Exhibit 99.2

ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
(FORMERLY FIRST COBALT CORP.)
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(EXPRESSED IN THOUSANDS OF CANADIAN DOLLARS)
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
General
This Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Electra Battery Materials Corporation (“Electra” or the “Company”) (“MD&A”) was prepared on November 16, 2023 and provides analysis of the Company’s financial results for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2023 and 2022. The Company prepares its condensed interim consolidated financial statements in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”). The following information should be read in conjunction with the accompanying condensed interim consolidated financial statements for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2023 and 2022 with accompanying notes which have been prepared following IAS 34, Interim Financial Reporting (“IAS 34”). All dollar figures are expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars unless otherwise stated. Financial Statements are available at www.sedarplus.ca and the Company’s website www.electrabmc.com.
Company Overview
Electra was incorporated on July 13, 2011 under the Business Corporations Act of British Columbia and on September 4, 2018, the Company filed a Certificate of Continuance into Canada and adopted Articles of Continuance as a Federal Company under the Canada Business Corporations Act (the “CBCA”). On December 6, 2021, the Company changed its name from First Cobalt Corp. to Electra Battery Materials Corporation to better align with its strategic vision. The Corporation is in the business of battery materials refining and the acquisition and exploration of cobalt-copper resource properties. The Corporation is focused on building a diversified portfolio of assets that are highly leveraged to the battery materials market with assets located in North America, with the intent of providing a North American supply of battery materials. The Corporation has two significant North American assets:
| (i) | a hydrometallurgical refinery located in Ontario, Canada (the “Refinery”); and |
| (ii) | the Iron Creek Project in Idaho, the Corporation’s flagship mineral project (the “Iron Creek Project”). |
Electra is a public company whose common shares are listed on the TSX Venture Exchange (TSX-V) and NASDAQ and trade under the symbol ELBM in both cases. The Company began trading on the NASDAQ on April 27, 2022.
The Company’s registered and records office is Suite 2400, Bay-Adelaide Centre, 333 Bay Street, Toronto, Ontario, M5H 2T6. The Company’s head office is located at 133 Richmond Street W, Suite 602, Toronto, Ontario, M5H 2L3.
Q3 2023 Highlights and Recent Events
Battery Recycling
Electra launched a black mass trial late in 2022 at its Ontario refinery complex to recover high-value elements found in shredded lithium-ion batteries. Using its proprietary hydrometallurgical process, Electra successfully completed the first plant-scale recycling of black mass material in North America and confirmed the recovery of a number of critical metals, including lithium, nickel, cobalt, copper, manganese, and graphite, needed for North America’s EV battery supply chain, surpassing initial expectations.
To date, Electra has produced quality nickel-cobalt mixed hydroxide, graphite, and lithium carbonate products in its black mass recycling trial.
In Q2 2023, Electra completed a desktop scoping study to evaluate the potential economics of developing a standalone black mass process plant within its refinery complex capable of processing 2,500 tonnes of black mass material per annum. The Phase 1 facility could be scaled over time as the market for battery recycling expands.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
Highlights from Electra’s desktop scoping study include:
| · | Internal estimate of capital spend is approximately $8.1 million. |
| · | The internal rate of return is estimated at 127%. |
| · | The payback period is estimated at between 1 and 2 years. |
Electra’s desktop scoping study was based on a number of assumptions, including annual processing of 2,500 tonnes of black mass, metal prices using analysts’ long-term forecasts, recovery rates consistent with those achieved to date, and $12.6 million of committed capital comprised of $8.1 million for capital costs and $4.5 million in working capital.
On July 17, 2023, the Corporation announced the first customer shipment of the nickel-cobalt mixed hydroxide precipitate product (“MHP”) produced at its refinery complex north from recycled battery material.
On October 2, 2023, Electra provided an update on its battery materials recycling trial, confirming improved recoveries of high-value elements, higher metal content in saleable products produced, and reduced use of reagents. Combined, the improvements pave the way for higher-quality customer products and improved economics for continuous battery materials recycling operations.
Key highlights of Electra black mass trial through end of Q3 2023 include:
| · | Electra has processed 40 tonnes of black mass material in a plant scale setting, believed to be the first of its kind in North America. |
| · | Recovery rates for all targeted metals have improved since the start of the trial in late December 2022. |
| · | Recovery rates for manganese have improved by more than 50% from results achieved in a lab setting. |
| · | Metal content contained in the nickel-cobalt mixed hydroxide precipitate (MHP) produced from the recycling process has increased in the range of 5 to 10% since the start of the trial. An increase in metal content results in a higher value saleable product, thereby improving the potential economics of continuous recycling operations. |
| · | Approximately 20 tonnes of nickel-cobalt MHP product have been shipped to customers to date. |
| · | Reagent requirements have been reduced and in some cases alternative, less costly reagents have been used for improved overall metal recovery. Further, some of the reagent additions substituted have reduced overall impurity levels within the process. The reduction in reagent use and substitution of certain reagents are expected to lower operating expenses, thereby improving the economics of continuous recycling operations. |
As a result of the successes achieved, the Corporation announced that it will continue to process black mass material at its refinery complex into the fourth quarter of 2023. Electra anticipates providing a detailed summary report of its key findings from its black mass trial in the fourth quarter of 2023.
As of November 16, 2023, Electra’s black mass recycling capabilities remain at the evaluation stage and the decision to commercialize these capabilities remains subject to financing, additional feasibility and engineering work to incorporate process modifications arising from the demonstration plant, vendor selection process, and the successful evaluation of samples by customers.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
Electra anticipates completing its black mass trial and making refinements to its desktop project economics for launching continuous black mass recycling operations in Q4, 2023. The Company’s ability to run a plant scale test has put Electra at the forefront of battery materials recycling using hydrometallurgical processes.
Commercial Agreement with LG Energy Solution
On July 24, 2023, the Company announced that its contract to supply battery grade cobalt to LG Energy Solution was extended and expanded beyond the terms initially announced in September 2022. Electra plans to supply LG Energy Solution with up to 19,000 tonnes of battery grade cobalt over a five-year period beginning in 2025. In the initial 2022 agreement, Electra agreed to supply LGES with 7,000 tonnes of battery grade cobalt from 2023 to 2025.
Private Placement
On August 11, 2023, The Company announced the close of a brokered private placement and concurrent non-brokered private placement for gross proceeds of $21.5 million. The total includes the exercise of the full over-allotment option granted to the syndicate of Agents. The Company intends to use the net proceeds; to advance its black mass recycling strategy and cobalt refinery; for working capital to retire existing payables; and for general corporate purposes.
Joint Venture with Three Fires to Recycle Lithium-ion battery waste in Ontario
On May 2, 2023, Electra announced the signing of a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with the Three Fires Group (“Three Fires”), a First Nations group focused on generating wealth and prosperity for its members from economic and infrastructure opportunities.
Under the planned joint venture, Electra and the Three Fires will collaborate to source and process lithium-ion battery waste generated by manufacturers of current and future battery cells, electric vehicles, and energy storage systems. The waste will be processed at a facility to be located in southern Ontario and produce black mass material that will be further refined using Electra’s proprietary hydrometallurgical process at its refinery complex north of Toronto. The recycling of black mass material is designed to recover high value elements, including lithium, nickel, cobalt, copper, manganese, and graphite.
As part of the MOU, Electra and the Three Fires Group have agreed to work together to secure a net-zero industrial facility that can be used to shred and separate lithium-ion batteries and produce black mass material. The joint-venture partners have also agreed to collaborate on the development of economic studies of sourcing of engineering, procurement, construction, and management requirements necessary to launch the battery waste recycling facility.
On June 26, 2023 Electra announced that it received a commitment for a strategic investment from the Three Fires Group in support of advancing the Company’s battery materials park north of Toronto and accelerating its battery recycling strategy in North America. As Three Fires was unable to secure funding for its strategic investment commitment in advance of the close of Electra’s private placement on August 11, the contemplated investment did not occur. The parties have agreed to revisit the investment at a later date.
Nasdaq Delisting Notification
On September 22, 2023, Electra announced that it received notice from The Nasdaq Stock Market LLC (“Nasdaq”) on September 21, 2023, stating that the Company is not in compliance with the minimum bid price requirement of US$1.00 per share under Nasdaq’s Listing Rule 5550(a)(2) based upon the closing bid price of the Company's common shares for the 30 consecutive business days prior to the date of the Notice. The Corporation has 180 calendar days from the date of the Notice, or until March 19, 2024, to regain compliance with the Minimum Bid Requirement, during which time the Company’s common shares will continue to trade on Nasdaq.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
Change in Auditors
On September 19, 2023, the Corporation announced a change in auditors from KPMG LLP (“Former to MNP LLP, Chartered Professional Accountants effective September 18, 2023. At the request of the Corporation, KPMG resigned as the auditor of Electra effective September 14, 2023. Electra’s Board of Directors appointed MNP as the Corporation’s auditor effective September 18, 2023 until the next Annual General Meeting of the Corporation.
