Filed Pursuant to Rule 424(b)(3)
No. 333-278221
PROXY STATEMENT FOR
STOCKHOLDER MEETING OF
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
PROSPECTUS FOR THE REGISTRATION OF
64,295,053 SHARES OF COMMON STOCK;
9,698,225 WARRANTS AND
9,698,225 RIGHTS OF
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
To the Stockholders of Global Star Acquisition Inc.:
You are cordially invited to attend the special meeting of the Stockholders of Global Star Acquisition Inc. (“Global Star”), which will be held at 9:30 a.m., Eastern time, on February 3, 2025 (the “Special Meeting”). Global Star will be holding the Special Meeting via teleconference using the following dial-in information:
Global Star Acquisition Inc. Virtual Shareholder Meeting Information:
Meeting Date: February 3, 2025
Meeting Time: 9:30 a.m. Eastern Time
Special Meeting-meeting webpage (information, webcast, telephone access and replay):
https://www.cstproxy.com/globalstarspac/bc2025
Telephone access (listen-only):
Within the U.S. and Canada:
1 800-450-7155 (toll-free)
Outside of the U.S. and Canada:
+1 857-999-9155 (standard rates apply)
Conference ID: 7921345#
Global Star is Delaware company incorporated as a blank check company for the purpose of entering into a merger, share exchange, asset acquisition, stock purchase, recapitalization, reorganization or other similar business combination with one or more businesses or entities, which Global Star refer to as a “target business.”
Global Star has entered into a merger agreement, dated as of June 15, 2023, as amended on March 11, 2024, June 28, 2024, July 25, 2024 and December 11, 2024 (the “Merger Agreement”), which provides for a business combination between Global Star and K Enter Holdings, Inc., a Delaware corporation (“K Enter”). Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, the business combination will be effected in two steps: (i) subject to the approval and adoption of the Merger Agreement by the stockholders of Global Star, Global Star will reincorporate to Cayman Islands by merging with and into K Wave Media Ltd, a Cayman Islands exempted company and wholly owned subsidiary of Global Star (“PubCo”), with PubCo remaining as the surviving publicly traded entity (the “Reincorporation Merger”) and (ii) one (1) business day following the Reincorporation Merger, GLST Merger Sub, Inc. (“Merger Sub”), a Delaware corporation and wholly owned subsidiary of PubCo, will be merged with and into K Enter, resulting in K Enter being a wholly owned subsidiary of PubCo (the “Acquisition Merger”). The Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger are collectively referred to herein as the “Business Combination.” On July 13, 2023, PubCo and Merger Sub executed a written joinder agreement to become parties to the Merger Agreement, accordingly, the Merger Agreement is by and among Global Star, PubCo, Merger Sub, and K Enter. The aggregate consideration for the Acquisition Merger is $590,000,000, payable in the form of 59,000,000 newly issued PubCo’s Ordinary Shares (as defined below) valued at $10.00 per share. K Enter currently has limited operations and does not presently own a controlling interest in any other entities.
At the Special Meeting, Global Star stockholders will be asked to consider and vote upon the following proposals:
Proposal 1. Reincorporation Merger — to consider and vote on a proposal to adopt and approve the merger agreement, dated as of June 15, 2023, as modified by the joinder agreement, dated July 13, 2023, the First Amendment, dated March 11, 2024, the Second Amendment, dated June 28, 2024, the Third Amendment to Merger Agreement, dated July 25, 2024 and the Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement, dated December 11, 2024 (the “Merger Agreement”), by and among Global Star Acquisition Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Global Star”), K Enter Holdings Inc., a Delaware corporation (“K Enter”), K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (“PubCo”) and GLST Merger Sub, Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Merger Sub”), to effect Global Star’s initial business combination pursuant to which, among other things, (1) Global Star will merge with and into PubCo that is a wholly owned subsidiary of Global Star, with PubCo being the surviving corporation in such merger, thereby consummating a change in Global Star’s domicile from a Delaware corporation to a Cayman Islands exempted company (the “Reincorporation Merger”). Global Star refers to this as the “Reincorporation Merger Proposal” or “Proposal No. 1;” A copy of the Merger Agreement is attached to the accompanying proxy statement as Annex A;
Proposal 2. Acquisition Merger — to consider and vote on a proposal to adopt and approve the subsequent merger set forth in the Merger Agreement, pursuant to which the K Enter will merge with and into Merger Sub that is a wholly owned subsidiary of PubCo, with K Enter as the surviving corporation in such merger, thereby consummating PubCo’s acquisition, through its Merger Sub, of K Enter (the “Acquisition Merger”), and, after giving effect to the Acquisition Merger, K Enter being a wholly owned subsidiary of PubCo. Global Star refers to this as the “Acquisition Merger Proposal” or “Proposal No. 2;” The Reincorporation Merger, the Acquisition Merger and such other transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement are hereinafter collectively referred as the “Business Combination” and Proposals 1 and 2 are collectively referred to as the “Business Combination Proposals”.
Proposal 3. The Governance Proposal — to consider and vote, on a non-binding advisory basis, on four separate governance proposals relating to the following material differences between Global Star’s current amended and restated certificate of incorporation (the “GLST Charter”) and PubCo’s Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association (the “PubCo Charter”). These four separate governance proposals are collectively referred to as the “Governance Proposal”:
a. through the Reincorporation Merger, Global Star shall merge with and into PubCo and Global Star, the Delaware corporation, shall cease to exist and PubCo shall be the surviving company and the name of the surviving company will be “K Wave Media, Ltd.”;
b. following the Reincorporation Merger the authorized shares of the surviving corporation shall change from (i) 100,000,000 shares of Global Star Class A Common Stock, 10,000,000 shares of Global Star Class B Common Stock and 1,000,000 shares of preferred stock to (ii) $100,000 divided into 990,000,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares and 10,000,000 PubCo Preference Shares;
c. deleting the forum selection provision providing for concurrent jurisdiction in the Court of Chancery and the federal district court for the District of Delaware for claims arising under the Securities Act and the PubCo Charter adopts the Cayman Islands as the exclusive forum for certain shareholder litigation; provided, however, that this exclusive forum provision shall not apply to any action or suits brought to enforce any liability or duty created by the United States Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the Exchange Act, or any claim for which the federal district courts of the United States of America are, as a matter of the laws of the United States, the sole and exclusive forum for determination of such a claim; and
d. deleting the election to not be governed by Section 203 of the DGCL and limiting certain corporate takeovers by interested shareholders.
A copy of the form of PubCo’s Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association is attached to this proxy statement/ prospectus as Annex B. Global Star refers to this as the “Governance Proposal” or “Proposal No. 3;”
Proposal 4. Election of Directors of PubCo Proposal — to consider and vote on a proposal to approve PubCo’s Board of Directors (the “PubCo Board”) in regards to the following persons: Pyeung Ho Choi, Young Jae Lee, Tan Chin Hwee, Ted Kim, Han Jae Kim, Hyung Seok Cho and Tae Woo Kim to serve on PubCo’s Board of Directors. Global Star refers to this as the “Director Proposal” or “Proposal No. 4;”;
Proposal 5. The PubCo 2023 Equity Incentive Plan Proposal — to consider and vote on a proposal to approve PubCo’s 2023 Equity Incentive Plan (the “Incentive Plan”). Global Star refers to this as the “Incentive Plan Proposal” or “Proposal No. 5.” A copy of the Incentive Plan is attached to the accompanying proxy statement as Annex C.
Proposal 6. The Adjournment Proposal — to approve a proposal to adjourn the Special Meeting under certain circumstances, which is more fully described in the accompanying proxy statement/prospectus. Global Star refers to this as the “Adjournment Proposal” or “Proposal No. 6” and, together with the Reincorporation Merger Proposal, the Acquisition Merger Proposal, and the Incentive Plan Proposal, the “Proposals.”
Upon the closing of the Acquisition Merger, (i) each share of K Enter capital stock, if any, that is owned by Company or Merger Sub (or any other subsidiary of Company) or K Enter (as treasury stock or otherwise), will automatically be cancelled and retired without any conversion, (ii) each share of K Enter preferred stock issued and outstanding shall be deemed converted into shares of K Enter common stock, (iii) each share of K Enter common stock issued and outstanding, including shares of K Enter common stock deemed outstanding as a result of the mandatory conversion of K Enter preferred stock, shall be converted into the right to receive a number of PubCo Ordinary Shares equal to the Conversion Ratio, and (iv) each share of Merger Sub common stock issued and outstanding shall be converted into and become one newly issued, fully paid and nonassessable share of K Enter common stock. Conversion Ratio means the quotient obtained by dividing (a) 59,000,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares, by (b) the Aggregate Fully Diluted K Enter Common Shares. Aggregate Fully Diluted K Enter Common Shares means the sum of (a) all shares of K Enter common stock that are issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Closing; plus (b) the aggregate shares of K Enter common stock issuable upon conversion of all shares of K Enter preferred stock that are issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Closing; plus (c) the aggregate shares of K Enter common stock issuable upon full conversion, exercise or exchange of any other securities of K Enter outstanding immediately prior to the Closing directly or indirectly convertible into or exchangeable or exercisable for K Enter.
It is anticipated that, upon consummation of the Business Combination, Global Star’s public stockholders will own approximately 3.3% of the issued PubCo Ordinary Shares, the Sponsor (as defined below) and Initial Stockholders will own approximately 4.5% of the issued PubCo Ordinary Shares, and K Enter’s current stockholders will own approximately 92.2% of the issued PubCo Ordinary Shares. These relative percentages assume that (i) none of Global Star’s existing public stockholders exercise their redemption rights, as discussed herein; and (ii) there is no exercise or conversion of PubCo Warrants. The exercise of the PubCo Warrants by some, but not all, of the warrant holders will result in dilution to the former Global Star public stockholders not exercising such PubCo Warrants.
If any of Global Star’s existing public stockholders exercise their redemption rights, the anticipated percentage ownership of Global Star’s existing stockholders will be reduced. For example, if 25% of Global Star’s public stockholders exercise their redemption rights, then the PubCo Ordinary Shares would be owned 92.6% by the K Enter stockholders, 2.8% by the former Global Star public stockholders and 4.6% by the Sponsor and Initial Stockholders. Further, if 25% of Global Star’s public stockholders exercise their redemption rights and all of the Global Star warrants and convertible securities are exercised, then the PubCo Ordinary Shares would be owned 79.7% by the K Enter stockholders, 2.4% by the former Global Star public stockholders and 4.0% by the Sponsor and Initial Stockholders Alternatively, if 100% of Global Star’s public stockholders exercise their redemption rights, then the PubCo Ordinary Share would be owned 93.9% by the K Enter stockholders, 1.4% by the former Global Star public stockholders and 4.7% by the Sponsor and Initial Stockholders. Likewise, if 100% of Global Star’s public stockholders exercise their redemption rights and all of the Global Star warrants and convertible securities are exercised, then the PubCo Ordinary Shares would be owned 80.7% by the K Enter stockholders, 1.3% by the former Global Star public stockholders and 4.1% by the Sponsor and Initial Stockholders No stockholder will have a controlling interest in PubCo. Further, both Global Star and K Enter have agreed to use their best efforts to complete a $50 million PIPE Financing that would result in further dilution, but the amount of such dilution cannot be determined until the terms of the PIPE Financing have been negotiated. You should read “Summary of the Proxy Statement/Prospectus — The Business Combination and the Merger Agreement” and “Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Financial Statements” for further information.
The closing of the business combination is subject to certain conditions, including K Enter’s acquisition of the controlling equity interests of the Six Korean Entities. K Enter currently has limited operations and does not presently own a controlling interest in any other entities. For more information, see the questions and answers titled “When is the acquisition of the Six Korean Entities expected to occur?” and “What if there are material developments or changes relating to the acquisition by K Enter of the Six Korean Entities prior to the Special Meeting?” and “What if K Enter’s acquisition of the Six Korean Entities does not occur prior to the Special Meeting?” in the Section titled “Questions and Answers about the Business Combination and the Special Meeting” beginning on page 6.
K Enter’s acquisition of the Six Korean Entities is a closing condition to the Business Combination, and while this condition can be waived, Global Star does not currently intend to waive this condition. K Enter expects to close the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of the Six Korean Entities within 24 to 72 hours after this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 is declared effective by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”). In addition, Global Star will not mail proxy materials to its shareholders for the Special Meeting until after K Enter closes the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities. PubCo shall include the date that K Enter completes the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all Six Korean Entities in its Form 424B3 Prospectus to be filed with the SEC after this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 is declared effective by the SEC.
In the event that K Enter does not complete the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities, PubCo will file a post-effective amendment to its Registration Statement on Form F-4 (the “Post-Effective Amendment”) disclosing that K Enter did not complete its contemplated acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities (and the material information concerning such event) and Global Star will not mail proxy materials to its shareholders for the Special Meeting (or hold its Special Meeting) until after the Post-Effective Amendment is declared effective by the SEC. Global Star’s shareholders will not be able to vote for or against the Business Combination until after they receive a definitive proxy statement, which will only be mailed after the later of (i) the successful consummation of the acquisition of the controlling interests of all of the Six Korean Entities or (ii) the declaration of effectiveness by the SEC of the Post-Effective Amendment.
As of January 3, 2025, K Enter completed the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of each of the Six Korean Entities.
Global Star’s Initial Stockholders and the Sponsor, who as of the record date, owned 2,798,225 shares of GLST Common Stock, or approximately 69.1% of the issued and outstanding GLST Common Stock, have agreed to vote their respective shares in favor of each of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal and the Acquisition Merger Proposal and are expected to vote in favor of the Incentive Plan Proposal, the Adjournment Proposal and the Director Proposal. As a result, the affirmative vote of the shares of GLST Common Stock held by the Initial Stockholders and the Sponsor is sufficient to approve each of the Proposals.
Global Star common shares are currently listed on the Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol “GLST.” PubCo intends to apply to list the PubCo Ordinary Shares and PubCo Warrants on the Nasdaq Stock Market under the symbols “KWM” and “KWMW” respectively, in connection with the closing of the Business Combination. Global Star cannot assure you that the PubCo Ordinary Shares and PubCo Warrants will be approved for listing on Nasdaq.
Investing in PubCo securities involves a high degree of risk. See “Risk Factors” beginning on page 36 for a discussion of information that should be considered in connection with an investment in PubCo securities.
As of January 3, 2025, there was approximately $4.3 million in Global Star’s trust account. On January 3, 2025, the last sale price of GLST Common Stock was $11.97.
Global Star’ stockholders are not entitled to exercise appraisal or dissenters rights in connection with the Business Combination. Pursuant to Global Star’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation, Global Star is providing its public stockholders with the opportunity to redeem all or a portion of their shares of GLST Common Stock at a per-share price, payable in cash, equal to the aggregate amount then on deposit in Global Star’s trust account as of two business days prior to the consummation of the Business Combination, including interest, less taxes payable, divided by the number of then outstanding shares of GLST Common Stock that were sold as part of the GLST Units in Global Star’s initial public offering (“IPO”), subject to the limitations described herein. Global Star estimates that the per-share price at which public shares may be redeemed from cash held in the trust account will be approximately $11.45 per share, subject to reduction for the payment of taxes, at the time of the Special Meeting. Global Star’s public stockholders may elect to redeem their shares even if they vote for the Reincorporation Merger or do not vote at all. Global Star has no specified maximum redemption threshold under the Global Star’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation. It is a condition to closing under the Merger Agreement, however, that Global Star has, in the aggregate, not less than $5,000,001 of net tangible assets or is otherwise exempt from the provisions of Rule 419 promulgated under the Securities Act. If redemptions by Global Star public stockholders cause Global Star to be unable to meet this closing condition, then Global Star may not be required to consummate the Business Combination, although Global Star and K Enter may, in their sole discretion, waive this condition. In the event that Global Star waives this condition, Global Star does not intend to seek additional stockholder approval or to extend the time period in which its public stockholders can exercise their redemption rights. Holders of outstanding GLST Warrants and GLST Rights do not have redemption rights in connection with the Business Combination.
Global Star is providing this proxy statement/prospectus and accompanying proxy card to its stockholders in connection with the solicitation of proxies to be voted at the Special Meeting and at any adjournments or postponements of the Special Meeting. The Sponsor and K Enter, which own approximately 19.26% and 2.0%, respectively, of GLST Common Stock as of the record date, are expected to vote their Common Stock in favor of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal and the Acquisition Merger Proposal, which transactions comprise the Business Combination, and intend to vote for the Incentive Plan Proposal and the Adjournment Proposal, although there is no agreement in place with respect to voting on those proposals.
Each stockholder’s vote is very important. Whether or not you plan to attend the Special Meeting in person, please submit your proxy card without delay. Global Star’s stockholders may revoke proxies at any time before they are voted at the meeting. Voting by proxy will not prevent a stockholder from voting in person if such stockholder subsequently chooses to attend the Special Meeting. If you are a holder of record and you attend the Special Meeting and wish to vote in person, you may withdraw your proxy and vote in person. Assuming that a quorum is present, attending the Special Meeting either in person or by proxy and abstaining from voting will have the same effect as voting against all the Proposals. And broker non-votes will have no effect on any of the Proposals.
If you sign, date and return your proxy card without indicating how you wish to vote, your proxy will be voted in favor of each of the Proposals presented at the Special Meeting. If you fail to return your proxy card or fail to instruct your bank, broker or other nominee how to vote, and do not attend the Special Meeting in person, the effect will be that your shares will not be counted for purposes of determining whether a quorum is present at the Special Meeting of stockholders and, if a quorum is present, will have the effect of a vote against the Business Combination Proposal and no effect on the adjournment proposal. If you are a stockholder of record and you attend the Special Meeting and wish to vote in person, you may withdraw your proxy and vote in person.
Global Star encourages you to read this proxy statement/prospectus carefully. In particular, you should review the matters discussed under the caption “Risk Factors” beginning on page 36.
Global Star board of directors has unanimously approved the Merger Agreement and unanimously recommends that Global Star stockholders vote “FOR” approval of each of the Proposals. When you consider Global Star board of director’s recommendation of these Proposals, you should keep in mind that Global Star’s directors and officers have interests in the Business Combination that may conflict or differ from your interests as a stockholder. See the section titled “Proposals to be Considered by Global Star Stockholders: The Business Combination — Interests of Global Star’s Directors and Executive Officers in the Business Combination.”
On behalf of the Global Star board of directors, I thank you for your support and Global Star looks forward to the successful consummation of the Business Combination.
If you have any questions or need assistance voting your ordinary shares, please contact Laurel Hill Advisory Group, LLC, Global Star’s proxy solicitor, by calling (855)-414-2266, or banks and brokers can call collect at (516) 396-7902, or by emailing GLST@laurelhill.com. The notice of the stockholder meeting and the proxy statement/prospectus relating to the Business Combination will be available at https://www.cstproxy.com/globalstarspac/bc2025.
The accompanying proxy statement/prospectus provides stockholders of Global Star with detailed information about the Business Combination and other matters to be considered at the stockholder meeting of Global Star. Global Star encourages you to read the entire accompanying proxy statement/prospectus, including the Annexes and other documents referred to therein, carefully and in their entirety. In particular, when you consider the recommendation of the board of directors of Global Star to vote in favor of the proposals described in this proxy statement/prospectus, you should keep in mind that Global Star’s directors and officers have interests in the Business Combination that are different from, in addition to or may conflict with your interests as a shareholder. For instance, the Sponsor, and the officers and directors of Global Star who have invested in the Sponsor entity, will benefit from the completion of the Business Combination and may be incentivized to complete an acquisition of a less favorable target company or on terms less favorable to stockholders rather than liquidate. See the section entitled “Interests of Global Star’s Directors and Officers in the Business Combination” for a further discussion. You should also carefully consider the risk factors described in “Risk Factors” beginning on page 36 of the accompanying proxy statement/prospectus.
NEITHER THE SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION NOR ANY STATE SECURITIES REGULATORY AGENCY HAS APPROVED OR DISAPPROVED THE TRANSACTIONS DESCRIBED IN THE ACCOMPANYING PROXY STATEMENT/PROSPECTUS, PASSED UPON THE MERITS OR FAIRNESS OF THE BUSINESS COMBINATION OR RELATED TRANSACTIONS OR PASSED UPON THE ADEQUACY OR ACCURACY OF THE DISCLOSURE IN THE ACCOMPANYING PROXY STATEMENT/PROSPECTUS. ANY REPRESENTATION TO THE CONTRARY CONSTITUTES A CRIMINAL OFFENSE.
The accompanying proxy statement/prospectus is dated January 7, 2025, and is first being mailed to Global Star’s stockholders on or about January 7, 2025.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
1641 International Drive Unit 208
McLean, VA
NOTICE OF STOCKHOLDER MEETING
TO BE HELD ON FEBRUARY 3, 2025
TO THE STOCKHOLDERS OF GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.:
NOTICE IS HEREBY GIVEN that a meeting of the stockholders (the “stockholder meeting”) of Global Star Acquisition Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Global Star”), will be held on February 3, 2025, at 9:30 Eastern Time at https://www.cstproxy.com/globalstarspac/bc2025, unless the stockholder meeting is adjourned. Global Star also intends to hold the stockholder meeting through a “virtual” or online method. You will be able to attend the stockholder meeting online, vote and submit your questions during the stockholder meeting by visiting https://www.cstproxy.com/globalstarspac/bc2025. To register and receive access to the stockholder meeting, registered stockholders and beneficial stockholders (those holding shares through a stock brokerage account or by a bank or other holder of record) will need to follow the instructions applicable to them provided in this proxy statement/prospectus.
Proposal 1. Reincorporation Merger — to consider and vote on a proposal to adopt and approve the merger agreement, dated as of June 15, 2023, as modified by the joinder agreement, dated July 13, 2023, the First Amendment, dated March 11, 2024, the Second Amendment, dated June 28, 2024, the Third Amendment to Merger Agreement, dated July 25, 2024 and the Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement, dated December 11, 2024 (the “Merger Agreement”), by and among Global Star Acquisition Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Global Star”), K Enter Holdings Inc., a Delaware corporation (“K Enter”), K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (“PubCo”) and GLST Merger Sub, Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Merger Sub”), to effect Global Star’s initial business combination pursuant to which, among other things, (1) Global Star will merge with and into PubCo that is a wholly owned subsidiary of Global Star, with PubCo being the surviving corporation in such merger, thereby consummating a change in Global Star’s domicile from a Delaware corporation to a Cayman Islands exempted company (the “Reincorporation Merger”). Global Star refers to this as the “Reincorporation Merger Proposal” or “Proposal No. 1;” A copy of the Merger Agreement is attached to the accompanying proxy statement as Annex A;
Proposal 2. Acquisition Merger — to consider and vote on a proposal to adopt and approve the subsequent merger set forth in the Merger Agreement, pursuant to which the K Enter will merge with and into Merger Sub that is a wholly owned subsidiary of PubCo, with K Enter as the surviving corporation in such merger, thereby consummating PubCo’s acquisition, through its Merger Sub, of K Enter (the “Acquisition Merger”), and, after giving effect to the Acquisition Merger, K Enter being a wholly owned subsidiary of PubCo. Global Star refers to this as the “Acquisition Merger Proposal” or “Proposal No. 2;” The Reincorporation Merger, the Acquisition Merger and such other transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement are hereinafter collectively referred as the “Business Combination” and Proposals 1 and 2 are collectively referred to as the “Business Combination Proposals”.
Proposal 3. The Governance Proposal — to consider and vote, on a non-binding advisory basis, on four separate governance proposals relating to the following material differences between Global Star’s current amended and restated certificate of incorporation (the “GLST Charter”) and PubCo’s Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association (the “PubCo Charter”). These four separate governance proposals are collectively referred to as the “Governance Proposal”:
a. through the Reincorporation Merger, Global Star shall merge with and into PubCo and Global Star, the Delaware corporation, shall cease to exist and PubCo shall be the surviving corporation and the name of the surviving corporation will be “K Wave Media, Ltd.”;
b. following the Reincorporation Merger the authorized shares of the surviving corporation shall change from (i) 100,000,000 shares of Global Star Class A Common Stock, 10,000,000 shares of Global Star Class B Common Stock and 1,000,000 shares of preferred stock to (ii) $100,000 divided into 990,000,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares and 10,000,000 PubCo Preference Shares;
c. deleting the forum selection provision providing for concurrent jurisdiction in the Court of Chancery and the federal district court for the District of Delaware for claims arising under the Securities Act and the PubCo Charter adopts the Cayman Islands as the exclusive forum for certain shareholder litigation; provided, however, that this exclusive forum provision shall not apply to any action or suits brought to enforce any liability or duty created by the United States Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the Exchange Act, or any claim for which the federal district courts of the United States of America are, as a matter of the laws of the United States, the sole and exclusive forum for determination of such a claim; and
d. deleting the election to not be governed by Section 203 of the DGCL and limiting certain corporate takeovers by interested shareholders.
A copy of the form of PubCo’s Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association is attached to this proxy statement/ prospectus as Annex B. Global Star refers to this as the “Governance Proposal” or “Proposal No. 3;”
Proposal 4. Election of Directors of PubCo Proposal — to consider and vote on a proposal to approve PubCo’s Board of Directors (the “PubCo Board”) in regards to the following persons: Pyeung Ho Choi, Young Jae Lee, Tan Chin Hwee, Ted Kim, Han Jae Kim, Hyung Seok Cho and Tae Woo Kim to serve on PubCo’s Board of Directors. Global Star refers to this as the “Director Proposal” or “Proposal No. 4;”;
Proposal 5. The PubCo 2023 Equity Incentive Plan Proposal — to consider and vote on a proposal to approve PubCo’s 2023 Equity Incentive Plan (the “Incentive Plan”). Global Star refers to this as the “Incentive Plan Proposal” or “Proposal No. 5.” A copy of the Incentive Plan is attached to the accompanying proxy statement as Annex C.
Proposal 6. The Adjournment Proposal — to approve a proposal to adjourn the Special Meeting under certain circumstances, which is more fully described in the accompanying proxy statement/prospectus. Global Star refers to this as the “Adjournment Proposal” or “Proposal No. 6” and, together with the Reincorporation Merger Proposal, the Acquisition Merger Proposal, and the Incentive Plan Proposal, the “Proposals.”
All of the proposals set forth above are sometimes collectively referred to herein as the “Proposals.” The Reincorporation Merger Proposal and the Acquisition Merger Proposal are dependent upon each other. It is important for you to note that in the event that either of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal or the Acquisition Merger Proposal is not approved, then Global Star will not consummate the Business Combination. If Global Star does not consummate the Business Combination and fails to complete an initial business combination by February 22, 2025 (or June 22, 2025 in the event Global Star extends the time it has to complete an initial business combination to the fullest extent), Global Star will be required to dissolve and liquidate.
As of December 13, 2024, there were 3,214,100 shares of GLST Common Stock issued and outstanding and entitled to vote. Only Global Star stockholders who hold shares of record as of the close of business on December 13, 2024 are entitled to vote at the Special Meeting or any adjournment of the Special Meeting. This proxy statement/prospectus is first being mailed to Global Star stockholders on or about January 7, 2025. Approval of each of the Proposals will require the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the issued and outstanding GLST Common Stock present and entitled to vote at the Special Meeting or any adjournment thereof. Assuming that a quorum is present, attending the Special Meeting either in person or by proxy and abstaining from voting will have the same effect as voting against the Proposals and failing to instruct your bank, brokerage firm or nominee to attend and vote your shares will have no effect on any of the Proposals.
This proxy statement/prospectus and accompanying proxy card is being provided to Global Star’s stockholders in connection with the solicitation of proxies to be voted at the stockholder meeting and at any adjournment of the stockholder meeting. Whether or not you plan to attend the stockholder meeting, all of Global Star’s stockholders are urged to read the accompanying proxy statement/prospectus, including the Annexes and other documents referred to therein, carefully and in their entirety. You should also carefully consider the risk factors described in “Risk Factors” beginning on page 36 of the accompanying proxy statement/prospectus.
After careful consideration, the board of directors of Global Star has unanimously approved the Merger Agreement and recommends that stockholders vote “FOR” the adoption of the Merger Agreement and “FOR” all other proposals presented to Global Star’s stockholders in the accompanying proxy statement/prospectus. When you consider the recommendation of these proposals by the board of directors of Global Star, you should keep in mind that Global Star’s directors and officers have interests in the Business Combination that may conflict with your interests as a shareholder. See the section entitled “Business Combination Proposals — Interests of Global Star’s Directors and Executive Officers in the Business Combination” in this proxy statement/prospectus for a further discussion of these considerations.
Pursuant to the Existing Governing Documents, a public shareholder may request that Global Star redeem all or a portion of its public shares for cash if the Business Combination is consummated. As a holder of public shares, you will be entitled to receive cash for any public shares to be redeemed only if you:
| (i) | (a) hold public shares or (b) if you hold public shares through units, you elect to separate your units into the underlying public shares, GLST Warrants and GLST Rights prior to exercising your redemption rights with respect to the public shares; |
| (ii) | submit a written request to Global Star’s transfer agent in which you (a) request that Global Star redeem all or a portion of your public shares for cash, and (b) identify yourself as the beneficial holder of the public shares and provide your legal name, phone number and address; and (c) deliver your public shares to Continental, Global Star’s transfer agent, physically or electronically through The Depository Trust Company; and |
| (iii) | deliver your certificates for public shares (if any) along with the redemption forms to Continental, Global Star’s transfer agent, physically or electronically through The Depository Trust Company (“DTC”). |
Holders must complete the procedures for electing to redeem their public shares in the manner described above prior to 5:00 pm, Eastern Time, on January 30, 2025 (two business days before the scheduled vote at the stockholder meeting) in order for their shares to be redeemed.
Holders of units must elect to separate the units into the underlying public shares, GLST Warrants and GLST Rights prior to exercising redemption rights with respect to the public shares. Public holders that hold their units in an account at a brokerage firm or bank, must notify their broker or bank that they elect to separate the units into the underlying public shares, GLST Warrants and GLST Rights, or if a holder holds units registered in its own name, the holder must contact Global Star’s transfer agent directly and instruct them to do so. The redemption rights include the requirement that a holder must identify itself in writing as a beneficial holder and provide its legal name, phone number and address to Global Star’s transfer agent in order to validly redeem its shares. Public stockholders may elect to redeem public shares regardless of if or how they vote in respect of the Business Combination Proposals and regardless of whether they hold public shares on the record date. If the Business Combination is not consummated, the public shares will be returned to the respective holder, broker or bank. If the Business Combination is consummated, and if a public shareholder properly exercises its right to redeem all or a portion of the public shares that it holds and timely delivers its shares to Global Star’s transfer agent, PubCo will redeem such public shares for a per-share price, payable in cash, equal to the pro rata portion of the trust account established at the consummation of Global Star’s initial public offering (the “Trust Account”), calculated as of two business days prior to the consummation of the Business Combination. For illustrative purposes, based on approximately $4,364,690 in the Trust Account and 380,875 shares subject to possible redemption, in each case, as of December 13, 2024, this would have amounted to approximately $11.45 per issued and outstanding public share, subject to reduction for the payment of taxes. If a holder of public shares exercises its redemption rights in full, then such holder will be electing to exchange its public shares for cash and will no longer own public shares. See “Stockholder Meeting of Global Star — Redemption Rights” in this proxy statement/prospectus for a detailed description of the procedures to be followed if you wish to redeem your public shares for cash.
On behalf of Global Star’s board of directors, I would like to thank you for your support and look forward to the successful completion of the Business Combination.
| | Sincerely, |
| | |
| | /s/ Anthony Ang |
| | Anthony Ang
Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of Directors |
NEITHER THE SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION NOR ANY STATE SECURITIES REGULATORY AGENCY HAS APPROVED OR DISAPPROVED THE TRANSACTIONS DESCRIBED IN THE ACCOMPANYING PROXY STATEMENT/PROSPECTUS OR THE SECURITIES TO BE ISSUED, PASSED UPON THE MERITS OR FAIRNESS OF THE BUSINESS COMBINATION OR RELATED TRANSACTIONS OR PASSED UPON THE ADEQUACY OR ACCURACY OF THE DISCLOSURE IN THE ACCOMPANYING PROXY STATEMENT/PROSPECTUS. ANY REPRESENTATION TO THE CONTRARY CONSTITUTES A CRIMINAL OFFENSE.
The accompanying proxy statement/prospectus is dated January 7, 2025, and is first being mailed to stockholders on or about January 7, 2025.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| ANNEX A | | MERGER AGREEMENT, FIRST AMENDMENT TO THE MERGER AGREEMENT, SECOND AMENDMENT TO THE MERGER AGREEMENT AND THIRD AMENDMENT TO THE MERGER AGREEMENT | | A-1 |
| ANNEX B | | FORM OF PUBCO’S AMENDED AND RESTATED MEMORANDUM AND ARTICLES OF ASSOCIATION | | B-1 |
| ANNEX C | | FORM OF PUBCO’S 2024 EQUITY INCENTIVE PLAN | | C-1 |
| ANNEX D | | FORM OF AMENDED AND RESTATED REGISTRATION RIGHTS AGREEMENT | | D-1 |
| ANNEX E | | FORM OF LOCK-UP AGREEMENT | | E-1 |
| ANNEX F | | FAIRNESS OPINION LETTER, DATED JUNE 9, 2023, BY EVEREDGE PTE, LTD. AND OPINION OF EVEREDGE PTE., LTD., DATED JUNE 9, 2023 | | F-1 |
| ANNEX G | | FAIRNESS OPINION LETTER, DATED MARCH 12, 2024, REVISED APRIL 29, 2024, BY EVEREDGE PTE, LTD AND OPINION OF EVEREDGE PTE., LTD., DATED MARCH 12, 2024, REVISED APRIL 29, 2024. | | G-1 |
ABOUT THIS PROXY STATEMENT/PROSPECTUS
This document, which forms part of a registration statement on Form F-4 filed by PubCo (File No. 333-278221) with the SEC, constitutes a prospectus of PubCo under Section 5 of the Securities Act, with respect to the issuance of (i) the PubCo Ordinary Shares to Global Star’s stockholders, (ii) the PubCo Warrants to holders of GLST Warrants in exchange for the GLST Warrants, (iii) the PubCo Rights in exchange for the GLST Rights (iv) the PubCo Ordinary Shares underlying the PubCo Rights, (v) PubCo Ordinary Shares to the stockholders of K Enter and (vi) the investors in the PIPE Financing, if the Business Combination is consummated. This document also constitutes a notice of meeting and a proxy statement under Section 14(a) of the Exchange Act, with respect to the Special Meeting at which Global Star’s stockholders will be asked to consider and vote upon the Proposals to approve the Reincorporation Merger, the Acquisition Merger, the Incentive Plan Proposal and the Adjournment Proposal.
This proxy statement/prospectus does not constitute an offer to sell, or a solicitation of an offer to buy, any securities, or the solicitation of a proxy, in any jurisdiction to or from any person to whom it is not lawful to make any such offer or solicitation in such jurisdiction.
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION
As a foreign private issuer, after the consummation of the Business Combination, PubCo will be required to file its Annual Report on Form 20-F with the SEC no later than four months following its fiscal year end. Global Star files reports, proxy statements and other information with the SEC as required by the Exchange Act. You can read Global Star’s SEC filings, including this proxy statement/prospectus, over the Internet at the SEC’s website at http://www.sec.gov.
Information and statements contained in this proxy statement/prospectus, or any annex to this proxy statement/prospectus, are qualified in all respects by reference to the copy of the relevant contract or other annex filed with this proxy statement/prospectus.
If you would like additional copies of this proxy statement/prospectus, or if you have questions about the Business Combination, you should contact Global Star’s proxy solicitor, Laurel Hill Advisory Group, LLC, individual call toll-free at (855) 414-2266 and banks and brokers call at (516) 396-7902.
All information contained in this proxy statement/prospectus relating to Global Star, PubCo and Merger Sub has been supplied by Global Star, and all such information relating to K Enter has been supplied by K Enter. Information provided by either of Global Star or K Enter does not constitute any representation, estimate or projection of the other party.
Neither Global Star, PubCo, Merger Sub nor K Enter has authorized anyone to give any information or make any representation about the Business Combination or their companies that is different from, or in addition to, that contained in this proxy statement/prospectus or in any of the materials that have been incorporated into this proxy statement/prospectus by reference. Therefore, if anyone does give you any such information, you should not rely on it. If you are in a jurisdiction where offers to exchange or sell, or solicitations of offers to exchange or purchase, the securities offered by this proxy statement/prospectus or the solicitation of proxies is unlawful, or if you are a person to whom it is unlawful to direct these types of activities, then the offer presented in this proxy statement/prospectus does not extend to you. The information contained in this proxy statement/prospectus speaks only as of the date of this proxy statement/prospectus unless the information specifically indicates that another date applies.
USE OF CERTAIN TERMS
Unless otherwise stated in this proxy statement/prospectus references to the following terms shall be defined as follows:
| ● | “2023 Plan” or the “Incentive Plan” refer to PubCo 2023 Share Incentive Plan; |
| ● | “Acquisition Merger” refer to the merger, described in the Merger Agreement, between K Enter and Merger Sub, whereby K Enter is the surviving corporation; |
| ● | “Business Combination” refer to the closing of the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement, including the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger; |
| ● | “Closing Date” refer to the date on which the Business Combination is consummated; |
| ● | “Exchange Act” refer to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended; |
| ● | “First Amendment” refer to the First Amendment to Merger Agreement, dated March 11, 2024, by and among Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub; |
| | ● | “Founder Shares” means the outstanding shares of GLST Class B Common Stock held by the Sponsor, Global Star’s directors and affiliates of Global Star’s management team in the total amount of 2,140,000 shares. |
| | | |
| | ● | “Fourth Amendment” means the Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement, dated December 11, 2024, by and among Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub; |
| ● | “Global Star” or “GLST” or the “Company” refer to Global Star Acquisition Inc., a Delaware corporation; |
| ● | “GLST Charter” refers to GLST’s Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, filed with the Delaware Secretary of State on September 19, 2022. |
| | ● | “GLST Common Stock” refers collectively to GLST Class A Common Stock, $0.0001 par value per share and GLST Class B Common Stock, $0.0001 par value per share; |
| | ● | “GLST Class A Common Stock” are to Global Star’s Class A Common Stock, $0.0001 par value per share;, sold as part of the units in the IPO (whether they are purchased in the IPO or thereafter in the open market) |
| ● | “GLST Class B Common Stock” are to Global Star’s Class B Common Stock, $0.0001 par value per share; |
| ● | “GLST Rights” are to the rights sold as part of the units in the IPO (whether they are purchased in the IPO or thereafter in the open market). The GLST Rights entitle the holder to receive 1/10 of one share of GLST Class A Common Stock upon the consummation of the Business Combination; |
| | ● | “GLST Warrants” are to redeemable warrants sold as part of the units in the IPO (whether they are purchased in the IPO or thereafter in the open market, including warrants that may be acquired by Global Star’s sponsor or its affiliates in this offering or thereafter in the open market). The GLST Warrants entitle the holder to purchase one share of GLST Class A Common Stock for $11.50 per share; |
| | ● | “GLST Units” are to Global Star Units sold in the IPO at a price of $10 per unit (whether they are purchased in the IPO or thereafter in the open market, including warrants that may be acquired by Global Star’s sponsor or its affiliates in this offering or thereafter in the open market). The GLST Units consist of one share of Class A Common Stock, one GLST Warrant and one GLST Right; |
| ● | “IFRS” refer to International Financial Reporting Standards issued by the IFRS Foundation and the International Accounting Standards Board. |
| | ● | “Initial Stockholders” are the initial stockholders of Global Star, including Anthony Ang, Nicholas Khoo, Shan Cui, Stephen Drew, Argon Lam Chun Win, Yang Kan Chong, Hai Chwee Chew and Jukka Rannila and excluding the Sponsor. |
| | ● | “IPO” refer to the initial public offering of 8,000,000 units of Global Star consummated on September 22, 2022; |
| ● | “Joinder Agreement” refer to as the Joinder Agreement, dated July 13, 2023, entered into among PubCo, Merger Sub, Global Star and K Enter. |
| ● | “K Enter” refers to K Enter Holdings Inc., a Delaware corporation; |
| ● | “K Enter Charter” refers to K Enter’s Second Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, filed with the Delaware Secretary of State on May 31, 2023. |
| ● | “K Enter Common Stock” refer to the shares of K Enter’s common stock, $0.0001 par value per share. |
| ● | “Merger Agreement” refer to the Merger Agreement, dated June 15, 2023, by and between Global Star and K Enter, as modified by the Joinder Agreement, dated July 13, 2023, the First Amendment to Merger Agreement, dated March 11, 2024, the Second Amendment to Merger Agreement, dated June 28, 2024, the Third Amendment to Merger Agreement to Merger Agreement, dated July 25, 2024 and the Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement dated December 11, 2024; |
| ● | “Merger Sub” refer to GLST Merger Sub, Inc., a Delaware corporation; |
| | ● | “New K Enter” refers to K Enter after the closing of the six (6) equity purchase agreements with (1) Play Company Co., Ltd.; (2) Solaire Partners LLC; (3) Apeitda Co., Ltd.; (4) The LAMP Co., Ltd.: (5) Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd.; and (6) Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd. |
| ● | “PIPE Financing” refers to Global Star’s plan to use its best efforts to consummate a capital raise of $50,000,000, with the assistance and cooperation of K Enter, with the closing to occur simultaneously with the closing of the Business Combination. |
| ● | “Plan of Merger” refers to the statutory plan of merger to be filed with the Registrar of Companies in the Cayman Islands to effect the Reincorporation Merger; |
| | ● | “Preferred Stock” refers to the Series A Preferred Stock and the Series A-1 Preferred Stock combined. |
| ● | “Private Rights” are to the rights sold as part of the Private Units sold in the private placement that occurred simultaneously with the closing of the IPO. The Private Rights entitle the holder to receive 1/10 of one share of GLST Class A Common Stock upon the consummation of the Business Combination; |
| ● | “Private Warrants” are to the redeemable warrants sold as part of the Private Units sold in the private placement that occurred simultaneously with the closing of the IPO. The Private Warrants entitle the holder to purchase one share of GLST Class A Common Stock for $11.50 per share; |
| ● | “Private Units” are to the private units sold in the private placement that occurred simultaneously with the closing of the IPO at $10 per unit. The Private Units consist of one share of Class A Common Stock, one Private Warrant and one Private Right; |
| ● | “PubCo” or “K Wave” or the “Registrant” refer to K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company; |
| ● | “PubCo Ordinary Shares” or “K Wave Ordinary Shares” refer to PubCo’s ordinary shares; |
| ● | “PubCo Rights” or “K Wave Rights” refer to PubCo’s rights which entitle the holder to receive 1/10 of one PubCo Ordinary Share upon the consummation of the Acquisition Merger; |
| ● | “PubCo Warrants” or “K Wave Warrants” refer to PubCo’s redeemable warrants which entitle the holder to purchase one PubCo Ordinary Share for $11.50; |
| ● | “PubCo Charter” or “K Wave Charter” refers to PubCo’s Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association, to be in effect upon the consummation of the Business Combination. |
| ● | “public shares” are to shares of Global Star Class A Common Stock sold as part of the units in the IPO (whether they are purchased in this offering or thereafter in the open market); |
| ● | “Reincorporation Merger” refer to the merger, described in the Merger Agreement, between Global Star and PubCo, whereby PubCo is the surviving corporation. |
| | ● | “Representative” refer to EF Hutton, division of Benchmark Investments LLC, the underwriter for the Global Star initial public offering, now known as D. Boral Capital LLC. |
| | | |
| | ● | “Second Amendment” refer to the Second Amendment to Merger Agreement, dated June 28, 2024, by an among Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub; |
| | | |
| | ● | “Series A Preferred Stock” refer to the shares of K Enter’s Series A Convertible Preferred Stock, $0.0001 par value per share. |
| | | |
| | ● | “Series A-1 Preferred Stock” refer to the shares of K Enter’s Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock, $0.0001 par value per share. |
| | | |
| | ● | “Sponsor” refer to Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC; |
| ● | “Seven Korean Entities” refers to (1) Play Company Co., Ltd., (2) Solaire Partners LLC, (3) Apeitda Co., Ltd., (4)The LAMP Co., Ltd., (5) Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd., (6) Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd. and (7) First Virtual Lab Inc., collectively; |
| ● | “Six Korean Entities” refers to (1) Play Company Co., Ltd., (2) Solaire Partners LLC, (3) Apeitda Co., Ltd., (4)The LAMP Co., Ltd., (5) Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd., and (6) Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd., collectively; |
| | ● | “Third Amendment” refer to the Third Amendment to Merger Agreement, dated July 25, 2024, by an among Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub; |
| ● | “US Dollars,” “$,” or “US$” refer to the legal currency of the United States; and |
| ● | “U.S. GAAP” refer to accounting principles generally accepted in the United States. |
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT THE BUSINESS COMBINATION AND THE SPECIAL MEETING
| Q: | What is the purpose of this document? |
| A: | Global Star is proposing to consummate the Business Combination. The Business Combination consists of the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger, each of which are described in this proxy statement/prospectus. In addition, the Merger Agreement is attached to this proxy statement/prospectus as Annex A, and is incorporated into this proxy statement/prospectus by reference. This proxy statement/prospectus contains important information about the Business Combination and the other matters to be acted upon at the Special Meeting. You are encouraged to carefully read this proxy statement/prospectus, including “Risk Factors” and all the annexes hereto. |
Approval of the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger will each require the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the issued and outstanding GLST Common Stock present and entitled to vote at the Special Meeting or any adjournment thereof.
| Q: | What is being voted on at the Special Meeting? |
| A: | Below are the Proposals that the Global Star’s stockholders are being asked to vote on: |
| ● | The Reincorporation Merger Proposal to approve the Reincorporation Merger; |
| ● | The Acquisition Merger Proposal to approve the Acquisition Merger; |
| ● | The Governance Proposal to approve, on a non-binding advisory basis, four separate governance proposals relating to material differences between Global Star’s current amended and restated certificate of incorporation and PubCo’s Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Incorporation; |
| | ● | The Director Proposal to elect the following persons: Pyeung Ho Choi, Young Jae Lee, Tan Chin Hwee, Ted Kim, Han Jae Kim, Hyung Seok Cho and Tae Woo Kim to serve on PubCo’s Board of Directors; |
| ● | The Incentive Plan Proposal to approve PubCo’s Incentive Plan; and |
| ● | The Adjournment Proposal to approve the adjournment of the Special Meeting in the event Global Star does not receive the requisite stockholder vote to approve the above Proposals. |
Approval of each of the Proposals requires the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the issued and outstanding GLST Common Stock present and entitled to vote at the Special Meeting or any adjournment thereof;.
| Q: | Will Global Star or K Enter be raising any financing in connection with the Business Combination? |
| A: | Global Star and K Enter intend to use their best efforts to raise $50 million in a PIPE financing transaction or pre-PIPE financing transaction (i.e., a capital raise by K Enter prior to the Business Combination) in connection with the closing of the Business Combination. The PIPE or pre-PIPE financing may take the form of equity financing or debt financing, including convertible debt. A PIPE or pre-PIPE financing is not a condition to the closing of the Business Combination. If successful in securing such a financing, the proceeds of the financing will be used by PubCo to fund its working capital for operations and to fund future acquisitions by PubCo. In the event Global Star is able to secure a PIPE or pre-PIPE financing, such financing will have a dilutive effect on the shareholders of PubCo. Currently, Global Star has not received any commitments for a PIPE financing and there can be no assurances that Global Star will be able to consummate a PIPE or pre-PIPE financing in connection with the Business Combination. If Global Star and K Enter are unable to raise a PIPE or pre-PIPE Financing prior to the closing of the Business Combination, PubCo will fund its working capital from cash flow from operations and PubCo plans to use its best efforts to complete a capital raise of $20 million to $50 million through a public or private equity offering or a debt offering following the closing of the Business Combination. However, there can be no assurances that PubCo will be able to raise additional capital through a public or private equity or debt offering following the closing of the Business Combination. K Enter will not require a capital raise to complete the acquisitions of the controlling interests of the Six Korean Entities because the only consideration to be tendered by K Enter to consummate the closing of the acquisitions of the controlling interests of the Six Korean Entities is shares of common stock of K Enter. Pursuant to the share purchase agreement between K Enter and the current owner of Play Company, PubCo is required to pay to the current owner of Play Company (i) a payment of 18.1 billion won (approximately $13.2 million within three months of the closing of the Business Combination, (ii) a payment of 9.05 billion won (approximately $6.57 million) by January 31, 2025 and (iii) a payment of 9.05 billion won (approximately $6.57 million) by January 31, 2026. Due to the fact that Global Star has approximately $13 million dollars in its trust account, absent a capital raise before or after the closing of the Business Combination, PubCo may not have sufficient funds to make the post-closing payments to the current owner of Play Company. If PubCo does not have the available cash to make the required payment to the current owner of Play Company, PubCo may negotiate with the current owner of Play Company to modify the post-closing payments or to extend the due dates for the post-closing payments. Global Star and K Enter believe that funds from the operations may not be sufficient to pay the second and third payments timely. Therefore, a capital raise post-completion of the Business Combination may become necessary. Also, the failure to raise adequate PIPE financing will delay PubCo’s ability to invest in new media content, which will adversely impact revenues and cash flow during 2024 and 2025. |
| Q: | Are any of the proposals conditioned on one another? |
| A: | Yes, the Reincorporation Merger Proposal and the Acquisition Merger Proposal are dependent upon each other. It is important for you to note that in the event that either of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal or the Acquisition Merger Proposal is not approved, Global Star will not consummate the Business Combination. If Global Star does not consummate the Business Combination and fails to complete an initial business combination by February 22, 2025 (unless Global Star elects to extend the time it has to complete the initial business combination to June 22, 2025), Global Star will be required to dissolve and liquidate. Adoption of the Adjournment Proposal is not conditioned upon the adoption of any of the other Proposals. |
| Q: | Do any of Global Star’s directors or officers have interests that may conflict with my interests with respect to the Business Combination? |
| A: | Global Star’s directors and officers may have interests in the Business Combination that are different from your interests as a stockholder. Global Star’s Sponsor and officers and directors purchased 2,300,000 shares of GLST Class B Common Stock, which we refer to herein as “Founder Shares,” for an aggregate purchase price of $25,000 and 498,225 Private Units for which they paid an aggregate purchase price of $4,982,250. Specifically: the Sponsor owns 2,798,225 shares of GLST Common Stock; Anthony Ang and Ted Kim beneficially own 1,640,000 shares of GLST Common Stock by virtue of serving as the managing members of the Sponsor, and Mr. Ang also owns 300,000 shares of GLST Common Stock directly; Nicholas Khoo owns 50,000 shares of GLST Common Stock; and Stephen Drew owns 20,000 shares of GLST Common Stock. In addition, on July 12, 2023, the Sponsor sold 160,000 Founder Shares to K Enter for $1,600,000. Thereafter, the Sponsor loaned the $1.6 million to Global Star in exchange for an unsecured, non-interest-bearing promissory note, $1.5 million of which will be converted into 150,000 Global Star Units in connection with the completion of the Business Combination. Stephen Drew, a director of Global Star served as a director of K Enter Holdings, Inc. from January 3, 2023 to April 25, 2023. Also, Ted Kim, the manager of the Sponsor and a co-founder and director of K Enter, owns 19,564 shares or 10.12% of the shares of common stock of K Enter based on the shares of K Enter to be issued and outstanding immediately prior to the closing of the Business Combination through his ownership and control of Global Fund LLC, which owns 12,000 shares, and Lodestar USA, Inc., which owns 7,564 shares. Further, Global Star officers and directors collectively own shares of common stock of K Enter representing approximately 8,537 shares or 4.3% of the outstanding shares of K Enter common stock based on the shares of K Enter to be issued and outstanding immediately prior to the closing of the Business Combination. Specifically, Stephen Drew owns 6,000 shares of K Enter common stock, Yang Kan Chong owns 1,337 shares of K Enter common stock, Jukka Rannila, beneficially through Assai OY, owns 600 shares of K Enter common stock. Nicholas Aaron Khoo, the Company’s Chief Operating Officer, owns 600 shares of K Enter common stock, prior to the closing of the Business Combination. All of such investments will expire worthless if a business combination is not consummated; on the other hand, if a business combination is consummated, such investments could earn a positive rate of return on their overall investment in the combined company, even if other holders of Global Star’s common stock experience a negative rate of return. |
In addition, if the Trust Account is liquidated, including in the event Global Star is unable to complete an initial business combination within the required time period, the Sponsor has agreed to indemnify Global Star to the extent any claims by a third party for services rendered or products sold to us, or any claims by a prospective target business with which Global Star has discussed entering into an acquisition agreement, reduce the amount of funds in the Trust Account to below the lesser of (i) $10.25 per public share and (ii) the actual amount per public share held in the Trust Account as of the date of the liquidation of the Trust Account, if less than $10.25 per public share is then held in the Trust Account due to reductions in the value of the trust assets, less taxes payable, (y) shall not apply to any claims by a third party or a target which executed a waiver of any and all rights to the monies held in the Trust Account (whether or not such waiver is enforceable) and (z) shall not apply to any claims under the Company’s indemnity of the underwriters of Global Star’s IPO against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), but only if such a third party or target business has not executed a waiver of any and all rights to seek access to the Trust Account.
Further, none of Global Star’s officers or directors has received any cash compensation for services rendered to the Company, and all of the current members of Global Star’s Board are expected to continue to serve as directors at least through the date of the special meeting to vote on a business combination and may even continue to serve following any business combination and receive compensation thereafter.
The exercise of Global Star’s directors’ and officers’ discretion in agreeing to changes or waivers in the terms of the Business Combination may result in a conflict of interest when determining whether such changes or waivers are appropriate and in Global Star stockholders’ best interests.
| Q: | When and where is the Special Meeting? |
| A: | The Special Meeting will take place on February 3, 2025, at 9:30 a.m., Eastern Time. Global Star will be holding its Special Meeting as a teleconference using the following dial-in information: |
| | 1 800-450-7155 | |
| | US Toll Free | |
| | | |
| | +1 857-999-9155 | |
| | International Toll | |
| | | |
| | 7921345# | |
| | Participant Passcode | |
| Q: | Who may vote at the Special Meeting? |
| A: | Only holders of record of GLST Class A Common Stock and GLST Class B Common Stock as of the close of business on December 13, 2024 (the record date) may vote at the Special Meeting. As of December 13, 2024, there were 994,100 shares of GLST Class A Common Stock and 2,300,000 shares of GLST Class B Common Stock outstanding and entitled to vote. Please see the section titled “The Special Meeting — Record Date; Who is Entitled to Vote” for further information. |
| Q: | What is the quorum requirement for the Special Meeting? |
| A: | Shareholders representing a majority of the shares of capital stock issued and outstanding as of the record date and entitled to vote at the Special Meeting must be present in person or represented by proxy in order to hold the Special Meeting and conduct business. This is called a quorum. GLST Common Stock will be counted for purposes of determining if there is a quorum if the stockholder (i) is present and entitled to vote at the meeting, or (ii) has properly submitted a proxy card or voting instructions through a broker, bank or custodian. In the absence of a quorum, the Special Meeting will be adjourned to the next business day at the same time and place or to such other time and place as the directors may determine. |
| Q: | What vote is required to approve the Proposals? |
| A: | Approval of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal and the Acquisition Merger Proposal will require the affirmative vote of the holders of sixty-five percent (65%) of the issued and outstanding GLST Common Stock. Approval of the Governance Proposal, the Incentive Plan Proposal and the Adjournment Proposal will require the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the issued and outstanding GLST Common Stock present and entitled to vote at the Special Meeting or any adjournment thereof. Under the Director Proposal, directors are elected by a plurality of the votes cast. Since the Reincorporation Merger Proposal and the Acquisition Merger Proposal require the affirmative vote of a majority sixty-five percent (65%) of the issued and outstanding GLST Common Stock, abstaining from voting or failing to instruct your bank, brokerage firm or nominee to attend and vote your shares will have the same effect as voting “AGAINST” these Proposals; however, abstaining from voting or failing to instruct your bank, brokerage firm or nominee to attend and vote your shares will have no effect on any of the Director Election Proposal, the Incentive Plan Proposal or the Adjournment Proposal. |
| Q: | How will the Initial Stockholders and the Sponsor vote? |
| A: | Global Star’s Initial Stockholders and the Sponsor, who as of the record date, owned 2,798,225 shares of GLST Common Stock, or approximately 69.1% of the issued and outstanding GLST Common Stock, have agreed to vote their respective shares in favor of each of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal and the Acquisition Merger Proposal and are expected to vote in favor of the Incentive Plan Proposal, the Adjournment Proposal and the Director Proposal. As a result, the affirmative vote of the shares of GLST Common Stock held by the Initial Stockholders and the Sponsor is sufficient to approve each of the Proposals. |
| Q: | What do I need to do now? |
| A: | Global Star urges you to read carefully and consider the information contained in this proxy statement/prospectus, including the annexes, and consider how the Business Combination will affect you as a Global Star stockholder. You should vote as soon as possible in accordance with the instructions provided in this proxy statement/prospectus and on the enclosed proxy card. |
| Q: | Do I need to attend the Special Meeting to vote my shares? |
| A: | No. You are invited to attend the Special Meeting to vote on the Proposals described in this proxy statement/prospectus. However, you do not need to attend the Special Meeting to vote your GLST Common Stock. Instead, you may submit your proxy by signing, dating and returning the applicable enclosed proxy card in the pre-addressed postage paid envelope. Your vote is important. Global Star encourages you to vote as soon as possible after carefully reading this proxy statement/prospectus. |
| Q: | Am I required to vote against the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger Proposal in order to have my GLST Common Stock redeemed? |
| A: | No. You are not required to vote against the Reincorporation Merger Proposal and the Acquisition Merger Proposal in order to have the right to demand that Global Star redeem your GLST Common Stock for cash equal to your pro rata share of the aggregate amount then on deposit in the trust account (including interest earned on your pro rata portion of the trust account, net of taxes payable) before payment of deferred underwriting commissions. These redemption rights in respect of the GLST Common Stock are sometimes referred to herein as “redemption rights.” If the Business Combination is not completed, holders of GLST Common Stock electing to exercise their redemption rights will not be entitled to receive such payments and their GLST Common Stock will be returned to them. |
| Q: | How do I exercise my redemption rights? |
| A: | If you are a public stockholder and you seek to have your shares redeemed, you must (i) demand, no later than 5:00 p.m., Eastern time on January 30, 2025 (two business days before the Special Meeting), that Global Star redeem your shares for cash, and (ii) submit your request in writing to Global Star’s transfer agent, at the address listed at the end of this section and deliver your shares to Global Star’s transfer agent (physically, or electronically using the DWAC (Deposit/Withdrawal At Custodian) system) at least two business days prior to the vote at the Special Meeting. |
Any corrected or changed written demand of redemption rights must be received by Global Star’s transfer agent two business days prior to the Special Meeting. No demand for redemption will be honored unless the holder’s shares have been delivered (either physically or electronically) to the transfer agent at least two business days prior to the vote at the Special Meeting.
Public stockholders may seek to have their shares redeemed regardless of whether they vote for or against the Business Combination and whether or not they are holders of GLST Common Stock as of the record date. Any public stockholder who holds GLST Common Stock on or before January 30, 2025 (two (2) business days before the Special Meeting) will have the right to demand that his, her or its shares be redeemed for a pro rata share of the aggregate amount then on deposit in the trust account, less any taxes then due but not yet paid, at the consummation of the Business Combination. If you have questions regarding the certification of your position or delivery of your shares, please contact:
Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company
1 State Street, 30th Floor
New York, NY 10004
Attn. Mark Zimkind
E-mail: spacredemptions@continentalstock.com
| A: | If you were a holder of record of GLST Common Stock on December 13, 2024, the record date for the Special Meeting, you may vote with respect to the Proposals in person at the Special Meeting, or by submitting a proxy by mail so that it is received prior to 9:30 a.m. Eastern Time on February 3, 2025, in accordance with the instructions provided to you under the section titled “The Special Meeting.” If you hold your shares in “street name,” which means your shares are held of record by a broker, bank or other nominee, your broker or bank or other nominee may provide voting instructions (including any telephone or Internet voting instructions). You should contact your broker, bank or nominee in advance to ensure that votes related to the shares you beneficially own will be properly counted. In this regard, you must provide the record holder of your shares with instructions on how to vote your shares or, if you wish to attend the Special Meeting and vote in person, obtain a proxy from your broker, bank or nominee. |
| Q: | If my shares are held in “street name” by my bank, brokerage firm or nominee, will they automatically vote my shares for me? |
| A: | No. Under Nasdaq rules, your broker, bank or nominee cannot vote your GLST Common Stock with respect to non-discretionary matters unless you provide instructions on how to vote in accordance with the information and procedures provided to you by your broker, bank or nominee. Global Star believes the Proposals are non-discretionary and, therefore, your broker, bank or nominee cannot vote your GLST Common Stock without your instruction. Broker non-votes will not be considered present for the purposes of establishing a quorum and will have no effect on the Proposals. If you do not provide instructions with your proxy, your bank, broker or other nominee may submit a proxy card expressly indicating that it is NOT voting your GLST Common Stock; this indication that a bank, broker or nominee is not voting your GLST Common Stock is referred to as a “broker non-vote.” Your bank, broker or other nominee can vote your GLST Common Stock only if you provide instructions on how to vote. You should instruct your broker to vote your GLST Common Stock in accordance with directions you provide. |
| Q: | What if I abstain from voting or fail to instruct my bank, brokerage firm or nominee? |
| A: | Global Star will count a properly executed proxy marked “ABSTAIN” with respect to a particular Proposal as present for the purposes of determining whether a quorum is present at the Special Meeting of Global Star stockholders. For purposes of approval, an abstention on any Proposals will have the same effect as a vote “AGAINST” such Proposal. |
| Q: | What happens if I sell my GLST Common Stock before the Special Meeting? |
| A: | The record date for the Special Meeting is earlier than the date that the Business Combination is expected to be consummated. If you transfer your GLST Common Stock after the record date, but before the Special Meeting, unless the transferee obtains from you a proxy to vote those shares, you would retain your right to vote at the Special Meeting. However, you would not be entitled to receive any PubCo Ordinary Shares following the consummation of the Business Combination because only Global Star’s stockholders at the time of the consummation of the Business Combination will be entitled to receive PubCo Ordinary Shares in connection with the Business Combination. |
| Q: | Will I experience dilution as a result of the Business Combination? |
| A: | Prior to the Business Combination, Global Star’s public stockholders who hold shares issued in the IPO own approximately 28.1% of Global Star’s issued and outstanding shares of common stock. After giving effect to the Business Combination and to (i) the issuance of the 59,000,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares in the Acquisition Merger and excluding the 5,900,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares reserved and authorized for issuance under the Incentive Plan upon closing; (ii) the issuance of up to 1,137,006 PubCo Ordinary Shares to the Global Star stockholders in connection with the Reincorporation Merger (assuming there are no Global Star stockholders who exercise their redemption rights); (iii) issuance of up to 920,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares are issued upon conversion of the PubCo Rights); (iv) assuming no exercise of the PubCo Warrants, Global Star’s current public stockholders will own approximately 3.3% of the issued share capital of PubCo. |
Stockholders exercising their redemption rights will retain their Global Star warrants, which will automatically convert into PubCo Warrants. As of the record date for the Special Meeting, there are 9,200,000 Global Star warrants outstanding with an aggregate market value of $276,000 based on the closing price as of January 3, 2025. The future exercise of these warrants will result in dilution to Public Stockholders. Stockholders exercising their redemption rights also will retain their public rights, each of which will automatically convert into one-tenth of a share of PubCo common stock upon the closing of the Business Combination.
Each Global Star Right will automatically convert into one PubCo Right in connection with the Reincorporation Merger. Each 10 PubCo Rights will convert into one PubCo Ordinary Share in connection with the Acquisition Merger. In order to receive a single PubCo Ordinary Share, a rights holder must hold 10 PubCo Rights. There will be no issuance of fractional PubCo Ordinary Shares and those holding fewer than 10 PubCo Rights will not be entitled to receive any PubCo Ordinary Shares.
The following summarizes the pro forma shares of K Wave ordinary shares issued and outstanding immediately after the Business Combination, presented under the five scenarios listed below:
| | | No Additional Redemptions | | | 25% Redemptions | | | 50% Redemptions | | | 75% Redemptions | | | Maximum Redemptions | |
| | | Shares | | | % | | | Shares | | | % | | | Shares | | | % | | | Shares | | | % | | | Shares | | | % | |
| K Enter stockholders(1) | | | 59,160,000 | | | | 93.1 | % | | | 59,160,000 | | | | 93.3 | % | | | 59,160,000 | | | | 93.4 | % | | | 59,160,000 | | | | 93.5 | % | | | 59,160,000 | | | | 93.7 | % |
| Global Star public stockholders(2) | | | 1,300,875 | | | | 2.1 | % | | | 1,205,656 | | | | 2.0 | % | | | 1,110,438 | | | | 1.8 | % | | | 1,015,219 | | | | 1.7 | % | | | 920,000 | | | | 1.4 | % |
| Sponsor and Insider Stockholders(3)(5) | | | 2,943,747 | | | | 4.6 | % | | | 2,943,747 | | | | 4.6 | % | | | 2,943,747 | | | | 4.6 | % | | | 2,943,747 | | | | 4.6 | % | | | 2,943,747 | | | | 4.7 | % |
| Representative Shares | | | 115,000 | | | | 0.2 | % | | | 115,000 | | | | 0.2 | % | | | 115,000 | | | | 0.2 | % | | | 115,000 | | | | 0.2 | % | | | 115,000 | | | | 0.2 | % |
| Total Shares outstanding at Closing, not reflecting potential sources of dilution(5) | | | 63,519,622 | | | | 100 | % | | | 63,424,403 | | | | 100 | % | | | 63,329,185 | | | | 100 | % | | | 63,233,966 | | | | 100 | % | | | 63,138,747 | | | | 100 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Shares outstanding at Closing, not reflecting potential sources of dilution(5) | | | 63,519,622 | | | | 86.0 | % | | | 63,424,403 | | | | 86.0 | % | | | 63,329,185 | | | | 86.0 | % | | | 63,233,966 | | | | 85.9 | % | | | 63,138,747 | | | | 86.0 | % |
| Total Pro Forma Equity at Closing | | $ | 168,680,177 | | | | | | | $ | 167,607,875 | | | | | | | $ | 166,535,573 | | | | | | | $ | 165,463,271 | | | | | | | $ | 164,390,969 | | | | | |
| Per Share Pro Forma Book Value of Shares outstanding at Closing(4) | | $ | 2.66 | | | | | | | $ | 2.64 | | | | | | | $ | 2.63 | | | | | | | $ | 2.62 | | | | | | | $ | 2.60 | | | | | |
| (1) | Includes 59,000,000 K Wave Ordinary Shares to be issued upon consummation of the Business Combination as follows: (i) 30,878,682 K Wave Ordinary shares issued in exchange for 101,202 shares of K Enter common stock owned by the currently existing stockholders of K Enter, including, the 4,997 shares of K Enter common stock owned by GF Korea and the 1,202 shares of K Enter common stock owned by Lodestar USA; (ii) 12,448,256 K Wave Ordinary shares issued in exchange for 40,798 shares of K Enter common stock owned by the Preferred Stock owners after the conversion of the 40,798 shares of Preferred Stock into shares of K Enter common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination and (iii) 15,673,062 K Wave Ordinary shares to be issued in exchange for 51,367 shares of K Enter common stock that will be owned by the owners of Six Korean Entities following K Enter acquisition of the controlling equity interests in the Six Korean Entities and 160,000 K Wave Ordinary shares to be issued in exchange 160,000 shares of Global Star Founder Shares currently owned by K Enter. |
| (2) | Includes 9,200,000 public shares at June 30, 2024 less 4,052,066 shares redeemed in September 2023, 4,010,928 shares redeemed in June 2024 and 756,131 shares redeemed in November 2024 plus 9,200,000 Public Rights automatically converted into 920,000 shares of Global Star common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination. |
| (3) | Includes (a) 1,640,000 Founder Shares owned by the Sponsor, (b) 498,225 shares underlying the Private Units plus 498,225 Private Rights automatically converted into 49,822 shares of common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination owned by the Sponsor, (c) 150,000 shares of common stock underlying the Convertible Note plus 150,000 Convertible Note Rights automatically converted into 15,000 shares of common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination owned by the Sponsor, (d) 90,700 shares of common stock from loans converted to shares, and (e) 500,000 Founder Shares owned by the Initial Stockholders. |
| (4) | The per share pro forma book value of the shares is calculated as Pro forma equity / pro forma shares. Global Star and K Enter intend to use their best efforts to raise $50 million in a PIPE Financing in connection with the closing of the Business Combination, but the PIPE Financing is not a condition to the closing of the Business Combination. If successful in securing a PIPE financing, the proceeds of the PIPE financing will be used by PubCo to fund its working capital for operations and to fund future acquisitions by PubCo. In the event Global Star is able to secure a PIPE financing, such financing will have a dilutive effect on the shareholders of PubCo. Currently, Global Star has not received any commitments for a PIPE financing and there can be no assurances that Global Star will be able to consummate a PIPE financing in connection with the Business Combination. |
| (5) | Excludes 19,300 shares potentially to be issued to the Sponsor if an additional $193,000 were to be drawn on the Global Star loan and converted into Global Star Class B common stock. Accordingly, K Wave is registering up to an aggregate amount of 64,295,053 Ordinary Shares to be issued in connection with Business Combination on this proxy statement/prospectus. |
| | | No Additional Redemptions | | | 25% Redemptions | | | 50% Redemptions | | | 75% Redemptions | | | Maximum Redemptions | |
| | | Shares | | | % | | | Shares | | | % | | | Shares | | | % | | | Shares | | | % | | | Shares | | | % | |
| K Enter stockholders(1) | | | 59,160,000 | | | | 93.1 | % | | | 59,160,000 | | | | 93.3 | % | | | 59,160,000 | | | | 93.4 | % | | | 59,160,000 | | | | 93.5 | % | | | 59,160,000 | | | | 93.7 | % |
| Global Star public stockholders(2) | | | 1,300,875 | | | | 2.1 | % | | | 1,205,656 | | | | 2.0 | % | | | 1,110,438 | | | | 1.8 | % | | | 1,015,219 | | | | 1.7 | % | | | 920,000 | | | | 1.4 | % |
| Sponsor and Insider Stockholders(3)(5) | | | 2,943,747 | | | | 4.6 | % | | | 2,943,747 | | | | 4.6 | % | | | 2,943,747 | | | | 4.6 | % | | | 2,943,747 | | | | 4.6 | % | | | 2,943,747 | | | | 4.7 | % |
| Representative Shares | | | 115,000 | | | | 0.2 | % | | | 115,000 | | | | 0.2 | % | | | 115,000 | | | | 0.2 | % | | | 115,000 | | | | 0.2 | % | | | 115,000 | | | | 0.2 | % |
| Total Shares outstanding at Closing, not reflecting potential sources of dilution(6) | | | 63,519,622 | | | | 100 | % | | | 63,424,403 | | | | 100 | % | | | 63,329,185 | | | | 100 | % | | | 63,233,966 | | | | 100 | % | | | 63,138,747 | | | | 100 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Shares outstanding at Closing, not reflecting potential sources of dilution(6) | | | 63,519,622 | | | | 86.0 | % | | | 63,424,403 | | | | 86.0 | % | | | 63,329,185 | | | | 86.0 | % | | | 63,233,966 | | | | 85.9 | % | | | 63,138,747 | | | | 86.0 | % |
| Potential sources of dilution: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Shares underlying Global Star Public Warrants | | | 9,200,000 | | | | 12.5 | % | | | 9,200,000 | | | | 12.5 | % | | | 9,200,000 | | | | 12.5 | % | | | 9,200,000 | | | | 12.5 | % | | | 9,200,000 | | | | 12.4 | % |
| Shares underlying Global Star Placement Warrants | | | 498,225 | | | | 0.7 | % | | | 498,225 | | | | 0.7 | % | | | 498,225 | | | | 0.7 | % | | | 498,225 | | | | 0.7 | % | | | 498,225 | | | | 0.7 | % |
| Shares underlying K Enter convertible senior unsecured notes(5) | | | 450,000 | | | | 0.6 | % | | | 450,000 | | | | 0.6 | % | | | 450,000 | | | | 0.6 | % | | | 450,000 | | | | 0.6 | % | | | 450,000 | | | | 0.6 | % |
| Shares underlying Global Star convertible note warrants | | | 150,000 | | | | 0.2 | % | | | 150,000 | | | | 0.2 | % | | | 150,000 | | | | 0.2 | % | | | 150,000 | | | | 0.3 | % | | | 150,000 | | | | 0.3 | % |
| Total Shares outstanding at Closing | | | 73,817,847 | | | | 100 | % | | | 73,722,628 | | | | 100 | % | | | 73,627,410 | | | | 100 | % | | | 73,532,191 | | | | 100 | % | | | 73,436,972 | | | | 100 | % |
| Total Pro Forma Equity at Closing | | $ | 168,680,177 | | | | | | | $ | 167,607,875 | | | | | | | $ | 166,535,573 | | | | | | | $ | 165,463,271 | | | | | | | $ | 164,390,969 | | | | | |
| Per Share Pro Forma Book Value of Shares outstanding at Closing(4) | | $ | 2.29 | | | | | | | $ | 2.27 | | | | | | | $ | 2.26 | | | | | | | $ | 2.25 | | | | | | | $ | 2.24 | | | | | |
| (1) | Includes 59,000,000 K Wave Ordinary Shares to be issued upon consummation of the Business Combination as follows: (i) 30,878,682 K Wave Ordinary shares issued in exchange for 101,202 shares of K Enter common stock owned by the currently existing stockholders of K Enter, including, the 4,997 shares of K Enter common stock owned by GF Korea and the 1,202 shares of K Enter common stock owned by Lodestar USA; (ii) 12,448,256 K Wave Ordinary shares issued in exchange for 40,798 shares of K Enter common stock owned by the Preferred Stock owners after the conversion of the 40,798 shares of Preferred Stock into shares of K Enter common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination and (iii) 15,673,062 K Wave Ordinary shares to be issued in exchange for 51,367 shares of K Enter common stock that will be owned by the owners of Six Korean Entities following K Enter acquisition of the controlling equity interests in the Six Korean Entities and 160,000 K Wave Ordinary shares to be issued in exchange 160,000 shares of Global Star Founder Shares currently owned by K Enter. |
| (2) | Includes 9,200,000 public shares at June 30, 2024 less 4,052,066 shares redeemed in September 2023, 4,010,928 shares redeemed in June 2024 and 756,131 shares redeemed in November 2024 plus 9,200,000 Public Rights automatically converted into 920,000 shares of Global Star common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination. |
| (3) | Includes (a) 1,640,000 Founder Shares owned by the Sponsor, (b) 498,225 shares underlying the Private Units plus 498,225 Private Rights automatically converted into 49,822 shares of common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination owned by the Sponsor, (c) 150,000 shares of common stock underlying the Convertible Note plus 150,000 Convertible Note Rights automatically converted into 15,000 shares of common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination owned by the Sponsor, (d) 90,700 shares of common stock from loans converted to shares and (e) 500,000 Founder Shares owned by the Initial Stockholders. |
| (4) | The per share pro forma book value of the shares is calculated as Pro forma equity / total pro forma shares. Global Star and K Enter intend to use their best efforts to raise $50 million in a PIPE Financing in connection with the closing of the Business Combination, but the PIPE Financing is not a condition to the closing of the Business Combination. If successful in securing a PIPE financing, the proceeds of the PIPE financing will be used by PubCo to fund its working capital for operations and to fund future acquisitions by PubCo. In the event Global Star is able to secure a PIPE financing, such financing will have a dilutive effect on the shareholders of PubCo. Currently, Global Star has not received any commitments for a PIPE financing and there can be no assurances that Global Star will be able to consummate a PIPE financing in connection with the Business Combination. |
| (5) | In this table we have assumed a $10 per share conversion price, however we note the conversion price in the convertible senior unsecured notes are subject to downward adjustment to a floor price of $4 per share. In the event the conversion price is adjusted downward from $10 per share to the floor price of $4 per share, the number of shares underlying the K Enter convertible senior unsecured notes would be 1,125,000 shares. |
| (6) | Excludes 19,300 shares potentially to be issued to the Sponsor if an additional $193,000 were to be drawn on the Global Star loan and converted into Global Star Class B common stock. Accordingly, K Wave is registering up to an aggregate amount of 64,295,053 Ordinary Shares to be issued in connection with Business Combination on this proxy statement/prospectus. |
| Q: | Are K Enter’s shareholders required to approve the Acquisition Merger? |
| A: | Yes. K Enter’s shareholders’ approval of the Acquisition Merger and the Merger Agreement is required to consummate the Business Combination. |
| Q: | Is the consummation of the Business Combination subject to any conditions? |
| A: | Yes. The obligations of each of Global Star, K Enter, Merger Sub and PubCo to consummate the Business Combination are subject to conditions, as more fully described in the section titled “Summary of the Proxy Statement/Prospectus — The Business Combination and the Merger Agreement” in this proxy statement/prospectus. |
| Q: | Do I have appraisal rights or dissenters’ rights if I object to the proposed Business Combination?1 |
| A: | No appraisal or dissenters’ rights are available to holders of Global Star shares or units in connection with the Business Combination Proposal; however, public shareholders can exercise their redemption rights as described herein. The Global Star board of directors has determined that the redemption proceeds payable to public shareholders who exercise their redemption rights represent the fair value of the public shares. Please see the section titled “The Special Meeting — Redemption Rights” for the procedures to be followed if you wish to redeem your ordinary shares for cash. |
| Q: | Can I change my vote after I have mailed my proxy card? |
| A: | Yes. You may change your vote at any time before your proxy is voted at the Special Meeting. You may revoke your proxy by executing and returning a proxy card dated later than the previous one, or by attending the Special Meeting in person and casting your vote by hand or by ballot (as applicable) or by submitting a written revocation stating that you would like to revoke your proxy that Global Star’s proxy solicitor receives prior to the Special Meeting. If you hold your GLST Common Stock through a bank, brokerage firm or nominee, you should follow the instructions of your bank, brokerage firm or nominee regarding the revocation of proxies. If you are a record holder, you should send any notice of revocation or your completed new proxy card, as the case may be, to: |
Laurel Hill Advisory Group, LLC
2 Robbins Lane, Suite 201
Jericho, NY 11753
(855)-414-2266
Email: GLST@laurelhill.com
| Q: | Should I send in my stock certificates now? |
| A: | Yes. Global Star’s stockholders who intend to have their shares redeemed should send their certificates or tender their shares electronically no later than two business days before the Special Meeting. Please see the section titled “The Special Meeting — Redemption Rights” for the procedures to be followed if you wish to redeem your ordinary shares for cash. |
| Q: | When is the Business Combination expected to occur? |
| A: | Assuming the requisite stockholder approvals are received, Global Star expects that the Business Combination will occur as soon as practicable following the Special Meeting, but only after the registration of the plans of merger by the Registrar of Companies of the Cayman Islands with respect to the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger. |
| Q: | When is the acquisition by K Enter of the Six Korean Entities expected to occur? |
| A: | Subject to satisfaction of the applicable conditions precedent in the equity purchase agreements, Global Star expects that K Enter’s acquisition of the Six Korean Entities will close shortly after the proxy statement/prospectus is declared effective and prior to Global Star’s mailing of the proxy statement to its stockholders in connection with the Special Meeting. K Enter will close the share purchase agreement with Play Company first and thereafter, K Enter will close the share purchase agreements with the remaining five of the Six Korean Entities. K Enter’s acquisition of the Six Korean Entities is a closing condition to the Business Combination, and Global Star does not currently intend to waive this condition. |
| Q: | What if there are material developments or changes relating to the acquisition by K Enter of the Six Korean Entities prior to the Special Meeting? |
| A: | Global Star will advise its stockholders of the closing of the acquisition of the Six Korean Entities by filing a Current Report on Form 8-K. Global Star will circulate updated or supplemental proxy materials to its stockholders if any material changes to K Enter’s planned acquisition of the Six Korean Entities occur prior to the Special Meeting including if there is any adjustment to the Merger Consideration or if anything other than the successful acquisition by K Enter of the Six Korean Entities occurs. The updated or supplemental proxy materials shall describe such material changes or developments and, as appropriate, provide additional disclosure regarding these developments in describing the background of the Business Combination, any changes to the Merger Consideration, any changes to the Second Fairness Opinion or the applicability thereof, or updated pro forma financial information and such other information as may be appropriate. |
| Q: | What if K Enter’s acquisition of the Six Korean Entities does not occur prior to the Special Meeting? |
| A: | K Enter’s acquisition of the Six Korean Entities is a closing condition to the Business Combination, and while this condition can be waived, however Global Star does not currently intend to waive this condition. K Enter expects to close the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of the Six Korean Entities within 24 to 72 hours after this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 is declared effective by the SEC. In addition, Global Star will not mail proxy materials to its shareholders for the Special Meeting until after K Enter closes the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities. PubCo shall include the date that K Enter completes the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all Six Korean Entities in its Form 424B3 Prospectus to be filed with the SEC after this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 is declared effective by the SEC. In the event that K Enter does not complete the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities, PubCo will file a post-effective amendment to its Registration Statement on Form F-4 (the “Post-Effective Amendment”) disclosing that K Enter did not complete its contemplated acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities (and the material information concerning such event) and Global Star will not mail proxy materials to its shareholders for the Special Meeting (or hold its Special Meeting) until after the Post-Effective Amendment is declared effective by the SEC. Global Star’s shareholders will not be able to vote for or against the Business Combination until after they receive a definitive proxy statement, which will only be mailed after the later of (i) the successful consummation of the acquisition of the controlling interests of all of the Six Korean Entities or (ii) the declaration of effectiveness by the SEC of the Post-Effective Amendment. |
| | As of January 3, 2025, K Enter completed the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of each of the Six Korean Entities. |
| A: | PubCo will be managed by its Board of Directors. Messrs. Pyeung Ho Choi, Young Jae Lee, Tan Chin Hwee, Ted Kim, Han Jae Kim, Hyung Seok Cho and Tae Woo Kim shall be the members of the Board of Directors of PubCo. For more information on PubCo’s current and anticipated management, see the section titled “PubCo’s Directors and Executive Officers after the Business Combination” in this proxy statement/prospectus. |
| Q: | Is there a deadline for the Business Combination to occur? What happens if the Business Combination is not consummated? |
| A: | At a Special Meeting of Stockholders held on November 27, 2024, the stockholders of Global Star approved amendments to Global Star’s Current Charter and the Trust Agreement to extend the deadline for completing a business combination from December 22, 2024 (the “Prior Termination Date”) to up to June 22, 2025 via six one-month extensions provided the Sponsor deposits into the Trust Account extension payments equal to the lesser of $60,000 or $0.02 per outstanding share of common stock sold in the IPO as of the applicable deadline date for each one-month extension. In order to fund these extension payments and interim working capital needs, the Sponsor made a $1.6 million loan to Global Star in exchange for an unsecured, non-interest-bearing promissory note (the “Convertible Note”) in the amount of $1.6 million. The Convertible Note is payable in full upon completion of the Business Combination, and up to $1,500,000 due under the Convertible Note may be converted into Global Star Units, each consisting of one share of GLST Class A Common Stock, one GLST Warrant and one GLST Right, at the conversion rate of $10.00 per unit. On December 4, 2024, Global Star deposited $7,617.50 into the Trust and on December 12, 2024, Global Star deposited $7,617.50 into the Trust, to extend the date by which Global Star must complete a business combination to February 22, 2025 (the “Extended Date”). Global Star can extend the Extended Date to June 22, 2025, by depositing the sum of $7,617.50 into the Trust Account for each such one-month extension (the “New Termination Date”). |
| | If Global Star fails to consummate a business combination prior to the earlier of the Extended Date or the New Termination Date (as it may be extended as described above), Global Star will (i) cease all operations except for the purpose of winding up, (ii) as promptly as reasonably possible but not more than ten business days thereafter, redeem the public shares, at a per-share price, payable in cash, equal to the aggregate amount then on deposit in the Trust Account, including interest earned on the funds held in the Trust Account and not previously released to pay taxes (less up to $100,000 of interest to pay dissolution expenses), divided by the number of then outstanding public shares, which redemption will completely extinguish the rights of the holders of public shares as shareholders (including the right to receive further liquidating distributions, if any), and (iii) as promptly as reasonably possible following such redemption, subject to the approval of Global Star’s remaining shareholders and the board of directors, dissolve and liquidate, subject in each case to Global Star’s obligations under Delaware law to provide for claims of creditors and the requirements of other applicable law. In that event, there will be no distribution from the Trust Account with respect to rights, which will expire worthless in the event of Global Star’s winding up. In the event of a liquidation, Sponsor and directors and officers will not receive any monies held in the Trust Account as a result of their ownership of the Founder Shares and Private Placement Units. |
| Q: | What happens to the funds deposited in the trust account following the Business Combination? |
| A: | Following the closing of the Business Combination, holders of GLST Common Stock exercising redemption rights will receive their per share redemption price out of the funds in the trust account. The balance of the funds will be released to PubCo and utilized to fund working capital needs of PubCo. As of December 13, 2024, there was approximately $4,364,690 in Global Star’s trust account. Global Star estimates that approximately $11.45 per outstanding share issued in Global Star’s IPO, subject to reduction for the payment of taxes, will be paid to the public investors exercising their redemption rights, subject to reduction for the payment of taxes. Any funds remaining in the trust account after such uses will be used for future working capital and other corporate purposes of the combined entity. |
| Q: | What are the U.S. federal income tax consequences of exercising my redemption rights? |
| A: | In the event that a U.S. Holder elects to redeem its GLST Common Stock for cash, the treatment of the transaction for U.S. federal income tax purposes will depend on whether the redemption qualifies as sale or exchange of the GLST Common Stock under Section 302 of the Internal Revenue Code (the “Code”) or is treated as a distribution under Section 301 of the Code. If the redemption qualifies as a sale or exchange of the GLST Common Stock, the U.S. Holder will be treated as recognizing capital gain or loss equal to the difference between the amount realized on the redemption and such U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in the GLST Common Stock surrendered in such redemption transaction. Any such capital gain or loss generally will be long-term capital gain or loss if the U.S. Holder’s holding period for the GLST Common Stock redeemed exceeds one year. Long-term capital gains recognized by non-corporate U.S. Holders will be eligible to be taxed at reduced rates. The deductibility of capital losses is subject to limitations. |
Further, because the Reincorporation Merger will occur immediately prior to the redemption of GLST Common Stock, U.S. Holders exercising redemption rights will be subject to the potential tax consequences of the Reincorporation Merger. All U.S. Holders considering exercising redemption rights with respect to their GLST Common Stock are urged to consult with their tax advisors with respect to the potential tax consequences to them of the Reincorporation Merger and exercise of redemption rights.
See the section titled “Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences — Certain U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of Exercising Redemption Rights.”
| Q: | Will holders of GLST Common Stock, GLST Rights or GLST Warrants be subject to U.S. federal income tax on the PubCo Ordinary Shares or PubCo Warrants received in the Business Combination? |
| A: | Subject to the limitations and qualifications described in “Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Business Combination,” the Reincorporation Merger will qualify as a “reorganization” within the meaning of Section 368 of the Code, and, as a result, a U.S. Holder (as defined below) should not recognize gain or loss on the exchange of GLST Common Stock, GLST Rights, or GLST Warrants for PubCo Ordinary Shares or PubCo Warrants, as applicable, pursuant to the Reincorporation Merger. The discussion in “Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Business Combination” reflects the opinion of Nelson Mullins as to the material U.S. federal income tax consequences of the Business Combination to U.S. Holders of GLST Common Stock, GLST Rights, or GLST Warrants, subject to the limitations, exceptions, beliefs, assumptions, and qualifications described therein and otherwise herein (including uncertainty as to whether the Business Combination will be taxable for such U.S. Holders). |
If the Reincorporation Merger does not qualify as a reorganization, then a U.S. Holder that exchanges its GLST Common Stock, GLST Rights, or GLST Warrants for the consideration under the Business Combination will recognize gain or loss equal to the difference between (i) the fair market value of the PubCo Ordinary Shares and PubCo Warrants received and (ii) the U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in the GLST Common Stock, GLST Rights, and GLST Warrants exchanged.
Further, because the Reincorporation Merger will occur immediately prior to the redemption of GLST Common Stock, U.S. Holders exercising redemption rights will be subject to the potential tax consequences of the Reincorporation Merger. All U.S. Holders considering exercising redemption rights with respect to their GLST Common Stock are urged to consult with their tax advisors with respect to the potential tax consequences to them of the Reincorporation Merger and exercise of redemption rights.
For a more detailed discussion of certain U.S. federal income tax consequences of the Reincorporation Merger and the Business Combination, see the section titled “Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Business Combination” in this proxy statement/prospectus. Holders should consult their own tax advisors to determine the tax consequences to them (including the application and effect of any state, local or other income and other tax laws) of the Business Combination.
| Q: | Who can help answer my questions? |
| A: | If you have questions about the Proposals or if you need additional copies of this proxy statement/prospectus or the enclosed proxy card you should contact Global Star’s proxy solicitor at: |
Laurel Hill Advisory Group, LLC
2 Robbins Lane, Suite 201
Jericho, NY 11753
(855)-414-2266
Email: GLST@laurelhill.com
You may also obtain additional information about Global Star from documents filed with the SEC by following the instructions in the section titled “Where You Can Find More Information.”
DELIVERY OF DOCUMENTS TO GLOBAL STAR’S STOCKHOLDERS
Pursuant to the rules of the SEC, Global Star and vendors that it employs to deliver communications to its stockholders are permitted to deliver to two or more stockholders sharing the same address a single copy of this proxy statement/prospectus, unless Global Star has received contrary instructions from one or more of such stockholders. Upon written or oral request, Global Star will deliver a separate copy of this proxy statement/prospectus to any stockholder at a shared address to which a single copy of this proxy statement/prospectus was delivered and who wishes to receive separate copies in the future. Stockholders receiving multiple copies of the proxy statement may likewise request that Global Star deliver single copies of this proxy statement/prospectus in the future. Stockholders may notify Global Star of their requests by contacting Global Star’s proxy solicitor as follows:
Laurel Hill Advisory Group, LLC
2 Robbins Lane, Suite 201
Jericho, NY 11753
(855)-414-2266
Email: GLST@laurelhill.com
SUMMARY OF THE PROXY STATEMENT/PROSPECTUS
This summary highlights selected information from this proxy statement/prospectus but may not contain all of the information that may be important to you. Accordingly, Global Star encourages you to read carefully this entire proxy statement/prospectus, including the Merger Agreement attached as Annex A, the PubCo’s Memorandum and Articles of Association attached as Annex B, the Incentive Plan attached as Annex C and, the Escrow Agreement attached as Annex D. Please read these documents carefully as they are the legal documents that govern the Business Combination and your rights in the Business Combination.
Unless otherwise specified, all share calculations assume no exercise of the redemption rights by Global Star’s stockholders.
The Parties to the Business Combination
Global Star Acquisition Inc.
Formation. Global Star is a blank check company incorporated on July 24, 2019, as a Delaware corporation whose business purpose is to effect a merger, capital stock exchange, asset acquisition, stock purchase, reorganization, or similar business combination with one or more businesses, (the “Business Combination”). Global Star is an emerging growth company and, as such, Global Star is subject to all the risks associated with emerging growth companies.
Initial Public Offering. On September 22, 2022, the Company consummated its initial public offering (the “IPO”) of 8,000,000 units (the “Units”). Each Unit consists of one share of Class A Common Stock of the Company, par value $0.0001 per share (“Class A Common Stock”), one redeemable GLST Warrant, with each whole GLST Warrant entitling the holder thereof to purchase one share of Class A Common Stock for $11.50 per share, and one GLST Right, with each GLST Right entitling the holder to receive one-tenth of one share of Class A Common Stock. The Units were sold at a price of $10.00 per Unit, generating gross proceeds to the Company of $80,000,000. Simultaneously with the consummation of the closing of the IPO, the Company consummated the private placement of an aggregate of 456,225 units (the “IPO Private Placement Units”) to the Sponsor, at a price of $10.00 per Private Placement Unit, generating total gross proceeds of $4,562,250 (the “IPO Private Placement”).
At the time of the IPO, the underwriters were granted a 45-day over-allotment option to purchase up to 1,200,000 additional Units to cover overallotments, if any (the “Over-Allotment Units”). Subsequently, on September 30, 2022, the underwriters exercised their over-allotment option to purchase 1,200,000 Over-Allotment Units. On October 4, 2022, the Company closed on the Over-Allotment Units through the sale of 1,200,000 Units at a purchase price of $10.00 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $12.0 million.
Simultaneously with the sale of the Over-Allotment Units, the Company consummated the private placement of an aggregate of 42,000 units (the “Over-Allotment Private Placement Units” and together with the IPO Private Placement Units, the “Private Placement Units”) to the Sponsor, at a price of $10.00 per Over-Allotment Private Placement Units, generating total gross proceeds of $420,000
A total of $94,300,000 comprising proceeds from the IPO and proceeds of the Private Placement, net of the underwriting commissions, discounts, and IPO expenses, was deposited in a trust account established for the benefit of the Company’s public stockholders.
Global Star’s management team is led by Anthony Ang, Global Star’s Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) who is a global executive with over 40 years of senior management experience. His broad expertise covers international marketing, investment promotion, manufacturing, and fund management. Mr. Ang currently holds various senior positions including independent director on boards of public companies, Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary of the Republic of Singapore to the Republic of Tunisia, and the Chairman and director for a crowd funded real estate investment platform, and a digital asset exchange.
Global Star’s units, public shares, public warrants, and public rights are each traded on the Nasdaq Stock Market under the symbols “GLSTU,” “GLST”, “GLSTW,” and “GLSTR” respectively. Global Star’s units commenced public trading on September 22, 2022, and public shares, public warrants and public rights commenced separate public trading on November 10, 2022. Global Star’s Class B Common Stock is not listed on any exchange.
K Enter Holdings Inc.
K Enter Holdings Inc. (“K Enter”) was formed on January 4, 2023, under the laws of the State of Delaware. K Enter was formed as a holding company for the purpose of acquiring six diversified entertainment operating companies based in Korea, engaged in the entertainment content and IP creation businesses (the “Six Korean Entities”). K Enter has entered into agreements to acquire controlling equity interests in each of the Six Korean Entities. The Six Korean Entities to be acquired by K Enter include: an IP merchandising company - Play Company Co., Ltd., four K content production companies - Apeitda Production, Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd., The LAMP Co., Ltd., and Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd., and a specialized K content private equity company - Solaire Partners LLC. K Enter also has an internal K drama production team. Following K Enter’s acquisition of the controlling equity interests in each of the Six Korean Entities, as a combined company (referred to herein as “New K Enter”), New K Enter expects these companies to provide a significant amount of synergy, however the timing and extent of such synergies is uncertain.
K Enter currently has limited operations and does not presently own a controlling interest in any other entities. K Enter’s acquisition of the Six Korean Entities is a closing condition to the Business Combination, and while this condition can be waived, however Global Star does not currently intend to waive this condition. K Enter expects to close the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of the Six Korean Entities within 24 to 72 hours after this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 is declared effective by the SEC. In addition, Global Star will not mail proxy materials to its shareholders for the Special Meeting until after K Enter closes the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities. PubCo shall include the date that K Enter completes the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all Six Korean Entities in its Form 424B3 Prospectus to be filed with the SEC after this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 is declared effective by the SEC.
In the event that K Enter does not complete the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities, PubCo will file a post-effective amendment to its Registration Statement on Form F-4 (the “Post-Effective Amendment”) disclosing that K Enter did not complete its contemplated acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities (and the material information concerning such event) and Global Star will not mail proxy materials to its shareholders for the Special Meeting (or hold its Special Meeting) until after the Post-Effective Amendment is declared effective by the SEC. Global Star’s shareholders will not be able to vote for or against the Business Combination until after they receive a definitive proxy statement, which will only be mailed after the later of (i) the successful consummation of the acquisition of the controlling interests of all of the Six Korean Entities or (ii) the declaration of effectiveness by the SEC of the Post-Effective Amendment.
As of January 3, 2025, K Enter completed the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of each of the Six Korean Entities.
For more information, see the questions and answers titled “When is the acquisition of the Six Korean Entities expected to occur?” and “What if there are material developments or changes relating to the acquisition by K Enter of the Six Korean Entities prior to the Special Meeting?” and “What if K Enter’s acquisition of the Six Korean Entities does not occur prior to the Special Meeting?” in the Section titled “Questions and Answers about the Business Combination and the Special Meeting” beginning on page 6.
On April 12, 2023, K Enter entered into a share purchase agreement with Sungkwon Kim, King Bear Film LLC (the “FVL SPA”) to acquire a majority equity interest First Virtual Lab Inc. (“First Virtual”), a content virtualization company. The FVL SPA was terminated and amended by the execution of two agreements, namely the Termination and Amendment to the Share Purchase Agreement and the Shareholders Agreement, dated January 31, 2024, by and among Sungkwon Kim, King Bear Film LLC and K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “SPA Amendment”) and the Share Purchase Agreement, dated January 31, 2024, by and among King Bear Film LLC and K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “KB Agreement” and collectively with the SPA Amendment the “New FVL Agreements”). Pursuant to the New FVL Agreements the purchase price for K Enter’s acquisition of a controlling interest in First Virtual was reduced from approximately $20 million to approximately $8 million.
K Enter learned that three separate lawsuits were filed in or about December 2023, concerning First Virtual, its principal Sungkwon Kim and certain other parties (collectively referred to as the “Prototype Lawsuits”). Two lawsuits are pending in the Chancery Court of the State of Delaware and one lawsuit in Korea. The Delaware lawsuits are entitled: Prototype Lab, Inc., a Korean corporation, Craig Bernard, individually and on behalf of Prototype Groupe, Inc. a Delaware corporation, Culley Bunker, individually and on behalf of Prototype Groupe, Inc. a Delaware corporation v. King Bear Film, LLC, a California limited liability company, John C. Kim a/k/a Chang Kun Kim, SunkKwon Kim and Patrick Han a/k/a Chung Ho Han and assigned Case No. 2023-1257-NAC and In Re Prototype Groupe, Inc., a Delaware corporation and assigned Case No. 2023-1287-NAC. The Korean lawsuit is entitled: Prototype Holding Co. Ltd. and Ju-yeon Lee v. Sungkwon Kim. Due to the pendency of the Prototype Lawsuits, on March 5, 2024, the New FVL Agreements relating to the acquisition of a majority equity stake in First Virtual were terminated pursuant to a Termination Agreement and Re-Purchase Option Agreement, dated March 5, 2024, by and among Sungkwon Kim, King Bear Film LLC and K Enter (the “FVL Termination and Option Agreement”). Pursuant to the FVL Termination and Option Agreement, the New FVL Agreements are terminated and Sungkwon Kim and King Bear Film LLC have an option, for a period of five (5) years, to compel K Enter to acquire a 51% equity interest in First Virtual from Sungkwon Kim and King Bear Film LLC at the then current fair market value provided the Prototype Lawsuits are resolved in a manner acceptable to K Enter, in K Enter’s sole discretion. While no definitive action has been taken to terminate the FVL Termination and Option Agreement, K Enter currently views the acquisition of a controlling interest in First Virtual pursuant to the FVL Termination and Option Agreement as uncertain due to the uncertainty as to the outcome of the Prototype Lawsuits and there can be no assurance that K Enter will acquire a controlling interest in First Virtual pursuant to the FVL Termination and Option Agreement.
The financial projections and other financial information included in or informing the First Fairness Opinion are premised on the successful acquisition of all Seven Korean Entities, including First Virtual. The Second Fairness Opinion described in this proxy statement is premised on the successful acquisition of all Six Korean Entities and do not assume the acquisition of First Virtual. The financial projections informing the Second Fairness Opinion vary significantly from the actual results achieved in 2023 and the results for the first six months of 2024. For example, the revenues of the Six Korean Entities for the six (6) months ended June 30, 2024 represent approximately 48% of the revenue of the Six Korean companies for 2023 and approximately 18% of the projected revenues for 2024.
We believe that the reasons for the deviation between the financial projections and the performance is due to two key factors. First, (i) the seasonal nature of Play Company’s merchandising business, (ii) unexpected delays in some of the merchandising projects previously planned for the first half of the year, and (iii) slower-than-expected progress in developing new business opportunities, among other factors each contributed to the decline in performance. Second, the financial projections upon which the Second Fairness Opinion is based assumed that K Enter acquired the Six Korean Entities and the Business Combination closed on or before March 31, 2024, which did not occur. The fact the Business Combination did not close prior to March 31, 2024, caused a delay in the planned investments into the content production businesses, mainly the K Enter Drama Team as well as the Lamp, Bidangil and Anseilen which resulted in a reduction of the combined number of projects projected for the K Enter Drama Team as well as the Lamp, Bidangil and Studio Anseilen. Management is addressing these challenges by actively seeking business development opportunities for our planned subsidiaries. Accordingly, Global Star’s board of directors has determined that no purchase price adjustment is appropriate due to the failure to meet projected 2024 financial results of operations. Further, Global Star and K Enter management continue to believe that the assumptions underlying the projections are reasonable for future periods.
We believe that any production revenues not realized in 2024 due to this delay in closing the Business Combination can be made up in the following year. We believe the delay in closing the Business Combination is projected to reduce revenue for the K Enter Drama Team as well as the Lamp, Bidangil and Studio Anseilen by approximately $30 million in 2024. Thus, our stated 2024 projected revenue on a consolidated basis of $191 million could decline to approximately $161 million. The $30 million represents a lost opportunity in three to four movies and dramas by for the K Enter Drama Team as well as the Lamp, Bidangil and Studio Anseilen. This is because once K Enter acquires a controlling stake in these companies, various synergy creating activities were planned, such as deal-flow sharing, co-production and strategic relationships, which we expect will help PubCo become an integrated content management company. In 2024, the following 13 content productions were planned earlier in the year, and it is now our belief that not all 13 will be produced but possibly 9 or 10. K Enter believes that some of the content production projects identified in the tables below as in the “In development” stage may or may not be produced in 2024 due to the delay in closing the Business Combination, which may result in the 2024 revenues for those companies to be reduced in the aggregate of up to $30 million.
| Name of Drama | | Producer | | Stage | | Potential Cost of Delay |
| Trigger | | Bidangil | | Producing | | |
| Aema | | The Lamp | | Producing | | |
| Freelancer | | K Enter Drama Team | | Delayed Producing | | $10 million |
| I will survive | | Anseilen | | In development | | $5 million |
| Human Withdrawal | | K Enter Drama Team | | Delayed Producing | | $10 million |
| Your Honor | | Anseilen | | In development | | $5 million |
| Name of Film | | Producer | | Stage | | Potential Cost of Delay |
| Resonance | | Bidangil | | Post-production | | |
| Bidangil Film 2024 | | Bidangil | | In development | | $5 million |
| Starlight is Falling | | The Lamp | | Post-production | | |
| Escape | | The Lamp | | Released | | |
| Moral Hazard | | The Lamp | | Post-production | | |
| Star of Disgust | | Apeitda | | Released | | |
| The Lamp Film 2024 | | The Lamp | | In development | | $5 million |
Initially, we assumed the Business Combination would close by the end of March 2024. However with a decline in ad revenue and a glut of movies that had been produced but not released, content creators are in great need of securing reputable producers with a certain capacity to fund their new projects, K Enter believes the long-term business prospects of content production will not be impacted by this delay.
Despite the current delays, K Enter is carrying out the following management activities to overcome this delay, and we plan to minimize the impact on content sales through the following endeavors.
| | - | Integrated management activities through PubCo: PubCo’s content production personnel will be in charge of the overall management of the four content-focused subsidiaries. PubCo will carry out various synergy-creating activities, such as deal-flow sharing, co-production, strategic relationships, etc., and help PubCo become an integrated content management company. The synergy between content-focused subsidiaries and merchandising will also be sought and promoted, whereas if the popular content is created by one of the content-focused subsidiaries, K Enter’s planned merchandising subsidiary, “Play Company,” will be encouraged to monetize by turning the subject content into merchandise products. |
| | | |
| | - | Solaire Partners’ and Play Company’s projected revenue is not affected by the timing for K Enter going public. Apeitda’s 2024 revenue forecast is also not affected by K Enter’s timing for going public. |
The second fairness opinion already reflects lower-than-expected revenue for 2023 and the removal of FVL. We do not believe further projection modifications are necessary as any change in projections will be short-term and will not impact K Enter’s long-term viability.
The financial projections upon which the Second Fairness Opinion is based assumed that the Business Combination would occur on or before March 31, 2024. K Enter believes the delay in closing the Business Combination is expected to reduce New K Enter’s projected financial results of operations for 2024 because it will delay PubCo’s investment in new media content production, which is expected to drive revenues. The delay in closing the Business Combination is not expected to adversely impact PubCo’s projected results for 2025 or subsequent years, as it does not reflect a long-term trend, but rather a short-term delay in implementing business strategies. The expected reduction in PubCo’s projected revenues does not impact the Second Fairness Opinion dated March 12, 2024 (as updated on April 29, 2024), which was issued as of March 12, 2024.
The financial projections upon which the First Fairness Opinion and the Second Fairness Opinion are based should not be viewed as public guidance. The financial projections were not prepared with a view toward public disclosure, or complying with the published guidelines of the SEC regarding projections or the guidelines established by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants for preparation and presentation of prospective financial information, but, in the view of Global Star’s management, were prepared on a reasonable basis, reflecting the best currently available estimates and judgments, and present, to the best knowledge and belief of Global Star’s management, the expected course of action and revenues that Global Star anticipates generating, assuming the assumptions incorporated in the financial projections are themselves realized. Global Star’s management believes the assumptions included in the financial projections to be reasonable, based on currently available information and professional judgement and experience, which are inherently uncertain and difficult to predict and many of which are beyond Global Star’s control.
The financial projections are not included in this joint proxy statement/prospectus in order to induce any Global Star shareholders to vote in favor of any of the proposals at the Special Meeting. The assumptions incorporated in the financial projections are not based on the historical financial performance of the Six Korean Companies, but rather on the projections and estimates of K Enter’s management derived from management experience and industry information, including information applicable to established companies and related industries, which are not representative of PubCo’s expected business upon consummation of the Business Combination and may not be representative of PubCo’s future plans or performance. The financial projections were developed in good faith by K Enter’s management team based on their reasonable best estimates and taking into account the assumptions set forth herein.
The inclusion of financial projections in this joint proxy statement/information statement/prospectus should not be regarded as an indication that the Global Star Board, or their respective affiliates, advisors or other representatives considered, or now considers, the financial projections necessarily to be predictive of actual future results or to support or fail to support your decision whether to vote for or against the proposed Business Combination. Neither PubCo, Global Star nor K Enter nor any of their respective affiliates intends to, and, except to the extent required by applicable law, each of them expressly disclaims any obligation to, update, revise or correct the financial projections to reflect circumstances existing or arising after the date such financial projections were generated or to reflect the occurrence of future events, even if any or all of the assumptions underlying the financial projections are shown to be in error or any of the financial projections otherwise would not be realized. We and PubCo will not refer back to the financial projections in future periodic reports filed under the Exchange Act.
The financial projections are susceptible to multiple interpretations and periodic revisions based on actual experience and business developments. The financial projections also reflect numerous estimates and assumptions with respect to general business, economic, regulatory, market and financial conditions. Neither PubCo’s management, K Enter’s management nor Global Star’s management, nor any of their respective representatives has made or makes any representations to any person regarding the ultimate performance of PubCo relative to the financial projections. The financial projections are forward looking statements that are inherently subject to significant uncertainties and contingencies, many of which are beyond PubCo’s control. The various risks and uncertainties include those set forth in the “Risk Factors,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and “Cautionary Statement Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” sections of this joint proxy statement/information statement/prospectus, respectively, and risks and uncertainties inherent in the assumptions further described below.
For more information on K Enter, please see the sections entitled “Business of K Enter” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations of K Enter.”
The Business Combination and the Merger Agreement
The Merger Agreement was entered into by and among Global Star and K Enter and certain other parties on June 15, 2023. On June 13, 2023, PubCo and Merger Sub executed the Joinder Agreement and became parties to the Merger Agreement. On March 11, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub executed the First Amendment to Merger Agreement. On June 28, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Second Amendment to Merger Agreement. On July 25, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Third Amendment to Merger Agreement. On December 11, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement. Pursuant to the terms of the Merger Agreement, the Business Combination will be completed through a two-step process consisting of the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger.
The Reincorporation Merger
At least one (1) business day prior to the Acquisition Merger, Global Star will reincorporate to Cayman Islands by merging with and into the PubCo, a Cayman Islands exempted company and wholly owned subsidiary of Global Star. The separate corporate existence of Global Star will cease and PubCo will continue as the surviving corporation. In connection with the Reincorporation Merger, all outstanding GLST Units will separate into their individual components of GLST Common Stock, GLST Rights and GLST Warrants and will cease separate existence and trading. Upon the consummation of the Business Combination, the current equity holdings of the Global Star stockholders shall be exchanged as follows:
| (i) | Each share of GLST Common Stock, issued and outstanding immediately prior to the effective time of the Reincorporation Merger (other than any redeemed shares), will automatically be cancelled and cease to exist and for each share of such GLST Common Stock, PubCo shall issue to each Global Star stockholder (other than Global Star stockholders who exercise their redemption rights in connection with the Business Combination) one validly issued PubCo Ordinary Share, which, unless explicitly stated herein, shall be fully paid; |
| (ii) | Each GLST Warrant issued and outstanding immediately prior to effective time of the Reincorporation Merger will convert into a PubCo Warrant to purchase one PubCo Ordinary Share at a price of $11.50 per whole share; and |
| (iii) | The holders of GLST Rights issued and outstanding immediately prior to the effective time of the Reincorporation Merger will receive one- PubCo Right in exchange for the cancellation of each GLST Right. |
The Acquisition Merger
At least one (1) business day after the Reincorporation Merger, Merger Sub, a Delaware corporation and wholly owned subsidiary of PubCo, will be merged with and into K Enter, resulting in K Enter being a wholly owned subsidiary of PubCo.
The aggregate consideration for the Acquisition Merger is $590,000,000, payable in the form of 59,000,000 newly issued PubCo Ordinary Shares valued at $10.00 per share to K Enter and its shareholders. At the closing of the Acquisition Merger, the issued and outstanding shares in K Enter held by the former K Enter shareholders will be cancelled and ceased to exist, in exchange for the issue of an aggregate of 59,000,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares. 5,900,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares will be reserved and authorized for issuance under the Incentive Plan upon closing. At the closing of the Acquisition Merger, the one fully paid share in Merger Sub held by PubCo will become one fully paid share in the surviving corporation, so that K Enter will become a wholly owned subsidiary of PubCo.
The foregoing description of the Merger Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the actual agreement, a form of which is included as part of Annex A hereto. For more information about the Business Combination, please see the sections titled “Proposal No. 1 — The Reincorporation Merger Proposal” and “Proposal No. 2 — The Acquisition Merger Proposal.” A copy of the Merger Agreement is attached to this proxy statement/prospectus as Annex A.
Post-Business Combination Structure and Impact on the Public Float
The following charts illustrate the ownership structure of Global Star before the Business Combination, the ownership structure of PubCo following the Business Combination and a chart depicting the structure of the organization following the Business Combination. The equity interests shown in the diagrams below were calculated based on the assumptions that (i) no Global Star stockholder exercises its redemption, (ii) none of the parties in the chart below purchase GLST Common Stock in the open market and (iii) there are no other issuances of equity by Global Star prior to or in connection with the consummation of the Business Combination. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the ownership percentages set forth below do not take into account the 5,900,000 PubCo’s outstanding Ordinary Shares reserved and authorized for issuance under the Incentive Plan and do not take into account the exercise of any PubCo Warrants.
OWNERSHIP STRUCTURE OF GLOBAL STAR BEFORE THE BUSINESS COMBINATION
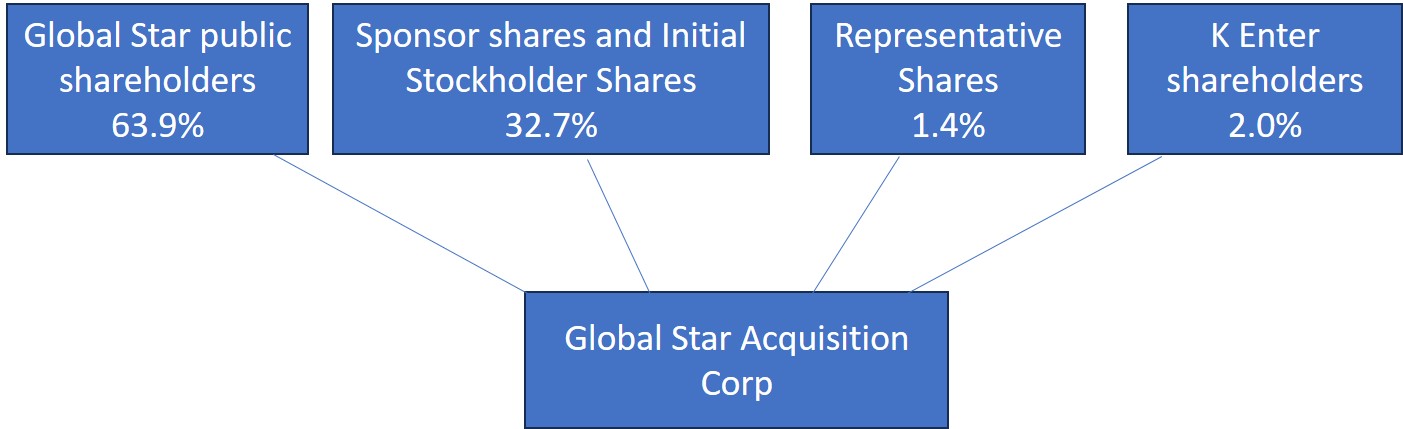
K ENTER’S ACQUISITION OF THE SIX KOREAN ENTITIES
K Enter’s acquisition of the Six Korean Entities is a closing condition to the Business Combination, and while this condition can be waived, however Global Star does not currently intend to waive this condition. K Enter expects to close the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of the Six Korean Entities within 24 to 72 hours after this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 is declared effective by the SEC. In addition, Global Star will not mail proxy materials to its shareholders for the Special Meeting until after K Enter closes the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities. PubCo shall include the date that K Enter completes the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all Six Korean Entities in its Form 424B3 Prospectus to be filed with the SEC after this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 is declared effective by the SEC.
In the event that K Enter does not complete the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities, PubCo will file a post-effective amendment to its Registration Statement on Form F-4 (the “Post-Effective Amendment”) disclosing that K Enter did not complete its contemplated acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities (and the material information concerning such event) and Global Star will not mail proxy materials to its shareholders for the Special Meeting (or hold its Special Meeting) until after the Post-Effective Amendment is declared effective by the SEC. Global Star’s shareholders will not be able to vote for or against the Business Combination until after they receive a definitive proxy statement, which will only be mailed after the later of (i) the successful consummation of the acquisition of the controlling interests of all of the Six Korean Entities or (ii) the declaration of effectiveness by the SEC of the Post-Effective Amendment.
As of January 3, 2025, K Enter completed the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of each of the Six Korean Entities.
K Enter’s acquisition of 100% equity interest in Play Company
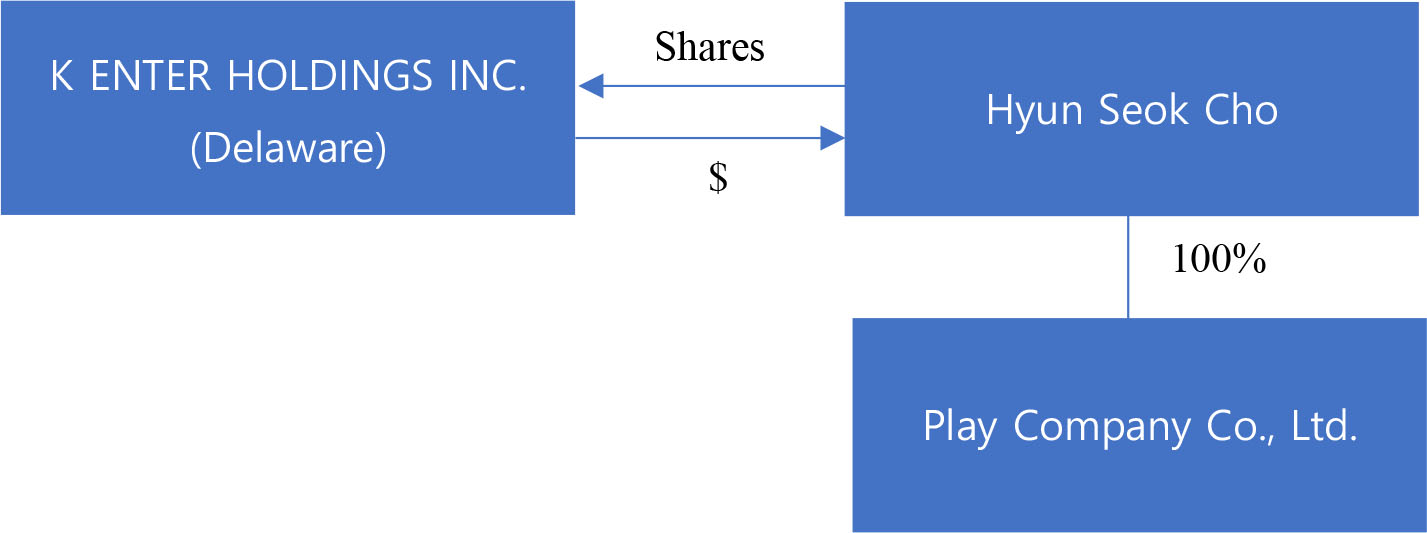
K Enter’s acquisition of equity interests in the five remaining Six Korean Entities will occur after the closing of the share purchase agreement concerning Play Company and prior to the Special Meeting of Global Star stockholders to vote to approve the Business Combination.
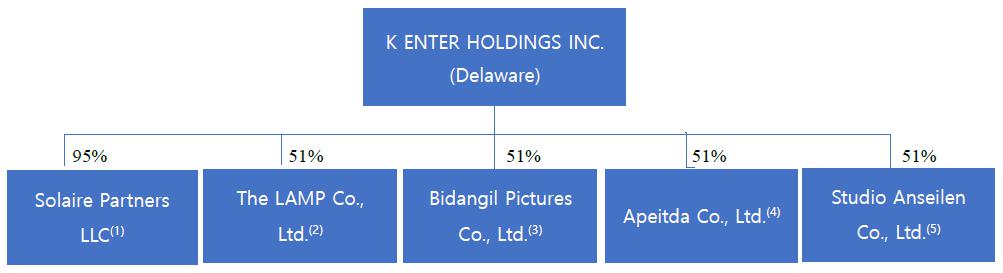
| (1) | The remaining 5% equity interest of Solaire Partners will be beneficially owned by the following persons: Choi, Pyeungho (3.0%); Lee, Youngjae (1.2%); Song, Hyojeong (0.2%); CY Holdings Co., Ltd. (0.2%); Park, Sukyung (0.1%); Hyun, Nayoung (0.1%); Lee, Myeonghyeon (0.1%); and Kim, Minsoon (0.1%). |
| (2) | The remaining 49% equity interest of The LAMP Co., Ltd. will be beneficially owned by the following person: Park, Eun Kyung (49%). |
| (3) | The remaining 49% equity interest of Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd. will be beneficially owned by the following persons: Yoon, In Beom (24.5%) and Kim, Soo Jin (24.5%). |
| (4) | The remaining 49% equity interest of Apeitda Co., Ltd. will be beneficially owned by the following persons: Jung, Byung Gil (39%) and Seo, Soon Yeo (10%). |
| (5) | The remaining 49% equity interest of Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd. will be beneficially owned by the following persons: Kim, Seung Ho (16.3%); Shin, Kyung Soo (16.3%); and Park, Joon Woo (16.3%). |
BUSINESS COMBINATION
Subject to satisfaction of the applicable conditions precedent in the Merger Agreement, following K Enter’s acquisition of the Six Korean Entities, Global Star expects the Business Combination to occur in the following order:
Reincorporation Merger (following the Special Meeting of Global Star)
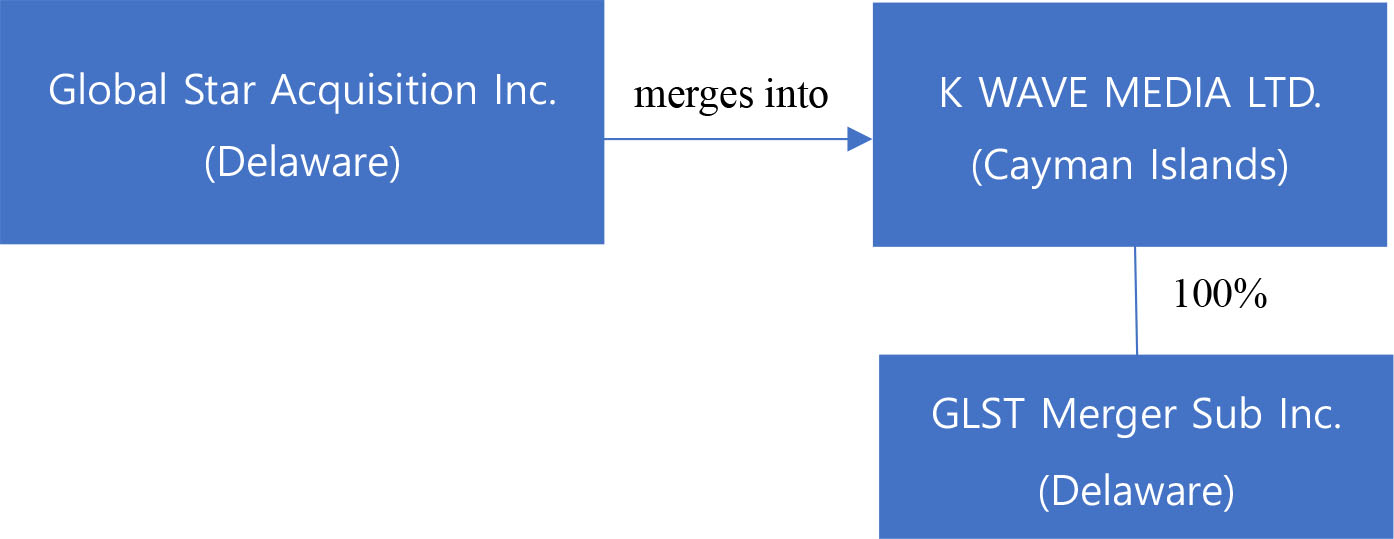
Acquisition Merger (one business day following the Reincorporation Merger)
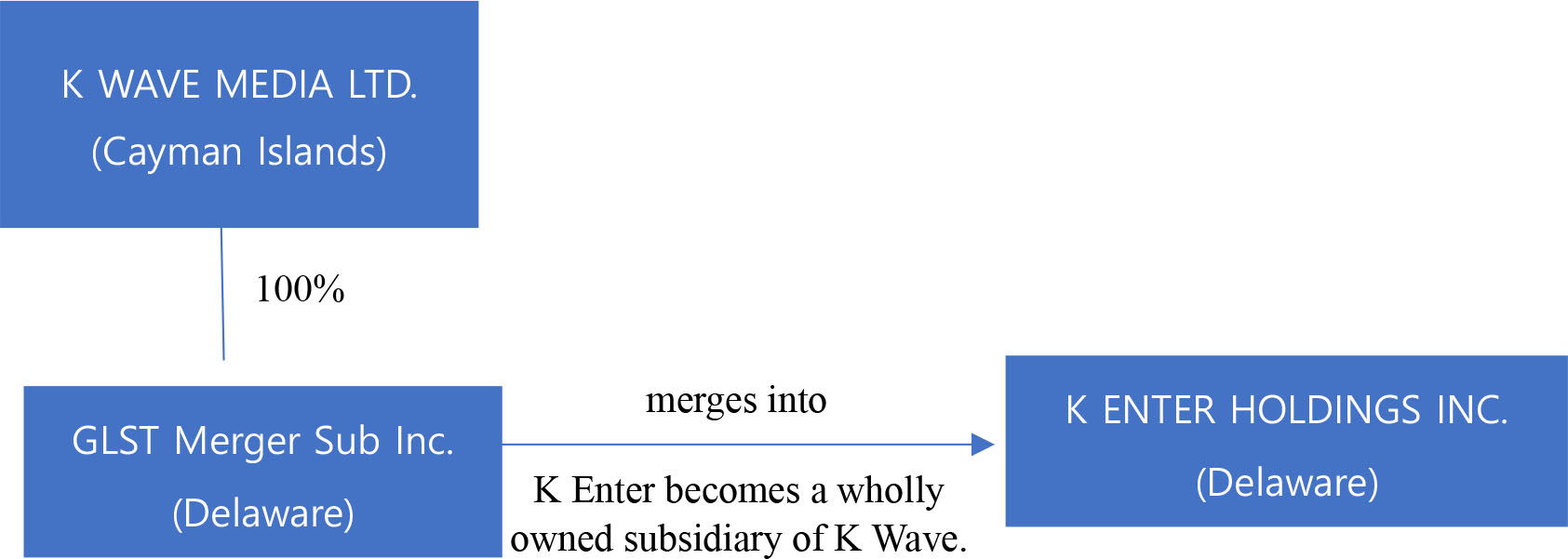
OWNERSHIP STRUCTURE OF PUBCO FOLLOWING THE BUSINESS COMBINATION
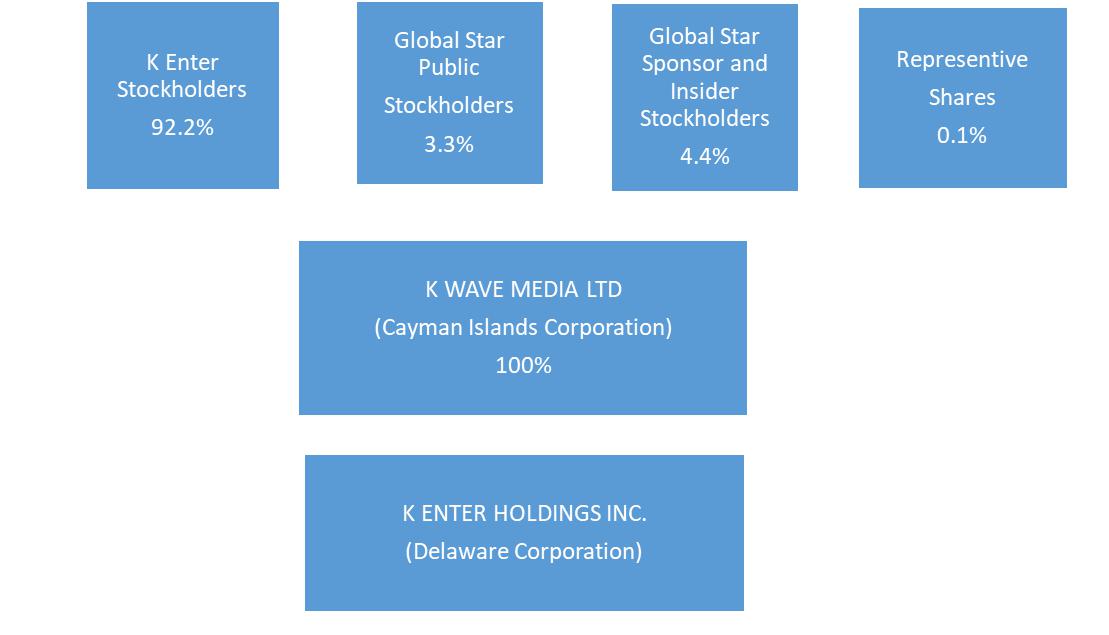
CHART DEPICTING THE STRUCTURE OF PUBCO FOLLOWING THE BUSINESS COMBINATION
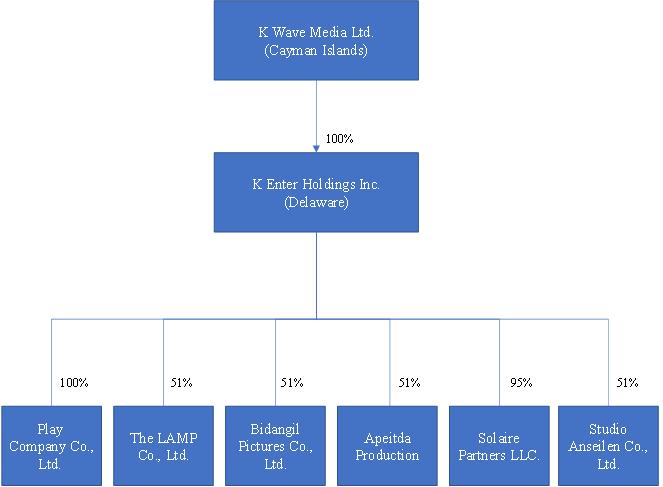
If the actual facts are different than these assumptions, the percentage ownership retained by Global Star’s public stockholders following the business combination will be different. The public warrants and private placement warrants will become exercisable 30 days after the completion of the Business Combination and will expire five years after the completion of the Business Combination or earlier upon redemption or liquidation.
Management and Board of Directors Following the Business Combination
Effective as of the closing of the Business Combination, the board of directors of PubCo will consist of seven (7) members. All members of the PubCo board of directors will be designated by K Enter and a majority of whom will be considered “independent” under Nasdaq’s listing standards. See section titled “PubCo’s Directors and Executive Officers after the Business Combination” for additional information.
Other Documents Relating to the Business Combination
Lock-Up Agreement
At the Closing, PubCo, the Sponsor, certain former stockholders of K Enter, and certain other persons and entities, will enter into lock-up agreements (the “Lock-Up Agreements”) with respect to the PubCo Ordinary Shares and PubCo Warrants held by the Sponsor immediately following the Closing, and the PubCo Ordinary Shares held by certain K Enter stockholders immediately following the Closing (the “Lock-Up Shares”), pursuant to which, each Holder agreed not to offer, sell, contract to sell, pledge, grant any option to purchase, or otherwise dispose of, directly or indirectly, any Lock-Up Shares during the application lock-up period, on the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in the Lock-Up Agreement. Lock-up period means, (i) with respect to 50% of the Lock-up Shares, the earlier of (A) six months after the Closing and (B) the date on which the closing price of the PubCo’s Ordinary Shares equals or exceeds $12.50 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, rights issuances, reorganizations and recapitalizations) for any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period commencing after the date hereof and (ii) with respect to the remaining 50% Lock-up Shares (or Ordinary Shares issuable upon conversion thereof), six months after the Closing. The Lock-Up Agreements will apply to (i) approximately 83% of the PubCo Ordinary Shares, consisting of 2,798,225 Ordinary Shares owned by the Sponsor, Stephen Drew and Nicholas Khoo and 49,424,300 Ordinary Shares owned by the former K Enter stockholders (ii) 498,225 Ordinary Shares underlying warrants held by the Sponsor (approximately 5.14% of the outstanding warrants) and (iii) 49,822 Ordinary Shares underlying rights owned by the Sponsor (approximately 5.14% of the rights).
The foregoing description of the Lock-Up Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the actual agreement, a form of which is included as part of Annex A hereto.
Registration Rights Agreement
At the Closing, PubCo, the Sponsor, certain former stockholders of Global Star, and certain former stockholders of K Enter, will enter into a registration rights agreement (the “Registration Rights Agreement”), pursuant to which PubCo will be obligated to file a registration statement to register the resale, pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, of certain securities of PubCo held by the parties to the Registration Rights Agreement. The Registration Rights Agreement will also provide the Sponsor, the Initial Stockholders, and certain former stockholders of K Enter with unlimited “piggy-back” registration rights, subject to certain requirements and customary conditions.
The Registration Rights Agreement amends and restates the registration rights agreement that was entered into by the Company, the Sponsor and the other parties thereto in connection with the Company’s initial public offering. The Registration Rights Agreement will terminate on the earlier of (a) the five year anniversary of the date of the Registration Rights Agreement or (b) with respect to any holder, on the date that such holder no longer holds any Registrable Securities (as defined therein).
The foregoing description of the Registration Rights Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the actual agreement, a form of which is included as part of Annex A hereto.
Redemption Rights
Pursuant to Global Star’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation, Global Star’s public stockholders may elect to have their shares redeemed for cash at the applicable redemption price per share equal to the quotient obtained by dividing (i) $4,377,240 the approximate aggregate amount on deposit in the trust account as of two business days prior to the consummation of the Business Combination, including interest (without deduction for taxes payable), by (ii) the total number of then-outstanding public shares. As of December 13, 2024, this would have amounted to approximately $11.45 per share, subject to reduction for the payment of taxes.
You will be entitled to receive cash for any public shares to be redeemed only if you:
| (i) | (x) hold public GLST Common Stock or (y) hold public GLST Common Stock through GLST Units and you elect to separate your GLST Units into the underlying public GLST Common Stock, public GLST Rights and public GLST Warrants prior to exercising your redemption rights with respect to the public GLST Common Stock; and |
| (ii) | prior to 5:00 p.m., Eastern Time, on January 30, 2025 (a) submit a written request to the transfer agent that Global Star redeem your public shares for cash and (b) deliver your public shares to the transfer agent, physically or electronically through DTC. |
Holders of outstanding GLST Units must separate the underlying GLST Common Stock, GLST Warrants and GLST Rights prior to exercising redemption rights with respect to the GLST Common Stock. If GLST Units are registered in a holder’s own name, the holder must deliver the certificate for its GLST Units to the transfer agent with written instructions to separate the GLST Units into their individual component parts. This must be completed far enough in advance to permit the mailing of the certificates back to the holder so that the holder may then exercise his, her or its redemption rights upon the separation of the GLST Common Stock from the GLST Units.
If a broker, dealer, commercial bank, trust company or other nominee holds GLST Units for an individual or entity (such individual or entity, the “beneficial owner”), the beneficial owner must instruct such nominee to separate the beneficial owner’s GLST Units into their individual component parts. The beneficial owner’s nominee must send written instructions by facsimile to the transfer agent. Such written instructions must include the number of GLST Units to be separated and the nominee holding such GLST Units. The beneficial owner’s nominee must also initiate electronically, using DTC’s DWAC system, a withdrawal of the relevant GLST Units and a deposit of an equal number of GLST Common Stock, GLST Warrants and GLST Rights. This must be completed far enough in advance to permit the nominee to exercise the beneficial owner’s redemption rights upon the separation of the GLST Common Stock from the GLST Units. While this is typically done electronically the same business day, beneficial owners should allow at least one full business day to accomplish the separation. If beneficial owners fail to cause their GLST Common Stock to be separated in a timely manner, they will likely not be able to exercise their redemption rights.
Any request for redemption, once made, may be withdrawn at any time up to two business days immediately preceding the Special Meeting. Furthermore, if a stockholder delivered his certificate for redemption and subsequently decided prior to the date immediately preceding the Special Meeting not to elect redemption, he may simply request that the transfer agent return the certificate (physically or electronically).
Notwithstanding the foregoing, a holder of the public shares, together with any affiliate of his or her or any other person with whom he or she is acting in concert or as a “group” (as defined in Section 13(d)-(3) of the Exchange Act) will be restricted from seeking redemption rights with respect to more than 15% of the GLST Common Stock.
If a holder exercises its redemption rights, then such holder will be exchanging its public shares for cash and will no longer own shares of the post-Business Combination company. Such a holder will be entitled to receive cash for its public shares only if it properly demands redemption and delivers its shares (either physically or electronically) to Global Star’s Transfer Agent in accordance with the procedures described herein. Please see the section titled “The Special Meeting — Redemption Rights” for the procedures to be followed if you wish to redeem your public shares for cash.
A redemption payment will only be made in the event that the Business Combination is consummated. If the Business Combination is not completed for any reason, then public stockholders who exercised their redemption rights would not be entitled to receive the redemption payment. In such case, Global Star will promptly return the share certificates to the public stockholder.
At a Special Meeting of Stockholders held on November 27, 2024, the stockholders of Global Star approved amendments to Global Star’s Current Charter and the Trust Agreement to extend the deadline for completing a business combination from December 22, 2024 (the “Prior Termination Date”) to up to June 22, 2025 via six one-month extensions provided the Sponsor deposits into the Trust Account extension payments equal to the lesser of $60,000 or $0.02 per outstanding share of common stock sold in the IPO as of the applicable deadline date for each one-month extension. In order to fund these extension payments and interim working capital needs, the Sponsor made a $1.6 million loan to Global Star in exchange for an unsecured, non-interest-bearing promissory note (the “Convertible Note”) in the amount of $1.6 million. The Convertible Note is payable in full upon completion of the Business Combination, and up to $1,500,000 due under the Convertible Note may be converted into Global Star Units, each consisting of one share of GLST Class A Common Stock, one GLST Warrant and one GLST Right, at the conversion rate of $10.00 per unit.
On December 4, 2024, Global Star deposited $7,617.50 into the Trust and on December 12, 2024, Global Star deposited $7,617.50 into the Trust, to extend the date by which Global Star must complete a business combination to February 22, 2025 (the “Extended Date”). Global Star can extend the Extended Date to June 22, 2025, by depositing the sum of $7,617.50 into the Trust Account for each such one-month extension (the “New Termination Date”). The extension payments were funded from the proceeds of a loan Sponsor made to Global Star in the principal amount of $1,600,000 (the “Loan”). The Loan is evidenced by a promissory note, dated July 31, 2023, issued by Global Star to the Sponsor (the “Note”). At the election of the Sponsor, up to $1,500,000 of the unpaid principal amount of the Note will be converted into GLST Private Units at a price of $10.00 per unit (the “Conversion Units”) in lieu of cash repayment. The principal balance of the Note is payable by Global Star on the later of: (i) December 31, 2023, or (ii) the date on which Global Star consummates a Business Combination. No interest shall accrue on the unpaid principal balance of the Note.
If Global Star fails to consummate a business combination prior to the earlier of the Extended Date or the New Termination Date (as it may be extended as described above), Global Star will (i) cease all operations except for the purpose of winding up, (ii) as promptly as reasonably possible but not more than ten business days thereafter, redeem the public shares, at a per-share price, payable in cash, equal to the aggregate amount then on deposit in the Trust Account, including interest earned on the funds held in the Trust Account and not previously released to pay taxes (less up to $100,000 of interest to pay dissolution expenses), divided by the number of then outstanding public shares, which redemption will completely extinguish the rights of the holders of public shares as shareholders (including the right to receive further liquidating distributions, if any), and (iii) as promptly as reasonably possible following such redemption, subject to the approval of Global Star’s remaining shareholders and the board of directors, dissolve and liquidate, subject in each case to Global Star’s obligations under Delaware law to provide for claims of creditors and the requirements of other applicable law. In that event, there will be no distribution from the Trust Account with respect to Global Star’s rights, which will expire worthless in the event of Global Star’s winding up. In the event of a liquidation, Global Star’s Sponsor and directors and officers will not receive any monies held in the Trust Account as a result of their ownership of the Founder Shares and Private Placement Units.
The Proposals
At the Special Meeting, the Global Star’s stockholders will be asked to vote on the following:
| ● | the Reincorporation Merger Proposal; |
| ● | the Acquisition Merger Proposal; |
| ● | the Incentive Plan Proposal; and |
| ● | the Adjournment Proposal. |
Please see the sections titled “The Special Meeting” on page 88 for more information on the foregoing Proposals.
Voting Securities, Record Date
As of December 13, 2024, there were 3,294,100 shares of GLST Common Stock issued and outstanding. Only Global Star’s stockholders who hold shares of GLST Common Stock of record as of the close of business on December 13, 2024 are entitled to vote at the Special Meeting or any adjournment of the Special Meeting. Approval of the Proposals will require the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the issued and outstanding GLST Common Stock present and entitled to vote at the Special Meeting.
As of December 13, 2024, the Initial Stockholders collectively owned and are entitled to vote 500,000 shares of GLST Common Stock, or approximately 15.2% of Global Star’s outstanding shares. With respect to the Business Combination, the Initial Stockholders and the Sponsor, which own 2,138,225, or approximately 65% of Global Star’s outstanding shares as of the record date, have agreed to vote their GLST Common Stock in favor of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal and the Acquisition Merger Proposal, and intends to vote for the other Proposals although there is no agreement in place with respect to voting on the Proposals.
IPO Underwriting Agreement
The underwriters for the Global Star’s IPO, which was completed on September 22, 2022, are entitled to a deferred fee of $0.35 per unit sold in the IPO or $3,220,000. The deferred fee will become payable to the underwriters from the amounts held in the Trust Account solely in the event that Global Star completes the Business Combination, subject to the terms of the underwriting agreement.
The following table sets forth the effective underwriting fee (inclusive of the 2.0% fee that was previously paid by Global Star at the closing of its IPO) at three redemption scenarios after giving effect to the redemptions in connection with the Special Meeting:
| | | Minimum
Redemption
Scenario | | | 50% Redemption
Scenario | | | Maximum
Redemption
Scenario | |
| Underwriting Fee(1) | | $ | 5,060,000 | | | $ | 5,060,000 | | | $ | 5,060,000 | |
| IPO Proceeds Remaining in Trust Account at December 13, 2024 | | $ | 4,364,690 | | | | 2,182,345 | | | | 0 | |
| Effective Underwriting Fee(2) | | | 116.5 | % | | | 232.6 | % | | | NA | |
| (1) | The underwriting fee consists of the $1,840,000 underwriting fee paid at the close of the IPO, after giving effect to the underwriter’s exercise of the over-allotment option, and the $3,220,000 deferred fee due at the close of the Business Combination. |
| (2) | The effective underwriting fee is calculated by dividing the IPO fee in dollars divided by the IPO proceeds in dollars remaining in the trust account at each redemption scenario. |
Anticipated Accounting Treatment
Prior to the Business Combination, K Enter will acquire controlling equity interests in the Six Korean Entities.
The acquisition of the Six Korean Entities by K Enter will occur with the acquisition of Play Company closing first and the acquisitions of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company closing subsequently. After the acquisition of all Six Korean Entities is completed, the collective combined company will be referred to as New K Enter solely for purposes of the discussion of the accounting treatment as New K Enter simply refers to K Enter after acquisition of the Six Korean Entities.
The acquisition of Play Company by K Enter will be accounted for in accordance with the acquisition method of accounting under IFRS 3, with Play Company considered to be the acquirer and predecessor of K Enter. As Play Company’s basis of accounting is IFRS, K Enter’s basis of accounting (following the acquisition of Play Company) will be IFRS.
The acquisitions of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company by K Enter will also be accounted for in accordance with the acquisition method of accounting under IFRS 3, with K Enter (following the acquisition of Play Company, its predecessor) considered to be the acquirer of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company. The results of operations of each of the acquired Six Korean Entities other than Play Company will be included in the consolidated financial statements from the date of the acquisition forward. New K Enter’s basis of accounting will be IFRS, consistent with that of its predecessor, Play Company.
The overall impact of the accounting conclusions set out above will be that the financial statements of Play Company will become those of K-Enter post-consummation and will not experience a change in basis as a result of the application of the acquisition method while each of K Enter and the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company will experience a change in basis as a result of the application of the acquisition method and will be reflected in the consolidated financial statements of Play Company on a prospective basis post-consummation.
The Business Combination is accounted for as a capital reorganization, with no goodwill or other intangible assets recorded, in accordance with IFRS 2. Under this method of accounting, K Wave Media, as the successor to Global Star in the Reincorporation Merger, is treated as the “acquired” company for financial reporting purposes. This determination was primarily based on the assumption that:
| | ● | New K Enter’s existing stockholders will hold a majority of the voting rights of PubCo post Business Combination under the No Additional Redemption Scenario and Maximum Redemption Scenario; |
| | | |
| | ● | By virtue of such estimated voting interest upon the Closing, New K Enter’s existing stockholders will have the ability to control decisions regarding the election and removal of directors and officers of the Combined Company following the Closing; |
| ● | New K Enter will have control over the Board; |
| ● | New K Enter’s operations will substantially comprise the ongoing operations of PubCo; |
| ● | New K Enter is the larger entity in terms of substantive operations and employee base; and |
| ● | New K Enter’s senior management will comprise the senior management of PubCo. |
Another determining factor was that Global Star does not meet the definition of a “business” pursuant to IFRS 3, and thus, for accounting purposes, the Business Combination will be accounted for as a capital reorganization within the scope of IFRS 2, where New K Enter issues stock for the net assets of Global Star. The net assets of Global Star are stated at historical cost, with no goodwill or intangible assets recorded. Any excess of the fair value of shares issued to Global Star over the fair value of Global Star’s identifiable net assets acquired represents compensation for the service of a stock exchange listing for its shares and is expensed as incurred.
The determination that Play Company will be considered the acquirer of K Enter for financial reporting purposes was primarily based on the assumption that:
| ● | Play Company’s existing stockholders will hold a large minority voting interest in New K Enter where no other owner has a significant voting interest; |
| ● | Play Company’s CEO has the ability to appoint the senior management of New K Enter |
| ● | Play Company’s CEO has the ability to appoint a majority of directors of New K Enter’s board of directors; |
| ● | Play Company’s operations will substantially comprise the ongoing operations of New K Enter; and |
| ● | Play Company is the larger entity in terms of substantive operations and employee base. |
Under the acquisition method of accounting, the preliminary purchase price is allocated to the underlying tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their respective fair market values, with the excess purchase price, if any, allocated to goodwill. Costs related to the transaction are expensed as incurred.
Regulatory Approvals
The Reincorporation Merger, the Acquisition Merger and the other transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement are not subject to any additional U.S. federal or state regulatory requirements or approvals, or any regulatory requirements or approvals under the laws of the Cayman Islands, except for the registration by the Registrar of Companies in the Cayman Islands of the plans of merger.
Interests of Certain Persons in the Business Combination
When you consider the recommendation of Global Star board of directors in favor of adoption of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal, the Acquisition Merger Proposal and the other related Proposals, you should keep in mind that Global Star’s directors and officers have interests in the Business Combination that are different from, or in addition to, your interests as a stockholder, including the following:
| | ● | the fact that the Sponsor and Global Star’s directors and officers hold 2,140,000 Founder Shares for which they paid an aggregate purchase price of $25,000 and, 498,225 Private Units for which they paid an aggregate purchase price of $4,982,250. Specifically: the Sponsor owns 2,798,225 shares of GLST Common Stock; Anthony Ang and Ted Kim beneficially own 1,640,000 shares of GLST Common Stock by virtue of serving as the managing members of the Sponsor, and Mr. Ang also owns 300,000 shares of GLST Common Stock directly; Nicholas Khoo owns 50,000 shares of GLST Common Stock; and Stephen Drew owns 20,000 shares of GLST Common Stock. In addition, (i) on July 31, 2023, the Sponsor loaned $1,600,000 to Global Star in exchange for a non-interest-bearing promissory note, $1.5 million of which will be converted into 150,000 shares of Global Star common stock upon completion of the Business Combination and then the balance of $100,000 will be paid to the Sponsor (the “Note”) and (ii) on August 19, 2024, the Sponsor loaned $120,000 to K Enter, evidenced by a non-interest bearing promissory note (the “K Enter Note”) due and payable on the earlier of November 18, 2024 or five days after PubCo’s registration statement on Form F-4 is declared effective. The Founder Shares, Private Units, the Note and the K Enter Note have a total current value of $35.1 million, based on September 10, 2024 closing price of the GLST Common Stock and the GLST Units, which was $11.07 and 11.34, respectively. All of such investments will expire worthless if a business combination is not consummated; on the other hand, if a business combination is consummated, such investments could earn a positive rate of return for the Sponsor and Global Star’s directors and officers since their overall investment in such investments, even if other holders of Global Star’s common stock experience a negative rate of return, due to having initially purchased the Founder Shares for $25,000; |
| | ● | the fact that, if the Trust Account is liquidated, including in the event Global Star is unable to complete an initial business combination within the required time period, the Sponsor has agreed to indemnify Global Star to the extent any claims by a third party for services rendered or products sold to us, or any claims by a prospective target business with which Global Star has discussed entering into an acquisition agreement, reduce the amount of funds in the Trust Account to below the lesser of (i) $10.25 per public share and (ii) the actual amount per public share held in the Trust Account as of the date of the liquidation of the Trust Account, if less than $10.25 per public share is then held in the Trust Account due to reductions in the value of the trust assets, less taxes payable, (y) shall not apply to any claims by a third party or a target which executed a waiver of any and all rights to the monies held in the Trust Account (whether or not such waiver is enforceable) and (z) shall not apply to any claims under the Company’s indemnity of the underwriters of Global Star’s IPO against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), but only if such a third party or target business has not executed a waiver of any and all rights to seek access to the Trust Account; |
| | ● | certain officers and directors of Global Star and affiliates of the Sponsor collectively own shares of common stock of K Enter. Ted Kim, the manager of the Sponsor and a co-founder and director of K Enter, owns 19,564 shares or 10.12% of the shares of common stock of K Enter based on the shares of K Enter to be issued and outstanding immediately prior to the closing of the Business Combination through his ownership and control of Global Fund LLC, which owns 12,000 shares, and Lodestar USA, Inc., which owns 7,564 shares. Further, Global Star officers and directors collectively own shares of common stock of K Enter representing approximately 8,537 shares or 4.3% of the outstanding shares of K Enter common stock based on the shares of K Enter to be issued and outstanding immediately prior to the closing of the Business Combination. Specifically, Stephen Drew owns 6,000 shares of K Enter common stock, Yang Kan Chong owns 1,337 shares of K Enter common stock, Jukka Rannila, beneficially through Assai OY, owns 600 shares of K Enter common stock. Nicholas Aaron Khoo, the Company’s Chief Operating Officer, owns 600 shares of K Enter common stock, prior to the closing of the Business Combination. All of such investments could expire worthless if a business combination is not consummated; and |
| | ● | the fact that none of Global Star’s officers or directors has received any cash compensation for services rendered to the Company, and all of the current members of Global Star’s Board are expected to continue to serve as directors at least through the date of the special meeting to vote on a business combination and may even continue to serve following any business combination and receive compensation thereafter. |
The exercise of Global Star’s directors’ and officers’ discretion in agreeing to changes or waivers in the terms of the transaction may result in a conflict of interest when determining whether such changes or waivers are appropriate and in Global Star’s stockholders’ best interest; and
| | ● | If the Business Combination with K Enter is completed, K Enter will designate all members of the board of directors. |
Global Star’s board of directors considered these conflicts of interest in negotiating and recommending the Business Combination and concluded that the merits of the Business Combination outweighed the potential conflicts and did not materially influence the negotiations with K Enter. In making this determination, Global Star’s board of directors also considered the fairness opinion obtained from Everedge Pte Ltd. Global Star’s certificate of incorporation includes a waiver of the corporate opportunity doctrine whereby directors and officers are required to present corporate opportunities to Global Star. Global Star does not believe that this waiver had any impact on the negotiations with K Enter.
Recommendations of Global Star’s Board of Directors to Global Star’s Stockholders
After careful consideration of the terms and conditions of the Merger Agreement, the Global Star board of directors has determined that Business Combination and the transactions contemplated thereby are fair to and in the best interests of Global Star and its stockholders. In reaching its decision with respect to the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger, the Global Star board of directors reviewed various industry and financial data and the due diligence and evaluation materials provided by K Enter. Global Star board of directors recommends that Global Star’s stockholders vote:
| ● | FOR the Reincorporation Merger Proposal; |
| ● | FOR the Acquisition Merger Proposal; |
| ● | FOR the Governance Proposal |
| ● | FOR the Director Proposal |
| ● | FOR the Incentive Plan Proposal; and |
| ● | FOR the Adjournment Proposal. |
SUMMARY RISK FACTORS
In evaluating the Business Combination and the Proposals to be considered and voted on at the Global Star Special Meeting, you should carefully review and consider the risk factors set forth under the section entitled “Risk Factors” beginning on page 36 of this proxy statement/prospectus. Some of these risks related to are summarized below. References in the summary below to “K Enter” generally refer to K Enter in the present tense or PubCo from and after the Business Combination.
The following summarizes certain principal factors that make an investment in the Combined Company speculative or risky, all of which are more fully described in the “Risk Factors” section below. This summary should be read in conjunction with the “Risk Factors” section and should not be relied upon as an exhaustive summary of the material risks facing Global Star’s, K Enter’s and/or the PubCo’s business.
Risks Related to K Enter
| | ● | K Enter has a limited operating history with a history of losses and expects to incur significant expenses for the near term. |
| | | |
| | ● | If K Enter fails to manage its growth effectively, its business could be harmed. |
| | | |
| | ● | K Enter’s business strategy may not be successfully implemented, which could negatively impact its financial results and stock price. |
| | | |
| | ● | The risk that K Enter fails to successfully and timely consummate its acquisition of one or more of the Six Korean Entities. |
| | | |
| | ● | Changes in the markets in which K Enter competes, including but not limited to with respect to its competitive landscape, technology evolution, changes in entertainment choices or regulatory changes. |
| | | |
| | ● | The risk that K Enter will need to raise additional capital to execute the business plan, which may not be available on acceptable terms or at all. |
| | | |
| | ● | K Enter’s business is highly specialized and dependent on a continuing demand for Korean entertainment content. |
| | | |
| | ● | K Enter may fail to adequately obtain, maintain, enforce and protect K Enter’s intellectual property and may not be able to prevent third parties from unauthorized use of K Enter’s intellectual property and proprietary technology. |
| | | |
| | ● | K Enter’s business depends on the success of its marketing strategies. |
| | | |
| | ● | K Enter’s success is dependent on the continued leadership and experience of K Enter management team, and the loss of their services may have a material and adverse effect on K Enter’s operations and financial condition. |
| | | |
| | ● | We may lose or fail to attract and retain key management personnel and salaried employees. |
| | | |
| | ● | The requirements of being a public company may strain K Enter’s resources and distract its management, which could make it difficult to manage the business, particularly after K Enter is no longer an “emerging growth company.” |
| | | |
| | ● | K Enter may incur material losses and costs as a result of warranty claims and product liability and intellectual property infringement actions that may be brought against K Enter. |
| | | |
| | ● | K Enter’s business could be adversely affected by computer malware, viruses, ransomware, hacking, phishing attacks and security threats, including cybersecurity threats and related disruptions, which could result in security and privacy breaches and interruption in service. |
| | | |
| | ● | The risk that K Enter may not be able to develop and maintain effective internal controls. |
Risks Related to New K Enter’s Business and Industry
Risks Related to K Enter’s Business
| | ● | Failure to comply with applicable anti-corruption legislation and other governmental laws and regulations could result in fines, criminal penalties and materially adversely affect its business, financial condition and results of operations. |
| | | |
| | ● | The continuation or worsening of the COVID-19 pandemic, or other similar public health developments, could have an adverse effect on business, results of operations, and financial condition. |
Risks Related to Global Star’s Business and the Business Combination
| | ● | Global Star will be forced to liquidate the Trust Account if it cannot consummate a business combination by February 22, 2025 (unless Global Star elects to extend the time it has to complete the initial business combination to June 22, 2025). In the event of a liquidation, Global Star’s public stockholders will receive a pro rata portion of the funds in the Trust Account and the GLST Warrants and GLST Rights will expire worthless. |
| | ● | The risk that the Business Combination may not be completed in a timely manner or at all, which may adversely affect the price of the securities |
| | | |
| | ● | You must tender your Public Shares in order to validly seek redemption at the Global Star Special Meeting of stockholders. |
| | | |
| | ● | If third parties bring claims against Global Star, the proceeds held in trust could be reduced and the per-share Public Share liquidation price received by Global Star’s stockholders may be less than $10.00. |
| | | |
| | ● | If Global Star’s due diligence investigation of K Enter was inadequate, then stockholders of Global Star following the Business Combination could lose some or all of their investment. |
Risks Related to the Combined Company Common Stock
| | ● | The market price of the PubCo Common Stock is likely to be highly volatile, and you may lose some or all of your investment. |
| | | |
| | ● | Volatility in the PubCo’s share price could subject the Combined Company to securities class action litigation. |
SECURITIES AND DIVIDENDS
Global Star’s units, common stock, warrants and rights are each quoted on the Nasdaq, under the symbols “GLSTU,” “GLST,” “GLSTW,” and “GLSTR,” respectively. Each GLST Unit consists of one share of common stock, one warrant entitling its holder to purchase one share of common stock at a price of $11.50 per whole share, and one right to receive one-tenth (1/10) of one share of common stock upon the consummation of the Business Combination. Global Star’s units commenced trading on Nasdaq on September 22, 2022. Global Star’s common stock, public rights and public warrants commenced trading on Nasdaq on November 10, 2022.
Global Star has not paid any cash dividends on its common stock to date and does not intend to pay cash dividends prior to the completion of a business combination. The payment of cash dividends in the future will be dependent upon Global Star’s revenues and earnings, if any, capital requirements and general financial condition subsequent to completion of a business combination. The payment of any dividends subsequent to the Business Combination will be within the discretion of the PubCo board of directors. It is the present intention of Global Star board of directors to retain all earnings, if any, for use in its business operations and, accordingly, Global Star’s board does not anticipate declaring any dividends in the foreseeable future.
K Enter’s securities are not currently publicly traded. K Enter is applying to list the PubCo Ordinary Shares and PubCo Warrants on Nasdaq in connection with the Business Combination.
RISK FACTORS
Stockholders should carefully consider the following risk factors, together with all of the other information included in this proxy statement/prospectus before they decide whether to vote or instruct their vote to be cast to approve the Proposals described in this proxy statement/prospectus. These risks could have a material adverse effect on the business, financial condition and results of operations of PubCo following the business combination, and could adversely affect the trading price of PubCo’s securities following the business combination.
Risk Factors Relating to K Enter’s Business, the Six Korean Entities’ Business, and New K Enter’s Business
K Enter is a holding company with limited independent operations as a drama production studio in South Korea. K Enter plans to acquire controlling interests in the Six Korean Entities following the effectiveness of this proxy statement/prospectus and before the closing of the Business Combination. Specifically, K Enter expects to acquire a controlling interest in the following companies: (1) Apeitda Co., Ltd, Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd., The LAMP Co., Ltd., and Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd., each of which is in the content production business, (the “Production Companies”); (2) Play Company Co., Ltd., which is in the content merchandising business, (the “Merchandising Company”); and (3) Solaire Partner LLC, which is in content investment business, (the “Investment Company”). Following the closing of K Enter’s acquisition of the controlling interests in the Six Korean Entities, K Enter is referred to herein as “New K Enter.”
K Enter does not have any operational history except for its newly formed drama production studio. Thus, the risks apply primarily to the Six Korean Entities that face these risks as well as future risks to New K Enter once it has been formed.
K Enter’s acquisition of the Six Korean Entities is a closing condition to the Business Combination, and while this condition can be waived, however Global Star does not currently intend to waive this condition. K Enter expects to close the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of the Six Korean Entities within 24 to 72 hours after this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 is declared effective by the SEC. In addition, Global Star will not mail proxy materials to its shareholders for the Special Meeting until after K Enter closes the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities. PubCo shall include the date that K Enter completes the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all Six Korean Entities in its Form 424B3 Prospectus to be filed with the SEC after this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 is declared effective by the SEC.
In the event that K Enter does not complete the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities, PubCo will file a post-effective amendment to its Registration Statement on Form F-4 (the “Post-Effective Amendment”) disclosing that K Enter did not complete its contemplated acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities (and the material information concerning such event) and Global Star will not mail proxy materials to its shareholders for the Special Meeting (or hold its Special Meeting) until after the Post-Effective Amendment is declared effective by the SEC. Global Star’s shareholders will not be able to vote for or against the Business Combination until after they receive a definitive proxy statement, which will only be mailed after the later of (i) the successful consummation of the acquisition of the controlling interests of all of the Six Korean Entities or (ii) the declaration of effectiveness by the SEC of the Post-Effective Amendment.
As of January 3, 2025, K Enter completed the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of each of the Six Korean Entities.
After each risk factor set forth below in this section, K Enter has identified in a parenthetical the business category to which the risk factor is applicable. Specifically, for each risk factor K Enter has provided the applicable business category: K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, and Investment Company.
K Enter is a recently formed company with limited business operations of its own and has not generated any revenues to date. K Enter plans to acquire controlling equity interests in the Six Korean Entities. Further, as K Enter has limited business operations of its own, it will depend primarily on the revenue and profits generated by the businesses of the Six Korean Entities in which it plans to acquire controlling interests. (K Enter)
K Enter was formed on January 4, 2023 and is a holding company which recently commenced operations as a drama production studio in South Korea. K Enter expects to fund operations using cash on hand and raising additional proceeds. There are no assurances, however, that K Enter will be able to generate the revenue necessary to support its cost structure or that it will be successful in obtaining the level of financing necessary for its operations. K Enter executed equity purchase agreement with the Six Korean Entities to acquire a controlling interest in each of the Six Korean Entities. The Business Combination is conditioned on K Enter acquiring each a controlling interest in each of the Six Korean Entities. The financial projections and other financial information included in or informing the First Fairness Opinion are premised on the acquisition of all Seven Korean Entities (including First Virtual), while the Second Fairness Opinion described in this proxy statement is premised on the successful acquisition of all Six Korean Entities (i.e., not including First Virtual). Moreover, the financial projections informing the Second Fairness Opinion vary significantly from the actual results achieved for the year ended December 31, 2023 and the results for the first six months of 2024. For example, the revenues of the Six Korean Entities for the six (6) months ended June 30, 2024 represent approximately 48% of the revenue of the Six Korean companies for 2023 and approximately 18% of the projected revenues for 2024.
The financial projections upon which the Second Fairness Opinion is based assumed that the Business Combination would occur on or before March 31, 2024. K Enter believes the delay in closing the Business Combination is expected to reduce New K Enter’s projected financial results of operations for 2024 because it will delay PubCo’s investment in new media content production, which is expected to drive revenues. The delay in closing the Business Combination is not expected to adversely impact PubCo’s projected results for 2025 or subsequent years, as it does not reflect a long-term trend, but rather a short-term delay in implementing business strategies. In addition, 2024 revenues were adversely impacted by (i) the seasonal nature of Play Company’s merchandising business, (ii) unexpected delays in some of the merchandising projects previously planned for the first half of the year, and (iii) slower-than-expected progress in developing new business opportunities in merchandising, among other factors. The expected reduction in PubCo’s projected revenues does not impact the Second Fairness Opinion dated March 12, 2024 (as updated on April 29, 2024), which was issued as of March 12, 2024. Global Star’s board of directors has determined that no purchase price adjustment is appropriate due to the negative deviation in performance from projected 2024 financial results of operations.
In the event K Enter successfully acquires controlling interests in all of the Six Korean Entities, then there is a risk that K Enter will not be able to manage the Six Korean Entities or the regulatory compliance activities for each of the Six Korean Entities. K Enter cannot guarantee that K Enter will be able to keep abreast of the changing legal and regulatory landscapes for each of the jurisdictions in which K Enter and the Six Korean Entities are expected to operate. If K Enter fails to manage the Six Korean Entities or the applicable regulatory compliance matters for each of the Six Korean Entities, then PubCo’s business and financial results may be harmed.
Additionally, as a holding company, K Enter will rely on earning generated by the businesses of the Six Korean Entities for distributions or payments for cash flow. Therefore, PubCo’s ability to fund and conduct PubCo’s business, service any debt, and pay dividends, if any, in the future may depend on the ability of K the Six Korean Entities to make upstream cash distributions or payments to us, which may be impacted, for example, by their ability to generate sufficient cash flow or limitations on the ability to repatriate funds, whether as a result of currency liquidity restrictions, monetary or exchange controls, regulatory restrictions, or otherwise. Further, the Six Korean Entities’ ability to make payments to K Enter will depend on:
| | ● | covenants contained in any debt agreements to which K Enter may then be subject, including any debt agreements of K Enter’s planned subsidiaries; |
| | ● | covenants contained in other agreements to which K Enter or K Enter’s planned subsidiaries are or may become subject; |
| | ● | business and tax considerations; and |
| | ● | applicable law, including any restrictions under South Korean law that may be imposed on K Enter’s planned subsidiaries and their affiliates, that would restrict its ability to make payments to K Enter. |
K Enter cannot assure that the operating results of K Enter’s planned subsidiaries at any given time will be sufficient to make distributions or other payments to us.
K Enter was formed to be an intellectual property (“IP”) entertainment company primarily through the acquisition, management, and development of companies in the entertainment business focusing on IP development and production, merchandising and IP ownership and investing and then moving into to other areas in the future such as virtualization and music. K Enter also created an in-house production company to develop, acquire and produce dramas and movies. To complement our existing portfolio and expand our influence, K Enter. actively pursues strategic partnerships, licensing agreements, and joint ventures within the entertainment industry. This allows us to access content development resources, studio facilities, and distribution channels apart from the six Korean entities. The objective of K Enter is to curate a portfolio of the best content. Recently, we signed a licensing agreement for the adaptation of the historical novel “Rabbit,” based on real-life female spy operations during the Korean War, into visual content (film, TV series). Through this agreement, we anticipate developing engaging visual content depicting historical narratives to resonate with global audiences. A link to the agreement is provided here Rabbit Link. Additionally, as part of our ongoing efforts to adapt to changes in viewer preferences, we are actively developing non-scripted TV show series including “Sexy100” (working title). A link to the agreement is provided here S100 Link.
Acquiring controlling stakes in the Six Korean Entities alongside the three core capabilities will form the cornerstone of our initial growth. Longer term, K Enter plans to actively pursue additional acquisitions, strategic partnerships, licensing agreements, and joint ventures within the entertainment industry. K Enter believe this strategy will allows it to access content development resources, studio facilities, and distribution channels apart from the Six Korean Entities.
PubCo’s inability to pay scheduled cash payment to the current owner of Play Company that are due following the closing of the Business Combination could negatively affect the business of PubCo.
Pursuant to the share purchase agreement between K Enter and the current owner of Play Company, PubCo is required to pay to the current owner of Play Company (i) a payment of 18.1 billion won (approximately $13.7 million within three months of the closing of the Business Combination, (ii) a payment of 9.05 billion won (approximately $6.87 million) by January 31, 2025 and (iii) a payment of 9.05 billion won (approximately $6.87 million) by January 31, 2026. Due to the fact that Global Star has approximately $13 million in its Trust Account, absent a capital raise before or after the closing of the Business Combination, PubCo may not have sufficient funds to make the post-closing payments to the current owner of Play Company. If PubCo does not have the available cash to make the required payment to the current owner of Play Company, PubCo may be subject to certain risks under the share purchase agreement such as the possibility of litigation. Specifically, Section 7.5(8) of the Share Purchase Agreement provides following the Closing of the Share Purchase Agreement the right of the non-breaching party to claim damages against the breaching party shall be the sole and exclusive remedy available to the non-breaching party for any monetary claims arising out of the breaching parties actions. Additionally, Section 2.3 of the Share Purchase Agreement between the owner of Play Company and K Enter provides that, in the event K Enter fails to pay the Purchase Price when due, the Purchaser shall pay to the Seller a default interest on such unpaid amount as calculated at the rate of fifteen percent (15%) per annum for the period from the relevant due date until the day immediately preceding the date of actual payment. Accordingly, in the event PubCo fails to make the payments that are due to the current owner of Play Company following the Closing of the Share Purchase Agreement, PubCo may be subject to a lawsuit commenced by the current owner of Play Company for monetary damages, including default interest at the rate of fifteen percent (15%) per annum until such obligations are paid. Such a lawsuit and the damages that may be potentially awarded to the current owner of Play Company could have a material adverse impact on the financial condition and/or results of operations of PubCo.
Risk factors impacting New K Enter (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company)
Competition within the broader entertainment industry may be intense and we expect that the Six Korean Entities’ existing and potential customers may be attracted to competing forms of entertainment, such as television, gaming and sporting events, as well as other entertainment options on the Internet. If the Six Korean Entities’ offerings may not be popular, New K Enter’s business may be harmed. (K Enter, Production, Merchandising)
Though New K Enter has yet to be formed, we expect New K Enter to operate in the global motion pictures industry within the broader entertainment industry with New K Enter’s mostly Korean offerings. We expect that New K Enter’s customers face a vast array of entertainment choices. Other forms of entertainment, such as television, gaming, and sporting events, may be more well-established and may be perceived by post-acquisition New K Enter’s customers to offer greater variety, affordability, interactivity and enjoyment. We expect that New K Enter will compete with these other forms of entertainment for the discretionary time and income of New K Enter’s customers. If we may be unable to sustain sufficient interest in the Six Korean Entities’ Korean entertainment offerings in comparison to other forms of entertainment, including new forms of entertainment, we expect that New K Enter’s business model may not continue to be viable.
The specific industries in which the Six Korean Entities operate may be characterized by dynamic customer demand and technological advances, and there may be intense competition among entertainment providers. A number of established, well-financed companies producing motion pictures, episodic content, or other relevant IPs and services may compete with the Six Korean Entities’ offerings, and other well-capitalized companies may introduce competitive IPs. Such competitors may spend more money and time on developing and testing content and services, undertake more extensive marketing campaigns, adopt more aggressive pricing or promotional policies or otherwise develop more commercially successful content or services than the Six Korean Entities’, which may negatively impact the Six Korean Entities’ business. The Six Korean Entities’ competitors may also develop content, features, or services that may be similar to theirs or that achieve greater market acceptance. Such competitors may also undertake more far-reaching and successful content development efforts or marketing campaigns, or may adopt more aggressive pricing policies. Furthermore, new competitors offering Korean motion pictures and episodic content may compete directly against the Six Korean Entities. There has also been considerable consolidation among competitors in the Korean entertainment industries and such consolidation and future consolidation may result in the formation of larger competitors with increased financial resources and altered cost structures, which may enable them to offer more competitive content, gain a larger market share, acquire the Six Korean Entities’ key partners, decrease cost per user acquisition, expand offerings and broaden their geographic scope of operations. If we may not be able to maintain or improve the Six Korean Entities’ market share, or if their offerings may not be accepted by the markets in which we operate, we expect that New K Enter’s business may suffer.
We expect that New K Enter may experience substantial fluctuations in its operating results and growth rate. (K Enter, Production Companies, Investment and Merchandising Company)
We may not be able to accurately forecast post-acquisition New K Enter’s growth rate in content IP development, investment and merchandizing. New K Enter may base its expense levels and investment plans on sales estimates. A significant portion of the Six Korean Entities’ expenses and investments may be fixed, and we may not be able to adjust their spending quickly enough if their sales may be less than expected.
The Six Korean Entities revenue growth may not achieve our expectations. The Six Korean Entities’ revenue and operating profit growth may depend on the continued growth of demand for the content and services offered by the Six Korean Entities or their customers, and their business may be affected by general economic and business conditions worldwide. A softening of demand, whether caused by changes in customer preferences or a weakening of the Korea, U.S. or global economies, may result in decreased revenue or growth.
The Six Korean Entities’ sales and operating results for content merchandizing may also fluctuate for many other reasons, including due to risks described elsewhere in this section and the following:
| ● | the Six Korean Entities expected ability to retain and increase sales to existing customers, attract new customers, and satisfy New K Enter’s customers’ demands; |
| | ● | the Six Korean Entities expected ability to retain and expand New K Enter’s network of customers; |
| | ● | the Six Korean Entities expected ability to offer content on favorable terms, manage inventory, and fulfill orders; |
| | ● | the Six Korean Entities expected introduction of competitive stores, websites, content, services, price decreases, or improvements; |
| | ● | the Six Korean Entities expected changes in usage or adoption rates of the Internet, e-commerce, electronic devices, and web services, inside or outside the U.S.; |
| | ● | the Six Korean Entities expected timing, effectiveness, and costs of expansion and upgrades of post-acquisition New K Enter’s systems and infrastructure; |
| | ● | the expected success of New K Enter’s geographic, service, and content line expansions; |
| | ● | the expected extent to which New K Enter raise capital, and the terms of any such financing for, New K Enter’s current operations and future growth; |
| | ● | the expected outcomes of legal proceedings and claims, which may include significant monetary damages or injunctive relief and may have a material adverse impact on post-acquisition New K Enter’s operating results; |
| | ● | variations in the mix of content and services the Six Korean Entities sell; |
| | ● | expected variations in post-acquisition New K Enter’s level of merchandise and vendor returns; |
| | ● | the expected extent to which we offer free shipping, continue to reduce prices worldwide, and provide additional benefits to post-acquisition New K Enter’s customers; |
| | ● | expected factors affecting post-acquisition New K Enter’s reputation or brand image; |
| | ● | the extent to which we invest in technology and content, fulfillment, and other expense categories; |
| | ● | increases in the prices of fuel and gasoline, as well as increases in the prices of other energy products and commodities like paper and packing supplies; |
| | ● | the expected extent to which post-acquisition New K Enter’s equity-method investees record significant operating and non-operating items; |
| | ● | the expected extent to which operators of the networks between post-acquisition New K Enter’s customers and its successfully charge fees to grant its customers unimpaired and unconstrained access to its online services; |
| | ● | our expected ability to collect amounts owed to us when they become due; |
| | ● | the expected extent to which use of post-acquisition New K Enter’s services may be affected by spyware, viruses, phishing and other spam emails, denial of service attacks, data theft, computer intrusions, outages, and similar events; |
| | ● | terrorist attacks and armed hostilities; |
| | ● | supply chain issues either in chip shortages; and |
| | ● | potential long lead time in the developments, investments, productions and distributions of IP content. |
The Six Korean Entities international operations in content production, content merchandizing and content investment expose us to a number of risks (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company).
The Six Korean Entities’ specializing operations (content production, content merchandizing and content investment) currently involve some level of international activities and efforts that we believe will be significant to post-acquisition New K Enter’s revenues and profits, and we plan to further expand the Six Korean Entities’ international reach of those operations. However, while expanding into new international market segments, the Six Korean Entities may have relatively little operating experience in newly expanded segments and may not benefit from any first-to-market advantages or otherwise succeed in these segments. It may be costly to establish, develop, and maintain more committed international operations, and promote post-acquisition New K Enter’s brand internationally. The post-acquisition New K Enter’s international operations may not be profitable on a sustained basis due to the Six Korean Entities’ limited experience and knowledge in newly expanded segments.
In addition to risks described elsewhere in this section, we expect that the post-acquisition New K Enter’s international sales and operations may be subject to a number of risks, including:
| | ● | local economic and political conditions; |
| | ● | government regulation and compliance requirements (such as regulation of New K Enter’s IP content and service offerings and of competition), restrictive governmental actions (such as trade protection measures, including export duties and quotas and custom duties and tariffs), nationalization, and restrictions on foreign ownership; |
| | ● | restrictions on sales or distribution of certain content or services and uncertainty regarding liability for certain IP content, including uncertainty as a result of less Internet-friendly legal systems, local laws, lack of legal precedent, and varying rules, regulations, and practices regarding the physical and digital distribution of media content and enforcement of intellectual property rights; |
| | ● | business licensing or certification requirements, such as for imports, exports, web services, and electronic devices; |
| | ● | limitations on the repatriation and investment of funds and foreign currency exchange restrictions; |
| | ● | limited technology infrastructure; |
| | ● | shorter payable and longer receivable cycles and the resultant negative impact on cash flow; |
| | ● | laws and regulations regarding consumer and data protection, privacy, network security, encryption, payments, and restrictions on pricing or discounts; |
| | ● | lower levels of consumer spending and fewer opportunities for growth compared to the U.S.; |
| | ● | lower levels of credit card usage and increased payment risk; |
| | ● | difficulty in staffing, developing, and managing foreign operations as a result of distance, language, and cultural differences; |
| | ● | different employee/employer relationships and the existence of works councils and labor unions; |
| | ● | compliance with the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and other applicable U.S. and foreign laws prohibiting corrupt payments to government officials and other third parties; |
| | ● | laws and policies of the U.S. and other jurisdictions affecting trade, foreign investment, loans, and taxes; and |
| | ● | geopolitical events, including war and terrorism. |
As international physical, e-commerce, and other services grow, competition may intensify, including through adoption of evolving business models. Local companies may have a substantial competitive advantage because of their greater understanding of, and focus on, the local customer, as well as their more established local brand names. We may not be able to hire, train, retain, and manage required personnel, which may limit the post-acquisition New K Enter’s international growth.
The Six Korean Entities’ technology, content and brands are subject to the threat of piracy, unauthorized copying and other forms of intellectual property infringement. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company)
We regard the Six Korean Entities’ technology, content and brands as proprietary and take measures to protect their technology, content and brands and other confidential information from infringement. Piracy and other forms of unauthorized copying and use of the Six Korean Entities’ technology, content and brands may become persistent, and policing is difficult. Further, the laws of some countries in which the Six Korean Entities’ products are or may be distributed either do not protect the Six Korean Entities’ intellectual property rights to the same extent as the laws of the United States, or are poorly enforced. Legal protection of the Six Korean Entities’ rights may be ineffective in such countries. In addition, although we take steps to enforce and police the Six Korean Entities’ rights, factors such as the proliferation of technology designed to circumvent the protection measures used by the Six Korean Entities’ business partners or by us, the availability of broadband access to the Internet, the refusal of Internet service providers or platform holders to remove infringing content in certain instances, and the proliferation of online channels through which infringing product is distributed all have contributed to a general expansion in unauthorized copying of technology, content and brands.
We may not be able to prevent others from unauthorized use of the Six Korean Entities’ intellectual property, which we expect could harm New K Enter’s business and competitive position. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company)
K Enter, the Production Companies and the Merchandising Company are each engaged in the “IP content business,” which refers to a business that focuses on creating, managing, licensing, and monetizing intellectual property (IP) content such as TV shows, movies, dramas and music. At the heart of K Enter’s and the Production Companies content business is the creation of original content or the acquisition of rights to existing content from creators, artists, or other sources, such as films and TV shows that are valuable intellectual property. In the case of the Merchandising Company it involves the merchandise sales of IP Content based on a popular musicians, TV shows and movies. K Enter, the Production Companies and the Merchandising Company regard their IP, including copyrights, registered trademark and pending trademarks, service marks, domain names, trade secrets, proprietary technologies and similar intellectual property as critical to New K Enter’s success. The, IP rights we expect New K Enter to own upon the closing of the Business Combination are limited to the IP Content that is currently owned by the Apeitda and Bidangil, which are two of the Six Korean Entities.
Specifically, Bidangil owns 100% for the movies it produced: The Chaser, Forbidden Quest and The Showdown. For these works Bidangil owns the copyrights, the exploitation rights including distribution, sales, licensing, and remake rights as well as a certain percentage of the net profit share rights of these works. Bidangil also owns partial IP rights (noted in parentheses) to the following works it produced: The Scam (50%), A Werewolf Boy (40%), The Royal Tailor (40%), Perfect Proposal (40%), Phantom Detective (40%), and Resonance (50%). For these works both the copyrights and net profit share rights are maintained in the percentages noted in the parentheses. Likewise, Apeitda owns 100% of the intellectual property rights for the movie Action boys and 50% of the intellectual property rights for the movie Villainess. The significance of the intellectual property is that K Enter believes that holding the intellectual property rights of content will help increase PubCo’s revenues not just directly from content creation, but also from leveraging and exploiting that IP content across other mediums such as webtoons and additional revenue sources such as merchandising. In addition, securing the intellectual property rights will enable us to seek better distribution terms of our IP content, provide greater artistic freedom for the artists that work with PubCo and ultimately allow PubCo to secure better creators and content. The intellectual property rights relating to the merchandise produced and sold by Play Company are owned and retained by the respective K Pop agencies who contract with Play Company. We will rely on trademark law, trade secret protection and confidentiality and license agreements with New K Enter’s employees and others to protect New K Enter’s proprietary rights. One of the objectives of PubCo is to be able to own the intellectual property rights of the content it creates. K Enter is working towards this goal but as of now Six Korean Entites own limited intellectual property as noted above.
K Enter, the Production Companies and the Merchandising Company have invested significant resources to develop their IP content and acquire licenses and permissions to use and distribute the IP content of others. We believe that failure to maintain or protect these rights could harm New K Enter’s business. In addition, any unauthorized use of the intellectual property owned by K Enter, the Production Companies and/or the Merchandising Company by third parties may adversely affect New K Enter’s future revenues and reputation. The significance of the intellectual property is that New K Enter believes that owning and exploiting IP of content will help increase our revenues not just directly from content creation but also from leveraging that IP across other mediums such as webtoons and additional revenue sources such as merchandising. In addition, securing the IP will enable New K Enter to seek better distribution terms for its content, provide greater artistic freedom for the artists that work with New K Enter and ultimately allow us to secure better creators of content as well as additional IP content.
Policing unauthorized use of proprietary technology is difficult and expensive. We expect to rely on a combination of copyright, trademark and trade secret laws and restrictions on disclosure to protect the intellectual property rights of K Enter, the Production Companies and the Merchandising Company. Further, New K Enter plans to require every employee and consultant to execute proprietary information and invention agreements prior to commencing work. Despite such efforts there can be no assurances that New K Enter will be able to adequately protect it IP content or other proprietary rights. Third parties may attempt to copy or otherwise obtain and use the IP content and intellectual property of K Enter, the Production Companies and the Merchandising Company or seek court declarations that their conduct does not infringe upon the IP content and intellectual property rights of K Enter, the Production Companies and the Merchandising Company. From time to time, New K Enter may have to resort to litigation to enforce the IP content and intellectual property rights of K Enter, the Production Companies and the Merchandising Company, which could result in substantial costs and diversion of our resources.
Our quarterly and annual operating results after the business combination may fluctuate due to seasonality in the Six Korean Entities’ business. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company)
The Six Korean Entities’ business may be subject to seasonal variations based on the timing of their Enter’s IP content releases. Release dates may be determined by several factors, including the timing of holiday periods, geographical release dates and competition in the market, and more recently, the timing of release dates has been affected by the pandemic.
This seasonal pattern of business requires significant use of working capital, mainly to prepare inventory during the months prior to the holiday season, and requires accurate forecasting of demand for specific IP offerings during the holiday season in order to avoid losing potential sales of popular IP content offerings or producing excess inventory that may be less popular with consumers. The Six Korean Entities’ failure to accurately predict and respond to consumer demand, resulting in under producing popular IP offerings and/or overproducing less popular IP offerings, would reduce the Six Korean Entities’ total sales and harm their results of operations.
As a result of the seasonal nature of the Six Korean Entities’ business, we would be significantly and adversely affected, in a manner disproportionate to the impact on a company with sales spread more evenly throughout the year, by unforeseen events such as a natural disaster, a terrorist attack, economic shock or pandemic that harms the retail environment or consumer buying patterns during the Six Korean Entities’ key selling season, or by events such as strikes or port delays or other supply chain challenges that interfere with the shipment of goods, particularly from the Far East, during the important months leading up to the holiday shopping season.
We may experience fluctuations in the Six Korean Entities’ operating results, which make their future results difficult to predict and may cause our operating results to fall below expectations. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company)
We expect the future New K Enter’s financial results to fluctuate in the future due to the nature of the Six Korean Entities’ business. These fluctuations may be due to a variety of factors, some of which may be outside of the Six Korean Entities’ control and may not fully reflect the underlying performance of their business.
For example, consumer engagement in the Six Korean Entities’ entertainment offerings may decline or fluctuate as a result of a number of factors, including the popularity of Korean culture, the customer’s taste in Asian movies, the Six Korean Entities’ ability to improve and innovate, outages and disruptions of online services, the services offered by the Six Korean Entities’ competitors, the Six Korean Entities’ marketing and advertising efforts or declines in consumer activity generally as a result of economic downturns, among others. Any decline or fluctuation in the recurring portion of the Six Korean Entities’ business may have a negative impact on our post-acquisition business, financial condition, results of operations or prospects.
We may be unable to maintain or acquire licenses or approvals to incorporate intellectual property owned by others in the Six Korean Entities’ IP content offerings. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company)
The Six Korean Entities’ IP content offerings may incorporate intellectual property owned by others. Relatedly, content that we distribute across various platforms may incorporate motions pictures of New K Enter’s associated parties and other third parties.
Additionally, the Six Korean Entities’ content offerings may incorporate motion pictures intellectual property owned by third parties. Exhibition of such content on different platforms, such as movie theatre or traditional media television or subscription video on demand platforms, may require additional licensing that may be difficult or costly to obtain. If the platforms on which content is distributed, redistributed and/or embedded change their policies relating to how content exhibited or published on the platform may be used, it may impact the Six Korean Entities’ ability to develop, distribute and exhibit engaging content and negatively impact their operations. If the Six Korean Entities are unable to maintain their licenses, rights and approvals or obtain additional licenses, rights and approvals with significant commercial value, their ability to develop successful and engaging IP content may be adversely affected and their operations may be negatively impacted.
The Six Korean Entities’ IP content and brand names may be subject to intellectual property infringement, including in jurisdictions that do not adequately protect brands and intellectual property rights. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company)
We regard the Six Korean Entities’ brand, IP content and other intellectual property as proprietary and we expect to take measures to protect New K Enter’s assets from infringement post-acquisition. We expect to be aware that potential unauthorized use of the Six Korean Entities’ brands and content may occur, and if a significantly greater amount were to occur, it may negatively impact New K Enter’s business. Further, the Six Korean Entities’ IP content offerings may be available worldwide and the laws of some countries either do not protect their content, brands and intellectual property to the same extent as the laws of the U.S. or may be poorly enforced. Legal protection of the Six Korean Entities’ rights may be ineffective in countries with weaker intellectual property enforcement mechanisms. In addition, certain third parties may register the Six Korean Entities’ intellectual property rights without authorization in foreign countries. Successfully registering such intellectual property rights may limit or restrict the Six Korean Entities’ ability to offer content and services based on such rights in those countries. Although we take steps to enforce and police the Six Korean Entities’ rights, our practices and methodologies may not be effective against all eventualities.
As a producer, investor, and distributor of IP content, the Six Korean Entities may face liability and expenses for legal claims based on the nature and content of the materials that they create or distribute, including materials provided by third parties. If they are required to pay damages or expenses in connection with these legal claims, we expect that New K Enter’s business and results of operations may be harmed. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company)
We expect to display the Six Korean Entities’ and its original IP content and third-party IP content on New K Enter’s websites and in its marketing materials. As a result, New K Enter may face potential liabilities including, but not limited to, copyright or trademark infringements and content misuse. New K Enter will generally rely on the “fair use” exception for New K Enter’s use of third-party brand names and marks, but these third parties may disagree, and the laws governing the fair use of these third-party materials are imprecise and adjudicated on a case-by-case basis in Korea. The Six Korean Entities also produce IP content we believe to be original. While we do not believe that such IP content infringe on any third-party copyrights or other intellectual property rights, companies that adopt business models similar to us may take the position that some of our IP content infringe on their intellectual property rights. These claims could divert management time and attention away from New K Enter’s business and result in significant costs to investigate and defend, regardless of the merit of these claims. The general liability insurance New K Enter plans to maintain may not cover potential claims of this type or may not be adequate to indemnify New K Enter for all liability that may be imposed. Any imposition of liability that is not covered by insurance, or is in excess of insurance coverage, could materially adversely affect New K Enter business, financial condition and results of operations and the price of PubCo’s securities.
The Six Korean Entities’ dependence on third-party relationships with IP content producers and distribution channels to develop and distribute IP content is critical to the success of New K Enter’s business. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company)
New K Enter plans to rely on the Six Korean Entities’ third party relationships with Korean IP content producers and distribution channels to develop and distribute IP content. New K Enter’s financial performance may be adversely affected by the Six Korean Entities’ relationships with content producers and distribution channels. Some of the Six Korean Entities’ content producers may have their own or other distribution capabilities in the markets in which they operate. These third-party content producers and distribution channels may decide, or be required by their respective parent companies, to use their intracompany distribution or content production capabilities rather than publishing such content with the Six Korean Entities. New K Enter’s business may be harmed if the content producers and distribution channels with which the Six Korean Entities work stop or reduce the amount of content they produce for the Six Korean Entities, or otherwise demand less favorable terms to them.
Risk factors impacting New K Enter (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
If the Six Korean Entities fails to respond to or capitalize on the rapid technological development in the video, music, gaming, and entertainment industry, including changes in entertainment delivery formats, New K Enter’s business may be harmed. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
The video, music, gaming, and entertainment industry continues to experience frequent change driven by technological development, including developments with respect to the formats through which music, films, television programming, games, and other content may be delivered to consumers. With rapid technological changes and expanded digital content offerings, the scale and scope of these changes have accelerated in recent years. For example, consumers may be increasingly accessing television, film and other episodic content on streaming and digital content networks, such as Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Hulu, Disney+ and Apple TV+.
Many motion pictures and episodic content offerings have gone direct to streaming channels and not produced a physical content format. Direct release to streaming channels may be likely to continue. Technological as well as other changes caused by the pandemic may have caused significant disruption to the retail distribution of film and episodic content offerings and have caused and may in the future cause a negative impact on sales of New K Enter’s content and other forms of monetization of content. New K Enter may lose opportunities to capitalize on changing market dynamics, technological innovations or consumer tastes if the Six Korean Entities do not adapt its content offerings or distribution capabilities in a timely manner. The overall effect that technological development and new digital distribution platforms have on the revenue and profits the Six Korean Entities derive from their movie content, including from merchandise sales derived from such content, and the additional costs associated with changing markets, media platforms and technologies, may be unpredictable. If the Six Korean Entities fails to accurately assess and effectively respond to changes in technology and consumer behavior in the entertainment industry, the post-acquisition New K Enter’s business may be harmed.
Failure to protect or enforce the Six Korean Entities’ intellectual property rights or the costs involved in such enforcement may harm New K Enter’s business, financial condition and results of operations. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
We expect New K Enter to rely on trademark, copyright, patent, trade secret, and domain-name-protection laws to protect the Six Korean Entities’ proprietary rights. In Korea and internationally, the Six Korean Entities’ may have filed various applications to protect aspects of their intellectual property, and they may hold a number of issued IPs in multiple jurisdictions. New K Enter may acquire additional companies or their portfolios, which may require significant cash expenditures. However, third parties may knowingly or unknowingly infringe the proprietary rights of New K Enter’s subsidiaries, third parties may challenge proprietary rights held by New K Enter’s operating subsidiaries, and pending and future trademark and patent applications may not be approved. In addition, effective intellectual property protection may not be available in every country in which the Six Korean Entities’ operates or intends to operate its business. In any of these cases, the Six Korean Entities may be required to expend significant time and expense to prevent infringement or to enforce their rights. There may be no assurance that others may not offer content or services that are substantially similar to the Six Korean Entities’ and compete with their business.
Circumstances outside the Six Korean Entities’ control may pose a threat to their intellectual property rights. For example, effective intellectual property protection may not be available in the United States or other countries from which the Six Korean Entities’ content offerings may be accessible. Also, the efforts the Six Korean Entities have taken to protect their proprietary rights may not be sufficient or effective. Any significant impairment of the Six Korean Entities’ intellectual property rights may harm their business or its ability to compete. Also, protecting the Six Korean Entities’ intellectual property rights may be costly and time-consuming. Any unauthorized disclosure or use of the Six Korean Entities’ intellectual property may make it more expensive to do business, thereby harming their operating results. Furthermore, if the Six Korean Entities are unable to protect their proprietary rights or prevent unauthorized use or appropriation by third parties, the value of the Six Korean Entities’ brand and other intangible assets may be diminished, and competitors may be able to more effectively mimic the Six Korean Entities’ offerings and services. The occurrence of any of these events may seriously harm New K Enter’s business post-acquisition of the Six Korean Entities.
We currently face concentration risk within Play Company Co. Ltd. (K Enter, Merchandise Company)
Currently, Play Company faces concentration risk due to its reliance on HYBE Co., Ltd. (“HYBE”), as a major business partner in its merchandising business.
Historically, in 2021 and 2022, Play Company’s dependence on HYBE, a K-pop agency, accounted for 86% and 80% of the total revenues of Play Company. In 2023, Play Company’s dependency on HYBE decreased, but HYBE continued to contribute approximately 52% of Play Company’s total revenues in 2023. Play Company recognizes the risks associated with this level of dependency and is actively working towards diversifying its revenue sources to mitigate these risks.
| Play Company’s Concentration of HYBE | | | | | | | | Unit: % | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2022 | | | 2023 | |
| HYBE share of Total Play Revenues | | | 86 | % | | | 80 | % | | | 52 | % |
| BTS share of Total Play Revenues | | | 72 | % | | | 67 | % | | | 24 | % |
Play Company’s written agreement with Weverse Company Inc. provided for a term from September 28, 2022 to Feb. 5, 2023. Play Company’s written agreement UMJ provided for a term from January 1 2022 to Dec. 31 2022. The formal, comprehensive agreement (producing, publishing, and distributing merchandise) between Play Company and HYBE has also expired. However, based on an informal understanding between Play Company and HYBE, despite the expiration of the Weverse Agreement and the UMJ Agreement, Play Company has continued to distribute and release products covered by those agreements in 2023. An example of this is the release of BTS Permission to Dance in Las Vegas merchandise on November 27, 2023.
However, recently, HYBE created a limited, distribution only agreement with Play Company targeting the first half of 2024. This distribution agreement with HYBE was signed on March 19, 2024 for four specific merchandise products. This one-year distribution agreement is projected to yield limited revenues to Play Company in 2024. Principal terms of the distribution agreement between Hybe Co., Ltd. (Hybe) and Play Company Corp. are the following. Contract period : One year. January 26, 2024 – January 25, 2025. Distribution agreement entered into by Play Company to distribute video publications or other publications (pictures, photo books, DVDs, etc).The scope of the global distribution covers four specific projects by artists TXT and ENHYPEN. Play Company earns revenues and profits by purchasing the merchandise from HYBE at a discount to the suggested manufacturer’s price and selling it to customers at a higher price.
Play Company is in the process of negotiating new agreements with HYBE and its subsidiaries for 2025 and 2026, but there is no guarantee any such agreements will be executed and whether the terms will revert back to a comprehensive agreement noted previously. If the agreement is not executed or if the terms are changed Play Company runs the risk that revenue will decline from HYBE. K Pop agencies, like HYBE, can exert significant buyer power over Play Company and can impact the revenues of Play Company. The change in the business agreement terms with HYBE in 2024 was a possibility the executive management of Play Company had considered and contingencies were made to replace the possible loss of HYBE-related revenues with new opportunities:
| 1. | In December 2023, Play Company entered into a new agreement with SM Entertainment, a major K-Pop agencies that manage top-tier K-Pop artists including Aespa, whose third extended play (EP) album sold over 2 million copies globally and ranked top-10 on the Billboard 200. Under this new agreement, Play Company is provided with exclusive video merchandising rights for all K-Pop artists under SM Entertainment’s management. Play Company expects to generate a sufficient amount of video merchandising revenues from this new agreement to replace a meaningful proportion of the possible reduction of HYBE-related revenues. Such SM-related revenues is planned to be incurred and recorded during the second half of the financial year of 2024 with new SM-related video merchandises released for the Christmas and winter season. |
| | 2. | Play Company has also widened its merchandise types and lineups for other, non-HYBE-related artists for who Play Company has merchandising rights under existing agreements. Such new non-video merchandises include light sticks and concert-related collectibles from which Play Company expects to generate a considerable amount of new revenues during the second half of the financial year of 2024. |
| | 3. | Play Company has been strengthening and extending its merchandise retail and distribution networks in Japan, and is expected to record higher merchandising distribution revenues for some of the non-HYBE-related artists, for who Play Company has existing merchandising rights, in 2024 than prior years. |
| | | |
| | 4. | Play Company is in active pursuit of securing new merchandising rights for other artists with whom it has no prior business relationships. Following its successful engagement with SM Entertainment, Play Company aims to enter similar exclusive business relationships with other major K-Pop agencies to generate additional video merchandise revenues, as well as non-K-Pop merchandise. |
The financial projections provided within this document for Play Company did account for the possible reduction of HYBE-related revenues. The projections for 2024 and beyond did not assume a continued dependent relationship with HYBE but anticipated gains from the above-stated new business opportunities. As of now, we expect that Play Company will be able to generate revenues equivalent to the projected revenues for the financial year of 2024.
For the first half of 2024, Play Company generated approximately $3 million in revenue from HYBE and we expect another $2 million from HYBE during the second half of 2024. Play Company is scheduled to release a total of 32 products for 2024, of which 28 are to be released from late June and the second half of 2024. Of the 17 products from SM, 15 are scheduled during the second half of 2024. This is because the new two-year contract from SM was entered into in December of 2023. Play Company needed time to plan, design, and make the products related to SM Entertainment artists. Despite our ongoing-efforts to diversify our sources of revenues so that we will not be dependent on specific K-Pop Agencies and related video-merchandise there is no assurance that we will achieve our intended goals.
On December 22, 2023 we entered into a new agreement with SM Entertainment Co., Ltd. (“SM Entertainment”), a major K-pop agency, to create video merchandise for all of their artists. Revenues from SM Entertainment could take some years to build to the levels achieved by HYBE. The Principal terms of the agreement between SM Entertainment and Play Company Corp. are the following. Contract period : December 23, 2023 – December 31, 2025. Automatically renewed for one year if neither party expresses intention to terminate. Worldwide collaborative agreement to produce, publish, distribute merchandise of SM Entertainment artists using various video materials by SM Entertainment and Play Company. The net profit earned on this project will be allocated among the two parties according to a set ratio between Play Company and SM Entertainment. A different, higher ratio is set for SM Entertainment’s artists NCT, NCT Dream and NCT127.
In the arrangements with K Pop agencies, like HYBE and SM Entertainment, these agencies or their clients retain ownership of the intellectual property rights relating to the merchandise that is created by Play Company.
New K Enter may be subject to risks related to online payment methods, including third-party payment processing-related risks. (K Enter, Merchandise Company)
We expect that New K Enter will accept payments using a variety of methods, including ACH, wire transfers, credit card and debit cards. As New K Enter offers new payment options to consumers, it may be subject to additional regulations, compliance requirements, fraud, and other risks. New K Enter may also rely on third parties to provide payment processing services, and for certain payment methods, New K Enter will pay interchange and other fees, which may increase over time and raise New K Enter’s operating costs and affect ability to achieve or maintain profitability. New K Enter may be also subject to payment card association operating rules and certification requirements, including the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, or PCI-DSS, and rules governing electronic funds transfers, which may change or be reinterpreted to make it difficult or impossible for New K Enter to comply. If New K Enter (or a third-party processing payment card transactions on New K Enter’s behalf) suffer a security breach affecting payment card information, it may have to pay onerous and significant fines, penalties and assessments arising out of the major card brands’ rules and regulations, contractual indemnifications or liability contained in merchant agreements and similar contracts, and New K Enter may lose its ability to accept payment cards for payment for its goods and services, which may materially impact New K Enter’s operations and financial performance.
As New K Enter’s business changes in the future, it may be subject to different rules under existing standards, which may require new assessments that involve costs above what Play Company currently pays for compliance. As New K Enter offer new payment options to consumers, including by way of integrating emerging mobile and other payment methods, New K Enter may be subject to additional regulations, compliance requirements and fraud. If New K Enter fails to comply with the rules or requirements of any provider of a payment method it accepts, if the volume of fraud in New K Enter’s transactions limits or terminates its rights to use payment methods we currently accept, or if a data breach occurs relating to New K Enter’s payment systems, New K Enter may, among other things, be subject to fines or higher transaction fees and may lose, or face restrictions placed upon, New K Enter ability to accept credit card payments from consumers or facilitate other types of online payments.
The Six Korean Entities’ may occasionally receive orders placed with fraudulent data, and we expect that New K Enter may ultimately be held liable for the unauthorized use of a cardholder’s card number in an illegal activity and be required by card issuers to pay charge-back fees. Charge-backs may result not only in New K Enter’s loss of fees earned with respect to the payment, but also may leave us liable for the underlying money transfer amount. If New K Enter’s charge-back rate becomes excessive, card associations also may require us to pay fines or refuse to process New K Enter’s transactions. In addition, we may be subject to additional fraud risk if third-party service providers or New K Enter’s employees fraudulently use consumer information for their own gain or facilitate the fraudulent use of such information. Overall, we may have little recourse if we process a criminally fraudulent transaction.
New K Enter may not realize the anticipated benefits of acquisitions or investments in IP content, or those benefits may be delayed or reduced in their realization. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
Acquisitions, investments and mechanizations in IP content may be crucial components of the expected growth and the development of New K Enter’s business. Acquisitions may broaden and diversify New K Enter’s brand holdings and content offerings may and allow New K Enter to build additional capabilities and competencies.
New K Enter cannot be certain that the IP content it may acquire, or acquire an interest in, may achieve or maintain popularity with consumers in the future or that any such acquisitions or investments may allow New K Enter to more effectively market its brands, develop its competencies or grow its business. In some cases, New K Enter expects that the integration of the Six Korean Entities that New K enter plans to acquire and incorporate into its operations may create development, marketing and other operating, revenue or cost synergies which may produce greater revenue growth and profitability and, where applicable, cost savings, operating efficiencies and other advantages. However, New K Enter cannot be certain that these synergies, efficiencies and cost savings will be realized. Even if achieved, these benefits may be delayed or reduced in their realization. In other cases, New K Enter may acquire or invest in IP that it believes to have strong and creative management, in which case New K Enter may plan to operate them more autonomously rather than fully integrating them into its operations. New K Enter may not be certain that the key talented individuals who own such IP content would continue to work for New K Enter after the acquisition or that they would develop popular and profitable content, entertainment or services in the future. New K Enter cannot guarantee that any acquisition or investment it may make will be successful or beneficial, and such acquisitions may consume significant amounts of management attention and other resources, which may negatively impact other aspects of New K Enter’s business.
New K Enter will face competition and if it is unable to compete effectively with existing or new competitors, New K Enter’s revenues, market share and profitability may not achieve its expectations. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New K Enter will have many competitors in the motion picture and broader entertainment industry. Some of the current and potential competitors have greater resources, longer histories, more customers, and/or greater brand recognition than New K Enter, Such competitors may secure better IP content deals, adopt more aggressive marketing, and devote more resources to technology, infrastructure, content delivery, and other areas. New K Enter competes in Korea and internationally with a wide array of large and small IP content development, IP content investment firms, virtual IP content production companies and movie studios. In addition, New K Enter competes with companies who may be focused on building their brands across multiple consumer categories, including through entertainment offerings other than motion pictures and episodic content. Across New K Enter’s business, it face competitors who may be constantly monitoring and attempting to anticipate consumer tastes and trends, seeking content which may appeal to consumers, and introducing new content that compete with New K Enter’s content for consumer acceptance and purchase.
Competition may intensify, including with the development of new business models and the entry of new and well-funded competitors, and as New K Enter’s competitors enter into business combinations or alliances and established companies in other market segments expand to become competitive with New K Enter’s business. In addition, new and enhanced technologies, including search, digital content, and electronic devices, may increase New K Enter’s competition. The Internet may facilitate competitive entry and content offerings comparison, and increased competition may reduce New K Enter’s business profits.
New K Enter’s expansion into new IP content offerings, services, technologies, and geographic regions subjects New K Enter to additional business, legal, financial, and competitive risks. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New K Enter may have limited or no relevant expertise in its future IP content development and merchandizing, and it customers may not adopt to New K Enter’s IP content offerings. These offerings may present new and difficult technology and content delivery challenges, and New K Enter may be subject to claims if customers of these offerings experience service disruptions or failures or other quality issues. In addition, profitability, if any, in New K Enter’s newer business activities may be lower than in its existing activities, and New K Enter may not be successful enough in these newer activities to recoup its investments in them. If any of this were to occur, it may damage New K Enter’s reputation, limit its growth, and negatively affect New K Enter’s results from operations.
Misalignment with public and consumer tastes and preferences for entertainment offerings may negatively impact demand for New K Enter’s IP content, which may have an adverse effect on New K Enter’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New K Enter plans to develop, invest in, and merchandize entertainment content, the success of which may depend substantially on consumer interests and preferences that frequently change in unpredictable ways. The success of New K Enter’s business may depend on its ability to consistently create popular content, and to engage popular talent, that may meet the changing preferences of the broad consumer market and may respond to competition from an expanding array of entertainment choices facilitated by technological developments in the availability and delivery of digital content. Misalignment of New K Enter’s IP content if New K Enter may not be successful in responding to rapidly changing public and consumer tastes and preferences, may impact demand for New K Enter’s IP content offerings and its business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects may be materially affected.
Inflation may cause New K Enter’s investment and development costs as well as operating and administrative expenses to grow more rapidly than net sales, which may result in lower gross margins and lower net earnings (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
Market variables, such as inflation of labor rates and fuel, freight and energy costs, across multiple geographic regions, have and may continue to increase potentially causing New K Enter to be unable to efficiently manage its development costs and operating and administrative expenses in a way that would enable New K Enter to leverage its revenue growth into higher net earnings. In addition, New K Enter’s inability to pass on such increases in development costs to the consumers in a timely manner, or at all, may cause New K Enter’s operating and administrative expenses to grow, which may result in lower gross profit margins and lower net earnings.
The current inflation levels have not materially impacted New K Enter’s day-to-day operations. However, inflation affects the cost of production and demand for New K Enter’s merchandise products, film and drama and food and beverage segment (the smallest segment). New K Enter competes with limited consumer and teenager’s budgets for entertainment and K Pop merchandise goods.
K Pop video merchandise customers are the least price sensitive among New K Enter’s clientele. New K Enter’s merchandise is purchased by fans who are very loyal to their artists, and this results in a lower price elasticity. New K Enter believes that product sales volume is driven by product quality that meets the needs of fans and the timely release of these goods.
In the case for film production, inflation impacts New K Enter’s break-even point. Higher movie ticket prices and lower consumer disposable income also lowers demand. The main customers of dramas are broadcasting companies and Over-the-Top or OTT companies, and although production costs are increasing due to inflation New K Enter believes these firms have been willing to invest in high-quality content.
The food and beverage segment is particularly sensitive to inflation with rising material costs and wages directly impacting New K Enter’s costs. Consumers with lower disposable income and intense competition in the market makes it more difficult to pass on the increased costs to New K Enter’s customers.
Weakness in the economy, market trends and other conditions affecting the profitability and financial stability of New K Enter’s expected consumers may negatively impact New K Enter’s expected sales growth and results of operations. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
Economic, political and industry trends will affect New K Enter’s business environments. We expect that New K Enter will serve an industry in which the demand for its content and services may be sensitive to the production activity, capital spending and demand for content and services of New K Enter’s customers. Some of these customers (including distributors) operate in markets that maybe subject to cyclical fluctuations resulting from market uncertainty, trade and tariff policies, costs of goods sold, currency exchange rates, central bank interest rate fluctuations, economic downturns, recessions, foreign competition, offshoring of production, oil and natural gas prices, geopolitical developments, labor shortages, inflation, natural or human induced disasters, extreme weather, outbreaks of pandemic disease such as the COVID-19 pandemic, inflation, deflation, and a variety of other factors beyond our control. Any of these factors may cause customers to idle, delay purchases, reduce wholesale purchasing levels, or experience reductions in the demand.
Any of these events may also reduce the volume of content and services these customers purchase from New K Enter or impair the ability of New K Enter’s customers to make full and timely payments and may cause increased pressure on New K Enter’s selling prices and terms of sale.
New K Enter’s expansions may place a strain on its management, operational, financial, and other resources. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New K Enter’s business may plan on operations of expansions, including increasing New K Enter’s IP acquisitions, service offerings and scaling New K Enter’s infrastructure to support its IP merchandizing businesses. This expansion may increase the complexity of New K Enter’s business and may place strain on New K Enter’s management, personnel, operations, systems, technical performance, financial resources, and internal financial control and reporting functions. New K Enter may not be able to manage growth effectively, which may damage New K Enter’s reputation, limit its growth, and negatively affect New K Enter’s operating results.
Consumer interests change rapidly and acceptance of New K Enter’s IP content offerings may be influenced by factors beyond New K Enter’s control. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
The interests of families, individuals, fans and audiences evolve extremely quickly and may change from year to year and by geography. To be successful, New K Enter plans to correctly anticipate the types of IP content patterns which may capture consumers’ interests and imagination, and quickly develop and introduce innovative IP offerings which may compete successfully for consumers’ limited time, attention and spending. This challenge may be more difficult with the ever-increasing utilization of technology, social media and digital media in entertainment offerings, and the increasing breadth of entertainment available to consumers. Evolving consumer tastes and shifting interests, coupled with an ever-changing and expanding pipeline of entertainment and consumer properties and content which compete for consumer interest and acceptance, create an environment in which some content offerings may fail to achieve consumer acceptance, and other IP content offerings may be popular during a certain period of time but then be rapidly replaced. As a result, New K Enter’s IP content offerings may have short consumer life cycles.
Consumer acceptance of New K Enter’s or its partners’ entertainment offerings may be also affected by outside factors, such as reviews, promotions, the quality and acceptance of films and television programs, music, video games, and content released into the marketplace at or near the same time, the availability of alternative forms of entertainment and leisure time activities, general economic conditions and public tastes generally, all of which may change rapidly and most of which may be beyond New K Enter’s control. There may be no assurance that television programs and films, video games, video movies New K Enter distributes may obtain favorable reviews or ratings, that films, video games, video movies New K Enter distributes may be popular with consumers and perform well in New K Enter’s distribution channels.
If New K Enter devotes time and resources to distributing and marketing content that consumers do not accept or do not find interesting enough to buy in sufficient quantities to be profitable to New K Enter, New K Enter’s revenues and profits may decline, and New K Enter’s business performance may be harmed. Similarly, if New K Enter’s IP offerings fail to correctly anticipate consumer interests, New K Enter’s revenues and earnings may be reduced.
Failure to successfully operate New K Enter’s information systems and implement new technology effectively may disrupt New K Enter’s business or reduce New K Enter’s sales or profitability. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New K Enter may rely on various information technology systems and software applications to manage many aspects of its businesses, including content development, communications with New K Enter’s affiliates and partners, sale and delivery of New K Enter’s New K Enter New K Enter New K Enter content, royalty and financial reporting and various other processes and transactions. New K Enter may be dependent on the integrity, security and consistent operations of these systems and related back-up systems. These systems may be subject to damage or interruption from power outages, computer and telecommunications failures, computer viruses, malware and other cybersecurity breaches, catastrophic events such as hurricanes, fires, floods, earthquakes, tornadoes, acts of war or terrorism and usage errors by New K Enter’s employees or partners. The efficient operation and successful growth of New K Enter’s business may depend on these information systems, including New K Enter’s New K Enter ability to operate them effectively and to select and implement appropriate upgrades or new technologies and systems and adequate disaster recovery systems successfully. The failure of New K Enter’s information systems or third-party hosted technology to perform as designed or New K Enter’s failure to implement and operate them effectively may disrupt New K Enter’s business, require significant capital investments to remediate a problem or subject New K Enter to liability.
The products and internal systems of the Six Korean Entities that New K Enter expects to acquire, rely on software and hardware that is highly technical, and any errors, bugs, or vulnerabilities in these systems, or failures to address or mitigate technical limitations in New K Enter’s systems, could adversely affect New K Enter’s business. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
The Six Korean Entities’ products and internal systems rely on software and hardware, including software and hardware developed or maintained internally and/or by third parties, that is highly technical and complex. In addition, the Six Korean Entities’ products and internal systems depend on the ability of such software and hardware to store, retrieve, process, and manage immense amounts of data. The software and hardware on which they rely upon may contain, and will in the future may further contain, errors, bugs, or vulnerabilities, and their systems are subject to certain technical limitations that may compromise the Six Korean Entities’ ability to meet their objectives. Some errors, bugs, or vulnerabilities inherently may be difficult to detect and may only be discovered after the code has been released for external or internal use. Errors, bugs, vulnerabilities, design defects, or technical limitations within the software and hardware on which the Six Korean Entities rely upon have in the past led to, and may in the future lead to, outcomes including a negative experience for users and marketers who use their products, compromised ability of the Six Korean Entities’ products to perform in a manner consistent with their terms, contracts, or policies, delayed product introductions or enhancements, targeting, measurement, or billing errors, compromised ability to protect the data of the Six Korean Entities’ users and/or their intellectual property or other data, or reductions in the Six Korean Entities’ ability to provide some or all of their services. For example, the Six Korean Entities make commitments to their users as to how their data will be used within and across products, and the Six Korean Entities’ systems are subject to errors, bugs and technical limitations that may prevent them from fulfilling these commitments reliably. In addition, any errors, bugs, vulnerabilities, or defects in New K Enter’s systems or the software and hardware on which New K Enter relies, failures to properly address or mitigate the technical limitations in the Six Korean Entities’ systems, or associated degradations or interruptions of service or failures to fulfil commitments to their users may in the future lead to outcomes including damage to our reputation, loss of users, loss of marketers, loss of revenue, regulatory inquiries, litigation, or liability for fines, damages, or other remedies, any of which could adversely affect the post-acquisition New K Enter’s business and financial results.
If New K Enter’s electronic data is compromised, New K Enter’s business may be significantly harmed. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New K Enter and its subsidiaries may maintain significant amounts of data electronically in locations around the United States and in the cloud. This data may relate to all aspects of New K Enter’s business, including the Six Korean Entities’ and post-acquisition New K Enter’s content under development, and also may contain certain customer, consumer, supplier, partner and employee data. New K Enter may maintain systems and processes designed to protect this data, but notwithstanding such protective measures, there may be a risk of intrusion, cyber-attacks or tampering that may compromise the integrity and privacy of this data. Cyber-attacks may be increasing in their frequency, sophistication and intensity, and may be becoming increasingly difficult to detect. They may be often carried out by motivated, well-resourced, skilled and persistent actors, including nation states, organized crime groups, “hacktivists” and employees or contractors acting with malicious intent. Cyber-attacks may include the deployment of harmful malware and key loggers, ransomware, a denial-of-service attack, a malicious website, the use of social engineering and other means to affect the confidentiality, integrity and availability of the Six Korean Entities’ and New K Enter’s technology systems and data. Cyber-attacks may also include information system attacks, which may cause a delay in the development, investment and distribution of New K Enter’s IP content. In addition, we expect that the New K Enter may provide confidential and proprietary information to its and the Six Korean Entities’ third-party business partners in certain cases where doing so may be necessary to conduct New K Enter’s business. While New K Enter obtains assurances from those parties that they have systems and processes in place to protect such data, and where applicable, that they may take steps to assure the protections of such data by third parties, those partners may also be subject to data intrusion or otherwise compromise the protection of such data. Any compromise of the confidential data of New K Enter’s customers, consumers, suppliers, partners, employees or ourselves, or failure to prevent or mitigate the loss of or damage to this data through breach of New K Enter’s information technology systems or other means may substantially disrupt New K Enter’s operations, harm New K Enter’s customers, consumers, employees and other business partners, damage New K Enter’s reputation, violate applicable laws and regulations, subject New K Enter to potentially significant costs and liabilities and may result in a loss of business that may be material.
New K Enter’s failure to raise additional capital or generate cash flows necessary to expand its operations and invest in the future which may reduce New K Enter’s ability to compete successfully and adversely affect New K Enter’s results of operations. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New K Enter may need to raise additional funds following the closing of the Business Combination, and New K Enter may not be able to obtain additional debt or equity financing on favorable terms or at all. If New K Enter raises additional equity financing, you may experience significant dilution of your ownership interests. If New K Enter raises additional debt financing, New K Enter may be required to accept terms that restrict New K Enter’s ability to incur additional indebtedness, may force New K Enter to maintain specified liquidity or other ratios or may restrict New K Enter’s ability to pay dividends or make acquisitions. If New K Enter needs additional capital and may not raise it on acceptable terms, or at all, New K Enter may not be able to, among other things:
| | ● | make the post closing payments to the owner of Play Company as called for the Play Company stock purchase agreement; |
| | | |
| | ● | invest in New K Enter’s business and continue to grow New K Enter’s brand and expand New K Enter’s fan base; |
| | ● | hire and retain employees, including celebrities, influences, and content creators as well as other employees and staff, including engineers, operations personnel, financial and accounting staff, and sales and marketing staff; |
| | ● | respond to competitive pressures or unanticipated working capital requirements; or |
| | ● | pursue opportunities for acquisitions of, investments in, or strategic alliances and joint ventures with complementary businesses. |
We expect New K Enter will face risks related to health epidemics and other widespread outbreaks of contagious disease, which may disrupt New K Enter’s expected operations and impact its expected operating results. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
Significant outbreaks of contagious diseases, and other adverse public health developments, may have a material impact on New K Enter’s business operations and operating results. Since the global outbreak of COVID-19, nearly every country has throughout the world have been affected by the spread of the virus, including Korea and the United States, and has implemented various emergency measures to contain the virus outbreak, including travel restrictions, restrictions on public gatherings and required in-home quarantine. As New K Enter has a presence in these locations, these measures may affect the health of New K Enter’s employee and ability to travel and work remotely.
Moreover, during and since the Covid-19 pandemic, the film exhibition industry has suffered from a decline in attendance in revenues and attendance as well as delays in film production. In this environment, some high budget movies have failed to recoup production and distribution costs. New K Enter cannot predict how the Covid-19 pandemic or other pandemics may impact New K Enter’s operations and financial results.
Economic downturns and political and market conditions beyond New K Enter’s control may adversely affect New K Enter’s business, financial condition and results of operations. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New K Enter’s financial performance may be subject to global, Korea and U.S. economic conditions and their impact on levels of spending by customers and advertisers. Economic recessions may have had, and may continue to have, far reaching adverse consequences across many industries, including the global entertainment and movie industries, which may adversely affect New K Enter’s business and financial condition. Due to international trade and monetary policy and other changes, there may appear to be an increasing risk of a recession. If the national and international economic recovery slows or stalls, these economies may experience another recession or any of the relevant regional or local economies suffers a downturn, New K Enter may experience a material adverse effect on New K Enter’s business, financial condition, results of operations or prospects.
In addition, changes in general market, economic and political conditions in domestic and foreign economies or financial markets, including fluctuation in stock markets resulting from, among other things, trends in the economy as a whole may reduce customers’ disposable income. Any one of these changes may have a material adverse effect on New K Enter’s business, financial condition, results of operations or prospects.
Reductions in discretionary consumer spending may have an adverse effect on New K Enter’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New K Enter’s expected business may be particularly sensitive to reductions from time to time in discretionary consumer spending. Demand for entertainment and leisure activities, including movies and TV series, may be affected by changes in the economy and consumer tastes, both of which may be difficult to predict and beyond New K Enter’s control. Unfavorable changes in general economic conditions, including recessions, economic slowdowns, sustained high levels of unemployment, and rising prices or the perception by consumers of weak or weakening economic conditions, may reduce New K Enter’s customers’ disposable income or result in fewer individuals engaging in entertainment and leisure activities, such as movie going or online streaming. As a result, New K Enter may not ensure that demand for future offerings may remain constant. Adverse developments affecting economies throughout the world, including a general tightening of availability of credit, decreased liquidity in certain financial markets, increased interest rates, foreign exchange fluctuations, increased energy costs, acts of war or terrorism, transportation disruptions, natural disasters, declining consumer confidence, sustained high levels of unemployment or significant declines in stock markets, as well as concerns regarding pandemics, epidemics and the spread of contagious diseases may lead to a further reduction in discretionary spending on leisure activities, such as movie going or online streaming. Any significant or prolonged decrease in consumer spending on entertainment or leisure activities may adversely affect the demand for New K Enter’s expected offerings, reducing New K Enter’s expected cash flows and revenues, and thereby materially harming New K Enter’s expected business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Changes in foreign currency exchange rates may significantly impact New K Enter’s expected reported financial performance. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New K Enter’s expected global operations mean it will transact business in many different jurisdictions with many different currencies. As a result, if the exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and a local currency for an international market in which New K Enter has significant sales or operations changes, New K Enter’s financial results as reported in U.S. dollars, may be meaningfully impacted even if New K Enter’s business in the local currency is not significantly affected. Similarly, New K Enter’s expenses may be significantly impacted, in U.S. dollar terms, by exchange rates, meaning the profitability of New K Enter’s business in U.S. dollar terms may be negatively impacted by exchange rate movements which New K Enter does not control. Depreciation in key currencies may have a significant negative impact on New K Enter’s revenues and earnings as they may be reported in U.S. dollars.
The Six Korean Entities’ business involves risks of liability claims for media content, which may adversely affect their business, results of operations and financial condition. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
As a developer, investor and distributor of media content, New K Enter may face potential liability for defamation, invasion of privacy, negligence, copyright or trademark infringement, and other claims based on the nature and content of the materials distributed. These types of claims have been brought, sometimes successfully, against producers and distributors of media content. Any imposition of liability that may be not covered by insurance or may be in excess of insurance coverage may have a material adverse effect on New K Enter’s business, results of operation and financial condition.
The Six Korean Entities’ relies on information technology and other systems and platforms, and any failures, errors, defects or disruptions in their systems or platforms may diminish New K Enter’s brand and reputation, subject New K Enter to liability, disrupt its business, affect its ability to scale technical infrastructure and adversely affect its operating results and growth prospects. New K Enter’s IP content and other software applications and systems, and the third-party platforms upon which they may be made available may contain undetected errors. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
The Six Korean Entities’ technology infrastructure may be important to the performance of their offerings and to customer satisfaction. New K Enter will devote resources to network and data security to protect the Six Korean Entities’ systems and data. However, New K Enter’s systems may not be designed with the necessary reliability and redundancy to avoid performance delays or outages that may be harmful to the Six Korean Entities’ business. We may not assure you that the measures New K Enter will take to prevent or hinder cyber-attacks and protect New K Enter’s systems, data and customer information and to prevent outages, data or information loss, fraud and to prevent or detect security breaches, including a disaster recovery strategy for server and equipment failure and back-office systems and the use of third parties for certain cybersecurity services, may provide absolute security. We may in the future experience website disruptions, outages and other performance problems due to a variety of factors, including infrastructure changes, human or software errors and capacity constraints. To date, the Six Korean Entities have not had a material impact from such disruptions; however, future disruptions from unauthorized access to, fraudulent manipulation of, or tampering with their computer systems and technological infrastructure, or those of third parties, may result in a wide range of negative outcomes, each of which may materially adversely affect their business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. Additionally, the Six Korean Entities’ content may contain errors, bugs, flaws or corrupted data, and these defects may only become apparent after their launch. If a particular content offering may be unavailable when customers attempt to access it or navigation through platforms may be slower than they expect, customers may be less likely to return to the Six Korean Entities’ content as often, if at all. Furthermore, programming errors, defects and data corruption may disrupt the Six Korean Entities’ operations, may adversely affect the experience of the Six Korean Entities’ customers, harm the Six Korean Entities’ reputation, cause the Six Korean Entities’ customers to stop utilizing their platforms, divert the Six Korean Entities’ resources and delay market acceptance of their offerings, any of which may result in legal liability to the Six Korean Entities, harm their business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
If the Six Korean Entities’ customer base and engagement continue to grow, and the amount and types of offerings continue to grow and evolve, the Six Korean Entities may need an increasing amount of technical infrastructure, including network capacity and computing power, to continue to satisfy the Six Korean Entities’ customers’ needs. Such infrastructure expansion may be complex, and unanticipated delays in completing these projects or availability of components may lead to increased project costs, operational inefficiencies, or interruptions in the delivery or degradation of the quality of the Six Korean Entities’ offerings. In addition, there may be issues related to this infrastructure that may be not identified during the testing phases of design and implementation, which may only become evident after the Six Korean Entities’ has started to fully use the underlying equipment or software, that may further degrade the customer experience or increase their costs. As such, New K Enter may fail to continue to effectively scale and grow its technical infrastructure to accommodate increased demands. In addition, the post-acquisition New K Enter’s business may be subject to interruptions, delays or failures resulting from adverse weather conditions, other natural disasters, power loss, terrorism, cyber-attacks, public health emergencies (such as COVID-19) or other catastrophic events. We believe that if New K Enter’s customers have a negative experience with is content offerings, or if New K Enter’s brand or reputation may be negatively affected, customers may be less inclined to continue or resume enjoying its content or recommend its content to other potential customers. As such, a failure or significant interruption in New K Enter’s service may harm its reputation, business and operating results.
Despite the Six Korean Entities’ security measures, their information technology and infrastructure may be vulnerable to attacks by hackers or breached due to employee error, malfeasance or other disruptions. Any such breach may compromise Six Korean Entities’ networks and the information stored there may be accessed, publicly disclosed, lost or stolen. Any such access, disclosure or other loss of information may result in legal claims or proceedings, liability under laws that protect the privacy of personal information, and regulatory penalties, disruption of Six Korean Entities’ operations and the services they provides to customers, damage to New K Enter’s reputation, and a loss of confidence in New K Enter’s content and services, which may adversely affect New K Enter’s business. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
The secure maintenance and transmission of customer information will be an important element of New K Enter’s operations. The Six Korean Entities’ information technology and other systems that maintain and transmit customer information, or those of service providers, business partners or employee information may be compromised by a malicious third-party penetration of New K Enter’s network security, or that of a third-party service provider or business partner, or impacted by intentional or unintentional actions or inactions by their employees, or those of a third-party service provider or business partner. As a result, the Six Korean Entities’ customers’ information may be lost, disclosed, accessed or taken without their customers’ consent. New K Enter and its Korean subsidiaries may not provide assurance that they may not experience any cyberattacks in the future and such cyberattacks may have a material impact on New K Enter’s operations or financial results.
Six Korean Entities rely on encryption and authentication technology licensed from third parties in an effort to securely transmit confidential and sensitive information, including credit card numbers. Advances in computer capabilities, new technological discoveries or other developments may result in the whole or partial failure of this technology to protect transaction data or other confidential and sensitive information from being breached or compromised. In addition, websites may be often attacked through compromised credentials, including those obtained through phishing and credential stuffing. The Six Korean Entities’ security measures, and those of their third-party service providers, may not detect or prevent all attempts to breach the Six Korean Entities’ systems, denial-of-service attacks, viruses, malicious software, break-ins, phishing attacks, social engineering, security breaches or other attacks and similar disruptions that may jeopardize the security of information stored in or transmitted by their websites, networks and systems or that they or such third parties otherwise maintain, including payment card systems, which may subject the Six Korean Entities or New K Enter to fines or higher transaction fees or limit or terminate their access to certain payment methods. New K Enter, its Korean subsidiaries and such third parties may not anticipate or prevent all types of attacks until after they have already been launched. Further, techniques used to obtain unauthorized access to or sabotage systems change frequently and may not be known until launched against them or their third-party service providers.
In addition, security breaches may also occur as a result of non-technical issues, including intentional or inadvertent breaches by New K Enter’s employees or by third parties. These risks may increase over time as the complexity and number of technical systems and applications New K Enter uses also increases. Breaches of New K Enter’s security measures or those of New K Enter’s third-party service providers or cybersecurity incidents may result in unauthorized access to New K Enter’s sites, networks and systems; unauthorized access to and misappropriation of customer information, including customers’ personally identifiable information, or other confidential or proprietary information of ourselves or third parties; viruses, worms, spyware or other malware being served from New K Enter’s sites, networks or systems; deletion or modification of content or the display of unauthorized content on New K Enter’s sites; interruption, disruption or malfunction of operations; costs relating to breach remediation, deployment of additional personnel and protection technologies, response to governmental investigations and media inquiries and coverage; engagement of third-party experts and consultants; litigation, regulatory action and other potential liabilities. If any of these breaches of security should occur and be material, New K Enter’s reputation and brand may be damaged, New K Enter’s business may suffer, New K Enter may be required to expend significant capital and other resources to alleviate problems caused by such breaches, and New K Enter may be exposed to a risk of loss, litigation or regulatory action and possible liability. New K Enter may not guarantee that recovery protocols and backup systems may be sufficient to prevent data loss. Actual or anticipated attacks may cause New K Enter to incur increasing costs, including costs to deploy additional personnel and protection technologies, train employees and engage third-party experts and consultants.
In addition, any party who may be able to illicitly obtain a customer’s password may access the customer’s transaction data or personal information, resulting in the perception that New K Enter’s systems may be insecure. Any compromise or breach of New K Enter’s security measures, or those of New K Enter’s third-party service providers, may violate applicable privacy, data protection, data security, network and information systems security and other laws and cause significant legal and financial exposure, adverse publicity and a loss of confidence in New K Enter’s security measures, which may have a material adverse effect on New K Enter’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
New K Enter addresses cyber security risks and plan to strengthen New K Enter’s security by working with an IT consulting firm to mitigate potential security breaches of customer information, business partners and employee information. Breaches at third-party providers can also directly impact us. New K Enter is bolstering in-house capabilities and risk management measures including data backup and recovery, investment in advanced technologies but also recognize the need to leverage the expertise of cybersecurity professionals. New K Enter plans to evaluate New K Enter’s consultant’s recommendations regarding assessing, identifying, and mitigating these risks to develop a comprehensive plan to manage cybersecurity risks. New K Enter plans to keep the board informed of these discussions, the implementation plan and proactively engage with them on New K Enter’s cybersecurity efforts.
New K Enter’s data is stored both in the U.S. and in Korea and New K Enter will maintain security to ensure the continued integrity of New K Enter’s business operation while weighing costs and the need to minimize potential impacts to New K Enter’s business.
The Six Korean Entities rely on third-party service providers with respect to their platforms and to deliver their offerings to customers on their platforms, and any disruption of or interference with their use of such services may adversely affect New K Enter’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
The Six Korean Entities currently maintain and support their operations using private cloud infrastructure, which may be built using third-party platform and datacenter providers. In addition, as we expect New K Enter to enter new jurisdictions, New K Enter may rely on third-party providers of cloud infrastructure services. New K Enter may not have control over the operations of the facilities or infrastructure of any third-party service providers, including third-party platform providers, that New K Enter expect to use. Such third parties’ facilities may be vulnerable to damage or interruption from natural disasters, cybersecurity attacks, terrorist attacks, power outages and similar events or acts of misconduct. New K Enter’s platform’s continuing and uninterrupted performance may be important to New K Enter’s success. We expect that in New K Enter will experience interruptions, delays and outages in service and availability from these third-party service providers from time to time due to a variety of factors, including infrastructure changes, human or software errors, website hosting disruptions and capacity constraints. In addition, any changes in these third parties’ service levels may adversely affect New K Enter’s ability to meet the requirements of New K Enter’s customers. As New K Enter’s platform’s continuing and uninterrupted performance may be important to its success, sustained or repeated system failures would reduce the attractiveness of New K Enter’s offerings. It may become increasingly difficult to maintain and improve New K Enter’s performance, especially during peak usage times, as New K Enter expands and the usage of New K Enter’s offerings increases.
In the event that any of the Six Korean Entities’ agreements with these third-party service providers may be terminated, New K Enter may experience significant costs or downtime in connection with the transfer to, or the addition of, new platform providers, data site providers or cloud infrastructure service providers. Although alternative providers may host New K Enter’s platform on a substantially similar basis, such transition may potentially be disruptive and New K Enter may incur significant one-time costs.
Any of the above circumstances or events may harm New K Enter’s reputation and brand, reduce the availability or usage of New K Enter’s platform, lead to a significant loss of revenue, increase New K Enter’s costs and impair New K Enter’s ability to attract new customers, any of which may adversely affect New K Enter’s business, financial condition and results of operations.
New K Enter plans to have a significant level of operations outside of the United States, which subjects New K Enter to additional costs and risks that may adversely affect its operating results. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
We expect a significant portion of New K Enter’s operations will be, after the acquisition of the Six Korean Entities, located in Korea.
Compliance with Korean and U.S. laws and regulations that apply to New K Enter’s international operations may increase New K Enter’s cost of doing business. As a result of New K Enter’s international operations, New K Enter may be subject to a variety of risks and challenges in managing an organization operating in various countries, including those related to:
| | ● | challenges caused by distance as well as language and cultural differences; |
| | ● | general economic conditions in each country or region; |
| | ● | political unrest, terrorism and the potential for other hostilities; |
| | ● | public health risks, particularly in areas in which New K Enter has significant operations; |
| | ● | longer payment cycles and difficulties in collecting accounts receivable; |
| | ● | overlapping or changes in tax regimes; |
| | ● | difficulties in transferring funds from certain countries; |
| | ● | laws such as the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, and local laws which also prohibit corrupt payments to governmental officials; and |
| | ● | reduced protection for intellectual property rights in some countries. |
If New K Enter is unable to expand or manage New K Enter’s existing development operations, New K Enter may not realize, in whole or in part, the anticipated business projections, which in turn may materially adversely affect New K Enter’s business, financial condition, and results of operations. Moreover, the financial projections contained in the Second Fairness Opinion are based on the assumption that K Enter acquired the Six Korean Entities and the Business Combination closed on or before March 31, 2024, which did not occur. Accordingly, the delay in K Enter’s acquisition of the Six Korean Entities and the closing of the Business Combination beyond March 31, 2024, will reduce PubCo’s projected revenues for 2024, but is not expected to have a materially adverse impact on PubCo’s revenues for the fiscal years 2025 through 2028.
The financial projections upon which the Second Fairness Opinion is based assumed that the Business Combination would occur on or before March 31, 2024. K Enter believes the delay in closing the Business Combination is expected to reduce New K Enter’s projected financial results of operations for 2024 because it will delay PubCo’s investment in new media content production, which is expected to drive revenues. The delay in closing the Business Combination is not expected to adversely impact PubCo’s projected results for 2025 or subsequent years, as it does not reflect a long-term trend, but rather a short-term delay in implementing business strategies. The expected reduction in PubCo’s projected revenues does not impact the Second Fairness Opinion dated March 12, 2024 (as updated on April 29, 2024), which was issued as of March 12, 2024. Global Star’s board of directors has determined that no purchase price adjustment is appropriate due to the negative deviation in performance from projected 2024 financial results of operations.
New K Enter expects, from time to time, to be subject to various legal proceedings which, if adversely determined, may cause New K Enter to incur substantial losses. An adverse outcome in one or more of such proceedings may adversely affect New K Enter’s business. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
From time to time, during the normal course of operating New K Enter’s business, New K Enter may be subject to various legal proceedings. Because New K Enter may not accurately predict the outcome of any action, it may be possible that, as a result of current and/or future litigation, New K Enter may be subject to adverse judgments or settlements, some of which may not be covered under New K Enter’s insurance policies. Any litigation to which New K Enter may be a party may result in an onerous or unfavorable judgment that may not be reversed upon appeal, or in payments of substantial monetary damages or fines, the posting of bonds requiring significant collateral, letters of credit or similar instruments, or New K Enter may decide to settle lawsuits on similarly unfavorable terms. These proceedings may also result in reputational harm, criminal sanctions, consent decrees or orders preventing New K Enter from offering certain content or requiring a change in New K Enter’s business practices in costly ways or requiring development of non-infringing or otherwise altered content. Litigation and other claims and regulatory proceedings against New K Enter may result in unexpected disciplinary actions, legal expenses and liabilities. Any of the foregoing may have a material adverse effect on New K Enter’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
If Internet and other technology-based service providers experience service interruptions, New K Enter’s ability to conduct its business may be impaired and New K Enter’s business, financial condition and results of operations may be adversely affected. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
A substantial portion of New K Enter’s network infrastructure may be provided by third parties, including Internet service providers and other technology-based service providers. See “—New K Enter relies on third-party service providers with respect to New K Enter’s platform and to deliver New K Enter’s offerings to customers on New K Enter’s platform, and any disruption of or interference with New K Enter’s use of such services may adversely affect New K Enter’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.” New K Enter requires technology-based service providers to implement cyber-attack-resilient systems and processes. However, if Internet service providers experience service interruptions, including because of cyber-attacks, or due to an event causing an unusually high volume of Internet use (such as during the COVID-19 pandemic or other public health emergency), communications over the Internet may be interrupted and impair New K Enter’s ability to conduct New K Enter’s business. Internet service providers and other technology-based service providers may in the future roll out upgraded or new mobile or other telecommunications services, such as 5G or 6G services, which may not be successful and thus may impact the ability of New K Enter’s customers to access New K Enter’s platform or offerings in a timely fashion or at all. In addition, New K Enter’s ability to process e-commerce transactions may depend on bank processing and credit card systems. To prepare for system problems, New K Enter may continuously seek to strengthen and enhance New K Enter’s current facilities and the capabilities of New K Enter’s system infrastructure and support. Nevertheless, there may be no assurance that the Internet infrastructure or New K Enter’s own network systems may continue to be able to meet the demand placed on New K Enter by the continued growth of the Internet, the overall online streaming communities and the motion picture industry and New K Enter’s customers. Any difficulties these providers face, including the potential of certain network traffic receiving priority over other traffic (such as lack of net neutrality), may adversely affect New K Enter’s business, and New K Enter may exercise little control over these providers, which may increase New K Enter’s vulnerability to problems with the services they provide. Any system failure as a result of reliance on third parties, such as network, software or hardware failure, including as a result of cyber-attacks, which causes a loss of New K Enter’s customers’ property or personal information or a delay or interruption in New K Enter’s online services and content, including New K Enter’s ability to handle existing or increased traffic, may result in a loss of anticipated revenue, interruptions to New K Enter’s platform and offerings, cause New K Enter to incur significant legal, remediation and notification costs, degrade the customer experience and cause customers to lose confidence in New K Enter’s offerings, any of which may have a material adverse effect on New K Enter’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
The Six Korean Entities’ growth may depend, in part, on the success of their current and future strategic relationships with third parties. Overreliance on certain third parties, or their inability to extend existing relationships of their predecessor entities or agree to new relationships may cause unanticipated costs for The Six Korean Entities and impact their financial performance in the future. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
The Six Korean Entities may, in the future, rely on relationships with movie directors, IP investment and development firms, advertisers, marketing firms and other third parties in order to attract customers to their contents. These relationships may, along with providers of online services, search engines, social media, directories and other websites and ecommerce businesses, direct consumers to their platforms. In addition, many of the parties with whom the Six Korean Entities may have advertising arrangements through relationships of their predecessor entities provide advertising services to other companies, including other gaming platforms with whom the Six Korean Entities may compete. While the Six Korean Entities believe there may be other third parties that may drive customers to their platforms, adding or transitioning to them may disrupt their business and increase their costs. In the event that any of the Six Korean Entities’ future relationships fails to provide services to them in accordance with the terms of their arrangement, or at all, and the Six Korean Entities may not be able to find suitable alternatives, this may impact their ability to attract consumers cost effectively and harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
New K Enter’s growth may depend on its ability to attract and retain customers, and the loss of its customers, failure to attract new customers in a cost-effective manner, or failure to effectively manage New K Enter’s growth may adversely affect its business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New K Enter’s ability to achieve growth in revenue in the future may depend, in large part, upon New K Enter’s ability to attract new customers to New K Enter’s content offerings, retain existing customers of New K Enter’s content offerings and reactivate customers in a cost-effective manner. Achieving growth in New K Enter’s community of customers may require New K Enter to increasingly engage in sophisticated and costly sales and marketing efforts, which may not make sense in terms of return on investment. New K Enter expects to use a variety of free and paid marketing channels, in combination with compelling offers and exciting games to achieve New K Enter’s objectives. If the search engines on which New K Enter relies modify their algorithms, change their terms, or if the prices at which New K Enter may purchase listings increase, then New K Enter’s costs may increase, and fewer customers may click through to New K Enter’s website. If links to New K Enter’s website may not be displayed prominently in online search results, if fewer customers click through to New K Enter’s website, if New K Enter’s other digital marketing campaigns may not be effective, of it the costs of attracting customers using any of New K Enter’s current methods significantly increase, then New K Enter’s ability to efficiently attract new customers may be reduced, New K Enter’s revenue may decline and New K Enter’s business, financial condition and results of operations may be harmed.
New K Enter may invest in or acquire other businesses, and its business may suffer if New K Enter is unable to successfully integrate acquired businesses into New K Enter or otherwise manage the growth associated with multiple acquisitions. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
As part of New K Enter’s business strategy, New K Enter may make acquisitions as opportunities arise to add new or complementary businesses, content, or entertainment offerings. In some cases, the costs of such acquisitions may be substantial, including as a result of professional fees and due diligence efforts. There may be no assurance that the time and resources expended on pursuing a particular acquisition may result in a completed transaction, or that any completed transaction may ultimately be successful. In addition, New K Enter may be unable to identify suitable acquisition or strategic investment opportunities, or may be unable to obtain any required financing or regulatory approvals, and therefore may be unable to complete such acquisitions or strategic investments on favorable terms, if at all. New K Enter may decide to pursue acquisitions with which New K Enter’s investors may not agree and New K Enter may not assure investors that any acquisition or investment may be successful or otherwise provide a favorable return on investment. In addition, acquisitions and the integration thereof require significant time and resources and place significant demands on New K Enter’s management, as well as on New K Enter’s operational and financial infrastructure. In addition, if New K Enter fails to successfully close transactions or integrate new teams, or integrate the content and technologies associated with these acquisitions into New K Enter’s company, New K Enter’s business may be seriously harmed. Acquisitions may expose New K Enter to operational challenges and risks, including:
| | ● | the ability to profitably manage acquired businesses or successfully integrate the acquired businesses’ operations, personnel, financial reporting, accounting and internal controls, technologies and content into New K Enter’s business; |
| | ● | incurrence of indebtedness and the expense of integrating acquired businesses, including significant administrative, operational, economic, geographic or cultural challenges in managing and integrating the expanded or combined operations; |
| | ● | entry into jurisdictions or acquisition of content or technologies with which New K Enter has limited or no prior experience, and the potential of increased competition with new or existing competitors as a result of such acquisitions; |
| | ● | diversion of management’s attention and the over-extension of New K Enter’s operating infrastructure and New K Enter’s management systems, information technology systems, and internal controls and procedures, which may be inadequate to support growth; |
| | ● | the ability to fund New K Enter’s capital needs and any cash flow shortages that may occur if anticipated revenue is not realized or is delayed, whether by general economic or market conditions, or unforeseen internal difficulties; and |
| | ● | the ability to retain or hire qualified personnel required for expanded operations. |
New K Enter’s acquisition strategy may not succeed if New K Enter is unable to remain attractive to target companies or expeditiously close transactions. Issuing common shares to fund an acquisition would cause economic dilution to existing shareholders. If New K Enter develops a reputation for being a difficult acquirer or having an unfavorable work environment, or target companies view New K Enter’s common shares unfavorably, New K Enter may be unable to consummate key acquisition transactions essential to New K Enter’s corporate strategy and New K Enter’s business may be seriously harmed.
New K Enter’s success may depend on the performance of its current and future employees, including certain key employees. Recruitment and retention of these individuals may be vital to growing New K Enter’s business and meeting its business plans. The loss of any of New K Enter’s key executives or other key employees may harm its business. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
K Enter depends on a limited number of key personnel to manage and operate New K Enter’s business, including New K Enter’s Chairman - Pyeong Ho Choi, Interim Chief Executive Officer - Tan Chin Hwee and New K Enter’s Chief Financial Officer – Jun Jong. The leadership of New K Enter’s current executive officers may have been a useful element in building New K Enter’s operations, and the departure, death or disability of any one of New K Enter’s executive officers or other extended or permanent loss of any of their services, or any negative market or industry perception with respect to any of them or their loss, may have a material adverse effect on New K Enter’s business.
In addition, certain of New K Enter’s other employees may have made significant contributions to their growth and success. New K Enter believes its success and New K Enter’s ability to compete and grow may depend in large part on the efforts and talents of New K Enter’s employees and on New K Enter’s ability to retain highly skilled personnel. The competition for these types of personnel may be intense and New K Enter may compete with other potential employers for the services of New K Enter’s employees. As a result, New K Enter may not succeed in retaining the executives and other key employees that New K Enter needs. Employees, particularly analysts and engineers, may be in high demand, and New K Enter may devote significant resources to identifying, hiring, training, successfully integrating and retaining these employees. New K Enter may not provide assurance that New K Enter may be able to attract or retain such highly qualified personnel in the future. In addition, the loss of employees or the inability to hire additional skilled employees as necessary may result in significant disruptions to New K Enter’s business, and the integration of replacement personnel may be time-consuming and expensive and cause additional disruptions to New K Enter’s business.
The unexpected loss of services of one or more of these key employees may have a material adverse effect on New K Enter’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. Additionally, as New K Enter grows and develop the infrastructure of a public company, New K Enter may find it difficult to maintain New K Enter’s entrepreneurial, innovative and team-based culture. New K Enter’s retention and recruiting may require significant increases in compensation expense as New K Enter transitions to a public company, which would adversely affect New K Enter’s results of operation. If New K Enter does not succeed in attracting, hiring, and integrating excellent personnel, or retaining and motivating existing personnel, New K Enter may be unable to grow effectively and New K Enter’s business may be harmed.
Digital piracy may adversely impact the Six Korean Entities’ business. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
A substantial portion of the Six Korean Entities’ revenue comes from the distribution of music and digital content which is potentially subject to unauthorized consumer copying and widespread digital dissemination without an economic return to us, including as a result of “stream-ripping.” In its Engaging with Music 2021 report, IFPI surveyed 43,000 people to examine the ways in which music consumers engaged with recorded music across 21 countries. Of those surveyed, 30% had used illegal or unlicensed methods to listen to or download music, and 14% had used unlicensed social media platforms for music purposes, the leading form of music piracy. Organized industrial piracy may also lead to decreased revenues. The potential impact of digital piracy on legitimate music revenues and subscriptions is hard to quantify, but we believe that illegal file sharing and other forms of unauthorized activity, including stream manipulation, have a substantial negative impact on music revenues. If the Six Korean Entities fail to obtain appropriate relief through the judicial process or the complete enforcement of judicial decisions issued in their favor (or if judicial decisions are not in their favor), if New K Enter is unsuccessful in its efforts to lobby governments to enact and enforce stronger legal penalties for copyright infringement or if it fails to develop effective means of protecting and enforcing the Six Korean Entities’ intellectual property (whether copyrights or other intellectual property rights such as patents, trademarks and trade secrets) or their music entertainment-related products or services, New K Enter’s results of operations, financial position and prospects may suffer.
Post-acquisition New K Enter’s insurance may not provide adequate levels of coverage against claims. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
We expect New K Enter will maintain insurance that we believe may be customary for businesses of its size and type. However, there may be types of losses New K Enter may incur that may not be insured against or that New K Enter believes may not be economically reasonable to insure. Moreover, any loss incurred may exceed policy limits and policy payments made to New K Enter may not be made on a timely basis. Such losses may adversely affect New K Enter’s business prospects, results of operations, cash flows and financial condition.
New K Enter’s business will be subject to complex and evolving U.S. and foreign laws and regulations regarding privacy, data use and data protection, content, competition, consumer protection, and other matters. Many of these laws and regulations are subject to change and uncertain interpretation, and could result in claims, changes to New K Enter’s business practices, monetary penalties, increased cost of operations, or declines in user growth or engagement, or otherwise harm New K Enter’s business. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
We expect that New K Enter will be subject to a variety of laws and regulations that involve matters central to its business, including privacy, data use, data protection and personal information, rights of publicity, content, intellectual property, advertising, marketing, distribution, data security, data retention and deletion, data localization and storage, data disclosure, artificial intelligence, electronic contracts and other communications, competition, protection of minors, consumer protection, telecommunications, product liability, e-commerce, taxation, economic or other trade prohibitions or sanctions, anti-corruption and political law compliance, securities law compliance, and online payment services. The introduction of new products, expansion of New K Enter’s activities in certain jurisdictions, or other actions that New K Enter may take may subject New K Enter to additional laws, regulations, or other government scrutiny. In addition, foreign data protection, privacy, content, competition, and other laws and regulations can impose different obligations or be more restrictive than those in the United States.
Since the Six Korean Entities’ operations are based in Korea, where most of their users are domiciled, New K Enter and its subsidiaries are expected to be subject to, among others, the Personal Information Protection Act and related legislation, regulations and orders (the “PIPA”), the Act on the Promotion of Information and Communications Network Utilization and Protection of Information Act (Korea), and the Credit Information Act in Korea that specifically regulates certain sensitive personal information. PIPA requires consent by the consumer with respect to the use of his or her data and requires the persons responsible for management of personal data to take the necessary technological and managerial measures to prevent data breaches and, among other duties, to notify the Personal Information Protection Commission of any data breach incidents within 24 hours. Failure to comply with PIPA in any manner may subject these persons responsible to personal liability for not obtaining such consent in an appropriate manner or for such breaches, including even negligent breaches, and violators face varying penalties ranging from monetary penalties to imprisonment. New K Enter strives to take the necessary technological and managerial measures to comply with PIPA, including the implementation of privacy policies concerning the collection, use, and disclosure of subscriber data on New K Enter’s apps and websites, and New K Enter regularly reviews and updates New K Enter’s policies and practices. Despite these efforts to comply with PIPA, these rules are complex and evolving, subject to interpretation by government regulators which may change over time and therefore New K Enter is subject to the risk of claims by regulators of failure to comply with PIPA. Any failure, or perceived failure, by New K Enter and its subsidiaries to comply with such policies, laws, regulations, and other legal obligations and regulatory guidance could adversely affect New K Enter’s reputation, brand, and business, and may result in claims, proceedings, or actions, including criminal proceedings, against New K Enter and certain of New K Enter’s executive officers by governmental entities or others or other liabilities. Any such claim, proceeding, or action, could hurt New K Enter’s reputation, brand, and business, force New K Enter to incur significant expenses in defense of such proceedings, distract New K Enter’s management, increase New K Enter’s costs of doing business, result in a loss of customers and merchants, and could have an adverse effect on New K Enter’s business, financial condition, and results of operations.
These U.S. federal and state and foreign laws and regulations, which in some cases can be enforced by private parties in addition to government entities, are constantly evolving and can be subject to significant change. As a result, the application, interpretation, and enforcement of these laws and regulations are often uncertain, particularly in the new and rapidly evolving industry in which New K Enter operates, and may be interpreted and applied inconsistently from country to country and inconsistently with New K Enter’s current policies and practices. For example, regulatory or legislative actions affecting the manner in which New K Enter displays content to New K Enter’s users or obtain consent to various practices could adversely affect user growth and engagement. Such actions could affect the manner in which New K Enter provides its services or adversely affect New K Enter’s financial results.
We also expect that New K Enter will be subject to evolving laws and regulations that dictate whether, how, and under what circumstances New K Enter and its subsidiaries can transfer, process and/or receive certain data that is critical to our future operations, including data shared between countries or regions in which we operate and data shared among Six Korean Entities’ products and services. If, post acquiring the Six Korean Entities, New K Enter is unable to transfer data between and among countries and regions in which New K Enter operates, or if New K Enter is restricted from sharing data among New K Enter’s products and services, it could affect New K Enter’s ability to provide services, the manner in which New K Enter provides its services or New K Enter’s ability to target ads, which could adversely affect New K Enter’s financial results.
Proposed or new legislation and regulations could also significantly affect New K Enter’s business. Laws and regulations are evolving and subject to interpretation, and resulting limitations on New K Enter’s advertising services, or reductions of advertising by marketers, have to some extent adversely affected, and will continue to adversely affect, New K Enter’s advertising business. Changes to Six Korean Entities’ products or business practices as a result of these developments may adversely affect New K Enter’s advertising business. Similarly, there are a number of legislative proposals in the European Union, the United States, at both the federal and state level, as well as other jurisdictions that could impose new obligations or limitations in areas affecting New K Enter’s business. In addition, some countries are considering or have passed legislation implementing data protection requirements or requiring local storage and processing of data or similar requirements that could increase the cost and complexity of delivering New K Enter’s services.
For example, the European Union traditionally has imposed stricter obligations under its laws and regulations relating to privacy, data protection and consumer protection than the United States. In May 2018, the European Union’s new regulation governing data practices and privacy called the General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR, became effective and substantially replaced the data protection laws of the individual European Union member states. The law requires companies to meet more stringent requirements regarding the handling of personal data of individuals in the EU than were required under predecessor EU requirements. In the United Kingdom, a Data Protection Bill that substantially implements the GDPR also became law in May 2018. The law also increases the penalties for non-compliance, which may result in monetary penalties of up to €20.0 million or 4% of a company’s worldwide turnover, whichever is higher. The GDPR and other similar regulations require companies to give specific types of notice and in some cases seek consent from consumers and other data subjects before collecting or using their data for certain purposes, including some marketing activities. Outside of the European Union, many countries have laws, regulations, or other requirements relating to privacy, data protection, information security, and consumer protection, and new countries are adopting such legislation or other obligations with increasing frequency. Many of these laws may require consent from consumers for the use of data for various purposes, including marketing, which may reduce New K Enter’s ability to market New K Enter’s products. There is no harmonized approach to these laws and regulations globally. Consequently, New K Enter increases its risk of non-compliance with applicable foreign data protection laws by operating internationally. New K Enter may need to change and limit the way New K Enter uses personal information in operating New K Enter’s business and may have difficulty maintaining a single operating model that is compliant. In addition, various federal, state and foreign legislative and regulatory bodies, or self-regulatory organizations, may expand current laws or regulations, enact new laws or regulations or issue revised rules or guidance regarding privacy, data protection, information security and consumer protection. For example, California adopted the California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018 (“CCPA”), which provides new data privacy rights for consumers and new operational requirements for businesses. The CCPA includes a statutory damages framework and private rights of action against businesses that fail to comply with certain CCPA terms or implement reasonable security procedures and practices to prevent data breaches. The CCPA went into effect in January 2020. The effects of the CCPA potentially are significant, however, and may require New K Enter to modify New K Enter’s data processing practices and policies and to incur substantial costs and expenses in an effort to comply. As a general matter, compliance with laws, regulations, and any applicable rules or guidance from self-regulatory organizations relating to privacy, data protection, information security and consumer protection, may result in substantial costs and may necessitate changes to New K Enter’s business practices, which may compromise New K Enter’s growth strategy, adversely affect New K Enter’s ability to acquire customers, and otherwise adversely affect New K Enter’s business, financial condition and operating results.
These laws and regulations, as well as any associated claims, inquiries, or investigations or any other government actions, have in the past led to, and may in the future lead to, unfavorable outcomes including increased compliance costs, delays or impediments in the development of new products, negative publicity and reputational harm, increased operating costs, diversion of management time and attention, and remedies that harm New K Enter’s business, including fines or demands or orders that New K Enter modifies or ceases existing business practices.
Changes in tax laws or regulations that are applied adversely to New K Enter or its customers may have a material adverse effect on New K Enter’s business, cash flow, financial condition or results of operations. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New income, sales, use or other tax laws, statutes, rules, regulations or ordinances could be enacted at any time, which could affect the tax treatment of New K Enter’s earnings and adversely affect New K Enter’s operations, and New K Enter’s business and financial performance. Further, existing tax laws, statutes, rules, regulations or ordinances could be interpreted, changed, modified or applied adversely to us. There may be material adverse effects resulting from the legislation that New K Enter has not yet identified. No estimated tax provision has been recorded in the financial statements included herein for tax attributes that are incomplete or subject to change.
The foregoing items could have a material adverse effect on New K Enter’s business, cash flow, financial condition or results of operations. In addition, it is unclear how these U.S. federal income tax changes will affect state and local taxation, which often uses federal taxable income as a starting point for computing state and local tax liabilities. The impact of this tax legislation on holders of New K Enter’s common stock is also uncertain and could be adverse. New K Enter urges its stockholders and investors to consult with New K Enter’s legal and tax advisors with respect to this legislation and the potential tax consequences of investing in or holding New K Enter’s common stock.
Failure to comply with the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act could result in fines, criminal penalties and an adverse effect on New K Enter’s business. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New K Enter may operate in a number of countries throughout the world, including countries known to have a reputation for corruption. New K Enter is committed to doing business in accordance with applicable anti-corruption laws and have adopted a code of business conduct and ethics which is consistent and in full compliance with the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977, or the FCPA. New K Enter is subject, however, to the risk that we, New K Enter’s affiliated entities or New K Enter’s or their respective officers, directors, employees and agents may take actions determined to be in violation of such anti-corruption laws, including the FCPA. Any such violation could result in substantial fines, sanctions, civil and/or criminal penalties, curtailment of operations in certain jurisdictions, and might adversely affect New K Enter’s business, results of operations or financial condition. In addition, actual or alleged violations could damage New K Enter’s reputation and ability to do business. Furthermore, detecting, investigating, and resolving actual or alleged violations is expensive and can consume significant time and attention of New K Enter’s senior management.
Fluctuations in exchange rates could result in foreign currency exchange losses to New K Enter’s. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
The value of the Korean Won and other currencies against the U.S. dollar has fluctuated, and may continue to fluctuate and is affected by, among other things, changes in political and economic conditions. It is difficult to predict how market forces or Korean or U.S. government policy, including any interest rate increases by the Federal Reserve, may impact the exchange rate between the Korean Won and the U.S. dollar in the future.
A substantial percentage of New K Enter’s revenue and costs are denominated in Korean Won, and a significant portion of New K Enter’s financial assets are also denominated in Korean Won, while New K Enter anticipates that a substantial portion of any debt incurred will be denominated in U.S. dollars. New K Enter is a holding company and New K Enter may receive dividends, loans and other distributions on equity paid by New K Enter’s operating subsidiaries in Korea. Any significant fluctuations in the value of the Korean Won may materially and adversely affect New K Enter’s liquidity and cash flows. For example, the depreciation of the Korean Won and other foreign currencies against the U.S. dollar typically results in a material increase in the cost of hosting services and equipment purchased from outside of Korea and the cost of servicing debt denominated in currencies other than the Korean Won. As a result, any significant depreciation of the Korean Won or other major foreign currencies against the U.S. dollar may have a material adverse effect on New K Enter’s results of operations. If New K Enter decides to convert New K Enter’s Korean Won into U.S. dollars for the purpose of repaying principal or interest expense on any future U.S. dollar-denominated debt, making payments for dividends on New K Enter’s common stock, or other business purposes, depreciation of the Korean Won or other foreign currencies against the U.S. dollar would have a negative effect on the U.S. dollar amount New K Enter would receive. Conversely, to the extent that New K Enter needs to convert U.S. dollars into Korean Won for New K Enter’s operations, appreciation of the Korean Won against the U.S. dollar would have an adverse effect on the Korean Won amount New K Enter would receive.
Tensions with North Korea could have an adverse effect on New K Enter’s business, financial condition, and results of operations, and the price per share of PubCo’s ordinary shares may decrease. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
Relations between Korea and North Korea have fluctuated over the years. Tension between Korea and North Korea may increase or change abruptly as a result of current and future events. In particular, there have been heightened security concerns in recent years stemming from North Korea’s nuclear weapon and ballistic missile programs as well as its hostile military actions against Korea.
North Korea’s economy also faces severe challenges, which may further aggravate social and political pressures within North Korea. Since April 2018, North Korea has held a series of bilateral summit meetings with Korea and the United States to discuss peace and denuclearization of the Korean peninsula. However, North Korea has since resumed its missile testing, heightening tensions, and the outlook of such discussions remains uncertain.
Further tensions in North Korean relations could develop due to a leadership crisis, breakdown in high-level inter-Korea contacts or military hostilities. Alternatively, tensions may be resolved through reconciliatory efforts, which may include peace talks, alleviation of sanctions or reunification. New K Enter cannot assure you that future negotiations will result in a final agreement on North Korea’s nuclear program, including critical details such as implementation and timing, or that the level of tensions between Korea and North Korea will not escalate. Any increase in the level of tension between Korea and North Korea, an outbreak in military hostilities or other actions or occurrences, could adversely affect New K Enter’s business, prospects, financial condition, and results of operations and could lead to a decline in the price per share of New K Enter’s common stock.
There are special risks involved with investments in companies with significant Korean operations, including the possibility of restrictions being imposed by the Korean government in emergency circumstances, accounting and corporate disclosure standards that differ from those in other jurisdictions, and the risk of direct or vicarious criminal liability for executive officers of New K Enter and the Six Korean Entities. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
K Enter expects to acquire are all Six Korean Entities with significant operation in South Korea. New K Enter’s planned Korean subsidiaries and their affiliates operate in a business and cultural environment that is different from that of other countries. For example, under the Foreign Exchange Transaction Act of Korea, if the Korean government determines that in certain emergency circumstances, including sudden fluctuations in interest rates or exchange rates, extreme difficulty in stabilizing the balance of payments or substantial disturbance in the Korean financial and capital markets are likely to occur, it may impose any necessary restriction such as requiring Korean or foreign investors to obtain prior approval from the Minister of Economy and Finance of Korea prior to entering into a capital markets transaction, repatriating interest, dividends or sales proceeds arising from Korean securities or from the disposition of such securities or other transactions involving foreign exchange. Although investors will hold shares of New K Enter’s common stock, New K Enter’s subsidiaries may experience adverse risks and in turn could adversely impact New K Enter’s business, prospects, financial condition, and results of operations and could lead to a decline in the price per share of New K Enter’s common stock.
In addition, under Korean law, there are circumstances in which certain executive officers of a company may be investigated or held criminally liable either directly or vicariously for the actions of K Enter and its executives and employees. For example, complaints alleging infringement of intellectual property rights, breaches of certain Korean laws (e.g., labor standards laws and fair trade laws), and product-related claims may be investigated and prosecuted as criminal offenses with both K Enter and K Enter’s executive officers being named as defendants in such proceedings. These risks change over time.
As a result of these current and changing risks, New K Enter’s Korean subsidiaries and their affiliates’ executive officers may be named in the future in criminal investigations or proceedings stemming from New K Enter’s operations. In Korea, company executive officers being named in such investigations or proceedings is a common occurrence, even though in practice many such cases result in no liability to the individual. If New K Enter’s Korean subsidiaries and their affiliates’ executive officers were to be named in such criminal proceedings or held either directly or vicariously criminally liable for the actions of K Enter and its executives and employees, New K Enter’s business, financial condition, and results of operations may be harmed.
New K Enter’s planned transactions with the Six Korean Entities or with their affiliates may be restricted under Korean fair trade regulations. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New K Enter’s Korean subsidiaries enter into business relationships and transactions with their affiliates, which are subject to scrutiny by the Korean Fair Trade Commission (“KFTC”) as to, among other things, whether such relationships and transactions constitute undue financial support among companies in the same business group. If, in the future, the KFTC determines that New K Enter’s Korean subsidiaries have engaged in transactions that violate the fair trade laws and regulations, it may be subject to an administrative and/or criminal fine, surcharge or other actions, which may have an adverse effect on New K Enter’s business, financial condition, and results of operations.
K Enter’s Korean operations, the Six Korean Entities and a group of companies affiliated with it may be designated an affiliated group under Korean law, which would require that group of companies to make certain disclosures and implement additional corporate governance requirements. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New K Enter’s Korean subsidiaries and a group of companies affiliated with it are likely to be designated as a business group subject to disclosure under the Korean Monopoly Regulation and Fair Trade Act. As described in greater detail in the section titled “Government Regulation-The Monopoly Regulation and Fair Trade Act”, such a designation would impose additional corporate governance and public disclosure requirements on this group of affiliated companies. These requirements would create additional costs of compliance and could subject this group of affiliated companies to greater regulatory scrutiny and risk of penalties for any failure to comply with the additional obligations imposed.
K Enter’s Korean operations and the Six Korean Entities are subject to certain requirements and restrictions under Korean law that may, in certain circumstances, require it to act in a manner that may not be in New K Enter’s or its shareholders’ best interest. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
Under applicable Korean law, directors of a Korean company, such as the Six Korean Entities, owe a fiduciary duty to K Enter itself rather than to its stockholders. This fiduciary duty obligates directors of a Korean company to perform their duties faithfully for the good of K Enter as a whole. As a result, if circumstances arise in which the good of New K Enter’s Korean subsidiaries conflicts with the good of K Enter Holdings or its stockholders, New K Enter’s Korean subsidiaries may not be permitted under applicable Korean law to act in a manner that is in the best interest of K Enter Holdings, as its parent, or New K Enter’s stockholders. For example, providing guarantees or collateral by New K Enter’s Korean subsidiaries in favor of K Enter Holdings, as its parent, without a justifiable cause and on other than arm’s length terms may cause breach of a fiduciary duty of directors to New K Enter’s Korean subsidiaries.
Approval by the board of directors of a Korean company is required for, among other things, all transactions between a director or major stockholder (including a 10% or more stockholder) and K Enter for the director’s or the major stockholder’s account. As a result, intercompany transactions between New K Enter and the Six Korean Entities (or any other Korean entity K Enter may own, from time to time), could arise in the future in which the directors of the Korean subsidiary are not able to act in New K Enter’s or its shareholders’ best interest as a result of competing interests of the subsidiary. Since substantially all of New K Enter’s operations are conducted by the Six Korean Entities, any such occurrence with respect to the Six Korean Entities could adversely affect New K Enter’s business, financial condition, and results of operations.
K Enter’s Korean operations and the Six Korean Entities’ transactions with related parties are subject to close scrutiny by the Korean tax authorities, which may result in adverse tax consequences. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
Under Korean tax law, there is an inherent risk that New K Enter’s transactions with its subsidiaries, affiliates or any other person or company that is related to New K Enter may be challenged by the Korean tax authorities if such transactions are viewed as having been made on terms that were not on an arm’s-length basis. If the Korean tax authorities determine that any of its transactions with related parties were on other than arm’s-length terms, it may not be permitted to deduct as expenses, or may be required to include as taxable income, any amount which is found to be undue financial support between related parties in such transaction, which may have adverse tax consequences for New K Enter and, in turn, may adversely affect New K Enter’s business, financial condition, and results of operations.
If New K Enter is deemed to have a “place of effective management” in Korea, New K Enter will be treated as a Korean company for the purpose of Korean corporate income tax with regards to New K Enter’s worldwide income. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
Under the Corporate Tax Act (“CTA”), as amended on December 31, 2022, a corporation having a “place of effective management” in Korea will be treated as a Korean company for the purposes of Korean corporate income tax. The CTA does not clearly define what constitutes “place of effective management.” However, there are court precedents which establish certain factors to consider for determining whether a foreign corporation can be considered as having a “place of effective management” in Korea. Such factors include, without limitation, considerations such as the location of Board of Directors’ meetings, etc. If New K Enter is deemed to have a “place of effective management” in Korea, New K Enter will be required to file annual corporate income tax returns with the Korean tax authorities and be subject to Korean corporate income tax. Currently, the applicable rates are 9.9% (inclusive of local corporate taxes) for taxable income up to 200 million Korean Won, 20.9% (inclusive of local corporate taxes) for taxable income exceeding 200 million Korean Won and less than 20 billion Korean Won, 23.1% (inclusive of local corporate taxes) for taxable income greater than 20 billion won and less than 300 billion Korean Won, and 26.4% (inclusive of local corporate tax) for taxable income greater than 300 billion Korean Won. Taxable income would include any worldwide income, such as dividends New K Enter receives from New K Enter’s Korean operating company and any interest income earned outside of Korea. If New K Enter is required to pay Korean corporate income tax, it may reduce New K Enter’s cash flow and negatively impact the returns to investors.
If New K Enter is deemed to have a “permanent establishment” in Korea, New K Enter will be subject to Korean corporate income tax with regards to any Korean source income attributable to or effectively connected with such permanent establishment. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
If New K Enter is deemed to have a “permanent establishment” as defined under Korean tax law, New K Enter would be required to file annual corporate income tax returns with the Korean tax office and be subject to Korean corporate income tax. The applicable rates are 9.9% (inclusive of local corporate taxes) for taxable income up to 200 million Korean Won, 20.9% (inclusive of local corporate taxes) for taxable income exceeding 200 million Korean Won and less than 20 billion Korean Won, 23.1% (inclusive of local corporate taxes) for taxable income greater than 20 billion won and less than 300 billion Korean Won, and 26.4% (inclusive of local corporate tax) for taxable income greater than 300 billion Korean Won. Taxable income includes any Korean source income attributable to or effectively connected with such permanent establishment, such as the dividends New K Enter expects to receive from the Six Korean Entities. If New K Enter is required to pay Korean corporate income tax, it may reduce New K Enter’s cash flow and negatively impact the returns to investors.
A focus on regulating copyright and patent infringement by the Korean government subjects New K Enter to extra scrutiny in New K Enter’s operations and could subject New K Enter to sanctions, fines, or other penalties, which could adversely affect New K Enter’s business and operations in Korea. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
The Korean government has recently focused on addressing copyright and patent infringement in Korea, particularly with respect to luxury and brand name merchandise. Despite measures New K Enter has taken to address copyright and patent infringement, the Korean government may subject New K Enter to sanctions, fines, or other penalties, which could adversely affect New K Enter’s business and operations in Korea.
New legislative proposals may expose New K Enter’s business to additional risks from litigation, regulation, and government investigations. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New K Enter expects to be subject to changing laws and regulations everywhere we does business, including in Korea. For example, on September 28, 2020, the Korean Ministry of Justice announced (i) a proposed amendment to the Korean Commercial Code to adopt a punitive damages system that would apply generally to all areas of business, and (ii) a proposed bill to introduce a class action litigation system in Korea.
Previously, punitive or exemplary damages have been available in Korea only in specific business fields. The proposed legislation would broaden the potential availability of such damages. Similarly, the proposal relating to class actions would make such litigation applicable to a broader scope of cases, would allow for a Korean style discovery process, jury trials in many cases, and would apply to claims whose cause arose before the bill’s enactment.
Additionally, on January 8, 2021, the main session of the Korean National Assembly passed a draft Bill on Punishment for Serious Accidents, etc. (the “Serious Accidents Act”), which came into effect January 27, 2022. The Serious Accidents Act imposes enhanced liability (including criminal liability) on businesses, managers, and individuals who are responsible for causing loss of life by failing to fulfill duties relating to workplace safety and health or risk prevention. The Serious Accidents Act provides the potential for criminal punishment, public disclosure of punishment, and monetary damages, including punitive damages up to five times the actual damages suffered. The Serious Accidents Act extends potential liability to a wider group of persons than under existing law, including those who oversee safety and health matters for the business concerned and also general managers of the business.
These are just some examples of how New K Enter’s business could be affected by changing regulations. If these proposals are enacted and implemented, the Six Korean Entities could face substantial costs and management could be required to spend significant time and attention on these matters, which would divert New K Enter’s focus from New K Enter’s core business. This could adversely affect New K Enter’s business, financial condition, and results of operations.
As New K Enter’s planned subsidiaries are incorporated in Korea, it may be more difficult to enforce judgments obtained in courts outside Korea. (K Enter, Production Companies, Merchandising Company, Investment Company)
New K Enter’s operations are primarily conducted outside of the United States. In addition, all but one of New K Enter’s directors and officers are non-residents of the United States, and all or a substantial portion of the assets of these non-residents are located outside the United States. New K Enter is a Delaware corporation and will continue to be a Delaware corporation after the closing of the Business Combination. As a result, while U.S. investors should be above to serve process within the United States on New K Enter, it may be difficult or impossible for U.S. investors to serve process within the United States upon PubCo, the Six Korean Entities or New K Enter’s directors and officers or to enforce a judgment against New K Enter for civil liabilities in U.S. courts. In addition, you should not assume that courts in the countries in which New K Enter or the Six Korean Entities are incorporated or where New K Enter’s or the assets of the Six Korean Entities are located (1) would enforce judgments of U.S. courts obtained in actions against New K Enter or the Six Korean Entities based upon the civil liability provisions of applicable U.S. federal and state securities laws or (2) would enforce, in original actions, liabilities against New K Enter or the Six Korean Entities based on those laws.
The preparation of PubCo’s financial statements involves the use of good faith estimates, judgments and assumptions, and PubCo’s financial statements may be materially affected if such good faith estimates, judgments or good faith assumptions prove to be inaccurate.
Financial statements prepared in accordance with IFRS, as issued by the International Accounting Standard Board, typically require the use of good faith estimates, judgments and assumptions that affect the reported amounts. Often, different estimates, judgments and assumptions could reasonably be used that would have a material effect on such financial statements, and changes in these estimates, judgments and assumptions may occur from period to period over time. Significant areas of accounting requiring the application of management’s judgment include, but are not limited to, determining the fair value of assets, share-based compensation and the timing and amount of cash flows from assets. These estimates, judgments and assumptions are inherently uncertain and, if PubCo’s estimates were to prove to be wrong, PubCo would face the risk that charges to income or other financial statement changes or adjustments would be required. Any such charges or changes would require a restatement of our financial statements and could harm PubCo’s business, including PubCo’s financial condition and results of operations and the price of PubCo’s securities. See “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” for a discussion of the accounting estimates, judgments and assumptions that PubCo believes are the most critical to an understanding of PubCo’s financial statements and its business.
If PubCo prepares its financial statements in accordance with IFRS following the Business Combination, there may be a significant effect on K Enter’s reported financial results.
The SEC permits foreign private issuers to file financial statements in accordance with IFRS as issued by IASB. At any time in the future, as a foreign private issuer, PubCo expects to prepare its financial statements in accordance with IFRS as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”). The application by PubCo of different accounting standards, a change in the rules of IFRS as issued by the IASB, or in the SEC’s acceptance of such rules, could have a significant effect on K Enter’s reported financial results. Additionally, U.S. GAAP is subject to interpretation by the Financial Accounting Standards Board, the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants, the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board, the SEC, and various bodies formed to promulgate and interpret appropriate accounting principles. IFRS are subject to interpretation by the IASB. A change in these principles or interpretations could have a significant effect on K Enter’s and PubCo’s reported financial results.
The JOBS Act permits “emerging growth companies” like Global Star to take advantage of certain exemptions from various reporting requirements applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies.
PubCo expects that it will qualify as an “emerging growth company” as defined in Section 2(a)(19) of the Securities Act, as modified by the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (the “JOBS Act”). The JOBS Act defines an emerging growth company as a company that has annual gross revenues less than $1.235 billion during its most recent fiscal year and has not sold common stock under a registration statement. A company will be classified as an emerging growth company for its first five fiscal years, unless: its gross revenues exceed $1.235 billion, it has issued over $1 billion in non-convertible debt over three years, or it becomes a large accelerated filer. SEC Rule 12b-2 provides that a large accelerated filer is a company that has a public float of greater than $700 million, has been filing periodic reports for at least 12 months, has previously filed at least one annual report (e.g. Form 10-K), and is not a smaller reporting company. That is, a large accelerated filer is simply an accelerated filer whose public float exceeds $700 million. As such, PubCo will take advantage of certain exemptions from various reporting requirements applicable to other public companies based on its status as an emerging growth company. Pursuant to Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, once PubCo is no longer an emerging growth company, PubCo may be required to furnish an attestation report on internal control over financial reporting issued by PubCo’s independent registered public accounting firm. When PubCo’s independent registered public accounting firm is required to undertake an assessment of its internal control over financial reporting, the cost of complying with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act will significantly increase, and management’s attention may be diverted from other business concerns, which could adversely affect PubCo’s business and results of operations.
As a foreign private issuer, PubCo will be exempt from a number of U.S. securities laws and rules promulgated thereunder and will be permitted to publicly disclose less information than U.S. public companies must. This may limit the information available to holders of the PubCo ordinary shares.
Following the completion of the Business Combination, PubCo will convert from a Delaware corporation to a Cayman Islands entity. As a result, PubCo will qualify as a “foreign private issuer,” as defined in the SEC’s rules and regulations, and, consequently, PubCo will not be subject to all of the disclosure requirements applicable to public companies organized within the United States. For example, PubCo will be exempt from certain rules under the Exchange Act that regulate disclosure obligations and procedural requirements related to the solicitation of proxies, consents or authorizations applicable to a security registered under the Exchange Act. In addition, PubCo’s officers and directors are exempt from the reporting and “short-swing” profit recovery provisions of Section 16 of the Exchange Act and related rules with respect to their purchases and sales of PubCo’s securities. For example, some of PubCo’s key executives may sell a significant amount of PubCo ordinary shares and such sales will not be required to be disclosed as promptly as public companies organized within the United States would have to disclose. Accordingly, once such sales are eventually disclosed, the price of PubCo ordinary shares may decline significantly. Moreover, PubCo will not be required to file periodic reports and financial statements with the SEC as frequently or as promptly as U.S. public companies. PubCo will also not be subject to Regulation FD under the Exchange Act, which would prohibit PubCo from selectively disclosing material nonpublic information to certain persons without concurrently making a widespread public disclosure of such information. Accordingly, there may be less publicly available information concerning PubCo than there is for U.S. public companies.
As a foreign private issuer, PubCo will file an annual report on Form 20-F within four months of the close of each fiscal year ended December 31 and furnish reports on Form 6-K relating to certain material events promptly after PubCo publicly announces these events. However, because of the above exemptions for foreign private issuers, which PubCo intends to rely on, PubCo shareholders will not be afforded the same information generally available to investors holding shares in public companies that are not foreign private issuers.
PubCo may lose its foreign private issuer status in the future, which could result in significant additional costs and expenses. This would subject PubCo to U.S. GAAP reporting requirements which may be difficult for it to comply with.
As a “foreign private issuer,” PubCo would not be required to comply with all of the periodic disclosure and current reporting requirements of the Exchange Act and related rules and regulations. Under those rules, the determination of foreign private issuer status is made annually on the last business day of an issuer’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter, and, accordingly, the next determination will be made with respect to Global Star on June 30, 2024.
In the future, PubCo could lose its foreign private issuer status if a majority of its ordinary shares are held by residents in the United States and it fails to meet any one of the additional “business contacts” requirements. Although PubCo intends to follow certain practices that are consistent with U.S. regulatory provisions applicable to U.S. companies, PubCo’s loss of foreign private issuer status would make such provisions mandatory. The regulatory and compliance costs to PubCo under U.S. securities laws if it is deemed a U.S. domestic issuer may be significantly higher. If PubCo is not a foreign private issuer, PubCo will be required to file periodic reports and prospectuses on U.S. domestic issuer forms with the SEC, which are more detailed and extensive than the forms available to a foreign private issuer. For example, PubCo would become subject to the Regulation FD, aimed at preventing issuers from making selective disclosures of material information. PubCo also may be required to modify certain of its policies to comply with good governance practices associated with U.S. domestic issuers. Such conversion and modifications will involve additional costs. In addition, PubCo may lose its ability to rely upon exemptions from certain corporate governance requirements of Nasdaq that are available to foreign private issuers. For example, Nasdaq’s corporate governance rules require listed companies to have, among other things, a majority of independent board members and independent director oversight of executive compensation, nomination of directors, and corporate governance matters. Nasdaq rules also require shareholder approval of certain share issuances, including approval of equity compensation plans. As a foreign private issuer, PubCo would be permitted to follow home country practice in lieu of the above requirements. As long as PubCo relies on the foreign private issuer exemption to certain of Nasdaq’s corporate governance standards, a majority of the directors on its board of directors are not required to be independent directors, its remuneration committee is not required to be comprised entirely of independent directors and it will not be required to have a nominating and corporate governance committee. Also, PubCo would be required to change its basis of accounting from IFRS as issued by the IASB to U.S. GAAP, which may be difficult and costly for it to comply with. If PubCo loses its foreign private issuer status and fails to comply with U.S. securities laws applicable to U.S. domestic issuers, PubCo may have to de-list from Nasdaq and could be subject to investigation by the SEC, Nasdaq and other regulators, among other materially adverse consequences.
Because PubCo is incorporated under the laws of the Cayman Islands and its Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association designates the courts of the Cayman Islands to have exclusive jurisdiction over certain matters, you may face difficulties in protecting your interests, and your ability to protect your rights through the U.S. Federal courts may be limited.
PubCo is an exempted company incorporated under the laws of the Cayman Islands. PubCo’s Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association designates the courts of the Cayman Islands to have exclusive jurisdiction over any claim or dispute arising out of or in connection with the Memorandum, the Articles or otherwise related in any way to each Member’s shareholding in the Company, including but not limited to: (a) any derivative action or proceeding brought on behalf of the Company; (b) any action asserting a claim of breach of any fiduciary or other duty owed by any current or former Director, Officer or other employee of the Company to the Company or the Members; (c) any action asserting a claim arising pursuant to any provision of the Companies Act (as revised) of the Cayman Islands, PubCo’s Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association and (d) any action asserting a claim against the Company governed by the “Internal Affairs Doctrine” (as such concept is recognized under the laws of the United States of America); provided, however, that this exclusive forum provision shall not apply to any action or suits brought to enforce any liability or duty created by the United States Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the Exchange Act, or any claim for which the federal district courts of the United States of America are, as a matter of the laws of the United States, the sole and exclusive forum for determination of such a claim. As a result, it may be difficult for investors to effect service of process within the United States upon PubCo’s directors or officers, or enforce judgments obtained in the United States courts against PubCo’s directors or officers.
PubCo’s corporate affairs will be governed by its amended and restated memorandum and articles of association, the Companies Act (as the same may be supplemented or amended from time to time) and the common law of the Cayman Islands. PubCo will also be subject to the federal securities laws of the United States. The rights of shareholders to take action against the directors, actions by minority shareholders and the fiduciary responsibilities of PubCo’s directors to PubCo under Cayman Islands law are to a large extent governed by the common law of the Cayman Islands. The common law of the Cayman Islands is derived in part from comparatively limited judicial precedent in the Cayman Islands as well as from English common law, the decisions of whose courts are of persuasive authority, but are not binding on a court in the Cayman Islands. The rights of PubCo’s shareholders and the fiduciary responsibilities of PubCo’s directors under Cayman Islands law are different from what they would be under statutes or judicial precedent in some jurisdictions in the United States. In particular, the Cayman Islands has a different body of securities laws as compared to the United States, and certain states, such as Delaware, may have more fully developed and judicially interpreted bodies of corporate law. In addition, Cayman Islands companies may not have standing to initiate a shareholders derivative action in a Federal court of the United States.
PubCo has been advised by Harneys Cayman Islands, its Cayman Islands legal counsel, that the courts of the Cayman Islands are unlikely (i) to recognize or enforce against it judgments of courts of the United States predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the federal securities laws of the United States or any state; and (ii) in original actions brought in the Cayman Islands, to impose liabilities against it predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the federal securities laws of the United States or any state, so far as the liabilities imposed by those provisions are penal in nature. In those circumstances, although there is no statutory enforcement in the Cayman Islands of judgments obtained in the United States, the courts of the Cayman Islands will recognize and enforce a foreign money judgment of a foreign court of competent jurisdiction without retrial on the merits based on the principle that a judgment of a competent foreign court imposes upon the judgment debtor an obligation to pay the sum for which judgment has been given provided certain conditions are met. For a foreign judgment to be enforced in the Cayman Islands, such judgment must be final and conclusive and for a liquidated sum, and must not be in respect of taxes or a fine or penalty, inconsistent with a Cayman Islands judgment in respect of the same matter, impeachable on the grounds of fraud or obtained in a manner, or be of a kind the enforcement of which is, contrary to natural justice or the public policy of the Cayman Islands (awards of punitive or multiple damages may well be held to be contrary to public policy). A Cayman Islands court may stay enforcement proceedings if concurrent proceedings are being brought elsewhere.
As a result of all of the above, public shareholders may have more difficulty in protecting their interests in the face of actions taken by management, members of the board of directors or controlling shareholders than they would as public shareholders of a corporation incorporated in the United States.
It may be difficult to enforce a U.S. judgment against PubCo or its directors and officers outside the United States, or to assert U.S. securities law claims outside of the United States.
A number of PubCo directors and executive officers are not residents of the United States, and the majority of its assets and the assets of these persons are located outside the United States. As a result, it may be difficult or impossible for investors to effect service of process upon PubCo within the United States or other jurisdictions, including judgments predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the federal securities laws of the United States. Additionally, it may be difficult to assert U.S. securities law claims in actions originally instituted outside of the United States. Foreign courts may refuse to hear a U.S. securities law claim because foreign courts may not be the most appropriate forum in which to bring such a claim. Even if a foreign court agrees to hear a claim, it may determine that the law of the jurisdiction in which the foreign court resides, and not U.S. law, is applicable to the claim. Further, if U.S. law is found to be applicable, the content of applicable U.S. law must be proved as a fact, which can be a time-consuming and costly process, and certain matters of procedure would still be governed by the law of the jurisdiction in which the foreign court resides.
As a company incorporated in the Cayman Islands, PubCo is permitted to adopt certain home country practices in relation to corporate governance matters that differ significantly from Nasdaq corporate governance listing standards; these practices may afford less protection to shareholders than they would enjoy if PubCo complied fully with Nasdaq corporate governance listing standards.
PubCo is a company incorporated in the Cayman Islands, and has applied for listing of the PubCo ordinary shares on Nasdaq. Nasdaq market rules permit a foreign private issuer like PubCo to follow the corporate governance practices of its home country. Certain corporate governance practices in the Cayman Islands, which is PubCo’s home country, may differ significantly from Nasdaq corporate governance listing standards.
Among others, PubCo will not be required to: (i) have a majority of the board be independent; (ii) have a compensation committee consisting entirely of independent directors; (iii) have a minimum of three members on the audit committee; (iv) obtain shareholders’ approval for issuance of securities in certain situations; or (v) have regularly scheduled executive sessions with only independent directors each year.
Provisions in the PubCo’s governance documents may inhibit a takeover of PubCo, which could limit the price investors might be willing to pay in the future for PubCo ordinary shares and could entrench management.
PubCo’s governance documents will contain provisions that may discourage unsolicited takeover proposals that shareholders may consider to be in their best interests. These provisions include that PubCo’s board of directors will be classified into three classes of directors. As a result, in most circumstances, a person can gain control of the board only by successfully engaging in a proxy contest at two or more annual general meetings. PubCo may issue additional shares without shareholder approval and such additional shares could be utilized for a variety of corporate purposes, including future offerings to raise additional capital, acquisitions and employee benefit plans. The ability for PubCo to issue additional shares could render more difficult or discourage an attempt to obtain control of PubCo by means of a proxy contest, tender offer, merger or otherwise that could involve the payment of a premium over prevailing market prices for PubCo ordinary shares.
Risk Factors Relating to Global Star’s Business
Throughout this section, references to “Global Star,” refer to Global Start Acquisition Inc. unless the context requires otherwise.
If we are deemed to be an investment company for purposes of the Investment Company Act, we would be required to institute burdensome compliance requirements and our activities would be severely restricted and, as a result, we may abandon our efforts to consummate a business combination and liquidate the Company.
On January 24, 2024, the SEC adopted the final rules, relating to, among the others, the extent to which special purpose acquisition companies or SPACs like Global Star could become subject to regulation under the Investment Company Act (the “SPAC Final Rules”). The SPAC Final Rules provide that whether a SPAC is an investment company subject to the Investment Company Act is based on particular facts and circumstances. A specific duration period of a SPAC is not the sole determinant, but one of the long-standing factors to consider in determination of a SPAC’s status under the Investment Company Act. A SPAC could be deemed as an investment company at any stage of its operation. The determination of a SPAC’s status as an investment company includes analysis of a SPAC’s activities, depending upon the facts and circumstances, including but not limited to, the nature of SPAC assets and income, the activities of a SPAC’s officers, directors and employees, the duration of a SPAC, the manner a SPAC holding itself out to investors, and the merging with an investment company. The SPAC Final Rules will become effective 125 days after publication in the Federal Register.
Since the consummation of its IPO, the Company has deposited the proceeds of its IPO (including proceeds of the full exercise of over-allotment options), net of certain expenses and working capital, into the Trust Account to invest in U.S. government securities with a maturity of 185 days or less or in money market funds meeting certain conditions under Rule 2a-7 under the Investment Company Act which invest only in direct U.S. government treasury obligations. As a result, it is possible that a claim could be made that the Company has been operating as an unregistered investment company. If the Company was deemed to be an investment company for purposes of the Investment Company Act, it might be forced to abandon its efforts to complete an initial business combination and instead be required to liquidate. If the Company is required to liquidate, its investors would not be able to realize the benefits of owning stock in a successor operating business, such as any appreciation in the value of the Company’s securities following such a transaction, the Company’s warrants and rights would expire worthless and shares of GLST Common Stock would have no value apart from their pro rata entitlement to the funds then-remaining in the Trust Account.
If we are deemed to be an investment company for purposes of the Investment Company Act, our activities would be severely restricted. In addition, we would be subject to additional burdensome regulatory requirements and expenses for which we have not allotted funds. As a result, unless the Company is able to modify its activities so that we would not be deemed an investment company under the Investment Company Act, we may abandon our efforts to consummate a business combination and instead liquidate the Company. If we are required to liquidate the Company, our investors would not be able to realize the benefits of owning shares or investing in a successor operating business, including the potential appreciation in the value of our units, shares, warrants and rights following such a transaction, and our warrants and rights would expire worthless.
Global Star will be forced to liquidate the trust account if it cannot consummate a business combination by June 22, 2025, Global Star’s public stockholders will receive $10.25 per share and the Global Star rights will expire worthless.
If Global Star is unable to complete a business combination by June 22, 2025 (unless Global Star obtains stockholder approval to extend the time it has to complete its initial business combination), and is forced to liquidate, the per-share liquidation distribution will be $10.25, plus interest earned on amounts held in trust that have not been used to pay for taxes. Furthermore, there will be no distribution with respect to the GLST Rights, which will expire worthless as a result of Global Star’s failure to complete a business combination.
You must tender your GLST Common Stock in order to validly seek redemption at the Special Meeting.
In connection with tendering your shares for redemption, you must elect either to physically tender your stock certificates to Global Star’s transfer agent by two (2) business days before the Special Meeting, or deliver your GLST Common Stock to the transfer agent electronically using The Depository Trust Company’s DWAC System, which election would likely be determined based on the manner in which you hold your ordinary shares. The requirement for physical or electronic delivery by two (2) business days before the Special Meeting ensures that a redeeming holder’s election to redeem is irrevocable once the Business Combination is consummated. Any failure to observe these procedures will result in your loss of redemption rights in connection with the vote on the Business Combination.
If third parties bring claims against Global Star, the proceeds held in trust could be reduced and the per-share liquidation price received by Global Star’s stockholders may be less than $10.25.
Global Star’s placing of funds in trust may not protect those funds from third party claims against Global Star. Although the Sponsor has agreed to indemnify us, in the event the Trust Account is liquidated, to the extent any claims by a third party for services rendered or products sold to us, or any claims by a prospective target business with which Global Star has discussed entering into an acquisition agreement, reduce the amount of funds in the Trust Account to below the lesser of (i) $10.25 per public share and (ii) the actual amount per public share held in the Trust Account as of the date of the liquidation of the Trust Account, if less than $10.25 per public share is then held in the Trust Account due to reductions in the value of the trust assets, less taxes payable, (y) shall not apply to any claims by a third party or a target which executed a waiver of any and all rights to the monies held in the Trust Account (whether or not such waiver is enforceable) and (z) shall not apply to any claims under the Company’s indemnity of the underwriters of Global Star’s IPO against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), but only if such a third party or target business has not executed a waiver of any and all rights to seek access to the Trust Account, there can be no assurance that the Sponsor will be able to pay such amounts. Therefore, the per-share distribution from the trust account for Global Star’s stockholders may be less than $10.00 due to such claims.
Additionally, if Global Star is forced to file a bankruptcy case or an involuntary bankruptcy case is filed against it which is not dismissed, the proceeds held in the trust account could be subject to applicable bankruptcy law, and may be included in Global Star’s bankruptcy estate and subject to the claims of third parties with priority over the claims of its stockholders. To the extent any bankruptcy claims deplete the trust account, Global Star may not be able to return $10.25 to Global Star’s public stockholders.
Any distributions received by Global Star’s stockholders could be viewed as an unlawful payment if it was proved that immediately following the date on which the distribution was made, Global Star was unable to pay its debts as they fell due in the ordinary course of business and the value of its assets does not exceed its liabilities.
Global Star’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation provides that it will continue in existence only until June 22, 2025 (assuming the deadline for consummation is extended in accordance with the amended and restated certificate of incorporation). If Global Star is unable to consummate a transaction within the required time period, upon notice from Global Star, the trustee of the trust account will distribute the amount in its trust account to its public stockholders. Concurrently, Global Star shall pay, or reserve for payment, from funds not held in trust, its liabilities and obligations, although Global Star cannot assure you that there will be sufficient funds for such purpose. Global Star also cannot assure you that a creditor or stockholder will not file a petition with the Delaware court which, if successful, may result in Global Star’s liquidation being subject to the supervision of that court. Such events might delay distribution of some or all of Global Star’s assets to its public stockholders.
Thereafter, Global Star’s sole business purpose will be to voluntarily liquidate and dissolve in accordance with Delaware law. In such a situation under Delaware law, a liquidator would be appointed and, subject to the terms of the required plan of liquidation, the liquidator would give at least 21 days’ notice to creditors of his intention to make a distribution by notifying known creditors (if any) and by placing a public advertisement. However, in practice the procedure to be followed by the liquidator will be subject to the terms of the plan of liquidation and the certificate of incorporation of Global Star and the mentioned notice may not necessarily delay the distribution of assets particularly if the liquidator is satisfied that no creditors would be adversely affected as a consequence of a distribution before this time period has expired. In practice, as soon as the affairs of Global Star are fully-wound up, the liquidator would normally lay a final report and accounts before a final general meeting which must be called by a public notice at least one month before it takes place. After the final meeting, the liquidator must make a return to the registrar confirming the date on which the meeting was held and three months after the date of such filing Global Star is dissolved. It is Global Star’s intention to liquidate the trust account to its public stockholders as soon as reasonably possible and Global Star’s Sponsor and Initial Stockholders have agreed to take any such action necessary to liquidate the trust account and to dissolve Global Star as soon as reasonably practicable if Global Star does not complete a business combination within the required time period. Pursuant to Global Star’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation, failure to consummate a business combination by February 22, 2025 (unless Global Star elects to extend the time it has to complete the initial business combination to June 22, 2025), will trigger an automatic winding up of Global Star.
If Global Star is forced to enter into an insolvent liquidation, any distributions received by Global Star stockholders could be viewed as an unlawful payment if it was proved that immediately following the date on which the distribution was made, Global Star was unable to pay its debts as they fall due in the ordinary course of business. As a result, a liquidator could seek to recover all amounts received by Global Star stockholders. Furthermore, Global Star board of directors may be viewed as having breached its fiduciary duties to its creditors and/or may have acted in bad faith, and thereby exposing itself and Global Star to claims of damages, by paying public stockholders from the trust account prior to addressing the claims of creditors. Global Star cannot assure you that claims will not be brought against it for these reasons.
If Global Star’s due diligence investigation of K Enter was inadequate, then Global Star stockholders following the Business Combination could lose some or all of their investment.
Even though Global Star conducted a due diligence investigation of K Enter, it cannot be sure that this diligence uncovered all material issues that may be present inside K Enter or its business, or that it would be possible to uncover all material issues through a customary amount of due diligence, or that factors outside of K Enter and its business and outside of its control will not later arise.
All of Global Star’s Sponsor, officers and directors beneficially own GLST Common Stock, GLST Warrants and GLST Rights and will not participate in liquidation distributions and, therefore, they may have a conflict of interest in determining whether the Business Combination is appropriate.
All of Global Star’s Sponsor, officers and directors collectively beneficially own an aggregate of 2,140,000 shares of GLST Common Stock and 498,225 GLST Private Units. Such individuals/entities have waived their rights to redeem these shares (including shares underlying the units), or to receive distributions with respect to these shares upon the liquidation of the trust account if Global Star is unable to consummate a business combination. Accordingly, the GLST Common Stock, as well as the GLST Units purchased by Global Star’s officers and directors, will be worthless if Global Star does not consummate a business combination. Based on a market price of $11.69 per share of GLST Common Stock and $11.32 per GLST Unit on December 3, 2024, the aggregate value of these shares and units was approximately $30.7 million. The GLST Common Stock acquired prior to the IPO, as well as the GLST Units will be worthless if Global Star does not consummate a business combination. Consequently, Global Star’s Sponsor’, officers’ and directors’ discretion in identifying and selecting K Enter as a suitable target business may result in a conflict of interest when determining whether the terms, conditions and timing of the Business Combination are appropriate and in Global Star stockholders’ best interest.
Global Star is requiring stockholders who wish to redeem their shares of common stock in connection with the Business Combination to comply with specific requirements for redemption that may make it more difficult for them to exercise their redemption rights prior to the deadline for exercising their rights.
Global Star is requiring public stockholders who wish to redeem their shares of common stock to either tender their certificates to Global Star’s transfer agent or deliver their shares to the transfer agent electronically using the Depository Trust Company’s, or DTC, DWAC System two (2) business days before the Special Meeting. In order to obtain a physical certificate, a stockholder’s broker and/or clearing broker, DTC and Global Star’s transfer agent will need to act to facilitate this request. It is Global Star’s understanding that stockholders should generally allot at least two weeks to obtain physical certificates from the transfer agent. However, because Global Star does not have any control over this process or over the brokers or DTC, it may take significantly longer than two weeks to obtain a physical stock certificate. While Global Star has been advised that it takes a short time to deliver shares through the DWAC System, Global Star cannot assure you of this fact. Accordingly, if it takes longer than Global Star anticipates for stockholders to deliver their shares, stockholders who wish to redeem may be unable to meet the deadline for exercising their redemption rights and thus may be unable to redeem their shares of common stock.
Global Star will require its public stockholders who wish to redeem their shares of common stock in connection with the Business Combination to comply with specific requirements for redemption described above, such redeeming stockholders may be unable to sell their securities when they wish to in the event that the Business Combination is not consummated.
If Global Star requires public stockholders who wish to redeem their shares of common stock in connection with the Business Combination to comply with specific requirements for redemption as described above and the Business Combination is not consummated, Global Star will promptly return such certificates to its public stockholders. Accordingly, investors who attempted to redeem their shares of common stock in such a circumstance will be unable to sell their securities after the failed acquisition until Global Star has returned their securities to them. The market price for Global Star’s ordinary shares may decline during this time and you may not be able to sell your securities when you wish to, even while other stockholders that did not seek redemption may be able to sell their securities.
The Initial Stockholders, including the officers and directors, control a substantial interest in Global Star and thus may influence certain actions requiring a stockholder vote.
Global Star’s Sponsor and Initial Stockholders, including the officers and directors, collectively own approximately 56.8% of its issued and outstanding shares of common stock. However, if a significant number of Global Star stockholders vote, or indicate an intention to vote, against the Business Combination, Global Star’s Initial Stockholders or the affiliates, could make such purchases in the open market or in private transactions in order to influence the vote.
If the Business Combination’s benefits do not meet the expectations of financial or industry analysts, the market price of PubCo’s securities may decline after the Business Combination.
The market price of PubCo’s securities may decline as a result of the Business Combination if:
| ● | PubCo does not achieve the perceived benefits of the acquisition as rapidly as, or to the extent anticipated by, financial or industry analysts; or |
| ● | The effect of the Business Combination on the financial statements is not consistent with the expectations of financial or industry analysts. |
Accordingly, investors may experience a loss as a result of decreasing stock prices.
Global Star’s directors and officers may have certain conflicts in determining to recommend the acquisition of K Enter, since certain of their interests, and certain interests of their affiliates and associates, are different from, or in addition to, your interests as a stockholder.
Global Star’s management and directors have interests in and arising from the Business Combination that are different from, or in addition to, your interests as a stockholder, which could result in a real or perceived conflict of interest. These interests include the following:
| | ● | the fact that the Sponsor and Global Star’s directors and officers hold 2,140,000 Founder Shares for which they paid an aggregate purchase price of $25,000 and, 498,225 Private Units for which they paid an aggregate purchase price of $4,982,250. Specifically: the Sponsor owns 2,798,225 shares of GLST Common Stock; Anthony Ang and Ted Kim beneficially own 1,640,000 shares of GLST Common Stock by virtue of serving as the managing members of the Sponsor, and Mr. Ang also owns 300,000 shares of GLST Common Stock directly; Nicholas Khoo owns 50,000 shares of GLST Common Stock; and Stephen Drew owns 20,000 shares of GLST Common Stock. In addition, (i) on July 31, 2023, the Sponsor loaned $1,600,000 to Global Star in exchange for a non-interest-bearing promissory note, $1.5 million of which will be converted into 150,000 shares of Global Star common stock upon completion of the Business Combination and then the balance of $100,000 will be paid to the Sponsor (the “Note”) and (ii) on August 19, 2024, the Sponsor loaned $120,000 to K Enter, evidenced by a non-interest bearing promissory note (the “K Enter Note”) due and payable on the earlier of November 18, 2024 or five days after PubCo’s registration statement on Form F-4 is declared effective. The Founder Shares, Private Units, the Note and the K Enter Note have a total current value of $35.1 million, based on September 10, 2024 closing price of the GLST Common Stock and the GLST Units, which was $11.07 and 11.34, respectively. All of such investments will expire worthless if a business combination is not consummated; on the other hand, if a business combination is consummated, such investments could earn a positive rate of return for the Sponsor and Global Star’s directors and officers since their overall investment in such investments, even if other holders of Global Star’s common stock experience a negative rate of return, due to having initially purchased the Founder Shares for $25,000; |
| | ● | the fact that, if the Trust Account is liquidated, including in the event Global Star is unable to complete an initial business combination within the required time period, the Sponsor has agreed to indemnify Global Star to the extent any claims by a third party for services rendered or products sold to us, or any claims by a prospective target business with which Global Star has discussed entering into an acquisition agreement, reduce the amount of funds in the Trust Account to below the lesser of (i) $10.25 per public share and (ii) the actual amount per public share held in the Trust Account as of the date of the liquidation of the Trust Account, if less than $10.25 per public share is then held in the Trust Account due to reductions in the value of the trust assets, less taxes payable, (y) shall not apply to any claims by a third party or a target which executed a waiver of any and all rights to the monies held in the Trust Account (whether or not such waiver is enforceable) and (z) shall not apply to any claims under the Company’s indemnity of the underwriters of Global Star’s IPO against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), but only if such a third party or target business has not executed a waiver of any and all rights to seek access to the Trust Account; |
| | ● | certain officers and directors of the Company and affiliates of the Sponsor collectively own shares of common stock of K Enter for which they paid an aggregate purchase price of $8,600. Ted Kim, the manager of the Sponsor and a co-founder and director of K Enter, owns 19,564 shares or 10.12% of the shares of common stock of K Enter based on the shares of K Enter to be issued and outstanding immediately prior to the closing of the Business Combination through his ownership and control of Global Fund LLC, which owns 12,000 shares, and Lodestar USA, Inc., which owns 7,564 shares. Further, Global Star officers and directors collectively own shares of common stock of K Enter representing approximately 8,537 shares or 4.3% of the outstanding shares of K Enter common stock based on the shares of K Enter to be issued and outstanding immediately prior to the closing of the Business Combination. Specifically, Stephen Drew owns 6,000 shares of K Enter common stock, Yang Kan Chong owns 1,337 shares of K Enter common stock, Jukka Rannila, beneficially through Assai OY, owns 600 shares of K Enter common stock. Nicholas Aaron Khoo, the Company’s Chief Operating Officer, owns 600 shares of K Enter common stock, prior to the closing of the Business Combination. All of such investments could expire worthless if a business combination is not consummated; and |
| | ● | the fact that none of Global Star’s officers or directors has received any cash compensation for services rendered to the Company, and all of the current members of Global Star’s Board are expected to continue to serve as directors at least through the date of the special meeting to vote on a business combination and may even continue to serve following any business combination and receive compensation thereafter. |
| ● | The exercise of Global Star’s directors’ and officers’ discretion in agreeing to changes or waivers in the terms of the transaction may result in a conflict of interest when determining whether such changes or waivers are appropriate and in Global Star’s stockholders’ best interest; and |
| | ● | If the Business Combination with K Enter is completed, K Enter will designate all members of the board of directors. |
Global Star’s board of directors considered these conflicts of interest in negotiating and recommending the Business Combination and concluded that the merits of the Business Combination outweighed the potential conflicts and did not materially influence the negotiations with K Enter. In making this determination, Global Star’s board of directors also considered the fairness opinion obtained from EverEdge Pte Ltd. Global Star’s certificate of incorporation includes a waiver of the corporate opportunity doctrine whereby directors and officers are required to present corporate opportunities to Global Star. Global Star does not believe that this waiver had any impact on the negotiations with K Enter.
Global Star will incur significant transaction costs in connection with transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement.
Global Star will incur significant transaction costs in connection with the Business Combination. If the Business Combination is not consummated, Global Star may not have sufficient funds to seek an alternative business combination and may be forced to voluntarily liquidate and subsequently dissolve.
Risk Factors Relating to the Business Combination
Global Star and K Enter have incurred and expect to incur significant costs associated with the Business Combination. Whether or not the Business Combination is completed, the incurrence of these costs will reduce the amount of cash available to be used for other corporate purposes by Global Star if the Business Combination is completed or by Global Star if the Business Combination is not completed.
Global Star and K Enter expect to incur significant costs associated with the Business Combination. Whether or not the Business Combination is completed, Global Star expects to incur approximately $675,000 in expenses. These expenses will reduce the amount of cash available to be used for other corporate purposes by Global Star if the Business Combination is completed or by Global Star if the Business Combination is not completed.
Global Star may not be able to complete an initial business combination with a U.S. target company since such initial business combination may be subject to U.S. foreign investment regulations and review by a U.S. government entity such as the Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States (“CFIUS”), or ultimately prohibited.
One of Global Star’s directors is a citizen of a country other than the United States. In addition, K Enter, the company with which Global Star entered into the Business Combination Agreement is a Delaware corporation that will have operations in Korea and certain of its directors are citizens of countries other than the United States. While Global Star believes that the nature of Global Star’s business, and the nature of the businesses of K Enter should not make the transaction subject to U.S. foreign regulations or review by a U.S. government entity, it is possible that the Business Combination may be subject to a CFIUS review, the scope of which was expanded by the Foreign Investment Risk Review Modernization Act of 2018 (“FIRRMA”), to include certain non-passive, non-controlling investments in sensitive U.S. businesses and certain acquisitions of real estate even with no underlying U.S. business. FIRRMA, and subsequent implementing regulations that are now in force, also subjects certain categories of investments to mandatory filings. If the Business Combination falls within CFIUS’s jurisdiction, Global Star may determine that Global Star is required to make a mandatory filing or that Global Star will submit a voluntary notice to CFIUS, or to proceed with the initial business combination without notifying CFIUS and risk CFIUS intervention, before or after closing the initial business combination. CFIUS may decide to block or delay Global Star’s initial business combination, impose conditions to mitigate national security concerns with respect to such initial business combination or order Global Star to divest all or a portion of a U.S. business of the combined company without first obtaining CFIUS clearance, which may limit the attractiveness of or prevent Global Star from pursuing certain initial business combination opportunities that Global Star believes would otherwise be beneficial to Global Star and Global Star’s shareholders. As a result, the pool of potential targets with which Global Star could complete an initial business combination may be limited, and Global Star may be adversely affected in terms of competing with other special purpose acquisition companies which do not have similar foreign ownership issues.
Moreover, the process of government review, whether by the CFIUS or otherwise, could be lengthy and Global Star has limited time to complete Global Star’s initial business combination. If Global Star cannot complete Global Star’s initial business combination by February 22, 2025 (unless Global Star elects to extend the time it has to complete the initial business combination to June 22, 2025), because the review process drags on beyond such timeframe or because Global Star’s initial business combination is ultimately prohibited by CFIUS or another U.S. government entity, Global Star may be required to liquidate. This will also cause you to lose the investment opportunity in a target company and the chance of realizing future gains on your investment through any price appreciation in the combined company.
Global Star does not believe that either Global Star or Global Star’s Sponsor constitute a “foreign person” under CFIUS rules and regulations. However, if Global Star was to be considered a “foreign person” under CFIUS rules that may affect national security, Global Star could be subject to such foreign ownership restrictions and/or CFIUS review. If the Business Combination falls within the scope of applicable foreign ownership restrictions, Global Star may be unable to consummate the Business Combination. In addition, if the Business Combination falls within CFIUS’ jurisdiction, Global Star may be required to make a mandatory filing or determine to submit a voluntary notice to CFIUS, or to proceed with the Business Combination without notifying CFIUS and risk CFIUS intervention, before or after closing the Business Combination Although Global Star does not believe Global Star or Global Star’s sponsor are a “foreign person,” CFIUS may take a different view and decide to block or delay the business combination, impose conditions to mitigate national security concerns with respect to the business combination, order Global Star to divest all or a portion of a U.S. business of the combined company if Global Star had proceeded without first obtaining CFIUS clearance, or impose penalties if CFIUS believes that the mandatory notification requirement applied.
Additionally, the laws and regulations of other U.S. government entities may impose review or approval procedures on account of any foreign ownership by the Sponsor. If Global Star were to seek an initial business combination other than the Business Combination, the pool of potential targets with which Global Star could complete an initial business combination may be limited as a result of any such regulatory restriction. Moreover, the process of any government review, whether by CFIUS or otherwise, could be lengthy. Because Global Star has only a limited time to complete the Business Combination, Global Star’s failure to obtain any required approvals within the requisite time period may require Global Star to liquidate. Global Star cannot assure you that the per share distribution from the Trust Account, if Global Star liquidates, will not be less than $10.25. As a result, if Global Star liquidates, Global Star’s public shareholders may receive less than $10.25 per share, and Global Star’s rights will expire worthless. This will also cause you to lose any potential investment opportunity in the Business Combination and the chance of realizing future gains on your investment through any price appreciation in the combined company post-closing of the Business Combination.
Our stockholders may not have the same benefits as an investor in an underwritten public offering.
Global Star is already a publicly traded company. Therefore, the merger and the transactions described in this proxy statement/prospectus are not an underwritten initial public offering of securities of the combined company and differ from an underwritten initial public offering in several significant ways. For example, like other business combinations and spin-offs, in connection with the merger, our stockholders will not receive the benefits of the diligence that would customarily be performed by the underwriters in an underwritten public offering. Investors in an underwritten public offering may benefit from the role of the underwriters in such an offering. In an underwritten public offering, an issuer initially sells its securities to the public market via one or more underwriters, who distribute or resell such securities to the public. Underwriters have liability under the U.S. securities laws for material misstatements or omissions in a registration statement pursuant to which an issuer sells securities. Because the underwriters have a “due diligence” defense to any such liability by, among other things, conducting a reasonable investigation, the underwriters and their counsel conduct a due diligence investigation of the issuer. Due diligence entails engaging legal, financial and/or other experts to perform an investigation as to the accuracy of an issuer’s disclosure regarding, among other things, its business and financial results. In making their investment decision, investors have the benefit of such diligence in underwritten public offerings. Our stockholders must rely on the information in this proxy statement/prospectus and will not have the benefit of an independent review and investigation of the type normally performed by an independent underwriter in a public securities offering. While private investors and management in a business combination undertake a certain level of due diligence, it is not necessarily the same level of due diligence undertaken by an underwriter in a public securities offering.
In addition, because there are no underwriters engaged in connection with the merger, prior to the opening of trading on the Nasdaq on the trading day immediately following the Closing, there will be no traditional “roadshow” or book building process, and no price at which underwriters initially sold shares to the public to help inform efficient and sufficient price discovery with respect to the initial post-closing trades on the Nasdaq. Therefore, buy and sell orders submitted prior to and at the opening of initial post-closing trading of our securities will not have the benefit of being informed by a published price range or a price at which the underwriters initially sold shares to the public, as would be the case in an underwritten initial public offering. There will be no underwriters assuming risk in connection with an initial resale of our securities or helping to stabilize, maintain or affect the public price of our securities following the Closing. Moreover, we will not engage in, and have not and will not, directly or indirectly, request financial advisors to engage in, any special selling efforts or stabilization or price support activities in connection with our securities that will be outstanding immediately following the Closing. No assurance can be given that brokerage firms will, in the future, want to conduct any offerings on the combined company’s behalf. All of these differences from an underwritten public offering of the combined company’s securities could result in a more volatile price for the combined company’s securities.
Such differences from an underwritten public offering may present material risks to unaffiliated investors that would not exist if K Enter became a publicly listed company through an underwritten initial public offering instead or upon completion of the merger.
In the event that a significant number of GLST Common Stock are redeemed, the PubCo Ordinary Shares may become less liquid following the Business Combination.
If a significant number of GLST Common Stock are redeemed, PubCo may be left with a significantly smaller number of stockholders. As a result, trading in the shares of PubCo following the Business Combination may be limited and your ability to sell your shares in the market could be adversely affected.
Global Star may waive one or more of the conditions to the Business Combination without resoliciting Global Star stockholder approval for the Business Combination.
Global Star may agree to waive, in whole or in part, some of the conditions to its obligations to complete the Business Combination, to the extent permitted by applicable laws. The Global Star board of directors will evaluate the materiality of any waiver to determine whether amendment of this proxy statement/prospectus and resolicitation of proxies is warranted.
In some instances, if the Global Star board of directors determines that a waiver is not sufficiently material to warrant resolicitation of Global Star stockholders, Global Star has the discretion to complete the Business Combination without seeking further stockholder approval. For example, it is a condition to Global Star’s obligations to close the Business Combination that there be no restraining order, injunction or other order restricting K Enter’s conduct of its business, however, if the Global Star board of directors determines that any such order or injunction is not material to the business of K Enter, then the Global Star board of directors may elect to waive that condition and close the Business Combination.
Global Star stockholders will experience immediate dilution as a consequence of the issuance of PubCo Ordinary Shares as consideration in the Business Combination. Having a minority share position may reduce the influence that Global Star’s current stockholders have on the management of Global Star.
After the Business Combination, assuming (i) there are no redemptions of Global Star’s shares and (ii) there is no exercise of the PubCo Warrants, Global Star’s current public stockholders will own approximately 3.3% of the issued share capital of PubCo, Global Star’s Initial Stockholders, current directors, officers and affiliates will own approximately 4.5% of the issued share capital of PubCo, and K Enter shareholders will own approximately 92.2% of the issued share capital of PubCo (excluding the 5,900,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares reserved and authorized for issuance under the Incentive Plan). Assuming maximum redemptions by holders of Global Star’s outstanding ordinary shares, Global Star’s current public stockholders will own approximately 1.4% of the issued share capital of PubCo, Global Star’s current directors, officers and affiliates will own approximately 4.7% of the issued share capital of PubCo, and K Enter shareholders will own approximately 93.9% of the issued share capital of PubCo (excluding the 5,900,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares reserved and authorized for issuance under the Incentive Plan). The minority position of the former Global Star’s stockholders will give them limited influence over the management and operations of the post-Business Combination company.
Global Star and K Enter intend to use their best efforts to raise $50 million in a PIPE Financing in connection with the closing of the Business Combination. A PIPE Financing is not a condition to the closing of the Business Combination. If successful in securing a PIPE Financing, the proceeds of the PIPE Financing will be used by PubCo to fund its working capital for operations and to fund future acquisitions by PubCo. In the event Global Star is able to secure a PIPE Financing, such financing will have a dilutive effect on the shareholders of PubCo. Currently, Global Star has not received any commitments for a PIPE Financing and there can be no assurances that Global Star will be able to consummate a PIPE Financing in connection with the Business Combination.
Since Global Star has no operating history and Global Star faces mandatory liquidation should its initial business combination not be consummated by February 22, 2025 (unless Global Star extends the time period it has to complete its initial business combination to June 22, 2025), management of Global Star has determined that these factors raise substantial doubt about Global Star’s ability to continue as a going concern.
Global Star is a blank check company with no operating history or results. Global Star has until February 22, 2025 (unless Global Star elects to extend the time it has to complete the initial business combination to June 22, 2025) to consummate a Business Combination. If a Business Combination is not consummated by such deadline, then Global Star is subject to mandatory liquidation and potential subsequent dissolution. Global Star’s management has determined that the liquidation, should a Business Combination not occur, and potential subsequent dissolution raises substantial doubt about Global Star’s ability to continue as a going concern. See the section titled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations of Global Star—Liquidity and Capital Resources.”
Our management has identified material weaknesses in Global Star’s internal control over financial reporting and Global Star may not be able to remediate these weaknesses. Additionally, Global Star’s management may identify material weaknesses in the future that could adversely affect investor confidence, impair the value of Global Star’s securities, and increase Global Star’s cost of raising capital.
There can be no assurance as to how quickly or effectively Global Star can remediate the material weaknesses in Global Star’s internal control over financial reporting or that additional material weaknesses will not be identified in the future. Any failure to remedy additional weaknesses or deficiencies in Global Star’s internal control over financial reporting that may be discovered in the future or to implement new or improved controls, or difficulties encountered in the implementation of such controls, could harm Global Star’s operating results, cause Global Star to fail to meet Global Star’s reporting obligations or result in material misstatements in Global Star’s financial statements. Any such failure could, in turn, affect the future ability of Global Star’s management to certify that Global Star’s internal control over financial reporting is effective. Ineffective internal control over financial reporting could also subject Global Star to the scrutiny of the SEC and other regulatory bodies which could cause investors to lose confidence in Global Star’s reported financial information and subject Global Star to civil or criminal penalties or shareholder litigation, which could have an adverse effect on the trading price of Global Star’s securities. In addition, if identify additional deficiencies in Global Star’s internal control over financial reporting, the disclosure of that fact, even if quickly remedied, could reduce the market’s confidence in Global Star’s financial statements and harm Global Star’s share price. Furthermore, additional deficiencies could result in future non-compliance with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (“Sarbanes-Oxley”). Such non-compliance could subject Global Star to a variety of administrative sanctions, including review by the SEC or other regulatory authorities.
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial and accounting officer, Global Star conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of its disclosure controls and procedures as of the end of the year ended December 31, 2023, as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act. Global Star is experiencing difficulty in the accounting and reporting related to the existence of assets and corresponding income, as well as the accounting and reporting for the completeness and accuracy of our liabilities and the corresponding income and expenses. Additionally, Global Star has not evidenced oversight of Global Star’s financial statements and disclosures as of December 31, 2023. These material weaknesses in the disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2023, have not been remediated and therefore Global Star’s disclosure controls were not effective. In light of the material weakness, Global Star has made control improvements, including enhancing the efficacy of its review processes to identify and appropriately apply applicable accounting requirements to better evaluate and understand the nuances of the accounting standards that apply to the treatment and reporting of related party transactions in Global Star’s consolidated financial statements. Global Star’s plans at this time also include providing enhanced access to accounting literature, research materials and documents and increased communication among Global Star’s management and third-party professionals with whom Global Star consults regarding related party accounting applications. Furthermore, in light of this material weakness, Global Star performed additional analysis as deemed necessary to ensure that Global Star’s consolidated financial statements were prepared in accordance with GAAP. Global Star continues to evaluate steps to remediate the identified material weakness. These remediation measures may be time consuming and costly and thee is no assurance that these initiatives will ultimately have the intended effects.
Risks Factors Relating to an Investment in PubCo Ordinary Shares and Public Warrants
Certain judgments obtained against PubCo by PubCo’s shareholders may not be enforceable.
PubCo is a company incorporated under the laws of the Cayman Islands. K Enter conducts most of its operations in the Republic of Korea and substantially all of its operations outside of the United States. Most of K Enter’s assets are located in the Republic of Korea, and substantially all of K Enter’s assets are located outside of the United States. In addition, after the Business Combination, most of PubCo’s senior executive officers reside within the Republic of Korea for a significant portion of the time and most are Korean nationals. Substantially all of the assets of these persons are located outside the United States. As a result, it may be difficult or impossible for you to bring an action against PubCo or against these individuals in the United States in the event that you believe that your rights have been infringed under the U.S. federal securities laws or otherwise. Even if you are successful in bringing an action of this kind, the laws of the Cayman Islands and of the Republic of Korea may render you unable to enforce a judgment against PubCo’s assets or the assets of K Enter’s directors and officers. For more information regarding the relevant laws of the Cayman Islands and the Republic of Korea, see “Comparison of Shareholder Rights — Enforceability of Civil Liabilities under the U.S. Securities Laws.”
Currently, there is no public market for the ordinary shares of PubCo. Global Star stockholders cannot be sure that an active trading market will develop for or of the market price of the ordinary shares of PubCo they will receive or that PubCo will successfully obtain authorization for listing on the Nasdaq.
Upon the consummation of the Business Combination, each ordinary share of K Enter will be converted into the right to receive one ordinary share of PubCo. PubCo is a newly formed entity and prior to this transaction it has not issued any securities in the U.S. markets or elsewhere nor has there been extensive information about it, its businesses, or its operations publicly available. Global Star, K Enter and PubCo have agreed to use their best efforts to cause the ordinary shares of PubCo to be issued in the Business Combination to be approved for listing on the Nasdaq prior to the effective time of the Business Combination. However, the listing of shares on the Nasdaq does not ensure that a market for the ordinary shares of PubCo will develop or the price at which the shares will trade. No assurance can be provided as to the demand for or trading price of the ordinary shares of PubCo following the closing of the Business Combination and the ordinary shares of PubCo may trade at a price less than the current market price of the common stock of Global Star.
Even if PubCo is successful in developing a public market, there may not be enough liquidity in such market to enable shareholders to sell their ordinary shares. If a public market for the combined PubCo’s ordinary shares does not develop, investors may not be able to re-sell their ordinary shares, rendering their shares illiquid and possibly resulting in a complete loss of their investment. PubCo cannot predict the extent to which investor interest in PubCo will lead to the development of an active, liquid trading market. The trading price of and demand for the ordinary shares of PubCo following completion of the Business Combination and the development and continued existence of a market and favorable price for the ordinary shares of PubCo will depend on a number of conditions, including the development of a market following, including by analysts and other investment professionals, the businesses, operations, results and prospects of PubCo, general market and economic conditions, governmental actions, regulatory considerations, legal proceedings and developments or other factors. These and other factors may impair the development of a liquid market and the ability of investors to sell shares at an attractive price. These factors also could cause the market price and demand for the ordinary shares of PubCo to fluctuate substantially, which may limit or prevent investors from readily selling their shares and may otherwise affect negatively the price and liquidity of the ordinary shares of PubCo. Many of these factors and conditions are beyond the control of PubCo or PubCo shareholders.
PubCo’s share price may be volatile and could decline substantially.
The market price of PubCo’s ordinary shares may be volatile, both because of actual and perceived changes in Global Star’s financial results and prospects, and because of general volatility in the stock market. The factors that could cause fluctuations in PubCo’s share price may include, among other factors discussed in this section, the following:
| ● | actual or anticipated variations in the financial results and prospects of Global Star or other companies in the retail business; |
| ● | changes in financial estimates by research analysts; |
| ● | changes in the market valuations of other entertainment content companies; |
| ● | announcements by PubCo or its competitors of new education services, expansions, investments, acquisitions, strategic partnerships or joint ventures; |
| ● | mergers or other business combinations involving PubCo; |
| ● | additions and departures of key personnel and senior management; |
| ● | changes in accounting principles; |
| ● | the passage of legislation or other developments affecting PubCo or its industry; |
| ● | the trading volume of PubCo’s ordinary shares in the public market; |
| ● | the release of lockup, escrow or other transfer restrictions on PubCo’s outstanding equity securities or sales of additional equity securities; |
| ● | potential litigation or regulatory investigations; |
| ● | changes in economic conditions, including fluctuations in global and the Republic of Korea’s economies; |
| ● | financial market conditions; |
| ● | natural disasters, terrorist acts, acts of war or periods of civil unrest; and |
| ● | the realization of some or all of the risks described in this section. |
In addition, the stock markets have experienced significant price and trading volume fluctuations from time to time, and the market prices of the equity securities of retailers have been extremely volatile and are sometimes subject to sharp price and trading volume changes. These broad market fluctuations may materially and adversely affect the market price of PubCo’s ordinary shares.
The sale or availability for sale of substantial amounts of ordinary shares could adversely affect their market price.
Sales of substantial amounts of the ordinary shares in the public market after the completion of the Business Combination, or the perception that these sales could occur, could adversely affect the market price of the PubCo Ordinary Shares and could materially impair PubCo’s ability to raise capital through equity offerings in the future. The PubCo Ordinary Shares listed after the Business Combination will be freely tradable without restriction or further registration under the Securities Act. In connection with the Business Combination, K Enter and its directors, executive officers and existing shareholders will exchange the ordinary shares of K Enter held by them for PubCo Ordinary Shares upon the consummation of the Business Combination and have agreed, subject to certain exceptions, not to sell any PubCo Ordinary Shares for 180 days after the date of this prospectus without the prior written consent of PubCo. Shares of PubCo to be held by K Enter’s certain existing shareholders after the Business Combination may be sold in the public market in the future subject to the restrictions in Rule 144 and Rule 701 under the Securities Act and the applicable lockup agreements. There will be 63,519,622 outstanding and issued PubCo Ordinary Shares immediately after the Business Combination, assuming no additional redemptions. PubCo cannot predict what effect, if any, market sales of securities held by PubCo’s significant shareholders or any other holders or the availability of these securities for future sale will have on the market price of the PubCo Ordinary Shares.
PubCo may redeem your unexpired warrants prior to their exercise at a time that is disadvantageous to you, thereby making your warrants worthless.
PubCo has the ability to redeem outstanding PubCo Warrants at any time after they become exercisable and prior to their expiration, at a price of $0.01 per warrant, provided that the last reported sales price of its Ordinary Shares equals or exceeds $18.00 per share (as adjusted for share splits, share capitalizations, rights issuances, subdivisions, reorganizations, recapitalizations and the like) for any 20 trading days within a 30 trading-day period ending on the third trading day prior to the date we send the notice of redemption to the warrant holders, provided that there is an effective registration statement covering the Ordinary Shares issuable upon exercise of the PubCo Warrants, and a current prospectus relating thereto, available throughout the 30-day redemption period or PubCo has elected to require the exercise of the PubCo Warrants on a “cashless basis;” provided, however, that if and when the PubCo Warrants become redeemable by PubCo, PubCo may not exercise such redemption right if the issuance of Ordinary Shares upon exercise of the PubCo Warrants is not exempt from registration or qualification under applicable state blue sky laws or PubCo is unable to effect such registration or qualification.
If PubCo so elects to redeem the PubCo Warrants, PubCo will fix the redemption date and provide notice of redemption by first-class mail to the registered holders of the PubCo Warrants to be redeemed at their addresses as they appear on the registration books. PubCo also will file a Current Report on Form 8-K with the SEC on or before the mailing date of the redemption notice. Redemption of the outstanding warrants could force warrantholders (i) to exercise PubCo Warrants and pay the exercise price therefor at a time when it may be disadvantageous for them, (ii) to sell PubCo Warrants at the then-current market price when they might otherwise wish to hold their warrants or (iii) to accept the nominal redemption price which, at the time the outstanding warrants are called for redemption, is likely to be substantially less than the market value of the PubCo Warrants.
If securities or industry analysts do not publish research or publish inaccurate or unfavorable research about PubCo or its business, its ordinary shares price and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for PubCo’s ordinary shares will depend in part on the research and reports that securities or industry analysts publish about PubCo or its business. Securities and industry analysts do not currently, and may never, publish research on PubCo. If no securities or industry analysts commence coverage of PubCo, the trading price for its ordinary shares would likely be negatively impacted. In the event securities or industry analysts initiate coverage, if one or more of the analysts who cover PubCo downgrade its securities or publish inaccurate or unfavorable research about its business, its stock price would likely decline. If one or more of these analysts cease coverage of PubCo or fail to publish reports on PubCo, demand for its ordinary shares could decrease, which might cause its ordinary share price and trading volume to decline.
PubCo’s amended and restated memorandum and articles of association that will become effective prior to the completion of the Business Combination contains anti-takeover provisions that could have a material adverse effect on the rights of holders of the ordinary shares of PubCo.
In connection with the Business Combination, PubCo will adopt an amended and restated memorandum and articles of association that will become effective immediately prior to the consummation of the Business Combination. PubCo’s post-closing memorandum and articles of association will contain provisions to limit the ability of others to acquire control of PubCo or cause PubCo to engage in change-of-control transactions. These provisions could have the effect of depriving PubCo shareholders of an opportunity to sell their shares at a premium over prevailing market prices by discouraging third parties from seeking to obtain control of PubCo in a tender offer or similar transaction. For example, PubCo’s board of directors will have the authority, subject to any resolution of the shareholders to the contrary, to issue preference shares in one or more series and to fix their designations, powers, preferences, privileges, and relative participating, optional or special rights and the qualifications, limitations or restrictions, including dividend rights, conversion rights, voting rights, terms of redemption and liquidation preferences, any or all of which may be greater than the rights associated with PubCo’s ordinary shares. Preference shares could be issued quickly with terms calculated to delay or prevent a change in control of PubCo or make removal of management more difficult. If PubCo’s board of directors decides to issue preference shares, the price of the ordinary shares of PubCo may fall and the voting and other rights of the holders of the ordinary shares of PubCo may be materially and adversely affected.
Risk Factors Relating to PubCo
If PubCo ceases to qualify as a foreign private issuer, it would be required to convert the financials to US GAAP from IFRS in order comply fully with the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act applicable to U.S. domestic issuers, and it would incur significant additional legal, accounting and other expenses that it would not incur as a foreign private issuer.
As a foreign private issuer, PubCo will be exempt from the rules under the Exchange Act prescribing the furnishing and content of proxy statements, and its officers, directors and principal shareholders will be exempt from the reporting and short-swing profit recovery provisions contained in Section 16 of the Exchange Act. In addition, it will not be required under the Exchange Act to file periodic reports and financial statements with the SEC as frequently or as promptly as United States domestic issuers, and it will not be required to disclose in its periodic reports all of the information that United States domestic issuers are required to disclose. In addition, PubCo would be required to report its financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP, which could result in significant additional expenses and impact PubCo’s financial results due to the change in accounting framework. If it ceases to qualify as a foreign private issuer in the future, it would incur significant additional expenses that could have a material adverse effect on its results of operations.
Because PubCo is a foreign private issuer and is exempt from certain Nasdaq corporate governance standards applicable to U.S. issuers, you will have less protection than you would have if it were a domestic issuer.
PubCo’s status as a foreign private issuer exempts it from compliance with certain Nasdaq corporate governance requirements if it instead complies with the statutory requirements applicable to a Cayman Islands exempted company. The statutory requirements of PubCo’s home country of Cayman Islands, do not strictly require a majority of its board to consist of independent directors. Thus, although a director must act in the best interests of PubCo, it is possible that fewer board members will be exercising independent judgment and the level of board oversight on the management of Global Star may decrease as a result. In addition, the Nasdaq Listing Rules also require U.S. domestic issuers to have an independent compensation committee with a minimum of two members, a nominating committee, and an independent audit committee with a minimum of three members. PubCo, as a foreign private issuer, with the exception of needing an independent audit committee composed of at least three members, is not subject to these requirements. The Nasdaq Listing Rules may also require shareholder approval for certain corporate matters that PubCo’s home country’s rules do not. Following Cayman Islands governance practices, as opposed to complying with the requirements applicable to a U.S. company listed on Nasdaq, may provide less protection to you than would otherwise be the case.
Although as a Foreign Private Issuer PubCo is exempt from certain corporate governance standards applicable to US domestic issuers, if PubCo cannot satisfy, or continue to satisfy, the initial listing requirements and other rules of Nasdaq, PubCo’s securities may not be listed or may be delisted, which could negatively impact the price of its securities and your ability to sell them.
PubCo will seek to have its securities approved for listing on Nasdaq in connection with the Business Combination. PubCo cannot assure you that it will be able to meet those initial listing requirements at that time. Even if PubCo’s securities are listed on Nasdaq, it cannot assure you that its securities will continue to be listed on Nasdaq.
In addition, following the Business Combination, in order to maintain its listing on Nasdaq, PubCo will be required to comply with certain rules of Nasdaq, including those regarding minimum stockholders’ equity, minimum share price, minimum market value of publicly held shares, and various additional requirements. Even if PubCo initially meets the listing requirements and other applicable rules of Nasdaq, PubCo may not be able to continue to satisfy these requirements and applicable rules. If PubCo is unable to satisfy Nasdaq criteria for maintaining its listing, its securities could be subject to delisting.
If Nasdaq does not list PubCo’s securities, or subsequently delists its securities from trading, PubCo could face significant consequences, including:
| ● | a limited availability for market quotations for its securities; |
| ● | reduced liquidity with respect to PubCo’s securities; |
| ● | a determination that its ordinary shares is a “penny stock,” which will require brokers trading in PubCo’s Ordinary Shares to adhere to more stringent rules and possibly result in a reduced level of trading activity in the secondary trading market for PubCo’s Ordinary Shares; |
| ● | limited amount of news and analyst coverage; and |
| ● | a decreased ability to issue additional securities or obtain additional financing in the future. |
A potential failure to maintain effective internal control over financial reporting in accordance with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act could have a material adverse effect on PubCo’s business, financial condition, and results of operations. PubCo may be unable to accurately report PubCo’s financial results or prevent fraud if Global Star cannot maintain an effective system of internal controls over PubCo’s financial reporting.
PubCo will be subject to reporting obligations under the U.S. securities laws. The Securities and Exchange Commission, or the “SEC,” as required by Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, or the “Sarbanes-Oxley Act,” adopted rules requiring every public company to include a management report on such company’s internal controls over financial reporting in its annual report, which contains management’s assessment of the effectiveness of the company’s internal controls over financial reporting. PubCo will be an “emerging growth company,” and are expected to first include a management report on PubCo’s internal controls over financial reporting in PubCo’s annual report in the PubCo’s second annual report after the close of the business combination. PubCo’s management may conclude that PubCo’s internal controls over PubCo’s financial reporting are not effective, and PubCo’s reporting obligations as a public company will place a significant strain on PubCo’s management, operational and financial resources, and systems for the foreseeable future, which will increase PubCo’s operating expenses.
The establishment of effective internal controls over financial reporting is necessary for PubCo to produce reliable financial reports and are important to help prevent fraud. PubCo’s failure to achieve and maintain effective internal controls over financial reporting could consequently result in the loss of investor confidence in the reliability of PubCo’s financial statements, which in turn could harm PubCo’s business and negatively impact the trading price of PubCo’s stock. PubCo anticipate that it will incur considerable costs and devote significant management time and efforts and other resources to comply with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act.
K Enter identified material weaknesses in its internal control over financial reporting which, if not corrected, could affect the reliability of K Enter’s financial statements and have other adverse consequences.
K Enter has identified material weaknesses in its internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023 which relate to: (a) the design and operation of K Enter’s information technology general controls; (b) K Enter’s overall closing and financial reporting processes, including accounting for significant and unusual transactions, (c) general segregation of duties, including the review and approval of journal entries and (d) the design, implementation and operation for process level control activities related to equity transactions.
A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of K Enter’s financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. These deficiencies could result in additional misstatements to K Enter’s financial statements that would be material and would not be prevented or detected on a timely basis.
K Enter’s management has concluded that these material weaknesses in K Enter’s internal control over financial reporting are due to the fact that, prior to this proxy statement, K Enter was a private company with limited resources and did not have the necessary business processes and related internal control formally designed and implemented coupled with the appropriate resources with the appropriate level of experience and technical expertise to oversee K Enter’s business processes and controls surrounding information technology general controls and K Enter’s closing and financial reporting processes.
K Enter’s management has developed a remediation plan to address the remaining material weaknesses. Specifically, (a) to alleviate the information technology control issue, K Enter plans to implement Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and financial solution, which will allow personnel to implement workflow controls; (b) to alleviate the overall closing and financial reporting processes, including accounting for significant and unusual transactions, K Enter plans to hire internal personnel and external advisors with relevant public reporting experience and conduct training for K Enter’s personnel in GAAP reporting requirements; (c) to alleviate the segregation of duties issue, K Enter plans to leverage ERP system configuration and workflow while expanding the accounting team and reviewing roles; (d) to alleviate the lack of a formal journal entry review and approval process, K Enter will be implementing work flow steps within the ERP system to ensure all journal entries are approved before posting to the general ledger ; and (e) to alleviate the lack of process level control activities relate to equity transactions, K Enter plans to improve the review process including the documentation of the assessment of equity transactions and the engagement of external advisors to review management’s accounting analysis. The material weaknesses will not be considered remediated until management concludes, through testing, that these controls are effective. K Enter’s management will monitor the effectiveness of K Enter’s remediation plans and will make changes management determines to be appropriate.
Play Company identified material weaknesses in its internal control over financial reporting which, if not corrected, could affect the reliability of Play Company’s financial statements and have other adverse consequences.
Play Company has identified material weaknesses in its internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2022 which relate to: (a) Play Company did not have sufficient skilled personnel with requisite IFRS reporting knowledge and experience and (b) Play Company did not have sufficient entity level controls and sufficiently designed internal controls and financial reporting policies and procedures including segregation of duties that are commensurate with IFRS reporting requirements.
A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of Play Company’s respective financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. These deficiencies could result in additional misstatements to Play Company’s financial statements that would be material and would not be prevented or detected on a timely basis.
Play Company’s management has concluded that these material weaknesses in Play Company’s respective internal control over financial reporting are due to the fact that, prior to this proxy statement, Play Company was a private company with limited resources and did not have the necessary business processes and related internal control formally designed and implemented coupled with the appropriate resources with the appropriate level of experience and technical expertise to oversee Play Company’s business processes and controls surrounding information technology general controls and Play Company’s closing and financial reporting processes.
To remediate the material weaknesses described above, Play Company’s management plans to (a) continue to establish a comprehensive and effective internal control system with the assistance from third-party consulting firm which shall provide relevant professional advisory services; (b) continue to assess Play Company’s standardized processes to further enhance the effectiveness of Play Company’s financial review, including the analysis and monitoring of financial information in a consistent and thorough manner; and (c) hire internal personnel and external advisors with relevant public reporting experience and conduct training for Play Company’s personnel in IFRS reporting requirements.
If not remediated, these material weaknesses could result in further material misstatements to K Enter’s annual or interim financial statements that would not be prevented or detected on a timely basis, or in delayed filing of required periodic reports. If K Enter is unable to assert that its internal control over financial reporting is effective, or when required in the future, if PubCo’s independent registered public accounting firm is unable to express an unqualified opinion as to the effectiveness of the internal control over financial reporting, investors may lose confidence in the accuracy and completeness of PubCo’s financial reports, the market price of PubCo Common Stock could be adversely affected and PubCo could become subject to litigation or investigations by the Nasdaq, the SEC or other regulatory authorities, which could require additional financial and management resources.
K Enter’s management has identified material weaknesses in K Enter’s internal control over financial reporting and K Enter may not be able to remediate these weaknesses. Additionally, K Enter’s management may identify material weaknesses in the future that could adversely affect investor confidence, impair the value of K Wave’s securities, and increase K Wave’s cost of raising capital.
There can be no assurance as to how quickly or effectively K Enter can remediate the material weaknesses in K Enter’s internal control over financial reporting or that additional material weaknesses will not be identified in the future. Any failure to remedy additional weaknesses or deficiencies in K Enter’s internal control over financial reporting that may be discovered in the future or to implement new or improved controls, or difficulties encountered in the implementation of such controls, could harm K Enter’s operating results, cause PubCo to fail to meet K Enter’s reporting obligations or result in material misstatements in K Enter’s financial statements. Any such failure could, in turn, affect the future ability of K Enter’s management to certify that K Enter’s internal control over financial reporting is effective. Ineffective internal control over financial reporting could also subject K Enter to the scrutiny of the SEC and other regulatory bodies which could cause investors to lose confidence in K Enter’s reported financial information and subject K Enter to civil or criminal penalties or shareholder litigation, which could have an adverse effect on the trading price of K Enter’s securities. In addition, if identify additional deficiencies in K Enter’s internal control over financial reporting, the disclosure of that fact, even if quickly remedied, could reduce the market’s confidence in K Enter’s financial statements and harm K Wave’s share price. Furthermore, additional deficiencies could result in future non-compliance with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (“Sarbanes-Oxley”). Such non-compliance could subject K Enter to a variety of administrative sanctions, including review by the SEC or other regulatory authorities.
Play Company’s management has identified material weaknesses in Play Company’s internal control over financial reporting and Play Company may not be able to remediate these weaknesses. Additionally, Play Company’s management may identify material weaknesses in the future that could adversely affect investor confidence, impair the value of K Wave’s securities, and increase K Wave’s cost of raising capital.
There can be no assurance as to how quickly or effectively Play Company can remediate the material weaknesses in K Enter’s internal control over financial reporting or that additional material weaknesses will not be identified in the future. Any failure to remedy additional weaknesses or deficiencies in Play Company’s internal control over financial reporting that may be discovered in the future or to implement new or improved controls, or difficulties encountered in the implementation of such controls, could harm Play Company’s operating results, cause PubCo to fail to meet Play Company’s reporting obligations or result in material misstatements in Play Company’s financial statements. Any such failure could, in turn, affect the future ability of Play Company’s management to certify that Play Company’s internal control over financial reporting is effective. Ineffective internal control over financial reporting could also subject Play Company to the scrutiny of the SEC and other regulatory bodies which could cause investors to lose confidence in Play Company’s reported financial information and subject Play Company to civil or criminal penalties or shareholder litigation, which could have an adverse effect on the trading price of Play Company’s securities. In addition, if identify additional deficiencies in Play Company’s internal control over financial reporting, the disclosure of that fact, even if quickly remedied, could reduce the market’s confidence in Play Company’s financial statements and harm K Wave’s share price. Furthermore, additional deficiencies could result in future non-compliance with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (“Sarbanes-Oxley”). Such non-compliance could subject Play Company to a variety of administrative sanctions, including review by the SEC or other regulatory authorities.
The directors and officers of Pubco will own 52.8% of PubCo’s Ordinary Shares following the closing of the Business Combination.
The directors and officers of Pubco will own 33,888,244 Ordinary Shares representing 52.80% of PubCo following the closing of the Business Combination, assuming no additional shares of Global Star common stock are redeemed. The directors and officers of Pubco will own 33,888,244 Ordinary Shares representing 53.75% of PubCo following the closing of the Business Combination, assuming 1,137,006 additional shares of Global Star common stock are redeemed. Accordingly, following the closing of the Business Combination and directors and officers of PubCo, if they vote together as a group may be able to approve matters submitted to a vote of shareholders of PubCo provide such matter only requires a simple majority of PubCo shareholders to approve.
K Enter may face litigation and other risks as a result of the material weakness in its internal control over financial reporting.
As a result of (i) any potential material weakness in internal control over financial reporting arising out of the Business Combination, (ii) any changes made to accounting procedures with respect to PubCo’s business or those of its subsidiaries following the Business Combination, or (iii) other matters raised or that may in the future be raised by the SEC, PubCo may face potential for litigation or other disputes, including, among others, claims invoking the federal and state securities laws, contractual claims or other claims arising from the Restatement and material weaknesses in PubCo’s internal control over financial reporting and the preparation of PubCo’s financial statements. As of the date of this proxy statement/prospectus, PubCo has no knowledge of any such litigation or dispute. However, PubCo can provide no assurance that such litigation or dispute will not arise in the future. Any such litigation or dispute, whether successful or not, could have a material adverse effect on PubCo’s business, results of operations and financial condition or its ability to complete the Business Combination.
You may face difficulties in protecting your interests, and your ability to protect your rights through U.S. courts may be limited, because PubCo is incorporated under Cayman Islands law.
