UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
FORM 10-K
| | | | | |
| ☑ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended: December 31, 2024
OR | | | | | |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
Commission file number: 001-41520
Noble Corporation plc
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter) | | | | | | | | | | | |
| England and Wales | | 98-1644664 |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. employer identification number) |
2101 City West Boulevard, Suite 600, Houston, Texas, 77042
(Address of principal executive offices) (Zip Code)
Registrant’s Telephone Number, Including Area Code: (281) 276-6100
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | | | | | | |
| Title of each class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| A Ordinary Shares, par value $0.00001 per share | NE | New York Stock Exchange |
| Tranche 1 Warrants of Noble Corporation plc | NE WS | New York Stock Exchange |
| Tranche 2 Warrants of Noble Corporation plc | NE WSA | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☑
Indicate by check mark whether each registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether each registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether each registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer | ☑ | | Accelerated filer | ☐ |
| Non-accelerated filer | ☐ | | Smaller reporting company | ☐ |
| | | Emerging growth company | ☐ |
| | | | |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☑
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to 240.D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether each registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☑
As of June 28, 2024, the aggregate market value of the registered shares of Noble Corporation plc held by non-affiliates was $5.1 billion based on the closing price of such shares on such date as reported on the New York Stock Exchange.
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed all documents and reports required to be filed by Section 12, 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 subsequent to the distribution of securities under a plan confirmed by a court. Yes ☑ No ☐
Number of shares outstanding at February 14, 2025: Noble Corporation plc — 159,191,313
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Items 10, 11, 12, 13, and 14 of Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K will be incorporated by reference from the proxy statement for the 2025 Annual Meeting of Stockholders of Noble Corporation plc to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Page |
| PART I | | | | |
| Item 1. | | | | |
| Item 1A. | | | | |
| Item 1B. | | | | |
| Item 1C. | | | | |
| Item 2. | | | | |
| Item 3. | | | | |
| Item 4. | | | | |
| | | | | |
| PART II | | | | |
| Item 5. | | | | |
| Item 6. | | | | |
| Item 7. | | | | |
| Item 7A. | | | | |
| Item 8. | | | | |
| Item 9. | | | | |
| Item 9A. | | | | |
| Item 9B. | | | | |
| Item 9C. | | | | |
| | | | | |
| PART III | | | | |
| Item 10. | | | | |
| Item 11. | | | | |
| Item 12. | | | | |
| Item 13. | | | | |
| Item 14. | | | | |
| | | | | |
| PART IV | | | | |
| Item 15. | | | | |
| Item 16. | | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | | |
Forward-Looking Statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K (“Annual Report”) includes “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (“the Exchange Act”). All statements other than statements of historical facts included in this report or in the documents incorporated by reference, are forward looking statements, including those regarding expected financial performance, revenues, expected utilization, and fleet status, stacking of rigs, effects of new rigs on the market revenues, the impact of the Diamond Transaction, operating expenses, cash flows, contract status, tenders, terms and duration, dayrates, termination and extensions, contract backlog, the availability, delivery, mobilization, stacking or reactivation, contract commencement, relocation or other movement of rigs and the timing thereof, contract claims, capital expenditures, insurance maintenance and renewals, access to financing, rig demand, peak oil, the offshore drilling market, oil prices, production levels among members of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (“OPEC”) and other oil and gas producing nations (together with OPEC, “OPEC+”), and any expectations we may have with respect thereto, our future financial position, business strategy, impairments, repayment of debt, credit ratings, liquidity, borrowings under any credit facilities or other instruments, sources of funds, cost inflation, planned acquisitions or divestitures of assets, governmental regulations and permitting, taxes and tax rates, indebtedness covenant compliance, dividends and distributable reserves, share repurchases, progress, plans and goals related to environmental, social, and governance matters; the outcome of tax disputes, assessments and settlements, and expense management, the outcome of any dispute, litigation, audit or investigation, plans, foreign currency requirements, results of joint ventures, general economic, market, including inflation and recessions, trends and outlook, general political conditions, including political tensions, conflicts and war, timing, benefits or results of acquisitions or dispositions, and timing for compliance with any new regulations. When used in this report or in the documents incorporated by reference, the words “anticipate,” “believe,” “continue,” “could,” “estimate,” “expect,” “intend,” “may,” “might,” “on track,” “plan,” “possible,” “potential,” “predict,” “project,” “should,” “would,” “shall,” “target,” “will,” and similar expressions are intended to be among the terms that identify forward-looking statements. Although we believe that the expectations reflected in such forward-looking statements are reasonable, we cannot assure you that such expectations will prove to be correct. These forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and we undertake no obligation to revise or update any forward-looking statement for any reason, except as required by law. Actual results may differ materially from any future results expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements and the expectations expressed in forward-looking statements are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties and assumptions, which include, but are not limited to: a decline in the price of oil or gas, reduced demand for oil and gas products and increased regulation of drilling and production, price competition and cyclicality in the offshore drilling industry, offshore rig supply, dayrates and demand for rigs, contract duration, renewal, terminations and repricing, national oil companies and governmental clients, contract backlog, customer and geographic concentration, operational hazards and risks, labor force unionization, labor interruptions and labor regulations, major natural disasters, catastrophic event, acts of war, terrorism or social unrest, pandemic, or other similar event, joint ventures as well as investments in associates, international operations and related mobilization and demobilization of rigs, operational interruptions, delays, upgrades, refurbishment and repair of rigs and any related delays and cost overruns or reduced payment of dayrates, impacts of inflation, renewal of insurance, protection of sensitive information, operational technology systems and critical data, the ability to attract and retain skilled personnel or the increased cost in doing so, supplier capacity constraints or shortages in parts or equipment, supplier production disruptions, supplier quality and sourcing issues or price increases, future mergers, acquisitions or dispositions of businesses or assets or other strategic transactions, hurricanes and windstorm damage, responding to long-term changes in the energy mix, nonperformance of suppliers or third-party subcontractors, risks related to the Diamond Transaction and related integration, compliance with governmental laws and regulations, increasing attention to environmental, social and governance matters, including climate change and accountability for public statements about ESG efforts, compliance with anti-bribery or anti-corruption, international trade laws and regulations, litigation, our ability to maintain effective disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting, impairments on property and equipment, including rigs and related capital spares, operating and financial restrictions, and maintenance of covenants in our debt documents, tax disputes, or tax challenges as well as the “Risk Factors” referenced or described in Part I, Item 1A. “Risk Factors” of this Annual Report and in our other filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”). We cannot control such risk factors and other uncertainties, and in many cases, we cannot predict the risks and uncertainties that could cause our actual results to differ materially from those indicated by the forward-looking statements. You should consider these risks and uncertainties when you are evaluating us. Future quarterly dividends and other shareholder returns will be subject to, amongst other things, approval by the Board of Directors and may be modified as market conditions dictate.
Risk Factors Summary
The following is a summary of the principal risks that could adversely affect our business, operating results, and financial condition.
Risks Related to Our Business and Operations
▪our business depends on the level of activity in the oil and gas industry;
▪the offshore contract drilling industry is a highly competitive and cyclical business;
▪an oversupply of offshore rigs;
▪our ability to renew or replace existing contracts;
▪contracting with national oil companies;
▪our current backlog of contract drilling revenue may not be ultimately realized;
▪our substantial dependence on several customers and geographic locations;
▪operating hazards inherent to the offshore drilling business;
▪risks associated with unionization efforts, labor interruptions, and labor regulations;
▪a major natural disaster, catastrophic event, acts of war, terrorism or social unrest, pandemic, or other similar event;
▪risks associated with participation in joint ventures and investments in associates;
▪risks relating to operations in international locations;
▪upgrades, refurbishment, operating, and maintenance costs of our rigs as well as related operational interruptions and delays in operations;
▪inflation may adversely affect our operating results;
▪obtaining and maintaining insurance;
▪our and our service providers’ failure to adequately protect sensitive information and operational technology systems and critical data;
▪our failure to attract and retain skilled personnel;
▪supplier capacity constraints or shortages in parts or equipment or price increases;
▪risks associated with future mergers, acquisitions, or dispositions of businesses or assets;
▪our failure to achieve the intended benefits of the Diamond Transaction;
▪seasonal weather events, including in the United States Gulf of America, also known as the United States Gulf of Mexico (the “US Gulf”), and related windstorm damage or liabilities;
▪our failure to effectively and timely respond to the impact of long-term changes in the energy mix;
▪the potential for substandard performance or nonperformance by third-party suppliers and subcontractors upon which we rely;
▪risks associated with creating and executing new business models;
Regulatory and Legal Risks
▪the impact of governmental laws and regulations on our costs and drilling activity;
▪increasing attention to environmental, social, and governance matters (“ESG”), including climate change;
▪changes in, compliance with, or our failure to comply with certain laws and regulations;
▪compliance with laws and regulations relating to environmental, social, and governance matters;
▪violations of anti-bribery or anti-corruption laws;
▪compliance with complex laws and regulations governing international trade;
▪we are, or in the future, could be subject to litigation;
Financial, Tax, and Governance Risks
•we may record impairment charges on property and equipment;
•the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement, the indentures for the 2030 Notes and the Diamond Second Lien Notes (each as defined herein), and future facilities may contain various restrictive covenants limiting the discretion of our management in operating our business;
•the impact of a loss of a major tax dispute or a successful tax challenge to our operating structure, intercompany pricing policies, or the taxable presence of our subsidiaries in certain countries on our tax rate on our worldwide earnings;
•variance in our effective income tax rate;
•fluctuations in exchange rates;
•the interest of certain majority shareholders;
•the uncertainty of future dividends or future share repurchases;
•our structure as a holding company that is dependent upon cash flows from subsidiaries, joint ventures, and associates; and
•dilutive effects on shareholders from future equity sales and warrant exercises.
For a more complete discussion of the material risks facing our business, see Part I, Item 1A, “Risk Factors” below.
PART I
Item 1. Business.
Overview
Noble Corporation plc, a public limited company incorporated under the laws of England and Wales, is a leading offshore drilling contractor for the oil and gas industry. We provide contract drilling services to the international oil and gas industry with our global fleet of mobile offshore drilling units. We focus on a high-specification fleet of floating and jackup rigs and the deployment of our drilling rigs in oil and gas basins around the world. Noble and its predecessors have been engaged in the contract drilling of oil and gas wells since 1921. As of December 31, 2024, our fleet of 40 drilling rigs consisted of 27 floaters and 13 jackups.
On September 30, 2022 (the “Merger Effective Date”), pursuant to a business combination agreement, dated November 10, 2021 (as amended, the “Business Combination Agreement”), by and among Noble (as defined below), Noble Corporation, an exempted company incorporated in the Cayman Islands with limited liability (“Noble Cayman”), Noble Newco Sub Limited, a Cayman Islands exempted company and a direct, wholly owned subsidiary of Noble (“Merger Sub”), and The Drilling Company of 1972 A/S, a Danish public limited liability company (“Maersk Drilling”), Noble Cayman merged with and into Merger Sub (the “Merger”), with Merger Sub surviving the Merger as a wholly owned subsidiary of Noble. As a result of the Merger, Noble became the ultimate parent of Noble Cayman and its respective subsidiaries.
On October 3, 2022 (the “Closing Date”), pursuant to the Business Combination Agreement, Noble completed a voluntary tender exchange offer to Maersk Drilling’s shareholders (the “Offer” and, together with the Merger and the other transactions contemplated by the Business Combination Agreement, the “Business Combination”) and because Noble acquired more than 90% of the issued and outstanding shares of Maersk Drilling, nominal value Danish krone (“DKK”) 10 per share (“Maersk Drilling Shares”), Noble redeemed all remaining Maersk Drilling Shares not exchanged in the Offer for, at the election of the holder, either A ordinary shares, par value $0.00001 per share, of Noble (“Ordinary Shares”) or cash (or, for those holders that did not make an election, only cash), under Danish law by way of a compulsory purchase (the “Compulsory Purchase”) which was completed in early November 2022. Upon completion of the Compulsory Purchase, Maersk Drilling became a wholly owned subsidiary of Noble.
On June 9, 2024, Noble entered into an agreement and plan of merger (the “Diamond Merger Agreement”) with Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc. (“Diamond”), Dolphin Merger Sub 1, Inc., and Dolphin Merger Sub 2, Inc., under which Noble would acquire Diamond in a stock plus cash transaction (the “Diamond Transaction”). On September 4, 2024 (the “Diamond Closing Date”), Noble completed its acquisition of Diamond.
For additional information, see “Note 2 — Acquisitions and Divestitures” to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
As a result of the Merger, Noble became the successor issuer to Noble Cayman for purposes of and pursuant to the Exchange Act. References in this Annual Report on Form 10-K to “Noble,” the “Company,” “we,” “us,” and “our” refer collectively to (i) Noble Cayman and its consolidated subsidiaries prior to the Merger Effective Date, (ii) Noble and its consolidated subsidiaries (including Noble Cayman) on and after the Merger Effective Date, and (iii) Noble and its consolidated subsidiaries on and after the Diamond Closing Date, as applicable.
Contract Drilling Services
We report our contract drilling operations as a single reportable segment, Contract Drilling Services, which reflects how we manage our business. The mobile offshore drilling units comprising our offshore rig fleet operate in a global market for contract drilling services and are often redeployed to different regions due to changing demands of our customers, which consist primarily of large, integrated, independent, and government-owned or controlled oil and gas companies throughout the world.
We typically provide contract drilling services under an individual contract on a dayrate basis. Each contract’s final terms and conditions are the result of negotiations with our customers, and many contracts are awarded through a competitive bidding process. The following terms generally describe the key aspects of our contracts:
•contract duration extending over a specific period of time or a period necessary to drill a defined number of wells;
•payment of compensation to us (generally in US dollars although some customers, typically national oil companies, require a part of the compensation to be paid in local currency) on a “daywork” basis, so that we receive a fixed amount for each day (“dayrate”) that the drilling unit is operating under contract (a lower rate or no compensation is payable during periods of equipment breakdown and repair or adverse weather or in the event operations are interrupted by other conditions, some of which may be beyond our control);
•provisions permitting early termination of the contract by the customer (i) if the unit is lost or destroyed, (ii) if operations are suspended for a specified period of time due to breakdown of equipment or breach of contract, or (iii) for convenience with the payment of contractually specified termination amounts;
•provisions allowing the impacted party to terminate the contract if specified “force majeure” events beyond the contracting parties’ control occur for a defined period of time;
•payment by us of the operating expenses of the drilling unit, including labor costs and the cost of incidental supplies;
•provisions that allow us to recover our mobilization and demobilization costs associated with moving a drilling unit from one regional location to another which, under certain market conditions, may not allow us to receive full reimbursement of such costs;
•provisions that allow us to recover certain cost increases from our customers in certain long-term contracts;
•provisions that require us to lower dayrates for documented cost decreases in certain long-term contracts; and
•provisions that allocate responsibility and liability through indemnification provisions for risks related to personal injury, property damage or loss, environmental damages, damage to the reservoir, and other matters.
Under our drilling contracts, liability with respect to personnel and property is typically assigned on a “knock-for-knock” basis, which means that we and our customers assume liability for our respective personnel and property, generally irrespective of the fault or negligence of the party indemnified. In addition, our customers may indemnify us in certain instances for damage to our down-hole equipment and, in some cases, our subsea equipment. Also, we generally obtain a mutual waiver of consequential losses in our drilling contracts.
Our customers typically assume responsibility for and indemnify us from loss or liability resulting from pollution or contamination, including third-party damages and clean-up and removal, arising from operations under the contract and originating below the surface of the water. We are generally responsible for pollution originating above the surface of the water and emanating from our drilling units. Additionally, our customers typically indemnify us for liabilities incurred as a result of a blow-out or cratering of the well and underground reservoir loss or damage. In the current market, we are under increasing pressure to accept exceptions to the above-described allocations of risk and, as a result, take on more risk. In such cases where we agree, we generally limit the exposure with a monetary cap and other restrictions.
During periods of depressed market conditions, our customers may attempt to renegotiate or repudiate their contracts with us although we seek to enforce our rights under our contracts. The renegotiation may include changes to key contract terms, such as pricing, termination, and risk allocation.
For a discussion of our backlog of commitments for contract drilling services, please read Part II, Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations— Contract Drilling Services Backlog.”
Drilling Fleet
Noble is a leading offshore drilling contractor for the oil and gas industry. Noble owns and operates one of the most modern, versatile, and technically advanced fleets of mobile offshore drilling units in the offshore drilling industry. Noble provides, through its subsidiaries, contract drilling services with a fleet of 40 offshore drilling units, consisting of 27 floaters and 13 jackups at the date of this report, focused largely on ultra-deepwater and harsh environment drilling opportunities in both established and emerging regions worldwide. Each type of drilling rig is described further below. Several factors determine the type of unit most suitable for a particular job, the most significant of which include the water depth and the environment of the intended drilling location, whether the drilling is being done over a platform or other structure, and the intended well depth. At December 31, 2024, our fleet was operating in Africa, Far East Asia, the Middle East, the North Sea, Oceania, South America, and the US Gulf. Our fleet consists of the following types of mobile offshore drilling units:
Floaters. A drillship is a type of floating drilling unit that is based on the ship-based hull of the vessel and equipped with modern drilling equipment that gives it the capability of easily transitioning from various worldwide locations and carrying high capacities of equipment while being able to drill ultra-deepwater oil and gas wells in up to 12,000 feet of water. Drillships can stay directly over the drilling location without anchors in open seas using a dynamic positioning system
(“DPS”), which coordinates position references from satellite signals and acoustic seabed transponders with the drillship's six to eight thrusters to keep the ship directly over the well that is being drilled. Drillships are selected to drill oil and gas wells for programs that require a high level of simultaneous operations, where drilling loads are expected to be high, or where there are occurrences of high ocean currents, where the drillship's hull shape is the most efficient. Noble's fleet consists of 19 drillships capable of water depths from 10,000 feet to 12,000 feet.
Semisubmersible drilling units are designed as a floating drilling platform incorporating one or several pontoon hulls, which are submerged in the water to lower the center of gravity and make this type of drilling unit exceptionally stable in the open sea. Semisubmersible drilling units are generally categorized in terms of the water depth in which they are capable of operating, from the mid-water range of 300 feet to 4,000 feet, the deepwater range of 4,000 feet to 7,500 feet, to the ultra-deepwater range of 7,500 feet to 12,000 feet as well as by their generation, or date of construction. This type of drilling unit typically exhibits excellent stability characteristics, providing a stable platform for drilling in even rough seas. Semisubmersible drilling units hold their position over the drilling location using either an anchored mooring system or a DPS and may be self-propelled. Noble’s fleet consists of 8 moored ultra-deepwater semisubmersible drilling units.
Jackups. Jackup drilling units are designed to provide drilling solutions in depths ranging from less than 100 feet to as deep as 500 feet of water with drilling hook loads up to 2,500,000 pounds. Jackup rigs can be used in open water exploration locations, as well as over fixed, bottom-supported platforms. A jackup drilling unit is a towed mobile vessel consisting of a floating hull equipped with three or four legs, which are lowered to the seabed at the drilling location. The hull is then elevated out of the water by the jacking system using the legs to support the weight of the hull and drilling equipment against the seabed. Once the hull is elevated to the desired level, or jacked up, the drilling package can be extended out over an existing production platform or the open water location and drilling can commence. Noble’s fleet of 13 jackups consists of high-specification units capable of drilling in up to 500 feet of water.
The following table presents certain information concerning our offshore fleet at February 18, 2025. We own and operate all of the units included in the table.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Name | | Make | | Year Built (1) | | Water Depth Rating (feet) (2) | | Drilling Depth Capacity (feet) | | Location | | Status (3) |
| Floaters—27 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Drillships—19 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Noble Bob Douglas | | GustoMSC P10000 | | 2013 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | Guyana | | Active |
| Noble Don Taylor | | GustoMSC P10000 | | 2013 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | Guyana | | Active |
| Noble Faye Kozack | | Samsung 96000 | | 2013 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | Brazil | | Active |
| Noble Gerry de Souza | | Samsung 120000 Double Hull | | 2011 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | Nigeria | | Active |
| Noble Globetrotter I | | Globetrotter Class | | 2011 | | 10,000 | | 30,000 | | US Gulf | | Active |
| Noble Globetrotter II | | Globetrotter Class | | 2013 | | 10,000 | | 30,000 | | US Gulf | | Available |
| Noble Sam Croft | | GustoMSC P10000 | | 2014 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | Guyana | | Active |
| Noble Stanley Lafosse | | Samsung 96000 | | 2014 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | US Gulf | | Active |
| Noble Tom Madden | | GustoMSC P10000 | | 2014 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | Guyana | | Active |
Pacific Meltem (4) | | Samsung 96000 | | 2014 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | Las Palmas | | Stacked |
Pacific Scirocco (4) | | Samsung 120000 Double Hull | | 2011 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | Las Palmas | | Stacked |
| Noble Valiant | | Samsung 96000 | | 2014 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | US Gulf | | Active |
| Noble Venturer | | Samsung 96000 | | 2014 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | Namibia | | Active |
| Noble Viking | | Samsung 96000 | | 2014 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | Malaysia | | Active |
| Noble Voyager | | Samsung 96000 | | 2015 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | Curacao | | Available |
| Noble BlackRhino | | Gusto P10000 | | 2014 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | US Gulf | | Active |
| Ocean BlackHawk | | Gusto P10000 | | 2014 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | US Gulf | | Active |
| Ocean BlackHornet | | Gusto P10000 | | 2014 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | US Gulf | | Active |
| Ocean BlackLion | | Gusto P10000 | | 2015 | | 12,000 | | 40,000 | | US Gulf | | Active |
| Semisubmersibles—8 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Noble Deliverer | | DSS21-DPS2 | | 2010 | | 10,000 | | 40,000 | | Malaysia | | Available |
| Noble Developer | | DSS21-DPS2 | | 2009 | | 10,000 | | 40,000 | | Trinidad & Tobago | | Active |
| Noble Discoverer | | DSS21-DPS2 | | 2009 | | 10,000 | | 40,000 | | Colombia | | Active |
| Noble Patriot | | Bingo 3000 | | 1983 | | 1,500 | | 20,000 | | UK | | Active |
| Ocean Apex | | Enhanced Victory | | 1976/2014 | | 6,000 | | 30,000 | | Australia | | Active |
| Ocean Courage | | F&G ExD Millennium | | 2009 | | 10,000 | | 40,000 | | Brazil | | Active |
| Ocean Endeavor | | Enhanced Victory | | 1975/2006 | | 10,000 | | 35,000 | | UK | | Active |
| Ocean GreatWhite | | Moss CS-60E | | 2016 | | 10,000 | | 35,000 | | UK | | Active |
| Independent Leg Cantilevered Jackups—13 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Harsh environment—8 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Noble Highlander | | F&G JU-2000E | | 2016 | | 400 | | 30,000 | | Denmark | | Stacked |
| Noble Mick O’Brien | | F&G JU-3000N | | 2013 | | 400 | | 35,000 | | Qatar | | Active |
| Noble Regina Allen | | F&G JU-3000N | | 2013 | | 400 | | 30,000 | | Argentina | | Active |
| Noble Resilient | | MCS CJ50-X100 MC | | 2008 | | 350 | | 30,000 | | UK | | Active |
| Noble Resolute | | MCS CJ50-X100 MC | | 2008 | | 350 | | 30,000 | | Netherlands | | Active |
| Noble Resolve | | MCS CJ50-X100 MC | | 2009 | | 350 | | 30,000 | | Poland | | Active |
| Noble Tom Prosser | | F&G JU-3000N | | 2014 | | 400 | | 30,000 | | Malaysia | | Active |
| Noble Reacher | | MCS CJ50-X100 MC | | 2009 | | 350 | | 30,000 | | Denmark | | Active |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Ultra-harsh environment—5 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Noble Innovator | | MCS CJ70-150MC | | 2003 | | 492 | | 30,000 | | UK | | Active |
| Noble Integrator | | MCS CJ70-X150 MD | | 2015 | | 492 | | 40,000 | | Norway | | Active |
| Noble Interceptor | | MCS CJ70-X150 MD | | 2014 | | 492 | | 40,000 | | Denmark | | Available |
| Noble Intrepid | | MCS CJ70-X150 MD | | 2014 | | 492 | | 40,000 | | UK | | Active |
| Noble Invincible | | MCS CJ70-X150 MD | | 2016 | | 492 | | 40,000 | | Norway | | Active |
(1) All of our current rigs were delivered to the Company new from the shipyard.
(2) Rated water depth for drillships and semisubmersibles reflects the maximum water depth for which a floating rig has been designed for drilling operations.
(3) Rigs listed as “active” are operating, preparing to operate, or under contract; rigs listed as “available” are actively seeking contracts and may include those that are idle or warm stacked; rigs listed as “stacked” are idle without a contract, have reduced or no crew, or are not actively marketed in present market conditions.
(4) In February 2025, we committed to a plan to sell the Pacific Meltem and Pacific Scirocco.
Market
The offshore contract drilling industry is a highly competitive and cyclical business. Demand for offshore drilling services is driven by the offshore exploration and development programs of oil and gas operators, which in turn are influenced by many factors. Those factors include, but are not limited to, the price and price stability of oil and gas, the relative cost and carbon footprint of offshore resources within each operator’s broader energy portfolio, global macroeconomic conditions, world energy demand, the operator’s strategy toward renewable energy sources, environmental considerations, and governmental policies.
In the provision of offshore contract drilling services, success in securing contracts is primarily governed by price, a rig’s availability, drilling capabilities and technical specifications, and the drilling contractor’s safety performance record. Other factors include experience of the workforce, process efficiency, condition of equipment, operating integrity, reputation, industry standing, and client relations.
We maintain a global operational presence and compete in many of the major offshore oil and gas basins worldwide with a primary focus on the deepwater and ultra-deepwater market and the harsh and ultra-harsh environment jackup and floater markets. All our drilling rigs are mobile, and we may reposition our drilling rigs among regions for a variety of reasons, including in response to customer requirements. We compete in both the jackup and floating rig markets, each of which may have different supply and demand dynamics at a given period in time or in different regions.
We have one of the youngest and highest specification fleets of global scale in the industry, with diversification across asset classes, geographic regions, and customers. The Company has a track record of industry-leading utilization, coupled with a commitment to best-in-class safety performance and customer satisfaction. We strive to be a leader in industry innovation and first-mover in sustainability.
The offshore drilling industry has historically experienced significant volatility and change. In recent years, however, oil prices have generally remained at levels that are supportive of offshore exploration and development activity. While ongoing geopolitical and macroeconomic factors continue to create some uncertainty relating to future global energy demand, global offshore rig demand has generally remained robust since 2021. During 2023 and 2024, the total level of global floater and jackup demand exceeded 2020 early pre-pandemic highs, albeit with some moderation over the past 12 months as upstream capital discipline has resulted in a slight reduction in contracted offshore rig demand compared to early 2024 peak levels. As a result, utilization and leading edge dayrates for certain rig classes have recently plateaued or decreased. A further softening of utilization in 2025 could result in corresponding dayrate pressure in certain situations due to a more competitive bidding environment.
The global rig supply has come down from historic highs as Noble and other offshore drilling contractors have retired less capable and idle assets. Concurrently, the incoming supply of newbuild offshore drilling rigs has diminished materially, with several newbuild rigs stranded in shipyards. However, we expect many of these stranded newbuild rigs may continue to make their way into the global market over the next few years.
Although the market outlook in our business varies by geographical region and water depth, we remain encouraged by the long-term outlook in the ultra-deepwater floater market, with overall demand having increased from 2020 lows. Our customers continue to focus on our highest specification floaters, which represents the majority of our floater fleet. While
we remain encouraged about overall rig demand, to the extent global macroeconomic concerns become more prevalent, we could experience downward pressure on oil and gas prices as well as overall rig demand for both floaters and jackups.
As of the date of this report, the majority of our jackup fleet is positioned in the North Sea. While we have seen generally stable demand in the UK and southern North Sea in recent years, overall activity levels in the region remain subdued compared to historical levels. Similarly, the ultra-harsh environment jackup market in Norway also remains below historical levels despite the market being attractive to operators given it is characterized by low-cost and low-emission barrels.
Returning to the broader offshore drilling market, while there are a number of multi-year contracts out for tender, the overall market remains characterized by generally shorter-term contracts. This leads to an increased number of rig contract start-ups, both with different customers and among different regions, which may require incremental resources and costs. Additionally, this has resulted in, and is likely to continue to result in, lower overall effective utilization for our fleet driven by more idle time between contracts.
The energy transition from hydrocarbons to renewables poses a challenge to the oil and gas sector and our market. Energy rebalancing trends have accelerated in recent years as evidenced by promulgated or proposed government policies and commitments by many of our customers to further invest in sustainable energy sources. Our industry could be further challenged as resource holders and policy makers continue to evaluate and calibrate strategies and capital flows to address global energy needs. Ultimately, however, there continues to be a global dependence on products made from hydrocarbons and on the combustion of hydrocarbons to provide reliable and affordable energy. Low-cost and low-emission barrels are expected to be the most attractive conventional source to meet energy needs both currently and in the future. Global energy demand is predicted to increase over the coming decades, and we expect that offshore oil and gas will continue to play an important and lasting role in meeting this demand.
While inflationary pressures in our industry have eased since 2023, our cost profile remains sensitive to global labor market conditions, capital intensive repair and maintenance scopes on our rigs, global trade and sanctions regimes, and geopolitical crises and their respective regional and global ramifications. Each of these factors has the potential to adversely impact our ability to conduct our day-to-day operations and manage costs.
Significant Customers
During the three years ended December 31, 2024, we principally conducted our contract drilling operations in Africa, Far East Asia, the Middle East, the North Sea, Oceania, South America, and the US Gulf. The following table sets forth revenues from our customers as a percentage of our consolidated operating revenues:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Exxon Mobil Corporation (“ExxonMobil”) | | 22.1 | % | | 24.5 | % | | 32.3 | % |
| Shell plc | | 12.3 | % | | 13.6 | % | | 12.0 | % |
| TotalEnergies | | 6.3 | % | | 10.5 | % | | 9.7 | % |
No other customer accounted for more than 10 percent of our consolidated operating revenues in 2024, 2023, or 2022.
Human Capital
At December 31, 2024, we had approximately 5,000 employees, excluding approximately 1,400 persons we engaged through labor contractors or agencies. Approximately 80% percent of our workforce is located offshore. Certain of our employees and contractors in international markets, such as Norway and Denmark, are represented by labor unions and work under collective bargaining or similar agreements, which are subject to periodic renegotiation, and we consider our employee relations to be satisfactory.
For additional information, please read Part I, Item 1A, “Risk Factors—Risk Related to Our Business and Operations—Unionization efforts, labor interruptions and labor regulations could have a material adverse effect on our operations.”
Our compliance program is focused on promoting adherence with high ethical standards and applicable laws and setting the tone for an ethical business practices and work environment throughout the Company. The Noble Code, Noble’s code of business conduct and ethics (the “Code of Conduct”), encompasses our commitments to our Core Values of safety, environmental stewardship, honesty and integrity, respect, and performance. The Code of Conduct also includes our responsibility and commitment to follow all applicable laws as well as our own internal policies, and extends requirements to any supplier or third party who works with Noble to comply with similar fundamental principles.
Operating our business in a socially responsible way is integral to our identity. Internally, our employee-focused programs, such as training and continuing education, our promotion and advancement program, focus on inclusion and culture, recruitment initiatives, and retirement and benefits, are key to our commitment to the personal and professional growth of our workforce. Externally, our dedication is evidenced by our affiliations and how we contribute to and invest in the communities where we operate.
Talent Management. Noble is committed to a number of initiatives that directly support our employee talent management. As part of these initiatives, Noble is committed to the promotion of equal opportunity and non-discrimination and aspires to not only promote an environment and culture of inclusion, but also provide healthy working conditions that enable our employees to reach their full potential.
In order to enable regular feedback loops and a continuous focus on employee engagement, we implement semi-annual Employee Engagement Surveys, results of which are shared with the organization and leaders engage their teams in a conversation regarding the results and subsequent actions. Noble also focuses on enabling performance through continuous conversations between the leader and the employee. The conversations are intended to take place at least twice a year and follow a structured framework pertaining to contributions, engagement, and development, and incorporate two-way feedback.
We also identify high-performing and high-potential individuals within Noble and aspire to ensure succession planning regarding all critical positions. We focus on engagement and retention of such individuals by aspiring to offer experiences and opportunities that demonstrate our commitment to their ongoing growth.
Safety and Environmental Stewardship. Noble is committed to operating with excellent health, safety, and environmental (“HSE”) performance as part of our business strategy in order to add further value for employees, customers, and shareholders. All personnel, regardless of job or position onboard our vessels or at any Noble facility, has the authorization and obligation to immediately stop any unsafe act, practice, or job that poses an unaddressed or unreasonable risk or danger to people or the environment. Noble’s pursuit of exceptional HSE performance begins with our strong corporate culture and by starting SAFE every day: one tour, one task and one person at a time. SAFE is an acronym for the phrase: follow Standards, be Accountable, stay Focused, achieve Excellence. Daily, the crew onboard each rig works together to achieve specific safety and environmental objectives and if all objectives are met, then the day is counted as a SAFE Day. Under our SAFE Day program, in 2024, our rigs achieved the SAFE objectives 98.6% of available days, which has remained flat compared to 2023 performance. As of December 31, 2024, this metric is only available for vessels owned by Noble prior to the Diamond Transaction. As integration activities are completed throughout 2025, all current Noble vessels will utilize this program.
Training and Continuing Education. We place considerable value on the training and development of our employees. Accordingly, we conduct formal and informal meetings with employees, regular executive-led podcasts, issue periodic publications of Company activities, and other matters of interest to the Company’s OneNoble app and offer a variety of training, including in-house through NobleAdvances, our state-of-the-art training facility in Texas. Noble has learned that technical skills are not enough to keep pace in our fast-changing offshore environments. NobleAdvances allows us to deliver scenario-based drilling and marine training with a strong focus on communication, biases, and emergency decision making. This approach is designed to enable Noble employees to execute our procedures effectively and solve complex technical problems in challenging offshore conditions.
Environmental Responsibility
Climate change is an environmental, social, and economic challenge facing everyone today. We are committed to continuous improvement and a sustainable energy future supported by our efforts to protect the environment throughout our operations and safely provide reliable and efficient services to allow access to resources essential for human and economic prosperity. There is ongoing attention concerning the global climate and the effect of greenhouse gas (“GHG”) emissions. Various regulators have proposed or adopted rules requiring the monitoring and reporting of GHG emissions from specified sources in the United States, including, among other things, certain offshore activities relating to oil and gas production. As such, we regularly assess the environmental impact of operations, focusing on the reduction of GHG emissions, operational discharges, water use, and waste. Furthermore, we actively look to collaborate with our customers to evaluate economic alternatives for reducing the carbon footprint of our drilling rigs.
Available Information
Our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act are available free of charge at our website as soon as reasonably practicable after such material is electronically filed with or furnished with the SEC. The SEC
maintains an internet site that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC at http://www.sec.gov.
Our website address is http://www.noblecorp.com. Investors should also note that we announce material financial information in SEC filings, press releases, and public conference calls. Based on guidance from the SEC, we may use the investor relations section of our website to communicate with our investors. It is possible that the financial and other information (including fleet status reports) posted there could be deemed to be material information. Noble may also use social media channels including, but not limited to, Noble's accounts on LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter, to communicate with investors and the public about its business, services, and other matters, and those communications could be deemed to be material information. Documents and information on our website or our social media channels are not incorporated by reference herein.
Item 1A. Risk Factors.
You should carefully consider the following risk factors in addition to the other information included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Each of these risk factors could affect our business, operating results, and financial condition as well as affect an investment in our shares.
Risks Related to Our Business and Operations
Our business depends on the level of activity in the oil and gas industry. Adverse developments affecting the industry, including a decline in the price of oil or gas, reduced demand for oil and gas products, and increased regulation of drilling and production, have in the past had, and may in the future, have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Demand for drilling services depends on a variety of economic and political factors and the level of activity in offshore oil and gas exploration and development and production markets around the world. The price of oil and gas and market anticipation of potential changes in the price, significantly affect this level of activity, as well as dayrates that we can charge customers for our services. Crude oil prices remain volatile; for example, Brent crude reached a low of $9.12 in 2020 and a 5-year high of $133.18 in 2022.
Higher prices do not necessarily translate into increased drilling activity because our customers typically take into account a number of considerations when they decide to invest in offshore oil and gas resources, including expectations regarding future commodity prices and demand for hydrocarbons. While the price of oil and gas remains volatile, the level of activity in offshore oil and gas exploration and development can be extremely volatile and can be affected by numerous factors beyond our control, including:
▪worldwide production, current demand, and our customer’s views of future demand for oil and gas;
▪changes in the rate of economic growth in the global economy;
▪the cost of exploring for, developing, producing, and delivering oil and gas;
▪the ability of OPEC and OPEC+ to set and maintain production levels and pricing;
▪expectations regarding future energy prices;
▪increased supply of oil and gas resulting from onshore hydraulic fracturing activity and shale development;
▪the relative cost of offshore oil and gas exploration versus onshore oil and gas production;
▪potential acceleration in the investment, development, and the price and availability of alternative fuels or energy sources;
▪allocation of capital to exploration and production operations within customers’ broader portfolios;
▪the level of production in non-OPEC+ countries;
▪inventory levels and the cost and availability of storage and transportation of oil, gas, and their related products;
▪worldwide financial instability or recessions;
▪regulatory restrictions or any moratorium on offshore drilling or the availability of offshore lease or concession areas;
▪the discovery rate of new oil and gas reserves either onshore or offshore;
▪the rate of decline of existing and new oil and gas reserves;
▪available pipeline and other oil and gas transportation capacity;
▪oil refining capacity;
▪the ability of oil and gas companies to raise capital;
▪limitations on liquidity and available credit;
▪advances in exploration, development, and production technology either onshore or offshore;
▪technical advances affecting energy consumption, including the displacement of hydrocarbons;
▪merger, acquisition, and divestiture activity among oil and gas industry participants;
▪the availability of, and access to, suitable locations from which hydrocarbons can be produced;
▪adverse weather and sea conditions, including hurricanes, typhoons, cyclones, winter storms, and rough seas;
▪the occurrence or threat of a major natural disaster, catastrophic event, epidemic, or pandemic diseases, as well as any governmental response to such occurrence or threat;
▪changes in and compliance with tax laws, regulations, and policies;
▪changes in and compliance with environmental laws, regulations, and other initiatives, including those involving alternative energy sources, the phase-out of fossil fuel consuming vehicles, and the risks of global climate change;
▪the political environment of oil-producing countries or regions, including uncertainty or instability resulting from civil disorder, geopolitical instability, border disputes, or an outbreak or escalation of armed hostilities or acts of war or terrorism, such as the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, Middle East conflicts, and the Guyana-Venezuela dispute, and their respective regional and global ramifications; and
▪the laws, regulations, and policies of governments regarding exploration and development of their oil and gas reserves or speculation regarding future laws or regulations.
Adverse developments affecting the industry as a result of factors such as those listed above, including a decline in the price of oil and gas from their current levels or the failure of the price of oil and gas to consistently remain at or above a level that encourages our customers to expand their capital spending, the inability of our customers to access capital on economically advantageous terms, including as a result of the increasing focus on climate change by investors, a global recession, reduced demand for oil and gas products, or a perception that the demand for hydrocarbons will significantly decrease, increased supply due to the development of new onshore drilling and production technologies, and increased regulation of drilling and production, particularly if several developments were to occur in a short period of time, would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations. However, increases in near-term commodity prices do not necessarily translate into increased offshore drilling activity because customers’ expectations of longer-term future commodity prices and expectations regarding future demand for hydrocarbons typically have a greater impact on demand for our rigs. The level of oil and gas prices has had, and may in the future have, a material effect on demand for our services, and future declines in prices would likely have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
The offshore contract drilling industry is a highly competitive and cyclical business with intense price competition. If we are unable to compete successfully, our profitability may be materially reduced.