KPMG did not issue any modified opinions on the annual financial statements of the Corporation for the two fiscal years preceding the date its resignation nor for any interim financial information for any subsequent period preceding the date of its resignation. There are no reportable events including disagreements, consultations, or unresolved issues as defined in National Instrument 51-102 – Continuous Disclosure Obligations (“NI 51-102”) (Part 4.11) between Electra and KPMG.
Strategic Business Review Process
The Company initiated a process in the first quarter of 2023 to evaluate potential strategic alternatives to maximize shareholder value, and close funding gap to complete the construction and commissioning of cobalt refinery project. BMO Capital Markets was retained to assist with the process. Electra’s Board of Directors evaluated a range of alternatives identified by the process including but not limited to a potential equity investment from a strategic partner and merger opportunities with other entities. As of November 16, 2023 none of these strategic options have been approved or ratified by the Company’s Board of Directors. The Company continues to explore these strategic alternatives, and there is no assurance that this process will culminate in any transaction or alternative.
Detailed Outlook and Overview of Current Programs
The Company’s vision is to provide sustainable battery materials to the EV industry in North America. The Company owns two main assets – the Refinery located in Ontario, Canada and the Iron Creek cobalt-copper project located in Idaho, United States. It also has a royalty over several silver and cobalt properties in Ontario known as the Cobalt Camp.
The Company has been progressing plans to create an integrated battery materials park in Ontario, Canada. The first phase of this plan involves recommissioning and expanding the Refinery to become the only refiner of battery-grade cobalt sulfate in North America. Electra’s primary focus is advancing the construction and commissioning of the Refinery. Another phase of the Company’s strategic plan revolves around recycled battery materials (known as black mass) as additional feedstock for the Refinery, with commercial, metallurgical, and engineering activities on the potential incorporation of black mass into the Refinery being conducted in parallel with the cobalt refinery project. The Company commissioned the black mass demonstration plant in 2022 and recovered a number of critical metals, including lithium, nickel, cobalt, copper, manganese, and graphite, needed for North America’s EV battery supply chain, surpassing initial expectations. The Company finalized the black mass desktop study and decided to integrate black mass recycling to its sustainable battery materials strategy. The Company continues with exploration activity in Idaho, and released an updated 43-101 report for Iron Creek.
The Company’s mission is to be one of the most sustainable producers of battery materials and continues to build upon its solid Environmental and Social Governance (“ESG”) foundation. Cobalt is a key element in fueling the lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles and for electric battery storage, both of which are essential technologies in the reduction of global carbon emissions.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
The Company strives to be a leader amongst its peer group in ESG. The Company will provide a clean and ethical supply of cobalt for the EV market from large, commercial mining operations that provide ethically sourced cobalt and the highest quality cobalt hydroxide globally. As a member of the Cobalt Institute, the Company will follow the Cobalt Industry Responsible Assessment Framework (CIRAF), an industry-wide risk management tool that helps cobalt supply chain players identify production and sourcing related risks. Electra also committed to the Responsible Minerals Initiative, which will include a third-party audit of the systems in place to responsibly source minerals in line with current global standards.
The Refinery is projected to have a lower quartile carbon intensity cobalt by virtue of hydro powered mining operations supplying its hydrometallurgical refining operation. In October 2020, results were released from an independent Life Cycle Assessment (“LCA”) which affirmed the low carbon footprint of the Refinery. The report concluded that the environmental impacts associated with refining cobalt at the Refinery will be materially lower than the published impacts of a leading Chinese refiner.
The Company takes a proactive, risk-based approach to environmental management and human rights with robust measures intended to minimize the environmental impact of operations and prevent the use of child labor at any level in the supply chain. Electra believes that these and other ESG practices will help it establish a premium brand of cobalt sulfate for the electric vehicle market. The Company’s first sustainability report was published on February 24, 2023.
The Cobalt Refinery Complex
The Company is working towards restarting its wholly owned Refinery in Ontario, Canada as the first phase in a multi-phase strategy to create an integrated battery materials park in North America. In 2020, the Company announced the results of an engineering study on the expansion of the Refinery that demonstrated that the facility could become a significant, globally competitive producer of cobalt sulfate for the electric vehicle market. The engineering study determined the Refinery could produce 25,000 tonnes of battery-grade cobalt sulfate annually (equating to approximately 5,000 tonnes of cobalt contained in sulfate), which would represent approximately 5% of the total refined cobalt market and 100% of the North American cobalt sulfate supply. The study indicated strong operating margins at the asset level. In November 2021, the Company announced it would invest in additional capacity for its crystallizer circuit, which will result in installed capacity of 6,500 tonnes of annual cobalt production.
Electra continues to make progress on the construction, procurement, and commissioning of its cobalt refinery project. Through September 30, 2023, Electra’s progress can be measured by several key developments, including:
| · | Completed recommissioning of the analytical lab, feed material handling system (including ball mill and mixing station), leach circuit, filter presses and reagent handling systems. |
| · | Completed the erection of the solvent extraction building. |
| · | Completed construction of the cobalt sulfate loadout facility. |
| · | Received the majority of long lead and custom fabricated equipment from suppliers around the world, thereby reducing the schedule risk associated with final construction. |
While constructing its crystallization circuit, the final stage in the cobalt sulfate refining process, the Corporation took delivery of a falling film evaporator vessel that was damaged in transit. Custom-built for the Corporation, the vessel is used to vaporize water from the cobalt solution before it can be crystallized into cobalt sulfate. The evaporator vessel is valued at approximately $881, and measures approximately 60 feet in length and five feet in diameter. Subsequent inspection of the damaged equipment has determined that the falling film evaporator vessel is suitable for installation. The damaged equipment has since been repaired on site. The Corporation uses microchips throughout its refinery complex as part of the process control system to regulate equipment and integrate various circuits and systems together. Global supply shortages of microchips resulted in delays to delivery of several process control system components. Although the Corporation advanced the construction of its refinery project, it was unable to progress fully on some work projects pending delivery of the process control components. As a result of the impact of critical equipment being damaged enroute to the Corporation’s complex north of Toronto, ongoing supply chain disruptions and inflationary pressure, the Corporation on February 14, 2023 withdrew its guidance issued on August 11, 2022, and November 9, 2022, for its fourth quarter ending December 31, 2022 along with any forward-looking statements previously made on the timing of the commissioning, capital spend and production of its cobalt sulfate refinery.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
In conjunction with this, on February 14, 2023, the Corporation announced a review of the refinery project scope, scheduling, and capital expenditures and completed the re-baseline engineering report in second quarter of 2023.
The re-baseline engineering report estimated that the total capital costs are now at $155 to $167 million, of which approximately $82.7 million has been capitalized as of September 30, 2023. The increase in capital costs has been driven by supply chain disruptions, and inflationary pressures that negatively impacted all aspects of the refinery project, including contractor labour rate, costs for concrete, steel, piping, and freight. The Company had disclosed previously that estimated capital costs for completing its refinery project would be between $100 and $105 million. As noted above, the Company has completed a $21.5 million private placement on August 11, 2023 (for a net proceed of approximately $20.1 million), but additional financing will be required to complete the refinery.
Management reevaluated the project feasibility with independently verified re-baselined costs and remains steadfast in its conviction to pursue the project, given its strategic importance to the North American battery supply chain and potential long-term benefit to shareholders.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
Black Mass Recycling
Black mass is the industry term used to describe the material remaining once expired lithium-ion batteries are shredded and all casings removed. Black mass contains high-value elements, including lithium, nickel, cobalt, manganese, copper, and graphite, that once recovered, can be recycled to produce new lithium-ion batteries.
Established North American battery recyclers have focused on collecting and shredding of batteries with the resulting black mass material primarily being exported to Asia or treated domestically by a pyrometallurgical smelting process that has a higher carbon footprint and lower metal recoveries than hydrometallurgical processes.
Recycling black mass through hydrometallurgical refining processes like Electra’s is expected to increasingly become a key feature of the EV battery supply chain given the strong demand for critical minerals and the looming supply deficit of metals such as nickel and cobalt. According to data from McKinsey & Company, available battery material for recycling is expected to grow by 20% per year through 2040.
Black Mass recycling is the centrepiece of the Company’s second phase of the Battery Materials Park strategy. In the first quarter of 2023 the Company invested $896 in the black mass recycling demonstration plant. The operations and activities were completed using existing and new equipment as well as external experts and the Company’s employees.
