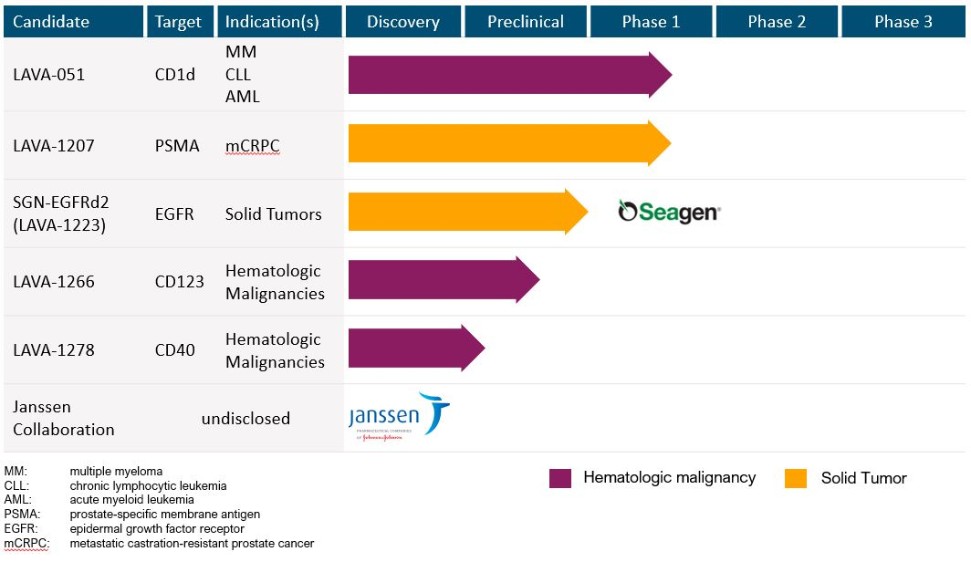
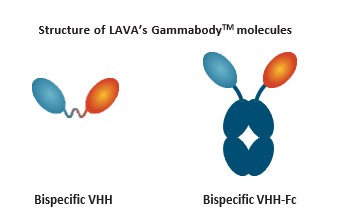
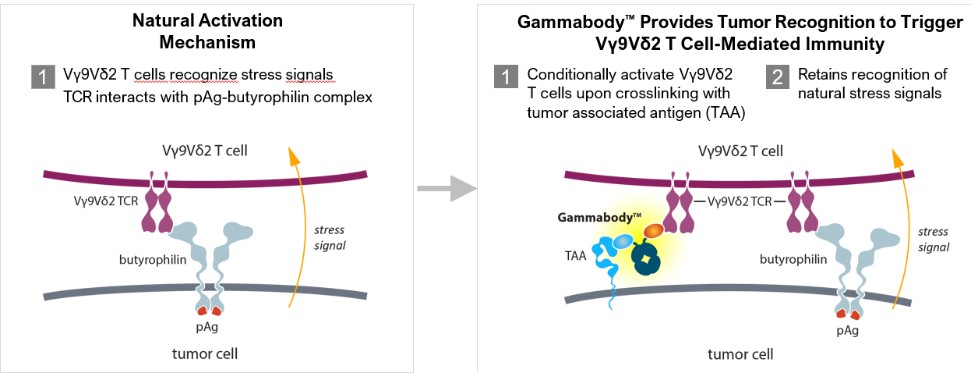
Other healthcare laws and compliance requirements
In the United States, our activities are potentially subject to regulation by various federal, state and local authorities in addition to the FDA, including but not limited to, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, or CMS, other divisions of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (such as the Office of Inspector General and the Health Resources and Service Administration), the Department of Justice, or the DOJ, and individual U.S. Attorney offices within the DOJ, and state and local governments. For example, research, sales, marketing activities and scientific/educational grant programs must comply with the anti-fraud and abuse provisions of the Social Security Act, the False Claims Act, transparency laws, the health information privacy and security laws, similar state laws, and regulations, each as amended, as applicable.
The federal Anti-Kickback Statute prohibits, among other things, any person or entity, from knowingly and willfully offering, paying, soliciting or receiving any remuneration, directly or indirectly, overtly or covertly, in cash or in kind, to induce or in return for purchasing, leasing, ordering or arranging for the purchase, lease or order of any item or service for which payment may be made, in whole or in part, under Medicare, Medicaid or other federal healthcare programs.
The federal false claims laws, including the FCA, which can be enforced by private citizens through civil qui tam actions and civil monetary penalty laws prohibit any person or entity from, among other things, knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, a false or fraudulent claim for payment to, or approval by, federal healthcare programs, or knowingly making, using, or causing to be made or used a false record or statement material to a false or fraudulent claim to the federal government.
We may be subject to data privacy and security regulations by both the federal government and the states in which we conduct our business. HIPAA, as amended by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act, or HITECH, and its implementing regulations, impose requirements relating to the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information on certain healthcare providers, healthcare clearinghouses, and health plans, known as covered entities, and independent contractors, or agents of covered entities that receive or obtain individually identifiable health information in connection with providing a service on behalf of a covered entity, known as a business associates, as well as their covered subcontractors. Among other things, HITECH makes HIPAA’s privacy and security standards directly applicable to business associates. HITECH also created four new tiers of civil monetary penalties, amended HIPAA to make civil and criminal penalties directly applicable to business associates, and gave state attorneys general new authority to file civil actions for damages or injunctions in federal courts to enforce HIPAA and seek attorneys’ fees and costs associated with pursuing federal civil actions.
In Europe, we are subject to Regulation (EU) 2016/679, the General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR, in relation to our collection, control, processing and other use of personal data. The GDPR is directly applicable in each European Union Member State, however, it provides that European Member States may introduce further conditions, including limitations which could limit our ability to collect, use and share personal data (including health and medical information), or could cause our compliance costs to increase, ultimately having an adverse impact on our business. These changes may lead to additional compliance costs and could increase our overall risk.
We are also subject to European Union rules with respect to cross-border transfers of personal data out of the European Union and European Economic Area (EEA). Recent developments in the EU have created complexity and uncertainty regarding transfers of personal data from the EEA to the United States. As supervisory authorities issue further guidance on personal data export mechanisms, including circumstances where the standard contractual clauses cannot be used, and/or start taking enforcement action, we could suffer additional costs, complaints and/or regulatory investigations or fines, and/or if we are otherwise unable to transfer personal data between and among countries and regions in which we operate, it could affect the manner in which we provide our services, the geographic location or segregation of our relevant systems and operations, and could adversely affect our financial results.
Additionally, the federal Physician Payments Sunshine Act, or the Sunshine Act, within the ACA, and its implementing regulations, require that certain manufacturers of drugs, devices, biological and medical supplies for which payment is available under Medicare, Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program (with certain exceptions) report annually to CMS information related to certain payments or other