The offshore contract drilling industry is a highly competitive and cyclical business characterized by high capital and operating costs and evolving capability of newer rigs. Drilling contracts are traditionally awarded on a competitive bid basis. Price competition, rig availability, location, suitability, and technical specifications are the primary factors in determining which rig is qualified for a job, and additional factors such as experience of the workforce, operating efficiency, safety performance record, condition of equipment, operating integrity, reputation, industry standing, and customer relations are also often considered. Our future success and profitability will partly depend upon our ability to keep pace with our customers’ demands with respect to these factors. In the past several years, the pace of consolidation in our industry has increased, and may continue to increase, leading to the creation of a number of larger and financially stronger competitors. If we are unable, or our customers believe that we are unable, to compete with the scale and financial strength of certain of our competitors, it could harm our ability to maintain existing drilling contracts and secure new ones.
Further, if current competitors implement new or differentiated technical capabilities, services or specifications, which may be more attractive to our customers or price their product offerings more competitively, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations. We may face competitive pressure to develop, implement, or acquire certain new technologies at a substantial cost. We cannot be certain that we will be able to continue to develop and implement new technologies or services offered.
Our industry is cyclical. Periods of low demand or excess rig supply intensify the competition in the industry and have resulted in, and may continue to result in, many of our rigs earning substantially lower dayrates or being idle for long periods of time. Although, since the 2014 peak, the industry has experienced a rationalization and correction of the global offshore rig supply, we continue to experience competition from newbuild rigs, including rigs that have been stranded in shipyards, that have either already entered the market or are available to enter the market. The entry of these rigs into the market has resulted in, and may in the future result in, lower dayrates for both newbuilds and existing rigs rolling off their current contracts. In addition, our competitors may relocate rigs to geographic markets in which we operate, which could exacerbate any excess rig supply, or depress the current rationalization and correction of offshore rig supply, and result in lower dayrates and utilization in those regions.
In addition, our customers continue to seek more favorable terms with respect to allocation of risk under offshore drilling contracts. Our drilling contracts provide for varying levels of risk allocation and indemnification from our customers. Our customers have historically assumed most of the responsibility for and indemnified us from loss, damage, or other liability resulting from pollution or environmental damage, including clean-up and removal and third-party damages arising from operations under the contract when the source of the pollution originates from the well or reservoir, including those resulting from blow-outs or loss of well control. However, we regularly are required to assume certain amounts of liability for pollution and environmental damage caused by our negligence, which liability generally has higher caps, or may even have unlimited liability, where the damage is caused by our gross negligence or willful misconduct. We still face resistance with some customers when attempting to allocate less risk to us and lower caps for damage caused by our gross negligence or willful misconduct or reduce our exposure with respect pollution or environmental damage. Our contracts may also be subject to judicial review and application of public policy principles whereby relevant authorities could decide that certain contractual indemnities in current or future contracts are not enforceable. Going forward, we could decide or be required to retain more risk in the future, resulting in higher risk of losses, which could be material. Moreover, we may not be able to maintain adequate insurance in the future at rates that we consider reasonable or be able to obtain insurance against current or future risks.
We have not been, and may continue not to be, able to renew or replace certain expiring contracts, and our customers have sought, and may seek in the future, to terminate, renegotiate, or repudiate our drilling contracts and have had, and may have in the future, financial difficulties that prevent them from meeting their obligations under our drilling contracts.
Our ability to renew contracts that expire or obtain new contracts and the terms of any such contracts will depend on market conditions and our customers' expectations and assumptions of future oil prices and other factors.
Depending on market conditions, we have also experienced customers seeking price reductions for our services, payment deferrals, and termination of our contracts; customers seeking to not perform under our contracts pursuant to a force majeure claim; and customers that are unable or unwilling to timely pay outstanding receivables owed to us, all of which present liquidity challenges for us. Our customers may generally terminate our drilling contracts if a drilling rig is destroyed or lost or if we have to suspend drilling operations for a specified period of time as a result of a breakdown of equipment or, in some cases, due to other events beyond the control of either party. In the case of nonperformance and under certain other conditions, our drilling contracts generally allow our customers to terminate without any payment to us. The terms of some of our drilling contracts permit the customer to terminate the contract after a specified notice period by tendering contractually specified termination amounts or, in some cases, without any payment. These termination payments, if any, may not fully compensate us for the loss of a contract. The early termination of a contract may result in a rig being idle for an extended period of time and a reduction in our contract backlog and associated revenue, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations. Moreover, if any of our long-term contracts were to be terminated early, such termination could affect our future earnings flow and could have a material adverse effect on our future financial condition and results of operations even if we were to receive the contractually specified termination amount.
During periods of depressed market conditions, we are subject to an increased risk of our customers seeking to renegotiate or repudiate their contracts. The ability of our customers to perform their obligations under drilling contracts with us may also be adversely affected by the financial condition of the customer, restricted credit markets, economic downturns, and industry downturns. We may elect to renegotiate the rates we receive under our drilling contracts downward if we determine that to be a reasonable business solution. If our customers cancel or are unable to perform their obligations under their drilling contracts, including their payment obligations, and we are unable to secure new contracts on a timely basis on substantially similar terms or if we elect to renegotiate our drilling contracts and accept terms that are less favorable to us, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Drilling contracts with national oil companies may expose us to greater risks than we normally assume in drilling contracts with non-governmental customers.
Contracts with national oil companies are often non-negotiable and may expose us to greater commercial, political, and operational risks than we assume in other contracts, such as exposure to materially greater environmental liability and other claims for damages (including consequential damages) and personal injury related to our operations, or the risk that the contract may be terminated by our customer without cause on short-term notice, contractually or by governmental action, under certain conditions that may not provide us an early termination payment, collection risks, and political risks. In
addition, our ability to resolve disputes or enforce contractual provisions may be negatively impacted under these contracts. We can provide no assurance that the increased risk exposure will not have an adverse impact on our future operations or that we will not increase the number of rigs contracted to national oil companies with additional contractual risks.
Our current backlog of contract drilling revenue may not be ultimately realized.
Generally, contract backlog only includes future revenues under signed drilling contracts. We may not be able to perform under these contracts as a result of operational or other breaches or due to events beyond our control, and we may not ultimately execute a definitive agreement in cases where one does not currently exist. Moreover, we can provide no assurance that our customers will be able to or willing to fulfill their contractual commitments to us or that they will not seek to renegotiate or repudiate their contracts or, for certain customers, reallocate term among contracted rigs, especially during an industry downturn. The terms of some of our drilling contracts permit the customer to terminate the contract after specified notice periods by tendering contractually specified termination amounts or, in certain cases, without any payment. In estimating backlog, we make certain assumptions about applicable dayrates under our longer-term contracts which have dayrate adjustment mechanisms (like certain of our contracts with ExxonMobil, AkerBP, Tullow, and Petrobras). In addition, from time to time, we may report anticipated commitments under letters of intent or awards for which definitive agreements have not yet been, but are expected to be, signed. We cannot assure you that actual results will mirror these assumptions. Our inability to perform under our contractual obligations, execute definitive agreements, our customers’ inability or unwillingness to fulfill their contractual commitments to us, including as a result of contract repudiations or our decision to accept less favorable terms on our drilling contracts, or the failure of actual results to reflect the assumptions we use to estimate backlog for certain contracts, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
A substantial portion of our business is dependent on several of our customers as well as dependent on several geographic areas and the disruption of business with any of these customers or disruption of business within these geographic areas could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Any concentration of customers increases the risks associated with any possible termination or nonperformance of drilling contracts, failure to renew contracts or award new contracts, or reduction of their drilling programs. In addition, the concentration of operations within a geographic area increases the impact of terrorism, piracy, or political or social unrest, changes in local laws and regulations, as well as severe weather events, should they occur within an area of concentration. As of December 31, 2024, ExxonMobil, BP, and Petrobras represented approximately 37.2%, 13.1%, and 12.6% of our contract backlog, respectively, and operations within Guyana, the US Gulf, and the North Sea accounted for approximately 37.2%, 21.9%, and 18.5% of our contract backlog, respectively. ExxonMobil and Shell plc accounted for approximately 22.1% and 12.3%, respectively, of our consolidated operating revenues for the year ended December 31, 2024, and operations in the US Gulf, Guyana, and the North Sea accounted for approximately 22.4%, 22.1%, and 17.8%, respectively, of our consolidated operating revenues for the year ended December 31, 2024. This concentration of customers increases the risks associated with any possible termination or nonperformance of contracts in addition to our exposure to credit risk. If any of these customers were to terminate or fail to perform their obligations under their contracts and we were not able to find other customers for the affected drilling units promptly, our financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected. Additionally, the concentration of operations in specific geographies increases the risks associated with terrorism, piracy, political or social unrest, changes in local laws and regulations, as well as severe weather events within those regions, should they occur. If we were forced to cease drilling operations in any of these regions for any reason and we were not able to redeploy to other regions promptly, our financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
Our business may be impacted by numerous operating hazards.
Our operations are subject to many hazards inherent in the drilling business, including:
•loss of well control or blowout;
•fire;
•navigation hazards, such as collisions or groundings of offshore equipment;
•helicopter accidents;
•seabed punch-throughs of a jackup rig;
•mechanical or technological equipment failures;
•failure to comply with environmental, health, and safety requirements;
•loss of well integrity (such as pipe or cement failures and casing collapses);
•adverse weather or sea conditions (caused by events including hurricanes, typhoons, tsunamis, cyclones, and winter storms, which may increase in frequency and severity as a result of climate change);
•loop currents or eddies;
•toxic gas emanating from the well; and
•improper handling, release, or disposal of hazardous materials.
These hazards could cause personal injury, including claims of post-traumatic stress or loss of life, suspend drilling operations, result in regulatory investigation or penalties, seriously damage or destroy property and equipment, result in claims by employees, customers, or third parties, cause environmental damage, and cause substantial damage to oil and gas producing formations or facilities. Operations also may be suspended because of machinery breakdowns, abnormal drilling conditions, and failure of subcontractors to perform or supply goods or services or personnel shortages. The occurrence of any of the hazards we face could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Unionization efforts, labor interruptions, and labor regulations could have a material adverse effect on our operations.
Certain of our employees and contractors in international markets, such as Australia, certain African countries, Brazil, Norway, Denmark, and the United Kingdom, are represented by labor unions and work under collective bargaining or similar agreements, which are subject to periodic renegotiation, and efforts may be made from time to time to unionize other portions of our workforce. Although we have not experienced any labor disruptions, strikes, or other forms of labor unrest in connection with our personnel, there can be no assurance that labor disruptions by employees and contractors will not occur in the future. Further, unionized employees of third parties on whom we rely may be involved in labor disruptions, strikes, or other forms of labor unrest, causing operational disruptions. Such actions could result in the occurrence of additional costs, as well as limitations on our ability to operate or provide services to our customers, which may materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations. In addition strikes may occur in connection with annual salary negotiations with respect to unionized employees or contractors. If future labor strikes force us to shut down any of our operations, such interruption in operations could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations. Additionally, legislation has been introduced in the US Congress that could encourage additional unionization efforts in the United States, as well as increase the chances that such efforts succeed. Additional unionization efforts, if successful, could materially increase our labor costs and operating restrictions.
A major natural disaster, catastrophic event, acts of war, terrorism, social unrest, pandemic, or other similar event could have a materially adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations, or have other adverse consequences.
Our business, financial condition, results of operations, access to capital markets, and borrowing costs may be adversely affected by a major natural disaster or catastrophic event, including civil unrest, geopolitical instability, war, terrorist attacks, pandemics, or other (actual or threatened) public health emergencies such as the COVID-19 outbreak, or other events beyond our control, and measures taken in response thereto.
Acts of terrorism and social unrest, brought about by world political events or otherwise, such as the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, Middle East conflicts, and the Guyana-Venezuela dispute, and their respective regional and global ramifications, have caused instability in the world’s financial and insurance markets in the past and may occur in the future. Such acts could be directed against companies such as ours. In addition, acts of terrorism, piracy, and social unrest could lead to increased volatility in prices for crude oil and natural gas and could affect the markets for drilling services. Insurance premiums could increase and coverage may be unavailable in the future. Government regulations may effectively preclude us from engaging in business activities in certain countries. These regulations could be amended to cover countries where we currently operate or where we may wish to operate in the future.
Our drilling contracts do not generally provide indemnification against loss of capital assets or loss of revenues resulting from acts of terrorism, piracy, or political or social unrest. We have limited insurance for our assets providing coverage for physical damage losses resulting from risks, such as terrorist acts, piracy, vandalism, sabotage, civil unrest, expropriation, and acts of war, and we do not carry insurance for loss of revenues resulting from such risks.
Public health emergencies have created and may in the future create, significant volatility and uncertainty and economic and financial market disruption. Governmental authorities implemented, and may implement in the future, numerous measures attempting to contain and mitigate the effects of pandemics and outbreaks, including travel bans and restrictions, quarantines, shelter in place orders, and shutdowns. Due to travel restrictions and mandatory quarantine measures, we experienced, and may in the future experience again, increased difficulties, delays, and expenses in moving our personnel to and from our operating locations. We may be unable to pass these increased expenses to our customers. Further, we have previously, and may in the future have to, temporarily shut down operations of one or more of our rigs if there is a pandemic, outbreak, or other public health emergency or vacancies of essential positions due to related infections, which could have a material negative impact on our business, financial condition, and results of operations. Additionally, disruptions to the ability of our suppliers, manufacturers, and service providers to supply labor, parts, equipment, or services in the jurisdictions in which we operate, whether as a result of government actions, labor shortages, travel restrictions, the inability to source labor, parts or equipment from affected locations, or other effects related to pandemics, outbreaks or other public health emergencies, have increased our operating costs and the risk of rig downtime and negatively impacted our ability to meet commitments to customers and may do so in the future.
We face risks associated with our participation in certain joint ventures as well as investments in associates.
We have made investments in certain joint ventures and as well as investments in associates. Such investments are often entered into to satisfy local requirements, including local content requirements, in certain jurisdictions and the terms of the investment agreements vary depending on the counterparty and jurisdiction involved. For example, we currently have joint ventures with local owners or partners that were entered into in the ordinary course of business to satisfy local content requirements in certain African countries, countries in the Middle East, Mexico, and other applicable jurisdictions in which we operate. Investments in joint ventures or associates over which we have partial or joint control are subject to the risk that the other owners or partners in such joint venture or associate, who may have different business or investment strategies compared to ours or with whom we may have a disagreement or dispute, may have the ability to block business, financial, or management decisions (such as the decision to distribute dividends or appoint members of management) which may be crucial to the success of our investment in the joint venture or associate, or could otherwise implement initiatives which may be contrary to our interests. In addition, such joint venture owners or partners may be unable, or unwilling, to fulfill their obligations under the relevant agreements (for example, by not contributing working capital or other resources), or may experience financial, operational, or other difficulties that may adversely impact our investment in a particular joint venture or associate. In addition, such joint venture owners or associates may lack sufficient controls and procedures which could expose us to risk. If any of the foregoing were to occur, such occurrence could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We are exposed to risks relating to operations in international locations, including the mobilization and demobilization of our rigs to and from such locations.
We operate in various regions throughout the world that may expose us to political or governmental risks and other uncertainties, including risks of:
•seizure, nationalization, or expropriation of property or equipment;
▪monetary policies, capital controls, government credit rating downgrades and potential defaults, and any potential shutdown of the United States government;
▪foreign currency fluctuations and devaluations;
▪limitations on the ability to repatriate income or capital;
▪complications associated with repairing and replacing equipment in remote locations;
▪repudiation, nullification, modification, or renegotiation of contracts;
▪limitations on insurance coverage, such as war risk coverage, in certain areas;
▪import-export quotas, wage and price controls, and imposition of sanctions, tariffs, or other trade restrictions;
▪operating delays as a result of excess governmental scrutiny or oversight;
▪compliance with and changes in taxation rules or policies;
▪compliance with and changes in regulatory or financial requirements, including local ownership, presence, local immigration, and visa requirements for personnel or labor requirements;
▪complexity involving conflicts of law between jurisdictions in which we operate;
▪other forms of government regulation and economic conditions that are beyond our control and that create operational uncertainty;
▪corruption, payment of bribes to government officials, money laundering, or kleptocracy (i.e., political corruption in which the government seeks personal gain and status at the expense of the governed); and
▪terrorism, piracy, civil, or international disturbances or conflict, such as the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, Middle East conflicts, and the Guyana-Venezuela dispute, and their respective regional and global ramifications.
Further, we operate or have operated in certain less-developed countries with legal and regulatory systems that are not as mature as those in more developed countries, which can lead to greater uncertainty in legal matters and proceedings. Examples of challenges of operating in these countries include:
•ongoing changes in Brazilian laws related to the importation of rigs and equipment that may impose bonding, insurance, or duty-payment requirements;
•ongoing audits, including customs audits;
•procedural requirements for temporary import permits, which may be difficult to obtain; and
•the effect of certain temporary import permit regimes, where the duration of the permit does not coincide with the general term of the drilling contract.
Our ability to do business in a number of jurisdictions is subject to maintaining required licenses and permits and complying with applicable laws and regulations. For example, all of our drilling units are subject to regulatory requirements of the flag state, the country where a drilling unit is registered. The applicable flag state requirements are consistent with international maritime standards. In addition, each of our drilling units must assessed by a classification society, which conducts surveys and reviews for physical and operational compliance with the rules of the classification society and the requirements of the flag state, signifying that such drilling rig has been constructed, maintained, crewed, and operated in accordance with the rules of the classification society and complies with applicable rules and regulations of the flag state (also referred to as being “in-class”). If any drilling unit is deemed or otherwise found to be “out of class”, it will no longer be permitted to operate, certain contractual obligations will be voided, canceled, or withdrawn (e.g., drilling contracts, insurance contracts, etc.), and the unit will be prohibited from entering the waters of most countries.
Jurisdictions where we operate may attempt to increase or impose requirements for our drilling units to operate in such jurisdiction, such as certain local ownership or content requirements or registration under the flag of that jurisdiction, or similar measures, resulting in our inability or being prevented from operating in a country imposing such requirements or measures.
Any such inability to carry on operations in jurisdictions where we operate or desire to operate, or our failure to comply with any other laws and regulations of the countries where we operate, could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations. Some governments favor or effectively require the awarding of drilling contracts to local contractors, require use of a local agent, require partial local ownership, or require foreign contractors to employ citizens of, or purchase supplies from, a particular jurisdiction. In addition, some governments frequently intervene in their economy and occasionally make significant changes in policy and regulations. An example is the Brazilian government's actions to control inflation and other policies and regulations which have often involved, among other measures, changes in interest rates, changes in tax policies, changes in legislation, wage controls, price controls, currency devaluations, capital controls, and limits on imports of goods and services. These practices have and may adversely affect our ability to compete and our results of operations.
In addition, the offshore drilling industry is a global market requiring flexibility for rigs, depending on their technical capability, to relocate and operate in various environments and jurisdictions, moving from one area to another. The mobilization of rigs is expensive and time-consuming and can be impacted by several factors including, but not limited to, governmental regulation and customs practices, availability of tugs and tow vessels, weather, currents, political instability, civil unrest, and military actions, such as the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, Middle East conflicts, and the Guyana-Venezuela dispute, and their respective regional and global ramifications, and rigs may as a result become stranded. Some jurisdictions enforce strict technical requirements on the rigs requiring substantial physical modification to the rigs before they can be utilized. Such modifications may require significant capital expenditures and, as a result, may limit the use of the rigs in those jurisdictions in the future. In addition, mobilization carries the risk of damage to the rig. Failure to mobilize a rig in accordance with the deadlines set by a specific customer contract could result in a loss of compensation, liquidated damages, or the cancellation or termination of the contract. In some cases, we may not be paid for the time that a rig is out
of service during mobilization. In addition, in the hope of securing future contracts, we may choose to mobilize a rig to another geographic market without a customer contract in place. If no customer contracts are obtained, we would be required to absorb these costs. Mobilization and relocating activities could, therefore, have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Operating and maintenance costs of our rigs may be significant and may not correspond to revenue earned.
Our operating expenses and maintenance costs depend on a variety of factors, including crew costs, costs of provisions, equipment, insurance, maintenance and repairs, shipyard costs, supply chain disruptions, and inflation, many of which are beyond our control. Our total operating costs are generally related to the number of drilling rigs in operation and the cost level in each country or region where such drilling rigs are located. Equipment maintenance costs fluctuate depending upon the type of activity that the drilling rig is performing, the age and condition of the equipment, and the timing of the drilling rig special periodic surveys (SPS). While operating revenues may fluctuate as a function of changes in dayrate, costs for operating a rig may not be proportional to the dayrate received and may vary based on a variety of factors, including the scope and length of required rig preparations and the duration of the contractual period over which such expenditures are amortized. Any investments in our rigs may not result in an increased dayrate for or income from such rigs. A disproportionate change in the amount of operating and maintenance costs in comparison to dayrates could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Inflation may adversely affect our operating results.
Inflationary factors such as increases in labor costs, material costs, changes in tariff and sanctions regimes, and overhead costs may adversely affect our operating results and cash flows. We have experienced increases in the cost of labor and materials during 2023 and 2024, and inflationary pressures may continue into 2025. Inflation, including a continuation of inflation at the current rate, may have an adverse effect on our ability to maintain current levels of gross margin and general and administrative expenses as a percentage of total revenue, if our dayrates do not increase sufficiently to cover these increased costs, as well as result in increases in our capital expenditures. Most of our contracts have dayrates that are fixed over the contract term. While some of our long-term contracts contain rate adjustment provisions, they can be based on market fluctuations rather than cost increases. To the extent a drilling contract provides for escalations attributable to inflation in our costs, those adjustments will lag the impact of inflationary pressures and may not reflect the full impact to us of any cost inflation. As drilling contracts with such provisions expire or are terminated, there can be no assurance that future drilling contracts will contain similar provisions, which may reduce our margins in inflationary environments. In addition, inflation is often, and has recently been, accompanied by higher interest rates. Such higher interest rates may affect our ability to enter into future traditional debt financing, as high inflation may result in an increase in the cost to borrow. Future increases in interest rates may negatively impact our cost of capital and ability to access capital markets.
Operational interruptions, maintenance, or repair work may delay commencement of operations or cause our customers to suspend or reduce payment of dayrates until operation of the respective drilling rig is resumed, which may lead to loss of revenue, payment of liquidated damages, termination, or renegotiation of the drilling contract.
If our drilling rigs are idle for reasons that are not related to the ability of the rig to operate, our customers may be entitled to pay a waiting, or standby, rate that is lower than the full operational rate. In addition, if our drilling rigs are taken out of service for maintenance and repair for a period of time that exceeds the scheduled maintenance periods set forth in our drilling contracts, we may not be entitled to payment of full dayrates until the rig is able to work. Several factors could cause operational interruptions, including:
•breakdowns of equipment and other unforeseen engineering problems;
•work stoppages, including labor strikes;
•shortages of material and skilled labor;
•shipyard availability, failures, and difficulties;
•delays in repairs by suppliers;
•surveys by government and maritime authorities;
•periodic classification surveys;
•delays imposed by or resulting from compliance with permits, laws, regulations, or litigation;
•severe weather, strong ocean currents, or harsh operating conditions;
•force majeure events; and
•the occurrence or threat of epidemic or pandemic diseases, or any government response to such occurrence or threat.
Several of these factors have been exacerbated by global supply chain disruptions, including disruptions due to COVID-19, the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, Middle East conflicts, and the Guyana-Venezuela dispute, labor strikes at critical points in a supply chain, and their respective regional and global ramifications. If a delay of commencement of operations, or interruption of operations, exceeds a determined period, our customers may have the right to pay a rate that is significantly lower than the waiting rate for a period of time, may be entitled to liquidated damages, and may have a right to terminate the drilling contracts related to the subject rig. Suspension of drilling contract payments, payment of liquidated damages, prolonged payment of reduced rates, or termination of any drilling contract as a result of an interruption of operations as described herein could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We may have difficulty obtaining or maintaining insurance in the future and our insurance coverage and contractual indemnity rights may not protect us against all the risks and hazards we face.
We do not procure insurance coverage for all of the potential risks and hazards we may face. Furthermore, no assurance can be given that we will be able to obtain insurance against all of the risks and hazards we face or that we will be able to obtain or maintain adequate insurance at rates and with deductibles or retention amounts that we consider commercially reasonable. Some insurance carriers may decide not to offer insurance to companies operating in the oil and gas industry, potentially resulting in less available insurance capacity and/or higher rates. In addition, our insurance carriers may interpret our insurance policies such that they do not cover losses for which we make claims.
Although we maintain insurance in the geographic areas in which we operate, pollution, reservoir damage, and environmental risks generally are not fully insurable. Our insurance policies may not adequately cover our losses or may have exclusions of coverage for some losses. We do not have insurance coverage for all risk exposures. For example, we carry no loss of hire insurance for any rigs in our fleet. In addition, our insurance may not cover losses associated with pandemics. Furthermore, the damage sustained to offshore oil and gas assets in the United States as a result of hurricanes has negatively impacted certain aspects of the energy insurance market, resulting in more restrictive and expensive coverage for US named windstorm perils due to the price or lack of availability of coverage. Accordingly, we have primarily self-insured the rigs in the US Gulf for property damage resulting from named windstorm perils, and only have windstorm third-party liability coverage for all rigs, subject to certain limits. We will continue to monitor the insurance market conditions in the future and may decide not to, or be unable to, purchase named windstorm coverage for some or all of the rigs operating in the US Gulf.
Under our drilling contracts, liability with respect to personnel and property is customarily assigned on a “knock-for-knock” basis, which means that we and our customers assume liability for our respective personnel and property, irrespective of the fault or negligence of the party indemnified. Although our drilling contracts generally provide for indemnification from our customers for certain liabilities, including liabilities resulting from pollution or environmental damage originating below the surface of the water, enforcement of these contractual rights to indemnity may be limited by public policy and other considerations and, in any event, may not adequately cover our losses from such incidents. There can also be no assurance that those parties with contractual obligations to indemnify us will necessarily be in a financial position to do so. During depressed market periods, such as the one in which we recently operated, the contractual indemnity provisions we are able to negotiate in our drilling contracts may require us to assume more risk than we would during normal market periods.
If a significant accident or other loss occurs and is not fully covered by insurance or contractual indemnity, it could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Our failure to adequately protect our sensitive information and operational technology systems and critical data and our service providers’ failure to protect their systems and data could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
Our day-to-day operations increasingly depend on information and operational technology systems that we manage, and other systems that our third parties, such as our service providers, vendors, and equipment providers, manage, including critical systems on our drilling units. These systems are subject to risks associated with growing and evolving cyber incidents or attacks or other disruptions. These risks include, but may not be limited to, human error, power outages, computer and telecommunication failures, natural disasters, fraud or malice, social engineering or phishing attacks, viruses or malware, and other cyberattacks, such as denial-of-service or ransomware attacks. Entities or groups, including
cybercriminals, competitors, and nation state actors, have mounted cyber-attacks on businesses and other organizations solely to disable or disrupt computer systems, disrupt operations, and, in some cases, steal data. In addition, the United States government has issued public warnings that indicate energy assets and companies engaging in significant transactions, such as acquisitions, might be specific targets of cyber security threats. Geopolitical tensions or conflicts, such as the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, and the increased adoption of artificial intelligence technologies, may further heighten the risk of cyber security threats.
Also, many of our non-operational employees work remotely a significant amount of their time, which has created certain operational risks, such as an increased risk of security breaches or other cyber incidents or attacks, loss of data, fraud, and other disruptions as more fully outlined, above. Working remotely has significantly increased the use of technological and online telecommunication services and remote networking, which enable employees to work outside of our corporate infrastructure and, in some cases, use their own personal equipment. This remote work model has resulted in an increased demand for technological resources and may expose us to additional risks of cyber-incidents or attacks, security breaches, loss of data, fraud, and other disruptions as a consequence of more employees accessing sensitive and critical information remotely. Due to the nature of cyber-attacks, breaches to our systems or our service or equipment providers’ systems could go undetected for a prolonged period of time. A breach could also compromise or originate from our customers’, vendors’, or other third-party systems or networks outside of our control. A security breach may result in legal claims or proceedings against us by our shareholders, employees, customers, vendors, and governmental authorities, both in the United States and internationally.
The Company maintains a cyber security program, which includes administrative, technical, and organizational safeguards. A significant cyberattack or incident, either with our systems or a critical third-party systems, could disrupt our operations and result in downtime, loss of revenue, harm to the Company's reputation, or the loss, theft, corruption, or unauthorized release of our critical data or those with whom we do business, as well as result in higher costs to correct and remedy the effects of such incidents, including potential extortion, unforeseen payments associated with ransomware, or ransom demands. If our, or our service or equipment providers’, safeguards maintained for protecting against cyber incidents or attacks prove to be insufficient, and an incident were to occur, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, reputation, and results of operations. Additionally, it may be difficult to determine the best way to investigate, mitigate, contain, and remediate the harm caused by a cyber incident. Such efforts may not be successful, and we may make errors or fail to take necessary actions. It may take considerable time for us to investigate and evaluate the full impact of incidents, particularly for sophisticated attacks. These factors may inhibit our ability to provide prompt, full, and reliable information about the incident to our customers, partners, regulators, and the public. Even though we carry cyber insurance that may provide insurance coverage under certain circumstances, we might suffer losses as a result of a security breach or cyber incident that exceeds the coverage available under our policy or for which we do not have coverage, and we cannot be certain that cyber insurance will continue to be available to us on commercially reasonable terms, or at all.
In addition, Noble is subject to a variety of continuously evolving and developing laws and regulations in the United States and abroad governing, or proposed to govern, cyber security, data privacy and protection, and the unauthorized disclosure of confidential or protected information, including the UK Data Protection Act, the EU General Data Protection Regulation, the Data Protection Law, as revised, of the Cayman Islands, the California Consumer Privacy Act, as amended by the California Privacy Rights Act, the Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act, and other similar legislation in domestic and international jurisdictions, which pose increasingly complex compliance challenges and potentially elevate costs. Any failure to comply with these laws and regulations could result in significant penalties and legal liability. These laws and regulations are continuously evolving and developing, creating significant uncertainty as privacy and data protection laws may be interpreted and applied differently from country to country and may create inconsistent or conflicting requirements. Any failure, or perceived failure, by Noble or third-party service providers to comply with Noble’s privacy or security policies or privacy-related legal obligations, or any compromise of security that results in the unauthorized release or transfer of personal data, may result in loss of revenue, reputational harm, and could be subject to legal or regulatory claims or proceedings, including enforcement actions under data privacy or disclosure regulations, which may result in significant expenditures, fines, or liabilities and could have an adverse effect on our operating results and financial condition.
Upgrades, refurbishment, and repair of rigs are subject to risks, including delays and cost overruns, that could have an adverse impact on our available cash resources and results of operations.
We will continue to make upgrades, refurbishment, and repair expenditures to our fleet from time to time, some of which may be unplanned. In addition, we may reactivate rigs that have been cold or warm stacked and make selective acquisitions of rigs. Our customers may also require certain upgrade projects for our rigs. These projects typically become more time consuming and expensive the older the fleet becomes and are subject to risks of cost overruns or delays inherent in any large construction project as a result of numerous factors, including the following:
▪shortages of equipment, materials, or skilled labor;
▪work stoppages and labor disputes;
▪unscheduled delays in the delivery of ordered materials and equipment;
▪local customs strikes or related work slowdowns that could delay importation of equipment or materials;
▪weather interferences;
▪difficulties in obtaining necessary permits or approvals or in meeting permit or approval conditions;
▪design and engineering problems;
▪inadequate regulatory support infrastructure in the local jurisdiction;
▪latent damages or deterioration to hull, equipment, and machinery in excess of engineering estimates and assumptions;
▪unforeseen increases in the cost of equipment, labor, and raw materials, particularly steel due to inflation or other factors;
▪unanticipated actual or purported change orders;
▪customer acceptance delays;
▪disputes with shipyards and suppliers;
▪delays in, or inability to obtain, access to funding;
▪shipyard availability, failures, and difficulties, including as a result of financial problems of shipyards or their subcontractors; and
▪failure or delay of third-party equipment vendors or service providers.
The failure to complete a rig upgrade, refurbishment, or repair on time, or at all, may result in related loss of revenues, liquidated damages, penalties, or delay, renegotiation, or cancellation of a drilling contract or the recognition of an asset impairment. Additionally, capital expenditures could materially exceed our planned capital expenditures. Moreover, when our rigs are undergoing upgrade, refurbishment, and repair, they may not earn a dayrate during the period they are out of service. If we experience substantial delays and cost overruns in our shipyard projects, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Failure to attract and retain skilled personnel or an increase in personnel costs could adversely affect our operations.
Our employees are vital to our success. We require skilled personnel to operate and provide technical services and support for our drilling units. In the past, during periods of high demand for drilling services and increasing worldwide industry fleet size, shortages of qualified personnel have occurred and competition for personnel has intensified. During periods of reduced demand, there have been, and in the future may be, layoffs of qualified personnel (including offshore personnel), who often find work with competitors or leave the industry. As a result, if market conditions improve following a period of reduced demand and we seek to reactivate warm or cold stacked rigs, move rigs to a new locale, upgrade our working rigs, or purchase additional rigs, we may face shortages of qualified personnel, which would impair our ability to attract qualified personnel for our new or existing drilling units, impair the timeliness and quality of our work, and create upward pressure on personnel costs, any of which could adversely affect our operations.
In addition, our ability to retain our key business leaders is critical. The market for highly skilled workers and leaders in our industry is extremely competitive and we may need to invest significant amounts of cash and equity to attract and retain new employees. We may never realize returns on these investments. In order to help attract, retain, and motivate qualified employees, we use equity-based awards and performance-based cash incentive awards. Sustained declines in our stock price, or lower stock price performance relative to competitors, can reduce the retention value of our equity-based awards,
which can impact the competitiveness of our compensation. The unexpected loss of members of management, qualified personnel, or a significant number of employees due to disease, disability, or death, could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Supplier capacity constraints or shortages in parts or equipment, supplier production disruptions, supplier quality, and sourcing issues or price increases could increase our operating costs, decrease our revenues, and adversely impact our operations.
Our reliance on third-party suppliers, manufacturers, and service providers to secure equipment used in our drilling operations exposes us to volatility in the quality, price, and availability of such items. Certain specialized parts and equipment we use in our operations may be available only from a single or small number of suppliers. During periods of reduced demand, many of these third-party suppliers reduced their inventories of parts and equipment and, in some cases, reduced their production capacity, and may do so in the future. Moreover, the global supply chain has experienced challenges and disruptions in recent years, resulting in shortages of, shipping delays, and increased pricing pressures on, among other things, certain raw materials and labor. If the market for our services improves and we seek to reactivate warm or cold stacked rigs, upgrade our working rigs, or purchase additional rigs, these reductions and global supply chain constraints could make it more difficult for us to find equipment and parts for our rigs. A disruption or delay in the deliveries from such third-party suppliers, capacity constraints, production disruptions, price increases (including those related to inflation, the imposition of tariffs and supply chain disruptions), defects or quality-control issues, recalls, or other decreased availability or servicing of parts and equipment could adversely affect our ability to reactivate rigs, upgrade working rigs, purchase additional rigs, or meet our commitments to customers on a timely basis, adversely impact our operations and revenues by resulting in uncompensated downtime, reduced dayrates, the incurrence of liquidated damages, or other penalties or the cancellation or termination of contracts, or increase our operating costs.
We may experience risks associated with future mergers, acquisitions, dispositions of businesses or assets, or other strategic transactions.
As part of our business strategy, and as evidenced by the Pacific Drilling Merger (as defined herein). the Business Combination with Maersk Drilling and the acquisition of Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc., we have pursued and completed, and may continue to pursue, mergers, acquisitions, dispositions of businesses or assets, or other strategic transactions that we believe will enable us to strengthen or broaden our business. We may be unable to implement this element of our strategy if we cannot identify suitable companies, businesses or assets, reach agreement on potential strategic transactions on acceptable terms, manage the impacts of such transactions on our business, or for other reasons. Moreover, mergers, acquisitions, dispositions, and other strategic transactions involve various risks, including, among other things, (i) difficulties relating to integrating or disposing of a business, including changes to our employee workforce and unanticipated changes in customer, vendor, and other third-party relationships, (ii) failure to integrate operations and internal controls, including those related to financial reporting, disclosure, and cyber security and data protection, (iii) diversion of management’s attention from day-to-day operations, (iv) failure to realize the anticipated benefits of such transactions, such as cost savings and revenue enhancements, (v) potentially substantial transaction costs associated with such transactions, (vi) failure to identify significant issues at the target during the due diligence process, which could result in financial or legal exposure, and (vii) potential impairment resulting from the overpayment for an acquisition.
Future mergers or acquisitions may require us to obtain additional equity or debt financing, which may not be available on attractive terms. Moreover, to the extent a transaction financed by non-equity consideration results in goodwill, it will reduce our tangible net worth, which might have an adverse effect on credit availability.
We may not achieve the intended benefits of the Diamond Transaction, and the Diamond Transaction may disrupt its current plans or operations.
We closed the Diamond Transaction in September 2024. There can be no assurance that we will be able to successfully integrate Diamond assets or otherwise realize the expected benefits of the Diamond Transaction. Difficulties in integrating Diamond into Noble may result in Noble performing differently than expected, in operational challenges or in the failure to realize anticipated synergies and efficiencies in the expected time frame or at all. The anticipated benefits and cost savings of the merger may not be realized fully or at all, may take longer to realize than expected, or could have other adverse effects that Noble does not currently foresee. These anticipated benefits include an assumption, as of the closing date, that Noble is able to realize annual pre-tax cost synergies of approximately $100 million, in which case the Diamond Transaction may not be accretive to earnings per share, may not improve Noble’s balance sheet position, may not enhance Noble’s ability to deliver, and may not generate additional free cash flow.
Following completion of the Diamond Transaction, the combined Company’s success will depend, in part, on Noble’s ability to manage the expansion resulting from the Diamond Transaction, which poses numerous risks and uncertainties. The integration of the two companies may result in material challenges, including the diversion of management’s attention from ongoing business concerns; attracting, motivating, and retaining key management and other employees; retaining or attracting business, customer, and operational relationships; the possibility of faulty assumptions underlying expectations regarding the integration process and associated expenses; consolidating corporate and administrative infrastructures, including integrating enterprise resource planning systems, and eliminating duplicative operations; coordinating geographically separate organizations; unanticipated issues in integrating information technology, communications, and other systems; as well as potential unknown liabilities, unforeseen expenses relating to integration, or delays associated with the acquisition. Additionally, if relationships with customers, distributors, suppliers, vendors, landlords, and other business partners are adversely affected by the Diamond Transaction, or if Noble, following completion of the Diamond Transaction, loses the benefits of certain contracts of Diamond, Noble’s business, prospects, liquidity, and financial performance could suffer. Further, the market price of Ordinary Shares may decline as a result of completing the Diamond Transaction if, among other things, it is unable to achieve the expected benefits and synergies of the Diamond Transaction.
At certain locations where we operate, there is an increased potential for seasonal weather events that could lead to limits or restrictions on our ability to operate, damage to our assets and equipment, liabilities or claims, operational delays for recovery and repair, liability claims, impacts on customer and vendor contracts, regulatory fines and penalties, and uninsured losses, which could adversely affect our business.
Certain areas of the world where we operate, such as the US Gulf, South Atlantic, the North Sea, Southwest Pacific, South China Sea, and Southeast Indian Ocean, experience significant weather events, typically on a seasonal basis, manifesting as an unnamed wind event or of a magnitude that places it in a category of tropical cyclone, hurricane, typhoon, or extratropical cyclone. While such weather events are tracked, forecasted, and reported by recognized meteorological institutions, information upon which we rely when contracting and operating our drilling rigs, are merely projections and the actual course, speed, and/or severity of any one event could ultimately be unexpected and lead to an unanticipated encounter and or impact, exposing our assets and personnel to extreme wind and sea conditions that could result in limits or restrictions on our ability to operate, injuries or loss of life, damage to or a loss of our assets and equipment, liabilities or claims, operational delays for recovery and repair, impacts on customer and vendor contracts, regulatory fines and penalties, and/or uninsured losses, which could adversely affect our business and financial performance. Moreover, a potential result of climate change is more frequent or more severe weather events. To the extent such weather events become more frequent or more severe, the risks associated with severe weather events could intensify.
Failure to effectively and timely respond to the impact of long-term changes in the energy mix could adversely affect our business, results of operations, and cash flows.