In February 2023 the Company completed the first plant-scale recycling of black mass material in North America and recovered critical metals, including nickel, cobalt and graphite, needed for the electric vehicle (EV) battery supply chain using its proprietary hydrometallurgical process. On March 13, 2023, the Company announced that it progressed the demonstration plant to also recover lithium in its black mass recycling trial. Also, in March 2023 the Company produced mixed hydroxide precipitate (MHP) at contained metal grades for nickel and cobalt above the quoted market specification and more recently began recycling lithium carbonate product. The black mass recycling trial is also recovering copper, graphite, and manganese.
Recoveries within the MHP circuit are achieving results equivalent to and at times above bench scale results. Electra attributes its success to the refinery team continuously optimizing circuit performance as more black mass is processed. Electra delivered its first nickel-cobalt mixed hydroxide precipitate product (“MHP”) on July 17, 2023.
On April 30, 2023, Electra completed a desktop study. Based on the findings of this study, the Black Mass Project was deemed to be a viable investment opportunity for Electra Battery Materials to pursue. Further analysis and engineering work will be required to fully evaluate the project's feasibility and mitigate the risks and challenges associated with execution and future expansion.
Electra’s desktop scoping study was based on a number of assumptions, including annual processing of 2,500 tonnes of black mass, metal prices using analysts’ long-term forecasts, recovery rates consistent with those achieved to date, and $12.6 million of committed capital comprised of $8.1 million for capital costs and $4.5 million in working capital. At this time, black mass recycling capabilities remain at the evaluation stage and the decision to commercialize these capabilities remains subject to financing, additional feasibility and engineering work to incorporate process modifications arising from the demonstration plant, vendor selection process, and the successful evaluation of samples by customers. Subject to these conditions, expansion to 2,500 tonnes per annum could occur in 2024 pending the securing of financing for the project and installation of additional vessels and equipment within the existing footprint of the refinery complex being utilized for the black mass trial.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
From an ESG perspective, Electra’s hydrometallurgical recycling plant is estimated to be five times less carbon intensive than a comparable production facility using a pyrometallurgical process with a similar electricity grid as found in China and four times lower than a similar facility in the state of Michigan. Electra’s proprietary hydrometallurgical process produces less waste and enables the recovery of high value lithium and by-products that pyrometallurgical process cannot recover.
The Iron Creek Project
Following the acquisition of US Cobalt in June of 2018, the Company commenced an extensive drill program at Iron Creek. In October 2018, the Company filed a technical report supporting the maiden resource estimate for the Iron Creek Project in Idaho. A second phase drill campaign was initiated to conduct infill drilling to upgrade a portion of the inferred resources to the indicated category for mine planning and to improve the confidence for future engineering studies. As a secondary priority, this campaign increased the resource along strike and at depth. An updated mineral resources estimate (MRE) was completed in November, 2019 by the company by Ristorcelli and Schlitt.
The unpatented mining claims included within the Iron Creek Project have no expiration date if the annual claim maintenance fees are paid by August 31 of each year. These fees have been paid in full to September 1, 2024. The patents are not subject to annual claim-maintenance fees, but applicable real and immovable property taxes are payable to Lemhi County annually. The total annual land holding costs are estimated to be $92 (US$69). Certain claims within the land package are governed by underlying agreements (Redcastle JV, CAS Option Agreement) which require milestone payments and/or earn in obligations for Electra to maintain their exploration rights on those claims. On January 23, 2023, the Company updated mineral resource for the Iron Creek Project (the “2023 MRE”) as prepared by QPs Martin Perron, P.Eng. and Marc R. Beauvais, P.Eng. of InnovExplo, using all available information. The 2023 MRE includes a new mineral resource estimate based on all drilling conducted through the end of 2022. The new resource was calculated using a net smelter return calculation (NSR) model with assumptions shown in section 14.13 of the 2023 MRE. The resulting model calculated an indicated mineral resource of 4.45 million tonnes at 0.19% Co and 0.73% Cu and an inferred mineral resource of 1.23 million tonnes at 0.08% Co and 1.34% Cu. The mineralization remains open along strike and downdip. The resource does not include the Ruby target which has insufficient drilling to effectively calculate a volume and grade of mineralization. Management believes that there is potential to continue to expand the size of the Iron Creek resource and continue drilling at the Ruby target to evaluate the viability of that target. In 2022, the Company commenced drilling with Titan Drilling out of Elko, Nevada completing six holes for 1,674 m. One hole was completed on the east side of the Iron Creek Project to infill between the edge of the resource boundary and the drill intercepts in the 2021 step-out program. The remaining 3 collars with two wedges were completed on the Ruby target to evaluate the depth extent of Ruby zone. All holes intercepted significant cobalt mineralization confirming the depth extent and continuity of the Ruby zone.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
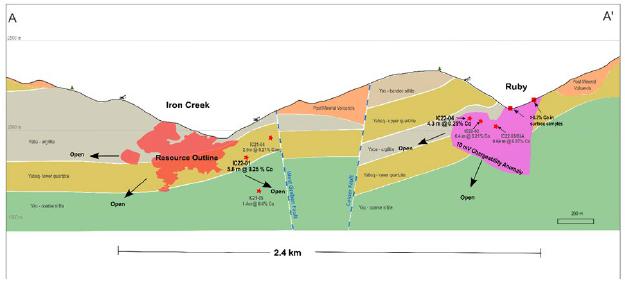
Figure 2. Schematic cross-section of the Iron Creek and Ruby properties using a 100m cutting envelope. Drillholes projected up to 200m into the plain of the section to show relative locations of targeting in 2021 and 2022. IC21-04 and IC21-05 are labeled as reported on May 9, 2022. IC22-02 and IC22-03/3A are labeled as reported on October 5, 2022. IC22-01 and IC22-04 are labeled as reported on December 14th, 2022. Resource outline is based on Ristorcelli and Schmitt (2019) and includes both the indicated and inferred categories. Section has not been updated with the 2023 resource outline.
On December 14, 2022, the Corporation announced the acquisition of a cobalt property (the “CAS Property”) in proximity to the Corporation’s projects in Idaho. The new cobalt property was acquired for $2,034 (US$1,500), payable over 10 years upon completion of specific milestones. The underlying claim owner will retain a 1.5% NSR which can be purchased by Electra for $662 (US$500) within one year of commercial production from the CAS Property.
The Cobalt Camp
On January 31, 2023, the Company completed the sale of the remaining assets of Canadian Cobalt Camp consisting of Keely-Frontier patents which Kuya did not own, as well as their associated asset retirement obligations. To complete the sale, Kuya issued to the Company 3,108,108 shares at a deemed price of $0.37 per share (being the share price equivalent to the VWAP prior to issuance) comprised of 2,702,703 shares as consideration for the $1,000 sale price and an additional 405,405 to settle $150 of payables to the Company. Kuya has also agreed to enter into a royalty agreement with the Company whereby it will grant the Company a two percent royalty on net smelter returns from commercial products derived from the remaining assets. The Company will retain a right of first offer to refine any base metal concentrates produced from the assets at the Company’s Ontario refinery.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
EXPLORATION AND EVALUATION ASSETS
The Company is focused on building a North American battery materials supply chain. The Company’s Iron Creek Project in Idaho, U.S. is its flagship mineral property and a new, upgraded resource estimate was published in March, 2023. The Iron Creek property includes patented and unpatented claims totalling approximately 3,260 hectares as well as 600 metres of underground drifting from three adits. Other cobalt-copper targets exist on the Company’s property away from the Iron Creek resource.
| | | Balance | | | | | | | | | | | | Balance | |
| | | December 31, | | | Acquisition | | | Impairment | | | Reclassification | | | September 30, | |
| | | 2022 | | | Costs | | | Reversal | | | to Held for Sale | | | 2023 | |
| Iron Creek | | $ | 87,693 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 87,693 | |
| Total | | $ | 87,693 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 87,693 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Balance | | | | | | | | | | | Balance | |
| | | December 31, | | | Acquisition | | | Impairment | | | Reclassification | | | December 31, | |
| | | 2021 | | | Costs | | | Reversal | | | to Held for Sale | | | 2022 | |
| Iron Creek | | $ | 87,661 | | | $ | 32 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 87,693 | |
| Cobalt Camp, Ontario | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,338 | | | | (1,338 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | $ | 87,661 | | | $ | 32 | | | $ | 1,338 | | | $ | (1,338 | ) | | $ | 87,693 | |
In 2020, the Company reversed a portion of previously recorded impairment charges relating to the Cobalt Camp because of the announced sale transaction with Kuya related to the Keeley Joint-Venture. These assets were reclassified as held for sale as at December 31, 2020 and the sale transaction was completed during 2021. Similarly, in 2022 the Company entered a purchase option with Kuya to sell the remaining Cobalt Camp patents under the Joint-Venture created in 2020. These assets were classified as held for sale as at December 31, 2022 with the sale completing January 31, 2023.