PubCo is an exempted company incorporated under the laws of the Cayman Islands. PubCo’s corporate affairs are governed by its memorandum and articles of association, the Companies Act (As Revised) of the Cayman Islands and the common law of the Cayman Islands. The rights of shareholders to take action against PubCo’s directors, actions by PubCo’s minority shareholders and the fiduciary duties of PubCo’s directors to PubCo under Cayman Islands law are to a large extent governed by the common law of the Cayman Islands. The common law of the Cayman Islands is derived in part from comparatively limited judicial precedent in the Cayman Islands as well as from the common law of England, the decisions of whose courts are of persuasive authority, but are not binding, on a court in the Cayman Islands. The rights of PubCo’s shareholders and the fiduciary duties of PubCo’s directors under Cayman Islands law are not as clearly established as they would be under statutes or judicial precedent in some jurisdictions in the United States. In particular, the Cayman Islands have a less developed body of securities laws than the United States. Some U.S. states, such as Delaware, have more fully developed and judicially interpreted bodies of corporate law than the Cayman Islands. In addition, Cayman Islands companies may not have standings to initiate a shareholder derivative action in a federal court of the United States.
Shareholders of Cayman Islands exempted companies like PubCo have no general rights under Cayman Islands law to inspect corporate records or to obtain copies of lists of shareholders of these companies. PubCo’s directors have discretion under its articles of association that will become effective immediately prior to completion of the Business Combination to determine whether or not, and under what conditions, its corporate records may be inspected by its shareholders, but are not obliged to make them available to its shareholders. This may make it more difficult for you to obtain the information needed to establish any facts necessary for a shareholder motion or to solicit proxies from other shareholders in connection with a proxy contest.
As a result of all of the above, PubCo’s public shareholders may have more difficulty in protecting their interests in the face of actions taken by PubCo’s management, users of the board of directors or controlling shareholders than they would as public shareholders of a company incorporated in the United States.
Future changes to U.S. and non-U.S. tax laws could adversely affect PubCo.
The U.S. Congress and other government agencies in jurisdictions where PubCo and its affiliates will do business have had an extended focus on issues related to the taxation of multinational corporations. One example is in the area of “base erosion and profit shifting,” including situations where payments are made between affiliates from a jurisdiction with high tax rates to a jurisdiction with lower tax rates. As a result, the tax laws in the countries in which PubCo and its affiliates do business could change on a prospective or retroactive basis, and any such changes could adversely affect PubCo and its affiliates.
Global Star may be subject to the Excise Tax included in the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 in connection with redemptions after December 31, 2022.
On August 16, 2022, President Biden signed into law the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, which, among other things, imposes a 1% excise tax on any publicly traded domestic corporation that repurchases its stock after December 31, 2022 (the “Excise Tax”). The Excise Tax is imposed on the fair market value of the repurchased stock, with certain exceptions. Because New K Enter is expected to continue to be treated as a U.S. corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 7874 of the Code following the Reincorporation Merger and because Global Star’s securities will trade on Nasdaq, New K Enter will be a “covered corporation” within the meaning of the Inflation Reduction Act. While not free from doubt, absent any further guidance from the U.S. Department of the Treasury (the “Treasury”), who has been given authority to provide regulations and other guidance to carry out and prevent the abuse or avoidance of the Excise Tax, the Excise Tax may apply to any redemptions after December 31, 2022, including redemptions in connection with the Business Combination, unless an exemption is available. Generally, issuances of securities in connection with an initial business combination transaction (including any PIPE transaction at the time of an initial business combination), as well as any other issuances of securities not in connection with an initial business combination, would be expected to reduce the amount of the Excise Tax in connection with redemptions occurring in the same calendar year, but the number of securities redeemed may exceed the number of securities issued. In addition, the Excise Tax would be payable by us, and not by the redeeming holder. Further, based on recently issued interim guidance from the IRS and Treasury, subject to certain exceptions, the Excise Tax should not apply in the event of Global Star’s liquidation.
The Business Combination may be a taxable event for U.S. Holders of GLST Common Stock, GLST Warrants, and GLST Rights.
Subject to the limitations and qualifications described in “Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Business Combination,” the Reincorporation Merger will qualify as a “reorganization” within the meaning of Section 368 of the Code and, as a result, a U.S. Holder (as defined below) should not recognize gain or loss on the exchange of GLST Common Stock, the GLST Rights, or GLST Warrants for PubCo Ordinary Shares or PubCo Warrants, as applicable, pursuant to the Business Combination.
If the Reincorporation Merger does not qualify as a reorganization, a U.S. Holder that exchanges its GLST Common Stock, GLST Rights, or GLST Warrants for the consideration under the Business Combination will recognize gain or loss equal to the difference between (i) the fair market value of the PubCo Ordinary Shares and PubCo Warrants received and (ii) the U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in the GLST Common Stock, GLST Rights, and GLST Warrants exchanged.
THE SPECIAL MEETING OF GLOBAL STAR STOCKHOLDERS
General
Global Star is furnishing this proxy statement/prospectus to the Global Star stockholders as part of the solicitation of proxies by Global Star board of directors for use at the Special Meeting to be held on February 3, 2025 and at any adjournment or postponement thereof. This proxy statement/prospectus is first being furnished to Global Star’s stockholders on or about January 7, 2025, in connection with the vote on the Reincorporation Merger Proposal, the Acquisition Merger Proposal, the Governance Proposal, the Director Proposal, the Incentive Plan Proposal and the Adjournment Proposal. This document provides you with the information you need to know to be able to vote or instruct your vote to be cast at the Special Meeting.
Date, Time and Place
The Special Meeting will be held on February 3, 2025 at 9:30 a.m. Eastern Time, or such other date, time and place to which such meeting may be adjourned or postponed. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Global Star will be holding the Special Meeting as a teleconference using the following dial-in information:
US Toll Free: 1 800-450-7155
International Toll: +1 857-999-9155
Participant Passcode: 7921345#
Purpose of the Special Meeting
At the Special Meeting, Global Star is asking holders of GLST Common Stock to approve the following Proposals:
| ● | The Reincorporation Merger Proposal to approve the Reincorporation Merger; |
| ● | The Acquisition Merger Proposal to approve the Acquisition Merger; |
| ● | The Governance Proposal to approve, on an advisory basis, four separate governance proposals; |
| ● | The Director Proposal to elect seven (7) nominees to serve as PubCo’s board of directors until the next annual meeting of stockholders; |
| ● | The Incentive Plan Proposal to approve PubCo’s Incentive Plan; and |
| ● | The Adjournment Proposal to approve the adjournment of the Special Meeting in the event Global Star does not receive the requisite stockholder vote to approve the above Proposals. |
Recommendation of Global Star’s Board of Directors
Global Star board of directors:
| ● | has determined that each of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal, the Acquisition Merger Proposal, the Governance Proposal, the Director Proposal, the Incentive Plan Proposal and the Adjournment Proposal, are fair to, and in the best interests of, Global Star and its stockholders; |
| ● | has approved the Reincorporation Merger Proposal, the Acquisition Merger Proposal, the Governance Proposal, the Director Proposal, the Incentive Plan Proposal and the Adjournment Proposal; and |
| ● | recommends that the Global Star stockholders vote “FOR” each of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal, the Acquisition Merger Proposal, the Governance Proposal, the Director Proposal, the Incentive Plan Proposal and the Adjournment Proposal. |
Global Star board of directors have interests that may be different from or in addition to your interests as a stockholder. See “The Business Combination — Interests of Certain Persons in the Business Combination” in this proxy statement/prospectus for further information.
Record Date; Who is Entitled to Vote
Global Star has fixed the close of business on December 13, 2024, as the record date for determining those Global Star stockholders entitled to notice of and to vote at the Special Meeting. As of the close of business on December 13, 2024, there were 3,294,100 GLST Common Stock outstanding and entitled to vote. Each holder of GLST Common Stock is entitled to one vote per share on each of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal, the Acquisition Merger Proposal, the Governance Proposal, the Director Proposal, the Incentive Plan Proposal and the Adjournment Proposal.
As of the record date, the Initial Stockholders and the Sponsor collectively own and are entitled to vote approximately 37.4% of the outstanding shares of GLST Common Stock and have agreed to vote their GLST Common Stock acquired by them in favor of the Reincorporation Proposal and the Acquisition Merger Proposal. The Initial Stockholders and the Sponsor also are expected to vote their shares in favor of the Governance Proposal, the Director Proposal and the Adjournment Proposal.
Quorum and Required Vote for the Proposals
A quorum of Global Star stockholders is necessary to hold a valid meeting. A quorum will be present at the Special Meeting if a majority of the shares of capital stock issued and outstanding as of the record date and entitled to vote at the Special Meeting is represented in person or by proxy. A Global Star holder present in person or by proxy and abstaining from voting at the Special Meeting will count as present for the purposes of establishing a quorum but broker non-votes will not.
Approval of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal, the Acquisition Merger Proposal and the Governance Proposal will require the affirmative vote of sixty-five percent (65%) of the issued and outstanding shares of Global Star entitled to vote at the Special Meeting. Approval of the Incentive Plan Proposal and the Adjournment Proposal will require the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the issued and outstanding ordinary shares of Global Star present and entitled to vote at the Special Meeting. Approval of the Director Proposal will be determined by a plurality of votes cast, meaning that the nominee for each open board seat who receives the most votes will be elected. Attending the Special Meeting either in person or by proxy and abstaining from voting will have the same effect as voting against the Reincorporation Merger Proposal, the Acquisition Merger Proposal and the Governance Proposal but will have no effect on the voting on the other Proposals.
Global Star’s Initial Stockholders and the Sponsor, who as of the record date, owned 2,798,225 shares of GLST Common Stock, or approximately 69.1% of the issued and outstanding GLST Common Stock, have agreed to vote their respective shares in favor of each of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal and the Acquisition Merger Proposal and are expected to vote in favor of the Director Proposal, the Incentive Plan Proposal and the Adjournment Proposal. As a result, the affirmative vote of the shares of GLST Common Stock held by the Initial Stockholders and the Sponsor is sufficient to approve each of the Proposals. As Global Star does not expect any other persons to be nominated for election as directors at the Special Meeting, the affirmative vote of the shares of GLST Common Stock held by the Initial Stockholders and the Sponsor is sufficient to approve the Director Proposal.
Voting Your Shares
Each share of GLST Common Stock that you own in your name entitles you to one vote for each Proposal on which such shares are entitled to vote at the Special Meeting. Your proxy card shows the number of shares of GLST Common Stock that you own.
There are two ways to ensure that your GLST Common Stock are voted at the Special Meeting:
| ● | You can cause your shares to be voted by signing and returning the enclosed proxy card. If you submit your proxy card, your “proxy,” whose name is listed on the proxy card, will vote your shares as you instruct on the proxy card. If you sign and return the proxy card but do not give instructions on how to vote your shares, your shares will be voted, as recommended by the Global Star board of directors, “FOR” the adoption of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal, the Acquisition Merger Proposal, the Incentive Plan Proposal and the Adjournment Proposal. Votes received after a matter has been voted upon at the Special Meeting will not be counted. |
| ● | You can attend the Special Meeting and vote in person. Global Star will give you a ballot when you arrive. However, if your shares are held in the name of your broker, bank or another nominee, you must get a proxy from the broker, bank or other nominee. That is the only way Global Star can be sure that the broker, bank or nominee has not already voted your shares. |
IF YOU RETURN YOUR PROXY CARD WITHOUT AN INDICATION OF HOW YOU WISH TO VOTE, YOUR SHARES WILL BE VOTED IN FAVOR OF THE REINCORPORATION MERGER PROPOSAL AND THE ACQUISITION MERGER PROPOSAL (AS WELL AS THE OTHER PROPOSALS). IN ORDER TO REDEEM YOUR SHARES, YOU MUST TENDER YOUR SHARES TO GLOBAL STAR’S TRANSFER AGENT AT LEAST TWO BUSINESS DAYS PRIOR TO THE SPECIAL MEETING. YOU MAY TENDER YOUR SHARES FOR REDEMPTION BY EITHER DELIVERING YOUR STOCK CERTIFICATE TO THE TRANSFER AGENT OR BY DELIVERING YOUR SHARES ELECTRONICALLY USING THE DEPOSITORY TRUST COMPANY’S DWAC SYSTEM. IF THE BUSINESS COMBINATION IS NOT COMPLETED, THEN THESE TENDERED SHARES WILL NOT BE REDEEMED FOR CASH AND WILL BE RETURNED TO THE APPLICABLE STOCKHOLDER. IF YOU HOLD THE SHARES IN STREET NAME, YOU WILL NEED TO INSTRUCT THE ACCOUNT EXECUTIVE AT YOUR BROKER OR BANK TO WITHDRAW THE SHARES FROM YOUR ACCOUNT IN ORDER TO EXERCISE YOUR REDEMPTION RIGHTS.
Revoking Your Proxy
If you give a proxy, you may revoke it at any time before it is exercised by doing any one of the following:
| ● | you may send another proxy card with a later date; |
| ● | if you are a record holder, you may notify Global Star’s proxy solicitor, Laurel Hill Advisory Group, LLC at 2 Robbins Lane, Suite 201 Jericho, NY 11753, in writing before the Special Meeting that you have revoked your proxy; or |
| ● | you may attend the Special Meeting, revoke your proxy, and vote in person, as indicated above. |
Who Can Answer Your Questions About Voting Your Shares
If you have any questions about how to vote or direct a vote in respect of your ordinary shares, you may call Laurel Hill Advisory Group, LLC, Global Star’s proxy solicitor, with individual call toll-free at (855) 414-2266 and banks and brokers call at (516) 396-7902.
No Additional Matters May Be Presented at the Special Meeting
This Special Meeting has been called only to consider the approval of the Proposals.
Appraisal or Dissenters Rights
Global Star stockholders are not entitled to exercise appraisal rights with respect to any of the matters to come before the Special Meeting.
Redemption Rights
Pursuant to Global Star’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation, a holder of GLST Common Stock has the right to have its public shares redeemed for cash equal to its pro rata share of the trust account (net of taxes payable) in connection with the Business Combination.
If you are a public stockholder and you seek to have your shares redeemed, you must (i) demand, no later than 5:00 p.m., Eastern time on January 30, 2025, (two (2) business days before the Special Meeting), that Global Star redeem your shares into cash; and (ii) submit your request in writing to Global Star’s transfer agent, at the address listed at the end of this section and deliver your shares to Global Star’s transfer agent physically or electronically using the DWAC system at least two (2) business days prior to the vote at the Special Meeting. In order to validly request redemption, you must either make a request for redemption on the proxy card or separately send a request in writing to Global Star’s transfer agent. The proxy card or separate request must be signed by the applicable stockholder in order to validly request redemption. A stockholder is not required to submit a proxy card or vote in order to validly exercise redemption rights.
You may tender the GLST Common Stock for which you are electing redemption by two (2) business days before the Special Meeting by either:
| ● | Delivering certificates representing Global Star’s ordinary shares to Global Star’s transfer agent, or |
| ● | Delivering the GLST Common Stock electronically through the DWAC system. |
Global Star stockholders will be entitled to redeem their GLST Common Stock for a full pro rata share of the trust account (currently anticipated to be no less than approximately $10.25 per share) net of taxes payable.
Any corrected or changed written demand of redemption rights must be received by Global Star’s transfer agent two (2) business days prior to the Special Meeting. No demand for redemption will be honored unless the holder’s shares have been delivered (either physically or electronically) to the transfer agent at least two (2) business days prior to the vote at the Special Meeting.
Public stockholders may seek to have their shares redeemed regardless of whether they vote for or against the Business Combination and whether or not they are holders of GLST Common Stock as of the record date. Any public stockholder who holds GLST Common Stock on or before January 30, 2025, (two (2) business days before the Special Meeting) will have the right to demand that his, her or its shares be redeemed for a pro rata share of the aggregate amount then on deposit in the trust account, less any taxes then due but not yet paid, at the consummation of the Business Combination.
In connection with tendering your shares for redemption, you must elect either to physically tender your stock certificates to Global Star’s transfer agent or deliver your shares to the transfer agent electronically using The Depository Trust Company’s DWAC System, in each case, two (2) business days before the Special Meeting.
Through the DWAC system, this electronic delivery process can be accomplished by contacting your broker and requesting delivery of your shares through the DWAC system. Delivering shares physically may take significantly longer. In order to obtain a physical stock certificate, a stockholder’s broker and/or clearing broker, DTC, and Global Star’s transfer agent will need to act together to facilitate this request. There is a nominal cost associated with the above-referenced tendering process and the act of certificating the shares or delivering them through the DWAC system. The transfer agent will typically charge the tendering broker $45 and the broker would determine whether or not to pass this cost on to the redeeming holder. It is Global Star’s understanding that Global Star stockholders should generally allot at least two weeks to obtain physical certificates from the transfer agent. Global Star does not have any control over this process or over the brokers or DTC, and it may take longer than two weeks to obtain a physical stock certificate. Global Star stockholders who request physical stock certificates and wish to redeem may be unable to meet the deadline for tendering their shares before exercising their redemption rights and thus will be unable to redeem their shares.
In the event that a stockholder tenders its shares and decides prior to the consummation of the Business Combination that it does not want to redeem its shares, the stockholder may withdraw the tender. In the event that a stockholder tenders shares and the Business Combination is not completed, these shares will not be redeemed for cash and the physical certificates representing these shares will be returned to the stockholder promptly following the determination that the Business Combination will not be consummated. Global Star anticipates that a stockholder who tenders shares for redemption in connection with the vote to approve the Business Combination would receive payment of the redemption price for such shares soon after the completion of the Business Combination.
If properly demanded by Global Star public stockholders, Global Star will redeem each share into a pro rata portion of the funds available in the trust account, calculated as of two business days prior to the anticipated consummation of the Business Combination. As of the record date, this would amount to approximately $11.45 per share, subject to reduction for the payment of taxes. If you exercise your redemption rights, you will be exchanging your GLST Common Stock for cash and will no longer own the shares. If Global Star is unable to complete the Business Combination by February 22, 2025 (unless Global Star elects to extend the time it has to complete the initial business combination to June 22, 2025), it will liquidate and dissolve and public stockholders would be entitled to receive approximately $10.25 per share upon such liquidation, plus the pro rata share of interest earned on amounts held in trust that have not been used to pay for taxes.
Holders of outstanding GLST Units must separate the underlying GLST Common Stock, GLST Warrants and GLST Rights prior to exercising redemption rights with respect to the GLST Common Stock. If GLST Units are registered in a holder’s own name, the holder must deliver the certificate for its GLST Units to the transfer agent with written instructions to separate the GLST Units into their individual component parts. This must be completed far enough in advance to permit the mailing of the certificates back to the holder so that the holder may then exercise his, her or its redemption rights upon the separation of the GLST Common Stock from the GLST Units.
If a broker, dealer, commercial bank, trust company or other nominee holds GLST Units for an individual or entity (such individual or entity, the “beneficial owner”), the beneficial owner must instruct such nominee to separate the beneficial owner’s GLST Units into their individual component parts. The beneficial owner’s nominee must send written instructions by facsimile to the transfer agent. Such written instructions must include the number of GLST Units to be separated and the nominee holding such GLST Units. The beneficial owner’s nominee must also initiate electronically, using DTC’s DWAC system, a withdrawal of the relevant GLST Units and a deposit of an equal number of GLST Common Stock, GLST Warrants and GLST Rights. This must be completed far enough in advance to permit the nominee to exercise the beneficial owner’s redemption rights upon the separation of the GLST Common Stock from the GLST Units. While this is typically done electronically the same business day, beneficial owners should allow at least one full business day to accomplish the separation. If beneficial owners fail to cause their GLST Common Stock to be separated in a timely manner, they will likely not be able to exercise their redemption rights.
Tendering Common Stock Certificates in connection with Redemption Rights
Global Star is requiring the Global Star public stockholders seeking to exercise their redemption rights, whether they are record holders or hold their shares in “street name,” to either tender their certificates to Global Star’s transfer agent, or to deliver their shares to the transfer agent electronically using Depository Trust Company’s DWAC System, at the holder’s option at least two (2) business days prior to the Special Meeting. There is a nominal cost associated with the above-referenced tendering process and the act of certificating the shares or delivering them through the DWAC System. The transfer agent will typically charge the tendering broker $45.00 and it would be up to the broker whether to pass this cost on to the redeeming holder. However, this fee would be incurred regardless of whether Global Star requires holders seeking to exercise redemption rights to tender their ordinary shares. The need to deliver ordinary shares is a requirement of exercising redemption rights regardless of the timing of when such delivery must be effectuated.
Any request for redemption, once made, may be withdrawn at any time up to the business day immediately preceding the consummation of the Business Combination. Furthermore, if a stockholder delivered his certificate for redemption and subsequently decided prior to the date immediately preceding the consummation of the Business Combination not to elect redemption, he may simply request that the transfer agent return the certificate (physically or electronically).
A redemption payment will only be made in the event that the Business Combination is consummated. If the Business Combination is not completed for any reason, then public stockholders who exercised their redemption rights would not be entitled to receive the redemption payment. In such case, Global Star will promptly return the share certificates to the public stockholder.
Proxies and Proxy Solicitation Costs
Global Star is soliciting proxies on behalf of the Global Star board of directors. This solicitation is being made by mail but also may be made by telephone or in person. Global Star and its directors, officers and employees may also solicit proxies in person, by telephone or by other electronic means. Any solicitation made and information provided in such a solicitation will be consistent with the written proxy statement/prospectus and proxy card. Morrow Sodali LLC, a proxy solicitation firm that Global Star has engaged to assist it in soliciting proxies, will be paid its customary fee and out-of-pocket expenses.
Global Star will ask banks, brokers and other institutions, nominees and fiduciaries to forward its proxy materials to their principals and to obtain their authority to execute proxies and voting instructions. Global Star will reimburse them for their reasonable expenses.
If you send in your completed proxy card, you may still vote your shares in person if you revoke your proxy before it is exercised at the Special Meeting.
PROPOSAL NO. 1
THE REINCORPORATION MERGER PROPOSAL
The discussion in this proxy statement/prospectus of the Business Combination and the principal terms of the Merger Agreement, is subject to, and is qualified in its entirety by reference to, the Merger Agreement. The full text of the Merger Agreement is attached hereto as Annex A, which is incorporated by reference herein.
Purpose of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal
The purpose of the Reincorporation Merger is to establish a Cayman Islands exempted company as the parent entity of K Enter that would be a “foreign private issuer” as that term is defined under the Exchange Act. As a result of the Reincorporation Merger, the Global Star stockholders will no longer be stockholders of Global Star and (other than the Global Star stockholders who exercise their redemption rights) will become shareholders of PubCo, a foreign private issuer. As a foreign private issuer, PubCo is exempt from compliance with certain of the rules under the Exchange Act.
As a foreign private issuer, PubCo will be exempt from the rules under the Exchange Act, prescribing the furnishing and content of proxy statements, and its officers, directors and principal shareholders will be exempt from the reporting and short-swing profit recovery provisions contained in Section 16 of the Exchange Act. In addition, PubCo will not be required under the Exchange Act to file quarterly periodic reports and financial statements with the SEC, and will not be required to disclose in its periodic reports all of the information that U.S. domestic issuers are required to disclose. PubCo will also be permitted to follow corporate governance practices in accordance with Cayman Islands law in lieu of most of the corporate governance rules set forth by Nasdaq. As a result, PubCo’s corporate governance practices differ in some respects from those required to be followed by U.S. companies listed on a national securities exchange.
Summary of the Reincorporation Merger
The Merger Agreement was entered into by and among Global Star and K Enter on June 15, 2023. On July 13, 2023, PubCo and Merger Sub executed the Joinder Agreement and became parties to the Merger Agreement. On March 11, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub executed the First Amendment to Merger Agreement. On June 28, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub executed the Second Amendment to Merger Agreement. On July 25, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub executed the Third Amendment to Merger Agreement. On December 11, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub executed the Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement. Upon the approval of the Merger Agreement by the Global Star stockholders, PubCo and Global Star will execute the Plan of Merger, which shall be filed with the Registrar of Companies in the Cayman Islands with certain other documents on or prior to the Closing Date. On the Closing Date and concurrently with the Acquisition Merger, Global Star will reincorporate to Cayman Islands by merging with and into the PubCo, a Cayman Islands exempted company and wholly owned subsidiary of Global Star. The separate corporate existence of Global Star will cease and PubCo will continue as the surviving corporation. In connection with the Reincorporation Merger, all outstanding GLST Units will separate into their individual components of GLST Common Stock, GLST Rights and GLST Warrants and will cease separate existence and trading. Upon the consummation of the Business Combination, the current equity holdings of the Global Star stockholders shall be exchanged as follows:
| | (i) | Each share of GLST Common Stock issued and outstanding immediately prior to the effective time of the Reincorporation Merger (other than any redeemed shares) will automatically be cancelled and cease to exist and, for each share of such GLST Common Stock, PubCo shall issue to each Global Star stockholder (other than Global Star stockholders who exercise their redemption rights in connection with the Business Combination) one validly issued PubCo Ordinary Share, which, unless explicitly stated herein, shall be fully paid; |
| | | |
| | (ii) | Each GLST Warrant issued and outstanding immediately prior to effective time of the Reincorporation Merger will convert into a PubCo Warrant to purchase one PubCo Ordinary Share at a price of $11.50 per whole share; and |
| | | |
| | (iii) | The holders of GLST Rights issued and outstanding immediately prior to the effective time of the Reincorporation Merger will receive one PubCo Right in exchange for the cancellation of each GLST Right. |
Differences between PubCo’s Memorandum and Articles of Association and GLST’s Certificate of Incorporation
Following is a summary of the material differences between the Memorandum and Articles of Association of PubCo to be in effect following the Business Combination and Global Star’s current amended and restated certificate of incorporation:
| ● | The name of the new public entity will be “K Wave Media Ltd.” as opposed to “Global Star Acquisition Inc.”; |
| | ● | PubCo’s authorized share capital is $100,000 divided into 990,000,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares and 10,000,000 PubCo Preference Shares, as opposed to Global Star which has authorized capital stock of 100,000,000 shares of Global Star Class A Common Stock, 10,000,000 shares of Global Star Class B Common Stock and 1,000,000 shares of preferred stock; |
| ● | PubCo’s corporate existence is perpetual as opposed to Global Star’s corporate existence terminating if a business combination is not consummated by Global Star within a specified period of time; and |
| ● | PubCo’s constitutional documents do not include the various provisions applicable only to special purpose acquisition corporations that Global Star’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation contains. |
Authorized but unissued ordinary shares may enable PubCo’s board of directors to render it more difficult or to discourage an attempt to obtain control of PubCo and thereby protect continuity of or entrench its management, which may adversely affect the market price of PubCo’s securities. For example, if, in the due exercise of its fiduciary obligations, for example, PubCo’s board of directors were to determine that a takeover proposal were not in the best interests of PubCo, such shares could be issued by the board of directors without shareholder approval in one or more private placements or other transactions that might prevent or render more difficult or make more costly the completion of any attempted takeover transaction by diluting voting or other rights of the proposed acquirer or insurgent stockholder group, by creating a substantial voting block in institutional or other hands that might support the position of the incumbent board of directors, by effecting an acquisition that might complicate or preclude the takeover, or otherwise. The authorization of additional shares will, however, enable PubCo to have the flexibility to authorize the issuance of shares in the future for financing its business, for acquiring other businesses, for forming strategic partnerships and alliances and for stock dividends and stock splits. PubCo currently has no such plans, proposals, or arrangements, written or otherwise, to issue any of the additional authorized shares for such purposes.
A copy of PubCo’s Memorandum and Articles of Association, as will be in effect upon consummation of the Business Combination, is attached to this proxy statement/prospectus as Annex B. See also the Section entitled Comparison of Shareholder’s Rights on page 336 of this proxy statement/prospectus.
Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of The Business Combination
The following is a general discussion of the material U.S. federal income tax consequences (i) of the Business Combination to U.S. Holders (defined below) of GLST Common Stock (excluding any redeemed shares), GLST Rights, and GLST Warrants (collectively, the “Global Star securities”), (ii) of the Acquisition Merger to U.S. Holders of K Enter Common Stock, (iii) of the subsequent ownership and disposition of PubCo Ordinary Shares and PubCo Warrants (collectively, the “PubCo securities”) received in the Business Combination and (iv) exercise of redemption rights by Global Star stockholders that are U.S. Holders. In addition, the following includes a general discussion of certain U.S. federal income tax consequences of the Business Combination to Global Star, K Enter, and PubCo.
This discussion is based on provisions of the Code, the Treasury Regulations promulgated thereunder (whether final, temporary, or proposed), administrative rulings of the IRS, and judicial decisions, all as in effect on the date hereof, and all of which are subject to differing interpretations or change, possibly with retroactive effect. This discussion does not purport to be a complete analysis or listing of all potential U.S. federal income tax considerations that may apply to a holder as a result of the Business Combination or as a result of the ownership and disposition of Global Star securities. In addition, this discussion does not address all aspects of U.S. federal income taxation that may be relevant to particular holders nor does it take into account the individual facts and circumstances of any particular holder that may affect the U.S. federal income tax consequences to such holder, and accordingly, is not intended to be, and should not be construed as, tax advice. This discussion does not address the U.S. federal 3.8% Medicare tax imposed on certain net investment income or any aspects of U.S. federal taxation other than those pertaining to the income tax, nor does it address any tax consequences arising under any U.S. state and local, or non-U.S. tax laws. Holders should consult their own tax advisors regarding such tax consequences in light of their particular circumstances.
No ruling has been requested or will be obtained from the IRS regarding the U.S. federal income tax consequences of the Business Combination or any other related matter; thus, there can be no assurance that the IRS will not challenge the U.S. federal income tax treatment described below or that, if challenged, such treatment will be sustained by a court.
This summary is limited to considerations relevant to U.S. Holders that hold Global Star securities, K Enter Common Stock, and, after the completion of the Business Combination, PubCo securities, as “capital assets” within the meaning of section 1221 of the Code (generally, property held for investment). This discussion does not address all aspects of U.S. federal income taxation that may be important to holders in light of their individual circumstances, including holders subject to special treatment under the U.S. tax laws, such as, for example:
| ● | banks or other financial institutions, underwriters, or insurance companies; |
| ● | traders in securities who elect to apply a mark-to-market method of accounting; |
| ● | real estate investment trusts and regulated investment companies; |
| ● | tax-exempt organizations, qualified retirement plans, individual retirement accounts, or other tax-deferred accounts; |
| ● | expatriates or former long-term residents of the United States; |
| ● | subchapter S corporations, partnerships or other pass-through entities or investors in such entities; |
| ● | dealers or traders in securities, commodities or currencies; |
| ● | persons subject to the alternative minimum tax; |
| ● | U.S. persons whose “functional currency” is not the U.S. dollar; |
| ● | persons who received shares of GLST Common Stock or K Enter Common Stock through the issuance of restricted stock under an incentive plan or through a tax-qualified retirement plan or otherwise as compensation; |
| ● | persons who own (directly or through attribution) 5% or more (by vote or value) of the outstanding shares of GLST Common Stock, K Enter Common Stock, or, after the Business Combination, the issued PubCo Ordinary Shares (excluding treasury shares); |
| ● | holders holding Global Star securities, K Enter Common Stock, or, after the Business Combination, PubCo securities, as a position in a “straddle,” as part of a “synthetic security” or “hedge,” as part of a “conversion transaction,” or other integrated investment or risk reduction transaction; or |
| ● | the Sponsor or its affiliates. |
As used in this proxy statement/prospectus, the term “U.S. Holder” means a beneficial owner of Global Star securities, K Enter Common Stock, and, after the Business Combination, PubCo securities received in the Business Combination, that is, for U.S. federal income tax purposes:
| ● | an individual who is a citizen or resident of the United States; |
| ● | a corporation (or other entity that is classified as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes) that is created or organized in or under the laws of the United States or any State thereof or the District of Columbia; |
| ● | an estate the income of which is subject to U.S. federal income tax regardless of its source; or |
| ● | a trust (i) if a court within the United States is able to exercise primary supervision over the administration of the trust and one or more U.S. persons have the authority to control all substantial decisions of the trust, or (ii) that has a valid election in effect under applicable Treasury Regulations to be treated as a U.S. person for U.S. federal income tax purposes. |
A “Non-U.S. Holder” means a beneficial owner of Global Star securities, K Enter Common Stock, and, after the Business Combination, PubCo securities that is neither a U.S. Holder nor a partnership (or an entity or arrangement treated as a partnership) for U.S. federal income tax purposes.
If a partnership, including for this purpose any entity or arrangement that is treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes, holds Global Star securities, K Enter Common Stock, and, after the completion of the Business Combination, PubCo securities received in the Business Combination, the U.S. federal income tax treatment of a partner in such partnership will generally depend on the status of the partner and the activities of the partnership. A holder that is a partnership and the partners in such partnership should consult their own tax advisors with regard to the U.S. federal income tax consequences of the Business Combination and the subsequent ownership and disposition of PubCo securities received in the Business Combination.
Because GLST Units will be separated into their component parts immediately prior to the consummation of the Business Combination, a beneficial owner of a GLST Unit should be treated as the owner of the underlying component Global Star securities for U.S. federal income tax purposes. The discussion below with respect to Global Star securities should also apply to holders of GLST Units (as the deemed owner of the underlying component Global Star securities).
THIS SUMMARY DOES NOT PURPORT TO BE A COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS OR DESCRIPTION OF ALL POTENTIAL U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSEQUENCES OF THE BUSINESS COMBINATION. GLOBAL STAR STOCKHOLDERS AND K ENTER STOCKHOLDERS SHOULD CONSULT WITH THEIR TAX ADVISORS REGARDING THE PARTICULAR TAX CONSEQUENCES TO THEM OF THE BUSINESS COMBINATION AND OF THE OWNERSHIP AND DISPOSITION OF PUBCO SECURITIES AFTER THE BUSINESS COMBINATION, INCLUDING THE APPLICABILITY AND EFFECTS OF U.S. FEDERAL, STATE, LOCAL, AND OTHER TAX LAWS.
U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Business Combination to U.S. Holders
The following discussion, “— U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Business Combination to U.S. Holders,” constitutes the opinion of Nelson Mullins Riley & Scarborough LLP, counsel to Global Star, as to the material U.S. federal income tax consequences of the Business Combination to the U.S. Holders of Global Star securities, subject to the limitations, exceptions, beliefs, assumptions, and qualifications described in such opinion and otherwise herein.
Tax Residence of PubCo for U.S. Federal Income Tax Purposes
Under current U.S. federal income tax law, a corporation generally will be considered to be resident for U.S. federal income tax purposes in its place of organization or incorporation. Accordingly, under the generally applicable U.S. federal income tax rules, PubCo, which is a Cayman Islands-incorporated entity, would generally be classified as a non-U.S. corporation (and, therefore, not a U.S. tax resident). Section 7874 of the Code and the regulations promulgated thereunder, however, contain specific rules (more fully discussed below) that may cause a non-U.S. corporation to be treated as a U.S. corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Although PubCo is incorporated under the laws of the Cayman Islands, PubCo expects that PubCo will be taxed as a U.S. corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 7874 of the Code, and that PubCo will be liable for U.S. federal income tax on its income like any other U.S. corporation, and certain distributions made by PubCo to Non-U.S. Holders of PubCo securities would be subject to U.S. withholding tax.
Under section 7874 of the Code, a corporation created or organized outside the United States (i.e., a non-U.S. corporation) will nevertheless be treated as a U.S. corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes (and, therefore, be a U.S. tax resident subject to U.S. federal income tax on its worldwide income) if (1) the non-U.S. corporation directly or indirectly acquires substantially all of the assets held directly or indirectly by a U.S. corporation, (2) the non-U.S. corporation’s expanded affiliated group does not have substantial business activities in the non-U.S. corporation’s country of organization or incorporation relative to the expanded affiliated group’s worldwide activities (the “substantial business activities test”), and (3) the shareholders of the acquired U.S. corporation hold at least 80% (by either vote or value) of the stock of the non-U.S. acquiring corporation after the acquisition by reason of holding shares in the U.S. acquired corporation, as determined under complex share ownership rules described below, which are uncertain in their application in many circumstances and are intended to increase the percentage ownership for these purposes (the “Ownership Test”). For this purpose, “expanded affiliated group” generally means the foreign acquiring corporation and all subsidiary corporations in which such foreign corporation owns, directly or indirectly, more than 50% of the stock (by vote and value) after the foreign acquiring corporation’s acquisition of the assets of the U.S. corporation.
In the Business Combination, PubCo will directly acquire all of Global Star’s assets through Global Star merging with and into PubCo, with PubCo remaining as the surviving publicly traded entity. As a result, the determination of whether PubCo will be treated as a U.S. corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes will depend on the application of the substantial business activities test and the Ownership Test.
PubCo is not expected to satisfy the substantial business activities test based on its activities in the Cayman Islands after the completion of the Business Combination. Accordingly, PubCo must determine whether the Ownership Test has been met.
Based on the complex rules for determining share ownership under Section 7874 of the Code and Treasury Regulations promulgated thereunder and certain factual assumptions, former Global Star stockholders are expected to be treated as holding more than 80% (by both vote and value) of PubCo stock by reason of their former ownership of Global Star common stock for these purposes. Therefore, PubCo is expected to satisfy the Ownership Test, and PubCo is expected to be treated as a U.S. corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 7874 of the Code.
This following discussion assumes that Section 7874 of the Code continues to apply to treat PubCo as a U.S. corporation for all purposes under the Code. If, for some reason (e.g., future repeal of Section 7874 of the Code), PubCo were no longer treated as a U.S. corporation under the Code, the U.S. federal income tax consequences described herein could be materially and adversely affected.
Qualification of the Reincorporation Merger as a Reorganization
The Reincorporation Merger will qualify as a “reorganization” within the meaning of Section 368 of the Code. However, U.S. Holders should be aware that the completion of the Business Combination is not conditioned on the receipt of an opinion of counsel that the Business Combination qualifies as a reorganization, and that PubCo has not requested and does not intend to request a ruling from the IRS with respect to the U.S. federal income tax treatment of the Business Combination. There can be no assurance that the IRS will not take a contrary position to views expressed herein or that a court will not agree with a contrary position of the IRS.
If the Reincorporation Merger Qualifies as a Reorganization
Because the Reincorporation Merger will qualify as a reorganization under the provisions of Section 368 of the Code, a U.S. Holder that exchanges its Global Star securities pursuant to the Business Combination will not recognize gain or loss on the exchange of Global Star securities for PubCo securities. The aggregate adjusted tax basis of a U.S. Holder in the PubCo Ordinary Shares received as a result of the Business Combination will equal the aggregate adjusted tax basis of the GLST Common Stock and the GLST Rights surrendered in the exchange, and the aggregate adjusted tax basis in the PubCo Warrants received as a result of such exchange will equal the aggregate adjusted tax basis of the GLST Warrants surrendered in the exchange. A U.S. Holder’s holding period for the PubCo securities received in the exchange will include the holding period for the Global Star securities surrendered in the exchange.
U.S. Holders should consult their own tax advisors as to the particular consequences to them of the exchange of Global Star securities for PubCo securities pursuant to the Business Combination, the qualification of the Reincorporation Merger as a reorganization.
If the Reincorporation Merger Does Not Qualify as a Reorganization
If the Reincorporation Merger fails to qualify as a Reorganization, a U.S. Holder that exchanges its Global Star securities for the consideration under the Business Combination will recognize gain or loss equal to the difference between (i) the sum of the fair market value of the PubCo securities received and (ii) the U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in the Global Star securities exchanged. A U.S. Holder’s aggregate tax basis in the PubCo securities received will be the fair market value of those securities on the date the U.S. Holder receives them. The U.S. Holder’s holding period for the PubCo securities received pursuant to the Business Combination will begin on the day after the date the U.S. Holder receives such PubCo securities.
Such gain or loss will be a capital gain or loss and will be a long-term capital gain or loss if the U.S. Holder’s holding period for the Global Star securities exceeds one year at the time of the Business Combination. Long-term capital gains of non-corporate U.S. Holders, including individuals, currently are subject to reduced rates of U.S. federal income taxation. The deductibility of capital losses is subject to limitations under the Code.
U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Acquisition Merger to U.S. Holders of K Enter Common Stock
The following discussion, “—U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Acquisition Merger to U.S. Holders of K Enter Common Stock,” constitutes the opinion of Loeb & Loeb, counsel to K Enter, as to the material U.S. federal income tax consequences of the Acquisition Merger to U.S. Holders of K Enter Common Stock, subject to the limitations, exceptions, beliefs, assumptions, and qualifications described in such opinion and otherwise herein.
Neither K Enter nor Global Star has requested, and neither intends to request, a ruling from the IRS as to the U.S. federal income tax consequences of the Acquisition Merger. A tax opinion represents the legal judgment of counsel rendering the opinion and is not binding on the IRS. Consequently, no assurance can be given that the IRS will not assert, or that a court would not sustain, a position that the Acquisition Merger does not constitute a “reorganization.” Accordingly, each U.S. Holder is urged to consult its tax advisor with respect to the particular tax consequence of the Acquisition Merger to such holder.
Subject to the qualifications and limitations set forth herein, the Acquisition Merger will qualify as a “reorganization” within the meaning of Section 368(a) of the Code, and U.S. Holders of K Enter Common Stock generally should not recognize any gain or loss as a result of the Acquisition Merger. Pursuant to the Acquisition Merger, U.S. Holders of K Enter Common Stock will receive shares of PubCo Ordinary Shares in exchange for their shares of K Enter Common Stock. Each U.S. Holder’s tax basis in the shares of PubCo Ordinary Shares received in the Acquisition Merger will be the same as his, her or its tax basis in the shares of K Enter Common Stock surrendered in the Acquisition Merger in exchange therefor. The holding period of the shares of PubCo Ordinary Shares received in the Acquisition Merger by the U.S. Holder will include the holding period of the shares of K Enter Common Stock surrendered in the Acquisition Merger in exchange therefor. The rules under Section 368 of the Code, however, are complex and there is limited guidance as to their application in the context of a transaction or series of transactions like those contemplated by the Business Combination. Accordingly, no assurance can be given as to whether U.S. Holders will recognize gain, if any, as a result of the Acquisition Merger.
If the Acquisition Merger fails to qualify as a “reorganization” under Section 368(a) of the Code, a U.S. Holder of K Enter Common Stock would recognize gain or loss in an amount equal to the difference (i) the fair market value of the aggregate merger consideration received in exchange for such surrendered K Enter Common Stock upon completion of the Acquisition Merger and (ii) the holder’s basis in the K Enter Common Stock surrendered. Gain or loss will be calculated separately for each block K Enter Common Stock (generally shares acquired at the same cost in a single transaction) surrendered. Such gain or loss generally will be capital gain or loss, and will be long-term capital gain or loss if such K Enter Common Stock have been held for more than one year at the time of the Acquisition Merger. Long-term capital gain of non-corporate U.S. Holders (including individuals) generally is taxed at reduced U.S. federal income tax rates. The deductibility of capital losses is subject to limitations. A U.S. Holder’s tax basis in shares of PubCo Ordinary Shares received in the Acquisition Merger would be equal to the fair market value thereof as of the Effective Time, and the U.S. Holder’s holding period in such shares would begin on the day following the Acquisition Merger.
All U.S. Holders are urged to consult their tax advisors as to the tax consequences to them of the Acquisition Merger under such holder’s particular circumstances.
U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of Ownership and Disposition of PubCo Securities
U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences to U.S. Holders
The following discussion is a summary of certain material U.S. federal income tax consequences of the ownership and disposition of PubCo securities to U.S. Holders who receive such PubCo securities pursuant to the Business Combination.
Distribution on PubCo Ordinary Shares
The gross amount of any distribution on PubCo Ordinary Shares that is made out of PubCo’s current and accumulated profits (as determined for U.S. federal income tax purposes) will generally be taxable to a U.S. Holder as ordinary dividend income on the date such distribution is actually or constructively received by such U.S. Holder. Any such dividends paid to corporate U.S. Holders generally will qualify for a dividends received deduction (pursuant to which a portion of the dividend may be deducted) if the requisite holding period is satisfied. Subject to applicable requirements and limitations, dividends paid to a non-corporate U.S. Holder generally will constitute “qualified dividends” that will be subject to tax at the preferential tax rate accorded to long-term capital gains.
Non-corporate U.S. Holders that do not meet a minimum holding period requirement or that elect to treat the dividend income as “investment income” pursuant to Section 163(d)(4) of the Code (dealing with the deduction for investment interest expense) will not be eligible for the reduced rates of taxation applicable to qualified dividends. In addition, the rate reduction will not apply to dividends if the recipient of a dividend is obligated to make related payments with respect to positions in substantially similar or related property. This disallowance applies even if the minimum holding period has been met.
To the extent that the amount of any distribution made by PubCo on the PubCo Ordinary Shares exceeds PubCo’s current and accumulated earnings and profits for a taxable year (as determined under U.S. federal income tax principles), the distribution will first be treated as a tax-free return of capital, causing a reduction (but not below zero) in the adjusted basis of the U.S. Holder’s PubCo Ordinary Shares, and to the extent the amount of the distribution exceeds the U.S. Holder’s tax basis, the excess will be taxed as capital gain recognized on a sale or exchange as described below under “— Sale, Exchange, Redemption or Other Taxable Disposition of PubCo Securities.” However, PubCo may not calculate earnings and profits in accordance with U.S. federal income tax principles. In such event, a U.S. Holder should expect to generally treat distributions PubCo makes as dividends.
Sale, Exchange, Redemption or Other Taxable Disposition of PubCo Securities
A U.S. Holder will generally recognize gain or loss on any sale, exchange, redemption, or other taxable disposition of PubCo Ordinary Shares and PubCo Warrants in an amount equal to the difference between the amount realized on the disposition and such U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in such PubCo Ordinary Shares or PubCo Warrants. Any gain or loss recognized by a U.S. Holder on a taxable disposition of PubCo Ordinary Shares or PubCo Warrants will generally be capital gain or loss and will be long-term capital gain or loss if the holder’s holding period in the PubCo Ordinary Shares or PubCo Warrants exceeds one year at the time of the disposition. Preferential tax rates may apply to long-term capital gains of non-corporate U.S. Holders (including individuals). The amount of gain or loss recognized will generally be equal to the difference between (i) the sum of the amount of cash and the fair market value of any property received in such disposition and (ii) the U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in its PubCo securities so disposed of. A U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in its shares of PubCo securities will generally equal the U.S. Holder’s acquisition cost for such shares (or, in the case of PubCo Ordinary Shares received upon exercise of a warrant, the U.S. Holder’s initial basis for such PubCo Ordinary Shares, as discussed below), less any prior distributions treated as a return of capital. Long-term capital gains recognized by non-corporate U.S. Holders are generally eligible for reduced rates of tax. If the U.S. Holder’s holding period for the PubCo securities so disposed of is one year or less, any gain on a sale or other taxable disposition of the shares would be subject to short-term capital gain treatment and would be taxed at ordinary income tax rates. The deductibility of capital losses is subject to limitations.
Exercise or Lapse of a PubCo Warrant
Except as discussed below with respect to the cashless exercise of a PubCo Warrant, a U.S. Holder generally will not recognize gain or loss upon the acquisition of a PubCo ordinary share on the exercise of a PubCo Warrant for cash. A U.S. Holder’s tax basis in a PubCo ordinary share received upon exercise of the PubCo Warrant generally will be an amount equal to the sum of the U.S. Holder’s tax basis in the PubCo Warrant exchanged therefor and the exercise price. The U.S. Holder’s holding period for a PubCo ordinary share received upon exercise of the PubCo Warrant will begin on the date following the date of exercise (or possibly the date of exercise) of the PubCo Warrants and will not include the period during which the U.S. Holder held the PubCo Warrants. If a PubCo Warrant is allowed to lapse unexercised, a U.S. Holder generally will recognize a capital loss equal to such holder’s tax basis in the PubCo Warrant.
The tax consequences of a cashless exercise of a warrant are not clear under current tax law. A cashless exercise may be tax-free, either because the exercise is not a gain realization event or because the exercise is treated as a recapitalization for U.S. federal income tax purposes. In either tax-free situation, a U.S. Holder’s basis in the PubCo Ordinary Shares received would equal the holder’s basis in the PubCo Warrant. If the cashless exercise were treated as not being a gain recognition event, a U.S. Holder’s holding period in the PubCo Ordinary Shares would be treated as commencing on the date following the date of exercise (or possibly the date of exercise) of the PubCo Warrant. If the cashless exercise were treated as a recapitalization, the holding period of the PubCo ordinary share would include the holding period of the PubCo Warrant.
It is also possible that a cashless exercise could be treated in part as a taxable exchange in which gain or loss would be recognized. In such event, a U.S. Holder would recognize gain or loss with respect to the portion of the exercised PubCo Warrants treated as surrendered to pay the exercise price of the PubCo Warrants (the “surrendered warrants”). The U.S. Holder would recognize capital gain or loss with respect to the surrendered warrants in an amount generally equal to the difference between (i) the fair market value of the PubCo Ordinary Shares that would have been received with respect to the surrendered warrants in a regular exercise of the PubCo Warrants and (ii) the sum of the U.S. Holder’s tax basis in the surrendered warrants and the aggregate cash exercise price of such warrants (if they had been exercised in a regular exercise). In this case, a U.S. Holder’s tax basis in the PubCo Ordinary Shares received would equal the U.S. Holder’s tax basis in the PubCo Warrants exercised plus (or minus) the gain (or loss) recognized with respect to the surrendered warrants. A U.S. Holder’s holding period for the PubCo Ordinary Shares would commence on the date following the date of exercise (or possibly the date of exercise) of the PubCo Warrant.
Due to the absence of authority on the U.S. federal income tax treatment of a cashless exercise, there can be no assurance which, if any, of the alternative tax consequences and holding periods described above would be adopted by the IRS or a court of law. Accordingly, U.S. Holders should consult their tax advisors regarding the tax consequences of a cashless exercise.
U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences to Non-U.S. Holders
Distributions on PubCo Ordinary Shares
Distributions of cash or property to a Non-U.S. Holder in respect of PubCo Ordinary Shares will generally constitute dividends for U.S. federal income tax purposes to the extent paid from PubCo’s current or accumulated earnings and profits, as determined under U.S. federal income tax principles. If a distribution exceeds PubCo’s current and accumulated earnings and profits, the excess will generally be treated first as a tax-free return of capital to the extent of the Non-U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in the PubCo Ordinary Shares. Any remaining excess will be treated as capital gain and will be treated as described below under “— Sale, Exchange, Redemption or Other Taxable Disposition of PubCo Securities.”
Dividends paid to a Non-U.S. Holder of PubCo Ordinary Shares generally will be subject to withholding of U.S. federal income tax at a 30% rate, unless such Non-U.S. Holder is eligible for a reduced rate of withholding tax under an applicable income tax treaty and provides proper certification of its eligibility for such reduced rate as described below. However, dividends that are effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business by the Non-U.S. Holder within the United States (and, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, are attributable to a U.S. permanent establishment or fixed base of the Non-U.S. Holder) are not subject to such withholding tax, provided certain certification and disclosure requirements are satisfied (generally by providing an IRS FormW-8ECI). Instead, such dividends are subject to United States federal income tax on a net income basis in the same manner as if the Non-U.S. Holder were a United States person as defined under the Code. Any such effectively connected dividends received by a foreign corporation may be subject to an additional “branch profits tax” at a 30% rate or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty.
A Non-U.S. Holder of PubCo Ordinary Shares who wishes to claim the benefit of an applicable treaty rate and avoid backup withholding, as discussed below, for dividends will be required (a) to complete the applicable IRS FormW-8 and certify under penalty of perjury that such holder is not a United States person as defined under the Code and is eligible for treaty benefits or (b) if the PubCo Ordinary Shares are held through certain foreign intermediaries, to satisfy the relevant certification requirements of applicable United States Treasury Regulations. Special certification and other requirements apply to certain Non-U.S. Holders that are pass-through entities rather than corporations or individuals.
A Non-U.S. Holder of PubCo Ordinary Shares eligible for a reduced rate of U.S. withholding tax pursuant to an income tax treaty may obtain a refund of any excess amounts withheld by timely filing an appropriate claim for refund with the IRS. Non-U.S. Holders are urged to consult their own tax advisors regarding their entitlement to the benefits under any applicable income tax treaty.
Sale, Exchange, Redemption or Other Taxable Disposition of PubCo Securities
In general, a Non-U.S. Holder will not be subject to U.S. federal income or, subject to the discussion below under the headings “Information Reporting and Backup Withholding” and “Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act,” withholding tax on any gain realized upon the sale or other disposition of PubCo Ordinary Shares unless:
| | ● | the gain is effectively connected with a trade or business carried on by the Non-U.S. Holder within the United States and, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, is attributable to a U.S. permanent establishment of the Non-U.S. Holder; |
| | | |
| | ● | the Non-U.S. Holder is an individual and is present in the United States for 183 days or more in the taxable year of disposition and certain other conditions are satisfied; or |
| | | |
| | ● | PubCo is or has been a U.S. real property holding corporation (a “USRPHC”) for U.S. federal income tax purposes at any time within the shorter of the five-year period ending on the date of the disposition or the Non-U.S. Holder’s holding period for such securities disposed of, and either (A) PubCo Ordinary Shares are not considered to be regularly traded on an established securities market or (B) such Non-U.S. Holder has owned or is deemed to have owned, at any time during the shorter of the five-year period preceding such disposition and such Non-U.S. Holder’s holding period more than 5% of the outstanding PubCo Ordinary Shares. PubCo believes that PubCo currently is not, and PubCo does not anticipate it becoming, a USRPHC. |
Gain that is effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business in the United States generally will be subject to U.S. federal income tax, net of certain deductions, at regular U.S. federal income tax rates. If the Non-U.S. Holder is a foreign corporation, the branch profits tax described above also may apply to such effectively connected gain. An individual Non-U.S. Holder who is subject to U.S. federal income tax because the Non-U.S. Holder was present in the United States for 183 days or more during the year of sale or other disposition of Global Star’s securities will generally be subject to a flat 30% tax on the gain derived from such sale or other disposition, which may be offset by U.S. source capital losses, provided the Non-U.S. Holder has timely filed U.S. federal income tax returns with respect to such losses.
Exercise or Lapse of a PubCo Warrant
The U.S. federal income tax treatment of a Non-U.S. Holder’s exercise of a PubCo Warrant, or the lapse of a PubCo Warrant held by a Non-U.S. Holder, generally will correspond to the U.S. federal income tax treatment of the exercise or lapse of a warrant by a U.S. Holder, as described under “— U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences to U.S. Holders — Exercise or Lapse of a PubCo Warrant,” above, although to the extent a cashless exercise results in a taxable exchange, the consequences would be similar to those described under “— Sale, Exchange, Redemption or Other Taxable Disposition of PubCo Common Stock,” above for a Non-U.S. Holder’s gain on the sale or other disposition of PubCo securities.
Certain U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of Exercising Redemption Rights
U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences to U.S. Holders
In the event that a U.S. Holder elects to redeem its GLST Common Stock for cash, the treatment of the transaction for U.S. federal income tax purposes will depend on whether the redemption qualifies as sale or exchange of the GLST Common Stock under Section 302 of the Code. If the redemption qualifies as a sale or exchange of the GLST Common Stock, the U.S. Holder will be treated as recognizing capital gain or loss equal to the difference between the amount realized on the redemption and such U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in the GLST Common Stock surrendered in such redemption transaction. Any such capital gain or loss generally will be long-term capital gain or loss if the U.S. Holder’s holding period for the GLST Common Stock redeemed exceeds one year. Long-term capital gains recognized by non-corporate U.S. Holders will be eligible to be taxed at reduced rates. The deductibility of capital losses is subject to limitations.
If the redemption does not qualify as a sale or exchange of GLST Common Stock, the U.S. Holder will be treated as receiving a corporate distribution. Such distributions generally will constitute dividends for U.S. federal income tax purposes to the extent paid from Global Star’s current or accumulated earnings and profits, as determined under U.S. federal income tax principles. Distributions in excess of current and accumulated earnings and profits will constitute a return of capital that will be applied against and reduce (but not below zero) the U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in the GLST Common Stock. Any remaining excess will be treated as gain realized on the sale or other disposition of the ordinary shares. Dividends paid to a U.S. Holder that is a taxable corporation generally will qualify for the dividends received deduction if the requisite holding period is satisfied. With certain exceptions (including, but not limited to, dividends treated as investment income for purposes of investment interest deduction limitations) and provided certain holding period requirements are met, dividends paid to a non-corporate U.S. Holder generally will constitute “qualified dividends” that will be subject to tax at the maximum tax rate accorded to long-term capital gains. However, it is unclear whether the redemption rights with respect to the GLST Common Stock may prevent a U.S. Holder from satisfying the applicable holding period requirements with respect to the dividends received deduction or the preferential tax rate on qualified dividend income, as the case may be.
Whether a redemption qualifies for sale or exchange treatment will depend largely on the total number of shares of GLST Common Stock treated as held by the U.S. Holder (including any GLST Common Stock constructively owned by the U.S. Holder as a result of owning GLST Warrants or GLST Rights) relative to all of the shares of GLST Common Stock outstanding both before and after the redemption. The redemption of GLST Common Stock generally will be treated as a sale or exchange of the GLST Common Stock (rather than as a corporate distribution) if the redemption (i) is “substantially disproportionate” with respect to the U.S. Holder, (ii) results in a “complete termination” of the U.S. Holder’s interest in Global Star or (iii) is “not essentially equivalent to a dividend” with respect to the U.S. Holder. These tests are explained more fully below.
In determining whether any of the foregoing tests are satisfied, a U.S. Holder takes into account not only GLST Common Stock actually owned by the U.S. Holder, but also shares of GLST Common Stock that are constructively owned by it. A U.S. Holder may constructively own, in addition to stock owned directly, stock owned by certain related individuals and entities in which the U.S. Holder has an interest or that have an interest in such U.S. Holder, as well as any stock the U.S. Holder has a right to acquire by exercise of an option, which would generally include GLST Common Stock which could be acquired pursuant to the exercise of the GLST Warrants or GLST Rights. In order to meet the substantially disproportionate test, the percentage of Global Star’s outstanding voting stock actually and constructively owned by the U.S. Holder immediately following the redemption of the GLST Common Stock must, among other requirements, be less than 80% of the percentage of Global Star’s outstanding voting stock actually and constructively owned by the U.S. Holder immediately before the redemption. There will be a complete termination of a U.S. Holder’s interest if either (i) all of the shares of the GLST Common Stock actually and constructively owned by the U.S. Holder are redeemed or (ii) all of the shares of the GLST Common Stock actually owned by the U.S. Holder are redeemed and the U.S. Holder is eligible to waive, and effectively waives in accordance with specific rules, the attribution of stock owned by certain family members and the U.S. Holder does not constructively own any other GLST Common Stock. The redemption of the GLST Common Stock will not be essentially equivalent to a dividend if a U.S. Holder’s conversion results in a “meaningful reduction” of the U.S. Holder’s proportionate interest in Global Star. Whether the redemption will result in a meaningful reduction in a U.S. Holder’s proportionate interest in Global Star will depend on the particular facts and circumstances. However, the IRS has indicated in a published ruling that even a small reduction in the proportionate interest of a small minority stockholder in a publicly held corporation who exercises no control over corporate affairs may constitute such a “meaningful reduction.” A U.S. Holder should consult with its own tax advisors as to the tax consequences of a redemption.
If none of the foregoing tests is satisfied, then the redemption will be treated as a corporate distribution. After the application of those rules regarding corporate distributions, any remaining tax basis of the U.S. Holder in the redeemed ordinary shares will be added to the U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in its remaining GLST Common Stock, or, if it has none, to the U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in its GLST Warrants or possibly in other GLST Common Stock constructively owned by it.
Because the Reincorporation Merger will occur prior to the redemption of U.S. Holders that exercise redemption rights with respect to GLST Common Stock, U.S. Holders exercising such redemption rights, will be subject to the potential tax consequences as a result of the Reincorporation Merger (as discussed further above). All U.S. Holders are urged to consult their tax advisors as to the tax consequences to them of a redemption of all or a portion of their GLST Common Stock pursuant to an exercise of redemption rights.
U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences to Non-U.S. Holders
The characterization for U.S. federal income tax purposes of the redemption of a Non-U.S. Holder’s GLST Common Stock as a sale or exchange under Section 302 of the Code or as a corporate distribution under Section 301 of the Code generally will correspond to the U.S. federal income tax characterization of such a redemption of a U.S. Holder’s GLST Common Stock, as described above, and the corresponding consequences will be as described below.
Because the Reincorporation Merger will occur prior to the redemption of Non-U.S. Holders that exercise redemption rights with respect to GLST Common Stock, Non-U.S. Holders exercising such redemption rights, will be subject to the potential tax consequences as a result of the Reincorporation Merger (as discussed further above). All Non-U.S. Holders are urged to consult their tax advisors as to the tax consequences to them of a redemption of all or a portion of their GLST Common Stock pursuant to an exercise of redemption rights.
Redemption Treated as Sale or Exchange
Any gain realized by a Non-U.S. Holder on the redemption of GLST Common Stock that is treated as a sale or exchange under Section 302 of the Code generally will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax unless:
| | ● | the gain is effectively connected with a trade or business of the Non-U.S. Holder in the United States (and, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, is attributable to a United States permanent establishment or fixed base of the Non-U.S. Holder); |
| | | |
| | ● | the Non-U.S. Holder is an individual who is present in the United States for a period or periods aggregating 183 days or more in the taxable year of the disposition, and certain other conditions are met; or |
| | | |
| | ● | Global Star is or has been a “United States real property holding corporation” for U.S. federal income tax purposes at any time during the shorter of the five-year period ending on the date of disposition or the Non-U.S. Holder’s holding period for such GLST Common Stock redeemed, and either (A) shares of GLST Common Stock are not considered to be regularly traded on an established securities market or (B) such Non-U.S. Holder has owned or is deemed to have owned, at any time during the shorter of the five-year period preceding such disposition and such Non-U.S. Holder’s holding period more than 5% of the outstanding shares of GLST Common Stock. There can be no assurance that shares of GLST Common Stock will be treated as regularly traded on an established securities market for this purpose. |
A non-corporate Non-U.S. Holder described in the first bullet point immediately above will be subject to tax on the net gain derived from the sale under regular graduated U.S. federal income tax rates. An individual Non-U.S. Holder described in the second bullet point immediately above will be subject to a flat 30% tax on the gain derived from the sale, which may be offset by certain United States source capital losses, even though the individual is not considered a resident of the United States, provided that the individual has timely filed U.S. federal income tax returns with respect to such losses. If a Non-U.S. Holder that is a corporation falls under the first bullet point immediately above, it will be subject to tax on its net gain in the same manner as if it were a United States person as defined under the Code and, in addition, may be subject to the branch profits tax equal to 30% (or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty) of its effectively connected earnings and profits, subject to adjustments.
If the last bullet point immediately above applies to a Non-U.S. Holder, gain recognized by such Non-U.S. Holder on the redemption of GLST Common Stock generally will be subject to tax at generally applicable U.S. federal income tax rates. In addition, Global Star may be required to withhold U.S. income tax at a rate of 15% of the amount realized upon such redemption. Global Star would generally be classified as a “U.S. real property holding corporation” if the fair market value of Global Star’s “United States real property interests” equals or exceeds 50% of the sum of the fair market value of Global Star’s worldwide real property interests and Global Star’s other assets used or held for use in a trade or business, as determined for U.S. federal income tax purposes. However, Global Star believes that Global Star is not and have not been at any time since Global Star’s formation a U.S. real property holding corporation and Global Star does not expect to be a U.S. real property holding corporation immediately after the Business Combination is completed.
Redemption Treated as Corporate Distribution
With respect to any redemption treated as a corporate distribution under Section 301 of the Code, provided such dividends are not effectively connected with the Non-U.S. Holder’s conduct of a trade or business within the United States, GLST will be required to withhold U.S. tax from the gross amount of the dividend at a rate of 30%, unless such Non-U.S. Holder is eligible for a reduced rate of withholding tax under an applicable income tax treaty and provides proper certification of its eligibility for such reduced rate (usually on an IRS Form W-8BEN or W-8BEN-E). Any distribution not constituting a dividend will be treated first as reducing (but not below zero) the Non-U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in its shares of the GLST Common Stock and, to the extent such distribution exceeds the Non-U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis, as gain realized from the sale or other disposition of the GLST Common Stock, which will be treated as described above.
This withholding tax does not apply to dividends paid to a Non-U.S. Holder who provides a Form W-8ECI, certifying that the dividends are effectively connected with the Non-U.S. Holder’s conduct of a trade or business within the United States. Instead, the effectively connected dividends will be subject to regular U.S. income tax as if the Non-U.S. Holder were a U.S. resident, subject to an applicable income tax treaty providing otherwise. A Non-U.S. corporation receiving effectively connected dividends may also be subject to an additional “branch profits tax” imposed at a rate of 30% (or a lower treaty rate).
Information Reporting and Backup Withholding
In general, information reporting requirements will apply to dividends received by U.S. Holders of PubCo Ordinary Shares (including constructive dividends), and the proceeds received on the disposition of PubCo Ordinary Shares and PubCo Warrants effected within the United States (and, in certain cases, outside the United States), in each case, other than U.S. Holders that are exempt recipients (such as corporations). Information reporting requirements will also apply to redemptions from U.S. Holders of GLST Common Stock. Backup withholding (currently at a rate of 24%) may apply to such amounts if the U.S. Holder fails to provide an accurate taxpayer identification number (generally on an IRS Form W-9 provided to the paying agent or the U.S. Holder’s broker) or is otherwise subject to backup withholding. A Non-U.S. Holder may have to comply with certification procedures to establish that it is not a United States person for U.S. federal income tax purposes or otherwise establish an exemption in order to avoid information reporting and backup withholding requirements or to claim a reduced rate of withholding under an applicable income tax treaty. The amount of any backup withholding from a payment to a Non-U.S. Holder will generally be allowed as a credit against such Non-U.S. Holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability and may entitle such Non-U.S. Holder to a refund, provided that the required information is furnished by such Non-U.S. Holder to the IRS in a timely manner.
Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Any amounts withheld under the backup withholding rules may be allowed as a refund or credit against a holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability, if any, provided the required information is timely furnished to the IRS.
Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act
Sections 1471 through 1474 of the Code and the Treasury Regulations and administrative guidance promulgated thereunder (commonly referred as the “Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act” or “FATCA”) generally impose withholding at a rate of 30% in certain circumstances on dividends in respect of, and (subject to the proposed Treasury Regulations discussed below) gross proceeds from the sale or other disposition of, securities (including PubCo securities) which are held by or through certain foreign financial institutions (including investment funds), unless any such institution (i) enters into, and complies with, an agreement with the IRS to report, on an annual basis, information with respect to interests in, and accounts maintained by, the institution that are owned by certain U.S. persons and by certain non-U.S. entities that are wholly or partially owned by U.S. persons and to withhold on certain payments, or (ii) if required under an intergovernmental agreement between the United States and an applicable foreign country, reports such information to its local tax authority, which will exchange such information with the U.S. authorities. An intergovernmental agreement between the United States and an applicable foreign country may modify these requirements. Accordingly, the entity through which PubCo securities are held will affect the determination of whether such withholding is required. Similarly, dividends in respect of, and (subject to the proposed Treasury Regulations discussed below) gross proceeds from the sale or other disposition of, PubCo securities held by an investor that is a non-financial non-U.S. entity that does not qualify under certain exceptions will generally be subject to withholding at a rate of 30%, unless such entity either (i) certifies to the applicable withholding agent that such entity does not have any “substantial United States owners” or (ii) provides certain information regarding the entity’s “substantial United States owners,” which will in turn be provided to the U.S. Department of Treasury.
Under the applicable Treasury Regulations and administrative guidance, withholding under FATCA generally applies to payments of dividends in respect of PubCo Ordinary Shares. While withholding under FATCA generally would also apply to payments of gross proceeds from the sale or other disposition of securities (including PubCo securities), proposed Treasury Regulations eliminate FATCA withholding on payments of gross proceeds entirely. Taxpayers generally may rely on these proposed Treasury Regulations until final Treasury Regulations are issued. All holders should consult their tax advisors regarding the possible implications of FATCA on their investment in PubCo securities.
Required Vote
Approval of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal requires the affirmative vote of the holders of sixty-five percent (65%) of the GLST Common Stock outstanding as of the record date. Adoption of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal is conditioned upon the adoption of the Acquisition Merger Proposal. It is important for you to note that in the event that either of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal or the Acquisition Merger Proposal is not approved, then Global Star will not consummate the Business Combination.
Recommendation of Global Star’s Board of Directors
After careful consideration, Global Star board of directors determined that the Reincorporation Merger forming part of the Business Combination with K Enter is in the best interests of Global Star and its stockholders. On the basis of the foregoing, Global Star board of directors has approved and declared advisable the Business Combination with K Enter and recommends that you vote or give instructions to vote “FOR” adoption of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal.
PROPOSAL NO. 2
THE ACQUISITION MERGER PROPOSAL
The discussion in this proxy statement/prospectus of the Business Combination and the principal terms of the Merger Agreement, as amended, is subject to, and is qualified in its entirety by reference to, the Merger Agreement. The full text of the Merger Agreement is attached hereto as Annex A, which is incorporated by reference herein.
General Description of the Acquisition Merger
Acquisition Merger with K Enter; Acquisition Merger Consideration
K Enter’s acquisition of the Six Korean Entities is a closing condition to the Business Combination, and while this condition can be waived, however Global Star does not currently intend to waive this condition. K Enter expects to close the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of the Six Korean Entities within 24 to 72 hours after this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 is declared effective by the SEC. In addition, Global Star will not mail proxy materials to its shareholders for the Special Meeting until after K Enter closes the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities. PubCo shall include the date that K Enter completes the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all Six Korean Entities in its Form 424B3 Prospectus to be filed with the SEC after this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 is declared effective by the SEC.
In the event that K Enter does not complete the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities, PubCo will file a post-effective amendment to its Registration Statement on Form F-4 (the “Post-Effective Amendment”) disclosing that K Enter did not complete its contemplated acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of all of the Six Korean Entities (and the material information concerning such event) and Global Star will not mail proxy materials to its shareholders for the Special Meeting (or hold its Special Meeting) until after the Post-Effective Amendment is declared effective by the SEC. Global Star’s shareholders will not be able to vote for or against the Business Combination until after they receive a definitive proxy statement, which will only be mailed after the later of (i) the successful consummation of the acquisition of the controlling interests of all of the Six Korean Entities or (ii) the declaration of effectiveness by the SEC of the Post-Effective Amendment.
As of January 3, 2025, K Enter completed the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of each of the Six Korean Entities.
At least one (1) business day after the Reincorporation Merger, Merger Sub, a Delaware corporation and wholly owned subsidiary of PubCo, will be merged with and into K Enter, resulting in K Enter being a wholly owned subsidiary of PubCo.
The aggregate consideration for the Acquisition Merger is $590,000,000, payable in the form of 59,000,000 newly issued PubCo Ordinary Shares valued at $10.00 per share to K Enter and its shareholders. At the closing of the Acquisition Merger, the issued and outstanding shares in K Enter held by the former K Enter shareholders will be cancelled and ceased to exist, in exchange for the issue of an aggregate of 59,000,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares. 5,900,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares will be reserved and authorized for issuance under the Incentive Plan upon closing. At the closing of the Acquisition Merger, the fully paid shares in Merger Sub held by PubCo will become fully paid shares in the surviving corporation, so that K Enter will become a wholly owned subsidiary of PubCo.
Upon the closing of the Business Combination, PubCo board of directors will consist of seven directors, all of whom will be designated by K Enter and a majority of whom will be “independent” under Nasdaq’s listing standards. See section titled “PubCo’s Directors and Executive Officers after the Business Combination” for additional information. While the Merger Agreement contemplates that the Sponsor will have the right to designate a certain number of directors, the Sponsor has waived this right.
According to the PubCo Charter, the authorized share capital of post-closing company is $100,000 divided into 990,000,000 ordinary shares of par value of $0.0001 each and 10,000,000 preference shares of par value US$0.0001 each. After the consummation of the Business Combination, PubCo will be a “foreign private issuer” under the U.S. securities laws and the rules of Nasdaq. For more information about the foreign private issuer, please see the sections titled “PubCo’s Directors and Executive Officers After the Business Combination — Foreign Private Issuer Status.”
After the Business Combination, assuming (i) there are no additional redemptions of Global Star’s shares and (ii) there is no exercise of the PubCo Warrants, Global Star’s current public stockholders will own approximately 3.3% of the issued share capital of PubCo, Global Star’s current directors, officers and affiliates will own approximately 4.5% of the issued share capital of PubCo, and K Enter shareholders will own approximately 92.2% of the issued share capital of PubCo (excluding the 5,900,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares reserved and authorized for issuance under the Incentive Plan). Assuming maximum redemptions by holders of Global Star’s outstanding ordinary shares, Global Star’s current public stockholders will own approximately 1.4% of the issued share capital of PubCo, Global Star’s current directors, officers and affiliates will own approximately 4.7% of the issued share capital of PubCo, and K Enter shareholders will own approximately 93.9% of the issued share capital of PubCo (excluding the 5,900,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares reserved and authorized for issuance under the Incentive Plan).
The closing of the business combination is subject to certain conditions, including K Enter’s acquisition of the controlling equity interests of the Six Korean Entities. K Enter currently has limited operations and does not presently own a controlling interest in any other entities. For more information, see the questions and answers titled “When is the acquisition of the Six Korean Entities expected to occur?” and “What if there are material developments or changes relating to the acquisition by K Enter of the Six Korean Entities prior to the Special Meeting?” and “What if K Enter’s acquisition of the Six Korean Entities does not occur prior to the Special Meeting?” in the Section titled “Questions and Answers about the Business Combination and the Special Meeting” beginning on page 6.
Assuming the Reincorporation Merger Proposal and the Acquisition Merger Proposal are approved, Global Star expects to close the Business Combination by February 10, 2025.
Representations and Warranties
K Enter makes certain representations and warranties (with certain exceptions set forth in the disclosure schedule to the Merger Agreement) relating to, among other things: (a) proper corporate organization of K Enter and similar corporate matters; (b) authorization, execution, delivery and enforceability of the Merger Agreement and other transaction documents; (c) absence of conflicts; (d) capital structure; (e) accuracy of charter documents and corporate records; (f) required consents and approvals; (g) financial information; (h) absence of certain changes or events; (i) title to assets and properties; (j) material contracts; (k) ownership of real property; (l) licenses and permits; (m) compliance with laws, including those relating to foreign corrupt practices and money laundering; (n) ownership of intellectual property; (o) customers and suppliers; (p) employment and labor matters; (q) taxes matters; (r) environmental matters; (s) brokers and finders; (t) that K Enter is not an investment company; and (u) other customary representations and warranties.
Global Star, PubCo and Merger Sub (collectively “Purchaser Parties”) make certain representations and warranties relating to, among other things: (a) proper corporate organization and similar corporate matters; (b) authorization, execution, delivery and enforceability of the Merger Agreement and other transaction documents; (c) litigation; (d) brokers and finders; (e) capital structure; (f) validity of share issuance; (g) minimum trust fund amount; and (h) validity of Nasdaq Stock Market listing; (i) SEC filing requirements and financial statements; (j) material contracts; (k) compliance with laws, including those relating to foreign corrupt practices and money laundering.
Conduct Prior to Closing; Covenants
Each of K Enter and Global Star has agreed to, and cause its subsidiaries to, operate the business in the ordinary course, consistent with past practices, prior to the closing of the transactions (with certain exceptions) and not to take certain specified actions without the prior written consent of the other party.
The Merger Agreement also contains covenants providing for:
| ● | Each party providing access to their books and records and providing information relating to their respective business to the other party, its legal counsel and other representatives; |
| ● | K Enter delivering the financial statements required by Global Star to make applicable filings with the SEC; |
| ● | Cooperation in making certain filings with the SEC; and |
Conditions to Closing
General Conditions
Consummation of the Merger Agreement and the transactions herein is conditioned on, among other things, (i) the absence of any order or provisions of any applicable law making the transactions illegal or otherwise preventing or imposing any condition on the transactions; (ii) all applicable waiting periods, if any, under the Hart-Scott-Rodino Act shall have expired or been terminated and each consent required to consummate the Business Combination shall have been obtained and be in full force and effect; (iii) Global Star shall, after giving effect to any redemptions, have net tangible assets of at least $5,000,001 or (iv) be otherwise exempt from the provisions of Rule 419 promulgated under the Securities Act; (v) Global Star shall have received approval from its stockholders of the Business Combination Proposals, the Governance Proposal and the Incentive Plan Proposal; (vi) the Business Combination shall have been approved by K Enter’s stockholders; (vii) PubCo’s initial listing application with Nasdaq or an alternate exchange, as applicable, in connection with the transactions contemplated by this Agreement shall have been conditionally approved and, immediately following the Business Combination, PubCo shall satisfy any applicable initial and continuing listing requirements of such exchange Nasdaq or an Alternate Exchange, as applicable, and PubCo shall not have received any notice of non-compliance therewith, and the shares to be issued in connection with the Business Combination shall have been approved for listing on Nasdaq or an alternate exchange, as applicable; (viii) this Registration Statement shall have become effective in accordance with the provisions of the Securities Act, no stop order suspending the effectiveness of this Registration Statement shall have been issued by the SEC that remains in effect and no proceeding seeking such a stop order shall have been initiated by the SEC and not withdrawn; (ix) the Reincorporation Merger shall have been consummated and the applicable certificates filed in the appropriate jurisdictions; (x) the acquisition by K Enter of a controlling interest in the Six Korean Entities shall have been consummated; and (xi) the joinder to the Merger Agreement shall have been executed by PubCo and Merger Sub.
K Enter’s Conditions to Closing
The obligations of K Enter to consummate the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement, in addition to the conditions described above, are conditioned upon each of the following, among other things:
| ● | Purchaser Parties complying with all of their obligations under the Merger Agreement in all material respects; |
| | ● | subject to applicable materiality qualifiers, the representations and warranties of Purchaser Parties being true on and as of the closing date of the transactions; |
| ● | Purchaser Parties complying with the reporting requirements under the applicable Securities Act and Exchange Act; |
| | ● | There having been no material adverse effect to Purchaser Parties that is continuing; and |
| | | |
| | ● | The size and composition of PubCo’s post-closing board of directors shall have been approved. |
Purchaser Parties’ Conditions to Closing
The obligations of Purchaser Parties to consummate the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement, in addition to the conditions described above in the first paragraph of this section, are conditioned upon each of the following, among other things:
| ● | K Enter and its subsidiaries complying with all of the obligations under the Merger Agreement in all material respects; |
| | ● | subject to applicable materiality qualifiers, the representations and warranties of K Enter and its subsidiaries being true on and as of the closing date of the transactions; |
| ● | there having been no material adverse effect to the business of K Enter, Play Company or Solaire Partners, taken as a whole, that is continuing; and |
| | ● | K Enter shall have obtained certain specified third-party consents. |
Termination
The Merger Agreement may be terminated and/or abandoned at any time prior to the closing, whether before or after approval of the proposals being presented to Global Star stockholders, by:
| ● | Written agreement of Global Star and K Enter; |
| | ● | either Global Star or K Enter, if the closing has not occurred by June 22, 2025, provided that no material breach of this Agreement by the party seeking to terminate this Agreement shall have occurred or have been made; |
| ● | Global Star, if K Enter has materially breached any representation, warranty, agreement or covenant contained in the Merger Agreement; |
| ● | K Enter, if Global Star has materially breached any representation, warranty, agreement or covenant contained in the Merger Agreement; or |
| ● | Either K Enter or Global Star if the Business Combination is permanently enjoined, prohibited or prevented by the terms of a final, non-appealable government order. |
The foregoing description of the Merger Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the actual agreement, a form of which is included as part of Annex A hereto.
In addition to the Merger Agreement, the following agreements will be entered into in connection with the closing of the business combination.
Lock-Up Agreement
At the Closing, PubCo, the Sponsor, certain former stockholders of K Enter, and certain other persons and entities, will enter into lock-up agreements (the “Lock-Up Agreements”) with respect to PubCo Ordinary Shares and PubCo Warrants held by the Sponsor immediately following the Closing, and PubCo Ordinary Shares held by certain K Enter stockholders immediately following the Closing (the “Lock-Up Shares”), pursuant to which, each Holder agreed not to offer, sell, contract to sell, pledge, grant any option to purchase, or otherwise dispose of, directly or indirectly, any Lock-Up Shares during the application lock-up period, on the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in the Lock-Up Agreement. Lock-up period means, (i) with respect to 50% of the Lock-up Shares, the earlier of (A) six months after the Closing and (B) the date on which the closing price of the PubCo’s Ordinary Shares equals or exceeds $12.50 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, rights issuances, reorganizations and recapitalizations) for any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period commencing after the date hereof and (ii) with respect to the remaining 50% Lock-up Shares (or Ordinary Shares issuable upon conversion thereof), six months after the Closing. The Lock-Up Agreements will apply to (i) approximately 83% of the PubCo Ordinary Shares, consisting of 2,798,225 Ordinary Shares owned by the Sponsor, Stephen Drew and Nicholas Khoo and 49,424,300 Ordinary Shares owned by the former K Enter stockholders (ii) 498,225 Ordinary Shares underlying warrants held by the Sponsor (approximately 5.14% of the outstanding warrants) and (iii) 49,822 Ordinary Shares underlying rights owned by the Sponsor (approximately 5.14% of the rights).
The foregoing description of the Lock-Up Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the actual agreement, a form of which is included as part of Annex A hereto.
Registration Rights Agreement
At the Closing, PubCo, the Sponsor, certain former stockholders of Global Star, and certain former stockholders of K Enter, will enter into a registration rights agreement (the “Registration Rights Agreement”), pursuant to which PubCo will be obligated to file a registration statement to register the resale, pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, of certain securities of PubCo held by the parties to the Registration Rights Agreement. The Registration Rights Agreement will also provide the Sponsor, the Initial Stockholders, and certain former stockholders of K Enter with unlimited “piggy-back” registration rights, subject to certain requirements and customary conditions.
The Registration Rights Agreement amends and restates the registration rights agreement that was entered into by the Company, the Sponsor and the other parties thereto in connection with the Company’s initial public offering. The Registration Rights Agreement will terminate on the earlier of (a) the five year anniversary of the date of the Registration Rights Agreement or (b) with respect to any holder, on the date that such holder no longer holds any Registrable Securities (as defined therein).
The foregoing description of the Lock-Up Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the actual agreement, a form of which is included as part of Annex A hereto.
Interests of Certain Persons in the Business Combination
When you consider the recommendation of Global Star board of directors in favor of adoption of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal, the Acquisition Merger Proposal and the other related Proposals, you should keep in mind that Global Star’s directors and officers have interests in the Business Combination that are different from, or in addition to, your interests as a stockholder, including the following:
| | ● | If the Business Combination is not completed by June 22, 2025, Global Star will be required to liquidate. In such event, the 2,140,000 Founder Shares purchased by the Sponsor and Initial Stockholders for $25,000 and the 498,225 Private Units acquired by the Sponsor and the Initial Stockholders for $4,982,250 prior to the IPO as well as the $1,600,000 the Sponsor loaned to Global Star in exchange for a promissory note and the $120,000 the Sponsor loaned to K Enter will be worthless. Such securities and promissory note had an aggregate market value of approximately $32.4 million based on December 3 , 2024, closing price of GLST Common Stock of $11.69 and of GLST Units of $11.32; |
| ● | Certain officers and directors of the Company own shares of common stock of K Enter. Specifically, the following directors own shares of common stock of K Enter as follows: Stephen Drew owns 6,000 shares of K Enter common stock, Yang Kan Chong owns 1,337 shares of K Enter common stock and Jukka Rannila, beneficially through Assai OY, owns 600 shares of K Enter common stock. Nicholas Aaron Khoo the Company’s Chief Operating Officer owns 600 shares of K Enter common stock; |
| ● | The exercise of Global Star’s directors’ and officers’ discretion in agreeing to changes or waivers in the terms of the transaction may result in a conflict of interest when determining whether such changes or waivers are appropriate and in Global Star’s stockholders’ best interest; and |
| ● | If the Business Combination with K Enter is completed, K Enter will designate all members of the board of directors. |
Anticipated Accounting Treatment
Prior to the Business Combination, K Enter will acquire controlling equity interests in the Six Korean Entities.
The acquisition of the Six Korean Entities by K Enter will occur with the acquisition of Play Company closing first and the acquisitions of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company closing subsequently. After the acquisition of all Six Korean Entities is completed, the collective combined company will be referred to as New K Enter solely for purposes of the discussion of the accounting treatment as New K Enter simply refers to K Enter after acquisition of the Six Korean Entities.
The acquisition of Play Company by K Enter will be accounted for in accordance with the acquisition method of accounting under IFRS 3, with Play Company considered to be the acquirer and predecessor of K Enter. As Play Company’s basis of accounting is IFRS, K Enter’s basis of accounting (following the acquisition of Play Company) will be IFRS.
The acquisitions of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company by K Enter will also be accounted for in accordance with the acquisition method of accounting under IFRS 3, with K Enter (following the acquisition of Play Company, its predecessor) considered to be the acquirer of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company. The results of operations of each of the acquired Six Korean Entities other than Play Company will be included in the consolidated financial statements from the date of the acquisition forward. New K Enter’s basis of accounting will be IFRS, consistent with that of its predecessor, Play Company.
The overall impact of the accounting conclusions set out above will be that the financial statements of Play Company will become those of K-Enter post-consummation and will not experience a change in basis as a result of the application of the acquisition method while each of K Enter and the five Korean Entities other than Play Company will experience a change in basis as a result of the application of the acquisition method and will be reflected in the consolidated financial statements of Play Company on a prospective basis post-consummation.
The Business Combination is accounted for as a capital reorganization, with no goodwill or other intangible assets recorded, in accordance with IFRS 2. Under this method of accounting, K Wave Media, as the successor to Global Star in the Reincorporation Merger, is treated as the “acquired” company for financial reporting purposes. This determination was primarily based on the assumption that:
| | ● | New K Enter’s existing stockholders will hold a majority of the voting rights of PubCo post Business Combination under the No Additional Redemption Scenario and Maximum Redemption Scenario; |
| | | |
| | ● | By virtue of such estimated voting interest upon the Closing, New K Enter’s existing stockholders will have the ability to control decisions regarding the election and removal of directors and officers of the Combined Company following the Closing; |
| | ● | New K Enter will have control over the Board; |
| | ● | New K Enter’s operations will substantially comprise the ongoing operations of PubCo; |
| | ● | New K Enter is the larger entity in terms of substantive operations and employee base; and |
| | ● | New K Enter’s senior management will comprise the senior management of PubCo. |
Another determining factor was that Global Star does not meet the definition of a “business” pursuant to IFRS 3, and thus, for accounting purposes, the Business Combination will be accounted for as a capital reorganization within the scope of IFRS 2, where New K Enter issues stock for the net assets of Global Star. The net assets of Global Star are stated at historical cost, with no goodwill or intangible assets recorded. Any excess of the fair value of shares issued to Global Star over the fair value of Global Star’s identifiable net assets acquired represents compensation for the service of a stock exchange listing for its shares and is expensed as incurred.
The determination that Play Company will be considered the acquirer of K Enter for financial reporting purposes was primarily based on the assumption that:
| | ● | Play Company’s existing stockholders will hold a large minority voting interest in New K Enter where no other owner has a significant voting interest; |
| | ● | Play Company’s CEO has the ability to appoint the senior management of New K Enter |
| | ● | Play Company’s CEO has the ability to appoint a majority of directors of New K Enter’s board of directors; |
| | ● | Play Company’s operations will substantially comprise the ongoing operations of New K Enter; and |
| | ● | Play Company is the larger entity in terms of substantive operations and employee base. |
Under the acquisition method of accounting, the preliminary purchase price is allocated to the underlying tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their respective fair market values, with the excess purchase price, if any, allocated to goodwill. Costs related to the transaction are expensed as incurred.
Regulatory Approvals
The Reincorporation Merger, the Acquisition Merger and the other transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement are not subject to any additional U.S. federal or state regulatory requirements or approvals, or any regulatory requirements or approvals under the laws of the Cayman Islands, except for the registration by the Registrar of Companies in the Cayman Islands of the plans of merger.
Background of the Business Combination
Global Star is a blank check company incorporated on July 24, 2019, as a Delaware corporation whose business purpose is to effect a merger, capital stock exchange, asset acquisition, stock purchase, reorganization, or similar business combination with one or more businesses, (the “Business Combination”). Global Star’s efforts to identify a prospective target business initially were focused on fintech and proptech companies, with a preference for the South East Asia region.
On September 22, 2022, Global Star consummated its initial public offering of 8,000,000 units. Each Unit consisted of one share of Class A Common Stock of Global Star, par value $0.0001 per share, one redeemable warrant, with each whole warrant entitling the holder thereof to purchase one share of Class A Common Stock for $11.50 per share, and one Right, with each Right entitling the holder to receive one-tenth of one share of Class A Common Stock. The units were sold at a price of $10.00 per unit, generating gross proceeds to Global Star of $80,000,000.
At the time of the initial public offering, the underwriters were granted a 45-day over-allotment option to purchase up to 1,200,000 additional Units to cover overallotments, if any. Subsequently, on September 30, 2022, the underwriters exercised their over-allotment option to purchase 1,200,000 over-allotment units. On October 4, 2022 Global Star closed on the over-allotment units through the sale of 1,200,000 units at a purchase of $10.00 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $12.0 million.
Simultaneously with the consummation of the closing of the initial public offering and the following over-allotment, Global Star consummated the private placement of an aggregate of 498,225 units to the Sponsor, at a price of $10.00 per Private Placement Unit, generating total gross proceeds of $4,982,225.
A total of $94,300,000 comprising proceeds from the initial public offering and proceeds of the private placement, net of the underwriting commissions, discounts, and initial public offering expenses, was deposited in a trust account established for the benefit of Global Star’s public stockholders. The Cotto Wealth Management Group at Morgan Stanley is managing the trust account. Before the successful conclusion of its initial public offering, neither Global Star nor anyone on its behalf contacted any prospective target or had any substantive discussions, formal or otherwise, with respect to a merger transaction with Global Star. Following the initial public offering, the management team and board members initiated contact with and were approached by numerous potential targets and advisors. Global Star established a transparent and systematic process for selecting and vetting potential targets, which involved collecting information on the targets presented, shortlisting, developing criteria for ranking and assessment, and conducting due diligence. A pipeline for the targets was set up to assemble data and information on potential merger targets.
Based on these criteria and multiple conversations with the targets and its own internal discussion, Global Star developed a target candidate shortlist. As part of the assessment process, the management team ranked all the potential targets based on certain criteria such as revenue, earnings, sector, technology, etc. and organized a weekly call for the management to discuss the deals with the directors. The assessment also included signing of non-disclosure agreements where needed to access data rooms for detailed information on the targets.
In accordance with this process, Global Star engaged in discussions with multiple targets, ultimately narrowing the list down to five targets from various sectors: (A) fintech, (B) artificial intelligence (“AI”), (C) renewable energy, (D) luxury branded products and (E) K-content (K Enter). Global Star conducted additional due diligence and sent non-exclusive term sheets to the above 5 candidates in February and March 2023. In November and December 2022, Global Star management held meetings with representatives of potential acquisition targets in Singapore, Japan, Korea, Malaysia and Europe.
Ted Kim, a managing member of the Sponsor and a director of K Enter, introduced Global Star to K Enter in late January 2023, as a potential acquisition target. K Enter was formed by 5 individuals, including Mr. Kim, Pyeung Ho Choi, Jae Young Lee (“Dale Lee”), Hyuk Jin Lee and Mina Kim (collectively the “K Enter Co-Founders”) following discussions among the K Enter Co-Founders in November 2023. The K Enter Co-Founder’s agreed in November 2023, that Mr. Choi and Dale Lee, who are officers of Solaire Partners LLC, a Korean based entertainment venture capital fund, would lead K Enter and identify and negotiate acquisition agreements to enable K Enter to acquire controlling interests in a number of Korean entertainment companies. As of mid-January 2023, K Enter had identified and commenced negotiation with the Seven Korean Entities. Towards the end of January 2023, Mr. Kim learned that Dale Lee was traveling on business to Singapore. Since Anthony Ang, the CEO of Global Star is based in Singapore, Mr. Kim decided to see if Dale Lee could meet with Mr. Ang in Singapore and so Mr. Kim introduced K Enter to Global Star as a potential acquisition target.
Global Star decided to apply the following additional conditions to the targets:
| ● | Requirement for the targets to purchase a minimum of USD $1 million worth of Founder Shares from the Sponsor in lieu of a usual break fee for the merger agreement in order for to increase deal certainty and provide additional capital to extend the timeframe for closing the transaction; and |
| ● | No minimum cash closing conditions, with private investment in public equity (“PIPE”) fund raising to be the primary responsibility of the target, with Global Star playing a supporting role. |
With these conditions, the 5 targets were then narrowed down to 2 final choices, namely targets (B) and (E) in April 2023 that accepted the additional conditions.
Global Star was actively engaged with the two targets from early April until June 2023. One of these targets, referred to as Target B, is a 5-year-old Emotive AI company with revenue and profitability. However, in order to facilitate the merger process and meet the above conditions relating to the purchase of Founder Shares from the Sponsor and the closing of a PIPE transaction, Target B needed to raise approximately USD $5-10 million in a PIPE. To gain a comprehensive understanding of the business, Global Star’s management team, led by the chief executive officer and chief operating officer, visited Target B in Kuala Lumpur on February 28, 2023, and conducted three subsequent discussions, including a Zoom presentation to the Board on March 3, 2023. The negotiations with Target B continued until Global Star executed the Merger Agreement with K Enter, as Global Star desired to preserve a second option in light of the limited time frame for Global Star to complete a business combination.
The other target, referred to as Target E / K Enter, was a newly constituted holding company planning to acquire seven K-content related companies.
On February 8, 2023, the chief executive officers of Global Star and K Enter (Anthony Ang and Young Jae Lee) met in person in Singapore to discuss the possibility of a business combination. This was the only introductory meeting between K Enter and Global Star on February 8, 2023. At that time, K Enter was actively negotiating to acquire the Seven Korean Entities. Global Star had no involvement in the negotiations between K Enter and those six companies or the formation of K Enter. As K Enter had been recently formed, the discussions focused on the businesses that K Enter sought to acquire. While Global Star would have preferred to acquire a company with active operations, the prospect of acquiring K Enter and the Seven Korean Entities presented an attractive opportunity. The identification and the selection of the Seven Korean Entities was managed by Mr. Choi and Dale Lee.
When Dale Lee and Mr. Ang met in Singapore on February 8, 2023, K Enter had already identified and commenced the process of negotiating the acquisition of the controlling interests of the Seven Korean Entities, subject to due diligence, valuation and execution of definitive documentation. K Enter advised Mr. Ang that K Enter preferred an all-stock deal for the Seven Korean Entities to reduce capital requirements and to align the interests of the owners and managers of the acquired companies with the success of PubCo.
The owner of Play Company sought additional cash payments in connection with the transaction. Given the importance of Play Company to the success of PubCo, K Enter was willing to agree to these payments but spread-out the payments into three future installments. The owner of Play Company will also join the board of the New K Enter and this way, he will continue to have incentive to make sure Play Company performs good post completion of the business combination. The better Play Company performs, the easier it is for K Enter to make the payment to the. owner of Play Company.
Other than K Enter’s acquisition of Solaire Partners LLC, Global Star was not aware of any conflicts of interest between K Enter and any of the potential target companies. K Enter informed Global Star that K Enter’s operating companies would be a major factor when it comes to determining whether it will be a suitable target for Global Star. The mere fact K Enter was a recently formed, did not raise significant concern because K Enter’s business plan was to acquire the Seven Korean Entities which either had experienced operators or years of successful operating history. Global Star’s primary focus was whether the management of K Enter was qualified and presented a sense of integrity and transparency. Throughout February and until the signing of the merger agreement, Global Star’s confidence in K Enter and its management team grew after seeing K Enter execution the agreements to acquire controlling interests of the Seven Korean Entities and by engaging some of the most prominent Korean entertainment people under K Enter.
The February 8, 2023 meeting in Singapore between K Enter’s former CEO Dale Lee and Global Star’s CEO Anthony Ang commenced good faith negotiation and discussion about the possible merger between the two companies. During the February 8, 2023 meeting, due diligence matters relating to the Seven Korean Entities were discussed, and shortly thereafter Global Star was provided access to K Enter’s data room, which contained detailed financial information of Seven Korean Entities as well as legal and business due diligence reports of the Seven Korean Entities to be acquired.
Thereafter, Global Star proposed a videoconference to further explore the possibilities of a merger. Global Star was informed that one of the Seven Korean Entities, Anseilen was newly created in March 2023. K Enter explained that they value “people” capacity above all. Although it is a newly created entity, its management team comes from “SBS” content production team. SBS is widely considered one of Korea’s best content production and broadcasting companies and with that kind of pedigree, K Enter stated that Anseilen will be a new powerhouse content production studio in Korea. As one of the Seven Korean Entities with valuation of about $6 million for 51%, Global Star thought Anseilen, although a newly created entity, was a good addition to K Enter acquisition targets.
In February and March 2023, Global Star continued its due diligence on K Enter and the Seven Korean Entities, with the assistance of two Korean law firms engaged by K Enter, Ehoo Law Group and Lee & Ko. Among the due diligence documents GLST reviewed was a “valuation report” on K Enter (the “KPMG Valuation Report”) assuming the acquisition of the Seven Korean Entities prepared by KPMG Samjong Accounting Corp (“Samjong KPMG”), a member firm of the KPMG global organization of member firms. The KPMG Valuation Report is attached to this proxy statement/prospectus as Exhibit 99.10. KPMG, assuming K Enter completes the purchase of the Seven Korean Entities, conducted a detailed valuation on K Enter based on DCF method and revenue multiples and proposed a valuation range of $580 million ~$650 million utilizing a discounted cash flow analysis, a forward trading enterprise value to sales multiple analysis, a forward trading enterprise value to EBITDA multiples analysis and a transaction multiple analysis.
Global Star did not engage Samjong KPMG to prepare this valuation report, and neither Global Star nor K Enter nor any of their affiliates has had any material relationship with Samjong KPMG over the last two years. Global Star reviewed the KPMG valuation report and considered it in its analysis setting the valuation. However, because Samjong KPMG was engaged by K Enter, it was not given more weight than any other valuation metric. Given the fact that Samjong KPMG was engaged by K Enter, and the conflict of interest discussed elsewhere, rather than relying on the KPMG valuation analysis, Global Star ultimately obtained a separate fairness opinion from EverEdge Pte Ltd.
The KPMG valuation report was based upon pro forma financial projections for the Seven Korean Entities provided to Global Star for fiscal years 2023 through 2027 (“First K Enter Pro Forma Projections”), assuming that K Enter had consummated the acquisition of the Seven Korean Entities. These original financial projections, are set forth in Annex F. These projections have been updated as discussed below, and the updated projections are included in Annex G. In preparing its valuation report, Samjong KPMG assumed that the financial information and projections, estimates and assumptions provided by K Enter were complete and accurate. The financial projections contained in Annex G are based on the assumption that K Enter acquired the Six Korean Entities and the Business Combination closed on or before March 31, 2024, which did not occur. Accordingly, the delay in K Enter’s acquisition of the Six Korean Entities and the closing of the Business Combination beyond March 31, 2024, will reduce PubCo’s projected revenues for 2024, but is not expected to have a materially adverse impact on PubCo’s revenues for the fiscal years 2025 through 2028.
The discounted cash flow analyses provided by KPMG Samjong Accounting Corp were based on the 5-year business plans from 2023 to 2027 of K Enter Holdings and its six potential subsidiary companies, as follows:
For the discounted cash flow analysis, KPMG applied the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) of approximately 11.2%, based on market date including market capitalization, equity risk premiums and market volatility, as of December 31, 2022, of U.S. publicly traded peer companies engaging in similar businesses to K Enter Holdings and its 6 potential subsidiary companies, including AMC Entertainment Holdings Inc, Chicken Soup for the Soul Entertainment Inc, Fox Corp, Lions Gate Entertainment Corp, Madison Square Garden Entertainment Corp, Netflix Inc, Paramount Global, Liberty Media Corp - Liberty SiriusXM, the Walt Disney Co, Warner Bros Discovery Inc, Warner Music Group Corp and Cinedigm Corp. The equity value of K Enter Holdings has been estimated within a range from USD 587 million to USD 715 million.
For the peer trading multiple analysis, KPMG collected both actual and projected financial data, including annual revenues, net debts and market capitalizations, of the above-listed U.S. publicly traded peer companies, from global databases including Capital IQ and Bloomberg, to estimate the forward trading multiples in 2023 and 2025. For the peer transaction multiple analysis, KPMG collected actual financial data, including annual revenues, net debts, market capitalizations and offering data, for the IPO transactions of the U.S. publicly traded companies from January 1, 2018, to January 3, 2023.
On April 5, 2023, the videoconference took place, with CEO/Chairman Anthony Ang and other members of Global Star (Shan Cui, Nicholas Khoo, Jukka Rannila, Argon Lam, Yang Kan Chong, Stephen Drew and Hai Chwee Chew), and representatives of K Enter, led by Chairman Choi, Mr. Dale Lee, CEO, and other representatives of K Enter (Young Jae Lee, Chae Yeon Kim, Yang Jae Kim and Ted Kim). During the videoconference, K Enter’s management team provided further color around K Enter’s product and business development progress, which, at the time, included acquisition of six entertainment focused operating companies in Korea. They also answered Global Star’s questions related to K Enter’s financials and projected financing needs. There was no discussion of valuation during this meeting, although the parties agreed to expect a term sheet from Global Star to K Enter sometime in early April 2023, with Global Star taking note of K Enter’s 2022 pro forma revenue of approximately USD $150 million with $14 million in EBITDA.
Subsequently, on April 9, 2023, Global Star presented its first term sheet proposing various terms and conditions for the merger, including but not limited to a pre-money equity value of $610 million for K Enter based on the pro forma revenue and EBITDA numbers provided by K Enter (including K Enter’s pro forma revenue of $150 million with $14 million in EBITDA), and various other terms and conditions, including:
| ● | K Enter using its best efforts to secure at least $50 million in PIPE financing at $10.00 per share concurrent with the closing of the Business Combination. |
| ● | A purchase of 100,000 shares of common stock of Global Star by K Enter or its designee from the Sponsor, for a total purchase price of $1 million; |
| ● | An extendable mutual exclusivity period of 6 weeks; |
| ● | The expansion of the post-merger board of directors to consist of 6 directors and one additional member to be determined by Global Star; |
| ● | A lock-up period of 6 months after the closing of the transaction for shares held by all K Enter’s existing shareholders; and |
| ● | An equity compensation plan worth of 1% of the combined company’s outstanding shares as of the closing of the transaction for the post-closing management for attracting other talented employees. This 1% later changed to 10% to allow the parties more leeway for attracting talented employees following the Business Combination. |
Given that the valuation proposed by Global Star was generally consistent with the KPMG Valuation Report, K Enter agreed to the $610 million valuation at that time. Global Star and K Enter also agreed that the closing of the business combination would be conditioned upon the acquisitions of controlling equity interest of only Play Company Co., Ltd and Solaire Partners LLC. Although Global Star believed all Seven Operating Companies were important, without these two, the merger will not be successful for several reasons. One, Play Company Co., Ltd was contributing more than 80% of revenue and is the only music related company of the Seven. Two of the Seven Operating Companies did not have any revenue in 2022 so compared to these, having Play Company Co., Ltd under K Enter, Global Star believed was in integral part of creating a successful holding company. Without Solaire Partners LLC, it was all not clear whether all the movie and drama studios will remain confident and be an integral part of K Enter. After all, the movie and drama studios decided to join K Enter largely in part due to Solaire Partner LLC’s reputation and track record. Global Star realized early on, that without these two, K Enter will be a much less attractive company to merge with. This view aligned with K Enter’s decision to acquire 95% of Solaire Partners and 100% of Play Company but only 51% of other six operating companies. This decision was based on both difficulty in reaching agreement with the sellers of the other six companies on valuation and K Enter’s desire to give greater incentives to management of the five other companies to achieve success.
In the event K Enter does not acquire a controlling interest in any of the remaining six companies, then Global Star and K Enter reached a mutual understanding that Global Star and K Enter will adjust to the base consideration to be paid to K Enter in the planned business combination. If such an event occurs K Wave will file a proxy supplement explaining such event. In the event of any material changes occur regarding the planned acquisitions by K Enter occur prior to the Special Meeting, Global Star will promptly circulate updated or supplemental proxy materials to its stockholders.
On April 11, 2023, K Enter’s management and board of directors responded to Global Star’s emailed term sheet, accepting all of its terms and conditions presented by Global Star’s management team, including subjecting most shares to a lock-up period of 6 months post business combination, no minimum cash requirement for closing, and the purchase of at least $1 million worth of founder shares from the sponsor entity to fund the extension and operating cash of Global Star. Both parties executed the non-binding term sheet on April 11, 2023, which included the purchase price of $610 million. The signed term sheet also included a provision for a 1% equity incentive plan and a best-effort basis $50 million PIPE raise, which was mutually agreed upon as K Enter’s responsibility.
K Enter was willing to accept the two new conditions but indicated that it might require more time for preparation and restructuring exercises.
K Enter was introduced by Ted Kim, a managing member of the Sponsor and who is also a director and a co-founder of K Enter and Stephen Drew who is a director of Global Star and a member of the Sponsor and is also a shareholder of K-Enter, the remaining members of the Global Star Board, on the advice of counsel, determined that there was a potential conflict of interest in its consideration of the transaction. The Global Star Board decided to engage EverEdge Pte Ltd on April 12, 2023 to provide a fairness opinion with respect to the transaction. In connection with the fairness opinion, Global Star provided EverEdge with the First K Enter Pro Forma Projections previously provided by K Enter.
On May 3, 2023, the working group, including Global Star, K Enter, K Enter’s legal counsel Loeb & Loeb, LLP, Global Star’s legal counsel Nelson Mullins Riley & Scarborough LLP, K Enter’s accounting advisor KPMG, and Korea side legal counsel Lee & Ko., held an initial virtual kickoff conference call. Following the conference, the working group granted access to K Enter’s virtual data room to facilitate further due diligence.
After reviewing the materials in the virtual data room, which included an investor presentation, business plan, KPMG valuation report, financial and legal due diligence reports, product overviews of would-be subsidiaries, intellectual property rights, extensive Q&As, future expansion plans, a list of competitors and potential partners, barriers to entry, market size, and financial modeling assumptions, Global Star, along with its financial, accounting and legal teams held virtual due diligence calls with K Enter’s management team on a weekly basis starting from May 2023. The due diligence calls covered a range of topics, including the history of K Enter, its growth strategy, how its various entities complement one another, its area of focus, the competitive landscape, organic and add-on growth strategies, and more.
The following topics were the main discussion points during May 2023:
From Global Star, Anthony Ang (CEO), Nicholas Khoo (COO), Stephen Drew (Director) led the inquiries into K Enter. From the K Enter, Young Jae (Dale) Lee (former CEO), Pyeong Ho Choi (Chairman of the Board) mostly provided the responses with the help of some of its officers and directors.
| | ● | How K Enter plans to strengthen its core business of content production and the music related merchandise sales. How the reliance on BTS for merchandizing can be lessened and what it plans to do in case K Enter via Play Company Co., Ltd does not get the exclusive right to sell merchandizing belonging to BTS K Enter management responded as follows: K Enter plans to increase its content production revenue by increasing both the number of productions and the amount of investment going into such production. The four studios have more than enough production capacity but what they lack is the amount of “good capital” available to them. K Enter, along with Solaire as a co-investor, plans to provide reasonable amount of funding for the content production and this will increase both the number of production and the associated revenue from the content production business. For music related merchandising, K Enter management stated that diversifying client base for Play beyond BTS/Korea/Japan will be much more feasible after going public due to enhanced credibility and reputation as a public entity subsidiary and this should allow Play to tap into other foreign stars and K drama/movie stars. K Enter stated that Play Company is actively seeking contracts with other K-pop management companies such as SM Entertainment, possibly obtaining a bulk contract allowing Play to manufacture merchandising for every artist belonging to SM Entertainment. If this were to happen, K Enter stated that it will be an excellent step towards reducing over-reliance on a particular group such as BTS. |
| ● | K Enter’s detailed business plan, mainly focused on content production and music related merchandising sales. |
| ● | How the reliance on BTS for merchandizing can be lessened and what it plans to do in case K Enter via Play Company Co., Ltd does not get the exclusive right to sell merchandizing belong to BTS |
| ● | Of the four movie and drama studios, how did COVID-19 affect these studios during 2020-2022, and how does it plan to produce more content starting in 2023 and whether any of them have a stable contract with world-leading content platforms such as Netflix and Disney in the light of the fact that Netflix announced on May 12, 2023, that it will invest $2.5 billion into Korean content production. |
| | | |
| | | K Enter management responded as follows: During 2020-2022 when Korea was under the influence of Covid-19, most movie studios suffered and even in 2023, the number of movie goers in South Korea was only 50% of pre-covid numbers. But in 2024, the South Korean movie industry is expected to recover to pre-covid levels. |
| ● | How much money (investment) is typically required per average K drama series or movie, how the revenue is recognized and how early in the production the investment needs to be made. |
| | | |
| | | K Enter management responded as follows: The “average” number varies, but it is widely understood among the K content producers that the average cost of producing K drama/movie has increased substantially, and often exceeding $5 million~$10 million. In order to secure revenue from this content, one must invest at the “script” stage, meaning one has to provide certain “commitment” early before production starts and provide the committed capital when called for. For this reason, K Enter stated it is vital that it goes public as soon as possible. |
| ● | Current problems with Korean content production and why there seems to be less money left for the studios in Korea even after they produce world-class content. |
| ● | K Enter’s plan to bring a “paradigm shift” into Korean content production by making a larger capital investment in K content, which typically does not allow any carried or loyalty income, rather than relying solely on outside investors. K Enter plans include funding at least 20-30% of production costs to improve its bottom line significantly once they produce a world-class content. |
| ● | How going public in the U.S. and potential cooperation with U.S.-based tech companies for virtual technology and other AI-related technology will bring a mutual benefit to both the U.S. tech partners and K Enter’s movie and drama studios. |
| | | |
| | | K Enter responded as follows: That the future of content business, whether drama or movie, largely depends on the “technology” side of the business. That is, increasingly, contents that utilizes “virtual” technology tend to reduce both the production cost and time, some say by as much as 30%. One of the biggest K drama hits of 2023 was a drama called “Moving”. It extensively utilized virtual studio technologies and became a global hit. K Enter will actively seek strategic relationship agreements with U.S. based virtual and AI studies for the purpose of cutting both the production time and costs. This will undoubtedly bring mutual benefit to all parties involved. |
| ● | How Solaire Partners LLC, as a content-focused venture capital fund, can source great deal flow for K Enter and together produce world-class content and, once that is achieved, how K Enter’s merchandizing business will be able to utilize the opportunity to generate additional merchandising revenue for these new stars. |
| | | |
| | | K Enter management responded with its opinion that Solaire is already considered one of the best content investors in Korea as it has already invested in over 200 movies and dramas and that Solaire’s network and access to content deal-flow is second to none in Korea. Without this unique access to the best of Korean content focused deal-flow, it is rather difficult to invest in Korea’ best content. Solaire made it clear that they do not plan to sell their existing rights to K Enter but rather engage in “co-investment” with K Enter so K Enter can instantly access some of the best content deal-flows in Korea that took Solaire years to develop. This will reduce the opportunity cost for K Enter and allow K Enter to instantly become a mainstream investor in Korean content production. |
| | ● | Although the term sheet executed by the parties provided for the $610 million valuation proposed by Global Star, K Enter argued that the valuation should be closer to US $1 billion, reflecting its current and future plans and expected organic growth and acquisition opportunities for this new platform. The Global Star team rejected the revision to the valuation in light of the uncertainties about whether these growth objectives could be achieved, in particular the growth plan based on add-on acquisitions. K Enter noted that earlier that year in January of 2023, a competing company “Kakao Entertainment Co. Ltd” announced a capital raise of 1.2 trillion won (about $970 million at that time) based on their 2022 revenue of approximately $1.5 billion with negative EBITDA of approximately $12 million. The two investors who invested the 1.2 trillion won together took about 10% of Kakao Entertainment Co., Ltd. This investment reflected approximately 5x revenue multiple while K Enter’s asking valuation which was about 4x of its 2022 revenue of the Seven Korean Entities. |
| ● | Why K content producing studios have limited IP rights. K Enter explained that when investors provide close to 100% of production cost, the Korean studios that actually produce content do not get to keep much of IP rights. The “Squid Game”, the biggest Netflix hit ever, generates significant merchandising revenues three years after the show ended, but it is Netflix that gets to enjoy the IP rights on all Squid Game related costumes, not the Korean studio that produced the world record hit. K Enter explained that only “good capital” and “timely investment” will bring more IP rights to the actual studios that produce these world class content. |
| ● | K Enter management responded as follows: In order to bring a positive “paradigm shift” to K content production, and music merchandizing sales, K Enter management passionately stated it is vital for it to list on the best stock market in the world. It needs to raise good capital, form partnership with world class technology companies in the space of virtual and AI technology which in turn will reduce both the production cost and time, gain exposure to global audience, and the best way to go about doing this was to merge with a US SPAC quickly. Global Star agreed this is very good strategy indeed. Also, the parties discussed that there is no diversified entertainment company listed in the U.S. with focus on Korean entertainment. |
Between May 2-5, 2023, the Global Star management team (CEO and COO) also visited Seoul to meet with K Enter executives and conduct in-depth due diligence. During this visit, Global Star executives Anthony Ang and Nicholas Khoo met with Xeno Investment Asia, an unaffiliated investor, regarding a possible investment in K Enter. During the visit, both the CEO and COO met with key members of K Enter and the CEOs of its planned subsidiaries. They also conducted on-site inspections and held in-person Q&A sessions during the three-day business trip. Xeno Investment Asia and its affiliate JVC Inc. ultimately invested $5 million in Series A Preferred Stock issued by K Enter.
As a result of this trip and their on-site inspection and meetings, Global Star’s CEO and COO concluded the following:
| ● | K Enter was established on a solid business foundation, spearheaded by the Solaire team, including strong industry veterans Mr. Choi Pyeong Ho and Dale Lee, renowned for their leadership in the Korean media investment sector. The leadership extended to its subsidiaries, with each headed by highly respected professionals in their respective fields. Among them is Mr. Cho Hyung Seok from PLAY Company, recognized as a leader in Korea for specialized planning and filming, content production, product design, and the manufacturing of albums and merchandise for the K-Pop industry, alongside celebrated directors in the K-Drama sector. |
| ● | The strategic plan of K Enter revolves around an integrated model designed to facilitate the identification, financing, production, and monetization of intellectual properties (IPs) within the Korean content industry. The overarching mission is to revolutionize the sector by alleviating the challenges faced by smaller K content creators, who are often overshadowed by larger financial and Over-The-Top (OTT) entities. By democratizing the industry, the K Enter platform aims to empower content creators by providing the necessary resources to fund and distribute their creative works. |
| ● | The Korean content industry has witnessed remarkable growth over the past two decades, thanks to the dedicated support of the Korean government and the business community. This has positioned the sector as a magnet for the nation’s top young talents, contributing to the global K content phenomenon. Today, the industry stands as a highly attractive and investible domain. |
| ● | Global Star should commission an independent valuation by EverEdge Global, a specialized valuation firm based in Singapore, to reinforce our financial assessment rather than rely on the Samjong KPMG report. |
On June 7, 2023, Loeb & Loeb and K Enter shared the first draft of the Merger Agreement which contemplated a two-step structure for the merger. Between June 7 and June 14, 2023, Global Star and Nelson Mullins shared a response draft of the Merger Agreement with K Enter and Loeb & Loeb, clarifying various aspects of the two-step structure of the business combination transaction. This involved a reincorporation merger to change Global Star’s domicile from Delaware to the Cayman Islands, as well as addressing representations and warranties, covenants, closing conditions, and a form of lock-up agreement, registration rights agreement and form of equity incentive plan. Under the terms of the lock-up agreement, the Sponsor, certain shareholders of K Enter and selected persons and entities would agree not to sell their shares of K Wave for a specified period following the closing of the Business Combination Merger. The Lock-Up Agreements will apply to (i) approximately 83% of the PubCo Ordinary Shares, consisting of 2,798,225 Ordinary Shares owned by the Sponsor, Stephen Drew and Nicholas Khoo and 49,424,300 Ordinary Shares owned by the former K Enter stockholders (ii) 498,225 Ordinary Shares underlying warrants held by the Sponsor (approximately 5.14% of the outstanding warrants) and (iii) 49,822 Ordinary Shares underlying rights owned by the Sponsor (approximately 5.14% of the rights). The registration rights agreement grants rights to such persons to require K Wave to register their shares of K Wave during the five year period following the closing of the Business Combination Merger. The joinder agreement provided for the execution of the Merger Agreement upon the formation of K Wave and Merger Sub.
On June 14, 2023, Global Star’s Board met to review the terms of the Business Combination with K Enter and the proposed definitive documentation. The Board also reviewed proposed resolutions to approve the entry into the Merger Agreement. During the meeting, Global Star’s management provided the Board with a comprehensive overview of K Enter’s business and strategy. The results and findings of K Enter’s due diligence process, financial analyses, and comparable transactions backed by the KPMG valuation report, financial and legal due diligence reports, and the fairness opinion secured at Global Star’s request were also presented. Global Star’s board of directors considered the conflicts of interest discussed elsewhere in this proxy statement/prospectus in negotiating and recommending the Business Combination and concluded that the merits of the Business Combination outweighed the potential conflicts and did not materially influence the negotiations with K Enter. The Global Star Board unanimously determined that proceeding with a business combination transaction with K Enter, based on the reviewed documents, was in the best interests of Global Star. The Board authorized Global Star’s officers to execute the merger agreement, leading to the execution of a definitive merger agreement with K Enter on June 15, 2023. On June 15, 2023, Global Star announced the Business Combination.
After signing the Merger Agreement, Global Star and K Enter’s management held a teleconference to finalize the terms of the founder shares purchase. Initially, K Enter was to purchase 100,000 shares of common stock of Global Star from Global Star’s Sponsor for a total purchase price of $1 million. However, Global Star’s management realized that the audit process of the six planned subsidiaries might take longer than expected and requested an increase in the amount of Founder Shares from the Sponsor from $1 million to $1.6 million. After careful consideration and discussion, K Enter accepted this increased amount.
On July 12, 2023, the two companies executed a share purchase agreement, whereby K Enter agreed to purchase 160,000 founder shares from the sponsor entity at $10 per share, totaling $1.6 million. The funds obtained from this transaction will be loaned to Global Star from its Sponsor and used for either extension purposes or as operating cash for Global Star.
On July 13, 2023, PubCo and Merger Sub executed a written joinder agreement to become parties to the Merger Agreement.
In September 2023, the share purchase agreements between K Enter and six of the Seven Korean Entities were revised to amend and clarify the consideration to the paid for the shares constituting the controlling interests of the Seven Korean Entities and the timing of the closings of the share purchase agreements. This amendment was intended to clarify that the steps of the transaction, with K Enter acquiring the companies, followed by the Reincorporation Merger and the Business Combination Merger, as the initial agreement erroneously skipped the first step of the transaction. The amendment further adjusted the language regarding the closing date to add flexibility as to the timing of closing. In addition, the share purchase agreements were amended to eliminate the stockholder approval requirement in order to permit the acquisition of the acquired companies prior to the Global Star shareholder meeting to approve the Business Combination.
On November 6, 2023, K Enter provided to Global Star updated pro forma financial projections for the Seven Korean Entities for fiscal years 2024 through 2028 (“Updated K Enter Pro Forma Projections”), assuming that K Enter had completed the acquisition of each of the Seven Korean Entities, including First Virtual, which was later eliminated from the Business Combination. The Updated K Enter Pro Forma Projections are included as part of Annex G.
The financial results of the Six Korean Entities for the six months ended June 30, 2024 vary significantly from the financial results for 2023 and the financial projections for 2024. We believe that deviation between the financial projections and the performance is due to two key factors. First, (i) the seasonal nature of Play Company’s merchandising business, (ii) unexpected delays in some of the merchandising projects previously planned for the first half of the year, and (iii) slower-than-expected progress in developing new business opportunities in merchandising, among other factors each contributed to the decline in performance. Second, the financial projections upon which the Second Fairness Opinion is based assumed that the Business Combination would occur on or before March 31, 2024. K Enter believes the delay in closing the Business Combination has reduced K Enter’s projected financial results of operations for 2024 because it delayed PubCo’s investment in new media content production, which is expected to drive revenues. The delay in closing the Business Combination is not expected to adversely impact PubCo’s projected results for 2025 or subsequent years, as it does not reflect a long-term trend, but rather a short-term delay in implementing business strategies. The expected reduction in PubCo’s projected revenues does not impact the Second Fairness Opinion dated March 12, 2024 (as updated on April 29, 2024), which was issued as of March 12, 2024. Global Star’s board of directors has determined that the assumptions regarding projections for future years remain reasonable and that no purchase price adjustment is appropriate due to the expected decline in projected 2024 financial results of operations.
The Updated K Enter Pro Forma Projections included adjusted revenue and EBITDA projections for each of the years. In the Updated K Enter Pro Forma Projections, the revenue projections for 2023 were reduced from $189 million to $94 million and reduced in 2024 from $289 million to $191 million. The revenue projections were increased in 2025 from $315 million to $355 million, increased in 2026 from $405 million to $493 million and increased in 2027 from $501 million to $627 million. Based on discussions between Anthony Ang, Nicholas Khoo and Stephen Drew from Global Star and Young Jae Lee and Jun Jung from K-Enter, Mr. Lee and Mr. Jung explained that the higher revenue growth was primarily caused by an increase in the number of titles in drama and film production, a new category of unscripted shows was added, the ability to bring additional management companies and artists that was not expected when the initial projections were prepared and newly-projected expansion into Southeast Asia. We foresee greater revenue in the outer years as we establish a steady portfolio of films and dramas and curate a portfolio of the best content from Asia. K Enter’s primary aim is to uncover intellectual properties (IPs) that possess distinctive Asian characteristics including those from Korea, which will also appeal to a global audience. As we gather more resources, talents, and companies under K Enter, we will be able to leverage a wider network of contacts in the entertainment industry, and acquire even better content, companies and artists. Specifically, the Updated K Enter Pro Forma Projections reflect the opportunity for K Enter to acquire a music-focused management company, signing a “bulk contract” with multiple artists rather than signing individual artists and the acquisition of a “webtoons” company. With respect to the plan to obtain bulk contracts with management companies, on December 30, 2023, Play Company executed a two-year bulk contract with SM Entertainment, Korea’s first music-focused, publicly-traded management company.
K Enter’s vision is to become a leading, diversified, IP-focused entertainment company. Its initial focus of operation is Korea, and as for Korean entertainment, K-POP or K-music is arguably the most robust and fastest-growing sector in “Korean Entertainment.” Without some exposure to K-POP, it is doubtful K Enter will fully emerge as “a leading diversified, IP-focused entertainment company” out of Korea. There are many so-called “medium” or “small” music label management firms in Korea in addition to the “big four” or YG, SM Entertainment, HYBE, and JYP. In order to fulfill our vision, K Enter may consider, in the future, adding music capabilities by buying a controlling stake in one of these smaller music labels or music-focused management companies, which will create obvious synergy with one of the operating companies of K Enter, Play Company. Play Company is already one of the largest K-POP-focused merchandising companies in Korea that do not own any music label or K-POP-focused management companies.
Webtoons, or internet-based cartoons, is another fast-growing entertainment sector in which Korean Entities tend to dominate. Korea’s biggest webtoon company, Naver Webtoon, announced its plan to list on Nasdaq with a $4 billion valuation in the summer 2024. The webtoon market size is expected to be $56 billion~$80 billion by 2030 from about $5 billion in 2022. K Enter will be uniquely positioned to acquire smaller but exceptional webtoon companies based in Korea as there are dozens of webtoon companies that are too small to go public on their own but can be an integral part of K Enter. This is because about 1/3~1/2 of all K dramas or movies are based on webtoon/anime. Having a webtoon-focused subsidiary will create an obvious synergy with other K Enter subsidiaries focused on movies and dramas.
We note, however, that no definitive agreements or prospects have been identified either in music label management, music-focused management company or in Webtoons. K Enter expects PubCo to fund future acquisitions using cash on hand and raising additional proceeds. There are no assurances, however, that the Company will be able to generate the revenue necessary to support its cost structure or that it will be successful in obtaining the level of financing necessary for its operations.
K Enter’s failure to get listed on Nasdaq will significantly lower its chance of acquiring a controlling stake in webtoon companies or other K-POP label or music-focused management companies.
Global Star’s management reviewed these changes and felt they were reasonable adjustments based on changed circumstances that had not been anticipated when the initial projections were prepared. Global Star’s Board reviewed the changes with its management and discussed what this meant for the transaction and the valuation of K Enter. The decrease in revenues in 2023 and 2024 were more than offset by the gains in revenues for 2025, 2026 and 2027, but the Global Star Board felt they were harder to evaluate given their distance in the future. In addition, the Updated K Enter Pro Form Projections included projections for 2028, which were not available previously.
As a result, on December 6, 2023, Global Star decided that given the changes that it should re-engage EverEdge to update its fairness opinion in light of the updates to the K Enter financial projections.
The parties have continued and expect to continue regular discussions in connection with, and to facilitate, the Business Combination.
The First K Enter Forecasts, the Updated K Enter Forecasts, the First K Enter Projections and the Updated K Enter Projections included in this document have been prepared by, and are the responsibility of, K Enter’s management. Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers has not audited, reviewed, examined, compiled nor applied agreed-upon procedures with respect to the accompanying First K Enter Forecasts, the Updated K Enter Forecasts, the First K Enter Projections and the Updated K Enter Projections and, accordingly, Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers does not express an opinion or any other form of assurance with respect thereto. The Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers report included in this proxy statement/prospectus relates to K Enter’s previously issued financial statements. It does not extend to the First K Enter Forecasts and Projections, or the Updated K Enter Forecasts and Projections and should not be read to do so.
The actual results for the Six Korean Entities for the year ended December 31, 2023 were significantly lower than the projected results in the K Enter Forecasts and the Updated K Enter Forecasts. Moreover, the Updated K Enter Forecasts assumed a closing date of March 31, 2024, which did not occur. This delay in closing the Business Combination has prevented PubCo from making investments in new content, and accordingly, PubCo is not expected to achieve the projected results for the year ended December 31, 2024. PubCo does not expect the fact that the Business Combination did not close before March 31, 2024, to impact projected results for 2025 and subsequent years. The Board of Directors of Global Star has determined that no valuation adjustment was necessitated or appropriate based on PubCo’s failure to achieve projected results for 2023 and 2024.
Relationship with First Virtual.
On April 12, 2023, K Enter entered into a share purchase agreement with Sungkwon Kim, King Bear Film LLC (the “FVL SPA”) to acquire a majority equity interest First Virtual, a content virtualization company. The FVL SPA was terminated and amended by the execution of two agreements, namely the Termination and Amendment to the Share Purchase Agreement and the Shareholders Agreement, dated January 31, 2024, by and among Sungkwon Kim, King Bear Film LLC and K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “SPA Amendment”) and the Share Purchase Agreement, dated January 31, 2024, by and among King Bear Film LLC and K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “KB Agreement” and collectively with the SPA Amendment the “New FVL Agreements”). Pursuant to the New FVL Agreements the purchase price for K Enter’s acquisition of a controlling interest in First Virtual was reduced from approximately $20 million to approximately $8 million. K Enter proposed this purchase price reduction to First Virtual in light of the completion by First Virtual of a spin-off of one of its divisions resulting in a reduction in value.
K Enter determined to terminate the share purchase agreement with First Virtual and enter into the New FVL Agreements upon learning that three separate lawsuits were filed in or about December 2023, concerning First Virtual, its principal Sungkwon Kim and certain other parties (collectively referred to as the “Prototype Lawsuits”). In K Enter’s view, these lawsuits, if successful, could significantly impact the business of First Virtual and the viability of a business combination with First Virtual. Two lawsuits are pending in the Chancery Court of the State of Delaware and one lawsuit in Korea. The Delaware lawsuits are entitled: Prototype Lab, Inc., a Korean corporation, Craig Bernard, individually and on behalf of Prototype Groupe, Inc. a Delaware corporation, Culley Bunker, individually and on behalf of Prototype Groupe, Inc. a Delaware corporation v. King Bear Film, LLC, a California limited liability company, John C. Kim a/k/a Chang Kun Kim, SunkKwon Kim and Patrick Han a/k/a Chung Ho Han and assigned Case No. 2023-1257-NAC and In Re Prototype Groupe, Inc., a Delaware corporation and assigned Case No. 2023-1287-NAC. The Korean lawsuit is entitled: Prototype Holding Co. Ltd. and Ju-yeon Lee v. Sungkwon Kim. Due to the pendency of the Prototype Lawsuits, on March 5, 2024, the New FVL Agreements relating to the acquisition of a majority equity stake in First Virtual were terminated pursuant to a Termination Agreement and Re-Purchase Option Agreement, dated March 5, 2024, by and among Sungkwon Kim, King Bear Film LLC and K Enter (the “FVL Termination and Option Agreement”). Pursuant to the FVL Termination and Option Agreement, the New FVL Agreements are terminated and Sungkwon Kim and King Bear Film LLC have an option, for a period of five (5) years, to compel K Enter to acquire a 51% equity interest in First Virtual from Sungkwon Kim and King Bear Film LLC at the then current fair market value provided the Prototype Lawsuits are resolved in a manner acceptable to K Enter, in K Enter’s sole discretion. While the FVL Termination and Option Agreement provides that First Virtual may compel K Enter to acquire First Virtual in the event the Prototype Lawsuits are resolved in a manner satisfactory to K Enter. While no definitive action has been taken to terminate the FVL Termination and Option Agreement, K Enter currently views the acquisition of a controlling interest in First Virtual pursuant to the FVL Termination and Option Agreement as uncertain due to the uncertainty as to the outcome of the Prototype Lawsuits and there can be no assurance that K Enter will acquire a controlling interest in First Virtual pursuant to the FVL Termination and Option Agreement.
Based on the termination of the New FVL Agreement Global Star and K Enter agreed to decrease the base merger consideration Global Star will issue to the stockholders of K Enter in connection with the Business Combination. On March 11, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the First Amendment to Merger Agreement, which among other things decrease the base merger consideration from $610 million to $590 million that Global Star will issue to the stockholders of K Enter. Accordingly, pursuant to the Merger Agreement, as amended PubCo will issue 59,000,000 ordinary shares of PubCo to the stockholders of K Enter in exchange for all of the shares of common stock of K Enter. The $20 million purchase price reduction was based on the original valuation K Enter had placed on First Virtual. After a review of the $20 million reduction of the base merger consideration proposed by K Enter, Global Star confirmed that merger consideration of $590 million was appropriate and fair.
As a result of the termination of the share purchase agreement with First Virtual, Global Star requested an update from EverEdge of its prior fairness opinion. No new projections were provided to EverEdge; rather, EverEdge simply eliminated First Virtual from the projections. On March 1, 2024, EverEdge advised the board of directors of Global Star that the removal of First Virtual was unlikely to have a significant impact on its fairness opinion.
Accordingly, on March 11, 2024, the board of directors of Global Star approved an amendment to the Merger Agreement eliminating First Virtual from the companies included in the Merger Agreement and a purchase price reduction from $610 million to $590 million. On March 12, 2024, EverEdge presented an updated fairness opinion to Global Star’s board of directors confirming that the terms of the Merger Agreement were fair to the public stockholders of Global Star from a financial point of view. On April 29, 2024, EverEdge provided a revised fairness opinion based on the fairness opinion it delivered on March 12, 2024. The financial projections contained in the Second Fairness Opinion are based on the assumption that K Enter acquired the Six Korean Entities and the Business Combination closed on or before March 31, 2024, which did not occur. Accordingly, the delay in K Enter’s acquisition of the Six Korean Entities and the closing of the Business Combination beyond March 31, 2024, will reduce PubCo’s projected revenues for 2024, but is not expected to have a materially adverse impact on PubCo’s revenues for the fiscal years 2025 through 2028.
The financial projections upon which the Second Fairness Opinion is based assumed that the Business Combination would occur on or before March 31, 2024. K Enter believes the delay in closing the Business Combination is expected to reduce New K Enter’s projected financial results of operations for 2024 because it will delay PubCo’s investment in new media content production, which is expected to drive revenues. The delay in closing the Business Combination is not expected to adversely impact PubCo’s projected results for 2025 or subsequent years, as it does not reflect a long-term trend, but rather a short-term delay in implementing business strategies. The expected reduction in PubCo’s projected revenues does not impact the Second Fairness Opinion dated March 12, 2024 (as updated on April 29, 2024), which was issued as of March 12, 2024. Global Star’s board of directors has determined that no purchase price adjustment is appropriate due to the expected decline in projected 2024 financial results of operations.
On June 28, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Second Amendment to Merger Agreement, which extended the outside date for the parties to consummate the closing of the Business Combination from June 22, 2024 to December 22, 2024.
On July 25, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Third Amendment to Merger Agreement, which conditioned the closing of the Business Combination on K Enter’s prior consummation of the acquisition of the controlling equity interests in the Six Korean Entities. Global Star and K Enter entered into the Third Amendment to Merger Agreement because they believe that each of the Six Korean Entities is important to the success of PubCo, as well as to provide greater clarity to investors as to the nature of PubCo’s business following the consummation of the Business Combination. On December 11, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement, which extended the outside date for the parties to consummate the closing of the Business Combination from December 22, 2024 to June 22, 2025.
As of January 3, 2025, K Enter completed the acquisitions of the controlling equity interests of each of the Six Korean Entities.
Following K Enter’s acquisition of the controlling equity intrests of The Lamp, Apieitda, Bidangil and Anseilen, our objective is to support them both managerially and financially to ensure their success. Given the unique nature of the content business, where much depends on key creators like the CEO or director, there was a risk that essential creators, the owners of the company we were acquiring, might simply leave after we acquired their company. We believe that motivating these individuals is paramount. K Enter acquired a 51% equity interest in the production companies based on the strategy that having the creative personnel retain 49%, a significant stake in their business, would better motivate the production resources and align K Enter’s success with their success. This is an established practice in the local market. Aligning economic interests with the owner/creators, was our primary objective in implementing this arrangement, which we believe will lead to greater success.
The Global Star Board of Directors’ Reasons for the Approval of the Business Combination
The decision-making process regarding the transaction with K Enter was designed to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the proposal. The Board of Directors of Global Star engaged in extensive consultations with Global Star management and sought advice from its legal counsel, considering their expertise and experience. Multiple factors were carefully considered and assessed, with no specific relative weights assigned to any particular factor, thus ensuring a well-rounded decision-making process.
In order to reach a well-informed determination, the Board of Directors of Global Star engaged in detailed discussions concerning the results of management’s due diligence activities. These activities encompassed the following:
| ● | Regular Communication: To gain a deep understanding of the formation of K Enter, its business model, and the popularity of K-Content and Korea’s media industry, regular weekly calls were conducted between management and the Board as soon as K Enter became a viable target in early April 2023. These discussions provided valuable insights into K Enter’s business potential and projected financial performance. |
| ● | Comprehensive Examination: A diligent examination was undertaken, covering various aspects such as business, accounting, legal, tax, insurance, and operational considerations. This thorough analysis also shed light on the growth potential of the K-content sector and its market comparable, enabling the Board of Global Star to better assess the transaction’s viability. |
| ● | Financial and Valuation Analyses: The Board of Directors reviewed the Fairness Opinion, which determined that the consideration to be paid in the Business Combination was fair to the shareholders of Global Star from a financial point of view. |
The Board carefully evaluated multiple critical factors that supported its decision to proceed with the Merger Agreement and related transactions, including but not limited to:
| ● | Global Cultural Mainstream Rise: K-Content has experienced a significant increase in its worldwide cultural influence since its introduction to global markets in the early 2000s. The widespread adoption of K-Content across diverse categories is a testament to its emergence and status as a prominent global cultural phenomenon. The burgeoning interest in content and intellectual property (IP) creation and distribution from South Korea is experiencing a remarkable upsurge. According to research firm Media Partners Asia, South Korea is the single largest producer of successful shows in Asia. It is also the largest producer of hit series globally for Netflix outside of the United States. Netflix reported that more than 60% of its customers watched a South Korean show in 2022. |
In fact, according to a study by London and L.A.-based consultancy Ampere Analysis, South Korea rivals the United States in New Scripted Shows’ Global Internet Popularity. In 2022, 32 U.S. titles ranked in a top 100 of most globally popular new scripted TV shows released that year. 30 South Korean series made the same Top 100. This is even more surprising given that the United States produced some 360 new scripted shows, while South Korea produced only 140, meaning a much higher proportion of South Korean produced shows were in the top 100 list.
| ● | Strong Investment interest: The success of K Content has attracted international investments on top of strong local support by the South Korean government and domestic private sector players. Separately, Reuters also reported on April 24, 2023 that Netflix has just announced that it will spend $2.5 billion over the next four years in the country to fund more productions and work with local South Korean organizations to groom talents. According to Media Partners Asia. following Netflix’s lead, some of the world’s largest media businesses and streaming services such as Disney+, Apple TV+ and Amazon.com (Prime) are scrambling for deals that would step up their investment in the country. |
| ● | Value Chain Integration: The competitive landscape in global content markets has evolved, highlighting the importance of integrated capabilities as a crucial success factor. Major global players, such as Netflix, Disney, Paramount, CJ ENM, and Kakao, have actively pursued funding or acquisition of independent studios to enhance their internal value chains. |
| | ● | K Enter’s Comprehensive Capabilities: Upon completion of the business combination, K Enter will possess a harmonized ensemble of content, investment firms, content production studios, and content merchandise production. K Enter is in the process of developing virtual tech capabilities. This integration covers all core aspects of the content value chain, ensuring that K Enter is well placed as a competitive player and marking a significant milestone in the history of the South Korean media and content industry. |
| ● | Top-Tier Creative Talents: K Enter following the closing of its planned acquisition of the Six Korean Entities will possess an extensive pool of commercially successful and critically acclaimed producers, directors, and writers for films and TV series. The popularity of its content offerings across various categories and distribution outlets underscores its ability to attract and retain top-tier creative talents. |
| ● | IP-Based Business Model: K Enter strategically integrates content investment, production, and merchandising capabilities to create a risk-managed, IP-based business model. This approach provides structured downside protections as a production studio and potential upsides as an IP rights holder, ensuring a balanced and sustainable business model. |
| ● | Robust Financial Performance and Growth Potential: Upon the completion of K Enter’s acquisition of Play Company, K Enter will have a solid revenue base and be profitable. It has both short-term and long-term plans to maximize synergies and growth potential through content coverage and value chain expansion. |
| ● | World-Class Leadership Team: K Enter comprises a management, operational, and administrative team dedicated to supporting its proposed subsidiaries’ core businesses. The experienced management team possesses proven expertise in content investment, business strategy, and corporate finance, ensuring effective leadership and operational excellence. |
| ● | Strong Barriers to Entry: As one of the first K Content companies to be listed on NASDAQ, K Enter has secured an advantage based on a differentiated business model with value chain integration and unique IPs, exceptional talents, and strong growth pipeline. |
While evaluating the Business Combination, the Board acknowledged various uncertainties, risks, and potential negative factors, including but not limited to:
| ● | Future Financial Performance: The risk that future financial performance may not meet expectations due to factors within or beyond Global Star’s control, including industry disruptions, economic cycles and macroeconomic factors. The potential impact of these factors on the transaction’s outcome should be carefully considered. |
| ● | Potential for Growth not Achieved: The risk that the anticipated benefits of the Business Combination, such as K Enter’s future movie production performance, may not be fully realized or may take longer than expected. Close monitoring and effective management of these potential risks are necessary. |
| ● | Liquidation of Global Star: In the event that the Business Combination fails, there may be risks and costs to the business, potentially diverting management focus and resources from other opportunities and leading to the expiration of rights and liquidation of Global Star. However, K Enter’s purchase of USD 1.6 million shares of Global Star helps mitigate this risk. |
| ● | Stockholder Vote: The risk that stockholders may not provide the necessary votes to approve the Business Combination. This risk should be carefully considered in light of potential implications for the transaction. |
| ● | Closing Conditions: Where the subject deal does not require minimum closing cash, a more successful completion of the Business Combination may depend on raising funds from Pre-PIPE and PIPE investors. K Enter has committed to taking primary responsibility for raising funds, and Global Star will play a supporting role. |
| ● | Litigation: There is a possibility of legal challenges to the Business Combination, which could result in an adverse judgment preventing its consummation. Proper legal analysis and contingency planning are crucial in mitigating potential legal risks. |
| ● | Listing Risks: The challenges associated with preparing K Enter, a private entity, for the applicable disclosure and listing requirements as a publicly traded company on the Nasdaq. While the Board considered this risk, it did not find it to be a significant impediment to the consummation of the Business Combination. |
| ● | Other Risks: Various additional risks associated with the Business Combination, the business of GSA, and the business of K Enter are described in detail under “Risk Factors.” A comprehensive review of these risk factors is important to gain a holistic understanding of the potential risks involved. |
| | ● | In addition to the above, the Board considered the inherent conflicts of interest in the transaction, specifically that certain officers and directors of the Company and affiliates of the Sponsor collectively own shares of common stock of K Enter. Ted Kim, the manager of the Sponsor and a co-founder and director of K Enter, owns 19,564 shares or 10.12% of the shares of common stock of K Enter based on the shares of K Enter to be issued and outstanding immediately prior to the closing of the Business Combination through his ownership and control of Global Fund LLC, which owns 12,000 shares, and Lodestar USA, Inc., which owns 7,564 shares. Further, Global Star officers and directors collectively own shares of common stock of K Enter representing approximately 8,537 shares or 4.3% of the outstanding shares of K Enter common stock based on the shares of K Enter to be issued and outstanding immediately prior to the closing of the Business Combination. Specifically, Stephen Drew owns 6,000 shares of K Enter common stock, Yang Kan Chong owns 1,337 shares of K Enter common stock, Jukka Rannila, beneficially through Assai OY, owns 600 shares of K Enter common stock. Nicholas Aaron Khoo, the Company’s Chief Operating Officer, owns 600 shares of K Enter common stock, prior to the closing of the Business Combination. All of such investments could expire worthless if a business combination is not consummated; and |
| | ● | Global Star’s board of directors considered these conflicts of interest in negotiating and recommending the Business Combination and concluded that the merits of the Business Combination outweighed the potential conflicts and did not materially influence the negotiations with K Enter. In making this determination, Global Star’s board of directors also considered the fairness opinion obtained from Everedge Pte Ltd. |
When reviewing the information provided in this document, it is essential to exercise caution and consider the factors discussed under “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements.”
Opinion of Global Star’s Financial Advisor
Global Star initially engaged EverEdge Pte. Ltd. (“EverEdge”) on April 12, 2023 to act as its financial advisor in connection with the Business Combination and to render an opinion as to whether the Acquisition Merger is fair to the public stockholders of Global Star from a financial point of view. EverEdge delivered the first fairness opinion on June 9, 2023 (the “First Fairness Opinion”). Global Star re-engaged EverEdge to update the Fairness Opinion since (i) the Seven Korean Entities had failed to achieve their original projections in 2023 and (ii) First Virtual Lab Inc. had been withdrawn from the group of the Seven Korean Entities to be acquired by K Enter with a reduction in the Merger Consideration from $610 million to $590 million. EverEdge delivered its updated fairness opinion (the “Second Fairness Opinion”) to Global Star on March 12, 2024, as revised on April 29, 2024. On April 29, 2024 EverEdge revised its March 12, 2024 fairness opinion and delivered the same, as revised, to Global Star. These revisions consisted of (i) adjustments to reflect the elimination of First Virtual from the Business Combination, (ii) the reduction of the Merger Consideration from $610 million to $590 million due to the elimination of First Virtual from the Business Combination and (iii) adding detail regarding how the comparable companies were selected for purposes of the Second Fairness Opinion. The First Fairness Opinion and the Second Fairness Opinion are incorporated by reference in their entireties into this proxy statement, and the analyses accompanying each, respectively, are attached as Annex F and Annex G.
First Fairness Opinion by EverEdge
Pursuant to the engagement proposal dated April 12, 2023, EverEdge was engaged by Global Star to act as its financial advisor in connection with the business combination involving Global Star and K Enter, to evaluate the proposed transaction with K Enter (the “Business Combination”). As part of this engagement, Global Star requested that EverEdge evaluate the facts of the Business Combination and provide an opinion as to whether the purchase consideration of US$610 million (the “Transaction Consideration”) for 100% of the outstanding equity and equity equivalents of K Enter (including its acquisition/merger targets, including options, warrants or other securities that have the right to acquire or convert into equity securities of K Enter Holdings Inc.), is fair to the public stockholders of Global Star from a financial point of view.
The full text of the First Fairness Opinion, which sets forth, among other things, the procedures followed, assumptions made, matters considered, and qualifications and limitations on the scope of review undertaken in rendering its opinion is attached as Annex F and is incorporated by reference in its entirety into this proxy statement. EverEdge’s opinion was addressed to, and provided for the information and benefit of, the relevant officers in Global Star in connection with their evaluation of the Proposed Transaction. The opinion does not constitute a recommendation to the relevant officers in Global Star or to any other persons in respect of the Proposed Transaction, including as to how any holder of Global Star’s shares should vote or act in respect of the Proposed Transaction. EverEdge’s opinion does not address the relative merits of the Proposed Transaction as compared to other business or financial strategies that might be available to Global Star, nor does it address the underlying business decision of Global Star to engage in the Proposed Transaction.
In connection with rendering the First Fairness Opinion, EverEdge performed the necessary analyses, giving consideration, to the following information:
| ● | The financial terms and conditions of the non-binding Letter of Intent (the “Original Agreement”) dated April 11, 2023, between Global Star and K Enter Holdings Inc.; |
| | ● | The K Enter Pro Forma Projections provided by the management of K Enter Holdings Inc. (“K Enter Forecasts”), which are included in pages F-12 through F-19 of Annex F; |
| ● | Corporate Presentation Decks of K Enter Holdings Inc. prepared by KPMG Samjong Accounting Corp. (“KPMG”); |
| ● | K Enter Holdings Inc. corporate structure documents including the Articles of Incorporation dated January 4, 2023 and List of Shareholders as of April 28, 2023; |
| ● | Other available public information (i.e., various equity analyst reports, annual reports, and public information about comparable companies), information available from the virtual data room and relevant market data from knowledge databases such as FactSet; |
| ● | Confirmation with Management on key assumptions around discount rate, industry EV/Revenue and EV/EBITDA multiples, and working capital and found them to be reasonable based on industry research; |
| ● | Comparable statistics for companies in segments of the Film entertainment and production industry as well as the Gaming/Webtoons/OTT Platforms industry. |
For purposes of its analysis and opinion, EverEdge assumed and relied upon the accuracy and completeness of the financial and other information publicly available, and all of the information supplied or otherwise made available to, discussed with, or reviewed by EverEdge, without any independent verification of such information (and assumed no responsibility or liability for any independent verification of such information), and further relied upon the assurances of the management of Global Star that they were not aware of any facts or circumstances that would make such information inaccurate or misleading. With respect to the K Enter Forecasts, EverEdge assumed that they were reasonably prepared on bases reflecting the best currently available estimates and good faith judgments of the management of K Enter as to its future financial performance. EverEdge expressed no view as to the K Enter Forecasts nor the assumptions on which they were based.
For purposes of its analysis and opinion, EverEdge assumed, in all respects material to its analysis, that the representations and warranties of each party contained in the Original Agreement were true and correct, that each party would perform all of the covenants and agreements required to be performed by it under the Original Agreement and that all conditions to the consummation of the Proposed Transaction would be satisfied without waiver or modification thereof. EverEdge further assumed, in all respects material to its analysis, that all governmental, regulatory, or other consents, approvals or releases necessary for the consummation of the Proposed Transaction would be obtained without any delay, limitation, restriction or condition that would have an adverse effect on the consummation of the Proposed Transaction or reduce the contemplated benefits to Global Star or Global Star’s equity holders (including holders of options, warrants, and other convertible securities).
EverEdge did not conduct a physical inspection of the properties nor facilities of K Enter. EverEdge did not evaluate the solvency or fair value of K Enter under any state or federal laws relating to bankruptcy, insolvency, or similar matters. EverEdge’s opinion is necessarily based upon information made available to EverEdge as of April 20, 2023 and financial, economic, market, and other conditions as they existed and as could be evaluated as of that date. Subsequent developments may affect EverEdge’s opinion and EverEdge does not have any obligation to update, revise, or reaffirm its opinion.
EverEdge was not asked to pass upon, and expressed no opinion with respect to, any matter other than the fairness of the Transaction Consideration to the public equity holders (including holders of options, warrants, and other convertible securities) of Global Star’s shares, from a financial point of view. EverEdge did not express any view on, and its opinion does not address, the fairness of the Proposed Transaction to creditors or other constituencies of Global Star, nor as to the fairness of the amount or nature of any compensation to be paid or payable to any of the officers, directors, or employees of K Enter, or any class of such persons, whether relative to the Proposed Transaction or otherwise. EverEdge was not asked to, nor did it express any view on, and its opinion does not address, any other term or aspect of the Original Agreement or the Transaction Consideration, including, without limitation, the structure or form of the Proposed Transaction, or any term or aspect of any other agreements or instruments contemplated by the Original Agreement or entered into or amended in connection with the Original Agreement.
EverEdge’s opinion does not address the relative merits of the Proposed Transaction as compared to other business or financial strategies that might be available to Global Star, nor does it address the underlying business decision of Global Star to engage in the Proposed Transaction. EverEdge has assumed the accuracy and completeness of assessments by Global Star and its advisors with respect to legal, regulatory, accounting, and tax matters. The credit, financial, and stock markets have been experiencing unusual volatility and EverEdge expressed no opinion or view as to any potential effects of such volatility on the parties or the Proposed Transaction.
Set forth below is a summary of the material financial analyses reviewed by EverEdge with the management of Global Star on May 16, 2023 in connection with rendering its opinion. The following summary, however, does not purport to be a complete description of the analyses performed by EverEdge. The order of the analyses described and the results of these analyses do not represent relative importance or weight given to these analyses by EverEdge. Except as otherwise noted, the following quantitative information, to the extent that it is based on market data, is based on market data that existed on or before April 20, 2023, and is not necessarily indicative of current nor future market conditions.
Summary of EverEdge’s Financial Analysis of K Enter
The valuation of the financial adequacy of the Transaction Consideration is carried out on a stand-alone basis using different valuation methods. The implied equity value of K Enter is calculated as at the date of valuation of December 31, 2022.
The discounted cash flow (“DCF”) method is of key importance in the context of EverEdge’s valuation. The valuation considerations are supplemented by the application of market-based methods based on the trading multiples of comparable companies (Guideline Public Traded Companies Method) and prices paid in past transactions (Guideline Transaction Method). The implied equity value resulting from the DCF method, and from the respective market-based valuations is then compared with the Transaction Consideration. Valuations based on trading and transaction multiples are performed to cross-check against the DCF valuation.
The following provides an overview of the valuation methods used:
Income Approach - Discounted Cash Flow Analysis Method
In the DCF method, the value of K Enter is derived by discounting the expected future free cash flows with the appropriate weighted average cost of capital (“WACC”) at the defined date of valuation. The application of the DCF method to determine enterprise value is the preferred method used by industry practitioners.
EverEdge performed a DCF analysis to calculate the implied enterprise value (and resulting equity value) of K Enter Holdings Inc., utilizing management estimates of the unlevered, after-tax free cash flows that K Enter is expected to generate over the five-year period from FY 2023 to FY 2027 (“Explicit Period”) based on the K Enter Forecasts, approved by the management of K Enter.
For purposes of its discounted cash flow analyses, unlevered free cash flow is defined as net income after tax, plus depreciation and amortization expenses, plus after-tax interest expenses, less capital expenditures, less working capital investments, and plus/(less) other non-cash expenses/(gains).
The proportion of cash flow that relates to the time after the explicit period into perpetuity is reflected as the terminal value (“TV”). EverEdge calculated the terminal value of K Enter using the Gordon Growth Model by applying a stable growth rate of 5.1% to estimate the terminal year unlevered free cash flow reflected in the K Enter Forecasts, for a business in a steady state of growth under the premise of a going concern.
Discounting the unlevered, after-tax free cashflows for the explicit period, as well as the calculated terminal value with a time weighted WACC of 13.8%, in a range between 13.6% to 14.1% from FY2023 to FY2027, gives the present value of free cash flow to firm (“FCFF”). The sum of these present-valued free cash flow to firm results in the enterprise value as at the defined date of valuation. The time weighted WACC is determined based on EverEdge’s determination of the capital structure and company specific risk profile of K Enter, in conjunction with industry and economic indicators as of the defined date of valuation.
In a final step to derive the equity value from the enterprise value, non-operating assets (mainly cash and cash equivalents) as of December 31, 2022 are added to the enterprise value, and total financial debt and debt equivalents (mainly interest-bearing short-term and long-term financial debt) as of December 31, 2022 are deducted from the enterprise value. This results in the equity value of K Enter as of the defined date of valuation.
The results of the calculations are as follows:
| DCF Method (KRW ‘million) | | Downside
(WACC +50 bp) | | | Base | | | Upside
(WACC -50 bp) | |
| Net Present Value of FCFF over Forecast Period | | | 142,926 | | | | 147,175 | | | | 151,603 | |
| Net Present Value of Terminal Value | | | 544,833 | | | | 633,114 | | | | 746,200 | |
| Total Enterprise Value at Date of Valuation | | | 687,759 | | | | 780,289 | | | | 897,803 | |
| Add: Operating Assets at Date of Valuation | | | 36,827 | | | | 36,827 | | | | 36,827 | |
| Less: Total Financial Debt at Date of Valuation | | | (16,047 | ) | | | (16,047 | ) | | | (16,047 | ) |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (KRW ‘m) | | | 708,539 | | | | 801,069 | | | | 918,583 | |
| KRW/USD at Date of Valuation | | | 1,261.9 | | | | 1,261.9 | | | | 1,261.9 | |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (USD ‘m) | | | 561.5 | | | | 634.8 | | | | 727.9 | |
EverEdge’s determination of equity value using the DCF method is a median value of USD 634.8 million, in a value range between USD 561.5 million and USD 727.9 million based on a change in WACC by ±50 basis points.
Market Approach – Guideline Public Traded Companies (GPTC) Method
The valuation based on forward trading multiples is used to cross-check the DCF valuation. The GPTC Method is a market indicator used to value a business, based on trading multiples derived from publicly traded companies that are similar to the target company. The significance of the forward trading multiples valuation may be limited as both the business model of K Enter and the specific situation of the comparable companies may differ. EverEdge reviewed and compared certain financial information of K Enter to corresponding trading multiples and financial ratios for the following selected publicly traded comparable companies in selected segments of the Film entertainment and production industry as well as the Gaming/Webtoons/OTT Platforms industry (referred to in this section as the “Comparable Companies”):
Comparable Companies (Film & Entertainment): United States
| | ● | AMC Entertainment Holdings Inc. | | ● | Netflix, Inc. |
| | ● | Fox Corporation | | ● | Paramount Global |
| | ● | Lions Gate Entertainment | | ● | Liberty Media Corp. |
| | ● | Madison Square Garden Entertainment Corp. | | ● | Walt Disney Company |
| | ● | Warner Music Group Corp. | | ● | Warner Bros. Discovery, Inc. |
Comparable Companies (Direct Film & Drama Production): South Korea
| | ● | ContentreeJoongAng Corp. | | ● | Astory Co., Ltd |
| | ● | KX Innovation Co., Ltd | | ● | Chorokbaem Media Co., Ltd |
| | ● | Wysiwyg Studios Co., Ltd | | ● | Next Entertainment World Co., Ltd |
| | ● | SHOWBOX Corp. | | | |
Comparable Companies (CGI / VFX): South Korea and United States
| | ● | Dexter Studios Co., Ltd | | ● | Autodesk, Inc. |
Comparable Companies (DVD and Merchandise): South Korea
Comparable Companies (Gaming / Webtoons / OTT Platforms): South Korea
| | ● | Kakao Corp. | | ● | Barunson Entertainment & Arts Corp. |
| | ● | Kakao Entertainment Co., Ltd (Private) | | ● | DoubleDown Interactive Co., Ltd |
| | ● | Incross Co., Ltd | | ● | Com2us Corporation |
Although none of the Comparable Companies listed above are directly comparable to K Enter, EverEdge selected these companies based on its professional judgment due to similar operating industries with business characteristics that, for purposes of its analysis, EverEdge considered as close proxies the business characteristics of K Enter for the business lines presented in the K Enter Forecasts.
For each of the Comparable Companies identified above, the Enterprise Value-to-EBITDA (EV/EBITDA) multiple as well as an Enterprise-to-Revenue (EV/Revenue) multiple were selected as the comparable valuation metrics to determine the implied enterprise value of K Enter, as reflected in the most recent public filings made by the Comparable Companies and consensus estimates obtained from publicly available equity research analysts’ projections made available by FactSet as of the date of valuation.
Based on the list of identified Comparable Companies, EverEdge has derived an average EV/EBITDA multiple of 16.5x, in a range between 14.7x and 19.6x, and an average EV/Revenue multiple of 3.2x, in a range between 2.5x and 3.7x. K Enter’s implied enterprise value under this method is computed by applying the derived trading multiples to the FY2025 EBITDA and FY2023 Revenue forecasts, and discounted commensurately over the relevant time horizon to the defined date of valuation.
Certain valuation adjustments were also applied to determine the adjusted enterprise value. A discount to trading multiples adjustment of 20.4% is applied to account for both the lack of marketability as well as the unique risk profile of K Enter relative to the publicly traded Comparable Companies.
As the trading multiples derived from Comparable Companies have generally factored in a discount for lack of control to reflect the fair value of a minority stake in a publicly traded company, a control premium on 27.4% was also applied to adjust the enterprise value from a minority stake perspective of the GPTC method to an enterprise value on a controlling basis.
Lastly, non-operating assets (mainly cash and cash equivalents) as of December 31, 2022 are added, and total financial debt and debt equivalents (mainly interest-bearing short-term and long-term financial debt) as of December 31, 2022 are deducted to derive the equity value from the enterprise value.
The results of the calculations are as follows:
| EV/EBITDA Multiples (KRW ‘million) | | 25th
Percentile | | | Median | | | 75th
Percentile | |
| FY 2025 EBITDA | | | 69,465 | | | | 69,465 | | | | 69,465 | |
| Unadjusted EV/EBITDA Multiple | | | 14.7 | x | | | 16.5 | x | | | 19.6 | x |
| Minus: Discount to Trading Multiples (%) | | | (20.4 | %) | | | (20.4 | %) | | | (20.4 | %) |
| Adjusted EV/EBITDA Multiple | | | 11.7 | x | | | 13.2 | x | | | 15.6 | x |
| Enterprise Value on a Non-Controlling, Non-Marketable Basis | | | 811,710 | | | | 913,530 | | | | 1,086,079 | |
| Add: Control Premium (%) | | | 27.4 | % | | | 27.4 | % | | | 27.4 | % |
| Control Premium | | | 222,408 | | | | 250,307 | | | | 297,586 | |
| Enterprise Value on a Controlling, Non-Marketable Basis | | | 1,034,118 | | | | 1,163,837 | | | | 1,383,665 | |
| WACC (%) | | | 13.8 | % | | | 13.8 | % | | | 13.8 | % |
| Discount Factor | | | 0.72 | | | | 0.72 | | | | 0.72 | |
| Enterprise Value at Date of Valuation | | | 746,489 | | | | 840,128 | | | | 998,813 | |
| Add: Operating Assets at Date of Valuation | | | 36,827 | | | | 36,827 | | | | 36,827 | |
| Less: Total Financial Debt at Date of Valuation | | | (16,047 | ) | | | (16,047 | ) | | | (16,047 | ) |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (KRW ‘m) | | | 767,269 | | | | 860,908 | | | | 1,019,593 | |
| KRW/USD at Date of Valuation | | | 1,261.9 | | | | 1,261.9 | | | | 1,261.9 | |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (USD ‘m) | | | 608.0 | | | | 682.2 | | | | 808.0 | |
EverEdge’s determination of equity value using the forward trading FY2025 EV/EBITDA multiples under the GPTC method results in a median equity value of USD 682.2 million, in a value range between USD 608.0 million and USD 808.0 million.
| EV/Revenue Multiples (KRW ‘million) | | 25th
Percentile | | | Median | | | 75th
Percentile | |
| FY 2023 Revenue | | | 250,563 | | | | 250,563 | | | | 250,563 | |
| Unadjusted EV/Revenue Multiple | | | 2.5 | x | | | 3.2 | x | | | 3.7 | x |
| Minus: Discount to Trading Multiples (%) | | | (20.40 | %) | | | (20.40 | %) | | | (20.40 | %) |
| Adjusted EV/Revenue Multiple | | | 2.0 | x | | | 2.5 | x | | | 2.9 | x |
| Enterprise Value on a Non-Controlling, Non-Marketable Basis | | | 490,912 | | | | 631,608 | | | | 737,437 | |
| Add: Control Premium (%) | | | 27.4 | % | | | 27.4 | % | | | 27.4 | % |
| Control Premium | | | 134,510 | | | | 173,061 | | | | 202,058 | |
| Enterprise Value on a Controlling, Non-Marketable Basis | | | 625,422 | | | | 804,669 | | | | 939,495 | |
| WACC (%) | | | 14.1 | % | | | 14.1 | % | | | 14.1 | % |
| Discount Factor | | | 0.94 | | | | 0.94 | | | | 0.94 | |
| Enterprise Value at Date of Valuation | | | 585,600 | | | | 753,435 | | | | 879,676 | |
| Add: Operating Assets at Date of Valuation | | | 36,827 | | | | 36,827 | | | | 36,827 | |
| Less: Total Financial Debt at Date of Valuation | | | (16,047 | ) | | | (16,047 | ) | | | (16,047 | ) |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (KRW ‘m) | | | 606,380 | | | | 774,215 | | | | 900,456 | |
| KRW/USD at Date of Valuation | | | 1,261.9 | | | | 1,261.9 | | | | 1,261.9 | |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (USD ‘m) | | | 480.5 | | | | 613.5 | | | | 713.5 | |
EverEdge’s determination of equity value using the forward trading FY2023 EV/Revenue multiples under the GPTC method results in a median equity value of USD 613.5 million, in a value range between USD 480.5 million and USD 713.5 million.
Market Approach – Guideline Transaction Method (GTM)
EverEdge also used the Guideline Transaction Method (GTM) as a third valuation methodology, to calculate the implied enterprise value (and resulting equity value) of K Enter, by analyzing comparable transactions in the marketplace.
EverEdge relied on identifying relevant transactions that are similar to K Enter in terms of industry, size, growth prospects, and other relevant characteristics. K Enter’s implied enterprise value (and resulting equity value) under this method was computed by multiplying the FY2025 EBITDA by the transaction EV/EBITDA multiple, then discounted commensurately over the forecast period to the defined date of valuation.
The results of the calculations are as follows:
| Transaction Multiples (KRW ‘million) | | 25th
Percentile | | | Median | | | 75th
Percentile | |
| FY 2025 EBITDA | | | 69,465 | | | | 69,465 | | | | 69,465 | |
| Transaction EV/EBITDA Multiple | | | 14.3 | x | | | 14.8 | x | | | 15.3 | x |
| Undiscounted Enterprise Value | | | 993,356 | | | | 1,028,089 | | | | 1,062,822 | |
| WACC (%) | | | 13.8 | % | | | 13.8 | % | | | 13.8 | % |
| Discount Factor | | | 0.72 | | | | 0.72 | | | | 0.72 | |
| Enterprise Value at Date of Valuation | | | 717,064 | | | | 742,137 | | | | 767,209 | |
| Add: Operating Assets at Date of Valuation | | | 36,827 | | | | 36,827 | | | | 36,827 | |
| Less: Total Financial Debt at Date of Valuation | | | (16,047 | ) | | | (16,047 | ) | | | (16,047 | ) |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (KRW ‘m) | | | 737,844 | | | | 762,917 | | | | 787,989 | |
| KRW/USD at Date of Valuation | | | 1,261.9 | | | | 1,261.9 | | | | 1,261.9 | |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (USD ‘m) | | | 584.7 | | | | 604.6 | | | | 624.4 | |
Conclusion
Based on its analyses and value considerations as well as the results presented, in the First Fairness Opinion, EverEdge considered the Transaction Consideration of US$610 million to be fair to the public stockholders of Global Star from a financial point of view. This conclusion is based on the following considerations:
| | 1. | The Transaction Consideration is supported by the DCF valuation. |
| | 2. | The Transaction Consideration is within the value range resulting from the application of trading and transaction multiples. |
Implied Equity Value of Target (US$ ‘m)
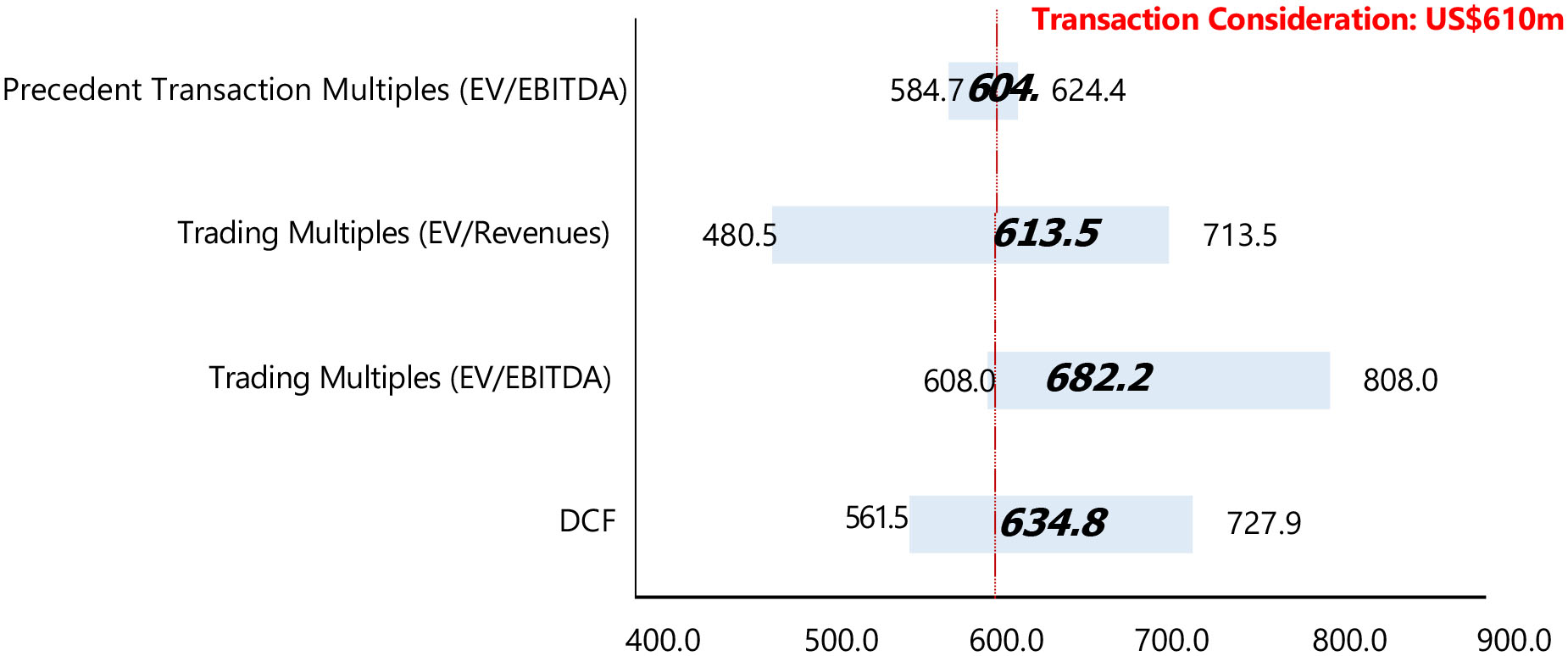
Miscellaneous
The foregoing summary of certain financial analyses does not purport to be a complete description of the analyses or data presented by EverEdge. In connection with the evaluation of the Proposed Transaction by Global Star, EverEdge performed a variety of financial and comparative analyses for purposes of rendering its opinion. The preparation of a fairness opinion is a complex process and is not necessarily susceptible to partial analysis or summary descriptions. Selecting portions of the analyses or of the summary described above, without considering the analyses as a whole, may create an incomplete view of the processes underlying EverEdge’s opinion. In arriving at its fairness determination, EverEdge considered the results of all the analyses and did not draw, in isolation, conclusions from or with regard to any one analysis or factor considered by it for purposes of its opinion. Rather, EverEdge made its determination as to fairness on the basis of its experience and professional judgment after considering the results of all the analyses. In addition, EverEdge may have given certain analyses and factors more or less weight than others and may have deemed certain assumptions more or less probable than others. As a result, the range of valuations resulting from any particular analysis or combination of analyses described above should not be taken to be the view of EverEdge with respect to the actual value of K Enter. Further, EverEdge’s analyses involve complex considerations and judgments concerning financial and operating characteristics and other factors that could affect the acquisition, public trading or other values of the companies used, including judgments and assumptions with regard to industry performance, general business, economic, market and financial conditions and other matters, many of which are beyond the control of Global Star or its advisors.
EverEdge prepared these analyses for the purpose of providing an opinion to the relevant officers in Global Star as to the fairness of the Transaction Consideration to the public equity holders(including holders of options, warrants, and other convertible securities) of Global Star, from a financial point of view. These analyses do not purport to be appraisals or to necessarily reflect the prices at which the business or securities may be sold at. Any estimates contained in these analyses are not necessarily indicative of actual future results, which may be significantly more or less favorable than those suggested by such estimates. Accordingly, estimates used in, and the results derived from, EverEdge’s analyses are inherently subject to substantial uncertainty, and EverEdge assumes no responsibility if future results are materially different from those forecasted in such estimates.
The K Enter Projections used by EverEdge for the First Fairness Opinion are set forth in pages F-12 through F-19 of Annex F to this proxy statement.
Supplemental Information: Calculation of consolidated unlevered free cash flows for the Target
| Fiscal Year | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Calendar | | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | | 31-Dec-27 | | | | 31-Dec-28 | |
| PlayCompany CFO | | | | 11,952 | | | | 16,561 | | | | 23,844 | | | | 32,728 | | | | 37,332 | |
| The Lamp CFO | | | | 481 | | | | 1,572 | | | | 3,127 | | | | 7,336 | | | | 11,049 | |
| Bidangil CFO | | | | 2,545 | | | | 772 | | | | 3,144 | | | | 5,275 | | | | 6,152 | |
| Apeitda CFO | | | | (302 | ) | | | 2,080 | | | | 5,762 | | | | 7,291 | | | | 14,307 | |
| Studio Anseilen CFO | | | | (10,294 | ) | | | (6,356 | ) | | | 2,734 | | | | 13,261 | | | | 21,711 | |
| Solaire Partners CFO | | | | 12 | | | | 2,773 | | | | 7,000 | | | | 11,990 | | | | 21,874 | |
| FVL CFO | | | | 163 | | | | 540 | | | | 2,051 | | | | 2,525 | | | | 2,646 | |
| K-Enter Drama Team CFO | | | | 60 | | | | 1,257 | | | | 1,560 | | | | 2,526 | | | | 3,837 | |
| Consolidated Cash Flow from Operations (CFO) | | | | 4,617 | | | | 19,199 | | | | 49,223 | | | | 82,931 | | | | 118,908 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| PlayCompany CFI | | | | (1,506 | ) | | | (1,606 | ) | | | (1,741 | ) | | | (1,819 | ) | | | (1,875 | ) |
| The Lamp CFI | | | | (51 | ) | | | (51 | ) | | | (52 | ) | | | (53 | ) | | | (54 | ) |
| Bidangil CFI | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Apeitda CFI | | | | (46 | ) | | | (47 | ) | | | (48 | ) | | | (48 | ) | | | (49 | ) |
| Studio Anseilen CFI | | | | (235 | ) | | | (238 | ) | | | (243 | ) | | | (247 | ) | | | (252 | ) |
| Solaire Partners CFI | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| FVL CFI | | | | (2 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (3 | ) |
| K-Enter Drama Team CFI | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Consolidated Cash Flow from Investments (CFI) | | | | (1,839 | ) | | | (1,945 | ) | | | (2,087 | ) | | | (2,171 | ) | | | (2,232 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Consolidated Unlevered Free Cash Flows to Firm | | | | 2,778 | | | | 17,253 | | | | 47,135 | | | | 80,761 | | | | 116,676 | |
Supplemental Information: Market Approach – Overview of Comparable Companies
| General Information | | | | | | | | | Profitability | | | Valuation Multiples | |
| Company Name | | Country | | | Market Cap
(KRW mil.) | | | Annual Revenue
(KRW mil.) | | | Gross
Profit Margin | | | | | | | | | | |
| ContentreeJoongAng corp. | | South Korea | | | | 320,332 | | | | 852,051 | | | | 12.4 | % | | | 13.2 | % | | | (8.6 | %) | | | 2.0 | x |
| KX Innovation Co., Ltd. | | South Korea | | | | 230,307 | | | | 326,266 | | | | 41.6 | % | | | 31.5 | % | | | 24.3 | % | | | 1.2 | x |
| Wysiwyg Studios Co., Ltd. | | South Korea | | | | 497,752 | | | | 186,345 | | | | 4.8 | % | | | (6.4 | %) | | | (13.7 | %) | | | 2.3 | x |
| SHOWBOX Corp. | | South Korea | | | | 187,914 | | | | 56,684 | | | | 9.3 | % | | | 69.8 | % | | | (5.6 | %) | | | 3.4 | x |
| Astory Co., Ltd. | | South Korea | | | | 124,115 | | | | 71,680 | | | | 21.2 | % | | | 12.8 | % | | | 12.0 | % | | | 2.2 | x |
| Next Entertainment World Co., Ltd. | | South Korea | | | | 123,345 | | | | 155,617 | | | | 22.2 | % | | | 6.9 | % | | | 4.7 | % | | | 1.4 | x |
| Dexter Studios Co., Ltd. | | South Korea | | | | 183,219 | | | | 65,906 | | | | 9.5 | % | | | 5.4 | % | | | (3.8 | %) | | | 2.2 | x |
| Kakao Corp. | | South Korea | | | | 22,447,047 | | | | 7,106,837 | | | | 54.6 | % | | | 16.2 | % | | | 8.2 | % | | | 3.2 | x |
| Incross Co.,Ltd. | | South Korea | | | | 132,927 | | | | 53,308 | | | | 52.4 | % | | | 39.4 | % | | | 36.8 | % | | | 1.0 | x |
| AfreecaTV Co., Ltd. | | South Korea | | | | 766,701 | | | | 314,977 | | | | 55.9 | % | | | 31.5 | % | | | 26.2 | % | | | 1.3 | x |
| Barunson Entertainment & Arts Corp. | | South Korea | | | | 51,959 | | | | 26,033 | | | | 15.0 | % | | | (25.9 | %) | | | (28.3 | %) | | | 2.9 | x |
| AMC Entertainment Holdings, Inc. Class A | | United States | | | | 1,701,802 | | | | 3,911 | | | | 18.1 | % | | | 0.2 | % | | | (9.9 | %) | | | 2.1 | x |
| Fox Corporation Class B | | United States | | | | 17,942,482 | | | | 14,913 | | | | 32.3 | % | | | 21.3 | % | | | 18.5 | % | | | 1.3 | x |
| Lions Gate Entertainment Corp Class A | | United States | | | | 2,585,406 | | | | 3,855 | | | | 35.0 | % | | | 48.3 | % | | | 0.5 | % | | | 1.5 | x |
| Madison Square Garden Entertainment Corp. | | United States | | | | 1,873,989 | | | | 851 | | | | 34.2 | % | | | 21.6 | % | | | 13.0 | % | | | 2.8 | x |
| Liberty Media Corp. Series C Liberty SiriusXM | | United States | | | | 34,418,910 | | | | 9,003 | | | | 47.3 | % | | | 28.9 | % | | | 22.1 | % | | | 6.0 | x |
| Walt Disney Company | | United States | | | | 218,876,515 | | | | 88,454 | | | | 27.2 | % | | | 16.0 | % | | | 9.9 | % | | | 2.5 | x |
| Warner Bros. Discovery, Inc. Series A | | United States | | | | 32,876,907 | | | | 33,817 | | | | 18.2 | % | | | 14.4 | % | | | (6.9 | %) | | | 1.6 | x |
| Warner Music Group Corp. Class A | | United States | | | | 22,041,707 | | | | 6,037 | | | | 41.9 | % | | | 19.6 | % | | | 14.1 | % | | | 3.4 | x |
| Average | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2.4 | x |
| Median | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2.2 | x |
| 30th Percentile (Low) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 1.6 | x |
| 70th Percentile (High) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2.8 | x |
Supplemental Information: Market Approach – Overview of Comparable Companies (Continued)
General Information | | | | | | | | | Profitability | | | Valuation Multiples | |
| Company Name | | Country | | | Market Cap
(KRW mil.) | | | EBITDA
(KRW mil.) | | | Gross
Profit Margin | | | EBITDA
Margin | | | EBIT Margin | | | EV/EBITDA | |
| ContentreeJoongAng corp. | | South Korea | | | | 320,332 | | | | 112,674 | | | | 12.4 | % | | | 13.2 | % | | | (8.6 | %) | | | 12.4 | x |
| SHOWBOX Corp. | | South Korea | | | | 187,914 | | | | 39,563 | | | | 9.3 | % | | | 69.8 | % | | | (5.6 | %) | | | 7.6 | x |
| Astory Co., Ltd. | | South Korea | | | | 124,115 | | | | 9,199 | | | | 21.2 | % | | | 12.8 | % | | | 12.0 | % | | | 27.7 | x |
| Dexter Studios Co., Ltd. | | South Korea | | | | 183,219 | | | | 3,583 | | | | 9.5 | % | | | 5.4 | % | | | (3.8 | %) | | | 15.1 | x |
| Autodesk, Inc. | | United States | | | | 60,240,185 | | | | 1,140 | | | | 89.5 | % | | | 23.1 | % | | | 20.1 | % | | | 39.7 | x |
| Kakao Corp. | | South Korea | | | | 22,447,047 | | | | 1,149,008 | | | | 54.6 | % | | | 16.2 | % | | | 8.2 | % | | | 21.9 | x |
| AMC Entertainment Holdings, Inc. Class A | | United States | | | | 1,701,802 | | | | 9 | | | | 18.1 | % | | | 0.2 | % | | | (9.9 | %) | | | 14.6 | x |
| Fox Corporation Class B | | United States | | | | 17,942,482 | | | | 3,175 | | | | 32.3 | % | | | 21.3 | % | | | 18.5 | % | | | 6.1 | x |
| Madison Square Garden Entertainment Corp. | | United States | | | | 1,873,989 | | | | 184 | | | | 34.2 | % | | | 21.6 | % | | | 13.0 | % | | | 11.6 | x |
| Netflix, Inc. | | United States | | | | 267,637,788 | | | | 19,996 | | | | 39.4 | % | | | 63.2 | % | | | 17.8 | % | | | 10.3 | x |
| Liberty Media Corp. Series C Liberty SiriusXM | | United States | | | | 34,418,910 | | | | 2,598 | | | | 47.3 | % | | | 28.9 | % | | | 22.1 | % | | | 29.2 | x |
| Walt Disney Company | | United States | | | | 218,876,515 | | | | 14,113 | | | | 27.2 | % | | | 16.0 | % | | | 9.9 | % | | | 15.3 | x |
| Warner Bros. Discovery, Inc. Series A | | United States | | | | 32,876,907 | | | | 4,867 | | | | 18.2 | % | | | 14.4 | % | | | (6.9 | %) | | | 9.9 | x |
| Warner Music Group Corp. Class A | | United States | | | | 22,041,707 | | | | 1,182 | | | | 41.9 | % | | | 19.6 | % | | | 14.1 | % | | | 17.4 | x |
| Average | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 16.4 | x |
| Median | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 14.6 | x |
| 30th Percentile (Low) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 10.6 | x |
| 70th Percentile (High) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 17.0 | x |
Supplemental Information: Market Approach – Overview of Comparable Precedent Transactions
| General Information | | | | | Profitability | | | Valuation Multiples | |
| Date | | Target | | Country | | Industry | | Deal Value
(USD mil.) | | | Enterprise
Value (USD mil.) | | | EBITDA
(USD mil.) | | | EV/EBITDA | |
| 3-Jan-2022 | | Warner Music Group Corp. | | United States | | Music Entertainment | | | 900 | | | | 25,514 | | | | 1,017 | | | | 25.1 | x |
| 22-Mar-2021 | | Paramount Global | | United States | | Broadcasting / Media / Entertainment | | | 750 | | | | 73,884 | | | | 5,157 | | | | 14.3 | x |
| 25-Jan-2021 | | AMC Networks Inc. | | United States | | Media / Entertainment | | | 994 | | | | 4,477 | | | | 705 | | | | 6.4 | x |
| Average | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 15.3 | x |
| Median | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 14.3 | x |
The issuance of EverEdge’s First Fairness Opinion was approved by an opinion committee of EverEdge.
Pursuant to the terms of EverEdge’s engagement letter with Global Star, EverEdge was entitled to receive a fee of SG$29,500. Global Star has also agreed to reimburse EverEdge for any reasonable and documented out-of-pocket expenses (including any travel or search costs) and to indemnify EverEdge for certain liabilities arising out of its engagement.
Global Star engaged EverEdge to act as a supplier of the fairness opinion based on EverEdge’s qualifications, experience, and reputation. EverEdge is a global advisory and transaction firm specializing in intangible assets and is regularly engaged in business valuation practices.
Second Fairness Opinion by Everedge
EverEdge Pte. Ltd. (“EverEdge”) subsequently was re-engaged by Global Star Acquisition Inc. (the “SPAC”), to act as its financial advisor in connection with the business combination involving Global Star and K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “Target”), to evaluate the proposed merger transaction (the “New Proposed Transaction”). As part of this engagement, Global Star requested that EverEdge evaluate the facts of the New Proposed Transaction in light of the revised projections presented by K-Enter and provide an opinion as to whether the purchase consideration of US$590 million (the “Transaction Consideration”) for 100% of the outstanding equity and equity equivalents of K Enter (including its acquisition/merger targets, including options, warrants or other securities that have the right to acquire or convert into equity securities of K Enter), is fair to the public stockholders of Global Star from a financial point of view. Based on the analyses described in Annex G, EverEdge concluded that the Transaction Consideration is fair to the public stockholders of Global Star from a financial point of view.
The full text of EverEdge’s written opinion dated March 12, 2024 as subsequently revised on April 29, 2024, which sets forth, among other things, the procedures followed, assumptions made, matters considered, and qualifications and limitations on the scope of review undertaken in rendering its opinion is incorporated by reference in its entirety into this proxy statement. In addition, the supporting analyses and projections provided by K Enter are described in Annex G. EverEdge’s opinion was addressed to, and provided for the information and benefit of, the relevant officers in Global Star in connection with their evaluation of the New Proposed Transaction. The opinion does not constitute a recommendation to the relevant officers in Global Star or to any other persons in respect of the New Proposed Transaction, including as to how any holder of Global Star’s shares should vote or act in respect of the New Proposed Transaction. The Second Fairness Opinion does not address the relative merits of the New Proposed Transaction as compared to other business or financial strategies that might be available to Global Star, nor does it address the underlying business decision of Global Star to engage in the New Proposed Transaction.
In connection with rendering the Second Fairness Opinion, EverEdge performed the necessary analyses, giving consideration, to the following information:
| ● | The terms and conditions of the Non-Binding Letter of Intent dated 11 April 2023, the Share Purchase Agreement dated 15 June 2023, the Termination Agreement and Re-Purchase Option Agreement dated 5 March 2024, and the First Amendment to Merger Agreement dated 11 March 2024 (collectively referred to as the “New Proposed Transaction Agreements”); |
| | ● | The Updated K Enter Pro Forma Projections provided by the management of K Enter Holdings Inc. (“Revised K Enter Forecasts”); |
| | ● | Corporate Presentation Decks of K Enter prepared by KPMG Samjong Accounting Corp. (“KPMG”); |
| | ● | The following conflicts of interest: Global Star’s Sponsor and officers and directors purchased 2,300,000 shares of GLST Class B Common Stock, which we refer to herein as “Founder Shares,” for an aggregate purchase price of $25,000 and 498,225 Private Units for which they paid an aggregate purchase price of $4,982,250. Specifically: the Sponsor owns 2,798,225 shares of GLST Common Stock; Anthony Ang and Ted Kim beneficially own 1,640,000 shares of GLST Common Stock by virtue of serving as the managing members of the Sponsor, and Mr. Ang also owns 300,000 shares of GLST Common Stock directly; Nicholas Khoo owns 50,000 shares of GLST Common Stock; and Stephen Drew owns 20,000 shares of GLST Common Stock. In addition, on July 12, 2023, the Sponsor sold 160,000 Founder Shares to K Enter for $1,600,000. Thereafter, the Sponsor loaned the $1.6 million to Global Star in exchange for an unsecured, non-interest-bearing promissory note, $1.5 million of which will be converted into 150,000 Global Star Units in connection with the completion of the Business Combination. Stephen Drew, a director of Global Star served as a director of K Enter Holdings, Inc. from January 3, 2023 to April 25, 2023. Furthermore, we noted that other officers and directors of Global Star also hold shares in K Enter, and Global Star has provided full disclosure regarding these relationships and shareholdings as follows: Ted Kim, the manager of the Sponsor and a co-founder and director of K Enter, owns 19,564 shares or 10.12% of the shares of common stock of K Enter based on the shares of K Enter to be issued and outstanding immediately prior to the closing of the Business Combination through his ownership and control of Global Fund LLC, which owns 12,000 shares, and Lodestar USA, Inc., which owns 7,564 shares. Further, Global Star officers and directors collectively own shares of common stock of K Enter representing approximately 8,537 shares or 4.3% of the outstanding shares of K Enter common stock based on the shares of K Enter to be issued and outstanding immediately prior to the closing of the Business Combination. Specifically, Stephen Drew owns 6,000 shares of K Enter common stock, Yang Kan Chong owns 1,337 shares of K Enter common stock, Jukka Rannila, beneficially through Assai OY, owns 600 shares of K Enter common stock. Nicholas Aaron Khoo, the Company’s Chief Operating Officer, owns 600 shares of K Enter common stock, prior to the closing of the Business Combination. All of such investments will expire worthless if a business combination is not consummated; on the other hand, if a business combination is consummated, such investments could earn a positive rate of return on their overall investment in the combined company, even if other holders of Global Star’s common stock experience a negative rate of return. |
| ● | K Enter Holdings Inc. corporate structure documents including the Articles of Incorporation dated 4 January 2023 and List of Shareholders as of 28 April 2023; |
| ● | Other available public information (i.e., various equity analyst reports, annual reports, and public information about comparable companies), information available from the virtual data room and relevant market data from knowledge databases such as FactSet; |
| ● | Confirmation with Management on key assumptions around discount rate, industry EV/Revenue and EV/EBITDA multiples, and working capital and found them to be reasonable based on industry research; |
| ● | Comparable statistics for companies in segments of the Film entertainment and production industry as well as the Gaming/Webtoons/OTT Platforms industry. |
For purposes of its analysis and opinion, EverEdge assumed and relied upon the accuracy and completeness of the financial and other information publicly available, and all of the information supplied or otherwise made available to, discussed with, or reviewed by EverEdge, without any independent verification of such information (and assumed no responsibility or liability for any independent verification of such information), and further relied upon the assurances of the management of Global Star that they were not aware of any facts or circumstances that would make such information inaccurate or misleading. With respect to the K Enter Forecasts, EverEdge assumed that they were reasonably prepared on bases reflecting the best currently available estimates and good faith judgments of the management of K Enter Holdings Inc. as to its future financial performance. EverEdge expressed no view as to the Revised K Enter Forecasts nor the assumptions on which they were based.
For purposes of its analysis and opinion, EverEdge assumed, in all respects material to its analysis, that the representations and warranties of each party contained in the New Proposed Transaction Agreements were true and correct, that each party would perform all of the covenants and agreements required to be performed by it under the New Proposed Transaction Agreements and that all conditions to the consummation of the New Proposed Transaction would be satisfied without waiver or modification thereof. EverEdge further assumed, in all respects material to its analysis, that all governmental, regulatory, or other consents, approvals or releases necessary for the consummation of the New Proposed Transaction would be obtained without any delay, limitation, restriction or condition that would have an adverse effect on the consummation of the New Proposed Transaction or reduce the contemplated benefits to K Enter or K Enter’s equity holders (including holders of options, warrants, and other convertible securities).
EverEdge did not conduct a physical inspection of the properties nor facilities of K Enter. EverEdge did not evaluate the solvency or fair value of K Enter under any state or federal laws relating to bankruptcy, insolvency, or similar matters. The Second Fairness Opinion is necessarily based upon information made available to EverEdge as of 12 March 2024 and financial, economic, market, and other conditions as they existed and as could be evaluated as of that date. Subsequent developments may affect the Second Fairness Opinion and EverEdge does not have any obligation to update, revise, or reaffirm its opinion.
EverEdge was not asked to pass upon, and expressed no opinion with respect to, any matter other than the fairness of the Transaction Consideration to the holders (including holders of options, warrants, and other convertible securities) of the Target’s shares, from a financial point of view. EverEdge did not express any view on, and its opinion does not address, the fairness of the New Proposed Transaction to creditors or other constituencies of Global Star, nor as to the fairness of the amount or nature of any compensation to be paid or payable to any of the officers, directors, or employees of K Enter, or any class of such persons, whether relative to the New Proposed Transaction or otherwise. EverEdge was not asked to, nor did it express any view on, and its opinion does not address, any other term or aspect of the New Proposed Transaction Agreements or the Transaction Consideration, including, without limitation, the structure or form of the New Proposed Transaction, or any term or aspect of any other agreements or instruments contemplated by the New Proposed Transaction Agreements or entered into or amended in connection with the New Proposed Transaction Agreements.
EverEdge’s Second Fairness Opinion does not address the relative merits of the New Proposed Transaction as compared to other business or financial strategies that might be available to Global Star, nor does it address the underlying business decision of Global Star to engage in the New Proposed Transaction. EverEdge has assumed the accuracy and completeness of assessments by Global Star and its advisors with respect to legal, regulatory, accounting, and tax matters. The credit, financial, and stock markets have been experiencing unusual volatility and EverEdge expressed no opinion or view as to any potential effects of such volatility on the parties or the New Proposed Transaction.
Summary of EverEdge’s Financial Analysis of K Enter
The valuation of the financial adequacy of the Transaction Consideration is carried out on a stand-alone basis using different valuation methods. The implied equity value of K Enter is calculated as at the date of valuation of December 31, 2023.
The discounted cash flow (“DCF”) method is of key importance in the context of EverEdge’s valuation. The valuation considerations are supplemented by the application of market-based methods based on the trading multiples of comparable companies (Guideline Public Traded Companies Method) and prices paid in past transactions (Guideline Transaction Method). The implied equity value resulting from the DCF method, and from the respective market-based valuations is then compared with the Transaction Consideration. Valuations based on trading and transaction multiples are performed to cross-check against the DCF valuation.
The following provides an overview of the valuation methods used:
Income Approach - Discounted Cash Flow Analysis Method
In the DCF method, the value of K Enter is derived by discounting the expected future free cash flows with the appropriate weighted average cost of capital (“WACC”) at the defined date of valuation. The application of the DCF method to determine enterprise value is the preferred method used by industry practitioners.
EverEdge performed a DCF analysis to calculate the implied enterprise value (and resulting equity value) of K Enter Holdings Inc., utilizing management estimates of the unlevered, after-tax free cash flows that K Enter is expected to generate over the five-year period from FY 2024 to FY 2028 (“Explicit Period”) based on the Revised K Enter Forecasts, approved by the management of K Enter. The performance of K-Enter over the Explicit Period consolidates the performance of the six Korean Entities and the K Enter Drama team, which forms part of the New Proposed Transaction, under the premise that Global Star will complete the acquisition of all aforementioned entities. While EverEdge assumed that significant synergies among the entities will occur post-transaction that will potentially improve K-Enter’s profitability, no explicit values were assigned thereto in the financial analysis and the computation of unlevered free cash flows given the uncertainties around the estimation of any such potential synergies. The consolidation was performed on a sum-of-the-parts basis.
For purposes of its discounted cash flow analyses, unlevered free cash flow is defined as net income after tax, plus depreciation and amortization expenses, plus after-tax interest expenses, less capital expenditures, less working capital investments, and plus/(less) other non-cash expenses/(gains).
The proportion of cash flow that relates to the time after the Explicit Period into perpetuity is reflected as the terminal value (“TV”). EverEdge calculated the terminal value of K Enter using the Gordon Growth Model by applying a stable growth rate of 4.5% to estimate the terminal year unlevered free cash flow reflected in the K Enter Forecasts, for a business in a steady state of growth under the premise of a going concern.
Discounting the unlevered, after-tax free cashflows for the Explicit Period, as well as the calculated terminal value with a time weighted WACC of 12.6%, in a range between 12.8% to 12.4% from FY2024 to FY2028, gives the present value of free cash flow to firm (“FCFF”). The sum of these present-valued free cash flow to firm results in the enterprise value as at the defined date of valuation. The time-weighted WACC is determined based on EverEdge’s determination of the capital structure and company specific risk profile of K Enter, in conjunction with industry and economic indicators as of the defined date of valuation.
In a final step to derive the equity value from the enterprise value, non-operating assets (mainly cash and cash equivalents) estimated as of December 31, 2023 are added to the enterprise value, and total financial debt and debt equivalents (mainly interest-bearing short-term and long-term financial debt) as of December 31, 2023 are deducted from the enterprise value. This results in the equity value of K Enter as of the defined date of valuation.
The results of the calculations are as follows:
| DCF Method (KRW ‘million) | | Downside
(WACC +50 bp) | | | Base | | | Upside
(WACC -50 bp) | |
| Net Present Value of FCFF over Forecast Period | | | 748,952 | | | | 167,578 | | | | 172,882 | |
| Net Present Value of Terminal Value | | | 162,496 | | | | 878,262 | | | | 1,047,125 | |
| Total Enterprise Value at Date of Valuation | | | 911,448 | | | | 1,045,840 | | | | 1,220,007 | |
| Add:Non- Operating Assets at Date of Valuation | | | 11,053 | | | | 11,053 | | | | 11,053 | |
| Less: Total Financial Debt at Date of Valuation | | | (7,076 | ) | | | (7,076 | ) | | | (7,076 | ) |
| Less: Non-controlling interest | | | (269,273 | ) | | | (269,273 | ) | | | (269,273 | ) |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (KRW ‘m) | | | 646,151 | | | | 780,543 | | | | 954,710 | |
| KRW/USD at Date of Valuation | | | 1,300.4 | | | | 1,300.4 | | | | 1,300.4 | |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (USD ‘m) | | | 496.9 | | | | 600.2 | | | | 734.2 | |
EverEdge’s determination of equity value using the DCF method is a median value of USD 600.2 million, in a value range between USD 496.9 million and USD 734.2 million based on a change in WACC by ±50 basis points.
Market Approach – Guideline Public Traded Companies (GPTC) Method
The valuation based on forward trading multiples is used to cross-check the DCF valuation. The GPTC Method is a market indicator used to value a business, based on trading multiples derived from publicly traded companies that are similar to the target company. The significance of the forward trading multiples valuation may be limited as both the business model of K Enter and the specific situation of the comparable companies may differ. EverEdge reviewed and compared certain information of K Enter (business activity, revenue sources, geography) to the following selected publicly traded comparable companies in selected segments of the Film entertainment and production industry as well as the Gaming/Webtoons/OTT Platforms industry (referred to in this section as the “Comparable Companies”):
Comparable Companies (Film & Entertainment): United States
| | ● | AMC Entertainment Holdings Inc. | | ● | Netflix, Inc. |
| | ● | Fox Corporation | | ● | Paramount Global |
| | ● | Lions Gate Entertainment | | ● | Liberty Media Corp. |
| | ● | Madison Square Garden Entertainment Corp. | | ● | Walt Disney Company |
| | ● | Warner Music Group Corp. | | ● | Warner Bros. Discovery, Inc. |
Comparable Companies (Direct Film & Drama Production): South Korea
| | ● | ContentreeJoongAng Corp. | | ● | Astory Co., Ltd |
| | ● | KX Innovation Co., Ltd | | ● | Chorokbaem Media Co., Ltd* |
| | ● | Wysiwyg Studios Co., Ltd | | ● | Next Entertainment World Co., Ltd |
| | ● | SHOWBOX Corp. | | | |
Comparable Companies (DVD and Merchandise): South Korea
Comparable Companies (Gaming / Webtoons / OTT Platforms): South Korea
| | ● | Kakao Corp. | | ● | Barunson Entertainment & Arts Corp. |
| | ● | Incross Co., Ltd. | | ● | DoubleDown Interactive Co., Ltd* |
| | ● | AfreecaTV Co., Ltd. | | ● | Com2us Corporation |
| * | Certain identified comparable companies have been assessed to be outliers and are subsequently excluded from the analysis. |
Our analysis concentrated on identifying companies with industries closely resembling that of the Target, particularly within the film and/or music production sectors in South Korea or the United States. We emphasize that while none of the Comparable Companies listed above are directly comparable to the Target, EverEdge selected these companies due to the similar operating industries with business characteristics that, for the purposes of its analysis, EverEdge considered as close proxies to the business characteristics of the Target for the business lines presented in the K Enter Forecasts. Despite notable differences in scale and financial standing, these identified companies were deemed relevant for comparison purposes due to their shared industry focus.
Moreover, while the Target may be a newly established entity, several of the Six Korean Entities to be acquired as subsidiaries—specifically Play Company, Bidangil Pictures, The Lamp Pictures, Apeitda and Solaire Partners—each boast, what we believe is, a well-established operational history. Studio Anseilen which was established in 2023, is the most newly established entity. While Studio Anseilen cannot be categorized as having a well-established operational history, its founders, Kyung-su Shin, Jun-Woo Park, Seung-Ho Kim, are 3 of the top Korean executive producers who previously worked for SBS, one of the leading Korean TV broadcasting channels and have shown in the past to have created some of Korea’s most famous dramas such as an adaptation of the webtoons show Taxi Driver. This drama about how a former special forces soldier who delivers revenge for victims of injustice while working for a secret organization that fronts as a taxi company. Taxi Driver was very well received by audiences in Korea and was one of the top 4 most watched dramas in SBS history in its Friday and Saturday drama time slot. We believe the founders of Studia Anseilen, who will continue with the company after the closing of the Business Combination, have the potential to create hit IP content for Studio Anseilen. It is important to also recognize that market capitalization and operating history alone do not necessarily equate direct comparability. Factors such as the industry alignment, business model nuances, geographic focus, and product diversity, which we have considered, also play significant roles in assessing relevance.
Finally we also exercised discretion in excluding companies with negative operating results or exceptionally high valuation multiples deemed outliers, as these factors could potentially distort the integrity of our analysis.
For each of the Comparable Companies identified above, the Enterprise Value-to-EBITDA (EV/EBITDA) multiple as well as an Enterprise-to-Revenue (EV/Revenue) multiple were selected as the comparable valuation metrics to determine the implied enterprise value of K Enter, as reflected in the most recent public filings made by the Comparable Companies and consensus estimates obtained from publicly available equity research analysts’ projections made available by FactSet as of the date of valuation.
Based on the list of identified Comparable Companies, EverEdge has derived an average EV/EBITDA multiple of 16.4x, in a range between 10.6x and 17.0x, and an average EV/Revenue multiple of 2.4x, in a range between 1.6x and 2.8x. To address the company-specific risk profile and size of K Enter in relation to publicly traded Comparable Companies, an additional discount to trading multiples of 20.4% has been applied to both the EV/EBITDA and EV/Revenue multiples. Consequently, the adjusted average EV/EBITDA multiple stands at 13.1x, in a range between 8.4x and 13.5x, while the adjusted average EV/Revenue multiple is 1.9x, in a range between 1.3x to 2.3x.
As a logical continuation of the foregoing analysis, the implied enterprise value of K Enter is determined through the application of adjusted trading multiples to the projected FY2026 EBITDA and FY2026 Revenue figures. This calculation operates on the assumption that the K Enter’s revenue and profitability will exhibit stability from FY2026, a consequence of the business stabilization process occurring post-2023 and the synergistic effects realized among subsidiaries. The valuation methodology employs forward-looking financials representing FY2026 EBITDA and FY2026 Revenue.
As the trading multiples derived from Comparable Companies have generally factored in a discount for lack of control to reflect the fair value of a minority stake in a publicly traded company, a control premium on 26.1% was also applied to adjust the enterprise value from a minority stake perspective of the GPTC method to an enterprise value on a controlling basis.
Subsequently, the resultant forward-looking enterprise values are discounted commensurately with the relevant time horizon, concluding at the defined date of valuation.
In a final step, non-operating assets (mainly cash and cash equivalents) estimated as of 31 December 2023 are added, and total financial debt and debt equivalents (mainly interest-bearing short-term and long-term financial debt) and non-controlling interests as of 31 December 2023 are deducted to derive the equity value from the enterprise value.
The results of the calculations are as follows:
| EV/EBITDA Multiples (KRW ‘million) | | 25th
Percentile | | | Median | | | 75th
Percentile | |
| FY 2026 EBITDA | | | 58,586 | | | | 58,586 | | | | 58,586 | |
| Unadjusted EV/EBITDA Multiple | | | 10.6 | x | | | 16.4 | x | | | 17.0 | x |
| Minus: Discount to Trading Multiples (%) | | | (20.4 | %) | | | (20.4 | %) | | | (20.4 | %) |
| Adjusted EV/EBITDA Multiple | | | 8.4 | x | | | 13.1 | x | | | 13.5 | x |
| Enterprise Value on a Non-Controlling, Non-Marketable Basis | | | 492,379 | | | | 765,692 | | | | 790,679 | |
| Add: Control Premium (%) | | | 26.1 | % | | | 26.1 | % | | | 26.1 | % |
| Control Premium | | | 128,511 | | | | 199,846 | | | | 206,367 | |
| Enterprise Value on a Controlling, Non-Marketable Basis | | | 620,891 | | | | 965,537 | | | | 997,046 | |
| WACC (%) | | | 12.6 | % | | | 12.6 | % | | | 12.6 | % |
| Discount Factor | | | 0.74 | | | | 0.74 | | | | 0.74 | |
| Enterprise Value at Date of Valuation | | | 460,642 | | | | 716,337 | | | | 739,714 | |
| Add: Non-Operating Assets at Date of Valuation | | | 11,053 | | | | 11,053 | | | | 11,053 | |
| Less: Total Financial Debt at Date of Valuation | | | (7,076 | ) | | | (7,076 | ) | | | (7,076 | ) |
| Less:Non-controlling Interest | | | (269,273 | ) | | | (269,273 | ) | | | (269,273 | ) |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (KRW ‘m) | | | 195,345 | | | | 451,040 | | | | 474,417 | |
| KRW/USD at Date of Valuation | | | 1,300.4 | | | | 1,300.4 | | | | 1,300.4 | |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (USD ‘m) | | | 150.2 | | | | 346.8 | | | | 364.8 | |
EverEdge’s determination of equity value using the forward trading FY2026 EV/EBITDA multiples under the GPTC method results in a median equity value of USD 346.8 million, in a value range between USD 150.2 million and USD 364.8 million.
| EV/REVENUE Multiples (KRW ‘million) | | 25th
Percentile | | | Median | | | 75th
Percentile | |
| FY 2026 REVENUE | | | 614,805 | | | | 614,805 | | | | 614,805 | |
| Unadjusted EV/Revenue Multiple | | | 1.6 | x | | | 2.4 | x | | | 2.8 | x |
| Minus: Discount to Trading Multiples (%) | | | (20.4 | %) | | | (20.4 | %) | | | (20.4 | %) |
| Adjusted EV/Revenue Multiple | | | 1.3 | x | | | 1.9 | x | | | 2.3 | x |
| Enterprise Value on a Non-Controlling, Non-Marketable Basis | | | 781,854 | | | | 1,170,281 | | | | 1,388,353 | |
| Add: Control Premium (%) | | | 26.1 | % | | | 26.1 | % | | | 26.1 | % |
| Control Premium | | | 204,064 | | | | 305,443 | | | | 362,360 | |
| Enterprise Value on a Controlling, Non-Marketable Basis | | | 985,918 | | | | 1,475,724 | | | | 1,750,714 | |
| WACC (%) | | | 12.6 | % | | | 12.6 | % | | | 12.6 | % |
| Discount Factor | | | 0.74 | | | | 0.74 | | | | 0.74 | |
| Enterprise Value at Date of Valuation | | | 731,475 | | | | 1,094,847 | | | | 1,298,863 | |
| Add: Non-Operating Assets at Date of Valuation | | | 11,053 | | | | 11,053 | | | | 11,053 | |
| Less: Total Financial Debt at Date of Valuation | | | (7,076 | ) | | | (7,076 | ) | | | (7,076 | ) |
| Less: Non-controlling Interest | | | (269,273 | ) | | | (269,273 | ) | | | (269,273 | ) |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (KRW ‘m) | | | 466,161 | | | | 829,551 | | | | 1,033,567 | |
| KRW/USD at Date of Valuation | | | 1,300.4 | | | | 1,300.4 | | | | 1,300.4 | |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (USD ‘m) | | | 358.5 | | | | 637.9 | | | | 794.8 | |
EverEdge’s determination of equity value using the forward trading FY2026 EV/Revenue multiples under the GPTC method results in a median equity value of USD 637.9 million, in a value range between USD 358.5 million and USD 794.8 million.
Market Approach – Guideline Transaction Method (GTM)
EverEdge also used the Guideline Transaction Method (GTM) as a third valuation methodology, to calculate the implied enterprise value (and resulting equity value) of K Enter, by analyzing comparable transactions in the marketplace.
EverEdge relied on identifying relevant transactions that are similar to K Enter in terms of industry, size, growth prospects, and other relevant characteristics. K Enter’s implied enterprise value (and resulting equity value) under this method was computed by multiplying the FY2026 EBITDA by the transaction EV/EBITDA multiple, then discounted commensurately over the forecast period to the defined date of valuation.
The results of the calculations are as follows:
| Transaction Multiples (KRW ‘million) | | 25th
Percentile | | | Median | | | 75th
Percentile | |
| FY 2026 EBITDA | | | 58,586 | | | | 58,586 | | | | 58,586 | |
| Transaction EV/EBITDA Multiple | | | 14.3 | x | | | 14.8 | x | | | 15.3 | x |
| Undiscounted Enterprise Value | | | 837,781 | | | | 867,074 | | | | 896,367 | |
| WACC (%) | | | 12.6 | % | | | 12.6 | % | | | 12.6 | % |
| Discount Factor | | | 0.74 | | | | 0.74 | | | | 0.74 | |
| Enterprise Value at Date of Valuation | | | 621,554 | | | | 643,287 | | | | 665,020 | |
| Add: Non-Operating Assets at Date of Valuation | | | 11,053 | | | | 11,053 | | | | 11,053 | |
| Less: Total Financial Debt at Date of Valuation | | | (7,076 | ) | | | (7,076 | ) | | | (7,076 | ) |
| Less: Non-controlling Interest | | | (269,273 | ) | | | (269,273 | ) | | | (269,273 | ) |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (KRW ‘m) | | | 356,258 | | | | 377,990 | | | | 399,723 | |
| KRW/USD at Date of Valuation | | | 1,300.4 | | | | 1,300.4 | | | | 1,300.4 | |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (USD ‘m) | | | 274.0 | | | | 290.7 | | | | 307.4 | |
Conclusion
Based on its analyses and value considerations as well as the results presented, in the Second Fairness Opinion, EverEdge considered the Transaction Consideration of US$590 million to be fair to the public stockholders of Global Star from a financial point of view. This conclusion is based on the following considerations:
| 1. | The significance of the valuation range derived from the Precedent Transaction Multiples approach is deemed minimal due to the limited pool of comparable precedent transactions. |
| 2. | While we assume that significant synergies between subsidiaries will occur post-transaction that will potentially improve Target’s profitability, no explicit values were assigned thereto in the financial analysis. Consequently, the valuation range derived from EV/EBITDA trading multiples is assessed to be understated. |
| 3. | The Transaction Consideration is supported by the DCF valuation. |
| 4. | The Transaction Consideration is within the value range resulting from the application of EV/Revenue trading multiples. |
Implied Equity Value of Target (US$ ‘m)
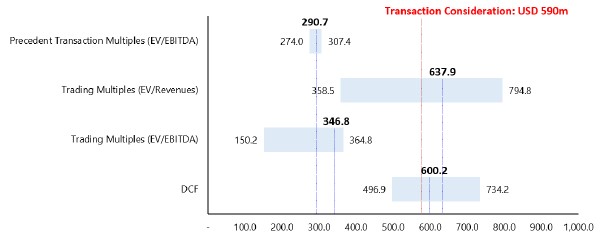
Miscellaneous
The foregoing summary of certain financial analyses does not purport to be a complete description of the analyses or data presented by EverEdge. In connection with the evaluation of the New Proposed Transaction by Global Star, EverEdge performed a variety of financial and comparative analyses for purposes of rendering its opinion. The preparation of a fairness opinion is a complex process and is not necessarily susceptible to partial analysis or summary descriptions. Selecting portions of the analyses or of the summary described above, without considering the analyses as a whole, may create an incomplete view of the processes underlying EverEdge’s opinion. In arriving at its fairness determination, EverEdge considered the results of all the analyses and did not draw, in isolation, conclusions from or with regard to any one analysis or factor considered by it for purposes of its opinion. Rather, EverEdge made its determination as to fairness on the basis of its experience and professional judgment after considering the results of all the analyses. In addition, EverEdge may have given certain analyses and factors more or less weight than others and may have deemed certain assumptions more or less probable than others. As a result, the range of valuations resulting from any particular analysis or combination of analyses described above should not be taken to be the view of EverEdge with respect to the actual value of K Enter. Further, EverEdge’s analyses involve complex considerations and judgments concerning financial and operating characteristics and other factors that could affect the acquisition, public trading or other values of the companies used, including judgments and assumptions with regard to industry performance, general business, economic, market and financial conditions and other matters, many of which are beyond the control of Global Star or its advisors.
EverEdge prepared these analyses for the purpose of providing an opinion to the relevant officers in Global Star as to the fairness to the public stockholders of Global Star, from a financial point of view, of the Transaction Consideration to the public stockholders (including holders of options, warrants, and other convertible securities) of K Enter’s shares. These analyses do not purport to be appraisals or to necessarily reflect the prices at which the business or securities may be sold at. Any estimates contained in these analyses are not necessarily indicative of actual future results, which may be significantly more or less favorable than those suggested by such estimates. Accordingly, estimates used in, and the results derived from, EverEdge’s analyses are inherently subject to substantial uncertainty, and EverEdge assumes no responsibility if future results are materially different from those forecasted in such estimates.
The issuance of the Second Fairness Opinion was approved by an opinion committee of EverEdge.
Pursuant to the terms of EverEdge’s engagement letter with Global Star, EverEdge was entitled to receive a total fee of SG$49,500, which represented an additional SG$20,000 for rendering the Second Fairness Opinion. Global Star has also agreed to reimburse EverEdge for any reasonable and documented out-of-pocket expenses (including any travel or search costs) and to indemnify EverEdge for certain liabilities arising out of its engagement.
Global Star engaged EverEdge to act as a supplier of the Second Fairness Opinion based on EverEdge’s qualifications, experience, and reputation as well as its familiarity with K-Enter due to its issuance of the First Fairness Opinion. EverEdge is a global advisory and transaction firm specializing in intangible assets and is regularly engaged in business valuation practices.
Required Vote
Approval of the Acquisition Merger Proposal requires the affirmative vote of the holders of sixty-five percent (65%) of the outstanding GLST Common Stock as of the record date. Adoption of the Acquisition Merger Proposal is conditioned upon the adoption of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal. It is important for you to note that in the event that either of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal or the Acquisition Merger Proposal is not approved, then Global Star will not consummate the Business Combination.
Recommendation of Global Star’s Board of Directors
After careful consideration, Global Star board of directors determined that the Acquisition Merger forming part of the Business Combination with K Enter is in the best interests of Global Star and its stockholders. On the basis of the foregoing, Global Star board of directors has approved and declared advisable the Business Combination with K Enter and recommends that you vote or give instructions to vote “FOR” the Acquisition Merger Proposal. Global Star’s directors have interests that may be different from, or in addition to your interests as a stockholder. See the section titled “The Acquisition Merger Proposal — Interests of Certain Persons in the Acquisition” in this proxy statement/prospectus for further information.
Supplemental Information: K Enter Forecasts
A summary of the 5-year financial forecasts for the entities contracted to be subsidiaries of K Enter are provided below. All figures shown in these exhibits are presented in KRW millions.
Play Company Co., Ltd.
The financial forecasts for Play Company set forth below mainly consist of: (i) the financial projections for the content merchandising business of Play Company and (ii) the financial projections for the food & beverage business of Play Company’s subsidiary, Play F&B.
(i) The content merchandising business produces and distributes seasonal merchandises (called “titles”) of certain K-Pop artists of whom Play Company has exclusive merchandising rights. The projected growth in revenues assumes an increase in (a) the number of such artists of who it has exclusive merchandising rights and (b) the number of titles per such artist. Specifically, the number of artists and titles is projected to grow from 29 titles for 17 artists in 2024 to 51 titles for 20 artists in 2028. Such artists include certain K-Pop artists contracted with various K-Pop agencies including HYBE (only limited number of artists and titles for HYBE in the projections reflecting adjusted business terms), SM Entertainment, KQ Entertainment and JYP Entertainment. The average selling prices and quantities per title are projected to grow approximately 2% and 3%, respectively. The projected growth in gross profit margins is mainly due to the increasing proportion of merchandising rights with non-HYBE artists, in which Play Company has favorable terms and conditions regarding minimum guarantees and profit sharing terms with each agency.
The HYBE-related “video merchandise” revenues are forecasted to decrease to KRW 9.9 billion in 2024 from KRW 34.5 billion in 2023 in line with the change in the business agreements with HYBE in 2024. The forecasted HYBE-related revenues are expected to gradually increase to KRW 33.7 billion in 2028 in accordance with Play Company’s plan to expand its coverage of projects and artists from HYBE under the current business terms and do not reflect its effort to revert the business terms back to the comprehensive agreement noted previously.
The SM-related “video merchandise” revenues are forecasted to be at a relatively low level of KRW 13.9 billion in 2024 considering it is the first year of the business relationship between Play Company and SM and are expected to grow rapidly to KRW 66.0 billion in 2028 following Play Company’s plan to expand its coverage of projects and artist from SM under the current exclusive business terms.
Other K-Pop agency-related “video merchandise” revenues are forecasted to increase to KRW 82.3 billion in 2028 in accordance with Play Company’s plan to increase the sales volume of video merchandises for other non-HYBE K-Pop artists who Play Company has merchandising rights under existing agreements from the expansion of its distribution networks in Japan, as disclosed at page 45. The forecasted increase in other K-pop agency-related revenues is also in line with Play Company’s plan and effort to secure new merchandising rights for artists with whom Play Company has no prior business relationships. Following its successful engagement with SM, Play Company aims to enter into similar exclusive business relationships with other major K-Pop agencies. Please do note, however, that there are no material agreements, negotiations or discussions for disclosure at this moment for such exclusive business relationships.
Other revenues include revenues from distributing any non-video merchandises which have been marginal until 2023. As contingencies to the expected reduction in the HYBE-related “video merchandise” revenues in 2024, Play Company has been diversifying its merchandise types and lineups to light sticks and other concert-related collectible, merchandises and even non-K Pop merchandise. The forecasted increase in other revenues is in accordance with Play Company’s plan and effort for the sales of such new merchandises for other non-HYBE K-Pop artists, as well as merchandise for famous actors, webtoons, dramas and entertainment shows. Please do note, however, that there are no material agreements, negotiations or discussions for disclosure at this moment in relation to such sales of new merchandises. Other revenues also include a small amount of revenues from filming, editing and designing services which are forecasted to remain at current levels.
(ii) The food & beverage business consists of 4 main brands including “OUR Bakery”, “Kinda Katsu”, “OUR Bagel” and “Golden Chatters”. The projected growth in revenues is mainly according to Play F&B’s plan to increase the number of restaurants (including both directly-managed locations and franchised locations) for these 4 main brands. Specifically, the number of restaurants for these 4 main brands is projected to grow from 21 locations (16 directly-managed and 11 franchised locations) in 2024 to 96 locations (21 directly-managed and 75 franchised locations) in 2028. Revenue per restaurant is projected to remain consistent. The projected growth in gross profit margins assumes the increasing proportion of franchised restaurants, from which Play F&B earns franchising right revenues with very limited costs for providing food supplies to each franchised location.
| Fiscal Year | | 2023
(Forecast) | | | 2023
Actual1 | | | | 2024
(Forecast) | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Calendar | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | | 31-Dec-27 | | | | 31-Dec-28 | |
| PlayCo Revenues | | | 76,804 | | | | 49,772 | | | | | 105,519 | | | | 164,579 | | | | 228,832 | | | | 283,626 | | | | 312,989 | |
| - HYBE-Related Video Merchandise | | | 56,834 | | | | 34,529 | | | | | 9,958 | | | | 15,268 | | | | 21,087 | | | | 26,879 | | | | 33,682 | |
| SM Ent-Related Video Merchandise | | | - | | | | - | | | | | 13,930 | | | | 26,041 | | | | 38,475 | | | | 57,415 | | | | 65,986 | |
| - Other Video Merchandise | | | 11,425 | | | | 12,936 | | | | | 18,057 | | | | 32,404 | | | | 55,093 | | | | 75,008 | | | | 82,335 | |
| - Other Merchandise & Services | | | 8,546 | | | | 2,307 | | | | | 63,574 | | | | 90,867 | | | | 114,177 | | | | 124,324 | | | | 130,986 | |
| PlayF&B Revenues | | | 18,390 | | | | 17,709 | | | | | 21,841 | | | | 26,712 | | | | 33,574 | | | | 39,099 | | | | 44,560 | |
| Total Revenues | | | 95,194 | | | | 67,481 | | | | | 127,361 | | | | 191,291 | | | | 262,405 | | | | 322,725 | | | | 357,548 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | | | | | | 33.8 | % | | | 50.2 | % | | | 37.2 | % | | | 23.0 | % | | | 10.8 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| PlayCo COGS | | | (62,083 | ) | | | 42,787 | | | | | (94,025 | ) | | | (149,760 | ) | | | (205,090 | ) | | | (250,579 | ) | | | (276,478 | ) |
| PlayF&B COGS | | | (18,780 | ) | | | 15,415 | | | | | (19,079 | ) | | | (21,483 | ) | | | (24,781 | ) | | | (27,227 | ) | | | (29,507 | ) |
| Total COGS | | | (80,863 | ) | | | 58,202 | | | | | (113,104 | ) | | | (171,243 | ) | | | (229,871 | ) | | | (277,806 | ) | | | (305,985 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | 14,331 | | | | 9,279 | | | | | 14,256 | | | | 20,048 | | | | 32,534 | | | | 44,919 | | | | 51,564 | |
| GP Margin | | | 15.1 | % | | | 13.8 | % | | | | 11.2 | % | | | 10.5 | % | | | 12.4 | % | | | 13.9 | % | | | 14.4 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| PlayCo SG&A Expenses | | | (2,957 | ) | | | (2,803 | ) | | | | (3,445 | ) | | | (3,694 | ) | | | (3,991 | ) | | | (4,284 | ) | | | (4,598 | ) |
| PlayF&B SG&A Expenses | | | (1,148 | ) | | | (1,146 | ) | | | | (1,423 | ) | | | (1,547 | ) | | | (1,695 | ) | | | (1,841 | ) | | | (1,998 | ) |
| Total SG&A Expenses | | | (4,105 | ) | | | (3,949 | ) | | | | (4,868 | ) | | | (5,241 | ) | | | (5,686 | ) | | | (6,126 | ) | | | (6,596 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | 4.3 | % | | | 5.9 | % | | | | 3.8 | % | | | 2.7 | % | | | 2.2 | % | | | 1.9 | % | | | 1.8 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBITDA | | | 10,226 | | | | 5,330 | | | | | 9,389 | | | | 14,807 | | | | 26,848 | | | | 38,793 | | | | 44,968 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | 10.7 | % | | | 7.9 | % | | | | 7.4 | % | | | 7.7 | % | | | 10.2 | % | | | 12.0 | % | | | 12.6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| PlayCo Depreciation & Amortization Expenses PlayF&B Depreciation & Amortization | | | (188 | ) | | | | | | | | (192 | ) | | | (195 | ) | | | (199 | ) | | | (202 | ) | | | (206 | ) |
| Expenses | | | (1,213 | ) | | | | | | | | (1,314 | ) | | | (1,411 | ) | | | (1,542 | ) | | | (1,617 | ) | | | (1,668 | ) |
| Adjusted for Consolidation | | | (1,303 | ) | | | | | | | | (1,303 | ) | | | (1,303 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (2,705 | ) | | | (3,284 | ) | | | | (2,809 | ) | | | (2,910 | ) | | | (1,741 | ) | | | (1,819 | ) | | | (1,875 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBIT | | | 7,521 | | | | 2,046 | | | | | 6,580 | | | | 11,897 | | | | 25,106 | | | | 36,974 | | | | 43,093 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | 7.9 | % | | | 3.0 | % | | | | 5.2 | % | | | 6.2 | % | | | 9.6 | % | | | 11.5 | % | | | 12.1 | % |
| 1 | This column has been added to reflect actual results of Play Company for the year ended December 31, 2023 as the actual results deviated significantly from projected 2023 results. |
Supplemental Information: K Enter Forecasts (Continued)
The financial forecasts for (1) The LAMP, (2) Bidangil Pictures, (3) Apeitda and (4) Studio Anseilen on the following pages mainly consist of financial projections for the drama and film production businesses, in which The LAMP, Bidangil Pictures, Apeitda and Studio Anseilen produce and distribute dramas and films to global streaming platforms, TV channels and theatres. Projected revenues for 2024 for these companies assumes a closing date of March 31, 2024, which did not occur. The delay in closing beyond this date also delays planned investment in content production, which will adversely impact 2024 revenues.
The projected growth in revenues assumes an increase in the number of dramas and films produced and distributed each year. Specifically, the numbers of dramas and films produced are projected to grow from 9 or 10 dramas and films in 2024 to 15 dramas and 11 films in 2028, collectively for the 4 content production studios.
More precisely, between the years 2024~2027, the following productions are planned.
| Years | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Bidangil: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Film | | | 2 | | | | 2 | | | | 3 | | | | 3 | | | | 3 | |
| Drama | | | 1 | | | | 1 | | | | 1 | | | | 1 | | | | 1 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| The Lamp | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Film | | | 4 | | | | 3 | | | | 2 | | | | 2 | | | | 3 | |
| Drama | | | 1 | | | | 1 | | | | 1 | | | | 2 | | | | 2 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Apeitda | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Film | | | 1 | | | | 2 | | | | 3 | | | | 3 | | | | 3 | |
| Drama | | | | | | | | | | | 1 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Anseillen | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Film | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Drama | | | 2 | | | | 4 | | | | 5 | | | | 5 | | | | 6 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| K Enter Drama Team | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Film | | | | | | | 1 | | | | 1 | | | | 2 | | | | 2 | |
| Drama | | | 2 | | | | 3 | | | | 4 | | | | 5 | | | | 6 | |
The projected growth in gross profit margins assumes an increase in margins for dramas and films sold to global streaming platforms. Specifically, such margins are projected to grow on average 5% in 2024 to 20 - 30% in 2028. Such expected increase in margins for dramas and films sold to global streaming platforms will be attained as the 5 content production studios gain negotiating powers collectively on such platforms.
1. The LAMP Co., Ltd.
| Fiscal Year | | 2023
(Forecast) | | | 2023
Actual1 | | | | 2024
(Forecast) | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Calendar | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | | 31-Dec-27 | | | | 31-Dec-28 | |
| Drama Revenues | | | 4,073 | | | | 463 | | | | | 8,400 | | | | 17,522 | | | | 19,388 | | | | 42,694 | | | | 46,800 | |
| Film Revenues | | | 11,485 | | | | 20,374 | | | | | 16,124 | | | | 16,819 | | | | 25,375 | | | | 27,669 | | | | 45,600 | |
| Total Revenues | | | 15,559 | | | | 20,837 | | | | | 24,524 | | | | 34,341 | | | | 44,763 | | | | 70,363 | | | | 92,400 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | | | | | | 57.6 | % | | | 40.0 | % | | | 30.3 | % | | | 57.2 | % | | | 31.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Drama COGS | | | (3,849 | ) | | | (146 | ) | | | | (7,980 | ) | | | (15,750 | ) | | | (16,500 | ) | | | (34,500 | ) | | | (36,000 | ) |
| Film COGS | | | (10,898 | ) | | | (19,363 | ) | | | | (14,762 | ) | | | (15,270 | ) | | | (22,900 | ) | | | (24,590 | ) | | | (40,560 | ) |
| Total COGS | | | (14,747 | ) | | | (19,509 | ) | | | | (22,742 | ) | | | (31,020 | ) | | | (39,400 | ) | | | (59,090 | ) | | | (76,560 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | 812 | | | | 1,328 | | | | | 1,782 | | | | 3,321 | | | | 5,363 | | | | 11,273 | | | | 15,840 | |
| GP Margin | | | 5.2 | % | | | 6.4 | % | | | | 7.3 | % | | | 9.7 | % | | | 12.0 | % | | | 16.0 | % | | | 17.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total SG&A Expenses | | | (838 | ) | | | (652 | ) | | | | (1,035 | ) | | | (1,105 | ) | | | (1,186 | ) | | | (1,341 | ) | | | (1,479 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | 5.4 | % | | | 3.13 | % | | | | 4.2 | % | | | 3.2 | % | | | 2.7 | % | | | 1.9 | % | | | 1.6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
EBITDA | | | (26 | ) | | | 676 | | | | | 747 | | | | 2,216 | | | | 4,176 | | | | 9,932 | | | | 14,361 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | (0.2 | %) | | | 3.24 | % | | | | 3.0 | % | | | 6.5 | % | | | 9.3 | % | | | 14.1 | % | | | 15.5 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (50 | ) | | | (78 | ) | | | | (51 | ) | | | (51 | ) | | | (52 | ) | | | (53 | ) | | | (54 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
EBIT | | | (75 | ) | | | 598 | | | | | 696 | | | | 2,164 | | | | 4,124 | | | | 9,879 | | | | 14,307 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | (0.5 | %) | | | 2.87 | % | | | | 2.8 | % | | | 6.3 | % | | | 9.2 | % | | | 14.0 | % | | | 15.5 | % |
| 1 | This column has been added to reflect actual results of the Lamp for the year ended December 31, 2023 as the actual results deviated significantly from projected 2023 results. |
2. Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd
| Fiscal Year | | 2023
(Forecast) | | | 2023
Actual1 | | | | 2024
(Forecast) | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Calendar | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | | 31-Dec-27 | | | | 31-Dec-28 | |
| Drama Revenues | | | 9,000 | | | | 7,378 | | | | | 21,000 | | | | 20,460 | | | | 23,100 | | | | 21,347 | | | | 23,400 | |
| Film Revenues | | | 370 | | | | 368 | | | | | 10,700 | | | | 37,440 | | | | 39,024 | | | | 42,900 | | | | 46,800 | |
| Total Revenues | | | 9,370 | | | | 7,746 | | | | | 31,700 | | | | 57,900 | | | | 62,124 | | | | 64,247 | | | | 70,200 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | | | | | | 238.3 | % | | | 82.7 | % | | | 7.3 | % | | | 3.4 | % | | | 9.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Drama COGS | | | (8,100 | ) | | | (7,070 | ) | | | | (18,900 | ) | | | (18,600 | ) | | | (21,000 | ) | | | (17,250 | ) | | | (18,000 | ) |
| Film COGS | | | (345 | ) | | | (19 | ) | | | | (9,520 | ) | | | (34,200 | ) | | | (35,650 | ) | | | (39,270 | ) | | | (42,840 | ) |
| Total COGS | | | (8,445 | ) | | | (7,070 | ) | | | | (28,420 | ) | | | (52,800 | ) | | | (56,650 | ) | | | (56,520 | ) | | | (60,840 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | 924 | | | | 676 | | | | | 3,280 | | | | 5,100 | | | | 5,474 | | | | 7,727 | | | | 9,360 | |
| GP Margin | | | 9.9 | % | | | 8.7 | % | | | | 10.3 | % | | | 8.8 | % | | | 8.8 | % | | | 12.0 | % | | | 13.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total SG&A Expenses | | | (1,063 | ) | | | (693 | ) | | | | (1,072 | ) | | | (1,095 | ) | | | (1,128 | ) | | | (1,156 | ) | | | (1,186 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | 11.3 | % | | | 8.9 | % | | | | 3.4 | % | | | 1.9 | % | | | 1.8 | % | | | 1.8 | % | | | 1.7 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
EBITDA | | | (138 | ) | | | (17 | ) | | | | 2,208 | | | | 4,005 | | | | 4,346 | | | | 6,571 | | | | 8,174 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | (1.5 | %) | | | (0.2 | %) | | | | 7.0 | % | | | 6.9 | % | | | 7.0 | % | | | 10.2 | % | | | 11.6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | - | | | | (66 | ) | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
EBIT | | | (138 | ) | | | (83 | ) | | | | 2,208 | | | | 4,005 | | | | 4,346 | | | | 6,571 | | | | 8,174 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | (1.5 | %) | | | (1.1 | %) | | | | 7.0 | % | | | 6.9 | % | | | 7.0 | % | | | 10.2 | % | | | 11.6 | % |
| 1 | This column has been added to reflect actual results of Bidangil Pictures for the year ended December 31, 2023 as the actual results deviated significantly from projected 2023 results. |
3. Apeitda Co., Ltd
| Fiscal Year | | 2023
(Forecast) | | | 2023
Actual1 | | | | 2024
(Forecast) | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Calendar | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | | 31-Dec-27 | | | | 31-Dec-28 | |
| Drama Revenues | | | | | | | - | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 19,388 | | | | 21,347 | | | | 46,800 | |
| Film Revenues | | | 329 | | | | 90 | | | | | 104 | | | | 38,850 | | | | 37,750 | | | | 41,038 | | | | 44,400 | |
| Total Revenues | | | 329 | | | | 90 | | | | | 104 | | | | 38,850 | | | | 57,138 | | | | 62,384 | | | | 91,200 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | | | | | | (68.4 | %) | | | 373.1 | x | | | 47.1 | % | | | 9.2 | % | | | 46.2 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Drama COGS | | | | | | | - | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (16,500 | ) | | | (17,250 | ) | | | (36,000 | ) |
| Film COGS | | | (1 | ) | | | (26 | ) | | | | (95 | ) | | | (37,000 | ) | | | (33,900 | ) | | | (36,090 | ) | | | (38,280 | ) |
| Total COGS | | | (1 | ) | | | (26 | ) | | | | (95 | ) | | | (37,000 | ) | | | (50,400 | ) | | | (53,340 | ) | | | (74,280 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | 327 | | | | 64 | | | | | 9 | | | | 1,850 | | | | 6,738 | | | | 9,044 | | | | 16,920 | |
| GP Margin | | | 99.6 | % | | | 71.1 | % | | | | 8.5 | % | | | 4.8 | % | | | 11.8 | % | | | 14.5 | % | | | 18.6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total SG&A Expenses | | | (287 | ) | | | (244 | ) | | | | (292 | ) | | | (299 | ) | | | (308 | ) | | | (316 | ) | | | (324 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | | | | | 271 | % | | | | 281.7 | % | | | 0.8 | % | | | 0.5 | % | | | 0.5 | % | | | 0.4 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
EBITDA | | | 40 | | | | (180 | ) | | | | (284 | ) | | | 1,551 | | | | 6,430 | | | | 8,729 | | | | 16,596 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | 12.3 | % | | | (200 | %) | | | | (273.2 | %) | | | 4.0 | % | | | 11.3 | % | | | 14.0 | % | | | 18.2 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (45 | ) | | | (76 | ) | | | | (46 | ) | | | (47 | ) | | | (48 | ) | | | (48 | ) | | | (49 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
EBIT | | | (5 | ) | | | (256 | ) | | | | (330 | ) | | | 1,504 | | | | 6,382 | | | | 8,680 | | | | 16,547 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | (1.4 | %) | | | (284 | %) | | | | (317.4 | %) | | | 3.9 | % | | | 11.2 | % | | | 13.9 | % | | | 18.1 | % |
| 1 | This column has been added to reflect actual results of Apeitda for the year ended December 31, 2023 as the actual results deviated significantly from projected 2023 results. |
4. Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd
| Fiscal Year | | 2023
(Forecast) | | | 2023
Actual1 | | | | 2024
(Forecast) | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Calendar | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | | 31-Dec-27 | | | | 31-Dec-28 | |
| Drama Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | 17,535 | | | | 39,225 | | | | 66,779 | | | | 86,082 | | | | 119,700 | |
| Film Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Revenues | | | - | | | | 0 | | | | | 17,535 | | | | 39,225 | | | | 66,779 | | | | 86,082 | | | | 119,700 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 123.7 | % | | | 70.2 | % | | | 28.9 | % | | | 39.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Drama COGS | | | | | | | | | | | | (16,700 | ) | | | (35,000 | ) | | | (56,353 | ) | | | (69,069 | ) | | | (91,890 | ) |
| Film COGS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total COGS | | | - | | | | 0 | | | | | (16,700 | ) | | | (35,000 | ) | | | (56,353 | ) | | | (69,069 | ) | | | (91,890 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | - | | | | 0 | | | | | 835 | | | | 4,226 | | | | 10,426 | | | | 17,013 | | | | 27,810 | |
| GP Margin | | | 10.3 | % | | | - | | | | | 4.8 | % | | | 10.8 | % | | | 15.6 | % | | | 19.8 | % | | | 23.2 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total SG&A Expenses | | | - | | | | (348 | ) | | | | (1,367 | ) | | | (1,396 | ) | | | (1,436 | ) | | | (1,471 | ) | | | (1,509 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | | | | | - | | | | | 7.8 | % | | | 3.6 | % | | | 2.2 | % | | | 1.7 | % | | | 1.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
EBITDA | | | - | | | | (348 | ) | | | | (532 | ) | | | 2,830 | | | | 8,990 | | | | 15,541 | | | | 26,301 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | | | | | - | | | | | (3.0 | %) | | | 7.2 | % | | | 13.5 | % | | | 18.1 | % | | | 22.0 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | - | | | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
EBIT | | | - | | | | (348 | ) | | | | (532 | ) | | | 2,830 | | | | 8,990 | | | | 15,541 | | | | 26,301 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | | | | | - | | | | | (3.0 | %) | | | 7.2 | % | | | 13.5 | % | | | 18.1 | % | | | 22.0 | % |
| 1 | This column has been added to reflect actual results of Anseilen for the year ended December 31, 2023 as the actual results deviated significantly from projected 2023 results. |
Supplemental Information: K Enter Forecasts (Continued)
Solaire Partners LLC
The financial forecasts for Solaire Partners, consists of projected commissions and expenses for managing content investment funds. The projected growth in revenues assumes Solaire will be able to launch new content investment funds each year. Specifically, the number of funds under management is expected to grow from 8 funds in 2024 to 16 funds in 2028. The commission rate is projected to remain consistent at 1.5% of the assets under management.
| Fiscal Year | | 2023
(Forecast) | | | 2023
Actual1 | | | | 2024
(Forecast) | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Calendar | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | | 31-Dec-27 | | | | 31-Dec-28 | |
| Commission for fund management | | | 1,742 | | | | 1,714 | | | | | 2,850 | | | | 5,746 | | | | 6,857 | | | | 7,636 | | | | 7,867 | |
| Direct Investment | | | 34 | | | | 2 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other revenue | | | 25 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Revenues | | | 1,801 | | | | 1,716 | | | | | 2,850 | | | | 5,746 | | | | 6,857 | | | | 7,636 | | | | 7,867 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | | | | | | 58.2 | % | | | 101.6 | % | | | 19.3 | % | | | 11.4 | % | | | 3.0 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total COGS | | | (32 | ) | | | (146 | ) | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | 1,770 | | | | 1,570 | | | | | 2,850 | | | | 5,746 | | | | 6,857 | | | | 7,636 | | | | 7,867 | |
| GP Margin | | | 98.2 | % | | | 91.5 | % | | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total SG&A Expenses | | | (1,364 | ) | | | (1,644 | ) | | | | (2,004 | ) | | | (3,217 | ) | | | (3,626 | ) | | | (4,037 | ) | | | (4,475 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | 75.7 | % | | | 95.8 | % | | | | 70.3 | % | | | 56.0 | % | | | 52.9 | % | | | 52.9 | % | | | 56.9 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
EBITDA | | | 406 | | | | (74 | ) | | | | 846 | | | | 2,528 | | | | 3,231 | | | | 3,600 | | | | 3,392 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | 22.5 | % | | | (4.3 | %) | | | | 29.7 | % | | | 44.0 | % | | | 47.1 | % | | | 47.1 | % | | | 43.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (2 | ) | | | (67 | ) | | | | (2 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (3 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
EBIT | | | 403 | | | | (141 | ) | | | | 844 | | | | 2,526 | | | | 3,228 | | | | 3,597 | | | | 3,389 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | 22.4 | % | | | (8.2 | %) | | | | 29.6 | % | | | 44.0 | % | | | 47.1 | % | | | 47.1 | % | | | 43.1 | % |
| 1 | This column has been added to reflect actual results of Solaire Partners for the year ended December 31, 2023 as the actual results deviated significantly from projected 2023 results. |
Supplemental Information: K Enter Forecasts (Continued)
K Enter Drama Team
The financial forecasts for the K Enter Drama Team set forth below mainly consists of financial projections for the drama and film production businesses, in which the K Enter Drama Team produces and distributes dramas and films to global streaming platforms, TV channels and theatres. The projected growth in revenues assumes an increase in the number of dramas and films produced and distributed each year. Specifically, the numbers of dramas and films produced are projected to grow from 2 dramas and no films in 2024 to 6 dramas and 2 films in 2028, collectively for the K Enter Drama Team. The projected growth in gross profit margins assumes an increase in margins for dramas and films sold to global streaming platforms. Specifically, such margins are projected to grow on average 5% in 2024 to 20 - 30% in 2028. Such expected increase in margins for dramas and films sold to global streaming platforms will be attained as the K Enter Drama Team gains negotiating power on such platforms.
The financial forecasts for IP Investment and Additional Businesses for the K Enter Drama Team set forth below is based on the assumption that K Enter Drama Team will be able to (i) invest in film production and attain investment returns and (ii) develop additional content businesses other than the existing drama and film production businesses.
(i) For IP Investment, K Enter assumes it will be able to invest from its own principal investment account in selected films that Solaire decides to invest with its content investment funds. Specifically, the number of film investments is expected to grow from 1 film in 2024 to 3 films in 2028. The amount of investment per film is expected to grow from KRW 10 billion in 2024 to KRW 15 billion in 2028, and the expected return per investment is expected to grow from 10% in 2024 to 20% in 2028.
(ii) For Additional Businesses, K Enter assumes it will be able to develop new content businesses including non-script show production, music production and digital content production. K Enter plans to generate KRW 10 billion in 2024 to KRW 17 billion in 2028 from such Additional Businesses.
| Fiscal Year | | 2023
(Forecast) | | | 2023
Actual1 | | | | 2024
(Forecast) | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Calendar | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | | 31-Dec-27 | | | | 31-Dec-28 | |
| Drama Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | 23,845 | | | | 36,436 | | | | 60,390 | | | | 89,484 | | | | 110,700 | |
| Film Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | - | | | | 11,419 | | | | 12,375 | | | | 27,669 | | | | 30,000 | |
| IP Investment (Film) | | | | | | | | | | | | 11,000 | | | | 12,656 | | | | 28,750 | | | | 32,313 | | | | 54,000 | |
| Additional Business | | | | | | | | | | | | 10,000 | | | | 11,500 | | | | 13,225 | | | | 15,209 | | | | 17,490 | |
| Total Revenues | | | 0 | | | | 0 | | | | | 44,845 | | | | 72,011 | | | | 114,740 | | | | 164,674 | | | | 212,190 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 60.6 | % | | | 59.3 | % | | | 43.5 | % | | | 28.9 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Drama COGS | | | | | | | | | | | | (21,968 | ) | | | (33,375 | ) | | | (50,626 | ) | | | (71,490 | ) | | | (84,780 | ) |
| Film COGS | | | | | | | | | | | | - | | | | (10,500 | ) | | | (11,000 | ) | | | (24,590 | ) | | | (26,280 | ) |
| IP Investment COGS (Film) | | | | | | | | | | | | (10,000 | ) | | | (11,250 | ) | | | (25,000 | ) | | | (27,500 | ) | | | (45,000 | ) |
| Additional Business COGS | | | | | | | | | | | | (8,500 | ) | | | (9,775 | ) | | | (11,241 | ) | | | (12,927 | ) | | | (14,867 | ) |
| Total COGS | | | | | | | - | | | | | (40,468 | ) | | | (64,900 | ) | | | (97,867 | ) | | | (136,508 | ) | | | (170,927 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | | | | | - | | | | | 4,377 | | | | 7,111 | | | | 16,873 | | | | 28,166 | | | | 41,264 | |
| GP Margin | | | | | | | | | | | | 9.8 | % | | | 9.9 | % | | | 14.7 | % | | | 17.1 | % | | | 19.4 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total SG&A Expenses | | | (10,494 | ) | | | (382 | ) | | | | (11,954 | ) | | | (11,832 | ) | | | (12,307 | ) | | | (12,750 | ) | | | (13,224 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | 26.7 | % | | | 16.4 | % | | | 10.7 | % | | | 7.7 | % | | | 6.2 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBITDA | | | (10,494 | ) | | | (382 | ) | | | | (7,577 | ) | | | (4,721 | ) | | | 4,566 | | | | 15,417 | | | | 28,040 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | | | | | | | | | | (16.9 | %) | | | (6.6 | %) | | | 4 | % | | | 9.4 | % | | | 13.2 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (115 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | | (235 | ) | | | (238 | ) | | | (243 | ) | | | (247 | ) | | | (252 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBIT | | | (10,609 | ) | | | (385 | ) | | | | (7,812 | ) | | | (4,959 | ) | | | 4,323 | | | | 15,170 | | | | 27,788 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | | | | | | | | | | (17.4 | %) | | | (6.9 | %) | | | 3.8 | % | | | 9.2 | % | | | 13.1 | % |
PROPOSAL NO. 3
THE GOVERNANCE PROPOSALS
Overview
Global Star is asking Global Star’s stockholders to vote upon, on a non-binding advisory basis, a proposal to approve certain differences between Global Star and PubCo including the governance provisions set forth in PubCo’s Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association, as compared to the Existing Charter. These proposals are being presented in accordance with SEC guidance and will each be voted upon on an advisory basis. The vote on each of these proposals are not binding on Global Star or Global Star’s Board.
In the judgment of the Board, these provisions are necessary to adequately address the needs of PubCo. Furthermore, the Business Combination is not conditioned upon the separate approval of the Governance Proposals.
Governance Proposals
The following is a summary of the material differences between the Existing Charter and PubCo’s Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association applicable to the Governance Proposals. This summary is qualified by reference to the complete text of PubCo’s Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association, a copy of which is attached to this proxy statement/prospectus as Annex B. Global Star urges all stockholders to read PubCo’s Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association in their entirety for a more complete description of its terms. Additionally, as the Existing Charter is governed by the Delaware General Corporation Law and PubCo’s Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association will be governed by the Companies Act (As Revised) of the Cayman Islands) (the “Companies Act”), Global Star encourages stockholders to carefully consult the information set out under the “Description of PubCo’s Share Capital — Comparison of Rights of PubCo Shareholders and GLOBAL STAR stockholders” section of this proxy statement/prospectus.
| | | Global Star Existing Charter | | PubCo Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association |
| Governance Proposal A — Merger and Name Change | | Existing Charter provides that Global Star is a Delaware corporation named Global Star Acquisition, Inc. | | Through the Reincorporation Merger, Global Star will merge with and into PubCo, which shall be the surviving corporation as will be named K Wave Media, Ltd. |
| | | | | |
| Governance Proposal B — Authorized Shares of Common Stock | | Existing Charter authorizes the issuance of up to 100,000,000 shares of Class A Common Stock, par value $0.0001 per share, 10,000,000 shares of Class B Common Stock, par value $0.0001 per share and 1,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.0001 per share. | | The Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association (“Amended Articles”) authorize 990,000,000 ordinary shares of a par value of US$0.0001 each, each is entitled to one vote and 10,000,000 preference shares of a par value of US$0.0001 each. |
| | | | | |
| Governance Proposal C — Exclusive Forum | | Global Star’s Existing Charter adopts Delaware as the exclusive forum for certain stockholder litigation. | | Amended Articles adopts the Cayman Islands as the exclusive forum for certain shareholder litigation; provided, however, that this exclusive forum provision shall not apply to any action or suits brought to enforce any liability or duty created by the United States Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the Exchange Act, or any claim for which the federal district courts of the United States of America are, as a matter of the laws of the United States, the sole and exclusive forum for determination of such a claim. |
| | | | | |
| Governance Proposal D — Corporate Takeovers | | Global Star’s Existing Charter provides that Global Star is subject to Section 203 of the DGCL relating to business combinations with interested shareholders and includes additional restrictions on business combinations with interested shareholders. | | Amended Articles eliminate these provisions. |
Reasons
Governance Proposal A — Change of Name
The change in name from Global Star to K Wave Media, Ltd. will better reflect the nature of PubCo’s business after the Business Combination.
Governance Proposal B — Authorized Shares of Common Stock
The greater number of authorized shares of share capital is desirable for PubCo to have sufficient shares to issue the Merger Consideration in the Business Combination and have enough additional authorized shares for financing its business, for acquiring other businesses, for forming strategic partnerships and alliances and for share dividends and share subdivisions and to issue upon exercise of potential equity grants made in the future.
Governance Proposal C — Exclusive Forum
Following the Closing of the Business Combination, PubCo will be the ultimate parent company and PubCo is a Cayman Islands exempted company. Accordingly, Global Star’s Board has determined it is in the best interest of the stockholders to remove the Delaware exclusive forum provision in the Existing Charter and adopt a Cayman Islands exclusive forum for certain shareholder litigation through the adoption of the Amended Articles.
PubCo’s Amended Articles designates the courts of the Cayman Islands to have exclusive jurisdiction over any claim or dispute arising out of or in connection with the Memorandum, the Articles or otherwise related in any way to each Member’s shareholding in the Company, including but not limited to: (a) any derivative action or proceeding brought on behalf of the Company; (b) any action asserting a claim of breach of any fiduciary or other duty owed by any current or former Director, Officer or other employee of the Company to the Company or the Members; (c) any action asserting a claim arising pursuant to any provision of the Companies Act (as revised) of the Cayman Islands, PubCo’s Amended Articles and (d) any action asserting a claim against the Company governed by the “Internal Affairs Doctrine” (as such concept is recognised under the laws of the United States of America). This exclusive forum provision does not apply to any action or suits brought to enforce any liability or duty created by the United States Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the Exchange Act, or any claim for which the federal district courts of the United States of America are, as a matter of the laws of the United States, the sole and exclusive forum for determination of such a claim.
As a result, it may be difficult for investors to litigate against PubCo or to enforce judgments obtained in the United States courts against PubCo or its directors or officers.
Governance Proposal D — Corporate Takeovers
Global Star’s Board has determined that following the Closing of the Business Combination, PubCo will not require the anti-takeover provisions or the restrictions on business combinations with interested shareholders. that were contained in the Existing Charter. Accordingly, in adopting the Amended Articles the Global Star Board did not include such anti-takeover provisions or restrictions on business combinations with interested shareholders.
Vote Required for Approval
Each of the Governance Proposals, each of which is a non-binding vote, assuming that a quorum is present at the Special Meeting, will be approved only if holders of at least sixty-five percent (65%) of the issued and outstanding shares of GLST Common Stock as of the record date vote “FOR” each of the Governance Proposals. Accordingly, attending the Meeting either in person or by proxy and abstaining from voting will have the same effect as voting “AGAINST” each of the Governance Proposals and failing to instruct your bank, brokerage firm or nominee to attend and vote your shares will have no effect on any of the Governance Proposals.
As discussed above, the Governance Proposals are advisory votes and therefore are not binding on Global Star or Global Star’s Board. Furthermore, the Business Combination is not conditioned on the separate approval of the Governance Proposals. Accordingly, regardless of the outcome of the non-binding advisory vote on these proposals, the Amended Articles will be the charter of PubCo upon consummation of the Business Combination.
The Initial Stockholders have agreed to vote any shares of Global Star common stock owned by them in favor of the Governance Proposals.
Board Recommendation
THE BOARD RECOMMENDS A VOTE “FOR” ADOPTION OF EACH OF THE GOVERNANCE PROPOSALS UNDER PROPOSAL NO. 3.
PROPOSAL NO. 4
THE DIRECTOR PROPOSAL
Election of Directors
Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, Global Star has agreed to take all necessary action, including causing the directors of Global Star to resign, so that effective at the Closing, K Wave’s board of directors will consist of seven individuals, at least five (5) of whom shall qualify as independent directors under the Nasdaq rules.
It is proposed that K Wave’s board of directors consist of the directors shown in the table below, to serve in the class indicated:
| Name | | Age | | Position |
| Pyeung Ho Choi | | 66 | | Co-Founder and Chairman of K Enter |
| Young Jae Lee | | 49 | | Co-Founder of K Enter |
| Tan Chin Hwee | | 52 | | Director, Executive Chairman and Interim CEO of K Enter |
| Ted Kim | | 53 | | Founder of Global Star, Managing Member of Sponsor and Director of K Enter |
| Han Jae (Patrick) Kim | | 35 | | Director of K Enter and Managing Partner of Sui Generis Partners |
| Hyun Seok Cho | | 46 | | CEO of Play Co., Ltd. |
| Tae Woo Kim | | 41 | | CFO of Play Co., Ltd. |
Information regarding each nominee is set forth in the section titled “Management After the Business Combination.”
Resolution to be Voted Upon
The full text of the resolution to be proposed is as follows:
“RESOLVED, as an ordinary resolution, to elect Pyeung Ho Choi, Young Jae Lee, Tan Chin Hwee, Ted Kim, Han Jae (Patrick) Kim, Hyun Seok Cho and Tae Woo Kim to serve on K Wave’s board of directors until the 2024 annual meetings of stockholders, as applicable, and until their respective successors are duly elected and qualified or until their earlier death, resignation or removal.”
Vote Required for Approval
The election of each director nominee must be approved by an ordinary resolution under Cayman Islands law, being the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the Global Star Ordinary Shares who, being present in person (including virtually) or represented by proxy and entitled to vote at the Shareholder Meeting, vote at the Shareholder Meeting. Abstentions and broker non-votes, while considered present for the purposes of establishing a quorum, will not count as a vote cast and will have no effect on the outcome of the vote on the Director Proposal.
Unless authority is withheld or the shares are subject to a broker non-vote, the proxies solicited by the Global Star Board will be voted “FOR” the election of these nominees. In case any of the nominees becomes unavailable for election to the K Wave Board, an event that is not anticipated, the persons named as proxies, or their substitutes, will have full discretion and authority to vote or refrain from voting for any other candidate in accordance with their judgment. Any shares not voted “FOR” a particular nominee (whether due to a direction to withhold authority or a broker non-vote) will not be counted in the nominee’s favor.
The Director Proposal is conditioned upon the approval (or waiver) of the Reincorporation Merger Proposal and the Business Combination Proposal.
Following consummation of the Business Combination, the election of K Wave Board will be governed by the Proposed Articles of Association and Proposed Bylaws and the laws of the Cayman Islands.
Recommendation of the Global Star Board
THE GLOBAL STAR BOARD UNANIMOUSLY RECOMMENDS THAT ITS SHAREHOLDERS VOTE “FOR” EACH OF THE NOMINEES IN THE DIRECTOR PROPOSAL.
PROPOSAL NO. 5
THE INCENTIVE PLAN PROPOSAL
Global Star is asking Global Star’s shareholders to approve and adopt the K Wave Media, Ltd. 2023 Equity Incentive Plan and the material terms thereunder.
The 2023 Plan is described in more detail below. A copy of the 2023 Plan is included in this proxy statement/prospectus as Annex D.
Overview
The following is a summary description of the 2023 Plan as proposed to be approved by Global Star in connection with the Business Combination. The summary is not a complete statement of the 2023 Plan and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the complete text of the 2023 Plan, a copy of which is attached hereto as Annex D. Global Star’s stockholders should refer to the 2023 Plan for more complete and detailed information about the terms and conditions of the 2023 Plan. In the event of a conflict between the information in this description and the terms of the 2023 Plan, the 2023 Plan shall control. Unless the context otherwise requires, references in this summary description to “we”, “us” and “our” generally refer to Global Star in the present tense or K Wave from and after the Business Combination.
Background of the 2023 Plan
On June 15, 2023, the Global Star Board approved, subject to the approval by Global Star’s stockholders, the 2023 Plan. The 2023 Plan will become effective on the Closing Date and, if shareholder approval is obtained, K Wave will be authorized to grant awards to eligible service providers as described below. If the 2023 Plan is not approved by Global Star’s shareholders, the 2023 Plan will not become effective and K Wave will not be able to grant equity awards under the 2023 Plan. Global Star believes K Wave’s ability to recruit and retain top talent will be adversely affected if the 2023 Plan is not approved.
Summary of the 2023 Plan
Purpose of the 2023 Plan
The purpose of the 2023 Plan is to secure and retain the services of employees, directors and consultants, to provide incentives for such persons to exert maximum efforts for K Wave’s success and to provide a means by which such persons may be given an opportunity to benefit from increases in value of the K Wave Ordinary Shares through the granting of awards under the 2023 Plan. Global Star believes that the awards to be issued under the 2023 Plan will motivate award recipients to offer their maximum effort to K Wave and help focus them on the creation of long-term value consistent with the interests of K Wave shareholders. Global Star believes that grants of incentive awards are necessary to enable K Wave to attract and retain top talent.
Awards
The 2023 Plan provides for the grant of incentive stock options (“ISOs”) within the meaning of Section 422 of the Code, to K Wave employees and subsidiary corporations’ employees, and for the grant of non-statutory stock options (“NSOs”), stock appreciation rights, restricted stock awards, restricted stock unit awards, and other forms of awards to K Wave’s employees, directors and consultants and any of K Wave’s affiliates’ employees and consultants. Upon the closing of the Business Combination, K Wave expects there to be approximately 15 employees of K Wave, including 5 executive officers, 6 non-employee directors and 1 consultant eligible to be granted awards under the 2023 Plan.
Authorized Shares
Initially, the maximum number of shares of the K Wave Ordinary Shares that may be issued under the 2023 Plan after it becomes effective will be 5,900,000 of the outstanding shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares, which amount shall automatically increase on January 1 of each year for a period of ten years commencing on January 1, 2024 and ending on (and including) January 1, 2033, in an amount equal to five percent (5%) of the total number of shares of Stock outstanding on December 31 of the preceding year; provided, however, that the Board may act prior to January 1st of a given year to provide that the increase for such year will be a lesser number of shares of stock. The total number of PubCo ordinary shares that will be reserved for issuance under the K Wave Media will be 59 million shares for the New K Enter, and approximately $2.8 million shares for the sponsor of the Global Star. In addition, depending on the amount of Pre-PIPE or PIPE raised, as well as the redemption rate from Global Star’s existing shareholders, additional shares will be reserved and issued.
Shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares subject to awards that will be granted under the 2023 Plan that expire or terminate without being exercised in full will not reduce the number of shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares available for issuance under the 2023 Plan. The settlement of any portion of an award in cash will not reduce the number of K Wave Ordinary Shares available for issuance under the 2023 Plan. Shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares withheld under an award to satisfy the exercise, strike or purchase price of an award or to satisfy a tax withholding obligation will not reduce the number of shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares that will be available for issuance under the 2023 Plan. With respect to a stock appreciation right, only shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares that are issued upon settlement of the stock appreciation right will count towards reducing the number of shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares available for issuance under the 2023 Plan. If any shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares issued pursuant to an award are forfeited back to or repurchased or reacquired by K Wave due to forfeiture, cancellation or expiration, the shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares that are forfeited or repurchased or reacquired will revert to and again become available for issuance under the 2023 Plan.
Plan Administration
K Wave’s board of directors, or a duly authorized committee of K Wave’s board of directors, will administer the 2023 Plan. K Wave’s board of directors, or a duly authorized committee of K Wave’s board of directors, may, in accordance with the terms of the 2023 Plan, delegate to one or more of K Wave’s officers the authority to (i) designate employees (other than officers) to be recipients of specified awards, and to the extent permitted by applicable law, the terms of such awards; and (ii) determine the number of shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares to be subject to such awards granted to such employees. Under the 2023 Plan, K Wave’s board of directors, or a duly authorized committee of K Wave’s board of directors, will have the authority to determine: award recipients; how and when each award will be granted; the types of awards to be granted; the provisions of each award, including the period of exercisability and the vesting conditions applicable to an award; the number of shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares or cash equivalent subject to each award; and the fair market value applicable to an award.
Under the 2023 Plan, (i) K Wave’s board of directors will not, without stockholder approval, (a) reduce the exercise or strike price of an option or stock appreciation right (other than in connection with a capitalization adjustment), and (b) at any time when the exercise or strike price of an option or stock appreciation right is above the fair market value of a share of K Wave Ordinary Shares, cancel and re-grant or exchange such option or stock appreciation right for a new award with a lower (or no) purchase price or for cash, and (ii) a participant’s rights under any award will not be materially adversely impaired by any amendment without the participant’s written consent.
K Wave will also designate a plan administrator to administer the day-to-day operations of the 2023 Plan.
Stock Options
Options will be granted under stock option agreements adopted by K Wave’s board of directors. Each option will be designated in writing as an ISO or an NSO. K Wave’s board of directors will determine the exercise price for stock options, within the terms and conditions of the 2023 Plan, except the exercise price of a stock option generally will not be less than 100% (or 110% in the case of ISOs granted to a person who owns or is deemed to own stock possessing more than 10% of K Wave’s total combined voting power or that of any of K Wave’s parent or subsidiary corporations, or a ten percent stockholder) of the fair market value of K Wave Ordinary Shares on the date of grant. Options granted under the 2023 Plan will vest at the rate specified in the stock option agreement as will be determined by K Wave’s board of directors. The terms and conditions of separate options need not be identical.
No option will be exercisable after the expiration of ten years (or five years in the case of ISOs granted to a ten percent stockholder) or a shorter period specified in the applicable award agreement. Unless the terms of an optionholder’s stock option agreement, or other written agreement between K Wave and the recipient, provide otherwise, if an optionholder’s service relationship with K Wave or any of K Wave’s affiliates ceases for any reason other than disability, death or cause, the optionholder may generally exercise any vested options for a period of three months following the cessation of service. If an optionholder’s service relationship with K Wave or any of K Wave’s affiliates ceases due to death, or an optionholder dies within a certain period following cessation of service, the optionholder or a beneficiary may generally exercise any vested options for a period of 18 months following the date of death. If an optionholder’s service relationship with K Wave or any of K Wave’s affiliates ceases due to disability, the optionholder may generally exercise any vested options for a period of 12 months following the cessation of service. In the event of a termination for cause, options generally terminate upon the termination date. An optionholder may not exercise an option at any time that the issuance of shares upon such exercise would violate applicable law. Unless provided otherwise in the optionholder’s stock option agreement or other written agreement between an optionholder and us, if an optionholder’s service relationship with K Wave or any of K Wave’s affiliates ceases for any reason other than for cause and, at any time during the last thirty days of the applicable post-termination exercise period: (i) the exercise of the optionholder’s option would be prohibited solely because the issuance of shares of Ordinary Shares upon such exercise would violate applicable law, or (ii) the immediate sale of any shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares issued upon such exercise would violate K Wave’s trading policy, then the applicable post-termination exercise period will be extended to the last day of the calendar month that begins after the date the award would otherwise expire, with an additional extension of the exercise period to the last day of the next calendar month to apply if any of the foregoing restrictions apply at any time during such extended exercise period. There is no limitation as to the maximum permitted number of extensions. However, in no event may an option be exercised beyond the expiration of its term.
Acceptable consideration for the purchase of K Wave Ordinary Shares issued upon the exercise of a stock option will be determined by K Wave’s board of directors and may include (i) cash or check, bank draft or money order payable to us; (ii) a broker-assisted cashless exercise; (iii) subject to certain conditions, the tender of shares of K Wave’s Ordinary Shares previously owned by the optionholder; (iv) a net exercise of the option if it is an NSO; or (v) other legal consideration acceptable to K Wave’s board of directors.
Unless K Wave’s board of directors provides otherwise, options or stock appreciation rights generally will not be transferable except by will or the laws of descent and distribution. Subject to approval of K Wave’s board of directors or a duly authorized officer, an option may be transferred pursuant to a domestic relations order.
Limitations on ISOs
The aggregate fair market value, determined at the time of grant, of K Wave Ordinary Shares with respect to ISOs that are exercisable for the first time by an optionholder during any calendar year under all of K Wave’s stock plans or plans of K Wave’s affiliates may not exceed $100,000. Options or portions thereof that exceed such limit will generally be treated as NSOs. No ISO may be granted to any person who, at the time of the grant, owns or is deemed to own stock possessing more than 10% of K Wave’s total combined voting power or that of any of K Wave’s parent or subsidiary corporations unless (i) the option exercise price is at least 110% of the fair market value of the stock subject to the option on the date of grant; and (ii) the term of the ISO does not exceed five years from the date of grant.
Restricted Stock Unit Awards
Subject to the terms of the 2023 Plan, each restricted stock unit award will have such terms and conditions as determined by K Wave’s board of directors. A restricted stock unit award represents a participant’s right to be issued on a future date the number of shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares that is equal to the number of restricted stock units subject to the award. A participant will not have voting or any other rights as a stockholder of K Wave’s with respect to any restricted stock unit award (unless and until shares are actually issued in settlement of a vested restricted stock unit award). A restricted stock unit award will be granted in consideration for a participant’s services to K Wave or an affiliate, such that the participant will not be required to make any payment to K Wave (other than such services) with respect to the grant or vesting of the restricted stock unit award, or the issuance of any shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares pursuant to the restricted stock unit award. K Wave’s board of directors may determine that restricted stock unit awards may be granted in consideration for any form of legal consideration that may be acceptable to K Wave’s board of directors and permissible under applicable law. A restricted stock unit award may be settled by cash, delivery of stock (or any combination of K Wave Ordinary Shares and cash), or in any other form of consideration determined by K Wave’s board of directors and set forth in the restricted stock unit award agreement. At the time of grant, K Wave’s board of directors may impose such restrictions or conditions on the award of restricted stock units that delay delivery to a date following the vesting of the award. Additionally, dividend equivalents may be paid or credited in respect of shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares covered by a restricted stock unit award. Except as otherwise provided in the applicable award agreement, or other written agreement between K Wave and the recipient, restricted stock unit awards that have not vested will be forfeited once the participant’s continuous service ends for any reason.
Restricted Stock Awards
Restricted stock awards will be granted under restricted stock award agreements adopted by K Wave’s board of directors. A restricted stock award may be awarded in consideration for cash, check, bank draft or money order, past services to K Wave or any of K Wave’s affiliates, or any other form of legal consideration that may be acceptable to K Wave’s board of directors and permissible under applicable law. K Wave’s board of directors will determine the terms and conditions of restricted stock awards, including vesting and forfeiture terms. Dividends may be paid or credited with respect to shares subject to a restricted stock award, as determined by K Wave’s board of directors and specified in the applicable restricted stock award agreement. If a participant’s service relationship with K Wave ends for any reason, K Wave may receive any or all of the shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares held by the participant that have not vested as of the date the participant terminates service with K Wave through a forfeiture condition or a repurchase right.
Stock Appreciation Rights
Stock appreciation rights will be granted under stock appreciation right agreements adopted by K Wave’s board of directors and denominated in shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares equivalents. The terms of separation stock appreciation rights need not be identical. K Wave’s board of directors will determine the purchase price or strike price for a stock appreciation right, which generally will not be less than 100% of the fair market value of K Wave Ordinary Shares on the date of grant. A stock appreciation right granted under the 2023 Plan will vest at the rate specified in the stock appreciation right agreement as will be determined by K Wave’s board of directors. Stock appreciation rights may be settled in cash or shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares (or any combination of K Wave Ordinary Shares and cash) or in any other form of payment, as determined by K Wave’s board of directors and specified in the stock appreciation right agreement.
Our board of directors will determine the term of stock appreciation rights granted under the 2023 Plan, up to a maximum of ten years. If a participant’s service relationship with us or any of K Wave’s affiliates ceases for any reason other than cause, disability, or death, the participant may generally exercise any vested stock appreciation right for a period of three months following the cessation of service. If a participant’s service relationship with K Wave or any of K Wave’s affiliates ceases due to death, or a participant dies within a certain period following cessation of service, the participant or a beneficiary may generally exercise any vested stock appreciation rights for a period of 18 months following the date of death. If a participant’s service relationship with K Wave or any of K Wave’s affiliates ceases due to disability, the participant may generally exercise any vested stock appreciation rights for a period of 12 months following the cessation of service. In the event of a termination for cause, stock appreciation rights generally terminate upon the termination date. A holder of a stock appreciation right may not exercise a stock appreciation right at any time that the issuance of shares upon such exercise would violate applicable law. Unless provided otherwise in the stock appreciation right agreement or other written agreement between the participant and us, if a participant’s service relationship with K Wave or any of K Wave’s affiliates ceases for any reason other than for cause and, at any time during the last thirty days of the applicable post-termination exercise period: (i) the exercise of the participant’s stock appreciation right would be prohibited solely because the issuance of shares upon such exercise would violate applicable law, or (ii) the immediate sale of any shares issued upon such exercise would violate K Wave’s trading policy, then the applicable post-termination exercise period will be extended to the last day of the calendar month that begins after the date the award would otherwise expire, with an additional extension of the exercise period to the last day of the next calendar month to apply if any of the foregoing restrictions apply at any time during such extended exercise period. There is no limitation as to the maximum permitted number of extensions. However, in no event may a stock appreciation right be exercised beyond the expiration of its term.
Other Stock Awards
K Wave’s board of directors will be permitted to grant other awards, based in whole or in part by reference to, or otherwise based on, K Wave Ordinary Shares, either alone or in addition to other awards. K Wave’s board of directors will have the sole and complete discretion to determine the persons to whom and the time or times at which other stock awards will be granted, the number of shares under the other stock award (or cash equivalent) and all other terms and conditions of such awards.
Non-Employee Director Compensation Limit
The aggregate value of all compensation granted or paid following the effective date of the 2023 Plan to any individual for service as a non-employee director with respect to any fiscal year, including awards granted under the 2023 Plan (valued based on the grant date fair value for financial reporting purposes) and cash fees paid by K Wave to such non-employee director, will not exceed $500,000 in total value.
Changes to Capital Structure
In the event there is a specified type of change in K Wave’s capital structure, such as a stock split, reverse stock split, or recapitalization, K Wave’s board of directors will appropriately and proportionately adjust (i) the class(es) and maximum number of shares subject to the 2023 Plan and the maximum number of shares by which the share reserve may annually increase pursuant to the 2023 Plan; (ii) the class(es) and maximum number of shares that may be issued on the exercise of ISOs; and (iii) the class(es) and number of shares and exercise price, strike price, or purchase price, if applicable, of all outstanding awards granted under the 2023 Plan.
Corporate Transactions
In the event of a corporate transaction (as defined below), unless otherwise provided in a participant’s award agreement or other written agreement with K Wave or one of K Wave’s affiliates or unless otherwise expressly provided by K Wave’s board of directors at the time of grant, any awards outstanding under the 2023 Plan may be assumed, continued or substituted for, in whole or in part, by any surviving or acquiring corporation (or its parent company), and any reacquisition or repurchase rights held by K Wave with respect to K Wave Ordinary Shares issued pursuant to awards may be assigned to the successor (or its parent company). If the surviving or acquiring corporation (or its parent company) does not assume, continue or substitute for such awards, then (i) with respect to any such awards that are held by participants whose continuous service has not terminated prior to the effective time of the corporate transaction, or current participants, the vesting (and exercisability, if applicable) of such awards will be accelerated in full (or, in the case of awards with performance-based vesting with multiple vesting levels depending on the level of performance, unless provided otherwise in the applicable award agreement, vesting will accelerate at 100% of the target level) to a date prior to the effective time of the corporate transaction (contingent upon the effectiveness of the corporate transaction) as K Wave’s board of directors determines (or, if K Wave’s board of directors does not determine such a date, to the date that is five days prior to the effective time of the corporate transaction), and such awards will terminate if not exercised (if applicable) at or prior to the effective time of the corporate transaction, and any reacquisition or repurchase rights held by K Wave with respect to such awards will lapse (contingent upon the effectiveness of the corporate transaction); and (ii) any such awards that are held by persons other than current participants will terminate if not exercised (if applicable) prior to the occurrence of the corporate transaction, except that any reacquisition or repurchase rights held by K Wave with respect to such awards will not terminate and may continue to be exercised notwithstanding the corporate transaction.
In the event an award will terminate if not exercised prior to the effective time of a corporate transaction, K Wave’s board of directors may provide, in its sole discretion, that the holder of such award may not exercise such award but instead will receive a payment, in such form as may be determined by K Wave’s board of directors, equal in value to the excess (if any) of (i) the value of the property the participant would have received upon the exercise of the award, over (ii) any per share exercise price payable by such holder, if applicable. As a condition to the receipt of an award, a participant will be deemed to have agreed that the award will be subject to the terms of any agreement under the 2023 Plan governing a corporate transaction involving us.
Under the 2023 Plan, a “corporate transaction” generally will be the consummation, in a single transaction or in a series of related transactions, of (i) a sale or other disposition of all or substantially all, as determined by K Wave’s board of directors, of the consolidated assets of K Wave and K Wave’s subsidiaries; (ii) a sale or other disposition of at least 50% of K Wave’s outstanding securities; (iii) a merger, consolidation or similar transaction following which K Wave is not the surviving corporation; or (iv) a merger, consolidation or similar transaction following which K Wave is the surviving corporation but the shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares outstanding immediately prior to such transaction are converted or exchanged into other property by virtue of the transaction.
Transferability
Except as expressly provided in the 2023 Plan or the form of award agreement, awards granted under the 2023 Plan may not be transferred or assigned by a participant. After the vested shares subject to an award have been issued, or in the case of a restricted stock award and similar awards, after the issued shares have vested, the holder of such shares is free to assign, hypothecate, donate, encumber or otherwise dispose of any interest in such shares provided that any such actions are in compliance with the provisions herein, the terms of K Wave’s trading policy and applicable law.
Clawback/Recovery
All awards granted under the 2023 Plan will be subject to recoupment in accordance with any clawback policy that K Wave is required to adopt pursuant to the listing standards of any national securities exchange or association on which K Wave’s securities are listed or as is otherwise required by the Dodd-Frank Act or other applicable law and any clawback policy that K Wave otherwise adopts, to the extent applicable and permissible under applicable law. In addition, K Wave’s board of directors may impose such other clawback, recovery or recoupment provisions in an award agreement as K Wave’s board of directors determines necessary or appropriate, including but not limited to a reacquisition right in respect of previously acquired shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares or other cash or property upon the occurrence of cause.
Amendment or Termination
K Wave’s board of directors may accelerate the time at which an award granted under the 2023 Plan may first be exercised or the time during which an award grant under the 2023 Plan or any part thereof will vest, notwithstanding the provisions in the award agreement stating the time at which it may first be exercised or the time during which it will vest. K Wave’s board of directors will have the authority to amend, suspend, or terminate the 2023 Plan at any time, provided that such action does not materially impair the existing rights of any participant without such participant’s written consent. Certain material amendments will also require the approval of K Wave’s stockholders. No ISOs may be granted after the tenth anniversary of the date K Wave’s board of directors adopts the 2023 Plan. No awards may be granted under the 2023 Plan while it is suspended or after it is terminated.
Certain U.S. Federal Income Tax Aspects of Awards under the 2023 Plan
The following is a general summary under current law of the material federal income tax consequences to participants in the 2023 Plan under U.S. law. This summary deals with the general tax principles that apply and is provided only for general information. Certain types of taxes, such as state and local income taxes and taxes imposed by jurisdictions outside the United States, are not discussed. Tax laws are complex and subject to change and may vary depending on individual circumstances and from locality to locality. The summary does not discuss all aspects of income taxation that may be relevant to a participant in light of his or her personal investment circumstances and this summarized tax information is not tax advice.
Section 162(m) of the Code
K Wave will be entitled to a tax deduction in connection with an award under the 2023 Plan only in an amount equal to the ordinary income realized by the participant at the time the participant recognizes the income. Section 162(m) of the Internal Revenue Code places a limit of $1 million on the amount of compensation that K Wave may deduct as a business expense in any year with respect to certain of K Wave’s most highly paid executive officers. While K Wave’s board of directors considers the deductibility of compensation as one factor in determining executive compensation, K Wave’s board of directors retains the discretion to pay compensation (including through the issuance of awards) that is not deductible as it believes that it is in the best interests of K Wave’s stockholders to maintain flexibility in K Wave’s approach to executive compensation and to structure a program that K Wave considers to be the most effective in attracting, motivating and retaining key employees.
Stock Options
A participant will not recognize taxable income at the time an option is granted, and K Wave will not be entitled to a tax deduction at that time. A participant will recognize compensation taxable as ordinary income (and subject to income tax withholding in respect of an employee) upon exercise of an NSO equal to the excess of the fair market value of the shares purchased over their purchase price, and K Wave will be entitled to a corresponding deduction, except to the extent the deduction limits of Section 162(m) of the Code apply. A participant will not recognize income (except for purposes of the alternative minimum tax) upon exercise of an ISO. If the shares acquired by exercise of an ISO are held for at least two years from the date the option was granted and one year from the date it was exercised, any gain or loss arising from a subsequent disposition of those shares will be taxed as long-term capital gain or loss, and K Wave will not be entitled to any deduction. If, however, such shares are disposed of within either of the above-described periods, then in the year of that disposition, the participant will recognize compensation taxable as ordinary income equal to the excess of the lesser of (i) the amount realized upon that disposition, and (ii) the excess of the fair market value of those shares on the date of exercise over the exercise price, and K Wave will be entitled to a corresponding deduction, except to the extent the deduction limits of Section 162(m) of the Code apply.
Stock Appreciation Rights
A participant will not recognize taxable income at the time a stock appreciation right is granted, and K Wave will not be entitled to a tax deduction at that time. Upon exercise, the participant will recognize compensation taxable as ordinary income (and subject to income tax withholding in respect of an employee) in an amount equal to the fair market value of any shares delivered and the amount of cash paid upon settlement. This amount is deductible by K Wave as a compensation expense, except to the extent the deduction limits of Section 162(m) of the Code apply.
Restricted Stock
A participant will not recognize taxable income at the time restricted stock is granted, and K Wave will not be entitled to a tax deduction at that time, unless the participant makes an election to be taxed at that time. If such an election is made, the participant will recognize compensation taxable as ordinary income (and subject to income tax withholding in respect of an employee) at the time of the grant in an amount equal to the excess of the fair market value for the shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares at such time over the amount, if any, paid for those shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares. If such election is not made, the participant will recognize compensation taxable as ordinary income (and subject to income tax withholding in respect of an employee) at the time the restrictions constituting a substantial risk of forfeiture lapse in an amount equal to the excess of the fair market value of the shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares at such time over the amount, if any, paid for those shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares. The amount of ordinary income recognized by making the above-described election or upon the lapse of restrictions is deductible by K Wave as compensation expense, except to the extent the deduction limits of Section 162(m) of the Code apply.
Restricted Stock Units
A participant will not recognize taxable income at the time that restricted stock units are granted, and K Wave will not be entitled to a tax deduction at that time. Upon settlement of restricted stock units, the participant will recognize compensation taxable as ordinary income (and subject to income tax withholding in respect of an employee) in an amount equal to the fair market value of any shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares or other consideration delivered and the amount of any cash paid by us. The amount of ordinary income recognized is deductible by K Wave as compensation expense, except to the extent the deduction limits of Section 162(m) of the Code apply.
Other Stock Awards
The tax consequences associated with any other stock award will vary depending on the specific terms of such award. Among the relevant factors are whether or not the award has a readily ascertainable fair market value, whether or not the award is subject to forfeiture provisions or restrictions on transfer, the nature of the property to be received by the participant under the award, and the participant’s holding period and tax basis for the award or underlying shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares.
The tax consequences for equity awards outside of the United States may differ significantly from the U.S. federal income tax consequences described above.
New Plan Benefits
The awards, if any, that will be made to eligible persons under the 2023 Plan will be subject to the discretion of the compensation committee of K Wave. Therefore, Global Star cannot currently determine the benefits or number of shares of K Wave Ordinary Shares subject to awards that may be granted in the future and a new plan benefits table is thus not provided.
Resolution to be Voted Upon
The full text of the resolution to be proposed is as follows:
“RESOLVED, AS AN ORDINARY RESOLUTION THAT the K Wave Media, Ltd. 2023 Equity Incentive Plan, a copy of which is attached to this proxy statement/prospectus as Annex D, to be effective upon the consummation of the Business Combination, be and is hereby approved and adopted.”
Vote Required for Approval
The Equity Incentive Plan Proposal requires the approval of an ordinary resolution under Cayman Islands law, being the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the Global Star Common Stock who, being present in person (including virtually) or represented by proxy and entitled to vote at the Shareholder Meeting, vote at the Shareholder Meeting. Abstentions and broker non-votes, while considered present for the purposes of establishing a quorum, will not count as a vote cast and will have no effect on the outcome of the vote on the Incentive Plan Proposal.
The Incentive Plan Proposal is conditioned on the approval of each of the other Proposals.
Recommendation of the Global Star Board
THE GLOBAL STAR BOARD UNANIMOUSLY RECOMMENDS THAT GLOBAL STAR SHAREHOLDERS VOTE “FOR” THE APPROVAL OF THE INCENTIVE PLAN PROPOSAL.
PROPOSAL NO. 6
THE ADJOURNMENT PROPOSAL
Purpose of the Adjournment Proposal
In the event there are not sufficient votes for the adoption of the Reincorporation Merger, the Acquisition Merger Proposal, the Governance Proposals, the Director Election Proposal and the Incentive Plan Proposal, the Global Star board of directors may adjourn the Special Meeting to a later date, or dates, if necessary, to permit further solicitation of proxies. In no event will Global Star seek adjournment which would result in soliciting of proxies, having a stockholder vote, or otherwise consummating a business combination after February 22, 2025 (unless Global Star elects to extend the time it has to complete the initial business combination to June 22, 2025).
Required Vote
Approval of the Adjournment Proposal requires the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the GLST Common Stock as of the record date represented in person or by proxy at the Special Meeting and entitled to thereon. Adoption of the Adjournment Proposal is not conditioned upon the adoption of any of the other Proposals.
Recommendation of Global Star’s Board of Directors
The Global Star board of directors recommends a vote “FOR” adoption of the Adjournment Proposal.
Risks Related to the Redemption
Public stockholders who wish to redeem their public shares for a pro rata portion of the Trust Account must comply with specific requirements for redemption that may make it more difficult for them to exercise their redemption rights prior to the deadline. If stockholders fail to comply with the redemption requirements specified in this proxy statement/prospectus, they will not be entitled to redeem their public shares for a pro rata portion of the funds held in the Trust Account.
Risks if the Adjournment Proposal is Not Approved
If the Adjournment Proposal is not approved, and an insufficient number of votes have been obtained to authorize the consummation of the Business Combination, the Global Star Board will not have the ability to adjourn the stockholder meeting to a later date in order to solicit further votes, and, therefore, the Business Combination will not be approved, and, therefore, the Business Combination may not be consummated.
Risks if the Business Combination is not Consummated
Global Star cannot assure you that Global Star will be able to complete the Business Combination or any other transaction prior to June 22, 2025 (unless Global Star extends the time period it has to complete its initial business combination), the date by which Global Star is required to complete a business combination.
If Global Star is not able to complete the Business Combination with K Enter nor able to complete another business combination by June 22, 2025 (unless Global Star extends the time period it has to complete its initial business combination), Global Star would cease all operations except for the purpose of winding up and Global Star would redeem its public shares and liquidate the Trust Account, in which case Global Star’s public stockholders may only receive approximately $11.45 per share, subject to reduction for the payment of taxes, and Global Star’s warrants will expire worthless.
SELECTED HISTORICAL FINANCIAL INFORMATION OF Global Star
Global Star is providing the following selected historical financial data to assist you in your analysis of the financial aspects of the Business Combination. The following tables present Global Star’s selected historical financial information for the periods and as of the dates indicated. The information was derived from Global Star’s financial statements included elsewhere in this proxy statement/prospectus.
The information is only a summary and should be read In conjunction with, and is qualified by reference to, “Global Star’s Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and the financial statements and notes thereto included elsewhere in this proxy statement/prospectus and. Global Star’s historical results are not necessarily indicative of future results, and the results for any interim period are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected for a full fiscal year.
| | | For the
Nine Months Ended
September 30,
2024 | | | For the
Year Ended
December 31,
2023 | | | For the
Year Ended
December 31,
2022 | | | For the
Year Ended
December 31,
2021 | |
| Selected Statement of Operations Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total expenses | | $ | 1,700,833 | | | $ | 2,126,947 | | | $ | 547,868 | | | $ | 1,699 | |
| Other income – income earned on Investments held in Trust Account | | $ | 1,596,528 | | | $ | 3,942,920 | | | $ | 844,178 | | | $ | - | |
| Provision for income taxes | | $ | (315,369 | ) | | $ | (795,729 | ) | | $ | (135,321 | ) | | $ | - | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders | | $ | (404,644 | ) | | $ | 1,044,077 | | | $ | 168,814 | | | $ | (1,699 | ) |
| Per Share Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average number of shares of redeemable Class A Common Stock outstanding | | | 4,136,294 | | | | 7,823,408 | | | | 2,481,096 | | | | - | |
| Basic and diluted net income (loss) per share of redeemable Class A Common Stock | | $ | (0.06 | ) | | $ | 0.10 | | | $ | 0.04 | | | $ | - | |
| Weighted average number of shares of non-redeemable Class A and Class B Common Stock outstanding | | | 2,300,000 | | | | 2,913,225 | | | | 2,238,462 | | | | 2,000,000 | |
| Basic and diluted net income (loss) per share of Class A and Class B Common Stock | | $ | (0.06 | ) | | $ | 0.10 | | | $ | 0.04 | | | $ | (0.00 | ) |
| | | September 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | | | December 31,
2021 | |
| Selected Balance Sheet Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total assets | | $ | 13,342,114 | | | $ | 57,295,453 | | | $ | 96,293,292 | | | $ | 81,071 | |
| Total liabilities | | $ | 8,392,053 | | | $ | 6,889,246 | | | $ | 3,823,629 | | | $ | 58,980 | |
| Class A Common Stock that may be redeemed in connection with the Business Combination (approximately $11.31, $10.80 and $10.30 per share, respectively) | | $ | 12,857,261 | | | $ | 55,575,390 | | | $ | 94,797,761 | | | $ | - | |
| Total stockholders’ (deficit) equity | | $ | (7,907,200 | ) | | $ | (5,169,183 | ) | | $ | (2,328,098 | ) | | $ | 22,091 | |
| | | For the
Nine Months Ended
September 30,
2024 | | | For the
Year Ended
December 31,
2023 | | | For the
Year Ended
December 31,
2022 | | | For the
Year Ended
December 31,
2021 | |
| Selected Cash Flow Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash (used in) provided by operating activities | | $ | (1,710,887 | ) | | $ | (1,582,347 | ) | | $ | (461,825 | ) | | $ | 16,000 | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | | $ | 44,384,560 | | | $ | 43,369,841 | | | $ | (94,300,000 | ) | | $ | - | |
| Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | | $ | (43,788,448 | ) | | $ | (41,158,140 | ) | | $ | 95,639,385 | | | $ | (16,000 | ) |
SELECTED HISTORICAL FINANCIAL INFORMATION OF K ENTER
K Enter is providing the following selected historical financial data to assist you in your analysis of the financial aspects of the Business Combination. The following tables present K Enter’s selected historical financial information for the periods and as of the dates indicated. The information was derived from K Enter’s financial statements included elsewhere in this proxy statement/prospectus.
The information is only a summary and should be read in conjunction with, and is qualified by reference to, “K Enter’s Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and the financial statements and notes thereto included elsewhere in this proxy statement/prospectus. K Enter’s historical results are not necessarily indicative of future results, and the results for any interim period are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected for a full fiscal year.
| | | Nine months ended
September 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from
January 4, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| Selected Statement of Operations Data: | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | $ | 470,052 | | | $ | 208,704 | |
| Operating expenses | | | | | | | | |
| Cost of revenues | | | 411,121 | | | | 207,153 | |
| General and Administrative | | | 10,519,714 | | | | 8,954,316 | |
| Loss From Operations | | | (10,460,783 | ) | | | (8,952,765 | ) |
| Other income (expense) | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | | 388 | | | | 7,956 | |
| Other expense | | | (3,833 | ) | | | 13,863 | |
| Total other expense | | | (3,445 | ) | | | 21,819 | |
| Net loss | | $ | (10,464,228 | ) | | $ | (8,930,946 | ) |
| Per Share Data: | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding | | | 94,478 | | | | 76,540 | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share of common stock | | $ | (110.76 | ) | | $ | (116.68 | ) |
| | | September 30, | | | December 31, | |
| | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
| Selected Balance Sheet Data: | | | | | | | | |
| Total assets | | $ | 8,805,000 | | | $ | 8,778,338 | |
| Total liabilities | | $ | 8,386,253 | | | $ | 2,766,234 | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | | $ | 418,747 | | | $ | 6,012,104 | |
| | | Nine months ended
September 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from
January 4, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| Selected Cash Flow Data: | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash used in operating activities | | $ | (4,068,117 | ) | | $ | (8,002,540 | ) |
| Net cash used in investing activities | | $ | (1,060 | ) | | $ | (2,637,390 | ) |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | | $ | 1,809,499 | | | $ | 13,121,268 | |
MARKET PRICE AND DIVIDEND INFORMATION
Global Star’s units, public shares, public warrants, and public rights are each traded on the Nasdaq Stock Market under the symbols “GLSTU,” “GLST”, “GLSTW,” and “GLSTR” respectively. Global Star’s units commenced public trading on September 22, 2022, and Global Star’s public shares, public warrants and public rights commenced separate public trading on November 10, 2022. Global Star’s Class B Common Stock is not listed on any exchange.
The most recent closing price of the units, public shares, public warrants and public rights as of December 11, 2024, the last trading day before announcement of the execution of the Merger Agreement, was $11.32, $11.50, $0.01, and $0.1669, respectively. As of December 13, 2024, the record date for the stockholder meeting, the closing price for each unit, ordinary share, redeemable warrant and right was $11.96, $11.33, $0.01 and $0.11, respectively.
Holders of the units, public shares, public warrants, and public rights should obtain current market quotations for their securities. The market price of Global Star’s securities could vary at any time before the Business Combination.
Holders
As of December 13, 2024, there were 4 holders of record of shares of Global Star’s common stock, 1 holder of record of Global Star’s public warrants and 1 holder of record of Global Star’s public rights. A substantially greater number of holders of common stock are “street name” or beneficial holders whose shares of record are held by banks, brokers, and other financial institutions. As a result, Global Star is unable to estimate the total number of stockholders represented by the record holders of Global Star’s common stock public warrants or public rights.
See “Beneficial Ownership of Securities.”
Dividend Policy
Global Star has not paid any cash dividends on Global Star’s common stock to date and do not intend to pay cash dividends prior to the completion of Global Star’s Business Combination. The payment of cash dividends in the future will be dependent upon Global Star’s revenues and earnings, if any, capital requirements and general financial condition subsequent to completion of Global Star’s initial business combination. The payment of any cash dividends subsequent to Global Star’s initial business combination will be within the discretion of Global Star’s board of directors at such time. In addition, Global Star’s board of directors is not currently contemplating and does not anticipate declaring any stock dividends in the foreseeable future. Further, if Global Star incurs any indebtedness in connection with Global Star’s initial business combination, Global Star’s ability to declare dividends may be limited by restrictive covenants Global Star may agree to in connection therewith.
Price Range of K Enter’s Securities
Historical market price information regarding K Enter is not provided because there is no public market for K Enter’s securities. For information regarding K Enter’s liquidity and capital resources, see “K Enter’s Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources.”
BUSINESS OF K ENTER
OVERVIEW
K Enter was formed to be an intellectual property (“IP”) entertainment company primarily through the acquisition, management, and development of companies in the Korean entertainment business focusing on IP development and production, merchandising and IP ownership and investing and then moving into to other areas in the future such as virtualization and music. K Enter also created an in-house production company to develop, acquire and produce dramas and movies.
K Enter’s vision is to become a leading tech and IP-based diversified entertainment company. As K Enter works on fulfilling its vision the first step will be acquiring a controlling equity interest in the following Korean entertainment companies: Apeitda Co., Ltd., Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd., The LAMP Co., Ltd., Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd., Play Company Co., Ltd. and Solaire Partners LLC (collectively the “Six Korean Entities”) which combine three initial capabilities, K Enter believes, are necessary to carry out its business plan. They include content production, content merchandising, and content investment. K Enter has a plan to develop virtual production capabilities in the future through K Enter’s internal tech team and in collaboration with content virtualization companies. The combined three capabilities noted below and the developing capability will serve as an initial foundation for K Enter’s growth.
| 1. | Content production (4 companies). The equity interest to be acquired is 51% in each of the following production studios. |
| ② | Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd. |
| ④ | Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd. |
| 2. | Content merchandising (1 company). The equity interest to be acquired is 100%. |
| 3. | Content investment (1 company). The equity interest to be acquired is 95%. |
Below K Enter describes the four initial capabilities and the businesses of the Six Korean Entities that K Enter plans to acquire prior to the closing of the business combination with Global Star Acquisition, Inc. (the “Business Combination”).
The three initial capabilities defined
K Enter’s content production will initially be in film and drama production, through its acquisition of the following production studios Apeitda Co., Ltd., Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd., The LAMP Co., Ltd., Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd., which are four of the Six Korean Entities K Enter plans to acquire prior to the Business Combination.
Content production entails overseeing the entire process of bringing a film or drama to life including taking an initial idea, developing a script, securing actors and a director, financing the project, producing the content, marketing the content so that the work can be brought to the viewer.
Content merchandising means the enhancement of the fan experience through the IP merchandise K Enter creates and sells, which also helps artists maintain a strong bond with their fanbase. K Enter will engage in content merchandising through the Play Company Co., Ltd. (“Play Company’), an IP content merchandising company, which is one of the Six Korean Entities, K Enter plans to acquire prior to the Business Combination. The Korean music industry generated $8.4 billion in sales in 2022 according to the Korea Creative Content Agency. (See: Korea Creative Content Agency (KOCCA), “2022 Yearly Analysis of Content Industry Trends”, p.6 (2022 kocca.kr)). In 2022 over 74 million physical K Pop CDs were sold according to the Korean Culture and Information Service (See : KOCIS, Dec. 26, 2022 News Release, (kocis.go.kr)), almost 30% higher than the previous year. As a comparison 33.4 million CDs were sold in the U.S. in 2022 according to the Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA, Year-end 2022 RIAA Revenue Statistics, (RIAA.com)). Korea also exported $233 million in physical album sales in 2022 (See : KOCCA, “Korea Creative Content Agency, S. Korea’s exports of K-Pop albums hit record high of US$233 million in 2022”, Jan. 17, 2023, (kocca.kr)). While buying CDs may seem outdated when music streaming is the most popular way to listen to music, many fans in Korea purchase CDs to show their support and increase an artist’s popularity ranking. CDs and the accompanying package in Korea are also bought many times for the inherent value it has to the fan as a collector’s item. The CDs can contain valuable photo cards (some which are traded on the market), merchandise, and to fans valuable raffle tickets which allows ticket holders to attend fan meetings, conduct video calls with their artist, etc. During COVID-19, the opportunity to conduct a video call gained great value to fans rather than in person meetings, and this new form of engaging with fans has become very well accepted. It is not uncommon for some fans to buy more than one CD.
This behavior of buying CDs spills over to the purchase of the specialized video merchandise created by Play Company Co., Ltd., one of the Six Korean Entities. Fans of K-Pop artists such as BTS have purchased specialized video merchandise created by Play Company to show support for their artist. These fans have been known to buy billboards and ads to congratulate their artists on their birthday. The fans also derive satisfaction from owning unique and exclusive video merchandise that is treated as a collectible item. The video package, for example, contains unique footage with behind-the-scenes videos and photos of the artists in concerts, music videos, dance practices and intimate aspects of their everyday lives. They also usually include special photo albums, stickers, and post cards of the artists. The items included depends on the type of item that is most popular at that time. Items have varied from masking tapes and badges to key rings.
Content investing by K Enter, will initially entail investing in the production of film and drama through Solaire Partners LLC, a venture capital firm that specializes in investment into movies, dramas and content related companies, which is one of the Six Korean Entities, K Enter plans to acquire prior to the Business Combination. Revenues are derived from the management fees it receives and performance fees. Solaire Partners LLC’s investment capabilities will also be leveraged to select which films and dramas will be produced by K Enter.
The contribution of each of the Six Korean Entities to total pro forma revenues is noted in tabular form below.
Contribution of each entity to total pro forma revenues in 2022
| Unit : $ Millions, % | |
| Entity | | Revenues | | | % of Total | |
| K Enter | | | - | | | | 0 | % |
| Apeitda | | | 3.3 | | | | 2 | % |
| Bidangil | | | 0.3 | | | | 0 | % |
| The Lamp | | | 13.9 | | | | 9 | % |
| Studio Anseilen | | | - | | | | 0 | % |
| Play | | | 130.8 | | | | 87 | % |
| Solaire | | | 1.4 | | | | 1 | % |
| Total | | | 149.8 | | | | 100 | % |
Contribution of each entity to total pro forma revenues in 2023
| Unit : $ Millions, % | |
| Entity | | Revenues | | | % of Total | |
| K Enter | | | 0.2 | | | | 0 | % |
| Apeitda | | | 0.1 | | | | 0 | % |
| Bidangil | | | 5.9 | | | | 8 | % |
| The Lamp | | | 15.9 | | | | 21 | % |
| Studio Anseilen | | | - | | | | 0 | % |
| Play | | | 51.6 | | | | 69 | % |
| Solaire | | | 1.3 | | | | 2 | % |
| Total | | | 75.1 | | | | 100 | % |
Contribution of each entity to total pro forma revenues in June YTD 2024
| Unit : $ Millions, % | |
| Entity | | Revenues | | | % of Total | |
| K Enter | | | 0.4 | | | | 1 | % |
| Apeitda | | | 0.1 | | | | 0 | % |
| Bidangil | | | 5.7 | | | | 19 | % |
| The Lamp | | | 9.3 | | | | 31 | % |
| Studio Anseilen | | | - | | | | 0 | % |
| Play | | | 14.1 | | | | 47 | % |
| Solaire | | | 0.7 | | | | 2 | % |
| Total | | | 30.1 | | | | 100 | % |
Aggregate consideration to be paid by K Enter for the control interests of the Six Korean Entities.
Stock Consideration payable to each of the Six Korean Entities (assuming PubCo’s Ordinary Shares are valued at $10.00 per share).
| Name | | Value of
K Enter
common stock
to be issued
(US $) | | | Number of
shares | |
| Play Company Co., Ltd. | | | 92,622,072 | | | | 30,356 | |
| The LAMP Co., Ltd | | | 22,229,487 | | | | 7,286 | |
| Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd | | | 14,819,658 | | | | 4,857 | |
| Apeitda Co., Ltd. | | | 11,114,743 | | | | 3,643 | |
| Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd. | | | 5,593,695 | | | | 1,833 | |
| Solaire Partners LLC. | | | 10,351,966 | | | | 3,393 | |
| Total | | | 156,731,621 | | | | 51,367 | |
| * | Exchange rate: 1,375.558 applied. |
Additional consideration payable to the owner Play Company (the “PC Seller”)
Cash payments payable to the PC Seller.
| Payment Date | | Purchase Price
(US $) | | | Present Value
(US $) | |
| Within three (3) months from the listing date | | | 13,172,862 | | | | 12,624,805 | |
| January 31, 2025 | | | 6,574,407 | | | | 6,228,303 | |
| January 31, 2026 | | | 6,574,407 | | | | 5,863,270 | |
| Total | | | 26,321,676 | | | | 24,716,377 | |
Potential earn out payments potentially payable to the PC Seller.
In the event the business of Play Company, following its acquisition by K Enter, achieves a certain annual average net profit for Fiscal Years 2023 to 2025, then PubCo shall be required to make additional payments to the PC Seller as follows: (i) if the average net profit for the Play Company business for said years is less than 75% (KRW 12.105 Billion) of the target amount separately agreed between the Parties (KRW 16.14 Billion) or exceeds 125% of the said target amount (KRW 20.175 Billion), then PubCo shall pay to the PC Seller in cash (KRW) on January 31, 2027 and January 31, 2028 (for the purpose of this Section, the “Payment Date,” respectively), an amount calculated by multiplying the achieved percentage based on the annual average net profit for Fiscal Years 2023 to 2025 by KRW 9.05 Billion, and (ii) if the average net profit for the said years is not less than 75% of the target amount (KRW 12.105 Billion) and not greater than 125% of the target amount (KRW 20.175 Billion), PubCo shall pay KRW 9.05 Billion to the PC Seller on each Payment Date. Each earn out payment above shall be deemed as an adjustment to the Purchase Price.
An additional payment in cash may be owed to the PC Seller if the shares of PubCo that the shares of New K Enter’s common stock convert into at the closing of the Acquisition Merger are sold during the three-month period (the “Sale Period”) following the six-month lock-up period of the newly issued shares of PubCo at a per share price less than the per share value at closing of the Acquisition Merger for the shortfall in share price. The amount to be paid will be reduced by (i) any realized gains from the sale of additional shares of PubCo by the PC Seller between the end of the Sale Period and December 31, 2026, and (ii) the unrealized gain as of December 31, 2026 for the shares that continue to be held by the PC Seller (calculated as the number of remaining shares of PubCo times the difference of (i) the average closing price of PubCo from December 1, 2026 to December 31, 2026 and (ii) the per-share value of PubCo at the closing of the Acquisition Merger).
The PC Seller and K Enter have also entered into a call option agreement prior to the Closing date under which the PC Seller will be granted an option to acquire the shares of Play F&B Co., Ltd. held by Play Company within three years from the Closing Date. The exercise price for the call option will be the book value of Play F&B Co., Ltd. on the financial statements of Play Company as of the end of Fiscal Year 2022 prepared in accordance with K-GAAP.
Company and Industry Background
| 1. | K Enter businesses engaged in content production (following the business combination) : Apeitda Co., Ltd, Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd., The LAMP Co., Ltd., Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd. |
Products and Service offered
The products and services provided
| Apeitda | Bidangil | The Lamp | Studio Anseilen |
| Film production for the global audience | Film and drama production for the global audience | Drama and film production for the global audience | Drama production for the global audience |
Revenues generated (In June YTD 2024, 2023 and 2022)
$21.9 million in revenues were generated by the four companies in 2023 and $17.5 million in 2022. A breakdown by company is shown below. Revenues are generated primarily from providing media productions services.
2023 and 2022 Revenues and share of total 6 company revenue Unit : $ Millions, %
| Year | Apeitda | Bidangil | The Lamp | Studio Anseilen |
| June YTD 2024 | 0 (0%) | 5.7 (19.0%) | 9.3 (30.8%) | 0 (0%) |
| 2023 | 0.0 (0.1%) | 5.9 (7.8%) | 15.9 (21.2%) | 0 (0%) |
| 2022 | 3.2 (2.1%) | 0.3 (0.2%) | 13.9 (9.3%) | 0 (0%) |
Note : Studio Anseilen was newly established (Mar. 2023)
Contribution to total revenue
The total revenues of $15.0 million in June YTD 2024 would have represented 49.8% of the combined revenues of all six companies.
The total revenues of $21.9 million in 2023 would have represented 29.2% of the combined revenues of all six companies.
The total revenues of $17.5 million in 2022 would have represented 11.6% of the combined revenues of all six companies
Current operational status of business
| Upcoming Film & Drama Lineup (1) |
| Format | | Title | | Production | | Expected | | Director | | Writer | | Starring | | Status |
| Drama | | Trigger | | Bidangil Pictures | | 2025 | | Kwon Oh-Seung | | Kwon Oh-Seung | | Kim Nam-Gil | | A Netflix Original series / Currently in production |
| | | Aema | | The Lamp Pictures | | 2025 | | Lee Hae-Young | | Lee Hae-Young | | Lee Haree | | A Netflix Original series / Currently in production |
| | | Scarecrow | | Studio Anseilen | | TBD | | Park Jun-Woo | | Lee Ji-Hyun | | TBD | | A TV series / Currently in development |
| | | Ace Club | | Bidangil Pictures | | TBD | | TBD | | Kim Jia | | TBD | | An OTT original series / Currently in development |
| Film | | Escape | | The LAMP pictures | | 2024 | | Lee Jong-Pil | | Kwon Sung-Hwi | | Lee Je-Hoon, Koo Kyo-Hwan | | A theatrical release / To be released on July 3, 2024 |
| | | Resonance | | Bidangil Pictures | | 2024 | | Jung Da-Won | | Jung Da-Won | | Jin Seon-Kyu | | A theatrical release / Currently in post-production |
| | | Starlight is Falling | | The LAMP Pictures | | 2024 | | Choi Kuk-Hee | | Choi Kuk-Hee | | Esom | | A theatrical release / Currently in post-production |
| | | Virus | | The LAMP Pictures | | 2024 | | Kang Yi-Kwan | | Kang Yi-Kwan | | Bae Doona | | A theatrical release / Currently in post-production |
| | | Pavane | | The LAMP Pictures | | 2025 | | Son Yong-Ho | | Son Yong-Ho | | TBD | | A theatrical release / Currently in production |
| | | Blood for Blood | | Bidangil Pictures | | TBD | | Son Yong-Ho | | Son Yong-Ho | | TBD | | A theatrical release / Currently in development |
 | |  | |  | |  | |  |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Trigger | | Aema | | Resonance | | Escape | | Virus |
Note (1) The summary lists are selected examples to illustrate certain capabilities of K Enter and do not, by themselves, reflect the track record of K Enter as a whole.
In the drama segment, we highlight two primary projects that started production in 2023. It is the production of Aema (The Lamp) and Trigger (Bidangil). Aema is a Netflix original series. According to Netflix’s press release it is a fictional comedy revealing the harsh realities of actors behind the glitzy veneer of Korean show business in the 80s. Trigger is also a Netflix original series. The series has been described in the local press as an action thriller set in gun-free South Korea and the societal impact when firearms suddenly become widely available. Studio Anseilen as well as K Enter’s own drama production team are in pre-production work for projects that are expected to start production in 2024.
In the film segment, Bidangil is currently in production for two movies Resonance and Starlight is Falling. The Lamp is currently in production of Escape.
Change following business combination and future business activity
The objective for K Enter’s drama and film production business is to develop a diverse portfolio of shows with global appeal. K Enter aims to curate a wide range of shows and facilitate partnerships with distributors to showcase K Enter’s work to audiences in Korea, Southeast Asia, and beyond. K Enter’s expansion strategy involves not only drama and thrillers but also venturing into other genres such as romantic comedies.
We believe that the high quality of K Enter’s content will enhance its marketability, facilitating distribution. Utilizing K Enter’s in-house expertise in developing merchandising, we also intend to establish stronger connections with K Enter’s audience. Additionally, by retaining intellectual property (IP) rights for K Enter’s productions, we anticipate achieving greater financial returns from K Enter’s creative endeavors.
Timeline and status of developing such capabilities
Drama and film production is currently underway, and K Enter’s plan is to expand these efforts further. We will leverage K Enter’s in-house resources and invest in high-quality content to enrich K Enter’s portfolio. 2024 will mark the initiation of this journey, and we believe it will serve as a foundational year to strengthen and diversify K Enter’s collection of shows.
Industry in which Apeitda Co., Ltd, Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd., The LAMP Co., Ltd., Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd. will compete (following the business combination) : Content production industry
Industry overview and market opportunity
The Korean content market is estimated to produce around $114 billion in revenues in 2022 and has grown at 5.5% CAGR since 2017. (See: Korea Creative Content Agency (KOCCA), “2022 Yearly Analysis of Content Industry Trends”, p.6 (2022 kocca.kr)). This industry includes sectors such as content that is broadcasted (TV shows, dramas, etc), publishing, games, music, animation, movies, etc.). Korean content has gained popularity in Northeast Asia, including Japan and China, and has spread to Southeast Asia, the United States, and Europe. With the development of digital transmission technology, the spread of social media platforms like YouTube, and the growth of global content platforms like Netflix, Korean content has gained significant attention worldwide. As a market, the Korean content industry is the 7th largest in the world estimated to be a $70.2 billion market (See: KOCCA, “2022 Content Industry White Paper, Ministry of culture, Sports and Tourism”, p. 98, (Kocca.kr)) Exports have also been growing to $13.3 billion in 2022 and has grown at 8.5% CAGR since 2017. Among the most popular TV shows on Netflix, Korean content occupies 52% of the non-English content, while the United States occupies 66% of the total, including English content, and Korean content occupies 18% (Source : Netflix). Korean content is also popular globally, with 30 out of 100 TV shows worldwide being Korean content, compared to 32 from the United States. (See : Variety, “Korea Rivals the U.S. in New Scripted Shows’s Global Internet Popularity”, Jun. 28, 2023, (variety.com)) Due to its high popularity overseas, CNBC, CNN, Reuters, CBS reported Netflix announced it would invest approximately $2.5 billion in Korean content over the next three years. The content industry is the third-largest exporter in the Korean economy, making it an important driving force for the economy. Additionally, Korea has a base of an eager and discerning audience. In 2019, South Korea had the highest number of moviegoers per capita, with 220 million visits to theaters, and an average of 4.37 movie admissions per person, making it the country with the highest movie consumption in the world. (Source: KOFIC, “2022 A review of the Korean Movie Industry”, Korea Film Council, p. 14, (Kofic)) K Enter plans to compete in this industry with its internal drama production company and through its proposed acquisitions of Apeitda Co., Ltd., Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd., The LAMP Co., Ltd., and Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
Customers
Customers for content production are primarily companies that provide content to audiences. They include companies that distribute content such as traditional TV broadcasters, cable companies, streaming companies, Internet Protocol Television (IPTV) operators and major cinema chains that distribute, produce, and invest in movies such as CJ ENM, Lotte Entertainment. These customers have points of contact with the end audience. Our content production companies expect its customer base to broaden globally as Apeitda grow. Our content production companies’ customers also include the end audience that watch its content and are the ultimate evaluators of the quality of the work.
Suppliers
Movies and dramas are collaborative efforts involving a team of experts which contribute to the final product. Some of the major contributors are listed below. Directors: They determine and oversee the visual and directorial direction of the content. Writers: They are responsible for developing the story and script for the content. Actors: They portray the main characters of the content, breathing life into the story. Cinematographers: They contribute to filming and implementing the visual style. Art Directors: They design and create the aesthetic elements and settings of the content. Studio set providers. They provide and construct the necessary shooting spaces. CG/VFX (Computer Graphics/Visual Effects): They enhance the visual elements through computer-generated graphics and special effects. Additionally, investors who provide funding for content production can also be considered suppliers.
Sales & Marketing
Sales and marketing play crucial roles in the revenue aspect of the films and TV series production industry. In marketing IP video content, we plan to focus on the following elements:
(1) Trailers and Promotional Materials: the video content trailers, and promotional materials capture the interest of the audience, encouraging them to make reservations or watch the video content in advance. These visual media materials play a vital role in highlighting the core story and compelling characters of the video content. Extensive advertising and various promotions are carried out to increase the exposure of trailers and promotional materials, aiming to establish high awareness and preference among the video content’s primary customers, the audience.
(2) Social Media Marketing: In recent years, social media marketing has emerged as a critical element in the video content marketing. Social media platforms enable direct interaction with the public and are used to quickly disseminate information about the video content. Various social media channels such as Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube are leveraged to increase the frequency of exposure to the video content among the audience. Efforts are made to encourage audience interest in the video content encountered through social media, ultimately leading to the video content attendance.
(3) Special Events and Premieres: the video content-related special events and premieres provide audiences with the opportunity for direct interaction with actors, directors, producers, and others involved in the video content. This can elevate audience affinity for the video content and potentially lead to viral marketing.
(4) Reviews and Press Coverage: the video content reviews and press coverage can emphasize the strengths of the video content and create a positive impression among audiences. Therefore, press releases and reviews related to the video content are disseminated to contribute to the video content’s success through media promotion All these elements collectively contribute to the marketing strategies employed within the video content industry.
Competition
Our content production companies face numerous competitors in the video content production industry. Every production studio that creates film or drama video content is a competitor of K Enter. Among them, SLL, formerly known as JTBC Studios, is a well-known Korean drama production, distribution and K-pop agency that will compete directly with K Enter related to K content as well as Studio Dragon Corp. Kakao Entertainment Co., Ltd is another, much bigger competitor in the market.
Competitive Strength
First K-Enter has numerous talented and experienced creators who will provide a diverse range of quality content. One strength of K Enter lies in its ability to secure investment. Content production typically requires substantial funding, and acquiring this funding can be time-consuming and challenging. K Enter can directly invest in content projects. It can also leverage its content-specialized venture capital firm Solaire Partners, which we believe will provide sufficient financing to secure the IP content of attractive projects which can lead to greater profitability. Furthermore, K Enter does not own its own streaming platform. This offers flexibility to collaborate independently with various platforms globally and maximize potential earnings.
K Enter is also committed to securing virtual production capabilities. K Enter is pursuing various avenues including using its internal tech team K Enter is confident that these collective efforts will ultimately enable K Enter to achieve its goal of securing virtual production capabilities. K Enter is bolstering the team that will be working on this initiative. K Enter tech team now includes advisers Lee Joung Jae and Kim Seung Mo, VFX specialists at Rabbit Walks, a video production specialist firm creating video commercials, exhibitions, and VR special effects.
| 2 | K Enter business engaged in content merchandising (following the business combination) : Play company Co, Ltd. |
Products and Service offered
Play’s primary focus is on creating specialized video merchandise for renowned K-pop artists, with notable examples including BTS. Play also engages in the food and beverage industry, which contributed approximately 10% to the overall sales in 2022.
Revenue generated (In June YTD 2024, 2023 and 2022)
$14.1 million in revenues were generated in June YTD 2024, $51.6 million in 2023 and $130.8 million in 2022. Revenues were generated primarily from the sale of specialized video merchandise packages. Approximately 26% of revenues in 2023 were generated from food and beverages in the form of baked goods and coffee. In 2022 10% of revenues came from food and beverages.
Contribution to total revenue
Total revenues were $14.1 million in June YTD 2024 they would have represented 46.6% of the combined revenues of all six companies.
Total revenues were $51.6 million in 2023 they would have represented 68.7% of the combined revenues of all six companies.
Total revenues were $130.8 million in 2022 they would have represented 87.3% of the combined revenues of all six companies.
Current operational status of business :
We highlight some key projects this year including the release of the following merchandise :
| - | BTS Permission to Dance in Las Vegas on November 27, 2023. |
| - | Stray Kids 2nd World Tour Maniac Concert, 2nd world tour. |
| - | ATEEZ Summer photobook and DVD. Note ATEEZ recently debuted at #1 in the billboard chart. |
In 2022 approximately 80% of sales have come from HYBE specifically from its two subsidiaries Weverse Company Inc. and Universal Music Japan. In 2023 52% of sales came from HYBE specifically from its two subsidiaries Weverse Company Inc. and Universal Music Japan.
The material terms of the agreement outlines the terms at which Play Company will provide DVDs, Digital Codes, and other merchandise of HYBE’s artists to Weverse Company Inc. and Universal Music Japan. In the Weverse Company Inc. agreement the supply price is determined at a discount of the local selling price in Korea as well as Japan.
Play Company’s written agreement with Weverse Company Inc. provided for a term from September 28, 2022 to Feb. 5, 2023. Play Company’s written agreement UMJ provided for a term from January 1 2022 to Dec. 31 2022. The formal, comprehensive agreement (producing, publishing, and distributing merchandise) between Play Company and HYBE has also expired. However, based on an informal understanding between Play Company and HYBE, despite the expiration of the Weverse Agreement and the UMJ Agreement, Play Company has continued to distribute and release products covered by those agreements in 2023. An example of this is the release of BTS Permission to Dance in Las Vegas merchandise on November 27, 2023.
However, recently, HYBE created a limited, distribution only agreement with Play Company targeting the first half of 2024. This distribution agreement with HYBE was signed on March 19, 2024 for four specific merchandise products. This one-year distribution agreement is projected to yield limited revenues to Play Company in 2024. A copy of a redacted version of Play Company’s agreement with Hybe, dated January 26, 2024 is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.56. Play Company is in the process of negotiating new agreements with HYBE and its subsidiaries for 2025 and 2026 but there is no guarantee any such agreements will be executed and whether the terms will revert back to a comprehensive agreement noted previously. If the agreement is not executed or if the terms are changed Play Company runs the risk that revenue will decline from HYBE.K Pop agencies can exert significant buyer power over Play Company.
On December 22, 2023 we entered into a new agreement with SM Entertainment Co., Ltd., a major K-pop agency, to create video merchandise for all of their artists. Revenues from SM Entertainment could take some years to build to the levels achieved by HYBE. A copy of a redacted version of Play Company’s agreement with SM Entertainment, dated December 12, 2023, is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.57.
Change following business combination and future business activity
Play plans to continue its ongoing efforts to elevate the visibility of K-pop artists. To achieve this, we aim to collaborate with leading talent management groups such as HYBE, JYP, and others, and working closely with their most popular artists. Furthermore, Play is committed to expanding its footprint in international markets, with a specific focus on Japan and Southeast Asian regions. Play recognizes the global appeal of K-pop and aim to capitalize on this by growing Play’s business in creating specialized video merchandise tailored for K-pop fans worldwide. This strategic approach aligns with Play’s vision to not only strengthen its presence in the domestic market but also to establish Play as a prominent player in the global K-pop merchandise industry.
Timeline and status of developing such capabilities
The most immediate priority is to continue to develop and expand fandom-targeted merchandisable IP of K Pop artists that will resonate with fans. Play will also expand its merchandising business in Japan by partnering with top tier K Pop and J Pop artists. Approximately 40% of 2022 revenues came from Japan.
Within the next two years we aim to enter new markets with a particular emphasis on Southeast Asia. By understanding and meeting the unique demands of each market, we aim to cultivate a global fan base for Play’s specialized merchandise. In addition, we want to create a new portfolio of collectible merchandise for non K Pop content including from film and TV series.
Industry in which Play company Co., Ltd. will compete (following the business combination): Content merchandising industry
According to the Korean Creative Content Agency’s analysis of the second half of 2022 and annual trends in the content industry, the revenue of the Korean music industry reached $8.58 billion in 2022. This industry has grown at a 11.9% CAGR since 2014. (See: Korea Creative Content Agency (KOCCA), “2014 and 2022 Yearly Analysis of Content Industry Trends”, p.7 and p. 6 (2014 kocca.kr), (2022 kocca.kr)). This industry consists of several segments including physical albums, digital music, performances, and licensing. During COVID-19, off-line performances were not held for about two years, but online streaming performances were introduced as an alternative. Since then performers have introduced live streaming systems in concert venues to simultaneously hold offline and online hybrid performances. Many agencies are now broadcasting performances to platforms such as cinemas. Against this backdrop, K-Pop merchandising (“MD”) market has been growing and we expect it to become larger. We estimate the four major entertainment agencies in Korea (HYBE Co., Ltd., JYP Entertainment Corporation, SM Entertainment Co., Ltd., YG Entertainment Inc.) earned $592 million in MD sales and licensing in 2022, accounting for more than 23% of their total revenues. (Source : KB Securities, May 2, 2023, Focusing on what only Hybe can do, p.6, (kbsec.com); Daishin Securities, September 6, 2022, Entertainment p. 62, (daishin.com) SM 2022 Quarterly Earnings Reports; Samsung Securities, May 12, 2023, YG Entertainment, p.2 (samsungpop.com); and Kyobo Securities, July 12, 2023, JYP Ent, p.2, (mk.co.kr), internal company estimates.) Merchandise purchase by K-Pop fans is driven by emotion and we find that they will purchase multiple physical CDs to obtain a specific item that is randomly placed in CDs or to obtain tickets to attend fan meetings. The specialized video merchandise we provide appeals to the same fan base. These fans have been willing to purchase higher ticket amounts. We expect the demand for merchandise will expand beyond just music related goods to photos, clothing, accessories, cosmetics, food, and beverages. In addition, we expect demand for K-Pop merchandise to grow internationally. Major entertainment agencies in Korea have opened pop-up stores related to K-Pop merchandise. K Enter plans to compete in the content merchandising industry through its proposed acquisition of Play Company.
Customers
The main customers of Play Company are K-pop agencies that work with K-Pop artists such as HYBE Co., Ltd., JYP Entertainment Corporation. While we work with large agencies we also work with smaller agencies with budding stars as well as other popular Korean music genres other than K-Pop that have a strong fan base in Korea. The fans of the K-Pop artists are also important customers that evaluate the quality of Play’s video merchandise as well as the ancillary photo albums, calendars and other items that are included in Play’s merchandise package.
Suppliers
Play’s suppliers are also the talent agencies that work with K-Pop stars that supply the video content in its video merchandise. Play also work with manufacturers of photo albums, printing services and other suppliers for the packaged merchandise we create.
Sales & Marketing
Play’s sales and marketing is focused on supporting music talent agencies (such as HYBE Co., Ltd., JYP Entertainment Corporation, KQ Entertainment Co., Ltd.) which manage the artists and the distributors (such as Weverse, HYBE Co., Ltd., Universal) of the merchandise goods. Play works closely with both parties to design an attractive merchandise to be released, including special gifts, photo cards, and other inducements such as the opportunity to have a video call with their favorite artist that will be included in the package. Play also works with lesser known artists and talent agencies to develop new talent which could turn out to be the next stars. Play started working with some of the biggest K-Pop artists long before they became famous.
Competition
Play believes its main competitors are the internal teams within major music talent agencies. Talent agencies could bring these capabilities in house, but the competencies required to produce, manufacture, and distribute quality video merchandise is not necessarily their core competency. Talent agencies have come to understand the tight deadlines Play Company works under to deliver this video merchandise and have come to appreciate the value of one-stop solution that Play Company provides. We are aware of other companies including Copan Global that competes with us. While some players can create the merchandising materials, we believe many are not able to produce the critical specialized video content that is included as part of the package. In terms of the quality of the video content we believe we create the highest quality content. Play Company’s competitiveness comes from its ability to produce, film, and edit to create superior video productions of the artist in their natural state especially during concerts.
Competitive Strength
Play Company’s video merchandises are planned to be released in regular intervals during the year. This is a model Play Company first developed. The merchandise is released during specific times and events such as concerts, album releases and fan meetings. Play Company’s ability to produce a merchandise package consisting of quality video merchandise and other goods that fans (primarily female teenagers) will want, and then manufacture, and distribute these goods on time is one of its competitive strength. New, desirable, goods must be continuously created yet be consistent with the image of the artist. Play Company is also a pioneer by providing a full service end-to-end solution to talent agencies by designing, producing, and distributing video merchandise. This turnkey approach is also a unique competitive strength. Management companies that have worked with Play company have seen the benefit of additional meaningful sales and profits from video merchandise products which tangibly benefit both the artist and their K-pop agency and have thus been willing partners.
| 4 | K Enter business engaged in content investment (following the business combination) : Solaire Partners LLC. |
Products and Service offered
Investments into the cultural content sector particularly movies.
Revenue generated (In June YTD 2024, 2023 and 2022)
$0.7 million in revenues were generated by Solaire in June YTD 2024, $1.3 million in 2023, and $1.4 million in 2022. Revenues are generated from investment management revenues in exchange from investment management services the includes fund administration, fund compliance, fund transfer agent and fund distribution services. Investment management services are calculated as a contractual percent of the fund Solaire Partners manages for its clients. For successful projects profit sharing also contributes to revenues.
Contribution to total revenue:
Total revenues of $0.7 million in June YTD 2024 would have represented 2.3% of the combined revenues of all Six Korean Entities combined.
Total revenues of $1.3 million in 2023 would have represented 1.7% of the combined revenues of all Six Korean Entities combined.
Total revenues of $1.4 million in 2022 would have represented 0.9% of the combined revenues of all Six Korean Entities combined.
Current operational status of business
In 2023 of the five Korean films that were invited to the Cannes Film festival, Solaire had invested in two of the films Sleep and Hopeless. In Sleep Solaire was the main investor of the film.
Among the top 10 box office hits in 2023 Solaire was the main investor in two of the films. Sleep and The Day. Sleep surpassed the break-even point solely through the box office revenue with a cumulative audience of 1.47 million. It is currently available on IPTV, OTT. Profitability of this movie will increase as it is broadcast overseas and through the revenues from ancillary rights. Sleep was recently made available on Netflix in Korea.
The day was released on November 22, 2023. As of December 15, 2023 over 7.7 million have watched the movie at the box office. We expect this movie to be screened for an extended period. The break even has already been surpassed through the box office revenue. Additional revenues from movie theatres and from VOD is expected which will further improve profitability. Solaire Partners has recorded a cumulative Assets Under Management of $112 million (Period covers Jan. 1, 2017-Aug. 31, 2023, from internal company documents)
Solaire and Maybank Asset Management Singapore PTE. LTD. established a Variable Capital Company (VCC), a collective investment scheme, in Singapore on November 23, 2023. The fund name is K-Wave Fund 1. In the coming months the VCC is expected to attract capital directly from foreign investors primarily from Asia to invest in the Korean content industry. Solaire was also successful in launching its $16 million Korean Film Scale-Up Fund II in September of 2023. This would be the 8th VC fund launched by Solaire.
Change following business combination and future business activity
Solaire Partners will continue to be dedicated to investing in the expanding Korean cultural content industry. One change, however, involves actively supporting K Enter in its content investment initiatives. Solaire Partners’ role extends beyond traditional investment to providing strategic advice, assisting in the selection of content that possesses the potential to resonate with a global audience.
Timeline and status of developing such capabilities
Solaire will grow by leveraging the capabilities it currently has today.
Industry in which Solaire Partners LLC will compete (following the business combination) : Content Investment industry
Korea’s cultural venture capital market is estimated to be $2.5 billion. (See: Korea Creative Content Agency (KOCCA), “2022 Half and Yearly Analysis of Content Industry Trends”, p. 97, (kocca.kr)). The Korean cultural industry consists of various sectors such as film, drama, music, games, and e-sports. Growth has been driven in part by government policies to support the growth of this industry, and the increase in both individual and institutional investors who want to invest in the growth of this industry. The Korean content investment industry is driven primarily by venture capital firms, strategic investors that both invest and distribute content such as CJ ENM and Lotte Entertainment as well as financial investors. Financial investors are primarily securities firms, banks, insurers, and other financial firms. Another important player in the content investment industry is KVIC, a venture capital specialist managing fund of funds that is backed by the Korean government, Solaire expects to continue to seek investments from strategic investors, financial investors as well as KVIC. In addition, Solaire has established a VCC fund in Singapore, a collective investment scheme which is expected to attract capital directly from foreign investors primarily from Asia to invest in the content industry. The name of the VCC fund is the K-Wave Fund and its overall investment objective, through multiple sub-funds, shall consist of investments across multiple asset classes, including Korean movies, drama and content companies. The managers of the fund are Solaire and Maybank Asset Management, a Malaysian bank. The K-Wave fund pays 2% management fee based on the total fund size per year and a 20% performance fee based on the gains that exceed the 15% IRR hurdle rate at time of liquidation. Solaire is entitled to 75% of the management fee and Maybank Asset Management is entitled to 25% of the management fee and Solaire is entitled to 100% of the performance fee.
Customers
Solaire is a specialized VC firm focused on cultural content. Solaire in the past has secured some part of their funding from the Korea Venture Investment Corporation, a government agency, and other public agencies such as the Regional Film Council. Large Korean institutional financial investors and major cinema chains that distribute, produce, and invest in movies also fund Solaire’s projects. Past performance is not indicative of future performance and there can be no assurance that prior investors in Solaire projects will invest in K Enter’s projects.
Suppliers
Investment targets include production companies who require investments for their production. Solaire reviews on average 250 movie scenarios every year from production companies that seek investments. Solaire also invests in the projects of major cinema chains that distribute, produce, and invest in movies. Within this environment suppliers can also be customers.
Sales & Marketing
In the context of content investment, sales and marketing are relevant when creating a fund. Sales efforts are directed at potential investors, including the following segments: Financial Investors (Banks, Securities Firms, etc.): Seeking Profit and Stability - Investors looking to pursue investment returns. Strategic Investors (Production Companies, Distributors, etc.): Synergy and Collaboration - Investors aiming to align their internal investment portfolio with the fund’s objectives. Public Investors (Korea Venture Capital, Regional Film Commission, etc.): Achieving Social Goals - Government or public sector entities seeking to achieve specific social objectives through their investments.
The stages of fund sales targeting these investors are as follows:
(1) Targeting: Identifying potential investors that align with the characteristics of the fund, such as film or drama-related projects, and understanding their key needs.
(2) Proposal Writing: Creating a detailed proposal that explains the fund’s objectives, strategies, and potential profitability.
(3) Meetings and Presentations: Conducting presentations based on the proposal, addressing investors’ questions comprehensively, and emphasizing the advantages of the investment.
(4) Negotiation and Terms Definition: Engaging in negotiations with investors and defining investment conditions, amounts, and other terms.
(5) Contract Signing: Finalizing the negotiation process by signing the investment agreement.
Solaire Partners has several marketing strengths when it comes to establishing and operating funds for customers and suppliers, as follows:
1. Solaire Partners has a well-balanced team composed of content industry experts with extensive experience in content investment and a financial professional holding a CFA qualification. With a deep understanding of the content industry and significant expertise in business development and M&A, the team brings a high level of expertise to the table.
2. Solaire Partners has formed a wide-reaching network of industry players both domestically and internationally, known for their competitive IP production capabilities. Through years of content investment and collaboration, Solaire Partners has established strong relationships with proven producers and directors, providing access to high-quality information about their projects and opportunities to invest in their projects.
3. Solaire Partners is recognized and trusted as a specialized venture capital (“VC”) firm in the field of cultural content by government agencies in South Korea. It has a history of being selected as the General Partner (GP) for cultural content funds backed by government institutions. Solaire Partners has also successfully developed and operated South Korea’s first cultural content index fund with funding primarily from financial institutions such as banks, securities firms, and insurance companies.
Past performance is not indicative of future performance. Thus, the fact that Solaire had projects in the past, does not mean that K Enter’s will have successful project in the future.
Competition
Competitors in the cultural venture capital industry include Daesung Private Equity, a listed company in KOSDAQ with an AUM of $254 million, and KC Ventures specializing in cultural content with an AUM of $119 million. See Disclosure Information of Venture Capital Analysis (DIVA), (vcs.go.kr).
Solaire Partners competes with other VC firms that specialize in the content sector. There are others venture capital firms that invest in the content sector as part of a broader investment strategy.
Competitive Strength
Solaire Partners has a unique funding approach, unlike most Korean cultural VCs that initially rely on investments from the Korea Venture Investment Corp (“KVIC”), Solaire Partners initiated its business using funds from financial investors to create movie investment funds. KVIC is a venture capital specialist managing fund of funds that is backed by the Korean government. While some of Solaire’s investment funds have received funding from KVIC, other Solaire investment funds have raised funds from sources other than KVIC. Solaire has devised diverse investment strategies.
This was made possible due to the Solaire team’s deep understanding of the Korean content industry, which they gained through years of experience in the sector. Unlike other VCs, many of which have financial backgrounds and venture into cultural content VC, Solaire Partners’ team brings a deeper industry-specific knowledge. Solaire Partners has recorded a cumulative AUM of $112 million (Period covers Jan. 1, 2017-Aug. 31, 2023, from internal company documents). In over six years, Solaire Partners’ has invested in 178 movies, with 49% of invested commercial movies (production cost over $2.3 million) surpassing break even. This is significant as the percentage of Korean commercial movies in the market that achieve break-even is typically around 33%. See KOFIC, “2021 and 2022 Korean Film Market Analysis Report”, p 101, (2021 kofic.or.kr), p. 101-102 (2022 kofic.or.kr).
Past performance is not indicative of future performance and there can be no assurance that investors in Solaire Partners will be able to obtain investors in future K Enter’s projects nor that K Enter’s future projects will be successful.
K Enter’s goal and vision
To achieve its goals K Enter plans to initially secure the intellectual property (“IP”) rights for quality drama and film content (as measured in terms of audience reception or artistic merit) instead of following the traditional content production business model in Korea where streaming companies have provided content producers a certain level of markup (5-10%) above the cost of production while taking the full IP rights of what is produced. By having K Enter or one of the Six Korean Entities invest in at least 30% of the production cost of films and drama K Enter will be able to secure its share of IP rights. K Enter believes that by owning the IP rights of quality content, K Enter will be able to monetize on the value of this IP as it is distributed globally. Additionally, K Enter will nurture, enable film and drama creators to expand by providing them with an alternative source of financing. This contrasts with the existing practice where creators rely primarily on local major cinema chains and streaming (subscription video on demand companies) for financing. Leveraging Solaire Partners’ expertise, K Enter expects to be able to invest in film and drama and content companies.
K Enter will also help creators distribute their content globally and find a wider audience for their work. K content popularity on global streaming platforms has increased in part because it is cost efficient (20-30% of Hollywood costs) and in recent years has become one of the most popular forms of non-English content especially in Asia. In the case of Squid Games it cost Netflix $2.4 million per episode vs. $8 million for Stranger Things and $10 million for The Crown according to Variety. Squid Games beat Stranger Things in terms of viewership during the first 91 days since release to become one of Netflix’s most popular series ever. Over 2.2 billion hours were viewed for Squid Games. According to KOCCA K content exports (including video games, music, animation, movies, TV series, etc.) grew from $4.3 billion in 2011 to $13.3 billion by 2022. (See: Korea Creative Content Agency (KOCCA), “2014 and 2022 2nd Half and Yearly Analysis of Content Industry Trends”, p. 18. p. 8, (2014 kocca.kr), (2022 kocca.kr)) K content has been growing in worldwide popularity and K Enter believes there is still room for continued growth.
K Enter’s ultimate vision is to become a leading tech and IP-based total entertainment company, covering a wide spectrum of content genres, formats, and technologies. Even after the acquisition of the Six Korean Entities, K Enter plans to expand its business capabilities and market presence by recruiting new talents and acquiring accretive M&A targets. K Enter’s company vision is focused on creating an IP-based business model, global expansion and ecosystem expansion.

IP-Based business model
| | (1) | K Enter plans to integrate core capabilities to create an IP-based business model maximizing synergic value creations with content IPs |
| | (2) | K Enter plans to extend content investment to secure and fully capture market potentials of content IPs |
| (3) | Financing and profit-sharing alternatives for creators to existing outsourcing models for global streaming platforms |
Global Expansion
| | (1) | K Enter plans to expand to Southeast Asia and Japan, by developing local distribution networks and co-production partnerships |
| (2) | Expecting strong co-production opportunities in Southeast Asia by transferring K Content expertise in producing local content |
| | (3) | Long-term K Enter wants to enter into American and European markets based upon New K Enter’s strong track records in Asian markets |
Ecosystem Expansion
| | (1) | K Enter plans to identify innovative opportunities for crossover synergies between different content genres, formats and technologies |
| | (2) | K Enter plans to acquire new business capabilities to expand the IP-based ecosystem through recruiting new talents and executing M&A transactions, in such areas as webtoons, animations, music, talent management, games and interactive content |
K Enter aims to create a diversified content ecosystem by acquiring controlling equity interests in the Six Korean Entities and then seeking out additional strategic acquisitions spanning from video content to gaming and interactive content. In the future, K Enter plans to expand video capabilities and expand into webtoons and webnovels to adapt as IP sources for film and TV series production, and then K Enter expects to acquire talented musicians, actors and creators and tech-based interactive content capabilities to fully leverage its IP libraries
K Enter’s Directors and Executive Officers
The current directors and executive officers of K Enter are as follows:
| Name | | Age | | Position |
| Pyeung Ho Choi | | 66 | | Co-Founder and Chairman |
| Ted Kim | | 53 | | Co-Founder of K Enter and Director |
| Tan Chin Hwee | | 52 | | Director and Executive Chairman and Interim Chief Executive Officer |
| Hyuk Jin Lee | | 51 | | Director |
| Han Jae Kim (Patrick Kim) | | 35 | | Director |
| Young Jae Lee | | 49 | | Co-Founder and Director |
| Jun Jong | | 53 | | Chief Financial Officer |
| Jeong Hoon Bae | | 45 | | Head of Content Production |
Board of Directors of K Enter
Pyeung-ho Choi:
Mr. Pyeung-ho Choi is the co-founder and Chairman of K Enter Holdings Inc. and the founder and CEO of Solaire Partners LLC, one of the leading Korean content VC firm and one of the pioneers in the Korean entertainment industry. Prior to Solaire Partners LLC, Choi was the appointed President Fund Manager of the Union Global Contents Investment Fund at Union Investment Partners Inc. from 2012 to 2016. At a size of US $120 million, the Fund partnered with major Korean distributors and financiers, the Korean government, and foreign investors, with an aim to invest in international co-productions to globalize the Korean film and content industry. Through Choi’s vast experience in content investment, the Union Global Contents Investment Fund collaborated with Korean companies, directors, and actors, in co-productions with countries including the United States, China, and Japan.
Before joining Union Investment Partners, Choi was the CEO of SidusFNH at Korea Telecom Group, where he oversaw the company’s film financing, production, and distribution operations. He spearheaded the aggregation and digital distribution of content through multiple new media platforms that Korea Telecom Group owned and operated from 2008 to 2011; these platforms included IPTV, Internet VOD, Satellite TV, and mobile.
Choi began his entertainment industry career at CJ Group, where he was one of the founding members of CJ Entertainment (CJENM). He served as Executive Vice President at CJENM from 2000 to 2007 after serving as General Manager of strategic planning and international business teams from 1995 to 1999. He played a critical role in shaping CJ Group’s film business portfolio, including: the inception of CJ Entertainment through the CJ Group’s investment in DreamWorks SKG in the United States; the joint venture that distributed CJ films across Asia; the formation of CJ Group’s exhibition arm, CGV, that became Korea’s largest exhibitor, initially jointly established by CJ Group, Golden Harvest, and Village Roadshow. During his 12 year tenure at CJ Entertainment, Choi financed and distributed a number of notable Korean films that introduced many talented Korean directors and actors. He launched filmed entertainment, music licensing, TV drama series, animation, and cable broadcasting businesses. In 1982, he started at the Samsung Group in business planning at CJ CheilJedang Corporation, where he was responsible for business strategy planning, M&A, overseas business and export, and overseas marketing. From 1987 to 1994, he served as head of the strategy planning team and head of the overseas business team.
Choi holds a Ph.D. in holographic engineering, a Master’s degree in 3D contents from Kwangwoon University, and a Bachelor’s degree in chemical engineering from Youngnam University.
Ted Kim:
Mr. Kim is the co-founder and a member of the board of directors of K Enter. Mr. Kim founded Global Fund LLC in August 2013, a US-based private equity firm that focuses on investing in high-growth companies across various industries and geographies, including the pre-IPO period, and has been serving as its Managing Partner ever since. Global Fund LLC is also the managing member of Tribeca Global SPAC Fund I, III, and IV LLC which were founded during 2021 and 2022. Mr. Kim is a highly experienced and disciplined private equity specialist who has successfully launched and closed multiple U.S.-based private equity funds. Mr. Kim has also been a member of the Korea-America Business Summit, Washington D.C., since 2019. He co-founded Global Star Acquisition I LLC in September 2022, the sponsoring entity for the US Nasdaq listed SPAC “Global Star Acquisition Inc.”, and has been serving as its Managing Member ever since. He also co-founded K Enter Holdings Inc. in January 2023. Mr. Kim is also an Attorney at Law focusing on mergers and acquisitions and cross-border transactions. He was a Guest Lecturer at Tsinghua University in 2005 on American venture capitalism. Mr. Kim received his Juris Doctor degree from the Pennsylvania State University’s Dickinson School of Law in May 1997. He received his Bachelor of Arts degree in Finance and Politics, a double major, from the Catholic University of America in May 1993.
Tan Chin Hwee:
Mr. Tan is appointed as the Chairman of SGTraDex Services. SGTraDex is built upon the foundation of the Emerging Stronger Taskforce Alliance for Action and formed through a collaborative effort across public and private stakeholders. Chin Hwee was also nominated as a member of the Trade and Connectivity Standards Committee under the Singapore Standards Council (SSC)/MTI, which facilitates the development, promotion and review of standards in Singapore.
Mr. Tan also serves as the current Chief Executive Officer, Asia Pacific of Trafigura. He joined Trafigura in 2016 and is responsible for continuing the growth of Trafigura’s business across the region. Trafigura was the largest amongst the only three Singapore companies to appear in the Fortune Global 500 list and it ranked top 22 globally. Chin Hwee has more than 25 years of experience in management and financial roles. Prior to joining Trafigura, he was most recently the founder of the Asian operations of alternative investment firm Apollo Global Management, and before that, managing director at hedge fund Amaranth Advisors.
Mr. Tan has sat on the boards of various organizations in the public and private sectors. The positions he held include: member of the Resource Panel for Government Parliamentary Committee for Finance and Trade and Industry; member of the Advisory Panel for Youth Corps Singapore; member of the Advisory Panel for the Ministry of Education; member of the Advisory Panel for the Ministry of Culture, Community and Youth; board member of Lien Aid Limited (Singapore), the endowment fund for KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital; advisory board member of Shanghai Jiao Tong University’s Shanghai Advanced Institute of Finance; non-executive and independent director of Keppel REIT (until June 2017); member of Nanyang Technological University’s board of trustees; member of Hwa Chong Institution executive committee board; member of the Monetary Authority of Singapore’s Finance Centre Advisory Panel; and member of the Maritime and Port Authority of Singapore’s International Maritime Centre (IMC) 2030 Advisory Committee.
Mr. Tan holds a Bachelor of Accountancy degree, graduating with Second Class Upper Honours in 1995 from NTU. He has an MBA from Yale University and completed a postgraduate course at Harvard Kennedy School. He is a Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) and is both an Australian and a Singapore-registered Certified Public Accountant (CPA). He was also the past President of CFA Society Singapore
Youngjae Lee
Youngjae Lee currently serves as a director and co-founder of K Enter Holdings Inc and Chief Executive Officer of Solaire Partners LLC. Youngjae Lee served as the Chief Executive Officer of K Enter Holdings, Inc. from inception until July 5, 2024. Youngjae Lee co-founded K Enter Holdings Inc. and Solaire Partners LLC in October 2023 and June 2007, respectively. Youngjae Lee worked at KT from 2000 to 2016, where he undertook various positions such as a team member, deputy director, and project leader. During his stay at KT, Mr. Lee oversaw subsidiaries such as NTC and Mongol Telecom, handled mergers and acquisitions planned by KT, led business developments of KT, and was responsible for various in-house consulting tasks. While overseeing KT’s Russian telecommunications subsidiary NTC in Vladivostok, he contributed to its growth and exit strategy and made it the largest telecommunications operator in the Far East region. From Apil 2006 to September 2010, he served as the Chief Financial Officer and the Chief Information Officer at Sidus FNH, a movie production company acquired by KT as its strategy to enter the Korean content media industry. This experience equipped him with insights into the content industry, where he introduced real-time production management systems to enhance budget efficiency in movie productions. Starting in October 2010, Mr. Lee was responsible for overseas subsidiaries and international telecommunications operators within KT’s in-house consulting department. During this period he made substantial contributions to the growth of KT’s subsidiaries East Telecom and EVO in Uzbekistan by conducting management assessments and formulating growth strategies. His efforts led to KT’s recognitions such as Outstanding Employee Award in 2011, and further responsibilities such as Project Manager position for the Game Changer Project at Botswana’s government-owned telecommunications company, BoFiNet in 2015. Through Mr. Lee’s initiative, BoFiNet gained global recognition in 2016 as the most innovative telecommunications company. In 2017, Mr. Lee founded Solaire Partners, a venture capital firm specializing in content investments. Solaire Partners has amassed assets under management (AUM) amounting to USD $112 million and secured investments of USD $44 million from the South Korean government for four distinct funds, with Mr. Lee taking on the role of manager for three of these funds. Solaire Partners has invested in approximately 200 films, with 49% surpassing the break-even point, significantly outperforming the market average of 33% and even surpassing the 16% market average return. Under Mr. Lee’s leadership, Solaire Partners has achieved substantial success by investing in various films and content, leveraging South Korean commercial film industry data to enhance investment strategies and yield higher returns. Furthermore, Solaire Partners has been diversifying investments into the digital human and virtual production studio sectors to lead the paradigm shift in the Korean content industry. Mr. Lee received a degree in Business Administration from Chungbuk National University in 2000. He furthered his education by participating in the Global MBA program at Sungkyunkwan University and attending Indiana University’s Kelly Business School as an exchange student, enhancing his academic background class of 2015. He also holds the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) qualification, demonstrating his expertise in financial matters. Currently, he serves as an instructor for the Cultural Content segment of the Korean Venture Capital Association’s Venture Capitalist program, starting in 2021.
Han Jae Kim (Patrick Kim)
Patrick Kim is a Co-Founder and Managing Partner of Sui Generis Partners. He has more than 10 years of capital market, investment banking, private equity, and venture capital experience, is also a member of Investment Committee of Sui Generis Partners. He additionally serves as an external advisor for Naviator Capital. At Sui Generis, he oversees an investment framework that originated, managed, and monitored a diverse portfolio of early-stage venture investment, mainly in SaaS/Cloud Software and Content/Entertainment sectors. Prior to establishing Sui Generis in 2021, Patrick was an investment professional at BRV Capital Management from 2018 to 2021, one of prominent tech-focused private equity across Asia and the US, where he was responsible for Growth Capital and Late-Stage Venture Capital investment in the US and Europe along with his team in Seoul Office. Prior to joining BRV Capital Management, Patrick worked at BGC Partners Hong Kong and Daewoo Securities Hong Kong, responsible for originating, structuring, and executing equity, debt, and structured offering across a broad range of products and asset classes for both primary and secondary market.