Our long-term success depends on our ability to effectively respond to the impact of long-term changes in the energy mix, which could require adapting our fleet and business to potentially changing government requirements, customer preferences, and customer base, as well as engaging with existing and potential customers and suppliers to develop or implement solutions designed to reduce or to decarbonize oil and gas operations or to advance renewable and other alternative energy sources. If the energy mix landscape changes faster than anticipated or in a manner that we do not anticipate, demand for our services could be adversely affected. Furthermore, if we fail to, or are perceived not to, effectively implement a strategy regarding long-term changes in the energy mix, or if investors or financial institutions shift funding away from companies in fossil fuel-related industries, our access to capital or the market for our securities could be negatively impacted. Additionally, if we fail to, or are perceived not to, effectively respond to long-term changes in the energy mix, we may experience diminished reputation or sentiment, an inability to attract and retain talent and/or a loss of customers or vendors.
We rely on third-party suppliers and subcontractors to provide or complete parts, crew, and equipment, as applicable, for our projects and our operations may be adversely affected by the substandard performance or nonperformance of those suppliers or third-party subcontractors due to production disruptions, quality and sourcing issues, price increases, or consolidation of suppliers and sub-contractors as well as equipment breakdowns.
Our reliance on third-parties such as suppliers, manufacturers, subcontractors, and other service providers for equipment, services, and labor used in our drilling operations exposes us to volatility in the quality, price, and availability of such resources. Certain specialized parts, crew, and equipment used in our operations may be available only from a single or a small number of suppliers. A disruption in the deliveries from such third-party suppliers, capacity constraints, production
disruptions, price increases, defects or quality-control issues, recalls, or other decrease in the availability or servicing of parts and equipment could adversely affect our ability to meet our commitments towards our customers, adversely impact operations and revenues by resulting in uncompensated downtime, reduced day rates under the relevant drilling contracts, cancellation or termination of contracts, or increased operating costs. In addition, consolidation of suppliers may limit our ability to obtain supplies and services when needed at an acceptable cost or at all.
Equipment deficiencies or breakdowns, whether due to faulty parts, quality control issues, or inadequate installation, may result in increased maintenance costs and could adversely affect our operations and revenues by resulting in financial downtime. For example, we have a multi-year maintenance project to overhaul jacking gears on certain jackup rigs involving significant costs. If mitigation measures put in place are not effective, it could lead to significant financial downtime, adversely affect our ability to meet our commitments with our customers, potential cancellation or termination of drilling contracts, suspension or termination of operations, regulatory penalties or sanctions, or property, environmental, and other damage claims by customers or other third parties, which may in turn have a material adverse effect on the our business, financial condition, results of operations, and reputation. Subcontractors are used to perform certain services and to provide certain input in areas where we do not have requisite expertise and are engaged on some parts of our projects, but may be used for a majority of the services in respect of new business models. The subcontracting of work exposes us to risks associated with planning interface nonperformance, delayed performance, or substandard performance by our subcontractors. Any inability to hire qualified subcontractors could hinder successful completion of a project. Further, our employees may not have the requisite skills to be able to monitor or control the performance of these subcontractors. We may suffer losses on contracts if the amounts we are required to pay for subcontractor services exceed original estimates. Remedial or mitigating actions, such as requiring contractual obligations from subcontractors that are similar to those we have with our customers, and requesting parent guarantees from subcontractors to cover nonperformance, may not be available or sufficient to mitigate these risks. For example, we have experienced issues with the performance of some of our key suppliers in the past, in particular in relation to delays in the delivery and maintenance of subsea well-control equipment. Such issues could have a negative effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We face risks associated with creating and executing new business models, particularly when such business models involve a risk profile, remuneration, or financial scheme that is different from a conventional drilling contract.
We are exploring, and have in the past, implemented various degrees of innovative business models with customers and partners in order to expand our share of the value chain, while simultaneously creating better outcomes for our customers and long-term resilience of our business through increased customer collaboration, differentiation, and utilization. Although such business model innovation is intended to offer further earnings opportunities, there are risks associated with creating and executing new business models, particularly when such business models involve a risk profile, remuneration, or financial scheme that is different from our conventional drilling contracts.
Two broad categories of business models include:
(i)offering integrated services or integrating new services into offerings to customers as an integrated service provider with the objective of improving efficiencies; and
(ii)exploring alternative financial models focused on risk and reward sharing through, among other things, bonus-malice schemes, deferred payments, fixed pricing, or co-investments, enabling operators to develop fields that would otherwise be economically challenged.
However, forecasting the success of any new business model is inherently uncertain and depends on a number of factors both within and outside our control. Our actual revenue and profit generated from such business models may be significantly greater or less than forecasts. In addition, the efficiencies anticipated from new business models may fail to be realized, the costs may be higher, and the counterparty risk greater than expected. In addition, as we create and execute more new business models and expand into other parts of the value chain, our risk profile may continue to shift. Entering into new business models could have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Regulatory and Legal Risks
Changes in, compliance with, or our failure to comply with certain laws and regulations could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations by adding to our costs, or negatively impact our operations by causing delays or limiting activity.
Our business is affected by public policy and laws and regulations relating to the energy industry in the geographic areas where we do or seek to operate or otherwise have a presence, including laws and regulations relating to the environment (including climate change and greenhouse gas (“GHG”) emissions and regulations that for economic, environmental, social, or other reasons curtail or encumber our ability to operate competitively or negatively impact exploration, development, and production of oil and gas. We may be required to make significant capital expenditures to comply with governmental laws and regulations. Governments in some countries are increasingly active in regulating and controlling the ownership of concessions, the exploration for oil and gas, and other aspects of the oil and gas industries.
There is increasing worldwide attention concerning the issue of climate change and the effect of GHGs, sustainability, and long-term changes in the energy mix. This increased attention has led to and may result in additional environmental laws or regulations that may unfavorably impact our business, or that of our suppliers and our customers. In addition, increasing attention to the risks of climate change has resulted in an increased possibility of litigation or investigations brought by public and private entities against oil and gas companies in connection with their GHG emissions. However, it is not possible at this time to predict the timing and effect of climate related laws and regulations, the adoption of additional GHG legislation, regulations or other measures at the international, federal, state, or local levels.
The modification of existing laws or regulations or the adoption of new laws or regulations that curtail or encumber our ability to operate competitively or negatively impact exploration, development, and production of oil and gas could materially and adversely affect our business by limiting drilling opportunities, increasing our cost of doing business, discouraging our customers from drilling for hydrocarbons, disrupting revenue through permitting or similar delays, or subjecting us to liability. In the United States, the issuance of federal leases or other similar initiatives have been the subject of efforts to reform federal leasing practices and may result in the development of additional restrictions on offshore drilling, limitations on the availability of offshore leases, or restrictions on the ability to obtain required permits, which could have a material adverse impact on our operations by reducing drilling opportunities and the demand for our services.
There have been various legal developments in the UK in 2024, some of which are still evolving (including an increase in and extension of an energy profits levy and changes to environmental impact assessment standards), which have reduced oil and gas exploration and development activities in the North Sea. These developments could reduce the demand for our services.
In addition, efforts have been made and continue to be made in the international community toward the adoption or enhancement of international treaties or protocols related to protecting the environment, reducing climate change, reducing the use of hydrocarbon-based fuel reductions, and encouraging the implementation of GHG emission pledges. Fuel conservation measures, alternative fuel requirements and increasing consumer demand for alternatives to oil and gas could reduce demand for oil and gas. These measures may result in a reduced global reliance on and future demand for oil and gas, which could have a material impact on our business.
Many countries have or appear to be progressing toward enacting varying requirements for GHG monitoring, reporting, and emissions control or reduction, such as the United States which, in November 2024, announced final rules to implement the “Waste Emissions Charge” required under 2022’s Inflation Reduction Act. The Waste Emissions Charge imposes a fee on GHG and waste emissions from certain oil and gas facilities that exceed specified intensity levels and is part of the United States’ Methane Emissions Reduction Plan. While we are subject to certain federal GHG monitoring and reporting requirements, our operations have not been materially impacted by existing international, federal, state, and local climate change initiatives. However, new legislation and regulatory programs to reduce GHG emissions, or increased reporting obligations, could increase our cost of doing business, discourage our customers from drilling for hydrocarbons, or otherwise have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations. Our operations are subject to various laws and regulations in countries in which we operate, including laws and regulations relating to:
▪the environment and the health and safety of personnel;
▪the importing, exporting, equipping, and operation of drilling rigs;
▪finance and currency exchange controls;
▪oil and gas exploration and development;
▪taxation of local and offshore earnings and earnings of expatriate personnel; and
▪use and compensation of local employees, contractors, and suppliers, and involvement of foreign contractors.
Public and governmental scrutiny of the energy industry has resulted in increased regulations being proposed and often implemented. In addition, existing regulations might be revised or reinterpreted, new laws, regulations, and permitting requirements might be adopted or become applicable to us, our rigs, our customers, our vendors, or our service providers, and future changes in laws and regulations could significantly increase our costs and could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations. In addition, we may be required to post additional surety bonds to secure performance, tax, customs, and other obligations relating to our rigs in jurisdictions where bonding requirements are already in effect and in other jurisdictions where we may operate in the future. These requirements would increase the cost of operating in these countries, which could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
From time to time, new rules, regulations, and requirements regarding oil and gas development have been proposed and implemented by BOEM, BSEE, or the United States Congress, as well as other jurisdictions outside the United States, that could materially limit or prohibit, and increase the cost of, offshore drilling. For example, following a years’ long rule making process, both BSEE and BOEM updated and expanded their respective offshore decommissioning financial assurance and bonding requirements. The updated requirements, which were finalized by BSEE in 2023 and BOEM in 2024, are stricter than previous requirements and may increase the costs of operating on the Outer Continental Shelf. BOEM and BSEE could issue new rules relating to well control equipment and operational requirements that fall under their authority in the future. Future actions taken by the United States to limit the availability of new oil and gas leases on the Outer Continental Shelf, or delays imposed by or resulting from compliance with permits, laws, regulations, or litigation would adversely impact the offshore oil and gas industry and impact demand for our services.
We are also subject to increasing regulatory requirements and scrutiny in certain jurisdictions and other countries, including the North Sea. New rules, regulations, and requirements, including the adoption of new safety requirements and policies relating to the approval of drilling permits, restrictions on oil and gas development and production activities in the US Gulf and elsewhere, implementation of safety and environmental management systems, mandatory third-party compliance audits, and the promulgation of numerous Notices to Lessees or similar new regulatory requirements outside of the United States, may impact our operations by causing increased costs, delays, and operational restrictions. If new regulations, policies, operating procedures, and the possibility of increased legal liability resulting from the adoption or amendment of rules and regulations applicable to our operations in the United States or other jurisdictions are viewed by our current or future customers as a significant impairment to expected profitability on projects, then they could discontinue or curtail their offshore operations in the impacted region, thereby, adversely affecting our operations by limiting drilling opportunities or resulting in materially increased costs.
Finally, many scientists have concluded that increasing concentrations of GHGs in the Earth’s atmosphere and climate change may produce significant physical effects on weather conditions, such as increased frequency and severity of droughts, storms, floods, and other climatic events. If any such effects were to occur, they could adversely affect or delay demand for the oil or natural gas produced or cause us to incur significant costs in preparing for or responding to the effects of climatic events themselves. Potential adverse effects could include disruption of our and our customers’ operations, including, for example, damages to our facilities from winds or floods, increases in our costs of operation, or reductions in the efficiency of our operations, impacts on our personnel, supply chain, or distribution chain, as well as potentially increased costs for insurance coverages in the aftermath of such effects. Any of these events could have an adverse effect on our assets and operations.
Increasing attention and expanding requirements relating to environmental, social, and governance matters compounded by the varied and expansive scope of ESG standards, ESG rating criteria, our sustainability and ESG disclosures, and the perception and expectations of the public, may negatively impact our business and financial results.
In recent years, regulators, investors, and the general public have been giving increasing attention to corporate activities that relate to environmental, social, and governance matters. As part of this, ESG has been advanced by advocacy groups in many jurisdictions where they continue to campaign for governmental and private action in connection with ESG criteria and initiatives, including through the investment and voting practices of individual and institutional investors and investment advisers, public company rating agencies, and others in or connected to the investing community. The attention
of advocacy groups and expansion of regulatory requirements regarding ESG performance, commitments, and disclosures, including those relating to climate change and reduction of carbon emissions, is evidenced by initiatives such as the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, as well as by the new strategy adopted by the International Maritime Organization in July 2023 to advance the prevention and control of marine pollution through the reduction of GHG emissions from ships.
Stakeholders and members of the investment community continue to screen and assess companies such as ours for sustainability and ESG performance information measured against the expanded list of ESG metrics advanced by the various ESG standards and ESG ratings sources. Within the ESG context, there continues to be a public and governmental concentration on environmental matters as compared to social and governance matters, with a focus on environment related company practices, performance, and compliance, particularly with respect to data on waste stream management, including discharges, emissions, and reduction commitments regarding carbon dioxide, hydrocarbons, and fluorinated materials in various states of matter. In addition, developments in the law could result in ESG commitments and disclosures being subjected to increased scrutiny. If we are unable to positively manage our ESG performance, effectively administer our ESG tracking and reporting, clearly communicate our ESG strategy and commitments and meet publicly disclosed targets such as our goal to reduce carbon intensity by 20% by 2030 (as defined in our disclosures), we could experience additional costs and financial penalties, increased scrutiny from the investment community, special interest groups, and enforcement authorities, miss or be excluded from business opportunities, have delayed or cancelled projects, experience a reduction in our equity share price, or encounter limitations to our access to financing or capital, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our operations, earnings, cash flows, and financial condition.
Any violation of anti-bribery, anti-corruption, or anti-fraud laws, including the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, the United Kingdom Bribery Act, or other applicable laws and regulations could result in significant expenses, divert management attention, and otherwise have a negative impact on the Company.
In the conduct and operation of our business, particularly in countries with a reputation of illegal activities that include government corruption, bribery, money laundering, and human rights issues, we are subject to the risk that we, our affiliated entities, agents, or service providers, or their respective officers, directors, employees, and agents may take action determined to be in violation of such local laws or laws applicable to us and those acting on our behalf, including the US Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977 (the “FCPA”), the United Kingdom Bribery Act 2010 (the “UK Bribery Act”), the United Kingdom Modern Slavery Act 2015 (the “UK Modern Slavery Act”), and similar laws. Any violation of the FCPA, UK Bribery Act, UK Slavery Act, or local or other applicable laws could result in substantial fines, sanctions, civil, and/or criminal penalties against the Company and implicate members of our senior management or Board, and curtailment of operations in certain jurisdictions and might adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations. In addition, actual or alleged violations could damage our reputation and ability or qualification to do business with specific customers or in certain other jurisdictions. Further, detecting, investigating, and resolving actual or alleged violations is expensive and would consume significant time and attention of our senior management.
Any failure to comply with the complex laws and regulations governing international trade could adversely affect our operations.
The shipment of goods, services, and technology across international borders subjects our business to extensive trade laws and regulations. Import activities are governed by unique customs laws and regulations in each of the countries of operation. Moreover, many countries and governing bodies, including the United States, European Union and the United Kingdom, control the export and re-export of certain goods, services, and technology and impose related export recordkeeping and reporting obligations. Governments and governing bodies may also impose economic sanctions against certain countries, persons and other entities that may restrict or prohibit transactions involving such countries, persons, and entities. US, EU and UK sanctions, in particular, are targeted against certain countries that are heavily involved in the petroleum and petrochemical industries, which includes drilling activities.
The laws and regulations concerning import activity, export recordkeeping and reporting, export control, and economic sanctions are complex and constantly changing. These laws and regulations may be enacted, amended, enforced, or interpreted in a manner materially impacting our operations. Shipments can be delayed and denied export or entry for a variety of reasons, some of which are outside our control and some of which may result from failure to comply with existing legal and regulatory regimes. Shipping delays or denials could cause unscheduled operational downtime. Any failure to comply with applicable legal and regulatory trading obligations could also result in criminal and civil penalties and
sanctions, such as fines, imprisonment, debarment from government contracts, seizure of shipments, and loss of import and export privileges.
Currently, we do not, nor do we intend to, operate in countries that are subject to significant sanctions and embargoes imposed by certain countries or governing bodies such as the US, UK or EU or in countries identified by such bodies as state sponsors of terrorism, such as the Crimean region of the Ukraine, Cuba, Iran, North Korea, and Syria. These sanctions and embargo laws and regulations vary in their application, as they do not all apply to the same covered persons or proscribe the same activities, and such sanctions and embargo laws and regulations may be amended or strengthened over time. There can be no assurance that we will be in compliance in the future, particularly as the scope of certain laws may be unclear and may be subject to changing interpretations. Any such violation could result in fines or other penalties and could result in some investors deciding, or being required, to divest their interest, or not to invest, in us. In addition, certain institutional investors may have investment policies or restrictions that prevent them from holding securities of companies that have contracts with countries identified by certain governing bodies, including the US, UK and EU, as state sponsors of terrorism or with countries that are otherwise subject to sanctions and embargo laws. In addition, our reputation and the market for our securities may be adversely affected if we engage in certain other activities, such as entering into drilling contracts with individuals or entities in countries subject to significant sanctions and embargo laws.
We are, or in the future could be, subject to investigations, litigation and claims that could have an adverse effect on us.
We are, from time to time, involved in various claims, investigations and litigation. These matters may include, among other things, contract disputes, personal injury claims, asbestos, and other toxic tort claims, environmental claims or proceedings, employment matters, issues related to employee or representative conduct, governmental claims for taxes, duties, customs or other regulatory findings and litigation that arises in the ordinary course of our business. Although we intend to defend or pursue such matters vigorously, we cannot predict with certainty the outcome or effect of any claim, investigation or other litigation matter, and there can be no assurance as to the ultimate outcome of any claim, investigation or litigation. Investigations, claims and litigation may have an adverse effect on us because of potential negative outcomes, legal fees, the allocation of management’s time and attention, and other factors.
We could also face increased climate-related litigation with respect to our operations both in the US and around the world. Governmental and other entities in various US states, such as California and New York, have filed lawsuits against energy companies. These suits allege damages as a result of climate change, and the plaintiffs are seeking unspecified damages and abatement under various tort theories. Similar lawsuits may be filed in other jurisdictions both in the US and globally. Though we are not currently a party to any such lawsuit, these suits present uncertainty regarding the extent to which companies who are not producing oil or gas, but who are engaged in such production, such as offshore drillers, face an increased risk of liability stemming from climate change, which risk would also adversely impact the oil and gas industry and impact demand for our services.
Financial, Tax, and Governance Risks
We may record impairment charges on property and equipment, including rigs and related capital spares.
We evaluate the impairment of property and equipment, which include rigs and related capital spares, whenever events or changes in circumstances, including a decision to cold stack, retire, or sell rigs, indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. An impairment loss on our property and equipment may exist when the estimated undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use of the asset and its eventual disposition are less than its carrying amount. Any impairment loss recognized represents the excess of the asset’s carrying value over the estimated fair value. As part of this analysis, we make assumptions and estimates regarding future market conditions. To the extent actual results do not meet our estimated assumptions, for a given rig or piece of equipment, we may take an impairment loss in the future. In addition, we may also take an impairment loss on capital spares and other capital equipment when we deem the value of those items has declined due to factors like obsolescence, deterioration or damage. Based upon our impairment analyses for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, we did not record any impairment charges. There can be no assurance that we will not have to take additional impairment charges in the future if depressed market conditions return, or that we will be able to return cold stacked rigs to service in the time frame and at the reactivation costs or at the dayrates that we projected. It is reasonably possible that the estimate of undiscounted cash flows may change in the near term, resulting in the need to write down the affected assets to their corresponding estimated fair values.
The 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement, the indenture for the 2030 Notes, and the indenture for the Diamond Second Lien Notes each contain various restrictive covenants limiting the discretion of our management in operating our business.
The 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement contains various restrictive covenants that may limit our management’s discretion in certain respects. In particular, the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement limits the ability of Noble Finance II LLC (“Noble Finance II”) and the ability of its restricted subsidiaries to, among other things and subject to certain limitations and exceptions, (i) incur, assume or guarantee additional indebtedness, (ii) pay dividends or distributions on capital stock or redeem or repurchase capital stock, (iii) make investments, (iv) repay, redeem, or amend certain indebtedness, (v) sell stock of its subsidiaries, (vi) transfer or sell assets, (vii) create, incur, or assume liens, (viii) enter into transactions with certain affiliates, (ix) merge or consolidate with or into any other person or undergo certain other fundamental changes, and (x) enter into certain burdensome agreements. In addition, the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement obligates Noble Finance II LLC and its restricted subsidiaries to comply with certain financial maintenance covenants and, under certain conditions, to make mandatory prepayments and reduce the amount of credit available under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility, all as described in Part II, Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations — Liquidity and Capital Resources — Amended and Restated Senior Secured Revolving Credit Agreement.” Such mandatory prepayments and commitment reductions may affect cash available for use in the Company’s business. Our failure to comply with these covenants could result in an event of default which, if not cured or waived, could result in all obligations under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility to be declared due and payable immediately and all commitments thereunder to be terminated.
The 8.000% Senior Notes due 2030 (the “2030 Notes”) are fully and unconditionally guaranteed, jointly and severally, by the direct and indirect subsidiaries of Noble Finance II that are Credit Parties (as defined herein) under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility. The ability of Noble Finance II to comply with the covenants and restrictions contained in the indenture for the 2030 Notes may be affected by events beyond its control. If market or other economic conditions deteriorate, our ability to comply with these covenants and restrictions may be impaired. A failure to comply with the covenants, ratios, or tests in the indenture, if not cured or waived, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations. Our existing and future indebtedness may have cross-default and cross-acceleration provisions. Upon the triggering of any such provision, the relevant creditor may:
▪not be required to lend any additional amounts to Noble Finance II;
▪elect to declare all borrowings outstanding due to them, together with accrued and unpaid interest and fees, to be due and payable;
▪have the ability to require Noble Finance II to apply all of its available cash to repay such borrowings; and/or
▪prevent Noble Finance II from making debt service payments under its other agreements, any of which could result in an event of default under the 2030 Notes.
If any of our existing indebtedness were to be accelerated, there can be no assurance that we would have, or be able to obtain, sufficient funds to repay such indebtedness in full. Even if new financing were available, it may be on terms that are less attractive than the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility or the 2030 Notes or it may not be on terms that are acceptable to us.
In addition, the Diamond 8.500% Senior Secured Second Lien Notes due October 2030 (the “Diamond Second Lien Notes”) are issued by Diamond Foreign Asset Company and Diamond Finance, LLC (collectively, the “Issuers”) and are fully and unconditionally guaranteed, jointly and severally, on a senior secured basis by Noble Offshore Drilling, Inc. (formerly known as Dolphin Merger Sub 2, Inc. and as successor by merger with Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc.) (“NODI”), and each of its existing restricted subsidiaries (other than the Issuers) and by certain of NODI’s future restricted subsidiaries.
The indenture governing the Diamond Second Lien Notes contains covenants that, among other things, restrict NODI’s ability and the ability of certain of its subsidiaries to: (i) incur additional debt and issue certain preferred stock; (ii) incur or create liens; (iii) make certain dividends, distributions, investments, and other restricted payments; (iv) sell or otherwise dispose of certain assets; (v) engage in certain transactions with affiliates; and (vi) merge, consolidate, amalgamate, or sell, transfer, lease, or otherwise dispose of all or substantially all of the assets of NODI and such subsidiaries. A failure to comply with the covenants, ratios, or tests in the indenture, if not cured or waived, could result in the outstanding principal amount, together with accrued and unpaid interest and fees, becoming immediately due and payable and could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
A loss of a major tax dispute or a successful tax challenge to our operating structure, intercompany pricing policies, or the taxable presence of our subsidiaries in certain countries could result in a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Tax returns that we file and/or tax payments that we make will be subject to review and examination. If any tax authority successfully challenges our operational structure, intercompany pricing policies, the taxable presence of our subsidiaries in certain countries, or other material tax positions, if the terms of certain tax treaties are interpreted in a manner that is adverse to our structure, or if we lose a material tax dispute in any country, our effective tax rate on our worldwide earnings, income tax expense, and/or operating expense could increase substantially and result in a material adverse effect on our financial condition. In addition, Noble may have exposures with respect to the tax audits and tax disputes of certain third parties which were under a joint taxation contribution arrangement with certain subsidiaries that Noble acquired in the Business Combination.
Our consolidated effective income tax rate may vary substantially from one reporting period to another.
We cannot provide any assurances as to what our consolidated effective income tax rate will be because of, among other matters, uncertainty regarding the nature and extent of our business activities in any particular jurisdiction in the future and the tax laws of such jurisdictions, as well as potential changes in tax laws, regulations, or treaties or the interpretation or enforcement thereof, changes in the administrative practices and precedents of tax authorities or any reclassification or other matter, such as changes in applicable accounting rules, that increases the amounts we have provided for income taxes or deferred tax assets and liabilities in our consolidated financial statements. For example, certain countries within which we operate or own substantial assets have enacted changes to their tax laws in response to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development’s (“OECD”) ongoing Base Erosion and Profit Shifting initiatives and these and other countries may enact changes to their tax laws or practices in the future (prospectively or retroactively), which may have a material adverse effect on our financial position, operating results and/or cash flows.
In addition, as a result of frequent changes in the taxing jurisdictions in which our drilling rigs are operated and/or owned, changes in the overall level of our income and changes in tax laws, our consolidated effective income tax rate may vary substantially from one reporting period to another. Income tax rates imposed in the tax jurisdictions in which our subsidiaries conduct operations vary, as does the tax base to which the rates are applied. In some cases, tax rates may be applicable to gross revenues, statutory or negotiated deemed profits, or other bases utilized under local tax laws, rather than to net income. Our drilling rigs frequently move from one taxing jurisdiction to another to perform contract drilling services. In some instances, the movement of drilling rigs among taxing jurisdictions will involve the transfer of ownership of the drilling rigs among our subsidiaries. If we are unable to mitigate the negative consequences of any change in law, audit, business activity, or other matter, this could cause our consolidated effective income tax rate to increase and cause a material adverse effect on our financial position, operating results, and/or cash flows.
Fluctuations in exchange rates and nonconvertibility of currencies could result in losses to us.
We may experience currency exchange losses when revenues are received or expenses are paid in nonconvertible currencies, when we do not hedge an exposure to a foreign currency, when the result of a hedge is a loss or if any counterparty to our hedge were to experience financial difficulties. We may also incur losses as a result of an inability to collect revenues due to a shortage of convertible currency available to the country of operation, controls over currency exchange or controls over the repatriation of income or capital.
Certain shareholders own a significant portion of our outstanding equity securities, and their interests may not always coincide with the interests of other holders of the Ordinary Shares.
A large percentage of the Ordinary Shares are held by a relatively small number of investors. As a result, these investors could have significant influence over all matters presented to our shareholders for approval, including election and removal of our directors, change in control transactions, and the outcome of all actions requiring a majority shareholder approval.
The interests of these investors may not always coincide with the interests of the other holders of the Ordinary Shares, and the concentration of control in these investors may limit other shareholders’ ability to influence corporate matters. The concentration of ownership and voting power of these investors may also delay, defer, or even prevent an acquisition by a third party or other change of control of our Company, and may make some transactions more difficult or impossible without their support, even if such events are in the best interests of our other shareholders. In addition, the concentration of voting power may adversely affect the trading price of the Ordinary Shares. A large percentage of the Ordinary Shares are held by a relatively small number of investors.
Holders of the Ordinary Shares may not receive dividends on their Ordinary Shares, and we may decrease or suspend our dividend on, or our repurchases of, our Ordinary Shares.
Holders of the Ordinary Shares are entitled to receive only such dividends as our Board of Directors may declare and pay out of funds legally available for such payments. Such may be paid only out of Noble’s “distributable reserves” as determined by reference to relevant statutory accounts in accordance with English law, and additionally as permitted under our credit facilities and other financing arrangements. Therefore, Noble is not permitted to pay dividends out of share capital, which includes share premium. We are not required to pay a dividend or effect share repurchases, and any determination to pay dividends and other distributions in cash, stock, or property, or to effect share repurchases by us in the future, including determinations as to the amount of any such dividend, distribution, or repurchase, will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors. Our payment of dividends and share repurchases may vary from historical practices or our stated expectations. The timing and amount, if any, of dividends and share repurchases is discretionary and will be dependent on many factors, including our expectations regarding our ability to generate sufficient cash flows, and our results of operations, financial condition, cash requirements, future business prospects, capital requirements, contractual and indenture restrictions, and other factors deemed relevant by our Board of Directors.
We are a holding company, and we are dependent upon cash flow from subsidiaries, joint ventures, and associates to meet our obligations.
We currently conduct our operations through our subsidiaries, including joint ventures and associates, and our operating income and cash flow are generated by such entities. As a result, cash we obtain from our subsidiaries, joint ventures, and associates is the principal source of funds necessary to meet our debt service obligations. Unless they are guarantors of our indebtedness, such entities do not have any obligation to pay amounts due on our indebtedness or to make funds available for that purpose. Contractual provisions or laws, as well as such entities’ financial condition, debt covenants, and operating requirements, may also limit our ability to obtain the cash that we require to pay our debt service obligations. Applicable tax laws may also subject such payments to us by such entities to further taxation.
Future sales or the availability for sale of substantial amounts of the Ordinary Shares or the exercise of warrants issued pursuant to the Plan would have a dilutive effect to shareholders of the Company and the perception that these sales may occur, could adversely affect the trading price of the Ordinary Shares, and could impair our ability to raise capital through future sales of equity securities.
As of February 14, 2025, there were 159,191,313 Ordinary Shares outstanding. In addition, as of February 14, 2025, 886,427 Tranche 1 Warrants, 942,606 Tranche 2 Warrants, and 2,773,456 Tranche 3 Warrants were outstanding and exercisable. We also have 5,255,631 Ordinary Shares authorized and reserved for issuance pursuant to equity awards under the Noble Corporation plc 2022 Long-Term Incentive Plan.
A large percentage of the Ordinary Shares (or warrants exercisable for Ordinary Shares) are held by a relatively small number of investors.
Sales of a substantial number of the Ordinary Shares in the public markets, exercise of a substantial number of warrants, or even the perception that these sales or exercises might occur, could impair our ability to raise capital for our operations through a future sale of, or pay for acquisitions using, our equity securities.
As of February 14, 2025, the Mandatory Exercise Condition (as defined in the applicable warrant agreement) for the Tranche 1 Warrants and the Tranche 2 Warrants had been satisfied. Between January 1, 2024, and December 31, 2024, an aggregate of 245,210 Ordinary Shares were issued pursuant to exercise of Tranche 1 Warrants, Tranche 2 Warrants, and Tranche 3 Warrants. These exercises, and continued exercises of these warrants into Ordinary Shares pursuant to the terms of the outstanding warrants, will have a dilutive effect to the holdings of our existing shareholders.
We used Ordinary Shares for part of the consideration in the Diamond Transaction and may issue Ordinary Shares or other securities from time to time as consideration for future acquisitions and investments. If any such acquisition or investment is significant, the number of Ordinary Shares, or the number or aggregate principal amount, as the case may be, of other securities that we may issue may in turn be substantial. We may also grant registration rights covering those Ordinary Shares or other securities in connection with any such acquisitions and investments. For example, in connection with the Business Combination with Maersk Drilling, we issued a significant number of Ordinary Shares as consideration and granted registration rights to a recipient thereof, pursuant to which we have filed a registration statement with the SEC to facilitate potential future sales of such Ordinary Shares by them.
We cannot predict the effect that future sales of Ordinary Shares will have on the price at which the Ordinary Shares trade or the size of future issuances of Ordinary Shares or the effect, if any, that future issuances will have on the market price of the Ordinary Shares. Sales of substantial amounts of the Ordinary Shares, or the perception that such sales could occur, may adversely affect the trading price of the Ordinary Shares.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments.
None.
Item 1C. Cyber Security.
Risk Management and Strategy
Cyber security risk management at Noble, along with all enterprise risks, is part of the Company’s Enterprise Risk Management Program and risks from cyber security threats are assessed, identified, and managed by our Information Security Team. The Information Security Team reports to the Chief Information Officer (“CIO”). The Information Security Team is composed of the Director of Information Security, managers, and security analysts.
The Information Security Team is responsible for all of Noble’s cyber security-related activities such as advising on governance requirements, setting cyber security policies, standards, and procedures, reporting, determining current risk appetite, setting security posture, evaluating security maturity, and ensuring compliance to cyber security frameworks. The team monitors both internal and external threats, potential compromising internet-based attacks, phishing activities, and aims to adapt with protective measures.
The Director of Information Security and information security managers carry broad manager level cyber security certifications, and the technical teams carry relevant specific technical certifications related to both Information Technology and Operational Technology security.
Noble’s cyber security program encompasses mandatory cyber training, awareness, phishing exercises, and cyber security incident response plan testing to assist with our cyber security risk management process and ensure various applicable implemented cyber controls are working as intended.
Noble works with various third-party partners to help execute and advise on cyber security and evaluate maturity assessments as needed.
Noble has a process of monitoring all third parties with direct access into the Noble network via various implemented security tools that act as both detective and preventive controls. All third parties with such direct access are also monitored via procurement processes and are subject to specific legal terms and conditions. Noble also engages with various third-party partners in order to share intelligence regarding external threats. For any cyber incidents, Noble may engage applicable third-party partners for forensic purposes.
Noble also engages with various cyber security service providers, such as Crowdstrike, Fortinet, NTT, and Microsoft, which share applicable reports with Noble.
In the last fiscal year, Noble has not identified any known cyber security threats, incidents, or exposures that have materially affected Noble’s business strategy, results of operations, or financial condition, but Noble faces certain ongoing cyber security risks that, if realized, could materially and adversely affect Noble. This does not guarantee that future incidents or threats will not have a material impact or that we are not currently the subject of an undetected incident or threat that may have such an impact. Potential cyber security risks to Noble are shared in Part I, Item 1A, “Risk Factors,” which should be read in conjunction with the foregoing information.
Governance
The Audit Committee of the Board provides oversight of the Company’s cyber security program. The Information Security Team keeps management informed about initiatives, threats, incidents, training, and best practices on an on-going basis via circulated memos or meetings.
In addition to reporting through the Audit Committee and Enterprise Risk Management Program, the Board may periodically include cyber security as an independent agenda item and engages with the CIO and Information Security Team as well as external experts on cyber security matters.
The Information Security Team advises the CIO via cyber reports on prevention, detection, mitigation, and remediation of cyber security incidents. The CIO is responsible for the Information Security Team risk strategy, assessment, exceptions, risk acceptance, and management of the Company’s material risks from cyber security risk appetites. Ongoing assessments cover applicable information technology and operations technology systems, applications, and software used to support Noble’s corporate and rig operations. The outcome of these various assessments influences the IT risk appetite and risk identification, and acceptance is discussed and shared with the CIO, executive management, the Audit Committee, and the Board of Directors.
The CIO has extensive cyber security knowledge and skills gained from over ten years of relevant work experience at Noble including two years as Deputy CIO as well as Director, IT prior to the merger with Maersk Drilling with responsibility for cyber security. The CIO has multiple years of experience managing OT data and secure remote access for data management on and offshore. Prior to serving as Director, IT the CIO was the Manager, Business Systems responsible for application management and Enterprise Architecture. The Information Security Team advises the CIO on prevention, detection, mitigation, and remediation of cyber security incidents.
Item 2. Properties.
The description of our rig fleet included under “Part I, Item 1, Business” is incorporated by reference herein. We lease office space in Houston, Texas, where our corporate headquarters are located. In addition, we own and lease operational, administrative, and marketing offices, as well as other sites used primarily for operations, storage, and maintenance and repairs for drilling rigs and equipment in various locations worldwide.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings.
As of December 31, 2024, we were involved in a number of lawsuits, regulatory matters, disputes, and claims, asserted and unasserted, all of which have arisen in the ordinary course of our business and for which we do not expect the liability, if any, to have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position, results of operations, or cash flows. We cannot predict with certainty the outcome or effect of any of the matters referred to above or of any such other pending or threatened litigation or legal proceedings. We can provide no assurance that our beliefs or expectations as to the outcome or effect of any lawsuit or claim or dispute will prove correct and the eventual outcome of these matters could materially differ from management’s current estimates.
Additional information regarding legal proceedings is presented in “Note 12 — Commitments and Contingencies” to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures.
Not applicable.
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters, and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities.
Market for Shares and Related Shareholder Information
Our shares are listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol “NE”.
On February 14, 2025, there were 159,191,313 Ordinary Shares outstanding held by 8 shareholder accounts of record. This figure does not include an estimate of the indeterminate number of beneficial holders whose shares may be held of record by brokerage firms and clearing agencies.
Exercises of Warrants
During the three months ended December 31, 2024:
•19,787 Ordinary Shares were issued to holders of our Tranche 1 Warrants pursuant to exercises of 36,920 Tranche 1 Warrants; and
•12,660 Ordinary Shares were issued to holders of our Tranche 2 Warrants pursuant to exercises of 23,449 Tranche 2 Warrants; and
•24 Ordinary Shares were issued to holders of our Tranche 2 Warrants pursuant to exercises of 38 Tranche 2 Warrants; and
•4,189 Ordinary Shares were issued to holders of Diamond Warrants pursuant to exercises of 18,162 Diamond Warrants.
Such Ordinary Shares, as the case may be, were issued pursuant to the exemptions from the registration requirements of the Securities Act under Section 4(a)(2) under the Securities Act or Section 1145 of the Bankruptcy Code, as the case may be. For more information on the terms of exercise and other features of the warrants, see “Note 7 — Equity” to our consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Share Repurchases
The following table presents information about our purchases of equity securities for the three months ended December 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Period | | Total Number of Shares Purchased (1) | | Average Price Paid per Share | | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of a Publicly Announced Plan or Program (1) | | Approximate Dollar Value of Shares that may yet be Purchased Under a Plan or Program (1) |
| October 1 - 31, 2024 | | — | | | $ | — | | | — | | | $ | 440,174,211 | |
| November 1 - 30, 2024 | | 1,081,487 | | | $ | 33.85 | | | 1,081,487 | | | $ | 403,539,117 | |
| December 1- 31, 2024 | | 423,398 | | | $ | 31.52 | | | 423,398 | | | $ | 390,184,935 | |
| Total | | 1,504,885 | | | | | 1,504,885 | | | $ | 390,184,935 | |
(1)Subject to restrictions under applicable law discussed in “Note 7 — Equity” to our consolidated financial statements, we announced a share repurchase plan on November 2, 2022, to purchase up to $400 million of outstanding Ordinary Shares or Warrants. On October 22, 2024, Noble’s Board of Directors authorized an increased share repurchase authorization of up to an additional $400 million. The authorization does not have a fixed expiration and may be modified, suspended, or discontinued at any time. The program does not obligate us to acquire any particular amount of shares. All repurchased shares were subsequently cancelled.
Dividends
The declaration and payment of dividends require the authorization of the Board of Directors. Such may be paid only out of Noble’s “distributable reserves” as determined by reference to relevant statutory accounts in accordance with English law. Therefore, Noble is not permitted to pay dividends out of share capital, which includes share premium. The payment of future dividends will depend on our results of operations, financial condition, cash requirements, future business prospects, contractual and indenture restrictions, and other factors deemed relevant by our Board of Directors.
Stock Performance Graph
The chart below presents a comparison of the cumulative total returns, assuming $100 was invested at the beginning of the period for Noble, the Standard & Poor's 500 Index (“S&P 500”), the PHLX Oil Service Sector Index (“OSX”), and the Dow Jones US Oil Equipment and Services. Total return assumes the reinvestment of dividends, if any, in the security on the ex-dividend date. This graph depicts the past performance for the period from June 9, 2021, the day our Noble Cayman Shares began trading on the NYSE, through December 31, 2024, and in no way should be used to predict future share performance. In connection with the Business Combination with Maersk Drilling, prior to the opening of trading on September 30, 2022, the Noble Cayman Shares were suspended from trading on the NYSE. The Ordinary Shares began regular-way trading on the NYSE using Noble Cayman’s trading history under the ticker symbol “NE” immediately following the suspension of trading of the Noble Cayman Shares.