SUMMARY OF QUARTERLY RESULTS
Key financial information for the three months ended September 30, 2023, as well as the quarters spanning the most recent preceding fiscal years, are summarized as follows, reported in thousands of Canadian dollars except for per share amounts.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
| | | September 30, | | | June 30, | | | March 31, | | | December 31, | |
| | | 2023 | | | 2023 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | ($) | | | | ($) | | | | ($) | | | | ($) | |
| Financial Position | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current Assets | | | 17,384 | | | | 8,556 | | | | 14,521 | | | | 13,518 | |
| Exploration and Evaluation Assets | | | 87,693 | | | | 87,693 | | | | 87,693 | | | | 87,693 | |
| Total Assets | | | 210,307 | | | | 198,977 | | | | 198,766 | | | | 187,524 | |
| Current Liabilities | | | 72,939 | | | | 24,952 | | | | 28,556 | | | | 54,109 | |
| Long-term Liabilties | | | 6,224 | | | | 54,888 | | | | 63,739 | | | | 6,906 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operations | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| General and administrative | | | 680 | | | | 424 | | | | 900 | | | | 811 | |
| Consulting and professional fees | | | 1,149 | | | | 1,647 | | | | 600 | | | | 187 | |
| Exploration and evaluation expenditures | | | 259 | | | | 276 | | | | 77 | | | | 614 | |
| Investor relations and marketing | | | 194 | | | | 161 | | | | 33 | | | | 203 | |
| Refinery, engineering and metallurgical studies | | | 628 | | | | 335 | | | | 624 | | | | 1,381 | |
| Refinery, permitting and environmental expenses | | | 47 | | | | 59 | | | | 28 | | | | 64 | |
| Salary and benefits | | | 891 | | | | 1,291 | | | | 1,328 | | | | 2,038 | |
| Share-based payments | | | 317 | | | | 326 | | | | 218 | | | | 259 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | | | 4,165 | | | | 4,519 | | | | 3,808 | | | | 5,557 | |
| Net Income (Loss) | | | (9,223 | ) | | | 12,002 | | | | (21,803 | ) | | | 10,315 | |
| Income (Loss) per Share | | | (0.20 | ) | | | 0.33 | | | | (0.61 | ) | | | 0.31 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | September 30, | | | | June 30, | | | | March 31, | | | | December 31, | |
| | | | 2022 | | | | 2022 | | | | 2022 | | | | 2021 | |
| | | | ($) | | | | ($) | | | | ($) | | | | ($) | |
| Financial Position | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current Assets | | | 25,650 | | | | 45,601 | | | | 56,578 | | | | 61,935 | |
| Exploration and Evaluation Assets | | | 87,661 | | | | 87,661 | | | | 87,661 | | | | 87,661 | |
| Total Assets | | | 170,919 | | | | 176,355 | | | | 171,258 | | | | 167,611 | |
| Current Liabilities | | | 8,684 | | | | 11,078 | | | | 6,039 | | | | 4,708 | |
| Long-term Liabilties | | | 50,105 | | | | 47,094 | | | | 61,057 | | | | 62,939 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operations | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| General and administrative | | | 668 | | | | 377 | | | | 69 | | | | 170 | |
| Consulting and professional fees | | | 1,024 | | | | 932 | | | | 586 | | | | 977 | |
| Exploration and evaluation expenditures | | | 1,336 | | | | 1,084 | | | | 394 | | | | 2,931 | |
| Investor relations and marketing | | | 233 | | | | 318 | | | | 246 | | | | 492 | |
| Refinery, engineering and metallurgical studies | | | 548 | | | | 327 | | | | 93 | | | | 436 | |
| Refinery, permitting and environmental expenses | | | 3 | | | | 33 | | | | 28 | | | | 182 | |
| Salary and benefits | | | 722 | | | | 529 | | | | 624 | | | | 1,222 | |
| Share-based payments | | | 285 | | | | 304 | | | | 434 | | | | 185 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | | | 4,819 | | | | 3,904 | | | | 2,474 | | | | 6,595 | |
| Net Income (Loss) | | | (7,628 | ) | | | 7,534 | | | | 2,330 | | | | (15,494 | ) |
| Income (Loss) per Share | | | (0.24 | ) | | | 0.23 | | | | 0.08 | | | | (0.55 | ) |
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
The following are highlights from the Company’s results of operations for the three months ended September 30, 2023 and 2022:
| | · | Included in Net Loss of $9,223 for three months ended September 30, 2023 is $4,436 of fair value adjustments relating to the 2028 Notes. |
| · | Exploration and evaluation expenditures were $259 for the three months ended September 30, 2023, compared to $1,336 for the three months ended September 30, 2022. The decrease was caused by a reduction in drilling expenses and professional fees related to Iron Creek. |
| · | Consulting and professional fees expenses were $1,149 for the three months ended September 30, 2023, compared to $1,024 for the three months ended September 30, 2022. These costs have increased due to higher legal fees relating to financing matters. |
| · | Salary and benefits were $891 for the three months ended September 30, 2023, compared to $722 for the three months ended June 30, 2022. The increase is due to higher headcounts at the Toronto office compared to the same period in the prior year. |
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS FOR THE NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
The following are highlights from the Company’s results of operations for the nine months ended September 30, 2023 and 2022:
| · | Included in Net Loss of $19,199 for nine months ended September 30, 2023 are net loss of $6,546 from fair value adjustments relating to the 2028 Notes and US dollar warrants. The main drivers of these fair value adjustments were volatility of Company’s share price and decrease in the Company’s share price during the year. |
| · | General and administrative expenses were $2,004 for the nine months ended September 30, 2023, compared to $1,114 for the nine months ended September 30, 2022. These costs have increased due to higher head office costs due to the expansion of Toronto office compared to the same period in the prior year. |
| · | Consulting and professional fees expenses were $3,396 for the nine months ended September 30, 2023, compared to $2,542 for the nine months ended September 30, 2022. These costs have increased due to higher legal fees relating to financing matters. |
| · | Salary and benefits were $3,510 for the nine months ended September 30, 2023, compared to $1,875 for the nine months ended September 30, 2022. The increase is a result of the higher headcounts at the Toronto office compared to the same period in the prior year. |
| · | Refinery, engineering, and metallurgical studies costs were $1,587 for the nine months ended September 30, 2023, compared to $968 for the nine months ended September 30, 2022. Costs in first nine months of 2023 included approximately $1,707 relating to black mass project. This was offset by $250 received from the Ontario government relating to cost reimbursement of nickel sulfate studies which were completed in 2022. |
| · | Investor relations and marketing expenses were $388 for the nine months ended September 30, 2023, compared to $797 for the nine months ended September 30, 2022. The decreased costs are due to timing of spending and cost-cutting measures implemented, including reducing the use of third-party vendors by performing more work. |
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
CAPITAL STRUCTURE
As of the date of this MD&A, the Company has 55,841,329 common shares issued and outstanding, which includes 19,545,454 common shares issued as part of private placement completed on August 11, 2023. In addition, there are outstanding share purchase warrants and stock options for a further 33,724,658 (which includes 19,545,454 warrants issued as part of August 11, 2023 private placement plus 900,000 broker warrants) and 967,116 common shares, respectively. Also, during the third quarter, the Company issued 660,802 common shares to make an interest payment to a convertible note holder. The Company currently has 497,291 Deferred Share Units (DSUs), 420,754 Restricted Share Units (RSUs) and 34,029 Performance Share Units (PSUs) issued under its Long-Term Incentive Plan.