Mr. Kim graduated from Peking University with a Bachelor of Economics degree, concentrating in Finance.
Hyukjin Lee:
Hyukjin is a Vice President at IDG Capital, a leading investment firm focused on developing extraordinary companies through its expertise in private equity, and venture capital. Throughout his 27 year career in the financial services industry, he has served as fund manager, M&A strategist, PE manager and venture capitalist. By combining both the macro perspective and micro perspective from venture capital and private equity he has successfully invested in three unicorn companies in a row. Prior to IDG Capital he worked in leading firms such as Hanwha Investment and Hyundai Investment Trust.
Hyukjin graduated with a B.A. degree in Economics from Korea University
Management of K Enter
Executive Chairman and Interim Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) : Tan Chin Hwee See description above.
Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”) : Jun Jong
Jun is currently the CFO of K Enter. He started his career at Samsung electronics in 1995, performing foreign subsidiary management, investment, and planning. Following Samsung he transitioned to the Hartford Financial Services in Tokyo, Japan and Hartford, CT in 2000. As part of the startup team of Hartford Life Insurance K.K.’s Tokyo operations he helped launch the Japan operations where he performed strategic planning, financial analysis, and investor relations during the period it expanded from startup to USD 15 billion in AUM.
Subsequently he was Assistant Vice President of business development and strategy for The Hartford Financial Services Group’s wealth management group until 2013, developing enterprise-wide business opportunities, supporting M&A transactions and divestiture of non-core businesses.
More recently Jun has worked in private equity performing value creation and business development activities in portfolio companies, capital raising activities and LP management.
Jun received a Bachelor of Arts degree in economics from Dartmouth College and an MBA from the Tuck School of Business at Dartmouth.
Chief Accounting Officer (“CAO”) : Jihun Byun
Jihun Byun, CPA, is currently the CAO of K Enter holdings, managing the accounting field of the company. He brings with him a diverse set of experience primarily in accounting, M&A, and corporate governance restructuring more than 10 years. He worked as general manager in corporate center at Wonik corporations, own several KOSDAQ listed corporations in the semiconductor/display, secondary battery, beauty, and digital healthcare sectors.
Jihun received a Bachelor of Arts degree in business from Sogang University.
Head of Content Production: Jeong Hoon Bae
Jeong Hoon Bae, K Enter’s Head of the Content Production, is a veteran, executive producer in Korea who has worked in the TV drama industry for 21 years. He started as an assistant director (AD) at the SBS TV drama department from 2003 to 2007 helping to produce numerous dramas. SBS, is one of the leading Korean broadcasting channels. Subsequently he worked at TVN, a pay television network owned by CJ E&M. Next he worked at Bone Factory a TV drama production company, as executive producer creating popular works such as “You’re Beautiful” which was part of the first generation of Korean dramas to be aired in Asia and Japan.
Subsequently he worked at Huayi Brothers as executive producer creating miniseries for Korean broadcasting channels. Subsequently he worked as CEO of Big Pictures where he created several dramas that were aired in JTBC. Subsequently he was the senior vice president and executive producer of Ace Factory, where he led drama planning, production, distribution, and investment. Jong-Hoon Bae also worked on projects for streaming companies such as “The Grid” for Disney+. One of his earlier works “My Name” was also released on Netflix.
Jeong Hoon Bae has a Bachelor of Arts in statistics and communications from SungkyunKwan University
Capabilities and the Six Korean Entities to be acquired
Below is a description of the businesses of the Six Korean Entities that K Enter plans to acquire prior to the closing of the Business Combination.
1. Content Production
Four production companies as well as an in-house drama company provide K Enter with a base to provide film and drama content. These companies have within them a previous record of producing quality content and commercial success. K Enter’s drama in-house production capabilities is led by Bae Jung Hoon and Lee Jae Ha, two very experienced executive producers. Bae Jeong Hoon is a former vice president of Ace Factory, one of the leading independent studios in Korea.

| 1) | Apeitda Co., Ltd. (“Apeitda”) |
Established in 2013, Apeitda’s main business is a film production studio and is led by Jung Byung-gil and his brother Jung Byung-sik. Apeitda’s focus has been on action and thriller movies such as The Villainess and Carter which received recognition from Hollywood for its unique camerawork to create a sense of realism in action films. The Villainess was invited to premiere at the Cannes Film Festival as part of the Midnight Screening section. Another movie, Confession of Murder was remade in Japan in 2017.
Apeitda’s principal offices are located at 156, Ohyeon-ro, Gangbuk-gu, Seoul, Korea.
Apeitda currently has three full time employees, not including sub-contractors.
Apeitda owns IP rights to two movies. It owns 100% of the IP rights of Action Boys and 50% of The Villainess.
K Enter’s Agreements with Apeitda
On April 9, 2023, K Enter entered into a Stock Purchase Agreement with Jung Byunggil to acquire 51% of Apeitda (the “Apeitda SPA”) in consideration of a purchase price of 15,300,000,000 Korean Won in shares of K Enter on the day preceding the closing date of the Apeitda SPA, which as of June 30, 2024 equaled approximately $11.1 million or 3,643 shares of K Enter Common Stock. The closing of the Apeitda SPA is to occur as soon as the subject registration statement becomes effective. In connection with the Apeitda SPA, the shares retained by the minority shareholders do not have any economic, voting or other rights that differ from the shares purchased by K Enter. On September 14, 2023, K Enter and Apeitda entered into an amendment of the Apeitda SPA (the “Apeitda Amendment”) which provided among other things that the closing of the Apeitda SPA will occur on January 5, 2024 or on such other date as designated by K Enter, provided all conditions precedent have been satisfied.
On April 24, 2023, K Enter entered into an Equity Pledge Agreement with each of the Apeitda Shareholders (the “Apeitda EPA”), pursuant to which each Apeitda Shareholder pledged certain percentages of his or her equity interests in the Apeitda in the total amount of 51% outstanding equity interest of Apeitda to K Enter to guarantee the performance of Apeitda’s obligations under the relevant SPA Agreement. Under the terms of the Apeitda EPA, in the event that Apeitda Shareholders breach their respective contractual obligations under the subject SPA Agreements, K Enter, as pledgee, will be entitled to certain rights, including, but not limited to, the right to transfer an ownership interest in favor of K Enter. All of the Apeitda Shareholders also agreed that upon the occurrence of any event of default, as set forth in the Apeitda EPA, K Enter is entitled to dispose the pledged equity interest in accordance with applicable Korean laws. Each of Apeitda’s Shareholders further agreed not to dispose of the pledged equity interests or take any actions that would prejudice K Enter’s interest. The Apeitda EPA is effective until the earlier of (i) the date of the “closing” of the subject Apeitda SPA; (ii) the date as of which the subject Apeitda SPA is duly terminated; or (iii) the date as of which all of the obligations secured by the pledge shall have been duly performed.
The purposes of the Apeitda EPA is to (1) guarantee the performance of the Apeitda Shareholders obligations to convey their pledged shares under the Apeitda SPA, (2) make sure any of Apeitda’s Shareholders do not and will not transfer or assign the pledged equity interests, or create or allow any encumbrance that would prejudice K Enter’s interests without K Enter’s prior written consent, and (3) provide K Enter effective control over the pledged equity interests of Apeitda to ensure the closing of the Apeitda SPA. In the event that Apeitda or its shareholder(s) breaches its contractual obligations under the Apeitda SPA, K Enter will be entitled to foreclose on and dispose all of Apeitda’s issued and outstanding equity interests, have the right to (1) dispose of the pledged equity of Apeitda and (2) require Apeitda to pay all payments due or damages incurred by K Enter. However, during the term of the Apeitda EPA, the pledgors shall retain all voting and economic rights with respect to the pledged equity interests.
On April 24, 2023, K Enter entered into a Letter of Consent for Disposal with each Apeitda Shareholder (the “Apeitda DA”) which irrevocably granted K Enter an irrevocable right to dispose of the subject shares in the event of any default on the part of the Apeitda
The Apeitda DA shall remain effective until all of the equities in Apeitda that are to be purchased by K Enter under the Apeitda SPA (i.e. 51% outstanding equity interest of Apeitda) are transferred to K Enter and/or an entity designated by K Enter.
The Apeitda SPA, together with the Apeitda EPA and the Apeitda DA, together enable K Enter to exercise effective control over Apeitda.
The foregoing description of the Apeitda SPA, Apeitda Amendment, Apeitda EPA and Apeitda DA does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the actual agreements, English translations of the original Korean versions are attached hereto as Exhibit 10.10.
| 2) | Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd. (“Bidangil”) |
Established in 2005 and led by Soo-Jin Kim and In-beom Yoo. Bidangil is a production studio that has produced over 10 movies including thrillers such as The Chaser and Korea’s first space based sci fi movie Space Sweepers which was released on Netflix. Another characteristics of Bidangil is that it has had successfully uncovered talented new directors, including Na Hongjin for The Chaser and Jo Sunghee for A Werewolf Boy and Space Sweepers. Bidangil also has created a distinctive portfolio of films with unique story lines and settings.

Bidangil’s principal offices are located on the 5th floor, Yeoksam-ro 220-gil, Gangnam-gu, Seoul and has 5 employees.
Bidangil currently has 5 full time employees, not including sub-contractors.
Bidangil owns intellectual property rights for the following movies it has produced.
Bidangil owns partial IP rights to the following works:
| | 5. | Phantom Detective (40%) |
Share Purchase Agreement
Under the Stock Purchase Agreement (the “Bidangil SPA”) executed on April 10, 2023 among each of the Bidangil’s Shareholders and the K Enter, K Enter will acquire 51% of Bidangil in consideration of a purchase price of 20,400,000,000 Korean Won in shares of K Enter on the day preceding the closing of the Bidangil SPA, which as of June 30, 2024 equaled approximately $14.8 million or 4,857 shares of K Enter Common Stock. The closing of the Bidangil SPA is to occur as soon as the subject registration statement becomes effective. In connection with the Bidangil SPA, the shares retained by the minority shareholders do not have any economic, voting or other rights that differ from the shares purchased by K Enter. On September 14, 2023, K Enter and Bidangil entered into an amendment of the Bidangil SPA (the “Bidangil Amendment”) which provided among other things that the closing of the Bidangil SPA will occur on January 5, 2024 or on such other date as designated by K Enter, provided all conditions precedent have been satisfied.
Equity Pledge Agreement
Under the Equity Pledge Agreement dated April 24, 2023 (the “Bidangil EPA”), Bidangil and each of the Bidangil Shareholders pledged certain percentages of his or her equity interests in the Bidangil in the total amount of 51% outstanding equity interest of Bidangil to K Enter to guarantee the performance of Bidangil’s obligations under the Bidangil SPA. Under the terms of the Bidangil EPA, in the event that the Bidangil Shareholders breach their respective contractual obligations under the subject SPA Agreements, K Enter, as pledgee, will be entitled to certain rights, including, but not limited to, the right to transfer an ownership interest in favor of K Enter. All of the Bidangil’s Shareholders also agreed that upon the occurrence of any event of default, as set forth in the Bidangil EPA, K Enter is entitled to dispose the pledged equity interest in accordance with applicable Korean laws. Each of Bidangil’s Shareholder further agreed not to dispose of the pledged equity interests or take any actions that would prejudice K Enter’s interest.
The Bidangil EPA is effective the earlier of (i) the date of the “closing” of the subject Bidangil SPA; (ii) the date as of which the subject Bidangil SPA is duly terminated; or (iii) the date as of which all of the obligations secured by the pledge shall have been duly performed.
The purposes of the Bidangil EPA are to (1) guarantee the performance of the Bidangil Shareholders obligations to convey their pledged shares under the Bidangil SPA, (2) make sure any Bidangil’s Shareholders do not and will not transfer or assign the pledged equity interests, or create or allow any encumbrance that would prejudice K Enter’s interests without K Enter’s prior written consent, and (3) provide K Enter effective control over the pledged equity interests of Bidangil to ensure the closing of the Bidangil SPA. In the event that Bidangil or its shareholder(s) breaches its contractual obligations under the Bidangil SPA, K Enter will be entitled to foreclose on and dispose all of Bidangil’s issued and outstanding equity interests, have the right to (1) dispose of the pledged equity of Bidangil and (2) require Bidangil to pay all payments due or damages incurred by K Enter. However, during the term of the Bidangil EPA, the pledgors shall retain all voting and economic rights with respect to the pledged equity interests.
Letter of Consent for Disposal
Under the Letter of Consent for Disposal dated April 24, 2023 (the “Bidangil DA”), each Bidangil Shareholder irrevocably granted K Enter an irrevocable right to dispose of the subject shares in the event of any default on the part of the Bidangil.
The Bidangil DA shall remain effective until all of the equities in Bidangil that are to be purchased by K Enter under the Bidangil SPA (i.e. 51% outstanding equity interest of Bidangil) are transferred to K Enter and/or an entity designated by K Enter.
The Bidangil SPA, together with the Bidangil EPA and the Bidangil DA, together enable K Enter to exercise effective control over Bidangil.
The foregoing description of the Bidangil SPA, Bidangil Amendment, Bidangil EPA and Bidangil DA does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the actual agreements, English translations of the original Korean versions are attached hereto as Exhibit 10.11.
| 3) | The LAMP Co., Ltd. (“Lamp”) |
Established in 2023. Led by Park eun-kyung, The Lamp is a film and TV series production studio specializing in thought-provoking yet commercially successful movies including ‘A Taxi Driver’, ‘Mal-Mo-E’ and ‘Samjin Company English Class’. A Taxi Driver, for example, achieved commercial success attracting 12.2 million viewers at the box office. The Lamp has received awards at various film festivals and awards for content quality, including Blue Dragon Awards, Baeksang Art Awards and Houston International Film Festival. One of her current projects includes Aema, a Netflix original series that is scheduled for release in 2025. In Netflix’s press release of September 11, 2023, it confirmed the production of its upcoming series Aema, a fictional comedy. Netflix described it as a fictional comedy revealing the harsh realities of actors behind the glitzy veneer of Korean show business in the 80s.

The Lamp’s principal offices are located at 1st floor, Samseong-ro 119-gil 37-9, Ganagnam-gu Seoul.
The Lamp currently has 4 full time employees, not including sub-contractors.
The Lamp currently owns no real estate property. It used to own 3 properties.
Share Purchase Agreement
Under the Stock Purchase Agreement executed on April 10, 2023 (the “Lamp SPA”), among each of the Lamp’s Shareholders and the K Enter, K Enter will acquire 51% of Lamp in consideration of a purchase price of 30,600,000,000 Korean Won in shares of K Enter on the day preceding the closing of the Lamp SPA, which as of June 30, 2024 equaled approximately $22.2 million or 7,286 shares of K Enter Common Stock. The closing of the Lamp SPA is to occur as soon as the subject registration statement becomes effective. In connection with the Lamp SPA, the shares retained by the minority shareholders do not have any economic, voting or other rights that differ from the shares purchased by K Enter. On September 14, 2023, K Enter and Lamp entered into an amendment of the Lamp SPA (the “Lamp Amendment”) which provided among other things that the closing of the Lamp SPA will occur on January 5, 2024 or on such other date as designated by K Enter, provided all conditions precedent have been satisfied.
Share Pledge Agreement
The Lamp Pledge Agreement is dated April 24, 2023 and effective until June 15, 2024 (the “Lamp EPA”) and can be extended by mutual written consent. K Enter shall cancel or terminate the Lamp EPA upon “closing” of the Lamp SPA.
Under the Lamp EPA, Lamp and each of the Lamp Shareholder pledged certain percentages of his or her equity interests in the Lamp in the total amount of 51% outstanding equity interest of Lamp to K Enter to guarantee the performance of Lamp’s obligations under the Lamp SPA. Under the terms of the Lamp EPA, in the event that the Lamp Shareholders breach their respective contractual obligations under the Lamp SPA, K Enter, as pledgee, will be entitled to certain rights, including, but not limited to, the right to transfer an ownership interest in favor of K Enter. All of the Lamp Shareholders also agreed that upon the occurrence of any event of default, as set forth in the Lamp EPA, K Enter is entitled to dispose the Lamp pledged equity interest in accordance with applicable Korean laws. Each of Lamp’s Shareholder further agreed not to dispose of the pledged equity interests or take any actions that would prejudice K Enter’s interest.
The purpose of the Lamp EPA is to (1) guarantee the performance of the Lamp Shareholders obligations to convey their pledged shares under the Lamp SPA, (2) make sure any Lamp’s Shareholders do not and will not transfer or assign the pledged equity interests, or create or allow any encumbrance that would prejudice K Enter’s interests without K Enter’s prior written consent, and (3) provide K Enter effective control over the pledged equity interests of Lamp to ensure the closing of the Lamp SPA. In the event that Lamp or its shareholder(s) breaches its contractual obligations under the Lamp SPA, K Enter will be entitled to foreclose on and dispose all of Lamp’s issued and outstanding equity interests, have the right to (1) dispose of the pledged equity of Lamp and (2) require Lamp to pay all payments due or damages incurred by K Enter. However, during the term of the Lamp EPA, the pledgors shall retain all voting and economic rights with respect to the pledged equity interests.
Letter of Consent for Disposal
Under the Letter of Consent for Disposal dated April 24, 2023 (the “Lamp DA”), each Lamp Shareholder irrevocably granted K Enter an irrevocable right to dispose of the subject shares in the event of any default on the part of the Lamp.
The Lamp DA shall remain effective until the 100% equities in Lamp are transferred to K Enter and/or an entity designated by K Enter.
The Lamp SPA, together with the Lamp EPA and the Lamp DA enable K Enter to exercise effective control over Lamp.
The foregoing description of the Lamp SPA, Lamp Amendment, Lamp EPA and Lamp DA does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the actual agreements, English translations of the original Korean versions are attached hereto as Exhibit 10.12.
| 4) | Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd. (“Anseilen”) |
Anseilen’s main business is production studio for multi-form TV series and movies. While it is a newly established entity (March 2023), it is led by Kyung-su Shin, Jun-Woo Park, Seung-Ho Kim, 3 top executive producers who worked for SBS, one of the leading Korean TV broadcasting channels. They have created some of Korea’s most famous dramas such as an adaptation of the webtoons taxi driver and other works such as the First Responders’ and ‘Twenty-Five Twenty-One’.

Anseilen’s principal offices are located at 37, Almata-gil, Dongjak-gu, 107 Dong 902 Ho, Seoul, Korea 06939.
Anseilen currently has 4 full time employees, not including sub-contractors.
Share Purchase Agreement
Under the Stock Purchase Agreement executed on April 9, 2023 (the “Anseilen SPA”) among each of the Anseilen Shareholders and the K Enter, K Enter will acquire 51% of Anseilen in consideration of a purchase price of 7,700,000,000 Korean Won in shares of K Enter on the day preceding the closing of the Anseilen SPA, which as of June 30, 2024 equaled approximately $5.6 million or 1,833 shares of K Enter Common Stock. The closing of the Anseilen SPA is to occur as soon as the subject registration statement becomes effective. In connection with the Anseilen SPA, the shares retained by the minority shareholders do not have any economic, voting or other rights that differ from the shares purchased by K Enter. On September 14, 2023, K Enter and Anseilen entered into an amendment of the Anseilen SPA (the “Anseilen Amendment”) which provided among other things that the closing of the Anseilen SPA will occur on January 5, 2024 or on such other date as designated by K Enter, provided all conditions precedent have been satisfied.
Equity Pledge Agreement
The Equity Pledge Agreement is effective until the earlier of (i) the date of the “closing” of the subject Anseilen SPA; (ii) the date as of which the subject Anseilen SPA is duly terminated; or (iii) the date as of which all of the obligations secured by the pledge shall have been duly performed.
Under the Anseilen EPA, Anseilen and each of the Anseilen’s Shareholder pledged certain percentages of his or her equity interests in the Anseilen in the total amount of 100% outstanding equity interest of Anseilen to K Enter to guarantee the performance of Anseilen’s obligations under the Anseilen SPA. Under the terms of the Anseilen EPA, in the event that the Anseilen Shareholders breach their respective contractual obligations under the Anseilen SPA, K Enter, as pledgee, will be entitled to certain rights, including, but not limited to, the right to transfer an ownership interest in favor of K Enter. All of the Anseilen Shareholders also agreed that upon the occurrence of any event of default, as set forth in the Anseilen EPA, K Enter is entitled to dispose the pledged equity interest in accordance with applicable Korean laws. Each of Anseilen’s Shareholder further agreed not to dispose of the pledged equity interests or take any actions that would prejudice K Enter’s interest.
The purposes of the Anseilen EPA is to (1) guarantee the performance of the Anseilen Shareholders obligations to convey their pledged shares under the Anseilen SPA, (2) make sure any Anseilen’s Shareholders do not and will not transfer or assign the pledged equity interests, or create or allow any encumbrance that would prejudice K Enter’s interests without K Enter’s prior written consent, and (3) provide K Enter effective control over the pledged equity interests of Anseilen to ensure the closing of the Anseilen SPA. In the event that Anseilen or its shareholder(s) breaches its contractual obligations under the Anseilen SPA, K Enter will be entitled to foreclose on and dispose all of Anseilen s issued and outstanding equity interests, have the right to (1) dispose of the pledged equity of Anseilen and (2) require Anseilen to pay all payments due or damages incurred by K Enter. However, during the term of the Anseilen EPA, the pledgors shall retain all voting and economic rights with respect to the pledged equity interests.
Letter of Consent for Disposal
Under the Letter of Consent for Disposal dated April 24, 2023 (the “Anseilen DA”), each Anseilen Shareholder irrevocably granted K Enter an irrevocable right to dispose of the subject shares in the event of any default on the part of the Anseilen.
The Anseilen DA shall remain effective until all of the equities in Anseilen that are to be purchased by K Enter under the Anseilen SPA (i.e. 51% outstanding equity interest of Anseilen) are transferred to K Enter and/or an entity designated by K Enter.
The Anseilen SPA, together with the Anseilen EPA, and the Anseilen DA enable K Enter to exercise effective control over Anseilen.
The foregoing description of the Anseilen SPA, Anseilen Amendment, Anseilen EPA and Anseilen DA does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the actual agreements, English translations of the original Korean versions are attached hereto as Exhibit 10.13.
2. Content merchandising
Play Company Co., Ltd. (“Play Company”)
K Enter believes Play Company to be one of the leading producer and distributor of specialized video merchandise products in Korea. Play Company has been the trusted partner of K Pop groups such as BTS, Twice, Seventeen and 25 other artists. Through this video merchandise, Play Company enhances the fan experience and strengthens the engagement between artists and fans. Play Company is a pioneer in this full-service end-to end solution to talent agencies by designing, producing, and distributing video merchandise. Play Company’s video merchandises are planned to be released in regular intervals during the year. This is a model Play Company first developed. The merchandise is released during specific times, occasions, and events such as concerts, album releases, fan meetings, end of year review of the artist’s activities. These programs are created under tight deadlines. Play Company’s ability to produce quality video merchandise, manufacture, and distribute, these goods on time is its competitive strength.
Samples of Merchandise that Play Company Releases

Management companies that have worked with Play company have seen the benefit of additional meaningful sales and profits from video merchandise products which tangibly benefit both the artist and their K-pop agency and have thus been willing partners. Merchandising and licensing revenues have been growing for the top four agencies. In 2022 it is estimated that merchandising and licensing accounted for more than 23% of revenues at the top four agencies. The specialized video merchandise is the primary business of Play Company. The non-video merchandise such as clothes account for only approximately 10% of Play Company’s revenues.
Play Company’s key priorities include maintaining and developing a portfolio of K-Pop stars willing to collaborate with Play Company, expanding the Japan business which already accounts for approximately 44% of its revenues by signing on J-pop artists, and entering new foreign markets. Play Company intends to capitalize on the increasing popularity of K-Pop globally. One measure of this popularity is seen in the total number of YouTube views during March 2021 and February 2022. BTS, Black Pink and Twice generated 27.5 billion YouTube views globally. 95% of views were from outside of Korea. (See: Korea Joongang Daily, “As K-Pop Goes Global, Koreans Fall Behind When it Comes to Consumption” April 5, 2022, (joins.com)) In Japan 15 of top the 50 albums in 2022 were from K-Pop bands according to Oricon, Japan’s music chart authority.
Play Company will also create collectibles for non K-Pop fandoms in movies, dramas and other content. Play Company has in the past created merchandising and animation products for actors. With the added network Play Company gains through its content production business, greater effort will be placed in nurturing this non K-pop segment. In addition to its core video merchandise business, Play Company also operates a bakery and restaurant business, which accounts for approximately 10% of its overall revenues.
K Enter believes Play Company’s main competitors are the internal teams within major music talent agencies. Talent agencies could bring these capabilities in house, but the competencies required to produce, manufacture, and distribute quality video merchandise is not necessarily their core competency. Talent agencies have come to understand the tight deadlines Play Company works under to deliver this video merchandise and have come to appreciate the value of one-stop solution that Play Company provides. In terms of the quality of the video content K Enter believes K Enter creates the highest quality content. Play Company’s competitiveness comes from its ability to produce, film, and edit to create superior video productions of the artist in their natural state especially during concerts.
Play Company’s subsidiary (“Play F&B”) is engaged in the food and beverage business, as well as licensing its intellectual property in the food and beverage business. Play F&B operates a retail bakery-café business and franchising business under the concept names “Our Bakery”. As of June 30, 2023, retail operations consist of 15 Play F&B-owned bakery-cafes and 7 franchise-operated bakery-cafes located in South Korea and China.
Play Company’s principal offices are located at 20th Fl., E Business Tower, Nurikum Square Building A, 396 World Cup Buk-ro, Mapo-gu, Seoul, South Korea, 03940. Play Company owns no real property. Its office is leased.
Play Company currently has 244 full time employees, not including sub-contractors of which 203 work in the F&B group.
Share Purchase Agreement
Under the Stock Purchase Agreement executed on March 31, 2023 (the “Play SPA”) among each of the Play Company’s Shareholders and the K Enter, K Enter will acquire 100% of Play Company in consideration of a purchase price of 127,498,912,820 Korean Won in shares of K Enter on the day preceding the closing of the Play SPA, which as of June 30, 2024 equaled approximately $92.6 million or 30,356 shares of K Enter Common Stock, plus a cash payment due as follows: (1) 18,133,103,403 Korean Won or approximately $13,172,862 payable within three months of the date PubCo’s shares are listed for trading; (2) 9,050,000,000 Korean Won or approximately $6,574,407 payable on or before January 31, 2025; and (3) 9,050,000,000 Korean Won or approximately $6,574,407 payable on or before January 31, 2026. The closing of the Play SPA is to occur as soon as the subject registration statement becomes effective.
An additional payment in cash may be owed to the owner of Play Company if the shares of PubCo that shares of the K Enter’s common stock convert to at closing of the Acquisition Merger are sold during the three-month period (the “Sale Period”) following the six-month lock-up period of the newly issued shares of PubCo at a per share price less than the per-share value at closing of the Acquisition Merger for the shortfall in share price. The amount to be paid will be reduced by (i) any gains from the sale of shares of PubCo by the owner of Play Company between the end of the Sale Period and December 31, 2026 and (ii) any unrealized gain as of December 31, 2026 for the shares of PubCo that remain held by the owner of Play Company (calculated as the number of remaining shares of PubCo times the difference of (i) the average closing price of PubCo from December 1, 2026 to December 31, 2026 and (ii) the per-share value of PubCo at the closing of the Acquisition Merger).
As part of the Play SPA, the owner of Play Company was provided a call option agreement, whereby the owner of Play Company has the option to acquire the shares of Play F&B, a subsidiary of Play Company, within three years from the closing date of the acquisition between K Enter and Play Company at a price of 504.8 million Korean Won or approximately $0.4 million as of June 30, 2023, which is the book value of Play F&B as of December 31, 2022.
On September 30, 2023, K Enter and Play Company entered into an amendment of the Play Company SPA (the “Play Amendment”) which provided among other things, that (i) the purchase price changed from KRW 163,732,018,000 to KRW 163,732,016,220, effecting a change in the aggregate value of the K Enter shares to be issued to Play Company from KRW 127,500,000,000 to KRW 127,498,912,820, but did not change the cash payment to Play Company portion of the purchase price set forth in the Play SPA, and (ii) the closing of the Play SPA will occur on January 5, 2024 or on such other date as designated by K Enter, provided all conditions precedent have been satisfied.
Equity Pledge Agreement
The Equity Pledge Agreement is effective the earlier of (i) the date of the “closing” of the subject Play SPA; (ii) the date as of which the subject Play SPA is duly terminated; or (iii) the date as of which all of the obligations secured by the pledge shall have been duly performed and can be extended by mutual written consent (the “Play EPA”). K Enter shall cancel or terminate the Equity Pledge Agreement upon “closing” of the Play SPA.
Under the Play EPA, Play Company and each of the Play Company Shareholder pledged certain percentages of his or her equity interests in the Play Company in the total amount of 100% outstanding equity interest of Play Company to K Enter to guarantee the performance of Play Company’s obligations under the Play SPA. Under the terms of the Play EPA, in the event that the Play Company Shareholders breach their respective contractual obligations under the Play SPA, K Enter, as pledgee, will be entitled to certain rights, including, but not limited to, the right to transfer ownership interest in favor of K Enter. All of Play Company Shareholders also agreed that upon occurrence of any event of default, as set forth in the Play EPA, K Enter is entitled to dispose the pledged equity interest in accordance with applicable Korean laws. Each of Company’s Shareholder further agreed not to dispose of the pledged equity interests or take any actions that would prejudice K Enter’s interest.
The purposes of the Play EPA are to (1) guarantee the performance of the Play Company Shareholders obligations to convey their pledged shares under the Play SPA, (2) make sure any Play Company’s Shareholder do not and will not transfer or assign the pledged equity interests, or create or allow any encumbrance that would prejudice K Enter’s interests without K Enter’s prior written consent, and (3) provide K Enter effective control over the pledged equity interests of Play Company to ensure the closing of the Play Company SPA. In the event that Play Company or its shareholder(s) breaches its contractual obligations under the Play SPA, K Enter will be entitled to foreclose on and dispose all of Play Company’s issued and outstanding equity interests, have the right to (1) dispose of the pledged equity of Play Company and (2) require Play Company to pay all payments due or damages incurred by K Enter. However, during the term of the Play EPA, the pledgors shall retain all voting and economic rights with respect to the pledged equity interests.
Letter of Consent for Disposal
Under the Letter of Consent for Disposal dated April 12, 2023 (the “Play DA”), each Play Company Shareholder irrevocably granted K Enter an irrevocable right to dispose of the subject shares in the event of any default on the part of the Play Company.
The Play DA shall remain effective until all of the equities in Play that are to be purchased by K Enter under the Play SPA (i.e. 100% outstanding equity interest of Play) are transferred to K Enter and/or an entity designated by K Enter.
The Play SPA, together with the Play EPA, and the Play DA enable K Enter to exercise effective control over Play Company.
The foregoing description of the Play SPA, Play Amendment, Play EPA and Play DA does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the actual agreements, English translations of the original Korean versions are attached hereto as Exhibit 10.15.
3. Content Investment
Solaire Partners, LLC (“Solaire”)
Solaire is a content-specialized private equity firm based in Korea that invests in movies, dramas, and content companies since 2017. It is led by their CEO, Pyeungho Choi and Solaire’s team of content and finance experts with extensive experience in the entertainment industry. Solaire follows a disciplined project selection process, followed by a thorough hands-on, value add approach to investments. It monitors, reviews and shapes marketing and distribution strategy (teaser, poster, setting release date, distribution), scenario development, and participates in the casting of a project. Solaire Partners has invested in some of the highest-grossing films out of Korea. It has also invested in entertainment tech companies that digitize content or produce super IP.
Among its distinctions, it has created Korea’s first and only movie investment fund based on proprietary movie data. The fund invests to capture the returns of the broad segment of Korean commercial movies. Solaire has invested over $138 million in over 200 content projects in the last five years. Solaire Partners has received distinctions from the Korean government as one of the leading venture capitalist firms in the cultural content sector and has secured the investments from some of the largest financial institutions in Korea such as Samsung Securities, Industrial Bank of Korea that have started to invest in the movie industry.
Solaire Partners in addition to financing movies through its venture capital business plans to create a VCC fund in Singapore, a collective investment scheme which is expected to attract capital from investors primarily from Asia. On a pro forma basis the revenues of Solaire Partners would have accounted for approximately 1.3% of New K Enter’s total revenues in 2022. Solaire Partners derives revenues through a management fee (around 2%) on the amount invested. Solaire’s revenues in terms of the entire group in 2022 was relatively small. K Enter expects Solaire Partners LLC’s share of total New K Enter revenues to remain at these levels.
Solaire Partners priority includes helping K Enter extend the investment scope from films to TV series and other formats of content including webtoons and animation and expanding K Enter’s business globally.
Solaire Partners’ distinctiveness stems from the fact that its members are content specialists who also possess finance capabilities. This combination allows Solaire Partners to approach investments in the content industry with a deeper understanding of the creative and artistic aspects, rather than solely focusing on the financial aspects of a project. In addition, due to their extensive experience and expertise in the content industry, Solaire Partners has built a strong network in this industry. Strong relationships with influential producers and directors have allowed it to become the anchor investor in acclaimed movies such as “Parasite” and “Decision to Leave.” This showcases their ability to identify and support promising projects and talent.
Solaire Partners competes with other VC firms that invest in the contents industry. Some like Solaire invest exclusively in the content sector. There are others that invest in the content sector as part of a broader investment strategy.
Solaire is located at 11F, Telepia Bldg, 527, Eonju-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul Korea 06138. Solaire Partners’ owns no real property. Its office is leased.
Solaire Partners currently has 7 full time employees, not including sub-contractors.
Solaire Partners does not own any intellectual property.
Equity Purchase Agreement
Under the Equity Purchase Agreement executed on March 31, 2023 (the “Solaire SPA”) among each of the Solaire Partners’ Shareholders and the K Enter, K Enter will acquire 95% of Solaire Partners in consideration of a purchase price of 14,250,000,000 Korean Won in shares of K Enter on the day preceding the closing of the Solaire SPA, which as of June 30, 2024 equaled approximately $10.4 million or 3,393 shares of K Enter Common Stock. The closing of the Solaire SPA is to occur as soon as the subject registration statement becomes effective. In connection with the Solaire SPA, the shares retained by the minority shareholders do not have any economic, voting or other righs that differ from the shares purchased by K Enter. On September 14, 2023, K Enter and Solaire entered into an amendment of the Solaire SPA (the “Solaire Amendment”) which provided among other things that the closing of the Solaire SPA will occur on January 5, 2024 or on such other date as designated by K Enter, provided all conditions precedent have been satisfied.
Equity Pledge Agreement
The Equity Pledge Agreement is effective until the earlier of (i) the date of the “closing” of the subject Solaire SPA; (ii) the date as of which the subject Solaire SPA is duly terminated; or (iii) the date as of which all of the obligations secured by the pledge shall have been duly performed and can be extended by mutual written consent (the “Solaire EPA”). K Enter shall cancel or terminate the Equity Pledge Agreement upon “closing” of the subject Solaire SPA.
Under the Solaire EPA, Solaire Partners and each of the Solaire Partners’ Shareholder pledged certain percentages of his or her equity interests in the Solaire Partners in the total amount of 95% outstanding equity interest of Solaire Partners to K Enter to guarantee the performance of Solaire Partners’ obligations under the Solaire SPA. Under the terms of the Solaire EPA, in the event that the Solaire Partners Shareholders breach their respective contractual obligations under the Solaire SPA, K Enter, as pledgee, will be entitled to certain rights, including, but not limited to, the right to transfer ownership interest in favor of K Enter. All of the Solaire Partners Shareholders also agreed that upon occurrence of any event of default, as set forth in the Solaire EPA, K Enter is entitled to dispose the pledged equity interest in accordance with applicable Korean laws. Each of Solaire Partners’ Shareholder further agreed not to dispose of the pledged equity interests or take any actions that would prejudice K Enter’s interest.
The purposes of the Solaire EPA are to (1) guarantee the performance of the Solaire Partners Shareholders obligations to convey their pledged shares under the Solaire SPA, (2) make sure any Solaire Partners’ Shareholders do not and will not transfer or assign the pledged equity interests, or create or allow any encumbrance that would prejudice K Enter’s interests without K Enter’s prior written consent, and (3) provide K Enter effective control over the pledged equity interests of Solaire to ensure the closing of the Solaire SPA. In the event that Solaire or its shareholder(s) breaches its contractual obligations under the Solaire SPA, K Enter will be entitled to foreclose on and dispose all of Solaire Partners’ issued and outstanding equity interests, have the right to (1) dispose of the pledged equity of Solaire Partners and (2) require Solaire Partners to pay all payments due or damages incurred by K Enter. However, during the term of the Solaire EPA, the pledgors shall retain all voting and economic rights with respect to the pledged equity interests.
Letter of Consent for Disposal
Under the Letter of Consent for Disposal dated April 24, 2023 (the “Solaire DA”), each Solaire Partners Shareholder irrevocably granted K Enter an irrevocable right to dispose of the subject shares in the event of any default on the part of the Solaire.
The Solaire DA shall remain effective until all of the equities in Solaire Partners that are to be purchased by K Enter under the Solaire SPA (i.e. 95% outstanding equity interest of Solaire Partners) are transferred to K Enter and/or an entity designated by K Enter.
The Solaire SPA, together with the Solaire EPA, and the Solaire DA enable K Enter to exercise effective control over Solaire Partners.
The foregoing description of the Solaire SPA, Solaire Amendment, Solaire EPA and Solaire DA does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the actual agreements, English translations of the original Korean versions are attached hereto as Exhibit 10.16.
K Enter’s Relationship with First Virtual Lab, Inc. (“First Virtual”)
First Virtual is an emerging company with plans to establish virtual production capabilities. It currently has no revenues. The content virtualization capability First Virtual develops is dependent to how quickly First Virtual establishes a virtual studio, acquires clients and generates revenues. First Virtual was established in 2020, plans to provide virtual production, computer graphics (CG), and visual effects (VFX).
First Virtual is led by CEO Kim Sung-kwon. First Virtual ’s objective is to meet the increasing demand for virtual production infrastructure and digital assets in Korea. The virtual production capabilities of First Virtual can provide producers greater efficiency and can help save cost and time while enhancing the audience experience through an immersive and realistic experience. First Virtual plans to expand its tech-based entertainment portfolio by launching additional visual effects businesses in collaboration with global partners.
Virtual production globally is expected to increase 18.2% from 2023 to 2030 to reach $6.7 billion globally according to Grandview research. COVID was a catalyst for virtual production and showed the potential gains in efficiency with digital production.
First Virtual principal office is located at Unit 2803, GIFC Tower located at 240 Kintex-ro, Ilsanseo-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do.
First Virtual currently has seven full time employees, not including sub-contractors.
K Enter’s Agreements with the Shareholders First Virtual
1. Original Agreement
Share Purchase Agreement
Under the Stock Purchase Agreement executed on April 12, 2023 (the “FVL SPA”) among each of the First Virtual’s Shareholders and the K Enter, K Enter will acquire 51% of First Virtual in consideration of a purchase price of 25,500,000,000 Korean Won in shares of K Enter on the day preceding the closing of the FVL SPA, which as of June 30, 2024 equaled approximately $18.5 million or 6,071 shares of K Enter Common Stock. The closing of the FVL SPA is to occur as soon as the subject registration statement becomes effective.
Equity Pledge Agreement
The Equity Pledge Agreement is effective the earlier of (i) the date of the “closing” of the subject FVL SPA; (ii) the date as of which the subject FVL SPA is duly terminated; or (iii) the date as of which all of the obligations secured by the pledge shall have been duly performed and can be extended by mutual written consent (the “FVL EPA”). K Enter shall cancel or terminate the FVL EPA upon “closing” of the FVL SPA
Under the FVL EPA, First Virtual and each of the First Virtual Shareholders pledged certain percentages of his or her equity interests in the First Virtual in the total amount of 51% outstanding equity interest of First Virtual to K Enter to guarantee the performance of First Virtual’s obligations under the FLV SPA. Under the terms of the FVL EPA, in the event that the First Virtual Shareholders breach their respective contractual obligations under the FVL SPA, K Enter, as pledgee, will be entitled to certain rights, including, but not limited to, the right to transfer ownership interest in favor of K Enter. All of the First Virtual Shareholders also agreed that upon occurrence of any event of default, as set forth in the FVL EPA, K Enter is entitled to dispose the pledged equity interest in accordance with applicable Korean laws. Each of First Virtual’s Shareholder further agreed not to dispose of the pledged equity interests or take any actions that would prejudice K Enter’s interest.
The purposes of the FVL EPA are to (1) guarantee the performance of First Virtual’s obligations under the FVL SPA, (2) make sure any First Virtual Shareholders do not and will not transfer or assign the pledged equity interests, or create or allow any encumbrance that would prejudice K Enter’s interests without K Enter’s prior written consent, and (3) provide K Enter effective over the pledged equity interests of First Virtual to ensure the closing of the First Virtual SPA. In the event that First Virtual or its shareholder(s) breaches its contractual obligations under the FVL SPA, K Enter will be entitled to foreclose on and dispose all of First Virtual’s issued and outstanding equity interests, have the right to (1) dispose of the pledged equity of First Virtual and (2) require First Virtual to pay the fund and all any payment due or damages incurred. However, during the term of the FVL EPA, the pledgors shall retain all voting and economic rights with respect to the pledged equity interests.
Letter of Consent for Disposal
Under the Letter of Consent for Disposal dated April 24, 2023 (the “FVL DA”), each First Virtual Shareholder irrevocably granted K Enter an irrevocable right to dispose of the subject shares in the event of any default on the part of the First Virtual.
The FVL DA shall remain effective until all of the equities in First Virtual that are to be purchased by K Enter under the FVL SPA (i.e. 51% outstanding equity interest of First Virtual) are transferred to K Enter and/or an entity designated by K Enter.
The FVL SPA, together with the FVL EPA, and the FVL DA enable K Enter to exercise effective control over First Virtual.
The foregoing description of the FVL SPA, FVL EPA and FVL DA does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the actual agreements, English translations of the original Korean versions are attached hereto as Exhibit 10.14.
The FVL SPA, together with the FVL EPA, and the FVL DA were terminated and amended by the execution of two agreements, namely the Termination and Amendment to the Share Purchase Agreement and the Shareholders Agreement, dated January 31, 2024, by and among Sungkwon Kim, King Bear Film LLC and K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “SPA Amendment”) and the Share Purchase Agreement, dated January 31, 2024, by and among King Bear Film LLC and K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “KB Agreement” and collectively with the SPA Amendment the “New FVL Agreements”). Pursuant to the New FVL Agreements the purchase price for K Enter’s acquisition of a controlling interest in First Virtual was reduced from approximately $20 million to approximately $8 million. Copies of the SPA Amendment and the KB Agreement are attached hereto as Exhibits 10.19 and 10.20, respectively.
K Enter has recently learned that in or about December 2023, three separate lawsuits were filed concerning First Virtual, its principal Sungkwon Kim and certain other parties (collectively referred to as the “Prototype Lawsuits”). Two lawsuits are pending in the Chancery Court of the State of Delaware and one lawsuit in Korea. The Delaware lawsuits are entitled: Prototype Lab, Inc., a Korean corporation, Craig Bernard, individually and on behalf of Prototype Groupe, Inc. a Delaware corporation, Culley Bunker, individually and on behalf of Prototype Groupe, Inc. a Delaware corporation v. King Bear Film, LLC, a California limited liability company, John C. Kim a/k/a Chang Kun Kim, SunkKwon Kim and Patrick Han a/k/a Chung Ho Han and assigned Case No. 2023-1257-NAC and In Re Prototype Groupe, Inc., a Delaware corporation and assigned Case No. 2023-1287-NAC. The Korean lawsuit is entitled: Prototype Holding Co. Ltd. and Ju-yeon Lee v. Sungkwon Kim. Due to the pendency of the Prototype Lawsuits, on March 5, 2024, the New FVL Agreements relating to the acquisition of a majority equity stake in First Virtual were terminated pursuant to a Termination Agreement and Re-Purchase Option Agreement, dated March 5, 2024, by and among Sungkwon Kim, King Bear Film LLC and K Enter (the “FVL Termination and Option Agreement”). Pursuant to the FVL Termination and Option Agreement, the New FVL Agreements are terminated and Sungkwon Kim and King Bear Film LLC have an option, for a period of five (5) years, to compel K Enter to acquire a 51% equity interest in First Virtual from Sungkwon Kim and King Bear Film LLC at the then current fair market value provided the Prototype Lawsuits are resolved in a manner acceptable to K Enter. While no definitive action has been taken to terminate the FVL Termination and Option Agreement, K Enter currently views the acquisition of a controlling interest in First Virtual pursuant to the FVL Termination and Option Agreement as uncertain due to the uncertainty as to the outcome of the Prototype Lawsuits and there can be no assurance that K Enter will acquire a controlling interest in First Virtual pursuant to the FVL Termination and Option Agreement. A copy of the FVL Termination and Option Agreement are attached hereto as Exhibit 10.44.
Based on the termination of the New FVL Agreements, Global Star and K Enter agreed to decrease the base merger consideration Global Star will issue to the stockholders of K Enter in connection with the Business Combination. On March 11, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the First Amendment to Merger Agreement, which among other things decreased the base merger consideration from $610 million to $590 million that Global Star will issue to the stockholders of K Enter. Accordingly, pursuant to the First Amendment to Merger Agreement, PubCo will issue 59,000,000 ordinary shares of PubCo to the stockholders of K Enter in exchange for all of the shares of common stock of K Enter.
Key factors affecting New K Enter’s results of operation following the closing of the Business Combination.
The following are key factors affecting the results of New K Enter’s operation
1. New K Enter competes with large, established companies from many different segments of an entertainment industry which is rapidly evolving and being reshaped. Traditional TV’s influence has waned while streaming has become a more important means to consume content. Non-traditional players such as YouTube, a tech company, has become a powerful alternative to professionally produced content. More narrowly, New K Enter competes with major content creators associated with cinema chains, Korean conglomerates which have entered the entertainment industry, traditional broadcasters, large domestic and international streaming companies, and other companies that provide entertainment such as YouTube.
2. Considerable growth and execution risk. New K Enter’s success will depend on its ability to grow and execute on the tasks laid out in its roadmap and extract synergies from its business. New K Enter will need to prioritize, focus, execute, and coordinate the activities of the various entities and integrate them under New K Enter while successfully guiding them toward its common vision.
3. New K Enter faces concentration risk within Play Company Co. Ltd. Historically, in 2021 and 2022, Play Company’s dependence on HYBE, a K-pop agency, accounted for 86% and 80% of the total revenues of Play Company Co., Ltd. As of December of 2023 (Year-to-Date), this dependency on HYBE has decreased but still contributes to 65% of Play Company’s total revenues. New K Enter recognizes the risks associated with this level of dependency and are actively working towards diversifying Play Company’s revenue sources to mitigate these risks. The addition of SM Entertainment, a top tier K-pop agency, as a customer in December 21, 2023 will contribute to decreasing this risk.
4. While managing existing operating companies for profitable growth, New K Enter will need to continue to add capabilities to manage its growth and achieve its vision as well as strengthen its internal structure and processes.
5. Sustainability of K content. There are concerns that the global interest in K content may wane, stagnate and that the global penetration of K content has been reached. New K Enter feels there is room for greater growth and that Korean content will continue to provide great value with the potential to become a global hit.
6. New K Enter is a business that relies primarily on the work of producers, directors, and artists. New K Enter’s performance could be impacted by any negative factors that could impede their ability to work.
7. During COVID-19 movie attendance was severely limited. While movie attendance has increased it has not recovered fully to pre COVID-19 levels. The speed at which movie theatre attendance normalizes to pre-COVID levels impacts New K Enter’s operations.
The primary laws in Korea that may be applicable to New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities, include the following:
| (1) | The privacy and data protection laws in Korea that may be applicable to New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities, include the following: |
| 1. | Personal Information Protection Act (the “PIPA”): The PIPA aims to protect the freedom and rights of individuals, and further, to realize the dignity and value of the individuals, by prescribing matters related to the processing and protection of personal information. The primary enforcing authority of the PIPA is the Personal Information Protection Commission. |
| | (i) | New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities are expected to collect personal information from employees and customers in the course of their business operations. Consequently, it is anticipated that New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities may retain the collected personal information internally or provide it to third parties. For K Enter and/or its subsidiaries to be able to provide the collected personal information, it is important to note that they will be required to obtain separate consent from the data subjects. |
| | (ii) | According to the PIPA, New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities, as data handlers, are obligated to obtain consent from data subjects to collect and use their personal information as a general rule. Furthermore, they are only allowed to use the collected personal information strictly within the scope of the purposes for which it was collected (Article 15(1), the PIPA). When obtaining consent, data subjects must be provided with information regarding: (a) the purpose of collection; (b) the specific items of personal information being collected; (d) the retention and usage period; and (d) the data subject’s right to withhold consent and any disadvantages of doing so (if any) (Article 15(2), the PIPA). Additionally, if New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities intend to share the collected personal information with third parties, they are required to obtain explicit consent from data subjects for such third-party provision after providing them with certain statutorily-prescribed information (Article 17(1) and (2), the PIPA). |
| | (iii) | If New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities fail to comply with the various obligations required by the PIPA, they may be subject to administrative and/or criminal penalties, depending on the nature of the violation. For instance, in cases where personal information is used for purposes beyond the scope prescribed by the PIPA or is provided to third parties without the consent of the data subject, the responsible individual may be subject to imprisonment of up to five (5) years or fines of up to KRW 50 million as criminal penalty, and the corporate entity to which the responsible individual belongs may also be subject to fines of up to KRW 50 million (Items 1 and 2, Article 71; Article 74, the PIPA). In addition, in cases where personal information is processed without obtaining consent for collection and use, administrative penalties of up to 3% of the total annual sales (excluding sales unrelated to the violation) or up to KRW 2 billion may be imposed (Item 1, Article 64-2 of the PIPA). Moreover, refusing to provide goods or services due to a customer’s failure to provide their consent for the collection of personal information may be subject to administrative fines of up to KRW 30 million (Item 1, Article 75(2), the PIPA). |
| 2. | Act on the Promotion of Data Industry and the Activation of Data Use (the “Data Industries Act”): The objective of this Act to contribute to the enhancement of citizens’ quality of life and the advancement of the national economy by establishing necessary provisions related to the promotion of data production, trade, and utilization. The Data Industries Act is governed by the MSIT. |
| | (i) | The Data Industries Act governs the institutional foundation for fostering the data industry, including the promotion of data production, utilization, distribution, and trade. New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities are expected to produce various entertainment-related products and services in the course of their business operations, which will likely involve the use of various “data” regulated under the Data Industries Act. In such cases, they may be subject to the regulations and potentially eligible for various supports provided by the Data Industries Act. |
| (ii) | Under the Data Industries Act, data transaction businesses and others are required to report their business activities to the MSIT (Article 16, the Data Industries Act). Businesses that have duly reported may be eligible for various forms of support, including data platform support, support for fostering data transaction businesses, and tax incentives. |
| 3. | Act on Promotion of Information and Communications Network Utilization and Information Protection (the “Network Act”): The objective of this Act is to enhance the well-being of citizens and promote public welfare by fostering the effective utilization of information and communication networks. The Network Act is regulated by the Ministry of Science and ICT (the “MSIT”) and the Korea Communications Commission (the “KCC”). |
| | (i) | New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities are expected to utilize a range of information and communication networks, including the Internet, as part of their business operations, which may encompass activities such as marketing, sales and information publishing, and the collection of personal information. The Network Act regulates various activities that utilize information and communication networks, including those using telecommunications facilities and computer technology. |
| | (ii) | For instance, New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities may be regulated as “information providers” under the Network Act in the course of their business operations. In such cases, if the content (including text, audio, and video information) falls under harmful media content for minors as defined by the Youth Protection Act, it must be appropriately labeled as such (Article 42, the Network Act). |
| | (iii) | Failure by New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities to comply with the various obligations required under the Network Act may result in administrative fines, fines, or imprisonment, depending on the nature of the violation. For example, if they provide content for profit without appropriately marking it as harmful to minors in violation of Article 42 of the Network Act, they may be subject to imprisonment for up to two (2) years or fines of up to KRW 20 million (Article 73, the Network Act). |
The aforementioned privacy and data protection-related laws of Korea outline key requirements that New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities are required to comply with while conducting their business, including obtaining consent from data subjects when collecting, using, and transferring their personal information, as well as various reporting and labeling obligations.
In the course of conducting business activities involving the processing of personal information, New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities have consistently endeavored to operate their businesses in compliance with these laws, and they remain dedicated to upholding this commitment in the future.
The employment laws in Korea that may be applicable to K Enter and/or its subsidiaries include the following:
| 1. | Labor Standards Act: The purpose of this Act is to establish the standards for terms and conditions of employment in conformity with the Constitution of Korea, thereby securing and improving the fundamental living standards of employees and achieving a well-balanced development of the national economy. The Labor Standards Act is administered by the Ministry of Employment and Labor. |
| | (i) | New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities are expected to employ officers and employees within Korea for their business activities, which will entail certain responsibilities as per Korea’s Labor Standards Act, such as wage payment, provision of leave, and payment of retirement benefits. The Labor Standards Act and related labor regulations in Korea establish various obligations related to employment-related activities within the country, and New K-Enter will be required to comply with these regulations. Some of the exemplary requirements are as follows: |
| | - | Statutory allowances: Under the Labor Standards Act, an employer like New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities will be obligated to pay a designated percentage increase in wages (the “statutory allowances”) for extended, nighttime, and holiday work performed by employees (Article 56, the Labor Standards Act). Employers must also make additional payments if wages fall short of the statutory allowances (Article 49, the Labor Standards Act,). This obligation to pay statutory allowances applies regardless of the form of compensation for employees (e.g., hourly wage system, comprehensive wage system). |
| | - | Employment arrangements: KNew K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities are likely to use temporary workers in various fields, such as janitorial services, security, and UI design, and may engage in business outsourcing through service contracts. It also appears that they will use short-term and part-time workers in different roles. Under the Act on the Protection of Fixed-term and Part-time Employees (the “Fixed-term Employees Act”), employers are prohibited from treating employees who work short-term differently from regular employees who perform similar or equivalent tasks solely due to their short-term contract status (Article 8(2), the Fixed-term Employees Act). Violation of this provision may result in corrective orders by the Labor Relations Commission (Article 12, the Fixed-term Employees Act) and administrative fines of up to KRW 100 million for non-compliance with the ordered corrections (Article 24, the Fixed-term Employees Act). |
Additionally, it is important to note that regardless of the form of a contract, if the user company directly supervises and manages temporary workers, the situation may be considered as what is defined as “temporary placement of workers” under the Act on the Protection, etc. of Temporary Agency Workers (the “Temporary Workers Act”). In such cases, receiving work services from an unlicensed temporary work agency is prohibited (Article 7(3), the Temporary Workers Act), and violation thereof may result in (i) imprisonment for up to three (3) years or a fine of up to KRW 30 million (Item 2, Article 43, the Temporary Workers Act), and (ii) the obligation to directly employ the temporary workers (Item 5, Article 6-2(1), the Temporary Workers Act).
The aforementioned employment-related laws regulate various aspects of labor conditions in Korea, including obligations related to working hours (with a maximum of 52 hours per week), the supervision and management of contractors and service providers, the prohibition of discriminatory treatment of fixed-term workers, the obligation to provide retirement benefits for employees with more than one year of service, and the payment of wages in accordance with labor standards related to working hours and overtime.
New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities have consistently endeavored to operate their businesses in compliance with these employment-related legal requirements, and they remain dedicated to upholding this commitment in the future.
Other laws that may be relevant to New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities include the following:
New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities are expected to be engaged in businesses such as video content production and distribution, which may be subject to various laws and regulations, including the following:
| 1. | Commercial Act: The Commercial Act regulates various aspects related to the establishment, organization, and operation of companies. It is primarily governed by the Ministry of Justice. |
| 2. | Broadcasting Act: The objective of this Act is to safeguard viewers’ rights, foster democratic public opinion, and enrich national culture. It also seeks to advance the field of broadcasting and promote public welfare by upholding broadcasting’s freedom and independence while reinforcing broadcasters’ societal obligations. |
| 3. | Act on the Promotion of Newspapers, Etc. (the “Newspapers Act”): This Act aims to support the expansion of press freedom and the fostering of public opinion in a democratic manner by upholding the liberty and autonomy of newspaper publication and promoting social responsibility within the newspaper industry. |
| 4. | Promotion of the Motion Pictures and Video Products Act (“Motion Pictures Act”): The objective of this Act is to contribute to enhancing the cultural life of the people and promoting the national culture by upgrading the motion pictures and video products qualitatively and promoting the development of the film and video culture and its industry. |
| 5. | Framework Act on the Promotion of Cultural Industries (the “Cultural Industries Act”): The purpose of this Act is to enrich the quality of the nation’s cultural life and foster economic growth by setting forth the framework for developing cultural industries and enhancing its competitiveness. |
| 6. | Internet Multimedia Broadcasting Business Act (the “Internet Broadcasting Act”): This Act seeks to safeguard the rights and interests of users, promote the advancement of associated technologies and industries, protect the public interest in broadcasting, and enhance national culture. |
The department responsible for governing the Broadcasting Act, the Newspapers Act, the Motion Pictures Act, and the Cultural Industries Act is the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism, while the Internet Broadcasting Act is administered by the MSIT and the KCC.
New K Enter and/or the Six Korean Entities have consistently endeavored to operate their businesses in compliance with the regulations prescribed under the aforementioned laws, and they remain dedicated to upholding this commitment in the future.
Legal Proceedings.
K Enter is not aware of any pending or threatened legal proceedings involving K Enter.
Real Property.
On April 27, 2023, K Enter entered into a two-year written lease with ZoaZoa Inc., as landlord (“Lease 1”) for 1,743 square feet of office space located at 32-15 Nonhyeon-dong, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Korea commencing on May 27, 2023. At inception, total gross rental payments due under this operating lease approximated $136,198 and a security deposit due approximated $75,666. A copy of Lease 1 is attached to this proxy statement/prospectus as Exhibit 10.21.
On June 1, 2023, K Enter entered into a two-year written lease with Solaire Partners, as landlord (“Lease 2”) for 2,520 square feet of office space located at 11F, Telepia Building, 527, Eonju-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Korea 06138 commencing on June 1, 2023. Solaire Partners, one of the Six Korean Entities, is the landlord under the Lease 2. At inception, total gross rental payments due under this operating lease approximated $103,926 and a security deposit due approximated $75,704. A copy of Lease 2 is attached to this proxy statement/prospectus as Exhibit 10.22.
Employees
K Enter Holdings has 4 Executive officers including a Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, Chief Accounting Officer, Chief Strategy Officer. All the Executive officers are full time employees devoted to the global growth of K Enter.
K Enter Holdings currently operates a US Headquarter and a branch office in Korea with a total of 17 employees. There are two employees in the U.S. The remainder are in Korea. Most of the workforce is concentrated in business management and the accounting department. This team will be complemented by the 343 employees following the closing of the acquisitions of controlling interests in the Six Korean Entities.
There currently are no unions and no pending or threatened lawsuits with employee.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF
FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS OF K ENTER
The following discussion and analysis should be read in conjunction with “Selected Financial Information of K Enter” and the audited and unaudited financial statements and related notes that are included elsewhere in this proxy statement/prospectus. The discussion and analysis should also be read together with K Enter’s pro forma financial information for the period ended December 31, 2023 and as of December 31, 2023 (in the section entitled “Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Financial Information”). In addition to historical information, this discussion contains forward-looking statements that involve risks, uncertainties, and assumptions that could cause K Enter’s actual results to differ materially from management’s expectations due to a number of factors, including those discussed in the sections entitled “Risk Factors” and “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” appearing elsewhere in this proxy statement/prospectus of Form F-4. Factors which could cause such differences are discussed herein. Unless otherwise specifically noted or the context otherwise requires, all references in this section to “K Enter” refers to K Enter Holdings Inc. prior to the consummation of the Business Combination, which will become the business of PubCo following the consummation of the Business Combination.
Business Overview
K Enter was formed on January 4, 2023, under the laws of the State of Delaware, to become a leading tech and intellectual property (“IP”) based diversified entertainment company. To fulfill this vision, the Company established and internal Korean drama production team and entered into equity purchase agreements to acquire a controlling equity interest in six separate Korean entertainment companies (collectively, the “Six Korean Entities”) in order to combine initial capabilities believed to serve as the foundation for the Company’s growth – content production, content merchandising, and content investment. The Six Korean Entities include one Korean content-specialized private equity firm, one Korean drama production company, three Korean movie production companies, and one IP merchandising company.
Business Combinations and Public Company Costs
Merger Agreement with Global Star
On June 15, 2023, we announced that we entered into a Merger Agreement with Global Star, a publicly traded special purpose acquisition company and certain of its subsidiaries. On March 11, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub executed the First Amendment to Merger Agreement. On June 28, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Second Amendment to Merger Agreement. On July 25, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Third Amendment to Merger Agreement. On December 11, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement. Under the terms of the proposed transaction, the estimated combined enterprise value of the surviving entity following the proposed transaction is approximately $590.0 million, which is based on an assumed share price of PubCo’s Ordinary Shares of $10.00 per share. The actual fair value, which will be determined on the acquisition date, may be significantly different from the estimated combined enterprise value disclosed herein. The transaction is expected to close during the fourth quarter of 2024 and remains subject to customary Closing conditions. See the rest of this proxy statement/prospectus for additional information regarding the Business Combination, including the sections entitled “Proposal No. 1 The Reincorporation Merger Proposal” and Proposal No. 2 The Acquisition Merger Proposal.”
While the legal acquirer in the Business Combination is Global Star, for financial accounting and reporting purposes under International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”), based on K Enter’s initial analysis, we believe we will be the accounting acquirer and the business combination will be accounted for as a “reverse recapitalization.” A reverse recapitalization does not result in a new basis of accounting, and the financial statements of the combined entity represent the continuation of K Enter’s financial statements in many respects. Under this method of accounting, Global Star will be treated as the acquired entity whereby we will be deemed to have issued common stock for the net assets and equity of Global Star consisting mainly of cash, accompanied by a simultaneous equity recapitalization of Global Star (the “Recapitalization”).
Upon consummation of the Business Combination, the most significant change in K Enter’s future reported financial position and results is expected to be an estimated increase in cash (on a pro forma basis as compared to K Enter’s balance sheet at June 30, 2024) of approximately $0.1 million, assuming maximum stockholder redemptions permitted under the Business Combination, an estimated increase of $12.9 million, assuming no stockholder redemptions. Total direct and incremental transaction costs are estimated at approximately $24.2 million, assuming maximum stockholder redemptions permitted under the Business Combination, $24.3 million assuming no stockholder redemptions. Total direct and incremental transaction costs will be treated as a reduction of the cash proceeds and deducted from the combined company’s additional paid-in-capital or added to the combined company’s accumulated deficit. See the section entitled “Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Financial Information.”
As a consequence of the Business Combination, we will become the successor to an SEC-registered and NASDAQ-listed company which will require us to hire additional personnel and implement procedures and processes to address public company regulatory requirements and customary practices. We expect to incur additional annual expenses as a public company for, among other things, directors’ and officers’ liability insurance, director fees and additional internal and external accounting, legal and administrative resources, including increased audit and legal fees.
K Enter expect its capital and operating expenditures will increase significantly in connection with K Enter’s ongoing activities as we:
| ● | complete the acquisition of the Six Korean Entities |
| ● | increase K Enter’s investment in marketing, advertising, sales infrastructure for K Enter’s products and services; |
| ● | obtain, maintains and improves K Enter’s operational, financials and management information systems; |
| ● | hire additional personnel; |
| ● | obtain, maintains, expands and protects its intellectual property portfolio; and |
| ● | operate a public company |
On June 28, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Second Amendment to Merger Agreement, which extended the outside date for the parties to consummate the closing of the Business Combination from June 22, 2024 to December 22, 2024.
On July 25, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Third Amendment to Merger Agreement, which conditioned the closing of the Business Combination on K Enter’s prior consummation of the acquisition of the controlling equity interests in the Six Korean Entities.
On December 11, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement, which extended the outside date for the parties to consummate the closing of the Business Combination from December 22, 2024 to June 22, 2025.
Acquisitions of Six Korean Entities
As part of the Business Combination, we will acquire controlling equity interests in the Six Korean Entities to assist us in achieving K Enter’s vision to become a leading tech and IP-based diversified entertainment company. These acquisitions will combine three initial capabilities, we believe, are necessary to carry out K Enter’s business plan, which include content production, content merchandising, and content investment.
Content production entails overseeing the entire process of bringing a film or drama to life including taking an initial idea, developing a script, securing actors and a director, financing the project, producing the content, marketing the content so that the work can be brought to the viewer. K Enter’s content production will initially be in film and drama production, through the acquisition of the following production studios Apeitda Co., Ltd., Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd., The LAMP Co., Ltd., Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd., which are four of the Six Korean Entities we plan to acquire prior to the Business Combination.
Content merchandising means the enhancement of the fan experience through the IP merchandise we create and sell, which also helps artists maintain a strong bond with their fanbase. We will engage in content merchandising through the Play Company Co., Ltd. (“Play Company”), an IP content merchandising company, which is one of the Six Korean Entities, K Enter plans to acquire prior to the Business Combination.
Content investing will initially entail investing in the production of film and drama through Solaire Partners LLC., a venture capital firm that specializes in investment into movies, dramas and content related companies, which is one of the Six Korean Entities, we plan to acquire prior to the Business Combination.
The acquisition of the Six Korean Entities by K Enter will occur with the acquisition of Play Company closing first and the acquisitions of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company closing subsequently. After the acquisition of all Six Korean Entities is completed, the collective combined company will be referred to as New K Enter.
The acquisition of Play Company by K Enter will be accounted for in accordance with the acquisition method of accounting under IFRS 3, with Play Company considered to be the acquirer and predecessor of K Enter. As Play Company’s basis of accounting is IFRS, the combined K Enter – Play Company entity basis of accounting will be IFRS.
The acquisitions of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company by the combined K Enter – Play Company entity will be accounted for in accordance with the acquisition method of accounting under IFRS 3, with the combined K Enter – Play Company entity considered to be the acquirer of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company. The results of operations of each of the acquired Six Korean Entities will be included in the consolidated financial statements from the date of the acquisition forward. As the combined K Enter – Play Company entity basis of accounting is IFRS, New K Enter’s basis of accounting will be IFRS.
Under the acquisition method of accounting, the preliminary purchase price is allocated to the underlying tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their respective fair market values, with the excess purchase price, if any, allocated to goodwill. Costs related to the transaction are expensed as incurred.
Recent Developments
During October 2023, K Enter entered into an agreement to issue 615 shares of Series A-1 for gross proceeds of $369,000. If any founding member shareholder(s) owning together more than 20% of the Company decide to sell its shares, the investor was provided the right, but not an obligation, to participate in the relevant sale along with the founding member shareholder(s) with the identical terms and conditions given to the lead seller. As of the date these unaudited financial statements were issued, the investor has not yet transferred consideration for this agreement to the Company.
During January 2024, we entered into an agreement with a six-month term to engage an exclusive US-based financial advisor and placement agent (the “Advisor”) in connection with a pre-PIPE financing transaction in exchange for 7.0% of the gross proceeds from an equity investment and 5.0% of the gross proceeds from a debt investment. The Advisor may elect to receive up to 50.0% of the compensation owed in common equity of K Enter or the entity that survives the transaction. Additionally, the Advisor will earn a fee of $500,000 in the form of K Enter common stock at the closing of the business combination if a minimum of $5,000,000 of investment (debt or equity) is secured by the Advisor. No investment commitments have been secured to date.
On January 31, 2024, K Enter entered into the Stock Purchase Agreement with Solaire Partners LLC, which the company acquired 1,000 shares of Play Company Co., Ltd totaling 1,741,000,000 Korean Won ($1,324,015 at September 30, 2024).
On January 31, 2024, an amendment was made to the share purchase agreement, originally entered into on April 12, 2023, with the CEO of First Virtual, and the share purchase agreement with the shareholder of First Virtual was renewed due to the spin-off of the First Virtual, which was executed in October 2023. As a result of this amendment, the value of shares to be exchanged has been decreased to 10,199,577,468 Korean won.
On March 5, 2024, K Enter entered into the Termination and Re-Purchase Option Agreement with the owners of First Virtual, which terminated all agreements entered into in connection with the original equity purchase agreement. The major conditions in the agreement are followings.
| ● | The Company shall repurchase shares if the related suits are finally resolved by a final, non-appealable judgment or the involved parties’ mutually agreed settlement with prejudice of all claims related to and arising from the related suits in each case in a manner satisfactory to the Company as determined by the Company at its sole discretion based on what is considered legally and commercially reasonable. |
| ● | The repurchase price shall be the fair market value, which shall be determined by an accounting firm selected by both parties’ mutual agreement. The transaction shall be consummated within 15 days after the determination of the fair value, excluding the date of government approval if required. The term of this agreement shall be effective and in force only for the time period between the agreement date and the five year anniversary thereof. |
Based on the termination of the New FVL Agreements, Global Star and K Enter agreed to decrease the base merger consideration Global Star will issue to the stockholders of K Enter in connection with the Business Combination. On March 11, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the First Amendment to Merger Agreement, which among other things decreased the base merger consideration from $610 million to $590 million that Global Star will issue to the stockholders of K Enter. Accordingly, pursuant to the First Amendment to Merger Agreement, PubCo will issue 59,000,000 ordinary shares of PubCo to the stockholders of K Enter in exchange for all of the shares of common stock of K Enter.
While no definitive action has been taken to terminate the FVL Termination and Option Agreement, K Enter currently views the acquisition of a controlling interest in First Virtual pursuant to the FVL Termination and Option Agreement as uncertain due to the uncertainty as to the outcome of the Prototype Lawsuits and there can be no assurance that K Enter will acquire a controlling interest in First Virtual pursuant to the FVL Termination and Option Agreement.
In June 2024, K Enter issued two convertible senior unsecured notes (the “Notes”) in the aggregate amount of $4,500,000. The Notes have a maturity date of 3 years and will pay an annual coupon rate of 3% to be paid semi-annually until the maturity date of the Notes.
Under one Note (the “$1.5MM Note”), which is in the principal amount of $1,500,000, the proceeds shall be wired to K Enter as follows:
| (1) | 25% of the committed amount at the time of signing this definitive agreement, |
| (2) | 25% at the time SEC declares effectiveness on the F-4, and |
| (3) | the remaining 50% at the time of shareholder approval and going public. |
Under the other Note (the “$3MM Note”), which is in the principal amount of $3,000,000, the proceeds shall be wired to K Enter as follows:
| (1) | 25% of the committed amount at the time of signing this definitive agreement, |
| (2) | 50% at the time SEC declares effectiveness on the F-4, and |
| (3) | the remaining 25% at the time of shareholder approval and going public. |
From the time K Enter issued the Notes and until the closing of the Business Combination, the Notes will be convertible, at the option of the holders, at a conversion price per share of $1,200 per share. The Post-Merger Conversion Price for the Notes shall be the greater of the following:
| ● | 60% discount to the 5-day average of the volume-weighted average prices of ordinary shares over 5 consecutive trading days following the conversion notice date, and |
| ● | a Floor price of $4 per share. |
Upon execution of the $1.5MM Note, K Enter received $375,000 pursuant to the $1.5MM Note. pon execution of the $3MM Note, K Enter received $750,000 pursuant to the $3MM Note. On October 3, 2024, K Enter received $300,000 pursuant to the $3MM Note and on October 18, 2024, K Enter received $1,200,000 pursuant to the $3MM Note. Accordingly, K Enter is not due any payment under the $3MM Note at the time SEC declares effectiveness on the F-4.
On, August 9, 2024, K Enter entered into an extension agreement on the convertible bond with Prototype Groupe Inc to extend the maturity date to August 9, 2025. The Loan bears interest at the rate of 5.96% per annum. If there are any overdue payments, Prototype shall bear a late payment interest rate of the Applicable Federal Rate plus 10% additional interest.
On August 19. 2024, Global Star Acquisition I LLC loaned K Enter $120,000. The loan is for a term of three months or within five business days after K Enter F4 registration statement becomes effective, whichever is earlier and bears no interest. The proceeds of the loan will be used to fund the operations of K Enter. On October 18. 2024, K Enter repaid $120,000 of Global Star Acquisition I LLC loan, leaving a balance of $0.00 on the loan.
Comparability of Financial Information
Our results of operations and statement of assets and liabilities may not be comparable between prospective periods as a result of the Business Combination.
Key factors Affecting Operating Results
We believe that K Enter’s performance and future success depend on several factors that present significant opportunities for us but also pose risks and challenges, including those discussed below and in the section entitled “Risk Factors—Risks related to K Enter’s Business and Industry.
Limited Operating History
While we do not have significant past operating history, K Enter’s management is aware that the future operating results and K Enter’s future financial condition may be different than K Enter’s past operating results and financial condition. Major factors that will have a material impact on future financial results and condition include whether investments in the development of new motion pictures or new IP content achieve significant commercial success. Even if significant commercial success is achieved, K Enter’s business plan is complex and there are many factors which could impact K Enter’s operating results and financial conditions including delays in projects, opportunity cost of divesting management and financial resources away from other IP content and volatility in the demand for K Enter’s products and services. For more information, please see the section entitled “Risk Factors — Risks Related to K Enter Holdings Inc.’s Business and Industry”
Government Regulation
We plan to have significant international sales and operations that are subject to government regulation and compliance requirements (such as regulation of K Enter’s IP content and service offerings, competition, censorship of content, data privacy), restrictive governmental actions (such as trade protection measures, including export duties and quotas and custom duties and tariffs), nationalization, and restrictions on foreign ownership. Compliance with international and U.S. laws and regulations that apply to K Enter’s international operations may increase K Enter’s cost of doing business. For more information, please see the section entitled “Risk Factors — Risks Related to K Enter Holdings Inc.’s Business and Industry”
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in accordance with GAAP, expressed in U.S. dollars. References to GAAP issued by the FASB in these accompanying notes to the financial statements are to the FASB Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”).
Key Components of Statement of Operations
Revenue
K Enter’s operating income was driven by videography services for television programs.
General and Administrative Expense
General and administrative expenses consist of personnel-related expenses for K Enter’s administrative functions, expenses for outside professional services, including legal, audit and accounting services, as well as expenses for facilities, depreciation, and travel costs. Personnel-related expenses consist of salaries, benefits, and share-based compensation.
We expect K Enter’s general and administrative expenses to increase for the foreseeable future as we complete the acquisition of the controlling equity interests in the Six Korean Entities, scale headcount with the growth of K Enter’s business, and as a result of operating as a public company, including compliance with the rules and regulations of the SEC, legal, audit, additional insurance expense, investor relations activities and other administrative and professional services.
Other Income (Expense)
Other income (expense) consists primarily of the realized gain on transactions that are denominated in a currency other than K Enter’s reporting currency.
Results of Operations
Presented below is a summary of K Enter’s results of operations:
| | | For the
nine months Ended
September 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from
January 4, 2023
(inception) to
September 30,
2023 | |
| Statement of Profit or Loss: | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | $ | 470,052 | | | | - | |
| Operating expenses | | | | | | | | |
| Cost of revenues | | | 411,121 | | | | - | |
| General and Administrative | | | 10,519,714 | | | | 5,310,902 | |
| Loss From Operations | | | (10,460,783 | ) | | | (5,310,902 | ) |
| Other income (expense) | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | | 388 | | | | 83 | |
| Other income (expense) | | | (3,833 | ) | | | 12,603 | |
| Total other income (expense) | | | (3,445 | ) | | | 12,686 | |
| Net loss | | $ | (10,464,228 | ) | | | (5,298,216 | ) |
For the period ended September 30, 2024, K Enter’s operating income was driven by it’s a service agreement, which realized revenues totaling $0.47 million and this is attributable to the agreement entered into in October 2023 for the videography service for the television programs.
For the period ended September 30, 2024, K Enter’s operating expenses are primarily driven by payroll related costs to run its internal Korean drama production and operating team and advisory fees paid to auditor, financial and legal experts.
K Enter’s operating expenses increased for the period ended September 30, 2024 as compared to the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to September 30, 2023 by $5.62 million, or 105.8%. This is attributable to an increase in payroll and payroll related expenses of $0.89 million associated with an increased employee headcount in 2024 compared to 2023, an increase in advisory fees paid of $3.67 million, and the share-based compensation expenses of $0.41 million for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to September 30, 2023.
For the period ended September 30, 2024, K Enter’s other expense is comprised of interest expense of $26,691, partially offset by gains on valuation of short-term financial instruments of $22,436.
Cash Flow
Presented below is a summary of K Enter’s operating, investing and financing cash flows:
| | | For the
period Ended
September 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from
January 4, 2023
(inception) to
September 30,
2023 | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | | $ | (4,068,117 | ) | | | (4,835,398 | ) |
| Investing activities | | | (1,060 | ) | | | (4,171,327 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | 1,809,499 | | | | 13,121,268 | |
| Effect of exchange rates on cash | | | (99,742 | ) | | | 20,775 | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | | $ | (2,359,420 | ) | | | 4,135,318 | |
The cash flow used in K Enter’s operating activities for the period ended September 30, 2024 primarily relate to K Enter’s net loss of $10.5 million, adjusted for changes in K Enter’s working capital accounts.
K Enter’s cash flows used in operating activities decreased for the period ended September 30, 2024 as compared to the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to September 30, 2023 by $0.8 million due to an increase in share-based compensation expenses of $0.4 million, a decrease in cash outflows from accrued expenses and other current liabilities of $3.4 million, and a decrease in cash outflows from account payables of $0.3 million for the period ended September 30, 2024, partially offset by an increase in net loss of $5.2 million.
The cash flow used in K Enter’s investing activities for the period ended September 30, 2024 primarily relates to K Enter’s purchase of property and equipment for less than $0.01 million.
K Enter’s cash flow used in investing activities decreased for the period ended September 30, 2024 as compared to the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to September 30, 2023 by $4.2 million due to the advances made under receivables of $1.5 million, the purchase of convertible debt security of $1.0 million, and purchase of investment in equity securities of $1.6 million for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, that did not recur for the period ended September 30, 2024.
The cash flow generated in K Enter’s financing activities for the period ended September 30, 2024 primarily relates to the issuance of convertible notes of $1.1 million and the proceeds from short-term borrowings of $0.8 million.
The cash flow provided by financing activities decreased for the period ended September 30, 2024 as compared to the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to September 30, 2023 by $11.3 million and primarily relates to the proceeds from the issuance of preferred shares of $10.6 million for period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to September 30, 2023, that did not recur for the period ended September 30, 2024.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
K Enter has incurred significant losses and negative cash flows from operations, net loss was $10,464,228 for the nine months period ended September 30, 2024. During the nine months period ended September 30, 2024, K Enter had negative cash flows from operations of $4,068,117. As of September 30, 2024, K Enter’s accumulated deficit was $19,395,174. K Enter has funded its operations to date through equity and debt financing and has cash equivalents of $166,262 as of September 30, 2024. K Enter monitors its cash flow projections on a current basis and takes active measures to obtain the funding it requires to continue its operations. However, these cash flow projections are subject to various uncertainties concerning their fulfilment such as the ability to increase revenues by attracting and expanding its customer base and completing additional financing. K Enter expects to fund operations using cash on hand and raising additional proceeds. There are no assurances, however, that the Company will be able to generate the revenue necessary to support its cost structure or that it will be successful in obtaining the level of financing necessary for its operations. These conditions raise substantial doubt as to K Enter’s ability to continue as a going concern.
Historically, K Enter’s primary sources of liquidity have been cash flows from contributions from founders, the issuance of Series A convertible preferred stock, and the issuance of Series A-1 convertible preferred stock. As of September 30, 2024, we had an aggregate cash balance of $166,262 and net working capital of $3.5 million.
We intend to operate with its current cash on hand. In the future, we may borrow money and sell equity to finance K Enter’s operations. As we have a limited operating history, K Enter’s liquidity and capital resources may change substantially from past results.
Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including K Enter’s revenue growth rate, the timing of the acquisitions of the controlling interests in the Six Korean Entities, the timing and extent of spending to support future sales and marketing and research and development efforts. In order to finance these opportunities, we may need to raise additional financing. While there can be no assurances, if additional capital is required, we intend to raise such capital through operations, additional issuances of convertible preferred stock, and through the Business Combination. If additional financing is required from outside sources, we may not be able to raise it on terms acceptable to us or at all. If we are unable to raise additional capital when desired, K Enter’s business, results of operations and financial condition would be materially and adversely affected.
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
We manage K Enter’s use of cash in the operation of K Enter’s business to support the execution of K Enter’s primary strategic goals of launching K Enter’s internal Korean drama production team and acquiring the controlling interests in the Six Korean Entities. We primarily use cash for capital investments, purchases of equity shares in related parties, loans, including purchases of bonds, to companies that will assist us in achieving K Enter’s strategic goals, acquisitions of businesses and general and administrative costs.
Our cash requirements beyond twelve months are for operating leases – Refer to Note 11 of the notes to the financial statement for further information of K Enter’s obligations and the timing of expected payments.
Related Parties
Two of K Enter’s directors, one of whom is the Chairman of K Enter’s board of directors, are also senior officers of Solaire Partners, which is one of the Six Korean Entities.
K Enter entered into a two-year operating lease for one of its office spaces commencing in June 2023 with Solaire Partners as the landlord. At inception, total gross rental payments due under this operating lease approximated $104,452 and a security deposit due approximated $76,087. For the period from January 1, 2024 to September 30, 2024, K Enter made $39,170 of rental payments associated with this operating lease. As of September 30, 2024, $34,265 associated with the present value of lease payments is included as components of lease liabilities, current – related party and lease liabilities, noncurrent – related party on the accompanying balance sheet, $76,087 associated with the security deposit is included as a component of other assets, noncurrent – related party on the accompanying balance sheet, and $27,869 associated with the lease is included as a component of accounts payable – related party.
During January 2024, K Enter purchased 1,000 shares of Play Company Co., Ltd. Common Stock for an aggregate purchase price of $1,324,015 from Solaire Partners LLC.
On April 22, 2024, Young Jae Lee, K Enter’s director and former Chief Executive Officer, loaned K Enter $136.888 (the “1st Lee Loan”). On May 3, 2024, K Enter repaid $76,049 of the 1st Lee Loan, leaving a balance of $60,839 on the 1st Lee Loan. The 1st Lee Loan is for a term of six months and bears interest at the rate of 4.6% per annum. The proceeds of the 1st Lee Loan will be used to fund the operations of K Enter. The 1st Lee Loan is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.50. On October 23, 2024, Mr. Lee and K Enter extended the maturity date of the 1st Lee Loan to the earlier of June 30, 2025 or within 5 business days after this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 becomes effective. A copy of the loan extension agreement between Mr. Lee and K Enter is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.66.
On April 23, 2024, Young Jae Lee, K Enter’s director and former Chief Executive Officer, loaned K Enter $190,123 (the “2nd Lee Loan”). On May 3, 2024, K Enter repaid $190,123 of the 2nd Lee Loan, leaving a balance of $0.00 on the 2nd Lee Loan. The 2nd Lee Loan is for a term of three months and bears interest at the rate of 4.6% per annum. The proceeds of the 2nd Lee Loan will be used to fund the operations of K Enter. The 2nd Lee Loan is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.51.
On April 26, 2024, Bidangil Pictures Co.,Ltd. loaned K Enter $102,666 (the “Bidangil Loan”). The loan is unsecured, for a term of three months and bears interest at the rate of 3% per annum. The proceeds of the loan will be used to fund the operations of K Enter. The Bidangil Loan is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.53. On October 25, 2024, K Enter entered into an extension agreement on the loan with Bidangil Pictures Co.,Ltd. to amend the maturity date to June 30, 2025 or within five business days after K Wave Media Ltd F-4 registration statement becomes effective. A copy of the loan extension agreement between The Bidangil and K Enter is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.67.
On May 3, 2024, Young Jae Lee, K Enter’s director and former Chief Executive Officer, loaned K Enter $266,172 (the “3rd Lee Loan”). The 3rd Lee Loan is for a term of six months and bears interest at the rate of 4.6% per annum. The proceeds of the 3rd Lee Loan will be used to fund the operations of K Enter. The 3rd Lee Loan is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.52. On November 3, 2024, K Enter entered into an extension agreement on the 3rd Lee Loan to amend the maturity date to April 30, 2025 or within five days after the K Wave Media Ltd registration statement on Form F-4 is declared effective by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. A copy of the loan extension agreement between Mr. Lee and K Enter is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.68.
On June 4, 2024, K Enter issued a convertible senior unsecured note in the principal amount of $3,000,000 to Innocus Global Group Pte. Ltd., an entity owned by Jaekeun (Jason) Kim, a nominee director PubCo (the “$3MM Note”). The $3MM Note has a maturity date of 3 years and will pay an annual coupon rate of 3% to be paid semi-annually until the maturity date of the $3MM Notes. Under the $3MM Note, the proceeds shall be wired to K Enter as follows: (i) 25% of the committed amount at the time of signing this definitive agreement, (ii) 50% at the time SEC declares effectiveness on the F-4, and (iii) the remaining 25% at the time of shareholder approval and going public. From the time K Enter issued the $3MM Note and until the closing of the Business Combination, the $3MM Note will be convertible, at the option of the holder, at a conversion price per share of $1,200 per share. The Post-Merger Conversion Price for the Notes shall be the greater of (a) a 60% discount to the 5-day average of the volume-weighted average prices of ordinary shares over 5 consecutive trading days following the conversion notice date, and (b) a Floor price of $4 per share. On October 3, 2024, K Enter received $300,000 pursuant to the $3MM Note and on October 18, 2024, K Enter received $1,200,000 pursuant to the $3MM Note. Accordingly, K Enter is not due any payment under the $3MM Note at the time SEC declares effectiveness on the F-4.
On August 19. 2024, Global Star Acquisition I LLC loaned K Enter $120,000(the “Global Star Acquisition Loan”). The loan is for a term of three months or within five business days after K Wave Media Ltd F-4 registration statement becomes effective, whichever is earlier and bears no interest. The proceeds of the loan will be used to fund the operations of K Enter. The Global Star Acquisition Loan is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.55.
On August 31, 2024, K Enter issued Jae Ha Lee, an employee of K Enter, 1,932 shares ($1,044,111, $540.43 per share) of K Enter’s common stock in consideration for services rendered and to be rendered to K Enter.
On August 31, 2024, K Enter reacquired a total of 1,376 shares of treasury stock at no cost which were initially given to two employees under the employment agreements.
On September 12, 2024, one founder of K Enter transferred a total of 688 shares ($371,816, $540.43 per share) of the founder to an employee at par value. K Enter recognized the transaction as a share-based compensation at fair value, which is included within general and administrative expenses on the accompanying statement of operations and comprehensive loss of K Enter.
On September 24, 2024, K Enter entered into a share subscription agreement with GF Korea Inc. (the “GF Agreement”) pursuant to which K Enter issued 4,997 shares ($2,700,529 or $540.43 per share) of K Enter’s common stock to GF Korea, Inc. The GF Agreement closed on September 25, 2024 and K Enter issued the 4,997 shares of K Enter’s common stock to GF Korea, which will be converted to 1,524,681 PubCo ordinary shares based on an estimated 305.1192809:1 conversion ratio calculated with a foreign exchange rate of KRW 1,376.55 / USD $1.00 in the Business Combination. K Enter entered into the GF Agreement for the purpose of transferring certain of K Enter’s payment obligations to gain greater financial flexibility. Mina Kim, a co-founder of K Enter, is the CEO of GF Korea and Mina Kim’s spouse is the owner of GF Korea.
On September 25, 2024, Innocus Global Group Pte, Ltd., an entity owned by Jaekeun (Jason) Kim, a nominee director PubCo, entered into an agreement to purchase 250 shares of K Enter’s Series A-1 Preferred Stock for gross proceeds of $150,000. Each issued share of Series A-1 Preferred Stock is convertible into common stock of K Enter on a one-for-one basis.
Ted Kim, a director and co-founder, of K Enter is also a managing member of Global Star Acquisition 1, LLC, the sponsor, to Global Star, the entity from which K Enter purchased 160,000 shares of Global Star Class B common stock. On September 29, 2024, K Enter entered into an agreement with Lodestar USA, Inc. (the “Lodestar Agreement”) pursuant to which K Enter issued 1,202 shares ($649,597, $540.43 per share) of K Enter’s common stock to Lodestar USA, Inc. in consideration for services rendered to K Enter by Ted Kim, the owner of Lodestar USA Inc. Ted Kim owns 19,564 shares or 10.12% of the shares of common stock of K Enter based on the shares of K Enter to be issued and outstanding immediately prior to the closing of the Business Combination through his ownership and control of Global Fund LLC, which owns 12,000 shares, and Lodestar USA, Inc., which owns 7,564 shares.
On September 30, 2024, K Enter issued Tan Chin Hwee, a director, Executive Chairman and Interim CEO of K Enter, 168 shares ($90,792, $540.43 per share) of K Enter’s common stock in consideration for services rendered and to be rendered to K Enter.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
During the period presented, we did not have any relationships with unconsolidated organizations or financial partnerships, such as structured finance or special purpose entities, which were established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements.
Critical Accounting Estimates
Our financial statements have been prepared in accordance with GAAP. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities as of the balance sheet date, as well as the reported expenses incurred during the reporting period. Management bases its estimates on historical experience and in various other assumptions believed to be reasonable, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities. Actual results could differ from those estimates, and such differences could be material to K Enter’s financial statements.
We believe the accounting policies discussed below are critical to understanding K Enter’s historical and future performance, as these policies relate to more significant areas involving management’s judgments and estimates.
While K Enter’s significant accounting policies are described in the notes to K Enter’s financial statements, we believe that the following accounting policies require a greater degree of judgment and complexity. Accordingly, these are the policies we believe are most critical to aid in fully understanding and evaluating K Enter’s financial condition and results of operations.
See Summary of Significant Accounting Policies under Note 2 in the notes to the financial statements for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023 for more information about K Enter’s significant accounting policies.
Estimating Fair Value of Convertible Debt Security
We do not have a history of market price for the obligor on K Enter’s convertible debt security because the obligor is not publicly traded. As such, the fair value of the convertible debt security was determined using the Tsiveriotis-Fernandes model (the “T-F Model”).
The T-F Model separates convertible hybrid instruments into equity value and debt value. The risk-neutral probability is applied to the equity value, discounted at the risk-free interest rate, while the debt value is discounted at the risk interest rate reflecting the credit risk of the obligor. The model calculates each value separately and measures the value of the hybrid financial product through the summation of these two values, known as the blended discount model. The T-F Model distinguishes discount rates that align with the expected future cash flows inherent in the option structure within complex financial instruments, which aligns with the characteristics of cash flows.
The following assumptions were used in determining the fair value of the convertible debt security as of September 30, 2024:
| Risk-neutral probability | | | % |
| Risk-free interest rate | | | 4.18 | % |
| Risk interest rate reflect the credit risk of the obligor | | | 14.69 | % |
Estimating Fair Value of Convertible Notes
The fair value of the convertible notes was determined using the Probability Weighted Return Model. The convertible notes issued contain a right to convert the notes into the common shares. The Probability Weighted Return Model separates the embedded conversion features associated with the convertible notes separately from the host contract as the economic characteristics and risks of the embedded conversion feature are not closely related to the economic characteristics and risks of the host contract. The carrying amount of the convertible notes was determined for the difference between the fair value of the embedded conversion features and the principal amount of the convertible notes. The difference between the carrying value and principal amount of the convertible notes represents the discount on notes that was amortized to interest expense over the terms of the convertible notes using the effective interest rate method.
Leveraged adjusted guideline volatility for public companies was utilized in determining the fair value of the convertible notes because we do not have a history of market price on convertible notes as we are not publicly traded.
The following assumptions were used in determining the fair value of the convertible bond as of September 30, 2024:
| Risk-free interest rate | | | 3.58 | % |
| Debt rate | | | 6.62 | % |
Estimating Fair Value of Common Stock
We do not have a history of market price for K Enter’s common stock because it is not publicly traded. As such, the fair value of K Enter’s common stock was determined by K Enter’s board of directors as of the date shares of common stock were issued from treasury shares, by considering a number of objective and subjective factors, including:
| ● | Our business, financial condition and results of operations, including related industry trends affecting K Enter’s operations and the progress of conversations concerning: |
| ○ | the potential acquisitions of controlling equity interests of the Six Korean Entities |
| ○ | a potential merger with Global Star and the eventual execution of the Merger Agreement |
| ○ | a capital rise through the issuance of convertible preferred stock |
| ● | Our forecasted operating performance and projected future cash flows; |
| ● | the lack of an active market for K Enter’s common stock and K Enter’s convertible preferred stock; |
| ● | the likelihood of securing additional financing beyond the ongoing Series A and Series A-1 capital raises |
| ● | liquidation preferences, redemption rights and other rights and privileges of K Enter’s common stock and convertible preferred stock; |
| ● | market multiples of K Enter’s comparable public peers; and |
| ● | market conditions affecting K Enter’s industry. |
In connection with estimating the fair value of K Enter’s common stock at the time shares of common stock were issued from K Enter’s treasury shares, we obtained a third-party valuation from an independent valuation firm. The valuation dated as of September 30, 2024 was conducted in accordance with the framework of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants’ Technical Practice Aid, Valuation of Privately-Held-Company Equity Securities Issued as Compensation utilizing an option pricing model (the “OPM”)
The OPM estimated K Enter’s enterprise value by asserting the September 2024 Series A-1 issuances to third parties was transacted at a fair value of $600.00 per share. The OPM utilizes the recent sale of the Preferred Series A-1 shares to a third-party as the best indicator of fair value in order to estimate the fair value of the respective classes of equity. We used a market approach, whereby we applied the recent transaction method for each outcome, or management estimations to estimate the implied equity value.
The OPM utilizes K Enter’s best estimates of the timing and likelihood of two scenarios, (a) merger with a special purpose acquisition company (“SPAC”) and (b) sale, in order to estimate the fair value of the respective classes of equity. For each scenario, we used either a market approach, whereby we applied the precedent transaction method for each outcome, or management estimations to estimate the implied equity value.
The equity value was allocated until the Series A-1 Preferred was equal to the sale price and allocated to each of the equity–linked instruments using an OPM. Based on the structure of the Company’s equity linked instruments, we developed breakpoints based on the conversion prices and exercise prices of the various preferred stock, and outstanding options and warrants. These breakpoints were used to allocate value as each instrument would be exercised/converted as it was in the money. We calculated allocation percentages for each equity–linked instrument. The value of each tranche was determined by subtracting the value of the previous tranche, which is multiplied by the applicable allocation percentages, and summed to yield the total value of each equity–linked instrument. The total value for each class of equity was then divided by the respective shares outstanding for that class to determine the per share value. The resulting value per share was the indicated present value, on a non-marketable basis.
For the valuation used to establish the fair value of K Enter’s common stock as of September 30, 2024, the following assumptions were used:
| | | SPAC
Merger
Scenario | | | Sale
Scenario | |
| Probability | | | 90.0 | % | | | 10.0 | % |
| Time to liquidity event | | | 0.33 years | | | | 2.5 years | |
| Risk free rate | | | NA | | | | 4.38 | % |
| Volatility | | | NA | | | | 28.2 | % |
| Discount for lack of marketability | | | NA | | | | 4.6 | % |
There is inherent uncertainty in K Enter’s forecasts and projections, and if we had made different assumptions and estimates than those described previously, the amount of K Enter’s share-based compensation expense, net loss, and net loss per share amounts could have been materially different.
The per-share fair value of K Enter’s common stock were newly issued or issued from K Enter’s treasury shares during the period from January 1, 2024 to September, 2024, were $540.43 with six months restriction and 566.36 with no restriction. The difference in fair value per share of common stock newly issued or issued from treasury shares is driven by the length of the restricted period for which the underlying share of common stock cannot be sold by the individual.
We were formed on January 4, 2023 for the purpose of acquiring the Six Korean Entities. We entered into equity purchase agreements with the Six Korean Entities between March 2023 and April 2023, all of which are contingent upon PubCo’s proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 being declared effective by the SEC. We entered into conversations with Global Star, a special purpose acquisition company in February 2023, and we executed a term sheet with Global Star in April 2023 to consummate a business combination. On June 15, 2023, we executed a Merger Agreement with Global Star to consummate the Business Combination. The completion of the equity purchase agreements with the Six Korean Entities prior to the consummation of the Business Combination is the primary driver of the increase in the estimated fair value of the common stock from the date of the common stock issuances from K Enter’s treasury shares to the estimated merger price of approximately $3,051 per share on an as converted basis.
We believe that it is reasonable to expect that the completion of the equity purchase agreements with the Six Korean Entities will add value to the shares of K Enter’s common stock as the entities are operational and revenue generating entities with balance sheets that will be combined with ours subsequent to the transaction consummation. We believe that it is reasonable to expect that the completion of the Business Combination will add value to the shares of K Enter’s common stock because they will have increased liquidity and marketability. We believe that the preceding estimates are a reasonable description of the value that market participants would place on K Enter’s common stock as of the valuation date.
Income Taxes
We recognize deferred taxes for temporary differences between the basis of assets and liabilities for financial statement and income tax purposes. As a pre-revenue company we generate net operating losses that would be available to carryforward to future years and applied against future taxable income.
Under Section 382 of the Code, substantial changes in K Enter’s ownership may limit the amount of net operating loss carryforwards that could be utilized annually in the future to offset K Enter’s taxable income. Specifically, the limitation may arise in the event of a cumulative change in K Enter’s ownership of more than 50% within a three-year period. Any such limitation may significantly reduce the utilization of K Enter’s net operating loss carry forwards before they expire. We have not completed a study to assess whether an ownership change has occurred, or whether there have been multiple ownership changes since K Enter’s inception, due to the significant costs and complexities associated with the study. However, we believe it is likely that transaction that have occurred in the past, alone or together with the closing of the Business Combination and other transactions that may occur in the future, would trigger an ownership change pursuant to Section 382, which could limit the amount of net operating loss carryforwards that could be utilized annually in the future to offset out taxable income, if any.
For additional information on K Enter’s accounting policy on income taxes, see Note 2 – Summary of significant accounting policies – Income Taxes and Note 16 – Income Taxes in the accompanying audited financial statements.
Emerging Growth Company Status
We intend to rely on the other exemptions and reduced reporting requirements provided by the JOBS Act. Subject to certain conditions set forth in the JOBS Act, if, as an emerging growth company, we intend to rely on such exemptions, we are not required to, among other things: (a) provide an auditor’s attestation report on K Enter’s system of internal control over financial reporting pursuant to Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act; (b) provide all of the compensation disclosure that may be required of non-emerging growth public companies under the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act; (c) comply with any requirement that may be adopted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board regarding mandatory audit firm rotation or a supplement to the auditor’s report providing additional information about the audit and the financial statements (auditor discussion and analysis); and (d) disclose certain executive compensation-related items such as the correlation between executive compensation and performance comparison of the Chief Executive Officer’s compensation to median employee compensation.
We will remain an emerging growth company under the JOBS Act until the earliest of (a) the day of K Enter’s first fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the Closing, (b) the last date of K Enter’s fiscal year in which we have total annual gross revenue of at least $1.235 billion, (c) the date on which we are deemed to be a “large accelerated filer” under the rules of the SEC with at least $700.0 million of outstanding securities held by non-affiliates or (d) the date on which we have issued more than $1.0 billion in non-convertible debt securities during the previous three years.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
We are exposed to a variety of market and other risks, including the effects of interest rate changes, foreign currency fluctuations, inflation, and the availability of funding sources.
Interest Rate Risk
We hold cash and cash equivalents for working capital purposes. We do not have material exposure with respect to investments, as any investments that we enter into are primarily highly liquid investments. As of September 30, 2024, we had a cash balance of $166,262, consisting of operating accounts which are not affected by changes in the general level of U.S. interest rates.
Foreign Currency Risk
We conduct K Enter’s operations through two branches, one located in the United States and one in Korea. The transactions of each branch are primarily denominated in the U.S. dollar and the Korean Won, respectively, the functional currency. We have elected to use a reporting currency of the U.S. dollar. As foreign exchange rates change, the U.S. dollar equivalent of K Enter’s existing foreign currency assets, liabilities, commitments and forecasted foreign currency revenues and expenses will change. We are evaluating the best method to manage K Enter’s exposure to foreign currency fluctuations to reduce volatility of earnings and cash flow in order to allow management to focus on core business issues and challenges.
The economic and political conditions in the countries we are currently in and plan to operate in could impact K Enter’s ability to manage K Enter’s exposure to foreign currency fluctuations in those countries or repatriate cash from those countries.
Inflation Risk
We do not believe that inflation currently has a material effect on K Enter’s business. Inflation may become a greater risk in the event of changes in current economic and governmental fiscal policy.
New Accounting Pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements are issued by the FASB or other standard setting bodies that are adopted by use as of the specified effective date. Unless otherwise discussed, we believe that the impact of recently issued standards that are not yet effective will not have a material impact on K Enter’s financial position or results of operations under adoption.
See Recent Accounting Pronouncements issued, not yet adopted under Note 1 – Nature of Operations and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies in the notes to the financial statement for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023 for more information about recent accounting pronouncements, the timing of their adoption and K Enter’s assessment, to the extent we have made one, of their potential impact on K Enter’s financial condition and results of operations.
Subsequent Event
On October 3, 2024, K Enter received $300,000 pursuant to the $3MM Note and on October 18, 2024, K Enter received $1,200,000 pursuant to the $3MM Note. Accordingly, K Enter is not due any payment under the $3MM Note at the time SEC declares effectiveness on the F-4.
On October 18. 2024, K Enter repaid $120,000 of Global Star Acquisition I LLC loan, leaving a balance of $0.00 on the loan.
On October 23, 2024, K Enter entered into an extension agreement on the 1st Lee Loan to amend the maturity date to June 30, 2025 or within five days after the K Wave Media Ltd registration statement on Form F-4 is declared effective by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. The Loan bears interest at the rate of 4.6% per annum.
On October 25, 2024, K Enter entered into an extension agreement on the loan with Bidangil Pictures Co.,Ltd. to amend the maturity date to June 30, 2025 or within five business days after K Wave Media Ltd F-4 registration statement becomes effective. The Loan is for a term of three months and bears interest at the rate of 3% per annum.
On November 3, 2024, K Enter entered into an extension agreement on the 3rd Lee Loan to amend the maturity date to April 30, 2025 or within five days after the K Wave Media Ltd registration statement on Form F-4 is declared effective by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. The Loan bears interest at the rate of 4.6% per annum.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF
FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS OF Play Company
References to the “Play Company” refer to Play Company Co., Ltd. The following discussion and analysis of Play Company’s financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with (in each case, included elsewhere herein): (i) Play Company’s audited financial statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 (and related notes) and (ii) Play Company’s unaudited financial statements as of June 30, 2024 and for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 (and related notes). Certain information contained in the discussion and analysis set forth below includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties.
Business Overview
Play Company Co., Ltd. (“Play Company”) sells its entertainment content and services and food and beverage products, as well as licenses its intellectual property in the food and beverage business. Play Company offers made-to-order services to plan projects, design merchandise and deliver customized products to its customers who are primarily music talent agencies that work with K-Pop artists, and operates a retail bakery-café business and franchising business under the concept names “Our Bakery”. As of June 30, 2024, retail operations consist of 12 Company-owned bakery-cafes and 16 franchise-operated bakery-cafes located in South Korea and China. Accordingly, Play Company has identified two operating segments for which Play Company’s management reviews discrete financial information as it makes decisions about its business – Content and Food and Beverage.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”), as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”), expressed in Korean Won.
Key Components of Statement of Operations
Play Company’s reporting currency is the Korean Won and its operating results and cash flows have been translated to U.S. dollar using the following exchange rates that represent the average daily rate in place for the respective period:
| | ● | At the period exchange rate as of June 30, 2024 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,376.55 for the balance sheet; |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the six months ended June 30, 2024 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,350.04 for the statements of operations and cash flow; |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the six months ended June 30, 2023 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,296.17 for the statements of operations and cash flow; |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the year ended December 31, 2023 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,306.76 for the statements of operations and cash flow; and |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the year ended December 31, 2022 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,291.78 for the statements of operations and cash flow. |
Results of Operations
A summary of Play Company’s operating results as translated to the U.S. dollar prepared under IFRS is as follows:
Comparison of Six Months Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Income Statement: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | | ₩ | 18,982 | | | $ | 14,060,309 | | | ₩ | 41,512 | | | $ | 32,026,963 | |
| Cost of sales | | | (16,838 | ) | | | (12,471,866 | ) | | | (36,900 | ) | | | (28,468,564 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 2,144 | | | | 1,588,443 | | | | 4,612 | | | | 3,558,399 | |
| Operating expenses | | | (1,829 | ) | | | (1,354,527 | ) | | | (1,710 | ) | | | (1,319,365 | ) |
| Operating income | | | 315 | | | | 233,916 | | | | 2,902 | | | | 2,239,034 | |
| Other income (expense) | | | (735 | ) | | | (544,642 | ) | | | 481 | | | | 371,344 | |
| Profit(Loss) before taxes | | | (420 | ) | | | (310,726 | ) | | | 3,383 | | | | 2,610,378 | |
| Income tax benefit (expense) | | | 61 | | | | 45,438 | | | | (913 | ) | | | (705,002 | ) |
| Net income | | ₩ | (359 | ) | | $ | (265,288 | ) | | ₩ | 2,470 | | | $ | 1,905,376 | |
For the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023, Play Company’s operating income was driven by its content segment, which realized revenues totaling Korean Won 11,480 million ($8.5 million) and Korean Won 32,277 million ($24.9 million), respectively, and its food and beverage segment, which realized revenues of Korean Won 7,502 ($5.6 million) and Korean Won 9,236 million ($7.1 million), respectively.
The operating result for the first half of the year represents only 14.9% of Play Company’s forecasted revenue of Korean Won 127.4 billion for the financial year of 2024 and also marks a 54% decline year-over-year compared to Korean Won 41.5 billion of revenues for the first half of 2023. This relatively low performance is largely attributable to (i) the seasonal nature of Play Company’s merchandising business, (ii) unexpected delays in some of the merchandising projects previously planned for the first half of the year, and (iii) slower-than-expected progress in developing new business opportunities, among other factors.
(i) Seasonal nature of business: As stated within this document, Play Company’s main business is the production and distribution of merchandise of K-Pop artists. The majority of these fan-targeted products are photo and video albums for the summer season (July and August) and seasons’ greetings products for the winter season (November and December). Due to this disproportionate lineup, Play Company typically generates significantly more revenue during the second half of the year. For the financial year of 2024, Play Company has a strong lineup of season’s greetings products and plans to generate substantial revenues from these products in the second half of the year.
(ii) Unexpectedly delayed projects: As stated within this document, Play Company entered into a new business agreement with SM Entertainment in December 2023 and has been developing new merchandise projects for K-Pop artists from SM Entertainment. Since this is the first year of business cooperation between Play Company and SM Entertainment, the two companies needed to work closely to align their teamwork. As a result, several projects that were initially planned for release in the first half of the year have been adjusted, revised and delayed to ensure quality improvements. Play Company is currently focusing on releasing the delayed projects according to the revised schedule, aiming to generate substantial revenue in the second half of the year.
(iii) New business development: As stated in this document, Play Company has been preparing for several new business opportunities to offset the anticipated decline in HYBE-related revenues in 2024. These opportunities include expanding its distribution networks in Japan and diversifying its merchandise offerings, such as light sticks and other concert-related collectibles. The slower-than-expected progress in developing these opportunities contributed to the relatively low performance in the first half of the year but has resulted in significant achievements, such as identifying potential business partners for opening pop-up stores in Japan. Play Company is currently investing substantial effort and resources to launch these new business initiatives, aiming to generate meaningful revenue in the second half of the year.
Play Company is actively implementing strategies to address and overcome the current challenges, as mentioned above. Play Company, however, runs the risk of generating annual results that fall well short of forecasted revenue if it (i) fails to distribute and sell the expected quantities of its season’s greetings merchandise, (ii) encounters further delays or cancellations of its merchandising projects rescheduled for the second half of the year, or (iii) experiences further delays or setbacks in the development of its new business opportunities. Acknowledging this risk, we have been closely cooperating with and supporting the executive management of Play Company to help meet its forecasted revenue for the financial year of 2024.
Play Company’s gross profit has decreased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 2,468 million ($2.0 million), or 53.5%, corresponding to a decrease in revenue of Korean Won 22,530 million ($18.0 million), or 54.3%. This is primarily attributable to a group of projects associated K-pop boybands, which generated Korean Won 19.3 million for the six months ended June 30, 2023. These projects were completed prior to the six months ended June 30, 2024. For the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023, three of Play Company’s customers account for 59.7% and 82.4%, respectively, of total content segment revenue and 36.1% and 64.1%, respectively, of total Play Company revenue.
For the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023, Play Company’s operating expenses are primarily driven by payroll and payroll related costs of Korean Won 1,016 million ($1 million) and Korean Won 1,016 million ($0.8 million), respectively. Additional components of operating expenses consisted of severance of Korean Won 189 million ($0.1 million) and Korean Won 90 million ($0.1 million), respectively, non-income taxes of Korean Won 16 million ($0.0 million) and Korean Won 103 million ($0.1 million), respectively, depreciation expense of Korean Won 333 million ($0.2 million) and Korean Won 324 million ($0.2 million) respectively, and other administrative costs of Korean Won 275 million ($0.2 million) and Korean Won 177 million ($0.1 million) respectively, for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023.
Play Company’s operating expenses increased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 119 million ($35,167), or 7.0%. This is primarily attributable to an increase in bad debt expenses of Korean Won 116 million ($0.1 million).
For the six months ended June 30, 2024, Play Company has executed only a partial number of targeted projects in 2024 due to unexpected delays in launching the projects as decided by some customers, although Play Company had more than enough production capacity.
Play Company’s cost of sales are closely related to the revenues generated because Play Company’s cost of sales primarily consist of costs incurred in connection with the manufacturing of the video merchandises. Therefore, the related manufacturing costs correlatedly decrease if the revenue declines.
For the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023, Play Company’s other income (expense) is comprised of
| | ● | finance income of $0.13 million and $1.11 million, respectively, primarily attributable to gains on foreign currency translation of less than $0.1 million and $0.27 million, respectively, gains on foreign currency transactions of less than $0.1 million and $0.10 million, respectively. Interest income earned from interest bearing notes and accounts was $0.11 million and $0.20 million, respectively. Gains on disposal of financial instruments of $0.48 million of was recognized for the six months ended June 30, 2023 that did not recur for the six months ended June 30, 2024. |
| | ● | finance costs of $0.7 million in both periods presented, primarily attributable to interest expense relating to lease liabilities of $0.5 and $0.5 million, respectively, and losses on foreign currency transactions of less than $0.1 million and $0.2 million, respectively, and losses on foreign currency translation of $0.1 million and less than $0.1 million, respectively. |
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Year Ended
December 31,
2023 | | | Year Ended
December 31,
2022 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Income Statement: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | | ₩ | 67,481 | | | $ | 51,640,054 | | | ₩ | 169,022 | | | $ | 130,844,562 | |
| Cost of sales | | | (60,837 | ) | | | (46,555,654 | ) | | | (150,752 | ) | | | (116,701,165 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 6,644 | | | | 5,084,400 | | | | 18,270 | | | | 14,143,397 | |
| Operating expenses | | | (3,147 | ) | | | (2,408,011 | ) | | | (5,108 | ) | | | (3,954,428 | ) |
| Operating income | | | 3,497 | | | | 2,676,389 | | | | 13,162 | | | | 10,188,969 | |
| Other income (expense) | | | 56 | | | | 42,647 | | | | (590 | ) | | | (456,869 | ) |
| Profit before taxes | | | 3,553 | | | | 2,719,036 | | | | 12,572 | | | | 9,732,100 | |
| Income tax benefit (expense) | | | (761 | ) | | | (582,186 | ) | | | (2,687 | ) | | | (2,090,160 | ) |
| Net income (loss) | | ₩ | 2,792 | | | $ | 2,136,850 | | | ₩ | 9,885 | | | $ | 7,651,940 | |
For the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, Play Company’s operating income was driven by its content segment, which realized revenues totaling Korean Won 49,772 million ($38.1 million) and Korean Won 151,859 million ($117.6 million), respectively, and its food and beverage segment, which realized revenues of Korean Won 17,709 ($13.6 million) and Korean Won 17,164 million ($13.3 million), respectively.
Play Company’s gross profit has decreased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 11,626 million ($9.1 million), or 63.6% corresponding to a decrease in revenue of Korean Won 101,541 million ($79.2 million), or 60.1%. This is attributable to a group of projects has been completed during the year ended December 31, 2023. For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, three of Play Company’s customers account for 81.4% and 85%, respectively, of total content segment revenue and 60.0% and 76.4%, respectively, of total Play Company revenue.
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, Play Company’s operating expenses are primarily driven by payroll and payroll related costs of Korean Won 2,874 million ($2.2 million) and Korean Won 2,975 million ($2.3 million), respectively. Additional components of operating expenses consisted of severance of Korean Won 370 million ($0.4 million) and Korean Won 306 million ($0.2 million), respectively, non-income taxes of Korean Won 129 million (less than $0.1 million) and Korean Won 125 million (less than $0.1 million), respectively, depreciation expense of Korean Won 649 million ($0.5 million) and Korean Won 645 million ($0.5 million) respectively, and other administrative costs of Korean Won 476 million ($0.4 million) and Korean Won 397 million ($0.3 million) respectively, for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022.
Play Company’s operating expenses decreased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 1,961 million ($1.5 million), or 38.4%, and is attributable to a decrease in uncollectable accounts that were written off of Korean Won 525 million ($0.4 million), a decrease in payroll and payroll related expenses of Korean Won 362 million ($0.4 million) associated with a decreased employee headcount in 2023 compared to 2022, and a decrease in impairment loss on property and equipment of Korean Won 13 million (less than $0.1 million).
For the year ended December 31, 2023, Play Company has executed only a partial number of targeted projects in 2023 due to a fewer number of agreements with other k-pop managements, although Play Company had more than enough production capacity.
Play Company’s operating expenses are closely related to the revenues generated because Play Company’s operating expenses primarily consist of costs incurred in connection with the manufacturing of the video merchandises. Therefore, the related manufacturing costs correlatedly decrease if the revenue declines.
Play Company may generate revenue from agreements that have been entered into, or may be entered into in the future as Play Company is actively seeking contracts with other K-pop management companies, possibly obtaining a bulk contract allowing Play Company to manufacture merchandising for every artist belonging to other K-pop management companies.
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, Play Company’s other income (expense) is comprised of
| ● | finance income of $1.3 million and $0.9 million, respectively, primarily attributable to gains on foreign currency translation of $0.3 million and $0.1 million, respectively, gains on foreign currency transactions of $0.2 million and $0.4 million, respectively. Interest income earned from interest bearing notes and accounts was $0.3 million and $0.4 million, respectively. Gains on disposal of financial instruments of $0.5 million of was recognized for the year ended December 31, 2023 that did not occur for the year ended December 31, 2022. |
| ● | finance costs of $1.3 million and $1.4 million, respectively, primarily attributable to interest expense relating to lease liabilities of $0.8 and $0.6 million, respectively, and losses on foreign currency transactions of $0.2 million and $0.6 million, respectively, and losses on foreign currency translation of less than $0.1 million and $0.1 million, respectively. |
Cash Flow:
A summary of Play Company’s operating, investing, and financing cash flows prepared under IFRS is as follows:
Comparison of Six Months Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | | ₩ | (3,089 | ) | | $ | (2,288,105 | ) | | ₩ | (12,639 | ) | | $ | (9,751,377 | ) |
| Investing activities | | | (351 | ) | | | (259,951 | ) | | | (1,598 | ) | | | (1,233,079 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | (813 | ) | | | (601,988 | ) | | | (9,470 | ) | | | (7,305,899 | ) |
| Effect of exchange rates on cash | | | (133 | ) | | | (98,469 | ) | | | 349 | | | | 269,446 | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | (4,386 | ) | | $ | (3,248,513 | ) | | ₩ | (23,358 | ) | | $ | (18,020,909 | ) |
Play Company’s cash flows used in operating activities decreased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 9,550 million ($7.5 million). This is primarily attributable to a decrease in payments for trade payables of Korean Won 27,635 million ($21.3 million), offset by a decrease in net income of Korean Won 2,828 million ($2.2 million), a decrease in the collection of trade receivables of Korean Won 5,549 million ($4.4 million), and an increase in the payment of prepaid expenses of Korean Won 6,895 million($5.1 million) for the six months ended June 30, 2024.
Operational cash flow reflects the similar trend of fluctuation of revenue and operating expenses.
Play Company’s cash flows used in investing activities decreased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 1,247 million ($1.0 million) and is primarily attributable to a decrease in cash outflows from borrowings of Korean Won 3,984 million ($3.1 million), and a decrease in cash outflows from the purchase of of property, plant and equipment of Korean Won 450 million ($351,996), and a decrease in cash inflows from the disposal of other financial assets of Korean Won 3,185 million ($2,466,962)
Play Company’s cash flows used in financing activities decreased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 8,657 million ($6.7 million) and primarily relates to the acquisition of treasury shares for the six months ended June 30, 2023 that did not recur for the six months ended June 30, 2024.
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Year Ended
December 31,
2023 | | | Year Ended
December 31,
2022 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | | ₩ | (8,378 | ) | | $ | (6,410,933 | ) | | ₩ | 26,185 | | | $ | 20,270,421 | |
| Investing activities | | | (1,790 | ) | | | (1,369,862 | ) | | | (5,040 | ) | | | (3,901,752 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | (12,190 | ) | | | (9,328,274 | ) | | | (1,763 | ) | | | (1,364,926 | ) |
| Effect of exchange rates on cash | | | 362 | | | | 276,657 | | | | 96 | | | | 74,731 | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | (21,996 | ) | | $ | (16,832,412 | ) | | ₩ | 19,478 | | | $ | 15,078,474 | |
Play Company’s cash flows used in operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2023 was Korean Won 8,378 million ($6.4 million), compared to Korean Won 26,185 million ($20.2 million) of cash flows provided by operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2022. This is primarily attributable to a decrease in net income of Korean Won 7,092 million ($5.5 million), a decrease in accounts payable of Korean Won 21,321 million ($16.3 million) due to the payments made for purchase of inventories, and a payment made for income taxes of Korean Won 3,177 million ($2.4 million) during the year ended December 31, 2023.
The decrease in net cash provided by operating activities in 2023 compared to 2022 was mainly due to a decrease in cash collected from Play Company’s customers primarily as result of a decrease in Play Company’s revenue. Also, Play Company incurred a cash outflow due to the payment made in 2023 for the inventories purchased in 2022. Play Company’s operating expenses are closely related to the revenues generated because Play Company’s operating expenses primarily consist of costs incurred in connection with the manufacturing of the video merchandises. Moreover, operational cash flow reflects the similar trend of fluctuation of revenue and operating expenses.
Play Company’s cash flows used in investing activities decreased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 3,250 million ($2.5 million). This is primarily attributable to the proceeds from the short-term financial instruments of Korean Won 4,136 million ($3.2 million).
Play Company’s cash flows used in financing activities increased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 10,427 million ($8.0 million) and primarily relates to the acquisition of treasury shares for the year ended December 31, 2023. An improvement in Play Company’s sales in 2024 would help resolve the negative cash flows we experienced in 2023. In the event our cash flows do not improve, PubCo will seek to raise capital through both equity and debt financing with reasonable terms post going public.
Liquidity and Capital Resources:
Historically, Play Company’s sources of liquidity have been cash flows from the issuance of common stock and the generation of net income. As of June 30, 2024, Play Company had an aggregate cash balance of Korean Won 4,200 million ($3,051,114) and net working capital deficit of Korean Won 1,867 million ($1,356,598).
Play Company intends to operate with its current cash on hand and the profits it anticipates earning in the future. Play Company intends to expand its current business operations, including providing additional offerings such as obtaining intellectual property rights and expand its international footprint. Play Company may need to borrow money or sell equity to finance its operations and planned growth.
Play Company’s future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including its revenue growth rate, potential acquisitions, the timing and extent of spending to support future sales and marketing efforts. In order to finance these opportunities, Play Company may need to raise additional financing. While there can be no assurances, if additional capital is required, Play Company intends to raise such capital through operations or additional issuances of equity. If additional financing is required from outside sources, Play Company may not be able to raise it on terms acceptable to it or at all. If Play Company is unable to raise additional capital when desired, Play Company’s business, results of operations and financial condition would be materially and adversely affected.
Related Parties
The related parties of Play Company’s comprise key management personnel and entities controlled by or affiliated with key management personnel. As of June 30, 2024, Play Company entered into revenue and purchase agreement with related parties. Under the agreements, total gross revenue of approximately $3.0 million and total gross expense of approximately $0.1 million were generated.
As of June 30, 2024, $0.9 million of accounts payable and $2.0 million of borrowings are outstanding as Play Company entered into the agreements for acquisition of treasury stock and borrowing with Chief Executive Officer for the six months ended June 30, 2023. Play Company is provided guarantees for the borrowings obtained from financial institutions by Chief Executive Officer.
See Related Parties under Note 18 in the notes to the condensed consolidated financial statement for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 for more information about transactions entered into with related parties.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
During the period presented, Play Company did not have any relationships with unconsolidated organizations or financial partnerships, such as structured finance or special purpose entities, which were established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements.
Critical Accounting Estimates
Play Company’s consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with IFRS as issued by the IASB. The preparation of these financial statements requires Play Company to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities as of the balance sheet date, as well as the reported expenses incurred during the reporting period. Management bases its estimates on historical experience and in various other assumptions believed to be reasonable, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities. Actual results could differ from those estimates, and such differences could be material to Play Company’s consolidated financial statements.
Play Company believes the accounting policies discussed in the notes to Play Company’s consolidated financial statements are critical to understanding Play Company’s historical and future performance, as these policies relate to more significant areas involving management’s judgments and estimates.
See Summary of Material Accounting Policies under Note 5 in the notes to the consolidated financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 for more information about Play Company’s material accounting policies.
Impairment assessment on CGU
Play Company estimates the recoverable amount of an individual asset, and if it is impossible to measure the individual recoverable amount of an asset, Play Company estimates the recoverable amount of cash-generating unit (“CGU”). The value in use is estimated by applying a weighted average cost of capital that reflects current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the asset or CGU for which estimated future cash flows have not been adjusted, to the estimated future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset or CGU.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, Play Company performed impairment test for Food and Beverages operating segment. Play Company identifies each of bakery-cafés as CGU. As the individual CGUs are tested for impairment at the same time as the group of CGUs containing the goodwill, Play Company tested the individual CGUs for impairment before the group of CGUs is tested.
The recoverable amount of each CGU is determined based on its value in use. Value in use is calculated using the estimated cash flow based on 5-year business plan approved by management. The estimated revenue and operating expenditures on Play Company’s products used in the forecast was determined considering external sources and Play Company’s experience. Management estimated the future cash flows based on its past performance and forecasts on consumer inflation rate. The key assumptions used in the estimation of value in use for Food and Beverages CGU include revenue and operating expenditures for the forecast period, growth rates for subsequent years (“terminal growth rate”), and discount rate. Terminal growth rate and the discount rate used in the estimation of value in use are as follows
| | | Weighted average
cost of capital | | | Terminal
growth rate | |
| 2023 | | | 10.7 | % | | | 1.0 | % |
| 2022 | | | 11.4 | % | | | 1.0 | % |
The discount rate was calculated using the weighted average cost of equity capital and debt and the beta of equity capital was calculated as the average of four Korean listed companies in the same industry and Play Company. Cost of debt was calculated using the yield rate of non-guaranteed corporate bond considering Play Company’s credit rating and debt ratio was determined using the average of the debt ratios of the four Korean listed companies in the same industry and Play Company. Play Company calculates the value in use of Food and Beverages CGU using post-tax cash flows and a post-tax discount rate.
As a result of the impairment test for goodwill for groups of Food and Beverages CGUs, the recoverable amount exceeded its carrying amount by Korean Won 4,778,529 thousand in 2023 (2022: Korean Won 6,575,660 thousand). The recoverable amount exceeded its carrying amount accounts 18.9% of the amount of value in use (2022: 24.9%). The value in use determined for this CGU is sensitive to the discount rate and terminal growth rate used in the discounted cash flow model.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
Play Company’s operating activities expose itself to a variety of financial risks: market risk, credit risk and liquidity risk from which Play Company’s risk management program focuses on minimizing any adverse effects on its financial performance. Play Company operates financial risk management policies and programs that closely monitor and respond to each risk factor.
See Summary of Play Company’s financial risk management under Note 27 in the notes to the consolidated financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 for more information.
New Accounting Pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements are issued by the IASB or other standard setting bodies that are adopted by use as of the specified effective date. Unless otherwise discussed, Play Company believes that the impact of recently issued standards that are not yet effective will not have a material impact on Play Company’s consolidated financial position or results of operations under adoption.
See Recent Accounting Pronouncements issued, not yet adopted under Note 5 Material accounting policies in the notes to the financial statement for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 for more information about recent accounting pronouncements, the timing of their adoption and Play Company’s assessment, to the extent Play Company has made one, of their potential impact on Play Company’s consolidated financial condition and results of operations.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF
FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS OF SOLAIRE
References to the “Solaire” refer to Solaire Partners, LLC. The following discussion and analysis of Solaire’s financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with (in each case, included elsewhere herein): (i) Solaire’s audited financial statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 (and related notes) and (ii) Solaire’s unaudited financial statements as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 and for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 (and related notes). Certain information contained in the discussion and analysis set forth below includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties.
Business Overview
Solaire Partners, LLC (“Solaire”) is a content-specialized private equity firm based in Korea that invests in movies, dramas, and content companies since 2017. It is led by their CEO, Pyeungho Choi and Solaire’s team of content and finance experts with extensive experience in the entertainment industry. Solaire follows a disciplined project selection process, followed by a thorough hands-on, value add approach to investments. It monitors, reviews and shapes marketing and distribution strategy (teaser, poster, setting release date, distribution), scenario development, and participates in the casting of a project. Solaire has invested in some of the highest-grossing films out of Korea. It has also invested in entertainment tech companies that digitize.
Among its distinctions, it has created Korea’s first and only movie investment fund based on proprietary movie data. The fund invests to capture the returns of the broad segment of Korean commercial movies. Solaire has invested over $138 million in over 200 content projects in the last five years. Solaire has received distinctions from the Korean government as one of the leading venture capitalist firms in the cultural content sector and has secured the investments from some of the largest financial institutions in Korea such as Samsung Securities, Industrial Bank of Korea that have started to invest in the movie industry.
The revenues of Solaire would account for approximately 1.8% of New K Enter’s total revenues in 2023 on a pro forma basis. Solaire derives revenues through a management fee (around 1%) on the amount invested. Solaire expect its share of total New K Enter revenues to remain at these levels.
Solaire’s priority includes helping K Enter extend the investment scope from films to TV series and other formats of content including webtoons and animation and expanding K Enter’s business globally.
Solaire’s distinctiveness stems from the fact that its all members have a various experience in contents investment and also possess finance capabilities. This combination allows Solaire to approach investments in the content industry with a deeper understanding of the creative and artistic aspects, rather than solely focusing on the financial aspects of a project. In addition, due to their extensive experience and expertise in the content industry, Solaire has built a strong network in this industry. Strong relationships with influential producers and directors have allowed it to become the anchor investor in acclaimed movies such as “Parasite” and “Decision to Leave.” This showcases their ability to identify and support promising projects and talent.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”), as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”), expressed in Korean Won.
Key Components of Statement of Operations
Solaire’s reporting currency is the Korean Won and its operating results and cash flows have been translated to U.S. dollar using the following exchange rates that represent the average daily rate in place for the respective period:
| | ● | At the period exchange rate as of June 30, 2024 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,376.55 for the balance sheet; |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the six months ended June 30, 2024 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,350.04 for the statements of operations and cash flow; |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the six months ended June 30, 2023 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,296.17 for the statements of operations and cash flow; |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the year ended December 31, 2023 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,306.76 for the statements of operations and cash flow; and |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the year ended December 31, 2022 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,291.78 for the statements of operations and cash flow. |
Results of Operations
A summary of Solaire’s operating results is as follows:
Comparison of Six Months Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Income Statement: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | | ₩ | 960 | | | $ | 710,935 | | | ₩ | 852 | | | $ | 656,980 | |
| Cost of sales | | | (26 | ) | | | (19,128 | ) | | | (25 | ) | | | (18,974 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 934 | | | | 691,807 | | | | 827 | | | | 638,006 | |
| Operating expenses | | | (1,043 | ) | | | (772,425 | ) | | | (1,070 | ) | | | (825,827 | ) |
| Operating income | | | (109 | ) | | | (80,618 | ) | | | (243 | ) | | | (187,821 | ) |
| Other expense, net | | | 76 | | | | 56,178 | | | | (1 | ) | | | (390 | ) |
| Loss before taxes | | | (33 | ) | | | (24,440 | ) | | | (244 | ) | | | (188,211 | ) |
| Income tax expense | | | (3 | ) | | | (2,426 | ) | | | (12 | ) | | | (9,097 | ) |
| Net income | | ₩ | (36 | ) | | $ | (26,866 | ) | | ₩ | (256 | ) | | $ | (197,308 | ) |
For the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023, Solaire’s operating income was driven by its content investment segment, which realized revenues totaling Korean Won 960 million ($710,935) and Korean Won 852 million ($656,979), respectively.
Solaire’s gross profit has increased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 107 million ($53,802), or 12.9% corresponding to an increase in revenue of Korean Won 108 million ($53,956), or 12.7%. This is attributable to an increase in investment management revenue resulting from investment funds that were established during the second half of 2023. For the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023, four of Solaire’s customers account for 100% and 100% of total Solaire revenue, respectively.
For the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023, Solaire’s operating expenses are primarily driven by payroll and payroll related costs, commissions expenses, share-based payments for both periods presented.
Solaire’s operating expenses decreased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 27 million ($53,402), or 2.5%. This is primarily attributable to an increase in payroll and payroll related costs of Korean Won 148 million ($113,962) associated with an increased average salary of the management, an increase in commission expenses of Korean Won 244 million ($188,244) associated with the development of software, and a decrease in share-based payments of Korean Won 421 million ($324,999) associated with the shares transferred to the employees that was held by Solaire Partners’ largest shareholder during the six months ended June 30, 2023.
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Year Ended
December 31,
2023 | | | Year Ended
December 31,
2022 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Income Statement: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | | ₩ | 1,716 | | | $ | 1,313,449 | | | ₩ | 1,855 | | | $ | 1,435,916 | |
| Cost of sales | | | (146 | ) | | | (111,904 | ) | | | (61 | ) | | | (47,184 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 1,570 | | | | 1,201,545 | | | | 1,794 | | | | 1,388,732 | |
| Operating expenses | | | (1,755 | ) | | | (1,343,224 | ) | | | (1,248 | ) | | | (966,338 | ) |
| Operating income | | | (185 | ) | | | (141,679 | ) | | | 546 | | | | 422,394 | |
| Other expense, net | | | (77 | ) | | | (58,604 | ) | | | (7 | ) | | | (4,943 | ) |
| Profit (Loss) before taxes | | | (262 | ) | | | (200,283 | ) | | | 539 | | | | 417,451 | |
| Income tax expense | | | (39 | ) | | | (30,264 | ) | | | (111 | ) | | | (85,851 | ) |
| Net income | | ₩ | (301 | ) | | $ | (230,547 | ) | | ₩ | 428 | | | $ | 331,600 | |
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, Solaire’s operating income was driven by its content investment segment, which realized revenues totaling Korean Won 1,716 million ($1,313,449) and Korean Won 1,855 million ($1,435,916), respectively.
Solaire’s gross profit has decreased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 224 million ($187,187), or 12.5% corresponding to a decrease in revenue of Korean Won 139 million ($122,467), or 7.5%. For the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, three of Solaire’s customers account for 95% and 93% of total Solaire revenue, respectively.
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, Solaire’s operating expenses are primarily driven by payroll and payroll related costs, depreciation expenses, insurance expenses for both periods presented.
Solaire’s operating expenses increased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 507 million ($376,886), or 40.6%. This is primarily attributable to share-based payments of Korean Won 421 million ($322,365) during the year ended December 31, 2023, which did not incur for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Cash Flows
A summary of Solaire’ operating, investing, and financing cash flows is as follows:
Comparison of Six Months Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | | ₩ | (288 | ) | | $ | (213,280 | ) | | ₩ | 357 | | | $ | 275,761 | |
| Investing activities | | | 108 | | | | 79,738 | | | | (150 | ) | | | (115,664 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | (71 | ) | | | (52,379 | ) | | | (40 | ) | | | (31,243 | ) |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | (251 | ) | | $ | (185,921 | ) | | ₩ | 167 | | | $ | 128,854 | |
Solaire’s net cash flows used in operating activities for the six months ended June 30, 2024 was Korean Won 288 million ($213,280), compared to Korean Won 357 million ($275,761) of net cash flows provided by operating activities for the six months ended June 30, 2023. This is primarily attributable to an increase in Solaire’s income tax paid by Korean Won 136 million ($104,434), a decrease in share-based payments of Korean Won 421 million ($324,999), and a decrease in cash inflows of Korean Won 218 million ($161,939) from the project investment assets.
Solaire’s net cash flows provided by investing activities for the six months ended June 30, 2024 was Korean Won 108 million ($79,738), compared to Korean Won 150 million ($115,664) of net cash flows used in investing activities for the six months ended June 30, 2023. This is primarily attributable to a decrease in lease receivable of Korean Won 43 million ($31,591), a decrease in leasehold deposit of Korean Won 65 million ($48,147), and the payment made for leasehold deposit of Korean Won 150 million ($115,726) for the six months ended June 30, 2023 that did not recur for the six months ended June 30, 2024.
Solaire’s cash flows used in financing activities increased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 31 million ($21,136) and primarily relates to the repayment of borrowings for the six months ended June 30, 2023 that did not recur for the six months ended June 30, 2024.
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Year Ended
December 31,
2023 | | | Year Ended
December 31,
2022 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | | ₩ | 417 | | | $ | 319,212 | | | ₩ | 77 | | | $ | 59,262 | |
| Investing activities | | | (115 | ) | | | (88,447 | ) | | | (5 | ) | | | (3,866 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | (31 | ) | | | (23,435 | ) | | | (219 | ) | | | (169,350 | ) |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | 271 | | | $ | 207,330 | | | ₩ | (147 | ) | | $ | (113,954 | ) |
Net cash flows provided by operating activities increased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 340 million ($259,950). This is primarily attributable to a decrease in Solaire’s net income by Korean Won 730 million ($562,148), offset by an increase in share-based payments of Korean Won 421 million ($322,365) during the year ended December 31, 2023, contribution paid to plan assets of Korean Won 182 million ($141,161), a decrease in trade receivables of Korean Won 144 million ($111,198), the refund of income tax expense of Korean Won 131 million ($100,414), and an increase in investment withholdings of Korean Won 237 million ($183,767).
Net cash flows used in investing activities increased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 110 million ($84,581). This is primarily attributable to the advance made for leasehold deposit of Korean Won 150 million ($114,788).
Net cash flows used in financing activities decreased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 188 million ($145,915) and primarily relates to the repayment of borrowings for the year ended December 31, 2022 that did not recur for the year ended December 31, 2023.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Historically, Solaire’s sources of liquidity have been cash flows from fundraising and the generation of net income. As of June 30, 2024, Solaire had an aggregate cash balance of Korean Won 92 million ($66,758) and net working capital of Korean Won 388 million ($281,507).
Solaire intends to operate with its current cash on hand and the profits it anticipates earning in the future. Solaire intends to expand it current business operations through oversea fund raising and exploit investment opportunities to scale up its profit. Solaire may need to borrow money or sell equity to finance its operations and planned growth.
Solaire’s future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including its revenue growth rate, potential acquisitions, the timing and extent of spending to support future sales and marketing efforts. In order to finance these opportunities, Solaire may need to raise additional financing. While there can be no assurances, if additional capital is required, Solaire intends to raise such capital through operations or additional issuances of equity. If additional financing is required from outside sources, Solaire may not be able to raise it on terms acceptable to it or at all. If Solaire is unable to raise additional capital when desired, Solaire’s business, results of operations and financial condition would be materially and adversely affected.
Related Parties
The related parties of Solaire comprise individuals, entities with significant influence over the Company, and associates. Solaire entered into multiple investment management agreements with said associates, pursuant to which Solaire will deliver investment management services.
See Related Parties under Note 15 in the notes to the financial statement for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 for more information about transactions entered into with related parties.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
During the periods presented, Solaire did not have any relationships with unconsolidated entities or financial partnerships, such as structured finance or special purpose entities, which were established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements.
Critical Accounting Estimates
Solaire’s financial statements have been prepared in accordance with IFRS as issued by the IASB. The preparation of these financial statements requires Solaire to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities as of the reporting dates, as well as the reported income and expenses incurred during the reporting period. Management bases its estimates on historical experience and in various other assumptions believed to be reasonable, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities. Actual results could differ from those estimates, and such differences could be material to Solaire’s financial statements.
Solaire believes the accounting policies discussed in the notes to Solaire’s financial statements are critical to understanding Solaire’s historical and future performance, as these policies relate to more significant areas involving management’s judgments and estimates.
See Summary of Material Accounting Policies in Note 5 to the financial statements as of and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 for more information about Solaire’s material accounting policies.
Equity-accounted investees
In determining whether Solaire has significant influence, Solaire takes into account whether Solaire directly or indirectly holds 20% or more of the voting rights over the investee, whether Solaire participates in the board or other decision-making body equivalent thereto of the investees, or whether Solaire’s potential voting rights will affect these rights.
Although Solaire holds less than 20% of equity interests in investment fund, investments in such investees were classified as investments in associates as Solaire can exercise significant influence over financial and operating policy decisions as a general partner.
Financial Instruments – Fair values and risk management
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market is determined by using valuation techniques. Solaire uses its judgment to select a variety of methods and make assumptions that are mainly based on market conditions existing at the end of each reporting period.
These valuation techniques use as much market observable information as possible and use the least amount of Solaire-specific information. At this time, if all the significant input variables required to measure the fair value are observable, the financial instruments are classified as Level 2. If more than one significant input variable is not based on observable market information, the item is included in Level 3.
The valuation techniques used to measure the fair value of a financial instrument include:
| | ● | Market price or dealer price of a similar financial instrument |
| | | |
| | ● | The fair value of derivative instruments is determined by discounting the amount to present value using the leading exchange rate as of the end of the reporting period |
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
Solaire’s operating activities expose itself to a variety of financial risks: credit risk and liquidity risk from which Solaire’s risk management program focuses on minimizing any adverse effects on its financial performance. Solaire operates financial risk management policies and programs that closely monitor and respond to each risk factor.
See Summary of Solaire’s financial risk management under Note 24 in the notes to the financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 for more information.
New Accounting Pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements are issued by the IASB or other standard setting bodies that are adopted by use as of the specified effective date. Unless otherwise discussed, Solaire believes that the impact of recently issued standards that are not yet effective will not have a material impact on Solaire’s financial statements upon adoption.
See Recent Accounting Pronouncements issued, not yet adopted in Note 5 Material accounting policies in the notes to the financial statement for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 for more information about recent accounting pronouncements, the timing of their adoption and Solaire’s assessment, to the extent Solaire has made one, of their potential impact on Solaire’s financial condition and results of operations.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF
FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS OF APEITDA
References to the “Apeitda” refer to Apeitda Co., Ltd. The following discussion and analysis of Apeitda’s financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with (in each case, included elsewhere herein): (i) Apeitda’s audited financial statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 (and related notes) and (ii) Apeitda’s unaudited financial statements as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 and for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023(and related notes). Certain information contained in the discussion and analysis set forth below includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties.
Business Overview
Established in 2013, Apeitda Co., Ltd. (“Apeitda”)’s main business is a film production studio and is led by Jung Byung-gil and his brother Jung Byung-sik. Apeitda’s focus has been on action and thriller movies such as The Villainess and Carter which received recognition from Hollywood for its unique camerawork to create a sense of realism in action films.
Apeitda is actively involved in the film production business, producing both domestic and foreign movies. As a forward-thinking production company with a commitment to original ideas, Apeitda creates content that remains true to the fundamental values of entertainment and visual enjoyment. Apeitda’s portfolio includes films spanning various genres, from commercial blockbusters to independent features. Notably, Apeitda’s recent success in the box office was marked by the global streaming of the action film “Carter” on Netflix, solidifying its position as a production company capable of delivering world-class films.
Looking ahead, Apeitda has ambitious plans for numerous upcoming projects set to be streamed on global OTT channels like Amazon and Netflix. This strategic move reflects its dedication to further expanding its capabilities as a global film production studio.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”), as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”), expressed in Korean Won.
Key Components of Statement of Operations
Apeitda’s reporting currency is the Korean Won and its operating results and cash flows have been translated to U.S. dollar using the following exchange rates that represent the average daily rate in place for the respective period:
| | ● | At the period exchange rate as of June 30, 2024 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,376.55 for the balance sheet; |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the six months ended June 30, 2024 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,350.04 for the statements of operations and cash flow; |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the six months ended June 30, 2023 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,296.17 for the statements of operations and cash flow; |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the year ended December 31, 2023 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,306.76 for the statements of operations and cash flow; and |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the year ended December 31, 2022 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,291.78 for the statements of operations and cash flow. |
Results of Operations
A summary of Apeitda’s operating results is as follows:
Comparison of Six Months Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Income Statement: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | | ₩ | 1 | | | $ | 393 | | | ₩ | - | | | $ | - | |
| Cost of sales | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Gross profit | | | 1 | | | | 393 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Operating expenses | | | (200 | ) | | | (147,554 | ) | | | (186 | ) | | | (143,260 | ) |
| Operating profit (loss) | | | (199 | ) | | | (147,161 | ) | | | (186 | ) | | | (143,260 | ) |
| Other income (expense), net | | | 18 | | | | 13,443 | | | | 46 | | | | 35,529 | |
| Loss before taxes | | | (181 | ) | | | (133,718 | ) | | | (140 | ) | | | (107,731 | ) |
| Income tax benefit (expense) | | | (7 | ) | | | (5,183 | ) | | | 13 | | | | 10,402 | |
| Net income (loss) | | ₩ | (188 | ) | | $ | (138,901 | ) | | ₩ | (127 | ) | | $ | (97,329 | ) |
For the six months ended June 30, 2024, Apeitda’s operating income was driven by its content production segment, which realized revenues totalling less than Korean Won 1 million ($393) from one of the media production project which was released to the public in January 2024. For the six months ended June 30, 2023, Apeitda had not entered into any production agreements yet to provide the film production service. As such, for the six months ended June 30, 2023, Apeitda had not generated any revenue.
Apeitda’s gross profit has increased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by less than Korean Won 1 million ($393), corresponding to an increase in revenue of less than Korean Won 1 million ($393).
For the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023, Apeitda’s operating expenses are primarily driven by payroll and payroll related costs, depreciation expenses, commissions expenses and other bad debt expenses for both periods presented.
Apeitda’s operating expenses increased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 14 million ($4,294), or 7.5%. This is primarily attributable to a decrease in commission expenses of Korean Won 17 million ($12,350) associated with professional consulting fees, an increase in advertising expenses of Korean Won 20 million ($14,814) due to Apeitda’s marketing efforts, a decrease in entertainment expenses of Korean Won 11 million ($7,964), and an increase in impairment of prepayment of Korean Won 30 million ($22,222) which incurred due to the delay in completing the projects.
Apeitda typically takes approximately three years to complete a content project. Apeitda currently has no content projects in the production stage, but Apeitda may generate revenue from agreements Apeitda has entered into, or may enter into, with respect to Apeitda’s content project candidates, as well as content projects in production stage in the future. Apeitda’s ability to generate content revenues will depend on the successful development of its content project candidates.
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Year Ended
December 31,
2023 | | | Year Ended
December 31,
2022 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Income Statement: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | | ₩ | 90 | | | $ | 68,873 | | | ₩ | 4,240 | | | $ | 3,282,042 | |
| Cost of sales | | | (26 | ) | | | (20,259 | ) | | | (3,952 | ) | | | (3,059,364 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 64 | | | | 48,614 | | | | 288 | | | | 222,678 | |
| Operating expenses | | | (321 | ) | | | (245,456 | ) | | | (291 | ) | | | (224,973 | ) |
| Operating profit (loss) | | | (257 | ) | | | (196,842 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (2,295 | ) |
| Other income (expense), net | | | 87 | | | | 66,258 | | | | (4 | ) | | | (3,459 | ) |
| Loss before taxes | | | (170 | ) | | | (130,584 | ) | | | (7 | ) | | | (5,754 | ) |
| Income tax benefit | | | 15 | | | | 11,181 | | | | 66 | | | | 50,992 | |
| Net income (loss) | | ₩ | (155 | ) | | $ | (119,403 | ) | | ₩ | 59 | | | $ | 45,238 | |
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, Apeitda’s operating income was driven by its content production segment, which realized revenues totaling Korean Won 90 million ($68,873) and Korean Won 4,240 million ($3,282,042), respectively.
Apeitda’s gross profit has decreased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 224 million ($174,064), or 77.7% corresponding to a decrease in revenue of Korean Won 4,150 million ($3,213,169), or 97.9%. For the year ended December 31, 2023, Apeitda has no content reached the production stage. For the year ended December 31, 2022, one of Apeitda’s customers account for 99.7% of total Apeitda revenue.
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, Apeitda’s operating expenses are primarily driven by payroll and payroll related costs, depreciation expenses, and commissions expenses for both periods presented.
Apeitda’s operating expenses increased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 30 million ($20,483), or 10.3%. This is primarily attributable to an increase in depreciation expenses of Korean Won 44 million ($33,210) due to Apeitda’s newly acquired lease assets placed in service during the fourth quarter of 2023, offset by a decrease in bonus paid of Korean Won 8 million ($6,004) associated with a decrease in revenue for the year ended December 31, 2023.
Apeitda typically takes approximately three years to complete a content project. Apeitda currently has no content projects in the production stage, but Apeitda may generate revenue from agreements Apeitda has entered into, or may enter into, with respect to Apeitda’s content project candidates, as well as content projects in production stage in the future. Apetida’s ability to generate content revenues will depend on the successful development of its content project candidates.
Cash Flows
A summary of Apeitda’s operating, investing and financing cash flows prepared under IFRS is as follows:
Comparison of Six Months Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | | ₩ | (113 | ) | | $ | (83,584 | ) | | ₩ | (22 | ) | | $ | (17,251 | ) |
| Investing activities | | | 9 | | | | 6,811 | | | | (53 | ) | | | (40,853 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | (80 | ) | | | (59,258 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
| Effect of exchange rates on cash | | | 1 | | | | 785 | | | | 1 | | | | 393 | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | (183 | ) | | $ | (135,246 | ) | | ₩ | (74 | ) | | $ | (57,711 | ) |
Net cash flows used in operating activities increased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 91 million ($66,333). This is primarily attributable to an increase in Apeitda’s net loss by Korean Won 61 million ($41,572), a decrease in accounts receivable as no revenue generated by Korean Won 213 million ($164,654) for the six months ended June 30, 2024, and income tax refund received of Korean Won 254 million ($195,564).
Net cash flows provided by investing activities for the six months ended June 30, 2024 was Korean Won 9 million ($6,811), compared to Korean Won 53 million ($40,853) of net cash flows used in investing activities for the six months ended June 30, 2023. This is primarily attributable to an acquisition of long-term investment securities of Korean Won 36 million ($26,306), an increase in disposal of long-term investment securities of Korean Won 27 million ($19,656), and an acquisition of property, plant, and equipment of Korean Won 70 million ($54,314) for the six months ended June 30, 2023 that did not recur for the six months ended June 30, 2024.
Net cash flows used in financing activities increased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 80 million ($59,258). This is primarily attributable to the repayment of long-term borrowings of Korean Won 80 million ($59,258).
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Year Ended
December 31,
2023 | | | Year Ended
December 31, 2022 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | | ₩ | (159 | ) | | $ | (121,559 | ) | | ₩ | (85 | ) | | $ | (65,395 | ) |
| Investing activities | | | 428 | | | | 327,256 | | | | (960 | ) | | | (743,452 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | (83 | ) | | | (63,439 | ) | | | (8 | ) | | | (5,748 | ) |
| Effect of exchange rates on cash | | | - | | | | 10 | | | | - | | | | (233 | ) |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | 186 | | | $ | 142,268 | | | ₩ | (1,053 | ) | | $ | (814,828 | ) |
Net cash flows used in operating activities increased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 74 million ($56,164). This is primarily attributable to a decrease in net income of Korean Won 214 million ($164,641), a decrease in income tax expense of Korean Won 51 million ($39,811) corresponding to a decrease in revenue, and a decrease in prepayments of Korean Won 110 million ($84,659) due to a less film production projects for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022.
Net cash flows provided by investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2023 was Korean Won 428 million ($327,256), compared to Korean Won 960 million ($743,452) of net cash flows used in investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2022. This is primarily attributable to a decrease in the fluctuation of short-term financial instruments of Korean Won 1,000 million ($769,689) and a decrease in leasehold deposit of Korean Won 345 million ($267,073) as leasehold deposit payment did not recur for the year ended December 31, 2023.
Net cash flows used in financing activities increased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 75 million ($57,691). This is primarily attributable to the repayments of short-term borrowings made during the year ended December 31, 2023.
Based on management’s forecasts, the day-to-day operations and expenditure requirements are anticipated to be sufficiently funded by the cash held by Apeitda and securing other forms of investment and/or financing. As Apeitda’s operating expense consist primarily of costs incurred in connection with the production costs of the content projects, the operating expenses to be incurred in the future will be sufficiently funded by the potential investment.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Historically, Apeitda’s sources of liquidity have been cash flows from the generation of net income. As of June 30, 2024, Apeitda had an aggregate cash balance of Korean Won 477 million ($346,532) and net working capital of Korean Won 307 million ($223,344).
Related Parties
The related parties of Apeitda comprise two of Apeitda’s Chief Executive Officers, who are also the shareholders of Apeitda, and other related parties. Apeitda entered into multiple agreements for leasing the office space and loans with related parties.
See Related Parties under Note 12 in the notes to the financial statement for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 for more information about transactions entered into with related parties.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
During the periods presented, Apeitda did not have any relationships with unconsolidated organizations or financial partnerships, such as structured finance or special purpose entities, which were established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements.
Critical Accounting Estimates
Apeitda’s financial statements have been prepared in accordance with IFRS as issued by the IASB. The preparation of these financial statements requires Apeitda to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities as of the reporting dates, as well as the reported income and expenses incurred during the reporting period. Management bases its estimates on historical experience and in various other assumptions believed to be reasonable, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities. Actual results could differ from those estimates, and such differences could be material to Apeitda’s financial statements.
Apeitda believes the accounting policies discussed in the notes to Apeitda’s financial statements are critical to understanding Apeitda’s historical and future performance, as these policies relate to more significant areas involving management’s judgments and estimates.
See Summary of Material Accounting Policies in Note 5 to the financial statements as of and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 for more information about Apeitda’s material accounting policies.
Measurement of defined benefit obligations: key actuarial assumptions
Apeitda’s net obligation in respect of defined benefit plans is calculated separately for each plan by estimating the amount of future benefit that employees have earned in the current and prior periods, discounting that amount and deducting the fair value of any plan assets.
The calculation of defined benefit obligations is performed annually by a qualified actuary using the projected unit credit method. When the calculation results in a potential asset for Apeitda, the recognized asset is limited to the present value of economic benefits available in the form of any future refunds from the plan or reductions in future contributions to the plan. To calculate the present value of economic benefits, consideration is given to any applicable minimum funding requirements.
Uncertain tax treatments
Apeitda establishes additional current tax liabilities for income taxes when, despite the belief that tax positions are fully supportable, there remain positions that do not meet the minimum probability threshold, which is a tax position that is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by the applicable taxation authority. The impact of current tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions, as well as the related net interest and penalties, is included in income taxes in the statements of operations.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
Apeitda’s operating activities expose itself to a variety of financial risks: market risk, credit risk and liquidity risk from which Apeitda’s risk management program focuses on minimizing any adverse effects on its financial performance. Apeitda operates financial risk management policies and programs that closely monitor and respond to each risk factor.
See Summary of Apeitda’s financial risk management under Note 21 in the notes to the financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 for more information.
New Accounting Pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements are issued by the IASB or other standard setting bodies that are adopted by use as of the specified effective date. Unless otherwise discussed, Apeitda believes that the impact of recently issued standards that are not yet effective will not have a material impact on Apeitda’s financial position or results of operations adoption.
See Recent Accounting Pronouncements issued, not yet adopted in Note 5 Material accounting policies in the notes to the financial statement for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 for more information about recent accounting pronouncements, the timing of their adoption and Apeitda’s assessment, to the extent Apeitda has made one, of their potential impact on Apeitda’s financial statements upon operations.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF
FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS OF THE LAMP
References to the “The Lamp” refer to The LAMP Co., Ltd. The following discussion and analysis of The Lamp’s financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with (in each case, included elsewhere herein): (i) The Lamp’s audited financial statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 (and related notes) and (ii) The Lamp’s unaudited financial statements as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 and for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 (and related notes). Certain information contained in the discussion and analysis set forth below includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties.
Business Overview
The Lamp Co., Ltd. is actively involved in the production of video content, encompassing both domestic and international films and dramas. The Lamp’s commitment to the video content industry is evident in its ongoing contributions through content planning, development, and production. Boasting top-tier hits in the history of the Korean box office, The Lamp has also garnered numerous awards for The Lamp work in both domestic and international realms.
Recent endeavors include a strategic focus on attracting investments and producing content for OTT streaming platforms such as Netflix and Wavve. Through these initiatives, The Lamp is consistently broadening the global reach of its content. Adapting to the dynamic landscape of the rapidly growing content industry, The Lamp currently possesses a diverse portfolio of intellectual properties (IPs), including musicals and novels. The Lamp’s dedication to enhancing content competitiveness is unwavering, as The Lamp continually expands its repertoire of IPs to meet the evolving demands of the market.
Established in 2023. Led by Park Un-kyoung, The Lamp is a film and TV series production studio specializing in thought-provoking yet commercially successful movies including ‘A Taxi Driver’, ‘Mal-Mo-E’ and ‘Samjin Company English Class’. A Taxi Driver, for example, achieved commercial success attracting 12.2 million viewers at the box office. The Lamp has received awards at various film festivals and awards for content quality, including Blue Dragon Awards, Baeksang Art Awards and Houston International Film Festival. One of her current projects includes Aema, a Netflix original series that is scheduled for release in 2025. In Netflix’s press release of September 11, 2023, it confirmed the production of its upcoming series Aema, a fictional comedy.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”), as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”), expressed in Korean Won.
Key Components of Statement of Operations
The Lamp’s reporting currency is the Korean Won and its operating results and cash flows have been translated to U.S. dollar using the following exchange rates that represent the average daily rate in place for the respective period:
| | ● | At the period exchange rate as of June 30, 2024 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,376.55 for the balance sheet; |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the six months ended June 30, 2024 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,350.04 for the statements of operations and cash flow; |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the six months ended June 30, 2023 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,296.17 for the statements of operations and cash flow; |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the year ended December 31, 2023 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,306.76 for the statements of operations and cash flow; and |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the year ended December 31, 2022 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,291.78 for the statements of operations and cash flow. |
Results of Operations
A summary of The Lamp’s operating results is as follows:
Comparison of Six Months Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Income Statement: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | | ₩ | 12,532 | | | $ | 9,282,449 | | | ₩ | 8,981 | | | $ | 6,928,724 | |
| Cost of sales | | | (11,590 | ) | | | (8,585,214 | ) | | | (8,936 | ) | | | (6,893,844 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 942 | | | | 697,235 | | | | 45 | | | | 34,880 | |
| Operating expenses | | | (493 | ) | | | (364,945 | ) | | | (391 | ) | | | (301,850 | ) |
| Operating income (loss) | | | 449 | | | | 332,289 | | | | (346 | ) | | | (266,970 | ) |
| Other expense, net | | | (58 | ) | | | (43,238 | ) | | | (4 | ) | | | (3,097 | ) |
| Profit(Loss) before taxes | | | 391 | | | | 289,051 | | | | (350 | ) | | | (270,067 | ) |
| Income tax benefit (expense) | | | (82 | ) | | | (60,424 | ) | | | 40 | | | | 30,504 | |
| Net income (loss) | | ₩ | 309 | | | $ | 228,628 | | | ₩ | (310 | ) | | $ | (239,563 | ) |
For the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023, The Lamp’s operating income(loss) was driven by its content production segment, which realized revenues totalling Korean Won 12,532 million ($9,282,449) and Korean Won 8,981 million ($6,928,724), respectively.
The Lamp’s gross profit has increased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 897 million ($662,355), or 1,993.3%, corresponding to an increase in revenue of Korean Won 3,551 million ($2,353,725), or 39.5%. This is attributable to more content projects on the production stage during the six months ended June 30, 2024 compared to during the six months ended June 30, 2023. For the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023, three of The Lamp’s customers account for 97% and 88%, respectively, of total revenue.
For the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023, The Lamp’s operating expenses are primarily driven by payroll and payroll related costs, depreciation expenses, supplies expenses, rent expenses, commission expenses, and other bad debt expenses for both periods presented.
The Lamp’s operating expenses increased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 102 million ($63,095), or 26.1%. This is primarily attributable to an increase in payroll and payroll related costs of Korean Won 43 million ($32,191) corresponding to an increased average salary of the management, a decrease in bad debt expense of Korean Won 90 million ($66,665), and a decrease in miscellaneous income of Korean Won 55 million ($40,375) associated with the government grants received for the six months ended June 30, 2023.
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Year Ended
December 31,
2023 | | | Year Ended
December 31,
2022 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Income Statement: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | | ₩ | 20,837 | | | $ | 15,945,434 | | | ₩ | 17,966 | | | $ | 13,907,699 | |
| Cost of sales | | | (19,509 | ) | | | (14,929,569 | ) | | | (17,117 | ) | | | (13,250,789 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 1,328 | | | | 1,015,865 | | | | 849 | | | | 656,910 | |
| Operating expenses | | | (750 | ) | | | (573,991 | ) | | | (661 | ) | | | (511,719 | ) |
| Operating income | | | 578 | | | | 441,874 | | | | 188 | | | | 145,191 | |
| Other income (expense), net | | | (59 | ) | | | (45,107 | ) | | | (410 | ) | | | (317,607 | ) |
| Profit (loss) before tax | | | 519 | | | | 396,767 | | | | (222 | ) | | | (172,416 | ) |
| Income tax benefit | | | 19 | | | | 14,386 | | | | 20 | | | | 15,508 | |
| Net income (loss) | | ₩ | 538 | | | $ | 411,153 | | | ₩ | (202 | ) | | $ | (156,908 | ) |
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, The Lamp’s operating income was driven by its content production segment, which realized revenues totaling Korean Won 20,837 million ($15,945,434) and Korean Won 17,966 million ($13,907,699), respectively.
The Lamp’s gross profit has increased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 479 million ($358,955), or 56.4% corresponding to an increase in revenue of Korean Won 2,871 million ($2,037,735), or 16.0%. This is attributable to a more content projects during the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to during the year ended December 31, 2022. For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, five of The Lamp’s customers account for 100% and 89%, respectively, of total revenue.
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, The Lamp’s operating expenses are primarily driven by payroll and payroll related costs, depreciation expenses, supplies expenses and other bad debt expenses for both periods presented.
The Lamp’s operating expenses increased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 89 million ($62,272), or 13.5%. This is primarily attributable to an increase in payroll and payroll related costs of Korean Won 16 million ($12,381) corresponding to an increase in a number of employees, increase in bad debt expense of Korean Won 85 million ($65,046), an increase in commission expenses of Korean Won 21 million ($15,715), and an increase in miscellaneous income of Korean Won 32 million ($24,585) associated with the government grants received for the year ended December 31, 2023.
Cash Flows
A summary of The Lamp’s operating, investing and financing cash flows is as follows:
Comparison of Six Months Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | | ₩ | (149 | ) | | $ | (110,668 | ) | | ₩ | 1,124 | | | $ | 867,203 | |
| Investing activities | | | 36 | | | | 26,311 | | | | 273 | | | | 210,263 | |
| Financing activities | | | (56 | ) | | | (41,424 | ) | | | (104 | ) | | | (79,863 | ) |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | (169 | ) | | $ | (125,781 | ) | | ₩ | 1,293 | | | $ | 997,603 | |
Net cash flows used in operating activities for the six months ended June 30, 2024 was Korean Won 149 million ($110,668), compared to Korean Won 1,124 million ($867,203) of net cash flows provided by operating activities for the six months ended June 30, 2023. This is primarily attributable to an increase in net income of Korean Won 619 million ($468,190) as The Lamp entered into a new contract for the film production project, an increase in trade receivables of Korean Won 1,077 million ($801,427)corresponding to an increase in the number of the film production projects, a decrease in contract liabilities related to in-progress content projects of Korean Won 535 million ($422,073), and a decrease in accounts payable of Korean Won 449 million ($349,800).
Net cash flows provided by investing activities decreased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 237 million ($183,952). This is primarily attributable to a decrease in long-term investment securities collection of Korean Won 329 million ($254,131).
Net cash flows used in financing activities decreased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 48 million ($38,439). This is primarily attributable to an increase in cash and cash equivalents of Korean Won 72 million ($55,364) associated with the spin-off and repayments made of short-term borrowings of Korean Won 30 million ($22,222).
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Year Ended
December 31,
2023 | | | Year Ended
December 31,
2022 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | | ₩ | 876 | | | $ | 670,014 | | | ₩ | (106 | ) | | $ | (82,286 | ) |
| Investing activities | | | 225 | | | | 172,125 | | | | (895 | ) | | | (693,192 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | (124 | ) | | | (94,517 | ) | | | 1,159 | | | | 897,084 | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | 977 | | | $ | 747,622 | | | ₩ | 158 | | | $ | 121,606 | |
Net cash flows provided by operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2023 was Korean Won 876 million ($670,014), compared to Korean Won 106 million ($82,286) of net cash flows used in operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2022. This is primarily attributable to an increase in net income of Korean Won 740 million ($568,062) as The Lamp entered into a new contract for the film production project, an increase in bad debt expenses of Korean Won 85 million ($64,869), and an increase in interest expense of Korean Won 31 million ($23,196).
Net cash flows provided by investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2023 was Korean Won 225 million ($172,125), compared to Korean Won 895 million ($693,192) of net cash flows used in investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2022. This is primarily attributable to a decrease short-term loans of Korean Won 622 million ($481,313) and advances made of Korean Won 800 million ($619,301) for content projects.
Net cash flows used in financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2023 was Korean Won 124 million ($94,517), compared to Korean Won 1,159 million ($897,084) of net cash flows provided by financing activities the year ended December 31, 2022. This is primarily attributable to a decrease in cash and cash equivalents of Korean Won 1,044 million ($1,323,798) associated with the spin-off and the repayment of lease liabilities of Korean Won 65 million ($19,031).
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Historically, The Lamp’s sources of liquidity have been cash flows from the generation of net income. As of June 30, 2024, The Lamp had an aggregate cash balance of Korean Won 1,750 million ($1,271,372) and net working capital deficit of Korean Won 825 million ($599,503).
The Lamp intends to operate with its current cash on hand and the profits it anticipates earning in the future. The Lamp intends to expand its current business operations, including increasing drama and movie projects with global OTT and expanding its international footprint. The Lamp may need to borrow money or sell equity to finance its operations and planned growth.
The Lamp’s future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including its revenue growth rate, potential acquisitions, the timing and extent of spending to support future sales and marketing efforts. In order to finance these opportunities, The Lamp may need to raise additional financing. While there can be no assurances, if additional capital is required, The Lamp intends to raise such capital through operations or additional issuances of equity. If additional financing is required from outside sources, The Lamp may not be able to raise it on terms acceptable to it or at all. If The Lamp is unable to raise additional capital when desired, The Lamp’s business, results of operations and financial condition would be materially and adversely affected.
Related Parties
The related parties of The Lamp comprise the Chief Executive Officers of The Lamp, who is also the shareholder of The Lamp, and other related parties. The Lamp entered into multiple agreements for loans with related parties.
See Related Parties under Note 13 in the notes to the financial statement for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 for more information about transactions entered into with related parties.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
During the periods presented, The Lamp did not have any relationships with unconsolidated entities or financial partnerships, such as structured finance or special purpose entities, which were established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements.
Critical Accounting Estimates
The Lamp’s financial statements have been prepared in accordance with IFRS as issued by the IASB. The preparation of these financial statements requires The Lamp to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities as of the reporting dates, as well as the reported income and expenses incurred during the reporting period. Management bases its estimates on historical experience and in various other assumptions believed to be reasonable, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities. Actual results could differ from those estimates, and such differences could be material to The Lamp’s financial statements.
The Lamp believes the accounting policies discussed in the notes to The Lamp’s financial statements are critical to understanding The Lamp’s historical and future performance, as these policies relate to more significant areas involving management’s judgments and estimates.
See Summary of Material Accounting Policies in Note 5 to the financial statements as of and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 for more information about The Lamp’s material accounting policies.
Measurement of defined benefit obligations: key actuarial assumptions
The Lamp’s net obligation in respect of defined benefit plans is calculated separately for each plan by estimating the amount of future benefit that employees have earned in the current and prior periods, discounting that amount and deducting the fair value of any plan assets.
The calculation of defined benefit obligations is performed annually by a qualified actuary using the projected unit credit method. When the calculation results in a potential asset for The Lamp, the recognized asset is limited to the present value of economic benefits available in the form of any future refunds from the plan or reductions in future contributions to the plan. To calculate the present value of economic benefits, consideration is given to any applicable minimum funding requirements.
Uncertain tax treatments
The Lamp establishes additional current tax liabilities for income taxes when, despite the belief that tax positions are fully supportable, there remain positions that do not meet the minimum probability threshold, which is a tax position that is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by the applicable taxation authority. The impact of current tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions, as well as the related net interest and penalties, is included in income taxes in the statements of operations.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
The Lamp’s operating activities expose itself to a variety of financial risks: market risk, credit risk and liquidity risk from which The Lamp’s risk management program focuses on minimizing any adverse effects on its financial performance. The Lamp operates financial risk management policies and programs that closely monitor and respond to each risk factor.
See Summary of The Lamp’s financial risk management under Note 22 in the notes to the combined financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 for more information.
New Accounting Pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements are issued by the IASB or other standard setting bodies that are adopted by use as of the specified effective date. Unless otherwise discussed, The Lamp believes that the impact of recently issued standards that are not yet effective will not have a material impact on The Lamp’s financial statements upon adoption.
See Recent Accounting Pronouncements issued, not yet adopted in Note 5 Material accounting policies in the notes to the financial statement for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 for more information about recent accounting pronouncements, the timing of their adoption and The Lamp’s assessment, to the extent The Lamp has made one, of their potential impact on The Lamp’s financial condition and results of operations.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF
FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS OF BIDANGIL PICTURES
References to the “Bidangil” refer to Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd. The following discussion and analysis of Bidangil’s financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with (in each case, included elsewhere herein): (i) Bidangil’s audited financial statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 (and related notes) and (ii) Bidangil’s unaudited financial statements as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 and for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 (and related notes). Certain information contained in the discussion and analysis set forth below includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties.
Business Overview
Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd. (“Bidangil”) is engaged in the vibrant landscape of content production, covering a spectrum that includes both domestic and international movies and dramas. Distinguished by a world-class production sense and a highly efficient production system, Bidangil actively pursues innovation by venturing into diverse genres within the film industry. Many acclaimed directors play pivotal roles in shaping the landscape of K-content, and Bidangil stands out as an exceptional production studio, skillfully navigating the intersection of artistic quality and commercial success.
Established in 2005 and led by Kim, Soo Jin and Yoon, In Bum. Bidangil is a production studio that has produced over 10 movies including thrillers such as The Chaser and Korea’s first space-based sci-fi movie Space Sweepers which was released on Netflix. Bidangil has also been successful in discovering talented new directors, including Na Hongjin for The Chaser and Jo Sunghee for A Werewolf Boy and Space Sweepers. Bidangil also has created a distinctive portfolio of films with unique story lines and settings.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”), as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”), expressed in Korean Won.
Key Components of Statement of Operations
Bidangil’s reporting currency is the Korean Won and its operating results and cash flows have been translated to U.S. dollar using the following exchange rates that represent the average daily rate in place for the respective period:
| | ● | At the period exchange rate as of June 30, 2024 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,376.55 for the balance sheet; |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the six months ended June 30, 2024 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,350.04 for the statements of operations and cash flow; |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the six months ended June 30, 2023 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,296.17 for the statements of operations and cash flow; |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the year ended December 31, 2023 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,306.76 for the statements of operations and cash flow; and |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the year ended December 31, 2022 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,291.78 for the statements of operations and cash flow. |
Results of Operations
A summary of Bidangil’s operating results is as follows:
Comparison of Six Months Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Income Statement: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | | ₩ | 14,557 | | | $ | 10,782,558 | | | ₩ | 72 | | | $ | 55,569 | |
| Cost of sales | | | (13,798 | ) | | | (10,220,720 | ) | | | (15 | ) | | | (11,477 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 759 | | | | 561,838 | | | | 57 | | | | 44,092 | |
| Operating expenses | | | (340 | ) | | | (251,172 | ) | | | (360 | ) | | | (278,152 | ) |
| Operating income (loss) | | | 419 | | | | 310,666 | | | | (303 | ) | | | (234,060 | ) |
| Other income, net | | | 28 | | | | 20,389 | | | | 79 | | | | 61,182 | |
| Profit(Loss) before taxes | | | 447 | | | | 331,055 | | | | (224 | ) | | | (172,878 | ) |
| Income tax expense | | | (38 | ) | | | (28,425 | ) | | | (2 | ) | | | (1,652 | ) |
| Net income (loss) | | ₩ | 409 | | | $ | 302,630 | | | ₩ | (226 | ) | | $ | (174,530 | ) |
For the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023, Bidangil’s operating income (loss) was driven by its content production segment, which realized revenues totalling Korean Won 14,557 million ($10,782,558) and Korean Won 72 million ($55,569), respectively.
Bidangil’s gross profit has increased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 702 million ($517,746), or 1,231.6%, corresponding to an increase in revenue of Korean Won 14,485 million ($10,726,989), or 20,118.1%. This is attributable to an increase in media production revenue due to a new agreement initiated in August 2023. For the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023, three of Bidangil Pictures’ customers account for 99.9% and 89.1%, respectively, of total revenue.
For the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023, Bidangil’s operating expenses are primarily driven by payroll and payroll related costs, depreciation expenses, and commissions expenses for both periods presented.
Bidangil’s operating expenses decreased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 20 million ($26,980), or 5.6%. This is primarily attributable to an increase in bonus paid of Korean Won 4 million ($2,963) and a decrease in commissions expenses of Korean Won 32 million ($23,838) associated with outsourcing fees due to a decrease in the use of outsourcing companies.
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Year Ended
December 31,
2023 | | Year Ended
December 31,
2022 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) |
| Income Statement: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | | ₩ | 7,746 | | | $ | 5,927,700 | | | ₩ | 423 | | | $ | 327,723 | |
| Cost of sales | | | (7,070 | ) | | | (5,410,029 | ) | | | (353 | ) | | | (273,338 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 676 | | | | 517,671 | | | | 70 | | | | 54,385 | |
| Operating expenses | | | (725 | ) | | | (555,119 | ) | | | (741 | ) | | | (573,679 | ) |
| Operating loss | | | (49 | ) | | | (37,448 | ) | | | (671 | ) | | | (519,294 | ) |
| Other income, net | | | 234 | | | | 178,982 | | | | 70 | | | | 54,088 | |
| Profit (Loss) before taxes | | | 185 | | | | 141,534 | | | | (601 | ) | | | (465,206 | ) |
| Income tax benefit (expense) | | | 2 | | | | 1,165 | | | | (4 | ) | | | (3,023 | ) |
| Net income (loss) | | ₩ | 187 | | | $ | 142,699 | | | ₩ | (605 | ) | | $ | (468,229 | ) |
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, Bidangil’s revenue was derived from its content production segment, which realized revenues totaling Korean Won 7,746 million ($5,927,700) and Korean Won 423 million ($327,723), respectively.
Bidangil’s gross profit has increased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 606 million ($463,286), or 862.9% corresponding to an increase in revenue of Korean Won 7,323 million ($5,599,977), or 1,729.7%. This is attributable to an increase in proportion of profit-sharing revenue that has higher gross profit margins as the revenue is generated from the contents that are completed for the production in prior periods. For the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, three of Bidangil Pictures’ customers accounted for 99.2% and 95%, respectively, of total revenue.
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, Bidangil’s operating expenses were primarily comprised of payroll and payroll related costs, depreciation expenses, and commissions expenses for both periods presented.
Bidangil’s operating expenses decreased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 16 million ($18,560), or 2.2%. This is primarily attributable to a decrease in bonus paid of Korean Won 44 million ($33,671), a decrease in depreciation expenses of Korean Won 15 million ($11,514), a decrease in commissions expenses of Korean Won 23 million ($17,347) associated with professional consulting fee for research and development efforts for new products, and a decrease in miscellaneous income of Korean Won 100 million ($76,518) associated with government grants for content production, and an increase in other income of Korean Won 36 million ($27,473) during the year ended December 31, 2022.
Cash Flows
A summary of Bidangil’s operating, investing, and financing cash flows is as follows:
Comparison of Six Months Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | | ₩ | (1,102 | ) | | $ | (815,934 | ) | | ₩ | (465 | ) | | $ | (358,587 | ) |
| Investing activities | | | 1,385 | | | $ | 1,026,263 | | | ₩ | (63 | ) | | $ | (48,985 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | (2,244 | ) | | $ | (1,662,499 | ) | | ₩ | (42 | ) | | $ | (32,262 | ) |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | (1,961 | ) | | $ | (1,452,170 | ) | | ₩ | (570 | ) | | $ | (439,834 | ) |
Net cash flows used in operating activities increased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 637 million ($457,347). This is primarily attributable to a decrease in net loss by Korean Won 635 million ($477,159), a decrease in prepaid expenses of Korean Won 3,142 million ($2,327,454), an increase in accrued expenses of Korean Won 887 million ($655,856), partially offset by a decrease in contract liabilities of Korean Won 5,793 million ($4,291,234) as one of the content projects are nearing completion.
Net cash flows provided by investing activities for the six months ended June 30, 2024 was Korean Won 1,385 million ($1,026,263), compared to Korean Won 63 million ($48,985) of net cash flows used in investing activities for the six months ended June 30, 2023. This is attributable to the payment made of Korean Won 468 million ($422,959) for the purchase of short-term investment securities and the proceeds from disposal of short-term investment securities of Korean Won 121 million ($15,008). This is also attributable to proceeds from short-term loans collected of Korean Won 953 million ($705,535) and short-term loans paid of Korean Won 135 million ($99,997).
Net cash flows used in financing activities increased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 2,202 million ($1,630,237). This is primarily attributable to the purchase of treasury shares of Korean Won 2,000 million ($1,481,438).
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Year Ended
December 31,
2023 | | | Year Ended
December 31,
2022 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | | ₩ | 2,088 | | | $ | 1,598,066 | | | ₩ | 125 | | | $ | 97,043 | |
| Investing activities | | | 1,293 | | | | 989,446 | | | | (2,708 | ) | | | (2,096,067 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | (685 | ) | | | (524,298 | ) | | | 684 | | | | 529,538 | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | 2,696 | | | $ | 2,063,214 | | | ₩ | (1,899 | ) | | $ | (1,469,486 | ) |
Net cash flows provided by operating activities increased for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 by Korean Won 1,963 million ($1,501,023). This is primarily attributable to an increase in prepaid expenses of Korean Won 4,127 million ($3,158,058) and an increase in contract liabilities Korean Won 6,183 million ($4,731,519) associated with a new content project initiated during the year ended December 31, 2023.
Net cash flows provided by investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2023 was Korean Won 1,293 million ($989,446), compared to Korean Won 2,708 million ($2,096,067) of net cash flows used in investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2022. This is primarily attributable to the payment made of Korean Won 3,526 million ($2,668,094) for the purchase of short-term investment securities and the proceeds from disposal of short-term investment securities of Korean Won 7,600 million ($5,809,876).
Net cash flows used in financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2023 was Korean Won 685 million ($524,298), compared to Korean Won 684 million ($529,538) of net cash flows provided by in financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2022. This is primarily attributable to the repayment of Korean Won 1,402 million ($1,079,530) made due to the cancellation of contract for issuing new shares during the year ended December 31, 2023.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Historically, Bidangil’s sources of liquidity have been cash flows from the generation of net income. As of June 30, 2024, Bidangil had an aggregate cash balance of Korean Won 1,763 million ($1,280,687) and net working capital of Korean Won 2,190 million ($1,590,878).
Bidangil intends to operate with its current cash on hand and the profits it anticipates earning in the future. Bidangil intends to expand its current business operations, increasing drama and movie projects with global OTT and expanding its international footprint. Bidangil may need to borrow money or sell equity to finance its operations and planned growth.
Bidangil’s future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including its revenue growth rate, potential acquisitions, the timing and extent of spending to support future sales and marketing efforts. In order to finance these opportunities, Bidangil may need to raise additional financing. While there can be no assurances, if additional capital is required, Bidangil intends to raise such capital through operations or additional issuances of equity. If additional financing is required from outside sources, Bidangil may not be able to raise it on terms acceptable to it or at all. If Bidangil is unable to raise additional capital when desired, Bidangil’s business, results of operations and financial condition would be materially and adversely affected.
Related Parties
The related parties of Bidangil comprise two of Chief Executive Officers, who are also the shareholder of Bidangil. Bidangil entered into a loan agreement with two of Bidangil’s Chief Executive Officers.
See Related Parties under Note 13 in the notes to the financial statement for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 for more information about transactions entered into with related parties.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
During the periods presented, Bidangil did not have any relationships with unconsolidated entities or financial partnerships, such as structured finance or special purpose entities, which were established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements.
Critical Accounting Estimates
Bidangil’s financial statements have been prepared in accordance with IFRS as issued by the IASB. The preparation of these financial statements requires Bidangil to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities as of the reporting dates, as well as the reported income and expenses incurred during the reporting period. Management bases its estimates on historical experience and in various other assumptions believed to be reasonable, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities. Actual results could differ from those estimates, and such differences could be material to Bidangil’s financial statements.
Bidangil believes the accounting policies discussed in the notes to Bidangil’s financial statements are critical to understanding Bidangil’s historical and future performance, as these policies relate to more significant areas involving management’s judgments and estimates.
See Summary of Material Accounting Policies in Note 5 to the financial statements as of and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 for more information about Bidangil’s material accounting policies.
Uncertain tax treatments
Bidangil establishes additional current tax liabilities for income taxes when, despite the belief that tax positions are fully supportable, there remain positions that do not meet the minimum probability threshold, which is a tax position that is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by the applicable taxation authority. The impact of current tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions, as well as the related net interest and penalties, is included in income taxes in the statements of operations.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
Bidangil’s operating activities expose itself to a variety of financial risks: market risk, credit risk and liquidity risk from which Bidangil’s risk management program focuses on minimizing any adverse effects on its financial performance. Bidangil operates financial risk management policies and programs that closely monitor and respond to each risk factor.
See Summary of Bidangil’s financial risk management under Note 22 in the notes to the financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 for more information.
New Accounting Pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements are issued by the IASB or other standard setting bodies that are adopted by use as of the specified effective date. Unless otherwise discussed, Bidangil believes that the impact of recently issued standards that are not yet effective will not have a material impact on Bidangil’s financial statements upon adoption.
See Recent Accounting Pronouncements issued, not yet adopted in Note 5 Material accounting policies in the notes to the financial statement for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 for more information about recent accounting pronouncements, the timing of their adoption and Bidangil’s assessment, to the extent Bidangil has made one, of their potential impact on Bidangil’s financial condition and results of operations.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF
FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS OF ANSEILEN
References to the “Anseilen” refers to Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd. The following discussion and analysis of Anseilen’s financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with (in each case, included elsewhere herein) ): (i) Anseilen’s audited financial statements as of December 31, 2023 (and related notes) and (ii) Anseilen’s unaudited financial statements as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 and for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 (and related notes). Certain information contained in the discussion and analysis set forth below includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties.
Business Overview
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd. (“Anseilen”) is engaged in the video content production business, spanning movies and dramas, and including IP planning and development. Anseilen’s team comprises accomplished directors who have played key roles in shaping the landscape of K-drama, contributing invaluable expertise to the creation of global video content. Recognizing the evolving trends in the video content market that demand diversity, Anseilen strategically plans and develops new content, drawing on Anseilen’s extensive experience across various formats, including plays, classics, novels, foreign dramas, and documentaries.
In alignment with the global demand for content, Anseilen is actively working on projects slated for streaming on platforms such as Disney and Netflix. Anseilen’s upcoming productions aim to lead the way in the ever-changing landscape of video content trends. Through the independent directorial skills and the synergy derived from Studio Anseilen’s seasoned directors, Anseilen plans to spearhead the emergence of fresh and innovative video content.
Anseilen’s main business is production studio for multi-form TV series and movies. While it is a newly established entity (March 2023), it is led by Kyung-su Shin, Jun-Woo Park, Seung-Ho Kim, 3 top executive producers who worked for SBS, one of the leading Korean TV broadcasting channels. They have created some of Korea’s most famous dramas such as an adaptation of the webtoons taxi driver and other works such as the First Responders’ and ‘Twenty-Five Twenty-One’.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”), as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”), expressed in Korean Won.
Key Components of Statement of Operations
Anseilen’s reporting currency is the Korean Won and its operating results and cash flows have been translated to U.S. dollar using the following exchange rates that represent the average daily rate in place for the respective period:
| | ● | At the period exchange rate as of June 30, 2024 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,376.55 for the balance sheet; |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the six months ended June 30, 2024 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,350.04 for the statements of operations and cash flow; and |
| | | |
| | ● | At the average exchange rate for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 of US$1.00 to KRW 1,296.17 for the statements of operations and cash flow. |
Results of Operations
A summary of Anseilen’s operating results is as follows:
Comparison of Six Months Ended June 30, 2024 and the Period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
| | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2024 | | | For the Period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Statement of Profit or Loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating expenses | | ₩ | (256 | ) | | $ | (189,643 | ) | | ₩ | (59 | ) | | $ | (45,400 | ) |
| General and Administrative | | | (256 | ) | | | (189,905 | ) | | | (59 | ) | | | (45,400 | ) |
| Other operating income, net | | | - | | | | 262 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Operating loss | | | (256 | ) | | | (189,643 | ) | | | (59 | ) | | | (45,400 | ) |
| Other income | | | - | | | | 82 | | | | - | | | | 2 | |
| Interest income | | | - | | | | 82 | | | | - | | | | 2 | |
| Net loss | | ₩ | (256 | ) | | $ | (189,561 | ) | | ₩ | (59 | ) | | $ | (45,398 | ) |
For the six months ended June 30, 2024 and the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023, Anseilen’s operating expenses consist of personnel-related expenses for administrative functions and expenses for outside professional services, including legal, audit and accounting services. Personnel-related expenses consist of salaries and severance.
Anseilen’s operating expenses increased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 197 million ($144,242), or 333.9%. This is primarily attributable to an increase in the average salary amount for the management.
Cash Flows
A summary of Anseilen’s operating, investing, and financing cash flows is as follows:
Comparison of Six Months Ended June 30, 2024 and the Period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
| | | Six Months Ended
June 30,
2024 | | | For the period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | (In millions of Korean won and US dollar) | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | | ₩ | (54 | ) | | $ | (40,039 | ) | | ₩ | 844 | | | $ | 651,335 | |
| Investing activities | | | - | | | | - | | | | (80 | ) | | | (61,720 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | - | | | | - | | | | 14 | | | | 10,759 | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | (54 | ) | | $ | (40,039 | ) | | ₩ | 778 | | | $ | 600,374 | |
Net cash flows used in operating activities for the six months ended June 30, 2024 was Korean Won 54 million ($40,039), compared to Korean Won 844 million ($651,335) of net cash flows provided by operating activities for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023. This is primarily attributable to an increase in Anseilen’s net loss by Korean Won of 197 million ($144,162) and decrease in changes in the working capital accounts by Korean Won of 701 million ($547,281).
Net cash flows used in investing activities decreased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 80 million ($61,720). This is due to advances of leasehold deposit receivables of Korean Won 50 million ($38,575) and purchase of investment securities of Korean Won 30 million ($23,145) for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023, which did not recur for the six months ended June 30, 2024.
Net cash flows provided by financing activities decreased for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 by Korean Won 14 million ($10,759). This is primarily attributable to the proceeds received from the common shares issued, which did not recur for the six months ended June 30, 2024.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Historically, Anseilen’s sources of liquidity have been cash flows from the payments received from K Enter Holdings. During June 2023, Anseilen entered into the agreement with K Enter Holdings to receive payment totaling Korean Won 1,000 million ($758,840) by June 30, 2025. Also, Anseilen has received totaling Korean Won 250 million ($181,613) by June 30, 2024. As of June 30, 2024, Anseilen had an aggregate cash balance of Korean Won 222 million ($161,158) and net working capital of Korean Won 221 million ($160,761).
Anseilen intends to operate with its current cash on hand and the profits it anticipates earning in the future. Anseilen intends to expand its current business operations, including providing additional offerings such as producing intellectual property rights of K-Drama and expand its international footprint. Anseilen may need to borrow money or sell equity to finance its operations and planned growth.
Anseilen’s future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including its revenue growth rate, potential acquisitions, the timing and extent of spending to support future sales and marketing efforts. In order to finance these opportunities, Anseilen may need to raise additional financing. While there can be no assurances, if additional capital is required, Anseilen intends to raise such capital through operations or additional issuances of equity. If additional financing is required from outside sources, Anseilen may not be able to raise it on terms acceptable to it or at all. If Anseilen is unable to raise additional capital when desired, Anseilen’s business, results of operations and financial condition would be materially and adversely affected.
Related Parties
The related parties of Anseilen comprise shareholders of the Company and other related parties.
See Related Parties under Note 11 in the notes to the financial statement for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 for more information about transactions entered into with related parties.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
During the period presented, Anseilen did not have any relationships with unconsolidated entities or financial partnerships, such as structured finance or special purpose entities, which were established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements.
Critical Accounting Estimates
Anseilen’s financial statements have been prepared in accordance with IFRS as issued by the IASB. The preparation of these financial statements requires Anseilen to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities as of the reporting date, as well as the reported income and expenses incurred during the reporting period. Management bases its estimates on historical experience and in various other assumptions believed to be reasonable, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities. Actual results could differ from those estimates, and such differences could be material to Anseilen’s financial statements.
Anseilen believes the accounting policies discussed in the notes to Anseilen’s financial statements are critical to understanding Anseilen’s historical and future performance, as these policies relate to more significant areas involving management’s judgments and estimates.
See Summary of Material Accounting Policies in Note 5 to the financial statements as of and for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023 for more information about Anseilen’s significant accounting policies.
Measurement of defined benefit obligations: key actuarial assumptions
Anseilen’s net obligation in respect of defined benefit plans is calculated separately for each plan by estimating the amount of future benefit that employees have earned in the current and prior periods, discounting that amount and deducting the fair value of any plan assets.
The calculation of defined benefit obligations is performed annually by a qualified actuary using the projected unit credit method. When the calculation results in a potential asset for Anseilen, the recognized asset is limited to the present value of economic benefits available in the form of any future refunds from the plan or reductions in future contributions to the plan. To calculate the present value of economic benefits, consideration is given to any applicable minimum funding requirements.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
Anseilen’s operating activities expose itself to a variety of financial risks: market risk, credit risk and liquidity risk from which Anseilen’s risk management program focuses on minimizing any adverse effects on its financial performance. Anseilen operates financial risk management policies and programs that closely monitor and respond to each risk factor.
See Summary of Anseilen’s financial risk management under Note 19 in the notes to the financial statements for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023 for more information.
New Accounting Pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements are issued by the IASB or other standard setting bodies that are adopted by use as of the specified effective date. Unless otherwise discussed, Anseilen believes that the impact of recently issued standards that are not yet effective will not have a material impact on Anseilen’s financial statements upon adoption.
See Recent Accounting Pronouncements issued, not yet adopted in Note 5 Material accounting policies in the notes to the financial statement for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023 for more information about recent accounting pronouncements, the timing of their adoption and Anseilen’s assessment, to the extent Anseilen has made one, of their potential impact on Anseilen’s financial condition and results of operations.
K WAVE’S BUSINESS
Overview
Formation. K Wave Media Ltd. (“K Wave” or “PubCo”), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Global Star Acquisition Inc. (“Global Star”), was incorporated on June 22 2023 as a Cayman Islands exempted company. K Wave was formed for the purpose of becoming the ultimate parent company following the transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement. K Wave maintains one direct wholly owned subsidiary, GLST Merger Sub Inc. (“Merger Sub”), a Delaware corporation. Merger Sub was incorporated to facilitate the consummation of the Merger Agreement. As of the date of the proxy statement/prospectus K Wave and Merger Sub have nominal assets and no operations.
Business Combination Activities. On June 15, 2023, Global Star entered into the Merger Agreement with K Enter, pursuant to which the Company plans to consummate a business combination transaction with K Enter. On July 13, 2023, K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company and wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company (the “PubCo”), and GLST Merger Sub Inc., a Delaware corporation and wholly-owned subsidiary of PubCo (the “Merger Sub”) became parties to the Business Combination Agreement pursuant to a previously disclosed written joinder agreement. On March 11, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the First Amendment to Merger Agreement. On June 28, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Second Amendment to Merger Agreement. On July 25, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Third Amendment to Merger Agreement. Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, the Business Combination will be effected in two steps: (i) subject to the approval and adoption of the Merger Agreement by the stockholders of Global Star, Global Star will reincorporate to Cayman Islands by merging with and into K Wave, with K Wave remaining as the surviving publicly traded entity (the “Reincorporation Merger”); (ii) one (1) business day following the Reincorporation Merger, Merger Sub will be merged with and into K Enter, resulting in K Enter being a wholly owned subsidiary of K Wave. However, the consummation of the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement is subject to numerous conditions, and there can be no assurances that such conditions will be satisfied.
Planned Business Operations, K Wave plans to be engaged in the “IP content business,” which refers to a business that focuses on creating, investing in, managing, licensing, and monetizing intellectual property (IP) content such as TV shows, movies, dramas and music. At the heart of K Wave’s IP content business is the creation of original content or the acquisition of rights to existing content from creators, artists, or other sources, such as films and TV shows that are valuable intellectual property. In the case of the Merchandising Company it involves the merchandise sales of IP Content based on a popular musicians, TV shows and movies. K Wave regards its IP content, including copyrights, registered trademark and pending trademarks, service marks, domain names, trade secrets, proprietary technologies and similar intellectual property as critical to its success. K Wave will rely on trademark law, trade secret protection and confidentiality and license agreements with employees and others to protect K Wave’s proprietary rights.
Corporate Information. K Wave’s offices are located at:
K Wave Media
c/o Maples Corporate Services Limited
PO Box 309, Ugland House
Grand Cayman, KY1-1104
Cayman Islands
(703) 790-0717
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF
FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS OF K Wave media ltd.
References to the “K Wave Media” refers to K Wave Media Ltd. The following discussion and analysis of K Wave Media Ltd.’s financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with (in each case, included elsewhere herein) (i) K Wave Media Ltd.’s audited financial statements as of December 31, 2023 and for the period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to December 31 (and related notes) and (ii) K Wave Media Ltd.’s unaudited financial statements as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 and for the six month ended June 30, 2024 and the period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 (and related notes). Certain information contained in the discussion and analysis set forth below includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties.
Business Overview
K Wave Media Ltd. (“the Company”), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Global Star Acquisition Inc. (“Global Star”), was incorporated on June 22, 2023 and the Company’s registered office is at c/o Maples Corporate Services Limited PO Box 309, Ugland House Grand Cayman, KY1-1104 Cayman Islands. The Company was formed for the purpose of becoming the ultimate parent company following the transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement. The Company maintains one direct wholly owned subsidiary, GLST Merger Sub Inc. (“Merger Sub”), a Delaware corporation. Merger Sub was incorporated to facilitate the consummation of the Business Combination Agreement. As of June 30, 2024, Merger Sub had no operations. The Company and Merger Sub are together referred to as the “Group”.
Global Star has entered into a merger agreement, dated as of June 15, 2023, and as amended on March 11, 2024, June 28, 2024, July 25, 2024 and December 11, 2024 (as it may be amended from time to time, the “Merger Agreement”), which provides for a Business Combination between Global Star and K Enter Holdings, Inc., a Delaware corporation (“K Enter”). Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, the Business Combination will be effected in two steps: (i) subject to the approval and adoption of the Merger Agreement by the stockholders of Global Star, Global Star will reincorporate to Cayman Islands by merging with and into the Company, with the Company remaining as the surviving publicly traded entity (the “Reincorporation Merger”); (ii) one (1) business day following the Reincorporation Merger, Merger Sub will be merged with and into K Enter, resulting in K Enter being a wholly owned subsidiary of the Group.
In connection with the December 11, 2024, amendment to the Merger Agreement, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement, which extended the outside date for the parties to consummate the closing of the Business Combination from December 22, 2024 to June 22, 2025.
As of June 30, 2024, the Company issued 5,000,000 shares of the Company’s ordinary shares. Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, the Company expects to cancel all the outstanding 5,000,000 shares of the Company’s ordinary shares as of the effective date of the Business Combination. Also, the Company expects to issue a total of 59,000,000 ordinary shares of the Company at a price of $10 per share as consideration for a total of 193,367 shares of K Enter. This consists of (1) 30,878,682 K Wave Ordinary shares issued in exchange for 101,202 shares of K Enter common stock owned by the currently existing stockholders of K Enter, including, the 4,997 shares of K Enter common stock owned by GF Korea and the 1,202 shares of K Enter common stock owned by Lodestar USA; (2) 12,448,256 K Wave Ordinary shares issued in exchange for 40,798 shares of K Enter common stock owned by the Preferred Stock owners after the conversion of the 40,798 shares of Preferred Stock into shares of K Enter common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination and (3) 15,673,062 K Wave Ordinary shares to be issued in exchange for 51,367 shares of K Enter common stock that will be owned by the owners of Six Korean Entities following K Enter acquisition of the controlling equity interests in the Six Korean Entities, all based on an estimated 305.1192809:1 conversion ratio calculated using a foreign exchange rate as of June 30, 2024, of KRW 1,376.55 / USD $1.00. The total ordinary shares of the Company to be issued to the stockholders of K Enter in connection with the closing of the Business Combination will be 59,000,000 ordinary shares.
Following the consummation of the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement, the Group will be the surviving publicly-traded entity. However, the consummation of the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement is subject to numerous conditions, and there can be no assurances that such conditions will be satisfied.
Results of operations
Present below is a summary of K Wave Media’s operating results is as follows:
Comparison of Six Month Ended June 30, 2024 and the Period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to June 30,2023
| | | Six months ended
June 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from
June 22, 2023
(inception) through
June 30,
2023 | |
| Statement of Profit or Loss: | | | | | | | | |
| Operating expenses | | $ | - | | | $ | (3,882 | ) |
| General and Administrative | | | - | | | | (3,882 | ) |
| Loss From Operations | | | - | | | | (3,882 | ) |
| Other income | | | - | | | | - | |
| Interest income | | | - | | | | - | |
| Net loss | | $ | - | | | $ | (3,882 | ) |
K Wave Media’s all expenses decreased for the six month ended June 30, 2024 as compared to the period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023, by $3,882, or 100%. For the period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023, K Wave Media’s all expenses have been related to initial start-up costs incurred with setting up a legal entity. As of June 30, 2024, the Company had no operations and the Company expects to incur the operating expenses after becoming the ultimate parent company following the transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement.
Liquidity and capital resources
As of June 30, 2024, we had no cash or cash equivalents.
From inception to June 30, 2024, we did not have any operating, investing, or financing cash flows.
Contractual obligations and commitments
As of June 30, 2024, we have no contractual obligations and commitments outside of our related party transaction with K Wave Media.
Off-balance sheet arrangements
As of June 30, 2024, we do not have any off-balance sheet arrangements.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
We prepare our Financial Statements in accordance with the IFRS issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”). Refer to “Note3 - Material accounting policies” in the accompanying Financial Statements for discussion of the accounting policies applied by us. From inception to December 31, 2023, we did not have operating activities or become party to transactions requiring the application of significant, difficult, subjective, or complex accounting judgements.
Quantitative and qualitative disclosures about market risk
As of June 30, 2024, we had no material exposure to market risk.
GLOBAL STAR’S BUSINESS
Overview
Formation. Global Star is a blank check company incorporated on July 24, 2019, as a Delaware corporation whose business purpose is to effect a merger, capital stock exchange, asset acquisition, stock purchase, reorganization, or similar business combination with one or more businesses, (the “Business Combination”). Global Star is an emerging growth company and, as such, Global Star is subject to all the risks associated with emerging growth companies.
Under the Existing Charter, Global Star must consummate the Business Combination by February 22, 2025 (unless Global Star elects to extend the time it has to complete the initial business combination to June 22, 2025). If Global Star is unable to complete its initial business combination by February 22, 2025 (unless Global Star elects to extend the time it has to complete the initial business combination to June 22, 2025), it will (i) cease all operations except for the purpose of winding up, (ii) as promptly as reasonably possible but no more than five business days thereafter, redeem 100% of the outstanding public shares, at a per share price, payable in cash, equal to the aggregate amount then on deposit in the Trust Account, including interest earned (net of taxes payable), divided by the number of then outstanding public shares, which redemption will completely extinguish public stockholders’ rights as stockholders (including the right to receive further liquidation distributions, if any), subject to applicable law, and (iii) as promptly as reasonably possible following such redemption, subject to the approval of the remaining stockholders and the Board, proceed to commence a voluntary liquidation and thereby a formal dissolution of Global Star, subject in each case to its obligations to provide for claims of creditors and the requirements of applicable law.
Offering Proceeds Held in Trust. On September 22, 2022, the Company consummated its initial public offering (the “IPO”) of 8,000,000 units (the “Units”). Each Unit consists of one share of Class A Common Stock of the Company, par value $0.0001 per share (“Class A Common Stock”), one redeemable warrant (“Warrant”), with each whole Warrant entitling the holder thereof to purchase one share of Class A Common Stock for $11.50 per share, and one Right, with each Right entitling the holder to receive one-tenth of one share of Class A Common Stock. The Units were sold at a price of $10.00 per Unit, generating gross proceeds to the Company of $80,000,000.
Simultaneously with the consummation of the closing of the IPO, the Company consummated the private placement of an aggregate of 456,225 units (the “IPO Private Placement Units”) to the Sponsor, at a price of $10.00 per Private Placement Unit, generating total gross proceeds of $4,562,250 (the “IPO Private Placement”).
At the time of the IPO, the underwriters were granted a 45-day over-allotment option to purchase up to 1,200,000 additional Units to cover overallotments, if any (the “Over-Allotment Units”). Subsequently, on September 30, 2022, the underwriters exercised their over-allotment option to purchase 1,200,000 Over-Allotment Units. On October 4, 2022 the Company closed on the Over-Allotment Units through the sale of 1,200,000 Units at a purchase price of $10.00 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $12.0 million.
Simultaneously with the sale of the Over-Allotment Units, the Company consummated the private placement of an aggregate of 42,000 units (the “Over-Allotment Private Placement Units” and together with the IPO Private Placement Units, the “Private Placement Units”) to the Sponsor, at a price of $10.00 per Over-Allotment Private Placement Units, generating total gross proceeds of $420,000.
A total of $94,300,000 comprising proceeds from the IPO and proceeds of the Private Placement, net of the underwriting commissions, discounts, and IPO expenses, was deposited in a trust account established for the benefit of the Company’s public stockholders.
At a Special Meeting of Stockholders held on June 11, 2024, the stockholders of Global Star approved amendments to Global Star’s Current Charter and the Trust Agreement to extend the deadline for completing a business combination from June 22, 2024 (the “Prior Termination Date”) to up to December 22, 2024 via six one-month extensions provided the Sponsor deposits into the Trust Account extension payments equal to the lesser of $60,000 or $0.02 per outstanding share of common stock sold in the IPO as of the applicable deadline date for each one-month extension.
On June 18, 2024, Global Star deposited $22,740 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to July 22, 2024. On July 17, 2024, Global Star deposited $22,740 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to August 22, 2024. On August 19, 2024, Global Star deposited $22,740 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to September 22, 2024. On September 17, 2024, Global Star deposited $22,740 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to October 22, 2024. On October 17, 2024, Global Star deposited $22,740 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to November 22, 2024. On November 18, 2024, Global Star deposited $22,740 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to December 22, 2024.
The extension payments were funded from the proceeds of a loan Sponsor made to Global Star in the principal amount of $1,600,000 (the “Loan”). The Loan is evidenced by a promissory note, dated July 31, 2023, issued by Global Star to the Sponsor (the “Note”). At the election of the Sponsor, up to $1,500,000 of the unpaid principal amount of the Note will be converted into GLST Private Units at a price of $10.00 per unit (the “Conversion Units”) in lieu of cash repayment. The principal balance of the Note is payable by Global Star on the later of: (i) December 31, 2023, or (ii) the date on which Global Star consummates a Business Combination. No interest shall accrue on the unpaid principal balance of the Note.
Then, on November 27, 2024, Global Star held a Special Meeting of its Stockholders (the “Meeting”). At the Meeting, Global Star’s stockholders approved the Charter Amendment which extends the date by which Global Star must consummate its initial business combination from December 22, 2024 to June 22, 2025, subject to the approval of the Board of Directors of Global Star (the “Board”) provided the sponsor or its designees deposit into the trust account the lesser of (i) $60,000 or (ii) $0.02 per share for each public share that is not redeemed in connection with the Meeting, prior to the commencement of each extension period. At the Meeting shareholders holding 756,131 shares of common stock exercised their right to redeem their shares for cash at a price of approximately $11.39 per share of the funds in the Trust Account. As a result an aggregate of $8,613,436, net of interest withdrawn for taxes of $110,751, was removed from the Trust Account to pay such holders. Following the redemption, Global Star’s remaining shares of GLST Class A Common Stock outstanding were 380,875. Global Star has disclosed further details of the Meeting in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC on November 27, 2024. On December 4, 2024, Global Star deposited $7,617.50 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to January 22, 2025. On December 12, 2024, Global Star deposited $7,617.50 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to February 22, 2025.
If Global Star fails to consummate a business combination prior to the earlier of the Extended Date or the New Termination Date (as it may be extended as described above), Global Star will (i) cease all operations except for the purpose of winding up, (ii) as promptly as reasonably possible but not more than ten business days thereafter, redeem the public shares, at a per-share price, payable in cash, equal to the aggregate amount then on deposit in the Trust Account, including interest earned on the funds held in the Trust Account and not previously released to pay taxes (less up to $100,000 of interest to pay dissolution expenses), divided by the number of then outstanding public shares, which redemption will completely extinguish the rights of the holders of public shares as shareholders (including the right to receive further liquidating distributions, if any), and (iii) as promptly as reasonably possible following such redemption, subject to the approval of Global Star’s remaining shareholders and the board of directors, dissolve and liquidate, subject in each case to Global Star’s obligations under Delaware law to provide for claims of creditors and the requirements of other applicable law. In that event, there will be no distribution from the Trust Account with respect to Global Star’s rights, which will expire worthless in the event of Global Star’s winding up. In the event of a liquidation, Global Star’s Sponsor and directors and officers will not receive any monies held in the Trust Account as a result of their ownership of the Founder Shares and Private Placement Units.
Business Combination Activities. On June 15, 2023, Global Star entered into the Merger Agreement with K Enter, pursuant to which the Company plans to consummate a business combination transaction with K Enter. On July 13, 2023, K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company and wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company (the “PubCo”), and GLST Merger Sub Inc., a Delaware corporation and wholly-owned subsidiary of PubCo (the “Merger Sub”) became parties to the Business Combination Agreement pursuant to a previously disclosed written joinder agreement. On March 11, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the First Amendment to Merger Agreement. On June 28, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Second Amendment to Merger Agreement. On July 25, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Third Amendment to Merger Agreement. On December 11, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement. In the event that the Business Combination is not consummated by February 22, 2025 (unless Global Star elects to extend the time it has to complete the initial business combination to June 22, 2025), Global Star’s corporate existence will cease and Global Star will distribute the funds held in the trust account to Global Star’s public shareholders.
Corporate Information. Global Star’s executive offices are located at:
1641 International Drive Unit 208
McLean, VA 22102
Telephone: (703) 790-0717
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF
FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS OF GLOBAL STAR
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with Global Star’s Financial Statements and footnotes thereto contained in this report.
References to the “Global Star” refer to Global Star Acquisition Inc. The following discussion and analysis of Global Star’s financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with Global Star’s audited financial statements and related notes included herein. The following discussion and analysis of Global Star’s financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with Global Star’s unaudited financial statements and the notes thereto contained elsewhere in this Report. Certain information contained in the discussion and analysis set forth below includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties.
Overview
Global Star is a blank check company incorporated in the State of Delaware on July 24, 2019, whose business purpose is to effect a merger, capital stock exchange, asset acquisition, stock purchase, reorganization, or similar business combination with one or more businesses, which Global Star refers to as Global Star’s initial business combination (the “Business Combination”). To date, Global Star’s efforts have been limited to organizational activities as well as activities related to the initial public offering (the “IPO”) and the completion of Global Star’s Business Combination.
Global Star’s sponsor is Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (the “Sponsor”). The registration statement for the Global Star’s Initial Public Offering was declared effective on September 19, 2022. On September 22, 2022, Global Star consummated the IPO of 8,000,000 units, at $10.00 per unit, with each unit consisting of one share of Class A Common Stock, par value $0.0001 per share (“GLST Class A Common Stock”), one redeemable warrant (“Warrant”), each whole Warrant entitling the holder thereof to purchase one share of GLST Class A Common Stock at an exercise price of $11.50 per share, and one Right, with each Right entitling the holder to receive one-tenth of one share of GLST Class A Common Stock (“Right”), generating gross proceeds of $80,000,000. On September 22, 2022, simultaneously with the consummation of the closing of the IPO, Global Star consummated the private placement of an aggregate of 456,225 units (the “Private Placement Unit”) to the Sponsor, at a price of $10.00 per Private Placement Unit, generating total gross proceeds of $4,562,250 (the “Private Placement”).
At the time of the IPO, the underwriters were granted a 45-day over-allotment option to purchase up to 1,200,000 additional Units to cover overallotments (the “Over-Allotment Units”). On September 30, 2022, the underwriters exercised their over-allotment option to purchase 1,200,000 Over-Allotment Units. On October 4, 2022, Global Star closed on the over-allotment through the sale of 1,200,000 at Over-Allotment Units a purchase of $10.00 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $12,000,000.
Simultaneously with the sale of the Over-Allotment Units, Global Star consummated the private placement of an aggregate of 42,000 units (the “Over- Allotment Private Placement Units” and together with the IPO Private Placement Units, the “Private Placement Units”) to the Sponsor, at a price of $10.00 per Over-Allotment Private Placement Units, generating total gross proceeds of $420,000.
A total of $94,300,000 comprised of the proceeds from the IPO and the proceeds of the Private Placement, net of the underwriting commissions, discounts, and offering expenses, was deposited in a trust account established for the benefit of Global Star’s public stockholders (the “Trust Account”). The proceeds held in the Trust Account are invested in United States “government securities” within the meaning of Section 2(a)(16) of the Investment Company Act with a maturity of 180 days or less or in money market funds meeting certain conditions under Rule 2a-7 promulgated under the Investment Company Act which invest only in direct U.S. government treasury obligations. Except with respect to interest earned on the funds held in the Trust Account that may be released to Global Star to pay Global Star income or other tax obligations as described in the initial public offering, the proceeds will not be released from the trust account until the earlier of the completion of a business combination or the redemption of all or a portion of the outstanding public shares if Global Star has not completed a business combination within the time required time period.
Global Star intends to effectuate Global Star’s Business Combination using cash from the proceeds of the IPO and the Private Placement, the proceeds of the sale of Global Star’s shares in connection with the Business Combination, shares which may be issued to the owners of the target, debt issued to bank or other lenders or the owners of the target, or a combination of the foregoing.
Special Meetings
On August 22, 2023, the Company held a Special Meeting of Stockholders (the “August 2023 Meeting”). At the August 2023 Meeting, the Company’s stockholders approved the Charter Amendment, which extends the date by which the Company must consummate its initial business combination from September 22, 2023 to June 22, 2024, subject to the approval of the Board of Directors of the Company (the “Board”), provided the sponsor or its designees deposit into the trust account a monthly amount equal to $125,000, prior to the commencement of each extension period (the “Extension”). The Company filed the Charter Amendment with the Office of the Secretary of State of Delaware on August 28, 2023, a copy of which is attached as Exhibit 3.1 in the Form 8-K filed with the SEC on August 28, 2023 and is incorporated by reference herein. At the Meeting, Stockholders holding 4,052,066 shares of common stock exercised their right to redeem their shares for cash at a price of approximately $10.53 per share of the funds in the Trust Account. As a result, an aggregate of $42,680,726 was removed from the Trust Account to pay such holders. Following the redemption, the Company’s remaining shares of Class A common stock outstanding were 5,147,934. The Company made 9 monthly payments of $125,000 to extend the period of time it has to consummate its initial business combination to June 22, 2024.
On June 11, 2024, the Company held a Special Meeting of Stockholders (the “June 2024 Meeting”). At the Meeting, the Company’s stockholders approved the Charter Amendment, which further extends the date by which the Company must consummate its initial business combination by an additional six-months pursuant to six one-month extensions, from June 22, 2024 to December 22, 2024 (the “Second New Termination Date”), provided that the sponsor or its designees deposit into the trust account the lesser of: (i) $60,000 and (ii) 0.02 per share for each public share that is not redeemed in connection with the June 2024 Meeting. At the June 2024 Meeting, Stockholders holding 4,010,928 shares of common stock exercised their right to redeem their shares for cash at an approximate price of $11.12 per share of the funds in the Trust Account. As a result, $44,605,448 was removed from the Trust Account to pay such holders. The Company made six monthly extension payments in the Trust Account to extend the period of time it has to consummate its initial business combination to December 22, 2024.
Then, on November 27, 2024, Global Star held a Special Meeting of its Stockholders (the “Meeting”). At the Meeting, Global Star’s stockholders approved the Charter Amendment which extends the date by which Global Star must consummate its initial business combination from December 22, 2024 to June 22, 2025, subject to the approval of the Board of Directors of Global Star (the “Board”) provided the sponsor or its designees deposit into the trust account the lesser of (i) $60,000 or (ii) $0.02 per share for each public share that is not redeemed in connection with the Meeting, prior to the commencement of each extension period. At the Meeting shareholders holding 756,131 shares of common stock exercised their right to redeem their shares for cash at a price of approximately $11.39 per share of the funds in the Trust Account. As a result an aggregate of $8,613,436, net of interest withdrawn for taxes of $110,751, was removed from the Trust Account to pay such holders. Following the redemption, Global Star’s remaining shares of GLST Class A Common Stock outstanding were 380,875. Global Star has disclosed further details of the Meeting in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC on November 27, 2024. On December 4, 2024, Global Star deposited $7,617.50 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to January 22, 2025. On December 12, 2024, Global Star deposited $7,617.50 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to February 22, 2025.
Merger Agreement
On June 15, 2023, our Company and K Enter Holdings Inc., a Delaware corporation (the “K Enter”) entered into a definitive Merger Agreement, as amended on March 11, 2024, June 28, 2024, July 25, 2024 and December 11, 2024 (the “Merger Agreement”) pursuant to which, among other things, (i) we will merge with and into K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company, formed on June 22, 2023, and wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company (the “Purchaser”), with Purchaser continuing as the surviving corporation (the “Reincorporation Merger”) and (ii) GLST Merger Sub Inc., a Delaware corporation, formed on June 12, 2023 and wholly-owned subsidiary of Purchaser (the “Merger Sub”) will merge with and into K Enter, with K Enter surviving the merger as a wholly-owned subsidiary of Purchaser (the “Acquisition Merger”). The Reincorporation Merger, the Acquisition Merger and the other transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement, together, are referred to herein as the “Proposed Business Combination”. Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, the parent of the combined company will be named “K Wave Media Ltd.” and we expect that the securities of the parent of the combined company will be listed on The Nasdaq Stock Market.
In connection with the December 11, 2024, amendment to the Merger Agreement, Global Star, K Enter, PubCo and Merger Sub entered into the Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement, which extended the outside date for the parties to consummate the closing of the Business Combination from December 22, 2024 to June 22, 2025.
Merger Consideration
Upon the effective time of the Reincorporation Merger, (i) each issued and outstanding share of common stock of the Company (the “Company Common Stock”), other than Company Common Stock that are owned by the Company as treasury shares or any Company Common Stock owned by any direct or indirect wholly owned subsidiary of the Company, will be converted automatically into one ordinary share of the Purchaser (the “Purchaser Ordinary Share”), and (ii) each issued and outstanding warrant of the Company will convert automatically into a warrant to purchase one Purchaser Ordinary Share at a price of $11.50 per whole share (the “Purchaser Warrant”), (iii) each issued and outstanding right of the Company shall convert automatically into a right to receive one-tenth (1/10) of one Purchaser Ordinary Share at the closing of a business combination (the “Purchaser Right”), and (iv) each issued and outstanding unit of the Company shall separate and convert automatically into one Purchaser Ordinary Share, one Purchaser Warrant and one Purchaser Right. Each of the Purchaser Warrants and Purchaser Rights shall have, and be subject to, the same terms and conditions set forth in the applicable agreements governing the warrants of the Company and the rights of the Company, respectively. At the closing of the Reincorporation Merger, all common stock, warrants, rights, units, and other securities of the Company shall cease to be outstanding and shall automatically be canceled and retired and shall cease to exist.
Upon the closing of the Acquisition Merger, (i) each share of K Enter capital stock, if any, that is owned by Company or Merger Sub (or any other subsidiary of Company) or K Enter (as treasury stock or otherwise), will automatically be cancelled and retired without any conversion, (ii) each share of K Enter preferred stock issued and outstanding shall be deemed converted into shares of K Enter common stock, (iii) each share of K Enter common stock issued and outstanding, including shares of K Enter common stock deemed outstanding as a result of the mandatory conversion of K Enter preferred stock, shall be converted into the right to receive a number of Purchaser Ordinary Shares equal to the Conversion Ratio, and (iv) each share of Merger Sub common stock issued and outstanding shall be converted into and become one newly issued, fully paid and nonassessable share of K Enter common stock. Conversion Ratio means the quotient obtained by dividing (a) 59,000,000 Purchaser Ordinary Shares, by (b) the Aggregate Fully Diluted K Enter Common Shares. Aggregate Fully Diluted K Enter Common Shares means the sum of (a) all shares of K Enter common stock that are issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Closing; plus (b) the aggregate shares of K Enter common stock issuable upon conversion of all shares of K Enter preferred stock that are issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Closing; plus (c) the aggregate shares of K Enter common stock issuable upon full conversion, exercise or exchange of any other securities of K Enter outstanding immediately prior to the Closing directly or indirectly convertible into or exchangeable or exercisable for K Enter.
Conditions to Closing
The Closing is subject to certain customary conditions, including, among other things, (i) approval by the Company’s stockholders of the Merger Agreement and related proposals, (ii) approval by K Enter’s shareholders of the Merger Agreement, (iii) the effectiveness of a registration statement on Form F-4 (the “Registration Statement”) to be filed by Purchaser relating to the Business Combination, which will contain a proxy statement of the Company in connection with its solicitation for proxies for the vote by stockholders of the Company in connection with the Business Combination and other matters as described in the Registration Statement, (iv) the approval for Purchaser’s initial listing application with Nasdaq or an alternate exchange, (v) the Company having at least $5,000,001 of net tangible assets, (vi) the accuracy of each party’s representations and warranties, except generally as would not have a Material Adverse Effect and in the case of certain fundamental representations, in all material respects, (vii) compliance by each party with pre-closing covenants in all material respects, (viii) the absence of any legal restraints or injunctions enjoining or prohibiting the consummation of the Business Combination, (ix) the receipt, expiration or termination of applicable government approvals and antitrust waiting periods, (x) the Reincorporation Merger has been consummated and the applicable certificates has filed in the appropriate jurisdictions, (xi) the acquisition of certain entities of the Six Korean Entities have been consummated, and (xii) the Purchaser and Merger Sub having entered into a joinder to the merger agreement.
Covenants, Representations and Warranties
The parties to the Merger Agreement have made covenants that are customary for transactions of this nature, including, among others, obligations on (i) the parties to conduct, as applicable, their respective businesses in the ordinary course and consistent with past practice through the Closing, (ii) the parties to not initiate any negotiations or enter into any agreements for certain alternative transactions, (iii) the Company and Purchaser to jointly prepare the Registration Statement, and Purchaser to file the Registration Statement, and the Company to take certain other actions for the Company to obtain the requisite approval of stockholders of the Company of certain proposals regarding the Business Combination, and (v) the Company to exercise its right to extend its deadline to complete its initial business combination.
The parties to the Merger Agreement have made representations and warranties that are customary for transactions of this nature. The representations and warranties of the respective parties to the Merger Agreement generally will not survive the Closing.
Termination
The Merger Agreement may be terminated by either K Enter or the Company under certain circumstances, including, among others, (i) by written consent of both K Enter or the Company, (ii) by either K Enter or the Company if the Closing has not occurred by the earlier of June 22, 2024 and the material breach or violation of any representation, warranty, covenant or obligation by the party seeking to terminate the Merger Agreement was not the cause of, or resulted in, the failure of the Closing to occur on or before June 22, 2024, (iii) by either K Enter or the Company if the Business Combination is permanently enjoined, prohibited or prevented by the terms of a final, non-appealable governmental order, (iv) by either K Enter or the Company if the other party has materially breached their respective representations or covenants under the Merger Agreement and has not timey cured such breach.
Following the termination of the Merger Agreement, there shall be no liability on the part of any party except for certain provisions that survive the termination.
The foregoing description of the Merger Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the Merger Agreement, copy of which, is filed as Exhibit 2.1 in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC on June 22, 2023.
Lock-Up Agreement
At the Closing, Purchaser, Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (the “Sponsor”), certain former stockholders of K Enter (such stockholders, the “Target Holders”), and other persons and entities (collectively, the “Holders” and each, a “Holder”), will enter into lock-up agreements (the “Lock-Up Agreements”) with respect to the Purchaser Ordinary Shares and Purchaser Warrants held by the Sponsor immediately following the Closing, and the Purchaser Ordinary Shares held by the Target Holders immediately following the Closing (the “Lock-Up Shares”), pursuant to which, each Holder agreed not to offer, sell, contract to sell, pledge, grant any option to purchase, or otherwise dispose of, directly or indirectly, any Lock-Up Shares during the application lock-up period, on the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in the Lock-Up Agreement. Lock-up period means, (i) with respect to 50% of the Lock-up Shares, the earlier of (A) six months after the Closing and (B) the date on which the closing price of the Purchaser’s Ordinary Shares equals or exceeds $12.50 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, rights issuances, reorganizations and recapitalizations) for any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period commencing after the date hereof and (ii) with respect to the remaining 50% Lock-up Shares (or Ordinary Shares issuable upon conversion thereof), six months after the Closing.
The foregoing description of the Lock-Up Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the Lock-Up Agreement, a form of which is filed as Exhibit 10.1 in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC on June 22, 2023.
Registration Rights Agreement
The Merger Agreement contemplates that, at the Closing, the Purchaser, the Sponsor, certain former stockholders of the Company (such stockholders, together with the Sponsor, the “Company Holders”), and certain former stockholders of K Enter, will enter into a registration rights agreement (the “Registration Rights Agreement”), pursuant to which Purchaser will be obligated to file a registration statement to register the resale, pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, of certain securities of Purchaser held by the parties to the Registration Rights Agreement. The Registration Rights Agreement will also provide the Sponsor, the Company Holders, the Target Holders with unlimited “piggy-back” registration rights, subject to certain requirements and customary conditions.
The Registration Rights Agreement amends and restates the registration rights agreement that was entered into by the Company, the Sponsor and the other parties thereto in connection with the Company’s initial public offering. The Registration Rights Agreement will terminate on the earlier of (a) the five year anniversary of the date of the Registration Rights Agreement or (b) with respect to any holder, on the date that such holder no longer holds any Registrable Securities (as defined therein).
The foregoing description of the Registration Rights Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the Registration Rights Agreement, a form of which is filed as Exhibit 10.2 in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC on June 22, 2023.
Joinder Agreement
A form of Joinder Agreement was included as an exhibit to the Merger Agreement to be executed by Purchaser and Merger Sub, following their formation, to bind them to the terms and conditions of the Merger Agreement. On July 13, 2023, the Purchaser and the Merger Sub executed the Joinder Agreement by and between the Company, K Enter, the Purchaser and Merger Sub. Pursuant to the Joinder Agreement, the Purchaser and Merger Sub agreed to become a party to, to be bound by, and to comply with the terms and conditions of the Merger Agreement.
The foregoing description of the Joinder Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the Joinder Agreement, copy of which, or the form of which, is filed as Exhibit 10.1 on the Company’s Form 8-K as filed with the SEC on July 18, 2023.
Purchase Agreement
In connection with this Merger Agreement, on July 12, 2023, the Company entered into a Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) by and between the Company, K Enter, and Global Star Acquisition I LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (the “Sponsor”). Pursuant to the Purchase Agreement, K Enter purchased from the Sponsor 160,000 shares of Class B common stock (“the SPAC Securities”) for an aggregate purchase price of $1,600,000 (the “Purchase Price”), which was payable within 10 days from the effective date of the Purchase Agreement.
In addition to the payment of the Purchase Price, K Enter acknowledged that (x) it is an accredited investor as defined by Rule 501 of the Securities Act, (y) and has knowledge and experience in financial and business matters and in investments of this type and is capable of evaluating the merits and risks of the SPAC Securities and of making an informed investment decision. K Enter further acknowledged and agreed that the SPAC Securities: (a) are subject to limitations on transfer, (b) are being acquired pursuant to an exemption from registration under the Securities Act with no present intention to distribute them to any person in violation of the Securities Act or any applicable U.S. state, (c) will not be sold except in compliance with the Securities Act and any applicable U.S. state securities laws, and in accordance with any limitations set forth in any applicable lock-up agreements applicable to the SPAC Securities.
The foregoing description of the Purchase Agreement is a summary only and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the full text of the Purchase Agreement, a copy of which is attached as Exhibit 10.2 in the Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 17, 2023.
First Amendment
On March 11, 2024, the Company, K Enter, Purchaser, and Merger Sub entered into a First Amendment to the Merger Agreement (the “First Amendment”) to amend certain of the terms of the Merger Agreement. The First Amendment (i) reduces the base value of the merger consideration to be received by Company shareholders from $610 million to $590 million, and (ii) removes in its entirety respective references to the “Share Purchase Agreement” dated April 12, 2023 with certain sellers of First Virtual Lab Inc. from its disclosure schedules and includes the “Termination Agreement and Re-Purchase Option Agreement, dated March 5, 2024, by and among Sungkwon Kim, King Bear Film LLC and K Enter Holdings Inc” to the disclosure schedule. Pursuant to Section 141(f) of the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware and Section 4.5 of the Company’s bylaws, the board approved and authorized the First Amendment on March 11, 2024. The board obtained an updated fairness opinion with respect to the First Amendment. The modification in the purchase consideration was made in connection with the cessation of the planned acquisition of a majority equity stake in First Virtual Lab Inc.
The foregoing description of the First Amendment is a summary only and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the full text of the Purchase Agreement, a copy of which is attached as Exhibit in the Form 8-K filed with the SEC on March 14, 2024.
Second, Third and Fourth Amendments to the Merger Agreement
On June 28, 2024, the Company entered into a Second Amendment to the Business Combination Agreement (the “Second BCA Amendment”), by and among K Enter, K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (the “K Wave Media Ltd.”), and GLST Merger Sub Inc., a Delaware corporation (the “GLST Merger Sub Inc.”) to extend the outside date by which the parties’ must consummate the business combination. Other than the extension of the date to December 22, 2024, by which we must consummate a business combination, all of the terms, covenants, agreements, and conditions of the BCA remain in full force and effect in accordance with its original terms. On July 25, 2024, the Company entered into a Third Amendment to the Business Combination Agreement (the “Third BCA Amendment”), by and among K Enter, K Wave Media Ltd., and GLST Merger Sub Inc. to amend the conditions to the parties’ obligations to consummate the business combination. Other than the amendment to the condition to the obligations of the parties whereby K Enter must complete its acquisition of the controlling equity interests of (1) Play Company Co. Ltd., (2) Solaire Partners LLC, (3) Apeitda Co., Ltd., (4) The LAMP Co., Ltd., (5) Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd., and (6) Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd., all of the terms, covenants, agreements, and conditions of the BCA remain in full force and effect in accordance with its original terms. On December 11, 2024, the Company entered into a Fourth Amendment to the Business Combination Agreement (the “Fourth BCA Amendment”), by and among K Enter, K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (the “K Wave Media Ltd.”), and GLST Merger Sub Inc., a Delaware corporation (the “GLST Merger Sub Inc.”) to extend the outside date by which the parties’ must consummate the business combination from December 22, 2024 to June 22, 2025. Other than the extension of the date to June 22, 2025, by which we must consummate a business combination, all of the terms, covenants, agreements, and conditions of the BCA remain in full force and effect in accordance with its original terms.
The foregoing description of the Second BCA Amendment, Third BCA Amendment and Fourth BCA Amendment (the “BCA Amendments”) do not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the BCA Amendments, copies of which, are filed as part of Annex A and as Exhibits 2.2, 2.3 and 2.5 attached hereto.
Results of Operations
As of September 30, 2024, the Company had not commenced any operations. All activity for the period from July 24, 2019 (inception) through September 30, 2024, relates to organizational activities and identifying a target company for a business combination. We will not generate any operating revenues until after the completion of our initial Business Combination, at the earliest. We will generate non-operating income in the form of interest income on cash and cash equivalents from the proceeds derived from the IPO. The Company has selected December 31 as its fiscal year end. We expect to continue to incur significant costs in the pursuit of our Business Combination. We cannot assure you that our plans to complete our Business Combination will be successful.
For the three months ended September 30, 2024, we had net loss of $107,629, which consists of operating costs of $248,771, which primarily consist of legal, professional and advisory fees as well as insurance expense, and a provision for income taxes of $28,906 offset by interest income on marketable securities held in the Trust Account of $165,372 and interest income – bank of $4,676.
For the nine months ended September 30, 2024, we had net loss of $404,644, which consists of operating costs of $1,700,833, which primarily consist of legal, professional and advisory fees as well as insurance expense, and a provision for income taxes of $315,369 offset by interest income on marketable securities held in the Trust Account of $1,596,528 and interest income – bank of $15,030.
For the three months ended September 30, 2023, we had net income of $108,936, which consists of interest income on marketable securities held in the Trust Account of $1,058,863 and interest income – bank of $5,468, offset by operating costs of $742,722, which primarily consist of legal, professional and advisory fees as well as insurance expense, and a provision for income taxes of $212,673.
For the nine months ended September 30, 2023, we had net income of $1,072,088, which consists of interest income on marketable securities held in the Trust Account of $3,214,400 and interest income – bank of $5,667 offset by operating costs of $1,503,601, which primarily consist of legal, professional and advisory fees as well as insurance expense, and a provision for income taxes of $644,378.
Franchise and Income Tax Withdrawals from Trust Account
Since completion of its IPO on September 22, 2022, and through September 30, 2024, the Company withdrew $1,684,187 from the Trust Account to pay its liabilities related to income and Delaware franchise taxes. Through September 30, 2024, the Company remitted $1,288,941 to the respective tax authorities, with the difference of $395,247 to be remitted as Company’s tax obligations become due. Inadvertently the Company used $3,108 of those funds to pay for working capital purposes and as such breached the Company’s charter. Subsequent to September 30, 2024, the Company received additional funds from the Sponsor under the terms of promissory note. As of September 30, 2024, the Company had accrued but unpaid income tax liability of $288,597 and accrued but unpaid Delaware franchise tax liability of $169,113. The Company remitted $830,000 in payment of its income tax liability for 2023 (including interest and penalties) on July 3, 2024, and intends to settle its obligations for income and Delaware Franchise taxes as they become due.
Liquidity, Capital Resources and Going Concern
On September 22, 2022, we consummated our Initial Public Offering of 8,000,000 Units at $10.00 per Unit, generating gross proceeds of $80,000,000. Simultaneously with the closing of our Initial Public Offering, we consummated the private placement of an aggregate of 456,225 Private Placement Units to our Sponsor at a price of $10.00 per Private Placement Unit, generating total gross proceeds of $4,562,250. On October 4, 2022, we closed on the over-allotment through the sale of 1,200,000 Units at a purchase of $10.00 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $12.0 million, and simultaneously with the exercise of the overallotment, we consummated the Private Placement of an additional 42,000 Private Placement Units to the Sponsor, generating gross proceeds of $420,000. A total of $96,982,250 was generated from our IPO.
Transaction costs amounted to $4,788,510 consisting of $920,000 of underwriting fees (net of underwriter reimbursements), $3,220,000 of deferred underwriting fees payable, which are held in a trust account with Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company acting as trustee (the “Trust Account”) and $648,510 of other offering costs related to the Initial Public Offering. The underwriters were also issued 115,000 shares of Class A common stock as representative shares, in connection with the IPO. Upon close of the Initial Public Offering, the Company recorded additional issuance costs of $79,338, the grant date fair value of the shares, with an offset to additional paid-in capital. As described in Note 6 — Commitments and Contingencies, of the Notes to the Condensed consolidated Financial Statements contained in this report, the $3,220,000 deferred underwriting fees are contingent upon the consummation of the Business Combination.
As of September 30, 2024, we had $392,139 of cash on our balance sheet, which is restricted for payment of Company’s taxes and a working capital deficit of $4,749,664. We intend to use the funds held outside of the Trust Account for identifying and evaluating prospective acquisition candidates, performing business due diligence on prospective target businesses, traveling to and from the offices, plants or similar locations of prospective target businesses, reviewing corporate documents and material agreements of prospective target businesses, selecting the target business to acquire and structuring, negotiating and consummating the Business Combination. The interest income earned on the investments in the Trust Account are unavailable to fund operating expenses.
As previously disclosed on July 31, 2023, in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC, we issued a promissory note (the “July 2023 Note”) in the principal amount of $1,600,000 to our Sponsor. The Note was issued in connection with a $1,600,000 loan the Sponsor has made to us for working capital expenses. If we complete the Business Combination, we would repay the Note out of the proceeds of the Trust Account released to us. Otherwise, the Note would be repaid only out of funds held outside the Trust Account. In the event that a Business Combination does not close, we may use a portion of the working capital held outside the trust account to repay the Note but no proceeds from the Trust Account would be used to repay the Note. At the election of the Sponsor, up to $1,500,000 of the unpaid principal amount of the Note may be converted into units of the Company at a price of $10.00 per unit (the “Conversion Units”) in lieu of cash repayment. The principal balance of the Note is payable by us on the later of: (i) December 31, 2023, or (ii) the date on which we consummate a Business Combination. No interest shall accrue on the unpaid principal balance of the Note. $1,586,000 was drawn and outstanding under the Note as of September 30, 2024.
On April 15, 2024, the Company issued a promissory note to the Sponsor in an amount of up to $1,000,000 for working capital needs. The note bears no interest and shall be payable by the Maker on the earlier of: (i) December 31, 2024 or (ii) the date on which Maker consummates an initial public offering of its securities. The principal balance may be prepaid at any time. As of September 30, 2024 $821,000 was drawn and outstanding under the promissory note.
On October 23, 2024, the Company amended the terms of the promissory note to allow conversion of up to $1,000,000 into Class B Common Stock of the Company at a price of $10.00 per unit in lieu of cash repayment, effective immediately prior to the Business Combination.
The issuance of the Note was made pursuant to the exemption from registration contained in Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended.
If the Company has not completed a Business Combination by February 22, 2025 (unless Global Star elects to extend the time it has to complete the initial business combination to June 22, 2025), the Company will (i) cease all operations except for the purpose of winding up, (ii) as promptly as reasonably possible but not more than ten business days thereafter, redeem the Public Shares, at a per-share price, payable in cash, equal to the aggregate amount then on deposit in the Trust Account, including interest earned on the funds held in the Trust Account and not previously released to pay taxes (less up to $100,000 of interest to pay dissolution expenses), divided by the number of then outstanding Public Shares, which redemption will completely extinguish Public Stockholders’ rights as stockholders (including the right to receive further liquidating distributions, if any), and (iii) as promptly as reasonably possible following such redemption, subject to the approval of the Company’s remaining stockholders and the Company’s board of directors, dissolve and liquidate, subject in each case to the Company’s obligations under Delaware law to provide for claims of creditors and the requirements of other applicable law. There will be no redemption rights or liquidating distributions with respect to the Company’s warrants, which will expire worthless if the Company fails to complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period.
Special Meetings, Extension and Trust Withdrawal from Trust Account
On August 22, 2023, we held a Special Meeting of Stockholders (the “August 2023 Meeting”). At the Meeting, our stockholders approved the Charter Amendment, which extends the date by which the Company must consummate its initial business combination by an additional nine-months pursuant to nine one-month extensions, from September 22, 2023 to June 22, 2024 (the “First New Termination Date”), subject to the approval of the Board of Directors of the Company (the “Board”), provided the sponsor or its designees deposit into the trust account a monthly amount equal to $125,000, prior to the commencement of each extension period (the “Extension”). We filed the Charter Amendment with the Office of the Secretary of State of Delaware on August 28, 2023, a copy of which is attached as Exhibit 3.1 in the Form 8-K filed with the SEC on August 28, 2023 and is incorporated by reference herein. At the Meeting, Stockholders holding 4,052,066 shares of common stock exercised their right to redeem their shares for cash at an approximate price of $10.53 per share of the funds in the Trust Account. As a result, for the period ended September 30, 2024, an aggregate of $44,605,448 was withdrawn from the Trust Account to pay such holders. Following the redemption, our remaining shares of Class A common stock outstanding were 5,147,934.
On June 11, 2024, we held a Special Meeting of Stockholders (the “June 2024 Meeting”). At the Meeting, our stockholders approved the Charter Amendment, which further extends the date by which the Company must consummate its initial business combination by an additional six-months pursuant to six one-month extensions, from June 22, 2024 to December 22, 2024 (the “Second New Termination Date”), provided that the sponsor or its designees deposit into the trust account approximately $22,740 prior to the commencement of each extension period. At the June 2024 Meeting, Stockholders holding 4,010,928 shares of common stock exercised their right to redeem their shares for cash at an approximate price of $11.12 per share of the funds in the Trust Account. As a result, $44,605,448 was removed from the Trust Account to pay such holders. We have made six monthly extension payments in the Trust Account to extend the period of time by which it has to consummate its initial business combination to December 22, 2024.
Then, on November 27, 2024, Global Star held a Special Meeting of its Stockholders (the “Meeting”). At the Meeting, Global Star’s stockholders approved the Charter Amendment which extends the date by which Global Star must consummate its initial business combination from December 22, 2024 to June 22, 2025, subject to the approval of the Board of Directors of Global Star (the “Board”) provided the sponsor or its designees deposit into the trust account the lesser of (i) $60,000 or (ii) $0.02 per share for each public share that is not redeemed in connection with the Meeting, prior to the commencement of each extension period. At the Meeting shareholders holding 756,131 shares of common stock exercised their right to redeem their shares for cash at a price of approximately $11.39 per share of the funds in the Trust Account. As a result an aggregate of $8,613,436, net of interest withdrawn for taxes of $110,751, was removed from the Trust Account to pay such holders. Following the redemption, Global Star’s remaining shares of GLST Class A Common Stock outstanding were 380,875. Global Star has disclosed further details of the Meeting in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC on November 27, 2024. On December 4, 2024, Global Star deposited $7,617.50 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to January 22, 2025. On December 12, 2024, Global Star deposited $7,617.50 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to February 22, 2025.
We have until February 22, 2025 (unless Global Star elects to extend the time it has to complete the initial business combination to June 22, 2025), to consummate a Business Combination. If we do not complete our initial business combination by February 22, 2025 (unless Global Star elects to extend the time it has to complete the initial business combination to June 22, 2025), or (i) as extended by our stockholders in accordance with our amended and restated certificate of incorporation or (ii) with respect to any other provision relating to stockholders’ rights or pre-initial business combination activity and (iii) waive their rights to liquidating distributions from the trust account with respect to any founder shares and placement shares held by them if we fail to complete our initial business combination prior to the Second New Termination date, the public stockholders will be entitled to liquidating distributions from the trust account with respect to any public shares they hold if we fail to complete our initial business combination within the prescribed time frame. Accordingly, it is our intention to redeem our public shares as soon as reasonably possible following the Second New Termination Date unless our initial business combination shall have occurred earlier and, therefore, we do not intend to comply with those procedures. As such, our public stockholders could potentially be liable for any claims to the extent of distributions received by them (but no more) and any liability of our stockholders may extend well beyond the third anniversary of such date.
As of September 30, 2024, we had cash of $392,139 in our operating bank accounts, $12,919,725 of marketable securities held in the Trust Account to be used for an initial Business Combination or to repurchase or redeem stock in connection therewith and a working capital deficit of $4,749,664. As of September 30, 2024, 49,454 of the amount on deposit in the Trust Account represented interest income that is available to pay our tax obligations, net of amounts previously withdrawn.
We may raise additional capital through loans or additional investments from the Sponsor or our stockholders, officers, directors, or third parties. Our officers and directors, the Sponsor or their affiliates may but are not obligated to loan us funds, from time to time, in whatever amount they deem reasonable in their sole discretion, to meet our working capital needs. Based on the foregoing, we do not believe we will have sufficient cash to meet our needs through the earlier of consummation of a Business Combination or June 22, 2024, or such earlier date as determine by our board of directors, the deadline to complete a Business Combination pursuant to our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation (unless otherwise amended by stockholders).
Off-Balance Sheet Financing Arrangements
We have no obligations, assets, or liabilities, which would be considered off-balance sheet arrangements as of September 30, 2024. We do not participate in transactions that create relationships with unconsolidated entities or financial partnerships, often referred to as variable interest entities, which would have been established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements. We have not entered into any off-balance sheet financing arrangements, established any special purpose entities, guaranteed any debt or commitments of other entities, or purchased any non-financial assets.
Contractual Obligations
We do not have any long-term debt, capital lease obligations, operating lease obligations or long-term liabilities, other than an agreement to pay the Sponsor a monthly fee up to $10,000 for office space, utilities, and secretarial and administrative support services. We began incurring these fees on September 22, 2022 and will continue to incur these fees monthly until the earlier of the completion of the Business Combination and our liquidation.
The underwriters are entitled to a deferred fee of $3,220,000 in the aggregate. The deferred fee will become payable to the underwriters from the amounts held in the Trust Account solely in the event that the Company completes a Business Combination, subject to the terms of the underwriting agreement.
In order to finance transaction costs in connection with the Business Combination, our Sponsor extended to us a line of credit of up to $1,600,000 pursuant to a Promissory Note dated July 31, 2023 (“Sponsor Working Capital Loan”). Such Sponsor Working Capital Loan is without interest and is to be repaid on the later of (i) December 31, 2023 or (ii) upon the consummation of a Business Combination. The Sponsor in its sole discretion may elect to convert up to $1,500,000 amount of the Sponsor Working Capital Loan into the Company’s Common Stock at a price of $10.00 per share in lieu of cash repayment. In the event that a Business Combination does not close, we may use a portion of proceeds held outside the Trust Account to repay the Sponsor Working Capital Loan, but no proceeds held in the Trust Account would be used to repay the Sponsor Working Capital Loans.
Agreements with Service Providers
From time to time the Company has entered into and may enter into agreements with various services providers and advisors, including investment banks, to help us identify targets, negotiate terms of potential Business Combinations, consummate a Business Combination and/or provide other services. In connection with these agreements, the Company may be required to pay such service providers and advisors fees in connection with their services to the extent that certain conditions, including the closing of a potential Business Combination, are met. If a Business Combination does not occur, the Company would not expect to be required to pay these contingent fees. There can be no assurance that the Company will complete a Business Combination.
On September 24, 2023, the Company engaged EF Hutton LLC, now known as D. Boral Capital LLC (“Boral Capital”) to act as the exclusive placement agent (“Placement Agent”) for the Company, in connection with the proposed offering by private placement of equity or equity-linked securities in the form of a PIPE, forward purchase arrangement or similar type of equity line financing (the “Placement”) to “qualified institutional buyers” as such term is defined in Rule 144A promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”) and to the institutional accredited investors as such term is defined in Regulation D promulgated under the Securities Act of the Company’s equity or equity-linked securities, including warrants, options or other rights to purchase such securities (collectively, the “Securities”). In case of successful Placements, a non-refundable cash placement fee (the “Placement Fee”), payable at each closing of a Placement, in an amount equal to seven percent (7.0%), as well as foreign placement fee of 1%, and reduced placement fee of 1% of the aggregate gross proceeds from the sale of all Securities in the Placement would be due and payable to Boral Capital.
On November 27, 2023, the Company engaged MZHCI, LLC, a MZ Group Company (“MZHCI”) as its public relations consultant starting from January 1, 2024 (the “MZHCI Agreement”). According to terms of the MZHCI Agreement, MZHCI will be paid a monthly fee of $10,000 for its services for the period of the Proposed Business Combination starting from January 1, 2023, which will increase to $14,000 (subject to 5% cost of living adjustment) upon closing of the Proposed Business Combination. In addition, upon a successful closing of the Proposed Business Combination, the Company will issue to MZHCI $150,000 worth of the Company’s restricted stock as valued on the first day of trading post-closing.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
We prepare our unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted principles, which require management to make estimates that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the balance sheet dates, as well as the reported amounts of revenues and expenses for the reporting periods. To the extent that there are material differences between these estimates and actual results, our financial condition or results of operations would be affected. We base our estimates on our own historical experience and other assumptions that we believe are reasonable taking into account our circumstances and future expectations based on the available information. We evaluate these estimates on an ongoing basis.
We consider an accounting estimate to be critical if (i) the accounting estimate requires to make assumptions about matters that were highly uncertain at the time when the accounting estimate was made; and (ii) changes in the estimate that are reasonably likely to occur from period to period or use of different estimates that we reasonably could have used in the current period, would have a material amount on our financial condition or results of operations. There are items in our financial statements that require estimation but are not deemed to be critical, as defined above.
For a detailed discussion of our significant accounting policies and related judgements, see Note 2– Summary of Significant Accounting Policies Basis of Presentation in the Notes to the Condensed consolidated Financial Statements included in this report.
Warrant Classification
The Private Placement Warrants are identical to the Public Warrants underlying the Units sold in the IPO. Company account for warrants as either equity-classified or liability-classified instruments based on an assessment of the warrant’s specific terms and applicable authoritative guidance in ASC 480 and ASC Topic 815, “Derivatives and Hedging” (“ASC 815”). The assessment considers whether the warrants are freestanding financial instruments pursuant to ASC 480, meet the definition of a liability pursuant to ASC 480, and whether the warrants meet all of the requirements for equity classification under ASC 815, including whether the warrants are indexed to our of common stock, among other conditions for equity classification. This assessment, which requires the use of professional judgment, is conducted at the time of warrant issuance and as of each subsequent quarterly period end date while the warrants are outstanding. For issued or modified warrants that meet all of the criteria for equity classification, the warrants are required to be recorded as a component of additional paid-in capital at the time of issuance. For issued or modified warrants that do not meet all the criteria for equity classification, the warrants are required to be recorded at their initial fair value on the date of issuance. The fair value of the warrants are remeasured at each balance sheet date with the change in the estimated fair value of the warrants recognized as a non-cash gain or loss on the statements of operations. We have analyzed the Public Warrants and Private Placement Warrants and determined they are considered to be freestanding instruments and do not exhibit any of the characteristics in ASC 480 and therefore are not classified as liabilities under ASC 480.
Class A Common Stock Subject to Possible Redemption
We account for our Class A common stock subject to possible redemption in accordance with the guidance in ASC Topic 480 “Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity.” Shares of Class A common stock subject to mandatory redemption are classified as a liability instrument and are measured at fair value. Conditionally redeemable shares of Class A common stock (including Class A common stock that features redemption rights that is either within the control of the holder or subject to redemption upon the occurrence of uncertain events not solely within our control) are classified as temporary equity. At all other times, shares of Class A common stock are classified as stockholders’ equity. Our Class A common stock features certain redemption rights that are considered to be outside of our control and subject to occurrence of uncertain future events. Accordingly, Class A common stock subject to possible redemption is presented at redemption value as temporary equity, outside of the stockholders’ deficit section of our condensed consolidated balance sheets.
Share-Based Payment Arrangements
We measure and recognize compensation expense for all share-based payments on their estimated fair values measured as of the grant date. These costs are recognized as an expense in the statements of operations upon vesting, once the applicable performance conditions are met, with an offsetting increase to additional paid-in capital. Forfeitures are recognized as they occur.
Net (Loss) Income per Common Share
Net (loss) income per common share of common stock is computed by dividing net (loss) income by the weighted average number of common shares issued and outstanding during the period. Subsequent measurement of the redeemable shares of Class A common stock is excluded from (loss) income per ordinary share as the redemption value approximates fair value. We calculate our earnings per share to allocate net (loss) income pro rata to shares of Class A and Class B common stock. This presentation contemplates a Business Combination as the most likely outcome, in which case, both classes of common stock share pro rata in the (loss) income of our Company.
Income Taxes
We account for income taxes under ASC 740, “Income Taxes.” ASC 740, Income Taxes, requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for both the expected impact of differences between the condensed consolidated financial statements and tax basis of assets and liabilities and for the expected future tax benefit to be derived from tax loss and tax credit carry forwards. ASC 740 additionally requires a valuation allowance to be established when it is more likely than not that all or a portion of deferred tax assets will not be realized. We also recognized accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits as income tax expense. We have identified the United States as our only “major” tax jurisdiction. We are subject to income taxation by major taxing authorities since inception. These examinations may include questioning the timing and amount of deductions, the nexus of income among various tax jurisdictions and compliance with federal and state tax laws. We do not expect that the total amount of unrecognized tax benefits will materially change over the next twelve months.
Recent Accounting Standards
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures (ASU 2023-09), which requires disclosure of incremental income tax information within the rate reconciliation and expanded disclosures of income taxes paid, among other disclosure requirements. ASU 2023-09 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. Early adoption is permitted. The Company’s management does not believe the adoption of ASU 2023-09 will have a material impact on its condensed consolidated financial statements and disclosures.
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED FINANCIAL INFORMATION
The following summary unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information (the “Summary Pro Forma Information”) gives effect to the transactions contemplated by the Business Combination and the acquisition of the Six Korean Entities. K Enter expects to close the equity purchases for the Six Korean Entities following the date this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 is declared effective by the SEC and before the closing of the Business Combination.
The historical financial statements of Global Star have been prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP and in its functional and presentation currency of the United States dollar (“USD”). The historical financial statements of the Six Korean Entities have been prepared in accordance with IFRS as issued by the IASB in its functional currency of the Korean Republic Won (KRW) and presentation currency of the USD. The historical financial statements of K Enter have been prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP and in its presentation currency of USD. The historical financial statements of K Wave Media Ltd have been prepared in accordance with IFRS as issued by the IASB in its presentational currency of USD.
The acquisition of the Six Korean Entities by K Enter will occur with the acquisition of Play Company closing first and the acquisitions of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company closing subsequently. After the acquisition of all Six Korean Entities is completed, the collective combined company will be referred to as New K Enter.
The acquisition of Play Company by K Enter will be accounted for in accordance with the acquisition method of accounting under IFRS 3, with Play Company considered to be the acquirer of K Enter. As Play Company’s basis of accounting is IFRS, K Enter post the acquisition of Play Company basis of accounting will be IFRS.
The acquisitions of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company by K Enter Post the acquisition of Play Company will be accounted for in accordance with the acquisition method of accounting under IFRS 3, with K Enter post the acquisition of Play Company considered to be the acquirer of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company. As K Enter post the acquisition of Play Company basis of accounting is IFRS, New K Enter’s basis of accounting will be IFRS.
Under the acquisition method of accounting, the preliminary purchase price is allocated to the underlying tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their respective fair market values, with the excess purchase price, if any, allocated to goodwill. Costs related to the transaction are expensed as incurred. K Enter and all Six Korean Entities are referred to as “New K Enter” in these unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements.
The Business Combination will be accounted for as a capital reorganization in accordance with IFRS 2 as Global Star does not meet the criteria to be determined a business under IFRS 3. Under this method of accounting, Global Star is treated as the acquired company for financial reporting purposes, and New K Enter is treated as the acquirer for financial statement reporting purposes.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information has been prepared using the assumptions below with respect to the potential redemption into cash of Global Star Class A Common Stock:
| | ● | Assuming No Additional Redemption: This presentation assumes that, after the redemptions of 4,052,066 shares of Global Star Class A Common Stock in August 2023 (the “August Redemptions”), the redemptions of 4,010,928 shares of Global Star Class A Common Stock in June 2024 (the “June Redemptions”), and the redemptions of 756,131 shares of Global Star Class A Common Stock in November 2024 (the “November Redemptions”), no public stockholders of Global Star exercise redemption rights with respect to their Public Shares upon consummation of the Business Combination. |
| | ● | Assuming Maximum Redemption: This presentation assumes that, after the August Redemptions, the June Redemptions, and the November Redemptions, Global Star public stockholders holding 380,875 shares of Global Star Class A Common Stock will exercise their redemption rights for $4.3 million upon consummation of the Business Combination at a redemption price of approximately $11.41 per share as of December 5, 2024, subject to reduction for the payment of taxes. The maximum redemption amount reflects the maximum number of Global Star’s Public Shares that can be redeemed. This scenario includes all adjustments contained in the “no additional redemption” scenario and presents additional adjustments to reflect the effect of the maximum redemptions. |
The following table sets out share ownership of Global Star on a pro forma basis assuming the No Additional Redemption Scenario and the Maximum Redemption Scenario for the year ended December 31, 2023:
| | | No Additional
Redemption | | | Maximum
Redemption | |
| Pro Forma Ownership | | Number of
Shares | | | Percent
Outstanding | | | Number of
Shares | | | Percent
Outstanding | |
| K Enter stockholders(1) | | | 59,160,000 | | | | 93.1 | % | | | 59,160,000 | | | | 93.7 | % |
| Global Star public stockholders(2) | | | 1,300,875 | | | | 2.1 | % | | | 920,000 | | | | 1.4 | % |
| Sponsor and Initial Stockholders(3)(4) | | | 2,943,747 | | | | 4.6 | % | | | 2,943,747 | | | | 4.7 | % |
| Representative Shares | | | 115,000 | | | | 0.2 | % | | | 115,000 | | | | 0.2 | % |
| Total shares outstanding(4) | | | 63,519,622 | | | | | | | | 63,138,747 | | | | | |
| (1) | Includes 59,000,000 K Wave Ordinary Shares to be issued upon consummation of the Business Combination as follows: (i) 30,878,682 K Wave Ordinary shares issued in exchange for 101,202 shares of K Enter common stock owned by the currently existing stockholders of K Enter, including, the 4,997 shares of K Enter common stock owned by GF Korea and the 1,202 shares of K Enter common stock owned by Lodestar USA; (ii) 12,448,256 K Wave Ordinary shares issued in exchange for 40,798 shares of K Enter common stock owned by the Preferred Stock owners after the conversion of the 40,798 shares of Preferred Stock into shares of K Enter common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination and (iii) 15,673,062 K Wave Ordinary shares to be issued in exchange for 51,367 shares of K Enter common stock that will be owned by the owners of Six Korean Entities following K Enter acquisition of the controlling equity interests in the Six Korean Entities and 160,000 K Wave Ordinary shares to be issued in exchange 160,000 shares of Global Star Founder Shares currently owned by K Enter. |
| (2) | Includes 9,200,000 public shares at June 30, 2024 less 4,052,066 shares redeemed in September 2023, 4,010,928 shares redeemed in June 2024, and 756,131 shares redeemed in November 2024 plus 9,200,000 Public Rights automatically converted into 920,000 shares of Global Star common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination. |
| (3) | Includes (a) 1,640,000 Founder Shares owned by the Sponsor as of June 30, 2024, (b) 498,225 shares underlying the Private Units as of June 30, 1014 plus 498,225 Private Rights automatically converted into 49,822 shares of common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination owned by the Sponsor, (c) 150,000 shares of common stock underlying the Convertible Note plus 150,000 Convertible Note Rights automatically converted into 15,000 shares of common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination owned by the Sponsor,(d) 90,700 shares of common stock underlying the Global Star loan, and (e) 500,000 Founder Shares owned by the Initial Stockholders as of June 30, 2024. |
| (4) | Excludes 19,300 shares to be potentially issued to the Sponsor if an additional $193,000 were to be drawn on the Global Star loan and converted into shares of Global Star Class B common stock. Accordingly, K Wave is registering up to an aggregate amount of 64,295,053 Ordinary Shares to be issued in connection with Business Combination on this proxy statement/prospectus. |
The following table sets out summary data derived from the unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet and the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations of PubCo. The summary unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet as of June 30, 2024 gives effect to the Business Combination as if it had occurred on June 30, 2024. The summary unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations for the six months ended June 30, 2024, and for the year ended December 31, 2023 give effect to the Business Combination as if it had occurred on January 1, 2023.
| | | Pro Forma Combined | |
| | | No Additional
Redemption
Scenario | | | Maximum
Redemption
Scenario | |
| Summary Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Statement of Operations Data for the Six Months Ended June 30, 2024 | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | | $ | (8,384,396 | ) | | $ | (8,384,396 | ) |
| Net loss per share – basic and diluted | | $ | (0.13 | ) | | $ | (0.13 | ) |
| Weighted average shares outstanding – basic and diluted(1) | | | 63,519,622 | | | | 63,138,747 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Summary Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Statement of Operations Data for the Year Ended December 31, 2023 | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | | $ | (96,454,828 | ) | | $ | (96,352,547 | ) |
| Net loss per share – basic and diluted | | $ | (1.52 | ) | | $ | (1.53 | ) |
| Weighted average shares outstanding – basic and diluted(1) | | | 63,519,622 | | | | 63,138,747 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Summary Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Balance Sheet Data as of June 30, 2024 | | | | | | | | |
| Total assets | | $ | 262,534,677 | | | $ | 258,188,338 | |
| Total liabilities | | $ | 93,854,500 | | | $ | 93,797,369 | |
| Total equity | | $ | 168,680,177 | | | $ | 164,390,969 | |
| (1) | Excludes 19,300 shares potentially to be issued to the Sponsor if an additional $193,000 were to be drawn on the Global Star loan and converted into Global Star Class B common stock. Accordingly, K Wave is registering up to an aggregate amount of 64,295,053 Ordinary Shares to be issued in connection with Business Combination on this proxy statement/prospectus. |
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED FINANCIAL INFORMATION
Introduction
The following unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet as of June 30, 2024, combines the historical unaudited balance sheets of Global Star, K Wave, and the Six Korean Entities as of June 30, 2024, giving pro forma effect to the Business Combination and the acquisition of the Six Korean Entities as if they each had occurred as of June 30, 2024.
The following unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations for the six months ended June 30, 2024 combines the historical unaudited statements of operations of Global Star, K Wave, and the Six Korean Entities for the six months ended June 30, 2024, on a pro forma basis as if the Business Combination and the acquisition of the Six Korean Entities as if they had each occurred on January 1, 2023.
The following unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2023 combines the historical audited statements of operations of Global Star for the year ended December 31, 2023, K Enter for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, K Wave for the period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, and the Six Korean Entities for the year ended December 31, 2023 (with the exception of Studio Anseilen, which is for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023), on a pro forma basis as if the Business Combination and the acquisition of the Six Korean Entities as if they had each occurred on January 1, 2023.
K Enter and the Six Korean Entities are referred to as “New K Enter” in these unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet as of June 30, 2024 and unaudited pro forma condensed combined statements of operations for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and for the year ended December 31, 2023 have been derived from (as applicable) (in each case, included elsewhere herein):
| | ● | the historical financial statements of K Wave as of June 30, 2024, for the six months then ended, and for the period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023; and |
| | | |
| | ● | the historical financial statements of K Enter as of June 30, 2024 and 2023, for the six months then ended, and for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023; and |
| | ● | the historical consolidated financial statements of Global Star as of June 30, 2024 and 2023, for the six months then ended, and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022; and |
| | ● | the historical consolidated financial statements of Play Company as of June 30, 2024 and for the six months then ended, and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022; and |
| | ● | the historical financial statements of LAMP as of June 30, 2024 and 2023 and for the six months then ended and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022; and |
| | ● | the historical financial statements of Bidangil as of June 30, 2024 and 2023 and for the six months then ended and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022; and |
| | ● | the historical financial statements of Apeitda as of June 30, 2024 and 2023 and for the six months then ended and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022; and |
| | ● | the historical financial statements of Anseilen as of June 30, 2024 and 2023 and for the six months then ended and for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023. |
| | ● | the historical financial statements of Solaire Partners as of June 30, 2024 and 2023 and for the six months then ended and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. |
The following unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information has been prepared in accordance with Article 11 of Regulation S-X.
This information should be read together with the financial statements and related notes, as applicable, of each of Global Star, Play Company, LAMP, Bidangil, Apeitda, Anseilen, Solaire Partners, K Wave. and K Enter included in this proxy statement/prospectus and Global Star’s, Play Company’s, LAMP’s, Bidangil’s, Apeitda’s, Ansilen’s, Solaire Partners’, K Wave’s and K Enter’s “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and other financial information included elsewhere herein (or as previously filed).
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED BALANCE SHEET
FOR K WAVE
AS OF JUNE 30, 2024 (1)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Scenario 1: No Additional
Redemption Scenario | | | Scenario 2: Maximum
Redemption Scenario | |
| | | K Wave
Media
(IFRS Historical) | | | New K Enter
Pro Forma
Combined
(IFRS Historical) | | | Global Star
(IFRS Historical -
Note 4) | | | Share Redemption
Adjustment and
Elimination
Adjustment | | | | | Global Star
Pro Forma
Adjusted
(IFRS Historical) | | | Transaction
Accounting
Adjustments | | | | | Pro Forma
Combined
(IFRS) | | | Transaction
Accounting
Adjustments | | | | | Pro Forma
Combined
(IFRS) | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | - | | | $ | 10,141,463 | | | $ | 1,353,525 | | | $ | - | | | | | | $ | 1,353,525 | | | $ | 4,346,339 | | | B | | | $ | 4,812,281 | | | $ | (4,346,339 | ) | | G | | | $ | 465,942 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (3,220,000 | ) | | C | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (7,768,635 | ) | | D | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 96,000 | | | L | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (15,094 | ) | | M | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (121,317 | ) | | O | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | | - | | | | 303,275 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 303,275 | | | | - | | | | | | | 303,275 | |
| Short-term investment securities | | | - | | | | 726,955 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 726,955 | | | | - | | | | | | | 726,955 | |
| Accounts receivable - trade, net | | | - | | | | 3,290,858 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 3,290,858 | | | | - | | | | | | | 3,290,858 | |
| Other receivables | | | - | | | | 20,574 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | | | | | | | | 20,574 | | | | - | | | | | | | 20,574 | |
| Other receivables - related parties | | | 50,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | (50,000 | ) | | W | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Preferred stock subscription receivable | | | - | | | | 519,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | - | | | | 519,000 | | | | - | | | | | | | 519,000 | |
| Convertible debt security | | | - | | | | 1,027,027 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | | | | | | | | 1,027,027 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,027,027 | |
| Deferred transaction costs | | | - | | | | 1,879,509 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | | | | | | | | 1,879,509 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,879,509 | |
| Short-term loans, net | | | - | | | | 687,416 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 687,416 | | | | - | | | | | | | 687,416 | |
| Accounts receivable - other, net | | | - | | | | 1,400,912 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,400,912 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,400,912 | |
| Value added tax receivables | | | - | | | | 478,218 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 478,218 | | | | - | | | | | | | 478,218 | |
| Other current financial assets | | | - | | | | 146,856 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 146,856 | | | | - | | | | | | | 146,856 | |
| Other current assets | | | - | | | | 8,650,652 | | | | 49,818 | | | | - | | | | | | | 49,818 | | | | - | | | | | | | 8,700,470 | | | | - | | | | | | | 8,700,470 | |
| Contract assets | | | - | | | | 380,370 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 380,370 | | | | - | | | | | | | 380,370 | |
| Current tax assets | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1 | |
| Inventories, net | | | - | | | | 995,671 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 995,671 | | | | - | | | | | | | 995,671 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total current assets | | | 50,000 | | | | 30,648,757 | | | | 1,403,343 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,403,343 | | | | (6,732,707 | ) | | | | | | 25,369,393 | | | | (4,346,339 | ) | | | | | | 21,023,054 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term financial instruments | | | - | | | | 230,740 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 230,740 | | | | - | | | | | | | 230,740 | |
| Long-term loans, net | | | - | | | | 94,491 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 94,491 | | | | - | | | | | | | 94,491 | |
| Long-term investment securities | | | - | | | | 1,259,710 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,259,710 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,259,710 | |
| Investments in associates and joint ventures | | | - | | | | 441,751 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 441,751 | | | | - | | | | | | | 441,751 | |
| Investment in subsidiary | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 50,000 | | | V | | | | 50,000 | | | | (50,000 | ) | | W | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Investment in equity securities | | | - | | | | 1,600,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,600,000 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,600,000 | |
| Investment in equity securities - related party | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Property, plant and equipment, including right-of-use assets | | | - | | | | 10,368,785 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 10,368,785 | | | | - | | | | | | | 10,368,785 | |
| Investment properties | | | - | | | | 2,142,139 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 2,142,139 | | | | - | | | | | | | 2,142,139 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets, net | | | - | | | | 11,045 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 11,045 | | | | - | | | | | | | 11,045 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets, net - related party | | | - | | | | 44,692 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 44,692 | | | | - | | | | | | | 44,692 | |
| Intangible Asset - Intellectual Property | | | - | | | | 16,705,549 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 16,705,549 | | | | - | | | | | | | 16,705,549 | |
| Intangible Asset - Customer relationships | | | - | | | | 11,329,202 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 11,329,202 | | | | - | | | | | | | 11,329,202 | |
| Intangible Asset - Trademarks | | | - | | | | 4,321,608 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 4,321,608 | | | | - | | | | | | | 4,321,608 | |
| Intangible Asset - Non-compete | | | - | | | | 187,953 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 187,953 | | | | - | | | | | | | 187,953 | |
| Intangible assets other than goodwill | | | - | | | | 3,420,367 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 3,420,367 | | | | - | | | | | | | 3,420,367 | |
| Goodwill | | | - | | | | 178,359,515 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 178,359,515 | | | | - | | | | | | | 178,359,515 | |
| Other non-current assets | | | - | | | | 936,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 936,000 | | | | - | | | | | | | 936,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other non-current assets - related party | | | - | | | | 72,682 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 72,682 | | | | - | | | | | | | 72,682 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | - | | | | 1,602,895 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,602,895 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,602,895 | |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | | - | | | | 3,429,047 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 3,429,047 | | | | - | | | | | | | 3,429,047 | |
| Defined benefit assets | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Deferred tax assets | | | - | | | | 607,113 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 607,113 | | | | - | | | | | | | 607,113 | |
| Investments held in Trust Account | | | - | | | | - | | | | 12,686,133 | | | | (8,613,436 | ) | | A-2 | | | | 3,961,947 | | | | (4,346,339 | ) | | B | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (110,750 | ) | | A-2 | | | | | | | | 263,075 | | | J | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 121,317 | | | O | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total non-current assets | | | - | | | | 237,165,284 | | | | 12,686,133 | | | | (8,674,186 | ) | | | | | | 4,011,947 | | | | (4,011,947 | ) | | | | | | 237,165,284 | | | | - | | | | | | | 237,165,284 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total assets | | $ | 50,000 | | | $ | 267,814,041 | | | $ | 14,089,476 | | | $ | (8,674,186 | ) | | | | | $ | 5,415,290 | | | $ | (10,744,654 | ) | | | | | $ | 262,534,677 | | | $ | (4,346,339 | ) | | | | | $ | 258,188,338 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | $ | - | | | $ | 18,119,869 | | | $ | 1,393,590 | | | $ | - | | | | | | $ | 1,393,590 | | | $ | (1,455,767 | ) | | D | | | $ | 18,057,692 | | | $ | (57,131 | ) | | D | | | $ | 18,000,561 | |
| Trade and other payables - related party | | | - | | | | 1,277,613 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,277,613 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,277,613 | |
| Other current financial liabilities | | | - | | | | 66,458 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 66,458 | | | | - | | | | | | | 66,458 | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | - | | | | 1,498,521 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,498,521 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,498,521 | |
| Contract liabilities | | | - | | | | 2,108,530 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 2,108,530 | | | | - | | | | | | | 2,108,530 | |
| Other payables | | | 7,257 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 7,257 | | | | - | | | | | | | 7,257 | |
| Other payables - related parties | | | 5,550 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 50,000 | | | V | | | | 50,000 | | | | (50,000 | ) | | W | | | | 5,550 | | | | - | | | | | | | 5,550 | |
| Defined severance benefits, current | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Short-term borrowings | | | - | | | | 3,520,073 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 3,520,073 | | | | - | | | | | | | 3,520,073 | |
| Short-term borrowings - related party | | | - | | | | 313,720 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 313,720 | | | | - | | | | | | | 313,720 | |
| Current portion of long-term borrowings, net | | | - | | | | 32,661 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 32,661 | | | | - | | | | | | | 32,661 | |
| Current lease liabilities | | | - | | | | 1,387,822 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,387,822 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,387,822 | |
| Lease liability, current - related party | | | - | | | | 44,692 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 44,692 | | | | - | | | | | | | 44,692 | |
| Current tax liabilities | | | - | | | | 481,910 | | | | 1,082,528 | | | | (110,750 | ) | | A-2 | | | | 971,778 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,453,688 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,453,688 | |
| Due to Sponsor | | | - | | | | - | | | | 15,094 | | | | - | | | | | | | 15,094 | | | | (15,094 | ) | | M | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Excise tax payable attributable to redemption of common stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | 872,861 | | | | - | | | | | | | 872,861 | | | | - | | | | | | | 872,861 | | | | - | | | | | | | 872,861 | |
| Promissory note - related party | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,311,000 | | | | - | | | | | | | 2,311,000 | | | | (2,407,000 | ) | | L | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 96,000 | | | L | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Consideration payable | | | - | | | | 13,797,492 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 13,797,492 | | | | - | | | | | | | 13,797,492 | |
| Contingent consideration payable | | | - | | | | 5,972,887 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 5,972,887 | | | | - | | | | | | | 5,972,887 | |
| Accrued franchise tax payable | | | - | | | | - | | | | 136,713 | | | | - | | | | | | | 136,713 | | | | - | | | | | | | 136,713 | | | | - | | | | | | | 136,713 | |
| Accrued expenses | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 12,807 | | | | 48,622,248 | | | | 5,811,786 | | | | (60,750 | ) | | | | | | 5,751,036 | | | | (3,831,861 | ) | | | | | | 50,554,230 | | | | (57,131 | ) | | | | | | 50,497,099 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other non-current payables | | | - | | | | 298,101 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 298,101 | | | | - | | | | | | | 298,101 | |
| Long-term borrowings, excluding current portion, net | | | - | | | | 1,486,639 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,486,639 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,486,639 | |
| Other non-current financial liabilities | | | - | | | | 239,730 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 239,730 | | | | - | | | | | | | 239,730 | |
| Other non-current non-financial liabilities | | | - | | | | 39,541 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 39,541 | | | | - | | | | | | | 39,541 | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | | - | | | | 907,651 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 907,651 | | | | - | | | | | | | 907,651 | |
| Convertible note | | | | | | | - | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Derivative liabilities | | | - | | | | 548,361 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 548,361 | | | | - | | | | | | | 548,361 | |
| Contract liabilities | | | - | | | | 653,808 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 653,808 | | | | - | | | | | | | 653,808 | |
| Other non-current provisions | | | - | | | | 459,209 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 459,209 | | | | - | | | | | | | 459,209 | |
| Non-current lease liabilities | | | - | | | | 8,521,184 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 8,521,184 | | | | - | | | | | | | 8,521,184 | |
| Lease liability, non-current - related party | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | | - | | | | 7,493,698 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 7,493,698 | | | | - | | | | | | | 7,493,698 | |
| Deferred underwriting commissions | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,220,000 | | | | - | | | | | | | 3,220,000 | | | | (3,220,000 | ) | | C | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Warrant liabilities | | | - | | | | - | | | | 240,516 | | | | - | | | | | | | 240,516 | | | | 3,720 | | | L | | | | 244,236 | | | | - | | | | | | | 244,236 | |
| Call option liability | | | - | | | | 4,731,239 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 4,731,239 | | | | - | | | | | | | 4,731,239 | |
| Earnout liability | | | - | | | | 1,194,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,194,000 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,194,000 | |
| Consideration payable, non-current | | | - | | | | 12,526,059 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 12,526,059 | | | | - | | | | | | | 12,526,059 | |
| Convertible senior unsecured notes | | | - | | | | 4,369,465 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 4,369,465 | | | | - | | | | | | | 4,369,465 | |
| Discount on note | | | - | | | | (412,651 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | (412,651 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (412,651 | ) |
| Class A common stock subject to possible redemption | | | - | | | | - | | | | 12,684,975 | | | | (8,613,436 | ) | | A-2 | | | | 4,071,539 | | | | (4,071,539 | ) | | G | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | - | | | | 43,056,034 | | | | 16,145,491 | | | | (8,613,436 | ) | | | | | | 7,532,055 | | | | (7,287,819 | ) | | | | | | 43,300,270 | | | | - | | | | | | | 43,300,270 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total liabilities | | | 12,807 | | | | 91,678,282 | | | | 21,957,277 | | | | (8,674,186 | ) | | | | | | 13,283,091 | | | | (11,119,680 | ) | | | | | | 93,854,500 | | | | (57,131 | ) | | | | | | 93,797,369 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Class A common stock subject to possible redemption | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EQUITY | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Global Star preferred stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| K Enter Series A-1 convertible preferred stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| K Enter Series A convertible preferred stock | | | - | | | | 355 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | (355 | ) | | Q | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| K Enter common stock | | | - | | | | 1,017 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | 4 | | | Q | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (985 | ) | | E | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (36 | ) | | R | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pubco ordinary shares | | | 50,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | 5,748 | | | E | | | | 6,353 | | | | (38 | ) | | G | | | | 6,315 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 152 | | | D | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (50,000 | ) | | W | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 453 | | | N | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Global Star Class A common stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | 62 | | | | - | | | | | | | 62 | | | | 38 | | | G | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 230 | | | I | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 97 | | | K | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 26 | | | L | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (453 | ) | | N | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Global Star Class B common stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | 230 | | | | - | | | | | | | 230 | | | | (230 | ) | | I | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| K Enter treasury stock | | | - | | | | (36 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | 36 | | | R | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Preferred stock subscription receivable | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Additional paid-in capital | | | - | | | | 169,661,493 | | | | - | | | | | | | | | | | - | | | | 11,918,472 | | | D | | | | 234,618,647 | | | | (4,346,301 | ) | | G | | | | 230,227,196 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (4,763 | ) | | E | | | | | | | | (45,150 | ) | | H | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (8,878,424 | ) | | F | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 4,071,501 | | | G | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 54,296,860 | | | H | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (97 | ) | | K | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,403,254 | | | L | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,150,000 | | | P | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 351 | | | Q | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share premium | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Other reserves | | | (1,376 | ) | | | (21,403,974 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | - | | | | (21,405,350 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (21,405,350 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Retained earnings (Accumulated deficit) | | | (11,431 | ) | | | 15,792,519 | | | | (7,868,093 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (7,868,093 | ) | | | 8,878,424 | | | F | | | | (56,623,858 | ) | | | 45,150 | | | H | | | | (56,521,577 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (54,296,860 | ) | | H | | | | | | | | 57,131 | | | D | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 263,075 | | | J | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (18,231,492 | ) | | D | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (1,150,000 | ) | | P | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | | | - | | | | (93,739 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | (93,739 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (93,739 | ) |
| Equity attributable to the equity holders of the Company | | | 37,193 | | | | 163,957,635 | | | | (7,867,801 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (7,867,801 | ) | | | 375,026 | | | | | | | 156,502,053 | | | | (4,289,208 | ) | | | | | | 152,212,845 | |
| Non-controlling interest | | | - | | | | 12,178,124 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 12,178,124 | | | | - | | | | | | | 12,178,124 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total equity | | | 37,193 | | | | 176,135,759 | | | | (7,867,801 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (7,867,801 | ) | | | 375,026 | | | | | | | 168,680,177 | | | | (4,289,208 | ) | | | | | | 164,390,969 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total equity and liabilities | | $ | 50,000 | | | $ | 267,814,041 | | | $ | 14,089,476 | | | $ | (8,674,186 | ) | | | | | $ | 5,415,290 | | | $ | (10,744,654 | ) | | | | | $ | 262,534,677 | | | $ | (4,346,339 | ) | | | | | $ | 258,188,338 | |
| (1) | The unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet for K Wave as of June 30, 2024, combines the unaudited pro forma combined balance sheet for New K Enter(2) as of June 30, 2024 with the historical unaudited balance sheet of Global Star as of June 30, 2024 and the historical unaudited balance sheet of K Wave as of June 30, 2024. |
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED BALANCE SHEET
FOR NEW K ENTER
AS OF JUNE 30, 2024 (2)
| | | Play Company
as converted
to USD
(IFRS
Historical) | | | LAMP
as converted
to USD
(IFRS
Historical) | | | Bidangil
as converted
to USD
(IFRS
Historical) | | | Apeitda
as converted
to USD
(IFRS
Historical) | | | Anseilen
as converted
to USD
(IFRS
Historical) | | | Solaire Partners
as converted
to USD
(IFRS
Historical) | | | K Enter
(IFRS
Historical -
Note 4) | | | Transaction
Accounting
Adjustments | | | | | | New K Enter
Pro Forma
Combined
(IFRS
Historical) | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 3,051,114 | | | $ | 1,271,372 | | | $ | 1,280,687 | | | $ | 346,532 | | | $ | 161,158 | | | $ | 66,758 | | | $ | 438,842 | | | $ | 3,375,000 | | | X | | | $ | 10,141,463 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 150,000 | | | Z | | | | | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | | 303,275 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 303,275 | |
| Short-term investment securities | | | 0 | | | | - | | | | 726,955 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 726,955 | |
| Accounts receivable - trade, net | | | 2,170,577 | | | | 839,555 | | | | 232 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 273,520 | | | | 6,974 | | | | - | | | | | | | 3,290,858 | |
| Other receivables | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 20,574 | | | | - | | | | | | | 20,574 | |
| Other receivables - related parties | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Preferred stock subscription receivable | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 369,000 | | | | 150,000 | | | Z | | | | 519,000 | |
| Convertible debt security | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,027,027 | | | | | | | | | | | 1,027,027 | |
| Deferred transaction costs | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,879,509 | | | | | | | | | | | 1,879,509 | |
| Short-term loans, net | | | 687,416 | | | | - | | | | 98,071 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (98,071 | ) | | A-1 | | | | 687,416 | |
| Accounts receivable - other, net | | | 73,934 | | | | 47,237 | | | | 531 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,341,176 | | | | - | | | | (61,435 | ) | | T | | | | 1,400,912 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (531 | ) | | A-1 | | | | | |
| Value added tax receivables | | | 440,264 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,631 | | | | 36,323 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 478,218 | |
| Other current financial assets | | | 29,058 | | | | - | | | | 18,161 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 99,637 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 146,856 | |
| Other current assets | | | 5,587,152 | | | | 1,711,732 | | | | 981,989 | | | | 1,706 | | | | 44 | | | | - | | | | 368,029 | | | | - | | | | | | | 8,650,652 | |
| Contract assets | | | - | | | | 135,591 | | | | 108,827 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 135,952 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 380,370 | |
| Current tax assets | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1 | |
| Inventories, net | | | 995,671 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 995,671 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total current assets | | | 13,338,461 | | | | 4,005,487 | | | | 3,215,453 | | | | 349,870 | | | | 197,525 | | | | 1,917,043 | | | | 4,109,955 | | | | 3,514,963 | | | | | | | 30,648,757 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term financial instruments | | | 230,740 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 230,740 | |
| Long-term loans, net | | | - | | | | 94,491 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 94,491 | |
| Long-term investment securities | | | 452,986 | | | | 581,163 | | | | - | | | | 56,297 | | | | 21,794 | | | | 147,470 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,259,710 | |
| Investments in associates and joint ventures | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 441,751 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 441,751 | |
| Investment in subsidiary | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Investment in equity securities | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,600,000 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,600,000 | |
| Investment in equity securities - related party | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,264,756 | | | | (1,264,756 | ) | | U | | | | - | |
| Property, plant and equipment, including right-of-use assets | | | 9,890,565 | | | | 80,700 | | | | 66,778 | | | | 191,829 | | | | 610 | | | | 39,878 | | | | 29,911 | | | | 68,514 | | | T | | | | 10,368,785 | |
| Investment properties | | | 2,142,139 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 2,142,139 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets, net | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 55,737 | | | | (44,692 | ) | | T | | | | 11,045 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets, net - related party | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 44,692 | | | | - | | | | | | | 44,692 | |
| Intangible Asset - Intellectual Property | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 16,705,549 | | | A | | | | 16,705,549 | |
| Intangible Asset - Customer relationships | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 11,329,202 | | | A | | | | 11,329,202 | |
| Intangible Asset - Trademarks | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,321,608 | | | A | | | | 4,321,608 | |
| Intangible Asset - Non-compete | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 187,953 | | | A | | | | 187,953 | |
| Intangible assets other than goodwill | | | 3,420,367 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 3,420,367 | |
| Goodwill | | | 2,373,855 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 175,985,660 | | | A | | | | 178,359,515 | |
| Other non-current assets | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,916,749 | | | | (908,067 | ) | | S | | | | 936,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (72,682 | ) | | T | | | | | |
| Other non-current assets - related party | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 72,682 | | | | - | | | | | | | 72,682 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | 1,171,540 | | | | 36,381 | | | | 104,657 | | | | 296,323 | | | | - | | | | 218 | | | | - | | | | (6,224 | ) | | T | | | | 1,602,895 | |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | | 1,622,222 | | | | 1,037,801 | | | | 386,183 | | | | - | | | | 382,841 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 3,429,047 | |
| Defined benefit assets | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Deferred tax assets | | | 494,492 | | | | 63,171 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 49,450 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 607,113 | |
| Investments held in Trust Account | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total non-current assets | | | 21,798,906 | | | | 1,893,707 | | | | 557,618 | | | | 544,449 | | | | 405,245 | | | | 678,767 | | | | 4,984,527 | | | | 206,302,065 | | | | | | | 237,165,284 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total assets | | $ | 35,137,367 | | | $ | 5,899,194 | | | $ | 3,773,071 | | | $ | 894,319 | | | $ | 602,770 | | | $ | 2,595,810 | | | $ | 9,094,482 | | | $ | 209,817,028 | | | | | | $ | 267,814,041 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | $ | 9,573,735 | | | $ | 1,541,784 | | | $ | 1,183,108 | | | $ | 13,881 | | | $ | 15,195 | | | $ | 1,308,853 | | | $ | 4,555,995 | | | $ | (72,682 | ) | | T | | | $ | 18,119,869 | |
| Trade and other payables - related party | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,278,144 | | | | (531 | ) | | A-1 | | | | 1,277,613 | |
| Other current financial liabilities | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 66,458 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 66,458 | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | 1,239,765 | | | | 114,698 | | | | 10,557 | | | | 94,845 | | | | 21,570 | | | | 17,086 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,498,521 | |
| Contract liabilities | | | - | | | | 1,825,487 | | | | 283,043 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 2,108,530 | |
| Other payables | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Other payables - related parties | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Defined severance benefits, current | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Short-term borrowings | | | 2,448,149 | | | | 1,071,519 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 405 | | | | - | | | | | | | 3,520,073 | |
| Short-term borrowings - related party | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 411,791 | | | | (98,071 | ) | | A-1 | | | | 313,720 | |
| Current portion of long-term borrowings, net | | | 18,132 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 14,529 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 32,661 | |
| Current lease liabilities | | | 1,203,834 | | | | 18,960 | | | | 61,653 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 94,699 | | | | 53,368 | | | | (44,692 | ) | | T | | | | 1,387,822 | |
| Lease liability, current - related party | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 44,692 | | | | - | | | | | | | 44,692 | |
| Current tax liabilities | | | 211,444 | | | | 32,542 | | | | 86,214 | | | | 3,271 | | | | - | | | | 148,439 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 481,910 | |
| Due to Sponsor | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Excise tax payable attributable to redemption of common stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Promissory note - related party | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Consideration payable | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 13,797,492 | | | A | | | | 13,797,492 | |
| Contingent consideration payable | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | | 5,972,887 | | | A | | | | 5,972,887 | |
| Accrued franchise tax payable | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Accrued expenses | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 14,695,059 | | | | 4,604,990 | | | | 1,624,575 | | | | 126,526 | | | | 36,765 | | | | 1,635,535 | | | | 6,344,395 | | | | 19,554,403 | | | | | | | 48,622,248 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other non-current payables | | | 298,101 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 298,101 | |
| Long-term borrowings, excluding current portion, net | | | 1,486,639 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,486,639 | |
| Other non-current financial liabilities | | | 239,730 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 239,730 | |
| Other non-current non-financial liabilities | | | 39,541 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 908,067 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (908,067 | ) | | S | | | | 39,541 | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | | 487,416 | | | | 202,217 | | | | - | | | | 108,750 | | | | 86,255 | | | | 23,013 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 907,651 | |
| Convertible note | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Derivative liabilities | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 135,710 | | | | 412,651 | | | X | | | | 548,361 | |
| Contract liabilities | | | - | | | | 653,808 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 653,808 | |
| Other non-current provisions | | | 449,708 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 9,501 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 459,209 | |
| Non-current lease liabilities | | | 8,517,371 | | | | 49,998 | | | | 7,861 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (54,046 | ) | | T | | | | 8,521,184 | |
| Lease liability, non-current - related party | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | | 691,937 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 6,801,761 | | | A | | | | 7,493,698 | |
| Deferred underwriting commissions | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Warrant liabilities | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Call option liability | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,731,239 | | | A | | | | 4,731,239 | |
| Earnout liability | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,194,000 | | | A | | | | 1,194,000 | |
| Consideration payable, non-current | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 12,526,059 | | | A | | | | 12,526,059 | |
| Convertible senior unsecured notes | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 994,465 | | | | 3,375,000 | | | X | | | | 4,369,465 | |
| Discount on note | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (412,651 | ) | | X | | | | (412,651 | ) |
| Class A common stock subject to possible redemption | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | 12,210,443 | | | | 906,023 | | | | 7,861 | | | | 108,750 | | | | 994,322 | | | | 32,514 | | | | 1,130,175 | | | | 27,665,946 | | | | | | | 43,056,034 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total liabilities | | | 26,905,502 | | | | 5,511,013 | | | | 1,632,436 | | | | 235,276 | | | | 1,031,087 | | | | 1,668,049 | | | | 7,474,570 | | | | 47,220,349 | | | | | | | 91,678,282 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Class A common stock subject to possible redemption | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EQUITY | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital | | | 363,227 | | | | 57 | | | | 36,323 | | | | 7,265 | | | | 10,897 | | | | 617,486 | | | | - | | | | (1,035,255 | ) | | A | | | | - | |
| Global Star preferred stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| K Enter Series A-1 convertible preferred stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| K Enter Series A convertible preferred stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 355 | | | | - | | | | | | | 355 | |
| K Enter common stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,000 | | | | 5 | | | A | | | | 1,017 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 12 | | | Y | | | | | |
| Pubco ordinary shares | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Global Star Class A common stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Global Star Class B common stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| K Enter treasury stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (57 | ) | | | 21 | | | Y | | | | (36 | ) |
| Preferred stock subscription receivable | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Additional paid-in capital | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 15,238,711 | | | | 141,948,607 | | | A | | | | 169,661,493 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 12,174,175 | | | Y | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 300,000 | | | Z | | | | | |
| Share premium | | | - | | | | (425,316 | ) | | | 36,323 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 306,022 | | | | - | | | | 82,971 | | | A | | | | - | |
| Other reserves | | | (20,139,218 | ) | | | - | | | | (1,452,908 | ) | | | (65,729 | ) | | | (766 | ) | | | (33,153 | ) | | | - | | | | 1,552,556 | | | A | | | | (21,403,974 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (1,264,756 | ) | | U | | | | | |
| Retained earnings (Accumulated deficit) | | | 27,911,826 | | | | 813,440 | | | | 3,520,897 | | | | 717,507 | | | | (438,448 | ) | | | 37,406 | | | | (13,526,358 | ) | | | 8,875,556 | | | A | | | | 15,792,519 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 54,901 | | | T | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (12,174,208 | ) | | Y | | | | | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (93,739 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (93,739 | ) |
| Equity attributable to the equity holders of the Company | | | 8,135,835 | | | | 388,181 | | | | 2,140,635 | | | | 659,043 | | | | (428,317 | ) | | | 927,761 | | | | 1,619,912 | | | | 150,514,585 | | | | | | | 163,957,635 | |
| Non-controlling interest | | | 96,030 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 12,082,094 | | | A | | | | 12,178,124 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total equity | | | 8,231,865 | | | | 388,181 | | | | 2,140,635 | | | | 659,043 | | | | (428,317 | ) | | | 927,761 | | | | 1,619,912 | | | | 162,596,679 | | | | | | | 176,135,759 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total equity and liabilities | | $ | 35,137,367 | | | $ | 5,899,194 | | | $ | 3,773,071 | | | $ | 894,319 | | | $ | 602,770 | | | $ | 2,595,810 | | | $ | 9,094,482 | | | $ | 209,817,028 | | | | | | $ | 267,814,041 | |
| (2) | The unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet for New K Enter as of June 30, 2024, combines the historical unaudited balance sheets of the Six Korean Entities as of June 30, 2024, with the historical unaudited balance sheet of K Enter as of June 30, 2024 as adjusted for conversion to IFRS (see also Note 4 — “IFRS Conversion and Presentation Alignment”). |
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS
FOR K WAVE
FOR THE SIX MONTHS ENDED JUNE 30, 2024 (3)
| | | | | | | | | | | | Scenario 1: No Additional
Redemption Scenario | | | Scenario 2: Maximum
Redemption Scenario | |
| | | K Wave
Media
(IFRS Historical) | | | New K
Enter Pro
Forma
Combined
(IFRS Historical) | | | Global Star
(IFRS
Historical -
Note 4) | | | Transaction
Accounting
Adjustments | | | | | | Pro Forma
Combined
(IFRS) | | | Transaction
Accounting
Adjustments | | | | | | Pro Forma
Combined
(IFRS) | |
| Sales revenue | | $ | - | | | $ | 34,492,242 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | | | | $ | 34,492,242 | | | $ | - | | | | | | $ | 34,492,242 | |
| Investment management revenue | | | - | | | | 696,403 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 696,403 | | | | - | | | | | | | 696,403 | |
| Investment revenue | | | - | | | | 1,020 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,020 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,020 | |
| Gains from investments in associates | | | - | | | | 13,511 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 13,511 | | | | - | | | | | | | 13,511 | |
| Cost of sales | | | - | | | | (31,539,346 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | (31,539,346 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (31,539,346 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | - | | | | 3,663,830 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 3,663,830 | | | | - | | | | | | | 3,663,830 | |
| Operating expenses | | | - | | | | - | | | | (1,452,062 | ) | | | 60,000 | | | BB | | | | (1,392,062 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (1,392,062 | ) |
| Selling, general, and administrative expenses | | | - | | | | (7,883,938 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | (7,883,938 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (7,883,938 | ) |
| Losses from investments in associates | | | - | | | | (19,128 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | (19,128 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (19,128 | ) |
| Stock-based compensation expense | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Other income | | | - | | | | 404,168 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 404,168 | | | | - | | | | | | | 404,168 | |
| Other expenses | | | - | | | | (2,370,063 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | (2,370,063 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (2,370,063 | ) |
| Transaction costs | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | - | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating income (loss) | | | - | | | | (6,205,130 | ) | | | (1,452,062 | ) | | | 60,000 | | | | | | | (7,597,192 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (7,597,192 | ) |
| Other income (expense) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Finance income | | | - | | | | 245,083 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 245,083 | | | | - | | | | | | | 245,083 | |
| Finance costs | | | - | | | | (862,272 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | | | | | (862,272 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (862,272 | ) |
| Change in fair value of warrant liability | | | - | | | | - | | | | (143,534 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (143,534 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (143,534 | ) |
| Loss on initial issuance of debt | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Interest income | | | - | | | | 344 | | | | 10,354 | | | | - | | | | | | | 10,698 | | | | - | | | | | | | 10,698 | |
| Other income (expense), net | | | - | | | | 13,841 | | | | | | | | - | | | | | | | 13,841 | | | | - | | | | | | | 13,841 | |
| Interest income on marketable securities held in Trust Account | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,431,156 | | | | (1,431,156 | ) | | AA | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Net income (loss) before taxes | | | - | | | | (6,808,134 | ) | | | (154,086 | ) | | | (1,371,156 | ) | | | | | | (8,333,376 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (8,333,376 | ) |
| Provision for taxes | | | - | | | | (51,020 | ) | | | (286,463 | ) | | | 286,463 | | | CC | | | | (51,020 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (51,020 | ) |
| Net income (loss) | | | - | | | | (6,859,154 | ) | | | (440,549 | ) | | | (1,084,693 | ) | | | | | | (8,384,396 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (8,384,396 | ) |
| Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interest in subsidiaries | | | - | | | | (928,158 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | | | | | (928,158 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (928,158 | ) |
| Income (loss) attributable to shareholders of New K Enter | | $ | - | | | $ | (5,930,996 | ) | | $ | (440,549 | ) | | $ | (1,084,693 | ) | | | | | $ | (7,456,238 | ) | | $ | - | | | | | | $ | (7,456,238 | ) |
| Basic and diluted net income per share | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic net income per share, Class A common stock subject to possible redemption | | | | | | | | | | $ | (0.06 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic net income per share, Class B common stock | | | | | | | | | | $ | (0.06 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pro forma weighted average number of shares outstanding - basic and diluted | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 63,519,622 | (7) | | | | | | | | | | 63,138,747 | (7) |
| Pro forma net loss per share - basic and diluted | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | (0.13 | ) | | | | | | | | | $ | (0.13 | ) |
| (3) | The unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations for K Wave for the six months ended June 30, 2024, combines the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statements of operations for the Six Korean Entities as converted to USD and K Enter(5) for the six months ended June 30, 2024 with the historical unaudited statement of operations of Global Star for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and the historical unaudited statement of operations of K Wave for the six months ended June 30, 2024. |
| (4) | Please refer to Note 8 — “Net Loss per Share” for details. |
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS
FOR NEW K ENTER
FOR THE SIX MONTHS ENDED JUNE 30, 2024 (5)
| | | Play Company
as converted
to USD
(IFRS Historical) | | | K Enter
(US GAAP
Historical) | | | Lamp
as converted
to USD
(IFRS Historical) | | | Bidangil
as converted to USD
(IFRS Historical) | | | Apeitda
as converted
to USD
(IFRS Historical) | | | Anseilen
as converted
to USD
(IFRS Historical) | | | Solaire Partners
as converted
to USD
(IFRS Historical) | | | Transaction
Accounting
Adjustments | | | | | | New K Enter
Pro Forma Combined
(IFRS Historical) | |
| Sales revenue | | $ | 14,060,309 | | | $ | 366,533 | | | $ | 9,282,449 | | | $ | 10,782,558 | | | $ | 393 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | | | | $ | 34,492,242 | |
| Investment management revenue | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 696,403 | | | | - | | | | | | | 696,403 | |
| Investment revenue | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,020 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,020 | |
| Gains from investments in associates | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 13,511 | | | | - | | | | | | | 13,511 | |
| Cost of sales | | | (12,471,866 | ) | | | (261,546 | ) | | | (8,585,214 | ) | | | (10,220,720 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | (31,539,346 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 1,588,443 | | | | 104,987 | | | | 697,235 | | | | 561,838 | | | | 393 | | | | - | | | | 710,934 | | | | - | | | | | | | 3,663,830 | |
| Operating expenses | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Selling, general, and administrative expenses | | | (1,521,986 | ) | | | (4,712,937 | ) | | | (344,753 | ) | | | (251,167 | ) | | | (125,311 | ) | | | (189,905 | ) | | | (772,435 | ) | | | 22,901 | | | FF | | | | (7,883,938 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 11,655 | | | GG | | | | | |
| Losses from investments in associates | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (19,128 | ) | | | | | | | | | | (19,128 | ) |
| Stock-based compensation expense | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | | | | | - | |
| Other income | | | 406,242 | | | | - | | | | 13,829 | | | | 1 | | | | 1 | | | | 262 | | | | 10 | | | | (3,981 | ) | | FF | | | | 404,168 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (11,655 | ) | | GG | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (541 | ) | | HH | | | | | |
| Other expenses | | | (238,783 | ) | | | - | | | | (34,022 | ) | | | (6 | ) | | | (22,244 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (2,078,778 | ) | | EE | | | | (2,370,063 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 3,229 | | | FF | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 541 | | | HH | | | | | |
| Transaction costs | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Operating income (loss) | | | 233,916 | | | | (4,607,950 | ) | | | 332,289 | | | | 310,666 | | | | (147,161 | ) | | | (189,643 | ) | | | (80,619 | ) | | | (2,056,628 | ) | | | | | | (6,205,130 | ) |
| Other income (expense) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Finance income | | | 127,882 | | | | - | | | | 5,707 | | | | 24,431 | | | | 21,356 | | | | 82 | | | | 65,625 | | | | | | | | | | | 245,083 | |
| Finance costs | | | (672,524 | ) | | | - | | | | (48,945 | ) | | | (4,043 | ) | | | (7,913 | ) | | | - | | | | (9,447 | ) | | | (119,400 | ) | | II | | | | (862,272 | ) |
| Change in fair value of warrant liability | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Loss on initial issuance of debt | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Interest income | | | - | | | | 344 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 344 | |
| Other income (expense), net | | | | | | | 13,841 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 13,841 | |
| Interest income on marketable securities held in Trust Account | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Net income (loss) before taxes | | | (310,726 | ) | | | (4,593,765 | ) | | | 289,051 | | | | 331,054 | | | | (133,718 | ) | | | (189,561 | ) | | | (24,441 | ) | | | (2,176,028 | ) | | | | | | (6,808,134 | ) |
| Provision for taxes | | | 45,438 | | | | - | | | | (60,424 | ) | | | (28,425 | ) | | | (5,183 | ) | | | - | | | | (2,426 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (51,020 | ) |
| Net income (loss) | | | (265,288 | ) | | | (4,593,765 | ) | | | 228,627 | | | | 302,629 | | | | (138,901 | ) | | | (189,561 | ) | | | (26,867 | ) | | | (2,176,028 | ) | | | | | | (6,859,154 | ) |
| Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interest in subsidiaries | | | (206,932 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (721,226 | ) | | DD | | | | (928,158 | ) |
| Income (loss) attributable to shareholders of New K Enter | | $ | (58,356 | ) | | $ | (4,593,765 | ) | | $ | 228,627 | | | $ | 302,629 | | | $ | (138,901 | ) | | $ | (189,561 | ) | | $ | (26,867 | ) | | $ | (1,454,802 | ) | | | | | $ | (5,930,996 | ) |
| Basic and diluted net income per share | | $ | (0.58 | ) | | $ | (116.68 | ) | | $ | 228.63 | | | $ | 30.26 | | | $ | (13.89 | ) | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (5) | The unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations for New K Enter for the six months ended June 30, 2024, combines the historical statements of operations of the Six Korean Entities for the six months ended June 30, 2024 as converted to USD, with the historical unaudited statement of operations of K Enter for the six months ended June 30, 2024, as adjusted for conversion to IFRS (see also Note 4 — “IFRS Conversion and Presentation Alignment”). |
| (6) | Please refer to Note 8 — “Net Loss per Share” for details. |
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS
FOR K WAVE
FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2023 (7)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Scenario 1: No Additional
Redemption Scenario | | | Scenario 2: Maximum
Redemption Scenario | |
| | | K Wave
Media
(IFRS Historical) | | | New K
Enter Pro
Forma
Combined
(IFRS Historical) | | | Global Star
(IFRS
Historical -
Note 4) | | | Transaction
Accounting
Adjustments | | | | | | Pro Forma
Combined
(IFRS) | | | Transaction
Accounting
Adjustments | | | | | | Pro Forma
Combined
(IFRS) | |
| Sales revenue | | $ | - | | | $ | 73,790,538 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | | | | $ | 73,790,538 | | | $ | - | | | | | | $ | 73,790,538 | |
| Investment management revenue | | | - | | | | 1,311,845 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,311,845 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,311,845 | |
| Investment revenue | | | - | | | | 1,601 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,601 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,601 | |
| Cost of sales | | | - | | | | (67,122,457 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | (67,122,457 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (67,122,457 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | - | | | | 7,981,527 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 7,981,527 | | | | - | | | | | | | 7,981,527 | |
| Operating expenses | | | - | | | | - | | | | (2,126,947 | ) | | | 121,666 | | | BB | | | | (2,005,281 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (2,005,281 | ) |
| Selling, general, and administrative expenses | | | (11,431 | ) | | | (15,452,931 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | (15,464,362 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (15,464,362 | ) |
| Losses from investments in associates | | | - | | | | (111,904 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | (111,904 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (111,904 | ) |
| Stock-based compensation expense | | | - | | | | (11,882,316 | ) | | | - | | | | (1,150,000 | ) | | EE | | | | (13,032,316 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (13,032,316 | ) |
| Other income | | | - | | | | 1,305,111 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,305,111 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,305,111 | |
| Other expenses | | | - | | | | (4,223,162 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | (4,223,162 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (4,223,162 | ) |
| Transaction costs | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (54,296,860 | ) | | CC | | | | (70,549,530 | ) | | | 45,150 | | | CC | | | | (70,447,249 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (9,527,943 | ) | | FF | | | | | | | | 57,131 | | | FF | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (6,724,727 | ) | | LL | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating income (loss) | | | (11,431 | ) | | | (22,383,675 | ) | | | (2,126,947 | ) | | | (71,577,864 | ) | | | | | | (96,099,917 | ) | | | 102,281 | | | | | | | (95,997,636 | ) |
| Other income (expense) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Finance income | | | - | | | | 1,643,380 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,643,380 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,643,380 | |
| Finance costs | | | - | | | | (1,697,771 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | (1,697,771 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (1,697,771 | ) |
| Change in fair value of warrant liability | | | - | | | | - | | | | 239,546 | | | | - | | | | | | | 239,546 | | | | - | | | | | | | 239,546 | |
| Loss on initial issuance of debt | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Interest income | | | - | | | | 7,956 | | | | 23,833 | | | | - | | | | | | | 31,789 | | | | - | | | | | | | 31,789 | |
| Other income (expense), net | | | - | | | | 13,863 | | | | | | | | - | | | | | | | 13,863 | | | | - | | | | | | | 13,863 | |
| Interest income on marketable securities held in Trust Account | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,942,920 | | | | (3,942,920 | ) | | AA | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Net income (loss) before taxes | | | (11,431 | ) | | | (22,416,248 | ) | | | 2,079,352 | | | | (75,520,784 | ) | | | | | | (95,869,111 | ) | | | 102,281 | | | | | | | (95,766,830 | ) |
| Provision for taxes | | | - | | | | (585,717 | ) | | | (795,729 | ) | | | 795,729 | | | DD | | | | (585,717 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (585,717 | ) |
| Net income (loss) | | | (11,431 | ) | | | (23,001,965 | ) | | | 1,283,623 | | | | (74,725,055 | ) | | | | | | (96,454,828 | ) | | | 102,281 | | | | | | | (96,352,547 | ) |
| Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interest in subsidiaries | | | - | | | | (1,830,493 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | | | | | (1,830,493 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (1,830,493 | ) |
| Income (loss) attributable to shareholders of New K Enter | | $ | (11,431 | ) | | $ | (21,171,472 | ) | | $ | 1,283,623 | | | $ | (74,725,055 | ) | | | | | $ | (94,624,335 | ) | | $ | 102,281 | | | | | | $ | (94,522,054 | ) |
| Basic and diluted net income per share | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic net income per share, Class A common stock subject to possible redemption | | | | | | | | | | $ | 0.12 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic net income per share, Class B common stock | | | | | | | | | | $ | 0.12 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pro forma weighted average number of shares outstanding - basic and diluted | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 63,519,622 | (7) | | | | | | | | | | 63,138,747 | (7) |
| Pro forma net loss per share - basic and diluted | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | (1.52 | ) | | | | | | | | | $ | (1.53 | ) |
| (7) | The unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations for K Wave for the year ended December 31, 2023, combines the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statements of operations for the Six Korean Entities as converted to USD and K Enter(5) for the year ended December 31, 2023 with the historical audited statement of operations of Global Star for the year ended December 31, 2023 and the historical audited statement of operations of K Wave for the year ended December 31, 2023. |
| (8) | Please refer to Note 8 — “Net Loss per Share” for details. |
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS
FOR NEW K ENTER
FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2023 (9)
| | | Play Company
as converted
to USD
(IFRS
Historical) | | | K Enter
(US GAAP
Historical) | | | Lamp
as converted
to USD
(IFRS
Historical) | | | Bidangil
as converted
to USD
(IFRS
Historical) | | | Apeitda
as converted
to USD
(IFRS
Historical) | | | Anseilen
as converted
to USD
(IFRS
Historical) | | | Solaire Partners
as converted
to USD
(IFRS
Historical) | | | Transaction
Accounting
Adjustments | | | | | | New K Enter
Pro Forma Combined
(IFRS
Historical) | |
| Sales revenue | | $ | 51,639,895 | | | $ | 208,704 | | | $ | 15,945,385 | | | $ | 5,927,682 | | | $ | 68,872 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | | | | $ | 73,790,538 | |
| Investment management revenue | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,311,845 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,311,845 | |
| Investment revenue | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,601 | | | | - | | | | | | | 1,601 | |
| Cost of sales | | | (46,555,511 | ) | | | (207,153 | ) | | | (14,929,523 | ) | | | (5,410,012 | ) | | | (20,258 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | (67,122,457 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 5,084,384 | | | | 1,551 | | | | 1,015,862 | | | | 517,670 | | | | 48,614 | | | | - | | | | 1,313,446 | | | | - | | | | | | | 7,981,527 | |
| Operating expenses | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Selling, general, and administrative expenses | | | (3,518,788 | ) | | | (8,954,316 | ) | | | (558,536 | ) | | | (581,127 | ) | | | (245,249 | ) | | | (264,906 | ) | | | (1,308,875 | ) | | | 42,637 | | | II | | | | (15,452,931 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (63,771 | ) | | JJ | | | | | |
| Losses from investments in associates | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (111,904 | ) | | | | | | | | | | (111,904 | ) |
| Stock-based compensation expense | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (11,882,316 | ) | | MM | | | | (11,882,316 | ) |
| Other income | | | 1,137,986 | | | | - | | | | 68,325 | | | | 27,552 | | | | 196 | | | | 467 | | | | 5 | | | | 6,809 | | | II | | | | 1,305,111 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 63,771 | | | JJ | | | | | |
| Other expenses | | | (27,202 | ) | | | - | | | | (83,778 | ) | | | (1,543 | ) | | | (402 | ) | | | - | | | | (34,350 | ) | | | (4,157,550 | ) | | HH | | | | (4,223,162 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 81,663 | | | II | | | | | |
| Transaction costs | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Operating income (loss) | | | 2,676,380 | | | | (8,952,765 | ) | | | 441,873 | | | | (37,448 | ) | | | (196,841 | ) | | | (264,439 | ) | | | (141,678 | ) | | | (15,908,757 | ) | | | | | | (22,383,675 | ) |
| Other income (expense) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Finance income | | | 1,334,550 | | | | - | | | | 37,222 | | | | 187,785 | | | | 67,229 | | | | 231 | | | | 16,363 | | | | | | | | | | | 1,643,380 | |
| Finance costs | | | (1,291,902 | ) | | | - | | | | (82,328 | ) | | | (8,803 | ) | | | (971 | ) | | | - | | | | (74,967 | ) | | | (238,800 | ) | | KK | | | | (1,697,771 | ) |
| Change in fair value of warrant liability | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Loss on initial issuance of debt | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Interest income | | | - | | | | 7,956 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 7,956 | |
| Other income (expense), net | | | | | | | 13,863 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | 13,863 | |
| Interest income on marketable securities held in Trust Account | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | - | |
| Net income (loss) before taxes | | | 2,719,028 | | | | (8,930,946 | ) | | | 396,767 | | | | 141,534 | | | | (130,583 | ) | | | (264,208 | ) | | | (200,282 | ) | | | (16,147,558 | ) | | | | | | (22,416,248 | ) |
| Provision for taxes | | | (582,185 | ) | | | - | | | | 14,386 | | | | 1,165 | | | | 11,181 | | | | - | | | | (30,264 | ) | | | - | | | | | | | (585,717 | ) |
| Net income (loss) | | | 2,136,843 | | | | (8,930,946 | ) | | | 411,153 | | | | 142,699 | | | | (119,402 | ) | | | (264,208 | ) | | | (230,546 | ) | | | (16,147,558 | ) | | | | | | (23,001,965 | ) |
| Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interest in subsidiaries | | | (263,886 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (1,566,607 | ) | | GG | | | | (1,830,493 | ) |
| Income (loss) attributable to shareholders of New K Enter | | $ | 2,400,729 | | | $ | (8,930,946 | ) | | $ | 411,153 | | | $ | 142,699 | | | $ | (119,402 | ) | | $ | (264,208 | ) | | $ | (230,546 | ) | | $ | (14,580,951 | ) | | | | | $ | (21,171,472 | ) |
| Basic and diluted net income per share | | $ | 24.01 | | | $ | (116.68 | ) | | $ | 411.15 | | | $ | 14.27 | | | $ | (11.94 | ) | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (9) | The unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations for New K Enter for the year ended December 31, 2023, combines the historical statements of operations of the Six Korean Entities for the year ended December 31, 2023 as converted to USD, with the historical audited statement of operations of K Enter for the period of January 4, 2023 (Inception) through December 31, 2023, as adjusted for conversion to IFRS (see also Note 4 — “IFRS Conversion and Presentation Alignment”). |
NOTES TO UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1 — Description of the Transactions
Proposed Transaction
Global Star has entered into the Merger Agreement, dated as of June 15, 2023, as amended on March 11, 2024, June 28, 2024, July 25, 2024 and December 11, 2024 (as it may be amended from time to time), which provides for a Business Combination between Global Star and K Enter. Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, the Business Combination will be effected in two steps: (i) subject to the approval and adoption of the Merger Agreement by the stockholders of Global Star, Global Star will reincorporate to Cayman Islands by merging with and into K Wave Media Ltd, a Cayman Islands exempted company and wholly owned subsidiary of Global Star (“PubCo”), with PubCo remaining as the surviving publicly traded entity (the “Reincorporation Merger”); (ii) one (1) business day following the Reincorporation Merger, GLST Merger Sub, Inc. (“Merger Sub”), a Delaware corporation and wholly owned subsidiary of PubCo, will be merged with and into K Enter, resulting in K Enter being a wholly owned subsidiary of PubCo (the “Acquisition Merger”). The Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger are collectively referred to herein as the “Business Combination.” On July 13, 2023, PubCo and Merger Sub executed a written joinder agreement to become parties to the Merger Agreement, accordingly, the Merger Agreement is by and among Global Star, PubCo, Merger Sub, and K Enter.
Upon the closing of the Reincorporation Merger, (i) each issued and outstanding share of common stock of Global Star, other than Global Star common stock owned by Global Star as treasury shares or any Global Star common stock owned by any direct or indirect wholly owned subsidiary of Global Star, will be converted into one ordinary share of PubCo (the “PubCo Ordinary Share”), (ii) each issued and outstanding warrant of Global Star will convert automatically into a warrant to purchase one PubCo Ordinary Share at a price of $11.50 per whole share (the “PubCo Warrant”), (iii) each issued and outstanding right of Global Star shall convert automatically into a right to receive one-tenth (1/10) of one PubCo Ordinary Share at the closing of a business combination (the “PubCo Right”), and (iv) each issued and outstanding unit of Global Star shall separate and convert automatically into one PubCo Ordinary Share, one PubCo Warrant, and one PubCo Right. At the closing of the Reincorporation Merger, all common stock, warrants, rights, units and other securities of Global Star shall cease to be outstanding and shall automatically be canceled and retired and shall cease to exist.
Upon the closing of the Acquisition Merger, (i) each share of K Enter capital stock, if any, that is owned by Global Star or Merger Sub (or any other subsidiary of Global Star) or K Enter (as treasury stock or otherwise), will automatically be cancelled and retired without any conversion, (ii) each share of K Enter preferred stock issued and outstanding shall be deemed converted into shares of K Enter common stock, (iii) each share of K Enter common stock issued and outstanding, including shares of K Enter common stock deemed outstanding as a result of the mandatory conversion of K Enter preferred stock, shall be converted into the right to receive a number of PubCo Ordinary Shares equal to the Conversion Ratio, and (iv) each share of Merger Sub common stock issued and outstanding shall be converted into and become one newly issued, fully paid and nonassessable share of K Enter common stock.
The total consideration for the Acquisition Merger is 59,000,000 newly issued PubCo Ordinary Shares, which have an estimated fair value at $10.00 per share (and, consequently, result in estimated consideration of $590,000,000) to K Enter and its shareholders. At the closing of the Acquisition Merger, the issued and outstanding shares in K Enter held by the former K Enter shareholders will be cancelled and cease to exist, in exchange for the issue of an aggregate of 59,000,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares. The actual fair value, which will be determined on the acquisition date, may be significantly different from the estimated New K Enter enterprise value disclosed herein and allocated to the respective entities as follows as a basis for the preparation of the pro forma financial statements:
| | | Play Company (1) | | | K Enter (2) | | | LAMP | | | Bidangil | | | Apeitda | | | Anseilen | | | Solaire Partners | | | Total | |
| Estimated fair value of common stock issued | | $ | 433,268,345 | | | $ | 92,622,072 | | | $ | 22,229,520 | | | $ | 14,819,658 | | | $ | 11,114,743 | | | $ | 5,593,694 | | | $ | 10,351,968 | | | $ | 590,000,000 | |
| Add: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proportionate share of non-controlling interest (3) | | | | | | | - | | | | 3,985,285 | | | | 4,088,106 | | | | 2,399,135 | | | | 1,343,826 | | | | 265,743 | | | | 12,082,095 | |
| Fair value of Earnout | | | | | | | 1,194,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,194,000 | |
| Contingent consideration payable | | | | | | | 5,972,887 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 5,972,887 | |
| Call option liability | | | | | | | 4,731,239 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,731,239 | |
| Cash to be paid | | | | | | | 26,323,551 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 26,323,551 | |
| Less: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Intangible assets identified | | | | | | | - | | | | 9,791,471 | | | | 7,841,262 | | | | 5,356,700 | | | | 4,008,621 | | | | 5,546,258 | | | | 32,544,312 | |
| Goodwill | | | | | | | 129,223,837 | | | | 18,081,572 | | | | 10,564,691 | | | | 8,617,685 | | | | 4,195,018 | | | | 5,302,859 | | | | 175,985,662 | |
| Net assets acquired (liabilities assumed) | | | | | | | 1,619,912 | | | | (1,658,238 | ) | | | 501,811 | | | | (460,507 | ) | | | (1,266,119 | ) | | | (231,406 | ) | | | | |
| (1) | Represents the estimated fair value of Play Company, the accounting acquirer, in accordance with the acquisition method of accounting under IFRS 3. As such, under the acquisition method, the net assets acquired of K Enter, the legal acquirer, will be recognized at their fair value, which approximates carrying value. |
| (2) | Represents the estimated fair value of K Enter, the legal acquirer, in which the acquisition will be accounted for in accordance with the acquisition method of accounting under IFRS 3, with Play Company considered to be the accounting acquirer of K Enter. |
| (3) | Proportionate share of non-controlling interest related to the net assets acquired/liabilities assumed of the respective entities based on the assumption that the Business Combination was consummated on June 30, 2024. |
For a description of the Business Combination and certain agreements executed in connection therewith, see “Summary of the Proxy Statement/Prospectus — The Business Combination and the Merger Agreement.”
Acquisition of the Six Korean Entities
K Enter expects to close the equity purchase for Play Company first and the acquisitions of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company closing subsequently, following the date this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 is declared effective by the SEC and before the closing of the Business Combination.
The acquisition of each of the Six Korean Entities by K Enter will be accounted for in accordance with the acquisition method of accounting under IFRS 3, with Play Company considered to be the acquirer of K Enter. As Play Company’s basis of accounting is IFRS, the combined K Enter – Play Company entity basis of accounting will be IFRS.
The acquisitions of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company by K Enter post the acquisition of Play Company will be accounted for in accordance with the acquisition method of accounting under IFRS 3, with K Enter post the acquisition of Play Company considered to be the acquirer of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company. As K Enter post the acquisition of Play Company basis of accounting is IFRS, New K Enter’s basis of accounting will be IFRS.
Under the acquisition method of accounting, the preliminary purchase price is allocated to the underlying tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their respective fair market values, with the excess purchase price, if any, allocated to goodwill. Costs related to the transaction are expensed as incurred. K Enter and Play Company are referred to as “New K Enter” in these unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements.
The Business Combination will be accounted for as a capital reorganization in accordance with IFRS 2 as Global Star does not meet the criteria to be determined a business under IFRS 3. Under this method of accounting, Global Star is treated as the acquired company for financial reporting purposes, and New K Enter is treated as the acquirer for financial statement reporting purposes.
Note 2 — Basis of Presentation and Accounting Policies
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information is for illustrative purposes only. The financial results may have been different had the companies always been combined. You should not rely on the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information as being indicative of the historical results that would have been achieved had the companies always been combined or the future results that PubCo will experience. New K Enter and Global Star have not had any historical relationship prior to the Business Combination. Accordingly, no pro forma adjustments were required to eliminate activities between the companies.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet and statements of operations reflects the acquisition of the Six Korean Entities that is expected to close following the date this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 is declared effective by the SEC and before the closing of the Business Combination as if it had occurred on June 30, 2024, and January 1, 2023, respectively.
The historical financial statements of the Six Korean Entities have been prepared in accordance with IFRS as issued by the IASB and in its presentation and functional currency of the Korean Republic Won (“KRW”). The historical financial statements of Global Star have been prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP and in its presentation and functional currency of the USD. The historical financial statements of K Enter have been prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP and in its presentation currency of USD. The historical financial statements of K Wave Media Ltd have been prepared in accordance with IFRS and in its presentation currency of USD. The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information reflects IFRS, the basis of accounting that will be used by PubCo. Global Star’s and K Enter’s historical financial statements have been converted from U.S. GAAP to IFRS to align with the basis of accounting that will be used by PubCo. See Note 4 – IFRS Conversion and Presentation Alignment.
The historical financial statements of the Six Korean Entities have been translated into and are presented in USD using the following exchange rates:
| | ● | at the period exchange rate as of June 30, 2024 of US$1.00 to KRW$1,376.55 for the balance sheet; |
| | | |
| | ● | the average exchange rate for the six months ended June 30, 2024 of US$1.00 to KRW$1,350.04 for the statement of operations for the period ending on the date; and |
| | | |
| | ● | the average exchange rate for the year ended December 31, 2023 of US$1.00 to KRW$1,306.764 for the statement of operations for the period ending on that date; |
Frist Extension
On August 22, 2023, Global Star held an extraordinary general meeting, at which Global Star’s stockholders approved First Amendment to the Charter extending the date by which Global Star had to complete a Business Combination from September 22, 2023 to June 22, 2024, provided the Sponsor or its designees deposit into the Trust Account an amount equal to $125,000, prior to the commencement of each extension period. Global Star filed the First Amendment to the Charter with the Office of the Secretary of State of Delaware on August 28, 2023, a copy of which is attached as Exhibit 3.4 to this report and is incorporated by reference herein. In connection with the approval of the extension, stockholders elected to redeem an aggregate of 4,052,066 shares of Class A Common Stock (the “August Redemptions”). As a result, an aggregate of approximately $42.7 million, or approximately $10.53 per share, was released from the Trust Account to pay such stockholders. In addition, the Global Star stockholders also approved the Charter Amendment to eliminate from the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation (the “GLST Charter”) the limitation that the Company shall not redeem Public Shares to the extent that such redemptions would cause the Company’s net tangible assets to be less than $5,000,001.
Second Extension
On June 11, 2024, Global Star held a Special Meeting of Stockholders (the “Meeting”). At the Meeting, Global Star’s stockholders approved the Second Amendment to the Charter, which extends the date by which Global Star must consummate its initial business combination from June 22, 2024 to December 22, 2024, subject to the approval of the Board of Directors of Global Star (the “Board”), provided the sponsor or its designees deposit into the trust account a monthly amount equal to the lesser of $60,000 or $0.02 per outstanding share of common stock sold in the IPO, prior to the commencement of each extension period (the “Extension”). Global Star filed the Second Amendment to the Charter with the Office of the Secretary of State of Delaware on June 14, 2024, a copy of which is attached as Exhibit 3.5 to this report and is incorporated by reference herein. At the Meeting, Stockholders holding 4,010,928 shares of common stock exercised their right to redeem their shares for cash at a price of approximately $11.17 per share of the funds in the Trust Account. As a result, an aggregate of $44,464,316, net of interest withdrawn for taxes of $350,301, was removed from the Trust Account to pay such holders. Following the redemption, Global Star’s remaining shares of GLST Class A Common Stock outstanding were 1,137,006. Global Star has disclosed further details of the Meeting in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC on June 17, 2024.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, Global Star deposited $125,000 into the Trust Account for each one-month extension to extend the SPAC Term from September 22, 2023, to December 22, 2023. Following December 31, 2023, Global Star deposited $125,000 into the Trust account on January 17, 2024, February 15, 2024, March 15, 2024, April 19, 2024 and May 21, 2024, to extend the SPAC Term to June 22, 2024. On June 18, 2024, Global Star deposited $22,740 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to July 22, 2024. On July 17, 2024, Global Star deposited $22,740 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to August 22, 2024. On August 19, 2024, Global Star deposited $22,740 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to September 22, 2024. On September 17, 2024, Global Star deposited $22,740 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to October 22, 2024. On October 17, 2024, Global Star deposited $22,740 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to November 22, 2024. On November 18, 2024, Global Star deposited $22,740 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to December 22, 2024.
Third Extension
On November 27, 2024, Global Star held a Special Meeting of its Stockholders (the “Meeting”). At the Meeting, Global Star’s stockholders approved the Charter Amendment which extends the date by which Global Star must consummate its initial business combination from December 22, 2024 to June 22, 2025, subject to the approval of the Board of Directors of Global Star (the “Board”) provided the sponsor or its designees deposit into the trust account the lesser of (i) $60,000 or (ii) $0.02 per share for each public share that is not redeemed in connection with the Meeting, prior to the commencement of each extension period. At the Meeting shareholders holding 756,131 shares of common stock exercised their right to redeem their shares for cash at a price of approximately $11.39 per share of the funds in the Trust Account. As a result an aggregate of $8,613,436, net of interest withdrawn for taxes of $110,751, was removed from the Trust Account to pay such holders. Following the redemption, Global Star’s remaining shares of GLST Class A Common Stock outstanding were 380,875. Global Star has disclosed further details of the Meeting in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC on November 27, 2024. On December 4, 2024, Global Star deposited $7,617.50 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to January 22, 2025. On December 12, 2024, Global Star deposited $7,617.50 into the Trust, to extend the SPAC Term to February 22, 2025.
Convertible Senior Unsecured Notes
In June 2024, K Enter issued two convertible senior unsecured notes (the “Notes”) in the aggregate amount of $4,500,000. The Notes have a maturity date of 3 years and will pay an annual coupon rate of 3% to be paid semi-annually until the maturity date of the Notes.
Under one Note (the “$1.5MM Note”), which is in the principal amount of $1,500,000, the proceeds shall be wired to K Enter as follows:
| (1) | 25% of the committed amount at the time of signing this definitive agreement, |
| (2) | 25% at the time SEC declares effectiveness on the F-4, and; |
| (3) | the remaining 50% at the time of shareholder approval and going public. |
Under the other Note (the “$3MM Note”), which is in the principal amount of $3,000,000, the proceeds shall be wired to K Enter as follows:
| | (1) | 25% of the committed amount at the time of signing this definitive agreement, |
| | | |
| | (2) | 50% at the time SEC declares effectiveness on the F-4, and |
| | | |
| | (3) | the remaining 25% at the time of shareholder approval and going public. |
From the time K Enter purchases the Note and until De-SPAC the Note will be convertible at a conversion price per share of USD $1,200 per share. The Post-Merger Conversion Prices shall be adjusted to the greater of the following:
| ● | 60% discount to the 5-day average of the volume-weighted average prices of ordinary shares over 5 consecutive trading days following the conversion notice date; |
| ● | and Floor price of $4 per share. |
As of June 5, 2024, K Enter has drawn 25% of the committed amounts on the Notes for an aggregate amount of $1,125,000. On October 3, 2024, K Enter received $300,000 pursuant to the $3MM Note and on October 18, 2024, K Enter received $1,20,000 pursuant to the $3MM Note. The accompanying unaudited pro forma balance sheet presents the total proceeds of the Notes in the aggregate amount of $4,500,000 as if the closing of the Business Combination had occurred on June 30, 2024.
Global Star has elected to provide the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information under two different redemption scenarios of Global Star public stock into cash as more fully described below:
| | ● | Scenario 1 — Assuming Additional No Redemptions: This presentation assumes that, after the August Redemptions, the June Redemptions, and the November Redemptions, no public stockholders of Global Star exercise redemption rights with respect to their Class A Common Stock upon consummation of the Business Combination. |
| | ● | Scenario 2 — Assuming Maximum Redemptions: This presentation assumes that Global Star public stockholders holding 380,875 shares of Global Star Class A Common Stock will exercise their redemption rights for $4.3 million upon consummation of the Business Combination at a redemption price of approximately $11.41 per share, as of December 5, 2024 subject to reduction for the payment of taxes. The maximum redemption amount reflects the maximum number of Global Star’s Class A Common Stock that can be redeemed. This scenario includes all adjustments contained in the “no additional redemptions” scenario and presents additional adjustments to reflect the effect of the maximum redemptions. |
The following summarizes the pro forma shares of K Wave ordinary shares issued and outstanding immediately after the Business Combination, presented under the two scenarios listed above:
| | | No Additional
Redemptions | | | Maximum
Redemptions | |
| Pro Forma Ownership | | Number of
Shares | | | Percent
Outstanding | | | Number of
Shares | | | Percent
Outstanding | |
| K Enter stockholders(1) | | | 59,160,000 | | | | 93.1 | % | | | 59,160,000 | | | | 93.7 | % |
| Global Star public stockholders(2)(4) | | | 1,300,875 | | | | 2.1 | % | | | 920,000 | | | | 1.4 | % |
| Sponsor and Initial Stockholders(3) | | | 2,943,747 | | | | 4.6 | % | | | 2,943,747 | | | | 4.7 | % |
| Representative Shares | | | 115,000 | | | | 0.2 | % | | | 115,000 | | | | 0.2 | % |
| Total shares outstanding(4) | | | 63,519,622 | | | | | | | | 63,138,747 | | | | | |
| (1) | Includes 59,000,000 K Wave Ordinary Shares to be issued upon consummation of the Business Combination as follows: (i) 30,878,682 K Wave Ordinary shares issued in exchange for 101,202 shares of K Enter common stock owned by the currently existing stockholders of K Enter, including, the 4,997 shares of K Enter common stock owned by GF Korea and the 1,202 shares of K Enter common stock owned by Lodestar USA; (ii) 12,448,256 K Wave Ordinary shares issued in exchange for 40,798 shares of K Enter common stock owned by the Preferred Stock owners after the conversion of the 40,798 shares of Preferred Stock into shares of K Enter common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination and (iii) 15,673,062 K Wave Ordinary shares to be issued in exchange for 51,367 shares of K Enter common stock that will be owned by the owners of Six Korean Entities following K Enter acquisition of the controlling equity interests in the Six Korean Entities and 160,000 K Wave Ordinary shares to be issued in exchange 160,000 shares of Global Star Founder Shares currently owned by K Enter. |
| (2) | Includes 9,200,000 public shares at June 30, 2024 less 4,052,066 shares redeemed in September 2023, 4,010,928 shares redeemed in June 2024, and 756,131 shares redeemed in November 2024, plus 9,200,000 Public Rights automatically converted into 920,000 shares of common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination. |
| (3) | Includes (a) 1,640,000 Founder Shares owned by the Sponsor as of June 30, 2024, (b) 498,225 shares underlying the Private Units as of June 30, 2024 plus 498,225 Private Rights automatically converted into 49,822 shares of common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination owned by the Sponsor, (c) 240,700 shares of common stock underlying the Convertible Note plus 240,700 Convertible Note Rights automatically converted into 24,070 shares of common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination owned by the Sponsor and (d) 500,000 Founder Shares owned by the Initial Stockholders as of June 30, 2024. |
| (4) | Excludes 19,300 shares potentially to be issued to the Sponsor if an additional $193,000 were to be drawn on the Global Star and converted into Global Star Class B common stock. Accordingly, K Wave is registering up to an aggregate amount of 64,295,053 Ordinary Shares to be issued in connection with Business Combination on this proxy statement/prospectus. |
The pro forma adjustments do not have an income tax effect as they are either (i) incurred by legal entities that are not subject to a corporate income tax, or (ii) permanently non-deductible or non-taxable based on the laws of the relevant jurisdiction.
The share amounts and ownership percentages set forth above are not indicative of voting percentages and do not take into account GLST Warrants that will remain outstanding immediately following the Business Combination and may be exercised thereafter.
Upon consummation of the Business Combination, management will perform a comprehensive review of the entity’s accounting policies. As a result of the review, management may identify differences between the accounting policies of the entities which, when conformed, could have a material impact on the financial statements of the post-combination company. Management did not identify any differences that would have a material impact on the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information. As a result, the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information does not assume any differences in accounting policies.
Note 3 — Accounting for the Transactions
The Business Combination is accounted for as a capital reorganization in accordance with IFRS 2. Under this method of accounting, Global Star is treated as the “acquired” company for financial reporting purposes and New K Enter is treated as the acquirer for financial statement reporting purposes. This determination was primarily based on the assumption that:
| | ● | New K Enter’s existing stockholders will hold a majority of the voting rights of PubCo post Business Combination under the No Additional Redemption Scenario and Maximum Redemption Scenario; |
| | | |
| | ● | By virtue of such estimated voting interest upon the Closing, New K Enter’s existing stockholders will have the ability to control decisions regarding the election and removal of directors and officers of New K Enter following the Closing; |
| | ● | New K Enter will have control over the Board; |
| | ● | New K Enter’s operations will substantially comprise the ongoing operations of PubCo; |
| ● | New K Enter is the larger entity in terms of substantive operations and employee base; and |
| | ● | New K Enter’s senior management will comprise the senior management of PubCo. |
Another determining factor was that Global Star does not meet the definition of a “business” pursuant to IFRS 3, and thus, for accounting purposes, the Business Combination will be accounted for as a capital reorganization within the scope of IFRS 2, where New K Enter issues stock for the net assets of Global Star. The net assets of Global Star are stated at historical cost, with no goodwill or intangible assets recorded. Any excess of the fair value of shares issued to Global Star over the fair value of Global Star’s identifiable net assets acquired represents compensation for the service of a stock exchange listing for its shares and is expensed as incurred.
The acquisition of Play Company by K Enter will be accounted for in accordance with the acquisition method of accounting under IFRS 3, with Play Company considered to be the acquirer of K Enter for financial reporting purposes. As Play Company’s basis of accounting is IFRS, K Enter’s basis of accounting (following the acquisition of Play Company) will be IFRS.
The acquisitions of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company by K Enter will also be accounted for in accordance with the acquisition method of accounting under IFRS 3, with K Enter (following the acquisition of Play Company, its predecessor) considered to be the acquirer of each of the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company. New K Enter’s basis of accounting will be IFRS, consistent with that of its predecessor, Play Company.
The overall impact of the accounting conclusions set out above will be that the financial statements of Play Company will become those of K-Enter post-consummation and will not experience a change in basis as a result of the application of the acquisition method while each of K Enter and the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company will experience a change in basis as a result of the application of the acquisition method and will be reflected in the consolidated financial statements of Play Company on a prospective basis post-consummation.
This determination was primarily based on the assumption that:
| ● | Play Company’s existing stockholders will hold a large minority voting interest in New K Enter where no other owner has a significant voting interest; |
| ● | Play Company’s CEO has the ability to appoint a majority of directors of New K Enter’s board of directors; |
| | ● | Play Company’s CEO has the ability to appoint the senior management of New K Enter; |
| ● | Play Company’s operations will substantially comprise the ongoing operations of New K Enter; and |
| ● | Play Company is the larger entity in terms of substantive operations and employee base. |
Under the acquisition method of accounting, the preliminary purchase price is allocated to the underlying tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their respective fair market values, with the excess purchase price, if any, allocated to goodwill. Costs related to the transaction are expensed as incurred.
Note 4 — IFRS Conversion and Presentation Alignment
The historical financial information of Global Star has been adjusted to give effect to the differences between U.S. GAAP and IFRS as issued by the IASB for the purposes of the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information. Two adjustments required to convert Global Star’s financial statements from U.S. GAAP to IFRS for purposes of the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information were to (i) reclassify Global Star Class A Common Stock subject to redemption to non-current financial liabilities under IFRS 2, as stockholders have the right to require Global Star to redeem the common stock and Global Star has an irrevocable obligation to deliver cash or another financial instrument for such redemption, and (ii) reclassify GLST Warrants from equity (under U.S. GAAP) to non-current financial liabilities under IAS 32 measured at fair value through profit or loss, due to the “cashless” settlement provisions in the warrant agreement.
There were no adjustments required to adjust the historical financial information of K Enter to give effect to the differences between U.S. GAAP and IFRS as issued by the IASB for the purposes of the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information.
Further, as part of the preparation of the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information, certain reclassifications were made to align Global Star’s historical financial information and K Enter’s historical financial information in accordance with the presentation of Play Company’s historical financial information.