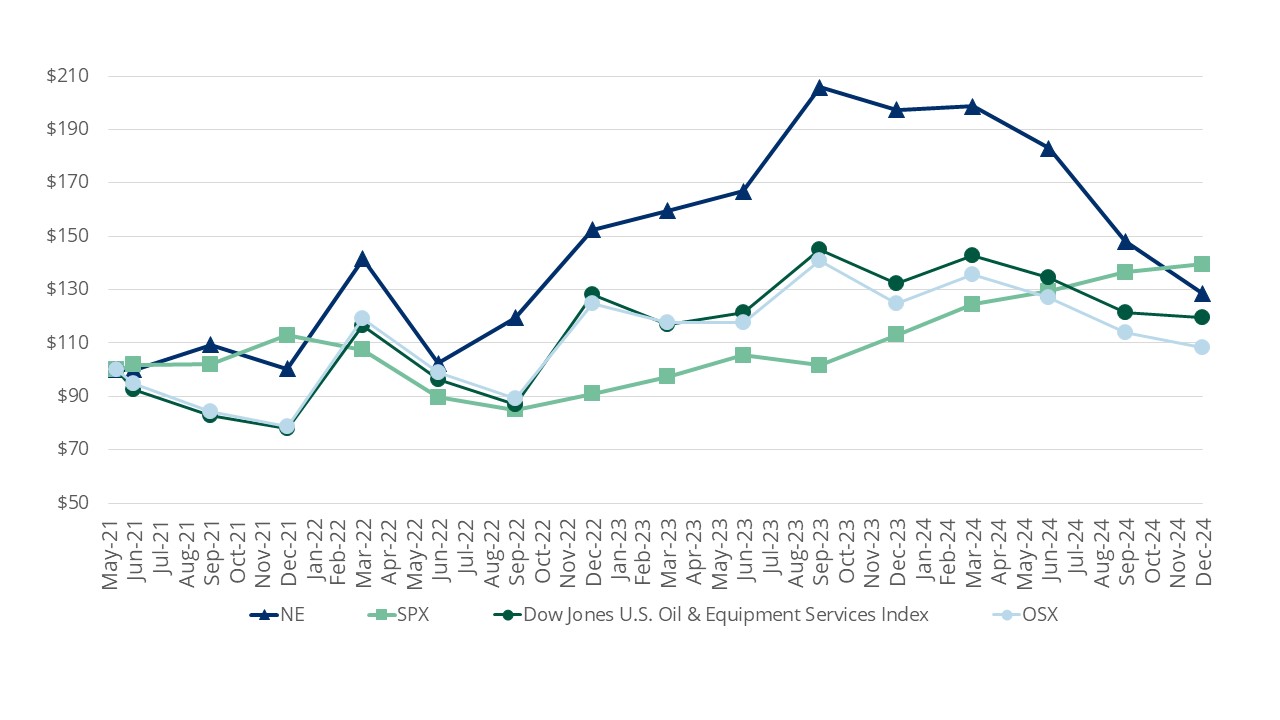
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Indexed Returns |
| Company / Index | | June 9,
2021 | | December 31,
2021 | | December 31,
2022 | | December 31,
2023 | | December 31,
2024 | | | | |
| Noble Corporation plc | | $ | 100.00 | | | $ | 100.24 | | | $ | 152.36 | | | $ | 197.37 | | | $ | 128.69 | | | | | |
| S&P 500 Index | | 100.00 | | | 112.95 | | | 90.99 | | | 113.04 | | | 139.39 | | | | | |
| Dow Jones US Oil Equipment & Services Index | | 100.00 | | | 77.84 | | | 127.98 | | | 132.25 | | | 119.55 | | | | | |
| OSX Index | | 100.00 | | | 78.50 | | | 124.90 | | | 125.00 | | | 108.16 | | | | | |
The above graph and related information shall not be deemed “soliciting material” or to be “filed” with the SEC, nor shall such information be incorporated by reference into any future filing under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act, except to the extent that we specifically incorporate it by reference into such filing.
Item 6. [Reserved].
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
The following discussion is intended to assist you in understanding our financial position at December 31, 2024 and 2023, and our results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022.
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and related notes contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024, filed by Noble.
Executive Overview
Noble is a leading offshore drilling contractor for the oil and gas industry. We provide contract drilling services to the international oil and gas industry with our global fleet of mobile offshore drilling units. Our business strategy is centered around providing efficient, reliable, and safe offshore drilling services to our customers. We have one of the youngest and highest specification fleets of global scale in the industry, with diversification across asset classes, geographic regions, and customers. The Company has a track record of industry-leading utilization coupled with a commitment to best-in-class safety performance and customer satisfaction. We strive to be the leader in industry innovation and a first-mover in sustainability.
Our fleet consists predominately of technologically advanced units, equipped with sophisticated systems and components prepared to execute our customers’ complicated offshore drilling programs safely and with greater efficiency. We are primarily focused on the ultra-deepwater market and the harsh and ultra-harsh environment jackup markets, which typically are more technically challenging markets to operate in.
We emphasize safe operations, environmental stewardship, and superior performance through a structured management system, the employment of qualified and well-trained crews and onshore support staff, the care of our surroundings and the neighboring communities where we operate, and other activities advancing our environmental sustainability, social responsibility, and good governance. We also manage rig operating costs through the implementation and continuous improvement of innovative systems and processes, which includes the use of data analytics and predictive maintenance technology.
As of the filing date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, our fleet of 40 drilling rigs consists of 27 floaters and 13 jackups strategically deployed worldwide. We typically employ each drilling unit under an individual contract, and many contracts are awarded based upon a competitive bidding process.
We report our contract drilling operations as a single reportable segment, Contract Drilling Services, which reflects how we manage our business. The mobile offshore drilling units comprising our offshore rig fleet operate in a global market for contract drilling services and are often redeployed to different regions due to changing demands of our customers, which consist primarily of large, integrated, independent, and government-owned or controlled oil and gas companies throughout the world.
For the year ended December 31, 2024, our financial and operating results include:
•operating revenues totaling $3.1 billion;
•net income of $448.4 million or $2.96 per diluted share;
•net cash provided by operating activities totaling $655.5 million;
•no funds drawn down on the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility as of December 31, 2024, and
•a year end cash balance of $247.3 million.
Demand for our services is driven by the offshore exploration and development programs of oil and gas operators, which in turn are influenced by many factors. Those factors include, but are not limited to, the price and price stability of oil and gas, the relative cost and carbon footprint of offshore resources within each operator’s broader energy portfolio, global macroeconomic conditions, world energy demand, the operator’s strategy toward renewable energy sources, environmental considerations, and governmental policies.
Outlook
In recent years, oil prices have generally remained at levels that are supportive of offshore exploration and development activity and global rig demand recovered to eclipse pre-pandemic levels, albeit with some moderation over the past 12 months. Current demand and utilization levels are supported by the combination of resilient commodity prices, heightened focus on energy security, the capital intensity of depletion replacement, and relative attractiveness of offshore plays with respect to both cost and carbon emissions. The increase in global rig demand since 2021 has had a positive impact on dayrates for most rig classes although dayrates have generally plateaued more recently.
The global rig supply has come down from historic highs as Noble and other offshore drilling contractors have retired less capable and idle assets. Concurrently, the incoming supply of newbuild offshore drilling rigs has diminished materially, with several newbuild rigs stranded in shipyards. However, we expect many of these stranded newbuild rigs may continue to make their way into the global market over the next few years.
Although the market outlook in our business varies by geographical region and water depth, we remain encouraged by the long-term outlook in the ultra-deepwater floater market. However, within this ultra-deepwater market, our customers continue to focus on our highest specification floaters, which represents the majority of our floater fleet. Assuming current market fundamentals, continued customer prioritization towards these highest specification floaters is likely to result in lower utilization for our lower specification drillships and our semi-submersibles. Demand for midwater semisubmersibles is primarily driven by brownfield activity in mature basins, especially in Northwest Europe, South America, and the Asia Pacific regions, where a generally stable level of baseload demand is supported by infield drilling and plug and abandonment requirements. Despite some recent contract suspensions in select jackup markets, we have also observed an overall demand increase in the global jackup market since 2020. While we remain encouraged about overall long-term rig demand, to the extent global macroeconomic concerns become more prevalent and produce downward pressure on oil and gas prices, we could experience downward pressure on overall rig demand for both floaters and jackups.
Returning to the broader offshore drilling market, while there are a number of multi-year contracts out for tender, the overall market remains characterized by generally shorter-term contracts. This leads to an increased number of rig contract start-ups, both with different customers and among different regions, which may require incremental resources and costs. Additionally, this has resulted in, and is likely to continue to result in, lower overall effective utilization for our fleet driven by more idle time between contracts.
The energy transition from hydrocarbons to renewables poses a challenge to the oil and gas sector and our market. Energy rebalancing trends have accelerated in recent years as evidenced by promulgated or proposed government policies and commitments by many of our customers to further invest in sustainable energy sources. Our industry could be further challenged as resource holders and policy makers continue to evaluate and calibrate strategies and capital flows to address global energy needs. Ultimately, however, there continues to be a global dependence on products made from hydrocarbons and on the combustion of hydrocarbons to provide reliable and affordable energy. Low-cost and low-emission barrels are expected to be the most attractive conventional source to meet energy needs both currently and in the future. Global energy demand is predicted to increase over the coming decades, and we expect that offshore oil and gas will continue to play an important and lasting role in meeting this demand.
We expect inflationary pressures to persist, which has led, and may continue to lead, to increased costs of services. Additionally, we expect supply chain disruptions to continue, and potentially accelerate, as geopolitical crises, such as the Russia-Ukraine conflict, Middle East conflicts, the Guyana-Venezuela dispute, and their respective regional and global ramifications, may negatively impact our ability to conduct our day-to-day operations. Additionally, the impact of new or increased tariffs or trade wars could have an inflationary impact on the costs of certain products and services as well as potentially contribute to further supply chain disruptions.
Contract Drilling Services Backlog
We maintain a backlog of commitments for contract drilling services. Our contract drilling services backlog reflects estimated future revenues attributable to signed drilling contracts. While backlog did not include any letters of intent as of December 31, 2024, in the past we have included in backlog certain letters of intent that we expect to result in binding drilling contracts. As of December 31, 2024, contract drilling services backlog totaled approximately $6.1 billion.
We calculate backlog for any given unit and period by multiplying the full contractual operating dayrate for such unit by the number of days remaining in the period, and include certain assumptions based on the terms of certain contractual arrangements, discussed in the notes to the table below. The reported contract drilling services backlog does not include amounts representing revenues for mobilization, demobilization, and contract preparation, which are not expected to be
significant to our contract drilling services revenues, amounts constituting reimbursables from customers, or amounts attributable to uncommitted option periods under drilling contracts or letters of intent.
The table below presents the amount of our contract drilling services backlog and the percent of available operating days committed for the periods indicated:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Year Ended December 31, (1) |
| | Total | | 2025 | | 2026 | | 2027 | | 2028 | | 2029 |
| | (In thousands) |
| Contract Drilling Services Backlog | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Floaters (2) | | $ | 5,243,084 | | | $ | 2,412,325 | | | $ | 1,547,270 | | | $ | 818,441 | | | $ | 463,718 | | | $ | 1,330 | |
Jackups (3) | | 849,914 | | 398,001 | | 267,233 | | 184,680 | | — | | — |
| Total | | $ | 6,092,998 | | | $ | 2,810,326 | | | $ | 1,814,503 | | | $ | 1,003,121 | | | $ | 463,718 | | | $ | 1,330 | |
Percent of Available Days Committed (4) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Floaters | | | | 60 | % | | 38 | % | | 23 | % | | 13 | % | | — | % |
| Jackups | | | | 51 | % | | 24 | % | | 14 | % | | — | % | | — | % |
| Total | | | | 57 | % | | 34 | % | | 20 | % | | 9 | % | | — | % |
(1)Represents a twelve-month period beginning January 1. Some of our drilling contracts provide customers with certain early termination rights and, in limited cases, those termination rights require minimal or no notice and minimal financial penalties.
(2)Noble entered into a multi-year Commercial Enabling Agreement (the “CEA”) with ExxonMobil in February 2020. Under the CEA, dayrates for the rigs are repriced on March 1 and September 1 each year to the projected market rate at the time the new rate goes into effect, subject to a scale-based discount and a performance bonus that appropriately aligns the interests of Noble and ExxonMobil. Under the CEA, the table above includes awarded and remaining current contract term to August 18, 2028, related to each of the four following rigs: the Noble Tom Madden, Noble Bob Douglas, Noble Don Taylor, and Noble Sam Croft. Under the CEA, ExxonMobil may reassign remaining contract term among rigs, subject to maintaining certain minimum contract term on the rig from which term is removed.
(3)In 2022, Noble renewed its five-year Framework Agreement with Aker BP for the provision of ultra-harsh environment jackup rigs, the Noble Integrator and Noble Invincible, for activities offshore Norway. Under the Framework Agreement, different rate structures apply reflecting different operating modes, agreed incentive schemes, and adjustments for operating expenses. Rate structures are adjusted annually to reflect market conditions.
(4)Percent of available days committed is calculated by dividing the total number of days our rigs are operating under contract for such period by the product of the number of our rigs, including cold-stacked rigs, and the number of calendar days in such period.
The amount of actual revenues earned and the actual periods during which revenues are earned may be materially different than the backlog amounts and backlog periods presented in the table above due to various factors, including, but not limited to, shipyard and maintenance projects, unplanned downtime, the operation of market benchmarks for dayrate resets, achievement of bonuses, weather conditions, reduced standby or mobilization rates, and other factors that result in applicable dayrates lower than the full contractual operating dayrate. In addition, amounts included in the backlog may change because drilling contracts may be varied or modified by mutual consent or customers may exercise early termination rights contained in some of our drilling contracts or decline to enter into a drilling contract after executing a letter of intent. As a result, our backlog as of any particular date may not be indicative of our actual operating results for the periods for which the backlog is calculated. See Part I, Item 1A, “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Business and Operations—Our current backlog of contract drilling revenue may not be ultimately realized.”
As of December 31, 2024, ExxonMobil, BP, and Petrobras represented approximately 37.2%, 13.1%, and 12.6% of our backlog, respectively.
Results of Operations
Results for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023
Net income for the year ended December 31, 2024, was $448.4 million, or $2.96 per diluted share, on operating revenues of $3.1 billion compared to net income for the year ended December 31, 2023, of $481.9 million, or $3.32 per diluted share, on operating revenues of $2.6 billion.
Key Operating Metrics
Operating results for our contract drilling services segment are dependent on three primary metrics: operating days, dayrates, and operating costs. We also track rig utilization, which is a function of operating days and the number of rigs in our fleet. For more information on operating costs, see “Contract Drilling Services” below.
The following table presents the average rig utilization, operating days, and average dayrates for our rig fleet for the periods indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Average Rig Utilization (1) | | Operating Days (2) | | Average Dayrates (2) | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | Year Ended December 31, | | Year Ended December 31, | | |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2024 | | 2023 | | |
| Floaters | | 69 | % | | 73 | % | | 5,372 | | | 5,067 | | | $ | 427,192 | | | $ | 382,041 | | | |
| Jackups | | 77 | % | | 64 | % | | 3,678 | | | 3,272 | | | 153,321 | | | 128,161 | | | |
| Total | | 72 | % | | 69 | % | | 9,050 | | | 8,339 | | | $ | 315,883 | | | $ | 282,392 | | | |
(1)We define utilization for a specific period as the total number of days our rigs are operating under contract, divided by the product of the total number of our rigs, including cold stacked rigs, and the number of calendar days in such period. Information reflects our policy of reporting on the basis of the number of available rigs in our fleet.
(2)An operating day is defined as a calendar day during which a rig operated under a drilling contract. We define average dayrates as revenue from contract drilling services earned per operating day. Average dayrates have not been adjusted for the non-cash amortization related to favorable and unfavorable customer contract intangibles.
Contract Drilling Services
The following table presents the operating results for our contract drilling services segment for the period indicated (dollars in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, | | Change |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | $ | | % |
| Operating revenues: | | | | | | | | |
| Contract drilling services | | $ | 2,918,767 | | | $ | 2,461,715 | | | $ | 457,052 | | | 19 | % |
Reimbursables and other (1) | | 139,051 | | | 127,303 | | | 11,748 | | | 9 | % |
| | $ | 3,057,818 | | | $ | 2,589,018 | | | $ | 468,800 | | | 18 | % |
| Operating costs and expenses: | | | | | | | | |
| Contract drilling services | | $ | 1,687,164 | | | $ | 1,452,281 | | | $ | 234,883 | | | 16 | % |
Reimbursables (1) | | 105,479 | | | 91,642 | | | 13,837 | | | 15 | % |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 428,626 | | | 301,345 | | | 127,281 | | | 42 | % |
| General and administrative | | 140,499 | | | 128,413 | | | 12,086 | | | 9 | % |
| Merger and integration costs | | 109,424 | | | 60,335 | | | 49,089 | | | 81 | % |
| Gain on sale of operating assets, net | | (17,357) | | | — | | | (17,357) | | | — | % |
| Hurricane losses and (recoveries), net | | — | | | (19,703) | | | 19,703 | | | (100) | % |
| | 2,453,835 | | | 2,014,313 | | | 439,522 | | | 22 | % |
| Operating income (loss) | | $ | 603,983 | | | $ | 574,705 | | | $ | 29,278 | | | 5 | % |
(1)We record reimbursements from customers for out-of-pocket expenses as operating revenues and the related direct costs as operating expenses. Changes in the amount of these reimbursables generally do not have a material effect on our financial position, results of operations, or cash flows.
Contract Drilling Services Revenues
The following table provides information about contract drilling services revenues and costs by rig types (dollars in millions except average dayrates):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years Ended December 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 |
| | | Floaters | | Jackups | | Floaters | | Jackups |
| Contract drilling services revenues | | $ | 2,350 | | | $ | 569 | | | $ | 2,010 | | | $ | 452 | |
| Contract drilling services costs | | $ | 1,306 | | | $ | 381 | | | $ | 1,112 | | | $ | 340 | |
| Average rig utilization | | | 69 | % | | 77 | % | | 73 | % | | 64 | % |
| Operating days | | | 5,372 | | | 3,678 | | | 5,067 | | | 3,272 | |
| Average dayrates | | | $ | 427,192 | | | $ | 153,321 | | | $ | 382,041 | | | $ | 128,161 | |
| Total rigs | — Beginning | | 19 | | | 13 | | | 19 | | | 13 | |
| — Acquired | | 11 | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| — Disposed | | (3) | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| — Ending | | 27 | | | 13 | | | 19 | | | 13 | |
Floaters. During the year ended December 31, 2024, floaters generated revenue of $2.3 billion, as compared to $2.0 billion in year ended December 31, 2023. The increase in revenue was mainly attributable to $297.0 million provided by the additional floaters acquired in connection with the Diamond Transaction. The increase also included $285.6 million from an increase in average dayrates during the current year, excluding rigs acquired in the Diamond Transaction, and $42.0 million received from a contract termination fee. These increases were partly offset by $265.6 million from rigs with net changes in operating days during the current year, excluding rigs acquired in the Diamond Transaction. Additionally, floater revenue from net non-cash amortization related to off-market customer contract assets and liabilities decreased $19.5 million during the current year. For additional information, see “Note 2 — Acquisitions and Divestitures” to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Jackups. During the year ended December 31, 2024, jackups generated revenue of $569.1 million, as compared to $451.6 million in year ended December 31, 2023. The increase in revenue was mainly attributable to $60.5 million from an increase in average dayrates during the current year and $91.5 million from rigs with net changes in operating days during the current year. Additionally, jackup revenue from net non-cash amortization related to off-market customer contract assets and liabilities decreased $27.1 million during the current year.
Operating Costs and Expenses
Floaters. During the year ended December 31, 2024, total contract drilling services cost related to floaters was $1.3 billion, as compared to $1.1 billion in year ended December 31, 2023. The primary drivers of this increase were $180.1 million related to the additional floaters acquired in connection with the Diamond Transaction and $32.0 million predominately driven by labor and transportation costs across the fleet. These increases were partially offset by insurance proceeds received for a certain rig totaling $18.1 million. For additional information, see “Note 2 — Acquisitions and Divestitures” to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Jackups. During the year ended December 31, 2024, total contract drilling services cost related to jackups was $381.2 million, as compared to $340.0 million in year ended December 31, 2023. The primary drivers of the aggregate increase of $99.0 million related to labor costs, repairs and maintenance, operations support, and other costs across the fleet due to increased activity. These increases were partially offset by a decrease of $58.0 million after the completion of disposal activities regarding certain rigs.
Depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization totaled $428.6 million and $301.3 million during the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Depreciation and amortization increased by $127.3 million in the current year primarily due to the timing of capital additions that were placed in service as compared to retirements among the periods as well as an incremental amount added in connection with the Diamond Transaction.
General and administrative. General and administrative expenses totaled $140.5 million and $128.4 million during the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. The increase was primarily a result of the Diamond Transaction and other individually insignificant items within certain corporate charges such as professional fees, corporate leases, and employee related costs.
Merger and integration costs. Noble incurred $109.4 million and $60.3 million of merger and integration costs during the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, primarily as a result of the Diamond Transaction and the Business Combination with Maersk Drilling. During the current period, $84.5 million and $25.0 million of costs related directly to the Diamond Transaction and the Business Combination with Maersk Drilling, respectively. Costs incurred prior to 2024 related to the Business Combination with Maersk Drilling in October 2022. A majority of the costs attributable to the Diamond Transaction related to the closing of the transaction and included charges for professional fees, severance, and share-based compensation. For additional information, see “Note 2 — Acquisitions and Divestitures” and “Note 3 — Merger and Integration Costs” to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Gain on sale of operating assets, net. During the year ended December 31, 2024, we sold the Noble Explorer for total proceeds of $25.0 million, $21.5 million of which was received in the fourth quarter of 2023, resulting in a pre-tax gain of $17.4 million.
Hurricane losses and recoveries, net. During the year ended December 31, 2024, costs in connection with the Hurricane Ida incident were offset by accrued recoveries. During the year ended December 31, 2023, Noble recognized $31.8 million of costs, which was offset by the recognition of insurance recoveries of $51.5 million. For additional information, see “Note 12 — Commitments and Contingencies” to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Other Income and Expenses
Interest expense, net of amounts capitalized. Interest expense totaled $94.2 million and $59.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Interest expense primarily relates to our 2030 Notes which, in part, refinanced prior debt assumed in the Business Combination with Maersk Drilling in October 2022, as well as the Diamond Second Lien Notes. For additional information, see “Note 6 — Debt“ to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Gain (loss) on extinguishment of debt, net. Noble recognized loss on extinguishment of debt of $26.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, related to the redemption of the remaining balance on notes and refinancing of other debt. For additional information, see “Note 6 — Debt” to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Interest income and other, net. Noble recognized other expenses of $17.4 million and other income of $18.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2024, Noble made a tax contribution repayment of $4.0 million related to a joint taxation scheme with A.P. Møller Holding A/S. For the year ended December 31, 2023, other income primarily related to the recognition of approximately $19.1 million of compensation under the same arrangement. For additional information, see “Note 10 — Income Taxes” to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Gain on bargain purchase. Noble recognized a $5.0 million gain on the bargain purchase of Maersk Drilling for the year ended December 31, 2023. For additional information, see “Note 2 — Acquisitions and Divestitures” to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Income tax benefit (provision). Noble recorded an income tax provision of $44.0 million and $30.3 million during the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
During the year ended December 31, 2024, our tax provision included tax benefits of $123.6 million related to releases of valuation allowances primarily in Luxembourg, and a net tax benefit of $20.2 million related to changes in uncertain tax positions. Such tax benefits were offset by various recurring quarterly accruals of $187.8 million primarily in Guyana, Nigeria, the United States, Switzerland, and Luxembourg.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, our tax provision included tax benefits of $187.2 million related to releases of valuation allowances in Luxembourg, Guyana, Switzerland, and Norway, and a tax benefit of $6.8 million related to uncertain tax position releases. Such tax benefits were offset by tax expenses related to uncertain tax positions of $20.9 million in various countries, contract fair value amortization of $23.7 million, and various recurring quarterly accruals of $179.6 million primarily in Guyana, Switzerland, and Luxembourg.
2023 Compared to 2022
Information related to a comparison of our results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to the year ended December 31, 2022, is included in Part II, Item 7, “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition
and Results of Operations” of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023, filed with the SEC on February 23, 2024.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Sources and Uses of Cash
Our principal sources of capital in 2024 were cash generated from operating activities as well as net proceeds from the issuance of additional 2030 Notes (as defined below). Cash on hand during the current period was primarily used for the following:
•cash consideration and fees related to the Diamond Transaction;
•normal recurring operating expenses;
•capital expenditures;
•fees and expenses related to merger and integration costs;
•share repurchases and dividend payments; and
•certain contractual cash obligations and commitments.
Our anticipated cash flow needs, both in the short term and long term, may also include repurchases, redemptions, or repayments of debt and interest.
We currently expect to fund our cash flow needs with cash generated by our operations, cash on hand, proceeds from sales of assets, or borrowings under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility, and we believe this will provide us with sufficient liquidity to fund our cash flow needs over the next 12 months. Subject to market conditions and other factors, we may also issue equity or long-term debt securities to fund our cash flow needs and for other purposes. We have been incurring expenses and capital costs related to incidents regarding one floater and one jackup. These incurred costs related to each rig each exceeded the applicable deductible. We received partial insurance recoveries in 2024 for each of these claims and we continue to seek insurance recoveries for the remainder of the incurred and anticipated costs.
Net cash provided by operating activities was $655.5 million and $574.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Net cash provided by operating activities increased mainly due to improvements in cash flows from operating assets and liabilities, with key drivers being an increase in payments from customers offset by a reduction in payments to vendors, as well as the Diamond Transaction. We had working capital balances of $448.5 million and $420.1 million at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
Net cash used in investing activities was $959.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2024, and consisted of capital expenditures on routine projects associated with overhauls and upgrades on various rigs and net cash paid related to the closing of the Diamond Transaction. Net cash used in investing activities was $366.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, and consisted of capital expenditures on routine projects associated with overhauls and upgrades on various rigs in the newly combined fleet.
Net cash provided by financing activities was $188.1 million and net cash used in financing activities was $325.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. The year ended December 31, 2024, included the issuance of an additional $824.0 million of 2030 Notes. We also repurchased 8.4 million of our Ordinary Shares for total of $300.0 million, made dividend payments to our shareholders of $277.8 million, and paid $66.1 million in taxes withheld on vested employee share-based compensation awards. The year ended December 31, 2023, included the repayment of the DSF Credit Facility in full, the redemption of notes, the repayment of the New DNB Credit Facility, totaling $673.4 million, and the $600.0 million issuance of the initial 2030 Notes. We also repurchased 2.3 million of our Ordinary Shares for a total of $94.8 million and made dividend payments to our shareholders of $98.8 million.
At December 31, 2024, we had a total contract drilling services backlog of approximately $6.1 billion, which includes a commitment of 57% of available days for 2025. For additional information regarding our backlog, see “Contract Drilling Services Backlog.”
Capital Additions
Capital additions totaled $520.3 million and $454.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Capital additions for the year ended December 31, 2024, consisted of the following:
•$312.5 million for sustaining capital;
•$169.8 million in major projects, including subsea and other related projects;
•$34.3 million for rebillable capital and contract modifications; and
•$3.7 million for capitalized interest.
Our total capital additions estimate for 2025, net of reimbursements, is expected to range between $375.0 million and $425.0 million. We expect to fund these capital additions with cash generated by our operations and cash on hand.
From time to time we consider possible projects and may have certain events that would require expenditures that are not included in our capital budget, and such unbudgeted expenditures could be significant. In addition, while liquidity and preservation of capital remains our top priority, we will continue to evaluate acquisitions of drilling units from time to time.
Amended and Restated Senior Secured Revolving Credit Agreement
In April 2023, certain subsidiaries of Noble amended and restated the senior secured revolving credit agreement, dated February 5, 2021, by entering into an Amended and Restated Senior Secured Revolving Credit Agreement, dated as of April 18, 2023 (as amended and otherwise modified from time to time, the “2023 Revolving Credit Agreement”), by and among Noble Finance II, Noble International Finance Company (“NIFCO”), Noble Drilling A/S, and each other designated borrower from time to time party thereto, as borrowers (the “Borrowers”), the lenders and issuing banks party thereto from time to time and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, collateral agent, and security trustee. The revolving credit facility under the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement (the “2023 Revolving Credit Facility”) provides for commitments of $550.0 million with maturity in April 2028. The guarantors under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility are the same subsidiaries of Noble Finance II that are or will be guarantors of the 2030 Notes.
As of December 31, 2024, we had no borrowings outstanding and $24.8 million of letters of credit issued under our 2023 Revolving Credit Facility and an additional $126.8 million in letters of credit and surety bonds issued under bilateral arrangements. For additional information about the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility, see “Note 6 — Debt” to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
8.000% Senior Notes due 2030
In April 2023, Noble Finance II, a wholly owned subsidiary of Noble, issued $600.0 million in aggregate principal amount of its 8.000% Senior Notes due 2030 (“Initial 2030 Notes”). The Initial 2030 Notes were issued pursuant to an indenture, dated April 18, 2023 (as supplemented or otherwise modified from time to time, the “Noble Indenture”), among Noble Finance II, the subsidiaries of Noble Finance II party thereto, as guarantors (the “Guarantors”), and U.S. Bank Trust Company, National Association, as trustee. In August 2024, Noble Finance II issued an additional $800.0 million in aggregate principal amount of its 8.000% Senior Notes due 2030 (the “Additional 2030 Notes” and, together with the Initial 2030 Notes, the “2030 Notes”) at a premium of 103% bringing the total outstanding principal amount to $1.4 billion. The Additional 2030 Notes were issued pursuant to the Noble Indenture and the net proceeds from the offering of the Additional 2030 Notes were primarily used to fund the cash consideration in the Diamond Transaction and to pay any premiums, fees, and expenses related to the issuance of the Additional 2030 Notes. As of December 31, 2024, we had outstanding $1.4 billion aggregate principal amount of our 2030 Notes. For additional information about the 2030 Notes, see “Note 6 — Debt” to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Diamond Second Lien Notes due 2030
In connection with the Diamond Transaction, the Company assumed $550.0 million aggregate principal amount of 8.500% Senior Secured Second Lien Notes due October 2030 (the “Diamond Second Lien Notes”) issued pursuant to an indenture, dated as of September 21, 2023 (as supplemented and otherwise modified from time to time, the “Diamond Second Lien Indenture”), among Diamond Foreign Asset Company and Diamond Finance, LLC, as issuers, Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc., the other guarantors party thereto and HSBC Bank USA, National Association, as trustee and as collateral agent. As of December 31, 2024, we had outstanding $550.0 million aggregate principal amount of our Diamond Second Lien Notes. For additional information about the Diamond Second Lien Notes, see “Note 6 — Debt” to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Diamond Credit Agreement
In connection with the Diamond Transaction, the Company terminated Diamond’s $300.0 million senior secured revolving credit facility (the “Diamond Revolving Credit Facility”) under a credit agreement, dated as of April 23, 2021 (as amended and otherwise modified, the “Diamond Credit Agreement”), among Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc., Diamond Foreign Asset Company, as borrower, the lenders party thereto from time to time and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as administrative agent, collateral agent, and issuing lender. The revolving commitments under the Diamond Credit Agreement were scheduled to mature in April 2026. At the time of the Diamond Transaction and the termination of the commitments under the Diamond Credit Agreement, Diamond had no outstanding borrowings under the Diamond Credit Agreement. For additional information about the Diamond Credit Agreement, see “Note 6 — Debt” to our consolidated
financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Dividends
Our most recent quarterly dividend, totaling approximately $79.7 million (or $0.50 per share), was declared on November 5, 2024, and paid on December 19, 2024, to shareholders of record at close of business on December 5, 2024. During the year ended December 31, 2024, we declared dividends of approximately $278.3 million, including accrued dividends, (or $1.80 per share), and made cash dividend payments of approximately $277.8 million.
On February 17, 2025, our Board of Directors approved a declaration of a quarterly cash interim dividend on our Ordinary Shares of $0.50 per share. This dividend is to be payable on March 20, 2025, to shareholders of record at close of business on March 5, 2025.
The declaration and payment of dividends require authorization of the Board of Directors, provided that such dividends on issued share capital may be paid only out of the Company’s “distributable reserves” as determined by reference to relevant statutory accounts in accordance with English law. The Company is not permitted to pay dividends out of share capital, which includes share premiums. The payment of future dividends will depend on our results of operations, financial condition, cash requirements, future business prospects, the availability of sufficient distributable reserves, contractual and indenture restrictions, and other factors deemed relevant by our Board of Directors.
Share Repurchases
Under English law, the Company is only permitted to purchase its own Ordinary Shares by way of an “off-market purchase” pursuant to a contract approved by shareholders (except where the purchase is for the purposes of, or pursuant to, any employees’ share scheme). Such purchases may be paid for either (i) out of Noble’s “distributable reserves” as determined by reference to relevant statutory accounts in accordance with English law or (ii) from the proceeds of a fresh issue of shares made for the purpose of financing the purchase. As of the date of this report, we have shareholder authority to repurchase up to 15% per annum of the issued share capital of the Company as of the beginning of each fiscal year for a five-year period commencing on September 28, 2022 (subject to an overall aggregate maximum of 20.6 million Ordinary Shares). During the year ended December 31, 2024, we repurchased 8.4 million of our Ordinary Shares pursuant to such authority. All repurchased shares were subsequently cancelled.
Summary of Contractual Cash Obligations and Commitments
We have $196.0 million of net long-term tax reserves for uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties, which are included in “Other liabilities” due to the difficulty in making reasonably reliable estimates of the timing of cash settlements to taxing authorities. See “Note 10 — Income Taxes” to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
At December 31, 2024, no long-term debt is due in the next twelve months and $2.0 billion will be due subsequent to 2025. See “Note 6 — Debt” to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We may seek to refinance all or a portion of our long-term debt obligations, including the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility, though any such refinancing transactions are subject to market and other conditions and there are no assurances that we will complete any such transactions, in whole or in part, or as to the amount or timing of any such transactions.
At December 31, 2024, $13.0 million of pension obligations will be due in the next twelve months and the remainder of $127.3 million will be due subsequent to 2025. See “Note 11 — Employee Benefit Plans” to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. In addition, $9.5 million is due on a long-term basis under the Danish Holiday Act of 2020.
For a description of our operating and finance lease obligations, refer to “Note 9 — Leases” to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
At December 31, 2024, we had other commitments that we are contractually obligated to fulfill with cash if the obligations are called. These obligations include letters of credit that guarantee our performance as it relates to our drilling contracts, tax, and other obligations in various jurisdictions. We expect to comply with the underlying performance requirements and we expect obligations under these letters of credit and surety bonds will not be called. At December 31, 2024, $30.6 million letters of credit and commercial commitments will expire in the next twelve months and the remainder of $121.0 million will expire subsequent to 2025.
We expect to fund these obligations and commitments with cash generated by our operations and cash on hand.
Unaudited Condensed Consolidating Financial Information
The Noble Indenture contains a covenant that requires Noble Finance II to furnish to holders of the 2030 Notes certain financial information relating to Noble Finance II and its restricted subsidiaries. The Diamond Second Lien Indenture contains a covenant that requires NODI to furnish to holders of the Diamond Second Lien Notes certain financial information relating to NODI and its subsidiaries.
The summarized financial information below reflects combined accounts of Noble Finance II, NODI, and all other subsidiaries of Noble. The financial information is presented on a combined basis and intercompany balances and transactions between entities have been eliminated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Noble Corporation plc and Subsidiaries |
| | Unaudited Condensed Consolidating Selected Financials |
| | December 31, 2024 |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | Consolidated Noble Finance II LLC | | Consolidated Noble Offshore Drilling, Inc. (1) | | Other
Non-guarantor Subsidiaries
of Noble | | Consolidating Adjustments | | Total |
| Balance Sheets | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 131,703 | | | $ | 114,999 | | | $ | 601 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 247,303 | |
| Total current assets | | 1,683,839 | | | 524,251 | | | 124,851 | | | (944,077) | | | 1,388,864 | |
| Total current liabilities | | 694,321 | | | 324,049 | | | 1,508,473 | | | (1,586,481) | | | 940,362 | |
| Total debt | | 1,401,214 | | | 1,244,357 | | | — | | | (665,385) | | | 1,980,186 | |
| Total shareholders' equity | | 4,535,081 | | | 861,791 | | | 4,017,807 | | | (4,763,293) | | | 4,651,386 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Noble Corporation plc and Subsidiaries |
| | Unaudited Condensed Consolidating Selected Financials |
| | Twelve Months Ended December 31, 2024 |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | Consolidated Noble Finance II LLC | | Consolidated Noble Offshore Drilling, Inc. (1) | | Other
Non-guarantor Subsidiaries
of Noble | | Consolidating Adjustments | | Total |
| Statements of Operations | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating revenues | | $ | 2,721,156 | | | $ | 336,542 | | | $ | 120 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 3,057,818 | |
| Operating costs and expenses | | 2,010,731 | | | 334,722 | | | 108,382 | | | — | | | 2,453,835 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 379,551 | | | 49,075 | | | — | | | — | | | 428,626 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Statements of Cash Flows | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | | $ | 792,859 | | | $ | (39,696) | | | $ | (97,688) | | | $ | — | | | $ | 655,475 | |
| Capital expenditures | | (536,658) | | | (38,477) | | | (180) | | | — | | | (575,315) | |
| Proceeds from disposal of assets, net | | (690) | | | 10,730 | | | 13,257 | | | — | | | 23,297 | |
| Dividend payments | | — | | | — | | | (277,831) | | | — | | | (277,831) | |
(1)Consolidated Noble Offshore Drilling, Inc. from merger effective date on September 4, 2024.
Critical Accounting Estimates
We prepare our consolidated financial statements in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (“US GAAP”), which require us to make estimates that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues, expenses, and related disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which
form the basis for making judgments about the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from our estimates and assumptions and any such differences could be material to our consolidated financial statements. The following accounting policies involve critical accounting estimates because they are particularly dependent on estimates and assumptions made by Noble about matters that are inherently uncertain.
Recoverability of Assets
We evaluate our property and equipment and intangible assets for impairment whenever there are changes in facts that suggest that the value of the asset is not recoverable. An impairment loss is recognized when and to the extent that an asset's carrying value exceeds its estimated fair value. To the extent actual results do not meet our estimated assumptions for a given rig, piece of equipment or intangible customer contract, we may take an impairment loss in the future. In determining the fair value of the assets, we make significant assumptions and estimates regarding future market conditions using significant unobservable inputs representative of a Level 3 fair value measurement. Critical assumptions used in our estimate include projected dayrates, utilization, and discount rate. These projections involve uncertainties that rely on assumptions about current and future market conditions, timing of future contract awards, and marketability of a unit. It can be difficult to determine the fair value based on the cyclical nature of our business, demand for offshore drilling rigs in different markets, and changes in economic conditions.
During the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, no impairment charges were recognized.
Impairment assessment inherently involves management judgments as to assumptions about expected future cash flows and the impact of market conditions on those assumptions. Due to the many variables inherent in this estimation, differences in assumptions may have a material effect on the results of our impairment analysis.
Income Taxes
We estimate income taxes and file tax returns in each of the taxing jurisdictions in which we operate and are required to file a tax return. At the end of each year, an estimate for income taxes is recorded in the financial statements. Tax returns are generally filed in the subsequent year. A reconciliation of the estimate to the final tax return is done at that time, which will result in changes to the original estimate. We believe that our tax return positions are appropriately supported, but tax authorities can challenge certain of our tax positions.
We currently operate, and have in the past operated, in a number of countries throughout the world and our tax returns filed in those jurisdictions are subject to review and examination by tax authorities within those jurisdictions. We recognize uncertain tax positions that we believe have a greater than 50% likelihood of being sustained upon challenge by a tax authority. We cannot predict or provide assurance as to the ultimate outcome of any existing or future assessments. A change in judgment related to the expected ultimate resolution of uncertain tax positions will be recognized in earnings in the quarter of such change. We believe that our reserve for uncertain tax positions, including related interest and penalties, is adequate. As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Company had $196.0 million and $202.3 million of net long-term tax reserves for unrecognized tax benefits, including interest and penalties, which are included in “Other liabilities.” The amounts ultimately paid upon resolution of audits could be materially different from the amounts previously included in our income tax expense and, therefore, could have a material impact on our tax provision, net income and cash flows.