The following warrants were outstanding at the date of this MD&A:
| Grant Date | | Expiry Date | | Number of warrants
outstanding | | | Weighted
Average
Exercise Price | |
| United States Dollar denominated warrants | | | | | | | | | | |
| November 15, 2022 | | November 15, 2025 | | | 2,483,150 | | | US$ | 3.10 | |
| February 13, 2023 | | February 13, 2028 | | | 10,796,054 | | | US$ | 2.48 | |
| Total United States Dollar denominated warrants | | | | | 13,279,204 | | | US$ | 2.60 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Canadian Dollar denominated warrants | | | | | | | | | | |
| August 11, 2023 | | August 11, 2025 | | | 19,545,454 | | | $ | 1.74 | |
| August 11, 2023 | | August 11, 2025 | | | 900,000 | | | $ | 1.10 | |
| Total Canadian Dollar denominated warrants | | | | | 20,445,454 | | | $ | 1.71 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total warrants outstanding | | | | | 33,724,658 | | | | | |
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
The following incentive stock options were outstanding and exercisable at the date of this MD&A:
| | | Options Outstanding | | | Options Exercisable | |
Exercise
Price | | | Number of
Shares Issuable
on Exercise | | | Weighted
Average
Remaining Life
(Years) | | | Weighted
Average
Exercise Price | | | Number of
Shares Issuable
on Exercise | | | Weighted
Average
Exercise Price | |
| $ | 1.04 | | | 50,000 | | | 4.89 | | | $ | 1.04 | | | - | | | $ | 1.04 | |
| $ | 2.40 | | | 323,350 | | | 2.46 | | | $ | 2.40 | | | - | | | $ | 2.40 | |
| $ | 2.52 | | | 108,332 | | | 0.42 | | | $ | 2.52 | | | 108,333 | | | $ | 2.52 | |
| $ | 2.61 | | | 27,778 | | | 1.91 | | | $ | 2.61 | | | 27,778 | | | $ | 2.61 | |
| $ | 2.88 | | | 16,667 | | | 0.50 | | | $ | 2.88 | | | 16,667 | | | $ | 2.88 | |
| $ | 3.21 | | | 105,000 | | | 2.94 | | | $ | 3.21 | | | - | | | $ | 3.21 | |
| $ | 3.24 | | | 55,556 | | | 0.39 | | | $ | 3.24 | | | 55,556 | | | $ | 3.24 | |
| $ | 4.38 | | | 30,000 | | | 3.73 | | | $ | 4.38 | | | 10,000 | | | $ | 4.38 | |
| $ | 4.63 | | | 19,444 | | | 3.65 | | | $ | 4.63 | | | 6,481 | | | $ | 4.63 | |
| $ | 5.40 | | | 176,822 | | | 2.48 | | | $ | 5.40 | | | 58,941 | | | $ | 5.40 | |
| $ | 5.76 | | | 19,444 | | | 3.50 | | | $ | 5.76 | | | 6,481 | | | $ | 5.76 | |
| $ | 6.21 | | | 29,167 | | | 1.70 | | | $ | 6.21 | | | 19,444 | | | $ | 6.21 | |
| $ | 7.29 | | | 5,556 | | | 1.39 | | | $ | 7.29 | | | 5,556 | | | $ | 7.29 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Grand Total | | | 967,116 | | | 2.30 | | | $ | 3.36 | | | 315,237 | | | $ | 3.69 | |
The following units were outstanding at the date of this MD&A:
| Type | | | Outstanding | |
| Deferred Share Units | | | | 497,291 | |
| Restricted Share Units | | | | 420,754 | |
| Performance Share Units | | | | 34,029 | |
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
CAPITAL STRUCTURE, RESOURCES & LIQUIDITY
Capital Structure
The Company manages its capital structure to maximize its financial flexibility, adjusting it in response to changes in economic conditions and the risk characteristics of the underlying assets and business opportunities. The Company does not presently utilize any quantitative measures to monitor its capital but rather relies on the expertise of the Company’s management to sustain the future development of the business. Management reviews its capital management approach on an ongoing basis and believes that this, given the relative size of the Company, is appropriate.
The Company will continue to adjust its capital structure based on Management’s assessment of the best capital mix to effectively advance its assets. With the settlement of the 2026 Notes and issuances of the 2028 Notes in February 2023, the Company has increased the debt component of its capital structure with a par value of $67,938 (US$50,250) outstanding after an early conversion of $672 (US$500) of notes in February 2023 and $334 (US$250) in April 2023. As of November 16, 2023, the Company had $67,938 (US$50,250) of convertible notes.
On August 11, 2023, the Company completed a private placement for gross proceeds of $21,500 (net proceeds of $20,116), consisting of a brokered placement for $16,500 and a non-brokered placement for $5,000 (the “Offering”). Under the terms of the Offering, the Company has issued 19,545,454 units, at a price of $1.10 per unit. Each unit consists of one common share of the Company and one common share purchase warrant. Each warrant entitles the holder thereof to purchase one common share at a price of $1.74 at any time on or before August 10, 2025. As consideration for services under the brokered Offering, the Company paid to the agents a cash commission of $990 equivalent to 6% of gross proceed of brokered placement and issued to the agents 900,000 non-transferable broker warrants of the Company entitling the holder to acquire one common share at a price of $1.10 at any time on or before August 10, 2025.
In addition to its cash on hand, the Company has previously executed contribution agreements with the Government of Ontario and the Government of Canada for aggregate funding towards the refinery construction of $10,000, of which $4,898 has been received to date. The Company continues to be in active discussions with both Government of Canada and Province of Ontario for the remaining $5,102, as well as pursuing additional opportunities under various government programs for funding towards both refinery and battery recycling.
The Company is also actively pursuing various alternatives including equity and debt financing to increase its liquidity and capital resources to fund the projected Refinery expenditures. The Company will also need working capital funding for the purchase of other consumables before the startup of operations.
Liquidity
In February 2023, the Company closed on the 2028 Notes with a principal balance of US$51,000 and settled the previous 2026 Notes with a principal balance of US$36,000 for a net proceed of US$15,000 ($20,013), before interest payment of $1,656 and transaction costs of $2,275. The 2028 Notes reduced the minimum liquidity balance requirement under the 2026 Notes from US$7,500 to US$2,000. The Company also was required to have a United States registration statement providing for the resale of the underlying Common Stock deliverable on the conversion of the debenture and warrant indenture by May 15, 2023. The Company had previously received a waiver on this covenant from all indenture holders until August 31, 2023 but the waiver was not extended as of September 30, 2023, hence the Company was in default of the registration covenant. As the Company did not have a US registration statement, the Company was unable to deliver freely tradable common stock to settle interest payment on August 15, 2023, hence the Company was also in default of interest payment covenant. On November 14, 2023, subsequent to period end, the Company received a temporary waiver on both covenants, where the indenture holders agreed to waive their rights and remedies under registration default until December 31, 2023, and waive their rights and remedies under the interest payment default until a new interest payment date, which will be seventh trading day after the effectiveness of the registration statement providing for the resale of the underlying Common Stock. The Company is actively working on completing the registration statement prior to December 31, 2023, but if the Company is unable to complete this, the Company will continue to seek additional waivers from the indenture holders prior to expiry. However, there are no assurances that the indenture holders will accommodate further waivers the Company will seek. If the Company is unable to provide a registration statement and is not successful in obtaining suitable waivers, it would result in an event of default under the bond and warrant indenture which provides the indenture holders the right to demand repayment of the instrument. These conditions indicate the existence of a material uncertainty that results in substantial doubt as to the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
The Company’s objective in managing liquidity risk is to maintain sufficient liquidity to meet operational and asset advancement requirements as well as ensuring compliance with minimum liquidity balance covenant of US$2,000.
At September 30, 2023, the Company had cash of $15,053 (December 31, 2022 - $7,952) and marketable securities of $625 (December 31, 2022 - $433), compared to accounts payable and accrued liabilities of $9,615 (December 31, 2022 - $18,864).
Cash requirements for the Refinery expansion from September 30, 2023, through to the expected completed commissioning are estimated to be significantly higher than the previously estimated. At this time, the Company does not have sufficient financial resources necessary to complete the construction and final commissioning of the Refinery and will require additional financing in 2023 and 2024 to continue operations, complete the construction of the Refinery, advance its battery recycling strategy, purchase the required feedstock as the Refinery enters its operating phase and remain in compliance with the minimum liquidity covenant under the 2028 Notes. Failure to remain in compliance with the liquidity terms, in addition to the Company being unable to provide a United States registration statement or obtain suitable waivers, may result in the instrument becoming due before the contractual maturity.
The Company had the following summarized Cash flows:
| | | Nine months ended | | | Nine months ended | |
| | | September 30, | | | September 30, | |
| | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| Cash Flows used in operating activities | | $ | (17,040 | ) | | $ | (9,259 | ) |
| Cash Flows used in investing activities | | | (12,513 | ) | | | (32,608 | ) |
| Cash Flows provided by financing activities | | | 36,587 | | | | 1,943 | |
| Changes in cash during the period | | | 7,034 | | | | (39,924 | ) |
| Effect of exchange rates on cash | | | 67 | | | | 240 | |
| Cash – Beginning of the period | | | 7,952 | | | | 58,626 | |
| Cash – End of the period | | $ | 15,053 | | | $ | 18,942 | |
Cash used in operating activities was $17,040 during the nine months ended September 30, 2023, compared to $9,259 used in operating activities during the nine months ended September 30, 2022. The increase in cash used in operating activities was driven primarily by change in working capital.
Cash used in investing activities was $12,513 during the nine months ended September 30, 2023, compared to cash out flows from investing activities of $32,608 during the nine months ended September 30, 2022. The cash outflow from investing activities relate to prepayments of solvent extraction and crystalizing equipment, the construction of the solvent extraction facility and installation of related equipment as well as general construction costs and advancement of the cobalt crystallizer unit and facility which will be utilized in the expanded Refinery.