BALANCE SHEET
FOR GLOBAL STAR
AS OF JUNE 30, 2024
| | | Global Star
(US GAAP
Historical) | | | IFRS Conversion
and Presentation
Alignment | | | Global Star
(IFRS
Historical) | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 1,353,525 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 1,353,525 | |
| Other current assets | | | 49,818 | | | | - | | | | 49,818 | |
| Total current assets | | | 1,403,343 | | | | - | | | | 1,403,343 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Investments held in Trust Account | | | 12,686,133 | | | | - | | | | 12,686,133 | |
| Total non-current assets | | | 12,686,133 | | | | - | | | | 12,686,133 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total assets | | $ | 14,089,476 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 14,089,476 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | | - | | | | 1,393,590 | | | | 1,393,590 | |
| Promissory note - related party | | | 2,311,000 | | | | - | | | | 2,311,000 | |
| Excise tax payable attributable to redemption of common stock | | | 872,861 | | | | - | | | | 872,861 | |
| Current tax liabilities | | | 1,082,528 | | | | - | | | | 1,082,528 | |
| Due to Sponsor | | | 15,094 | | | | - | | | | 15,094 | |
| Accrued franchise tax payable | | | 136,713 | | | | - | | | | 136,713 | |
| Accrued expenses | | | 1,393,590 | | | | (1,393,590 | ) | | | - | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 5,811,786 | | | | - | | | | 5,811,786 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Deferred underwriting commissions | | | 3,220,000 | | | | - | | | | 3,220,000 | |
| Warrant liabilities | | | - | | | | 240,516 | | | | 240,516 | |
| Class A common stock subject to possible redemption | | | - | | | | 12,684,975 | | | | 12,684,975 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | 3,220,000 | | | | 12,925,491 | | | | 16,145,491 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total liabilities | | | 9,031,786 | | | | 12,925,491 | | | | 21,957,277 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Class A common stock subject to possible redemption | | | 12,684,975 | | | | (12,684,975 | ) | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EQUITY | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Global Star preferred stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Global Star Class A common stock | | | 62 | | | | - | | | | 62 | |
| Global Star Class B common stock | | | 230 | | | | - | | | | 230 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Retained earnings (Accumulated deficit) | | | (7,627,577 | ) | | | (240,516 | ) | | | (7,868,093 | ) |
| Total stockholders’ equity | | | (7,627,285 | ) | | | (240,516 | ) | | | (7,867,801 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total equity and liabilities | | $ | 14,089,476 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 14,089,476 | |
| (1) | IFRS Conversion |
| (2) | Presentation Alignment |
STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS
FOR GLOBAL STAR
FOR THE SIX MONTHS ENDED JUNE 30, 2024
| | | Global Star
(US GAAP
Historical) | | | IFRS Conversion
and Presentation
Alignment | | | Global Star
(IFRS
Historical) | |
| Operating expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operational costs | | | (1,452,062 | ) | | | - | | | | (1,452,062 | ) |
| Total operating expenses | | | (1,452,062 | ) | | | - | | | | (1,452,062 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss from operations | | | (1,452,062 | ) | | | - | | | | (1,452,062 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other income (expense) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Change in fair value of over-allotment liability | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Change in fair value of warrant liability | | | - | | | | (143,534 | ) | | | (143,534 | ) |
| Interest income | | | 10,354 | | | | - | | | | 10,354 | |
| Interest income on marketable securities held in Trust Account | | | 1,431,156 | | | | - | | | | 1,431,156 | |
| Net income before taxes | | | (10,552 | ) | | | (143,534 | ) | | | (154,086 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | �� |
| Provision for taxes | | | (286,463 | ) | | | - | | | | (286,463 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | $ | (297,015 | ) | | $ | (143,534 | ) | | $ | (440,549 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted net income per share, redeemable Class A common stock | | $ | (0.04 | ) | | | | | | $ | (0.06 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted net income per share, Class B common stock | | $ | (0.04 | ) | | | | | | $ | (0.06 | ) |
STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS
FOR GLOBAL STAR
FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2023
| | | Global Star
(US GAAP
Historical) | | | IFRS Conversion
and Presentation
Alignment | | | Global Star
(IFRS
Historical) | |
| Operating expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operational costs | | | (2,126,947 | ) | | | - | | | | (2,126,947 | ) |
| Total operating expenses | | | (2,126,947 | ) | | | - | | | | (2,126,947 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss from operations | | | (2,126,947 | ) | | | - | | | | (2,126,947 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other income (expense) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Change in fair value of over-allotment liability | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Change in fair value of warrant liability | | | - | | | | 239,546 | | | | 239,546 | |
| Interest income | | | 23,833 | | | | - | | | | 23,833 | |
| Interest income on marketable securities held in Trust Account | | | 3,942,920 | | | | - | | | | 3,942,920 | |
| Net income before taxes | | | 1,839,806 | | | | 239,546 | | | | 2,079,352 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Provision for taxes | | | (795,729 | ) | | | - | | | | (795,729 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | $ | 1,044,077 | | | $ | 239,546 | | | $ | 1,283,623 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted net income per share, redeemable Class A common stock | | $ | 0.10 | | | | | | | $ | 0.12 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted net income per share, Class B common stock | | $ | 0.10 | | | | | | | $ | 0.12 | |
BALANCE SHEET
FOR K ENTER
AS OF JUNE 30, 2024
| | | K Enter
(US GAAP
Historical) | | | IFRS Conversion
and Presentation
Alignment | | | K Enter
(IFRS
Historical) | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 438,842 | | | | - | | | | 438,842 | |
| Accounts receivable | | | 6,974 | | | | - | | | | 6,974 | |
| Other receivables | | | 20,574 | | | | - | | | | 20,574 | |
| Convertible debt security | | | 1,027,027 | | | | - | | | | 1,027,027 | |
| Deferred transaction costs | | | 1,879,509 | | | | - | | | | 1,879,509 | |
| Preferred stock subscription receivable | | | - | | | | 369,000 | | | | 369,000 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | | 368,029 | | | | - | | | | 368,029 | |
| Total current assets | | | 3,740,955 | | | | 369,000 | | | | 4,109,955 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Investment in equity securities | | | 1,600,000 | | | | - | | | | 1,600,000 | |
| Investment in equity securities - related party | | | 1,264,756 | | | | - | | | | 1,264,756 | |
| Property, plant and equipment, net | | | 29,911 | | | | - | | | | 29,911 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets, net | | | 55,737 | | | | - | | | | 55,737 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets, net - related party | | | 44,692 | | | | - | | | | 44,692 | |
| Other non-current assets | | | 1,916,749 | | | | - | | | | 1,916,749 | |
| Other non-current assets - related party | | | 72,682 | | | | - | | | | 72,682 | |
| Total non-current assets | | | 4,984,527 | | | | - | | | | 4,984,527 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total assets | | $ | 8,725,482 | | | $ | 369,000 | | | $ | 9,094,482 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | | - | | | | 4,555,995 | | | | 4,555,995 | |
| Trade and other payables - related party | | | | | | | 1,278,144 | | | | 1,278,144 | |
| Accounts payable | | | 1,137,490 | | | | (1,137,490 | ) | | | - | |
| Accounts payable - related party | | | 1,278,144 | | | | (1,278,144 | ) | | | - | |
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | | | 3,418,505 | | | | (3,418,505 | ) | | | - | |
| Short-term borrowings | | | 405 | | | | | | | | 405 | |
| Short-term borrowings - related party | | | 411,791 | | | | | | | | 411,791 | |
| Defined severance benefits, current | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Lease liability, current | | | 53,368 | | | | - | | | | 53,368 | |
| Lease liability, current - related party | | | 44,692 | | | | - | | | | 44,692 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 6,344,395 | | | | - | | | | 6,344,395 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Defined severance benefits, non-current | | | 994,465 | | | | - | | | | 994,465 | |
| Derivative liabilities | | | 135,710 | | | | - | | | | 135,710 | |
| Lease liability, non-current | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Lease liability, non-current - related party | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total liabilities | | | 7,474,570 | | | | - | | | | 7,474,570 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Equity | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Series A-1 convertible preferred stock | | | - | | | | | | | | | |
| Series A convertible preferred stock | | | 355 | | | | - | | | | 355 | |
| Common stock | | | 1,000 | | | | - | | | | 1,000 | |
| Treasury stock | | | (57 | ) | | | - | | | | (57 | ) |
| Preferred stock subscription receivable | | | (369,000 | ) | | | 369,000 | | | | - | |
| Additional paid-in capital | | | 15,238,711 | | | | - | | | | 15,238,711 | |
| Accumulated deficit | | | (13,524,711 | ) | | | (1,647 | ) | | | (13,526,358 | ) |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income | | | (95,386 | ) | | | 1,647 | | | | (93,739 | ) |
| Total stockholders’ equity | | | 1,250,912 | | | | 369,000 | | | | 1,619,912 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | $ | 8,725,482 | | | $ | 369,000 | | | $ | 9,094,482 | |
| (2) | Presentation Alignment |
STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS
FOR K ENTER
FOR THE SIX MONTHS ENDED JUNE 30, 2024
| | | K Enter
(US GAAP
Historical) | | | IFRS Conversion
and Presentation
Alignment | | | K Enter
(IFRS
Historical) | |
| Revenue | | | 366,533 | | | | - | | | | 366,533 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cost of revenue | | | (261,546 | ) | | | | | | | (261,546 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 104,987 | | | | - | | | | 104,987 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | (4,712,937 | ) | | | - | | | | (4,712,937 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating income (loss) | | | (4,607,950 | ) | | | - | | | | (4,607,950 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other income (expense) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income (expense), net | | | 344 | | | | - | | | | 344 | |
| Other income (expense), net | | | 13,841 | | | | - | | | | 13,841 | |
| Total other expense | | | 14,185 | | | | - | | | | 14,185 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Provision for taxes | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | | | (4,593,765 | ) | | | - | | | | (4,593,765 | ) |
STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS
FOR K ENTER
FOR THE PERIOD FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) THROUGH DECEMBER 31, 2023
| | | K Enter
(US GAAP
Historical) | | | IFRS
Conversion
and
Presentation
Alignment | | | K Enter
(IFRS
Historical) | |
| Revenue | | | 208,704 | | | | - | | | | 208,704 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cost of revenue | | | (207,153 | ) | | | | | | | (207,153 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 1,551 | | | | - | | | | 1,551 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | (8,954,316 | ) | | | - | | | | (8,954,316 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating income (loss) | | | (8,952,765 | ) | | | - | | | | (8,952,765 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other income (expense) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income (expense), net | | | 7,956 | | | | - | | | | 7,956 | |
| Other income (expense), net | | | 13,863 | | | | - | | | | 13,863 | |
| Total other expense | | | 21,819 | | | | - | | | | 21,819 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Provision for taxes | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | | | (8,930,946 | ) | | | - | | | | (8,930,946 | ) |
Note 5 — Adjustments and Reclassifications to Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Balance Sheet as of December 31, 2023
The pro forma adjustments to the unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet as of June 30, 2024, are as follows:
| | A. | Reflects the allocation, on a preliminary basis, of the cost associated with the acquisition of K Enter and the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company as if the acquisition had occurred on June 30, 2024. Play Company was determined to be the accounting acquirer under IFRS 3. The final allocation of the purchase consideration will be determined after the completion of a thorough analysis to determine the fair value of all assets acquired and liabilities assumed, but in no event later than one year following the completion of the transaction. Accordingly, the final acquisition accounting adjustments could differ materially from the unaudited pro forma adjustments presented herein. Any increase or decrease in the fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed, as compared to the information shown herein, could also change the portion of the purchase consideration allocable to goodwill and could impact the operating results of New K Enter due to differences in the allocation of the purchase consideration, depreciation and amortization related to some of these assets and liabilities. The preliminary allocation of the purchase price is as follows: |
| | | K Enter | | | LAMP | | | Bidangil | | | Apeitda | | | Anseilen | | | Solaire Partners | | | Total | |
| Estimated fair value of common stock issued (51,367 shares) | | $ | 92,622,072 | | | $ | 22,229,521 | | | $ | 14,819,658 | | | $ | 11,114,743 | | | $ | 5,593,694 | | | $ | 10,351,967 | | | $ | 156,731,655 | |
| Fair value of Earnout(b) | | | 1,194,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,194,000 | |
| Contingent consideration payable(e) | | | 5,972,887 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 5,972,887 | |
| Call option liability(c) | | | 4,731,239 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,731,239 | |
| Proportionate share of non-controlling interest(k) | | | - | | | | 3,985,285 | | | | 4,088,106 | | | | 2,399,135 | | | | 1,343,826 | | | | 265,743 | | | | 12,082,094 | |
| Cash to be paid(d) | | | 26,323,551 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 26,323,551 | |
| Total consideration | | | 130,843,749 | | | | 26,214,806 | | | | 18,907,764 | | | | 13,513,878 | | | | 6,937,520 | | | | 10,617,710 | | | | 207,035,426 | |
| Allocated to: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash | | $ | 438,842 | | | $ | 1,271,372 | | | $ | 1,280,687 | | | $ | 346,532 | | | $ | 161,158 | | | $ | 66,758 | | | $ | 3,565,349 | |
| Accounts receivable - trade | | | 6,974 | | | | 839,555 | | | | 232 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 273,520 | | | | 1,120,281 | |
| Value added tax receivable | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,631 | | | | 36,323 | | | | - | | | | 37,954 | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Short-term investment securities | | | - | | | | - | | | | 726,955 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 726,955 | |
| Other receivables, contract assets and current assets | | | 388,603 | | | | 1,894,560 | | | | 1,109,508 | | | | 1,707 | | | | 44 | | | | 1,576,765 | | | | 4,971,187 | |
| Short-term loans, net | | | - | | | | - | | | | 98,071 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 98,071 | |
| Property, plant and equipment, net | | | 29,911 | | | | 80,700 | | | | 66,778 | | | | 191,829 | | | | 610 | | | | 39,878 | | | | 409,706 | |
| Long-term loans, net | | | - | | | | 94,491 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 94,491 | |
| Convertible debt security | | | 1,027,027 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,027,027 | |
| Deferred transaction costs | | | 1,879,509 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,879,509 | |
| Preferred stock subscription receivable | | | 369,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 369,000 | |
| Long-term investment securities | | | - | | | | 581,163 | | | | - | | | | 56,297 | | | | 21,794 | | | | 147,470 | | | | 806,724 | |
| Investments in associates and joint ventures | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 441,751 | | | | 441,751 | |
| Investment in equity securities | | | 1,600,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,600,000 | |
| Investment in equity securities - related parties | | | 1,264,756 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,264,756 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets, net | | | 55,737 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 55,737 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets, related party | | | 44,692 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 44,692 | |
| Other non-current assets | | | 1,916,749 | | | | 1,137,353 | | | | 490,840 | | | | 296,323 | | | | 382,841 | | | | 49,668 | | | | 4,273,774 | |
| Other non-curent assets, related party | | | 72,682 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 72,682 | |
| Accounts payable, accrued expenses, contract liabilities and other current liabilities | | | (4,555,995 | ) | | | (3,367,271 | ) | | | (1,466,151 | ) | | | (13,881 | ) | | | (15,195 | ) | | | (1,308,853 | ) | | | (10,727,346 | ) |
| Accounts payable - related party | | | (1,278,144 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (1,278,144 | ) |
| Current portion of long-term borrowings | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (14,529 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (14,529 | ) |
| Lease liability, current | | | (53,368 | ) | | | (18,960 | ) | | | (61,653 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (94,699 | ) | | | (228,680 | ) |
| Short term borrowings | | | (405 | ) | | | (1,071,519 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (1,071,924 | ) |
| Short-term borrowings - related party | | | (411,791 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (411,791 | ) |
| Other current financial liabilities | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (66,458 | ) | | | (66,458 | ) |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | - | | | | (114,698 | ) | | | (10,557 | ) | | | (94,845 | ) | | | (21,570 | ) | | | (17,086 | ) | | | (258,756 | ) |
| Current tax liability | | | - | | | | (32,542 | ) | | | (86,214 | ) | | | (3,271 | ) | | | - | | | | (148,439 | ) | | | (270,466 | ) |
| Redeemable convertible preference shares | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Lease liability - related party | | | (44,692 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (44,692 | ) |
| Other non-current liabilities, contract liabilities, and provisions | | | - | | | | (653,808 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (908,067 | ) | | | (9,501 | ) | | | (1,571,376 | ) |
| Other non-current financial liabilities | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Long-term borrowings | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | | - | | | | (202,217 | ) | | | - | | | | (108,750 | ) | | | (86,255 | ) | | | (23,013 | ) | | | (420,235 | ) |
| Derivative liabilities | | | (135,710 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (135,710 | ) |
| Defined severance benefits non-current | | | (994,465 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (994,465 | ) |
| Lease liability, non-current | | | - | | | | (49,998 | ) | | | (7,861 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (57,859 | ) |
| Long-term lease liability, related party | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Deferred tax liability(j) | | | - | | | | (2,046,419 | ) | | | (1,638,824 | ) | | | (1,119,550 | ) | | | (837,802 | ) | | | (1,159,167 | ) | | | (6,801,762 | ) |
| Net assets acquired (liabilities assumed) | | | 1,619,912 | | | | (1,658,238 | ) | | | 501,811 | | | | (460,507 | ) | | | (1,266,119 | ) | | | (231,406 | ) | | | (1,494,547 | ) |
| Excess of purchase price over net tangible assets acquired, aggregate fair value purchase consideration, non-controlling interest, and net liabilities assumed before allocation to identifiable intangible assets and goodwill | | $ | 129,223,837 | | | $ | 27,873,044 | | | $ | 18,405,953 | | | $ | 13,974,385 | | | $ | 8,203,639 | | | $ | 10,849,116 | | | $ | 208,529,973 | |
Management made an initial determination that approximately $32.5 million of the excess of the purchase price over the net assets acquired (liabilities assumed), non-controlling interest, and aggregate fair value purchase consideration should be allocated to identifiable intangible assets. The unidentified excess of the purchase price over the fair value of the net assets acquired has been recorded as goodwill.
| | (a) | The Six Korean Entities will be issued an estimated aggregate 51,367 shares of K Enter common stock, par value $0.0001, at a value of approximately $3,051 per share. The price per share was calculated as follows: |
| | Estimated New K Enter enterprise value* | | $ | 590,000,000 | |
| | Total expected shares of K Enter common stock to be issued** | | | 193,367 | |
| | Value per share of K Enter common stock | | $ | 3,051 | |
| * | The estimated New K Enter enterprise value is based on an assumed share price of PubCo’s Ordinary Shares of $10.00 per share. The actual fair value, which will be determined on the acquisition date, may be significantly different from the estimated New K Enter enterprise value disclosed herein and allocated to the respective entities as follows as a basis for the preparation of the pro forma financial statement: |
| | | Enterprise
Value | |
| Existing K Enter Shareholders | | $ | 433,268,345 | |
| Play Company | | | 92,622,072 | |
| Lamp | | | 22,229,521 | |
| Bidangil | | | 14,819,658 | |
| Apeitda | | | 11,114,743 | |
| Anseilen | | | 5,593,694 | |
| Solaire Partners | | | 10,351,967 | |
| Total | | $ | 590,000,000 | |
| ** | The number of total expected shares of K Enter stock to be issued is derived by adding the expected 51,367 shares of K Enter Common Stock to be issued to the sellers of the Six Korean Entities in connection with the closing of the six executed share purchase agreements, as amended plus the 40,798 shares of K Enter Common Stock to be issued to the holders of K Enter’s Series A Preferred Stock and K Enter’s Series A-1 Preferred Stock, upon conversion of such shares of preferred stock to K Enter Common Stock upon the closing of the Business Combination, plus the existing 101,202 shares of K Enter Common Stock held by the current stockholders of K Enter as of the state of the proxy statement/prospectus. |
| | (b) | The Earnout was determined to be part of the business combination (i.e., consideration) and therefore in accordance with IFRS 3, such contingent consideration will be measured at fair value at the acquisition date and included within the calculation of goodwill. The liability-classified arrangement is recorded at fair value at initial recognition; measurement is updated at each reporting date, with changes recognized in the income statement each reporting period until the arrangement is settled or derecognized. The terms of the Earnout state that depending on the achievement by Play Company of the annual average net profit for Fiscal Years 2023 to 2025, New K Enter shall make additional payments to the Seller as follows: (1) if the average net profit for the said years is less than 75% (KRW 12.105 billion) of the target amount separately agreed between the Parties (KRW 16.14 billion) or exceeds 125% of the said target amount (KRW 20.175 billion), New K Enter shall pay to the Seller in cash (KRW) on January 31, 2027 and January 31, 2028 (the “Payment Date”, respectively) an amount calculated by multiplying the achieved percentage based on the annual average net profit for Fiscal Years 2023 to 2025 by KRW 9.05 billion and (ii) if the average net profit for the said years is no less than 75% of the target amount (KRW 12.105 billion) and no greater than 125% of the target amount (KRW 20.175 billion) New K Enter shall pay KRW 9.05 billion to the Seller on each Payment Date. Each payment above shall be deemed as an adjustment to the Purchase Price. The Earnout was valued with a Monte Carlo Model simulation. The fair value was the discounted cash flow from the date of payment. The net profit was assumed to grow at a specified industry growth rate and fluctuate with the projected earnings volatility. The projected earnings volatility was based upon guideline public companies. |
| | (c) | In accordance with IAS 32 and IFRS 9, the call option liability is representative of a financial liability to potentially issue equity shares and/or transfer assets of the combined entity; therefore, the call option liability will be measured at fair value at the acquisition date and included within the calculation of goodwill. The liability-classified arrangement is recorded at fair value at initial recognition; measurement is updated at each reporting date, with changes recognized in the income statement each reporting period until the arrangement is settled or derecognized. The fair value pricing of the call option liability was determined by applying the binomial option pricing model. The assumptions utilized in the option pricing model included: (a) equity share price of 10,010,425,600 KRW, (b) volatility of 43.75%, and (c) risk-free rate of 3.642% |
| | (d) | Pursuant to the Play Company equity purchase agreement, an aggregate of KRW 36,233,103,400 (or approximately USD $24,716,377) will be paid as follows: |
| | Payment Date | | Purchase
Price (KRW) | | | Purchase
Price
(USD) | | | Present
Value
(USD) | |
| | Within 3 months from the listing date | | | 18,133,103,400 | | | | 13,172,074 | | | | 12,624,805 | |
| | January 31, 2025 | | | 9,050,000,000 | | | | 6,574,407 | | | | 6,228,303 | |
| | January 31, 2026 | | | 9,050,000,000 | | | | 6,574,407 | | | | 5,863,270 | |
| | Total | | | 36,233,103,400 | | | | 26,320,888 | | | | 24,716,377 | |
| | (e) | An additional payment in cash may be owed to the owner of Play Company if the shares of PubCo that the shares of New K Enter’s common stock convert to at closing of the Acquisition Merger are sold during the three-month period (the “Sale Period”) following the six-month lock-up period of the newly issued shares of PubCo at a per share price less than the per share value at closing of the Acquisition Merger for the shortfall in share price. The amount to be paid will be reduced by (i) any realized gains from the sale of additional shares of PubCo by the owner of Play Company between the end of the Sale Period and December 31, 2026, and (ii) the unrealized gain as of December 31, 2026 for the shares that remain held by the owner of Play Company (calculated as the number of remaining shares of PubCo times the difference of (i) the average closing price of PubCo from December 1, 2026 to December 31, 2026 and (ii) the per-share value of PubCo at the closing of the Acquisition Merger). The contingent consideration liability is recorded at fair value determined using a Black Scholes model that values the put option related to the Shortfall payment obligation as detailed in the Shares Purchase Agreement. |
| (f) | Trademarks were valued based on a Relief of Royalty Method (“RRM”) with a 5-year life. RRM determines the value of an intangible asset by calculating how much a company would save in hypothetical royalty payments if it we to own the asset rather than licensing it from a third party. |
| | | |
| (g) | IP/Technology was valued based on a Multi-Period Excess Earnings Method (“MPEE”) for LAMP, Bidangil, Apeitda, and Anseilen. The expected life was 10 years. MPEE is a financial valuation model that estimates revenues and cash flows derived from the intangible asset and then deducts portions of the cash flow that can be attributed to supporting assets, such as a brand name or fixed assets, that contributed to the generation of the cash flows. IP/Technology was valued based on RRM for Solaire Partners. The expected life was 5 years. |
| | | |
| | (h) | Customer relationships/bases were valued using MPEE. The expected life for LAMP was 8 years, the expected life for Bidangil was 8 years, the expected life for Apeitda was 8 years, and the expected life for Solaire Partners was 8.4 years. |
| | | |
| (i) | Non-competes were valued using a With and Without Method (“WWM”) with a 5-year term for Bidangil, Apeitda, Anseilen, and Solaire Partners and a 4 year term for LAMP. WWM calculates the difference between two discounted cash flow models: one that represents the status quo for the business enterprise with the asset in place, and another without it. |
| | (j) | The table below presents the calculation of the deferred tax liability on the intangible assets recorded in Entry (A) in the unaudited pro forma balance sheet of New K Enter using a tax rate of 20.9%: |
| | | | K Enter | | | LAMP | | | Bidangil | | | Apeitda | | | Anseilen | | | Solaire Partners | | | Total | |
| | Trademark(f) | | $ | - | | | $ | 771,690 | | | $ | 1,246,843 | | | $ | 1,166,862 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 1,136,213 | | | $ | 4,321,608 | |
| | Intellectual property(g) | | | - | | | | 4,689,566 | | | | 3,696,932 | | | | 2,523,645 | | | | 3,964,811 | | | | 1,830,595 | | | | 16,705,549 | |
| | Customer relationships(h) | | | - | | | | 4,314,056 | | | | 2,857,448 | | | | 1,648,652 | | | | - | | | | 2,509,046 | | | | 11,329,202 | |
| | Non-competes(i) | | | - | | | | 16,159 | | | | 40,039 | | | | 17,541 | | | | 43,810 | | | | 70,404 | | | | 187,953 | |
| | Goodwill | | | 129,223,837 | | | | 18,081,572 | | | | 10,564,691 | | | | 8,617,685 | | | | 4,195,018 | | | | 5,302,859 | | | | 175,985,662 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Total | | $ | 129,223,837 | | | $ | 27,873,043 | | | $ | 18,405,953 | | | $ | 13,974,385 | | | $ | 8,203,639 | | | $ | 10,849,117 | | | $ | 208,529,974 | |
| * | The goodwill for K Enter is supported by the following qualitative factor: |
| ● | Synergic growth between (a) content production and investment businesses, in which K Enter secures IP rights of its films and TV series for additional distribution and advertisement revenues and (b) content production and merchandising businesses, in which K Enter produces goods and merchandises for its films and TV series for additional merchandising revenues. |
This is further supported by the following qualitative factors:
| ● | Organic growth of the content production business, assuming an increase in the production of films and TV series collectively by the four studios (Anseilen, Apeitda, Bidangil and Lamp) and K Enter’s internal production team; |
| | |
| ● | Organic growth of the content merchandising business, assuming an increase in the IP rights coverage for merchandising by Play Company, reflecting Play Company’s recent contract with SM Entertainment; |
| | |
| ● | Organic growth of the content investment business, assuming a serial launching of new content investment funds by Solaire Partners. |
| | (k) | As part of the acquisition, the sellers of the Six Korean entities other than Play maintained their respective non-controlling interests. The following table presents the proportionate share of the non-controlling interest recorded to goodwill for each company calculated on the intangible assets identified and the net assets acquired (liabilities assumed), net of the deferred tax liability: |
| Company | | Net Assets Acquired (Liabilities Assumed) (USD) | | | Intangible Assets Identified (USD) | | | Deferred Tax Liability (USD) | | | Subtotal | | | Non-Controlling
Interest % | | | Total Non-Controlling Interest Recorded to Goodwill (USD) | |
| LAMP | | $ | 388,181 | | | $ | 9,791,471 | | | $ | (2,046,418 | ) | | $ | 8,133,234 | | | | 49.00 | % | | $ | 3,985,285 | |
| Bidangil | | | 2,140,635 | | | | 7,841,262 | | | | (1,638,824 | ) | | | 8,343,073 | | | | 49.00 | % | | | 4,088,106 | |
| Apeitda | | | 659,043 | | | | 5,356,700 | | | | (1,119,550 | ) | | | 4,896,193 | | | | 49.00 | % | | | 2,399,135 | |
| Anseilen | | | (428,317 | ) | | | 4,008,621 | | | | (837,802 | ) | | | 2,742,502 | | | | 49.00 | % | | | 1,343,826 | |
| Solaire Partners | | | 927,761 | | | | 5,546,258 | | | | (1,159,168 | ) | | | 5,314,851 | | | | 5.00 | % | | | 265,743 | |
| | | $ | 3,687,303 | | | $ | 32,544,312 | | | $ | (6,801,762 | ) | | $ | 29,429,853 | | | | | | | $ | 12,082,094 | |
| | B. | Reflects the liquidation and reclassification of $4.3 million of funds held in the Trust Account to cash that becomes available following the Business Combination. |
| | C. | Reflects the settlement of deferred underwriting fees payable upon the closing of the Business Combination. |
| | | |
| | D. | Represents preliminary estimated transaction costs expected to be incurred by Global Star of approximately $1.3 million under the no additional redemption scenario and the maximum redemption scenario and by New K Enter of $24.3 million and $24.2 million, under the no additional redemption scenario and the maximum redemption scenario respectively, for legal, accounting, underwriting, due diligence, and other fees incurred as part of the Business Combination. The costs for Global Star are accounted for as a reduction in the combined cash account with a corresponding reduction in accumulated deficit. |
| | | Under the no redemption scenario, for the New K Enter transaction costs of $24.3 million, $6.2 million has been paid and $3.4 million has been accrued as of the date of the pro forma balance sheet date, $9.6 million is reflected as an adjustment to accumulated deficit and $5.2 million is included as an adjustment to additional paid-in capital. Under the maximum redemption scenario, for the New K Enter transaction costs of $24.2 million, $6.2 million has been paid and $3.4 million has been accrued as of the date of the pro forma balance sheet date, $9.5 million is reflected as an adjustment to accumulated deficit and $5.2 million is included as an adjustment to additional paid-in capital. The adjustment to accumulated losses includes $9.6 million and $9.5 million related to success fees, for the no additional redemption and the maximum redemption scenarios, respectively, with a corresponding increase to trade and other payables as 30% of the success fee is due three months after the Combined Company is listed and traded publicly and 70% of the success fee is due twelve months after the Combined Company is listed and traded publicly. These transaction costs are non-recurring. In each scenario for New K Enter, $8.5 million of the K Enter transaction costs are being paid in shares of K Enter common stock. The 4,997 shares of K Enter common stock were converted to 1,524,681 shares of Pubco, par value of $0.0001 per share at a value of $10 per share. A net amount of $6.7 million was recorded to accumulated deficit for the difference between the value of the shares issued and the value of the debt transferred. |
| | | |
| | | For the Global Star transaction costs, $0.9 million has been accrued and $0.2 million has been paid as of the pro forma balance sheet date. The amount of $0.9 million is reflected as an adjustment to accumulated deficit. The Global Star estimated transaction costs exclude the deferred underwriting commissions included (C) above. |
| | E. | Represents the exchange of outstanding New K Enter shares into 57,475,319 PubCo Ordinary Shares at par value of $0.0001 per share. These shares plus the 1,524,681 shares presented as being issued to satisfy K Enter transaction expenses, as described in (D) above, total the 59,000,000 New K Enter shares to be issued at the consummation of the Business Combination. |
| | | |
| | F. | Represents the elimination of Global Star’s historical accumulated losses after recording the transaction costs to be incurred by Global Star as described in (D) above, the interest earned in the Trust as described in (J) below and the stock-based compensation as described in (P) below. |
| | G. | The No Additional Redemption Scenario assumes that, after the August Redemptions, the June Redemptions, and the November Redemptions, no Global Star stockholders exercise their redemption rights for cash and the Class A Common Stock subject to redemption amounting to $4.0 million would be transferred to permanent equity. The Maximum Redemption Scenario reflects the redemption, after the August Redemptions and the June Redemptions, of 380,875 shares of Global Star Class A Common Stock for aggregate redemption payments of $4.3 million at a redemption price of approximately $11.41 per share as of December 5, 2024, subject to reduction for the payment of taxes. |
| | H. | In the No Additional Redemption Scenario, represents the preliminary estimated expense recognized, in accordance with IFRS 2, for the excess of the deemed costs of the shares issued by PubCo and the fair value of Global Star’s identifiable net assets at the date of the Business Combination, resulting in a $54.3 million increase to accumulated deficit. In the Maximum Redemption Scenario, represents the preliminary estimated expense recognized, in accordance with IFRS 2, for the excess of the deemed costs of the shares issued by PubCo and the fair value of Global Star’s identifiable net assets at the date of the Business Combination, resulting in a $54.3 million increase to accumulated deficit. The fair value of shares issued was estimated based on a market price of $11.53 per share (as of October 18, 2024). The value is preliminary and will change based on fluctuations in the share price of the Global Star common stock through the Closing Date. In the No Additional Redemption Scenario, a one percent change in the market price per share would result in a change of $0.5 million in the estimated expense. In the Maximum Redemption Scenario, a one percent change in the market price per share would result in a change of $0.5 million in the estimated expense. |
| | | | No Additional
Redemption
Scenario | | | Maximum
Redemption
Scenario | |
| | | | Shares | | | Dollars | | | Shares | | | Dollars | |
| | Global Star shareholders | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Public shareholders(1) | | | 1,300,875 | | | | | | | | 920,000 | | | | | |
| | Sponsor and other shareholders(2) | | | 3,058,747 | | | | | | | | 3,058,747 | | | | | |
| | Deemed costs of shares to be issued to Global Star shareholders | | | | | | $ | 50,266,442 | | | | | | | $ | 45,874,953 | |
| | Net assets of Global Star as of June 30, 2024 | | | | | | | 5,057,690 | | | | | | | | 5,057,690 | |
| | Less: Global Star Transaction Costs | | | | | | | (123,406 | ) | | | | | | | (123,406 | ) |
| | Less: Global Star Warrant liabilities | | | | | | | (240,516 | ) | | | | | | | (240,516 | ) |
| | Less: Effect of November redemptions and interest withdrawal | | | | | | | (8,724,186 | ) | | | | | | | (8,724,186 | ) |
| | Less: Effect of maximum redemption of shares | | | | | | | - | | | | | | | | (4,346,339 | ) |
| | Adjusted net assets (liabilities) of Global Star as of June 30, 2024 | | | | | | | (4,030,418 | ) | | | | | | | (8,376,757 | ) |
| | Difference – being IFRS 2 charge for listing services | | | | | | $ | 54,296,860 | | | | | | | $ | 54,251,710 | |
| (1) | Includes 9,200,000 Public Rights automatically converted into 920,000 shares of common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination. |
| (2) | Includes 498,225 Private Rights automatically converted into 49,822 shares of common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination and includes 240,700 Convertible Note Rights automatically converted into 24,070 shares of common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination. |
| | I. | Reflects the conversion of Global Star Class B Common Stock into Class A Common Stock on a one-for-one basis upon consummation of the Business Combination. |
| | J. | Reflects the net effect of interest earned in the Trust Account subsequent to June 30, 2024. |
| | K. | Reflects the conversion of 9,698,225 GLST Rights into 969,823 ordinary shares upon the closing of the Business Combination. |
| | L. | Reflects additional draws on the Global Star April 15, 2024, promissory note of $96,000 subsequent to June 30, 2024. Reflects the conversion of $1.5 million of the July 31, 2023, Global Star Working Capital Loan into 150,000 GLST Units at a price of $10.00 per unit upon consummation of the Business Combination. Each unit consists of one share of GLST Class A Common Stock, one GLST Warrant, and one GLST Right. Also reflects the conversion of 150,000 GLST Rights into 15,000 shares of GLST Class A Common Stock upon the closing of the Business Combination. The warrants were recorded as non-current financial liabilities under IAS 32.Reflects the conversion of $100,000 of the Global Star July 31, 2023, Working Capital Loan and $807,000 of the Global Star April 15, 2024, promissory note into shares of Global Star Class B common stock at a price of $10.00 per share upon the consummation of the business combination. |
| | M. | Reflects the payment of the amount Due to Sponsor upon consummation of the Business Combination. |
| | | |
| | N. | Reflects the conversion of GLST Class A Common Stock into PubCo ordinary shares upon consummation of the Business Combination. |
| | |
| | O. | Reflects the extension payments made to the Trust Account subsequent to June 30, 2024. |
| | | |
| | P. | Reflects the recognition of stock-based compensation related to the sale of Founders Shares to Global Star’s directors and strategic advisors upon consummation of the Business Combination. |
| | | |
| | Q. | Reflects the conversion of 35,484 shares of K Enter Series A preferred stock to New K Enter common stock, par value $0.01, and the conversion of 5,314 shares of K Enter Series A-1 preferred stock to New K Enter common stock, par value $0.01, at a conversion ratio of 1:1 at the consummation of the business combination. |
| | | |
| | R. | Reflects the retirement of New K Enter treasury stock upon consummation of the Business Combination. |
| | S. | Reflects the elimination upon consolidation of the intercompany balances for advances paid by K Enter to Anseilen for content development. |
| | | |
| | T. | Reflects the elimination upon consolidation of legal fees paid by Solaire Partners on behalf of K Enter and the sublease agreement between K Enter and Solaire Partners. |
| | U. | Reflects the elimination of the Investment in Play Company related to the 1,000 shares of Play Company owned by Solaire Partners. |
| | V. | Reflects the adjustment to Global Star historical balance sheet to reverse the consolidation of its wholly-owned subsidiary, K Wave Media, Ltd. |
| | | |
| | W. | Reflects the intercompany elimination upon consolidation of the intercompany accounts of Global Star and K Wave Media Ltd. |
| | X. | Reflects the proceeds of $3.4 million from the convertible senior unsecured debt and the bifurcation of the conversion option at a fair value of $0.4 million. |
| Y. | Reflects the share-based compensation recognized by K Enter for the issuance of 2,100 shares of K Enter treasury stock and 1,202 shares and 688 shares of K Enter common stock, par value $0.01 at a fair value of $10 per share, subsequent to June 30, 2024.The 688 shares of K Enter common stock were transferred from a K Enter co-founder to a K Enter employee to compensate the employee on behalf of K Enter for services rendered to K Enter and were expensed as share-based compensation. |
| Z. | Reflects the issuance of 500 shares of K Enter Series A-1 preferred stock issued at $600 subsequent to June 30, 2024, for $150,000 cash received and $150,000 recorded as subscription receivable. |
| A-1. | Reflects the intercompany elimination upon consolidation of the short-term borrowing from Bidangil to K Enter. |
| | A-2 | Reflects the redemption of 756,131 shares of Global Star Class A common stock at approximately $11.41 per share for $8.6 million and the withdrawal of $0.1 million of interest income from the Trust to pay certain tax obligations, subsequent to June 30, 2024. |
Note 6 — Adjustments and Reclassifications to Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Statement of Operations for the Six Months Ended June 30, 2024
The pro forma adjustments included in the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations for the six months ended June 30, 2024 are as follows:
| | AA. | Reflects the elimination of interest income generated from the investments held in the Trust Account. |
| | | |
| | BB. | Reflects the elimination of administrative service fees that will cease to be paid upon the closing of the Business Combination. |
| | | |
| | CC. | Reflects the income tax impacts of the pre-tax transaction adjustments. |
| | | |
| | DD. | Reflects the recognition of net loss attributable to non-controlling interests in the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company. |
| | | |
| | EE. | Reflects the amortization of Intellectual Property, Trademarks, Non-competes and Customer Relationships intangible assets recognized on New K Enter. |
| | | K Enter | | | Lamp | | | Bidangil | | | Apeitda | | | Anseilen | | | Solaire Partners | | | Total | |
| Intellectual Property (USD) | | $ | - | | | $ | 4,689,566 | | | $ | 3,696,932 | | | $ | 2,523,645 | | | $ | 3,964,811 | | | $ | 1,830,595 | | | $ | 16,705,549 | |
| Useful Life | | | | | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 5 | | | | | |
| Customer Relationships (USD) | | $ | - | | | $ | 4,314,056 | | | $ | 2,857,448 | | | $ | 1,648,652 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 2,509,046 | | | $ | 11,329,202 | |
| Useful Life | | | | | | | 8 | | | | 8 | | | | 8 | | | | - | | | | 8.4 | | | | | |
| Trademarks (USD) | | $ | - | | | $ | 771,690 | | | $ | 1,246,843 | | | $ | 1,166,862 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 1,136,213 | | | $ | 4,321,608 | |
| Useful Life | | | | | | | 5 | | | | 5 | | | | 5 | | | | - | | | | 5 | | | | | |
| Non-competes (USD) | | $ | - | | | $ | 16,159 | | | $ | 40,039 | | | $ | 17,541 | | | $ | 43,810 | | | $ | 70,404 | | | $ | 187,953 | |
| Useful Life | | | | | | | 4 | | | | 5 | | | | 5 | | | | 5 | | | | 5 | | | | | |
| Annual Amortization | | $ | - | | | $ | 1,166,591 | | | $ | 984,251 | | | $ | 695,327 | | | $ | 405,243 | | | $ | 906,138 | | | $ | 4,157,550 | |
| 6 months Amortization | | $ | - | | | $ | 583,296 | | | $ | 492,126 | | | $ | 347,664 | | | $ | 202,622 | | | $ | 453,070 | | | $ | 2,078,778 | |
| | FF. | Reflects the elimination upon consolidation of the sublease agreement between K Enter. |
| | | |
| | GG. | Reflects the elimination upon consolidation of the intercompany balances related to the consulting transaction between K Enter and Solaire Partners. |
| | | |
| | HH. | Reflects the elimination upon consolidation of the short-term borrowing from Bidangil to K Enter. |
| | | |
| | II. | Reflects the amortization of the debt discount of $0.09 million, and accrual of interest expense at an annual coupon rate of 3% of $0.07 million. |
Note 7 — Adjustments and Reclassifications to Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Statement of Operations for the Year Ended December 31, 2023
The pro forma adjustments included in the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | AA. | Reflects the elimination of interest income generated from the investments held in the Trust Account. |
| | BB. | Reflects the elimination of administrative service fees that will cease to be paid upon the closing of the Business Combination. |
| | | |
| | CC. | Represents the preliminary estimated expense recognized, in accordance with IFRS 2, for the excess of the deemed costs of the shares issued by PubCo over the fair value of Global Star’s identifiable net assets at the date of the Business Combination, as described in (H) above. This cost is a non-recurring item. |
| | | |
| | DD. | Reflects the income tax impacts of the pre-tax transaction adjustments. |
| | | |
| | EE. | Reflects the recognition of stock-based compensation related to the sale of Founders Shares to Global Star’s directors and strategic advisors at the consummation of the Business Combination. |
| | | |
| | FF. | Reflects the expenses incurred by New K Enter for transaction costs related to accounting, advisory and valuation services. |
| | GG. | Reflects the recognition of net loss attributable to non-controlling interests in the Six Korean Entities other than Play Company. |
| | | |
| | HH. | Reflects the amortization of Intellectual Property, Trademarks, Non-competes and Customer Relationships intangible assets recognized on New K Enter. |
| | | K Enter | | | Lamp | | | Bidangil | | | Apeitda | | | Anseilen | | | Solaire Partners | | | Total | |
| Intellectual Property (USD) | | $ | - | | | $ | 4,689,566 | | | $ | 3,696,932 | | | $ | 2,523,645 | | | $ | 3,964,811 | | | $ | 1,830,595 | | | $ | 16,705,549 | |
| Useful Life | | | | | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 5 | | | | | |
| Customer Relationships (USD) | | $ | - | | | $ | 4,314,056 | | | $ | 2,857,448 | | | $ | 1,648,652 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 2,509,046 | | | $ | 11,329,202 | |
| Useful Life | | | | | | | 8 | | | | 8 | | | | 8 | | | | - | | | | 8.4 | | | | | |
| Trademarks (USD) | | $ | - | | | $ | 771,690 | | | $ | 1,246,843 | | | $ | 1,166,862 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 1,136,213 | | | $ | 4,321,608 | |
| Useful Life | | | | | | | 5 | | | | 5 | | | | 5 | | | | - | | | | 5 | | | | | |
| Non-competes (USD) | | $ | - | | | $ | 16,159 | | | $ | 40,039 | | | $ | 17,541 | | | $ | 43,810 | | | $ | 70,404 | | | $ | 187,953 | |
| Useful Life | | | | | | | 4 | | | | 5 | | | | 5 | | | | 5 | | | | 5 | | | | | |
| Annual Amortization | | $ | - | | | $ | 1,166,591 | | | $ | 984,251 | | | $ | 695,327 | | | $ | 405,243 | | | $ | 906,138 | | | $ | 4,157,550 | |
| 6 months Amortization | | $ | - | | | $ | 583,296 | | | $ | 492,126 | | | $ | 347,664 | | | $ | 202,622 | | | $ | 453,070 | | | $ | 2,078,778 | |
| II. | Reflects the elimination upon consolidation of the sublease agreement between K Enter. |
| JJ. | Reflects the elimination upon consolidation of the intercompany balances related to the consulting transaction between K Enter and Solaire Partners. |
| KK. | Reflects the amortization of the debt discount of $0.2 million, and accrual of interest expense at an annual coupon rate of 3% of $0.1 million. |
| LL. | Reflects the expense recognized for the K Enter shares issued for the satisfaction of transaction expenses as described in (D) above. |
| | | |
| | MM. | Reflects the share-based compensation recognized by K Enter for the 2,100 shares of K Enter treasury stock issued and the 1,202 shares and 688 shares of K Enter common stock issued as described in adjustment Y above. The 688 shares of K Enter common stock were transferred from a K Enter co-founder to a K Enter employee to compensate the employee on behalf K Enter for services rendered to K Enter and were expensed as share-based compensation. |
Note 8 — Net Loss per Share
Represents the loss per share calculated using the historical weighted average shares outstanding, and the issuance of additional shares in connection with the Business Combination, assuming the shares were outstanding since January 1, 2023. As the Business Combination is being reflected as if it had occurred at the beginning of the period presented, the calculation of weighted average shares outstanding for basic and diluted net loss per share assumes that the shares issued in connection with the Business Combination have been outstanding for the entire period presented. If the number of public shares described under the “Assuming Maximum Redemptions” scenario described above are redeemed, this calculation is retroactively adjusted to eliminate such shares for the entire period.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information has been prepared assuming two alternative levels of redemption of PubCo’s public shares:
| | | For the
Six Months Ended
June 30, 2024
and for the
Year Ended
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | No Additional
Redemption
Scenario | | | Maximum
Redemption
Scenario | |
| Weighted average shares outstanding – basic and diluted | | | | | | | | |
| K Enter stockholders(1) | | | 59,160,000 | | | | 59,160,000 | |
| Global Star public stockholders(2) | | | 1,300,875 | | | | 920,000 | |
| Sponsor and Initial Stockholders(3)(4) | | | 2,943,747 | | | | 2,943,747 | |
| Representative Shares | | | 115,000 | | | | 115,000 | |
| Total(4) | | | 63,519,622 | | | | 63,138,747 | |
| (1) | Includes 59,000,000 K Wave Ordinary Shares to be issued upon consummation of the Business Combination as follows: (i) 30,878,682 K Wave Ordinary shares issued in exchange for 101,202 shares of K Enter common stock owned by the currently existing stockholders of K Enter, including, the 4,997 shares of K Enter common stock owned by GF Korea and the 1,202 shares of K Enter common stock owned by Lodestar USA; (ii) 12,448,256 K Wave Ordinary shares issued in exchange for 40,798 shares of K Enter common stock owned by the Preferred Stock owners after the conversion of the 40,798 shares of Preferred Stock into shares of K Enter common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination and (iii) 15,673,062 K Wave Ordinary shares to be issued in exchange for 51,367 shares of K Enter common stock that will be owned by the owners of Six Korean Entities following K Enter acquisition of the controlling equity interests in the Six Korean Entities and 160,000 K Wave Ordinary shares to be issued in exchange 160,000 shares of Global Star Founder Shares currently owned by K Enter. |
| (2) | Includes 9,200,000 public shares at June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 less 4,052,066 shares redeemed in September 2023, 4,010,928 shares redeemed in June 2024, and 756,131 shares redeemed in November 2024, plus 9,200,000 Public Rights automatically converted into 920,000 shares of common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination. |
| (3) | Includes (a) 1,640,000 Founder Shares owned by the Sponsor as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023, (b) 498,225 shares underlying the Private Units as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 plus 498,225 Private Rights automatically converted into 49,822 shares of common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination owned by the Sponsor, (c) 150,000 shares of common stock underlying the Convertible Note plus 150,000 Convertible Note Rights automatically converted into 15,000 shares of common stock upon consummation of the Business Combination owned by the Sponsor (d) 90,700 shares underlying the Global Star loan converted to Global Star Class B common stock upon the consummation of the business combination, and (e) 500,000 Founder Shares owned by the Initial Shareholders as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023. |
| (4) | Excludes 19,300 shares potentially to be issued to the Sponsor if an additional $193,000 were to be drawn on the Global Star loan and converted to Global Star Class B common stock. Accordingly, K Wave is registering up to an aggregate amount of 64,295,053 Ordinary Shares to be issued in connection with Business Combination on this proxy statement/prospectus. |
| | | For the
Six Months Ended
June 30,
2024 | |
| | | No Additional
Redemption
Scenario | | | Maximum
Redemption
Scenario | |
| Pro forma net loss | | $ | (8,384,396 | ) | | $ | (8,384,396 | ) |
| Weighted average shares outstanding – basic and diluted(2) | | | 63,519,622 | | | | 63,138,747 | |
| Net loss per share – basic and diluted | | $ | (0.13 | ) | | $ | (0.13 | ) |
| Excluded securities:(1) | | | | | | | | |
| GLST Public Warrants | | | 9,200,000 | | | | 9,200,000 | |
| Sponsor Private Placement Warrants | | | 498,225 | | | | 498,225 | |
| Convertible Note Warrants | | | 150,000 | | | | 150,000 | |
| Shares attributed to the Convertible Senior Unsecured Debt | | | 450,000 | | | | 450,000 | |
| | | For the
Year Ended
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | No Additional
Redemption
Scenario | | | Maximum
Redemption
Scenario | |
| Pro forma net loss | | $ | (96,454,828 | ) | | $ | (96,352,547 | ) |
| Weighted average shares outstanding – basic and diluted | | | 63,519,622 | | | | 63,138,747 | |
| Net loss per share – basic and diluted | | $ | (1.52 | ) | | $ | (1.53 | ) |
| Excluded securities:(1) | | | | | | | | |
| GLST Public Warrants | | | 9,200,000 | | | | 9,200,000 | |
| Sponsor Private Placement Warrants | | | 498,225 | | | | 498,225 | |
| Convertible Note Warrants | | | 150,000 | | | | 150,000 | |
| Shares attributed to the Convertible Senior Unsecured Debt | | | 450,000 | | | | 450,000 | |
| (1) | The potentially dilutive outstanding securities were excluded from the computation of pro forma net income per share, basic and diluted, because their effect would have been anti-dilutive. |
| (2) | Excludes 19,300 shares potentially to be issued to the Sponsor if an additional $193,000 were to be drawn on the Global Star loan and converted into Global Star Class B common stock. Accordingly, K Wave is registering up to an aggregate amount of 64,295,053 Ordinary Shares to be issued in connection with Business Combination on this proxy statement/prospectus. |
COMPARATIVE HISTORICAL AND UNAUDITED
PRO FORMA COMBINED PER SHARE FINANCIAL INFORMATION
The following table sets forth summary historical comparative share information for Global Star, Play Company and K Enter, respectively, and unaudited pro forma condensed combined per share information after giving effect to the Business Combination presented under two scenarios:
| | ● | Scenario 1 — Assuming No Additional Redemptions: This presentation assumes that, after the August Redemptions and the June Redemptions, no public stockholders of Global Star exercise redemption rights with respect to their Class A Common Stock upon consummation of the Business Combination. |
| | ● | Scenario 2 — Assuming Maximum Redemptions: This presentation assumes that Global Star public stockholders holding 380,875 shares of Global Star Class A Common Stock will exercise their redemption rights for $4.3 million upon consummation of the Business Combination at a redemption price of approximately $11.41 per share, as of December 5, 2024, subject to reduction for the payment of taxes. The maximum redemption amount reflects the maximum number of Global Star’s Class A Common Stock that can be redeemed. This scenario includes all adjustments contained in the “no additional redemptions” scenario and presents additional adjustments to reflect the effect of the maximum redemptions. |
This information is only a summary and should be read in conjunction with the historical financial statements of Global Star, Play Company, LAMP, Bidangil, Apeitda, Anseilen, Solaire Partners, K Wave Media Ltd and K Enter and related notes that are included elsewhere in this proxy statement/prospectus. The unaudited pro forma combined per share information of Global Star, Play Company, LAMP, Bidangil, Apeitda, Anseilen, Solaire Partners, K Wave Media Ltd and K Enter is derived from, and should be read in conjunction with, the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this proxy statement/prospectus.
The unaudited pro forma combined income per share information below does not purport to represent the earnings per share which would have occurred had the companies been combined during the period presented, nor earnings per share for any future date or period. The unaudited pro forma combined book value per share information below does not purport to represent what the value of Global Star, Play Company, and K Enter would have been had the companies been combined during the period presented.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Combined Pro Forma | |
| June 30, 2024 | | Play company (Historical) | | | LAMP
(Historical) | | | Bidangil
(Historical) | | | Apeitda
(Historical) | | | Anseilen
(Historical) | | | Solaire Partners
(Historical) | | | K Enter
(Historical) | | | K Wave Media Ltd
(Historical) | | | Global Star
(Historical) | | | Assuming No
Additional
Redemptions | | | Assuming Maximum Redemptions | |
| Net Income (Loss) | | | (265,288 | ) | | | 228,627 | | | | 302,629 | | | | (138,901 | ) | | | (189,561 | ) | | | (26,867 | ) | | | (4,593,765 | ) | | | - | | | | (440,549 | ) | | | (8,384,396 | ) | | | (8,384,396 | ) |
| Shareholders’ Equity (Deficit) | | | 8,231,865 | | | | 388,181 | | | | 2,140,635 | | | | 659,043 | | | | (428,317 | ) | | | 927,761 | | | | 1,250,912 | | | | 37,193 | | | | (7,867,801 | ) | | | 168,680,177 | | | | 164,390,969 | |
| Shareholders’ Book Value per Share* | | | N/A | | | | N/A | | | | N/A | | | | N/A | | | | N/A | | | | N/A | | | | N/A | | | | N/A | | | $ | (1.03 | ) | | $ | 2.66 | | | $ | 2.60 | |
| Cash dividends | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average shares - Basic and diluted(1) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 7,642,436 | | | | 63,519,622 | | | | 63,138,747 | |
| Net income (loss) per share - Basic and diluted | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | (0.06 | ) | | $ | (0.13 | ) | | $ | (0.13 | ) |
| * | Book value = shareholders’ equity/shares outstanding |
| (1) | Excludes 19,300 shares potentially to be issued to the Sponsor if an additional $193,000 were to be drawn on the Global Star loan and converted into Global Star Class B common stock. Accordingly, K Wave is registering up to an aggregate amount of 64,295,053 Ordinary Shares to be issued in connection with Business Combination on this proxy statement/prospectus. |
DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS, EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION AND
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE OF GLOBAL STAR
Directors and Executive Officers
Global Star’s current directors and executive officers are as follows:
Name | | Age | | Position |
| Anthony Ang | | 68 | | Chief Executive Officer and Director |
| Nicholas Khoo | | 45 | | Chief Operating Officer |
| Shan Cui | | 51 | | Chief Financial Officer |
| Stephen Drew | | 53 | | Director |
| Lam Chun Wing | | 45 | | Independent Director |
| Yang Kan Chong | | 68 | | Independent Director |
| Hai Chwee Chew | | 67 | | Independent Director |
| Jukka Rannila | | 46 | | Independent Director |
The experience of Global Star’s directors and executive officers is as follows:
Anthony Ang, Global Star’s Chairman and CEO is a global executive with over 40 years of senior management experience. His broad expertise covers international marketing, investment promotion, manufacturing, and fund management. Mr. Ang started his career at the Singapore Economic Development Board in 1980, and his last position was Regional Director for North America (based in the United States for six years) responsible for the promotion of investments from North America. He went on to become Group General Manager of Armstrong Industrial Corporation, a Singapore precision engineering company that he helped list on the Singapore Exchange in 1995. Mr. Ang then joined Vertex Management as Senior Vice President (Investment) in 1999, a leading venture Capital firm with its headquarters in Singapore and subsequently GIC Real Estate Pte. Ltd. (a unit of the Sovereign wealth fund of the Singapore Government) as Executive Vice President for Admin and Corporate Affairs in 2001. Mr. Ang went on to serve as founding Executive Director of Majulah Connection, a consulting and networking organization sponsored by the Government of Singapore. In 2006, Mr. Ang joined the ARA Group, a leading real estate fund management house with its headquarters in Singapore and asset under management (“AUM”) of $140 billion. From 2008 to 2010, Mr. Ang served as the CEO of ARA Asia Dragon Limited (“ADF”), the flagship private equity real estate fund of the ARA Group. ADF had a committed capital of $1.13 billion and was focused on investments across Asia. Mr. Ang was responsible for raising the fund with global investors and overseeing its investments of over fourteen assets. From February 2010 to December 2016, Mr. Ang served as the CEO and Executive Director of ARA Asset Management (Fortune) Pte. Ltd. (a subsidiary of the ARA Group), as the manager of Fortune Real Estate Investment Trust (“Fortune REIT”) with HK$36 billion of retail assets in Hong Kong. During his tenure at Fortune REIT, Mr. Ang was recognized as “Best CEO (Third)” and “Best CEO (First)” for Hong Kong in 2013 and 2014 respectively for successfully expanding Fortune REIT, by the Annual Best Managed Companies Poll by FinanceAsia. From March 2017 to July 2021, Mr. Ang served as CEO of Sasseur Asset Management Pte Ltd (SGX: CRPU), where he led the listing process for the initial public offering of Sasseur Real Estate Investment Trust (“Sasseur REIT”) (AUM US$1.2 billion) in March 2018. In 2019, under Mr. Ang’s leadership, Sasseur REIT was recognized as the “REIT of the Year” and “Best Retail REIT (platinum)” in Singapore. Mr. Ang was awarded “Best CEO (platinum)” in Singapore in 2019 and 2020 by The Fortune Times Award.
Mr. Ang currently holds various senior positions. Since January 2016, Mr. Ang has served as an independent director of Yong Tai Bhd, a property development company listed on Bursa Malaysia, the Malaysian stock exchange. Since April 2017, Mr. Ang has served as an independent director with Heatec Jietong Holding Ltd., a marine industry manufacturing and service company that is listed on the Singapore Exchange. From October 2022, Mr. Ang has served as an independent director with EuroSport Global Limited, a distributor of ultra-luxury automobiles that is listed on the Singapore Exchange. Mr Ang was also appointed as an executive director of Sunrise Shares Holding Limited, an investment holding company listed on the Singapore Exchange in September 2023. Mr. Ang has represented his country as the Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary of the Republic of Singapore to the Republic of Tunisia since September 2017. In that role he represents the interests of Singapore and helps to maintain the relations of amity and concord between the two countries. In December 2020, Mr. Ang began his position as a director at Truufin Pte. Ltd., where he provides guidance for the company in the Fintech industry. Mr. Ang has served as a director of Sinospring Venture Ltd. (Singapore) since May 2021 and as a director of GCIC Ltd since June 2021, both of which are consultancy services companies. In the education consultancy services industry, Mr. Ang has served as a director of ITE Education Services Pte. Ltd. since July 2021. Finally, Mr. Ang currently serves as the Chairman and director for RV SG Pte Ltd, a crowd funded real estate investment platform since November 2021, and as Chairman and director of Singapore Digital Exchange Pte. Ltd., a digital exchange of cryptocurrency and digital assets in Singapore since December 2021 and an Executive director of SquareDog Robotics Pte Ltd since December 2022. Mr. Ang holds a Bachelor of Science in Mechanical Engineering degree with First Class Honors from the Imperial College of Science and Technology at the University of London. He also obtained an MBA degree and an International Directorship Certificate from INSEAD, France in and completed a Marketing Management Program at the Graduate School of Business at Stanford University.
Nicholas Khoo, Global Star’s Chief Operating Officer’s diversified career spans over 20 years within technology, video games, fintech, real estate, and consulting industries. In the financial services industry, Mr. Khoo has led Asia Pacific and Japan for Visa Inc’s Cybersource Managed Services from 2012 to 2017. Mr. Khoo is a known figure in the esports and video games industry, serving as an Advisor to the Board of the Global Esports Federation since December 2019. Mr. Khoo also serves as an investment committee member of the Tribeca Global SPAC Fund since September 2021 and the Global Fund since October 2021. He also serves as an Investment Committee Advisor to MSW Ventures Asia Fund X, a venture capital fund focused on Southeast Asia since May 2023. Mr. Khoo has experience in the public sector as he has served on various official boards and committees in Singapore including the Gambling Regulatory Authority, National Crime Prevention Council, and the Internet and Media Advisory Committee. Mr. Khoo was the valedictorian when he graduated with a Master of Business Administration from Arcadia University.
Shan Cui, Global Star’s Chief Financial Officer, has more than 20 years of financial management, consulting, and audit experience. Ms. Cui currently serves and an Independent Director and Audit Committee Chair of MicroAlgo Inc. (NASDAQ: ALGO) and as an Independent Director and Audit Committee Chair of Flag Ship Acquisition Corporation a pre-IPO SPAC. Ms. Cui served as a director and audit committee chair of Venus Acquisition Corporation (NASDAQ: VENA), a special purpose acquisition company that closed its initial public offering in February 2021 and completed its acquisition of MicroAlgo Inc. in December 2022. From June 2020 to May 2021, Ms. Cui served as a director and audit committee chair of WiMi Hologram Cloud Inc. (NASDAQ: WIMI), a holographic cloud comprehensive technical solution provider. She also served as a director and audit chair for Addentax Group Corp. (OTCQB: ATGX), a garment manufacturer and logistics service provider based in China, from April 2020 to April 2021. From April 2019 to October 2019, Ms. Cui served as a director and audit committee chair for Greenland Acquisition Corporation, a special purpose acquisition company that closed its business combination with Zhongchai Holding (Hong Kong) Limited in October 2019, forming Greenland Technologies Holding Corporation (NASDAQ: GTEC). Since 2010, Ms. Cui has served as a Managing Director of Capital First International, which provides consulting services to SPAC, private equity, venture capital and growth companies. From February 2011 to February 2013, she served as chief financial officer at Lizhan Environmental Corporation, a then Nasdaq-listed company engaged in the manufacturing and distribution of green leather materials. From 2009 to 2010, she was the manager of planning and analysis for Greene, Tweed & Company, a manufacturer of high-performance engineering parts and products for the aerospace, oilfield, and semi-conductor industries. Prior to Greene, Tweed & Company, Ms. Cui served as a senior finance manager at Ikon Office Solutions from 2005 to 2008, group CFO of Invista from 2003 to 2004, manager of strategic planning and analysis for General Time Corporation from 1998 to 2001, and senior vice president for Seaboard Corporation from 1996 to 1998. Ms. Cui holds an MBA degree from Georgia State University in the United States and completed her undergraduate studies in English at Ocean University of China.
Stephen Drew serves as a non-independent member of Global Star’s board of directors. Mr. Drew has 25 years of experience in private equity, investment banking, real estate, and Fintech-related businesses. Stephen Drew, a director of Global Star served as a director of K Enter Holdings, Inc. from January 3, 2023 to April 25, 2023. Mr. Drew began his career at Wall Street firms Citigroup and Gruntal & Co. In the real estate financing and investing arena, Mr. Drew acted as the principal of Pinnacle Funding for over ten years, where he managed over 50 professional investors. Mr. Drew was also a member of Greenwich Realty Capital LLC from 2017 to 2019, where he managed commercial real estate development. From 2019 to 2020, Mr. Drew served as a Managing Member of Tribeca Realty Capital LLC, the US-based partner of a $27.5 billion asset manager based in Asia for equity investments and is responsible for successfully closing hundreds of millions in transactions. Since 2018, Mr. Drew has served as a Managing Partner of Global Fund LLC, a sponsor affiliate. Since 2021, Mr. Drew has also served as a Managing Partner of Tribeca Global SPAC Fund LLC. Currently a Director at Global Star Acquisition Inc. Mr. Drew studied Finance at Central Connecticut State University.
Argon Lam Chun Win Global Star’s independent director, currently serves as a Vice President of a leading fund management company granted the Type 4 and Type 9 license by the Hong Kong Securities and Futures Commission for providing investment consultancy services and segregated fund management. Mr. Lam brings a deep understanding of investment performance and has served as a Vice President of two additional leading fund management companies from 2016 to the present. He brings vast experience and a developed insight to serving the needs of customers seeking excellent investment performance. His expertise continues to serve the Company and its shareholders well.
Yang Kan Chong, Global Star’s independent director, serves as a member of Global Star’s board of directors and as Chairman of Global Star’s Compensation Committee. Mr. Chong brings thirty years of expertise in the areas of energy, oil, gas, power, and infrastructure in the international arena. He is experienced in senior management in multi- and crossed-cultural environments. Mr. Chong holds a strong network of key contacts in the financial industry, and has accumulated extensive experience in treasury, financial management, and capital operation. Mr. Chong has previously served as Managing Director of Asia Petroleum Technology Pte Ltd, President and CEO of the U.S.-listed China New Energy Group Company, Group Deputy CEO of the Singapore-listed China EnerSave Limited, and several U.S. energy giants and Singapore Government-linked companies. From 2018 to 2019, Mr. Chong served as an independent director of China Star Food Group Ltd. Since 2016, Mr. Chong has acted as a Director of Sport Lifestyle Initiative Pte Ltd., a Singapore sport education company. Finally, since 2020, Mr. Chong works as an Investment Committee Member and Equity Partner of Global Fund LLC, a sponsor affiliate. He holds a Master of Science Degree (Mechanical Engineering) accredited by the National University of Singapore and a Bachelor of Engineering Degree (Mechanical and Production) accredited by the University of Singapore.
Hai Chwee Chew, Global Star’s independent director, serves as a member of Global Star’s board of directors and as Chairman of Global Star’s audit committee. Mr. Chew is an entrepreneur who has served in the positions of Independent Director, Executive Director, CFO, COO, and CEO in Asian and U.S. multi-national and local organizations. Mr. Chew’s career includes having held positions as Executive Director of United Fibre Systems Ltd listed in SGX (Singapore Exchange), Executive Director and CEO of NASDAQ listed Pacific Internet Ltd, and CEO of Bright Vision Community Hospital. He was also an Independent Director and Audit Chairman of The Stratech Group Ltd, a SGX listed company. Mr. Chew has also served as the CFO and Finance Director of KFC/Pizza Hut/Taco Bell Singapore, Delifrance Asia, Black and Decker Asia and Vickers Systems Ltd Asia Pacific. Mr. Chew’s entrepreneurial skills were highlighted in his successful founding of Silveray Pte Ltd in 2008, a wheelchair transportation company. Mr. Chew grew Silveray Pte Ltd from scratch to a current fleet size of 71 minibuses specializing in transporting people on wheelchairs, which he sold in November 2021. Mr. Chew is a member of Singapore Institute of Directors and Singapore Red Cross Fund-Raising Committee. He also serves as a District Councilor as well as Vice Chairman of Finance Committee of South West Central Development Committee (CDC), which serves the people in the Southwest Region of Singapore under the Mayor of SW CDC. He has previously served on the Council of Singapore Red Cross and was the Chairman for Singapore’s Red Cross Committee for Humanitarian Assistance and International Relief (CHAIR), during which he was honored with the Singapore Red Cross Outstanding Service Award in Sept 2019 by the President of Singapore. He has also served on the Board of Ang Mo Kio (“AMK”)-Thye Hua Kwan (“THK”) Hospital, was a member of AMK-THK Medi-fund Committee, and a member of THK Moral Society audit committee. Since 2010, Mr. Chew has served as an independent director to Pacific Andes Resources Development Ltd. Since 2012, Mr. Chew has acted as an independent director and audit chair of the University of Las Vegas for their Singapore campus. Mr. Chew holds an MBA degree and a Bachelor of Science degree in Accounting, summa cum laude, from the University of South Alabama. He has completed an Executive Program at INSEAD, France for Global CFOs.
Jukka Rannila, Global Star’s independent director serves as a member of Global Star’s board of directors and audit committee. Mr. Rannila is a seasoned professional with vast experience in investment management and real estate. From 2013 to 2020 Mr. Rannila served as the Chairman of the board of directors of Berlin Invest 3 Oy, from 2012-2020 with Berlin Invest 2 Oy, and from 2011 to 2022 with Berlin Invest Oy, where he oversaw residential real estate portfolios. Mr. Rannila currently serves as a board member of the investment management company for the Berlin Invest Oy groups, Confido Kiinteistöhallinta Oy, where he oversees a residential real estate portfolio in Berlin, Germany. Similarly, since 2018, Mr. Rannila has acted as a member of the board of Revelon Oy (formerly Assai Commercial Oy), where he oversees a commercial real estate portfolio in the greater Helsinki area. Since 2004, Mr. Rannila has acted as a board member and investment manager of Assai Oy, where he is responsible for the operations and investment portfolio of listed and non-listed companies in the family office. Since 2009, Mr. Rannila has acted as chairman of the board of Nosh Company Oy, where he co-directs a high growth fashion and design group of companies. Currently, Mr. Rannila also co-directs a high growth robotics company with international expansion, Trussmatic Oy. Similarly, since 2018, Mr. Rannila co-directs a high growth manufacturing group of companies through his director position with Tikli Group Oy. More recently, in 2021, Mr. Rannila manages all operations of Warp Bridge Oy, a SPV investing in a venture capital fund, as a Managing Director. Mr., Rannila studied at the University of Manchester in the Department of Accounting and Finance.
Number and Terms of Officers and Directors
Global Star has six directors since the completion of Global Star’s IPO. Global Star’s board of directors is divided into three classes with only one class of directors being elected in each year and each class (except for those directors appointed prior to Global Star’s first annual meeting of stockholders) serving a three-year term. In accordance with Nasdaq corporate governance requirements, Global Star is not required to hold an annual meeting until one year after Global Star’s first fiscal year end following Global Star’s listing on Nasdaq. The term of office of the first class of directors, consisting of Hai Chwee Chew and Jukka Rannila will expire at Global Star’s first annual meeting of stockholders. The term of office of the second class of directors, consisting of Stephen Drew, Lam Chun Wing, and Yang Kan Chong will expire at the second annual meeting of stockholders. The term of office of the third class director, consisting of Anthony Ang, will expire at the third annual meeting of stockholders.
Our officers are appointed by the board of directors and serve at the discretion of the board of directors, rather than for specific terms of office. Global Star’s board of directors is authorized to appoint persons to the offices set forth in Global Star’s bylaws as it deems appropriate. Global Star’s bylaws provide that Global Star’s officers may consist of a Chairman of the Board, Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, President, Vice Presidents, Secretary, Treasurer, Assistant Secretaries, and such other offices as may be determined by the board of directors.
On October 24, 2022, Benny Kan resigned from the Board for personal reasons. Mr. Kan was an independent director and served on the Audit Committee of the Board. His resignation was effective on November 15, 2022. The Board named Argon Lam to serve as Director in the place of Mr. Kan. On January 12, 2023, Global Star’s board of directors appointed Argon Lam, to serve as a member of both the Compensation Committee of the Board and the Audit Committee of the Board, effective immediately. On the same day, the Board also appointed Jukka Rannila to serve as a member of the Compensation Committee of the Board, effective immediately. On January 12, 2023, the Company issued a press release announcing the appointments of Argon Lam and Jukka Rannila to serve as members of the Compensation Committee, and the appointment of Argon Lam to serve as a member of the Audit Committee. A copy of the press release is attached to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on January 12, 2023 available at www.sec.gov.
Director Independence
Nasdaq listing standards require that a majority of Global Star’s board of directors be independent. An “independent director” is defined generally as a person other than an officer or employee of the company or its subsidiaries or any other individual having a relationship which in the opinion of the company’s board of directors, would interfere with the director’s exercise of independent judgment in carrying out the responsibilities of a director. Global Star’s board of directors has determined that Lam Chun Wing, Yang Kan Chong, Hai Chwee Chew, and Jukka Rannila are “independent directors” as defined in the Nasdaq listing standards and applicable SEC rules. Global Star’s independent directors will have regularly scheduled meetings at which only independent directors are present.
Executive Officer and Director Compensation
After the completion of Global Star’s initial business combination, members of Global Star’s management team who remain with Global Star may be paid consulting or management fees from the combined company. All of these fees will be fully disclosed to stockholders, to the extent then known, in the proxy solicitation materials or tender offer materials furnished to Global Star’s stockholders in connection with the Business Combination. Global Star has not established any limit on the amount of such fees that may be paid by the combined company to Global Star’s members of management. It is unlikely the amount of such compensation will be known at the time of the Business Combination because the directors of the post-combination business will be responsible for determining executive officer and director compensation. Any compensation to be paid to Global Star’s executive officers will be determined, or recommended to the board of directors for determination, either by a compensation committee constituted solely by independent directors or by a majority of the independent directors on Global Star’s board of directors.
Global Star does not intend to take any action to ensure that members of Global Star’s management team maintain their positions with Global Star after the completion of Global Star’s initial business combination, although it is possible that some or all of Global Star’s executive officers and directors may negotiate employment or consulting arrangements to remain with Global Star after Global Star’s initial business combination. The existence or terms of any such employment or consulting arrangements to retain their positions with Global Star may influence Global Star’s management’s motivation in identifying or selecting a target business but Global Star does not believe that the ability of Global Star’s management to remain with Global Star after the completion of Global Star’s initial business combination will be a determining factor in Global Star’s decision to proceed with any potential business combination. Global Star is not party to any agreements with Global Star’s executive officers and directors that provide for benefits upon termination of employment.
Committees of the Board of Directors
Our board of directors has two standing committees: an audit committee and a compensation committee. Subject to phase-in rules and a limited exception, Nasdaq rules and Rule 10A-3 of the Exchange Act require that the audit committee of a listed company be comprised solely of independent directors, and Nasdaq rules require that the compensation committee of a listed company be comprised solely of independent directors. Global Star’s audit and compensation committees are staffed with the following independent directors.
| Standing Committees Audit | | Compensation |
| Argon Lam Chun Win | | Argon Lam Chun Win |
| Hai Chwee Chew | | Yang Kang Chong |
| Jukka Rannila | | Jukka Rannila |
Each of Messrs. Lam, Chew, Chong, and Rannila meet the independent director standard under Nasdaq listing standards and under Rule 10-A-3(b)(1) of the Exchange Act.
Audit Committee
Global Star has established an audit committee. Each member of the audit committee is financially literate, and Global Star’s board of directors has determined that each of Messer Lam, Chew and Rannila, qualifies as an “Audit Committee Financial Expert” as defined in applicable SEC rules.
Global Star has adopted an audit committee charter, which details the principal functions of the audit committee, including:
| | ● | appointing, compensating, and overseeing Global Star’s independent registered public accounting firm; |
| ● | reviewing and approving the annual audit plan for the company; |
| | ● | overseeing the integrity of Global Star’s financial statements and Global Star’s compliance with legal and regulatory requirements; |
| ● | discussing the annual audited financial statements and unaudited quarterly financial statements with management and the independent registered public accounting firm; |
| | ● | pre-approving all audit services and permitted non-audit services to be performed by Global Star’s independent registered public accounting firm, including the fees and terms of the services to be performed; |
| ● | appointing or replacing the independent registered public accounting firm; |
| | ● | establishing procedures for the receipt, retention, and treatment of complaints (including anonymous complaints) Global Star receives concerning accounting, internal accounting controls, auditing matters or potential violations of law; |
| | ● | monitoring Global Star’s environmental sustainability and governance practices; |
| | ● | establishing procedures for the receipt, retention and treatment of complaints received by Global Star regarding accounting, internal accounting controls or reports which raise material issues regarding Global Star’s financial statements or accounting policies; |
| | ● | approving audit and non-audit services provided by Global Star’s independent registered public accounting firm; |
| | ● | discussing earnings press releases and financial information provided to analysts and rating agencies; |
| | ● | discussing with management Global Star’s policies and practices with respect to risk assessment and risk management; |
| | ● | reviewing any material transaction between Global Star’s Chief Financial Officer that has been approved in accordance with Global Star’s Code of Ethics for its officers, and providing prior written approval of any material transaction between Global Star and its President; and |
| | ● | producing an annual report for inclusion in Global Star’s proxy statement, in accordance with applicable rules and regulations. The audit committee is a separately designated standing committee established in accordance with Section 3(a)(58)(A) of the Exchange Act. |
Compensation Committee
Global Star has established a compensation committee of Global Star’s board of directors as delineated above with independent directors. Global Star has adopted a compensation committee charter, which details the principal functions of the compensation committee, including:
| | ● | reviewing and approving corporate goals and objectives relevant to Global Star’s President’s compensation, evaluating Global Star’s President’s performance in light of those goals and objectives, and setting Global Star’s President’s compensation level based on this evaluation; |
| | ● | setting salaries and approving incentive compensation and equity awards, as well as compensation policies, for all other officers who file reports of their ownership, and changes in ownership, of the company’s common stock under Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act (the “Section 16 Officers”), as designated by Global Star’s board of directors; |
| | ● | making recommendations to the board of directors with respect to incentive compensation programs and equity-based plans that are subject to board approval; |
| | ● | any employment or severance agreements with Global Star’s Section 16 Officers; |
| | ● | granting any awards under equity compensation plans and annual bonus plans to Global Star’s President and the Section 16 Officers; |
| | ● | approving the compensation of Global Star’s directors; and |
| | ● | producing an annual report on executive compensation for inclusion in Global Star’s proxy statement, in accordance with applicable rules and regulations. |
Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation
None of Global Star’s executive officers currently serves, and in the past year has not served, as a member of the compensation committee of any entity that has one or more executive officers serving on Global Star’s board of directors.
Corporate Governance and Nominating Committee
Global Star does not have a standing nominating committee though Global Star intends to form a corporate governance and nominating committee as and when required to do so by law or Nasdaq rules. In accordance with Rule 5605 of the Nasdaq rules, a majority of the independent directors may recommend a director nominee for selection by the board of directors. The board of directors believes that the independent directors can satisfactorily carry out the responsibility of properly selecting or approving director nominees without the formation of a standing nominating committee. Global Star’s independent directors will participate in the consideration and recommendation of director nominees. In accordance with Rule 5605 of the Nasdaq rules, all such directors are independent. As there is no standing nominating committee, Global Star does not have a nominating committee charter in place.
The board of directors will also consider director candidates recommended for nomination by Global Star’s stockholders during such times as they are seeking proposed nominees to stand for election at the next annual meeting of stockholders (or, if applicable, a special meeting of stockholders). Global Star’s stockholders that wish to nominate a director for election to Global Star’s board of directors should follow the procedures set forth in Global Star’s bylaws.
Global Star has not formally established any specific, minimum qualifications that must be met or skills that are necessary for directors to possess. In general, in identifying and evaluating nominees for director, the board of directors considers educational background, diversity of professional experience, knowledge of Global Star’s business, integrity, professional reputation, independence, wisdom, and the ability to represent the best interests of Global Star’s stockholders.
The primary function of the corporate governance and nominating committee include:
| | ● | identifying individuals qualified to become members of the board of directors and making recommendations to the board of directors regarding nominees for election; |
| | ● | reviewing the independence of each director and making a recommendation to the board of directors with respect to each director’s independence; |
| | ● | developing and recommending to the board of directors the corporate governance principles applicable to Global Star and reviewing its corporate governance guidelines at least annually; |
| | ● | making recommendations to the board of directors with respect to the membership of the audit, compensation, and corporate governance and nominating committees; |
| | ● | overseeing the evaluation of the performance of the board of directors and its committees on a continuing basis, including an annual self-evaluation of the performance of the corporate governance and nominating committee; |
| | ● | considering the adequacy of Global Star’s governance structures and policies, including as they relate to Global Star’s environmental sustainability and governance practices; |
| | ● | considering director nominees recommended by stockholders; and |
| | ● | reviewing Global Star’s overall corporate governance and reporting to the board of directors on its findings and any recommendations. |
Guidelines for Selecting Director Nominees
The guidelines for selecting nominees, which is specified in the charter adopted by us, generally provides that person to be nominated:
| | ● | should possess personal qualities and characteristics, accomplishments, and reputation in the business community; |
| | ● | should have current knowledge and contacts in the communities in which Global Star does business and, in Global Star’s industry, or other industries relevant to Global Star’s business; |
| | ● | should have the ability and willingness to commit adequate time to the board of directors and committee matters; |
| | ● | should demonstrate ability and willingness to commit adequate time to the board of directors and committee matters; |
| | ● | should possess the fit of the individual’s skills and personality with those of other directors and potential directors in building a board of directors that is effective, collegial, and responsive to Global Star’s needs; and |
| | ● | should demonstrate diversity of viewpoints, background, experience, and other demographics, and all aspects of diversity in order to enable the board of directors to perform its duties and responsibilities effectively, including candidates with a diversity of age, gender, nationality, race, ethnicity, and sexual orientation. |
Each year in connection with the nomination of candidates for election to the board of directors, the corporate governance and nominating committee will evaluate the background of each candidate, including candidates that may be submitted by Global Star’s stockholders.
Code of Ethics
Global Star has adopted a Code of Ethics applicable to Global Star’s directors, officers, and employees. Global Star has filed a copy of Global Star’s Code of Ethics and Global Star’s audit committee charter as exhibits to the registration statement. You are able to review these documents by accessing Global Star’s public filings at the SEC’s web site at www.SEC.gov. In addition, a copy of the Code of Ethics will be provided without charge upon request from us.
Conflicts of Interest
Subject to pre-existing fiduciary or contractual duties as described below, Global Star’s officers and directors have agreed to present any business opportunities presented to them in their capacity as a director or officer of Global Star’s company to us. Certain of Global Star’s officers and directors presently have fiduciary or contractual obligations to other entities pursuant to which such officer or director is or will be required to present a business combination opportunity. Accordingly, if any of Global Star’s officers or directors becomes aware of a business combination opportunity which is suitable for an entity to which he or she has then-current fiduciary or contractual obligations, he or she will honor his or her fiduciary or contractual obligations to present such opportunity to such entity. Global Star believes, however, that the fiduciary duties or contractual obligations of Global Star’s officers or directors will not materially affect Global Star’s ability to complete Global Star’s initial business combination. Global Star’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation provides that Global Star renounces Global Star’s interest in any corporate opportunity offered to any director or officer unless such opportunity is expressly offered to such person solely in his or her capacity as a director or officer of Global Star’s company and such opportunity is one Global Star is legally and contractually permitted to undertake and would otherwise be reasonable for Global Star to pursue, and to the extent the director or officer is permitted to refer that opportunity to Global Star without violating another legal obligation.
Our officers and directors may become officers or directors of another special purpose acquisition company with a class of securities intended to be registered under the Exchange Act, even prior to Global Star entering into a definitive agreement for Global Star’s initial business combination. Potential investors should also be aware of the following other potential conflicts of interest:
| | ● | None of Global Star’s officers or directors is required to commit his or her full time to Global Star’s affairs and, accordingly, may have conflicts of interest in allocating his or her time among various business activities. |
| | ● | In the course of their other business activities, Global Star’s officers and directors may become aware of investment and business opportunities which may be appropriate for presentation to Global Star as well as the other entities with which they are affiliated. Global Star’s management may have conflicts of interest in determining to which entity a particular business opportunity should be presented. |
| | ● | Our Initial Stockholders have agreed to waive their redemption rights with respect to any founder shares, placement shares and any public shares held by them in connection with the consummation of Global Star’s initial business combination. Additionally, Global Star’s Initial Stockholders have agreed to waive their redemption rights with respect to any founder shares and placement shares held by them if Global Star fails to consummate Global Star’s initial business combination within 12 months from the closing of this offering (or up to 21 months by depositing into the trust account for each one-month extension $264,000, or $303,600 if the underwriters’ over-allotment option is exercised in full ($0.033 per unit in either case), or as extended by the Company’s stockholders in accordance with Global Star’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation). Neither the Sponsor or the Initial Stockholders received any additional consideration for these waivers. If Global Star does not complete its initial business combination within such applicable time period, the proceeds of the sale of the placement units held in the trust account will be used to fund the redemption of Global Star’s public shares, and the placement securities will expire worthless. With certain limited exceptions, the founder shares will not be transferable, assignable by Global Star’s sponsor until the earlier to occur of: (A) twelve months after the completion of Global Star’s initial business combination and (B) subsequent to Global Star’s initial business combination, (x) if the reported last sale price of Global Star’s Class A Common Stock equals or exceeds $12.00 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, right issuances, reorganizations, recapitalizations and the like) for any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period commencing at least six months after Global Star’s initial business combination, or (y) the date on which Global Star completes a liquidation, merger, capital stock exchange, reorganization or other similar transaction that results in all of Global Star’s stockholders having the right to exchange their shares of common stock for cash, securities or other property. With certain limited exceptions, the placement units, placement shares and placement warrants and the Class A Common Stock underlying such warrants, will not be transferable, assignable or saleable by Global Star’s sponsor or its permitted transferees until 30 days after the completion of Global Star’s initial business combination. Since Global Star’s sponsor and officers and directors may directly or indirectly own common stock and warrants following this offering, Global Star’s officers and directors may have a conflict of interest in determining whether a particular target business is an appropriate business with which to effectuate Global Star’s initial business combination. |
| | ● | Our officers and directors may have a conflict of interest with respect to evaluating a particular business combination if the retention or resignation of any such officers and directors was included by a target business as a condition to any agreement with respect to Global Star’s initial business combination. |
| | ● | Our sponsor, officers or directors may have a conflict of interest with respect to evaluating a business combination and financing arrangements as we may obtain loans from Global Star’s sponsor or an affiliate of Global Star’s sponsor or any of Global Star’s officers or directors to finance transaction costs in connection with an intended initial business combination. Up to $1,500,000 of such working capital loans may be converted into GLST Units, at a price of $10.00 per unit at the option of the lender, upon consummation of Global Star’s initial business combination. The units would be identical to the placement units. |
The conflicts described above may not be resolved in Global Star’s favor. In general, officers and directors of a corporation incorporated under the laws of the State of Delaware are required to present business opportunities to a corporation if:
| | ● | the corporation could financially undertake the opportunity; |
| | ● | the opportunity is within the corporation’s line of business; and |
| | ● | it would not be fair to Global Star’s company and its stockholders for the opportunity not to be brought to the attention of the corporation. |
Accordingly, as a result of multiple business affiliations, Global Star’s officers and directors may have similar legal obligations relating to presenting business opportunities meeting the above-listed criteria to multiple entities. Furthermore, Global Star’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation provides that Global Star renounces its interest in any corporate opportunity offered to any director or officer unless such opportunity is expressly offered to such person solely in his or her capacity as a director or officer of Global Star’s company and such opportunity is one Global Star is legally and contractually permitted to undertake and would otherwise be reasonable for Global Star to pursue, and to the extent the director or officer is permitted to refer that opportunity to Global Star without violating another legal obligation. Below is a table summarizing the entities to which Global Star’s executive officers and directors currently have fiduciary duties or contractual obligations:
| Individual(1) | | Entity(2) | | Entity’s Business | | Affiliation |
| Anthony Ang | | Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Government of Singapore | | Representations of the Interests of the Republic of Singapore | | Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Yong Tai Bhd. | | Property Development | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Heatec Jietong Holding Ltd. | | Manufacturing and Services, Marine Industry | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Better World Asset Management Ltd. | | Management Consultancy Services | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Sinospring Venture Ltd. | | Management Consultancy Services | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | GCIC Ltd. | | Management Consultancy Services | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Seascape Investments Pte. Ltd. | | Management Consultancy Services | | Director |
| | | ITE Education Services Pte. Ltd. | | Education Consultancy Services | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Truufin Pte. Ltd. | | Fintech | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | RV SG Pte Ltd. | | Real Estate Fund Management | | Chairman |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Singapore Digital Exchange Pte Ltd. | | Digital Exchange | | Chairman |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Imperiale Investment Holdings Ltd. | | Investment Holdings | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| Nicholas Khoo | | COMEBACK PTE. Ltd. | | Counseling Services | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | KHOO CAP ONE PTE. Ltd. | | Consulting | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | KHOO CAP TWO PTE. Ltd. | | Investment | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | KHOO CAP THREE PTE. Ltd. | | Investment | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Goku Ventures PTE, Ltd. | | Consulting | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Khoo Tech | | Consulting | | Sole Proprietor |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Hatten Land Ltd. | | Real Estate | | Independent Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Tribeca Global SPAC Fund LLC | | Finance | | Investment Committee Member |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Global Fund LLC | | Finance | | Investment Committee Member |
| | | | | | | |
| | | A.D. VENTURE | | Venture Capital | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| Stephen Drew | | Tribeca Global SPAC Fund IV LLC | | Investments | | Investment Committee Member |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Global Fund LLC | | Finance | | Managing Partner |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Tribeca Global SPAC Fund I LLC | | Investments | | Investment Committee Member |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Tribeca Global SPAC Fund III LLC | | Investments | | Investment Committee Member |
| | | | | | | |
| Chun Wing Lam | | IPG Wealth Management Limited | | Wealth Management Fund | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Golden Great China Fund Management Ltd. | | Finance | | First Vice President |
| Yang Kan Chong | | Tribeca Global SPAC Fund IV LLC | | Investments | | Investment Committee Member |
| | | | | | | |
| Global Fund LLC | | Finance | | Managing Director and Investment Committee Member |
| | | | | |
| Hai Chwee Chew | | Surecanlah | | Consultancy/Investment | | CEO/Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Pacific Andes Resources Dept. | | Global Supply/Fishing | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | University of Las Vegas, Singapore | | Education | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| Jukka Rannila | | Assai Oy | | Investments | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Nosh Company Oy | | Fashion and Design | | Chairman of the Board |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Tikli Group Oy | | Manufacturing | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Warp Bridge Oy | | Investments | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Confido Kiinteistöhallinta Oy | | Residential Real Estate Investments | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Trussmatic Oy | | Robotics | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Assai Commercial Oy | | Commercial Real Estate | | Director |
| | | | | | | |
| | | Global Fund LLC | | Finance | | Investment Committee Member |
| | | | | | | |
| Shan Cui | | Venus Acquisition Corp. | | SPAC | | Director |
| (1) | Each person has a fiduciary duty with respect to the listed entities next to their respective names. |
| (2) | Each of the entities listed in this table has priority and preference relative to Global Star’s company with respect to the performance by each individual listed in this table of his obligations and the presentation by each such individual of business opportunities. |
Accordingly, if any of the above executive officers or directors becomes aware of a business combination opportunity which is suitable for any of the above entities to which he or she has current fiduciary or contractual obligations, he or she will honor his or her fiduciary or contractual obligations to present such business combination opportunity to such entity, and only present it to Global Star if such entity rejects the opportunity. Global Star is not prohibited from pursuing an initial business combination with a company that is affiliated with Global Star’s sponsor, officers or directors. In the event Global Star seeks to complete Global Star’s initial business combination with such a company, we, or a committee of independent directors, would obtain an opinion from an independent investment banking firm or another independent entity that commonly renders valuation opinions, that such an initial business combination is fair to Global Star’s company from a financial point of view. In the event that Global Star submits its initial business combination to Global Star’s public stockholders for a vote, pursuant to the letter agreement, Global Star’s sponsor, officers and directors have agreed to vote any founder shares or placement shares held by them and any public shares purchased during or after the offering (including in open market and privately negotiated transactions) in favor of Global Star’s initial business combination.
Executive Compensation
None of Global Star’s executive officers or directors have received any cash compensation for services rendered to us. Global Star may pay consulting, finder or success fees to Global Star’s Initial Stockholders, officers, directors, or their affiliates for assisting Global Star in consummating its initial business combination. In addition, Global Star’s Initial Stockholders, executive officers, and directors, or any of their respective affiliates will be reimbursed for any out-of-pocket expenses incurred in connection with activities on Global Star’s behalf such as identifying potential target businesses and performing due diligence on suitable business combinations. There is no limit on the amount of out-of-pocket expenses reimbursable by us.
After Global Star’s initial business combination, members of Global Star’s management team who remain with Global Star may be paid consulting, management, or other fees from the combined company with any and all amounts being fully disclosed to shareholders, to the extent then known, in the proxy solicitation materials furnished to Global Star’s shareholders. The amount of such compensation may not be known at the time of a shareholder meeting held to consider an initial business combination, as it will be up to the directors of the post-combination business to determine executive and director compensation. In this event, such compensation will be publicly disclosed at the time of its determination in a Current Report on Form 8-K, as required by the SEC. Since Global Star’s formation, Global Star has not granted any stock options or stock appreciation rights or any other awards under long-term incentive plans to any of Global Star’s executive officers or directors.
Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation
None of Global Star’s executive officers currently serves, and in the past year has not served, as a member of the compensation committee of any entity that has one or more executive officers serving on the Global Star Board.
Code of Business Conduct and Ethics
Global Star has adopted a code of ethics applicable to Global Star’s directors, officers and employees (“Code of Ethics”). A copy of the Code of Ethics will be provided without charge upon request from us. Global Star intends to disclose any amendments to or waivers of certain provisions of Global Star’s Code of Ethics in a Current Report on Form 8-K.
Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance
Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act requires Global Star’s officers, directors and persons who beneficially own more than ten percent of Global Star’s ordinary shares to file reports of ownership and changes in ownership with the SEC. These reporting persons are also required to furnish Global Star with copies of all Section 16(a) forms they file.
PUBCO’S DIRECTORS AND EXECUTIVE OFFICERS
AFTER THE BUSINESS COMBINATION
PubCo’s Directors and Executive Officers
Following the closing of the Business Combination PubCo’s directors and executive officers shall be as follows:
| Name | | Age | | Position |
| Pyeung Ho Choi | | 66 | | Co-Founder and Chairman |
| Young Jae Lee | | 49 | | Co-Founder and Director |
| Ted Kim | | 53 | | Co-Founder of K Enter and Director |
| Tan Chin Hwee(1) | | 52 | | Director, Executive Chairman and Interim CEO |
| Hyung Seok Cho | | 46 | | Director |
| Tae Woo Kim | | 41 | | Director |
| Han Jae Kim (Patrick Kim) | | 35 | | Director |
| Jaekeun (Jason) Kim | | 43 | | Director |
| Jun Jong(2) | | 53 | | CFO |
| Jihun Byun(3) | | 45 | | CAO |
| Jeong Hoon Bae | | 45 | | Head of Content Production |
| (1) | The form of Tan Chin Hwee’s employment agreement with PubCo is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.47. |
| (2) | The form of Jun Jong’s employment agreement with PubCo is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.48. |
| (3) | The form of Jihun Byun’s employment agreement with PubCo is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.49. |
PubCo’s Board Members
Pyeung-ho Choi. Mr. Pyeung-ho Choi is expected to serve as Chairman of PubCo. Mr. Pyeung-ho Choi is the co-founder and Chairman of K Enter Holdings Inc. and the founder and CEO of Solaire Partners LLC, one of the leading Korean content VC firm and one of the pioneers in the Korean entertainment industry. Prior to Solaire Partners LLC, Mr. Choi was the appointed President Fund Manager of the Union Global Contents Investment Fund at Union Investment Partners Inc. from 2012 to 2016. At a size of US $120 million, the fund partnered with major Korean distributors and financiers, the Korean government, and foreign investors, with an aim to invest in international co-productions to globalize the Korean film and content industry. Through Mr. Choi’s vast experience in content investment, the Union Global Contents Investment Fund collaborated with Korean companies, directors, and actors in co-productions with countries including the United States, China, and Japan. Before joining Union Investment Partners, Choi was the Chief Executive Officer of Sidus FNH at Korea Telecom Group, where he oversaw the company’s film financing, production, and distribution operations. He spearheaded the aggregation and digital distribution of content through multiple new media platforms that Korea Telecom Group owned and operated from 2008 to 2011; these platforms included IPTV, Internet VOD, Satellite TV, and mobile.
Mr. Choi began his entertainment industry career at CJ Group, where he was one of the founding members of CJ Entertainment (CJENM). He served as Executive Vice President at CJENM from 2000 to 2007 after serving as General Manager of strategic planning and international business teams from 1995 to 1999. He played a critical role in shaping CJ Group’s film business portfolio, including: the inception of CJ Entertainment through the CJ Group’s investment in DreamWorks SKG in the United States; the joint venture that distributed CJ films across Asia; the formation of CJ Group’s exhibition arm, CGV, that became Korea’s largest exhibitor, initially jointly established by CJ Group, Golden Harvest, and Village Roadshow. During his 12 year tenure at CJ Entertainment, Choi financed and distributed a number of notable Korean films that introduced many talented Korean directors and actors. He launched filmed entertainment, music licensing, TV drama series, animation, and cable broadcasting businesses. In 1982, he started at the Samsung Group in business planning at CJ CheilJedang Corporation, where he was responsible for business strategy planning, M&A, overseas business and export, and overseas marketing. From 1987 to 1994, he served as head of the strategy planning team and head of the overseas business team. Mr. Choi holds a Ph.D. in holographic engineering, a Master’s degree in 3D contents from Kwangwoon University, and a Bachelor’s degree in chemical engineering from Youngnam University.
Young Jae Lee. Mr. Youngjae Lee is expected to serve as a member of the board of directors of PubCo. Youngjae Lee co-founded K Enter Holdings Inc. and Solaire Partners LLC in October 2023 and June 2007, respectively, and has been serving as their Chief Executive Officer since then. Youngjae Lee worked at KT from 2000 to 2016, where he undertook various positions such as a team member, deputy director, and project leader. During his stay at KT, Mr. Lee oversaw subsidiaries such as NTC and Mongol Telecom, handled mergers and acquisitions planned by KT, led business developments of KT, and was responsible for various in-house consulting tasks. While overseeing KT’s Russian telecommunications subsidiary NTC in Vladivostok, he contributed to its growth and exit strategy and made it the largest telecommunications operator in the Far East region. From Apil 2006 to September 2010, he served as the Chief Financial Officer and the Chief Information Officer at Sidus FNH, a movie production company acquired by KT as its strategy to enter the Korean content media industry. This experience equipped him with insights into the content industry, where he introduced real-time production management systems to enhance budget efficiency in movie productions. Starting in October 2010, Mr. Lee was responsible for overseas subsidiaries and international telecommunications operators within KT’s in-house consulting department. During this period he made substantial contributions to the growth of KT’s subsidiaries East Telecom and EVO in Uzbekistan by conducting management assessments and formulating growth strategies. His efforts led to KT’s recognitions such as Outstanding Employee Award in 2011, and further responsibilities such as Project Manager position for the Game Changer Project at Botswana’s government-owned telecommunications company, BoFiNet in 2015. Through Mr. Lee’s initiative, BoFiNet gained global recognition in 2016 as the most innovative telecommunications company. In 2017, Mr. Lee founded Solaire Partners, a venture capital firm specializing in content investments. Solaire Partners has amassed assets under management (AUM) amounting to USD $112 million and secured investments of USD $44 million from the South Korean government for four distinct funds, with Mr. Lee taking on the role of manager for three of these funds. Up until the date of this prospectus, Solaire Partners invested in approximately 200 films, with 49% surpassing the break-even point, significantly outperforming the market average of 33% and even surpassing the 16% market average return. Under Mr. Lee’s leadership, Solaire Partners has achieved substantial success by investing in various films and content, leveraging South Korean commercial film industry data to enhance investment strategies and yield higher returns. Furthermore, Solaire Partners has been diversifying investments into the digital human and virtual production studio sectors to lead the paradigm shift in the Korean content industry. Mr. Lee received a degree in Business Administration from Chungbuk National University in 2000. He furthered his education by participating in the Global MBA program at Sungkyunkwan University and attending Indiana University’s Kelly Business School as an exchange student, enhancing his academic background class of 2015. He also holds the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) qualification, demonstrating his expertise in financial matters. Currently, he serves as an instructor for the Cultural Content segment of the Korean Venture Capital Association’s Venture Capitalist program, starting in 2021.
Ted Kim. Mr. Kim is expected to serve as a member of the board of directors of PubCo. Mr. Kim founded Global Fund LLC in August 2013, a US-based private equity firm that focuses on investing in high-growth companies across various industries and geographies, including the pre-IPO period, and has been serving as its Managing Partner ever since. Global Fund LLC is also the managing member of Tribeca Global SPAC Fund I, III, and IV LLC which were founded during 2021 and 2022. Mr. Kim is a highly experienced and disciplined private equity specialist who has successfully launched and closed multiple U.S.-based private equity funds. Mr. Kim has also been a member of the Korea-America Business Summit, Washington D.C., since 2019. He co-founded Global Star Acquisition I LLC in September 2022, the sponsoring entity for the US Nasdaq listed SPAC “Global Star Acquisition Inc.”, and has been serving as its Managing Member ever since. He also co-founded K Enter Holdings Inc. in January 2023. Mr. Kim is also an Attorney at Law focusing on mergers and acquisitions and cross-border transactions. He was a Guest Lecturer at Tsinghua University in 2005 on American venture capitalism. Mr. Kim received his Juris Doctor degree from the Pennsylvania State University’s Dickinson School of Law in May 1997. He received his Bachelor of Arts degree in Finance and Politics, a double major, from the Catholic University of America in May 1993.
Tan Chin Hwee. Mr. Tan Chin Hwee is expected to serve as PubCo’s Executive Chairman, Interim Chief Executive Officer and as a member of the board of directors of PubCo. Mr. Tan has been serving as the Chairman of SGTraDex Services since 2021. SGTraDex is built upon the foundation of the Emerging Stronger Taskforce Alliance for Action and formed through a collaborative effort across public and private stakeholders. Mr. Tan was nominated as a member of the Trade and Connectivity Standards Committee under the Singapore Standards Council (SSC)/MTI in 2021, which facilitates the development, promotion and review of standards in Singapore. Mr. Tan has been serving as the Chief Executive Officer of Asia Pacific of Trafigura since 2016. He joined Trafigura in 2016 as Chief Executive Officer of Asia Pacific and is responsible for continuing the growth of Trafigura’s business across the region. Trafigura was the largest amongst the only three Singapore companies to appear in the Fortune Global 500 list and it ranked top 22 globally. Mr. Tan has more than 25 years of experience in management and financial roles. Prior to joining Trafigura, he was most recently the founder of the Asian operations of alternative investment firm Apollo Global Management, and before that, managing director at hedge fund Amaranth Advisors. In addition, Mr. Tan has sat on the boards of various organizations in the public and private sectors. The positions he held include: member of the Resource Panel for Government Parliamentary Committee for Finance and Trade and Industry; member of the Advisory Panel for Youth Corps Singapore; member of the Advisory Panel for the Ministry of Education; member of the Advisory Panel for the Ministry of Culture, Community and Youth; board member of Lien Aid Limited (Singapore), the endowment fund for KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital; advisory board member of Shanghai Jiao Tong University’s Shanghai Advanced Institute of Finance; non-executive and independent director of Keppel REIT (until June 2017); member of Nanyang Technological University’s board of trustees; member of Hwa Chong Institution executive committee board; member of the Monetary Authority of Singapore’s Finance Centre Advisory Panel; and member of the Maritime and Port Authority of Singapore’s International Maritime Centre (IMC) 2030 Advisory Committee. Mr. Tan holds a Bachelor of Accountancy degree, graduating with Second Class Upper Honours in 1995 from NTU. He has an MBA from Yale University and completed a postgraduate course at Harvard Kennedy School. He is a Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) and is both an Australian and a Singapore-registered Certified Public Accountant (CPA). He was also the past President of CFA Society Singapore.
Hyeng Seok Cho. Mr. Cho began his career at Between Corporation which was formed by former members of the DVD team of Samsung’s content division. Next, he worked at SBS, one of the leading Korean broadcasting channels. He oversaw the division that produced DVDs of Korean dramas and movies as well as K pop artists. Building on his experience working with K pop artists he founded Play Company (Play) in 2012. He currently serves as its CEO. Play works with Korea’s top tier K pop talent agencies and pioneered a full service end-to-end solution of designing, producing, and distributing video merchandise. This model has allowed talent agencies and artists to see meaningful sales and profits from video merchandise products. In 2022 Play’s revenues exceeded $134 million. The artists Play has worked with includes BTS, Seventeen, Twice, Enhypen, TXT, Stray Kids, GOT7, ATEEZ, Block.B, CRAVITY, ASTRO, and Monsta X. Under his leadership Play has broadened the offerings of merchandise products and has even expanded to creating merchandise for popular Korea actors such as Lee Joon-gi, Park Bo-gum, and Kim Seon-ho. Cho Hyung Seok is a graduate of Kwangwoon University and holds a Bachelor’s degree in chemistry.
Tae Woo Kim. Tae Woo Kim is currently the CFO of Play Company Co., Ltd. managing the financial planning, budgeting, forecasting and the financial operations of the company. He brings with him a diverse set of experience primarily in the content industry. He has worked in strategic planning at JTBC, a major broadcasting network in Korea known for its entertainment, drama and variety shows. He also worked in strategic planning in T-broad holdings, a large cable operator. In addition to his experience in the content industry he also worked in strategic planning at Boryung holdings, a holding company of Boryung, a KOSDAQ listed pharmaceutical company. He has also worked in strategic planning in SF Innovation, a Korean fast food restaurant operator. Tae Woo received a Bachelor of Arts degree in business from Korea University.
Han Jae Kim (Patrick Kim). Mr. Han Jae Kim (Patrick Kim) is expected to serve as a member of the board of directors of PubCo. Patrick Kim has been serving as the Co-Founder and Managing Partner of Sui Generis Partners since November 2021. He has more than 10 years of capital market, investment banking, private equity, and venture capital experience. He is also a member of Investment Committee of Sui Generis Partners since November 2021. He additionally serves as an external advisor for Naviator Capital. At Sui Generis, he oversees an investment framework that originated, managed, and monitored a diverse portfolio of early-stage venture investment, mainly in SaaS/Cloud Software and Content/Entertainment sectors. Prior to establishing Sui Generis in 2021, Patrick Kim was an investment professional at BRV Capital Management from January 2018 to December 2021, one of the most prominent tech-focused private equity firms across Asia and the US. During his stay at BRV Capital Management, Patrick Kim was responsible for Growth Capital and Late-Stage Venture Capital investment in the US and Europe. Prior to joining BRV Capital Management, Patrick Kim worked at BGC Partners Hong Kong and Daewoo Securities Hong Kong, responsible for originating, structuring, and executing equity, debt, and structured offering across a broad range of products and asset classes for both primary and secondary markets. Patrick Kim graduated from Peking University with a Bachelor of Economics degree, concentrating in Finance.
Jaekeun (Jason) Kim. Mr. Jaekeun Kim (Jason Kim) is expected to serve as a member of the board of directors of PubCo. Jason Kim is a seasoned investor and private equity specialist and he currently owns and operates Naviator Global Holdings LLC in Abu Dhabi, taking on the role of Founding Partner. His leadership has been pivotal in transforming investment strategies across multiple assets, establishing the firm as an influential player in the region. Prior to that, he founded and operated Innocus Global Group Pte, a Singapore-based investment firm, from March 2022 until March 2024, during which time he provided key regional strategies and investments across multiple assets. Since January 2016, he has also maintained the CEO position of “EQ Investment Inc.” a private equity fund based in Seoul, Korea. From late 2014 to late 2015, Jason served as a Regional Director at JD Capital in Beijing, focusing on investment opportunities in South Korea and Japan. Following this, Jason ascended to the role of Chief Executive Officer at EQ Investments Inc. in Seoul, a position he has held since January 2016. In this role, Jason has been instrumental in providing business consultancy services and guiding acquisitions of targeted properties and assets. Jason Kim embarked on his professional career as an Equity Research Intern at Mariners Investment Advisory Group in New York in early 2011. Shortly thereafter, he moved to Bloomberg Japan LLC in Tokyo, where Jason worked as a Credit Analyst from June 2011 to June 2012. Jason earned a Bachelor of Arts and Sciences in Economics and Sociology from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign in December 2007 and a Master of International Affairs from Columbia University School of International Affairs in New York, in May 2011, where he specialized in International Finance with an East Asia focus.
PubCo’s Executive Officers
Jun Jong. Mr. Jun Jong is expected to serve as the Chief Financial Officer of PubCo. He is currently the Chief Financial Officer of K Enter Holdings Inc. Mr. Jong started his career at Samsung electronics in 1995, performing various responsibilities such as foreign subsidiary management, investment, and planning. Following is work at Samsung, he joined the Hartford Financial Services in Tokyo, Japan and Hartford, Ct in 2000. He was one of the early startup members of Hartford Life Insurance K.K.’s Tokyo operations to launch the Japan operations where he performed strategic planning, financial analysis and investor relations, during which period it expanded to USD $15 billion in AUM. Subsequently he served as the Assistant Vice President for Business Development and Strategy for The Hartford Financial Services Group’s wealth management group until 2013, developing enterprise-wide business opportunities, supporting mergers and acquisitions transactions and divestiture of non-core businesses. More recently, Mr. Jong worked in private equity performing value creation and business development activities in portfolio companies, capital raising activities and LP management. Jun received a Bachelor of Arts degree in economics from Dartmouth College and an MBA from the Tuck School of Business at Dartmouth.
Jihun Byun, CPA, is currently the CAO of K Enter holdings, managing the accounting field of the company. He brings with him a diverse set of experience primarily in accounting, M&A, and corporate governance restructuring more than 10 years. He worked as general manager in corporate center at Wonik corporations, own several KOSDAQ listed corporations in the semiconductor/display, secondary battery, beauty, and digital healthcare sectors.
Jihun received a Bachelor of Arts degree in business from Sogang University.
Jeong Hoon Bae. Mr. Jeong Hoon Bae is expected to serve as the Head of Content Production of PubCo. Mr. Bae is a veteran and popular executive producer in Korea who has worked in the TV drama industry for 21 years. He started his career as an Assistant Director at drama department of SBS TV, one of the leading Korean broadcasting channels, from 2003 to 2007, helping to produce numerous dramas. Subsequently, he worked at TVN, a pay television network owned by CJ E&M. Next he worked at Bone Factory, a TV drama production company, as executive producer and created popular works such as “You’re Beautiful”, which was part of the first generation of Korean dramas to be aired in Asia and Japan. Subsequently he worked at Huayi Brothers as its executive producer, creating mini series for Korean broadcasting channels. Subsequently he worked as the Chief Executive Officer of Big Pictures, where he created several dramas that were aired in JTBC. Subsequently he was the senior vice president and executive producer of Ace Factory, where he led drama planning, production, distribution, and investment. Mr. Bae also worked on projects for streaming companies such as “The Grid” for Disney+. One of his earlier works “My Name” was also released on Netflix. Jeong Hoon Bae has a Bachelor of Arts in statistics and communications from SungkyunKwan University.
The directors and officers of Pubco will own 33,888,244 Ordinary Shares representing 52.8% of PubCo following the closing of the Business Combination, assuming no additional shares of Global Star common stock are redeemed.
PubCo’s Advisory Board
Michael Harpster. Mr. Harpster started his film career in 1970 with a small film company, New Line Cinema, releasing foreign films for the non-theatrical US market. In 1972, Mr. Harpster moved to New York City and became the head of Marketing for New Line. Key benchmarks in New Line’s growth were films like Jean Luc Godard’s Sympathy for the Devil and Reefer Madness. In 1984, Mr. Harpster participated in the development and marketing of the first A Nightmare On Elm Street, which grossed well over $57 million on a $1.1 million dollar budget. In 2021, A Nightmare on Elm Street was selected for preservation in the United States National Film Registry by the Library of Congress as being “culturally, historically, or aesthetically significant”. That first Nightmare led to a number of sequels and an approach to filmmaking and releasing that became known as “niche marketing” and lad to a number of high impact and low-cost films that were major successes for New Line in the “80 and 1990’s including films like House Party, the first Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles, The Mask. and many more. As President of Marketing at New Line, Mr. Harpster has devised campaigns for and released well over 200 feature films. He participated in an IPO and oversaw the development of video marketing with RCA Columbia. New Line Cinema was sold to Turner and then to Warner Brothers. It is one of the few independent film firms that prospered for over 40 years and its alumni are a virtual who’s who in Hollywood today. It became worth well over $4 billion. In 1995 Mr. Harpster broke open the “faith” market in the US with the release of The Omega Code which ended up selling well over 2,000,000 video units. In 2007, Mr Harpster worked with the award-winning producer, Moctezuma Esparza to raise funding for Maya Releasing, an effort directed to the Latin market. In 2011, Mr. Harpster became interested in the Asian market and consulted with several Asian producers including Yasushi Akimoto the founder of the well-known singing group AKB 48. In 2014 Mr. Harpster established his own consulting group, Orange Gove Media and continues to work today to help investors identify lucrative and safe media investments.
Faith Chu. Mr. Faith Chu has been serving as the Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of IPG Wealth Management LLC since January 2012. He has 40 years of experience in international finance and investment. He worked in AIG and AIA over 28 years since 1983. He was involved in numerous investment projects. He was appointed as the director of financial companies. He is experienced in strategic management, sales and marketing, capital allocation, and he has cultivated a lot of successful leaders and entrepreneurs. He is the founder of IPG Integrity Group, Chairman of Golden Great China Fund Management Limited. He is also the founder and president of HappyMen Foundation, and the co-founder of Hong Kong International Blockchain and Financial Association (HKIBFA). He was also the guest lecturer of Tsinghua University, Peking University, Zhongshan University and City University of Hong Kong. Mr. Chu is a member of the following institutes: Asia Pacific Financial Services Association (APFinSA), The Institute of Financial Accountants(IFA), Chartered Insurance Agency Management(CIAM), LIMRA International, Registered Financial Planner Institute(RFP).
Global Star Management and Directors who will join PubCo’s Advisory Board
Anthony Ang. Mr. Anthony Ang currently serves as the Chairman and CEO of Global Star Acquisition Inc. He is a global executive with over 40 years of senior management experience. His broad expertise covers international marketing, investment promotion, manufacturing, and fund management. Mr. Ang started his career at the Singapore Economic Development Board in 1980, and his last position was Regional Director for North America (based in the United States for six years) responsible for the promotion of investments from North America. He went on to become Group General Manager of Armstrong Industrial Corporation, a Singapore precision engineering company that he helped list on the Singapore Exchange in 1995. Mr. Ang then joined Vertex Management as Senior Vice President (Investment) in 1999, a leading venture Capital firm with its headquarters in Singapore and subsequently GIC Real Estate Pte. Ltd. (a unit of the Sovereign wealth fund of the Singapore Government) as Executive Vice President for Admin and Corporate Affairs in 2001. Mr. Ang went on to serve as founding Executive Director of Majulah Connection, a consulting and networking organization sponsored by the Government of Singapore. In 2006, Mr. Ang joined the ARA Group, a leading real estate fund management house with its headquarters in Singapore and asset under management (“AUM”) of $140 billion. From 2008 to 2010, Mr. Ang served as the CEO of ARAAsia Dragon Limited (“ADF”), the flagship private equity real estate fund of the ARA Group. ADF had a committed capital of $1.13 billion and was focused on investments across Asia. Mr. Ang was responsible for raising the fund with global investors and overseeing its investments of over fourteen assets. From February 2010 to December 2016, Mr. Ang served as the CEO and Executive Director of ARA Asset Management (Fortune) Pte. Ltd. (a subsidiary of the ARA Group), as the manager of Fortune Real Estate Investment Trust (“Fortune REIT”) with HK$36 billion of retail assets in Hong Kong. During his tenure at Fortune REIT, Mr. Ang was recognized as “Best CEO (Third)” and “Best CEO (First)” for Hong Kong in 2013 and 2014 respectively for successfully expanding Fortune REIT, by the Annual Best Managed Companies Poll by FinanceAsia. From March 2017 to July 2021, Mr. Ang served as CEO of Sasseur Asset Management Pte Ltd (SGX:CRPU), where he led the listing process for the initial public offering of Sasseur Real Estate Investment Trust (“Sasseur REIT”) (AUM US$1.2 billion) in March 2018. In 2019, under Mr. Ang’s leadership, Sasseur REIT was recognized as the “REIT of the Year” and “Best Retail REIT (platinum)” in Singapore. Mr. Ang was awarded “Best CEO (platinum)” in Singapore in 2019 and 2020 by The Fortune Times Award. Mr. Ang currently holds various senior positions. Since January 2016, Mr. Ang has served as an independent director of Yong Tai Bhd, a property development company listed on Bursa Malaysia, the Malaysian stock exchange. Since April 2017, Mr. Ang has served as an independent director with Heatec Jietong Holding Ltd., a marine industry manufacturing and service company that is listed on the Singapore Exchange. Mr. Ang has represented his country as the Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary of the Republic of Singapore to the Republic of Tunisia since September 2017. In that role he represents the interests of Singapore and helps to maintain the relations of amity and concord between the two countries. In December 2020, Mr. Ang began his position as a director at Truufin Pte. Ltd., where he provides guidance for the company in the Fintech industry. Mr. Ang has served as a director of Sinospring Venture Ltd. (Singapore) since May 2021 and as a director of GCIC Ltd since June 2021, both of which are consultancy services companies. In the education consultancy services industry, Mr. Ang has served as a director of ITE Education Services Pte. Ltd. since July 2021. Finally, Mr. Ang currently serves as the Chairman and director for R. Vantage Pte. Ltd. (Singapore), a crowd funded real estate investment platform since November 2021, and as Chairman and director of Singapore Digital Exchange Pte. Ltd., a digital exchange of cryptocurrency and digital assets in Singapore since December 2021. Mr. Ang holds a Bachelor of Science in Mechanical Engineering degree with First Class Honors from the Imperial College of Science and Technology at the University of London. He also obtained an MBA degree and an International Directorship Certificate from INSEAD, France in and completed a Marketing Management Program at the Graduate School of Business at Stanford University.
Nicholas Aaron Khoo. Mr. Khoo currently serves as the Chief Operating Officer of Global Star Acquisition Inc. Mr. Khoo has a diversified career that spans over 20 years within the technology, gaming, fintech, real estate, and consulting industries. In the financial services and consulting industry, Mr. Khoo has led Asia Pacific and Japan for Visa Inc’s Cybersource Managed Services from 2012 to 2017. In the real estate industry, Mr. Khoo has served as an independent director of Hatten Land Ltd. since January 2022. Mr. Khoo is a known figure in the esports and video games industry, serving as an advisor to the board of the Global Esports Federation. Mr. Khoo also serves as an investment committee member of the Tribeca Global SPAC Fund since September 2021. Since October 2021, he has also served as an Investment Committee Member of Global Fund, a sponsor affiliate. Mr. Khoo has experience in the public sector as he has served on various official boards and committees in Singapore including the Gambling Regulatory Authority, National Crime Prevention Council, and the Internet and Media Advisory Committee. Mr. Khoo was the valedictorian when he graduated with a Masters of Business Administration from Arcadia University.
Jukka Rannila. Mr. Rannila currently serves as a board member of Global Star Acquisition Inc. He is a seasoned professional with vast experience in investment management and real estate. From 2013 to 2020, Mr. Rannila served as the Chairman of the board of directors of Berlin Invest 3 Oy, from 2012-2020 with Berlin Invest 2 Oy, and from 2011 to 2022 with Berlin Invest Oy, where he oversaw residential real estate portfolios. Mr. Rannila currently serves as a board member of the investment management company for the Berlin Invest Oy groups, Confido Kiinteistöhallinta Oy, where he oversees a residential real estate portfolio in Berlin, Germany. Similarly, since 2018, Mr. Rannila has acted as a member of the board of Assai Commercial Oy, where he oversees a commercial real estate portfolio in the greater Helsinki area. Since 2004, Mr. Rannila has acted as a board member and investment manager of Assai Oy, where he is responsible for the operations and investment portfolio of listed and non-listed companies in the family office. Since 2009, Mr. Rannila has acted as chairman of the board of Nosh Company Oy, where he co-directs a high growth fashion and design group of companies. Currently, Mr. Rannila also co-directs a high growth robotics company with international expansion, Trussmatic Oy. Similarly, since 2018, Mr. Rannila co-directs a high growth manufacturing group of companies through his director position with Tikli Group Oy. More recently in 2021, Mr. Rannila manages all operations of Warp Bridge Oy, a SPV investing in a venture capital fund, as a Managing Director. Mr. Rannila studied at the University of Manchester in the Department of Accounting and Finance.
Stephen Drew. Mr. Stephen Drew currently serves as a non-independent member of Global Star Acquisition Inc.’s board of directors. Mr. Drew has 25 years of experience in private equity, investment banking, real estate, and Fintech-related businesses. Stephen Drew, a director of Global Star served as a director of K Enter Holdings, Inc. from January 3, 2023 to April 25, 2023. Mr. Drew began his career at Wall Street firms Citigroup and Gruntal & Co. In the real estate financing and investing arena, Mr. Drew acted as the principal of Pinnacle Funding for over ten years, where he managed over 50 professional investors. Mr. Drew was also a member of Greenwich Realty Capital LLC from 2017 to 2019, where he managed commercial real estate development. From 2019 to 2020, Mr. Drew served as a Managing Member of Tribeca Realty Capital LLC, the US-based partner of a $27.5 billion asset manager based in Asia for equity investments and is responsible for successfully closing hundreds of millions in transactions. Since 2018, Mr. Drew has served as a Managing Partner of Global Fund LLC, a sponsor affiliate. Since 2021, Mr. Drew has also served as a Managing Partner of Tribeca Global SPAC Fund LLC. Mr. Drew studied Finance at Central Connecticut State University.
On March 22, 2020, Mr. Ted Kim voluntarily petitioned the United States Bankruptcy Court for the Eastern District of Virginia for personal bankruptcy under Chapter 7 of the United States Bankruptcy Code and was assigned Case No. 2010885BFK. Mr. Kim was discharged in December 2020 and the matter was terminated in December 2020. There were no allegations of fraud made in the proceedings. Except for Mr. Kim, none of PubCo’s proposed executive officers or directors has filed a petition for personal bankruptcy or has been affiliated with any company that has filed for bankruptcy within the last ten years.
FOREIGN PRIVATE ISSUER STATUS
Following the Business Combination, PubCo will qualify as a “foreign private issuer” as defined under SEC rules. Even after PubCo no longer qualifies as an emerging growth company, as long as PubCo continues to qualify as a foreign private issuer under SEC rules, PubCo is exempt from certain SEC rules that are applicable to U.S. domestic public companies, including:
| ● | the rules requiring domestic filers to issue financial statements prepared under U.S. GAAP; |
| ● | the sections of the Exchange Act regulating the solicitation of proxies, consents or authorizations in respect of a security registered under the Exchange Act; |
| ● | the sections of the Exchange Act requiring insiders to file public reports of their share ownership and trading activities and liability for insiders who profit from trades made in a short period of time; |
| ● | the rules under the Exchange Act requiring the filing with the SEC of quarterly reports on Form 10-Q containing financial statements and other specified information, and current reports on Form 8-K upon the occurrence of specified significant events; and |
| ● | the selective disclosure rules by issuers of material non-public information under Regulation FD. |
Notwithstanding these exemptions, PubCo will file with the SEC, within four months after the end of each fiscal year, or such applicable time as required by the SEC, an annual report on Form 20-F containing financial statements audited under International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) by an independent registered public accounting firm.
PubCo may take advantage of these exemptions until such time as PubCo is no longer a foreign private issuer. PubCo would cease to be a foreign private issuer at such time as more than 50% of its outstanding voting securities are held by U.S. residents and any of the following three circumstances applies: (1) the majority of its executive officers or directors are U.S. citizens or residents, (2) more than 50% of its assets are located in the United States or (3) its business is administered principally in the United States.
Both foreign private issuers and emerging growth companies also are exempt from certain more stringent executive compensation disclosure rules. Thus, even if PubCo no longer qualifies as an emerging growth company, but remains a foreign private issuer, PubCo will continue to be exempt from the more stringent compensation disclosures required of companies that are neither an emerging growth company nor a foreign private issuer.
In addition, because PubCo will qualify as a foreign private issuer under SEC rules following the Business Combination, PubCo is permitted to follow the corporate governance practices of Cayman Islands (the jurisdiction in which PubCo is organized) in lieu of certain Nasdaq corporate governance requirements that would otherwise be applicable to PubCo. For example, under Cayman Islands law, PubCo is not required to have a board of directors comprised of a majority of directors meeting the independence standards described in Nasdaq Listing Rules. In addition, under Cayman Islands law, PubCo is not required to have a compensation committee or a nominations committee that is comprised solely of independent directors.
If at any time PubCo ceases to be a foreign private issuer, PubCo will take all action necessary to comply with the SEC and Nasdaq Listing Rules.
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS
The following table sets forth information regarding (i) the actual beneficial ownership of Global Star Common Stock as of September 24, 2024, and (ii) expected beneficial ownership of PubCo common stock immediately following the Closing, assuming that no Public Shares are redeemed, and alternatively that 1,137,006 Public Shares are redeemed, by:
| ● | each person who is, or is expected to be, the beneficial owner of more than 5% of issued and outstanding shares of Global Star Common Stock or of PubCo common stock; |
| ● | each of our current executive officers and directors; |
| ● | each person who will become an executive officer or director of PubCo post-Business Combination; and |
| ● | all executive officers and directors of Global Star as a group pre-Business Combination and all executive officers and directors of PubCo post-Business Combination. |
Beneficial ownership is determined according to the rules of the SEC, which generally provide that a person has beneficial ownership of a security if he, she or it possesses sole or shared voting or investment power over that security, including options and warrants that are currently exercisable or exercisable within 60 days. Unless otherwise indicated, Global Star believes that all persons named in the table have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares of Global Star Common Stock beneficially owned by them.
In the event the aggregate cash consideration required to pay for all shares of common stock that are validly submitted for redemption (plus any amount required to satisfy cash conditions pursuant to the terms of the Merger Agreement) exceeds the aggregate amount of cash available to us, we may be unable to complete the Business Combination or redeem any shares. Upon such event, all shares of common stock submitted for redemption will be returned to the holders thereof, and we instead may search for an alternate business combination.
The beneficial ownership of shares of Global Star Common Stock pre-Business Combination is based on 4,050,231 shares of Global Star Common Stock (including 1,137,006 shares of Company’s redeemable Class A Common Stock, 613,225 shares of Company’s non-redeemable Class A Common Stock, and 2,300,000 shares of Class B Common Stock) issued and outstanding as of September 24, 2024. Class A Ordinary Shares underlying the Private Placement Warrants held by the Sponsor are not required to be, and are not, included in the table below because these securities are not exercisable within 60 days of this proxy statement.
The expected beneficial ownership of shares of PubCo common stock post-Business Combination assuming none of the Public Shares are redeemed has been determined based upon the following: (i) that no Public Stockholders exercise their redemption rights (no redemptions scenario), (ii) that none of the investors set forth in the table below has purchased or purchases shares of Global Star Common Stock (pre-Business Combination) or PubCo Ordinary Shares (post-Business Combination), (iii) that 63,512,622 PubCo Ordinary Shares will be issued in the Business Combination, and (iv) there will be an aggregate of 63,512,622 PubCo Ordinary Shares issued and outstanding at Closing.
The expected beneficial ownership of shares of PubCo common stock post-Business Combination assuming the maximum number of Public Shares have been redeemed has been determined based on the following: (i) that holders of 1,137,006 Public Shares exercise their redemption rights (maximum redemption scenario), (ii) that none of the investors set forth in the table below has purchased or purchases shares of Global Star Class A Common Stock (pre-Business Combination) or PubCo common stock (post-Business Combination), (iii) that 63,138,747 PubCo Ordinary Shares are issued in the Business Combination, and (iv) there will be an aggregate of 63,138,747 PubCo Ordinary Shares are issued and outstanding at Closing. In the event the aggregate cash consideration required to pay for all shares of common stock that are validly submitted for redemption (plus any amount required to satisfy cash conditions pursuant to the terms of the Merger Agreement) exceeds the aggregate amount of cash available to us, we may be unable to complete the Business Combination or redeem any shares. Upon such event, all shares of common stock submitted for redemption will be returned to the holders thereof, and we instead may search for an alternate business combination.
Unless otherwise indicated, we believe that all persons named in the table have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares beneficially owned by them.
| | | Before the Business Combination | | | After the
Business Combination | |
| | | | | | Assuming No
Redemption | | | Assuming
Maximum
Redemption | |
| Name and Address of Beneficial Owner | | Number of
shares of
Global Star
Common
Stock | | | %(6) | | | Number of
shares of
PubCo
Common
Stock | | | %(7) | | | Number of
shares of
PubCo
Common
Stock | | | %(8) | |
| Directors and Executive Officers Pre-Business Combination | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Anthony Ang(1)(2) | | | 2,438,225 | | | | 60.20 | % | | | 2,488,047 | | | | 3.92 | % | | | 2,488,047 | | | | 3.94 | % |
| Ted Kim(1)(2)(3) | | | 2,438,225 | | | | 60.20 | % | | | 8,457,400 | | | | 13.31 | % | | | 8,457,400 | | | | 13.39 | % |
| Nicholas Khoo(2) | | | 50,000 | | | | 1.23 | % | | | 233,072 | | | | 0.37 | % | | | 233,072 | | | | 0.37 | % |
| Shan Cui(2) | | | 50,000 | | | | 1.23 | % | | | 50,000 | | | | 0.08 | % | | | 50,000 | | | | 0.08 | % |
| Stephen Drew(2) | | | 20,000 | | | | * | | | | 1,850,716 | | | | 2.91 | % | | | 1,850,716 | | | | 2.93 | % |
| Argon Lam Chun Win(2) | | | 20,000 | | | | * | | | | 20,000 | | | | 0.03 | % | | | 20,000 | | | | 0.03 | % |
| Yang Kan Chong(2) | | | 20,000 | | | | * | | | | 427,944 | | | | 0.67 | % | | | 427,944 | | | | 0.68 | % |
| Hai Chwee Chew(2) | | | 20,000 | | | | * | | | | 20,000 | | | | 0.03 | % | | | 20,000 | | | | 0.03 | % |
| Jukka Rannila | | | 20,000 | | | | * | | | | 203,072 | | | | 0.32 | % | | | 203,072 | | | | 0.32 | % |
| All pre-Business Combination directors and executive officers as a group (9 individuals) | | | 2,638,225 | | | | 65.14 | % | | | 11,262,204 | | | | 17.73 | % | | | 11,262,204 | | | | 17.84 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Directors and Executive Officers Post-Business Combination | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pyeung Ho Choi(3) | | | | | | | | | | | 4,960,495 | | | | 7.81 | % | | | 4,960,495 | | | | 7.86 | % |
| Young Jae Lee(4) | | | | | | | | | | | 4,334,219 | | | | 6.82 | % | | | 4,334,219 | | | | 6.86 | % |
| Ted Kim(1)(2)(3) | | | | | | | | | | | 8,457,400 | | | | 13.31 | % | | | 8,457,400 | | | | 13.39 | % |
| Tan Chin Hwee(4) | | | | | | | | | | | 559,894 | | | | 0.88 | % | | | 559,894 | | | | 0.89 | % |
| Hyung Seok Cho(4) | | | | | | | | | | | 9,262,207 | | | | 14.58 | % | | | 9,262,207 | | | | 14.67 | % |
| Tae Woo Kim(4) | | | | | | | | | | | 209,922 | | | | 0.33 | % | | | 209,922 | | | | 0.33 | % |
| Jihun Byun(4) | | | | | | | | | | | 209,922 | | | | 0.33 | % | | | 209,922 | | | | 0.33 | % |
| Jung Hoon Bae(4) | | | | | | | | | | | 589,490 | | | | 0.93 | % | | | 589,490 | | | | 0.93 | % |
| Jae Keun Kim(4) | | | | | | | | | | | 5,161,603 | | | | 8.13 | % | | | 5,161,603 | | | | 8.18 | % |
| All post-Business Combination directors and executive officers as a group (9 individuals) | | | | | | | | | | | 33,745,152 | | | | 53.13 | % | | | 33,745,152 | | | | 53.45 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Five Percent Holders: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC(1)(2) | | | 2,438,225 | | | | 60.02 | % | | | 2,488,047 | | | | 3.92 | % | | | 2,488,047 | | | | 3.94 | % |
| * | means less than 1% |
| | |
| (1) | Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC, Global Star’s sponsor, is the record holder of 2,438,225 shares of Global Star common stock that will be converted into shares of PubCo Ordinary Shares on a 1-for-1 basis in the Reincorporation Merger. Anthony Ang, Global Star’s Chairman and Chief Executive Officer and Ted Kim, are managing members of Global Star’s Sponsor. By virtue of this relationship, Mr. Ang and Mr. Kim may be deemed to share beneficial ownership of the securities held of record by Global Star’s Sponsor. Mr. Ang and Mr. Kim disclaim any such beneficial ownership except to the extent of his pecuniary interest. The business address of Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC, Mr. Ang and Mr. Kim is 1641 International Drive, Unit 208, McLean, VA. |
| (2) | Interests shown before the Business Combination consist solely of founder shares, classified as shares of Class B Common Stock, as well as placement shares after the IPO. Founder shares are convertible into shares of Class A Common Stock on a one-for-one basis, subject to adjustment. These shares will be converted into Pubco Ordinary Shares on a 1-for-1 basis. The business address of Mr. Khoo, Mr. Cui, Mr. Drew, Mr. Win, Mr. Chong, Mr. Chew and Mr. Rannila is 1641 International Drive, Unit 208, McLean, VA. |
| (3) | Ted Kim is the beneficial owner of 19,564 shares of K Enter common stock through his ownership and control of Global Fund LLC, which owns 12,000 shares of K Enter common stock, and Lodestar USA, Inc. which owns 7,564 shares of K Enter common stock. The 19,564 shares of K Enter common stock beneficially owned by Mr. Kim through his ownership and control of Global Fund LLC and Lodestar USA, Inc. will be converted into an aggregate amount of 5,969,353 PubCo Ordinary Shares in the Business Combination. |
| (4) | The business address of Pyeung Ho Choi, Young Jae Lee, Tan Chin Hwee, Hyung Seok Cho, Tae Woo Kim, Jihun Byun, Jung Hoon Bae and Jae Keun Kim is 16192 Coastal Highway, Lewes DE 19958. |
| (5) | Jae Keun Kim is the beneficial owner of 16,917 shares of K Enter common stock as follows 250 shares of K Enter common stock he owns individually and through his ownership and control of Xeno Investment Asia, which owns 10,000 shares of K Enter common stock, and JVC Inc. which owns 6,667 shares of K Enter common stock. The 16,917 shares of K Enter common stock beneficially owned by Mr. Kim individually and through his ownership and control of Xeno Investment Asia and JVC Inc. will be converted into an aggregate amount of 5,161,603 PubCo Ordinary Shares in the Business Combination. |
| (6) | This % is based upon 4,050,231 shares of Global Star common stock outstanding as of November 21, 2024. |
| (7) | This % is based upon 64,275,753 shares of K Wave ordinary shares outstanding after the Business Combination assuming no redemptions of Global Star common stock. |
| (8) | This % is based upon 63,138,747 shares of K Wave ordinary shares outstanding after the Business Combination assuming maximum redemptions of Global Star common stock. |
The holders of the founder shares have agreed (a) to vote any founder shares owned by it in favor of any business combination and (b) not to redeem any founder shares in connection with a stockholder vote to approve a proposed initial business combination. Global Star’s sponsor and Global Star’s executive officers and directors are deemed to be Global Star’s “promoters” as such term is defined under the federal securities laws.
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED PERSON TRANSACTIONS
Certain Relationships and Related Person Transactions-Global Star
Founder Shares
On February 14, 2022, Global Star’s sponsor purchased 2,875,000 founder shares for an aggregate purchase price of $25,000, or approximately $0.009 per share. On April 5, 2022, Global Star’s sponsor transferred 300,000 founder shares to Anthony Ang, 50,000 shares to Nicholas Khoo, 50,000 shares to Shan Cui, 20,000 shares to Stephen Drew, 20,000 shares to Kan Mun Wai Benny, 20,000 shares to Yang Kan Chong, 20,000 shares to Hai Chwee Chew, and 20,000 shares to Jukka Rannila. On July 26, 2022 Global Star’s sponsor surrendered 575,000 founder shares to the Company for cancellation, for no consideration. The number of founder shares issued was determined based on the expectation that such founder shares would represent 20% of the outstanding shares upon completion of this offering (excluding the placement units and underlying securities). The shares transferred to the officers and directors have a grant date fair value of $2.30 per unit or an aggregate of $1,150,000 and the expense associated with these awards will be recognized upon successful business combination. The Company measured the fair value of the shares on the grant date of the award utilizing a valuation model which considers certain assumptions.
Private Placement Units
Our sponsor purchased an aggregate of 456,225 placement units at a price of $10.00 per unit for an aggregate purchase price of $4,562,250. If the over-allotment option is exercised in full, the amount of placement units sold will be 498,225 for an aggregate purchase price of $4,982,250. Simultaneously with the sale of the Over-Allotment Units, Global Star consummated the private placement of an aggregate of 42,000 units (the “Over-Allotment Private Placement Units” and together with the IPO Private Placement Units, the “Private Placement Units”) to the Sponsor, at a price of $10.00 per Over-Allotment Private Placement Units, generating total gross proceeds of $420,000.
Administrative Services Agreement
On September 22, 2022, Global Star entered into an Administrative Services Agreement, as it may be amended from time to time, with Global Star’s sponsor, pursuant to which Global Star paid its Sponsor $10,000 per month for office space, utilities, secretarial, administrative and support services. Upon completion of the business combination, Global Star’s liquidation or reaching $160,000, Global Star would cease paying these monthly fees. For each of the three and six months ended June 30, 2023 Global Star incurred $31,666 and $61,666, respectively, of expenses pursuant to this agreement. For each of the three and six months ended June 30, 2023, Global Star paid $40,000 and $80,000 respectively. As of June 30, 2023 Global Star had a prepaid balance of $10,000 which is included in prepaid expenses and other current assets on Global Star’s condensed consolidated balance sheets. As of December 31, 2023, the Global Star incurred $121,666 (including a catch up payment of $1,666 for the previous year) of administrative fees.
Promissory Notes — Related Party
On February 14, 2022, Global Star’s sponsor issued an unsecured promissory note to the Company (the “Promissory Note”), pursuant to which the Company may borrow up to an aggregate principal amount of $300,000. Upon closing of the Initial Public Offering, the Company repaid the outstanding balance in full.
On July 31, 2023, the Sponsor loaned Global Star, $1,600,000 pursuant to a non-interest bearing promissory note dated July 31, 2023 to fund working capital expenses (the “Sponsor Working Capital Loan”). The Sponsor Working Capital Loan is without interest and is to be repaid on the later of (i) December 31, 2023 or (ii) upon the consummation of a Business Combination. Simultaneously with the closing of the business Combination the Sponsor shall convert $1,500,000 of the principal amount of the Sponsor Working Capital Loan into the Global Star’s Private Units at a price of $10.00 per unit and the remaining $100,000 shall be paid to the Sponsor in cash. In the event that a Business Combination does not close, Global Star may use a portion of proceeds held outside the Trust Account to repay the Sponsor Working Capital Loan, but no proceeds held in the Trust Account will be used to repay the Sponsor Working Capital Loan. As of September 30, 2023, the amount due under the Sponsor Working Capital Loan was $1,600,000.
Certain Relationships and Related Person Transactions-K Enter
One of K Enter’s directors, Ted Kim, is also the manager of Global Star Acquisition I, LLC, the sponsor, to Global Star. On September 29, 2024, K Enter entered into an agreement with Lodestar USA, Inc. (the “Lodestar Agreement”) pursuant to which K Enter issued 1,202 shares of K Enter’s common stock to Lodestar USA, Inc. in consideration for services rendered to K Enter by Ted Kim, the owner of Lodestar USA Inc. Ted Kim owns 19,564 shares or 10.12% of the shares of common stock of K Enter based on the shares of K Enter to be issued and outstanding immediately prior to the closing of the Business Combination through his ownership and control of Global Fund LLC, which owns 12,000 shares, and Lodestar USA, Inc., which owns 7,564 shares.
Two of K Enter’s directors, Pyeung-ho Choi, who is the Chairman of K Enter and Young Jae Lee, who is the Chief Executive Officer of K Enter, are also senior officers of Solaire Partners, one of the Six Korean Entities.
On September 24, 2024, K Enter entered into a share subscription agreement with GF Korea Inc. (the “GF Agreement”) pursuant to which K Enter issued 4,997 shares of K Enter’s common stock to GF Korea Inc. (“GF Korea”) in consideration for GF Korea Inc. assuming certain payment obligations of K Enter in the aggregate $8.52 million owed to its service providers of K Enter. The GF Agreement closed on September 25, 2024 and K Enter issued the 4,997 shares of K Enter’s common stock to GF Korea, which will be converted to 1,524,681 PubCo ordinary shares (305.1192809 : 1 conversion ratio at f/x rate KRW 1,376.55 / USD $1.00) in the Business Combination. K Enter entered into the GF Agreement for the purpose of transferring certain of K Enter’s payment obligations to gain greater financial flexibility. Mina Kim, a co-founder of K Enter, is the CEO of GF Korea and Mina Kim’s spouse is the owner of GF Korea.
On September 30, 2024, K Enter issued Tan Chin Hwee, a director, Executive Chairman and Interim CEO of K Enter, 168 shares of K Enter’s common stock in consideration for services rendered and to be rendered to K Enter.
On September 25, 2024, Innocus Global Group Pte, Ltd., an entity owned by Jaekeun (Jason) Kim, a nominee director PubCo, entered into an agreement to purchase 250 shares of K Enter’s Series A-1 Preferred Stock for gross proceeds of $150,000. Each issued share of Series A-1 Preferred Stock is convertible into common stock of K Enter on a one-for-one basis.
On August 31, 2024, K Enter issued Jae Ha Lee, an employee of K Enter, 1,932 shares of K Enter’s common stock in consideration for services rendered and to be rendered to K Enter.
On June 4, 2024, K Enter issued a convertible senior unsecured note in the principal amount of $3,000,000 to Innocus Global Group Pte, Ltd., an entity owned by Jaekeun (Jason) Kim, a nominee director PubCo (the “$3MM Note”). The $3MM Note has a maturity date of 3 years and will pay an annual coupon rate of 3% to be paid semi-annually until the maturity date of the $3MM Notes. Under the $3MM Note, the proceeds shall be wired to K Enter as follows: (i) 25% of the committed amount at the time of signing this definitive agreement, (ii) 50% at the time SEC declares effectiveness on the F-4, and (iii) the remaining 25% at the time of shareholder approval and going public. From the time K Enter issued the $3MM Note and until the closing of the Business Combination, the $3MM Note will be convertible, at the option of the holder, at a conversion price per share of $1,200 per share. The Post-Merger Conversion Price for the Notes shall be the greater of (a) a 60% discount to the 5-day average of the volume-weighted average prices of ordinary shares over 5 consecutive trading days following the conversion notice date, and (b) a Floor price of $4 per share. On October 3, 2024, K Enter received $300,000 pursuant to the $3MM Note and on October 18, 2024, K Enter received $1,200,000 pursuant to the $3MM Note. Accordingly, K Enter is not due any payment under the $3MM Note at the time SEC declares effectiveness on the F-4.
On April 22, 2024 Young Jae Lee, K Enter’s director and former Chief Executive Officer, loaned K Enter $130,762 (the “1st Lee Loan”). On May 3, 2024, K Enter repaid $72,645 of the 1st Lee Loan, leaving a balance of $58,116 on the 1st Lee Loan. The 1st Lee Loan is for a term of six months and bears interest at the rate of 4.6% per annum. The proceeds of the 1st Lee Loan will be used to fund the operations of K Enter. The 1st Lee Loan is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.50. On October 23, 2024, Mr. Lee and K Enter extended the maturity date of the 1st Lee Loan to the earlier of June 30, 2025 or within 5 business days after this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 becomes effective. A copy of the loan extension agreement between Mr. Lee and K Enter is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.66.
On April 25, 2024 Young Jae Lee, K Enter’s director and former Chief Executive Officer, loaned K Enter $181,613 (the “2nd Lee Loan”). On May 3, 2024, K Enter repaid $181,613 of the 2nd Lee Loan, leaving a balance of $0.00 on the 2nd Lee Loan. The 2nd Lee Loan is for a term of three months and bears interest at the rate of 4.6% per annum. The proceeds of the 2nd Lee Loan will be used to fund the operations of K Enter. The 2nd Lee Loan is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.51.
On May 3, 2024 Young Jae Lee, K Enter’s director and former Chief Executive Officer, loaned K Enter $254,259 (the “3rd Lee Loan”). The 3rd Lee Loan is for a term of six months and bears interest at the rate of 4.6% per annum. The proceeds of the 3rd Lee Loan will be used to fund the operations of K Enter. The 3rd Lee Loan is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.52.
On April 26, 2024, Bidangil Pictures Co.,Ltd. loaned the $98,071 (the “Bidangil Loan”). The loan is unsecured, for a term of three months and bears interest at the rate of 3% per annum. The proceeds of the loan will be used to fund the operations of K Enter. The Bidangil Loan is attached hereto as Exhibit 10.53.
On May 25, 2023, K Enter entered into a production development agreement with Studio Anseilen, one of the Six Korean Entities, to advance Studio Anseilen $726,454 for content development. The advance does not accrue interest, is not secured and is evidenced by an agreement dated May 25, 2023, a copy of which is attached to this proxy statement/prospectus as Exhibit 10.23.
On June 1, 2023, K Enter entered into a two-year written lease with Solaire Partners, as landlord (“Lease 2”) for 2,520 square feet of office space located at 11F, Telepia Building, 527, Eonju-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Korea 06138 commencing on June 1, 2023. Solaire Partners., one of the Six Korean Entities, is the landlord under the Lease 2. At inception, total gross rental payments due under this operating lease approximated $99,777 and a security deposit due approximated $72,682. A copy of Lease 2 is attached to this proxy statement/prospectus as Exhibit 10.22.
Solaire Partners advised K Enter approximately $121,448 through the payment of K Enter’s administrative expenses during the period January 4, 2023 through June 30, 2023. As of June 30, 2023, K Enter owed $49,101 to Solaire related to this advance and is included as a component of accrued expenses and other current liabilities on the accompanying balance sheet. This advance from Solaire Partners has been fully repaid by K Enter.
During August 2023, K Enter purchased a $1,000,000 convertible bond from Prototype Groupe, Inc. (“Prototype Groupe”), a company that operates in virtual studio technology and who First Virtual, which is a Korean company K Enter had an agreement to acquire a controlling equity interest. Virtualization remains a future strategic initiative for K Enter, but its management has decided to terminate the planned acquisition of First Virtual, an emerging company with plans to establish virtual production capabilities. The share purchase agreement with First Virtual has been terminated but includes a re-purchase option. K Enter currently views the acquisition of a controlling interest in First Virtual pursuant to the FVL Termination and Option Agreement as uncertain due to the uncertainty as to the outcome of the Prototype Lawsuits and there can be no assurance that K Enter will acquire a controlling interest in First Virtual pursuant to the FVL Termination and Option Agreement. First Virtual has a 19% ownership interest in the Prototype Groupe. The convertible bond is due and payable on demand after August 10, 2024. The convertible bond will bear interest at a fixed rate equal to the Applicable Federal Rate for short term loans as of the date of the bond (4.96%). At K Enter’s option, at any time prior to payment in full of the principal amount and all accrued interest, the convertible bond can be converted into such number of shares of common stock of Prototype Groupe equal to the entire principal amount of the convertible bond and all accrued and unpaid interest thereon, divided by $7.40 per share in case the pre-money valuation of Prototype Groupe shall meet or exceed $94,800,000. In the event the pre-money valuation is below $94,800,000, the conversion price shall be proportionally reduced. If the convertible bond is not repaid or converted through K Enter’s voluntary election and Prototype Groupe issues and sells shares of its equity securities before the maturity date resulting in gross proceeds of $10,000,000 (excluding the conversion of this bond), then at any time on or after the maturity date, Prototype Groupe shall have the option to (a) repay all outstanding principal and accrued unpaid interest of the convertible bond or (b) convert all or any portion of the outstanding principal and accrued unpaid interest of the convertible bond into such number of its common shares equal to the principal amount and all accrued unpaid interest thereon to be converted divided by the conversion price. A copy of the convertible bond with Prototype Groupe is attached to this proxy statement/prospectus as Exhibit 10.24.
During September 2023, K Enter advanced $1,452,908 to Studio V Plus Co., Ltd. at an interest rate of 3.00% per annum that is due and payable on November 6, 2023. The advance is unsecured and is evidence by a loan agreement dated September 6, 2023 (the “Loan Agreement”), a copy of which is attached to this proxy statement/prospectus as Exhibit 10.25. Studio V Plus Co., Ltd. has repaid K Enter all sums due under the Loan Agreement by the due date.
SHARES ELIGIBLE FOR FUTURE SALE
According to the Memorandum and Articles of Association of PubCo the authorized share capital of post-closing company is $100,000 divided into 990,000,000 ordinary shares of par value of $0.0001 each and 10,000,000 preference shares of par value of $0.0001 each. All of PubCo’s Ordinary Shares issued in connection with the Reincorporation Merger will be freely transferable by persons other than by PubCo’s “affiliates” without restriction under the Securities Act, subject to the restrictions detailed below. PubCo’s Ordinary Shares issued in the Acquisition Merger will also be registered at the closing, but will be subject to the lock-up agreements described below. Sales of substantial amounts of PubCo Ordinary Shares in the public market could adversely affect prevailing market prices of PubCo’s Ordinary Shares. Prior to the Business Combination, there has been no public market for PubCo’s Ordinary Shares. PubCo intends to apply for listing of PubCo’s Ordinary Shares and PubCo’s Warrants on Nasdaq, but it cannot be assured that a regular trading market will develop in PubCo Ordinary Shares or PubCo Warrants.
Transfer of Ordinary Shares
Subject to applicable securities laws in relevant jurisdictions and PubCo’s Memorandum and Articles of Association, the fully paid-up ordinary shares are freely transferable. Shares may be transferred by a duly signed instrument of transfer in any usual common form or in a form acceptable to the directors and the applicable securities laws in the relevant jurisdictions. The directors may decline to register any transfer unless, among other things, evidence of payment of any stamp duty payable with respect to the transfer is provided together with other evidence as the directors may require to show the right of the transferor to make the transfer. PubCo will replace lost or destroyed certificates for shares upon notice to PubCo and upon, among other things, the applicant furnishing evidence and indemnity as the directors may require and the payment of all applicable fees.
Lock-up Agreement
At the Closing, PubCo, the Sponsor, certain former stockholders of K Enter, and certain other persons and entities, will enter into lock-up agreements (the “Lock-Up Agreements”) with respect to PubCo Ordinary Shares and PubCo Warrants held by the Sponsor immediately following the Closing, and PubCo Ordinary Shares held by certain K Enter stockholders immediately following the Closing (the “Lock-Up Shares”), pursuant to which, each Holder agreed not to offer, sell, contract to sell, pledge, grant any option to purchase, or otherwise dispose of, directly or indirectly, any Lock-Up Shares during the application lock-up period, on the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in the Lock-Up Agreement. Lock-up period means, (i) with respect to 50% of the Lock-up Shares, the earlier of (A) six months after the Closing and (B) the date on which the closing price of the PubCo’s Ordinary Shares equals or exceeds $12.50 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, rights issuances, reorganizations and recapitalizations) for any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period commencing after the date hereof and (ii) with respect to the remaining 50% Lock-up Shares (or Ordinary Shares issuable upon conversion thereof), six months after the Closing. The Lock-Up Agreements will apply to (i) approximately 83% of the PubCo Ordinary Shares, consisting of 2,798,225 Ordinary Shares owned by the Sponsor, Stephen Drew and Nicholas Khoo and 49,424,300 Ordinary Shares owned by the former K Enter stockholders (ii) 498,225 Ordinary Shares underlying warrants held by the Sponsor (approximately 5.14% of the outstanding warrants) and (iii) 49,822 Ordinary Shares underlying rights owned by the Sponsor (approximately 5.14% of the rights).
PubCo Options
In connection with the Business Combination, Global Star and K Enter have agreed that PubCo shall adopt the 2023 Plan. The 2023 Plan provides for the issuance of up to an aggregate of 5,900,000 of PubCo Ordinary Shares. Upon the closing of the Business Combination, options to purchase an aggregate number of 5,900,000 PubCo Ordinary Shares may be immediately granted and outstanding. See “PubCo’s Directors and Executive Officers after the Business Combination—Share Incentive Plan.”
Regulation S
Regulation S under the Securities Act provides an exemption from registration requirements in the United States for offers and sales of securities that occur outside the United States. Rule 903 of Regulation S provides the conditions to the exemption for a sale by an issuer, a distributor, their respective affiliates or anyone acting on their behalf, while Rule 904 of Regulation S provides the conditions to the exemption for a resale by persons other than those covered by Rule 903. In each case, any sale must be completed in an offshore transaction, as that term is defined in Regulation S, and no directed selling efforts, as that term is defined in Regulation S, may be made in the United States.
PubCo is a foreign issuer as defined in Regulation S. As a foreign issuer, securities that PubCo sells outside the United States pursuant to Regulation S are not considered to be restricted securities under the Securities Act, and, subject to the offering restrictions imposed by Rule 903, are freely tradable without registration or restrictions under the Securities Act, unless the securities are held by PubCo’s affiliates. Generally, subject to certain limitations, holders of PubCo’s restricted shares who are not affiliates of PubCo or who are affiliates of PubCo by virtue of their status as an officer or director of PubCo may, under Regulation S, resell their restricted shares in an “offshore transaction” if none of the shareholder, its affiliate nor any person acting on their behalf engages in directed selling efforts in the United States and, in the case of a sale of PubCo restricted shares by an officer or director who is an affiliate of PubCo solely by virtue of holding such position, no selling commission, fee or other remuneration is paid in connection with the offer or sale other than the usual and customary broker’s commission that would be received by a person executing such transaction as agent. Additional restrictions are applicable to a holder of PubCo restricted shares who will be an affiliate of PubCo other than by virtue of his or her status as an officer or director of PubCo.
PubCo is not claiming the potential exemption offered by Regulation S in connection with the offering of newly issued shares outside the United States and will register all of the newly issued shares under the Securities Act.
Rule 144
All of PubCo Ordinary Shares that will be outstanding upon the consummation of the Business Combination, other than those equity shares issued and registered in connection with the Business Combination, are “restricted securities” as that term is defined in Rule 144 under the Securities Act and may be sold publicly in the United States only if they are subject to an effective registration statement under the Securities Act or pursuant to an exemption from the registration requirement such as those provided by Rule 144 and Rule 701 promulgated under the Securities Act. In general, beginning 90 days after the date of this proxy statement/prospectus, a person (or persons whose shares are aggregated) who, at the time of a sale, is not, and has not been during the three months preceding the sale, an affiliate of PubCo and has beneficially owned PubCo’s restricted securities for at least six months will be entitled to sell the restricted securities without registration under the Securities Act, subject only to the availability of current public information about PubCo. Persons who are affiliates of PubCo and have beneficially owned PubCo’s restricted securities for at least six months may sell a number of restricted securities within any three-month period that does not exceed the greater of the following:
| ● | 1% of the then issued equity shares of the same class which, immediately after the Business Combination, will equal 701,960 equity shares (assuming no additional redemptions by holders of Global Star shares and not including the PIPE Shares); or |
| ● | the average weekly trading volume of PubCo Ordinary Shares of the same class during the four calendar weeks preceding the date on which notice of the sale is filed with the SEC. |
Sales by affiliates of PubCo under Rule 144 are also subject to certain requirements relating to manner of sale, notice and the availability of current public information about PubCo.
Rule 701
In general, under Rule 701 of the Securities Act as currently in effect, each of PubCo’s employees, consultants or advisors who purchases equity shares from PubCo in connection with a compensatory stock plan or other written agreement executed prior to the consummation of the Business Combination is eligible to resell those equity shares in reliance on Rule 144, but without compliance with some of the restrictions, including the holding period, contained in Rule 144. However, the Rule 701 shares would remain subject to lock-up arrangements and would only become eligible for sale when the lock-up period expires.
Registration Rights
In connection with the transactions, Global Star, PubCo and K Enter entered into Backstop Agreements with a number of investors. The Backstop Agreement will provide that holders of the PIPE Shares can, at any time after the consummation of the Business Combination and subject to certain conditions set forth in the Backstop Agreement, make up to two demands that PubCo register the applicable PubCo Ordinary Shares. In addition, pursuant to the Backstop Agreement, the holders of PIPE Shares have certain “piggy-back” registration rights with respect to registration statements filed subsequent to the consummation of the Business Combination.
DESCRIPTION OF PUBCO’S SECURITIES
PubCo or K Wave Media Ltd is a Cayman Islands exempted company and its affairs are governed by the memorandum and articles of association, as amended and restated from time to time, and Companies Act (As Revised) of the Cayman Islands, referred to herein as the “Companies Act” below, and the common law of the Cayman Islands.
PubCo currently has only one class of issued ordinary shares, which have identical rights in all respects and rank equally with one another. The share capital of PubCo is $100,000 divided into 990,000,000 ordinary shares of par value of $0.0001 each and 10,000,000 preference shares or a par value US$0.0001 each.
PubCo Ordinary Shares
The following includes a summary of the terms of PubCo Ordinary Shares, based on its Memorandum and Articles of Association and Cayman Islands law. Immediately prior to the consummation of the Reincorporation Merger, PubCo shall amend its memorandum and articles of association, which amendment is referred to herein as the “Memorandum and Articles of Association.” According to the Memorandum and Articles of Association, the authorized share capital of post-closing company is $100,000 divided into 990,000,000 ordinary shares of par value of $0.0001 each and 10,000,000 preference shares or a par value US$0.0001 each.
General. Immediately prior to the consummation of the Business Combination, PubCo’s authorized share capital is $100,000 divided into 990,000,000 ordinary shares of par value of $0.0001 each and 10,000,000 preference shares or a par value US$0.0001 each. All of PubCo’s issued and outstanding ordinary shares are fully paid and non-assessable. Certificates representing the ordinary shares are issued in registered form. PubCo may not issue share to bearer. PubCo’s shareholders who are non-residents of the Cayman Islands may freely hold and transfer their ordinary shares.
Dividends. The holders of PubCo’s ordinary shares are entitled to such dividends as may be declared by its Board of Directors subject to its Memorandum and Articles of Association and the Companies Act. In addition, PubCo’s shareholders may by ordinary resolution declare a dividend, but no dividend may exceed the amount recommended by its directors. PubCo’s Memorandum and Articles of Association provide that no dividend or other distribution shall be paid except out of the realised or unrealised profits of the Company, out of the share premium account or as otherwise permitted by law. Dividends may also be declared and paid out of share premium account or any other fund or account which can be authorized for this purpose in accordance with the Companies Act. No dividend may be declared and paid unless PubCo’s directors determine that, immediately after the payment, PubCo will be able to pay its debts as they become due in the ordinary course of business and PubCo has funds lawfully available for such purpose.
Voting Rights. In respect of all matters subject to a shareholders’ vote, each PubCo ordinary share is entitled to one vote. Voting at any meeting of shareholders is by poll and not on a show of hands.
A quorum required for a meeting of shareholders consists of holders of a majority of the Shares being individuals present in person or by proxy or, if a corporation or other non-natural person, by its duly authorized representative or proxy shall be a quorum. As a Cayman Islands exempted company, PubCo is not obliged by the Companies Act to call shareholders’ annual general meetings. PubCo’s Memorandum and Articles of Association provide that PubCo may (but are not obliged to) in each year hold a general meeting as its annual general meeting in which case PubCo will specify the meeting as such in the notices calling it, and the annual general meeting will be held at such time and place as may be determined by its directors. We, however, will hold an annual shareholders’ meeting during each fiscal year, as required by the Listing Rules at the Nasdaq. Each general meeting, other than an annual general meeting, shall be an extraordinary general meeting. Shareholders’ annual general meetings and any other general meetings of PubCo’s shareholders may be called by a majority of its Board of Directors or its chairman. PubCo’s Memorandum and Articles of Association provide its shareholders with the right to put any proposals before annual general meetings. Shareholders seeking to bring business before the annual general meeting or to nominate candidates for appointment as directors at the annual general meeting must deliver notice to the principal executive offices of PubCo not less than 120 calendar days before the date of PubCo’s proxy statement released to shareholders in connection with the previous year’s annual general meeting or, if the Company did not hold an annual general meeting the previous year, or if the date of the current year’s annual general meeting has been changed by more than 30 days from the date of the previous year’s annual general meeting, then the deadline shall be set by the board of Directors with such deadline being a reasonable time before PubCo begins to print and send its related proxy materials.
An ordinary resolution is a resolution passed by a simple majority of the shareholders, as being entitled to do so, vote in person or by proxy at a general meeting, and includes a unanimous written resolution. In computing the majority when a poll is demanded regard shall be had to the number of votes to which each Member is entitled by the Articles, while a special resolution is a resolution passed by no less than two-thirds of the shareholders as, being entitled to do so, vote in person or by proxy at a general meeting, and includes a unanimous written resolution. A special resolution will be required for important matters such as a change of name or making changes to PubCo’s Memorandum and Articles of Association.
Transfer of Ordinary Shares. Subject to the restrictions in PubCo’s Memorandum and Articles of Association as set out below, any of PubCo’s shareholders may transfer all or any of his or her ordinary shares by an instrument of transfer in the usual or common form or any other form approved by PubCo’s Board of Directors.
PubCo’s Board of Directors may, in its absolute discretion, decline to register any transfer of any ordinary share which is not fully paid up or on which PubCo has a lien. PubCo’s Board of Directors may also decline to register any transfer of any ordinary share unless:
| ● | the instrument of transfer is lodged with us, accompanied by the certificate for the ordinary shares to which it relates and such other evidence as PubCo’s Board of Directors may reasonably require to show the right of the transferor to make the transfer; |
| ● | the instrument of transfer is in respect of only one class of shares; |
| ● | the instrument of transfer is properly stamped, if required; |
| ● | in the case of a transfer to joint holders, the number of joint holders to whom the ordinary share is to be transferred does not exceed four; and |
| ● | a fee of such maximum sum as the Nasdaq may determine to be payable or such lesser sum as PubCo’s directors may from time to time require is paid to PubCo in respect thereof. |
If PubCo’s directors refuse to register a transfer they shall, within two months after the date on which the instrument of transfer was lodged, send to each of the transferor and the transferee notice of such refusal.
The registration of transfers may, after compliance with any notice required of the Nasdaq, be suspended and the register closed at such times and for such periods as PubCo’s Board of Directors may from time to time determine, provided, however, that the registration of transfers shall not be suspended nor the register closed for more than 30 days in any year as PubCo’s board may determine.
Liquidation. On a return of capital on winding up or otherwise (other than on conversion, redemption or purchase of ordinary shares), if the assets available for distribution amongst PubCo’s shareholders shall be more than sufficient to repay the whole of the share capital at the commencement of the winding up, the surplus shall be distributed amongst PubCo’s shareholders in proportion to the par value of the shares held by them at the commencement of the winding up, subject to a deduction from those shares in respect of which there are monies due, of all monies payable to PubCo for unpaid calls or otherwise. If PubCo’s assets available for distribution are insufficient to repay all of the paid-up capital, the assets will be distributed so that the losses are borne by PubCo’s shareholders in proportion to the par value of the shares held by them. Any distribution of assets or capital to a holder of ordinary share will be the same in any liquidation event.
Redemption, Repurchase and Surrender of Ordinary Shares. PubCo may issue shares on terms that such shares are subject to redemption, at PubCo’s option or at the option of the holders thereof, on such terms and in such manner as may be determined, before the issue of such shares, by PubCo’s Board of Directors or by a special resolution of PubCo’s shareholders. PubCo may also repurchase any of its shares provided that the manner and terms of such purchase have been approved by its Board of Directors or are otherwise authorized by its Memorandum and Articles of Association. Under the Companies Act, the redemption or repurchase of any share may be paid out of PubCo’s profits or out of the proceeds of a fresh issue of shares made for the purpose of such redemption or repurchase, or out of capital (including share premium account and capital redemption reserve) if the company can, immediately following such payment, pay its debts as they fall due in the ordinary course of business. In addition, under the Companies Act no such share may be redeemed or repurchased (a) unless it is fully paid up, (b) if such redemption or repurchase would result in there being no shares outstanding, or (c) if the company has commenced liquidation. In addition, PubCo may accept the surrender of any fully paid share for no consideration.
Variations of Rights of Shares. If at any time PubCo’s share capital is divided into different classes or series of shares, the rights attached to any class or series of shares (unless otherwise provided by the terms of issue of the shares of that class or series), whether or not PubCo is being wound-up, be varied without the consent of the holders of the issued shares of that class where such variation is considered by the directors of PubCo not to have a material adverse effect upon such rights; otherwise, any such variation shall be made only with the consent in writing of the holders of not less than two-thirds of the issued shares of that class, or with the approval of a resolution passed by a majority of not less than two-thirds of the votes cast at a separate meeting of the holders of the shares of that class. For the avoidance of doubt, the directors of PubCo reserve the right, notwithstanding that any such variation may not have a material adverse effect, to obtain consent from the holders of shares of the relevant class. To any such meeting all the provisions of PurCo’s Charter relating to general meetings shall apply mutatis mutandis, except that the necessary quorum shall be one person holding or representing by proxy at least one-third of the issued shares of the class and that any holder of Shares of the class present in person or by proxy may demand a poll.
Inspection of Books and Records. Holders of PubCo Ordinary Shares have no general right under Cayman Islands law to inspect or obtain copies of PubCo’s list of shareholders or its corporate records. However, PubCo will provide its shareholders with annual audited financial statements. See “Where You Can Find Additional Information.”
Issuance of Additional Shares. PubCo’s Memorandum and Articles of Association authorize its Board of Directors to issue additional ordinary shares from time to time as its Board of Directors shall determine, to the extent of available authorized but unissued shares.
PubCo’s Memorandum and Articles of Association also authorize its Board of Directors to establish from time to time one or more series of preferred shares and to determine, with respect to any series of preferred shares, the terms and rights of that series, including:
| ● | the designation of the series; |
| ● | the number of shares of the series; |
| ● | the dividend rights, dividend rates, conversion rights, voting rights; and |
| ● | the rights and terms of redemption and liquidation preferences. |
PubCo’s Board of Directors may issue preferred shares without action by its shareholders to the extent authorized but unissued. Issuance of these shares may dilute the voting power of holders of ordinary shares.
Anti-Takeover Provisions. Some provisions of PubCo’s Memorandum and Articles of Association may discourage, delay or prevent a change of control of PubCo or management that shareholders may consider favorable, including provisions that authorize PubCo’s Board of Directors to issue preferred shares in one or more series and to designate the price, rights, preferences, privileges and restrictions of such preferred shares without any further vote or action by its shareholders.
Exempted Company. PubCo is an exempted company with limited liability under the Companies Act. The Companies Act distinguishes between ordinary resident companies and exempted companies. Any company that is registered in the Cayman Islands but conducts business mainly outside the Cayman Islands may apply to be registered as an exempted company. The requirements for an exempted company are essentially the same as for an ordinary company except that an exempted company:
| ● | does not have to file an annual return of its shareholders with the Registrar of Companies; |
| ● | is not required to open its register of members for inspection; |
| ● | does not have to hold an annual general meeting; |
| ● | may issue shares with no par value; |
| ● | may obtain an undertaking against the imposition of any future taxation (such undertakings are usually given for 20 years in the first instance); |
| ● | may register by way of continuation in another jurisdiction and be deregistered in the Cayman Islands; |
| ● | may register as a limited duration company; and |
| ● | may register as a segregated portfolio company. |
“Limited liability” means that the liability of each shareholder is limited to the amount unpaid by the shareholder on that shareholder’s shares of the company.
PubCo Warrants
Set forth below is also a description of PubCo Options and PubCo Warrants that will be issued and outstanding upon the consummation of the Business Combination.
The following summary is not complete and is subject to, and is qualified in its entirety by reference to, the provisions of the Memorandum and Articles of Association attached as Annex B to this proxy statement/prospectus.
PubCo Warrants will have the same terms as the GLST Warrants. Each PubCo Warrant entitles the holder thereof to purchase one PubCo Ordinary Share at a price of $11.50 per full share. PubCo will not issue fractional shares. As a result, a warrant holder must exercise its PubCo Warrants in multiples of two, at a price of $11.50 per full share, subject to adjustment, to validly exercise PubCo Warrants. PubCo Warrants will become exercisable on the later of (i) 12 months from the closing of this offering and (ii) 30 days after the completion of the Business Combination. the PubCo Warrants will expire five years after the consummation of the Business Combination.
PubCo may redeem the outstanding PubCo Warrants (excluding the private warrants that are part of the Private Units), in whole and not in part, at a price of $0.01 per warrant:
| | ● | at any time while PubCo Warrants are exercisable, |
| ● | upon a minimum of 30 days’ prior written notice of redemption, |
| ● | if, and only if, the last sales price of PubCo Ordinary Shares equals or exceeds $18.00 per share for any 20 trading days within a 30 trading day period ending three business days before PubCo sends the notice of redemption, and |
| | ● | if, and only if, there is a current registration statement in effect with respect to PubCo Ordinary Shares underlying PubCo Warrants at the time of redemption and for the entire 30-day trading period referred to above and continuing each day thereafter until the date of redemption. |
If the foregoing conditions are satisfied and PubCo issues a notice of redemption, each warrant holder can exercise his, her or its PubCo Warrant prior to the scheduled redemption date. However, the price of PubCo Ordinary Shares may fall below the $18.00 trigger price as well as the $11.50 warrant exercise price per full share after the redemption notice is issued and not limit PubCo’s ability to complete the redemption.
If PubCo calls PubCo Warrants for redemption as described above, PubCo’s management will have the option to require all warrant holders that wish to exercise PubCo Warrants to do so on a “cashless basis.” In such event, each warrant holder would pay the exercise price by surrendering the whole PubCo Warrant for that number of PubCo Ordinary Shares equal to the quotient obtained by dividing (x) the product of the number of PubCo Ordinary Shares underlying PubCo Warrants, multiplied by the difference between the exercise price of PubCo Warrants and the “fair market value” (as defined below) by (y) the fair market value. The “fair market value” shall mean the average reported last sale price of PubCo Ordinary Shares for the 10 trading days ending on the third trading day prior to the date on which the notice of redemption is sent to the warrant holders. Whether PubCo will exercise its option to require all warrant holders to exercise their PubCo Warrants on a “cashless basis” will depend on a variety of factors including the price of PubCo Ordinary Shares at the time PubCo Warrants are called for redemption, PubCo’s cash needs at such time and concerns regarding dilutive share issuances.
COMPARISON OF SHAREHOLDERS’ RIGHTS
In connection with the Business Combination, holders of Global Star Common Stock will become shareholders of PubCo and their rights will be governed by the Cayman Islands law and the Memorandum and Articles of Association. Currently, the rights of Global Star stockholders are governed by the laws of the State of Delaware and Global Star’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation.
This section describes the material differences between the rights of Global Star stockholders and the proposed rights of PubCo’s shareholders. This summary is not complete and does not cover all of the differences between the Cayman Islands laws and Delaware laws affecting corporations and their shareholders or all the differences between Global Star’s and PubCo’s organizational documents. The summary is therefore subject to the complete text of the relevant provisions of the Cayman Islands laws and Delaware laws and Global Star’s and PubCo’s organizational documents. For information on Global Star’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation see the section titled, “Where You Can Find More Information” in this proxy statement/prospectus. For a summary of PubCo’s Memorandum and Articles of Association, see the section titled “Description of PubCo’s Securities” in this proxy statement/prospectus and see the full text of PubCo’s Memorandum and Articles of Association attached to this proxy statement/prospectus as Annex B.
| Cayman Islands | | Delaware |
| Shareholder Meetings |
| |
| ● | Held at a time and place as designated in the Articles of Association. PubCo’s Articles of Association provide that PubCo’s board may designate such time and place. | | ● | Held at such time or place as designated in the certificate of incorporation or the by-laws, or if not so designated, as determined by the board of directors |
| | | |
| ● | May be held within or outside the Cayman Islands | | ● | May be held within or without Delaware |
| | | |
| ● | Notice: at least 5 clear days’ notice | | ● | Notice: |
| | | |
| ● | Our Articles of Association provides that a general meeting of the company may be called by the chairman or a majority of PubCo’s board or by the holders of at least one-third of all votes attached to all issued shares entitled to vote at PubCo’s general meetings. | | ● | Whenever shareholders are required to take any action at a meeting, a written notice of the meeting shall be given which shall state the place, if any, date and hour of the meeting, and the means of remote communication, if any. |
| | | |
| ● | Notices shall be in writing and may be given to any shareholder of PubCo either personally or by sending it by courier, post, telex, fax or email to such shareholder or to such shareholder’s address as shown in the Register of Members (or where the notice is given by email by sending it to the email address provided by such shareholder). Notice may also be served by Electronic Communication in accordance with the rules and regulations of the Designated Stock Exchange, the Securities and Exchange Commission and/or any other competent regulatory authority or by placing it on the Company’s Website. | | ● | Written notice shall be given not less than 10 nor more than 60 days before the meeting. |
| Cayman Islands | | Delaware |
| Shareholders’ Voting Rights |
| |
| ● | Our Articles of Association provide shareholders may take any action requiring an ordinary or special resolution passed at a meeting of shareholders without a meeting if their consent to such ordinary or special resolution is in writing and is signed by all shareholders entitled to vote on such resolution, in accordance with the procedure in PubCo’s articles of association. | | ● | Any action required to be taken by meeting of shareholders may be taken without meeting if consent is in writing and is signed by all the shareholders entitled to vote |
| | | |
| ● | Any person authorized to vote may authorize another person or persons to act for him by proxy if permitted by the Articles of Association. PubCo’s Articles of Association permit such proxies. | | ● | Any person authorized to vote may authorize another person or persons to act for him by proxy. |
| | | | | |
| ● | Quorum is as designated in the Articles of Association. Quorum in PubCo’s Articles of Association is holders of a majority of the shares being individuals present in person or by proxy or if a corporation or other non-natural person by its duly authorised representative or proxy. | | ● | For stock corporations, certificate of incorporation or by-laws may specify the number to constitute a quorum but in no event shall a quorum consist of less than one-third of shares entitled to vote at a meeting. In the absence of such specifications, a majority of shares entitled to vote shall constitute a quorum. |
| | | |
| ● | The Memorandum and Articles of Association may provide for cumulative voting in the election of directors. PubCo’s Articles of Association do not provide for cumulative voting. | | ● | The certificate of incorporation may provide for cumulative voting. |
| | | |
| ● | Our Articles of Association provide that the rights attached to any class of shares may be varied, modified or abrogated with the consent in writing of the holders of not less than two-thirds of the issued shares of that class, or with the sanction of a resolution passed by a majority of not less than two-thirds of the votes cast at a separate meeting of the holders of the Shares of that class. | | | |
| | | | | |
| Directors |
| |
| ● | Our Articles of Association provide that the number of directors shall not be less than 1 director. | | ● | Board must consist of at least one member. |
| | | |
| ● | Maximum number of directors can be changed by Ordinary Resolution (as defined therein). | | ● | Number of board members shall be fixed by the by-laws, unless the certificate of incorporation fixes the number of directors, in which case a change in the number shall be made only by amendment of the certificate. |
| | | |
| ● | If the board is authorized to change the number of directors actually appointed, provided that the number still falls within the maximum and the minimum number of directors as set out in the Articles of Association, it can do so provided that it complies with the procedure set out in the Articles of Association. PubCo’s Articles of Association permit PubCo’s board to appoint and remove directors. | | | |
| Cayman Islands | | Delaware |
| Fiduciary Duties |
| | |
| ● | In summary, directors and officers owe the following fiduciary duties: | | ● | Directors and officers must act in good faith, with the care of a prudent person, and in the best interest of the corporation as a whole. |
| | | | |
| | ● | Duty to act in good faith in what the directors believe to be in the best interests of the company as a whole; | | ● | Directors and officers must refrain from self-dealing, usurping corporate opportunities and receiving improper personal benefits. |
| | | | |
| | ● | Duty to exercise powers for the purposes for which those powers were conferred and not for a collateral purpose; | | ● | Decisions made by directors and officers on an informed basis, in good faith and in the honest belief that the action was taken in the best interest of the corporation will be protected by the “business judgment rule.” |
| | | | | | |
| | ● | Directors should not improperly fetter the exercise of future discretion; | | | |
| | | | | |
| | ● | Duty to exercise powers fairly as between different groups of shareholders; | | | |
| | | | | |
| | ● | Duty not to put himself in a position of conflict between their duty to the company and their personal interests; and | | | |
| | | | | |
| | ● | Duty to exercise independent judgment. | | | |
| | | | | |
| ● | In addition to the above, directors also owe a duty of care which is not fiduciary in nature. This duty has been defined as a requirement to act as “a reasonably diligent person” having both: | | | |
| | | | | |
| | ● | the general knowledge, skill and experience that may reasonably be expected of a person carrying out the same functions as are carried out by that director in relation to the company, and | | | |
| | | | | |
| | ● | the nature of the company, the nature of the decision and the position of the director and the responsibilities undertaken. | | | |
| | | | | |
| ● | As set out above, directors have a duty not to put themselves in a position of conflict and this includes a duty not to engage in self-dealing, or to otherwise benefit as a result of his position. However, in some instances a breach of this duty can be forgiven and/or authorized in advance by the shareholders provided that there is full disclosure by the directors. This can be done by way of permission granted in the Articles of Association or alternatively by shareholder approval at general meetings. | | | |
| Cayman Islands | | Delaware |
| Shareholders’ Derivative Actions | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ● | Generally speaking, the company is the proper plaintiff in any action. However, based on English authorities, which would in all likelihood be of persuasive authority and be applied by a court in the Cayman Islands, exceptions to the foregoing principle apply in circumstances in which: | | ● | In any derivative suit instituted by a shareholder of a corporation, it shall be averred in the complaint that the plaintiff was a shareholder of the corporation at the time of the transaction of which he complains or that such shareholder’s stock thereafter devolved upon such shareholder by operation of law. |
| | | | | | |
| | ● | Those who control the company have refused a request by the shareholders to move the company to bring the action; | | ● | Complaint shall set forth with particularity the efforts of the plaintiff to obtain the action by the board or the reasons for not making such effort. |
| | | | | | |
| | ● | Those who control the company have refused to do so for improper reasons such that they are perpetrating a “fraud on the minority” (this is a legal concept and is different to “fraud” in the sense of dishonesty); | | ● | Such action shall not be dismissed or compromised without the approval of the Chancery Court. |
| | | | | | |
| | ● | a company is acting or proposing to act illegally or beyond the scope of its authority; or | | ● | Shareholders of a Delaware corporation that redeemed their shares, or whose shares were canceled in connection with dissolution, would not be able to bring a derivative action against the corporation after the shares have been redeemed or canceled. |
| | | | | | |
| | ● | the act complained of, although not beyond the scope of the authority, could only be effected if duly authorized by more than the number of votes which have actually been obtained. | | | |
| | | | | |
| | ● | Once a shareholder has relinquished his, her or its shares (whether by redemption or otherwise), it is generally the case that they could no longer bring a derivative action as they would no longer be a registered shareholder. | | | |
ENFORCEABILITY OF CIVIL LIABILITIES UNDER U.S. SECURITIES LAWS
Cayman Islands
PubCo was incorporated in the Cayman Islands in order to enjoy the following benefits:
| ● | political and economic stability; |
| ● | an effective judicial system; |
| ● | the absence of exchange control or currency restrictions; and |
| ● | the availability of professional and support services. |
However, certain disadvantages accompany incorporation in the Cayman Islands. These disadvantages include, but are not limited to, the following:
| ● | the Cayman Islands has a less developed body of securities laws as compared to the United States and these securities laws provide significantly less protection to investors; and |
| ● | Cayman Islands companies may not have standing to sue before the federal courts of the United States. |
Our memorandum and articles of association do not contain provisions requiring that disputes, including those arising under the securities laws of the United States, between us, PubCo’s officers, directors and shareholders, be arbitrated.
Substantially all of PubCo’s operations are conducted outside the United States, and all of PubCo’s assets are located outside the United States. A majority of PubCo’s directors and officers are nationals or residents of jurisdictions other than the United States and a substantial portion of their assets are located outside the United States. As a result, it may be difficult for a shareholder to effect service of process within the United States upon these persons, or to enforce against PubCo or them judgments obtained in United States courts, including judgments predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the securities laws of the United States or any state in the United States.
PubCo will appoint Cogency Global Inc. as its agent upon whom process may be served in any action brought against it under the securities laws of the United States after the consummation of the Business Transactions.
Maples and Calder (Cayman) LLP, PubCo’s counsel as to Cayman Islands law has advised PubCo that there is uncertainty as to whether the courts of the Cayman Islands, would:
| | ● | recognize or enforce judgments of United States courts obtained against PubCo or its directors or officers predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the securities laws of the United States or any state in the United States; or |
| | ● | entertain original actions brought in each respective jurisdiction against PubCo or its directors or officers predicated upon the securities laws of the United States or any state in the United States. |
Maples and Calder (Cayman) LLP has informed PubCo that it is uncertain whether the courts of the Cayman Islands will allow shareholders of PubCo’s company to originate actions in the Cayman Islands based upon securities laws of the United States. In addition, there is uncertainty with regard to Cayman Islands law related to whether a judgment obtained from the U.S. courts under civil liability provisions of U.S. securities laws will be determined by the courts of the Cayman Islands as penal or punitive in nature. If such a determination is made, the courts of the Cayman Islands will not recognize or enforce the judgment against a Cayman Islands company, such as PubCo. As the courts of the Cayman Islands have yet to rule on making such a determination in relation to judgments obtained from U.S. courts under civil liability provisions of U.S. securities laws, it is uncertain whether such judgments would be enforceable in the Cayman Islands. Maples and Calder (Cayman) LLP has further informed PubCo that although there is no statutory enforcement in the Cayman Islands of judgments obtained in the federal or state courts of the United States (and the Cayman Islands are not a party to any treaties for the reciprocal enforcement or recognition of such judgments), a judgment obtained in such jurisdiction will be recognized and enforced in the courts of the Cayman Islands at common law, without any reexamination of the merits of the underlying dispute, by an action commenced on the foreign judgment debt in the Grand Court of the Cayman Islands, provided such judgment (a) is given by a foreign court of competent jurisdiction, (b) imposes on the judgment debtor a liability to pay a liquidated sum for which the judgment has been given, (c) is final, (d) is not in respect of taxes, a fine or a penalty, and (e) was not obtained in a manner and is not of a kind the enforcement of which is contrary to natural justice or the public policy of the Cayman Islands.
LEGAL MATTERS
The validity of PubCo Ordinary Shares and PubCo Warrants to acquire PubCo Ordinary Shares will be passed upon by Maples and Calder (Cayman) LLP, Cayman Islands counsel to PubCo, and Nelson Mullins Riley & Scarborough LLP, PubCo’s U.S. Counsel respectively. Certain legal matters relating to U.S. law will be passed upon for K Enter by Loeb & Loeb LLP. Certain legal matters relating to Cayman Islands law will be passed upon for K Enter by Maples and Calder (Cayman) LLP.
CHANGE IN PLAY COMPANY’S CERTIFYING ACCOUNTANT
On July 24, 2023, Play Company engaged Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers (“PwC Korea”), as the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm to audit the consolidated financial statements for Play Company as of December 31, 2022, December 31, 2021 and January 1, 2021 and for each of the two fiscal years in the period ended December 31, 2022 in accordance with IFRS and PCAOB standards. Play Company’s Directors approved the engagement of PwC Korea.
As of December 31, 2022, December 31, 2021 and January 1, 2021 and for each of the two fiscal years in the period ended December 31, 2022, E-JUNG Accounting Corporation performed the audit of Play Company’s consolidated financial statements prepared under Korean Generally Accepted Accounting Principles and issued its statutory audit reports in accordance with Korean Standards on Auditing. E-Jung Accounting Corporation continues to serve as Play Company’s statutory auditor in Korea.
The statutory audit reports of E-JUNG Accounting Corporation on the Company’s consolidated financial statements as of December 31, 2022, December 31, 2021 and January 1, 2021 and for each of the two fiscal years in the period ended December 31, 2022 contained no adverse opinion or disclaimer of opinion and were not qualified or modified as to uncertainty, audit scope or accounting principle.
During the fiscal years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 and the subsequent interim period through July 24, 2023, there have been (i) no disagreements within the meaning of Item 16F(a)(1)(iv) of Form 20-F with E-JUNG Accounting Corporation on any matter of accounting principles or practices, financial statement disclosure, or auditing scope or procedure, which disagreements, if not resolved to the satisfaction of E-JUNG Accounting Corporation, would have caused them to make reference thereto in their reports on the financial statements for such years, and (ii) no “reportable events” within the meaning of Item 16F(a)(1)(v) of Form 20-F.
Subsequent to the appointment of PwC Korea, Play Company and PwC Korea identified certain material weaknesses in Play Company’s internal control over financial reporting and errors in Play Company’s previously-issued financial statements based on Korean GAAP. See “Risk Factors — Play Company management has identified material weaknesses in Play Company’s internal control over financial reporting and Play Company may not be able to remediate these weaknesses. Additionally, Play Company’s management may identify material weaknesses in the future that could adversely affect investor confidence, impair the value of PubCo’s securities, and increase PubCo’s cost of raising capital.”
Play Company provided E-JUNG Accounting Corporation with a copy of the disclosures it is making in this proxy statement/prospectus on Form F-4 and has requested that E-JUNG Accounting Corporation furnish a letter addressed to the Securities and Exchange Commission stating whether or not it agrees with the statements made herein. A copy of such letter is filed as Exhibit 16.1 to this Registration Statement on Form F-4.
During the fiscal years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 and the subsequent interim period through July 24, 2023, neither Play Company nor anyone acting on its behalf consulted with PwC Korea regarding (i) the application of accounting principles to a specific transaction, either completed or proposed, or the type of audit opinion that might be rendered on Play Company’s financial statements and neither a written report nor oral advice was provided to Play Company that PwC Korea concluded was an important factor considered by Play Company in reaching a decision as to any accounting, auditing, or financial reporting issue, (ii) any matter that was the subject of a disagreement within the meaning of Item 16F(a)(1)(iv) of Form 20-F, or (iii) any “reportable event” within the meaning of Item 16F(a)(1)(v) of Form 20-F.
EXPERTS
The financial statements of Global Star Acquisition Inc. as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 appearing in this proxy statement/prospectus have been audited by Marcum LLP, independent registered public accounting firm, as set forth in their report thereon appearing elsewhere herein and have been included herein (which contains an explanatory paragraph relating to substantial doubt about the ability of Global Star Acquisition Inc. to continue as a going concern as described in Note 1 to the financial statements). Such financial statements are included in reliance upon such report and upon the authority of such firm as experts in accounting and auditing.
The financial statements of K Wave Media Ltd. as of December 31, 2023 and for the period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023 included in this proxy statement/prospectus have been so included in reliance on the report of Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers, an independent registered public accounting firm, given on the authority of said firm as experts in auditing and accounting.
The financial statements of K Enter Holdings Inc. as of December 31, 2023 and for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023 included in this proxy statement/prospectus have been so included in reliance on the reports of Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers, an independent registered public accounting firm, given on the authority of said firm as experts in auditing and accounting.
The financial statements of Play Company Co., Ltd. as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022 and for the years then ended included in this proxy statement/prospectus have been so included in reliance on the report of Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers, an independent registered public accounting firm, given on the authority of said firm as experts in auditing and accounting.
The financial statements of Solaire Partners LLC. as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022 and for the years then ended included in this proxy statement/prospectus have been so included in reliance on the report of Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers, an independent registered public accounting firm, given on the authority of said firm as experts in auditing and accounting.
The financial statements of Apeitda Co., Ltd. as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022 and for the years then ended included in this proxy statement/prospectus have been so included in reliance on the report of Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers, an independent registered public accounting firm, given on the authority of said firm as experts in auditing and accounting.
The financial statements of the LAMP Co., Ltd. as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022 and for the years then ended included in this proxy statement/prospectus have been so included in reliance on the report of Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers, an independent registered public accounting firm, given on the authority of said firm as experts in auditing and accounting.
The financial statements of Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd. as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022 and for the years then ended included in this proxy statement/prospectus have been so included in reliance on the report of Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers, an independent registered public accounting firm, given on the authority of said firm as experts in auditing and accounting.
The financial statements of Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd. as of December 31, 2023 and for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023 included in this proxy statement/prospectus have been so included in reliance on the report (which contains an explanatory paragraph relating to the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern as described in Note 2 to the financial statements) of Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers, an independent registered public accounting firm, given on the authority of said firm as experts in auditing and accounting.
SHAREHOLDER PROPOSALS AND OTHER MATTERS
Management of Global Star knows of no other matters which may be brought before the Special Meeting. If any matter other than the Business Combination or related matters should properly come before the Special Meeting, however, the persons named in the enclosed proxies will vote proxies in accordance with their judgment on those matters.
DELIVERY OF DOCUMENTS TO SHAREHOLDERS
Pursuant to the rules of the SEC, Global Star and its agents that deliver communications to its stockholders are permitted to deliver to two or more stockholders sharing the same address a single copy of Global Star’s proxy statement/prospectus. Upon written or oral request, Global Star will deliver a separate copy of this proxy statement/prospectus to any stockholder at a shared address who wishes to receive separate copies of such documents in the future. Shareholders receiving multiple copies of such documents may likewise request that Global Star deliver single copies of such documents in the future. Shareholders may notify Global Star of their requests by calling or writing Global Star at its principal executive offices at 555 Madison Avenue, Room 543, New York, NY 10022, Attn: Wei Chen.
WHERE YOU CAN FIND ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Global Star is subject to the informational requirements of the Exchange Act, and is required to file reports, any proxy statements and other information with the SEC.
Neither Global Star, PubCo nor K Enter has authorized anyone to provide you with information that differs from that contained in this proxy statement/prospectus. You should not assume that the information contained in this proxy statement/prospectus is accurate as on any date other than the date of this proxy statement/prospectus, and neither the mailing of this proxy statement/prospectus to Global Star stockholders nor the consummation of the Business Combination shall create any implication to the contrary.
This proxy statement/prospectus does not constitute an offer to sell, or a solicitation of an offer to buy, any securities, or the solicitation of a proxy, in any jurisdiction to or from any person to whom it is not lawful to make any such offer or solicitation in such jurisdiction.
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
INDEX TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| Unaudited financial statements of K Wave Media Ltd. as of June 30, 2024 and 2023 | | |
| Condensed Consolidated Interim Statements of Financial Position as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 | | F-6 |
| Condensed Consolidated Interim Statements of Operations for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 | | F-7 |
| Condensed Consolidated Interim Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Deficit (Equity) for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 | | F-8 |
| Condensed Consolidated Interim Statements of Cash Flows for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 | | F-9 |
| Notes to Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements | | F-10 – F-13 |
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
INDEX TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
INDEX TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
INDEX TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| Condensed Financial Statements (Unaudited): | | |
| Condensed Balance Sheets as of September 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 | | F-95 |
| Condensed Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss for the nine months ended September 30, 2024 and for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) through September 30, 2023 | | F-96 |
| Condensed Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity for the nine months ended September 30, 2024 and for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) through September 30, 2023 | | F-97 |
| Condensed Statements of Cash Flows for the nine months ended September 30, 2024 and for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) through September 30, 2023 | | F-98 |
| Notes to Condensed Financial Statements | | F-99 – F-111 |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD.
INDEX TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD.
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
INDEX TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
APEITDA CO., LTD
INDEX TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
APEITDA CO. LTD.
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
INDEX TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
THE LAMP CO. LTD.
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
INDEX TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO. LTD.
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
STUDIO ANSEILEN CO., LTD.
INDEX TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| Unaudited financial statements of Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd as of June 30, 2024 and 2023 | | |
| Condensed Interim Statements of Financial Position as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 | | F-543 |
| Condensed Interim Statements of Operations for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 | | F-544 |
| Condensed Interim Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Deficit (Equity) for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and from period March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 | | F-545 |
| Condensed Interim Statements of Cash Flows for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 | | F-546 |
| Notes to Condensed Interim Financial Statements | | F-547 – F-557 |
STUDIO ANSEILEN CO. LTD.
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023
| | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | |
| Other receivables – related parties | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | | $ | 50,000 | | | $ | 50,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | | | | | | | |
| Other payables | | | 7,256 | | | | 7,256 | |
| Other payables – related parties | | | 5,551 | | | | 5,551 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | | $ | 12,807 | | | $ | 12,807 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | | | | | | | |
| Common stock | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | |
| Other reserves | | | (1,376 | ) | | | (1,376 | ) |
| Accumulated deficit | | | (11,431 | ) | | | (11,431 | ) |
| Total stockholders’ equity | | | 37,193 | | | | 37,193 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | $ | 50,000 | | | $ | 50,000 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed consolidated interim financial statements.
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
For the six-month period ended June 30, 2024 and period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
| | | Six months ended
June 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from
June 22, 2023
(inception) to
June 30,
2023 | |
| Revenue | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
| Operating expenses | | | | | | | | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | - | | | | 3,882 | |
| Total operating cost and expenses | | | - | | | | 3,882 | |
| Loss from operations | | | - | | | | (3,882 | ) |
| Net loss | | $ | - | | | $ | (3,882 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Comprehensive loss | | $ | - | | | $ | (3,882 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding, basic and diluted | | | 5,000,000 | | | | 5,000,000 | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share of common stock | | $ | - | | | $ | (0.001 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed consolidated interim financial statements.
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
For the six-month period ended June 30, 2024 and period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
| | | Common stock | | | Other | | | Accumulated | | | | |
| | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Reserves | | | Deficit | | | Total | |
| Balance, June 22, 2023 (inception) | | | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
| Shares issued for related party receivable | | | 5,000,000 | | | | 50,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 50,000 | |
| Other reserves | | | - | | | | - | | | | (1,376 | ) | | | - | | | | (1,376 | ) |
| Net loss | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (3,882 | ) | | | (3,882 | ) |
| Balance, June 30, 2023 | | | 5,000,000 | | | $ | 50,000 | | | $ | (1,376 | ) | | $ | (3,882 | ) | | $ | 44,742 | |
| Balance, January 1, 2024 | | | 5,000,000 | | | $ | 50,000 | | | $ | (1,376 | ) | | $ | (11,431 | ) | | $ | 37,193 | |
| Net loss | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Balance, June 30, 2024 | | | 5,000,000 | | | $ | 50,000 | | | $ | (1,376 | ) | | $ | (11,431 | ) | | $ | 37,193 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed consolidated interim financial statements.
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the six-month period ended June 30, 2024 and period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
| | | Six Months ended
June 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from
June 22, 2023
(inception) to
June 30,
2023 | |
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | | $ | - | | | $ | (3,882 | ) |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash used in operations: | | | | | | | | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
| Other payables | | | - | | | | 3,288 | |
| Other payables – related parties | | | - | | | | 594 | |
| CASH USED IN OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | - | | | | - | |
| CASH USED IN INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES | | | - | | | | - | |
| CASH USED IN FINANCING ACTIVITIES | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period | | | - | | | | - | |
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of period | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed consolidated interim financial statements.
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the six-month period ended June 30, 2024 and period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
1. General Information
K Wave Media Ltd. (“the Company”), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Global Star Acquisition Inc. (“Global Star”), was incorporated on June 22 2023 and the Company’s registered office is at c/o Maples Corporate Services Limited PO Box 309, Ugland House Grand Cayman, KY1-1104 Cayman Islands. The Company was formed for the purpose of becoming the ultimate parent company following the transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement. The Company maintains one direct wholly owned subsidiary, GLST Merger Sub Inc. (“Merger Sub”), a Delaware corporation. Merger Sub was incorporated to facilitate the consummation of the Business Combination Agreement. As of June 30, 2024, Merger Sub had no operations. The Company and Merger Sub are together referred to as the “Group”.
Global Star entered into a merger agreement, dated as of June 15, 2023 and as amended on March 11, 2024, June 28, 2024, and July 25, 2024 (the “Merger Agreement”), which provides for a Business Combination between Global Star and K Enter Holdings, Inc., a Delaware corporation (“K Enter”). Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, the Business Combination will be effected in two steps: (i) subject to the approval and adoption of the Merger Agreement by the stockholders of Global Star, Global Star will reincorporate to Cayman Islands by merging with and into the Company, with the Company remaining as the surviving publicly traded entity (the “Reincorporation Merger”); (ii) one (1) business day following the Reincorporation Merger, the Merger Sub will be merged with and into K Enter, resulting in K Enter being a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company.
On July 13, 2023, the Company and the Merger Sub executed a written Joinder Agreement to become parties to the Merger Agreement to comply with the terms and conditions of the Merger Agreement, accordingly, the Merger Agreement is by and among Global Star, the Company, Merger Sub, and K Enter.
As of June 30, 2024, the Company issued 5,000,000 shares of the Company’s ordinary shares. Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, the Company expects to cancel all the outstanding 5,000,000 shares of the Company’s ordinary shares as of the effective date of the Business Combination. In connection with the Reincorporation Merger, the Company expects to issue 4,519,622 ordinary shares of the Company to the stockholders of Global Star, assuming no additional redemptions by the public stockholders of Global Star. Also, pursuant to the Merger Agreement the Company expects to issue a total of 59,000,000 ordinary shares of the Company as consideration for a total of 193,367 shares of K Enter. This consists of 101,202 shares of outstanding K Enter’s common stock, 51,367 shares of K Enter common stock to be issued to the owners of the Six Korean Entities pursuant to the equity purchase agreement based on an estimated 305.1:1 conversion ratio calculated with a foreign exchange rate of KRW 1,376.55 / USD $1.00, and 40,798 K Wave shares of common stock to be issued to the holders of K Enter’s Series A Preferred Stock and Series A-1 Preferred Stock based on the conversion of the of K Enter Series A Preferred Stock and Series A-1 Preferred Stock. The total ordinary shares of the Company to be issued to the stockholders of K Enter will be 59,000,000 ordinary shares in connection with the closing of the Business Combination. Following the consummation of all the transactions contemplated by the Business Combination, the total outstanding shares of the Company will be 63,519,622, assuming no additional redemptions by the public stockholders of Global Star.
Following the consummation of the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement, the Company will be the surviving publicly-traded entity. However, the consummation of the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement is subject to numerous conditions, and there can be no assurances that such conditions will be satisfied.
The condensed consolidated financial statements of the Company were authorized for initial issuance on October 25, 2024, except for the matters disclosed in Note 5 as to which the date is December 23, 2024.
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the six-month period ended June 30, 2024 and period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
2. Basis of Accounting
These interim consolidated financial statements for the six month period ended June 30, 2024 and period from June 22, 2023 to June 30,2023 have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) IAS 34 Interim Financial Reporting as issued by International Accounting Standard Board (“IASB”), and should be read in conjunction with the Group’s last annual consolidated financial statements as at and for the year ended December 31, 2023 (“last annual financial statements”). They do not include all of the information required for a complete set of financial statements prepared in accordance with IFRS Accounting Standards. However, selected explanatory notes are included to explain events and transactions that are significant to an understanding of the changes in the Group’s financial position and performance since the last annual financial statements. The costs of business operations are paid by K Enter and therefore no accounting transactions have been recorded for 6 months in 2024.
The number of shares used to calculate diluted loss per share of common shares attributable to common shareholders is the same as the number of shares used to calculate basic loss per share of common shares attributable to common shareholders for the period presented because there were no potentially dilutive securities outstanding during the period.
The loss per share presented in the statement of operations and comprehensive loss is based on the following for the six-month period ended June 30, 2024 and period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023:
| | | Six months ended June 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from
June 22, 2023
(inception) to
June 30,
2023 | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share: | | | | | | | | |
| Numerator | | | | | | | | |
| Allocation of net loss | | $ | - | | | $ | (3,882 | ) |
| Denominator: | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted weighted average number of shares outstanding | | | 5,000,000 | | | | 5,000,000 | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share | | $ | - | | | $ | (0.001 | ) |
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the six-month period ended June 30, 2024 and period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
3. Significant accounting policies
Significant accounting policies and method of computation used in the preparation of the condensed consolidated interim financial statements are consistent with those of the last annual financial statements for the period ended December 31, 2023, except for the changes as described below.
Income tax expense
Income tax expense for the interim period is recognized based on management’s best estimate of the weighted average annual income tax rate expected for the full financial year. The estimated average annual effective income tax rate is applied to the pre-tax income of the interim period.
| i. | New and amended standards or interpretations adopted by the Group |
The Group has applied the following standards and interpretations for the first time for their annual reporting period commencing January 1, 2024.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements
The amendments to IAS 1 clarify that the classification of liabilities as current or non-current should be based on rights that are in existence at the end of the reporting period and that the classification is unaffected by management’s intentions or expectations about whether an entity will exercise its right to defer settlement of a liability. The amendments also introduce a definition of settlement to make clear that settlement includes the transfer to the counterparty of the entity’s own equity instruments, however, it would be excluded if an option to settle the liability by the transfer of the entity’s own equity instruments is recognized separately from the liability as an equity component of a compound financial instrument. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Group’s interim financial statements.
IAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows, and IFRS 7, Financial Instruments: Disclosures
The amendments add to the disclosure objectives in IAS 7, Statement of Cash Flows, that information about supplier financing arrangements should be disclosed to enable users of financial statements to assess the impact of those arrangements on the Group’s liabilities and cash flows. The amendments also amend IFRS 7, Financial Instruments: Disclosures, to add supplier financing arrangements as an example of a requirement to disclose information about an entity’s exposure to concentrations of liquidity risk. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Group’s interim financial statements.
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the six-month period ended June 30, 2024 and period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
IFRS 16 Leases
The amendments add requirements for the subsequent measurement of sale-and-leaseback transactions that are accounted for as sales in accordance with IFRS 15, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. The amendments require the seller lessee to calculate the ‘lease payments’ or ‘revised lease payments’ in a way that does not result in the seller-lessee recognizing any gain or loss for the rights of use that the seller-lessee continues to retain after the lease commences. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Group’s interim financial statements.
| ii. | New and amended standards or interpretations not yet adopted by the Group |
The following new accounting standards and interpretations that have been published that are not mandatory for June 30, 2024 reporting periods and have not been early adopted by the Group.
IAS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates
The amendments require exchangeability of two currencies should be assessed in order to clarify reporting of foreign currency transactions in the absence of normal-functioning foreign exchange market. The amendments also require applicable spot exchange rate should be determined when the assessment indicates two currencies lack exchangeability. The amendments are effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2025, with early application permitted.
4. Share capital
Details of share capital as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| Number of authorized shares | | | 5,000,000 | | | | 5,000,000 | |
| Value per share | | $ | 0.01 | | | $ | 0.01 | |
| Number of shares issued | | | 5,000,000 | | | | 5,000,000 | |
| Common shares | | $ | 50,000 | | | $ | 50,000 | |
During June 2023, the Group entered into an agreement to issue 5,000,000 shares of common shares for gross proceeds of $50,000. Each ordinary share maintains one voting right. The entire amount of this equity is held by Global Star and recorded as a receivable under the caption Other receivables - related parties in the Group’s condensed Consolidated Statements of Financial Position.
5. EVENTS UP TO DECEMBER 23, 2024 SUBSEQUENT TO THE DATE THAT THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS WERE AUTHORIZED FOR INITIAL ISSUANCE, OCTOBER 25, 2024
On December 11, 2024, Global Star, K Enter, the Company and Merger Sub (the “Parties”) entered into the Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement, which extended the Outside Date for the parties to consummate the closing of the Business Combination from December 22, 2024 to June 22, 2025.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Shareholder of
K Wave Media Ltd.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statement of financial position of K Wave Media Ltd. and its subsidiary (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2023, and the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss, of changes in equity and of cash flows for the period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, including the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023 in conformity with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s consolidated financial statements based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit of these consolidated financial statements in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud.
Our audit included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audit also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
| /s/ Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers | |
| | |
| Seoul, KOREA | |
| May 13, 2024 | |
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2024.
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As of December 31, 2023
| | | December 31,
2023 | |
| ASSETS | | | | |
| Other receivables – related parties | | | 50,000 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | | $ | 50,000 | |
| | | | | |
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | | | |
| Other payables | | | 7,256 | |
| Other payables – related parties | | | 5,551 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | | $ | 12,807 | |
| | | | | |
| STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | | | |
| Common stock | | | 50,000 | |
| Other reserves | | | (1,376 | ) |
| Accumulated deficit | | | (11,431 | ) |
| Total stockholders’ equity | | | 37,193 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | $ | 50,000 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
For the period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
| | | For the
period from
June 22, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| Revenue | | $ | - | |
| Operating expenses | | | | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | 11,431 | |
| Total operating cost and expenses | | | 11,431 | |
| Loss from operations | | | (11,431 | ) |
| Net loss | | $ | (11,431 | ) |
| | | | | |
| Comprehensive loss | | $ | (11,431 | ) |
| | | | | |
| Weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding, basic and diluted | | | 5,000,000 | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share of common stock | | $ | (0.002 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
For the period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
| | | Common stock | | | Other | | | Accumulated | | | | |
| | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Reserves | | | Deficit | | | Total | |
| Balance, June 22, 2023 (inception) | | | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
| Shares issued for related party receivable | | | 5,000,000 | | | | 50,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 50,000 | |
| Other reserves | | | - | | | | - | | | | (1,376 | ) | | | - | | | | (1,376 | ) |
| Net loss | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (11,431 | ) | | | (11,431 | ) |
| Balance, December 31, 2023 | | | 5,000,000 | | | $ | 50,000 | | | $ | (1,376 | ) | | $ | (11,431 | ) | | $ | 37,193 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
For the period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
| | | For the
period from
June 22, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | | |
| Net loss | | $ | (11,431 | ) |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash used in operations: | | | | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | |
| Other payables | | | 7,257 | |
| Other payables – related parties | | | 4,174 | |
| CASH USED IN OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | - | |
| | | | | |
| CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | - | |
| CASH USED IN INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | - | |
| | | | | |
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES | | | - | |
| CASH USED IN FINANCING ACTIVITIES | | | - | |
| | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period | | | - | |
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of period | | $ | - | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
1. General Information
K Wave Media Ltd. (“the Company”), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Global Star Acquisition Inc. (“Global Star”), was incorporated on June 22 2023 and the Company’s registered office is at c/o Maples Corporate Services Limited PO Box 309, Ugland House Grand Cayman, KY1-1104 Cayman Islands. The Company was formed for the purpose of becoming the ultimate parent company following the transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement. The Company maintains one direct wholly owned subsidiary, GLST Merger Sub Inc. (“Merger Sub”), a Delaware corporation. Merger Sub was incorporated to facilitate the consummation of the Business Combination Agreement. As of December 31, 2023, Merger Sub had no operations. The Company and Merger Sub are together referred to as the “Group”.
Global Star entered into a merger agreement, dated as of June 15, 2023 (as it may be amended from time to time, the “Merger Agreement”), which provides for a Business Combination between Global Star and K Enter Holdings, Inc., a Delaware corporation (“K Enter”). Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, the Business Combination will be effected in two steps: (i) subject to the approval and adoption of the Merger Agreement by the stockholders of Global Star, Global Star will reincorporate to Cayman Islands by merging with and into the Company, with the Company remaining as the surviving publicly traded entity (the “Reincorporation Merger”); (ii) one (1) business day following the Reincorporation Merger, the Merger Sub will be merged with and into K Enter, resulting in K Enter being a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company.
On July 13, 2023, the Company and the Merger Sub executed a written Joinder Agreement to become parties to the Merger Agreement to comply with the terms and conditions of the Merger Agreement, accordingly, the Merger Agreement is by and among Global Star, the Company, Merger Sub, and K Enter.
Following the consummation of the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement, the Company will be the surviving publicly-traded entity. However, the consummation of the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement is subject to numerous conditions, and there can be no assurances that such conditions will be satisfied.
2. Basis of Accounting
These consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with the International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”), on the historical cost basis, and in the presentation currency USD. All amounts are in actual USD unless otherwise stated. These consolidated financial statements were authorized for issuance by the board of directors on May 13, 2024.
The number of shares used to calculate diluted loss per share of common shares attributable to common shareholders is the same as the number of shares used to calculate basic loss per share of common shares attributable to common shareholders for the period presented because there were no potentially dilutive securities outstanding during the period.
The loss per share presented in the statement of operations and comprehensive loss is based on the following for the period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023:
| | | Common Stock | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share: | | | | |
| Numerator | | | | |
| Allocation of net loss | | $ | (11,431 | ) |
| Denominator: | | | | |
| Basic and diluted weighted average number of shares outstanding | | | 5,000,000 | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share | | $ | (0.002 | ) |
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from June 22, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
3. Material accounting policies
The material following accounting policies followed by the Group in preparation of its financial statements are as follows:
| A. | Financial assets and Financial liabilities |
Financial instruments are any form of contract that gives rise to a financial asset in one company and a financial liability or equity instrument in another company. A financial asset or financial liability is included in the balance sheet when the entity becomes a party to the contractual terms of the instrument. Other financial liabilities and other financial assets, including liabilities to and receivables from related parties, are valued at amortized cost. A financial asset is removed from the balance sheet when the contractual right to cash flow from the asset has ceased or been settled. The same applies where the risks and benefits associated with the holding are essentially transferred to another party and the entity no longer has control over the financial asset. A financial liability is derecognized when the agreed obligation has been fulfilled or ceased.
| B. | Transaction costs in issuing equity securities, organization costs, and other service fees |
When issuing common stock, incremental costs directly attributable to the equity transaction that otherwise would have been avoided are accounted for as a deduction from equity while other issuing related costs and organization costs are expensed as incurred. $1,376 is deducted from equity while $3,882 is expensed as incurred. $7,549 service fees are expensed as incurred. $5,551 is owed to Global Star and recorded as a payable under the caption Other payables - related parties in the Group’s Consolidated Statement of Financial Position.
4. Share capital
Details of share capital as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | December 31,
2023 | |
| Number of authorized shares | | | 5,000,000 | |
| Value per share | | $ | 0.01 | |
| Number of shares issued | | | 5,000,000 | |
| Common shares | | $ | 50,000 | |
During June 2023, the Group entered into an agreement to issue 5,000,000 shares of common shares for gross proceeds of $50,000. Each ordinary share maintains one voting right. The entire amount of this equity is held by Global Star and recorded as a receivable under the caption Other receivables - related parties in the Group’s Consolidated Statement of Financial Position.
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Stockholders and Board of Directors of
Global Star Acquisition Inc.
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Global Star Acquisition Inc. (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the related consolidated statements of income, changes in stockholders’ (deficit) equity and cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2023, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2023, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Explanatory Paragraph – Going Concern
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As described in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company is a Special Purpose Acquisition Corporation that was formed for the purpose of completing a merger, capital stock exchange, asset acquisition, stock purchase, reorganization or similar business combination with one or more businesses or entities on or before March 22, 2024 (or up to June 22, 2024, in the event the Company extends the term to the fullest). The Company entered into a definitive merger agreement with a business combination target on June 15, 2023; however, the completion of this transaction is subject to the approval of the Company’s stockholders among other conditions. There is no assurance that the Company will obtain the necessary approvals, satisfy the required closing conditions, raise the additional capital it needs to fund its operations, and complete the transaction prior to March 22, 2024, if at all. The Company also has no approved plan in place to extend the business combination deadline and fund operations for any period of time after March 22, 2024, in the event that it is unable to complete a business combination by that date. These matters raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans with regard to these matters are also described in Note 1. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that may be necessary should the Company be unable to continue as a going concern.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Marcum LLP
Marcum LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2021.
New York, NY
March 15, 2024
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
| | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | |
| Current Assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 1,506,914 | | | $ | 877,560 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | | 80,782 | | | | 231,528 | |
| Total Current Assets | | | 1,587,696 | | | | 1,109,088 | |
| Other assets | | | - | | | | 49,526 | |
| Marketable securities held in Trust Account | | | 55,707,757 | | | | 95,134,678 | |
| Total Assets | | $ | 57,295,453 | | | $ | 96,293,292 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES, COMMON STOCK SUBJECT TO POSSIBLE REDEMPTION AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | | $ | 781,967 | | | $ | 184,204 | |
| Accrued offering costs | | | - | | | | 67,414 | |
| Accrued franchise tax payable | | | 59,313 | | | | 201,596 | |
| Income taxes payable | | | 796,065 | | | | 135,321 | |
| Excise tax payable attributable to redemption of common stock | | | 426,807 | | | | - | |
| Promissory note - related party | | | 1,590,000 | | | | - | |
| Due to Sponsor | | | 15,094 | | | | 15,094 | |
| Total Current Liabilities | | | 3,669,246 | | | | 603,629 | |
| Deferred underwriting commission | | | 3,220,000 | | | | 3,220,000 | |
| Total Liabilities | | $ | 6,889,246 | | | $ | 3,823,629 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES (Note 6) | | | | | | | | |
| Class A common stock subject to possible redemption; 5,147,934 and 9,200,000 shares issued and outstanding at redemption value of $10.80 and $10.30 per share at December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | | | 55,575,390 | | | | 94,797,761 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Stockholders’ deficit: | | | | | | | | |
| Preferred stock, $0.0001 par value; 1,000,000 shares authorized; none issued and outstanding | | | - | | | | - | |
| Class A common stock, $0.0001 par value, 100,000,000 shares authorized, 613,225 shares issued and outstanding (excluding 5,147,934 and 9,200,000 shares subject to possible redemption at December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively) | | | 62 | | | | 62 | |
| Class B common stock, $0.0001 par value, 10,000,000 shares authorized, 2,300,000 shares issued and outstanding | | | 230 | | | | 230 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | | | - | | | | - | |
| Accumulated deficit | | | (5,169,475 | ) | | | (2,328,390 | ) |
| Total Stockholders’ Deficit | | | (5,169,183 | ) | | | (2,328,098 | ) |
| Total Liabilities, Common Stock Subject to Possible Redemption and Stockholders’ Deficit | | $ | 57,295,453 | | | $ | 96,293,292 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
| | | For the Year Ended | |
| | | December 31, | | | December 31, | |
| | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| OPERATING EXPENSES | | | | | | | | |
| Administration fee - related party | | $ | 121,666 | | | $ | 32,000 | |
| General and administrative | | | 2,005,281 | | | | 515,868 | |
| TOTAL OPERATING EXPENSES | | | (2,126,947 | ) | | | (547,868 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| OTHER INCOME | | | | | | | | |
| Income earned on Investments held in Trust Account | | | 3,942,920 | | | | 844,178 | |
| Interest income | | | 23,833 | | | | 206 | |
| Change in fair value of over-allotment liability | | | - | | | | 7,619 | |
| TOTAL OTHER INCOME | | | 3,966,753 | | | | 852,003 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Income before provision for income taxes | | | 1,839,806 | | | | 304,135 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Provision for income taxes | | | (795,729 | ) | | | (135,321 | ) |
| Net income | | $ | 1,044,077 | | | $ | 168,814 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average number of shares of redeemable Class A common stock outstanding, basic and diluted | | | 7,823,408 | | | | 2,481,096 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted net income per share of redeemable Class A common stock | | $ | 0.10 | | | $ | 0.04 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average number of shares of non-redeemable Class A and B common stock outstanding, basic and diluted | | | 2,913,225 | | | | 2,238,462 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted net income per share of non-redeemable Class A and B common stock | | $ | 0.10 | | | $ | 0.04 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ (DEFICIT) EQUITY
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2023 AND 2022
| | | Class A | | | Class B | | | Additional | | | | | | Stockholders’ | |
| | | Common Stock | | | Common Stock(1)(2)(3) | | | Paid-In | | | Accumulated | | | (Deficit) | |
| | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Capital | | | Deficit | | | Equity | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2021 | | | - | | | $ | - | | | | 2,300,000 | | | $ | 230 | | | $ | 24,770 | | | $ | (2,909 | ) | | $ | 22,091 | |
| Sale of Units in Public Offering, net of offering costs | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 436,226 | | | | - | | | | 436,226 | |
| Proceeds from Private Placement Units, net of offering costs | | | 498,225 | | | | 50 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,952,607 | | | | - | | | | 4,952,607 | |
| Proceeds from Sale of Rights, net of costs | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 61,072 | | | | - | | | | 61,072 | |
| Class A common stock issued to representative | | | 115,000 | | | | 12 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 79,338 | | | | - | | | | 79,350 | |
| Remeasurement adjustment of Class A ordinary shares to redemption value | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (5,554,013 | ) | | | (2,494,295 | ) | | | (8,048,308 | ) |
| Net income | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 168,814 | | | | 168,814 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2022 | | | 613,225 | | | $ | 62 | | | | 2,300,000 | | | $ | 230 | | | $ | - | | | $ | (2,328,390 | ) | | $ | (2,328,098 | ) |
| Remeasurement adjustment of Class A ordinary shares to redemption value | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (3,458,355 | ) | | | (3,458,355 | ) |
| Excise tax payable attributable to redemption of common stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (426,807 | ) | | | (426,807 | ) |
| Net income | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,044,077 | | | | 1,044,077 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | | | 613,225 | | | $ | 62 | | | | 2,300,000 | | | $ | 230 | | | $ | - | | | $ | (5,169,475 | ) | | $ | (5,169,183 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| | | For the Year Ended | |
| | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities: | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | $ | 1,044,077 | | | $ | 168,814 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash used in operating activities: | | | | | | | | |
| Income earned on Investments held in Trust Account | | | (3,942,920 | ) | | | (844,178 | ) |
| Change in fair value of overallotment liability | | | - | | | | (7,619 | ) |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
| Prepaid expenses | | | 150,746 | | | | 25,071 | |
| Other current assets | | | - | | | | (231,528 | ) |
| Other assets | | | 49,526 | | | | (49,526 | ) |
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | | | 597,763 | | | | 184,204 | |
| Accrued income taxes | | | 660,744 | | | | 135,321 | |
| Accrued franchise tax payable | | | (142,283 | ) | | | 200,000 | |
| Advances from related party | | | - | | | | (42,384 | ) |
| Net cash used in Operating Activities | | | (1,582,347 | ) | | | (461,825 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Cash Flows from Investing Activities: | | | | | | | | |
| Investment of cash into Trust Account | | | (500,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Cash withdrawn from Trust Account to pay franchise and income taxes | | | 1,189,115 | | | | - | |
| Cash withdrawn from Trust Account in connection with redemption | | | 42,680,726 | | | | - | |
| Cash deposited into Trust Account | | | - | | | | (94,300,000 | ) |
| Net Cash provided by (used in) Investing Activities | | | 43,369,841 | | | | (94,300,000 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Cash Flows from Financing Activities: | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from sale of Units in Public Offering | | | - | | | | 92,000,000 | |
| Proceeds from sale of Private Placement Warrants | | | - | | | | 4,982,250 | |
| Payment of underwriter discounts and commissions | | | - | | | | (920,000 | ) |
| Proceeds from sponsor | | | - | | | | 25,000 | |
| Proceeds from sponsor note | | | - | | | | 185,000 | |
| Repayment of sponsor note | | | - | | | | (185,000 | ) |
| Due from Sponsor | | | - | | | | 15,094 | |
| Payment of offering costs | | | (67,414 | ) | | | (462,959 | ) |
| Proceeds from promissory note - related party | | | 1,590,000 | | | | - | |
| Redemption of common stock | | | (42,680,726 | ) | | | - | |
| Net cash (used in) provided by Financing Activities | | | (41,158,140 | ) | | | 95,639,385 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Net change in cash | | | 629,354 | | | | 877,560 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | | | 877,560 | | | | - | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | | $ | 1,506,914 | | | $ | 877,560 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Supplemental disclosure of non-cash financing activities: | | | | | | | | |
| Deferred offering costs included in accrued offering costs | | $ | - | | | $ | 52,414 | |
| Deferred underwriting costs | | $ | - | | | $ | 3,220,000 | |
| Class A Ordinary Shares remeasurement to redemption value | | $ | 3,458,355 | | | $ | 8,048,308 | |
| Excise tax payable attributable to redemption of common stock | | $ | 426,807 | | | $ | - | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Supplemental disclosure of information: | | | | | | | | |
| Income taxes paid | | $ | 134,985 | | | $ | - | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1 — DESCRIPTION OF ORGANIZATION, BUSINESS OPERATIONS AND GOING CONCERN
Global Star Acquisition Inc. (the “Company”) is a blank check company incorporated in the State of Delaware on July 24, 2019, whose business purpose is to effect a merger, capital stock exchange, asset acquisition, stock purchase, reorganization, or similar business combination with one or more businesses, which we refer to as our initial business combination. To date, our efforts have been limited to organizational activities as well as activities related to the initial public offering and the completion of its initial Business Combination.
As of December 31, 2023, the Company had two wholly-owned subsidiaries, GLST Merger Sub, Inc., a majority-owned subsidiary of the Company incorporated in Delaware on June 12, 2023 (“GLST Merger Sub”), and K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company formed on June 22, 2023 (See “Merger Agreement” section below).
As of December 31, 2023, the Company had not commenced any operations. All activity for the period from July 24, 2019 (inception) through December 31, 2023, relates to organizational activities and identifying a target company for a business combination. The Company will not generate any operating revenues until after the completion of its initial Business Combination, at the earliest. The Company generates non-operating income in the form of interest income on the proceeds derived from the Offering placed in Trust Account. The Company has selected December 31 as its fiscal year end.
The Company’s sponsor is Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (the “Sponsor”). The registration statement for the Company’s Initial Public Offering was declared effective on September 19, 2022.
On September 22, 2022, the Company consummated its initial public offering (the “IPO”) of 8,000,000 units (the “Units” and, with respect to the shares of Class A common stock included in the Units sold, the “Public Shares”). Each Unit consists of one share of Class A common stock of the Company, par value $0.0001 per share (“Class A Common Stock”), one redeemable warrant of the Company (“Warrant”), with each whole Warrant entitling the holder thereof to purchase one share of Class A Common Stock for $11.50 per share, and one Right, with each Right entitling the holder to receive one-tenth of one share of Class A Common Stock. The Units were sold at a price of $10.00 per Unit, generating gross proceeds to the Company of $80,000,000. On October 4, 2022, the Company closed on the over-allotment through the sale of 1,200,000 Units at a purchase of $10.00 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $12.0 million.
Simultaneously with the consummation of the closing of the Offering, the Company consummated the private placement of an aggregate of 456,225 units (the “Private Placement Units”) to Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC, the sponsor of the Company (the “Sponsor”), at a price of $10.00 per Private Placement Unit, generating total gross proceeds of $4,562,250 (the “Private Placement”) (see Note 4).
On October 4, 2022, the Company consummated the closing of the sale of 1,200,000 additional units at a price of $10 per unit upon receiving notice of the underwriters’ election to exercise their overallotment option generating additional gross proceeds of $12.0 million. Simultaneously with the exercise of the overallotment, the Company consummated the Private Placement of an additional 42,000 Private Placement Units to the Sponsor, generating gross proceeds of $420,000.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Transaction costs amounted to $4,788,510 consisting of $920,000 of underwriting fees (net of underwriter reimbursements), $3,220,000 of deferred underwriting fees payable, which are held in a trust account with Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company acting as trustee (the “Trust Account”) and $648,510 of other offering costs related to the Initial Public Offering. The underwriters were also issued 115,000 shares of Class A common stock as representative shares, in connection with the IPO. Upon close of the Initial Public Offering, the Company recorded additional issuance costs of $79,338, the grant date fair value of the shares, with an offset to additional paid-in capital. As described in Note 6, the $3,220,000 deferred underwriting fees are contingent upon the consummation of the Business Combination within 21 months from the closing of the IPO pursuant to nine one-month extensions, from September 22, 2023 until June 22, 2024, provided that the Sponsor (or its affiliates or permitted designees) will deposit into the Trust Account $125,000 for each such one-month extension until June 22, 2024, unless the closing of the Company’s initial business combination shall have occurred. (See “Special Meeting” section below).
Nasdaq rules provide that at least 90% of the gross proceeds from the IPO and the sale of the placement units be deposited in a trust account. Of the net proceeds of the IPO and the sale of the placement units, $94,300,000, $10.25 per unit, was placed into a trust account (the “Trust Account”) established for the benefit of the holders of the outstanding Public Shares (the “public stockholders”), with Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company acting as trustee and Morgan Stanley Wealth Management acting as investment manager. These proceeds include $3,220,000 in deferred underwriting commissions.
The proceeds in the trust account may be invested in U.S. government securities, within the meaning set forth in Section 2(a)(16) of the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended (the “Investment Company Act”), with a maturity of 185 days or less or in any open-ended investment company that holds itself out as a money market fund meeting the conditions of Rule 2a-7 of the Investment Company Act, as determined by the Company, until the earlier of: (i) the consummation of a Business Combination or (ii) the distribution of the Trust Account to the Company’s stockholders, as described below.
Special Meeting
On August 22, 2023, the Company held a Special Meeting of Stockholders (the “Meeting”). At the Meeting, the Company’s stockholders approved the Charter Amendment, which extends the date by which the Company must consummate its initial business combination by an additional nine-months pursuant to nine one-month extensions, from September 22, 2023 to June 22, 2024 (the “New Termination Date”), subject to the approval of the Board of Directors of the Company (the “Board”), provided the sponsor or its designees deposit into the trust account a monthly amount equal to $125,000, prior to the commencement of each extension period (the “Extension”). The Company filed the Charter Amendment with the Office of the Secretary of State of Delaware on August 28, 2023, a copy of which is attached as Exhibit 3.1 in the Form 8-K filed with the SEC on August 28, 2023 and is incorporated by reference herein. At the Meeting, Stockholders holding 4,052,066 shares of common stock exercised their right to redeem their shares for cash at an approximate price of $10.53 per share of the funds in the Trust Account. As a result, for the period ended December 31, 2023, an aggregate of $42,680,726 was withdrawn from the Trust Account to pay such holders. Following the redemption, the Company’s remaining shares of Class A common stock outstanding were 5,147,934. The Company has made four monthly payments of $125,000 in the Trust Account to extend the period of time it has to consummate its initial business combination to January 22, 2024 (see Note 11).
The Company will provide its holders of the outstanding Public Shares (the “public stockholders”) with the opportunity to redeem all or a portion of their Public Shares upon the completion of a Business Combination either (i) in connection with a stockholder meeting called to approve the Business Combination or (ii) by means of a tender offer. In connection with a proposed Business Combination, the Company may seek stockholder approval of a Business Combination at a meeting called for such purpose at which stockholders may seek to redeem their shares, regardless of whether they vote for or against a Business Combination. The Company will proceed with a Business Combination only if the Company has net tangible assets of at least $5,000,001 either immediately prior to or upon such consummation of a Business Combination and, if the Company seeks stockholder approval, a majority of the outstanding shares voted are voted in favor of the Business Combination.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The Company will have until March 22, 2024 (or up to June 22, 2024, in the event the Company extends the term to the fullest), to consummate a Business Combination. If we do not complete our initial business combination by June 22, 2024, or (i) as extended by the Company’s stockholders in accordance with our amended and restated certificate of incorporation or (ii) with respect to any other provision relating to stockholders’ rights or pre-initial business combination activity and (iii) waive their rights to liquidating distributions from the trust account with respect to any founder shares and placement shares held by them if we fail to complete our initial business combination prior to the New Termination date, the public stockholders will be entitled to liquidating distributions from the trust account with respect to any public shares they hold if we fail to complete our initial business combination within the prescribed time frame. Accordingly, it is our intention to redeem our public shares as soon as reasonably possible following the New Termination Date unless our initial business combination shall have occurred earlier and, therefore, we do not intend to comply with those procedures. As such, our public stockholders could potentially be liable for any claims to the extent of distributions received by them (but no more) and any liability of our stockholders may extend well beyond the third anniversary of such date (see Note 10).
Our sponsor has agreed that it will be liable to us if and to the extent any claims by a third party (other than the independent public accounting firm) for services rendered or products sold to us, or a prospective target business with which we have entered into a written letter of intent, confidentiality or similar agreement or business combination agreement, reduce the amount of funds in the trust account to below the lesser of (i) $10.25 per public share and (ii) the actual amount per public share held in the trust account due to reductions in the value of the trust assets as of the date of the liquidation of the trust account, if less than $10.25 per public share due to reductions in the value of the trust assets, less taxes payable, provided that such liability will not apply to any claims by a third party or prospective target business who executed a waiver of any and all rights to the monies held in the trust account (whether or not such waiver is enforceable) nor will it apply to any claims under our indemnity of the underwriters of the IPO against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act. In the event that any such executed waiver is deemed to be unenforceable against such third party, the Sponsor shall not be responsible to the extent of any liability for such third-party claims. The Sponsor shall have the right to defend against any such claim with counsel of its choice reasonably satisfactory to the Company if, within 15 days following written receipt of notice of the claim to the Sponsor, the Sponsor notifies the Company in writing that it shall undertake such defense. We have not asked our sponsor to reserve for such indemnification obligations, nor have we independently verified whether our sponsor has sufficient funds to satisfy its indemnity obligations and believe that our sponsor’s only assets are securities of our company. Therefore, we cannot assure you that our sponsor would be able to satisfy those obligations. None of our officers or directors will indemnify us for claims by third parties including, without limitation, claims by vendors and prospective target businesses.
Liquidity and Going Concern
As of December 31, 2023, the Company had cash of $1,506,914 in its operating bank accounts, including $723,012 restricted for payment of the Company’s tax obligations, $55,707,757 of marketable securities held in the Trust Account to be used for an initial Business Combination or to repurchase or redeem stock in connection therewith and working capital deficit of $2,081,550. As of December 31, 2023, $2,441,434 of the amount on deposit in the Trust Account represented interest income that was available to pay the Company’s tax obligations. From the date of the IPO and through December 31, 2023, the Company has withdrawn an aggregate of $1,189,115 for payment of its income and franchise taxes, out of which amount $723,012 remained in the Company’s operating account for payment of income taxes for 2023.
The Company may raise additional capital through loans or additional investments from the Sponsor or its shareholders, officers, directors, or third parties. The Company’s officers and directors, the Sponsor or their affiliates may, but are not obligated to loan us funds, from time to time, in whatever amount they deem reasonable in their sole discretion, to meet the Company’s working capital needs. Based on the foregoing, the Company believes it will not have sufficient cash to meet its needs through the earlier of consummation of a Business Combination or June 22, 2024.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
However, if the Company’s estimate of the costs of identifying a target business, undertaking in-depth due diligence and negotiating a Business Combination are more than the actual amount necessary to do so, or if the Company’s shareholders approve an extension to the mandatory liquidation date beyond 21 months from the closing of the IPO, the Company may have insufficient funds available to operate its business prior to a Business Combination. Moreover, the Company may need to obtain additional financing either to complete a Business Combination or because it becomes obligated to redeem a significant number of its Public Shares upon completion of a Business Combination, in which case the Company may issue additional securities or incur debt in connection with such Business Combination. Subject to compliance with applicable securities laws, the Company would only complete such financing simultaneously with the completion of a Business Combination. If the Company does not complete a Business Combination because it does not have sufficient funds available, it will be forced to cease operations and liquidate the Trust Account. In addition, following our Business Combination, if cash on hand is insufficient, the Company may need to obtain additional financing in order to meet its obligations.
If the Company does not consummate a Business Combination by March 22, 2024 (or up to June 22, 2024 in the event the company extends the term to the fullest), there will be a mandatory liquidation and subsequent dissolution of the Company. In connection with the Company’s assessment of going concern considerations in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board’s (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 205-40, “Presentation of Financial Statements - Going Concern,” the Company has determined that the liquidity condition due to insufficient working capital and mandatory liquidation, should a Business Combination not occur, and potential subsequent dissolution raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern for at least one year from the date that the consolidated financial statements are issued. No adjustments have been made to the carrying amounts of assets or liabilities should the Company be required to liquidate after 12 months from the closing of the Public Offering (or up to 21 months from the closing of the Public Offering if the Company extends the period of time to consummate a Business Combination). The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustment that might be necessary, if the Company is unable to continue as a going concern.
Merger Agreement
On June 15, 2023, the Company and K Enter Holdings Inc., a Delaware corporation (the “K Enter”) executed of a definitive Merger Agreement (as amended by that certain First Amendment, the “Merger Agreement”) pursuant to which, among other things, (i) the Company will merge with and into K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company, formed on June 22, 2023, and wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company (the “Purchaser”), with Purchaser continuing as the surviving corporation (the “Reincorporation Merger”) and (ii) GLST Merger Sub Inc., a Delaware corporation, formed on June 12, 2023, and wholly-owned subsidiary of Purchaser (the “Merger Sub”) will merge with and into K Enter, with K Enter surviving the merger as a wholly-owned subsidiary of Purchaser (the “Acquisition Merger”). The Reincorporation Merger, the Acquisition Merger and the other transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement, together, are referred to herein as the “Proposed Business Combination”. Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, the parent of the combined company will be named “K Wave Media Ltd.” and the Company expects that the securities of the parent of the combined company will be listed on The Nasdaq Stock Market.
Merger Consideration
Upon the effective time of the Reincorporation Merger, (i) each issued and outstanding share of common stock of the Company (the “Company Common Stock”), other than Company Common Stock that are owned by the Company as treasury shares or any Company Common Stock owned by any direct or indirect wholly owned subsidiary of the Company, will be converted automatically into one ordinary share of the Purchaser (the “Purchaser Ordinary Share”), and (ii) each issued and outstanding warrant of the Company will convert automatically into a warrant to purchase one Purchaser Ordinary Share at a price of $11.50 per whole share (the “Purchaser Warrant”), (iii) each issued and outstanding right of the Company shall convert automatically into a right to receive one-tenth (1/10) of one Purchaser Ordinary Share at the closing of a business combination (the “Purchaser Right”), and (iv) each issued and outstanding unit of the Company shall separate and convert automatically into one Purchaser Ordinary Share, one Purchaser Warrant and one Purchaser Right. Each of the Purchaser Warrants and Purchaser Rights shall have, and be subject to, the same terms and conditions set forth in the applicable agreements governing the warrants of the Company and the rights of the Company, respectively. At the closing of the Reincorporation Merger, all common stock, warrants, rights, units, and other securities of the Company shall cease to be outstanding and shall automatically be canceled and retired and shall cease to exist.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Upon the closing of the Acquisition Merger, (i) each share of K Enter capital stock, if any, that is owned by Company or Merger Sub (or any other subsidiary of Company) or K Enter (as treasury stock or otherwise), will automatically be cancelled and retired without any conversion, (ii) each share of K Enter preferred stock issued and outstanding shall be deemed converted into shares of K Enter common stock, (iii) each share of K Enter common stock issued and outstanding, including shares of K Enter common stock deemed outstanding as a result of the mandatory conversion of K Enter preferred stock, shall be converted into the right to receive a number of Purchaser Ordinary Shares equal to the Conversion Ratio, and (iv) each share of Merger Sub common stock issued and outstanding shall be converted into and become one newly issued, fully paid and nonassessable share of K Enter common stock. Conversion Ratio means the quotient obtained by dividing (a) 59,000,000 Purchaser Ordinary Shares, by (b) the Aggregate Fully Diluted K Enter Common Shares. Aggregate Fully Diluted K Enter Common Shares means the sum of (a) all shares of K Enter common stock that are issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Closing; plus (b) the aggregate shares of K Enter common stock issuable upon conversion of all shares of K Enter preferred stock that are issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Closing; plus (c) the aggregate shares of K Enter common stock issuable upon full conversion, exercise or exchange of any other securities of K Enter outstanding immediately prior to the Closing directly or indirectly convertible into or exchangeable or exercisable for K Enter.
Conditions to Closing
The Closing is subject to certain customary conditions, including, among other things, (i) approval by the Company’s stockholders of the Merger Agreement and related proposals, (ii) approval by K Enter’s shareholders of the Merger Agreement, (iii) the effectiveness of a registration statement on Form F-4 (the “Registration Statement”) to be filed by Purchaser relating to the Business Combination, which will contain a proxy statement of the Company in connection with its solicitation for proxies for the vote by stockholders of the Company in connection with the Business Combination and other matters as described in the Registration Statement, (iv) the approval for Purchaser’s initial listing application with Nasdaq or an alternate exchange, (v) the Company having at least $5,000,001 of net tangible assets, (vi) the accuracy of each party’s representations and warranties, except generally as would not have a Material Adverse Effect and in the case of certain fundamental representations, in all material respects, (vii) compliance by each party with pre-closing covenants in all material respects, (viii) the absence of any legal restraints or injunctions enjoining or prohibiting the consummation of the Business Combination, (ix) the receipt, expiration or termination of applicable government approvals and antitrust waiting periods, (x) the Reincorporation Merger has been consummated and the applicable certificates has filed in the appropriate jurisdictions, (xi) the acquisition of certain entities of the Six Korean Entities have been consummated, and (xii) the Purchaser and Merger Sub having entered into a joinder to the merger agreement.
The foregoing description of the Merger Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the Merger Agreement, copy of which, is filed as Exhibit 2.1 in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC on June 22, 2023.
Lock-Up Agreement
At the Closing, Purchaser, Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (the “Sponsor”), certain former stockholders of K Enter (such stockholders, the “Target Holders”), and other persons and entities (collectively, the “Holders” and each, a “Holder”), will enter into lock-up agreements (the “Lock-Up Agreements”) with respect to the Purchaser Ordinary Shares and Purchaser Warrants held by the Sponsor immediately following the Closing, and the Purchaser Ordinary Shares held by the Target Holders immediately following the Closing (the “Lock-Up Shares”), pursuant to which, each Holder agreed not to offer, sell, contract to sell, pledge, grant any option to purchase, or otherwise dispose of, directly or indirectly, any Lock-Up Shares during the application lock-up period, on the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in the Lock-Up Agreement. Lock-up period means, (i) with respect to 50% of the Lock-up Shares, the earlier of (A) six months after the Closing and (B) the date on which the closing price of the Purchaser’s Ordinary Shares equals or exceeds $12.50 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, rights issuances, reorganizations and recapitalizations) for any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period commencing after the date hereof and (ii) with respect to the remaining 50% Lock-up Shares (or Ordinary Shares issuable upon conversion thereof), six months after the Closing.
The foregoing description of the Lock-Up Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the Lock-Up Agreement, a form of which is filed as Exhibit 10.1 in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC on June 22, 2023.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Registration Rights Agreement
The Merger Agreement contemplates that, at the Closing, the Purchaser, the Sponsor, certain former stockholders of the Company (such stockholders, together with the Sponsor, the “Company Holders”), and certain former stockholders of K Enter, will enter into a registration rights agreement (the “Registration Rights Agreement”), pursuant to which Purchaser will be obligated to file a registration statement to register the resale, pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, of certain securities of Purchaser held by the parties to the Registration Rights Agreement. The Registration Rights Agreement will also provide the Sponsor, the Company Holders, the Target Holders with unlimited “piggy-back” registration rights, subject to certain requirements and customary conditions.
The Registration Rights Agreement amends and restates the registration rights agreement that was entered into by the Company, the Sponsor and the other parties thereto in connection with the Company’s initial public offering. The Registration Rights Agreement will terminate on the earlier of (a) the five year anniversary of the date of the Registration Rights Agreement or (b) with respect to any holder, on the date that such holder no longer holds any Registrable Securities (as defined therein).
The foregoing description of the Registration Rights Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the Registration Rights Agreement, a form of which is filed as Exhibit 10.2 in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC on June 22, 2023.
Purchase Agreement
In connection with this Merger Agreement, on July 12, 2023, the Company entered into a Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) by and between the Company, K Enter, and Global Star Acquisition I LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (the “Sponsor”). Pursuant to the Purchase Agreement, K Enter will purchase from the Sponsor 160,000 shares of Class B common stock (“the SPAC Securities”) for an aggregate purchase price of $1,600,000 (the “Purchase Price”) payable within 10 days from the effective date of the Purchase Agreement.
In addition to the payment of the Purchase Price, K Enter acknowledged that (x) it is an accredited investor as defined by Rule 501 of the Securities Act, (y) and has knowledge and experience in financial and business matters and in investments of this type and is capable of evaluating the merits and risks of the SPAC Securities and of making an informed investment decision. K Enter further acknowledged and agreed that the SPAC Securities: (a) are subject to limitations on transfer, (b) are being acquired pursuant to an exemption from registration under the Securities Act with no present intention to distribute them to any person in violation of the Securities Act or any applicable U.S. state, (c) will not be sold except in compliance with the Securities Act and any applicable U.S. state securities laws, and in accordance with any limitations set forth in any applicable lock-up agreements applicable to the SPAC Securities.
The foregoing description of the Purchase Agreement is a summary only and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the full text of the Purchase Agreement, a copy of which is attached as Exhibit 10.2 in the Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 17, 2023.
First Amendment
On March 11, 2024, the Company, K Enter, Purchaser, and Merger Sub entered into a First Amendment to the Merger Agreement (the “First Amendment”) to amend certain of the terms of the Merger Agreement. The First Amendment (i) reduces the base value of the merger consideration to be received by Company shareholders from $610 million to $590 million, and (ii) removes in its entirety respective references to the “Share Purchase Agreement” dated April 12, 2023 with certain sellers of First Virtual Lab Inc. from its disclosure schedules and includes the “Termination Agreement and Re-Purchase Option Agreement, dated March 5, 2024, by and among Sungkwon Kim, King Bear Film LLC and K Enter Holdings Inc” to the disclosure schedule. Pursuant to Section 141(f) of the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware and Section 4.5 of the Company’s bylaws, the board approved and authorized the First Amendment on March 11, 2024. The board obtained an updated fairness opinion with respect to the First Amendment. The modification in the purchase consideration was made in connection with the cessation of the planned acquisition of a majority equity stake in First Virtual Lab Inc.
The foregoing description of the First Amendment is a summary only and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the full text of the Purchase Agreement, a copy of which is attached as Exhibit in the Form 8-K filed with the SEC on March 14, 2024.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Risks and Uncertainties
Management continues to evaluate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the industry, the geopolitical conditions resulting from the invasion of Ukraine by Russia and subsequent sanctions against Russia, Belarus and related individuals and entities and the status of debt and equity markets, as well as protectionist legislation in our target markets, and has concluded that while it is reasonably possible that these factors could have a negative effect on the Company’s financial position, results of its operations, and/or search for a target company, the specific impact is not readily determinable as of the date of the consolidated financial statements. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of these uncertainties.
Inflation Reduction Act of 2022
On August 16, 2022, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (the “IR Act”) was signed into federal law. The IR Act provides for, among other things, a new U.S. federal 1% excise tax on certain repurchases of stock by publicly traded U.S. domestic corporations and certain U.S. domestic subsidiaries of publicly traded foreign corporations occurring on or after January 1, 2023. The excise tax is imposed on the repurchasing corporation itself, not its shareholders from which shares are repurchased. The amount of the excise tax is generally 1% of the fair market value of the shares repurchased at the time of the repurchase. However, for purposes of calculating the excise tax, repurchasing corporations are permitted to net the fair market value of certain new stock issuances against the fair market value of stock repurchases during the same taxable year. In addition, certain exceptions apply to the excise tax. The U.S. Department of the Treasury (the “Treasury”) has been given authority to provide regulations and other guidance to carry out and prevent the abuse or avoidance of the excise tax.
On August 22, 2023, in connection with the implementation of the Extension, the Company’s public stockholders elected to redeem 4,052,066 Public Shares for a total of $42,680,726. As such the Company has recorded a 1% excise tax liability in the amount of $426,807 on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2023. The liability does not impact the Company’s consolidated statements of income and is offset against additional paid-in capital or accumulated deficit if additional paid-in capital is not available. This liability will be reevaluated and remeasured at the end of each quarterly period.
NOTE 2 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES BASIS OF PRESENTATION
The accompanying consolidated financial statements are presented in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“US GAAP”) and pursuant to the rules and regulations of the SEC.
Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly owned subsidiary where the Company has the ability to exercise control. All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. Activities in relation to the noncontrolling interest are not considered to be significant and are, therefore, not presented in the accompanying consolidated financial statements.
Emerging Growth Company
The Company is an “emerging growth company,” as defined in Section 2(a) of the Securities Act, as modified by the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (the “JOBS Act”), and it may take advantage of certain exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies including, but not limited to, not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in its periodic reports and proxy statements, and exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Further, Section 102(b)(1) of the JOBS Act exempts emerging growth companies from being required to comply with new or revised financial accounting standards until private companies (that is, those that have not had a Securities Act registration statement declared effective or do not have a class of securities registered under the Exchange Act) are required to comply with the new or revised financial accounting standards. The JOBS Act provides that a company can elect to opt out of the extended transition period and comply with the requirements that apply to non-emerging growth companies but any such election to opt out is irrevocable. The Company has elected not to opt out of such extended transition period which means that when a standard is issued or revised and it has different application dates for public or private companies, the Company, as an emerging growth company, can adopt the new or revised standard at the time private companies adopt the new or revised standard. This may make comparison of the Company’s consolidated financial statements with another public company which is neither an emerging growth company nor an emerging growth company which has opted out of using the extended transition period difficult or impossible because of the potential differences in accounting standards used.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period.
Making estimates requires management to exercise significant judgment. It is at least reasonably possible that the estimate of the effect of a condition, situation or set of circumstances that existed at the date of the consolidated financial statements, which management considered in formulating its estimate, could change in the near term due to one or more future confirming events. Accordingly, the actual results could differ significantly from those estimates.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all short-term investments with an original maturity of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents. The Company’s operating account is classified as cash equivalent in the Company’s consolidated balance sheet.
Marketable Securities Held in Trust Account
At December 31, 2023 and 2022, substantially all of the assets held in the Trust Account were held in money market funds that invest in U.S. Treasury Securities. The Company accounts for its marketable securities as Trading Securities under ASC 320, where securities are presented at fair value on the consolidated balance sheets and with unrealized gains or losses, if any, presented on the consolidated statements of income. From the date of the IPO and through December 31, 2023, the Company withdrew an aggregate of $1,189,115 of interest earned on the Trust Account to pay its income and franchise taxes, out of which $723,012 remained in the Company’s operating account as of December 31, 2023, restricted for payment of tax obligations.
Offering Costs
The Company complies with the requirements of the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) ASC340-10-S99-1and SEC Staff Accounting Bulletin (“SAB”) Topic 5A, “Expenses of Offering.” Offering costs were allocated to the separable financial instruments issued in the Initial Public Offering. Offering costs, including underwriter fees, associated with the Units were allocated between temporary equity and the Public Warrants and the Public Rights by the relative fair value method. Offering costs of $648,510 consisted principally of costs incurred in connection with preparation for the Initial Public Offering. The Company issued 115,000 shares of Class A Common Stock to the representative of the underwriter for services related to the Initial Public Offering. The shares have a grant date fair value of $79,338.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Class A Common Stock Subject to Possible Redemption
The Company accounts for its Class A common stock subject to possible redemption in accordance with the guidance in ASC Topic 480 “Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity.” Class A common stock subject to mandatory redemption is classified as a liability instrument and is measured at fair value. Conditionally redeemable common stock (including common stock that features redemption rights that is either within the control of the holder or subject to redemption upon the occurrence of uncertain events not solely within the Company’s control) is classified as temporary equity. At all other times, common stock is classified as stockholders’ equity. The Company’s Class A common stock features certain redemption rights that are considered to be outside of the Company’s control and subject to occurrence of uncertain future events. Accordingly, on December 31, 2023 and 2022, Class A common stock subject to possible redemption is presented at redemption value as temporary equity, outside of the stockholders’ deficit section of the Company’s consolidated balance sheets.
The Company recognizes changes in the redemption value immediately as they occur and adjusts the carrying value of redeemable common stock to equal the redemption value at the end of each reporting period. Increases or decreases in the carrying amount of redeemable common stock are affected by charges against additional paid-in capital and accumulated deficit.
At December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Class A common stock reflected in the consolidated balance sheets is reconciled in the following table:
| Gross proceeds from IPO and exercise of the over-allotment option | | $ | 92,000,000 | |
| Less: | | | | |
| Transaction costs allocated to the Class A common stock | | | (4,726,147 | ) |
| Proceeds allocated to Public Rights and Warrants | | | (524,400 | ) |
| Plus: | | | | |
| Remeasurement adjustment of Class A common stock to redemption value | | | 8,048,308 | |
| Class A common stock subject to possible redemption at December 31, 2022 | | $ | 94,797,761 | |
| Plus: | | | | |
| Remeasurement adjustment of Class A common stock to redemption value | | | 3,458,355 | |
| Less: | | | | |
| Redemption of Class A common stock subject to redemption | | | (42,680,726 | ) |
| Class A common stock subject to possible redemption at December 31, 2023 | | $ | 55,575,390 | |
Warrant Classification
The Company accounts for warrants as either equity-classified or liability-classified instruments based on an assessment of the warrant’s specific terms and applicable authoritative guidance in ASC 480 and ASC Topic 815, “Derivatives and Hedging” (“ASC 815”). The assessment considers whether the warrants are freestanding financial instruments pursuant to ASC 480, meet the definition of a liability pursuant to ASC 480, and whether the warrants meet all of the requirements for equity classification under ASC 815, including whether the warrants are indexed to the Company’s own common stock, among other conditions for equity classification. This assessment, which requires the use of professional judgment, is conducted at the time of warrant issuance and as of each subsequent quarterly period end date while the warrants are outstanding.
For issued or modified warrants that meet all of the criteria for equity classification, the warrants are required to be recorded as a component of additional paid-in capital at the time of issuance. For issued or modified warrants that do not meet all the criteria for equity classification, the warrants are required to be recorded at their initial fair value on the date of issuance. The fair value of the warrants are remeasured at each balance sheet date with the change in the estimated fair value of the warrants recognized as a non-cash gain or loss on the consolidated statements of operations. The Company has analyzed the Public Warrants (as defined in Note 3) and Private Placement Warrants and determined they are considered to be freestanding instruments and do not exhibit any of the characteristics in ASC 480 and therefore are not classified as liabilities under ASC 480.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Income Taxes
The Company complies with the accounting and reporting requirements of ASC Topic 740, “Income Taxes,” which requires an asset and liability approach to financial accounting and reporting for income taxes. Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are computed for differences between the financial statement and tax bases of assets and liabilities that will result in future taxable or deductible amounts, based on enacted tax laws and rates applicable to the periods in which the differences are expected to affect taxable income. Valuation allowances are established, when necessary, to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized.
ASC Topic 740 prescribes a recognition threshold and a measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. For those benefits to be recognized, a tax position must be more-likely-than-not to be sustained upon examination by taxing authorities. The Company recognizes accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits, if any, as income tax expense. There were no unrecognized tax benefits and no amounts accrued for interest and penalties as of December 31, 2023 and 2022. The Company is currently not aware of any issues under review that could result in significant payments, accruals or material deviation from its position. The Company is subject to income tax examinations by major taxing authorities since inception.
Net Income Per Share
The Company complies with accounting and disclosure requirements of FASB ASC Topic 260, “Earnings Per Share”. Net income per share of common stock is computed by dividing net income by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Subsequent measurement of the redeemable shares of Class A common stock are excluded from income per shares of common stock as the redemption value approximates fair value.
The Company calculates its earnings per share by allocating net income pro rata to shares of redeemable Class A and non-redeemable Class A and B common stock. This presentation contemplates a Business Combination as the most likely outcome, in which case, both classes of common stock share pro rata in the income of the Company.
The calculation of diluted income per share of common stock does not consider the effect of the warrants issued in connection with the (i) Initial Public Offering, and (ii) the private placement since the exercise of the warrants is contingent upon the occurrence of future events. The warrants are exercisable to purchase 9,698,225 shares of Class A common stock in the aggregate. As a result, diluted net income per share of common stock is the same as basic net income per share of common stock for the period presented.
The following table reflects the calculation of basic and diluted net income per share of common stock (in dollars, except per share amounts):
| | | Year Ended | | | Year Ended | |
| | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | Redeemable
Class A | | | Non-Redeemable
Class A & B | | | Redeemable
Class A | | | Non-Redeemable
Class A & B | |
| Numerator: Basic and diluted net income per share of common stock | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Allocation of net income | | $ | 760,782 | | | $ | 283,295 | | | $ | 88,746 | | | $ | 80,068 | |
| Denominator: Basic and diluted weighted average shares outstanding | | | 7,823,408 | | | | 2,913,225 | | | | 2,481,096 | | | | 2,238,462 | |
| Basic and diluted income per share of common stock | | $ | 0.10 | | | $ | 0.10 | | | $ | 0.04 | | | $ | 0.04 | |
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist of a cash account in a financial institution, which, at times, may exceed the Federal Depository Insurance Corporation coverage limit of $250,000. The Company has not experienced losses on these accounts.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Fair value is defined as the price that would be received for sale of an asset or paid for transfer of a liability, in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. GAAP establishes a three-tier fair value hierarchy, which prioritizes the inputs used in measuring fair value. The hierarchy gives the highest priority to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1 measurements) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3 measurements). These tiers include:
| | ● | Level 1, defined as observable inputs such as quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical instruments in active markets; |
| | | |
| | ● | Level 2, defined as inputs other than quoted prices in active markets that are either directly or indirectly observable such as quoted prices for similar instruments in active markets or quoted prices for identical or similar instruments in markets that are not active; and |
| | | |
| | ● | Level 3, defined as unobservable inputs in which little or no market data exists, therefore requiring an entity to develop its own assumptions, such as valuations derived from valuation techniques in which one or more significant inputs or significant value drivers are unobservable. |
In some circumstances, the inputs used to measure fair value might be categorized within different levels of the fair value hierarchy. In those instances, the fair value measurement is categorized in its entirety in the fair value hierarchy based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
Share-Based Payment Arrangements
The Company accounts for share-based payments in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718, “Compensation—Stock Compensation,” (“ASC 718”) which requires that all equity awards be accounted for at their “fair value.” The Company measures and recognizes compensation expense for all share-based payments on their estimated fair values measured as of the grant date. These costs are recognized as an expense in the Consolidated statements of Operations upon vesting, once the applicable performance conditions are met, with an offsetting increase to additional paid-in capital. Forfeitures are recognized as they occur.
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures (ASU 2023-09), which requires disclosure of incremental income tax information within the rate reconciliation and expanded disclosures of income taxes paid, among other disclosure requirements. ASU 2023-09 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. Early adoption is permitted. The Company’s management does not believe the adoption of ASU 2023-09 will have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements and disclosures.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 3 — INITIAL PUBLIC OFFERING
Pursuant to the Initial Public Offering, the Company sold 8,000,000 Units at a price of $10.00 per Unit generating gross proceeds of $80,000,000. Each Unit consists of one share of Common stock, one redeemable warrant (“Public Warrant”) and one right (“Public Right). Each whole Public Warrant will entitle the holder to purchase one share of Common stock at a price of $11.50 per share, subject to adjustment (see Note 7). Each Public Right entitles the holder to receive one-tenth of one share of Common Stock upon the consummation of the business combination. On October 4, 2022, the Company consummated the closing of the sale of 1,200,000 additional units at a price of $10 per unit upon receiving notice of the underwriters’ election to exercise their overallotment option generating additional gross proceeds of $12.0 million and incurred additional offering costs of $412,500 in underwriting fees, of which $262,500 are for deferred underwriting commissions.
NOTE 4 — PRIVATE PLACEMENT
Simultaneously with the closing of the Initial Public Offering, the Company consummated the private sale (the “Private Placement”) of an aggregate of 456,225 units (the “Private Placement Units”) to the Sponsor at a purchase price of $10.00 per Private Placement Unit, generating gross proceeds to the Company in the amount of $4,562,250. Simultaneously with the exercise of the overallotment, the Company consummated the Private Placement of an additional 42,000 Private Placement Units to the Sponsor, generating gross proceeds of $420,000.
The proceeds from the sale of the Placement Units will be added to the net proceeds from the Public Offering held in the Trust Account. The Placement Units are identical to the Units sold in the Public Offering, except for the placement warrants (“Private Placement Warrants”), as described in Note 7. If the Company does not complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period, the proceeds from the sale of the Placement Units will be used to fund the redemption of the Public Shares (subject to the requirements of applicable law) and the Private Placement Warrants and the rights underlying the Placement Units (“Private Rights”) will expire worthless.
NOTE 5 — RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Founder Shares
During the year ended December 31, 2021, the Sponsor agreed to purchase 2,300,000 shares of the Company’s Common stock (the “Founder Shares”) for $25,000. On February 14, 2022, the Sponsor received the 2,875,000 shares and paid the Company $25,000 in full satisfaction of the outstanding receivable. The Founder Shares include an aggregate of up to 300,000 shares subject to forfeiture to the extent that the underwriters’ over-allotment is not exercised in full or in part, so that the number of Founder Shares will equal, on an as-converted basis, approximately 20% of the Company’s issued and outstanding shares of common stock after the Initial Public Offering (see Note 9).In accordance with ASC 505, “Equity”, all shares, and the associated amounts have been retroactively restated to account for this share issuance. On April 5, 2022, the Sponsor entered into share transfer agreements (collectively, the “Share Transfer Agreements”) for an aggregate of 500,000 founder shares to the Company’s officers and directors (subject to certain performance conditions discussed in Note 8). On July 26, 2022, the Sponsor surrendered 575,000 founder shares to the Company for cancellation, for no consideration. All share amounts have been retroactively restated to reflect this surrender.
The Sponsor and each Insider agrees that (i) 50% of the Founder Shares (or shares of Common Stock issuable upon conversion thereof) will not be transferred, assigned or sold until the earlier of (A) six months after the date of the consummation of the Company’s initial business combination and (B) the date on which the closing price of the Company’s common stock equals or exceeds $12.50 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, reorganizations and recapitalizations) for any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period commencing after the Company’s initial business combination and (i) the remaining 50% of the Founder Shares (or shares of Common Stock issuable upon conversion thereof) will not be transferred, assigned, sold or released from escrow until six months after the date of the consummation of the Company’s initial business combination.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Due to Related Party
Prior to September 30, 2022, and in connection with the close of the overallotment on October 4, 2022, the Company received $112,250 which should have been deposited into the Sponsor’s bank account. The amount was transferred to the Trust Account prior to December 31, 2022.
At the close of the Initial Public Offering, a related party deposited $25,000 greater than the agreed upon initial investment. The Company repaid this amount in full, and no balance related to this transaction was outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
Due to Sponsor
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the outstanding balance due to the Sponsor was $15,094, which represents certain amounts paid by Sponsor on behalf of the Company.
Promissory Notes — Related Party Working Capital Loan
On February 14, 2022, the Sponsor issued an unsecured promissory note to the Company (the “Promissory Note”), pursuant to which the Company may borrow up to an aggregate principal amount of $300,000, which was fully drawn prior to Initial Public Offering. Upon closing of the Initial Public Offering, the Company repaid the outstanding balance in full.
In order to finance transaction costs in connection with the Business Combination, our Sponsor extended to us a line of credit of up to $1,600,000 pursuant to a Promissory Note dated July 31, 2023 (“Sponsor Working Capital Loan”). Such Sponsor Working Capital Loan is without interest and is to be repaid on the later of (i) December 31, 2023 or (ii) upon the consummation of a Business Combination. The Sponsor in its sole discretion may elect to convert up to $1,500,000 amount of the Sponsor Working Capital Loan into the Company’s Common Stock at a price of $10.00 per share in lieu of cash repayment. The conversion options embedded in the Sponsor Working Capital Loan are considered related to those of an equity instrument. As a result, this would be considered a contract that would be issued or held by the Company that is (i) indexed to its own stock and (ii) classified in stockholders’ equity the Company’s statement of financial position; therefore, this embedded feature meets the scope exception criteria under ASC 815-10-15-74(a) and is not accounted for as a derivative instrument within the scope of ASC 815.
In the event that a Business Combination does not close, we may use a portion of proceeds held outside the Trust Account to repay the Sponsor Working Capital Loan, but no proceeds held in the Trust Account would be used to repay the Sponsor Working Capital Loans. As of December 31, 2023, the amount outstanding under the Sponsor Working Capital Loan was $1,590,000.
Advances From Related Party
The Sponsor paid certain offering costs on behalf of the Company and advanced working capital to the Company. These advances are due on demand and are non-interest bearing. Upon close of the Initial Public Offering, the Company repaid the outstanding balance of $119,720 in full.
Administrative Support Agreement
The Sponsor has agreed to make available, or cause to be made available, to the Company, or any successor location of Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC, certain office space, utilities and secretarial and administrative support as may be reasonably required by the Company. In exchange therefore, the Company shall pay the Sponsor the sum of $10,000 per month on the Initial Public Offering date and continuing monthly thereafter until the Termination Date. For the year ended The Company incurred $121,666 (including a catch up payment of $1,666 for the previous year) and $32,000 of expenses pursuant to this agreement for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 6 — COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Registration Rights
Pursuant to a registration rights agreement entered into on September 22, 2022, the holders of the Founder Shares, Private Placement Warrants (and the underlying shares of Class A common stock) and any warrants that may be issued upon conversion of the Working Capital Loans (and the underlying shares of common stock) are entitled to registration rights. The holders of these securities will be entitled to make up to three demands, excluding short form registration demands, that the Company register such securities. The holders of the majority of the securities can elect to exercise these registration rights at any time after the Company consummates a Business Combination. In addition, the holders have certain “piggy-back” registration rights with respect to registration statements filed subsequent to the completion of a Business Combination. The registration rights agreement does not contain liquidated damages or other cash settlement provisions resulting from delays in registering the Company’s securities. The Company will bear the expenses incurred in connection with the filing of any such registration statements.
Underwriting Agreement
The Company granted the underwriters a 45-day option from the date of Initial Public Offering to purchase up to 1,200,000 additional Units to cover over-allotments, if any, at the Initial Public Offering price less the underwriting discounts and commissions. On October 4, 2022, the Company consummated the closing of the sale of 1,200,000 additional units at a price of $10 per unit upon receiving notice of the underwriters’ election to exercise their overallotment option generating additional gross proceeds of $12.0 million and incurred additional offering costs of $412,500 in underwriting fees, of which $262,500 are for deferred underwriting commissions. Simultaneously with the exercise of the overallotment, the Company consummated the Private Placement of an additional 42,000 Private Placement Units to the Sponsor, generating gross proceeds of $420,000.
The underwriters were paid a cash underwriting discount of $0.20 per Unit, or $1,840,000, upon the closing of the Initial Public Offering. The underwriters reimbursed $920,000 to the Company for certain expenses in connection with the IPO. In addition, the underwriters are entitled to a deferred fee of $0.35 per Unit, or $3,220,000. The deferred fee will become payable to the underwriters from the amounts held in the Trust Account solely in the event that the Company completes a Business Combination, subject to the terms of the underwriting agreement.
The underwriters were also issued 115,000 of Class A common stock as representative shares, in connection with our IPO. The Representative Shares have been deemed compensation by FINRA and the lock up period expired on March 19, 2023. The Company recorded additional issuance costs of $79,338, the grant date fair value of the shares, with an offset to additional paid-in capital.
Service Provider Agreement
From time to time the Company has entered into and may enter into agreements with various services providers and advisors, including investment banks, to help us identify targets, negotiate terms of potential Business Combinations, consummate a Business Combination and/or provide other services. In connection with these agreements, the Company may be required to pay such service providers and advisors fees in connection with their services to the extent that certain conditions, including the closing of a potential Business Combination, are met. If a Business Combination does not occur, the Company would not expect to be required to pay these contingent fees. There can be no assurance that the Company will complete a Business Combination.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
On September 24, 2023, the Company has engaged EF Hutton, division of Benchmark Investments, LLC (“EF Hutton”) to act as the exclusive placement agent (“Placement Agent”) for the Company, in connection with the proposed offering by private placement of equity or equity-linked securities in the form of a PIPE, forward purchase arrangement or similar type of equity line financing (the “Placement”) to “qualified institutional buyers” as such term is defined in Rule 144A promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”) and to the institutional accredited investors as such term is defined in Regulation D promulgated under the Securities Act of the Company’s equity or equity-linked securities, including warrants, options or other rights to purchase such securities (collectively, the “Securities”). In case of successful Placements, a non-refundable cash placement fee (the “Placement Fee”), payable at each closing of a Placement, in an amount equal to seven percent (7.0%), as well as foreign placement fee of 1% and reduced placement fee of 1% of the aggregate gross proceeds from the sale of all Securities in the Placement would be due and payable to EF Hutton.
On November 27, 2023, the Company engaged MZHCI, LLC, a MZ Group Company (“MZHCI”) as its public relations consultant starting from January 1, 2024 (the “MZHCI Agreement”). According to terms of the MZHCI Agreement, MZHCI will be paid a monthly fee of $10,000 for its services for the period of the Proposed Business Combination starting from January 1, 2024, which will increase to $14,000 (subject to 5% cost of living adjustment) upon closing of the Proposed Business Combination. In addition, upon a successful closing of the Proposed Business Combination, the Company will issue to MZHCI $150,000 worth of the Company’s restricted stock as valued on the first day of trading post-closing.
Joinder Agreement
A form of Joinder Agreement was included as an exhibit to the Merger Agreement to be executed by Purchaser and Merger Sub, following their formation, to bind them to the terms and conditions of the Merger Agreement. On July 13, 2023, the Purchaser and the Merger Sub executed the Joinder Agreement by and between the Company, K Enter, the Purchaser and Merger Sub. Pursuant to the Joinder Agreement, the Purchaser and Merger Sub agreed to become a party to, to be bound by, and to comply with the terms and conditions of the Merger Agreement.
The foregoing description of the Joinder Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the Joinder Agreement, copy of which, or the form of which, is filed as Exhibit 10.1 on the Company’s Form 8-K as filed with the SEC on July 18, 2023.
Purchase Agreement
In connection with the Merger Agreement the Company entered into a Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) by and between the Company, K Enter, and the Sponsor. Pursuant to the Purchase Agreement, K Enter will purchase from the Sponsor 160,000 shares of Class B common stock (“the SPAC Securities”) for an aggregate purchase price of $1,600,000 (the “Purchase Price”) payable within 10 days from the effective date of the Purchase Agreement.
In addition to the payment of the Purchase Price, K Enter acknowledged that (x) it is an accredited investor as defined by Rule 501 of the Securities Act, (y) and has knowledge and experience in financial and business matters and in investments of this type and is capable of evaluating the merits and risks of the SPAC Securities and of making an informed investment decision. K Enter further acknowledged and agreed that the SPAC Securities: (a) are subject to limitations on transfer, (b) are being acquired pursuant to an exemption from registration under the Securities Act with no present intention to distribute them to any person in violation of the Securities Act or any applicable U.S. state, (c) will not be sold except in compliance with the Securities Act and any applicable U.S. state securities laws, and in accordance with any limitations set forth in any applicable lock-up agreements applicable to the SPAC Securities
The foregoing description of the Purchase Agreement is a summary only and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the full text of the Purchase Agreement, a copy of which is attached as Exhibit 10.2 on the Company’s Form 8-K as filed with the SEC on July 18, 2023.
NOTE 7 — STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
Preferred Stock—The Company is authorized to issue 1,000,000 preferred shares with a par value of $0.0001 per share with such designation, rights and preferences as may be determined from time to time by the Company’s Board of Directors. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, there were no preferred shares issued or outstanding.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Class A Common Stock—The Company is authorized to issue 100,000,000 shares of Class A common stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share. Holders of the Company’s Class A common stock are entitled to one vote for each share. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, there were 613,225 shares of Class A Common Stock issued and outstanding (excluding 5,147,934 and 9,200,000 shares of Class A Common Stock subject to possible redemption), respectively.
Class B Common Stock—The Company is authorized to issue 10,000,000 shares of Class B common stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share. Holders of Class B common stock are entitled to one vote for each share. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, there were 2,300,000 shares of Class B common stock issued and outstanding, respectively.
Only holders of the Class B common stock will have the right to vote on the election of directors prior to the Business Combination. Holders of Class A common stock and holders of Class B common stock will vote together as a single class on all matters submitted to a vote of our stockholders except as otherwise required by law. In connection with our initial business combination, we may enter into a stockholder agreement or other arrangements with the stockholders of the target or other investors to provide for voting or other corporate governance arrangements that differ from those in effect upon completion of our IPO.
The shares of Class B common stock will automatically convert into Class A common stock at the time of a Business Combination, or earlier at the option of the holder, on a one-for-one basis, subject to adjustment. In the case that additional shares of Class A common stock, or equity-linked securities, are issued or deemed issued in excess of the amounts issued in the Initial Public Offering and related to the closing of a Business Combination, the ratio at which shares of Class B common stock shall convert into shares of Class A common stock will be adjusted (unless the holders of a majority of the then-outstanding shares of Class B common stock agree to waive such adjustment with respect to any such issuance or deemed issuance) so that the number of shares of Class A common stock issuable upon conversion of all shares of Class B common stock will equal, in the aggregate, on an as-converted basis, 20% of the sum of the total number of all shares of common stock outstanding upon the completion of Initial Public Offering plus all shares of Class A common stock and equity-linked securities issued or deemed issued in connection with a Business Combination (net of the number of shares of Class A common stock redeemed in connection with a Business Combination), excluding any shares or equity-linked securities issued or issuable to any seller of an interest in the target to us in a Business Combination.
Only holders of the Common stock will have the right to vote on the election of directors prior to the Business Combination. Holders of Common stock will vote together as a single class on all matters submitted to a vote of our stockholders except as otherwise required by law. In connection with our initial business combination, we may enter into a stockholder agreement or other arrangements with the stockholders of the target or other investors to provide for voting or other corporate governance arrangements that differ from those in effect upon completion of our IPO.
Warrants—As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, there are 9,200,000 Public Warrants outstanding. Public Warrants may only be exercised for a whole number of shares. No fractional warrants will be issued upon separation of the Units and only whole warrants will trade. The Public Warrants will become exercisable on the later of (a) 30 days after the completion of a Business Combination and (b) 12 months from the closing of the Initial Public Offering. The Public Warrants will expire five years after the completion of a Business Combination or earlier upon redemption or liquidation.
The Company will not be obligated to deliver any shares of Class A common stock pursuant to the exercise of a warrant and will have no obligation to settle such warrant exercise unless a registration statement under the Securities Act covering the issuance of the shares of Class A common stock issuable upon exercise of the warrants is then effective and a current prospectus relating to those shares of Class A common stock is available, subject to the Company satisfying its obligations with respect to registration, or a valid exemption from registration is available. No warrant will be exercisable for cash or on a cashless basis, and the Company will not be obligated to issue any shares to holders seeking to exercise their warrants, unless the issuance of the shares upon such exercise is registered or qualified under the securities laws of the state of residence of the exercising holder, or an exemption from registration is available.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The Company has agreed that as soon as practicable, but in no event later than 15 business days after the closing of a Business Combination, the Company will use its commercially reasonable efforts to file, and within 60 business days following a Business Combination to have declared effective, a registration statement covering the issuance of the shares of Class A common stock issuable upon exercise of the warrants and to maintain a current prospectus relating to those shares of Class A common stock until the warrants expire or are redeemed. Notwithstanding the above, if the Class A common stock is at the time of any exercise of a warrant not listed on a national securities exchange such that it satisfies the definition of a “covered security” under Section 18(b)(1) of the Securities Act, the Company may, at its option, require holders of Public Warrants who exercise their warrants to do so on a “cashless basis” in accordance with Section 3(a)(9) of the Securities Act and, in the event the Company so elects, the Company will not be required to file or maintain in effect a registration statement, but will use its commercially reasonable efforts to register or qualify the shares under applicable blue sky laws to the extent an exemption is not available.
Once the warrants become exercisable, the Company may redeem the outstanding Public Warrants:
| | ● | in whole and not in part; |
| | | |
| | ● | at a price of $0.01 per Public Warrant; |
| | | |
| | ● | upon a minimum of 30 days’ prior written notice of redemption, or the 30-day redemption period to each warrant holder; and |
| | | |
| | ● | if, and only if, the last reported sale price of the Class A common stock equals or exceeds $18.00 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, reorganization, recapitalizations and the like) for any 20 trading days within a 30-trading day period ending on the third trading day prior to the date on which the Company sends the notice of redemption to warrant holders. |
If and when the warrants become redeemable by the Company, the Company may exercise its redemption right even if it is unable to register or qualify the underlying securities for sale under all applicable state securities laws.
If the Company calls the Public Warrants for redemption, as described above, its management will have the option to require any holder that wishes to exercise the Public Warrants to do so on a “cashless basis,” as described in the warrant agreement. The exercise price and number of common stock issuable upon exercise of the Public Warrants may be adjusted in certain circumstances including in the event of a stock dividend, extraordinary dividend or recapitalization, reorganization, merger, or consolidation. However, except as described below, the Public Warrants will not be adjusted for issuances of common stock at a price below its exercise price. Additionally, in no event will the Company be required to net cash settle the Public Warrants. If the Company is unable to complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period and the Company liquidates the funds held in the Trust Account, holders of Public Warrants will not receive any of such funds with respect to their Public Warrants, nor will they receive any distribution from the Company’s assets held outside of the Trust Account with respect to such Public Warrants. Accordingly, the Public Warrants may expire worthless.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, there are 498,225 Private Placement Warrants outstanding. The Private Placement Warrants are identical to the Public Warrants underlying the Units sold in the Initial Public Offering. The Company accounts for the warrants issued in connection with the Initial Public Offering in accordance with the guidance contained in ASC815-40. Such guidance provides that the warrants are not precluded from equity classification. Equity-classified contracts are initially measured at fair value (or allocated value). Subsequent changes in fair value are not recognized as long as the contracts continue to be classified in equity.
The Private Placement Warrants are identical to the Public Warrants underlying the Units sold in the Initial Public Offering, except that the Private Placement Warrants (including the shares of Class A common stock issuable upon the exercise of the Private Placement Warrants) will not be transferable, assignable or salable until 30 days after the completion of a Business Combination, subject to certain limited exceptions. Additionally, the Private Placement Warrants held by Stifel Venture will not be exercisable more than five years from the commencement of sales of the Initial Public Offering in accordance with FINRA Rule 5110(g)(8)(A).
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Rights—Except in cases where the Company is not the surviving company in a business combination, each holder of a right will automatically receive one-tenth (1/10) of one share of Class A common stock upon consummation of the initial business combination. The Company will not issue fractional shares in connection with an exchange of rights. Fractional shares will either be rounded down to the nearest whole share or otherwise addressed in accordance with the applicable provisions of United States law.
The Company accounts for the rights issued in connection with the Initial Public Offering in accordance with the guidance contained in ASC815-40. Such guidance provides that the rights are not precluded from equity classification. Equity-classified contracts are initially measured at fair value (or allocated value). Subsequent changes in fair value are not recognized as long as the contracts continue to be classified in equity.
NOTE 8 — STOCK BASED COMPENSATION
The sale of the Founder Shares to the Company’s director nominees and strategic advisors is in the scope of ASC 718. Under ASC 718, stock-based compensation associated with equity-classified awards is measured at fair value upon the grant date. The Company has assessed the fair value associated with the Founder Shares granted. The fair value of the 500,000 Founder Shares granted to the Company’s officers and directors was $1,150,000 or $2.30 per share (see Note 5). The Founder Shares were granted subject to the following performance condition: (i) the occurrence of a Business Combination. Compensation expense related to the Founder Shares is recognized only when the performance conditions are probable of occurrence under the applicable accounting literature in this circumstance.
As of December 31, 2023, there are 500,000 shares that remain unvested as the Company determined that a Business Combination is not considered probable. Therefore, the remaining fair value of stock-based compensation expense associated with these shares totaling $1,150,000 has not been recognized. Stock-based compensation would be recognized at the date a Business Combination is considered probable (i.e., upon consummation of a Business Combination) in an amount equal to the number of Founder Shares times the grant date fair value per share (unless subsequently modified) less the amount initially received for the purchase of the Founder Shares.
NOTE 9 — FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
The Public Warrants were valued at $0.05 per warrant at the Initial Public Offering. Significant inputs included a risk free rate of 3.74%, volatility of 1.5%, probability of business combination of 7%, dividend of $0 and life of 5.88 years.
The Company follows the guidance in ASC 820 for its financial assets and liabilities that arere-measured and reported at fair value at each reporting period, and non-financial assets and liabilities that are re-measured and reported at fair value at least annually. The fair value of the Company’s financial assets and liabilities reflects management’s estimate of amounts that the Company would have received in connection with the sale of the assets or paid in connection with the transfer of the liabilities in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. In connection with measuring the fair value of its assets and liabilities, the Company seeks to maximize the use of observable inputs (market data obtained from independent sources) and to minimize the use of unobservable inputs (internal assumptions about how market participants would price assets and liabilities).
The following table presents information about the Company’s assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and indicates the fair value hierarchy of the valuation inputs the Company utilized to determine such fair value:
| | | Description | | | Level | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Marketable securities held in Trust Account | | | | | | 1 | | | $ | 55,707,757 | | | $ | 95,134,678 | |
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 10 — TAXES
A reconciliation of the federal income tax rate to the Company’s effective tax rate is as follows:
| | | For the
Year Ended
December 31,
2023 | | | For the
Year Ended
December 31,
2022 | |
| U.S. federal statutory rate | | | 21.0 | % | | | 21.0 | % |
| Change in Fair Value of Warrants | | | 0.0 | % | | | (0.5 | )% |
| Business combination expenses | | | 8.4 | % | | | 0.00 | % |
| Meals & entertainment | | | 0.1 | % | | | 0.00 | % |
| Fines and penalties | | | 0.2 | % | | | 0.00 | % |
| Valuation allowance | | | 13.6 | % | | | 24.0 | % |
| Income tax provision | | | 43.3 | % | | | 44.5 | % |
The effective tax rate differs from the statutory rate of 21% for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 primarily due to the business combination, meals and entertainment expenses, penalties, and changes in valuation allowance for the deferred assets.
Below is breakdown of the income tax provision:
| | | For the
Year Ended
December 31,
2022 | | | For the
Year Ended
December 31,
2022 | |
| Federal: | | | | | | | | |
| Current | | $ | 796,065 | | | $ | 135,321 | |
| Deferred | | | (250,221 | ) | | | (73,052 | ) |
| State and local: | | | | | | | | |
| Current | | | - | | | | - | |
| Deferred | | | - | | | | - | |
| Change in valuation allowance | | | 250,221 | | | | 73,052 | |
| Total tax provision | | $ | 796,065 | | | $ | 135,321 | |
In assessing the realization of the deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion of all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which temporary differences representing net future deductible amounts become deductible. Management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income and tax planning strategies in making this assessment. After consideration of all of the information available, management believes that significant uncertainty exists with respect to future realization of the deferred tax assets and has therefore established a full valuation allowance. For the year ended December 31, 2023, the change in the valuation allowance was $250,221. For the year ended December 31, 2022, the change in the valuation allowance was $73,052.
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes. Significant components of the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows at December 31:
| | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Start up costs | | $ | 323,273 | | | $ | 73,052 | |
| Total deferred tax assets | | | 323,273 | | | | 71,302 | |
| Valuation Allowance | | | (323,273 | ) | | | (71,302 | ) |
| Net deferred tax asset | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 11 — SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
The Company evaluated subsequent events and transactions that occurred after the balance sheet date through the date that the consolidated financial statements were issued. Based upon this review, other than as disclosed below or within these consolidated financial statements, the Company did not identify any subsequent events that would have required recognition or disclosure in the consolidated financial statements.
Subsequent to December 31, 2023, the Company made two monthly payments in its Trust Account for Extension through March 22, 2024.
As further disclosed in Note 1, on March 11, 2024, the Company, K Enter, Purchaser, and Merger Sub entered into a First Amendment to the Merger Agreement (the “First Amendment”) to amend certain of the terms of the Merger Agreement.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
| | | September 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | (Unaudited) | | | (Audited) | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | |
| Current Assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 392,139 | | | $ | 1,506,914 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | | 30,250 | | | | 80,782 | |
| Total Current Assets | | | 422,389 | | | | 1,587,696 | |
| Marketable securities held in Trust Account | | | 12,919,725 | | | | 55,707,757 | |
| Total Assets | | $ | 13,342,114 | | | $ | 57,295,453 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES, COMMON STOCK SUBJECT TO POSSIBLE REDEMPTION AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | | $ | 1,419,388 | | | $ | 781,967 | |
| Accrued franchise tax payable | | | 169,113 | | | | 59,313 | |
| Income taxes payable | | | 288,597 | | | | 796,065 | |
| Excise tax payable attributable to redemption of common stock | | | 872,861 | | | | 426,807 | |
| Promissory note - related party | | | 2,407,000 | | | | 1,590,000 | |
| Due to Sponsor | | | 15,094 | | | | 15,094 | |
| Total Current Liabilities | | | 5,172,053 | | | | 3,669,246 | |
| Deferred underwriting commission | | | 3,220,000 | | | | 3,220,000 | |
| Total Liabilities | | $ | 8,392,053 | | | $ | 6,889,246 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES (Note 6) | | | | | | | | |
| Class A common stock subject to possible redemption; 1,137,006 and 5,761,159 shares issued and outstanding at redemption value of $11.31 and $10.80 per share at September 30, 2024, and December 31, 2023, respectively | | | 12,857,261 | | | | 55,575,390 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Stockholders’ deficit: | | | | | | | | |
| Preferred stock, $0.0001 par value; 1,000,000 shares authorized; none issued and outstanding | | | - | | | | - | |
| Class A common stock, $0.0001 par value, 100,000,000 shares authorized, 613,225 shares issued and outstanding (excluding 1,137,006 and 5,147,934 shares subject to possible redemption at September 30, 2024, and December 31, 2023, respectively) | | | 62 | | | | 62 | |
| Class B common stock, $0.0001 par value, 10,000,000 shares authorized, 2,300,000 shares issued and outstanding | | | 230 | | | | 230 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | | | - | | | | - | |
| Accumulated deficit | | | (7,907,492 | ) | | | (5,169,475 | ) |
| Total Stockholders’ Deficit | | | (7,907,200 | ) | | | (5,169,183 | ) |
| Total Liabilities, Common Stock Subject to Possible Redemption and Stockholders’ Deficit | | $ | 13,342,114 | | | $ | 57,295,453 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(UNAUDITED)
| | | For the
Three Months Ended
September 30, | | | For the
Nine Months Ended
September 30, | |
| | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
| OPERATING EXPENSES | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| General and administrative | | $ | 218,771 | | | $ | 742,722 | | | $ | 1,610,833 | | | $ | 1,503,601 | |
| Administration fee - related party | | | 30,000 | | | | - | | | | 90,000 | | | | - | |
| TOTAL OPERATING EXPENSES | | | (248,771 | ) | | | (742,722 | ) | | | (1,700,833 | ) | | | (1,503,601 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| OTHER INCOME | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Income earned on Investments held in Trust Account | | | 165,372 | | | | 1,058,863 | | | | 1,596,528 | | | | 3,214,400 | |
| Interest income | | | 4,676 | | | | 5,468 | | | | 15,030 | | | | 5,667 | |
| TOTAL OTHER INCOME | | | 170,048 | | | | 1,064,331 | | | | 1,611,558 | | | | 3,220,067 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss before provision for income taxes | | | (78,723 | ) | | | 321,609 | | | | (89,275 | ) | | | 1,716,466 | |
| Provision for income taxes | | | (28,906 | ) | | | (212,673 | ) | | | (315,369 | ) | | | (644,378 | ) |
| Net (loss) income | | $ | (107,629 | ) | | $ | 108,936 | | | $ | (404,644 | ) | | $ | 1,072,088 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average number of shares of redeemable Class A common stock outstanding, basic and diluted | | | 1,750,231 | | | | 8,403,811 | | | | 4,136,294 | | | | 9,338,258 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted net (loss) income per share of redeemable Class A common stock | | $ | (0.03 | ) | | $ | 0.01 | | | $ | (0.06 | ) | | $ | 0.09 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average number of shares of non-redeemable Class A and B common stock outstanding, basic and diluted | | | 2,300,000 | | | | 2,300,000 | | | | 2,300,000 | | | | 2,300,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted net (loss) income per share of Class A and Class B common stock | | $ | (0.03 | ) | | $ | 0.01 | | | $ | (0.06 | ) | | $ | 0.09 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
(UNAUDITED)
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2024 AND 2023
| | | Class A
Common Stock | | | Class B
Common Stock | | | Additional
Paid-In | | | Accumulated | | | Total
Stockholders’ | |
| | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Capital | | | Deficit | | | Deficit | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | | | 613,225 | | | $ | 62 | | | | 2,300,000 | | | $ | 230 | | | $ | - | | | $ | (5,169,475 | ) | | $ | (5,169,183 | ) |
| Remeasurement adjustment of Class A ordinary shares to redemption value | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (909,438 | ) | | | (909,438 | ) |
| Net loss | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (212,370 | ) | | | (212,370 | ) |
| Balance as of March 31, 2024 | | | 613,225 | | | | 62 | | | | 2,300,000 | | | | 230 | | | | - | | | | (6,291,283 | ) | | | (6,290,991 | ) |
| Remeasurement adjustment of Class A ordinary shares to redemption value | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (805,595 | ) | | | (805,595 | ) |
| Excise tax payable attributable to redemption of common stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (446,054 | ) | | | (446,054 | ) |
| Net loss | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (84,645 | ) | | | (84,645 | ) |
| Balance as of June 30, 2024 | | | 613,225 | | | | 62 | | | | 2,300,000 | | | | 230 | | | | - | | | | (7,627,577 | ) | | | (7,627,285 | ) |
| Remeasurement adjustment of Class A ordinary shares to redemption value | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (172,286 | ) | | | (172,286 | ) |
| Net loss | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (107,629 | ) | | | (107,629 | ) |
| Balance as of September 30, 2024 | | | 613,225 | | | $ | 62 | | | | 2,300,000 | | | $ | 230 | | | $ | - | | | $ | (7,907,492 | ) | | $ | (7,907,200 | ) |
| | | Class A | | | Class B | | | Additional | | | | | | Total | |
| | | Common Stock | | | Common Stock | | | Paid-in | | | Accumulated | | | Stockholders’ | |
| | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Capital | | | Deficit | | | Deficit | |
| Balance – January 1, 2023 | | | 613,225 | | | $ | 62 | | | | 2,300,000 | | | $ | 230 | | | $ | - | | | $ | (2,328,390 | ) | | $ | (2,328,098 | ) |
| Remeasurement adjustment of Class A common stock to redemption value | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (757,933 | ) | | | (757,933 | ) |
| Net income | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 415,378 | | | | 415,378 | |
| Balance – March 31, 2023 | | | 613,225 | | | | 62 | | | | 2,300,000 | | | | 230 | | | | - | | | | (2,670,945 | ) | | | (2,670,653 | ) |
| Remeasurement adjustment of Class A common stock to redemption value | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (865,899 | ) | | | (865,899 | ) |
| Net income | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 547,774 | | | | 547,774 | |
| Balance – June 30, 2023 | | | 613,225 | | | | 62 | | | | 2,300,000 | | | | 230 | | | | - | | | | (2,989,070 | ) | | | (2,988,778 | ) |
| Remeasurement adjustment of Class A common stock to redemption value | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (27,532 | ) | | | (27,532 | ) |
| Excise tax payable attributable to redemption of common stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (426,807 | ) | | | (426,807 | ) |
| Net income | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 108,936 | | | | 108,936 | |
| Balance – September 30, 2023 | | | 613,225 | | | $ | 62 | | | | 2,300,000 | | | $ | 230 | | | $ | - | | | $ | (3,334,473 | ) | | $ | (3,334,181 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(UNAUDITED)
| | | For the
Nine Months Ended
September 30, | |
| | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | | | | | | | |
| Net (loss) income | | $ | (404,644 | ) | | $ | 1,072,088 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net (loss) income to net cash used in operating activities: | | | | | | | | |
| Investment income earned on investment held in Trust Account | | | (1,596,528 | ) | | | (3,214,400 | ) |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | | 50,532 | | | | 111,834 | |
| Other assets | | | - | | | | 49,526 | |
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | | | 637,421 | | | | 425,150 | |
| Accrued franchise taxes | | | 109,800 | | | | (145,457 | ) |
| Income taxes payable | | | (507,468 | ) | | | 644,378 | |
| Net cash used in operating activities | | | (1,710,887 | ) | | | (1,056,881 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | |
| Investment of cash into Trust Account | | | (715,960 | ) | | | (125,000 | ) |
| Cash withdrawn from Trust Account to pay franchise and income taxes | | | 495,072 | | | | 1,189,115 | |
| Cash withdrawn from Trust Account for working capital purposes | | | 44,605,448 | | | | 42,680,726 | |
| Net cash provided by investing activities | | | 44,384,560 | | | | 43,744,841 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | | | | | | | |
| Redemption of common stock | | | (44,605,448 | ) | | | (42,680,726 | ) |
| Proceeds from borrowings under promissory note – related party | | | 821,000 | | | | 1,600,000 | |
| Repayment of promissory note – related party | | | (4,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Payment of offering costs | | | - | | | | (67,414 | ) |
| Net cash used in financing activities | | $ | (43,788,448 | ) | | $ | (41,148,140 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Net change in cash | | | (1,114,775 | ) | | | 1,539,820 | |
| Cash at beginning of period | | | 1,506,914 | | | | 877,560 | |
| Cash at end of period | | $ | 392,139 | | | $ | 2,417,380 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Non-cash investing and financing activities: | | | | | | | | |
| Remeasurement of Class A common stock to redemption value | | $ | 1,887,319 | | | $ | 1,651,364 | |
| Excise tax payable attributable to redemption of common stock | | $ | 446,054 | | | $ | 426,807 | |
| Supplementary information: | | | | | | | | |
| Income taxes paid | | $ | 822,837 | | | $ | - | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1 — DESCRIPTION OF ORGANIZATION, BUSINESS OPERATIONS AND GOING CONCERN
Global Star Acquisition, Inc. (the “Company”) is a blank check company incorporated in the State of Delaware on July 24, 2019, whose business purpose is to effect a merger, capital stock exchange, asset acquisition, stock purchase, reorganization, or similar business combination with one or more businesses, which we refer to as our initial business combination. To date, our efforts have been limited to organizational activities as well as activities related to the initial public offering and the completion of its initial Business Combination.
As of September 30, 2024, the Company had two wholly-owned subsidiaries, GLST Merger Sub, Inc., a majority-owned subsidiary of the Company incorporated in Delaware on June 12, 2023 (“GLST Merger Sub”), and K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company formed on June 22, 2023 (See “Merger Agreement” section below).
As of September 30, 2024, the Company had not commenced any operations. All activity for the period from July 24, 2019 (inception) through September 30, 2024, relates to organizational activities and identifying a target company for a business combination. The Company will not generate any operating revenues until after the completion of its initial Business Combination, at the earliest. The Company generates non-operating income in the form of interest income on the proceeds derived from the Offering placed in Trust Account. The Company has selected December 31 as its fiscal year end.
The Company’s sponsor is Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (the “Sponsor”). The registration statement for the Company’s Initial Public Offering was declared effective on September 19, 2022.
On September 22, 2022, the Company consummated its initial public offering (the “IPO”) of 8,000,000 units (the “Units” and, with respect to the shares of Class A common stock included in the Units sold, the “Public Shares”). Each Unit consists of one share of Class A common stock of the Company, par value $0.0001 per share (“Class A Common Stock”), one redeemable warrant of the Company (“Warrant”), with each whole Warrant entitling the holder thereof to purchase one share of Class A Common Stock for $11.50 per share, and one Right, with each Right entitling the holder to receive one-tenth of one share of Class A Common Stock. The Units were sold at a price of $10.00 per Unit, generating gross proceeds to the Company of $80,000,000. On October 4, 2022, the Company closed on the over-allotment through the sale of 1,200,000 Units at a purchase of $10.00 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $12.0 million.
Simultaneously with the consummation of the closing of the Offering, the Company consummated the private placement of an aggregate of 456,225 units (the “Private Placement Units”) to Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC, the sponsor of the Company (the “Sponsor”), at a price of $10.00 per Private Placement Unit, generating total gross proceeds of $4,562,250 (the “Private Placement”) (see Note 4).
On October 4, 2022, the Company consummated the closing of the sale of 1,200,000 additional units at a price of $10 per unit upon receiving notice of the underwriters’ election to exercise their overallotment option generating additional gross proceeds of $12.0 million. Simultaneously with the exercise of the overallotment, the Company consummated the Private Placement of an additional 42,000 Private Placement Units to the Sponsor, generating gross proceeds of $420,000.
Transaction costs amounted to $4,788,510 consisting of $920,000 of underwriting fees (net of underwriter reimbursements), $3,220,000 of deferred underwriting fees payable, which are held in a trust account with Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company acting as trustee (the “Trust Account”) and $648,510 of other offering costs related to the Initial Public Offering. The underwriters were also issued 115,000 shares of Class A common stock as representative shares, in connection with the IPO. Upon close of the Initial Public Offering, the Company recorded additional issuance costs of $79,338, the grant date fair value of the shares, with an offset to additional paid-in capital. As described in Note 6, the $3,220,000 deferred underwriting fees are contingent upon the consummation of the Business Combination within 27 months from the closing of the IPO pursuant to six one-month extensions, from June 22, 2023 until December 22, 2024, provided that the Sponsor (or its affiliates or permitted designees) will deposit into the Trust Account $22,740 for each such one-month extension until December 22, 2024, unless the closing of the Company’s initial business combination shall have occurred. (See “Special Meetings” section below).
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1 — DESCRIPTION OF ORGANIZATION, BUSINESS OPERATIONS AND GOING CONCERN (CONTINUED)
Nasdaq rules provide that at least 90% of the gross proceeds from the IPO and the sale of the placement units be deposited in a trust account. Of the net proceeds of the IPO and the sale of the placement units, $94,300,000, $10.25 per unit, was placed into a trust account (the “Trust Account”) established for the benefit of the holders of the outstanding Public Shares (the “public stockholders”), with Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company acting as trustee and Morgan Stanley Wealth Management acting as investment manager. These proceeds include $3,220,000 in deferred underwriting commissions.
The proceeds in the trust account may be invested in U.S. government securities, within the meaning set forth in Section 2(a)(16) of the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended (the “Investment Company Act”), with a maturity of 185 days or less or in any open-ended investment company that holds itself out as a money market fund meeting the conditions of Rule 2a-7 of the Investment Company Act, as determined by the Company, until the earlier of: (i) the consummation of a Business Combination or (ii) the distribution of the Trust Account to the Company’s stockholders, as described below.
On August 19, 2024, the Company received a letter (the “MVLS Deficiency Notice”) from the listing qualifications department staff (the “Staff”) of The Nasdaq Stock Market (“Nasdaq”) notifying the Company that from July 5, 2024 to August 14, 2024, the Company’s Market Value of Listed Securities (“MVLS”) was below the minimum of $50 million required for continued listing on The Nasdaq Global Market pursuant to Nasdaq Listing Rule 5450(b)(2)(A) (the “MVLS Requirement”).
The MVLS Deficiency Notice has no immediate effect on the listing of the Company’s common stock, and the Company’s common stock continues to trade on the Nasdaq Global Market under the symbol “GLST.”
In accordance with Nasdaq Listing Rule 5810(c)(3)(C), the Company has 180 calendar days from the date of the MVLS Deficiency Notice, or until February 17, 2025 (the “Compliance Date”), to regain compliance with respect to the MVLS Requirement. The MVLS Deficiency Notice states that to regain compliance with the MVLS Requirement, the Company’s MVLS must close at $50 million or more for a minimum of ten consecutive business days during the compliance period ending on the Compliance Date.
If the Company does not regain compliance by the Compliance Date, Nasdaq will provide written notice to the Company that its securities are subject to delisting. At that time, the Company may appeal any such delisting determination. However, there can be no assurance that, if the Company receives a delisting notice from the Staff and appeals the delisting determination, such appeal would be successful. Alternatively, the Company may consider applying for transfer to The Nasdaq Capital Market (the “Capital Market”).
Special Meetings
On August 22, 2023, the Company held a Special Meeting of Stockholders (the “August 2023 Meeting”). At the Meeting, the Company’s stockholders approved the Charter Amendment, which extends the date by which the Company must consummate its initial business combination by an additional nine-months pursuant to nine one-month extensions, from September 22, 2023 to June 22, 2024 (the “First New Termination Date”), subject to the approval of the Board of Directors of the Company (the “Board”), provided the sponsor or its designees deposit into the trust account a monthly amount equal to $125,000, prior to the commencement of each extension period (the “Extension”). The Company filed the Charter Amendment with the Office of the Secretary of State of Delaware on August 28, 2023, a copy of which is attached as Exhibit 3.1 in the Form 8-K filed with the SEC on August 28, 2023 and is incorporated by reference herein. At the Meeting, Stockholders holding 4,052,066 shares of common stock exercised their right to redeem their shares for cash at an approximate price of $10.53 per share of the funds in the Trust Account. As a result, for the period ended September 30, 2024, an aggregate of $44,605,448 was withdrawn from the Trust Account to pay such holders. Following the redemption, the Company’s remaining shares of Class A common stock outstanding were 5,147,934. The Company has made nine monthly payments of $125,000 in the Trust Account to extend the period of time it has to consummate its initial business combination to January 22, 2024 (see Note 11). The Company will provide its holders of the outstanding Public Shares (the “public stockholders”) with the opportunity to redeem all or a portion of their Public Shares upon the completion of a Business Combination either (i) in connection with a stockholder meeting called to approve the Business Combination or (ii) by means of a tender offer. In connection with a proposed Business Combination, the Company may seek stockholder approval of a Business Combination at a meeting called for such purpose at which stockholders may seek to redeem their shares, regardless of whether they vote for or against a Business Combination. The Company will proceed with a Business Combination only if the Company has net tangible assets of at least $5,000,001 either immediately prior to or upon such consummation of a Business Combination and, if the Company seeks stockholder approval, a majority of the outstanding shares voted are voted in favor of the Business Combination.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1 — DESCRIPTION OF ORGANIZATION, BUSINESS OPERATIONS AND GOING CONCERN (CONTINUED)
On June 11, 2024, the Company held a Special Meeting of Stockholders (the “June 2024 Meeting”). At the Meeting, the Company’s stockholders approved the Charter Amendment, which further extends the date by which the Company must consummate its initial business combination by an additional six-months pursuant to six one-month extensions, from June 22, 2024 to December 22, 2024 (the “Second New Termination Date”), provided that the sponsor or its designees deposit into the trust account approximately $22,740 prior to the commencement of each extension period. At the June 2024 Meeting, Stockholders holding 4,010,928 shares of common stock exercised their right to redeem their shares for cash at an approximate price of $11.12 per share of the funds in the Trust Account. As a result, $44,605,448 was removed from the Trust Account to pay such holders. The Company has made five monthly extension payments in the Trust Account to extend the period of time by which it has to consummate its initial business combination to November 22, 2024.
The Company has until November 22, 2024 (or up to December 22, 2024, in the event the Company extends the term to the fullest), to consummate a Business Combination. If we do not complete our initial business combination by December 22, 2024, or (i) as extended by the Company’s stockholders in accordance with our amended and restated certificate of incorporation or (ii) with respect to any other provision relating to stockholders’ rights or pre-initial business combination activity and (iii) waive their rights to liquidating distributions from the trust account with respect to any founder shares and placement shares held by them if we fail to complete our initial business combination prior to the Second New Termination date, the public stockholders will be entitled to liquidating distributions from the trust account with respect to any public shares they hold if we fail to complete our initial business combination within the prescribed time frame. Accordingly, it is our intention to redeem our public shares as soon as reasonably possible following the Second New Termination Date unless our initial business combination shall have occurred earlier and, therefore, we do not intend to comply with those procedures. As such, our public stockholders could potentially be liable for any claims to the extent of distributions received by them (but no more) and any liability of our stockholders may extend well beyond the third anniversary of such date.
Our sponsor has agreed that it will be liable to us if and to the extent any claims by a third party (other than the independent public accounting firm) for services rendered or products sold to us, or a prospective target business with which we have entered into a written letter of intent, confidentiality or similar agreement or business combination agreement, reduce the amount of funds in the trust account to below the lesser of (i) $10.25 per public share and (ii) the actual amount per public share held in the trust account due to reductions in the value of the trust assets as of the date of the liquidation of the trust account, if less than $10.25 per public share due to reductions in the value of the trust assets, less taxes payable, provided that such liability will not apply to any claims by a third party or prospective target business who executed a waiver of any and all rights to the monies held in the trust account (whether or not such waiver is enforceable) nor will it apply to any claims under our indemnity of the underwriters of the IPO against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act. In the event that any such executed waiver is deemed to be unenforceable against such third party, the Sponsor shall not be responsible to the extent of any liability for such third-party claims. The Sponsor shall have the right to defend against any such claim with counsel of its choice reasonably satisfactory to the Company if, within 15 days following written receipt of notice of the claim to the Sponsor, the Sponsor notifies the Company in writing that it shall undertake such defense. We have not asked our sponsor to reserve for such indemnification obligations, nor have we independently verified whether our sponsor has sufficient funds to satisfy its indemnity obligations and believe that our sponsor’s only assets are securities of our company. Therefore, we cannot assure you that our sponsor would be able to satisfy those obligations. None of our officers or directors will indemnify us for claims by third parties including, without limitation, claims by vendors and prospective target businesses.
Franchise and Income Tax Withdrawals from Trust Account
Since completion of its IPO on September 22, 2022, and through September 30, 2024, the Company withdrew $1,684,187 from the Trust Account to pay its liabilities related to income and Delaware franchise taxes. Through September 30, 2024, the Company remitted $1,288,941 to the respective tax authorities, with the difference of $395,247 to be remitted as Company’s tax obligations become due. Inadvertently the Company used $3,108 of those funds to pay for working capital purposes and as such breached the Company’s charter. Subsequent to September 30, 2024, the Company received additional funds from the Sponsor under the terms of promissory note. As of September 30, 2024, the Company had accrued but unpaid income tax liability of $288,597 and accrued but unpaid Delaware franchise tax liability of $169,113. The Company remitted $830,000 in payment of its income tax liability for 2023 (including interest and penalties) on July 3, 2024, and intends to settle its obligations for income and Delaware Franchise taxes as they become due.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1 — DESCRIPTION OF ORGANIZATION, BUSINESS OPERATIONS AND GOING CONCERN (CONTINUED)
Liquidity and Going Concern
As of September 30, 2024, the Company had cash of $392,139 in its operating bank accounts, which is restricted for payment of the Company’s tax obligations (as described above). The Company had 12,919,725 of marketable securities held in the Trust Account to be used for an initial Business Combination or to repurchase or redeem stock in connection therewith and working capital deficit of $4,749,664. From the date of the IPO and through September 30, 2024, the Company has withdrawn an aggregate of $1,684,187 for payment of its income and franchise taxes.
The Company may raise additional capital through loans or additional investments from the Sponsor or its shareholders, officers, directors, or third parties. The Company’s officers and directors, the Sponsor or their affiliates may, but are not obligated to loan us funds, from time to time, in whatever amount they deem reasonable in their sole discretion, to meet the Company’s working capital needs. Based on the foregoing, the Company believes it will not have sufficient cash to meet its needs through the earlier of consummation of a Business Combination or December 22, 2024.
However, if the Company’s estimate of the costs of identifying a target business, undertaking in-depth due diligence and negotiating a Business Combination are more than the actual amount necessary to do so, or if the Company’s shareholders approve an extension to the mandatory liquidation date beyond 21 months from the closing of the IPO, the Company may have insufficient funds available to operate its business prior to a Business Combination. Moreover, the Company may need to obtain additional financing either to complete a Business Combination or because it becomes obligated to redeem a significant number of its Public Shares upon completion of a Business Combination, in which case the Company may issue additional securities or incur debt in connection with such Business Combination. Subject to compliance with applicable securities laws, the Company would only complete such financing simultaneously with the completion of a Business Combination. If the Company does not complete a Business Combination because it does not have sufficient funds available, it will be forced to cease operations and liquidate the Trust Account. In addition, following our Business Combination, if cash on hand is insufficient, the Company may need to obtain additional financing in order to meet its obligations.
If the Company does not consummate a Business Combination by December 22, 2024, there will be a mandatory liquidation and subsequent dissolution of the Company. In connection with the Company’s assessment of going concern considerations in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board’s (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 205-40, “Presentation of Financial Statements - Going Concern,” the Company has determined that the liquidity condition due to insufficient working capital and mandatory liquidation, should a Business Combination not occur, and potential subsequent dissolution raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern for at least one year from the date that the consolidated financial statements are issued. No adjustments have been made to the carrying amounts of assets or liabilities should the Company be required to liquidate after 12 months from the closing of the Public Offering. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustment that might be necessary, if the Company is unable to continue as a going concern.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1 — DESCRIPTION OF ORGANIZATION, BUSINESS OPERATIONS AND GOING CONCERN (CONTINUED)
Merger Agreement
On June 15, 2023, the Company and K Enter Holdings Inc., a Delaware corporation (the “K Enter”) executed of a definitive Merger Agreement (as amended by that certain First Second and Third Amendments, the “Merger Agreement”) pursuant to which, among other things, (i) the Company will merge with and into K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company, formed on June 22, 2023, and wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company (the “Purchaser”), with Purchaser continuing as the surviving corporation (the “Reincorporation Merger”) and (ii) GLST Merger Sub Inc., a Delaware corporation, formed on June 12, 2023, and wholly-owned subsidiary of Purchaser (the “Merger Sub”) will merge with and into K Enter, with K Enter surviving the merger as a wholly-owned subsidiary of Purchaser (the “Acquisition Merger”). The Reincorporation Merger, the Acquisition Merger and the other transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement, together, are referred to herein as the “Proposed Business Combination”. Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, the parent of the combined company will be named “K Wave Media Ltd.” and the Company expects that the securities of the parent of the combined company will be listed on The Nasdaq Stock Market.
Merger Consideration
Upon the effective time of the Reincorporation Merger, (i) each issued and outstanding share of common stock of the Company (the “Company Common Stock”), other than Company Common Stock that are owned by the Company as treasury shares or any Company Common Stock owned by any direct or indirect wholly owned subsidiary of the Company, will be converted automatically into one ordinary share of the Purchaser (the “Purchaser Ordinary Share”), and (ii) each issued and outstanding warrant of the Company will convert automatically into a warrant to purchase one Purchaser Ordinary Share at a price of $11.50 per whole share (the “Purchaser Warrant”), (iii) each issued and outstanding right of the Company shall convert automatically into a right to receive one-tenth (1/10) of one Purchaser Ordinary Share at the closing of a business combination (the “Purchaser Right”), and (iv) each issued and outstanding unit of the Company shall separate and convert automatically into one Purchaser Ordinary Share, one Purchaser Warrant and one Purchaser Right. Each of the Purchaser Warrants and Purchaser Rights shall have, and be subject to, the same terms and conditions set forth in the applicable agreements governing the warrants of the Company and the rights of the Company, respectively. At the closing of the Reincorporation Merger, all common stock, warrants, rights, units, and other securities of the Company shall cease to be outstanding and shall automatically be canceled and retired and shall cease to exist.
Upon the closing of the Acquisition Merger, (i) each share of K Enter capital stock, if any, that is owned by Company or Merger Sub (or any other subsidiary of Company) or K Enter (as treasury stock or otherwise), will automatically be cancelled and retired without any conversion, (ii) each share of K Enter preferred stock issued and outstanding shall be deemed converted into shares of K Enter common stock, (iii) each share of K Enter common stock issued and outstanding, including shares of K Enter common stock deemed outstanding as a result of the mandatory conversion of K Enter preferred stock, shall be converted into the right to receive a number of Purchaser Ordinary Shares equal to the Conversion Ratio, and (iv) each share of Merger Sub common stock issued and outstanding shall be converted into and become one newly issued, fully paid and nonassessable share of K Enter common stock. Conversion Ratio means the quotient obtained by dividing (a) 59,000,000 Purchaser Ordinary Shares, by (b) the Aggregate Fully Diluted K Enter Common Shares. Aggregate Fully Diluted K Enter Common Shares means the sum of (a) all shares of K Enter common stock that are issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Closing; plus (b) the aggregate shares of K Enter common stock issuable upon conversion of all shares of K Enter preferred stock that are issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Closing; plus (c) the aggregate shares of K Enter common stock issuable upon full conversion, exercise or exchange of any other securities of K Enter outstanding immediately prior to the Closing directly or indirectly convertible into or exchangeable or exercisable for K Enter.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1 — DESCRIPTION OF ORGANIZATION, BUSINESS OPERATIONS AND GOING CONCERN (CONTINUED)
Conditions to Closing
The Closing is subject to certain customary conditions, including, among other things, (i) approval by the Company’s stockholders of the Merger Agreement and related proposals, (ii) approval by K Enter’s shareholders of the Merger Agreement, (iii) the effectiveness of a registration statement on Form F-4 (the “Registration Statement”) to be filed by Purchaser relating to the Business Combination, which will contain a proxy statement of the Company in connection with its solicitation for proxies for the vote by stockholders of the Company in connection with the Business Combination and other matters as described in the Registration Statement, (iv) the approval for Purchaser’s initial listing application with Nasdaq or an alternate exchange, (v) the Company having at least $5,000,001 of net tangible assets, (vi) the accuracy of each party’s representations and warranties, except generally as would not have a Material Adverse Effect and in the case of certain fundamental representations, in all material respects, (vii) compliance by each party with pre-closing covenants in all material respects, (viii) the absence of any legal restraints or injunctions enjoining or prohibiting the consummation of the Business Combination, (ix) the receipt, expiration or termination of applicable government approvals and antitrust waiting periods, (x) the Reincorporation Merger has been consummated and the applicable certificates has filed in the appropriate jurisdictions, (xi) the acquisition of certain entities of the Six Korean Entities have been consummated, and (xii) the Purchaser and Merger Sub having entered into a joinder to the merger agreement.
The foregoing description of the Merger Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the Merger Agreement, copy of which, is filed as Exhibit 2.1 in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC on June 22, 2023.
Lock-Up Agreement
At the Closing, Purchaser, Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (the “Sponsor”), certain former stockholders of K Enter (such stockholders, the “Target Holders”), and other persons and entities (collectively, the “Holders” and each, a “Holder”), will enter into lock-up agreements (the “Lock-Up Agreements”) with respect to the Purchaser Ordinary Shares and Purchaser Warrants held by the Sponsor immediately following the Closing, and the Purchaser Ordinary Shares held by the Target Holders immediately following the Closing (the “Lock-Up Shares”), pursuant to which, each Holder agreed not to offer, sell, contract to sell, pledge, grant any option to purchase, or otherwise dispose of, directly or indirectly, any Lock-Up Shares during the application lock-up period, on the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in the Lock-Up Agreement. Lock-up period means, (i) with respect to 50% of the Lock-up Shares, the earlier of (A) six months after the Closing and (B) the date on which the closing price of the Purchaser’s Ordinary Shares equals or exceeds $12.50 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, rights issuances, reorganizations and recapitalizations) for any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period commencing after the date hereof and (ii) with respect to the remaining 50% Lock-up Shares (or Ordinary Shares issuable upon conversion thereof), six months after the Closing.
The foregoing description of the Lock-Up Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the Lock-Up Agreement, a form of which is filed as Exhibit 10.1 in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC on June 22, 2023.
Registration Rights Agreement
The Merger Agreement contemplates that, at the Closing, the Purchaser, the Sponsor, certain former stockholders of the Company (such stockholders, together with the Sponsor, the “Company Holders”), and certain former stockholders of K Enter, will enter into a registration rights agreement (the “Registration Rights Agreement”), pursuant to which Purchaser will be obligated to file a registration statement to register the resale, pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, of certain securities of Purchaser held by the parties to the Registration Rights Agreement. The Registration Rights Agreement will also provide the Sponsor, the Company Holders, the Target Holders with unlimited “piggy-back” registration rights, subject to certain requirements and customary conditions.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1 — DESCRIPTION OF ORGANIZATION, BUSINESS OPERATIONS AND GOING CONCERN (CONTINUED)
The Registration Rights Agreement amends and restates the registration rights agreement that was entered into by the Company, the Sponsor and the other parties thereto in connection with the Company’s initial public offering. The Registration Rights Agreement will terminate on the earlier of (a) the five year anniversary of the date of the Registration Rights Agreement or (b) with respect to any holder, on the date that such holder no longer holds any Registrable Securities (as defined therein).
The foregoing description of the Registration Rights Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the Registration Rights Agreement, a form of which is filed as Exhibit 10.2 in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC on June 22, 2023.
Purchase Agreement
In connection with this Merger Agreement, on July 12, 2023, the Company entered into a Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) by and between the Company, K Enter, and Global Star Acquisition I LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (the “Sponsor”). Pursuant to the Purchase Agreement, K Enter purchased from the Sponsor 160,000 shares of Class B common stock (“the SPAC Securities”) for an aggregate purchase price of $1,600,000 (the “Purchase Price”), which was payable within 10 days from the effective date of the Purchase Agreement.
In addition to the payment of the Purchase Price, K Enter acknowledged that (x) it is an accredited investor as defined by Rule 501 of the Securities Act, (y) and has knowledge and experience in financial and business matters and in investments of this type and is capable of evaluating the merits and risks of the SPAC Securities and of making an informed investment decision. K Enter further acknowledged and agreed that the SPAC Securities: (a) are subject to limitations on transfer, (b) are being acquired pursuant to an exemption from registration under the Securities Act with no present intention to distribute them to any person in violation of the Securities Act or any applicable U.S. state, (c) will not be sold except in compliance with the Securities Act and any applicable U.S. state securities laws, and in accordance with any limitations set forth in any applicable lock-up agreements applicable to the SPAC Securities.
The foregoing description of the Purchase Agreement is a summary only and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the full text of the Purchase Agreement, a copy of which is attached as Exhibit 10.2 in the Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 17, 2023.
First Amendment
On March 11, 2024, the Company, K Enter, Purchaser, and Merger Sub entered into a First Amendment to the Merger Agreement (the “First Amendment”) to amend certain of the terms of the Merger Agreement. The First Amendment (i) reduces the base value of the merger consideration to be received by Company shareholders from $610 million to $590 million, and (ii) removes in its entirety respective references to the “Share Purchase Agreement” dated April 12, 2023 with certain sellers of First Virtual Lab Inc. from its disclosure schedules and includes the “Termination Agreement and Re-Purchase Option Agreement, dated March 5, 2024, by and among Sungkwon Kim, King Bear Film LLC and K Enter Holdings Inc” to the disclosure schedule. Pursuant to Section 141(f) of the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware and Section 4.5 of the Company’s bylaws, the board approved and authorized the First Amendment on March 11, 2024. The board obtained an updated fairness opinion with respect to the First Amendment. The modification in the purchase consideration was made in connection with the cessation of the planned acquisition of a majority equity stake in First Virtual Lab Inc.
Second and Third Amendment
On June 28, 2024, the Company entered into a Second Amendment to the Business Combination Agreement (the “Second BCA Amendment”), by and among K Enter, K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (the “K Wave Media Ltd.”), and GLST Merger Sub Inc., a Delaware corporation (the “GLST Merger Sub Inc.”) to extend the outside date by which the parties’ must consummate the business combination. Other than the extension of the date to December 22, 2024, by which we must consummate a business combination, all of the terms, covenants, agreements, and conditions of the BCA remain in full force and effect in accordance with its original terms. On July 25, 2024, the Company entered into a Third Amendment to the Business Combination Agreement (the “Third BCA Amendment”), by and among K Enter, K Wave Media Ltd., and GLST Merger Sub Inc. to amend the conditions to the parties’ obligations to consummate the business combination. Other than the amendment to the condition to the obligations of the parties whereby K Enter must complete its acquisition of the controlling equity interests of (1) Play Company Co. Ltd., (2) Solaire Partners LLC, (3) Apeitda Co., Ltd., (4) The LAMP Co., Ltd., (5) Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd., and (6) Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd., all of the terms, covenants, agreements, and conditions of the BCA remain in full force and effect in accordance with its original terms.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1 — DESCRIPTION OF ORGANIZATION, BUSINESS OPERATIONS AND GOING CONCERN (CONTINUED)
The foregoing description of the Second BCA Amendment and Third BCA Amendment (the “BCA Amendments”) do not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the BCA Amendments, copies of which, are filed as Exhibit 2.1 and 2.2 in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 31, 2024.
Risks and Uncertainties
Management continues to evaluate the impact of various factors, including the geopolitical conditions resulting from the invasion of Ukraine by Russia and subsequent sanctions against Russia, Belarus and related individuals and entities and the status of debt and equity markets, as well as protectionist legislation in our target markets, and has concluded that while it is reasonably possible that these factors could have a negative effect on the Company’s financial position, results of its operations, and/or search for a target company, the specific impact is not readily determinable as of the date of the consolidated financial statements. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of these uncertainties.
Inflation Reduction Act of 2022
On August 16, 2022, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (the “IR Act”) was signed into federal law. The IR Act provides for, among other things, a new U.S. federal 1% excise tax on certain repurchases of stock by publicly traded U.S. domestic corporations and certain U.S. domestic subsidiaries of publicly traded foreign corporations occurring on or after January 1, 2023. The excise tax is imposed on the repurchasing corporation itself, not its shareholders from which shares are repurchased. The amount of the excise tax is generally 1% of the fair market value of the shares repurchased at the time of the repurchase. However, for purposes of calculating the excise tax, repurchasing corporations are permitted to net the fair market value of certain new stock issuances against the fair market value of stock repurchases during the same taxable year. In addition, certain exceptions apply to the excise tax. The U.S. Department of the Treasury (the “Treasury”) has been given authority to provide regulations and other guidance to carry out and prevent the abuse or avoidance of the excise tax.
On August 22, 2023, in connection with the implementation of the Extension, the Company’s public stockholders elected to redeem 4,052,066 Public Shares for a total of $42,680,726. As such the Company has recorded a 1% excise tax liability in the amount of $426,807 on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets as of August 22, 2023. On June 25, 2024, in connection with the implementation of the Second Extension, the Company’s public stockholders elected to redeem 4,010,928 Public Shares for a total of $44,605,448. As such the Company has recorded a 1% excise tax liability in the amount of $446,054 on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets as of September 30, 2024. The total liability of $872,861 recorded as of September 30, 2024 does not impact the Company’s consolidated statements of income and is offset against additional paid-in capital or accumulated deficit if additional paid-in capital is not available. This liability will be reevaluated and remeasured at the end of each quarterly period.
During the second quarter of 2024, the Internal Revenue Service issued final regulations with respect to the timing and payment of the Excise Tax. These regulations provided that the filing and payment deadline for any liability incurred during the period from January 1, 2023 to December 31, 2023 would be October 31, 2024. The Company has filed its excise tax return and is currently evaluating its options with respect to this obligation. Any amount of such Excise Tax not paid in full, will be subject to additional interest and penalties which are currently estimated at 10% interest per annum and a 5% underpayment penalty per month or portion of a month up to 25% of the total liability for any amount that is unpaid from November 1, 2024 until paid in full.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 2 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES BASIS OF PRESENTATION
The accompanying condensed consolidated financial statements are presented in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“US GAAP”) and pursuant to the rules and regulations of the SEC.
Certain information and note disclosures normally included in the financial statements prepared in accordance with US GAAP have been condensed consolidated. As such, the information included in these financial statements should be read in conjunction with the audited financial statements as of December 31, 2023 filed with the SEC on Form 10-K. In the opinion of the Company’s management, these condensed consolidated financial statements include all adjustments, which are only of a normal and recurring nature, necessary for a fair statement of the Company’s financial position as of September 30, 2024 and the Company’s results of operations and cash flows for the periods presented. The results of operations for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2024 are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for the full year ending December 31, 2024.
Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly owned subsidiary where the Company has the ability to exercise control. All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. Activities in relation to the noncontrolling interest are not considered to be significant and are, therefore, not presented in the accompanying consolidated financial statements.
Emerging Growth Company
The Company is an “emerging growth company,” as defined in Section 2(a) of the Securities Act, as modified by the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (the “JOBS Act”), and it may take advantage of certain exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies including, but not limited to, not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in its periodic reports and proxy statements, and exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved.
Further, Section 102(b)(1) of the JOBS Act exempts emerging growth companies from being required to comply with new or revised financial accounting standards until private companies (that is, those that have not had a Securities Act registration statement declared effective or do not have a class of securities registered under the Exchange Act) are required to comply with the new or revised financial accounting standards. The JOBS Act provides that a company can elect to opt out of the extended transition period and comply with the requirements that apply to non-emerging growth companies but any such election to opt out is irrevocable. The Company has elected not to opt out of such extended transition period which means that when a standard is issued or revised and it has different application dates for public or private companies, the Company, as an emerging growth company, can adopt the new or revised standard at the time private companies adopt the new or revised standard. This may make comparison of the Company’s condensed consolidated financial statements with another public company which is neither an emerging growth company nor an emerging growth company which has opted out of using the extended transition period difficult or impossible because of the potential differences in accounting standards used.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 2 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES BASIS OF PRESENTATION (CONTINUED)
Use of Estimates
The preparation of condensed consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the condensed consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period.
Making estimates requires management to exercise significant judgment. It is at least reasonably possible that the estimate of the effect of a condition, situation or set of circumstances that existed at the date of the condensed consolidated financial statements, which management considered in formulating its estimate, could change in the near term due to one or more future confirming events. Accordingly, the actual results could differ significantly from those estimates.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all short-term investments with an original maturity of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents. The Company’s operating account is classified as cash equivalent in the Company’s condensed consolidated balance sheet.
Marketable Securities Held in Trust Account
At September 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023, substantially all of the assets held in the Trust Account were held in money market funds that invest in U.S. Treasury Securities. The Company accounts for its marketable securities as Trading Securities under ASC 320, where securities are presented at fair value on the condensed consolidated balance sheets and with unrealized gains or losses, if any, presented on the condensed consolidated statements of income. From the date of the IPO and through September 30, 2024, the Company withdrew an aggregate of $1,684,187 of interest earned on the Trust Account to pay its income and franchise taxes and remitted $1,288,941 to respective tax authorities. The remaining balance of $392,139 is available for payment of Company’s tax liabilities as of September 30, 2024.
Offering Costs
The Company complies with the requirements of the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) ASC340-10-S99-1and SEC Staff Accounting Bulletin (“SAB”) Topic 5A, “Expenses of Offering.” Offering costs were allocated to the separable financial instruments issued in the Initial Public Offering. Offering costs, including underwriter fees, associated with the Units were allocated between temporary equity and the Public Warrants and the Public Rights by the relative fair value method. Offering costs of $648,510 consisted principally of costs incurred in connection with preparation for the Initial Public Offering. The Company issued 115,000 shares of Class A Common Stock to the representative of the underwriter for services related to the Initial Public Offering. The shares have a grant date fair value of $79,338.
Class A Common Stock Subject to Possible Redemption
The Company accounts for its Class A common stock subject to possible redemption in accordance with the guidance in ASC Topic 480 “Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity.” Class A common stock subject to mandatory redemption is classified as a liability instrument and is measured at fair value. Conditionally redeemable common stock (including common stock that features redemption rights that is either within the control of the holder or subject to redemption upon the occurrence of uncertain events not solely within the Company’s control) is classified as temporary equity. At all other times, common stock is classified as stockholders’ equity. The Company’s Class A common stock features certain redemption rights that are considered to be outside of the Company’s control and subject to occurrence of uncertain future events. Accordingly, on September 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023, Class A common stock subject to possible redemption is presented at redemption value as temporary equity, outside of the stockholders’ deficit section of the Company’s condensed consolidated balance sheets.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 2 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES BASIS OF PRESENTATION (CONTINUED)
The Company recognizes changes in the redemption value immediately as they occur and adjusts the carrying value of redeemable common stock to equal the redemption value at the end of each reporting period. Increases or decreases in the carrying amount of redeemable common stock are affected by charges against additional paid-in capital and accumulated deficit.
At September 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023, the Class A common stock reflected in the condensed consolidated balance sheets is reconciled in the following table:
| Gross proceeds from IPO and exercise of the over-allotment option | | $ | 92,000,000 | |
| Less: | | | | |
| Transaction costs allocated to the Class A common stock | | | (4,726,147 | ) |
| Proceeds allocated to Public Rights and Warrants | | | (524,400 | ) |
| Plus: | | | | |
| Remeasurement adjustment of Class A common stock to redemption value | | | 8,048,308 | |
| Class A common stock subject to possible redemption at December 31, 2022 | | $ | 94,797,761 | |
| Plus: | | | | |
| Remeasurement adjustment of Class A common stock to redemption value | | | 3,458,355 | |
| Less: | | | | |
| Redemption of Class A common stock subject to redemption | | | (42,680,726 | ) |
| Class A common stock subject to possible redemption at December 31, 2023 | | $ | 55,575,390 | |
| Plus: | | | | |
| Remeasurement adjustment of Class A common stock to redemption value | | | 909,438 | |
| Class A common stock subject to possible redemption at March 31, 2024 | | $ | 56,484,828 | |
| Plus: | | | | |
| Remeasurement adjustment of Class A common stock to redemption value | | | 805,595 | |
| Less: | | | | |
| Redemption of Class A common stock subject to redemption | | | (44,605,448 | ) |
| Class A common stock subject to possible redemption at June 30, 2024 | | $ | 12,684,975 | |
| Plus: | | | | |
| Remeasurement adjustment of Class A common stock to redemption value | | | 172,286 | |
| Class A common stock subject to possible redemption at September 30, 2024 | | $ | 12,857,261 | |
Warrant Classification
The Company accounts for warrants as either equity-classified or liability-classified instruments based on an assessment of the warrant’s specific terms and applicable authoritative guidance in ASC 480 and ASC Topic 815, “Derivatives and Hedging” (“ASC 815”). The assessment considers whether the warrants are freestanding financial instruments pursuant to ASC 480, meet the definition of a liability pursuant to ASC 480, and whether the warrants meet all of the requirements for equity classification under ASC 815, including whether the warrants are indexed to the Company’s own common stock, among other conditions for equity classification. This assessment, which requires the use of professional judgment, is conducted at the time of warrant issuance and as of each subsequent quarterly period end date while the warrants are outstanding.
For issued or modified warrants that meet all of the criteria for equity classification, the warrants are required to be recorded as a component of additional paid-in capital at the time of issuance. For issued or modified warrants that do not meet all the criteria for equity classification, the warrants are required to be recorded at their initial fair value on the date of issuance. The fair value of the warrants are remeasured at each balance sheet date with the change in the estimated fair value of the warrants recognized as a non-cash gain or loss on the condensed consolidated statements of operations. The Company has analyzed the Public Warrants (as defined in Note 3) and Private Placement Warrants and determined they are considered to be freestanding instruments and do not exhibit any of the characteristics in ASC 480 and therefore are not classified as liabilities under ASC 480.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 2 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES BASIS OF PRESENTATION (CONTINUED)
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes under ASC 740, “Income Taxes.” ASC 740, Income Taxes, which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for both the expected impact of differences between the condensed consolidated financial statements and tax basis of assets and liabilities and for the expected future tax benefit to be derived from tax loss and tax credit carry forwards. ASC 740 additionally requires a valuation allowance to be established when it is more likely than not that all or a portion of deferred tax assets will not be realized. The Company does not expect that the total amount of unrecognized tax benefits will materially change over the next twelve months.
While ASC 740 identifies usage of the effective annual tax rate (“ETR”) for purposes of an interim provision, it does allow for estimating individual elements in the current period if they are significant, unusual or infrequent. Computing the ETR for the Company is complicated due to the potential impact of the Company’s change in fair value of warrants (or any other change in fair value of a complex financial instrument), the timing of any potential business combination expenses and the actual interest income that will be recognized during the year. The Company has taken a position as to the calculation of income tax expense in the current period based on 740-270-25-3 which states, “If an entity is unable to estimate a part of its ordinary income (or loss) or the related tax (or benefit) but is otherwise able to make a reliable estimate, the tax (or benefit) applicable to the item that cannot be estimated shall be reported in the interim period in which the item is reported.” The Company believes its calculation to be a reliable estimate and allows it to properly take into account the unusual elements that can impact its annualized book income and its impact on ETR. As such, the Company is computing its taxable income (loss) and associated income tax provision based on actual results through September 30, 2024.
ASC Topic 740 prescribes a recognition threshold and a measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. For those benefits to be recognized, a tax position must be more-likely-than-not to be sustained upon examination by taxing authorities. The Company recognizes accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits and income taxes, if any, as income tax expense. There were no unrecognized tax benefits and no amounts accrued for interest and penalties as of September 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023.
The Company has identified the United States as our only “major” tax jurisdiction. The Company is subject to income tax examinations by major taxing authorities since inception. These examinations may include questioning the timing and amount of deductions, the nexus of income among various tax jurisdictions and compliance with federal and state tax laws. The Company does not expect that the total amount of unrecognized tax benefits will materially change over the next twelve months and is currently not aware of any issues under review that could result in significant payments, accruals or material deviation from its position.
As of September 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 the Company’s deferred tax asset had a full valuation allowance recorded against it. Our effective tax rate was (36.7%) and (353.3%) for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2024, respectively, 66.1% and 37.5% for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2023, respectively. The effective tax rate differs from the statutory tax rate of 21.0% for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2024 and 2023, due to non-deductible meals & entertainment expenses, tax penalties, business combination costs and changes in the valuation allowance on the deferred tax assets.
Net (Loss) Income Per Share
The Company complies with accounting and disclosure requirements of FASB ASC Topic 260, “Earnings Per Share”. Net (loss) income per share of common stock is computed by dividing net (loss) income by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Subsequent measurement of the redeemable shares of Class A common stock are excluded from (loss) income per shares of common stock as the redemption value approximates fair value.
The Company calculates its earnings per share by allocating net (loss) income pro rata to shares of redeemable Class A and non-redeemable Class A and B common stock. This presentation contemplates a Business Combination as the most likely outcome, in which case, both classes of common stock share pro rata in the (loss) income of the Company.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 2 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES BASIS OF PRESENTATION (CONTINUED)
The calculation of diluted (loss) income per share of common stock does not consider the effect of the warrants issued in connection with the (i) Initial Public Offering, and (ii) the private placement since the exercise of the warrants is contingent upon the occurrence of future events. The warrants are exercisable to purchase 9,698,225 shares of Class A common stock in the aggregate. As a result, diluted net (loss) income per share of common stock is the same as basic net (loss) income per share of common stock for the period presented.
The following table reflects the calculation of basic and diluted net (loss) income per share of common stock (in dollars, except per share amounts):
| | | For the Three Months Ended September 30, | | | For the Nine Months Ended September 30, | |
| | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
| | | Redeemable
Class A | | | Non-Redeemable
Class A And Class B | | | Redeemable
Class A | | | Non-Redeemable
Class A And Class B | | | Redeemable
Class A | | | Non-Redeemable
Class A And Class B | | | Redeemable
Class A | | | Non-Redeemable
Class A And Class B | |
| Basic and diluted net (loss) income per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Numerator: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Allocation of net (loss) income | | $ | (46,510 | ) | | $ | (61,119 | ) | | $ | 85,528 | | | $ | 23,408 | | | $ | (260,045 | ) | | $ | (144,599 | ) | | $ | 860,218 | | | $ | 211,870 | |
| Denominator: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average shares outstanding | | | 1,750,231 | | | | 2,300,000 | | | | 8,403,811 | | | | 2,300,000 | | | | 4,136,294 | | | | 2,300,000 | | | | 9,338,258 | | | | 2,300,000 | |
| Basic and diluted net (loss) income per share | | $ | (0.03 | ) | | $ | (0.03 | ) | | $ | 0.01 | | | $ | 0.01 | | | $ | (0.06 | ) | | $ | (0.06 | ) | | $ | 0.09 | | | $ | 0.09 | |
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist of a cash account in a financial institution, which, at times, may exceed the Federal Depository Insurance Corporation coverage limit of $250,000. The Company has not experienced losses on these accounts.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Fair value is defined as the price that would be received for sale of an asset or paid for transfer of a liability, in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. GAAP establishes a three-tier fair value hierarchy, which prioritizes the inputs used in measuring fair value. The hierarchy gives the highest priority to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1 measurements) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3 measurements). These tiers include:
| | ● | Level 1, defined as observable inputs such as quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical instruments in active markets; |
| | | |
| | ● | Level 2, defined as inputs other than quoted prices in active markets that are either directly or indirectly observable such as quoted prices for similar instruments in active markets or quoted prices for identical or similar instruments in markets that are not active; and |
| | | |
| | ● | Level 3, defined as unobservable inputs in which little or no market data exists, therefore requiring an entity to develop its own assumptions, such as valuations derived from valuation techniques in which one or more significant inputs or significant value drivers are unobservable. |
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 2 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES BASIS OF PRESENTATION (CONTINUED)
In some circumstances, the inputs used to measure fair value might be categorized within different levels of the fair value hierarchy. In those instances, the fair value measurement is categorized in its entirety in the fair value hierarchy based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
Share-Based Payment Arrangements
The Company accounts for share-based payments in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718, “Compensation—Stock Compensation,” (“ASC 718”) which requires that all equity awards be accounted for at their “fair value.” The Company measures and recognizes compensation expense for all share-based payments on their estimated fair values measured as of the grant date. These costs are recognized as an expense in the Condensed consolidated statements of Operations upon vesting, once the applicable performance conditions are met, with an offsetting increase to additional paid-in capital. Forfeitures are recognized as they occur.
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures (ASU 2023-09), which requires disclosure of incremental income tax information within the rate reconciliation and expanded disclosures of income taxes paid, among other disclosure requirements. ASU 2023-09 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. Early adoption is permitted. The Company’s management does not believe the adoption of ASU 2023-09 will have a material impact on its condensed consolidated financial statements and disclosures.
NOTE 3 — INITIAL PUBLIC OFFERING
Pursuant to the Initial Public Offering, the Company sold 8,000,000 Units at a price of $10.00 per Unit generating gross proceeds of $80,000,000. Each Unit consists of one share of Common stock, one redeemable warrant (“Public Warrant”) and one right (“Public Right). Each whole Public Warrant will entitle the holder to purchase one share of Common stock at a price of $11.50 per share, subject to adjustment (see Note 7). Each Public Right entitles the holder to receive one-tenth of one share of Common Stock upon the consummation of the business combination. On October 4, 2022, the Company consummated the closing of the sale of 1,200,000 additional units at a price of $10 per unit upon receiving notice of the underwriters’ election to exercise their overallotment option generating additional gross proceeds of $12.0 million and incurred additional offering costs of $412,500 in underwriting fees, of which $262,500 are for deferred underwriting commissions.
NOTE 4 — PRIVATE PLACEMENT
Simultaneously with the closing of the Initial Public Offering, the Company consummated the private sale (the “Private Placement”) of an aggregate of 456,225 units (the “Private Placement Units”) to the Sponsor at a purchase price of $10.00 per Private Placement Unit, generating gross proceeds to the Company in the amount of $4,562,250. Simultaneously with the exercise of the overallotment, the Company consummated the Private Placement of an additional 42,000 Private Placement Units to the Sponsor, generating gross proceeds of $420,000.
The proceeds from the sale of the Placement Units will be added to the net proceeds from the Public Offering held in the Trust Account. The Placement Units are identical to the Units sold in the Public Offering, except for the placement warrants (“Private Placement Warrants”), as described in Note 7. If the Company does not complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period, the proceeds from the sale of the Placement Units will be used to fund the redemption of the Public Shares (subject to the requirements of applicable law) and the Private Placement Warrants and the rights underlying the Placement Units (“Private Rights”) will expire worthless.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 5 — RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Founder Shares
During the year ended December 31, 2021, the Sponsor agreed to purchase 2,300,000 shares of the Company’s Common stock (the “Founder Shares”) for $25,000. On February 14, 2022, the Sponsor received the 2,875,000 shares and paid the Company $25,000 in full satisfaction of the outstanding receivable. The Founder Shares include an aggregate of up to 300,000 shares subject to forfeiture to the extent that the underwriters’ over-allotment is not exercised in full or in part, so that the number of Founder Shares will equal, on an as-converted basis, approximately 20% of the Company’s issued and outstanding shares of common stock after the Initial Public Offering (see Note 9). In accordance with ASC 505, “Equity”, all shares, and the associated amounts have been retroactively restated to account for this share issuance. On April 5, 2022, the Sponsor entered into share transfer agreements (collectively, the “Share Transfer Agreements”) for an aggregate of 500,000 founder shares to the Company’s officers and directors (subject to certain performance conditions discussed in Note 8). On July 26, 2022, the Sponsor surrendered 575,000 founder shares to the Company for cancellation, for no consideration. All share amounts have been retroactively restated to reflect this surrender. K Enter purchased 160,000 Founder Shares from the Sponsor pursuant to the Purchase Agreement discussed herein. In accordance with the Purchase Agreement, the Sponsor owns 2,140,000 Founder Shares.
The Sponsor and each Insider agrees that (i) 50% of the Founder Shares (or shares of Common Stock issuable upon conversion thereof) will not be transferred, assigned or sold until the earlier of (A) six months after the date of the consummation of the Company’s initial business combination and (B) the date on which the closing price of the Company’s common stock equals or exceeds $12.50 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, reorganizations and recapitalizations) for any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period commencing after the Company’s initial business combination and (i) the remaining 50% of the Founder Shares (or shares of Common Stock issuable upon conversion thereof) will not be transferred, assigned, sold or released from escrow until six months after the date of the consummation of the Company’s initial business combination.
Due to Related Party
Prior to September 30, 2022, and in connection with the close of the overallotment on October 4, 2022, the Company received $112,250 which should have been deposited into the Sponsor’s bank account. The amount was transferred to the Trust Account prior to December 31, 2022.
At the close of the Initial Public Offering, a related party deposited $25,000 greater than the agreed upon initial investment. The Company repaid this amount in full, and no balance related to this transaction was outstanding as of September 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023.
Due to Sponsor
As of September 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023, the outstanding balance due to the Sponsor was $15,094, which represents certain amounts paid by Sponsor on behalf of the Company.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 5 — RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS (CONTINUED)
Promissory Notes — Related Party Working Capital Loan
On February 14, 2022, the Sponsor issued an unsecured promissory note to the Company (the “Promissory Note”), pursuant to which the Company may borrow up to an aggregate principal amount of $300,000, which was fully drawn prior to Initial Public Offering. Upon closing of the Initial Public Offering, the Company repaid the outstanding balance in full.
In order to finance transaction costs in connection with the Business Combination, our Sponsor extended to us a line of credit of up to $1,600,000 pursuant to a Promissory Note dated July 31, 2023 (“Sponsor Working Capital Loan”). Such Sponsor Working Capital Loan is without interest and is to be repaid on the later of (i) December 31, 2023 or (ii) upon the consummation of a Business Combination. The Sponsor in its sole discretion may elect to convert up to $1,500,000 amount of the Sponsor Working Capital Loan into the Company’s Common Stock at a price of $10.00 per share in lieu of cash repayment. The conversion options embedded in the Sponsor Working Capital Loan are considered related to those of an equity instrument. As a result, this would be considered a contract that would be issued or held by the Company that is (i) indexed to its own stock and (ii) classified in stockholders’ equity the Company’s statement of financial position; therefore, this embedded feature meets the scope exception criteria under ASC 815-10-15-74(a) and is not accounted for as a derivative instrument within the scope of ASC 815.
In the event that a Business Combination does not close, we may use a portion of proceeds held outside the Trust Account to repay the Sponsor Working Capital Loan, but no proceeds held in the Trust Account would be used to repay the Sponsor Working Capital Loans. As of September 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023, the amount outstanding under the Sponsor Working Capital Loan was $1,586,000 and $1,590,000, respectively.
On April 15, 2024, the Company issued a promissory note to the Sponsor in an amount of up to $1,000,000 for working capital needs. The note bears no interest and shall be payable by the Maker on the earlier of: (i) December 31, 2024 or (ii) the date on which Maker consummates an initial public offering of its securities. The principal balance may be prepaid at any time. As of September 30, 2024, $821,000 was drawn and outstanding under the promissory note.
On October 23, 2024, the Company amended the terms of the promissory note to allow conversion of up to $1,000,000 into Class B Common Stock of the Company at a price of $10.00 per unit in lieu of cash repayment, effective immediately prior to the Business Combination.
Advances From Related Party
The Sponsor paid certain offering costs on behalf of the Company and advanced working capital to the Company. These advances are due on demand and are non-interest bearing. Upon close of the Initial Public Offering, the Company repaid the outstanding balance of $119,720 in full.
Administrative Support Agreement
The Sponsor has agreed to make available, or cause to be made available, to the Company, or any successor location of Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC, certain office space, utilities and secretarial and administrative support as may be reasonably required by the Company. In exchange therefore, the Company shall pay the Sponsor the sum of $10,000 per month on the Initial Public Offering date and continuing monthly thereafter until the Termination Date. The Company incurred $30,000 and $90,000 of expenses pursuant to this agreement for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2024, respectively. For each of the three and nine months ended September 30, 2023 the Company incurred $30,000 and $91,666, respectively, of expenses pursuant to this agreement.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 6 — COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Registration Rights
Pursuant to a registration rights agreement entered into on September 22, 2022, the holders of the Founder Shares, Private Placement Warrants (and the underlying shares of Class A common stock) and any warrants that may be issued upon conversion of the Working Capital Loans (and the underlying shares of common stock) are entitled to registration rights. The holders of these securities will be entitled to make up to three demands, excluding short form registration demands, that the Company register such securities. The holders of the majority of the securities can elect to exercise these registration rights at any time after the Company consummates a Business Combination. In addition, the holders have certain “piggy-back” registration rights with respect to registration statements filed subsequent to the completion of a Business Combination. The registration rights agreement does not contain liquidated damages or other cash settlement provisions resulting from delays in registering the Company’s securities. The Company will bear the expenses incurred in connection with the filing of any such registration statements.
Underwriting Agreement
The Company granted the underwriters a 45-day option from the date of Initial Public Offering to purchase up to 1,200,000 additional Units to cover over-allotments, if any, at the Initial Public Offering price less the underwriting discounts and commissions. On October 4, 2022, the Company consummated the closing of the sale of 1,200,000 additional units at a price of $10 per unit upon receiving notice of the underwriters’ election to exercise their overallotment option generating additional gross proceeds of $12.0 million and incurred additional offering costs of $412,500 in underwriting fees, of which $262,500 are for deferred underwriting commissions. Simultaneously with the exercise of the overallotment, the Company consummated the Private Placement of an additional 42,000 Private Placement Units to the Sponsor, generating gross proceeds of $420,000.
The underwriters were paid a cash underwriting discount of $0.20 per Unit, or $1,840,000, upon the closing of the Initial Public Offering. The underwriters reimbursed $920,000 to the Company for certain expenses in connection with the IPO. In addition, the underwriters are entitled to a deferred fee of $0.35 per Unit, or $3,220,000. The deferred fee will become payable to the underwriters from the amounts held in the Trust Account solely in the event that the Company completes a Business Combination, subject to the terms of the underwriting agreement.
The underwriters were also issued 115,000 of Class A common stock as representative shares, in connection with our IPO. The Representative Shares have been deemed compensation by FINRA and the lock up period expired on March 19, 2023. The Company recorded additional issuance costs of $79,338, the grant date fair value of the shares, with an offset to additional paid-in capital.
Service Provider Agreement
From time to time the Company has entered into and may enter into agreements with various services providers and advisors, including investment banks, to help us identify targets, negotiate terms of potential Business Combinations, consummate a Business Combination and/or provide other services. In connection with these agreements, the Company may be required to pay such service providers and advisors fees in connection with their services to the extent that certain conditions, including the closing of a potential Business Combination, are met. If a Business Combination does not occur, the Company would not expect to be required to pay these contingent fees. There can be no assurance that the Company will complete a Business Combination.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 6 — COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES (CONTINUED)
On September 24, 2023, the Company has engaged EF Hutton, division of Benchmark Investments, LLC (“EF Hutton”) to act as the exclusive placement agent (“Placement Agent”) for the Company, in connection with the proposed offering by private placement of equity or equity-linked securities in the form of a PIPE, forward purchase arrangement or similar type of equity line financing (the “Placement”) to “qualified institutional buyers” as such term is defined in Rule 144A promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”) and to the institutional accredited investors as such term is defined in Regulation D promulgated under the Securities Act of the Company’s equity or equity-linked securities, including warrants, options or other rights to purchase such securities (collectively, the “Securities”). In case of successful Placements, a non-refundable cash placement fee (the “Placement Fee”), payable at each closing of a Placement, in an amount equal to seven percent (7.0%), as well as foreign placement fee of 1% and reduced placement fee of 1% of the aggregate gross proceeds from the sale of all Securities in the Placement would be due and payable to EF Hutton.
On November 27, 2023, the Company engaged MZHCI, LLC, a MZ Group Company (“MZHCI”) as its public relations consultant starting from January 1, 2024 (the “MZHCI Agreement”). According to terms of the MZHCI Agreement, MZHCI will be paid a monthly fee of $10,000 for its services for the period of the Proposed Business Combination starting from January 1, 2024, which will increase to $14,000 (subject to 5% cost of living adjustment) upon closing of the Proposed Business Combination. In addition, upon a successful closing of the Proposed Business Combination, the Company will issue to MZHCI $150,000 worth of the Company’s restricted stock as valued on the first day of trading post-closing.
Joinder Agreement
A form of Joinder Agreement was included as an exhibit to the Merger Agreement to be executed by Purchaser and Merger Sub, following their formation, to bind them to the terms and conditions of the Merger Agreement. On July 13, 2023, the Purchaser and the Merger Sub executed the Joinder Agreement by and between the Company, K Enter, the Purchaser and Merger Sub. Pursuant to the Joinder Agreement, the Purchaser and Merger Sub agreed to become a party to, to be bound by, and to comply with the terms and conditions of the Merger Agreement.
The foregoing description of the Joinder Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the Joinder Agreement, copy of which, or the form of which, is filed as Exhibit 10.1 on the Company’s Form 8-K as filed with the SEC on July 18, 2023.
Purchase Agreement
In connection with the Merger Agreement, on July 12, 2023, the Company entered into a Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) by and between the Company, K Enter, and the Sponsor. Pursuant to the Purchase Agreement, K Enter purchased from the Sponsor 160,000 shares of Class B common stock (“the SPAC Securities”) for an aggregate purchase price of $1,600,000 (the “Purchase Price”), which was payable within 10 days from the effective date of the Purchase Agreement.
In addition to the payment of the Purchase Price, K Enter acknowledged that (x) it is an accredited investor as defined by Rule 501 of the Securities Act, (y) and has knowledge and experience in financial and business matters and in investments of this type and is capable of evaluating the merits and risks of the SPAC Securities and of making an informed investment decision. K Enter further acknowledged and agreed that the SPAC Securities: (a) are subject to limitations on transfer, (b) are being acquired pursuant to an exemption from registration under the Securities Act with no present intention to distribute them to any person in violation of the Securities Act or any applicable U.S. state, (c) will not be sold except in compliance with the Securities Act and any applicable U.S. state securities laws, and in accordance with any limitations set forth in any applicable lock-up agreements applicable to the SPAC Securities
The foregoing description of the Purchase Agreement is a summary only and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the full text of the Purchase Agreement, a copy of which is attached as Exhibit 10.2 on the Company’s Form 8-K as filed with the SEC on July 18, 2023.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 7 — STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
Preferred Stock—The Company is authorized to issue 1,000,000 preferred shares with a par value of $0.0001 per share with such designation, rights and preferences as may be determined from time to time by the Company’s Board of Directors. As of September 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023, there were no preferred shares issued or outstanding.
Class A Common Stock—The Company is authorized to issue 100,000,000 shares of Class A common stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share. Holders of the Company’s Class A common stock are entitled to one vote for each share. As of September 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023, there were 613,225 shares of Class A Common Stock issued and outstanding (excluding 1,137,006 shares of Class A Common Stock subject to possible redemption), respectively.
Class B Common Stock—The Company is authorized to issue 10,000,000 shares of Class B common stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share. Holders of Class B common stock are entitled to one vote for each share. As of September 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023, there were 2,300,000 shares of Class B common stock issued and outstanding, respectively.
Only holders of the Class B common stock will have the right to vote on the election of directors prior to the Business Combination. Holders of Class A common stock and holders of Class B common stock will vote together as a single class on all matters submitted to a vote of our stockholders except as otherwise required by law. In connection with our initial business combination, we may enter into a stockholder agreement or other arrangements with the stockholders of the target or other investors to provide for voting or other corporate governance arrangements that differ from those in effect upon completion of our IPO.
The shares of Class B common stock will automatically convert into Class A common stock at the time of a Business Combination, or earlier at the option of the holder, on a one-for-one basis, subject to adjustment. In the case that additional shares of Class A common stock, or equity-linked securities, are issued or deemed issued in excess of the amounts issued in the Initial Public Offering and related to the closing of a Business Combination, the ratio at which shares of Class B common stock shall convert into shares of Class A common stock will be adjusted (unless the holders of a majority of the then-outstanding shares of Class B common stock agree to waive such adjustment with respect to any such issuance or deemed issuance) so that the number of shares of Class A common stock issuable upon conversion of all shares of Class B common stock will equal, in the aggregate, on an as-converted basis, 20% of the sum of the total number of all shares of common stock outstanding upon the completion of Initial Public Offering plus all shares of Class A common stock and equity-linked securities issued or deemed issued in connection with a Business Combination (net of the number of shares of Class A common stock redeemed in connection with a Business Combination), excluding any shares or equity-linked securities issued or issuable to any seller of an interest in the target to us in a Business Combination.
Only holders of the Common stock will have the right to vote on the election of directors prior to the Business Combination. Holders of Common stock will vote together as a single class on all matters submitted to a vote of our stockholders except as otherwise required by law. In connection with our initial business combination, we may enter into a stockholder agreement or other arrangements with the stockholders of the target or other investors to provide for voting or other corporate governance arrangements that differ from those in effect upon completion of our IPO.
Warrants—As of September 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023, there are 9,200,000 Public Warrants outstanding. Public Warrants may only be exercised for a whole number of shares. No fractional warrants will be issued upon separation of the Units and only whole warrants will trade. The Public Warrants will become exercisable on the later of (a) 30 days after the completion of a Business Combination and (b) 12 months from the closing of the Initial Public Offering. The Public Warrants will expire five years after the completion of a Business Combination or earlier upon redemption or liquidation.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 7 — STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT (CONTINUED)
The Company will not be obligated to deliver any shares of Class A common stock pursuant to the exercise of a warrant and will have no obligation to settle such warrant exercise unless a registration statement under the Securities Act covering the issuance of the shares of Class A common stock issuable upon exercise of the warrants is then effective and a current prospectus relating to those shares of Class A common stock is available, subject to the Company satisfying its obligations with respect to registration, or a valid exemption from registration is available. No warrant will be exercisable for cash or on a cashless basis, and the Company will not be obligated to issue any shares to holders seeking to exercise their warrants, unless the issuance of the shares upon such exercise is registered or qualified under the securities laws of the state of residence of the exercising holder, or an exemption from registration is available.
The Company has agreed that as soon as practicable, but in no event later than 15 business days after the closing of a Business Combination, the Company will use its commercially reasonable efforts to file, and within 60 business days following a Business Combination to have declared effective, a registration statement covering the issuance of the shares of Class A common stock issuable upon exercise of the warrants and to maintain a current prospectus relating to those shares of Class A common stock until the warrants expire or are redeemed. Notwithstanding the above, if the Class A common stock is at the time of any exercise of a warrant not listed on a national securities exchange such that it satisfies the definition of a “covered security” under Section 18(b)(1) of the Securities Act, the Company may, at its option, require holders of Public Warrants who exercise their warrants to do so on a “cashless basis” in accordance with Section 3(a)(9) of the Securities Act and, in the event the Company so elects, the Company will not be required to file or maintain in effect a registration statement, but will use its commercially reasonable efforts to register or qualify the shares under applicable blue sky laws to the extent an exemption is not available.
Once the warrants become exercisable, the Company may redeem the outstanding Public Warrants:
| | ● | in whole and not in part; |
| | | |
| | ● | at a price of $0.01 per Public Warrant; |
| | | |
| | ● | upon a minimum of 30 days’ prior written notice of redemption, or the 30-day redemption period to each warrant holder; and |
| | | |
| | ● | if, and only if, the last reported sale price of the Class A common stock equals or exceeds $18.00 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, reorganization, recapitalizations and the like) for any 20 trading days within a 30-trading day period ending on the third trading day prior to the date on which the Company sends the notice of redemption to warrant holders. |
If and when the warrants become redeemable by the Company, the Company may exercise its redemption right even if it is unable to register or qualify the underlying securities for sale under all applicable state securities laws.
If the Company calls the Public Warrants for redemption, as described above, its management will have the option to require any holder that wishes to exercise the Public Warrants to do so on a “cashless basis,” as described in the warrant agreement. The exercise price and number of common stock issuable upon exercise of the Public Warrants may be adjusted in certain circumstances including in the event of a stock dividend, extraordinary dividend or recapitalization, reorganization, merger, or consolidation. However, except as described below, the Public Warrants will not be adjusted for issuances of common stock at a price below its exercise price. Additionally, in no event will the Company be required to net cash settle the Public Warrants. If the Company is unable to complete a Business Combination within the Combination Period and the Company liquidates the funds held in the Trust Account, holders of Public Warrants will not receive any of such funds with respect to their Public Warrants, nor will they receive any distribution from the Company’s assets held outside of the Trust Account with respect to such Public Warrants. Accordingly, the Public Warrants may expire worthless.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 7 — STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT (CONTINUED)
As of September 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023, there are 498,225 Private Placement Warrants outstanding. The Private Placement Warrants are identical to the Public Warrants underlying the Units sold in the Initial Public Offering. The Company accounts for the warrants issued in connection with the Initial Public Offering in accordance with the guidance contained in ASC815-40. Such guidance provides that the warrants are not precluded from equity classification. Equity-classified contracts are initially measured at fair value (or allocated value). Subsequent changes in fair value are not recognized as long as the contracts continue to be classified in equity.
The Private Placement Warrants are identical to the Public Warrants underlying the Units sold in the Initial Public Offering, except that the Private Placement Warrants (including the shares of Class A common stock issuable upon the exercise of the Private Placement Warrants) will not be transferable, assignable or salable until 30 days after the completion of a Business Combination, subject to certain limited exceptions. Additionally, the Private Placement Warrants held by Stifel Venture will not be exercisable more than five years from the commencement of sales of the Initial Public Offering in accordance with FINRA Rule 5110(g)(8)(A).