Our gross deferred tax asset balance at year end reflects the application of our income tax accounting policies and is based on management’s estimates, judgments, and assumptions regarding realizability. If it is more likely than not that a portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized in a future period, the deferred tax assets will be reduced by a valuation allowance based on management’s estimates. In evaluating our ability to recover our deferred tax assets, in full or in part, we consider all available positive and negative evidence, including our past operating results and our forecast of future earnings, future taxable income, and prudent and feasible tax planning strategies. The assumptions utilized in determining future taxable income require significant judgment. Although we believe our assumptions, judgments, and estimates are reasonable, changes in tax laws or our interpretation of tax laws and the resolution of any tax audits could have a material impact our consolidated financial statements.
Claims Reserves
We maintain various levels of self-insured retention for certain losses including property damage, loss of hire, employment practices liability, employers’ liability, and general liability, among others. We accrue for property damage and loss of hire charges on a per event basis.
Employment practices liability claims are accrued based on actual claims during the year. Maritime employer’s liability claims are generally estimated using actuarial determinations. General liability claims are estimated by our internal claims department by evaluating the facts and circumstances of each claim (including incurred but not reported claims) and
making estimates based upon historical experience with similar claims. The amount of our loss reserves for personal injury and protection claims is based on an analysis performed by a third-party actuary which uses our historical loss patterns and trends as well as industry data to estimate the unpaid loss and allocated loss adjustment expense. Claim severity experienced in each year, ranging from minor incidents to permanent disability or injuries requiring extensive medical care, is a key driver of the variability around our reserve estimates. These estimates are further subject to uncertainty because the ultimate disposition of claims incurred is subject to the outcome of events which have not yet transpired. Accordingly, we may be required to increase or decrease our reserve levels. At December 31, 2024, loss reserves for personal injury and protection claims totaled $164.1 million, of which $149.2 million was included in “Other current liabilities” and $14.9 million in “Other long-term liabilities” in the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets. At December 31, 2023, loss reserves for personal injury and protection claims totaled $63.9 million of which $21.9 million was included in “Other current liabilities” and $42.0 million in “Other long-term liabilities” in the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Business Combinations
We follow the acquisition method of accounting for business combinations. Assets acquired and liabilities assumed are recognized at the date of acquisition at their respective estimated fair value. Any excess of the purchase price over the fair value amounts assigned to assets and liabilities is recorded as goodwill. To the extent the estimated fair value of the net assets acquired exceeded the purchase price, we recognize a bargain purchase gain. Changes in these judgments or estimates can have a material impact on the valuation of the respective assets and liabilities acquired and our results of operations in periods after acquisition. The allocation of the purchase price may be modified up to one year after the acquisition date as more information is obtained about the fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed.
Our estimates of fair value of the acquired property and equipment and contract intangibles require us to use significant unobservable inputs, representative of a Level 3 fair value measurement. Critical assumptions used in our estimate include projected dayrates, utilization, and discount rate. These projections involve uncertainties that rely on assumptions about current and future market conditions, timing of future contract awards, demand for our services, and marketability of a unit. It can be difficult to determine the fair value based on the cyclical nature of our business, demand for offshore drilling rigs in different markets, and changes in economic conditions.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk.
Market risk is the potential for loss due to a change in the value of a financial instrument as a result of fluctuations interest rates, currency exchange rates, or equity prices, as further described below.
Interest Rate Risk
We are subject to market risk exposure related to changes in interest rates on borrowings under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility and may be subject to similar exposure on future borrowing arrangements. Borrowings under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility, if any, bear interest at the term secured overnight financing rate (“SOFR”) plus 0.10% (subject to a 0.00% floor) plus an applicable margin, which is currently 3.00%, or a base rate stated in the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement plus an applicable margin, which is currently 2.00%.
As of December 31, 2024, we had no borrowings outstanding under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility and $24.8 million of performance letters of credit outstanding thereunder.
Because they bear interest at a fixed rate, the fair value of the 2030 Notes and the Diamond Second Lien Notes will fluctuate based on changes in market expectations for interest rates and perceptions of our credit risk. The fair value of our total debt was $2.0 billion as of December 31, 2024.
Foreign Currency Risk
Although we are a UK company, we define foreign currency as any non-US dollar denominated currency. Our functional currency is the US dollar. However, outside the United States, a portion of our expenses are incurred in local currencies. Therefore, when the US dollar weakens (strengthens) in relation to the currencies of the countries in which we operate, our expenses reported in US dollars will increase (decrease).
We are exposed to risks on future cash flows to the extent that foreign currency expenses exceed revenues denominated in the same foreign currency. In order to help manage this potential risk, we periodically enter into derivative instruments to manage our net exposure to fluctuations in currency exchange rates. We have documented policies and procedures to monitor and control the use of derivative instruments. We do not engage in derivative transactions for speculative or trading purposes, nor are we a party to leveraged derivatives.
Several of our regional shorebases have a significant amount of their cash operating expenses payable in foreign currencies. In order to limit the potential risk of currency fluctuations, we periodically enter into forward contracts, which have historically settled monthly in the operations’ respective local currencies. All of these contracts had a maturity of less than 12 months. Based on current projections, a 10% increase in the average exchange rates of all foreign currencies would hypothetically increase our future estimated operating expenses by approximately $20.6 million.
Market Risk
We have a US noncontributory defined benefit pension plan that covers certain salaried employees and a US noncontributory defined benefit pension plan that covers certain hourly employees, whose initial date of employment is prior to August 1, 2004 (collectively referred to as our “qualified US plans”). These plans are governed by the Noble Drilling Employees’ Retirement Trust. The benefits from these plans are based primarily on years of service and, for the salaried plan, employees’ compensation near retirement. These plans are designed to qualify under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (“ERISA”), and our funding policy is consistent with funding requirements of ERISA and other applicable laws and regulations. We make cash contributions, or utilize credits available to us, for the qualified US plans when required. The benefit amount that can be covered by the qualified US plans is limited under ERISA and the Internal Revenue Code of 1986. Therefore, we maintain an unfunded, nonqualified excess benefit plan designed to maintain benefits for specified employees at the formula level in the qualified salary US plan. We refer to the qualified US plans and the excess benefit plan collectively as the “US plans.”
In addition to the US plans, Noble Drilling (Land Support) Limited, an indirect, wholly-owned subsidiary of Noble, maintains a pension plan that covers all of its salaried, non-union employees, whose most recent date of employment is prior to April 1, 2014 (referred to as our “non-US plan”). Benefits are based on credited service and employees’ compensation, as defined by the non-US plan.
The Company’s pension plan assets are exposed to the market prices of debt and equity securities. Changes to the pension plan asset values can impact the Company’s pension expense, funded status, and future minimum funding requirements. The Company aims to reduce risk through asset diversification and by investing in long duration fixed-income securities that have a duration similar to that of its pension liabilities. At December 31, 2024, the value of the investments in the pension funds was $202.1 million, and a hypothetical 10.0% decrease in the value of the investments in the fund would have reduced the value of the fund by approximately $20.2 million. A significant decline in the value of pension assets could require Noble to increase funding of its pension plans in future periods, which could adversely affect cash flows in those periods. In addition, a decline in the fair value of these plan assets, in the absence of additional cash contributions to the plans by Noble, could increase the amount of pension cost required to be recorded in future periods by Noble.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
The following financial statements are filed in this Item 8:
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of Noble Corporation plc
Opinions on the Financial Statements and Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Noble Corporation plc and its subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, and the related consolidated statements of operations, of comprehensive income (loss), of equity and of cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2024, including the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). We also have audited the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2024 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the COSO.
Basis for Opinions
The Company's management is responsible for these consolidated financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A. Our responsibility is to express opinions on the Company’s consolidated financial statements and on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud, and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audits of the consolidated financial statements included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
As described in Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting, management has excluded Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc. (“Diamond”) from its assessment of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024 because it was acquired by the Company in a purchase business combination during 2024. We have also excluded Diamond from our audit of internal control over financial reporting. Diamond is a wholly-owned subsidiary whose total assets and total revenues excluded from management’s assessment and our audit of internal control over financial reporting represent approximately 29% and 11%, respectively, of the related consolidated financial statement amounts as of and for the year ended December 31, 2024.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are
recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current period audit of the consolidated financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (i) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the consolidated financial statements and (ii) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Acquisition of Diamond - Fair Value of Mobile Offshore Drilling Units
As described in Notes 1 and 2 to the consolidated financial statements, on September 4, 2024, the Company completed its acquisition of Diamond. The acquisition resulted in $1.8 billion of property and equipment, net being recorded, of which a significant portion related to mobile offshore drilling units. Management determined the fair value of the mobile offshore drilling units using the discounted cash flows expected to be generated from the drilling assets over their remaining useful lives. Assumptions used in management’s assessment included, but were not limited to, timing of future contract awards and expected operating dayrates, operating costs, rig utilization rates, tax rates, discount rate, capital expenditures, synergies, market values, and estimated economic useful lives of the rigs.
The principal considerations for our determination that performing procedures relating to the fair value of mobile offshore drilling units acquired in the acquisition of Diamond is a critical audit matter are (i) the significant judgment by management when developing the fair value estimate of the mobile offshore drilling units acquired; (ii) a high degree of auditor judgment, subjectivity, and effort in performing procedures and evaluating management’s significant assumptions related to the expected operating dayrates, operating costs, rig utilization rates, tax rates, discount rate, synergies, and estimated economic useful lives of the rigs; and (iii) the audit effort involved the use of professionals with specialized skill and knowledge.
Addressing the matter involved performing procedures and evaluating audit evidence in connection with forming our overall opinion on the consolidated financial statements. These procedures included testing the effectiveness of controls relating to the valuation of the mobile offshore drilling units acquired. These procedures also included, among others (i) reading the purchase agreement; (ii) testing management’s process for developing the fair value estimate of the mobile offshore drilling units acquired; (iii) evaluating the appropriateness of the discounted cash flow models; (iv) testing the completeness and accuracy of underlying data used in the discounted cash flow models; and (v) evaluating the reasonableness of the significant assumptions used by management related to the expected operating dayrates, operating costs, rig utilization rates, tax rates, discount rate, synergies, and estimated economic useful lives of the rigs. Evaluating management’s assumptions related to the expected operating dayrates, operating costs, rig utilization rates, tax rates, synergies, and estimated economic useful lives of the rigs involved considering (i) the current and past performance of the mobile offshore drilling units; (ii) the consistency with external market and industry data; and (iii) whether these assumptions were consistent with evidence obtained in other areas of the audit. Professionals with specialized skill and knowledge were used to assist in evaluating the appropriateness of the discounted cash flow models and the reasonableness of the discount rate assumption.
| | |
|
| /s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP |
| |
| Houston, Texas |
| February 18, 2025 |
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 1994.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(In thousands, except share amounts)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| ASSETS | | | | |
| Current assets | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 247,303 | | | $ | 360,794 | |
| Accounts receivable, net | | 796,961 | | | 548,844 | |
| Taxes receivable | | 56,389 | | | 39,845 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | 288,211 | | | 112,265 | |
| Total current assets | | 1,388,864 | | | 1,061,748 | |
| Intangible assets | | 214 | | | 10,128 | |
| Property and equipment, at cost | | 6,904,731 | | | 4,591,936 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | | (868,914) | | | (467,600) | |
| Property and equipment, net | | 6,035,817 | | | 4,124,336 | |
| | | | |
| Other assets | | 539,873 | | | 311,225 | |
| Total assets | | $ | 7,964,768 | | | $ | 5,507,437 | |
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | | |
| Current liabilities | | | | |
| | | | |
| Accounts payable | | $ | 397,622 | | | $ | 395,165 | |
| Accrued payroll and related costs | | 116,877 | | | 97,313 | |
| Taxes payable | | 78,900 | | | 56,420 | |
| Interest payable | | 36,075 | | | 10,707 | |
| Other current liabilities | | 310,888 | | | 82,075 | |
| Total current liabilities | | 940,362 | | | 641,680 | |
| Long-term debt | | 1,980,186 | | | 586,203 | |
| Deferred income taxes | | 9,202 | | | 11,416 | |
| Noncurrent contract liabilities | | 8,580 | | | 50,863 | |
| Other liabilities | | 375,052 | | | 296,035 | |
| Total liabilities | | 3,313,382 | | | 1,586,197 | |
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 12) | | | | |
| Shareholders' equity | | | | |
| Common stock, $0.00001 par value; 158,946,711 and 140,773,750 ordinary shares outstanding as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively | | 1 | | | 1 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | | 4,236,172 | | | 3,377,048 | |
| Retained earnings | | 411,244 | | | 541,159 | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | | 3,969 | | | 3,032 | |
| Total shareholders' equity | | 4,651,386 | | | 3,921,240 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | | $ | 7,964,768 | | | $ | 5,507,437 | |
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(In thousands, except per share amounts)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Operating revenues | | | | | | |
| Contract drilling services | | $ | 2,918,767 | | | $ | 2,461,715 | | | $ | 1,332,841 | |
| Reimbursables and other | | 139,051 | | | 127,303 | | | 81,006 | |
| | 3,057,818 | | | 2,589,018 | | | 1,413,847 | |
| Operating costs and expenses | | | | | | |
| Contract drilling services | | 1,687,164 | | | 1,452,281 | | | 897,096 | |
| Reimbursables | | 105,479 | | | 91,642 | | | 64,427 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 428,626 | | | 301,345 | | | 146,879 | |
| General and administrative | | 140,499 | | | 128,413 | | | 82,177 | |
| Merger and integration costs | | 109,424 | | | 60,335 | | | 84,668 | |
| (Gain) loss on sale of operating assets, net | | (17,357) | | | — | | | (90,230) | |
| Hurricane losses and (recoveries), net | | — | | | (19,703) | | | 60 | |
| | 2,453,835 | | | 2,014,313 | | | 1,185,077 | |
| Operating income (loss) | | 603,983 | | | 574,705 | | | 228,770 | |
| Other income (expense) | | | | | | |
| Interest expense, net of amounts capitalized | | (94,211) | | | (59,139) | | | (42,722) | |
| Gain (loss) on extinguishment of debt, net | | — | | | (26,397) | | | (8,912) | |
| Interest income and other, net | | (17,438) | | | 18,069 | | | 14,365 | |
| Gain on bargain purchase | | — | | | 5,005 | | | — | |
| | | | | | |
| Income (loss) before income taxes | | 492,334 | | | 512,243 | | | 191,501 | |
| Income tax benefit (provision) | | (43,981) | | | (30,341) | | | (22,553) | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 448,353 | | | $ | 481,902 | | | $ | 168,948 | |
| Basic earnings (loss) per share | | $ | 3.01 | | | $ | 3.48 | | | $ | 1.99 | |
| Diluted earnings (loss) per share | | $ | 2.96 | | | $ | 3.32 | | | $ | 1.73 | |
| Weighted Average Shares Outstanding | | | | | | |
| Basic | | 148,733 | | | 138,380 | | | 85,055 | |
| Diluted | | 151,639 | | | 145,197 | | | 97,607 | |
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 448,353 | | | $ | 481,902 | | | $ | 168,948 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Net changes in pension and other postretirement plan assets and benefit obligations recognized in other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax provision (benefit) of $(457), $(940), and $(928) for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively | | 937 | | | (615) | | | (1,742) | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net | | 937 | | | (615) | | | (1,742) | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | | $ | 449,290 | | | $ | 481,287 | | | $ | 167,206 | |
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 448,353 | | | $ | 481,902 | | | $ | 168,948 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash flow from operating activities: | | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 428,626 | | | 301,345 | | | 146,879 | |
| Amortization of intangible assets and contract liabilities, net | | (60,032) | | | (106,776) | | | (5,352) | |
| Gain on bargain purchase | | — | | | (5,005) | | | — | |
| (Gain) loss on extinguishment of debt, net | | — | | | 26,397 | | | 8,912 | |
| (Gain) loss on sale of operating assets, net | | (17,357) | | | — | | | (90,230) | |
| | | | | | |
| Deferred income taxes | | (42,647) | | | (98,093) | | | (25,628) | |
| Amortization of share-based compensation | | 43,797 | | | 37,680 | | | 35,251 | |
| Other costs, net | | (13,964) | | | (8,036) | | | (323) | |
| Changes in components of working capital and other operating activities: | | | | | | |
| Change in taxes receivable | | (15,263) | | | (7,374) | | | 23,344 | |
| Net changes in other operating assets and liabilities | | (116,038) | | | (47,703) | | | 19,184 | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | | 655,475 | | | 574,337 | | | 280,985 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | |
| Capital expenditures | | (575,315) | | | (409,581) | | | (174,319) | |
| Proceeds from insurance claims | | 23,297 | | | 18,809 | | | — | |
| Cash acquired (used) in business combinations, net | | (417,041) | | | — | | | 166,607 | |
| Proceeds from disposal of assets, net | | 10,040 | | | 24,264 | | | 381,026 | |
| Other investing activities | | — | | | — | | | 2,458 | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | | (959,019) | | | (366,508) | | | 375,772 | |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | | | | | |
| Issuance of debt | | 824,000 | | | 600,000 | | | 350,000 | |
| Repayments of debt | | — | | | (673,411) | | | (627,323) | |
| Borrowing on credit facilities | | 35,000 | | | — | | | 220,000 | |
| Repayments of credit facilities | | (35,000) | | | — | | | (220,000) | |
| Debt issuance costs | | (10,002) | | | (24,914) | | | (641) | |
| Debt extinguishment costs | | — | | | (25,697) | | | — | |
| Compulsory purchase payment | | — | | | — | | | (69,924) | |
| Warrant exercises | | 1,443 | | | 485 | | | 1,004 | |
| Share repurchases | | (299,989) | | | (94,826) | | | (15,000) | |
| Dividend payments | | (277,831) | | | (98,804) | | | — | |
| Taxes withheld employee stock transactions | | (66,057) | | | (8,624) | | | (5,888) | |
| Finance lease payments | | (6,064) | | | — | | | — | |
| Other | | 22,578 | | | — | | | — | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | | 188,078 | | | (325,791) | | | (367,772) | |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash | | (115,466) | | | (117,962) | | | 288,985 | |
| Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash, beginning of period | | 367,745 | | | 485,707 | | | 196,722 | |
| Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash, end of period | | $ | 252,279 | | | $ | 367,745 | | | $ | 485,707 | |
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EQUITY
(In thousands) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Shares | | Additional
Paid-in
Capital | | Retained
Earnings (Accumulated Deficit) | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive
Income (Loss) | | Total
Equity |
| | Balance | | Par Value | | | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2021 | | 60,172 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 1,393,255 | | | $ | 101,982 | | | $ | 5,389 | | | $ | 1,500,627 | |
| Employee related equity activity: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amortization of share-based compensation | | — | | | — | | | 35,252 | | | — | | | — | | | 35,252 | |
| Issuance of share-based compensation shares | | 834 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Shares withheld for taxes on equity transactions | | — | | | — | | | (5,888) | | | — | | | — | | | (5,888) | |
| Warrants exercised | | 9,827 | | | — | | | 1,004 | | | — | | | — | | | 1,004 | |
| Share repurchases | | (407) | | | — | | | — | | | (15,000) | | | — | | | (15,000) | |
| Issuance of common stock for Maersk Drilling merger | | 60,107 | | | — | | | 1,800,130 | | | — | | | — | | | 1,800,130 | |
| Settlement of Compulsory Purchase Interest | | 4,148 | | | — | | | 123,754 | | | — | | | — | | | 123,754 | |
| Net income (loss) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 168,948 | | | — | | | 168,948 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (1,742) | | | (1,742) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | | 134,681 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 3,347,507 | | | $ | 255,930 | | | $ | 3,647 | | | $ | 3,607,085 | |
| Employee related equity activity: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amortization of share-based compensation | | — | | | — | | | 37,680 | | | — | | | — | | | 37,680 | |
| Issuance of share-based compensation shares | | 501 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Shares withheld for taxes on equity transactions | | — | | | — | | | (8,624) | | | — | | | — | | | (8,624) | |
| Warrants exercised | | 7,939 | | | — | | | 485 | | | — | | | — | | | 485 | |
| Share repurchases | | (2,347) | | | — | | | — | | | (94,826) | | | — | | | (94,826) | |
| Dividends | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (101,847) | | | — | | | (101,847) | |
| Net income (loss) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 481,902 | | | — | | | 481,902 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (615) | | | (615) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | | 140,774 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 3,377,048 | | | $ | 541,159 | | | $ | 3,032 | | | $ | 3,921,240 | |
| Employee related equity activity: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amortization of share-based compensation | | — | | | — | | | 43,797 | | | — | | | — | | | 43,797 | |
| Issuance of share-based compensation shares | | 2,131 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Shares withheld for taxes on equity transactions | | — | | | — | | | (66,057) | | | — | | | — | | | (66,057) | |
| Warrants exercised | | 245 | | | — | | | 1,443 | | | — | | | — | | | 1,443 | |
| Share repurchases | | (8,443) | | | — | | | — | | | (299,989) | | | — | | | (299,989) | |
| Issuance of common stock for Diamond Offshore Drilling merger | | 24,240 | | | — | | | 879,941 | | | — | | | — | | | 879,941 | |
| Dividends | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (278,279) | | | — | | | (278,279) | |
| Net income (loss) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 448,353 | | | — | | | 448,353 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 937 | | | 937 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2024 | | 158,947 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 4,236,172 | | | $ | 411,244 | | | $ | 3,969 | | | $ | 4,651,386 | |
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Note 1 — Organization and Significant Accounting Policies
Noble Corporation plc, a public limited company incorporated under the laws of England and Wales (“Noble”), is a leading offshore drilling contractor for the oil and gas industry. We provide contract drilling services to the international oil and gas industry with our global fleet of mobile offshore drilling units. Noble and its predecessors have been engaged in the contract drilling of oil and gas wells since 1921. As of December 31, 2024, our fleet of 40 drilling rigs consisted of 27 floaters and 13 jackups.
We report our contract drilling operations as a single reportable segment, Contract Drilling Services, which reflects how we manage our business. The mobile offshore drilling units comprising our offshore rig fleet operate in a global market for contract drilling services and are often redeployed to different regions due to changing demands of our customers, which consist primarily of large, integrated, independent, and government-owned or controlled oil and gas companies throughout the world.
On September 30, 2022 (the “Merger Effective Date”), pursuant to a business combination agreement, dated November 10, 2021 (as amended, the “Business Combination Agreement”), by and among Noble, Noble Corporation, an exempted company incorporated in the Cayman Islands with limited liability (“Noble Cayman”), Noble Newco Sub Limited, a Cayman Islands exempted company and a direct, wholly owned subsidiary of Noble (“Merger Sub”), and The Drilling Company of 1972 A/S, a Danish public limited liability company (“Maersk Drilling”), Noble Cayman merged with and into Merger Sub (the “Merger”), with Merger Sub surviving the Merger as a wholly owned subsidiary of Noble. As a result of the Merger, Noble became the ultimate parent of Noble Cayman and its respective subsidiaries.
On October 3, 2022 (the “Closing Date”), pursuant to the Business Combination Agreement, Noble completed a voluntary tender exchange offer to Maersk Drilling’s shareholders (the “Offer” and, together with the Merger and the other transactions contemplated by the Business Combination Agreement, the “Business Combination”) and because Noble acquired more than 90% of the issued and outstanding shares of Maersk Drilling, nominal value Danish krone (“DKK”) 10 per share (“Maersk Drilling Shares”), Noble redeemed all remaining Maersk Drilling Shares not exchanged in the Offer for, at the election of the holder, either A ordinary shares, par value $0.00001 per share, of Noble (“Ordinary Shares”) or cash (or, for those holders that did not make an election, only cash), under Danish law by way of a compulsory purchase (the “Compulsory Purchase”), which was completed in early November 2022. Upon completion of the Compulsory Purchase Maersk Drilling became a wholly owned subsidiary of Noble. The Merger is accounted for as a business combination in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 805, Business Combinations (“ASC 805”), where Noble is the accounting acquirer.
On June 9, 2024, Noble entered into an agreement and plan of merger (the “Diamond Merger Agreement”) with Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc. (“Diamond”), Dolphin Merger Sub 1, Inc., and Dolphin Merger Sub 2, Inc., under which Noble would acquire Diamond in a stock plus cash transaction (the “Diamond Transaction”). On September 4, 2024 (the “Diamond Closing Date”), Noble completed its acquisition of Diamond. The merger is accounted for as a business combination in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 805, where Noble is the accounting acquirer.
See “Note 2 — Acquisitions and Divestitures” for additional information.
As a result of the Merger, Noble became the successor issuer to Noble Cayman for purposes of and pursuant to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (“the Exchange Act”). References in this Annual Report on Form 10-K to “Noble,” the “Company,” “we,” “us,” and “our” refer collectively to (i) Noble Cayman and its consolidated subsidiaries prior to the Merger Effective Date, (ii) Noble and its consolidated subsidiaries (including Noble Cayman) on and after the Merger Effective Date, and (iii) Noble and its consolidated subsidiaries on and after the Diamond Closing Date, as applicable.
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include our accounts and those of our wholly-owned subsidiaries and entities in which we hold a controlling financial interest.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (“US GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amount
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Certain accounting policies involve judgments and uncertainties to such an extent that there is reasonable likelihood that materially different amounts could have been reported under different conditions, or if different assumptions had been used. We evaluate our estimates and assumptions on a regular basis. We base our estimates on historical experience and various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates and assumptions used in preparation of our consolidated financial statements.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand, demand deposits with banks, and all highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less. Our cash, cash equivalents, and short-term investments are subject to potential credit risk, and certain of our cash accounts carry balances greater than the federally insured limits. Cash and cash equivalents are primarily held by major banks or investment firms. Our cash management and investment policies restrict investments to lower risk, highly liquid securities and we perform periodic evaluations of the relative credit standing of the financial institutions with which we conduct business.
Restricted Cash
We classify restricted cash balances in current assets if the restriction is expected to expire or otherwise be resolved within one year and in other assets if the restriction is expected to expire or otherwise be resolved in more than one year. As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, our restricted cash balance consisted of $5.0 million and $7.0 million, respectively. All restricted cash is recorded in “Prepaid expenses and other current assets.” As of December 31, 2024, our restricted cash balance was related to cash collateral for Company rig performance guarantees and other performance obligations.
Accounts Receivable
We record accounts receivable at the amount we invoice our clients, net of allowance for credit losses. We provide an allowance for uncollectible accounts, as necessary. Our allowance for doubtful accounts was zero as of both December 31, 2024 and 2023.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment is stated at cost, reduced by provisions to recognize economic impairment. Major replacements and improvements are capitalized. When assets are sold, retired, or otherwise disposed of, the cost and related accumulated depreciation are eliminated from the accounts and the gain or loss is recognized. Drilling equipment and facilities are depreciated using the straight-line method over their estimated useful lives as of the date placed in service or date of major refurbishment. Estimated useful lives of our drilling equipment range from three to 30 years. Other property and equipment is depreciated using the straight-line method over useful lives ranging from two to 40 years.
Interest is capitalized on long-term construction projects using the weighted average cost of debt outstanding during the period of construction.
Scheduled maintenance of equipment is performed based on the number of hours operated in accordance with our preventative maintenance program. Routine repair and maintenance costs are charged to expense as incurred; however, the costs of the overhauls and asset replacement projects that benefit future periods and which typically occur every three to five years are capitalized when incurred and depreciated over an equivalent period. These overhauls and asset replacement projects are included in “Drilling equipment and facilities” in “Note 5 — Property and Equipment.”
We evaluate our property and equipment for impairment whenever there are changes in facts that suggest that the value of the asset is not recoverable. As part of this analysis, we make assumptions and estimates regarding future market conditions. When circumstances indicate that the carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable, management compares the carrying value to the expected undiscounted pre-tax future cash flows for the associated rig for which identifiable cash flows are independent of cash flows of other assets. If the expected undiscounted pre-tax future cash flows are lower than the carrying value, the net capitalized costs are reduced to fair value. An impairment loss is recognized to the extent that an asset's carrying value exceeds its estimated fair value. Fair value is generally estimated using a discounted cash flow model. The expected future cash flows used for impairment assessment and related fair value measurements are typically based on judgmental assessments of, but are not limited to, timing of future contract awards and expected operating dayrates, operating costs, utilization rates, discount rates, capital expenditures, reactivation costs, estimated economic useful lives and, in certain cases, our belief that a drilling unit is no longer marketable and is unlikely to
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
return to service in the near to medium term, and considering all available information at the date of assessment. During the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, we did not identify any impairment triggers for our property and equipment.
Fair Value Measurements
We measure certain of our assets and liabilities based on a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value. The three-level hierarchy, from highest to lowest level of observable inputs, are as follows:
Level 1 — Valuations based on quoted prices in active markets for identical assets;
Level 2 — Valuations based on observable inputs that do not meet the criteria for Level 1, including quoted prices in inactive markets and quoted prices in active markets for similar but not identical instruments; and
Level 3 — Valuations based on unobservable inputs.
Our cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash, accounts receivable, marketable securities, and accounts payable are by their nature short term. As a result, the carrying values included in our Consolidated Balance Sheets approximate fair value.
Business Combinations
In connection with our acquisitions, we apply the acquisition method of accounting. Accordingly, we record the acquired assets and assumed liabilities at fair value and recognize goodwill to the extent the consideration transferred exceeded the fair value of the net assets acquired. To the extent the fair value of the net assets acquired exceeded the consideration transferred, we recognize a bargain purchase gain. Changes in these judgments or estimates can have a material impact on the valuation of the respective assets and liabilities acquired and our results of operations in periods after acquisition. The allocation of the purchase price may be modified up to one year after the acquisition date as more information is obtained about the fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed. We estimate the fair values of the acquired assets and assumed liabilities as of the date of the acquisition. See “Note 2 — Acquisitions and Divestitures” for further information.
Revenue Recognition
The activities that primarily drive the revenue earned in our drilling contracts include (i) providing a drilling rig and the crew and supplies necessary to operate the rig, (ii) mobilizing and demobilizing the rig to and from the drill site, and (iii) performing rig preparation activities and/or modifications required for the contract. Consideration received for performing these activities may consist of dayrate drilling revenue, mobilization and demobilization revenue, contract preparation revenue, and reimbursement revenue. We account for these integrated services provided within our drilling contracts as a single performance obligation satisfied over time and comprised of a series of distinct time increments in which we provide drilling services.
Our standard drilling contracts require that we operate the rig at the direction of the customer throughout the contract term (which is the period we estimate to benefit from the corresponding activities and generally ranges from two to 60 months). The activities performed and the level of service provided can vary hour to hour. Our obligation under a standard contract is to provide whatever level of service is required by the operator, or customer, over the term of the contract. We are, therefore, under a stand-ready obligation throughout the entire contract duration. Consideration for our stand-ready obligation corresponds to distinct time increments, though the rate may be variable depending on various factors, and is recognized in the period in which the services are performed. The total transaction price is determined for each individual contract by estimating both fixed and variable consideration expected to be earned over the term of the contract. We have elected to exclude from the transaction price measurement all taxes assessed by a governmental authority. See further discussion regarding the allocation of the transaction price to the remaining performance obligations below.
The amount estimated for variable consideration may be subject to interrupted or restricted rates and is only included in the transaction price to the extent that it is probable that a significant reversal of previously recognized revenue will not occur throughout the term of the contract (“constrained revenue”). When determining if variable consideration should be constrained, management considers whether there are factors outside the Company’s control that could result in a significant reversal of revenue as well as the likelihood and magnitude of a potential reversal of revenue. These estimates are reassessed each reporting period as required.
Dayrate Drilling Revenue. Our drilling contracts generally provide for payment on a dayrate basis, with higher rates for periods when the drilling unit is operating and lower rates or zero rates for periods when drilling operations are interrupted or restricted. The dayrate invoices billed to the customer are typically determined based on the varying rates applicable to the specific activities performed on an hourly basis. Such dayrate consideration is allocated to the distinct hourly increment
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
it relates to within the contract term and, therefore, recognized in line with the contractual rate billed for the services provided for any given hour.
Mobilization/Demobilization Revenue. We may receive fees (on either a fixed lump-sum or variable dayrate basis) for the mobilization and demobilization of our rigs. These activities are not considered to be distinct within the context of the contract and, therefore, the associated revenue is allocated to the overall performance obligation and the associated pre-operating costs are deferred. We record a contract liability for mobilization fees received and a deferred asset for costs. Both revenue and pre-operating costs are recognized ratably over the initial term of the related drilling contract.
In most contracts, there is uncertainty as to the amount of expected demobilization revenue due to contractual provisions that stipulate that certain conditions must be present at contract completion for such revenue to be received and as to the amount thereof, if any. For example, contractual provisions may require that a rig demobilize a certain distance before the demobilization revenue is payable or the amount may vary dependent upon whether or not the rig has additional contracted work within a certain distance from the wellsite. Therefore, the estimate for such revenue may be constrained, as described earlier, depending on the facts and circumstances pertaining to the specific contract. We assess the likelihood of receiving such revenue based on past experience and knowledge of the market conditions. In cases where demobilization revenue is expected to be received upon contract completion, it is estimated as part of the overall transaction price at contract inception and recognized in earnings ratably over the initial term of the contract with an offset to an accretive contract asset.
Contract Preparation Revenue. Some of our drilling contracts require downtime before the start of the contract to prepare the rig to meet customer requirements. At times, we may be compensated by the customer for such work (on either a fixed lump-sum or variable dayrate basis). These activities are not considered to be distinct within the context of the contract and, therefore, the related revenue is allocated to the overall performance obligation and recognized ratably over the initial term of the related drilling contract. We record a contract liability for contract preparation fees received, which is amortized ratably to contract drilling revenue over the initial term of the related drilling contract.
Bonuses, Penalties, and Other Variable Consideration. We may receive bonus increases to revenue or penalty decreases to revenue. Based on historical data and ongoing communication with the operator/customer, we are able to reasonably estimate this variable consideration. We will record such estimated variable consideration and remeasure our estimates at each reporting date.
Capital Modification Revenue. From time to time, we may receive fees from our customers for capital improvements to our rigs to meet contractual requirements (on either a fixed lump-sum or variable dayrate basis). Such revenue is allocated to the overall performance obligation and recognized ratably over the initial term of the related drilling contract as these activities are integral to our drilling activities and are not considered to be a stand-alone service provided to the customer within the context of our contracts. We record a contract liability for such fees and recognize them ratably as contract drilling revenue over the term of the related drilling contract commencing when the asset is ready for its intended use.
Revenues Related to Reimbursable Expenses. We generally receive reimbursements from our customers for the purchase of supplies, equipment, personnel services, and other services provided at their request in accordance with a drilling contract or other agreement. Such reimbursable revenue is variable and subject to uncertainty, as the amounts received and timing thereof is highly dependent on factors outside of our influence. Accordingly, reimbursable revenue is constrained revenue and not included in the total transaction price until the uncertainty is resolved, which typically occurs when the related costs are incurred on behalf of a customer. We are generally considered a principal in such transactions and record the associated revenue at the gross amount billed to the customer as “Reimbursables and other” in our Consolidated Statements of Operations. Such amounts are recognized ratably over the period within the contract term during which the corresponding goods and services are to be consumed.
Deferred revenues from drilling contracts totaled $101.9 million and $43.1 million at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Such amounts are included in either “Other current liabilities” or “Other liabilities” in the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets, based upon our expected time of recognition. Related expenses deferred under drilling contracts totaled $37.1 million and $4.4 million at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, and are included in either “Prepaid expenses and other current assets” or “Other assets” in the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets, based upon our expected time of recognition.
We record reimbursements from customers for “out-of-pocket” expenses as revenues and the related direct cost as operating expenses.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Income Taxes
Income taxes are based on the laws and rates in effect in the countries in which operations are conducted or in which we or our subsidiaries are considered resident for income tax purposes. In certain circumstances, we expect that, due to changing demands of the offshore drilling markets and the ability to redeploy our offshore drilling units, certain of such units will not reside in a location long enough to give rise to future tax consequences. As a result, no deferred tax asset or liability has been recognized in these circumstances. Should our expectations change regarding the length of time an offshore drilling unit will be used in a given location, we will adjust deferred taxes accordingly.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the anticipated future tax effects of temporary differences between the financial statement basis and the tax basis of our assets and liabilities using the applicable jurisdictional tax rates at year end. A valuation allowance for deferred tax assets is recorded when it is more likely than not that the deferred tax asset will not be realized in a future period.
We operate through various subsidiaries in numerous countries throughout the world, including the United States. Consequently, we are subject to changes in tax laws, treaties, and regulations or the interpretation or enforcement thereof in the United States, UK, and any other jurisdictions in which we or any of our subsidiaries operate or are resident. Our income tax expense is based upon our interpretation of the tax laws in effect in various countries at the time that the expense was incurred. If the IRS or other taxing authorities do not agree with our assessment of the effects of such laws, treaties, and regulations, this could have a material adverse effect on us including the imposition of a higher effective tax rate on our worldwide earnings or a reclassification of the tax impact of our significant corporate restructuring transactions. The Company has adopted an accounting policy to look through the outside basis of partnerships and all other flow-through entities and exclude these from the computation of deferred taxes.
Insurance Recoveries
The Company maintains insurance coverage for personal injuries, property damage, and certain other losses sustained during operations. Recoveries from insurance are recorded when a loss has been recognized and realization is probable, and are measured at the lower of the loss recognized or the probable recovery. Timing differences may occur between the loss recognized, damage costs, capital expenditures made to repair or restore properties, and recognition and receipt of insurance proceeds reflected in the Company’s financial statements. Costs, as well as insurance recoveries, related to the Hurricane Ida event in 2021 are presented in “Hurricane losses and (recoveries), net” on the Consolidated Statements of Operations. See “Note 12 — Commitments and Contingencies” for additional information.
Claims Reserves
We maintain various levels of self-insured retention for certain losses including property damage, loss of hire, employment practices liability, employers’ liability, and general liability, among others. We accrue for property damage and loss of hire charges on a per event basis.
Employment practices liability claims are accrued based on actual claims during the year. Maritime employer’s liability claims are generally estimated using actuarial determinations. General liability claims are estimated by our internal claims department by evaluating the facts and circumstances of each claim (including incurred but not reported claims) and making estimates based upon historical experience with similar claims. At December 31, 2024, loss reserves for personal injury and protection claims totaled $164.1 million, of which $149.2 million was included in “Other current liabilities” and $14.9 million in “Other long-term liabilities” in the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets. At December 31, 2023, loss reserves for personal injury and protection claims totaled $63.9 million of which $21.9 million was included in “Other current liabilities” and $42.0 million in “Other long-term liabilities” in the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Earnings per Share
Our unvested share-based payment awards, which contain non-forfeitable rights to dividends, are participating securities and are included in the computation of earnings per share pursuant to the two-class method. The two-class method allocates undistributed earnings between common shares and participating securities. The diluted earnings per share calculation under the two-class method also includes the dilutive effect of potential shares issued in connection with stock warrants and options. The dilutive effect of stock warrants and options is determined using the Treasury Stock Method. The diluted earnings per share calculation is adjusted for mandatory exercise, under the Treasury Stock Method, if the condition is met at the balance sheet date. At December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Mandatory Exercise Condition (as defined in the applicable warrant agreement) set forth in the warrant agreements for the Tranche 1 Warrants and the Tranche 2 Warrants was satisfied. See “Note 4 — Income (Loss) Per Share” for additional information.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Share-Based Compensation Plans
We record the grant date fair value of share-based compensation arrangements as compensation cost using a straight-line method over the service period. Share-based compensation is expensed or capitalized based on the nature of the employee’s activities. The Company classified certain awards that will be settled in cash as liability awards. The fair value of a liability-classified award is determined on a quarterly basis beginning at the grant date until final vesting. Changes in the fair value of liability-classified awards are expensed or capitalized based on the nature of the employee’s activities over the vesting period of the award.