Cash flows provided by financing activities were $36,587 during the nine months ended September 30, 2023 compared to the $1,943 from financing activities during the nine months ended September 30, 2022. The change was primarily driven by net proceeds from 2028 Notes, which was completed on February 13, 2023 and private placement that took place on August 11, 2023.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
There can be no assurances that the Company will be successful in obtaining other sources of funding; failure to obtain additional capital could result in the delay or indefinite postponement of further advancement of the Company’s assets.
COMMITMENTS
The Company’s commitments relate to purchase and services commitments for work programs relating to refinery expansion and payments under financing arrangements. The Company had the following commitments as of September 30, 2023:
| | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | Thereafter | | | Total | |
| Purchase commitments | | $ | 3,491 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 3,491 | |
| Convertible notes payments | | | 5,797 | | | | 6,262 | | | | 6,064 | | | | 6,064 | | | | 73,326 | | | | 97,513 | |
| Government loan payments | | | - | | | | 1,032 | | | | 1,032 | | | | 1,032 | | | | 1,887 | | | | 4,983 | |
| Royalty payments | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 675 | | | | 4,690 | | | | 5,365 | |
| Total | | $ | 9,288 | | | $ | 7,294 | | | $ | 7,096 | | | $ | 7,771 | | | $ | 79,903 | | | $ | 111,352 | |
1 The figures in the above table are as of September 30, 2023 as reported in the notes to the condensed interim consolidated financial statements. Convertible notes payments amounts are based on contractual maturities of 2028 Notes and assumption that it would remain outstanding until maturity. During the first 12 months of the term of the 2028 Notes, the Company may pay interest through the issuance of Common Shares. As discussed above, 2026 Notes were cancelled and replaced with 2028 Notes in February 2023.
2 Royalty payments are estimated amounts associated with the royalty agreements entered with the convertible debt holders as part of the 2028 Note offering. The estimated amounts and timing are subject to changes in sulfate prices, timing of completion of the refinery, reaching commercial operations and timing and amounts of sales.
The Company has recorded a provision for environmental remediation, reclamation and decommissioning for its Ontario assets. For the Refinery, a liability of $1,669 has been recorded, linked to the closure plan filed and accepted in March 2022 and updated in November 2022. In relation to the refinery closure plan, an amount of $3,450 has been posted via a surety bond with the Ministry of Northern Development, Mines, Natural Resources and Forestry (NDMNRF) as financial assurance.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
The Company’s related parties include key management personnel and companies related by way of directors or shareholders in common.
Key Management Personnel Compensation
During the nine months ended September 30, 2023 and 2022, the Company paid and/or accrued the following fees to management personnel and directors:
| | | | September 30,
2023 | | | September 30,
2022 | |
| Management | | | $ | 1,555 | | | $ | 1,116 | |
| Directors | | | | 61 | | | | 124 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | $ | 1,616 | | | $ | 1,240 | |
During the nine months ended September 30, 2023, the Company had share-based payments made to management and directors of $1,328 (September 30, 2022 - $553).
OFF BALANCE SHEET ARRANGEMENTS
The Company currently has no off-balance sheet arrangements.
FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
Financial assets and liabilities are classified in the fair value hierarchy according to the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. Assessment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurement requires judgement and may affect placement within the fair value hierarchy levels.
The hierarchy is as follows:
| · | Level 1 fair value measurements are those derived from quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that the entity can access at the measurement date. |
| · | Level 2 fair value measurements are those derived from inputs other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly. |
| · | Level 3 fair value measurements are those derived from inputs that are unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. |
Fair value estimates of financial instruments are made at a specific point in time, based on relevant information about financial markets and specific financial instruments. As these estimates are subjective in nature, involving uncertainties and matters of significant judgment, they cannot be determined with precision. Changes in assumptions can significantly affect estimated fair values.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
Financial Assets and Liabilities
The Company’s fair values of financial assets and liabilities were as follows:
| | | Carrying Value | | | September 30, 2023 | |
| | | Fair value
through profit or
loss | | | Amortized
cost | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total Fair
Value | |
| Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | - | | | $ | 15,053 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 15,053 | |
| Receivables | | | - | | | | 993 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 993 | |
| Marketable securities | | | 625 | | | | - | | | | 625 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 625 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | $ | 625 | | | $ | 16,046 | | | $ | 625 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 16,671 | |
| Liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | $ | - | | | $ | 9,615 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 9,615 | |
| Accrued Interest 1 | | | - | | | | 4,017 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,017 | |
| Government loan payable | | | - | | | | 4,228 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,228 | |
| Convertible notes payable 1 | | | 52,089 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 52,089 | | | | 52,089 | |
| Warrants – Convertible Notes 1 | | | 3,901 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,901 | | | | 3,901 | |
| Royalty 1 | | | - | | | | 2,432 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,432 | | | | 2,432 | |
| Other financial derivative liability | | | 111 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 111 | | | | 111 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | $ | 56,101 | | | $ | 20,292 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 58,533 | | | $ | 76,393 | |
1 Components of 2028 Notes Payable. During the first 12 months of the term of the 2028 Notes, the Company may pay interest through the issuance of Common Shares.
The level 3 liabilities consist of convertible notes and the US Dollar denominated warrants.
Convertible Notes Payable
For the convertible notes payable designated at fair value through profit or loss, the valuation is derived by a finite difference method, whereby the convertible debt as a whole is viewed as a hybrid instrument consisting of two components, an equity component (i.e., the conversion option) and a debt component, each with different risk. The key inputs in the valuation include risk-free rates, share price, equity volatility, and credit spread. As there are significant unobservable inputs used in the valuation, the convertible notes payable is included in Level 3.
The fair value of the convertible note payable has been estimated based on significant unobservable inputs which are equity volatility and credit spread. The Company used an equity volatility of 60%. If the Company had used an equity volatility that was higher or lower by 10%, the potential effect would be an increase of $3,193 or a decrease of $3,187 to the fair value of the convertible note payable. The Company used a credit spread of 28.0%. If the Company had used a credit spread that was higher or lower by 5%, the potential effect would be a decrease of $3,507 or an increase of $4,037 to the fair value of convertible note payable.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
Warrants – Convertible Notes
The Warrants issued in a foreign currency and accounted for at fair value through profit or loss are valued using a Monte Carlo Simulation Model to better model the variability in exercise date. The key inputs in the valuation include risk-free rates and equity volatility. As there are significant unobservable inputs used in the valuation, the financial derivative liability is included in Level 3.
The fair value of the Warrants has been estimated using a significant unobservable input which is equity volatility. The Company used an equity volatility of 60%. If the Company had used an equity volatility that was higher or lower by 10%, the potential effect would be an increase of $550 or a decrease of $632 to the fair value of the Warrants.
Royalty
The fair value of the Royalty has been estimated at inception using a discounted cash flow model. The key inputs in the valuation include the discount rate and cash flows estimates of future operating and gross revenues. As there are significant unobservable inputs used in the valuation, the Royalty is included in Level 3. A 10% increase or decrease in revenues would directly correspond to a same percentage change in royalty payments.
Other Financial Derivative Liabilities
The fair value adjustment on embedded derivative (US Warrant) issued in foreign currency as at September 30, 2023 was $111 (December 31, 2022 - $1,271). Warrants can be exercised at a time prior to expiry, the Company uses a Monte Carlo Simulation Model to better model the variability in exercise dates. The key inputs in the valuation include risk-free rates and equity volatility. As there are significant unobservable inputs used in the valuation, the financial derivative liability is included in Level 3.
The Company used an equity volatility of 67.57% (December 31, 2022 – 62.85%). If the Company had used an equity volatility that was higher or lower by 10%, the potential effect would be an increase of $32 (December 31, 2022 - $163) or a decrease of $66 (December 31, 2022 - $366) to the fair value of the embedded derivative.
RISK AND RISK MANAGEMENT
Financial Risk Factors
The Company’s risk exposure and the impact on the Company’s financial instruments are summarized below:
Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that the Company will not be able to meet its financial obligations as they fall due. The Company does not have sufficient financial resources necessary to complete the construction and final commissioning of the Refinery. The Company attempts to ensure there is sufficient access to funds to meet ongoing business requirements, considering its current cash position and potential funding sources. Although the Company has historically been successful in obtaining financing in the past, there can be no assurances that the Company will be able to obtain adequate financing in the future. This represents a material uncertainty that casts substantial doubt on the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. The Company has future obligations to pay semi-annual interest payments and the principal upon maturity related to the convertible debt. Starting in 2024 repayment of the interest-free Government loan will begin in 19 equal installments. The Company is subject to a minimum cash balance requirement of US $2,000. Failure to provide a United States registration statement by May 15, 2023 is considered an event of default under the 2028 bond and warrant indenture which provides the indenture holders the right to demand repayment of the instrument. The Company was in default of interest and registration covenant at September 30, 2023, but has received a waiver from all indenture holders subsequent to quarter-end. The Company is actively working on completing the US registration before the expiry of the registration waiver on December 31, 2023, but if the Company is unable to complete this, the Company will continue to seek additional waivers from the indenture holders prior to expiry. However, there are no assurances that the indenture holders will accommodate further waivers the Company will seek.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
At September 30, 2023, the Company had cash of $15,053 (December 31, 2022 - $7,952) and marketable securities of $625 (December 31, 2022 - $433), compared to accounts payable and accrued liabilities of $9,615 (December 31, 2022 - $18,864).