Rights—Except in cases where the Company is not the surviving company in a business combination, each holder of a right will automatically receive one-tenth (1/10) of one share of Class A common stock upon consummation of the initial business combination. The Company will not issue fractional shares in connection with an exchange of rights. Fractional shares will either be rounded down to the nearest whole share or otherwise addressed in accordance with the applicable provisions of United States law.
The Company accounts for the rights issued in connection with the Initial Public Offering in accordance with the guidance contained in ASC815-40. Such guidance provides that the rights are not precluded from equity classification. Equity-classified contracts are initially measured at fair value (or allocated value). Subsequent changes in fair value are not recognized as long as the contracts continue to be classified in equity.
NOTE 8 — STOCK BASED COMPENSATION
The sale of the Founder Shares to the Company’s director nominees and strategic advisors is in the scope of ASC 718. Under ASC 718, stock-based compensation associated with equity-classified awards is measured at fair value upon the grant date. The Company has assessed the fair value associated with the Founder Shares granted. The fair value of the 500,000 Founder Shares granted to the Company’s officers and directors was $1,150,000 or $2.30 per share (see Note 5). The Founder Shares were granted subject to the following performance condition: (i) the occurrence of a Business Combination. Compensation expense related to the Founder Shares is recognized only when the performance conditions are probable of occurrence under the applicable accounting literature in this circumstance.
As of September 30, 2024, there are 500,000 shares that remain unvested as the Company determined that a Business Combination is not considered probable. Therefore, the remaining fair value of stock-based compensation expense associated with these shares totaling $1,150,000 has not been recognized. Stock-based compensation would be recognized at the date a Business Combination is considered probable (i.e., upon consummation of a Business Combination) in an amount equal to the number of Founder Shares times the grant date fair value per share (unless subsequently modified) less the amount initially received for the purchase of the Founder Shares.
GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 9 — FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
The Public Warrants were valued at $0.05 per warrant at the Initial Public Offering. Significant inputs included a risk-free rate of 3.74%, volatility of 1.5%, probability of business combination of 7%, dividend of $0 and life of 5.88 years.
The Company follows the guidance in ASC 820 for its financial assets and liabilities that arere-measured and reported at fair value at each reporting period, and non-financial assets and liabilities that are re-measured and reported at fair value at least annually. The fair value of the Company’s financial assets and liabilities reflects management’s estimate of amounts that the Company would have received in connection with the sale of the assets or paid in connection with the transfer of the liabilities in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. In connection with measuring the fair value of its assets and liabilities, the Company seeks to maximize the use of observable inputs (market data obtained from independent sources) and to minimize the use of unobservable inputs (internal assumptions about how market participants would price assets and liabilities).
The following table presents information about the Company’s assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value as of September 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 and indicates the fair value hierarchy of the valuation inputs the Company utilized to determine such fair value:
| | | Description | | Level | | September 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Marketable securities held in Trust Account | | | | 1 | | $ | 12,919,725 | | | $ | 55,707,757 | |
NOTE 10 — SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
The Company evaluated subsequent events and transactions that occurred after the balance sheet date through the date that the condensed consolidated financial statements were issued. Based upon this review, or within these unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements, the Company did not identify any subsequent events that would have required recognition or disclosure in the unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements.
On October 23, 2024, the Company amended the terms of the promissory note to allow conversion of up to $1,000,000 into Class B Common Stock of the Company at a price of $10.00 per unit in lieu of cash repayment, effective immediately prior to the Business Combination.
On November 1, 2024, the Company filed a preliminary extension proxy with the SEC for a special meeting of its stockholders to amend its charter and trust agreement to reduce the payment required and extend the date by which the Company is required to complete the business combination from December 22, 2024 until March 22, 2025 by three one-month extensions, provided that the Sponsor (or its affiliates or permitted designees) deposit into the Trust Account an amount equal to the lesser of (x) $60,000 or (y) $0.02 per share for each public share that is not redeemed in connection with the Special Meeting for each one-month extension until March 22, 2025, unless the closing of the Company’s initial business combination has occurred.
NOTE 11. EVENTS UP TO DECEMBER 23, 2024 SUBSEQUENT TO THE DATE THAT THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS WERE AVAILABLE FOR INITIAL ISSUANCE, NOVEMBER 22, 2024
On December 11, 2024, K Wave Media, K Enter, the Company and Merger Sub (the “Parties”) entered into the Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement, which extended the Outside Date for the parties to consummate the closing of the Business Combination from December 22, 2024 to June 22, 2025.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
K Enter Holdings Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying balance sheet of K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2023, and the related statements of operations and comprehensive loss, of changes in stockholders’ equity and of cash flows for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, including the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit of these financial statements in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud.
Our audit included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audit also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers
Seoul, KOREA
March 25, 2024
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2023.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
BALANCE SHEET
| | | December 31,
2023 | |
| Current assets: | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 2,525,682 | |
| Other receivables | | | 70,906 | |
| Convertible debt security | | | 1,006,757 | |
| Deferred transaction costs | | | 1,363,241 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | | 227,416 | |
| Total current assets | | | 5,194,002 | |
| | | | | |
| Investment in equity securities | | | 1,600,000 | |
| Property and equipment, net | | | 33,598 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets, net | | | 95,191 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets, net – related party | | | 72,635 | |
| Other assets, noncurrent | | | 1,705,412 | |
| Other assets, noncurrent – related party | | | 77,500 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | | $ | 8,778,338 | |
| | | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | | |
| Accounts payable | | $ | 294,717 | |
| Accounts payable – related party | | | 16,828 | |
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | | | 2,237,710 | |
| Defined severance benefits, current | | | 2,462 | |
| Lease liabilities, current | | | 60,619 | |
| Lease liabilities, current – related party | | | 55,122 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 2,667,458 | |
| Defined severance benefits, noncurrent | | | 46,691 | |
| Lease liabilities, noncurrent | | | 34,571 | |
| Lease liabilities, noncurrent – related party | | | 17,514 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | 98,776 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | | | 2,766,234 | |
| | | | | |
| STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | | | |
| Series A-1 convertible preferred stock | | | - | |
| Series A convertible preferred stock | | | 355 | |
| Common stock | | | 1,000 | |
| Treasury stock | | | (57 | ) |
| Preferred stock subscription receivable | | | (369,000 | ) |
| Additional paid-in capital | | | 15,238,711 | |
| Accumulated deficit | | | (8,930,946 | ) |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income | | | 72,041 | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | | | 6,012,104 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | $ | 8,778,338 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
| | | For the
period from
January 4, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| Revenue | | $ | 208,704 | |
| Operating cost and expenses | | | | |
| Cost of revenue | | | 207,153 | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | 8,954,316 | |
| Total operating cost and expenses | | | 9,161,469 | |
| Loss from operations | | | (8,952,765 | ) |
| Other income (expense) | | | | |
| Interest income | | | 7,956 | |
| Other income | | | 13,863 | |
| Total other income, net | | | 21,819 | |
| Net loss | | $ | (8,930,946 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | | | | |
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | | | 65,284 | |
| Unrealized gain of available-for-sales | | | 6,757 | |
| Total other comprehensive loss, net | | | 72,041 | |
| Comprehensive loss | | $ | (8,858,905 | ) |
| | | | | |
| Weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding, basic and diluted | | | 76,540 | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share of common stock | | $ | (116.68 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
| | | Series A-1
Convertible
Preferred Stock | | | Series A
Convertible
Preferred Stock | | | Common stock | | | Treasury stock | | | Preferred Stock Subscription | | | Additional Paid-in | | | Accumulated | | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive | | | | |
| | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Receivables | | | Capital | | | Deficit | | | Income | | | Total | |
| Balance, January 4, 2023 (inception) | | | - | | | $ | - | | | | - | | | $ | - | | | | - | | | $ | - | | | | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
| Shares issued for Series A convertible preferred stock, net of issuance costs | | | - | | | | - | | | | 35,484 | | | | 355 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 10,600,609 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 10,600,964 | |
| Shares issued for Series A-1 convertible preferred stock | | | 4,814 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (369,000 | ) | | | 2,888,400 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,519,400 | |
| Shares issued for common stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 100,000 | | | | 1,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,000 | |
| Treasury stock shares acquired | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (12,074 | ) | | | (121 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (121 | ) |
| Shares issued for common stock from the Company’s treasury shares | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 6,353 | | | | 64 | | | | - | | | | 1,749,702 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,749,766 | |
| Net loss | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (8,930,946 | ) | | | | | | | (8,930,946 | ) |
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 65,284 | | | | 65,283 | |
| Unrealized gain of available-for-sales | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 6,757 | | | | 6,757 | |
| Balance, December 31, 2023 | | | 4,814 | | | $ | - | | | | 35,484 | | | $ | 355 | | | | 100,000 | | | $ | 1,000 | | | | (5,721 | ) | | $ | (57 | ) | | $ | (369,000 | ) | | $ | 15,238,711 | | | $ | (8,930,946 | ) | | $ | 72,041 | | | $ | 6,012,104 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
| | | For the
period from
January 4, 2023
(inception) through
December 31,
2023 | |
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | | |
| Net loss | | $ | (8,930,946 | ) |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash used in operations: | | | | |
| Share-based compensation | | | 1,749,741 | |
| Severance benefits | | | 48,559 | |
| Amortization of operating lease right-of-use assets | | | 36,638 | |
| Amortization of operating lease right-of-use assets – related party | | | 27,957 | |
| Depreciation expense | | | 4,198 | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | |
| Other receivables | | | (70,070 | ) |
| Deferred transaction costs | | | (212,079 | ) |
| Prepaid and other current assets | | | (224,895 | ) |
| Other assets, noncurrent | | | (1,684,800 | ) |
| Other assets, noncurrent – related party | | | (76,563 | ) |
| Accounts payable | | | 292,354 | |
| Accounts payable – related party | | | 16,625 | |
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | | | 1,085,336 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | (36,638 | ) |
| Lease liabilities – related party | | | (27,957 | ) |
| CASH USED IN OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | (8,002,540 | ) |
| | | | | |
| CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | | |
| Purchase of property and equipment | | | (37,390 | ) |
| Collection of short-term loans | | | 1,530,499 | |
| Advances of short-term loans | | | (1,530,499 | ) |
| Purchase of convertible debt security | | | (1,000,000 | ) |
| Purchase of investment in equity securities | | | (1,600,000 | ) |
| CASH USED IN INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | (2,637,390 | ) |
| | | | | |
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES | | | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of Series A-1 convertible preferred stock | | | 2,519,400 | |
| Proceeds from issuance of Series A convertible preferred stock, net of issuance costs | | | 10,600,964 | |
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock | | | 1,000 | |
| Purchase of treasury shares | | | (121 | ) |
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock from treasury shares | | | 25 | |
| CASH PROVIDED BY FINANCING ACTIVITIES | | | 13,121,268 | |
| | | | | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash | | | 44,345 | |
| | | | | |
| Change in cash and cash equivalents | | | 2,525,682 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period | | | - | |
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of period | | $ | 2,525,682 | |
| | | | | |
| Cash paid for interest | | $ | - | |
| Cash paid for taxes | | $ | - | |
| | | | | |
| Supplemental disclosure of noncash investing and financing activities: | | | | |
| Operating right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for lease obligations | | $ | 129,236 | |
| Operating right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for lease obligations – related party | | $ | 98,613 | |
| Deferred transaction costs included in Accrued Expenses | | $ | 1,151,162 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
1. NATURE OF OPERATIONS
K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “Company”), a Delaware corporation, was formed on January 4, 2023 to become a leading tech and intellectual property (“IP”) based diversified entertainment company. To fulfill this vision, the Company established an internal Korean drama production team and entered into equity purchase agreements to acquire a controlling equity interest in six separate Korean entertainment companies (collectively, the “Six Korean Entities”) in order to combine initial capabilities believed to serve as the foundation for the Company’s growth – content production, content merchandising, and content investment. The Six Korean Entities include one Korean content-specialized private equity firm, one Korean drama production company, three Korean movie production companies, and one IP merchandising company.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of Accounting: The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). References to GAAP in the accompanying financial statements are to the Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”).
Foreign Currency: The U.S. dollar is the reporting currency of the Company. The functional currency of the Company’s domestic branch and international branch is the U.S. dollar and Korean Won, respectively. The functional currencies are the local currencies used in the primary economic environment for each respective branch. Remeasurement gains and losses from transactions that are not denominated in the functional currency are recorded as other income (expense) in the statement of operations and comprehensive loss. The Company recognized realized gains of $15,979 on foreign currency transactions and balances within other income on the accompanying statement of operations and comprehensive loss for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023.
Assets and liabilities of the international branch are translated into U.S. dollars at the exchange rate in effect at the balance sheet date. Revenue and expenses are translated at average exchange rates in effect during the period. Foreign currency translation gains and losses are recorded in the cumulative translation adjustment account, which is a separate component of other comprehensive income.
Use of Estimates: The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make certain estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses in the financial statements and accompanying notes. The Company’s most significant estimates and judgments involve the valuation of share-based compensation and convertible debt security, including the fair value of common stock. Management bases its estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions believed to be reasonable, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities. Actual results could differ from those estimates, and such differences could be material to the Company’s financial statements.
Segment Information: ASC 280, Segment Reporting (“ASC 280”), defines operating segments as components of an enterprise where discrete financial information is available that is evaluated regularly by the chief operating decision-maker (“CODM”) in deciding how to allocate resources and in assessing performance. The Company operates as a single operating segment. The Company’s CODM is the chief executive officer, who has ultimate responsibility for the operating performance of the Company and the allocation of resources. The CODM uses cash flows as the primary measure to manage the business and does not segment the business for internal reporting or decision making.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
Cash and Cash Equivalents: Cash and cash equivalents comprise cash in bank which are subject to an insignificant risk of changes in value. The Company considers all short-term investments with an original maturity of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents. The Company did not have any cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023.
Fair Value Measurements: ASC 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures (“ASC 820”), clarifies that fair value is an exit price, representing the amount that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants. As such, fair value is a market-based measurement that should be determined based upon assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability. As a basis for considering such assumptions, ASC 820 establishes a three-tier fair value hierarchy, which prioritizes the inputs used in measuring fair value as follows:
Level 1: Quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets that the Company can assess at the measurement date.
Level 2: Significant other observable inputs other than level 1 prices such as quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities, quoted prices in markets that are not active or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market date.
Level 3: Significant unobservable inputs that reflect the Company’s own assumptions about the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability.
An asset’s or liability’s fair value measurement level within the fair value hierarchy is based on the lowest level of any input that is significant to the fair value measurement. Valuation techniques used need to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs.
Assets and liabilities measured at fair value are based on one or more of the following three valuation techniques noted in ASC 820:
| | ● | Market approach: Prices and other relevant information generated by market transactions involving identical or comparable assets and liabilities. |
| | | |
| | ● | Cost approach: Amount that would be required to replace the service capacity of an asset (replacement cost). |
| | | |
| | ● | Income approach: Techniques to convert future amounts to a single present value amount based upon market expectations (including present value techniques, option pricing, and excess earning models) |
The Company believes its valuation methods are appropriate and consistent with other market participants, however the use of different methodologies or assumptions to determine the fair value of certain financial instruments could result in a different fair value measurement at the reporting date.
The Company’s financial instruments with a carrying value that approximates fair value consists of cash, other receivables, accounts payable, accrued expenses and other current liabilities because of the short-term nature of these instruments. The Company’s financial assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis consist of the convertible debt security (see Note 5 and Note 10).
Other Receivables: Other receivables consists entirely of a refund for value add tax from the government, which is expected to be received within the next 12 months.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
Convertible Debt Security: Convertible debt security consists of a convertible bond purchased from a private company and is considered an available for sale debt securities with a private company that is recorded at fair value (see Note 5).
Prepaid Expenses and Other Current Assets: Prepaid expenses and other current assets consist entirely of advance payments to vendors which are expected to be recognized or realized within the next 12 months.
Deferred Transaction Costs: Commissions, legal fees and other costs that are direct and incremental costs related to a contemplated transaction are capitalized as deferred transaction costs until the consummation of the transaction. The costs will be reclassified to additional paid-in capital upon the closing of the transaction. If the transaction does not close, these transaction costs will be written off to general and administrative expenses at such time the transaction is determined to be unsuccessful. As of December 31, 2023, deferred transaction costs related to the Merger Agreement (see Note 3) totaled $1,363,241.
Investment in Equity Securities: Investments in equity securities that have a readily determinable fair value are reported at fair value. Changes in fair value between accounting periods are recorded in other income (expense) in the statement of operations and comprehensive loss. The Company has elected to account for investments in equity securities that do not have a readily determinable fair value under the measurement alternative permitted by ASC 321, Investments in Equity Securities (“ASC 321”). Under the measurement alternative, investments in equity securities that do not have a readily determinable fair value are recorded at cost, less impairment. The investment in equity securities without readily determinable fair values will be subsequently remeasured to fair value when observable price changes occur as of the date the transaction occurred or its impairment, with all changes in fair value reflected as a component of other income (expense) on the accompanying statement of operations and comprehensive loss. Realized gains or losses upon sale are recorded in other income (expense) in the statement of operations and comprehensive loss.
Property and Equipment, Net: Purchased and constructed property and equipment is recorded at cost. Property and equipment consists of office equipment and is depreciated using the straight-line method over a five year period.
Other Assets, Noncurrent: Other assets, noncurrent include security deposits on the Company’s office leases, capitalized implementation costs associated with the Company’s cloud computing arrangement, advances to production companies for content development, and advances to writers for content development which are not expected to be recognized or realized within the next 12 months.
The Company measures the capitalized implementation costs associated with its cloud computing arrangements for its accounting software at cost in accordance with ASC 350-40, Internal-use software (“ASC 350-40”), and will amortize these costs over the remaining life of the three-year hosting arrangement at the time the cloud computing arrangement is placed into service. Options to extend or terminate the hosting arrangement that are reasonably certain to be exercised will be included in the determination of the useful life at the time the cloud computing arrangement is placed into service.
The Company advanced money to additional production companies to fund the planning and development costs for the production of dramas. Certain contracts with production companies permit the Company to earn a set percentage of the profit of the drama. Other contracts with production companies require a separate agreement to be entered into that will define the Company’s role with the production of the drama (e.g., co-producer) as well as its investment stake in the drama. These factors will then be used to allocate the profits of the drama between the Company and the production company, at which point the recognition pattern of the costs will be determined. To the extent that the production of a drama developed using this advance is not approved, the planning and development costs paid by the Company will be reclassified to the statement of operations and comprehensive loss in the period the decision is made. Certain contracts permit the advance to be returned to the Company if a separate agreement is not entered into that will define the Company’s role with the production of the drama.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
The Company advanced money to writers to fund the writing of drama scripts for a set number of episodes for a set number of dramas. Payments are owed to the writers based on achievement of milestones which may include (1) contract execution (2) start of filming (3) filming completion (4) broadcasting schedule confirmation (5) approval to write a subsequent draft of a script (6) approval of a script. Certain contracts with writers permit a revenue share of the profit distribution of the drama.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets: The Company reviews long-lived assets, including property and equipment, for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that an asset group’s carrying amount may not be recoverable. The Company conducts its long-lived asset impairment analysis in accordance with ASC 360-10, Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets (“ASC 360-10”), which requires the Company to group assets and liabilities at the lowest level for which identifiable cash flows are largely independent of the cash flows of other assets and liabilities and evaluate the asset group against the sum of the undiscounted future cash flows. If the undiscounted cash flows do not indicate the carrying amount of the asset group is recoverable, an impairment charge is measured as the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset group exceeds its fair value. The Company did not record impairment losses for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023.
Leases: The Company’s determination of whether an arrangement contains a lease is based on an evaluation of whether the arrangement conveys the right to use and control specific property or equipment. The Company leases office facilities under operating leases primarily having initial terms of two years.
Leases are classified as either finance leases or operating leases. A lease is classified as a finance lease if any one of the following criteria are met: the lease transfers ownership of the asset by the end of the lease term, the lease contains an option to purchase the asset that is reasonably certain to be exercised, the lease term is for a major part of the remaining useful life of the asset or the present value of the lease payments equals or exceeds substantially all of the fair value of the asset. A lease is classified as an operating lease if it does not meet any one of these criteria.
The Company recognizes a lease liability and a right of use (“ROU”) asset at the commencement date of each lease. Lease payments may be fixed or variable; however, only fixed payments or in-substance fixed payments are included in the Company’s lease liability calculation. Lease agreements may include options to extend or terminate the lease which are included in the measurement of the lease liability when it is reasonably certain that the option will be exercised.
The lease liability is initially and subsequently recognized based on the present value of the contract’s fixed future lease payments. The discount rate used to calculate the present value is the implicit rate, if it is readily determinable, or the Company’s incremental borrowing rate. The Company’s incremental borrowing rate for a lease is the rate of interest it would have to pay on a collateralized basis to borrow an amount equal to the lease payments under similar terms and in a similar economic environment. For all leases entered into during the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, the ICE BofA BBB US Corporate Index Effective Yield in effect on the lease commencement date was used as the incremental borrowing rate.
Variable lease payments, such as periodic adjustments for inflation, reimbursement of real estate taxes, any variable common area maintenance and any other variable costs associated with the leased property, are expensed as incurred on the accompanying statement of operations and comprehensive loss and future variable rent obligations are not included within the lease liabilities on the balance sheet.
The depreciable life of right of use assets and leasehold improvements are limited by the expected lease term. None of the Company’s leases contain any material residual value guarantees or restrictive covenants.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
The Company accounts for fixed lease and non-lease components of a lease as a single lease component. Leases with an initial term of 12 months or less are not recorded on the balance sheet and are recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term within general administrative expenses on the accompanying statement of operations and comprehensive loss.
Rent expense for the Company’s operating leases, which may have escalating rentals over the term of the lease and may include rent holidays, is recorded on a straight-line basis over the initial lease term and those renewal or termination periods that are reasonably certain that the option to extend or terminate will be exercised. Payments received from landlords as incentives for leasehold improvements are recorded as a reduction of the operating lease right-of-use asset and amortized on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease as a reduction of rent expense.
Defined Severance Benefits: The Company accrues severance benefits for employees of Korean branch. Pursuant to the Employee Retirement Benefit Security Act of Korea, eligible employees with one or more years of service are entitled to severance payments upon the termination of their employment based on their length of service and pay rate.
The Company recognizes the defined severance benefits obligation in the balance sheets with a corresponding adjustment to operating expenses. The obligations are measured annually, or more frequently if there is a remeasurement event, based on the Company’s measurement date utilizing various actuarial assumptions and methodologies. The Company uses certain assumptions including, but not limited to, the selection of the: (i) discount rates; (ii) salary growth rates; and (iii) certain employee-related factors, such as turnover, retirement age and mortality. The Company reviews actuarial assumptions and make modifications to the assumptions based on current rates and trends when appropriate.
Revenue: The Company is a holding company which operates as a drama production studio. The Company provides the service for planning, producing, and selling the television programs such as dramas. The Company recognizes revenue using the input method for performance obligations to be satisfied over time, as the customers receive and use the benefits simultaneously. This determination is based on the actual costs incurred relative to the total expected costs. Payment for services is collected within a short period following transfer of control or commencement of delivery of services, as applicable.
Share-Based Compensation: The Company accounts for its share-based compensation awards in accordance with ASC 718, Compensation – Stock Compensation (“ASC 718”), under which share based payments that involve the issuance of shares of common stock from the Company’s treasury shares to employees and nonemployees and meet the criteria for equity-classified awards are recognized in the financial statements as share-based compensation expense based on the fair value of common stock on the date of issuance. The inputs and assumption used in determining the fair value of a share of common stock are management’s best estimates, but the estimates involve inherent uncertainties and the application of management judgment (see Note 7). Share-based compensation is recognized in the period the shares of common stock are issued from the Company’s treasury shares as the awards do not have a vesting period for employees or a specified contract period for nonemployees.
Other Comprehensive Loss: Other comprehensive loss reflects gains and losses that are recorded as a component of stockholders’ equity and are excluded from net loss and consists of foreign currency translation gains and losses related to the translation of the Company’s functional currency into its reporting currency.
Tax Incentives: In the normal course of business, the Company, or a third-party producing content on the Company’s behalf, may qualify for tax incentives through eligible spend on productions. The accounting for tax incentives is dependent on the particular type of incentive, including the nature of the benefit and the location where the incentive is earned. In general, tax incentives are realized as cash receipts and may be received prior to or after a title was launched. Tax incentives are generally accounted for as a reduction to the cost basis of the Company’s content assets and reduces cost of revenue when the content is sold on the statement of operations and comprehensive loss. For the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, there were no tax incentives received.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
Income Taxes: The Company accounts for income taxes in accordance with authoritative guidance, which requires the use of the asset and liability method. Under this method, deferred income tax assets and liabilities are determined based upon the difference between the financial statement carrying amounts and the tax basis of assets and liabilities and are measured using the enacted tax rate expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which the differences are expected to be reversed.
Significant judgment is required in determining any valuation allowance recorded against deferred tax assets. In assessing the need for a valuation allowance, the Company considers all available evidence, including past operating results, estimates of future taxable income, and the feasibility of tax planning strategies.
In the event that the Company changes its determination as to the amount of deferred tax assets that can be realized, the valuation allowance is adjusted with a corresponding impact to the provision for income taxes in the period in which such determination is made.
The Company is required to evaluate the tax positions taken when preparing its tax returns to determine whether tax positions are “more-likely-than-not” of being sustained by the applicable tax authority. Tax benefits of positions not deemed to meet the “more-likely-than-not” threshold would be recorded as a tax expense in the current year. The amount recognized is subject to estimate and management judgment with respect to the likely outcome of each uncertain tax position. The amount that is ultimately sustained for an individual uncertain tax position or for all uncertain tax positions in the aggregate could differ from the amount that is initially recognized.
Earnings (Loss) per Share: Basic earnings (loss) per share (“EPS”) is computed using the two-class method as the Company had issued securities, other than common stock, that contractually entitle the holds to participate in dividends and earnings. Under the two-class method, all securities that meet the definition of a participating security, irrespective of whether the securities are convertible, nonconvertible, or potential common stock securities, are included in the computation of basic EPS. The two-class method requires earnings for the period to be allocated between common stock and participating securities based upon their respective rights to receive distributed and undistributed earnings.
Under the two-class method, for period with net income, basic net income per common share is computed by dividing the net income attributable to common stockholders by the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Net income attributable to common stockholders is computed by subtracting from net income the portion of current period earnings that the participating securities would have been entitled to receive pursuant to their dividend rights had all of the period’s earnings been distributed. No such adjustment to earnings is made during periods with a net loss, as the holders of the participating securities have no obligation to fund losses.
The number of shares used to calculate diluted loss per share of common shares attributable to common shareholders is the same as the number of shares used to calculate basic loss per share of common shares attributable to common shareholders for the period presented because there were no potentially dilutive securities outstanding during the period.
The earnings (loss) per share presented in the statement of operations and comprehensive loss is based on the following for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023:
| | | Common Stock | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share: | | | | |
| Numerator | | | | |
| Allocation of net loss | | $ | (8,930,946 | ) |
| Denominator: | | | | |
| Basic and diluted weighted average number of shares outstanding | | | 76,540 | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share | | $ | (116.68 | ) |
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
Emerging Growth Company: The Company is expected to be an “emerging growth company”, as defined in Section 2(a) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, (the “Securities Act”), as modified by the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (the “JOBS Act”). The JOBS Act provides that an emerging growth company can take advantage of an extended transition period for complying with new or revised accounting standards. Thus, an emerging growth company can delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. The Company has elected to take advantage of the extended transition period to comply with new or revised accounting standards and to adopt certain of the reduced disclosure requirements available to emerging growth companies. As a result of the accounting standards election, the Company will not be subject to the same implementation timeline for new or revised accounting standards as other public companies that are not emerging growth companies. At times, the Company may elect to early adopt a new or revised accounting standard.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements, not yet adopted: In October 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-06, Disclosure Agreements - Codification Amendments in Response to the SEC’s Disclosure Update and Simplification Initiative (ASU 2023-06). This amendment will impact various disclosure areas, including the statement of cash flows, accounting changes and error corrections, earnings per share, debt, equity, derivatives, and transfers of financial assets. The amendments in ASU 2023-06 will be effective on the date the related disclosures are removed from Regulation S-X or Regulation S-K by the SEC, and will no longer be effective if the SEC has not removed the applicable disclosure requirement by June 30, 2027. Early adoption is prohibited. We are currently evaluating the impacts of the amendment on our disclosures.
In November 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-07, Segment Reporting (Topic 280) (“ASC 280”): Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures (“ASU 2023-07”), that would enhance disclosures for significant segment expenses for all public entities required to report segment information in accordance with ASC 280. ASC 280 requires a public entity to report for each reportable segment a measure of segment profit or loss that its chief operating decision maker (“CODM”) uses to assess segment performance and to make decisions about resource allocations. The amendments in ASU 2023-07 improve financial reporting by requiring disclosure of incremental segment information on an annual and interim basis for all public entities to enable investors to develop more useful financial analyses. Currently, Topic 280 requires that a public entity disclose certain information about its reportable segments. For example, a public entity is required to report a measure of segment profit or loss that the CODM uses to assess segment performance and make decisions about allocating resources. ASC 280 also requires other specified segment items and amounts such as depreciation, amortization and depletion expense to be disclosed under certain circumstances. The amendments in ASU 2023-07 do not change or remove those disclosure requirements. The amendments in ASU 2023-07 also do not change how a public entity identifies its operating segments, aggregates those operating segments, or applies the quantitative thresholds to determine its reportable segments. The amendments in ASU 2023-07 are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. Early adoption is permitted. A public entity should apply the amendments in ASU 2023-07 retrospectively to all prior periods presented in the financial statements. We are currently evaluating the impact of this standard on our financial statements and related disclosures.
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures (“ASU 2023-09”). ASU 2023-09 is intended to enhance the transparency and decision usefulness of income tax disclosures. The amendments in ASU 2023-09 address investor requests for enhanced income tax information primarily through changes to the rate reconciliation and income taxes paid information. ASU 2023-09 will be effective for us in the annual period beginning October 1, 2025, though early adoption is permitted. We are still evaluating the presentational effect that ASU 2023-09 will have on our financial statements, but we expect considerable changes to our income tax footnote.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
3. BUSINESS COMBINATIONS
Merger Agreement with Global Star Acquisition Inc.
On June 15, 2023, and as amended on March 11 2024, the Company entered into a merger agreement (the “Merger Agreement”) with Global Star Acquisition Inc., a Delaware corporation, (“Global Star”) and GLST Merger Sub Inc., a Delaware corporation and wholly owned sub of Global Star, (“Merger Sub”). The Merger Agreement provides that Global Star will merge with and into K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (“K Wave Media” or “PubCo”), with PubCo continuing as the surviving publicly traded entity (the “Reincorporation Merger”). One day following the Reincorporation Merger, Merger Sub will be merged with and into K Enter, with K Enter the surviving corporation and resulting in K Enter being a wholly owned subsidiary of PubCo (“Acquisition Merger”).The Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger are collectively referred to herein as the “Business Combination”.
Key terms of the Merger Agreement include, but are not limited to, the following:
| ● | The consideration for Reincorporation Merger is expected to be settled by issuing: (a) one share of PubCo’s ordinary shares in exchange for each share of Global Star Class A common stock that is outstanding as of the effective time of the Reincorporation Merger and (b) one warrant to purchase one of PubCo’s ordinary shares at an exercise price of $11.50 in exchange for each share of each Global Star warrant that is outstanding as of the effective time of the Reincorporation Merger. |
| ● | Certain of Global Star’s stockholders have provided written consent, pursuant to which, among other things, such stockholders have approved the Merger Agreement and the Reincorporation Merger. Each issued and outstanding share of Global Star ‘s Class A common stock and each issued and outstanding Global Star right on an as-converted basis, will automatically be cancelled and converted into an equal number of shares of the PubCo’s ordinary shares in accordance with the Merger Agreement and each Global Star warrant shall be exchanged for a PubCo warrant. |
| ● | The aggregate consideration for the Acquisition Merger is $590,000,000 and is expected to be settled by issuing 59,000,000 shares of PubCo’s ordinary shares in exchange for an estimated 196,536 shares of Company common stock, including the shares of the Company’s common stock underlying the Company’s outstanding Series A and Series A-1 preferred stock at an exchange rate of approximately 300.199 shares of the Company’s common stock on an as converted basis for each ordinary share of the PubCo (the “Conversion Ratio”) at the time of the Acquisition Merger. |
| ● | Certain of the Company’s stockholders have provided written consent, pursuant to which, among other things, such stockholders have approved the Merger Agreement and the Acquisition Merger. Each issued and outstanding share of the Company’s common stock and each issued and outstanding share of convertible preferred stock on an as-converted basis will automatically be cancelled and converted into the right to receive the number of shares of the PubCo’s ordinary shares equal to the Conversion Ratio in accordance with the Acquisition Merger. |
| ● | The Merger Agreement is subject to the approval by the stockholders of the Company and Global Star. Holders of Global Star’s Class A Common Stock will have the opportunity to redeem their shares of Global Star Class A Common Stock for cash in connection with the Business Combination. |
In certain circumstances, including if the Merger Agreement has not been consummated by June 22, 2024, either party may elect to terminate the Merger Agreement.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
Acquisitions of Controlling Equity Interests in the Six Korean Entities
During March 2023, and as amended in December 2023, the Company entered into an equity purchase agreement with the owner of Play Company Corp (“Play Company”) to acquire 100% of the outstanding shares of common stock in exchange for 163,732,016,220 Korean Won ($126,828,676 at December 31, 2023), payable through the issuance of the shares of the Company’s common stock totaling 127,498,912,820 Korean Won ($98,762,104 at December 31, 2023) and in exchange for cash totaling 36,233,103,400 Korean Won ($28,066,573 at December 31, 2023). Additional payments in cash will be made to the owner of Play Company if the annual average net profit for fiscal years from 2023 to 2025 reaches specified thresholds, with payments due to the owner of Play Company on January 31, 2027 and January 31, 2028.
An additional payment in cash may be owed to the owner of Play Company if the shares of PubCo that shares of the Company’s common stock convert to at closing of the Acquisition Merger are sold during the three-month period (the “Sale Period”) following the six-month lock-up period of the newly issued shares of PubCo at a per share price less than the per-share value at closing of the Acquisition Merger for the shortfall in share price. The amount to be paid will be reduced by (i) any gains from the sale of shares of PubCo by the owner of Play Company between the end of the Sale Period and December 31, 2026 and (ii) any unrealized gain as of December 31, 2026 for the shares of PubCo that remain held by the owner of Play Company (calculated as the number of remaining shares of PubCo times the difference of (i) the average closing price of PubCo from December 1, 2026 to December 31, 2026 and (ii) the per-share value of PubCo at the closing of the Acquisition Merger).
During March 2023, and as amended in December 2023, the Company entered into an equity purchase agreement with the owners of Solaire Partners, LLC (“Solaire Partners”) to acquire 95% of the outstanding shares of common stock in exchange for shares of the Company’s common stock totaling 14,250,000,000 Korean Won ($11,038,212 at December 31, 2023).
During April 2023, and as amended in December 2023, the Company entered into an equity purchase agreement with the owners of Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd (“Anseilen”) to acquire 51% of the outstanding shares of common stock in exchange for shares of the Company’s common stock totaling 7,700,000,400 Korean Won ($5,964,508 at December 31, 2023).
During April 2023, and as amended in December 2023, the Company entered into an equity purchase agreement with the owner of Apeitda Co. Ltd (“Apeitda”) to acquire 51% of the outstanding shares of common stock in exchange for shares of the Company’s common stock totaling 15,300,000,000 Korean Won ($11,851,553 at December 31, 2023).
During April 2023, and as amended in December 2023, the Company entered into an equity purchase agreement with the owners of Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd. (“Bidangil”) to acquire 51% of the outstanding shares of common stock in exchange for shares of the Company’s common stock totaling 20,400,000,000 Koren Won ($15,802,071 at December 31, 2023).
During April 2023, and as amended in December 2023, the Company entered into an equity purchase agreement with the owner of The LAMP Co., Ltd. (“Lamp”) to acquire 51% of the outstanding shares of common stock in exchange for shares of the Company’s common stock totaling 30,600,000,000 Korean Won ($23,703,107 at December 31, 2023).
During April 2023, the Company entered into an equity purchase agreement with the owners of First Virtual Lab Inc.(“First Virtual”) to acquire 51% of the outstanding shares of common stock and preferred stock in exchange for shares of the Company’s common stock totaling 25,500,000,000 Korean Won ($19,752,589 at December 31, 2023). However, the Company entered into the termination agreement during March 2024, which terminated all agreements entered into in connection with the original equity purchase agreement.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
The number of shares of the Company’s common stock to be issued to the sellers of the Six Korean Entities at closing of the respective transactions will be adjusted by changes in exchange rates as the share purchase agreements are denominated in Korean Won and the Company’s equity transactions are denominated in U.S. Dollar.
In certain circumstances, including prior to the closing of the Merger Agreement and if the shares of PubCo, excluding the shares subject to a lock-up on the Nasdaq market, remain not issued or registered sixty days after the shareholder vote approving the merger, either party may elect to terminate the equity purchase agreements.
4. REVENUE
Details of total revenue was as follows:
| Revenue: | | | |
| Media production | | $ | 208,704 | |
| Geographic information: | | | |
| Korea | | $ | 208,704 | |
The Company’s total revenue has derived from sales to a single customer.
5. CONVERTIBLE DEBT SECURITY
During August 2023, the Company purchased a $1,000,000 convertible bond from Prototype Groupe, Inc. (“Prototype Groupe”). The convertible bond is due and payable on demand after August 10, 2024 and bears interest at a fixed rate equal to the Applicable Federal Rate for short term loans, which as of the date of the bond was 4.96%.
At the Company’s option, at any time prior to payment in full of the principal amount and all accrued interest, the convertible bond can be converted into such number of shares of common stock of Prototype Groupe equal to the entire principal amount of the convertible bond and all accrued and unpaid interest thereon, divided by $7.40 per share in case the pre-money valuation of Prototype Groupe shall meet or exceed $94,800,000. In the event the pre-money valuation is below $94,800,000, the conversion price shall be proportionally reduced.
If the convertible bond is not repaid or converted through the Company’s voluntary election and Prototype Groupe issues and sells shares of its equity securities before the maturity date resulting in gross proceeds of $10,000,000 (excluding the conversion of this bond), then at any time on or after the maturity date, Prototype Groupe shall have the option to (a) repay all outstanding principal and accrued unpaid interest of the convertible bond or (b) convert all or any portion of the outstanding principal and accrued unpaid interest of the convertible bond into such number of its common shares equal to the principal amount and all accrued unpaid interest thereon to be converted divided by the conversion price.
6. INVESTMENT IN EQUITY SECURITIES
During July 2023, the Company purchased 160,000 shares of Global Star Class B Common Stock (the “Founder Shares”) for an aggregate purchase price of $1,600,000 from Global Star Acquisition 1, LLC, the sponsor of Global Star (the “Sponsor”). The Company’s investment in the Founder Shares is recorded at cost minus impairment and adjusted for changes in observable prices.
As of December 31, 2023, there were no indicators of impairment and for the period between the date of acquisition and December 31, 2023, there were no observable price changes or sales of Founder Shares.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
7. STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
The Company was authorized to issue 100,000 shares of common stock at a par value of $0.01 when it was formed on January 4, 2023. The Company amended its certificate of incorporation on May 31, 2023 and again on August 31, 2023 in order to increase the shares of common stock it is authorized to issue to 10,000,000 shares of common stock at a par value of $0.0001 per share and 1,000,000 shares of preferred stock at a par value of $0.0001 per share, of which 45,000 shares have been designated as Series A Convertible Preferred Stock (“Series A”) and 15,000 shares have been designated as Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock (“Series A-1”) by the board of directors (the “Board”).
Common Stock: During January 2023, the Company issued 100,000 shares of common stock at a par value of $0.01 in exchange for proceeds of $1,000. As of December 31, 2023, 100,000 and 94,279 shares of common stock were issued and outstanding, respectively and the Company had reserved 40,298 shares of common stock for the conversion of Series A and Series A-1.
Convertible preferred stock: During the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, the Company issued shares of Series A as follows:
| | | Shares | | | Contracted
Gross proceeds | |
| May 2023 | | | 7,670 | | | $ | 2,271,884 | |
| June 2023 | | | 21,147 | | | | 6,344,100 | |
| September 2023 | | | 6,667 | | | | 2,000,000 | |
| Total | | | 35,484 | | | $ | 10,615,984 | |
During the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, the Company issued shares of Series A-1 as follows:
| | | Shares | | | Contracted
Gross proceeds | |
| August 2023 | | | 3,258 | | | $ | 1,954,800 | |
| September 2023 | | | 941 | | | | 564,600 | |
| Total | | | 4,199 | | | $ | 2,519,400 | |
During October 2023, the Company entered into an agreement to issue 615 shares of Series A-1 for gross proceeds of $369,000. If any founding member shareholder(s) owning together more than 20% of the Company decide to sell its shares, the investor was provided the right, but not an obligation, to participate in the relevant sale along with the founding member shareholder(s) with the identical terms and conditions given to the lead seller. As of the date these financial statements were issued, the investor has not yet transferred consideration for this agreement to the Company.
The rights, preferences, privileges and restrictions for Series A and Series A-1 (collectively, “Preferred Stock”) are as follows:
Dividends: The holders of Series A and Series A-1 are entitled to receive non-cumulative dividends at a rate of $3.00 and $6.00, respectively, as adjusted, per annum, payment of which is due only upon a deemed liquidation event. If any dividend on any share of common stock is paid, such dividend will be distributed among all holders of common stock and Preferred Stock in proportion to the number of shares of common stock into which the Preferred Stock shares may be converted. Dividends are payable when and if declared by the Board out of any assets legally available. No dividends have been declared or paid as of December 31, 2023.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
Conversion: Series A and Series A-1 are convertible into common stock at the option of the holder, according to a conversion ratio, subject to adjustment for stock splits, stock dividends, combinations, recapitalizations or the like ($300.00 and $600.00 per share, respectively, as of December 31, 2023). In the event of any subsequent capital raise involving the issuance of common stock, preferred stock or other equity-linked securities issued at a lower valuation than the Series A, a discount of 30% will apply to the conversion price of the Series A shares outstanding as of December 31, 2023.
Upon (i) the completion of a qualifying initial public offering that results in aggregate gross proceeds of at least $30,000,000 to the Company, (ii) the closing of a transaction or series of related transaction by merger, acquisition or other business combination involving the Company and a publicly traded special purpose acquisition company or other similar entity or (iii) vote or written consent of the majority of the then outstanding shares of Preferred Stock, all of the shares of Preferred Stock will be automatically converted into shares of common stock.
Redemption: The Preferred Stock are not mandatorily redeemable.
Voting: The Preferred Stock are given rights to vote for such matters as follows:
| i) | Electing directors to the board |
| ii) | Approving a merger of acquisition |
| iii) | Approving a stock compensation plan |
| iv) | Executive salaries and benefits |
| v) | Fundamental corporate structure changes, among other things |
Liquidation: In the event of any liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company, either voluntarily or involuntarily, the holders of Series A and Series A-1 are entitled to receive, on a pari passu basis, prior and in preference to any distribution to the holders of common stock, the greater of (i) an amount equal to $300.00 and $600.00 per share, respectively, as adjusted for stock splits, combinations, recapitalizations or the like, plus all accrued and unpaid dividends, or (ii) the amount that would be payable if the Preferred Stock were converted to common stock immediately prior to a liquidation or dissolution event. If the proceeds of such an event are insufficient to permit the full liquidation payment, the entire proceeds legally available for distribution will be distributed ratably on an equal basis among the holders of Preferred Stock in proportion to the preferential amount each such holder is otherwise entitled to receive. Any amounts remaining after such distribution will be distributed pro rata to the holders of common stock.
Protection Provisions: The holders of Series A and Series A-1 have certain protective provisions that permit the holders of Series A and Series A-1 the right of first refusal in the event the Company plans to raise additional capital that could cause potential dilution for the Series A and Series A-1 holder, where one investor has a minimum 10 calendar day notice period and all other investors have a minimum 15 day notice period.
Treasury Stock: During the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, 12,074 shares of common stock were repurchased from a shareholder for gross proceeds totaling $121 and 6,353 of shares of common stock were issued to employees and nonemployees, from the Company’s treasury shares, for gross proceeds totaling $64 (See Note 8). There were no service, market or performance conditions associated with the shares of common stock that were issued from the Company’s treasury shares, resulting in the employee and nonemployee obtaining the full benefits of a common stock shareholder upon the date of the issuance.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
The employment agreements for the employees issued shares of common stock from the Company’s treasury shares provide a restricted period during which the employees are prohibited from selling the shares of common stock and a clawback feature that requires the shares to be transferred back to the Company for no consideration if certain contingent events occur in the future. One of the employment agreements provides the employee the option of transferring shares back to the Company or paying a fee to the Company of 3,750,000,000 Korean Won ($2,904,793 at December 31, 2023).
The period during which employees are restricted from selling their shares was defined in their employment agreements and range from either six months from the Closing of the Acquisition Merger (See Note 3) for 1,932 of the shares of common stock issued from the Company’s treasury shares to one employee or two years from the date of employment (June 1, 2023) for 1,376 of the shares of common stock issued from the Company’s treasury shares to two employees. In accordance with ASC 718, the restrictive features associated with the employee’s ability to sell the shares of common stock will be considered in determining the fair value the shares of common stock issued out of the Company’s treasury shares issued to employees (See Note 8).
The certain contingent events that would result in the clawback feature taking effect were defined as a violation of the non-compete agreement or a resignation of employment without prior Company consent. In accordance with ASC 718, the clawback features were excluded from the determination of the estimated fair value of common stock issued from the Company’s treasury shares and the effect of these contingent features will be accounted for if and when the contingent event occurs.
8. SHARE-BASED COMPENSATION
Share-based compensation expense of $1,749,741 was recorded during the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, in connection with the issuance of shares of common stock from the Company’s treasury shares to employees and nonemployees (See Note 7) as the estimated fair value of such common stock as of the issuance date exceeded the consideration paid, if any, and is included within general and administrative expenses on the accompanying statement of operations and comprehensive loss.
The Company’s board of directors (the “Board”) determines the fair value of common stock at the time of issuance due to the absence of an active market for the Company’s common stock. The Board determined the fair value of such common stock by considering a number of objective and subjective factors, operating and financial performance, the lack of liquidity of capital stock, and general and industry-specific economic outlook, amongst other factors. The fair value of the underlying common stock will be determined by the Company’s Board until such time the Company’s common stock is listed on an established exchange or national market system.
In connection with estimating the fair value of common stock at the time shares of common stock were issued from the Company’s treasury shares an option pricing model (the “OPM”) and a probability-weighted expected return method (the “PWERM”) were utilized.
9. DEFINED SEVERANCE BENEFITS
Changes in defined severance benefits obligation were as follows:
| Balance as of January 3, 2023 (inception) | | $ | - | |
| Current service cost | | | 48,559 | |
| Actuarial losses | | | - | |
| Payments from plans | | | - | |
| Cumulative effects of foreign currency translation | | | 594 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | | $ | 49,153 | |
| Current | | | 2,462 | |
| Noncurrent | | | 46,691 | |
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
The principal actuarial assumptions used to determine defined severance benefits obligation were as follows:
| Discount rates | | | 4.70 | % |
| Salary growth rates | | | 3.38%+Experienced salary scale |
The expected maturity analysis of undiscounted defined severance benefits as of December 31, 2023 was as follows:
| | | Less than
1 year | | | Between
1-2 years | | | Between
2-5 years | | | Over
5 years | | | Total | |
| Expected Retirement Benefits | | $ | 2,462 | | | $ | 3,291 | | | $ | 9,976 | | | $ | 64,380 | | | $ | 80,109 | |
10. FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
The convertible debt security is classified within Level 3 value hierarchy because the value of the asset is based on the credit worthiness of the obligor, which is an unobservable input. The Company used a Tsiveriotis-Fernandes model (the “T-F Model”) to value the convertible debt security as of December 31, 2023.
Financial assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis are as follows:
| | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| Financial assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Convertible debt security | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 1,006,757 | | | $ | 1,006,757 | |
The table below presents the ranges of significant unobservable inputs used to value the Company’s Level 3 financial instruments. These ranges represent the significant unobservable inputs that were used in the valuation of each type of financial instrument. These inputs are not representative of the inputs that could have been used in the valuation of any one financial instrument. Valuation techniques and inputs for assets measured by the fair value hierarchy Level 3 are as follows:
| Classification | | Valuation technique | | Input |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | |
| Convertible debt security | | Tsiveriotis-Fernandes model | | Discount rate, stock price and volatility |
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances for the convertible debt security measured at fair value on a recurring basis using significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) is as follows:
| Balance as of January 3, 2023 (inception) | | $ | - | |
| Convertible debt security purchased | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Adjustment to fair value | | | 6,757 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | | $ | 1,006,757 | |
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
11. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property and equipment, net consisted of the following as of December 31, 2023:
| Office equipment | | $ | 37,847 | |
| | | | 37,847 | |
| Less: accumulated depreciation | | | (4,249 | ) |
| Property and equipment, net | | $ | 33,598 | |
Depreciation expense for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023 totaled $4,198 and was included within general and administrative expenses on the accompanying statement of operations and comprehensive loss.
12. PREPAID EXPENSES AND OTHER CURRENT ASSETS
Prepaid expenses and other current assets consisted of the following as of December 31, 2023:
| Advances to a production company for content development | | $ | 77,461 | |
| Advances to writers for development of content | | | 69,716 | |
| Prepaid cloud computing arrangement hosting services | | | 61,413 | |
| Accounting services | | | 18,826 | |
| | | $ | 227,416 | |
13. OTHER ASSETS, NONCURRENT
Other assets, noncurrent consisted of the following as of December 31, 2023:
| Advances to production companies for content development | | $ | 852,072 | |
| Advances to writers for development of content | | | 480,259 | |
| Capitalized implementation costs for cloud computing arrangement | | | 295,619 | |
| Security deposit for office lease | | | 77,462 | |
| | | $ | 1,705,412 | |
Other assets, noncurrent – related party consisted of a security deposit for an office lease totaling $77,500 (see Note 17).
14. ACCRUED EXPENSES AND OTHER CURRENT LIABILITIES
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities consisted of the following as of December 31, 2023:
| Accrued legal services | | $ | 1,468,900 | |
| Accrued accounting services | | | 667,906 | |
| Annual leave allowance | | | 65,272 | |
| Payroll withholding tax | | | 34,337 | |
| Other payable | | | 1,295 | |
| | | $ | 2,237,710 | |
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
15. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Operating Leases: The Company has obligations as a lessee for two office space leases, both of which are classified as operating leases. For the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, the total lease cost was $70,831.
The weighted average remaining lease term was 1.4 years and the weighted average discount rate was 5.7% as of December 31, 2023.
Future minimum payments of lease liabilities under the noncancelable operating leases are as follows at December 31, 2023:
| 2024 | | $ | 122,911 | |
| 2025 | | | 51,213 | |
| Total undiscounted lease payments | | | 174,124 | |
| Less: imputed interest | | | (6,297 | ) |
| Total future minimum payments | | $ | 167,826 | |
Legal Matters: From time to time, the Company may become subject to legal proceedings, claims and litigation arising in the ordinary course of business. The Company is not currently a party to any legal proceedings, nor is it aware of any pending or threatened litigation, that would have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, operating results, cash flows, or financing condition should such litigation be resolved unfavorably.
16. INCOME TAXES
The Company’s effective tax rate for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) the December 31, 2023 was zero percent. The effective tax rate may vary significantly from period to period and can be influenced by many factors. These factors include, but are not limited to, changes to the statutory rates in the jurisdictions where the Company has operations and changes in the valuation of deferred tax assets and liabilities. The difference between the effective tax rate and the federal statutory rate of 21.0% (Korea: 20.9%) primarily relates to certain nondeductible items, state and local income taxes, the absence of current income tax, and a full valuation allowance for deferred tax assets.
| Current taxes | | | | |
| United States | | $ | - | |
| Foreign - Korea | | | - | |
| Current taxes | | $ | - | |
| Deferred taxes | | | | |
| United States | | $ | - | |
| Foreign - Korea | | | - | |
| Deferred taxes | | $ | - | |
Deferred tax assets of the following as of December 31, 2023:
| Deferred tax assets | | | |
| Net operating loss carryforward | | $ | 1,837,180 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | 48,741 | |
| Defined severance benefits | | | 10,273 | |
| Others | | | (36,495 | ) |
| Total gross deferred tax assets | | | 1,859,699 | |
| Valuation allowance | | | (1,859,699 | ) |
| Net deferred tax assets | | $ | - | |
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
There are no deferred taxes that are directly charged to (credited from) equity for the years ended December 31, 2023.
The Company’s policy is to record estimated interest and penalties related to the underpayment of income taxes or unrecognized tax benefits as a component of its income tax provision. The Company has not recorded any interest or penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits through December 31, 2023.
In the normal course of business, the Company is subject to examination by federal and state jurisdictions where applicable based on the statute of limitations that apply in each jurisdiction. The Company is not currently under audit by the taxing jurisdictions to which the Company is subject.
17. RELATED PARTIES
Two of the Company’s directors, one of whom is the Executive Chairman and the other is also the Chief Executive Officer, are also senior officers of Solaire Partners. During the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023,
| ● | The Company entered into a two-year operating lease for one of its office spaces commencing in June 2023 with Solaire Partners as the landlord. At inception, total gross rental payments due under this operating lease approximated $103,946 and a security deposit due approximated $75,718. For the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, the Company made $30,656 of rental payments, and paid $77,500 for the security deposit associated with this operating lease. As of December 31, 2023, $72,636 associated with the present value of lease payments is included as components of lease liabilities, current – related party and lease liabilities, noncurrent – related party on the accompanying balance sheet, $77,500 associated with the security deposit is included as a component of other assets, noncurrent – related party. |
| ● | Solaire Partners paid an aggregate total of $59,499 of administrative expenses on the Company’s behalf, which is recorded as a component of general and administrative expenses on the accompanying statement of operations. This amount was repaid in full as of December 31, 2023. |
| ● | The Company entered into a one-year consulting services agreement with Solaire Partners commencing in August 2023 where Solaire Partners provides the Company with consulting services for certain aspects of its business operations in exchange for 200,000,000 Korean Won ($154,922 at December 31, 2023). The consulting services agreement will automatically renew on the expiration date if a new consulting services agreement is not reached or the current consulting services agreement is not terminated. For the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, 83,333,335 Korean Won, or $63,771, was associated with the consulting services agreement is included as a component of general and administrative expenses on the accompanying statement of operations. As of December 31, 2023, 16,666,667 Korean Won ($12,910 at December 31, 2023) is included as a component of accounts payable – related party. The consulting services agreement was terminated as of December 31, 2023. |
A director of the Company is also a managing member of Global Star Acquisition 1, LLC, the entity the Company purchased its shares of Global Star Class B common stock from.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FROM JANUARY 4, 2023 (INCEPTION) TO DECEMBER 31, 2023
18. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
The Company evaluated subsequent events and transactions that occurred after the balance sheet date up to March 25, 2024, the date that the financial statements were available to be issued. Based upon this review, the Company did not identify any subsequent events that would have required adjustment or disclosure in the financial statements.
On January 31, 2024, the Company entered into the Stock Purchase Agreement with Solaire Partners LLC, which the company acquired 1,000 shares of Play Company Co.,Ltd totaling 1,741,000,000 Korean Won.
On January 31, 2024, an amendment was made to the share purchase agreement, originally entered into on April 12, 2023, with the CEO of First Virtual, and the share purchase agreement with the shareholder of First Virtual was renewed due to the spin-off of the First Virtual, which was executed in October 2023. As a result of this amendment, the value of shares to be exchanged has been decreased to 10,199,577,468 Korean won.
On March 5, 2024, the Company entered into the Termination and Re-Purchase Option Agreement with the owners of First Virtual, which terminated all agreements entered into in connection with the original equity purchase agreement. The key conditions in the agreement are as follows.
| ● | The Company shall repurchase shares if the related suits are finally resolved by a final, non-appealable judgment or the involved parties’ mutually agreed settlement with prejudice of all claims related to and arising from the related suits in each case in a manner satisfactory to the Company as determined by the Company at its sole discretion based on what is considered legally and commercially reasonable. |
| ● | The repurchase price shall be the fair market value, which shall be determined by an accounting firm selected by both parties’ mutual agreement. The transaction shall be consummated within 15 days after the determination of the fair value, excluding the date of government approval if required. The term of this agreement shall be effective and in force only for the time period between the agreement date and the five year anniversary thereof. |
On March 11, 2024, the Merger Agreement dated June 15, 2023, was amended in connection with the Termination Agreement and Re-Purchase Option Agreement. The total estimated base amount for the transaction decreased from $610,000,000 to $590,000,000.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
CONDENSED BALANCE SHEETS
| | | September 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | |
| Current assets | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 166,262 | | | $ | 2,525,682 | |
| Accounts receivable | | | 3,802 | | | | - | |
| Other receivables | | | 10,138 | | | | 70,906 | |
| Convertible debt security | | | 945,946 | | | | 1,006,757 | |
| Deferred transaction costs | | | 2,103,520 | | | | 1,363,241 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | | 505,651 | | | | 227,416 | |
| Total current assets | | | 3,735,319 | | | | 5,194,002 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Investment in equity securities | | | 1,600,000 | | | | 1,600,000 | |
| Investment in equity securities - related party | | | 1,324,015 | | | | - | |
| Property and equipment, net | | | 29,343 | | | | 33,598 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets, net | | | 30,691 | | | | 95,191 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets, net - related party | | | 44,692 | | | | 72,635 | |
| Other assets, noncurrent | | | 1,968,258 | | | | 1,705,412 | |
| Other assets, noncurrent - related party | | | 72,682 | | | | 77,500 | |
| Total non-current assets | | | 5,069,681 | | | | 3,584,336 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | | $ | 8,805,000 | | | $ | 8,778,338 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | | | | | | | |
| Current liabilities | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts payable | | $ | 1,328,059 | | | $ | 294,717 | |
| Accounts payable - related party | | | 1,359,348 | | | | 16,828 | |
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | | | 3,959,242 | | | | 2,237,163 | |
| Short-term borrowings | | | 120,000 | | | | 405 | |
| Short-term borrowings - related party | | | 419,514 | | | | 142 | |
| Defined severance benefits, current | | | - | | | | 2,462 | |
| Lease liabilities, current | | | 28,955 | | | | 60,619 | |
| Lease liabilities, current - related party | | | 44,692 | | | | 55,122 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 7,259,810 | | | | 2,667,458 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Defined severance benefits, noncurrent | | | - | | | | 46,691 | |
| Convertible Note | | | 1,013,169 | | | | - | |
| Derivative liabilities | | | 113,274 | | | | - | |
| Lease liabilities, noncurrent | | | - | | | | 34,571 | |
| Lease liabilities, noncurrent - related party | | | - | | | | 17,514 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | 1,126,443 | | | | 98,776 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | | $ | 8,386,253 | | | $ | 2,766,234 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | | | | | | | |
| Series A-1 convertible preferred stock | | | - | | | | - | |
| Series A convertible preferred stock | | | 355 | | | | 355 | |
| Preferred stock subscription receivable | | | (519,000 | ) | | | (369,000 | ) |
| Common stock | | | 1,000 | | | | 1,000 | |
| Treasury Stock | | | - | | | | (57 | ) |
| Additional paid-in capital | | | 20,395,499 | | | | 15,238,711 | |
| Accumulated deficit | | | (19,395,174 | ) | | | (8,930,946 | ) |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income(loss) | | | (63,933 | ) | | | 72,041 | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | | $ | 418,747 | | | $ | 6,012,104 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | $ | 8,805,000 | | | $ | 8,778,338 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited financial statements.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
| | | Nine months ended
September 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from
January 4, 2023
(inception) through September 30,
2023 | |
| Revenue | | $ | 470,052 | | | $ | - | |
| Cost of revenues | | $ | 411,121 | | | $ | - | |
| Operating expenses | | | | | | | | |
| General and administrative expenses | | $ | 10,519,714 | | | $ | 5,310,902 | |
| Total operating expenses | | | 10,930,835 | | | | 5,310,902 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Loss from operations | | | (10,460,783 | ) | | | (5,310,902 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Other income (expense) | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | | 388 | | | | 83 | |
| Other income (expense) | | | (3,833 | ) | | | 12,602 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total other income (expense), net | | | (3,445 | ) | | | 12,685 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Income tax expense | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | | $ | (10,464,228 | ) | | $ | (5,298,217 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Other comprehensive loss | | | | | | | | |
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | | | (75,163 | ) | | | (89,561 | ) |
| Unrealized loss of available-for-investments | | | (60,811 | ) | | | - | |
| Comprehensive loss | | $ | (10,600,202 | ) | | $ | (5,387,777 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding, basic and diluted | | | 94,478 | | | | 70,496 | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share of common stock | | $ | (110.76 | ) | | $ | (75.16 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited financial statements.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
| | | Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock | | | Series A Convertible Preferred Stock | | | Common stock | | | Treasury stock | | | Preferred Stock Subscription | | | Additional Paid-in | | | Accumulated | | | Accumulated Other Comprehensive | | | | |
| | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Receivable | | | Capital | | | Deficit | | | Loss | | | Total | |
| Balance, January 4, 2023 (inception) | | | - | | | $ | - | | | | - | | | $ | - | | | | - | | | $ | - | | | | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
| Shares issued for common stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 100,000 | | | | 1,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,000 | |
| Shares issued for Series A convertible preferred stock, net of issuance costs | | | - | | | | - | | | | 35,484 | | | | 355 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 10,600,609 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 10,600,964 | |
| Shares issued for Series A-1 convertible preferred stock | | | 4,199 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,519,400 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,519,400 | |
| Treasury stock shares acquired | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (12,074 | ) | | | (121 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (121 | ) |
| Shares transferred back to the Company | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 6,353 | | | | 64 | | | | - | | | | 1,749,702 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,749,766 | |
| Net loss | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (5,298,216 | ) | | | - | | | | (5,298,216 | ) |
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (89,561 | ) | | | (89,561 | ) |
| Balance, September 30, 2023 | | | 4,199 | | | $ | - | | | | 35,484 | | | $ | 355 | | | | 100,000 | | | $ | 1,000 | | | | (5,721 | ) | | $ | (57 | ) | | $ | - | | | $ | 14,869,711 | | | $ | (5,298,216 | ) | | $ | (89,561 | ) | | $ | 9,483,232 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance, January 1, 2024 | | | 4,814 | | | $ | - | | | | 35,484 | | | $ | 355 | | | | 100,000 | | | $ | 1,000 | | | | (5,721 | ) | | $ | (57 | ) | | $ | (369,000 | ) | | $ | 15,238,711 | | | $ | (8,930,946 | ) | | $ | 72,041 | | | $ | 6,012,104 | |
| Shares issued for Series A-1 convertible preferred stock | | | 500 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (150,000 | ) | | | 300,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 150,000 | |
| Shares issued for common stock as a share-based compensation | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,202 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 649,597 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 649,597 | |
| Treasury stock returned | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (1,376 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | - | | | | | |
| Shares issued for common stock from the Company’s treasury shares | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,100 | | | | 7 | | | | - | | | | 1,134,896 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,134,903 | |
| Settlement of liabilities by issuance of shares | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 4,997 | | | | 50 | | | | - | | | | 2,700,479 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,700,529 | |
| Share-based compensation | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | - | | | | 371,816 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 371,816 | |
| Net loss | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (10,464,228 | ) | | | - | | | | (10,464,228 | ) |
| Unrealized Loss of Available-For-Investments | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (60,811 | ) | | | (60,811 | ) |
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (75,163 | ) | | | (75,163 | ) |
| Balance, September 30, 2024 | | | 5,314 | | | $ | - | | | | 35,484 | | | $ | 355 | | | | 101,202 | | | $ | 1,000 | | | | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | (519,000 | ) | | $ | 20,395,499 | | | $ | (19,395,174 | ) | | $ | (63,933 | ) | | $ | 418,747 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited financial statements.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| | | Nine Months ended September 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from
January 4, 2023
(inception) through
September 30,
2023 | |
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | | $ | (10,464,228 | ) | | $ | (5,298,216 | ) |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | | | | | | | | |
| Share-based compensation | | | 2,156,316 | | | | 1,749,741 | |
| Severance Benefits | | | 37,395 | | | | - | |
| Amortization of operating lease right-of-use assets | | | 79,200 | | | | 20,869 | |
| Amortization of operating lease right-of-use assets – related party | | | 13,276 | | | | 15,924 | |
| Depreciation expense | | | 5,711 | | | | 2,378 | |
| Interest expense | | | 1,443 | | | | - | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | | | (3,699 | ) | | | - | |
| Other receivables | | | 60,161 | | | | (45,722 | ) |
| Deferred transaction costs | | | - | | | | (185,000 | ) |
| Prepaid and other current assets | | | (267,321 | ) | | | (427,875 | ) |
| Other assets, noncurrent | | | (225,122 | ) | | | (1,647,631 | ) |
| Other assets, noncurrent – related party | | | 1,316 | | | | (76,851 | ) |
| Accounts payable | | | 1,026,746 | | | | 758,426 | |
| Accounts payable – related party | | | 17,743 | | | | 16,902 | |
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | | | 3,678,567 | | | | 319,816 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | (88,012 | ) | | | (26,630 | ) |
| Lease liabilities – related party | | | (13,275 | ) | | | (11,529 | ) |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | | (84,334 | ) | | | - | |
| CASH PROVIDED BY (USED IN) OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | (4,068,117 | ) | | | (4,835,398 | ) |
| CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | | | | | | |
| Purchase of property and equipment | | | (1,060 | ) | | | (35,075 | ) |
| Advances under note receivable | | | - | | | | (1,536,252 | ) |
| Purchase of convertible debt security | | | - | | | | (1,000,000 | ) |
| Purchase of investment in equity securities | | | - | | | | (1,600,000 | ) |
| CASH USED IN INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | (1,060 | ) | | | (4,171,327 | ) |
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of Series A-1convertible preferred stock, net of issuance costs | | | 150,000 | | | | 2,519,400 | |
| Proceeds from issuance of Series A convertible preferred stock, net of issuance costs | | | - | | | | 10,600,964 | |
| Proceeds from issuance of convertible notes, net of issuance costs | | | 1,125,000 | | | | - | |
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock, net of issuance costs | | | - | | | | 1,000 | |
| Purchase of treasury shares | | | - | | | | (121 | ) |
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock from treasury shares | | | - | | | | 25 | |
| Proceeds from short-term borrowings | | | 120,000 | | | | - | |
| Proceeds from short-term borrowings – related party | | | 674,137 | | | | - | |
| Repayment of short-term borrowings – related party | | | (259,638 | ) | | | - | |
| CASH PROVIDED BY FINANCING ACTIVITIES | | | 1,809,499 | | | | 13,121,268 | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash | | | (99,742 | ) | | | 20,775 | |
| Change in cash and cash equivalents | | | (2,359,420 | ) | | | 4,135,318 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period | | | 2,525,682 | | | | - | |
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of period | | $ | 166,262 | | | $ | 4,135,318 | |
| Supplemental disclosure of noncash investing and financing activities: | | | | | | | | |
| Outstanding payable related to acquisition of Play Company common stock. | | $ | 1,287,835 | | | $ | - | |
| Deferred transaction costs included in Accrued Expenses | | $ | 740,261 | | | $ | 677,482 | |
| Settlement of payables by issuance of common stock | | $ | 2,700,479 | | | $ | - | |
| Issuance of preferred stock | | $ | 150,000 | | | $ | - | |
| Operating right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for lease obligations | | | - | | | | 129,236 | |
| Operating right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for lease obligations – related party | | | - | | | | 98,613 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited financial statements.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED)
1. NATURE OF OPERATIONS AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “Company”), a Delaware corporation, was formed on January 4, 2023 to become a leading tech and intellectual property (“IP”) based diversified entertainment company. To fulfill this vision, the Company established an internal Korean drama production team and entered into equity purchase agreements to acquire a controlling equity interest in six separate Korean entertainment companies (collectively, the “Six Korean Entities”) in order to combine initial capabilities believed to serve as the foundation for the Company’s growth – content production, content merchandising, and content investment. The Six Korean Entities include one Korean content-specialized private equity firm, one Korean drama production company, three Korean movie production companies, and one IP merchandising company.
Basis of Accounting:
The accompanying unaudited interim financial statements of the Company have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”). These interim financial statements include normal recurring adjustments which are, in the opinion of management, necessary to provide a fair statement of the Company’s financial condition and results of operations for the periods presented. These interim financial statements are presented in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 270, “Interim Reporting” and, accordingly, do not include all of the information and note disclosures required by U.S. GAAP for complete financial statements. The results of operations for the nine months ended September 30, 2024 are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for a full year or for any other periods. The interim financial statements should be read in conjunction with the audited financial statements as of December 31, 2023.
There have been no material changes to the Company’s significant accounting policies as of and for the nine months ended September 30, 2024 as compared to the significant accounting policies described in the Company’s audited financial statements for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023
Going Concern:
The Company has incurred significant losses and negative cash flows from operations, net loss was $10,464,228 for the nine months period ended September 30, 2024. During the nine months period ended September 30, 2024, the Company had negative cash flows from operations of $4,068,117. As of September 30, 2024, the Company’s accumulated deficit was $19,395,174. The Company has funded its operations to date through equity and debt financing and has cash equivalents of $166,262 as of September 30, 2024. The Company monitors its cash flow projections on a current basis and takes active measures to obtain the funding it requires to continue its operations. However, these cash flow projections are subject to various uncertainties concerning their fulfilment such as the ability to increase revenues by attracting and expanding its customer base and completing additional financing. The Company expects to fund operations using cash on hand and raising additional proceeds. There are no assurances, however, that the Company will be able to generate the revenue necessary to support its cost structure or that it will be successful in obtaining the level of financing necessary for its operations. These conditions raise substantial doubt as to the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. These financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern and do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Emerging Growth Company:
The Company is expected to be an “emerging growth company”, as defined in Section 2(a) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, (the “Securities Act”), as modified by the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (the “JOBS Act”). The JOBS Act provides that an emerging growth company can take advantage of an extended transition period for complying with new or revised accounting standards. Thus, an emerging growth company can delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. The Company has elected to take advantage of the extended transition period to comply with new or revised accounting standards and to adopt certain of the reduced disclosure requirements available to emerging growth companies. As a result of the accounting standards election, the Company will not be subject to the same implementation timeline for new or revised accounting standards as other public companies that are not emerging growth companies. At times, the Company may elect to early adopt a new or revised accounting standard.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED)
Recent Accounting Pronouncements, not yet adopted:
In November 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-07, Segment Reporting (Topic 280) (“ASC 280”): Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures (“ASU 2023-07”), that would enhance disclosures for significant segment expenses for all public entities required to report segment information in accordance with ASC 280. ASC 280 requires a public entity to report for each reportable segment a measure of segment profit or loss that its chief operating decision maker (“CODM”) uses to assess segment performance and to make decisions about resource allocations. The amendments in ASU 2023-07 improve financial reporting by requiring disclosure of incremental segment information on an annual and interim basis for all public entities to enable investors to develop more useful financial analyses. Currently, Topic 280 requires that a public entity disclose certain information about its reportable segments. For example, a public entity is required to report a measure of segment profit or loss that the CODM uses to assess segment performance and make decisions about allocating resources. ASC 280 also requires other specified segment items and amounts such as depreciation, amortization and depletion expense to be disclosed under certain circumstances. The amendments in ASU 2023-07 do not change or remove those disclosure requirements. The amendments in ASU 2023-07 also do not change how a public entity identifies its operating segments, aggregates those operating segments, or applies the quantitative thresholds to determine its reportable segments. The amendments in ASU 2023-07 are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. Early adoption is permitted. A public entity should apply the amendments in ASU 2023-07 retrospectively to all prior periods presented in the financial statements. We are currently evaluating the impact of this standard on our financial statements and related disclosures.
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures (“ASU 2023-09”). ASU 2023-09 is intended to enhance the transparency and decision usefulness of income tax disclosures. The amendments in ASU 2023-09 address investor requests for enhanced income tax information primarily through changes to the rate reconciliation and income taxes paid information. ASU 2023-09 will be effective for us in the annual period beginning October 1, 2025, though early adoption is permitted. We are still evaluating the presentational effect that ASU 2023-09 will have on our financial statements, but we expect considerable changes to our income tax footnote.
In November 2024, the FASB issued ASU No. 2024-03, “Disaggregation of Income Statements Expenses (DISE)” (ASU 2024-03), which requires that a public entity provide additional disclosure of the nature of expenses included in the income statement. The new standard requires disclosures about specific types of expenses included in the expense captions presented on the face of the income statement as well as disclosures about selling expenses. ASU 2024-03 will be effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2026, and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2027, with retrospective application. The standard allows early adoption of these requirements. We are currently evaluating the impact of this standard on our financial statements and related disclosures.
2. BUSINESS COMBINATIONS
Merger Agreement with Global Star Acquisition, Inc.
On June 15, 2023, and as amended on March 11, 2024, June 28, 2024, and July 25, 2024, the Company entered into a Third Amendment to Merger Agreement (the “Third Merger Amendment”) with Global Star Acquisition Inc., a Delaware corporation, (“Global Star”) and GLST Merger Sub Inc., a Delaware corporation and wholly owned sub of Global Star, (“Merger Sub”). The Merger Agreement provides that Global Star will merge with and into K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (“K Wave Media” or “PubCo”), with PubCo continuing as the surviving publicly traded entity (the “Reincorporation Merger”). One day following the Reincorporation Merger, Merger Sub will be merged with and into K Enter, with K Enter the surviving corporation and resulting in K Enter being a wholly owned subsidiary of PubCo (“Acquisition Merger”). The Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger are collectively referred to herein as the “Business Combination”.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED)
Key terms of the Merger Agreement include, but are not limited to, the following:
| ● | The consideration for Reincorporation Merger is expected to be settled by issuing: (a) one share of PubCo’s ordinary shares in exchange for each share of Global Star Class A common stock that is outstanding as of the effective time of the Reincorporation Merger and (b) one warrant to purchase one of PubCo’s ordinary shares at an exercise price of $11.50 in exchange for each share of each Global Star warrant that is outstanding as of the effective time of the Reincorporation Merger. |
| ● | Certain of Global Star’s stockholders have provided written consent, pursuant to which, among other things, such stockholders have approved the Merger Agreement and the Reincorporation Merger. Each issued and outstanding share of Global Star ‘s Class A common stock and each issued and outstanding Global Star right on an as-converted basis, will automatically be cancelled and converted into an equal number of shares of the PubCo’s ordinary shares in accordance with the Merger Agreement and each Global Star warrant shall be exchanged for a PubCo warrant. |
| ● | The aggregate consideration for the Acquisition Merger is $590,000,000 and is expected to be settled by issuing 59,000,000 shares of PubCo’s ordinary shares in exchange for an estimated 193,367 shares of Company common stock, including the shares of the Company’s common stock underlying the Company’s outstanding Series A and Series A-1 preferred stock based on an estimated 305.1:1 conversion ratio calculated with a foreign exchange rate of KRW 1,376.55 / USD $1.00 on an as converted basis for each ordinary share of the PubCo (the “Conversion Ratio”) at the time of the Acquisition Merger. |
| ● | Certain of the Company’s stockholders have provided written consent, pursuant to which, among other things, such stockholders have approved the Merger Agreement and the Acquisition Merger. Each issued and outstanding share of the Company’s common stock and each issued and outstanding share of convertible preferred stock on an as-converted basis will automatically be cancelled and converted into the right to receive the number of shares of the PubCo’s ordinary shares equal to the Conversion Ratio in accordance with the Acquisition Merger. |
| ● | The Merger Agreement is subject to the approval by the stockholders of the Company and Global Star. Holders of Global Star’s Class A Common Stock will have the opportunity to redeem their shares of Global Star Class A Common Stock for cash in connection with the Business Combination. |
In certain circumstances, including if the Merger Agreement has not been consummated by December 22, 2024, either party may elect to terminate the Merger Agreement.
Acquisitions of Controlling Equity Interests in the Six Korean Entities
During March 2023, and as amended in December 2023, the Company entered into an equity purchase agreement with the owner of Play Company Corp (“Play Company”) to acquire 100% of the outstanding shares of common stock in exchange for 163,732,016,220 Korean Won ($124,516,720 at September 30, 2024), payable through the issuance of the shares of the Company’s common stock totaling 127,498,912,820 Korean Won ($96,961,772 at September 30, 2024) and in exchange for cash totaling 36,233,103,400 Korean Won ($27,554,948 at September 30, 2024). Additional payments in cash will be made to the owner of Play Company if the annual average net profit for fiscal years from 2023 to 2025 reaches specified thresholds, with payments due to the owner of Play Company on January 31, 2027 and January 31, 2028.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED)
An additional payment in cash may be owed to the owner of Play Company if the shares of PubCo that shares of the Company’s common stock convert to at closing of the Acquisition Merger are sold during the three-month period (the “Sale Period”) following the six-month lock-up period of the newly issued shares of PubCo at a per share price less than the per-share value at closing of the Acquisition Merger for the shortfall in share price. The amount to be paid will be reduced by (i) any gains from the sale of shares of PubCo by the owner of Play Company between the end of the Sale Period and December 31, 2026 and (ii) any unrealized gain as of December 31, 2026 for the shares of PubCo that remain held by the owner of Play Company (calculated as the number of remaining shares of PubCo times the difference of (i) the average closing price of PubCo from December 1, 2026 to December 31, 2026 and (ii) the per-share value of PubCo at the closing of the Acquisition Merger).
During March 2023, and as amended in December 2023 and in January 2024, the Company entered into an equity purchase agreement with the owners of Solaire Partners, LLC (“Solaire Partners”) to acquire 95% of the outstanding shares of common stock in exchange for shares of the Company’s common stock totaling 14,250,000,000 Korean Won ($10,836,996 at September 30, 2024).
During April 2023, and as amended in December 2023, the Company entered into an equity purchase agreement with the owners of Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd (“Anseilen”) to acquire 51% of the outstanding shares of common stock in exchange for shares of the Company’s common stock totaling 7,700,000,400 Korean Won ($5,855,781 at September 30, 2024).
During April 2023, and as amended in December 2023, the Company entered into an equity purchase agreement with the owner of Apeitda Co. Ltd (“Apeitda”) to acquire 51% of the outstanding shares of common stock in exchange for shares of the Company’s common stock totaling 15,300,000,000 Korean Won ($11,635,512 at September 30, 2024).
During April 2023, and as amended in December 2023, the Company entered into an equity purchase agreement with the owners of Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd. (“Bidangil”) to acquire 51% of the outstanding shares of common stock in exchange for shares of the Company’s common stock totaling 20,400,000,000 Koren Won ($15,514,016 at September 30, 2024).
During April 2023, and as amended in December 2023, the Company entered into an equity purchase agreement with the owner of The LAMP Co., Ltd. (“Lamp”) to acquire 51% of the outstanding shares of common stock in exchange for shares of the Company’s common stock totaling 30,600,000,000 Korean Won ($23,271,024 at September 30, 2024).
During April 2023, the Company entered into an equity purchase agreement with the owners of First Virtual Lab Inc.(“First Virtual”) to acquire 51% of the outstanding shares of common stock and preferred stock in exchange for shares of the Company’s common stock. The Company entered into the termination and re-purchase option agreement during March 2024, which terminated all agreements entered into in connection with the original equity purchase agreement. The Company shall repurchase shares if the related suits are finally resolved by a final, non-appealable judgment or the involved parties’ mutually agreed settlement with prejudice of all claims related to and arising from the related suits in each case in a manner satisfactory to the Company as determined by the Company at its sole discretion based on what is considered legally and commercially reasonable. The repurchase price shall be the fair market value, which shall be determined by an accounting firm selected by both parties’ mutual agreement. The transaction shall be consummated within 15 days after the determination of the fair value, excluding the date of government approval if required. The term of this agreement shall be effective and in force only for the time period between the agreement date and the five-year anniversary thereof.
The number of shares of the Company’s common stock to be issued to the sellers of the Six Korean Entities at closing of the respective transactions will be adjusted by changes in exchange rates as the share purchase agreements are denominated in Korean Won and the Company’s equity transactions are denominated in U.S. Dollar.
In certain circumstances, including prior to the closing of the Merger Agreement and if the shares of PubCo, excluding the shares subject to a lock-up on the Nasdaq market, remain not issued or registered sixty days after the shareholder vote approving the merger, either party may elect to terminate the equity purchase agreements.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED)
3. REVENUE
Details of total revenue was as follows:
| | | Nine months ended September 30,
2024 | | | Period from
January 4, 2023
(inception) to
September 30,
2023 | |
| Revenue | | | | | | | | |
| Media production | | $ | 470,052 | | | | - | |
| | | Nine months ended September 30,
2024 | | | Period from
January 4, 2023
(inception) to
September 30,
2023 | |
| Geographic information: | | | | | | | | |
| Korea | | $ | 470,052 | | | | - | |
4. CONVERTIBLE DEBT SECURITY
During August 2023, the Company purchased a $1,000,000 convertible bond from Prototype Group, Inc. (“Prototype Group”), a company that operates in virtual studio technology. The convertible bond was due and payable on demand after August 10, 2024 and the company entered into 1-year extension agreement with Prototype group, and bears interest at a fixed rate equal to the Applicable Federal Rate plus 1% additional interest for short term loans, which as of the date of the bond was 5.96%. If there are any overdue payments, Prototype shall bear a late payment interest rate of the Applicable Federal Rate plus 10% additional interest.
At the Company’s option, at any time prior to payment in full of the principal amount and all accrued interest, the convertible bond can be converted into such number of shares of common stock of Prototype Group equal to the entire principal amount of the convertible bond and all accrued and unpaid interest thereon, divided by $7.40 per share in case the pre-money valuation of Prototype Group shall meet or exceed $94,800,000. In the event the pre-money valuation is below $94,800,000, the conversion price shall be proportionally reduced.
If the convertible bond is not repaid or converted through the Company’s voluntary election and Prototype Group issues and sells shares of its equity securities before the maturity date resulting in gross proceeds of $10,000,000 (excluding the conversion of this bond), then at any time on or after the maturity date, Prototype Group shall have the option to (a) repay all outstanding principal and accrued unpaid interest of the convertible bond or (b) convert all or any portion of the outstanding principal and accrued unpaid interest of the convertible bond into such number of its common shares equal to the principal amount and all accrued unpaid interest thereon to be converted divided by the conversion price.
5. INVESTMENT IN EQUITY SECURITIES
During July 2023, the Company purchased 160,000 shares of Global Star Class B Common Stock (the “Founder Shares”) for an aggregate purchase price of $1,600,000 from Global Star Acquisition 1, LLC, the sponsor of Global Star (the “Sponsor”). During January 2024, the Company purchased 1,000 shares of Play Company Co., Ltd. Common Stock for an aggregate purchase price of $1,324,015 from Solaire Partners LLC. The Company’s investments are recorded at cost minus impairment and adjusted for changes in observable prices.
As of September 30, 2024, there were no indicators of impairment and for the period between the date of acquisition and September 30, 2024, there were no observable price changes or sales of Founder Shares and Play Company shares.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED)
6. STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
The Company was authorized to issue 100,000 shares of common stock at a par value of $0.01 when it was formed on January 4, 2023. The Company amended its certificate of incorporation on May 31, 2023 and again on August 31, 2023 in order to increase the shares of common stock it is authorized to issue to 10,000,000 shares of common stock at a par value of $0.0001 per share and 1,000,000 shares of preferred stock at a par value of $0.0001 per share, of which 45,000 shares have been designated as Series A Convertible Preferred Stock (“Series A”) and 15,000 shares have been designated as Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock (“Series A-1”) by the board of directors (the “Board”).
Common Stock: On September 29, 2024, the Company issued 1,202 shares ($649,597, $540.43 per share) of the Company’s common stock to Lodestar USA, Inc. in consideration for services rendered to the Company by Ted Kim, a co-founder and a director of the Company and the owner of Lodestar USA Inc. (See Note 14).
Convertible preferred stock: On September 21, 2024, the Company entered into an agreement to issue 250 shares of Series A-1 for gross proceeds of $150,000 (“Say Coon Loh Agreement”). Each issued Series A-1 shares are convertible into common stock of the Company on a one-for-one basis. On September 25, 2024, the Company entered into an agreement to issue 250 shares of Series A-1 for gross proceeds of $150,000 (“Innocus Global Agreement”). Each issued Series A-1 shares are convertible into common stock of the Company on a one-for-one basis. Currently, the Company has not received the proceeds of $150,000 from Innocus Global Agreement and recorded $150,000 as subscription receivable.
Treasury Stock: On August 31, 2024, the Company issued 1,932 shares ($1,044,111, $540.43 per share) of the Company’s common stock to one employee in consideration for services rendered. On August 31, 2024, a total of 1,376 shares of treasury stock were returned as a settlement for no consideration to the Company under the employment agreements, which were initially given to two employees. On September 24, 2024, the Company entered into a share subscription agreement with GF Korea Inc. (the “GF Agreement”) pursuant to which the Company issued 4,997 shares ($2,700,529, $540.43 per share) of the Company’s common stock to GF Korea Inc. The liabilities was paid with the shares and the difference between fair value of issued shares and liabilities was recognized as expense. On September 30, 2024, the Company issued Tan Chin Hwee, a director, Executive Chairman and Interim CEO of the Company, 168 shares ($90,792, $540.43 per share) of the Company’s common stock in consideration for services rendered. (See Note 14)
As of September 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023, 101,202 shares (no treasury share) and 94,279 shares (5,721 treasury shares) of common stock were issued and outstanding, respectively, and the Company reserved 40,798 shares and 40,298 shares of common stock for the conversion of Series A and Series A-1, respectively.
7. SHARE-BASED COMPENSATION
Share-based compensation expense of $2,156,316 was recorded during the period from January 1, 2024 to September 30, 2024, and $1,749,741 was recorded during the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) to September 30, 2023, in connection with the issuance of shares of common stock from the Company’s treasury shares to employees and nonemployees (See Note 6) as the estimated fair value of such common stock as of the issuance date exceeded the consideration paid, if any, and is included within general and administrative expenses on the accompanying statement of operations and comprehensive loss. Details of share-based compensation that the Company recognized as expense for the period from January 1, 2024 to September 30, 2024 are as follows:
| Grant date | | Holder | | Total shares | | | Share fair value | | | Total fair value | |
| August 31, 2024 | | Employee | | | 1,932 | | | $ | 540.43 | | | $ | 1,044,111 | |
| September 29, 2024 | | Lodestar USA | | | 1,202 | | | | 540.43 | | | | 649,597 | |
| September 30, 2024 | | Employee | | | 168 | | | | 540.43 | | | | 90,792 | |
| September 12, 2024 | | Employee* | | | 688 | | | | 540.43 | | | | 371,816 | |
| | | | | | 3,990 | | | | | | | | 2,156,316 | |
| * | One employee purchased 688 shares from a shareholder at a price lower than the fair value. The difference between the transaction price and the fair value was accounted for as an expense. |
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED)
The Company’s board of directors (the “Board”) determines the fair value of common stock at the time of issuance due to the absence of an active market for the Company’s common stock. The Board determined the fair value of such common stock by considering a number of objective and subjective factors, operating and financial performance, the lack of liquidity of capital stock, and general and industry-specific economic outlook, amongst other factors. The fair value of the underlying common stock will be determined by the Company’s Board until such time the Company’s common stock is listed on an established exchange or national market system.
In connection with estimating the fair value of common stock at the time shares of common stock were issued from the Company’s treasury shares an option pricing model (the “OPM”) was utilized.
8. EARNINGS PER SHARE
Basic earnings (loss) per share (“EPS”) is computed using the two-class method as the Company had issued securities, other than common stock, that contractually entitle the holds to participate in dividends and earnings. Under the two-class method, all securities that meet the definition of a participating security, irrespective of whether the securities are convertible, nonconvertible, or potential common stock securities, are included in the computation of basic EPS. The two-class method requires earnings for the period to be allocated between common stock and participating securities based upon their respective rights to receive distributed and undistributed earnings. Under the two-class method, for period with net income, basic net income per common share is computed by dividing the net income attributable to common stockholders by the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Net income attributable to common stockholders is computed by subtracting from net income the portion of current period earnings that the participating securities would have been entitled to receive pursuant to their dividend rights had all of the period’s earnings been distributed. No such adjustment to earnings is made during periods with a net loss, as the holders of the participating securities have no obligation to fund losses. The number of shares used to calculate diluted loss per share of common shares attributable to common shareholders is the same as the number of shares used to calculate basic loss per share of common shares attributable to common shareholders for the period presented because there were no potentially dilutive securities outstanding during the period.
The following table presents the calculation of basic and diluted earnings per share attributable to the stockholders:
| | | Nine months ended September 30,
2024 | | | Period from
January 4, 2023
(inception) to
September 30,
2023 | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share: | | | | | | | | |
| Numerator | | | | | | | | |
| Allocation of net loss | | $ | (10,464,228 | ) | | $ | (5,298,217 | ) |
| Denominator: | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted weighted average number of shares outstanding | | | 94,478 | | | | 70,496 | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share | | $ | (110.76 | ) | | $ | (75.16 | ) |
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED)
9. EMPLOYEE BENEFITS
Changes in defined severance benefits obligation were as follows:
| Balance as of January 1, 2024 | | $ | 49,153 | |
| Current service cost | | | 37,446 | |
| Included in profit or loss (*1) | | | (10,922 | ) |
| Benefits paid | | | (7,249 | ) |
| Payments from plans for the transition to a defined contribution retirement plan | | | (64,861 | ) |
| Cumulative effects of foreign currency translation | | | (3,567 | ) |
| Balance as of September 30, 2024 | | $ | - | |
| Current | | | - | |
| Noncurrent | | | - | |
| (*1) | The difference between the defined benefit obligations and the settled amount upon the transition of post-employment benefit. |
Effective May 3, 2024, the Company has transitioned from a defined benefit retirement plan to a defined contribution retirement plan. The expense recognized in relation to defined contribution plan for the period ended September 30, 2024 is $37,052.
10. CONVERTIBLE NOTES
In May 2024, The Company issued $1.13 million in aggregate principal amount of the convertible senior unsecured notes. The convertible notes contain a right to convert the notes into the common shares. The Company accounted the embedded conversion features associated with the convertible notes separately from the host contract as the economic characteristics and risks of the embedded conversion feature are not closely related to the economic characteristics and risks of the host contract. The Company accounted the embedded conversion feature as a derivative instrument and periodically measures its fair value in accordance with ASC 820. The Company determined the carrying amount of the convertible notes for the difference between the fair value of the embedded conversion features and the principal amount of the convertible notes. The difference between the carrying value and principal amount of the convertible notes represents the discount on notes that was amortized to interest expense over the terms of the convertible notes using the effective interest rate method.
Details of convertible notes issued and outstanding as of September 30, 2024 are as follows:
| | | September 30,
2024 | |
| Noncurrent | | | |
| Convertible Notes | | $ | 1,125,000 | |
| Discount on Notes | | | (111,831 | ) |
| | | $ | 1,013,169 | |
Amounts recognized in profit or loss and changes in fair value of derivative liabilities at fair value through profit or loss for the period ended September 30, 2024 are as follows:
| | | 1st | | | 2nd | | | Total | |
| Balance at 1 January | | $ | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Issuance | | | 90,473 | | | | 45,237 | | | | 135,710 | |
| Adjustment to fair value | | | (14,957 | ) | | | (7,479 | ) | | | (22,436 | ) |
| Balance at 30 September | | $ | 75,516 | | | | 37,758 | | | | 113,274 | |
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED)
Details of the convertible notes issued by the Company and outstanding as of September 30, 2024 are as follows:
| Series | | 1st | | 2nd |
| Type | | Convertible Notes | | Convertible Notes |
| Issuance amount | | 750,000 | | 375,000 |
| Coupon rate (%) | | 3% | | 3% |
| Issuance date | | 2024-06-04 | | 2024-06-05 |
| Maturity date | | 2027-06-03 | | 2027-06-04 |
| Principal redemption | | 1. | Redemption at maturity: Redeemed on the maturity date, at their outstanding principal amount, which has not been early redeemed. | | 1. | Redemption at maturity: Redeemed on the maturity date, at their outstanding principal amount, which has not been early redeemed. |
| Conversion price | | ● | Conversion before the business combination: Before the consummation of the Business Combination, the holders shall be entitled to convert the Pre-PIPE Notes into ordinary shares in the Company at the conversion price of $1,200 per share (the Pre-Merger Conversion Price). Upon the consummation of the Business Combination, 1 ordinary share of the Company shall be converted into 300 ordinary shares (1 share is worth $10.00) of a combined entity (the Combined Entity). | | ● | Conversion before the business combination: Before the consummation of the Business Combination, the Investor shall be entitled to convert the Pre-PIPE Notes into ordinary shares in the Company at the conversion price of $1,200 per share (the Pre-Merger Conversion Price). Upon the consummation of the Business Combination, 1 ordinary share of the Company shall be converted into 300 ordinary shares (1 share is worth $10.00) of a combined entity (the Combined Entity). |
| | | | | | | |
| | | ● | Conversion after the business combination Upon the consummation of the Business Combination, the Pre-PIPE Notes shall be a part of the Combined Entity and the Investor shall be entitled to convert the Pre- PIPE Notes into ordinary shares in the Combined Entity at the conversion price of $10 per share (the Post-Merger Conversion Price). | | ● | Conversion after the business combination Upon the consummation of the Business Combination, the Pre-PIPE Notes shall be a part of the Combined Entity and the Investor shall be entitled to convert the Pre- PIPE Notes into ordinary shares in the Combined Entity at the conversion price of $10 per share (the Post-Merger Conversion Price). |
| | | | | | | |
| | | The Post-Merger Conversion Prices shall be adjusted downwardly to the greater of the following: | | The Post-Merger Conversion Prices shall be adjusted downwardly to the greater of the following: |
| | | | | |
| | | ● | 60% discount to the 5-day average of the volume-weighted average prices of ordinary shares over 5 consecutive trading days following the conversion notice date; and | | ● | 60% discount to the 5-day average of the volume-weighted average prices of ordinary shares over 5 consecutive trading days following the conversion notice date; and |
| | | | | | | |
| | | ● | Floor price of $4 per share. | | ● | Floor price of $4 per share. |
| | | | | | | |
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED)
11. FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
The convertible debt security is classified within Level 3 value hierarchy because the value of the asset is based on the credit worthiness of the obligor, which is an unobservable input. The Company used a Tsiveriotis-Fernandes model (the “T-F Model”) to value the convertible debt security and Discounted Cash Flow method (the “DCF method”) to value the long-term investment security as of September 30, 2024.
Financial assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis are as follows:
| | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| Financial assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Convertible debt security | | $ | - | | | | - | | | | 945,946 | | | | 945,946 | |
| Financial liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivative liabilities | | $ | - | | | | - | | | | 113,274 | | | | 113,274 | |
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances for the convertible debt security measured at fair value on a recurring basis using significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) is as follows:
| Balance as of January 1, 2024 | | $ | 1,006,757 | |
| Adjustment to fair value | | | (60,811 | ) |
| Balance as of September 30, 2024 | | $ | 945,946 | |
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances for the derivative liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis using significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) is as follows:
| Balance as of January 1, 2024 | | $ | - | |
| Issuance | | | 135,710 | |
| Adjustment to fair value | | | (22,436 | ) |
| Balance as of September 30, 2024 | | $ | 113,274 | |
12. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Operating Leases: The Company has obligations as a lessee for two office space leases, both of which are classified as operating leases. For the period from January 1, 2024 to September 30, 2024, the total lease cost was $88,030.
The weighted average remaining lease term was 0.6 years, and the weighted average discount rate was 5.7% as of September 30, 2024.
Future minimum payments of lease liabilities under the noncancelable operating leases are as follows at September 30, 2024:
| 2024 | | | 30,168 | |
| 2025 | | | 44,576 | |
| Total undiscounted lease payments | | | 74,744 | |
| Less: imputed interest | | | (1,097 | ) |
| Total future minimum payments | | $ | 73,647 | |
Legal Matters: From time to time, the Company may become subject to legal proceedings, claims and litigation arising in the ordinary course of business. The Company is not currently a party to any legal proceedings, nor is it aware of any pending or threatened litigation, that would have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, operating results, cash flows, or financing condition should such litigation be resolved unfavorably.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED)
13. INCOME TAXES
The Company’s tax provision from income taxes for interim periods is determined using an estimate of the Company’s annual effective tax rate, adjusted for discrete items, if any, that are taken into account in the relevant period. Each quarter the Company updates the estimate of the annual effective tax rate, and if the estimated tax rate changes, the Company makes a cumulative adjustment. No income tax benefit was accrued for jurisdictions where the Company anticipates incurring a loss during the full fiscal year as the related deferred tax assets were fully offset by a valuation allowance. The Company’s resulting effective tax rate differs from the applicable statutory rate, primarily due to tax credits, the valuation allowance against deferred tax assets in loss making jurisdictions, and other permanent differences.
The Company’s policy is to record estimated interest and penalties related to the underpayment of income taxes or unrecognized tax benefits as a component of its income tax provision. The Company has not recorded any interest or penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits through September 30, 2024.
In the normal course of business, the Company is subject to examination by federal and state jurisdictions where applicable based on the statute of limitations that apply in each jurisdiction. The Company is not currently under audit by the taxing jurisdictions to which the Company is subject.
14. RELATED PARTIES
Two of the Company’s directors are also senior officers of Solaire Partners. A director of the Company is also a managing member of Global Star Acquisition 1, LLC, the entity the Company purchased its shares of Global Star Class B common stock from.
The Company entered into a two-year operating lease for one of its office spaces commencing in June 2023 with Solaire Partners as the landlord. At inception, total gross rental payments due under this operating lease approximated $104,452 and a security deposit due approximated $76,087. For the period from January 1, 2024 to September 30, 2024, the Company made $39,170 of rental payments associated with this operating lease. As of September 30, 2024, $34,265 associated with the present value of lease payments is included as components of lease liabilities, current – related party on the accompanying balance sheet, $76,087 associated with the security deposit is included as a component of other assets, noncurrent – related party on the accompanying balance sheet, and $27,869 associated with the lease is included as a component of accounts payable – related party.
During January 2024, the Company purchased 1,000 shares of Play Company Co., Ltd. Common Stock for an aggregate purchase price of $1,324,015 from Solaire Partners LLC.
On April 22, 2024, Young Jae Lee, the Company’s Director, loaned the Company $136.888 (the “1st Lee Loan”). On May 3, 2024, the Company repaid $76,049 of the 1st Lee Loan, leaving a balance of $60,839 on the 1st Lee Loan. The 1st Lee Loan is for a term of nine months and bears interest at the rate of 4.6% per annum. The proceeds of the 1st Lee Loan will be used to fund the operations of the Company.
On April 23, 2024, Young Jae Lee, the Company’s Director, loaned the Company $190,123 (the “2nd Lee Loan”). On May 3, 2024, the Company repaid $190,123 of the 2nd Lee Loan, leaving a balance of $0.00 on the 2nd Lee Loan. The 2nd Lee Loan is for a term of three months and bears interest at the rate of 4.6% per annum.
On April 26, 2024, Bidangil Pictures Co.,Ltd., loaned the Company $102,666. The Loan is for a term of three months and bears interest at the rate of 3% per annum. On July 26, 2024, the Company entered into the extension agreement with Bidangil in order to differ the maturity to October 23, 2024. The proceeds of the Loan will be used to fund the operations of the Company.
On May 3, 2024, Young Jae Lee, the Company’s Director, loaned the Company $266,172 (the “3rd Lee Loan”). The 3rd Lee Loan is for a term of nine months and bears interest at the rate of 4.6% per annum. The proceeds of the 3rd Lee Loan will be used to fund the operations of the Company.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED)
On June 4, 2024, the Company issued a convertible senior unsecured note in the principal amount of $3,000,000 to Innocus Global Group Pte Ltd., an entity owned by Jaekeun (Jason) Kim, a nominee director PubCo (the “Jason Note”). The Jason Note has a maturity date of 3 years and will pay an annual coupon rate of 3% to be paid semi-annually until the maturity date of the Jason Notes. Under the Jason Note, the proceeds shall be wired to the company as follows: (i) 25% of the committed amount at the time of signing this definitive agreement, (ii) 50% at the time SEC declares effectiveness on the F-4, and (iii) the remaining 25% at the time of shareholder approval and going public. From the time the company issued the Jason Note and until the closing of the Business Combination, the Jason Note will be convertible, at the option of the holder, at a conversion price per share of $1,200 per share. The Post-Merger Conversion Price for the Notes shall be the greater of (a) a 60% discount to the 5-day average of the volume-weighted average prices of ordinary shares over 5 consecutive trading days following the conversion notice date, and (b) a Floor price of $4 per share.
On August 19. 2024, Global Star Acquisition I LLC loaned the Company $120,000. The loan is for a term of three months or within five business days after K Wave Media Ltd F-4 registration statement becomes effective, whichever is earlier and bears no interest. The proceeds of the loan will be used to fund the operations of the Company.
On August 31, 2024, the Company issued 1,932 shares ($1,044,111, $540.43 per share) of the Company’s common stock to an employee of the Company, in consideration for services rendered.
On August 31, 2024, a total of 1,376 shares of treasury stock were returned as a settlement for no consideration to the Company under the employment agreements, which were initially given to two employees.
On September 12, 2024, one founder of the Company transferred a total of 688 shares ($371,816, $540.43 per share) of the founder to an employee at par value. The Company recognized the transaction as a share-based compensation at fair value (See Note 7), which is included within general and administrative expenses on the accompanying statement of operations and comprehensive loss.
On September 24, 2024, the Company entered into a share subscription agreement with GF Korea Inc. (the “GF Agreement”) pursuant to which the Company issued 4,997 shares ($2,700,529, $540.43 per share) of the Company’s common stock to GF Korea Inc. The liabilities was paid with the shares and the difference between fair value of issued shares and liabilities was recognized as expense.. The GF Agreement closed on September 25, 2024 and the company issued the 4,997 shares of its common stock to GF Korea Inc., which will be converted to 1,524,681 shares of Pubco based on an estimated 305.1:1 conversion ratio calculated with a foreign exchange rate of KRW 1,376.55 / USD $1.00 in the Business Combination. Pursuant to the GF Agreement, GF Korea Inc. shall sell the shares within sixty(60) days following the listing date on the NASDAQ Stock Market.; However, if any lock-up period is imposed under applicable laws, GF Korea shall sell those ordinary shares within sixty (60) days after the expiration of such lock-up period.
On September 25, 2024, Innocus Global Group Pte, Ltd., an entity owned by Jaekeun (Jason) Kim, a nominee director PubCo, entered into an agreement to purchase 250 shares of K Enter’s Series A-1 Preferred Stock for gross proceeds of $150,000. Each issued share of Series A-1 Preferred Stock is convertible into common stock of K Enter on a one-for-one basis.
On September 29, 2024, the Company entered into an agreement with Lodestar USA, Inc. (the “Lodestar Agreement”) pursuant to which the Company issued 1,202 shares ($649,597, $540.43 per share) of the Company’s common stock to Lodestar USA, Inc. in consideration for services rendered to the Company by Ted Kim, a co-founder and a director of the Company and the owner of Lodestar USA Inc. The Company’s common stock will be converted to 366,753 shares of Pubco based on an estimated 305.1:1 conversion ratio calculated with a foreign exchange rate of KRW 1,376.55 / USD $1.00. Ted Kim owns 19,564 shares or 10.12% of the shares of common stock of the company based on the shares of the company to be issued and outstanding immediately prior to the closing of the Business Combination through his ownership and control of Global Fund LLC, which owns 12,000 shares, and Lodestar USA, Inc., which owns 7,564 shares.
On September 30, 2024, the Company issued Tan Chin Hwee, a director, Executive Chairman and Interim CEO of the Company, 168 shares ($90,792, $540.43 per share) of the Company’s common stock in consideration for services rendered.
K ENTER HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED)
15. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
The Company evaluated subsequent events and transactions that occurred after the balance sheet date up to November 22, 2024, the date that the financial statements were available to be issued.
On October 3, 2024, the Company received $300,000 pursuant to the Jason Note and on October 18, 2024, the Company received $1,200,000 pursuant to the Jason Note. Accordingly, the Company is not due any payment under the Note at the time SEC declares effectiveness on the F-4.
On October 18. 2024, the Company repaid $120,000 of Global Star Acquisition I LLC loan, leaving a balance of $0.00 on the loan.
On October 23, 2024, the Company entered into an extension agreement on the 1st Lee Loan to amend the maturity date to June 30, 2025 or within five days after the K Wave Media Ltd registration statement on Form F-4 is declared effective by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. The Loan bears interest at the rate of 4.6% per annum.
On October 25, 2024, the Company entered into an extension agreement on the loan with Bidangil Pictures Co.,Ltd. to amend the maturity date to June 30, 2025 or within five business days after K Wave Media Ltd F-4 registration statement becomes effective. The Loan is for a term of three months and bears interest at the rate of 3% per annum.
On November 3, 2024, the Company entered into an extension agreement on the 3rd Lee Loan to amend the maturity date to April 30, 2025 or within five days after the K Wave Media Ltd registration statement on Form F-4 is declared effective by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. The Loan bears interest at the rate of 4.6% per annum.
16. EVENTS UP TO DECEMBER 23, 2024 SUBSEQUENT TO THE DATE THAT THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS WERE AVAILABLE FOR INITIAL ISSUANCE, NOVEMBER 22, 2024
On December 11, 2024, Global Star, K Wave Media, the Company and Merger Sub (the “Parties”) entered into the Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement, which extended the Outside Date for the parties to consummate the closing of the Business Combination from December 22, 2024 to June 22, 2025.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023
| | | Note | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | 17 | | ₩ | | | 4,200,011 | | | | 8,585,634 | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | 14 | | | | | 417,473 | | | | 419,391 | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | | | | | | 2,987,908 | | | | 6,754,011 | |
| - Related parties | | 18 | | | | | 365,584 | | | | 1,017,018 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 2,622,324 | | | | 5,736,993 | |
| Short-term loans, net | | 13 | | | | | 946,262 | | | | 859,900 | |
| - Related parties | | 18 | | | | | 685,388 | | | | 149,900 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 260,874 | | | | 710,000 | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | | | | | | 101,774 | | | | 351,166 | |
| - Related parties | | 18 | | | | | 16,647 | | | | 51,619 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 85,127 | | | | 299,547 | |
| Value added tax receivables | | | | | | | 606,046 | | | | 200,407 | |
| Other current assets | | | | | | | 7,690,994 | | | | 719,193 | |
| Other current financial assets | | | | | | | 40,000 | | | | 203,266 | |
| Contract assets | | | | | | | - | | | | 73,463 | |
| Inventories, net | | 9 | | | | | 1,370,591 | | | | 424,560 | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | | 18,361,059 | | | | 18,590,991 | |
| Long-term financial instruments | | 14 | | | | | 317,625 | | | | 307,729 | |
| Long-term investment securities | | 14 | | | | | 623,558 | | | | 640,739 | |
| Property, plant and equipment including right-of-use assets | | 15 | | | | | 13,614,858 | | | | 14,867,677 | |
| Intangible assets other than goodwill | | 11 | | | | | 4,708,306 | | | | 4,889,597 | |
| Goodwill | | 11 | | | | | 3,267,730 | | | | 3,267,730 | |
| Investment properties | | 10 | | | | | 2,948,761 | | | | 3,260,795 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | | | 1,612,684 | | | | 1,390,486 | |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | | | | | | 2,233,069 | | | | 2,606,623 | |
| Deferred tax assets | | 8 | | | | | 680,693 | | | | 565,144 | |
| Total non-current assets | | | | | | | 30,007,284 | | | | 31,796,520 | |
| Total assets | | | | ₩ | | | 48,368,343 | | | | 50,387,511 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed consolidated interim financial statements.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023
| | | Note | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | | | ₩ | | | 13,178,725 | | | | 14,407,610 | |
| - Related parties | | 18 | | | | | 1,201,951 | | | | 1,297,426 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 11,976,774 | | | | 13,110,184 | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | | | | | 1,706,598 | | | | 870,830 | |
| Short-term borrowings | | 13 | | | | | 3,370,000 | | | | 3,330,000 | |
| - Related parties | | 18 | | | | | 870,000 | | | | 830,000 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 2,500,000 | | | | 2,500,000 | |
| Current portion of long-term borrowings, net | | 13 | | | | | 24,960 | | | | 24,960 | |
| Current lease liabilities | | 13,15 | | | | | 1,657,138 | | | | 1,630,482 | |
| Current tax liabilities | | 8 | | | | | 291,063 | | | | 845,547 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | | 20,228,484 | | | | 21,109,429 | |
| Trade and other non-current payables | | | | | | | 410,351 | | | | 335,871 | |
| Long-term borrowings, excluding current portion, net | | 13 | | | | | 2,046,433 | | | | 2,008,041 | |
| - Related parties | | 18 | | | | | 2,040,193 | | | | 1,989,321 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 6,240 | | | | 18,720 | |
| Other non-current financial liabilities | | | | | | | 330,000 | | | | 200,000 | |
| Other non-current non-financial liabilities | | | | | | | 54,431 | | | | 109,764 | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | 7 | | | | | 670,952 | | | | 706,102 | |
| Other non-current provisions | | | | | | | 619,046 | | | | 674,148 | |
| Non-current lease liabilities | | 13,15 | | | | | 11,724,587 | | | | 12,878,027 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | 8 | | | | | 952,486 | | | | 676,406 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | | | | | 16,808,286 | | | | 17,588,359 | |
| Total liabilities | | | | ₩ | | | 37,036,770 | | | | 38,697,788 | |
| Equity | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital | | 12 | | ₩ | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | |
| Other reserves | | 12 | | | | | (27,722,641 | ) | | | (27,722,641 | ) |
| Retained earnings | | | | | | | 38,422,024 | | | | 38,500,808 | |
| Equity attributable to owners of the Parent Company | | | | | | | 11,199,383 | | | | 11,278,167 | |
| Non-controlling interest | | | | | | | 132,190 | | | | 411,556 | |
| Total equity | | | | | | | 11,331,573 | | | | 11,689,723 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | | | | ₩ | | | 48,368,343 | | | | 50,387,511 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed consolidated interim financial statements.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the Six-month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Note | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won except per share data) | |
| Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Content revenue | | 3,4 | | ₩ | | | 11,479,769 | | | | 32,276,753 | |
| - Related parties | | 18 | | | | | 4,046,663 | | | | 5,902,002 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 7,433,106 | | | | 26,374,751 | |
| F&B revenue | | 3,4 | | | | | 6,923,383 | | | | 8,963,370 | |
| - Related parties | | 18 | | | | | 29,992 | | | | 251 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 6,893,391 | | | | 8,963,119 | |
| Other revenue | | 3,4 | | | | | 578,827 | | | | 272,144 | |
| Total revenues | | | | | | | 18,981,979 | | | | 41,512,267 | |
| Cost of revenues | | | | | | | (16,837,518 | ) | | | (36,899,990 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | | | | | 2,144,461 | | | | 4,612,277 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | | | | | (2,054,742 | ) | | | (1,849,137 | ) |
| Other income | | | | | | | 548,442 | | | | 145,132 | |
| Other expenses | | | | | | | (322,366 | ) | | | (6,110 | ) |
| Operating profit | | | | | | | 315,795 | | | | 2,902,162 | |
| Finance income | | | | | | | 172,646 | | | | 1,418,336 | |
| - Related parties | | 18 | | | | | 60,750 | | | | 744,668 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 111,896 | | | | 673,668 | |
| Finance costs | | 13,15 | | | | | (907,934 | ) | | | (937,012 | ) |
| - Related parties | | 18 | | | | | (120,831 | ) | | | (36,182 | ) |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | (787,103 | ) | | | (900,829 | ) |
| Profit(Loss) before income tax | | | | | | | (419,493 | ) | | | 3,383,486 | |
| Income tax benefit (expense) | | 8 | | | | | 61,343 | | | | (913,800 | ) |
| Profit(Loss) for the period | | | | ₩ | | | (358,150 | ) | | | 2,469,686 | |
| Other comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Items that will not be reclassified to income or loss: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remeasurement of defined benefit liabilities | | 12 | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total comprehensive income(Loss) for the period | | | | ₩ | | | (358,150 | ) | | | 2,469,686 | |
| Profit (loss) attributable to: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Owners of the Parent Company | | | | | | | (78,784 | ) | | | 2,927,604 | |
| Non‑controlling interest | | | | | | | (279,366 | ) | | | (457,918 | ) |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) attributable to: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Owners of the Parent Company | | | | | | | (78,784 | ) | | | 2,927,604 | |
| Non-controlling interest | | | | | | | (279,366 | ) | | | (457,918 | ) |
| Earnings per share (in Korean won) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic earnings per share | | 5 | | ₩ | | | (933 | ) | | | 32,004 | |
| Diluted earnings per share | | 5 | | | | | (933 | ) | | | 32,004 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed consolidated interim financial statements.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
For the Six-month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | | | | | Attributable to owners of the Parent Company | | | Non- | | | | |
| | | Note | | | | Share
capital | | | Other
reserves | | | Retained
earnings | | | Total | | | controlling
interest | | | Total
equity | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at January 1, 2023 | | | | ₩ | | | 500,000 | | | | (667,927 | ) | | | 35,363,622 | | | | 35,195,695 | | | | 720,382 | | | | 35,916,077 | |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Profit (loss) for the period | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,927,604 | | | | 2,927,604 | | | | (457,918 | ) | | | 2,469,686 | |
| Transaction with owners, recognized directly in equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Treasury shares acquired | | | | | | | - | | | | (27,128,262 | ) | | | - | | | | (27,128,262 | ) | | | - | | | | (27,128,262 | ) |
| Balance at June 30, 2023 | | | | | | | 500,000 | | | | (27,796,189 | ) | | | 38,291,226 | | | | 10,995,037 | | | | 262,464 | | | | 11,257,501 | |
| Balance at January 1, 2024 | | | | | | | 500,000 | | | | (27,722,641 | ) | | | 38,500,808 | | | | 11,278,167 | | | | 411,556 | | | | 11,689,723 | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (78,784 | ) | | | (78,784 | ) | | | (279,366 | ) | | | (358,150 | ) |
| Balance at June 30, 2024 | | | | ₩ | | | 500,000 | | | | (27,722,641 | ) | | | 38,422,024 | | | | 11,199,383 | | | | 132,190 | | | | 11,331,573 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed consolidated interim financial statements.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the Six-month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Note | | | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | 17 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income(loss) for the period | | | | ₩ | | | (358,150 | ) | | | 2,469,686 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | | 17 | | | | | (1,900,652 | ) | | | (13,484,891 | ) |
| Interest received | | | | | | | 20,694 | | | | 20,216 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | | | (527,262 | ) | | | (489,030 | ) |
| Income taxes paid | | | | | | | (325,126 | ) | | | (1,156,886 | ) |
| Dividend received | | | | | | | 1,463 | | | | 1,463 | |
| Net cash inflow (outflow) from operating activities | | | | | | | (3,089,033 | ) | | | (12,639,442 | ) |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payments for short-term loans | | | | | | | (1,875,862 | ) | | | (3,660,676 | ) |
| - Related parties | | 18 | | | | | (1,724,988 | ) | | | (3,510,676 | ) |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | (150,874 | ) | | | (150,000 | ) |
| Proceeds from short-term loans | | | | | | | 1,489,500 | | | | 290,000 | |
| - Related parties | | | | | | | 1,189,500 | | | | 280,000 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 300,000 | | | | 10,000 | |
| Payments for long-term loans | | | | | | | - | | | | (1,000,000 | ) |
| - Related parties | | 18 | | | | | - | | | | (1,000,000 | ) |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Payments for other financial assets | | | | | | | (153,964 | ) | | | (141,104 | ) |
| Collection of other financial assets | | | | | | | 320,334 | | | | 3,505,154 | |
| Proceeds from disposal of property and equipment | | | | | | | 12,100 | | | | 3,365 | |
| Purchase of property and equipment | | | | | | | (144,540 | ) | | | (595,018 | ) |
| Proceeds from Lease Incentives | | | | | | | 1,486 | | | | - | |
| Net cash outflow in investing activities | | | | | | | (350,946 | ) | | | (1,598,279 | ) |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | 17 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from short-term borrowings | | | | | | | 80,000 | | | | - | |
| - Related parties | | 18 | | | | | 80,000 | | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Repayment of short-term borrowings | | | | | | | (40,000 | ) | | | - | |
| - Related parties | | 18 | | | | | (40,000 | ) | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Repayment of current portion of long-term borrowings | | | | | | | (12,480 | ) | | | (12,480 | ) |
| Acquisition of Treasury shares | | | | | | | - | | | | (8,677,100 | ) |
| Repayment of lease liabilities | | | | | | | (840,227 | ) | | | (780,107 | ) |
| Net cash outflow in financing activities | | | | | | | (812,707 | ) | | | (9,469,687 | ) |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | (132,937 | ) | | | 349,247 | |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | (4,252,686 | ) | | | (23,707,408 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the period | | | | | | | 8,585,634 | | | | 30,581,556 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of the period | | | | ₩ | | | 4,200,011 | | | | 7,223,395 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed consolidated interim financial statements.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
1. Reporting entity
The Parent Company
Play Company Co., Ltd. (“the Parent Company”) was incorporated in June 2012 and the Parent Company’s registered office is at Business Tower 20F, 396 World Cup buk-ro, Mapo-gu, Seoul, Korea. These condensed consolidated interim financial statements comprise the Parent Company and its subsidiary (together referred to as the “Group”). The Group generates revenue primarily through the sale of the Group’s entertainment content and services, and food and beverage products as well as through the licensing of the Group’s intellectual property in food and beverage business. The Parent Company primarily engages in the provision of goods to its customers by offering made-to-order services to plan the projects, design merchandise, and deliver customized products to its customers, utilizing the intellectual property associated with K-pop artists. Play F&B Co., Ltd. (the “Subsidiary”) operates a retail bakery-cafe business and franchising business under the concept names ‘Our Bakery’. As of June 30, 2024, retail operations consist of 12 Company-owned bakery-cafes and 16 franchise-operated bakery-cafes located in South Korea and China.
The Parent Company’s major shareholders and their respective percentage of ownership as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | Number of shares
(in shares) | | | Percentage of
ownership (%) | | | Number of shares
(in shares) | | | Percentage of
ownership (%) | |
| Cho, Hyeong Seok | | | 83,418 | | | | 83.4 | % | | | 83,418 | | | | 83.4 | % |
| Solaire Partners Co., LLC | | | 1,000 | | | | 1.0 | % | | | 1,000 | | | | 1.0 | % |
| Subtotal (outstanding) | | | 84,418 | | | | 84.4 | % | | | 84,418 | | | | 84.4 | % |
| Plus: Treasury shares | | | 15,582 | | | | 15.6 | % | | | 15,582 | | | | 15.6 | % |
| Total (issued) | | | 100,000 | | | | 100.0 | % | | | 100,000 | | | | 100.0 | % |
Consolidated Subsidiary
Details of the consolidated subsidiary as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Percentage of ownership (%) | | | | | |
| Subsidiary | | Location | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31, 2023 | | | Fiscal year end | | Main business |
| Play F&B | | Korea | | 67.1 | | | 67.1 | | | December | | Sale of food and beverages |
Condensed financial information of subsidiary
Condensed financial information of subsidiary as of and for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | June 30, 2024 | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Subsidiary | | Total
assets (*1) | | | Total
liabilities (*1) | | | Revenues (*1) | | | Loss
for the
period (*1) | |
| Play F&B | | | 17,412,153 | | | | 20,609,961 | | | | 7,502,210 | | | | (439,162 | ) |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | June 30, 2023 | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Subsidiary | | Total assets (*1) | | | Total
liabilities (*1) | | | Revenues (*1) | | | Loss for the
period (*1) | |
| Play F&B | | | 20,727,052 | | | | 23,741,610 | | | | 9,235,514 | | | | (1,286,621 | ) |
| (*1) | The condensed financial information was prepared based on amounts before eliminating intergroup transactions. |
2. Basis of Presentation and Material Accounting Policies
These interim financial statements for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 have been prepared in accordance with International Accounting Standards (“IAS”) 34 Interim Financial Reporting as issued by International Accounting Standard Board (“IASB”), and should be read in conjunction with the Group’s last annual consolidated financial statements as at and for the year ended December 31, 2023 (“last annual financial statements”). They do not include all of the information required for a complete set of financial statements prepared in accordance with IFRS Accounting Standards. However, selected explanatory notes are included to explain events and transactions that are significant to an understanding of the changes in the Group’s financial position and performance since the last annual financial statements.
| B. | Material Accounting Policies |
Material accounting policies and method of computation used in the preparation of the condensed consolidated interim financial statements are consistent with those of the last annual financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2023, except for the changes as described below.
Income tax expense
Income tax expense for the interim period is recognized based on management’s best estimate of the weighted average annual income tax rate expected for the full financial year. The estimated average annual effective income tax rate is applied to the pre-tax income of the interim period.
| i. | New and amended standards or interpretations adopted by the Group |
The Group has applied the following standards and interpretations for the first time for their annual reporting period commencing January 1, 2024.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements
The amendments to IAS 1 clarify that the classification of liabilities as current or non-current should be based on rights that are in existence at the end of the reporting period and that the classification is unaffected by management’s intentions or expectations about whether an entity will exercise its right to defer settlement of a liability. The amendments also introduce a definition of settlement to make clear that settlement includes the transfer to the counterparty of the entity’s own equity instruments, however, it would be excluded if an option to settle the liability by the transfer of the entity’s own equity instruments is recognized separately from the liability as an equity component of a compound financial instrument. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Group’s interim financial statements.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
IAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows, and IFRS 7, Financial Instruments: Disclosures
The amendments add to the disclosure objectives in IAS 7, Statement of Cash Flows, that information about supplier financing arrangements should be disclosed to enable users of financial statements to assess the impact of those arrangements on the Group’s liabilities and cash flows. The amendments also amend IFRS 7, Financial Instruments: Disclosures, to add supplier financing arrangements as an example of a requirement to disclose information about an entity’s exposure to concentrations of liquidity risk. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Group’s interim financial statements.
IFRS 16 Leases
The amendments add requirements for the subsequent measurement of sale-and-leaseback transactions that are accounted for as sales in accordance with IFRS 15, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. The amendments require the seller lessee to calculate the ‘lease payments’ or ‘revised lease payments’ in a way that does not result in the seller-lessee recognizing any gain or loss for the rights of use that the seller-lessee continues to retain after the lease commences. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Group’s interim financial statements.
| ii. | New and amended standards or interpretations not yet adopted by the Group |
The following new accounting standards and interpretations that have been published that are not mandatory for June 30, 2024 reporting periods and have not been early adopted by the Group.
IAS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates
The amendments require exchangeability of two currencies should be assessed in order to clarify reporting of foreign currency transactions in the absence of normal-functioning foreign exchange market. The amendments also require applicable spot exchange rate should be determined when the assessment indicates two currencies lack exchangeability. The amendments are effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2025, with early application permitted. The Group does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the Group’s interim financial statements.
IFRS 16 Leases – Lease Liability in a Sale and Leaseback
The amendments add requirements for the subsequent measurement of sale-and-leaseback transactions that are accounted for as sales in accordance with IFRS 15, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. The amendments require the seller-lessee to calculate the ‘lease payments’ or ‘revised lease payments’ in a way that does not result in the seller-lessee recognizing any gain or loss for the rights of use that the seller-lessee continues to retain after the lease commences. The amendments are effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, with early application permitted. The Group does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the Group’s interim financial statements.
IFRS 18 Presentation and Disclosure in Financial Statements
Items in the statement of profit or loss will need to be classified into one of five categories: operating, investing, financing, income taxes and discontinued operations. IFRS 18 requires the Company to present specified totals and subtotals: ‘Operating profit or loss’, ‘Profit or loss’ and ‘Profit or loss before financing and income taxes’. Information related to management-defined performance measures should be disclosed. IFRS 18 also provides enhanced guidance on the principles of aggregation and disaggregation which focus on grouping items based on their shared characteristics. The new standard should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2027, and earlier application is permitted. The Group is in review for the impact of this new standard on the financial statements.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
The consolidated financial statements have been prepared on the historical cost basis except for the following items, which are measured on an alternative basis on each reporting date.
| Items | | Measurement bases |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | Present value |
| Financial instruments measured at fair value through profit or loss (“FVTPL”) | | Fair value |
3. Operating segments
The Group’s operating segments have been identified to be each business unit, by which the Group provides different services and merchandise.
The Group assesses the performance of each operating segment based on operating profit, and there is no difference with the amounts reported on the consolidated statement of profit or loss, except for intergroup transactions.
The following summary describes the operations of each reportable segment.
| Operating segments | | Operations |
| Content | | Sale and distribution of content consumer products and providing production services |
| Food and beverages | | Sale of food and beverages products and licensing of the intellectual property |
The Group’s chief executive officer reviews the internal management reports of each business unit at least quarterly.
| B. | Information about reportable segments |
Information related to each reportable segment is set out below. Segment operating profit is used to measure performance because management believes that this information is the most relevant in evaluating the results of the respective segments relative to other entities that operate in the same industries.
The segment information for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | Six-month period ended June 30, 2024 | |
| | | | | Content | | | F&B | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Segment revenue | | ₩ | | | 11,479,769 | | | | 7,502,209 | | | | 18,981,978 | |
| Elimination of intersegment revenue | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Consolidated net revenue | | | | | 11,479,769 | | | | 7,502,209 | | | | 18,981,978 | |
| Depreciation/Amortization | | | | | 270,615 | | | | 1,401,830 | | | | 1,672,445 | |
| Segment operating profit | | | | | 475,802 | | | | (160,007 | ) | | | 315,795 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | | | Six-month period ended June 30, 2023 | |
| | | | | Content | | | F&B | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Segment revenue | | ₩ | | | 32,276,753 | | | | 9,235,514 | | | | 41,512,267 | |
| Elimination of intersegment revenue | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Consolidated net revenue | | | | | 32,276,753 | | | | 9,235,514 | | | | 41,512,267 | |
| Depreciation/Amortization | | | | | 373,616 | | | | 1,243,162 | | | | 1,616,778 | |
| Segment operating profit | | | | | 3,779,125 | | | | (876,963 | ) | | | 2,902,162 | |
Content segment and food and beverages segments are managed on a worldwide basis, but operate manufacturing facilities and sales offices primarily in Seoul, South Korea. The geographic information analyses the Group’s revenue by the customer’s country of domicile. In presenting the geographic information, segment revenue and non-current assets have been based on the geographic location of customers.
Summary of the Group’s operation by region based on the location of customers for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 16,860,856 | | | | 32,205,661 | |
| USA | | | | | 13 | | | | 368,059 | |
| Japan | | | | | 2,045,268 | | | | 8,927,495 | |
| Other | | | | | 75,841 | | | | 11,052 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 18,981,978 | | | | 41,512,267 | |
Summary of the Group’s non-current assets based on the location as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 28,385,406 | | | | 30,282,905 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Revenues from major customers that amount to 10% or more of the Group’s revenue for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Customer A (Content segment) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 4,046,663 | | | | 1,647,498 | |
| % | | | | | 21.32 | % | | | 3.16 | % |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 4,046,663 | | | | 1,647,498 | |
4. Revenue
The Group generates revenue primarily through the sale of the Group’s entertainment content and production services, and food and beverage products. Other sources of revenue include the franchise royalty fees from licensing of the Group’s intellectual property in food and beverage business.
Revenue from contracts with customers for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Revenue from contracts with customers | | ₩ | | | 18,981,979 | | | | 41,512,267 | |
| B. | Disaggregation of revenue from contracts with customers |
In the following table, revenue from contracts with customers is disaggregated by primary geographical market, major products and service lines and timing of revenue recognition. The table also includes a reconciliation of the disaggregated revenue with the Group’s reportable segments (see Note 3).
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Revenue from contracts with customers based on the service contract type, the timing of satisfaction of performance obligations, and by primary geographical market for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month period ended
June 30, 2024 | | | Six-month period ended
June 30, 2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Major products/service lines | | | | | | | | | | |
| Content goods and merchandises | | | | | | | | | | |
| Video Project & Merchandise Items | | ₩ | | | 8,124,822 | | | | 30,725,982 | |
| Others | | | | | 3,354,947 | | | | 1,550,771 | |
| Subtotal | | ₩ | | | 11,479,769 | | | | 32,276,753 | |
| F&B | | | | | | | | | | |
| Food and beverages | | ₩ | | | 6,923,383 | | | | 8,963,370 | |
| Franchise royalties and fees | | | | | 578,827 | | | | 272,144 | |
| Subtotal | | ₩ | | | 7,502,210 | | | | 9,235,514 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 18,981,979 | | | | 41,512,267 | |
| Timing of revenue recognition | | | | | | | | | | |
| At a point in time | | ₩ | | | 18,687,441 | | | | 41,240,123 | |
| Over time | | | | | 294,538 | | | | 272,144 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 18,981,979 | | | | 41,512,267 | |
The balance of contract liabilities from contracts with customers as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Contract assets | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 73,463 | |
The contract liabilities primarily relate to the advance consideration received from customers, for which revenue is recognized at a point in time when the product is delivered to the customer.
As of June 30, 2024, the Group has an advance payment to a vendor, for fulfilling a contract in which the Group acts as an agent. The advance payment amount as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are respectively as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Advance payment to a vendor(included in other current assets) | | ₩ | | | 6,959,034 | | | | - | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
5. Earnings per share
| A. | Basic earnings per share |
The calculation of basic Earning per share has been based on the following profit attributable to ordinary shareholders and weighted-average number of ordinary shares outstanding.
| i. | Profit attributable to ordinary shareholders (basic) |
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Profit for the period, attribute to the owners of Parent Company | | ₩ | | | (78,784 | ) | | | 2,927,604 | |
| Dividends on non-redeemable preference shares | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Profit attributable to ordinary shareholders | | ₩ | | | (78,784 | ) | | | 2,927,604 | |
| ii. | Weighted-average number of ordinary shares (basic) |
| | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | (In number of shares) | |
| Number of ordinary shares issued at January 1 | | | 84,418 | | | | 100,000 | |
| Effect of treasury shares held | | | - | | | | (8,523 | ) |
| Weighted-average number of ordinary shares for the six months ended June 30 | | | 84,418 | | | | 91,477 | |
| B. | Anti-diluted earnings per share |
Diluted earnings per share is not different from basic earnings per share as there is no dilution effects of potential ordinary shares for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023.
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In Korean Won) | |
| Basic earnings per share | | ₩ | | | (933 | ) | | | 32,004 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
6. Share-based payment arrangements
| A. | Description of share-based payment arrangements |
As of June 30, 2024, the Group had the following share-based payment arrangements.
| i. | Share option plan (Tandem awards) |
On December 31, 2021, the Parent Company established tandem award share option plan that entitle employees to a cash payment or shares of the Parent Company. Under these plan, holders of vested options are entitled to a cash payment or purchase shares at the exercise price. Currently, these plans are limited to employees. The share option plans granted to the employees were cancelled during the year ended December 31, 2022.
| ii. | Share option plan (cash-settled) |
On June 30, 2021, the Subsidiary granted 400 share options entitling employees to a cash payment after satisfying 2 vesting conditions below. The amount of the cash payment is determined based on the difference between the share price of the Group at the time of exercise and exercise price.
The key terms and conditions related to the grants under these plans are as follows:
Grant date/
employees entitled | | | Number of
instruments | | | Vesting conditions | | | Contractual life
of options | | | Type | | | Underlying
assets |
| Options granted to employees | | | | | | |
| As of June 30, 2021 | | | 400 | | | 2 years’ service from grant date and the Play F&B’s annual average Adjusted EBITDA (*1) equals or exceeds Korean Won 1,375,000 thousand at the date of exercise | | | 7 years | | | Cash-settled | | | Play F&B’s ordinary shares |
| (*1) | Adjusted EBITDA = Operating Income +Depreciation of PP&E +Amortization of Intangible Assets +Advertising & marketing expenses |
| B. | Measurement of fair values |
| i. | Cash-settled share-based payment arrangement |
The fair value of the employee share options has been measured using a binomial model.
The inputs used in the measurement of the fair values at grant date and measurement date of the cash-settled share-based payment arrangement are as follows:
Share appreciation rights
(cash- settled) | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In Korean Won) | |
| Fair value of option | | ₩ | | | 564,603 | | | | 504,547 | |
| Share price | | | | | 1,484,262 | | | | 1,247,333 | |
| Exercise price | | ₩ | | | 1,100,000 | | | | 1,100,000 | |
| Risk- free interest rate (based on government bonds) | | | | | 3.18 | % | | | 3.15 | % |
| Volatility (*) | | | | | 22.48 | % | | | 37.49 | % |
| (*) | Volatility has been based on an evaluation of the historical volatility of other companies’ share price, which are listed in KOSDAQ, particularly over the historical period commensurate with prior one year. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| C. | Reconciliation of outstanding share options |
The number and exercise prices of share options under the share option plan for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows.
| | | Six-month period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
Share option plan
(cash-settled) | | Number of
options | | | | Exercise
price | | | Number of
options | | | | Exercise
price | |
| | | (In Korean Won and number of options) | |
| Outstanding at January 1 | | | 400 | | ₩ | | | 1,100,000 | | | | 400 | | ₩ | | | 1,100,000 | |
| Cancelled during the year | | | - | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | - | |
| Exercised during the year | | | - | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | - | |
| Granted during the year | | | - | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | - | |
| Outstanding at June 30 | | | 400 | | | | | 1,100,000 | | | | 400 | | | | | 1,100,000 | |
| Exercisable at June 30 | | | - | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | ₩ | | | - | |
Details of the liabilities arising from the share option plan (cash-settled) are as follows.
| | | | | As of
June 30,
2024 | | | As of
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total carrying amount of liabilities for share-based payment | | ₩ | | | 225,841 | | | | 201,819 | |
| Total intrinsic value of liabilities for vested benefits | | | | | 153,705 | | | | 58,933 | |
7. Employee benefits
Details of defined benefit liability recognized as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Defined benefit liability | | ₩ | | | 670,952 | | | | 706,102 | |
The Group operates both the defined benefit plans and defined contribution plans as a retirement pension scheme. Defined benefit plans expose the Group to actuarial risks, such as longevity risk, currency risk, interest rate risk and market (investment) risk.
The expense recognized in relation to defined contribution plan for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 is Korean Won 147,814 thousand.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| A. | Movement in net defined benefit (asset) liability |
Details of reconciliation from the opening balances to the closing balances for the net defined benefit liability and its components as of June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Defined benefit obligation | | | Fair value of plan assets | | | Net defined Benefit liabilities | |
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | June 30,
2023 | | | June 30,
2024 | | | June 30,
2023 | | | June 30,
2024 | | | June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) |
| Beginning Balance | | ₩ | | | 706,102 | | | | 928,148 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 706,102 | | | | 928,148 | |
| Included in profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current service cost | | | | | 255,138 | | | | 303,459 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 255,138 | | | | 303,459 | |
| Interest expense | | | | | 15,559 | | | | 23,207 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 15,559 | | | | 23,207 | |
| Subtotal | | | | | 270,697 | | | | 326,666 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 270,697 | | | | 326,666 | |
| Other | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Benefits paid | | | | | (305,846 | ) | | | (311,360 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (305,846 | ) | | | (311,360 | ) |
| Subtotal | | | | | (305,846 | ) | | | (311,360 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (305,846 | ) | | | (311,360 | ) |
| Ending Balance | | ₩ | | | 670,952 | | | | 943,454 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 670,952 | | | | 943,454 | |
There are no contributions funded to its defined benefit plans as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023.
| C. | Employee benefit expenses |
| i. | Details of employee benefit expenses recognized for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows: |
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Wages and salaries | | ₩ | | | 3,938,796 | | | | 4,766,750 | |
| Expenses related to post-employment plans | | | | | 469,393 | | | | 348,207 | |
| Social security contributions | | | | | 206,297 | | | | 315,539 | |
| Fringe benefit | | | | | 282,408 | | | | 325,601 | |
| Cash settled Share-based payments | | | | | 24,022 | | | | 25,889 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 4,920,916 | | | | 5,781,986 | |
| ii. | Expenses are recognized in the condensed consolidated statements of comprehensive income (loss) as follows: |
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cost of revenues | | ₩ | | | 3,716,180 | | | | 4,676,317 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | | | 1,204,736 | | | | 1,105,669 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 4,920,916 | | | | 5,781,986 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
8. Income taxes
Details of income tax expenses for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current tax expense | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current year | | ₩ | | | 30,230 | | | | 971,478 | |
| Adjustments recognized related to prior period incomes (*) | | | | | (252,105 | ) | | | (4,780 | ) |
| | | ₩ | | | (221,875 | ) | | | 966,698 | |
| Deferred tax expense | | | | | | | | | | |
| Origination and reversal of temporary differences | | | | | 160,532 | | | | (52,898 | ) |
| Tax expense on continuing operations | | ₩ | | | (61,343 | ) | | | 913,800 | |
| (*) | In the normal course of business, the Group and its respective subsidiary are examined by taxation authority. The income tax refund (additional tax payments) are included in income taxes in the consolidated statements of operations. Our management regularly assesses the potential outcomes of these examinations and any future examinations for the current or prior years in determining the adequacy of its liabilities for income taxes. |
We establish additional current tax liabilities for income taxes when, despite the belief that tax positions are fully supportable, there remain positions that do not meet the minimum probability threshold, which is a tax position that is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by the applicable taxing authority. The impact of current tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions, as well as the related net interest and penalties, are included in income taxes in the consolidated statements of operations.
9. Inventories
Details of inventories as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Merchandise | | ₩ | | | 2,346,550 | | | | 1,110,974 | |
| Work in process | | | | | 307,719 | | | | 391,939 | |
| Allowance for Inventories valuation | | | | | (1,283,678 | ) | | | (1,078,353 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,370,591 | | | | 424,560 | |
In 2024, inventories amounted to Korean Won 14,993,791 thousand (2023: Korean Won 22,403,694 thousand) were recognized as an expense during the year and included in ‘cost of sales’.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
The Group recognizes the full provision for inventories with more than one year aging from the initiation of project according to the Group’s accounting policies. For inventories with less than one year aging from the initial production with an estimated recovery period exceeding one year, it is also recognized as a provision. Loss on valuation of inventories amounted to Korean Won 577,388 thousand (2023: Korean Won 203,141 thousand) and reversal of allowance for inventories valuation amounted to Korean Won 372,064 thousand (2023: Korean Won 489,714 thousand) were recognized during the six-month period ended June 30, 2024.
10. Investment properties
| A. | Reconciliation of carrying amount |
Details of Investment properties as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Book value | | ₩ | | | 4,277,447 | | | | 4,311,539 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | | | | | (1,328,686 | ) | | | (1,050,744 | ) |
| Carrying amount | | ₩ | | | 2,948,761 | | | | 3,260,795 | |
Changes in Investment properties for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance as of January 1 | | ₩ | | | 3,260,795 | | | | - | |
| Lease modification | | | | | (34,091 | ) | | | - | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (277,943 | ) | | | - | |
| Balance as of June 30 | | ₩ | | | 2,948,761 | | | | - | |
| B. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
Rental income recognized by the Group for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 was Korean Won 429,138 thousand (2023: nil). Depreciation expense, included in ‘cost of revenues’, was as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Depreciation | | ₩ | | | 277,943 | | | | - | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
11. Intangible assets and goodwill
| A. | Reconciliation of carrying amount |
Details of intangible assets as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| | | | | Book value | | | Accumulated
amortization | | | Carrying
amount | |
| Software | | ₩ | | | 487,309 | | | | (336,353 | ) | | | 150,956 | |
| Brand | | | | | 5,388,000 | | | | (830,650 | ) | | | 4,557,350 | |
| Goodwill | | | | | 3,267,730 | | | | - | | | | 3,267,730 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 9,143,039 | | | | (1,167,003 | ) | | | 7,976,036 | |
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| | | | | Book value | | | Accumulated
amortization | | | Carrying
amount | |
| Software | | ₩ | | | 487,309 | | | | (289,762 | ) | | | 197,547 | |
| Brand | | | | | 5,388,000 | | | | (695,950 | ) | | | 4,692,050 | |
| Goodwill | | | | | 3,267,730 | | | | | | | | 3,267,730 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 9,143,039 | | | | (985,712 | ) | | | 8,157,327 | |
Details of the changes in intangible assets for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month period ended June 30, 2024 | |
| | | | | Software | | | Brand | | | Goodwill | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 197,547 | | | | 4,692,050 | | | | 3,267,730 | | | | 8,157,327 | |
| Acquisitions | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Amortization | | | | | (46,591 | ) | | | (134,700 | ) | | | - | | | | (181,291 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 150,956 | | | | 4,557,350 | | | | 3,267,730 | | | | 7,976,036 | |
| | | | | Six-month period ended June 30, 2023 | |
| | | | | Software | | | Brand | | | Goodwill | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 290,947 | | | | 4,961,450 | | | | 3,267,730 | | | | 8,520,127 | |
| Acquisitions | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Amortization | | | | | (46,810 | ) | | | (134,700 | ) | | | - | | | | (181,510 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 244,137 | | | | 4,826,750 | | | | 3,267,730 | | | | 8,338,617 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
The classification of amortization in the statements of comprehensive income for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | ₩ | | | 181,291 | | | | 181,510 | |
12. Capital and reserves
| A. | Share capital and share premium |
Details of share capital and share premium as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In Korean won and number of shares) | |
| Number of authorized shares | | | | | 900,000 | | | | 900,000 | |
| Value per share | | ₩ | | | 5,000 | | | | 5,000 | |
| Number of shares issued | | | | | 100,000 | | | | 100,000 | |
| Common shares | | ₩ | | | 500,000,000 | | | | 500,000,000 | |
Holders of these shares are entitled to dividends as declared from time to time and are entitled to one vote per share at general meetings of the Group.
On March 24, 2023, the Group acquired a 15.6% interest of the Parent Company’s issued shares for approximately Korean Won 27,128,262 thousand.
Details of treasury shares for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | Numbers of
shares | | | Carrying
amount | | | Numbers of
shares | | | Carrying
amount | |
| | | | | (In Korean won and number of shares) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 15,582 | | | | 27,128,262 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Acquisition | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 15,582 | | | | 27,128,262 | |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 15,582 | | | | 27,128,262 | | | | 15,582 | | | | 27,128,262 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| B. | Other components of equity |
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liability | | ₩ | | | 151,921 | | | | 151,921 | |
| Other capital surplus | | | | | (746,300 | ) | | | (746,300 | ) |
| Treasury shares | | | | | (27,128,262 | ) | | | (27,128,262 | ) |
| Other components of equity | | ₩ | | | (27,722,641 | ) | | | (27,722,641 | ) |
13. Borrowings/payable and Loans/receivable
Borrowings as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term borrowings | | ₩ | | | 3,370,000 | | | | 3,330,000 | |
| Current portion of long-term borrowings, net | | | | | 24,960 | | | | 24,960 | |
| Current lease liabilities (*) | | | | | 1,657,138 | | | | 1,630,482 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 5,052,098 | | | | 4,985,442 | |
| Non-Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term borrowings, excluding current portion, net | | ₩ | | | 2,046,433 | | | | 2,008,041 | |
| Non-current lease liabilities (*) | | | | | 11,724,587 | | | | 12,878,027 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 13,771,020 | | | | 14,886,068 | |
| (*) | The interest rate related to lease liabilities reflects the incremental borrowing rate based on the Group’s credit. The amount of interest expense related to lease liabilities incurred during the six-month period ended June 30, 2024 is Korean Won 454,773 thousand (June 30, 2023: Korean Won 529,400 thousand). Additionally, the amount of short-term lease payments and low-value assets lease payments not included the measurement of lease liabilities during the six-month period ended June 30, 2024 are Korean Won 18,829 thousand (June 30, 2023: Korean Won 6,902 thousand). |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| A. | Terms and repayment schedule |
The terms and conditions of outstanding borrowings as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| | | Currency | | Nominal interest rate | | Maturity | | | Face
value | | | Carrying
amount | | | Face
value | | | Carrying
amount | |
| Secured borrowings (*1) | | KRW | | KORIBOR +1.692% | | 20-Dec-24 | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | |
| Secured borrowings (*2) | | KRW | | 5.923% | | 27-Feb-25 | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Secured borrowings (*3) | | KRW | | 5.9086% | | 27-Jun-25 | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Secured borrowings (*4) | | KRW | | KORIBOR +2.388% | | 16-Sep-25 | | | | 100,000 | | | | 31,200 | | | | 100,000 | | | | 43,680 | |
| Unsecured borrowings | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 700,000 | | | | 700,000 | | | | 700,000 | | | | 700,000 | |
| Unsecured borrowings | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 2,200,000 | | | | 2,040,193 | | | | 2,200,000 | | | | 1,989,321 | |
| Unsecured borrowings | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 180,000 | | | | 170,000 | | | | 130,000 | | | | 130,000 | |
| Total interest-bearing liabilities | | | | 5,680,000 | | | | 5,441,393 | | | | 5,630,000 | | | | 5,363,001 | |
| (*1) | As of June 30, 2024, the Group is provided a guarantee of Korean Won 412,775 thousand (2023: Korean Won 412,775 thousand) by the CEO of the Group. The Group provided the intellectual property(IP) rights as collateral. |
| (*2) | As of June 30, 2024, the Group is provided a guarantee of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand (2023: Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand) from the CEO of the Group. |
| (*3) | As of June 30, 2024, the Group is provided a guarantee of Korean Won 900,000 thousand (2023: Korean Won 900,000 thousand) by Korea Credit Guarantee Fund. |
| (*4) | As of June 30, 2024, the Group provides machines with a carrying amount of Korean Won 119,593 thousand (2023: Korean Won 133,948 thousand) as collaterals for the secured borrowings with equal amortization repayment condition. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| B. | Terms and collection schedule |
The terms and conditions of outstanding loans as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| | | Currency | | Nominal interest rate | | Maturity | | | Face
value | | | Carrying
amount | | | Face
value | | | Carrying
amount | |
| Cho Hyung Seok | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 69,267 | | | | 69,267 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Cho Mi Kyung (*1) | | KRW | | 2.00% | | 31-Aug-25 | | | | 400,000 | | | | - | | | | 400,000 | | | | - | |
| Bonanza Pictures | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Mar-21 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | |
| Coam payments (*2) | | KRW | | 12.00% | | 31-May-22 | | | | 200,000 | | | | 200,000 | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | |
| Jung Kyung Han | | KRW | | 3.00% | | 14-Sep-23 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | |
| Jung Kyung Han | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 874 | | | | 874 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Jung Bo Ram | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 43,721 | | | | 43,721 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| YY entertainment (*3) | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 150,000 | | | | - | | | | 150,000 | | | | 150,000 | |
| Second plan | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | |
| Second plan (*4) | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 100,000 | | | | 100,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Rainier Co., Ltd. | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 150,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Beacon Holdings, Inc. | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 100,000 | | | | 100,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Second plan (*4) | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 214,400 | | | | 214,400 | | | | 76,900 | | | | 76,900 | |
| Studio Cuat. Co., Ltd. (*4) | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 43,000 | | | | 43,000 | | | | 43,000 | | | | 43,000 | |
| Beacon Holdings, Inc. (*4) | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 85,000 | | | | 85,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | | | 1,646,262 | | | | 946,262 | | | | 1,259,900 | | | | 859,900 | |
| (*1) | The Group recognized a full provision for the balance of loan and accrued interest income. Accrued interest income as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are Korean Won 26,685 thousand and Korean Won 26,685 thousand, respectively. |
| (*2) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee by third party. |
| (*3) | The Group recognized a full provision for the balance of loan and accrued interest income as of June 30, 2024. Accrued interest income as of June 30, 2024 are Korean Won 6,333 thousand. |
| (*4) | The contract is automatically extended by one year if the loan is not collected until maturity date. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
14. Financial Instruments – Fair values and risk management
| A. | Accounting classifications and fair values |
The following table shows the carrying amounts and fair values of financial assets and financial liabilities, including their levels in the fair value hierarchy. It does not include fair value information for financial assets and financial liabilities not measured at fair value if the carrying amount is a reasonable approximation of fair value.
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of June 30, 2024 are as follows:
| | | | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Guaranteed Return Insurances (short-term) (*) | | ₩ | | | 7,473 | | | | - | | | | 7,473 | | | | - | | | | 7,473 | |
| Guaranteed Return Insurances (long-term) (*) | | | | | 317,625 | | | | - | | | | 317,625 | | | | - | | | | 317,625 | |
| Long-term investment securities | | | | | 623,558 | | | | 184,548 | | | | - | | | | 439,010 | | | | 623,558 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 948,656 | | | | 184,548 | | | | 325,098 | | | | 439,010 | | | | 948,656 | |
| (*) | The fair value of guaranteed return insurances classified at Level 2 in the fair value hierarchy is determined using an evaluation of surrender proceeds received from financial institutions. |
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Guaranteed Return Insurances (short-term) (*) | | ₩ | | | 9,391 | | | | - | | | | 9,391 | | | | - | | | | 9,391 | |
| Guaranteed Return Insurances (long-term) (*) | | | | | 307,729 | | | | - | | | | 307,729 | | | | - | | | | 307,729 | |
| Long-term investment securities | | | | | 640,739 | | | | 201,729 | | | | - | | | | 439,010 | | | | 640,739 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 957,859 | | | | 201,729 | | | | 317,120 | | | | 439,010 | | | | 957,859 | |
| (*) | The fair value of guaranteed return insurances classified at Level 2 in the fair value hierarchy is determined using an evaluation of surrender proceeds received from financial institutions. |
| B. | Measurement of fair values |
Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows:
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical asset or liability |
| ● | Level 2: all inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable (either directly that is, prices, or indirectly that is, derived from prices) for the asset or liability |
| ● | Level 3: unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
The fair value of financial instruments traded in an active market is determined based on the quoted market price as of the end of the reporting period. If the quoted prices are readily and regularly available through exchanges, sellers, brokers, industry groups, rating agencies or regulators and such prices represent actual market transactions that occur regularly between independent parties, they are considered active markets.
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market is determined using valuation techniques. These valuation techniques use as much market observable information as possible and use the least amount of group-specific information. At this time, if all the significant input variables required to measure the fair value are observable, the financial instruments are classified as Level 2.
If more than one significant input variable is not based on observable market information, the item is included in Level 3.
The valuation techniques used to measure the fair value of a financial instrument include:
| ● | Market price or dealer price of a similar financial instrument |
| ● | The fair value of derivative instruments is determined by discounting the amount to present value using the leading exchange rate as of the end of the reporting period |
15. Leases
The Group leases buildings and vehicles. The leases typically run for a period of 1 ~5 years, with an option to renew or terminate the lease after that date. The Group also leases water purifiers, copy machines, and others with contract terms of one to three years. These leases are short-term and/or leases of low-value items. The Group has elected not to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for these leases. Information about leases for which the Group is a lessee is presented below.
Right-of-use assets related to leased properties that do not meet the definition of investment property are presented as property, plant and equipment.
Details of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities recognized in the consolidated statements of financial position as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Acquisition price) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Buildings | | ₩ | | | 11,175,574 | | | | 16,820,786 | |
| Vehicles | | | | | 530,765 | | | | 267,776 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 11,706,339 | | | | 17,088,562 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Accumulated depreciation) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Buildings | | ₩ | | | (2,980,839 | ) | | | (1,879,717 | ) |
| Vehicles | | | | | (113,196 | ) | | | (119,274 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (3,094,035 | ) | | | (1,998,991 | ) |
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Net book value) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Buildings | | ₩ | | | 8,194,735 | | | | 14,941,069 | |
| Vehicles | | | | | 417,569 | | | | 148,502 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 8,612,304 | | | | 15,089,571 | |
Changes in right-of-use assets for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month period ended June 30, 2024 | |
| | | | | Building | | | Vehicles | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 9,268,936 | | | | 156,885 | | | | 9,425,821 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (602,554 | ) | | | (36,296 | ) | | | (638,850 | ) |
| Acquisitions | | | | | 56,084 | | | | 296,980 | | | | 353,064 | |
| Lease termination | | | | | (527,731 | ) | | | - | | | | (527,731 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 8,194,735 | | | | 417,569 | | | | 8,612,304 | |
| | | | | Six-month period ended June 30, 2023 | |
| | | | | Building | | | Vehicles | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 14,941,069 | | | | 148,502 | | | | 15,089,571 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (927,477 | ) | | | (38,089 | ) | | | (965,566 | ) |
| Acquisitions | | | | | 449,910 | | | | 93,157 | | | | 543,067 | |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 14,463,502 | | | | 203,570 | | | | 14,667,072 | |
| ii. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
Amounts recognized in profit or loss for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest expense relating to lease liabilities (included in finance cost) | | ₩ | | | 454,773 | | | | 529,400 | |
| Expense relating to short-term leases | | | | | 9,880 | | | | - | |
| Expense relating to leases of low-value assets excluding short-term leases | | | | | 8,949 | | | | 6,902 | |
| Gains on disposal of right-of-use assets | | | | | 96,251 | | | | - | |
| Expense relating to variable lease payments not included in the measurement of lease liabilities | | ₩ | | | 259,140 | | | | 455,761 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
The Company has revised the expense relating to variable lease payments not included in the measurement of lease liabilities for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2023 to be consistent with the classification as of June 30, 2024.
| iii. | Amounts recognized in statement of cash flows |
Amounts recognized in statements of cash flows for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total cash outflows of leases | | ₩ | | | 1,572,970 | | | | 1,772,170 | |
The Company has revised the total cash outflows of leases for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2023 to be consistent with the classification as of June 30, 2024.
Some property leases contain extension options exercisable by the Group. Where practicable, the Group seeks to include extension options in new leases to provide operational flexibility. The extension options held are exercisable only by the Group and not by the lessors. The Group assesses at the lease commencement date whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the extension options. The Group reassesses whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the options if there is a significant event or significant changes in circumstances within its control.
The Group has entered into a contract to pay revenue-based rent payment for a several lease agreements. If the revenue of the store that entered into the contract increase, the rent to be paid may proportionally increase. According to the contract, it is expected that 9 to 18% of sales will be paid.
The Group leases out its investment property consisting of its leased property.
The Group has classified these leases as operating leases because they do not transfer substantially all the risk and rewards incidental to the ownership of the assets. Note 10 sets out information about the operating leases of investment property.
Rental income recognized by the Group for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 was Korean Won 429,138 thousand (2023: nil).
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Maturity analysis of lease payments, showing the undiscounted lease payments to be received after June 30, 2024 and 2023 as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Less than 1 year | | ₩ | | | 832,031 | | | | - | |
| 1 ~ 2years | | | | | 132,728 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 964,759 | | | | - | |
16. Commitments
Key commitments the Group has entered into with financial institutions and others as of June 30, 2024 are as follows:
| Financial institutions | | Categories | | | | Credit limit | | | Borrowings amount | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Revolving credit (*1) | | ₩ | | | 2,000,000 | | | | - | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*2) | | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*3) | | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*4) | | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*5) | | | | | 100,000 | | | | 31,200 | |
| Shinhan Bank | | Revolving credit (*6) | | | | | 500,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 5,100,000 | | | | 2,531,200 | |
| (*1) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 2,400,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*2) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 412,775 thousand by the CEO of the Group. Also, the Group provides intellectual property (IP) rights as collateral for the borrowing. |
| (*3) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*4) | The Group is provided a guarantee of Korean Won 900,000 thousand by Korea Credit Guarantee Fund. |
| (*5) | The Group provides machinery as collateral for the borrowing. |
| (*6) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 600,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Key commitments the Group has entered into with financial institutions and others as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| Financial institutions | | Categories | | | | Credit limit | | | Borrowings amount | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Revolving credit (*1) | | ₩ | | | 2,000,000 | | | | - | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*2) | | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*3) | | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*4) | | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*5) | | | | | 100,000 | | | | 43,680 | |
| Shinhan Bank | | Revolving credit (*6) | | | | | 500,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 5,100,000 | | | | 2,543,680 | |
| (*1) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 2,400,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*2) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 412,775 thousand by the CEO of the Group. Also, the Group provides intellectual property (IP) rights as collateral for the borrowing. |
| (*3) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*4) | The Group is provided a guarantee of Korean Won 900,000 thousand by Korea Credit Guarantee Fund. |
| (*5) | The Group provides machinery as collateral for the borrowing. |
| (*6) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 600,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| B. | Guarantees by individuals |
Details of guarantees provided by individuals other than related parties as of June 30, 2024 are as follows:
| Guaranteed by | | Details of guarantee | | | | Guarantee limit | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Seoul Guarantee Insurance Company | | Performance guarantee, etc. | | ₩ | | | 916,157 | |
| Korea credit guarantee fund | | Loan guarantee | | | | | 900,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,816,157 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Details of guarantees provided by individuals other than related parties as of December 31, 2023are as follows:
| Guaranteed by | | Details of guarantee | | | | Guarantee limit | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Seoul Guarantee Insurance Company | | Performance guarantee, etc. | | ₩ | | | 808,693 | |
| Korea credit guarantee fund | | Loan guarantee | | | | | 900,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,708,693 | |
| C. | List of assets provided as collateral |
List of assets that the Group provided as collateral as of June 30, 2024and December 31, 2023are as follows:
| | | Counterparty receiving the collateral | | usage restrictions | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Provided as collateral for employee loans (*1) | | ₩ | | | 300,000 | | | | 300,000 | |
| Machinery | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Provided as collateral for short-term borrowings (*2) | | | | | 119,593 | | | | 133,948 | |
| (*1) | The Group provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 231,000 thousand as of June 30, 2024 (December 31, 2023 Korean Won 231,000 thousand) |
| (*2) | As of June 30, 2024 Industrial Bank of Korea has established a pledge of Korean Won 180,000 thousand (December 31, 2023: Korean Won 180,000 thousand) on the insurance coverage amount for property damage provided by Hyundai Marine & Fire Insurance Company. |
The Group provides intellectual property (IP) rights as collateral for the borrowing.
On March 31, 2023, the CEO, who is the dominant shareholder of the Group, entered into an equity interest exchange agreement with K Enter Holdings, for the purpose of listing on the NASDAQ through a merger with a SPAC company. The equity interest exchange agreement is effective upon the approval of the shareholders of K Enter Holdings and SPAC. Upon the approval, the CEO of the Group will exchange 83,418 shares with the equity interest of K Enter Holdings. Following the equity interest exchange transaction, the Parent Company is expected to be a subsidiary of K Enter Holdings.
On March 31, 2023, the CEO agreed to enter into a call option agreement prior to closing date of equity interest exchange agreement with K Enter Holdings, under which the CEO of Group will be granted with an option to acquire the shares of Play F&B Co., Ltd held by the Group within three years from the closing date of equity interest exchange agreement.
As of June 30, 2024 there is no change in shareholders and the call option has not been executed.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
17. Statement of Cash flows
Adjustments for income and expenses from operating activities for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Depreciation | | ₩ | | | 1,491,154 | | | | 1,435,268 | |
| Amortization | | | | | 181,291 | | | | 181,510 | |
| Bad debt expenses | | | | | 85,069 | | | | - | |
| Reversal of bad debt expenses | | | | | - | | | | (30,967 | ) |
| Other Bad debt expenses | | | | | 306,333 | | | | 3,967 | |
| Losses on valuation of short-term financial instruments | | | | | - | | | | 1,112 | |
| Losses on valuation of long-term financial instruments | | | | | 26,287 | | | | 3,219 | |
| Losses on valuation of long-term investment securities | | | | | - | | | | 15,550 | |
| Gains on valuation of long-term financial instruments | | | | | (13,347 | ) | | | (1,086 | ) |
| Gains on valuation of short-term financial instruments | | | | | (33 | ) | | | - | |
| Gains on valuation of long-term investment securities | | | | | - | | | | (64,625 | ) |
| Gains on disposal of short-term financial instruments | | | | | - | | | | (12,819 | ) |
| Gains on disposal of long-term financial instruments | | | | | - | | | | (622,539 | ) |
| Inventory valuation loss(reversal of loss) | | | | | 205,324 | | | | (286,573 | ) |
| Losses on foreign currency translation | | | | | 177,541 | | | | 63,827 | |
| Gains on foreign currency translation | | | | | (6,121 | ) | | | (349,295 | ) |
| Gains on disposal of right-of-use assets | | | | | (96,251 | ) | | | - | |
| Losses on disposal of property, plant and equipment | | | | | 3,480 | | | | 1,646 | |
| Gains on disposal of property, plant and equipment | | | | | (6,100 | ) | | | - | |
| Interest expenses | | | | | 657,385 | | | | 641,212 | |
| Interest income | | | | | (147,965 | ) | | | (234,612 | ) |
| Dividend income | | | | | (1,463 | ) | | | (1,463 | ) |
| Share-based payments expenses | | | | | 24,022 | | | | 25,889 | |
| Severance Benefits | | | | | 270,697 | | | | 326,666 | |
| Tax expenses | | | | | (61,343 | ) | | | 913,800 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 3,095,960 | | | | 2,009,687 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Changes in assets and liabilities from operating activities for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | ₩ | | | 373,553 | | | | (35,149 | ) |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | | | 833,326 | | | | - | |
| Other current assets | | | | | (6,922,634 | ) | | | 1,203,423 | |
| Accounts receivable – net | | | | | 3,716,013 | | | | 9,264,711 | |
| Accounts receivable – other, net | | | | | 39,821 | | | | 229,756 | |
| Trade and other payables | | | | | (1,097,399 | ) | | | (28,971,260 | ) |
| Inventories, net | | | | | (1,200,523 | ) | | | 3,125,301 | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | | | | (305,845 | ) | | | (311,360 | ) |
| Value added tax receivables | | | | | (432,924 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (4,996,612 | ) | | | (15,494,578 | ) |
Significant non-cash transactions for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Increase in restoration provisions | | ₩ | | | 26,833 | | | | 29,966 | |
| Transfer of construction in progress | | | | | - | | | | 112,778 | |
| Reclassification of Long-term borrowings | | | | | 12,480 | | | | 12,480 | |
| Reclassification of Non-current lease liabilities | | | | | 663,507 | | | | 989,235 | |
| Increase in Lease liabilities | | | | | 297,797 | | | | 448,739 | |
| Offset of Loans | | | | | - | | | | 14,804,782 | |
| Offset of Other receivables | | | | | - | | | | 646,380 | |
| Loan Reassignment: Involvement of the Parent company’s CEO | | | | | - | | | | 2,900,000 | |
| Payables related to the acquisition of treasury shares | | | | | - | | | | 3,000,000 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
The movements of liabilities to cash flows arising from financing activities for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Short-term
borrowings | | | Current portion of long-term borrowings | | | Long-term
borrowings | | | Current lease
liabilities | | | Non-current
lease liabilities | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at 1 January 2023 | | ₩ | | | 2,500,000 | | | | 24,960 | | | | 43,680 | | | | 1,630,237 | | | | 15,773,254 | | | | 19,972,131 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Repayment of borrowings | | | | | - | | | | (12,480 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (12,480 | ) |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (780,107 | ) | | | - | | | | (780,107 | ) |
| Reclassification | | | | | - | | | | 12,480 | | | | (12,480 | ) | | | 989,235 | | | | (989,235 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | (12,480 | ) | | | 209,128 | | | | (989,235 | ) | | | (792,587 | ) |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Borrowing assumed (*) | | | | | 700,000 | | | | - | | | | 2,200,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,900,000 | |
| New leases | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 448,739 | | | | 448,739 | |
| Interest expense | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 529,400 | | | | - | | | | 529,400 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (529,400 | ) | | | - | | | | (529,400 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 700,000 | | | | - | | | | 2,200,000 | | | | - | | | | 448,739 | | | | 3,348,739 | |
| Balance at 30 June 2023 | | ₩ | | | 3,200,000 | | | | 24,960 | | | | 2,231,200 | | | | 1,839,365 | | | | 15,232,758 | | | | 22,528,283 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at 1 January 2024 | | ₩ | | | 3,330,000 | | | | 24,960 | | | | 2,008,041 | | | | 1,630,482 | | | | 12,878,027 | | | | 19,871,510 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from borrowings | | | | | 80,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 80,000 | |
| Repayment of borrowings | | | | | (40,000 | ) | | | (12,480 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (52,480 | ) |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (840,227 | ) | | | - | | | | (840,227 | ) |
| Reclassification | | | | | - | | | | 12,480 | | | | (12,480 | ) | | | 663,507 | | | | (663,507 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 40,000 | | | | - | | | | (12,480 | ) | | | (176,720 | ) | | | (663,507 | ) | | | (812,707 | ) |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| New leases | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 297,797 | | | | - | | | | 297,797 | |
| Lease termination/lease modification | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (94,422 | ) | | | (489,933 | ) | | | (584,355 | ) |
| Interest expense | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 50,872 | | | | 454,773 | | | | - | | | | 505,645 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (454,773 | ) | | | - | | | | (454,773 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | 50,872 | | | | 203,375 | | | | (489,933 | ) | | | (235,686 | ) |
| Balance at 30 June 2024 | | ₩ | | | 3,370,000 | | | | 24,960 | | | | 2,046,433 | | | | 1,657,137 | | | | 11,724,587 | | | | 18,823,117 | |
| (*) | Prior to 2023, the Parent Company granted a loan amounting to Korean Won 1,700,000 thousand to its subsidiary. Upon consolidation, this intercompany transaction was offset. During 2023, the obligation, along with a new loan of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand borrowed by the subsidiary within the year, was transitioned to Cho Hyeong Seok, CEO of the Parent Company. This reallocated liability is presented as “borrowing assumed”, denoting a change in debtor, not the origination of a new loan. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash flows from other financing activities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Acquisition of Treasury shares | | | | | - | | | | (8,677,100 | ) |
18. Related parties
| A. | List of related parties |
List of related parties as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| Relationship | | Company |
| Other related parties | | FF Company Co., Ltd. (“FF Company”) |
| Other related parties | | OURcoffee gangnamjum Co.,Ltd. (“OURcoffee Gangnamjum”) |
| Other related parties | | SecondPlan Co.,Ltd. (“SecondPlan”) |
| Other related parties | | ThirdPlan Co., Ltd. (“ThirdPlan”) |
| Other related parties | | PLAYVERSE Co., Ltd. (“PLAYVERSE”) |
| Other related parties | | Studio Cuat. Co., Ltd. (“Studio Cuat”) |
| Other related parties | | Beacon Holdings, Inc. (“Beacon Holdings”) |
| B. | Transactions with related parties |
Details of transaction with related parties for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | Six-month period ended
June 30, 2024 | | | Six-month period ended
June 30, 2023 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Revenue | | | Finance
income | | | Purchases | | | Finance
Costs | | | Revenue | | | Finance
income | | | Purchases | | | Finance
Costs | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties | | FF Company | | ₩ | | | 4,046,663 | | | | - | | | | 5,084 | | | | - | | | | 5,902,002 | | | | - | | | | 16,049 | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | SecondPlan | | | | | 15,999 | | | | 5,635 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,890 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | ThirdPlan | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,442 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | Studio Cuat | | | | | 13,993 | | | | 986 | | | | 179,510 | | | | - | | | | 251 | | | | | | | | 383,330 | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | Beacon Holdings | | | | | - | | | | 2,958 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Key management personnel | | Cho Hyeong Seok | | | | | - | | | | 51,056 | | | | - | | | | 117,389 | | | | | | | | 78,457 | | | | | | | | 36,182 | |
| Key management personnel | | Jeong Bo Ram | | | | | - | | | | 116 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | | 664,321 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 4,076,655 | | | | 60,751 | | | | 184,594 | | | | 120,831 | | | | 5,902,253 | | | | 744,668 | | | | 399,379 | | | | 36,182 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| C. | Account balances with related parties |
The balances of receivables and payables to related parties as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Receivables | | | Loans | | | Payables | | | Borrowings | | | Receivables | | | Loans | | | Payables | | | Borrowings | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | | | | |
| Other related parties | | FF Company | | ₩ | | | 284,886 | | | | - | | | | 289 | | | | - | | | | 1,002,931 | | | | - | | | | 38,115 | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | SecondPlan | | | | | 92,909 | | | | 344,400 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 63,589 | | | | 106,900 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | ThirdPlan | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 5,877 | | | | 170,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,435 | | | | 130,000 | |
| Other related parties | | Studio Cuat | | | | | 1,181 | | | | 43,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,117 | | | | 43,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | Beacon Holdings | | | | | 2,958 | | | | 185,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Key management personnel | | Cho Hyeong Seok | | | | | 183 | | | | 69,267 | | | | 1,195,785 | | | | 2,740,193 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,256,876 | | | | 2,689,321 | |
| Key management personnel | | Jeong Bo Ram | | | | | 116 | | | | 43,721 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 382,233 | | | | 685,388 | | | | 1,201,951 | | | | 2,910,193 | | | | 1,068,637 | | | | 149,900 | | | | 1,297,426 | | | | 2,819,321 | |
| D. | Financial transactions with related parties |
Details of significant financial transactions with related parties for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | Six-month period ended
June 30, 2024 | | | Six-month period ended
June 30, 2023 | |
| Related party | | Company | | | | Loans | | | Collection (*1) | | | Borrowings | | | Repayment | | | Loans | | | Collection (*1) | | | Borrowings | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties | | Second Plan | | ₩ | | | 267,500 | | | | 30,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | ThirdPlan | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 80,000 | | | | 40,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | Studio Cuat | | | | | 19,500 | | | | 19,500 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | Beacon Holdings | | | | | 1,325,000 | | | | 1,140,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Key management personnel | | Cho Hyeong Seok (*2) | | | | | 69,267 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 10,738,538 | | | | 15,084,782 | | | | 2,900,000 | |
| Key management personnel | | Jeong Bo Ram | | | | | 43,721 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,905,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | | | ₩ | | | 1,724,988 | | | | 1,189,500 | | | | 80,000 | | | | 40,000 | | | | 11,738,538 | | | | 18,989,782 | | | | 2,900,000 | |
| (*1) | During 2023, the collection of loans related to with Second Plan and Jeong Bo Ram was due to a liability transfer to Cho Hyeong Seok, with no resulting cash inflows. |
| (*2) | During 2023, the Parent Company secured a loan of Korean Won 3,510,676 thousand from Cho Hyeong Seok. Cho Hyeong Seok then assumed obligations for loans amounting to Korean Won 7,227,862 thousand made by Play Company to third parties. Of this amount, Korean Won 2,900,000 thousand originally loaned by Play Company to Play F&B is now effectively a loan from Cho Hyeong Seok to the Group. In addition, the Parent Company received repayments of Korean Won 280,000 thousand, and an outstanding loan of Korean Won 14,804,782 thousand was offset against proceeds from the purchase of treasury share. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| E. | Commitments with related parties |
Commitments the Group has entered into with related parties as of June 30, 2024 are as follows:
| Related party | | Financial institutions | | Categories | | | | Credit limit | | | Borrowings amount | |
| | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Revolving credit (*1) | | ₩ | | | 2,000,000 | | | | - | |
| Key management personnel | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*2) | | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | |
| Key management personnel | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*3) | | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Key management personnel | | Shinhan Bank | | Revolving credit (*4) | | | | | 500,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 4,000,000 | | | | 1,500,000 | |
| (*1) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 2,400,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*2) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 412,775 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*3) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*4) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 600,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
Commitments the Group has entered into with related parties as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| Related party | | Financial institutions | | Categories | | | | Credit limit | | | Borrowings amount | |
| | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Revolving credit (*1) | | ₩ | | | 2,000,000 | | | | - | |
| Key management personnel | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*2) | | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | |
| Key management personnel | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*3) | | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Key management personnel | | Shinhan Bank | | Revolving credit (*4) | | | | | 500,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 4,000,000 | | | | 1,500,000 | |
| (*1) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 2,400,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*2) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 412,775 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*3) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*4) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 600,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
The CEO of the Group provides a joint guarantee of Korean Won 271,690 thousand for the vehicle lease from Mirae Asset Securities as of June 30, 2024.
The Group provides a joint guarantee of Korean Won 30,000 thousand for the payment guarantee to Second Plan as of December 31, 2023.
| F. | Key management personnel compensation |
The compensation for the key management personnel for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Short-term employee benefits | | ₩ | | | 597,223 | | | | 1,136,414 | |
| Post-employment benefits | | | | | 141,867 | | | | 11,565 | |
| Share-based payments | | | | | 18,017 | | | | 19,417 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 757,107 | | | | 1,167,396 | |
Compensation of the Group’s key management personnel includes salaries, non-cash benefits and contributions to a post-employment defined benefit plan and defined contribution plan.
Executive officers also participate in the Group’s share option plan.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders of
Play Company Co., Ltd.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of financial position of the Play Company Co., Ltd. and its subsidiary (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the related consolidated statements of comprehensive income, of changes in equity and of cash flows for the years then ended, including the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the years then ended in conformity with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits of these consolidated financial statements in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
| /s/ Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers | |
| | |
| Seoul, KOREA | |
| May 13, 2024 | |
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2023.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | 17,21,23,27,32 | | ₩ | | | 8,585,634 | | | | 30,581,556 | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | 21,27 | | | | | 419,391 | | | | 3,918,460 | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | 16,21,27 | | | | | 6,754,011 | | | | 14,461,525 | |
| - Related parties | | 33 | | | | | 1,017,018 | | | | 1,264,195 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 5,736,993 | | | | 13,197,330 | |
| Short-term loans, net | | 21,24,27 | | | | | 859,900 | | | | 5,182,254 | |
| - Related parties | | 33 | | | | | 149,900 | | | | 4,346,244 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 710,000 | | | | 836,010 | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | 16,21,27 | | | | | 351,166 | | | | 731,734 | |
| - Related parties | | 33 | | | | | 51,619 | | | | 621,071 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 299,547 | | | | 110,663 | |
| Value added tax receivables | | | | | | | 200,407 | | | | 2,065,640 | |
| Other current assets | | 14 | | | | | 719,193 | | | | 77,938 | |
| Other current financial assets | | 21,27 | | | | | 203,266 | | | | - | |
| Contract assets | | 7 | | | | | 73,463 | | | | - | |
| Inventories, net | | 15 | | | | | 424,560 | | | | 3,355,857 | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | | 18,590,991 | | | | 60,374,964 | |
| Long-term financial instruments | | 21,27 | | | | | 307,729 | | | | 279,932 | |
| Long-term loans, net | | 21,24,27 | | | | | - | | | | 2,413,972 | |
| - Related parties | | 33 | | | | | - | | | | 2,250,966 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | 163,006 | |
| Long-term investment securities | | 21,27 | | | | | 640,739 | | | | 536,234 | |
| Property, plant and equipment including right-of-use assets | | 19,30 | | | | | 14,867,677 | | | | 20,629,505 | |
| Intangible assets other than goodwill | | 20 | | | | | 4,889,597 | | | | 5,252,397 | |
| Goodwill | | 20 | | | | | 3,267,730 | | | | 3,267,730 | |
| Investment properties | | 18 | | | | | 3,260,795 | | | | - | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | 21,27 | | | | | 1,390,486 | | | | 1,707,777 | |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | 14 | | | | | 2,606,623 | | | | 539,296 | |
| Deferred tax assets | | 13 | | | | | 565,144 | | | | 885,517 | |
| Total non-current assets | | | | | | | 31,796,520 | | | | 35,512,360 | |
| Total assets | | | | ₩ | | | 50,387,511 | | | | 95,887,324 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | 21,25,27 | | ₩ | | | 14,407,610 | | | | 33,481,452 | |
| - Related parties | | 33 | | | | | 1,297,426 | | | | 237,858 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 13,110,184 | | | | 33,243,594 | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | | | | | 870,830 | | | | 370,676 | |
| Short-term borrowings | | 21,24,27 | | | | | 3,330,000 | | | | 2,500,000 | |
| - Related parties | | 33 | | | | | 830,000 | | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 2,500,000 | | | | 2,500,000 | |
| Current portion of long-term borrowings, net | | 21,24,27 | | | | | 24,960 | | | | 24,960 | |
| Current lease liabilities | | 24,30 | | | | | 1,630,482 | | | | 1,630,238 | |
| Current tax liabilities | | 13 | | | | | 845,547 | | | | 3,243,217 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | | 21,109,429 | | | | 41,250,543 | |
| Trade and other non-current payables | | 21,25,27 | | | | | 335,871 | | | | 227,593 | |
| Long-term borrowings, excluding current portion, net | | 21,24,27 | | | | | 2,008,041 | | | | 43,680 | |
| - Related parties | | 33 | | | | | 1,989,321 | | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 18,720 | | | | 43,680 | |
| Other non-current financial liabilities | | 21 | | | | | 200,000 | | | | - | |
| Other non-current non-financial liabilities | | | | | | | 109,764 | | | | - | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | 12 | | | | | 706,102 | | | | 928,148 | |
| Other non-current provisions | | 26 | | | | | 674,148 | | | | 711,086 | |
| Non-current lease liabilities | | 24,30 | | | | | 12,878,027 | | | | 15,773,254 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | 13 | | | | | 676,406 | | | | 1,036,943 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | | | | | 17,588,359 | | | | 18,720,704 | |
| Total liabilities | | | | ₩ | | | 38,697,788 | | | | 59,971,247 | |
| Equity | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital | | 22 | | ₩ | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | |
| Other reserves | | 22 | | | | | (27,722,641 | ) | | | (667,927 | ) |
| Retained earnings | | | | | | | 38,500,808 | | | | 35,363,622 | |
| Equity attributable to owners of the Parent Company | | | | | | | 11,278,167 | | | | 35,195,695 | |
| Non-controlling interest | | 28,29 | | | | | 411,556 | | | | 720,382 | |
| Total equity | | | | | | | 11,689,723 | | | | 35,916,077 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | | | | ₩ | | | 50,387,511 | | | | 95,887,324 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won except per share data) | |
| Revenues | | | | | | | | | | |
| Content revenue | | 6,7 | | ₩ | | | 49,771,824 | | | | 151,858,729 | |
| - Related parties | | 33 | | | | | 11,184,157 | | | | 4,167,544 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 38,587,667 | | | | 147,691,185 | |
| F&B revenue | | 6,7 | | | | | 16,984,621 | | | | 16,469,551 | |
| - Related parties | | 33 | | | | | 15,303 | | | | 8,529 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 16,969,318 | | | | 16,461,022 | |
| Other revenue | | 6,7 | | | | | 724,711 | | | | 694,108 | |
| Total revenues | | | | | | | 67,481,156 | | | | 169,022,388 | |
| Cost of revenues | | 8 | | | | | (60,837,065 | ) | | | (150,752,230 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | | | | | 6,644,091 | | | | 18,270,158 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | 8 | | | | | (4,598,226 | ) | | | (5,146,556 | ) |
| Other income | | 8 | | | | | 1,487,080 | | | | 84,462 | |
| Other expenses | | 8 | | | | | (35,547 | ) | | | (46,157 | ) |
| Operating profit | | | | | | | 3,497,398 | | | | 13,161,907 | |
| Finance income | | 9,21 | | | | | 1,743,941 | | | | 1,221,147 | |
| - Related parties | | 33 | | | | | 831,200 | | | | 215,988 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 912,741 | | | | 1,005,159 | |
| Finance costs | | 9,21,24,30 | | | | | (1,688,210 | ) | | | (1,811,321 | ) |
| - Related parties | | 33 | | | | | (176,597 | ) | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | (1,511,612 | ) | | | (1,811,321 | ) |
| Profit before income tax | | | | | | | 3,553,129 | | | | 12,571,733 | |
| Income tax expenses | | 13 | | | | | (760,779 | ) | | | (2,687,108 | ) |
| Profit for the year | | | | ₩ | | | 2,792,350 | | | | 9,884,625 | |
| Other comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Items that will not be reclassified to income or loss: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remeasurement of defined benefit liabilities | | 12,22 | | | | | 109,558 | | | | 143,829 | |
| Total comprehensive income for the year | | | | ₩ | | | 2,901,908 | | | | 10,028,454 | |
| Profit (loss) attributable to: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Owners of the Parent Company | | | | | | | 3,137,186 | | | | 10,189,718 | |
| Non-controlling interest | | 28,29 | | | | | (344,836 | ) | | | (305,093 | ) |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) attributable to: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Owners of the Parent Company | | | | | | | 3,210,734 | | | | 10,286,272 | |
| Non-controlling interest | | 28,29 | | | | | (308,826 | ) | | | (257,818 | ) |
| Earnings per share (in Korean won) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic earnings per share | | 10 | | ₩ | | | 35,683 | | | | 101,897 | |
| Diluted earnings per share | | 10 | | | | | 35,683 | | | | 101,897 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | | | | | Attributable to owners of the Parent Company | | | Non- | | | | |
| | | Note | | | | Share
capital | | | Other
reserves | | | Retained
earnings | | | Total | | | controlling
interest | | | Total
equity | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at January 1, 2022 | | | | ₩ | | | 500,000 | | | | (988,645 | ) | | | 25,173,904 | | | | 24,685,259 | | | | 1,273,314 | | | | 25,958,573 | |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Profit (loss) for the year | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 10,189,718 | | | | 10,189,718 | | | | (305,093 | ) | | | 9,884,625 | |
| Remeasurement of defined benefit liabilities | | 12 | | | | | - | | | | 96,554 | | | | - | | | | 96,554 | | | | 47,275 | | | | 143,829 | |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the year | | | | | | | - | | | | 96,554 | | | | 10,189,718 | | | | 10,286,272 | | | | (257,818 | ) | | | 10,028,454 | |
| Transaction with owners, recognized directly in equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Additional acquisition of non-controlling interest in subsidiary | | 31 | | | | | - | | | | (1,004,886 | ) | | | - | | | | (1,004,886 | ) | | | (295,114 | ) | | | (1,300,000 | ) |
| De-recognition of the obligation to purchase the Group’s own equity instruments | | 31 | | | | | - | | | | 1,229,050 | | | | - | | | | 1,229,050 | | | | - | | | | 1,229,050 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | | | | ₩ | | | 500,000 | | | | (667,927 | ) | | | 35,363,622 | | | | 35,195,695 | | | | 720,382 | | | | 35,916,077 | |
| Balance at January 1, 2023 | | | | | | | 500,000 | | | | (667,927 | ) | | | 35,363,622 | | | | 35,195,695 | | | | 720,382 | | | | 35,916,077 | |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Profit (loss) for the year | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,137,186 | | | | 3,137,186 | | | | (344,836 | ) | | | 2,792,350 | |
| Remeasurement of defined benefit liabilities | | | | | | | - | | | | 73,548 | | | | - | | | | 73,548 | | | | 36,010 | | | | 109,558 | |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the year | | | | | | | - | | | | 73,548 | | | | 3,137,186 | | | | 3,210,734 | | | | (308,826 | ) | | | 2,901,908 | |
| Transaction with owners, recognized directly in equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Acquisition of Treasury shares | | | | | | | - | | | | (27,128,262 | ) | | | - | | | | (27,128,262 | ) | | | - | | | | (27,128,262 | ) |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | | | | | | | 500,000 | | | | (27,722,641 | ) | | | 38,500,808 | | | | 11,278,167 | | | | 411,556 | | | | 11,689,723 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | 32 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | | ₩ | | | 2,792,350 | | | | 9,884,625 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | | 32 | | | | | (6,881,338 | ) | | | 19,396,280 | |
| Interest received | | | | | | | 70,995 | | | | 72,808 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | | | (1,184,042 | ) | | | (800,423 | ) |
| Income taxes paid | | | | | | | (3,176,978 | ) | | | (2,369,065 | ) |
| Dividend received | | | | | | | 1,463 | | | | 700 | |
| Net cash inflow(outflow) from operating activities | | | | | | | (8,377,550 | ) | | | 26,184,925 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payments for short-term loans | | | | | | | (3,840,576 | ) | | | (3,773,050 | ) |
| - Related parties | | 33 | | | | | (3,690,576 | ) | | | (520,050 | ) |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | (150,000 | ) | | | (3,253,000 | ) |
| Proceeds from short-term loans | | | | | | | 320,000 | | | | 2,700,000 | |
| - Related parties | | 33 | | | | | 310,000 | | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 10,000 | | | | 2,700,000 | |
| Payments for long-term loans | | | | | | | (1,000,000 | ) | | | (700,000 | ) |
| - Related parties | | 33 | | | | | (1,000,000 | ) | | | (700,000 | ) |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Payments for other financial assets | | | | | | | (610,093 | ) | | | (5,543,599 | ) |
| Collection of other financial assets | | | | | | | 4,135,728 | | | | 3,956,661 | |
| Collection of long-term financial instruments | | | | | | | - | | | | 63,138 | |
| Purchase of long-term investment securities | | | | | | | - | | | | (443,164 | ) |
| Proceeds from disposal of property and equipment | | | | | | | 4,293 | | | | - | |
| Purchase of property and equipment | | | | | | | (949,583 | ) | | | (3,166,783 | ) |
| Purchase of intangible assets | | | | | | | - | | | | (113,900 | ) |
| Proceeds from lease incentives | | | | | | | 150,150 | | | | 1,980,492 | |
| Net cash outflow from investing activities | | | | | | | (1,790,081 | ) | | | (5,040,205 | ) |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | 32 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from short-term borrowings | | | | | | | 130,000 | | | | - | |
| - Related parties | | 33 | | | | | 130,000 | | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Repayment of current portion of long-term borrowings | | | | | | | (24,960 | ) | | | (24,960 | ) |
| Acquisition of Treasury shares | | | | | | | (10,677,100 | ) | | | - | |
| Transaction with non-controlling interests | | | | | | | - | | | | (650,000 | ) |
| Repayment of lease liabilities | | | | | | | (1,617,756 | ) | | | (1,088,224 | ) |
| Net cash outflow for financing activities | | | | | | | (12,189,816 | ) | | | (1,763,184 | ) |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | 361,525 | | | | 96,536 | |
| Net increase(decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | (22,357,447 | ) | | | 19,381,536 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the year | | 17 | | | | | 30,581,556 | | | | 11,103,484 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of the year | | 17 | | ₩ | | | 8,585,634 | | | | 30,581,556 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
1. Reporting entity
The Parent Company
Play Company Co., Ltd. (“the Parent Company”) was incorporated in June 2012 and the Parent Company’s registered office is at Business Tower 20F, 396 World Cup buk-ro, Mapo-gu, Seoul, Korea. These consolidated financial statements comprise the Parent Company and its subsidiary (together referred to as the “Group”). The Group generates revenue primarily through the sale of the Group’s entertainment content and services, and food and beverage products as well as through the licensing of the Group’s intellectual property in food and beverage business. The Parent company primarily engages in the provision of goods to its customers by offering made-to-order services to plan the projects, design merchandise, and deliver customized products to its customers, utilizing the intellectual property associated with K-pop artists. Play F&B Co., Ltd. (the “Subsidiary”) operates a retail bakery-cafe business and franchising business under the concept names ‘Our Bakery’. As of December 31, 2023, retail operations consist of 12 Company-owned bakery-cafes and 16 franchise-operated bakery-cafes located in South Korea and China.
The Parent Company’s major shareholders and their respective percentage of ownership as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | Number of shares
(in shares) | | | Percentage of
ownership (%) | | | Number of shares
(in shares) | | | Percentage of
ownership (%) | |
| Cho, Hyeong Seok | | | 83,418 | | | | 83.4 | % | | | 100,000 | | | | 100.0 | % |
| Solaire Partners LLC. | | | 1,000 | | | | 1.0 | % | | | - | | | | - | |
| Subtotal (outstanding) | | | 84,418 | | | | 84.4 | % | | | - | | | | - | |
| Plus: Treasury shares | | | 15,582 | | | | 15.6 | % | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total (issued) | | | 100,000 | | | | 100.0 | % | | | 100,000 | | | | 100.0 | % |
Consolidated Subsidiary
Details of the consolidated subsidiary as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | Percentage of ownership (%) | | | | | |
| Subsidiary | | Location | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | | | Fiscal year end | | Main business |
| Play F&B | | Korea | | 67.1 | | | 67.1 | | | December | | Sale of food and beverages |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Condensed financial information of subsidiary
Condensed financial information of subsidiary as of and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | 2023 | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Subsidiary | | Total assets (*) | | | Total liabilities (*) | | | Revenues (*) | | | Profit for the period (*) | |
| Play F&B | | | 18,958,244 | | | | 21,716,891 | | | | 17,709,332 | | | | (1,140,267 | ) |
| | | 2022 | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Subsidiary | | Total assets (*) | | | Total liabilities (*) | | | Revenues (*) | | | Profit for the period (*) | |
| Play F&B | | | 21,559,281 | | | | 23,287,219 | | | | 17,163,659 | | | | (772,658 | ) |
| (*) | The condensed financial information was prepared based on amounts before eliminating intergroup transactions. |
2. Basis of Accounting
These consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) as issued by International Accounting Standard Board (“IASB”). These consolidated financial statements were authorized for issuance by the Company’s directors on May 13, 2024.
Details of the Group’s accounting policies, including changes thereto, are included in Note 5.
Basis of measurement
The consolidated financial statements have been prepared on the historical cost basis except for the following items, which are measured on an alternative basis on each reporting date.
| Items | | Measurement bases |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | Present value |
| Financial instruments measured at fair value through profit or loss (“FVTPL”) | | Fair value |
3. Functional and presentation currency
These consolidated financial statements are presented in Korean Won, which the Group’s functional currency. All amounts have been rounded to the nearest thousand, unless otherwise indicated.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
4. Use of judgements and estimates
In preparing these consolidated financial statements, management has made judgements and estimates that affect the application of the Group’s accounting policies and the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
Estimates and underlying assumptions are reviewed on an ongoing basis. Revisions to estimates are recognized prospectively.
Information about judgements made in applying accounting policies that have the most significant effects on the amounts recognized in the financial statements is included in the following notes:
Note 30(A): lease term: whether the Group is reasonably certain to exercise extension options.
| B. | Assumptions and estimation uncertainties |
Information about assumptions and estimation uncertainties at the reporting date that have a significant risk of resulting in a material adjustment to the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities within the next financial year is included in the following notes:
| ● | Note 20(C): goodwill impairment: The Group estimates the recoverable amount of an individual asset, and if it is impossible to measure the individual recoverable amount of an asset, the Group estimates the recoverable amount of cash-generating unit (“CGU”). The value in use is estimated by applying a weighted average cost of capital that reflects current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the asset or CGU for which estimated future cash flows have not been adjusted, to the estimated future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset or CGU. |
| i. | Measurement of fair values |
A number of the Group’s accounting policies and disclosures require the measurement of fair values for financial assets.
When measuring the fair value of a financial instruments measured at FVTPL, the Group uses observable market data as far as possible. Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows.
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
| ● | Level 2: inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly (i.e., as prices) or indirectly (i.e., derived from prices). |
| ● | Level 3: inputs for the asset or liability that are not based on observable market data (unobservable inputs). |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
If the inputs used to measure the fair value of an asset or a liability fall into different levels of the fair value hierarchy, then the fair value measurement is categorized in its entirety in the same level of the fair value hierarchy as the lowest level input that is significant to the entire measurement.
The Group recognizes transfers between levels of the fair value hierarchy at the end of the reporting period during which the change has occurred.
Further information about the assumptions made in measuring fair values is included in the following notes:
| ● | Note 11(B): share-based payment arrangements; |
| ● | Note 27(B): financial instruments. |
5. Material accounting policies
The material accounting policies followed by the Group in preparation of its consolidated financial statements are as follows:
| A. | New and amended standards or interpretations adopted by the Group |
The Group has applied the following standards and amendments for the first time for their annual reporting period commencing January 1, 2023.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements - Disclosure of Accounting Policies
The amendments to IAS 1 define and require entities to disclose their material accounting policies. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 8 Accounting policies, changes in accounting estimates and errors - Definition of Accounting Estimates
The amendments define accounting estimates and clarify how to distinguish them from changes in accounting policies. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 12 Income Taxes - Deferred Tax related to Assets and Liabilities arising from a Single Transaction
The amendments include an additional condition to the exemption to initial recognition of an asset or liability that a transaction does not give rise to equal taxable and deductible temporary differences at the time of the transaction. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 12 Income Taxes – International Tax Reform – Pillar Two Model Rules
The amendments provide a temporary relief from the accounting for deferred taxes arising from legislation enacted to implement the Pillar Two model rules, which aim to reform international corporate taxation for multinational enterprises, and require disclosure of related current tax effects, etc. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
New Standard: IFRS 17 Insurance Contract
IFRS 17 Insurance Contracts replaces IFRS 4 Insurance Contracts. This standard estimates future cash flows of an insurance contract and measures insurance liabilities using discount rates applied with assumptions and risks at the measurement date. The entity recognizes insurance revenue on an accrual basis including services (insurance coverage) provided to the policyholder by each annual period. In addition, investment components (Refunds due to termination/maturity) repaid to a policyholder even if an insured event does not occur, are excluded from insurance revenue, and insurance financial income or expense and the investment income or expense are presented separately to enable users of the information to understand the sources of income or expenses. This Standard do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
| B. | New and amended standards or interpretations not yet adopted by the Group |
The following new accounting standards and interpretations that have been published that are not mandatory for December 31, 2023 reporting periods and have not been early adopted by the Group.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements - Classification of Liabilities as Current or Non-current
The amendments clarify that liabilities are classified as either current or non-current, depending on the substantive rights that exist at the end of the reporting period. Classification is unaffected by the likelihood that an entity will exercise right to defer settlement of the liability or the expectations of management. Also, the settlement of liability includes the transfer of the entity’s own equity instruments, however, it would be excluded if an option to settle them by the entity’s own equity instruments if compound financial instruments is met the definition of equity instruments and recognized separately from the liability. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, and earlier application is permitted. The Group does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 7 Statements of Cash Flows and IFRS 7 Financial instruments disclosures - Supplier finance
These amendments require disclosures to enhance the transparency of supplier finance arrangements and their effects on an entity’s liabilities, cash flows and exposure to liquidity risk. The disclosure requirements are the IASB’s response to investors’ concerns that some companies’ supplier finance arrangements are not sufficiently visible, hindering investors’ analysis. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, with transitional reliefs in the first year. The Group does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 21 The effects of changes in foreign exchange rates - Lack of Exchangeability
The amendments add requirements to help entities to determine whether a currency is exchangeable into another currency at a measurement date for a specified purpose and the spot exchange rate to use when it is not. A currency is exchangeable when there is an ability to obtain the other currency (with a normal administrative delay), and the transaction would take place through a market or exchange mechanism that creates enforceable rights and obligations. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2025, and earlier application is permitted. The Group does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
IFRS 16 Leases – Lease Liability in a Sale and Leaseback
The amendments add requirements for the subsequent measurement of sale-and-leaseback transactions that are accounted for as sales in accordance with IFRS 15, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. The amendments require the seller-lessee to calculate the ‘lease payments’ or ‘revised lease payments’ in a way that does not result in the seller-lessee recognizing any gain or loss for the rights of use that the seller-lessee continues to retain after the lease commences. The amendments are effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, with early application permitted. The Group does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IFRS 18 Presentation and Disclosure in Financial Statements
Items in the statement of profit or loss will need to be classified into one of five categories: operating, investing, financing, income taxes and discontinued operations. IFRS 18 requires the Company to present specified totals and subtotals: ‘Operating profit or loss’, ‘Profit or loss’ and ‘Profit or loss before financing and income taxes’. Information related to management-defined performance measures should be disclosed. IFRS 18 also provides enhanced guidance on the principles of aggregation and disaggregation which focus on grouping items based on their shared characteristics. The new standard should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2027, and earlier application is permitted. The Company is in review for the impact of this new standard on the financial statements.
Basis of consolidation
The Group accounts for business combinations using the acquisition method when the acquired set of activities and assets meets the definition of a business and control is transferred to the Group. In determining whether a particular set of activities and assets is a business, the Group assesses whether the set of assets and activities acquired includes, at a minimum, an input and substantive process and whether the acquired set has the ability to produce outputs.
The consideration transferred in the acquisition is generally measured at fair value, as are the identifiable net assets acquired. Any goodwill that arises is tested annually for impairment. Any gain on a bargain purchase is recognized in profit or loss immediately. Transaction costs are expensed as incurred, except if related to the issue of debt or equity securities.
The consideration transferred does not include amounts related to the settlement of pre-existing relationships. Such amounts are generally recognized in profit or loss.
Any contingent consideration is measured at fair value at the date of acquisition. If an obligation to pay contingent consideration that meets the definition of a financial instrument is classified as equity, then it is not remeasured and settlement is accounted for within equity. Otherwise, other contingent consideration is remeasured at fair value at each reporting date and subsequent event changes in the fair value of the contingent consideration are recognized in profit or loss.
If share-based payment awards are required to be exchanged for awards held by the acquiree’s employees (acquiree’s awards), then all or a portion of the amount of the acquirer’s replacement awards is included in measuring the consideration transferred in the business combination. This determination is based on the market-based measure of the replacement awards compared with the market-based measure of the acquiree’s awards and the extent to which the replacement awards relate to pre-combination service.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Subsidiary is an entity controlled by the Group. The Group ‘controls’ an entity when it is exposed to, or has rights to, variable returns from its involvement with the entity and has the ability to affect those returns through its power over the entity. The financial statements of subsidiary are included in the consolidated financial statements from the date on which control commences until the date on which control ceases.
| iii. | Non-controlling interests |
Non-controlling interests are measured initially at their proportionate share of the acquiree’s identifiable net assets at the date of acquisition.
Changes in the Group’s interest in a subsidiary that do not result in a loss of control are accounted for as equity transactions.
When the Group loses control over a subsidiary, it derecognizes the assets and liabilities of the subsidiary, and any related non-controlling interests and other components of equity. Any resulting gain or loss is recognized in profit or loss. Any interest retained in the former subsidiary is measured at fair value when control is lost.
| v. | Interests in equity-accounted investees |
The Group’s interests in equity-accounted investees comprise interests in associates and a joint venture. Associates are those entities in which the Group has significant influence, but not control or joint control, over the financial and operating policies. A joint venture is an arrangement in which the Group has joint control, whereby the Group has rights to the net assets of the arrangement, rather than rights to its assets and obligations for its liabilities.
Interests in associates and the joint venture are accounted for using the equity method. They are initially recognized at cost, which includes transaction costs. Subsequent to initial recognition, the consolidated financial statements include the Group’s share of the profit or loss and other comprehensive income (“OCI”) of equity-accounted investees, until the date on which significant influence or joint control ceases.
| vi. | Transactions eliminated on consolidation |
Intra-group balances and transactions, and any unrealized income and expenses (except for foreign currency transaction gains or losses) arising from intra-group transactions, are eliminated. Unrealized gains arising from transactions with equity-accounted investees are eliminated against the investment to the extent of the Group’s interest in the investee. Unrealized losses are eliminated in the same way as unrealized gains, but only to the extent that there is no evidence of impairment.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| i. | Foreign currency transactions |
Transactions in foreign currencies are translated into the respective functional currencies of Group companies at the exchange rates at the dates of the transactions.
Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are translated into the functional currency at the exchange rate at the reporting date. Non-monetary assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value in a foreign currency are translated into the functional currency at the exchange rate when the fair value was determined. Non-monetary items that are measured based on historical cost in a foreign currency are translated at the exchange rate at the date of the transaction. Foreign currency differences are generally recognized in profit or loss and presented within finance costs. Translation differences on Non-monetary assets and liabilities carried at fair value are reported as part of the fair value gain or loss.
However, foreign currency differences arising from the translation of the following items are recognized in OCI:
| ● | an investment in equity securities designated as at FVOCI (except on impairment, in which case foreign currency differences that have been recognized in OCI are reclassified to profit or loss); |
| ● | a financial liability designated as a hedge of the net investment in a foreign operation to the extent that the hedge is effective; and |
| ● | qualifying cash flow hedges to the extent that the hedges are effective. |
| D. | Revenue from contracts with customers |
The Group generates revenue primarily through the sale of the Group’s entertainment content and services, and food and beverage products as well as through the licensing of the Group’s intellectual property in food and beverage business.
The Group determines revenue recognition by:
| ● | identifying the contract, or contracts, with a customer; |
| ● | identifying the performance obligations in each contract; |
| ● | determining the transaction price; |
| ● | allocating the transaction price to the performance obligations in each contract; and |
| ● | recognizing revenue when, or as, we satisfy performance obligations by transferring the promised goods or services. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Content revenue
Content revenues consist of sales of the physical and digital content consumer products and merchandises. The Group recognizes revenues from the sale of consumer products and merchandises after both (1) control of the products has been transferred to customers and (2) the underlying performance obligations have been satisfied.
Content revenues are recognized after deducting the estimated allowance for returns, which are accounted for as variable consideration when estimating the amount of revenue to recognize. Returns are estimated at contract inception and updated at the end of each reporting period as additional information becomes available.
Food and beverages revenue
Food and beverages revenues consist of sales of the consumer products including food and beverages. The Group recognizes revenues from the sale of consumer products after both (1) control of the products has been transferred to customers and (2) the underlying performance obligations have been satisfied.
Food and beverages revenues are recognized after deducting the estimated allowance for returns, which are accounted for as variable consideration when estimating the amount of revenue to recognize.
Other revenues
Under franchise agreements, the Group’s performance obligation is to provide a license to use Our Bakery’s trademarks and other intellectual property. Franchise royalties and fees are typically charged as a percentage of food and beverage revenues and are treated as variable consideration, recognized as the underlying food and beverage revenues occur.
Franchise agreements also contain a promise to provide training support and recipe teaching services to franchise-operated stores. A monthly franchise loyalty fee, based on gross food and beverage revenues, is charged, and recognized over time as these services are delivered.
An operating segment is a component of the Group that engages in business activities from which it may earn revenues and incur expenses, including revenues and expenses that relate to transactions with any of the Group’s other components. The chief operating decision-maker has been identified as the chief executive officer. The Group’s operating segments have been determined to be each business unit, for which the Group generates separately identifiable financial information that is regularly reported to the chief executive officer for the purpose of resource allocation and assessment of segment performance. The Group has two reportable segments as described in Note 6. Segment results that are reported to the chief operating decision maker include items directly attributable to a segment as well as those that can be allocated on a reasonable basis.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| i. | Short-term employee benefits |
Short-term employee benefits are employee benefits due to be settled within 12 months after the end of the period in which the employees render related services. When an employee has rendered a service to the Group during an accounting period, the Group recognizes the undiscounted amount of short-term employee benefits expected to be paid in exchange for that service.
| ii. | Share-based payment arrangements |
The grant-date fair value of equity-settled share-based payment arrangements granted to employees is generally recognized as an expense, with a corresponding increase in equity, over the vesting period of the awards. The amount recognized as an expense is adjusted to reflect the number of awards for which the related service and non-market performance conditions are expected to be met, such that the amount ultimately recognized is based on the number of awards that meet the related service and non-market performance conditions at the vesting date. For share-based payment awards with non-vesting conditions, the grant-date fair value of the share-based payment is measured to reflect such conditions and there is no true-up for differences between expected and actual outcomes.
The fair value of the amount payable to employees in respect of share-based payment arrangements, which are settled in cash, is recognized as an expense with a corresponding increase in liabilities, over the period during which the employees become unconditionally entitled to payment. The liability is remeasured at each reporting date and at settlement date based on the fair value of the share-based payment arrangements. Any changes in the liability are recognized in profit or loss.
The fair value of the share-based payment arrangements with cash alternatives granted to employees, which is sum of the fair values of the equity component and liabilities component, is recognized as an expense, with a corresponding increase in equity and liabilities, over the vesting period of the awards. The liability is remeasured at each reporting date and at settlement date based on the fair value of the share-based payment arrangements. Any changes in the liability are recognized in profit or loss.
| iii. | Defined contribution plans |
Obligations for contributions to defined contribution plans are expensed as the related service is provided. Prepaid contributions are recognized as an asset to the extent that a cash refund or a reduction in future payments is available.
The Group’s net obligation in respect of defined benefit plans is calculated separately for each plan by estimating the amount of future benefit that employees have earned in the current and prior periods, discounting that amount and deducting the fair value of any plan assets.
The calculation of defined benefit obligations is performed annually using the projected unit credit method. When the calculation results in a potential asset for the Group, the recognized asset is limited to the present value of economic benefits available in the form of any future refunds from the plan or reductions in future contributions to the plan. To calculate the present value of economic benefits, consideration is given to any applicable minimum funding requirements.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Remeasurements of the net defined benefit liability, which comprise actuarial gains and losses, the return on plan assets (excluding interest) and the effect of the asset ceiling (if any, excluding interest), are recognized immediately in OCI. The Group determines the net interest expense (income) on the net defined benefit liability (asset) for the period by applying the discount rate used to measure the defined benefit obligation at the beginning of the annual period to the then-net defined benefit liability (asset), taking into account any changes in the net defined benefit liability (asset) during the period as a result of contributions and benefit payments. Net interest expense and other expenses related to defined benefit plans are recognized in profit or loss.
When the benefits of a plan are changed or when a plan is curtailed, the resulting change in benefit that relates to past service or the gain or loss on curtailment is recognized immediately in profit or loss. The Group recognizes gains and losses on the settlement of a defined benefit plan when the settlement occurs.
| G. | Finance income and finance costs |
The Group’s finance income and finance costs include:
| ● | the net gain or loss on financial assets at FVTPL; |
| ● | the foreign currency gain or loss on financial assets and financial liabilities; |
The ‘effective interest rate’ is the rate that exactly discounts estimated future cash payments or receipts through the expected life of the financial instrument to:
| ● | the gross carrying amount of the financial asset; or |
| ● | the amortized cost of the financial liability. |
In calculating interest income and expense, the effective interest rate is applied to the gross carrying amount of the asset (when the asset is not credit-impaired) or to the amortized cost of the liability. However, for financial assets that have become credit-impaired subsequent to initial recognition, interest income is calculated by applying the effective interest rate to the amortized cost of the financial asset. If the asset is no longer credit-impaired, then the calculation of interest income reverts to the gross basis.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Income tax expense comprises current and deferred tax. It is recognized in profit or loss except to the extent that it relates to a business combination, or items recognized directly in equity or in OCI.
The Group has determined that interest and penalties related to income taxes, including uncertain tax treatments, do not meet the definition of income taxes, and therefore accounted for them under IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets.
Current tax comprises the expected tax payable or receivable on the taxable income or loss for the year and any adjustment to the tax payable or receivable in respect of previous years. The amount of current tax payable or receivable is the best estimate of the tax amount expected to be paid or received that reflects uncertainty related to income taxes, if any. It is measured using tax rates enacted or substantively enacted at the reporting date. Current tax also includes any tax arising from dividends.
Current tax assets and liabilities are offset only if certain criteria are met.
| - | Has a legally enforceable right to set off the recognized amounts; and |
| - | Intends either to settle on a net basis, or to realize the asset and settle the liability simultaneously. |
Deferred tax is recognized in respect of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for taxation purposes. Deferred tax is not recognized for:
| ● | temporary differences on the initial recognition of assets or liabilities in a transaction that is not a business combination and that affects neither accounting nor taxable profit or loss; |
| ● | temporary differences related to investments in subsidiary, associates and joint arrangements to the extent that the Group is able to control the timing of the reversal of the temporary differences and it is probable that they will not reverse in the foreseeable future; and |
| ● | taxable temporary differences arising on the initial recognition of goodwill. |
Deferred tax assets are recognized for unused tax losses, unused tax credits and deductible temporary differences to the extent that it is probable that future taxable profits will be available against which they can be used. Future taxable profits are determined based on the reversal of relevant taxable temporary differences. If the amount of taxable temporary differences is insufficient to recognize a deferred tax asset in full, then future taxable profits, adjusted for reversals of existing temporary differences, are considered, based on the business plans for individual subsidiary in the Group. Deferred tax assets are reviewed at each reporting date and are reduced to the extent that it is no longer probable that the related tax benefit will be realized; such reductions are reversed when the probability of future taxable profits improves.
The measurement of deferred tax reflects the tax consequences that would follow from the manner in which the Group expects, at the reporting date, to recover or settle the carrying amount of its assets and liabilities. For this purpose, the carrying amount of investment property measured at fair value is presumed to be recovered through sale, and the Group has not rebutted this presumption.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are offset only if certain criteria are met.
| - | Has a legally enforceable right to set off the recognized amounts; and |
| - | Intends either to settle on a net basis, or to realize the asset and settle the liability simultaneously. |
| I. | Cash and Cash Equivalents |
Cash and cash equivalents comprise cash on hand, deposits held at banks, and investment securities with maturities of three months or less from the acquisition date that are easily convertible to cash and subject to an insignificant risk of changes in their fair value.
Inventories are measured at the lower of cost and net realizable value. The cost of inventories is based on the first-in, first-out allocation method, and includes expenditures incurred in acquiring the inventories, production or conversion cost and other costs incurred in bringing them to their existing location and condition. Net realizable value is the estimated selling price in the ordinary course of business less the estimated costs of completion and the estimated selling expenses.
The Group makes adjustments to reduce the cost of inventory to its net realizable value, for estimated excess, obsolescence or impaired balances.
Property held by a lessee as a right-of-use asset to earn rentals or for capital appreciation or both is classified as investment property. Investment properties held by a lessee as a right-of-use assets are initially measured at its cost in accordance with IFRS 16. The Company remeasures the investment property held by a lessee as a right-of-use asset if necessary, in accordance with IFRS 16.
Among investment properties, land is not depreciated, and investment properties except land are depreciated on a straight-line basis according to the economic depreciation period. Depreciation methods, useful lives and residual values of investment properties are reviewed at each reporting period-end and if appropriate, the changes are accounted for as changes in accounting estimates.
| L. | Property, plant and equipment |
| i. | Recognition and measurement |
Items of property, plant and equipment are measured at cost, which includes capitalized borrowing costs, less accumulated depreciation and any accumulated impairment losses.
If significant parts of an item of property, plant and equipment have different useful lives, then they are accounted for as separate items (major components) of property, plant and equipment.
Any gain or loss on disposal of an item of property, plant and equipment is recognized in profit or loss.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| ii. | Subsequent expenditure |
Subsequent expenditure is capitalized only if it is probable that the future economic benefits associated with the expenditure will flow to the Group. The carrying amount of the replaced parts are derecognized and the repairs and maintenance expenses are recognized in profit or loss in the period they are incurred.
Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method to allocate the cost or revalued amounts of the assets, net of their residual values, over their estimated useful lives as follows:
| Machinery | | 5 ~ 8 years |
| Vehicles | | 5 years |
| Office equipment | | 5 ~ 8 years |
| Furniture and fixtures | | 5 ~ 8 years |
| Right-of-use assets | | 2 ~ 10 years |
Depreciation methods, useful lives and residual values are reviewed at each reporting date and adjusted if appropriate.
| M. | Intangible assets and goodwill |
| i. | Recognition and measurement |
Goodwill: Goodwill arising on the acquisition of subsidiary is measured at cost less accumulated impairment losses.
Other intangible assets: Other intangible assets, including trademarks that are acquired by the Group and have finite useful lives are measured at cost less accumulated amortization and any accumulated impairment losses.
| ii. | Subsequent expenditure |
Subsequent expenditure is capitalized only when it increases the future economic benefits embodied in the specific asset to which it relates. All other expenditure, including expenditure on internally generated goodwill and brands, is recognized in profit or loss as incurred.
Amortization is calculated using the straight-line method to allocate the cost or revalued amounts of the assets, net of their residual values, over their estimated useful lives as follows:
| Software | | 5 years |
| Other Intangible assets | | 20 years |
| Goodwill | | Indefinite |
Amortization methods, useful lives and residual values are reviewed at each reporting date and adjusted if appropriate.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| i. | Recognition and initial measurement |
Trade receivables and debt securities issued are initially recognized when they are originated. All other financial assets and financial liabilities are initially recognized when the Group becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the instrument.
A financial asset (unless it is a trade receivable without a significant financing component) or financial liability is initially measured at fair value plus or minus, for an item not at FVTPL, transaction costs that are directly attributable to its acquisition or issue. A trade receivable without a significant financing component is initially measured at the transaction price.
| ii. | Classification and subsequent measurement |
Financial assets
On initial recognition, a financial asset is classified as measured at:
| ● | FVOCI - debt investment; |
| ● | FVOCI - equity investment; |
Financial assets are not reclassified subsequent to their initial recognition unless the Group changes its business model for managing financial assets, in which case all affected financial assets are reclassified on the first day of the first reporting period following the change in the business model.
A financial asset is measured at amortized cost if it meets both of the following conditions and is not designated as at FVTPL:
| ● | it is held within a business model whose objective is to hold assets to collect contractual cash flows; and |
| ● | its contractual terms give rise on specified dates to cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. |
A debt investment is measured at FVOCI if it meets both of the following conditions and is not designated as at FVTPL:
| ● | it is held within a business model whose objective is achieved by both collecting contractual cash flows and selling financial assets; and |
| ● | its contractual terms give rise on specified dates to cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
On initial recognition of an equity investment that is not held for trading, the Group may irrevocably elect to present subsequent changes in the investment’s fair value in OCI. This election is made on an investment-by-investment basis.
All financial assets not classified as measured at amortized cost or FVOCI as described above are measured at FVTPL. This includes all derivative financial assets. On initial recognition, the Group may irrevocably designate a financial asset that otherwise meets the requirements to be measured at amortized cost or at FVOCI as at FVTPL if doing so eliminates or significantly reduces an accounting mismatch that would otherwise arise.
Financial assets - Business model assessment
The Group makes an assessment of the objective of the business model in which a financial asset is held at a portfolio level because this best reflects the way the business is managed and information is provided to management. The information considered includes:
| ● | the stated policies and objectives for the portfolio and the operation of those policies in practice. These include whether management’s strategy focuses on earning contractual interest income, maintaining a particular interest rate profile, matching the duration of the financial assets to the duration of any related liabilities or expected cash outflows or realizing cash flows through the sale of the assets; |
| ● | how the performance of the portfolio is evaluated and reported to the Group’s management; |
| ● | the risks that affect the performance of the business model (and the financial assets held within that business model) and how those risks are managed; |
| ● | how managers of the business are compensated - e.g. whether compensation is based on the fair value of the assets managed or the contractual cash flows collected; and |
| ● | the frequency, volume and timing of sales of financial assets in prior periods, the reasons for such sales and expectations about future sales activity. |
Transfers of financial assets to third parties in transactions that do not qualify for derecognition are not considered sales for this purpose, consistent with the Group’s continuing recognition of the assets.
Financial assets that are held for trading or are managed and whose performance is evaluated on a fair value basis are measured at FVTPL.
Financial assets - Assessment whether contractual cash flows are solely payments of principal and interest
For the purposes of this assessment, ‘principal’ is defined as the fair value of the financial asset on initial recognition. ‘Interest’ is defined as consideration for the time value of money and for the credit risk associated with the principal amount outstanding during a particular period of time and for other basic lending risks and costs (e.g. liquidity risk and administrative costs), as well as a profit margin.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
In assessing whether the contractual cash flows are solely payments of principal and interest, the Group considers the contractual terms of the instrument. This includes assessing whether the financial asset contains a contractual term that could change the timing or amount of contractual cash flows such that it would not meet this condition. In making this assessment, the Group considers:
| ● | contingent events that would change the amount or timing of cash flows; |
| ● | terms that may adjust the contractual coupon rate, including variable-rate features; |
| ● | prepayment and extension features; and |
| ● | terms that limit the Group’s claim to cash flows from specified assets (e.g. non-recourse features). |
A prepayment feature is consistent with the solely payments of principal and interest criterion if the prepayment amount substantially represents unpaid amounts of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding, which may include reasonable compensation for early termination of the contract. Additionally, for a financial asset acquired at a discount or premium to its contractual par amount, a feature that permits or requires prepayment at an amount that substantially represents the contractual par amount plus accrued (but unpaid) contractual interest (which may also include reasonable compensation for early termination) is treated as consistent with this criterion if the fair value of the prepayment feature is insignificant at initial recognition.
Financial assets - Subsequent measurement and gains and losses
Financial assets at FVTPL: These assets are subsequently measured at fair value. Net gains and losses, including any interest or dividend income, are recognized in profit or loss.
Financial assets at amortized cost: These assets are subsequently measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. The amortized cost is reduced by impairment losses. Interest income, foreign exchange gains and losses and impairment are recognized in profit or loss. Any gain or loss on derecognition is recognized in profit or loss.
Financial liabilities - Classification, subsequent measurement and gains and losses
Financial liabilities are classified as measured at amortized cost or FVTPL. A financial liability is classified as at FVTPL if it is classified as held-for-trading, it is a derivative or it is designated as such on initial recognition. Financial liabilities at FVTPL are measured at fair value and net gains and losses, including any interest expense, are recognized in profit or loss. Other financial liabilities are subsequently measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. Interest expense and foreign exchange gains and losses are recognized in profit or loss. Any gain or loss on derecognition is also recognized in profit or loss.
Financial assets
The Group derecognizes a financial asset when:
| ● | the contractual rights to the cash flows from the financial asset expire; or |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| ● | it transfers the rights to receive the contractual cash flows in a transaction in which either: |
| - | substantially all of the risks and rewards of ownership of the financial asset are transferred; or |
| - | the Group neither transfers nor retains substantially all of the risks and rewards of ownership and it does not retain control of the financial asset. |
The Group enters into transactions whereby it transfers assets recognized in its statement of financial position, but retains either all or substantially all of the risks and rewards of the transferred assets. In these cases, the transferred assets are not derecognized.
Financial liabilities
The Group derecognizes a financial liability when its contractual obligations are discharged or cancelled, or expire. The Group also derecognizes a financial liability when its terms are modified and the cash flows of the modified liability are substantially different, in which case a new financial liability based on the modified terms is recognized at fair value.
On derecognition of a financial liability, the difference between the carrying amount extinguished and the consideration paid (including any non-cash assets transferred or liabilities assumed) is recognized in profit or loss.
When changes were made to a financial asset or financial liability in addition to changes to the basis for determining the contractual cash flows required by interest rate benchmark reform, the Group first updated the effective interest rate of the financial asset or financial liability to reflect the change that is required by interest rate benchmark reform. After that, the Group applied the policies on accounting for modifications to the additional changes.
| i. | Non-derivative financial assets |
Financial instruments and contract assets
The Group recognizes loss allowances for ECLs on:
| ● | financial assets measured at amortized cost; |
| ● | debt investments measured at FVOCI; and |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The Group also recognizes loss allowances for ECLs on lease receivables, which are disclosed as part of trade and other receivables.
The Group measures loss allowances at an amount equal to lifetime ECLs, except for the following, which are measured at 12-month ECLs:
| ● | debt securities that are determined to have low credit risk at the reporting date; and |
| ● | other debt securities and bank balances for which credit risk (i.e. the risk of default occurring over the expected life of the financial instrument) has not increased significantly since initial recognition. |
Loss allowances for trade receivables (including lease receivables) and contract assets are always measured at an amount equal to lifetime ECLs.
When determining whether the credit risk of a financial asset has increased significantly since initial recognition and when estimating ECLs, the Group considers reasonable and supportable information that is relevant and available without undue cost or effort. This includes both quantitative and qualitative information and analysis, based on the Group’s historical experience and informed credit assessment, that includes forward-looking information.
The Group assumes that the credit risk on a financial asset has increased significantly if it is more than 12 months past due.
The Group considers a financial asset to be in default when:
| ● | the debtor is unlikely to pay its credit obligations to the Group in full, without recourse by the Group to actions such as realising security (if any is held). |
Lifetime ECLs are the ECLs that result from all possible default events over the expected life of a financial instrument.
12-month ECLs are the portion of ECLs that result from default events that are possible within the 12 months after the reporting date (or a shorter period if the expected life of the instrument is less than 12 months).
The maximum period considered when estimating ECLs is the maximum contractual period over which the Group is exposed to credit risk.
Measurement of ECLs
ECLs are a probability-weighted estimate of credit losses. Credit losses are measured as the present value of all cash shortfalls (i.e. the difference between the cash flows due to the entity in accordance with the contract and the cash flows that the Group expects to receive).
ECLs are discounted at the effective interest rate of the financial asset.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Credit-impaired financial assets
At each reporting date, the Group assesses whether financial assets carried at amortized cost and debt securities at FVOCI are credit-impaired. A financial asset is ‘credit-impaired’ when one or more events that have a detrimental impact on the estimated future cash flows of the financial asset have occurred.
Evidence that a financial asset is credit-impaired includes the following observable data:
| ● | significant financial difficulty of the debtor; |
| ● | a breach of contract such as a default or being more than 90 days past due; |
| ● | the restructuring of a loan or advance by the Group on terms that the Group would not consider otherwise; |
| ● | it is probable that the debtor will enter bankruptcy or other financial reorganization; or |
| ● | the disappearance of an active market for a security because of financial difficulties. |
Presentation of allowance for ECL in the statement of financial position
Loss allowances for financial assets measured at amortized cost are deducted from the gross carrying amount of the assets.
For debt securities at FVOCI, the loss allowance is charged to profit or loss and is recognized in OCI.
Write-off
The gross carrying amount of a financial asset is written off when the Group has no reasonable expectations of recovering a financial asset in its entirety or a portion thereof. For individual customers, the Group has a policy of writing off the gross carrying amount when the financial asset is 180 days past due based on historical experience of recoveries of similar assets. For corporate customers, the Group individually makes an assessment with respect to the timing and amount of write-off based on whether there is a reasonable expectation of recovery. The Group expects no significant recovery from the amount written off. However, financial assets that are written off could still be subject to enforcement activities in order to comply with the Group’s procedures for recovery of amounts due.
At each reporting date, the Group reviews the carrying amounts of its non-financial assets (other than biological assets, investment property, inventories, contract assets and deferred tax assets) to determine whether there is any indication of impairment. If any such indication exists, then the asset’s recoverable amount is estimated. Goodwill is tested annually for impairment.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
For impairment testing, assets are grouped together into the smallest group of assets that generates cash inflows from continuing use that are largely independent of the cash inflows of other assets or CGUs. Goodwill arising from a business combination is allocated to CGUs or groups of CGUs that are expected to benefit from the synergies of the combination.
The recoverable amount of an asset or CGU is the greater of its value in use and its fair value less costs of disposal. Value in use is based on the estimated future cash flows, discounted to their present value using a pre-tax discount rate that reflects current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the asset or CGU.
An impairment loss is recognized if the carrying amount of an asset or CGU exceeds its recoverable amount.
Impairment losses are recognized in profit or loss. The Group recognizes the impairment loss if there is any indication of impairment of individual CGU. And then, the Group performed impairment test of goodwill for groups of CGUs.
An impairment loss in respect of goodwill is not reversed. For other assets, an impairment loss is reversed only to the extent that the asset’s carrying amount does not exceed the carrying amount that would have been determined, net of depreciation or amortization, if no impairment loss had been recognized.
Provisions are determined by discounting the expected future cash flows at a pre-tax rate that reflects current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the liability. The unwinding of the discount is recognised as finance cost.
Building restoration: In accordance with the Group’s policy and applicable legal requirements, a provision for restoration in respect of leased buildings, and the related expense, is recognized when the lease term is commenced.
At inception of a contract, the Group assesses whether a contract is, or contains, a lease. A contract is, or contains, a lease if the contract conveys the right to control the use of an identified asset for a period of time in exchange for consideration.
At commencement or on modification of a contract that contains a lease component, the Group allocates the consideration in the contract to each lease component on the basis of its relative stand-alone prices. However, for the leases of property the Group has elected not to separate non-lease components and account for the lease and non-lease components as a single lease component.
The Group recognizes a right-of-use asset and a lease liability at the lease commencement date. The right-of-use asset is initially measured at cost, which comprises the initial amount of the lease liability adjusted for any lease payments made at or before the commencement date, plus any initial direct costs incurred and an estimate of costs to dismantle and remove the underlying asset or to restore the underlying asset or the site on which it is located, less any lease incentives received.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The right-of-use asset is subsequently depreciated using the straight-line method from the commencement date to the end of the lease term, unless the lease transfers ownership of the underlying asset to the Group by the end of the lease term or the cost of the right-of-use asset reflects that the Group will exercise a purchase option. In that case the right-of-use asset will be depreciated over the useful life of the underlying asset, which is determined on the same basis as those of property and equipment. In addition, the right-of-use asset is periodically reduced by impairment losses, if any, and adjusted for certain remeasurements of the lease liability.
The lease liability is initially measured at the present value of the lease payments that are not paid at the commencement date, discounted using the interest rate implicit in the lease or, if that rate cannot be readily determined, the Group’s incremental borrowing rate. Generally, the Group uses its incremental borrowing rate as the discount rate.
The Group determines its incremental borrowing rate by obtaining interest rates from various external financing sources and makes certain adjustments to reflect the terms of the lease and type of the asset leased.
Lease payments included in the measurement of the lease liability comprise the following:
| ● | fixed payments, including in-substance fixed payments; |
| ● | variable lease payments that depend on an index or a rate, initially measured using the index or rate as at the commencement date; |
| ● | amounts expected to be payable under a residual value guarantee; and |
| ● | the exercise price under a purchase option that the Group is reasonably certain to exercise, lease payments in an optional renewal period if the Group is reasonably certain to exercise an extension option, and penalties for early termination of a lease unless the Group is reasonably certain not to terminate early. |
The lease liability is measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. It is remeasured when there is a change in future lease payments arising from a change in an index or rate, if there is a change in the Group’s estimate of the amount expected to be payable under a residual value guarantee, if the Group changes its assessment of whether it will exercise a purchase, extension or termination option or if there is a revised in-substance fixed lease payment.
When the lease liability is remeasured in this way, a corresponding adjustment is made to the carrying amount of the right-of-use asset, or is recorded in profit or loss if the carrying amount of the right-of-use asset has been reduced to zero.
At the date of transition to IFRSs, The Group applies the following approach to all of its leases.
The Group measures that lease liability at the present value of the remaining lease payments, discounted using the lessee’s incremental borrowing rate at the date of transition to IFRSs.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The Group measures right-of-use asset at its carrying amount as if IFRS 16 had been applied since the commencement date of the lease, but discounted using the lessee’s incremental borrowing rate at the date of transition to IFRSs.
The Group uses hindsight in applying IFRS 16 such as the determination of lease term for contracts that contain options to extend or terminate a lease.
The Group has elected not to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for leases of low-value assets (leases for which the underlying asset is valued at USD 5,000 or less) and short-term leases (leases that have a lease term of 12 months or less at the commencement date), including IT equipment. The Group recognizes the lease payments associated with these leases as an expense on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
At inception or on modification of a contract that contains a lease component, the Group allocates the consideration in the contract to each lease component on the basis of their relative stand-alone prices.
When the Group acts as a lessor, it determines at lease inception whether each lease is a finance lease or an operating lease.
To classify each lease, the Group makes an overall assessment of whether the lease transfers substantially all of the risks and rewards incidental to ownership of the underlying asset. If this is the case, then the lease is a finance lease; if not, then it is an operating lease. As part of this assessment, the Group considers certain indicators such as whether the lease is for the major part of the economic life of the asset.
When the Group is an intermediate lessor, it accounts for its interests in the head lease and the sub-lease separately. It assesses the lease classification of a sub-lease with reference to the right-of-use asset arising from the head lease, not with reference to the underlying asset. If a head lease is a short-term lease to which the Group applies the exemption described above, then it classifies the sub-lease as an operating lease.
If an arrangement contains lease and non-lease components, then the Group applies IFRS 15 to allocate the consideration in the contract.
The Group applies the derecognition and impairment requirements in IFRS 9 to the net investment in the lease. The Group further regularly reviews estimated unguaranteed residual values used in calculating the gross investment in the lease.
The Group recognizes lease payments received under operating leases as income on a straight-line basis over the lease term as part of ‘other income’.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
‘Fair value’ is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date in the principal or, in its absence, the most advantageous market to which the Group has access at that date. The fair value of a liability reflects its non-performance risk.
A number of the Group’s accounting policies and disclosures require the measurement of fair values, for both financial and non-financial assets and liabilities.
When one is available, the Group measures the fair value of an instrument using the quoted price in an active market for that instrument. A market is regarded as ‘active’ if transactions for the asset or liability take place with sufficient frequency and volume to provide pricing information on an ongoing basis.
If there is no quoted price in an active market, then the Group uses valuation techniques that maximize the use of relevant observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The chosen valuation technique incorporates all of the factors that market participants would take into account in pricing a transaction.
The best evidence of the fair value of a financial instrument on initial recognition is normally the transaction price - i.e. the fair value of the consideration given or received. If the Group determines that the fair value on initial recognition differs from the transaction price and the fair value is evidenced neither by a quoted price in an active market for an identical asset or liability nor based on a valuation technique for which any unobservable inputs are judged to be insignificant in relation to the measurement, then the financial instrument is initially measured at fair value, adjusted to defer the difference between the fair value on initial recognition and the transaction price. Subsequently, that difference is recognised in profit or loss on an appropriate basis over the life of the instrument but no later than when the valuation is wholly supported by observable market data or the transaction is closed out.
Basic earnings per share is calculated by dividing the net profit for the period available to the ordinary shareholders by the weighted-average number of ordinary shares outstanding during the year.
Diluted earnings per share is calculated by dividing the profit for the year attributable to owners of the parent company from the consolidated statements of profit or loss by the weighted-average number of ordinary shares outstanding and potential dilutive shares. Potential dilutive shares are used in the calculation of dilutive earnings per share only when they have dilutive effects.
| T. | Concentration of Credit Risk |
The Group performs periodic credit evaluations of its customers’ financial condition and generally does not require collateral for customers on accounts receivable. The Group maintains reserves for potential credit losses, which are periodically reviewed.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Ordinary shares are classified as equity. Incremental costs directly attributable to the issuance of ordinary shares and share options are recognized as a deduction from equity, net of any tax effects.
When the Group repurchases its own shares, the amount of the consideration paid is recognized as a deduction from equity and classified as treasury shares. The gains or losses from the purchase, disposal, reissue, or retirement of treasury shares are directly recognized in equity being as transaction with owners.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
6. Operating segments
The Group’s operating segments have been identified to be each business unit, by which the Group provides different services and merchandise.
The Group assesses the performance of each operating segment based on operating profit, and there is no difference with the amounts reported on the consolidated statement of profit or loss, except for intergroup transactions.
The following summary describes the operations of each reportable segment.
| Operating segments | | Operations |
| Content | | Sale and distribution of content consumer products and providing production services |
| Food and beverages | | Sale of food and beverages products and licensing of the intellectual property |
The Group’s chief executive officer reviews the internal management reports of each business unit at least quarterly.
| B. | Information about reportable segments |
Information related to each reportable segment is set out below. Segment operating profit is used to measure performance because management believes that this information is the most relevant in evaluating the results of the respective segments relative to other entities that operate in the same industries.
The segment information for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Content | | | F&B | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Segment revenue | | ₩ | | | 49,771,824 | | | | 17,709,332 | | | | 67,481,156 | |
| Elimination of intersegment revenue | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Consolidated net revenue | | | | | 49,771,824 | | | | 17,709,332 | | | | 67,481,156 | |
| Depreciation/Amortization | | | | | 750,031 | | | | 2,534,001 | | | | 3,284,032 | |
| Segment operating profit(loss) | | | | | 3,802,307 | | | | (304,909 | ) | | | 3,497,398 | |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Content | | | F&B | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Segment revenue | | ₩ | | | 151,858,729 | | | | 17,163,659 | | | | 169,022,388 | |
| Elimination of intersegment revenue | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Consolidated net revenue | | | | | 151,858,729 | | | | 17,163,659 | | | | 169,022,388 | |
| Depreciation/Amortization | | | | | 733,182 | | | | 1,702,091 | | | | 2,435,273 | |
| Segment operating profit(loss) | | | | | 13,546,382 | | | | (384,475 | ) | | | 13,161,907 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Content segment and food and beverages segments are managed on a worldwide basis, but operate manufacturing facilities and sales offices primarily in Seoul, South Korea. The geographic information analyses the Group’s revenue by the customer’s country of domicile. In presenting the geographic information, segment revenue and non-current assets have been based on the geographic location of customers.
Summary of the Group’s operation by region based on the location of customers for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 54,892,741 | | | | 93,764,173 | |
| USA | | | | | 335,239 | | | | 9,879,723 | |
| Japan | | | | | 11,948,054 | | | | 64,996,330 | |
| Other | | | | | 305,122 | | | | 382,162 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 67,481,156 | | | | 169,022,388 | |
Summary of the Group’s non-current assets based on the location as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 30,282,905 | | | | 31,396,705 | |
Revenues from major customers that amount to 10% or more of the Group’s revenue for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Customer A (Content segment) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 17,859,876 | | | | 62,174,920 | |
| % | | | | | 26.47 | % | | | 36.79 | % |
| Customer B (Content segment) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | | | | 11,463,821 | | | | 62,713,081 | |
| % | | | | | 16.99 | % | | | 37.10 | % |
| Customer C (Content segment) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | | | | 11,184,157 | | | | 4,167,544 | |
| % | | | | | 16.57 | % | | | 2.47 | % |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 40,507,854 | | | | 129,055,545 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
7. Revenue
The Group generates revenue primarily through the sale of the Group’s entertainment content and production services, and food and beverage products. Other sources of revenue include the franchise royalty fees from licensing of the Group’s intellectual property in food and beverage business.
Revenue from contracts with customers for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Revenue from contracts with customers | | ₩ | | | 67,481,156 | | | | 169,022,388 | |
| B. | Disaggregation of revenue from contracts with customers |
In the following table, revenue from contracts with customers is disaggregated by major products and service lines and timing of revenue recognition. The table also includes a reconciliation of the disaggregated revenue with the Group’s reportable segments (see Note 6).
Revenue from contracts with customers based on the service contract type and the timing of satisfaction of performance obligations for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Major products/service lines | | | | | | | | | | |
| Content goods and merchandises | | | | | | | | | | |
| Video Project & Merchandise Items | | ₩ | | | 47,511,123 | | | | 150,972,943 | |
| Others | | | | | 2,260,701 | | | | 885,786 | |
| Subtotal | | ₩ | | | 49,771,824 | | | | 151,858,729 | |
| F&B | | | | | | | | | | |
| Food and beverages | | ₩ | | | 17,067,663 | | | | 16,469,551 | |
| Franchise royalties and fees | | | | | 641,669 | | | | 694,108 | |
| Subtotal | | ₩ | | | 17,709,332 | | | | 17,163,659 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 67,481,156 | | | | 169,022,388 | |
| Timing of revenue recognition | | | | | | | | | | |
| At a point in time | | ₩ | | | 66,925,610 | | | | 168,328,280 | |
| Over time | | | | | 555,546 | | | | 694,108 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 67,481,156 | | | | 169,022,388 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The balance of contract liabilities from contracts with customers as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Contract assets | | ₩ | | | 73,463 | | | | - | |
| Contract liabilities | | | | | - | | | | 801 | |
The contract liabilities primarily relate to the advance consideration received from customers, for which revenue is recognized at a point in time when the product is delivered to the customer.
The amount of Korean Won 801 thousand included in contract liabilities as of December 31, 2022 has been recognized as revenue in 2023.
No information is provided about remaining performance obligations as of December 31, 2023 or as of December, 31 2022 that have an original expected duration of one year or less, as allowed by IFRS 15.
8. Income and Expenses
Details of other income for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Gains on disposal of Property, Plant & Equipment | | ₩ | | | 928 | | | | - | |
| Gains on disposal of right-of-use assets | | | | | 1,042,833 | | | | - | |
| Rental income | | | | | 283,983 | | | | - | |
| Miscellaneous income | | | | | 159,336 | | | | 84,462 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,487,080 | | | | 84,462 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Details of other expenses for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other bad debt expenses | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 8,000 | |
| Losses on disposal of Property, Plant & Equipment | | | | | 31,975 | | | | - | |
| Impairment losses on Property, Plant & Equipment | | | | | 2,246 | | | | 15,583 | |
| Securities purchase expenses | | | | | - | | | | 188 | |
| Miscellaneous expenses | | | | | 1,326 | | | | 22,386 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 35,547 | | | | 46,157 | |
Details of classification of expenses by nature for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Changes in inventories | | ₩ | | | 2,931,297 | | | | (1,555,535 | ) |
| Raw materials and consumables | | | | | 4,989,957 | | | | 4,322,808 | |
| Employee benefits | | | | | 11,777,876 | | | | 11,483,075 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | 2,921,232 | | | | 2,082,277 | |
| Amortization of intangible assets | | | | | 362,800 | | | | 352,996 | |
| Commission paid | | | | | 21,501,616 | | | | 84,065,732 | |
| Outsourcing fee | | | | | 16,071,848 | | | | 48,710,311 | |
| Copyright fee | | | | | 1,348,620 | | | | 2,365,794 | |
| Rent | | | | | 856,282 | | | | 792,174 | |
| Supplies | | | | | 307,350 | | | | 470,966 | |
| Water and fuel expenses | | | | | 633,874 | | | | 444,240 | |
| Transportation | | | | | 369,182 | | | | 429,703 | |
| Bad debt expenses | | | | | 171,560 | | | | 696,977 | |
| Building Maintenance | | | | | 96,425 | | | | 201,353 | |
| Other expenses | | | | | 1,095,372 | | | | 1,035,915 | |
| Total | | | | | 65,435,291 | | | | 155,898,786 | |
Total expenses consist of cost of sales and selling, general and administrative expenses.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
9. Finance income and costs
Details of finance income and costs for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Finance income | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | ₩ | | | 406,933 | | | | 520,526 | |
| Dividend income | | | | | 1,462 | | | | 700 | |
| Realized gains on foreign currency transaction | | | | | 199,697 | | | | 529,995 | |
| Unrealized gains on foreign currency transaction | | | | | 376,295 | | | | 154,896 | |
| Gains on valuation of short-term financial instruments | | | | | 55 | | | | - | |
| Gains on valuation of long-term financial instruments | | | | | 7,241 | | | | 6,514 | |
| Gains on disposal of long-term investment securities | | | | | - | | | | 5,878 | |
| Gains on valuation of long-term investment securities | | | | | 116,900 | | | | 2,638 | |
| Gains on disposal of short-term loans | | | | | 12,819 | | | | - | |
| Gains on disposal of long-term loans | | | | | 622,539 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,743,941 | | | | 1,221,147 | |
| Finance costs | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expenses | | ₩ | | | 1,385,142 | | | | 810,047 | |
| Realized losses on foreign currency transaction | | | | | 255,886 | | | | 723,307 | |
| Unrealized losses on foreign currency transaction | | | | | 26,064 | | | | 149,586 | |
| Losses on valuation of short-term financial instruments | | | | | 6 | | | | 421 | |
| Losses on valuation of long-term financial instruments | | | | | 8,717 | | | | 5,263 | |
| Losses on disposal of long-term investment securities | | | | | - | | | | 4,090 | |
| Losses on valuation of long-term investment securities | | | | | 12,395 | | | | 118,607 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,688,210 | | | | 1,811,321 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
10. Earnings per share
| A. | Basic earnings per share |
The calculation of basic EPS has been based on the following profit attributable to ordinary shareholders and weighted-average number of ordinary shares outstanding.
| i. | Profit attributable to ordinary shareholders (basic) |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Profit for the year, attribute to the owners of Parent Company | | ₩ | | | 3,137,186 | | | | 10,189,718 | |
| Dividends on non-redeemable preference shares | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Profit attributable to ordinary shareholders | | ₩ | | | 3,137,186 | | | | 10,189,718 | |
| ii. | Weighted-average number of ordinary shares (basic) |
| | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | (In number of shares) | |
| Number of ordinary shares issued at January 1 | | | 100,000 | | | | 100,000 | |
| Effect of treasury shares held | | | (12,081 | ) | | | - | |
| Weighted-average number of ordinary shares at December 31 | | | 87,919 | | | | 100,000 | |
| B. | Anti-diluted earnings per share |
Diluted earnings per share is not different from basic earnings per share as there is no dilution effects of potential ordinary shares for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022.
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In Korean Won) | |
| Basic earnings per share | | ₩ | | | 35,683 | | | | 101,897 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
11. Share-based payment arrangements
| A. | Description of share-based payment arrangements |
As of December 31, 2023, the Group had the following share-based payment arrangements.
| i. | Share option plan (Tandem awards) |
On December 31, 2021, the Parent Company established tandem award share option plan that entitle employees to a cash payment or shares of the Parent Company. Under these plan, holders of vested options are entitled to a cash payment or purchase shares at the exercise price. Currently, these plans are limited to employees. The share option plans granted to the employees were cancelled during the year ended December 31, 2022.
| ii. | Share option plan (cash-settled) |
On June 30, 2021, the Subsidiary granted 400 share options entitling employees to a cash payment after satisfying 2 vesting conditions below. The amount of the cash payment is determined based on the difference between the share price of the Group at the time of exercise and exercise price.
The key terms and conditions related to the grants under these plans are as follows:
Grant date/
employees entitled | | | Number of
instruments | | | Vesting conditions | | | Contractual life
of options | | | Type | | | Underlying
assets |
| Options granted to employees | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of June 30, 2021 | | | 400 | | | 2 years’ service from grant date and the Play F&B’s annual average Adjusted EBITDA (*1) equals or exceeds Korean Won 1,375,000 thousand at the date of exercise | | | 7 years | | | Cash-settled | | | Play F&B’s ordinary shares |
| (*1) | Adjusted EBITDA = Operating Income +Depreciation of PP&E +Amortization of Intangible Assets +Advertising & marketing expenses |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| B. | Measurement of fair values |
| i. | Cash-settled share-based payment arrangement |
The fair value of the employee share options has been measured using a binomial model.
The inputs used in the measurement of the fair values at grant date and measurement date of the cash-settled share-based payment arrangement are as follows:
Share appreciation rights
(cash-settled) | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In Korean Won) | |
| Fair value of option | | ₩ | | | 504,547 | | | | 756,517 | |
| Share price | | | | | 1,247,333 | | | | 1,484,354 | |
| Exercise price | | ₩ | | | 1,100,000 | | | | 1,100,000 | |
| Risk-free interest rate (based on government bonds) | | | | | 3.15 | % | | | 3.8 | % |
| Volatility (*) | | | | | 37.49 | % | | | 37.5 | % |
| (*) | Volatility has been based on an evaluation of the historical volatility of other companies’ share price, which are listed in KOSDAQ, particularly over the historical period commensurate with prior one year. |
| C. | Reconciliation of outstanding share options |
The number and exercise prices of share options under the share option plan for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows.
| | | 2022 | |
Share option plan
(Either of equity-settled or cash-settled) | | Number of
options | | | | Exercise
price | |
| | | (In Korean Won and number of options) | |
| Outstanding at January 1 | | | 3,000 | | ₩ | | | 560,000 | |
| Cancelled during the year | | | (3,000 | ) | | | | (560,000 | ) |
| Outstanding at December 31 | | | - | | | | | - | |
| Exercisable at December 31 | | | - | | ₩ | | | - | |
| | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
Share option plan
(cash-settled) | | Number of
options | | | | Exercise
price | | | Number of
options | | | | Exercise
price | |
| | | (In Korean Won and number of options) | |
| Outstanding at January 1 | | | 400 | | ₩ | | | 1,100,000 | | | | 400 | | ₩ | | | 1,100,000 | |
| Outstanding at December 31 | | | 400 | | | | | 1,100,000 | | | | 400 | | | | | 1,100,000 | |
| Exercisable at December 31 | | | - | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | ₩ | | | - | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Details of the liabilities arising from the share option plan (cash-settled) are as follows.
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total carrying amount of liabilities for share-based payment | | ₩ | | | 201,819 | | | | 227,577 | |
| Total intrinsic value of liabilities for vested benefits | | | | | 58,933 | | | | 115,306 | |
The share option plans (Tandem awards) granted to the employees were cancelled during the year ended December 31, 2022.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
12. Employee benefits
Details of defined benefit liability recognized as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Defined benefit liability | | ₩ | | | 706,102 | | | | 928,148 | |
The Group operates both the defined benefit plans and defined contribution plans as a retirement pension scheme. Defined benefit plans expose the Group to actuarial risks, such as longevity risk, currency risk, interest rate risk and market (investment) risk.
The expense recognized in relation to defined contribution plan for the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 is Korean Won 435,139 thousand and 339,901 thousand respectively.
| A. | Movement in net defined benefit (asset) liability |
Details of reconciliation from the opening balances to the closing balances for the net defined benefit liability and its components for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | Defined benefit obligation | | | Fair value of plan assets | | | Net defined Benefit liabilities | |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at 1 January | | ₩ | | | 928,148 | | | | 796,366 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 928,148 | | | | 796,366 | |
| Included in profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current service cost | | | | | 514,505 | | | | 550,108 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 514,505 | | | | 550,108 | |
| Past service credit | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Interest expense | | | | | 31,375 | | | | 19,095 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 31,375 | | | | 19,095 | |
| Subtotal | | | | | 545,880 | | | | 569,203 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 545,880 | | | | 569,203 | |
| Included in OCI | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remeasurement loss(gain) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| - Demographic assumption | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| - Financial assumption | | | | | 49,584 | | | | (201,015 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 49,584 | | | | (201,015 | ) |
| - Adjustment based on experience | | | | | (159,142 | ) | | | 57,186 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (159,142 | ) | | | 57,186 | |
| Subtotal | | | | | (109,558 | ) | | | (143,829 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (109,558 | ) | | | (143,829 | ) |
| Other | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Benefits paid | | | | | (658,368 | ) | | | (293,592 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (658,368 | ) | | | (293,592 | ) |
| Subtotal | | | | | (658,368 | ) | | | (293,592 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (658,368 | ) | | | (293,592 | ) |
| Balance at 31 December | | ₩ | | | 706,102 | | | | 928,148 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 706,102 | | | | 928,148 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
There are no contributions funded to its defined benefit plans as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
| C. | Defined benefit obligation |
Details of actuarial assumptions used for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Discount rate | | 4.9% | | 5.6% |
| Future salary growth | | 6.1%~8.2% | | 6.1%~8.2% |
Assumptions regarding future longevity and standard salary scale have been based on issued by Korea Insurance Development Institute.
As of December 31, 2023, the weighted average duration of the defined benefit obligation was 10.8 years.
The Group measures the risk of actuarial assumption changes as a 1% fluctuation in the discount rate and future salary growth rate of the amounts of defined benefit obligation, which reflects the management’s assessment of the risk of actuarial assumption fluctuation that can reasonably occur. The impact of a 1% fluctuation in discount rates and future salary growth rates on the Group’s defined benefit obligation as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | Increased by 1% | | | Decreased by 1% | | | Increased by 1% | | | Decreased by 1% | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Discount rate | | ₩ | | | (68,906 | ) | | | 83,674 | | | | (84,764 | ) | | | 102,725 | |
| Future salary growth | | | | | 83,967 | | | | (70,331 | ) | | | 103,858 | | | | (87,055 | ) |
Although the analysis does not take account of the full distribution of cash flows expected under the plan, it does provide an approximation of the sensitivity of the assumptions shown.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| D. | Employee benefit expenses |
| i. | Details of employee benefit expenses recognized for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows: |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Wages and salaries | | ₩ | | | 9,641,567 | | | | 9,321,946 | |
| Expenses related to post-employment plans | | | | | 981,019 | | | | 909,103 | |
| Social security contributions | | | | | 582,545 | | | | 476,938 | |
| Fringe benefit | | | | | 598,503 | | | | 622,293 | |
| Cash-settled Share-based payments | | | | | (25,758 | ) | | | 152,795 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 11,777,876 | | | | 11,483,075 | |
| ii. | Expenses are recognized in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income (loss) as follows: |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cost of revenues | | ₩ | | | 9,290,041 | | | | 8,454,607 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | | | 2,487,835 | | | | 3,028,468 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 11,777,876 | | | | 11,483,075 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
13. Income taxes
| A. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current tax expense | | | | | | | | |
| Current year | | ₩ | | | 1,319,643 | | | | 2,827,858 | |
| Adjustments recognized related to prior period incomes (*) | | | | | (518,699 | ) | | | 539,038 | |
| | | ₩ | | | 800,944 | | | | 3,366,896 | |
| Deferred tax expense | | | | | | | | | | |
| Origination and reversal of temporary differences | | ₩ | | | (40,165 | ) | | | (679,788 | ) |
| Deferred taxes charged directly to equity | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Tax expense on continuing operations | | ₩ | | | 760,779 | | | | 2,687,108 | |
| (*) | In the normal course of business, the Group and its respective subsidiary are examined by taxation authority. Our management regularly assesses the potential outcomes of these examinations and any future examinations for the current or prior years in determining the adequacy of its liabilities for income taxes. |
We establish additional current tax liabilities for income taxes when, despite the belief that tax positions are fully supportable, there remain positions that do not meet the minimum probability threshold, which is a tax position that is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by the applicable taxation authority. The impact of current tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions, as well as the related net interest and penalties, are included in income taxes in the consolidated statements of operations.
| B. | Amounts recognized in OCI |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Before tax | | | Tax (expense) benefit | | | Net of tax | | | Before tax | | | Tax (expense) benefit | | | Net of tax | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Items that will not be reclassified to profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liability | | ₩ | | | 109,558 | | | | - | | | | 109,558 | | | | 143,829 | | | | - | | | | 143,829 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| C. | Reconciliation of effective tax rate |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) |
| Profit before income tax | | ₩ | | | 3,553,129 | | | | 12,571,733 | |
| Tax at the statutory income tax rate | | | | | 720,604 | | | | 2,743,781 | |
| Adjustments: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Tax-exempt income | | | | | (92 | ) | | | (42 | ) |
| Expenses not deductible for tax purposes | | | | | 37,369 | | | | 33,114 | |
| Tax credits | | | | | (124,290 | ) | | | (348,559 | ) |
| Changes in unrecognized deferred tax | | | | | (149,470 | ) | | | 81,485 | |
| Adjustments recognized related to prior period incomes | | | | | 121,794 | | | | 137,205 | |
| Other (differences in tax rate, etc) | | | | | 154,864 | | | | 40,124 | |
| Income tax expenses | | ₩ | | | 760,779 | | | | 2,687,108 | |
| Effective income tax rate | | | | | 21.4 | % | | | 21.4 | % |
| D. | Movement in deferred tax balances |
| i. | Movement in deferred tax balances as of December 31, 2023 |
| | | | | Tax effect | |
| | | | | Beginning | | | Increase (decrease) | | | Ending | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Accrued income | | ₩ | | | (119,556 | ) | | | 65,087 | | | | (54,469 | ) |
| Short-term financial instruments | | | | | 79,158 | | | | (5,151 | ) | | | 74,007 | |
| Inventories | | | | | (60,881 | ) | | | 281,440 | | | | 220,559 | |
| Property, plant and equipment including right-of-use assets | | | | | (3,600,206 | ) | | | 1,338,286 | | | | (2,261,920 | ) |
| Intangible assets other than goodwill | | | | | 15,853 | | | | (26,565 | ) | | | (10,712 | ) |
| Allowance for bad debts | | | | | 203,306 | | | | 64,495 | | | | 267,801 | |
| Investments in associate and subsidiary (*) | | | | | 805,615 | | | | 118,907 | | | | 924,522 | |
| Accrued expenses | | | | | 102,454 | | | | (102,454 | ) | | | - | |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 3,637,330 | | | | (648,430 | ) | | | 2,988,900 | |
| Provisions | | | | | 220,431 | | | | (27,787 | ) | | | 192,644 | |
| Investment property | | | | | - | | | | (681,506 | ) | | | (681,506 | ) |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | | | | 193,983 | | | | (50,843 | ) | | | 143,140 | |
| Brand | | | | | (1,036,943 | ) | | | 360,537 | | | | (676,406 | ) |
| Other | | | | | 869,670 | | | | (818,937 | ) | | | 50,733 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,310,214 | | | | (132,921 | ) | | | 1,177,293 | |
| Loss carried forward | | ₩ | | | 4,787 | | | | 504,909 | | | | 509,696 | |
| Carryover tax credit | | | | | 2,756,092 | | | | 1,490,363 | | | | 4,246,455 | |
| Unrecognized deferred tax liabilities (assets) (*) | | | | | (4,222,519 | ) | | | (1,822,187 | ) | | | (6,044,706 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets (liabilities) | | ₩ | | | (151,426 | ) | | | 40,164 | | | | (111,262 | ) |
| (*) | As of December 31, 2023, the Group did not recognize deferred income tax asset for the temporary difference relating to investments in subsidiary as it is not probable such temporary differences can be utilized in the foreseeable future. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| ii. | Movement in deferred tax balances as of December 31, 2022 |
| | | | | Tax effect | |
| | | | | Beginning | | | Increase (decrease) | | | Ending | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Accrued income | | ₩ | | | (18,943 | ) | | | (100,613 | ) | | | (119,556 | ) |
| Short-term financial instruments | | | | | 57,820 | | | | 21,338 | | | | 79,158 | |
| Inventories | | | | | (157,411 | ) | | | 96,530 | | | | (60,881 | ) |
| Property, plant and equipment including right-of-use assets | | | | | (1,817,912 | ) | | | (1,782,294 | ) | | | (3,600,206 | ) |
| Intangible assets other than goodwill | | | | | 21,348 | | | | (5,495 | ) | | | 15,853 | |
| Allowance for bad debts | | | | | 57,204 | | | | 146,102 | | | | 203,306 | |
| Investments in associate and subsidiary (*) | | | | | 580,612 | | | | 225,003 | | | | 805,615 | |
| Accrued expenses | | | | | (9,865 | ) | | | 112,319 | | | | 102,454 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 2,024,139 | | | | 1,613,191 | | | | 3,637,330 | |
| Provisions | | | | | 137,910 | | | | 82,521 | | | | 220,431 | |
| Derivatives | | | | | (23,100 | ) | | | 23,100 | | | | - | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | | | | 175,200 | | | | 18,783 | | | | 193,983 | |
| Brand | | | | | (1,150,787 | ) | | | 113,844 | | | | (1,036,943 | ) |
| Other | | | | | 447,723 | | | | 421,947 | | | | 869,670 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 323,938 | | | | 986,276 | | | | 1,310,214 | |
| Loss carried forward | | ₩ | | | 9,353 | | | | (4,566 | ) | | | 4,787 | |
| Carryover tax credit | | | | | 1,798,221 | | | | 957,871 | | | | 2,756,092 | |
| Unrecognized deferred tax liabilities (assets) (*) | | | | | (2,962,726 | ) | | | (1,259,793 | ) | | | (4,222,519 | ) |
| Deferred tax liabilities assets (liabilities) | | ₩ | | | (831,214 | ) | | | 679,788 | | | | (151,426 | ) |
| (*) | As of December 31, 2022, the Group did not recognize deferred income tax asset for the temporary difference relating to investments in subsidiary as it is not probable such temporary differences can be utilized in the foreseeable future. |
| E. | Deferred assets (liabilities) |
| i. | Details of unrecognized as deferred income tax assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows: |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Tax loss carryforwards | | ₩ | | | 509,696 | | | | 4,787 | |
| Tax credit carryforwards | | | | | 4,246,455 | | | | 2,756,092 | |
| Unrecognized temporary difference | | | | | 1,288,555 | | | | 1,461,640 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| ii. | Details of unused tax loss carryforwards and unused tax credit carryforwards that are not recognized as deferred income tax assets as of December 31, 2023 are as follows: |
| Year of expiration | | | | Unused loss
carryforwards | | | Unused tax credit carryforwards | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| 2024 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | |
| 2025 | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| 2026 | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| 2027 | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| 2028 | | | | | - | | | | 393,938 | |
| 2029 | | | | | - | | | | 297,000 | |
| After 2029 | | | | | 2,438,736 | | | | 3,555,517 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 2,438,736 | | | | 4,246,455 | |
| iii. | The timing of recovery of deferred tax assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows: |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Deferred tax assets | | | | | | | | | | |
| - Deferred tax assets to be recovered after more than 12 months | | ₩ | | | 510,711 | | | | 1,221,333 | |
| - Deferred tax assets to be recovered within 12 months | | | | | 516,316 | | | | 352,584 | |
| Sub-total | | | | | 1,027,027 | | | | 1,573,916 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| - Deferred tax liabilities to be recovered after more than 12 months | | | | | (1,126,473 | ) | | | (1,542,440 | ) |
| - Deferred tax liabilities to be recovered within 12 months | | | | | (11,816 | ) | | | (182,903 | ) |
| Sub-total | | | | | (1,138,289 | ) | | | (1,725,343 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets (liabilities), net | | ₩ | | | (111,262 | ) | | | (151,426 | ) |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Details of other assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current | | | | | | | | |
| Prepayments | | ₩ | | | 18,423 | | | | 3,500 | |
| Prepaid expenses (*) | | | | | 700,770 | | | | 74,438 | |
| Subtotal | | | | | 719,193 | | | | 77,938 | |
| Non-Current | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-current prepaid expenses (*) | | | | | 2,606,623 | | | | 539,296 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 3,325,816 | | | | 617,234 | |
| (*) | On July 2023, the Group granted a retention bonus to 7 employees, as a compensation for being employed for the next 5 years. Prepaid and Non-current prepaid expenses are expensed in a straight-line basis, during the employment period defined in the contract. |
15. Inventories
Details of inventories as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Merchandise | | ₩ | | | 1,110,974 | | | | 1,960,765 | |
| Work in process | | | | | 391,939 | | | | 2,871,439 | |
| Allowance for Inventories valuation | | | | | (1,078,353 | ) | | | (1,476,347 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 424,560 | | | | 3,355,857 | |
In 2023, inventories amounted to Korean Won 38,465,045 thousand (2022: Korean Won 65,875,206 thousand) were recognized as an expense during the year and included in ‘cost of sales’.
The Group recognizes the full provision for inventories with more than one year aging from the initiation of project according to the Company’s accounting policies. For inventories with less than one year aging from the initial production with an estimated recovery period exceeding one year, it is also recognized as a provision. Loss on valuation of inventories amounted to Korean Won 140,077 thousand (2022: Korean Won 1,358,651 thousand) and reversal of allowance for inventories valuation amounted to Korean Won 538,072 thousand (2022: Korean Won 215,553 thousand) were recognized during the year ended December 31, 2023.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| 16. | Trade and other receivables |
Details of trade and other receivables as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Trade receivable | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable — Trade | | ₩ | | | 7,192,166 | | | | 15,228,120 | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts (Accounts receivable) | | | | | (438,155 | ) | | | (766,595 | ) |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | ₩ | | | 6,754,011 | | | | 14,461,525 | |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other receivables | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accrued income | | ₩ | | | 46,893 | | | | 438,385 | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts (Accrued income) | | | | | (26,685 | ) | | | (26,685 | ) |
| Non-trade receivables | | | | | 830,958 | | | | 320,034 | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts (Non-trade receivables) | | | | | (500,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | ₩ | | | 351,166 | | | | 731,734 | |
Details of the changes in the loss allowance of trade and other receivables during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts (Trade receivable) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Beginning of the year | | ₩ | | | 766,595 | | | | 69,618 | |
| Bad debt expenses | | | | | - | | | | 696,977 | |
| Reversal of bad debt expenses | | | | | (328,440 | ) | | | - | |
| Ending of the year | | ₩ | | | 438,155 | | | | 766,595 | |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts (Other receivables) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Beginning of the year | | ₩ | | | 26,685 | | | | 18,685 | |
| Bad debt expenses - other | | | | | 500,000 | | | | 8,000 | |
| Ending of the year | | ₩ | | | 526,685 | | | | 26,685 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
17. Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| Cash on hand | | ₩ | | | 2,661 | | | | 2,827 | |
| Deposits in banks | | | | | 8,582,973 | | | | 30,578,729 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 8,585,634 | | | | 30,581,556 | |
The Group doesn’t have any restricted cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
18. Investment properties
| A. | Reconciliation of carrying amount |
Details of Investment properties as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Book value | | ₩ | | | 4,311,539 | | | | - | |
| Accumulated depreciation | | | | | (1,050,744 | ) | | | - | |
| Carrying amount | | ₩ | | | 3,260,795 | | | | - | |
Changes in Investment properties for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance as of January 1 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | |
| Transfer (*) | | | | | 3,483,371 | | | | - | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (222,576 | ) | | | - | |
| Balance as of December 31 | | ₩ | | | 3,260,795 | | | | - | |
| (*) | During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Group transferred Right-of-use assets to investment properties. (Note 19) |
| B. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
Rental income recognized by the Group during the year ended December 31, 2023 was Korean Won 283,983 thousand (2022: nil). Depreciation expense, included in ‘cost of revenues’, was as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Depreciation | | ₩ | | | 222,576 | | | | - | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
19. Property, plant and equipment
| A. | Reconciliation of carrying amount |
Details of property, plant and equipment as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | Book value | | | Accumulated depreciation | | | Carrying amount |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Machinery | | ₩ | | | 2,658,245 | | | | (830,223 | ) | | | 1,828,022 | |
| Vehicles | | | | | 51,419 | | | | (51,417 | ) | | | 2 | |
| Office equipment | | | | | 545,651 | | | | (262,359 | ) | | | 283,292 | |
| Construction-in-progress | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Furniture and fixtures | | | | | 4,668,349 | | | | (1,337,809 | ) | | | 3,330,540 | |
| Right-of-use assets | | | | | 12,104,207 | | | | (2,678,386 | ) | | | 9,425,821 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 20,027,871 | | | | (5,160,194 | ) | | | 14,867,677 | |
| | | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | Book value | | | Accumulated depreciation | | | Carrying amount | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Machinery | | ₩ | | | 2,641,962 | | | | (600,383 | ) | | | 2,041,579 | |
| Vehicles | | | | | 20,374 | | | | (16,299 | ) | | | 4,075 | |
| Office equipment | | | | | 452,831 | | | | (176,120 | ) | | | 276,711 | |
| Construction-in-progress | | | | | 9,950 | | | | - | | | | 9,950 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | | | | | 3,986,571 | | | | (778,952 | ) | | | 3,207,619 | |
| Right-of-use assets | | | | | 17,088,562 | | | | (1,998,991 | ) | | | 15,089,571 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 24,200,250 | | | | (3,570,745 | ) | | | 20,629,505 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Details of the changes in property, plant and equipment for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Machinery | | | Vehicles | | | Office
equipment | | | Construction-
in-progress | | | Furniture
and fixture | | | Right-of-use assets | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 2,041,579 | | | | 4,075 | | | | 276,711 | | | | 9,950 | | | | 3,207,619 | | | | 15,089,571 | | | | 20,629,505 | |
| Acquisitions | | | | | 172,534 | | | | - | | | | 92,819 | | | | - | | | | 684,228 | | | | 578,409 | | | | 1,527,990 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (345,202 | ) | | | (4,074 | ) | | | (86,238 | ) | | | - | | | | (559,061 | ) | | | (1,704,081 | ) | | | (2,698,656 | ) |
| Disposals | | | | | (50,839 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (50,839 | ) |
| Transfer (*1) | | | | | 9,950 | | | | 1 | | | | - | | | | (9,950 | ) | | | - | | | | (3,483,372 | ) | | | (3,483,371 | ) |
| Impairment loss (*2) | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (2,246 | ) | | | - | | | | (2,246 | ) |
| Lease modification | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (45,282 | ) | | | (45,282 | ) |
| Lease termination | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (1,009,424 | ) | | | (1,009,424 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 1,828,022 | | | | 2 | | | | 283,292 | | | | - | | | | 3,330,540 | | | | 9,425,821 | | | | 14,867,677 | |
| (*1) | During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Group transferred Right-of-use assets to investment properties because the Group decided to lease the building to a third party. (Note 18) |
| (*2) | The Group identified each bakery-café store as CGU and recognized impairment loss to bakery-café stores located in Garosu-gil and Jamwon. |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Machinery | | | Vehicles | | | Office
equipment | | | Construction-
in-progress | | | Furniture
and fixture | | | Right-of-use assets | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 1,124,834 | | | | 8,150 | | | | 320,471 | | | | 20,000 | | | | 1,615,335 | | | | 7,974,791 | | | | 11,063,581 | |
| Acquisitions | | | | | 421,201 | | | | - | | | | 21,607 | | | | 2,603,716 | | | | 88,110 | | | | 8,529,150 | | | | 11,663,784 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (235,991 | ) | | | (4,075 | ) | | | (65,367 | ) | | | - | | | | (385,623 | ) | | | (1,391,221 | ) | | | (2,082,277 | ) |
| Transfer | | | | | 731,535 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (2,613,766 | ) | | | 1,905,380 | | | | (23,149 | ) | | | - | |
| Impairment loss (*) | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (15,583 | ) | | | - | | | | (15,583 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 2,041,579 | | | | 4,075 | | | | 276,711 | | | | 9,950 | | | | 3,207,619 | | | | 15,089,571 | | | | 20,629,505 | |
| (*) | The Group identified each bakery-café store as CGU and recognized impairment loss to bakery-café stores located in Garosu-gil and Jamwon. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The classification of depreciation expenses in the statements of comprehensive income for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cost of revenues | | ₩ | | | 2,318,730 | | | | 1,706,191 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | | | 379,926 | | | | 376,086 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 2,698,656 | | | | 2,082,277 | |
| B. | Leased property, plant and equipment |
The Group leased the building and vehicles during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. As of December 31, 2023, Korean Won 9,425,821 thousand of right-of-use assets was recognized. (December 31, 2022: Korean Won 15,089,571 thousand of building, vehicles and other).
At the end of the 2023 and 2022, Korean Won 133,948 thousand of machinery and Korean Won 145,429 thousand of machinery are pledged as collateral for short-term borrowings provided from Industrial Bank of Korea.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
20. Intangible assets and goodwill
| A. | Reconciliation of carrying amount |
Details of intangible assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| | | | | Book value | | | Accumulated depreciation | | | Carrying amount | |
| Software | | ₩ | | | 487,309 | | | | (289,762 | ) | | | 197,547 | |
| Brand | | | | | 5,388,000 | | | | (695,950 | ) | | | 4,692,050 | |
| Goodwill | | | | | 3,267,730 | | | | - | | | | 3,267,730 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 9,143,039 | | | | (985,712 | ) | | | 8,157,327 | |
| | | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| | | | | Book value | | | Accumulated depreciation | | | Carrying amount | |
| Software | | ₩ | | | 487,309 | | | | (196,362 | ) | | | 290,947 | |
| Brand | | | | | 5,388,000 | | | | (426,550 | ) | | | 4,961,450 | |
| Goodwill | | | | | 3,267,730 | | | | - | | | | 3,267,730 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 9,143,039 | | | | (622,912 | ) | | | 8,520,127 | |
Details of the changes in intangible assets for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Software | | | Brand | | | Goodwill | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 290,947 | | | | 4,961,450 | | | | 3,267,730 | | | | 8,520,127 | |
| Amortization | | | | | (93,400 | ) | | | (269,400 | ) | | | - | | | | (362,800 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 197,547 | | | | 4,692,050 | | | | 3,267,730 | | | | 8,157,327 | |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Software | | | Brand | | | Goodwill | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 260,643 | | | | 5,230,850 | | | | 3,267,730 | | | | 8,759,223 | |
| Acquisitions | | | | | 113,900 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 113,900 | |
| Amortization | | | | | (83,596 | ) | | | (269,400 | ) | | | - | | | | (352,996 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 290,947 | | | | 4,961,450 | | | | 3,267,730 | | | | 8,520,127 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The classification of amortization in the statements of comprehensive income for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | ₩ | | | 362,800 | | | | 352,996 | |
| C. | Impairment assessment on CGU |
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Group performed impairment test for Food and Beverages operating segment. The Group identifies each of bakery-cafés as CGU. As the individual CGUs are tested for impairment at the same time as the group of CGUs containing the goodwill, the Group tested the individual CGUs for impairment before the group of CGUs is tested.
The recoverable amount of each CGU is determined based on its value in use. Value in use is calculated using the estimated cash flow based on 5-year business plan approved by management. The estimated revenue and operating expenditures on the Group’s products used in the forecast was determined considering external sources and the Group’s experience. Management estimated the future cash flows based on its past performance and forecasts on consumer inflation rate. The key assumptions used in the estimation of value in use for Food and Beverages CGU include revenue and operating expenditures for the forecast period, growth rates for subsequent years (“terminal growth rate”), and discount rate. Terminal growth rate and the discount rate used in the estimation of value in use are as follows.
| | | Weighted average
cost of capital | | | Terminal
growth rate | |
| 2023 | | | 10.7 | % | | | 1.0 | % |
| 2022 | | | 11.4 | % | | | 1.0 | % |
The discount rate was calculated using the weighted average cost of equity capital and debt and the beta of equity capital was calculated as the average of four Korean listed companies in the same industry and the Group. Cost of debt was calculated using the yield rate of non-guaranteed corporate bond considering the Group’s credit rating and debt ratio was determined using the average of the debt ratios of the four Korean listed companies in the same industry and the Group. The Group calculates the value in use of Food and Beverages CGU using post-tax cash flows and a post-tax discount rate.
As a result of the impairment test for goodwill for groups of Food and Beverages CGUs, the recoverable amount exceeded its carrying amount by Korean Won 4,778,529 thousand in 2023 (2022: Korean Won 6,575,660 thousand). The recoverable amount exceeded its carrying amount accounts 18.9% of the amount of value in use (2022: 24.9%). The value in use determined for this CGU is sensitive to the discount rate and terminal growth rate used in the discounted cash flow model.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The impact of a 0.5% fluctuation in discount rates and terminal growth rates on the value in use as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| 2023 | | 0.5% Increase | | | 0.5% Decrease | |
| Discount rate | | | (-) 4.6 | % | | | 5.1 | % |
| Terminal growth rate | | | 3.7 | % | | | (-) 3.3 | % |
| 2022 | | 0.5% Increase | | | 0.5% Decrease | |
| Discount rate | | | (-) 4.8 | % | | | 5.3 | % |
| Terminal growth rate | | | 3.9 | % | | | (-) 3.6 | % |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
21. Financial instruments by category
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at amortized cost | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | | | 8,585,634 | | | | 30,581,556 | |
| Short-term financial instruments (*) | | | | | 410,000 | | | | 3,910,000 | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | | | | 6,754,011 | | | | 14,461,525 | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | | | | 351,166 | | | | 731,734 | |
| Short-term loans, net | | | | | 859,900 | | | | 5,182,254 | |
| Other current financial assets | | | | | 203,266 | | | | - | |
| Long-term loans, net | | | | | - | | | | 2,413,972 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | 1,390,486 | | | | 1,707,777 | |
| Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term financial instruments (*) | | | | | 9,391 | | | | 8,460 | |
| Long-term financial instruments | | | | | 307,729 | | | | 279,932 | |
| Long-term investment securities | | | | | 640,739 | | | | 536,234 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 19,512,322 | | | | 59,813,444 | |
| (*) | Short-term financial instruments consist of time deposits and saving-based insurance. As of December 31, 2023, Korean Won 231,000 thousand of time deposits in banks are provided as collateral for employee loans and restricted for use. (December 31, 2022: Korean Won 3,900,000 thousand) |
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial liabilities at amortized cost | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables (*) | | ₩ | | | 12,086,332 | | | | 32,392,287 | |
| Short-term borrowings | | | | | 3,330,000 | | | | 2,500,000 | |
| Current portion of long-term borrowings, net | | | | | 24,960 | | | | 24,960 | |
| Trade and other non-current payables (*) | | | | | 134,052 | | | | 16 | |
| Long-term borrowings, excluding current portion, net | | | | | 2,008,041 | | | | 43,680 | |
| Other non-current financial liabilities | | | | | 200,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 17,783,385 | | | | 34,960,943 | |
| (*) | Trade and other payables that are not financial liabilities are excluded. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| A. | Classification of investment assets based on liquidity |
The classification of investment assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current investments | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fixed deposit – at amortized cost (*) | | ₩ | | | 410,000 | | | | 3,910,000 | |
| Saving based insurance – at FVTPL | | | | | 9,391 | | | | 8,460 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 419,391 | | | | 3,918,460 | |
| Non-Current investments | | | | | | | | | | |
| Saving based insurance – at FVTPL | | ₩ | | | 307,729 | | | | 279,932 | |
| Equity securities – at FVTPL | | | | | 637,478 | | | | 533,143 | |
| Debt securities – at FVTPL | | | | | 3,262 | | | | 3,091 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 948,469 | | | | 816,166 | |
| (*) | As of December 31, 2023, Korean Won 231,000 thousand of time deposits is provided as collateral for employee loans and restricted for use. (December 31, 2022: Korean Won 3,900,000 thousand) |
| B. | Equity Securities designated as at FVTPL |
The Group designated the investments shown below as equity securities at FVTPL because these equity securities represent investment that the Group intends to sell for strategic purposes.
| | | | | Fair value at December 31,
2023 | | | Fair value at December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Equity Securities (listed stocks) | | ₩ | | | 198,468 | | | | 178,393 | |
| Equity Securities (unlisted stocks) | | | | | 439,010 | | | | 354,750 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 637,478 | | | | 533,143 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| C. | Net gains and losses by category of financial instruments |
The net gains and losses by category of financial instruments for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Financial assets at
amortized cost | | | Financial assets at
fair value through
profit or loss | | | Financial
liabilities at
amortized cost | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest income | | ₩ | | | 406,933 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 406,933 | |
| interest expense | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (320,209 | ) | | | (320,209 | ) |
| Foreign currency differences | | | | | 294,087 | | | | - | | | | (45 | ) | | | 294,042 | |
| Gain or loss on disposal of financial instruments | | | | | 635,358 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 635,358 | |
| Gain or loss on valuation of investment securities | | | | | - | | | | 104,505 | | | | - | | | | 104,505 | |
| Gain or loss on valuation of financial instruments | | | | | - | | | | (1,427 | ) | | | - | | | | (1,427 | ) |
| Dividend income | | | | | - | | | | 1,463 | | | | - | | | | 1,463 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,336,378 | | | | 104,541 | | | | (320,254 | ) | | | 1,120,665 | |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Financial assets at
amortized cost | | | Financial assets at
fair value through
profit or loss | | | Financial
liabilities at
amortized cost | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest income | | ₩ | | | 520,526 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 520,526 | |
| interest expense | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (96,225 | ) | | | (96,225 | ) |
| Foreign currency differences | | | | | (191,335 | ) | | | - | | | | 3,333 | | | | (188,002 | ) |
| Gain or loss on disposal of investment securities | | | | | - | | | | 1,788 | | | | - | | | | 1,788 | |
| Gain or loss on valuation of investment securities | | | | | - | | | | (115,969 | ) | | | - | | | | (115,969 | ) |
| Gain or loss on valuation of financial instruments | | | | | - | | | | 830 | | | | - | | | | 830 | |
| Dividend income | | | | | - | | | | 700 | | | | - | | | | 700 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 329,191 | | | | (112,651 | ) | | | (92,892 | ) | | | 123,648 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
22. Capital and reserves
| A. | Share capital and share premium |
Details of share capital and share premium as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In Korean won and number of shares) | |
| Number of authorized shares | | | | | 900,000 | | | | 900,000 | |
| Value per share | | ₩ | | | 5,000 | | | | 5,000 | |
| Number of shares issued | | | | | 100,000 | | | | 100,000 | |
| Common shares | | ₩ | | | 500,000,000 | | | | 500,000,000 | |
Holders of these shares are entitled to dividends as declared from time to time and are entitled to one vote per share at general meetings of the Group.
On March 24, 2023, the Group acquired a 15.6% interest of the Parent Company’s issued shares for approximately Korean Won 27,128,262 thousand.
Details of treasury shares for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Number of
shares | | | Carrying
amount | | | Number of
shares | | | Carrying
amount | |
| | | | | (In Korean won and number of shares) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Acquisition | | | | | 15,582 | | | | 27,128,262 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 15,582 | | | | 27,128,262 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| B. | Other components of equity |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liability | | ₩ | | | 151,921 | | | | 78,373 | |
| Other capital surplus | | | | | (746,300 | ) | | | (746,300 | ) |
| Treasury shares | | | | | (27,128,262 | ) | | | - | |
| Other components of equity | | ₩ | | | (27,722,641 | ) | | | (667,927 | ) |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
23. Capital management
The Group’s policy is to maintain a strong capital base so as to maintain investor, creditor and market confidence and to sustain future development of the business. The Group monitors capital using a ratio of ‘net debt’ to ‘total equity’. Net debt is calculated as total liabilities (as shown in the statement of financial position) less cash and cash equivalents. The Group’s net debt to adjusted equity ratio as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows.
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total liabilities | | ₩ | | | 38,697,788 | | | | 59,971,247 | |
| Less: Cash and cash equivalents | | | | | (8,585,634 | ) | | | (30,581,556 | ) |
| Net debt | | | | | 30,112,154 | | | | 29,389,691 | |
| Total equity | | ₩ | | | 11,689,723 | | | | 35,916,077 | |
| Net debt to total equity ratio | | | | | 2.58 | | | | 0.82 | |
24. Borrowings/payable and Loans/receivable
Borrowings as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current Liabilities | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term borrowings | | ₩ | | | 3,330,000 | | | | 2,500,000 | |
| Current portion of long-term borrowings, net | | | | | 24,960 | | | | 24,960 | |
| Current lease liabilities (*) | | | | | 1,630,482 | | | | 1,630,238 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 4,985,442 | | | | 4,155,198 | |
| Non-Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term borrowings, excluding current portion, net | | ₩ | | | 2,008,041 | | | | 43,680 | |
| Non-current lease liabilities (*) | | | | | 12,878,027 | | | | 15,773,254 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 14,886,068 | | | | 15,816,934 | |
| (*) | The interest rate related to lease liabilities reflects the incremental borrowing rate based on the Group’s credit. The amount of interest expense related to lease liabilities incurred during the year ended December 31, 2023 is Korean Won 1,047,738 thousand (2022: Korean Won 704,560 thousand). Additionally, the amount of short-term lease payments and low-value assets lease payments not included in the measurement of lease liabilities during 2023 are Korean Won 23,157 thousand (2022: Korean Won 11,285 thousand) |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| A. | Terms and repayment schedule |
The terms and conditions of outstanding borrowings as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| | | Currency | | Nominal interest rate | | Maturity | | | Face value | | | Carrying amount | | | Face value | | | Carrying amount | |
| Secured borrowings (*1) | | KRW | | KORIBOR +1.62% | | 20-Dec-24 | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | |
| Secured borrowings (*2) | | KRW | | 5.92% | | 28-Feb-24 | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Secured borrowings (*3) | | KRW | | 5.91% | | 28-Jun-24 | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Secured borrowings (*4) | | KRW | | KORIBOR +2.39% | | 16-Sep-25 | | | | 100,000 | | | | 43,680 | | | | 100,000 | | | | 68,640 | |
| Unsecured borrowings | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 700,000 | | | | 700,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Unsecured borrowings | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 2,200,000 | | | | 1,989,321 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Unsecured borrowings | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 130,000 | | | | 130,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total interest-bearing liabilities | | | 5,630,000 | | | | 5,363,001 | | | | 2,600,000 | | | | 2,568,640 | |
| (*1) | As of December 31, 2023, the Group is provided a guarantee of Korean Won 412,775 thousand (2022: Korean Won 321,270 thousand) by the CEO of the Group. The Group provided the intellectual property(IP) rights as collateral. |
| (*2) | As of December 31, 2023, the Group is provided a guarantee of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand (2022: Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand) from the CEO of the Group. |
| (*3) | As of December 31, 2023, the Group is provided a guarantee of Korean Won 900,000 thousand (2022: Korean Won 900,000 thousand) by Korea Credit Guarantee Fund. |
| (*4) | As of December 31, 2023, the Group provides machines with a carrying amount of Korean Won 133,948 thousand (2022: Korean Won 145,429 thousand) as collaterals for the secured borrowings with equal amortization repayment condition. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| B. | Terms and collection schedule |
The terms and conditions of outstanding loans as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| | | Currency | | Nominal interest rate | | Maturity | | | Face value | | | Carrying amount | | | Face value | | | Carrying amount | |
| Cho Hyung Seok (*1) | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-20 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 926,194 | | | | 926,194 | |
| Cho Hyung Seok (*2) | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Oct-22 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,900,000 | | | | 2,900,000 | |
| Cho Hyung Seok (*2) | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-22 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 340,050 | | | | 340,050 | |
| Cho Hyung Seok (*1) | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Mar-23 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 180,000 | | | | 180,000 | |
| Cho Mi Kyung (*3) | | KRW | | 2.00% | | 31-Aug-25 | | | | 400,000 | | | | - | | | | 400,000 | | | | - | |
| Bonanza Pictures (*1) | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Mar-21 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 40,000 | | | | 40,000 | |
| Coam payments (*4) | | KRW | | 12.00% | | 31-May-22 | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | |
| OneTwo Six | | KRW | | 3.00% | | 27-Aug-23 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 250,000 | | | | 243,010 | |
| OneTwo Six | | KRW | | 3.00% | | 28-Jun-24 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 62,862 | | | | 58,773 | |
| Song Tae Ryul | | KRW | | 3.00% | | 14-Sep-23 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 23,000 | | | | 23,000 | |
| Jung Kyung Han | | KRW | | 3.00% | | 14-Sep-23 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | |
| Jung Kyung Han | | KRW | | 3.00% | | 31-Mar-24 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 110,000 | | | | 104,233 | |
| Jung Bo Ram | | KRW | | 1.50% | | 17-May-26 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 705,000 | | | | 571,246 | |
| Jung Bo Ram | | KRW | | 1.50% | | 14-Dec-26 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,500,000 | | | | 1,157,118 | |
| Jung Bo Ram | | KRW | | 1.50% | | 19-May-27 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 300,000 | | | | 235,845 | |
| Jung Bo Ram | | KRW | | 1.50% | | 08-Dec-27 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 400,000 | | | | 286,756 | |
| YY entertainment | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 150,000 | | | | 150,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Second Plan | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Second Plan (*1) | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 76,900 | | | | 76,900 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Studio Coite (*1) | | KRW | | 4.60% | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 43,000 | | | | 43,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | | | 1,259,900 | | | | 859,900 | | | | 8,667,106 | | | | 7,596,226 | |
| (*1) | The contract is automatically extended by one year if the loan is not collected until maturity date. |
| (*2) | In 2022, The maturity date of this loan was extended to October 31, 2023. |
| (*3) | The Group recognized a full provision for the balance of loan and accrued interest income as of January 1, 2021. Accrued interest income as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022 are Korean Won 26,685 thousand and Korean Won 26,685 thousand, respectively. |
| (*4) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee by third party. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
25. Trade and other payables
Trade and other payables as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Trade payables | | ₩ | | | 9,536,869 | | | | 30,866,150 | |
| Other payables | | | | | 2,016,077 | | | | 870,181 | |
| Accrued expenses | | | | | 2,854,664 | | | | 1,745,121 | |
| Trade and other non-current payables | | | | | 335,871 | | | | 227,593 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 14,743,481 | | | | 33,709,045 | |
26. Provisions
Provisions for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Site restoration | | | | | | | | | | |
| Beginning of the year | | ₩ | | | 711,086 | | | | 353,117 | |
| Provisions made during the year | | | | | 26,833 | | | | 350,837 | |
| Interest expense | | | | | 17,195 | | | | 9,262 | |
| Cancellation of lease | | | | | (78,722 | ) | | | - | |
| Lease modification | | | | | (2,244 | ) | | | - | |
| Provisions used during the year | | | | | - | | | | (2,130 | ) |
| Ending of the year | | ₩ | | | 674,148 | | | | 711,086 | |
The provision for building restoration relates mainly to buildings leased during 2023 and 2022. The provision has been estimated based on historical data associated with similar buildings.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
27. Financial Instruments – Fair values and risk management
| A. | Accounting classifications and fair values |
The following table shows the carrying amounts and fair values of financial assets and financial liabilities, including their levels in the fair value hierarchy. It does not include fair value information for financial assets and financial liabilities not measured at fair value if the carrying amount is a reasonable approximation of fair value.
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Guaranteed Return Insurances (short-term) (*) | | ₩ | | | 9,391 | | | | - | | | | 9,391 | | | | - | | | | 9,391 | |
| Guaranteed Return Insurances (long-term) (*) | | | | | 307,729 | | | | - | | | | 307,729 | | | | - | | | | 307,729 | |
| Long-term investment securities | | | | | 640,739 | | | | 201,729 | | | | - | | | | 439,010 | | | | 640,739 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 957,859 | | | | 201,729 | | | | 317,120 | | | | 439,010 | | | | 957,859 | |
| (*) | The fair value of guaranteed return insurances classified at Level 2 in the fair value hierarchy is determined using an evaluation of surrender proceeds received from financial institutions. |
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Guaranteed Return Insurances (short-term) (*) | | ₩ | | | 8,460 | | | | - | | | | 8,460 | | | | - | | | | 8,460 | |
| Guaranteed Return Insurances (long-term) (*) | | | | | 279,932 | | | | - | | | | 279,932 | | | | - | | | | 279,932 | |
| Long-term investment securities | | | | | 536,234 | | | | 181,484 | | | | - | | | | 354,750 | | | | 536,234 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 824,626 | | | | 181,484 | | | | 288,392 | | | | 354,750 | | | | 824,626 | |
| (*) | The fair value of guaranteed return insurances classified at Level 2 in the fair value hierarchy is determined using an evaluation of surrender proceeds received from financial institutions. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| B. | Measurement of fair values |
Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows:
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical asset or liability |
| ● | Level 2: all inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable (either directly that is, prices, or indirectly that is, derived from prices) for the asset or liability |
| ● | Level 3: unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. |
The fair value of financial instruments traded in an active market is determined based on the quoted market price as of the end of the reporting period. If the quoted prices are readily and regularly available through exchanges, sellers, brokers, industry groups, rating agencies or regulators and such prices represent actual market transactions that occur regularly between independent parties, they are considered active markets.
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market is determined using valuation techniques. These valuation techniques use as much market observable information as possible and use the least amount of group-specific information. At this time, if all the significant input variables required to measure the fair value are observable, the financial instruments are classified as Level 2.
If more than one significant input variable is not based on observable market information, the item is included in Level 3.
The valuation techniques used to measure the fair value of a financial instrument include:
| ● | Market price or dealer price of a similar financial instrument |
| ● | The fair value of derivative instruments is determined by discounting the amount to present value using the leading exchange rate as of the end of the reporting period |
| C. | Financial risk management |
The Group’s operating activities expose itself to a variety of financial risks: market risk, credit risk and liquidity risk from which the Group’s risk management program focuses on minimizing any adverse effects on its financial performance. The Group operates financial risk management policies and programs that closely monitor and respond to each risk factor.
Credit risk is the risk of financial loss to the Group if a customer or counterpart to a financial instrument fails to meet its contractual obligations and arises principally from the Group’s receivables from customers. In order to manage credit risk, the Group regularly evaluate the credit worthiness of each customer or counterparty considering the party’s financial information, past experience, its own trading records and other factors. In relation to the impairment of financial assets subsequent to initial recognition, the Group recognizes the changes in expected credit loss (“ECL”) in profit or loss at each reporting date. The carrying amount of a financial asset represents the maximum exposure to credit risk.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The maximum exposure to credit risk of the Group as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | | | 8,585,634 | | | | 30,581,556 | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | | | | 410,000 | | | | 3,910,000 | |
| Accounts receivable, net | | | | | 7,105,177 | | | | 15,193,259 | |
| Short-term loans, net | | | | | 859,900 | | | | 5,182,254 | |
| Other current financial assets | | | | | 203,266 | | | | - | |
| Long-term loans, net | | | | | - | | | | 2,413,972 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | 1,390,486 | | | | 1,707,777 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 18,554,463 | | | | 58,988,818 | |
Cash and cash equivalents and short-term financial instruments are deposited in financial institutions with strong credit rating. Accounts receivables of the Subsidiary are mainly due from payment processing companies and platform service providers, which in the Group believes have low levels of credit risk. In addition, the Parent Company’s exposure to credit risk is influenced mainly by the individual characteristics of each customer. The Group has established a credit policy under which each new customer is analyzed individually before the Group’s standard payment and delivery terms and conditions are offered. The Group’s review includes external ratings, if they are available, financial statements, credit agency information, industry information and in some cases bank references.
The Group monitors customer credit risk, customers are grouped according to their credit characteristics, including whether they are an individual or a legal entity, their geographic location, industry, trading history with the Group and existence of previous financial difficulties. The Group does not require collateral in respect of trade and other receivables. Expected credit losses (ECLs) and credit risk exposures for accounts as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
- Accounts receivables
| As of December 31, 2023 | | Expected loss rate | | | | | Carrying amount | | | Loss allowance | |
| | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Not due or overdue less than 90 days | | | 0.41 | % | | ₩ | | | 6,498,419 | | | | 26,871 | |
| More than 90 days ~ Less than 180 days | | | 0.00 | % | | | | | 4,229 | | | | - | |
| More than 180 days ~ Less than 270 days | | | 32.14 | % | | | | | 410,028 | | | | 131,793 | |
| More than 270 days ~ Less than 1 year | | | 0.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| More than 1 year | | | 100.00 | % | | | | | 279,491 | | | | 279,491 | |
| Total | | | | | | ₩ | | | 7,192,167 | | | | 438,155 | |
| As of December 31, 2022 | | Expected
loss rate | | | | | Carrying
amount | | | Loss
allowance | |
| | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Not due or overdue less than 90 days | | | 0.33 | % | | ₩ | | | 14,505,848 | | | | 44,340 | |
| More than 90 days ~ Less than 180 days | | | 15.68 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| More than 180 days ~ Less than 270 days | | | 28.47 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| More than 270 days ~ Less than 1 year | | | 58.33 | % | | | | | 40 | | | | 23 | |
| More than 1 year | | | 100.00 | % | | | | | 722,232 | | | | 722,232 | |
| Total | | | | | | ₩ | | | 15,228,120 | | | | 766,595 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Liquidity risk management includes the maintenance of sufficient cash and marketable securities, the availability of funds from appropriately committed credit lines, and the ability to settle market positions.
Financial liabilities of the Group by maturity according to the remaining period from December 31, 2023 to the contractual maturity date are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | Carrying Amount | | | Less than 3 months | | | 3 months ~ 1 year | | | 1~2 years | | | 2~5 years | | | More than 5 years | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Non-derivative financial liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade payables | | ₩ | | | 9,536,869 | | | | 9,527,035 | | | | 9,834 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 9,536,869 | |
| Other payable | | | | | 2,144,395 | | | | 1,452,795 | | | | 557,548 | | | | 134,052 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,144,395 | |
| Accrued expense | | | | | 539,120 | | | | 539,048 | | | | 72 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 539,120 | |
| Secured borrowings | | | | | 5,363,001 | | | | 1,072,843 | | | | 2,490,386 | | | | 2,320,406 | | | | 6,305 | | | | - | | | | 5,889,940 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 14,508,509 | | | | 752,242 | | | | 1,882,864 | | | | 2,499,840 | | | | 6,927,468 | | | | 6,399,847 | | | | 18,462,261 | |
| Other non-current financial liabilities | | | | | 200,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 200,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 200,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 32,291,894 | | | | 13,343,963 | | | | 4,940,704 | | | | 5,154,298 | | | | 6,933,773 | | | | 6,399,847 | | | | 36,772,585 | |
Financial liabilities of the Group by maturity according to the remaining period from December 31, 2022 to the contractual maturity date are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | Carrying Amount | | | Less than 3 months | | | 3 months ~ 1 year | | | 1~2 years | | | 2~5 years | | | More than 5 years | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Non-derivative financial liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade payables | | ₩ | | | 30,866,150 | | | | 30,866,150 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 30,866,150 | |
| Other payable | | | | | 870,197 | | | | 870,181 | | | | - | | | | 16 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 870,197 | |
| Accrued expense | | | | | 655,956 | | | | 655,956 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 655,956 | |
| Secured borrowings | | | | | 2,568,640 | | | | 1,033,761 | | | | 1,556,234 | | | | 27,024 | | | | 19,220 | | | | - | | | | 2,636,239 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 17,403,491 | | | | 602,420 | | | | 1,849,242 | | | | 2,484,965 | | | | 7,136,906 | | | | 7,119,186 | | | | 19,192,719 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 52,364,434 | | | | 34,028,468 | | | | 3,405,476 | | | | 2,512,005 | | | | 7,156,126 | | | | 7,119,186 | | | | 54,221,261 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The Group is exposed to foreign exchange risk arising from cash equivalents and accounts receivables primarily with respect to the US Dollar and Japanese Yen.
Financial assets and liabilities are exposed to foreign currency risk as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | Assets in
foreign currency | | | Liabilities in
foreign currency | | | Assets in
Korean Won | | | Liabilities in
Korean Won | |
| | | (Individual amounts in each foreign currency) | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| USD | | | 60,191 | | | | - | | | | 79,018 | | | | - | |
| JPY | | | 805,407,622 | | | | 5,448,213 | | | | 7,350,633 | | | | 49,724 | |
| Total | | | | | | | | | | | 7,429,651 | | | | 49,724 | |
| | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | Assets in
foreign currency | | | Liabilities in
foreign currency | | | Assets in
Korean Won | | | Liabilities in
Korean Won | |
| | | (Individual amounts in each foreign currency) | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| USD | | | 4,313,515 | | | | - | | | | 5,466,518 | | | | - | |
| JPY | | | 2,628,458,508 | | | | - | | | | 25,053,941 | | | | - | |
| Total | | | | | | | | | | | 30,520,459 | | | | - | |
The Group measures foreign exchange risk as a 10% fluctuation in the exchange rate of each foreign currency, which reflects the management’s assessment of the risk of exchange rate fluctuation that can be reasonably occur. The impact of a 10% fluctuation in foreign currency exchange rates on the Group’s profit or loss (before income tax effects) for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | Increased by 10% | | | Decreased by 10% | | | Decreased by 10% | | | Decreased by 10% | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| USD | | | 7,902 | | | | (7,902 | ) | | | 546,652 | | | | (546,652 | ) |
| JPY | | | 730,091 | | | | (730,091 | ) | | | 2,505,394 | | | | (2,505,394 | ) |
| Total | | | 737,993 | | | | (737,993 | ) | | | 3,052,046 | | | | (3,052,046 | ) |
The sensitivity analysis is based on monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies other than the functional currency as of the end of the reporting period.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The sensitivity analysis is based on borrowing under variable interest rate conditions as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | Increased by 100 bp | | | Decreased by 100 bp | | | Increased by 100 bp | | | Decreased by 100 bp | |
| | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) |
| Interest | | ₩ | | | 5,329 | | | | (5,329 | ) | | | 5,562 | | | | (5,562 | ) |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
28. Non-controlling interests
| A. | Summary of financial statements |
Summary of financial statements of the Group’s subsidiary that has material non-controlling interest, before any intercompany transactions eliminations for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| NCI percentage | | | | | 32.9 | % | | | 32.9 | % |
| Current assets | | ₩ | | | 1,873,566 | | | | 2,114,532 | |
| Non-current assets | | | | | 21,776,729 | | | | 24,406,198 | |
| Current liabilities | | | | | 6,838,358 | | | | 6,810,043 | |
| Non-current liabilities | | | | | 15,859,171 | | | | 17,514,118 | |
| Net assets | | | | | 952,766 | | | | 2,196,569 | |
| Revenue | | | | | 17,709,332 | | | | 17,163,659 | |
| Profit (loss) | | | | | (1,140,267 | ) | | | (772,658 | ) |
| OCI | | | | | 109,558 | | | | 143,829 | |
| Total comprehensive income | | ₩ | | | (1,030,709) | | | | (628,829 | ) |
| Cash flows from operation activities | | | | | (94,618 | ) | | | 1,909,605 | |
| Cash flows from investment activities | | | | | (860,374 | ) | | | (2,603,987 | ) |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | | | | 480,119 | | | | 115,318 | |
| Net increase(decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | | | (474,873) | | | | (579,064 | ) |
Movement in NCI for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Net assets attributable to NCI at beginning of the year | | ₩ | | | 720,382 | | | | 1,273,314 | |
| Profit allocated to NCI | | | | | (344,836 | ) | | | (305,093 | ) |
| OCI allocated to NCI | | | | | 36,011 | | | | 47,275 | |
| Transaction with non-controlling interest | | | | | - | | | | (295,114 | ) |
| Net assets attributable to NCI at the end of the year | | ₩ | | | 411,556 | | | | 720,382 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
29. Acquisition of non-controlling interests
In January 2022, the Group acquired an additional 9.9% interest in Play F&B, increasing its ownership from 57.2 to 67.1%. The carrying amount of Play F&B’s net assets in the Group’s consolidated financial statements on the date of the acquisition was Korean Won 2,980,954 thousand considering the brand and effect of deferred tax liability.
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Carrying amount of NCI acquired (₩ 2,980,954 thousand x 9.9%) | | ₩ | | | 295,114 | |
| Consideration paid to NCI | | | | | 1,300,000 | |
| A decrease in equity attributable to owners of the Company | | ₩ | | | (1,004,886) | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
30. Leases
The Group leases buildings and vehicles. The leases typically run for a period of 1 ~5 years, with an option to renew or terminate the lease after that date. The Group also leases water purifiers, copy machines, and others with contract terms of one to three years. These leases are short-term and/or leases of low-value items. The Group has elected not to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for these leases. Information about leases for which the Group is a lessee is presented below.
Right-of-use assets related to leased properties that do not meet the definition of investment property are presented as property, plant and equipment.
Details of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities recognized in the consolidated statements of financial position as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Acquisition price) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Buildings | | ₩ | | | 11,783,393 | | | | 16,820,786 | |
| Vehicles | | | | | 320,813 | | | | 267,776 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 12,104,206 | | | | 17,088,562 | |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Accumulated depreciation) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Buildings | | ₩ | | | (2,514,457) | | | | (1,879,717 | ) |
| Vehicles | | | | | (163,928 | ) | | | (119,274 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (2,678,385) | | | | (1,998,991 | ) |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Net book value) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Buildings | | ₩ | | | 9,268,936 | | | | 14,941,069 | |
| Vehicles | | | | | 156,885 | | | | 148,502 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 9,425,821 | | | | 15,089,571 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Changes in right-of-use assets for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Building | | | Vehicles | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance as of January 1, 2023 | | ₩ | | | 14,941,069 | | | | 148,502 | | | | 15,089,571 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (1,627,945 | ) | | | (76,136 | ) | | | (1,704,081 | ) |
| Acquisitions | | | | | 489,855 | | | | 88,554 | | | | 578,409 | |
| Transfer | | | | | (3,483,371 | ) | | | (1 | ) | | | (3,483,372 | ) |
| Lease termination | | | | | (1,009,424 | ) | | | - | | | | (1,009,424 | ) |
| Lease modification | | | | | (41,248 | ) | | | (4,034 | ) | | | (45,282 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | | ₩ | | | 9,268,936 | | | | 156,885 | | | | 9,425,821 | |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Building | | | Vehicles | | | Other | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance as of January 1, 2022 | | ₩ | | | 7,791,572 | | | | 158,100 | | | | 25,119 | | | | 7,949,672 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (1,327,134 | ) | | | (62,117 | ) | | | (1,970 | ) | | | (1,389,251 | ) |
| Acquisitions | | | | | 8,476,631 | | | | 52,519 | | | | | | | | 8,529,150 | |
| Transfer | | | | | | | | | | | | | (23,149 | ) | | | - | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2022 | | ₩ | | | 14,941,069 | | | | 148,502 | | | | - | | | | 15,089,571 | |
| ii. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
Amounts recognized in profit or loss for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest expense relating to lease liabilities (included in finance cost) | | ₩ | | | 1,047,738 | | | | 704,560 | |
| Expense relating to short-term leases | | | | | 6,268 | | | | - | |
| Expense relating to leases of low-value assets excluding short-term leases | | | | | 16,889 | | | | 11,285 | |
| Gains on disposal of right-of-use assets | | | | | 1,042,833 | | | | - | |
| Expense relating to variable lease payments not included in the measurement of lease liabilities | | ₩ | | | 853,983 | | | | 792,174 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The Company has revised the expense relating to variable lease payments not included in the measurement of lease liabilities for the year ended December 31, 2022 to be consistent with the classification as of December 31, 2023.
| iii. | Amounts recognized in statement of cash flows |
Amounts recognized in statements of cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total cash outflows of leases | | ₩ | | | 3,536,265 | | | | 2,594,294 | |
The Company has revised the total cash outflows of leases for the year ended December 31, 2022 to be consistent with the classification as of December 31, 2023.
Some property leases contain extension options exercisable by the Group. Where practicable, the Group seeks to include extension options in new leases to provide operational flexibility. The extension options held are exercisable only by the Group and not by the lessors. The Group assesses at the lease commencement date whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the extension options. The Group reassesses whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the options if there is a significant event or significant changes in circumstances within its control.
The Group has entered into a contract to pay revenue-based rent payment for a several lease agreements. If the revenue of the store that entered into the contract increase, the rent to be paid may proportionally increase. According to the contract, it is expected to pay 9 to 18% of sales will be paid.
The Group leases out its investment property consisting of its leased property.
The Group has classified these leases as operating leases because they do not transfer substantially all the risk and rewards incidental to the ownership of the assets. Note 18 sets out information about the operating leases of investment property.
Rental income recognized by the Group during the year ended December 31, 2023 was Korean Won 283,983 thousand (2022: nil).
Maturity analysis of lease payments, showing the undiscounted lease payments to be received after December 31, 2023 and 2022 as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Less than 1 year | | ₩ | | | 830,723 | | | | - | |
| 1 ~ 2years | | | | | 549,062 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,379,785 | | | | - | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
31. Commitments
Key commitments the Group has entered into with financial institutions and others as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| Financial institutions | | Categories | | | | Credit limit | | | Borrowings amount | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Revolving credit (*1) | | ₩ | | | 2,000,000 | | | | - | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*2) | | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*3) | | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*4) | | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*5) | | | | | 100,000 | | | | 43,680 | |
| Shinhan Bank | | Revolving credit (*6) | | | | | 500,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 5,100,000 | | | | 2,543,680 | |
| (*1) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 2,400,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*2) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 412,775 thousand by the CEO of the Group. Also, the Group provides intellectual property (IP) rights as collateral for the borrowing. |
| (*3) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*4) | The Group is provided a guarantee of Korean Won 900,000 thousand by Korea Credit Guarantee Fund. |
| (*5) | The Group provides machinery as collateral for the borrowing. |
| (*6) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 600,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Key commitments the Group has entered into with financial institutions and others as of December 31, 2022 are as follows:
| Financial institutions | | Categories | | | | Credit limit | | | Borrowings amount | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Revolving credit (*1) | | ₩ | | | 2,000,000 | | | | - | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*2) | | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*3) | | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*4) | | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*5) | | | | | 100,000 | | | | 68,640 | |
| Shinhan Bank | | Revolving credit (*6) | | | | | 500,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 5,100,000 | | | | 2,568,640 | |
| (*1) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 2,400,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*2) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 321,270 thousand by the CEO of the Group. Also, the Group provides intellectual property (IP) rights as collateral for the borrowing. |
| (*3) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*4) | The Group is provided a guarantee of Korean Won 900,000 thousand by Korea Credit Guarantee Fund. |
| (*5) | The Group provides machinery as collateral for the borrowing. |
| (*6) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 600,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
The Group has entered into an option contract giving its owner the right to buy the common shares of Play F&B owned by non-controlling shareholders of Play F&B on November 30, 2020. Details of the option rights obtained by the investors are as follows:
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Call Option | | Put Option |
| Exercise right holder | | Play Company, CEO of Play Company | | Non-controlling shareholders of Play F&B |
| | | | | |
| Exercise right obligor | | Non-controlling shareholders of Play F&B | | Play Company, CEO of Play Company |
| | | | | |
| Object of exercise | | Common shares | | Common shares |
| | | | | |
| Exercise period | | From the completion of closing date of Play F&B for the year ended December 31, 2022 to June 30, 2023 | | From the completion of closing date of Play F&B for the year ended December 31, 2022 to June 30, 2023 |
| | | | | |
| Exercise price (Per share) | | The greater of price of Korean Won 1,300 thousand per share or average annual EBITDA for 3 years (FY2020 – 2022) multiplied by 7 per shares issued | | The greater of price of Korean Won 1,300 thousand per share or average annual EBITDA for 3 years (FY2020 – 2022) multiplied by 7 per shares issued |
Financial liabilities of Korean Won 1,229,050 thousand, which had been recognized as derivative of Korean Won 598,644 thousand as of January 1, 2021, were recognized as of December 31, 2021 according to option contract. It was eliminated as the Group purchased the shares during the year ended December 31, 2022.
| Description | | Exercise right holder | | Exercise right obligator | | Exercise condition | | Rights |
| Right of first refusal | | Play Company, CEO of Play Company | | Existing shareholders of Play F&B | | In the case of Play Company and CEO agree existing shareholder’s transfer of their shares to third party | | Play Company may purchase the shares held by existing shareholders if shareholder intends to transfer with using preferential purchase rights. |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Drag-Along Right | | Play Company, CEO of Play Company | | Existing shareholders of Play F&B | | In the case of transferring the shares held by Play Company or CEO | | Play Company and CEO may request the existing shareholders to sell their shares on the same exercise condition. |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Tag-Along Right | | Existing shareholders of Play F&B | | Play Company, CEO of Play Company | | In the case of transferring the shares held by Play Company and CEO and not exercising Drag-Along right to existing shareholders | | Existing shareholder may request Play Company and CEO to sell its shares on the same exercise condition. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| B. | Guarantees by individuals |
Details of guarantees provided by individuals other than related parties as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| Guaranteed by | | Details of guarantee | | | | | Guarantee limit | |
| | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Seoul Guarantee Insurance Company | | Performance guarantee, etc. | | ₩ | | | | 808,693 | |
| Korea credit guarantee fund | | Loan guarantee | | | | | | 900,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | | 1,708,693 | |
Details of guarantees provided by individuals other than related parties as of December 31, 2022 are as follows:
| Guaranteed by | | Details of guarantee | | | | | Guarantee limit | |
| | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Seoul Guarantee Insurance Company | | Performance guarantee, etc. | | ₩ | | | | 844,512 | |
| Korea credit guarantee fund | | Loan guarantee | | | | | | 900,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | | 1,744,512 | |
| C. | List of assets provided as collateral |
List of assets that the Group provided as collateral as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | Counterparty receiving the collateral | | usage restrictions | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Provided as collateral for employee loans (*1) | | ₩ | | | 300,000 | | | | 3,900,000 | |
| Machinery | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Provided as collateral for short-term borrowings (*2) | | | | | 133,948 | | | | 145,429 | |
| (*1) | The Group provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 231,000 thousand as of December 31, 2023. (December 31, 2022: Korean Won 4,178,900 thousand) |
| (*2) | As of December 31, 2023, Industrial Bank of Korea has established a pledge of Korean Won 180,000 thousand (December 31, 2022 : Korean Won 180,000 thousand) on the insurance coverage amount for property damage provided by Hyundai Marine & Fire Insurance Company. |
| (*3) | The Group provides intellectual property (IP) rights as collateral for the borrowing. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
On March 31, 2023, the CEO, who is the dominant shareholder of the Group, entered into an equity interest exchange agreement with K Enter Holdings, for the purpose of listing on the NASDAQ through a merger with a SPAC company. The equity interest exchange agreement is effective upon the approval of the shareholders of K Enter Holdings and SPAC. Upon the approval, the CEO of the Group will exchange 83,418 shares with the equity interest of K Enter Holdings. Following the equity interest exchange transaction, the Parent Company is expected to be a subsidiary of K Enter Holdings.
On March 31, 2023, the CEO agreed to enter into a call option agreement prior to closing date of equity interest exchange agreement with K Enter Holdings, under which the CEO of Group will be granted with an option to acquire the shares of Play F&B Co., Ltd held by the Group within three years from the closing date of equity interest exchange agreement.
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
32. Statement of Cash flows
Adjustments for income and expenses from operating activities for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Depreciation | | ₩ | | | 2,921,232 | | | | 2,082,277 | |
| Amortization | | | | | 362,800 | | | | 352,996 | |
| Impairment loss | | | | | 2,246 | | | | 15,583 | |
| Bad debt expenses | | | | | 500,000 | | | | 696,977 | |
| Reversal of bad debt expenses | | | | | (328,439 | ) | | | - | |
| Other Bad debt expenses | | | | | - | | | | 8,000 | |
| Losses on valuation of short-term financial instruments | | | | | 6 | | | | 421 | |
| Losses on valuation of long-term financial instruments | | | | | 8,717 | | | | 5,263 | |
| Losses on valuation of long-term investment securities | | | | | 12,395 | | | | 118,607 | |
| Losses on disposal of long-term investment securities | | | | | - | | | | 4,090 | |
| Gains on disposal of long-term investment securities | | | | | - | | | | (5,878 | ) |
| Gains on valuation of long-term financial instruments | | | | | (7,241 | ) | | | (6,514 | ) |
| Gains on valuation of long-term investment securities | | | | | (116,900 | ) | | | (2,638 | ) |
| Gains on disposal of short-term financial instruments | | | | | (12,819 | ) | | | - | |
| Gains on disposal of long-term financial instruments | | | | | (622,539 | ) | | | - | |
| Gains on valuation of short-term financial instruments | | | | | (55 | ) | | | - | |
| Inventory valuation loss (gains) | | | | | (397,995 | ) | | | 1,143,098 | |
| Losses on foreign currency translation | | | | | 26,064 | | | | 149,586 | |
| Gains on foreign currency translation | | | | | (376,295 | ) | | | (154,896 | ) |
| Gains on disposal of right-of-use assets | | | | | (1,042,833 | ) | | | - | |
| Losses on disposal of property, plant and equipment | | | | | 31,975 | | | | - | |
| Gains on disposal of property, plant and equipment | | | | | (928 | ) | | | - | |
| Interest expenses | | | | | 1,385,142 | | | | 810,047 | |
| Interest income | | | | | (406,933 | ) | | | (520,526 | ) |
| Dividend income | | | | | (1,462 | ) | | | (700 | ) |
| Miscellaneous expenses | | | | | - | | | | 8,649 | |
| Miscellaneous income | | | | | - | | | | (6,028 | ) |
| Share-based payments expenses (reversal) | | | | | (25,758 | ) | | | 152,795 | |
| Severance Benefits | | | | | 545,880 | | | | 569,203 | |
| Tax expenses | | | | | 760,779 | | | | 2,687,108 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 3,217,039 | | | | 8,107,520 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Changes in assets and liabilities from operating activities for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | ₩ | | | 299,334 | | | | 9,264 | |
| Other current assets | | | | | (2,708,583 | ) | | | 257,134 | |
| Accounts receivable – trade, net | | | | | 7,951,197 | | | | 9,010,819 | |
| Accounts receivable – other, net | | | | | (303,948 | ) | | | (303,462 | ) |
| Trade and other payables | | | | | (19,972,438 | ) | | | 4,579,752 | |
| Inventories, net | | | | | 3,329,293 | | | | (2,698,635 | ) |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | | | | (658,367 | ) | | | (293,592 | ) |
| Value added tax receivables | | | | | 1,965,135 | | | | 727,480 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (10,098,377 | ) | | | 11,288,760 | |
Significant non-cash transactions for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Recognition of restoration provision | | ₩ | | | 26,833 | | | | 350,837 | |
| Transfer of construction in progress | | | | | 9,950 | | | | 2,613,766 | |
| Reclassification of long-term borrowings | | | | | 24,960 | | | | 24,960 | |
| Reclassification of Non-current lease liabilities | | | | | 1,911,047 | | | | 1,891,507 | |
| Increase in Lease liabilities | | | | | 612,220 | | | | 9,301,914 | |
| Offset of Loans | | | | | 14,804,782 | | | | - | |
| Offset of Other receivables | | | | | 646,380 | | | | - | |
| Loan Reassignment: Involvement of the Parent company’s CEO | | | | | 2,900,000 | | | | - | |
| Payables related to the acquisition of treasury shares | | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | - | |
| Reclassification of Investment properties | | | | | 3,483,371 | | | | - | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The movements of liabilities to cash flows arising from financing activities for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | Short-term
borrowings | | | Current portion of long-term borrowings | | | Long-term
borrowings | | | Current lease liabilities | | | Non-current lease liabilities | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at 1 January 2022 | | ₩ | | | 2,500,000 | | | | 24,960 | | | | 68,640 | | | | 837,785 | | | | 8,362,848 | | | | 11,794,233 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Repayment of borrowings | | | | | - | | | | (24,960 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (24,960 | ) |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (1,088,224 | ) | | | - | | | | (1,088,224 | ) |
| Reclassification (*1) | | | | | - | | | | 24,960 | | | | (24,960 | ) | | | 1,880,677 | | | | (1,891,508 | ) | | | (10,831 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | (24,960 | ) | | | 792,453 | | | | (1,891,508 | ) | | | (1,124,015 | ) |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | - | |
| New leases | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 9,301,914 | | | | 9,301,914 | |
| Interest expense | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 704,560 | | | | - | | | | 704,560 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (704,560 | ) | | | - | | | | (704,560 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 9,301,914 | | | | 9,301,914 | |
| Balance at 31 December 2022 | | ₩ | | | 2,500,000 | | | | 24,960 | | | | 43,680 | | | | 1,630,238 | | | | 15,773,254 | | | | 19,972,132 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at 1 January 2023 | | ₩ | | | 2,500,000 | | | | 24,960 | | | | 43,680 | | | | 1,630,238 | | | | 15,773,254 | | | | 19,972,132 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | - | |
| Proceeds from borrowings | | | | | 130,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 130,000 | |
| Repayment of borrowings | | | | | - | | | | (24,960 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (24,960 | ) |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (1,617,756 | ) | | | - | | | | (1,617,756 | ) |
| Reclassification | | | | | - | | | | 24,960 | | | | (24,960 | ) | | | 1,911,047 | | | | (1,911,047 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 130,000 | | | | - | | | | (24,960 | ) | | | 293,291 | | | | (1,911,047 | ) | | | (1,512,716 | ) |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | - | |
| Borrowing assumed (*2) | | | | | 700,000 | | | | - | | | | 2,200,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,900,000 | |
| Present value discount | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (282,734 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (282,734 | ) |
| New leases | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 612,220 | | | | 612,220 | |
| Lease termination / lease modification | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (293,047 | ) | | | (1,596,400 | ) | | | (1,889,447 | ) |
| Interest expense | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 72,055 | | | | 1,047,738 | | | | - | | | | 1,119,793 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (1,047,738 | ) | | | - | | | | (1,047,738 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 700,000 | | | | - | | | | 1,989,321 | | | | (293,047 | ) | | | (984,180 | ) | | | 1,412,094 | |
| Balance at 31 December 2023 | | ₩ | | | 3,330,000 | | | | 24,960 | | | | 2,008,041 | | | | 1,630,482 | | | | 12,878,027 | | | | 19,871,510 | |
| (*1) | The amount resulted from offsetting lease liabilities against other deposit receivables due to exercised purchase option. (2022: Korean Won 10,831 thousand) |
| (*2) | Prior to 2023, the Parent Company granted a loan amounting to Korean Won 1,700,000 thousand to its subsidiary. Upon consolidation, this intercompany transaction was offset. During 2023, the obligation, along with a new loan of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand borrowed by the subsidiary within the year, was transitioned to Cho Hyeong Seok, CEO of the Parent Company. This reallocated liability is presented as “borrowing assumed”, denoting a change in debtor, not the origination of a new loan. |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash flows from other financing activities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Acquisition of Treasury shares | | ₩ | | | (10,677,100 | ) | | | - | |
| Transaction with non-controlling interests | | | | | - | | | | (650,000 | ) |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
33. Related parties
| A. | List of related parties |
List of related parties as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| Relationship | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Other related parties | | FF Company Co., Ltd. (“FF Company”) | | FF Company Co., Ltd. (“FF Company”) |
| Other related parties | | OURcoffee gangnamjum Co.,Ltd. (“OURcoffee Gangnamjum”) | | OURcoffee gangnamjum Co.,Ltd. (“OURcoffee Gangnamjum”) |
| Other related parties | | SecondPlan Co.,Ltd. (“SecondPlan”) | | SecondPlan Co.,Ltd. (“SecondPlan”) |
| Other related parties | | ThirdPlan Co., Ltd. (“ThirdPlan”) | | ThirdPlan Co., Ltd. (“ThirdPlan”) |
| Other related parties | | PLAYVERSE Co., Ltd. (“PLAYVERSE”) | | PLAYVERSE Co., Ltd. (“PLAYVERSE”) |
| Other related parties | | Studio Cuat. Co., Ltd. (“Studio Cuat”) | | Studio Cuat. Co., Ltd. (“Studio Cuat”) |
| Other related parties | | Beacon Holdings, Inc. (“Beacon Holdings”) | | |
| B. | Transactions with related parties |
Details of transaction with related parties for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Revenue | | | Finance
income | | | Purchases | | | Finance
Costs | | | Revenue | | | Finance
income | | | Purchases | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties | | FF Company | | ₩ | | | 11,184,157 | | | | - | | | | 62,415 | | | | - | | | | 4,167,544 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | OURcoffee Gangnamjum | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 8,529 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | SecondPlan | | | | | 15,052 | | | | 3,041 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | ThirdPlan | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,435 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | PLAYVERSE | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 28,000 | |
| Other related parties | | Studio Cuat | | | | | 251 | | | | 194 | | | | 527,864 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 611,991 | |
| Key management personnel | | Cho Hyeong Seok | | | | | - | | | | 151,624 | | | | - | | | | 176,597 | | | | - | | | | 179,749 | | | | - | |
| Key management personnel | | Jeong Bo Ram | | | | | - | | | | 676,341 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 36,239 | | | | - | |
| Total | | | | ₩ | | | 11,199,460 | | | | 831,200 | | | | 590,279 | | | | 179,032 | | | | 4,176,073 | | | | 215,988 | | | | 639,991 | |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| C. | Account balances with related parties |
The balances of receivables and payables to related parties as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Receivables | | | Loans | | | Payables | | | Borrowings | | | Receivables | | | Loans | | | Payables | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties | | FF Company | | ₩ | | | 1,002,931 | | | | - | | | | 38,115 | | | | - | | | | 1,253,562 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | SecondPlan | | | | | 63,589 | | | | 106,900 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 10,633 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | ThirdPlan | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,435 | | | | 130,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | Studio Cuat | | | | | 2,117 | | | | 43,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 247,500 | | | | - | | | | 237,858 | |
| Key management personnel | | Cho Hyeong Seok | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,256,876 | | | | 2,689,321 | | | | 329,678 | | | | 4,346,244 | | | | - | |
| Key management personnel | | Jeong Bo Ram | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 43,893 | | | | 2,250,966 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,068,637 | | | | 149,900 | | | | 1,297,426 | | | | 2,819,321 | | | | 1,885,266 | | | | 6,597,210 | | | | 237,858 | |
| D. | Financial transactions with related parties |
Details of significant financial transactions with related parties for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| Related party | | Company | | | | Loans | | | Collection (*1) | | | Borrowings | | | Loans | | | Collection | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties | | Second Plan | | ₩ | | | 1,136,900 | | | | 1,030,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | ThirdPlan | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 130,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | Studio Cuat | | | | | 43,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Key management personnel | | Cho Hyeong Seok (*2) | | | | | 10,738,538 | | | | 15,084,782 | | | | 2,900,000 | | | | 520,050 | | | | - | |
| Key management personnel | | Jeong Bo Ram | | | | | - | | | | 2,905,000 | | | | - | | | | 700,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 11,918,438 | | | | 19,019,782 | | | | 3,030,000 | | | | 1,220,050 | | | | - | |
| (*1) | During 2023, the collection of loans related to Second Plan and Jeong Bo Ram was due to a liability transfer to Cho Hyeong Seok, with no resulting cash inflows. |
| (*2) | During the period, the Parent Company secured a loan of Korean Won 3,510,676 thousand from Cho Hyeong Seok. Cho Hyeong Seok then assumed obligations for loans amounting to Korean Won 7,227,862 thousand made by Play Company to third parties. Of this amount, Korean Won 2,900,000 thousand originally loaned by Play Company to Play F&B is now effectively a loan from Cho Hyeong Seok to the Group. In addition, the Parent Company received repayments of Korean Won 280,000 thousand, and an outstanding loan of Korean Won 14,804,782 thousand was offset against proceeds from the purchase of treasury share. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| E. | Commitments with related parties |
Commitments the Group has entered into with related parties as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| Related party | | Financial institutions | | Categories | | | | Credit limit | | | Borrowings amount | |
| | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Revolving credit (*1) | | ₩ | | | 2,000,000 | | | | - | |
| Key management personnel | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*2) | | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | |
| Key management personnel | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*3) | | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Key management personnel | | Shinhan Bank | | Revolving credit (*4) | | | | | 500,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 4,000,000 | | | | 1,500,000 | |
| (*1) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 2,400,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*2) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 412,775 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*3) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*4) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 600,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
Commitments the Group has entered into with related parties as of December 31, 2022 are as follows:
| Related party | | Financial institutions | | Categories | | | | Credit limit | | | Borrowings amount | |
| | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Revolving credit (*1) | | ₩ | | | 2,000,000 | | | | - | |
| Key management personnel | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*2) | | | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | |
| Key management personnel | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Small and medium-sized enterprise financing (*3) | | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Key management personnel | | Shinhan Bank | | Revolving credit (*4) | | | | | 500,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 4,000,000 | | | | 1,500,000 | |
| (*1) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 2,400,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*2) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 321,270 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*3) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
| (*4) | The Group is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 600,000 thousand by the CEO of the Group. |
PLAY COMPANY CO., LTD. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Details of the collateral the Group provides for the related parties as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| Related Party | | Financial institutions | | Collateral | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cho Hyeong Seok | | Industrial Bank of Korea | | Short-term financial instruments | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 3,530,000 | |
| F. | Key management personnel compensation |
The compensation for the key management personnel for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Short-term employee benefits | | ₩ | | | 1,426,806 | | | | 1,516,788 | |
| Post-employment benefits | | | | | 279,982 | | | | 91,773 | |
| Share-based payments | | | | | 38,530 | | | | 114,596 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,745,318 | | | | 1,723,157 | |
Compensation of the Group’s key management personnel includes salaries, non-cash benefits and contributions to a post-employment defined benefit plan and defined contribution plan.
Executive officers also participate in the Group’s share option plan.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023
| | | Note | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Assets | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | | ₩ | | | 91,896 | | | | 342,896 | |
| Short-term investment securities | | 11 | | | | | - | | | | 1,664,720 | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | | | | | | 376,513 | | | | 384,675 | |
| - Related parties | | 15 | | | | | 376,513 | | | | 384,675 | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | | | | | | 1,846,196 | | | | 118,633 | |
| - Related parties | | 15 | | | | | 1,827,768 | | | | 118,633 | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | 18,428 | | | | - | |
| Other current financial assets | | | | | | | 137,155 | | | | - | |
| - Related parties | | 15 | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | 137,155 | | | | - | |
| Contract assets | | | | | | | 187,146 | | | | 110,988 | |
| - Related parties | | 15 | | | | | 187,146 | | | | 110,988 | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | | 2,638,906 | | | | 2,621,912 | |
| Long-term investment securities | | 11 | | | | | 203,000 | | | | 12,180 | |
| Investments in associates | | 7,13 | | | | | 608,093 | | | | 669,043 | |
| Property and equipment including right-of-use asset | | 3,12 | | | | | 54,893 | | | | 83,659 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | | | 300 | | | | 231,846 | |
| - Related parties | | 15 | | | | | - | | | | 36,082 | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | 300 | | | | 195,764 | |
| Deferred tax assets | | 6 | | | | | 68,072 | | | | 64,863 | |
| Defined benefit assets | | 5 | | | | | - | | | | 21 | |
| Total non-current assets | | | | | | | 934,358 | | | | 1,061,612 | |
| Total assets | | | | ₩ | | | 3,573,264 | | | | 3,683,524 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | | | ₩ | | | 1,801,704 | | | | 1,830,848 | |
| - Related parties | | 15 | | | | | 308 | | | | 27,346 | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | 1,801,396 | | | | 1,803,502 | |
| Other current financial liabilities | | | | | | | 91,482 | | | | - | |
| - Related parties | | 15 | | | | | 91,482 | | | | - | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | | | | | 23,520 | | | | 26,988 | |
| Current tax liabilities | | 6 | | | | | 204,335 | | | | 211,124 | |
| Current Lease liabilities | | 10,12 | | | | | 130,358 | | | | 145,798 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | | 2,251,399 | | | | 2,214,758 | |
| Other non-current financial liabilities | | | | | | | - | | | | 87,123 | |
| - Related parties | | 15 | | | | | - | | | | 87,123 | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | 5 | | | | | 31,679 | | | | - | |
| Other non-current provisions | | | | | | | 13,078 | | | | 12,989 | |
| Non-current Lease liabilities | | 10,12 | | | | | - | | | | 55,275 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | | | | | 44,757 | | | | 155,387 | |
| Total liabilities | | | | ₩ | | | 2,296,156 | | | | 2,370,145 | |
| Equity | | | | | | | |
| Share capital | | 1,8 | | ₩ | | | 850,000 | | | | 850,000 | |
| Share premium | | 8,9 | | | | | 421,254 | | | | 421,254 | |
| Other reserves | | 8 | | | | | (45,637 | ) | | | (45,637 | ) |
| Retained earnings | | | | | | | 51,491 | | | | 87,762 | |
| Total equity | | | | | | | 1,277,108 | | | | 1,313,379 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | | | | ₩ | | | 3,573,264 | | | | 3,683,524 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed interim financial statements.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Note | | | | Six-month period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Operating income | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Investment management revenue | | 3,4 | | | | | 940,172 | | | | 849,708 | |
| - Related parties | | 15 | | | | | 940,172 | | | | 849,708 | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Investment revenue | | 3,4 | | | | | 1,378 | | | | 1,849 | |
| - Related parties | | 15 | | | | | 5 | | | | - | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | 1,373 | | | | 1,849 | |
| Gains from investments in associates | | 7 | | | | | 18,241 | | | | - | |
| - Related parties | | 15 | | | | | 18,241 | | | | - | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | 959,791 | | | | 851,557 | |
| Operating expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | | | | | (1,042,818 | ) | | | (1,060,447 | ) |
| Losses from investments in associates | | 7 | | | | | (25,823 | ) | | | (24,594 | ) |
| | | | | | | | (1,068,641 | ) | | | (1,085,041 | ) |
| Other income | | | | | | | 13 | | | | 878 | |
| Other expense | | | | | | | - | | | | (10,842 | ) |
| Operating loss | | 3 | | | | | (108,837 | ) | | | (243,448 | ) |
| Finance income | | | | | | | 88,596 | | | | 4,995 | |
| - Related parties | | 15 | | | | | 81,654 | | | | 4,796 | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | 6,942 | | | | 199 | |
| Finance costs | | | | | | | (12,754 | ) | | | (5,501 | ) |
| - Related parties | | 15 | | | | | (4,360 | ) | | | (673 | ) |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | (8,394 | ) | | | (4,828 | ) |
| Loss before income tax | | | | | | | (32,995 | ) | | | (243,954 | ) |
| Income tax expenses | | 6 | | | | | (3,276 | ) | | | (11,790 | ) |
| Loss for the period | | | | ₩ | | | (36,271 | ) | | | (255,744 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Items that will not be reclassified to income or loss: | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Remeasurement of defined benefit liabilities | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | ₩ | | | (36,271 | ) | | | (255,744 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed interim financial statements.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Note | | | | Share capital | | | Share
premium | | | Other
reserves | | | Retained earnings | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at January 1, 2023 | | 1 | | ₩ | | | 850,000 | | | | - | | | | (32,913 | ) | | | 389,032 | | | | 1,206,119 | |
| Total comprehensive income for the period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (255,744 | ) | | | (255,744 | ) |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (255,744 | ) | | | (255,744 | ) |
| Share-based Payment | | | | | | | - | | | | 421,254 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 421,254 | |
| Balance at June 30, 2023 | | | | ₩ | | | 850,000 | | | | 421,254 | | | | (32,913 | ) | | | 133,288 | | | | 1,371,629 | |
| Balance at January 1, 2024 | | 1 | | ₩ | | | 850,000 | | | | 421,254 | | | | (45,637 | ) | | | 87,762 | | | | 1,313,379 | |
| Total comprehensive income for the period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (36,271 | ) | | | (36,271 | ) |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (36,271 | ) | | | (36,271 | ) |
| Balance at June 30, 2024 | | 1 | | ₩ | | | 850,000 | | | | 421,254 | | | | (45,637 | ) | | | 51,491 | | | | 1,277,108 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed interim financial statements.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Note | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | 14 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | | ₩ | | | (36,271 | ) | | | (255,744 | ) |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities | | | | | | | (235,710 | ) | | | 495,174 | |
| Interest received | | | | | | | 5,625 | | | | 199 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | | | (8,306 | ) | | | (4,815 | ) |
| Income taxes refunded(paid) | | | | | | | (13,274 | ) | | | 122,620 | |
| Net cash inflow(outflow) from operating activities | | | | ₩ | | | (287,936 | ) | | | 357,434 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | 14 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment for other non-current financial assets | | | | | | | - | | | | (150,000 | ) |
| Collection of other non-current financial assets | | | | | | | 65,000 | | | | 80 | |
| Collection of lease receivables | | | | | | | 42,650 | | | | - | |
| Net cash inflow(outflow) in investing activities | | | | ₩ | | | 107,650 | | | | (149,920 | ) |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | 14 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from short-term borrowings | | | | | | | 14,000 | | | | - | |
| Repayment of short-term borrowings | | | | | | | (14,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Repayment of lease liabilities | | | | | | | (70,714 | ) | | | (40,496 | ) |
| Net cash outflow in financing activities | | | | ₩ | | | (70,714 | ) | | | (40,496 | ) |
| Net increase(decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | (251,000 | ) | | | 167,018 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the period | | | | | | | 342,896 | | | | 71,965 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of the period | | | | ₩ | | | 91,896 | | | | 238,983 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed interim financial statements.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
1. Reporting entity
The Company
Solaire Partners LLC. (“the Company”) was incorporated in June 2017 and the Company’s registered office is at 527 Eonju-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Republic of Korea. The Company is investment management company focusing on contents. The Company primarily generates revenue from the investment in securities of Korean content companies and commissions received from the customers from providing the investment management services.
The Company’s major shareholders and their respective percentage of ownership as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | Share Capital
(₩) | | | Ownership
(%) | | | Share Capital
(₩) | | | Ownership
(%) | |
| Choi, Pyeung Ho | | | 514,250,000 | | | | 60.5 | % | | | 514,250,000 | | | | 60.5 | % |
| Lee, Young Jae | | | 208,250,000 | | | | 24.5 | % | | | 208,250,000 | | | | 24.5 | % |
| Song, Hyo Jeong | | | 42,500,000 | | | | 5.0 | % | | | 42,500,000 | | | | 5.0 | % |
| CY Holdings Co., Ltd | | | 42,500,000 | | | | 5.0 | % | | | 42,500,000 | | | | 5.0 | % |
| Park, Su Kyung | | | 17,000,000 | | | | 2.0 | % | | | 17,000,000 | | | | 2.0 | % |
| Hyun, Na Young | | | 8,500,000 | | | | 1.0 | % | | | 8,500,000 | | | | 1.0 | % |
| Lee, Myung Hyun | | | 8,500,000 | | | | 1.0 | % | | | 8,500,000 | | | | 1.0 | % |
| Kim, Min Soo | | | 8,500,000 | | | | 1.0 | % | | | 8,500,000 | | | | 1.0 | % |
| Total | | | 850,000,000 | | | | 100.0 | % | | | 850,000,000 | | | | 100.0 | % |
2. Basis of Presentation and Significant Accounting Policies
These condensed interim financial statements for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) IAS 34 Interim Financial Reporting as issued by International Accounting Standard Board (“IASB”), and should be read in conjunction with the Company’s last annual financial statements as at and for the period ended December 31, 2023 (“last annual financial statements”). They do not include all of the information required for a complete set of financial statements prepared in accordance with IFRS Accounting Standards. However, selected explanatory notes are included to explain events and transactions that are significant to an understanding of the changes in the Company’s financial position and performance since the last annual financial statements.
| B. | Significant Accounting Policies |
Significant accounting policies and method of computation used in the preparation of the condensed interim financial statements are consistent with those of the last annual financial statements for the period ended December 31, 2023, except for the changes as described below.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Income tax expense
Income tax expense for the interim period is recognized based on management’s best estimate of the weighted average annual income tax rate expected for the full financial period. The estimated average annual effective income tax rate is applied to the pre-tax income of the interim period.
| i. | New and amended standards or interpretations adopted by the Company |
The Company has applied the following standards and interpretations for the first time for their annual reporting period commencing January 1, 2024.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements
The amendments to IAS 1 clarify that the classification of liabilities as current or non-current should be based on rights that are in existence at the end of the reporting period and that the classification is unaffected by management’s intentions or expectations about whether an entity will exercise its right to defer settlement of a liability. The amendments also introduce a definition of settlement to make clear that settlement includes the transfer to the counterparty of the entity’s own equity instruments, however, it would be excluded if an option to settle the liability by the transfer of the entity’s own equity instruments is recognized separately from the liability as an equity component of a compound financial instrument. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Company’s interim financial statements.
IAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows, and IFRS 7, Financial Instruments: Disclosures
The amendments add to the disclosure objectives in IAS 7, Statement of Cash Flows, that information about supplier financing arrangements should be disclosed to enable users of financial statements to assess the impact of those arrangements on the Company’s liabilities and cash flows. The amendments also amend IFRS 7, Financial Instruments: Disclosures, to add supplier financing arrangements as an example of a requirement to disclose information about an entity’s exposure to concentrations of liquidity risk. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Company’s interim financial statements.
IFRS 16 Leases
The amendments add requirements for the subsequent measurement of sale-and-leaseback transactions that are accounted for as sales in accordance with IFRS 15, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. The amendments require the seller lessee to calculate the ‘lease payments’ or ‘revised lease payments’ in a way that does not result in the seller-lessee recognizing any gain or loss for the rights of use that the seller-lessee continues to retain after the lease commences. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Group’s interim financial statements.
| ii. | New and amended standards or interpretations not yet adopted by the Company |
The following new accounting standards and interpretations that have been published that are not mandatory for June 30, 2024 reporting periods and have not been early adopted by the Company.
IAS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates
The amendments require exchangeability of two currencies should be assessed in order to clarify reporting of foreign currency transactions in the absence of normal-functioning foreign exchange market. The amendments also require applicable spot exchange rate should be determined when the assessment indicates two currencies lack exchangeability. The amendments are effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2025, with early application permitted.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
The financial statements have been prepared on the historical cost basis except for the following items, which are measured on an alternative basis on each reporting date.
| Items | | Measurement bases |
| Financial instruments measured at fair value through profit or loss (“FVTPL”) | | Fair value |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | Present value |
3. Operating segments
The Company’s operating segments have been identified to be a single business unit, by which the Company provides the services for investment fund management.
The following summary describes the operations of each reportable segment.
| Reportable segments | | Operations |
| Investment management | | Providing investment management services to investment funds |
| B. | Information about reportable segments |
Information related to each reportable segment is set out below. Segment operating loss is used to measure performance because management believes that this information is the most relevant in evaluating the results of the respective segments relative to other entities that operate in the same industries.
The segment information for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Segment revenue | | ₩ | | | 959,791 | | | | 851,557 | |
| Depreciation/Amortization | | | | | (28,766 | ) | | | (36,828 | ) |
| Segment operating loss | | | | | (108,837 | ) | | | (243,448 | ) |
Investment and commission revenues are managed and operated in Seoul, Korea. The geographic information analyses the Company’s revenue by the customer’s country of domicile. In presenting the geographic information, segment revenue and non-current assets have been based on the geographic location of customers.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Summary of the Company’s operation by region based on the location of customers for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30, 2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 959,791 | | | | 851,557 | |
Summary of the Company’s non-current assets based on the location as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 662,987 | | | | 752,702 | |
Revenues from major customers that amount to 10% or more of the Company’s revenue for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 390,668 | | | | 371,918 | |
| % | | | | | 41 | % | | | 44 | % |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 272,427 | | | | 286,377 | |
| % | | | | | 28 | % | | | 34 | % |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 202,770 | | | | - | |
| % | | | | | 21 | % | | | - | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 92,548 | | | | 191,414 | |
| % | | | | | 10 | % | | | 22 | % |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 958,413 | | | | 849,709 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
4. Operating income
| A. | Operating income streams |
The Company generates revenue primarily through providing the services for investment management for initial exhibition in theaters.
Revenue from contracts with customers and other income for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Revenue from contracts with customers | | ₩ | | | 941,550 | | | | 851,557 | |
| Other sources of operating income (*) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gains from investments in associates | | | | | 18,241 | | | | - | |
| | | ₩ | | | 959,791 | | | | 851,557 | |
| (*) | Other sources of operating income consists of the entity’s interest in the profit of associates accounted for by the equity method, and gains from disposal of investments in associates. |
| B. | Disaggregation of revenue from contracts with customers |
In the following table, revenue from contracts with customers is disaggregated by primary geographical market, major products and service lines and timing of revenue recognition. The table also includes a reconciliation of the disaggregated revenue with the Company’s reportable segments. (See Note 3)
Revenue from contracts with customers based on the service contract type, the timing of satisfaction of performance obligations, and by primary geographical market for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30, 2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Major products/service lines | | | | | | | | | | |
| Investment management revenue | | ₩ | | | 940,172 | | | | 849,708 | |
| Investment revenue | | | | | 1,378 | | | | 1,849 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 941,550 | | | | 851,557 | |
| Timing of revenue recognition | | | | | | | | | | |
| Over time | | | | | 941,550 | | | | 851,557 | |
| Revenue from contracts with customers | | | | | 941,550 | | | | 851,557 | |
| Other sources of operating income | | | | | 18,241 | | | | - | |
| External revenue as reported in Note 3 | | ₩ | | | 959,791 | | | | 851,557 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
5. Employee benefits
Details of Net defined benefit liability(asset) recognized as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Defined benefit asset | | ₩ | | | (321,017 | ) | | | (314,885 | ) |
| Defined benefit liability | | | | | 352,696 | | | | 314,864 | |
| Net defined benefit liability(asset) | | ₩ | | | 31,679 | | | | (21 | ) |
The Company operates defined benefit plans as a retirement pension scheme. Defined benefit plans expose the Company to actuarial risks, such as longevity risk, interest rate risk and market (investment) risk.
| A. | Movement in net defined benefit liability(asset) |
Details of reconciliation from the opening balances to the closing balances for the net defined benefit liability(asset) and its components as of June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Defined benefit obligation | | | Fair value of plan assets | | | Net defined benefit liabilities (asset) | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | June 30, 2023 | | | June 30,
2024 | | | June 30,
2023 | | | June 30, 2024 | | | June 30,
2023 | |
| Beginning Balance | | ₩ | | | 314,864 | | | | 243,736 | | | | 314,885 | | | | 246,218 | | | | (21 | ) | | | (2,482 | ) |
| Included in profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current service cost | | | | | 34,451 | | | | 26,275 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 34,451 | | | | 26,275 | |
| Interest | | | | | 3,381 | | | | 4,686 | | | | 6,132 | | | | 6,154 | | | | (2,751 | ) | | | (1,468 | ) |
| Subtotal | | | | | 37,832 | | | | 30,961 | | | | 6,132 | | | | 6,154 | | | | 31,700 | | | | 24,807 | |
| Ending Balance | | ₩ | | | 352,696 | | | | 274,697 | | | | 321,017 | | | | 252,372 | | | | 31,679 | | | | 22,325 | |
There are no contributions funded to its defined benefit plans as of June 30, 2024. In 2023, the Company contributed Korean Won 64,096 thousand to the defined benefit plans.
Details of plan assets as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash | | ₩ | | | 78 | | | | 76 | |
| Time deposits | | | | | 320,939 | | | | 314,809 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 321,017 | | | | 314,885 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Most of the plan assets are invested in one-year time deposits.
Company invests in financial instruments with guaranteed principal to manage risks to plan assets, and there are no separate restrictions on refundability.
Company reviews the level of fund reserves every year and has a policy to compensate for the deficit in the plan assets.
The estimated contribution for 2024 is Korean Won 66,841 thousand.
| C. | Employee benefit expenses |
| i. | Details of employee benefit expenses recognized for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows: |
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Wages and salaries | | ₩ | | | 581,281 | | | | 442,996 | |
| Defined benefits plan expenses | | | | | 31,700 | | | | 24,807 | |
| Social security contributions | | | | | 22,327 | | | | 21,056 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 635,308 | | | | 488,859 | |
| ii. | Expenses are recognized in the condensed statements of comprehensive income (loss) as follows: |
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | ₩ | | | 635,308 | | | | 488,859 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
6. Income taxes
Details of income tax expenses for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month period ended
June 30, 2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current tax expense | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current period | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 9,055 | |
| Adjustments recognized related to prior period incomes (*) | | | | | 6,483 | | | | 11,790 | |
| | | | | | 6,483 | | | | 20,845 | |
| Deferred tax expense | | | | | | | | | | |
| Origination and reversal of temporary differences | | ₩ | | | (3,207 | ) | | | (9,055 | ) |
| Deferred taxes charged directly to equity | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Tax expense on continuing operations | | ₩ | | | 3,276 | | | | 11,790 | |
| (*) | In the normal course of business, the Company is examined by taxation authority. Our management regularly assesses the potential outcomes of these examinations and any future examinations for the current or prior years in determining the adequacy of its liabilities for income taxes. |
The Company establish additional current tax liabilities for income taxes when, despite the belief that tax positions are fully supportable, there remain positions that do not meet the minimum probability threshold, which is a tax position that is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by the applicable taxing authority. The impact of current tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions, as well as the related net interest and penalties, are included in income taxes in the statements of operations.