Litigation Contingencies
We are involved in legal proceedings, claims, and regulatory, tax, or government inquiries and investigations that arise in the ordinary course of business. Certain of these matters include speculative claims for substantial or indeterminate amounts of damages. We record a liability when we believe that it is both probable that a loss has been incurred and the amount can be reasonably estimated. If we determine that a loss is reasonably possible and the loss or range of loss can be estimated, we disclose the possible loss in the notes to the consolidated financial statements.
We review the developments in our contingencies that could affect the amount of the provisions that has been previously recorded, and the matters and related possible losses disclosed. We make adjustments to our provisions and changes to our disclosures accordingly to reflect the impact of negotiations, settlements, rulings, advice of legal counsel, and updated information. Significant judgment is required to determine both the probability and the estimated amount.
Foreign Currency
Although we are a UK company, our functional currency is the US dollar, and we define any non-US dollar denominated currency as “foreign currencies.” In non-US locations where the US dollar has been designated as the functional currency (based on an evaluation of factors including the markets in which the subsidiary operates, inflation, generation of cash flow, financing activities, and intercompany arrangements), local currency transaction gains and losses are included in net income or loss.
Derivative Financial Instruments
We have used foreign currency forward contracts and interest rate swaps in order to manage our exposure to fluctuations in currency exchange and interest rates, respectively. The contracts are not entered into for trading purposes. The Company has not designated these derivative instruments as hedges. We recognize the derivatives at fair value on the Consolidated Balance Sheets and, where applicable, such contracts covered by master netting agreements are reported net. Gross positive fair values are netted with gross negative fair values by counterparty. Realized gains and losses as well as changes in the fair values of derivative financial instruments are recognized in the income statement in “Interest income and other, net.”
Accounting Pronouncements
Accounting Standards Adopted.
In November 2023, the FASB issued ASU No. 2023-07 ("ASU 2023-07"), Segment Reporting (Topic 280): Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures, which requires, among other things, the following: (i) enhanced disclosures about significant segment expenses that are regularly provided to the chief operating decision maker and included in a segment's reported measure of profit or loss, (ii) disclosure of the amount and description of the composition of other segment items, as defined in ASU 2023-07, by reportable segment, and (iii) reporting the disclosures about each reportable segment's profit or loss and assets on an annual and interim basis.
Recently Issued Accounting Standards.
In November 2024, the FASB issued ASU No. 2024-04 ("ASU 2024-04"), Debt—Debt with Conversion and Other Options (Subtopic 470-20). The Board is issuing this Update to improve the relevance and consistency in application of the induced conversion guidance in Subtopic 470-20, Debt— Debt with Conversion and Other Options. When the terms of a convertible debt instrument are changed to induce conversion of the instrument, current generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) provide guidance for determining whether the transaction should be accounted for as an induced conversion (as opposed to a debt extinguishment). The induced conversion guidance was written in the context of share-settled convertible debt before cash convertible instruments became prevalent in the marketplace. The Company continues to assess the potential impact of this pronouncement.
In November 2024, the FASB issued ASU No. 2024-03 ("ASU 2024-03"), Income Statement—Reporting Comprehensive Income—Expense Disaggregation Disclosures (Subtopic 220-40): Disaggregation of Income Statement Expenses. The
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
amendments in this Update require disclosure, in the notes to financial statements, of specified information about certain costs and expenses. An entity is not precluded from providing additional voluntary disclosures that may provide investors with additional decision-useful information. The amendments in this Update are effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2026, and interim reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2027. Early adoption is permitted. The Company continues to assess the potential impact of this pronouncement.
In December 2023, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") No. 2023-09 ("ASU 2023-09"), Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures, which requires, among other things, the following for public business entities: (i) enhanced disclosures of specific categories of reconciling items included in the rate reconciliation, as well as additional information for any of these items meeting certain qualitative and quantitative thresholds, (ii) disclosure of the nature, effect, and underlying causes of each individual reconciling item disclosed in the rate reconciliation and the judgment used in categorizing them if not otherwise evident, and (iii) enhanced disclosures for income taxes paid, which includes federal, state, and foreign taxes, as well as for individual jurisdictions over a certain quantitative threshold. The amendments in ASU 2023-09 eliminate the requirement to disclose the nature and estimate of the range of the reasonably possible change in unrecognized tax benefits for the 12 months after the balance sheet date. The provisions of ASU 2023-09 are effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2024; early adoption is permitted. The Company continues to evaluate the potential impact of this pronouncement.
Note 2 — Acquisitions and Divestitures
Business Combination with Diamond Offshore Drilling
On the Diamond Closing Date, Noble completed its acquisition of Diamond. Pursuant to the terms and conditions set forth in the Diamond Merger Agreement, Diamond shareholders received 0.2316 shares of Noble, plus cash consideration of $5.65 per share for each share of Diamond.
Purchase Price Allocation
The Diamond Transaction has been accounted for using the acquisition method of accounting under ASC Topic 805, Business Combinations, with Noble being treated as the accounting acquirer. Under the acquisition method of accounting, the assets acquired and liabilities assumed of Diamond and its subsidiaries were recorded at their respective fair values on the Diamond Closing Date. Total consideration for the acquisition was $1.5 billion, which included $610.3 million in cash paid and $879.9 million in non-cash consideration, primarily related to Ordinary shares issued to legacy Diamond shareholders and the replacement of legacy Diamond RSUs (as defined below).
Determining the fair values of the assets and liabilities of Diamond and the consideration paid required judgment and certain assumptions to be made. The most significant fair value estimates related to the valuation of Diamond’s mobile offshore drilling units and other related tangible assets, the fair value of drilling contracts, and debt.
Offshore drilling units. The valuation of Diamond’s mobile offshore drilling units was determined using the discounted cash flows expected to be generated from the drilling assets over their remaining useful lives. Assumptions used in our assessment included, but were not limited to, future marketability of each unit in light of the current market conditions and its current technical specifications, timing of future contract awards and expected operating dayrates, operating costs, rig utilization rates, tax rates, discount rate, capital expenditures, synergies, market values, estimated economic useful lives of the rigs and, in certain cases, our belief that a drilling unit is no longer marketable and is unlikely to return to service in the near to medium term.
Diamond off-market contracts. The Company recorded, with the assistance of external valuation specialists, liabilities from drilling contracts that had unfavorable terms compared to the current market which were recorded on the Diamond Closing Date. The Company recognized the fair value adjustments as off-market contract liabilities recorded in “Noncurrent contract liabilities.”
Diamond debt. In connection with the Diamond Transaction, the Company assumed the Diamond Second Lien Notes (as defined herein) in an outstanding principal debt amount of $550.0 million and terminated the Diamond Revolving Credit Facility in the principal amount of $300.0 million, which was scheduled to mature in April 2026. The valuation of the Diamond Second Lien Notes was based on relevant market data as of the Diamond Closing Date and the term of the Diamond Second Lien Notes. Considering that the interest rate and implied yield for the Diamond Second Lien Notes were within a range of comparable market yields (with considerations for term and seniority), a fair value adjustment was recorded relating to the Diamond Second Lien Notes. For additional information, see “Note 6 — Debt.”
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
The following table represents the allocation of the total purchase price of Diamond to the identifiable assets acquired and the liabilities assumed based on the fair values as of the Diamond Closing Date. In connection with this acquisition, the Company incurred $84.5 million of acquisition related costs during the year ended December 31, 2024. The results of Diamond operations were included in the Company’s results of operations effective on the Diamond Closing Date. Upon completion of our assessment as of December 31, 2024, the Company concluded that no goodwill nor gain on bargain purchase should be recorded as appropriate under US GAAP.
| | | | | | | | |
| Purchase price consideration: | | |
| Fair value of Ordinary Shares transferred to legacy Diamond shareholders | | $ | 857,678 | |
| Fair value of replacement Diamond RSU Awards attributable to the purchase price | | 22,263 | |
| Cash paid to legacy Diamond shareholders | | 583,152 | |
| Cash paid to terminate the Diamond Revolving Credit Facility | | 308 | |
| Cash paid to settle contingent success fees | | 17,316 | |
| Cash paid for retention bonuses | | 4,422 | |
| Cash paid for short-term incentive plans | | 5,086 | |
| Total purchase price consideration | | $ | 1,490,225 | |
| | |
| Assets acquired: | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 193,243 | |
| Accounts receivable, net | | 193,194 | |
| Taxes receivable | | 6,971 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | 69,781 | |
| Total current assets | | 463,189 | |
| Property and equipment, net | | 1,817,986 | |
Assets held for sale (1) | | 5,300 | |
| Other assets | | 193,289 | |
| Total assets acquired | | 2,479,764 | |
| Liabilities assumed: | | |
| Accounts payable | | 82,805 | |
| Accrued payroll and related costs | | 36,791 | |
| Taxes payable | | 3,699 | |
| Interest payable | | 19,750 | |
| Other current liabilities | | 137,788 | |
| Total current liabilities | | 280,833 | |
| Long-term debt | | 580,250 | |
| Deferred income taxes | | 184 | |
| Noncurrent contract liabilities | | 27,663 | |
| Other liabilities | | 100,609 | |
| Total liabilities assumed | | 989,539 | |
| Net assets acquired | | $ | 1,490,225 | |
(1)During the third quarter of 2024, we sold the Ocean Valiant for total proceeds of $5.6 million. See “Note 5 — Property and Equipment.”
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Diamond Revenue and Net Income
The following table represents Diamond’s revenue and earnings included in Noble’s Consolidated Statements of Operations subsequent to the Diamond Closing Date of the Diamond Transaction.
| | | | | | | | |
| | Period from
September 4, 2024
through
December 31, 2024 |
| Revenue | | $ | 336,542 | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 24,431 | |
Pro Forma Financial Information
The following unaudited pro forma summary presents the results of operations as if the Diamond Transaction had occurred on January 1, 2023. The pro forma summary uses estimates and assumptions based on information available at the time. Management believes the estimates and assumptions to be reasonable; however, actual results may have differed significantly from this pro forma financial information. The pro forma information does not reflect any synergy savings that might have been achieved from combining the operations and is not intended to reflect the actual results that would have occurred had the companies actually been combined during the periods presented.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Twelve Months Ended December 31, 2024 | | Twelve Months Ended December 31, 2023 |
| Revenue | | $ | 3,081,879 | | | $ | 3,672,860 | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 375,402 | | | $ | 358,549 | |
| Net income (loss) per share: | | | | |
| Basic | | $ | 2.26 | | | $ | 2.21 | |
| Diluted | | $ | 2.19 | | | $ | 2.09 | |
The pro forma results include, among others, (i) an increase to Diamond’s historically reported depreciation expense related to adjustments of property and equipment values, (ii) adjustments to reflect certain acquisition related costs incurred directly in connection with the Diamond Transaction as if it had occurred on January 1, 2023, and (iii) net adjustments to increase contract drilling services revenue related to off-market customer contract liabilities recognized in connection with the Diamond Transaction on a pro forma basis.
Business Combination with Maersk Drilling
On the Merger Effective Date, pursuant to the Business Combination Agreement, Noble Cayman merged with and into Merger Sub, with Merger Sub surviving the Merger as a wholly owned subsidiary of Noble, and (i) each Noble Cayman Share issued and outstanding prior to the effective time of the Merger (the “Merger Effective Time”) was converted into one newly and validly issued, fully paid, and non-assessable Ordinary Share of Noble and (ii) each Noble Cayman Warrant (as defined herein) issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Merger Effective Time was converted automatically into a warrant to acquire a number of Ordinary Shares equal to the number of Noble Cayman Shares underlying such warrant, with the same terms as were in effect immediately prior to the Merger Effective Time under the terms of the applicable Noble Cayman Warrant Agreement (as defined herein) (collectively, the “Warrants”). In addition, each award of restricted share units representing the right to receive Noble Cayman Shares, or value based on the value of Noble Cayman Shares (each, a “Noble Cayman RSU Award”), outstanding immediately prior to the Merger Effective Time ceased to represent a right to acquire Noble Cayman Shares (or value equivalent to Noble Cayman Shares) and was converted into the right to acquire, on the same terms and conditions as were applicable under the Noble Cayman RSU Award (including any vesting conditions), that number of Ordinary Shares equal to the number of Noble Cayman Shares subject to such Noble Cayman RSU Award immediately prior to the Merger Effective Time. As a result of the Merger, Noble became the ultimate parent of Noble Cayman and its respective subsidiaries effective as of the Merger Effective Time.
On the Closing Date, pursuant to the Business Combination Agreement, Noble completed the Offer and because Noble acquired more than 90% of the issued and outstanding Maersk Drilling Shares, Noble redeemed all remaining Maersk Drilling Shares not exchanged in the Offer for, at the election of the holder, either Ordinary Shares or cash (or, for those holders that do not make an election, only cash), under Danish law by way of the Compulsory Purchase. The Compulsory Purchase was completed in early November 2022, at which time Maersk Drilling became a wholly owned subsidiary of
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Noble. After the close of the Business Combination, Maersk Drilling was contributed by Noble to Noble Finance Company, an exempted company incorporated in the Cayman Islands with limited liability (“Finco”), in a common control transaction.
In connection with the Offer and the Compulsory Purchase, each Maersk Drilling Share was exchanged for either (i) 1.6137 newly and validly issued, fully paid and non-assessable Ordinary Shares (the “Exchange Ratio”) or (ii) cash consideration (payable in DKK). The Offer was subject to a cash consideration cap per Maersk Drilling shareholder of $1,000 and an aggregate cap on cash consideration payable to all Maersk Drilling shareholders of $50 million. Consequently, in relation to the Offer, Maersk Drilling shareholders who elected to receive cash consideration in the Offer received, as applicable, (i) $1,000 for the applicable portion of their Maersk Drilling Shares and the balance of Maersk Drilling Shares in Ordinary Shares in accordance with the Exchange Ratio or (ii) the amount corresponding to the total holding of their Maersk Drilling Shares if such holding of Maersk Drilling Shares represented a value equal to or less than $1,000 in the aggregate. The Compulsory Purchase was not subject to a cash consideration cap per holder or an aggregate cap for cash consideration.
In addition, each Maersk Drilling restricted stock unit award (a “Maersk Drilling RSU Award”) that was outstanding immediately prior to the acceptance time of the Offer (the “Acceptance Time”) was exchanged, at the Acceptance Time, with the right to receive, on the same terms and conditions as were applicable under the Maersk Drilling RSU Long-Term Incentive Programme for Executive Management 2019 and the Maersk Drilling RSU Long-Term Incentive Programme 2019 (including any vesting conditions), that number of Ordinary Shares equal to the product of (i) the number of Maersk Drilling Shares subject to such Maersk Drilling RSU Award immediately prior to the Acceptance Time and (ii) the Exchange Ratio, with any fractional Maersk Drilling Shares rounded to the nearest whole share. Upon such exchange, Maersk Drilling RSU Awards ceased to represent a right to receive Maersk Drilling Shares (or value equivalent to Maersk Drilling Shares).
In September 2021, eligible Maersk Drilling employees signed an addendum to their existing service agreements that provides for enhanced severance terms in the event of termination as well as a retention bonus (“Deal Completion Bonus”) to be paid irrespective of termination if a transaction with Noble were to close (the “Retention Addendum”). The Retention Addendum was entered into on September 20, 2021. The Deal Completion Bonus was paid on October 3, 2022, for five Maersk executives terminated immediately upon close and on October 31, 2022, for all other eligible individuals.
Purchase Price Allocation
The Business Combination has been accounted for using the acquisition method of accounting under ASC Topic 805, Business Combination, with Noble being treated as the accounting acquirer. Under the acquisition method of accounting, the assets and liabilities of Maersk Drilling and its subsidiaries were recorded at their respective fair values on the Closing Date. Total consideration for the acquisition was $2.0 billion, which included $5.6 million in net cash paid and $2.0 billion in non-cash consideration, primarily related to Ordinary Shares issued to legacy Maersk shareholders and the replacement of legacy Maersk Drilling RSU Awards.
Determining the fair values of the assets and liabilities of Maersk Drilling and the consideration paid required judgment and certain assumptions to be made. The most significant fair value estimates related to the valuation of Maersk Drilling’s mobile offshore drilling units and other related tangible assets and the fair value of drilling contracts and other intangibles.
Offshore Drilling Units. The valuation of Maersk Drilling’s mobile offshore drilling units was determined using either (i) the discounted cash flows expected to be generated from the drilling assets over their remaining useful lives or (ii) the cost to replace the drilling assets as adjusted by the current market for similar offshore drilling assets. Assumptions used in our assessment included, but were not limited to, future marketability of each unit in light of the current market conditions and its current technical specifications, timing of future contract awards and expected operating dayrates, operating costs, rig utilization rates, tax rates, discount rate, capital expenditures, synergies, market values, estimated economic useful lives of the rigs and, in certain cases, our belief that a drilling unit is no longer marketable and is unlikely to return to service in the near to medium term.
Compulsory Purchase. Noble redeemed all of the remaining 4.1 million shares of Maersk Drilling Shares not exchanged in the Offer for, at the election of the holder, either Ordinary Shares or cash (or, for those holders that did not make an election, only cash), as required under Danish law by way of the Compulsory Purchase. The Company recognized the Compulsory Purchase as a redeemable interest at fair value upon the closing of the Business Combination. The Company determined that the fair value of the Compulsory Purchase was $193.7 million utilizing inputs which included Noble share price and cash redemption amount as of the Closing Date. The Compulsory Purchase interest was derecognized in mid-November 2022, with a portion being offset to common stock when 4.1 million Ordinary Shares were issued, additional paid in capital of $123.8 million and the remainder being the amount paid in cash of $69.9 million.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Maersk Drilling Debt. On December 22, 2022, Maersk Drilling, as borrower, Noble Corporation plc, as parent guarantor, certain subsidiaries of Maersk Drilling party thereto, as guarantors, entered into a term loan (the “DNB Credit Facility”) under a term facility agreement, dated as of December 22, 2022 (as amended or otherwise modified from time to time), with DNB Bank ASA, New York Branch, as agent and security agent, and the other lenders party thereto. In connection with the Business Combination, the Company guaranteed the DNB Credit Facility and the DSF Credit Facility. The DSF Credit Facility had a floating interest rate that fluctuated based on market rates, thus fair value approximated the carrying amount. On February 23, 2023, the remaining amount under the DSF Credit Facility was paid in full using cash on hand. On April 18, 2023, we repaid all outstanding borrowings under the DNB Credit Facility. For additional information on the credit facilities see “Note 6 — Debt.”
Maersk Drilling Off-market Contracts. The Company recorded, with the assistance of external valuation specialists, intangible assets and liabilities from drilling contracts that had favorable and unfavorable terms compared to the current market which were recorded on the Closing Date. The Company recognized the fair value adjustments as off-market contract assets and liabilities recorded in “Intangible assets” and “Noncurrent contract liabilities,” respectively.
The following table represents the allocation of the total purchase price of Maersk Drilling to the identifiable assets acquired and the liabilities assumed based on the fair values as of the Closing Date. In connection with this acquisition, the Company incurred $24.9 million, $34.1 million, and $33.1 million of acquisition related costs during the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively. The results of Maersk Drilling operations were included in the Company’s results of operations effective on the Closing Date. The Business Combination resulted in a gain on bargain purchase due to the estimated fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired exceeding the purchase consideration transferred by $5.0 million and is shown as a gain on bargain purchase on Noble’s Consolidated Statement of Operations. Management reviewed the Maersk Drilling assets acquired and liabilities assumed as well as the assumptions utilized in estimating their fair values. Upon completion of our assessment as of September 30, 2023, the Company concluded that recording a gain on bargain purchase was appropriate and required under US GAAP.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
| | | | | | | | |
| Purchase price consideration: | | |
| Fair value of Ordinary Shares transferred to legacy Maersk shareholders | | $ | 1,793,351 | |
| Cash paid to legacy Maersk shareholders | | 887 | |
| Fair value of replacement Maersk Drilling RSU Awards attributable to the purchase price | | 6,780 | |
| Deal Completion Bonus | | 6,177 | |
| Fair Value of Compulsory Purchase | | 193,678 | |
| Total purchase price consideration | | $ | 2,000,873 | |
| | |
| Assets acquired: | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 172,205 | |
| Accounts receivable, net | | 250,251 | |
Taxes receivable (1) | | 18,987 | |
Prepaid expenses and other current assets (1) | | 43,168 | |
| Total current assets | | 484,611 | |
| Intangible assets | | 22,991 | |
| Property, plant, and equipment, net | | 2,756,096 | |
Other assets (1) | | 94,882 | |
| Total assets acquired | | 3,358,580 | |
| Liabilities assumed: | | |
| Current maturities of long-term debt | | 129,130 | |
| Accounts payable | | 130,273 | |
Accrued payroll and related costs (1) | | 23,884 | |
Taxes payable (1) | | 29,219 | |
| Interest payable | | 800 | |
Other current liabilities (1) | | 44,253 | |
| Total current liabilities | | 357,559 | |
| Long-term debt | | 596,692 | |
| Deferred income taxes | | 4,071 | |
| Noncurrent contract liabilities | | 237,703 | |
Other liabilities (1) | | 156,677 | |
| Total liabilities assumed | | 1,352,702 | |
| Net assets acquired | | 2,005,878 | |
Gain on bargain purchase (1) | | (5,005) | |
| Purchase price consideration | | $ | 2,000,873 | |
(1)During the nine months ended September 30, 2023, the Company recorded tax adjustments, which resulted in a net decrease in current taxes receivable and current taxes payable of $1.6 million and $9.0 million, respectively, a net increase in deferred tax assets of $25.2 million, a net increase in other current liabilities of $3.0 million, a net increase in reserves for uncertain tax positions of $13.1 million, and a net decrease in other tax liabilities of $14.6 million. Other adjustments were made to remeasure certain payroll tax related balances. As a result of the aforementioned adjustments, initial goodwill recognized on the purchase was revised to a gain on bargain purchase.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Maersk Drilling Revenue and Net Income
The following table represents Maersk Drilling’s revenue and earnings included in Noble’s Consolidated Statements of Operations subsequent to the Closing Date of the Business Combination.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Period from October 3, 2022, through December 31, 2022 | | |
| Revenue | | | | $ | 341,490 | | | |
| Net loss | | | | $ | 21,690 | | | |
Pro Forma Financial Information
The following unaudited pro forma summary presents the results of operations as if the Business Combination had occurred on February 6, 2021. The pro forma summary uses estimates and assumptions based on information available at the time. Management believes the estimates and assumptions to be reasonable; however, actual results may have differed significantly from this pro forma financial information. The pro forma information does not reflect any synergy savings that might have been achieved from combining the operations and is not intended to reflect the actual results that would have occurred had the companies actually been combined during the periods presented.
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Twelve Months Ended December 31, 2022 |
| Revenue | | | | $ | 2,218,117 | |
| Net income (loss) | | | | $ | (19,246) | |
| Net income (loss) per share | | | | |
| Basic | | | | $ | (0.14) | |
| Diluted | | | | $ | (0.14) | |
The pro forma results include, among others, (i) a reduction to Maersk Drilling’s historically reported depreciation expense related to adjustments of property and equipment values, (ii) adjustments to reflect certain acquisition related costs incurred directly in connection with the Business Combination as if it had occurred on February 6, 2021, (iii) an adjustment to reflect the gain on sale as if the Rig Transaction (discussed below) had occurred on February 6, 2021, and (iv) net adjustments to increase contract drilling services revenue related to off-market customer contract assets and liabilities recognized in connection with the Business Combination with Maersk Drilling on a pro forma basis.
Rig Transaction
On June 23, 2022, Noble and Shelf Drilling (North Sea), Ltd. and Shelf Drilling, Ltd. (together “Shelf Drilling”) entered into the sale by Noble and the purchase by Shelf Drilling of five jackup rigs known as the Noble Hans Deul, Noble Houston Colbert, Noble Lloyd Noble, Noble Sam Hartley, and Noble Sam Turner and all related support and infrastructure (collectively, and together with the related offshore and onshore personnel and related operations, the “Divestment Business”). On October 5, 2022, Noble and Shelf Drilling completed the sale (the “Rig Transaction”) as part of the Business Combination. The Rig Transaction addressed the potential concerns identified by the UK Competition and Markets Authority of the Business Combination and was approved by them in September 2022.
In connection with the Rig Transaction, the Divestment Business was transferred by Noble to Shelf Drilling for a purchase price of $375 million in cash which resulted in a gain of $85.1 million. As of the date of the Rig Transaction, Shelf Drilling gained control of the Noble Lloyd Noble. For a transition period following the completion of the Rig Transaction, Noble agreed to continue to operate the Noble Lloyd Noble under operating agreements with Shelf Drilling (the “NLN Charter Agreement”) and to provide certain other transition services to Shelf Drilling. Under the operating agreements, we agreed to remit the collections from our customers under the associated drilling contracts to Shelf Drilling, and Shelf Drilling agreed to reimburse us for our direct costs and expenses incurred while operating the Noble Lloyd Noble on behalf of Shelf Drilling (with certain exceptions). As of December 31, 2023, the NLN Charter Agreement is closed and the Noble Lloyd Noble is no longer operated by Noble.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Note 3 — Merger and Integration Costs
During the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, the Company incurred $109.4 million, $60.3 million, and $84.7 million, respectively, of merger and integration costs directly attributable to its merger and integration activities associated with the business combinations with Diamond Offshore and Maersk Drilling. Merger and integration costs consisted primarily of transaction-related acquisition costs, costs related to integration activities, severance costs, retention costs, professional fees, and other costs such as share-based compensation charges that are directly attributable to these activities. All merger and integration costs were expensed as incurred and recorded under “Merger and integration costs.”
Most merger and integration costs do not qualify for special accounting treatment as exit or disposal activities; however, during the year ended December 31, 2024, the Company incurred $4.1 million related to certain employee compensation that qualifies as exit or disposal activities. During the year ended December 31, 2022, the Company incurred $0.8 million related to certain employee compensation that qualifies as exit or disposal activities.
In connection with these activities, Noble has incurred various costs associated with contractual termination benefits, including severance, accelerated vesting of share-based compensation and other expenses. These termination benefits have been accounted for under ASC 712, “Compensation - Nonretirement Post-Employment Benefits” and ASC 718, “Compensation - Stock Compensation.”
Note 4 — Income (Loss) Per Share
The following table presents the computation of basic and diluted earnings per share:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Numerator: | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 448,353 | | | $ | 481,902 | | | $ | 168,948 | |
| Denominator: | | | | | | |
| Weighted average shares outstanding — basic | | 148,733 | | | 138,380 | | | 85,055 | |
| Dilutive effect of share-based awards | | 1,512 | | | 3,158 | | | 3,334 | |
| Dilutive effect of warrants | | 1,394 | | | 3,659 | | | 8,489 | |
Dilutive effect of compulsory purchase (1) | | — | | | — | | | 729 | |
| Weighted average shares outstanding — diluted | | 151,639 | | | 145,197 | | | 97,607 | |
| Per share data: | | | | | | |
| Basic | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 3.01 | | | $ | 3.48 | | | $ | 1.99 | |
| Diluted | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 2.96 | | | $ | 3.32 | | | $ | 1.73 | |
(1) Represents the dilutive effect on outstanding shares between when the Compulsory Purchase interest was recorded on the Closing Date and when it was derecognized in mid-November 2022.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Only those items having a dilutive impact on our basic income per share are included in diluted income per share. The following table displays the share-based instruments that have been excluded from diluted income per share since the effect would have been anti-dilutive:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| | | | | | |
Warrants (1) | | 2,774 | | | 2,774 | | | 2,774 | |
(1) Represents the total number of warrants outstanding which did not have a dilutive effect. In periods where the warrants are determined to be dilutive, the number of shares which will be included in the computation of diluted shares is determined using the Treasury Stock Method, adjusted for mandatory exercise provisions under the warrant agreements if applicable.
Note 5 — Property and Equipment
Property and equipment, at cost, for Noble consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Drilling equipment and facilities | | $ | 6,650,034 | | | $ | 4,338,229 | |
| Construction in progress | | 197,789 | | | 210,759 | |
| Other | | 56,908 | | | 42,948 | |
| Property and equipment, at cost | | $ | 6,904,731 | | | $ | 4,591,936 | |
Capital additions, including capitalized interest, during the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022 totaled $520.3 million, $454.3 million, and $193.6 million, respectively.
During 2024, we sold the Noble Explorer for total proceeds of $25.0 million, $21.5 million of which was received in the fourth quarter of 2023, resulting in a pre-tax gain of $17.4 million. Also, during 2024, we sold the Ocean Valiant and the Ocean Onyx for total proceeds of $5.6 million and $5.2 million, respectively.
During 2022, we sold the Divestment Business as part of the Rig Transaction for total net proceeds of $366.8 million, resulting in a gain of $85.1 million, and the Noble Clyde Boudreaux for total net proceeds of $14.2 million, resulting in a gain of $6.8 million.
Note 6 — Debt
Amended and Restated Senior Secured Revolving Credit Agreement
In April 2023, Noble entered into the Amended and Restated Senior Secured Revolving Credit Agreement, dated as of April 18, 2023, and as amended on June 24, 2024 (the “2023 Revolving Credit Agreement”), by and among Noble Finance II LLC (“Noble Finance II”), Noble International Finance Company, Noble Drilling A/S, and certain additional subsidiaries of Noble Finance II as from time to time designated by Noble Finance II, as borrowers, the lenders and issuing banks party thereto from time to time, and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, collateral agent, and security trustee. The revolving credit facility under the Revolving Credit Agreement (the “2023 Revolving Credit Facility”) provides for commitments of $550.0 million with maturity in 2028. The guarantors (the “Guarantors”) under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility are the same subsidiaries of Noble Finance II that are or will be guarantors of the 2030 Notes (as defined below). As of December 31, 2024, we had no borrowings outstanding and $24.8 million of letters of credit issued under the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement.
All obligations of the Borrowers under the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement, certain cash management obligations, certain letter of credit obligations and certain swap obligations are unconditionally guaranteed, on a joint and several basis, by Noble Finance II and certain of its direct and indirect subsidiaries (together with the Borrowers, the “Credit Parties”), including a guarantee by each Borrower of the obligations of each other Borrower under the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement. All such obligations, including the guarantees of the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility, are secured by senior priority liens on substantially all assets of, and the equity interests in, each Credit Party, including substantially all rigs owned by subsidiaries of Noble as of the date of the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement, along with certain other rigs in the future such
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
that collateral rigs shall generate at least 80% of the total revenue of all rigs owned by Noble Finance II and its restricted subsidiaries and the ratio of the aggregate rig value of the collateral rigs to the commitments under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility is at least 5.00 to 1.00, in each case, subject to certain exceptions and limitations described in the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement.
The loans outstanding under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility bear interest at a rate per annum equal to the applicable margin plus, at Noble Finance II’s option, either: (i) the Term SOFR Rate (as defined in the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement) plus 0.10% (subject to a 0.00% floor); or (ii) a base rate, determined as the greatest of (x) the prime loan rate as published in the Wall Street Journal, (y) the NYFRB Rate (as defined in the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement) plus 1/2 of 1%, and (z) the one-month Term SOFR Rate plus 0.10% (subject to a 0.00% floor) plus 1%. The applicable margin is initially 2.75% per annum for Term SOFR Rate loans and 1.75% per annum for base rate loans and will range based on the Consolidated Total Net Leverage Ratio (as defined in the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement, which allows for certain cash netting depending on the amount of loans and letters of credit outstanding under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility at the time of calculation), from 2.75% per annum to 3.75% per annum for Term SOFR Rate loans and 1.75% per annum to 2.75% per annum for base rate loans. The Borrowers are required to pay interest on (i) overdue principal at the rate equal to 2.00% per annum in excess of the applicable interest rate under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility, to the extent lawful, and (ii) overdue installments of interest, if any, without regard to any applicable grace period, at 2% in excess of the interest rate applicable to base rate loans, to the extent lawful.
The Borrowers are required to pay a quarterly commitment fee to each lender under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility, which accrues at a rate per annum equal to (i) during the period from and including the effective date of the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement to and including the third anniversary of the effective date of the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement, 0.50% on the average daily unused portion of each lender’s commitments under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility, (ii) during the period from the third anniversary of the effective date of the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement to and including the fourth anniversary of the effective date of the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement, 0.75% on the average daily unused portion of each lender’s commitments under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility, and (iii) thereafter, 1.00% on the average daily unused portion of each lender’s commitments under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility. The Borrowers are also required to pay customary letter of credit and fronting fees.
Borrowings under the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement may be used for working capital and other general corporate purposes. Availability of borrowings under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility is subject to the satisfaction of certain conditions, including that, after giving effect to any such borrowings and the application of the proceeds thereof, the aggregate amount of Available Cash (as defined in the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement) would not exceed $250.0 million.
Mandatory prepayments and, under certain circumstances, commitment reductions are required under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility in connection with certain asset sales (subject to reinvestment rights if no event of default exists). Available cash in excess of $250.0 million at the end of any month is also required to be applied to prepay loans (without a commitment reduction). The loans under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility may be voluntarily prepaid, and the commitments thereunder voluntarily terminated or reduced, by the Borrowers at any time without premium or penalty, other than customary breakage costs.
The 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement obligates Noble Finance II to comply with the following financial covenants:
•as of the last day of each fiscal quarter, the Interest Coverage Ratio (as defined in the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement) is not permitted to be less than 2.50 to 1.00; and
•as of the last day of each fiscal quarter, the Consolidated Total Net Leverage Ratio is not permitted to be greater than 3.00 to 1.00.
The 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement contains other affirmative and negative covenants, representations and warranties and events of default that Noble views as customary for a financing of this type. The occurrence of any event of default under the 2023 Revolving Credit Agreement would permit all obligations under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility to be declared due and payable immediately and all commitments thereunder to be terminated.
8.000% Senior Notes due 2030
On April 18, 2023, Noble Finance II, a wholly owned subsidiary of Noble, issued the $600.0 million in aggregate principal amount of its 8.000% Senior Notes due 2030 (the “Initial 2030 Notes”). On August 22, 2024, Noble Finance II issued an additional $800.0 million in aggregate principal amount of its 8.000% Senior Notes due 2030 (the “Additional 2030 Notes”
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
and, together with the Initial 2030 Notes, the “2030 Notes”) at a premium of 103% bringing the total outstanding principal amount to $1.4 billion. The 2030 Notes were issued pursuant to an indenture, dated as of April 18, 2023 (as supplemented or otherwise modified from time to time, the “Noble Indenture”), among Noble Finance II, the subsidiaries of Noble Finance II party thereto, as guarantors, and U.S. Bank Trust Company, National Association, as trustee, paying agent, and registrar.
The 2030 Notes are unconditionally guaranteed on a senior unsecured basis by the Guarantors and will be unconditionally guaranteed on the same basis by certain of Noble Finance II’s future subsidiaries that guarantee certain indebtedness of Noble Finance II and the Guarantors, including the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility.
The 2030 Notes will mature on April 15, 2030, and interest on the 2030 Notes is payable semi-annually in arrears on each April 15 and October 15, commencing October 15, 2023, to holders of record on the April 1 and October 1 immediately preceding the related interest payment date, at a rate of 8.000% per annum.
At any time prior to April 15, 2026, Noble Finance II may, from time to time, redeem up to 40% of the aggregate principal amount of 2030 Notes at a redemption price of 108% of the principal amount of the 2030 Notes redeemed, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but excluding, the redemption date (subject to the right of holders of record on the relevant record date to receive interest due on an interest payment date that is on or prior to the redemption date), in an amount not greater than the net cash proceeds of one or more equity offerings by Noble Finance II, subject to certain requirements. In addition, prior to April 15, 2026, Noble Finance II may redeem the 2030 Notes at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the 2030 Notes redeemed, plus an applicable make-whole premium and accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but excluding, the redemption date. At any time on or after April 15, 2026, Noble Finance II may redeem all or part of the 2030 Notes at fixed redemption prices (expressed as percentages of the principal amount) beginning at 104.00% and decreasing thereafter, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but excluding, the redemption date.
If a Change of Control Triggering Event (as defined in the Noble Indenture) occurs, each holder of 2030 Notes may require Noble Finance II to repurchase all or any part of that holder’s 2030 Notes for cash at a price equal to 101% of the aggregate principal amount of the 2030 Notes repurchased, plus any accrued and unpaid interest thereon, if any, to, but excluding, the date on which the 2030 Notes are repurchased (subject to the right of holders of record on the relevant record date to receive interest due on the relevant interest payment date).
The Noble Indenture contains customary covenants and events of default.
Diamond Second Lien Notes due 2030
On September 21, 2023, Diamond Foreign Asset Company and Diamond Finance, LLC (collectively referred to as the “Issuers”) issued $550.0 million aggregate principal amount of 8.500% Senior Secured Second Lien Notes due October 2030 (the “Diamond Second Lien Notes”) with interest payable semi-annually in arrears on April 1 and October 1 of each year, beginning on April 1, 2024. The Diamond Second Lien Notes are fully and unconditionally guaranteed, jointly and severally, on a senior secured basis by Noble Offshore Drilling, Inc. (formerly known as Dolphin Merger Sub 2, Inc. and as successor by merger with Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc.) (“NODI”) and each of its existing restricted subsidiaries (other than the Issuers) and by certain of NODI’s future restricted subsidiaries.
The Diamond Second Lien Notes obligate NODI and its subsidiaries to comply with an indenture dated as of September 21, 2023 (as supplemented and otherwise modified from time to time, the “Diamond Second Lien Indenture”), among the Issuers, NODI, certain of its subsidiaries party thereto, as guarantors, and HSBC Bank USA, National Association, as trustee and collateral agent. The Diamond Second Lien Indenture contains covenants that, among other things, restrict NODI’s ability and the ability of certain of its subsidiaries to: (i) incur additional debt and issue certain preferred stock; (ii) incur or create liens; (iii) make certain dividends, distributions, investments, and other restricted payments; (iv) sell or otherwise dispose of certain assets; (v) engage in certain transactions with affiliates; and (vi) merge, consolidate, amalgamate, or sell, transfer, lease, or otherwise dispose of all, or substantially all, of the assets of NODI and such subsidiaries taken as a whole. These covenants are subject to important exceptions and qualifications.
Noble Second Lien Notes
On April 18, 2023, we redeemed the remaining balance of approximately $173.7 million aggregate principal amount of outstanding notes using a portion of the proceeds from the offering of the Initial 2030 Notes, and recognized a loss of approximately $25.7 million.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Diamond Credit Agreement
On September 4, 2024, in connection with the closing of the Diamond Transaction, Noble terminated Diamond’s $300.0 million senior secured revolving credit facility under the Diamond Credit Agreement. The revolving commitments under the Diamond Credit Agreement were scheduled to mature on April 22, 2026. At the time of the Diamond Transaction and the termination of the commitments under the Diamond Credit Agreement, Diamond had no outstanding borrowings under the Diamond Credit Agreement.
DNB Credit Facility and New DNB Credit Facility
Upon the Closing Date, Noble guaranteed the DNB Credit Facility and on December 22, 2022, it was terminated and replaced with the New DNB Credit Facility (“New DNB Credit Facility”). On April 18, 2023, we repaid the $347.5 million of outstanding borrowings under the New DNB Credit Facility using a portion of the proceeds from the offering of the 2030 Notes, and recognized a loss of approximately $0.7 million.
DSF Credit Facility
The Company guaranteed a term loan (the “DSF Credit Facility”) under a term loan facility agreement, dated as of December 10, 2018 (as amended or otherwise modified from time to time), among Maersk Drilling Holding A/S, Maersk Drilling A/S, the subsidiaries of Maersk Drilling Holding A/S, and Danmarks Skibskredit A/S, as original lender, agent, and security agent, in connection with the Business Combination with Maersk Drilling that closed on October 3, 2022. The DSF Credit Facility was repaid in full and terminated on February 23, 2023, using cash on hand.
Debt Open Market Repurchases
In the third and fourth quarter of 2022, we purchased $42.3 million aggregate principal amount of our Second Lien Notes for approximately $48.1 million, plus accrued interest, as open market repurchases and recognized a loss of approximately $4.6 million.
Guarantees of Indebtedness
On the Closing Date of the Business Combination with Maersk Drilling, Noble guaranteed all of the obligations of Maersk Drilling and certain of its subsidiaries under the DNB Credit Facility, the DSF Credit Facility, and related financing documents. On February 23, 2023, the DSF Credit Facility was repaid in full and the related Noble guarantee was terminated. On April 18, 2023, the DNB Credit Facility was repaid in full and the related Noble guarantee was terminated.