Credit risk
Credit risk is the risk that one party to a financial instrument will fail to discharge an obligation and cause the other party to incur a financial loss. The Company’s primary exposure to credit risk is on its cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash which are being held with major Canadian banks that are high-credit quality financial institutions as determined by rating agencies.
Interest rate risk
Interest rate risk is the risk that the fair value of future cash flow of a financial instrument will fluctuate because of changes in market interest rate. The Company’s debt with Glencore was extinguished during 2021 and the Company currently does not have any financial instruments that are linked to LIBOR, SOFR, or any form of a floating market interest rate. Therefore, changes in the market interest rate does not have an impact on the Company as at September 30, 2023.
Foreign Currency Risk
Foreign currency risk is the risk that the fair value of future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because they are denominated in currencies that differ from the Company’s functional currency, Canadian Dollars. The Company is exposed to foreign currency risk on fluctuations related to cash, receivables, and accrued liabilities that are denominated in US Dollars. In addition, the Company’s 2028 Notes are denominated in US dollars and fluctuations in foreign exchange rates will impact the Canadian dollar amounts required to settle interest and principal payments for these convertible notes. The Company has not used derivative instruments to reduce its exposure to foreign currency risk nor has it entered foreign exchange contracts to hedge against gains or losses from foreign exchange.
BUSINESS RISKS AND UNCERTAINTIES
There are many risk factors facing companies involved in the mineral exploration industry. Risk Management is an ongoing exercise upon which the Company spends a substantial amount of time. While it is not possible to eliminate all the risks inherent to the industry, the Company strives to manage these risks, to the greatest extent possible. The following risks are most applicable to the Company.
Going Concern
As discussed above, the Company will require additional financing in 2023 and 2024 to continue operations, complete the construction of the Refinery, advance its battery recycling strategy, purchase required feedstock as the Refinery enters its operating phase and remain in compliance with minimum liquidity covenant under the 2028 Notes. The Company also was required to have a United States registration statement providing for the resale of the underlying Common Stock deliverable on the conversion of the debenture and warrant indenture by May 15, 2023. The Company was in default of interest and registration covenant at September 30, 2023, but has received a waiver from all indenture holders until December 31, 2023, subsequent to quarter-end. The Company is actively working on completing the US registration before the expiry of the registration waiver on December 31, 2023, but if the Company is unable to complete this, the Company will continue to seek additional waivers from the indenture holders prior to expiry However there are no assurances that the indenture holders will accommodate further waivers the Company will seek. If the Company is unable to provide a registration statement and is not successful in obtaining suitable waivers, it would result in an event of default under the bond and warrant indenture which provides the indenture holders the right to demand repayment of the instrument. The Company is actively pursuing various alternatives including equity and debt financing to increase its liquidity and capital resources. The Company is also in discussion with various parties on alternatives to finance the funding of feedstock purchases. Although the Company has historically been successful in obtaining financing in the past, there can be no assurances that the Company will be able to obtain adequate financing in the future. These represent material uncertainties that casts substantial doubt on the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Financial information presented does not include the adjustments to the amounts and classifications of assets and liabilities that would be necessary should the Company be unable to continue as a going concern. These adjustments may be material.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
These going concern risk factors are discussed further in Note 1 of the financial statements.
Financing
The Company has raised funds through grants, equity financing and debt arrangements to fund its operations and the advancement of the Refinery. The market price of natural resources, specifically cobalt prices, is highly speculative and volatile. Instability in prices may affect the interest in resource assets and the development of and production from such properties. This may adversely affect the Company’s ability to raise capital or obtain debt to fund corporate activities and growth initiatives. The completion of the Refinery project is dependent on additional financing.
Technical Capabilities of the Refinery
The Company’s strategic priority is the advancement of the Refinery, with significant engineering studies and metallurgical testing conducted to date. There is no assurance that the final refining process will have the capabilities to produce specific end products. The Company manages this risk by employing and contracting technical experts in metallurgy and engineering to support refinery process decisions.
Ability to meet Debt Service Obligations
The Company has debt obligations under the 2028 Notes, which include ongoing coupon payments and payment of principal at maturity. In the event, that the refinery construction is not completed as planned or sufficient cash flow from refinery operations is not generated, there is a risk that the Company may not have sufficient available capital to meet its debt obligations. Additionally, the Company is subject to certain covenants related to the 2028 Notes, which include minimum liquidity of US$2,000 and having a United States registration statement providing for the resale of the underlying Common Stock deliverable on the conversion of the debenture and warrant indenture. Should the Company breach a covenant or be unable to service the debt, the assets pledged may be transferred to the lenders.
Macroeconomic Risks
Political and economic instability (including Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and war in Israel), global or regional adverse conditions, such as pandemics or other disease outbreaks (including the COVID-19 global outbreak) or natural disasters, currency exchange rates, trade tariff developments, transport availability and cost, including import-related taxes, transport security, inflation and other factors are beyond the Company’s control. The macroeconomic environment remains challenging, and the Company’s results of operations could be materially affected by such macroeconomic conditions.
Industry and Mineral Exploration Risk
Mineral exploration is highly speculative, involves many risks and frequently is non-productive. There is no assurance that the Company’s exploration efforts will be successful. At present, the Company’s projects do not contain any proven or probable reserves. Success in establishing reserves is a result of several factors, including the quality of the project itself. Substantial expenditures are required to establish reserves or resources through drilling, to develop metallurgical processes, and to develop the mining and processing facilities and infrastructure at any site chosen for mining. Because of these uncertainties, no assurance can be given that planned exploration programs will result in the establishment of mineral resources or reserves. The Company may be subject to risks, which could not reasonably be predicted in advance. Events such as labour disputes, natural disasters or estimation errors are prime examples of industry-related risks. The Company attempts to balance this risk through ongoing risk assessments conducted by its technical team.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
Commodity Prices
The Company’s mineral exploration operations and its prospects are largely dependent on movements in the price of various minerals. Prices fluctuate daily and are affected by several factors well beyond the control of the Company. The mineral exploration industry in general is a competitive market and there is no assurance that, even if commercial quantities of proven and probable reserves are discovered, a profitable market may exist. The Company has not entered any price hedging programs.
Environmental
Exploration projects or operations are subject to the environmental laws and applicable regulations of the jurisdiction in which the Company operates. Environmental standards continue to evolve, and the trend is to a longer, more complete and rigid process. The Company reviews environmental matters on an ongoing basis. If and when appropriate, the Company will make appropriate provisions in its financial statements for any potential environmental liability.
Title of Assets
Although the Company conducts title reviews in accordance with industry practice prior to any purchase of resource assets, such reviews do not guarantee that an unforeseen defect in the chain on title will not arise and defeat our title to the purchased assets. If such a defect were to occur, our entitlement to the production from such purchased assets could be jeopardized.
Competition
The Company expects to compete in the burgeoning North American Critical Minerals Industry with the completion of the Cobalt Sulfate refinery. The industry is developing in Canada with new entrants expected in the short term. Many of these competitors have substantially longer histories in the industry as well as substantially greater financial, sales and marketing resources than the Company.
The Company engages in the highly competitive resource exploration industry. The Company competes directly and indirectly with major and independent resource companies in its exploration for and development of desirable resource properties. Many companies and individuals are engaged in this business, and the industry is not dominated by any single competitor or a small number of competitors. Many of such competitors have substantially greater financial, technical, sales, marketing, and other resources, as well as greater historical market acceptance than does the Company. The Company will compete with numerous industry participants for the acquisition of land and rights to prospects, and for the equipment and labour required to operate and develop such prospects.
Competition could materially and adversely affect the Company’s business, operating results and financial condition. Such competitive disadvantages could adversely affect the Company’s ability to participate in projects with favorable rates of return.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
Additional information on risks and uncertainties relating to Electra’s business is provided in Electra’s Annual Information Form dated April 4, 2023 under the heading “Risk Factors”.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES
The preparation of the Company’s financial statements in conformity with IFRS requires management to make judgments, estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities and contingent liabilities at the date of the financial statements and reported amounts of income and expenses during the reporting period. Estimates and assumptions are continuously evaluated and are based on management’s experience and other factors, including expectations of future events that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. However, actual outcomes may differ significantly from these estimates.