7. Equity-accounted investees
| A. | Acquisition cost of investments in associates |
Details of acquisition cost of investments in associates as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | Percentage of Ownership (*) | | | Acquisition Cost | | | Percentage of Ownership (*) | | | Acquisition Cost | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Investments in associates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 1.04 | % | | | 146,632 | | | | 1.04 | % | | | 200,000 | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 1.25 | % | | | 300,000 | | | | 1.25 | % | | | 300,000 | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 1.00 | % | | | 300,000 | | | | 1.00 | % | | | 300,000 | |
| SOLAIRESCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 1.04 | % | | | 88,000 | | | | 1.04 | % | | | 88,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | | | | | 834,632 | | | | | | | | 888,000 | |
| (*) | Although the Company holds less than 20% of equity interests in investment fund, investments in such investees were classified as investments in associates as the Company can exercise significant influence over financial and operating policy decisions as a general partner. |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| B. | Carrying amount of investments in associates |
Details of carrying amount of investments in associates as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | Percentage of Ownership (*) | | | Carrying Amount | | | Percentage of Ownership (*) | | | Carrying Amount | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Investments in associates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 1.04 | % | | | 61,630 | | | | 1.04 | % | | | 112,425 | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 1.25 | % | | | 187,911 | | | | 1.25 | % | | | 208,522 | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 1.00 | % | | | 276,612 | | | | 1.00 | % | | | 260,944 | |
| SOLAIRESCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 1.04 | % | | | 81,940 | | | | 1.04 | % | | | 87,152 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | | | | | 608,093 | | | | | | | | 669,043 | |
| (*) | Although the Company holds less than 20% of equity interests in investment fund, investments in such investees were classified as investments in associates as the Company can exercise significant influence over financial and operating policy decisions as a general partner. |
C. Movement of investments in associates
Details of the changes in investments in associates for the June 30, 2024 are as follows:
| | | | | January 1, 2024 | | | Capital contribution | | | Capital withdrawal | | | Gains(Losses) on disposal of investments in associates | | | Share in the
profit of associates | | | June 30, 2024 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Investments in associates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 112,425 | | | | - | | | | (53,368 | ) | | | - | | | | 2,573 | | | | 61,630 | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 208,522 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (20,611 | ) | | | 187,911 | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 260,944 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 15,668 | | | | 276,612 | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 87,152 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (5,212 | ) | | | 81,940 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 669,043 | | | | - | | | | (53,368 | ) | | | - | | | | (7,582 | ) | | | 608,093 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Details of the changes in investments in associates for the June 30, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | January 1, 2023 | | | Capital contribution | | | Capital withdrawal | | | Gains(Losses) on disposal of investments in associates | | | Share in the
profit of associates | | | June 30, 2023 | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Investments in associates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.8 | | | | | 35,636 | | | | - | | | | (17,000 | ) | | | - | | | | (2,092 | ) | | | 16,544 | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 158,861 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (5,906 | ) | | | 152,955 | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 264,846 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (9,634 | ) | | | 255,212 | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 290,086 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (6,961 | ) | | | 283,125 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 749,430 | | | | - | | | | (17,000 | ) | | | - | | | | (24,594 | ) | | | 707,836 | |
D. Summary of financial information of associates
Details of the summary of financial information of associates the June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | |
| | | | | Current assets | | | Investment asset | | | Total assets | | | Current liabilities | | | Total liabilities | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Investments in associates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 29,361 | | | | 5,944,369 | | | | 5,973,730 | | | | 26,437 | | | | 26,437 | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 1,523,565 | | | | 13,645,503 | | | | 15,169,067 | | | | 136,213 | | | | 136,213 | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 3,045,541 | | | | 24,803,172 | | | | 27,848,713 | | | | 187,500 | | | | 187,500 | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 125,816 | | | | 7,800,541 | | | | 7,926,357 | | | | 60,112 | | | | 60,112 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 4,724,283 | | | | 52,193,585 | | | | 56,917,867 | | | | 410,262 | | | | 410,262 | |
| | | | | Six-month period ended June 30, 2024 | |
| | | | | Investment income | | | Profit (Loss) for the period | | | Total Comprehensive Income (loss) | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Investments in associates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 106,298 | | | | 248,292 | | | | 248,292 | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 5,339 | | | | (1,648,873 | ) | | | (1,648,873 | ) |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 2,687,434 | | | | 1,566,790 | | | | 1,566,790 | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 4,415 | | | | (500,369 | ) | | | (500,369 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 2,803,486 | | | | (334,160 | ) | | | (334,160 | ) |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | Current assets | | | Investment asset | | | Total assets | | | Current liabilities | | | Total liabilities | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | | | | |
| Investments in associates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 3,149,532 | | | | 7,767,287 | | | | 10,916,819 | | | | 67,819 | | | | 67,819 | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 2,270,036 | | | | 14,561,389 | | | | 16,831,425 | | | | 149,698 | | | | 149,698 | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 1,084,379 | | | | 25,204,198 | | | | 26,288,577 | | | | 194,154 | | | | 194,154 | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 4,644,693 | | | | 3,800,000 | | | | 8,444,693 | | | | 78,079 | | | | 78,079 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 11,148,640 | | | | 51,332,874 | | | | 62,481,514 | | | | 489,750 | | | | 489,750 | |
| | | | | Six-month period ended June 30, 2023 | |
| | | | | Investment income | | | Profit (Loss) for the year | | | Total Comprehensive income | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Investments in associates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 320,188 | | | | (569,904 | ) | | | (569,904 | ) |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 33,539 | | | | (770,761 | ) | | | (770,761 | ) |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 9,274 | | | | (696,150 | ) | | | (696,150 | ) |
| SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.8 | | | | | 142,854 | | | | (234,559 | ) | | | (234,559 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 505,855 | | | | (2,271,374 | ) | | | (2,271,374 | ) |
8. Capital and reserves
Details of share capital as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Shares | | ₩ | | | 850,000 | | | | 850,000 | |
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Share Premium | | ₩ | | | 421,254 | | | | 421,254 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| C. | Other components of equity |
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liability | | ₩ | | | (45,637 | ) | | | (45,637 | ) |
9. Share-based payment arrangements
| A. | Measurement of fair values |
The fair value of the employee share options has been measured using a discounted cash flow method.
The inputs used in the measurement of the fair values at grant date are as follows:
Share option plan
(Either of equity-settled or cash-settled) | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Estimated fair value of Share (in aggregate) | | ₩ | | | 455,254 | |
| Transfer Price | | | | | 34,000 | |
| Fair Value of options | | ₩ | | | 421,254 | |
| Risk-free interest rate (based on government bonds) | | | | | 3.74 | % |
| Discount rate | | | | | 15.80 | % |
10. Borrowings/payable
Borrowings as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Lease liabilities (*) | | ₩ | | | 130,358 | | | | 145,798 | |
| Non-Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Lease liabilities (*) | | | | | - | | | | 55,275 | |
| (*) | The interest rate related to lease liabilities reflects the incremental borrowing rate based on the Company’s credit. The amount of interest expense related to lease liabilities incurred during the six-month period ended June 30, 2024 is Korean Won 8,306 thousand (six-month period ended June 30, 2023: Korean Won 4,815 thousand). Additionally, the amount of low-value assets lease payments not included in the measurement of lease liabilities during the six-month period ended June 30, 2024 is Korean Won 1,269 thousand (six-month period ended June 30, 2023: Korean Won 1,519 thousand). |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
11. Financial Instruments – Fair values and risk management
| A. | Accounting classifications and fair values |
The following table shows the carrying amounts and fair values of financial assets and financial liabilities, including their levels in the fair value hierarchy. It does not include fair value information for financial assets and financial liabilities not measured at fair value if the carrying amount is a reasonable approximation of fair value.
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of June 30, 2024 are as follows:
| | | | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term investment securities | | ₩ | | | 3,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,000 | | | | 3,000 | |
| Project investment | | | | | 200,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 200,000 | | | | 200,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 203,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 203,000 | | | | 203,000 | |
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term investment securities | | ₩ | | | 1,664,720 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,664,720 | | | | 1,664,720 | |
| Long-term investment securities | | | | | 3,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,000 | | | | 3,000 | |
| Project investment | | | | | 9,180 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 9,180 | | | | 9,180 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,676,900 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,676,900 | | | | 1,676,900 | |
Details of the changes in financial instruments for the years ended June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 1,676,900 | | | | 38,875 | |
| Acquisitions (*1) | | | | | 200,000 | | | | 1,741,000 | |
| Disposals (*2) | | | | | (1,673,900 | ) | | | (26,695 | ) |
| Valuation (*3) | | | | | - | | | | (76,280 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 203,000 | | | | 1,676,900 | |
| (*1) | On March 23, 2023, the Company acquired 1,000 shares of Play Company Co., Ltd., which represents 1% of total shares issued. Acquisition price per share is Korean Won 1,741 thousand. On April 23, 2024, the Company invest Korean Won 200 thousand for the purpose of planning and developing a movie. |
| (*2) | On January 31, 2024, the Company disposed of all shares of Play Company Co., Ltd. |
| (*3) | Unlisted stocks were revalued on December 31, 2023. |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| B. | Measurement of fair values |
Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows:
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 2: all inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable (either directly that is, prices, or indirectly that is, derived from prices) for the asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 3: unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. |
The fair value of financial instruments traded in an active market is determined based on the quoted market price as of the end of the reporting period. If the quoted prices are readily and regularly available through exchanges, sellers, brokers, industry groups, rating agencies or regulators and such prices represent actual market transactions that occur regularly between independent parties, they are considered active markets.
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market is determined using valuation techniques. These valuation techniques use as much market observable information as possible and use the least amount of Company-specific information. At this time, if all the significant input variables required to measure the fair value are observable, the financial instruments are classified as Level 2.
If more than one significant input variable is not based on observable market information, the item is included in Level 3.
The valuation techniques used to measure the fair value of a financial instrument include:
| ● | Market price or dealer price of a similar financial instrument |
| ● | The fair value of derivative instruments is determined by discounting the amount to present value using the leading exchange rate as of the end of the reporting period |
12. Leases
The company leases building. The leases typically run for a period of 1~3 years, with an option to renew or terminate the lease after that date. The company also leases printer with contract terms of one year. These leases are leases of low-value items. The company has elected not to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for these leases. Information about leases for which the company is a lessee is presented below.
Right-of-use assets related to leased properties that do not meet the definition of investment property are presented as property, plant and equipment.
Details of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities recognized in the statements of financial position as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Building) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Acquisition price | | ₩ | | | 102,888 | | | | 270,012 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | | | | | (55,731 | ) | | | (195,363 | ) |
| Book amount | | ₩ | | | 47,157 | | | | 74,649 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Changes in right-of-use assets for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | |
| | | | | Building | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance as of January 1, 2024 | | ₩ | | | 74,649 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (27,492 | ) |
| Balance as of June 30, 2024 | | ₩ | | | 47,157 | |
| | | | | June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | Building | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance as of January 1, 2023 | | ₩ | | | 86,739 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (35,963 | ) |
| Acquisitions | | | | | 328,232 | |
| Lease modification | | | | | 1,344 | |
| Provision of sublease | | | | | (218,931 | ) |
| Balance as of June 30, 2023 | | ₩ | | | 161,421 | |
| ii. | Amounts recognized in loss |
Amounts recognized in loss for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest expense relating to lease liabilities (included in finance cost) | | ₩ | | | 8,306 | | | | 4,815 | |
| Expense relating to leases of low-value assets excluding short-term leases | | ₩ | | | 1,269 | | | | 1,519 | |
| iii. | Amounts recognized in statement of cash flows |
Amounts recognized in statements of cash flows for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total cash outflows of leases | | ₩ | | | 80,289 | | | | 46,830 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
During six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 the Company has sub-leased a building that has been presented as a right-of-use asset.
During six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 the Company did not dispose of any right-of-use assets and therefore recognized no losses (six-month periods ended June 30, 2023: 10,842) on disposition of right-of-use asset.
During six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 the Company recognized interest income on lease receivables Korean Won 5,374 thousand (six-month periods ended June 30, 2023: 1,555).
13. Commitments
| A. | Amount of investment agreement |
The outstanding balances of contributions according to the investment agreements as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| June 30, 2024 | | | | Total amount
of investment
agreement | | | Cumulative investment | | | Outstanding Balance | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | ₩ | | | 200,000 | | | | 200,000 | | | | - | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 220,000 | | | | 88,000 | | | | 132,000 | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 300,000 | | | | 300,000 | | | | - | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 300,000 | | | | 300,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,020,000 | | | | 888,000 | | | | 132,000 | |
| December 31, 2023 | | | | Total amount
of investment
agreement | | | Cumulative investment | | | Outstanding Balance | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | ₩ | | | 200,000 | | | | 200,000 | | | | - | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 220,000 | | | | 88,000 | | | | 132,000 | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 300,000 | | | | 300,000 | | | | - | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 300,000 | | | | 300,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,020,000 | | | | 888,000 | | | | 132,000 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
On September 14, 2023, an amendment was made to the equity interest exchange agreement, originally entered into on March 31, 2023, between the CEO, other shareholders of the Company, and K Enter Holdings for the purpose of listing on the NASDAQ through a merger with a SPAC company. The equity interest exchange agreement is effective on the date designated by K Enter Holdings. Upon the effective date, the CEO and other shareholders of the Company will exchange 95.1% of its shares with the equity interest of K Enter Holdings. Following the equity interest exchange transaction, the Company is expected to be a subsidiary of K Enter Holdings.
14. Statement of Cash flows
Adjustments for income and expenses from operating activities for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Depreciation | | ₩ | | | 28,766 | | | | 36,828 | |
| Interest expenses | | | | | 12,754 | | | | 5,501 | |
| Interest income | | | | | (12,316 | ) | | | (4,995 | ) |
| Severance Benefits | | | | | 31,700 | | | | 24,807 | |
| Share-based payments expenses | | | | | - | | | | 421,254 | |
| Tax expenses | | | | | 3,276 | | | | 11,791 | |
| Gains on valuation of securities under equity method | | | | | (18,242 | ) | | | - | |
| Gains on disposition of Short-term investment securities | | | | | (76,280 | ) | | | - | |
| Losses on valuation of securities under equity method | | | | | 25,823 | | | | 24,594 | |
| Losses on disposition of right-of-use assets | | | | | - | | | | 10,842 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (4,519 | ) | | | 530,622 | |
Changes in assets and liabilities from operating activities for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other current liabilities | | ₩ | | | (3,468 | ) | | | (32,843 | ) |
| Other current assets | | | | | - | | | | (2,320 | ) |
| Accounts receivable - other | | | | | 6,870 | | | | (77,154 | ) |
| Trade and other payables | | | | | (29,145 | ) | | | (71,393 | ) |
| Accounts receivable - trade | | | | | (67,996 | ) | | | 104,567 | |
| Decrease(Increase) in Project investment | | | | | (190,820 | ) | | | 26,695 | |
| Decrease in securities under equity method | | | | | 53,368 | | | | 17,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (231,191 | ) | | | (35,448 | ) |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Significant non-cash transactions for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Increase in Lease liabilities | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 289,756 | |
| Increase in Short-term investment securities | | | | | - | | | | 1,741,000 | |
| Increase in Other non-current financial liabilities | | | | | - | | | | 100,050 | |
| Decrease in Short-term investment securities | | | | | 1,741,000 | | | | - | |
The movements of liabilities to cash flows arising from financing activities for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Other current
financial liabilities | | | Other non-current financial liabilities | | | Short-term borrowings | | | Current lease liabilities | | | Non-current lease liabilities | | | Total | |
| Balance at 1 January 2023 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 61,718 | | | | 23,366 | | | | 85,084 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (40,496 | ) | | | - | | | | (40,496 | ) |
| Reclassification | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 7,980 | | | | (7,980 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (32,516 | ) | | | (7,980 | ) | | | (40,496 | ) |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| New leases | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 150,289 | | | | 139,468 | | | | 289,757 | |
| Interest expense | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,815 | | | | - | | | | 4,815 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (4,815 | ) | | | - | | | | (4,815 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 150,289 | | | | 139,468 | | | | 289,757 | |
| Balance at 30 June 2023 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 179,491 | | | | 154,854 | | | | 334,345 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at 1 January 2024 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 87,123 | | | | - | | | | 145,798 | | | | 55,274 | | | | 288,195 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (70,714 | ) | | | - | | | | (70,714 | ) |
| Reclassification | | | | | 91,483 | | | | (91,483 | ) | | | - | | | | 55,274 | | | | (55,274 | ) | | | - | |
| Borrowing | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 14,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 14,000 | |
| Repayment | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (14,000 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (14,000 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 91,483 | | | | (91,483 | ) | | | - | | | | (15,440 | ) | | | (55,274 | ) | | | (70,714 | ) |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | | | | | - | | | | 4,360 | | | | - | | | | 8,306 | | | | - | | | | 12,666 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (8,306 | ) | | | - | | | | (8,306 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 4,360 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,360 | |
| Balance at 30 June 2024 | | ₩ | | | 91,483 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 130,358 | | | | - | | | | 221,841 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
15. Related parties
| A. | List of related parties |
List of related parties as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| Relationship | | June 30, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| Key management personnel | | Choi, Pyeung Ho | | Choi, Pyeung Ho |
| Key management personnel | | Lee, Young Jae | | Lee, Young Jae |
| Personnel with significant influence over the Company | | Song, Hyo Jeong | | Song, Hyo Jeong |
| Entities with significant influence over the Company | | CY Holdings Co., Ltd | | CY Holdings Co., Ltd |
| Personnel with significant influence over the Company | | Park, Su Kyung | | Park, Su Kyung |
| Personnel with significant influence over the Company | | Hyun, Na Young | | Hyun, Na Young |
| Personnel with significant influence over the Company | | Lee, Myung Hyun | | Lee, Myung Hyun |
| Personnel with significant influence over the Company | | Kim, Min Soo | | Kim, Min Soo |
| Other related parties | | K Enter Holdings INC | | K Enter Holdings INC |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 |
| Associates | | Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | Solaire Culture Plus Fund |
| Associates | | Solaire Main Movie Fund | | Solaire Main Movie Fund |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 |
| Other related parties | | Bluefire Studio Co., Ltd | | Bluefire Studio Co., Ltd |
| Other related parties | | Secret: Untold Melody Limited Company Specializing in The Cultural Industry | | Secret: Untold Melody Limited Company Specializing in The Cultural Industry |
| Other related parties | | Next Sohee Limited Company Specializing in The Cultural Industry | | Next Sohee Limited Company Specializing in The Cultural Industry |
| Other related parties | | Falling starlight Limited Company Specializing in The Cultural Industry | | Falling starlight Limited Company Specializing in The Cultural Industry |
| Other related parties | | Pupil Limited Company Specializing in The Cultural Industry | | - |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
B. Transactions with related parties
Details of transaction with related parties for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | Six-month period ended June 30, 2024 | | | Six-month period ended June 30, 2023 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Revenue | | | Purchases | | | Revenue | | | Purchases | |
| | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties (*1) | | K Enter Holdings INC | | ₩ | | | 81,654 | | | | 4,360 | | | | 2,430 | | | | 673 | |
| Key management personnel | | Lee, Young Jae | | | | | 3 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Personnel with significant influence over the Company | | Song, Hyo Jeong | | | | | 2 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Associates (*2) | | SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.8 | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,092 | |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 92,548 | | | | - | | | | 191,414 | | | | 5,905 | |
| Associates | | Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 272,427 | | | | 20,611 | | | | 286,377 | | | | 9,634 | |
| Associates | | Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 390,668 | | | | - | | | | 371,918 | | | | 6,962 | |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 202,770 | | | | 5,212 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,040,072 | | | | 30,183 | | | | 852,139 | | | | 25,266 | |
| (*1) | A gain of 76,280 thousand won from the disposal of Play Company Co., Ltd shares was included. |
| (*2) | Amounts before the liquidation during the year ended December 31, 2023. |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| C. | Account balances with related parties |
The balances of receivables and payables to related parties as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | June 30, 2024 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Receivables | | | Lease receivable | | | Payables | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Lee, Young Jae | | ₩ | | | 2,200 | | | | - | | | | 180 | |
| Personnel with significant influence over the Company | | Song, Hyo Jeong | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 128 | |
| Other related parties | | K Enter Holdings INC | | | | | 1,741,000 | | | | 84,568 | | | | 91,482 | |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 89,975 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 149,970 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Associates | | Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 136,213 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Associates | | Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 187,500 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 2,306,858 | | | | 84,568 | | | | 91,790 | |
| | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Receivables | | | Lease receivable | | | Payables | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Lee, Young Jae | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,949 | |
| Personnel with significant influence over the Company | | Song, Hyo Jeong | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,392 | |
| Other related parties | | K Enter Holdings INC | | | | | 27,498 | | | | 127,217 | | | | 87,123 | |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 87,238 | | | | - | | | | 24,005 | |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 76,550 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Associates | | Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 144,375 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Associates | | Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 187,500 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 523,161 | | | | 127,217 | | | | 114,469 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| D. | Financial transactions with related parties |
Details of significant financial transactions with related parties for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | Six-month
period ended June 30, 2024 | | | Six-month
period ended June 30, 2023 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Repayment | | | Borrowing | | | Repayment | | | Borrowing | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Choi, Pyeung Ho | | ₩ | | | 14,000 | | | | 14,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| E. | Capital contribution transactions with related parties |
Details of significant capital contribution transactions with related parties for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | Six-month
period ended June 30, 2024 | | | Six-month
period ended June 30, 2023 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Additional investment | | | Recovery of investment | | | Additional investment | | | Recovery of investment | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.8 (*) | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 17,000 | |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | - | | | | 53,368 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 53,368 | | | | - | | | | 17,000 | |
| (*) | Amounts before the liquidation during the year ended December 31, 2023. |
| F. | Key management personnel compensation |
The compensation for the key management personnel for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended June 30, 2024 | | | Six-month
period ended June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Short-term employee benefits | | ₩ | | | 394,245 | | | | 275,960 | |
| Defined benefits plan expenses | | | | | 20,373 | | | | 19,825 | |
Compensation of the Company’s key management personnel includes salaries, non-cash benefits and contributions to a post-employment defined benefit plan.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
16. Subsequent Events
On July 23, 2024, the Company entered into a credit line agreement with KB Kookmin Bank amounting to KRW 300 million, however as no funds have been withdrawn to date, there is currently no outstanding borrowed amount.
On August 9, 2024, the Company provided a guarantee for an investment made by Industrial Bank of Korea intended for movie production <pupil of the eye>. The investee for this investment is SPC(Special Purpose Company), which specializes in the cultural industry and is responsible for the production, and the investment amount is KRW 1.6 billion.
Report of Independent Auditors
To the management of
Solaire Partners LLC.
Opinion
We have audited the accompanying financial statements of Solaire Partners LLC. (the “Company”), which comprise the statements of financial position as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the related statements of comprehensive income, of changes in equity and of cash flows for the years then ended, including the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”).
In our opinion, the accompanying financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the years then ended in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
Basis for Opinion
We conducted our audit in accordance with auditing standards generally accepted in the United States of America (US GAAS). Our responsibilities under those standards are further described in the Auditors’ Responsibilities for the Audit of the Financial Statements section of our report. We are required to be independent of the Company and to meet our other ethical responsibilities, in accordance with the relevant ethical requirements relating to our audit. We believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our audit opinion.
Responsibilities of Management for the Financial Statements
Management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of the financial statements in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board, and for the design, implementation, and maintenance of internal control relevant to the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error.
In preparing the financial statements, management is responsible for assessing the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern for at least, but not limited to, twelve months from the end of the reporting period, disclosing, as applicable, matters related to going concern and using the going concern basis of accounting unless management either intends to liquidate the Company or to cease operations, or has no realistic alternative but to do so.
Auditors’ Responsibilities for the Audit of the Financial Statements
Our objectives are to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements as a whole are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error, and to issue an auditors’ report that includes our opinion. Reasonable assurance is a high level of assurance but is not absolute assurance and therefore is not a guarantee that an audit conducted in accordance with US GAAS will always detect a material misstatement when it exists. The risk of not detecting a material misstatement resulting from fraud is higher than for one resulting from error, as fraud may involve collusion, forgery, intentional omissions, misrepresentations, or the override of internal control. Misstatements are considered material if there is a substantial likelihood that, individually or in the aggregate, they would influence the judgment made by a reasonable user based on the financial statements.
In performing an audit in accordance with US GAAS, we:
| ● | Exercise professional judgment and maintain professional skepticism throughout the audit. |
| | | |
| ● | Identify and assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to fraud or error, and design and perform audit procedures responsive to those risks. Such procedures include examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. |
| | | |
| ● | Obtain an understanding of internal control relevant to the audit in order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control. Accordingly, no such opinion is expressed. |
| | | |
| ● | Evaluate the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonableness of significant accounting estimates made by management, as well as evaluate the overall presentation of the financial statements. |
| | | |
| ● | Conclude whether, in our judgment, there are conditions or events, considered in the aggregate, that raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern for a reasonable period of time. |
We are required to communicate with those charged with governance regarding, among other matters, the planned scope and timing of the audit, significant audit findings, and certain internal control-related matters that we identified during the audit.
| /s/ Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers | |
| | |
| Seoul, KOREA | |
| May 13, 2024 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Assets | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | 14,17,19,24,27 | | ₩ | | | 342,896 | | | | 71,965 | |
| Short-term investment securities | | 17,24 | | | | | 1,664,720 | | | | - | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | 13,17,24 | | | | | 384,675 | | | | 435,533 | |
| - Related parties | | 28 | | | | | 384,675 | | | | 435,533 | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | 13,17,24 | | | | | 118,633 | | | | - | |
| - Related parties | | 28 | | | | | 118,633 | | | | - | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other current assets | | 12 | | | | | - | | | | 520 | |
| Contract assets | | 7 | | | | | 110,988 | | | | - | |
| - Related parties | | 28 | | | | | 110,988 | | | | - | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Current tax assets | | 11 | | | | | - | | | | 133,237 | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | | 2,621,912 | | | | 641,255 | |
| Long-term investment securities | | 17,24 | | | | | 12,180 | | | | 38,875 | |
| Investments in associates | | 16 | | | | | 669,043 | | | | 749,430 | |
| Property and equipment including right-of-use asset | | 15,25 | | | | | 83,659 | | | | 93,608 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | 13,17,24 | | | | | 231,846 | | | | 59,056 | |
| - Related parties | | 28 | | | | | 36,082 | | | | - | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | 195,764 | | | | 59,056 | |
| Deferred tax assets | | 11 | | | | | 64,863 | | | | 26,887 | |
| Defined benefit assets | | 10 | | | | | 21 | | | | 2,482 | |
| Total non-current assets | | | | | | | 1,061,612 | | | | 970,338 | |
| Total assets | | | | ₩ | | | 3,683,524 | | | | 1,611,593 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | 17,22,24 | | ₩ | | | 1,830,848 | | | | 123,521 | |
| - Related parties | | 28 | | | | | 27,346 | | | | 30,721 | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | 1,803,502 | | | | 92,800 | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | | | | | 26,988 | | | | 50,206 | |
| Current tax liabilities | | 11 | | | | | 211,124 | | | | 146,663 | |
| Current Lease liabilities | | 21,24,25 | | | | | 145,798 | | | | 61,718 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | | 2,214,758 | | | | 382,108 | |
| Other non-current financial liabilities | | 17,24 | | | | | 87,123 | | | | - | |
| - Related parties | | 28 | | | | | 87,123 | | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | 10 | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other non-current provisions | | 23 | | | | | 12,989 | | | | - | |
| Non-current Lease liabilities | | 21,24,25 | | | | | 55,275 | | | | 23,366 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | | | | | 155,387 | | | | 23,366 | |
| Total liabilities | | | | ₩ | | | 2,370,145 | | | | 405,474 | |
| Equity | | | | | | | |
| Share capital | | 18 | | ₩ | | | 850,000 | | | | 850,000 | |
| Share premium | | 18,20 | | | | | 421,254 | | | | - | |
| Other reserves | | 10,18 | | | | | (45,637 | ) | | | (32,913 | ) |
| Retained earnings | | | | | | | 87,762 | | | | 389,032 | |
| Total equity | | | | | | | 1,313,379 | | | | 1,206,119 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | | | | ₩ | | | 3,683,524 | | | | 1,611,593 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Operating income | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Investment management revenue | | 6,7 | | | | | 1,714,271 | | | | 1,827,963 | |
| - Related parties | | 28 | | | | | 1,714,271 | | | | 1,825,952 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | 2,011 | |
| Investment revenue | | 6,7 | | | | | 2,092 | | | | 25,501 | |
| - Related parties | | 28 | | | | | 114 | | | | 1,391 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 1,978 | | | | 24,110 | |
| Gains from investments in associates | | 7 | | | | | - | | | | 1,424 | |
| - Related parties | | 28 | | | | | - | | | | 1,424 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | 1,716,363 | | | | 1,854,888 | |
| Operating expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | 8 | | | | | (1,710,391 | ) | | | (1,248,299 | ) |
| Losses from investments in associates | | 8 | | | | | (146,232 | ) | | | (60,952 | ) |
| | | | | | | | (1,856,623 | ) | | | (1,309,251 | ) |
| Other income | | 8 | | | | | 7 | | | | 3 | |
| Other expense | | 8 | | | | | (44,886 | ) | | | - | |
| Operating profit (loss) | | | | | | | (185,139 | ) | | | 545,640 | |
| Finance income | | 9,17,25 | | | | | 21,382 | | | | 4,720 | |
| - Related parties | | 28 | | | | | 8,826 | | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 12,556 | | | | 4,720 | |
| Finance costs | | 9,17,25 | | | | | (97,964 | ) | | | (11,105 | ) |
| - Related parties | | 28 | | | | | (4,825 | ) | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | (93,139 | ) | | | (11,105 | ) |
| Profit (loss) before income tax | | | | | | | (261,721 | ) | | | 539,255 | |
| Income tax expenses | | 11 | | | | | (39,549 | ) | | | (110,900 | ) |
| Profit (loss) for the year | | | | ₩ | | | (301,270 | ) | | | 428,355 | |
| Other comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Items that will not be reclassified to income or loss: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remeasurement of defined benefit liabilities | | 10,11,18 | | | | | (12,724 | ) | | | 34,734 | |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the year | | | | ₩ | | | (313,994 | ) | | | 463,089 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | Share capital | | | Share premium | | | Other reserves | | | Retained earnings | | | Total | |
| Balance at January 1, 2022 | | 1 | | ₩ | | | 850,000 | | | | - | | | | (67,647 | ) | | | (39,323 | ) | | | 743,030 | |
| Total comprehensive income for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Profit (loss) for the year | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 428,355 | | | | 428,355 | |
| Remeasurement of defined benefit liabilities | | 18 | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 34,734 | | | | - | | | | 34,734 | |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the year | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 34,734 | | | | 428,355 | | | | 463,089 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | | | | ₩ | | | 850,000 | | | | - | | | | (32,913 | ) | | | 389,032 | | | | 1,206,119 | |
| Balance at January 1, 2023 | | 1 | | ₩ | | | 850,000 | | | | - | | | | (32,913 | ) | | | 389,032 | | | | 1,206,119 | |
| Total comprehensive income for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Profit (loss) for the year | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (301,270 | ) | | | (301,270 | ) |
| Remeasurement of defined benefit liabilities | | 18 | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (12,724 | ) | | | - | | | | (12,724 | ) |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the year | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (12,724 | ) | | | (301,270 | ) | | | (313,994 | ) |
| Share-based Payment | | 18 | | | | | - | | | | 421,254 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 421,254 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | | 1 | | ₩ | | | 850,000 | | | | 421,254 | | | | (45,637 | ) | | | 87,762 | | | | 1,313,379 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Profit (loss) for the year | | | | ₩ | | | (301,270 | ) | | | 428,355 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile profit for the year to net cash provided by operating activities | | 27 | | | | | 594,658 | | | | (341,171 | ) |
| Interest received | | | | | | | 9,286 | | | | 474 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | | | (16,757 | ) | | | (11,105 | ) |
| Income taxes refunded(paid) | | | | | | | 131,217 | | | | - | |
| Net cash inflow from operating activities | | | | ₩ | | | 417,134 | | | | 76,553 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment for other non-current financial assets | | | | ₩ | | | (150,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Collection of lease receivables | | | | | | | 38,435 | | | | - | |
| Collection of other non-current financial assets | | | | | | | 80 | | | | - | |
| Purchase of property and equipment | | | | | | | (4,094 | ) | | | (4,994 | ) |
| Net cash outflow in investing activities | | | | ₩ | | | (115,579 | ) | | | (4,994 | ) |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | 27 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Repayments of Current portion of long-term borrowings | | | | ₩ | | | - | | | | (161,000 | ) |
| Collection of rent deposit | | | | | | | 100,050 | | | | - | |
| Repayment of lease liabilities | | | | | | | (130,674 | ) | | | (57,763 | ) |
| Net cash outflow in financing activities | | | | ₩ | | | (30,624 | ) | | | (218,763 | ) |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | 270,931 | | | | (147,204 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the year | | | | ₩ | | | 71,965 | | | | 219,169 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of the year | | 14 | | ₩ | | | 342,896 | | | | 71,965 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
1. Reporting entity
The Company
Solaire Partners LLC. (“the Company”) was incorporated in June 2017 and the Company’s registered office is at 112, Yeoksam-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Republic of Korea. The Company is investment management company focusing on contents. The Company primarily generates revenue from the investment in securities of Korean content companies and commissions received from the customers from providing the investment management services.
The Company’s major shareholders and their respective percentage of ownership as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | Number of
shares | | | Ownership
(%) | | | Number of
shares | | | Ownership
(%) | |
| Choi, Pyeung ho | | | 514,250,000 | | | | 60.5 | % | | | 548,250,000 | | | | 64.5 | % |
| Lee, Young Jae | | | 208,250,000 | | | | 24.5 | % | | | 208,250,000 | | | | 24.5 | % |
| Song, Hyo Jeong | | | 42,500,000 | | | | 5.0 | % | | | 42,500,000 | | | | 5.0 | % |
| CY Holdings Co., Ltd | | | 42,500,000 | | | | 5.0 | % | | | 42,500,000 | | | | 5.0 | % |
| Park, Su Kyung | | | 17,000,000 | | | | 2.0 | % | | | 8,500,000 | | | | 1.0 | % |
| Hyun, Na Young | | | 8,500,000 | | | | 1.0 | % | | | - | | | | - | |
| Lee, Myung Hyun | | | 8,500,000 | | | | 1.0 | % | | | - | | | | - | |
| Kim, Min Soo | | | 8,500,000 | | | | 1.0 | % | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | | 850,000,000 | | | | 100.0 | % | | | 850,000,000 | | | | 100.0 | % |
| (*) | On January 2, 2023, Choi Pyeung ho, the Company’s largest shareholder, transferred the Company’s shares to employees. (See Note 20) |
2. Basis of Accounting
These financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) as issued by International Accounting Standard Board (“IASB”). These financial statements were authorized for issuance by the management on May 13, 2024. (To-be updated)
Details of the Company’s accounting policies are included in Note 5.
Basis of measurement
The financial statements have been prepared on the historical cost basis except for the following items, which are measured on an alternative basis on each reporting date.
| Items | | Measurement bases |
| Financial instruments measured at fair value through profit or loss (“FVTPL”) | | Fair value |
| defined benefit plans – plan assets | | Fair value |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
3. Functional and presentation currency
These financial statements are presented in Korean Won, which the Company’s functional currency. All amounts have been rounded to the nearest thousand, unless otherwise indicated.
4. Use of judgements and estimates
In preparing these financial statements, management has made judgements and estimates that affect the application of the Company’s accounting policies and the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
Estimates and underlying assumptions are reviewed on an ongoing basis. Revisions to estimates are recognized prospectively.
Information about judgements made in applying accounting policies that have the most significant effects on the amounts recognized in the financial statements is included in the following notes:
Note 25(A): lease term: whether the Company is reasonably certain to exercise extension options.
| B. | Assumptions and estimation uncertainties |
Information about assumptions and estimation uncertainties at the reporting date that have a significant risk of resulting in a material adjustment to the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities within the next financial year is included in the following notes:
| ● | Note 16: Equity-accounted investees; |
In determining whether the Company has significant influence, the Company takes into account whether the Company directly or indirectly holds 20% or more of the voting rights over the investee, whether the Company participates in the board or other decision-making body equivalent thereto of the investees, or whether the Company’s potential voting rights will affect these rights.
| ● | Note 24(B): Financial Instruments – Fair values and risk management; |
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market is determined by using valuation techniques. The Company uses its judgment to select a variety of methods and make assumptions that are mainly based on market conditions existing at the end of each reporting period.
| i. | Measurement of fair values |
A number of the Company’s accounting policies and disclosures require the measurement of fair values, for financial assets.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
When measuring the fair value of a financial instruments measured at FVTPL, the Company uses observable market data as far as possible. Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows.
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
| ● | Level 2: inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly (i.e., as prices) or indirectly (i.e., derived from prices). |
| ● | Level 3: inputs for the asset or liability that are not based on observable market data (unobservable inputs). |
If the inputs used to measure the fair value of an asset or a liability fall into different levels of the fair value hierarchy, then the fair value measurement is categorized in its entirety in the same level of the fair value hierarchy as the lowest level input that is significant to the entire measurement.
The Company recognizes transfers between levels of the fair value hierarchy at the end of the reporting period during which the change has occurred.
Further information about the assumptions made in measuring fair values is included in the following notes:
| ● | Note 24(B): financial instruments. |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
5. Material accounting policies
The Company has consistently applied the following accounting policies to all periods presented in these financial statements, except if mentioned otherwise.
| A. | New and amended standards or interpretations adopted the Company |
The Company has applied the following standards and amendments for the first time for its annual reporting period commencing January 1, 2023.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements - Disclosure of Accounting Policies
The amendments to IAS 1 define and require entities to disclose their material accounting policies. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 8 Accounting policies, changes in accounting estimates and errors - Definition of Accounting Estimates
The amendments define accounting estimates and clarify how to distinguish them from changes in accounting policies. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 12 Income Taxes - Deferred Tax related to Assets and Liabilities arising from a Single Transaction
The amendments include an additional condition to the exemption to initial recognition of an asset or liability that a transaction does not give rise to equal taxable and deductible temporary differences at the time of the transaction. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 12 Income Taxes – International Tax Reform – Pillar Two Model Rules
The amendments provide a temporary relief from the accounting for deferred taxes arising from legislation enacted to implement the Pillar Two model rules, which aim to reform international corporate taxation for multinational enterprises, and require disclosure of related current tax effects, etc. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
New Standard: IFRS 17 Insurance Contract
IFRS 17 Insurance Contracts replaces IFRS 4 Insurance Contracts. This Standard estimates future cash flows of an insurance contract and measures insurance liabilities using discount rates applied with assumptions and risks at the measurement date. The entity recognizes insurance revenue on an accrual basis including services (insurance coverage) provided to the policyholder by each annual period. In addition, investment components (Refunds due to termination/maturity) repaid to a policyholder even if an insured event does not occur, are excluded from insurance revenue, and insurance financial income or expense and the investment income or expense are presented separately to enable users of the information to understand the sources of income or expenses. This Standard do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| B. | New and amended standards or interpretations not yet adopted |
The following new accounting standards and interpretations that have been published that are not mandatory for December 31, 2023 reporting periods and have not been early adopted by the Company.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements - Classification of Liabilities as Current or Non-current
The amendments clarify that liabilities are classified as either current or non-current, depending on the substantive rights that exist at the end of the reporting period. Classification is unaffected by the likelihood that an entity will exercise right to defer settlement of the liability or the expectations of management. Also, the settlement of liability includes the transfer of the entity’s own equity instruments, however, it would be excluded if an option to settle them by the entity’s own equity instruments if compound financial instruments is met the definition of equity instruments and recognized separately from the liability. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, and earlier application is permitted. The Company is in review for the impact of these amendments on the financial statements.
IAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows - IFRS 7 Financial Instruments: Disclosures – Supplier finance arrangements
When applying supplier finance arrangements, an entity shall disclose information about its supplier finance arrangements that enables users of financial statements to assess the effects of those arrangements on the entity’s liabilities and cash flows and on the entity’s exposure to liquidity risk. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, and earlier application is permitted. The Company does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 21 The effects of changes in foreign exchange rates - Lack of Exchangeability
The amendments add requirements to help entities to determine whether a currency is exchangeable into another currency at a measurement date for a specified purpose and the spot exchange rate to use when it is not. A currency is exchangeable when there is an ability to obtain the other currency (with a normal administrative delay), and the transaction would take place through a market or exchange mechanism that creates enforceable rights and obligations. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2025, and earlier application is permitted. The Company does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IFRS 16 – Lease Liability in a Sale and Leaseback
When subsequently measuring lease liabilities arising from a sale and leaseback, a seller-lessee shall determine lease payments or revised lease payments in a way that the seller-lessee would not recognize any amount of the gain or loss that relates to the right of use retained by the seller-lessee. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, and earlier application is permitted. The Company does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IFRS 18 Presentation and Disclosure in Financial Statements
Items in the statement of profit or loss will need to be classified into one of five categories: operating, investing, financing, income taxes and discontinued operations. IFRS 18 requires the Company to present specified totals and subtotals: ‘Operating profit or loss’, ‘Profit or loss’ and ‘Profit or loss before financing and income taxes’. Information related to management-defined performance measures should be disclosed. IFRS 18 also provides enhanced guidance on the principles of aggregation and disaggregation which focus on grouping items based on their shared characteristics. The new standard should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2027, and earlier application is permitted. The Company is in review for the impact of this new standard on the financial statements.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| C. | Revenue from contracts with customers |
The Company generates revenue primarily through providing the service for investment management for investment funds, investing in Korean theatrical films, and investing in content companies based in Korea.
The Company determines revenue recognition by:
| ● | identifying the contract, or contracts, with a customer; |
| ● | identifying the performance obligations in each contract; |
| ● | determining the transaction price; |
| ● | allocating the transaction price to the performance obligations in each contract; and |
| ● | recognizing revenue when, or as, we satisfy performance obligations by transferring the promised goods or services. |
Investment management revenue
The Company manages and operates the investment funds on behalf of investors and receives commissions from its customers. The investment management revenues are received in exchange for investment management services that include a series of fund administration services, fund compliance, fund transfer agent services and fund distribution services. Control of investment management services is transferred to the customer over time as these customers receive and consume the benefits provided by these services. Investment management revenues are calculated as a contractual percentage of financial assets the Company manages for clients on either a discretionary or non-discretionary basis. Investment management revenues are recognized for each distinct performance obligation identified in customer contracts when the performance obligation has been satisfied by transferring services to a customer over time.
Other revenues
Other revenues are from other sources, not from the contract with customers. Other sources of revenue are earned from investing in investment funds, which are investees accounted for using the equity method. An associate is an entity in which the Company has significant influence, but not control, over the entity’s financial and operating policies. Under this method of accounting, the Company typically records its proportionate share of the net earnings or losses of equity method investees and a corresponding increase or decrease to the investment balances. In addition, other sources of revenue are also earned from investing directly in content being produced such as theatrical films and television programs.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
An operating segment is a component of the Company that engages in business activities from which it may earn revenues and incur expenses, including revenues and expenses that relate to transactions with any of the Company’s other components. The chief operating decision-maker has been identified as the chief executive officer. The Company’s operating segments have been determined to be a single business unit, for which the Company generates identifiable financial information that is regularly reported to the chief executive officer for the purpose of resource allocation and assessment of segment performance. The Company has a reportable segment as described in note 6. Segment results that are reported to the chief operating decision maker include items directly attributable to a segment as well as those that can be allocated on a reasonable basis.
| i. | Short-term employee benefits |
Short-term employee benefits are employee benefits due to be settled within 12 months after the end of the period in which the employees render related services. When an employee has rendered a service to the Company during an accounting period, the Company recognizes the undiscounted amount of short-term employee benefits expected to be paid in exchange for that service.
The Company’s net obligation in respect of defined benefit plans is calculated separately for each plan by estimating the amount of future benefit that employees have earned in the current and prior periods, discounting that amount and deducting the fair value of any plan assets.
The calculation of defined benefit obligations is performed annually using the projected unit credit method. When the calculation results in a potential asset for the Company, the recognized asset is limited to the present value of economic benefits available in the form of any future refunds from the plan or reductions in future contributions to the plan. To calculate the present value of economic benefits, consideration is given to any applicable minimum funding requirements.
Remeasurements of the net defined benefit liability, which comprise actuarial gains and losses, the return on plan assets (excluding interest) and the effect of the asset ceiling (if any, excluding interest), are recognized immediately in OCI. The Company determines the net interest expense (income) on the net defined benefit liability (asset) for the period by applying the discount rate used to measure the defined benefit obligation at the beginning of the annual period to the then-net defined benefit liability (asset), taking into account any changes in the net defined benefit liability (asset) during the period as a result of contributions and benefit payments. Net interest expense and other expenses related to defined benefit plans are recognized in profit or loss.
When the benefits of a plan are changed or when a plan is curtailed, the resulting change in benefit that relates to past service or the gain or loss on curtailment is recognized immediately in profit or loss. The Company recognizes gains and losses on the settlement of a defined benefit plan when the settlement occurs.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| F. | Finance income and finance costs |
The Company’s finance income and finance costs include:
| ● | the net gain or loss on financial assets at FVTPL; |
| ● | the foreign currency gain or loss on financial assets and financial liabilities; |
The ‘effective interest rate’ is the rate that exactly discounts estimated future cash payments or receipts through the expected life of the financial instrument to:
| ● | the gross carrying amount of the financial asset; or |
| ● | the amortized cost of the financial liability. |
In calculating interest income and expense, the effective interest rate is applied to the gross carrying amount of the asset (when the asset is not credit-impaired) or to the amortized cost of the liability. However, for financial assets that have become credit-impaired subsequent to initial recognition, interest income is calculated by applying the effective interest rate to the amortized cost of the financial asset. If the asset is no longer credit-impaired, then the calculation of interest income reverts to the gross basis.
Income tax expense comprises current and deferred tax. It is recognized in profit or loss except to the extent that it relates to a business combination, or items recognized directly in equity or in OCI.
The Company has determined that interest and penalties related to income taxes, including uncertain tax treatments, do not meet the definition of income taxes, and therefore accounted for them under IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets.
Current tax comprises the expected tax payable or receivable on the taxable income or loss for the year and any adjustment to the tax payable or receivable in respect of previous years. The amount of current tax payable or receivable is the best estimate of the tax amount expected to be paid or received that reflects uncertainty related to income taxes, if any. It is measured using tax rates enacted or substantively enacted at the reporting date. Current tax also includes any tax arising from dividends.
Current tax assets and liabilities are offset only if certain criteria are met.
| - | Has a legally enforceable right to set off the recognized amounts; and |
| - | Intends either to settle on a net basis, or to realize the asset and settle the liability simultaneously. |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Deferred tax is recognized in respect of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for taxation purposes. Deferred tax is not recognized for:
| ● | temporary differences on the initial recognition of assets or liabilities in a transaction that is not a business combination and that affects neither accounting nor taxable profit or loss; |
| ● | temporary differences related to investments in subsidiaries, associates and joint arrangements to the extent that the Company is able to control the timing of the reversal of the temporary differences and it is probable that they will not reverse in the foreseeable future; and |
| ● | taxable temporary differences arising on the initial recognition of goodwill. |
Deferred tax assets are recognized for unused tax losses, unused tax credits and deductible temporary differences to the extent that it is probable that future taxable profits will be available against which they can be used. Future taxable profits are determined based on the reversal of relevant taxable temporary differences. If the amount of taxable temporary differences is insufficient to recognize a deferred tax asset in full, then future taxable profits, adjusted for reversals of existing temporary differences, are considered, based on the business plan of the Company. Deferred tax assets are reviewed at each reporting date and are reduced to the extent that it is no longer probable that the related tax benefit will be realized; such reductions are reversed when the probability of future taxable profits improves.
The measurement of deferred tax reflects the tax consequences that would follow from the manner in which the Company expects, at the reporting date, to recover or settle the carrying amount of its assets and liabilities. For this purpose, the carrying amount of investment property measured at fair value is presumed to be recovered through sale, and the Company has not rebutted this presumption.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are offset only if certain criteria are met.
| - | Has a legally enforceable right to set off the recognized amounts; and |
| - | Intends either to settle on a net basis, or to realize the asset and settle the liability simultaneously. |
| H. | Cash and Cash Equivalents |
Cash and cash equivalents comprise cash on hand, deposits held at banks, and investment securities with maturities of three months or less from the acquisition date that are easily convertible to cash and subject to an insignificant risk of changes in their fair value.
| i. | Recognition and measurement |
Items of property and equipment are measured at cost, which includes capitalized borrowing costs, less accumulated depreciation and any accumulated impairment losses.
If significant parts of an item of property and equipment have different useful lives, then they are accounted for as separate items (major components) of property and equipment.
Any gain or loss on disposal of an item of property and equipment is recognized in profit or loss.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| ii. | Subsequent expenditure |
Subsequent expenditure is capitalized only if it is probable that the future economic benefits associated with the expenditure will flow to the Company. The carrying amount of the replaced parts are derecognized and the repairs and maintenance expenses are recognized in profit or loss in the period they are incurred.
Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method to allocate the cost or revalued amounts of the assets, net of their residual values, over their estimated useful lives as follows:
| Office equipment | | 5 years |
| Right-of-use assets | | Lease term |
Depreciation methods, useful lives and residual values are reviewed at each reporting date and adjusted if appropriate.
| i. | Recognition and initial measurement |
Trade receivables and debt securities issued are initially recognized when they are originated. All other financial assets and financial liabilities are initially recognized when the Company becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the instrument.
A financial asset (unless it is a trade receivable without a significant financing component) or financial liability is initially measured at fair value plus or minus, for an item not at FVTPL, transaction costs that are directly attributable to its acquisition or issue. A trade receivable without a significant financing component is initially measured at the transaction price.
| ii. | Classification and subsequent measurement |
Financial assets
On initial recognition, a financial asset is classified as measured at:
| ● | FVOCI - debt investment; |
| ● | FVOCI - equity investment; |
Financial assets are not reclassified subsequent to their initial recognition unless the Company changes its business model for managing financial assets, in which case all affected financial assets are reclassified on the first day of the first reporting period following the change in the business model.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
A financial asset is measured at amortized cost if it meets both of the following conditions and is not designated as at FVTPL:
| ● | it is held within a business model whose objective is to hold assets to collect contractual cash flows; and |
| ● | its contractual terms give rise on specified dates to cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. |
A debt investment is measured at FVOCI if it meets both of the following conditions and is not designated as at FVTPL:
| ● | it is held within a business model whose objective is achieved by both collecting contractual cash flows and selling financial assets; and |
| ● | its contractual terms give rise on specified dates to cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. |
On initial recognition of an equity investment that is not held for trading, the Company may irrevocably elect to present subsequent changes in the investment’s fair value in OCI. This election is made on an investment-by-investment basis.
All financial assets not classified as measured at amortized cost or FVOCI as described above are measured at FVTPL. This includes all derivative financial assets. On initial recognition, the Company may irrevocably designate a financial asset that otherwise meets the requirements to be measured at amortized cost or at FVOCI as at FVTPL if doing so eliminates or significantly reduces an accounting mismatch that would otherwise arise.
Financial assets - Business model assessment
The Company makes an assessment of the objective of the business model in which a financial asset is held at a portfolio level because this best reflects the way the business is managed and information is provided to management. The information considered includes:
| ● | the stated policies and objectives for the portfolio and the operation of those policies in practice. These include whether management’s strategy focuses on earning contractual interest income, maintaining a particular interest rate profile, matching the duration of the financial assets to the duration of any related liabilities or expected cash outflows or realizing cash flows through the sale of the assets; |
| ● | how the performance of the portfolio is evaluated and reported to the Company’s management; |
| ● | the risks that affect the performance of the business model (and the financial assets held within that business model) and how those risks are managed; |
| ● | how managers of the business are compensated - e.g. whether compensation is based on the fair value of the assets managed or the contractual cash flows collected; and |
| ● | the frequency, volume and timing of sales of financial assets in prior periods, the reasons for such sales and expectations about future sales activity. |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Transfers of financial assets to third parties in transactions that do not qualify for derecognition are not considered sales for this purpose, consistent with the Company’s continuing recognition of the assets.
Financial assets that are held for trading or are managed and whose performance is evaluated on a fair value basis are measured at FVTPL.
Financial assets - Assessment whether contractual cash flows are solely payments of principal and interest
For the purposes of this assessment, ‘principal’ is defined as the fair value of the financial asset on initial recognition. ‘Interest’ is defined as consideration for the time value of money and for the credit risk associated with the principal amount outstanding during a particular period of time and for other basic lending risks and costs (e.g. liquidity risk and administrative costs), as well as a profit margin.
In assessing whether the contractual cash flows are solely payments of principal and interest, the Company considers the contractual terms of the instrument. This includes assessing whether the financial asset contains a contractual term that could change the timing or amount of contractual cash flows such that it would not meet this condition. In making this assessment, the Company considers:
| ● | contingent events that would change the amount or timing of cash flows; |
| ● | terms that may adjust the contractual coupon rate, including variable-rate features; |
| ● | prepayment and extension features; and |
| ● | terms that limit the Company’s claim to cash flows from specified assets (e.g. non-recourse features). |
A prepayment feature is consistent with the solely payments of principal and interest criterion if the prepayment amount substantially represents unpaid amounts of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding, which may include reasonable compensation for early termination of the contract. Additionally, for a financial asset acquired at a discount or premium to its contractual par amount, a feature that permits or requires prepayment at an amount that substantially represents the contractual par amount plus accrued (but unpaid) contractual interest (which may also include reasonable compensation for early termination) is treated as consistent with this criterion if the fair value of the prepayment feature is insignificant at initial recognition.
Financial assets - Subsequent measurement and gains and losses
Financial assets at FVTPL: These assets are subsequently measured at fair value. Net gains and losses, including any interest or dividend income, are recognized in profit or loss.
Financial assets at amortized cost: These assets are subsequently measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. The amortized cost is reduced by impairment losses. Interest income, foreign exchange gains and losses and impairment are recognized in profit or loss. Any gain or loss on derecognition is recognized in profit or loss.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Financial liabilities - Classification, subsequent measurement and gains and losses
Financial liabilities are classified as measured at amortized cost or FVTPL. A financial liability is classified as at FVTPL if it is classified as held-for-trading, it is a derivative or it is designated as such on initial recognition. Financial liabilities at FVTPL are measured at fair value and net gains and losses, including any interest expense, are recognized in profit or loss. Other financial liabilities are subsequently measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. Interest expense and foreign exchange gains and losses are recognized in profit or loss. Any gain or loss on derecognition is also recognized in profit or loss.
Financial assets
The Company derecognizes a financial asset when:
| ● | the contractual rights to the cash flows from the financial asset expire; or |
| ● | it transfers the rights to receive the contractual cash flows in a transaction in which either: |
| - | substantially all of the risks and rewards of ownership of the financial asset are transferred; or |
| - | the Company neither transfers nor retains substantially all of the risks and rewards of ownership and it does not retain control of the financial asset. |
The Company enters into transactions whereby it transfers assets recognized in its statement of financial position, but retains either all or substantially all of the risks and rewards of the transferred assets. In these cases, the transferred assets are not derecognized.
Financial liabilities
The Company derecognizes a financial liability when its contractual obligations are discharged or cancelled, or expire. The Company also derecognizes a financial liability when its terms are modified and the cash flows of the modified liability are substantially different, in which case a new financial liability based on the modified terms is recognized at fair value.
On derecognition of a financial liability, the difference between the carrying amount extinguished and the consideration paid (including any non-cash assets transferred or liabilities assumed) is recognized in profit or loss.
When changes were made to a financial asset or financial liability in addition to changes to the basis for determining the contractual cash flows required by interest rate benchmark reform, the Company first updated the effective interest rate of the financial asset or financial liability to reflect the change that is required by interest rate benchmark reform. After that, the Company applied the policies on accounting for modifications to the additional changes.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| i. | Non-derivative financial assets |
Financial instruments and contract assets
The Company recognizes loss allowances for ECLs on:
| ● | financial assets measured at amortized cost; and |
The Company also recognizes loss allowances for ECLs on lease receivables, which are disclosed as part of trade and other receivables.
The Company measures loss allowances at an amount equal to lifetime ECLs, except for the following, which are measured at 12-month ECLs:
| ● | debt securities that are determined to have low credit risk at the reporting date; and |
| ● | other debt securities and bank balances for which credit risk (i.e. the risk of default occurring over the expected life of the financial instrument) has not increased significantly since initial recognition. |
Loss allowances for trade receivables (including lease receivables) and contract assets are always measured at an amount equal to lifetime ECLs.
When determining whether the credit risk of a financial asset has increased significantly since initial recognition and when estimating ECLs, the Company considers reasonable and supportable information that is relevant and available without undue cost or effort. This includes both quantitative and qualitative information and analysis, based on the Company’s historical experience and informed credit assessment, that includes forward-looking information.
The Company assumes that the credit risk on a financial asset has increased significantly if it is more than 12 months past due.
The Company considers a financial asset to be in default when:
| ● | the debtor is unlikely to pay its credit obligations to the Company in full, without recourse by the Company to actions such as realizing security (if any is held). |
Lifetime ECLs are the ECLs that result from all possible default events over the expected life of a financial instrument.
12-month ECLs are the portion of ECLs that result from default events that are possible within the 12 months after the reporting date (or a shorter period if the expected life of the instrument is less than 12 months).
The maximum period considered when estimating ECLs is the maximum contractual period over which the Company is exposed to credit risk.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Measurement of ECLs
ECLs are a probability-weighted estimate of credit losses. Credit losses are measured as the present value of all cash shortfalls (i.e. the difference between the cash flows due to the entity in accordance with the contract and the cash flows that the Company expects to receive).
ECLs are discounted at the effective interest rate of the financial asset.
Credit-impaired financial assets
At each reporting date, the Company assesses whether financial assets carried at amortized cost are credit-impaired. A financial asset is ‘credit-impaired’ when one or more events that have a detrimental impact on the estimated future cash flows of the financial asset have occurred.
Evidence that a financial asset is credit-impaired includes the following observable data:
| ● | significant financial difficulty of the debtor; |
| ● | a breach of contract such as a default or being more than 90 days past due; |
| ● | the restructuring of a loan or advance by the Company on terms that the Company would not consider otherwise; |
| ● | it is probable that the debtor will enter bankruptcy or other financial reorganization; or |
| ● | the disappearance of an active market for a security because of financial difficulties. |
Presentation of allowance for ECL in the statement of financial position
Loss allowances for financial assets measured at amortized cost are deducted from the gross carrying amount of the assets.
Write-off
The gross carrying amount of a financial asset is written off when the Company has no reasonable expectations of recovering a financial asset in its entirety or a portion thereof. For individual customers, the Company has a policy of writing off the gross carrying amount when the financial asset is 180 days past due based on historical experience of recoveries of similar assets. For corporate customers, the Company individually makes an assessment with respect to the timing and amount of write-off based on whether there is a reasonable expectation of recovery. The Company expects no significant recovery from the amount written off. However, financial assets that are written off could still be subject to enforcement activities in order to comply with the Company’s procedures for recovery of amounts due.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
At each reporting date, the Company reviews the carrying amounts of its non-financial assets (other than biological assets, investment property, inventories, contract assets and deferred tax assets) to determine whether there is any indication of impairment. If any such indication exists, then the asset’s recoverable amount is estimated. Goodwill is tested annually for impairment.
For impairment testing, assets are grouped together into the smallest group of assets that generates cash inflows from continuing use that are largely independent of the cash inflows of other assets or CGUs. Goodwill arising from a business combination is allocated to CGUs or groups of CGUs that are expected to benefit from the synergies of the combination.
The recoverable amount of an asset or CGU is the greater of its value in use and its fair value less costs of disposal. Value in use is based on the estimated future cash flows, discounted to their present value using a pre-tax discount rate that reflects current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the asset or CGU.
An impairment loss is recognized if the carrying amount of an asset or CGU exceeds its recoverable amount.
Impairment losses are recognized in profit or loss. They are allocated first to reduce the carrying amount of any goodwill allocated to the CGU, and then to reduce the carrying amounts of the other assets in the CGU on a pro rata basis.
An impairment loss in respect of goodwill is not reversed. For other assets, an impairment loss is reversed only to the extent that the asset’s carrying amount does not exceed the carrying amount that would have been determined, net of depreciation or amortization, if no impairment loss had been recognized.
At inception of a contract, the Company assesses whether a contract is, or contains, a lease. A contract is, or contains, a lease if the contract conveys the right to control the use of an identified asset for a period of time in exchange for consideration.
At commencement or on modification of a contract that contains a lease component, the Company allocates the consideration in the contract to each lease component on the basis of its relative stand-alone prices. However, for the leases of property the Company has elected not to separate non-lease components and account for the lease and non-lease components as a single lease component.
The Company recognizes a right-of-use asset and a lease liability at the lease commencement date. The right-of-use asset is initially measured at cost, which comprises the initial amount of the lease liability adjusted for any lease payments made at or before the commencement date, plus any initial direct costs incurred and an estimate of costs to dismantle and remove the underlying asset or to restore the underlying asset or the site on which it is located, less any lease incentives received.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The right-of-use asset is subsequently depreciated using the straight-line method from the commencement date to the end of the lease term, unless the lease transfers ownership of the underlying asset to the Company by the end of the lease term or the cost of the right-of-use asset reflects that the Company will exercise a purchase option. In that case the right-of-use asset will be depreciated over the useful life of the underlying asset, which is determined on the same basis as those of property and equipment. In addition, the right-of-use asset is periodically reduced by impairment losses, if any, and adjusted for certain remeasurements of the lease liability.
The lease liability is initially measured at the present value of the lease payments that are not paid at the commencement date, discounted using the interest rate implicit in the lease or, if that rate cannot be readily determined, the Company’s incremental borrowing rate. Generally, the Company uses its incremental borrowing rate as the discount rate.
The Company determines its incremental borrowing rate by obtaining interest rates from various external financing sources and makes certain adjustments to reflect the terms of the lease and type of the asset leased.
Lease payments included in the measurement of the lease liability comprise the following:
| ● | fixed payments, including in-substance fixed payments; |
| ● | variable lease payments that depend on an index or a rate, initially measured using the index or rate as at the commencement date; |
| ● | amounts expected to be payable under a residual value guarantee; and |
| ● | the exercise price under a purchase option that the Company is reasonably certain to exercise, lease payments in an optional renewal period if the Company is reasonably certain to exercise an extension option, and penalties for early termination of a lease unless the Company is reasonably certain not to terminate early. |
The lease liability is measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. It is remeasured when there is a change in future lease payments arising from a change in an index or rate, if there is a change in the Company’s estimate of the amount expected to be payable under a residual value guarantee, if the Company changes its assessment of whether it will exercise a purchase, extension or termination option or if there is a revised in-substance fixed lease payment.
When the lease liability is remeasured in this way, a corresponding adjustment is made to the carrying amount of the right-of-use asset, or is recorded in profit or loss if the carrying amount of the right-of-use asset has been reduced to zero.
At the date of transition to IFRSs, The Company applies the following approach to all of its leases.
The Company measures that lease liability at the present value of the remaining lease payments, discounted using the lessee’s incremental borrowing rate at the date of transition to IFRSs.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The Company measures right-of-use asset at its carrying amount as if IFRS 16 had been applied since the commencement date of the lease, but discounted using the lessee’s incremental borrowing rate at the date of transition to IFRSs.
The Company uses hindsight in applying IFRS 16 such as the determination of lease term for contracts that contain options to extend or terminate a lease.
The Company has elected not to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for leases of low-value assets (leases for which the underlying asset is valued at USD 5,000 or less) and short-term leases (leases that have a lease term of 12 months or less at the commencement date), including IT equipment. The Company recognizes the lease payments associated with these leases as an expense on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
‘Fair value’ is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date in the principal or, in its absence, the most advantageous market to which the Company has access at that date. The fair value of a liability reflects its non-performance risk.
A number of the Company’s accounting policies and disclosures require the measurement of fair values, for both financial and non-financial assets and liabilities.
When one is available, the Company measures the fair value of an instrument using the quoted price in an active market for that instrument. A market is regarded as ‘active’ if transactions for the asset or liability take place with sufficient frequency and volume to provide pricing information on an ongoing basis.
If there is no quoted price in an active market, then the Company uses valuation techniques that maximize the use of relevant observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The chosen valuation technique incorporates all of the factors that market participants would take into account in pricing a transaction.
The best evidence of the fair value of a financial instrument on initial recognition is normally the transaction price - i.e. the fair value of the consideration given or received. If the Company determines that the fair value on initial recognition differs from the transaction price and the fair value is evidenced neither by a quoted price in an active market for an identical asset or liability nor based on a valuation technique for which any unobservable inputs are judged to be insignificant in relation to the measurement, then the financial instrument is initially measured at fair value, adjusted to defer the difference between the fair value on initial recognition and the transaction price. Subsequently, that difference is recognized in profit or loss on an appropriate basis over the life of the instrument but no later than when the valuation is wholly supported by observable market data or the transaction is closed out.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| N. | Equity-accounted investees |
Associates are entities over which the Company has significant influence over the financial and operating policy decisions. Generally, if the Company holds 20% or more of the voting power of the investee, it is presumed that the Company has significant influence.
Investments in associates are initially recognized at cost and equity method is applied after initial recognition. The carrying amount is increased or decreased to recognize the Company’s share of the profit or loss of the investee and changes in the investee’s equity after the date of acquisition. Distributions received from an investee reduce the carrying amount of the investment. Unrealized gains and losses resulting from transactions between the Company and associates are eliminated to the extent of the Company’s share in associates. If unrealized losses are an indication of an impairment that requires recognition in the consolidated financial statements, those losses are recognized for the period.
If associates use accounting policies other than those of the Company for like transactions and events in similar circumstances, if necessary, adjustments shall be made to make the associates’ accounting policies conform to those of the Company when the associates’ financial statements are used by the Company in applying the equity method.
If the Company’s share of losses of associates equals or exceeds its interest in the associates (including long-term interests that, in substance, form part of the Company’s net investment in the associates), the Company discontinues recognizing its share of further losses. After the Company’s interest is reduced to zero, additional losses are provided for, and a liability is recognized, only to the extent that the Company has incurred legal or constructive obligations or made payments on behalf of the investee.
The Company determines at each reporting period whether there is any objective evidence that the investments in the associates are impaired. If this is the case, the Company calculates the amount of impairment as the difference between the recoverable amount of the associates and its carrying amount and recognizes the amount as non-operating expenses in the consolidated statement of comprehensive income.
| O. | Concentration of Credit Risk |
The Company performs periodic credit evaluations of its customers’ financial condition and generally does not require collateral for customers on accounts receivable. The Company maintains reserves for potential credit losses, which are periodically reviewed.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
6. Operating segments
The Company’s operating segments have been identified to be a single business unit, by which the Company provides the services for investment fund management.
The following summary describes the operations of each reportable segment.
| Reportable segments | | Operations |
| Investment management | | Providing investment management services to investment funds |
| B. | Information about reportable segments |
Information related to each reportable segment is set out below. Segment operating profit is used to measure performance because management believes that this information is the most relevant in evaluating the results of the respective segments relative to other entities that operate in the same industries.
The segment information for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Segment revenue | | ₩ | | | 1,716,363 | | | | 1,854,888 | |
| Depreciation/Amortization | | | | | (93,126 | ) | | | (65,862 | ) |
| Segment operating profit (loss) | | | | | (185,139 | ) | | | 545,640 | |
Investment and commission revenues are managed and operated in Seoul, Korea. The geographic information analyses the Company’s revenue by the customer’s country of domicile. In presenting the geographic information, segment revenue and non-current assets have been based on the geographic location of customers.
Summary of the Company’s operating income by region based on the location of customers for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 1,716,363 | | | | 1,854,888 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Summary of the Company’s non-current assets based on the location as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 752,702 | | | | 843,038 | |
Revenues from major customers that amount to 10% or more of the Company’s revenue for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 748,459 | | | | 750,000 | |
| % | | | | | 44 | % | | | 40 | % |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 573,678 | | | | 602,260 | |
| % | | | | | 33 | % | | | 32 | % |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 302,276 | | | | 386,000 | |
| % | | | | | 18 | % | | | 21 | % |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,624,413 | | | | 1,738,260 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
7. Operating income
| A. | Operating income streams |
The Company generates operating income primarily through providing the services for investment management for initial exhibition in theaters.
Revenue from contracts with customers and other operating income for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Revenue from contracts with customers | | ₩ | | | 1,716,363 | | | | 1,853,464 | |
| Other sources of operating income (*) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gains from investments in associates | | | | | - | | | | 1,424 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,716,363 | | | | 1,854,888 | |
| (*) | Other sources of operating income consists of the entity’s interest in the profit of associates accounted for by the equity method, and gains from disposal of investments in associates. |
| B. | Disaggregation of revenue from contracts with customers |
In the following table, revenue from contracts with customers is disaggregated by primary geographical market, major products and service lines and timing of revenue recognition. The table also includes a reconciliation of the disaggregated revenue with the Company’s reportable segments. (See Note 6)
Revenue from contracts with customers based on the service contract type, the timing of satisfaction of performance obligations for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Major products/service lines | | | | | | | | |
| Investment management revenue | | ₩ | | | 1,714,271 | | | | 1,825,952 | |
| Investment revenue | | | | | 2,092 | | | | 25,501 | |
| Consulting revenue | | | | | - | | | | 2,011 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,716,363 | | | | 1,853,464 | |
| Timing of revenue recognition | | | | | | | | | | |
| Over time | | | | | 1,716,363 | | | | 1,853,464 | |
| Revenue from contracts with customers | | | | | 1,716,363 | | | | 1,853,464 | |
| Other sources of operating income | | | | | - | | | | 1,424 | |
| External operating income as reported in Note 6 | | ₩ | | | 1,716,363 | | | | 1,854,888 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The balance of contract assets and contract liabilities from contracts with customers as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Contract assets (Unbilled revenue) | | ₩ | | | 110,988 | | | | - | |
| Contract liabilities (Deferred revenue) | | | | | - | | | | - | |
The contract liabilities primarily relate to the advance consideration received from customers, for which revenue is recognized over time. This will be recognized as revenue when the Company satisfies the performance obligations.
The amount of Korean Won 23,912 thousand included in contract liabilities as of December 31, 2021 has been recognized as revenue in 2022.
No information is provided about remaining performance obligations as of December 31, 2023 or as of December, 31 2022 that have an original expected duration of one year or less, as allowed by IFRS 15.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
8. Income and Expenses
Details of other income for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other income | | ₩ | | | 7 | | | | 3 | |
Details of other expenses for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Donations | | ₩ | | | 30,000 | | | | - | |
| Losses on disposition of PP&E | | | | | 14,367 | | | | - | |
| Other expenses | | | | | 520 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 44,887 | | | | - | |
Details of classification of expenses by nature for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Losses from investments in associates | | ₩ | | | 146,232 | | | | 60,952 | |
| Employee benefits | | | | | 978,553 | | | | 1,057,021 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | | | 93,126 | | | | 65,862 | |
| Commission paid | | | | | 68,534 | | | | 10,710 | |
| Other expenses | | | | | 570,178 | | | | 114,706 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,856,623 | | | | 1,309,251 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
9. Finance income and costs
Details of finance income and costs for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Finance income | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | ₩ | | | 21,382 | | | | 4,720 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 21,382 | | | | 4,720 | |
| Finance costs | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expenses | | ₩ | | | 21,684 | | | | 11,105 | |
| Losses on valuation of short-term investment securities | | | | | 76,280 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 97,964 | | | | 11,105 | |
10. Employee benefits
Details of Net defined benefit liability(asset) recognized as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Defined benefit asset | | ₩ | | | (314,885 | ) | | | (246,218 | ) |
| Defined benefit liability | | | | | 314,864 | | | | 243,736 | |
| Net defined benefit liability(asset) | | ₩ | | | (21 | ) | | | (2,482 | ) |
The Company operates defined benefit plans as a retirement pension scheme. Defined benefit plans expose the Company to actuarial risks, such as longevity risk, interest rate risk and market (investment) risk.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| A. | Movement in net defined benefit liability(asset) |
Details of reconciliation from the opening balances to the closing balances for the net defined benefit liability(asset) and its components for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | Defined benefit obligation | | | Fair value of plan assets | | | Net defined benefit liabilities (asset) | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| Balance at 1 January | | ₩ | | | 243,736 | | | | 251,814 | | | | 246,218 | | | | - | | | | (2,482 | ) | | | 251,814 | |
| Included in profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current service cost | | | | | 56,091 | | | | 61,624 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 56,091 | | | | 61,624 | |
| Past service credit | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Interest | | | | | 9,394 | | | | 4,632 | | | | 7,943 | | | | 280 | | | | 1,451 | | | | 4,352 | |
| Subtotal | | | | | 65,485 | | | | 66,256 | | | | 7,943 | | | | 280 | | | | 57,542 | | | | 65,976 | |
| Included in OCI | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remeasurement loss(gain) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Demographic assumption | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Financial assumption | | | | | 16,645 | | | | (23,571 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 16,645 | | | | (23,571 | ) |
| Adjustment based on experience | | | | | 236 | | | | (15,680 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 236 | | | | (15,680 | ) |
| Return on plan assets excluding interest income | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,759 | | | | 227 | | | | (2,759 | ) | | | (227 | ) |
| Subtotal | | | | | 16,881 | | | | (39,251 | ) | | | 2,759 | | | | 227 | | | | 14,122 | | | | (39,478 | ) |
| Other | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Benefits paid | | | | | (11,238 | ) | | | (35,083 | ) | | | (6,131 | ) | | | - | | | | (5,107 | ) | | | (35,083 | ) |
| Contribution paid by the employer | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 64,096 | | | | 245,711 | | | | (64,096 | ) | | | (245,711 | ) |
| Subtotal | | | | | (11,238 | ) | | | (35,083 | ) | | | 57,965 | | | | 245,711 | | | | (69,203 | ) | | | (280,794 | ) |
| Balance at 31 December | | ₩ | | | 314,864 | | | | 243,736 | | | | 314,885 | | | | 246,218 | | | | (21 | ) | | | (2,482 | ) |
In 2023, the Company contributed Korean Won 64,096 thousand to the defined benefit plans. In 2022, the Company contributed Korean Won 245,711 thousand to the defined benefit plans.
Details of plan assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Cash | | ₩ | | | 76 | | | | 65 | |
| Time deposits | | | | | 314,809 | | | | 246,153 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 314,885 | | | | 246,218 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Most of the plan assets are invested in one-year time deposits.
Company invests in financial instruments with guaranteed principal to manage risks to plan assets, and there are no separate restrictions on refundability.
Company reviews the level of fund reserves every year and has a policy to compensate for the deficit in the plan assets.
The estimated contribution for 2024 is nil.
| C. | Defined benefit obligation |
Details of actuarial assumptions used for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Discount rate | | 3.9% | | 5.2% |
| Future salary growth | | 3.7% | | 3.7% |
Assumptions regarding future longevity and standard salary scale have been based on issued by Korea Insurance Development Institute.
As of December 31, 2023, the weighted average duration of the defined benefit obligation was 4.4 years.
The Company measures the risk of actuarial assumption changes as a 1% fluctuation in the discount rate and future salary growth rate of the amounts of defined benefit obligation, which reflects the management’s assessment of the risk of actuarial assumption fluctuation that can reasonably occur. The impact of a 1% fluctuation in discount rates and future salary growth rates on the Company’s defined benefit obligation as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | Increased by 1% | | | Decreased by 1% | | | Increased by 1% | | | Decreased by 1% | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Discount rate | | ₩ | | | (13,013 | ) | | | 14,572 | | | | (9,321 | ) | | | 10,469 | |
| Future salary growth | | | | | 14,470 | | | | (13,169 | ) | | | 10,535 | | | | (9,544 | ) |
Although the analysis does not take account of the full distribution of cash flows expected under the plan, it does provide an approximation of the sensitivity of the assumptions shown.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| D. | Employee benefit expenses |
| i. | Details of employee benefit expenses recognized for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows: |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Wages and salaries | | ₩ | | | 876,912 | | | | 954,492 | |
| Defined benefits plan expenses | | | | | 57,542 | | | | 65,976 | |
| Social security contributions | | | | | 44,099 | | | | 36,553 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 978,553 | | | | 1,057,021 | |
| ii. | Expenses are recognized in the statements of comprehensive income (loss) as follows: |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | ₩ | | | 978,553 | | | | 1,057,021 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
11. Income taxes
| A. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current tax expense | | | | | | | | |
| Current year | | ₩ | | | 24,875 | | | | 5,270 | |
| Adjustments recognized related to period income taxes (*) | | | | | 51,253 | | | | 98,312 | |
| | | | | | 76,128 | | | | 103,582 | |
| Deferred tax expense | | | | | | | | | | |
| Origination and reversal of temporary differences | | ₩ | | | (37,977 | ) | | | 12,062 | |
| Deferred taxes charged directly to equity | | | | | 1,398 | | | | (4,744 | ) |
| Tax expense on continuing operations | | ₩ | | | 39,549 | | | | 110,900 | |
| (*) | In the normal course of business, the Company and its respective subsidiary are examined by taxation authority. Our management regularly assesses the potential outcomes of these examinations and any future examinations for the current or prior years in determining the adequacy of its liabilities for income taxes. |
The Company establish additional current tax liabilities for income taxes when, despite the belief that tax positions are fully supportable, there remain positions that do not meet the minimum probability threshold, which is a tax position that is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by the applicable taxation authority. The impact of current tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions, as well as the related net interest and penalties, are included in income taxes in the statements of operations.
| B. | Amounts recognized in OCI |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Before tax | | | Tax (expense) benefit | | | Net of tax | | | Before tax | | | Tax (expense) benefit | | | Net of tax | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Items that will not be reclassified to profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liability | | ₩ | | | (14,122 | ) | | | 1,398 | | | | (12,724 | ) | | | 39,478 | | | | (4,744 | ) | | | 34,734 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| C. | Reconciliation of effective tax rate |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Profit (loss) before income tax | | ₩ | | | (261,721 | ) | | | 539,255 | |
| Tax at the statutory income tax rate | | | | | (25,910 | ) | | | 96,636 | |
| Adjustments: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Expenses not deductible for tax purposes | | | | | 455 | | | | 5,683 | |
| Tax credits | | | | | (13,740 | ) | | | (17,514 | ) |
| Adjustments recognized related to prior period incomes | | | | | 38,044 | | | | 65,291 | |
| Other (differences in tax rate, etc) | | | | | 40,700 | | | | (39,196 | ) |
| Income tax expenses | | ₩ | | | 39,549 | | | | 110,900 | |
| Effective income tax rate (*) | | | | | - | | | | 20.6 | % |
| (*) | The effective tax rate is not calculated as the Company incurred a loss before income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2023. |
| D. | Movement in deferred tax balances |
| i. | Movement in deferred tax balances as of December 31, 2023 |
| | | | | Tax effect | |
| | | | | Beginning | | | Increase
(decrease) | | | Ending | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 7,552 | | | | 7,552 | |
| Property and equipment including right-of-use assets | | | | | (8,731 | ) | | | 1,099 | | | | (7,632 | ) |
| Investments in associates | | | | | 12,453 | | | | 9,224 | | | | 21,677 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 8,423 | | | | 11,483 | | | | 19,906 | |
| Lease receivables | | | | | - | | | | (12,595 | ) | | | (12,595 | ) |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | | | | (5,216 | ) | | | 5,214 | | | | (2 | ) |
| Other | | | | | 4,282 | | | | 2,259 | | | | 6,541 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 11,211 | | | | 24,236 | | | | 35,447 | |
| Loss carried forward | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Carryover tax credit | | | | | 15,676 | | | | 13,740 | | | | 29,416 | |
| Deferred tax assets (liabilities) | | ₩ | | | 26,887 | | | | 37,976 | | | | 64,863 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| ii. | Movement in deferred tax balances as of December 31, 2022 |
| | | | | Tax effect | |
| | | | | Beginning | | | Increase (decrease) | | | Ending | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Property and equipment including right-of-use assets | | ₩ | | | (16,663 | ) | | | 7,932 | | | | (8,731 | ) |
| Investments in associates | | | | | 1,669 | | | | 10,784 | | | | 12,453 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 15,713 | | | | (7,290 | ) | | | 8,423 | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | | | | 27,700 | | | | (32,916 | ) | | | (5,216 | ) |
| Other | | | | | 10,530 | | | | (6,248 | ) | | | 4,282 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 38,949 | | | | (27,738 | ) | | | 11,211 | |
| Loss carried forward | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Carryover tax credit | | | | | - | | | | 15,676 | | | | 15,676 | |
| Deferred tax assets (liabilities) | | ₩ | | | 38,949 | | | | (12,062 | ) | | | 26,887 | |
| E. | Deferred assets (liabilities) |
| i. | The timing of recovery of deferred tax assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows: |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Deferred tax assets | | | | | | | | | | |
| - Deferred tax assets to be recovered after more than 12 months | | ₩ | | | 127,210 | | | | 37,178 | |
| - Deferred tax assets to be recovered within 12 months | | | | | 6,977 | | | | 3,656 | |
| Sub-total | | | | | 134,187 | | | | 40,834 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| - Deferred tax liabilities to be recovered after more than 12 months | | | | | (56,730 | ) | | | (13,947 | ) |
| - Deferred tax liabilities to be recovered within 12 months | | | | | (12,594 | ) | | | - | |
| Sub-total | | | | | (69,324 | ) | | | (13,947 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets (liabilities), net | | ₩ | | | 64,863 | | | | 26,887 | |
| ii. | Details of unused tax loss carryforwards and unused tax credit carryforwards that are recognized as deferred income tax assets as of December 31, 2023 are as follows: |
| Year of expiration | | | | Unused loss
carryforwards | | | Unused tax credit
carryforwards | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| After 2029 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 29,416 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
12. Other assets
Details of other assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Current | | | | | | | | | | |
| Prepaid expenses | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 520 | |
13. Trade and other receivables
Details of trade and other receivables as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Trade receivable | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable — Trade | | ₩ | | | 384,675 | | | | 435,533 | |
| Other receivables | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-trade receivables | | | | | 27,498 | | | | - | |
| Lease receivable(current) | | | | | 91,135 | | | | - | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | | | | | | |
| Leasehold deposit receivables | | | | | 195,464 | | | | 58,676 | |
| Other deposits receivables | | | | | 300 | | | | 380 | |
| Lease receivable(non-current) | | | | | 36,082 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 735,154 | | | | 494,589 | |
14. Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Deposits in banks | | ₩ | | | 342,896 | | | | 71,965 | |
The Company doesn’t have any restricted cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
15. Property and equipment
| A. | Reconciliation of carrying amount |
Details of property and equipment as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | Book value | | | Accumulated depreciation | | | Carrying amount | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Office equipment | | ₩ | | | 24,140 | | | | (15,129 | ) | | | 9,011 | |
| Right-of-use assets | | | | | 270,012 | | | | (195,363 | ) | | | 74,649 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 294,152 | | | | (210,492 | ) | | | 83,660 | |
| | | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | Book value | | | Accumulated depreciation | | | Carrying amount | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Office equipment | | ₩ | | | 20,046 | | | | (13,177 | ) | | | 6,869 | |
| Right-of-use assets | | | | | 190,929 | | | | (104,190 | ) | | | 86,739 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 210,975 | | | | (117,367 | ) | | | 93,608 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Details of the changes in property and equipment for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Office equipment | | | Right-of-use assets | | | Total | |
| | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 6,869 | | | | 86,739 | | | | 93,608 | |
| Acquisitions | | | | | 4,094 | | | | 308,663 | | | | 312,757 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (1,952 | ) | | | (91,174 | ) | | | (93,126 | ) |
| Lease modification | | | | | - | | | | (23,804 | ) | | | (23,804 | ) |
| Provision of sublease | | | | | - | | | | (205,775 | ) | | | (205,775 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 9,011 | | | | 74,649 | | | | 83,660 | |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Office equipment | | | Right-of-use assets | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 4,094 | | | | 150,382 | | | | 154,476 | |
| Acquisitions | | | | | 4,994 | | | | - | | | | 4,994 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (2,219 | ) | | | (63,643 | ) | | | (65,862 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 6,869 | | | | 86,739 | | | | 93,608 | |
The classification of depreciation expenses in the statements of comprehensive income for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | ₩ | | | 93,126 | | | | 65,862 | |
| B. | Leased property and equipment |
The Company leased the building during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. As of December 31, 2023, Korean Won 74,649 thousand of right-of-use assets was recognized. (December 31, 2022: Korean Won 86,739 thousand of building.).
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
16. Equity-accounted investees
| A. | Acquisition cost of investments in associates |
Details of acquisition cost of investments in associates as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | Percentage of Ownership (*) | | | Acquisition Cost | | | Percentage of Ownership (*) | | | Acquisition Cost | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Investments in associates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.8 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1.01 | % | | | 41,000 | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 1.04 | % | | | 200,000 | | | | 1.04 | % | | | 200,000 | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 1.25 | % | | | 300,000 | | | | 1.25 | % | | | 300,000 | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 1.00 | % | | | 300,000 | | | | 1.00 | % | | | 300,000 | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 1.04 | % | | | 88,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | | | | | 888,000 | | | | | | | | 841,000 | |
| (*) | Although the Company holds less than 20% of equity interests in investment fund, investments in such investees were classified as investments in associates as the Company can exercise significant influence over financial and operating policy decisions as a general partner. |
| B. | Carrying amount of investments in associates |
Details of carrying amount of investments in associates as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | Percentage of Ownership (*) | | | Carrying amount | | | Percentage of Ownership (*) | | | Carrying amount | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Investments in associates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.8 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1.01 | % | | | 35,636 | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 1.04 | % | | | 112,425 | | | | 1.04 | % | | | 158,862 | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 1.25 | % | | | 208,522 | | | | 1.25 | % | | | 264,846 | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 1.00 | % | | | 260,944 | | | | 1.00 | % | | | 290,086 | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 1.04 | % | | | 87,152 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | | | | | 669,043 | | | | | | | | 749,430 | |
| (*) | Although the Company holds less than 20% of equity interests in investment fund, investments in such investees were classified as investments in associates as the Company can exercise significant influence over financial and operating policy decisions as a general partner. |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| C. | Movement of investments in associates |
Details of the changes in investments in associates for the years ended December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | January 1, 2023 | | | Capital contribution | | | Capital withdrawal | | | Gains(Losses)
on disposal of
investments
in associates | | | Share in the profit of associates | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Investments in associates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.8 (*) | | ₩ | | | 35,636 | | | | - | | | | (22,155 | ) | | | - | | | | (13,481 | ) | | | - | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 158,862 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (46,437 | ) | | | 112,425 | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 264,846 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (56,324 | ) | | | 208,522 | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 290,086 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (29,142 | ) | | | 260,944 | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | - | | | | 88,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (848 | ) | | | 87,152 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 749,430 | | | | 88,000 | | | | (22,155 | ) | | | - | | | | (146,232 | ) | | | 669,043 | |
| (*) | Investment fund was liquidated during the year ended December 31, 2023. |
Details of the changes in investments in associates for the years ended December 31, 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | January 1, 2022 | | | Capital contribution | | | Capital withdrawal | | | Gains(Losses) on disposal of investments in associates | | | Share in the profit of associates | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Investments in associates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.5 (*) | | ₩ | | | 53,720 | | | | - | | | | (54,129 | ) | | | 409 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.6 (*) | | | | | 63,726 | | | | - | | | | (64,741 | ) | | | 1,015 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.8 | | | | | 37,401 | | | | 2,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (3,765 | ) | | | 35,636 | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 182,622 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (23,760 | ) | | | 158,862 | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 200,838 | | | | 90,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (25,992 | ) | | | 264,846 | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 117,520 | | | | 180,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (7,434 | ) | | | 290,086 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 655,827 | | | | 272,000 | | | | (118,870 | ) | | | 1,424 | | | | (60,951 | ) | | | 749,430 | |
| (*) | Investment fund was liquidated during the year ended December 31, 2022. |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
D. Summary of financial information of associates
Details of the summary of financial information of associates for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | Current assets | | | Investment asset | | | Total assets | | | Current liabilities | | | Total liabilities | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Investments in associates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | ₩ | | | 3,149,532 | | | | 7,767,287 | | | | 10,916,819 | | | | 67,819 | | | | 67,819 | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 2,270,036 | | | | 14,561,389 | | | | 16,831,425 | | | | 149,698 | | | | 149,698 | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 1,084,379 | | | | 25,204,198 | | | | 26,288,577 | | | | 194,154 | | | | 194,154 | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 4,644,693 | | | | 3,800,000 | | | | 8,444,693 | | | | 78,079 | | | | 78,079 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 11,148,640 | | | | 51,332,874 | | | | 62,481,514 | | | | 489,750 | | | | 489,750 | |
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Investment income | | | Profit (Loss) for the year | | | Total Comprehensive income | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Investments in associates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | ₩ | | | 350,251 | | | | (4,481,096 | ) | | | (4,481,096 | ) |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 40,872 | | | | (4,505,988 | ) | | | (4,505,988 | ) |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 11,332 | | | | (2,914,190 | ) | | | (2,914,190 | ) |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 12,202 | | | | (81,386 | ) | | | (81,386 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 414,657 | | | | (11,982,660 | ) | | | (11,982,660 | ) |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | Current assets | | | Investment asset | | | Total assets | | | Current liabilities | | | Total liabilities | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Investments in associates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.8 | | ₩ | | | 2,280 | | | | 3,533,273 | | | | 3,535,553 | | | | 1,093 | | | | 1,093 | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 3,143,154 | | | | 12,288,517 | | | | 15,431,671 | | | | 101,574 | | | | 101,574 | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 5,034,368 | | | | 16,307,633 | | | | 21,342,001 | | | | 154,286 | | | | 154,286 | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 3,222,693 | | | | 25,981,312 | | | | 29,204,004 | | | | 195,392 | | | | 195,392 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 11,402,495 | | | | 58,110,735 | | | | 69,513,229 | | | | 452,345 | | | | 452,345 | |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Investment income | | | Profit (Loss) for the year | | | Total Comprehensive income | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Investments in associates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.8 | | ₩ | | | 75,437 | | | | (373,090 | ) | | | (373,090 | ) |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 405,113 | | | | (2,292,929 | ) | | | (2,292,929 | ) |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 36,588 | | | | (2,070,164 | ) | | | (2,070,164 | ) |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 28,663 | | | | (743,382 | ) | | | (743,382 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 545,801 | | | | (5,479,565 | ) | | | (5,479,565 | ) |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
17. Financial instruments by category
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at amortized cost | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | | | 342,896 | | | | 71,965 | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | | | | 384,675 | | | | 435,533 | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | | | | 118,633 | | | | - | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | 231,846 | | | | 59,056 | |
| Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term investment securities | | | | | 1,664,720 | | | | - | |
| Long-term investment securities | | | | | 12,180 | | | | 38,875 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 2,754,950 | | | | 605,429 | |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial liabilities at amortized cost | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables (*) | | ₩ | | | 1,784,365 | | | | 90,858 | |
| Other non-current financial liabilities | | | | | 87,123 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,871,488 | | | | 90,858 | |
| (*) | Trade and other payables that are not financial liabilities are excluded. |
| A. | Classification of investment assets based on liquidity |
The classification of investment assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Equity securities – at FVTPL | | ₩ | | | 1,667,720 | | | | 3,000 | |
| Project investment | | | | | 9,180 | | | | 35,875 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,676,900 | | | | 38,875 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| B. | Equity Securities designated as at FVTPL |
The Company designated the investments shown below as equity securities at FVTPL because these equity securities represent investment that the Company intends to sell for strategic purposes.
| | | | | Fair value at December 31,
2023 | | | Fair value at December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Equity Securities (unlisted stocks) | | ₩ | | | 1,667,720 | | | | 3,000 | |
| C. | Net gains and losses by category of financial instruments |
The net gains and losses by category of financial instruments for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Financial assets at
amortized cost | | | Financial assets at
fair value through
profit or loss | | | Financial liabilities at amortized cost | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest income | | ₩ | | | 21,382 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 21,382 | |
| Interest expense | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (4,825 | ) | | | (4,825 | ) |
| Gain or loss on valuation of investment securities | | | | | - | | | | (76,280 | ) | | | - | | | | (76,280 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 21,382 | | | | (76,280 | ) | | | (4,825 | ) | | | (59,723 | ) |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Financial assets at
amortized cost | | | Financial liabilities at amortized cost | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest income | | ₩ | | | 4,720 | | | | - | | | | 4,720 | |
| Interest expense | | | | | - | | | | (2,583 | ) | | | (2,583 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 4,720 | | | | (2,583 | ) | | | 2,137 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
18. Capital and reserves
Details of share capital as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Shares | | ₩ | | | 850,000 | | | | 850,000 | |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Share Premium (*) | | ₩ | | 421,254 | | | | - | |
| (*) | On January 2, 2023, Choi Pyeung ho, the Company’s major shareholder, transferred the Company’s shares to the employees for less than fair value. |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liability | | ₩ | | | (45,637 | ) | | | (32,913 | ) |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
19. Capital management
The Company’s policy is to maintain a strong capital base so as to maintain investor, creditor and market confidence and to sustain future development of the business. The Company monitors capital using a ratio of ‘Net debt’ to ‘Total equity’. Net debt is calculated as total liabilities (as shown in the statement of financial position) less cash and cash equivalents. The Company’s net debt to total equity ratio as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows.
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total liabilities | | ₩ | | | 2,370,145 | | | | 405,474 | |
| Less: Cash and cash equivalents | | | | | (342,896 | ) | | | (71,965 | ) |
| Net debt | | | | | 2,027,249 | | | | 333,509 | |
| Total equity | | | | | 1,313,379 | | | | 1,206,119 | |
| Net debt to total equity ratio | | | | | 154.35 | % | | | 27.65 | % |
20. Share-based payment arrangements
| A. | Measurement of fair values |
The fair value of the employee share options has been measured using a discounted cash flow method.
The inputs used in the measurement of the fair values at grant date are as follows:
Share option plan
(Either of equity-settled or cash-settled) | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Estimated fair value of Share (in aggregate) | | ₩ | | | 455,254 | | | | - | |
| Transfer Price | | | | | 34,000 | | | | - | |
| Fair Value of options | | ₩ | | | 421,254 | | | | - | |
| Risk- free interest rate (based on government bonds) | | | | | 3.74 | % | | | - | |
| Discount rate | | | | | 15.80 | % | | | - | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
21. Borrowings
Borrowings as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Lease liabilities (*) | | ₩ | | | 145,798 | | | | 61,718 | |
| Non-Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Lease liabilities (*) | | | | | 55,275 | | | | 23,366 | |
| (*) | The interest rate related to lease liabilities reflects the incremental borrowing rate based on the Company’s credit. The amount of interest expense related to lease liabilities incurred during 2023 is Korean Won 16,757 thousand (2022: Korean Won 8,522 thousand). Additionally, the amount of low-value assets lease payments not included in the measurement of lease liabilities during 2023 is Korean Won 3,034 thousand (2022: Korean Won 2,640 thousand). |
22. Trade and other payables
Trade and other payables as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other payable | | ₩ | | | 1,784,364 | | | | 90,858 | |
| Accrued expenses | | | | | 46,484 | | | | 32,663 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,830,848 | | | | 123,521 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
23. Provisions
Provisions for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Site restoration | | | | | | | | | | |
| Beginning of the year | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | |
| Provisions made during the year | | | | | 12,888 | | | | - | |
| Interest expense | | | | | 101 | | | | - | |
| Ending of the year | | ₩ | | | 12,989 | | | | - | |
The provision for building restoration relates mainly to buildings leased during 2023. The provision has been estimated based on historical data associated with similar buildings.
24. Financial Instruments – Fair values and risk management
| A. | Accounting classifications and fair values |
The following table shows the carrying amounts and fair values of financial assets and financial liabilities, including their levels in the fair value hierarchy. It does not include fair value information for financial assets and financial liabilities not measured at fair value if the carrying amount is a reasonable approximation of fair value.
Carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term investment securities | | ₩ | | | 1,664,720 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,664,720 | | | | 1,664,720 | |
| Long-term investment securities | | | | | 3,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,000 | | | | 3,000 | |
| Project investment | | | | | 9,180 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 9,180 | | | | 9,180 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,676,900 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,676,900 | | | | 1,676,900 | |
Carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term investment securities | | ₩ | | | 3,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,000 | | | | 3,000 | |
| Project investment | | | | | 35,875 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 35,875 | | | | 35,875 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 38,875 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 38,875 | | | | 38,875 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Details of the changes in financial instruments for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 38,875 | | | | 3,468 | |
| Acquisitions (*1) | | | | | 1,741,000 | | | | 35,875 | |
| Disposals | | | | | (26,695 | ) | | | (468 | ) |
| Valuation (*2) | | | | | (76,280 | ) | | | - | |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 1,676,900 | | | | 38,875 | |
| (*1) | On March 23, 2023, the Company acquired 1,000 shares of Play Company Co., Ltd., which represents 1% of total shares issued. Acquisition price per share is Korean Won 1,741 thousand. |
| (*2) | Unlisted stocks were revalued on December 31, 2023. |
| B. | Measurement of fair values |
Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows:
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 2: all inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable (either directly that is, prices, or indirectly that is, derived from prices) for the asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 3: unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. |
The fair value of financial instruments traded in an active market is determined based on the quoted market price as of the end of the reporting period. If the quoted prices are readily and regularly available through exchanges, sellers, brokers, industry groups, rating agencies or regulators and such prices represent actual market transactions that occur regularly between independent parties, they are considered active markets.
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market is determined using valuation techniques. These valuation techniques use as much market observable information as possible and use the least amount of Company-specific information. At this time, if all the significant input variables required to measure the fair value are observable, the financial instruments are classified as Level 2.
If more than one significant input variable is not based on observable market information, the item is included in Level 3.
The valuation techniques used to measure the fair value of a financial instrument include:
| ● | Market price or dealer price of a similar financial instrument |
| ● | The fair value of derivative instruments is determined by discounting the amount to present value using the leading exchange rate as of the end of the reporting period |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| C. | Financial risk management |
The Company’s operating activities expose itself to a variety of financial risks: credit risk and liquidity risk from which the Company’s risk management program focuses on minimizing any adverse effects on its financial performance. The Company operates financial risk management policies and programs that closely monitor and respond to each risk factor.
Credit risk is the risk of financial loss to the Company if a customer or counterpart to a financial instrument fails to meet its contractual obligations and arises principally from the Company’s receivables from customers. In order to manage credit risk, the Company regularly evaluate the credit worthiness of each customer or counterparty considering the party’s financial information, past experience, its own trading records and other factors. In relation to the impairment of financial assets subsequent to initial recognition, the Company recognizes the changes in expected credit loss (“ECL”) in profit or loss at each reporting date. The carrying amount of a financial asset represents the maximum exposure to credit risk.
The maximum exposure to credit risk of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | | | 342,896 | | | | 71,965 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | 231,846 | | | | 59,056 | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | | | | 384,675 | | | | 435,533 | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | | | | 118,633 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,078,050 | | | | 566,554 | |
Cash and cash equivalents are deposited in financial institutions with strong credit rating. Accounts receivables are mainly due from investment funds, which management believes such customers are of low credit risk.
Liquidity risk management includes the maintenance of sufficient cash and marketable securities, the availability of funds from appropriately committed credit lines, and the ability to settle market positions. All assets and liabilities on the balance sheet and off-balance sheet transactions are subject to liquidity risk management.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Financial liabilities and off-balance sheet transactions of the Company by maturity according to the remaining period from December 31, 2023 to the contractual maturity date are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | Carrying Amount | | | Less than 3 months | | | 3 months ~ 1 year | | | 1~2 years | | | 2~5 years | | | More than 5 years | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Non-derivative financial liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other payables (*1) | | ₩ | | | 1,784,365 | | | | 43,365 | | | | 1,741,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,784,365 | |
| Other non-current financial liabilities | | | | | 87,123 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 100,050 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 100,050 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 201,073 | | | | 41,820 | | | | 111,600 | | | | 62,458 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 215,878 | |
| Off-balance sheet items | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Commitments (*2) | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 132,000 | | | | - | | | | 132,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 2,072,561 | | | | 85,185 | | | | 1,852,600 | | | | 162,508 | | | | 132,000 | | | | - | | | | 2,232,293 | |
| (*1) | Payables and accrued expense that are not financial liabilities are excluded. |
| (*2) | The Company classifies the amount, which is due to maintain the status of the member of investment fund in accordance with the agreement, based on its earliest contractual maturity. (Note 26) |
Financial liabilities of the Company by maturity according to the remaining period from December 31, 2022 to the contractual maturity date are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | Carrying Amount | | | Less than 3 months | | | 3 months ~ 1 year | | | 1~2 years | | | 2~5 years | | | More than 5 years | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Non-derivative financial liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other payables (*) | | ₩ | | | 90,858 | | | | 90,858 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 90,858 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 85,084 | | | | 16,500 | | | | 49,500 | | | | 23,407 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 89,407 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 175,942 | | | | 107,358 | | | | 49,500 | | | | 23,407 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 180,265 | |
| (*) | Payables and accrued expense that are not financial liabilities are excluded. |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
25. Leases
The Company leases building. The leases typically run for a period of 1~3 years, with an option to renew or terminate the lease after that date. The Company also leases printer with contract terms of one year. These leases is leases of low-value items. The Company has elected not to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for these leases. Information about leases for which the Company is a lessee is presented below.
Right-of-use assets related to leased properties that do not meet the definition of investment property are presented as property and equipment.
Details of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities recognized in the statements of financial position as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Building) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Acquisition price | | ₩ | | | 270,012 | | | | 190,929 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | | | | | (195,363 | ) | | | (104,190 | ) |
| Book amount | | ₩ | | | 74,649 | | | | 86,739 | |
Changes in right-of-use assets for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Building | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance as of January 1, 2023 | | ₩ | | | 86,739 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (91,174 | ) |
| Acquisitions | | | | | 308,663 | |
| Lease modification | | | | | (23,804 | ) |
| Provision of sublease | | | | | (205,775 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | | ₩ | | | 74,649 | |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Building | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance as of January 1, 2022 | | ₩ | | | 150,382 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (63,643 | ) |
| Acquisitions | | | | | - | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2022 | | ₩ | | | 86,739 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| ii. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
Amounts recognized in profit or loss for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest expense relating to lease liabilities (included in finance cost) | | ₩ | | | 16,757 | | | | 8,522 | |
| Expense relating to leases of low-value assets excluding short-term leases | | ₩ | | | 3,034 | | | | 2,640 | |
| iii. | Amounts recognized in statement of cash flows |
Amounts recognized in statement of cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total cash outflows of leases | | ₩ | | | 150,464 | | | | 68,924 | |
During the year ended December 31, 2023 the Company has sub-leased a building that has been presented as a right-of-use asset.
During the year ended December 31, 2023 the Company recognized a losses of Korean Won 14,367 thousand (2022: nil) on disposition of PP&E.
During the year ended December 31, 2023 the Company recognized interest income on lease receivables Korean Won 8,826 thousand (2022: nil).
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
26. Commitments
| A. | Amount of investment agreement |
The outstanding balances of contributions according to the investment agreements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| December 31, 2023 | | | | Total amount of
investment
agreement | | | Cumulative investment | | | Outstanding Balance | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | ₩ | | | 200,000 | | | | 200,000 | | | | - | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 220,000 | | | | 88,000 | | | | 132,000 | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 300,000 | | | | 300,000 | | | | - | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 300,000 | | | | 300,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,020,000 | | | | 888,000 | | | | 132,000 | |
| December 31, 2022 | | | | Total amount of
investment
agreement | | | Cumulative investment | | | Outstanding Balance | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.8 (*) | | ₩ | | | 55,000 | | | | 41,000 | | | | 14,000 | |
| SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 200,000 | | | | 200,000 | | | | - | |
| Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 300,000 | | | | 300,000 | | | | - | |
| Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 300,000 | | | | 300,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 855,000 | | | | 841,000 | | | | 14,000 | |
| (*) | As of December 31, 2022, obligation for unfunded balance was waived due to the termination of the investment period on the contract. |
On September 14, 2023, an amendment was made to the equity interest exchange agreement, originally entered into on March 31, 2023, between the CEO, other shareholders of the Company, and K Enter Holdings for the purpose of listing on the NASDAQ through a merger with a SPAC company. The equity interest exchange agreement is effective on the date designated by K Enter Holdings. Upon the effective date, the CEO and other shareholders of the Company will exchange 95.1% of its shares with the equity interest of K Enter Holdings. Following the equity interest exchange transaction, the Company is expected to be a subsidiary of K Enter Holdings.
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
27. Statement of Cash flows
Adjustments for income and expenses from operating activities for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Depreciation | | ₩ | | | 93,126 | | | | 65,862 | |
| Interest expenses | | | | | 21,684 | | | | 11,105 | |
| Interest income | | | | | (21,382 | ) | | | (4,720 | ) |
| Severance Benefits | | | | | 57,542 | | | | 65,976 | |
| Share-based payments expenses | | | | | 421,254 | | | | - | |
| Tax expenses | | | | | 39,549 | | | | 110,900 | |
| Gains on valuation of securities under equity method | | | | | - | | | | (1,424 | ) |
| Losses on valuation of short-term financial instruments | | | | | 76,280 | | | | - | |
| Losses on valuation of securities under equity method | | | | | 146,232 | | | | 60,952 | |
| Losses on disposition of PP&E | | | | | 14,367 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 848,652 | | | | 308,651 | |
Changes in assets and liabilities from operating activities for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other non-current liabilities | | ₩ | | | - | | | | (237,386 | ) |
| Other current liabilities | | | | | (23,218 | ) | | | 34,229 | |
| Other current assets | | | | | 520 | | | | (63 | ) |
| Accounts receivable - other | | | | | (29,139 | ) | | | 204,215 | |
| Trade and other payables | | | | | (33,673 | ) | | | (92,339 | ) |
| Accounts receivable - trade | | | | | 50,858 | | | | (93,368 | ) |
| Payment of severance | | | | | (5,107 | ) | | | (35,083 | ) |
| Net defined benefit asset | | | | | (64,096 | ) | | | (245,711 | ) |
| Contract liabilities | | | | | - | | | | (23,912 | ) |
| Contract assets | | | | | (110,988 | ) | | | 28,133 | |
| Decrease in Project investment | | | | | 26,695 | | | | 468 | |
| Increase in Project investment | | | | | - | | | | (35,875 | ) |
| Decrease in securities under equity method | | | | | 22,154 | | | | 118,870 | |
| Increase in securities under equity method | | | | | (88,000 | ) | | | (272,000 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (253,994 | ) | | | (649,822 | ) |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Significant non-cash transactions for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Increase in Lease liabilities (new contract) | | ₩ | | | 269,160 | | | | - | |
| Decrease in Lease liabilities (lease modification) | | | | | (22,498 | ) | | | - | |
| Increase in Short-term investment securities | | | | | 1,741,000 | | | | - | |
| Increase in Lease receivable | | | | | 173,656 | | | | - | |
The movements of liabilities to cash flows arising from financing activities for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | Other non-current financial liabilities | | | Current portion of
long-term
borrowings, net | | | Current lease liabilities | | | Non-current lease liabilities | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at 1 January 2022 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 161,000 | | | | 57,530 | | | | 85,317 | | | | 303,847 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Repayment of borrowings | | | | | - | | | | (161,000 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (161,000 | ) |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (57,763 | ) | | | - | | | | (57,763 | ) |
| Reclassification | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 61,951 | | | | (61,951 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | (161,000 | ) | | | 4,188 | | | | (61,951 | ) | | | (218,763 | ) |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 8,522 | | | | - | | | | 8,522 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (8,522 | ) | | | - | | | | (8,522 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Balance at 31 December 2022 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | 61,718 | | | | 23,366 | | | | 85,084 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at 1 January 2023 | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 61,718 | | | | 23,366 | | | | 85,084 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (130,674 | ) | | | - | | | | (130,674 | ) |
| Collection of rent deposit | | | | | 100,050 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Reclassification | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 237,252 | | | | (237,252 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 100,050 | | | | - | | | | 106,578 | | | | (237,252 | ) | | | (30,624 | ) |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| New leases | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 269,160 | | | | 269,160 | |
| Lease modification | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (22,498 | ) | | | - | | | | (22,498 | ) |
| Present value discount | | | | | (17,752 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (17,752 | ) |
| Interest expense | | | | | 4,825 | | | | - | | | | 16,757 | | | | - | | | | 21,582 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (16,757 | ) | | | - | | | | (16,757 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 87,123 | | | | - | | | | (22,498 | ) | | | 269,160 | | | | 233,735 | |
| Balance at 31 December 2023 | | ₩ | | | 87,123 | | | | - | | | | 145,798 | | | | 55,274 | | | | 288,195 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
28. Related parties
| A. | List of related parties |
List of related parties as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| Relationship | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Key management personnel | | Choi, Pyeung ho | | Choi, Pyeung ho |
| Key management personnel | | Lee, Young Jae | | Lee, Young Jae |
| Personnel with significant influence over the Company | | Song, Hyo Jeong | | Song, Hyo Jeong |
| Entities with significant influence over the Company | | CY Holdings Co., Ltd | | CY Holdings Co., Ltd |
| Personnel with significant influence over the Company | | Park, Su Kyung | | Park, Su Kyung |
| Personnel with significant influence over the Company | | Hyun, Na Young | | - |
| Personnel with significant influence over the Company | | Lee, Myung Hyun | | - |
| Personnel with significant influence over the Company | | Kim, Min Soo | | - |
| Other related parties | | K Enter Holdings INC | | - |
| Associates | | - (*) | | SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.8 |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE
INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE
INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | - |
| Associates | | Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | Solaire Culture Plus Fund |
| Associates | | Solaire Main Movie Fund | | Solaire Main Movie Fund |
| Other related parties | | Bluefire Studio Co., Ltd | | Bluefire Studio Co., Ltd |
| Other related parties | | Secret: Untold Melody Limited Company
Specializing in The Cultural Industry | | Secret: Untold Melody Limited Company
Specializing in The Cultural Industry |
| Other related parties | | Next Sohee Limited Company
Specializing in The Cultural Industry | | Next Sohee Limited Company
Specializing in The Cultural Industry |
| Other related parties | | Falling starlight Limited Company
Specializing in The Cultural Industry | | Falling starlight Limited Company
Specializing in The Cultural Industry |
| (*) | Investments in associates(SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.8) is excluded from related parties as they were liquidated during the year ended December 31, 2023. |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| B. | Transactions with related parties |
Details of transaction with related parties for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| Related party | | | Name of entity | | | | Revenues | | | Purchases | | | Revenues | | | Purchases | |
| | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | | Choi, Pyeung ho | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,583 | |
| Key management personnel | | | Lee, Young Jae | | | | | 67 | | | | - | | | | 811 | | | | - | |
| Personnel with significant influence over the Company | | | Song, Hyo Jeong | | | | | 48 | | | | - | | | | 580 | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | | K Enter Holdings INC | | | | | 8,826 | | | | 4,825 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Associates (*1) | | | SOLAIRE Contents
Investment Fund No.5 | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 17,154 | | | | 16,509 | |
| Associates (*1) | | | SOLAIRE Contents
Investment Fund No.6 | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 20,700 | | | | 19,366 | |
| Associates (*2) | | | SOLAIRE Contents
Investment Fund No.8 | | | | | - | | | | 13,481 | | | | 51,262 | | | | 3,765 | |
| Associates | | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 302,276 | | | | 46,436 | | | | 386,000 | | | | 23,761 | |
| Associates | | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 89,858 | | | | 848 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Associates | | | Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 573,678 | | | | 56,325 | | | | 602,260 | | | | 25,992 | |
| Associates | | | Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 748,459 | | | | 29,142 | | | | 750,000 | | | | 7,434 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,723,212 | | | | 151,057 | | | | 1,828,767 | | | | 99,410 | |
| (*1) | Amounts before the liquidation during the year ended December 31, 2022. |
| (*2) | Amounts before the liquidation during the year ended December 31, 2023. |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| C. | Account balances with related parties |
The balances of receivables and payables to related parties as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Receivables | | | Lease receivable | | | Payables | | | Receivables | | | Payables | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Lee, Young Jae | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,949 | | | | - | | | | 17,921 | |
| Personnel with significant influence over the Company | | Song, Hyo Jeong | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,392 | | | | - | | | | 12,800 | |
| Other related parties | | K Enter Holdings INC | | | | | 27,498 | | | | 127,217 | | | | 87,123 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.1 | | | | | 87,238 | | | | - | | | | 24,005 | | | | 97,293 | | | | - | |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 76,550 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Associates | | Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | 144,375 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 149,199 | | | | - | |
| Associates | | Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | 187,500 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 189,041 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 523,161 | | | | 127,217 | | | | 114,469 | | | | 435,533 | | | | 30,721 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| D. | Financial transactions with related parties |
Details of significant financial transactions with related parties for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Repayment | | | Borrowing | | | Repayment | | | Borrowing | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
Key management personnel
| | Choi, Pyeung ho | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | 161,000 | | | | - | |
| E. | Capital contribution transactions with related parties |
Details of significant capital contribution transactions with related parties for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Additional investment | | | Recovery of investment | | | Additional investment | | | Recovery of investment | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.5 | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 54,129 | |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.6 | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 64,741 | |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE Contents Investment Fund No.8 | | | | | - | | | | 22,155 | | | | 2,000 | | | | - | |
| Associates | | SOLAIRE SCALE-UP MOVIE INVESTMENT FUND NO.2 | | | | | 88,000 | | | | - | | | | | | | | | |
| Associates | | Solaire Culture Plus Fund | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 90,000 | | | | - | |
| Associates | | Solaire Main Movie Fund | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 180,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 88,000 | | | | 22,155 | | | | 272,000 | | | | 118,870 | |
SOLAIRE PARTNERS LLC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| F. | Key management personnel compensation |
The compensation for the key management personnel for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Short-term employee benefits | | ₩ | | | 552,935 | | | | 708,218 | |
| Defined benefits plan expenses | | | | | 41,084 | | | | 37,921 | |
Compensation of the Company’s key management personnel includes salaries, non-cash benefits and contributions to a post-employment defined benefit plan.
29. Subsequent Events
On January 31, 2024, the Company entered into the Stock Sell Agreement with K Enter Holdings, 1,000 shares of Play Company Co.,Ltd totaling 1,741,000,000 Korean Won.
APEITDA CO., LTD
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023
| | | Note | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | 11 | | ₩ | | | 477,019 | | | | 659,606 | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | | | | | | - | | | | 30 | |
| Other current assets | | | | | | | 2,348 | | | | 2,164 | |
| Value added tax receivable | | | | | | | 2,244 | | | | 384 | |
| Current tax assets | | | | | | | 2 | | | | 8,289 | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | | 481,613 | | | | 670,473 | |
| Long-term investment securities | | 9 | | | | | 77,496 | | | | 93,219 | |
| Property, plant and equipment including right-of-use assets | | 10 | | | | | 264,062 | | | | 301,006 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | | | 407,904 | | | | 385,494 | |
| - Related parties | | 12 | | | | | 407,904 | | | | 385,494 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | | | | | | - | | | | 30,000 | |
| Deferred tax assets | | 6 | | | | | - | | | | 15,771 | |
| Total non-current assets | | | | | | | 749,462 | | | | 825,490 | |
| Total assets | | | | ₩ | | | 1,231,075 | | | | 1,495,963 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | | | ₩ | | | 19,108 | | | | 19,119 | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | | | | | 130,559 | | | | 133,700 | |
| - Related parties | | 12 | | | | | 128,905 | | | | 128,905 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 1,654 | | | | 4,795 | |
| Current portion of long-term borrowings, net | | 8 | | | | | 20,000 | | | | 100,000 | |
| - Related parties | | 12 | | | | | 20,000 | | | | 100,000 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Current tax liabilities | | | | | | | 4,503 | | | | - | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | | 174,170 | | | | 252,819 | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | 5 | | | | | 149,700 | | | | 139,459 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | | | | | 149,700 | | | | 139,459 | |
| Total liabilities | | | | ₩ | | | 323,870 | | | | 392,278 | |
| Equity | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital | | 7 | | ₩ | | | 10,000 | | | | 10,000 | |
| Other reserves | | 7 | | | | | (90,479 | ) | | | (81,522 | ) |
| Retained earnings | | | | | | | 987,684 | | | | 1,175,207 | |
| Total equity | | | | | | | 907,205 | | | | 1,103,685 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | | | | ₩ | | | 1,231,075 | | | | 1,495,963 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed interim financial statements.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Note | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won except per share data) | |
| Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Contents revenue | | 3,4 | | ₩ | | | 530 | | | | - | |
| Cost of revenues | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Gross profit | | | | | | | 530 | | | | - | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | | | | | (169,175 | ) | | | (185,898 | ) |
| Other income | | | | | | | 1 | | | | 209 | |
| Other expenses | | | | | | | (30,030 | ) | | | - | |
| Operating loss | | | | | | | (198,674 | ) | | | (185,689 | ) |
| Finance income | | | | | | | 28,832 | | | | 47,051 | |
| - Related parties | | 12 | | | | | 22,410 | | | | 20,005 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 6,422 | | | | 27,046 | |
| Finance costs | | | | | | | (10,683 | ) | | | (1,000 | ) |
| Loss before income tax | | | | | | | (180,525 | ) | | | (139,638 | ) |
| Tax benefit (expense) | | 6 | | | | | (6,998 | ) | | | 13,483 | |
| Loss for the period | | | | ₩ | | | (187,523 | ) | | | (126,155 | ) |
| Other comprehensive loss | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Items that will not be reclassified to income or loss: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remeasurement of defined benefit liabilities | | | | | | | (8,957 | ) | | | - | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | ₩ | | | (196,480 | ) | | | (126,155 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed interim financial statements.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Note | | | | Share capital | | | Other components of equity | | | Retained earnings | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at January 1, 2023 | | | | ₩ | | | 10,000 | | | | (41,396 | ) | | | 1,331,237 | | | | 1,299,841 | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (126,155 | ) | | | (126,155 | ) |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (126,155 | ) | | | (126,155 | ) |
| Balance at June 30, 2023 | | | | ₩ | | | 10,000 | | | | (41,396 | ) | | | 1,205,082 | | | | 1,173,686 | |
| Balance at January 1, 2024 | | | | ₩ | | | 10,000 | | | | (81,522 | ) | | | 1,175,207 | | | | 1,103,685 | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (187,523 | ) | | | (187,523 | ) |
| Remeasurement of defined benefit liabilities | | | | | | | - | | | | (8,957 | ) | | | - | | | | (8,957 | ) |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | | | | - | | | | (8,957 | ) | | | (187,523 | ) | | | (196,480 | ) |
| Balance at June 30, 2024 | | | | ₩ | | | 10,000 | | | | (90,479 | ) | | | 987,684 | | | | 907,205 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed interim financial statements.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Note | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | 11 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | | ₩ | | | (187,523 | ) | | | (126,155 | ) |
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash provided by operating activities
| | | | | | | 60,867 | | | | 344,128 | |
| Interest received | | | | | | | 266 | | | | 313 | |
| Income taxes refund (paid) | | | | | | | 12,607 | | | | (241,380 | ) |
| Dividend received | | | | | | | 941 | | | | 734 | |
| Net cash outflow from operating activities | | | | ₩ | | | (112,842 | ) | | | (22,359 | ) |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchase of long-term investment securities | | | | | | | (35,514 | ) | | | - | |
| Disposal of long-term investment securities | | | | | | | 44,709 | | | | 17,447 | |
| Purchase of property and equipment | | | | | | | - | | | | (70,400 | ) |
| Net cash inflow (outflow) in investing activities | | | | ₩ | | | 9,195 | | | | (52,953 | ) |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | 11 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Repayment of long-term borrowings | | | | | | | (80,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Net cash outflow in financing activities | | | | ₩ | | | (80,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | 1,060 | | | | 510 | |
| Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | (183,647 | ) | | | (75,313 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the period | | | | | | | 659,606 | | | | 473,696 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of the period | | | | ₩ | | | 477,019 | | | | 398,893 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed interim financial statements.
APEITDA CO., LTD
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
1. Reporting entity
The Company
Apeitda Co., Ltd. (“the Company”) was incorporated in January 2013 and the Company’s registered office is at 156, Ohyeon-ro, Gangbuk-gu, Seoul, Korea. The Company is primarily providing the media production service that consists of planning, producing, and selling the theatrical films and television programs. The Company is a specialized film production company with expertise in action and thriller genres.
The Company’s major shareholders and their respective percentage of ownership as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | Number of
shares | | | Ownership
(%) | | | Number of
shares | | | Ownership (%) | |
| Jung, Byung Gil | | | 9,000 | | | | 90 | % | | | 9,000 | | | | 90 | % |
| Seo, Sun Yeo | | | 1,000 | | | | 10 | % | | | 1,000 | | | | 10 | % |
| Total | | | 10,000 | | | | 100 | % | | | 10,000 | | | | 100 | % |
2. Basis of Presentation and Significant Accounting Policies
These condensed interim financial statements for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 have been prepared in accordance with International Accounting Standards (“IAS”) 34 Interim Financial Reporting as issued by International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”), and should be read in conjunction with the Company’s last annual financial statements as at and for the year ended December 31, 2023 (“last annual financial statements”). They do not include all of the information required for a complete set of financial statements prepared in accordance with IFRS. However, selected explanatory notes are included to explain events and transactions that are significant to an understanding of the changes in the Company’s financial position and performance since the last annual financial statements.
| B. | Material Accounting Policies |
Material accounting policies and method of computation used in the preparation of the condensed interim financial statements are consistent with those of the last annual financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2023, except for the changes as described below.
Income tax expense
Income tax expense for the interim period is recognized based on management’s best estimate of the weighted average annual income tax rate expected for the full financial year. The estimated average annual effective income tax rate is applied to the pre-tax income of the interim period.
APEITDA CO., LTD
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| i. | New and amended standards or interpretations adopted by the Company |
The Company has applied the following standards and interpretations for the first time for their annual reporting period commencing January 1, 2024.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements
The amendments to IAS 1 clarify that the classification of liabilities as current or non-current should be based on rights that are in existence at the end of the reporting period and that the classification is unaffected by management’s intentions or expectations about whether an entity will exercise its right to defer settlement of a liability. The amendments also introduce a definition of settlement to make clear that settlement includes the transfer to the counterparty of the entity’s own equity instruments, however, it would be excluded if an option to settle the liability by the transfer of the entity’s own equity instruments is recognized separately from the liability as an equity component of a compound financial instrument. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Company’s interim financial statements.
IAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows, and IFRS 7, Financial Instruments: Presentation
The amendments add to the disclosure objectives in IAS 7, Statement of Cash Flows, that information about supplier financing arrangements should be disclosed to enable users of financial statements to assess the impact of those arrangements on the Company’s liabilities and cash flows. The amendments also amend IAS 7, Financial Instruments: Presentation, to add supplier financing arrangements as an example of a requirement to disclose information about an entity’s exposure to concentrations of liquidity risk. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Company’s interim financial statements.
IAS 16 Leases
The amendments add requirements for the subsequent measurement of sale-and-leaseback transactions that are accounted for as sales in accordance with IAS 15, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. The amendments require the seller lessee to calculate the ‘lease payments’ or ‘revised lease payments’ in a way that does not result in the seller-lessee recognizing any gain or loss for the rights of use that the seller-lessee continues to retain after the lease commences. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Company’s interim financial statements.
| ii. | New and amended standards or interpretations not yet adopted by the Company |
The following new accounting standards and interpretations that have been published that are not mandatory for June 30, 2024 reporting periods and have not been early adopted by the Company.
IAS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates
The amendments require exchangeability of two currencies should be assessed in order to clarify reporting of foreign currency transactions in the absence of normal-functioning foreign exchange market. The amendments also require applicable spot exchange rate should be determined when the assessment indicates two currencies lack exchangeability. The amendments are effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2025, with early application permitted.
APEITDA CO., LTD
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
The financial statements have been prepared on the historical cost basis except for the following items, which are measured on an alternative basis on each reporting date.
| Items | | Measurement bases |
| Financial instruments measured at fair value through profit or loss (“FVTPL”) | | Fair value |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | Present value |
3. Operating segments
The Company’s operating segments have been identified to be a single business unit, by which the Company provides media production services.
The following summary describes the operations of reportable segment.
| Operating segment | | Operations |
| Media Production | | Planning, producing, and selling the media content such as theatrical films and television programs |
The Company’s chief executive officer reviews the internal management reports at least quarterly.
Media production segment is managed and operated in Seoul, South Korea. The geographic information analyses the Company’s revenue by the customer’s country of domicile and other countries. In presenting the geographic information, segment revenue and non-current assets have been based on the geographic location of customers.
Summary of the Company’s operation by region based on the location of customers for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 530 | | | | - | |
Summary of the Company’s non-current assets based on the location as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 749,462 | | | | 809,720 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Revenues from major customers that amount to 10% or more of the Company’s revenue for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Customer A | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 530 | | | | - | |
| % | | | | | 100.0 | % | | | 0.0 | % |
4. Revenue
The Company generates revenue primarily through providing the services for planning, producing, and selling the media content such as theatrical films and television programs to third parties.
Revenue from contracts with customers for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Revenue from contracts with customers | | ₩ | | | 530 | | | | - | |
| B. | Disaggregation of revenue from contracts with customers |
In the following table, revenue from contracts with customers is disaggregated by major products and service lines and timing of revenue recognition.
Revenue from contracts with customers based on the service contract type and the timing of satisfaction of performance obligations for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Major products/service lines | | | | | | | | | | |
| Media production | | ₩ | | | 530 | | | | - | |
| Timing of revenue recognition | | | | | | | | | | |
| Over time | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | |
| At a point in time | | | | | 530 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 530 | | | | - | |
APEITDA CO., LTD
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
5. Employee benefits
Details of defined benefit liability recognized as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | ₩ | | | 149,700 | | | | 139,459 | |
The Company operates defined benefit plans as a retirement pension scheme. Defined benefit plans expose the Company to actuarial risks, such as longevity risk, currency risk, interest rate risk and market (investment) risk.
| A. | Movement in net defined benefit liability |
Details of reconciliation from the opening balances to the closing balances for the net defined benefit liability and its components as of June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Defined benefit obligation | | | Fair value of plan assets | | | Net defined Benefit liabilities | |
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | June 30,
2023 | | | June 30,
2024 | | | June 30,
2023 | | | June 30,
2024 | | | June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning Balance | | ₩ | | | 139,459 | | | | 80,707 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 139,459 | | | | 80,707 | |
| Included in profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current service cost | | | | | 7,156 | | | | 5,693 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 7,156 | | | | 5,693 | |
| Interest expense | | | | | 3,085 | | | | 2,165 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,085 | | | | 2,165 | |
| Ending Balance | | ₩ | | | 149,700 | | | | 88,565 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 149,700 | | | | 88,565 | |
There are no contributions funded to its defined benefit plans as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023.
| C. | Employee benefit expenses |
| i. | Details of employee benefit expenses recognized for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows: |
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Wages and salaries | | ₩ | | | 62,400 | | | | 62,886 | |
| Expenses related to post-employment plans | | | | | 10,241 | | | | 7,857 | |
| Fringe benefit | | | | | 3,232 | | | | 5,635 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 75,873 | | | | 76,378 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| ii. | Expenses are recognized in the condensed statements of comprehensive income (loss) as follows: |
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | ₩ | | | 75,873 | | | | 76,378 | |
6. Income taxes
Details of income tax expenses for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current tax expense | | | | | | | | | | |
| Adjustments recognized related to prior period incomes (*) | | ₩ | | | 184 | | | | 349 | |
| | | ₩ | | | 184 | | | | 349 | |
| Deferred tax income | | | | | | | | | | |
| Origination and reversal of temporary differences | | | | | 15,771 | | | | (13,832 | ) |
| Deferred taxes charged directly to equity | | | | | (8,957 | ) | | | - | |
| | | | | | 6,814 | | | | (13,832 | ) |
| Tax expense (benefit) on continuing operations | | ₩ | | | 6,998 | | | | (13,483 | ) |
| (*) | In the normal course of business, the Company is examined by taxing authority. Our management regularly assesses the potential outcomes of these examinations and any future examinations for the current or prior years in determining the adequacy of its liabilities for income taxes. |
The Company establishes additional current tax liabilities for income taxes when, despite the belief that tax positions are fully supportable, there remain positions that do not meet the minimum probability threshold, which is a tax position that is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by the applicable taxing authority. The impact of current tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions, as well as the related net interest and penalties, are included in income taxes in the statements of operations.
APEITDA CO., LTD
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
7. Capital and reserves
| A. | Share capital and share premium |
Details of share capital and share premium as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In Korean won and number of shares) | |
| Number of authorized shares | | | | | 40,000 | | | | 40,000 | |
| Value per share | | ₩ | | | 1,000 | | | | 1,000 | |
| Number of shares issued | | | | | 10,000 | | | | 10,000 | |
| Common shares | | ₩ | | | 10,000,000 | | | | 10,000,000 | |
| B. | Other components of equity |
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liability | | ₩ | | | (90,479 | ) | | | (81,522 | ) |
8. Borrowings
Borrowings as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current portion of long-term borrowings, net | | ₩ | | | 20,000 | | | | 100,000 | |
| A. | Terms and repayment schedule |
The terms and conditions of outstanding borrowings as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| | | Currency | | | Nominal interest rate | | | Maturity | | | Face
value | | | Carrying
amount | | | Face
value | | | Carrying
amount | |
| Unsecured borrowings | | KRW | | | - | | | 30-Sep-24 | | | | 20,000 | | | | 20,000 | | | | 100,000 | | | | 100,000 | |
| Total interest-bearing liabilities | | | | 20,000 | | | | 20,000 | | | | 100,000 | | | | 100,000 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
9. Financial Instruments – Fair values and risk management
| A. | Accounting classifications and fair values |
The following table shows the carrying amounts and fair values of financial assets and financial liabilities, including their levels in the fair value hierarchy. It does not include fair value information for financial assets and financial liabilities not measured at fair value if the carrying amount is a reasonable approximation of fair value.
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of June 30, 2024 are as follows:
| | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term investment securities | | | 77,496 | | | | 77,496 | | | | - | | | | - | |
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term investment securities | | | 93,219 | | | | 93,219 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| B. | Measurement of fair values |
Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows:
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 2: all inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable (either directly that is, prices, or indirectly that is, derived from prices) for the asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 3: unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. |
The fair value of financial instruments traded in an active market is determined based on the quoted market price as of the end of the reporting period. If the quoted prices are readily and regularly available through exchanges, sellers, brokers, industry groups, rating agencies or regulators and such prices represent actual market transactions that occur regularly between independent parties, they are considered active markets.
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market is determined using valuation techniques. These valuation techniques use as much market observable information as possible and use the least amount of company-specific information. At this time, if all the significant input variables required to measure the fair value are observable, the financial instruments are classified as Level 2.
If more than one significant input variable is not based on observable market information, the item is included in Level 3.
APEITDA CO., LTD
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
The valuation techniques used to measure the fair value of a financial instrument include:
| ● | Market price or dealer price of a similar financial instrument |
| ● | The fair value of derivative instruments is determined by discounting the amount to present value using the leading exchange rate as of the end of the reporting period |
10. Leases
The Company leases building. The leases typically run for a period of 5 years with an option to renew or terminate the lease after that date. The Company also leases vehicles and printer with contract terms of one year. These leases are short-term and/or leases of low-value items. The Company has elected not to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for these leases.
Information about leases for which the Company is a lessee is presented below.
Right-of-use assets related to leased properties that do not meet the definition of investment property are presented as property, plant and equipment.
Details of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities recognized in the statements of financial position as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Building) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Acquisition price | | ₩ | | | 259,838 | | | | 259,838 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | | | | | (83,148 | ) | | | (57,276 | ) |
| Net book value | | ₩ | | | 176,690 | | | | 202,562 | |
Changes in right-of-use assets for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning Balance | | ₩ | | | 202,562 | | | | 254,529 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (25,872 | ) | | | (25,872 | ) |
| Ending Balance | | ₩ | | | 176,690 | | | | 228,657 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Some property leases contain extension options exercisable by the Company. Where practicable, the Company seeks to include extension options in new leases to provide operational flexibility. The extension options held are exercisable only by the Company and not by the lessors. The Company assesses at the lease commencement date whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the extension options. The Company reassesses whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the options if there is a significant event or significant changes in circumstances within its control.
11. Statement of Cash flows
Adjustments for income and expenses from operating activities for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Depreciation | | ₩ | | | 36,944 | | | | 36,944 | |
| Impairment of prepayment | | | | | 30,000 | | | | - | |
| Gains on valuation of long-term investment securities | | | | | (4,156 | ) | | | (9,319 | ) |
| Losses on valuation of long-term investment securities | | | | | 10,683 | | | | 1,000 | |
| Gains on disposal of long-term investment securities | | | | | - | | | | (3,069 | ) |
| Gains on foreign currency translation | | | | | (1,059 | ) | | | (510 | ) |
| Interest income | | | | | (22,676 | ) | | | (33,419 | ) |
| Severance benefits | | | | | 10,241 | | | | 7,857 | |
| Dividend income | | | | | (941 | ) | | | (734 | ) |
| Tax expense (benefit) | | | | | 6,998 | | | | (13,483 | ) |
| Other bad debt expense | | | | | 30 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 66,064 | | | | (14,733 | ) |
Changes in assets and liabilities from operating activities for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | ₩ | | | (3,142 | ) | | | 137,250 | |
| Other current assets | | | | | (184 | ) | | | 1,534 | |
| Trade and other payables | | | | | (11 | ) | | | 732 | |
| Accounts receivable – net | | | | | - | | | | 213,419 | |
| Value added tax receivables | | | | | (1,860 | ) | | | 5,926 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (5,197 | ) | | | 358,861 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
The movements of liabilities to cash flows arising from financing activities for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Current portion of long-term borrowings, net | | | Long-term borrowings, excluding current portion, net | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at January 1, 2023 | | ₩ | | | 82,900 | | | | 100,000 | | | | 182,900 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Reclassification | | | | | 80,000 | | | | (80,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 162,900 | | | | 20,000 | | | | 182,900 | |
| Balance at June 30, 2023 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 182,900 | | | | 182,900 | |
| Balance at January 1, 2024 | | | | | 100,000 | | | | - | | | | 100,000 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Repayment of borrowings | | | | | (80,000 | ) | | | - | | | | (80,000 | ) |
| Balance at June 30, 2024 | | ₩ | | | 20,000 | | | | - | | | | 20,000 | |
12. Related parties
| A. | List of related parties |
List of related parties as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| Relationship | | Company |
| Key management personnel | | Jung, Byung Gil |
| Key management personnel | | Jung, Byung Shik |
| Other related parties | | Jung, Moon Young |
| Other related parties | | Dominico Inc. |
| B. | Transactions with related parties |
Details of transaction with related parties for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| Related party | | Name | | Interest income | | | Interest income | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties | | Jung, Moon Young | | | 22,410 | | | | 20,005 | |
| Total | | | 22,410 | | | | 20,005 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| C. | Account balances with related parties |
The balances of receivables and payables to related parties as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | Receivables | | | Borrowings | | | Other current non-financial
liabilities (*1) | | | Receivables | | | Borrowings | | | Other current non-financial
liabilities (*1) | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Jung, Byung Gil | ₩ | | - | | | | 20,000 | | | | 83,905 | | | | - | | | | 100,000 | | | | 83,905 | |
| Key management personnel | | Jung, Byung Shik | | | - | | | | - | | | | 45,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 45,000 | |
| Other related parties | | Jung, Moon Young (*2) | | | 600,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 600,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | | 600,000 | | | | 20,000 | | | | 128,905 | | | | 600,000 | | | | 100,000 | | | | 128,905 | |
| (*1) | The Company has entered into a service contract with the key management personnels and an unrelated film production company for the provision of services. Pursuant to this agreement, the key management personnels undertakes the provision of services while the Company acts in the capacity of an agency. The Company has received the service contract amount from the unrelated film production company during the year. As of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023, the outstanding amount payable to the key management personnels is related to this contract. In connection with this contract, the Company has neither recognized revenue from the received amount nor incurred expenses. |
| (*2) | This is the amount excluding the present value discount of 192,096 in thousands of Korean won (prior year: 214,506 in thousands of Korean won) for the lease deposit. |
| D. | Financial transactions with related parties |
Details of significant financial transactions with related parties for the years ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| Related party | | Name of related party | | | | Repayment | | | Repayment | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Jung, Byung Gil | | ₩ | | | 80,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 80,000 | | | | - | |
APEITDA CO., LTD
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| E. | Key management personnel compensation |
The compensation for the key management personnel for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Short-term employee benefits | | ₩ | | | 62,400 | | | | 53,400 | |
| Post-employment benefits | | | | | 10,241 | | | | 6,786 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 72,641 | | | | 60,186 | |
Compensation of the Company’s key management personnel includes salaries, non-cash benefits and contributions to a post-employment defined benefit plan.
13. Commitments
On September 14, 2023, an amendment was made to the equity interest exchange agreement, originally entered into on April 9, 2023, between the CEO, who is the dominant shareholder of the Company, and K Enter Holdings, Inc. for the purpose of listing on the NASDAQ through a merger with a SPAC company. The equity interest exchange agreement is effective on the date designated by K Enter Holdings, Inc. Upon the effective date, the CEO of the Company will exchange 5,100 shares with the equity interest of K Enter Holdings, Inc. Following the equity interest exchange transaction, the Company is expected to be a subsidiary of K Enter Holdings, Inc.
Report of Independent Auditors
To the management of
Apeitda Co., Ltd.
Opinion
We have audited the accompanying financial statements of Apeitda Co., Ltd. (the “Company”), which comprise the statements of financial position as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the related statements of comprehensive income, of changes in equity and of cash flows for the years then ended, including the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”).
In our opinion, the accompanying financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the years then ended in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
Basis for Opinion
We conducted our audit in accordance with auditing standards generally accepted in the United States of America (US GAAS). Our responsibilities under those standards are further described in the Auditors’ Responsibilities for the Audit of the Financial Statements section of our report. We are required to be independent of the Company and to meet our other ethical responsibilities, in accordance with the relevant ethical requirements relating to our audit. We believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our audit opinion.
Responsibilities of Management for the Financial Statements
Management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of the financial statements in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board, and for the design, implementation, and maintenance of internal control relevant to the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error.
In preparing the financial statements, management is responsible for assessing the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern for at least, but not limited to, twelve months from the end of the reporting period, disclosing, as applicable, matters related to going concern and using the going concern basis of accounting unless management either intends to liquidate the Company or to cease operations, or has no realistic alternative but to do so.
Auditors’ Responsibilities for the Audit of the Financial Statements
Our objectives are to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements as a whole are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error, and to issue an auditors’ report that includes our opinion. Reasonable assurance is a high level of assurance but is not absolute assurance and therefore is not a guarantee that an audit conducted in accordance with US GAAS will always detect a material misstatement when it exists. The risk of not detecting a material misstatement resulting from fraud is higher than for one resulting from error, as fraud may involve collusion, forgery, intentional omissions, misrepresentations, or the override of internal control. Misstatements are considered material if there is a substantial likelihood that, individually or in the aggregate, they would influence the judgment made by a reasonable user based on the financial statements.
In performing an audit in accordance with US GAAS, we:
| ● | Exercise professional judgment and maintain professional skepticism throughout the audit. |
| | | |
| ● | Identify and assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to fraud or error, and design and perform audit procedures responsive to those risks. Such procedures include examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. |
| | | |
| ● | Obtain an understanding of internal control relevant to the audit in order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control. Accordingly, no such opinion is expressed. |
| | | |
| ● | Evaluate the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonableness of significant accounting estimates made by management, as well as evaluate the overall presentation of the financial statements. |
| | | |
| ● | Conclude whether, in our judgment, there are conditions or events, considered in the aggregate, that raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern for a reasonable period of time. |
We are required to communicate with those charged with governance regarding, among other matters, the planned scope and timing of the audit, significant audit findings, and certain internal control-related matters that we identified during the audit.
| /s/ Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers | |
| | |
| Seoul, KOREA | |
| May 13, 2024 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | 14,16,18,21,23 | | ₩ | | | 659,606 | | | | 473,696 | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | 16,21 | | | | | - | | | | 500,000 | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | 13,16,21 | | | | | - | | | | 213,419 | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | 13,16,21 | | | | | 30 | | | | 30 | |
| Other current assets | | 12 | | | | | 2,164 | | | | 28,888 | |
| Value added tax receivable | | | | | | | 384 | | | | 6,806 | |
| Current tax assets | | | | | | | 8,289 | | | | - | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | | 670,473 | | | | 1,222,839 | |
| Long-term investment securities | | 16,21 | | | | | 93,219 | | | | 71,688 | |
| Property, plant and equipment including right-of-use assets | | 15,22 | | | | | 301,006 | | | | 377,465 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | 16,21 | | | | | 385,494 | | | | 344,131 | |
| - Related parties | | 24 | | | | | 385,494 | | | | 344,131 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | 12 | | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | |
| Deferred tax assets | | 11 | | | | | 15,771 | | | | - | |
| Total non-current assets | | | | | | | 825,490 | | | | 823,284 | |
| Total assets | | | | ₩ | | | 1,495,963 | | | | 2,046,123 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | 16,20,21 | | ₩ | | | 19,119 | | | | 90,479 | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | | | | | 133,700 | | | | 18,268 | |
| - Related parties | | 24 | | | | | 128,905 | | | | 13,750 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 4,795 | | | | 4,518 | |
| Contract liabilities | | 7 | | | | | - | | | | 90,000 | |
| Current portion of long-term borrowings, net | | 16,19,21,23 | | | | | 100,000 | | | | 82,900 | |
| - Related parties | | 24 | | | | | 100,000 | | | | 82,900 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Current tax liabilities | | | | | | | - | | | | 271,552 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | | 252,819 | | | | 553,199 | |
| Long-term borrowings, excluding current portion, net | | 16,19,21,23 | | | | | - | | | | 100,000 | |
| - Related parties | | 24 | | | | | - | | | | 100,000 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | 10 | | | | | 139,459 | | | | 80,707 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | 11 | | | | | - | | | | 12,376 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | | | | | 139,459 | | | | 193,083 | |
| Total liabilities | | | | ₩ | | | 392,278 | | | | 746,282 | |
| Equity | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital | | 17 | | ₩ | | | 10,000 | | | | 10,000 | |
| Other reserves | | 17 | | | | | (81,822 | ) | | | (41,396 | ) |
| Retained earnings | | | | | | | 1,175,207 | | | | 1,331,237 | |
| Total equity | | | | | | | 1,103,685 | | | | 1,299,841 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | | | | ₩ | | | 1,495,963 | | | | 2,046,123 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won except per share data) | |
| Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Contents revenue | | 6,7 | | ₩ | | | 90,000 | | | | 4,239,676 | |
| Cost of revenues | | 8 | | | | | (26,473 | ) | | | (3,952,025 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | | | | | 63,527 | | | | 287,651 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | 8 | | | | | (320,482 | ) | | | (226,861 | ) |
| - Related parties | | 24 | | | | | - | | | | (7,700 | ) |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | (320,483 | ) | | | (219,161 | ) |
| Other income | | 8 | | | | | 256 | | | | 1,280 | |
| Other expenses | | 8 | | | | | (526 | ) | | | (65,034 | ) |
| - Related parties | | 24 | | | | | - | | | | (65,000 | ) |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | (526 | ) | | | (34 | ) |
| Operating loss | | | | | | | (257,225 | ) | | | (2,964 | ) |
| Finance income | | 9,16 | | | | | 87,852 | | | | 24,127 | |
| - Related parties | | 24 | | | | | 41,362 | | | | 21,315 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 46,490 | | | | 2,812 | |
| Finance costs | | 9,16 | | | | | (1,269 | ) | | | (28,596 | ) |
| - Related parties | | 24 | | | | | - | | | | (275 | ) |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | (1,269 | ) | | | (28,321 | ) |
| Loss before income tax | | | | | | | (170,642 | ) | | | (7,433 | ) |
| Income tax benefit | | 11 | | | | | 14,612 | | | | 65,871 | |
| Profit (loss) for the year | | | | ₩ | | | (156,030 | ) | | | 58,438 | |
| Other comprehensive loss | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Items that will not be reclassified to income or loss: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remeasurement of defined benefit liabilities | | 10,17 | | | | | (40,126 | ) | | | (3,254 | ) |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the year | | | | ₩ | | | (196,156 | ) | | | 55,184 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | Share capital | | | Other components of equity | | | Retained earnings | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at January 1, 2022 | | | | ₩ | | | 10,000 | | | | (38,142 | ) | | | 1,272,799 | | | | 1,244,657 | |
| Total comprehensive income for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Profit for the year | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 58,438 | | | | 58,438 | |
| Remeasurement of defined benefit liabilities | | 17 | | | | | - | | | | (3,254 | ) | | | - | | | | (3,254 | ) |
| Total comprehensive income for the year | | | | | | | - | | | | (3,254 | ) | | | 58,438 | | | | 55,184 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | | | | ₩ | | | 10,000 | | | | (41,396 | ) | | | 1,331,237 | | | | 1,299,841 | |
| Balance at January 1, 2023 | | | | ₩ | | | 10,000 | | | | (41,396 | ) | | | 1,331,237 | | | | 1,299,841 | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the year | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (156,030 | ) | | | (156,030 | ) |
| Remeasurement of defined benefit liabilities | | 17 | | | | | - | | | | (40,126 | ) | | | - | | | | (40,126 | ) |
| Total comprehensive loss for the year | | | | | | | - | | | | (40,126 | ) | | | (156,030 | ) | | | (196,156 | ) |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | | | | ₩ | | | 10,000 | | | | (81,522 | ) | | | 1,175,207 | | | | 1,103,685 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | 23 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Profit (loss) for the year | | | | ₩ | | | (156,030 | ) | | | 58,438 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities | | | | | | | 260,798 | | | | (144,653 | ) |
| Interest received | | | | | | | 24,616 | | | | 1,660 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | | | - | | | | (275 | ) |
| Income taxes paid | | | | | | | (289,353 | ) | | | (251 | ) |
| Dividend received | | | | | | | 1,121 | | | | 606 | |
| Net cash outflow from operating activities | | | | ₩ | | | (158,848 | ) | | | (84,475 | ) |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Increase in other financial assets | | | | ₩ | | | - | | | | (345,000 | ) |
| Decrease in other financial assets | | | | | | | - | | | | 1,300 | |
| Disposal of short-term financial instruments | | | | | | | 500,000 | | | | - | |
| Purchase of short-term financial instruments | | | | | | | - | | | | (500,000 | ) |
| Purchase of long-term investment securities | | | | | | | (40,944 | ) | | | (107,769 | ) |
| Disposal of long-term investment securities | | | | | | | 38,989 | | | | 8,607 | |
| Purchase of property and equipment | | | | | | | (70,400 | ) | | | (17,514 | ) |
| Net cash inflow (outflow) in investing activities | | | | ₩ | | | 427,645 | | | | (960,376 | ) |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | 23 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment of long-term borrowings | | | | ₩ | | | (82,900 | ) | | | - | |
| - Related parties | | | | | | | (82,900 | ) | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Repayment of lease liabilities | | | | | | | - | | | | (7,425 | ) |
| Net cash outflow in financing activities | | | | ₩ | | | (82,900 | ) | | | (7,425 | ) |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | 13 | | | | (301 | ) |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | 185,897 | | | | (1,052,276 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the year | | 14 | | | | | 473,696 | | | | 1,526,273 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of the year | | 14 | | ₩ | | | 659,606 | | | | 473,696 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
1. Reporting entity
The Company
Apeitda Co., Ltd. (“the Company”) was incorporated in January 2013 and the Company’s registered office is at 156, Ohyeon-ro, Gangbuk-gu, Seoul, Korea. The Company is primarily providing the media production service that consists of planning, producing, and selling the theatrical films and television programs. The Company is specialized film production company with expertise in action and thriller genres.
The Company’s major shareholders and their respective percentage of ownership as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | Number of
shares | | | Ownership (%) | | | Number of
shares | | | Ownership (%) | |
| Jung, Byung Gil | | | 9,000 | | | | 90 | % | | | 9,000 | | | | 90 | % |
| Seo, Sun Yeo | | | 1,000 | | | | 10 | % | | | 1,000 | | | | 10 | % |
| Total | | | 10,000 | | | | 100 | % | | | 10,000 | | | | 100 | % |
2. Basis of Accounting
These financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) as issued by International Accounting Standard Board (“IASB”). These financial statements were authorized for issuance by the management on May 13, 2024.
Details of the Company’s accounting policies, including changes thereto, are included in Note 5.
Basis of measurement
The financial statements have been prepared on the historical cost basis except for the following items, which are measured on an alternative basis on each reporting date.
| Items | | Measurement bases |
| Financial instruments measured at fair value through profit or loss (“FVTPL”) | | Fair value |
3. Functional and presentation currency
These financial statements are presented in Korean Won, which the Company’s functional currency. All amounts have been rounded to the nearest thousand, unless otherwise indicated.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
4. Use of judgements and estimates
In preparing these financial statements, management has made judgements and estimates that affect the application of the Company’s accounting policies and the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
Estimates and underlying assumptions are reviewed on an ongoing basis. Revisions to estimates are recognized prospectively.
Information about judgements made in applying accounting policies that have the most significant effects on the amounts recognized in the financial statements is included in the following notes:
Note 5(C): revenue recognition: whether revenue from providing service is recognized over time or at a point in time; and
Note 22(A): lease term: whether the Company is reasonably certain to exercise extension options.
| B. | Assumptions and estimation uncertainties |
Information about assumptions and estimation uncertainties at the reporting date that have a significant risk of resulting in a material adjustment to the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities within the next financial year is included in the following notes:
| ● | Note 10(C) (i): measurement of defined benefit obligations: key actuarial assumptions; |
| ● | Note 11(A): uncertain tax treatments; |
| i. | Measurement of fair values |
A number of the Company’s accounting policies and disclosures require the measurement of fair values, for financial assets.
When measuring the fair value of a financial instruments measured at FVTPL, the Company uses observable market data as far as possible. Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows.
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
| ● | Level 2: inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly (i.e., as prices) or indirectly (i.e., derived from prices). |
| ● | Level 3: inputs for the asset or liability that are not based on observable market data (unobservable inputs). |
If the inputs used to measure the fair value of an asset or a liability fall into different levels of the fair value hierarchy, then the fair value measurement is categorized in its entirety in the same level of the fair value hierarchy as the lowest level input that is significant to the entire measurement.
The Company recognizes transfers between levels of the fair value hierarchy at the end of the reporting period during which the change has occurred.
Further information about the assumptions made in measuring fair values is included in the following notes:
| ● | Note 21(B): financial instruments. |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
5. Material accounting policies
The significant accounting policies followed by the Company in preparation of its financial statements are as follows:
| A. | New and amended standards or interpretations adopted by the Company |
The following new accounting standards and interpretations for the first time for their annual reporting period commencing January 1, 2023.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements - Disclosure of Accounting Policies
The amendments to IAS 1 define and require entities to disclose their material accounting policies. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 8 Accounting policies, changes in accounting estimates and errors - Definition of Accounting Estimates
The amendments define accounting estimates and clarify how to distinguish them from changes in accounting policies. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 12 Income Taxes - Deferred Tax related to Assets and Liabilities arising from a Single Transaction
The amendments include an additional condition to the exemption to initial recognition of an asset or liability that a transaction does not give rise to equal taxable and deductible temporary differences at the time of the transaction. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 12 Income Taxes – International Tax Reform – Pillar Two Model Rules
The amendments provide a temporary relief from the accounting for deferred taxes arising from legislation enacted to implement the Pillar Two model rules, which aim to reform international corporate taxation for multinational enterprises, and require disclosure of related current tax effects, etc. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
New Standard: IFRS 17 Insurance Contract
IFRS 17 Insurance Contracts replaces IFRS 4 Insurance Contracts. This Standard estimates future cash flows of an insurance contract and measures insurance liabilities using discount rates applied with assumptions and risks at the measurement date. The entity recognizes insurance revenue on an accrual basis including services (insurance coverage) provided to the policyholder by each annual period. In addition, investment components (Refunds due to termination/maturity) repaid to a policyholder even if an insured event does not occur, are excluded from insurance revenue, and insurance financial income or expense and the investment income or expense are presented separately to enable users of the information to understand the sources of income or expenses. This Standard do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| B. | New and and amended standards or interpretations not yet adopted |
The following new accounting standards and interpretations that have been published that are not mandatory for December 31, 2023 reporting periods and have not been early adopted by the Company.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements - Classification of Liabilities as Current or Non-current
The amendments clarify that liabilities are classified as either current or non-current, depending on the substantive rights that exist at the end of the reporting period. Classification is unaffected by the likelihood that an entity will exercise right to defer settlement of the liability or the expectations of management. Also, the settlement of liability includes the transfer of the entity’s own equity instruments, however, it would be excluded if an option to settle them by the entity’s own equity instruments if compound financial instruments is met the definition of equity instruments and recognized separately from the liability. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, and earlier application is permitted. The Company is in review for the impact of these amendments on the financial statements.
IAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows - IFRS 7 Financial Instruments: Disclosures – Supplier finance arrangements
When applying supplier finance arrangements, an entity shall disclose information about its supplier finance arrangements that enables users of financial statements to assess the effects of those arrangements on the entity’s liabilities and cash flows and on the entity’s exposure to liquidity risk. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, and earlier application is permitted. The Company does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 21 The effects of changes in foreign exchange rates - Lack of Exchangeability
The amendments add requirements to help entities to determine whether a currency is exchangeable into another currency at a measurement date for a specified purpose and the spot exchange rate to use when it is not. A currency is exchangeable when there is an ability to obtain the other currency (with a normal administrative delay), and the transaction would take place through a market or exchange mechanism that creates enforceable rights and obligations. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2025, and earlier application is permitted. The Company does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IFRS 16 – Lease Liability in a Sale and Leaseback
When subsequently measuring lease liabilities arising from a sale and leaseback, a seller-lessee shall determine lease payments or revised lease payments in a way that the seller-lessee would not recognize any amount of the gain or loss that relates to the right of use retained by the seller-lessee. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, and earlier application is permitted. The Company does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
IFRS 18 Presentation and Disclosure in Financial Statements
Items in the statement of profit or loss will need to be classified into one of five categories: operating, investing, financing, income taxes and discontinued operations. IFRS 18 requires the Company to present specified totals and subtotals: ‘Operating profit or loss’, ‘Profit or loss’ and ‘Profit or loss before financing and income taxes’. Information related to management-defined performance measures should be disclosed. IFRS 18 also provides enhanced guidance on the principles of aggregation and disaggregation which focus on grouping items based on their shared characteristics. The new standard should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2027, and earlier application is permitted. The Company is in review for the impact of this new standard on the financial statements.
Transactions in foreign currencies are translated into the functional currency of Company at the exchange rates at the dates of the transactions.
Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are translated into the functional currency at the exchange rate at the reporting date. Non-monetary assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value in a foreign currency are translated into the functional currency at the exchange rate when the fair value was determined. Non-monetary items that are measured based on historical cost in a foreign currency are translated at the exchange rate at the date of the transaction. Foreign currency differences are generally recognized in profit or loss and presented within finance costs. Translation differences on non-monetary assets and liabilities carried at fair value are reported as part of the fair value gain or loss.
| D. | Revenue from contracts with customers |
The Company generates revenue primarily through providing the media production service.
The Company determines revenue recognition by:
| ● | identifying the contract, or contracts, with a customer; |
| ● | identifying the performance obligations in each contract; |
| ● | determining the transaction price; |
| ● | allocating the transaction price to the performance obligations in each contract; and |
| ● | recognizing revenue when, or as, we satisfy performance obligations by transferring the promised goods or services. |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Media production revenue
The Company operates the media production business that consists of planning, producing, and selling the theatrical films and television programs. The Company identifies the license which is provided along with media product as combined output and recognizes revenue over time by measuring its progress based on cost incurred towards complete satisfaction of the performance obligation in accordance with Paragraph 35 (2) of IFRS 15 Revenue from contracts with customers. The percentage-of-completion for each contract is calculated by dividing the cumulative cost incurred in relation to service performed by the Company by estimated total contract costs.
The Company recognizes unbilled receivables from media production service as contract assets and recognizes receipts in advance for prepaid media production services as contract liabilities. The Company capitalizes the cost associated with the production, including development costs, direct costs, and production overhead per title as prepayments and prepaid expenses. The Company amortizes the capitalized asset in ‘Cost of revenues’ on the statements of comprehensive income based on the percentage-of-completion for each contract.
In addition to media production revenue, according to the terms of the contract with the customer, the Company is providing additional cable TV rights for the produced film with no other goods or services to be transferred to the customer under the contract apart from the obligation to provide licenses. The license agreement pertains to the right to use the entity’s intellectual property as that intellectual property exists at the point in time. This means that at the time of transferring the license, the customer can instruct the use of the license and obtain most of the remaining benefits arising from the license. For the rights, revenue is recognized at the point when the rights become available for use after the execution of the rights usage agreement.
An operating segment is a component of the Company that engages in business activities from which it may earn revenues and incur expenses, including revenues and expenses that relate to transactions with any of the Company’s other components. The chief operating decision-maker has been identified as the chief executive officer. The Company’s operating segment has been determined to be a single business unit, for which the Company generates identifiable financial information that is regularly reported to the chief executive officer for the purpose of resource allocation and assessment of segment performance. The Company has a reportable segment as described in Note 6. Segment results that are reported to the chief operating decision maker include items directly attributable to a segment as well as those that can be allocated on a reasonable basis.
| i. | Short-term employee benefits |
Short-term employee benefits are employee benefits due to be settled within 12 months after the end of the period in which the employees render related services. When an employee has rendered a service to the Company during an accounting period, the Company recognizes the undiscounted amount of short-term employee benefits expected to be paid in exchange for that service
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The Company’s net obligation in respect of defined benefit plans is calculated separately for each plan by estimating the amount of future benefit that employees have earned in the current and prior periods, discounting that amount and deducting the fair value of any plan assets.
The calculation of defined benefit obligations is performed annually using the projected unit credit method. When the calculation results in a potential asset for the Company, the recognized asset is limited to the present value of economic benefits available in the form of any future refunds from the plan or reductions in future contributions to the plan. To calculate the present value of economic benefits, consideration is given to any applicable minimum funding requirements.
Remeasurements of the net defined benefit liability, which comprise actuarial gains and losses, the return on plan assets (excluding interest) and the effect of the asset ceiling (if any, excluding interest), are recognized immediately in OCI. The Company determines the net interest expense (income) on the net defined benefit liability (asset) for the period by applying the discount rate used to measure the defined benefit obligation at the beginning of the annual period to the then-net defined benefit liability (asset), taking into account any changes in the net defined benefit liability (asset) during the period as a result of contributions and benefit payments. Net interest expense and other expenses related to defined benefit plans are recognized in profit or loss.
When the benefits of a plan are changed or when a plan is curtailed, the resulting change in benefit that relates to past service or the gain or loss on curtailment is recognized immediately in profit or loss. The Company recognizes gains and losses on the settlement of a defined benefit plan when the settlement occurs.
| G. | Finance income and finance costs |
The Company’s finance income and finance costs include:
| ● | the net gain or loss on financial assets at FVTPL; |
| ● | the foreign currency gain or loss on financial assets and financial liabilities; |
The ‘effective interest rate’ is the rate that exactly discounts estimated future cash payments or receipts through the expected life of the financial instrument to:
| ● | the gross carrying amount of the financial asset; or |
| ● | the amortized cost of the financial liability. |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
In calculating interest income and expense, the effective interest rate is applied to the gross carrying amount of the asset (when the asset is not credit-impaired) or to the amortized cost of the liability. However, for financial assets that have become credit-impaired subsequent to initial recognition, interest income is calculated by applying the effective interest rate to the amortized cost of the financial asset. If the asset is no longer credit-impaired, then the calculation of interest income reverts to the gross basis.
Income tax expense comprises current and deferred tax. It is recognized in profit or loss except to the extent that it relates to a business combination, or items recognized directly in equity or in OCI.
The Company has determined that interest and penalties related to income taxes, including uncertain tax treatments, do not meet the definition of income taxes, and therefore accounted for them under IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets.
Current tax comprises the expected tax payable or receivable on the taxable income or loss for the year and any adjustment to the tax payable or receivable in respect of previous years. The amount of current tax payable or receivable is the best estimate of the tax amount expected to be paid or received that reflects uncertainty related to income taxes, if any. It is measured using tax rates enacted or substantively enacted at the reporting date. Current tax also includes any tax arising from dividends.
Current tax assets and liabilities are offset only if certain criteria are met.
| - | has a legally enforceable right to set off the recognized amounts; and |
| - | intends either to settle on a net basis, or to realize the asset and settle the liability simultaneously. |
Deferred tax is recognized in respect of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for taxation purposes. Deferred tax is not recognized for:
| ● | temporary differences on the initial recognition of assets or liabilities in a transaction that is not a business combination and that affects neither accounting nor taxable profit or loss; |
| ● | temporary differences related to investments in subsidiaries, associates and joint arrangements to the extent that the Company is able to control the timing of the reversal of the temporary differences and it is probable that they will not reverse in the foreseeable future; and |
| ● | taxable temporary differences arising on the initial recognition of goodwill. |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Deferred tax assets are recognized for unused tax losses, unused tax credits and deductible temporary differences to the extent that it is probable that future taxable profits will be available against which they can be used. Future taxable profits are determined based on the reversal of relevant taxable temporary differences. If the amount of taxable temporary differences is insufficient to recognize a deferred tax asset in full, then future taxable profits, adjusted for reversals of existing temporary differences, are considered, based on the business plans for individual subsidiaries in the Company. Deferred tax assets are reviewed at each reporting date and are reduced to the extent that it is no longer probable that the related tax benefit will be realized; such reductions are reversed when the probability of future taxable profits improves.
The measurement of deferred tax reflects the tax consequences that would follow from the manner in which the Company expects, at the reporting date, to recover or settle the carrying amount of its assets and liabilities. For this purpose, the carrying amount of investment property measured at fair value is presumed to be recovered through sale, and the Company has not rebutted this presumption.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are offset only if certain criteria are met.
| - | has a legally enforceable right to set off the recognized amounts; and |
| - | intends either to settle on a net basis, or to realize the asset and settle the liability simultaneously. |
| I. | Cash and cash Equivalents |
Cash and cash equivalents comprise cash on hand, deposits held at banks, and investment securities with maturities of three months or less from the acquisition date that are easily convertible to cash and subject to an insignificant risk of changes in their fair value.
| J. | Property, plant and equipment |
| i. | Recognition and measurement |
Items of property, plant and equipment are measured at cost, which includes capitalized borrowing costs, less accumulated depreciation and any accumulated impairment losses.
If significant parts of an item of property, plant and equipment have different useful lives, then they are accounted for as separate items (major components) of property, plant and equipment.
Any gain or loss on disposal of an item of property, plant and equipment is recognized in profit or loss.
| ii. | Subsequent expenditure |
Subsequent expenditure is capitalized only if it is probable that the future economic benefits associated with the expenditure will flow to the Company. The carrying amount of the replaced parts are derecognized and the repairs and maintenance expenses are recognized in profit or loss in the period they are incurred.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method to allocate the cost or revalued amounts of the assets, net of their residual values, over their estimated useful lives as follows:
| Vehicles | | 5 years | |
| Office equipment | | 5 years | |
| Right-of-use assets | | 1 – 5 years | |
Depreciation methods, useful lives and residual values are reviewed at each reporting date and adjusted if appropriate.
| i. | Recognition and initial measurement |
Trade receivables and debt securities issued are initially recognized when they are originated. All other financial assets and financial liabilities are initially recognized when the Company becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the instrument.
A financial asset (unless it is a trade receivable without a significant financing component) or financial liability is initially measured at fair value plus or minus, for an item not at FVTPL, transaction costs that are directly attributable to its acquisition or issue. A trade receivable without a significant financing component is initially measured at the transaction price.
| ii. | Classification and subsequent measurement |
Financial assets
On initial recognition, a financial asset is classified as measured at:
Financial assets are not reclassified subsequent to their initial recognition unless the Company changes its business model for managing financial assets, in which case all affected financial assets are reclassified on the first day of the first reporting period following the change in the business model.
A financial asset is measured at amortized cost if it meets both of the following conditions and is not designated as at FVTPL:
| ● | it is held within a business model whose objective is to hold assets to collect contractual cash flows; |
| ● | its contractual terms give rise on specified dates to cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
A debt investment is measured at FVOCI if it meets both of the following conditions and is not designated as at FVTPL;
| ● | it is held within a business model whose objective is achieved by both collecting contractual cash flows and selling financial assets; and |
| ● | its contractual terms give rise on specified dates to cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. |
On initial recognition of an equity investment that is not held for trading, the Company may irrevocably elect to present subsequent changes in the investment’s fair value in OCI. This election is made on an investment-by-investment basis.
All financial assets not classified as measured at amortized cost or FVOCI as described above are measured at FVTPL. This includes all derivative financial assets. On initial recognition, the Company may irrevocably designate a financial asset that otherwise meets the requirements to be measured at amortized cost or at FVOCI as at FVTPL if doing so eliminates or significantly reduces an accounting mismatch that would otherwise arise.
Financial assets - Business model assessment
The Company makes an assessment of the objective of the business model in which a financial asset is held at a portfolio level because this best reflects the way the business is managed and information is provided to management. The information considered includes:
| ● | the stated policies and objectives for the portfolio and the operation of those policies in practice. These include whether management’s strategy focuses on earning contractual interest income, maintaining a particular interest rate profile, matching the duration of the financial assets to the duration of any related liabilities or expected cash outflows or realizing cash flows through the sale of the assets; |
| ● | how the performance of the portfolio is evaluated and reported to the Company’s management; |
| ● | the risks that affect the performance of the business model (and the financial assets held within that business model) and how those risks are managed; |
| ● | how managers of the business are compensated - e.g. whether compensation is based on the fair value of the assets managed or the contractual cash flows collected; and |
| ● | the frequency, volume and timing of sales of financial assets in prior periods, the reasons for such sales and expectations about future sales activity. |
Transfers of financial assets to third parties in transactions that do not qualify for derecognition are not considered sales for this purpose, consistent with the Company’s continuing recognition of the assets.
Financial assets that are held for trading or are managed and whose performance is evaluated on a fair value basis are measured at FVTPL.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Financial assets - Assessment whether contractual cash flows are solely payments of principal and interest
For the purposes of this assessment, ‘principal’ is defined as the fair value of the financial asset on initial recognition. ‘Interest’ is defined as consideration for the time value of money and for the credit risk associated with the principal amount outstanding during a particular period of time and for other basic lending risks and costs (e.g. liquidity risk and administrative costs), as well as a profit margin.
In assessing whether the contractual cash flows are solely payments of principal and interest, the Company considers the contractual terms of the instrument. This includes assessing whether the financial asset contains a contractual term that could change the timing or amount of contractual cash flows such that it would not meet this condition. In making this assessment, the Company considers:
| ● | contingent events that would change the amount or timing of cash flows; |
| ● | terms that may adjust the contractual coupon rate, including variable-rate features; |
| ● | prepayment and extension features; and |
| ● | terms that limit the Company’s claim to cash flows from specified assets (e.g. non-recourse features). |
A prepayment feature is consistent with the solely payments of principal and interest criterion if the prepayment amount substantially represents unpaid amounts of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding, which may include reasonable compensation for early termination of the contract. Additionally, for a financial asset acquired at a discount or premium to its contractual par amount, a feature that permits or requires prepayment at an amount that substantially represents the contractual par amount plus accrued (but unpaid) contractual interest (which may also include reasonable compensation for early termination) is treated as consistent with this criterion if the fair value of the prepayment feature is insignificant at initial recognition.
Financial assets - Subsequent measurement and gains and losses
Financial assets at FVTPL: These assets are subsequently measured at fair value. Net gains and losses, including any interest or dividend income, are recognized in profit or loss.
Financial assets at amortized cost: These assets are subsequently measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. The amortized cost is reduced by impairment losses. Interest income, foreign exchange gains and losses and impairment are recognized in profit or loss. Any gain or loss on derecognition is recognized in profit or loss.
Financial liabilities - Classification, subsequent measurement and gains and losses
Financial liabilities are classified as measured at amortized cost or FVTPL. A financial liability is classified as at FVTPL if it is classified as held-for-trading, it is a derivative or it is designated as such on initial recognition. Financial liabilities at FVTPL are measured at fair value and net gains and losses, including any interest expense, are recognized in profit or loss. Other financial liabilities are subsequently measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. Interest expense and foreign exchange gains and losses are recognized in profit or loss. Any gain or loss on derecognition is also recognized in profit or loss.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Financial assets
The Company derecognizes a financial asset when:
| ● | the contractual rights to the cash flows from the financial asset expire; or |
| ● | it transfers the rights to receive the contractual cash flows in a transaction in which either: |
| - | substantially all of the risks and rewards of ownership of the financial asset are transferred; or |
| - | the Company neither transfers nor retains substantially all of the risks and rewards of ownership and it does not retain control of the financial asset. |
The Company enters into transactions whereby it transfers assets recognized in its statement of financial position, but retains either all or substantially all of the risks and rewards of the transferred assets. In these cases, the transferred assets are not derecognized.
Financial liabilities
The Company derecognizes a financial liability when its contractual obligations are discharged or cancelled, or expire. The Company also derecognizes a financial liability when its terms are modified and the cash flows of the modified liability are substantially different, in which case a new financial liability based on the modified terms is recognized at fair value.
On derecognition of a financial liability, the difference between the carrying amount extinguished and the consideration paid (including any non-cash assets transferred or liabilities assumed) is recognized in profit or loss. When changes were made to a financial asset or financial liability in addition to changes to the basis for determining the contractual cash flows required by interest rate benchmark reform, the Company first updated the effective interest rate of the financial asset or financial liability to reflect the change that is required by interest rate benchmark reform. After that, the Company applied the policies on accounting for modifications to the additional changes.
| i. | Non-derivative financial assets |
Financial instruments and contract assets
The Company recognizes loss allowances for ECLs on:
| ● | financial assets measured at amortized cost; and |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The Company also recognizes loss allowances for ECLs on lease receivables, which are disclosed as part of trade and other receivables.
The Company measures loss allowances at an amount equal to lifetime ECLs, except for the following, which are measured at 12-month ECLs:
| ● | debt securities that are determined to have low credit risk at the reporting date; and |
| ● | other debt securities and bank balances for which credit risk (i.e. the risk of default occurring over the expected life of the financial instrument) has not increased significantly since initial recognition. |
Loss allowances for trade receivables (including lease receivables) and contract assets are always measured at an amount equal to lifetime ECLs.
When determining whether the credit risk of a financial asset has increased significantly since initial recognition and when estimating ECLs, the Company considers reasonable and supportable information that is relevant and available without undue cost or effort. This includes both quantitative and qualitative information and analysis, based on the Company’s historical experience and informed credit assessment, that includes forward-looking information.
The Company assumes that the credit risk on a financial asset has increased significantly if it is more than 12 months past due.
The Company considers a financial asset to be in default when:
| ● | the debtor is unlikely to pay its credit obligations to the Company in full, without recourse by the Company to actions such as realizing security (if any is held). |
Lifetime ECLs are the ECLs that result from all possible default events over the expected life of a financial instrument.
12-month ECLs are the portion of ECLs that result from default events that are possible within the 12 months after the reporting date (or a shorter period if the expected life of the instrument is less than 12 months).
The maximum period considered when estimating ECLs is the maximum contractual period over which the Company is exposed to credit risk.
Measurement of ECLs
ECLs are a probability-weighted estimate of credit losses. Credit losses are measured as the present value of all cash shortfalls (i.e. the difference between the cash flows due to the entity in accordance with the contract and the cash flows that the Company expects to receive).
ECLs are discounted at the effective interest rate of the financial asset.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Credit-impaired financial assets
At each reporting date, the Company assesses whether financial assets carried at amortized cost are credit-impaired. A financial asset is ‘credit-impaired’ when one or more events that have a detrimental impact on the estimated future cash flows of the financial asset have occurred.
Evidence that a financial asset is credit-impaired includes the following observable data:
| ● | significant financial difficulty of the debtor; |
| ● | a breach of contract such as a default or being more than 90 days past due; |
| ● | the restructuring of a loan or advance by the Company on terms that the Company would not consider otherwise; |
| ● | it is probable that the debtor will enter bankruptcy or other financial reorganization; or |
| ● | the disappearance of an active market for a security because of financial difficulties. |
Presentation of allowance for ECL in the statement of financial position
Loss allowances for financial assets measured at amortized cost are deducted from the gross carrying amount of the assets.
Write-off
The gross carrying amount of a financial asset is written off when the Company has no reasonable expectations of recovering a financial asset in its entirety or a portion thereof. For individual customers, the Company has a policy of writing off the gross carrying amount when the financial asset is 180 days past due based on historical experience of recoveries of similar assets. For corporate customers, the Company individually makes an assessment with respect to the timing and amount of write-off based on whether there is a reasonable expectation of recovery. The Company expects no significant recovery from the amount written off. However, financial assets that are written off could still be subject to enforcement activities in order to comply with the Company’s procedures for recovery of amounts due.
At each reporting date, the Company reviews the carrying amounts of its non-financial assets (other than biological assets, investment property, developing contents, contract assets and deferred tax assets) to determine whether there is any indication of impairment. If any such indication exists, then the asset’s recoverable amount is estimated. Goodwill is tested annually for impairment.
For impairment testing, assets are grouped together into the smallest group of assets that generates cash inflows from continuing use that are largely independent of the cash inflows of other assets or CGUs. Goodwill arising from a business combination is allocated to CGUs or groups of CGUs that are expected to benefit from the synergies of the combination.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The recoverable amount of an asset or CGU is the greater of its value in use and its fair value less costs of disposal. Value in use is based on the estimated future cash flows, discounted to their present value using a pre-tax discount rate that reflects current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the asset or CGU.
An impairment loss is recognized if the carrying amount of an asset or CGU exceeds its recoverable amount.
Impairment losses are recognized in profit or loss. They are allocated first to reduce the carrying amount of any goodwill allocated to the CGU, and then to reduce the carrying amounts of the other assets in the CGU on a pro rata basis.
An impairment loss in respect of goodwill is not reversed. For other assets, an impairment loss is reversed only to the extent that the asset’s carrying amount does not exceed the carrying amount that would have been determined, net of depreciation or amortization, if no impairment loss had been recognized.
At inception of a contract, the Company assesses whether a contract is, or contains, a lease. A contract is, or contains, a lease if the contract conveys the right to control the use of an identified asset for a period of time in exchange for consideration.
At commencement or on modification of a contract that contains a lease component, the Company allocates the consideration in the contract to each lease component on the basis of its relative stand-alone prices. However, for the leases of property the Company has elected not to separate non-lease components and account for the lease and non-lease components as a single lease component.
The Company recognizes a right-of-use asset and a lease liability at the lease commencement date. The right-of-use asset is initially measured at cost, which comprises the initial amount of the lease liability adjusted for any lease payments made at or before the commencement date, plus any initial direct costs incurred and an estimate of costs to dismantle and remove the underlying asset or to restore the underlying asset or the site on which it is located, less any lease incentives received.
The right-of-use asset is subsequently depreciated using the straight-line method from the commencement date to the end of the lease term, unless the lease transfers ownership of the underlying asset to the Company by the end of the lease term or the cost of the right-of-use asset reflects that the Company will exercise a purchase option. In that case the right-of-use asset will be depreciated over the useful life of the underlying asset, which is determined on the same basis as those of property and equipment. In addition, the right-of-use asset is periodically reduced by impairment losses, if any, and adjusted for certain remeasurements of the lease liability.
The lease liability is initially measured at the present value of the lease payments that are not paid at the commencement date, discounted using the interest rate implicit in the lease or, if that rate cannot be readily determined, the Company’s incremental borrowing rate. Generally, the Company uses its incremental borrowing rate as the discount rate.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The Company determines its incremental borrowing rate by obtaining interest rates from various external financing sources and makes certain adjustments to reflect the terms of the lease and type of the asset leased.
Lease payments included in the measurement of the lease liability comprise the following:
| ● | fixed payments, including in-substance fixed payments; |
| ● | variable lease payments that depend on an index or a rate, initially measured using the index or rate as at the commencement date; |
| ● | amounts expected to be payable under a residual value guarantee; and |
| ● | the exercise price under a purchase option that the Company is reasonably certain to exercise, lease payments in an optional renewal period if the Company is reasonably certain to exercise an extension option, and penalties for early termination of a lease unless the Company is reasonably certain not to terminate early. |
The lease liability is measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. It is remeasured when there is a change in future lease payments arising from a change in an index or rate, if there is a change in the Company’s estimate of the amount expected to be payable under a residual value guarantee, if the Company changes its assessment of whether it will exercise a purchase, extension or termination option or if there is a revised in-substance fixed lease payment.
When the lease liability is remeasured in this way, a corresponding adjustment is made to the carrying amount of the right-of-use asset, or is recorded in profit or loss if the carrying amount of the right-of-use asset has been reduced to zero.
At the date of transition to IFRSs, The Company applies the following approach to all of its leases.
The Company measures that lease liability at the present value of the remaining lease payments, discounted using the lessee’s incremental borrowing rate at the date of transition to IFRSs.
The Company measures right-of-use asset at its carrying amount as if IFRS 16 had been applied since the commencement date of the lease, but discounted using the lessee’s incremental borrowing rate at the date of transition to IFRSs.
The Company uses hindsight in applying IFRS 16 such as the determination of lease term for contracts that contain options to extend or terminate a lease.
The Company has elected not to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for leases of low-value assets (leases for which the underlying asset is valued at USD 5,000 or less) and short-term leases (leases that have a lease term of 12 months or less at the commencement date), including IT equipment. The Company recognizes the lease payments associated with these leases as an expense on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
‘Fair value’ is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date in the principal or, in its absence, the most advantageous market to which the Company has access at that date. The fair value of a liability reflects its non-performance risk.
A number of the Company’s accounting policies and disclosures require the measurement of fair values, for both financial and non-financial assets and liabilities.
When one is available, the Company measures the fair value of an instrument using the quoted price in an active market for that instrument. A market is regarded as ‘active’ if transactions for the asset or liability take place with sufficient frequency and volume to provide pricing information on an ongoing basis.
If there is no quoted price in an active market, then the Company uses valuation techniques that maximize the use of relevant observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The chosen valuation technique incorporates all of the factors that market participants would take into account in pricing a transaction.
The best evidence of the fair value of a financial instrument on initial recognition is normally the transaction price - i.e. the fair value of the consideration given or received. If the Company determines that the fair value on initial recognition differs from the transaction price and the fair value is evidenced neither by a quoted price in an active market for an identical asset or liability nor based on a valuation technique for which any unobservable inputs are judged to be insignificant in relation to the measurement, then the financial instrument is initially measured at fair value, adjusted to defer the difference between the fair value on initial recognition and the transaction price. Subsequently, that difference is recognized in profit or loss on an appropriate basis over the life of the instrument but no later than when the valuation is wholly supported by observable market data or the transaction is closed out.
| O. | Concentration of Credit Risk |
The Company performs periodic credit evaluations of its customers’ financial condition and generally does not require collateral for customers on accounts receivable. The Company maintains reserves for potential credit losses, which are periodically reviewed.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
6. Operating segments
The Company’s operating segments have been identified to be a single business unit, by which the Company provides media production services.
The following summary describes the operations of each reportable segment.
| Operating segment | | Operations |
| Media Production | | Planning, producing, and selling the media content such as theatrical films and television programs |
The Company’s chief executive officer reviews the internal management reports at least quarterly.
| B. | Information about reportable segments |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Segment revenue | | ₩ | | | 90,000 | | | | 4,239,676 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (76,459 | ) | | | (32,762 | ) |
| Segment operating loss | | | | | (257,225 | ) | | | (2,964 | ) |
Media production segment is managed and operated in Seoul, South Korea. The geographic information analyses the Company’s revenue by the customer’s country of domicile and other countries. In presenting the geographic information, segment revenue and non-current assets have been based on the geographic location of customers.
Summary of the Company’s operation by region based on the location of customers for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| USA | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 4,224,676 | |
| Korea | | | | | 90,000 | | | | 15,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 90,000 | | | | 4,239,676 | |
Summary of the Company’s non-current assets based on the location as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 809,720 | | | | 823,284 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Revenues from major customers that amount to 10% or more of the Company’s revenue for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Customer A | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 4,224,676 | |
| % | | | | | - | | | | 99.6 | % |
| Customer B | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | | | | 90,000 | | | | - | |
| % | | | | | 100 | % | | | - | |
7. Revenue
The Company generates revenue primarily through providing the services for planning, producing, and selling the media content such as theatrical films and television programs to third parties.
Revenue from contracts with customers for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Revenue from contracts with customers | | ₩ | | | 90,000 | | | | 4,239,676 | |
| B. | Disaggregation of revenue from contracts with customers |
In the following table, revenue from contracts with customers is disaggregated by major products and service lines and timing of revenue recognition.
Revenue from contracts with customers based on the service contract type and the timing of satisfaction of performance obligations for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Major products/service lines | | | | | | | | | | |
| Media production | | ₩ | | | 90,000 | | | | 4,239,676 | |
| Timing of revenue recognition | | | | | | | | | | |
| Over time | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 4,224,676 | |
| At a point in time | | | | | 90,000 | | | | 15,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 90,000 | | | | 4,239,676 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The balance of accounts receivables and contract liabilities from contracts with customers as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Account receivables – trade, net | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 213,419 | |
| Contract liabilities | | | | | - | | | | 90,000 | |
The contract liabilities primarily relate to the advance consideration received from customers for media production. This will be recognized as revenue when the Company satisfies the performance obligations.
The amount of contract liabilities as of December 31, 2022 has been recognized as revenue in 2023 is 90,000 thousand won (2022: Korean Won 494,256 thousand).
8. Income and Expenses
Details of other income for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Miscellaneous income | | ₩ | | | 256 | | | | 1,280 | |
Details of other expenses for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Impairment of prepaid expenses (*) | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 65,000 | |
| Miscellaneous expenses | | | | | 526 | | | | 34 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 526 | | | | 65,034 | |
| (*) | A full impairment was recognized in the previous period due to the discontinuation of the project. |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Details of classification of expenses by nature for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Subcontracted production and operating services | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 3,656,003 | |
| Employee benefits | | | | | 141,708 | | | | 122,449 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | 76,459 | | | | 32,762 | |
| Actor’s appearance fee | | | | | 19,300 | | | | 110 | |
| Staff and equipment, etc | | | | | 4,131 | | | | 281,729 | |
| Transportation | | | | | 26,261 | | | | 15,958 | |
| Rent | | | | | - | | | | 4,998 | |
| Entertainment | | | | | 20,250 | | | | 20,085 | |
| Supplies | | | | | 11,352 | | | | 24,770 | |
| Vehicle maintenance | | | | | 3,141 | | | | 6,832 | |
| Other | | | | | 44,353 | | | | 33,275 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 346,955 | | | | 4,178,886 | |
Total expenses consist of cost of revenues and selling, general and administrative expenses.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
9. Finance income and costs
Details of finance income and costs for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Finance income | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | ₩ | | | 65,979 | | | | 22,976 | |
| Dividend income | | | | | 1,121 | | | | 606 | |
| Unrealized gains on foreign currency translation | | | | | 13 | | | | - | |
| Gains on valuation of long-term instrument securities | | | | | 20,739 | | | | - | |
| Gains on disposal of long-term investment securities | | | | | - | | | | 545 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 87,852 | | | | 24,127 | |
| Finance costs | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expenses | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 275 | |
| Realized losses on foreign currency transaction | | | | | 106 | | | | - | |
| Unrealized losses on foreign currency transaction | | | | | - | | | | 301 | |
| Losses on valuation of long-term investment securities | | | | | 1,163 | | | | 28,020 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,269 | | | | 28,596 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
10. Employee benefits
Details of defined benefit liability recognized as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Defined benefit liability | | ₩ | | | 139,459 | | | | 80,707 | |
The Company operates defined benefit plans as a retirement pension scheme. Defined benefit plans expose the Company to actuarial risks, such as longevity risk, currency risk, interest rate risk and market (investment) risk.
| A. | Movement in net defined benefit asset (liability) |
Details of reconciliation from the opening balances to the closing balances for the net defined benefit liability and its components for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | Defined benefit obligation | | | Fair value of plan assets | | | Net defined benefit liabilities | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| Balance at January 1 | | ₩ | | | 80,706 | | | | 71,865 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 80,707 | | | | 71,865 | |
| Included in profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current service cost | | | | | 9,864 | | | | 9,562 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 9,863 | | | | 9,562 | |
| Interest cost | | | | | 4,354 | | | | 2,236 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,354 | | | | 2,236 | |
| Subtotal | | | | | 14,218 | | | | 11,798 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 14,217 | | | | 11,798 | |
| Included in OCI | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remeasurement loss(gain) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial assumption | | | | | 2,022 | | | | (15,999 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,022 | | | | (15,999 | ) |
| Adjustment based on experience | | | | | 42,513 | | | | 13,042 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 42,513 | | | | 13,042 | |
| Subtotal | | | | | 44,535 | | | | (2,957 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 44,535 | | | | (2,957 | ) |
| Balance at December 31 | | ₩ | | | 139,459 | | | | 80,706 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 139,459 | | | | 80,706 | |
There are no contributions funded to its defined benefit plans as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| C. | Defined benefit obligation |
Details of actuarial assumptions used for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Discount rate | | 4.60% | | 5.6% |
| Future salary growth | | 5.3%~7.4% | | 6.1%~8.2% |
Assumptions regarding future longevity and standard salary scale have been based on issued by Korea Insurance Development Institute.
As of December 31, 2023, the weighted-average duration of the defined benefit obligation was 9 years.
The Company measures the risk of actuarial assumption changes as a 1% fluctuation in the discount rate and future salary growth rate of the amounts of defined benefit obligation, which reflects the management’s assessment of the risk of actuarial assumption fluctuation that can reasonably occur. The impact of a 1% fluctuation in discount rates and future salary growth rates on the Company’s defined benefit obligation as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | Increased by 1% | | | Decreased by 1% | | | Increased by 1% | | | Decreased by 1% | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Discount rate | | ₩ | | | (11,682 | ) | | | 13,286 | | | | (6,921 | ) | | | 7,907 | |
| Future salary growth | | | | | 13,397 | | | | (11,983 | ) | | | 7,989 | | | | (7,111 | ) |
Although the analysis does not take account of the full distribution of cash flows expected under the plan, it does provide an approximation of the sensitivity of the assumptions shown.
| D. | Employee benefit expenses |
| i. | Details of employee benefit expenses recognized for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows: |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Wages and salaries | | ₩ | | | 117,300 | | | | 109,400 | |
| Defined benefits plan expenses | | | | | 14,218 | | | | 11,797 | |
| Fringe benefit | | | | | 10,190 | | | | 1,252 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 141,708 | | | | 122,449 | |
| ii. | Expenses are recognized in the statements of comprehensive income (loss) as follows: |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | ₩ | | | 141,708 | | | | 122,449 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
11. Income taxes
| A. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
| | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won and number of shares) | |
| Current tax expense | | | | | | | | |
| Current year | | | 8,217 | | | | 268,394 | |
| Adjustments recognized related to prior period incomes (*) | | | 910 | | | | 2,810 | |
| | | | 9,127 | | | | 271,204 | |
| Deferred tax income | | | | | | | | |
| Origination and reversal of temporary differences | | | (28,148 | ) | | | (330,866 | ) |
| Deferred taxes charged directly to equity | | | 4,409 | | | | (6,209 | ) |
| | | | (23,739 | ) | | | (337,075 | ) |
| Income tax benefit on continuing operations | | | (14,612 | ) | | | (65,871 | ) |
| (*) | In the normal course of business, the Company is examined by taxation authority. The Company’s management regularly assesses the potential outcomes of these examinations and any future examinations for the current or prior years in determining the adequacy of its liabilities for income taxes. |
The Company establishes additional current tax liabilities for income taxes when, despite the belief that tax positions are fully supportable, there remain positions that do not meet the minimum probability threshold, which is a tax position that is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by the applicable taxation authority. The impact of current tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions, as well as the related net interest and penalties, is included in income taxes in the statements of operations.
| B. | Amounts recognized in OCI |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Before tax | | | Tax (expense)
benefit | | | Net of tax | | | Before tax | | | Tax (expense)
benefit | | | Net of tax | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Items that will not be reclassified to profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liabilities | | ₩ | | | (44,535 | ) | | | 4,409 | | | | (40,126 | ) | | | 2,956 | | | | (6,209 | ) | | | (3,253 | ) |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| C. | Reconciliation of effective tax rate |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Loss before income tax | | ₩ | | | (170,642 | ) | | | (7,433 | ) |
| Tax at the statutory income tax rate | | | | | (16,894 | ) | | | (818 | ) |
| Adjustments: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Expenses not deductible for tax purposes | | | | | 1,310 | | | | 1,198 | |
| Tax credits | | | | | - | | | | (26,756 | ) |
| Adjustments recognized related to prior period incomes | | | | | 910 | | | | 2,810 | |
| Other (differences in tax rate, etc) | | | | | 62 | | | | (42,305 | ) |
| Income tax benefit | | ₩ | | | (14,612 | ) | | | (65,871 | ) |
| Effective income tax rate (*) | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| (*) | The effective tax rate is not calculated as the Company incurred a loss before income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. |
| D. | Movement in deferred tax balances |
| i. | Movement in deferred tax balances as of December 31, 2023 |
| | | | | Tax effect | |
| | | | | Beginning | | | Increase (decrease) | | | Ending | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Accounts receivable — Trade | | ₩ | | | (21,129 | ) | | | 21,129 | | | | - | |
| Prepayments | | | | | (5,509 | ) | | | 2,834 | | | | (2,675 | ) |
| Property, plant and equipment | | | | | (25,323 | ) | | | 3,111 | | | | (22,212 | ) |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | 25,331 | | | | (4,095 | ) | | | 21,236 | |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | | | | - | | | | (2,970 | ) | | | (2,970 | ) |
| Contract liabilities | | | | | 3,817 | | | | (6,290 | ) | | | (2,473 | ) |
| Short-term borrowings | | | | | (18,434 | ) | | | 18,107 | | | | (327 | ) |
| Long-term borrowings | | | | | 18,107 | | | | (18,107 | ) | | | - | |
| Withholdings | | | | | - | | | | 11,385 | | | | 11,385 | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | | | | 7,990 | | | | 5,817 | | | | 13,807 | |
| Others | | | | | 2,774 | | | | (2,774 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (12,376 | ) | | | 28,147 | | | | 15,771 | |
| Deferred tax assets (liabilities) | | ₩ | | | (12,376 | ) | | | 28,147 | | | | 15,771 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| ii. | Movement in deferred tax balances as of December 31, 2022 |
| | | | | Tax effect | |
| | | | | Beginning | | | Increase (decrease) | | | Ending | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Accounts receivable — Trade | | ₩ | | | - | | | | (21,129 | ) | | | (21,129 | ) |
| Prepaid expenses | | | | | (92,555 | ) | | | 92,555 | | | | - | |
| Prepayments | | | | | (5,643 | ) | | | 134 | | | | (5,509 | ) |
| Property, plant and equipment | | | | | (2,445 | ) | | | (22,878 | ) | | | (25,323 | ) |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | 3,853 | | | | 21,478 | | | | 25,331 | |
| Contract liabilities | | | | | (263,208 | ) | | | 267,025 | | | | 3,817 | |
| Short-term borrowings | | | | | (40,957 | ) | | | 22,523 | | | | (18,434 | ) |
| Long-term borrowings | | | | | 40,238 | | | | (22,131 | ) | | | 18,107 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 1,633 | | | | (1,633 | ) | | | - | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | | | | 15,811 | | | | (7,821 | ) | | | 7,990 | |
| Others | | | | | - | | | | 2,774 | | | | 2,774 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (343,273 | ) | | | 330,897 | | | | (12,376 | ) |
| Loss carried forward | | ₩ | | | 31 | | | | (31 | ) | | | - | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | ₩ | | | (343,242 | ) | | | 330,866 | | | | (12,376 | ) |
| E. | Deferred assets (liabilities) |
| i. | The timing of recovery of deferred tax assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows: |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Deferred tax assets | | | | | | | | | | |
| - Deferred tax assets to be recovered after more than 12 months | | ₩ | | | 35,043 | | | | 45,995 | |
| - Deferred tax assets to be recovered within 12 months | | | | | 11,385 | | | | 17,117 | |
| Sub-total | | | | | 46,428 | | | | 63,112 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| - Deferred tax liabilities to be recovered after more than 12 months | | | | | (25,182 | ) | | | (30,416 | ) |
| - Deferred tax liabilities to be recovered within 12 months | | | | | (5,475 | ) | | | (45,072 | ) |
| Sub-total | | | | | (30,657 | ) | | | (75,488 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets (liabilities), net | | ₩ | | | 15,771 | | | | (12,376 | ) |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
12. Other assets
Details of other assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current | | | | | | | | | | |
| Prepayments | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 26,473 | |
| Prepaid expenses | | | | | 2,164 | | | | 2,415 | |
| Non-current | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-current prepayments | | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 32,164 | | | | 58,888 | |
13. Trade and other receivables
Details of trade and other receivables as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Trade receivables | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable — Trade | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 213,419 | |
| Other receivables | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable — Other | | ₩ | | | 30 | | | | 30 | |
14. Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Deposits in banks | | ₩ | | | 645,917 | | | | 460,244 | |
| Foreign currency deposit in banks | | | | | 13,689 | | | | 13,452 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 659,606 | | | | 473,696 | |
The Company doesn’t have any restricted cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
15. Property, plant and equipment
| A. | Reconciliation of carrying amount |
Details of property, plant and equipment as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | Book value | | | Accumulated depreciation | | | Carrying amount | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Vehicles | | ₩ | | | 86,947 | | | | (52,925 | ) | | | 34,022 | |
| Office equipment | | | | | 16,778 | | | | (11,022 | ) | | | 5,756 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | | | | | 70,400 | | | | (11,734 | ) | | | 58,666 | |
| Right-of-use assets | | | | | 259,838 | | | | (57,276 | ) | | | 202,562 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 433,963 | | | | (132,957 | ) | | | 301,006 | |
| | | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | Book value | | | Accumulated depreciation | | | Carrying amount | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Vehicles | | ₩ | | | 86,947 | | | | (41,636 | ) | | | 45,311 | |
| Office equipment | | | | | 16,778 | | | | (9,553 | ) | | | 7,225 | |
| Construction in progress | | | | | 70,400 | | | | - | | | | 70,400 | |
| Right-of-use assets | | | | | 259,838 | | | | (5,309 | ) | | | 254,529 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 433,963 | | | | (56,498 | ) | | | 377,465 | |
Details of the changes in property and equipment for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Vehicles | | | Office
equipment | | | Furniture
and fixtures | | | Construction-
In progress | | | Right-of-Use
assets | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 45,311 | | | | 7,225 | | | | - | | | | 70,400 | | | | 254,529 | | | | 377,465 | |
| Replacement | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 70,400 | | | | (70,400 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (11,289 | ) | | | (1,469 | ) | | | (11,734 | ) | | | - | | | | (51,967 | ) | | | (76,459 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 34,022 | | | | 5,756 | | | | 58,666 | | | | - | | | | 202,562 | | | | 301,006 | |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Vehicles | | | Office
equipment | | | Construction-
In progress | | | Right-of-Use
assets | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 44,735 | | | | 2 | | | | - | | | | 17,737 | | | | 62,474 | |
| Acquisitions | | | | | 10,170 | | | | 7,345 | | | | 70,400 | | | | 259,838 | | | | 347,753 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (9,594 | ) | | | (122 | ) | | | - | | | | (23,046 | ) | | | (32,762 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 45,311 | | | | 7,225 | | | | 70,400 | | | | 254,529 | | | | 377,465 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The classification of depreciation expenses in the statements of comprehensive income for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | ₩ | | | 76,459 | | | | 32,762 | |
| B. | Leased property, plant and equipment |
The Company leased the building during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. As of December 31, 2023, Korean Won 202,562 thousand of right-of-use assets was recognized (December 31, 2022: Korean Won 254,529 thousand of building).
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
16. Financial instruments by category
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at amortized cost | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | | | 659,606 | | | | 473,696 | |
| Accounts receivable | | | | | 30 | | | | 213,449 | |
| Short-term financial instruments (*) | | | | | - | | | | 500,000 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | 385,494 | | | | 344,131 | |
| Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term investment securities | | | | | 93,219 | | | | 71,688 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,138,349 | | | | 1,602,964 | |
| (*) | Short-term financial instruments are consisted of time deposits. |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial liabilities at amortized cost | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables (*) | | ₩ | | | 19,119 | | | | 90,478 | |
| Current portion of long-term borrowings, net | | | | | 100,000 | | | | 82,900 | |
| Long-term borrowings, excluding current portion, net | | | | | - | | | | 100,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 119,119 | | | | 273,378 | |
| (*) | Trade and other payables that are not financial liabilities are excluded. |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| A. | Classification of investment assets |
The classification of investment assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current investments | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term financial instruments– at amortized cost (*) | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 500,000 | |
| Non-Current investments | | | | | | | | | | |
| Equity securities – at FVTPL | | ₩ | | | 93,219 | | | | 71,688 | |
| (*) | Short-term financial instruments are consisted of time deposits. |
| B. | Equity Securities as at FVTPL |
The Company recognized the investments shown below as equity securities at FVTPL because these equity securities represent investment that the Company intends to sell for strategic purposes.
| | | | | Fair value at
December 31,
2023 | | | Fair value at
December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Equity Securities (listed stocks) | | ₩ | | | 93,219 | | | | 71,688 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| C. | Net gains and losses by category of financial instruments |
The net gains and losses by category of financial instruments for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Financial assets at
amortized cost | | | Financial assets at fair
value through profit or loss | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest income | | ₩ | | | 65,979 | | | | - | | | | 65,979 | |
| Gain or loss on foreign currency transactions | | | | | (93 | ) | | | - | | | | (93 | ) |
| Gain or loss on valuation of long-term investment securities | | | | | - | | | | 19,576 | | | | 19,576 | |
| Dividend income | | | | | - | | | | 1,121 | | | | 1,121 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 65,886 | | | | 20,697 | | | | 86,583 | |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Financial assets at
amortized cost | | | Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest income | | ₩ | | | 22,976 | | | | - | | | | 22,976 | |
| Gain or loss on foreign currency transactions | | | | | (301 | ) | | | - | | | | (301 | ) |
| Gain or loss on disposal of long-term investment securities | | | | | - | | | | 545 | | | | 545 | |
| Gain or loss on valuation of long-term investment securities | | | | | - | | | | (28,020 | ) | | | (28,020 | ) |
| Dividend income | | | | | - | | | | 606 | | | | 606 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 22,675 | | | | (26,869 | ) | | | (4,194 | ) |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
17. Capital and reserves
| A. | Share capital and share premium |
Details of share capital and share premium as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In Korean won and number of shares) | |
| Number of authorized shares | | | | | 40,000 | | | | 40,000 | |
| Value per share | | ₩ | | | 1,000 | | | | 1,000 | |
| Number of shares issued | | | | | 10,000 | | | | 10,000 | |
| Common shares | | ₩ | | | 10,000,000 | | | | 10,000,000 | |
| B. | Other components of equity |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In Korean won and number of shares) | |
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liability | | ₩ | | | (81,522 | ) | | | (41,396 | ) |
18. Capital management
The Company’s policy is to maintain a strong capital base so as to maintain investor, creditor and market confidence and to sustain future development of the business. The Company monitors capital using a ratio of ‘net debt’ to ‘total equity’. Net debt is calculated as total liabilities (as shown in the statement of financial position) less cash and cash equivalents. The Company’s net debt to adjusted equity ratio as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows.
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In Korean won and number of shares) | |
| Total liabilities | | ₩ | | | 392,278 | | | | 746,281 | |
| Less: Cash and cash equivalents | | | | | (659,606 | ) | | | (473,696 | ) |
| Net debt | | ₩ | | | (267,328 | ) | | | 272,585 | |
| Total equity | | | | | 1,103,685 | | | | 1,299,842 | |
| Net debt to total equity ratio (*) | | | | | - | | | | 21 | % |
| (*) | The net debt to total equity ratio is not calculated as the Company’s net debt is negative for the year ended December 31, 2023. |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
19. Borrowings
Borrowings as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current portion of long-term borrowings, net | | ₩ | | | 100,000 | | | | 82,900 | |
| Total | | | | | 100,000 | | | | 82,900 | |
| Non-Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term borrowings, excluding current portion, net | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 100,000 | |
| Total | | | | | - | | | | 100,000 | |
| A. | Terms and repayment schedule |
The terms and conditions of outstanding borrowings as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| | | Currency | | | Nominal interest rate | | | Maturity | | | | Face value | | | Carrying amount | | | Face value | | | Carrying amount | |
| Unsecured borrowings | | KRW | | | - | | | - | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | 82,900 | | | | 82,900 | |
| Unsecured borrowings | | KRW | | | - | | | 30-Sep-24 | | | | | 100,000 | | | | 100,000 | | | | 100,000 | | | | 100,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 100,000 | | | | 100,000 | | | | 182,900 | | | | 182,900 | |
20. Trade and other payables
Trade and other payables as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other payable | | ₩ | | | 19,119 | | | | 90,479 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
21. Financial Instruments – Fair values and risk management
| A. | Accounting classifications and fair values |
The following table shows the carrying amounts and fair values of financial assets and financial liabilities, including their levels in the fair value hierarchy. It does not include fair value information for financial assets and financial liabilities not measured at fair value if the carrying amount is a reasonable approximation of fair value.
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| As of December 31, 2023 | | | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term investment securities | | ₩ | | | 93,219 | | | | 93,219 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 93,219 | |
| As of December 31, 2022 | | | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term investment securities | | ₩ | | | 71,688 | | | | 71,688 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 71,688 | |
| B. | Measurement of fair values |
Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows:
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical asset or liability. |
| ● | Level 2: all inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable (either directly that is, prices, or indirectly that is, derived from prices) for the asset or liability. |
| ● | Level 3: unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. |
The fair value of financial instruments traded in an active market is determined based on the quoted market price as of the end of the reporting period. If the quoted prices are readily and regularly available through exchanges, sellers, brokers, industry groups, rating agencies or regulators and such prices represent actual market transactions that occur regularly between independent parties, they are considered active markets.
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market is determined using valuation techniques. These valuation techniques use as much market observable information as possible and use the least amount of Company-specific information. At this time, if all the significant input variables required to measure the fair value are observable, the financial instruments are classified as Level 2.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
If more than one significant input variable is not based on observable market information, the item is included in Level 3.
The valuation techniques used to measure the fair value of a financial instrument include:
| ● | Market price or dealer price of a similar financial instrument |
| ● | The fair value of derivative instruments is determined by discounting the amount to present value using the leading exchange rate as of the end of the reporting period. |
| C. | Financial risk management |
The Company’s operating activities expose itself to a variety of financial risks: market risk, credit risk and liquidity risk from which the Company’s risk management program focuses on minimizing any adverse effects on its financial performance. The Company operates financial risk management policies and programs that closely monitor and respond to each risk factor.
Credit risk is the risk of financial loss to the Company if a customer or counterpart to a financial instrument fails to meet its contractual obligations and arises principally from the Company’s receivables from customers. In order to manage credit risk, the Company regularly evaluate the credit worthiness of each customer or counterparty considering the party’s financial information, past experience, its own trading records and other factors. In relation to the impairment of financial assets subsequent to initial recognition, the Company recognizes the changes in expected credit loss (“ECL”) in profit or loss at each reporting date. The carrying amount of a financial asset represents the maximum exposure to credit risk.
The maximum exposure to credit risk of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | | | 659,606 | | | | 473,696 | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | | | | - | | | | 500,000 | |
| Accounts receivable, net | | | | | 30 | | | | 213,449 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | 385,494 | | | | 344,131 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,045,130 | | | | 1,531,276 | |
Cash and cash equivalents and short-term financial instruments are deposited in financial institutions with strong credit rating.
The Company’s exposure to credit risk is influenced mainly by the individual characteristics of each customer. The Company has established a credit policy under which each new customer is analyzed individually before the Company’s standard payment and delivery terms and conditions are offered. The Company’s review includes external ratings, if they are available, financial statements, credit agency information, industry information and in some cases bank references.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The Company monitors customer credit risk, customers are grouped according to their credit characteristics, including whether they are an individual or a legal entity, their geographic location, industry, trading history with the Company and existence of previous financial difficulties. The Company does not require collateral in respect of trade and other receivables.
Expected credit losses (ECLs) and credit risk exposures for Accounts receivable as of December 31, 2022 are as follows:
| ① | Accounts receivable — trade |
| As of December 31, 2022 | | Expected loss rate | | | | | Carrying amount | | | Loss allowance | |
| | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Not due or overdue less than 90 days | | | 14.29 | % | | ₩ | | | 213,419 | | | | - | |
| More than 1 year | | | 100.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | | | | | ₩ | | | 213,419 | | | | - | |
| As of December 31, 2023 | | Expected loss rate | | | | | Carrying amount | | | Loss allowance | |
| | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Not due or overdue less than 90 days | | | 0.00 | % | | ₩ | | | 385,524 | | | | - | |
| More than 90 days ~ Less than 1year | | | 0.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| More than 1 year | | | 100.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | | | | | ₩ | | | 385,524 | | | | - | |
| As of December 31, 2022 | | Expected loss rate | | | | | Carrying amount | | | Loss allowance | |
| | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Not due or overdue less than 90 days | | | 0.00 | % | | ₩ | | | 344,161 | | | | - | |
| More than 90 days ~ Less than 1year | | | 0.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| More than 1 year | | | 100.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | | | | | ₩ | | | 344,161 | | | | - | |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Liquidity risk management includes the maintenance of sufficient cash and marketable securities, the availability of funds from appropriately committed credit lines, and the ability to settle market positions. Financial liabilities of the Company by maturity according to the remaining period from December 31, 2023 to the contractual maturity date are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | Carrying Amount | | | Less than 3 months | | | 3 months ~ 1 year | | | 1~2 years | | | 2~5 years | | | More than 5 years | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Non-derivative financial liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other payable (*) | | ₩ | | | 19,119 | | | | 19,119 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 19,119 | |
| Current portion of long-term borrowings, net | | | | | 100,000 | | | | - | | | | 100,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 100,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 119,119 | | | | 19,119 | | | | 100,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 119,119 | |
| (*) | Other payable excludes non-financial liabilities. |
Financial liabilities of the Company by maturity according to the remaining period from December 31, 2022 to the contractual maturity date are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | Carrying Amount | | | Less than 3 months | | | 3 months ~ 1 year | | | 1~2 years | | | 2~5 years | | | More than 5 years | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Non-derivative financial liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other payable (*) | | ₩ | | | 90,478 | | | | 90,478 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 90,478 | |
| Current portion of long-term borrowings, net | | | | | 82,900 | | | | - | | | | 82,900 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 82,900 | |
| Long-term borrowings, excluding current portion, net | | | | | 100,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 100,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 100,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 273,378 | | | | 90,478 | | | | 82,900 | | | | 100,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 273,378 | |
| (*) | Other payable excludes non-financial liabilities. |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The Company is exposed to foreign exchange risk arising from cash equivalents primarily with respect to the US Dollar. Financial assets are exposed to foreign currency risk as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| December 31, 2023 |
| (In U.S. Dollars) | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) |
| Assets in U.S. Dollars | | | Liabilities in U.S. Dollars | | | | Assets in Korean Won | | | Liabilities in Korean Won | |
| $ | 10,616 | | | | - | | ₩ | | | 13,689 | | | | - | |
| December 31, 2022 |
| (In U.S. Dollars) | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Assets in U.S. Dollars | | | Liabilities in U.S. Dollars | | | | Assets in Korean Won | | | Liabilities in Korean Won | |
| $ | 10,614 | | | | - | | ₩ | | | 13,452 | | | | - | |
The Company measures foreign exchange risk as a 10% fluctuation in the exchange rate of each foreign currency, which reflects the management’s assessment of the risk of exchange rate fluctuation that can be reasonably occur. The impact of a 10% fluctuation in foreign currency exchange rates on the Company’s profit or loss (before income tax effects) for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | Increased by
10% | | | Decreased by
10% | | | Decreased by
10% | | | Decreased by
10% | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| USD | | | 1,369 | | | | (1,369 | ) | | | 1,345 | | | | (1,345 | ) |
The sensitivity analysis is based on monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies other than the functional currency as of the end of the reporting period.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The Company’s marketable equity securities are susceptible to market price risk arising from the fluctuation in the price of the securities. The following table demonstrates the sensitivity analysis of a 10% change in the price of marketable equity securities on the Company’s statements of comprehensive income (before income tax effects) as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | Increased by 10% | | | Decreased by 10% | | | Increased by 10% | | | Decreased by 10% | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Gain (loss) on valuation of financial assets at fair value through profit or loss | | ₩ | | | 9,322 | | | | (9,322 | ) | | | 7,169 | | | | (7,169 | ) |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
22. Leases
The Company leases building. The leases typically run for a period of 5 years with an option to renew or terminate the lease after that date. The Company also leases vehicles and printer with contract terms of one year. These leases are short-term and/or leases of low-value items. The Company has elected not to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for these leases.
Information about leases for which the Company is a lessee is presented below.
Right-of-use assets related to leased properties that do not meet the definition of investment property are presented as property, plant and equipment.
Details of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities recognized in the statements of financial position as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Building) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Acquisition price | | ₩ | | | 259,838 | | | | 259,838 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | | | | | (57,276 | ) | | | (5,309 | ) |
| Net book value | | ₩ | | | 202,562 | | | | 254,529 | |
Changes in right-of-use assets for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 254,529 | | | | 17,737 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (51,967 | ) | | | (23,046 | ) |
| Acquisition | | | | | - | | | | 259,838 | |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 202,562 | | | | 254,529 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| ii. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
Amounts recognized in profit or loss for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest expense relating to lease liabilities (included in finance cost) | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 275 | |
| Expense relating to short-term leases | | | | | - | | | | 4,998 | |
| Expense relating to leases of low-value assets excluding short-term leases | | | | | - | | | | 220 | |
| iii. | Amounts recognized in statement of cash flows |
Amounts recognized in statements of cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total cash outflows of leases | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 12,918 | |
Some property leases contain extension options exercisable by the Company. Where practicable, the Company seeks to include extension options in new leases to provide operational flexibility. The extension options held are exercisable only by the Company and not by the lessors. The Company assesses at the lease commencement date whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the extension options. The Company reassesses whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the options if there is a significant event or significant changes in circumstances within its control.
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
23. Statement of Cash flows
Adjustments for income and expenses from operating activities for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Depreciation | | ₩ | | | 76,458 | | | | 32,762 | |
| Bad debt expenses | | | | | - | | | | 65,000 | |
| Gains on valuation of long-term investment securities | | | | | (20,739 | ) | | | - | |
| Losses on valuation of long-term investment securities | | | | | 1,163 | | | | 28,020 | |
| Gains on disposal of long-term investment securities | | | | | - | | | | (545 | ) |
| Gains on foreign currency translation | | | | | (13 | ) | | | - | |
| Losses on foreign currency translation | | | | | - | | | | 301 | |
| Interest expenses | | | | | - | | | | 275 | |
| Interest income | | | | | (65,979 | ) | | | (22,976 | ) |
| Severance benefits | | | | | 14,218 | | | | 11,797 | |
| Dividend income | | | | | (1,121 | ) | | | (606 | ) |
| Tax income | | | | | (14,611 | ) | | | (65,871 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (10,624 | ) | | | 48,157 | |
Changes in assets and liabilities from operating activities for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | ₩ | | | 115,433 | | | | 16,648 | |
| Other current assets | | | | | 26,724 | | | | 332,586 | |
| Trade and other payables | | | | | (959 | ) | | | (5,444 | ) |
| Accounts receivable | | | | | 213,419 | | | | (213,449 | ) |
| Value added tax receivable | | | | | 6,806 | | | | 81,106 | |
| Contract liabilities | | | | | (90,000 | ) | | | (404,256 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 271,423 | | | | (192,809 | ) |
Significant non-cash transactions for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Increase in accounts payable related to the acquisition of tangible assets | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 70,400 | |
| Increase in right-of-use assets due to lease agreements | | | | | - | | | | 259,838 | |
| Reclassification of long-term borrowings | | | | | 100,000 | | | | 82,900 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The movements of liabilities to cash flows arising from financing activities for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | Current portion of
long-term
borrowings, net | | | Long-term
borrowings, excluding current portion, net | | | Current lease liabilities | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at 1 January 2022 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 182,900 | | | | 7,425 | | | | 190,325 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (7,425 | ) | | | (7,425 | ) |
| Reclassification | | | | | 82,900 | | | | (82,900 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 82,900 | | | | (82,900 | ) | | | (7,425 | ) | | | (7,425 | ) |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 275 | | | | 275 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (275 | ) | | | (275 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Balance at 31 December 2022 | | ₩ | | | 82,900 | | | | 100,000 | | | | - | | | | 182,900 | |
| Balance at 1 January 2023 | | | | | 82,900 | | | | 100,000 | | | | - | | | | 182,900 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment of borrowings | | | | | (82,900 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (82,900 | ) |
| Reclassification | | | | | 100,000 | | | | (100,000 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 17,100 | | | | (100,000 | ) | | | - | | | | (82,900 | ) |
| Balance at 31 December 2023 | | ₩ | | | 100,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 100,000 | |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
24. Related parties
| A. | List of related parties |
List of related parties as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| Relationship | | Entity |
| Key management personnel | | Jung, Byung Shik |
| Key management personnel | | Jung, Byung Gil |
| Other related parties | | Jung, Moon Young |
| Other related parties | | Dominico Inc. |
| B. | Transactions with related parties |
Details of transaction with related parties for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| Related party | | Name of related party | | | | Interest Income | | | Purchases | | | Interest expense | | | Interest Income | | | Purchases | | | Interest expense | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties | | Jung, Moon Young | | ₩ | | | 41,362 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 21,315 | | | | 17,200 | | | | 275 | |
| Other related parties | | Dominico Inc. | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 65,000 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 41,362 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 21,315 | | | | 82,200 | | | | 275 | |
| C. | Account balances with related parties |
The balances of receivables and payables to related parties as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and are as follows:
| | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| Related party | | Name of
related party | | | | Receivables | | | Borrowings | | | Other current non-financial liabilities (*) | | | Receivables | | | Borrowings | | | Other current non-financial liabilities (*) | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Jung, Byung Gil | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 100,000 | | | | 83,905 | | | | - | | | | 182,900 | | | | 13,750 | |
| Key management personnel | | Jung, Byung Shik | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 45,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | Jung, Moon Young | | | | | 385,495 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 344,132 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 385,495 | | | | 100,005 | | | | 128,905 | | | | 344,132 | | | | 182,900 | | | | 13,750 | |
| (*) | The Company has entered into a service contract with the key management personnels and an unrelated film production company for the provision of services. Pursuant to this agreement, the key management personnels undertakes the provision of services while the Company acts in the capacity of an agency. The Company has received the service contract amount from the unrelated film production company during the year. As of December 31, 2023, the outstanding amount payable to the key management personnels is related to this contract. In connection with this contract, the Company has neither recognized revenue from the received amount nor incurred expenses. |
APEITDA CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| D. | Financial transactions with related parties |
Details of significant financial transactions with related parties for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| Related party | | Name of related party | | | | Payment of long-term borrowings | | | Leasehold deposit payment | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Jung, Byung Gil | | ₩ | | | 82,900 | | | | - | |
| Key management personnel | | Jung, Byung Shik | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | Jung, Moon Young | | | | | - | | | | 345,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 82,900 | | | | 345,000 | |
| E. | Key management personnel compensation |
The compensation for the key management personnel for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Short-term employee benefits | | ₩ | | | 111,300 | | | | 105,400 | |
| Post-employment benefits | | | | | 13,685 | | | | 11,458 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 124,985 | | | | 116,858 | |
Compensation of the Company’s key management personnel includes salaries, non-cash benefits and contributions to a defined benefit plan.
25. Commitments
On September 14, 2023, an amendment was made to the equity interest exchange agreement, originally entered into on April 9, 2023, between the CEO, who is the dominant shareholder of the Company, and K Enter Holdings, Inc. for the purpose of listing on the NASDAQ through a merger with a SPAC company. The equity interest exchange agreement is effective on the date designated by K Enter Holdings, Inc. Upon the effective date, the CEO of the Company will exchange 5,100 shares with the equity interest of K Enter Holdings, Inc. Following the equity interest exchange transaction, the Company is expected to be a subsidiary of K Enter Holdings, Inc.
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023
| | | Note | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | 12 | | ₩ | | | 1,750,107 | | | | 1,919,916 | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | | | | | | 1,155,690 | | | | 196,380 | |
| - Related parties | | | | | | | 20,000 | | | | 20,000 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 1,135,690 | | | | 176,380 | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | | | | | | 65,024 | | | | 7,287 | |
| - Related parties | | 13 | | | | | 1,127 | | | | 897 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 63,897 | | | | 6,390 | |
| Other current assets | | | | | | | 2,356,285 | | | | 2,270,256 | |
| Contract assets | | | | | | | 186,647 | | | | 158,697 | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | | 5,513,753 | | | | 4,552,536 | |
| Long-term loans, net | | 8 | | | | | 130,072 | | | | 130,087 | |
| - Related parties | | 13 | | | | | 130,072 | | | | 130,087 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Long-term investments | | 9 | | | | | 800,000 | | | | 800,000 | |
| - Related parties | | 13 | | | | | 800,000 | | | | 800,000 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Property, plant and equipment including right-of-use assets | | | | | | | 111,088 | | | | 374,001 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | | | 50,080 | | | | 147,406 | |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | | | | | | 1,428,585 | | | | 1,394,585 | |
| Deferred tax assets | | 6 | | | | | 86,957 | | | | 166,845 | |
| Total non-current assets | | | | | | | 2,606,782 | | | | 3,012,924 | |
| Total assets | | | | ₩ | | | 8,120,535 | | | | 7,565,460 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | | | ₩ | | | 2,122,342 | | | | 1,999,967 | |
| - Related parties | | 13 | | | | | 1,160,900 | | | | 1,138,798 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 961,442 | | | | 861,169 | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | | | | | 157,887 | | | | 69,553 | |
| Contract liabilities | | | | | | | 2,512,874 | | | | 2,210,942 | |
| Short-term borrowings | | 8 | | | | | 1,475,000 | | | | 1,505,000 | |
| Current lease liabilities | | 8 | | | | | 26,099 | | | | 62,797 | |
| Current tax liabilities | | | | | | | 44,796 | | | | 61,453 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | | 6,338,998 | | | | 5,909,712 | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | 5 | | | | | 278,362 | | | | 258,999 | |
| Non-current contract liabilities | | | | | | | 900,000 | | | | 900,000 | |
| Other non-current provisions | | | | | | | - | | | | 3,471 | |
| Non-current lease liabilities | | 8 | | | | | 68,824 | | | | 267,583 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | | | | | 1,247,186 | | | | 1,430,053 | |
| Total liabilities | | | | ₩ | | | 7,586,184 | | | | 7,339,765 | |
| Equity | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital | | 7 | | ₩ | | | 78 | | | | 78 | |
| Other reserves | | 7 | | | | | (585,468 | ) | | | (585,468 | ) |
| Retained earnings | | | | | | | 1,119,741 | | | | 811,085 | |
| Total equity | | | | | | | 534,351 | | | | 225,695 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | | | | ₩ | | | 8,120,535 | | | | 7,565,460 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Note | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won except per share data) | |
| Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Media production revenue | | 3,4 | | ₩ | | | 12,531,677 | | | | 8,980,804 | |
| - Related parties | | 13 | | | | | 87,280 | | | | 253,538 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 12,444,397 | | | | 8,727,266 | |
| Cost of revenues | | | | | | | 11,590,383 | | | | 8,935,593 | |
| Gross profit | | | | | | | 941,294 | | | | 45,211 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | | | | | (465,430 | ) | | | (341,736 | ) |
| Other income | | | | | | | 18,670 | | | | 54,608 | |
| Other expenses | | | | | | | (45,930 | ) | | | (104,121 | ) |
| Operating profit(loss) | | | | | | | 448,604 | | | | (346,038 | ) |
| Finance income | | | | | | | 7,705 | | | | 33,878 | |
| - Related parties | | 13 | | | | | 214 | | | | 623 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 7,491 | | | | 33,255 | |
| Finance costs | | 8,10 | | | | | (66,078 | ) | | | (37,892 | ) |
| - Related parties | | 13 | | | | | (24,718 | ) | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | (41,360 | ) | | | (37,892 | ) |
| Income(loss) before income tax | | | | | | | 390,231 | | | | (350,052 | ) |
| Income tax benefit (expenses) | | 6 | | | | | (81,575 | ) | | | 39,538 | |
| Income(loss) for the period | | | | ₩ | | | 308,656 | | | | (310,514 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total comprehensive income(loss) for the period | | | | ₩ | | | 308,656 | | | | (310,514 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | | | Net parent
investment | | | Share
capital | | | Other
reserves | | | Retained earnings | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at January 1, 2023 | | ₩ | | | 1,874,660 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,874,660 | |
| Total comprehensive income for the period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Income(Loss) for the period | | | | | (334,810 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 24,296 | | | | (310,514 | ) |
| Total comprehensive income for the period | | | | | (334,810 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 24,296 | | | | (310,514 | ) |
| Transaction directly recognized in equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Capital distribution from the Parent company | | | | | (2,125,240 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (2,125,240 | ) |
| Capital re-organization | | | | | 585,390 | | | | 78 | | | | (585,468 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
| Balance at June 30, 2023 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 78 | | | | (585,468 | ) | | | 24,296 | | | | (561,094 | ) |
| Balance at January 1, 2024 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 78 | | | | (585,468 | ) | | | 811,085 | | | | 225,695 | |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Income(loss) for the period | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 308,656 | | | | 308,656 | |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the period | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 308,656 | | | | 308,656 | |
| Balance at June 30, 2024 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 78 | | | | (585,468 | ) | | | 1,119,741 | | | | 534,351 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Note | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | 12 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income(loss) for the period | | | | ₩ | | | 308,656 | | | | (310,514 | ) |
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss(profit) to net cash provided by operating activities | | 12 | | | | | (399,037 | ) | | | 1,485,135 | |
| Interest received | | | | | | | 1,037 | | | | 455 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | | | (41,717 | ) | | | (37,532 | ) |
| Income taxes paid | | | | | | | (18,345 | ) | | | (13,504 | ) |
| Net cash inflow(outflow) from operating activities | | | | ₩ | | | (149,406 | ) | | | 1,124,040 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Disposal of long-term investments | | | | ₩ | | | 1,197 | | | | - | |
| Payments for other financial assets | | | | | | | (22,285 | ) | | | (62,210 | ) |
| Proceeds from other financial assets | | | | | | | 66,555 | | | | 4,200 | |
| Disposal of long-term investments | | | | | | | - | | | | 330,546 | |
| Purchase of property and equipment | | | | | | | (9,946 | ) | | | - | |
| Net cash inflow from investing activities | | | | ₩ | | | 35,521 | | | | 272,536 | |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | 12 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Repayment short-term borrowings | | | | ₩ | | | (30,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Capital distribution to the Parent company | | | | | | | - | | | | (71,758 | ) |
| Repayment of lease liabilities | | | | | | | (25,924 | ) | | | (31,755 | ) |
| Net cash outflow from financing activities | | | | ₩ | | | (55,924 | ) | | | (103,513 | ) |
| Net increase(decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | (169,809 | ) | | | 1,293,063 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the period | | | | | | | 1,919,916 | | | | 942,954 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of the period | | | | ₩ | | | 1,750,107 | | | | 2,236,017 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
1. Reporting entity
The LAMP Co., Ltd.
On February 15, 2023, Pluto Co., Ltd. (formerly, The LAMP Co., Ltd.) (“Pluto” or “Parent”) announced the proposed plan (“the Separation Proposal”) to establish a new company, The LAMP Co., Ltd. (formerly, The LAMP Pictures Co., Ltd.) (the “Company”) through a spin-off of its media production business. Before the spin-off, Pluto produced television programs and feature films including “Commitment”, “Three Summer Night”, “Love, Lies”, “Taxi Driver”, “Samjin Company English Class”, “Life is beautiful”, and “Phantom”. Following the spin-off, the Company primarily engaged in the business of media production for theatrical films and television programs, and the surviving split, Pluto, continued to engage in the remaining investment properties leasing business. The Company was separated from the remaining businesses of Pluto through the spin-off that resulted in the transfer of the media production business. The spin-off will permit the Company to strengthen competitiveness and concentrate its financial resources solely on its own operations in media content production industry and increase transparency in governance and stability in management.
In accordance with the Separation Proposal, the Company’s common shares were distributed pro rata to the shareholders of Pluto. On March 31, 2023, the date of spin-off, the spin-off of media production business was completed. The Company’s registered office is at 35 Dosan-daero 26 gil, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Korea. Park Un Kyoung, the CEO of the Company, holds 100% of ownership of the Company.
2. Basis of Presentation and Material Accounting Policies
These condensed interim financial statements for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 have been prepared in accordance with International Accounting Standards (“IAS”) 34 Interim Financial Reporting as issued by International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”), and should be read in conjunction with the Company’s last annual financial statements as at and for the year ended December 31, 2023 (“last annual financial statements”). They do not include all of the information required for a complete set of financial statements prepared in accordance with IFRS. However, selected explanatory notes are included to explain events and transactions that are significant to an understanding of the changes in the Company’s financial position and performance since the last annual financial statements.
These condensed interim financial statements are presented in a combined basis whereby combining the Pluto’s standalone financial statements using historical results of operation, cashflows and assets and liabilities attributable to the media production division before the spin-off as at March 31, 2023 with the Company’s interim financial statements after the spin-off as at March 31, 2023. The Company accounts the spin-off as a capital re-organization. On the basis that there is no substantive economic change, the Company incorporated the assets and liabilities of the Pluto at their pre-transaction carrying amounts.
| B. | Material Accounting Policies |
Significant accounting policies and method of computation used in the preparation of the condensed interim financial statements are consistent with those of the last annual financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2023, except for the changes as described below.
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Income tax expense
Income tax expense for the interim period is recognized based on management’s best estimate of the weighted average annual income tax rate expected for the full financial year. The estimated average annual effective income tax rate is applied to the pre-tax income of the interim period.
| i. | New and amended standards or interpretations adopted by the Company |
The Company has applied the following standards and interpretations for the first time for their annual reporting period commencing January 1, 2024.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements
The amendments to IAS 1 clarify that the classification of liabilities as current or non-current should be based on rights that are in existence at the end of the reporting period and that the classification is unaffected by management’s intentions or expectations about whether an entity will exercise its right to defer settlement of a liability. The amendments also introduce a definition of settlement to make clear that settlement includes the transfer to the counterparty of the entity’s own equity instruments, however, it would be excluded if an option to settle the liability by the transfer of the entity’s own equity instruments is recognized separately from the liability as an equity component of a compound financial instrument. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Company’s interim financial statements.
IAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows, and IFRS 7, Financial Instruments: Presentation
The amendments add to the disclosure objectives in IAS 7, Statement of Cash Flows, that information about supplier financing arrangements should be disclosed to enable users of financial statements to assess the impact of those arrangements on the Company’s liabilities and cash flows. The amendments also amend IFRS 7, Financial Instruments: Presentation, to add supplier financing arrangements as an example of a requirement to disclose information about an entity’s exposure to concentrations of liquidity risk. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Company’s interim financial statements.
IAS 16 Leases
The amendments add requirements for the subsequent measurement of sale-and-leaseback transactions that are accounted for as sales in accordance with IFRS 15, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. The amendments require the seller lessee to calculate the ‘lease payments’ or ‘revised lease payments’ in a way that does not result in the seller-lessee recognizing any gain or loss for the rights of use that the seller-lessee continues to retain after the lease commences. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Company’s interim financial statements.
| ii. | New and amended standards or interpretations not yet adopted by the Company |
The following new accounting standards and interpretations that have been published that are not mandatory for June 30, 2024 reporting periods and have not been early adopted by the Company.
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
IAS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates
The amendments require exchangeability of two currencies should be assessed in order to clarify reporting of foreign currency transactions in the absence of normal-functioning foreign exchange market. The amendments also require applicable spot exchange rate should be determined when the assessment indicates two currencies lack exchangeability. The amendments are effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2025, with early application permitted. The Company does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IFRS 16 – Lease Liability in a Sale and Leaseback
When subsequently measuring lease liabilities arising from a sale and leaseback, a seller-lessee shall determine lease payments or revised lease payments in a way that the seller-lessee would not recognize any amount of the gain or loss that relates to the right of use retained by the seller-lessee. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2025, and earlier application is permitted. The Company does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IFRS 18 Presentation and Disclosure in Financial Statements
Items in the statement of profit or loss will need to be classified into one of five categories: operating, investing, financing, income taxes and discontinued operations. IFRS 18 requires the Company to present specified totals and subtotals: ‘Operating profit or loss’, ‘Profit or loss’ and ‘Profit or loss before financing and income taxes’. Information related to management-defined performance measures should be disclosed. IFRS 18 also provides enhanced guidance on the principles of aggregation and disaggregation which focus on grouping items based on their shared characteristics. The new standard should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2027, and earlier application is permitted. The Company is in review for the impact of this new standard on the financial statements.
The financial statements have been prepared on the historical cost basis except for the following items, which are measured on an alternative basis on each reporting date.
| Items | | Measurement bases |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | Present value |
| Financial instruments measured at fair value through profit or loss (“FVTPL”) | | Fair value |
3. Operating segments
The Company’s operating segments have been identified to be a single unit, by which the Company provides the services for media production.
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
The following summary describes the operations of each reportable segment.
| Reportable segments | | Operations |
| Media Production | | Media production revenue |
Media production is managed and operated in Seoul, Korea. The geographic information analyses the Company’s revenue by the Company’s country of domicile and other countries. In presenting the geographic information, segment revenue has been based on the geographic location of customers.
Summary of the Company’s operation by the region for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 12,531,677 | | | | 8,980,804 | |
Summary of the Company’s non-current assets based on the location as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 1,539,672 | | | | 1,768,586 | |
Revenues by major customers for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Customer A (Media production segment) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 8,060,225 | | | | 933,659 | |
| % | | | | | 64 | % | | | 10 | % |
| Customer B (Media production segment) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 3,920,905 | | | | - | |
| % | | | | | 31 | % | | | 0 | % |
| Customer C (Media production segment) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 225,337 | | | | 6,972,281 | |
| % | | | | | 2 | % | | | 78 | % |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 12,206,467 | | | | 7,905,940 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
4. Revenue
The Company generates revenue primarily through providing the services for production of feature films for initial exhibition in theaters and production of television programs to third parties for internal television and streaming services.
Revenue from contracts with customers for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Revenue from contracts with customers | | ₩ | | | 12,531,677 | | | | 8,980,804 | |
| B. | Disaggregation of revenue from contracts with customers |
In the following table, revenue from contracts with customers is disaggregated by major products and service lines and timing of revenue recognition. The table also includes a reconciliation of the disaggregated revenue with the Company’s reportable segment. (see Note 3)
Revenue from contracts with customers based on the service contract type and the timing of satisfaction of performance obligations for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Major products/service lines | | | | | | | | | | |
| Media production | | ₩ | | | 12,531,677 | | | | 8,980,804 | |
| Timing of revenue recognition | | | | | | | | | | |
| Over time | | | | | 12,531,677 | | | | 8,980,804 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
5. Employee benefits
Details of defined benefit liability recognized as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Defined benefit liability | | ₩ | | | 278,362 | | | | 258,999 | |
The Company operates defined benefit plans as a retirement pension scheme. Defined benefit plans expose the Company to actuarial risks, such as longevity risk, interest rate risk and market (investment) risk.
| A. | Movement in net defined benefit (asset) liability |
Details of reconciliation from the opening balances to the closing balances for the net defined benefit liability and its components as of June 30, 2024 and 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | Defined benefit obligation | | | Fair value of plan assets | | | Net defined benefit liabilities | |
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | June 30,
2023 | | | June 30,
2024 | | | June 30,
2023 | | | June 30,
2024 | | | June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning Balance | | ₩ | | | 258,999 | | | | 156,092 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 258,999 | | | | 156,092 | |
| Included in profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current service cost | | | | | 14,155 | | | | 10,186 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 14,155 | | | | 10,186 | |
| Interest cost | | | | | 5,208 | | | | 3,942 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 5,208 | | | | 3,942 | |
| Subtotal | | | | | 19,363 | | | | 14,128 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 19,363 | | | | 14,128 | |
| Ending Balance | | ₩ | | | 278,362 | | | | 170,220 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 278,362 | | | | 170,220 | |
There are no contributions funded to its defined benefit plans as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023.
| C. | Employee benefit expenses |
| i. | Details of employee benefit expenses recognized for the years ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows: |
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Wages and salaries | | ₩ | | | 1,150,528 | | | | 1,009,838 | |
| Fringe benefit | | | | | 36,408 | | | | 47,841 | |
| Expenses related to post-employment defined benefit plans | | | | | 19,363 | | | | 14,128 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,206,299 | | | | 1,071,807 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| ii. | Expenses are recognized in the statements of comprehensive income (loss) as follows: |
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cost of revenues | | ₩ | | | 963,539 | | | | 872,507 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | | | 242,760 | | | | 199,300 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,206,299 | | | | 1,071,807 | |
6. Income taxes
Details of income tax expenses (benefit) for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current tax expenses (benefit) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current year | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | |
| Adjustments recognized related to prior period incomes (*) | | | | | 1,687 | | | | 1,075 | |
| | | | | | 1,687 | | | | 1,075 | |
| Deferred tax expenses (benefit) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Origination and reversal of temporary differences | | ₩ | | | 79,888 | | | | (40,613 | ) |
| Deferred taxes charged directly to equity | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Income tax expenses (benefit) | | ₩ | | | 81,575 | | | | (39,538 | ) |
| (*) | In the normal course of business, the Company is examined by taxation authority. The Company’s management regularly assesses the potential outcomes of these examinations and any future examinations for the current or prior years in determining the adequacy of its liabilities for income taxes. |
The Company establishes additional current tax liabilities for income taxes when, despite the belief that tax positions are fully supportable, there remain positions that do not meet the minimum probability threshold, which is a tax position that is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by the applicable taxation authority. The impact of current tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions, as well as the related net interest and penalties, are included in income taxes in the statements of operations.
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
7. Capital and other reserves
Details of share capital as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In Korean won and number of shares) | |
| Number of authorized shares | | | | | 4,000 | | | | 4,000 | |
| Value per share | | ₩ | | | 1,000 | | | | 1,000 | |
| Number of shares issued | | | | | 78 | | | | 78 | |
| Common shares | | ₩ | | | 78,000 | | | | 78,000 | |
Holder of these shares is entitled to dividends as declared from time to time and are entitled to one vote per share at general meetings of the Company.
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other reserves | | ₩ | | | (585,468 | ) | | | (585,468 | ) |
Upon the spin-off, the aggregate net parent investment and accumulated other comprehensive income are reclassified to share capital and other reserves.
8. Borrowings/payable and Loans/receivable
Borrowings as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term borrowings | | ₩ | | | 1,475,000 | | | | 1,505,000 | |
| Lease liabilities (*) | | | | | 26,099 | | | | 62,797 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,501,099 | | | | 1,567,797 | |
| Non-Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Lease liabilities (*) | | ₩ | | | 68,824 | | | | 267,583 | |
| (*) | The interest rate related to lease liabilities reflects the incremental borrowing rate based on the Company’s credit. The amount of interest expense related to lease liabilities incurred during the year ended June 30, 2024 is Korean Won 4,389 thousand (June 30, 2023: Korean Won 5,759 thousand). Additionally, the amount of short-term lease payments and low-value assets lease payments not included in the measurement of lease liabilities during the year ended June 30, 2024 is Korean Won 2,254,156 thousand (June 30, 2023: Korean Won 1,103,558 thousand). |
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| A. | Terms and repayment schedule |
The terms and conditions of outstanding borrowings as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| (In thousands of Korean won) | | Currency | | | Nominal interest rate | | | Maturity | | | Face
value | | | Carrying
amount | | | Face
value | | | Carrying
amount | |
| Secured bank borrowings (*1) | | KRW | | | 4.56% | | | 09-May-25 | | | | 520,000 | | | | 520,000 | | | | 520,000 | | | | 520,000 | |
| Secured bank borrowings (*2) | | KRW | | | CD + 1.37% | | | 22-Sep-24 | | | | 955,000 | | | | 955,000 | | | | 985,000 | | | | 985,000 | |
| Total | | | | 1,475,000 | | | | 1,475,000 | | | | 1,505,000 | | | | 1,505,000 | |
| (*1) | The Company has received a payment guarantee of Korean Won 468,000 thousand from Korea Credit Guarantee Fund as of June 30, 2024(December 31, 2023: Korean Won 468,000 thousand). The Company is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 52,000 thousand by the CEO of the Company as of June 30, 2024(December 31, 2023: Korean Won 62,400 thousand). |
| (*2) | The Company is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand by the CEO of the Company as of June 30, 2024(December 31, 2023: Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand). The borrowing will be repaid in monthly installments of 5,000 thousand. |
| B. | Terms and collection schedule |
The terms and conditions of outstanding loans as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| | | Currency | | | Nominal interest rate | | | Maturity | | | Face
value | | | Carrying
amount | | | Face
value | | | Carrying
amount | |
| Falling Starlight | | KRW | | | - | | | - | | | | 120,054 | | | | 120,054 | | | | 120,054 | | | | 120,054 | |
| Park, Un Kyoung | | KRW | | | 4.60% | | | 16-Jan-25 | | | | 10,000 | | | | 10,017 | | | | 10,000 | | | | 10,033 | |
| Total | | | | 130,054 | | | | 130,071 | | | | 130,054 | | | | 130,087 | |
9. Financial Instruments – Fair values and risk management
| A. | Accounting classifications and fair values |
The following table shows the carrying amounts and fair values of financial assets and financial liabilities, including their levels in the fair value hierarchy. It does not include fair value information for financial assets and financial liabilities not measured at fair value if the carrying amount is a reasonable approximation of fair value.
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of June 30, 2024 are as follows:
| | | | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term investments | | ₩ | | 800,000 | | | | - | | | - | | | 800,000 | | | 800,000 | |
Carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term investments | | ₩ | | 800,000 | | | | - | | | - | | | 800,000 | | | 800,000 | |
| B. | Measurement of fair values |
Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows:
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 2: all inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable (either directly that is, prices, or indirectly that is, derived from prices) for the asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 3: unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. |
The fair value of financial instruments traded in an active market is determined based on the quoted market price as of the end of the reporting period. If the quoted prices are readily and regularly available through exchanges, sellers, brokers, industry groups, rating agencies or regulators and such prices represent actual market transactions that occur regularly between independent parties, they are considered active markets.
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market is determined using valuation techniques. These valuation techniques use as much market observable information as possible and use the least amount of Company-specific information. At this time, if all the significant input variables required to measure the fair value are observable, the financial instruments are classified as Level 2.
If more than one significant input variable is not based on observable market information, the item is included in Level 3.
If the information is insufficient to measure fair value of the project investment, the Company recognizes gain on project settlements when the accumulated settlements exceed the project investment’s original invested amount. Before exceeding the project investment’s original invested amount, the settlements are recognized as the return of original project investment. The Company recognizes the valuation loss of the project investment based on its judgment as to whether the total amount of production costs and distribution fees could exceed the shared profit.
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
10. Leases
The Company leases vehicles. The leases typically run for a period of 5 years, with an option to renew or terminate the lease after that date. The Company also leases a building and vehicles with contract terms of one year. This lease is short-term item. The Company has elected not to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for these leases. Information about leases for which the Company is a lessee is presented below.
Right-of-use assets related to leased properties that do not meet the definition of investment property are presented as property, plant and equipment.
Details of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities recognized in the statements of financial position as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Acquisition price) | | | | | | | | |
| Building | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 417,533 | |
| Vehicles | | | | | 143,262 | | | | 143,262 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 143,262 | | | | 560,795 | |
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Accumulated depreciation) | | | | | | | | |
| Building | | ₩ | | | - | | | | (200,123 | ) |
| Vehicles | | | | | (45,526 | ) | | | (31,272 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (45,526 | ) | | | (231,395 | ) |
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Net book value) | | | | | | | | |
| Building | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 217,410 | |
| Vehicles | | | | | 97,736 | | | | 111,990 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 97,736 | | | | 329,400 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Changes in right-of-use assets for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month period ended
June 30, 2024 | |
| | | | | Building | | | Vehicles | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 217,410 | | | | 111,990 | | | | 329,400 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (17,397 | ) | | | (14,254 | ) | | | (31,651 | ) |
| Termination of lease agreement | | | | | (200,013 | ) | | | - | | | | (200,013 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 97,736 | | | | 97,736 | |
| | | | | Six-month period ended
June 30, 2023 | |
| | | | | Building | | | Vehicles | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 259,163 | | | | 140,643 | | | | 399,806 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (20,821 | ) | | | (14,254 | ) | | | (35,075 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 238,342 | | | | 126,389 | | | | 364,731 | |
| ii. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
Amounts recognized in profit or loss for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest expense relating to lease liabilities (included in finance cost) | | ₩ | | | 4,389 | | | | 5,759 | |
| Expense relating to short-term leases and leases of low-value assets | | | | | 2,254,156 | | | | 1,103,558 | |
The Company has revised the expense relating to short-term leases for the six months ended June 30, 2023 to be consistent with the classification as of June 30, 2024.
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| iii. | Amounts recognized in statement of cash flows |
Amounts recognized in statement of cash flows for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total cash outflows of leases | | ₩ | | | 2,333,056 | | | | 942,376 | |
The Company has revised the expense relating to short-term leases for the six months ended June 30, 2023 to be consistent with the classification as of June 30, 2024.
Some property leases contain extension options exercisable by the Company. The Company reflected extension options in measuring the lease liabilities. The extension options held are exercisable only by the Company and not by the lessors. The Company assesses at the lease commencement date whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the extension options. The Company reassesses whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the options if there is a significant event or significant changes in circumstances within its control.
11. Commitments and contingencies
Key commitments the Company has entered into with financial institutions and others as of June 30, 2024 are as follows:
| Financial institutions | | Categories | | | | Credit limit | | | Disbursed borrowing amount | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Woori Bank | | Corporate operating borrowings (*1) | | ₩ | | | 520,000 | | | | 520,000 | |
| Woori Bank | | Corporate operating borrowings (*2) | | | | | 955,000 | | | | 955,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,475,000 | | | | 1,475,000 | |
| (*1) | The Company has received a guarantee of Korean Won 468,000 thousand from Korea Credit Guarantee Fund as of June 30, 2024. The Company is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 52,000 thousand by the CEO of the Company as of June 30, 2024. |
| (*2) | The Company is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand by the CEO of the Company as of June 30, 2024. |
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Key commitments the Company has entered into with financial institutions and others as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| Financial institutions | | Categories | | | | Credit limit | | | Disbursed borrowing amount | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Woori Bank | | Corporate operating borrowings (*1) | | ₩ | | | 520,000 | | | | 520,000 | |
| Woori Bank | | Corporate operating borrowings (*2) | | | | | 985,000 | | | | 985,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,505,000 | | | | 1,505,000 | |
| (*1) | The Company has received a guarantee of Korean Won 468,000 thousand from Korea Credit Guarantee Fund as of December 31, 2023. The company is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 62,400 thousand by the CEO of the Company as of December 31, 2023. |
| (*2) | The Company is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand by the CEO of the Company as of December 31, 2023. |
Details of guarantees received as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| Guaranteed by | | Details of guarantee | | | | Guarantee limit | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) |
| Korea credit guarantee fund | | Payment guarantee | | ₩ | | | 468,000 | | | | 468,000 | |
The Company is jointly and severally responsible for the repayment of the liabilities owed by the Pluto before the spin-off.
12. Statement of Cash flows
Adjustments for income and expenses from operating activities for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Depreciation | | ₩ | | | 37,512 | | | | 38,173 | |
| Bad debt expenses | | | | | 10,000 | | | | 100,000 | |
| Interest expenses | | | | | 66,078 | | | | 37,892 | |
| Interest income | | | | | (2,611 | ) | | | (2,548 | ) |
| Losses on disposal of Property, Plant & Equipment | | | | | 35,334 | | | | - | |
| Gain on project settlements | | | | | (1,197 | ) | | | (31,330 | ) |
| Reversal of losses on valuation of long-term investments | | | | | (3,897 | ) | | | - | |
| Gain on disposal of Right-of-use assets | | | | | (18,569 | ) | | | - | |
| Severance benefits | | | | | 19,363 | | | | 14,128 | |
| Income tax expenses (benefit) | | | | | 81,575 | | | | (39,537 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 223,588 | | | | 116,778 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Changes in assets and liabilities from operating activities for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | ₩ | | | 88,335 | | | | 53,359 | |
| Other current assets | | | | | (86,030 | ) | | | (76,449 | ) |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | | | | (44,000 | ) | | | (179,500 | ) |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | | | | (952,936 | ) | | | 117,755 | |
| Trade and other payables | | | | | 98,024 | | | | 547,512 | |
| Contract liabilities | | | | | 301,932 | | | | 836,963 | |
| Contract assets | | | | | (27,950 | ) | | | 68,717 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (622,625 | ) | | | 1,368,357 | |
Significant non-cash transactions for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Unsettled distribution to Pluto due to spin-off | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 2,053,480 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
The movements of liabilities to cash flows arising from financing activities for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Short-term
borrowings | | | Current lease
liabilities | | | Non-current lease liabilities | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at January 1, 2023 | | ₩ | | | 520,000 | | | | 60,522 | | | | 334,404 | | | | 914,926 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | - | | | | (31,755 | ) | | | - | | | | (31,755 | ) |
| Reclassification | | | | | - | | | | 33,167 | | | | (33,167 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 1,412 | | | | (33,167 | ) | | | (31,755 | ) |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | | | | | - | | | | 5,758 | | | | - | | | | 5,758 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | - | | | | (5,758 | ) | | | - | | | | (5,758 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Balance at June 30, 2023 | | ₩ | | | 520,000 | | | | 61,934 | | | | 301,237 | | | | 883,171 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at January 1, 2024 | | | | | 1,505,000 | | | | 62,797 | | | | 267,583 | | | | 1,835,380 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | - | | | | (25,924 | ) | | | - | | | | (25,924 | ) |
| Repayment of borrowings | | | | | (30,000 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (30,000 | ) |
| Reclassification | | | | | - | | | | 13,232 | | | | (13,232 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (30,000 | ) | | | (12,692 | ) | | | (13,232 | ) | | | (55,924 | ) |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | | | | | - | | | | 4,389 | | | | - | | | | 4,389 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | - | | | | (4,389 | ) | | | - | | | | (4,389 | ) |
| Termination of lease agreement | | | | | - | | | | (24,006 | ) | | | (185,527 | ) | | | (209,533 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | (24,006 | ) | | | (185,527 | ) | | | (209,533 | ) |
| Balance at June 30, 2024 | | ₩ | | | 1,475,000 | | | | 26,099 | | | | 68,824 | | | | 1,569,923 | |
13. Related parties
| A. | List of related parties |
List of related parties as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| Relationship | | Entity |
| Other related parties | | Falling Starlight Limited Company Specializing in The Cultural Industry (hereafter referred to as “Falling Starlight”) |
| Other related parties | | Pluto Co., Ltd. |
| Key management personnel | | Park, Un Kyoung |
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| B. | Transactions with related parties |
Details of transaction with related parties for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | Six-month period ended June 30, 2024 | | | Six-month period ended June 30, 2023 | |
| | | | | | | Revenue | | | Interest income | | | Interest expense | | | Revenue | | | Interest income | |
| | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties | | Falling Starlight | | ₩ | | | 87,280 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 253,538 | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | Pluto Co., Ltd. | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 24,718 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Key management personnel | | Park, Un Kyoung | | | | | - | | | | 214 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 623 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 87,280 | | | | 214 | | | | 24,718 | | | | 253,538 | | | | 623 | |
| C. | Account balances with related parties |
The balances of receivables and payables to related parties as of June 30, 2024 are as follows:
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Receivables | | | Loans | | | Project
investments | | | Payables | |
| Other related parties | | Falling Starlight | | ₩ | | | 20,000 | | | | 120,054 | | | | 800,000 | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | Pluto | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,160,900 | |
| Key management personnel | | Park, Un Kyoung | | | | | 1,127 | | | | 10,017 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 21,127 | | | | 130,071 | | | | 800,000 | | | | 1,160,900 | |
The balances of receivables and payables to related parties as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Receivables | | | Loans | | | Project
investments | | | Payables | |
| Other related parties | | Falling Starlight | | ₩ | | | 20,000 | | | | 120,054 | | | | 800,000 | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | Pluto | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,138,798 | |
| Key management personnel | | Park, Un Kyoung | | | | | 897 | | | | 10,033 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 20,897 | | | | 130,087 | | | | 800,000 | | | | 1,138,798 | |
| D. | Financing and investing transactions with related parties |
Details of significant financing and investing transactions with related parties for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | Six-month period ended
June 30, 2024 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | Increase in accrued income | |
| | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Park, Un Kyoung | | | 229 | |
| | | | | | Six-month period ended
June 30, 2023 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | Increase in accrued income | |
| | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Park, Un Kyoung | | | 226 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| E. | Commitments with related parties |
During the year ended December 31, 2022, the Company entered into an agreement with Falling Starlight for the production service and profit sharing.
As of June 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company has been satisfying its performance obligation for production service in accordance with the agreement and has received the consideration for the service provided. After the release of the content, the Company is entitled to share the profits in accordance with the agreed profit-sharing ratio.
The Company is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 1,252,000 thousand by the CEO of the Company as of June 30, 2024.
| F. | Transactions with key management personnel |
The compensation for the key management personnel for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Short-term employee benefits | | ₩ | | | 142,000 | | | | 94,500 | |
| Post-employment benefits | | | | | 13,804 | | | | 9,654 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 155,804 | | | | 104,154 | |
Compensation of the Company’s key management personnel includes salaries, non-cash benefits and contributions to a post-employment defined benefit plan.
14. Subsequent events
On September 20, 2024, the Company entered into an agreement to extend the maturity date of the secured bank borrowings of Korean Won 955,000 thousand to September 23, 2025.
Report of Independent Auditors
To the management of
The LAMP Co., Ltd.
Opinion
We have audited the accompanying financial statements of The LAMP Co., Ltd. (the “Company”), which comprise the statements of financial position as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the related statements of comprehensive income, of changes in equity and of cash flows for the years then ended, including the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”).
In our opinion, the accompanying financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the years then ended in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
Basis for Opinion
We conducted our audit in accordance with auditing standards generally accepted in the United States of America (US GAAS). Our responsibilities under those standards are further described in the Auditors’ Responsibilities for the Audit of the Financial Statements section of our report. We are required to be independent of the Company and to meet our other ethical responsibilities, in accordance with the relevant ethical requirements relating to our audit. We believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our audit opinion.
Responsibilities of Management for the Financial Statements
Management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of the financial statements in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board, and for the design, implementation, and maintenance of internal control relevant to the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error.
In preparing the financial statements, management is responsible for assessing the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern for at least, but not limited to, twelve months from the end of the reporting period, disclosing, as applicable, matters related to going concern and using the going concern basis of accounting unless management either intends to liquidate the Company or to cease operations, or has no realistic alternative but to do so.
Auditors’ Responsibilities for the Audit of the Financial Statements
Our objectives are to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements as a whole are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error, and to issue an auditors’ report that includes our opinion. Reasonable assurance is a high level of assurance but is not absolute assurance and therefore is not a guarantee that an audit conducted in accordance with US GAAS will always detect a material misstatement when it exists. The risk of not detecting a material misstatement resulting from fraud is higher than for one resulting from error, as fraud may involve collusion, forgery, intentional omissions, misrepresentations, or the override of internal control. Misstatements are considered material if there is a substantial likelihood that, individually or in the aggregate, they would influence the judgment made by a reasonable user based on the financial statements.
In performing an audit in accordance with US GAAS, we:
| ● | Exercise professional judgment and maintain professional skepticism throughout the audit. |
| | | |
| ● | Identify and assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to fraud or error, and design and perform audit procedures responsive to those risks. Such procedures include examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. |
| | | |
| ● | Obtain an understanding of internal control relevant to the audit in order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control. Accordingly, no such opinion is expressed. |
| | | |
| ● | Evaluate the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonableness of significant accounting estimates made by management, as well as evaluate the overall presentation of the financial statements. |
| | | |
| ● | Conclude whether, in our judgment, there are conditions or events, considered in the aggregate, that raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern for a reasonable period of time. |
We are required to communicate with those charged with governance regarding, among other matters, the planned scope and timing of the audit, significant audit findings, and certain internal control-related matters that we identified during the audit.
| /s/ Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers | |
| | |
| Seoul, KOREA | |
| May 13, 2024 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | 14,16,18,22,25 | | ₩ | | | 1,919,916 | | | | 942,954 | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | 7,13,16,22 | | | | | 196,380 | | | | 118,558 | |
| - Related parties | | 26 | | | | | 20,000 | | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 176,380 | | | | 118,558 | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | 13,16,22 | | | | | 7,287 | | | | 3,554 | |
| - Related parties | | 26 | | | | | 897 | | | | 437 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 6,390 | | | | 3,117 | |
| Short-term loans, net | | 16,19,22 | | | | | - | | | | 100,054 | |
| - Related parties | | 26 | | | | | - | | | | 100,054 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other current assets | | 12 | | | | | 2,270,255 | | | | 1,089,346 | |
| Contract assets | | 7 | | | | | 158,697 | | | | 130,588 | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | | 4,552,535 | | | | 2,385,054 | |
| Long-term loans, net | | 16,19,22 | | | | | 130,087 | | | | 10,063 | |
| - Related parties | | 26 | | | | | 130,087 | | | | 10,063 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Long-term investments | | 9,16,22 | | | | | 800,000 | | | | 1,096,100 | |
| - Related parties | | 26 | | | | | 800,000 | | | | 800,000 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | 296,100 | |
| Property, plant and equipment including right-of-use assets | | 15,23 | | | | | 374,000 | | | | 411,808 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | 16,22 | | | | | 147,406 | | | | 93,225 | |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | 12 | | | | | 1,394,586 | | | | 1,630,585 | |
| Deferred tax assets | | 11 | | | | | 166,846 | | | | 104,457 | |
| Total non-current assets | | | | | | | 3,012,925 | | | | 3,346,238 | |
| Total assets | | | | ₩ | | | 7,565,460 | | | | 5,731,292 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | 16,20 | | ₩ | | | 1,999,967 | | | | 350,011 | |
| - Related parties | | | | | | | 1,138,798 | | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 861,169 | | | | 350,011 | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | | | | | 69,553 | | | | 56,940 | |
| Contract liabilities | | 7 | | | | | 2,210,942 | | | | 1,430,167 | |
| Short-term borrowings | | 16,19,22 | | | | | 1,505,000 | | | | 520,000 | |
| Current lease liabilities | | 19,22,23 | | | | | 62,797 | | | | 60,522 | |
| Current tax liabilities | | 11 | | | | | 61,453 | | | | 45,047 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | | 5,909,712 | | | | 2,462,687 | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | 10,27 | | | | | 258,999 | | | | 156,092 | |
| Non-current contract liabilities | | 7 | | | | | 900,000 | | | | 900,000 | |
| Other non-current provisions | | 21 | | | | | 3,471 | | | | 3,448 | |
| Non-current lease liabilities | | 19,22,23 | | | | | 267,583 | | | | 334,405 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | | | | | 1,430,053 | | | | 1,393,945 | |
| Total liabilities | | | | ₩ | | | 7,339,765 | | | | 3,856,632 | |
| Equity | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net parent investment | | 17 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 1,874,660 | |
| Share capital | | 17 | | | | | 78 | | | | - | |
| Other reserves | | 17,28 | | | | | (585,468 | ) | | | - | |
| Retained earnings | | | | | | | 811,085 | | | | - | |
| Total equity | | | | | | | 225,695 | | | | 1,874,660 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | | | | ₩ | | | 7,565,460 | | | | 5,731,292 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Revenues | | | | | | | | | | |
| Media production revenue | | 6,7 | | ₩ | | | 20,836,856 | | | | 17,965,687 | |
| - Related parties | | 26 | | | | | 432,411 | | | | 5,567,067 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 20,404,445 | | | | 12,398,620 | |
| Cost of revenues | | 8 | | | | | (19,509,364 | ) | | | (17,117,104 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | | | | | 1,327,492 | | | | 848,583 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | 8 | | | | | (729,875 | ) | | | (687,562 | ) |
| Other income | | 8 | | | | | 89,285 | | | | 57,158 | |
| Other expenses | | 8 | | | | | (109,479 | ) | | | (30,624 | ) |
| Operating Profit | | | | | | | 577,423 | | | | 187,555 | |
| Finance income | | 9,16 | | | | | 48,640 | | | | 13,145 | |
| - Related parties | | 26 | | | | | 430 | | | | 501 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 48,210 | | | | 12,644 | |
| Finance costs | | 9,16,22 | | | | | (107,583 | ) | | | (423,424 | ) |
| - Related parties | | 26 | | | | | (57,521 | ) | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | (50,062 | ) | | | (423,424 | ) |
| Profit(Loss) before income tax | | | | | | | 518,480 | | | | (222,724 | ) |
| Income tax benefit | | 11 | | | | | 18,799 | | | | 20,035 | |
| Income(Loss) for the year | | | | ₩ | | | 537,279 | | | | (202,689 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Items that will not be reclassified to income or loss: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remeasurement of defined benefit liabilities | | 10,17 | | | | | (61,004 | ) | | | 24,016 | |
| Total comprehensive income(loss) for the year | | | | ₩ | | | 476,275 | | | | (178,673 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | Net parent investment | | | Share capital | | | Other
reserves | | | Retained
earnings | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at January 1, 2022 | | | | ₩ | | | 1,375,276 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,375,276 | |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the year | | | | | | | (202,689 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (202,689 | ) |
| Remeasurement of defined benefit liabilities | | 17 | | | | | 24,016 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 24,016 | |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the year | | | | | | | (178,673 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (178,673 | ) |
| Transaction directly recognized in equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Capital contribution from Parent company | | | | | | | 678,057 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 678,057 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | | | | ₩ | | | 1,874,660 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,874,660 | |
| Balance at January 1, 2023 | | | | ₩ | | | 1,874,660 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,874,660 | |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Income (loss) for the year | | | | | | | (334,810 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 872,089 | | | | 537,279 | |
| Remeasurement of defined benefit liabilities | | 17 | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (61,004 | ) | | | (61,004 | ) |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the year | | | | | | | (334,810 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 811,085 | | | | 476,275 | |
| Transaction directly recognized in equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Capital distribution to the Parent company | | | | | | | (2,125,240 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (2,125,240 | ) |
| Capital re-organization | | | | | | | 585,390 | | | | 78 | | | | (585,468 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | | | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 78 | | | | (585,468 | ) | | | 811,085 | | | | 225,695 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE LAMP CO., LTD.
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | 25 | | | | | | | | |
| Net income(loss) | | | | ₩ | | | 537,279 | | | | (202,689 | ) |
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash provided by(used in) operating activities | | | | | | | 398,172 | | | | 91,179 | |
| Interest received | | | | | | | 1,995 | | | | 2,071 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | | | (48,130 | ) | | | (6,349 | ) |
| Income taxes refunded(paid) | | | | | | | (13,770 | ) | | | 9,493 | |
| Net cash inflow(outflow) from operating activities | | | | ₩ | | | 875,546 | | | | (106,295 | ) |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payments for short-term loans | | | | ₩ | | | - | | | | (621,750 | ) |
| - Related parties | | 26 | | | | | - | | | | (621,750 | ) |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Proceeds from short-term loans | | | | | | | - | | | | 521,696 | |
| - Related parties | | 26 | | | | | - | | | | 521,696 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Payments for long-term loans | | | | | | | (20,000 | ) | | | (10,000 | ) |
| - Related parties | | 26 | | | | | (20,000 | ) | | | (10,000 | ) |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Payments for other financial assets | | | | | | | (64,730 | ) | | | (180,668 | ) |
| Proceeds from other financial assets | | | | | | | 13,410 | | | | 186,093 | |
| Purchase of long-term investments | | | | | | | - | | | | (800,000 | ) |
| - Related parties | | 26 | | | | | - | | | | (800,000 | ) |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Disposal of long-term investments | | | | | | | 336,246 | | | | 9,178 | |
| Purchase of property and equipment | | | | | | | (40,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Net cash inflow(outflow) from investing activities | | | | ₩ | | | 224,926 | | | | (895,451 | ) |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | 25 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from short-term borrowings | | | | ₩ | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 520,000 | |
| Repayments of short-term borrowings | | | | | | | (15,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Capital contribution(distribution) from(to) Parent company | | | | | | | (1,043,963 | ) | | | 678,057 | |
| Repayment of lease liabilities | | | | | | | (64,547 | ) | | | (39,223 | ) |
| Net cash inflow(outflow) from financing activities | | | | ₩ | | | (123,510 | ) | | | 1,158,834 | |
| Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | 976,962 | | | | 157,088 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the year | | 14 | | | | | 942,954 | | | | 785,866 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of the year | | 14 | | ₩ | | | 1,919,916 | | | | 942,954 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
1. Reporting entity
The LAMP Co., Ltd. (formerly, The LAMP Pictures Co., Ltd.)
On February 15, 2023, Pluto Co., Ltd. (formerly, The LAMP Co., Ltd.) (“Pluto” or “Parent”) announced the proposed plan (“the Separation Proposal”) to establish a new company, The LAMP Co., Ltd. (formerly, The LAMP Pictures Co., Ltd.) (the “Company”) through a spin-off of its media production business. Before the spin-off, Pluto produced television programs and feature films including “Commitment”, “Three Summer Night”, “Love, Lies”, “Taxi Driver”, “Samjin Company English Class”, “Life is beautiful”, and “Phantom”. Following the spin-off, the Company primarily engaged in the business of media production for theatrical films and television programs, and the surviving split, Pluto, continued to engage in the remaining investment properties leasing business. The Company was separated from the remaining businesses of Pluto through the spin-off that resulted in the transfer of the media production business. The spin-off will permit the Company to strengthen competitiveness and concentrate its financial resources solely on its own operations in media content production industry and increase transparency in governance and stability in management.
In accordance with the Separation Proposal, the Company’s common shares were distributed pro rata to the shareholders of Pluto. On March 31, 2023, the date of spin-off, the spin-off of media production business was completed. The Company’s registered office is at 35 Dosan-daero 26 gil, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Korea. Park Un Kyoung, the CEO of the Company, holds 100% of ownership of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
2. Basis of Accounting
These financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) as issued by International Accounting Standard Board (“IASB”). These financial statements were authorized for issuance by the director on May 13, 2024.
These financial statements are presented in a combined basis whereby combining the Pluto’s standalone financial statements using historical results of operation, cashflows and assets and liabilities attributable to the media production division before the spin-off as at March 31, 2023 with the Company’s financial statements after the spin-off as at March 31, 2023. The Company accounts the spin-off as a capital re-organization. On the basis that there is no substantive economic change, the Company incorporated the assets and liabilities of the Pluto at their pre-transaction carrying amounts.
Details of the Company’s accounting policies, including changes thereto, are included in Note 5.
Basis of measurement
The financial statements have been prepared on the historical cost basis except for the following items, which are measured on an alternative basis on each reporting date.
| Items | | Measurement basis |
| Financial instruments measured at fair value through profit or loss (“FVTPL”) | | Fair value |
3. Functional and presentation currency
These financial statements are presented in Korean Won, which the Company’s functional currency. All amounts have been rounded to the nearest thousand, unless otherwise indicated.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
4. Use of judgements and estimates
In preparing these financial statements, management has made judgements and estimates that affect the application of the Company’s accounting policies and the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
Estimates and underlying assumptions are reviewed on an ongoing basis. Revisions to estimates are recognized prospectively.
Information about judgements made in applying accounting policies that have the most significant effects on the amounts recognized in the financial statements is included in the following notes:
Note 4(B): revenue recognition: whether revenue from providing service is recognized over time or at a point in time and the methods used to recognize revenue;
Note 23(A): lease term: whether the Company is reasonably certain to exercise extension options.
| B. | Assumptions and estimation uncertainties |
Information about assumptions and estimation uncertainties at the reporting date that have a significant risk of resulting in a material adjustment to the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities within the next financial year is included in the following notes:
| ● | Note 10(C) (i): measurement of defined benefit obligations: key actuarial assumptions; |
| ● | Note 11(E): uncertain tax treatments; |
| i. | Measurement of fair values |
A number of the Company’s accounting policies and disclosures require the measurement of fair values for financial assets.
When measuring the fair value of a financial instruments, the Company uses observable market data as far as possible. Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows.
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
| ● | Level 2: inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly (i.e., as prices) or indirectly (i.e., derived from prices). |
| ● | Level 3: inputs for the asset or liability that are not based on observable market data (unobservable inputs). |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
If the inputs used to measure the fair value of an asset or a liability fall into different levels of the fair value hierarchy, then the fair value measurement is categorized in its entirety in the same level of the fair value hierarchy as the lowest level input that is significant to the entire measurement.
The Company recognizes transfers between levels of the fair value hierarchy at the end of the reporting period during which the change has occurred.
Further information about the assumptions made in measuring fair values is included in the following notes:
| ● | Note 22(B): financial instruments. |
5. Material accounting policies
The Company has consistently applied the following accounting policies to all periods presented in these financial statements, except if mentioned otherwise.
| A. | New and amended standards or interpretations adopted the Company |
The Company has applied the following standards and amendments for the first time for its annual reporting period commencing January 1, 2023.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements - Disclosure of Accounting Policies
The amendments to IAS 1 define and require entities to disclose their material accounting policies. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 8 Accounting policies, changes in accounting estimates and errors - Definition of Accounting Estimates
The amendments define accounting estimates and clarify how to distinguish them from changes in accounting policies. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 12 Income Taxes - Deferred Tax related to Assets and Liabilities arising from a Single Transaction
The amendments include an additional condition to the exemption to initial recognition of an asset or liability that a transaction does not give rise to equal taxable and deductible temporary differences at the time of the transaction. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 12 Income Taxes – International Tax Reform – Pillar Two Model Rules
The amendments provide a temporary relief from the accounting for deferred taxes arising from legislation enacted to implement the Pillar Two model rules, which aim to reform international corporate taxation for multinational enterprises, and require disclosure of related current tax effects, etc. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
New Standard: IFRS 17 Insurance Contract
IFRS 17 Insurance Contracts replaces IFRS 4 Insurance Contracts. This Standard estimates future cash flows of an insurance contract and measures insurance liabilities using discount rates applied with assumptions and risks at the measurement date. The entity recognizes insurance revenue on an accrual basis including services (insurance coverage) provided to the policyholder by each annual period. In addition, investment components (Refunds due to termination/maturity) repaid to a policyholder even if an insured event does not occur, are excluded from insurance revenue, and insurance financial income or expense and the investment income or expense are presented separately to enable users of the information to understand the sources of income or expenses. This Standard do not have a significant impact on the financial statements.
| B. | New and amended standards or interpretations not yet adopted |
The following new accounting standards and interpretations that have been published that are not mandatory for December 31, 2023 reporting periods and have not been early adopted by the Company.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements - Classification of Liabilities as Current or Non-current
The amendments clarify that liabilities are classified as either current or non-current, depending on the substantive rights that exist at the end of the reporting period. Classification is unaffected by the likelihood that an entity will exercise right to defer settlement of the liability or the expectations of management. Also, the settlement of liability includes the transfer of the entity’s own equity instruments, however, it would be excluded if an option to settle them by the entity’s own equity instruments if compound financial instruments is met the definition of equity instruments and recognized separately from the liability. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, and earlier application is permitted. The Company is in review for the impact of these amendments on the financial statements.
IAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows - IFRS 7 Financial Instruments: Disclosures – Supplier finance arrangements
When applying supplier finance arrangements, an entity shall disclose information about its supplier finance arrangements that enables users of financial statements to assess the effects of those arrangements on the entity’s liabilities and cash flows and on the entity’s exposure to liquidity risk. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, and earlier application is permitted. The Company does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 21 The effects of changes in foreign exchange rates - Lack of Exchangeability
The amendments add requirements to help entities to determine whether a currency is exchangeable into another currency at a measurement date for a specified purpose and the spot exchange rate to use when it is not. A currency is exchangeable when there is an ability to obtain the other currency (with a normal administrative delay), and the transaction would take place through a market or exchange mechanism that creates enforceable rights and obligations. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2025, and earlier application is permitted. The Company does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
IFRS 16 – Lease Liability in a Sale and Leaseback
When subsequently measuring lease liabilities arising from a sale and leaseback, a seller-lessee shall determine lease payments or revised lease payments in a way that the seller-lessee would not recognize any amount of the gain or loss that relates to the right of use retained by the seller-lessee. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, and earlier application is permitted. The Company does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IFRS 18 Presentation and Disclosure in Financial Statements
Items in the statement of profit or loss will need to be classified into one of five categories: operating, investing, financing, income taxes and discontinued operations. IFRS 18 requires the Company to present specified totals and subtotals: ‘Operating profit or loss’, ‘Profit or loss’ and ‘Profit or loss before financing and income taxes’. Information related to management-defined performance measures should be disclosed. IFRS 18 also provides enhanced guidance on the principles of aggregation and disaggregation which focus on grouping items based on their shared characteristics. The new standard should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2027, and earlier application is permitted. The Company is in review for the impact of this new standard on the financial statements.
| C. | Revenue from contracts with customers |
The Company generates revenue primarily through providing the media production service.
The Company determines revenue recognition by:
| ● | identifying the contract, or contracts, with a customer; |
| ● | identifying the performance obligations in each contract; |
| ● | determining the transaction price; |
| ● | allocating the transaction price to the performance obligations in each contract; and |
| ● | recognizing revenue when, or as, we satisfy performance obligations by transferring the promised goods or services. |
Media production revenue
The Company operates the media production business that consists of planning, producing, and selling the theatrical films and television programs. The Company identifies the license which is provided along with media product as combined output and recognizes revenue over time by measuring its progress based on cost incurred towards complete satisfaction of the performance obligation of media production in accordance with Paragraph 35 (3) of IFRS 15 Revenue from contracts with customers. The percentage-of-completion for each contract is calculated by dividing the cumulative cost incurred in relation to service performed by the Company by estimated total contract costs. The Company is also eligible to receive its share of profits from film distributors once the film generates profits beyond the break-even point, which is considered as variable consideration and recognized as the revenue on the settlement date.
The Company recognizes unbilled receivables from media production service as contract assets and recognizes receipts in advance for prepaid media production services as contract liabilities. The Company capitalizes the cost associated with the production, including development costs, direct costs, and production overhead per title as prepayments and prepaid expenses. The Company amortizes the capitalized asset in ‘Cost of revenues’ on the combined statements of comprehensive income based on the percentage-of-completion for each contract.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
An operating segment is a component of the Company that engages in business activities from which it may earn revenues and incur expenses. The Company has one reportable segment, for which it generates separately identifiable financial information that is regularly reported to the chief operating decision maker for the purpose of resource allocation and assessment of segment performance.
| E. | Common control transactions |
The Company accounts the Spin-off as a capital re-organization. On the basis that there is no substantive economic change, the Company incorporates the assets and liabilities of the Pluto at their pre-transaction carrying amounts.
| i. | Short-term employee benefits |
Short-term employee benefits are employee benefits due to be settled within 12 months after the end of the period in which the employees render related services. When an employee has rendered a service during an accounting period, the Company recognizes the undiscounted amount of short-term employee benefits expected to be paid in exchange for that service.
The Company’s net obligation in respect of defined benefit plans is calculated separately for each plan by estimating the amount of future benefit that employees have earned in the current and prior periods, discounting that amount and deducting the fair value of any plan assets.
The calculation of defined benefit obligations is performed annually by a qualified actuary using the projected unit credit method. When the calculation results in a potential asset for the Company, the recognized asset is limited to the present value of economic benefits available in the form of any future refunds from the plan or reductions in future contributions to the plan. To calculate the present value of economic benefits, consideration is given to any applicable minimum funding requirements.
Remeasurements of the net defined benefit liability, which comprise actuarial gains and losses, the return on plan assets (excluding interest) and the effect of the asset ceiling (if any, excluding interest), are recognized immediately in OCI. The Company determines the net interest expense (income) on the net defined benefit liability (asset) for the period by applying the discount rate used to measure the defined benefit obligation at the beginning of the annual period to the then-net defined benefit liability (asset), taking into account any changes in the net defined benefit liability (asset) during the period as a result of contributions and benefit payments. Net interest expense and other expenses related to defined benefit plans are recognized in profit or loss.
When the benefits of a plan are changed or when a plan is curtailed, the resulting change in benefit that relates to past service or the gain or loss on curtailment is recognized immediately in profit or loss. The Company recognizes gains and losses on the settlement of a defined benefit plan when the settlement occurs.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| G. | Finance income and finance costs |
The Company’s finance income and finance costs include:
| ● | the net gain or loss on settlement and/or impairment of project investments; |
| ● | the foreign currency gain or loss on financial assets and financial liabilities; |
The ‘effective interest rate’ is the rate that exactly discounts estimated future cash payments or receipts through the expected life of the financial instrument to:
| ● | the gross carrying amount of the financial asset; or |
| ● | the amortized cost of the financial liability. |
In calculating interest income and expense, the effective interest rate is applied to the gross carrying amount of the asset (when the asset is not credit-impaired) or to the amortized cost of the liability. However, for financial assets that have become credit-impaired subsequent to initial recognition, interest income is calculated by applying the effective interest rate to the amortized cost of the financial asset. If the asset is no longer credit-impaired, then the calculation of interest income reverts to the gross basis.
Income tax expense comprises current and deferred tax. It is recognized in profit or loss except to the extent that it relates to a business combination, or items recognized directly in equity or in OCI.
The Company has determined that interest and penalties related to income taxes, including uncertain tax treatments, do not meet the definition of income taxes, and therefore accounted for them under IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets.
Current tax comprises the expected tax payable or receivable on the taxable income or loss for the year and any adjustment to the tax payable or receivable in respect of previous years. The amount of current tax payable or receivable is the best estimate of the tax amount expected to be paid or received that reflects uncertainty related to income taxes, if any. It is measured using tax rates enacted or substantively enacted at the reporting date. Current tax also includes any tax arising from dividends.
Current tax assets and liabilities are offset only if certain criteria are met.
| ● | Has a legally enforceable right to set off the recognized amounts; and |
| ● | Intends either to settle on a net basis, or to realize the asset and settle the liability simultaneously. |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Deferred tax is recognized in respect of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for taxation purposes. Deferred tax is not recognized for:
| ● | temporary differences on the initial recognition of assets or liabilities in a transaction that is not a business combination and that affects neither accounting nor taxable profit or loss; |
| ● | temporary differences related to investments in subsidiaries, associates and joint arrangements to the extent that the Company is able to control the timing of the reversal of the temporary differences and it is probable that they will not reverse in the foreseeable future; and |
| ● | taxable temporary differences arising on the initial recognition of goodwill. |
Deferred tax assets are recognized for unused tax losses, unused tax credits and deductible temporary differences to the extent that it is probable that future taxable profits will be available against which they can be used. Future taxable profits are determined based on the reversal of relevant taxable temporary differences. If the amount of taxable temporary differences is insufficient to recognize a deferred tax asset in full, then future taxable profits, adjusted for reversals of existing temporary differences, are considered, based on the business plans of the Company. Deferred tax assets are reviewed at each reporting date and are reduced to the extent that it is no longer probable that the related tax benefit will be realized; such reductions are reversed when the probability of future taxable profits improves.
The measurement of deferred tax reflects the tax consequences that would follow from the manner in which the Company, at the reporting date, to recover or settle the carrying amount of its assets and liabilities.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are offset only if certain criteria are met.
| ● | Has a legally enforceable right to set off the recognized amounts; and |
| ● | Intends either to settle on a net basis, or to realize the asset and settle the liability simultaneously. |
| I. | Cash and Cash Equivalents |
Cash and cash equivalents comprise cash on hand, deposits held at banks, and investment securities with maturities of three months or less from the acquisition date that are easily convertible to cash and subject to an insignificant risk of changes in their fair value.
| J. | Property, plant and equipment |
| i. | Recognition and measurement |
Items of property, plant and equipment are measured at cost, which includes capitalized borrowing costs, less accumulated depreciation and any accumulated impairment losses.
If significant parts of an item of property, plant and equipment have different useful lives, then they are accounted for as separate items (major components) of property, plant and equipment.
Any gain or loss on disposal of an item of property, plant and equipment is recognized in profit or loss.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| ii. | Subsequent expenditure |
Subsequent expenditure is capitalized only if it is probable that the future economic benefits associated with the expenditure will flow to the Company. The carrying amount of the replaced parts are derecognized and the repairs and maintenance expenses are recognized in profit or loss in the period they are incurred.
Depreciation is calculated to write off the cost of items of property, plant and equipment less their estimated residual values using the straight-line method over their estimated useful lives, and is generally recognized in profit or loss. Land is not depreciated.
The estimated useful lives of property, plant and equipment for current and comparative periods are as follows:
| Office equipment | | 5 years |
| Furniture and fixtures | | 5 years |
| Right-of-use assets | | 5 – 10 years |
Depreciation methods, useful lives and residual values are reviewed at each reporting date and adjusted if appropriate.
| i. | Recognition and initial measurement |
Trade receivables and debt securities issued are initially recognized when they are originated. All other financial assets and financial liabilities are initially recognized when the Company becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the instrument.
A financial asset (unless it is a trade receivable without a significant financing component) or financial liability is initially measured at fair value plus or minus, for an item not at FVTPL, transaction costs that are directly attributable to its acquisition or issue. A trade receivable without a significant financing component is initially measured at the transaction price.
| ii. | Classification and subsequent measurement |
Financial assets
On initial recognition, a financial asset is classified as measured at:
| ● | FVOCI - debt investment; |
| ● | FVOCI - equity investment; |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Financial assets are not reclassified subsequent to their initial recognition unless the Company changes its business model for managing financial assets, in which case all affected financial assets are reclassified on the first day of the first reporting period following the change in the business model.
A financial asset is measured at amortized cost if it meets both of the following conditions and is not designated as at FVTPL:
| ● | it is held within a business model whose objective is to hold assets to collect contractual cash flows; and |
| ● | its contractual terms give rise on specified dates to cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. |
A debt investment is measured at FVOCI if it meets both of the following conditions and is not designated as at FVTPL:
| ● | it is held within a business model whose objective is achieved by both collecting contractual cash flows and selling financial assets; and |
| ● | its contractual terms give rise on specified dates to cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. |
On initial recognition of an equity investment that is not held for trading, the Company may irrevocably elect to present subsequent changes in the investment’s fair value in OCI. This election is made on an investment-by-investment basis.
All financial assets not classified as measured at amortized cost or FVOCI as described above are measured at FVTPL. This includes all derivative financial assets. On initial recognition, the Company may irrevocably designate a financial asset that otherwise meets the requirements to be measured at amortized cost or at FVOCI as at FVTPL if doing so eliminates or significantly reduces an accounting mismatch that would otherwise arise.
Financial assets - Business model assessment
The Company makes an assessment of the objective of the business model in which a financial asset is held at a portfolio level because this best reflects the way the business is managed and information is provided to management. The information considered includes:
| ● | the stated policies and objectives for the portfolio and the operation of those policies in practice. These include whether management’s strategy focuses on earning contractual interest income, maintaining a particular interest rate profile, matching the duration of the financial assets to the duration of any related liabilities or expected cash outflows or realizing cash flows through the sale of the assets; |
| ● | how the performance of the portfolio is evaluated and reported to the Company’s management; |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| ● | the risks that affect the performance of the business model (and the financial assets held within that business model) and how those risks are managed; |
| ● | how managers of the business are compensated - e.g. whether compensation is based on the fair value of the assets managed or the contractual cash flows collected; and |
| ● | the frequency, volume and timing of sales of financial assets in prior periods, the reasons for such sales and expectations about future sales activity. |
Transfers of financial assets to third parties in transactions that do not qualify for derecognition are not considered sales for this purpose, consistent with the Company’s continuing recognition of the assets.
Financial assets that are held for trading or are managed and whose performance is evaluated on a fair value basis are measured at FVTPL.
Financial assets - Assessment whether contractual cash flows are solely payments of principal and interest
For the purposes of this assessment, ‘principal’ is defined as the fair value of the financial asset on initial recognition. ‘Interest’ is defined as consideration for the time value of money and for the credit risk associated with the principal amount outstanding during a particular period of time and for other basic lending risks and costs (e.g. liquidity risk and administrative costs), as well as a profit margin.
In assessing whether the contractual cash flows are solely payments of principal and interest, the Company considers the contractual terms of the instrument. This includes assessing whether the financial asset contains a contractual term that could change the timing or amount of contractual cash flows such that it would not meet this condition. In making this assessment, the Company considers:
| ● | contingent events that would change the amount or timing of cash flows; |
| ● | terms that may adjust the contractual coupon rate, including variable-rate features; |
| ● | prepayment and extension features; and |
| ● | terms that limit the Company’s claim to cash flows from specified assets (e.g. non-recourse features). |
A prepayment feature is consistent with the solely payments of principal and interest criterion if the prepayment amount substantially represents unpaid amounts of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding, which may include reasonable compensation for early termination of the contract. Additionally, for a financial asset acquired at a discount or premium to its contractual par amount, a feature that permits or requires prepayment at an amount that substantially represents the contractual par amount plus accrued (but unpaid) contractual interest (which may also include reasonable compensation for early termination) is treated as consistent with this criterion if the fair value of the prepayment feature is insignificant at initial recognition.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Financial assets - Subsequent measurement and gains and losses
Financial assets at FVTPL: These assets are subsequently measured at fair value. Net gains and losses, including any interest or dividend income, are recognized in profit or loss.
Financial assets at amortized cost: These assets are subsequently measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. The amortized cost is reduced by impairment losses. Interest income, foreign exchange gains and losses and impairment are recognized in profit or loss. Any gain or loss on derecognition is recognized in profit or loss.
Financial liabilities - Classification, subsequent measurement and gains and losses
Financial liabilities are classified as measured at amortized cost or FVTPL. A financial liability is classified as at FVTPL if it is classified as held-for-trading, it is a derivative or it is designated as such on initial recognition. Financial liabilities at FVTPL are measured at fair value and net gains and losses, including any interest expense, are recognized in profit or loss. Other financial liabilities are subsequently measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. Interest expense and foreign exchange gains and losses are recognized in profit or loss. Any gain or loss on derecognition is also recognized in profit or loss.
Financial assets
The Company derecognizes a financial asset when:
| ● | the contractual rights to the cash flows from the financial asset expire; or |
| ● | it transfers the rights to receive the contractual cash flows in a transaction in which either: |
| - | substantially all of the risks and rewards of ownership of the financial asset are transferred; or |
| - | the Company neither transfers nor retains substantially all of the risks and rewards of ownership and it does not retain control of the financial asset. |
The Company enters into transactions whereby it transfers assets recognized in its statement of financial position, but retains either all or substantially all of the risks and rewards of the transferred assets. In these cases, the transferred assets are not derecognized.
Financial liabilities
The Company derecognizes a financial liability when its contractual obligations are discharged or cancelled, or expire. The Company also derecognizes a financial liability when its terms are modified and the cash flows of the modified liability are substantially different, in which case a new financial liability based on the modified terms is recognized at fair value.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
On derecognition of a financial liability, the difference between the carrying amount extinguished and the consideration paid (including any non-cash assets transferred or liabilities assumed) is recognized in profit or loss.
When changes were made to a financial asset or financial liability in addition to changes to the basis for determining the contractual cash flows required by interest rate benchmark reform, the Company first updated the effective interest rate of the financial asset or financial liability to reflect the change that is required by interest rate benchmark reform. After that, the Company applied the policies on accounting for modifications to the additional changes.
| i. | Non-derivative financial assets |
Financial instruments and contract assets
The Company recognizes loss allowances for ECLs on:
| ● | financial assets measured at amortized cost; and |
The Company also recognizes loss allowances for ECLs on lease receivables, which are disclosed as part of trade and other receivables.
The Company measures loss allowances at an amount equal to lifetime ECLs, except for the following, which are measured at 12-month ECLs:
| ● | debt securities that are determined to have low credit risk at the reporting date; and |
| ● | other debt securities and bank balances for which credit risk (i.e. the risk of default occurring over the expected life of the financial instrument) has not increased significantly since initial recognition. |
Loss allowances for trade receivables (including lease receivables) and contract assets are always measured at an amount equal to lifetime ECLs.
When determining whether the credit risk of a financial asset has increased significantly since initial recognition and when estimating ECLs, the Company considers reasonable and supportable information that is relevant and available without undue cost or effort. This includes both quantitative and qualitative information and analysis, based on the Company’s historical experience and informed credit assessment, that includes forward-looking information.
The Company assumes that the credit risk on a financial asset has increased significantly if it is more than 30 days past due.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The Company considers a financial asset to be in default when:
| ● | the debtor is unlikely to pay its credit obligations to the Company in full, without recourse by the Company to actions such as realizing security (if any is held); or |
| ● | the financial asset is more than 90 days past due. |
Lifetime ECLs are the ECLs that result from all possible default events over the expected life of a financial instrument.
12-month ECLs are the portion of ECLs that result from default events that are possible within the 12 months after the reporting date (or a shorter period if the expected life of the instrument is less than 12 months).
The maximum period considered when estimating ECLs is the maximum contractual period over which the Company is exposed to credit risk.
Measurement of ECLs
ECLs are a probability-weighted estimate of credit losses. Credit losses are measured as the present value of all cash shortfalls (i.e. the difference between the cash flows due to the entity in accordance with the contract and the cash flows that the Company expects to receive).
ECLs are discounted at the effective interest rate of the financial asset.
Credit-impaired financial assets
At each reporting date, the Company assesses whether financial assets carried at amortized cost are credit-impaired. A financial asset is ‘credit-impaired’ when one or more events that have a detrimental impact on the estimated future cash flows of the financial asset have occurred.
Evidence that a financial asset is credit-impaired includes the following observable data:
| ● | significant financial difficulty of the debtor; |
| ● | a breach of contract such as a default or being more than 90 days past due; |
| ● | the restructuring of a loan or advance by the Company on terms that the Company would not consider otherwise; |
| ● | it is probable that the debtor will enter bankruptcy or other financial reorganization; or |
| ● | the disappearance of an active market for a security because of financial difficulties. |
Presentation of allowance for ECL in the statement of financial position
Loss allowances for financial assets measured at amortized cost are deducted from the gross carrying amount of the assets.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Write-off
The gross carrying amount of a financial asset is written off when the Company has no reasonable expectations of recovering a financial asset in its entirety or a portion thereof. For individual customers, the Company has a policy of writing off the gross carrying amount when the financial asset is 180 days past due based on historical experience of recoveries of similar assets. For corporate customers, the Company individually makes an assessment with respect to the timing and amount of write-off based on whether there is a reasonable expectation of recovery. The Company expects no significant recovery from the amount written off. However, financial assets that are written off could still be subject to enforcement activities in order to comply with the Company’s procedures for recovery of amounts due.
At each reporting date, the Company reviews the carrying amounts of its non-financial assets (other than biological assets, investment property, developing contents, contract assets and deferred tax assets) to determine whether there is any indication of impairment. If any such indication exists, then the asset’s recoverable amount is estimated. Goodwill is tested annually for impairment.
For impairment testing, assets are grouped together into the smallest group of assets that generates cash inflows from continuing use that are largely independent of the cash inflows of other assets or CGUs. Goodwill arising from a business combination is allocated to CGUs or groups of CGUs that are expected to benefit from the synergies of the combination.
The recoverable amount of an asset or CGU is the greater of its value in use and its fair value less costs of disposal. Value in use is based on the estimated future cash flows, discounted to their present value using a pre-tax discount rate that reflects current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the asset or CGU.
An impairment loss is recognized if the carrying amount of an asset or CGU exceeds its recoverable amount.
Impairment losses are recognized in profit or loss. They are allocated first to reduce the carrying amount of any goodwill allocated to the CGU, and then to reduce the carrying amounts of the other assets in the CGU on a pro rata basis.
An impairment loss in respect of goodwill is not reversed. For other assets, an impairment loss is reversed only to the extent that the asset’s carrying amount does not exceed the carrying amount that would have been determined, net of depreciation or amortization, if no impairment loss had been recognized.
At inception of a contract, the Company assesses whether a contract is, or contains, a lease. A contract is, or contains, a lease if the contract conveys the right to control the use of an identified asset for a period of time in exchange for consideration.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
At commencement or on modification of a contract that contains a lease component, the Company allocates the consideration in the contract to each lease component on the basis of its relative stand-alone prices. However, for the leases of property the Company has elected not to separate non-lease components and account for the lease and non-lease components as a single lease component.
The Company recognizes a right-of-use asset and a lease liability at the lease commencement date. The right-of-use asset is initially measured at cost, which comprises the initial amount of the lease liability adjusted for any lease payments made at or before the commencement date, plus any initial direct costs incurred and an estimate of costs to dismantle and remove the underlying asset or to restore the underlying asset or the site on which it is located, less any lease incentives received.
The right-of-use asset is subsequently depreciated using the straight-line method from the commencement date to the end of the lease term, unless the lease transfers ownership of the underlying asset to the Company by the end of the lease term or the cost of the right-of-use asset reflects that the Company will exercise a purchase option. In that case the right-of-use asset will be depreciated over the useful life of the underlying asset, which is determined on the same basis as those of property and equipment. In addition, the right-of-use asset is periodically reduced by impairment losses, if any, and adjusted for certain remeasurements of the lease liability.
The lease liability is initially measured at the present value of the lease payments that are not paid at the commencement date, discounted using the interest rate implicit in the lease or, if that rate cannot be readily determined, the Company’s incremental borrowing rate. Generally, the Company uses its incremental borrowing rate as the discount rate.
The Company determines its incremental borrowing rate by obtaining interest rates from various external financing sources and makes certain adjustments to reflect the terms of the lease and type of the asset leased.
Lease payments included in the measurement of the lease liability comprise the following:
| ● | fixed payments, including in-substance fixed payments; |
| ● | variable lease payments that depend on an index or a rate, initially measured using the index or rate as at the commencement date; |
| ● | amounts expected to be payable under a residual value guarantee; and |
| ● | the exercise price under a purchase option that the Company is reasonably certain to exercise, lease payments in an optional renewal period if the Company is reasonably certain to exercise an extension option, and penalties for early termination of a lease unless the Company is reasonably certain not to terminate early. |
The lease liability is measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. It is remeasured when there is a change in future lease payments arising from a change in an index or rate, if there is a change in the Company’s estimate of the amount expected to be payable under a residual value guarantee, if the Company changes its assessment of whether it will exercise a purchase, extension or termination option or if there is a revised in-substance fixed lease payment.
When the lease liability is remeasured in this way, a corresponding adjustment is made to the carrying amount of the right-of-use asset, or is recorded in profit or loss if the carrying amount of the right-of-use asset has been reduced to zero.
At the date of transition to IFRSs, the Company applies the following approach to all of its leases.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The Company measures that lease liability at the present value of the remaining lease payments, discounted using the lessee’s incremental borrowing rate at the date of transition to IFRSs.
The Company measures right-of-use asset at its carrying amount as if IFRS 16 had been applied since the commencement date of the lease, but discounted using the lessee’s incremental borrowing rate at the date of transition to IFRSs.
The Company uses hindsight in applying IFRS 16 such as the determination of lease term for contracts that contain options to extend or terminate a lease.
The Company has elected not to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for leases of low-value assets (leases for which the underlying asset is valued at USD 5,000 or less) and short-term leases (leases that have a lease term of 12 months or less at the commencement date). The Company recognizes the lease payments associated with these leases as an expense on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
‘Fair value’ is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date in the principal or, in its absence, the most advantageous market to which the Company has access at that date. The fair value of a liability reflects its non-performance risk.
A number of the Company’s accounting policies and disclosures require the measurement of fair values, for both financial and non-financial assets and liabilities.
When one is available, the Company measures the fair value of an instrument using the quoted price in an active market for that instrument. A market is regarded as ‘active’ if transactions for the asset or liability take place with sufficient frequency and volume to provide pricing information on an ongoing basis.
If there is no quoted price in an active market, then the Company uses valuation techniques that maximize the use of relevant observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The chosen valuation technique incorporates all of the factors that market participants would take into account in pricing a transaction.
The best evidence of the fair value of a financial instrument on initial recognition is normally the transaction price - i.e. the fair value of the consideration given or received. If the Company determines that the fair value on initial recognition differs from the transaction price and the fair value is evidenced neither by a quoted price in an active market for an identical asset or liability nor based on a valuation technique for which any unobservable inputs are judged to be insignificant in relation to the measurement, then the financial instrument is initially measured at fair value, adjusted to defer the difference between the fair value on initial recognition and the transaction price. Subsequently, that difference is recognized in profit or loss on an appropriate basis over the life of the instrument but no later than when the valuation is wholly supported by observable market data or the transaction is closed out.
| O. | Concentration of Credit Risk |
The Company performs periodic credit evaluations of its customers’ financial condition and generally does not require collateral for customers on accounts receivable. The Company maintains reserves for potential credit losses, which are periodically reviewed.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
6. Operating segments
The Company’s operating segments have been identified to be a single unit, by which the Company provides the services for media production.
The following summary describes the operations of each reportable segment.
| Reportable segments | | Operations |
| Media Production | | Media production revenue |
| B. | Information about reportable segments |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Segment revenue | | ₩ | | | 20,836,856 | | | | 17,965,687 | |
| Depreciation/Amortization | | | | | (77,808 | ) | | | (50,767 | ) |
| Segment operating profit (loss) | | | | | 577,423 | | | | 187,555 | |
Media production is managed and operated in Seoul, Korea. The geographic information analyses the Company’s revenue by the Company’s country of domicile and other countries. In presenting the geographic information, segment revenue has been based on the geographic location of customers.
Summary of the Company’s operation by region based on the location of customers for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 20,836,856 | | | | 17,965,687 | |
Summary of the Company’s non-current assets based on the location as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 1,768,586 | | | | 2,042,395 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Revenues by major customers for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Customer A (Media production segment) | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 10,938,655 | | | | - | |
| % | | | | | 53 | % | | | 0 | % |
| Customer B (Media production segment) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 8,274,728 | | | | 237,726 | |
| % | | | | | 40 | % | | | 1 | % |
| Customer C (Media production segment) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 530,890 | | | | 7,576,164 | |
| % | | | | | 3 | % | | | 42 | % |
| Customer D (Media production segment) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 463,012 | | | | 2,737,387 | |
| % | | | | | 2 | % | | | 15 | % |
| Customer E (*1, Media production segment) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 432,411 | | | | 5,567,067 | |
| % | | | | | 2 | % | | | 31 | % |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 20,639,696 | | | | 16,118,344 | |
| (*1) | Customer E is a related party of the Company. |
7. Revenue
The Company generates revenue primarily through providing the services for production of feature films for initial exhibition in theaters and production of television programs to third parties for internal television and streaming services.
Revenue from contracts with customers as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Revenue from contracts with customers | | ₩ | | | 20,836,856 | | | | 17,965,687 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| B. | Disaggregation of revenue from contracts with customers |
In the following table, revenue from contracts with customers is disaggregated by major products and service lines and timing of revenue recognition. The table also includes a reconciliation of the disaggregated revenue with the Company’s reportable segment. (see Note 6)
Revenue from contracts with customers based on the service contract type and the timing of satisfaction of performance obligations for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Major products/service lines | | | | | | | | | | |
| Media production | | ₩ | | | 20,836,856 | | | | 17,965,687 | |
| Timing of revenue recognition | | | | | | | | | | |
| Over time | | | | | 20,836,856 | | | | 17,965,687 | |
The balance of accounts receivables and contract liabilities from contracts with customers as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | ₩ | | | 196,380 | | | | 118,558 | |
| Contract asset (Unbilled receivables) | | | | | 158,697 | | | | 130,588 | |
| Contract liabilities (Deferred revenue) | | | | | 2,210,942 | | | | 1,430,167 | |
| Non-current | | | | | | | | | | |
| Contract liabilities (Deferred revenue) | | ₩ | | | 900,000 | | | | 900,000 | |
The contract liabilities primarily relate to the advance consideration received from customers for media production service, for which revenue is recognized over time. This will be recognized as revenue when the Company satisfies the performance obligations.
The amount of Korean Won 1,306,160 thousand included in contract liabilities as of December 31, 2022 has been recognized as revenue in 2023. (2022: 2,092,097 thousand)
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
8. Income and Expenses
Details of other income for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Grants for film production | | ₩ | | | 66,300 | | | | 29,700 | |
| Miscellaneous income | | | | | 22,985 | | | | 27,459 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 89,285 | | | | 57,159 | |
Details of other expenses for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other bad debt expenses | | ₩ | | | 105,000 | | | | 20,000 | |
| Miscellaneous expenses | | | | | 4,479 | | | | 10,624 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 109,479 | | | | 30,624 | |
Details of classification of expenses by nature for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Outsourcing Fee | | ₩ | | | 13,985,841 | | | | 12,040,281 | |
| Employee benefits | | | | | 1,372,480 | | | | 2,107,558 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | 77,809 | | | | 50,767 | |
| Commission paid | | | | | 63,236 | | | | 43,100 | |
| Transportation | | | | | 917,159 | | | | 890,088 | |
| Rent | | | | | 2,436,273 | | | | 2,114,703 | |
| Supplies | | | | | 1,271,958 | | | | 469,322 | |
| Other expenses | | | | | 114,483 | | | | 88,847 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 20,239,239 | | | | 17,804,666 | |
Total expenses consist of cost of sales and selling, general and administrative expenses.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
9. Finance income and costs
Details of finance income and costs for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Finance income | | | | | | | | | | |
| Reversal of loss on valuation of long-term investments | | ₩ | | | 39,355 | | | | - | |
| Gain on project settlements | | | | | 3,999 | | | | 8,997 | |
| Interest income | | | | | 5,286 | | | | 4,148 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 48,640 | | | | 13,145 | |
| Finance costs | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expenses | | ₩ | | | 107,583 | | | | 19,524 | |
| Losses on valuation of long-term investments (*1) | | | | | - | | | | 403,900 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 107,583 | | | | 423,424 | |
| (*1) | The Company recognized the valuation loss of the project investment in Life is beautiful based on the forecast the total amount of production costs and distribution fees exceed the shared profit. |
10. Employee benefits
Details of defined benefit liability recognized as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Defined benefit liability | | ₩ | | | 258,999 | | | | 156,092 | |
The Company operates defined benefit plans as a retirement pension scheme. Defined benefit plans expose the Company to actuarial risks, such as longevity risk, interest rate risk and market (investment) risk.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| A. | Movement in net defined benefit (asset) liability |
Details of reconciliation from the opening balances to the closing balances for the net defined benefit liability and its components as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | Defined benefit obligation | | | Fair value of plan assets | | | Net defined benefit liabilities | |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at 1 January | | ₩ | | | 156,092 | | | | 164,975 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 156,092 | | | | 164,975 | |
| Included in profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current service cost | | | | | 20,542 | | | | 23,670 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 20,542 | | | | 23,670 | |
| Past service credit | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Interest cost | | | | | 7,948 | | | | 4,126 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 7,948 | | | | 4,126 | |
| Subtotal | | | | | 28,490 | | | | 27,796 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 28,490 | | | | 27,796 | |
| Included in OCI | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remeasurement loss(gain) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Demographic assumption | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Financial assumption | | | | | 17,816 | | | | (23,745 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 17,816 | | | | (23,745 | ) |
| Adjustment based on experience | | | | | 56,601 | | | | (2,999 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 56,601 | | | | (2,999 | ) |
| Return on plan assets excluding interest income | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Subtotal | | | | | 74,417 | | | | (26,744 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 74,417 | | | | (26,744 | ) |
| Other | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Benefits paid | | | | | - | | | | (9,935 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (9,935 | ) |
| Subtotal | | | | | - | | | | (9,935 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (9,935 | ) |
| Balance at 31 December | | ₩ | | | 258,999 | | | | 156,092 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 258,999 | | | | 156,092 | |
There are no contributions funded to its defined benefit plans as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
| C. | Defined benefit obligation |
Details of actuarial assumptions used for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Discount rate | | 4.20% | | 5.30% |
| Future salary growth | | 6.10%~8.20% | | 6.10%~8.20% |
Assumptions regarding future longevity have been based on published statistics and mortality tables.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the weighted average duration of the defined benefit obligation was 6.7 years and 6.8 years, respectively.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The Company measures the risk of actuarial assumption changes as a 1% fluctuation in the discount rate and future salary growth rate of the amounts of defined benefit obligation, which reflects the management’s assessment of the risk of actuarial assumption fluctuation that can be reasonably occur. The impact of a 1% fluctuation in discount rates and future salary growth rates on the Company’s defined benefit obligation as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | Increased by 1% | | | Decreased by 1% | | | Increased by 1% | | | Decreased by 1% | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Discount rate | | ₩ | | | (16,283 | ) | | | 18,227 | | | | (10,007 | ) | | | 11,176 | |
| Future salary growth | | | | | 18,158 | | | | (16,524 | ) | | | 11,258 | | | | (10,257 | ) |
Although the analysis does not take account of the full distribution of cash flows expected under the plan, it does provide an approximation of the sensitivity of the assumptions shown.
| D. | Employee benefit expenses |
| i. | Details of employee benefit expenses recognized for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows: |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Wages and salaries | | ₩ | | | 1,257,852 | | | | 1,931,925 | |
| Fringe benefit | | | | | 86,139 | | | | 147,837 | |
| Expenses related to post-employment defined benefit plans | | | | | 28,490 | | | | 27,796 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,372,481 | | | | 2,107,558 | |
| ii. | Expenses are recognized in the statements of comprehensive income (loss) as follows: |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cost of revenues | | ₩ | | | 965,955 | | | | 1,719,286 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | | | 406,525 | | | | 388,272 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,372,481 | | | | 2,107,558 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
11. Income taxes
| A. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In Korean won and number of shares) | |
| Current tax expenses (benefit) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current year | | ₩ | | | 24,614 | | | | 26,708 | |
| Adjustments recognized related to prior period incomes (*) | | | | | 5,563 | | | | 6,300 | |
| | | | | | 30,177 | | | | 33,008 | |
| Deferred tax expenses (benefit) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Origination and reversal of temporary differences | | ₩ | | | (62,389 | ) | | | (50,315 | ) |
| Deferred taxes charged directly to equity | | | | | 13,413 | | | | (2,728 | ) |
| Income tax expenses (benefit) | | ₩ | | | (18,799 | ) | | | (20,035 | ) |
| (*) | In the normal course of business, the Company is examined by taxation authority. The Company’s management regularly assesses the potential outcomes of these examinations and any future examinations for the current or prior years in determining the adequacy of its liabilities for income taxes. |
The Company establish additional current tax liabilities for income taxes when, despite the belief that tax positions are fully supportable, there remain positions that do not meet the minimum probability threshold, which is a tax position that is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by the applicable taxation authority. The impact of current tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions, as well as the related net interest and penalties, are included in income taxes in the statements of operations.
| B. | Amounts recognized in OCI |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Before tax | | | Tax (expense) benefit | | | Net of tax | | | Before tax | | | Tax (expense) benefit | | | Net of tax | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Items that will not be reclassified to profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liability | | ₩ | | | (74,418 | ) | | | 13,413 | | | | (61,004 | ) | | | 26,744 | | | | (2,728 | ) | | | 24,016 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| C. | Reconciliation of effective tax rate |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Profit before income tax | | ₩ | | | 518,480 | | | | (222,724 | ) |
| Tax at the statutory income tax rate | | | | | 86,362 | | | | (26,999 | ) |
| Adjustments: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Expenses not deductible for tax purposes | | | | | 3,661 | | | | 4,039 | |
| Tax credits | | | | | (18,110 | ) | | | (29,790 | ) |
| Adjustments recognized related to prior period incomes | | | | | 5,563 | | | | 6,300 | |
| Changes in unrecognized deferred tax assets | | | | | (1,186 | ) | | | 1,186 | |
| Change in tax rates | | | | | (102,326 | ) | | | 21,982 | |
| Other | | | | | 7,237 | | | | 3,247 | |
| Income tax expenses (benefit) | | ₩ | | | (18,799 | ) | | | (20,035 | ) |
| Effective income tax rate (*) | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| (*) | The effective tax rate is not calculated as the Company recognized tax benefit for the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. |
| D. | Movement in deferred tax balances |
| i. | Movement in deferred tax balances as of December 31, 2023 |
| | | | | Tax effect | |
| | | | | Beginning | | | Increase (decrease) | | | Ending | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | ₩ | | | 15,453 | | | | 38,678 | | | | 54,131 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 39,098 | | | | 29,951 | | | | 69,049 | |
| Right-of-use assets | | | | | (39,581 | ) | | | (29,264 | ) | | | (68,845 | ) |
| Contract liabilities | | | | | 153,466 | | | | 273,726 | | | | 427,192 | |
| Contract assets | | | | | (17,837 | ) | | | (30,639 | ) | | | (48,476 | ) |
| Prepaid expenses | | | | | (96,550 | ) | | | (312,989 | ) | | | (409,539 | ) |
| Prepayments | | | | | (25,474 | ) | | | (73,335 | ) | | | (98,809 | ) |
| Other | | | | | 63,519 | | | | 159,475 | | | | 222,994 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 92,094 | | | | 55,603 | | | | 147,697 | |
| Loss carried forward | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Carryover tax credit | | | | | 13,549 | | | | 5,600 | | | | 19,149 | |
| Unrecognized deferred tax assets | | | | | (1,186 | ) | | | 1,186 | | | | - | |
| Deferred tax assets | | ₩ | | | 104,457 | | | | 62,389 | | | | 166,846 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| ii. | Movement in deferred tax balances as of December 31, 2022 |
| | | | | Tax effect | |
| | | | | Beginning | | | Increase (decrease) | | | Ending | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | ₩ | | | 18,147 | | | | (2,694 | ) | | | 15,453 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 33,076 | | | | 6,022 | | | | 39,098 | |
| Right-of-use assets | | | | | (33,101 | ) | | | (6,480 | ) | | | (39,581 | ) |
| Contract liabilities | | | | | 258,704 | | | | (105,238 | ) | | | 153,466 | |
| Contract assets | | | | | (7,956 | ) | | | (9,881 | ) | | | (17,837 | ) |
| Prepaid expenses | | | | | (210,338 | ) | | | 113,788 | | | | (96,550 | ) |
| Prepayments | | | | | (65,395 | ) | | | 39,921 | | | | (25,474 | ) |
| Other | | | | | 27,258 | | | | 36,261 | | | | 63,519 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 20,395 | | | | 71,699 | | | | 92,094 | |
| Loss carried forward | | ₩ | | | 33,747 | | | | (33,747 | ) | | | - | |
| Carryover tax credit | | | | | - | | | | 13,549 | | | | 13,549 | |
| Unrecognized deferred tax assets | | | | | - | | | | (1,186 | ) | | | (1,186 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets | | ₩ | | | 54,142 | | | | 50,315 | | | | 104,457 | |
| E. | Details of unused tax loss carryforwards and unused tax credit carryforwards |
| i. | Details of unused tax loss carryforwards and unused tax credit carryforwards as of December 31, 2023 are as follows: |
| Year of expiration | | | | Unused loss
carryforwards | | | Unused tax credit
carryforwards | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| 2024 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | |
| 2025 | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| 2026 | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| 2027 | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| 2028 | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| 2029 | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| After 2029 | | | | | - | | | | 19,149 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 19,149 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| ii. | The timing of recovery of deferred tax assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows: |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Deferred tax assets | | | | | | | | | | |
| - Deferred tax assets to be recovered after more than 12 months | | ₩ | | | 262,710 | | | | 257,325 | |
| - Deferred tax assets to be recovered within 12 months | | | | | 579,367 | | | | 195,471 | |
| Sub-total | | | | | 842,077 | | | | 452,796 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| - Deferred tax liabilities to be recovered after more than 12 months | | | | | (402,784 | ) | | | (223,696 | ) |
| - Deferred tax liabilities to be recovered within 12 months | | | | | (272,447 | ) | | | (124,643 | ) |
| Sub-total | | | | | (675,231 | ) | | | (348,339 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets (liabilities), net | | ₩ | | | 166,846 | | | | 104,457 | |
12. Other assets
Details of other assets for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current | | | | | | | | |
| Prepayments | | ₩ | | | 5,246 | | | | 44 | |
| Prepaid expenses (*1) | | | | | 1,959,519 | | | | 1,068,119 | |
| Value added tax receivables | | | | | 305,490 | | | | 21,182 | |
| Non-current | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-current prepayments (*2) | | | | | 1,394,586 | | | | 1,630,586 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 3,664,841 | | | | 2,719,931 | |
| (*1) | The amount of Korean Won 749,552 thousand included in prepaid expenses as of December 31, 2022 has been recognized as cost of revenues in 2023. (2022: Korean Won 1,771,764 thousand) |
| (*2) | The Company recognized an impairment loss amounting to Korean Won 105,000 thousand in 2023. (2022: Korean Won 20,000 thousand) |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
13. Trade and other receivables
Details of trade and other receivables as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Trade receivable | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable — Trade | | ₩ | | | 196,380 | | | | 118,558 | |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other receivables | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accrued income | | ₩ | | | 6,325 | | | | 3,117 | |
| Non-trade receivables | | | | | 962 | | | | 437 | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | ₩ | | | 7,287 | | | | 3,554 | |
14. Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash on hand | | ₩ | | | 3,214 | | | | 1,218 | |
| Deposits in banks | | | | | 1,916,702 | | | | 941,736 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,919,916 | | | | 942,954 | |
The Company doesn’t have any restricted cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
15. Property, plant and equipment
| A. | Reconciliation of carrying amount |
Details of property and equipment as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | Book value | | | Accumulated depreciation | | | Carrying amount | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Office equipment | | ₩ | | | 22,304 | | | | (16,796 | ) | | | 5,508 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | | | | | 52,700 | | | | (13,608 | ) | | | 39,092 | |
| Right-of-use assets | | | | | 560,795 | | | | (231,395 | ) | | | 329,400 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 635,799 | | | | (261,799 | ) | | | 374,000 | |
| | | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | Book value | | | Accumulated depreciation | | | Carrying amount | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Office equipment | | ₩ | | | 22,304 | | | | (13,267 | ) | | | 9,037 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | | | | | 12,700 | | | | (9,735 | ) | | | 2,965 | |
| Right-of-use assets | | | | | 560,795 | | | | (160,989 | ) | | | 399,806 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 595,799 | | | | (183,991 | ) | | | 411,808 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Details of the changes in property and equipment for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Office
equipment | | | Furniture
and fixture | | | Right-of-Use
assets | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 9,037 | | | | 2,965 | | | | 399,806 | | | | 411,808 | |
| Acquisitions | | | | | - | | | | 40,000 | | | | - | | | | 40,000 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (3,529 | ) | | | (3,873 | ) | | | (70,406 | ) | | | (77,808 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 5,508 | | | | 39,092 | | | | 329,400 | | | | 374,000 | |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Office
equipment | | | Furniture
and fixture | | | Right-of-Use
assets | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 12,893 | | | | 5,504 | | | | 300,916 | | | | 319,313 | |
| Acquisitions | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 143,262 | | | | 143,262 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (3,856 | ) | | | (2,539 | ) | | | (44,372 | ) | | | (50,767 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 9,037 | | | | 2,965 | | | | 399,806 | | | | 411,808 | |
The classification of depreciation expenses in the statements of comprehensive income for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | ₩ | | | 77,808 | | | | 50,767 | |
| B. | Leased property, plant and equipment |
During 2023 and 2022, the Company leased vehicles and building and recognized right-of-use assets of Korean Won 329,400 thousand. (December 31, 2022: Korean Won 399,806 thousand of vehicles and building)
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
16. Financial instruments by category
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at amortized cost | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | | | 1,919,916 | | | | 942,954 | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | | | | 196,380 | | | | 118,558 | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | | | | 7,287 | | | | 3,554 | |
| Short-term loans, net | | | | | - | | | | 100,054 | |
| Long-term loans, net | | | | | 130,087 | | | | 10,063 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | 147,406 | | | | 93,224 | |
| Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term investments | | | | | 800,000 | | | | 1,096,100 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 3,201,076 | | | | 2,364,507 | |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial liability at amortized cost | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables (*) | | ₩ | | | 1,995,641 | | | | 308,786 | |
| Short-term borrowings | | | | | 1,505,000 | | | | 520,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 3,500,641 | | | | 828,786 | |
| (*) | Annual leave allowance for employees are excluded. |
| A. | Classification of investment assets |
The classification of investment assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Non-Current investments | | | | | | | | | | |
| Equity investments – at FVTPL (*) | | ₩ | | | 800,000 | | | | 1,096,100 | |
| (*) | Equity investments consist of profit-sharing project investment asset. |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| B. | Project investment designated as at FVTPL |
The Company designated the investments shown below as equity investments at FVTPL because there is no contractual obligation for repayment and it does not qualify as a cash flow with principal and interest payments.
| | | | | Fair value at
December 31,
2023 | | | Fair value at
December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Life is beautiful (2022 film) | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 296,100 | |
| Falling starlight | | | | | 800,000 | | | | 800,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 800,000 | | | | 1,096,100 | |
| C. | Net gains and losses by category of financial instruments |
The net gains and losses by category of financial instruments as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Financial assets at
amortized cost | | | Financial assets at
fair value through
profit or loss | | | Financial liabilities
at amortized cost | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Gain on project settlements | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 3,999 | | | | - | | | | 3,999 | |
| Interest income | | | | | 5,286 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 5,286 | |
| Interest expense | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (96,512 | ) | | | (96,512 | ) |
| Reversal of losses on valuation of long-term investments | | | | | - | | | | 39,355 | | | | - | | | | 39,355 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 5,286 | | | | 43,354 | | | | (96,512 | ) | | | (47,872 | ) |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Financial assets at
amortized cost | | | Financial assets at
fair value through
profit or loss | | | Financial liabilities
at amortized cost | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Gain on project settlements | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 8,997 | | | | - | | | | 8,997 | |
| Interest income | | | | | 4,148 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,148 | |
| Interest expense | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (13,152 | ) | | | (13,152 | ) |
| Losses on valuation of long-term investment securities | | | | | - | | | | (403,900 | ) | | | - | | | | (403,900 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 4,148 | | | | (394,903 | ) | | | (13,152 | ) | | | (403,907 | ) |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
17. Capital and reserves
Details of share capital as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In Korean won and number of shares) | |
| Number of authorized shares | | | | | 4,000 | |
| Value per share | | ₩ | | | 1,000 | |
| Number of shares issued | | | | | 78 | |
| Common shares | | ₩ | | | 78,000 | |
Holders of these shares are entitled to dividends as declared from time to time and are entitled to one vote per share at general meetings of the Company.
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other reserves | | ₩ | | | (585,468 | ) | | | - | |
Upon the spin-off, the aggregate net parent investment and accumulated other comprehensive income are reclassified to share capital and other reserves.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
18. Capital management
The Company’s policy is to maintain a strong capital base so as to maintain investor, creditor and market confidence and to sustain future development of the business. The Company monitors capital using a ratio of ‘net debt’ to ‘total equity’. Net debt is calculated as total liabilities (as shown in the statement of financial position) less cash and cash equivalents. The Company’s net debt to total equity ratio as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows.
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total liabilities | | ₩ | | | 7,339,765 | | | | 3,856,632 | |
| Less: Cash and cash equivalents | | | | | (1,919,916 | ) | | | (942,954 | ) |
| Net debt | | | | | 5,419,849 | | | | 2,913,678 | |
| Total equity | | ₩ | | | 225,695 | | | | 1,874,660 | |
| Net debt to total equity ratio | | | | | 24.01 | | | | 1.55 | |
19. Borrowings/payable and Loans/receivable
Borrowings as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term borrowings | | ₩ | | | 1,505,000 | | | | 520,000 | |
| Lease liabilities (*) | | | | | 62,797 | | | | 60,522 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,567,797 | | | | 580,522 | |
| Non-Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Lease liabilities (*) | | ₩ | | | 267,583 | | | | 334,405 | |
| (*) | The interest rate related to lease liabilities reflects the incremental borrowing rate based on the Company’s credit. The amount of interest expense related to lease liabilities incurred during 2023 is Korean Won 11,049 thousand (2022: Korean Won 6,349 thousand). Additionally, the amount of short-term lease payments not included in the measurement of lease liabilities during 2023 is Korean Won 68,292 thousand (2022: Korean Won 43,930 thousand). |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| A. | Terms and repayment schedule |
The terms and conditions of outstanding borrowings as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | Currency | | | Nominal
interest rate | | | Maturity | | | Face value | | | Carrying amount | | | Face value | | | Carrying amount | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Secured bank borrowings (*1) | | KRW | | | 4.87% | | | 10-May-24 | | | | 520,000 | | | | 520,000 | | | | 520,000 | | | | 520,000 | |
| Secured bank borrowings (*2) | | KRW | | | CD + 1.37% | | | 22-Sep-24 | | | | 985,000 | | | | 985,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total interest-bearing liabilities | | | | 1,505,000 | | | | 1,505,000 | | | | 520,000 | | | | 520,000 | |
| (*1) | The Company has received a payment guarantee of Korean Won 468,000 thousand (2022: Korean Won 494,000 thousand) from Korea Technology Finance Corporation as of December 31, 2023. The Company is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 62,400 thousand by the CEO of the Company as of December 31, 2023. |
| (*2) | The Company is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand by the CEO of the Company as of December 31, 2023. The borrowing will be repaid in monthly installments of 5,000 thousand. |
| B. | Terms and collection schedule |
The terms and conditions of outstanding loans as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | Currency | | | Nominal
interest rate | | | Maturity | | | Face value | | | Carrying amount | | | Face value | | | Carrying amount | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Falling Starlight Limited Company Specializing in The Cultural Industry | | KRW | | | - | | | - | | | | 120,054 | | | | 120,054 | | | | 100,054 | | | | 100,054 | |
| Park, Un Kyoung | | KRW | | | 4.60% | | | 16-Jan-25 | | | | 10,000 | | | | 10,033 | | | | 10,000 | | | | 10,063 | |
| Total | | | | 130,054 | | | | 130,087 | | | | 110,054 | | | | 110,117 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
20. Trade and other payables
Trade and other payables as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other payable | | ₩ | | | 1,312,995 | | | | 105,917 | |
| Accrued expenses | | | | | 686,973 | | | | 244,093 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,999,967 | | | | 350,010 | |
21. Provisions
Provisions for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Site restoration | | | | | | | | | | |
| Beginning of the year | | ₩ | | | 3,448 | | | | 3,425 | |
| Interest expense | | | | | 23 | | | | 23 | |
| Ending of the year | | ₩ | | | 3,471 | | | | 3,448 | |
The provision for building restoration relates to buildings leased during 2022 and 2023. The provision has been estimated based on historical data associated with similar buildings.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
22. Financial Instruments – Fair values and risk management
| A. | Accounting classifications and fair values |
The following table shows the carrying amounts and fair values of financial assets and financial liabilities, including their levels in the fair value hierarchy. It does not include fair value information for financial assets and financial liabilities not measured at fair value if the carrying amount is a reasonable approximation of fair value.
Carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term investments | | ₩ | | 800,000 | | | - | | | - | | | 800,000 | | | 800,000 | |
Carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term investments | | ₩ | | 1,096,100 | | | - | | | - | | | 1,096,100 | | | 1,096,100 | |
| B. | Measurement of fair values |
Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows:
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 2: all inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable (either directly that is, prices, or indirectly that is, derived from prices) for the asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 3: unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. |
The fair value of financial instruments traded in an active market is determined based on the quoted market price as of the end of the reporting period. If the quoted prices are readily and regularly available through exchanges, sellers, brokers, industry groups, rating agencies or regulators and such prices represent actual market transactions that occur regularly between independent parties, they are considered active markets.
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market is determined using valuation techniques. These valuation techniques use as much market observable information as possible and use the least amount of Company-specific information. At this time, if all the significant input variables required to measure the fair value are observable, the financial instruments are classified as Level 2.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
If more than one significant input variable is not based on observable market information, the item is included in Level 3.
If the information is insufficient to measure fair value of the project investment, the Company recognizes gain on project settlements when the accumulated settlements exceed the project investment’s original invested amount. Before exceeding the project investment’s original invested amount, the settlements are recognized as the return of original project investment. The Company recognizes the valuation loss of the project investment based on its judgment as to whether the total amount of production costs and distribution fees could exceed the shared profit.
| C. | Financial risk management |
The Company’s operating activities expose itself to a variety of financial risks: market risk, credit risk and liquidity risk from which the Company’s risk management program focuses on minimizing any adverse effects on its financial performance. The Company operates financial risk management policies and programs that closely monitor and respond to each risk factor.
Credit risk is the risk of financial loss to the Company if a customer or counterpart to a financial instrument fails to meet its contractual obligations and arises principally from the Company’s receivables from customers. In order to manage credit risk, the Company regularly evaluate the credit worthiness of each customer or counterparty considering the party’s financial information, past experience, its own trading records and other factors. In relation to the impairment of financial assets subsequent to initial recognition, the Company recognizes the changes in expected credit loss (“ECL”) in profit or loss at each reporting date. The carrying amount of a financial asset represents the maximum exposure to credit risk.
The maximum exposure to credit risk of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | | | 1,919,916 | | | | 942,954 | |
| Accounts receivable, net | | | | | 203,667 | | | | 122,112 | |
| Short-term loans, net | | | | | - | | | | 100,054 | |
| Long-term loans, net | | | | | 130,087 | | | | 10,063 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | 147,406 | | | | 93,224 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 2,401,076 | | | | 1,268,407 | |
Cash and cash equivalents are deposited in financial institutions with strong credit rating. The Company’s exposure to credit risk is influenced mainly by the individual characteristics of each customer. The Company has established a credit policy under which each new customer is analyzed individually before the Company’s standard payment and delivery terms and conditions are offered. The Company’s review includes external ratings, if they are available, financial statements, credit agency information, industry information and in some cases bank references.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The Company monitors customer credit risk, customers are grouped according to their credit characteristics, including whether they are an individual or a legal entity, their geographic location, industry, trading history with the Company and existence of previous financial difficulties. The Company does not require collateral in respect of trade and other receivables. Expected credit losses (ECLs) and credit risk exposures for accounts and other receivables as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
- Accounts receivables
| As of December 31, 2023 | | Expected loss rate | | | | | Carrying amount | | | Loss allowance | |
| | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Not due or overdue less than 90 days | | | 0.00 | % | | ₩ | | | 203,667 | | | | - | |
| More than 90 days ~ Less than 1 year | | | 0.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| More than 1 year | | | 100.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | | | | | ₩ | | | 203,667 | | | | - | |
| As of December 31, 2022 | | Expected loss rate | | | | | Carrying amount | | | Loss allowance | |
| | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Not due or overdue less than 90 days | | | 0.00 | % | | ₩ | | | 122,112 | | | | - | |
| More than 90 days ~ Less than 1 year | | | 0.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| More than 1 year | | | 100.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | | | | | ₩ | | | 112,112 | | | | - | |
Liquidity risk management includes the maintenance of sufficient cash and marketable securities, the availability of funds from appropriately committed credit lines, and the ability to settle market positions.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Financial liabilities of the Company by maturity according to the remaining period from December 31, 2023 to the contractual maturity date are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | Carrying Amount | | | Less than 3 months | | | 3 months ~ 1 year | | | 1~2 years | | | 2~5 years | | | More than 5 years | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Payables (*) | | ₩ | | | 1,312,994 | | | | 238,741 | | | | 1,074,253 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,312,994 | |
| Accrued expense (*) | | | | | 682,647 | | | | 472,164 | | | | 210,483 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 682,647 | |
| Short-term borrowings | | | | | 1,505,000 | | | | 33,985 | | | | 1,517,736 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,551,721 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 330,379 | | | | 18,947 | | | | 56,840 | | | | 75,786 | | | | 194,527 | | | | 7,580 | | | | 353,680 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 3,831,020 | | | | 763,837 | | | | 2,859,312 | | | | 75,786 | | | | 194,527 | | | | 7,580 | | | | 3,901,042 | |
| (*) | Payables and accrued expense exclude non-financial liabilities. |
Financial liabilities of the Company by maturity according to the remaining period from December 31, 2022 to the contractual maturity date are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | Carrying Amount | | | Less than 3 months | | | 3 months ~ 1 year | | | 1~2 years | | | 2~5 years | | | More than 5 years | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Payables (*) | | ₩ | | | 69,897 | | | | 69,009 | | | | 888 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 69,897 | |
| Accrued expense (*) | | | | | 238,889 | | | | 101,354 | | | | 137,536 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 238,889 | |
| Short-term borrowings | | | | | 520,000 | | | | 7,257 | | | | 523,790 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 531,047 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 394,927 | | | | 18,567 | | | | 56,840 | | | | 75,786 | | | | 224,833 | | | | 53,060 | | | | 429,086 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,223,713 | | | | 196,187 | | | | 719,054 | | | | 75,786 | | | | 224,833 | | | | 53,060 | | | | 1,268,920 | |
| (*) | Payables and accrued expense exclude non-financial liabilities. |
The sensitivity analysis is based on borrowing under variable interest rate conditions as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | Increased by 100 bp | | | Decreased by 100 bp | | | Increased by 100 bp | | | Decreased by 100 bp | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest | | ₩ | | | 7,250 | | | | (7,250 | ) | | | 5,200 | | | | (5,200 | ) |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
23. Leases
The Company leases buildings and vehicles. The leases typically run for a period of 5 to 10 years, with an option to renew or terminate the lease after that date. The Company also leases vehicles with contract terms of one year. This lease is short-term item. The Company has elected not to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for these leases. Information about leases for which the Company is a lessee is presented below.
Right-of-use assets related to leased properties that do not meet the definition of investment property are presented as property, plant and equipment.
Details of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities recognized in the statements of financial position as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Acquisition price) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Building | | ₩ | | | 417,533 | | | | 417,533 | |
| Vehicles | | | | | 143,262 | | | | 143,262 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 560,795 | | | | 560,795 | |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Accumulated depreciation) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Building | | ₩ | | | (200,123 | ) | | | (158,370 | ) |
| Vehicles | | | | | (31,272 | ) | | | (2,619 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (231,395 | ) | | | (160,989 | ) |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Net book value) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Building | | ₩ | | | 217,410 | | | | 259,163 | |
| Vehicles | | | | | 111,990 | | | | 140,643 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 329,400 | | | | 399,806 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Changes in right-of-use assets for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Building | | | Vehicles | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance as of January 1, 2023 | | ₩ | | | 259,163 | | | | 140,643 | | | | 399,806 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (41,753 | ) | | | (28,653 | ) | | | (70,406 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | | ₩ | | | 217,410 | | | | 111,990 | | | | 329,400 | |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Building | | | Vehicles | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance as of January 1, 2022 | | ₩ | | | 300,916 | | | | - | | | | 300,916 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (41,753 | ) | | | (2,619 | ) | | | (44,372 | ) |
| Acquisitions | | | | | - | | | | 143,262 | | | | 143,262 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2022 | | ₩ | | | 259,163 | | | | 140,643 | | | | 399,806 | |
| ii. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
Amounts recognized in profit or loss for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest expense relating to lease liabilities (included in finance cost) | | ₩ | | | 11,049 | | | | 6,349 | |
| Expense relating to short-term leases | | | | | 2,436,273 | | | | 2,114,703 | |
The Company has revised the expense relating to short-term leases for the year ended December 31, 2022 to be consistent with the classification as of December 31, 2023.
| iii. | Amounts recognized in statement of cash flows |
Amounts recognized in statement of cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total cash outflows of leases | | ₩ | | | 2,511,869 | | | | 2,160,275 | |
The Company has revised the total cash outflows for leases for the year ended December 31, 2022 to be consistent with the classification as of December 31, 2023.
Some property leases contain extension options exercisable by the Company. The Company reflected extension options in measuring the lease liabilities. The extension options held are exercisable only by the Company and not by the lessors. The Company assesses at the lease commencement date whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the extension options. The Company reassesses whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the options if there is a significant event or significant changes in circumstances within its control.
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
24. Commitments
Key commitments the Company has entered into with financial institutions and others as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| Financial institutions | | Categories | | | | Credit limit | | | Disbursed
borrowing
amount | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Woori Bank | | Corporate operating borrowings (*1) | | ₩ | | | 520,000 | | | | 520,000 | |
| Woori Bank | | Corporate operating borrowings (*2) | | | | | 985,000 | | | | 985,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,505,000 | | | | 1,505,000 | |
| (*1) | The Company has received a payment guarantee of Korean Won 468,000 thousand (2022: Korean Won 494,000 thousand) from Korea Technology Finance Corporation as of December 31, 2023. The Company is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 62,400 thousand by the CEO of the Company as of December 31, 2023. |
| (*2) | The Company is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 1,200,000 thousand by the CEO of the Company as of December 31, 2023. |
On September 14, 2023, an amendment was made to the equity interest exchange agreement, originally entered into on March 31, 2023, between the CEO, who is the dominant shareholder of the Company, and K Enter Holdings for the purpose of listing on the NASDAQ through a merger with a SPAC company. The equity interest exchange agreement is effective on the date designated by K Enter Holdings. Upon the effective date, the CEO of the Company will exchange 40 shares with the equity interest of K Enter Holdings. Following the equity interest exchange transaction, the Company is expected to be a subsidiary of K Enter Holdings.
Details of guarantees received as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| Guaranteed by | | Details of guarantee | | | Guarantee limit | |
| | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea credit guarantee fund | | Payment guarantee | | | 468,000 | |
Details of guarantees received as of December 31, 2022 are as follows:
| Guaranteed by | | Details of guarantee | | | Guarantee limit | |
| | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea credit guarantee fund | | Payment guarantee | | | 494,000 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
25. Statement of Cash flows
Adjustments for income and expenses from operating activities for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Depreciation | | ₩ | | | 77,808 | | | | 50,767 | |
| Bad debt expenses | | | | | 105,000 | | | | 20,000 | |
| Interest expenses | | | | | 107,583 | | | | 19,524 | |
| Interest income | | | | | (5,286 | ) | | | (4,148 | ) |
| Gain on project settlements | | | | | (3,999 | ) | | | (8,997 | ) |
| (Reversal of) losses on valuation of long-term investments | | | | | (39,355 | ) | | | 403,900 | |
| Severance benefits | | | | | 28,490 | | | | 27,796 | |
| Income tax expenses | | | | | (18,799 | ) | | | (20,035 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 251,442 | | | | 488,807 | |
Changes in assets and liabilities from operating activities for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | ₩ | | | 12,612 | | | | 261 | |
| Other current assets | | | | | (1,180,909 | ) | | | 1,076,690 | |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | | | | 131,000 | | | | (315,917 | ) |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | | | | (77,888 | ) | | | 163,046 | |
| Trade and other payables | | | | | 509,249 | | | | (390,815 | ) |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | | | | - | | | | (9,935 | ) |
| Contract liabilities | | | | | 780,775 | | | | (801,685 | ) |
| Contract assets | | | | | (28,109 | ) | | | (119,273 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 146,730 | | | | (397,628 | ) |
Significant non-cash transactions for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Unsettled distribution to Pluto due to Spin-off | | ₩ | | | 1,081,277 | | | | - | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The movements of liabilities to cash flows arising from financing activities for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | Short-term
borrowings | | | Current lease
liabilities | | | Non-current
lease liabilities | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at 1 January 2022 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 33,835 | | | | 266,853 | | | | 300,688 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | - | |
| Proceeds from borrowings | | | | | 520,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 520,000 | |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | - | | | | (39,223 | ) | | | - | | | | (39,223 | ) |
| Reclassification | | | | | - | | | | 65,910 | | | | (65,910 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | | | | 520,000 | | | | 26,687 | | | | (65,910 | ) | | | 480,777 | |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| New leases | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 133,462 | | | | 133,462 | |
| Interest expense | | | | | - | | | | 6,349 | | | | - | | | | 6,349 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | - | | | | (6,349 | ) | | | - | | | | (6,349 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | 133,462 | | | | 133,462 | |
| Balance at 31 December 2022 | | ₩ | | | 520,000 | | | | 60,522 | | | | 334,405 | | | | 914,927 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at 1 January 2023 | | | | | 520,000 | | | | 60,522 | | | | 334,405 | | | | 914,927 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from borrowings | | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Repayment of borrowings | | | | | (15,000 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (15,000 | ) |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | - | | | | (64,547 | ) | | | - | | | | (64,547 | ) |
| Reclassification | | | | | - | | | | 66,822 | | | | (66,822 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 985,000 | | | | 2,275 | | | | (66,822 | ) | | | 920,453 | |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | | | | | - | | | | 11,049 | | | | - | | | | 11,049 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | - | | | | (11,049 | ) | | | - | | | | (11,049 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Balance at 31 December 2023 | | ₩ | | | 1,505,000 | | | | 62,797 | | | | 267,583 | | | | 1,835,380 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
26. Related parties
| A. | List of related parties |
List of related parties as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| Relationship | | Entity |
| Other related parties | | - | Falling Starlight Limited Company Specializing in The Cultural Industry (hereafter referred to as “Falling Starlight”) |
| | | - | Pluto Co., Ltd |
| Key management personnel | | - | Park, Un Kyoung |
| B. | Transactions with related parties |
Details of transaction with related parties for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | 2023 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Revenue | | | Interest income | | | Interest expenses | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties | | Falling Starlight | | ₩ | | | 432,411 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | Pluto | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 57,521 | |
| Key management personnel | | Park, Un Kyoung | | | | | - | | | | 430 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 432,411 | | | | 430 | | | | 57,521 | |
| | | | | | | 2022 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Revenue | | | Interest income | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties | | Falling Starlight | | ₩ | | | 5,567,067 | | | | - | |
| Key management personnel | | Park, Un Kyoung | | | | | - | | | | 501 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 5,567,067 | | | | 501 | |
| C. | Account balances with related parties |
The balances of receivables and payables to related parties as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Receivables | | | Loans | | | Project investment | | | Payables | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties | | Falling Starlight | | ₩ | | | 20,000 | | | | 120,054 | | | | 800,000 | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | Pluto (*) | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,138,798 | |
| Key management personnel | | Park, Un Kyoung | | | | | 897 | | | | 10,033 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 20,897 | | | | 130,087 | | | | 800,000 | | | | 1,138,798 | |
| (*) | On March 31, 2023, the date of spin-off, the Company agreed to pay Korean Won 2,053,480 thousand to Pluto in accordance with the Separation Proposal. As of December 31, 2023, the payables to Pluto is Korean Won 1,138,798 thousand after the settlement during the period ended December 31, 2023. |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The balances of receivables and payables to related parties as of December 31, 2022 are as follows:
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Receivables | | | Loans | | | Project investment | | | Payables | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties | | Falling Starlight | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 100,054 | | | | 800,000 | | | | - | |
| Key management personnel | | Park, Un Kyoung | | | | | 437 | | | | 10,063 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 437 | | | | 110,117 | | | | 800,000 | | | | - | |
| D. | Financing and investing transactions with related parties |
Details of significant financing and investing transactions with related parties for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | 2023 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Loans | | | Increase in project
investment | | | Increase in
accrued income | | | Capital
distribution | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties | | Falling Starlight | | ₩ | | | 20,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | Pluto | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,043,964 | |
| Key management personnel | | Park, Un Kyoung | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 460 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 20,000 | | | | - | | | | 460 | | | | 1,043,964 | |
| | | | | | | 2022 | |
| Related party | | Name of entity | | | | Loans | | | Increase in project investment | | | Increase in
accrued income | | | Capital
contribution | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties | | Falling Starlight | | ₩ | | | 100,054 | | | | 800,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other related parties | | Pluto | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 678,057 | |
| Key management personnel | | Park, Un Kyoung | | | | | 10,000 | | | | - | | | | 501 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 110,054 | | | | 800,000 | | | | 501 | | | | 678,057 | |
THE LAMP CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| E. | Commitments with related parties |
During the year ended December 31, 2022, the Company entered into an agreement with Falling Starlight for the production service and profit sharing.
As of December 31, 2023, the Company has been satisfying its performance obligation for production service in accordance with the agreement and has received the consideration for the service provided. After the release of the content, the Company is entitled to share the profits in accordance with the agreed profit-sharing ratio.
The Company is provided a joint guarantee of Korean Won 1,262,400 thousand by the CEO of the Company as of December 31, 2023.
| F. | Transactions with key management personnel |
The compensation for the key management personnel for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Short-term employee benefits | | ₩ | | | 205,500 | | | | 161,500 | |
| Post-employment benefits | | | | | 19,468 | | | | 17,781 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 224,968 | | | | 179,281 | |
Compensation of the Company’s key management personnel includes salaries, non-cash benefits and contributions to a post-employment defined benefit plan.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023
| | | Note | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | 12 | | ₩ | | | 1,762,929 | | | | 3,723,417 | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | 10 | | | | | 1,000,690 | | | | 1,537,640 | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | 4 | | | | | 320 | | | | 2,647 | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | | | | | | 730 | | | | 42,665 | |
| - Related parties | | 13 | | | | | - | | | | 42,664 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 730 | | | | 1 | |
| Short-term loans, net | | 7 | | | | | 135,000 | | | | 952,500 | |
| - Related parties | | 13 | | | | | - | | | | 952,500 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 135,000 | | | | - | |
| Other current assets | | 4 | | | | | 1,351,757 | | | | 5,070,905 | |
| Other current financial assets | | | | | | | 25,000 | | | | 49,000 | |
| Contract assets | | 4 | | | | | 149,806 | | | | 143,835 | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | | 4,426,232 | | | | 11,522,609 | |
| Property, plant and equipment including right-of-use assets | | 11 | | | | | 91,923 | | | | 138,006 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | | | 144,066 | | | | 131,620 | |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | | | | | | 531,600 | | | | 441,600 | |
| Total non-current assets | | | | | | | 767,589 | | | | 711,226 | |
| Total assets | | | | ₩ | | | 5,193,821 | | | | 12,233,835 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | | | ₩ | | | 1,628,608 | | | | 1,060,087 | |
| Other current financial liabilities | | 9 | | | | | - | | | | 200,200 | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | | | | | 14,531 | | | | 40,010 | |
| Contract liabilities | | 4 | | | | | 389,623 | | | | 6,182,960 | |
| Current Lease liabilities | | 9,11,12 | | | | | 84,869 | | | | 95,509 | |
| Current tax liabilities | | 6 | | | | | 118,679 | | | | 72,520 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | | 2,236,310 | | | | 7,651,286 | |
| Non-current Lease liabilities | | 9,11,12 | | | | | 10,821 | | | | 44,421 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | | | | | 10,821 | | | | 44,421 | |
| Total liabilities | | | | ₩ | | | 2,247,131 | | | | 7,695,707 | |
| Equity | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital | | 8 | | ₩ | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | |
| Share premium | | 8 | | | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | |
| Other reserves | | 8 | | | | | (2,000,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Retained earnings | | | | | | | 4,846,690 | | | | 4,438,128 | |
| Equity attributable to owners of the Parent Company | | | | | | | 2,946,690 | | | | 4,538,128 | |
| Total equity | | | | | | | 2,946,690 | | | | 4,538,128 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | | | | ₩ | | | 5,193,821 | | | | 12,233,835 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed consolidated interim financial statements.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Note | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Media production revenue | | 3,4 | | ₩ | | | 14,556,885 | | | | 72,027 | |
| Cost of revenues | | | | | | | (13,798,380 | ) | | | (14,876 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | | | | | 758,505 | | | | 57,151 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | | | | | (339,086 | ) | | | (374,787 | ) |
| Other income | | | | | | | 1 | | | | 15,906 | |
| Other expenses | | | | | | | (8 | ) | | | (1,651 | ) |
| Operating profit (loss) | | | | | | | 419,412 | | | | (303,381 | ) |
| Finance income | | | | | | | 32,983 | | | | 98,341 | |
| - Related parties | | 13 | | | | | 2,154 | | | | 21,148 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 30,829 | | | | 77,193 | |
| Finance costs | | | | | | | (5,458 | ) | | | (19,039 | ) |
| Profit (Loss) before income tax | | | | | | | 446,937 | | | | (224,079 | ) |
| Income tax expense | | 6 | | | | | (38,375 | ) | | | (2,141 | ) |
| Profit (Loss) for the period | | | | ₩ | | | 408,562 | | | | (226,220 | ) |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | ₩ | | | 408,562 | | | | (226,220 | ) |
| Profit (loss) attributable to: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Owners of the Parent Company | | | | | | | 408,562 | | | | (226,220 | ) |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) attributable to: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Owners of the Parent Company | | | | | | | 408,562 | | | | (226,220 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed consolidated interim financial statements.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Note | | | | Share capital | | | Capital surplus | | | Other components of equity | | | Retained earnings | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) |
| Balance at January 1, 2023 | | | | ₩ | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | | | | - | | | | 4,251,655 | | | | 4,351,655 | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (226,220 | ) | | | (226,220 | ) |
| Balance at June 30, 2023 | | | | ₩ | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | | | | - | | | | 4,025,435 | | | | 4,125,435 | |
| Balance at January 1, 2024 | | | | ₩ | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | | | | - | | | | 4,438,128 | | | | 4,538,128 | |
| Total comprehensive income for the period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Profit for the period | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 408,562 | | | | 408,562 | |
| Transaction with owners, recognized directly in equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Acquisition of treasury stock | | 8 | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (2,000,000 | ) | | | - | | | | (2,000,000 | ) |
| Balance at June 30, 2024 | | | | ₩ | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | | | | (2,000,000 | ) | | | 4,846,690 | | | | 2,946,690 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed consolidated interim financial statements.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| | | Note | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | 12 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Profit (Loss) for the period | | | | ₩ | | | 408,562 | | | | (226,220 | ) |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities | | | | | | | (1,567,856 | ) | | | (274,791 | ) |
| Interest received | | | | | | | 55,425 | | | | 47,463 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | | | (5,458 | ) | | | (5,361 | ) |
| Income taxes refund (paid) | | | | | | | 7,783 | | | | (5,881 | ) |
| Net cash outflow from operating activities | | | | ₩ | | | (1,101,544 | ) | | | (464,790 | ) |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Disposal of short-term financial instruments | | | | ₩ | | | 2,551,823 | | | | 2,430,545 | |
| Purchase of short-term financial instruments | | | | | | | (2,001,527 | ) | | | (2,469,888 | ) |
| Decrease in other current financial assets | | | | | | | 24,000 | | | | - | |
| Increase in other current financial assets | | | | | | | - | | | | (25,000 | ) |
| Proceeds from other non-current financial assets | | | | | | | - | | | | 850 | |
| Increase in other non-current financial assets | | | | | | | (6,300 | ) | | | - | |
| Payments for short-term loans | | | | | | | (135,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Collection of short-term loans | | | | | | | 952,500 | | | | - | |
| - Related parties | | | | | | | 952,500 | | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Net cash inflow (outflow) in investing activities | | | | ₩ | | | 1,385,496 | | | | (63,493 | ) |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | 12 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Repayment in investment withholdings | | | | ₩ | | | (200,200 | ) | | | - | |
| Acquisition of treasury shares | | | | | | | (2,000,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Repayment of lease liabilities | | | | | | | (44,240 | ) | | | (41,817 | ) |
| Net cash outflow in financing activities | | | | ₩ | | | (2,244,440 | ) | | | (41,817 | ) |
| Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | (1,960,488 | ) | | | (570,099 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the period | | | | | | | 3,723,417 | | | | 1,027,292 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of the period | | | | ₩ | | | 1,762,929 | | | | 457,193 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed consolidated interim financial statements.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
1. Reporting entity
The Parent Company
Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd. (“the Parent Company”) was incorporated in February 2005 and the Parent Company’s registered office is at 220, Yeoksam-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Korea. These condensed financial statements comprise the Parent Company and its subsidiary (together referred to as the “Group”). The Group generates revenue primarily through providing the media production services. The Parent Company is primarily providing the media production service that consists of planning, producing, and selling the theatrical films and television programs. Trigger Limited Company Specializing in The Cultural Industry (the “Subsidiary”) is engaged in the business of planning, development and production of the film Trigger.