Fair Value of Debt
Fair value represents the amount at which an instrument could be exchanged in a current transaction between willing parties. The estimated fair value of our debt instruments was based on the quoted market prices for similar issues or on the current rates offered to us for debt of similar remaining maturities (Level 2 measurement). The fair value of the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility approximates its respective carrying amount as its interest rate is variable and reflective of market rates.
The following table presents the carrying value, net of unamortized debt issuance costs and discounts or premiums, and the estimated fair value of our total debt, not including the effect of unamortized debt issuance costs, respectively:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| | Carrying
Value | | Estimated Fair Value | | Carrying
Value | | Estimated Fair Value |
| Senior secured notes | | | | | | | | |
| 8.000% Senior Notes due April 2030 | | $ | 1,401,214 | | | $ | 1,414,266 | | | $ | 586,203 | | | $ | 626,472 | |
| 8.500% Senior Secured Second Lien Notes due October 2030 | | 578,972 | | | 571,428 | | | — | | | — | |
| Credit facility | | | | | | | | |
| Amended and Restated Senior Secured Revolving Credit Facility matures April 2028 | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Total debt | | 1,980,186 | | | 1,985,694 | | | 586,203 | | | 626,472 | |
| Less: Current maturities of long-term debt | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Long-term debt | | $ | 1,980,186 | | | $ | 1,985,694 | | | $ | 586,203 | | | $ | 626,472 | |
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Note 7 — Equity
Noble Share Capital. As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, there were approximately 158.9 million and 140.8 million Ordinary Shares outstanding, respectively.
With respect to the Business Combination, at the Merger Effective Time, Noble issued 70.4 million Ordinary Shares to the former holders of Noble Cayman Shares. Further, at the Merger Effective Time, Noble issued 14.5 million Warrants exercisable for Ordinary Shares to former holders of Noble Cayman Warrants (defined wherein). In connection with the completion of the Exchange Offer, Noble issued 60.1 million Ordinary Shares to the former holders of Maersk Drilling shares.
On September 4, 2024, Noble issued 24.2 million Ordinary Shares to the former shareholders of Diamond, in connection with the closing of the Diamond acquisition. Further, Noble assumed all outstanding and unexercised warrants of Diamond, which were exercisable for 90 days from the effective time of the Diamond acquisition. As of December 4, 2024, the warrants assumed from Diamond are no longer exercisable and have expired in accordance with their terms.
Additional changes to share capital occurred as a result of, among other actions, the vesting of restricted stock units and performance based restricted stock units to our employees and directors, the cancellation of Ordinary Shares denoted as excess shares in the voluntary share exchange as a result of the Exchange Offer, the issuance of Ordinary Shares pursuant to the exercise of warrants, and share repurchases under the Company’s authorized share repurchase plan.
In addition, as of December 31, 2024, 0.9 million Tranche 1 Warrants, 0.9 million Tranche 2 Warrants and 2.8 million Tranche 3 Warrants were outstanding and exercisable. We also have 6.8 million Ordinary Shares authorized and reserved for issuance pursuant to equity awards under the Noble Corporation plc 2022 Long-Term Incentive Plan.
Our most recent quarterly dividend, totaling approximately $79.7 million (or $0.50 per share), was declared on November 5, 2024, and paid on December 19, 2024, to shareholders of record at close of business on December 5, 2024. During the years ended December 31, 2024, and 2023, we declared dividends of approximately $278.3 million and $101.8 million (or $1.80 and $0.70 per share cumulatively), respectively, and made cash dividend payments of approximately $277.8 million and $98.8 million, respectively. Approximately $3.5 million and $3.0 million was accrued related to dividend equivalent rights as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
The declaration and payment of dividends require the authorization of the Board of Directors. Such may be paid only out of Noble’s “distributable reserves” as determined by reference to relevant statutory accounts in accordance with English law. Therefore, Noble is not permitted to pay dividends out of share capital, which includes share premium. The payment of future dividends will depend on our results of operations, financial condition, cash requirements, future business prospects, contractual and indenture restrictions, and other factors deemed relevant by our Board of Directors.
Share Repurchases
Under English law, the Company is only permitted to purchase its own Ordinary Shares by way of an “off-market purchase” pursuant to a contract approved by shareholders (except where the purchase is for the purposes of, or pursuant to, any employees’ share scheme). Such purchases may be paid for either (i) out of Noble’s “distributable reserves” as determined by reference to relevant statutory accounts in accordance with English law or (ii) from the proceeds of a fresh issue of shares made for the purpose of financing the purchase. As of the date of this report, we have shareholder authority to repurchase up to 15% per annum of the issued share capital of the Company as of the beginning of each fiscal year for a five-year period commencing on September 28, 2022 (subject to an overall aggregate maximum of 20.6 million Ordinary Shares). During the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, we repurchased 8.4 million and 2.3 million of our Ordinary Shares pursuant to such authority. All repurchased shares were subsequently cancelled.
Warrants
On the Merger Effective Date, immediately prior to the Merger Effective Time, we had outstanding 6.2 million Noble Cayman Tranche 1 Warrants, 5.6 million Noble Cayman Tranche 2 Warrants and 2.8 million Noble Cayman Tranche 3 Warrants (together with the Noble Cayman Tranche 1 Warrants and the Noble Cayman Tranche 2 Warrants, the “Noble Cayman Warrants”). At the Merger Effective Time, each Noble Cayman Warrant outstanding immediately prior to the Merger Effective Time was converted automatically into a Warrant to acquire a number of Ordinary Shares equal to the number of
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Noble Cayman Shares underlying such Noble Cayman Warrant, with the same terms as were in effect immediately prior to the Merger Effective Time under the terms of the applicable Noble Cayman Warrant Agreement.
The Tranche 1 Warrants of Noble (the “Tranche 1 Warrants”) are exercisable for one Ordinary Share per warrant at an exercise price of $19.27 per warrant, the Tranche 2 Warrants of Noble (the “Tranche 2 Warrants”) are exercisable for one Ordinary Share per warrant at an exercise price of $23.13 per warrant, and the Tranche 3 Warrants of Noble (the “Tranche 3 Warrants”) are exercisable for one Ordinary Share per warrant at an exercise price of $124.40 per warrant (in each case as may be adjusted from time to time pursuant to the applicable Warrant Agreement). The Tranche 1 Warrants and the Tranche 2 Warrants are exercisable until 5:00 p.m., Eastern time, on February 4, 2028, and the Tranche 3 Warrants are exercisable until 5:00 p.m., Eastern time, on February 4, 2026. The Tranche 1 Warrants and the Tranche 2 Warrants have Black-Scholes protections, including in the event of a Fundamental Transaction (as defined in the applicable warrant agreement). The Tranche 1 Warrants and the Tranche 2 Warrants also provide that while the Mandatory Exercise Condition (as defined in the applicable Warrant Agreement) set forth in the applicable Warrant Agreement has occurred and is continuing, Noble or the Required Mandatory Exercise Warrantholders (as defined in the applicable Warrant Agreement) have the right and option (but not the obligation) to cause all or a portion of the Warrants to be exercised on a cashless basis. In the case of Noble, under the Mandatory Exercise Condition, all of the Tranche 1 Warrants or the Tranche 2 Warrants (as applicable) would be exercised. In the case of electing Required Mandatory Exercise Warrantholders, under the Mandatory Exercise Condition, all of their respective Tranche 1 Warrants or Tranche 2 Warrants (as applicable) would be exercised. Mandatory exercises entitle the holder of each Warrant subject thereto to (i) the number of Ordinary Shares issuable upon exercise of such Warrant on a cashless basis and (ii) an amount payable in cash, Ordinary Shares or a combination thereof (in Noble’s sole discretion) equal to the Black-Scholes Value (as defined in the applicable Warrant Agreement) with respect to the number of Ordinary Shares withheld upon exercise of such Warrant on a cashless basis. At December 31, 2024, the Mandatory Exercise Condition set forth in the Warrant Agreements for the Tranche 1 Warrants and the Tranche 2 Warrants was satisfied.
In connection with the automatic conversion of the Noble Cayman Warrants into Warrants at the Merger Effective Time, (i) the Tranche 1 Warrant Agreement, dated as of February 5, 2021, by and among Noble Cayman, Computershare Inc. and Computershare Trust Company, N.A. (together, “Computershare”), (ii) the Tranche 2 Warrant Agreement, dated as of February 5, 2021, by and among Noble Cayman and Computershare, and (iii) the Tranche 3 Warrant Agreement, dated as of February 5, 2021, by and among Noble Cayman and Computershare (collectively, the “Noble Cayman Warrant Agreements”) were terminated, and Noble entered into (a) a new Tranche 1 Warrant Agreement, dated as of the Merger Effective Date, by and among Noble and Computershare, (b) a new Tranche 2 Warrant Agreement, dated as of the Merger Effective Date, by and among Noble and Computershare, and (c) a new Tranche 3 Warrant Agreement, dated as of the Merger Effective Date, by and among Noble and Computershare (collectively, the “Warrant Agreements”). The Warrant Agreements have substantially similar terms as were in effect immediately prior to the Merger Effective Time pursuant to the Noble Cayman Warrant Agreements.
Share-Based Compensation Plans
Stock Plans. In connection with the Merger, on the Merger Effective Date, the Company adopted the Noble Corporation plc 2022 Long-Term Incentive Plan (the “2022 LTIP”), which permits grants of options, stock appreciation rights, stock or stock unit awards, or cash awards, any of which may be structured as a performance award, from time to time to employees and non-employee directors who are to be granted awards under the 2022 LTIP, and authorized and reserved approximately 5.9 million Ordinary Shares for equity incentive awards to be granted under such plan. The Company assumed, under the 2022 LTIP, all outstanding awards as well as any rights and obligations of Noble Cayman thereunder. On the Merger Effective Date, each Noble Cayman RSU Award outstanding immediately prior to the Merger Effective Time ceased to represent a right to acquire Noble Cayman Shares (or value equivalent to Noble Cayman Shares) and was converted into the right to acquire, on the same terms and conditions as were applicable under the Noble Cayman RSU Award (including any vesting conditions), that number of Ordinary Shares equal to the number of Noble Cayman Shares subject to such Noble Cayman RSU Award immediately prior to the Merger Effective Time.
The Company also approved the adoption, effective as of October 3, 2022, of (i) the Noble Corporation plc RSU Long-Term Incentive Program for Executive Management 2022 and (ii) the Noble Corporation plc RSU Long-Term Incentive Program 2022, under which the Company assumed all outstanding awards of Maersk Drilling granted under the Maersk Drilling RSU Long-Term Incentive Program for Executive Management 2019 and the Maersk Drilling RSU Long-Term Incentive Program 2019, respectively. Each Maersk Drilling RSU Award that was outstanding immediately prior to the Acceptance Time was exchanged, at the Acceptance Time, with the right to receive, on the same terms and conditions as were applicable under
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
the Maersk Drilling RSU Long-Term Incentive Program for Executive Management 2019 and the Maersk Drilling RSU Long-Term Incentive Program 2019 (including any vesting conditions), that number of Ordinary Shares equal to the product of (i) the number of Maersk Drilling Shares subject to such Maersk Drilling RSU Award immediately prior to the Acceptance Time and (ii) the Exchange Ratio, with any fractional Maersk Drilling Shares rounded to the nearest whole share. Upon such exchange, Maersk Drilling RSU Awards ceased to represent a right to receive Maersk Drilling Shares (or value equivalent to Maersk Drilling Shares).
In addition to assuming any outstanding awards granted under the plans listed in the two preceding paragraphs (including the shares underlying such awards) and the award agreements evidencing the grants of such awards, the Company assumed the remaining shares available for issuance under each applicable plan, including any awards granted to the Company’s directors or executive officers, in each case subject to adjustments to such awards in the manner set forth in the Business Combination Agreement.
Effective May 21, 2024, shareholders of the Company approved an amendment to the 2022 LTIP which increased the maximum number of shares that may be issued under the 2022 LTIP to 10,688,623 Ordinary Shares.
On September 4, 2024, in connection with the closing of the acquisition of Diamond, the Company assumed the Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc. 2021 Long-Term Stock Incentive Plan (the “Diamond LTIP”) and each Diamond RSU (as defined below) outstanding thereunder. Effective November 6, 2024, the Company also assumed the remaining shares available for issuance under the Diamond LTIP which, after adjustments under the Diamond Merger Agreement, totaled 1,556,404 Ordinary Shares.
Restricted Stock Units (“RSUs”). We awarded both Time Vested RSUs (“TVRSUs”) and Performance Vested RSUs (“PVRSUs”) under the 2022 LTIP.
On the Merger Effective Date, each Noble Cayman RSU Award outstanding immediately prior to the Merger Effective Time ceased to represent a right to acquire Noble Cayman Shares (or value equivalent to Noble Cayman Shares) and was converted into the right to acquire, on the same terms and conditions as were applicable under the Noble Cayman RSU Award (including any vesting conditions), that number of Ordinary Shares equal to the number of Noble Cayman Shares subject to such Noble Cayman RSU Award immediately prior to the Merger Effective Time.
On September 4, 2024, in connection with the closing of the acquisition of Diamond, each performance-vesting and time-vesting restricted stock unit covering shares of Diamond (together "Diamond RSUs") held by key employees were assumed by Noble and represented the right to receive shares in Noble. The Diamond RSUs were assumed by Noble on substantially the same terms and conditions (including vesting conditions) as applicable to the original Diamond RSUs prior to the closing of the acquisition.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, to the extent that a Diamond RSU vested as of the acquisition (including any awards that vested as a result of a termination of employment at or immediately after the acquisition), such awards were instead settled in cash or shares of Diamond, as applicable, immediately prior to the acquisition and any such shares of Diamond were treated the same as other Diamond shares.
The TVRSUs generally vest over a three-year period. The number of PVRSUs which vest will depend on the degree of achievement of specified corporate performance criteria generally over a three-year performance period. These criteria consist of market and performance-based criteria. Dividend equivalent rights are accrued and accumulated as dividends are declared, and payable upon vesting of the TVRSUs and PVRSUs.
The TVRSUs are valued on the date of award at our underlying share price. The total compensation expense for units that ultimately vest is recognized on a straight-line basis over the service period. The shares and related nominal value are recorded when the RSU vests and additional paid-in capital is adjusted as the share-based compensation cost is recognized for financial reporting purposes.
In 2024, 2023, and 2022, 40% of the TVRSUs granted to non-employee directors will be settled in cash and accounted for as liability awards, which were valued on the date of grant based on the estimated fair value of the Company’s share price. Under the fair value method for liability-classified awards, compensation expense is remeasured each reporting period at fair value based upon the closing price of the Company’s Ordinary Shares.
Each PVRSU represents the right to receive Ordinary Shares at a future date based on our performance against specified targets. The ultimate number of shares issued and the related compensation cost recognized is based on a comparison of
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
the final performance metrics to the specified targets. For performance-based awards, compensation expense is recognized based on the number of Ordinary Shares expected to be issued and the market price per Ordinary Share on the date of grant. Over the performance period, the number of shares expected to be issued is adjusted upward or downward based upon the probability of achievement of the performance targets. The market-based awards are valued on the date of grant based on the estimated fair value. Estimated fair value is determined based on numerous assumptions, including an estimate of the likelihood that our stock price performance will achieve the targeted thresholds and the expected forfeiture rate. The fair value is calculated using a Monte Carlo Simulation Model. The assumptions used to value the market-based awards include historical volatility and risk-free interest rates over a time period commensurate with the remaining term prior to vesting, as follows, for the respective grant dates:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| | | January 26, 2024 | | February 3, 2023 | | February 3, 2022 |
| Valuation assumptions: | | | | | | |
Expected volatility rate (1) | | 44.1 | % | | 83.0 | % | | 74.8 | % |
| Risk-free interest rate | | 4.16 | % | | 3.96 | % | | 1.42 | % |
(1)Expected dividend yield is included in the model via its impact on the historical volatility rate, which is based on daily returns inclusive of dividends.
Additionally, similar assumptions were made for each of the companies included in the defined index and the peer group of companies in order to simulate the future outcome using the Monte Carlo Simulation Model. For market-based awards, compensation expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the vesting terms.
A summary of the RSUs awarded during the periods indicated is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Equity-classified TVRSUs | | | | | | |
| Units awarded | | 839,773 | | | 384,995 | | | 988,750 | |
| Weighted-average award date fair value | | $ | 40.54 | | | $ | 39.54 | | | $ | 27.85 | |
| Weighted-average vesting period (years) | | 2.37 | | 2.90 | | 2.94 |
| Liability-classified TVRSUs | | | | | | |
| Units awarded | | 14,123 | | | 12,918 | | | 20,120 | |
| Weighted-average award date fair value | | $ | 44.34 | | | $ | 39.58 | | | $ | 31.25 | |
| Weighted-average vesting period (years) | | 1.00 | | 1.00 | | 1.00 |
| PVRSUs | | | | | | |
| Units awarded | | 257,574 | | | 223,635 | | | 295,372 | |
| Weighted-average award date fair value | | $ | 50.06 | | | $ | 45.88 | | | $ | 28.97 | |
| Three-year performance period end date December 31 | | 2026 | | 2025 | | 2024 |
During the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, we awarded 21,171, 19,376, and 30,180 shares equity-classified TVRSUs and 14,123, 12,918, and 20,120 shares liability-classified TVRSUs, respectively, to our non-employee directors.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
A summary of the status of non-vested RSUs at December 31, 2024 and 2023, and changes for the years then ended is presented below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Equity-Classified TVRSUs
Outstanding | | Weighted
Average
Award Date
Fair Value | | PVRSUs Outstanding (1) (2) | | Weighted
Average
Award Date
Fair Value |
| Non-vested RSUs at December 31, 2022 | | 1,539,550 | | | $ | 20.51 | | | 1,753,214 | | | $ | 19.58 | |
| Awarded | | 384,995 | | | 39.54 | | | 223,635 | | | 45.88 | |
| Vested | | (719,871) | | | 20.26 | | | (1,461,236) | | | 18.16 | |
| Forfeited | | (19,281) | | | 30.93 | | | — | | | — | |
| Non-vested RSUs at December 31, 2023 | | 1,185,393 | | | $ | 26.64 | | | 515,613 | | | $ | 36.19 | |
| Awarded | | 839,773 | | | 40.54 | | | 257,574 | | | 50.06 | |
| Vested | | (943,847) | | | 25.12 | | | (293,537) | | | 28.97 | |
| Forfeited | | (47,305) | | | 39.98 | | | (1,835) | | | 28.97 | |
| Non-vested RSUs at December 31, 2024 | | 1,034,014 | | | $ | 39.05 | | | 477,815 | | | $ | 48.13 | |
(1)For awards granted, the number of PVRSUs shown equals the shares that would vest if the “target” level of performance is achieved. The minimum number of convertible shares is zero and the “maximum” level of performance is 200% of the amounts shown.
(2)For awards granted during 2022, the minimum number of convertible shares is 36,929 and the “maximum” level of performance is 179% of the amounts shown.
We granted 14,123 and 12,918 liability-classified TVRSUs at a weighted average grant date fair value of $44.34 and $39.58, during the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. During the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, 12,918 and 2,672 units vested, respectively, and no units were forfeited during either period. At December 31, 2024 and 2023, we had 14,123 and 12,918 liability-classified TVRSUs outstanding with an associated total liability of $0.4 million and $0.6 million, respectively.
At December 31, 2024 and 2023, there was $22.7 million and $14.5 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to the equity-classified TVRSUs, to be recognized over a remaining weighted average period of 1.53 and 0.99 years, respectively. In addition, at December 31, 2024 and 2023, the immaterial amounts of unrecognized compensation cost related to the liability-classified TVRSUs are to be recognized over a remaining weighted average period of 0.11 and 0.09 years, respectively.
At December 31, 2024 and 2023, there was $11.3 million and $12.6 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to the PVRSUs, to be recognized over a remaining weighted average period of 1.54 and 1.43 years, respectively. The total potential compensation for PVRSUs is recognized over the service period regardless of whether the performance thresholds are ultimately achieved.
Share-based amortization recognized during the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, related to all restricted stock, excluding amounts included in merger and integration costs, totaled $27.9 million ($25.4 million net of income tax) and $37.4 million ($35.2 million net of income tax), respectively.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Note 8 — Revenue and Customers
Disaggregation of Revenue
The following table provides information about contract drilling revenue by rig types:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Floaters | | $ | 2,349,644 | | | $ | 2,010,113 | | | $ | 997,819 | |
| Jackups | | 569,123 | | | 451,602 | | | 335,022 | |
| Total | | $ | 2,918,767 | | | $ | 2,461,715 | | | $ | 1,332,841 | |
Contract Balances
Accounts receivable are recognized when the right to consideration becomes unconditional based upon contractual billing schedules. Payment terms on invoiced amounts are typically 30 to 60 days. Customer contract assets and liabilities generally consist of deferred revenue and contract costs resulting from past transactions related to the provision of services under contracts with customers. Current contract asset and liability balances are included in “Prepaid expenses and other current assets” and “Other current liabilities”, respectively, and noncurrent contract assets and liabilities are included in “Other assets” and “Other liabilities”, respectively, on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. Off-market customer contract assets and liabilities have been recognized in connection with our emergence from Chapter 11 and the Business Combination with Maersk Drilling and are included in “Intangible assets” and “Noncurrent contract liabilities”, respectively.
The following table provides information about contract assets and contract liabilities from contracts with customers:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| Current customer contract assets | | $ | 26,049 | | | $ | 4,208 | |
| Noncurrent customer contract assets | | 11,042 | | | 208 | |
| Total customer contract assets | | 37,091 | | | 4,416 | |
| | | | |
| Current deferred revenue | | (61,506) | | | (19,679) | |
| Noncurrent deferred revenue | | (40,439) | | | (23,393) | |
| Total deferred revenue | | $ | (101,945) | | | $ | (43,072) | |
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Significant changes in the remaining performance obligation contract assets and the contract liabilities balances for the year ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Contract Assets | | Contract Liabilities |
| Net balance at December 31, 2021 | | $ | 5,744 | | | $ | (27,755) | |
| | | | |
| Additions to deferred costs | | 34,187 | | | — | |
| Additions to deferred revenue | | — | | | (108,971) | |
| Amortization of deferred costs | | (19,875) | | | — | |
| Amortization of deferred revenue | | — | | | 55,521 | |
| Reclassification to held for sale and subsequent derecognition | | (8,519) | | | 21,408 | |
| Total | | 5,793 | | | (32,042) | |
| | | | |
| Net balance at December 31, 2022 | | $ | 11,537 | | | $ | (59,797) | |
| | | | |
| Additions to deferred costs | | 19,575 | | | — | |
| Additions to deferred revenue | | — | | | (60,430) | |
| Amortization of deferred costs | | (26,696) | | | — | |
| Amortization of deferred revenue | | — | | | 77,155 | |
| Total | | (7,121) | | | 16,725 | |
| | | | |
| Net balance at December 31, 2023 | | $ | 4,416 | | | $ | (43,072) | |
| | | | |
| Additions to deferred costs | | 55,323 | | | — | |
| Additions to deferred revenue | | — | | | (134,359) | |
| Amortization of deferred costs | | (22,648) | | | — | |
| Amortization of deferred revenue | | — | | | 75,486 | |
| Total | | 32,675 | | | (58,873) | |
| | | | |
| Net balance at December 31, 2024 | | $ | 37,091 | | | $ | (101,945) | |
Contract Costs
Certain direct and incremental costs incurred for upfront preparation, initial rig mobilization and modifications are costs of fulfilling a contract and are recoverable. These recoverable costs are deferred and amortized ratably to contract drilling expense as services are rendered over the initial term of the related drilling contract. Certain of our contracts include capital rig enhancements used to satisfy our performance obligations.
Future Amortization of Deferred Revenue
The following table reflects revenue expected to be recognized in the future related to deferred revenue, by rig type, at the end of the reporting period:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2025 | | 2026 | | 2027 | | 2028 | | | | Total |
| Floaters | | $ | 54,747 | | | $ | 15,170 | | | $ | 11,522 | | | $ | 5,532 | | | | | $ | 86,971 | |
| Jackups | | 6,759 | | | 4,708 | | | 3,499 | | | 8 | | | | | 14,974 | |
| Total | | $ | 61,506 | | | $ | 19,878 | | | $ | 15,021 | | | $ | 5,540 | | | | | $ | 101,945 | |
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
The revenue included above consists of expected mobilization, demobilization, and upgrade revenue for unsatisfied performance obligations. The amounts are derived from the specific terms within drilling contracts that contain such provisions, and the expected timing for recognition of such revenue is based on the estimated start date and duration of each respective contract based on information known at December 31, 2024. The actual timing of recognition of such amounts may vary due to factors outside of our control. We have taken the optional exemption, permitted by accounting standards, to exclude disclosure of the estimated transaction price related to the variable portion of unsatisfied performance obligations at the end of the reporting period, as our transaction price is based on a single performance obligation consisting of a series of distinct hourly, or more frequent, periods, the variability of which will be resolved at the time of the future services.
Off-market Customer Contract Assets and Liabilities
Upon emergence from Chapter 11 bankruptcy, the Company recognized fair value adjustments of $113.4 million related to intangible assets for certain favorable customer contracts, which were fully amortized as of August 2023. In addition, in connection with the Business Combination with Maersk Drilling, the Company recognized additional fair value adjustments of $23.0 million, related to intangible assets for certain favorable customer contracts. These intangible assets will be amortized as a reduction of contract drilling services revenue from the Closing Date through the remainder of the contracts.
In connection with the Business Combination with Maersk Drilling and the Diamond Transaction, the Company recognized a fair value adjustments of $237.7 million and $27.7 million, respectively, related to certain unfavorable customer contracts acquired. These liabilities will be amortized as an increase to contract drilling services revenue from the Closing Date and the Diamond Closing Date through the remainder of the contracts.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Unfavorable contacts | | Favorable
contracts | |
| Balance at December 31, 2021 | | $ | — | | | $ | 61,849 | | |
| Additions | | (237,703) | | | 22,991 | | |
| Amortization | | 55,820 | | | (50,468) | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | | $ | (181,883) | | | $ | 34,372 | | |
| Additions | | — | | | — | | |
| Amortization | | 131,020 | | | (24,244) | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | | $ | (50,863) | | | $ | 10,128 | | |
| Additions | | (27,663) | | | — | | |
| Amortization | | 69,946 | | | (9,914) | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2024 | | $ | (8,580) | | | $ | 214 | | |
Estimated future amortization over the expected remaining contract periods:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2025 | | | | | | Total |
| Unfavorable contracts | | $ | 8,580 | | | | | | | $ | 8,580 | |
| Favorable contracts | | (214) | | | | | | | (214) | |
| Total | | $ | 8,366 | | | | | | | $ | 8,366 | |
Note 9 — Leases
Leases
We determine if an arrangement is a lease at inception. Our lease agreements are primarily for real estate, equipment, storage, dock space, and automobiles and are included within “Other assets”, “Other current liabilities”, and “Other liabilities” on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. In connection with the Diamond Transaction, the Company assumed several leases entered into by Diamond consisting of operating leases for corporate and shorebases offices, office and information technology equipment, employee housing, onshore storage yards, and certain rig equipment and tools as well as finance
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
leases for well control equipment used on the drillships. The finance leases commenced in 2016 and also include an option to purchase the leased equipment at the end of the respective lease term.
As most of our leases do not provide an explicit rate, we use our incremental borrowing rate based on the information available at commencement date in determining the present value of lease payments. Certain of our lease agreements include options to extend or terminate the lease, which we do not include in our minimum lease terms unless management is reasonably certain to exercise.
Supplemental balance sheet information related to leases was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| Operating leases | | | | |
| Right-of-use assets | | $ | 78,993 | | | $ | 24,528 | |
Current lease liabilities | | $ | 14,844 | | | $ | 10,581 | |
| Long-term lease liabilities | | $ | 65,981 | | | $ | 15,082 | |
| Weighted average remaining lease term (years) | | 7.49 | | 4.34 |
| Weighted average discount rate | | 6.6 | % | | 7.6 | % |
| | | | |
Finance leases (1) | | | | |
| Right-of-use assets | | $ | 34,346 | | | $ | — | |
Current lease liabilities | | $ | 22,722 | | | $ | — | |
| Long-term lease liabilities | | $ | 11,270 | | | $ | — | |
| Weighted average remaining lease term (years) | | 1.47 | | — | |
| Weighted average discount rate | | 5.8 | % | | — | % |
(1)Includes finance leases acquired in the Diamond Transaction.
The components of lease cost were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Operating lease cost | | $ | 31,162 | | | $ | 12,615 | | | $ | 6,095 | |
| Finance lease cost: | | | | | | |
| Amortization of right-of-use assets | | 7,766 | | | — | | | — | |
| Interest on lease liabilities | | 734 | | | — | | | — | |
| Short-term lease cost | | 3,819 | | | 6,185 | | | 5,741 | |
| Variable lease cost | | 675 | | | 928 | | | 948 | |
| Total lease cost | | $ | 44,156 | | | $ | 19,728 | | | $ | 12,784 | |
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Supplemental cash flow information related to leases was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Operating leases | | | | | | |
| Operating cash flows used | | $ | 20,857 | | | $ | 13,369 | | | $ | 6,676 | |
Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for a lease liability (1) | | 45,313 | | | 9,614 | | | 19,841 | |
| | | | | | |
| Finance leases | | | | | | |
| Operating cash flows used | | $ | 560 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Financing cash flows used | | 6,064 | | | — | | | — | |
Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for a lease liability (1) | | 42,113 | | | — | | | — | |
(1)Includes right-of-use assets acquired in business combinations.
Maturities of lease liabilities as of December 31, 2024, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Operating Leases | | Finance Leases |
| 2025 | | $ | 17,850 | | | $ | 24,049 | |
| 2026 | | 16,720 | | | 11,430 | |
| 2027 | | 14,629 | | | — | |
| 2028 | | 10,905 | | | — | |
| 2029 | | 7,403 | | | — | |
| Thereafter | | 43,025 | | | — | |
| Total lease payments | | 110,532 | | | 35,479 | |
| Less: Interest | | (29,707) | | | (1,487) | |
| Present value of lease liability | | $ | 80,825 | | | $ | 33,992 | |
Note 10 — Income Taxes
Noble is a tax resident in the UK and, as such, is subject to UK corporation tax on its taxable profits and gains. Noble Cayman was incorporated in the Cayman Islands and, therefore, not subject to tax in any jurisdiction. With respect to Noble, a UK tax exemption is available in respect of qualifying dividends income and capital gains related to the sale of qualifying participations. We operate in various countries throughout the world, including the United States. The income or loss of the non-UK subsidiaries of Noble is not subject to UK corporation tax.
Consequently, we have taken account of the above exemption and provided for income taxes based on the laws and rates in effect in the countries in which operations are conducted, or in which we, or our subsidiaries, have a taxable presence for income tax purposes.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
The components of the net deferred taxes are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| Deferred tax assets | | | | |
| United States: | | | | |
| Net operating loss carry forwards | | $ | 65,686 | | | $ | 2,338 | |
| Excess of net tax basis over remaining book basis | | 14,418 | | | 18,527 | |
| Disallowed interest deduction carryforwards | | 66,632 | | | — | |
| Tax credits carryover | | 2,606 | | | — | |
| Deferred pension plan amounts | | 1,065 | | | 356 | |
| Accrued expenses not currently deductible | | 21,208 | | | 6,613 | |
| Unfavorable contract value | | 936 | | | — | |
| Other | | 3,066 | | | — | |
| Non-United States: | | | | |
| Net operating loss carry forwards | | 1,683,210 | | | 1,407,964 | |
| Excess of net tax basis over remaining book basis | | 456,302 | | | 305,840 | |
| Tax credits carryover | | 341 | | | 15,274 | |
| Transition attribute | | 959,985 | | | 956,187 | |
| Disallowed interest deduction carryforwards | | 30,427 | | | 30,982 | |
| | | | |
| Unfavorable contract value | | 1,858 | | | 3,081 | |
| Accrued expenses not currently deductible | | 8,701 | | | — | |
| Other | | 1,952 | | | 1,669 | |
| Deferred tax assets | | 3,318,393 | | | 2,748,831 | |
| Less: valuation allowance | | (2,964,740) | | | (2,512,571) | |
| Net deferred tax assets | | $ | 353,653 | | | $ | 236,260 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | | | |
| United States: | | | | |
| Excess of net book basis over remaining tax basis | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Favorable contract value | | — | | | — | |
| Deferred revenue | | (7,218) | | | (11,423) | |
| Other | | (3,019) | | | (1,809) | |
| Non-United States: | | | | |
| Excess of net book basis over remaining tax basis | | — | | | (10,137) | |
| Favorable contract value | | — | | | (1,573) | |
| Other | | (4,255) | | | (4,495) | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | (14,492) | | | (29,437) | |
| Net deferred tax assets (liabilities) | | $ | 339,161 | | | $ | 206,823 | |
Income (loss) before income taxes consists of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| United States | | $ | 51,948 | | | $ | 17,619 | | | $ | (43,381) | |
| Non-United States | | 440,386 | | | 494,624 | | | 234,882 | |
| Total | | $ | 492,334 | | | $ | 512,243 | | | $ | 191,501 | |
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Income tax provision (benefit) consists of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Current- United States | | $ | 9,061 | | | $ | 2,940 | | | $ | 1,058 | |
| Current- Non-United States | | 77,567 | | | 125,494 | | | 47,123 | |
| Deferred- United States | | 2,559 | | | 3,703 | | | (2,886) | |
| Deferred- Non-United States | | (45,206) | | | (101,796) | | | (22,742) | |
| Total | | $ | 43,981 | | | $ | 30,341 | | | $ | 22,553 | |
The following is a reconciliation of our reserve for uncertain tax positions, excluding interest and penalties:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Gross balance at beginning of period | | $ | 134,934 | | | $ | 132,979 | | | $ | 63,443 | |
| Additions based on tax positions related to current year | | 1,439 | | | 25,363 | | | 1,296 | |
| Additions for tax positions of prior years | | 41,961 | | | 10,087 | | | 69,163 | |
| Reductions for tax positions of prior years | | (20,960) | | | (29,113) | | | (687) | |
| Expiration of statutes | | (310) | | | — | | | (236) | |
| Tax settlements | | (42,296) | | | (4,382) | | | — | |
| Gross balance at end of period | | 114,768 | | | 134,934 | | | 132,979 | |
| Related tax benefits | | (3,705) | | | (78) | | | (384) | |
| Net reserve at end of period | | $ | 111,063 | | | $ | 134,856 | | | $ | 132,595 | |
The liabilities related to our reserve for uncertain tax positions, included in “Other liabilities” on our Consolidated Balance Sheets, are comprised of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| Reserve for uncertain tax positions, excluding interest and penalties | | $ | 111,063 | | | $ | 134,856 | |
| Interest and penalties | | 86,804 | | | 67,455 | |
| Reserve for uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties | | $ | 197,867 | | | $ | 202,311 | |
At December 31, 2024 and 2023, the reserves for uncertain tax positions totaled $197.9 million (net of related tax benefits of $3.7 million) and $202.3 million (net of related tax benefits of $0.1 million), respectively. If a portion or all of the December 31, 2024 and 2023, reserves listed above are not realized, the provision for income taxes could be reduced by up to $196.0 million and $188.0 million, respectively.
It is reasonably possible that our existing liabilities related to our reserve for uncertain tax positions may fluctuate in the next 12 months primarily due to the completion of open audits or the expiration of statutes of limitation.
We include, as a component of our “Income tax benefit (provision)”, potential interest and penalties related to recognized tax contingencies within our global operations. Interest and penalties resulted in an income tax expense of $5.9 million, $24.1 million, and $2.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
During the year ended December 31, 2024, our tax provision included a net tax benefit of $123.6 million related to releases of valuation allowances primarily in Luxembourg, and a net tax benefit of $20.2 million related to changes in uncertain tax positions. Such tax benefits were offset by various recurring quarterly accruals of $187.8 million primarily in Guyana, Nigeria, the United States, Switzerland, and Luxembourg.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, our tax provision included tax benefits of $187.2 million related to releases of valuation allowances in Luxembourg, Guyana, Switzerland, and Norway, and a tax benefit of $6.8 million related to uncertain tax position releases. Such tax benefits were offset by tax expenses related to uncertain tax positions of
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
$20.9 million in various countries, contract fair value amortization of $23.7 million, and various recurring quarterly accruals of $179.6 million primarily in Guyana, Switzerland, and Luxembourg.
During the year ended December 31, 2022, our tax provision included tax benefits of $42.1 million related to releases of valuation allowances in Guyana and Luxembourg, $1.3 million related primarily to other deferred tax adjustments, and $6.6 million related to a reduction in legacy Maersk tax contingencies primarily due to favorable foreign exchange movements. Such tax benefits were offset by tax expenses of $2.3 million related to the sale of the Remedy Rigs, $10.8 million related to contract fair value amortization, and various recurring items comprised of Guyana excess withholding tax on gross revenue of $34.7 million and annual current and deferred tax expense accruals of $24.9 million primarily in Luxembourg, Switzerland, US, Norway, and Ghana.
Our gross deferred tax asset balance at year-end reflects the application of our income tax accounting policies and is based on management’s estimates, judgments, and assumptions regarding realizability. If it is more likely than not that a portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized in a future period, the deferred tax assets will be reduced by a valuation allowance based on management’s estimates.
In deriving the $123.6 million change in valuation allowance, where applicable we relied on sources of income attributable to the reversal of taxable temporary differences in the same periods as the relevant tax attributes and projected taxable income for the period covered by our relevant existing drilling contracts based on the assumption that the relevant rigs will be owned by the current rig owners during the relevant existing drilling contract periods. Given the mobile nature of our assets, we are not able to reasonably forecast the jurisdiction of our taxable income from future drilling contracts. We also have limited objective positive evidence in historical periods. Accordingly, in determining the amount of deferred tax benefits to recognize, we did not consider projected book income beyond the conclusion of existing drilling contracts with the exception of interest income projected to be generated over a finite period beyond the conclusion of the relevant existing drilling contracts. As new drilling contracts are executed, we will reassess the amount of deferred tax assets that are realizable. Finally, once we have established sufficient objective positive evidence for historical periods, we may consider reliance on forecasted taxable income from future drilling contracts.
Our tax benefits related to transition attributes in Switzerland are scheduled to expire by 2036. Our net operating losses in Switzerland are scheduled to expire between 2027 and 2031. Our net operating losses in Luxembourg are scheduled to expire between 2033 and 2038; however, a portion of the tax losses has no expiration date.
We conduct business globally and, as a result, we file numerous income tax returns in the US and in non-US jurisdictions. In the normal course of business, we are subject to examination by taxing authorities throughout the world, including, but not limited to, jurisdictions such as Egypt, Ghana, Guyana, Mexico, and the United Kingdom. We are no longer subject to US Federal income tax examinations for years before 2021 and non-US income tax examinations for years before 2000.
In Denmark, prior to the Merger, Maersk Drilling was subject to a mandatory joint taxation scheme with all other Danish entities under the common control of A.P. Møller Holding A/S. To the extent Maersk Drilling incurred tax losses in Denmark until the Merger, such losses may be utilized by other jointly taxed entities. Noble may be compensated through a joint taxation contribution when such losses are utilized. In the event that A.P. Møller Holding A/S or any jointly taxed entity is subject to audits for years and periods prior to and until the Merger and such audits result in adjustments to relevant tax returns, adjustments to the prior year joint tax contributions may be required. This could result in additional compensation to Noble or refunds payable by Noble to A.P. Møller Holding A/S or to any previous joint taxation group administration company of previously received joint taxation contributions. Since the Merger and through December 31, 2024, Noble has recognized a benefit for tax contribution payments of approximately $21.1 million from A.P. Møller Holding A/S and an expense for a tax contribution repayment of $4.0 million to A.P. Møller Holding A/S under this arrangement. For the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, an expense of $4.0 million and net benefits of approximately $19.1 million, respectively, are included in “Interest income and other, net” on our Consolidated Statements of Operations. Additionally, for the year ended December 31, 2023, approximately $2.0 million is recorded and included as a benefit in “Income tax benefit (provision)” on our Consolidated Statement of Operations.