Areas requiring a significant degree of judgment relate to the recoverability and measurement of deferred tax assets and liabilities, the ability to continue as a going concern and the capitalization of development costs. Actual results may differ from those estimates and judgments.
Areas requiring a significant degree of estimation or judgement that have the most significant effect on the amounts recognized in the Company’s condensed interim consolidated financial statements are as follows:
| · | Exploration and Evaluation Assets |
The net carrying value of each mineral property is reviewed regularly for conditions that suggest potential indications of impairment. This review requires significant judgment. Factors considered in the assessment of asset impairment include, but are not limited to, whether there has been a significant adverse change in the legal, regulatory, accessibility, title, environmental or political factors that could affect the property’s value; whether exploration activities produced results that are not promising such that no more work is being planned in the foreseeable future and management’s assessment of likely proceeds from the disposition of the property.
| · | Financial Derivative Liability |
The Financial Derivative Liability values relating to convertible note and US dollar denominated warrants involve significant estimation. The fair value of financial derivative liability was determined at inception and is reviewed and adjusted on a quarterly basis or when conversions take place. Factors considered in the fair value of the financial derivative liability are risk free rate, the Company’s share price, equity volatility, and credit spread.
| · | Environmental rehabilitation |
Management’s determination of the Company’s decommissioning and rehabilitation provision is based on the reclamation and closure activities it anticipates as being required, the additional contingent mitigation measures it identifies as potentially being required and its assessment of the likelihood of such contingent measures being required, and its estimate of the probable costs and timing of such activities and measures. Significant estimations must be made when determining such reclamation and closure activities and measures required and potentially required.
The net carrying value of the Refinery asset is reviewed regularly for conditions that suggest potential indications of impairment. The review requires significant judgment. Factors considered in the assessment of asset impairment include, but are not limited to, whether there has been a significant adverse change in the technological, market, economic or legal environment in which the entity operates; and internal indicators that the economic performance of the asset will be worse than expected.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
The assessment of fair values, including those of the CGUs for purposes of testing for impairment of the refinery for potential impairment, require the use of estimates and assumptions for future operating performance and capital requirements, as well as future long-term commodity prices, discount rates, earnings multiple and foreign exchange rates. Changes in any of the assumptions or estimates used in determining the fair values could impact the impairment analysis.
The valuation of Convertible Notes Payable and Warrants relating to the Convertible Note Arrangement are carried at fair values and involves significant estimation. The fair values were determined at inception and are reviewed and adjusted on a quarterly basis or when conversions take place. Factors considered in the fair value of these components are risk free rate, the Company’s share price, equity volatility and credit spread.
FUTURE CHANGES IN ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND INITIAL ADOPTION
Future changes in accounting policies and initial adoption are disclosed in Note 3 of the financial statements.
INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
The President and Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer of the Company are responsible for designing internal controls over financial reporting or causing them to be designed under their supervision to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with IFRS. From the second quarter 2022, up to and including this disclosure, Management concluded that internal control over financial reporting was not designed effectively as of September 30, 2023, due to material weaknesses in Internal Control over Financial Reporting (ICFR).
A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the Company’s annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected in a timely basis. Management has identified the following material weaknesses:
| · | An ineffective control environment resulting from the combination of an insufficient number of trained financial reporting and accounting personnel with the appropriate skills and knowledge about the design, implementation, and operation of ICFR and inadequate IT tools and resources to ensure the relevance, timeliness and quality of information used in control activities. |
| · | Management has not designed or implemented a control monitoring process necessary to identify control weaknesses and remediations in a timely manner necessary to ensure the reliability of its ICFR. |
| · | Control deficiencies in the procurement, payment and receiving processes resulting from a lack of formal processes to ensure adherence to the Company’s delegation of authority policy, inconsistent matching of receipts to goods and services to supporting documentation and inconsistent receiving processes affecting the timing of recognition of assets and liabilities at the Company’s refinery project. |
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
As a consequence of the above, the Company had ineffective control activities related to the design of process level and financial statement close controls which had a pervasive impact on the Company's ICFR. Management has taken a number of steps to start addressing these weaknesses, including the following:
| · | Filled some of the recent vacancies in the finance team with more experienced employees. |
| · | Began working on a new ERP system implementation and targeting Q3 2024 go-live. |
| · | Signed a service agreement with a procurement and A/P software provider in October 2023 to help address some of the IT deficiencies on a more immediate basis. Management expects to go live before the end of 2023. |
| · | Providing progress updates on improving the Company’s ICFR to the Board / Audit Committee at quarterly meetings. |
Management intends to continue to further these efforts and are working towards designing processes for monitoring controls.
Other than those listed above, there have been no changes in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting during the 3 and 9 months ended September 30, 2023, that have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Disclosure Controls and Procedures (DCP) have not been designed to provide reasonable assurance that all relevant information required to be disclosed by the Company is accumulated and communicated to senior management as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. As disclosed in the previous quarter, the Company’s President and Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer note similar weaknesses in the disclosure controls and procedures as in the ICFR. The Company’s President and Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded, based on their evaluation of the design of the disclosure controls and procedures that because of the material weaknesses in our ICFR described above our DCP were not designed effectively at September 30, 2023.
Limitations of Controls and Procedures
The Company’s management, including the President and Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, believes that any internal controls over financial reporting and disclosure controls and procedures, no matter how well designed, can have inherent limitations. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance that the objectives of the control system are met.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
NON-GAAP FINANCIAL MEASURES
This MD&A contains “specified financial measures” within the meaning of NI 52-112, specifically, EBITDA which is a non-GAAP financial measure. Management believes that the use of this measure assists analysts, investors, and other stakeholders of the Company in understanding and assessing operating performance and for planning and forecasting future operating periods. The specified financial measures used in this MD&A do not have any standardized meaning prescribed by IFRS and may not be comparable to similar measures presented by other issuers. Accordingly, these specified financial measures should not be considered in isolation, or as a substitute for, analysis of the Company’s recognized measures presented in accordance with IFRS.
EBITDA is calculated as the Company’s Income (Loss) before taxes and adding back the impacts of interest expense, depreciation, and amortization. EBITDA is a non-GAAP financial measure and can be reconciled as follows for the three months ended September 30, 2023:
| | | Nine months ended September 30, 2023 | |
| | | Refinery | | | Corporate
and Other | | | Total | |
| Loss before taxes | | | (3,264 | ) | | | (15,935 | ) | | | (19,199 | ) |
| Add back (remove): | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | | - | | | | (206 | ) | | | (206 | ) |
| Depreciation expense | | | - | | | | 42 | | | | 42 | |
| EBITDA | | | (3,264 | ) | | | (16,099 | ) | | | (19,363 | ) |
CAUTIONARY STATEMENT REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This MD&A contains certain statements that may be deemed “forward-looking statements”, including statements regarding developments in the Company’s operations in future periods, adequacy of financial resources and plans and objectives of the Company. All statements in this document, other than statements of historical fact, which address events or developments that the Company expects to occur, are forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements are statements that are not historical facts and are generally, but not always, identified by the words “expects”, “plans”, “anticipates”, “believes”, “intends”, “estimates”, “projects”, “potential”, “interprets” and similar expressions, or events or conditions that “will”, “would”, “may”, “could” or “should” occur. Forward-looking statements in this document include statements regarding the advancement of the Refinery, future exploration programs, liquidity, and effects of accounting policy changes.
Although the Company believes the expectations expressed in such forward-looking statements are based on reasonable assumptions, such statements are not guarantees of future performance and actual results may differ materially from those in forward-looking statements. Factors that could cause the actual results to differ materially from those in forward-looking statements include market prices, exploration success, a successful outcome of the work in support of the recommissioning of the Refinery, continued availability of capital and financing, inability to obtain required regulatory or governmental approvals and general economic, market or business conditions. Investors are cautioned that any such statements are not guarantees of future performance and actual results or developments may differ materially from those projected in the forward-looking statements. Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on this forward-looking information.
ELECTRA BATTERY MATERIALS CORPORATION
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(expressed in thousands of Canadian dollars)
Forward-looking statements are based on the beliefs, estimates and opinions of the Company’s management on the date the statements are made. The Company undertakes no obligation to update these forward-looking statements if Management’s beliefs, estimates, opinions, or other factors should change except as required by law.
These statements are based on several assumptions including, among others, assumptions regarding general business and economic conditions, the timing of the receipt of regulatory and governmental approvals for the work programs described herein, the ability of the Company and other relevant parties to satisfy stock exchange and other regulatory requirements promptly, the availability of financing for the Company’s proposed work programs on its assets on reasonable terms and the ability of third-party service providers to deliver services promptly. The foregoing list of assumptions is not exhaustive. Events or circumstances could cause results to differ materially.