The Parent Company’s major shareholders and their respective percentage of ownership as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | Number of
shares | | | Ownership
(%) | | | Number of
shares | | | Ownership
(%) | |
| Yoon, In Bum | | | 4,750 | | | | 47.50 | % | | | 5,000 | | | | 50 | % |
| Kim, Soo Jin | | | 4,750 | | | | 47.50 | % | | | 5,000 | | | | 50 | % |
| Treasury shares | | | 500 | | | | 5.00 | % | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | | 10,000 | | | | 100 | % | | | 10,000 | | | | 100 | % |
Consolidated Subsidiary
Details of the consolidated subsidiary as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Percentage of ownership (%) | | | | | |
| Subsidiary | | Location | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | | | Fiscal year end | | Main business |
| Trigger Limited Company Specializing in The Cultural Industry | | Korea | | 100 | | | 100 | | | December | | Planning, development and production of the film Trigger |
The Parent Company established a special purpose company to plan, develop and manage the production of the new project ‘Trigger’ as of April 5, 2023. The initial capital amounted to Korean won 10,000 thousand, but no capital has been contributed as of June 30, 2024.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
2. Basis of Presentation and Material Accounting Policies
These condensed interim consolidated financial statements for the six months ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 have been prepared in accordance with International Accounting Standards (“IAS”) 34 Interim Financial Reporting as issued by International Accounting Standard Board (“IASB”), and should be read in conjunction with the Group’s last annual consolidated financial statements as at and for the year ended December 31, 2023 (“last annual financial statements”). They do not include all of the information required for a complete set of financial statements prepared in accordance with IFRS. However, selected explanatory notes are included to explain events and transactions that are significant to an understanding of the changes in the Group’s financial position and performance since the last annual financial statements.
| B. | Material Accounting Policies |
Material accounting policies and method of computation used in the preparation of the condensed consolidated interim financial statements are consistent with those of the last annual financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2023, except for the changes as described below.
Income tax expense
Income tax expense for the interim period is recognized based on management’s best estimate of the weighted average annual income tax rate expected for the full financial year. The estimated average annual effective income tax rate is applied to the pre-tax income of the interim period.
| i. | New and amended standards or interpretations adopted by the Group |
The Group has applied the following standards and amendments for the first time for their annual reporting period commencing January 1, 2024.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements
The amendments to IAS 1 clarify that the classification of liabilities as current or non-current should be based on rights that are in existence at the end of the reporting period and that the classification is unaffected by management’s intentions or expectations about whether an entity will exercise its right to defer settlement of a liability. The amendments also introduce a definition of settlement to make clear that settlement includes the transfer to the counterparty of the entity’s own equity instruments, however, it would be excluded if an option to settle the liability by the transfer of the entity’s own equity instruments is recognized separately from the liability as an equity component of a compound financial instrument. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Group’s interim financial statements.
IAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows, and IFRS 7, Financial Instruments: Presentation
The amendments add to the disclosure objectives in IAS 7, Statement of Cash Flows, that information about supplier financing arrangements should be disclosed to enable users of financial statements to assess the impact of those arrangements on the Group’s liabilities and cash flows. The amendments also amend IFRS 7, Financial Instruments: Presentation, to add supplier financing arrangements as an example of a requirement to disclose information about an entity’s exposure to concentrations of liquidity risk. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Group’s interim financial statements.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
IAS 16 Leases
The amendments add requirements for the subsequent measurement of sale-and-leaseback transactions that are accounted for as sales in accordance with IFRS 15, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. The amendments require the seller lessee to calculate the ‘lease payments’ or ‘revised lease payments’ in a way that does not result in the seller-lessee recognizing any gain or loss for the rights of use that the seller-lessee continues to retain after the lease commences. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Group’s interim financial statements.
| ii. | New and amended standards or interpretations not yet adopted by the Group |
The following new accounting standards and interpretations that have been published that are not mandatory for June 30, 2024 reporting periods and have not been early adopted by the Group.
IAS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates
The amendments require exchangeability of two currencies should be assessed in order to clarify reporting of foreign currency transactions in the absence of normal-functioning foreign exchange market. The amendments also require applicable spot exchange rate should be determined when the assessment indicates two currencies lack exchangeability. The amendments are effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2025, with early application permitted.
3. Operating segments
The Group’s operating segments have been identified to be a single business unit, by which the Group provides media production services.
The following summary describes the operations of reportable segment.
| Operating segment | | Operations |
| Media Production | | Planning, producing, and selling the media content such as theatrical films and television programs |
The Group’s chief executive officer reviews the internal management reports at least quarterly.
Media production is managed and operated in Seoul, South Korea. The geographic information analyses the Group’s revenue by the customer’s country of domicile. In presenting the geographic information, segment revenue and non-current assets have been based on the geographic location of customers.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Summary of the Group’s operation by the region based on the location of customers for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 49,502 | | | | 72,027 | |
| USA | | | | | 14,507,383 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 14,556,885 | | | | 72,027 | |
Summary of the Group’s non-current assets based on the location as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 767,589 | | | | 711,226 | |
Revenues from major customers that amount to 10% or more of the Group’s revenue for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Customer A | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 14,507,383 | | | | - | |
| % | | | | | 99.66 | % | | | - | |
| Customer B | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 31,156 | | | | 48,150 | |
| % | | | | | 0.21 | % | | | 66.85 | % |
| Customer C | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 5,971 | | | | 15,991 | |
| % | | | | | 0.04 | % | | | 22.20 | % |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 14,544,510 | | | | 64,141 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
4. Revenue
The Group generates revenue primarily through providing the services for production of feature films for initial exhibition in theaters and production of television programs to third parties for internal television and streaming services.
Revenue from contracts with customers for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Revenue from contracts with customers | | ₩ | | | 14,556,885 | | | | 72,027 | |
| B. | Disaggregation of revenue from contracts with customers |
In the following table, revenue from contracts with customers is disaggregated by major products and service lines and timing of revenue recognition (see Note 3).
Revenue from contracts with customers based on the service contract type and the timing of satisfaction of performance obligations for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Major products/service lines | | | | | | | | | | |
| Media production | | ₩ | | | 14,556,885 | | | | 72,027 | |
| Timing of revenue recognition | | | | | | | | | | |
| At a point in time | | ₩ | | | 43,531 | | | | 56,036 | |
| Over time | | | | | 14,513,354 | | | | 15,991 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 14,556,885 | | | | 72,027 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
The balance of contract assets from contracts with customers as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | ₩ | | | 320 | | | | 2,647 | |
| Contract asset (Unbilled receivables) | | | | | 149,806 | | | | 143,835 | |
| Contract liabilities (Deferred revenue) | | | | | 389,623 | | | | 6,182,960 | |
The contract liabilities primarily relate to the advance consideration received from customers for media production service, for which revenue is recognized over time. This will be recognized as revenue when the Group satisfies the performance obligations.
| D. | Asset recognized from costs to fulfil a Contract |
The Group recognized the expenses related to the screenplay for the film and drama production as assets, which are presented under “other assets” in the statement of financial position.
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Deferred contract fulfilment costs (*) | | ₩ | | | 985,244 | | | | 4,128,054 | |
| (*) | This is presented within ‘other assets’ in the consolidated statements of financial position. |
The costs relate directly to the contract, generate resources that will be used in satisfying the contract and are expected to be recovered. They were therefore recognized as an asset from costs to fulfil a contract. The asset is amortized as expense on a basis that is consistent with the transfer to the customer of the services to which the asset related over the term of the specific film production contract.
5. Employee benefits
The expenses recognized in relation to defined contribution plan for the period ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are Korean Won 37,642 thousand and Korean Won 28,775 thousand.
| A. | Employee benefit expenses |
| i. | Details of employee benefit expenses recognized for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows: |
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Wages and salaries | | ₩ | | | 216,500 | | | | 186,990 | |
| Expenses related to post-employment plans | | | | | 37,642 | | | | 28,775 | |
| Fringe benefit | | | | | 16,470 | | | | 22,485 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 270,612 | | | | 238,250 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| ii. | Expenses are recognized in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income (loss) as follows: |
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | ₩ | | | 270,612 | | | | 238,250 | |
6. Income taxes
Details of income tax expenses for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current tax expense | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current year | | ₩ | | | 36,674 | | | | - | |
| Adjustments recognized related to prior period incomes (*) | | | | | 1,701 | | | | 2,141 | |
| Tax expense on continuing operations | | ₩ | | | 38,375 | | | | 2,141 | |
| (*) | In the normal course of business, the Group is examined by taxation authority. The Group’s management regularly assesses the potential outcomes of these examinations and any future examinations for the current or prior years in determining the adequacy of its liabilities for income taxes. |
The Group establish additional current tax liabilities for income taxes when, despite the belief that tax positions are fully supportable, there remain positions that do not meet the minimum probability threshold, which is a tax position that is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by the applicable taxing authority. The impact of current tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions, as well as the related net interest and penalties, are included in income taxes in the consolidated statements of operations.
As of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023, the Group did not recognize deferred income tax asset for the temporary difference as it is not probable such loss carried forward and carryover tax credit can be utilized in the foreseeable future.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
7. Loans receivable
The terms and conditions of outstanding loans as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| | | Currency | | | Nominal interest rate | | | Face
value | | | Carrying
amount | | | Face
value | | | Carrying
amount | |
| Key management personnel | | KRW | | | 4.60% | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 952,500 | | | | 952,500 | |
| K Enter Holdings | | KRW | | | 3.00% | | | | 135,000 | | | | 135,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total loans receivable | | | | 135,000 | | | | 135,000 | | | | 952,500 | | | | 952,500 | |
| Less: Current portion | | | | (135,000 | ) | | | (135,000 | ) | | | (952,500 | ) | | | (952,500 | ) |
| Long-term loans receivable | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
8. Capital and reserves
| A. | Share capital and share premium |
Details of share capital and share premium as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In Korean won and number of shares) | |
| Number of authorized shares | | | | | 40,000 | | | | 40,000 | |
| Value per share | | ₩ | | | 5,000 | | | | 5,000 | |
| Number of shares issued | | | | | 10,000 | | | | 10,000 | |
| Common shares | | ₩ | | | 50,000,000 | | | | 50,000,000 | |
| B. | Other components of equity |
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Share premium | | ₩ | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | |
On January 31, 2024, the Group acquired a 5% interest of the Parent Company’s issued shares for Korean Won 2,000,000 thousand.
Details of treasury shares as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | Number of
shares | | | Carrying
amount | | | Number of
shares | | | Carrying
amount | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won and number of shares) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Acquisition | | | | | 500 | | | | 2,000,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 500 | | | | 2,000,000 | | | | - | | | | - | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
9. Borrowings
Borrowings as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Lease liabilities (*1) | | ₩ | | | 84,869 | | | | 95,509 | |
| Investment withholdings (*2) | | | | | - | | | | 200,200 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 84,869 | | | | 295,709 | |
| Non-Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Lease liabilities (*1) | | ₩ | | | 10,821 | | | | 44,421 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 10,821 | | | | 44,421 | |
| (*1) | The interest rate related to lease liabilities reflects the incremental borrowing rate based on the Group’s credit. The amount of interest expense related to lease liabilities incurred during the year ended June 30, 2024 is Korean Won 5,458 thousand (June 30, 2023: Korean Won 5,361 thousand). Additionally, the amount of short-term lease payments and low-value assets lease payments not included in the measurement of lease liabilities during the period ended June 30, 2024 is Korean Won 16,533 thousand (June 30, 2023: Korean Won 7,354 thousand). |
| (*2) | The amount corresponds to a payment made in accordance with the share subscription agreement with G&G Production, dated October 17, 2022. Notably, no shares were issued as a consequence of this subscription payment. On December 20, 2023, an additional agreement was established, outlining the complete refund of the subscription payment by June 30, 2024. A refund of 800,800 thousand Korean Won was processed and remitted to G&G Production as of June 30, 2024(December 31, 2023: 600,600 thousand Korean Won). |
10. Financial Instruments – Fair values and risk management
| A. | Accounting classifications and fair values |
The following table shows the carrying amounts and fair values of financial assets and financial liabilities, including their levels in the fair value hierarchy. It does not include fair value information for financial assets and financial liabilities not measured at fair value if the carrying amount is a reasonable approximation of fair value.
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of June 30, 2024 are as follows:
| | | | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | ₩ | | | 1,000,690 | | | | - | | | | 1,000,690 | | | | - | | | | 1,000,690 | |
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | ₩ | | | 1,537,640 | | | | - | | | | 1,537,640 | | | | - | | | | 1,537,640 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| B. | Measurement of fair values |
Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows:
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 2: all inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable (either directly that is, prices, or indirectly that is, derived from prices) for the asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 3: unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. |
The fair value of financial instruments traded in an active market is determined based on the quoted market price as of the end of the reporting period. If the quoted prices are readily and regularly available through exchanges, sellers, brokers, industry groups, rating agencies or regulators and such prices represent actual market transactions that occur regularly between independent parties, they are considered active markets.
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market is determined using valuation techniques. These valuation techniques use as much market observable information as possible and use the least amount of group-specific information. At this time, if all the significant input variables required to measure the fair value are observable, the financial instruments are classified as Level 2.
If more than one significant input variable is not based on observable market information, the item is included in Level 3.
The valuation techniques used to measure the fair value of a financial instrument include:
| ● | Market price or dealer price of a similar financial instrument |
| ● | The fair value of derivative instruments is determined by discounting the amount to present value using the leading exchange rate as of the end of the reporting period |
11. Leases
The Group leases building and vehicles. The leases typically run for a period of 1~5 years, with an option to renew or terminate the lease after that date. The Group also leases printer with contract terms of one year. These leases are short-term and/or leases of low-value items. The Group has elected not to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for these leases. Information about leases for which the Group is a lessee is presented below.
Right-of-use assets related to leased properties that do not meet the definition of investment property are presented as property, plant and equipment.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
Details of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities recognized in the consolidated statements of financial position as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Acquisition price) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Buildings | | ₩ | | | 470,856 | | | | 470,856 | |
| Vehicles | | | | | 127,097 | | | | 127,097 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 597,953 | | | | 597,953 | |
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Accumulated depreciation) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Buildings | | ₩ | | | (392,708 | ) | | | (359,301 | ) |
| Vehicles | | | | | (113,327 | ) | | | (100,651 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (506,035 | ) | | | (459,952 | ) |
| | | | | June 30, 2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Carrying amount) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Buildings | | ₩ | | | 78,148 | | | | 111,555 | |
| Vehicles | | | | | 13,770 | | | | 26,446 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 91,918 | | | | 138,001 | |
| ii. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
Amounts recognized in profit or loss for the years ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest expense relating to lease liabilities (included in finance cost) | | ₩ | | | 5,458 | | | | 5,361 | |
| Expense relating to short-term leases | | | | | 15,098 | | | | 6,678 | |
| Expense relating to leases of low-value assets excluding short-term leases | | | | | 1,435 | | | | 676 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| iii. | Amounts recognized in statement of cash flows |
Amounts recognized in statement of cash flows for the years ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total cash outflows of leases | | ₩ | | | 68,888 | | | | 54,532 | |
12. Statement of Cash flows
Adjustments for income and expenses from operating activities for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Depreciation | | ₩ | | | 46,083 | | | | 36,183 | |
| Gains on disposal of short-term financial instruments | | | | | (12,657 | ) | | | - | |
| Gains on valuation of short-term financial instruments | | | | | (690 | ) | | | (24,407 | ) |
| Losses on valuation of short-term financial instruments | | | | | - | | | | 13,678 | |
| Interest expenses | | | | | 5,458 | | | | 5,361 | |
| Interest income | | | | | (19,637 | ) | | | (73,934 | ) |
| Income tax expenses | | | | | 38,375 | | | | 2,141 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 56,932 | | | | (40,978 | ) |
Changes in assets and liabilities from operating activities for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | ₩ | | | (25,478 | ) | | | 4,040 | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | | | | 2,328 | | | | 802 | |
| Other current assets | | | | | 3,719,148 | | | | (544 | ) |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | | | | (90,000 | ) | | | (323,836 | ) |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | | | | 2 | | | | (3,874 | ) |
| Trade and other payables | | | | | 568,521 | | | | 80,590 | |
| Contract assets | | | | | (5,971 | ) | | | 9,009 | |
| Contract liabilities | | | | | (5,793,337 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (1,624,788 | ) | | | (233,813 | ) |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
The movements of liabilities to cash flows arising from financing activities for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Current Lease liabilities | | | Non-current
lease liabilities | | | Current
investment withholdings | | | Non-current
investment withholdings | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at 1 January 2023 | | ₩ | | | 79,232 | | | | 78,064 | | | | 150,800 | | | | 650,000 | | | | 958,096 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | (41,817 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (41,817 | ) |
| Reclassification | | | | | 45,293 | | | | (45,293 | ) | | | 650,000 | | | | (650,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 3,476 | | | | (45,293 | ) | | | 650,000 | | | | (650,000 | ) | | | (41,817 | ) |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | | | | | 5,361 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 5,361 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | (5,361 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (5,361 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Balance at 30 June 2023 | | ₩ | | | 82,708 | | | | 32,771 | | | | 800,800 | | | | - | | | | 916,279 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at 1 January 2024 | | ₩ | | | 95,509 | | | | 44,421 | | | | 200,200 | | | | - | | | | 340,130 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | (44,240 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (44,240 | ) |
| Repayment of investment withholdings | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (200,200 | ) | | | - | | | | (200,200 | ) |
| Reclassification | | | | | 33,600 | | | | (33,600 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (10,640 | ) | | | (33,600 | ) | | | (200,200 | ) | | | - | | | | (244,440 | ) |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | | | | | 5,458 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 5,458 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | (5,458 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (5,458 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Balance at 30 June 2024 | | ₩ | | | 84,869 | | | | 10,821 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 95,690 | |
13. Related parties
| A. | List of related parties |
List of related parties as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| Relationship | | Name |
| Key management personnel | | Yoon, In Bum |
| Key management personnel | | Kim, Soo Jin |
| B. | Account balances with related parties |
The balances of receivables to related parties as of June 30, 2024 and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| Related party | | Name | | | | Receivables | | | Receivables | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Yoon, In Bum | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 497,582 | |
| Key management personnel | | Kim, Soo Jin | | | | | - | | | | 497,582 | |
| Total | | | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 995,164 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2024 and 2023
| C. | Financial transactions with related parties |
Details of significant financial transactions with related parties for the Period ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | Six-month
period ended June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended June 30,
2023 | |
| Related party | | Name | | | | Increase in
accrued income | | | Collection (*) | | | Increase in
accrued income | | | Collection (*) | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Yoon, In Bum | | ₩ | | | 1,077 | | | | (498,659 | ) | | | 10,574 | | | | - | |
| Key management personnel | | Kim, Soo Jin | | | | | 1,077 | | | | (498,659 | ) | | | 10,574 | | | | - | |
| Total | | | | ₩ | | | 2,154 | | | | (997,318 | ) | | | 21,148 | | | | - | |
| (*) | Collection includes the accrued interest amounting to Korean Won 44,818 thousand. |
| D. | Key management personnel compensation |
The compensation for the key management personnel for the six-month periods ended June 30, 2024 and 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Six-month
period ended June 30,
2024 | | | Six-month
period ended June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Wages and salaries | | ₩ | | | 168,000 | | | | 132,000 | |
| Post-employment benefits | | | | | 33,600 | | | | 26,400 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 201,600 | | | | 158,400 | |
14. Commitments
On September 14, 2023, an amendment was made to the equity interest exchange agreement, originally entered into on April 10, 2023, between the CEOs, who is the dominant shareholder of the Parent Company, and K Enter Holdings, Inc. for the purpose of listing on the NASDAQ through a merger with a SPAC company. The equity interest exchange agreement is effective on the date designated by K Enter Holdings, Inc. Upon the effective date, the CEOs of the Group will exchange 5,100 shares with the equity interest of K Enter Holdings, Inc. Following the equity interest exchange transaction, the Parent Company is expected to be a subsidiary of K Enter Holdings, Inc.
Report of Independent Auditors
To the management of
Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd.
Opinion
We have audited the accompanying consolidated financial statements of Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd. and its subsidiaries (the “Company”), which comprise the consolidated statements of financial position as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the related consolidated statements of comprehensive income, of changes in equity and of cash flows for the years then ended, including the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”).
In our opinion, the accompanying consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the years then ended in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
Basis for Opinion
We conducted our audit in accordance with auditing standards generally accepted in the United States of America (US GAAS). Our responsibilities under those standards are further described in the Auditors’ Responsibilities for the Audit of the Consolidated Financial Statements section of our report. We are required to be independent of the Company and to meet our other ethical responsibilities, in accordance with the relevant ethical requirements relating to our audit. We believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our audit opinion.
Responsibilities of Management for the Consolidated Financial Statements
Management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of the consolidated financial statements in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board, and for the design, implementation, and maintenance of internal control relevant to the preparation and fair presentation of consolidated financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error.
In preparing the consolidated financial statements, management is responsible for assessing the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern for at least, but not limited to, twelve months from the end of the reporting period, disclosing, as applicable, matters related to going concern and using the going concern basis of accounting unless management either intends to liquidate the Company or to cease operations, or has no realistic alternative but to do so.
Auditors’ Responsibilities for the Audit of the Consolidated Financial Statements
Our objectives are to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements as a whole are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error, and to issue an auditors’ report that includes our opinion. Reasonable assurance is a high level of assurance but is not absolute assurance and therefore is not a guarantee that an audit conducted in accordance with US GAAS will always detect a material misstatement when it exists. The risk of not detecting a material misstatement resulting from fraud is higher than for one resulting from error, as fraud may involve collusion, forgery, intentional omissions, misrepresentations, or the override of internal control. Misstatements are considered material if there is a substantial likelihood that, individually or in the aggregate, they would influence the judgment made by a reasonable user based on the consolidated financial statements.
In performing an audit in accordance with US GAAS, we:
| ● | Exercise professional judgment and maintain professional skepticism throughout the audit. |
| | | |
| ● | Identify and assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to fraud or error, and design and perform audit procedures responsive to those risks. Such procedures include examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. |
| | | |
| ● | Obtain an understanding of internal control relevant to the audit in order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control. Accordingly, no such opinion is expressed. |
| | | |
| ● | Evaluate the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonableness of significant accounting estimates made by management, as well as evaluate the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. |
| | | |
| ● | Conclude whether, in our judgment, there are conditions or events, considered in the aggregate, that raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern for a reasonable period of time. |
We are required to communicate with those charged with governance regarding, among other matters, the planned scope and timing of the audit, significant audapit findings, and certain internal control-related matters that we identified during the audit.
| /s/ Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers | |
| | |
| Seoul, KOREA | |
| May 13, 2024 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | 14,17,19,22,24 | | ₩ | | | 3,723,417 | | | | 1,027,292 | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | 17,22 | | | | | 1,537,640 | | | | 2,728,688 | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | 7,13,17,22 | | | | | 2,647 | | | | 1,804 | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | 13,17,22 | | | | | 42,665 | | | | 50,778 | |
| - Related parites | | 25 | | | | | 42,664 | | | | 42,648 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 1 | | | | 8,130 | |
| Short-term loans — net | | 15,17,22 | | | | | 952,500 | | | | - | |
| - Related parties | | 25 | | | | | 952,500 | | | | - | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other current assets | | 12 | | | | | 5,070,905 | | | | 1,725 | |
| Other current financial assets | | 17,22 | | | | | 49,000 | | | | - | |
| Contract assets | | 7 | | | | | 143,834 | | | | 151,703 | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | | 11,522,609 | | | | 3,961,990 | |
| Long-term loans, net | | 15,17,22 | | | | | - | | | | 927,120 | |
| - Related parties | | 25 | | | | | - | | | | 927,120 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Property, plant and equipment including right-of-use assets | | 16,23 | | | | | 138,006 | | | | 145,730 | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | 17,22 | | | | | 131,620 | | | | 131,503 | |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | 12 | | | | | 441,600 | | | | 383,600 | |
| Total non-current assets | | | | | | | 711,226 | | | | 1,587,953 | |
| Total assets | | | | ₩ | | | 12,233,835 | | | | 5,549,943 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | 17,21,22 | | ₩ | | | 1,060,087 | | | | 150,635 | |
| Other current financial liabilities | | 17,20,22 | | | | | 200,200 | | | | 150,800 | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | | | | | 40,010 | | | | 7,377 | |
| Contract liabilities | | 7 | | | | | 6,182,960 | | | | - | |
| Current Lease liabilities | | 20,22,23 | | | | | 95,509 | | | | 79,232 | |
| Current tax liabilities | | | | | | | 72,520 | | | | 82,180 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | | 7,651,286 | | | | 470,224 | |
| Non-current Lease liabilities | | 20,22,23 | | | | | 44,421 | | | | 78,064 | |
| Other non-current financial liabilities | | 17,20,22 | | | | | - | | | | 650,000 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | | | | | 44,421 | | | | 728,064 | |
| Total liabilities | | | | ₩ | | | 7,695,707 | | | | 1,198,288 | |
| Equity | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital | | 18 | | ₩ | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | |
| Share premium | | 18 | | | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | |
| Retained earnings | | | | | | | 4,438,128 | | | | 4,251,655 | |
| Equity attributable to owners of the Parent Company | | | | | | | 4,538,128 | | | | 4,351,655 | |
| Total equity | | | | | | | 4,538,128 | | | | 4,351,655 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | | | | ₩ | | | 12,233,835 | | | | 5,549,943 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Media production revenue | | 6,7 | | ₩ | | | 7,746,081 | | | | 423,346 | |
| Total Revenues | | | | | | | 7,746,081 | | | | 423,346 | |
| Cost of revenues | | 8 | | | | | (7,069,610 | ) | | | (353,093 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | | | | | 676,471 | | | | 70,253 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | 8 | | | | | (759,395 | ) | | | (837,135 | ) |
| Other income | | 8 | | | | | 36,004 | | | | 99,624 | |
| Other expenses | | 8 | | | | | (2,016 | ) | | | (3,556 | ) |
| Operating loss | | | | | | | (48,936 | ) | | | (670,814 | ) |
| Finance income | | 9,17 | | | | | 245,390 | | | | 85,473 | |
| - Related parties | | 25 | | | | | 42,664 | | | | 42,648 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 202,726 | | | | 42,825 | |
| Finance costs | | 9,17 | | | | | (11,504 | ) | | | (15,602 | ) |
| Profit (loss) before income tax | | | | | | | 184,950 | | | | (600,943 | ) |
| Income tax benefit (expenses) | | 11 | | | | | 1,523 | | | | (3,906 | ) |
| Profit (loss) for the year | | | | ₩ | | | 186,473 | | | | (604,849 | ) |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the year | | | | ₩ | | | 186,473 | | | | (604,849 | ) |
| Profit (loss) attributable to: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Owners of the Parent Company | | | | ₩ | | | 186,473 | | | | (604,849 | ) |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) attributable to: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Owners of the Parent Company | | | | ₩ | | | 186,473 | | | | (604,849 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | Share capital | | | Capital surplus | | | Retained earnings | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at January 1, 2022 | | | | ₩ | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | | | | 4,894,504 | | | | 4,994,504 | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the year | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (604,849 | ) | | | (604,849 | ) |
| Transaction with owners, recognized directly in equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Dividends | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (38,000 | ) | | | (38,000 | ) |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | | | | ₩ | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | | | | 4,251,655 | | | | 4,351,655 | |
| Balance at January 1, 2023 | | | | ₩ | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | | | | 4,251,655 | | | | 4,351,655 | |
| Total comprehensive income for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Profit for the year | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 186,473 | | | | 186,473 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | | | | ₩ | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | | | | 4,438,128 | | | | 4,538,128 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| | | Note | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | 24 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Profit (loss) for the year | | | | ₩ | | | 186,473 | | | | (604,849 | ) |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities | | | | | | | 1,862,599 | | | | 837,414 | |
| Interest received | | | | | | | 58,849 | | | | 52,315 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | | | (11,504 | ) | | | (15,602 | ) |
| Income taxes paid | | | | | | | (8,128 | ) | | | (143,920 | ) |
| Net cash inflow from operating activities | | | | ₩ | | | 2,088,289 | | | | 125,358 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Disposal of short-term financial instruments | | | | ₩ | | | 8,300,231 | | | | 700,000 | |
| Purchase of short-term financial instruments | | | | | | | (6,933,733 | ) | | | (3,407,657 | ) |
| Payments for short-term loans | | | | | | | (25,380 | ) | | | - | |
| Payments for other current financial assets | | | | | | | (49,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Proceeds from other non-current financial assets | | | | | | | 850 | | | | - | |
| Net cash inflow (outflow) in investing activities | | | | ₩ | | | 1,292,968 | | | | (2,707,657 | ) |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | 24 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Repayment of investment withholdings | | | | | | | (600,600 | ) | | | - | |
| Receipt of investment withholdings | | | | | | | - | | | | 800,800 | |
| Repayment of lease liabilities | | | | | | | (84,532 | ) | | | (78,754 | ) |
| Payments for dividends | | | | | | | - | | | | (38,000 | ) |
| Net cash inflow (outflow) in financing activities | | | | ₩ | | | (685,132 | ) | | | 684,046 | |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | 2,696,125 | | | | (1,898,254 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the year | | 14 | | | | | 1,027,292 | | | | 2,925,546 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of the year | | 14 | | ₩ | | | 3,723,417 | | | | 1,027,292 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
1. Reporting entity
The Parent Company
Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd. (“the Parent Company”) was incorporated in February 2005 and the Parent Company’s registered office is at 220, Yeoksam-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Korea. These consolidated financial statements comprise the Parent Company and its subsidiary (together referred to as the “Group”). The Group generates revenue primarily through providing the media production services. The Parent Company is primarily providing the media production service that consists of planning, producing, and selling the theatrical films and television programs. Trigger Limited Company Specializing in The Cultural Industry (the “Subsidiary”) is engaged in the business of planning, development and production of the film Trigger.
The Parent Company’s major shareholders and their respective percentage of ownership as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | Number of shares | | | Ownership (%) | | | Number of shares | | | Ownership (%) | |
| Yoon, In Bum | | | 5,000 | | | | 50 | % | | | 5,000 | | | | 50 | % |
| Kim, Soo Jin | | | 5,000 | | | | 50 | % | | | 5,000 | | | | 50 | % |
| Total | | | 10,000 | | | | 100 | % | | | 10,000 | | | | 100 | % |
Consolidated Subsidiary
Details of the consolidated subsidiary as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | Percentage of ownership (%) | | | | | |
| Subsidiary | | Location | | | December 31,
2023 | | | Fiscal year end | | Main business |
Trigger Limited
Company Specializing
in The Cultural Industry | | Korea | | | 100 | | | December | | Planning, development
and production of
the film Trigger |
Changes in the Group’s consolidated subsidiary for the year ended December 31, 2023 is as follows
| Type | | | Company | | | Reason |
| Addition | | | Trigger Limited Company Specializing in The Cultural Industry | | | Establishment |
The Parent Company established a special purpose company to plan, develop and manage the production of the new project ‘Trigger’ as of April 5, 2023. The initial capital amounted to Korean won 10,000 thousand, but no capital has been contributed as of December 31, 2023.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
2. Basis of Accounting
These consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) as issued by International Accounting Standard Board (“IASB”). These consolidated financial statements were authorized for issuance by the management on May 13, 2024.
Details of the Group’s accounting policies are included in Note 5.
Basis of measurement
The consolidated financial statements have been prepared on the historical cost basis except for the following items, which are measured on an alternative basis on each reporting date.
| Items | | Measurement bases |
| Financial instruments measured at fair value through profit or loss (“FVTPL”) | | Fair value |
3. Functional and presentation currency
These consolidated financial statements are presented in Korean Won, which the Group’s functional currency. All amounts have been rounded to the nearest thousand, unless otherwise indicated.
4. Use of judgements and estimates
In preparing these consolidated financial statements, management has made judgements and estimates that affect the application of the Group’s accounting policies and the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
Estimates and underlying assumptions are reviewed on an ongoing basis. Revisions to estimates are recognized prospectively.
Information about judgements made in applying accounting policies that have the most significant effects on the amounts recognized in the consolidated financial statements is included in the following note:
Note 5(E): revenue recognition: whether revenue from providing service is recognized over time or at a point in time; and
Note 23(A): lease term: whether the Group is reasonably certain to exercise extension options.
| B. | Assumptions and estimation uncertainties |
Information about assumptions and estimation uncertainties at the reporting date that have a significant risk of resulting in a material adjustment to the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities within the next financial year is included in the following notes:
| ● | Note 11(A): uncertain tax treatments; |
| ● | Note 11(C): movement in deferred tax balances; |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| i. | Measurement of fair values |
A number of the Group’s accounting policies and disclosures require the measurement of fair values, for financial assets.
When measuring the fair value of a financial instruments measured at FVTPL, the Group uses observable market data as far as possible. Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows.
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
| ● | Level 2: inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly (i.e., as prices) or indirectly (i.e., derived from prices). |
| ● | Level 3: inputs for the asset or liability that are not based on observable market data (unobservable inputs). |
If the inputs used to measure the fair value of an asset or a liability fall into different levels of the fair value hierarchy, then the fair value measurement is categorized in its entirety in the same level of the fair value hierarchy as the lowest level input that is significant to the entire measurement.
The Group recognizes transfers between levels of the fair value hierarchy at the end of the reporting period during which the change has occurred.
Further information about the assumptions made in measuring fair values is included in the following note:
| ● | Note 22(B): financial instruments. |
5. Material accounting policies
The principal accounting policies followed by the Group in preparation of its consolidated financial statements are as follows:
| A. | New and amended standards or interpretations adopted by the Group |
The following new accounting standards and interpretations for the first time for their annual reporting period commencing January 1, 2023.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements - Disclosure of Accounting Policies
The amendments to IAS 1 define and require entities to disclose their material accounting policies. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the consolidated financial statements.
IAS 8 Accounting policies, changes in accounting estimates and errors - Definition of Accounting Estimates
The amendments define accounting estimates and clarify how to distinguish them from changes in accounting policies. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the consolidated financial statements.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
IAS 12 Income Taxes - Deferred Tax related to Assets and Liabilities arising from a Single Transaction
The amendments include an additional condition to the exemption to initial recognition of an asset or liability that a transaction does not give rise to equal taxable and deductible temporary differences at the time of the transaction. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the consolidated financial statements.
IAS 12 Income Taxes – International Tax Reform – Pillar Two Model Rules
The amendments provide a temporary relief from the accounting for deferred taxes arising from legislation enacted to implement the Pillar Two model rules, which aim to reform international corporate taxation for multinational enterprises, and require disclosure of related current tax effects, etc. The amendments do not have a significant impact on the consolidated financial statements.
New Standard: IFRS 17 Insurance Contract
IFRS 17 Insurance Contracts replaces IFRS 4 Insurance Contracts. This Standard estimates future cash flows of an insurance contract and measures insurance liabilities using discount rates applied with assumptions and risks at the measurement date. The entity recognizes insurance revenue on an accrual basis including services (insurance coverage) provided to the policyholder by each annual period. In addition, investment components (Refunds due to termination/maturity) repaid to a policyholder even if an insured event does not occur, are excluded from insurance revenue, and insurance financial income or expense and the investment income or expense are presented separately to enable users of the information to understand the sources of income or expenses. This Standard do not have a significant impact on the consolidated financial statements.
| B. | New and amended standards or interpretations not yet adopted |
The following new accounting standards and interpretation that have been published that are not mandatory for December 31, 2023 reporting periods and have not been early adopted by the Group.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements - Classification of Liabilities as Current or Non-current
The amendments clarify that liabilities are classified as either current or non-current, depending on the substantive rights that exist at the end of the reporting period. Classification is unaffected by the likelihood that an entity will exercise right to defer settlement of the liability or the expectations of management. Also, the settlement of liability includes the transfer of the entity’s own equity instruments, however, it would be excluded if an option to settle them by the entity’s own equity instruments if compound financial instruments is met the definition of equity instruments and recognized separately from the liability. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, and earlier application is permitted. The Group is in review for the impact of these amendments on the consolidated financial statements.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
IAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows - IFRS 7 Financial Instruments: Disclosures – Supplier finance arrangements
When applying supplier finance arrangements, an entity shall disclose information about its supplier finance arrangements that enables users of financial statements to assess the effects of those arrangements on the entity’s liabilities and cash flows and on the entity’s exposure to liquidity risk. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, and earlier application is permitted. The Group does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the consolidated financial statements.
IAS 21 The effects of changes in foreign exchange rates - Lack of Exchangeability
The amendments add requirements to help entities to determine whether a currency is exchangeable into another currency at a measurement date for a specified purpose and the spot exchange rate to use when it is not. A currency is exchangeable when there is an ability to obtain the other currency (with a normal administrative delay), and the transaction would take place through a market or exchange mechanism that creates enforceable rights and obligations. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2025, and earlier application is permitted. The Company does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IFRS 16 – Lease Liability in a Sale and Leaseback
When subsequently measuring lease liabilities arising from a sale and leaseback, a seller-lessee shall determine lease payments or revised lease payments in a way that the seller-lessee would not recognize any amount of the gain or loss that relates to the right of use retained by the seller-lessee. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, and earlier application is permitted. The Group does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the consolidated financial statements.
IFRS 18 Presentation and Disclosure in Financial Statements
Items in the statement of profit or loss will need to be classified into one of five categories: operating, investing, financing, income taxes and discontinued operations. IFRS 18 requires the Company to present specified totals and subtotals: ‘Operating profit or loss’, ‘Profit or loss’ and ‘Profit or loss before financing and income taxes’. Information related to management-defined performance measures should be disclosed. IFRS 18 also provides enhanced guidance on the principles of aggregation and disaggregation which focus on grouping items based on their shared characteristics. The new standard should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2027, and earlier application is permitted. The Company is in review for the impact of this new standard on the financial statements.
Subsidiary is an entity controlled by the Group. The Group ‘controls’ an entity when it is exposed to, or has rights to, variable returns from its involvement with the entity and has the ability to affect those returns through its power over the entity. The financial statements of subsidiary are included in the consolidated financial statements from the date on which control commences until the date on which control ceases.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| ii. | Non-controlling interests |
Non-controlling interests are measured initially at their proportionate share of the acquiree’s identifiable net assets at the date of acquisition.
Changes in the Group’s interest in a subsidiary that do not result in a loss of control are accounted for as equity transactions.
When the Group loses control over a subsidiary, it derecognizes the assets and liabilities of the subsidiary, and any related non-controlling interests and other components of equity. Any resulting gain or loss is recognized in profit or loss. Any interest retained in the former subsidiary is measured at fair value when control is lost.
Transactions in foreign currencies are translated into the respective functional currencies of Group at the exchange rates at the dates of the transactions.
Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are translated into the functional currency at the exchange rate at the reporting date. Non-monetary assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value in a foreign currency are translated into the functional currency at the exchange rate when the fair value was determined. Non-monetary items that are measured based on historical cost in a foreign currency are translated at the exchange rate at the date of the transaction. Foreign currency differences are generally recognized in profit or loss and presented within finance costs. Translation differences on Non-monetary assets and liabilities carried at fair value are reported as part of the fair value gain or loss.
| E. | Revenue from contracts with customers |
The Group generates revenue primarily through providing the media production service.
The Group determines revenue recognition by:
| ● | identifying the contract, or contracts, with a customer; |
| ● | identifying the performance obligations in each contract; |
| ● | determining the transaction price; |
| ● | allocating the transaction price to the performance obligations in each contract; and |
| ● | recognizing revenue when, or as, we satisfy performance obligations by transferring the promised goods or services. |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Media production revenue
The Group operates the media production business that consists of planning, producing, and selling the theatrical films and television programs. The Group identifies the license which is provided along with media product as combined output and recognizes revenue over time by measuring its progress based on cost incurred towards complete satisfaction of the performance obligation in accordance with Paragraph 35 (2) and (3) of IFRS 15 Revenue from contracts with customers. The percentage-of-completion for each contract is calculated by dividing the cumulative cost incurred in relation to service performed by the Group by estimated total contract costs.
The Group recognizes unbilled receivables from media production service as contract assets and recognizes receipts in advance for prepaid media production services as contract liabilities. The Group capitalizes the cost associated with the production, including development costs, direct costs, and production overhead per title as prepayments and prepaid expenses. The Group amortizes the capitalized asset in ‘Cost of revenues’ on the consolidated statements of comprehensive income based on the percentage-of-completion for each contract.
An operating segment is a component of the Group that engages in business activities from which it may earn revenues and incur expenses, including revenues and expenses that relate to transactions with any of the Group’s other components. The chief operating decision-maker has been identified as the chief executive officer. The Group’s operating segment has been determined to be a single business unit, for which the Group generates identifiable financial information that is regularly reported to the chief executive officer for the purpose of resource allocation and assessment of segment performance. The Group has a reportable segment as described in Note 6. Segment results that are reported to the chief operating decision maker include items directly attributable to a segment as well as those that can be allocated on a reasonable basis.
| i. | Short-term employee benefits |
Short-term employee benefits are employee benefits due to be settled within 12 months after the end of the period in which the employees render related services. When an employee has rendered a service to the Group during an accounting period, the Group recognizes the undiscounted amount of short-term employee benefits expected to be paid in exchange for that service
| ii. | Defined contribution plans |
Obligations for contributions to defined contribution plans are expensed as the related service is provided. Prepaid contributions are recognized as an asset to the extent that a cash refund or a reduction in future payments is available.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| H. | Finance income and finance costs |
The Group’s finance income and finance costs include:
| ● | the net gain or loss on financial assets at FVTPL; |
| ● | the foreign currency gain or loss on financial assets and financial liabilities; |
The ‘effective interest rate’ is the rate that exactly discounts estimated future cash payments or receipts through the expected life of the financial instrument to:
| ● | the gross carrying amount of the financial asset; or |
| ● | the amortized cost of the financial liability. |
In calculating interest income and expense, the effective interest rate is applied to the gross carrying amount of the asset (when the asset is not credit-impaired) or to the amortized cost of the liability. However, for financial assets that have become credit-impaired subsequent to initial recognition, interest income is calculated by applying the effective interest rate to the amortized cost of the financial asset. If the asset is no longer credit-impaired, then the calculation of interest income reverts to the gross basis.
Income tax expense comprises current and deferred tax. It is recognized in profit or loss except to the extent that it relates to a business combination, or items recognized directly in equity or in OCI.
Current tax comprises the expected tax payable or receivable on the taxable income or loss for the year and any adjustment to the tax payable or receivable in respect of previous years. The amount of current tax payable or receivable is the best estimate of the tax amount expected to be paid or received that reflects uncertainty related to income taxes, if any. It is measured using tax rates enacted or substantively enacted at the reporting date. Current tax also includes any tax arising from dividends.
Current tax assets and liabilities are offset only if certain criteria are met.
| - | Has a legally enforceable right to set off the recognized amounts; and |
| - | Intends either to settle on a net basis, or to realize the asset and settle the liability simultaneously. |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Deferred tax is recognized in respect of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for taxation purposes. Deferred tax is not recognized for:
| ● | temporary differences on the initial recognition of assets or liabilities in a transaction that is not a business combination and that affects neither accounting nor taxable profit or loss; |
| ● | temporary differences related to investments in subsidiaries, associates and joint arrangements to the extent that the Group is able to control the timing of the reversal of the temporary differences and it is probable that they will not reverse in the foreseeable future; and |
| ● | taxable temporary differences arising on the initial recognition of goodwill. |
Deferred tax assets are recognized for unused tax losses, unused tax credits and deductible temporary differences to the extent that it is probable that future taxable profits will be available against which they can be used. Future taxable profits are determined based on the reversal of relevant taxable temporary differences. If the amount of taxable temporary differences is insufficient to recognize a deferred tax asset in full, then future taxable profits, adjusted for reversals of existing temporary differences, are considered, based on the business plans for individual subsidiaries in the Group. Deferred tax assets are reviewed at each reporting date and are reduced to the extent that it is no longer probable that the related tax benefit will be realized; such reductions are reversed when the probability of future taxable profits improves.
The measurement of deferred tax reflects the tax consequences that would follow from the manner in which the Group expects, at the reporting date, to recover or settle the carrying amount of its assets and liabilities. For this purpose, the carrying amount of investment property measured at fair value is presumed to be recovered through sale, and the Group has not rebutted this presumption.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are offset only if certain criteria are met.
| - | Has a legally enforceable right to set off the recognized amounts; and |
| - | Intends either to settle on a net basis, or to realize the asset and settle the liability simultaneously. |
| J. | Cash and Cash Equivalents |
Cash and cash equivalents comprise cash on hand, deposits held at banks, and investment securities with maturities of three months or less from the acquisition date that are easily convertible to cash and subject to an insignificant risk of changes in their fair value.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| K. | Property, plant and equipment |
| i. | Recognition and measurement |
Items of property, plant and equipment are measured at cost, which includes capitalized borrowing costs, less accumulated depreciation and any accumulated impairment losses.
If significant parts of an item of property, plant and equipment have different useful lives, then they are accounted for as separate items (major components) of property, plant and equipment.
Any gain or loss on disposal of an item of property, plant and equipment is recognized in profit or loss.
| ii. | Subsequent expenditure |
Subsequent expenditure is capitalized only if it is probable that the future economic benefits associated with the expenditure will flow to the Group. The carrying amount of the replaced parts are derecognized and the repairs and maintenance expenses are recognized in profit or loss in the period they are incurred.
Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method to allocate the cost of the assets, net of their residual values, over their estimated useful lives as follows:
| Office equipment | | 5 years |
| Furniture and fixtures | | 5 years |
| Right-of-use assets | | 5~7 years |
Depreciation methods, useful lives and residual values are reviewed at each reporting date and adjusted if appropriate.
| i. | Recognition and initial measurement |
Trade receivables and debt securities issued are initially recognized when they are originated. All other financial assets and financial liabilities are initially recognized when the Group becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the instrument.
A financial asset (unless it is a trade receivable without a significant financing component) or financial liability is initially measured at fair value plus or minus, for an item not at FVTPL, transaction costs that are directly attributable to its acquisition or issue. A trade receivable without a significant financing component is initially measured at the transaction price.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| ii. | Classification and subsequent measurement |
Financial assets
On initial recognition, a financial asset is classified as measured at:
Financial assets are not reclassified subsequent to their initial recognition unless the Group changes its business model for managing financial assets, in which case all affected financial assets are reclassified on the first day of the first reporting period following the change in the business model.
A financial asset is measured at amortized cost if it meets both of the following conditions and is not designated as at FVTPL:
| ● | it is held within a business model whose objective is to hold assets to collect contractual cash flows; and |
| ● | its contractual terms give rise on specified dates to cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. A debt investment is measured at FVOCI if it meets both of the following conditions and is not designated as at FVTPL: |
| ● | it is held within a business model whose objective is achieved by both collecting contractual cash flows and selling financial assets; and |
| ● | its contractual terms give rise on specified dates to cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. |
On initial recognition of an equity investment that is not held for trading, the Group may irrevocably elect to present subsequent changes in the investment’s fair value in OCI. This election is made on an investment-by-investment basis.
All financial assets not classified as measured at amortized cost or FVOCI as described above are measured at FVTPL. This includes all derivative financial assets. On initial recognition, the Group may irrevocably designate a financial asset that otherwise meets the requirements to be measured at amortized cost or at FVOCI as at FVTPL if doing so eliminates or significantly reduces an accounting mismatch that would otherwise arise.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Financial assets - Business model assessment
The Group makes an assessment of the objective of the business model in which a financial asset is held at a portfolio level because this best reflects the way the business is managed and information is provided to management. The information considered includes:
| ● | the stated policies and objectives for the portfolio and the operation of those policies in practice. These include whether management’s strategy focuses on earning contractual interest income, maintaining a particular interest rate profile, matching the duration of the financial assets to the duration of any related liabilities or expected cash outflows or realizing cash flows through the sale of the assets; |
| ● | how the performance of the portfolio is evaluated and reported to the Group’s management; |
| ● | the risks that affect the performance of the business model (and the financial assets held within that business model) and how those risks are managed; |
| ● | how managers of the business are compensated - e.g. whether compensation is based on the fair value of the assets managed or the contractual cash flows collected; and |
| ● | the frequency, volume and timing of sales of financial assets in prior periods, the reasons for such sales and expectations about future sales activity. |
Transfers of financial assets to third parties in transactions that do not qualify for derecognition are not considered sales for this purpose, consistent with the Group’s continuing recognition of the assets.
Financial assets that are held for trading or are managed and whose performance is evaluated on a fair value basis are measured at FVTPL.
Financial assets - Assessment whether contractual cash flows are solely payments of principal and interest
For the purposes of this assessment, ‘principal’ is defined as the fair value of the financial asset on initial recognition. ‘Interest’ is defined as consideration for the time value of money and for the credit risk associated with the principal amount outstanding during a particular period of time and for other basic lending risks and costs (e.g. liquidity risk and administrative costs), as well as a profit margin.
In assessing whether the contractual cash flows are solely payments of principal and interest, the Group considers the contractual terms of the instrument. This includes assessing whether the financial asset contains a contractual term that could change the timing or amount of contractual cash flows such that it would not meet this condition. In making this assessment, the Group considers:
| ● | contingent events that would change the amount or timing of cash flows; |
| ● | terms that may adjust the contractual coupon rate, including variable-rate features; |
| ● | prepayment and extension features; and |
| ● | terms that limit the Group’s claim to cash flows from specified assets (e.g. non-recourse features). |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
A prepayment feature is consistent with the solely payments of principal and interest criterion if the prepayment amount substantially represents unpaid amounts of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding, which may include reasonable compensation for early termination of the contract. Additionally, for a financial asset acquired at a discount or premium to its contractual par amount, a feature that permits or requires prepayment at an amount that substantially represents the contractual par amount plus accrued (but unpaid) contractual interest (which may also include reasonable compensation for early termination) is treated as consistent with this criterion if the fair value of the prepayment feature is insignificant at initial recognition.
Financial assets - Subsequent measurement and gains and losses
Financial assets at FVTPL: These assets are subsequently measured at fair value. Net gains and losses, including any interest or dividend income, are recognized in profit or loss.
Financial assets at amortized cost: These assets are subsequently measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. The amortized cost is reduced by impairment losses. Interest income, foreign exchange gains and losses and impairment are recognized in profit or loss. Any gain or loss on derecognition is recognized in profit or loss.
Financial liabilities - Classification, subsequent measurement and gains and losses
Financial liabilities are classified as measured at amortized cost or FVTPL. A financial liability is classified as at FVTPL if it is classified as held-for-trading, it is a derivative or it is designated as such on initial recognition. Financial liabilities at FVTPL are measured at fair value and net gains and losses, including any interest expense, are recognized in profit or loss. Other financial liabilities are subsequently measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. Interest expense and foreign exchange gains and losses are recognized in profit or loss. Any gain or loss on derecognition is also recognized in profit or loss.
Financial assets
The Group derecognizes a financial asset when:
| ● | the contractual rights to the cash flows from the financial asset expire; or |
| ● | it transfers the rights to receive the contractual cash flows in a transaction in which either: |
| - | substantially all of the risks and rewards of ownership of the financial asset are transferred; or |
| - | the Group neither transfers nor retains substantially all of the risks and rewards of ownership and it does not retain control of the financial asset. |
The Group enters into transactions whereby it transfers assets recognized in its statement of financial position, but retains either all or substantially all of the risks and rewards of the transferred assets. In these cases, the transferred assets are not derecognized.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Financial liabilities
The Group derecognizes a financial liability when its contractual obligations are discharged or cancelled, or expire. The Group also derecognizes a financial liability when its terms are modified and the cash flows of the modified liability are substantially different, in which case a new financial liability based on the modified terms is recognized at fair value.
On derecognition of a financial liability, the difference between the carrying amount extinguished and the consideration paid (including any non-cash assets transferred or liabilities assumed) is recognized in profit or loss.
When changes were made to a financial asset or financial liability in addition to changes to the basis for determining the contractual cash flows required by interest rate benchmark reform, the Group first updated the effective interest rate of the financial asset or financial liability to reflect the change that is required by interest rate benchmark reform. After that, the Group applied the policies on accounting for modifications to the additional changes.
| i. | Non-derivative financial assets |
Financial instruments and contract assets
The Group recognizes loss allowances for ECLs on:
| ● | financial assets measured at amortized cost; and |
The Group also recognizes loss allowances for ECLs on lease receivables, which are disclosed as part of trade and other receivables.
The Group measures loss allowances at an amount equal to lifetime ECLs, except for the following, which are measured at 12-month ECLs:
| ● | debt securities that are determined to have low credit risk at the reporting date; and |
| ● | other debt securities and bank balances for which credit risk (i.e. the risk of default occurring over the expected life of the financial instrument) has not increased significantly since initial recognition. |
Loss allowances for trade receivables (including lease receivables) and contract assets are always measured at an amount equal to lifetime ECLs.
When determining whether the credit risk of a financial asset has increased significantly since initial recognition and when estimating ECLs, the Group considers reasonable and supportable information that is relevant and available without undue cost or effort. This includes both quantitative and qualitative information and analysis, based on the Group’s historical experience and informed credit assessment, that includes forward-looking information.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The Group assumes that the credit risk on a financial asset has increased significantly if it is more than 12 months past due.
The Group considers a financial asset to be in default when:
| ● | the debtor is unlikely to pay its credit obligations to the Group in full, without recourse by the Group to actions such as realizing security (if any is held). |
Lifetime ECLs are the ECLs that result from all possible default events over the expected life of a financial instrument.
12-month ECLs are the portion of ECLs that result from default events that are possible within the 12 months after the reporting date (or a shorter period if the expected life of the instrument is less than 12 months).
The maximum period considered when estimating ECLs is the maximum contractual period over which the Group is exposed to credit risk.
Measurement of ECLs
ECLs are a probability-weighted estimate of credit losses. Credit losses are measured as the present value of all cash shortfalls (i.e. the difference between the cash flows due to the entity in accordance with the contract and the cash flows that the Group expects to receive).
ECLs are discounted at the effective interest rate of the financial asset.
Credit-impaired financial assets
At each reporting date, the Group assesses whether financial assets carried at amortized cost are credit-impaired. A financial asset is ‘credit-impaired’ when one or more events that have a detrimental impact on the estimated future cash flows of the financial asset have occurred.
Evidence that a financial asset is credit-impaired includes the following observable data:
| ● | significant financial difficulty of the debtor; |
| ● | the restructuring of a loan or advance by the Group on terms that the Group would not consider otherwise; |
| ● | it is probable that the debtor will enter bankruptcy or other financial reorganization; or |
| ● | the disappearance of an active market for a security because of financial difficulties. |
Presentation of allowance for ECL in the statement of financial position
Loss allowances for financial assets measured at amortized cost are deducted from the gross carrying amount of the assets.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Write-off
The gross carrying amount of a financial asset is written off when the Group has no reasonable expectations of recovering a financial asset in its entirety or a portion thereof. For individual customers, the Group has a policy of writing off the gross carrying amount when the financial asset is 180 days past due based on historical experience of recoveries of similar assets. For corporate customers, the Group individually makes an assessment with respect to the timing and amount of write-off based on whether there is a reasonable expectation of recovery. The Group expects no significant recovery from the amount written off. However, financial assets that are written off could still be subject to enforcement activities in order to comply with the Group’s procedures for recovery of amounts due.
At each reporting date, the Group reviews the carrying amounts of its non-financial assets (other than biological assets, investment property, developing contents, contract assets and deferred tax assets) to determine whether there is any indication of impairment. If any such indication exists, then the asset’s recoverable amount is estimated.
At inception of a contract, the Group assesses whether a contract is, or contains, a lease. A contract is, or contains, a lease if the contract conveys the right to control the use of an identified asset for a period of time in exchange for consideration.
At commencement or on modification of a contract that contains a lease component, the Group allocates the consideration in the contract to each lease component on the basis of its relative stand-alone prices. However, for the leases of property the Group has elected not to separate non-lease components and account for the lease and non-lease components as a single lease component.
The Group recognizes a right-of-use asset and a lease liability at the lease commencement date. The right-of-use asset is initially measured at cost, which comprises the initial amount of the lease liability adjusted for any lease payments made at or before the commencement date, plus any initial direct costs incurred and an estimate of costs to dismantle and remove the underlying asset or to restore the underlying asset or the site on which it is located, less any lease incentives received.
The right-of-use asset is subsequently depreciated using the straight-line method from the commencement date to the end of the lease term, unless the lease transfers ownership of the underlying asset to the Group by the end of the lease term or the cost of the right-of-use asset reflects that the Group will exercise a purchase option. In that case the right-of-use asset will be depreciated over the useful life of the underlying asset, which is determined on the same basis as those of property and equipment. In addition, the right-of-use asset is periodically reduced by impairment losses, if any, and adjusted for certain remeasurements of the lease liability.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The lease liability is initially measured at the present value of the lease payments that are not paid at the commencement date, discounted using the interest rate implicit in the lease or, if that rate cannot be readily determined, the Group’s incremental borrowing rate. Generally, the Group uses its incremental borrowing rate as the discount rate.
The Group determines its incremental borrowing rate by obtaining interest rates from various external financing sources and makes certain adjustments to reflect the terms of the lease and type of the asset leased.
Lease payments included in the measurement of the lease liability comprise the following:
| ● | fixed payments, including in-substance fixed payments; |
| ● | variable lease payments that depend on an index or a rate, initially measured using the index or rate as at the commencement date; |
| ● | amounts expected to be payable under a residual value guarantee; and |
| ● | the exercise price under a purchase option that the Group is reasonably certain to exercise, lease payments in an optional renewal period if the Group is reasonably certain to exercise an extension option, and penalties for early termination of a lease unless the Group is reasonably certain not to terminate early. |
The lease liability is measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. It is remeasured when there is a change in future lease payments arising from a change in an index or rate, if there is a change in the Group’s estimate of the amount expected to be payable under a residual value guarantee, if the Group changes its assessment of whether it will exercise a purchase, extension or termination option or if there is a revised in-substance fixed lease payment.
When the lease liability is remeasured in this way, a corresponding adjustment is made to the carrying amount of the right-of-use asset, or is recorded in profit or loss if the carrying amount of the right-of-use asset has been reduced to zero.
At the date of transition to IFRSs, The Group applies the following approach to all of its leases.
The Group measures that lease liability at the present value of the remaining lease payments, discounted using the lessee’s incremental borrowing rate at the date of transition to IFRSs.
The Group measures right-of-use asset at its carrying amount as if IFRS 16 had been applied since the commencement date of the lease, but discounted using the lessee’s incremental borrowing rate at the date of transition to IFRSs.
The Group uses hindsight in applying IFRS 16 such as the determination of lease term for contracts that contain options to extend or terminate a lease.
The Group has elected not to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for leases of low-value assets (leases for which the underlying asset is valued at USD 5,000 or less) and short-term leases (leases that have a lease term of 12 months or less at the commencement date), including IT equipment. The Group recognizes the lease payments associated with these leases as an expense on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
‘Fair value’ is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date in the principal or, in its absence, the most advantageous market to which the Group has access at that date. The fair value of a liability reflects its non-performance risk.
A number of the Group’s accounting policies and disclosures require the measurement of fair values, for both financial and non-financial assets and liabilities.
When one is available, the Group measures the fair value of an instrument using the quoted price in an active market for that instrument. A market is regarded as ‘active’ if transactions for the asset or liability take place with sufficient frequency and volume to provide pricing information on an ongoing basis.
If there is no quoted price in an active market, then the Group uses valuation techniques that maximize the use of relevant observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The chosen valuation technique incorporates all of the factors that market participants would take into account in pricing a transaction.
The best evidence of the fair value of a financial instrument on initial recognition is normally the transaction price - i.e. the fair value of the consideration given or received. If the Group determines that the fair value on initial recognition differs from the transaction price and the fair value is evidenced neither by a quoted price in an active market for an identical asset or liability nor based on a valuation technique for which any unobservable inputs are judged to be insignificant in relation to the measurement, then the financial instrument is initially measured at fair value, adjusted to defer the difference between the fair value on initial recognition and the transaction price. Subsequently, that difference is recognized in profit or loss on an appropriate basis over the life of the instrument but no later than when the valuation is wholly supported by observable market data or the transaction is closed out.
| P. | Concentration of Credit Risk |
The Group performs periodic credit evaluations of its customers’ financial condition and generally does not require collateral for customers on accounts receivable. The Group maintains reserves for potential credit losses, which are periodically reviewed.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
6. Operating segments
The Group’s operating segments have been identified to be a single business unit, by which the Group provides media production services.
The following summary describes the operations of each reportable segment.
| Reportable segment | | Operations |
| Media Production | | Planning, producing, and selling the media content such as theatrical films and television programs |
The Group’s chief executive officer reviews the internal management reports at least quarterly.
| B. | Information about reportable segments |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Segment revenue | | ₩ | | | 7,746,081 | | | | 423,346 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | 84,999 | | | | 81,645 | |
| Segment operating loss | | | | | (48,936 | ) | | | (670,814 | ) |
Media production is managed and operated in Seoul, South Korea. The geographic information analyses the Group’s revenue by the customer’s country of domicile. In presenting the geographic information, segment revenue and non-current assets have been based on the geographic location of customers.
Summary of the Group’s revenues by region based on the location of customers for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 188,823 | | | | 423,346 | |
| USA | | | | | 7,557,258 | | | | - | |
| Total | | | | | 7,746,081 | | | | 423,346 | |
Summary of the Group’s non-current assets based on the location as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Korea | | ₩ | | | 711,226 | | | | 660,833 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Revenues from major customers that amount to 10% or more of the Group’s revenue for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Customer A (Media production segment) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 17,132 | | | | 333,285 | |
| % | | | | | 0.2 | % | | | 79 | % |
| Customer B (Media production segment) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 7,557,258 | | | | - | |
| % | | | | | 97.6 | % | | | - | |
| Customer C (Media production segment) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | ₩ | | | 104,734 | | | | 73,928 | |
| % | | | | | 1.4 | % | | | 17 | % |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 7,679,124 | | | | 407,213 | |
7. Revenue
The Group generates revenue primarily through providing the services for production of feature films for initial exhibition in theaters.
Revenue from contracts with customers as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Revenue from contracts with customers | | ₩ | | | 7,746,081 | | | | 423,346 | |
| B. | Disaggregation of revenue from contracts with customers |
In the following table, revenue from contracts with customers is disaggregated by major products and service lines and timing of revenue recognition. The table also includes a reconciliation of the disaggregated revenue with the Group’s reportable segments (see Note 6).
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Revenue from contracts with customers based on the service contract type and the timing of satisfaction of performance obligations for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Major products/service lines | | | | | | | | | | |
| Media production | | ₩ | | | 7,746,081 | | | | 423,346 | |
| Timing of revenue recognition | | | | | | | | | | |
| At a point in time | | ₩ | | | 171,691 | | | | 90,061 | |
| Over time | | | | | 7,574,390 | | | | 333,285 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 7,746,081 | | | | 423,346 | |
The balance of contract assets from contracts with customers as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | ₩ | | | 2,647 | | | | 1,804 | |
| Contract asset (Unbilled receivables) | | ₩ | | | 143,835 | | | | 151,703 | |
| Contract liabilities (Deferred revenue) | | ₩ | | | 6,182,960 | | | | - | |
The contract liabilities primarily relate to the advance consideration received from customers for media production service, for which revenue is recognized over time. This will be recognized as revenue when the Group satisfies the performance obligations.
| D. | Asset recognized from costs to fulfil a Contract |
The Group recognized the expenses related to the screenplay for the film and drama production as assets, which are presented under “Other assets” in the statement of financial position.
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Deferred contract fulfilment costs (*) | | ₩ | | | 4,128,054 | | | | - | |
| (*) | This is presented within ‘other assets’ in the statements of financial position. |
The costs relate directly to the contract, generate resources that will be used in satisfying the contract and are expected to be recovered. They were therefore recognized as an asset from costs to fulfil a contract. The asset is amortized as expense on a basis that is consistent with the transfer to the customer of the services to which the asset related over the term of the specific film production contract.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
8. Income and Expenses
Details of other income for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Grants for film production | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 21,600 | |
| Reversal for impairment of prepayments (*) | | | | | 20,000 | | | | 77,715 | |
| Miscellaneous income | | | | | 103 | | | | 309 | |
| Debt forgiveness gain | | | | | 15,901 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 36,004 | | | | 99,624 | |
| (*) | Recouping prepaid directing fees that were previously acknowledged as a prepayment impairment in the past. |
Details of other expenses for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Miscellaneous expenses | | | 2,016 | | | | 3,556 | |
Details of classification of expenses by nature for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Subcontracted production and operating services | | ₩ | | | 690,459 | | | | 245,760 | |
| Employee benefits | | | | | 557,970 | | | | 590,178 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | | | 84,999 | | | | 81,645 | |
| Actor’s appearance fee | | | | | 1,673,030 | | | | - | |
| Staff and equipment, etc | | | | | 3,290,008 | | | | 133,752 | |
| Transportation | | | | | 147,706 | | | | - | |
| Rent | | | | | 816,587 | | | | 49,273 | |
| Supplies | | | | | 485,067 | | | | - | |
| Other | | | | | 83,179 | | | | 89,620 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 7,829,005 | | | | 1,190,228 | |
Total expenses consist of cost of sales and selling, general and administrative expenses.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
9. Finance income and costs
Details of finance income and costs for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) | |
| Finance income | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | ₩ | | | 69,940 | | | | 64,443 | |
| Gains on disposal of short-term financial instruments | | | | | 137,811 | | | | - | |
| Gains on valuation of short-term financial instruments | | | | | 37,639 | | | | 21,030 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 245,390 | | | | 85,473 | |
| Finance costs | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expenses | | ₩ | | | 11,504 | | | | 15,602 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 11,504 | | | | 15,602 | |
10. Employee benefits
The expenses recognized in relation to defined contribution plan for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are Korean Won 79,537 thousand and Korean Won 86,217 thousand.
| A. | Employee benefit expenses |
| i. | Details of employee benefit expenses recognized for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows: |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Wages and salaries | | ₩ | | | 437,543 | | | | 463,400 | |
| Expenses related to post-employment plans | | | | | 79,537 | | | | 86,217 | |
| Fringe benefit | | | | | 40,890 | | | | 40,561 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 557,970 | | | | 590,178 | |
| ii. | Expenses are recognized in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income (loss) as follows: |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | ₩ | | | 557,970 | | | | 590,178 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
11. Income taxes
| A. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
| | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current tax expense | | | | | | | | |
| Current year | | | - | | | | - | |
| Adjustments recognized related to prior period incomes (*) | | | (1,523 | ) | | | 3,906 | |
| Tax expense(benefit) on continuing operations | | | (1,523 | ) | | | 3,906 | |
| (*) | In the normal course of business, the Group is examined by taxation authority. The Group’s management regularly assesses the potential outcomes of these examinations and any future examinations for the current or prior years in determining the adequacy of its liabilities for income taxes. |
The Group establish additional current tax liabilities for income taxes when, despite the belief that tax positions are fully supportable, there remain positions that do not meet the minimum probability threshold, which is a tax position that is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by the applicable taxation authority. The impact of current tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions, as well as the related net interest and penalties, are included in income taxes in the consolidated statements of operations.
| B. | Reconciliation of effective tax rate |
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Profit (loss) before income tax | | ₩ | | | 184,950 | | | | (600,943 | ) |
| Tax at the statutory income tax rate | | | | | 18,310 | | | | (66,104 | ) |
| Adjustments: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Expenses not deductible for tax purposes | | | | | 1,658 | | | | - | |
| Changes in unrecognized deferred tax assets | | | | | (15,085 | ) | | | 58,360 | |
| Adjustments recognized related to prior period incomes | | | | | (1,523 | ) | | | 3,906 | |
| Differences in tax rate | | | | | (4,883 | ) | | | 7,744 | |
| Income tax expenses (benefit) | | ₩ | | | (1,523 | ) | | | 3,906 | |
| Effective income tax rate (*) | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| (*) | The effective tax rate is not calculated as the Group incurred a income tax benefit for the year ended December 31, 2023 and a loss before income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2022. |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| C. | Movement in deferred tax balances |
| i. | Movement in deferred tax balances as of December 31, 2023 |
| | | | | Tax effect | |
| | | | | Beginning | | | Increase (decrease) | | | Ending | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Contract assets | | ₩ | | | (584,353 | ) | | | 951,597 | | | | 367,244 | |
| Prepayments | | | | | 539,340 | | | | (540,651 | ) | | | (1,311 | ) |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 3,137 | | | | (1,051 | ) | | | 2,086 | |
| Others | | | | | 10,703 | | | | (374,236 | ) | | | (363,533 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (31,173 | ) | | | 35,659 | | | | 4,486 | |
| Loss carried forward | | ₩ | | | 85,649 | | | | (55,677 | ) | | | 29,972 | |
| Carryover tax credit | | | | | 2,119,665 | | | | 35,429 | | | | 2,155,094 | |
| Unrecognized deferred tax income asset (*) | | | | | (2,174,141 | ) | | | (15,411 | ) | | | (2,189,552 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets (liabilities) | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| (*) | As of December 31, 2023, the Group did not recognize deferred income tax asset for the temporary difference as it is not probable such loss carried forward and carryover tax credit can be utilized in the foreseeable future. |
| ii. | Movement in deferred tax balances as of December 31, 2022 |
| | | | | Tax effect | |
| | | | | Beginning | | | Increase (decrease) | | | Ending | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Contract assets | | ₩ | | | (612,645 | ) | | | 28,292 | | | | (584,353 | ) |
| Prepayments | | | | | 565,205 | | | | (25,865 | ) | | | 539,340 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 4,271 | | | | (1,134 | ) | | | 3,137 | |
| Others | | | | | 39,285 | | | | (28,582 | ) | | | 10,703 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (3,884 | ) | | | (27,289 | ) | | | (31,173 | ) |
| Loss carried forward | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 85,649 | | | | 85,649 | |
| Carryover tax credit | | | | | 2,119,665 | | | | - | | | | 2,119,665 | |
| Unrecognized deferred tax income assets (*) | | | | | (2,115,781 | ) | | | (58,360 | ) | | | (2,174,141 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets (liabilities) | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| (*) | As of December 31, 2022, the Group did not recognize deferred income tax asset for the temporary difference as it is not probable such loss carried forward and carryover tax credit can be utilized in the foreseeable future. |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| D. | Deferred assets (liabilities) |
| i. | Details of unrecognized as deferred income tax assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows: |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Unrecognized temporary difference | | ₩ | | | 4,486 | | | | - | |
| Loss carried forward | | | | | 29,972 | | | | 54,476 | |
| Carryover tax credit | | | | | 2,155,094 | | | | 2,119,665 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 2,189,552 | | | | 2,174,141 | |
| ii. | The timing of recovery of deferred tax assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows: |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Deferred tax assets | | | | | | | | | | |
| - Deferred tax assets to be recovered after more than 12 months | | ₩ | | | 2,275,843 | | | | 2,285,630 | |
| - Deferred tax assets to be recovered within 12 months | | | | | 949,054 | | | | 858,414 | |
| Sub-total | | | | | 3,224,897 | | | | 3,144,044 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| - Deferred tax liabilities to be recovered after more than 12 months | | | | | (132,409 | ) | | | (115,155 | ) |
| - Deferred tax liabilities to be recovered within 12 months | | | | | (902,936 | ) | | | (854,748 | ) |
| Sub-total | | | | | (1,035,345 | ) | | | (969,903 | ) |
| Unrecognized deferred tax assets | | | | | (2,189,552 | ) | | | (2,174,141 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets (liabilities), net | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
12. Other assets
Details of other assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current | | | | | | | | | | |
| Prepaid expenses | | ₩ | | | 4,129,482 | | | | 1,725 | |
| Value added tax receivables | | | | | 941,424 | | | | - | |
| | | | | | 5,070,904 | | | | 1,725 | |
| Non-current | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-current prepayments | | | | | 441,600 | | | | 383,600 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 5,512,505 | | | | 385,325 | |
13. Trade and other receivables
Details of trade and other receivables as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Trade receivable | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable — Trade | | ₩ | | | 2,647 | | | | 1,804 | |
| Other receivables | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accrued income | | | | | 42,664 | | | | 42,648 | |
| Non-trade receivables | | | | | 1 | | | | 8,130 | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | | | | 42,665 | | | | 50,778 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 45,312 | | | | 52,582 | |
14. Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Deposits in banks | | ₩ | | | 3,723,417 | | | | 1,027,292 | |
The Group doesn’t have any restricted cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
15. Loans receivable
The terms and conditions of outstanding loans as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| | | Currency | | | Nominal interest rate | | | Face value | | | Carrying amount | | | Face value | | | Carrying amount | |
| Key management personnel | | KRW | | | 4.60% | | | | 927,120 | | | | 927,120 | | | | 927,120 | | | | 927,120 | |
| Key management personnel | | KRW | | | 4.60% | | | | 25,380 | | | | 25,380 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total loans receivable | | | | 952,500 | | | | 952,500 | | | | 927,120 | | | | 927,120 | |
| Less: Current portion | | | | (952,500 | ) | | | (952,500 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
| Long-term loans receivable | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 927,120 | | | | 927,120 | |
16. Property, plant and equipment
| A. | Reconciliation of carrying amount |
Details of property, plant and equipment as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | Book value | | | Accumulated depreciation | | | Carrying amount | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Office equipment | | ₩ | | | 6,067 | | | | (6,063 | ) | | | 4 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | | | | | 2,500 | | | | (2,499 | ) | | | 1 | |
| Right-of-use assets | | | | | 597,953 | | | | (459,952 | ) | | | 138,001 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 606,520 | | | | (468,514 | ) | | | 138,006 | |
| | | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | Book value | | | Accumulated depreciation | | | Carrying amount | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Office equipment | | ₩ | | | 6,067 | | | | (6,063 | ) | | | 4 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | | | | | 2,500 | | | | (2,499 | ) | | | 1 | |
| Right-of-use assets | | | | | 520,678 | | | | (374,953 | ) | | | 145,725 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 529,245 | | | | (383,515 | ) | | | 145,730 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Details of the changes in property and equipment for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Office
equipment | | | Furniture and fixture | | | Right-of-Use
assets | | | Total | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 4 | | | | 1 | | | | 145,725 | | | | 145,730 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (84,999 | ) | | | (84,999 | ) |
| Lease modification | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 77,275 | | | | 77,275 | |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 4 | | | | 1 | | | | 138,001 | | | | 138,006 | |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Office
equipment | | | Furniture and fixture | | | Right-of-Use
assets | | | Total | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | 4 | | | | 1 | | | | 227,370 | | | | 227,375 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (81,645 | ) | | | (81,645 | ) |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 4 | | | | 1 | | | | 145,725 | | | | 145,730 | |
The classification of depreciation expenses in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cost of revenues | | ₩ | | | 18,400 | | | | - | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | | | 66,599 | | | | 81,645 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 84,999 | | | | 81,645 | |
| B. | Leased property, plant and equipment |
The Group leased the building and vehicles during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. The amount of right-of-use assets recognized by category is as follows.
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Buildings | | ₩ | | | 111,555 | | | | 93,861 | |
| Vehicles | | | | | 26,446 | | | | 51,864 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 138,001 | | | | 145,725 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
17. Financial instruments by category
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at amortized cost | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | | | 3,723,417 | | | | 1,027,292 | |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | | | | 2,647 | | | | 1,804 | |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | | | | 42,665 | | | | 50,778 | |
| Short-term loans, net | | | | | 952,500 | | | | - | |
| Long-term loans, net | | | | | - | | | | 927,120 | |
| Other current financial assets | | | | | 49,000 | | | | - | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | 131,620 | | | | 131,504 | |
| Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | | | | 1,537,640 | | | | 2,728,688 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 6,439,489 | | | | 4,867,186 | |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial liabilities at amortized cost | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables (*) | | ₩ | | | 894,333 | | | | 64,418 | |
| Other current financial liabilities | | | | | 200,200 | | | | 150,800 | |
| Other non-current financial liabilities | | | | | - | | | | 650,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,094,533 | | | | 865,218 | |
| (*) | Trade and other payables that are not financial liabilities are excluded. |
| A. | Classification of investment assets |
The classification of investment assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current investments | | | | | | | | | | |
| Debt securities – at FVTPL | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 2,728,688 | |
| Other securities – at FVTPL | | | | | 1,537,640 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,537,640 | | | | 2,728,688 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| B. | Net gains and losses by category of financial instruments |
The net gains and losses by category of financial instruments for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Financial assets at amortized cost | | | Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest income | | ₩ | | | 58,616 | | | | 11,324 | | | | 69,940 | |
| Gain on disposal of short-term financial instruments | | | | | - | | | | 137,811 | | | | 137,811 | |
| Gain on valuation of short-term financial instruments | | | | | - | | | | 37,639 | | | | 37,639 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 58,616 | | | | 186,774 | | | | 245,390 | |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Financial assets at amortized cost | | | Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest income | | ₩ | | | 55,909 | | | | 8,534 | | | | 64,443 | |
| Gain on valuation of short-term financial instruments | | | | | - | | | | 21,030 | | | | 21,030 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 55,909 | | | | 29,564 | | | | 85,473 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
18. Capital and reserves
| A. | Share capital and share premium |
Details of share capital and share premium as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | (In Korean won and number of shares) | |
| Number of authorized shares | | | | 40,000 | | | | 40,000 | |
| Value per share | | ₩ | | 5,000 | | | | 5,000 | |
| Number of shares issued | | | | 10,000 | | | | 10,000 | |
| Common shares | | ₩ | | 50,000,000 | | | | 50,000,000 | |
Holders of these shares are entitled to dividends as declared from time to time and are entitled to one vote per share at general meetings of the Group.
| B. | Other components of equity |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Share premium | | ₩ | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
19. Capital management
The Group’s policy is to maintain a strong capital base so as to maintain investor, creditor and market confidence and to sustain future development of the business. The Group monitors capital using a ratio of ‘net debt’ to ‘adjusted equity’. Net debt is calculated as total liabilities (as shown in the statement of financial position) less cash and cash equivalents. The Group’s net debt to adjusted equity ratio as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows.
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total liabilities | | ₩ | | | 7,695,707 | | | | 1,198,288 | |
| Less: Cash and cash equivalents | | | | | (3,723,417 | ) | | | (1,027,292 | ) |
| Net debt | | | | | 3,972,290 | | | | 170,996 | |
| Total equity | | ₩ | | | 4,538,128 | | | | 4,351,655 | |
| Net debt to total equity ratio | | | | | 87.5 | % | | | 3.9 | % |
20. Borrowings/payable
Borrowings as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current Liabilities | | | | | | | | |
| Lease liabilities (*1) | | | 95,509 | | | | 79,232 | |
| Investment withholdings (*2) | | | 200,200 | | | | 150,800 | |
| Total | | | 295,709 | | | | 230,032 | |
| Non-Current liabilities | | | | | | | | |
| Lease liabilities (*1) | | | 44,421 | | | | 78,064 | |
| Investment withholdings (*2) | | | - | | | | 650,000 | |
| Total | | | 44,421 | | | | 728,064 | |
| (*1) | The interest rate related to lease liabilities reflects the incremental borrowing rate based on the Group’s credit. The amount of interest expense related to lease liabilities incurred during the year ended December 31, 2023 is Korean Won 11,504 thousand (2022: Korean Won 15,602 thousand). Additionally, the amount of short-term lease payments and low-value assets lease payments not included in the measurement of lease liabilities during 2023 is Korean Won 31,629 thousand (2022: Korean Won 1,333 thousand). |
| (*2) | The amount corresponds to a payment made in accordance with the share subscription agreement with G&G Production, dated October 17, 2022. Notably, no shares were issued as a consequence of this subscription payment. On December 20, 2023, an additional agreement was established, outlining the complete refund of the subscription payment by June 30, 2024. A refund of 600,600 thousand Korean Won was processed and remitted to G&G Production as of December 31, 2023. |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
21. Trade and other payables
Trade and other payables as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other payable | | ₩ | | | 381,377 | | | | 22,222 | |
| Accrued expenses | | | | | 678,710 | | | | 128,413 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,060,087 | | | | 150,635 | |
22. Financial Instruments – Fair values and risk management
| A. | Accounting classifications and fair values |
The following table shows the carrying amounts and fair values of financial assets and financial liabilities, including their levels in the fair value hierarchy. It does not include fair value information for financial assets and financial liabilities not measured at fair value if the carrying amount is a reasonable approximation of fair value.
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | | 1,537,640 | | | | - | | | | 1,537,640 | | | | - | | | | 1,537,640 | |
Carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as December 31, 2022 are as follows:
| | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term financial instruments | | | 2,728,688 | | | | - | | | | 2,728,688 | | | | - | | | | 2,728,688 | |
| B. | Measurement of fair values |
Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows:
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 2: all inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable (either directly that is, prices, or indirectly that is, derived from prices) for the asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 3: unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The fair value of financial instruments traded in an active market is determined based on the quoted market price as of the end of the reporting period. If the quoted prices are readily and regularly available through exchanges, sellers, brokers, industry groups, rating agencies or regulators and such prices represent actual market transactions that occur regularly between independent parties, they are considered active markets.
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market is determined using valuation techniques. These valuation techniques use as much market observable information as possible and use the least amount of Company-specific information. At this time, if all the significant input variables required to measure the fair value are observable, the financial instruments are classified as Level 2.
If more than one significant input variable is not based on observable market information, the item is included in Level 3.
The valuation techniques used to measure the fair value of a financial instrument include:
| ● | Market price or dealer price of a similar financial instrument |
| ● | The fair value of derivative instruments is determined by discounting the amount to present value using the leading exchange rate as of the end of the reporting period |
| C. | Financial risk management |
The Group’s operating activities expose itself to a variety of financial risks: market risk, credit risk and liquidity risk from which the Group’s risk management program focuses on minimizing any adverse effects on its financial performance. The Group operates financial risk management policies and programs that closely monitor and respond to each risk factor.
Credit risk is the risk of financial loss to the Group if a customer or counterpart to a financial instrument fails to meet its contractual obligations and arises principally from the Group’s receivables from customers. In order to manage credit risk, the Group regularly evaluate the credit worthiness of each customer or counterparty considering the party’s financial information, past experience, its own trading records and other factors. In relation to the impairment of financial assets subsequent to initial recognition, the Group recognizes the changes in expected credit loss (“ECL”) in profit or loss at each reporting date. The carrying amount of a financial asset represents the maximum exposure to credit risk.
The maximum exposure to credit risk of the Group as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | | | 3,723,417 | | | | 1,027,292 | |
| Accounts receivable, net | | | | | 45,312 | | | | 52,582 | |
| Short-term loans, net | | | | | 952,500 | | | | - | |
| Long-term loans, net | | | | | - | | | | 927,120 | |
| Other current financial assets | | | | | 49,000 | | | | - | |
| Other non-current financial assets | | | | | 131,620 | | | | 131,503 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 4,901,849 | | | | 2,138,497 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Cash and cash equivalents are deposited in financial institutions with strong credit rating. The Group’s exposure to credit risk is influenced mainly by the individual characteristics of each customer. The Group has established a credit policy under which each new customer is analyzed individually before the Group’s standard payment and delivery terms and conditions are offered. The Group’s review includes external ratings, if they are available, financial statements, credit agency information, industry information and in some cases bank references.
The Group monitors customer credit risk, customers are grouped according to their credit characteristics, including whether they are an individual or a legal entity, their geographic location, industry, trading history with the Group and existence of previous financial difficulties. The Group does not require collateral in respect of trade and other receivables. Expected credit losses (ECLs) and credit risk exposures for accounts and other receivables as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
① Accounts receivables— trade, net
| As of December 31, 2023 | | Expected loss rate | | | | | Carrying amount | | | Loss allowance | |
| | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Not due or overdue less than 90 days | | | 0.00 | % | | ₩ | | | 2,647 | | | | - | |
| More than 90 days ~ Less than 1year | | | 0.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| More than 1 year | | | 100.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | | | | | ₩ | | | 2,647 | | | | - | |
| As of December 31, 2022 | | Expected loss rate | | | | | Carrying amount | | | Loss allowance | |
| | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Not due or overdue less than 90 days | | | 0.00 | % | | ₩ | | | 1,804 | | | | - | |
| More than 90 days ~ Less than 1year | | | 0.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| More than 1 year | | | 100.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | | | | | ₩ | | | 1,804 | | | | - | |
② Other receivables
| As of December 31, 2023 | | Expected loss rate | | | | | Carrying amount | | | Loss allowance | |
| | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Not due or overdue less than 90 days | | | 0.00 | % | | ₩ | | | 223,285 | | | | - | |
| More than 90 days ~ Less than 1year | | | 0.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| More than 1 year | | | 100.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | | | | | ₩ | | | 223,285 | | | | - | |
| As of December 31, 2022 | | Expected loss rate | | | | | Carrying amount | | | Loss allowance | |
| | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Not due or overdue less than 90 days | | | 0.00 | % | | ₩ | | | 176,281 | | | | - | |
| More than 90 days ~ Less than 1year | | | 0.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| More than 1 year | | | 100.00 | % | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | | | | | ₩ | | | 176,281 | | | | - | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Liquidity risk management includes the maintenance of sufficient cash and marketable securities, the availability of funds from appropriately committed credit lines, and the ability to settle market positions.
Financial liabilities of the Group by maturity according to the remaining period from December 31, 2023 to the contractual maturity date are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | Carrying Amount | | | Less than 3 months | | | 3 months ~ 1 year | | | 1~2 years | | | 2~5 years | | | More than 5 years | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Non-derivative financial liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other payables (*) | | ₩ | | | 381,377 | | | | 381,377 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 381,377 | |
| Accrued expense (*) | | | | | 512,956 | | | | 512,956 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 512,956 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 139,930 | | | | 24,849 | | | | 74,547 | | | | 50,731 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 150,127 | |
| Investment withholdings | | | | | 200,200 | | | | - | | | | 200,200 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 200,200 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,234,463 | | | | 919,182 | | | | 274,747 | | | | 50,731 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,244,660 | |
| (*) | Trade and other payables and accrued expense exclude non-financial liabilities. |
Financial liabilities of the Group by maturity according to the remaining period from December 31, 2022 to the contractual maturity date are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2022 | |
| | | | | Carrying Amount | | | Less than 3 months | | | 3 months ~ 1 year | | | 1~2 years | | | 2~5 years | | | More than 5 years | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Non-derivative financial liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other payables (*) | | ₩ | | | 22,222 | | | | 22,222 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 22,222 | |
| Accrued expense (*) | | | | | 42,196 | | | | 42,196 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 42,196 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | | | 157,296 | | | | 23,589 | | | | 70,767 | | | | 71,856 | | | | 2,371 | | | | - | | | | 168,583 | |
| Investment withholdings | | | | | 800,800 | | | | - | | | | 150,800 | | | | 650,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 800,800 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,022,514 | | | | 88,007 | | | | 221,567 | | | | 721,856 | | | | 2,371 | | | | - | | | | 1,033,801 | |
| (*) | Trade and other payables and accrued expense exclude non-financial liabilities. |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
23. Leases
The Group leases building and vehicles. The leases typically run for a period of 1~5 years, with an option to renew or terminate the lease after that date. The Group also leases printer with contract terms of one year. These leases are short-term and/or leases of low-value items. The Group has elected not to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for these leases. Information about leases for which the Group is a lessee is presented below.
Right-of-use assets related to leased properties that do not meet the definition of investment property are presented as property, plant and equipment.
Details of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities recognized in the consolidated statements of financial position as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Acquisition price) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Buildings | | ₩ | | | 470,856 | | | | 393,581 | |
| Vehicles | | | | | 127,097 | | | | 127,097 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 597,953 | | | | 520,678 | |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Accumulated depreciation) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Buildings | | ₩ | | | (359,301 | ) | | | (299,721 | ) |
| Vehicles | | | | | (100,651 | ) | | | (75,232 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (459,952 | ) | | | (374,953 | ) |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Right-of-use assets (Carrying amount) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Buildings | | ₩ | | | 111,555 | | | | 93,860 | |
| Vehicles | | | | | 26,446 | | | | 51,865 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 138,001 | | | | 145,725 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Changes in right-of-use assets for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Building | | | Vehicles | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance as of January 1, 2023 | | ₩ | | | 93,860 | | | | 51,865 | | | | 145,725 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (59,580 | ) | | | (25,419 | ) | | | (84,999 | ) |
| Lease modification | | | | | 77,275 | | | | - | | | | 77,275 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | | ₩ | | | 111,555 | | | | 26,446 | | | | 138,001 | |
| | | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | Building | | | Vehicles | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance as of January 1, 2022 | | ₩ | | | 150,086 | | | | 77,284 | | | | 227,370 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | (56,226 | ) | | | (25,419 | ) | | | (81,645 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2022 | | ₩ | | | 93,860 | | | | 51,865 | | | | 145,725 | |
| ii. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
Amounts recognized in profit or loss for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest expense relating to lease liabilities (included in finance cost) | | ₩ | | | 11,504 | | | | 15,602 | |
| Expense relating to short-term leases | | | | | 30,284 | | | | - | |
| Expense relating to leases of low-value assets excluding short-term leases | | | | | 1,345 | | | | 1,333 | |
| iii. | Amounts recognized in statement of cash flows |
Amounts recognized in statement of cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total cash outflows of leases | | ₩ | | | 127,665 | | | | 95,689 | |
Some property leases contain extension options exercisable by the Group. Where practicable, the Group seeks to include extension options in new leases to provide operational flexibility. The extension options held are exercisable only by the Group and not by the lessors. The Group assesses at the lease commencement date whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the extension options. The Group reassesses whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the options if there is a significant event or significant changes in circumstances within its control.
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
24. Statement of Cash flows
Adjustments for income and expenses from operating activities for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Depreciation | | ₩ | | | 84,999 | | | | 81,645 | |
| Gains on disposal of short-term investment securities | | | | | (137,811 | ) | | | - | |
| Gains on valuation of short-term investment securities | | | | | (37,639 | ) | | | (21,030 | ) |
| Debt forgiveness gain | | | | | (15,901 | ) | | | - | |
| Interest expenses | | | | | 11,504 | | | | 15,602 | |
| Interest income | | | | | (69,940 | ) | | | (64,443 | ) |
| Tax expenses | | | | | (1,523 | ) | | | 3,906 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | (166,311 | ) | | | 15,680 | |
Changes in assets and liabilities from operating activities for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | ₩ | | | 32,634 | | | | (9,269 | ) |
| Accounts receivable — trade, net | | | | | (843 | ) | | | 1,278,748 | |
| Other current assets | | | | | (5,069,181 | ) | | | (923 | ) |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | | | | (58,000 | ) | | | (201,400 | ) |
| Accounts receivable — other, net | | | | | 8,119 | | | | (2,971 | ) |
| Trade and other payables | | | | | 925,353 | | | | (224,166 | ) |
| Contract assets | | | | | 7,868 | | | | (18,285 | ) |
| Contract liabilities | | | | | 6,182,960 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 2,028,910 | | | | 821,734 | |
Significant non-cash transactions for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Reclassification of long-term loans | | ₩ | | | 927,120 | | | | - | |
| Increase in lease liabilities due to lease agreements | | | | | 67,166 | | | | - | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The movements of liabilities to cash flows arising from financing activities for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | Current Lease liabilities | | | Non-current
lease liabilities | | | Current
investment withholdings | | | Non-current
investment withholdings | | | Total | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at 1 January 2022 | | ₩ | | | 72,685 | | | | 163,365 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 236,050 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | (78,754 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (78,754 | ) |
| Receipt of investment withholdings | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 150,800 | | | | 650,000 | | | | 800,800 | |
| Reclassification | | | | | 85,301 | | | | (85,301 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 6,547 | | | | (85,301 | ) | | | 150,800 | | | | 650,000 | | | | 722,046 | |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | | | | | 15,602 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 15,602 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | (15,602 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (15,602 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Balance at 31 December 2022 | | ₩ | | | 79,232 | | | | 78,064 | | | | 150,800 | | | | 650,000 | | | | 958,096 | |
| Balance at 1 January 2023 | | ₩ | | | 79,232 | | | | 78,064 | | | | 150,800 | | | | 650,000 | | | | 958,096 | |
| Changes from financing cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment of lease liabilities | | | | | (84,532 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (84,532 | ) |
| Repayment of investment withholdings | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (600,600 | ) | | | - | | | | (600,600 | ) |
| Reclassification | | | | | 96,959 | | | | (96,959 | ) | | | 650,000 | | | | (650,000 | ) | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 12,427 | | | | (96,959 | ) | | | 49,400 | | | | (650,000 | ) | | | (685,132 | ) |
| Other changes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Lease modification | | | | | 3,850 | | | | 63,316 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 67,166 | |
| Interest expense | | | | | 11,504 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 11,504 | |
| Interest paid | | | | | (11,504 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (11,504 | ) |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 3,850 | | | | 63,316 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 67,166 | |
| Balance at 31 December 2023 | | ₩ | | | 95,509 | | | | 44,421 | | | | 200,200 | | | | - | | | | 340,130 | |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
25. Related parties
| A. | List of related parties |
List of related parties as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| Relationship | | Name |
| Key management personnel | | Yoon, In Bum |
| Key management personnel | | Kim, Soo Jin |
| B. | Account balances with related parties |
The balances of receivables and payables to related parties as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | December 31,
2023 | | | December 31,
2022 | |
| Related party | | Name | | | | Receivables | | | Receivables | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Yoon, In Bum | | ₩ | | | 497,582 | | | | 484,884 | |
| Key management personnel | | Kim, Soo Jin | | | | | 497,582 | | | | 484,884 | |
| Total | | | | ₩ | | | 995,164 | | | | 969,768 | |
| C. | Financial transactions with related parties |
Details of significant financial transactions with related parties for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| Related party | | Name | | | | Loans | | | Increase in accrued income | | | Collection (*) | | | Increase in accrued income | | | Collection (*) | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Key management personnel | | Yoon, In Bum | | ₩ | | | 12,690 | | | | 21,332 | | | | (21,324 | ) | | | 21,324 | | | | (20,278 | ) |
| Key management personnel | | Kim, Soo Jin | | | | | 12,690 | | | | 21,332 | | | | (21,324 | ) | | | 21,324 | | | | (20,278 | ) |
| Total | | | | | 25,380 | | | | 42,664 | | | | (42,648 | ) | | | 42,648 | | | | (40,556 | ) |
| (*) | Collection includes the accrued interest (2023: Korean Won 42,648 thousand, 2022 : Korean Won 40,556 thousand). |
BIDANGIL PICTURES CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
| D. | Transactions with key management personnel |
The compensation for the key management personnel for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Wages and salaries | | ₩ | | | 363,000 | | | | 408,000 | |
| Post-employment benefits | | | | | 72,600 | | | | 81,600 | |
Compensation of the Group’s key management personnel includes salaries, non-cash benefits and contributions to a defined contribution plan (See Note 10).
26. Commitments
On September 14, 2023, an amendment was made to the equity interest exchange agreement, originally entered into on April 10, 2023, between the CEOs, who is the dominant shareholder of the Parent Company, and K Enter Holdings, Inc. for the purpose of listing on the NASDAQ through a merger with a SPAC company. The equity interest exchange agreement is effective on the date designated by K Enter Holdings, Inc. Upon the effective date, the CEOs of the Group will exchange 5,100 shares with the equity interest of K Enter Holdings, Inc. Following the equity interest exchange transaction, the Parent Company is expected to be a subsidiary of K Enter Holdings, Inc.
27. Subsequent Events
In accordance with the resolution of Shareholder’s meeting on January 31, 2024, the Parent Company acquired 500 shares of treasury stock at Korean won 2,000 million as of January 31, 2024.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As of June 30, 2024, and December 31, 2023
| | | | | | | June 30, | | | December 31, | |
| | | Note | | | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | 10 | | ₩ | | | 221,842 | | | | 275,897 | |
| Other current financial assets | | | | | | | 50,000 | | | | 50,000 | |
| Other current assets | | | | | | | 61 | | | | 26,465 | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | | 271,903 | | | | 352,362 | |
| Long-term investments | | 8 | | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | |
| Property, plant, and equipment | | | | | | | 840 | | | | 945 | |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | | | | | | 527,000 | | | | 360,000 | |
| - Related parties | | 11 | | | | | 60,000 | | | | 60,000 | |
| - Non-related parties | | | | | | | 467,000 | | | | 300,000 | |
| Total non-current assets | | | | | | | 557,840 | | | | 390,945 | |
| Total assets | | | | ₩ | | | 829,743 | | | | 743,307 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | | | ₩ | | | 20,915 | | | | 2,715 | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | | | | | 29,693 | | | | 1,931 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | | 50,608 | | | | 4,646 | |
| Other non-current non-financial liabilities | | 7 | | | | | 1,250,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | | | | | | 118,735 | | | | 72,347 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | | | | | 1,368,735 | | | | 1,072,347 | |
| Total liabilities | | | | | | | 1,419,343 | | | | 1,076,993 | |
| Equity | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital | | 6 | | | | | 15,000 | | | | 15,000 | |
| Other reserves | | 6 | | | | | (1,054 | ) | | | (1,054 | ) |
| Accumulated deficit | | | | | | | (603,546 | ) | | | (347,632 | ) |
| Total equity | | | | | | | (589,600 | ) | | | (333,686 | ) |
| Total liabilities and equity | | | | ₩ | | | 829,743 | | | | 743,307 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the Six-Month Period Ended June 30, 2024, and Period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
| | | Note | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from March 6, 2023
(inception) to
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Revenue | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cost of revenue | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Gross profit | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Selling, general, and administrative expenses | | | | | | | (256,379 | ) | | | (58,845 | ) |
| Operating loss | | | | | | | (256,379 | ) | | | (58,845 | ) |
| Other income | | | | | | | 354 | | | | - | |
| Other expense | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Finance income | | | | | | | 111 | | | | 3 | |
| Loss before income tax | | | | | | | (255,914 | ) | | | (58,842 | ) |
| Income tax income (expenses) | | 5 | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Loss for the period | | | | | | | (255,914 | ) | | | (58,842 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | ₩ | | | (255,914 | ) | | | (58,842 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
For the Six-Month Period Ended June 30, 2024, and Period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
| | | Note | | | | Share
capital | | | Other
components
of equity | | | Accumulated
deficit | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) |
| Balance at March 6, 2023 (inception) | | | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (58,842 | ) | | | (58,842 | ) |
| Transaction with owners, recognized directly in equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Shares issued | | 11 | | | | | 15,000 | | | | (1,054 | ) | | | - | | | | 13,946 | |
| Balance at June 30, 2023 | | | | ₩ | | | 15,000 | | | | (1,054 | ) | | | (58,842 | ) | | | (44,896 | ) |
| Balance at January 1, 2024 | | | | ₩ | | | 15,000 | | | | (1,054 | ) | | | (347,632 | ) | | | (333,686 | ) |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (255,914 | ) | | | (255,914 | ) |
| Balance at June 30, 2024 | | | | ₩ | | | 15,000 | | | | (1,054 | ) | | | (603,546 | ) | | | (589,600 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the Six-Month Period Ended June 30, 2024, and Period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
| | | Note | | | | Six-month
period ended June 30,
2024 | | | For the period from March 6, 2023
(inception) to
June 30,
2023 | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | | ₩ | | | (255,914 | ) | | | (58,842 | ) |
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash provided by operating activities | | 10 | | | | | 201,763 | | | | 903,080 | |
| Interest received | | | | | | | 111 | | | | 3 | |
| Income taxes paid | | | | | | | (15 | ) | | | - | |
| Net cash provided(used) by operating activities | | | | ₩ | | | (54,055 | ) | | | 844,241 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payments for other current financial assets | | | | | | | - | | | | (50,000 | ) |
| Purchases of long-term investments | | | | | | | - | | | | (30,000 | ) |
| Net cash outflow in investing activities | | | | ₩ | | | - | | | | (80,000 | ) |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from issues of shares | | | | | | | - | | | | 15,000 | |
| Share issue cost | | | | | | | - | | | | (1,054 | ) |
| Net cash inflow in financing activities | | | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 13,946 | |
| Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | (54,055 | ) | | | 778,187 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the period | | | | | | | 275,897 | | | | - | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of the period | | | | ₩ | | | 221,842 | | | | 778,187 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Period Ended June 30, 2024, and Period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
1. Reporting entity
The Company
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd. (“the Company”) was incorporated in March 2023 and the Company’s registered office is at B 907, 606, Hosu-ro, Ilsandong-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea. The Company is primarily providing the media production service that consists of planning, producing, and selling the television programs.
The Company’s major shareholders and their respective percentage of ownership as of June 30, 2024, and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | Number of
shares | | | Ownership
(%) | | | Number of
shares | | | Ownership
(%) | |
| Park, Jun Woo | | | 1,000 | | | | 33.33 | | | | 1,000 | | | | 33.33 | |
| Shin, Kyung Soo | | | 1,000 | | | | 33.33 | | | | 1,000 | | | | 33.33 | |
| Kim, Seung Ho | | | 1,000 | | | | 33.33 | | | | 1,000 | | | | 33.33 | |
| Total | | | 3,000 | | | | 100 | | | | 3,000 | | | | 100 | |
2. Basis of Presentation and Significant Accounting Policies
These condensed interim financial statements for the six-month period ended June 30, 2024, and period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 have been prepared in accordance with International Accounting Standards (“IAS”) 34 Interim Financial Reporting as issued by International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”), and should be read in conjunction with the Company’s last annual financial statements as at and for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023 (“last annual financial statements”). They do not include all of the information required for a complete set of financial statements prepared in accordance with IFRS. However, selected explanatory notes are included to explain events and transactions that are significant to an understanding of the changes in the Company’s financial position and performance since the last annual financial statements.
Going concern
The Company has incurred significant losses and negative cash flows from operations, net loss was 255,914 thousand Korean Won for the six-month period ended June 30, 2024. During the six-months period ended June 30, 2024, the Company had negative cash flows from operations of 54,055 thousand Korean Won. As of June 30, 2024, the Company’s accumulated deficit was 603,546 thousand Korean Won. The Company has funded its operations to date through equity and debt financing and has cash equivalents of 221,842 thousand Korean Won as of June 30, 2024. The Company monitors its cash flow projections on a current basis and takes active measures to obtain the funding it requires to continue its operations. However, these cash flow projections are subject to various uncertainties concerning their fulfilment such as the ability to increase revenues by attracting and expanding its customer base and completing additional financing. The Company expects to fund operations using cash on hand and raising additional proceeds. There are no assurances, however, that the Company will be able to generate the revenue necessary to support its cost structure or that it will be successful in obtaining the level of financing necessary for its operations. These conditions raise substantial doubt as to the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. These financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern and do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Period Ended June 30, 2024, and Period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
Based on management’s forecasts, the day-to-day operations and expenditure requirements as described above are anticipated to be funded by the cash generated through the new commitments from K Enter Holdings. On June 21, 2024, the Company received a non-binding loan letter of intent (“LOI”) from K Enter Holdings, 1,000,000 thousand Korean Won loan, which will be used for the Company’s content development. In addition, the Company received a separate non-binding loan LOI from K Enter Holdings to support the Company’s day-to-day operational expenditure. The maximum loan amount, conditions, and execution timing will be discussed in detail depending on the company’s future business environment.
| B. | Significant Accounting Policies |
Significant accounting policies and method of computation used in the preparation of the condensed interim financial statements are consistent with those of the last annual financial statements for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, except for the changes as described below.
Income tax expense
Income tax expense for the interim period is recognized based on management’s best estimate of the weighted average annual income tax rate expected for the full financial year. The estimated average annual effective income tax rate is applied to the pre-tax income of the interim period.
| i. | New and amended standards or interpretations adopted by the Company |
The Company has applied the following standards and interpretations for the first time for their annual reporting period commencing January 1, 2024.
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements
The amendments to IAS 1 clarify that the classification of liabilities as current or non-current should be based on rights that are in existence at the end of the reporting period and that the classification is unaffected by management’s intentions or expectations about whether an entity will exercise its right to defer settlement of a liability. The amendments also introduce a definition of settlement to make clear that settlement includes the transfer to the counterparty of the entity’s own equity instruments, however, it would be excluded if an option to settle the liability by the transfer of the entity’s own equity instruments is recognized separately from the liability as an equity component of a compound financial instrument. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Company’s interim financial statements.
IAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows, and IFRS 7, Financial Instruments: Presentation
The amendments add to the disclosure objectives in IAS 7, Statement of Cash Flows, that information about supplier financing arrangements should be disclosed to enable users of financial statements to assess the impact of those arrangements on the Company’s liabilities and cash flows. The amendments also amend IFRS 7, Financial Instruments: Presentation, to add supplier financing arrangements as an example of a requirement to disclose information about an entity’s exposure to concentrations of liquidity risk. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Company’s interim financial statements.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Period Ended June 30, 2024, and Period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
IFRS 16 Leases
The amendments add requirements for the subsequent measurement of sale-and-leaseback transactions that are accounted for as sales in accordance with IFRS 15, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. The amendments require the seller lessee to calculate the ‘lease payments’ or ‘revised lease payments’ in a way that does not result in the seller-lessee recognizing any gain or loss for the rights of use that the seller-lessee continues to retain after the lease commences. The application of amendments does not have a significant impact on the Company’s interim financial statements.
| ii. | New and amended standards or interpretations not yet adopted by the Company |
The following new accounting standards and interpretations that have been published that are not mandatory for June 30, 2024, reporting period and have not been early adopted by the Company.
IFRS 18 Presentation and Disclosure in Financial Statements
Items in the statement of profit or loss will need to be classified into one of five categories: operating, investing, financing, income taxes and discontinued operations. IFRS 18 requires the Company to present specified totals and subtotals: ‘Operating profit or loss’, ‘Profit or loss’ and ‘Profit or loss before financing and income taxes’. Information related to management-defined performance measures should be disclosed. IFRS 18 also provides enhanced guidance on the principles of aggregation and disaggregation which focus on grouping items based on their shared characteristics. The new standard should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2027, and earlier application is permitted. The Company is in review for the impact of this new standard on the financial statements.
IAS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates
The amendments require exchangeability of two currencies should be assessed to clarify reporting of foreign currency transactions in the absence of normal-functioning foreign exchange market. The amendments also require applicable spot exchange rate should be determined when the assessment indicates two currencies lack exchangeability. The amendments are effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2025, with early application permitted.
C. Basis of measurement
These financial statements have been prepared on the historical cost basis except for the following items, which are measured on an alternative basis on each reporting date.
| Items | | Measurement bases |
| Financial instruments measured at FVTPL | | Fair value |
3. Operating segments
The Company’s operating segments have been identified to be a single business unit, by which the Company provides media production services.
The following summary describes the operations of the reportable segment.
| Reportable segment | | Operations |
| Media Production | | Planning, producing, and selling the media content such as television programs |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Period Ended June 30, 2024, and Period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
4. Employee benefits
Details of defined benefit liability recognized as of June 30, 2024, and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Defined benefit liability | | ₩ | | | 118,735 | | | | 72,347 | |
The Company operates the defined benefit plans as a retirement pension scheme. Defined benefit plans expose the Company to actuarial risks, such as longevity risk, interest rate risk and market (investment) risk.
| A. | Movement in net defined benefit (asset) liability |
Details of reconciliation from the opening balances to the closing balances for the net defined benefit liability and its components for the six-month period ended June 30, 2024, and period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | Defined benefit obligation | | | Fair value of Plan assets | | | Net defined Benefit liabilities | |
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | June 30,
2023 | | | June 30,
2024 | | | June 30,
2023 | | | June 30,
2024 | | | June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | | | | | | | |
| Beginning Balance | | ₩ | | | 72,347 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 72,347 | | | | - | |
| Included in profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current service cost | | | | | 44,852 | | | | 22,673 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 44,852 | | | | 22,673 | |
| Interest cost | | | | | 1,536 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,536 | | | | - | |
| Ending Balance | | ₩ | | | 118,735 | | | | 22,673 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 118,735 | | | | 22,673 | |
B. Plan assets
There are no contributions funded to its defined benefit plans as of June 30, 2024, and December 31, 2023.
| C. | Employee benefit expenses |
| i. | Details of employee benefit expenses recognized for the six-month period ended June 30, 2024, and from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 are as follows: |
| | | | | Six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | For the period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) |
| Wages and salaries | | ₩ | | | 171,000 | | | | 29,876 | |
| Expenses related to post-employment plans | | | | | 46,388 | | | | 22,673 | |
| Fringe benefit | | | | | 18,129 | | | | 1,176 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 235,517 | | | | 53,725 | |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Period Ended June 30, 2024, and Period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
| ii. | Expenses are recognized in the statements of comprehensive income (loss) as follows: |
| | | | | Six-month period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Selling, general, and administrative expenses | | ₩ | | | 235,517 | | | | 53,725 | |
5. Income Tax
Income tax expense is recognized based on management’s best estimate of the average annual effective income tax rate expected for the full financial year multiplied by the pre-tax income of the interim reporting period. We did not calculate the expected weighted average annual effective Income tax rate for the interim reporting period due to expected pre-tax losses for the fiscal year ending December 31, 2024.
6. Capital and reserves
A. Share capital and share premium
Details of share capital and share premium as of June 30, 2024, and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) |
| Number of authorized shares | | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Value per share | | ₩ | | | 5 | | | | 5 | |
| Number of shares issued | | | | | 3,000 | | | | 3,000 | |
| Common shares | | ₩ | | | 15,000 | | | | 15,000 | |
Holders of these shares are entitled to dividends as declared from time to time and are entitled to one vote per share at general meetings of the Company.
| B. | Other components of equity |
Details of other components of equity as of June 30, 2024, and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Share issue cost | | ₩ | | | (1,054 | ) | | | (1,054 | ) |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Period Ended June 30, 2024, and Period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
7. Contract liabilities
Contract liabilities as of June 30, 2024, and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | June 30,
2024 | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Contract liabilities | | | 1,250,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
The Company received 250,000 thousand Korean Won in June 2024, and 1,000,000 thousand Korean Won in May 2023 from K Enter Holdings for the purpose of planning and developing a drama. In accordance with the terms of the contract with K Enter Holdings, the Company received payment before having completed performance obligations and recognized contract liabilities.
8. Financial Instruments – Fair values and risk management
| A. | Accounting classifications and fair values |
The following table shows the carrying amounts and fair values of financial assets and financial liabilities, including their levels in the fair value hierarchy. It does not include fair value information for financial assets and financial liabilities not measured at fair value if the carrying amount is a reasonable approximation of fair value.
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of June 2024 are as follows:
| | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Project investment | | | 30,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | |
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Project investment | | | 30,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | |
| B. | Measurement of fair values |
Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows:
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 2: all inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable (either directly that is, prices, or indirectly that is, derived from prices) for the asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 3: unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Period Ended June 30, 2024, and Period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
The fair value of financial instruments traded in an active market is determined based on the quoted market price as of the end of the reporting period. If the quoted prices are readily and regularly available through exchanges, sellers, brokers, industry groups, rating agencies or regulators and such prices represent actual market transactions that occur regularly between independent parties, they are considered active markets.
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market is determined using valuation techniques. These valuation techniques use as much market observable information as possible and use the least amount of Company-specific information. At this time, if all the significant input variables required to measure the fair value are observable, the financial instruments are classified as Level 2.
If more than one significant input variable is not based on observable market information, the item is included in Level 3.
If the information is insufficient to measure fair value of the project investment, the Company recognizes gain on project settlements when the accumulated settlements exceed the project investment’s original invested amount. Before exceeding the project investment’s original invested amount, the settlements are recognized as the return of original project investment. The Company recognizes the valuation loss of the project investment based on its judgment as to whether the total amount of production costs and distribution fees could exceed the shared profit.
9. Leases
The Company leases an office. The lease typically run for a period of 1 year, with an option to renew or terminate the lease after that date. The Company has elected not to recognize right-of-use asset and lease liability for this lease. Information about lease for which the Company is a lessee is presented below.
| i. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss. |
Amounts recognized in profit or loss for the six-month period ended June 30, 2024, and period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 are as follows:
| | | For the
six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) |
| Expense relating to short-term leases | | | 12,000 | | | | - | |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Period Ended June 30, 2024, and Period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
| ii. | Amounts recognized in statement of cash flows. |
Amounts recognized in statements of cash flows for the six-month period ended June 30, 2024, and period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | For the
six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) |
| Total cash outflows of leases | | ₩ | | | 12,000 | | | | - | |
The lease contains an extension option exercisable by the Company. Where practicable, the Company seeks to include extension option in new lease to provide operational flexibility. The extension option held is exercisable only by the Company and not by the lessor. The Company assesses at the lease commencement date whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the extension option. The Company reassesses whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the option if there is a significant event or significant changes in circumstances within its control.
10. Statement of cash flows
Adjustments for income from operating activities for the six-month period ended June 30, 2024, and period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | For the
six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | For the period from
March 6, 2023 (inception) to
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) |
| Interest income | | ₩ | | | (111 | ) | | | (3 | ) |
| Severance Benefits | | | | | 46,388 | | | | 22,673 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | 105 | | | | - | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 46,382 | | | | 22,670 | |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Period Ended June 30, 2024, and Period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
Changes in assets and liabilities from operating activities for the six-month period ended June 30, 2024, and period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | For the
six-month period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) |
| Other current assets | | ₩ | | | 26,419 | | | | (6,215 | ) |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | | | | (167,000 | ) | | | (120,000 | ) |
| Trade and other payables | | | | | 18,200 | | | | 2,128 | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | | | 27,762 | | | | 4,497 | |
| Other non-current non-financial liabilities | | | | | 250,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 155,381 | | | | 880,410 | |
11. Related parties
| A. | List of related parties |
List of related parties as of June 30, 2024, and December 31, 2023 are as follows:
| Relationship | | Name |
| Key management personnel | | Park, Jun Woo |
| Key management personnel | | Shin, Kyung Soo |
| Key management personnel | | Kim, Seung Ho |
| Other related parties | | Shining park Co., Ltd. |
| Other related parties | | Its story Co., Ltd. |
| Other related parties | | Poseidon pictures Co., Ltd. |
| B. | Transactions with related parties |
Details of transactions with related parties for the six-month period ended June 30, 2024, and period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | | | For the
six-month
period ended June 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to June 30,
2023 | |
| Related party | | Name | | | | Acquisition of
prepayments | | | Acquisition of
prepayments | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties | | Its story Co., Ltd. | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 60,000 | |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Period Ended June 30, 2024, and Period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
| C. | Account balances with related parties. |
There are no balances of receivables and payables to related parties as of June 30, 2024, and December 31, 2023.
| D. | Financial transactions with related parties |
There are no significant financial transactions with related parties for the six-month ended June 30, 2024, and period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023.
| E. | Transactions with key management personnel |
The compensation for the key management personnel for the six-month period ended June 30, 2024, and period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | For the six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | For the period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Short-term employee benefits | | ₩ | | | 150,000 | | | | 29,876 | |
| Post-employment benefits | | | | | 44,724 | | | | 22,673 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 194,724 | | | | 52,549 | |
Compensation of the Company’s key management personnel include salaries, non-cash benefits and contributions to a post-employment defined benefit plan.
| F. | Financial Transactions with key management personnel |
Details of significant financial transaction the key management personnel for the six-month period ended June 30, 2024, and period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023 are as follows:
| | | | | For the
six-month
period ended
June 30,
2024 | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
June 30,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Shares issued | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 15,000 | |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six-Month Period Ended June 30, 2024, and Period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to June 30, 2023
12. Commitments
On September 14, 2023, an amendment was made to the equity interest exchange agreement, originally entered into on April 9, 2023, between the CEOs, who are the dominant shareholders of the Company, and K Enter Holdings for the purpose of listing on NASDAQ through a merger with a SPAC company. The equity interest exchange agreement is effective on the date designated by K Enter Holdings. The effective date has not been designated as of the end of the reporting period but is expected to be designated in the future. Upon the effective date, the CEOs of the Company will exchange each of 510 shares with the equity interest of K Enter Holdings. Following the equity interest exchange transaction, the Company is expected to be a subsidiary of K Enter Holdings.
Report of Independent Auditors
To the Board of Directors of
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
Opinion
We have audited the accompanying financial statements of Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd. (the “Company”), which comprise the statement of financial position as of December 31, 2023, and the related statements of comprehensive income, of changes in equity and of cash flows for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, including the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”).
In our opinion, the accompanying financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
Basis for Opinion
We conducted our audit in accordance with auditing standards generally accepted in the United States of America (US GAAS). Our responsibilities under those standards are further described in the Auditors’ Responsibilities for the Audit of the Financial Statements section of our report. We are required to be independent of the Company and to meet our other ethical responsibilities, in accordance with the relevant ethical requirements relating to our audit. We believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our audit opinion.
Material Uncertainty Related to Going Concern
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 2 to the financial statements, the Company incurred a net loss and has a net total deficit, and has stated that these events or conditions indicate that a material uncertainty exists that may cast significant doubt on the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s evaluation of the events and conditions and management’s plans regarding these matters are also described in Note 2. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty. Our opinion is not modified with respect to this matter.
Responsibilities of Management for the Financial Statements
Management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of the financial statements in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board, and for the design, implementation, and maintenance of internal control relevant to the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error.
In preparing the financial statements, management is responsible for assessing the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern for at least, but not limited to, twelve months from the end of the reporting period, disclosing, as applicable, matters related to going concern and using the going concern basis of accounting unless management either intends to liquidate the Company or to cease operations, or has no realistic alternative but to do so.
Auditors’ Responsibilities for the Audit of the Financial Statements
Our objectives are to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements as a whole are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error, and to issue an auditors’ report that includes our opinion. Reasonable assurance is a high level of assurance but is not absolute assurance and therefore is not a guarantee that an audit conducted in accordance with US GAAS will always detect a material misstatement when it exists. The risk of not detecting a material misstatement resulting from fraud is higher than for one resulting from error, as fraud may involve collusion, forgery, intentional omissions, misrepresentations, or the override of internal control. Misstatements are considered material if there is a substantial likelihood that, individually or in the aggregate, they would influence the judgment made by a reasonable user based on the financial statements.
In performing an audit in accordance with US GAAS, we:
| ● | Exercise professional judgment and maintain professional skepticism throughout the audit. |
| | | |
| ● | Identify and assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to fraud or error, and design and perform audit procedures responsive to those risks. Such procedures include examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. |
| | | |
| ● | Obtain an understanding of internal control relevant to the audit in order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control. Accordingly, no such opinion is expressed. |
| | | |
| ● | Evaluate the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonableness of significant accounting estimates made by management, as well as evaluate the overall presentation of the financial statements. |
| | | |
| ● | Conclude whether, in our judgment, there are conditions or events, considered in the aggregate, that raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern for a reasonable period of time. |
We are required to communicate with those charged with governance regarding, among other matters, the planned scope and timing of the audit, significant audit findings, and certain internal control-related matters that we identified during the audit.
| /s/ Samil PricewaterhouseCoopers | |
| | |
| Seoul, KOREA | |
| May 13, 2024 | |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As of December 31, 2023
| | | Note | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | 12,14,16,19,21 | | ₩ | | | 275,897 | |
| Other current financial assets | | 14,19 | | | | | 50,000 | |
| Other current assets | | 11 | | | | | 26,465 | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | | 352,362 | |
| Long-term investments | | 14,19 | | | | | 30,000 | |
| Property and equipment | | 13 | | | | | 945 | |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | 11 | | | | | 360,000 | |
| - Related parties | | 22 | | | | | 60,000 | |
| - Non related parties | | | | | | | 300,000 | |
| Total non-current assets | | | | | | | 390,945 | |
| Total assets | | | | ₩ | | | 743,307 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | 14,17,19 | | ₩ | | | 2,715 | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | 11 | | | | | 1,931 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | | 4,646 | |
| Other non-current non-financial liabilities | | 11,18 | | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | 9 | | | | | 72,347 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | | | | | 1,072,347 | |
| Total liabilities | | | | | | | 1,076,993 | |
| Equity | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital | | 15 | | | | | 15,000 | |
| Other reserves | | 15 | | | | | (1,054 | ) |
| Accumulated deficit | | | | | | | (347,632 | ) |
| Total equity | | | | | | | (333,686 | ) |
| Total liabilities and equity | | | | ₩ | | | 743,307 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
STATEMENT OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
| | | Note | | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Revenue | | 6 | | ₩ | | | - | |
| Cost of revenue | | | | | | | - | |
| Gross profit | | | | | | | - | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | 7 | | | | | (348,550 | ) |
| Operating loss | | | | | | | (348,550 | ) |
| Finance income | | 8,14 | | | | | 303 | |
| Other income | | 7 | | | | | 614 | |
| Loss before income tax | | | | | | | (347,632 | ) |
| Income tax expenses | | 10 | | | | | - | |
| Loss for the period | | | | | | | (347,632 | ) |
| Other comprehensive loss | | | | ₩ | | | - | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | ₩ | | | (347,632 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
| | | Note | | | | Share capital | | | Other components of equity | | | Accumulated deficit | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Balance at March 6, 2023 (inception) | | 15 | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (347,632 | ) | | | (347,632 | ) |
| Transaction with owners, recognized directly in equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Shares issued | | | | | | | 15,000 | | | | (1,054 | ) | | | - | | | | 13,946 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | | 15 | | ₩ | | | 15,000 | | | | (1,054 | ) | | | (347,632 | ) | | | (333,686 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
| | | Note | | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | 21 | | | | | | |
| Net loss | | | | ₩ | | | (347,632 | ) |
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash provided by operating activities | | 21 | | | | | 690,376 | |
| Interest received | | 21 | | | | | 303 | |
| Income taxes paid | | | | | | | (46 | ) |
| Net cash inflow in operating activities | | | | ₩ | | | 343,001 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | |
| Payments for other current financial assets | | | | | | | (50,000 | ) |
| Purchases of long-term investments | | | | | | | (30,000 | ) |
| Purchase of property and equipment | | | | | | | (1,050 | ) |
| Net cash outflow in investing activities | | | | ₩ | | | (81,050 | ) |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from issues of shares | | | | | | | 15,000 | |
| Share issue cost | | | | | | | (1,054 | ) |
| Net cash inflow in financing activities | | | | ₩ | | | 13,946 | |
| Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | 275,897 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the period | | 12 | | | | | - | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of the period | | 12 | | ₩ | | | 275,897 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
1. Reporting entity
The Company
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd. (“the Company”) was incorporated in March 2023 and the Company’s registered office is at B 907, 606, Hosu-ro, Ilsandong-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea. The Company is primarily providing the media production service that consists of planning, producing, and selling the television programs.
The Company’s major shareholders and their respective percentage of ownership as of December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | Number of shares | | | Ownership (%) | |
| Park, Jun Woo | | | 1,000 | | | | 33.33 | |
| Shin, Kyung Soo | | | 1,000 | | | | 33.33 | |
| Kim, Seung Ho | | | 1,000 | | | | 33.33 | |
| Total | | | 3,000 | | | | 100.0 | |
2. Basis of Accounting
These financial statements for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) as issued by International Accounting Standard Board (“IASB”). These financial statements were authorized for issuance by the board of directors on May 13, 2024.
Details of the Company’s accounting policies are included in Note 5.
Going concern
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern which is dependent upon the Company receiving the proceeds from the loans or securing other forms of investment and/or financing. The Company incurred a loss of Korean Won 347,632 thousand for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, and had net total deficit of Korean Won 347,632 thousand as of December 31, 2023. The Company acknowledges that there is a risk that the quantum and timing of cash flows sufficient to sustain operations may not be achievable and that management forecasts regarding cash flow from operations may prove inaccurate. The continuation of the Company’s activities is dependent on the availability of adequate financial support. The Company has stated that these conditions indicate that a material uncertainty exists that may cast significant doubt on the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Based on management’s forecasts, the day-to-day operations and expenditure requirements as described above are anticipated to be funded by the cash generated through the new commitments from K Enter Holdings. On March 11, 2024, the Company received a non-binding loan letter of intent (“LOI”) from K Enter Holdings, 1,000,000 thousand Korean Won loan, which will be used for the Company’s content development. In addition, the Company received a separate non-binding loan LOI from K Enter Holdings to support the Company’s day-to-day operational expenditure. The maximum loan amount, conditions, and execution timing will be discussed in detail depending on the company’s future business environment.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
Basis of measurement
These financial statements have been prepared on the historical cost basis except for the following items, which are measured on an alternative basis on each reporting date.
| Items | | Measurement bases |
| Financial instruments measured at FVTPL | | Fair value |
3. Functional and presentation currency
These financial statements are presented in Korean Won, which the Company’s functional currency. All amounts have been rounded to the nearest thousand, unless otherwise indicated.
4. Use of judgements and estimates
In preparing these financial statements, management has made judgements and estimates that affect the application of the Company’s accounting policies and the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
Estimates and underlying assumptions are reviewed on an ongoing basis. Revisions to estimates are recognized prospectively.
| A. | Assumptions and estimation uncertainties |
Information about assumptions and estimation uncertainties at the reporting date that have a significant risk of resulting in a material adjustment to the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities within the next financial year is included in the following notes:
| - | Note 9: measurement of defined benefit obligations: key actuarial assumptions; |
5. Material accounting policies
The material accounting policies followed by the Company in preparation of its financial statements are as follows:
| A. | New and amended standards or interpretations not yet adopted by the Company |
The following new accounting standards and interpretations that have been published that are not mandatory for December 31, 2023, reporting periods and have not been early adopted by the Company.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements - Classification of Liabilities as Current or Non-current
The amendments clarify that liabilities are classified as either current or non-current, depending on the substantive rights that exist at the end of the reporting period. Classification is unaffected by the likelihood that an entity will exercise right to defer settlement of the liability or the expectations of management. Also, the settlement of liability includes the transfer of the entity’s own equity instruments, however, it would be excluded if an option to settle them by the entity’s own equity instruments if compound financial instruments is met the definition of equity instruments and recognized separately from the liability. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, and earlier application is permitted. The Company is in review for the impact of these amendments on the financial statements.
IAS 7 Statements of Cash Flows and IFRS 7 Financial instruments disclosures - Supplier finance
These amendments require disclosures to enhance the transparency of supplier finance arrangements and their effects on an entity’s liabilities, cash flows and exposure to liquidity risk. The disclosure requirements are the IASB’s response to investors’ concerns that some companies’ supplier finance arrangements are not sufficiently visible, hindering investors’ analysis. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, with transitional reliefs in the first year. The Company does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IAS 21 The effects of changes in foreign exchange rates - Lack of Exchangeability
The amendments add requirements to help entities to determine whether a currency is exchangeable into another currency at a measurement date for a specified purpose and the spot exchange rate to use when it is not. A currency is exchangeable when there is an ability to obtain the other currency (with a normal administrative delay), and the transaction would take place through a market or exchange mechanism that creates enforceable rights and obligations. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2025, and earlier application is permitted. The Company does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IFRS 16 – Lease Liability in a Sale and Leaseback
When subsequently measuring lease liabilities arising from a sale and leaseback, a seller-lessee shall determine lease payments or revised lease payments in a way that the seller-lessee would not recognize any amount of the gain or loss that relates to the right of use retained by the seller-lessee. The amendments should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2024, and earlier application is permitted. The Company does not expect that these amendments have a significant impact on the financial statements.
IFRS 18 Presentation and Disclosure in Financial Statements
Items in the statement of profit or loss will need to be classified into one of five categories: operating, investing, financing, income taxes and discontinued operations. IFRS 18 requires the Company to present specified totals and subtotals: ‘Operating profit or loss’, ‘Profit or loss’ and ‘Profit or loss before financing and income taxes’. Information related to management-defined performance measures should be disclosed. IFRS 18 also provides enhanced guidance on the principles of aggregation and disaggregation which focus on grouping items based on their shared characteristics. The new standard should be applied for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2027, and earlier application is permitted. The Company is in review for the impact of this new standard on the financial statements.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
Transactions in foreign currencies are translated into the functional currency of the Company at the exchange rates at the dates of the transactions.
Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are translated into the functional currency at the exchange rate at the reporting date. Non-monetary assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value in a foreign currency are translated into the functional currency at the exchange rate when the fair value was determined. Non-monetary items that are measured based on historical cost in a foreign currency are translated at the exchange rate at the date of the transaction. Foreign currency differences are generally recognized in profit or loss and presented within finance costs. Translation differences on non-monetary assets and liabilities carried at fair value are reported as part of the fair value gain or loss.
However, foreign currency differences arising from the translation of the following items are recognized in OCI:
| ● | an investment in equity securities designated as at FVOCI); |
| ● | a financial liability designated as a hedge of the net investment in a foreign operation to the extent that the hedge is effective; and |
| ● | qualifying cash flow hedges to the extent that the hedges are effective. |
| C. | Revenue from contracts with customers |
The Company generates revenue primarily through providing the media production service.
The Company determines revenue recognition by:
| ● | identifying the contract, or contracts, with a customer; |
| ● | identifying the performance obligations in each contract; |
| ● | determining the transaction price; |
| ● | allocating the transaction price to the performance obligations in each contract; and |
| ● | recognizing revenue when, or as, we satisfy performance obligations by transferring the promised goods or services. |
Media production revenue
The Company operates the media production business that consists of planning, producing, and selling the theatrical films and television programs. The Company identifies the license which is provided along with media product as combined output and recognizes revenue over time by measuring its progress based on cost incurred towards complete satisfaction of the performance obligation of media.
The Company recognizes unbilled receivables from media production service as contract assets and recognizes receipts in advance for prepaid media production services as contract liabilities.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
An operating segment is a component of the Company that engages in business activities from which it may earn revenues and incur expenses, including revenues and expenses that relate to transactions with any of the Company’s other components. The chief operating decision-maker has been identified as the chief executive officer. The Company’s operating segment has been determined to be a single business unit, for which the Company generates identifiable financial information that is regularly reported to the chief executive officer for the purpose of resource allocation and assessment of segment performance. The Company has a reportable segment as described in Note 6. Segment results that are reported to the chief operating decision maker include items directly attributable to a segment as well as those that can be allocated on a reasonable basis.
| i. | Short-term employee benefits |
Short-term employee benefits are employee benefits due to be settled within 12 months after the end of the period in which the employees render related services. When an employee has rendered a service to the Company during an accounting period, the Company recognizes the undiscounted amount of short-term employee benefits expected to be paid in exchange for that service.
The Company’s net obligation in respect of defined benefit plans is calculated separately for each plan by estimating the amount of future benefit that employees have earned in the current and prior periods, discounting that amount and deducting the fair value of any plan assets.
The calculation of defined benefit obligations is performed annually using the projected unit credit method. When the calculation results in a potential asset for the Company, the recognized asset is limited to the present value of economic benefits available in the form of any future refunds from the plan or reductions in future contributions to the plan. To calculate the present value of economic benefits, consideration is given to any applicable minimum funding requirements.
Remeasurements of the net defined benefit liability, which comprise actuarial gains and losses, the return on plan assets (excluding interest) and the effect of the asset ceiling (if any, excluding interest), are recognized immediately in OCI. The Company determines the net interest expense (income) on the net defined benefit liability (asset) for the period by applying the discount rate used to measure the defined benefit obligation at the beginning of the annual period to the then-net defined benefit liability (asset), taking into account any changes in the net defined benefit liability (asset) during the period as a result of contributions and benefit payments. Net interest expense and other expenses related to defined benefit plans are recognized in profit or loss.
When the benefits of a plan are changed or when a plan is curtailed, the resulting change in benefit that relates to past service or the gain or loss on curtailment is recognized immediately in profit or loss. The Company recognizes gains and losses on the settlement of a defined benefit plan when the settlement occurs.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
| F. | Finance income and finance costs |
The Company’s finance income and finance costs include:
| ● | the net gain or loss on settlement of project investments; |
| ● | the foreign currency gain or loss on financial assets and financial liabilities; |
The ‘effective interest rate’ is the rate that exactly discounts estimated future cash payments or receipts through the expected life of the financial instrument to:
| ● | the gross carrying amount of the financial asset; or |
| ● | the amortized cost of the financial liability. |
In calculating interest income and expense, the effective interest rate is applied to the gross carrying amount of the asset (when the asset is not credit-impaired) or to the amortized cost of the liability. However, for financial assets that have become credit-impaired subsequent to initial recognition, interest income is calculated by applying the effective interest rate to the amortized cost of the financial asset. If the asset is no longer credit-impaired, then the calculation of interest income reverts to the gross basis.
Income tax expense comprises current and deferred tax. It is recognized in profit or loss except to the extent that it relates to a business combination, or items recognized directly in equity or in OCI.
The Company has determined that interest and penalties related to income taxes, including uncertain tax treatments, do not meet the definition of income taxes, and therefore accounted for them under IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets.
Current tax comprises the expected tax payable or receivable on the taxable income or loss for the year and any adjustment to the tax payable or receivable in respect of previous years. The amount of current tax payable or receivable is the best estimate of the tax amount expected to be paid or received that reflects uncertainty related to income taxes, if any. It is measured using tax rates enacted or substantively enacted at the reporting date. Current tax also includes any tax arising from dividends.
Current tax assets and liabilities are offset only if certain criteria are met.
| - | Has a legally enforceable right to set off the recognized amounts; and |
| - | Intends either to settle on a net basis, or to realize the asset and settle the liability simultaneously. |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
Deferred tax is recognized in respect of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for taxation purposes. Deferred tax is not recognized for:
| ● | temporary differences on the initial recognition of assets or liabilities in a transaction that is not a business combination and that affects neither accounting nor taxable profit or loss and does not give rise to equal taxable and deductible temporary differences; |
| ● | temporary differences related to investments in subsidiaries, associates and joint arrangements to the extent that the Company is able to control the timing of the reversal of the temporary differences and it is probable that they will not reverse in the foreseeable future; and |
| ● | taxable temporary differences arising on the initial recognition of goodwill. |
Deferred tax assets are recognized for unused tax losses, unused tax credits and deductible temporary differences to the extent that it is probable that future taxable profits will be available against which they can be used. Future taxable profits are determined based on the reversal of relevant taxable temporary differences. If the amount of taxable temporary differences is insufficient to recognize a deferred tax asset in full, then future taxable profits, adjusted for reversals of existing temporary differences, are considered, based on the business plans for individual subsidiaries in the Company. Deferred tax assets are reviewed at each reporting date and are reduced to the extent that it is no longer probable that the related tax benefit will be realized; such reductions are reversed when the probability of future taxable profits improves.
The measurement of deferred tax reflects the tax consequences that would follow from the manner in which the Company expects, at the reporting date, to recover or settle the carrying amount of its assets and liabilities. For this purpose, the carrying amount of investment property measured at fair value is presumed to be recovered through sale, and the Company has not rebutted this presumption.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are offset only if certain criteria are met.
| - | Has a legally enforceable right to set off the recognized amounts; and |
| - | Intends either to settle on a net basis, or to realize the asset and settle the liability simultaneously. |
| H. | Cash and cash Equivalents |
Cash and cash equivalents comprise deposits held at banks with maturities of three months or less from the acquisition date that are easily convertible to cash and subject to an insignificant risk of changes in their fair value.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
| i. | Recognition and measurement |
Items of property and equipment are measured at cost, which includes capitalized borrowing costs, less accumulated depreciation and any accumulated impairment losses.
If significant parts of an item of property and equipment have different useful lives, then they are accounted for as separate items (major components) of property and equipment.
Any gain or loss on disposal of an item of property and equipment is recognized in profit or loss.
| ii. | Subsequent expenditure |
Subsequent expenditure is capitalized only if it is probable that the future economic benefits associated with the expenditure will flow to the Company. The carrying amount of the replaced parts are derecognized and the repairs and maintenance expenses are recognized in profit or loss in the period they are incurred.
Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method to allocate the cost or revalued amounts of the assets, net of their residual values, over their estimated useful lives as follows:
Depreciation methods, useful lives and residual values are reviewed at each reporting date and adjusted if appropriate.
| i. | Recognition and initial measurement |
Trade receivables and debt securities issued are initially recognized when they are originated. All other financial assets and financial liabilities are initially recognized when the Company becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the instrument.
A financial asset (unless it is a trade receivable without a significant financing component) or financial liability is initially measured at fair value plus or minus, for an item not at FVTPL, transaction costs that are directly attributable to its acquisition or issue. A trade receivable without a significant financing component is initially measured at the transaction price.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
| ii. | Classification and subsequent measurement |
Financial assets
On initial recognition, a financial asset is classified as measured at:
Financial assets are not reclassified subsequent to their initial recognition unless the Company changes its business model for managing financial assets, in which case all affected financial assets are reclassified on the first day of the first reporting period following the change in the business model.
A financial asset is measured at amortized cost if it meets both of the following conditions and is not designated as at FVTPL:
| ● | it is held within a business model whose objective is to hold assets to collect contractual cash flows; and |
| ● | its contractual terms give rise on specified dates to cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. |
A debt investment is measured at FVOCI if it meets both of the following conditions and is not designated as at FVTPL:
| ● | it is held within a business model whose objective is achieved by both collecting contractual cash flows and selling financial assets; and |
| ● | its contractual terms give rise on specified dates to cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. |
On initial recognition of an equity investment that is not held for trading, the Company may irrevocably elect to present subsequent changes in the investment’s fair value in OCI. This election is made on an investment-by-investment basis.
All financial assets not classified as measured at amortized cost or FVOCI as described above are measured at FVTPL. This includes all derivative financial assets. On initial recognition, the Company may irrevocably designate a financial asset that otherwise meets the requirements to be measured at amortized cost or at FVOCI as at FVTPL if doing so eliminates or significantly reduces an accounting mismatch that would otherwise arise.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
Financial assets - Business model assessment
The Company makes an assessment of the objective of the business model in which a financial asset is held at a portfolio level because this best reflects the way the business is managed, and information is provided to management. The information considered includes:
| ● | the stated policies and objectives for the portfolio and the operation of those policies in practice. These include whether management’s strategy focuses on earning contractual interest income, maintaining a particular interest rate profile, matching the duration of the financial assets to the duration of any related liabilities or expected cash outflows or realizing cash flows through the sale of the assets; |
| ● | how the performance of the portfolio is evaluated and reported to the Company’s management; |
| ● | the risks that affect the performance of the business model (and the financial assets held within that business model) and how those risks are managed; |
| ● | how managers of the business are compensated - e.g. whether compensation is based on the fair value of the assets managed or the contractual cash flows collected; and |
| ● | the frequency, volume and timing of sales of financial assets in prior periods, the reasons for such sales and expectations about future sales activity. |
Transfers of financial assets to third parties in transactions that do not qualify for derecognition are not considered sales for this purpose, consistent with the Company’s continuing recognition of the assets.
Financial assets that are held for trading or are managed and whose performance is evaluated on a fair value basis are measured at FVTPL.
Financial assets - Assessment whether contractual cash flows are solely payments of principal and interest
For the purposes of this assessment, ‘principal’ is defined as the fair value of the financial asset on initial recognition. ‘Interest’ is defined as consideration for the time value of money and for the credit risk associated with the principal amount outstanding during a particular period of time and for other basic lending risks and costs (e.g. liquidity risk and administrative costs), as well as a profit margin.
In assessing whether the contractual cash flows are solely payments of principal and interest, the Company considers the contractual terms of the instrument. This includes assessing whether the financial asset contains a contractual term that could change the timing or amount of contractual cash flows such that it would not meet this condition. In making this assessment, the Company considers:
| ● | contingent events that would change the amount or timing of cash flows; |
| ● | terms that may adjust the contractual coupon rate, including variable-rate features; |
| ● | prepayment and extension features; and |
| ● | terms that limit the Company’s claim to cash flows from specified assets (e.g. non-recourse features). |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
A prepayment feature is consistent with the solely payments of principal and interest criterion if the prepayment amount substantially represents unpaid amounts of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding, which may include reasonable compensation for early termination of the contract. Additionally, for a financial asset acquired at a discount or premium to its contractual par amount, a feature that permits or requires prepayment at an amount that substantially represents the contractual par amount plus accrued (but unpaid) contractual interest (which may also include reasonable compensation for early termination) is treated as consistent with this criterion if the fair value of the prepayment feature is insignificant at initial recognition.
Financial assets - Subsequent measurement and gains and losses
Financial assets at FVTPL: These assets are subsequently measured at fair value. Net gains and losses, including any interest or dividend income, are recognized in profit or loss.
Financial assets at amortized cost: These assets are subsequently measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. The amortized cost is reduced by impairment losses. Interest income, foreign exchange gains and losses and impairment are recognized in profit or loss. Any gain or loss on derecognition is recognized in profit or loss.
Financial liabilities - Classification, subsequent measurement and gains and losses
Financial liabilities are classified as measured at amortized cost or FVTPL. A financial liability is classified as at FVTPL if it is classified as held-for-trading, it is a derivative or it is designated as such on initial recognition. Financial liabilities at FVTPL are measured at fair value and net gains and losses, including any interest expense, are recognized in profit or loss. Other financial liabilities are subsequently measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. Interest expense and foreign exchange gains and losses are recognized in profit or loss. Any gain or loss on derecognition is also recognized in profit or loss.
Financial assets
The Company derecognizes a financial asset when:
| ● | the contractual rights to the cash flows from the financial asset expire; or |
| ● | it transfers the rights to receive the contractual cash flows in a transaction in which either: |
| - | substantially all of the risks and rewards of ownership of the financial asset are transferred; or |
| - | the Company neither transfers nor retains substantially all of the risks and rewards of ownership and it does not retain control of the financial asset. |
The Company enters into transactions whereby it transfers assets recognized in its statement of financial position, but retains either all or substantially all of the risks and rewards of the transferred assets. In these cases, the transferred assets are not derecognized.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
Financial liabilities
The Company derecognizes a financial liability when its contractual obligations are discharged or cancelled or expire. The Company also derecognizes a financial liability when its terms are modified and the cash flows of the modified liability are substantially different, in which case a new financial liability based on the modified terms is recognized at fair value.
On derecognition of a financial liability, the difference between the carrying amount extinguished and the consideration paid (including any non-cash assets transferred or liabilities assumed) is recognized in profit or loss.
When changes were made to a financial asset or financial liability in addition to changes to the basis for determining the contractual cash flows required by interest rate benchmark reform, the Company first updated the effective interest rate of the financial asset or financial liability to reflect the change that is required by interest rate benchmark reform. After that, the Company applied the policies on accounting for modifications to the additional changes.
| i. | Non-derivative financial assets |
Financial instruments and contract assets
The Company recognizes loss allowances for expected credit losses(“ECL”) on:
| ● | financial assets measured at amortized cost; and |
The Company also recognizes loss allowances for ECLs on lease receivables, which are disclosed as part of trade and other receivables.
The Company measures loss allowances at an amount equal to lifetime ECLs, except for the following, which are measured at 12-month ECLs:
| ● | debt securities that are determined to have low credit risk at the reporting date; and |
| ● | other debt securities and bank balances for which credit risk (i.e. the risk of default occurring over the expected life of the financial instrument) has not increased significantly since initial recognition. |
Loss allowances for trade receivables (including lease receivables) and contract assets are always measured at an amount equal to lifetime ECLs.
When determining whether the credit risk of a financial asset has increased significantly since initial recognition and when estimating ECLs, the Company considers reasonable and supportable information that is relevant and available without undue cost or effort. This includes both quantitative and qualitative information and analysis, based on the Company’s historical experience and informed credit assessment, that includes forward-looking information.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
The Company assumes that the credit risk on a financial asset has increased significantly if it is more than 12 months past due.
The Company considers a financial asset to be in default when:
| ● | the debtor is unlikely to pay its credit obligations to the Company in full, without recourse by the Company to actions such as realizing security (if any is held). |
Lifetime ECLs are the ECLs that result from all possible default events over the expected life of a financial instrument.
12-month ECLs are the portion of ECLs that result from default events that are possible within the 12 months after the reporting date (or a shorter period if the expected life of the instrument is less than 12 months).
The maximum period considered when estimating ECLs is the maximum contractual period over which the Company is exposed to credit risk.
Measurement of ECLs
ECLs are a probability-weighted estimate of credit losses. Credit losses are measured as the present value of all cash shortfalls (i.e. the difference between the cash flows due to the entity in accordance with the contract and the cash flows that the Company expects to receive).
ECLs are discounted at the effective interest rate of the financial asset.
Credit-impaired financial assets
At each reporting date, the Company assesses whether financial assets carried at amortized cost are credit-impaired. A financial asset is ‘credit-impaired’ when one or more events that have a detrimental impact on the estimated future cash flows of the financial asset have occurred.
Evidence that a financial asset is credit-impaired includes the following observable data:
| ● | significant financial difficulty of the debtor; |
| ● | the restructuring of a loan or advance by the Company on terms that the Company would not consider otherwise; |
| ● | it is probable that the debtor will enter bankruptcy or other financial reorganization; or |
| ● | the disappearance of an active market for a security because of financial difficulties. |
Presentation of allowance for ECL in the statement of financial position
Loss allowances for financial assets measured at amortized cost are deducted from the gross carrying amount of the assets.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
Write-off
The gross carrying amount of a financial asset is written off when the Company has no reasonable expectations of recovering a financial asset in its entirety or a portion thereof. For individual customers, the Company has a policy of writing off the gross carrying amount when the financial asset is 180 days past due based on historical experience of recoveries of similar assets. For corporate customers, the Company individually makes an assessment with respect to the timing and amount of write-off based on whether there is a reasonable expectation of recovery. The Company expects no significant recovery from the amount written off. However, financial assets that are written off could still be subject to enforcement activities in order to comply with the Company’s procedures for recovery of amounts due.
At each reporting date, the Company reviews the carrying amounts of its non-financial assets (other than biological assets, investment property, developing contents, contract assets and deferred tax assets) to determine whether there is any indication of impairment. If any such indication exists, then the asset’s recoverable amount is estimated. Goodwill is tested annually for impairment.
For impairment testing, assets are grouped together into the smallest group of assets that generates cash inflows from continuing use that are largely independent of the cash inflows of other assets or CGUs. Goodwill arising from a business combination is allocated to CGUs or groups of CGUs that are expected to benefit from the synergies of the combination.
The recoverable amount of an asset or CGU is the greater of its value in use and its fair value less costs of disposal. Value in use is based on the estimated future cash flows, discounted to their present value using a pre-tax discount rate that reflects current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the asset or CGU.
An impairment loss is recognized if the carrying amount of an asset or CGU exceeds its recoverable amount.
Impairment losses are recognized in profit or loss. They are allocated first to reduce the carrying amount of any goodwill allocated to the CGU, and then to reduce the carrying amounts of the other assets in the CGU on a pro rata basis.
An impairment loss in respect of goodwill is not reversed. For other assets, an impairment loss is reversed only to the extent that the asset’s carrying amount does not exceed the carrying amount that would have been determined, net of depreciation or amortization, if no impairment loss had been recognized.
At inception of a contract, the Company assesses whether a contract is, or contains, a lease. A contract is, or contains, a lease if the contract conveys the right to control the use of an identified asset for a period of time in exchange for consideration.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
At commencement or on modification of a contract that contains a lease component, the Company allocates the consideration in the contract to each lease component on the basis of its relative stand-alone prices. However, for the leases of property the Company has elected not to separate non-lease components and account for the lease and non-lease components as a single lease component.
The Company recognizes a right-of-use asset and a lease liability at the lease commencement date. The right-of-use asset is initially measured at cost, which comprises the initial amount of the lease liability adjusted for any lease payments made at or before the commencement date, plus any initial direct costs incurred and an estimate of costs to dismantle and remove the underlying asset or to restore the underlying asset or the site on which it is located, less any lease incentives received.
The right-of-use asset is subsequently depreciated using the straight-line method from the commencement date to the end of the lease term, unless the lease transfers ownership of the underlying asset to the Company by the end of the lease term or the cost of the right-of-use asset reflects that the Company will exercise a purchase option. In that case the right-of-use asset will be depreciated over the useful life of the underlying asset, which is determined on the same basis as those of property and equipment. In addition, the right-of-use asset is periodically reduced by impairment losses, if any, and adjusted for certain remeasurements of the lease liability.
The lease liability is initially measured at the present value of the lease payments that are not paid at the commencement date, discounted using the interest rate implicit in the lease or, if that rate cannot be readily determined, the Company’s incremental borrowing rate. Generally, the Company uses its incremental borrowing rate as the discount rate.
The Company determines its incremental borrowing rate by obtaining interest rates from various external financing sources and makes certain adjustments to reflect the terms of the lease and type of the asset leased.
Lease payments included in the measurement of the lease liability comprise the following:
| ● | fixed payments, including in-substance fixed payments; |
| ● | variable lease payments that depend on an index or a rate, initially measured using the index or rate as at the commencement date; |
| ● | amounts expected to be payable under a residual value guarantee; and |
| ● | the exercise price under a purchase option that the Company is reasonably certain to exercise, lease payments in an optional renewal period if the Company is reasonably certain to exercise an extension option, and penalties for early termination of a lease unless the Company is reasonably certain not to terminate early. |
The lease liability is measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. It is remeasured when there is a change in future lease payments arising from a change in an index or rate, if there is a change in the Company’s estimate of the amount expected to be payable under a residual value guarantee, if the Company changes its assessment of whether it will exercise a purchase, extension or termination option or if there is a revised in-substance fixed lease payment.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
When the lease liability is remeasured in this way, a corresponding adjustment is made to the carrying amount of the right-of-use asset, or is recorded in profit or loss if the carrying amount of the right-of-use asset has been reduced to zero.
The Company uses hindsight in applying IFRS 16 such as the determination of lease term for contracts that contain options to extend or terminate a lease.
The Company has elected not to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for leases of low-value assets (leases for which the underlying asset is valued at USD 5,000 or less) and short-term leases (leases that have a lease term of 12 months or less at the commencement date). The Company recognizes the lease payments associated with these leases as an expense on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
‘Fair value’ is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date in the principal or, in its absence, the most advantageous market to which the Company has access at that date. The fair value of a liability reflects its non-performance risk.
A number of the Company’s accounting policies and disclosures require the measurement of fair values, for both financial and non-financial assets and liabilities.
When one is available, the Company measures the fair value of an instrument using the quoted price in an active market for that instrument. A market is regarded as ‘active’ if transactions for the asset or liability take place with sufficient frequency and volume to provide pricing information on an ongoing basis.
If there is no quoted price in an active market, then the Company uses valuation techniques that maximize the use of relevant observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The chosen valuation technique incorporates all of the factors that market participants would take into account in pricing a transaction.
The best evidence of the fair value of a financial instrument on initial recognition is normally the transaction price - i.e. the fair value of the consideration given or received. If the Company determines that the fair value on initial recognition differs from the transaction price and the fair value is evidenced neither by a quoted price in an active market for an identical asset or liability nor based on a valuation technique for which any unobservable inputs are judged to be insignificant in relation to the measurement, then the financial instrument is initially measured at fair value, adjusted to defer the difference between the fair value on initial recognition and the transaction price. Subsequently, that difference is recognised in profit or loss on an appropriate basis over the life of the instrument but no later than when the valuation is wholly supported by observable market data, or the transaction is closed out.
| N. | Concentration of credit risk |
The Company performs periodic credit evaluations of its customers’ financial condition and generally does not require collateral for customers on accounts receivable. The Company maintains reserves for potential credit losses, which are periodically reviewed.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
6. Operating segments
The Company’s operating segments have been identified to be a single business unit, by which the Company provides media production services.
The following summary describes the operations of the reportable segment.
| Reportable segment | | Operations |
| Media Production | | Planning, producing, and selling the media content such as television programs |
7. Income and Expenses
Details of other income for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Miscellaneous income | | | 614 | |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
Details of classification of expenses by nature for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Employee benefits (Note 9 (D)) | | | | | 320,372 | |
| Service fees | | | | | 5,732 | |
| Rent | | | | | 12,000 | |
| Supplies | | | | | 5,422 | |
| Taxes & dues | | | | | 909 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | | | 105 | |
| Other expenses | | | | | 4,010 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 348,550 | |
Total expenses consist of cost of sales and selling, general and administrative expenses.
8. Finance income
Details of finance income for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Finance income | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | ₩ | | | 303 | |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
9. Employee benefits
Details of defined benefit liability recognized as of December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Defined benefit liability | | ₩ | | | 72,347 | |
The Company operates the defined benefit plans as a retirement pension scheme. Defined benefit plans expose the Company to actuarial risks, such as longevity risk, interest rate risk and market (investment) risk.
| A. | Movement in net defined benefit (asset) liability |
Details of reconciliation from the opening balances to the closing balances for the net defined benefit liability and its components as of December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | Defined benefit obligation | | | Fair value of Plan assets | | | Net defined Benefit liabilities | |
| | | | | For the period from March 6, 2023
(inception) to December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning Balance | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Included in profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current service cost | | | | | 72,347 | | | | - | | | | 72,347 | |
| Ending Balance | | ₩ | | | 72,347 | | | | - | | | | 72,347 | |
There are no contributions funded to its defined benefit plans as of December 31, 2023.
| C. | Defined benefit obligation |
Details of actuarial assumptions used for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 |
| Discount rate | | 4.50% |
| Future salary growth | | 2.88% |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
Assumptions regarding future longevity and standard salary scale have been based on issued by Korea Insurance Development Institute.
As of December 31, 2023, the weighted-average duration of the defined benefit obligation was 8.6 years.
The expected maturity analysis of undiscounted defined severance benefits as of December 31, 2023 was as follows:
| | | | | Less than
1 year | | | Between
1-2 years | | | Between
2-5 years | | | Over
5 years | | | Total | |
| Expected Retirement Benefits | | ₩ | | | 4,564 | | | | 4,550 | | | | 13,496 | | | | 87,210 | | | | 109,820 | |
The Company measures the risk of actuarial assumption changes as a 1% fluctuation in the discount rate and future salary growth rate of the amounts of defined benefit obligation, which reflects the management’s assessment of the risk of actuarial assumption fluctuation that can reasonably occur. The impact of a 1% fluctuation in discount rates and future salary growth rates on the Company’s defined benefit obligation as of December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | Increased by 1% | | | Decreased by 1% | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Discount rate | | ₩ | | | (5,819 | ) | | | 6,578 | |
| Future salary growth | | | | | 6,625 | | | | (5,964 | ) |
Although the analysis does not take account of the full distribution of cash flows expected under the plan, it does provide an approximation of the sensitivity of the assumptions shown.
| D. | Employee benefit expenses |
| i. | Details of employee benefit expenses recognized for the period ended December 31, 2023, are as follows: |
| | | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Wages and salaries | | ₩ | | | 231,000 | |
| Expenses related to post-employment plans | | | | | 72,347 | |
| Fringe benefit | | | | | 17,025 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 320,372 | |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
10. Income Tax
| A. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
| | | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current tax expense | | | | | | |
| Current period | | ₩ | | | - | |
The Company establish additional current tax liabilities for income taxes when, despite the belief that tax positions are fully supportable, there remain positions that do not meet the minimum probability threshold, which is a tax position that is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by the applicable taxation authority. The impact of current tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions, as well as the related net interest and penalties, are included in income taxes in the statements of operations.
| B. | Reconciliation of effective tax rate |
| | | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Loss before income tax | | ₩ | | | (347,632 | ) |
| Tax benefit at the statutory income tax rate | | | | | (34,416 | ) |
| Adjustments: | | | | | | |
| Changes in unrecognized loss carried forward | | | | | 34,520 | |
| Other | | | | | (104 | ) |
| Income tax expenses | | ₩ | | | - | |
| Effective income tax rate (*) | | | | | - | |
| (*) | The effective tax rate is not calculated as the Company incurred a loss before income taxes for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023. |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
| C. | Movement in deferred tax balances |
| i. | Movement in deferred tax balances as of December 31, 2023 |
| | | | | Tax effect | |
| | | | | Beginning | | | Increase
(decrease) | | | Ending | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Property and equipment | | | | | - | | | | 183 | | | | 183 | |
| Defined benefit liabilities | | | | | - | | | | 7,162 | | | | 7,162 | |
| Non-current prepayments | | | | | - | | | | (11,879 | ) | | | (11,879 | ) |
| Other payables | | | | | - | | | | 269 | | | | 269 | |
| Total | | | | | - | | | | (4,265 | ) | | | (4,265 | ) |
| Loss carried forward | | ₩ | | | - | | | | 38,785 | | | | 38,785 | |
| Unrecognized deferred tax income asset (*) | | | | | - | | | | (34,520 | ) | | | (34,520 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets (liabilities) | | ₩ | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| (*) | As of December 31, 2023, the Company did not recognize deferred income tax asset for the temporary difference as it is not probable such loss carried forward can be utilized in the foreseeable future. |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
| D. | Deferred assets (liabilities) |
| i. | Details of unrecognized as deferred income tax assets as of December 31, 2023, is as follows: |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Loss carried forward | | ₩ | | | 34,520 | |
| ii. | The timing of recovery of deferred tax assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2023, is as follows: |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Deferred tax assets | | | | | | |
| - Deferred tax assets to be recovered after more than 12 months | | ₩ | | | 11,611 | |
| - Deferred tax assets to be recovered within 12 months | | | | | 269 | |
| Sub-total | | | | | 11,880 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | | | | | |
| - Deferred tax liabilities to be recovered after more than 12 months | | | | | (11,880 | ) |
| - Deferred tax liabilities to be recovered within 12 months | | | | | - | |
| Sub-total | | | | | (11,880 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets (liabilities), net (*) | | ₩ | | | - | |
| (*) | Deferred tax assets have not been recognized because it is not probable that sufficient taxable profit will be available against which part or all of the deferred tax assets can be utilized. |
| iii. | Details of unused tax loss carryforwards that are recognized as deferred income tax assets as of December 31, 2023, are as follows: |
| Year of expiration | | | | Unused loss
carryforwards | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| After 2029 | | ₩ | | | 34,520 | |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
11. Other assets and liabilities
Details of other assets as of December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current | | | | | | |
| Value added tax receivables | | | | | 26,419 | |
| Current tax asset | | | | | 46 | |
| Non-current | | | | | | |
| Non-current prepayments (*) | | | | | 360,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 386,465 | |
| (*) | Prepayments to drama production company and writer for scenario developments. |
Details of other liabilities as of December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Current | | | | | | |
| Withholdings | | | | | 1,931 | |
| Non-current | | | | | | |
| Contract liabilities (*) | | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 1,001,931 | |
| (*) | The contract liabilities primarily relate to the advance consideration received from the counterparty for drama scenario development service. |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
12. Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Deposits in banks | | ₩ | | | 275,897 | |
The Company doesn’t have any restricted cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023.
13. Property and equipment
| A. | Reconciliation of carrying amount |
Details of property and equipment as of December 31, 2023, is as follows:
| | | | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | | | Book value | | | Accumulated depreciation | | | Carrying amount | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Office equipment | | ₩ | | | 1,050 | | | | (105 | ) | | | 945 | |
Details of the changes in property and equipment for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, is as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | Office equipment | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Beginning balance | | ₩ | | | - | |
| Acquisitions | | | | | 1,050 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | 105 | |
| Ending balance | | ₩ | | | 945 | |
The classification of depreciation expenses in the statements of comprehensive income for the years ended December 31, 2023, is as follows:
| | | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | ₩ | | | 105 | |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
14. Financial instruments by category
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at amortized cost | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | | | 275,897 | |
| Other current financial assets (*) | | | | | 50,000 | |
| Subtotal | | ₩ | | | 325,897 | |
| Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss | | | | | | |
| Long-term investments | | | | | 30,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 355,897 | |
| (*) | Other current financial assets consist of a rent deposit. |
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial liabilities at amortized cost | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | ₩ | | | 2,715 | |
| A. | Classification of investment assets based on liquidity |
The classification of investment assets as of December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Non-Current investments | | | | | | |
| Project investment (*) | | ₩ | | | 30,000 | |
| (*) | An investment in a film production company. |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
| B. | Net gains and losses by category of financial instruments |
The net gains and losses by category of financial instruments for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | Financial assets at amortized cost | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest income | | ₩ | | | 303 | |
15. Capital and reserves
| A. | Share capital and share premium |
Details of share capital and share premium as of December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Number of authorized shares | | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Value per share | | ₩ | | | 5 | |
| Number of shares issued | | | | | 3,000 | |
| Common shares | | ₩ | | | 15,000 | |
Holders of these shares are entitled to dividends as declared from time to time and are entitled to one vote per share at general meetings of the Company.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
| B. | Other components of equity |
Details of other components of equity as of December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Share issue cost | | ₩ | | | (1,054 | ) |
16. Capital management
The Company’s policy is to maintain a strong capital base so as to maintain investor, creditor and market confidence and to sustain future development of the business. The Company monitors capital using a ratio of ‘net debt’ to ‘total capital’. Net debt is calculated as total liabilities (as shown in the statement of financial position) less cash and cash equivalents. The Company’s net debt to total capital ratio as of December 31, 2023, is as follows.
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total liabilities | | ₩ | | | 1,076,993 | |
| Less: Cash and cash equivalents | | | | | (275,897 | ) |
| Net debt | | | | | 801,096 | |
| Total equity | | | | | (333,686 | ) |
| Total capital | | ₩ | | | 467,410 | |
| Net debt to total capital ratio | | | | | 171 | % |
17. Trade and other payables
Trade and other payables as of December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other payables | | ₩ | | | 2,715 | |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
18. Contract liabilities
Contract liabilities as of December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Contract liabilities | | ₩ | | | 1,000,000 | |
The Company received Korean Won 1,000,000 thousand in May 2023 from K Enter Holdings for the purpose of planning and developing a drama. In accordance with the terms of the contract with K Enter Holdings, the Company received payment before having completed performance obligations and recognized contract liabilities.
19. Financial Instruments – Fair values and risk management
| A. | Accounting classifications and fair values |
The following table shows the carrying amounts and fair values of financial assets and financial liabilities, including their levels in the fair value hierarchy. It does not include fair value information for financial assets and financial liabilities not measured at fair value if the carrying amount is a reasonable approximation of fair value.
The carrying amounts of financial instruments by category as of December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | Fair value | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Financial assets at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Project investment | | 30,000 | | | - | | | - | | | 30,000 | | | 30,000 | |
Details of the changes in project investment intangible assets for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023 |
| | | | | Beginning balance | | Acquisitions | | | Ending balance | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean Won) |
| Project investment | | ₩ | | - | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
| B. | Measurement of fair values |
Fair values are categorized into different levels in a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used in the valuation techniques as follows:
| ● | Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 2: all inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable (either directly that is, prices, or indirectly that is, derived from prices) for the asset or liability; |
| ● | Level 3: unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. |
The fair value of financial instruments traded in an active market is determined based on the quoted market price as of the end of the reporting period. If the quoted prices are readily and regularly available through exchanges, sellers, brokers, industry groups, rating agencies or regulators and such prices represent actual market transactions that occur regularly between independent parties, they are considered active markets.
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market is determined using valuation techniques. These valuation techniques use as much market observable information as possible and use the least amount of Company-specific information. At this time, if all the significant input variables required to measure the fair value are observable, the financial instruments are classified as Level 2.
If more than one significant input variable is not based on observable market information, the item is included in Level 3.
The valuation techniques used to measure the fair value of a project investment include:
| ● | Total amount of production costs and distribution fees |
| ● | Estimated amount of shared profit |
| C. | Financial risk management |
The Company’s operating activities expose itself to a variety of financial risks: market risk, credit risk and liquidity risk from which the Company’s risk management program focuses on minimizing any adverse effects on its financial performance. The Company operates financial risk management policies and programs that closely monitor and respond to each risk factor.
Credit risk is the risk of financial loss to the Company if a customer or counterpart to a financial instrument fails to meet its contractual obligations and arises principally from the Company’s receivables from customers. In order to manage credit risk, the Company regularly evaluate the credit worthiness of each customer or counterparty considering the party’s financial information, past experience, its own trading records and other factors. In relation to the impairment of financial assets subsequent to initial recognition, the Company recognizes the changes in expected credit loss (“ECL”) in profit or loss at each reporting date. The carrying amount of a financial asset represents the maximum exposure to credit risk.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
The maximum exposure to credit risk of the Company as of December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | ₩ | | | 275,897 | |
| Other current financial assets | | | | | 50,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 325,897 | |
Cash and cash equivalents are deposited in financial institutions with strong credit rating. The Company’s exposure to credit risk is influenced mainly by the individual characteristics of each customer. The Company has established a credit policy under which each new customer is analyzed individually before the Company’s standard payment and delivery terms and conditions are offered. The Company’s review includes external ratings, if they are available, financial statements, credit agency information, industry information and in some cases bank references.
The Company monitors customer credit risk, customers are grouped according to their credit characteristics, including whether they are an individual or a legal entity, their geographic location, industry, trading history with the Company and existence of previous financial difficulties. The Company does not require collateral in respect of trade and other receivables.
Liquidity risk management includes the maintenance of sufficient cash and marketable securities, the availability of funds from appropriately committed credit lines, and the ability to settle market positions.
Financial liabilities of the Company by maturity according to the remaining period from December 31, 2023, to the contractual maturity date are as follows:
| | | December 31, 2023 | |
| | | Carrying
Amount | | | Less than
3 months | | | 3 months
~ 1 year | | | 1~2 years | | | 2~5 years | | | More than
5 years | | | Total | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) |
| Non-derivative financial liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other payables | | | 2,715 | | | | 2,715 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,715 | |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
20. Leases
The Company leases an office. The lease typically run for a period of 1 year, with an option to renew or terminate the lease after that date. The Company has elected not to recognize right-of-use asset and lease liability for this lease. Information about lease for which the Company is a lessee is presented below.
| i. | Amounts recognized in profit or loss |
Amounts recognized in profit or loss for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | For the
period from
March 6,
2023 | |
| | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Expense relating to short-term leases | | | 12,000 | |
| ii. | Amounts recognized in statement of cash flows |
Amounts recognized in statements of cash flows for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Total cash outflows of leases | | ₩ | | | 12,000 | |
The lease contains extension option exercisable by the Company. Where practicable, the Company seeks to include extension option in new lease to provide operational flexibility. The extension option held is exercisable only by the Company and not by the lessor. The Company assesses at the lease commencement date whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the extension option. The Company reassesses whether it is reasonably certain to exercise the option if there is a significant event or significant changes in circumstances within its control.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
21. Statement of cash flows
Adjustments for income from operating activities for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Interest income | | ₩ | | | (303 | ) |
| Severance Benefits | | | | | 72,347 | |
| Depreciation | | | | | 105 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 72,149 | |
Changes in assets and liabilities from operating activities for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other current assets | | ₩ | | | (26,419 | ) |
| Other non-current non-financial assets | | | | | (360,000 | ) |
| Trade and other payables | | | | | 2,715 | |
| Other current non-financial liabilities | | | | | 1,931 | |
| Other non-current non-financial liabilities | | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 618,227 | |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
22. Related parties
| A. | List of related parties |
List of related parties as of December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| Relationship | | Name |
| Key management personnel | | Park, Jun Woo |
| Key management personnel | | Shin, Kyung Soo |
| Key management personnel | | Kim, Seung Ho |
| Other related parties | | Shining park Co., Ltd. |
| Other related parties | | Its story Co., Ltd. |
| Other related parties | | Poseidon pictures Co., Ltd. |
| B. | Transactions with related parties |
Details of transactions with related parties for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| Related party | | Name | | | | Acquisition of prepayments | |
| | | | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Other related parties | | Its story Co., Ltd. | | ₩ | | | 60,000 | |
| C. | Account balances with related parties |
There are no balances of receivables and payables to related parties as of December 31, 2023.
| D. | Financial transactions with related parties |
There are no significant financial transactions with related parties for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023.
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
| E. | Transactions with key management personnel |
The compensation for the key management personnel for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, are as follows:
| | | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Short-term employee benefits | | ₩ | | | 196,000 | |
| Post-employment benefits | | | | | 70,718 | |
| Total | | ₩ | | | 266,718 | |
Compensation of the Company’s key management personnel includes salaries, contributions to a post-employment defined benefit plan.
| F. | Financial Transactions with key management personnel |
Details of significant financial transaction the key management personnel for the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023, is as follows:
| | | | | For the
period from
March 6, 2023
(inception) to
December 31,
2023 | |
| | | | | (In thousands of Korean won) | |
| Shares issued | | ₩ | | | 15,000 | |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the period from March 6, 2023 (inception) to December 31, 2023
23. Commitments
On September 14, 2023, an amendment was made to the equity interest exchange agreement, originally entered into on April 9, 2023, between the CEOs, who is the dominant shareholders of the Company, and K Enter Holdings for the purpose of listing on the NASDAQ through a merger with a SPAC company. The equity interest exchange agreement is effective on January 5, 2024, or the date designated by K Enter Holdings. Upon the effective date, the CEOs of the Company will exchange each of 510 shares with the equity interest of K Enter Holdings. Following the equity interest exchange transaction, the Company is expected to be a subsidiary of K Enter Holdings.
Annex A
EXECUTION VERSION
MERGER AGREEMENT
dated
June 15, 2023
by and among
K Enter Holdings Inc., a Delaware corporation (the “Company”),
Global Star Acquisition Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Parent”),
K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (“Purchaser”)
and
GLST Merger Sub Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Merger Sub”)
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| | | | | Page |
| |
ARTICLE I DEFINITIONS | | A-2 |
| | |
1.1 | | Definitions | | A-2 |
1.2 | | Construction | | A-14 |
| |
ARTICLE II REINCORPORATION MERGER | | A-15 |
| | |
2.1 | | Reincorporation Merger | | A-15 |
2.2 | | Reincorporation Effective Time | | A-15 |
2.3 | | Effect of the Reincorporation Merger | | A-16 |
2.4 | | Charter Documents | | A-16 |
2.5 | | Effect of Issued Securities of Parent | | A-16 |
2.6 | | Cancellation of Purchaser Ordinary Shares | | A-17 |
2.7 | | Surrender of Securities | | A-17 |
2.8 | | Lost Stolen or Destroyed Certificates | | A-17 |
2.9 | | U.S. Tax Treatment | | A-17 |
2.10 | | Taking of Necessary Action; Further Action | | A-17 |
| |
ARTICLE III ACQUISITION MERGER | | A-18 |
| | |
3.1 | | Acquisition Merger | | A-18 |
3.2 | | Closing; Effective Time | | A-18 |
3.3 | | Effect of Acquisition Merger | | A-18 |
3.4 | | Company Charter; Company Bylaws | | A-18 |
3.5 | | Directors and Officers of Surviving Corporation | | A-19 |
3.6 | | Directors and Officers of Purchaser | | A-19 |
3.7 | | Taking of Necessary Action; Further Action | | A-19 |
3.8 | | U.S. Tax Treatment | | A-19 |
3.9 | | Effect of the Acquisition Merger on Company Capital Stock | | A-20 |
3.10 | | Dissenting Shares | | A-20 |
3.11 | | Surrender and Payment | | A-21 |
3.12 | | Consideration Spreadsheet | | A-21 |
3.13 | | Adjustment | | A-22 |
3.14 | | No Fractional Shares | | A-22 |
3.15 | | Taking of Necessary Action; Further Action | | A-22 |
3.16 | | No Further Ownership Rights in Company Capital Stock | | A-22 |
3.17 | | Transfers of Ownership | | A-22 |
| |
ARTICLE IV REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES OF THE COMPANY | | A-23 |
| | |
4.1 | | Corporate Existence and Power | | A-23 |
4.2 | | Authorization | | A-23 |
4.3 | | Governmental Authorization | | A-24 |
4.4 | | Non-Contravention | | A-24 |
4.5 | | Capitalization | | A-24 |
4.6 | | No Subsidiaries | | A-25 |
4.7 | | Corporate Records | | A-25 |
4.8 | | Consents | | A-25 |
TABLE OF CONTENTS CONTINUED
| | | | | Page |
| | |
4.9 | | Liabilities; Indebtedness | | A-25 |
4.10 | | [RESERVED] | | A-26 |
4.11 | | Absence of Certain Changes | | A-26 |
4.12 | | Properties; Title to the Company’s Assets | | A-26 |
4.13 | | Litigation | | A-26 |
4.14 | | Contracts | | A-26 |
4.15 | | Licenses and Permits | | A-27 |
4.16 | | Compliance with Laws | | A-28 |
4.17 | | Intellectual Property | | A-28 |
4.18 | | Employees; Employment Matters | | A-31 |
4.19 | | Withholding | | A-32 |
4.20 | | Employee Benefits | | A-32 |
4.21 | | Real Property | | A-33 |
4.22 | | Tax Matters | | A-33 |
4.23 | | [RESERVED] | | A-34 |
4.24 | | Finders’ Fees | | A-34 |
4.25 | | Directors and Officers | | A-35 |
4.26 | | Anti-Money Laundering Laws | | A-35 |
4.27 | | Insurance | | A-36 |
4.28 | | Related Party Transactions | | A-36 |
4.29 | | No Trading or Short Position | | A-36 |
4.30 | | Not an Investment Company | | A-36 |
| |
ARTICLE V REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES OF PARENT PARTIES | | A-36 |
| | |
5.1 | | Corporate Existence and Power | | A-36 |
5.2 | | Purchaser; Merger Sub | | A-37 |
5.3 | | Corporate Authorization | | A-37 |
5.4 | | Governmental Authorization | | A-37 |
5.5 | | Non-Contravention | | A-37 |
5.6 | | Finders’ Fees | | A-37 |
5.7 | | Issuance of Shares | | A-38 |
5.8 | | Capitalization | | A-38 |
5.9 | | Information Supplied | | A-39 |
5.10 | | Trust Fund | | A-39 |
5.11 | | Listing | | A-40 |
5.12 | | Board Approval | | A-40 |
5.13 | | Parent SEC Documents and Financial Statements | | A-40 |
5.14 | | Certain Business Practices | | A-42 |
5.15 | | Anti-Money Laundering Laws | | A-43 |
5.16 | | Affiliate Transactions | | A-43 |
5.17 | | Litigation | | A-43 |
5.18 | | Expenses, Indebtedness and Other Liabilities | | A-43 |
5.19 | | Brokers and Other Advisors | | A-43 |
5.20 | | Tax Matters | | A-43 |
5.21 | | Not an Investment Company | | A-44 |
| |
ARTICLE VI COVENANTS OF THE PARTIES PENDING CLOSING | | A-44 |
| | |
6.1 | | Conduct of the Business | | A-44 |
6.2 | | Exclusivity | | A-47 |
TABLE OF CONTENTS CONTINUED
| | | | | Page |
| | |
6.3 | | Access to Information | | A-48 |
6.4 | | Notices of Certain Events | | A-48 |
6.5 | | Registration Statement/Proxy Statement; Other Filings | | A-49 |
6.6 | | Trust Account | | A-52 |
6.7 | | Obligations of Purchaser and Merger Sub | | A-52 |
6.8 | | Cooperation with Regulatory Approvals | | A-52 |
6.9 | | Formation; Joinder | | A-53 |
| |
ARTICLE VII COVENANTS OF THE COMPANY | | A-53 |
| | |
7.1 | | Reporting; Compliance with Laws; No Insider Trading | | A-53 |
7.2 | | Company’s Stockholder Approval | | A-53 |
7.3 | | Company Financial Information | | A-53 |
| |
ARTICLE VIII COVENANTS OF ALL PARTIES HERETO | | A-54 |
| | |
8.1 | | Reasonable Best Efforts; Further Assurances | | A-54 |
8.2 | | Compliance with SPAC Agreements | | A-55 |
8.3 | | Confidentiality | | A-55 |
8.4 | | Directors’ and Officers’ Indemnification and Liability Insurance | | A-55 |
8.5 | | Parent Public Filings; Nasdaq | | A-56 |
8.6 | | Certain Tax Matters | | A-56 |
8.7 | | Purchaser Equity Incentive Plan | | A-57 |
8.8 | | Extension of Time to Consummate a Business Combination | | A-58 |
8.9 | | Section 16 Matters | | A-58 |
8.10 | | Lock-Up Agreement | | A-58 |
| |
ARTICLE IX CONDITIONS TO CLOSING | | A-58 |
| | |
9.1 | | Condition to the Obligations of the Parties | | A-58 |
9.2 | | Conditions to Obligations of the Parent Parties | | A-59 |
9.3 | | Conditions to Obligations of the Company | | A-60 |
| |
ARTICLE X TERMINATION | | A-61 |
| | |
10.1 | | Termination Without Default | | A-61 |
10.2 | | Termination Upon Default | | A-62 |
10.3 | | Effect of Termination | | A-62 |
| |
ARTICLE XI MISCELLANEOUS | | A-62 |
| | |
11.1 | | Notices | | A-62 |
11.2 | | Amendments; No Waivers; Remedies | | A-63 |
11.3 | | Arm’s Length Bargaining; No Presumption Against Drafter | | A-64 |
11.4 | | Publicity | | A-64 |
11.5 | | Expenses | | A-64 |
11.6 | | No Assignment or Delegation | | A-64 |
11.7 | | Governing Law | | A-64 |
11.8 | | Counterparts; Electronic Signatures | | A-64 |
11.9 | | Entire Agreement | | A-65 |
11.10 | | Severability | | A-65 |
TABLE OF CONTENTS CONTINUED
| | | | | Page |
| | |
11.11 | | Further Assurances | | A-65 |
11.12 | | Third Party Beneficiaries | | A-65 |
11.13 | | Waiver | | A-65 |
11.14 | | No Other Representations; No Reliance | | A-65 |
11.15 | | Waiver of Jury Trial | | A-67 |
11.16 | | Submission to Jurisdiction | | A-68 |
11.17 | | Attorneys’ Fees | | A-68 |
11.18 | | Remedies | | A-68 |
11.19 | | Non-Recourse | | A-69 |
| | | | |
| Exhibit A | | – | | Form of Lock-Up Agreement |
| Exhibit B | | – | | Form of Amended and Restated Registration Rights Agreement |
| Exhibit C | | – | | Form of Purchaser Equity Incentive Plan |
| Exhibit D | | – | | Form of Joinder |
MERGER AGREEMENT
MERGER AGREEMENT dated as of June 15, 2023 (this “Agreement”), by and among K Enter Holdings Inc., a Delaware corporation (the “Company”), Global Star Acquisition Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Parent”), Purchaser (as defined below) and Merger Sub (as defined below).
W I T N E S E T H:
A. The Company is a recently formed holding company for the purpose of acquiring (i) Solaire Partners Ltd. (“Solaire Partners”), a Korean contents-specialized investment firm, (ii) The LAMP Pictures Co., Ltd. (“The LAMP”), a Korean film production studio, (iii) Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd. (“Bidangil Pictures”), a Korean film production studio, (iv) Apeitda Co., Ltd. (“Apeitda”), a Korean film production studio, (v) Studio ANSEILLEN (“Studio ANSEILLEN”), a Korean TV series production studio, (vi) First Virtual Lab Inc. (“First Virtual Lab” or “FVL”), a Korean virtual production and visual effects studio, and (vii) Play Company Co., Ltd. (“Play Company”), a Korean contents merchandise producer, which in turn owns 67.1% of the issued and outstanding equity interests in Play F&B Co., Ltd. (“Play F&B”), a Korean food and beverage company (such entities, collectively, the “Target Entities”) (the “Business”);
B. Prior to the date hereof, the Company has entered into definitive acquisition agreements (the “Acquisition Agreements”) to acquire the Target Entities, but has not consummated the acquisition of any of the Target Entities;
C. Prior to the Closing, the Company intends to consummate the acquisition of the Target Entities upon the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in the Acquisition Agreements;
D. Parent is a blank check company formed for the purpose of effecting a merger, capital stock exchange, asset acquisition, stock purchase, reorganization or similar business combination with one or more businesses;
E. Following the date of this Agreement, Parent shall form Purchaser as a Cayman Islands exempted and wholly owned subsidiary of Parent, to be formed for the sole purpose of the merger of Parent with and into Purchaser, in which Purchaser will be the surviving corporation (the “Reincorporation Merger”). Following the formation of Purchaser, Parent shall cause Purchaser to enter into the Joinder (as defined below);
F. Following the date of this Agreement, Parent shall form Merger Sub as a Delaware corporation and wholly owned subsidiary of Purchaser, to be formed for the sole purpose of the Acquisition Merger (as defined below). Following the formation of Merger Sub, Parent shall cause Merger Sub to enter into the Joinder;
G. Upon the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in this Agreement, and in accordance with the Delaware General Corporation Law, as amended (the “DGCL”), Merger Sub will merge with and into the Company, after which the Company will be the surviving corporation (the “Surviving Corporation”) and a wholly-owned subsidiary of Purchaser (the “Acquisition Merger”);
H. Parent hereto intends that, (i) for United States federal and applicable state income tax purposes, the Reincorporation Merger will qualify as a “reorganization” within the meaning of Section 368(a) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”) and the Treasury Regulations promulgated thereunder, and this Agreement is intended to constitute a “plan of reorganization” within the meaning of Section 368 of the Code and Treasury Regulations Sections 1.368-2(g) and 1.368-3(a) for purposes of Sections 354, 361 and 368 of the Code (a “Plan of Reorganization”) with respect to the Reincorporation Merger and (ii) Purchaser will be treated as a United States domestic corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 7874(b) of the Code following the Reincorporation Merger ((i) and (ii) taken together, the “Reincorporation Intended Tax Treatment”);
I. Each of the parties hereto intends that, for United States federal and applicable state income tax purposes, the Acquisition Merger will qualify as a “reorganization” within the meaning of Section 368(a) of the Code and the Treasury Regulations promulgated thereunder, to which each of Parent, Purchaser and the Company are to be parties under Section 368(b) of the Code (the “Acquisition Intended Tax Treatment”), and this Agreement is intended to constitute a “Plan of Reorganization” with respect to the Acquisition Merger;
J. Prior to the date hereof, Parent has obtained an opinion from EverEdge Pte. Ltd. that the Acquisition Merger is fair to Parent from a financial point of view; and
K. The Boards of Directors of each of the Company, Parent, Purchaser and Merger Sub have unanimously (i) approved and declared advisable this Agreement and the transactions contemplated by this Agreement and the Ancillary Agreements to which they are or will be party, including the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger, and the performance of their respective obligations hereunder or thereunder, on the terms and subject to the conditions set forth herein or therein, (ii) determined that this Agreement and such transactions are fair to, and in the best interests of, them and their respective stockholders, (iii) resolved to recommend that their respective stockholders approve the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger and such other transactions contemplated hereby and adopt this Agreement and the Ancillary Agreements to which they are or will be a party and the performance of such party of their obligations hereunder and thereunder and (iv) in the case of Parent, resolved to recommend that its stockholders approve each of the Parent Proposals.
In consideration of the mutual representations, warranties, covenants and agreements set forth in this Agreement, and other good and valuable consideration, the receipt and sufficiency of which are hereby acknowledged, the parties hereby agree as follows:
ARTICLE I
DEFINITIONS
1.1 Definitions.
“Acquisition Intended Tax Treatment” has the meaning specified in the recitals to this Agreement.
“Acquisition Merger” has the meaning set forth in the recitals to this Agreement.
“Action” means any legal action, litigation, suit, claim, hearing, proceeding or investigation by or before any Authority.
“Additional Parent SEC Documents” has the meaning set forth in Section 5.13(a).
“Affiliate” means, with respect to any Person, any other Person directly or indirectly Controlling, Controlled by or under common Control with such Person, whether through one or more intermediaries or otherwise.
“Affordable Care Act” has the meaning set forth in Section 4.20(i).
“Aggregate Fully Diluted Company Common Shares” means the sum, without duplication, of (a) all shares of Company Common Stock that are issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Effective Time; plus (b) the aggregate shares of Company Common Stock issuable upon conversion of all shares of Company Preferred Stock that are issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Effective Time; plus (c) the aggregate shares of Company Common Stock issuable upon full conversion, exercise or exchange of any other securities of the Company outstanding immediately prior to the Effective Time directly or indirectly convertible into or exchangeable or exercisable for Company Common Stock.
“Aggregate Merger Consideration” means a number of Purchaser Ordinary Shares equal to the quotient obtained by dividing (a) the Base Purchase Price, by (b) $10.00.
“Agreement” has the meaning set forth in the preamble.
“Alternate Exchange” means The Nasdaq Capital Market, The Nasdaq Global Select Market, NYSE, NYSE American, or any successor thereto.
“Alternative Proposal” has the meaning set forth in Section 6.2(b).
“Alternative Transaction” has the meaning set forth in Section 6.2(a).
“Ancillary Agreements” means (i) the Lock-Up Agreement, the Registration Rights Agreement and the Joinder and (ii) for the purposes of Sections 4.2, 4.3 and 4.4 only, the Acquisition Agreements.
“Anti-Corruption Laws” has the meaning set forth in Section 4.26(a).
“Anti-Money Laundering Laws” has the meaning set forth in Section 4.26(a).
“Antitrust Laws” means any applicable domestic or foreign, supranational, national, federal, state, municipality or local Laws that are designed to prohibit, restrict or regulate actions having the purpose or effect of monopolization or restraint of trade, including the HSR Act.
“Authority” means any federal, state, provincial, municipal, local, foreign, multinational or supra-national government, governmental authority or regulatory body thereof, or political subdivision thereof, or any commission, department, board, bureau, authority, agency or instrumentality of such government, governmental authority, regulatory body or political subdivision, or any self-regulated organization or other non-governmental regulatory authority or quasi-governmental authority exercising executive, legislative, judicial, regulatory or administrative functions (to the extent that the rules, regulations or orders of such organization or authority have the force of Law), or any arbitrator, arbitration panel, court, tribunal, mediator or similar judicial body of competent jurisdiction.
“Base Purchase Price” means $610,000,000.
“Books and Records” means all books and records, ledgers, employee records, customer lists, files, correspondence, and other records of every kind (whether written, electronic, or otherwise embodied) owned or controlled by a Person in which a Person’s assets, liabilities, operations, the business or its transactions are otherwise reflected, other than stock books and minute books.
“Business” has the meaning set forth in the recitals to this Agreement.
“Business Day” means any day other than a Saturday, Sunday or a legal holiday on which commercial banking institutions in New York, New York are authorized or required by Law to close for business, excluding as a result of “stay at home,” “shelter-in-place,” “non-essential employee” or any other similar orders or restrictions or the closure of any physical branch locations at the direction of any Authority so long as the electronic funds transfer systems, including for wire transfers, of commercially banking institutions in New York, New York are generally open for use by customers on such day.
“Cayman Companies Act” means Companies Act (Revised) of the Cayman Islands, as the same may be amended from time to time.
“Cayman Registrar” has the meaning specified in Section 2.2.
“Certificate of Merger” has the meaning set forth in Section 3.2.
“Closing” has the meaning set forth in Section 3.2.
“Closing Consideration Spreadsheet” has the meaning set forth in Section 3.12(a).
“Closing Date” has the meaning set forth in Section 3.2.
“COBRA” means collectively, the requirements of Sections 601 through 606 of ERISA and Section 4980B of the Code.
“Code” means the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended.
“Company” has the meaning set forth in the preamble.
“Company Capital Stock” means Company Common Stock and Company Preferred Stock.
“Company Charter” means the Second Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of the Company as filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware on May 31, 2023, as amended and in effect on the date of this Agreement.
“Company Common Stock” means the common stock, par value $0.0001 per share, of the Company.
“Company Consent” has the meaning set forth in Section 4.8.
“Company Cure Period” has the meaning set forth in Section 10.2(a).
“Company Exclusively Licensed IP” means any and all Company Licensed IP that is exclusively licensed to or purported to be exclusively licensed to the Company.
“Company Financial Statements” has the meaning set forth in Section 7.3.
“Company Fundamental Representations” means the representations and warranties of the Company set forth in Section 4.1 (Corporate Existence and Power), Section 4.2 (Authorization), Section 4.3 (Government Authorization), Section 4.4 (Non-Contravention), Section 4.5(a) (other than the last sentence of Section 4.5(a)) (Capitalization), Section 4.5(b) (Capitalization), Section 4.6 (Subsidiaries) and Section 4.24 (Finders’ Fees).
“Company Information Systems” has the meaning set forth in Section 4.17(n).
“Company IP” means, collectively, any and all Company Owned IP and Company Licensed IP.
“Company Licensed IP” means any and all Intellectual Property owned by a third Person and licensed to or purported to be licensed, in whole or in part, to the Company or that the Company otherwise has a right to use or purports to have a right to use.
“Company Owned IP” means any and all Intellectual Property owned or purported to be owned, in whole or in part, by the Company, in each case, whether exclusively, jointly with another Person or otherwise.
“Company Preferred Stock” means the Series A Preferred Stock of the Company.
“Company Securityholder” means each Person who holds Company Capital Stock.
“Company Stockholders” means, at any given time, the holders of Company Capital Stock.
“Company Stockholder Approval” has the meaning set forth in Section 4.2(b).
“Company Stockholder Written Consent” has the meaning set forth in Section 7.2(a).
“Company Stockholder Written Consent Deadline” has the meaning set forth in Section 7.2(a).
“Confidential Information” means any information, knowledge or data concerning the businesses and affairs of the Company, or any suppliers, customers or agents of the Company that is not already generally available to the public, including any Intellectual Property.
“Confidentiality Agreement” means the Confidentiality Agreement, dated as of January 6, 2023, by and between the Company and Parent.
“Contracts” means the contracts, agreements, leases (including equipment leases, car leases and capital leases), licenses, Permits, commitments, client contracts, statements of work (SOWs), sales and purchase orders and similar instruments, oral or written, to which the Company is a party or by which any of its properties or assets is bound.
“Control” of a Person means the possession, directly or indirectly, of the power to direct or cause the direction of the management and policies of such Person, whether through the ownership of voting securities, by contract, or otherwise. “Controlled,” “Controlling” and “under common Control with” have correlative meanings.
“Conversion Ratio” means the quotient obtained by dividing (a) the number of Purchaser Ordinary Shares constituting the Aggregate Merger Consideration, by (b) the Aggregate Fully Diluted Company Common Shares.
“Copyleft Licenses” means all licenses or other Contracts to Software that requires as a condition of use, modification, or distribution of such Software that other Software or technology incorporated into, derived from, or distributed with such Software (i) be disclosed or distributed in source code form, (ii) be licensed for the purpose of making derivative works or (iii) be redistributable at no or minimal charge.
“Copyrights” has the meaning set forth in the definition of “Intellectual Property.”
“COVID-19” means SARS CoV-2 or COVID-19, and any evolutions thereof.
“COVID-19 Measures” means any quarantine, “shelter in place,” “stay at home,” workforce reduction, social distancing, shut down, closure, sequester, safety or similar Law, governmental Order, Action, directive, guidelines or recommendations promulgated by any Authority that has jurisdiction over the Company, Parent or their Subsidiaries, as applicable, including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization, in each case, in connection with or response to COVID-19, including the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act and the Families First Coronavirus Response Act.
“Data Protection Laws” means all applicable Laws in any applicable jurisdiction governing the Processing, privacy, security, or protection of Personal Information, and all regulations or guidance issued thereunder.
“DGCL” has the meaning set forth in the recitals to this Agreement.
“Dissenting Shares” has the meaning set forth in Section 3.10.
“Domain Names” has the meaning set forth in the definition of “Intellectual Property.”
“Effective Time” has the meaning set forth in Section 3.2.
“Enforceability Exceptions” has the meaning set forth in Section 4.2(a).
“ERISA” means the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974.
“ERISA Affiliate” means each entity, trade or business that is, or was at the relevant time, a member of a group described in Section 414(b), (c), (m) or (o) of the Code or Section 4001(b)(1) of ERISA that includes or included the Company, or that is, or was at the relevant time, a member of the same “controlled group” as the Company pursuant to Section 4001(a)(14) of ERISA.
“Exchange Act” means the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
“Exchange Agent” has the meaning set forth in Section 3.11(a).
“Exchange Fund” has the meaning set forth in Section 3.11(a).
“Excluded Matter” means any one or more of the following: (a) any change in general economic or political conditions; (b) conditions generally affecting the industries in which such Person or its Subsidiaries operates; (c) any changes in financial, banking or securities markets in general or any change in prevailing interest rates; (d) acts of war (whether or not declared), armed hostilities or terrorism, or the escalation thereof; (e) the taking of any action required or permitted by this Agreement or any action or omission taken by the Company at the written request of Parent or any action or omission taken by Parent or Merger Sub with the written consent or at the request of the Company; (f) any changes in applicable Laws (including any COVID-19 Measures) or accounting rules (including U.S. GAAP) or the enforcement, implementation or interpretation; (g) the announcement, pendency or completion of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement; (h) any natural or man-made disaster, acts of God or epidemic, pandemic or other disease outbreak (including COVID-19 and any COVID-19 Measures) or the worsening thereof; or (i) any failure by a party to meet any internal or published projections, forecasts or revenue or earnings
predictions (it being understood that the facts or occurrences giving rise or contributing to such failure that are not otherwise excluded from the definition of a “Material Adverse Effect” may be taken into account in determining whether there has been a Material Adverse Effect); provided, however, that the exclusions provided in the foregoing clauses (a) through (d), clause (f) and clause (h) shall not apply to the extent that Parent and Merger Sub, taken as a whole, on the one hand, or the Company, on the other hand, is disproportionately affected by any such exclusions or any change, event or development to the extent resulting from any such exclusions relative to all other similarly situated companies that participate in the industry in which they operate. In addition, the amount of the Parent Redemption Amount or the failure to obtain the Parent Stockholder Approval shall not be deemed to be a Material Adverse Effect on or with respect to Purchaser.
“Export Control Laws” has the meaning set forth in Section 4.26(a).
“HSR Act” shall mean the Hart-Scott-Rodino Antitrust Improvements Act of 1976, as amended, and any rules or regulations promulgated thereunder.
“Indebtedness” means with respect to any Person, (a) all obligations of such Person for borrowed money, including with respect thereto, all interests, fees and costs, (b) all obligations of such Person evidenced by bonds, debentures, notes or similar instruments, (c) all obligations of such Person under conditional sale or other title retention agreements relating to property purchased by such Person, (d) all obligations of such Person issued or assumed as the deferred purchase price of property or services (other than accounts payable to creditors for goods and services incurred in the ordinary course of business consistent with past practices), (e) all Indebtedness of others secured by (or for which the holder of such Indebtedness has an existing right, contingent or otherwise, to be secured by) any lien or security interest on property owned or acquired by such Person, whether or not the obligations secured thereby have been assumed, (f) all obligations of such Person under leases required to be accounted for as capital leases under U.S. GAAP, (g) all guarantees by such Person of the Indebtedness of another Person, (h) all liability of such Person with respect to any hedging obligations, including interest rate or currency exchange swaps, collars, caps or similar hedging obligations, (i) any unfunded or underfunded liabilities pursuant to any pension or nonqualified deferred compensation plan or arrangement and any earned but unpaid compensation (including salary, bonuses and paid time off) for any period prior to the Closing Date, and (j) any agreement to incur any of the same.
“Intellectual Property” means any and all of the worldwide intellectual property rights and proprietary rights associated with any of the following, whether registered, unregistered or registrable, to the extent recognized in a particular jurisdiction: discoveries, inventions, ideas, technology, trade secrets, and Software, in each case whether or not patentable or copyrightable (including proprietary or confidential information, systems, methods, processes, procedures, practices, algorithms, formulae, techniques, knowledge, results, protocols, models, designs, drawings, specifications, materials, technical data or information, know-how, research, methodologies, customer lists, business plans, databases, collections of data, and other information related to the development, marketing, pricing, distribution, cost, sales and manufacturing) (collectively, “Trade Secrets”); trade names, trademarks, service marks, trade dress, product configurations, other indications of origin, registrations thereof or applications for registration therefor, together with the goodwill associated with the foregoing (collectively, “Trademarks”); patents, patent applications, invention disclosures, utility models, industrial designs, supplementary protection certificates, and certificates of inventions, including all re-issues, continuations, divisionals, continuations-in-part, provisionals, priority documents, re-examinations, renewals, counterparts, extensions, substitutions, counterparts, and validations thereof (“collectively, “Patents”); works of authorship, copyrights, copyrightable materials, copyright registrations and applications for copyright registration (collectively, “Copyrights”); domain names and URLs (collectively, “Domain Names”); rights of privacy and publicity and in social media accounts; and identifiers, and other intellectual property; and all embodiments and fixations thereof and related documentation and registrations and all additions, improvements and accessions thereto.
“Interim Period” has the meaning set forth in Section 6.1(a).
“International Trade Control Laws” has the meaning set forth in Section 4.26(a).
“IP Contracts” means, collectively, any and all Contracts to which the Company is a party or by which any of its properties or assets are bound, in any case under which the Company (i) is granted a right (including option rights, rights of first offer, first refusal, first negotiation, etc.) in or to any Intellectual Property of a third Person, (ii) grants a right (including option rights, rights of first offer, first refusal, first negotiation, etc.) to a third Person in or to any Intellectual Property owned or purported to be owned by the Company or (iii) has entered into an agreement not to assert or sue with respect to any Intellectual Property (including settlement agreements and co-existence arrangements), in each case other than (A) “shrink wrap” or other licenses for generally commercially available software (including Publicly Available Software) or hosted services, (B) customer, distributor or channel partner Contracts on Company’s standard forms, (C) Contracts with the Company’s employees or contractors on Company’s standard forms, and (D) customary non-disclosure agreements entered into in the ordinary course of business consistent with past practices (subparts (A)-(D) collectively, the “Standard Contracts”).
“IPO” means the initial public offering of Parent pursuant to the Prospectus.
“IRS” means the United States Internal Revenue Service.
“Joinder” means the joinder to this Agreement, in substantially the form attached hereto as Exhibit D, which shall be entered into by Purchaser and Merger Sub following their formation.
“Key Employee” means the individuals listed on Schedule 1.1(b).
“Knowledge of the Company” or “to the Company’s Knowledge” means the actual knowledge after reasonable inquiry of the individuals listed on Schedule 1.1(c).
“Knowledge of Parent” or “to Parent’s Knowledge” means the actual knowledge after reasonable inquiry of Anthony Ang and Shan Cui.
“Law” means any domestic or foreign, supranational, national, federal, state, municipality or local law, statute, ordinance, code, rule, or regulation.
“Lien” means, with respect to any property or asset, any mortgage, lien, license, deed of trust, pledge, charge, claim, security interest or encumbrance of any kind in respect of such property or asset, any option, right of first offer or right of first refusal in respect of such property or asset, and any conditional sale or voting agreement or proxy, including any agreement to give any of the foregoing.
“Lock-Up Agreement” means the agreement, in substantially the form attached hereto as Exhibit A, restricting the sale, transfer or other disposition of Purchaser Ordinary Shares received by certain of the Company Securityholders and holders of Parent Common Shares at the Closing in connection with the Reincorporation Merger and Acquisition Merger, which shall be effective as of the Closing.
“Material Adverse Effect” means any fact, effect, event, development, change, state of facts, condition, circumstance, violation or occurrence (an “Effect”) that, individually or together with one or more other contemporaneous Effect, (i) has or would reasonably be expected to have a materially adverse effect on the financial condition, assets, liabilities, business or results of operations of the Company, on the one hand, or on Parent and Merger Sub, on the other hand, taken as a whole; or (ii) prevents or materially impairs or would reasonably be expected to prevent or materially impair the ability of the Company Securityholders and the Company, on the one hand, or on Parent and Merger Sub, on the other hand to consummate the Reincorporation Merger, the Acquisition Merger and the other transactions contemplated by this Agreement in accordance with the terms and conditions of this Agreement; provided, however, that, solely in the case of the foregoing clause (i), a Material Adverse Effect shall not be deemed to include Effects (and solely to the extent of such Effects) resulting from an Excluded Matter.
“Material Contracts” has the meaning set forth in Section 4.14(a). “Material Contracts” shall not include any Contracts that are also Plans.
“Merger Sub” means (a) prior to the execution of the Joinder, Parent, and (b) from and following the execution of the Joinder, GLST Merger Sub Inc., a Delaware corporation and wholly-owned subsidiary of Purchaser.
“Merger Sub Common Stock” has the meaning set forth in Section 5.8(c).
“Nasdaq” means The Nasdaq Global Market.
“Offer Documents” has the meaning set forth in Section 6.5(a).
“Order” means any decree, order, judgment, writ, award, injunction, stipulation, determination, award, rule or consent of or by an Authority.
“Other Filings” means any filings to be made by Parent required under the Exchange Act, Securities Act or any other United States federal, foreign or blue sky laws, other than the Registration Statement and the other Offer Documents.
“Outside Closing Date” has the meaning set forth in Section 10.1(a).
“Parent” has the meaning set forth in the preamble.
“Parent Board Recommendation” has the meaning set forth in Section 5.12(a).
“Parent Charter” means the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Parent as filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware on September 19, 2022.
“Parent Class A Common Stock” means the Class A common stock, par value $0.0001 per share, of Parent.
“Parent Class B Common Stock” means the Class B common stock, par value $0.0001 per share, of Parent.
“Parent Common Share” means a share of Parent Class A Common Stock and/or a share of Parent Class B Common Stock, as applicable.
“Parent Cure Period” has the meaning set forth in Section 10.2(b).
“Parent Financial Statements” means all of the financial statements of Parent included in the Parent SEC Documents and any amendments to such financial statements.
“Parent Fundamental Representations” means the representations and warranties of Parent set forth in Section 5.1 (Corporate Existence and Power), Section 5.3 (Corporate Authorization), Section 5.4 (Governmental Authorization), Section 5.5 (Non-Contravention), Section 5.6 (Finders’ Fees), Section 5.7 (Issuance of Shares), and Section 5.8 (Capitalization).
“Parent Parties” has the meaning set forth in ARTICLE V.
“Parent Private Warrant” means a warrant to purchase one (1) share of Parent Class A Common Stock at an exercise price of $11.50 per share that was included in the Parent Units sold to the Sponsor in a private placement at the time of the consummation of the IPO.
“Parent Proposals” has the meaning set forth in Section 6.5(e).
“Parent Public Warrant” means a warrant to purchase one (1) share of Parent Class A Common Stock at an exercise price of $11.50 per share that was included in the Parent Units sold in the IPO.
“Parent Redemption Amount” has the meaning set forth in Section 6.6.
“Parent Right” means a right entitling the holder thereof to receive one-tenth (1/10) of one share of Parent Class A common stock upon consummation of Parent’s initial business combination that was included in the Parent Units sold in the IPO.
“Parent Rights Agreement” means the Rights Agreement, dated as of September 22, 2022, between Parent and Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company, as rights agent.
“Parent SEC Documents” has the meaning set forth in Section 5.13(a).
“Parent Stockholder Approval” means the requisite approval under the Parent Charter, the DGCL or any other applicable Law, by holders of Parent Common Shares of this Agreement, the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger.
“Parent Stockholder Meeting” has the meaning set forth in Section 6.5(a).
“Parent Unit” means each unit of Parent consisting of one share of Parent Class A Common Stock, one Parent Warrant and one Parent Right, which units were sold in the IPO.
“Parent Warrant” shall mean a Parent Private Warrant and/or a Parent Public Warrant, as applicable.
“Parent Warrant Agreement” means the Warrant Agreement, dated as of September 22, 2022, between Parent and Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company, as warrant agent.
“Patents” has the meaning set forth in the definition of “Intellectual Property.”
“Permit” means each license, franchise, permit, order, approval, consent or other similar authorization required to be obtained and maintained by the Company under applicable Law to carry out or otherwise affecting, or relating in any way to, the Business.
“Permitted Liens” means (a) all defects, exceptions, restrictions, easements, rights of way and encumbrances disclosed in policies of title insurance which have been made available to Parent; (b) mechanics’, carriers’, workers’, repairers’ and similar statutory Liens arising or incurred in the ordinary course of business consistent with past practices for amounts (i) that are not delinquent, (ii) that are not material to the business, operations and financial condition of the Company so encumbered, either individually or in the aggregate, and (iii) not resulting from a breach, default or violation by the Company of any Contract or Law; (c) liens for Taxes (i) not yet due and delinquent or (ii) which are being contested in good faith by appropriate proceedings (and for which adequate accruals or reserves have been established on the Company Financial Statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP); and (d) the Liens set forth on Schedule 1.1(e).
“Person” means an individual, corporation, partnership (including a general partnership, limited partnership or limited liability partnership), limited liability company, association, trust, Authority or other entity or organization of any other kind.
“Personal Information” means any data or information regarding or capable of being associated with an identifiable natural person or device, or that otherwise constitutes personal data, personal health information, protected health information, personally identifiable information, personal information or similar defined term under any Data Protection Law.
“Plan” means each “employee benefit plan” within the meaning of Section 3(3) of ERISA and all other compensation and benefits plans, policies, programs, arrangements or payroll practices, including multiemployer plans within the meaning of Section 3(37) of ERISA, and each other stock purchase, stock option, restricted stock, severance, retention, employment (other than any employment offer letter in such form as previously provided to Parent that is terminable “at will” without any contractual obligation on the part of the Company to make any severance, termination, change of control, or similar payment), consulting, change-of-control, collective bargaining, bonus, incentive, deferred compensation, employee loan, fringe benefit and other benefit plan, agreement, program, policy, commitment or other arrangement, whether or not subject to ERISA, whether formal or informal, oral or written, in each case, that is sponsored, maintained, contributed or required to be contributed to by the Company, or under which the Company has any current or potential liability, but excluding in each case any statutory plan, program or arrangement that is required under applicable law and maintained by any Authority.
“Plan of Reorganization” has the meaning set forth in the recitals to this Agreement.
“Process,” “Processed” or “Processing” means any operation or set of operations performed upon Personal Information or sets of Personal Information, whether or not by automated means, such as collection, recording, organization, structuring, storage, adaptation or alteration, retrieval, consultation, use, disclosure, dissemination, or otherwise making available, alignment or combination, restriction, securing, erasure, or destruction.
“Prohibited Party” has the meaning set forth in Section 4.26(b).
“Prospectus” means the final IPO prospectus of Parent, dated September 19, 2022.
“Proxy Statement” has the meaning set forth in Section 6.5(a).
“Proxy Statement/Prospectus” has the meaning set forth in Section 6.5(a).
“Publicly Available Software” means each of any Software that contains, or is derived in any manner (in whole or in part) from, any Software that is distributed as free software, “copyleft,” open source software (e.g. Linux), or under similar licensing and distribution models, including but not limited to any of the following: (A) the GNU General Public License (GPL) or Lesser/Library GPL (LGPL), (B) the Artistic License (e.g., PERL), (C) the Mozilla Public License, (D) the Netscape Public License, (E) the Sun Community Source License (SCSL), (F) the Sun Industry Source License (SISL) and (G) the Apache Server License, including for the avoidance of doubt all Software licensed under a Copyleft License.
“Purchaser” means (a) prior to the execution of the Joinder, Parent, and (b) from and following the execution of the Joinder, K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company and wholly-owned subsidiary of Parent.
“Purchaser Equity Incentive Plan” has the meaning set forth in Section 8.7.
“Purchaser Ordinary Shares” means the ordinary shares of Purchaser.
“Purchaser Right” has the meaning set forth in Section 2.5(b).
“Purchaser Warrant” has the meaning set forth in Section 2.5(b).
“Real Property” means, collectively, all real properties and interests therein (including the right to use), together with all buildings, fixtures, trade fixtures, plant and other improvements located thereon or attached thereto; all rights arising out of use thereof (including air, water, oil and mineral rights); and all subleases, franchises, licenses, permits, easements and rights-of-way which are appurtenant thereto.
“Reincorporation Effective Time” has the meaning set forth in Section 2.2.
“Reincorporation Intended Tax Treatment” has the meaning specified in the recitals to this Agreement.
“Reincorporation Merger” has the meaning set forth in the recitals to this Agreement.
“Reincorporation Merger Certificate” has the meaning set forth in Section 2.2.
“Reincorporation Plan of Merger” has the meaning set forth in Section 2.2.
“Registered Exclusively Licensed IP” means any and all Company Exclusively Licensed IP that is the subject of a registration or an application for registration, including issued patents and patent applications.
“Registered IP” means collectively, any and all Registered Owned IP and Registered Exclusively Licensed IP.
“Registered Owned IP” means any and all Intellectual Property constituting Company Owned IP or filed in the name of the Company, that in each instance is the subject of a registration or an application for registration, including issued patents and patent applications.
“Registration Rights Agreement” means the amended and restated registration rights agreement, in substantially the form attached hereto as Exhibit B, which shall be effective as of the Closing.
“Registration Statement” has the meaning set forth in Section 6.5(a).
“Representatives” of a Person means the officers, directors, Affiliates, members, partners, managers, attorneys, accountants, consultants, employees, representatives and agents of such Person.
“Required Parent Proposals” has the meaning set forth in Section 6.5(e).
“Sanctions Laws” has the meaning set forth in Section 4.26(a).
“Sarbanes-Oxley Act” means the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
“SEC” means the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission.
“Securities Act” means the Securities Act of 1933, as amended.
“Series A Preferred Stock” has the meaning set forth in Section 4.5(a).
“Software” means computer software, programs, and databases (including development tools, library functions, and compilers) in any form, including in or as Internet Web sites, web content, links, source code, object code, operating systems, database management code, utilities, graphical user interfaces, menus, images, icons, forms, methods of processing, software engines, platforms, and data formats, together with all versions, updates, corrections, enhancements and modifications thereof, and all related specifications, documentation, developer notes, comments, and annotations.
“Sponsor” means Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC, a Delaware limited liability company.
“Standard Contracts” has the meaning set forth in the definition of IP Contracts.
“Subsidiary” means, with respect to any Person, each entity of which at least fifty percent (50%) of the capital stock or other equity or voting securities are Controlled or owned, directly or indirectly, by such Person.
“Surviving Corporation” has the meaning set forth in the recitals to this Agreement.
“Tangible Personal Property” means all tangible personal property and interests therein, including machinery, computers and accessories, furniture, office equipment, communications equipment, automobiles, laboratory equipment and other equipment owned or leased by the Company and other tangible property.
“Tax Return” means any return, information return, declaration, claim for refund of Taxes, report or any similar statement, and any amendment thereto, including any attached schedule and supporting information, whether on a separate, consolidated, combined, unitary or other basis, that is filed or required to be filed with any Taxing Authority in connection with the determination, assessment, collection or payment of a Tax or the administration of any Law relating to any Tax.
“Tax(es)” means any U.S. federal, state or local or non-U.S. taxes imposed by any Taxing Authority including any income (net or gross), gross receipts, profits, windfall profit, sales, use, goods and services, ad valorem, franchise, license, withholding, employment, social security, workers compensation, unemployment compensation, employment, payroll, transfer, excise, import, real property, escheat, personal property, intangible property, occupancy, recording, minimum, alternative minimum, and other taxes (including any governmental charge, fee, levy, or custom duty imposed by an Authority that is the nature of a tax), together with any interest, penalty, additions to tax or additional amount imposed with respect thereto.
“Taxing Authority” means the IRS and any other Authority responsible for the collection, assessment or imposition of any Tax or the administration of any Law relating to any Tax.
“Terminating Company Breach” has the meaning set forth in Section 10.2(a).
“Terminating Parent Breach” has the meaning set forth in Section 10.2(b).
“Trade Secrets” has the meaning set forth in the definition of “Intellectual Property.”
“Trademarks” has the meaning set forth in the definition of “Intellectual Property.”
“Transaction Litigation” has the meaning set forth in Section 8.1(c).
“Transfer Taxes” means any and all transfer, documentary, sales, use, real property, stamp, excise, recording, registration, value added and other similar Taxes, fees and costs (including any associated penalties and interest) incurred in connection with the transactions contemplated by this Agreement.
“Trust Account” has the meaning set forth in Section 5.10.
“Trust Agreement” has the meaning set forth in Section 5.10.
“Trustee” has the meaning set forth in Section 5.10.
“U.S. GAAP” means U.S. generally accepted accounting principles, consistently applied.
1.2 Construction.
(a) References to particular sections and subsections, schedules, and exhibits not otherwise specified are cross-references to sections and subsections, schedules, and exhibits of this Agreement. Captions are not a part of this Agreement, but are included for convenience, only.
(b) The words “herein,” “hereof,” “hereunder,” and words of similar import refer to this Agreement as a whole and not to any particular provision of this Agreement; and, unless the context requires otherwise, “party” means a party signatory hereto.
(c) Any use of the singular or plural, or the masculine, feminine or neuter gender, includes the others, unless the context otherwise requires; the word “including” means “including without limitation”; the word “or” means “and/or”; the word “any” means “any one, more than one, or all”; and, unless otherwise specified, any financial or accounting term has the meaning of the term under United States generally accepted accounting principles as consistently applied heretofore by the Company. Any reference in this Agreement to a Person’s directors shall include any member of such Person’s governing body.
(d) Unless otherwise specified, any reference to any agreement (including this Agreement), instrument, or other document includes all schedules, exhibits, or other attachments referred to therein, and any reference to a statute or other law means such law as amended, restated, supplemented or otherwise modified from time to time and includes any rule, regulation, ordinance or the like promulgated thereunder, in each case, as amended, restated, supplemented or otherwise modified from time to time.
(e) Any reference to a numbered schedule means the same-numbered section of the disclosure schedule. Any reference in a schedule contained in the disclosure schedules delivered by a party hereunder shall be deemed to be an exception to (or, as applicable, a disclosure for purposes of) the applicable representations and warranties (or applicable covenants) that are contained in the section or subsection of this Agreement that corresponds to such schedule and any other representations and warranties of such party that are contained in this Agreement to which the relevance of such item thereto is reasonably apparent on its face. The mere inclusion of an item in a schedule as an exception to (or, as
applicable, a disclosure for purposes of) a representation or warranty shall not be deemed an admission that such item represents a material exception or material fact, event or circumstance or that such item would have a Material Adverse Effect or establish any standard of materiality to define further the meaning of such terms for purposes of this Agreement. Nothing in the disclosure schedules constitutes an admission of any liability or obligation of the disclosing party to any third party or an admission to any third party, including any Authority, against the interest of the disclosing party, including any possible breach of violation of any Contract or Law. Summaries of any written document in the disclosure schedules do not purport to be complete and are qualified in their entirety by the written document itself. The disclosures schedules and the information and disclosures contained therein are intended only to qualify and limit the representations and warranties of the parties contained in this Agreement, and shall not be deemed to expand in any way the scope or effect of any of such representations and warranties.
(f) If any action is required to be taken or notice is required to be given within a specified number of days following a specific date or event, the day of such date or event is not counted in determining the last day for such action or notice. If any action is required to be taken or notice is required to be given on or before a particular day which is not a Business Day, such action or notice shall be considered timely if it is taken or given on or before the next Business Day.
(g) To the extent that any Contract, document, certificate or instrument is represented and warranted to by the Company to be given, delivered, provided or made available by the Company, such Contract, document, certificate or instrument shall be deemed to have been given, delivered, provided and made available to Parent or its Representatives, if such Contract, document, certificate or instrument shall have been posted not later than two (2) days prior to the date of this Agreement to the electronic data site maintained on behalf of the Company for the benefit of the Parent and its Representatives and the Parent and its Representatives have been given access to the electronic folders containing such information.
ARTICLE II
REINCORPORATION MERGER
2.1 Reincorporation Merger. On the day that is at least one Business Day prior to the date of the Effective Time, and subject to and upon the terms and conditions of this Agreement, and in accordance with the applicable provisions of the DGCL and the Cayman Companies Act, respectively, Parent shall be merged with and into Purchaser, the separate corporate existence of Parent shall cease and Purchaser shall continue as the surviving corporation. Purchaser as the surviving corporation after the Reincorporation Merger is hereinafter sometimes referred to as the “Reincorporation Surviving Corporation”.
2.2 Reincorporation Effective Time. The parties hereto shall cause the Reincorporation Merger to be consummated by filing a certificate of merger (the “Reincorporation Merger Certificate”) with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware, in accordance with the relevant provisions of the DGCL, and filing a plan of merger (the “Reincorporation Plan of Merger”) (and other documents required by the Cayman Companies Act) with the Registrar of Companies of the Cayman Islands (the “Cayman Registrar”), in accordance with the relevant provisions of the Cayman Companies Act. The effective time of the Reincorporation Merger shall be the later of the acceptance of the Reincorporation Merger Certificate and the time that Reincorporation Plan of Merger is duly registered by the Cayman Registrar, or such later time as specified in the Reincorporation Merger Certificate and Reincorporation Plan of Merger, being the “Reincorporation Effective Time”.
2.3 Effect of the Reincorporation Merger. At the Reincorporation Effective Time, the effect of the Reincorporation Merger shall be as provided in this Agreement, the Reincorporation Merger Certificate, the Reincorporation Plan of Merger and the applicable provisions of the DGCL and the Cayman Companies Act. Without limiting the generality of the foregoing, and subject thereto, at the Reincorporation Effective Time, all the property, rights, privileges, agreements, powers and franchises, debts, liabilities, duties and obligations of Parent prior to the Reincorporation Effective Time shall become the property, rights, privileges, agreements, powers and franchises, debts, liabilities, duties and obligations of the Reincorporation Surviving Corporation, which shall include the assumption by the Reincorporation Surviving Corporation of any and all agreements, covenants, duties and obligations of Parent set forth in this Agreement to be performed after the Reincorporation Effective Time, and all securities of the Reincorporation Surviving Corporation issued and outstanding as a result of the conversion under Section 2.5 hereof shall be listed on the public trading market on which the Parent Common Shares were trading prior to Reincorporation Merger.
2.4 Charter Documents. At the Reincorporation Effective Time, the Parent Charter and the bylaws of Parent, as in effect immediately prior to the Reincorporation Effective Time, shall cease and the Memorandum and Articles of Association of Purchaser, as in effect immediately prior to the Reincorporation Effective Time, shall be the Memorandum and Articles of Association of the Reincorporation Surviving Corporation, provided that the name of the Reincorporation Surviving Corporation shall be “K Wave Media Ltd.”.
2.5 Effect of Issued Securities of Parent.
(a) Conversion of Parent Common Shares. At the Reincorporation Effective Time, each issued and outstanding Parent Common Share (other than those described in Section 2.5(c)) shall be converted automatically into one Purchaser Ordinary Share. At the Reincorporation Effective Time, all Parent Common Shares shall cease to be outstanding and shall automatically be canceled and retired and shall cease to exist. The holders of issued and outstanding Parent Common Shares immediately prior to the Reincorporation Effective Time, as evidenced by the stockholder register of Parent (the “Stockholder Register”), shall cease to have any rights with respect to such Parent Common Shares, except as provided herein or by Law. Each holder of Parent Common Shares listed on the Stockholder Register shall thereafter have the right to receive the same number of Purchaser Ordinary Shares only. Each certificate (if any) previously evidencing Parent Common Shares shall be exchanged for a certificate representing the same number of Purchaser Ordinary Shares upon the surrender of such certificate in accordance with Section 2.6.
(b) Parent Warrants, Parent Rights and Parent Units. At the Reincorporation Effective Time, (i) each issued and outstanding Parent Warrant shall convert automatically into a warrant to purchase one Purchaser Ordinary Share at a price of $11.50 per whole share (the “Purchaser Warrant”), (ii) each issued and outstanding Parent Right shall convert automatically into a right to receive one-tenth (1/10) of one Purchaser Ordinary Share at the closing of a business combination (the “Purchaser Right”), and (iii) each issued and outstanding Parent Unit shall separate and convert automatically into one Purchaser Ordinary Share, one Purchaser Warrant and one Purchaser Right. At the Reincorporation Effective Time, all Parent Warrants, Parent Rights and Parent Units shall cease to be outstanding and shall automatically be canceled and retired and shall cease to exist. Each of the Purchaser Warrants and Purchaser Rights shall have, and be subject to, the same terms and conditions set forth in the applicable agreements governing the Parent Warrants and Parent Rights, respectively, that are outstanding immediately prior to the Reincorporation Effective Time. At or prior to the Reincorporation Effective Time, Purchaser shall take all corporate action necessary to reserve for future issuance, and shall maintain such reservation for so long as any of the Purchaser Warrants and Purchaser Rights remain outstanding, a sufficient number of Parent Ordinary Shares for delivery upon the exercise of the Purchaser Warrants and Purchaser Rights after the Reincorporation Effective Time.
(c) Cancellation of Parent Common Shares Owned by Parent. At the Reincorporation Effective Time, if there are any Parent Common Shares that are owned by Parent as treasury shares or any Parent Common Shares owned by any direct or indirect wholly owned subsidiary of Parent immediately prior to the Reincorporation Effective Time, such shares shall be canceled and extinguished without any conversion thereof or payment therefor.
(d) No Liability. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in this Section 2.5, none of the Reincorporation Surviving Corporation, Parent, Purchaser or any party hereto shall be liable to any person for any amount properly paid to a public official pursuant to any applicable abandoned property, escheat or similar law.
2.6 Cancellation of Purchaser Ordinary Shares. At the Reincorporation Effective Time, any security of Purchaser issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Reincorporation Effective Time shall be canceled and extinguished without any conversion thereof or payment therefor.
2.7 Surrender of Securities. All securities issued upon the surrender of the Parent Common Shares in accordance with the terms hereof shall be deemed to have been issued in full satisfaction of all rights pertaining to such securities, provided that any restrictions on the sale and transfer of the Parent Common Shares shall also apply to the Purchaser Ordinary Shares so issued in exchange.
2.8 Lost Stolen or Destroyed Certificates. In the event any certificates shall have been lost, stolen or destroyed, Purchaser shall issue in exchange for such lost, stolen or destroyed certificates or securities, as the case may be, upon the making of an affidavit of that fact by the holder thereof, such securities; provided, however, that the Reincorporation Surviving Corporation may, in its discretion and as a condition precedent to the issuance thereof, require the owner of such lost, stolen or destroyed certificates to deliver a bond in such sum as it may reasonably direct as indemnity against any claim that may be made against Reincorporation Surviving Corporation with respect to the certificates alleged to have been lost, stolen or destroyed.
2.9 U.S. Tax Treatment. For U.S. Federal income tax purposes, each of the parties intends that the Reincorporation Merger qualifies for the Reincorporation Intended Tax Treatment. The parties to this Agreement hereby (i) adopt this Agreement insofar as it relates to the Reincorporation Merger as a “plan of reorganization” within the meaning of Treasury Regulation Section 1.368-2(g), (ii) agree to file and retain such information as shall be required under Treasury Regulation Section 1.368-3, and (iii) agree to file all Tax and other informational returns on a basis consistent with such characterization and not otherwise to take any position or action inconsistent with such characterization. None of the parties knows of any fact or circumstance (without conducting independent inquiry or diligence of the other relevant party), or has taken or will take any action, if such fact, circumstance or action would be reasonably expected to impede the Reincorporation Intended Tax Treatment. Each of the parties acknowledge and agree that each such party (i) has had the opportunity to obtain independent legal and tax advice with respect to the transactions contemplated by this Agreement, and (ii) is responsible for paying its own Taxes, including any adverse Tax consequences that may result if the Reincorporation Merger is determined not to qualify as a tax-deferred reorganization under Section 368(a) of the Code.
2.10 Taking of Necessary Action; Further Action. If, at any time after the Reincorporation Effective Time, any further action is necessary or desirable to carry out the purposes of this Agreement and to vest the Reincorporation Surviving Corporation with full right, title and interest in, to and under, or possession of, all assets, property, rights, privileges, powers and franchises of Parent and Purchaser, the officers and directors of the Parent and Purchaser are fully authorized in the name and on behalf of their respective corporations or otherwise to take, and will take, all lawful action necessary or desirable to accomplish such purpose or acts, so long as such action is not inconsistent with this Agreement.
ARTICLE III
ACQUISITION MERGER
3.1 Acquisition Merger. Upon the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in this Agreement, on the Closing Date, in accordance with the DGCL, (a) Merger Sub shall be merged with and into the Company, (b) the separate corporate existence of Merger Sub shall thereupon cease, and the Company shall be the Surviving Corporation, and (c) the Surviving Corporation shall become a wholly-owned Subsidiary of Purchaser.
3.2 Closing; Effective Time. Unless this Agreement is earlier terminated in accordance with ARTICLE X, the closing of the Acquisition Merger (the “Closing”) shall take place virtually on the second (2nd) Business Day after the satisfaction or waiver (to the extent permitted by applicable Law) of the conditions set forth in ARTICLE IX (other than those conditions that by their terms are to be satisfied at the Closing, but subject to the satisfaction or waiver thereof), or at such other place and time as the Company and the Parent Parties may mutually agree. The parties may participate in the Closing via the exchange of signature pages via email or other electronic means. The date on which the Closing actually occurs is hereinafter referred to as the “Closing Date”. Subject to the provisions of this Agreement, at the Closing, the Company shall file with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware a certificate of merger, in form and substance reasonably acceptable to the Company and Parent, executed in accordance with the relevant provisions of the DGCL (the “Certificate of Merger”). The Acquisition Merger shall become effective upon the filing of the Certificate of Merger or at such later time as is agreed to by the parties and specified in the Certificate of Merger (the time at which the Acquisition Merger becomes effective is herein referred to as the “Effective Time”).
3.3 Effect of Acquisition Merger. At the Effective Time, the effect of the Acquisition Merger shall be as provided in this Agreement, the Certificate of Merger and the applicable provisions of the DGCL. Without limiting the generality of the foregoing, and subject thereto, at the Effective Time, all the assets, property, rights, privileges, immunities, powers and franchises of the Company and Merger Sub shall vest in the Surviving Corporation and all debts, liabilities and duties of the Company and Merger Sub shall become the debts, liabilities and duties of the Surviving Corporation, which shall include the assumption by the Surviving Corporation of any and all agreements, covenants, duties and obligations of the Company and Merger Sub set forth in this Agreement to be performed after the Effective Time.
3.4 Company Charter; Company Bylaws.
(a) At the Effective Time, the certificate of incorporation of the Company shall, in accordance with the terms thereof and the DGCL, be amended and restated in its entirety as set forth in an exhibit to the Certificate of Merger, and, as so amended and restated, shall be the certificate of incorporation of the Surviving Corporation until duly amended in accordance with the terms thereof and the DGCL.
(b) The bylaws of the Company as in effect immediately prior to the Effective Time shall be the bylaws of the Surviving Corporation, until thereafter amended in accordance with the terms thereof, the certificate of incorporation of the Surviving Corporation and applicable Law.
3.5 Directors and Officers of Surviving Corporation.
(a) At the Effective Time, the initial directors of the Surviving Corporation shall consist of the same persons serving on Purchaser’s Board of Directors in accordance with Section 3.6, and such directors shall hold office until their successors shall have been duly elected or appointed and qualified or until their earlier death, resignation or removal in accordance with the Surviving Corporation’s certificate of incorporation and bylaws.
(b) At the Effective Time, the officers of the Company shall become the initial officers of the Surviving Corporation and shall hold office until their respective successors are duly elected or appointed and qualified, or until their earlier death, resignation or removal.
3.6 Directors and Officers of Purchaser. At the Effective Time, Purchaser’s Board of Directors will consist of seven (7) directors. The Company shall have the right to designate ____ (__) directors and the Sponsor shall have the right to designate ___ (__) directors. At least a majority of the Board of Directors shall qualify as independent directors under Nasdaq or Alternate Exchange rules, as applicable. At or prior to the Closing, Purchaser will provide each member of Purchaser’s post-Closing Board of Directors with a customary director indemnification agreement, in form and substance reasonable acceptable to the directors, to be effective upon the Closing (or if later, such director’s appointment). The officers of the Company shall become the initial officers of Purchaser as of immediately after the Effective Time, with such individuals holding the titles set forth opposite their names until their respective successors are duly elected or appointed and qualified, or until their earlier death, resignation or removal.
3.7 Taking of Necessary Action; Further Action. If, at any time after the Closing, any further action is necessary or desirable to carry out the purposes of this Agreement and to vest the Surviving Corporation with full right, title and interest in, to and under, or possession of, all assets, property, rights, privileges, powers and franchises of the Company and Merger Sub, the officers and directors of the Company and Merger Sub are fully authorized in the name and on behalf of their respective corporations or otherwise to take, and will take, all lawful action necessary or desirable to accomplish such purpose or acts, so long as such action is not inconsistent with this Agreement.
3.8 U.S. Tax Treatment. For U.S. federal and applicable state or local income tax purposes, each of the parties intends that the Acquisition Merger qualifies for the Acquisition Intended Tax Treatment. The parties to this Agreement hereby (i) adopt this Agreement insofar as it relates to the Acquisition Merger as a “plan of reorganization” within the meaning of Treasury Regulation Section 1.368-2(g), (ii) agree to file and retain such information as shall be required under Treasury Regulation Section 1.368-3, and (iii) agree to file all Tax and other informational returns on a basis consistent with such characterization and not otherwise to take any position or action inconsistent with such characterization. None of the parties knows of any fact or circumstance (without conducting independent inquiry or diligence of the other relevant party), or has taken or will take any action, if such fact, circumstance or action would be reasonably expected to impede the Acquisition Intended Tax Treatment. Each of the parties acknowledge and agree that each such party (i) has had the opportunity to obtain independent legal and tax advice with respect to the transactions contemplated by this Agreement and (ii) is responsible for paying its own Taxes, including any adverse Tax consequences that may result if the Acquisition Merger is determined not to qualify as a tax-deferred reorganization under Section 368(a) of the Code.
3.9 Effect of the Acquisition Merger on Company Capital Stock. At the Effective Time, as a result of the Acquisition Merger and without any action on the part of Parent, Purchaser, Merger Sub, the Company or the holders of any shares of capital stock of any of them:
(a) Cancellation of Certain Shares of Company Capital Stock. Each share of Company Capital Stock, if any, that is owned by Parent or Merger Sub (or any other Subsidiary of Parent) or the Company (as treasury stock or otherwise), will automatically be cancelled and retired without any conversion thereof and will cease to exist, and no consideration will be delivered in exchange therefor. Each share of Company Capital Stock, if any, held immediately prior to the Effective Time by the Company as treasury stock shall be automatically canceled and extinguished, and no consideration shall be paid with respect thereto.
(b) Treatment of Shares of Company Preferred Stock. Each share of Company Preferred Stock issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Effective Time (other than any such shares of Company Preferred Stock cancelled pursuant to Section 3.9(a)) shall, in accordance with Section 5.1 of the Company Charter, be deemed converted into shares of Company Common Stock and shall be treated pursuant to Section 3.9(c).
(c) Conversion of Company Common Stock. Each share of Company Common Stock issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Effective Time (including shares of Company Common Stock deemed outstanding as a result of the mandatory conversion of the Company Preferred Stock pursuant to Section 3.9(b)) (other than any such shares of Company Common Stock cancelled pursuant to Section 3.9(a) and any Dissenting Shares) shall be converted into the right to receive a number of Purchaser Ordinary Shares equal to the Conversion Ratio. At the Effective Time, all shares of Company Common Stock converted into the right to receive a portion of the Aggregate Merger Consideration pursuant to this Section 3.9(c), shall no longer be outstanding and shall automatically be canceled and shall cease to exist, and each holder of shares of Company Common Stock shall thereafter cease to have any rights with respect to such securities, except the right to receive a portion of the Aggregate Merger Consideration into which such shares of Company Common Stock shall have been converted in the Acquisition Merger.
(d) Conversion of Merger Sub Capital Stock. Each share of Merger Sub Common Stock issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Effective Time shall be converted into and become one newly issued, fully paid and nonassessable share of common stock of the Surviving Corporation.
3.10 Dissenting Shares. Notwithstanding any provision of this Agreement to the contrary and to the extent applicable under Section 262 of the DGCL, shares of Company Capital Stock issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Effective Time (other than shares of Company Capital Stock cancelled in accordance with Section 3.9(a)) and held by a holder who has not voted in favor of adoption of this Agreement or consented thereto in writing and who is entitled to demand and has properly exercised and perfected appraisal rights of such shares in accordance with Section 262 of the DGCL (such shares of Company Capital Stock being referred to collectively as the “Dissenting Shares” until such time as such holder fails to perfect or otherwise waives, withdraws, or loses such holder’s appraisal rights under the DGCL with respect to such shares) shall not be converted into a right to receive a portion of the Aggregate Merger Consideration, but instead shall be entitled to only such rights as are granted by Section 262 of the DGCL; provided, however, that if, after the Effective Time, such holder fails to perfect, waives, withdraws, or loses such holder’s right to appraisal pursuant to Section 262 of the DGCL or if a court of competent jurisdiction shall determine that such holder is not entitled to the relief provided by Section 262 of the DGCL, such shares of Company Capital Stock shall be treated as if they had been converted as of the
Effective Time into the right to receive a portion of the Aggregate Merger Consideration to which such holder is entitled in accordance with Section 3.9(c), without interest thereon, upon transfer of such shares. The Company shall promptly provide Parent with written notice of any demands received by the Company for appraisal of shares of Company Capital Stock, any withdrawal of any such demand and any other demand, notice or instrument delivered to the Company prior to the Effective Time pursuant to the DGCL that relates to such demand, and Parent shall have the opportunity to participate in all negotiations and proceedings with respect to such demands.
3.11 Surrender and Payment.
(a) Exchange Fund. On or prior to the Closing Date, Purchaser shall deposit, or shall cause to be deposited, with Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company (the “Exchange Agent”) for the benefit of the Company Stockholders, for exchange in accordance with this ARTICLE III, the number of Purchaser Ordinary Shares sufficient to deliver the Aggregate Merger Consideration payable pursuant to this Agreement (such Purchaser Ordinary Shares, the “Exchange Fund”). Purchaser shall cause the Exchange Agent, pursuant to irrevocable instructions, to pay the Aggregate Merger Consideration out of the Exchange Fund in accordance with the Closing Consideration Spreadsheet and the other applicable provisions contained in this Agreement. The Exchange Fund shall not be used for any other purpose other than as contemplated by this Agreement.
(b) Exchange Procedures. As soon as practicable following the Effective Time, and in any event within two (2) Business Days following the Effective Time (but in no event prior to the Effective Time), Purchaser shall cause the Exchange Agent to deliver to each Company Stockholder, as of immediately prior to the Effective Time, represented by book-entry, such Company Stockholder’s applicable portion of the Aggregate Merger Consideration from the Exchange Fund.
(c) Termination of Exchange Fund. Any portion of the Exchange Fund relating to the Aggregate Merger Consideration that remains undistributed to the Company Stockholders for two (2) years after the Effective Time shall be delivered to Purchaser, upon demand, and any Company Stockholders who have not theretofore complied with this Section 3.11 shall thereafter look only to Purchaser for their portion of the Aggregate Merger Consideration. Any portion of the Exchange Fund remaining unclaimed by Company Stockholders as of a date which is immediately prior to such time as such amounts would otherwise escheat to or become property of any Authority shall, to the extent permitted by applicable Law, become the property of Purchaser free and clear of any claims or interest of any person previously entitled thereto.
3.12 Consideration Spreadsheet.
(a) At least five (5) Business Days prior to the Closing, the Company shall deliver to Parent a spreadsheet (the “Closing Consideration Spreadsheet”), prepared by the Company in good faith and detailing the following, in each case, as of immediately prior to the Effective Time:
(i) the name and address of record of each Company Stockholder and the number and class, type or series of shares of Company Capital Stock held by each, and in the case of shares of each series of Company Preferred Stock, the number of shares of Company Common Stock into which such shares of Company Preferred Stock are convertible;
(ii) the number of Aggregate Fully Diluted Company Common Shares;
(iii) detailed calculations of each of the following (in each case, determined without regard to withholding):
(A) the Aggregate Merger Consideration; and
(B) the Conversion Ratio.
(b) The contents of the Closing Consideration Spreadsheet delivered by the Company hereunder shall be subject to reasonable review and comment by Parent, but the Company shall, in all events, remain solely responsible for the contents of the Closing Consideration Spreadsheet. The parties agree that Parent shall be entitled to rely on the Closing Consideration Spreadsheet in making payments under ARTICLE III.
3.13 Adjustment. The shares comprising the Aggregate Merger Consideration and Conversion Ratio shall be adjusted to reflect appropriately the effect of any stock split, reverse stock split, stock dividend, recapitalization, reclassification, combination, exchange of shares or other like change with respect to Parent Common Shares occurring prior to the date the shares comprising the Aggregate Merger Consideration are issued.
3.14 No Fractional Shares. No fractional Purchaser Ordinary Shares, or certificates or scrip representing fractional Purchaser Ordinary Shares, will be issued upon the conversion of the Company Capital Stock pursuant to the Acquisition Merger, and such fractional share interests will not entitle the owner thereof to vote or to any rights of a stockholder of Purchaser. Any holder of a share of Company Capital Stock who would otherwise be entitled to receive a fraction of a Purchaser Ordinary Share (after aggregating all fractional Purchaser Ordinary Shares issuable to such holder) shall, in lieu of such fraction of a share, be paid in cash the dollar amount (rounded to the nearest whole cent), without interest, determined by multiplying such fraction by $10.00.
3.15 Taking of Necessary Action; Further Action. If, at any time after the Closing, any further action is necessary or desirable to carry out the purposes of this Agreement and to vest the Surviving Corporation with full right, title and interest in, to and under, or possession of, all assets, property, rights, privileges, powers and franchises of the Company and Merger Sub, the officers and directors of the Surviving Corporation are fully authorized in the name and on behalf of the Company and Merger Sub, to take all lawful action necessary or desirable to accomplish such purpose or acts, so long as such action is not inconsistent with this Agreement.
3.16 No Further Ownership Rights in Company Capital Stock. All consideration paid or payable in respect of shares of Company Capital Stock hereunder, or upon the exercise of the appraisal rights described in Section 3.10, shall be deemed to have been paid or payable in full satisfaction of all rights pertaining to such shares of Company Capital Stock and from and after the Effective Time, no holder of Company Capital Stock shall have any ownership right in the Company and there shall be no further registration of transfers of shares of Company Capital Stock on the stock transfer books of the Surviving Corporation.
3.17 Transfers of Ownership. If any certificate for Purchaser Ordinary Shares is to be issued in a name other than that in which the Company Capital Stock certificate surrendered in exchange therefor is registered, it will be a condition of the issuance thereof that the certificate so surrendered will be properly endorsed (or accompanied by an appropriate instrument of transfer) and otherwise in proper form for transfer and that the person requesting such exchange will have paid to Purchaser or any agent designated by it any transfer or other Taxes required by reason of the issuance of a certificate for securities of Purchaser in any name other than that of the registered holder of the certificate surrendered, or established to the satisfaction of Purchaser or any agent designated by it that such tax has been paid or is not payable.
ARTICLE IV
REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES OF THE COMPANY
Except as set forth in the disclosure schedules delivered by the Company to Parent prior to the execution of this Agreement (with specific reference to the particular section or subsection of this Agreement to which the information set forth in such disclosure letter relates (which qualify (a) the correspondingly numbered representation, warranty or covenant specified therein and (b) such other representations, warranties or covenants where its relevance as an exception to (or disclosure for purposes of) such other representation, warranty or covenant is reasonably apparent on its face or cross-referenced), the Company hereby represents and warrants to Parent that each of the following representations and warranties are true, correct and complete as of the date of this Agreement and as of the Closing Date (except for representations and warranties that are made as of a specific date, which are made only as of such date).
4.1 Corporate Existence and Power. The Company is a corporation or legal entity duly organized, validly existing and in good standing (with respect to jurisdictions that recognize that concept) under the laws of the jurisdiction of its incorporation. The Company has all requisite power and authority, corporate and otherwise, to own, lease or otherwise hold and operate its properties and other assets and to carry on the Business as presently conducted and as proposed to be conducted. The Company is duly licensed or qualified to do business and is in good standing (with respect to jurisdictions that recognize that concept) in each jurisdiction in which the nature of its business or the ownership, leasing or operation of its properties or other assets makes such qualification, licensing or good standing necessary, except where the failure to be so qualified, licensed or in good standing, individually or in the aggregate, has not had and would not reasonably be expected to have a Material Adverse Effect in respect of the Company. The Company has made available to Parent, prior to the date of this Agreement, complete and accurate copies of the organizational documents of the Company, in each case as amended to the date hereof. The Company has not taken any action in violation or derogation of its organizational documents.
4.2 Authorization.
(a) The Company has all requisite corporate power and authority to execute and deliver this Agreement and the Ancillary Agreements to which it is a party and to consummate the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby, in the case of the Acquisition Merger, subject to receipt of the Company Stockholder Approval. The execution and delivery by the Company of this Agreement and the Ancillary Agreements to which it is a party and the consummation by the Company of the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby have been duly authorized by all necessary corporate action on the part of the Company. No other corporate proceedings on the part of the Company are necessary to authorize this Agreement or the Ancillary Agreements to which it is a party or to consummate the transactions contemplated by this Agreement (other than, in the case of the Acquisition Merger, the receipt of the Company Stockholder Approval) or the Ancillary Agreements. This Agreement and the Ancillary Agreements to which the Company is a party have been duly executed and delivered by the Company and, assuming the due authorization, execution and delivery by each of the other parties hereto and thereto, this Agreement and the Ancillary Agreements to which the Company is a party constitute a legal, valid and binding obligation of the Company, enforceable against the Company in accordance with their respective terms, subject to bankruptcy, insolvency, fraudulent transfer, moratorium, reorganization or similar Laws affecting the rights of creditors generally and the availability of equitable remedies (the “Enforceability Exceptions”).
(b) By resolutions duly adopted (and not thereafter modified or rescinded) by the requisite vote of the Board of Directors of the Company, the Board of Directors of the Company has (i) approved the execution, delivery and performance by the Company of this Agreement, the Ancillary Agreements to which it is a party and the consummation of the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby, including the Acquisition Merger, on the terms and subject to the conditions set forth herein and therein; (ii) determined that this Agreement, the Ancillary Agreements to which it is a party, and the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby, upon the terms and subject to the conditions set forth herein, are advisable and fair to and in the best interests of the Company and the Company Stockholders; (iii) directed that the adoption of this Agreement be submitted to the Company Stockholders for consideration and recommended that all of the Company Stockholders adopt this Agreement. The affirmative vote or written consent of Persons holding a majority of the votes represented by all outstanding shares of Company Capital Stock entitled to vote thereon is required to, and shall be sufficient to, approve this Agreement and the transactions contemplated hereby (the “Company Stockholder Approval”). The Company Stockholder Approval is the only vote or consent of any of the holders of Company Capital Stock necessary to adopt this Agreement and approve the Acquisition Merger and the consummation of the other transactions contemplated hereby.
4.3 Governmental Authorization. None of the execution, delivery or performance by the Company of this Agreement or any Ancillary Agreement to which the Company is or will be a party, or the consummation of the transactions contemplated hereby or thereby, requires any consent, approval, license, Order or other action by or in respect of, or registration, declaration or filing with, any Authority other than the filing of the Certificate of Merger with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware pursuant to the DGCL, except for SEC or Nasdaq approval required to consummate the transactions contemplated hereunder.
4.4 Non-Contravention. None of the execution, delivery or performance by the Company of this Agreement or any Ancillary Agreement to which the Company is or will be a party or the consummation by the Company of the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby does or will (a) contravene or conflict with the Company Charter or the bylaws of the Company, (b) contravene or conflict with or constitute a violation of any provision of any Law or Order binding upon or applicable to the Company or to any of its properties, rights or assets, (c) except for the Contracts listed on Schedule 4.8 requiring Company Consents (but only as to the need to obtain such Company Consents), (i) require consent, approval or waiver under, (ii) constitute a default under or breach of (with or without the giving of notice or the passage of time or both), (iii) violate, (iv) give rise to any right of termination, cancellation, amendment or acceleration of any right or obligation of the Company or to a loss of any material benefit to which the Company is entitled, in the case of each of clauses (i) – (iv), under any provision of any Permit, Contract or other instrument or obligations binding upon the Company or any of its properties, rights or assets, (d) result in the creation or imposition of any Lien (except for Permitted Liens) on any of the Company’s properties, rights or assets, or (e) require any consent, approval or waiver from any Person pursuant to any provision of the organizational documents of the Company, except for such consent, approval or waiver which shall be obtained (and a copy provided to Parent) prior to the Closing.
4.5 Capitalization.
(a) The authorized capital stock of the Company consists of 10,000,000 shares of Company Common Stock and 1,000,000 shares of preferred stock, $0.0001 par value per share, of which 45,000 shares of preferred stock are designated “Series A Preferred Stock” (the “Series A Preferred Stock”). There are 91,222 shares of Company Common Stock and 7,670.40 shares of Series A Preferred Stock are issued and outstanding as of the date of this Agreement. There are 7,670.40 shares of Company Common Stock that may be issued upon the conversion or exchange of outstanding Series A Preferred Stock. No other shares of capital stock or other voting securities of the Company are authorized, issued, reserved for
issuance or outstanding. All issued and outstanding shares of Company Common Stock and Company Preferred Stock are duly authorized, validly issued, fully paid and non-assessable and were issued in compliance with all applicable Laws (including any applicable securities laws) and in compliance with the Company Charter and the bylaws of the Company. No shares of Company Common Stock or Company Preferred Stock are subject to or were issued in violation of any purchase option, right of first refusal, preemptive right, subscription right or any similar right (including under any provision of the DGCL, the Company Charter or any Contract to which the Company is a party or by which the Company or any of its properties, rights or assets are bound). As of the date of this Agreement, all outstanding shares of Company Capital Stock are owned of record by the Persons set forth on Schedule 4.5(a) in the amounts set forth opposite their respective names.
(b) Except for the Company Preferred Stock, there are no (i) outstanding warrants, options, agreements, convertible securities, performance units or other commitments or instruments pursuant to which the Company is or may become obligated to issue or sell any of its shares of Company Capital Stock or other securities, (ii) outstanding obligations of the Company to repurchase, redeem or otherwise acquire outstanding capital stock of the Company or any securities convertible into or exchangeable for any shares of capital stock of the Company, (iii) treasury shares of capital stock of the Company, (iv) bonds, debentures, notes or other Indebtedness of the Company having the right to vote (or convertible into, or exchangeable for, securities having the right to vote) on any matters on which stockholders of the Company may vote, are issued or outstanding, (v) preemptive or similar rights to purchase or otherwise acquire shares or other securities of the Company (including pursuant to any provision of Law, the Company Charter or any Contract to which the Company is a party), (vi) Liens (including any right of first refusal, right of first offer, proxy, voting trust, voting agreement or similar arrangement) with respect to the sale or voting of shares or securities of the Company (whether outstanding or issuable), or (vii) any stock appreciation, phantom stock or similar rights with respect to the Company.
4.6 No Subsidiaries. The Company does not have any Subsidiaries. For the avoidance of doubt, the Target Entities shall not be deemed Subsidiaries of the Company for any purpose under this Agreement, regardless of whether or not the transactions contemplated by the Acquisition Agreements have been consummated.
4.7 Corporate Records. All proceedings of the Board of Directors of the Company since January 4, 2023 (inception), including all committees thereof, and of the Company Stockholders, and all consents to actions taken thereby that are required by Law, the Company Charter or the bylaws of the Company, are accurately reflected in the minutes and records contained in the corporate minute books of the Company and made available to Parent. The stockholder ledger of the Company is true, correct and complete.
4.8 Consents. The Contracts listed on Schedule 4.8 are the only Contracts requiring a consent, approval, authorization, order or other action of or filing with any Person as a result of the execution, delivery and performance of this Agreement or any Ancillary Agreement to which the Company is or will be a party or the consummation of the transactions contemplated hereby or thereby (each of the foregoing, a “Company Consent”).
4.9 Liabilities; Indebtedness.
(a) The Company has no material liabilities or obligations of the type that would be required to be set forth on a balance sheet prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP, except for (i) liabilities arising in the ordinary course of business, and (ii) liabilities specifically set forth on Schedule 4.9(a).
(b) Except as set forth on Schedule 4.9(b), the Company does not have any Indebtedness.
4.10 [RESERVED].
4.11 Absence of Certain Changes. From January 4, 2023 (inception) until the date of this Agreement, (a) the Company has conducted its businesses in the ordinary course and in a manner consistent with past practice; (b) there has not been any Material Adverse Effect in respect of the Company; (c) the Company has not taken any action that, if taken after the date of this Agreement and prior to the consummation of the Merger, would require the consent of Parent pursuant to Section 6.1 and Parent has not given consent; and (d) to the knowledge of the Company, there has not been any Material Adverse Effect with respect to the Company, Play Company and Solaire Partners, taken as a whole.
4.12 Properties; Title to the Company’s Assets.
(a) All items of Tangible Personal Property have no material defects, are in good operating condition and repair in all material respects and function in accordance with their intended uses (ordinary wear and tear excepted), have been properly maintained in all material respects and are suitable for their present uses and meet all specifications and warranty requirements with respect thereto. All of the material Tangible Personal Property is located at the offices of the Company.
(b) The Company has good, valid and marketable title in and to, or in the case of the assets which are leased or licensed pursuant to Contracts, a valid leasehold interest or license in or a right to use all of the tangible assets of the type that would be required to be set forth on a balance sheet prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP. Except as set forth on Schedule 4.12, no such tangible asset is subject to any Lien other than Permitted Liens. The Company’s assets constitute all of the rights, properties, and assets of any kind or description whatsoever, including goodwill, necessary for the Company to operate the Business immediately after the Closing in substantially the same manner as the Business is currently being conducted.
4.13 Litigation. There is no Action pending or, to the Knowledge of the Company, threatened against or affecting the Company, any of the officers or directors of the Company, the Business, any of the Company’s rights, properties or assets or any Contract before any Authority or which in any manner challenges or seeks to prevent, enjoin, alter or delay the transactions contemplated by this Agreement or any Ancillary Agreement. There are no outstanding judgments against the Company or any of its rights, properties or assets. The Company or any of its rights, properties or assets is not, nor has been since January 4, 2023 (inception), subject to any Action by any Authority.
4.14 Contracts.
(a) Schedule 4.14(a) sets forth a true, complete and accurate list, as of the date of this Agreement, of all of the following Contracts as amended to date which are currently in effect (collectively, “Material Contracts”):
(i) all Contracts that require annual payments or expenses incurred by, or annual payments or income to, the Company of $500,000 or more (other than Contracts entered into in the ordinary course of business consistent with past practices);
(ii) each Contract with any current employee of the Company (A) which has continuing obligations for payment of an annual compensation of at least $500,000, and which is not terminable for any reason or no reason upon reasonable notice without payment of any penalty, severance or other obligation; (B) providing for severance or post-termination payments or benefits to such employee (other than COBRA obligations); or (C) providing for a payment or benefit upon the consummation of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement or any Ancillary Agreement or as a result of a change of control of the Company;
(iii) all Contracts creating a joint venture, strategic alliance, limited liability company or partnership arrangement to which the Company or any Subsidiary is a party;
(iv) all Contracts relating to any acquisitions or dispositions of material assets by the Company (other than acquisitions or dispositions of inventory in the ordinary course of business consistent with past practices), including the Acquisition Agreements;
(v) all IP Contracts, separately identifying all such IP Contracts under which the Company is obligated to pay royalties thereunder and all such IP Contracts under which the Company is entitled to receive royalties thereunder;
(vi) all Contracts creating or otherwise relating to outstanding Indebtedness (other than intercompany Indebtedness) in the aggregate that are valued at $500,000 or greater;
(vii) all Contracts relating to the voting or control of the equity interests of the Company or the election of directors of the Company (other than the organizational or constitutive documents of the Company);
(viii) all Contracts that may be terminated, or the provisions of which may be altered, as a result of the consummation of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement or any Ancillary Agreement; and
(ix) all Contracts under which any of the benefits, compensation or payments (or the vesting thereof) will be increased or accelerated by the consummation of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement or any Ancillary Agreement, or the amount or value thereof will be calculated on the basis of, the transactions contemplated by this Agreement or any Ancillary Agreement.
(b) Each Material Contract is (i) a valid and binding agreement, (ii) in full force and effect and (iii) enforceable by and against the Company and each counterparty that is party thereto, subject, in the case of this clause (iii), to the Enforceability Exceptions. Neither the Company nor, to the Company’s Knowledge, any other party to a Material Contract is in material breach or default (whether with or without the passage of time or the giving of notice or both) under the terms of any such Material Contract. The Company has not assigned, delegated or otherwise transferred any of its rights or obligations under any Material Contract or granted any power of attorney with respect thereto.
(c) The Company is in compliance in all material respects with all covenants, including all financial covenants, in all notes, indentures, bonds and other instruments or Material Contracts establishing or evidencing any Indebtedness. The consummation and closing of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement shall not cause or result in an event of default under any instruments or Material Contracts establishing or evidencing any Indebtedness.
4.15 Licenses and Permits. Schedule 4.15 sets forth a true, complete and correct list of each Permit held by the Company that is required under applicable Law to permit the Company to own, operate, use and maintain their assets in the manner in which they are now operated and maintained and to carry out or conduct the Business, together with the name of the Authority issuing the same. Such Permits are valid
and in full force and effect, and none of the Permits will be terminated or impaired or become terminable as a result of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement or any Ancillary Agreement. The Company has all Permits necessary to operate the Business, and each of the Permits is in full force and effect. The Company is not in material breach or violation of, or material default under, any such Permit, and, to the Company’s Knowledge, no basis (including the execution of this Agreement and the other Ancillary Agreements to which the Company is a party and the consummation of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement or any Ancillary Agreement) exists which, with notice or lapse of time or both, would reasonably constitute any such breach, violation or default or give any Authority grounds to suspend, revoke or terminate any such Permit. The Company has not received any written (or, to the Company’s Knowledge, oral) notice from any Authority regarding any material violation of any Permit. There has not been and there is not any pending or, to the Company’s Knowledge, threatened Action, investigation or disciplinary proceeding by or from any Authority against the Company involving any material Permit.
4.16 Compliance with Laws. Neither the Company nor, to the Knowledge of the Company, any Representative or other Person acting on behalf of the Company, is in violation in any material respect of, and, since January 4, 2023 (inception), no such Person has failed to be in compliance in all material respects with, all applicable Laws and Orders. Since January 4, 2023 (inception), (i) no event has occurred or circumstance exists that (with or without notice or due to lapse of time) would reasonably constitute or result in a violation by the Company of, or failure on the part of the Company to comply with, or any liability suffered or incurred by the Company in respect of any violation of or material noncompliance with, any Laws, Orders or policies by Authority that are or were applicable to it or the conduct or operation of its business or the ownership or use of any of its assets and (ii) no Action is pending, or to the Knowledge of the Company, threatened, alleging any such violation or noncompliance by the Company. Since January 4, 2023 (inception), the Company has not been threatened in writing or, to the Company’s Knowledge, orally to be charged with, or given written or, to the Company’s Knowledge, oral notice of any violation of any Law or any judgment, order or decree entered by any Authority.
4.17 Intellectual Property.
(a) The Company or any of its Subsidiary is the sole and exclusive owner of each item of Company Owned IP, free and clear of any Liens (except for Permitted Liens). The Company or any of its Subsidiary is the sole and exclusive licensee of each item of Company Exclusively Licensed IP, free and clear of any Liens (except for Permitted Liens). The Company or any of its Subsidiary has a valid right to use the Company Licensed IP.
(b) Schedule 4.17(b) sets forth a true, correct and complete list of all (i) Registered IP; (ii) Domain Names constituting Company Owned IP; and (iii) all social media handles constituting Company Owned IP; accurately specifying as to each of the foregoing, as applicable: (A) the filing number, issuance or registration number, or other identify details, including filing and issuance dates; (B) the record owner and nature of the ownership; (C) the jurisdictions, registrar or platform by or in which such Registered Owned IP has been issued, registered, or in which an application for such issuance or registration has been filed; and (D) any liens or security interests that apply.
(c) To the Knowledge of the Company, all Registered Owned IP that constitute issued Patents are valid and enforceable. All Registered Exclusively Licensed IP that constitute issued Patents are subsisting and, to the Knowledge of the Company, valid and enforceable. As of the date of this Agreement, no Registered Owned IP, and to the Knowledge of the Company no Registered Exclusively Licensed IP, is or has been involved in any litigation, interference, opposition, reissue, reexamination, revocation, inter parties review, nullity, cancellation or Uniform Domain Name Dispute-Resolution Policy proceeding or equivalent proceeding, and no such proceeding has been threatened in writing with respect thereto. Since January 4, 2023 (inception), there have been no claims filed, served or threatened in writing, or to the
Knowledge of the Company orally threatened, against the Company contesting the validity, use, ownership, enforceability, patentability, registrability, or scope of any Registered IP. The Registered Owned IP is currently in compliance with formal legal requirements of the applicable intellectual property office and all registration, maintenance and renewal fees currently due in connection with any Registered Owned IP, and to the Knowledge of the Company all Registered Exclusively Licensed IP, have been paid and all documents, recordations and certificates in connection therewith have been filed with the authorities in the United States or foreign jurisdictions, as the case may be, for the purposes of prosecuting, maintaining and perfecting such rights and recording the Company’s ownership or interests therein.
(d) Since January 4, 2023 (inception), there have been no claims filed, served or threatened in writing, or to the Knowledge of the Company orally threatened, against the Company alleging any conflict with, infringement, misappropriation, or other violation of any Intellectual Property of a third Person (including any unsolicited written offers to license any such Intellectual Property). There are no Actions pending that involving a claim against the Company by a third Person alleging infringement or misappropriation of such third Person’s Intellectual Property. To the Knowledge of the Company, since January 4, 2023 (inception), no third Person has conflicted with, infringed, misappropriated, or otherwise violated any Company IP.
(e) Since January 4, 2023 (inception), the Company has not filed, served, or threatened a third Person with any claims alleging any conflict with, infringement, misappropriation, or other violation of any Company IP. There are no Actions pending that involving a claim against a third Person the Company alleging infringement or misappropriation of Company IP. The Company is not subject to any Order that adversely restricts the use, transfer, registration or licensing of any such Intellectual Property by the Company.
(f) Except as disclosed on Schedule 4.17(f), each employee, agent, consultant, and contractor who has contributed to or participated in the creation or development of any Registered IP on behalf of the Company or any predecessor in interest thereto has executed a form of proprietary information and/or inventions agreement or similar written Contract with the Company under which such Person: (i) has assigned all right, title and interest in and to such Intellectual Property to the Company (or such predecessor in interest, as applicable); and (ii) is obligated to maintain the confidentiality of the Company’s confidential information both during and after the term of such Person’s employment or engagement.
(g) No government funding or facility of a university, college, other educational institution or research center was used in the development of any item of Registered IP or to the Knowledge of the Company any item of Company Exclusively Licensed IP.
(h) None of the execution, delivery or performance by the Company of this Agreement or any of the Ancillary Agreements to which the Company is or will be a party or the consummation by the Company of the transactions contemplated hereby or thereby will (i) cause any item of Company Owned IP, or any material item of Company Licensed IP immediately prior to the Closing, to not be owned, licensed or available for use by the Company on substantially the same terms and conditions immediately following the Closing or (ii) require any additional payment obligations by the Company in order to use or exploit any other such Intellectual Property to the same extent as the Company was permitted immediately before the Closing.
(i) Except with respect to the agreements listed on Schedule 4.14(a)(i), the Company is not obligated under any Contract to make any payments by way of royalties, fees, or otherwise to any owner or licensor of, or other claimant to, any Intellectual Property.
(j) The Company has exercised reasonable efforts necessary to maintain, protect and enforce the secrecy, confidentiality and value of all Trade Secrets and all other material Confidential Information, in each instance that are at least consistent with efforts undertaken by third Persons in the industry within which the Business is a part. No Company IP is subject to any technology or source code escrow arrangement or obligation. No person other than the Company and its employees and contractors (i) has a right to access or possess any source code of the Software constituting the Company Owned IP, or (ii) will be entitled to obtain access to or possession of such source code as a result of the execution, delivery and performance of by the Company of this Agreement. The Company is in actual possession and control of the source code of any Software constituting Company Owned IP and all related documentation and materials.
(k) To the Knowledge of the Company, the Privacy Policy accurately describes the Company’s collection, disclosure and use of Personal Information and materially complies with all applicable Data Protection Laws. To the Knowledge of the Company, none of the marketing materials and/or advertisements made, or provided by, or on behalf of the Company have been inaccurate in a material way, misleading in a material way, or unfair or deceptive in material violation of applicable Data Protection Laws.
(l) In connection with its Processing of any Personal Information, the Company is in material compliance with all applicable Data Protection Laws. To the Knowledge of the Company, there are no written complaints or audits, proceedings, investigations or claims pending against the Company by any Authority, or by any Person, in respect of Processing of Personal Information by or on behalf of the Company. Without limiting the generality of the foregoing, to the Knowledge of the Company, since January 4, 2023 (inception), the Company has not experienced any material loss, damage or unauthorized access, use, disclosure or modification, or breach of security of Personal Information maintained by or on behalf of the Company (including by any agent, subcontractor or vendor of the Company) for which the Company would be required to make a report to a governmental authority, a data subject, or any other Person.
(m) To the Knowledge of the Company, the Software that constitutes Company Owned IP and all Software that is used by the Company is free of all viruses, worms, Trojan horses and other material known contaminants and does not contain any bugs, errors, or problems of a material nature that would disrupt its operation or have an adverse impact on the operation of other Software. The Company is in material compliance with all Publicly Available Software license terms applicable to any Publicly Available Software licensed to or used by the Company. The Company has not received any written (or, to the Knowledge of the Company, oral) notice from any Person that it is in breach of any license with respect to Publicly Available Software. None of the Software of the Company is subject to any Copyleft Licenses. The Company is in material compliance with all Publicly Available Software license terms applicable to any Publicly Available Software licensed to or used by the Company. The Company has used commercially reasonable efforts to maintain the confidentiality of the source code and confidential system documentation relating to all proprietary Software of the Company. Except with respect to Publicly Available Software or Intellectual Property licensed to a member of the Company pursuant to Material Contracts, no third party owns any Intellectual Property in any Software incorporated in or used with any Company Software.
(n) The “Company Information Systems” are defined as all IT systems used in or necessary for the operation of the business of the Company. The Company has implemented and maintained (or, where applicable, has required its vendors to maintain) in material compliance with the Company’s internal standards as well as its contractual obligations to other Persons (including any applicable warranties or other user instructions from vendors), commercially reasonable security, and adequate policies and procedures regarding the performance, security, confidentiality, availability, and integrity of the Company
Information Systems from unauthorized physical or virtual access, use, modification, acquisition, disclosure or other misuse. There has been no material breach, intrusion, unauthorized access to or use of the Company Information Systems or other security incident that has impacted the integrity or availability of the Company Information Systems, nor has there been any material downtime or unavailability of the Company Information Systems that resulted in a material disruption of the Business. The Company Information Systems and Company Software (i) are adequate and sufficient (including with respect to working condition and capacity) for the operations of the Business and perform in all material conformance with their documentation and functional specifications, (ii) operate and perform in all material respects as currently required and as currently contemplated to be required to conduct and operate the Business, and (iii) are free from any material software defect. There has been no malfunction, misconfiguration, vulnerability, or failure with respect to any Company Information System that has had a material effect on the operations of the Company. The Company has implemented commercially reasonable backup, anti-virus, malware protection, server patch, intrusion detection, and disaster recovery technology, policies and procedures and all other security and incident detection and response measures (including access control protocols and capabilities for AI/ML or training data).
(o) To the Company’s Knowledge, there has been no unauthorized access to or use of the Company Information Systems, nor has there been any downtime or unavailability of the Company Information Systems that resulted in a material disruption of the Business. The Company Information Systems are adequate and sufficient (including with respect to working condition and capacity) for the operations of the Business. There has been no failure with respect to any Company Information System that has had a material effect on the operations of the Company.
4.18 Employees; Employment Matters.
(a) The Company has made available to Parent or its counsel a true, correct and complete list of the employees of the Company as of the date hereof, setting forth the employee ID, location, title, current base salary or hourly rate for each such person.
(b) The Company is not a party to any collective bargaining agreement or similar labor agreement with respect to any employees of the Company. There is no unfair labor practice charge or complaint pending or, to the Knowledge of the Company, threatened, before any applicable Authority relating to employees of the Company.
(c) There are no pending or, to the Knowledge of the Company, threatened in writing material Actions against the Company under any worker’s compensation policy or long-term disability policy.
(d) The Company is in compliance in all material respects with all applicable Laws relating to employment or the engagement of labor, including but not limited to all applicable Laws relating to wages, hours, overtime, collective bargaining, equal employment opportunity, discrimination, harassment (including, but not limited to sexual harassment), retaliation, immigration, verification of identity and employment authorization of individuals employed in the United States, employee leave, disability rights or benefits, employment and reemployment rights of members and veterans of the uniformed services, paid time off/vacation, unemployment insurance, safety and health, workers’ compensation, pay equity, restrictive covenants, whistleblower rights, child labor, classification of employees and independent contractors, meal and rest breaks, reimbursement of business expenses, and the collection and payment of withholding or social security Taxes.
(e) Schedule 4.18(e) discloses each individual who is employed by the Company pursuant to a visa and the expiration date of such visa.
(f) To the Knowledge of the Company, no Key Employee is a party to or bound by any enforceable confidentiality agreement, non-competition agreement or other restrictive covenant (with any Person) that materially interferes with: (i) the performance by such Key Employee of his or her duties or responsibilities as an officer or employee of the Company or (ii) the Company’s business or operations. No Key Employee has given written notice of his or her intent to terminate his or her employment with the Company, nor has the Company provided written notice of its present intention to terminate the employment of any of the foregoing.
(g) Since January 4, 2023 (inception), the Company has not received written notice of any material claim or litigation relating to an allegation of discrimination, retaliation, harassment (including sexual harassment), or sexual misconduct; nor is there any outstanding obligation for the Company under any settlement relating to such matters and to the Knowledge of the Company, no such claim or litigation has been threatened in writing.
4.19 Withholding. Except as disclosed on Schedule 4.19, all reasonably anticipated obligations of the Company with respect to employees of the Company (except for those related to wages during the pay period immediately prior to the Closing Date and arising in the ordinary course of business consistent with past practices), whether arising by operation of Law, or by contract, for salaries, bonuses and vacation pay/paid time off to such employees in respect of the services rendered by any of them prior to the date hereof have been or will be paid by the Company or accrued on the Company Financial Statements prior to the Closing Date.
4.20 Employee Benefits.
(a) Schedule 4.20(a) sets forth a correct and complete list of all Plans. With respect to each Plan, the Company has made available to Parent or its counsel a true and complete copy, to the extent applicable, of: (i) each writing constituting a part of such Plan and all amendments thereto, including all plan documents, material employee communications, benefit schedules, trust agreements, and insurance contracts and other funding vehicles; (ii) the most recent annual reports on Form 5500 and accompanying schedules, if any; (iii) the current summary plan description and any material modifications thereto; (iv) the most recent annual financial and actuarial reports; (v) the most recent determination or advisory letter received by the Company from the Internal Revenue Service regarding the tax-qualified status of such Plan; and (vi) the most recent written results of all required compliance testing, if any.
(b) No Plan is (i) subject to Title IV or Section 302 of ERISA or Section 412 or 4971 of the Code or (ii) a “multiemployer plan” (as defined in Section 3(37) of ERISA). Neither the Company nor any ERISA Affiliate has withdrawn at any time since January 4, 2023 (inception) from any multiemployer plan, or incurred any withdrawal liability which remains unsatisfied.
(c) With respect to each Plan that is intended to qualify under Section 401(a) of the Code, such Plan, including its related trust, has received a determination letter (or may rely upon opinion letters in the case of any prototype plans) from the Internal Revenue Service that it is so qualified and that its trust is exempt from Tax under Section 501(a) of the Code, and, to the Knowledge of the Company, nothing has occurred with respect to the operation of any such Plan that could reasonably be expected to cause the loss of such qualification or exemption.
(d) There are no pending or, to the Knowledge of the Company, threatened Actions against or relating to the Plans, the assets of any of the trusts under such Plans or the Plan sponsor or the Plan administrator, or against any fiduciary of any Plan with respect to the operation of such Plan (other than routine benefits claims). No Plan is presently under audit or examination (nor has written notice been received of a potential audit or examination) by any Authority.
(e) Each Plan has been established, administered and funded in accordance with its terms and in compliance in all material respects with the applicable provisions of ERISA, the Code and other applicable Laws. All premiums due or payable with respect to insurance policies funding any Plan have been made or paid in full or, to the extent not required to be made or paid on or before the date hereof, have been fully reflected on the Company Financial Statements.
(f) None of the Plans provide retiree or post-employment health, disability, life insurance or other welfare benefits and the Company has no obligation to provide such benefits, except as may be required by Section 4980B of the Code, Section 601 of ERISA or any other applicable Law. There has been no violation of the “continuation coverage requirement” of “group health plans” as set forth in Section 4980B of the Code and Part 6 of Subtitle B of Title I of ERISA with respect to any Plan to which such continuation coverage requirements apply.
(g) Neither the execution and delivery of this Agreement nor the consummation of the transactions contemplated hereby will (either alone or in combination with another event) (i) result in any payment becoming due, or increase the amount of any compensation or benefits due, to any current or former employee of the Company with respect to any Plan; (ii) increase any benefits otherwise payable under any Plan; (iii) result in the acceleration of the time of payment or vesting of any such compensation or benefits; or (iv) result in the payment of any amount that would, individually or in combination with any other such payment, be an “excess parachute payment” within the meaning of Section 280G of the Code. No Person is entitled to receive any additional payment (including any tax gross-up or other payment) from the Company as a result of the imposition of the excise taxes required by Section 4999 of the Code or any taxes required by Section 409A of the Code.
(h) Each Plan that is a “nonqualified deferred compensation plan” (as defined in Section 409A(d)(1) of the Code) is in all material respects in documentary compliance with, and has been administered in all material respects in compliance with, Section 409A of the Code.
(i) Each Plan that is subject to the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 (the “Affordable Care Act”) has been established, maintained and administered in compliance with the requirements of the Affordable Care Act.
(j) All Plans subject to the laws of any jurisdiction outside of the United States (i) if they are intended to qualify for special tax treatment, meet all requirements for such treatment, and (ii) if they are intended to be funded and/or book-reserved, are fully funded and/or book reserved, as appropriate, based upon reasonable actuarial assumptions.
4.21 Real Property. The Company does not own, or otherwise have an interest in, any Real Property, including under any Real Property lease, sublease, space sharing, licenses or other occupancy agreements.
4.22 Tax Matters. Except as set forth on Schedule 4.22,
(a) (i) The Company has duly filed all material Tax Returns which are required to be filed by it, and has paid all material Taxes (whether or not shown on such Tax Returns) which have become due; (ii) all such Tax Returns are true, correct and complete and accurate in all material respects; (iii) there is no Action, pending or proposed in writing, with respect to a material amount of Taxes of the Company; (iv) no statute of limitations in respect of the assessment or collection of any Taxes of the Company for which a Lien may be imposed on any of the Company’s assets has been waived or extended (other than pursuant to extensions of time to file Tax Returns obtained in the ordinary course of business), which waiver
or extension is in effect; (v) the Company has duly withheld or collected and paid over to the applicable Taxing Authority all material Taxes required to be withheld or collected by the Company in connection with any amounts paid or owing to any employee, creditor, independent contractor or other third party; (vi) the Company has collected and remitted to the applicable Taxing Authority all material sales Taxes required to be collected by the Company; (vii) the Company has not requested any letter ruling from the IRS (or any comparable ruling from any other Taxing Authority); (viii) there is no Lien (other than Permitted Liens) for Taxes upon any of the assets of the Company; (ix) the Company has not received any written request from a Taxing Authority in a jurisdiction where the Company has not paid any Tax or filed Tax Returns asserting that the Company is or may be subject to Tax in such jurisdiction, and the Company does not have a permanent establishment (within the meaning of an applicable Tax treaty) or other fixed place of business in a country other than the country in which it is organized; (x) there is no outstanding power of attorney from the Company authorizing anyone (other than employees of the Company) to act on behalf of the Company in connection with any Tax, Tax Return or Action relating to any Tax or Tax Return of the Company; (xi) the Company is not a party to any Tax sharing, Tax indemnity or Tax allocation Contract (other than a contract entered into in the ordinary course of business consistent with past practices, the primary purpose of which is not related to Taxes); (xii) the Company has not been a member of an “affiliated group” within the meaning of Section 1504(a) of the Code filing a consolidated federal income Tax Return (other than a group the common parent of which was the Company); (xiii) the Company has no liability for the Taxes of any other Person: (1) under Treasury Regulation Section 1.1502-6 (or any similar provision of applicable Law), (2) as a transferee or successor or (3) otherwise by operation of applicable Law; (xiv) the Company is not a “United States real property holding corporation” within the meaning of Section 897(c)(2) of the Code during the applicable period specified in Section 897(c)(1)(A)(ii) of the Code; and (xv) the Company has not been a party to any “listed transaction” as defined in Section 6707A(c)(2) of the Code and Treasury Regulation Section 1.6011-4(b)(2).
(b) The Company will not be required to include any material item of income or exclude any material item of deduction for any taxable period ending after the Closing Date as a result of: (i) adjustment under Section 481 of the Code (or any corresponding or similar provision of state, local or non-U.S. income Tax Law) by reason of a change in method of accounting for a taxable period ending on or before the Closing Date; (ii) any “closing agreement” described in Section 7121 of the Code (or similar provision of state, local or non-U.S. Law) executed on or before the Closing Date; (iii) any installment sale or open sale transaction disposition made on or before the Closing Date (iv) any prepaid amount received on or before the Closing Date outside the ordinary course of business; or (v) any intercompany transaction or excess loss account described in Treasury Regulations under Section 1502 of the Code (or any corresponding or similar provision of state, local or non-U.S. income Tax Law).
(c) The Company is not aware of any fact or circumstance, nor has taken or agreed to take any action, that would reasonably be expected to prevent or impede the Reincorporation Merger from qualifying for the Reincorporation Intended Tax Treatment or the Acquisition Merger from qualifying for the Acquisition Intended Tax Treatment.
4.23 [RESERVED].
4.24 Finders’ Fees. Except as set forth on Schedule 4.24, there is no investment banker, broker, finder or other intermediary which has been retained by or is authorized to act on behalf of the Company or any of its Affiliates who might be entitled to any fee or commission from the Company, Merger Sub, Parent or any of its respective Affiliates upon consummation of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement or any of the Ancillary Agreements.
4.25 Directors and Officers. Schedule 4.25 sets forth a true, correct and complete list of all directors and officers of the Company.
4.26 Anti-Money Laundering Laws.
(a) The Company currently is in compliance with applicable Laws related to (i) anti-corruption or anti-bribery, including the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977, 15 U.S.C. §§78dd-1, et seq., and any other equivalent or comparable Laws of other countries (collectively, “Anti-Corruption Laws”), (ii) economic sanctions administered, enacted or enforced by any Authority (collectively, “Sanctions Laws”), (iii) export controls, including the U.S. Export Administration Regulations, 15 C.F.R. §§730, et seq., and any other equivalent or comparable Laws of other countries (collectively, “Export Control Laws”), (iv) anti-money laundering, including the Money Laundering Control Act of 1986, 18 U.S.C. §§1956, 1957, and any other equivalent or comparable Laws of other countries (collectively, “Anti-Money Laundering Laws”); (v) anti-boycott regulations, as administered by the U.S. Department of Commerce; and (vi) importation of goods, including Laws administered by the U.S. Customs and Border Protection, Title 19 of the U.S.C. and C.F.R., and any other equivalent or comparable Laws of other countries (collectively, “International Trade Control Laws”).
(b) Neither the Company nor, to the Knowledge of the Company, any Representative of the Company (acting on behalf of the Company), is or is acting under the direction of, on behalf of or for the benefit of a Person that is, (i) the subject of Sanctions Laws or identified on any sanctions or similar lists administered by an Authority, including the U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Specially Designated Nationals List, the U.S. Department of Commerce’s Denied Persons List and Entity List, the U.S. Department of State’s Debarred List, HM Treasury’s Consolidated List of Financial Sanctions Targets and the Investment Bank List, or any similar list enforced by any other relevant Authority, as amended from time to time, or any Person owned or controlled by any of the foregoing (collectively, “Prohibited Party”); (ii) the target of any Sanctions Laws; (iii) located, organized or resident in a country or territory that is, or whose government is, the target of comprehensive trade sanctions under Sanctions Laws, including, as of the date of this Agreement, Crimea, Cuba, Iran, North Korea, Sudan and Syria; or (iv) an officer or employee of any Authority or public international organization, or officer of a political party or candidate for political office. Neither the Company nor, to the Knowledge of the Company, any Representative of the Company (acting on behalf of the Company), (A) has participated in any transaction involving a Prohibited Party, or a Person who is the target of any Sanctions Laws, or any country or territory that was during such period or is, or whose government was during such period or is, the target of comprehensive trade sanctions under Sanctions Laws, (B) to the Knowledge of the Company, has exported (including deemed exportation) or re-exported, directly or indirectly, any commodity, software, technology, or services in violation of any applicable Export Control Laws or (C) has participated in any transaction in violation of or connected with any purpose prohibited by Anti-Corruption Laws or any applicable International Trade Control Laws, including support for international terrorism and nuclear, chemical, or biological weapons proliferation.
(c) The Company has not received written notice of, nor, to the Knowledge of the Company, any of its Representatives is or has been the subject of, any investigation, inquiry or enforcement proceedings by any Authority regarding any offense or alleged offense under Anti-Corruption Laws, Sanctions Laws, Anti-Money Laundering Laws, Export Control Laws or International Trade Control Laws (including by virtue of having made any disclosure relating to any offense or alleged offense) and, to the Knowledge of the Company, there are no circumstances likely to give rise to any such investigation, inquiry or proceeding.
4.27 Insurance. All forms of insurance owned or held by and insuring the Company are set forth on Schedule 4.27, and such policies are in full force and effect. All premiums with respect to such policies covering all periods up to and including the Closing Date have been or will be paid when due, no notice of cancellation or termination has been received with respect to any such policy which was not replaced on substantially similar terms prior to the date of such cancellation or termination and there is no claim by the Company or, to the Company’s Knowledge, any other Person pending under any of such insurance policies as to which coverage has been questioned, denied or disputed by the underwriters or issuers of such policies. There is no existing default or event which, with or without the passage of time or the giving of notice or both, would constitute noncompliance with, or a default under, any such policy or entitle any insurer to terminate or cancel any such policy. Such policies will not in any way be affected by or terminate or lapse by reason of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement or the Ancillary Agreements. The insurance policies to which the Company is a party are of at least like character and amount as are carried by like businesses similarly situated and sufficient for compliance with all requirements of all Material Contracts to which the Company is a party or by which the Company is bound.
4.28 Related Party Transactions. Except as set forth in Schedule 4.28, as contemplated by this Agreement or as provided in the Company Financial Statements, no Affiliate of the Company, current or former director, manager, officer or employee of any Person in the Company or any immediate family member or Affiliate of any of the foregoing (a) is a party to any Contract, or has otherwise entered into any transaction, understanding or arrangement, with the Company, (b) owns any asset, property or right, tangible or intangible, which is used by the Company, or (c) is a borrower or lender, as applicable, under any Indebtedness owed by or to the Company since January 4, 2023 (inception).
4.29 No Trading or Short Position. None of the Company or any of its managers and officers, members and employees has engaged in any short sale of Parent’s voting stock or any other type of hedging transaction involving Parent’s securities (including, without limitation, depositing shares of Parent’s securities with a brokerage firm where such securities are made available by the broker to other customers of the firm for purposes of hedging or short selling Parent’s securities).
4.30 Not an Investment Company. The Company is not an “investment company” within the meaning of the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended, and the rules and regulations promulgated thereunder.
ARTICLE V
REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES OF PARENT PARTIES
Except as disclosed in the Parent SEC Documents filed with or furnished to the SEC prior to the date of this Agreement (to the extent the qualifying nature of such disclosure is reasonably apparent from the content of such Parent SEC Documents, but excluding any risk factor disclosures or other similar cautionary or predictive statements therein), it being acknowledged that nothing disclosed in such Parent SEC Documents shall be deemed to modify or qualify the representations and warranties set forth in Sections 5.1, 5.3 or 5.8, Parent, Purchaser and Merger Sub (the “Parent Parties”) hereby represent and warrant to the Company that each of the following representations and warranties are true, correct and complete as of the date of this Agreement and as of the Closing Date:
5.1 Corporate Existence and Power. Parent is a corporation duly incorporated, validly existing and in good standing under the Laws of the State of Delaware. Purchaser is a company duly incorporated, validly existing and in good standing under the Laws of the Cayman Islands. Purchaser does not hold and has not held any material assets or incurred any material liabilities, and has not carried on any business activities other than in connection with the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger. Merger Sub is a corporation duly incorporated, validly existing and in good standing under the Laws of the State
of Delaware. Merger Sub does not hold and has not held any material assets or incurred any material liabilities, and has not carried on any business activities other than in connection with the Acquisition Merger. Each of the Parent Parties has all requisite power and authority, corporate and otherwise, to own and operate its properties and assets and to carry on its business as presently conducted.
5.2 Purchaser; Merger Sub. Each of Purchaser and Merger Sub was formed solely for the purpose of engaging in the transactions contemplated by this Agreement and activities incidental thereto. Either Parent or a wholly owned (direct or indirect) Subsidiary of Parent owns beneficially and of record all of the outstanding capital stock of Merger Sub.
5.3 Corporate Authorization. Each of the Parent Parties has all requisite corporate power and authority to execute and deliver this Agreement and the Ancillary Agreements to which it is a party and to consummate the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby, in the case of the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger, subject to receipt of the Parent Stockholder Approval. The execution and delivery by each of the Parent Parties of this Agreement and the Ancillary Agreements to which it is a party and the consummation by each of the Parent Parties of the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby have been duly authorized by all necessary corporate action on the part of such Parent Party. No other corporate proceedings on the part of such Parent Party are necessary to authorize this Agreement or the Ancillary Agreements to which it is a party or to consummate the transactions contemplated by this Agreement (other than the Parent Stockholder Approval) or the Ancillary Agreements. This Agreement and the Ancillary Agreements to which such Parent Party is a party have been duly executed and delivered by such Parent Party and, assuming the due authorization, execution and delivery by each of the other parties hereto and thereto (other than a Parent Party), this Agreement and the Ancillary Agreements to which such Parent Party is a party constitute a legal, valid and binding obligation of such Parent Party, enforceable against such Parent Party in accordance with their respective terms, subject to the Enforceability Exceptions.
5.4 Governmental Authorization. Assuming the accuracy of the representations and warranties of the Company set forth in Section 4.3, none of the execution, delivery or performance of this Agreement or any Ancillary Agreement by a Parent Party or the consummation by a Parent Party of the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby requires any consent, approval, license or other action by or in respect of, or registration, declaration or filing with any Authority except for (a) any SEC or Nasdaq filings and approval required to consummate the transactions contemplated hereunder, (b) filings with the Cayman Registrar pursuant to the Cayman Companies Act with respect to the Reincorporation Merger, (c) filings required to be made with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware pursuant to the DGCL in connection with the Reincorporation Merger, and (d) the filing of the Certificate of Merger with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware pursuant to the DGCL.
5.5 Non-Contravention. The execution, delivery and performance by a Parent Party of this Agreement or the consummation by a Parent Party of the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby do not and will not (a) contravene or conflict with the organizational or constitutive documents of the Parent Parties, or (b) contravene or conflict with or constitute a violation of any provision of any Law or any Order binding upon the Parent Parties.
5.6 Finders’ Fees. Except for the Persons identified on Schedule 5.6, there is no investment banker, broker, finder or other intermediary which has been retained by or is authorized to act on behalf of the Parent Parties or their Affiliates who might be entitled to any fee or commission from the Company or any of its Affiliates upon consummation of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement or any of the Ancillary Agreements.
5.7 Issuance of Shares. The Aggregate Merger Consideration, when issued in accordance with this Agreement, will be duly authorized and validly issued, and will be fully paid and nonassessable, and each such share comprising the Aggregate Merger Consideration shall be issued free and clear of preemptive rights and all Liens, other than transfer restrictions under applicable securities laws and the organizational or constitutive documents of Parent. The Aggregate Merger Consideration shall be issued in compliance with all applicable securities Laws and other applicable Laws and without contravention of any other person’s rights therein or with respect thereto.
5.8 Capitalization.
(a) As of the date of this Agreement, the authorized share capital of Parent is 111,000,000 shares, each with a par value of $0.0001 per share, consisting of (i) 110,000,000 shares of common stock, including 100,000,000 shares of Parent Class A Common Stock and (ii) 10,000,000 shares of Parent Class B Common Stock, and (ii) 1,000,000 shares of preferred stock, of which 9,200,000 shares of Parent Class A Common Stock (inclusive of shares of Parent Class A Common Stock included in any outstanding Parent Units), 2,300,000 shares Parent Class B Common Stock and no preferred stock issued and outstanding. As of the date of this Agreement, 9,200,000 Parent Public Warrants (inclusive of Parent Public Warrants included in any outstanding Parent Units) and 498,225 Parent Private Warrants are issued and outstanding. As of the date of this Agreement, 9,200,000 Parent Rights (inclusive of Parent Rights included in any outstanding Parent Units) are issued and outstanding. No other shares of capital stock or other voting securities of Parent are issued, reserved for issuance or outstanding. All issued and outstanding Parent Common Shares are duly authorized, validly issued, fully paid and nonassessable and are not subject to, and were not issued in violation of, any purchase option, right of first refusal, preemptive right, subscription right or any similar right under any provision of the DGCL, Parent’s organizational documents or any contract to which Parent is a party or by which Parent is bound. All outstanding Parent Warrants have been duly authorized and validly issued and constitute valid and binding obligations of Parent, enforceable against Parent in accordance with their terms, subject to the Enforceability Exceptions and are not subject to, and were not issued in violation of, any purchase option, right of first refusal, preemptive right, subscription right or any similar right under any provision of the DGCL, Parent’s organizational documents or any contract to which Parent is a party or by which Parent is bound. Except as set forth in Parent’s organizational documents, there are no outstanding contractual obligations of Parent to repurchase, redeem or otherwise acquire any Parent Common Shares or any capital equity of Parent. There are no outstanding contractual obligations of Parent to provide funds to, or make any investment (in the form of a loan, capital contribution or otherwise) in, any other Person. All outstanding Parent Units, Parent Common Shares and Parent Warrants have been issued in compliance with all applicable securities and other applicable Laws and were issued free and clear of all Liens other than transfer restrictions under applicable securities Laws and the organizational or constitute documents of Parent.
(b) All issued and outstanding Purchaser Ordinary Shares are duly authorized, validly issued, fully paid and nonassessable and are not subject to, and were not issued in violation of, any purchase option, right of first refusal, preemptive right, subscription right or any similar right under any provision of the Cayman Companies Act, Purchaser’s organizational documents or any contract to which Purchaser is a party or by which Purchaser is bound. There are no outstanding contractual obligations of Purchaser to repurchase, redeem or otherwise acquire any Purchaser Ordinary Shares or any equity capital of Purchaser. There are no outstanding contractual obligations of Purchaser to provide funds to, or make any investment (in the form of a loan, capital contribution or otherwise) in, any other Person.
(c) All issued and outstanding shares of common stock of Merger Sub (“Merger Sub Common Stock”) are duly authorized, validly issued, fully paid and nonassessable and are not subject to, and were not issued in violation of, any purchase option, right of first refusal, preemptive right, subscription right or any similar right under any provision of the DGCL, Merger Sub’s organizational documents or any contract to which Merger Sub is a party or by which Merger Sub is bound. There are no outstanding contractual obligations of Merger Sub to repurchase, redeem or otherwise acquire any shares of Merger Sub Common Stock or any equity capital of Merger Sub. There are no outstanding contractual obligations of Merger Sub to provide funds to, or make any investment (in the form of a loan, capital contribution or otherwise) in, any other Person.
5.9 Information Supplied. None of the information supplied or to be supplied by the Parent Parties expressly for inclusion or incorporation by reference in the Registration Statement, Proxy Statement/Prospectus or other Offer Documents will, (a) when the Registration Statement is first filed, (b) on the effective date of the Registration Statement, (c) on the date when the Proxy Statement/Prospectus is mailed to the Parent’s stockholders and (d) at the time of the Parent Stockholder Meeting, as the case may be, contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state any material fact required to be stated therein or necessary in order to make the statements therein, in light of the circumstances under which they are made, not misleading (subject to the qualifications and limitations set forth in the materials provided by Parent or included in the Parent SEC Documents, the Additional Parent SEC Documents, the Registration Statement or any Other Filing).
5.10 Trust Fund. As of the date of this Agreement, Parent has at least $97 million in the trust account established by Parent for the benefit of its public stockholders (the “Trust Account”) maintained by Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company (the “Trustee”), and held in trust by the Trustee pursuant to the Investment Management Trust Agreement dated as of September 22, 2022, between Parent and the Trustee (the “Trust Agreement”). The Trust Agreement is valid and in full force and effect and enforceable in accordance with its terms, except as may be limited by the Enforceability Exceptions, and has not been amended or modified except as set forth in the Parent SEC Documents. There are no separate agreements, side letters or other agreements or understandings (whether written or unwritten, express or implied) that would cause the description of the Trust Agreement in the Parent SEC Documents to be inaccurate in any material respect or that would entitle any Person (other than public stockholders of Parent holding shares of Parent Class A Common Stock sold in Parent’s IPO who shall have elected to redeem their Parent Class A Common Stock pursuant to the Parent Charter) to any portion of the proceeds in the Trust Account. Prior to the Closing, none of the funds held in the Trust Account may be released except in accordance with the Trust Agreement and the Parent Charter. Parent has performed all material obligations required to be performed by it to date under, and is not in material default or delinquent in performance or any other respect (claimed or actual) in connection with, the Trust Agreement, and, to the Knowledge of Parent, no event has occurred which, with due notice or lapse of time or both, would reasonably be expected to constitute such a material default thereunder. There are no claims or proceedings pending with respect to the Trust Account. Parent has not released any money from the Trust Account (other than as permitted by the Trust Agreement). As of the Effective Time, (i) the obligations of Parent to dissolve or liquidate pursuant to the Parent Charter shall terminate, and (ii) Parent shall have no obligation whatsoever pursuant to the Parent Charter to dissolve and liquidate the assets of Parent by reason of the consummation of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement. Following the Effective Time, no stockholder of Parent (other than the underwriters of the IPO or Authority for Taxes) shall be entitled to receive any amount from the Trust Account except to the extent a Parent’s public stockholder shall have elected to tender its shares of Parent Class A Common Stock for redemption pursuant to the Parent Charter (or in connection with an extension of Parent’s deadline to consummate a “Business Combination” as such term is defined in the Parent Charter).
5.11 Listing. The Parent Units are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Exchange Act and are listed for trading on Nasdaq under the symbol “GLSTU”. The Parent Class A Common Stock is registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Exchange Act and are listed for trading on Nasdaq under the symbol “GLST”. The issued and outstanding Parent Warrants are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Exchange Act and are listed for trading on Nasdaq under the symbol “GLSTW”. The issued and outstanding Parent Rights are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Exchange Act and are listed for trading on Nasdaq under the symbol “GLSTR”. Since its initial public offering, Parent has complied in all material respects with all applicable listing and corporate governance rules and regulations of Nasdaq. As of the date of this Agreement, there is no Action or proceeding pending or, to the Knowledge of Parent, threatened against Parent by the Nasdaq or the SEC with respect to any intention by such entity to deregister the Parent Units, the Parent Class A Common Stock, the Parent Warrants or the Parent Rights or prohibit or terminate the listing of the Parent Units, the Parent Class A Common Stock, the Parent Warrants or the Parent Rights on the Nasdaq or prohibit the transfer of the listing to an Alternate Exchange. None of Parent, Purchaser, Merger Sub or their respective Affiliates has taken any action in an attempt to terminate the registration of the Parent Units, the Parent Class A Common Stock, the Parent Warrants or the Parent Rights under the Exchange Act except as contemplated by this Agreement.
5.12 Board Approval.
(a) Parent’s Board of Directors (including any required committee or subgroup of such board) has unanimously (i) declared the advisability of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement, (ii) determined that the transactions contemplated hereby are in the best interests of the stockholders of Parent and (iii) determined that the transactions contemplated hereby constitutes a “Business Combination” as such term is defined in the Parent Charter and (iv) recommended to the Parent’s stockholders to adopt and approve each of the Parent Proposals (“Parent Board Recommendation”).
(b) Purchaser’s Board of Directors has, as of the date of this Agreement, unanimously (i) declared the advisability of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement and (ii) determined that the transactions contemplated hereby are in the best interests of its sole shareholder.
(c) Merger Sub’s Board of Directors has, as of the date of this Agreement, unanimously (i) declared the advisability of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement and (ii) determined that the transactions contemplated hereby are in the best interests of its sole stockholder.
5.13 Parent SEC Documents and Financial Statements.
(a) Parent has filed all forms, reports, schedules, statements and other documents, including any exhibits thereto, required to be filed or furnished by Parent with the SEC since Parent’s formation under the Exchange Act or the Securities Act, together with any amendments, restatements or supplements thereto, and will use commercially reasonable efforts to file all such forms, reports, schedules, statements and other documents required to be filed subsequent to the date of this Agreement (the “Additional Parent SEC Documents”). Parent has made available to the Company copies in the form filed with the SEC of all of the following, except to the extent available in full without redaction on the SEC’s website through EDGAR for at least two (2) Business Days prior to the date of this Agreement: (i) Parent’s Annual Reports on Form 10-K for each fiscal year of Parent beginning with the first year that Parent was required to file such a form, (ii) all proxy statements relating to Parent’s meetings of stockholders (whether annual or special) held, and all information statements relating to stockholder consents, since the beginning of the first fiscal year referred to in clause (i) above, (iii) its Form 8-Ks filed since the beginning of the first
fiscal year referred to in clause (i) above, and (iv) all other forms, reports, registration statements and other documents (other than preliminary materials if the corresponding definitive materials have been provided to the Company pursuant to this Section 5.13) filed by Parent with the SEC since Parent’s formation (the forms, reports, registration statements and other documents referred to in clauses (i) through (iv) above, whether or not available through EDGAR, collectively, as they have been amended, revised or superseded by a later filing, the “Parent SEC Documents”).
(b) Parent SEC Documents were, and the Additional Parent SEC Documents will be, prepared in all material respects in accordance with the requirements of the Securities Act, the Exchange Act, and the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, as the case may be, and the rules and regulations thereunder. Parent SEC Documents did not, and the Additional Parent SEC Documents will not, at the time they were or are filed, as the case may be, with the SEC (except to the extent that information contained in any Parent SEC Document or Additional Parent SEC Document has been or is amended, revised or superseded by a later filed Parent SEC Document or Additional Parent SEC Document, then on the date of such filing) contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact required to be stated therein or necessary in order to make the statements made therein, in the light of the circumstances under which they were made, not misleading; provided, however, that the foregoing does not apply to statements in or omissions in any information supplied or to be supplied by the Company expressly for inclusion or incorporation by reference in the Registration Statement or Other Filing.
(c) As used in this Section 5.13, the term “file” shall be broadly construed to include any manner in which a document or information is furnished, supplied or otherwise made available to the SEC.
(d) Except as not required in reliance on exemptions from various reporting requirements by virtue of Parent’s status as an “emerging growth company” within the meaning of the Securities Act, as modified by the JOBS Act, or “smaller reporting company” within the meaning of the Exchange Act, since its initial public offering, (i) Parent has established and maintained a system of internal controls over financial reporting (as defined in Rule 13a-15 and Rule 15d-15 under the Exchange Act) sufficient to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of Parent’s financial reporting and the preparation of Parent’s financial statements for external purposes in accordance with U.S. GAAP and (ii) Parent has established and maintained disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15 and Rule 15d-15 under the Exchange Act) designed to ensure that material information relating to Parent is made known to Parent’s principal executive officer and principal financial officer by others within Parent. Parent maintains and, for all periods covered by the Parent Financial Statements, has maintained Books and Records of Parent in the ordinary course of business in accordance with U.S. GAAP in all material respects and other applicable legal and accounting requirements.
(e) Parent has not taken any action prohibited by Section 402 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act.
(f) Since its initial public offering, Parent has complied in all material respects with all applicable listing and corporate governance rules and regulations of Nasdaq. The classes of securities representing the Parent Class A Common Stock, Parent Units, Parent Warrants and Parent Rights are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Exchange Act and are listed for trading on Nasdaq. As of the date of this Agreement, there is no material Proceeding pending or, to the Knowledge of Parent, threatened against Parent by Nasdaq or the SEC with respect to any intention by such entity to deregister the Parent Class A Common Stock, Parent Units, Parent Warrants or Parent Rights or prohibit or terminate the listing of the Parent Class A Common Stock, Parent Units, Parent Warrants or Parent Rights on Nasdaq or prohibit the transfer of the listing to Nasdaq. Parent has not taken any action that is designed to terminate the registration of the Parent Class A Common Stock, Parent Units, Parent Warrants and Parent Rights under the Exchange Act.
(g) The Parent SEC Documents contain true and complete copies of the applicable Parent Financial Statements. Except as disclosed in the Parent SEC Documents, the Parent Financial Statements (i) fairly present in all material respects the financial position of Parent as at the respective dates thereof, and the results of its operations, stockholders’ equity and cash flows for the respective periods then ended (subject, in the case of any unaudited interim financial statements, to normal year-end audit adjustments (none of which is material) and the absence of footnotes), (ii) were prepared in conformity with U.S. GAAP applied on a consistent basis during the periods involved (subject, in the case of any unaudited financial statements, to normal year-end audit adjustments (none of which is material) and the absence of footnotes), (iii) in the case of the audited Parent Financial Statements, were audited in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board for public companies and (iv) comply in all material respects with the applicable accounting requirements and with the rules and regulations of the SEC, the Exchange Act and the Securities Act in effect as of the respective dates thereof (including Regulation S-X or Regulation S-K, as applicable)
(h) Parent has established and maintains systems of internal accounting controls that are designed to provide, in all material respects, reasonable assurance that (i) all transactions are executed in accordance with management’s authorization and (ii) all transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of proper and accurate financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP and to maintain accountability for Parent’s and its Subsidiaries’ assets. Parent maintains and, for all periods covered by the Parent Financial Statements, has maintained books and records of Parent in the ordinary course of business that are accurate and complete and reflect the revenues, expenses, assets and liabilities of Parent in all material respects.
(i) Except as disclosed in the Parent SEC Documents, Parent has not received any written complaint, allegation, assertion or claim that there is (i) a “significant deficiency” in the internal controls over financial reporting of Parent to Parent’s Knowledge, (ii) a “material weakness” in the internal controls over financial reporting of Parent to Parent’s Knowledge or (iii) fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees of Parent who have a significant role in the internal controls over financial reporting of Parent.
5.14 Certain Business Practices. Neither Parent nor any Representative of Parent (acting on behalf of Parent) has (a) used any funds for unlawful contributions, gifts, entertainment or other unlawful expenses relating to political activity, (b) made any unlawful payment to foreign or domestic government officials, employees or political parties or campaigns, (c) violated any provision of the Anti-Corruption Laws or (d) made any other unlawful payment. Neither Parent nor any director, officer, or, to the Knowledge of Parent, any agent or employee of Parent (nor any Person acting on behalf of any of the foregoing, but solely in his or her capacity as a director, officer, employee or agent of Parent) has, since the IPO, directly or indirectly, given or agreed to give any gift or similar benefit in any material amount to any customer, supplier, governmental employee or other Person in order to assist Parent in connection with any actual or proposed transaction, which, if not given or continued in the future, would reasonably be expected to (i) adversely affect the business of Parent and (ii) subject Parent to suit or penalty in any private or governmental Action.
5.15 Anti-Money Laundering Laws. The operations of Parent are and have been at all times conducted in compliance with the Anti-Money Laundering Laws, and no Action involving Parent with respect to the Anti-Money Laundering Laws is pending or, to the Knowledge of Parent, threatened.
5.16 Affiliate Transactions. Except as described in Parent SEC Documents, there are no transactions, agreements, arrangements or understandings between Parent or any of its Subsidiaries, on the one hand, and any director, officer, employee, stockholder, warrant holder or Affiliate of Parent or any of its Subsidiaries, on the other hand.
5.17 Litigation. There is no (a) Action pending or, to the Knowledge of Parent, threatened against Parent or any of its Subsidiaries or that affects its or their assets or properties, or (b) Order outstanding against Parent or any of its Subsidiaries or that affects its or their assets or properties. Neither Parent nor any of its Subsidiaries is party to a settlement or similar agreement regarding any of the matters set forth in the preceding sentence that contains any ongoing obligations, restrictions or liabilities (of any nature) that are material to Parent and its Subsidiaries.
5.18 Expenses, Indebtedness and Other Liabilities. Except as set forth in Parent SEC Documents, Parent does not have any Indebtedness or other liabilities.
5.19 Brokers and Other Advisors. No broker, investment banker, financial advisor or other Person is entitled to any broker’s, finder’s, financial advisor’s or other similar fee or commission in connection with the Transactions based upon arrangements made by or on behalf of Parent or any of its Subsidiaries except for Persons, if any, whose fees and expenses shall be paid by Parent.
5.20 Tax Matters.
(a) (i) Parent has duly filed all material Tax Returns which are required to be filed it, and has paid all material Taxes (whether or not shown on such Tax Returns) which have become due; (ii) all such Tax Returns are true, correct and complete and accurate in all material respects; (iii) there is no Action, pending or proposed in writing, with respect to a material amount of Taxes of Parent; (iv) no statute of limitations in respect of the assessment or collection of any Taxes of Parent for which a Lien may be imposed on any of Parent’s assets has been waived or extended (other than pursuant to extensions of time to file Tax Returns obtained in the ordinary course of business), which waiver or extension is in effect; (v) Parent has collected and remitted to the applicable Taxing Authority all material sales Taxes required to be collected by Parent; (vi) Parent duly withheld or collected and paid over to the applicable Taxing Authority all material Taxes required to be withheld or collected by Parent in connection with any amounts paid or owing to any employee, creditor, independent contractor or other third party; (vii) Parent has not requested any letter ruling from the IRS (or any comparable ruling form any other Taxing Authority); (viii) there is no Lien (other than Permitted Liens) for Taxes upon any of the assets of Parent; (ix) Parent has not received any written request from a Taxing Authority in a jurisdiction where Parent has not paid any Tax or filed Tax Returns asserting that Parent is or may be subject to Tax in such jurisdiction, and Parent does not have a permanent establishment (within the meaning of an applicable Tax treaty) or other fixed place of business in a country other than the country in which it is organized; (x) there is no outstanding power of attorney from Parent authorizing anyone (other than employees of Parent) to act on behalf of Parent in connection with any Tax, Tax Return or Action relating to any Tax or Tax Return of Parent; (xi) Parent is not a party to any Tax sharing, Tax indemnity or Tax allocation Contract (other than a contract entered into in the ordinary course of business consistent with past practices, the primary purpose of which is not related to Taxes); (xii) Parent has not been a member of an “affiliated group” within the meaning of Section 1504(a)
of the Code filing a consolidated federal income Tax Return (other than a group the common parent of which was the Parent); (xiii) Parent has no liability for the Taxes of any other Person: (1) under Treasury Regulation Section 1.1502-6 (or any similar provision of applicable Law), (2) as a transferee or successor or (3) otherwise by operation of applicable Law; (xiv) the Parent is not a “United States real property holding corporation” within the meaning of Section 897(c)(2) of the Code during the applicable period specified in Section 897(c)(1)(A)(ii) of the Code; and (xv) the Parent has not been a party to any “listed transaction” as defined in Section 6707A(c)(2) of the Code and Treasury Regulation Section 1.6011-4(b)(2).
(b) Parent will not be required to include any material item of income or exclude any material item of deduction for any taxable period ending after the Closing Date as a result of: (i) any adjustment under Section 481 of the Code (or any corresponding or similar provision of state, local or non-US. Income Tax Law) by reason of a change in method of accounting for a taxable period ending on or before the Closing Date; (ii) any “closing agreement” described in Section 7121 of the Code (or similar provision of state, local or non-U.S. Law) executed on or before the Closing Date; (iii) any installment sale or open sale transaction disposition made on or before the Closing Date; (iv) any prepaid amount received on or before the Closing Date outside the ordinary course of business; or (v) any intercompany transaction or excess loss account described in Treasury Regulations under Section 1502 of the Code (or any corresponding or similar provision of state, local or non-U.S. income Tax Law).
(c) Parent is not aware of any fact or circumstance, nor has taken or agreed to take any action, that would reasonably be expected to prevent or impede the Reincorporation Merger from qualifying for the Reincorporation Intended Tax Treatment or the Acquisition Merger from qualifying for the Acquisition Intended Tax Treatment.
5.21 Not an Investment Company. Neither Parent nor Purchaser is an “investment company” within the meaning of the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended, and the rules and regulations promulgated thereunder.
ARTICLE VI
COVENANTS OF THE PARTIES PENDING CLOSING
6.1 Conduct of the Business. Each of the Company and Parent covenants and agrees that:
(a) Except as expressly contemplated by this Agreement or the Ancillary Agreements or as set forth on Schedule 6.1(a), from the date hereof until the earlier of the Closing Date and the termination of this Agreement in accordance with its terms (the “Interim Period”), each party shall conduct its business only in the ordinary course (including the payment of accounts payable and the collection of accounts receivable), consistent with past practices and use its commercially reasonable efforts to preserve intact its business and assets. Without limiting the generality of the foregoing, and except as expressly contemplated by this Agreement or the Ancillary Agreements, or as required by applicable Law, from the date hereof until the earlier of the Closing Date and the termination of this Agreement in accordance with its terms, without the other party’s prior written consent (which shall not be unreasonably conditioned, withheld or delayed), neither the Company, Parent, nor any of their Subsidiaries, shall be permitted to:
(i) amend, modify or supplement its certificate of incorporation or bylaws or other organizational or governing documents except as contemplated hereby, or engage in any reorganization, reclassification, liquidation, dissolution or similar transaction;
(ii) amend, waive any provision of, terminate prior to its scheduled expiration date, or otherwise compromise in any way or relinquish any material right under, any (A) in the case of the Company, any Material Contract or (B) in the case of Parent, material contract, agreement, lease, license or other right or asset of Parent, as applicable;
(iii) other than in the ordinary course of business consistent with past practice, modify, amend or enter into any contract, agreement, lease, license or commitment that extends for a term of one year or more or obligates the payment by the Company or Parent, as applicable, of more than $500,000 (individually or in the aggregate);
(iv) make any capital expenditures in excess of $500,000 (individually or in the aggregate);
(v) sell, lease, license or otherwise dispose of any of the Company’s or Parent’s, as applicable, material assets, except pursuant to existing contracts or commitments disclosed herein or in the ordinary course of business consistent with past practice;
(vi) solely in the case of the Company, (i) transfer, sell, assign, lease, license, sublicense, covenant not to assert, encumber, subject to a Lien (other than a Permitted Lien), abandon, allow to lapse, or otherwise dispose of any right, title or interest of the Company or its Subsidiaries in Company Owned IP (other than non-exclusive licenses of Company Owned IP granted to customers, end users, or service providers granted in the ordinary course of business); or (ii) disclose any Trade Secrets to any third party (other than pursuant to a written confidentiality agreement entered into in the ordinary course of business that contains reasonable protections therefor);
(vii) (A) pay, declare or promise to pay any dividends, distributions or other amounts with respect to its capital stock or other equity securities; (B) pay, declare or promise to pay any other amount to any stockholder or other equityholder in its capacity as such; and (C) except as contemplated hereby or by any Ancillary Agreement, amend any term, right or obligation with respect to any outstanding shares of its capital stock or other equity securities;
(viii) (A) make any loan, advance or capital contribution to any Person; (B) incur any Indebtedness including drawings under the lines of credit, in the case of the Company, in excess of an aggregate principal amount of $500,000 or such lesser amount if the aggregate principal amount of such new Indebtedness together with the aggregate principal amount all other Indebtedness of the Company would exceed $1,000,000 other than (1) loans evidenced by promissory notes made to Parent as working capital advances as described in the Prospectus and (2) intercompany Indebtedness; or (C) repay or satisfy any Indebtedness, other than the repayment of Indebtedness in accordance with the terms thereof;
(ix) suffer or incur any Lien, except for Permitted Liens, on the Company’s or Parent’s, as applicable, assets;
(x) delay, accelerate or cancel, or waive any material right with respect to, any receivables or Indebtedness owed to the Company or write off or make reserves against the same (other than in the ordinary course of business consistent with past practice);
(xi) merge or consolidate or enter a similar transaction with, or acquire all or substantially all of the assets or business of, any other Person; make any material investment in any Person; or be acquired by any other Person;
(xii) terminate or allow to lapse any insurance policy protecting any of the Company’s or Parent’s, as applicable, assets, unless simultaneously with such termination or lapse, a replacement policy underwritten by an insurance company of nationally recognized standing having comparable deductions and providing coverage equal to or greater than the coverage under the terminated or lapsed policy for substantially similar premiums or less is in full force and effect;
(xiii) waive, release, institute, compromise, settle or agree to settle any Legal Proceeding or any Action before any Authority, in each case, where such waiver, release, institution, compromise or settlement is in excess of $500,000 (exclusive of any amounts covered by insurance) or that imposes injunctive or other non-monetary relief on such party;
(xiv) except as required by U.S. GAAP, make any material change in its accounting principles, methods or practices or write down the value of its assets;
(xv) except (a) in connection with the exercise of rights under the terms of any of the Company Preferred Stock or (b) in connection with any preferred equity financing of the Company, issue, redeem or repurchase any capital stock, membership interests or other securities, or issue any securities exchangeable for or convertible into any shares of its capital stock or other securities, other than any redemption by Parent of Parent Class A Common Stock held by its public stockholders pursuant to the Parent Charter or as otherwise contemplated herein or in any Ancillary Agreement;
(xvi) (A) make, change or revoke any material Tax election; (B) change any material method of accounting; (C) settle or compromise any material claim, notice, audit report or assessment in respect of Taxes; (D) enter into any Tax allocation, Tax sharing, Tax indemnity or other closing agreement relating to any Taxes (other than a contract entered into in the ordinary course of business consistent with past practices, the primary purpose of which is not related to Taxes); (E) surrender or forfeit any right to claim a material Tax refund, or (F) take any action, or knowingly fail to take any action, which action or failure to act prevents or impedes, or could reasonably be expected to prevent or impede, the Reincorporation Intended Tax Treatment or the Acquisition Intended Tax Treatment;
(xvii) enter into any transaction with or distribute or advance any material assets or property to any of its Affiliates, other than the payment of salary and benefits in the ordinary course;
(xviii) solely in the case of the Company, other than as required by Law or by the terms of a Plan (A) increase the compensation, bonus, pension, welfare, fringe or other benefits, severance or termination pay of any of any employee of the Company or service provider of the Company at the level of manager or above, except for annual compensation increases in the ordinary course of business consistent with past practices, (B) accelerate the vesting or payment of any compensation or benefits of any employee or service provider of the Company, (C) enter into, amend, or terminate any Plan (or any plan, program, agreement or arrangement that would be a Plan if in effect on the date hereof) or grant, amend or terminate any awards thereunder, (D) make any loan to any present or former employee or other individual service provider of the Company, other than advancement of expenses in the ordinary course of business consistent with past practices, (E) enter into, amend or terminate any collective bargaining agreement or other agreement with a labor union or labor organization; or (F) adopt any severance or retention plan;
(xix) fail to duly observe and conform to any applicable Laws and Orders; or
(xx) agree or commit to do any of the foregoing.
(b) Neither party shall (i) take or agree to take any action that would be reasonably likely to cause any representation or warranty of such party to be inaccurate or misleading in any respect at, or as of any time prior to, the Closing Date or (ii) omit to take, or agree to omit to take, any action necessary to prevent any such representation or warranty from being inaccurate or misleading in any respect at any such time.
(c) Nothing in this Agreement is intended to give Parent or Merger Sub, directly or indirectly, the right to control or direct the Company’s operations prior to the Closing Date, and nothing in this Agreement is intended to give the Company, directly or indirectly, the right to control or direct Parent’s or its Subsidiaries’ operations prior to the Closing Date. Prior to the Closing Date, each of the Company, Parent and Merger Sub shall exercise, consistent with the terms and conditions of this Agreement, complete control and supervision over its and its Subsidiaries’ respective operations.
6.2 Exclusivity.
(a) During the Interim Period, neither the Company, on the one hand, nor Parent, on the other hand, shall, and such Persons shall cause each of their respective Representatives not to, without the prior written consent of the other party (which consent may be withheld in the sole and absolute discretion of the party asked to provide consent), directly or indirectly, (i) encourage, solicit, initiate, engage or participate in negotiations with any Person concerning any Alternative Transaction, (ii) take any other action intended or designed to facilitate the efforts of any Person relating to a possible Alternative Transaction, (iii) approve, recommend or enter into any Alternative Transaction or any contract or agreement related to any Alternative Transaction or (iv) otherwise cooperate in any way with, or assist or participate in, or knowingly facilitate or encourage any effort or attempt by any Person to do or seek to do any of the foregoing. Immediately following the execution of this Agreement, the Company, on the one hand, and Parent, on the other hand, shall, and shall cause each of their Representatives, to terminate any discussion or negotiation that may be ongoing with any Persons other than the Company or Parent, as applicable, concerning any Alternative Transaction. Each of the Company and Parent shall be responsible for any acts or omissions of any of its respective Representatives that, if they were the acts or omissions of the Company or Parent, as applicable, would be deemed a breach of such party’s obligations hereunder (it being understood that such responsibility shall be in addition to and not by way of limitation of any right or remedy the Company or Parent, as applicable, may have against such Representatives with respect to any such acts or omissions). For purposes of this Agreement, except as disclosed on Schedule 6.2(a), the term “Alternative Transaction” means any of the following transactions involving the Company or Parent (other than the transactions contemplated by this Agreement or the Ancillary Agreements): (A) any merger, consolidation, share exchange, business combination or other similar transaction, (B) with respect to the Company, any sale, lease, exchange, transfer or other disposition of all or a material portion of the assets of the Company or its Subsidiaries (other than in the ordinary course of business) in a single transaction or series of transactions, or (C) with respect to Parent, any other Business Combination.
(b) In the event that there is a proposal for, or an indication of interest in entering into, an Alternative Transaction, communicated in writing to the Company or Parent or any of their respective Representatives (each, an “Alternative Proposal”), such party shall as promptly as practicable (and in any event within one (1) Business Day after receipt thereof) advise the other parties to this Agreement, orally and in writing, of such Alternative Proposal and the material terms and conditions thereof (including any changes thereto) and the identity of the Person making any such Alternative Proposal. The Company and Parent shall keep each other informed on a reasonably current basis of material developments with respect to any such Alternative Proposal. As used herein with respect to Parent, the term “Alternative Proposal” shall not include the receipt by Parent of any unsolicited communications (including the receipt of draft non-disclosure agreements) in the ordinary course of business inquiring as to Parent’s interest in a potential target for a business combination; provided, however, that Parent shall inform the person initiating such communication of the existence of this Agreement.
6.3 Access to Information. During the Interim Period, the Company and Parent shall each, use its commercially reasonable efforts to, (a) continue to give the other party, its legal counsel and its other Representatives full access to the offices, properties and Books and Records, (b) furnish to the other party, its legal counsel and its other Representatives such information relating to the business of the Company or Parent as such Persons may request and (c) cause its employees, legal counsel, accountants and other Representatives to cooperate with the other party in its investigation of the Business (in the case of the Company) or the business of Parent (in the case of Parent); provided, that no investigation pursuant to this Section 6.3 (or any investigation made prior to the date hereof) shall affect any representation or warranty given by the Company or Parent; and provided, further, that any investigation pursuant to this Section 6.3 shall be conducted in such manner as not to interfere unreasonably with the conduct of the Business of the Company. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary expressed or implied in this Agreement, neither party shall be required to provide the access described above or disclose any information to the other party if doing so is, in such party’s reasonable judgement, reasonably likely to (i) result in a waiver of attorney-client privilege, work product doctrine or similar privilege or (ii) violate any contract to which it is a party or to which it is subject or applicable Law.
6.4 Notices of Certain Events. During the Interim Period, each of Parent and the Company shall promptly notify the other party of:
(a) any notice from any Person alleging or raising the possibility that the consent of such Person is or may be required in connection with the transactions contemplated by this Agreement or that the transactions contemplated by this Agreement might give rise to any Action or other rights by or on behalf of such Person or result in the loss of any rights or privileges of the Company (or Parent, post-Closing) to any such Person or create any Lien on any of the Company’s or Parent’s assets;
(b) any notice or other communication from any Authority in connection with the transactions contemplated by this Agreement or the Ancillary Agreements;
(c) any Actions commenced or threatened against, relating to or involving or otherwise affecting either party or any of their stockholders or their equity, assets or business or that relate to the consummation of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement or the Ancillary Agreements;
(d) any written notice from Nasdaq with respect to the listing of the securities of Parent;
(e) the occurrence of any fact or circumstance which constitutes or results, or would reasonably be expected to constitute or result in a Material Adverse Effect (including, in the case of the Company, any Material Adverse Effect with respect to the Company, Play Company and Solaire Partners, taken as a whole); and
(f) any inaccuracy of any representation or warranty of such party contained in this Agreement at any time during the term hereof, or any failure of such party to comply with or satisfy any covenant, condition or agreement to be complied with or satisfied by it hereunder, that would reasonably be expected to cause any of the conditions set forth in ARTICLE IX not to be satisfied.
6.5 Registration Statement/Proxy Statement; Other Filings.
(a) As promptly as practicable after the execution of this Agreement, Purchaser shall prepare, with the assistance, cooperation and commercially reasonable efforts of the Company, and file with the SEC a mutually acceptable Registration Statement on Form F-4, or other appropriate form, including any pre-effective or post-effective amendments or supplements thereto (the “Registration Statement”), which Registration Statement shall include a proxy statement of Parent (as amended, the “Proxy Statement”) and proxy materials for the purpose of soliciting proxies from holders of Parent Common Shares sufficient to obtain Parent Stockholder Approval at a meeting of holders of Parent Common Shares to be called and held for such purpose (the “Parent Stockholder Meeting”) and a prospectus pursuant to which the securities of Purchaser issuable in the Reincorporation Merger and Acquisition Merger shall be registered under the Securities Act (such prospectus, together with the Proxy Statement and any amendments or supplements thereto, the “Proxy Statement/Prospectus”). Purchaser shall promptly respond to any SEC comments on the Registration Statement. Purchaser also agrees to use its best efforts to obtain all necessary state securities law or “Blue Sky” permits and approvals required to carry out the transactions contemplated hereby, and the Company shall furnish all information concerning the Company, its Subsidiaries and any of their respective members or stockholders as may be reasonably requested in connection with any such action. Each of Parent, Purchaser and the Company agrees, as promptly as reasonably practicable, to furnish to the other party all information concerning itself, its Subsidiaries, officers, directors, managers, stockholders, and other equityholders and information regarding such other matters as may be reasonably necessary or advisable or as may be reasonably requested in connection with the preparation of the Registration Statement, the Proxy Statement/Prospectus, a Current Report on Form 8-K pursuant to the Exchange Act in connection with the signing of this Agreement and the Ancillary Agreements, a Current Report on Form 8-K pursuant to the Exchange Act in connection with the Closing of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement, or any other statement, filing, notice or application made by or on behalf of Parent, Purchaser, the Company or their respective Subsidiaries to any regulatory authority (including Nasdaq) in connection with the Reincorporation Merger, the Acquisition Merger and the other transactions contemplated hereby (the “Offer Documents”).
(b) Purchaser (i) shall permit the Company and its counsel to review and comment on the Registration Statement and Proxy Statement/Prospectus and any exhibits, amendments or supplements thereto (or other related documents); (ii) shall consider any such comments reasonably and in good faith; and (iii) shall not file the Registration Statement and Proxy Statement/Prospectus or any exhibit, amendment or supplement thereto without giving reasonable and good faith consideration to the comments of the Company. As promptly as practicable after receipt thereof, Purchaser shall provide to the Company and its counsel notice and a copy of all correspondence (or, to the extent such correspondence is oral, a summary thereof), including any comments from the SEC or its staff, between Purchaser or any of its Representatives, on the one hand, and the SEC or its staff or other government officials, on the other hand, with respect to the Registration Statement and Proxy Statement/Prospectus, and, in each case, shall consult with the Company and its counsel concerning any such correspondence. Purchaser shall not file any response letters to any comments from the SEC without consulting reasonably and in good faith with the Company. Purchaser will use its reasonable efforts to permit the Company’s counsel to participate in any calls, meetings or other communications with the SEC or its staff. Purchaser will advise the Company, promptly after it receives notice thereof, of the time when the Registration Statement and Proxy Statement/Prospectus or any amendment or supplement thereto has been filed with the SEC and the time when the Registration Statement declared effective or any stop order relating to the Registration Statement is issued.
(c) As soon as practicable following the date on which the Registration Statement is declared effective by the SEC, Parent shall distribute the Proxy Statement/Prospectus to the holders of Parent Common Shares and, pursuant thereto, shall call the Parent Stockholder Meeting in accordance with its organizational documents, the applicable Nasdaq rules and the applicable Laws of the State of Delaware and, subject to the other provisions of this Agreement, solicit proxies from such holders to vote in favor of the adoption of this Agreement and the approval of the transactions contemplated hereby and the other proposals presented to the holders of Parent Common Shares for approval or adoption at the Parent Stockholder Meeting.
(d) Parent and Purchaser shall comply with all applicable provisions of and rules under the Securities Act and Exchange Act, the applicable Nasdaq rules and all applicable Laws of the State of Delaware, in the preparation, filing and distribution of the Registration Statement and the Proxy Statement/Prospectus (or any amendment or supplement thereto), as applicable, the solicitation of proxies under the Proxy Statement/Prospectus and the calling and holding of the Parent Stockholder Meeting. Without limiting the foregoing, Parent and Purchaser shall ensure that each of the Registration Statement, as of the effective date of the Registration Statement, and the Proxy Statement/Prospectus, as of the date on which it is first distributed to the holders of Parent Common Shares, and as of the date of the Parent Stockholder Meeting, does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary in order to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which they were made, not misleading (provided, that Parent and Purchaser shall not be responsible for the accuracy or completeness of any information relating to the Company (or any other information) that is furnished by the Company expressly for inclusion in the Proxy Statement/Prospectus). The Company represents and warrants that the information relating to the Company supplied by the Company for inclusion in the Registration Statement or the Proxy Statement/Prospectus, as applicable, will not as of the effective date of the Registration Statement and the date on which the Proxy Statement/Prospectus (or any amendment or supplement thereto) is first distributed to the holders of Parent Common Shares or at the time of the Parent Stockholder Meeting does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary in order to make the statements made in light of the circumstances under which they were made, not misleading. If at any time prior to the Effective Time, a change in the information relating to Parent, Purchaser or the Company or any other information furnished by Parent, Purchaser, Merger Sub or the Company for inclusion in the Registration Statement or the Proxy Statement/Prospectus, which would make the preceding two sentences incorrect, should be discovered by Parent, Purchaser, Merger Sub or the Company, as applicable, such party shall promptly notify the other parties of such change or discovery and an appropriate amendment or supplement describing such information shall be promptly filed with the SEC and, to the extent required by Law, disseminated to the holders of Parent Common Shares. In connection therewith, Parent, Purchaser, Merger Sub and the Company shall instruct their respective employees, counsel, financial advisors, auditors and other authorized representatives to reasonably cooperate with Purchaser as relevant if required to achieve the foregoing.
(e) In accordance with the Parent Charter and applicable securities laws, rules and regulations, including the DGCL and rules and regulations of Nasdaq, in the Proxy Statement/Prospectus, Parent shall seek from the holders of Parent Common Shares the approval the following proposals: (i) the Parent Stockholder Approval; (ii) approval of Purchaser’s organizational documents (as may be subsequently amended by mutual written agreement of Parent and the Company at any time before the effectiveness of the Registration Statement) in connection with the Reincorporation Merger, including any separate or unbundled proposals as are required to implement the foregoing; (iii) approval of the issuance of securities of Purchaser in connection with the Reincorporation Merger and Acquisition Merger under applicable exchange listing rules; (iv) approval of the Purchaser Equity Incentive Plan (the proposals set forth in the foregoing clauses (i) through (iv), the “Required Parent Proposals”); (v) approval of Purchaser’s post-closing Board of Directors; (vi) all required approvals under Nasdaq rules of the issuance of Purchaser Common Shares in connection with any financing in connection with the transactions contemplated hereunder; (vii) approval to obtain any and all other approvals necessary or advisable to effect the consummation of the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger as reasonably determined by the Company and Parent; and (viii) approval to adjourn the Parent Stockholder Meeting, if necessary, to permit further solicitation of proxies because there are not sufficient votes to approve and adopt any of the foregoing (the proposals set forth in the forgoing clauses (i) through (viii) collectively, the “Parent Proposals”).
(f) Purchaser, with the assistance of Parent and the Company, shall use its reasonable best efforts to cause the Registration Statement to “clear” comments from the SEC and the Registration Statement to become effective as promptly as reasonably practicable thereafter. As soon as practicable after the Registration Statement is “cleared” by the SEC, Parent shall cause the Proxy Statement/Prospectus, together will all other Offer Documents, to be disseminated to holders of Parent Common Shares. The Offer Documents shall provide the public stockholders of Parent with the opportunity to redeem all or a portion of their shares of Parent Class A Common Stock, at a price per share equal to the pro rata share of the funds in the Trust Account, all in accordance with and as required by the Parent Charter, the Trust Agreement, applicable Law and any applicable rules and regulations of the SEC. In accordance with the Parent Charter, the proceeds held in the Trust Account will first be used for the redemption of the Parent Class A Common Stock held by Parent’s public stockholders who have elected to redeem such shares.
(g) Parent shall call and hold the Parent Stockholder Meeting as promptly as practicable after the effective date of the Registration Statement for the purpose of seeking the approval of each of the Parent Proposals, and Parent shall consult in good faith with the Company with respect to the date on which such meeting is to be held. Parent shall use reasonable best efforts to solicit from its stockholders proxies in favor of the approval and adoption of the Parent Proposals. Parent’s Board of Directors shall recommend that the holders of Parent Common Shares vote in favor of the Parent Proposals.
(h) The Company acknowledges that a substantial portion of the Proxy Statement/ Prospectus shall include disclosure regarding the Company and its management, operations and financial condition. Accordingly, the Company agrees to as promptly as reasonably practicable provide Purchaser with such information as shall be reasonably requested by Purchaser for inclusion in or attachment to the Proxy Statement/ Prospectus, and that such information is accurate in all material respects and complies as to form in all material respects with the requirements of the Exchange Act and the rules and regulations promulgated thereunder. The Company understands that such information shall be included in the Proxy Statement/ Prospectus or responses to comments from the SEC or its staff in connection therewith. In connection with the preparation and filing of the Registration Statement and any amendments thereto, the Company shall reasonably cooperate with Purchaser and shall make their directors, officers and appropriate senior employees reasonably available to Purchaser and its counsel in connection with the drafting of such filings and mailings and responding in a timely manner to comments from the SEC.
(i) Except as otherwise required by applicable Law, Parent covenants that none of Parent, Parent’s Board of Directors nor any committee thereof shall withdraw or modify, or propose publicly or by formal action of Parent, Parent’s Board of Directors or any committee thereof to withdraw or modify, in any manner adverse to the Company, the Parent Board Recommendation.
(j) Notwithstanding anything else to the contrary in this Agreement or any Ancillary Agreements, Parent and Purchaser may make any public filing with respect to the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger to the extent required by applicable Law, provided that prior to making any filing that includes information regarding the Company, Parent and Purchaser shall provide a copy of the filing to the Company and permit the Company to make revisions to protect confidential or proprietary information of the Company.
6.6 Trust Account. Upon satisfaction or waiver of the conditions set forth in ARTICLE IX and provision of notice thereof to the Trustee (which notice Parent shall provide to the Trustee in accordance with the terms of the Trust Agreement), (i) in accordance with and pursuant to the Trust Agreement, Parent (a) shall cause any documents, opinions and notices required to be delivered to the Trustee pursuant to the Trust Agreement to be so delivered and (b) shall use its commercially reasonable efforts to cause the Trustee to, and the Trustee shall thereupon be obligated to (1) immediately prior to the Reincorporation Merger, pay as and when due all amounts payable to Parent Class A Common Stock held by the public stockholders (the “Parent Redemption Amount”), (2) at the Closing, pay any unpaid transaction expenses, and (3) at the Closing, following the payment of unpaid transaction expenses in subparagraph (2), pay all remaining amounts then available in the Trust Account to Purchaser or the Surviving Corporation for immediate use, subject to this Agreement and the Trust Agreement, and (ii) thereafter, the Trust Account shall terminate, except as otherwise provided therein.
6.7 Obligations of Purchaser and Merger Sub. Parent shall take all action necessary to cause Purchaser and Merger Sub to perform their respective obligations under this Agreement and to consummate the transactions contemplated under this Agreement, upon the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in this Agreement.
6.8 Cooperation with Regulatory Approvals. Parent and the Company each will, and Parent and the Company will cause each of their respective Affiliates to, use reasonable best efforts to comply as promptly as practicable with all legal requirements which may be imposed on it under any applicable Antitrust Laws in connection with the transactions contemplated by this Agreement. Each party will promptly furnish to the other such information and assistance as the other may reasonably request in connection with its preparation of any filing or submission that is necessary under the HSR Act and any other applicable Antitrust Laws and will use reasonable best efforts to cause the expiration or termination of the applicable waiting periods as soon as practicable. Parent and the Company agree not to, and Parent and the Company agree to cause each of its Affiliates not to, extend any waiting period under the HSR Act and other applicable Antitrust Laws or enter into any agreement with any Authority to delay, or otherwise not to consummate as soon as practicable, any of the Transactions contemplated by this Agreement except with the prior written consent of the non-requesting party, which consent may be withheld in the sole discretion of the non-requesting party. Neither Parent nor the Company shall, and each shall use its reasonable best efforts to cause their respective Affiliates not to, directly or indirectly take any action, including, directly or indirectly, acquiring or investing in any Person or acquiring, leasing or licensing any assets, or agreement to do any of the foregoing, if doing so would reasonably be expected to impose any material delay in the obtaining of, or significantly increase the risk of not obtaining, any required approval under the HSR Act and any applicable Antitrust Laws. Without limiting the foregoing, Parent and the Company shall: (i) promptly inform the other of any communication to or from the U.S. Federal Trade Commission, the U.S. Department of Justice or any other Authority with respect to Antitrust Laws regarding the transactions contemplated by this Agreement; (ii) permit each other to review reasonably in advance any proposed substantive written communication to any such Authority and incorporate reasonable comments thereto; (iii) give the other prompt written notice of the commencement of any Action with respect to such transactions under Antitrust Laws; (iv) not agree to participate in any substantive meeting or discussion with any such Authority in respect of any filing, investigation or inquiry concerning this Agreement or the transactions contemplated by this Agreement with respect to Antitrust Laws unless, to the extent reasonably practicable, it consults with the other party in advance and, to the extent permitted by such Authority, gives the other party the opportunity to attend; (v) keep the other reasonably informed as to the status of any such Action; and (vi) promptly furnish each other with copies of all correspondence, filings (except for filings made under the HSR Act) and written communications (and memoranda setting forth the substance of all substantive oral communications) between such party and, and in the case of Parent, its Subsidiaries (if applicable) and their respective Representatives and advisors, on one hand, and any such Authority, on the other hand, in each case, with respect to this Agreement and the transactions contemplated by this Agreement with respect to Antitrust Laws; provided that materials required to be supplied pursuant to this section may be redacted (1) to remove references concerning the valuation of the Company, (2) as necessary to comply with contractual arrangements, (3) as necessary to comply with applicable Law, and (4) as necessary to address reasonable privilege or confidentiality concerns; provided further, that a party may reasonably designate any competitively sensitive material provided to another party under this Section 6.8 as “Outside Counsel Only”.
6.9 Formation; Joinder. As promptly as practicable after the date of this Agreement, and in any event within ten (10) Business Day following the date hereof, Parent shall take all action necessary to form (i) Purchaser as a Cayman Islands exempted and wholly owned subsidiary of Parent, to be formed for the sole purpose of the Reincorporation Merger and (ii) Merger Sub as a Delaware corporation and wholly owned subsidiary of Purchaser, to be formed for the sole purpose of the Acquisition Merger. Following the formation of Purchaser and Merger Sub, Parent shall cause Purchaser and Merger Sub to enter into the Joinder.
ARTICLE VII
COVENANTS OF THE COMPANY
7.1 Reporting; Compliance with Laws; No Insider Trading. During the Interim Period,
(a) The Company shall duly observe and conform in all material respects to all applicable Law, including the Exchange Act, and Orders.
(b) The Company shall not, and it shall direct its Representatives to not, directly or indirectly, (i) purchase or sell (including entering into any hedge transaction with respect to) any Parent Common Shares, Parent Units or Parent Warrants, except in compliance with all applicable securities Laws, including Regulation M under the Exchange Act; (ii) use or disclose or permit any other Person to use or disclose any information that Parent or its Affiliates has made or makes available to the Company and its Representatives in violation of the Exchange Act, the Securities Act or any other applicable securities Law; or (iii) disclose to any third party any non-public information about the Company, Parent, the Reincorporation Merger, the Acquisition Merger or the other transactions contemplated hereby or by any Ancillary Agreement.
7.2 Company’s Stockholder Approval.
(a) As promptly as reasonably practicable after the effective date of the Registration Statement, and in any event within five (5) Business Days following such date (the “Company Stockholder Written Consent Deadline”), the Company shall obtain and deliver to Parent a true and correct copy of a written consent (in form and substance reasonably satisfactory to Parent) evidencing the Company Stockholder Approval that is duly executed by the Company Stockholders that hold at least the requisite number and class of issued and outstanding shares of Company Capital Stock required to obtain the Company Stockholder Approval (the “Company Stockholder Written Consent”).
(b) The Company’s Board of Directors shall recommend that the Company Stockholders vote in favor of this Agreement, the Ancillary Agreements to which the Company is or will be a party, the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby and other related matters, and neither the Company’s Board of Directors, nor any committee thereof, shall withhold, withdraw, amend, modify, change or propose or resolve to withhold, withdraw, amend, modify or change, in each case in a manner adverse to Parent, the recommendation of the Company’s Board of Directors.
7.3 Company Financial Information. Following the date of this Agreement, the Company shall provide Parent the audited consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of June 30, 2023, and the related statements of operations, changes in stockholders’ equity and cash flows, for the period from January 4, 2023 (inception) through June 30, 2023, including the notes thereto (collectively, the “Company Financial
Statements”). Subsequent to the delivery of the Company Financial Statements, the Company’s consolidated interim financial information for each quarterly period thereafter shall be delivered to Parent no later than forty (40) calendar days following the end of each quarterly period. All of the financial statements to be delivered pursuant to this Section 7.3 shall be prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP, and shall fairly present, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of the dates thereof and the results of operations of the Company for the periods reflected therein, in accordance with U.S. GAAP, except as otherwise indicated in such statements and subject to year-end audit adjustments. The Company will promptly provide with additional Company financial information reasonably requested by Purchaser for inclusion in the Registration Statement, the Proxy Statement/Prospectus and any other filings to be made by Purchaser with the SEC.
ARTICLE VIII
COVENANTS OF ALL PARTIES HERETO
8.1 Reasonable Best Efforts; Further Assurances.
(a) Subject to the terms and conditions of this Agreement, each of Parent and the Company shall use its reasonable best efforts to take, or cause to be taken, all actions and to do, or cause to be done, all things necessary or desirable under applicable Laws, or as reasonably requested by the other parties, to consummate and implement expeditiously each of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement, including using its reasonable best efforts to (i) obtain all necessary actions, nonactions, waivers, consents, approvals and other authorizations from all applicable Authorities prior to the Effective Time; (ii) avoid an Action by any Authority, and (iii) execute and deliver any additional instruments reasonably necessary to consummate the transactions contemplated by this Agreement. The parties shall execute and deliver such other documents, certificates, agreements and other writings and take such other actions as may be reasonably necessary in order to consummate or implement expeditiously each of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement.
(b) Subject to applicable Law, each of the Company and Parent agrees to (i) reasonably cooperate and consult with the other regarding obtaining and making all notifications and filings with Authorities, (ii) furnish to the other such information and assistance as the other may reasonably request in connection with its preparation of any notifications or filings, (iii) keep the other reasonably apprised of the status of matters relating to the completion of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement, including promptly furnishing the other with copies of notices and other communications received by such party from, or given by such party to, any third party or any Authority with respect to such transactions, (iv) permit the other party to review and incorporate the other party’s reasonable comments in any communication to be given by it to any Authority with respect to any filings required to be made with, or action or nonactions, waivers, expirations or terminations of waiting periods, clearances, consents or orders required to be obtained from, such Authority in connection with execution and delivery of this Agreement and the consummation of the transactions contemplated by this Agreement and (v) to the extent reasonably practicable, consult with the other in advance of and not participate in any meeting or discussion relating to the transactions contemplated by this Agreement, either in person or by telephone, with any Authority in connection with the proposed transactions unless it gives the other party the opportunity to attend and observe; provided, however, that, in each of clauses (iii) and (iv) above, that materials may be redacted (A) to remove references concerning the valuation of such party and its Affiliates, (B) as necessary to comply with contractual arrangements or applicable Laws, and (C) as necessary to address reasonable attorney-client or other privilege or confidentiality concerns.
(c) During the Interim Period, Parent, on the one hand, and the Company, on the other hand, shall each notify the other in writing promptly after learning of any stockholder demands or other stockholder Action (including derivative claims) relating to this Agreement, any of the Ancillary Agreements or any matters relating thereto commenced against Parent, any of the Parent Parties or any of its or their respective Representatives in their capacity as a representative of a Parent Party or against the Company (collectively, the “Transaction Litigation”). Parent shall control the negotiation, defense and settlement of any such Transaction Litigation brought against Parent, Merger Sub or members of the boards of directors of Parent or Merger Sub and the Company shall control the negotiation, defense and settlement of any such Transaction Litigation brought against the Company or the members of its board of directors; provided, however, that in no event shall the Company or Parent settle, compromise or come to any arrangement with respect to any Transaction Litigation, or agree to do the same, without the prior written consent of the other party (not to be unreasonably withheld, conditioned or delayed; provided, that it shall be deemed to be reasonable for Parent (if the Company is controlling the Transaction Litigation) or the Company (if Parent is controlling the Transaction Litigation) to withhold, condition or delay its consent if any such settlement or compromise (A) does not provide for a legally binding, full, unconditional and irrevocable release of each Parent Party (if the Company is controlling the Transaction Litigation) or the Company (if the Parent is controlling the Transaction Litigation) and its respective Representative that is the subject of such Transaction Litigation, (B) provides for any non-monetary, injunctive, equitable or similar relief against any Parent Party (if the Company is controlling the Transaction Litigation) or the Company (if Parent is controlling the Transaction Litigation) or (C) contains an admission of wrongdoing or Liability by a Parent Party (if the Company is controlling the Transaction Litigation) or the Company (if Parent is controlling the Transaction Litigation) and its respective Representative that is the subject of such Transaction Litigation. Parent and the Company shall each (i) keep the other reasonably informed regarding any Transaction Litigation, (ii) give the other the opportunity to, at its own cost and expense, participate in the defense, settlement and compromise of any such Transaction Litigation and reasonably cooperate with the other in connection with the defense, settlement and compromise of any such Transaction Litigation, (iii) consider in good faith the other’s advice with respect to any such Transaction Litigation and (iv) reasonably cooperate with each other.
8.2 Compliance with SPAC Agreements. Parent shall (a) comply with the Trust Agreement, the Parent Warrant Agreement, the Parent Rights Agreement and the Underwriting Agreement, dated as of September 22, 2022, by and between Parent and EF Hutton, division of Benchmark Investments, LLC, as representative of the underwriters thereto, and (b) enforce the terms of the letter agreement, dated as of September 22, 2022, by and among Parent, the Sponsor and each of the officers and directors of Parent named therein.
8.3 Confidentiality. Except as necessary to complete the Registration Statement, the other Offer Documents or any Other Filings, the Company, on the one hand, and Parent and Merger Sub, on the other hand, shall comply with the Confidentiality Agreement.
8.4 Directors’ and Officers’ Indemnification and Liability Insurance.
(a) All rights to indemnification for acts or omissions occurring through the Closing Date now existing in favor of the current directors and officers of the Company or the Parent Parties and Persons who served as a director, officer, member, trustee or fiduciary of another corporation, partnership, joint venture, trust, pension or other employee benefit plan or enterprise at the request of the Company or the Parent Parties, as provided in their respective organizational documents or in any indemnification agreements shall survive the Acquisition Merger and shall continue in full force and effect in accordance with their terms. For a period of six (6) years after the Effective Time, Parent shall cause the organizational documents of Parent, its Subsidiaries, and the Surviving Corporation to contain provisions no less favorable with respect to exculpation and indemnification of and advancement of expenses than are set forth as of the date of this Agreement in the organizational documents of, with respect to Parent, Parent, and with respect to the Surviving Corporation, the Company, as applicable, to the extent permitted by applicable Law.
(b) Prior to the Closing, Parent and the Company shall reasonably cooperate in order to obtain directors’ and officers’ liability insurance for Parent and the Company that shall be effective as of Closing and will cover (i) those Persons who were directors and officers of the Company prior to the Closing and (ii) those Persons who will be the directors and officers of Parent and its Subsidiaries (including the Surviving Corporation after the Effective Time) at and after the Closing on terms not less favorable than the better of (x) the terms of the current directors’ and officers’ liability insurance in place for the Company’s directors and officers and (y) the terms of a typical directors’ and officers’ liability insurance policy for a company whose equity is listed on Nasdaq or an Alternate Exchange, as applicable, which policy has a scope and amount of coverage that is reasonably appropriate for a company of similar characteristics (including the line of business and revenues) as the Company.
(c) The provisions of this Section 8.4 are intended to be for the benefit of, and shall be enforceable by, each Person who will have been a director or officer of the Company or Parent for all periods ending on or before the Closing Date and may not be changed with respect to any officer or director without his or her written consent.