UK earnings are taxable in the United Kingdom at the UK statutory rate of 19%. Noble Cayman was incorporated in the Cayman Islands and, therefore, not subject to tax in any jurisdiction. Following the Business Combination with Maersk Drilling, Noble is a public limited company incorporated under the laws of England and Wales. The income or loss of our non-UK subsidiaries is not subject to UK income tax. UK earnings are taxable in the United Kingdom at the UK statutory rate
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
of 19% and 25% through March 31, 2023, and beginning on April 1, 2023, respectively. A reconciliation of tax rates outside of the United Kingdom to our Noble effective rate for 2024 is shown below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Effect of: | | | | | | |
| Tax rates which are different than UK or Cayman rates | | 37.3 | % | | 37.6 | % | | 34.9 | % |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Tax impact of valuation allowance | | (25.0) | % | | (36.1) | % | | (22.0) | % |
| Resolution of (reserve for) tax authority audits | | (3.4) | % | | 4.4 | % | | (1.1) | % |
| Total | | 8.9 | % | | 5.9 | % | | 11.8 | % |
At December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Company asserts that its unremitted earnings and/or book/tax outside basis differences in certain of its subsidiaries are either permanently reinvested or are not expected to result in a material taxable event in the foreseeable future. Therefore, no material deferred taxes have been recorded related to such earnings and/or investments.
Note 11 — Employee Benefit Plans
Defined Benefit Plans
Noble Drilling (Land Support) Limited (“NDLS”), an indirect, wholly-owned subsidiary of Noble, maintains a pension plan that covers all of its salaried, non-union employees, whose most recent date of employment is prior to April 1, 2014 (referred to as our ‘non-US plan’). Since May 2022, the NDLS pension trustees and covenant advisors have been communicating with Noble to understand the impact of the Rig Transaction and merger with Maersk Drilling and to negotiate appropriate mitigation including buyout of the Scheme to cover the pension obligations. The Pension Regulators advised on December 15, 2022 that it did not intend to investigate the transaction unless Noble and the pension trustees were unable to agree on mitigation or there was a material change to circumstances. Noble has provided a company guarantee from Noble Corporation plc to cover the full section 75 debts of NDLS and Noble Resources Limited (“NRL”), the two sponsoring entities of the pension scheme, and believes this is an appropriate mitigation to support the pension liabilities.
In addition to the non-US plan discussed above, we have a US noncontributory defined benefit pension plan that covers certain salaried employees and a US noncontributory defined benefit pension plan that covers certain hourly employees, whose initial date of employment is prior to August 1, 2004 (collectively referred to as our “qualified US plans”). These plans are governed by the Noble Drilling Employees’ Retirement Trust (the “Trust”). The benefits from these plans are based primarily on years of service and, for the salaried plan, employees' compensation near retirement. These plans are designed to qualify under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (“ERISA”), and our funding policy is consistent with funding requirements of ERISA and other applicable laws and regulations. We make cash contributions, or utilize credits available to us, for the qualified US plans when required. The benefit amount that can be covered by the qualified US plans is limited under ERISA and the Internal Revenue Code of 1986. Therefore, we maintain an unfunded, non-qualified excess benefit plan designed to maintain benefits for specified employees at the formula level in the qualified salaried US plan. We refer to the qualified US plans and the excess benefit plan collectively as the “US plans.”
During the fourth quarter of 2016, we approved amendments, effective as of December 31, 2016, to our non-US and US defined benefit plans. With these amendments, employees and alternate payees will accrue no future benefits under the plans after December 31, 2016. However, these amendments will not affect any benefits earned through that date.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
A reconciliation of the changes in projected benefit obligations (“PBO”) for our non-US and US plans is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| | Non-US | | US | | Non-US | | US |
| Benefit obligation at beginning of period | | $ | 36,329 | | | $ | 179,346 | | | $ | 36,975 | | | $ | 176,438 | |
| Interest cost | | 2,062 | | | 8,751 | | | 2,356 | | | 8,992 | |
| Actuarial loss (gain) | | (2,738) | | | (9,872) | | | (2,571) | | | 6,642 | |
| Benefits paid | | (2,257) | | | (11,388) | | | (2,481) | | | (10,619) | |
| Settlements and curtailments | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (2,107) | |
| Foreign exchange rate changes | | (279) | | | — | | | 2,050 | | | — | |
| Benefit obligation at end of period | | $ | 33,117 | | | $ | 166,837 | | | $ | 36,329 | | | $ | 179,346 | |
A reconciliation of the changes in fair value of plan assets is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| | | Non-US | | US | | Non-US | | US |
| Fair value of plan assets at beginning of period | | $ | 43,245 | | | $ | 172,793 | | | $ | 40,642 | | | $ | 173,738 | |
| Actual return on plan assets | | (2,403) | | | 2,389 | | | 2,749 | | | 11,594 | |
| Employer contributions | | — | | | 50 | | | — | | | 187 | |
| Benefits paid | | (2,257) | | | (11,388) | | | (2,481) | | | (10,619) | |
| Plan participants’ contributions | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (2,107) | |
| Foreign exchange rate changes | | (313) | | | — | | | 2,335 | | | — | |
| Fair value of plan assets at end of period | | $ | 38,272 | | | $ | 163,844 | | | $ | 43,245 | | | $ | 172,793 | |
The funded status of the plans is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| | | Non-US | | US | | Non-US | | US |
| Funded status | | $ | 5,155 | | | $ | (2,993) | | | $ | 6,916 | | | $ | (6,553) | |
Amounts recognized in the Consolidated Balance Sheets consist of:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| | | Non-US | | US | | Non-US | | US |
| Other assets (noncurrent) | | $ | 5,155 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 6,916 | | | $ | — | |
| Other liabilities (current) | | — | | | (59) | | | — | | | (66) | |
| Other liabilities (noncurrent) | | — | | | (2,934) | | | — | | | (6,487) | |
| Net amount recognized | | $ | 5,155 | | | $ | (2,993) | | | $ | 6,916 | | | $ | (6,553) | |
Amounts recognized in AOCI consist of:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| | | Non-US | | US | | Non-US | | US |
| Net actuarial (gain) loss | | $ | 7,761 | | | $ | (12,390) | | | $ | 5,857 | | | $ | (9,371) | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Deferred income tax (asset) liability | | (1,942) | | | 2,602 | | | (1,486) | | | 1,968 | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive (income) loss | | $ | 5,819 | | | $ | (9,788) | | | $ | 4,371 | | | $ | (7,403) | |
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Pension costs include the following components:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| | Non-US | | US | | Non-US | | US | | Non-US | | US |
| Interest cost | | $ | 2,062 | | | $ | 8,751 | | | $ | 2,356 | | | $ | 8,992 | | | $ | 1,368 | | | $ | 6,753 | |
| Return on plan assets | | (2,291) | | | (9,243) | | | (1,871) | | | (9,579) | | | (1,431) | | | (12,581) | |
| Amortization of prior service cost | | — | | | — | | | 238 | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Recognized net actuarial loss | | 99 | | | — | | | — | | | (231) | | | — | | | (22) | |
| Settlement and curtailment (gain) loss | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 70 | | | — | | | (121) | |
| Net pension benefit cost (gain) loss | | $ | (130) | | | $ | (492) | | | $ | 723 | | | $ | (748) | | | $ | (63) | | | $ | (5,971) | |
There are zero estimated net actuarial losses and prior service costs for the non-US plan and the US plans that will be amortized from AOCI into net periodic pension cost in 2025.
During the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, we adopted the Retirement Plan mortality tables with the Mortality Projection scale as issued by the Society of Actuaries for each of the respective years. The Retirement Plan 2024, 2023, and 2022 mortality tables represent the new standard for defined benefit mortality assumptions due to adjusted life expectancies. There were no increases in our pension liability on our US plans resulting from the adoption of these tables for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
Defined Benefit Plans—Disaggregated Plan Information
Disaggregated information regarding our non-US and US plans is summarized below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | | |
| | | Non-US | | US | | Non-US | | US | | | | | |
| Projected benefit obligation | | $ | 33,117 | | | $ | 166,837 | | | $ | 36,329 | | | $ | 179,346 | | | | | | |
| Accumulated benefit obligation | | 33,117 | | | 166,837 | | | 36,329 | | | 179,346 | | | | | | |
| Fair value of plan assets | | 38,272 | | | 163,844 | | | 43,245 | | | 172,793 | | | | | | |
The following table provides information related to those plans in which the PBO exceeded the fair value of the plan assets at December 31, 2024 and 2023. The PBO is the actuarially computed present value of earned benefits based on service to date and includes the estimated effect of any future salary increases. Employees and alternate payees have no longer accrued future benefits under the plans since December 31, 2016.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| | | Non-US | | US | | Non-US | | US |
| Projected benefit obligation | | $ | — | | | $ | 166,837 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 179,346 | |
| Fair value of plan assets | | — | | | 163,844 | | | — | | | 172,793 | |
The PBO for the unfunded excess benefit plan was $0.7 million at December 31, 2024, as compared to $0.8 million at December 31, 2023, and is included under “US” in the above tables.
The following table provides information related to those plans in which the accumulated benefit obligation (“ABO”) exceeded the fair value of plan assets at December 31, 2024 and 2023. The ABO is the actuarially computed present value of earned benefits based on service to date, but differs from the PBO in that it is based on current salary levels. Employees and alternate payees have no longer accrued future benefits under the plans since December 31, 2016.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| | | Non-US | | US | | Non-US | | US |
| Accumulated benefit obligation | | $ | — | | | $ | 166,837 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 179,346 | |
| Fair value of plan assets | | — | | | 163,844 | | | — | | | 172,793 | |
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
The ABO for the unfunded excess benefit plan was $0.7 million at December 31, 2024, as compared to $0.8 million at December 31, 2023, and is included under “US” in the above tables.
Defined Benefit Plans—Key Assumptions
The key assumptions for the plans are summarized below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| | | Non-US | | US | | Non-US | | US |
| Weighted-average assumptions used to determine benefit obligations: | | | | | | | | |
| Discount Rate | | 5.50% | | 5.50% - 5.63% | | 4.80% | | 4.95% - 5.04% |
| Rate of compensation increase | | N/A | | N/A | | N/A | | N/A |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| | | Non-US | | Non-US | | Non-US |
| Weighted-average assumptions used to determine periodic benefit cost: | | | | | | |
| Discount Rate | | 5.50% | | 5.00% | | 1.80% |
| Expected long-term return on assets | | 4.80% | | 4.60% | | 1.20% |
| Rate of compensation increase | | N/A | | N/A | | N/A |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| | | US | | US | | US |
| Weighted-average assumptions used to determine periodic benefit cost: | | | | | | |
| Discount Rate | | 4.95% - 5.04% | | 5.17% - 5.27% | | 2.63% - 2.89% |
| Expected long-term return on assets | | 5.00% - 5.60% | | 5.00% - 5.80% | | 5.00% - 5.80% |
| Rate of compensation increase | | N/A | | N/A | | N/A |
The discount rates used to calculate the net present value of future benefit obligations for our US plans is based on the average of current rates earned on long-term bonds that receive a Moody’s rating of “Aa” or better. We have determined that the timing and amount of expected cash outflows on our plans reasonably match this index. For our non-US plan, the discount rate used to calculate the net present value of future benefit obligations is determined by using a yield curve of high quality bond portfolios with an average maturity approximating that of the liabilities.
In developing the expected long-term rate of return on assets, we considered the current level of expected returns on risk free investments (primarily government bonds), the historical level of risk premium associated with the other asset classes in which the portfolio is invested and the expectations for future returns of each asset class. The expected return for each asset class was then weighted based on the target asset allocation to develop the expected long-term rate of return on assets for the portfolio. To assist us with this analysis, we employ third-party consultants for our US and non-US plans that use a portfolio return model.
Defined Benefit Plans—Plan Assets
Non-US Plan. As of December 31, 2024, the NDLS pension Scheme targets an asset allocation of 13.5% return-seeking securities (growth) and 86.5% in debt securities (matching) and adopts a de-risking strategy whereby the level of investment risk reduces as the Scheme’s funding level improves. The overall investment objective of the Scheme, as adopted by the Scheme’s Trustees, is to reach a fully funded position on the agreed de-risking basis of gilts -0.0% per annum. The objectives within the Scheme’s overall investment strategy is to outperform the cash + 4% per annum long term objective for growth assets and to sufficiently hedge interest rate and inflation risk within the matching portfolio in relation to the Scheme’s liabilities. By achieving these objectives, the Trustees believe the Scheme will be able to avoid significant volatility in the contribution rate and provide sufficient assets to cover the Scheme’s benefit obligations. To achieve this the Trustees have
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
given Mercer, the appointed investment manager, full discretion in the day-to-day management of the Scheme’s assets and implementation of the de-risking strategy, who in turn invests in multiple underlying investment managers where appropriate. The Trustees meet with Mercer periodically to review and discuss their investment performance.
The actual fair values of the non-US plan are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2024 |
| | | | Estimated Fair Value Measurements |
| | Carrying
Amount | | Quoted Prices in Active Markets (Level 1) | | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 340 | | | $ | 340 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Equity securities: | | | | | | | | |
| International companies | | 2,820 | | | 2,820 | | | — | | | — | |
| Fixed income securities: | | | | | | | | |
| Corporate bonds | | 35,112 | | | 35,112 | | | — | | | — | |
| Total | | $ | 38,272 | | | $ | 38,272 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2023 |
| | | | Estimated Fair Value Measurements |
| | Carrying
Amount | | Quoted Prices in Active Markets (Level 1) | | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 247 | | | $ | 247 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Equity securities: | | | | | | | | |
| International companies | | 5,560 | | | 5,560 | | | — | | | — | |
| Fixed income securities: | | | | | | | | |
| Corporate bonds | | 37,438 | | | 37,438 | | | — | | | — | |
| Total | | $ | 43,245 | | | $ | 43,245 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
US Plans. The fundamental objective of the US plan is to provide the capital assets necessary to meet the financial obligations made to plan participants. In order to meet this objective, the Investment Policy Statement depicts how the investment assets of the plan are to be managed in accordance with the overall target asset allocation of approximately 75.0% equity securities, 6.0% fixed income securities, and 19.0% in strategic opportunities. The target asset allocation is intended to generate sufficient capital to meet plan obligations and provide a portfolio rate of return equal to or greater than the return realized using appropriate blended, market benchmark over a full market cycle (usually a five to seven year time period). Actual allocations may deviate from the target range, however any deviation from the target range of asset allocations must be approved by the Trust’s governing committee.
For investments in mutual funds, the assets of the Trust are subject to the guidelines and limits imposed by such mutual fund’s prospectus and the other governing documentation at the fund level.
No Ordinary Shares of Noble were included in equity securities at either December 31, 2024 or 2023.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
The actual fair values of US plan assets are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2024 |
| | | | Estimated Fair Value Measurements |
| | Carrying
Amount | | Quoted Prices in Active Markets (Level 1) | | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 4,164 | | | $ | 4,164 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Equity securities: | | | | | | | | |
| United States | | 38,317 | | | 1,726 | | | 36,591 | | | — | |
| Fixed income securities: | | | | | | | | |
| Corporate bonds | | 91,129 | | | 86,991 | | | 4,138 | | | |
| Treasury bonds | | 30,234 | | | 30,234 | | | — | | | — | |
| Total | | $ | 163,844 | | | $ | 123,115 | | | $ | 40,729 | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2023 |
| | | | Estimated Fair Value Measurements |
| | Carrying
Amount | | Quoted Prices in Active Markets (Level 1) | | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 4,388 | | | $ | 4,388 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Equity securities: | | | | | | | | |
| United States | | 36,857 | | | — | | | 36,857 | | | — | |
| Fixed income securities: | | | | | | | | |
| Corporate bonds | | 100,377 | | | 96,373 | | | 4,004 | | | |
| Treasury bonds | | 31,171 | | | 31,171 | | | — | | | — | |
| Total | | $ | 172,793 | | | $ | 131,932 | | | $ | 40,861 | | | $ | — | |
Defined Benefit Plans—Cash Flows
In 2024, 2023, and 2022, we made no contributions to our non-US plan and contributions of $0.1 million, $0.2 million, and $0.4 million to our US plans, respectively. We expect our aggregate minimum contributions to our non-US and US plans in 2025, subject to applicable law, to be zero and $0.1 million, respectively. We continue to monitor and evaluate funding options based upon market conditions and may increase contributions at our discretion.
The following table summarizes our estimated benefit payments at December 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Payments by Period |
| | Total | | 2025 | | 2026 | | 2027 | | 2028 | | 2029 | | Thereafter |
| Estimated benefit payments | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-US plans | | $ | 25,709 | | | $ | 2,282 | | | $ | 2,331 | | | $ | 2,423 | | | $ | 2,499 | | | $ | 2,578 | | | $ | 13,596 | |
| US plans | | 114,653 | | | 10,733 | | | 10,989 | | | 11,215 | | | 11,378 | | | 11,548 | | | 58,790 | |
| Total estimated benefit payments | | $ | 140,362 | | | $ | 13,015 | | | $ | 13,320 | | | $ | 13,638 | | | $ | 13,877 | | | $ | 14,126 | | | $ | 72,386 | |
Other Benefit Plans. We sponsored a 401(k) Restoration Plan, which is a nonqualified, unfunded employee benefit plan under which specified employees may elect to defer compensation in excess of amounts deferrable under our 401(k) savings plan. At December 31, 2021, our liability for the 401(k) Restoration Plan was $2.8 million, and is included in “Accrued payroll and related costs.” In early 2022, the Noble Services Company LLC Board of Directors approved the termination of the 401(k) Restoration Plan, following which Noble distributed all benefits of the plan during the second quarter of 2022. No liabilities remained in the plan as of December 31, 2022. We do not provide post-retirement benefits (other than pensions) or any post-employment benefits to our employees.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
In 2005, we enacted a profit sharing plan, the Noble Services Company LLC Profit Sharing Plan, which covers eligible employees, as defined in the plan. Participants in the plan become fully vested in the plan after one year of service. On January 1, 2019, the 401(k) savings plan and the profit sharing plan were merged into the Noble Drilling Services LLC 401(k) and Profit Sharing Plan. Effective January 1, 2025, the profit-sharing plan was removed and there will be no future profit-sharing contributions made into the plan. We sponsor other retirement, health, and welfare plans, a 401(k) savings plan, and international savings plans for the benefit of our employees. The contributions to these plans aggregated approximately $32.0 million, $34.0 million, and $34.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
Profit sharing contributions were discretionary, required Board of Directors approval, and were made in the form of cash. No contributions were made for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
Note 12 — Commitments and Contingencies
Tax Matters
Audit claims of approximately $359.3 million at December 31, 2024, attributable to income and other business taxes remain outstanding and are under continued objection by Noble. Such audit claims are mostly attributable to Brazil, Egypt, Ghana, and Guyana. This remains under continued monitoring and evaluation on a quarterly basis as facts change and as audits and/or litigation continue to progress. We intend to vigorously defend our reported positions and currently believe the ultimate resolution of the audit claims will not have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial statements.
We operate in numerous countries throughout the world and our tax returns filed in those jurisdictions are subject to review and examination by tax authorities within those jurisdictions. We recognize uncertain tax positions that we believe have a greater than 50% likelihood of being sustained upon challenge by a tax authority. We cannot predict or provide assurance as to the ultimate outcome of any existing or future assessments.
Hurricane Ida Personal Injury Claims
In preparation for Hurricane Ida in the United States Gulf of America, also known as the United States Gulf of Mexico ( the “US Gulf”), in August 2021, the Noble Globetrotter II successfully secured the well it was drilling and detached from the blowout preventer without incident. However, during transit, the lower marine riser package and a number of riser joints separated from the rig, and certain other damage occurred. Due to the environmental conditions, a number of crew members were treated for injuries and released from medical care. We have had multiple parties, some of which are subject to a third-party contractual indemnity to our benefit, who have filed answers to the Limitation of Liability Action in the United States District Court Western District of Louisiana seeking damages related to physical and emotional harm allegedly suffered as a result of the Hurricane Ida incident. We are defending ourselves vigorously against these claims, although there is inherent risk in litigation, and we cannot predict or provide assurance as to the ultimate outcome of this lawsuit. As claims progress, the Company’s estimated loss could change from time to time, and any such change individually or in the aggregate could be material. We have insurance for such claims with a deductible of $5.0 million, in addition to contractual indemnity owed to us for a portion of the third-party claims; however, these protections may not adequately cover our losses and related claims, which could adversely affect our business. Timing differences are likely to exist between any losses incurred and the recognition and receipt of insurance proceeds reflected in the Company’s financial statements. Costs, as well as insurance recoveries, are presented in “Hurricane losses and (recoveries), net” on the Consolidated Statement of Operations.
Services Agreement
In February 2016, Diamond entered into a ten-year agreement with a subsidiary of Baker Hughes Company (formerly named Baker Hughes, a GE company) to provide services with respect to certain blowout preventer and related well control equipment on our drillships. Such services include management of maintenance, certification, and reliability with respect to such equipment. Future commitments under the contractual services agreements are estimated to be approximately $24.7 million annually. Total future commitments are projected to be $67.6 million in the aggregate over the remaining term of the agreement, including a $37.0 million commitment for the purchase of consumables and capital spare parts owned and controlled by the vendor at the end of the service arrangement.
Letters of Credit and Surety Bonds
As of December 31, 2024, we had $24.8 million of letters of credit issued under the 2023 Revolving Credit Facility and an additional $126.8 million in letters of credit and surety bonds issued under bilateral arrangements which guarantee our
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
performance as it relates to our drilling contracts, contract bidding, tax appeals, customs duties, and other obligations in various jurisdictions. We expect to comply with the underlying performance requirements and we expect obligations under these letters of credit and surety bonds will not be called.
Other Contingencies
We are a defendant in certain other claims and litigation arising out of operations in the ordinary course of business, including personal injury claims, the resolution of which, in the opinion of management, will not be material to our financial position, results of operations, or cash flows. There is inherent risk in any litigation or dispute and no assurance can be given as to the outcome of these claims.
Subsequent Event
Total current liabilities and total current assets as of December 31, 2024, include an accrual for an expected settlement of certain litigation and a related insurance recovery, which balances had previously been reflected as lesser, and non-current, amounts.
Note 13 — Segment and Related Information
We report our contract drilling operations as a single reportable segment, Contract Drilling Services, which reflects how we manage our business. The mobile offshore drilling units comprising our offshore rig fleet operate in a global market for contract drilling services and are often redeployed to different regions due to changing demands of our customers, which consist primarily of large, integrated, independent, and government-owned or controlled oil and gas companies throughout the world. Our reportable segment comprises the structure used by our Chief Executive Officer, who has been determined to be our chief operating decision maker (“CODM”), for assessing performance and allocating resources. We regularly provide management reports to the CODM that include a segment revenue amount and segment contract drilling services costs. Our CODM evaluates the segment’s operating performance based on operating revenues and operating income (loss). Refer to the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Operations for additional information.
As of December 31, 2024, our contract drilling services segment conducted drilling operations in Africa, Far East Asia, the Middle East, the North Sea, Oceania, South America, and the US Gulf. Included in our long-lived assets balance below is our property and equipment and right-of-use assets. We used the geographic location as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, of each drilling rig, operating lease, and finance lease for our property and equipment and right-of-use assets, respectively, for our long-lived assets geographic disclosure shown below.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
The following table presents revenues and long-lived assets by country based on the location of the service provided during the period:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Revenues | | Long-Lived Assets as of |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| Australia | | $ | 242,721 | | | $ | 154,860 | | | $ | 78,899 | | | $ | 59,202 | | | $ | 83,162 | |
| Brazil | | 107,014 | | | 92,022 | | | 33,208 | | | 315,084 | | | 114 | |
| Colombia | | 94,560 | | | 53,646 | | | — | | | 163,719 | | | 98,979 | |
| Denmark | | 75,971 | | | 88,914 | | | 40,806 | | | 333,618 | | | 508,715 | |
| Ghana | | 138,176 | | | 150,677 | | | 35,018 | | | — | | | 241,132 | |
Guinea Bissau
| | 13,947 | | | — | | | — | | | 300,962 | | | — | |
| Guyana | | 676,234 | | | 703,473 | | | 469,267 | | | 762,746 | | | 733,803 | |
| Malaysia | | 203,495 | | | 87,105 | | | 32,227 | | | 292,878 | | | 234,469 | |
| Mexico | | — | | | 139,595 | | | 30,788 | | | — | | | — | |
| Namibia | | 7,537 | | | 27 | | | 19 | | | 253,652 | | | — | |
| Netherlands | | 42,107 | | | 36,510 | | | 13,378 | | | 75,421 | | | 134,887 | |
| Nigeria | | 135,331 | | | 143,641 | | | — | | | 73,296 | | | 67,495 | |
| Norway | | 236,834 | | | 249,308 | | | 154,406 | | | 487,183 | | | 498,845 | |
| Suriname | | 82,082 | | | 108,532 | | | 133,680 | | | — | | | — | |
| Trinidad and Tobago | | — | | | 2,135 | | | 35,101 | | | 78,396 | | | 382,369 | |
| United Kingdom | | 190,804 | | | 65,710 | | | 55,632 | | | 755,712 | | | 353,656 | |
| United States | | 685,835 | | | 437,346 | | | 266,176 | | | 1,666,748 | | | 575,960 | |
| Other | | 125,170 | | | 75,517 | | | 35,242 | | | 530,539 | | | 235,881 | |
| Total | | $ | 3,057,818 | | | $ | 2,589,018 | | | $ | 1,413,847 | | | $ | 6,149,156 | | | $ | 4,149,467 | |
Significant Customers
The following table sets forth revenues from our customers as a percentage of our consolidated operating revenues:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Exxon Mobil Corporation (“ExxonMobil”) | | 22.1 | % | | 24.5 | % | | 32.3 | % |
| Shell plc | | 12.3 | % | | 13.6 | % | | 12.0 | % |
| TotalEnergies | | 6.3 | % | | 10.5 | % | | 9.7 | % |
No other customer accounted for more than 10% of our consolidated operating revenues in 2024, 2023, or 2022.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
Note 14 — Supplemental Financial Information
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows Information
Operating cash activities. The net effect of changes in other assets and liabilities on cash flows from operating activities is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Accounts receivable | | $ | (54,923) | | | $ | (80,042) | | | $ | (18,133) | |
| Other current assets | | (108,044) | | | (42,532) | | | 21,271 | |
| Other assets | | 40,146 | | | (27,177) | | | 16,861 | |
| Accounts payable | | (32,437) | | | 59,757 | | | 20,430 | |
| Other current liabilities | | 103,326 | | | 9,679 | | | (36,713) | |
| Other liabilities | | (64,106) | | | 32,612 | | | 15,468 | |
| Total net change in other assets and liabilities | | $ | (116,038) | | | $ | (47,703) | | | $ | 19,184 | |
Non-cash investing and financing activities. Additions to property and equipment, at cost for which we had accrued a corresponding liability in accounts payable as of December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 were $66.0 million, $114.7 million, and $70.0 million, respectively.
On October 3, 2022, Noble completed the Business Combination with Maersk Drilling, issuing 60.1 million Ordinary Shares valued at $1.8 billion, in exchange for $2.0 billion net assets acquired. Also in connection with the Business Combination, in mid-November 2022, the Compulsory Purchase interest was settled when 4.1 million Ordinary Shares were issued, resulting an increase in additional paid in capital of $123.8 million, and the remainder paid in cash of $69.9 million. See “Note 2 — Acquisitions and Divestitures” for additional information.
On September 4, 2024, Noble completed its acquisition of Diamond issuing 24.2 million Ordinary Shares valued at $879.9 million, in exchange for $1.5 billion net assets acquired. See “Note 2 — Acquisitions and Divestitures” for additional information.
Additional cash flow information is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended | | Year Ended | | Year Ended |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Cash paid during the period for: | | | | | | |
| Interest, net of amounts capitalized | | $ | 106,845 | | | $ | 52,361 | | | $ | 35,543 | |
Income taxes paid (refunded), net (1) | | 108,664 | | | 105,446 | | | 58,386 | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
(1)The net income taxes paid for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, includes withholding tax in Guyana of $48.9 million, $52.3 million, and $34.7 million on gross revenue, respectively. Excluding such withholding tax, the total tax payments would be $59.7 million, $53.1 million, and $23.7 million, respectively.
Note 15 — Information about Noble Finance II
8.000% Senior Notes due 2030
Noble Finance II, a wholly-owned, indirect subsidiary of Noble, is the issuer of the 2030 Notes and, one or more 100% wholly-owned, direct and indirect subsidiaries of Noble Finance II are the unconditional guarantors, or are otherwise obligated as of December 31, 2024, with respect to the 2030 Notes. See “Note 6 — Debt” for additional information.
The Noble Indenture contains a covenant that requires Noble Finance II to furnish to holders of the 2030 Notes certain financial information relating to Noble Finance II and its restricted subsidiaries. The obligation to furnish such information may be satisfied by providing financial information of Noble along with a description of the differences between such information and the financial information of Noble Finance II and its restricted subsidiaries on a standalone basis.
NOBLE CORPORATION plc AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unless otherwise indicated, dollar and share amounts in tables are in thousands)
The summarized financial information below reflects the consolidated accounts of Noble Finance II:
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2024 |
| Balance Sheet | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 131,703 | |
| Total current assets | | 1,683,839 | |
| Total current liabilities | | 694,321 | |
| Total debt | | 1,401,214 | |
| Total shareholders' equity | | 4,535,081 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | Twelve Months Ended December 31, 2024 |
| Statement of Operations | | |
| Operating revenues | | $ | 2,721,156 | |
| Operating costs and expenses | | 2,010,731 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 379,551 | |
| | |
| Statement of Cash Flows | | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | | $ | 792,859 | |
| Capital expenditures | | (536,658) | |
| Proceeds from disposal of assets, net | | (690) | |
| Dividend payments | | — | |
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Conclusions Regarding Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Robert W. Eifler, President and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) of Noble, and Richard B. Barker, Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) of Noble, have evaluated the disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”)) of Noble as of the end of the period covered by this report. On the basis of this evaluation, our Principal Executive Officer and Principal Financial Officer have concluded that Noble’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of December 31, 2024. Noble’s disclosure controls and procedures are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by Noble in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to management, including its principal executive and principal financial officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
In accordance with interpretive guidance issued by SEC staff, companies may exclude an acquired business from the assessment of internal control over financial reporting during the first year following the date on which the acquisition is completed and from the assessment of disclosure controls and procedures to the extent subsumed in such internal control over financial reporting. In accordance with this guidance, as the Company acquired Diamond on September 4, 2024, Management’s, including our Principal Executive Officer and Principal Financial Officer, evaluation and conclusion as to the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2024, excluded the portion of disclosure controls and procedures that are subsumed by internal control over financial reporting of Diamond. The total assets and total revenues of this acquired entity represented approximately 29% and 11% of our consolidated total assets and total revenues as of and for the year ended December 31, 2024, respectively.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The management of Noble is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) promulgated under the Exchange Act. Under the supervision of and with the participation of our management, including our Principal Executive Officer and our Principal Financial Officer, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on the framework Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in 2013. Based on this assessment, our management concluded that Noble maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024.
In accordance with interpretive guidance issued by SEC staff, management has excluded Diamond from the assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, as the Company acquired Diamond during the year ended December 31, 2024. The total assets and total revenues of this acquired entity represented approximately 29% and 11% of our consolidated total assets and total revenues as of and for the year ended December 31, 2024, respectively.
PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, the independent registered public accounting firm that audited our financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, has audited the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, as stated in their report, which is provided in Part II, Item 8, “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in Noble’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the quarter ended December 31, 2024, that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the internal control over financial reporting of Noble.
Limitations on the Effectiveness of Controls
Internal control over financial reporting includes the controls themselves, monitoring (including internal auditing practices), and actions taken to correct deficiencies as identified. There are inherent limitations to the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, however well designed, including the possibility of human error and the possible circumvention or overriding of controls. The design of an internal control system is also based in part upon assumptions and judgments made by management about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that an internal control will be effective under all potential future conditions. As a result, even an effective system of internal controls can provide no more than reasonable assurance with respect to the fair presentation of financial statements and the processes under which they were prepared.
Item 9B. Other Information.
Our directors and executive officers may from time to time enter into plans or other arrangements for the purchase or sale of our Ordinary Shares that are intended to satisfy the affirmative defense conditions of Rule 10b5-1(c) or may represent a non-Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement under the Exchange Act. During the three months ended December 31, 2024, no such plans or other arrangements were adopted, terminated, or modified.
Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections.
Not applicable.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers, and Corporate Governance.
Information in response to this item is incorporated by reference to our Proxy Statement relating to our 2025 Annual Meeting of Shareholders. The Proxy Statement will be filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Form 10-K pursuant to Regulation 14A under the Exchange Act.
Item 11. Executive Compensation.
Information in response to this item is incorporated by reference to our Proxy Statement relating to our 2025 Annual Meeting of Shareholders. The Proxy Statement will be filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Form 10-K pursuant to Regulation 14A under the Exchange Act.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.
Information in response to this item is incorporated by reference to our Proxy Statement relating to our 2025 Annual Meeting of Shareholders. The Proxy Statement will be filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Form 10-K pursuant to Regulation 14A under the Exchange Act.
Item 13. Certain Relationships, Related Transactions, and Directors’ Independence.
Information in response to this item is incorporated by reference to our Proxy Statement relating to our 2025 Annual Meeting of Shareholders. The Proxy Statement will be filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Form 10-K pursuant to Regulation 14A under the Exchange Act.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services.
Information in response to this item is incorporated by reference to our Proxy Statement relating to our 2025 Annual Meeting of Shareholders. The Proxy Statement will be filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Form 10-K pursuant to Regulation 14A under the Exchange Act.
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules.
(a)The following documents are filed as part of this report:
(1)A list of the financial statements filed as a part of this report is set forth in Part II, Item 8, “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” on page 53 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and is incorporated herein by reference. (2)Financial Statement Schedules:
All schedules are omitted because they are either not applicable or required information is shown in the financial statements or notes thereto.
(3)Exhibits:
The information required by this Item 15(a)(3) is set forth in the Index to Exhibits accompanying this Annual Report on Form 10-K and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary.
None.
Index to Exhibits
| | | | | | | | |
Exhibit
Number | | Exhibit |
| | |
| 2.1 | | |
| | |
2.2† | | |
| | |
| 2.3 | | |
| | |
| 2.4 | | |
| | |
| 3.1 | | |
| | |
| 4.1 | | |
| | |
| 4.2 | | |
| | |
| 4.3 | | Indenture, dated as of September 21, 2023, among Diamond Foreign Asset Company and Diamond Finance, LLC, as issuers, Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc., as a guarantor, the other subsidiaries of Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc. party thereto from time to time, as guarantors, and HSBC Bank USA, National Association, as trustee and collateral agent (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on September 22, 2023 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| | |
| 4.4 | | Supplemental Indenture, dated as of September 4, 2024, among Diamond Foreign Asset Company and Diamond Finance, LLC, as issuers, Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc., as existing company, Dolphin Merger Sub 2, Inc., (now known as Noble Offshore Drilling Inc.) as new company, and HSBC Bank USA, National Association, as trustee and collateral agent (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to the Noble'’s current Report on Form 8-K filed on September 4, 2024 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| | |
| 4.5** | | |
| | |
| | | | | | | | |
Exhibit
Number | | Exhibit |
| 10.1* | | |
| | |
| 10.2* | | |
| | |
| 10.3* | | |
| | |
| 10.4* | | |
| | |
| 10.5* | | |
| | |
| 10.6* | | |
| | |
| 10.7* | | |
| | |
| 10.8* | | |
| | |
| 10.9* | | |
| | |
| 10.10* | | |
| | |
10.11*^ | | |
| | |
10.12*^ | | |
| | |
| | | | | | | | |
Exhibit
Number | | Exhibit |
| 10.13 | | |
| | |
| 10.14 | | |
| | |
| 10.15 | | |
| | |
| 10.16 | | |
| | |
| 10.17 | | |
| | |
| 10.18 | | |
| | |
| 10.19 | | |
| | |
| 10.20 | | |
| | |
| 10.21* | | |
| | |
| 10.22** | | |
| | |
| 10.23 | | Amended and Restated Senior Secured Revolving Credit Agreement, dated as of April 18, 2023, by and among Noble Finance II LLC, Noble International Finance Company, Noble Drilling A/S, and any additional subsidiaries of Noble Finance II LLC as from time to time designated by Noble Finance II LLC as a designated borrower,as borrowers, the lenders and issuing banks party thereto from time to time and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, collateral agent and security trustee (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Noble’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 18, 2023 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| | |
| | | | | | | | |
Exhibit
Number | | Exhibit |
| 10.24 | | First Amendment to the Amended and Restated Senior Secured Revolving Credit Agreement, dated as of June 24, 2024 by and among Noble Finance II LLC, Noble International Finance Company, as a designated borrower, Noble Drilling A/S, as a designated borrower, the lenders party thereto and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Noble’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 27, 2024 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| | |
| 10.25 | | Amended and Restated Collateral Agreement and Intercreditor Agreement, dated as of September 21, 2023, among Noble Offshore Drilling, Inc. (formerly known as Dolphin Merger Sub 2, Inc. and as successor by merger with Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc.), as a grantor, Diamond Foreign Asset Company, as a grantor, the other grantors from time to time party thereto, HSBC Bank USA, National Association, as credit agreement administrative agent, notes trustee, and collateral agent and security trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on September 22, 2023 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| | |
| 10.26* | | |
| | |
| 10.27* | | |
| | |
| 10.28* | | |
| | |
| 19.1** | | |
| | |
| 21.1 | | |
| | |
| 23.1 | | |
| | |
| 31.1 | | |
| | |
| 31.2 | | |
| | |
| 32.1+ | | |
| | |
| 32.2+ | | |
| | |
| 97.1 | | |
| | |
| | | | | | | | |
Exhibit
Number | | Exhibit |
| 101.INS | | Inline XBRL Instance Document - the instance document does not appear in the Interactive Data File because its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document. |
| | |
| 101.SCH | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. |
| | |
| 101.CAL | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document. |
| | |
| 101.DEF | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. |
| | |
| 101.LAB | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. |
| | |
| 101.PRE | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. |
| | |
| 104 | | Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101). |
| | |
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
* Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
** Filed herewith.
† Certain portions of the exhibit have been omitted. The Company agrees to furnish a supplemental copy with any omitted information to the SEC upon request.
^ Certain personally identifiable information contained in this exhibit has been redacted pursuant to Item 601(a)(6) of Regulation S-K.
+ Furnished in accordance with Item 601(b)(32)(ii) of Regulation S-K.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
Noble Corporation plc, a public limited company incorporated under the laws of England and Wales
| | | | | | | | |
| February 18, 2025 | By: | /s/ Robert W. Eifler |
| | | Robert W. Eifler
President and Chief Executive Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | | | | | |
| /s/ Robert W. Eifler | | February 18, 2025 |
Robert W. Eifler
President and Chief Executive Officer, and Director
(Principal Executive Officer) | | Date |
| | |
| /s/ Richard B. Barker | | February 18, 2025 |
Richard B. Barker
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer
(Principal Financial Officer) | | Date |
| | |
| /s/ Jennifer Yeung | | February 18, 2025 |
Jennifer Yeung
Vice President, Chief Accounting Officer and Controller
(Principal Accounting Officer) | | Date |
| | |
| /s/ Charles M. Sledge | | February 18, 2025 |
Charles M. Sledge
Director and Chairman | | Date |
| | |
| /s/ Patrice Douglas | | February 18, 2025 |
Patrice Douglas
Director | | Date |
| | |
| /s/ Claus V. Hemmingsen | | February 18, 2025 |
Claus V. Hemmingsen
Director | | Date |
| | |
| /s/ Alan J. Hirshberg | | February 18, 2025 |
Alan J. Hirshberg
Director | | Date |
| | |
| /s/ Kristin H. Holth | | February 18, 2025 |
Kristin H. Holth
Director | | Date |
| | |
| /s/ H. Keith Jennings | | February 18, 2025 |
H. Keith Jennings
Director | | Date |
| | |
| /s/ Alastair J. Maxwell | | February 18, 2025 |
Alastair J. Maxwell Director | | Date |
| | |
| | | | | | | | |
| /s/ Ann D. Pickard | | February 18, 2025 |
Ann D. Pickard
Director | | Date |