(d) Prior to the Effective Time, the Company shall obtain and fully pay the premium for a six year prepaid “tail” policy for the extension of the directors’ and officers’ liability coverage of the Company’s existing directors’ and officers’ liability insurance policies, for claims reporting or discovery period of six years from and after the Effective Time, on terms and conditions providing coverage retentions, limits and other material terms (other than premiums payable) substantially equivalent to the current policies of directors’ and officers’ liability insurance maintained by the Company with respect to matters arising on or before the Effective Time, covering without limitation the transactions contemplated hereby.
8.5 Parent Public Filings; Nasdaq. During the Interim Period, Parent will keep current and timely file all of its public filings with the SEC and otherwise comply in all material respects with applicable securities Laws, and shall use its reasonable best efforts prior to the Closing to maintain the listing of the Parent Class A Common Stock, the Parent Units, the Parent Warrants and the Parent Rights on Nasdaq. During the Interim Period, Parent shall use its reasonable best efforts to cause (a) Parent’s initial listing application with Nasdaq or an Alternate Exchange, to be agreed mutually by Parent and the Company, in connection with the transactions contemplated by this Agreement to have been approved; (b) all applicable initial and continuing listing requirements of Nasdaq or an Alternate Exchange, as applicable, to be satisfied; and (c) the Parent Common Shares, including the shares comprising the Aggregate Merger Consideration, and the Parent Warrants to be approved for listing on Nasdaq or an Alternate Exchange, as applicable, subject to official notice of issuance, in each case, as promptly as reasonably practicable after the date of this Agreement and in any event prior to the Effective Time.
8.6 Certain Tax Matters.
(a) Each of Parent, Merger Sub and the Company shall use its reasonable best efforts to cause the Reincorporation Merger to qualify for the Reincorporation Intended Tax Treatment and the Merger to qualify for the Merger Intended Tax Treatment, and none of Parent, Merger Sub or the Company has taken or will take any action (or fail to take any action), if such action (or failure to act), whether before or after the Effective Time, would reasonably be expected to prevent or impede the Reincorporation Merger from qualifying for the Reincorporation Intended Tax Treatment, to prevent Purchaser from being treated as a domestic corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 7874(b) of the Code following the Reincorporation Merger, or the Acquisition Merger from qualifying for the Acquisition Intended Tax Treatment.
(b) Each of Parent, the Company, and their respective Affiliates shall file all Tax Returns consistent with the Reincorporation Intended Tax Treatment and Acquisition Tax Treatment (including attaching the statement described in Treasury Regulations Section 1.368-(a) on or with the its Tax Return for the taxable year of the Merger), and shall take no position inconsistent with the Reincorporation Intended Tax Treatment, the treatment of Purchaser as a domestic corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 7874(b) of the Code following the Reincorporation Merger, or the Acquisition Intended Tax Treatment (whether in audits, Tax Returns or otherwise), in each case, unless otherwise required by a Taxing Authority as a result of a “determination” within the meaning of Section 1313(a) of the Code.
(c) Parent and the Company shall promptly notify the other party in writing if, before the Closing Date, either such party knows or has reason to believe that the Reincorporation Merger may not qualify for the Reincorporation Intended Tax Treatment or that the Acquisition Merger may not qualify for the Acquisition Intended Tax Treatment (and whether the terms of this Agreement could be reasonably amended in order to facilitate such qualification, which amendments shall be made if the Company reasonably determines on the advice of its counsel that such amendments would be reasonably expected to result in the Reincorporation Intended Tax Treatment or the Acquisition Intended Tax Treatment and would not be commercially impracticable).
(d) Any and all Transfer Taxes shall be paid 50% by Parent and 50% by the Company. The Party required by Law to do so shall file all necessary Tax Returns and other documentation with respect to all such Transfer Taxes, and if required by applicable Law, the Parties shall, and shall cause their respective Affiliates to, join in the execution of any such Tax Returns and other document. Any expenses incurred in connection with the filing of such Tax Returns or other documentation shall be borne equally by Parent and the Company. Notwithstanding any other provision of this Agreement, the Parties shall (and shall cause their respective Affiliates to) cooperate in good faith to minimize, to the extent permissible under applicable Law, the amount of any such Transfer Taxes.
(e) In the event the SEC requests or requires a tax opinion regarding the (i) Reincorporation Intended Tax Treatment, Parent will use its commercially reasonable efforts to cause Nelson Mullins Riley & Scarborough LLP to deliver such tax opinion to Parent, or (ii) the Acquisition Intended Tax Treatment, the Company shall use its commercially reasonable efforts to cause Loeb & Loeb LLP to deliver such tax opinion to the Company. Each party shall use reasonable best efforts to execute and deliver customary tax representation letters to the applicable tax advisor in form and substance reasonably satisfactory to such advisor. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in this Agreement, Loeb & Loeb LLP shall not be required to provide any opinion to any party regarding the Reincorporation Intended Tax Treatment and Nelson Mullins Riley & Scarborough LLP shall not be required to provide any opinion to any party regarding the Acquisition Intended Tax Treatment.
8.7 Purchaser Equity Incentive Plan. Prior to the effective date of the Registration Statement, Purchaser shall adopt a new equity incentive plan in substantially the form attached hereto as Exhibit C, with such changes or modifications thereto as the Company and Parent may mutually agree (such agreement not to be unreasonably withheld, conditioned or delayed) (the “Purchaser Equity Incentive Plan”). The Purchaser Equity Incentive Plan shall have such number of shares available for issuance equal to one percent (1%) of the Purchaser Ordinary Shares to be issued and outstanding immediately after the Closing and shall include an “evergreen” provision that is mutually agreeable to the Company and Parent that will provide for an automatic increase on the first day of each fiscal year in the number of shares available for issuance under the Purchaser Equity Incentive Plan as mutually determined by the Company and Parent.
8.8 Extension of Time to Consummate a Business Combination. To the extent necessary or advisable to effect the consummation of the Acquisition Merger, Parent shall take all actions necessary to extend the period of time Parent is afforded under the Parent Charter to consummate an initial business combination to the Outside Closing Date (or such other date as the parties may agree in writing).
8.9 Section 16 Matters. Prior to the Effective Time, each of the Company and Parent shall take all such steps as may be required (to the extent permitted under applicable Law) to cause any dispositions of shares of the Company Common Stock or acquisitions of Purchaser Ordinary Shares (including, in each case, securities deliverable upon exercise, vesting or settlement of any derivative securities) resulting from the transactions contemplated hereby by each individual who may become subject to the subject to the reporting requirements of Section 16 of the Exchange Act to the extent necessary for such issuance to be an exempt acquisition pursuant to Rule 16b-3 promulgated under the Exchange Act.
8.10 Lock-Up Agreement. Prior to the Closing, (i) the Company shall cause certain Company Stockholders and (ii) Parent shall cause holders of Parent Common Shares to enter into a Lock-Up Agreement with Purchaser to be effective as of the Closing, pursuant to which the shares comprising the Aggregate Merger Consideration and the Purchaser Ordinary Shares received by such Persons at the Closing in connection with the Reincorporation Merger and Acquisition Merger shall be subject to a lock-up in accordance with the terms and conditions more fully set forth in the Lock-Up Agreement.
ARTICLE IX
CONDITIONS TO CLOSING
9.1 Condition to the Obligations of the Parties. The obligations of all of the parties to consummate the Closing are subject to the satisfaction or written waiver (where permissible) by Parent, Purchaser and the Company of all the following conditions:
(a) No provisions of any applicable Law and no Order shall be in effect restraining, prohibiting or imposing any condition on the consummation of the transactions contemplated hereby, including the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger.
(b) (i) All applicable waiting periods, if any, under the HSR Act with respect to the Acquisition Merger shall have expired or been terminated, and (ii) each consent, approval or authorization of any Authority required of Parent, its Subsidiaries, or the Company to consummate the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger set forth on Schedule 9.1(b) shall have been obtained and shall be in full force and effect.
(c) No Authority shall have issued an Order or enacted a Law, having the effect of prohibiting the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger or making the Reincorporation Merger and the Acquisition Merger illegal, which Order or Law is final and non-appealable.
(d) Parent shall (i) after giving effect to any redemption of the Parent Class A Common Stock in connection with the transactions contemplated by this Agreement, have net tangible assets of at least $5,000,001 or (ii) be otherwise exempt from the provisions of Rule 419 promulgated under the Securities Act.
(e) The Company Stockholder Approval shall have been obtained.
(f) Each of the Required Parent Proposals shall have been approved at the Parent Stockholder Meeting.
(g) Purchaser’s initial listing application with Nasdaq or an Alternate Exchange, as applicable, in connection with the transactions contemplated by this Agreement shall have been conditionally approved and, immediately following the Effective Time, Purchaser shall satisfy any applicable initial and continuing listing requirements of Nasdaq or an Alternate Exchange, as applicable, and Purchaser shall not have received any notice of non-compliance therewith, and the shares comprising the Aggregate Merger Consideration shall have been approved for listing on Nasdaq or an Alternate Exchange, as applicable.
(h) The Registration Statement shall have become effective in accordance with the provisions of the Securities Act, no stop order suspending the effectiveness of the Registration Statement shall have been issued by the SEC that remains in effect and no proceeding seeking such a stop order shall have been initiated by the SEC and not withdrawn.
(i) The Reincorporation Merger shall have been consummated and the applicable certificates filed in the appropriate jurisdictions.
(j) The acquisition of Play Company and Solaire Partners shall have been consummated.
(k) The Joinder shall have been executed by K Wave Media Ltd. and GLST Merger Sub Inc.
9.2 Conditions to Obligations of the Parent Parties. The obligation of the Parent Parties to consummate the Closing is subject to the satisfaction, or the waiver in Parent’s sole and absolute discretion, of all the following further conditions:
(a) The Company shall have duly performed or complied with, in all material respects, all of its obligations hereunder required to be performed or complied with (without giving effect to any materiality or similar qualifiers contained therein) by the Company at or prior to the Closing Date.
(b) The representations and warranties of the Company contained in this Agreement (disregarding all qualifications contained therein relating to materiality or Material Adverse Effect), other than the Company Fundamental Representations, shall be true and correct in all respects as of the date of this Agreement and as of the Closing Date, as if made at and as of such date (except to the extent that any such representation and warranty is made as of an earlier date, in which case such representation and warranty shall be true and correct at and as of such earlier date) except, in each case, for any failure of such representations and warranties (disregarding all qualifications and exceptions contained therein relating to materiality or Material Adverse Effect) to be so true and correct that would not in the aggregate have or reasonably be expected to have a Material Adverse Effect in respect of the Company.
(c) The Company Fundamental Representations (disregarding all qualifications and exceptions contained therein relating to materiality or Material Adverse Effect) shall be true and correct in all respects at and as of the date of this Agreement and as of the Closing Date, as if made as of such date (except to the extent that any such representation and warranty is expressly made as of a specific date, in which case such representation and warranty shall be true and correct at and as of such specific date), other than de minimis inaccuracies.
(d) Since the date of this Agreement, there shall not have occurred a Material Adverse Effect in respect of the Company, Play Company and Solaire Partners, taken as a whole, that is continuing.
(e) Parent shall have received a certificate, dated as of the Closing Date, signed by the Chief Executive Officer of the Company certifying the accuracy of the provisions of the foregoing clauses (a), (b), (c) and (d) of this Section 9.2.
(f) Parent shall have received a certificate, dated as of the Closing Date, signed by the Secretary of the Company attaching true, correct and complete copies of (i) the Company Charter, certified as of a recent date by the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware; (ii) the bylaws of the Company; (iii) copies of resolutions duly adopted by the Board of Directors of the Company authorizing this Agreement, the Ancillary Agreements to which the Company is a party and the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby and the Company Stockholder Written Consent; and (iv) a certificate of good standing of the Company, certified as of a recent date by the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware.
(g) Each of the Company and the Company Securityholders, as applicable, shall have executed and delivered to Parent a copy of each Ancillary Agreement to which the Company or such Company Securityholder, as applicable, is a party.
(h) The Company shall have delivered to Parent a duly executed certificate conforming to the requirements of Treasury Regulation Sections 1.897-2(h)(1)(i) and 1.1445-2(c)(3)(i), and a notice to be delivered to the United States Internal Revenue Service as required under Treasury Regulation Section 1.897-2(h)(2) together with written authorization for Parent to deliver such notice to the IRS on behalf of the Company following the Closing, each dated no more than thirty (30) days prior to the Closing Date and in form and substance as reasonably agreed upon by Parent and the Company.
(i) The Company shall have obtained each Company Consent set forth on Schedule 4.8.
9.3 Conditions to Obligations of the Company. The obligations of the Company to consummate the Closing is subject to the satisfaction, or the waiver in the Company’s sole and absolute discretion, of all of the following further conditions:
(a) The Parent Parties shall each have duly performed or complied with, in all material respects, all of its respective obligations hereunder required to be performed or complied with (without giving effect to any materiality or similar qualifiers contained therein) by the Parent Parties, as applicable, at or prior to the Closing Date.
(b) The representations and warranties of the Parent Parties contained in this Agreement (disregarding all qualifications contained therein relating to materiality or Material Adverse Effect), other than the Parent Fundamental Representations, shall be true and correct as of the date of this Agreement and as of the Closing Date, as if made at and as of such date (except to the extent that any such representation and warranty is made as of an earlier date, in which case such representation and warranty shall be true and correct at and as of such earlier date), except, in each case, for any failure of such representations and warranties (disregarding all qualifications and exceptions contained therein relating to materiality or Material Adverse Effect) to be so true and correct that would not in the aggregate have or reasonably be expected to have a Material Adverse Effect in respect of the Parent Parties.
(c) The Parent Fundamental Representations shall be true and correct in all respects at and as of the date of this Agreement and as of the Closing Date, as if made as of such date (except to the extent that any such representation and warranty is expressly made as of a specific date, in which case such representation and warranty shall be true and correct at and as of such specific date), other than de minimis inaccuracies.
(d) Since the date of this Agreement, there shall not have occurred a Material Adverse Effect in respect of the Parent Parties that is continuing.
(e) The Company shall have received a certificate, dated as of the Closing Date, signed by an authorized officer of the Parent Parties certifying the accuracy of the provisions of the foregoing clauses (a), (b), (c) and (d) of this Section 9.3.
(f) The Company shall have received a certificate, dated as of the Closing Date, signed by an authorized officer of Parent and Purchaser attaching true, correct and complete copies of resolutions duly adopted by the Board of Directors of Parent and Purchaser authorizing this Agreement, the Ancillary Agreements to which Parent or Purchaser, as applicable, is a party and the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby and the Parent Proposals.
(g) The Company shall have received a certificate, dated as of the Closing Date, signed by an authorized officer of Merger Sub attaching true, correct and complete copies of (i) copies of resolutions duly adopted by the Board of Directors and sole stockholder of Merger Sub authorizing this Agreement, the Ancillary Agreements to which Merger Sub is a party and the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby and (ii) a certificate of good standing of Merger Sub, certified as of a recent date by the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware.
(h) Each of Parent, Purchaser, Sponsor or other stockholder of Parent, as applicable, shall have executed and delivered to the Company a copy of each Ancillary Agreement to which Parent, Purchaser, Sponsor or such other stockholder of Parent, as applicable, is a party.
(i) The size and composition of Purchaser’s post-Closing Board of Directors shall have been appointed as set forth in Section 3.6.
ARTICLE X
TERMINATION
10.1 Termination Without Default.
(a) In the event that (i) the Closing of the transactions contemplated hereunder has not occurred on or before June 22, 2024 (the “Outside Closing Date”); and (ii) the material breach or violation of any representation, warranty, covenant or obligation under this Agreement by the party (i.e., Parent or Merger Sub, on one hand, or the Company, on the other hand) seeking to terminate this Agreement was not the cause of, or resulted in, the failure of the Closing to occur on or before the Outside Closing Date, then Parent or the Company, as applicable, shall have the right, at its sole option, to terminate this Agreement without liability to the other party. Such right may be exercised by Parent or the Company, as the case may be, giving written notice to the other at any time after the Outside Closing Date.
(b) In the event an Authority shall have issued an Order or enacted a Law, having the effect of prohibiting the Reincorporation Merger or the Acquisition Merger or making the Reincorporation Merger or the Acquisition Merger illegal, which Order or Law is final and non-appealable, Parent or the Company shall have the right, at its sole option, to terminate this Agreement without liability to the other party; provided, however, that the right to terminate this Agreement pursuant to this Section shall not be available to the Company or Parent if the failure by such party or its Affiliates to comply with any provision of this Agreement has been a substantial cause of, or substantially resulted in, such action by such Authority.
(c) This Agreement may be terminated at any time by mutual written consent of the Company and Parent duly authorized by each of their respective boards of directors.
10.2 Termination Upon Default.
(a) Parent may terminate this Agreement by giving written notice to the Company, without prejudice to any rights or obligations Parent or Merger Sub may have: (i) at any time prior to the Closing if the Company shall have breached any representation, warranty, agreement or covenant contained herein to be performed on or prior to the Closing, which has rendered or would reasonably be expected to render the satisfaction of any of the conditions set forth in Section 9.2(a) through 9.2(c) impossible (a “Terminating Company Breach”); except that, if such Terminating Company Breach is curable by the Company through the exercise of its reasonable best efforts, then, for a period of up to thirty (30) days after receipt by the Company of notice from Parent of such breach, but only as long as the Company continues to use its reasonable best efforts to cure such Terminating Company Breach (the “Company Cure Period”), such termination shall not be effective, and such termination shall become effective only if the Terminating Company Breach is not cured within the Company Cure Period; or (ii) at any time after the Company Stockholder Written Consent Deadline if the Company has not delivered the Company Stockholder Approval to Parent (provided, that upon the Company delivering the Company Stockholder Approval to Parent, Parent shall no longer have any right to terminate this Agreement under this clause (ii)).
(b) The Company may terminate this Agreement by giving written notice to Parent, without prejudice to any rights or obligations the Company may have, if at any time prior to the Closing, Parent shall have breached any of its covenants, agreements, representations, and warranties contained herein to be performed on or prior to the Closing, which has rendered or reasonably would render the satisfaction of any of the conditions set forth in Section 9.3(a) or 9.3(b) impossible (a “Terminating Parent Breach”); except that, if such Terminating Parent Breach is curable by Parent through the exercise of its reasonable best efforts, then, for a period of up to thirty (30) days after receipt by Parent of notice from the Company of such breach, but only as long as Parent continues to use its reasonable best efforts to cure such Terminating Parent Breach (the “Parent Cure Period”), such termination shall not be effective, and such termination shall become effective only if the Terminating Parent Breach is not cured within the Parent Cure Period.
10.3 Effect of Termination. If this Agreement is terminated pursuant to this ARTICLE X, this Agreement shall become void and of no further force or effect without liability of any party (or any stockholder, director, officer, employee, Affiliate, agent, consultant or representative of such party) to the other parties hereto; provided that, if such termination shall result from the willful breach by a party of its covenants and agreements hereunder or common law fraud or willful breach in connection with the transactions contemplated by this Agreement, such party shall not be relieved of liability to the other parties for any such willful breach or common law fraud. The provisions of Section 8.3, this Section 10.3 and ARTICLE XI, and the Confidentiality Agreement, shall survive any termination hereof pursuant to this ARTICLE X.
ARTICLE XI
MISCELLANEOUS
11.1 Notices. Any notice hereunder shall be sent in writing, addressed as specified below, and shall be deemed given: (a) if by hand, electronic mail, or nationally recognized overnight courier service, by 5:00 PM on a Business Day, addressee’s day and time, on the date of delivery, and if delivered after 5:00 PM, addressee’s day and time, on the first Business Day after such delivery; (b) if by email, on the date of transmission with affirmative confirmation of receipt; or (c) three (3) Business Days after mailing by prepaid certified or registered mail, return receipt requested. Notices shall be addressed to the respective parties as follows (excluding telephone numbers, which are for convenience only), or to such other address as a party shall specify to the others in accordance with these notice provisions:
if to the Company (or, following the Closing, the Surviving Corporation or Parent), to:
K Enter Holdings Inc.
16192 Coaster Highway
Lewes, Delaware 19958
Attention: Ted Kim, Director
E-mail: ted@globalfundpe.com
with a copy (which shall not constitute notice) to:
Loeb & Loeb LLP
345 Park Avenue
New York, NY 10154
Attention: Mitchell S. Nussbaum
E-mail: mnussbaum@loeb.com
if to Parent or Merger Sub (prior to the Closing):
Global Star Acquisition Inc.
1641 International Drive, Unit 208
McLean, VA 22102
Attention: Anthony Ang, Chief Executive Officer
E-mail:
with a copy (which shall not constitute notice) to:
Nelson Mullins Riley & Scarborough LLP
50 N. Laura Street, 41st Floor
Jacksonville, FL 32202
Attention: Daniel B. Nunn, Jr.
E-mail: daniel.nunn@nelsonmullins.com
Nelson Mullins Riley & Scarborough LLP
101 Constitution Avenue NW
Suite 900
Washington, D.C. 20001
Attention: Andy Tucker
E-mail: andy.tucker@nelsonmullins.com
11.2 Amendments; No Waivers; Remedies.
(a) This Agreement cannot be amended, except by a writing signed by each party, and cannot be terminated orally or by course of conduct. No provision hereof can be waived, except by a writing signed by the party against whom such waiver is to be enforced, and any such waiver shall apply only in the particular instance in which such waiver shall have been given.
(b) Neither any failure or delay in exercising any right or remedy hereunder or in requiring satisfaction of any condition herein nor any course of dealing shall constitute a waiver of or prevent any party from enforcing any right or remedy or from requiring satisfaction of any condition. No notice to or demand on a party waives or otherwise affects any obligation of that party or impairs any right of the party giving such notice or making such demand, including any right to take any action without notice or demand not otherwise required by this Agreement. No exercise of any right or remedy with respect to a breach of this Agreement shall preclude exercise of any other right or remedy, as appropriate to make the aggrieved party whole with respect to such breach, or subsequent exercise of any right or remedy with respect to any other breach.
(c) Except as otherwise expressly provided herein, no statement herein of any right or remedy shall impair any other right or remedy stated herein or that otherwise may be available.
(d) Notwithstanding anything to the contrary contained herein, no party shall seek, nor shall any party be liable for, punitive or exemplary damages under any tort, contract, equity or other legal theory with respect to any breach (or alleged breach) of this Agreement or any provision hereof or any matter otherwise relating hereto or arising in connection herewith.
11.3 Arm’s Length Bargaining; No Presumption Against Drafter. This Agreement has been negotiated at arm’s-length by parties of equal bargaining strength, each represented by counsel or having had but declined the opportunity to be represented by counsel and having participated in the drafting of this Agreement. This Agreement creates no fiduciary or other special relationship between the parties, and no such relationship otherwise exists. No presumption in favor of or against any party in the construction or interpretation of this Agreement or any provision hereof shall be made based upon which Person might have drafted this Agreement or such provision.
11.4 Publicity. Except as required by Law or applicable stock exchange rules and except with respect to the Additional Parent SEC Documents, the parties agree that neither they nor their Representatives shall issue any press release or make any other public disclosure prior to the Closing concerning the transactions contemplated hereunder without the prior approval of the other party hereto. If a party is required to make such a disclosure as required by Law or applicable stock exchange rules, the party making such determination will, if practicable in the circumstances, use reasonable commercial efforts to allow the other party reasonable time to comment on such disclosure in advance of its issuance.
11.5 Expenses. The costs and expenses in connection with this Agreement and the transactions contemplated hereby shall be paid by Parent after the Closing. If the Closing does not take place, each party shall be responsible for its own expenses.
11.6 No Assignment or Delegation. No party may assign any right or delegate any obligation hereunder, including by merger, consolidation, operation of law or otherwise, without the written consent of the other party. Any purported assignment or delegation without such consent shall be void.
11.7 Governing Law. This Agreement and all disputes or controversies arising out of or relating to this Agreement or the transactions contemplated hereby, including the applicable statute of limitations, shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the Laws of the State of Delaware, without giving effect to any choice of law or conflict of law provision or rule (whether of the State of Delaware or any other jurisdiction) that would cause the application of the Law of any jurisdiction other than the State of Delaware.
11.8 Counterparts; Electronic Signatures. This Agreement may be executed in counterparts, each of which shall constitute an original, but all of which shall constitute one agreement. This Agreement shall become effective upon delivery to each party of an executed counterpart or the earlier delivery to each party of original, photocopied, or electronically transmitted signature pages that together (but need not individually) bear the signatures of all other parties.
11.9 Entire Agreement. This Agreement, together with the Ancillary Agreements, sets forth the entire agreement of the parties with respect to the subject matter hereof and thereof and supersedes all prior and contemporaneous understandings and agreements related thereto (whether written or oral), all of which are merged herein. No provision of this Agreement or any Ancillary Agreement may be explained or qualified by any agreement, negotiations, understanding, discussion, conduct or course of conduct or by any trade usage. Except as otherwise expressly stated herein or in any Ancillary Agreement, there is no condition precedent to the effectiveness of any provision hereof or thereof. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the Confidentiality Agreement is not superseded by this Agreement or merged herein and shall continue in accordance with its terms, including in the event of any termination of this Agreement.
11.10 Severability. A determination by a court or other legal authority that any provision that is not of the essence of this Agreement is legally invalid shall not affect the validity or enforceability of any other provision hereof. The parties shall cooperate in good faith to substitute (or cause such court or other legal authority to substitute) for any provision so held to be invalid a valid provision, as alike in substance to such invalid provision as is lawful.
11.11 Further Assurances. Each party shall execute and deliver such documents and take such action, as may reasonably be considered within the scope of such party’s obligations hereunder, necessary to effectuate the transactions contemplated by this Agreement.
11.12 Third Party Beneficiaries. Except as provided in Section 8.4 and Section 11.19, neither this Agreement nor any provision hereof confers any benefit or right upon or may be enforced by any Person not a signatory hereto.
11.13 Waiver. The Company has read the Prospectus and understands that Parent has established the Trust Account for the benefit of the public stockholders of Parent and the underwriters of the IPO pursuant to the Trust Agreement and that, except for a portion of the interest earned on the amounts held in the Trust Account, Parent may disburse monies from the Trust Account only for the purposes set forth in the Trust Agreement. For and in consideration of Parent agreeing to enter into this Agreement, the Company, for itself and on behalf of the Company Securityholders, hereby agrees that it does not now and shall not at any time hereafter prior to the Closing have any right, title, interest or claim of any kind in or to any monies in the Trust Account as a result of, or arising out of, any negotiations, contracts or agreements with Parent and hereby agrees that it will not seek recourse against the Trust Account for any reason.
11.14 No Other Representations; No Reliance.
(a) NONE OF THE COMPANY, ANY COMPANY SECURITYHOLDER NOR ANY OF THEIR RESPECTIVE REPRESENTATIVES HAS MADE ANY REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, OF ANY NATURE WHATSOEVER RELATING TO THE COMPANY OR THE BUSINESS OR OTHERWISE IN CONNECTION WITH THE TRANSACTIONS CONTEMPLATED BY THIS AGREEMENT OR ANY ANCILLARY AGREEMENT, OTHER THAN THOSE REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES EXPRESSLY SET FORTH IN ARTICLE IV, IN EACH CASE, AS MODIFIED BY THE SCHEDULES TO THIS AGREEMENT. Without limiting the generality of the foregoing, neither the Company, any Company Securityholder nor any of their respective Representatives has made, and shall not be deemed to have made, any representations or warranties in the materials relating to the Company made available to Parent and its Representatives, including due diligence materials, or in any presentation of the business of the Company by management of the Company or others in connection with the transactions contemplated hereby, and no statement contained in any of such
materials or made in any such presentation shall be deemed a representation or warranty hereunder or otherwise or deemed to be relied upon by Parent or Merger Sub in executing, delivering and performing this Agreement, the Ancillary Agreements or the transactions contemplated hereby or thereby, in each case except for the representations and warranties set forth in ARTICLE IV as modified by the Schedules to this Agreement. It is understood that any cost estimates, projections or other predictions, any data, any financial information or any memoranda or offering materials or presentations, including any offering memorandum or similar materials made available by the Company, any Company Securityholder or their respective Representatives are not and shall not be deemed to be or to include representations or warranties of the Company or any Company Securityholder, and are not and shall not be deemed to be relied upon by Parent or Merger Sub in executing, delivering and performing this Agreement, the Ancillary Agreements and the transactions contemplated hereby or thereby, in each case except for the representations and warranties set forth in ARTICLE IV, in each case, as modified by the Schedules to this Agreement. Except for the specific representations and warranties expressly made by the Company in ARTICLE IV, in each case as modified by the Schedules: (a) Parent acknowledges and agrees that: (i) neither the Company, the Company Securityholders nor any of their respective Representatives is making or has made any representation or warranty, express or implied, at law or in equity, in respect of the Company, the business, assets, liabilities, operations, prospects or condition (financial or otherwise) of the Company, the nature or extent of any liabilities of the Company, the effectiveness or the success of any operations of the Company or the accuracy or completeness of any confidential information memoranda, projections, forecasts or estimates of earnings, or other information (financial or otherwise) regarding the Company furnished to Parent, Merger Sub or their respective Representatives or made available to Parent and its Representatives in any “data rooms,” “virtual data rooms,” management presentations or any other form in expectation of, or in connection with, the transactions contemplated hereby, or in respect of any other matter or thing whatsoever; and (ii) no Representative of any Company Securityholder or the Company has any authority, express or implied, to make any representations, warranties or agreements not specifically set forth in ARTICLE IV and subject to the limited remedies herein provided; (b) each of Parent and Merger Sub specifically disclaims that it is relying upon or has relied upon any such other representations or warranties that may have been made by any Person, and acknowledges and agrees that the Company Securityholders and the Company have specifically disclaimed and do hereby specifically disclaim any such other representation or warranty made by any Person; and (c) none of the Company, the Company Securityholders nor any other Person shall have any liability to Parent, Merger Sub or any other Person with respect to any such other representations or warranties, including projections, forecasts, estimates, plans or budgets of future revenue, expenses or expenditures, future results of operations, future cash flows or the future financial condition of the Company or the future business, operations or affairs of the Company.
(b) NONE OF PARENT, MERGER SUB NOR ANY OF THEIR RESPECTIVE REPRESENTATIVES HAS MADE ANY REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, OF ANY NATURE WHATSOEVER RELATING TO PARENT, MERGER SUB OR OTHERWISE IN CONNECTION WITH THE TRANSACTIONS CONTEMPLATED BY THIS AGREEMENT OR ANY ANCILLARY AGREEMENT, OTHER THAN THOSE REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES EXPRESSLY SET FORTH IN ARTICLE V, IN EACH CASE, AS MODIFIED BY THE SCHEDULES TO THIS AGREEMENT AND THE PARENT SEC DOCUMENTS. Without limiting the generality of the foregoing, neither Parent, Merger Sub nor any of their respective Representatives has made, and shall not be deemed to have made, any representations or warranties in the materials relating to Parent and Merger Sub made available to the Company and the Company Securityholders and their Representatives, including due diligence materials, or in any presentation of the business of Parent by management of Parent or others in connection with the transactions contemplated hereby, and no statement contained in any of such materials or made in any such presentation shall be deemed a representation or warranty hereunder or otherwise or deemed to be relied upon by the Company and the Company Securityholders in executing, delivering and performing this Agreement, the Ancillary Agreements or the
transactions contemplated hereby or thereby, in each case except for the representations and warranties set forth in ARTICLE V as modified by the Schedules to this Agreement and the Parent SEC Documents. It is understood that any cost estimates, projections or other predictions, any data, any financial information or any memoranda or offering materials or presentations, including any offering memorandum or similar materials made available by Parent, Merger Sub or their respective Representatives are not and shall not be deemed to be or to include representations or warranties of Parent and Merger Sub, and are not and shall not be deemed to be relied upon by the Company or Company Securityholders in executing, delivering and performing this Agreement, the Ancillary Agreement and the transactions contemplated hereby or thereby, in each case except for the representations and warranties set forth in ARTICLE V, in each case, as modified by the Schedules to this Agreement and the Parent SEC Documents. Except for the specific representations and warranties expressly made by Parent and Merger Sub in ARTICLE V, in each case as modified by the Schedules and the Parent SEC Documents: (a) the Company acknowledges and agrees that: (i) neither Parent, Merger Sub nor any of their respective Representatives is making or has made any representation or warranty, express or implied, at law or in equity, in respect of Parent, Merger Sub, the business, assets, liabilities, operations, prospects or condition (financial or otherwise) of Parent or Merger Sub, the nature or extent of any liabilities of Parent or Merger Sub, the effectiveness or the success of any operations of Parent or Merger Sub or the accuracy or completeness of any confidential information memoranda, projections, forecasts or estimates of earnings, or other information (financial or otherwise) regarding Parent or Merger Sub furnished to the Company, the Company Securityholders or their respective Representatives or made available to the Company, the Company Securityholders and their Representatives in any “data rooms,” “virtual data rooms,” management presentations or any other form in expectation of, or in connection with, the transactions contemplated hereby, or in respect of any other matter or thing whatsoever; and (ii) no Representative of Parent or Merger Sub has any authority, express or implied, to make any representations, warranties or agreements not specifically set forth in ARTICLE V and subject to the limited remedies herein provided; (b) the Company specifically disclaims that it is relying upon or has relied upon any such other representations or warranties that may have been made by any Person, and acknowledges and agrees that Parent and Merger Sub have specifically disclaimed and do hereby specifically disclaim any such other representation or warranty made by any Person; and (c) none of Parent, Merger Sub nor any other Person shall have any liability to the Company, the Company Securityholders or any other Person with respect to any such other representations or warranties, including projections, forecasts, estimates, plans or budgets of future revenue, expenses or expenditures, future results of operations, future cash flows or the future financial condition of Parent or the future business, operations or affairs of Parent.
11.15 Waiver of Jury Trial. THE PARTIES EACH HEREBY WAIVES, TO THE FULLEST EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, ANY RIGHT TO TRIAL BY JURY OF ANY PROCEEDING (I) ARISING UNDER THIS AGREEMENT OR UNDER ANY ANCILLARY AGREEMENT OR (II) IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH OR RELATED OR INCIDENTAL TO THE DEALINGS OF THE PARTIES IN RESPECT OF THIS AGREEMENT OR ANY ANCILLARY AGREEMENT OR ANY OF THE TRANSACTIONS RELATED HERETO OR THERETO OR ANY FINANCING IN CONNECTION WITH THE TRANSACTIONS CONTEMPLATED HEREBY OR ANY OF THE TRANSACTIONS CONTEMPLATED THEREBY, IN EACH CASE, WHETHER NOW EXISTING OR HEREAFTER ARISING, AND WHETHER IN CONTRACT, TORT, EQUITY, OR OTHERWISE. THE PARTIES EACH HEREBY AGREES AND CONSENTS THAT ANY SUCH PROCEEDING SHALL BE DECIDED BY COURT TRIAL WITHOUT A JURY AND THAT THE PARTIES MAY FILE AN ORIGINAL COUNTERPART OF A COPY OF THIS AGREEMENT WITH ANY COURT AS WRITTEN EVIDENCE OF THE CONSENT OF THE PARTIES HERETO TO THE WAIVER OF THEIR RIGHT TO TRIAL BY JURY. EACH PARTY CERTIFIES AND ACKNOWLEDGES THAT (A) NO REPRESENTATIVE, AGENT OR ATTORNEY OF ANY OTHER PARTY HAS REPRESENTED, EXPRESSLY OR OTHERWISE, THAT SUCH OTHER PARTY WOULD NOT, IN THE EVENT OF LITIGATION, SEEK TO ENFORCE THE FOREGOING WAIVER, (B) EACH SUCH PARTY UNDERSTANDS AND HAS CONSIDERED THE IMPLICATIONS OF THIS WAIVER, (C) EACH SUCH PARTY MAKES THIS WAIVER VOLUNTARILY AND (D) EACH SUCH PARTY HAS BEEN INDUCED TO ENTER INTO THIS AGREEMENT BY, AMONG OTHER THINGS, THE MUTUAL WAIVERS AND CERTIFICATIONS IN THIS SECTION 11.15.
11.16 Submission to Jurisdiction. Each of the Parties irrevocably and unconditionally submits to the exclusive jurisdiction of the Chancery Court of the State of Delaware (or, if the Chancery Court of the State of Delaware does not have jurisdiction, a federal court sitting in Wilmington, Delaware) (or any appellate courts thereof), for the purposes of any Action (a) arising under this Agreement or under any Ancillary Agreement or (b) in any way connected with or related or incidental to the dealings of the Parties in respect of this Agreement or any Ancillary Agreement or any of the transactions contemplated hereby or thereby, and irrevocably and unconditionally waives any objection to the laying of venue of any such Action in any such court, and further irrevocably and unconditionally waives and agrees not to plead or claim in any such court that any such Action has been brought in an inconvenient forum. Each Party hereby irrevocably and unconditionally waives, and agrees not to assert, by way of motion or as a defense, counterclaim or otherwise, in any Action (i) arising under this Agreement or under any Ancillary Agreement or (ii) in any way connected with or related or incidental to the dealings of the Parties in respect of this Agreement or any Ancillary Agreement or any of the transactions contemplated hereby or thereby, (A) any claim that it is not personally subject to the jurisdiction of the courts as described in this Section 11.16 for any reason, (B) that it or its property is exempt or immune from the jurisdiction of any such court or from any Action commenced in such courts (whether through service of notice, attachment prior to judgment, attachment in aid of execution of judgment, execution of judgment or otherwise) and (C) that (x) the Action in any such court is brought in an inconvenient forum, (y) the venue of such Action is improper or (z) this Agreement, or the subject matter hereof, may not be enforced in or by such courts. Each Party agrees that service of any process, summons, notice or document by registered mail to such Party’s respective address set forth in Section 11.1 shall be effective service of process for any such Action.
11.17 Attorneys’ Fees. In the event of any legal action initiated by any party arising under or out of, in connection with or in respect of, this Agreement, the prevailing party shall be entitled to reasonable attorneys’ fees, costs and expenses incurred in such action, as determined and fixed by the court.
11.18 Remedies. Except as otherwise expressly provided herein, any and all remedies provided herein will be deemed cumulative with and not exclusive of any other remedy conferred hereby, or by law or equity upon such Party, and the exercise by a Party of any one remedy will not preclude the exercise of any other remedy. The Parties agree that irreparable damage for which monetary damages, even if available, would not be an adequate remedy, would occur in the event that the Parties do not perform their respective obligations under the provisions of this Agreement (including failing to take such actions as are required of them hereunder to consummate the transactions contemplated by this Agreement) in accordance with their specific terms or otherwise breach such provisions. It is accordingly agreed that the Parties shall be entitled to an injunction or injunctions, specific performance and other equitable relief to prevent breaches of this Agreement and to enforce specifically the terms and provisions of this Agreement, in each case, without posting a bond or undertaking and without proof of damages and this being in addition to any other remedy to which they are entitled at law or in equity. Each of the Parties agrees that it will not oppose the granting of an injunction, specific performance and other equitable relief when expressly available pursuant to the terms of this Agreement on the basis that the other Parties have an adequate remedy at law or an award of specific performance is not an appropriate remedy for any reason at law or equity.
11.19 Non-Recourse. This Agreement may be enforced only against, and any dispute, claim or controversy based upon, arising out of or related to this Agreement or the transactions contemplated hereby may be brought only against, the entities that are expressly named as parties hereto and then only with respect to the specific obligations set forth in this Agreement with respect to such party. No past, present or future director, officer, employee, incorporator, member, partner, stockholder, agent, attorney, advisor, lender or representative or Affiliate of any named party to this Agreement (which Persons are intended third party beneficiaries of this Section 11.19) shall have any liability (whether in contract or tort, at law or in equity or otherwise, or based upon any theory that seeks to impose liability of an entity party against its owners or Affiliates) for any one or more of the representations, warranties, covenants, agreements or other obligations or liabilities of such named party or for any dispute, claim or controversy based on, arising out of, or related to this Agreement or the transactions contemplated hereby.
[The remainder of this page intentionally left blank; signature pages to follow]
IN WITNESS WHEREOF, the parties hereto have caused this Agreement to be duly executed as of the day and year first above written.
| |
| Parent: |
|
| GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC. |
| |
| By: | /s/ Anthony Ang |
| Name: Anthony Ang |
| Title: CEO |
|
| Company: |
|
| K ENTER HOLDINGS INC. |
| |
| By: | /s/ Young Jae Lee |
| Name: Young Jae Lee |
| Title: CEO |
[Signature Page to Merger Agreement]
FIRST AMENDMENT TO MERGER AGREEMENT
This First Amendment to Merger Agreement (this “Amendment”), dated as of March 11, 2024 is entered into by and among K Enter Holdings Inc., a Delaware corporation (the “Company”), Global Star Acquisition Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Parent”), K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (“Purchaser”), and GLST Merger Sub Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Merger Sub”).
RECITALS
WHEREAS, the Company, Parent, Purchaser, and Merger Sub are parties to that certain Merger Agreement dated as of June 15, 2023 (the “Original Merger Agreement”);
WHEREAS, on January 31, 2024, with the consent of Parent, the Share Purchase Agreement dated as of April 12, 2023 (the “Acquisition Agreement”) by and among Sungkwon Kim, King Bear Film LLC and K Enter Holdings Inc. relating to the acquisition of a majority equity stake in First Virtual Lab Inc. (“First Virtual Lab”) was terminated and amended by the execution of two agreements, namely the Termination and Amendment to the Share Purchase Agreement and the Shareholders Agreement, dated January 31, 2024, by and among Sungkwon Kim, King Bear Film LLC and K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “SPA Amendment”) and the Share Purchase Agreement, dated January 31, 2024, by and among King Bear Film LLC and K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “KB Agreement” and collectively with the SPA Amendment the “New FVL Agreements”);
WHEREAS, on March 5, 2024, with the consent of Parent, the New FVL Agreements relating to the acquisition of a majority equity stake in First Virtual Lab were terminated pursuant to a Termination Agreement and Re-Purchase Option Agreement, dated March 5, 2024, by and among Sungkwon Kim, King Bear Film LLC and K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “First Virtual Lab Termination Agreement”);
WHEREAS, in connection with the First Virtual Lab Termination Agreement, the Company, Parent, Purchaser and Merger Sub Members desire to decrease the Base Purchase Price and to amend the disclosure schedules delivered by the Company to Parent in connection with the execution of the Original Merger Agreement (the “Original Disclosure Schedules”), all as more fully set forth herein; and
WHEREAS, capitalized and other defined terms used in this Amendment and not otherwise defined herein have the respective meanings given to them in the Original Merger Agreement.
NOW, THEREFORE, in consideration of the mutual covenants and promises set forth in this Agreement, and other good and valuable consideration, the receipt and sufficiency of which are hereby acknowledged, the parties hereby agree as follows:
1. Amendment of the Original Merger Agreement.
(a) The definition of the “Base Purchase Price” contained in Section 1.1 of the Original Merger Agreement is hereby amended to read in its entirety as follows:
” “Base Purchase Price” means $590,000,000.”
2. Amendment of the Original Disclosure Schedules.
(a) Schedules 4.14, 6.1(a) and 6.2(a) are hereby amended to delete in its entirety the respective reference to the “Share Purchase Agreement dated as of April 12, 2023 with certain sellers of First Virtual Lab Inc.”
(b) Schedule 4.14 is hereby amended to add at the end thereof a reference to the First Virtual Lab Termination Agreement as follows:
“Termination Agreement and Re-Purchase Option Agreement, dated March 5, 2024, by and among Sungkwon Kim, King Bear Film LLC and K Enter Holdings Inc.”
3. Representations and Warranties of the Company. The Company hereby represents and warrants to Parent that each of the following representations and warranties are true, correct and complete as of the date of this Amendment and as of the Closing Date:
(a) The Company has all requisite corporate power and authority to execute and deliver this Amendment and to consummate the transactions contemplated hereby, in the case of the Merger, subject to receipt of the Company Stockholder Approval. The execution and delivery by the Company of this Amendment and the consummation by the Company of the transactions contemplated hereby have been duly authorized by all necessary corporate action on the part of the Company. No other corporate proceedings on the part of the Company are necessary to authorize this Amendment or to consummate the transactions contemplated by this Amendment (other than, in the case of the Merger, the receipt of the Company Stockholder Approval). This Amendment has been duly executed and delivered by the Company and, assuming the due authorization, execution and delivery by each of the other parties hereto, this Amendment constitutes a legal, valid and binding obligation of the Company, enforceable against the Company in accordance with its terms, subject to the Enforceability Exceptions.
(b) None of the execution, delivery or performance by the Company of this Amendment or the consummation by the Company of the transactions contemplated hereby does or will (a) contravene or conflict with the contravene or conflict with the organizational or constitutive documents of the Company, (b) contravene or conflict with or constitute a violation of any provision of any Law or Order binding upon or applicable to the Company or to any of its respective properties, rights or assets (c) (i) require consent, approval or waiver under, (ii) constitute a default under or breach of (with or without the giving of notice or the passage of time or both), (iii) violate, (iv) give rise to any right of termination, cancellation, amendment or acceleration of any right or obligation of the Company Parties or to a loss of any material benefit to which the Company is entitled, in the case of each of clauses (i) – (iv), under any provision of any Permit, Contract or other instrument or obligations binding upon the Company or any of its respective properties, rights or assets, (d) result in the creation or imposition of any Lien (except for Permitted Liens) on any of the Company’s properties, rights or assets, or (e) require any consent, approval or waiver from any Person pursuant to any provision of the organizational or constitutive documents of the Company.
4. Representations and Warranties of the Parent Parties. Parent, Purchaser and Merger Sub (the “Parent Parties”) hereby represent and warrant to the Company that each of the following representations and warranties are true, correct and complete as of the date of this Agreement and as of the Closing Date:
(a) Each of the Parent Parties has all requisite corporate power and authority to execute and deliver this Amendment and to consummate the transactions contemplated hereby, in the case of the Merger, subject to receipt of the Parent Stockholder Approval. The execution and delivery by each of the Parent Parties of this Amendment and the consummation by each of the Parent Parties of the transactions contemplated hereby have been duly authorized by all necessary corporate action on the part of such Parent Party. No other corporate proceedings on the part of such Parent Party are necessary to authorize this Amendment or to consummate the transactions contemplated by this Amendment (other than, in the case of the Merger, the receipt of the Parent Stockholder Approval). This Amendment has been duly executed and delivered by such Parent Party and, assuming the due authorization, execution and delivery by each of the other parties hereto and thereto (other than a Parent Party), this Amendment constitutes a legal, valid and binding obligation of such Parent Party, enforceable against such Parent Party in accordance with its terms, subject to the Enforceability Exceptions.
(b) The execution, delivery and performance by a Parent Party of this Amendment or the consummation by a Parent Party of the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby do not and will not (a) contravene or conflict with the organizational or constitutive documents of the Parent Parties, or (b) contravene or conflict with or constitute a violation of any provision of any Law or any Order binding upon the Parent Parties.
5. No Waiver. No waiver of any breach or default hereunder shall be considered valid unless in writing, and no such waiver shall be deemed a waiver of any subsequent breach or default of the same or similar nature.
6. Miscellaneous.
(a) Entire Agreement. The Original Merger Agreement (including the Original Disclosure Schedules), as amended by this Amendment, together with the Additional Agreements, sets forth the entire agreement of the parties with respect to the subject matter hereof and thereof and supersedes all prior and contemporaneous understandings and agreements related thereto (whether written or oral), all of which are merged herein.
(b) Ratification. Except as amended hereby, the terms and provisions of the Original Merger Agreement (including the Original Disclosure Schedules) shall remain unchanged and in full force and effect. In the event of any conflict between the terms of the Original Merger Agreement (including the Original Disclosure Schedules) and the terms of this Amendment, the terms of this Amendment shall govern and control.
(c) Counterparts; Electronic Signatures. This Agreement may be executed in counterparts, each of which shall constitute an original, but all of which shall constitute one agreement. This Agreement shall become effective upon delivery to each party of an executed counterpart or the earlier delivery to each party of original, photocopied, or electronically transmitted signature pages that together (but need not individually) bear the signatures of all other parties.
(d) Governing Law. This Agreement and all disputes or controversies arising out of or relating to this Agreement or the transactions contemplated hereby, including the applicable statute of limitations, shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the Laws of the State of Delaware, without giving effect to any choice of law or conflict of law provision or rule (whether of the State of Delaware or any other jurisdiction) that would cause the application of the Law of any jurisdiction other than the State of Delaware.
[Signature Page Follows]
* * * * *
IN WITNESS WHEREOF, the undersigned, intending to be legally bound hereby, have duly executed this Amendment as of the day and year first above written.
| | Parent: | | |
| | | | |
| | GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC. |
| | | | |
| | By: | /s/ Anthony Ang |
| | | Name: | Anthony Ang |
| | | Title: | CEO |
| | | | |
| | Purchaser: |
| | | | |
| | K WAVE MEDIA LTD. |
| | | | |
| | By: | /s/ Anthony Ang |
| | | Name: | Anthony Ang |
| | | Title: | Director |
| | | | |
| | Merger Sub: |
| | | | |
| | GLST MERGER SUB INC. |
| | | | |
| | By: | /s/ Anthony Ang |
| | | Name: | Anthony Ang |
| | | Title: | Director |
| | | | |
| | Company: |
| | | | |
| | K ENTER HOLDINGS INC. |
| | | | |
| | By: | /s/ Young Jae Lee |
| | | Name: | Young Jae Lee |
| | | Title: | CEO |
[Signature Page to First Amendment to Merger Agreement]
SECOND AMENDMENT TO MERGER AGREEMENT
This Second Amendment to Merger Agreement (this “Amendment”), dated as of June 28, 2024 is entered into by and among K Enter Holdings Inc., a Delaware corporation (the “Company”), Global Star Acquisition Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Parent”), K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (“Purchaser”), and GLST Merger Sub Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Merger Sub”).
RECITALS
WHEREAS, the Company, Parent, Purchaser, and Merger Sub are parties to that certain Merger Agreement dated as of June 15, 2023 (the “Original Merger Agreement”) as amended by the First Amendment to Merger Agreement, dated as of March 11, 2024 (the “First Amendment”);
WHEREAS, capitalized and other defined terms used in this Amendment and not otherwise defined herein have the respective meanings given to them in the Original Merger Agreement.
WHEREAS, the Company, Parent, Purchaser, and Merger Sub desire to amend the Original Merger Agreement as set forth herein.
NOW, THEREFORE, in consideration of the mutual covenants and promises set forth in this Agreement, and other good and valuable consideration, the receipt and sufficiency of which are hereby acknowledged, the parties hereby agree as follows:
1. Amendment of the Outside Closing Date. Section 10.1(a) of the Original Merger Agreement is hereby deleted amended to read in its entirety as follows:
10.1 Termination Without Default.
(a) In the event that (i) the Closing of the transactions contemplated hereunder has not occurred on or before December 22, 2024 (the “Outside Closing Date”); and (ii) the material breach or violation of any representation, warranty, covenant or obligation under this Agreement by the party (i.e., Parent or Merger Sub, on one hand, or the Company, on the other hand) seeking to terminate this Agreement was not the cause of, or resulted in, the failure of the Closing to occur on or before the Outside Closing Date, then Parent or the Company, as applicable, shall have the right, at its sole option, to terminate this Agreement without liability to the other party. Such right may be exercised by Parent or the Company, as the case may be, giving written notice to the other at any time after the Outside Closing Date.
2. Representations and Warranties of the Company. The Company hereby represents and warrants to Parent that each of the following representations and warranties are true, correct and complete as of the date of this Amendment and as of the Closing Date:
(a) The Company has all requisite corporate power and authority to execute and deliver this Amendment and to consummate the transactions contemplated hereby, in the case of the Merger, subject to receipt of the Company Stockholder Approval. The execution and delivery by the Company of this Amendment and the consummation by the Company of the transactions contemplated hereby have been duly authorized by all necessary corporate action on the part of the Company. No other corporate proceedings on the part of the Company are necessary to authorize this Amendment or to consummate the transactions contemplated by this Amendment (other than, in the case of the Merger, the receipt of the Company Stockholder Approval). This Amendment has been duly executed and delivered by the Company and, assuming the due authorization, execution and delivery by each of the other parties hereto, this Amendment constitutes a legal, valid and binding obligation of the Company, enforceable against the Company in accordance with its terms, subject to the Enforceability Exceptions.
(b) None of the execution, delivery or performance by the Company of this Amendment or the consummation by the Company of the transactions contemplated hereby does or will (a) contravene or conflict with the contravene or conflict with the organizational or constitutive documents of the Company, (b) contravene or conflict with or constitute a violation of any provision of any Law or Order binding upon or applicable to the Company or to any of its respective properties, rights or assets (c) (i) require consent, approval or waiver under, (ii) constitute a default under or breach of (with or without the giving of notice or the passage of time or both), (iii) violate, (iv) give rise to any right of termination, cancellation, amendment or acceleration of any right or obligation of the Company Parties or to a loss of any material benefit to which the Company is entitled, in the case of each of clauses (i) – (iv), under any provision of any Permit, Contract or other instrument or obligations binding upon the Company or any of its respective properties, rights or assets, (d) result in the creation or imposition of any Lien (except for Permitted Liens) on any of the Company’s properties, rights or assets, or (e) require any consent, approval or waiver from any Person pursuant to any provision of the organizational or constitutive documents of the Company.
3. Representations and Warranties of the Parent Parties. Parent, Purchaser and Merger Sub (the “Parent Parties”) hereby represent and warrant to the Company that each of the following representations and warranties are true, correct and complete as of the date of this Agreement and as of the Closing Date:
(a) Each of the Parent Parties has all requisite corporate power and authority to execute and deliver this Amendment and to consummate the transactions contemplated hereby, in the case of the Merger, subject to receipt of the Parent Stockholder Approval. The execution and delivery by each of the Parent Parties of this Amendment and the consummation by each of the Parent Parties of the transactions contemplated hereby have been duly authorized by all necessary corporate action on the part of such Parent Party. No other corporate proceedings on the part of such Parent Party are necessary to authorize this Amendment or to consummate the transactions contemplated by this Amendment (other than, in the case of the Merger, the receipt of the Parent Stockholder Approval). This Amendment has been duly executed and delivered by such Parent Party and, assuming the due authorization, execution and delivery by each of the other parties hereto and thereto (other than a Parent Party), this Amendment constitutes a legal, valid and binding obligation of such Parent Party, enforceable against such Parent Party in accordance with its terms, subject to the Enforceability Exceptions.
(b) The execution, delivery and performance by a Parent Party of this Amendment or the consummation by a Parent Party of the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby do not and will not (a) contravene or conflict with the organizational or constitutive documents of the Parent Parties, or (b) contravene or conflict with or constitute a violation of any provision of any Law or any Order binding upon the Parent Parties.
4. No Waiver. No waiver of any breach or default hereunder shall be considered valid unless in writing, and no such waiver shall be deemed a waiver of any subsequent breach or default of the same or similar nature.
5. Miscellaneous.
(a) Entire Agreement. The Original Merger Agreement (including the Original Disclosure Schedules and the First Amendment), as amended by this Amendment, together with the Additional Agreements, sets forth the entire agreement of the parties with respect to the subject matter hereof and thereof and supersedes all prior and contemporaneous understandings and agreements related thereto (whether written or oral), all of which are merged herein.
(b) Ratification. Except as amended hereby, the terms and provisions of the Original Merger Agreement (including the Original Disclosure Schedules and the First Amendment) shall remain unchanged and in full force and effect. In the event of any conflict between the terms of the Original Merger Agreement (including the Original Disclosure Schedules and the First Amendment) and the terms of this Amendment, the terms of this Amendment shall govern and control.
(c) Counterparts; Electronic Signatures. This Amendment may be executed in counterparts, each of which shall constitute an original, but all of which shall constitute one agreement. This Amendment shall become effective upon delivery to each party of an executed counterpart or the earlier delivery to each party of original, photocopied, or electronically transmitted signature pages that together (but need not individually) bear the signatures of all other parties.
(d) Governing Law. This Amendment and all disputes or controversies arising out of or relating to this Amendment or the transactions contemplated hereby, including the applicable statute of limitations, shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the Laws of the State of Delaware, without giving effect to any choice of law or conflict of law provision or rule (whether of the State of Delaware or any other jurisdiction) that would cause the application of the Law of any jurisdiction other than the State of Delaware.
[Signature Page Follows]
IN WITNESS WHEREOF, the undersigned, intending to be legally bound hereby, have duly executed this Amendment as of the day and year first above written.
| | Parent: |
| | GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC. |
| | | | |
| | By: | /s/ Anthony Ang |
| | | Name: | Anthony Ang |
| | | Title: | CEO |
| | | | |
| | Purchaser: |
| | K WAVE MEDIA LTD. |
| | |
| | By: | /s/ Anthony Ang |
| | Name: | Anthony Ang |
| | | Title: | Director |
| | | | |
| | Merger Sub: |
| | GLST MERGER SUB INC. |
| | |
| | By: | /s/ Anthony Ang |
| | Name: | Anthony Ang |
| | | Title: | Director |
| | | | |
| | Company: |
| | K ENTER HOLDINGS INC. |
| | |
| | By: | /s/ Young Jae Lee |
| | | Name: | Young Jae Lee |
| | | Title: | CEO |
THIRD AMENDMENT TO MERGER AGREEMENT
This Third Amendment to Merger Agreement (this “Amendment”), dated as of July 25, 2024 is entered into by and among K Enter Holdings Inc., a Delaware corporation (the “Company”), Global Star Acquisition Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Parent”), K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (“Purchaser”), and GLST Merger Sub Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Merger Sub”).
RECITALS
WHEREAS, the Company, Parent, Purchaser, and Merger Sub are parties to that certain Merger Agreement dated as of June 15, 2023 (the “Original Merger Agreement”) as amended by the First Amendment to Merger Agreement, dated as of March 11, 2024 (the “First Amendment”) and by the Second Amendment to Merger Agreement, dated as of June 28, 2024 (the “Second Amendment”);
WHEREAS, capitalized and other defined terms used in this Amendment and not otherwise defined herein have the respective meanings given to them in the Original Merger Agreement.
WHEREAS, the Company, Parent, Purchaser, and Merger Sub desire to amend the Original Merger Agreement as set forth herein.
NOW, THEREFORE, in consideration of the mutual covenants and promises set forth in this Agreement, and other good and valuable consideration, the receipt and sufficiency of which are hereby acknowledged, the parties hereby agree as follows:
1. Amendment of the Outside Closing Date. Section 9.1(j) of the Original Merger Agreement is hereby deleted and amended to read in its entirety as follows:
9.1 Condition to the Obligations of the Parties.
(j) The Company’s acquisition of controlling equity interests of (1) Play Company Co., Ltd., (2) Solaire Partners LLC, (3) Apeitda Co., Ltd., (4)The LAMP Co., Ltd., (5) Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd., and (6) Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd. shall have been consummated.
2. Representations and Warranties of the Company. The Company hereby represents and warrants to Parent that each of the following representations and warranties are true, correct and complete as of the date of this Amendment and as of the Closing Date:
(a) The Company has all requisite corporate power and authority to execute and deliver this Amendment and to consummate the transactions contemplated hereby, in the case of the Merger, subject to receipt of the Company Stockholder Approval. The execution and delivery by the Company of this Amendment and the consummation by the Company of the transactions contemplated hereby have been duly authorized by all necessary corporate action on the part of the Company. No other corporate proceedings on the part of the Company are necessary to authorize this Amendment or to consummate the transactions contemplated by this Amendment (other than, in the case of the Merger, the receipt of the Company Stockholder Approval). This Amendment has been duly executed and delivered by the Company and, assuming the due authorization, execution and delivery by each of the other parties hereto, this Amendment constitutes a legal, valid and binding obligation of the Company, enforceable against the Company in accordance with its terms, subject to the Enforceability Exceptions.
(b) None of the execution, delivery or performance by the Company of this Amendment or the consummation by the Company of the transactions contemplated hereby does or will (a) contravene or conflict with the contravene or conflict with the organizational or constitutive documents of the Company, (b) contravene or conflict with or constitute a violation of any provision of any Law or Order binding upon or applicable to the Company or to any of its respective properties, rights or assets (c) (i) require consent, approval or waiver under, (ii) constitute a default under or breach of (with or without the giving of notice or the passage of time or both), (iii) violate, (iv) give rise to any right of termination, cancellation, amendment or acceleration of any right or obligation of the Company Parties or to a loss of any material benefit to which the Company is entitled, in the case of each of clauses (i) – (iv), under any provision of any Permit, Contract or other instrument or obligations binding upon the Company or any of its respective properties, rights or assets, (d) result in the creation or imposition of any Lien (except for Permitted Liens) on any of the Company’s properties, rights or assets, or (e) require any consent, approval or waiver from any Person pursuant to any provision of the organizational or constitutive documents of the Company.
3. Representations and Warranties of the Parent Parties. Parent, Purchaser and Merger Sub (the “Parent Parties”) hereby represent and warrant to the Company that each of the following representations and warranties are true, correct and complete as of the date of this Agreement and as of the Closing Date:
(a) Each of the Parent Parties has all requisite corporate power and authority to execute and deliver this Amendment and to consummate the transactions contemplated hereby, in the case of the Merger, subject to receipt of the Parent Stockholder Approval. The execution and delivery by each of the Parent Parties of this Amendment and the consummation by each of the Parent Parties of the transactions contemplated hereby have been duly authorized by all necessary corporate action on the part of such Parent Party. No other corporate proceedings on the part of such Parent Party are necessary to authorize this Amendment or to consummate the transactions contemplated by this Amendment (other than, in the case of the Merger, the receipt of the Parent Stockholder Approval). This Amendment has been duly executed and delivered by such Parent Party and, assuming the due authorization, execution and delivery by each of the other parties hereto and thereto (other than a Parent Party), this Amendment constitutes a legal, valid and binding obligation of such Parent Party, enforceable against such Parent Party in accordance with its terms, subject to the Enforceability Exceptions.
(b) The execution, delivery and performance by a Parent Party of this Amendment or the consummation by a Parent Party of the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby do not and will not (a) contravene or conflict with the organizational or constitutive documents of the Parent Parties, or (b) contravene or conflict with or constitute a violation of any provision of any Law or any Order binding upon the Parent Parties.
4. No Waiver. No waiver of any breach or default hereunder shall be considered valid unless in writing, and no such waiver shall be deemed a waiver of any subsequent breach or default of the same or similar nature.
5. Miscellaneous.
(a) Entire Agreement. The Original Merger Agreement (including the Original Disclosure Schedules, the First Amendment and the Second Amendment), as amended by this Amendment, together with the Additional Agreements, sets forth the entire agreement of the parties with respect to the subject matter hereof and thereof and supersedes all prior and contemporaneous understandings and agreements related thereto (whether written or oral), all of which are merged herein.
(b) Ratification. Except as amended hereby, the terms and provisions of the Original Merger Agreement (including the Original Disclosure Schedules, the First Amendment and the Second Amendment) shall remain unchanged and in full force and effect. In the event of any conflict between the terms of the Original Merger Agreement (including the Original Disclosure Schedules, the First Amendment and the Second Amendment) and the terms of this Amendment, the terms of this Amendment shall govern and control.
(c) Counterparts; Electronic Signatures. This Amendment may be executed in counterparts, each of which shall constitute an original, but all of which shall constitute one agreement. This Amendment shall become effective upon delivery to each party of an executed counterpart or the earlier delivery to each party of original, photocopied, or electronically transmitted signature pages that together (but need not individually) bear the signatures of all other parties.
(d) Governing Law. This Amendment and all disputes or controversies arising out of or relating to this Amendment or the transactions contemplated hereby, including the applicable statute of limitations, shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the Laws of the State of Delaware, without giving effect to any choice of law or conflict of law provision or rule (whether of the State of Delaware or any other jurisdiction) that would cause the application of the Law of any jurisdiction other than the State of Delaware.
[Signature Page Follows]
IN WITNESS WHEREOF, the undersigned, intending to be legally bound hereby, have duly executed this Amendment as of the day and year first above written.
| | Parent: |
| | GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC. |
| | | | |
| | By: | /s/ Anthony Ang |
| | | Name: | Anthony Ang |
| | | Title: | CEO |
| | | | |
| | Purchaser: |
| | K WAVE MEDIA LTD. |
| | |
| | By: | /s/ Anthony Ang |
| | Name: | Anthony Ang |
| | | Title: | Director |
| | | | |
| | Merger Sub: |
| | GLST MERGER SUB INC. |
| | |
| | By: | /s/ Anthony Ang |
| | Name: | Anthony Ang |
| | | Title: | Director |
| | | | |
| | Company: |
| | K ENTER HOLDINGS INC. |
| | |
| | By: | /s/ Tan Chin Hwee |
| | | Name: | Tan Chin Hwee |
| | | Title: | Interim CEO |
FOURTH AMENDMENT TO MERGER AGREEMENT
This Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement (this “Amendment”), dated as of December 11, 2024 is entered into by and among K Enter Holdings Inc., a Delaware corporation (the “Company”), Global Star Acquisition Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Parent”), K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (“Purchaser”), and GLST Merger Sub Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Merger Sub”).
RECITALS
WHEREAS, the Company, Parent, Purchaser, and Merger Sub are parties to that certain Merger Agreement dated as of June 15, 2023 (the “Original Merger Agreement”) as amended by the First Amendment to Merger Agreement, dated as of March 11, 2024 (the “First Amendment”), as amended by the Second Amendment to Merger Agreement, dated as of June 28, 2024, and as amended by the Third Amendment to Merger Agreement, dated as of July 25, 2024;
WHEREAS, capitalized and other defined terms used in this Amendment and not otherwise defined herein have the respective meanings given to them in the Original Merger Agreement.
WHEREAS, the Company, Parent, Purchaser, and Merger Sub desire to amend the Original Merger Agreement as set forth herein.
NOW, THEREFORE, in consideration of the mutual covenants and promises set forth in this Agreement, and other good and valuable consideration, the receipt and sufficiency of which are hereby acknowledged, the parties hereby agree as follows:
1. Amendment of the Outside Closing Date. Section 10.1(a) of the Original Merger Agreement is hereby deleted amended to read in its entirety as follows:
10.1 Termination Without Default.
(a) In the event that (i) the Closing of the transactions contemplated hereunder has not occurred on or before June 22, 2025 (the “Outside Closing Date”); and (ii) the material breach or violation of any representation, warranty, covenant or obligation under this Agreement by the party (i.e., Parent or Merger Sub, on one hand, or the Company, on the other hand) seeking to terminate this Agreement was not the cause of, or resulted in, the failure of the Closing to occur on or before the Outside Closing Date, then Parent or the Company, as applicable, shall have the right, at its sole option, to terminate this Agreement without liability to the other party. Such right may be exercised by Parent or the Company, as the case may be, giving written notice to the other at any time after the Outside Closing Date.
2. Representations and Warranties of the Company. The Company hereby represents and warrants to Parent that each of the following representations and warranties are true, correct and complete as of the date of this Amendment and as of the Closing Date:
(a) The Company has all requisite corporate power and authority to execute and deliver this Amendment and to consummate the transactions contemplated hereby, in the case of the Merger, subject to receipt of the Company Stockholder Approval. The execution and delivery by the Company of this Amendment and the consummation by the Company of the transactions contemplated hereby have been duly authorized by all necessary corporate action on the part of the Company. No other corporate proceedings on the part of the Company are necessary to authorize this Amendment or to consummate the transactions contemplated by this Amendment (other than, in the case of the Merger, the receipt of the Company Stockholder Approval). This Amendment has been duly executed and delivered by the Company and, assuming the due authorization, execution and delivery by each of the other parties hereto, this Amendment constitutes a legal, valid and binding obligation of the Company, enforceable against the Company in accordance with its terms, subject to the Enforceability Exceptions.
(b) None of the execution, delivery or performance by the Company of this Amendment or the consummation by the Company of the transactions contemplated hereby does or will (a) contravene or conflict with the contravene or conflict with the organizational or constitutive documents of the Company, (b) contravene or conflict with or constitute a violation of any provision of any Law or Order binding upon or applicable to the Company or to any of its respective properties, rights or assets (c) (i) require consent, approval or waiver under, (ii) constitute a default under or breach of (with or without the giving of notice or the passage of time or both), (iii) violate, (iv) give rise to any right of termination, cancellation, amendment or acceleration of any right or obligation of the Company Parties or to a loss of any material benefit to which the Company is entitled, in the case of each of clauses (i) – (iv), under any provision of any Permit, Contract or other instrument or obligations binding upon the Company or any of its respective properties, rights or assets, (d) result in the creation or imposition of any Lien (except for Permitted Liens) on any of the Company’s properties, rights or assets, or (e) require any consent, approval or waiver from any Person pursuant to any provision of the organizational or constitutive documents of the Company.
3. Representations and Warranties of the Parent Parties. Parent, Purchaser and Merger Sub (the “Parent Parties”) hereby represent and warrant to the Company that each of the following representations and warranties are true, correct and complete as of the date of this Agreement and as of the Closing Date:
(a) Each of the Parent Parties has all requisite corporate power and authority to execute and deliver this Amendment and to consummate the transactions contemplated hereby, in the case of the Merger, subject to receipt of the Parent Stockholder Approval. The execution and delivery by each of the Parent Parties of this Amendment and the consummation by each of the Parent Parties of the transactions contemplated hereby have been duly authorized by all necessary corporate action on the part of such Parent Party. No other corporate proceedings on the part of such Parent Party are necessary to authorize this Amendment or to consummate the transactions contemplated by this Amendment (other than, in the case of the Merger, the receipt of the Parent Stockholder Approval). This Amendment has been duly executed and delivered by such Parent Party and, assuming the due authorization, execution and delivery by each of the other parties hereto and thereto (other than a Parent Party), this Amendment constitutes a legal, valid and binding obligation of such Parent Party, enforceable against such Parent Party in accordance with its terms, subject to the Enforceability Exceptions.
(b) The execution, delivery and performance by a Parent Party of this Amendment or the consummation by a Parent Party of the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby do not and will not (a) contravene or conflict with the organizational or constitutive documents of the Parent Parties, or (b) contravene or conflict with or constitute a violation of any provision of any Law or any Order binding upon the Parent Parties.
4. No Waiver. No waiver of any breach or default hereunder shall be considered valid unless in writing, and no such waiver shall be deemed a waiver of any subsequent breach or default of the same or similar nature.
5. Miscellaneous.
(a) Entire Agreement. The Original Merger Agreement (including the Original Disclosure Schedules and the First Amendment), as amended by this Amendment, together with the Additional Agreements, sets forth the entire agreement of the parties with respect to the subject matter hereof and thereof and supersedes all prior and contemporaneous understandings and agreements related thereto (whether written or oral), all of which are merged herein.
(b) Ratification. Except as amended hereby, the terms and provisions of the Original Merger Agreement (including the Original Disclosure Schedules and the First Amendment) shall remain unchanged and in full force and effect. In the event of any conflict between the terms of the Original Merger Agreement (including the Original Disclosure Schedules and the First Amendment) and the terms of this Amendment, the terms of this Amendment shall govern and control.
(c) Counterparts; Electronic Signatures. This Amendment may be executed in counterparts, each of which shall constitute an original, but all of which shall constitute one agreement. This Amendment shall become effective upon delivery to each party of an executed counterpart or the earlier delivery to each party of original, photocopied, or electronically transmitted signature pages that together (but need not individually) bear the signatures of all other parties.
(d) Governing Law. This Amendment and all disputes or controversies arising out of or relating to this Amendment or the transactions contemplated hereby, including the applicable statute of limitations, shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the Laws of the State of Delaware, without giving effect to any choice of law or conflict of law provision or rule (whether of the State of Delaware or any other jurisdiction) that would cause the application of the Law of any jurisdiction other than the State of Delaware.
[Signature Page Follows]
IN WITNESS WHEREOF, the undersigned, intending to be legally bound hereby, have duly executed this Amendment as of the day and year first above written.
| | Parent: |
| | |
| | GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION INC. |
| | |
| | By: | /s/ Anthony Ang |
| | | Name: | Anthony Ang |
| | | Title: | CEO |
| | |
| | Purchaser: |
| | |
| | K WAVE MEDIA LTD. |
| | |
| | By: | /s/ Anthony Ang |
| | | Name: | Anthony Ang |
| | | Title: | Director |
| | |
| | Merger Sub: |
| | |
| | GLST MERGER SUB INC. |
| | |
| | By: | /s/ Anthony Ang |
| | | Name: | Anthony Ang |
| | | Title: | Director |
| | |
| | Company: |
| | |
| | K ENTER HOLDINGS INC. |
| | |
| | By: | /s/ Tan, Chin Hwee |
| | | Name: | Tan, Chin Hwee |
| | | Title: | CEO |
[Signature Page to Fourth Amendment to Merger Agreement]
Annex B
THE COMPANIES ACT (As Revised)
OF THE CAYMAN ISLANDS
COMPANY LIMITED BY SHARES
AMENDED AND RESTATED
MEMORANDUM AND ARTICLES OF ASSOCIATION
OF
K Wave Media Ltd.
(adopted by special resolution dated [Date] and effective on [date])
THE COMPANIES ACT (As Revised)
OF THE CAYMAN ISLANDS
COMPANY LIMITED BY SHARES
AMENDED AND RESTATED
MEMORANDUM OF ASSOCIATION
OF
K Wave Media Ltd.
(adopted by special resolution dated [Date] and effective on [date])
| 1 | The name of the Company is K Wave Media Ltd. |
| 2 | The Registered Office of the Company shall be at the offices of Maples Corporate Services Limited, PO Box 309, Ugland House, Grand Cayman, KY1-1104, Cayman Islands, or at such other place within the Cayman Islands as the Directors may decide. |
| 3 | The objects for which the Company is established are unrestricted and the Company shall have full power and authority to carry out any object not prohibited by the laws of the Cayman Islands. |
| 4 | The liability of each Member is limited to the amount unpaid on such Member’s shares. |
| 5 | The share capital of the Company is US$100,000 divided into 990,000,000 ordinary shares of a par value of US$0.0001 each and 10,000,000 preference shares of a par value of US$0.0001 each. |
| 6 | The Company has power to register by way of continuation as a body corporate limited by shares under the laws of any jurisdiction outside the Cayman Islands and to be deregistered in the Cayman Islands. |
| 7 | Capitalised terms that are not defined in this Amended and Restated Memorandum of Association bear the respective meanings given to them in the Amended and Restated Articles of Association of the Company. |
THE COMPANIES ACT (As Revised)
OF THE CAYMAN ISLANDS
COMPANY LIMITED BY SHARES
AMENDED AND RESTATED
ARTICLES OF ASSOCIATION
OF
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
(adopted by special resolution dated [Date] and effective on [date])
| 1.1 | In the Articles Table A in the First Schedule to the Statute does not apply and, unless there is something in the subject or context inconsistent therewith: |
| | “Applicable Law” | | means, with respect to any person, all provisions of laws, statutes, ordinances, rules, regulations, permits, certificates, judgments, decisions, decrees or orders of any governmental authority applicable to such person. |
| | | | |
| | “Articles” | | means these amended and restated articles of association of the Company. |
| | | | |
| | “Audit Committee” | | means the audit committee of the board of directors of the Company established pursuant to the Articles, or any successor committee. |
| | | | |
| | “Auditor” | | means the person for the time being performing the duties of auditor of the Company (if any). |
| | | | |
| | “business day” | | means any day other than a Saturday, a Sunday or a legal holiday or a day on which banking institutions or trust companies are authorised or obligated by law to close in New York City. |
| | | | |
| | “Clearing House” | | means a clearing house recognised by the laws of the jurisdiction in which the Shares (or depositary receipts therefor) are listed or quoted on a stock exchange or interdealer quotation system in such jurisdiction. |
| | “Company” | | means the above named company. |
| | | | |
| | “Company’s Website” | | means the website of the Company and/or its web-address or domain name (if any). |
| | | | |
| | “Compensation Committee” | | means the compensation committee of the board of directors of the Company established pursuant to the Articles, or any successor committee. |
| | | | |
| | “Designated Stock Exchange” | | means any United States national securities exchange on which the securities of the Company are listed for trading, including The NASDAQ Global Market. |
| | | | |
| | “Directors” | | means the directors for the time being of the Company. |
| | | | |
| | “Dividend” | | means any dividend (whether interim or final) resolved to be paid on Shares pursuant to the Articles. |
| | | | |
| | “Electronic Communication” | | means a communication sent by electronic means, including electronic posting to the Company’s Website, transmission to any number, address or internet website (including the website of the Securities and Exchange Commission) or other electronic delivery methods as otherwise decided and approved by the Directors. |
| | | | |
| | “Electronic Record” | | has the same meaning as in the Electronic Transactions Act. |
| | | | |
| | “Electronic Transactions Act” | | means the Electronic Transactions Act (As Revised) of the Cayman Islands. |
| | | | |
| | “Exchange Act” | | means the United States Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or any similar United States federal statute and the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission thereunder, all as the same shall be in effect at the time. |
| | | | |
| | “Independent Director” | | has the same meaning as in the rules and regulations of the Designated Stock Exchange or in Rule 10A-3 under the Exchange Act, as the case may be. |
| | | | |
| | “Member” | | has the same meaning as in the Statute. |
| | | | |
| | “Memorandum” | | means the amended and restated memorandum of association of the Company. |
| | “Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee” | | means the nominating and corporate governance committee of the board of directors of the Company established pursuant to the Articles, or any successor committee. |
| | | | |
| | “Officer” | | means a person appointed to hold an office in the Company. |
| | | | |
| | “Ordinary Resolution” | | means a resolution passed by a simple majority of the Members as, being entitled to do so, vote in person or, where proxies are allowed, by proxy at a general meeting, and includes a unanimous written resolution. In computing the majority when a poll is demanded regard shall be had to the number of votes to which each Member is entitled by the Articles. |
| | | | |
| | “Ordinary Share” | | means an ordinary share of a par value of US$0.0001 in the share capital of the Company. |
| | | | |
| | “Preference Share” | | means a preference share of a par value of US$0.0001 in the capital of the Company. |
| | | | |
| | “Register of Members” | | means the register of Members maintained in accordance with the Statute and includes (except where otherwise stated) any branch or duplicate register of Members. |
| | | | |
| | “Registered Office” | | means the registered office for the time being of the Company. |
| | | | |
| | “Seal” | | means the common seal of the Company and includes every duplicate seal. |
| | | | |
| | “Securities and Exchange Commission” | | means the United States Securities and Exchange Commission. |
| | | | |
| | “Share” | | means an Ordinary Share or a Preference Share and includes any class or series, and a fraction, of a share in the Company. |
| | | | |
| | “Special Resolution” | | has the same meaning as in the Statute, and includes a unanimous written resolution. |
| | | | |
| | “Statute” | | means the Companies Act (As Revised) of the Cayman Islands. |
| | | | |
| | “Treasury Share” | | means a Share held in the name of the Company as a treasury share in accordance with the Statute. |
| (a) | words importing the singular number include the plural number and vice versa; |
| (b) | words importing the masculine gender include the feminine gender; |
| (c) | words importing persons include corporations as well as any other legal or natural person; |
| (d) | “written” and “in writing” include all modes of representing or reproducing words in visible form, including in the form of an Electronic Record; |
| (e) | “shall” shall be construed as imperative and “may” shall be construed as permissive; |
| (f) | references to provisions of any law or regulation shall be construed as references to those provisions as amended, modified, re-enacted or replaced; |
| (g) | any phrase introduced by the terms “including”, “include”, “in particular” or any similar expression shall be construed as illustrative and shall not limit the sense of the words preceding those terms; |
| (h) | the term “and/or” is used to mean both “and” as well as “or.” The use of “and/or” in certain contexts in no respects qualifies or modifies the use of the terms “and” or “or” in others. The term “or” shall not be interpreted to be exclusive and the term “and” shall not be interpreted to require the conjunctive (in each case, unless the context otherwise requires); |
| (i) | headings are inserted for reference only and shall be ignored in construing the Articles; |
| (j) | any requirements as to delivery under the Articles include delivery in the form of an Electronic Record; |
| (k) | any requirements as to execution or signature under the Articles including the execution of the Articles themselves can be satisfied in the form of an electronic signature as defined in the Electronic Transactions Act; |
| (l) | sections 8 and 19(3) of the Electronic Transactions Act shall not apply; |
| (m) | the term “clear days” in relation to the period of a notice means that period excluding the day when the notice is received or deemed to be received and the day for which it is given or on which it is to take effect; and |
| (n) | the term “holder” in relation to a Share means a person whose name is entered in the Register of Members as the holder of such Share. |
| 2 | Commencement of Business |
| 2.1 | The business of the Company may be commenced as soon after incorporation of the Company as the Directors shall see fit. |
| 2.2 | The Directors may pay, out of the capital or any other monies of the Company, all expenses incurred in or about the formation and establishment of the Company, including the expenses of registration. |
| 3 | Issue of Shares and other Securities |
| 3.1 | Subject to the provisions, if any, in the Memorandum (and to any direction that may be given by the Company in general meeting) and, where applicable, the rules and regulations of the Designated Stock Exchange, the Securities and Exchange Commission and/or any other competent regulatory authority or otherwise under Applicable Law, and without prejudice to any rights attached to any existing Shares, the Directors may allot, issue, grant options over or otherwise dispose of Shares in separate classes and/or series (including fractions of a Share) with or without preferred, deferred or other rights or restrictions, whether in regard to Dividends or other distributions, voting, return of capital or otherwise and to such persons, at such times and on such other terms as they think proper, and may also (subject to the Statute and the Articles) vary such rights. |
| 3.2 | The Company may issue rights, options, warrants or convertible securities or securities of similar nature conferring the right upon the holders thereof to subscribe for, purchase or receive any class or series of Shares or other securities in the Company on such terms as the Directors may from time to time determine. |
| 3.3 | The Company shall not issue Shares to bearer. |
| 3.4 | On or before the allotment of any Share, the Directors shall resolve the class and/or series to which such Share shall be classified and may, prior to the issue of any Share, reclassify such Share. Each class and/or series shall be specifically identified. Subject to the Statute and the Articles, the Directors may at any time re-name any Share. |
| 4.1 | The Company shall maintain or cause to be maintained the Register of Members in accordance with the Statute. |
| 4.2 | The Directors may determine that the Company shall maintain one or more branch registers of Members in accordance with the Statute. The Directors may also determine which register of Members shall constitute the principal register and which shall constitute the branch register or registers, and to vary such determination from time to time. |
| 5 | Closing Register of Members or Fixing Record Date |
| 5.1 | For the purpose of determining Members entitled to notice of, or to vote at any meeting of Members or any adjournment thereof, or Members entitled to receive payment of any Dividend or other distribution, or in order to make a determination of Members for any other purpose, the Directors may, after notice has been given by advertisement in an appointed newspaper or any other newspaper or by any other means in accordance with the rules and regulations of the Designated Stock Exchange, the Securities and Exchange Commission and/or any other competent regulatory authority or otherwise under Applicable Law, provide that the Register of Members shall be closed for transfers for a stated period which shall not in any case exceed 40 days. |
| 5.2 | In lieu of, or apart from, closing the Register of Members, the Directors may fix in advance or arrears a date as the record date for any such determination of Members entitled to notice of, or to vote at any meeting of the Members or any adjournment thereof, or for the purpose of determining the Members entitled to receive payment of any Dividend or other distribution, or in order to make a determination of Members for any other purpose. |
| 5.3 | If the Register of Members is not so closed and no record date is fixed for the determination of Members entitled to notice of, or to vote at, a meeting of Members or Members entitled to receive payment of a Dividend or other distribution, the date on which notice of the meeting is sent or the date on which the resolution of the Directors resolving to pay such Dividend or other distribution is passed, as the case may be, shall be the record date for such determination of Members. When a determination of Members entitled to vote at any meeting of Members has been made as provided in this Article, such determination shall apply to any adjournment thereof. |
| 6.1 | A Member shall only be entitled to a share certificate if the Directors resolve that share certificates shall be issued. Share certificates representing Shares, if any, shall be in such form as the Directors may determine. Share certificates shall be signed by one or more Directors or other person authorised by the Directors. The Directors may authorise certificates to be issued with the authorised signature(s) affixed by mechanical process. All certificates for Shares shall be consecutively numbered or otherwise identified and shall specify the Shares to which they relate. All certificates surrendered to the Company for transfer shall be cancelled and, subject to the Articles, no new certificate shall be issued until the former certificate representing a like number of relevant Shares shall have been surrendered and cancelled. |
| 6.2 | The Company shall not be bound to issue more than one certificate for Shares held jointly by more than one person and delivery of a certificate to one joint holder shall be a sufficient delivery to all of them. |
| 6.3 | If a share certificate is defaced, worn out, lost or destroyed, it may be renewed on such terms (if any) as to evidence and indemnity and on the payment of such expenses reasonably incurred by the Company in investigating evidence, as the Directors may prescribe, and (in the case of defacement or wearing out) upon delivery of the old certificate. |
| 6.4 | Every share certificate sent in accordance with the Articles will be sent at the risk of the Member or other person entitled to the certificate. The Company will not be responsible for any share certificate lost or delayed in the course of delivery. |
| 6.5 | Share certificates shall be issued within the relevant time limit as prescribed by the Statute, if applicable, or as the rules and regulations of the Designated Stock Exchange, the Securities and Exchange Commission and/or any other competent regulatory authority or otherwise under Applicable Law may from time to time determine, whichever is shorter, after the allotment or, except in the case of a Share transfer which the Company is for the time being entitled to refuse to register and does not register, after lodgement of a Share transfer with the Company. |
| 7.1 | Subject to the terms of the Articles, any Member may transfer all or any of their Shares by an instrument of transfer provided that such transfer complies with the rules and regulations of the Designated Stock Exchange, the Securities and Exchange Commission and/or any other competent regulatory authority or otherwise under Applicable Law. If the Shares in question were issued in conjunction with rights, options or warrants issued pursuant to the Articles on terms that one cannot be transferred without the other, the Directors shall refuse to register the transfer of any such Share without evidence satisfactory to them of the like transfer of such right, option or warrant. |
| 7.2 | The instrument of transfer of any Share shall be in writing in the usual or common form or in a form prescribed by the rules and regulations of the Designated Stock Exchange, the Securities and Exchange Commission and/or any other competent regulatory authority or otherwise under Applicable Law or in any other form approved by the Directors and shall be executed by or on behalf of the transferor (and if the Directors so require, signed by or on behalf of the transferee) and may be under hand or, if the transferor or transferee is a Clearing House or its nominee(s), by hand or by machine imprinted signature or by such other manner of execution as the Directors may approve from time to time. The transferor shall be deemed to remain the holder of a Share until the name of the transferee is entered in the Register of Members. |
| 8 | Redemption, Repurchase and Surrender of Shares |
| 8.1 | Subject to the provisions of the Statute, and, where applicable, the rules and regulations of the Designated Stock Exchange, the Securities and Exchange Commission and/or any other competent regulatory authority or otherwise under Applicable Law, the Company may: |
| (a) | issue Shares that are to be redeemed or are liable to be redeemed at the option of the Member or the Company. The redemption of such Shares shall be effected in such manner and upon such other terms as the Company may, by Special Resolution, determine before the issue of the Shares. |
| (b) | purchase its own Shares (including any redeemable Shares) in such manner and on such other terms as the Directors may agree with the relevant Member. |
For the avoidance of doubt, redemptions, repurchases and surrenders of Shares in the circumstances described in the Article above shall not require further approval of the Members.
| 8.2 | The Company may make a payment in respect of the redemption or purchase of its own Shares in any manner permitted by the Statute, including out of capital. |
| 8.3 | The Directors may accept the surrender for no consideration of any fully paid Share. |
| 9.1 | The Directors may, prior to the purchase, redemption or surrender of any Share, determine that such Share shall be held as a Treasury Share. |
| 9.2 | The Directors may determine to cancel a Treasury Share or transfer a Treasury Share on such terms as they think proper (including, without limitation, for nil consideration). |
| 10 | Variation of Rights of Shares |
| 10.1 | Subject to Article 3.1, if at any time the share capital of the Company is divided into different classes or series of Shares, all or any of the rights attached to any class (unless otherwise provided by the terms of issue of the Shares of that class) may, whether or not the Company is being wound up, be varied without the consent of the holders of the issued Shares of that class where such variation is considered by the Directors not to have a material adverse effect upon such rights; otherwise, any such variation shall be made only with the consent in writing of the holders of not less than two-thirds of the issued Shares of that class, or with the approval of a resolution passed by a majority of not less than two-thirds of the votes cast at a separate meeting of the holders of the Shares of that class. For the avoidance of doubt, the Directors reserve the right, notwithstanding that any such variation may not have a material adverse effect, to obtain consent from the holders of Shares of the relevant class. To any such meeting all the provisions of the Articles relating to general meetings shall apply mutatis mutandis, except that the necessary quorum shall be one person holding or representing by proxy at least one-third of the issued Shares of the class and that any holder of Shares of the class present in person or by proxy may demand a poll. |
| 10.2 | For the purposes of a separate class meeting, the Directors may treat two or more or all the classes or series of Shares as forming one class or series of Shares if the Directors consider that such class or series of Shares would be affected in the same way by the proposals under consideration, but in any other case shall treat them as separate classes or series of Shares. |
| 10.3 | The rights conferred upon the holders of the Shares of any class issued with preferred or other rights shall not, unless otherwise expressly provided by the terms of issue of the Shares of that class, be deemed to be varied by the creation or issue of further Shares ranking pari passu therewith or Shares issued with preferred or other rights. |
| 11 | Commission on Sale of Shares |
The Company may, in so far as the Statute permits, pay a commission to any person in consideration of that person subscribing or agreeing to subscribe (whether absolutely or conditionally) or procuring or agreeing to procure subscriptions (whether absolutely or conditionally) for any Shares. Such commissions may be satisfied by the payment of cash and/or the issue of fully or partly paid-up Shares. The Company may also on any issue of Shares pay such brokerage as may be lawful.
| 12 | Non Recognition of Trusts |
The Company shall not be bound by or compelled to recognise in any way (even when notified) any equitable, contingent, future or partial interest in any Share, or (except only as is otherwise provided by the Articles or the Statute) any other rights in respect of any Share other than an absolute right to the entirety thereof in the holder.
| 13.1 | The Company shall have a first and paramount lien on all Shares (whether fully paid-up or not) registered in the name of a Member (whether solely or jointly with others) for all debts, liabilities or engagements to or with the Company (whether presently payable or not) by such Member or their estate, either alone or jointly with any other person, whether a Member or not, but the Directors may at any time declare any Share to be wholly or in part exempt from the provisions of this Article. The registration of a transfer of any such Share shall operate as a waiver of the Company’s lien thereon. The Company’s lien on a Share shall also extend to any amount payable in respect of that Share. |
| 13.2 | The Company may sell, in such manner as the Directors think fit, any Shares on which the Company has a lien, if a sum in respect of which the lien exists is presently payable, and is not paid within 14 clear days after notice has been received or deemed to have been received by the holder of the Shares, or to the person entitled to it in consequence of the death or bankruptcy of the holder, demanding payment and stating that if the notice is not complied with the Shares may be sold. |
| 13.3 | To give effect to any such sale the Directors may authorise any person to execute an instrument of transfer of the Shares sold to, or in accordance with the directions of, the purchaser. The purchaser or their nominee shall be registered as the holder of the Shares comprised in any such transfer, and they shall not be bound to see to the application of the purchase money, nor shall their title to the Shares be affected by any irregularity or invalidity in the sale or the exercise of the Company’s power of sale under the Articles. |
| 13.4 | The net proceeds of such sale after payment of costs, shall be applied in payment of such part of the amount in respect of which the lien exists as is presently payable and any balance shall (subject to a like lien for sums not presently payable as existed upon the Shares before the sale) be paid to the person entitled to the Shares at the date of the sale. |
| 14.1 | Subject to the terms of the allotment and issue of any Shares, the Directors may make calls upon the Members in respect of any monies unpaid on their Shares (whether in respect of par value or premium), and each Member shall (subject to receiving at least 14 clear days’ notice specifying the time or times of payment) pay to the Company at the time or times so specified the amount called on the Shares. A call may be revoked or postponed, in whole or in part, as the Directors may determine. A call may be required to be paid by instalments. A person upon whom a call is made shall remain liable for calls made upon them notwithstanding the subsequent transfer of the Shares in respect of which the call was made. |
| 14.2 | A call shall be deemed to have been made at the time when the resolution of the Directors authorising such call was passed. |
| 14.3 | The joint holders of a Share shall be jointly and severally liable to pay all calls in respect thereof. |
| 14.4 | If a call remains unpaid after it has become due and payable, the person from whom it is due shall pay interest on the amount unpaid from the day it became due and payable until it is paid at such rate as the Directors may determine (and in addition all expenses that have been incurred by the Company by reason of such non-payment), but the Directors may waive payment of the interest or expenses wholly or in part. |
| 14.5 | An amount payable in respect of a Share on issue or allotment or at any fixed date, whether on account of the par value of the Share or premium or otherwise, shall be deemed to be a call and if it is not paid all the provisions of the Articles shall apply as if that amount had become due and payable by virtue of a call. |
| 14.6 | The Directors may issue Shares with different terms as to the amount and times of payment of calls, or the interest to be paid. |
| 14.7 | The Directors may, if they think fit, receive an amount from any Member willing to advance all or any part of the monies uncalled and unpaid upon any Shares held by that Member, and may (until the amount would otherwise become payable) pay interest at such rate as may be agreed upon between the Directors and the Member paying such amount in advance. |
| 14.8 | No such amount paid in advance of calls shall entitle the Member paying such amount to any portion of a Dividend or other distribution payable in respect of any period prior to the date upon which such amount would, but for such payment, become payable. |
| 15.1 | If a call or instalment of a call remains unpaid after it has become due and payable the Directors may give to the person from whom it is due not less than 14 clear days’ notice requiring payment of the amount unpaid together with any interest which may have accrued and any expenses incurred by the Company by reason of such non-payment. The notice shall specify where payment is to be made and shall state that if the notice is not complied with the Shares in respect of which the call was made will be liable to be forfeited. |
| 15.2 | If the notice is not complied with, any Share in respect of which it was given may, before the payment required by the notice has been made, be forfeited by a resolution of the Directors. Such forfeiture shall include all Dividends, other distributions or other monies payable in respect of the forfeited Share and not paid before the forfeiture. |
| 15.3 | A forfeited Share may be sold, re-allotted or otherwise disposed of on such terms and in such manner as the Directors think fit and at any time before a sale, re-allotment or disposition the forfeiture may be cancelled on such terms as the Directors think fit. Where for the purposes of its disposal a forfeited Share is to be transferred to any person the Directors may authorise some person to execute an instrument of transfer of the Share in favour of that person. |
| 15.4 | A person any of whose Shares have been forfeited shall cease to be a Member in respect of them and shall surrender to the Company for cancellation the certificate for the Shares forfeited and shall remain liable to pay to the Company all monies which at the date of forfeiture were payable by that person to the Company in respect of those Shares together with interest at such rate as the Directors may determine, but that person’s liability shall cease if and when the Company shall have received payment in full of all monies due and payable by them in respect of those Shares. |
| 15.5 | A certificate in writing under the hand of one Director or Officer that a Share has been forfeited on a specified date shall be conclusive evidence of the facts stated in it as against all persons claiming to be entitled to the Share. The certificate shall (subject to the execution of an instrument of transfer) constitute a good title to the Share and the person to whom the Share is sold or otherwise disposed of shall not be bound to see to the application of the purchase money, if any, nor shall their title to the Share be affected by any irregularity or invalidity in the proceedings in reference to the forfeiture, sale or disposal of the Share. |
| 15.6 | The provisions of the Articles as to forfeiture shall apply in the case of non-payment of any sum which, by the terms of issue of a Share, becomes payable at a fixed time, whether on account of the par value of the Share or by way of premium as if it had been payable by virtue of a call duly made and notified. |
| 16.1 | If a Member dies, the survivor or survivors (where they were a joint holder), or their legal personal representatives (where they were a sole holder), shall be the only persons recognised by the Company as having any title to the deceased Member’s Shares. The estate of a deceased Member is not thereby released from any liability in respect of any Share, for which the Member was a joint or sole holder. |
| 16.2 | Any person becoming entitled to a Share in consequence of the death or bankruptcy or liquidation or dissolution of a Member (or in any other way than by transfer) may, upon such evidence being produced as may be required by the Directors, elect, by a notice in writing sent by that person to the Company, either to become the holder of such Share or to have some person nominated by them registered as the holder of such Share. If they elect to have another person registered as the holder of such Share they shall sign an instrument of transfer of that Share to that person. The Directors shall, in either case, have the same right to decline or suspend registration as they would have had in the case of a transfer of the Share by the relevant Member before their death or bankruptcy or liquidation or dissolution, as the case may be. |
| 16.3 | A person becoming entitled to a Share by reason of the death or bankruptcy or liquidation or dissolution of a Member (or in any other case than by transfer) shall be entitled to the same Dividends, other distributions and other advantages to which they would be entitled if they were the holder of such Share. However, they shall not, before becoming a Member in respect of a Share, be entitled in respect of it to exercise any right conferred by membership in relation to general meetings of the Company and the Directors may at any time give notice requiring any such person to elect either to be registered or to have some person nominated by them registered as the holder of the Share (but the Directors shall, in either case, have the same right to decline or suspend registration as they would have had in the case of a transfer of the Share by the relevant Member before their death or bankruptcy or liquidation or dissolution or any other case than by transfer, as the case may be). If the notice is not complied with within 90 days of being received or deemed to be received (as determined pursuant to the Articles), the Directors may thereafter withhold payment of all Dividends, other distributions, bonuses or other monies payable in respect of the Share until the requirements of the notice have been complied with. |
| 17 | Amendments of Memorandum and Articles of Association and Alteration of Capital |
| 17.1 | The Company may by Ordinary Resolution: |
| (a) | increase its share capital by such sum as the Ordinary Resolution shall prescribe and with such rights, priorities and privileges annexed thereto, as the Company in general meeting may determine; |
| (b) | consolidate and divide all or any of its share capital into Shares of larger amount than its existing Shares; |
| (c) | convert all or any of its paid-up Shares into stock, and reconvert that stock into paid-up Shares of any denomination; |
| (d) | by subdivision of its existing Shares or any of them divide the whole or any part of its share capital into Shares of smaller amount than is fixed by the Memorandum or into Shares without par value; and |
| (e) | cancel any Shares that at the date of the passing of the Ordinary Resolution have not been taken or agreed to be taken by any person and diminish the amount of its share capital by the amount of the Shares so cancelled. |
| 17.2 | All new Shares created in accordance with the provisions of the preceding Article shall be subject to the same provisions of the Articles with reference to the payment of calls, liens, transfer, transmission, forfeiture and otherwise as the Shares in the original share capital. |
| 17.3 | Subject to the provisions of the Statute and the provisions of the Articles as regards the matters to be dealt with by Ordinary Resolution, the Company may by Special Resolution: |
| (b) | alter or add to the Articles; |
| (c) | alter or add to the Memorandum with respect to any objects, powers or other matters specified therein; and |
| (d) | reduce its share capital or any capital redemption reserve fund. |
| 18 | Offices and Places of Business |
Subject to the provisions of the Statute, the Company may by resolution of the Directors change the location of its Registered Office. The Company may, in addition to its Registered Office, maintain such other offices or places of business as the Directors determine.
| 19.1 | All general meetings other than annual general meetings shall be called extraordinary general meetings. |
| 19.2 | The Company may, but shall not (unless required by the Statute) be obliged to, in each year hold a general meeting as its annual general meeting, and shall specify the meeting as such in the notices calling it. Any annual general meeting shall be held at such time and place as the Directors shall appoint. At these meetings the report of the Directors (if any) shall be presented. |
| 19.3 | The Directors or the chairperson of the board of Directors may call general meetings, and, for the avoidance of doubt, the Members shall not have the ability to call general meetings. |
| 19.4 | Members seeking to bring business before the annual general meeting or to nominate candidates for appointment as Directors at the annual general meeting must deliver notice to the principal executive offices of the Company not less than 120 calendar days before the date of the Company’s proxy statement released to Members in connection with the previous year’s annual general meeting or, if the Company did not hold an annual general meeting the previous year, or if the date of the current year’s annual general meeting has been changed by more than 30 days from the date of the previous year’s annual general meeting, then the deadline shall be set by the board of Directors with such deadline being a reasonable time before the Company begins to print and send its related proxy materials. |
| 20 | Notice of General Meetings |
| 20.1 | At least 5 clear days’ notice shall be given of any general meeting. Every notice shall specify the place, the day and the hour of the meeting and the general nature of the business to be conducted at the general meeting and shall be given in the manner hereinafter mentioned or in such other manner if any as may be prescribed by the Company, provided that a general meeting of the Company shall, whether or not the notice specified in this Article has been given and whether or not the provisions of the Articles regarding general meetings have been complied with, be deemed to have been duly convened if it is so agreed: |
| (a) | in the case of an annual general meeting, by all of the Members entitled to attend and vote at the meeting; and |
| (b) | in the case of an extraordinary general meeting, by a majority in number of the Members having a right to attend and vote at the meeting, together holding not less than 95% in par value of the Shares giving that right. |
| 20.2 | The accidental omission to give notice of a general meeting to, or the non receipt of notice of a general meeting by, any person entitled to receive such notice shall not invalidate the proceedings of that general meeting. |
| 21 | Proceedings at General Meetings |
| 21.1 | No business shall be transacted at any general meeting unless a quorum is present. The holders of a majority of the Shares being individuals present in person or by proxy or if a corporation or other non-natural person by its duly authorised representative or proxy shall be a quorum. |
| 21.2 | A person may participate at a general meeting by conference telephone or other communications equipment by means of which all the persons participating in the meeting can communicate with each other. Participation by a person in a general meeting in this manner is treated as presence in person at that meeting. |
| 21.3 | A resolution (including a Special Resolution) in writing (in one or more counterparts) signed by or on behalf of all of the Members for the time being entitled to receive notice of and to attend and vote at general meetings (or, being corporations or other non-natural persons, signed by their duly authorised representatives) shall be as valid and effective as if the resolution had been passed at a general meeting of the Company duly convened and held. |
| 21.4 | If a quorum is not present within half an hour from the time appointed for the meeting to commence, the meeting shall stand adjourned to the same day in the next week at the same time and/or place or to such other day, time and/or place as the Directors may determine, and if at the adjourned meeting a quorum is not present within half an hour from the time appointed for the meeting to commence, the Members present shall be a quorum. |
| 21.5 | The Directors may, at any time prior to the time appointed for the meeting to commence, appoint any person to act as chairperson of a general meeting of the Company or, if the Directors do not make any such appointment, the chairperson, if any, of the board of Directors shall preside as chairperson at such general meeting. If there is no such chairperson, or if the person shall not be present within 15 minutes after the time appointed for the meeting to commence, or is unwilling to act, the Directors present shall elect one of their number to be chairperson of the meeting. |
| 21.6 | If no Director is willing to act as chairperson or if no Director is present within 15 minutes after the time appointed for the meeting to commence, the Members present shall choose one of their number to be chairperson of the meeting. |
| 21.7 | The chairperson may, with the consent of a meeting at which a quorum is present (and shall if so directed by the meeting) adjourn the meeting from time to time and from place to place, but no business shall be transacted at any adjourned meeting other than the business left unfinished at the meeting from which the adjournment took place. |
| 21.8 | When a general meeting is adjourned for 30 days or more, notice of the adjourned meeting shall be given as in the case of an original meeting. Otherwise it shall not be necessary to give any such notice of an adjourned meeting. |
| 21.9 | A resolution put to the vote of the meeting shall be decided on a poll. |
| 21.10 | A poll shall be taken as the chairperson directs, and the result of the poll shall be deemed to be the resolution of the general meeting at which the poll was demanded. |
| 21.11 | A poll demanded on the election of a chairperson or on a question of adjournment shall be taken forthwith. A poll demanded on any other question shall be taken at such date, time and place as the chairperson of the general meeting directs, and any business other than that upon which a poll has been demanded or is contingent thereon may proceed pending the taking of the poll. |
| 21.12 | In the case of an equality of votes the chairperson shall be entitled to a second or casting vote. |
| 22.1 | Subject to any rights or restrictions attached to any Shares, every Member present in any such manner shall have one vote for every Share of which they are the holder. |
| 22.2 | In the case of joint holders the vote of the senior holder who tenders a vote, whether in person or by proxy (or, in the case of a corporation or other non-natural person, by its duly authorised representative or proxy), shall be accepted to the exclusion of the votes of the other joint holders, and seniority shall be determined by the order in which the names of the holders stand in the Register of Members. |
| 22.3 | A Member of unsound mind, or in respect of whom an order has been made by any court, having jurisdiction in lunacy, may vote by their committee, receiver, curator bonis, or other person on such Member’s behalf appointed by that court, and any such committee, receiver, curator bonis or other person may vote by proxy. |
| 22.4 | No person shall be entitled to vote at any general meeting unless they are registered as a Member on the record date for such meeting nor unless all calls or other monies then payable by them in respect of Shares have been paid. |
| 22.5 | No objection shall be raised as to the qualification of any voter except at the general meeting or adjourned general meeting at which the vote objected to is given or tendered and every vote not disallowed at the meeting shall be valid. Any objection made in due time in accordance with this Article shall be referred to the chairperson whose decision shall be final and conclusive. |
| 22.6 | Votes may be cast either personally or by proxy (or in the case of a corporation or other non-natural person by its duly authorised representative or proxy). A Member may appoint more than one proxy or the same proxy under one or more instruments to attend and vote at a meeting. Where a Member appoints more than one proxy the instrument of proxy shall specify the number of Shares in respect of which each proxy is entitled to exercise the related votes. |
| 22.7 | A Member holding more than one Share need not cast the votes in respect of their Shares in the same way on any resolution and therefore may vote a Share or some or all such Shares either for or against a resolution and/or abstain from voting a Share or some or all of the Shares and, subject to the terms of the instrument appointing the proxy, a proxy appointed under one or more instruments may vote a Share or some or all of the Shares in respect of which they are appointed either for or against a resolution and/or abstain from voting a Share or some or all of the Shares in respect of which they are appointed. |
| 23.1 | The instrument appointing a proxy shall be in writing and shall be executed under the hand of the appointor or of their attorney duly authorised in writing, or, if the appointor is a corporation or other non natural person, under the hand of its duly authorised representative. A proxy need not be a Member. |
| 23.2 | The Directors may, in the notice convening any meeting or adjourned meeting, or in an instrument of proxy sent out by the Company, specify the manner by which the instrument appointing a proxy shall be deposited and the place and the time (being not later than the time appointed for the commencement of the meeting or adjourned meeting to which the proxy relates) at which the instrument appointing a proxy shall be deposited. In the absence of any such direction from the Directors in the notice convening any meeting or adjourned meeting or in an instrument of proxy sent out by the Company, the instrument appointing a proxy shall be deposited physically at the Registered Office not less than 48 hours before the time appointed for the meeting or adjourned meeting to commence at which the person named in the instrument proposes to vote. |
| 23.3 | The chairperson may in any event at their discretion declare that an instrument of proxy shall be deemed to have been duly deposited. An instrument of proxy that is not deposited in the manner permitted, or which has not been declared to have been duly deposited by the chairperson, shall be invalid. |
| 23.4 | The instrument appointing a proxy may be in any usual or common form (or such other form as the Directors may approve) and may be expressed to be for a particular meeting or any adjournment thereof or generally until revoked. An instrument appointing a proxy shall be deemed to include the power to demand or join or concur in demanding a poll. |
| 23.5 | Votes given in accordance with the terms of an instrument of proxy shall be valid notwithstanding the previous death or insanity of the principal or revocation of the proxy or of the authority under which the proxy was executed, or the transfer of the Share in respect of which the proxy is given unless notice in writing of such death, insanity, revocation or transfer was received by the Company at the Registered Office before the commencement of the general meeting, or adjourned meeting at which it is sought to use the proxy. |
| 24.1 | Any corporation or other non-natural person which is a Member may in accordance with its constitutional documents, or in the absence of such provision by resolution of its directors or other governing body, authorise such person as it thinks fit to act as its representative at any meeting of the Company or of any class of Members, and the person so authorised shall be entitled to exercise the same powers on behalf of the corporation which they represent as the corporation could exercise if it were an individual Member. |
| 24.2 | If a Clearing House (or its nominee(s)), being a corporation, is a Member, it may authorise such persons as it sees fit to act as its representative at any meeting of the Company or at any meeting of any class of Members provided that the authorisation shall specify the number and class or series of Shares in respect of which each such representative is so authorised. Each person so authorised under the provisions of this Article shall be deemed to have been duly authorised without further evidence of the facts and be entitled to exercise the same rights and powers on behalf of the Clearing House (or its nominee(s)) as if such person was the registered holder of such Shares held by the Clearing House (or its nominee(s)). |
| 25 | Shares that May Not be Voted |
Shares in the Company that are beneficially owned by the Company shall not be voted, directly or indirectly, at any meeting and shall not be counted in determining the total number of outstanding Shares at any given time.
| 26.1 | There shall be a board of Directors consisting of not less than one person (exclusive of alternate Directors) provided however that the Company may by Ordinary Resolution increase or reduce the limits in the number of Directors. |
| 26.2 | The Directors shall be divided into three classes: Class I, Class II and Class III. The number of Directors in each class shall be as nearly equal as possible. Upon the adoption of the Articles, the existing Directors shall by resolution classify themselves as Class I, Class II or Class III Directors. The Class I Directors shall stand appointed for a term expiring at the Company’s first annual general meeting, the Class II Directors shall stand appointed for a term expiring at the Company’s second annual general meeting and the Class III Directors shall stand appointed for a term expiring at the Company’s third annual general meeting. Commencing at the Company’s first annual general meeting, and at each annual general meeting thereafter, Directors appointed to succeed those Directors whose terms expire shall be appointed for a term of office to expire at the third succeeding annual general meeting after their appointment. Except as the Statute or other Applicable Law may otherwise require, in the interim between annual general meetings or extraordinary general meetings called for the appointment of Directors and/or the removal of one or more Directors and the filling of any vacancy in that connection, additional Directors and any vacancies in the board of Directors, including unfilled vacancies resulting from the removal of Directors for cause, may be filled by the vote of a majority of the remaining Directors then in office, although less than a quorum (as defined in the Articles), or by the sole remaining Director. All Directors shall hold office until the expiration of their respective terms of office and until their successors shall have been appointed and qualified. A Director appointed to fill a vacancy resulting from the death, resignation or removal of a Director shall serve for the remainder of the full term of the Director whose death, resignation or removal shall have created such vacancy and until their successor shall have been appointed and qualified. |
| 27.1 | Subject to the provisions of the Statute, the Memorandum and the Articles and to any directions given by Special Resolution, the business of the Company shall be managed by the Directors who may exercise all the powers of the Company. No alteration of the Memorandum or Articles and no such direction shall invalidate any prior act of the Directors which would have been valid if that alteration had not been made or that direction had not been given. A duly convened meeting of Directors at which a quorum is present may exercise all powers exercisable by the Directors. |
| 27.2 | All cheques, promissory notes, drafts, bills of exchange and other negotiable or transferable instruments and all receipts for monies paid to the Company shall be signed, drawn, accepted, endorsed or otherwise executed as the case may be in such manner as the Directors shall determine by resolution. |
| 27.3 | The Directors on behalf of the Company may pay a gratuity or pension or allowance on retirement to any Director who has held any other salaried office or place of profit with the Company or to their surviving spouse, civil partner or dependants and may make contributions to any fund and pay premiums for the purchase or provision of any such gratuity, pension or allowance. |
| 27.4 | The Directors may exercise all the powers of the Company to borrow money and to mortgage or charge its undertaking, property and assets (present and future) and uncalled capital or any part thereof and to issue debentures, debenture stock, mortgages, bonds and other such securities whether outright or as security for any debt, liability or obligation of the Company or of any third party. |
| 28 | Appointment and Removal of Directors |
| 28.1 | The Company may by Ordinary Resolution appoint any person to be a Director or may by Ordinary Resolution remove any Director. |
| 28.2 | The Directors may appoint any person to be a Director, either to fill a vacancy or as an additional Director provided that the appointment does not cause the number of Directors to exceed any number fixed by or in accordance with the Articles as the maximum number of Directors. |
| 29 | Vacation of Office of Director |
The office of a Director shall be vacated if:
| (a) | the Director gives notice in writing to the Company that they resign the office of Director; or |
| (b) | the Director is absent (for the avoidance of doubt, without being represented by proxy or an alternate Director appointed by them) from three consecutive meetings of the board of Directors without special leave of absence from the Directors, and the Directors pass a resolution that they have by reason of such absence vacated office; or |
| (c) | the Director dies, becomes bankrupt or makes any arrangement or composition with their creditors generally; or |
| (d) | the Director is found to be or becomes of unsound mind; or |
| (e) | all of the other Directors (being not less than two in number) determine that the Director should be removed as a Director, either by a resolution passed by all of the other Directors at a meeting of the Directors duly convened and held in accordance with the Articles or by a resolution in writing signed by all of the other Directors. |
| 30 | Proceedings of Directors |
| 30.1 | The quorum for the transaction of the business of the Directors may be fixed by the Directors, and unless so fixed shall be a majority of the Directors then in office. A person who holds office as an alternate Director shall, if their appointor is not present, be counted in the quorum. A Director who also acts as an alternate Director shall, if their appointor is not present, count twice towards the quorum. |
| 30.2 | Subject to the provisions of the Articles, the Directors may regulate their proceedings as they think fit. Questions arising at any meeting shall be decided by a majority of votes. In the case of an equality of votes, the chairperson shall have a second or casting vote. A Director who is also an alternate Director shall be entitled in the absence of their appointor to a separate vote on behalf of their appointor in addition to their own vote. |
| 30.3 | A person may participate in a meeting of the Directors or any committee of Directors by conference telephone or other communications equipment by means of which all the persons participating in the meeting can communicate with each other at the same time. Participation by a person in a meeting in this manner is treated as presence in person at that meeting. Unless otherwise determined by the Directors, the meeting shall be deemed to be held at the place where the chairperson is located at the start of the meeting. |
| 30.4 | A resolution in writing (in one or more counterparts) signed by all the Directors or all the members of a committee of the Directors or, in the case of a resolution in writing relating to the removal of any Director or the vacation of office by any Director, all of the Directors other than the Director who is the subject of such resolution (an alternate Director being entitled to sign such a resolution on behalf of their appointor and if such alternate Director is also a Director, being entitled to sign such resolution both on behalf of their appointor and in their capacity as a Director) shall be as valid and effectual as if it had been passed at a meeting of the Directors, or committee of Directors as the case may be, duly convened and held. |
| 30.5 | A Director or alternate Director may, or other officer of the Company on the direction of a Director or alternate Director shall, call a meeting of the Directors by at least two days’ notice in writing to every Director and alternate Director which notice shall set forth the general nature of the business to be considered unless notice is waived by all the Directors (or their alternates) either at, before or after the meeting is held. To any such notice of a meeting of the Directors all the provisions of the Articles relating to the giving of notices by the Company to the Members shall apply mutatis mutandis. |
| 30.6 | The continuing Directors (or a sole continuing Director, as the case may be) may act notwithstanding any vacancy in their body, but if and so long as their number is reduced below the number fixed by or pursuant to the Articles as the necessary quorum of Directors the continuing Directors or Director may act for the purpose of increasing the number of Directors to be equal to such fixed number, or of summoning a general meeting of the Company, but for no other purpose. |
| 30.7 | The Directors may elect a chairperson of their board and determine the period for which they are to hold office; but if no such chairperson is elected, or if at any meeting the chairperson is not present within five minutes after the time appointed for the meeting to commence, the Directors present may choose one of their number to be chairperson of the meeting. |
| 30.8 | All acts done by any meeting of the Directors or of a committee of the Directors (including any person acting as an alternate Director) shall, notwithstanding that it is afterwards discovered that there was some defect in the appointment of any Director or alternate Director, and/or that they or any of them were disqualified, and/or had vacated their office and/or were not entitled to vote, be as valid as if every such person had been duly appointed and/or not disqualified to be a Director or alternate Director and/or had not vacated their office and/or had been entitled to vote, as the case may be. |
| 30.9 | A Director but not an alternate Director may be represented at any meetings of the board of Directors by a proxy appointed in writing by that Director. The proxy shall count towards the quorum and the vote of the proxy shall for all purposes be deemed to be that of the appointing Director. |
A Director or alternate Director who is present at a meeting of the board of Directors at which action on any Company matter is taken shall be presumed to have assented to the action taken unless their dissent shall be entered in the minutes of the meeting or unless they shall file their written dissent from such action with the person acting as the chairperson or secretary of the meeting before the adjournment thereof or shall forward such dissent by registered post to such person immediately after the adjournment of the meeting. Such right to dissent shall not apply to a Director or alternate Director who voted in favour of such action.
| 32.1 | A Director or alternate Director may hold any other office or place of profit under the Company (other than the office of Auditor) in conjunction with their office of Director for such period and on such terms as to remuneration and otherwise as the Directors may determine. |
| 32.2 | A Director or alternate Director may act on their own or by, through or on behalf of their firm in a professional capacity for the Company and they or their firm shall be entitled to remuneration for professional services as if they were not a Director or alternate Director. |
| 32.3 | A Director or alternate Director may be or become a director or other officer of or otherwise interested in any company promoted by the Company or in which the Company may be interested as a shareholder, a contracting party or otherwise, and no such Director or alternate Director shall be accountable to the Company for any remuneration or other benefits received by them as a director or officer of, or from their interest in, such other company. |
| 32.4 | No person shall be disqualified from the office of Director or alternate Director or prevented by such office from contracting with the Company, either as vendor, purchaser or otherwise, nor shall any such contract or any contract or transaction entered into by or on behalf of the Company in which any Director or alternate Director shall be in any way interested be or be liable to be avoided, nor shall any Director or alternate Director so contracting or being so interested be liable to account to the Company for any profit realised by or arising in connection with any such contract or transaction by reason of such Director or alternate Director holding office or of the fiduciary relationship thereby established. A Director (or their alternate Director in their absence) shall be at liberty to vote in respect of any contract or transaction in which they are interested provided that the nature of the interest of any Director or alternate Director in any such contract or transaction shall be disclosed by them at or prior to its consideration and any vote thereon. |
| 32.5 | A general notice that a Director or alternate Director is a shareholder, director, officer or employee of any specified firm or company and is to be regarded as interested in any transaction with such firm or company shall be sufficient disclosure for the purposes of voting on a resolution in respect of a contract or transaction in which they have an interest, and after such general notice it shall not be necessary to give special notice relating to any particular transaction. |
The Directors shall cause minutes to be made in books kept for the purpose of recording all appointments of officers made by the Directors, all proceedings at meetings of the Company or the holders of any class of Shares and of the Directors, and of committees of the Directors, including the names of the Directors or alternate Directors present at each meeting.
| 34 | Delegation of Directors’ Powers |
| 34.1 | The Directors may delegate any of their powers, authorities and discretions, including the power to sub-delegate, to any committee consisting of one or more Directors (including, without limitation, the Audit Committee, the Compensation Committee and the Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee). They may also delegate to any managing director or any Director holding any other executive office such of their powers, authorities and discretions as they consider desirable to be exercised by that Director, provided that an alternate Director may not act as managing director and the appointment of a managing director shall be revoked forthwith if they cease to be a Director. Any such delegation may be made subject to any conditions the Directors may impose and either collaterally with or to the exclusion of their own powers and any such delegation may be revoked or altered by the Directors. Subject to any such conditions, the proceedings of a committee of Directors shall be governed by the Articles regulating the proceedings of Directors, so far as they are capable of applying. |
| 34.2 | The Directors may establish any committees, local boards or agencies or appoint any person to be a manager or agent for managing the affairs of the Company and may appoint any person to be a member of such committees, local boards or agencies. Any such appointment may be made subject to any conditions the Directors may impose, and either collaterally with or to the exclusion of their own powers and any such appointment may be revoked or altered by the Directors. Subject to any such conditions, the proceedings of any such committee, local board or agency shall be governed by the Articles regulating the proceedings of Directors, so far as they are capable of applying. |
| 34.3 | The Directors may adopt formal written charters for committees as may be required from time to time by the rules and regulations of the Designated Stock Exchange, the Securities and Exchange Commission and/or any other competent regulatory authority or otherwise under Applicable Law. Each of these committees shall be empowered to do all things necessary to exercise the rights of such committee set forth in the Articles and shall have such powers as the Directors may delegate pursuant to the Articles and as required by the rules and regulations of the Designated Stock Exchange, the Securities and Exchange Commission and/or any other competent regulatory authority or otherwise under Applicable Law. Each of the Audit Committee, the Compensation Committee and the Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee, if established, shall consist of such number of Directors as the Directors shall from time to time determine (or such minimum number as may be required from time to time by the rules and regulations of the Designated Stock Exchange, the Securities and Exchange Commission and/or any other competent regulatory authority or otherwise under Applicable Law). For so long as any class or series of Shares is listed on the Designated Stock Exchange, the Audit Committee, the Compensation Committee and the Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee shall be made up of such number of Independent Directors as is required from time to time by the rules and regulations of the Designated Stock Exchange, the Securities and Exchange Commission and/or any other competent regulatory authority or otherwise under Applicable Law. |
| 34.4 | The Directors may by power of attorney or otherwise appoint any person to be the agent of the Company on such conditions as the Directors may determine, provided that the delegation is not to the exclusion of their own powers and may be revoked by the Directors at any time. |
| 34.5 | The Directors may by power of attorney or otherwise appoint any company, firm, person or body of persons, whether nominated directly or indirectly by the Directors, to be the attorney or authorised signatory of the Company for such purpose and with such powers, authorities and discretions (not exceeding those vested in or exercisable by the Directors under the Articles) and for such period and subject to such conditions as they may think fit, and any such powers of attorney or other appointment may contain such provisions for the protection and convenience of persons dealing with any such attorneys or authorised signatories as the Directors may think fit and may also authorise any such attorney or authorised signatory to delegate all or any of the powers, authorities and discretions vested in them. |
| 34.6 | The Directors may appoint such Officers as they consider necessary on such terms, at such remuneration and to perform such duties, and subject to such provisions as to disqualification and removal as the Directors may think fit. Unless otherwise specified in the terms of their appointment an Officer may be removed by resolution of the Directors or Members. An Officer may vacate their office at any time if they give notice in writing to the Company that they resign their office. |
| 35.1 | Any Director (but not an alternate Director) may by writing appoint any other Director, or any other person willing to act, to be an alternate Director and by writing may remove from office an alternate Director so appointed by them. |
| 35.2 | An alternate Director shall be entitled to receive notice of all meetings of Directors and of all meetings of committees of Directors of which their appointor is a member, to attend and vote at every such meeting at which the Director appointing them is not personally present, to sign any written resolution of the Directors, and generally to perform all the functions of their appointor as a Director in their absence. |
| 35.3 | An alternate Director shall cease to be an alternate Director if their appointor ceases to be a Director. |
| 35.4 | Any appointment or removal of an alternate Director shall be by notice to the Company signed by the Director making or revoking the appointment or in any other manner approved by the Directors. |
| 35.5 | Subject to the provisions of the Articles, an alternate Director shall be deemed for all purposes to be a Director and shall alone be responsible for their own acts and defaults and shall not be deemed to be the agent of the Director appointing them. |
| 36 | No Minimum Shareholding |
The Company in general meeting may fix a minimum shareholding required to be held by a Director, but unless and until such a shareholding qualification is fixed a Director is not required to hold Shares.
| 37 | Remuneration of Directors |
| 37.1 | The remuneration to be paid to the Directors, if any, shall be such remuneration as the Directors shall determine. The Directors shall also be entitled to be paid all travelling, hotel and other expenses properly incurred by them in connection with their attendance at meetings of Directors or committees of Directors, or general meetings of the Company, or separate meetings of the holders of any class or series of Shares or debentures of the Company, or otherwise in connection with the business of the Company or the discharge of their duties as a Director, or to receive a fixed allowance in respect thereof as may be determined by the Directors, or a combination partly of one such method and partly the other. |
| 37.2 | The Directors may by resolution approve additional remuneration to any Director for any services which in the opinion of the Directors go beyond that Director’s ordinary routine work as a Director. Any fees paid to a Director who is also counsel, attorney or solicitor to the Company, or otherwise serves it in a professional capacity shall be in addition to their remuneration as a Director. |
| 38.1 | The Company may, if the Directors so determine, have a Seal. The Seal shall only be used by the authority of the Directors or of a committee of the Directors authorised by the Directors. Every instrument to which the Seal has been affixed shall be signed by at least one person who shall be either a Director or some Officer or other person appointed by the Directors for the purpose. |
| 38.2 | The Company may have for use in any place or places outside the Cayman Islands a duplicate Seal or Seals each of which shall be a facsimile of the common Seal of the Company and, if the Directors so determine, with the addition on its face of the name of every place where it is to be used. |
| 38.3 | A Director or Officer, representative or attorney of the Company may without further authority of the Directors affix the Seal over their signature alone to any document of the Company required to be authenticated by them under seal or to be filed with the Registrar of Companies in the Cayman Islands or elsewhere wheresoever. |
| 39 | Dividends, Distributions and Reserve |
| 39.1 | Subject to the Statute and this Article and except as otherwise provided by the rights attached to any Shares, the Directors may resolve to pay Dividends and other distributions on Shares in issue and authorise payment of the Dividends or other distributions out of the funds of the Company lawfully available therefor. A Dividend shall be deemed to be an interim Dividend unless the terms of the resolution pursuant to which the Directors resolve to pay such Dividend specifically state that such Dividend shall be a final Dividend. No Dividend or other distribution shall be paid except out of the realised or unrealised profits of the Company, out of the share premium account or as otherwise permitted by law. |
| 39.2 | Except as otherwise provided by the rights attached to any Shares, all Dividends and other distributions shall be paid according to the par value of the Shares that a Member holds. If any Share is issued on terms providing that it shall rank for Dividend as from a particular date, that Share shall rank for Dividend accordingly. |
| 39.3 | The Directors may deduct from any Dividend or other distribution payable to any Member all sums of money (if any) then payable by the Member to the Company on account of calls or otherwise. |
| 39.4 | The Directors may resolve that any Dividend or other distribution be paid wholly or partly by the distribution of specific assets and in particular (but without limitation) by the distribution of shares, debentures, or securities of any other company or in any one or more of such ways and where any difficulty arises in regard to such distribution, the Directors may settle the same as they think expedient and in particular may issue fractional Shares and may fix the value for distribution of such specific assets or any part thereof and may determine that cash payments shall be made to any Members upon the basis of the value so fixed in order to adjust the rights of all Members and may vest any such specific assets in trustees in such manner as may seem expedient to the Directors. |
| 39.5 | Except as otherwise provided by the rights attached to any Shares, Dividends and other distributions may be paid in any currency. The Directors may determine the basis of conversion for any currency conversions that may be required and how any costs involved are to be met. |
| 39.6 | The Directors may, before resolving to pay any Dividend or other distribution, set aside such sums as they think proper as a reserve or reserves which shall, at the discretion of the Directors, be applicable for any purpose of the Company and pending such application may, at the discretion of the Directors, be employed in the business of the Company. |
| 39.7 | Any Dividend, other distribution, interest or other monies payable in cash in respect of Shares may be paid by wire transfer to the holder or by cheque or warrant sent through the post directed to the registered address of the holder or, in the case of joint holders, to the registered address of the holder who is first named on the Register of Members or to such person and to such address as such holder or joint holders may in writing direct. Every such cheque or warrant shall be made payable to the order of the person to whom it is sent. Any one of two or more joint holders may give effectual receipts for any Dividends, other distributions, bonuses, or other monies payable in respect of the Share held by them as joint holders. |
| 39.8 | No Dividend or other distribution shall bear interest against the Company. |
| 39.9 | Any Dividend or other distribution which cannot be paid to a Member and/or which remains unclaimed after six months from the date on which such Dividend or other distribution becomes payable may, in the discretion of the Directors, be paid into a separate account in the Company’s name, provided that the Company shall not be constituted as a trustee in respect of that account and the Dividend or other distribution shall remain as a debt due to the Member. Any Dividend or other distribution which remains unclaimed after a period of six years from the date on which such Dividend or other distribution becomes payable shall be forfeited and shall revert to the Company. |
| 39.10 | Prior to the Deadline Date, the Directors may not resolve to pay Dividends and other distributions on Shares in issue and authorise payment of the Dividends or other distributions out of the funds of the Company lawfully available therefor. |
The Directors may at any time capitalise any sum standing to the credit of any of the Company’s reserve accounts or funds (including the share premium account and capital redemption reserve fund) or any sum standing to the credit of the profit and loss account or otherwise available for distribution; appropriate such sum to Members in the proportions in which such sum would have been divisible amongst such Members had the same been a distribution of profits by way of Dividend or other distribution; and apply such sum on their behalf in paying up in full unissued Shares for allotment and distribution credited as fully paid-up to and amongst them in the proportion aforesaid. In such event the Directors shall do all acts and things required to give effect to such capitalisation, with full power given to the Directors to make such provisions as they think fit in the case of Shares becoming distributable in fractions (including provisions whereby the benefit of fractional entitlements accrue to the Company rather than to the Members concerned). The Directors may authorise any person to enter on behalf of all of the Members interested into an agreement with the Company providing for such capitalisation and matters incidental or relating thereto and any agreement made under such authority shall be effective and binding on all such Members and the Company.
| 41.1 | The Directors shall cause proper books of account (including, where applicable, material underlying documentation including contracts and invoices) to be kept with respect to all sums of money received and expended by the Company and the matters in respect of which the receipt or expenditure takes place, all sales and purchases of goods by the Company and the assets and liabilities of the Company. Such books of account must be retained for a minimum period of five years from the date on which they are prepared. Proper books shall not be deemed to be kept if there are not kept such books of account as are necessary to give a true and fair view of the state of the Company’s affairs and to explain its transactions. |
| 41.2 | The Directors shall determine whether and to what extent and at what times and places and under what conditions or regulations the accounts and books of the Company or any of them shall be open to the inspection of Members not being Directors and no Member (not being a Director) shall have any right of inspecting any account or book or document of the Company except as conferred by Statute or authorised by the Directors or by the Company in general meeting. |
| 41.3 | The Directors may cause to be prepared and to be laid before the Company in general meeting profit and loss accounts, balance sheets, group accounts (if any) and such other reports and accounts as may be required by law. |
| 42.1 | The Directors may appoint an Auditor of the Company who shall hold office on such terms as the Directors determine. |
| 42.2 | Without prejudice to the freedom of the Directors to establish any other committee, if the Shares (or depositary receipts therefor) are listed or quoted on the Designated Stock Exchange, and if required by the rules and regulations of the Designated Stock Exchange, the Securities and Exchange Commission and/or any other competent regulatory authority or otherwise under Applicable Law, the Directors shall establish and maintain an Audit Committee as a committee of the Directors and shall adopt a formal written Audit Committee charter and review and assess the adequacy of the formal written charter on an annual basis. The composition and responsibilities of the Audit Committee shall comply with the rules and regulations of the Designated Stock Exchange, the Securities and Exchange Commission and/or any other competent regulatory authority or otherwise under Applicable Law. If the Shares (or depositary receipts therefor) are listed or quoted on the Designated Stock Exchange, the Company shall conduct an appropriate review of all related party transactions on an ongoing basis and shall utilise the Audit Committee for the review and approval of potential conflicts of interest. |
| 42.3 | The remuneration of the Auditor shall be fixed by the Audit Committee (if one exists). |
| 42.4 | If the office of Auditor becomes vacant by resignation or death of the Auditor, or by their becoming incapable of acting by reason of illness or other disability at a time when their services are required, the Directors shall fill the vacancy and determine the remuneration of such Auditor. |
| 42.5 | Every Auditor of the Company shall have a right of access at all times to the books and accounts and vouchers of the Company and shall be entitled to require from the Directors and Officers such information and explanation as may be necessary for the performance of the duties of the Auditor. |
| 42.6 | Auditors shall, if so required by the Directors, make a report on the accounts of the Company during their tenure of office at the next annual general meeting following their appointment in the case of a company which is registered with the Registrar of Companies as an ordinary company, and at the next extraordinary general meeting following their appointment in the case of a company which is registered with the Registrar of Companies as an exempted company, and at any other time during their term of office, upon request of the Directors or any general meeting of the Members. |
| 42.7 | At least one member of the Audit Committee shall be an “audit committee financial expert” as determined by the rules and regulations of the Designated Stock Exchange, the Securities and Exchange Commission and/or any other competent regulatory authority or otherwise under Applicable Law. The “audit committee financial expert” shall have such past employment experience in finance or accounting, requisite professional certification in accounting, or any other comparable experience or background which results in the individual’s financial sophistication. |
| 43.1 | Notices shall be in writing and may be given by the Company to any Member either personally or by sending it by courier, post, telex, fax or email to such Member or to such Member’s address as shown in the Register of Members (or where the notice is given by email by sending it to the email address provided by such Member). Notice may also be served by Electronic Communication in accordance with the rules and regulations of the Designated Stock Exchange, the Securities and Exchange Commission and/or any other competent regulatory authority or by placing it on the Company’s Website. |
| 43.2 | Where a notice is sent by: |
| (a) | courier; service of the notice shall be deemed to be effected by delivery of the notice to a courier company, and shall be deemed to have been received on the third day (not including Saturdays or Sundays or public holidays) following the day on which the notice was delivered to the courier; |
| (b) | post; service of the notice shall be deemed to be effected by properly addressing, pre paying and posting a letter containing the notice, and shall be deemed to have been received on the fifth day (not including Saturdays or Sundays or public holidays in the Cayman Islands) following the day on which the notice was posted; |
| (c) | telex or fax; service of the notice shall be deemed to be effected by properly addressing and sending such notice and shall be deemed to have been received on the same day that it was transmitted; |
| (d) | email or other Electronic Communication; service of the notice shall be deemed to be effected by transmitting the email to the email address provided by the intended recipient and shall be deemed to have been received on the same day that it was sent, and it shall not be necessary for the receipt of the email to be acknowledged by the recipient; and |
| (e) | placing it on the Company’s Website; service of the notice shall be deemed to have been effected one hour after the notice or document was placed on the Company’s Website. |
| 43.3 | A notice may be given by the Company to the person or persons which the Company has been advised are entitled to a Share or Shares in consequence of the death or bankruptcy of a Member in the same manner as other notices which are required to be given under the Articles and shall be addressed to them by name, or by the title of representatives of the deceased, or trustee of the bankrupt, or by any like description at the address supplied for that purpose by the persons claiming to be so entitled, or at the option of the Company by giving the notice in any manner in which the same might have been given if the death or bankruptcy had not occurred. |
| 43.4 | Notice of every general meeting shall be given in any manner authorised by the Articles to every holder of Shares carrying an entitlement to receive such notice on the record date for such meeting except that in the case of joint holders the notice shall be sufficient if given to the joint holder first named in the Register of Members and every person upon whom the ownership of a Share devolves because they are a legal personal representative or a trustee in bankruptcy of a Member where the Member but for their death or bankruptcy would be entitled to receive notice of the meeting, and no other person shall be entitled to receive notices of general meetings. |
| 44.1 | If the Company shall be wound up, the liquidator shall apply the assets of the Company in satisfaction of creditors’ claims in such manner and order as such liquidator thinks fit. Subject to the rights attaching to any Shares, in a winding up: |
| (a) | if the assets available for distribution amongst the Members shall be insufficient to repay the whole of the Company’s issued share capital, such assets shall be distributed so that, as nearly as may be, the losses shall be borne by the Members in proportion to the par value of the Shares held by them; or |
| (b) | if the assets available for distribution amongst the Members shall be more than sufficient to repay the whole of the Company’s issued share capital at the commencement of the winding up, the surplus shall be distributed amongst the Members in proportion to the par value of the Shares held by them at the commencement of the winding up subject to a deduction from those Shares in respect of which there are monies due, of all monies payable to the Company for unpaid calls or otherwise. |
| 44.2 | If the Company shall be wound up the liquidator may, subject to the rights attaching to any Shares and with the approval of a Special Resolution of the Company and any other approval required by the Statute, divide amongst the Members in kind the whole or any part of the assets of the Company (whether such assets shall consist of property of the same kind or not) and may for that purpose value any assets and determine how the division shall be carried out as between the Members or different classes of Members. The liquidator may, with the like approval, vest the whole or any part of such assets in trustees upon such trusts for the benefit of the Members as the liquidator, with the like approval, shall think fit, but so that no Member shall be compelled to accept any asset upon which there is a liability. |
| 45 | Indemnity and Insurance |
| 45.1 | Every Director and Officer (which for the avoidance of doubt, shall not include auditors of the Company), together with every former Director and former Officer (each an “Indemnified Person”) shall be indemnified out of the assets of the Company against any liability, action, proceeding, claim, demand, costs, damages or expenses, including legal expenses, whatsoever which they or any of them may incur as a result of any act or failure to act in carrying out their functions other than such liability (if any) that they may incur by reason of their own actual fraud, wilful neglect or wilful default. No Indemnified Person shall be liable to the Company for any loss or damage incurred by the Company as a result (whether direct or indirect) of the carrying out of their functions unless that liability arises through the actual fraud, wilful neglect or wilful default of such Indemnified Person. No person shall be found to have committed actual fraud, wilful neglect or wilful default under this Article unless or until a court of competent jurisdiction shall have made a finding to that effect. |
| 45.2 | The Company shall advance to each Indemnified Person reasonable attorneys’ fees and other costs and expenses incurred in connection with the defence of any action, suit, proceeding or investigation involving such Indemnified Person for which indemnity will or could be sought. In connection with any advance of any expenses hereunder, the Indemnified Person shall execute an undertaking to repay the advanced amount to the Company if it shall be determined by final judgment or other final adjudication that such Indemnified Person was not entitled to indemnification pursuant to this Article. If it shall be determined by a final judgment or other final adjudication that such Indemnified Person was not entitled to indemnification with respect to such judgment, costs or expenses, then such party shall not be indemnified with respect to such judgment, costs or expenses and any advancement shall be returned to the Company (without interest) by the Indemnified Person. |
| 45.3 | The Directors, on behalf of the Company, may purchase and maintain insurance for the benefit of any Director or Officer against any liability which, by virtue of any rule of law, would otherwise attach to such person in respect of any negligence, default, breach of duty or breach of trust of which such person may be guilty in relation to the Company. |
Unless the Directors otherwise prescribe, the financial year of the Company shall end on 31st December in each year and, following the year of incorporation, shall begin on 1st January in each year.
| 47 | Transfer by Way of Continuation |
If the Company is exempted as defined in the Statute, it shall, subject to the provisions of the Statute and with the approval of a Special Resolution, have the power to register by way of continuation as a body corporate under the laws of any jurisdiction outside the Cayman Islands and to be deregistered in the Cayman Islands.
| 48 | Mergers and Consolidations |
The Company shall have the power to merge or consolidate with one or more other constituent companies (as defined in the Statute) upon such terms as the Directors may determine and (to the extent required by the Statute) with the approval of a Special Resolution.
| 49.1 | To the fullest extent permitted by Applicable Law, no individual serving as a Director or an Officer (“Management”) shall have any duty, except and to the extent expressly assumed by contract, to refrain from engaging directly or indirectly in the same or similar business activities or lines of business as the Company. To the fullest extent permitted by Applicable Law, the Company renounces any interest or expectancy of the Company in, or in being offered an opportunity to participate in, any potential transaction or matter which may be a corporate opportunity for Management, on the one hand, and the Company, on the other. Except to the extent expressly assumed by contract, to the fullest extent permitted by Applicable Law, Management shall have no duty to communicate or offer any such corporate opportunity to the Company and shall not be liable to the Company or its Members for breach of any fiduciary duty as a Member, Director and/or Officer solely by reason of the fact that such party pursues or acquires such corporate opportunity for itself, directs such corporate opportunity to another person, or does not communicate information regarding such corporate opportunity to the Company. |
| 49.2 | Except as provided elsewhere in this Article, the Company hereby renounces any interest or expectancy of the Company in, or in being offered an opportunity to participate in, any potential transaction or matter which may be a corporate opportunity for both the Company and Management, about which a Director and/or Officer who is also a member of Management acquires knowledge. |
| 49.3 | To the extent a court might hold that the conduct of any activity related to a corporate opportunity that is renounced in this Article to be a breach of duty to the Company or its Members, the Company hereby waives, to the fullest extent permitted by Applicable Law, any and all claims and causes of action that the Company may have for such activities. To the fullest extent permitted by Applicable Law, the provisions of this Article apply equally to activities conducted in the future and that have been conducted in the past. |
| 50 | Exclusive Jurisdiction and Forum |
| 50.1 | Unless the Company consents in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the courts of the Cayman Islands shall have exclusive jurisdiction over any claim or dispute arising out of or in connection with the Memorandum, the Articles or otherwise related in any way to each Member’s shareholding in the Company, including but not limited to: |
| (a) | any derivative action or proceeding brought on behalf of the Company; |
| (b) | any action asserting a claim of breach of any fiduciary or other duty owed by any current or former Director, Officer or other employee of the Company to the Company or the Members; |
| (c) | any action asserting a claim arising pursuant to any provision of the Statute, the Memorandum or the Articles; or |
| (d) | any action asserting a claim against the Company governed by the “Internal Affairs Doctrine” (as such concept is recognised under the laws of the United States of America). |
| 50.2 | Each Member irrevocably submits to the exclusive jurisdiction of the courts of the Cayman Islands over all such claims or disputes. |
| 50.3 | Without prejudice to any other rights or remedies that the Company may have, each Member acknowledges that damages alone would not be an adequate remedy for any breach of the selection of the courts of the Cayman Islands as exclusive forum and that accordingly the Company shall be entitled, without proof of special damages, to the remedies of injunction, specific performance or other equitable relief for any threatened or actual breach of the selection of the courts of the Cayman Islands as exclusive forum. |
| 50.4 | This Article 50 shall not apply to any action or suits brought to enforce any liability or duty created by the United States Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the Exchange Act, or any claim for which the federal district courts of the United States of America are, as a matter of the laws of the United States, the sole and exclusive forum for determination of such a claim. |
Annex C
K WAVE MEDIA LTD.
2024 EQUITY INCENTIVE PLAN
Article I
PURPOSE
The purpose of this K Wave Media Ltd. 2024 Equity Incentive Plan (the “Plan”) is to benefit K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (the “Company”) and its stockholders, by assisting the Company and its subsidiaries to attract, retain and provide incentives to key management employees, directors, and consultants of the Company and its Affiliates, and to align the interests of such service providers with those of the Company’s stockholders. Accordingly, the Plan provides for the granting of Non-qualified Stock Options, Incentive Stock Options, Restricted Stock Awards, Restricted Stock Unit Awards, Stock Appreciation Rights, Performance Stock Awards, Performance Unit Awards, Unrestricted Stock Awards, Distribution Equivalent Rights or any combination of the foregoing.
Article II
DEFINITIONS
The following definitions shall be applicable throughout the Plan unless the context otherwise requires:
2.1 “Affiliate” shall mean (i) any person or entity that directly or indirectly controls, is controlled by or is under common control with the Company and/or (ii) to the extent provided by the Committee, any person or entity in which the Company has a significant interest. The term “control” (including, with correlative meaning, the terms “controlled by” and “under common control with”), as applied to any person or entity, means the possession, directly or indirectly, of the power to direct or cause the direction of the management and policies of such person or entity, whether through the ownership of voting or other securities, by contract or otherwise.
2.2 “Award” shall mean, individually or collectively, any Option, Restricted Stock Award, Restricted Stock Unit Award, Performance Stock Award, Performance Unit Award, Stock Appreciation Right, Distribution Equivalent Right or Unrestricted Stock Award.
2.3 “Award Agreement” shall mean a written agreement between the Company and the Holder with respect to an Award, setting forth the terms and conditions of the Award, as amended.
2.4 “Board” shall mean the Board of Directors of the Company.
2.5 “Base Value” shall have the meaning given to such term in Section 14.2.
2.6 “Cause” shall mean (i) if the Holder is a party to an employment or service agreement with the Company or an Affiliate which agreement defines “Cause” (or a similar term), “Cause” shall have the same meaning as provided for in such agreement, or (ii) for a Holder who is not a party to such an agreement, “Cause” shall mean termination by the Company or an Affiliate of the employment (or other service relationship) of the Holder by reason of the Holder’s
(A) intentional failure to perform reasonably assigned duties, (B) dishonesty or willful misconduct in the performance of the Holder’s duties, (C) involvement in a transaction which is materially adverse to the Company or an Affiliate, (D) breach of fiduciary duty involving personal profit, (E) willful violation of any law, rule, regulation or court order (other than misdemeanor traffic violations and misdemeanors not involving misuse or misappropriation of money or property), (F) commission of an act of fraud or intentional misappropriation or conversion of any asset or opportunity of the Company or an Affiliate, or (G) material breach of any provision of the Plan or the Holder’s Award Agreement or any other written agreement between the Holder and the Company or an Affiliate, in each case as determined in good faith by the Board, the determination of which shall be final, conclusive and binding on all parties.
2.7 “Change of Control” shall mean, except as otherwise provided in an Award Agreement, (i) for a Holder who is a party to an employment or consulting agreement with the Company or an Affiliate which agreement defines “Change of Control” (or a similar term), “Change of Control” shall have the same meaning as provided for in such agreement, or (ii) for a Holder who is not a party to such an agreement, “Change of Control” shall mean the satisfaction of any one or more of the following conditions (and the “Change of Control” shall be deemed to have occurred as of the first day that any one or more of the following conditions shall have been satisfied):
(a) Any person (as such term is used in paragraphs 13(d) and 14(d)(2) of the Exchange Act, hereinafter in this definition, “Person”), other than the Company or an Affiliate or an employee benefit plan of the Company or an Affiliate, becomes the beneficial owner (as defined in Rule 13d-3 under the Exchange Act), directly or indirectly, of securities of the Company representing more than fifty percent (50%) of the combined voting power of the Company’s then outstanding securities;
(b) The closing of a merger, consolidation or other business combination (a “Business Combination”) other than a Business Combination in which holders of the Shares immediately prior to the Business Combination have substantially the same proportionate ownership of the common stock or ordinary shares, as applicable, of the surviving corporation immediately after the Business Combination as immediately before;
(c) The closing of an agreement for the sale or disposition of all or substantially all of the Company’s assets to any entity that is not an Affiliate;
(d) The approval by the holders of shares of Shares of a plan of complete liquidation of the Company, other than a merger of the Company into any subsidiary or a liquidation as a result of which persons who were stockholders of the Company immediately prior to such liquidation have substantially the same proportionate ownership of shares of common stock or ordinary shares, as applicable, of the surviving corporation immediately after such liquidation as immediately before; or
(e) Within any twenty-four (24) month period, the Incumbent Directors shall cease to constitute at least a majority of the Board or the board of directors of any successor to the Company; provided, however, that any director elected to the Board, or nominated for election, by a majority of the Incumbent Directors then still in office, shall be deemed to be an Incumbent Director for purposes of this paragraph (e), but excluding, for this purpose, any such individual whose initial assumption of office occurs as a result of either an actual or threatened election contest with respect to the election or removal of directors or other actual or threatened solicitation of proxies or consents by or on behalf of an individual, entity or “group” other than the Board (including, but not limited to, any such assumption that results from paragraphs (a), (b), (c), or (d) of this definition).
Notwithstanding the foregoing, solely for the purpose of determining the timing of any payments pursuant to any Award constituting a “deferral of compensation” subject to Code Section 409A, a Change of Control shall be limited to a “change in the ownership of the Company,” a “change in the effective control of the Company,” or a “change in the ownership of a substantial portion of the assets of the Company” as such terms are defined in Section 1.409A-3(i)(5) of the U.S. Treasury Regulations.
2.8 “Code” shall mean the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, and any successor thereto. Reference in the Plan to any section of the Code shall be deemed to include any regulations or other interpretative guidance under such section, and any amendments or successor provisions to such section, regulations or guidance.
2.9 “Committee” shall mean a committee comprised of two (2) or more members of the Board who are selected by the Board as provided in Section 4.1.
2.10 “Company” shall have the meaning given to such term in the introductory paragraph, including any successor thereto.
2.11 “Consultant” shall mean any person, including an advisor, who is (i) engaged by the Company or an Affiliate to render consulting or advisory services and is compensated for such services, or (ii) serving as a member of the board of directors of an Affiliate and is compensated for such services. However, service solely as a Director, or payment of a fee for such service, will not cause a Director to be considered a “Consultant” for purposes of the Plan. Notwithstanding the foregoing, a person is treated as a Consultant under this Plan only if a Form S-8 Registration Statement under the Securities Act is available to register either the offer or the sale of the Company’s securities to such person.
2.12 “Director” shall mean a member of the Board or a member of the board of directors of an Affiliate, in either case, who is not an Employee.
2.13 “Distribution Equivalent Right” shall mean an Award granted under Article XIII of the Plan which entitles the Holder to receive bookkeeping credits, cash payments and/or Share distributions equal in amount to the distributions that would have been made to the Holder had the Holder held a specified number of Shares during the period the Holder held the Distribution Equivalent Right.
2.14 “Distribution Equivalent Right Award Agreement” shall mean a written agreement between the Company and a Holder with respect to a Distribution Equivalent Right Award.
2.15 “Effective Date” shall mean __________, 2025.
2.16 “Employee” shall mean any employee, including any officer, of the Company or an Affiliate.
2.17 “Exchange Act” shall mean the United States of America Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
2.18 “Fair Market Value” shall mean, as of any date, the value of a share of Stock determined as follows:
(a) If the Stock is listed on any established stock exchange or a national market system, the per share closing sales price for shares of Stock (or the closing bid, if no sales were reported) as quoted on such exchange or system on the day of determination, as reported in The Wall Street Journal or such other source as the Committee deems reliable;
(b) If the Stock is regularly quoted by a recognized securities dealer but selling prices are not reported, the Fair Market Value of a share of Stock will be the mean between the high bid and low asked per share prices for the Stock on the day of determination, as reported in The Wall Street Journal or such other source as the Committee deems reliable; or
(c) In the absence of an established market for the Stock, the Fair Market Value will be determined in good faith by the Committee (acting on the advice of an Independent Third Party, should the Committee elect in its sole discretion to utilize an Independent Third Party for this purpose).
(d) Notwithstanding the foregoing, the determination of Fair Market Value in all cases shall be in accordance with the requirements set forth under Section 409A of the Code to the extent necessary for an Award to comply with, or be exempt from, Section 409A of the Code.
2.19 “Family Member” of an individual shall mean any child, stepchild, grandchild, parent, stepparent, spouse, former spouse, sibling, niece, nephew, mother-in-law, father-in-law, son-in-law, daughter-in-law, brother-in-law or sister-in-law, including adoptive relationships, any person sharing the Holder’s household (other than a tenant or employee of the Holder), a trust in which such persons have more than fifty percent (50%) of the beneficial interest, a foundation in which such persons (or the Holder) control the management of assets, and any other entity in which such persons (or the Holder) own more than fifty percent (50%) of the voting interests.
2.20 “Holder” shall mean an Employee, Director or Consultant who has been granted an Award or any such individual’s beneficiary, estate or representative, who has acquired such Award in accordance with the terms of the Plan, as applicable.
2.21 “Incentive Stock Option” shall mean an Option which is designated by the Committee as an “incentive stock option” and conforms to the applicable provisions of Section 422 of the Code.
2.22 “Incumbent Director” shall mean, with respect to any period of time specified under the Plan for purposes of determining whether or not a Change of Control has occurred, the individuals who were members of the Board at the beginning of such period.
2.23 “Independent Third Party” means an individual or entity independent of the Company having experience in providing investment banking or similar appraisal or valuation services and with expertise generally in the valuation of securities or other property for purposes of this Plan. The Committee may utilize one or more Independent Third Parties.
2.24 “Non-qualified Stock Option” shall mean an Option which is not designated by the Committee as an Incentive Stock Option.
2.25 “Option” shall mean an Award granted under Article VII of the Plan of an option to purchase Shares and shall include both Incentive Stock Options and Non-qualified Stock Options.
2.26 “Option Agreement” shall mean a written agreement between the Company and a Holder with respect to an Option.
2.27 “Performance Criteria” shall mean the criteria selected by the Committee for purposes of establishing the Performance Goal(s) for a Holder for a Performance Period.
2.28 “Performance Goals” shall mean, for a Performance Period, the written goal or goals established by the Committee for the Performance Period based upon the Performance Criteria, which may be related to the performance of the Holder, the Company or an Affiliate.
2.29 “Performance Period” shall mean one or more periods of time, which may be of varying and overlapping durations, selected by the Committee, over which the attainment of the Performance Goals shall be measured for purposes of determining a Holder’s right to, and the payment of, a Performance Stock Award or a Performance Unit Award.
2.30 “Performance Stock Award” or “Performance Stock” shall mean an Award granted under Article XII of the Plan under which, upon the satisfaction of predetermined Performance Goals, Shares are paid to the Holder.
2.31 “Performance Stock Agreement” shall mean a written agreement between the Company and a Holder with respect to a Performance Stock Award.
2.32 “Performance Unit Award” or “Performance Unit” shall mean an Award granted under Article XI of the Plan under which, upon the satisfaction of predetermined Performance Goals, a cash payment shall be made to the Holder, based on the number of Units awarded to the Holder.
2.33 “Performance Unit Agreement” shall mean a written agreement between the Company and a Holder with respect to a Performance Unit Award.
2.34 “Plan” shall mean this K Wave Media Ltd. 2024 Equity Incentive Plan, as amended from time to time, together with each of the Award Agreements utilized hereunder.
2.35 “Restricted Stock Award” and “Restricted Stock” shall mean an Award granted under Article VIII of the Plan of Shares, the transferability of which by the Holder is subject to Restrictions.
2.36 “Restricted Stock Agreement” shall mean a written agreement between the Company and a Holder with respect to a Restricted Stock Award.
2.37 “Restricted Stock Unit Award” and “RSUs” shall refer to an Award granted under Article X of the Plan under which, upon the satisfaction of predetermined individual service-related vesting requirements, a payment in cash or Shares shall be made to the Holder, based on the number of Units awarded to the Holder.
2.38 “Restricted Stock Unit Agreement” shall mean a written agreement between the Company and a Holder with respect to a Restricted Stock Award.
2.39 “Restriction Period” shall mean the period of time for which Shares subject to a Restricted Stock Award shall be subject to Restrictions, as set forth in the applicable Restricted Stock Agreement.
2.40 “Restrictions” shall mean the forfeiture, transfer and/or other restrictions applicable to Shares awarded to an Employee, Director or Consultant under the Plan pursuant to a Restricted Stock Award and set forth in a Restricted Stock Agreement.
2.41 “Rule 16b-3” shall mean Rule 16b-3 promulgated by the Securities and Exchange Commission under the Exchange Act, as such may be amended from time to time, and any successor rule, regulation or statute fulfilling the same or a substantially similar function.
2.42 “Shares” or “Stock” shall mean the ordinary shares of the Company, par value $0.0001 per share.
2.43 “Stock Appreciation Right” or “SAR” shall mean an Award granted under Article XIV of the Plan of a right, granted alone or in connection with a related Option, to receive a payment equal to the increase in value of a specified number of Shares between the date of Award and the date of exercise.
2.44 “Stock Appreciation Right Agreement” shall mean a written agreement between the Company and a Holder with respect to a Stock Appreciation Right.
2.45 “Tandem Stock Appreciation Right” shall mean a Stock Appreciation Right granted in connection with a related Option, the exercise of some or all of which results in termination of the entitlement to purchase some or all of the Shares under the related Option, all as set forth in Article XIV.
2.46 “Ten Percent Stockholder” shall mean an Employee who, at the time an Option is granted to him or her, owns shares possessing more than ten percent (10%) of the total combined voting power of all classes of shares of the Company or of any parent corporation or subsidiary corporation thereof (both as defined in Section 424 of the Code), within the meaning of Section 422(b)(6) of the Code.
2.47 “Termination of Service” shall mean a termination of a Holder’s employment with, or status as a Director or Consultant of, the Company or an Affiliate, as applicable, for any reason, including, without limitation, Total and Permanent Disability or death, except as provided in Section 6.4. In the event Termination of Service shall constitute a payment event with respect to any Award subject to Code Section 409A, Termination of Service shall only be deemed to occur upon a “separation from service” as such term is defined under Code Section 409A and applicable authorities.
2.48 “Total and Permanent Disability” of an individual shall mean the inability of such individual to engage in any substantial gainful activity by reason of any medically determinable physical or mental impairment which can be expected to result in death or which has lasted or can be expected to last for a continuous period of not less than twelve (12) months, within the meaning of Section 22(e)(3) of the Code.
2.49 “Unit” shall mean a bookkeeping unit, which represents such monetary amount as shall be designated by the Committee in each Performance Unit Agreement, or represents one Share for purposes of each Restricted Stock Unit Award.
2.50 “Unrestricted Stock Award” shall mean an Award granted under Article IX of the Plan of Shares which are not subject to Restrictions.
2.51 “Unrestricted Stock Agreement” shall mean a written agreement between the Company and a Holder with respect to an Unrestricted Stock Award.
Article III
EFFECTIVE DATE OF PLAN
The Plan shall be effective as of the Effective Date, provided that the Plan is approved by the stockholders of the Company within twelve (12) months of such date.
Article IV
ADMINISTRATION
4.1 Composition of Committee. The Plan shall be administered by the Committee, which shall be appointed by the Board. If necessary, in the Board’s discretion, to comply with Rule 16b-3 under the Exchange Act or relevant securities exchange or inter-dealer quotation service, the Committee shall consist solely of two (2) or more Directors who are each (i) “non-employee directors” within the meaning of Rule 16b-3 and (ii) “independent” for purposes of any applicable listing requirements;. If a member of the Committee shall be eligible to receive an Award under the Plan, such Committee member shall have no authority hereunder with respect to his or her own Award.
4.2 Powers. Subject to the other provisions of the Plan, the Committee shall have the sole authority, in its discretion, to make all determinations under the Plan, including but not limited to (i) determining which Employees, Directors or Consultants shall receive an Award, (ii) the time or times when an Award shall be made (the date of grant of an Award shall be the date on which the Award is awarded by the Committee), (iii) what type of Award shall be granted, (iv) the term of an Award, (v) the date or dates on which an Award vests, (vi) the form of any payment to be made pursuant to an Award, (vii) the terms and conditions of an Award (including the forfeiture of the Award, and/or any financial gain, if the Holder of the Award violates any applicable restrictive covenant thereof), (viii) the Restrictions under a Restricted Stock Award, (ix) the number of Shares which may be issued under an Award, (x) Performance Goals applicable to any Award and certification of the achievement of such goals, and (xi) the waiver of any Restrictions or Performance Goals, subject in all cases to compliance with applicable laws. In making such determinations the Committee may take into account the nature of the services rendered by the respective Employees, Directors and Consultants, their present and potential contribution to the Company’s (or the Affiliate’s) success and such other factors as the Committee in its discretion may deem relevant.
4.3 Additional Powers. The Committee shall have such additional powers as are delegated to it under the other provisions of the Plan. Subject to the express provisions of the Plan, the Committee is authorized to construe the Plan and the respective Award Agreements executed hereunder, to prescribe such rules and regulations relating to the Plan as it may deem advisable to carry out the intent of the Plan, to determine the terms, restrictions and provisions of each Award and to make all other determinations necessary or advisable for administering the Plan. The Committee may correct any defect or supply any omission or reconcile any inconsistency in any Award Agreement in the manner and to the extent the Committee shall deem necessary, appropriate or expedient to carry it into effect. The determinations of the Committee on the matters referred to in this Article IV shall be conclusive and binding on the Company and all Holders.
4.4 Committee Action. Subject to compliance with all applicable laws, action by the Committee shall require the consent of a majority of the members of the Committee, expressed either orally at a meeting of the Committee or in writing in the absence of a meeting. No member of the Committee shall have any liability for any good faith action, inaction or determination in connection with the Plan.
Article V
SHARES SUBJECT TO PLAN AND LIMITATIONS THEREON
5.1 Authorized Shares. The Committee may from time to time grant Awards to one or more Employees, Directors and/or Consultants determined by it to be eligible for participation in the Plan in accordance with the provisions of Article VI. Subject to any adjustments as necessary pursuant to Article XV, the aggregate number of shares of Stock reserved and available for grant and issuance under the Plan is Ten Percent (10%) of the Stock outstanding. In addition, subject to any adjustments as necessary pursuant to Article XV, such aggregate number of shares of Stock will automatically increase on January 1 of each year for a period of ten years commencing on January 1, 2025 and ending on (and including) January 1, 2034, in an amount equal to Five Percent (5%) of the total number of shares of Stock outstanding on December 31 of the preceding year; provided, however, that the Board may act prior to January 1st of a given year to provide that the increase for such year will be a lesser number of shares of Stock. In the event that (i) any Option or other Award granted hereunder is exercised through the tendering of Stock (either actually or by attestation) or by the withholding of Stock by the Company, or (ii) tax or deduction liabilities arising from such Option or other Award are satisfied by the tendering of Stock (either actually or by attestation) or by the withholding of Stock by the Company, then in each such case the shares of Stock so tendered or withheld shall not be added back to the shares of Stock available for grant under the Plan. Only Shares underlying Awards under this Plan that are forfeited, canceled, or expire unexercised, shall be available again for issuance under the Plan.
5.2 Types of Shares. The Shares to be issued pursuant to the grant or exercise of an Award may consist of authorized but unissued Shares, Shares purchased on the open market or Shares previously issued and outstanding and reacquired by the Company.
5.3 Aggregate Incentive Stock Option Limit. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in Section 5.1, and subject to Article XV, the aggregate maximum number of shares of Stock that may be issued pursuant to the exercise of Incentive Stock Options is Five Percent (5%) shares.
5.4 Non-Employee Director Compensation Limit. The maximum number of shares of Stock that may be subject to an Award granted under the Plan during any single fiscal year to any non-employee director, when taken together with any cash fees paid to such non-employee director during such year in respect of his service as a non-employee director (including service as a member or chair of any committee of the Board), shall not exceed $5,000.00 in total value (calculating the value of any such Award based on the Fair Market Value on the date of grant of such Award for financial reporting purposes).
Article VI
ELIGIBILITY AND TERMINATION OF SERVICE
6.1 Eligibility. Awards made under the Plan may be granted solely to individuals who, at the time of grant, are Employees, Directors or Consultants. An Award may be granted on more than one occasion to the same Employee, Director or Consultant, and, subject to the limitations set forth in the Plan, such Award may include, a Non-qualified Stock Option, a Restricted Stock Award, a Restricted Stock Unit Award, an Unrestricted Stock Award, a Distribution Equivalent Right Award, a Performance Stock Award, a Performance Unit Award, a Stock Appreciation Right, a Tandem Stock Appreciation Right, or any combination thereof, and solely for Employees, an Incentive Stock Option.
6.2 Termination of Service. Except to the extent inconsistent with the terms of the applicable Award Agreement and/or the provisions of Section 6.3 or 6.4, the following terms and conditions shall apply with respect to a Holder’s Termination of Service with the Company or an Affiliate, as applicable:
(a) The Holder’s rights, if any, to exercise any then exercisable Options and/or Stock Appreciation Rights shall terminate:
(i) If such termination is for a reason other than the Holder’s Total and Permanent Disability or death, ninety (90) days after the date of such Termination of Service;
(ii) If such termination is on account of the Holder’s Total and Permanent Disability, one (1) year after the date of such Termination of Service; or
(iii) If such termination is on account of the Holder’s death, one (1) year after the date of the Holder’s death.
Upon such applicable date the Holder (and such Holder’s estate, designated beneficiary or other legal representative) shall forfeit any rights or interests in or with respect to any such Options and Stock Appreciation Rights. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the Committee, in its sole discretion, may provide for a different time period in the Award Agreement, or may extend the time period, following a Termination of Service, during which the Holder has the right to exercise any vested Non-qualified Stock Option or Stock Appreciation Right, which time period may not extend beyond the expiration date of the Award term.
(b) In the event of a Holder’s Termination of Service for any reason prior to the actual or deemed satisfaction and/or lapse of the Restrictions, vesting requirements, terms and conditions applicable to a Restricted Stock Award and/or Restricted Stock Unit Award, such Restricted Stock and/or RSUs shall immediately be canceled, and the Holder (and such Holder’s estate, designated beneficiary or other legal representative) shall forfeit any rights or interests in and with respect to any such Restricted Stock and/or RSUs.
6.3 Special Termination Rule. Except to the extent inconsistent with the terms of the applicable Award Agreement, and notwithstanding anything to the contrary contained in this Article VI, if a Holder’s employment with, or status as a Director of, the Company or an Affiliate shall terminate, and if, within ninety (90) days of such termination, such Holder shall become a Consultant, such Holder’s rights with respect to any Award or portion thereof granted thereto prior to the date of such termination may be preserved, if and to the extent determined by the Committee in its sole discretion, as if such Holder had been a Consultant for the entire period
during which such Award or portion thereof had been outstanding. Should the Committee effect such determination with respect to such Holder, for all purposes of the Plan, such Holder shall not be treated as if his or her employment or Director status had terminated until such time as his or her Consultant status shall terminate, in which case his or her Award, as it may have been reduced in connection with the Holder’s becoming a Consultant, shall be treated pursuant to the provisions of Section 6.2, provided, however, that any such Award which is intended to be an Incentive Stock Option shall, upon the Holder’s no longer being an Employee, automatically convert to a Non-qualified Stock Option. Should a Holder’s status as a Consultant terminate, and if, within ninety (90) days of such termination, such Holder shall become an Employee or a Director, such Holder’s rights with respect to any Award or portion thereof granted thereto prior to the date of such termination may be preserved, if and to the extent determined by the Committee in its sole discretion, as if such Holder had been an Employee or a Director, as applicable, for the entire period during which such Award or portion thereof had been outstanding, and, should the Committee effect such determination with respect to such Holder, for all purposes of the Plan, such Holder shall not be treated as if his or her Consultant status had terminated until such time as his or her employment with the Company or an Affiliate, or his or her Director status, as applicable, shall terminate, in which case his or her Award shall be treated pursuant to the provisions of Section 6.2.
6.4 Termination of Service for Cause. Notwithstanding anything in this Article VI or elsewhere in the Plan to the contrary, and unless a Holder’s Award Agreement specifically provides otherwise, in the event of a Holder’s Termination of Service for Cause, all of such Holder’s then outstanding Awards shall expire immediately and be forfeited in their entirety upon such Termination of Service.
Article VII
OPTIONS
7.1 Option Period. The term of each Option shall be as specified in the Option Agreement; provided, however, that except as set forth in Section 7.3, no Option shall be exercisable after the expiration of ten (10) years from the date of its grant. If the Option would expire at a time when the exercise of the Option would violate applicable securities laws, the expiration date applicable to the Option will be automatically extended to a date that is 30 calendar days following the date such exercise would no longer violate applicable securities laws (so long as such extension shall not violate Section 409A of the Code); provided, that in no event shall such expiration date be extended beyond the expiration of the option period.
7.2 Limitations on Exercise of Option. An Option shall be exercisable in whole or in such installments and at such times as specified in the Option Agreement
7.3 Special Limitations on Incentive Stock Options. To the extent that the aggregate Fair Market Value (determined at the time the respective Incentive Stock Option is granted) of Shares with respect to which Incentive Stock Options are exercisable for the first time by an individual during any calendar year under all plans of the Company and any parent corporation or subsidiary corporation thereof (both as defined in Section 424 of the Code) which provide for the grant of Incentive Stock Options exceeds One Hundred Thousand Dollars ($100,000) (or such other individual limit as may be in effect under the Code on the date of grant), the portion of such Incentive Stock Options that exceeds such threshold shall be treated as Non-qualified Stock Options. The Committee shall determine, in accordance with applicable provisions of the Code, Treasury Regulations and other administrative pronouncements, which of a Holder’s Options, which were intended by the Committee to be Incentive Stock Options when granted to the
Holder, will not constitute Incentive Stock Options because of such limitation, and shall notify the Holder of such determination as soon as practicable after such determination. No Incentive Stock Option shall be granted to an Employee if, at the time the Incentive Stock Option is granted, such Employee is a Ten Percent Stockholder, unless (i) at the time such Incentive Stock Option is granted the Option price is at least one hundred ten percent (110%) of the Fair Market Value of the Shares subject to the Incentive Stock Option, and (ii) such Incentive Stock Option by its terms is not exercisable after the expiration of five (5) years from the date of grant. No Incentive Stock Option shall be granted more than ten (10) years from the earlier of the Effective Date or date on which the Plan is approved by the Company’s stockholders. The designation by the Committee of an Option as an Incentive Stock Option shall not guarantee the Holder that the Option will satisfy the applicable requirements for “incentive stock option” status under Section 422 of the Code.
7.4 Option Agreement. Each Option shall be evidenced by an Option Agreement in such form and containing such provisions not inconsistent with the other provisions of the Plan as the Committee from time to time shall approve, including, but not limited to, provisions intended to qualify an Option as an Incentive Stock Option. An Option Agreement may provide for the payment of the Option price, in whole or in part, by the delivery of a number of Shares (plus cash if necessary) that have been owned by the Holder for at least six (6) months and having a Fair Market Value equal to such Option price, or such other forms or methods as the Committee may determine from time to time, in each case, subject to such rules and regulations as may be adopted by the Committee. Each Option Agreement shall, solely to the extent inconsistent with the provisions of Sections 6.2, 6.3, and 6.4, as applicable, specify the effect of Termination of Service on the exercisability of the Option. Moreover, without limiting the generality of the foregoing, a Non-qualified Stock Option Agreement may provide for a “cashless exercise” of the Option, in whole or in part, by (a) establishing procedures whereby the Holder, by a properly-executed written notice, directs (i) an immediate market sale or margin loan as to all or a part of Shares to which he is entitled to receive upon exercise of the Option, pursuant to an extension of credit by the Company to the Holder of the Option price, (ii) the delivery of the Shares from the Company directly to a brokerage firm and (iii) the delivery of the Option price from sale or margin loan proceeds from the brokerage firm directly to the Company, or (b) reducing the number of Shares to be issued upon exercise of the Option by the number of such Shares having an aggregate Fair Market Value equal to the Option price (or portion thereof to be so paid) as of the date of the Option’s exercise. An Option Agreement may also include provisions relating to: (i) subject to the provisions hereof, accelerated vesting of Options, including but not limited to, upon the occurrence of a Change of Control, (ii) tax matters (including provisions covering any applicable Employee wage withholding requirements) and (iii) any other matters not inconsistent with the terms and provisions of the Plan that the Committee shall in its sole discretion determine. The terms and conditions of the respective Option Agreements need not be identical.
7.5 Option Price and Payment. The price at which a Share may be purchased upon exercise of an Option shall be determined by the Committee; provided, however, that such Option price (i) shall not be less than the Fair Market Value of a Share on the date such Option is granted (or 110% of Fair Market Value for an Incentive Stock Option held by Ten Percent Stockholder, as provided in Section 7.3), and (ii) shall be subject to adjustment as provided in Article XV. The Option or portion thereof may be exercised by delivery of an irrevocable notice of exercise to the Company. The Option price for the Option or portion thereof shall be paid in full in the manner prescribed by the Committee as set forth in the Plan and the applicable Option Agreement, which manner, with the consent of the Committee, may include the withholding of Shares otherwise issuable in connection with the exercise of the Option. Separate share certificates shall be issued by the Company for those Shares acquired pursuant to the exercise of an Incentive Stock Option and for those Shares acquired pursuant to the exercise of a Non-qualified Stock Option.
7.6 Stockholder Rights and Privileges. The Holder of an Option shall be entitled to all the privileges and rights of a stockholder of the Company solely with respect to such Shares as have been purchased under the Option and for which share certificates have been registered in the Holder’s name.
7.7 Options and Rights in Substitution for Stock or Options Granted by Other Corporations. Options may be granted under the Plan from time to time in substitution for stock options held by individuals employed by entities who become Employees, Directors or Consultants as a result of a merger or consolidation of the employing entity with the Company or any Affiliate, or the acquisition by the Company or an Affiliate of the assets of the employing entity, or the acquisition by the Company or an Affiliate of stock or shares of the employing entity with the result that such employing entity becomes an Affiliate. Any substitute Awards granted under this Plan shall not reduce the number of Shares authorized for grant under the Plan.
7.8 Prohibition Against Repricing. Except to the extent (i) approved in advance by holders of a majority of the shares of the Company entitled to vote generally in the election of directors, or (ii) as a result of any Change of Control or any adjustment as provided in Article XV, the Committee shall not have the power or authority to reduce, whether through amendment or otherwise, the exercise price under any outstanding Option or Stock Appreciation Right, or to grant any new Award or make any payment of cash in substitution for or upon the cancellation of Options and/or Stock Appreciation Rights previously granted.
Article VIII
RESTRICTED STOCK AWARDS
8.1 Award. A Restricted Stock Award shall constitute an Award of Shares to the Holder as of the date of the Award which are subject to a “substantial risk of forfeiture” as defined under Section 83 of the Code during the specified Restriction Period. At the time a Restricted Stock Award is made, the Committee shall establish the Restriction Period applicable to such Award. Each Restricted Stock Award may have a different Restriction Period, in the discretion of the Committee. The Restriction Period applicable to a particular Restricted Stock Award shall not be changed except as permitted by Section 8.2.
8.2 Terms and Conditions. At the time any Award is made under this Article VIII, the Company and the Holder shall enter into a Restricted Stock Agreement setting forth each of the matters contemplated thereby and such other matters as the Committee may determine to be appropriate. The Company shall cause the Shares to be issued in the name of Holder, either by book-entry registration or issuance of one or more stock certificates evidencing the Shares, which Shares or certificates shall be held by the Company or the stock transfer agent or brokerage service selected by the Company to provide services for the Plan. The Shares shall be restricted from transfer and shall be subject to an appropriate stop-transfer order, and if any certificate is issued, such certificate shall bear an appropriate legend referring to the restrictions applicable to the Shares. After any Shares vest, the Company shall deliver the vested Shares, in book-entry or certificated form in the Company’s sole discretion, registered in the name of Holder or his or her legal representatives, beneficiaries or heirs, as the case may be, less any Shares withheld to pay withholding taxes. If provided for under the Restricted Stock Agreement, the Holder shall have the right to vote Shares subject thereto and to enjoy all other stockholder rights, including the entitlement to receive dividends on the Shares during the Restriction Period. At the time of such
Award, the Committee may, in its sole discretion, prescribe additional terms and conditions or restrictions relating to Restricted Stock Awards, including, but not limited to, rules pertaining to the effect of Termination of Service prior to expiration of the Restriction Period. Such additional terms, conditions or restrictions shall, to the extent inconsistent with the provisions of Sections 6.2, 6.3 and 6.4, as applicable, be set forth in a Restricted Stock Agreement made in conjunction with the Award. Such Restricted Stock Agreement may also include provisions relating to: (i) subject to the provisions hereof, accelerated vesting of Awards, including but not limited to accelerated vesting upon the occurrence of a Change of Control, (ii) tax matters (including provisions covering any applicable Employee wage withholding requirements) and (iii) any other matters not inconsistent with the terms and provisions of the Plan that the Committee shall in its sole discretion determine. The terms and conditions of the respective Restricted Stock Agreements need not be identical. All Shares delivered to a Holder as part of a Restricted Stock Award shall be delivered and reported by the Company or the Affiliate, as applicable, to the Holder at the time of vesting.
8.3 Payment for Restricted Stock. The Committee shall determine the amount and form of any payment from a Holder for Shares received pursuant to a Restricted Stock Award, if any, provided that in the absence of such a determination, a Holder shall not be required to make any payment for Shares received pursuant to a Restricted Stock Award, except to the extent otherwise required by law.
Article IX
UNRESTRICTED STOCK AWARDS
9.1 Award. Shares may be awarded (or sold) to Employees, Directors or Consultants under the Plan which are not subject to Restrictions of any kind, in consideration for past services rendered thereby to the Company or an Affiliate or for other valid consideration.
9.2 Terms and Conditions. At the time any Award is made under this Article IX, the Company and the Holder shall enter into an Unrestricted Stock Agreement setting forth each of the matters contemplated hereby and such other matters as the Committee may determine to be appropriate.
9.3 Payment for Unrestricted Stock. The Committee shall determine the amount and form of any payment from a Holder for Shares received pursuant to an Unrestricted Stock Award, if any, provided that in the absence of such a determination, a Holder shall not be required to make any payment for Shares received pursuant to an Unrestricted Stock Award, except to the extent otherwise required by law.
Article X
RESTRICTED STOCK UNIT AWARDS
10.1 Award. A Restricted Stock Unit Award shall constitute a promise to grant Shares (or cash equal to the Fair Market Value of Shares) to the Holder at the end of a specified vesting schedule. At the time a Restricted Stock Unit Award is made, the Committee shall establish the vesting schedule applicable to such Award. Each Restricted Stock Unit Award may have a different vesting schedule, in the discretion of the Committee. A Restricted Stock Unit shall not constitute an equity interest in the Company and shall not entitle the Holder to voting rights, dividends or any other rights associated with ownership of Shares prior to the time the Holder shall receive a distribution of Shares pursuant to Section 10.3.
10.2 Terms and Conditions. At the time any Award is made under this Article X, the Company and the Holder shall enter into a Restricted Stock Unit Agreement setting forth each of the matters contemplated thereby and such other matters as the Committee may determine to be appropriate. The Restricted Stock Unit Agreement shall set forth the individual service-based vesting requirement which the Holder would be required to satisfy before the Holder would become entitled to distribution pursuant to Section 10.3 and the number of Units awarded to the Holder. Such conditions shall be sufficient to constitute a “substantial risk of forfeiture” as such term is defined under Section 409A of the Code. At the time of such Award, the Committee may, in its sole discretion, prescribe additional terms and conditions or restrictions relating to Restricted Stock Unit Awards in the Restricted Stock Unit Agreement, including, but not limited to, rules pertaining to the effect of Termination of Service prior to expiration of the applicable vesting period. The terms and conditions of the respective Restricted Stock Unit Agreements need not be identical.
10.3 Distributions of Shares. The Holder of a Restricted Stock Unit shall be entitled to receive Shares or a cash payment equal to the Fair Market Value of a Share, or one Share, as determined in the sole discretion of the Committee and as set forth in the Restricted Stock Unit Agreement, for each Restricted Stock Unit subject to such Restricted Stock Unit Award, if the Holder satisfies the applicable vesting requirement. Such distribution shall be made no later than by the fifteenth (15th) day of the third (3rd) calendar month next following the end of the calendar year in which the Restricted Stock Unit first becomes vested (i.e., no longer subject to a “substantial risk of forfeiture”).
Article XI
PERFORMANCE UNIT AWARDS
11.1 Award. A Performance Unit Award shall constitute an Award under which, upon the satisfaction of predetermined individual and/or Company (and/or Affiliate) Performance Goals based on selected Performance Criteria, a cash payment shall be made to the Holder, based on the number of Units awarded to the Holder. At the time a Performance Unit Award is made, the Committee shall establish the Performance Period and applicable Performance Goals. Each Performance Unit Award may have different Performance Goals, in the discretion of the Committee. A Performance Unit Award shall not constitute an equity interest in the Company and shall not entitle the Holder to voting rights, dividends or any other rights associated with ownership of Shares.
11.2 Terms and Conditions. At the time any Award is made under this Article XI, the Company and the Holder shall enter into a Performance Unit Agreement setting forth each of the matters contemplated thereby and such other matters as the Committee may determine to be appropriate. The Committee shall set forth in the applicable Performance Unit Agreement the Performance Period, Performance Criteria and Performance Goals which the Holder and/or the Company would be required to satisfy before the Holder would become entitled to payment pursuant to Section 11.3, the number of Units awarded to the Holder and the dollar value or formula assigned to each such Unit. Such payment shall be subject to a “substantial risk of forfeiture” under Section 409A of the Code. At the time of such Award, the Committee may, in its sole discretion, prescribe additional terms and conditions or restrictions relating to Performance Unit Awards, including, but not limited to, rules pertaining to the effect of Termination of Service prior to expiration of the applicable performance period. The terms and conditions of the respective Performance Unit Agreements need not be identical.
11.3 Payments. The Holder of a Performance Unit shall be entitled to receive a cash payment equal to the dollar value assigned to such Unit under the applicable Performance Unit Agreement if the Holder and/or the Company satisfy (or partially satisfy, if applicable under the applicable Performance Unit Agreement) the Performance Goals set forth in such Performance Unit Agreement. All payments shall be made no later than by the fifteenth (15th) day of the third (3rd) calendar month next following the end of the Company’s fiscal year to which such performance goals and objectives relate.
Article XII
PERFORMANCE STOCK AWARDS
12.1 Award. A Performance Stock Award shall constitute a promise to grant Shares (or cash equal to the Fair Market Value of Shares) to the Holder at the end of a specified Performance Period subject to achievement of specified Performance Goals. At the time a Performance Stock Award is made, the Committee shall establish the Performance Period and applicable Performance Goals based on selected Performance Criteria. Each Performance Stock Award may have different Performance Goals, in the discretion of the Committee. A Performance Stock Award shall not constitute an equity interest in the Company and shall not entitle the Holder to voting rights, dividends or any other rights associated with ownership of Shares unless and until the Holder shall receive a distribution of Shares pursuant to Section 12.3.
12.2 Terms and Conditions. At the time any Award is made under this Article XII, the Company and the Holder shall enter into a Performance Stock Agreement setting forth each of the matters contemplated thereby and such other matters as the Committee may determine to be appropriate. The Committee shall set forth in the applicable Performance Stock Agreement the Performance Period, selected Performance Criteria and Performance Goals which the Holder and/or the Company would be required to satisfy before the Holder would become entitled to the receipt of Shares pursuant to such Holder’s Performance Stock Award and the number of Shares subject to such Performance Stock Award. Such distribution shall be subject to a “substantial risk of forfeiture” under Section 409A of the Code. If such Performance Goals are achieved, the distribution of Shares (or the payment of cash, as determined in the sole discretion of the Committee), shall be made in accordance with Section 12.3, below. At the time of such Award, the Committee may, in its sole discretion, prescribe additional terms and conditions or restrictions relating to Performance Stock Awards, including, but not limited to, rules pertaining to the effect of the Holder’s Termination of Service prior to the expiration of the applicable performance period. The terms and conditions of the respective Performance Stock Agreements need not be identical.
12.3 Distributions of Shares. The Holder of a Performance Stock Award shall be entitled to receive a cash payment equal to the Fair Market Value of a Share, or one Share, as determined in the sole discretion of the Committee, for each Performance Stock Award subject to such Performance Stock Agreement, if the Holder satisfies the applicable vesting requirement. Such distribution shall be made no later than by the fifteenth (15th) day of the third (3rd) calendar month next following the end of the Company’s fiscal year to which such performance goals and objectives relate.
Article XIII
DISTRIBUTION EQUIVALENT RIGHTS
13.1 Award. A Distribution Equivalent Right shall entitle the Holder to receive bookkeeping credits, cash payments and/or Share distributions equal in amount to the distributions that would have been made to the Holder had the Holder held a specified number of Shares during the specified period of the Award.
13.2 Terms and Conditions. At the time any Award is made under this Article XIII, the Company and the Holder shall enter into a Distribution Equivalent Rights Award Agreement setting forth each of the matters contemplated thereby and such other matters as the Committee may determine to be appropriate. The Committee shall set forth in the applicable Distribution Equivalent Rights Award Agreement the terms and conditions, if any, including whether the Holder is to receive credits currently in cash, is to have such credits reinvested (at Fair Market Value determined as of the date of reinvestment) in additional Shares or is to be entitled to choose among such alternatives. Such receipt shall be subject to a “substantial risk of forfeiture” under Section 409A of the Code and, if such Award becomes vested, the distribution of such cash or Shares shall be made no later than by the fifteenth (15th) day of the third (3rd) calendar month next following the end of the Company’s fiscal year in which the Holder’s interest in the Award vests. Distribution Equivalent Rights Awards may be settled in cash or in Shares, as set forth in the applicable Distribution Equivalent Rights Award Agreement. A Distribution Equivalent Rights Award may, but need not be, awarded in tandem with another Award (other than an Option or a SAR), whereby, if so awarded, such Distribution Equivalent Rights Award shall expire, terminate or be forfeited by the Holder, as applicable, under the same conditions as under such other Award.
13.3 Interest Equivalents. The Distribution Equivalent Rights Award Agreement for a Distribution Equivalent Rights Award may provide for the crediting of interest on a Distribution Rights Award to be settled in cash at a future date (but in no event later than by the fifteenth (15th) day of the third (3rd) calendar month next following the end of the Company’s fiscal year in which such interest is credited and vested), at a rate set forth in the applicable Distribution Equivalent Rights Award Agreement, on the amount of cash payable thereunder.
Article XIV
STOCK APPRECIATION RIGHTS
14.1 Award. A Stock Appreciation Right shall constitute a right, granted alone or in connection with a related Option, to receive a payment equal to the increase in value of a specified number of Shares between the date of Award and the date of exercise.
14.2 Terms and Conditions. At the time any Award is made under this Article XIV, the Company and the Holder shall enter into a Stock Appreciation Right Agreement setting forth each of the matters contemplated thereby and such other matters as the Committee may determine to be appropriate. The Committee shall set forth in the applicable Stock Appreciation Right Agreement the terms and conditions of the Stock Appreciation Right, including (i) the base value (the “Base Value”) for the Stock Appreciation Right, which shall be not less than the Fair Market Value of a Share on the date of grant of the Stock Appreciation Right, (ii) the number of Shares subject to the Stock Appreciation Right, (iii) the period during which the Stock Appreciation Right may be exercised; provided, however, that no Stock Appreciation Right shall be exercisable after the expiration of ten (10) years from the date of its grant, and (iv) any other special rules and/or requirements which the Committee imposes upon the Stock Appreciation Right. Upon the exercise of some or all of the portion of a Stock Appreciation Right, the Holder shall receive a payment from the Company, in cash or in the form of Shares having an equivalent Fair Market Value or in a combination of both, as determined in the sole discretion of the Committee, equal to the product of:
(a) The excess of (i) the Fair Market Value of a Share on the date of exercise, over (ii) the Base Value, multiplied by,
(b) The number of Shares with respect to which the Stock Appreciation Right is exercised.
14.3 Tandem Stock Appreciation Rights. If the Committee grants a Stock Appreciation Right which is intended to be a Tandem Stock Appreciation Right, the Tandem Stock Appreciation Right shall be granted at the same time as the related Option, and the following special rules shall apply:
(a) The Base Value shall be equal to or greater than the per Share exercise price under the related Option;
(b) The Tandem Stock Appreciation Right may be exercised for all or part of the Shares which are subject to the related Option, but solely upon the surrender by the Holder of the Holder’s right to exercise the equivalent portion of the related Option (and when a Share is purchased under the related Option, an equivalent portion of the related Tandem Stock Appreciation Right shall be canceled);
(c) The Tandem Stock Appreciation Right shall expire no later than the date of the expiration of the related Option;
(d) The value of the payment with respect to the Tandem Stock Appreciation Right may be no more than one hundred percent (100%) of the difference between the per Share exercise price under the related Option and the Fair Market Value of the Shares subject to the related Option at the time the Tandem Stock Appreciation Right is exercised, multiplied by the number of the Shares with respect to which the Tandem Stock Appreciation Right is exercised; and
(e) The Tandem Stock Appreciation Right may be exercised solely when the Fair Market Value of the Shares subject to the related Option exceeds the per Share exercise price under the related Option.
Article XV
RECAPITALIZATION OR REORGANIZATION
15.1 Adjustments to Shares. The shares with respect to which Awards may be granted under the Plan are Shares as presently constituted; provided, however, that if, and whenever, prior to the expiration or distribution to the Holder of Shares underlying an Award theretofore granted, the Company shall effect a subdivision or consolidation of the Shares or the payment of an Share dividend on Shares without receipt of consideration by the Company, the number of Shares with respect to which such Award may thereafter be exercised or satisfied, as applicable, (i) in the event of an increase in the number of outstanding Shares, shall be proportionately increased, and the purchase price per Share shall be proportionately reduced, and (ii) in the event of a reduction in the number of outstanding Shares, shall be proportionately reduced, and the purchase price per Share shall be proportionately increased. Notwithstanding the foregoing or any other provision of this Article XV, any adjustment made with respect to an Award (x) which is an Incentive Stock Option, shall comply with the requirements of Section 424(a) of the Code, and in no event shall any adjustment be made which would render any Incentive Stock Option granted under the Plan to be other than an “incentive stock option” for purposes of Section 422 of the Code, and (y) which is a Non-qualified Stock Option, shall comply with the requirements of Section 409A of the Code, and in no event shall any adjustment be made which would render any Non-qualified Stock Option granted under the Plan to become subject to Section 409A of the Code.
15.2 Recapitalization. If the Company recapitalizes or otherwise changes its capital structure, thereafter upon any exercise or satisfaction, as applicable, of a previously granted Award, the Holder shall be entitled to receive (or entitled to purchase, if applicable) under such Award, in lieu of the number of Shares then covered by such Award, the number and class of shares and securities to which the Holder would have been entitled pursuant to the terms of the recapitalization if, immediately prior to such recapitalization, the Holder had been the holder of record of the number of Shares then covered by such Award.
15.3 Other Events. In the event of changes to the outstanding Shares by reason of an extraordinary cash dividend, reorganization, merger, consolidation, combination, split-up, spin-off, exchange or other relevant change in capitalization occurring after the date of the grant of any Award and not otherwise provided for under this Article XV, any outstanding Awards and any Award Agreements evidencing such Awards shall be adjusted by the Board in its discretion in such manner as the Board shall deem equitable or appropriate taking into consideration the applicable accounting and tax consequences, as to the number and price of Shares or other consideration subject to such Awards. In the event of any adjustment pursuant to Sections 15.1, 15.2 or this Section 15.3, the aggregate number of Shares available under the Plan pursuant to Section 5.1 may be appropriately adjusted by the Board, the determination of which shall be conclusive. In addition, the Committee may make provision for a cash payment to a Holder or a person who has an outstanding Award.
15.4 Change of Control. The Committee may, in its sole discretion, at the time an Award is made or at any time prior to, coincident with or after the time of a Change of Control, cause any Award either (i) to be canceled in consideration of a payment in cash or other consideration in amount per share equal to the excess, if any, of the price or implied price per Share in the Change of Control over the per Share exercise, base or purchase price of such Award, which may be paid immediately or over the vesting schedule of the Award; (ii) to be assumed, or new rights substituted therefore, by the surviving corporation or a parent or subsidiary of such surviving corporation following such Change of Control; (iii) accelerate any time periods, or waive any other conditions, relating to the vesting, exercise, payment or distribution of an Award so that any Award to a Holder whose employment has been terminated as a result of a Change of Control may be vested, exercised, paid or distributed in full on or before a date fixed by the Committee; (iv) to be purchased from a Holder whose employment has been terminated as a result of a Change of Control, upon the Holder’s request, for an amount of cash equal to the amount that could have been obtained upon the exercise, payment or distribution of such rights had such Award been currently exercisable or payable; or (v) terminate any then outstanding Award or make any other adjustment to the Awards then outstanding as the Committee deems necessary or appropriate to reflect such transaction or change. The number of Shares subject to any Award shall be rounded to the nearest whole number.
15.5 Powers Not Affected. The existence of the Plan and the Awards granted hereunder shall not affect in any way the right or power of the Board or of the stockholders of the Company to make or authorize any adjustment, recapitalization, reorganization or other change of the Company’s capital structure or business, any merger or consolidation of the Company, any issue of debt or equity securities ahead of or affecting Shares or the rights thereof, the dissolution or liquidation of the Company or any sale, lease, exchange or other disposition of all or any part of its assets or business or any other corporate act or proceeding.
15.6 No Adjustment for Certain Awards. Except as hereinabove expressly provided, the issuance by the Company of shares of any class or securities convertible into shares of any class, for cash, property, labor or services, upon direct sale, upon the exercise of rights or warrants to subscribe therefor or upon conversion of shares or obligations of the Company convertible into such shares or other securities, and in any case whether or not for fair value, shall not affect previously granted Awards, and no adjustment by reason thereof shall be made with respect to the number of Shares subject to Awards theretofore granted or the purchase price per Share, if applicable.
Article XVI
AMENDMENT AND TERMINATION OF PLAN
The Plan shall continue in effect, unless sooner terminated pursuant to this Article XVI, until the tenth (10th) anniversary of the date on which it is adopted by the Board (except as to Awards outstanding on that date). The Board may amend, alter, suspend, discontinue, or terminate the Plan or any portion thereof at any time; provided that (i) no amendment to Section 7.8 (repricing prohibitions) shall be made without stockholder approval and (ii) no such amendment, alteration, suspension, discontinuation or termination shall be made without stockholder approval if such approval is necessary to comply with any tax or regulatory requirement applicable to the Plan (including, without limitation, as necessary to comply with any rules or requirements of any securities exchange or inter-dealer quotation system on which the Stock may be listed or quoted); provided, further, that any such amendment, alteration, suspension, discontinuance or termination that would materially and adversely affect the rights of any Holder or beneficiary of any Award theretofore granted shall not to that extent be effective without the consent of the affected Holder or beneficiary (unless such change is required in order to exempt the Plan or any Award from Section 409A of the Code).
Article XVII
MISCELLANEOUS
17.1 No Right to Award. Neither the adoption of the Plan by the Company nor any action of the Board or the Committee shall be deemed to give an Employee, Director or Consultant any right to an Award except as may be evidenced by an Award Agreement duly executed on behalf of the Company, and then solely to the extent and on the terms and conditions expressly set forth therein.
17.2 No Rights Conferred. Nothing contained in the Plan shall (i) confer upon any Employee any right with respect to continuation of employment with the Company or any Affiliate, (ii) interfere in any way with any right of the Company or any Affiliate to terminate the employment of an Employee at any time, (iii) confer upon any Director any right with respect to continuation of such Director’s membership on the Board, (iv) interfere in any way with any right of the Company or an Affiliate to terminate a Director’s membership on the Board at any time, (v) confer upon any Consultant any right with respect to continuation of his or her consulting engagement with the Company or any Affiliate, or (vi) interfere in any way with any right of the Company or an Affiliate to terminate a Consultant’s consulting engagement with the Company or an Affiliate at any time.
17.3 Other Laws; No Fractional Shares; Withholding. The Company shall not be obligated by virtue of any provision of the Plan to recognize the exercise of any Award or to otherwise sell or issue Shares in violation of any laws, rules or regulations, and any postponement of the exercise or settlement of any Award under this provision shall not extend the term of such Award. Neither the Company nor its directors or officers shall have any obligation or liability to a Holder with respect to any Award (or Shares issuable thereunder) (i) that shall lapse because of such postponement, or (ii) for any failure to comply with the requirements of any applicable law, rules or regulations, including but not limited to any failure to comply with the requirements of Section 409A of this Code. No fractional Shares shall be delivered, nor shall any cash in lieu of fractional Shares be paid. The Company shall have the right to deduct in cash (whether under this Plan or otherwise) in connection with all Awards any taxes required by law to be withheld and to require any payments required to enable it to satisfy its withholding obligations. In the case of any Award satisfied in the form of Shares, no Shares shall be issued unless and until arrangements satisfactory to the Company shall have been made to satisfy any tax withholding obligations applicable with respect to such Award. Subject to such terms and conditions as the Committee may impose, the Company shall have the right to retain, or the Committee may, subject to such terms and conditions as it may establish from time to time, permit Holders to elect to tender, Shares (including Shares issuable in respect of an Award) to satisfy, in whole or in part, the amount required to be withheld.
17.4 No Restriction on Corporate Action. Nothing contained in the Plan shall be construed to prevent the Company or any Affiliate from taking any corporate action which is deemed by the Company or such Affiliate to be appropriate or in its best interest, whether or not such action would have an adverse effect on the Plan or any Award made under the Plan. No Employee, Director, Consultant, beneficiary or other person shall have any claim against the Company or any Affiliate as a result of any such action.
17.5 Restrictions on Transfer. No Award under the Plan or any Award Agreement and no rights or interests herein or therein, shall or may be assigned, transferred, sold, exchanged, encumbered, pledged or otherwise hypothecated or disposed of by a Holder except (i) by will or by the laws of descent and distribution, or (ii) where permitted under applicable tax rules, by gift to any Family Member of the Holder, subject to compliance with applicable laws. An Award may be exercisable during the lifetime of the Holder only by such Holder or by the Holder’s guardian or legal representative unless it has been transferred by gift to a Family Member of the Holder, in which case it shall be exercisable solely by such transferee. Notwithstanding any such transfer, the Holder shall continue to be subject to the withholding requirements provided for under Section 17.3 hereof.
17.6 Beneficiary Designations. Each Holder may, from time to time, name a beneficiary or beneficiaries (who may be contingent or successive beneficiaries) for purposes of receiving any amount which is payable in connection with an Award under the Plan upon or subsequent to the Holder’s death. Each such beneficiary designation shall serve to revoke all prior beneficiary designations, be in a form prescribed by the Company and be effective solely when filed by the Holder in writing with the Company during the Holder’s lifetime. In the absence of any such written beneficiary designation, for purposes of the Plan, a Holder’s beneficiary shall be the Holder’s estate.
17.7 Rule 16b-3. It is intended that the Plan and any Award made to a person subject to Section 16 of the Exchange Act shall meet all of the requirements of Rule 16b-3. If any provision of the Plan or of any such Award would disqualify the Plan or such Award under, or would otherwise not comply with the requirements of, Rule 16b-3, such provision or Award shall be construed or deemed to have been amended as necessary to conform to the requirements of Rule 16b-3.
17.8 Clawback Policy. All Awards (including on a retroactive basis) granted under the Plan are subject to the terms of any Company forfeiture, incentive compensation recoupment, clawback or similar policy as it may be in effect from time to time, as well as any similar provisions of applicable laws, as well as any other policy of the Company that may apply to the Awards, such as anti-hedging or pledging policies, as they may be in effect from time to time. In particular, these policies and/or provisions shall include, without limitation, (i) any Company policy established to comply with applicable laws (including, without limitation, Section 304 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and Section 954 of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act), and/or (ii) the rules and regulations of the applicable securities exchange or inter-dealer quotation system on which the shares of Stock or other securities are listed or quoted, and these requirements shall be deemed incorporated by reference into all outstanding Award Agreements.
17.9 No Obligation to Notify or Minimize Taxes. The Company shall have no duty or obligation to any Holder to advise such Holder as to the time or manner of exercising any Award. Furthermore, the Company shall have no duty or obligation to warn or otherwise advise such Holder of a pending termination or expiration of an Award or a possible period in which the Award may not be exercised. The Company has no duty or obligation to minimize the tax consequences of an Award to any person.
17.10 Section 409A of the Code.
(a) Notwithstanding any provision of this Plan to the contrary, all Awards made under this Plan are intended to be exempt from or, in the alternative, comply with Section 409A of the Code and the authoritative guidance thereunder, including the exceptions for stock rights and short-term deferrals. The Plan shall be construed and interpreted in accordance with such intent. Each payment under an Award shall be treated as a separate payment for purposes of Section 409A of the Code.
(b) If a Holder is a “specified employee” (as such term is defined for purposes of Section 409A of the Code) at the time of his termination of service, no amount that is nonqualified deferred compensation subject to Section 409A of the Code and that becomes payable by reason of such termination of service shall be paid to the Holder (or in the event of the Holder’s death, the Holder’s representative or estate) before the earlier of (x) the first business day after the date that is six months following the date of the Holder’s termination of service, and (y) within 30 days following the date of the Holder’s death. For purposes of Section 409A of the Code, a termination of service shall be deemed to occur only if it is a “separation from service” within the meaning of Section 409A of the Code, and references in the Plan and any Award Agreement to “termination of service” or similar terms shall mean a “separation from service.” If any Award is or becomes subject to Section 409A of the Code, unless the applicable Award Agreement provides otherwise, such Award shall be payable upon the Holder’s “separation from service” within the meaning of Section 409A of the Code. If any Award is or becomes subject to Section 409A of the Code and if payment of such Award would be accelerated or otherwise triggered under a Change of Control, then the definition of Change of Control shall be deemed modified, only to the extent necessary to avoid the imposition of any additional tax under Section 409A of the Code, to mean a “change in control event” as such term is defined for purposes of Section 409A of the Code.
(c) Any adjustments made pursuant to Article XV to Awards that are subject to Section 409A of the Code shall be made in compliance with the requirements of Section 409A of the Code, and any adjustments made pursuant to Article XV to Awards that are not subject to Section 409A of the Code shall be made in such a manner as to ensure that after such adjustment, the Awards either (x) continue not to be subject to Section 409A of the Code or (y) comply with the requirements of Section 409A of the Code.
17.11 Indemnification. Each person who is or shall have been a member of the Committee or of the Board shall be indemnified and held harmless by the Company against and from any loss, cost, liability, or expense that may be imposed upon or reasonably incurred thereby in connection with or resulting from any claim, action, suit, or proceeding to which such person may be made a party or may be involved by reason of any action taken or failure to act under the Plan and against and from any and all amounts paid thereby in settlement thereof, with the Company’s approval, or paid thereby in satisfaction of any judgment in any such action, suit, or proceeding against such person; provided, however, that such person shall give the Company an opportunity, at its own expense, to handle and defend the same before he or she undertakes to handle and defend it on his or her own behalf. The foregoing right of indemnification shall not be exclusive and shall be independent of any other rights of indemnification to which such persons may be entitled under the Company’s Articles of Incorporation or By-laws, by contract, as a matter of law, or otherwise.
17.12 Other Benefit Plans. No Award, payment or amount received hereunder shall be taken into account in computing an Employee’s salary or compensation for the purposes of determining any benefits under any pension, retirement, life insurance or other benefit plan of the Company or any Affiliate, unless such other plan specifically provides for the inclusion of such Award, payment or amount received. Nothing in the Plan shall be construed to limit the right of the Company to establish other plans or to pay compensation to its employees, in cash or property, in a manner which is not expressly authorized under the Plan.
17.13 Limits of Liability. Any liability of the Company with respect to an Award shall be based solely upon the contractual obligations created under the Plan and the Award Agreement. None of the Company, any member of the Board nor any member of the Committee shall have any liability to any party for any action taken or not taken, in good faith, in connection with or under the Plan.
17.14 Governing Law. Except as otherwise provided herein, the Plan shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the internal laws of the State of Nevada applicable to contracts made and performed wholly within the State of Nevada, without giving effect to the conflict of law provisions thereof.
17.15 Subplans. The Board may from time to time establish one or more sub-plans under the Plan for purposes of satisfying applicable blue sky, securities or tax laws of various jurisdictions. The Board shall establish such sub-plans by adopting supplements to the Plan setting forth (i) such limitations on the Committee’s discretion under the Plan as the Board deems necessary or desirable and (ii) such additional terms and conditions not otherwise inconsistent with the Plan as the Board shall deem necessary or desirable. All supplements adopted by the Board shall be deemed to be part of the Plan, but each supplement shall apply only to Holders within the affected jurisdiction and the Company shall not be required to provide copies of any supplement to Holders in any jurisdiction that is not affected.
17.16 Notification of Election Under Section 83(b) of the Code. If any Holder, in connection with the acquisition of Stock under an Award, makes the election permitted under Section 83(b) of the Code, if applicable, the Holder shall notify the Company of the election within ten days of filing notice of the election with the Internal Revenue Service.
17.17 Paperless Administration. If the Company establishes, for itself or using the services of a third party, an automated system for the documentation, granting or exercise of Awards, such as a system using an internet website or interactive voice response, then the paperless documentation, granting or exercise of Awards by a Holder may be permitted through the use of such an automated system.
17.18 Broker-Assisted Sales. In the event of a broker-assisted sale of Stock in connection with the payment of amounts owed by a Holder under or with respect to the Plan or Awards: (a) any Stock to be sold through the broker-assisted sale will be sold on the day the payment first becomes due, or as soon thereafter as practicable; (b) the Stock may be sold as part of a block trade with other Holders in the Plan in which all participants receive an average price; (c) the applicable Holder will be responsible for all broker’s fees and other costs of sale, and by accepting an Award, each Holder agrees to indemnify and hold the Company harmless from any losses, costs, damages, or expenses relating to any such sale; (d) to the extent the Company or its designee receives proceeds of the sale that exceed the amount owed, the Company will pay the excess in cash to the applicable Holder as soon as reasonably practicable; (e) the Company and its designees are under no obligation to arrange for the sale at any particular price; and (f) if the proceeds of the sale are insufficient to satisfy the Holder’s applicable obligation, the Holder may be required to pay immediately upon demand to the Company or its designee an amount in cash sufficient to satisfy any remaining portion of the Holder’s obligation.
17.19 Data Privacy. As a condition for receiving any Award, each Holder explicitly and unambiguously consents to the collection, use and transfer, in electronic or other form, of personal data as described in this Section 17.19 by and among the Company and its subsidiaries and Affiliates exclusively for implementing, administering and managing the Holder’s participation in the Plan. The Company and its subsidiaries and Affiliates may hold certain personal information about a Holder, including the Holder’s name, address and telephone number; birthdate; social security, insurance number or other identification number; salary; nationality; job title(s); any Stock held in the Company or its subsidiaries and Affiliates; and Award details, to implement, manage and administer the Plan and Awards (the “Data”). The Company and its subsidiaries and Affiliates may transfer the Data amongst themselves as necessary to implement, administer and manage a Holder’s participation in the Plan, and the Company and its subsidiaries and Affiliates may transfer the Data to third parties assisting the Company with Plan implementation, administration and management. These recipients may be located in the Holder’s country, or elsewhere, and the Holder’s country may have different data privacy laws and protections than the recipients’ country. By accepting an Award, each Holder authorizes the recipients to receive, possess, use, retain and transfer the Data, in electronic or other form, to implement, administer and manage the Holder’s participation in the Plan, including any required Data transfer to a broker or other third party with whom the Company or the Holder may elect to deposit any Stock. The Data related to a Holder will be held only as long as necessary to implement, administer, and manage the Holder’s participation in the Plan. A Holder may, at any time, view the Data that the Company holds regarding the Holder, request additional information about the storage and processing of the Data regarding the Holder, recommend any necessary corrections to the Data regarding the Holder or refuse or withdraw the consents in this Section 17.19 in writing, without cost, by contacting the local human resources representative. The Company may cancel Holder’s ability to participate in the Plan and, in the Committee’s discretion, the Holder may forfeit any outstanding Awards if the Holder refuses or withdraws the consents in this Section 17.19.
17.20 Severability of Provisions. If any provision of the Plan is held invalid or unenforceable, such invalidity or unenforceability shall not affect any other provision of the Plan, and the Plan shall be construed and enforced as if such invalid or unenforceable provision had not been included in the Plan.
17.21 No Funding. The Plan shall be unfunded. The Company shall not be required to establish any special or separate fund or to make any other segregation of funds or assets to ensure the payment of any Award. Prior to receipt of Shares or a cash distribution pursuant to the terms of an Award, such Award shall represent an unfunded unsecured contractual obligation of the Company and the Holder shall have no greater claim to the Shares underlying such Award or any other assets of the Company or Affiliate than any other unsecured general creditor.
17.22 Headings. Headings used throughout the Plan are for convenience only and shall not be given legal significance.
Annex D
AMENDED AND RESTATED
REGISTRATION RIGHTS AGREEMENT
THIS AMENDED AND RESTATED REGISTRATION RIGHTS AGREEMENT (this “Agreement”), dated as of [●], 2025, is made and entered into by and among K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (the “Company”), Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (the “Sponsor”), certain former stockholders of Global Star Acquisition Inc., a Delaware corporation (the “Parent”) (such stockholders, together with the Sponsor, the “Parent Holders”), certain former shareholders of K Enter Holdings Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Target”), set forth on Schedule I hereto (such stockholders, the “Target Holders”), and other persons and entities (collectively with the Sponsor, the Parent Holders, the Target Holders and any person or entity who hereafter becomes a party to this Agreement pursuant to Section 5.2 or Section 5.10 of this Agreement, the “Holders” and each, a “Holder”).
RECITALS
WHEREAS, the Parent, the Sponsor and each of the other parties thereto are party to that certain Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of September 22, 2022 (the “Original RRA”);
WHEREAS, the Company has entered into that certain Merger Agreement, dated as of June 15, 2023 (as it may be amended, supplemented or otherwise modified from time to time, the “Merger Agreement”), by and among the Company, the Parent, GLST Merger Sub, Inc., a Delaware corporation and a direct, wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (“Merger Sub”), and Target, pursuant to which, among other things, (i) the Parent merged with and into the Company, with the Company continuing as the surviving corporation (the “Reincorporation Merger”) and (ii) Merger Sub merged with and into the Target (the “Acquisition Merger”), with the Target surviving the Acquisition Merger as a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company;
WHEREAS, on the date of the Reincorporation Merger, pursuant to the Merger Agreement, (i) each outstanding share of Class A common stock and Class B common stock of the Parent (other than shares redeemed pursuant to the Parent’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation) was converted automatically into one ordinary share of the Company (the “Ordinary Shares”), (ii) each issued and outstanding warrant of the Parent was converted automatically into a warrant to purchase one Ordinary Share (“Warrant”), each Warrant having, and being subject to, the same terms and conditions set forth in the applicable agreements governing the Parent’s warrants, (iii) each issued and outstanding right of the Parent was converted automatically into a right to receive one-tenth (1/10) of one Ordinary Share at the closing of a business combination (“Right”), each Right having, and being subject to, the same terms and conditions set forth in the applicable agreements governing the Parent’s rights, and (iv) each outstanding unit of the Parent separated and converted automatically into one Ordinary Share, and one Warrant and One Right;
WHEREAS, on the date hereof, pursuant to the Merger Agreement, the Target Holders received Ordinary Shares;
WHEREAS, pursuant to Section 5.5 of the Original RRA, the provisions, covenants and conditions set forth therein may be amended or modified upon the written consent of the Parent and the Holders (as defined in the Original RRA) of at least a majority-in-interest of the Registrable Securities (as defined in the Original RRA) at the time in question; and
WHEREAS, the Company and the Sponsor desire to amend and restate the Original RRA in its entirety and enter into this Agreement, pursuant to which the Company shall grant the Holders certain registration rights with respect to certain securities of the Company, as set forth in this Agreement.
NOW, THEREFORE, in consideration of the representations, covenants and agreements contained herein, and certain other good and valuable consideration, the receipt and sufficiency of which are hereby acknowledged, the parties hereto, intending to be legally bound, hereby agree as follows:
ARTICLE I
DEFINITIONS
1.1 Definitions. The terms defined in this Article I shall, for all purposes of this Agreement, have the respective meanings set forth below:
“Additional Holder” shall have the meaning given in Section 5.10.
“Additional Holder Ordinary Shares” shall have the meaning given in Section 5.10.
“Adverse Disclosure” shall mean any public disclosure of material non-public information, which disclosure, in the good faith judgment of the Chief Executive Officer or the Chief Financial Officer of the Company, after consultation with counsel to the Company, (a) would be required to be made in any Registration Statement or Prospectus in order for the applicable Registration Statement or Prospectus not to contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements contained therein (in the case of any prospectus and any preliminary prospectus, in the light of the circumstances under which they were made) not misleading, (b) would not be required to be made at such time if the Registration Statement were not being filed, declared effective or used, as the case may be, and (c) the Company has a bona fide business purpose for not making such information public.
“Agreement” shall have the meaning given in the Preamble hereto.
“Block Trade” shall have the meaning given in Section 2.4.1.
“Board” shall mean the Board of Directors of the Company.
“Closing” shall have the meaning given in the Merger Agreement.
“Closing Date” shall have the meaning given in the Merger Agreement.
“Commission” shall mean the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission.
“Company” shall have the meaning given in the Preamble hereto and includes the Company’s successors by recapitalization, merger, consolidation, spin-off, reorganization or similar transaction.
“Demanding Holder” shall have the meaning given in Section 2.1.4.
“Exchange Act” shall mean the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as it may be amended from time to time.
“Form S-1 Shelf” shall have the meaning given in Section 2.1.1.
“Form S-3 Shelf” shall have the meaning given in Section 2.1.1.
“Holder Information” shall have the meaning given in Section 4.1.2.
“Holders” shall have the meaning given in the Preamble hereto, for so long as such person or entity holds any Registrable Securities.
“Insider Letter” shall mean that certain letter agreement, dated September 22, 2022, by and among the Company, the Sponsor and each of the other parties thereto.
“Joinder” shall have the meaning given in Section 5.10.
“Lock-up Period” shall have the meaning ascribed to such term in the Lock-up Agreement, dated as of [●], 2025, by and among the Company and the Holders party thereto.
“Maximum Number of Securities” shall have the meaning given in Section 2.1.5.
“Merger Agreement” shall have the meaning given in the Recitals hereto.
“Merger Sub” shall have the meaning given in the Recitals hereto.
“Minimum Takedown Threshold” shall have the meaning given in Section 2.1.4.
“Misstatement” shall mean an untrue statement of a material fact or an omission to state a material fact required to be stated in a Registration Statement or Prospectus or necessary to make the statements in a Registration Statement or Prospectus (in the case of a Prospectus, in the light of the circumstances under which they were made) not misleading.
“Ordinary Shares” shall have the meaning given in the Recitals hereto.
“Original RRA” shall have the meaning given in the Recitals hereto.
“Other Coordinated Offering” shall have the meaning given in Section 2.4.1.
“Permitted Transferees” shall mean (a) with respect to the Sponsor and its respective Permitted Transferees, any person or entity to whom such Holder is permitted to transfer such Registrable Securities, subject to and in accordance with any applicable agreement between such Holder and/or their respective Permitted Transferees and the Company and any transferee thereafter; (b) with respect to the Target Holders and their respective Permitted Transferees, any person or entity to whom such Holder is permitted to transfer such Registrable Securities, subject to and in accordance with any applicable agreement between such Holder and/or their respective Permitted Transferees and the Company and any transferee thereafter; and (c) with respect to all other Holders and their respective Permitted Transferees, any person or entity to whom such Holder of Registrable Securities is permitted to transfer such Registrable Securities, subject to and in accordance with any applicable agreement between such Holder and/or their respective Permitted Transferees and the Company and any transferee thereafter.
“Piggyback Registration” shall have the meaning given in Section 2.2.1.
“Private Placement Warrants” shall mean the warrants held by certain Holders, included in the private placement units purchased by such Holders in the private placement that occurred concurrently with the closing of the Company’s initial public offering, including any warrants and Ordinary Shares issued or issuable upon conversion or exchange of such warrants.
“Prospectus” shall mean the prospectus included in any Registration Statement, as supplemented by any and all prospectus supplements and as amended by any and all post-effective amendments and including all material incorporated by reference in such prospectus.
“Registrable Security” shall mean (a) any outstanding Ordinary Shares and any other equity security (including the Private Placement Warrants and any other warrants to purchase Ordinary Shares and Ordinary Shares issued or issuable upon the exercise of any other equity security and any Ordinary Shares issued) of the Company held by a Holder immediately following the Closing (including any securities distributable pursuant to the Merger Agreement); (b) any outstanding Ordinary Shares or any other equity security (including warrants to purchase Ordinary Shares, and Ordinary Shares issued or issuable upon the exercise of any other equity security) of the Company acquired by a Holder following the date hereof to the extent that such securities are “restricted securities” (as defined in Rule 144) or are otherwise held by an “affiliate” (as defined in Rule 144) of the Company; (c) any Additional Holder Ordinary Shares; and (d) any other equity security of the Company or any of its subsidiaries issued or issuable with respect to any securities referenced in clause (a), (b) or (c) above by way of a stock dividend or stock split or in connection with a recapitalization, merger, consolidation, spin-off, reorganization or similar transaction; provided, however, that, as to any particular Registrable Security, such securities shall cease to be Registrable Securities upon the earliest to occur of: (A) a Registration Statement with respect to the sale of such securities shall have become effective under the Securities Act and such securities shall have been sold, transferred, disposed of or exchanged in accordance with such Registration Statement by the applicable Holder; (B)(i) such securities shall have been otherwise transferred, (ii) new certificates for such securities not bearing (or book entry positions not subject to) a legend restricting further transfer shall have been delivered by the Company and (iii) subsequent public distribution of such securities shall not require registration under the Securities Act; (C) such securities shall have ceased to be outstanding; (D) such securities may be sold without registration pursuant to Rule 144 or any successor rule promulgated under the Securities Act (but with no volume or other restrictions or limitations including as to manner or timing of sale); and (E) such securities have been sold to, or through, a broker, dealer or underwriter in a public distribution or other public securities transaction.
“Registration” shall mean a registration, including any related Shelf Takedown, effected by preparing and filing a registration statement, Prospectus or similar document in compliance with the requirements of the Securities Act, and the applicable rules and regulations promulgated thereunder, and such registration statement becoming effective.
“Registration Expenses” shall mean the documented, out-of-pocket expenses of a Registration, including, without limitation, the following:
(A) all registration, listing and filing fees, including fees with respect to filings required to be made with the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, Inc. and any national securities exchange on which the Ordinary Shares is then listed;
(B) fees and expenses of compliance with securities or blue sky laws (including reasonable fees and disbursements of outside counsel for the Underwriters in connection with blue sky qualifications of Registrable Securities);
(C) printing, messenger, telephone and delivery expenses;
(D) reasonable fees and disbursements of counsel for the Company;
(E) reasonable fees and disbursements of all independent registered public accountants of the Company incurred specifically in connection with such Registration; and
(F) in an Underwritten Offering or Other Coordinated Offering, reasonable fees and expenses of one (1) legal counsel selected by the majority-in-interest of the Demanding Holders.
“Registration Statement” shall mean any registration statement that covers Registrable Securities pursuant to the provisions of this Agreement, including the Prospectus included in such registration statement, amendments (including post-effective amendments) and supplements to such registration statement, and all exhibits to and all material incorporated by reference in such registration statement.
“Requesting Holders” shall have the meaning given in Section 2.1.5.
“Securities Act” shall mean the Securities Act of 1933, as amended from time to time.
“Shelf” shall mean the Form S-1 Shelf, the Form S-3 Shelf or any Subsequent Shelf Registration Statement, as the case may be.
“Shelf Registration” shall mean a registration of securities pursuant to a registration statement filed with the Commission in accordance with and pursuant to Rule 415 promulgated under the Securities Act (or any successor rule then in effect).
“Shelf Takedown” shall mean any proposed transfer or sale using a Registration Statement, including a Piggyback Registration.
“Sponsor” shall have the meaning given in the Preamble hereto.
“Subsequent Shelf Registration Statement” shall have the meaning given in Section 2.1.2.
“Target” shall have the meaning given in the Preamble hereto.
“Target Holders” shall have the meaning given in the Preamble hereto.
“Transfer” shall mean the (a) sale or assignment of, offer to sell, contract or agreement to sell, hypothecate, pledge, grant of any option to purchase or otherwise dispose of or agreement to dispose of, directly or indirectly, or establishment or increase of a put equivalent position or liquidation with respect to or decrease of a call equivalent position within the meaning of Section 16 of the Exchange Act with respect to, any security, (b) entry into any swap or other arrangement that transfers to another, in whole or in part, any of the economic consequences of ownership of any security, whether any such transaction is to be settled by delivery of such securities, in cash or otherwise, or (c) public announcement of any intention to effect any transaction specified in clause (a) or (b).
“Underwriter” shall mean a securities dealer who purchases any Registrable Securities as principal in an Underwritten Offering and not as part of such dealer’s market-making activities.
“Underwritten Offering” shall mean a Registration in which securities of the Company are sold to an Underwriter in a firm commitment underwriting for distribution to the public.
“Withdrawal Notice” shall have the meaning given in Section 2.1.6.
ARTICLE II
REGISTRATIONS AND OFFERINGS
2.1 Shelf Registration.
2.1.1 Filing. Within forty-five (45) calendar days following the Closing Date (the “Filing Date”), the Company shall submit to or file with the Commission a Registration Statement for a Shelf Registration on Form S-1 (the “Form S-1 Shelf”) or a Registration Statement for a Shelf Registration on Form S-3 (the “Form S-3 Shelf”), if the Company is then eligible to use a Form S-3 Shelf, in each case, covering the resale of all the Registrable Securities (determined as of two (2) business days prior to such submission or filing) on a delayed or continuous basis and shall use its reasonable best efforts to have such Shelf declared effective as soon as practicable after the filing thereof, but no later than the ninetieth (90th) calendar day following the Filing Date. Such Shelf shall provide for the resale of the Registrable Securities included therein pursuant to any method or combination of methods legally available to, and requested by, any Holder named therein. The Company shall maintain a Shelf in accordance with the terms hereof, and shall prepare and file with the Commission such amendments, including post-effective amendments, and supplements as may be necessary to keep a Shelf continuously effective, available for use to permit the Holders named therein to sell their Registrable Securities included therein and in compliance with the provisions of the Securities Act until such time as there are no longer any Registrable Securities. In the event the Company files a Form S-1 Shelf, the Company shall use its commercially reasonable efforts to convert the Form S-1 Shelf (and any Subsequent Shelf Registration Statement) to a Form S-3 Shelf as soon as practicable after the Company is eligible to use Form S-3. The Company’s obligation under this Section 2.1.1, shall, for the avoidance of doubt, be subject to Section 3.4.
2.1.2 Subsequent Shelf Registration. If any Shelf ceases to be effective under the Securities Act for any reason at any time while Registrable Securities are still outstanding, the Company shall, subject to Section 3.4, use its commercially reasonable efforts to as promptly as is reasonably practicable cause such Shelf to again become effective under the Securities Act (including using its commercially reasonable efforts to obtain the prompt withdrawal of any order suspending the effectiveness of such Shelf), and shall use its commercially reasonable efforts to as promptly as is reasonably practicable amend such Shelf in a manner reasonably expected to result in the withdrawal of any order suspending the effectiveness of such Shelf or file an additional registration statement as a Shelf Registration (a “Subsequent Shelf Registration Statement”) registering the resale of all Registrable Securities (determined as of two (2) business days prior to such filing), and pursuant to any method or combination of methods legally available to, and requested by, any Holder named therein. If a Subsequent Shelf Registration Statement is filed, the Company shall use its commercially reasonable efforts to (i) cause such Subsequent Shelf Registration Statement to become effective under the Securities Act as promptly as is reasonably practicable after the filing thereof (it being agreed that the Subsequent Shelf Registration Statement shall be an automatic shelf registration statement (as defined in Rule 405 promulgated under the Securities Act) if the Company is a well-known seasoned issuer (as defined in Rule 405 promulgated under the Securities Act) at the most recent applicable eligibility determination date) and (ii) keep such Subsequent Shelf Registration Statement continuously effective, available for use to permit the Holders named therein to sell their Registrable Securities included therein and in compliance with the provisions of the Securities Act until such time as there are no longer any Registrable Securities. Any such Subsequent Shelf Registration Statement shall be on Form S-3 to the extent that the Company is eligible to use such form. Otherwise, such Subsequent Shelf Registration Statement shall be on another appropriate form. The Company’s obligation under this Section 2.1.2, shall, for the avoidance of doubt, be subject to Section 3.4.
2.1.3 Additional Registration Statement(s). Subject to Section 3.4, in the event that any Holder holds Registrable Securities that are not registered for resale on a delayed or continuous basis, the Company, upon written request of such Holder, shall promptly use its commercially reasonable efforts to cause the resale of such Registrable Securities to be covered by filing a Subsequent Shelf Registration Statement and cause the same to become effective as soon as practicable after such filing and such Subsequent Shelf Registration Statement shall be subject to the terms hereof; provided, however, that the Company shall only be required to cause such Registrable Securities to be so covered twice per calendar year for each of the Sponsor and the Target Holders.
2.1.4 Requests for Underwritten Offerings. Subject to Section 3.4, at any time and from time to time following the expiration of the Lock-up Period, the Sponsor or a Target Holder (any of the Sponsor or a Target Holder being in such case, a “Demanding Holder”) may request to sell all or any portion of its Registrable Securities in an Underwritten Offering; provided that the Company shall only be obligated to effect an Underwritten Offering if such offering shall include Registrable Securities proposed to be sold by the Demanding Holder, either individually or together with other Demanding Holders, with a total offering price reasonably expected to exceed, in the aggregate, $25 million (the “Minimum Takedown Threshold”). All requests for Underwritten Offerings shall be made by giving written notice to the Company, which shall specify the approximate number of Registrable Securities proposed to be sold in the Underwritten Offering. Subject to Section 2.4.4, the Company shall have the right to select the Underwriters for such offering (which shall consist of one or more reputable nationally recognized investment banks), subject to the initial Demanding Holder’s prior approval (which shall not be unreasonably withheld, conditioned or delayed). The Sponsor and the Target Holders may each demand not more than one (1) Underwritten Offering pursuant to this Section 2.1.4 in any twelve (12) month period, for an aggregate of not more than two (2) Underwritten Offerings pursuant to this Section 2.1.4 in any twelve (12) month period. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in this Agreement, the Company may effect any Underwritten Offering pursuant to any then effective Registration Statement, including a Form S-3, that is then available for such offering.
2.1.5 Reduction of Underwritten Offering. If the managing Underwriter or Underwriters in an Underwritten Offering, in good faith, advises the Company, the Demanding Holders and the Holders requesting piggy back rights pursuant to this Agreement with respect to such Underwritten Offering (the “Requesting Holders”) (if any) in writing that the dollar amount or number of Registrable Securities that the Demanding Holders and the Requesting Holders (if any) desire to sell, taken together with all other Ordinary Shares or other equity securities that the Company desires to sell and all other Ordinary Shares or other equity securities, if any, that have been requested to be sold in such Underwritten Offering pursuant to separate written contractual piggy-back registration rights held by any other stockholders, exceeds the maximum dollar amount or maximum number of equity securities that can be sold in the Underwritten Offering without adversely affecting the proposed offering price, the timing, the distribution method, or the probability of success of such offering (such maximum dollar amount or maximum number of such securities, as applicable, the “Maximum Number of Securities”), then the Company shall include in such Underwritten Offering, before including any Ordinary Shares or other equity securities proposed to be sold by Company or by other holders of Ordinary Shares or other equity securities, (i) first, the Registrable Securities of the Demanding Holders that can be sold without exceeding the Maximum Number of Securities (pro rata based on the respective number of Registrable Securities that each Demanding Holder has requested be included in such Underwritten Offering and the aggregate number of Registrable Securities that all of the Demanding Holders have requested be included in such Underwritten Offering), (ii) second, to the extent that the Maximum Number of Securities has not been reached under the foregoing clause (i), the Registrable Securities of the Requesting Holders (if any) (pro rata based on the respective number of Registrable Securities that each Requesting Holder (if any) has requested be included in such Underwritten Offering and the aggregate number of Registrable Securities that all of the Requesting Holders have requested be included in such Underwritten Offering) that can be sold without exceeding the Maximum Number of Securities, (iii) third, to the extent that the Maximum Number of Securities has not been reached under the foregoing clauses (i) and (ii), the Ordinary Shares or other equity securities that the Company desires to sell, which can be sold without exceeding the Maximum Number of Securities, and (iv) fourth,
to the extent that the Maximum Number of Securities has not been reached under the foregoing clauses (i), (ii) and (iii), the Ordinary Shares or other equity securities of persons other than Holders of Registrable Securities that the Company is obligated to register in a Registration pursuant to separate written contractual arrangements with such persons that can be sold without exceeding the Maximum Number of Securities.
2.1.6 Withdrawal. Prior to the filing of the applicable “red herring” prospectus or prospectus supplement used for marketing such Underwritten Offering, a majority-in-interest of the Demanding Holders initiating an Underwritten Offering shall have the right to withdraw from such Underwritten Offering for any or no reason whatsoever upon written notification (a “Withdrawal Notice”) to the Company and the Underwriter or Underwriters (if any) of their intention to withdraw from such Underwritten Offering; provided that the Sponsor or a Holder may elect to have the Company continue an Underwritten Offering if the Minimum Takedown Threshold would still be satisfied by the Registrable Securities proposed to be sold in the Underwritten Offering by the Sponsor, the Target Holders or any of their respective Permitted Transferees, as applicable. If withdrawn, a demand for an Underwritten Offering shall constitute a demand for an Underwritten Offering by the withdrawing Demanding Holder for purposes of Section 2.1.4, unless such Demanding Holder reimburses the Company for all Registration Expenses with respect to such Underwritten Offering (or, if there is more than one Demanding Holder, a pro rata portion of such Registration Expenses based on the respective number of Registrable Securities that each Demanding Holder has requested be included in such Underwritten Offering); provided that, if the Sponsor or a Target Holder elects to continue an Underwritten Offering pursuant to the proviso in the immediately preceding sentence, such Underwritten Offering shall instead count as an Underwritten Offering demanded by the Sponsor or such Target Holder, as applicable, for purposes of Section 2.1.4. Following the receipt of any Withdrawal Notice, the Company shall promptly forward such Withdrawal Notice to any other Holders that had elected to participate in such Shelf Takedown. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in this Agreement, the Company shall be responsible for the Registration Expenses incurred in connection with a Shelf Takedown prior to its withdrawal under this Section 2.1.6, other than if a Demanding Holder elects to pay such Registration Expenses pursuant to the second sentence of this Section 2.1.6.
2.2 Piggyback Registration.
2.2.1 Piggyback Rights. Subject to Section 2.4.3, if the Company or any Holder proposes to conduct a registered offering of, or if the Company proposes to file a Registration Statement under the Securities Act with respect to the Registration of, equity securities, or securities or other obligations exercisable or exchangeable for, or convertible into equity securities, for its own account or for the account of stockholders of the Company (or by the Company and by the stockholders of the Company including, without limitation, an Underwritten Offering pursuant to Section 2.1), other than a Registration Statement (or any registered offering with respect thereto) (i) filed in connection with any employee stock option or other benefit plan, (ii) pursuant to a Registration Statement on Form S-4 (or similar form that relates to a transaction subject to Rule 145 under the Securities Act or any successor rule thereto), (iii) for an offering of debt that is convertible into equity securities of the Company, (iv) for a dividend reinvestment plan, (v) for an exchange offer or offering of securities solely to the Company’s existing securityholders, (vi) for a rights offering, (vii) for an equity line of credit or an at-the-market offering of securities, (viii) a Block Trade or (ix) an Other Coordinated Offering, then the Company shall give written notice of such proposed offering to all of the Holders of Registrable Securities as soon as practicable but not less than ten (10) days before the anticipated filing date of such Registration Statement or, in the case of an Underwritten Offering pursuant to a Shelf Registration, the applicable “red herring” prospectus or prospectus supplement used for marketing such offering, which notice shall (A) describe the amount and type of securities to be included in such offering, the intended method(s) of distribution, and the name of the proposed managing Underwriter or Underwriters, if any, in such offering, and (B) offer to all of the Holders of Registrable Securities the opportunity to include in such registered offering such number of Registrable Securities as such Holders may request in writing within five (5) days after receipt of such written notice (such registered
offering, a “Piggyback Registration”). Subject to Section 2.2.2, the Company shall, in good faith, cause such Registrable Securities to be included in such Piggyback Registration and, if applicable, shall use its commercially reasonable efforts to cause the managing Underwriter or Underwriters of such Piggyback Registration to permit the Registrable Securities requested by the Holders pursuant to this Section 2.2.1 to be included therein on the same terms and conditions as any similar securities of the Company included in such registered offering and to permit the sale or other disposition of such Registrable Securities in accordance with the intended method(s) of distribution thereof. The inclusion of any Holder’s Registrable Securities in a Piggyback Registration shall be subject to such Holder agreement to enter into an underwriting agreement in customary form with the Underwriter(s) selected for such Underwritten Offering.
2.2.2 Reduction of Piggyback Registration. If the managing Underwriter or Underwriters in an Underwritten Offering that is to be a Piggyback Registration, in good faith, advises the Company and the Holders of Registrable Securities participating in the Piggyback Registration in writing that the dollar amount or number of Ordinary Shares or other equity securities that the Company desires to sell, taken together with (i) the Ordinary Shares or other equity securities, if any, as to which Registration or a registered offering has been demanded pursuant to separate written contractual arrangements with persons or entities other than the Holders of Registrable Securities hereunder, (ii) the Registrable Securities as to which registration has been requested pursuant to Section 2.2 hereof, and (iii) the Ordinary Shares or other equity securities, if any, as to which Registration or a registered offering has been requested pursuant to separate written contractual piggy-back registration rights of persons or entities other than the Holders of Registrable Securities hereunder, exceeds the Maximum Number of Securities, then:
(a) if the Registration or registered offering is undertaken for the Company’s account, the Company shall include in any such Registration or registered offering (A) first, the Ordinary Shares or other equity securities that the Company desires to sell, which can be sold without exceeding the Maximum Number of Securities; (B) second, to the extent that the Maximum Number of Securities has not been reached under the foregoing clause (A), the Registrable Securities of Holders exercising their rights to register their Registrable Securities pursuant to Section 2.2.1, pro rata, based on the respective number of Registrable Securities that each Holder has requested be included in such Underwritten Offering and the aggregate number of Registrable Securities that the Holders have requested to be included in such Underwritten Offering, which can be sold without exceeding the Maximum Number of Securities; and (C) third, to the extent that the Maximum Number of Securities has not been reached under the foregoing clauses (A) and (B), the Ordinary Shares or other equity securities, if any, as to which Registration or a registered offering has been requested pursuant to separate written contractual piggy-back registration rights of persons or entities other than the Holders of Registrable Securities hereunder, which can be sold without exceeding the Maximum Number of Securities;
(b) if the Registration or registered offering is pursuant to a demand by persons or entities other than the Holders of Registrable Securities, then the Company shall include in any such Registration or registered offering (A) first, the Ordinary Shares or other equity securities, if any, of such requesting persons or entities, other than the Holders of Registrable Securities, which can be sold without exceeding the Maximum Number of Securities; (B) second, to the extent that the Maximum Number of Securities has not been reached under the foregoing clause (A), the Registrable Securities of Holders exercising their rights to register their Registrable Securities pursuant to Section 2.2.1, pro rata, based on the respective number of Registrable Securities that each Holder has requested be included in such Underwritten Offering and the aggregate number of Registrable Securities that the Holders have requested to be included in such Underwritten Offering, which can be sold without exceeding the Maximum Number of Securities; (C) third, to the extent that the Maximum Number of Securities has not been reached under the foregoing clauses (A) and (B), the Ordinary Shares or other equity securities that the Company desires to sell, which can be sold without exceeding the Maximum Number of Securities; and (D) fourth, to the extent that the Maximum Number of Securities has not been reached under the foregoing clauses (A), (B) and (C), the Ordinary Shares or other equity securities, if any, as to which Registration or a registered offering has been requested pursuant to separate written contractual piggy-back registration rights of persons or entities other than the Holders of Registrable Securities hereunder, which can be sold without exceeding the Maximum Number of Securities; and
(c) if the Registration or registered offering and Underwritten Offering is pursuant to a request by Holder(s) of Registrable Securities pursuant to Section 2.1 hereof, then the Company shall include in any such Registration or registered offering securities in the priority set forth in Section 2.1.5.
2.2.3 Piggyback Registration Withdrawal. Any Holder of Registrable Securities (other than a Demanding Holder, whose right to withdraw from an Underwritten Offering, and related obligations, shall be governed by Section 2.1.6) shall have the right to withdraw from a Piggyback Registration for any or no reason whatsoever upon written notification to the Company and the Underwriter or Underwriters (if any) of his, her or its intention to withdraw from such Piggyback Registration prior to the effectiveness of the Registration Statement filed with the Commission with respect to such Piggyback Registration or, in the case of a Piggyback Registration pursuant to a Shelf Registration, the filing of the applicable “red herring” prospectus or prospectus supplement with respect to such Piggyback Registration used for marketing such transaction. The Company (whether on its own good faith determination or as the result of a request for withdrawal by persons or entities pursuant to separate written contractual obligations) may withdraw a Registration Statement filed with the Commission in connection with a Piggyback Registration (which, in no circumstance, shall include a Shelf) at any time prior to the effectiveness of such Registration Statement. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in this Agreement (other than Section 2.1.6), the Company shall be responsible for the Registration Expenses incurred in connection with the Piggyback Registration prior to its withdrawal under this Section 2.2.3.
2.2.4 Unlimited Piggyback Registration Rights. For purposes of clarity, subject to Section 2.1.6, any Piggyback Registration effected pursuant to Section 2.2 hereof shall not be counted as a demand for an Underwritten Offering under Section 2.1.4 hereof.
2.3 Market Stand-off. In connection with any Underwritten Offering of equity securities of the Company (other than a Block Trade or Other Coordinated Offering), if requested by the managing Underwriters, each Holder that is (a) an executive officer, (b) a director or (c) Holder in excess of five percent (5%) of the outstanding Ordinary Shares (and for which it is customary for such a Holder to agree to a lock-up) agrees that it shall not Transfer any Ordinary Shares or other equity securities of the Company (other than those included in such offering pursuant to this Agreement), without the prior written consent of the Company, during the ninety (90)-day period (or such shorter time agreed to by the managing Underwriters) beginning on the date of pricing of such offering, except as expressly permitted by such lock-up agreement or in the event the managing Underwriters otherwise agree by written consent. Each such Holder agrees to execute a customary lock-up agreement in favor of the Underwriters to such effect (in each case on substantially the same terms and conditions as all such Holders).
2.4 Block Trades; Other Coordinated Offerings.
2.4.1 Notwithstanding any other provision of this Article II, but subject to Section 3.4, at any time and from time to time when an effective Shelf is on file with the Commission, if a Demanding Holder wishes to engage in (a) an underwritten registered offering not involving a “roadshow,” an offer commonly known as a “block trade” (a “Block Trade”), or (b) an “at the market” or similar registered offering through a broker, sales agent or distribution agent, whether as agent or principal (an “Other Coordinated Offering”), in each case, (x) with a total offering price reasonably expected to exceed $25 million in the aggregate or (y) with respect to all remaining Registrable Securities held by the Demanding
Holder, then such Demanding Holder shall notify the Company of the Block Trade or Other Coordinated Offering at least five (5) business days prior to the day such offering is to commence and the Company shall use its commercially reasonable efforts to facilitate such Block Trade or Other Coordinated Offering; provided that the Demanding Holders representing a majority of the Registrable Securities wishing to engage in the Block Trade or Other Coordinated Offering shall use commercially reasonable efforts to work with the Company and any Underwriters, brokers, sales agents or placement agents prior to making such request in order to facilitate preparation of the registration statement, prospectus and other offering documentation related to the Block Trade or Other Coordinated Offering.
2.4.2 Prior to the filing of the applicable “red herring” prospectus or prospectus supplement used in connection with a Block Trade or Other Coordinated Offering, a majority-in-interest of the Demanding Holders initiating such Block Trade or Other Coordinated Offering shall have the right to submit a Withdrawal Notice to the Company, the Underwriter or Underwriters (if any) and any brokers, sales agents or placement agents (if any) of their intention to withdraw from such Block Trade or Other Coordinated Offering. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in this Agreement, the Company shall be responsible for the Registration Expenses incurred in connection with a Block Trade or Other Coordinated Offering prior to its withdrawal under this Section 2.4.2.
2.4.3 Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in this Agreement, Section 2.2 shall not apply to a Block Trade or Other Coordinated Offering initiated by a Demanding Holder pursuant to this Agreement.
2.4.4 The Demanding Holder in a Block Trade or Other Coordinated Offering shall have the right to select the Underwriters and any brokers, sales agents or placement agents (if any) for such Block Trade or Other Coordinated Offering (in each case, which shall consist of one or more reputable nationally recognized investment banks).
2.4.5 A Demanding Holder in the aggregate may demand no more than two (2) Block Trades or Other Coordinated Offerings pursuant to this Section 2.4 in any twelve (12) month period. For the avoidance of doubt, any Block Trade or Other Coordinated Offering effected pursuant to this Section 2.4 shall not be counted as a demand for an Underwritten Offering pursuant to Section 2.1.4 hereof.
ARTICLE III
COMPANY PROCEDURES
3.1 General Procedures. If at any time the Company is required to effect the Registration of Registrable Securities hereunder, the Company shall use its commercially reasonable efforts to effect such Registration to permit the sale of such Registrable Securities in accordance with the intended plan of distribution thereof, and pursuant thereto the Company shall:
3.1.1 prepare and file with the Commission as soon as practicable a Registration Statement with respect to such Registrable Securities and use its commercially reasonable efforts to cause such Registration Statement to become effective and remain effective until all Registrable Securities covered by such Registration Statement are sold in accordance with the intended plan of distribution set forth in such Registration Statement or have ceased to be Registrable Securities;
3.1.2 prepare and file with the Commission such amendments and post-effective amendments to the Registration Statement, and such supplements to the Prospectus, as may be reasonably requested by any Holder that holds at least five percent (5%) of the Registrable Securities registered on such Registration Statement or any Underwriter of Registrable Securities or as may be required by the rules, regulations or instructions applicable to the registration form used by the Company or by the Securities Act or rules and regulations thereunder to keep the Registration Statement effective until all Registrable Securities covered by such Registration Statement are sold in accordance with the intended plan of distribution set forth in such Registration Statement or supplement to the Prospectus or have ceased to be Registrable Securities;
3.1.3 prior to filing a Registration Statement or Prospectus, or any amendment or supplement thereto, furnish without charge to the Underwriters, if any, and the Holders of Registrable Securities included in such Registration, and such Holders’ legal counsel, copies of such Registration Statement as proposed to be filed, each amendment and supplement to such Registration Statement (in each case including all exhibits thereto and documents incorporated by reference therein), the Prospectus included in such Registration Statement (including each preliminary Prospectus), and such other documents as the Underwriters and the Holders of Registrable Securities included in such Registration or the legal counsel for any such Holders may reasonably request in order to facilitate the disposition of the Registrable Securities owned by such Holders; provided that the Company shall have no obligation to furnish any documents publicly filed or furnished with the Commission pursuant to the Electronic Data Gathering, Analysis and Retrieval System (“EDGAR”);
3.1.4 prior to any public offering of Registrable Securities, use its commercially reasonable efforts to (i) register or qualify the Registrable Securities covered by the Registration Statement under such securities or “blue sky” laws of such jurisdictions in the United States as the Holders of Registrable Securities included in such Registration Statement (in light of their intended plan of distribution) may request (or provide evidence satisfactory to such Holders that the Registrable Securities are exempt from such registration or qualification) and (ii) take such action necessary to cause such Registrable Securities covered by the Registration Statement to be registered with or approved by such other governmental authorities as may be necessary by virtue of the business and operations of the Company and do any and all other acts and things that may be necessary or advisable to enable the Holders of Registrable Securities included in such Registration Statement to consummate the disposition of such Registrable Securities in such jurisdictions; provided, however, that the Company shall not be required to qualify generally to do business or as a dealer in securities in any jurisdiction where it would not otherwise be required to qualify or take any action to which it would be subject to general service of process or taxation in any such jurisdiction where it is not then otherwise so subject;
3.1.5 cause all such Registrable Securities to be listed on each national securities exchange on which similar securities issued by the Company are then listed;
3.1.6 provide a transfer agent or warrant agent, as applicable, and registrar for all such Registrable Securities no later than the effective date of such Registration Statement;
3.1.7 advise each seller of such Registrable Securities, promptly after it shall receive notice or obtain knowledge thereof, of the issuance of any stop order by the Commission suspending the effectiveness of such Registration Statement or the initiation or threatening of any proceeding for such purpose and promptly use its commercially reasonable efforts to prevent the issuance of any stop order or to obtain its withdrawal if such stop order should be issued;
3.1.8 at least five (5) days prior to the filing of any Registration Statement or Prospectus or any amendment or supplement to such Registration Statement or Prospectus (or such shorter period of time as may be (a) necessary in order to comply with the Securities Act, the Exchange Act, and the rules and regulations promulgated under the Securities Act or Exchange Act, as applicable or (b) advisable in order to reduce the number of days that sales are suspended pursuant to Section 3.4), furnish a copy thereof to each seller of such Registrable Securities or its counsel (excluding any exhibits thereto and any filing made under the Exchange Act that is to be incorporated by reference therein);
3.1.9 notify the Holders at any time when a Prospectus relating to such Registration Statement is required to be delivered under the Securities Act, of the happening of any event as a result of which the Prospectus included in such Registration Statement, as then in effect, includes a Misstatement, and then to correct such Misstatement as set forth in Section 3.4;
3.1.10 in the event of an Underwritten Offering, a Block Trade, an Other Coordinated Offering, or sale by a broker, placement agent or sales agent pursuant to such Registration, in each of the following cases to the extent customary for a transaction of its type, permit a representative of the Holders, the Underwriters or other financial institutions facilitating such Underwritten Offering, Block Trade, Other Coordinated Offering or other sale pursuant to such Registration, if any, and any attorney, consultant or accountant retained by such Holders or Underwriter to participate, at each such person’s or entity’s own expense, in the preparation of the Registration Statement, and cause the Company’s officers, directors and employees to supply all information reasonably requested by any such representative, Underwriter, financial institution, attorney, consultant or accountant in connection with the Registration; provided, however, that such representatives, Underwriters or financial institutions agree to confidentiality arrangements in form and substance reasonably satisfactory to the Company, prior to the release or disclosure of any such information;
3.1.11 obtain a “cold comfort” letter from the Company’s independent registered public accountants in the event of an Underwritten Offering, a Block Trade, an Other Coordinated Offering or sale by a broker, placement agent or sales agent pursuant to such Registration (subject to such broker, placement agent or sales agent providing such certification or representation reasonably requested by the Company’s independent registered public accountants and the Company’s counsel) in customary form and covering such matters of the type customarily covered by “cold comfort” letters for a transaction of its type as the managing Underwriter may reasonably request, and reasonably satisfactory to a majority-in-interest of the participating Holders;
3.1.12 in the event of an Underwritten Offering, a Block Trade, an Other Coordinated Offering or sale by a broker, placement agent or sales agent pursuant to such Registration, on the date the Registrable Securities are delivered for sale pursuant to such Registration, to the extent customary for a transaction of its type, obtain an opinion, dated such date, of counsel representing the Company for the purposes of such Registration, addressed to the participating Holders, the broker, placement agents or sales agent, if any, and the Underwriters, if any, covering such legal matters with respect to the Registration in respect of which such opinion is being given as the participating Holders, broker, placement agent, sales agent or Underwriter may reasonably request and as are customarily included in such opinions and negative assurance letters;
3.1.13 in the event of any Underwritten Offering, a Block Trade, an Other Coordinated Offering or sale by a broker, placement agent or sales agent pursuant to such Registration, enter into and perform its obligations under an underwriting or other purchase or sales agreement, in usual and customary form, with the managing Underwriter or the broker, placement agent or sales agent of such offering or sale;
3.1.14 make available to its security holders, as soon as reasonably practicable, an earnings statement covering the period of at least twelve (12) months beginning with the first day of the Company’s first full calendar quarter after the effective date of the Registration Statement which satisfies the provisions of Section 11(a) of the Securities Act and Rule 158 thereunder (or any successor rule then in effect), which requirement will be deemed satisfied if the Company timely files Forms 10-K, 10-Q, and 8-K as may be required to be filed under the Exchange Act and otherwise complies with Rule 158 under the Securities Act;
3.1.15 with respect to an Underwritten Offering pursuant to Section 2.1.4, use its commercially reasonable efforts to make available senior executives of the Company to participate in customary “road show” presentations that may be reasonably requested by the Underwriter in such Underwritten Offering; and
3.1.16 otherwise, in good faith, cooperate reasonably with, and take such customary actions as may reasonably be requested by the participating Holders, consistent with the terms of this Agreement, in connection with such Registration.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, the Company shall not be required to provide any documents or information to an Underwriter, broker, sales agent or placement agent if such Underwriter, broker, sales agent or placement agent has not then been named with respect to the applicable Underwritten Offering or other offering involving a registration as an Underwriter, broker, sales agent or placement agent, as applicable.
3.2 Registration Expenses. The Registration Expenses of all Registrations shall be borne by the Company. It is acknowledged by the Holders that the Holders shall bear all incremental selling expenses relating to the sale of Registrable Securities, such as Underwriters’ commissions and discounts, brokerage fees and, other than as set forth in the definition of “Registration Expenses,” all fees and expenses of any legal counsel representing the Holders.
3.3 Requirements for Participation in Registration Statement and Underwritten Offerings. Notwithstanding anything in this Agreement to the contrary, if any Holder does not provide the Company with its requested Holder Information, the Company may exclude such Holder’s Registrable Securities from the applicable Registration Statement or Prospectus if the Company determines, based on the advice of counsel, that it is necessary or advisable to include such information in the applicable Registration Statement or Prospectus and such Holder continues thereafter to withhold such information. In addition, no person or entity may participate in any Underwritten Offering or other offering for equity securities of the Company pursuant to a Registration initiated by the Company hereunder unless such person or entity (i) agrees to sell such person’s or entity’s securities on the basis provided in any underwriting, sales, distribution or placement arrangements approved by the Company and (ii) completes and executes all customary questionnaires, powers of attorney, indemnities, lock-up agreements, underwriting or other agreements and other customary documents as may be reasonably required under the terms of such underwriting, sales, distribution or placement arrangements. For the avoidance of doubt, the exclusion of a Holder’s Registrable Securities as a result of this Section 3.3 shall not affect the registration of the other Registrable Securities to be included in such Registration.
3.4 Suspension of Sales; Adverse Disclosure; Restrictions on Registration Rights.
3.4.1 Upon receipt of written notice from the Company that a Registration Statement or Prospectus contains a Misstatement, each of the Holders shall forthwith discontinue disposition of Registrable Securities until it has received copies of a supplemented or amended Prospectus correcting the Misstatement (it being understood that the Company hereby covenants to prepare and file such supplement or amendment as soon as reasonably practicable after the time of such notice), or until it is advised in writing by the Company that the use of the Prospectus may be resumed.
3.4.2 Subject to Section 3.4.4, if the filing, initial effectiveness or continued use of a Registration Statement in respect of any Registration at any time would (a) require the Company to make an Adverse Disclosure, (b) require the inclusion in such Registration Statement of financial statements that are unavailable to the Company for reasons beyond the Company’s control, or (c) in the good faith judgment of the majority of the Board such Registration, be seriously detrimental to the Company and the majority of the Board concludes as a result that it is essential to defer such filing, initial effectiveness or continued
use at such time, the Company may, upon giving prompt written notice of such action to the Holders (which notice shall not specify the nature of the event giving rise to such delay or suspension), delay the filing or initial effectiveness of, or suspend use of, such Registration Statement for the shortest period of time determined in good faith by the Company to be necessary for such purpose. In the event the Company exercises its rights under this Section 3.4.2, the Holders agree to suspend, immediately upon their receipt of the notice referred to above, their use of the Prospectus relating to any Registration in connection with any sale or offer to sell Registrable Securities until such Holder receives written notice from the Company that such sales or offers of Registrable Securities may be resumed, and in each case maintain the confidentiality of such notice and its contents.
3.4.3 Subject to Section 3.4.4, (a) during the period starting with the date sixty (60) days prior to the Company’s good faith estimate of the date of the filing of, and ending on a date one hundred and twenty (120) days after the effective date of, a Company-initiated Registration and provided that the Company continues to actively employ, in good faith, all commercially reasonable efforts to maintain the effectiveness of the applicable Shelf Registration Statement, or (b) if, pursuant to Section 2.1.4, Holders have requested an Underwritten Offering and the Company and Holders are unable to obtain the commitment of underwriters to firmly underwrite such offering, the Company may, upon giving prompt written notice of such action to the Holders, delay any other registered offering pursuant to Section 2.1.4 or 2.4.
3.4.4 The right to delay or suspend any filing, initial effectiveness or continued use of a Registration Statement pursuant to Section 3.4.2 or a registered offering pursuant to Section 3.4.3 shall be exercised by the Company, in the aggregate, for not more than ninety (90) consecutive calendar days or more than one hundred and twenty (120) total calendar days, in each case, during any twelve (12)-month period.
3.5 Reporting Obligations. As long as any Holder shall own Registrable Securities, the Company, at all times while it shall be a reporting company under the Exchange Act, covenants to file timely (or obtain extensions in respect thereof and file within the applicable grace period) all reports required to be filed by the Company after the date hereof pursuant to Sections 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act and to promptly furnish the Holders with true and complete copies of all such filings; provided that any documents publicly filed or furnished with the Commission pursuant to EDGAR shall be deemed to have been furnished or delivered to the Holders pursuant to this Section 3.5. The Company further covenants that it shall take such further action as any Holder may reasonably request, all to the extent required from time to time to enable such Holder to sell Ordinary Shares held by such Holder without registration under the Securities Act within the limitation of the exemptions provided by Rule 144 promulgated under the Securities Act (or any successor rule then in effect). Upon the request of any Holder, the Company shall deliver to such Holder a written certification of a duly authorized officer as to whether it has complied with such requirements.
ARTICLE IV
INDEMNIFICATION AND CONTRIBUTION
4.1 Indemnification.
4.1.1 The Company agrees to indemnify, to the extent permitted by law, each Holder of Registrable Securities, its officers, directors and agents and each person or entity who controls such Holder (within the meaning of the Securities Act), against all losses, claims, damages, liabilities and out-of-pocket expenses (including, without limitation, reasonable and documented outside attorneys’ fees) resulting from any untrue or alleged untrue statement of material fact contained in or incorporated by reference in any Registration Statement, Prospectus or preliminary Prospectus or any amendment thereof or supplement
thereto or any omission or alleged omission of a material fact required to be stated therein or necessary to make the statements therein not misleading (in the case of a Prospectus, in light of the circumstances in which they were made), except insofar as the same are caused by or contained in any information or affidavit so furnished in writing to the Company by such Holder expressly for use therein.
4.1.2 In connection with any Registration Statement in which a Holder of Registrable Securities is participating, such Holder shall furnish (or cause to be furnished) to the Company in writing such information and affidavits as the Company reasonably requests for use in connection with any such Registration Statement or Prospectus (the “Holder Information”) and, to the extent permitted by law, shall indemnify the Company, its directors, officers and agents and each person or entity who controls the Company (within the meaning of the Securities Act) against all losses, claims, damages, liabilities and reasonable and documented out-of-pocket expenses (including, without limitation, reasonable and documented outside attorneys’ fees) resulting from any untrue or alleged untrue statement of material fact contained or incorporated by reference in any Registration Statement, Prospectus or preliminary Prospectus or any amendment thereof or supplement thereto or any omission or alleged omission of a material fact required to be stated therein or necessary to make the statements therein not misleading (in the case of a Prospectus, in light of the circumstances in which they were made), but only to the extent that such untrue statement is contained in (or not contained in, in the case of an omission) any information or affidavit so furnished in writing by or on behalf of such Holder expressly for use therein; provided, however, that the obligation to indemnify shall be several, not joint and several, among such Holders of Registrable Securities, and the liability of each such Holder of Registrable Securities shall be in proportion to and limited to the net proceeds received by such Holder from the sale of Registrable Securities pursuant to such Registration Statement. The Holders of Registrable Securities shall indemnify the Underwriters, their officers, directors and each person or entity who controls such Underwriters (within the meaning of the Securities Act) to the same extent as provided in the foregoing with respect to indemnification of the Company.
4.1.3 Any person or entity entitled to indemnification herein shall (i) give prompt written notice to the indemnifying party of any claim with respect to which it seeks indemnification (provided that the failure to give prompt notice shall not impair any person’s or entity’s right to indemnification hereunder to the extent such failure has not materially prejudiced the indemnifying party) and (ii) unless in such indemnified party’s reasonable judgment a conflict of interest between such indemnified and indemnifying parties may exist with respect to such claim, permit such indemnifying party to assume the defense of such claim with counsel reasonably satisfactory to the indemnified party. If such defense is assumed, the indemnifying party shall not be subject to any liability for any settlement made by the indemnified party without its consent (but such consent shall not be unreasonably withheld). An indemnifying party who is not entitled to, or elects not to, assume the defense of a claim shall not be obligated to pay the fees and expenses of more than one counsel for all parties indemnified by such indemnifying party with respect to such claim, unless in the reasonable judgment of any indemnified party a conflict of interest may exist between such indemnified party and any other of such indemnified parties with respect to such claim. No indemnifying party shall, without the consent of the indemnified party, consent to the entry of any judgment or enter into any settlement which cannot be settled in all respects by the payment of money (and such money is so paid by the indemnifying party pursuant to the terms of such settlement) or which settlement includes a statement or admission of fault and culpability on the part of such indemnified party or which settlement does not include as an unconditional term thereof the giving by the claimant or plaintiff to such indemnified party of a release from all liability in respect to such claim or litigation.
4.1.4 The indemnification provided for under this Agreement shall remain in full force and effect regardless of any investigation made by or on behalf of the indemnified party or any officer, director or controlling person or entity of such indemnified party and shall survive the transfer of securities. The Company and each Holder of Registrable Securities participating in an offering also agrees to make such provisions as are reasonably requested by any indemnified party for contribution to such party in the event the Company’s or such Holder’s indemnification is unavailable for any reason.
4.1.5 If the indemnification provided under Section 4.1 from the indemnifying party is unavailable or insufficient to hold harmless an indemnified party in respect of any losses, claims, damages, liabilities and reasonable and documented out-of-pocket expenses referred to herein, then the indemnifying party, in lieu of indemnifying the indemnified party, shall contribute to the amount paid or payable by the indemnified party as a result of such losses, claims, damages, liabilities and reasonable and documented out-of-pocket expenses in such proportion as is appropriate to reflect the relative fault of the indemnifying party and the indemnified party, as well as any other relevant equitable considerations. The relative fault of the indemnifying party and indemnified party shall be determined by reference to, among other things, whether any action in question, including any untrue or alleged untrue statement of a material fact or omission or alleged omission to state a material fact, was made by (or not made by, in the case of an omission), or relates to information supplied by (or not supplied by in the case of an omission), such indemnifying party or indemnified party, and the indemnifying party’s and indemnified party’s relative intent, knowledge, access to information and opportunity to correct or prevent such action; provided, however, that the liability of any Holder under this Section 4.1.5 shall be limited to the amount of the net proceeds received by such Holder in such offering giving rise to such liability. The amount paid or payable by a party as a result of the losses or other liabilities referred to above shall be deemed to include, subject to the limitations set forth in Sections 4.1.1, 4.1.2 and 4.1.3 above, any legal or other fees, charges or out-of-pocket expenses reasonably incurred by such party in connection with any investigation or proceeding. The parties hereto agree that it would not be just and equitable if contribution pursuant to this Section 4.1.5 were determined by pro rata allocation or by any other method of allocation, which does not take account of the equitable considerations referred to in this Section 4.1.5. No person or entity guilty of fraudulent misrepresentation (within the meaning of Section 11(f) of the Securities Act) shall be entitled to contribution pursuant to this Section 4.1.5 from any person or entity who was not guilty of such fraudulent misrepresentation.
ARTICLE V
MISCELLANEOUS
5.1 Notices. Any notice or communication under this Agreement must be in writing and given by (i) deposit in the United States mail, addressed to the party to be notified, postage prepaid and registered or certified with return receipt requested, (ii) delivery in person or by courier service providing evidence of delivery, or (iii) transmission by hand delivery, electronic mail or facsimile. Each notice or communication that is mailed, delivered, or transmitted in the manner described above shall be deemed sufficiently given, served, sent, and received, in the case of mailed notices, on the third business day following the date on which it is mailed and, in the case of notices delivered by courier service, hand delivery, electronic mail or facsimile, at such time as it is delivered to the addressee (with the delivery receipt or the affidavit of messenger) or at such time as delivery is refused by the addressee upon presentation. Any notice or communication under this Agreement must be addressed, if to the Company, to: K Wave Media Ltd., [●], Attention: Youngjae Lee, Chief Executive Officer, or by e-mail: [●], and, if to any Holder, at such Holder’s address, electronic mail address or facsimile number as set forth in the Company’s books and records. Any party may change its address for notice at any time and from time to time by written notice to the other parties hereto, and such change of address shall become effective thirty (30) days after delivery of such notice as provided in this Section 5.1.
5.2 Assignment; No Third Party Beneficiaries.
5.2.1 This Agreement and the rights, duties and obligations of the Company hereunder may not be assigned or delegated by the Company in whole or in part.
5.2.2 Subject to Section 5.2.4 and Section 5.2.5, this Agreement and the rights, duties and obligations of a Holder hereunder may be assigned in whole or in part to such Holder’s Permitted Transferees to which it transfers Registrable Securities; provided that with respect to the Target Holders and the Sponsor, the rights hereunder that are personal to such Holders may not be assigned or delegated in whole or in part, except that (i) each of the Target Holders shall be permitted to transfer its rights hereunder as the Target Holders to one or more affiliates or any direct or indirect partners, members or equity holders of such Target Holder (it being understood that no such transfer shall reduce or multiply any rights of such Target Holder or such transferees) and (ii) the Sponsor shall be permitted to transfer its rights hereunder as the Sponsor to one or more affiliates or any direct or indirect partners, members or equity holders of the Sponsor (including the member of the Sponsor), which, for the avoidance of doubt, shall include a transfer of its rights in connection with a distribution of any Registrable Securities held by Sponsor to its members (it being understood that no such transfer shall reduce or multiply any rights of the Sponsor or such transferees).
5.2.3 This Agreement and the provisions hereof shall be binding upon and shall inure to the benefit of each of the parties and its successors and the permitted assigns of the Holders, which shall include Permitted Transferees.
5.2.4 This Agreement shall not confer any rights or benefits on any persons or entities that are not parties hereto, other than as expressly set forth in this Agreement and Section 5.
5.2.5 No assignment by any party hereto of such party’s rights, duties and obligations hereunder shall be binding upon or obligate the Company unless and until the Company shall have received (i) written notice of such assignment as provided in Section 5.1 hereof and (ii) the written agreement of the assignee, in a form reasonably satisfactory to the Company, to be bound by the terms and provisions of this Agreement (which may be accomplished by an addendum or certificate of joinder to this Agreement, including the joinder in the form of Exhibit A attached hereto). Any transfer or assignment made other than as provided in this Section 5.2 shall be null and void.
5.3 Counterparts. This Agreement may be executed in multiple counterparts (including facsimile or PDF counterparts), each of which shall be deemed an original, and all of which together shall constitute the same instrument, but only one of which need be produced.
5.4 Governing Law; Venue. NOTWITHSTANDING THE PLACE WHERE THIS AGREEMENT MAY BE EXECUTED BY ANY OF THE PARTIES HERETO, THE PARTIES EXPRESSLY AGREE THAT (1) THIS AGREEMENT SHALL BE GOVERNED BY AND CONSTRUED UNDER THE LAWS OF THE STATE OF DELAWARE, WITHOUT GIVING EFFECT TO PRINCIPLES OR RULES OF CONFLICT OF LAWS TO THE EXTENT SUCH PRINCIPLES OR RULES WOULD REQUIRE OR PERMIT THE APPLICATION OF LAWS OF ANOTHER JURISDICTION AND (2) THE VENUE FOR ANY ACTION TAKEN WITH RESPECT TO THIS AGREEMENT SHALL BE ANY STATE OR FEDERAL COURT IN THE STATE OF DELAWARE.
5.5 TRIAL BY JURY. EACH PARTY HERETO ACKNOWLEDGES AND AGREES THAT ANY CONTROVERSY WHICH MAY ARISE UNDER THIS AGREEMENT IS LIKELY TO INVOLVE COMPLICATED AND DIFFICULT ISSUES, AND, THEREFORE, EACH SUCH PARTY HEREBY IRREVOCABLY AND UNCONDITIONALLY WAIVES TO THE FULLEST EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW, ANY RIGHT SUCH PARTY MAY HAVE TO A TRIAL BY JURY IN RESPECT TO ANY ACTION DIRECTLY OR INDIRECTLY ARISING OUT OF, UNDER OR IN CONNECTION WITH OR RELATING TO THIS AGREEMENT OR THE TRANSACTIONS CONTEMPLATED BY THIS AGREEMENT.
5.6 Amendments and Modifications. Upon the written consent of (a) the Company and (b) the Holders of a majority of the total Registrable Securities, compliance with any of the provisions, covenants and conditions set forth in this Agreement may be waived, or any of such provisions, covenants or conditions may be amended or modified; provided, however, that notwithstanding the foregoing, any amendment hereto or waiver hereof shall also require the written consent of the Sponsor so long as the Sponsor and its affiliates hold, in the aggregate, at least five percent (5%) of the outstanding Ordinary Shares of the Company; provided, further, that notwithstanding the foregoing, any amendment hereto or waiver hereof shall also require the written consent of each Target Holder so long as such Target Holder and its respective affiliates hold, in the aggregate, at least five percent (5%) of the outstanding Ordinary Shares of the Company; and provided, further, that any amendment hereto or waiver hereof that adversely affects one Holder, solely in its capacity as a holder of the shares of capital stock of the Company, in a manner that is materially different from the other Holders (in such capacity) shall require the consent of the Holder so affected. No course of dealing between any Holder or the Company and any other party hereto or any failure or delay on the part of a Holder or the Company in exercising any rights or remedies under this Agreement shall operate as a waiver of any rights or remedies of any Holder or the Company. No single or partial exercise of any rights or remedies under this Agreement by a party shall operate as a waiver or preclude the exercise of any other rights or remedies hereunder or thereunder by such party.
5.7 Other Registration Rights. Other than as provided in the (i) Warrant Agreement, dated as of September 22, 2022, between the Company and Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company and (ii) Private Placement Units Purchase Agreement, dated as of September 22, 2022, between the Company and Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company, the Company represents and warrants that no person or entity, other than a Holder of Registrable Securities, has any right to require the Company to register any securities of the Company for sale or to include such securities of the Company in any Registration Statement filed by the Company for the sale of securities for its own account or for the account of any other person or entity. The Company hereby agrees and covenants that it will not grant rights to register any Ordinary Shares (or securities convertible into or exchangeable for Ordinary Shares) pursuant to the Securities Act that are more favorable, pari passu or senior to those granted to the Holders hereunder without (a) the prior written consent of (i) the Sponsor, for so long as the Sponsor and its affiliates hold, in the aggregate, at least five percent (5%) of the outstanding Ordinary Shares of the Company, and (ii) a Target Holder, for so long as such Target Holder and its affiliates hold, in the aggregate, at least five percent (5%) of the outstanding Ordinary Shares of the Company; or (b) granting economically and legally equivalent rights to the Holders hereunder such that the Holders shall receive the benefit of such more favorable or senior terms and/or conditions. Further, the Company represents and warrants that this Agreement supersedes any other registration rights agreement or agreement with similar terms and conditions and in the event of a conflict between any such agreement or agreements and this Agreement, the terms of this Agreement shall prevail.
5.8 Term. This Agreement shall terminate on the earlier of (a) the fifth (5th) anniversary of the date of this Agreement and (b) with respect to any Holder, on the date that such Holder no longer holds any Registrable Securities. The provisions of Section 3.5 and Article IV shall survive any termination.
5.9 Holder Information. Each Holder agrees, if requested in writing, to represent to the Company the total number of Registrable Securities held by such Holder in order for the Company to make determinations hereunder.
5.10 Additional Holders; Joinder. In addition to persons or entities who may become Holders pursuant to Section 5.2 hereof, subject to the prior written consent of each of the Sponsor (so long as the Sponsor and its affiliates hold, in the aggregate, at least five percent (5%) of the outstanding Ordinary Shares of the Company) and each Target Holder (so long as such Target Holder and its respective affiliates hold, in the aggregate, at least five percent (5%) of the outstanding Ordinary Shares of the Company), the
Company may make any person or entity who acquires Ordinary Shares or rights to acquire Ordinary Shares after the date hereof a party to this Agreement (each such person or entity, an “Additional Holder”) by obtaining an executed joinder to this Agreement from such Additional Holder in the form of Exhibit A attached hereto (a “Joinder”). Such Joinder shall specify the rights and obligations of the applicable Additional Holder under this Agreement. Upon the execution and delivery and subject to the terms of a Joinder by such Additional Holder, the Ordinary Shares then owned, or underlying any rights then owned, by such Additional Holder (the “Additional Holder Ordinary Shares”) shall be Registrable Securities to the extent provided herein and therein and such Additional Holder shall be a Holder under this Agreement with respect to such Additional Holder Ordinary Shares.
5.11 Severability. It is the desire and intent of the parties that the provisions of this Agreement be enforced to the fullest extent permissible under the laws and public policies applied in each jurisdiction in which enforcement is sought. Accordingly, if any particular provision of this Agreement shall be adjudicated by a court of competent jurisdiction to be invalid, prohibited or unenforceable for any reason, such provision, as to such jurisdiction, shall be ineffective, without invalidating the remaining provisions of this Agreement or affecting the validity or enforceability of this Agreement or affecting the validity or enforceability of such provision in any other jurisdiction. Notwithstanding the foregoing, if such provision could be more narrowly drawn so as not to be invalid, prohibited or unenforceable in such jurisdiction, it shall, as to such jurisdiction, be so narrowly drawn, without invalidating the remaining provisions of this Agreement or affecting the validity or enforceability of such provision in any other jurisdiction.
5.12 Entire Agreement; Restatement. This Agreement constitutes the full and entire agreement and understanding between the parties with respect to the subject matter hereof and supersedes all prior agreements and understandings relating to such subject matter. Upon the Closing, the Original RRA shall no longer be of any force or effect.
[SIGNATURE PAGES FOLLOW]
IN WITNESS WHEREOF, the undersigned have caused this Agreement to be executed as of the date first written above.
| |
| COMPANY: |
|
| K WAVE MEDIA LTD. |
| a Cayman Islands exempted company |
| |
| By: | |
| Name: |
| Title: |
|
| HOLDERS: |
|
| GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION 1 LLC |
| a Delaware limited liability company |
| |
| By: | |
| Name: |
| Title: |
|
| [Entity Holders] |
| a [●] |
| |
| By: | |
| Name: |
| Title: |
| | |
|
| [Individual Holders] |
[Signature Page to Amended and Restated Registration Rights Agreement]
Schedule I
Target Holders
Exhibit A
REGISTRATION RIGHTS AGREEMENT JOINDER
The undersigned is executing and delivering this joinder (this “Joinder”) pursuant to the Amended and Restated Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of [●], 2025 (as the same may hereafter be amended, the “Registration Rights Agreement”), among K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (the “Company”), and the other persons or entities named as parties therein. Capitalized terms used but not otherwise defined herein shall have the meanings provided in the Registration Rights Agreement.
By executing and delivering this Joinder to the Company, and upon acceptance hereof by the Company upon the execution of a counterpart hereof, the undersigned hereby agrees to become a party to, to be bound by, and to comply with the Registration Rights Agreement as a Holder of Registrable Securities in the same manner as if the undersigned were an original signatory to the Registration Rights Agreement, and the undersigned’s Ordinary Shares shall be included as Registrable Securities under the Registration Rights Agreement to the extent provided therein.
Accordingly, the undersigned has executed and delivered this Joinder as of the __________ day of __________, 20__.
|
Signature of Stockholder |
|
|
| Print Name of Stockholder |
| Its: |
| | |
| Agreed and Accepted as of |
| ____________, 20__ |
|
| K WAVE MEDIA LTD. |
| |
| By: | | |
| Name: | | |
| Its: | | |
Annex E
LOCK-UP AGREEMENT
THIS LOCK-UP AGREEMENT (this “Agreement”) is dated as of [●], 2025 by and among K Wave Media Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (the “Purchaser”), Global Star Acquisition 1 LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (the “Sponsor”), certain former shareholders of K Enter Holdings Inc., a Delaware corporation (the “Target”), set forth on Schedule I hereto (such stockholders, the “Target Holders”), and other persons and entities (collectively with the Sponsor, the Target Holders and any person or entity who hereafter becomes a party to this Agreement, the “Holders” and each, a “Holder”).
A. The Purchaser, Global Star Acquisition Inc., a Delaware corporation (the “Parent”), GLST Merger Sub, Inc., a Delaware corporation and direct wholly owned subsidiary of the Purchaser (“Merger Sub”), and the Target have entered into that certain Merger Agreement dated as of June 15, 2023 (as amended or modified from time to time, the “Merger Agreement”), pursuant to which, among other things, (i) the Parent merged with and into the Purchaser, with the Purchaser continuing as the surviving corporation (the “Reincorporation Merger”) and (ii) Merger Sub merged with and into the Target (the “Acquisition Merger”), with the Target surviving the Acquisition Merger as a wholly owned subsidiary of the Purchaser. Capitalized terms used, but not otherwise defined, herein shall have the meanings ascribed to such terms in the Merger Agreement.
B. As of the date hereof, the Sponsor is the holder of record and the beneficial owner of the Purchaser Ordinary Shares and Purchaser Warrants as set forth on Schedule I attached hereto.
C. On the date hereof, pursuant to the Merger Agreement, the Target Holders received Purchaser Ordinary Shares in exchange for their shares of Company Common Stock.
D. As a condition of, and as a material inducement for the Parent to enter into and consummate the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement, the Holder has agreed to execute and deliver this Agreement.
NOW, THEREFORE, for and in consideration of the mutual covenants and agreements set forth herein, and other good and valuable consideration, the receipt and sufficiency of which is hereby acknowledged, the parties, intending to be legally bound, agree as follows:
AGREEMENT
1. Lock-Up.
(a) During the applicable Lock-up Period provided in Section 1(d) hereof, the Holder agrees that it, he or she will not offer, sell, contract to sell, pledge, grant any option to purchase, or otherwise dispose of, directly or indirectly, any of the Lock-up Shares (as defined below), establish or increase a put equivalent position or liquidate with respect to or decrease a call equivalent position with respect to, any of the Lock-up Shares, enter into a transaction that would have the same effect, or enter into any swap, hedge or other arrangement that transfers, in whole or in part, any of the economic consequences of ownership of the Lock-up Shares, whether any of these transactions are to be settled by delivery of any such Lock-up Shares, in cash or otherwise, publicly disclose the intention to make any transaction specified above, or engage in any Short Sales (as defined below) with respect to the Lock-up Shares.
(b) In furtherance of the foregoing, during the applicable Lock-up Period, the Purchaser will (i) place a stop order on all the Lock-up Shares, including those which may be covered by a registration statement, and (ii) notify the Purchaser’s transfer agent in writing of the stop order and the restrictions on the Lock-up Shares under this Agreement and direct the Purchaser’s transfer agent not to process any attempts by the Holder to resell or transfer any Lock-up Shares, except in compliance with this Agreement.
(c) For purposes hereof, “Short Sales” include, without limitation, all “short sales” as defined in Rule 200 promulgated under Regulation SHO under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), and all types of direct and indirect stock pledges, forward sale contracts, options, puts, calls, swaps and similar arrangements (including on a total return basis), and sales and other transactions through non-U.S. broker dealers or foreign regulated brokers.
(d) The term “Lock-up Period” means, (i) with respect to 50% of the Lock-up Shares, the earlier of (A) six months after the date hereof and (B) the date on which the closing price of the Purchaser’s ordinary shares equals or exceeds $12.50 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, rights issuances, reorganizations and recapitalizations) for any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period commencing after the date hereof and (ii) with respect to the remaining 50% Lock-up Share (or Ordinary Shares issuable upon conversion thereof), six months after the date hereof.
(e) The term “Lock-up Shares” means (a) the Purchaser Ordinary Shares and Purchaser Warrants held by the Sponsor immediately following the Closing, and (b) the Purchaser Ordinary Shares held by the Target Holders immediately following the Closing; provided, however, that such Lock-up Shares shall not include Purchaser Ordinary Shares acquired by such Holder in open market transactions during the Lock-up Period.
2. Beneficial Ownership. The Holder hereby represents and warrants that it does not beneficially own, directly or through its nominees (as determined in accordance with Section 13(d) of the Exchange Act, and the rules and regulations promulgated thereunder), any Purchaser Ordinary Shares, or any economic interest in or derivative of such shares, other than the Lock-up Shares, as set on Schedule I attached hereto.
3. Permitted Transfer. Notwithstanding the foregoing, and subject to the conditions below, the undersigned may transfer Lock-up Shares in connection with (each, a “Permitted Transfer”) (a) transfers or distributions to the Holder’s direct or indirect affiliates (within the meaning of Rule 405 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”)) or to the estates of any of the foregoing; (b) transfers by bona fide gift or gifts to a member of the Holder’s immediate family or to a trust, the beneficiary of which is the Holder or a member of the Holder’s immediate family for estate planning purposes; (c) by virtue of a will, testamentary document or the laws of descent and distribution upon death of the Holder; (d) pursuant to a qualified domestic relations order or as required by a divorce settlement; (e) transfers to the Purchaser’s officers, directors or their affiliates; (f) pledges of Lock-up Shares as security or collateral in connection with a borrowing or the incurrence of any indebtedness by the Holder; provided, however, that such borrowing or incurrence of indebtedness is secured by either a portfolio of assets or equity interests issued by multiple issuers; (g) transfers pursuant to a bona fide third-party tender offer, merger, stock sale, recapitalization, consolidation or other transaction involving a change of control of the Purchaser or which results in all of the holders of Purchaser Ordinary Shares having the right to exchange their Purchaser Ordinary Shares for cash, securities or other property subsequent to the consummation of such transaction; provided, however, that in the event that such tender offer, merger, recapitalization, consolidation or other such transaction is not completed, the Lock-up Shares subject to this Agreement shall remain subject to this Agreement; (h) the establishment of a trading plan pursuant to Rule 10b5-1 promulgated under the Exchange Act; provided, however, that such plan does not provide for the transfer of Lock-up Shares during the applicable Lock-up Period; (i) transfers to satisfy tax withholding obligations in connection with the exercise of options to purchase Purchaser Ordinary Shares or the vesting of stock-based awards; and (j) transfers in payment on a “net exercise” or “cashless” basis of the exercise or purchase
price with respect to the exercise of options to purchase Purchaser Ordinary Shares; provided, however, that, in the case of any transfer pursuant to the foregoing clauses (a) through (e), it shall be a condition to any such transfer that (i) the transferee/donee agrees to be bound by the terms of this Agreement (including, without limitation, the restrictions set forth in the preceding sentence) to the same extent as if the transferee/donee were a party hereto; and (ii) each party (donor, donee, transferor or transferee) shall not voluntarily make, any filing or public announcement of the transfer or disposition prior to the expiration of the applicable Lock-up Period. Notwithstanding any restrictions set forth above, the Target Holders reserve the right to release a certain amount of Lock-up Shares to the extent such Target Holders are subject to tax liabilities resulting from the unrealized gains on the Purchaser Ordinary Shares they received pursuant to the closing of the Acquisition Merger, provided, however, that such Target Holders shall not be allowed to sell their Lock-up Shares, but will only be permitted to hypothecate or borrow money against such Lock-up Shares.
4. Representations and Warranties. Each of the parties hereto, by their respective execution and delivery of this Agreement, hereby represents and warrants to the others that (a) such party has the full right, capacity and authority to enter into, deliver and perform its respective obligations under this Agreement, (b) this Agreement has been duly executed and delivered by such party and is a binding and enforceable obligation of such party, enforceable against such party in accordance with the terms of this Agreement, and (c) the execution, delivery and performance of such party’s obligations under this Agreement will not conflict with or breach the terms of any other agreement, contract, commitment or understanding to which such party is a party or to which the assets or securities of such party are bound. The Holder has independently evaluated the merits of his/her/its decision to enter into and deliver this Agreement, and such Holder confirms that he/she/it has not relied on the advice of the Purchaser, the Purchaser’s legal counsel, the Parent, the Parent’s legal counsel, or any other person.
5. No Additional Fees/Payment. Other than the consideration specifically referenced herein, the parties hereto agree that no fee, payment or additional consideration in any form has been or will be paid to the Holder in connection with this Agreement.
6. Notices. Any notices required or permitted to be sent hereunder shall be sent in writing, addressed as specified below, and shall be deemed given: (a) if by hand, electronic mail, or nationally recognized overnight courier service, by 5:00 PM on a Business Day, addressee’s day and time, on the date of delivery, and if delivered after 5:00 PM on the first Business Day, addressee’s day and time, after such delivery; (b) if by email, on the date that transmission with affirmative confirmation of receipt; or (c) three (3) Business Days after mailing by prepaid certified or registered mail, return receipt requested. Notices shall be addressed to the respective parties as follows (excluding telephone numbers, which are for convenience only), or to such other address as a party shall specify to the others in accordance with these notice provisions:
(a) If to the Purchaser, to:
K Wave Media Ltd.
[Address]
[City], [State] [Zip]
Attention: [●], Chief Executive Officer
E-mail: [●]
with a copy to (which copy shall not constitute notice):
Loeb & Loeb LLP
345 Park Avenue
New York, NY 10154
Attention: Mitchell S. Nussbaum
E-mail: mnussbaum@loeb.com
(b) If to the Holder, to the address set forth on Schedule I attached hereto; or to such other address(es) as any party may have furnished to the others in writing in accordance herewith.
7. Enumeration and Headings. The enumeration and headings contained in this Agreement are for convenience of reference only and shall not control or affect the meaning or construction of any of the provisions of this Agreement.
8. Counterparts. This Agreement may be executed in any number of original, electronic or facsimile counterparts and each of such counterparts shall for all purposes be deemed to be an original, and all such counterparts shall together constitute but one and the same instrument. This Agreement shall become effective upon delivery to each party of an executed counterpart or the earlier delivery to each party of original, photocopied, or electronically transmitted signature pages that together (but need not individually) bear the signatures of all other parties.
9. Successors and Assigns. This Agreement and the terms, covenants, provisions and conditions hereof shall be binding upon, and shall inure to the benefit of, the respective heirs, successors and assigns of the parties hereto. The Holder hereby acknowledges and agrees that this Agreement is entered into for the benefit of and is enforceable by the Parent and its successors and assigns. No party hereto may, except as set forth herein, assign either this Agreement or any of its rights, interests, or obligations hereunder, including by merger, consolidation, operation of law or otherwise, without the prior written consent of the other parties. Any purported assignment or delegation in violation of this paragraph shall be void and ineffectual, and shall not operate to transfer or assign any interest or title to the purported assignee.
10. Severability. This Agreement shall be deemed severable, and a determination by a court or other legal authority that any provision that is not of the essence of this Agreement is legally invalid shall not affect the validity or enforceability of this Agreement or of any other term or provision hereof. Furthermore, the parties shall cooperate in good faith to substitute (or cause such court or other legal authority to substitute) for any provision so held to be invalid a valid provision, as alike in substance to such invalid or unenforceable provision as may be possible and be valid and enforceable.
11. Entire Agreement; Amendment. This Agreement constitutes the entire agreement and understanding of the parties hereto in respect of the subject matter hereof and supersedes all prior and contemporaneous understandings and agreements related hereto (whether written or oral), to the extent they relate in any way to the subject matter hereof or the transactions contemplated hereby. No provision of this Agreement may be explained or qualified by any agreement, negotiations, understanding, discussion, conduct or course of conduct or by any trade usage. Except as otherwise expressly stated herein, there is no condition precedent to the effectiveness of any provision hereof. This Agreement may not be changed, amended or modified as to any particular provision, except by a written instrument executed by all parties hereto, and cannot be terminated orally or by course of conduct. No provision hereof can be waived, except by a writing signed by the party against whom such waiver is to be enforced, and any such waiver shall apply only in the particular instance in which such waiver shall have been given.
12. Further Assurances. Each party shall do and perform, or cause to be done and performed, all such further acts and things, and shall execute and deliver all such other agreements, certificates, instruments and documents, as may reasonably be considered within the scope of such party’s obligations hereunder, in order to carry out the intent and accomplish the purposes of this Agreement and the consummation of the transactions contemplated hereby.
13. No Strict Construction. The language used in this Agreement will be deemed to be the language chosen by the parties to express their mutual intent, and no rules of strict construction will be applied against any party.
14. Dispute Resolution. Section 11.15 and 11.16 of the Merger Agreement is incorporated by reference herein to apply with full force to any disputes arising under this Agreement.
15. Governing Law. Section 11.7 of the Merger Agreement is incorporated by reference herein to apply with full force to any disputes arising under this Agreement.
[Signature Page Follows]
IN WITNESS WHEREOF, the parties hereto have caused this Agreement to be duly executed by their respective authorized signatories as of the date first indicated above.
| |
| PURCHASER: |
|
| K WAVE MEDIA LTD. |
| a Cayman Islands exempted company |
| |
| By: | |
| Name: |
| Title: |
|
| HOLDERS: |
|
| GLOBAL STAR ACQUISITION 1 LLC |
| a Delaware limited liability company |
| |
| By: | |
| Name: |
| Title: |
|
| [Entity Holders] |
| a [●] |
| |
| By: | |
| Name: |
| Title: |
|
|
| [Individual Holders] |
[Signature Page to Lock-up Agreement]
Schedule I
Lock-up Shares
| | | | |
Holder | | Purchaser Ordinary Shares | | Purchaser Warrants |
| | | | |
Annex F
| Private and Confidential | 9 June 2023 |
Global Star Acquisition Inc.
1641 International Drive
Unit 208
McLean, VA 22202 USA
Fairness Opinion Letter
Global Star Acquisition Inc. (the “SPAC”) entered into a Non-Binding Letter of Intent on 11 April 2023 (the “Original Agreement”) to execute the merger transaction with K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “Target”). The Original Agreement has a purchase consideration (the “Transaction Consideration”) of 100% of the outstanding equity and equity equivalents of the Target (including its acquisition/merger targets, including options, warrants or other securities that have the right to acquire or convert into equity securities of the Target), based on a pre-money Equity Value of US$610 million, provided to or for the benefit of the Target or the Target’s equity holders (including holders of options, warrants, and other convertible securities) (the “Proposed Transaction”). The deal structure will be determined between the SPAC and the Target based on the due diligence findings as well as business, legal, tax, accounting and other considerations.
The terms and conditions of the Proposed Transaction are more fully set forth in the Original Agreement.
The SPAC has engaged EverEdge Pte. Ltd. (“EverEdge”) as an independent valuation expert for the purpose of issuing an assessment of the fairness in relation to the Proposed Transaction from a financial point of view of the shareholders of the SPAC (“Fairness Opinion”). The entities that are contracted to be subsidiaries of the Target comprised of the following:
| ● | the LAMP Pictures Co., Ltd |
| ● | Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd |
| ● | Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd |
To provide this Fairness Opinion, we have performed the necessary analyses, giving consideration, to the following information:
| ● | The financial terms and conditions of the Original Agreement between the SPAC and the Target dated 11 April 2023; |
| ● | The financial terms and conditions of the Share Purchase Agreements between the shareholders of the entities that are contracted to be subsidiaries listed below and the Target; |
| ○ | Play Company Co., Ltd (Dated 31 March 2023) |
| ○ | Solaire Partners LLC (Dated 31 March 2023) |
| ○ | the LAMP Pictures Co., Ltd (Dated 10 April 2023) |
| ○ | First Virtual Lab Inc. (Dated 12 April 2023) |
| ○ | Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd (Dated 9 April 2023) |
| ○ | Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd (Dated 10 April 2023) |
| ○ | Apeitda Co., Ltd (Dated 9 April 2023) |
| ● | Management financial forecasts for a period of 5 years and provided by the management of K Enter Holdings Inc. (“K Enter Forecasts”); |
| ● | Corporate Presentation Decks of the Target prepared by KPMG Samjong Accounting Corp. (“KPMG”); |
| ● | K Enter Holdings Inc. corporate structure documents including the Articles of Incorporation dated 4 January 2023 and List of Shareholders as of 28 April 2023; |
| ● | Other available public information (i.e., various equity analyst reports, annual reports, and public information about comparable companies), information available from the virtual data room and relevant market data from knowledge databases such as FactSet; |
| ● | Confirmation with management on key assumptions around discount rate, industry EV/Revenue and EV/EBITDA multiples, and working capital and found them to be reasonable based on industry research; |
| ● | Comparable statistics for companies in segments of the Film entertainment and production industry as well as the Gaming/Webtoons/OTT Platforms industry. |
In addition, we have performed the value calculations and financial analyses that we have deemed necessary to provide the opinion below.
The first method used was the Market Approach - Guideline Public Traded Companies (GPTC) Method as the basis for the fairness opinion assessment. These public comparable companies were independently obtained by EverEdge. KPMG also provided comparable companies that were reviewed as a secondary comparison and were found to be similar to those used for the Fairness Opinion assessment.
We also used the Income Approach – Discounted Cash Flows Method as a secondary valuation method as well as the Market Method – Guideline Transaction Method (GTM) as a third valuation method, examining relevant and comparable market transaction data for the key inputs. Additional details of the analysis performed can be found in the associated proxy statement.
In our assessment, we have relied upon the correctness and completeness of the information provided by the Target, without independent verification. We have relied upon the assurances of the management of the SPAC that they are not aware of any facts or circumstances that would make such information or data inaccurate or misleading in any material respect. With respect to the K Enter Forecasts, we have assumed that they have been reasonably prepared on bases reflecting the best currently available estimates and good faith judgments of the management of K Enter Holdings Inc. as to its future financial performance. We have not made any physical inspection of the properties or assets of the Target. We have not evaluated the solvency or fair value of the Target under any laws relating to bankruptcy, insolvency, or similar matters. We have assumed that the Proposed
Transaction will be completed in accordance with the terms stated in the Original Agreement without further waiver, modification, or amendment of any material term, condition, or agreement after 11 April 2023 and that, in the course of obtaining the necessary governmental, regulatory and other approvals, consents, releases and waivers for the Proposed Transaction, no delay, limitation, restriction or condition, including any divestiture requirements or amendments or modifications, will be imposed that would have an adverse effect on the contemplated benefits of the Proposed Transaction. We are not responsible for conclusions based on erroneous or incomplete information provided to us.
Our assignment was finalized on 16 May 2023, after a period of comments from the management of the SPAC. Any events or information occurring after this date have not been subject to consideration.
EverEdge is retained by the SPAC to provide this Fairness Opinion in connection with the Proposed Transaction and will receive a fee of SG$29,500. EverEdge’s fee is not contingent upon, or related to, the size of the Transaction Consideration, or whether the Proposed Transaction is consummated.
We are providing this Fairness Opinion to the SPAC who may use this document only in its entirety in the communication with the shareholders of the SPAC concerning the Proposed Transaction. Our opinion expressed below must not be construed as a recommendation as to whether the shareholders of the SPAC should approve the Proposed Transaction.
Fairness Opinion Conclusion
Based on the work performed by EverEdge, and on the statements above, we are of the opinion that the Proposed Transaction, on the date of issue of this document, is fair from a financial point of view for the equity shareholders of Global Star Acquisition Inc.
Yours sincerely,
Tyler Capson
Chartered Valuer and Appraiser (CVA #100150)
Managing Director
EverEdge Pte. Ltd.
| Primary Reviewer: | Secondary Reviewer: |
| | |
| Stefan Tan | Ian Lim |
| Senior Valuation Analyst | Senior Manager, Valuations |
| EverEdge Pte. Ltd. | EverEdge Pte. Ltd. |
For further information please contact: | |
| | |
| EverEdge Pte. Ltd. | |
| 168 Robinson Road, | |
| #20-01, Capital Tower, | |
| Singapore 068912 | |
| Private and Confidential | 9 June 2023 |
Opinion of Global Star Acquisition Inc.’s Financial Advisor
Opinion of EverEdge Pte. Ltd.
Pursuant to the engagement proposal dated 12 April 2023, EverEdge Pte. Ltd. (“EverEdge”) was engaged by Global Star Acquisition Inc. (the “SPAC”), to act as its financial advisor in connection with the business combination involving the SPAC and K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “Target”), to evaluate the proposed merger transaction (the “Proposed Transaction”). As part of this engagement, the SPAC requested that EverEdge evaluate the facts of the Proposed Transaction and provide an opinion as to whether the purchase consideration of US$610 million (the “Transaction Consideration”) for 100% of the outstanding equity and equity equivalents of the Target (including its acquisition/merger targets, including options, warrants or other securities that have the right to acquire or convert into equity securities of the Target), is fair and reasonable.
The full text of the EverEdge’s written opinion dated 9 June 2023, which sets forth, among other things, the procedures followed, assumptions made, matters considered, and qualifications and limitations on the scope of review undertaken in rendering its opinion is incorporated by reference in its entirety into this proxy statement. EverEdge’s opinion was addressed to, and provided for the information and benefit of, the relevant officers in the SPAC in connection with their evaluation of the Proposed Transaction. The opinion does not constitute a recommendation to the relevant officers in the SPAC or to any other persons in respect of the Proposed Transaction, including as to how any holder of the SPAC’s shares should vote or act in respect of the Proposed Transaction. EverEdge’s opinion does not address the relative merits of the Proposed Transaction as compared to other business or financial strategies that might be available to the SPAC, nor does it address the underlying business decision of the SPAC to engage in the Proposed Transaction.
In connection with rendering its opinion, EverEdge have performed the necessary analyses, giving consideration, to the following information:
| ● | The financial terms and conditions of the non-binding Letter of Intent (the “Original Agreement”) dated 11 April 2023, between the SPAC and the Target; |
| ● | Management financial forecasts for a period of 5 years and provided by the management of K Enter Holdings Inc. (“K Enter Forecasts”); |
| ● | Corporate Presentation Decks of the Target prepared by KPMG Samjong Accounting Corp. (“KPMG”); |
| ● | K Enter Holdings Inc. corporate structure documents including the Articles of Incorporation dated 4 January 2023 and List of Shareholders as of 28 April 2023; |
| ● | Other available public information (i.e., various equity analyst reports, annual reports, and public information about comparable companies), information available from the virtual data room and relevant market data from knowledge databases such as FactSet; |
| ● | Confirmation with Management on key assumptions around discount rate, industry EV/Revenue and EV/EBITDA multiples, and working capital and found them to be reasonable based on industry research; |
| ● | Comparable statistics for companies in segments of the Film entertainment and production industry as well as the Gaming/Webtoons/OTT Platforms industry. |
For purposes of its analysis and opinion, EverEdge assumed and relied upon the accuracy and completeness of the financial and other information publicly available, and all of the information supplied or otherwise made available to, discussed with, or reviewed by EverEdge, without any independent verification of such information (and assumed no responsibility or liability for any independent verification of such information), and further relied upon the assurances of the management of the SPAC that they were not aware of any facts or circumstances that would make such information inaccurate or misleading. With respect to the K Enter Forecasts, EverEdge assumed that they were reasonably prepared on bases reflecting the best currently available estimates and good faith judgments of the management of K Enter Holdings Inc. as to its future financial performance. EverEdge expressed no view as to the K Enter Forecasts nor the assumptions on which they were based.
For purposes of its analysis and opinion, EverEdge assumed, in all respects material to its analysis, that the representations and warranties of each party contained in the Original Agreement were true and correct, that each party would perform all of the covenants and agreements required to be performed by it under the Original Agreement and that all conditions to the consummation of the Proposed Transaction would be satisfied without waiver or modification thereof. EverEdge further assumed, in all respects material to its analysis, that all governmental, regulatory, or other consents, approvals or releases necessary for the consummation of the Proposed Transaction would be obtained without any delay, limitation, restriction or condition that would have an adverse effect on the consummation of the Proposed Transaction or reduce the contemplated benefits to the Target or the Target’s equity holders (including holders of options, warrants, and other convertible securities).
EverEdge did not conduct a physical inspection of the properties nor facilities of the Target. EverEdge did not evaluate the solvency or fair value of the Target under any state or federal laws relating to bankruptcy, insolvency, or similar matters. EverEdge’s opinion is necessarily based upon information made available to EverEdge as of 20 April 2023 and financial, economic, market, and other conditions as they existed and as could be evaluated as of that date. Subsequent developments may affect EverEdge’s opinion and EverEdge does not have any obligation to update, revise, or reaffirm its opinion.
EverEdge was not asked to pass upon, and expressed no opinion with respect to, any matter other than the fairness to the equity holders (including holders of options, warrants, and other convertible securities) of the Target’s shares, from a financial point of view, of the Transaction Consideration. EverEdge did not express any view on, and its opinion does not address, the fairness of the Proposed Transaction to creditors or other constituencies of the Target, nor as to the fairness of the amount or nature of any compensation to be paid or payable to any of the officers, directors, or employees of the Target, or any class of such persons, whether relative to the Proposed Transaction or otherwise. EverEdge was not asked to, nor did it express any view on, and its opinion does not address, any other term or aspect of the Original Agreement or the Transaction Consideration, including, without limitation, the structure or form of the Proposed Transaction, or any term or aspect of any other agreements or instruments contemplated by the Original Agreement or entered into or amended in connection with the Original Agreement.
EverEdge’s opinion does not address the relative merits of the Proposed Transaction as compared to other business or financial strategies that might be available to the SPAC, nor does it address the underlying business decision of the SPAC to engage in the Proposed Transaction. EverEdge has assumed the accuracy and completeness of assessments by the SPAC and its advisors with respect to legal, regulatory, accounting, and tax matters. The credit, financial, and stock markets have been experiencing unusual volatility and EverEdge expressed no opinion or view as to any potential effects of such volatility on the parties or the Proposed Transaction.
Set forth below is a summary of the material financial analyses reviewed by EverEdge with the management of the SPAC on 16 May 2023 in connection with rendering its opinion. The following summary, however, does not purport to be a complete description of the analyses performed by EverEdge. The order of the analyses described and the results of these analyses do not represent relative importance or weight given to these analyses by EverEdge. Except as otherwise noted, the following quantitative information, to the extent that it is based on market data, is based on market data that existed on or before 20 April 2023, and is not necessarily indicative of current nor future market conditions.
Summary of EverEdge’s Financial Analysis of the Target
The valuation of the financial adequacy of the Transaction Consideration is carried out on a stand-alone basis using different valuation methods. The implied equity value of the Target is calculated as at the date of valuation of 31 December 2022.
The discounted cash flow (“DCF”) method is of key importance in the context of our valuation. The valuation considerations are supplemented by the application of market-based methods based on the trading multiples of comparable companies (Guideline Public Traded Companies Method) and prices paid in past transactions (Guideline Transaction Method). The implied equity value resulting from the DCF method, and from the respective market-based valuations is then compared with the Transaction Consideration. Valuations based on trading and transaction multiples are performed to cross-check against the DCF valuation.
The following provides an overview of the valuation methods used:
Income Approach – Discounted Cash Flow Analysis Method
In general, the value of the company is derived by discounting the expected future free cash flows with the appropriate weighted average cost of capital (“WACC”) at the defined date of valuation. The application of the DCF method to determine enterprise value is the preferred method used by industry practitioners.
EverEdge performed a DCF analysis to calculate the implied enterprise value (and resulting equity value) of the Target, utilizing management estimates of the unlevered, after-tax free cash flows that the Target is expected to generate over the five-year period from FY 2023 to FY 2027 (“Explicit Period”) based on the K Enter Forecasts, approved by the management of the Target.
For purposes of its discounted cash flow analyses, unlevered free cash flow is defined as net income after tax, plus depreciation and amortization expenses, plus after-tax interest expenses, less capital expenditures, less working capital investments, and plus/(less) other non-cash expenses/(gains).
The proportion of cash flow that relates to the time after the explicit period into perpetuity is reflected as the terminal value (“TV”). EverEdge calculated the terminal value of the Target using the Gordon Growth Model by applying a stable growth rate of 5.1% to estimate the terminal year unlevered free cash flow reflected in the K Enter Forecasts, for a business in a steady state of growth under the premise of a going concern.
Discounting the unlevered, after-tax free cashflows for the explicit period, as well as the calculated terminal value with a time weighted WACC of 13.8%, in a range between 13.6% to 14.1% from FY2023 to FY2027, gives the present value of free cash flow to firm (“FCFF”). The sum of these present-valued free cash flow to firm results in the enterprise value as at the defined date of valuation. The time weighted WACC is determined based on EverEdge’s determination of the capital structure and company specific risk profile of the Target, in conjunction with industry and economic indicators as of the defined date of valuation.
In a final step to derive the equity value from the enterprise value, non-operating assets (mainly cash and cash equivalents) as of 31 December 2022 are added to the enterprise value, and total financial debt and debt equivalents (mainly interest-bearing short-term and long- term financial debt) as of 31 December 2022 are deducted from the enterprise value. This results in the equity value of the Target as of the defined date of valuation.
The results of the calculations are as follows:
DCF Method (KRW ‘million) | | Downside
(WACC +50 bp) | | | Base | | | Upside
(WACC -50 bp) | |
| Net Present Value of FCFF over Forecast Period | | | 142,926 | | | | 147,175 | | | | 151,603 | |
| Net Present Value of Terminal Value | | | 544,833 | | | | 633,114 | | | | 746,200 | |
| Total Enterprise Value at Date of Valuation | | | 687,759 | | | | 780,289 | | | | 897,803 | |
| Add: Operating Assets at Date of Valuation | | | 36,827 | | | | 36,827 | | | | 36,827 | |
| Less: Total Financial Debt at Date of Valuation | | | (16,047 | ) | | | (16,047 | ) | | | (16,047 | ) |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (KRW ‘m) | | | 708,539 | | | | 801,069 | | | | 918,583 | |
| KRW/USD at Date of Valuation | | | 1,261.9 | | | | 1,261.9 | | | | 1,261.9 | |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (USD ‘m) | | | 561.5 | | | | 634.8 | | | | 727.9 | |
EverEdge’s determination of equity value using the DCF method is a median value of USD 634.8 million, in a value range between USD 561.5 million and USD 727.9 million based on a change in WACC by ±50 basis points.
Market Approach – Guideline Public Traded Companies (GPTC) Method
The valuation based on forward trading multiples is used to cross-check the DCF valuation. The GPTC Method is a market indicator used to value a business, based on trading multiples derived from publicly traded companies that are similar to the target company. The significance of the forward trading multiples valuation may be limited as both the business model of the Target and the specific situation of the comparable companies may differ. EverEdge reviewed and compared certain financial information of the Target to corresponding trading multiples and financial ratios for the following selected publicly traded comparable companies in selected segments of the Film entertainment and production industry as well as the Gaming/Webtoons/OTT Platforms industry (referred to in this section as the “Comparable Companies”):
Comparable Companies (Film & Entertainment): United States
| ● | AMC Entertainment Holdings Inc. | ● | Netflix, Inc. |
| ● | Fox Corporation | ● | Paramount Global |
| ● | Lions Gate Entertainment | ● | Liberty Media Corp. |
| ● | Madison Square Garden Entertainment Corp. | ● | Walt Disney Company |
| | ● | Warner Music Group Corp. | ● | Warner Bros. Discovery, Inc. |
Comparable Companies (Direct Film & Drama Production): South Korea
| | ● | ContentreeJoongAng Corp. | ● | Astory Co., Ltd |
| | ● | KX Innovation Co., Ltd | ● | Chorokbaem Media Co., Ltd |
| | ● | Wysiwyg Studios Co., Ltd | ● | Next Entertainment World Co., Ltd |
| | ● | SHOWBOX Corp. | | |
Comparable Companies (CGI / VFX): South Korea and United States
| | ● | Dexter Studios Co., Ltd | ● | Autodesk, Inc. |
Comparable Companies (DVD and Merchandise): South Korea
Comparable Companies (Gaming / Webtoons / OTT Platforms): South Korea
| | ● | Kakao Corp. | ● | Barunson Entertainment & Arts Corp. |
| | ● | Kakao Entertainment Co., Ltd (Private) | ● | DoubleDown Interactive Co., Ltd |
| | ● | Incross Co., Ltd | ● | Com2us Corporation |
| | ● | AfreecaTV Co., Ltd | | |
Although none of the Comparable Companies listed above are directly comparable to the Target, EverEdge selected these companies based on its professional judgment due to similar operating industries with business characteristics that, for purposes of its analysis, EverEdge considered as close proxies the business characteristics of the Target for the business lines presented in the K Enter Forecasts.
For each of the Comparable Companies identified above, the Enterprise Value-to-EBITDA (EV/EBITDA) multiple as well as an Enterprise-to-Revenue (EV/Revenue) multiple were selected as the comparable valuation metrics to determine the implied enterprise value of the Target, as reflected in the most recent public filings made by the Comparable Companies and consensus estimates obtained from publicly available equity research analysts’ projections made available by FactSet as of the date of valuation.
Based on the list of identified Comparable Companies, EverEdge has derived an average EV/EBITDA multiple of 16.5x, in a range between 14.7x and 19.6x, and an average EV/Revenue multiple of 3.2x, in a range between 2.5x and 3.7x. The Target’s implied enterprise value under this method is computed by applying the derived trading multiples to the FY2025 EBITDA and FY2023 Revenue forecasts, and discounted commensurately over the relevant time horizon to the defined date of valuation.
Certain valuation adjustments were also applied to determine the adjusted enterprise value. A discount to trading multiples adjustment of 20.4% is applied to account for both the lack of marketability as well as the unique risk profile of the Target relative to the publicly traded Comparable Companies.
As the trading multiples derived from Comparable Companies have generally factored in a discount for lack of control to reflect the fair value of a minority stake in a publicly traded company, a control premium on 27.4% was also applied to adjust the enterprise value from a minority stake perspective of the GPTC method to an enterprise value on a controlling basis.
Lastly, non-operating assets (mainly cash and cash equivalents) as of 31 December 2022 are added, and total financial debt and debt equivalents (mainly interest-bearing short-term and long-term financial debt) as of 31 December 2022 are deducted to derive the equity value from the enterprise value.
The results of the calculations are as follows:
EV/EBITDA Multiples
(KRW ‘million) | | 25th
Percentile | | | Median | | | 75th
Percentile | |
| FY 2025 EBITDA | | | 69,465 | | | | 69,465 | | | | 69,465 | |
| Unadjusted EV/EBITDA Multiple | | | 14.7 | x | | | 16.5 | x | | | 19.6 | x |
| Minus: Discount to Trading Multiples (%) | | | (20.4 | )% | | | (20.4 | )% | | | (20.4 | )% |
| Adjusted EV/EBITDA Multiple | | | 11.7 | x | | | 13.2 | x | | | 15.6 | x |
| Enterprise Value on a Non-Controlling, Non-Marketable Basis | | | 811,710 | | | | 913,530 | | | | 1,086,079 | |
| Add: Control Premium (%) | | | 27.4 | % | | | 27.4 | % | | | 27.4 | % |
| Control Premium | | | 222,408 | | | | 250,307 | | | | 297,586 | |
| Enterprise Value on a Controlling, Non-Marketable Basis | | | 1,034,118 | | | | 1,163,837 | | | | 1,383,665 | |
| WACC (%) | | | 13.8 | % | | | 13.8 | % | | | 13.8 | % |
| Discount Factor | | | 0.72 | | | | 0.72 | | | | 0.72 | |
| Enterprise Value at Date of Valuation | | | 746,489 | | | | 840,128 | | | | 998,813 | |
| Add: Operating Assets at Date of Valuation | | | 36,827 | | | | 36,827 | | | | 36,827 | |
| Less: Total Financial Debt at Date of Valuation | | | (16,047 | ) | | | (16,047 | ) | | | (16,047 | ) |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (KRW ‘m) | | | 767,269 | | | | 860,908 | | | | 1,019,593 | |
| KRW/USD at Date of Valuation | | | 1,261.9 | | | | 1,261.9 | | | | 1,261.9 | |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (USD ‘m) | | | 608.0 | | | | 682.2 | | | | 808.0 | |
EverEdge’s determination of equity value using the forward trading FY2025 EV/EBITDA multiples under the GPTC method results in a median equity value of USD 682.2 million, in a value range between USD 608.0 million and USD 808.0 million.
EV/Revenue Multiples
(KRW ‘million) | | 25th
Percentile | | | Median | | | 75th
Percentile | |
| FY 2023 Revenue | | | 250,563 | | | | 250,563 | | | | 250,563 | |
| Unadjusted EV/Revenue Multiple | | | 2.5 | x | | | 3.2 | x | | | 3.7 | x |
| Minus: Discount to Trading Multiples (%) | | | (20.40 | )% | | | (20.40 | )% | | | (20.40 | )% |
| Adjusted EV/Revenue Multiple | | | 2.0 | x | | | 2.5 | x | | | 2.9 | x |
| Enterprise Value on a Non-Controlling, Non-Marketable Basis | | | 490,912 | | | | 631,608 | | | | 737,437 | |
| Add: Control Premium (%) | | | 27.4 | % | | | 27.4 | % | | | 27.4 | % |
| Control Premium | | | 134,510 | | | | 173,061 | | | | 202,058 | |
| Enterprise Value on a Controlling, Non-Marketable Basis | | | 625,422 | | | | 804,669 | | | | 939,495 | |
| WACC (%) | | | 14.1 | % | | | 14.1 | % | | | 14.1 | % |
| Discount Factor | | | 0.94 | | | | 0.94 | | | | 0.94 | |
| Enterprise Value at Date of Valuation | | | 585,600 | | | | 753,435 | | | | 879,676 | |
| Add: Operating Assets at Date of Valuation | | | 36,827 | | | | 36,827 | | | | 36,827 | |
| Less: Total Financial Debt at Date of Valuation | | | (16,047 | ) | | | (16,047 | ) | | | (16,047 | ) |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (KRW ‘m) | | | 606,380 | | | | 774,215 | | | | 900,456 | |
| KRW/USD at Date of Valuation | | | 1,261.9 | | | | 1,261.9 | | | | 1,261.9 | |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (USD ‘m) | | | 480.5 | | | | 613.5 | | | | 713.5 | |
EverEdge’s determination of equity value using the forward trading FY2023 EV/Revenue multiples under the GPTC method results in a median equity value of USD 613.5 million, in a value range between USD 480.5 million and USD 713.5 million.
Market Approach – Guideline Transaction Method (GTM)
EverEdge also used the Guideline Transaction Method (GTM) as a third valuation methodology, to calculate the implied enterprise value (and resulting equity value) of the Target, by analyzing comparable transactions in the marketplace.
EverEdge relied on identifying relevant transactions that are similar to the Target in terms of industry, size, growth prospects, and other relevant characteristics. The Target’s implied enterprise value (and resulting equity value) under this method was computed by multiplying the FY2025 EBITDA by the transaction EV/EBITDA multiple, then discounted commensurately over the forecast period to the defined date of valuation.
The results of the calculations are as follows:
Transaction Multiples
(KRW ‘million) | | 25th
Percentile | | | Median | | | 75th
Percentile | |
| FY 2025 EBITDA | | | 69,465 | | | | 69,465 | | | | 69,465 | |
| Transaction EV/EBITDA Multiple | | | 14.3 | x | | | 14.8 | x | | | 15.3 | x |
| Undiscounted Enterprise Value | | | 993,356 | | | | 1,028,089 | | | | 1,062,822 | |
| WACC (%) | | | 13.8 | % | | | 13.8 | % | | | 13.8 | % |
| Discount Factor | | | 0.72 | | | | 0.72 | | | | 0.72 | |
| Enterprise Value at Date of Valuation | | | 717,064 | | | | 742,137 | | | | 767,209 | |
| Add: Operating Assets at Date of Valuation | | | 36,827 | | | | 36,827 | | | | 36,827 | |
| Less: Total Financial Debt at Date of Valuation | | | (16,047 | ) | | | (16,047 | ) | | | (16,047 | ) |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (KRW ‘m) | | | 737,844 | | | | 762,917 | | | | 787,989 | |
| KRW/USD at Date of Valuation | | | 1,261.9 | | | | 1,261.9 | | | | 1,261.9 | |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (USD ‘m) | | | 584.7 | | | | 604.6 | | | | 624.4 | |
Conclusion
Based on the analyses described above and an assessment and evaluation of all the information provided, EverEdge has come to the following conclusion with regard to the financial adequacy of the SPAC’s Proposed Transaction of the Target.

Based on our analyses and value considerations as well as the results presented, EverEdge considers the Transaction Consideration of US$ 610 million to be fair from a financial point of view. This conclusion is based on the following considerations:
| 1. | The Transaction Consideration is supported by the DCF valuation. |
| 2. | The Transaction Consideration is within the value range resulting from the application of trading and transaction multiples. |
Miscellaneous
The foregoing summary of certain financial analyses does not purport to be a complete description of the analyses or data presented by EverEdge. In connection with the evaluation of the Proposed Transaction by the SPAC, EverEdge performed a variety of financial and comparative analyses for purposes of rendering its opinion. The preparation of a fairness opinion is a complex process and is not necessarily susceptible to partial analysis or summary descriptions. Selecting portions of the analyses or of the summary described above, without considering the analyses as a whole, may create an incomplete view of the processes underlying EverEdge’s opinion. In arriving at its fairness determination, EverEdge considered the results of all the analyses and did not draw, in isolation, conclusions from or with regard to any one analysis or factor considered by it for purposes of its opinion. Rather, EverEdge made its determination as to fairness on the basis of its experience and professional judgment after considering the results of all the analyses. In addition, EverEdge may have given certain analyses and factors more or less weight than others and may have deemed certain assumptions more or less probable than others. As a result, the range of valuations resulting from any particular analysis or combination of analyses described above should not be taken to be the view of EverEdge with respect to the actual value of the Target. Further, EverEdge’s analyses involve complex considerations and judgments concerning financial and operating characteristics and other factors that could affect the acquisition, public trading or other values of the companies used, including judgments and assumptions with regard to industry performance, general business, economic, market and financial conditions and other matters, many of which are beyond the control of the SPAC or its advisors.
EverEdge prepared these analyses for the purpose of providing an opinion to the relevant officers in the SPAC as to the fairness, from a financial point of view, of the Transaction Consideration to the equity holders (including holders of options, warrants, and other convertible securities) of the Target’s shares. These analyses do not purport to be appraisals or to necessarily reflect the prices at which the business or securities may be sold at. Any estimates contained in these analyses are not necessarily indicative of actual future results, which may be significantly more or less favorable than those suggested by such estimates. Accordingly, estimates used in, and the results derived from, EverEdge’s analyses are inherently subject to substantial uncertainty, and EverEdge assumes no responsibility if future results are materially different from those forecasted in such estimates.
The issuance of EverEdge’s fairness opinion was approved by an opinion committee of EverEdge.
Pursuant to the terms of EverEdge’s engagement letter with the SPAC, EverEdge was entitled to receive a fee of SG$29,500. The SPAC has also agreed to reimburse EverEdge for any reasonable and documented out-of-pocket expenses (including any travel or search costs) and to indemnify EverEdge for certain liabilities arising out of its engagement.
The SPAC engaged EverEdge to act as a supplier of the fairness opinion based on EverEdge’s qualifications, experience, and reputation. EverEdge is a global advisory and transaction firm specializing in intangible assets and is regularly engaged in business valuation practices.
Supplemental Exhibits: K Enter Forecasts
A summary of the 5-year financial forecasts for the entities contracted to be subsidiaries of the Target are provided below. All figures shown in these exhibits are in KRW millions.
Play Company Co., Ltd
| Fiscal Year | | 2022 | | | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | |
| Calendar | | | 31-Dec-22 | | | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | | 31-Dec-27 | |
| PlayCo Revenues | | | 156,282 | | | | | 144,460 | | | | 143,131 | | | | 179,330 | | | | 216,833 | | | | 254,512 | |
| PlayF&B Revenues | | | 17,675 | | | | | 24,593 | | | | 28,657 | | | | 35,017 | | | | 41,766 | | | | 46,659 | |
| Total Revenues | | | 173,957 | | | | | 169,053 | | | | 171,789 | | | | 214,348 | | | | 258,599 | | | | 301,171 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | | (2.8 | )% | | | 1.6 | % | | | 24.8 | % | | | 20.6 | % | | | 16.5 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| PlayCo COGS | | | (139,138 | ) | | | | (130,108 | ) | | | (123,988 | ) | | | (154,769 | ) | | | (186,725 | ) | | | (220,080 | ) |
| PlayF&B COGS | | | (16,529 | ) | | | | (21,549 | ) | | | (23,971 | ) | | | (27,829 | ) | | | (32,185 | ) | | | (34,998 | ) |
| Total COGS | | | (155,667 | ) | | | | (151,656 | ) | | | (147,959 | ) | | | (182,598 | ) | | | (218,911 | ) | | | (255,079 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | 18,290 | | | | | 17,397 | | | | 23,830 | | | | 31,750 | | | | 39,689 | | | | 46,092 | |
| GP Margin | | | 10.5 | % | | | | 10.3 | % | | | 13.9 | % | | | 14.8 | % | | | 15.3 | % | | | 15.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| PlayCo SG&A Expenses | | | (2,766 | ) | | | | (2,326 | ) | | | (2,368 | ) | | | (2,414 | ) | | | (2,476 | ) | | | (2,545 | ) |
| PlayF&B SG&A Expenses | | | (1,398 | ) | | | | (1,652 | ) | | | (1,803 | ) | | | (1,941 | ) | | | (2,057 | ) | | | (2,188 | ) |
| Adjusted for Consolidation | | | (1,303 | ) | | | | (1,303 | ) | | | (1,303 | ) | | | (1,303 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total SG&A Expenses | | | (5,468 | ) | | | | (5,282 | ) | | | (5,474 | ) | | | (5,658 | ) | | | (4,533 | ) | | | (4,733 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | 3.1 | % | | | | 3.1 | % | | | 3.2 | % | | | 2.6 | % | | | 1.8 | % | | | 1.6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBITDA | | | 12,822 | | | | | 12,115 | | | | 18,355 | | | | 26,092 | | | | 35,156 | | | | 41,359 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | 7.4 | % | | | | 7.2 | % | | | 10.7 | % | | | 12.2 | % | | | 13.6 | % | | | 13.7 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| PlayCo Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (217 | ) | | | | (193 | ) | | | (197 | ) | | | (178 | ) | | | (191 | ) | | | (174 | ) |
| PlayF&B Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (998 | ) | | | | (1,198 | ) | | | (1,180 | ) | | | (1,234 | ) | | | (1,235 | ) | | | (1,031 | ) |
| Adjusted for Consolidation | | | (1,303 | ) | | | | (1,303 | ) | | | (1,303 | ) | | | (1,303 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (2,519 | ) | | | | (2,695 | ) | | | (2,680 | ) | | | (2,715 | ) | | | (1,426 | ) | | | (1,205 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBIT | | | 10,304 | | | | | 9,421 | | | | 15,675 | | | | 23,376 | | | | 33,729 | | | | 40,154 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | 5.9 | % | | | | 5.6 | % | | | 9.1 | % | | | 10.9 | % | | | 13.0 | % | | | 13.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net Interest Income/(Expense) | | | 312 | | | | | 1,246 | | | | 1,627 | | | | 2,410 | | | | 3,489 | | | | 4,872 | |
| Other Income (Expenses) | | | (1,555 | ) | | | | (1,555 | ) | | | (1,555 | ) | | | (1,555 | ) | | | (1,555 | ) | | | (1,555 | ) |
| PlayCo Total Other Income | | | (1,244 | ) | | | | (309 | ) | | | 72 | | | | 854 | | | | 1,933 | | | | 3,317 | |
| Net Interest Income/(Expense) | | | (122 | ) | | | | (78 | ) | | | (28 | ) | | | (9 | ) | | | 12 | | | | 30 | |
| Other Income (Expenses) | | | (8 | ) | | | | (8 | ) | | | (8 | ) | | | (8 | ) | | | (8 | ) | | | - | |
| PlayF&B Total Other Income | | | (130 | ) | | | | (86 | ) | | | (36 | ) | | | (17 | ) | | | 4 | | | | 30 | |
| Total Other Income Adjusted for Consolidation | | | 1,368 | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total Other Income | | | (6 | ) | | | | (395 | ) | | | 35 | | | | 837 | | | | 1,937 | | | | 3,347 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| PlayCo EBT | | | 12,917 | | | | | 11,524 | | | | 16,649 | | | | 22,824 | | | | 29,374 | | | | 35,029 | |
| PlayF&B EBT | | | (382 | ) | | | | 1,307 | | | | 2,848 | | | | 5,230 | | | | 7,528 | | | | 9,495 | |
| Total Adjustments for Consol | | | (1,239 | ) | | | | (2,607 | ) | | | (2,607 | ) | | | (2,607 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total EBT | | | 11,296 | | | | | 10,224 | | | | 16,890 | | | | 25,447 | | | | 36,901 | | | | 44,524 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| PlayCo Tax Expense | | | (2,434 | ) | | | | (2,170 | ) | | | (3,143 | ) | | | (4,369 | ) | | | (5,745 | ) | | | (6,932 | ) |
| PlayF&B Tax Expense | | | - | | | | | (265 | ) | | | (604 | ) | | | (1,129 | ) | | | (1,634 | ) | | | (2,067 | ) |
| Total Tax Expense | | | (2,434 | ) | | | | (2,435 | ) | | | (3,748 | ) | | | (5,498 | ) | | | (7,379 | ) | | | (8,999 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| PlayCo Net Profit after Tax | | | 10,483 | | | | | 9,354 | | | | 13,506 | | | | 18,455 | | | | 23,629 | | | | 28,097 | |
| PlayF&B Net Profit after Tax | | | (382 | ) | | | | 1,041 | | | | 2,243 | | | | 4,101 | | | | 5,893 | | | | 7,428 | |
| Net Profit after Tax | | | 10,101 | | | | | 10,395 | | | | 15,749 | | | | 22,556 | | | | 29,523 | | | | 35,525 | |
| NPAT Margin | | | 5.8 | % | | | | 6.1 | % | | | 9.2 | % | | | 10.5 | % | | | 11.4 | % | | | 11.8 | % |
The LAMP Pictures Co., Ltd
| Fiscal Year | | 2022 | | | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | |
| Calendar | | | 31-Dec-22 | | | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | | 31-Dec-27 | |
| Movie Revenues | | | | | | | | 5,184 | | | | 17,539 | | | | 10,000 | | | | 20,103 | | | | 20,206 | |
| Drama Revenues | | | | | | | | 23,131 | | | | 21,633 | | | | 43,500 | | | | 39,000 | | | | 53,000 | |
| Total Revenues | | | 17,244 | | | | | 28,314 | | | | 39,172 | | | | 53,500 | | | | 59,103 | | | | 73,206 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | | 64.2 | % | | | 38.3 | % | | | 36.6 | % | | | 10.5 | % | | | 23.9 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Movie COGS | | | | | | | | (3,246 | ) | | | (17,539 | ) | | | (10,000 | ) | | | (20,000 | ) | | | (20,000 | ) |
| Drama COGS | | | | | | | | (22,801 | ) | | | (17,833 | ) | | | (37,500 | ) | | | (30,000 | ) | | | (40,000 | ) |
| Total COGS | | | (15,856 | ) | | | | (26,047 | ) | | | (35,372 | ) | | | (47,500 | ) | | | (50,000 | ) | | | (60,000 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | 1,388 | | | | | 2,268 | | | | 3,800 | | | | 6,000 | | | | 9,103 | | | | 13,206 | |
| GP Margin | | | 10.3 | % | | | | 10.3 | % | | | 13.9 | % | | | 14.8 | % | | | 15.3 | % | | | 15.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total SG&A Expenses | | | (914 | ) | | | | (972 | ) | | | (1,042 | ) | | | (1,132 | ) | | | (1,180 | ) | | | (1,275 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | 3.1 | % | | | | 3.1 | % | | | 3.2 | % | | | 2.6 | % | | | 1.8 | % | | | 1.6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBITDA | | | 474 | | | | | 1,295 | | | | 2,758 | | | | 4,868 | | | | 7,923 | | | | 11,932 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | 7.2 | % | | | | 7.2 | % | | | 10.7 | % | | | 12.2 | % | | | 13.6 | % | | | 13.7 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (50 | ) | | | | (10 | ) | | | (13 | ) | | | (13 | ) | | | (16 | ) | | | (19 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBIT | | | 424 | | | | | 1,285 | | | | 2,745 | | | | 4,855 | | | | 7,908 | | | | 11,913 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | 2.5 | % | | | | 4.5 | % | | | 7.0 | % | | | 9.1 | % | | | 13.4 | % | | | 16.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-operating Gain/(Loss) | | | (352 | ) | | | | (362 | ) | | | (365 | ) | | | (369 | ) | | | (373 | ) | | | (378 | ) |
| Total EBT | | | 72 | | | | | 924 | | | | 2,380 | | | | 4,486 | | | | 7,535 | | | | 11,535 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Tax Expense | | | (18 | ) | | | | (156 | ) | | | (432 | ) | | | (832 | ) | | | (1,412 | ) | | | (2,172 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net Profit after Tax | | | 55 | | | | | 768 | | | | 1,948 | | | | 3,654 | | | | 6,123 | | | | 9,364 | |
| NPAT Margin | | | 0.3 | % | | | | 2.7 | % | | | 5.0 | % | | | 6.8 | % | | | 10.4 | % | | | 12.8 | % |
Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd
| Fiscal Year | | 2022 | | | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | |
| Calendar | | | 31-Dec-22 | | | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | | 31-Dec-27 | |
| Movie Revenues | | | 90 | | | | | 15,279 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 32,877 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 17,897 | |
| Drama Revenues | | | - | | | | | 14,917 | | | | 29,783 | | | | 30,500 | | | | 45,875 | | | | 67,825 | |
| Total Revenues | | | 90 | | | | | 30,196 | | | | 59,783 | | | | 63,377 | | | | 75,875 | | | | 85,722 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | | 33,344.7 | % | | | 98.0 | % | | | 6.0 | % | | | 19.7 | % | | | 13.0 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Movie COGS | | | (511 | ) | | | | (9,113 | ) | | | (30,000 | ) | | | (32,000 | ) | | | (30,000 | ) | | | (17,417 | ) |
| Drama COGS | | | - | | | | | (14,917 | ) | | | (27,083 | ) | | | (27,500 | ) | | | (40,875 | ) | | | (60,125 | ) |
| Total COGS | | | (511 | ) | | | | (24,030 | ) | | | (57,083 | ) | | | (59,500 | ) | | | (70,875 | ) | | | (77,542 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | (421 | ) | | | | 6,166 | | | | 2,700 | | | | 3,877 | | | | 5,000 | | | | 8,181 | |
| GP Margin | | | 10.3 | % | | | | 10.3 | % | | | 13.9 | % | | | 14.8 | % | | | 15.3 | % | | | 15.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total SG&A Expenses | | | (1,121 | ) | | | | (980 | ) | | | (994 | ) | | | (1,010 | ) | | | (1,031 | ) | | | (1,055 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | 3.1 | % | | | | 3.1 | % | | | 3.2 | % | | | 2.6 | % | | | 1.8 | % | | | 1.6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBITDA | | | (1,542 | ) | | | | 5,186 | | | | 1,706 | | | | 2,867 | | | | 3,969 | | | | 7,126 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | 7.2 | % | | | | 7.2 | % | | | 10.7 | % | | | 12.2 | % | | | 13.6 | % | | | 13.7 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | - | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBIT | | | (1,542 | ) | | | | 5,186 | | | | 1,706 | | | | 2,867 | | | | 3,969 | | | | 7,126 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | (1,707.7 | )% | | | | 17.2 | % | | | 2.9 | % | | | 4.5 | % | | | 5.2 | % | | | 8.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Other Income | | | 150 | | | | | 177 | | | | 178 | | | | 180 | | | | 182 | | | | 185 | |
| Total EBT | | | (1,392 | ) | | | | 5,363 | | | | 1,884 | | | | 3,047 | | | | 4,151 | | | | 7,311 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Tax Expense | | | - | | | | | - | | | | (69 | ) | | | (559 | ) | | | (769 | ) | | | (1,369 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net Profit after Tax | | | (1,392 | ) | | | | 5,363 | | | | 1,815 | | | | 2,488 | | | | 3,382 | | | | 5,942 | |
| NPAT Margin | | | (1,541.3 | )% | | | | 17.8 | % | | | 3.0 | % | | | 3.9 | % | | | 4.5 | % | | | 6.9 | % |
Apeitda Co., Ltd
| Fiscal Year | | 2022 | | | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | |
| Calendar | | | 31-Dec-22 | | | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | | 31-Dec-27 | |
| Movie Revenues | | | | | | | | 10,107 | | | | 10,107 | | | | 5,299 | | | | 15,000 | | | | 2,000 | |
| Drama Revenues | | | | | | | | - | | | | 5,500 | | | | 13,250 | | | | 20,500 | | | | 40,480 | |
| Total Revenues | | | 5,301 | | | | | 10,107 | | | | 15,607 | | | | 18,549 | | | | 35,500 | | | | 42,480 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | | 90.7 | % | | | 54.4 | % | | | 18.9 | % | | | 91.4 | % | | | 19.7 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Movie COGS | | | | | | | | (10,000 | ) | | | (10,000 | ) | | | (5,000 | ) | | | (15,000 | ) | | | (2,000 | ) |
| Drama COGS | | | | | | | | - | | | | (5,000 | ) | | | (12,500 | ) | | | (17,500 | ) | | | (34,500 | ) |
| Total COGS | | | (3,636 | ) | | | | (10,000 | ) | | | (15,000 | ) | | | (17,500 | ) | | | (32,500 | ) | | | (36,500 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | 1,665 | | | | | 107 | | | | 607 | | | | 1,049 | | | | 3,000 | | | | 5,980 | |
| GP Margin | | | 10.3 | % | | | | 10.3 | % | | | 13.9 | % | | | 14.8 | % | | | 15.3 | % | | | 15.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total SG&A Expenses | | | (210 | ) | | | | (189 | ) | | | (250 | ) | | | (255 | ) | | | (263 | ) | | | (271 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | 3.1 | % | | | | 3.1 | % | | | 3.2 | % | | | 2.6 | % | | | 1.8 | % | | | 1.6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBITDA | | | 1,455 | | | | | (82 | ) | | | 357 | | | | 794 | | | | 2,737 | | | | 5,709 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | 7.2 | % | | | | 7.2 | % | | | 10.7 | % | | | 12.2 | % | | | 13.6 | % | | | 13.7 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (18 | ) | | | | (79 | ) | | | (64 | ) | | | (61 | ) | | | (55 | ) | | | (55 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBIT | | | 1,437 | | | | | (161 | ) | | | 293 | | | | 732 | | | | 2,682 | | | | 5,654 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | 27.1 | % | | | | (1.6 | )% | | | 1.9 | % | | | 3.9 | % | | | 7.6 | % | | | 13.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Other Income | | | (26 | ) | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total EBT | | | 1,411 | | | | | (161 | ) | | | 293 | | | | 732 | | | | 2,682 | | | | 5,654 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Tax Expense | | | - | | | | | - | | | | (12 | ) | | | (119 | ) | | | (490 | ) | | | (1,054 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net Profit after Tax | | | 1,411 | | | | | (161 | ) | | | 281 | | | | 613 | | | | 2,192 | | | | 4,600 | |
| NPAT Margin | | | 26.6 | % | | | | (1.6 | )% | | | 1.8 | % | | | 3.3 | % | | | 6.2 | % | | | 10.8 | % |
Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd
| Fiscal Year | | 2022 | | | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | |
| Calendar | | | 31-Dec-22 | | | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | | 31-Dec-27 | |
| Total Revenues | | | - | | | | | - | | | | 26,563 | | | | 27,149 | | | | 29,592 | | | | 33,864 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2.2 | % | | | 9.0 | % | | | 14.4 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total COGS | | | - | | | | | - | | | | (24,827 | ) | | | (25,189 | ) | | | (27,060 | ) | | | (30,324 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | - | | | | | - | | | | 1,736 | | | | 1,960 | | | | 2,532 | | | | 3,540 | |
| GP Margin | | | 10.3 | % | | | | 10.3 | % | | | 13.9 | % | | | 14.8 | % | | | 15.3 | % | | | 15.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total SG&A Expenses | | | - | | | | | (889 | ) | | | (366 | ) | | | (373 | ) | | | (383 | ) | | | (394 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | 3.1 | % | | | | 3.1 | % | | | 3.2 | % | | | 2.6 | % | | | 1.8 | % | | | 1.6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBITDA | | | - | | | | | (889 | ) | | | 1,370 | | | | 1,587 | | | | 2,149 | | | | 3,146 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | 7.2 | % | | | | 7.2 | % | | | 10.7 | % | | | 12.2 | % | | | 13.6 | % | | | 13.7 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | - | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBIT | | | - | | | | | (889 | ) | | | 1,370 | | | | 1,587 | | | | 2,149 | | | | 3,146 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | | | | | | | | | | 5.2 | % | | | 5.8 | % | | | 7.3 | % | | | 9.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Other Income | | | - | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total EBT | | | - | | | | | (889 | ) | | | 1,370 | | | | 1,587 | | | | 2,149 | | | | 3,146 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Tax Expense | | | - | | | | | - | | | | (71 | ) | | | (282 | ) | | | (388 | ) | | | (578 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net Profit after Tax | | | - | | | | | (889 | ) | | | 1,299 | | | | 1,305 | | | | 1,761 | | | | 2,568 | |
| NPAT Margin | | | | | | | | | | | | 4.9 | % | | | 4.8 | % | | | 6.0 | % | | | 7.6 | % |
Solaire Partners LLC
| Fiscal Year | | 2022 | | | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | |
| Calendar | | | 31-Dec-22 | | | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | | 31-Dec-27 | |
| Total Revenues | | | 1,974 | | | | | 2,981 | | | | 5,218 | | | | 6,039 | | | | 6,516 | | | | 6,605 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | | 51.0 | % | | | 75.1 | % | | | 15.7 | % | | | 7.9 | % | | | 1.4 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total COGS | | | - | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | 1,974 | | | | | 2,981 | | | | 5,218 | | | | 6,039 | | | | 6,516 | | | | 6,605 | |
| GP Margin | | | 10.3 | % | | | | 10.3 | % | | | 13.9 | % | | | 14.8 | % | | | 15.3 | % | | | 15.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total SG&A Expenses | | | (1,748 | ) | | | | (1,478 | ) | | | (1,963 | ) | | | (3,059 | ) | | | (3,153 | ) | | | (3,256 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | 3.1 | % | | | | 3.1 | % | | | 3.2 | % | | | 2.6 | % | | | 1.8 | % | | | 1.6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBITDA | | | 226 | | | | | 1,502 | | | | 3,255 | | | | 2,981 | | | | 3,364 | | | | 3,349 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | 7.2 | % | | | | 7.2 | % | | | 10.7 | % | | | 12.2 | % | | | 13.6 | % | | | 13.7 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (3 | ) | | | | (3 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (2 | ) | | | (2 | ) | | | (1 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBIT | | | 223 | | | | | 1,499 | | | | 3,252 | | | | 2,978 | | | | 3,362 | | | | 3,347 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | | | | | | 50.3 | % | | | 62.3 | % | | | 49.3 | % | | | 51.6 | % | | | 50.7 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Other Income | | | - | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total EBT | | | 223 | | | | | 1,499 | | | | 3,252 | | | | 2,978 | | | | 3,362 | | | | 3,347 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Tax Expense | | | - | | | | | (265 | ) | | | (598 | ) | | | (546 | ) | | | (619 | ) | | | (616 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net Profit after Tax | | | 223 | | | | | 1,234 | | | | 2,654 | | | | 2,432 | | | | 2,743 | | | | 2,731 | |
| NPAT Margin | | | | | | | | | | | | 50.9 | % | | | 40.3 | % | | | 42.1 | % | | | 41.4 | % |
First Virtual Lab Inc.
| Fiscal Year | | 2022 | | | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | |
| Calendar | | | 31-Dec-22 | | | | | 31-Dec-23 | | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | | 31-Dec-27 | |
| Total Revenues | | | - | | | | | 12,490 | | | | 28,074 | | | | 34,814 | | | | 43,206 | | | | 54,592 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | | | | | | 124.8 | % | | | 24.0 | % | | | 24.1 | % | | | 26.4 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total COGS | | | - | | | | | (7,891 | ) | | | (19,993 | ) | | | (27,149 | ) | | | (34,723 | ) | | | (44,500 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | - | | | | | 4,599 | | | | 8,081 | | | | 7,665 | | | | 8,483 | | | | 10,092 | |
| GP Margin | | | 10.3 | % | | | | 10.3 | % | | | 13.9 | % | | | 14.8 | % | | | 15.3 | % | | | 15.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total SG&A Expenses | | | (728 | ) | | | | (1,275 | ) | | | (1,839 | ) | | | (2,689 | ) | | | (3,281 | ) | | | (3,602 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | 3.1 | % | | | | 3.1 | % | | | 3.2 | % | | | 2.6 | % | | | 1.8 | % | | | 1.6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBITDA | | | (728 | ) | | | | 3,324 | | | | 6,242 | | | | 4,977 | | | | 5,202 | | | | 6,490 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | 7.2 | % | | | | 7.2 | % | | | 10.7 | % | | | 12.2 | % | | | 13.6 | % | | | 13.7 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | - | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBIT | | | (728 | ) | | | | 3,324 | | | | 6,242 | | | | 4,977 | | | | 5,202 | | | | 6,490 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | | | | | | 26.6 | % | | | 22.2 | % | | | 14.3 | % | | | 12.0 | % | | | 11.9 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Other Income | | | - | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total EBT | | | (728 | ) | | | | 3,324 | | | | 6,242 | | | | 4,977 | | | | 5,202 | | | | 6,490 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Tax Expense | | | - | | | | | (709 | ) | | | (1,351 | ) | | | (1,073 | ) | | | (1,122 | ) | | | (1,406 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net Profit after Tax | | | (728 | ) | | | | 2,615 | | | | 4,891 | | | | 3,904 | | | | 4,079 | | | | 5,084 | |
| NPAT Margin | | | | | | | | | | | | 17.4 | % | | | 11.2 | % | | | 9.4 | % | | | 9.3 | % |
Annex G
 | |  |
| | | |
| | | |
| | Revised as of April 29, 2024 | |
| | | |
| Private and Confidential | | 12 March 2024 |
Global Star Acquisition Inc.
1641 International Drive
Unit 208
McLean, VA 22202 USA
Fairness Opinion Letter
Global Star Acquisition Inc. (the “SPAC”) entered into a Non-Binding Letter of Intent on 11 April 2023 and the Share Purchase Agreement dated 15 June 2023 (collectively referred to as the “Original Agreements”) to execute the merger transaction with K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “Target”). The Original Agreements have a purchase consideration of 100% of the outstanding equity and equity equivalents of the Target (including its acquisition/merger targets, including options, warrants or other securities that have the right to acquire or convert into equity securities of the Target), based on an initial pre-money Equity Value of US$610 million, provided to or for the benefit of the Target or the Target’s equity holders (including holders of options, warrants, and other convertible securities) (the “Original Proposed Transaction”).
However, following the execution of the Termination Agreement and Re-Purchase Option Agreement dated 5 March 2024 (the “First Virtual Lab Termination Agreement”), and the subsequent enactment of the First Amendment to Merger Agreement dated 11 March 2024 (the “Amendment of the Original Merger Agreement”), the purchase consideration was revised downwards to US$590 million (the “New Proposed Transaction”). The modification in the purchase consideration was made in connection with the cessation of the planned acquisition of a majority equity stake in First Virtual Lab Inc, as outlined in the Original Agreements.
The deal structure will be determined between the SPAC and the Target based on the due diligence findings as well as business, legal, tax, accounting and other considerations.
The terms and conditions of the New Proposed Transaction are more fully set forth in the Original Agreements, First Virtual Lab Termination Agreement and the Amendment to the Original Merger Agreement (collectively referred to as the “New Proposed Transaction Agreements”).
The SPAC has engaged EverEdge Pte. Ltd. (“EverEdge”) as an independent valuation expert for the purpose of issuing an assessment of the fairness in relation to the New Proposed Transaction from a financial point of view of the shareholders of the SPAC (“Fairness Opinion”). The entities that are contracted to be subsidiaries of the Target comprised of the following:
| ● | the LAMP Pictures Co., Ltd |
| ● | Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd |
| ● | Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd |
To provide this Fairness Opinion, we have performed the necessary analyses, giving consideration, to the following information:
| ● | The financial terms and conditions of the Original Agreements dated 11 April 2023 and 15 June 2023, the Termination Agreement and Re-Purchase Option Agreement dated 5 March 2024; and the First Amendment to Merger Agreement dated 11 March 2024; |
| ● | The financial terms and conditions of the Share Purchase Agreements between the shareholders of the entities that are contracted to be subsidiaries listed below and the Target; |
| ○ | Play Company Co., Ltd (Dated 31 March 2023) |
| ○ | Solaire Partners LLC (Dated 31 March 2023) |
| ○ | the LAMP Pictures Co., Ltd (Dated 10 April 2023) |
| ○ | Studio Anseilen Co., Ltd (Dated 9 April 2023) |
| ○ | Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd (Dated 10 April 2023) |
| ○ | Apeitda Co., Ltd (Dated 9 April 2023) |
| ● | Management financial forecasts for a period of 5 years and provided by the management of K Enter Holdings Inc. (“K Enter Forecasts”); |
| ● | Corporate Presentation Decks of the Target prepared by KPMG Samjong Accounting Corp. (“KPMG”); |
| ● | K Enter Holdings Inc. corporate structure documents including the Articles of Incorporation dated 4 January 2023 and List of Shareholders as of 28 April 2023; |
| ● | Other available public information (i.e., various equity analyst reports, annual reports, and public information about comparable companies), information available from the virtual data room and relevant market data from knowledge databases such as FactSet; |
| ● | Confirmation with management on key assumptions around discount rate, industry EV/Revenue and EV/EBITDA multiples, and working capital and found them to be reasonable based on industry research; |
| ● | Comparable statistics for companies in segments of the Film entertainment and production industry as well as the Gaming/Webtoons/OTT Platforms industry. |
In addition, we have performed the value calculations and financial analyses that we have deemed necessary to provide the opinion below.
The primary and preferred valuation method used was the Income Approach – Discounted Cash Flows (DCF) Method as the basis for the Fairness Opinion assessment.
We used the Market Approach - Guideline Public Traded Companies (GPTC) Method as a secondary valuation method to cross-check against the DCF valuation. These public comparable companies were independently obtained by EverEdge. KPMG also provided comparable companies that were reviewed as a secondary comparison and were found to be similar to those used for the Fairness Opinion assessment.
We also applied a third valuation method, using the Market Approach – Guideline Transaction Method (GTM) method, which examines the relevant and comparable market transaction data for the key inputs.
Valuations based on trading and transaction multiples are performed to cross-check against the DCF valuation. Additional details of the analyses across the valuation methodologies can be found in the associated proxy statement.
In our assessment, we have relied upon the correctness and completeness of the information provided by the Target, without independent verification. We have relied upon the assurances of the management of the SPAC that they are not aware of any facts or circumstances that would make such information or data inaccurate or misleading in any material respect. With respect to the K Enter Forecasts, we have assumed that they have been reasonably prepared on bases reflecting the best currently available estimates and good faith judgments of the management of K Enter Holdings Inc. as to its future financial performance. We have not made any physical inspection of the properties or assets of the Target. We have not evaluated the solvency or fair value of the Target under any laws relating to bankruptcy, insolvency, or similar matters. We have assumed that the New Proposed transaction will be completed in accordance with the terms stated in the New Proposed Transaction Agreements without further waiver, modification, or amendment of any material term, condition, or agreement after 11 April 2023 and that, in the course of obtaining the necessary governmental, regulatory and other approvals, consents, releases and waivers for the New Proposed Transaction, no delay, limitation, restriction or condition, including any divestiture requirements or amendments or modifications, will be imposed that would have an adverse effect on the contemplated benefits of the New Proposed Transaction. We are not responsible for conclusions based on erroneous or incomplete information provided to us.
In the course of our evaluation, EverEdge has revised our valuation analyses across all valuation methodologies using the updated set of K Enter financial forecasts provided by the management of K Enter Holdings Inc. Consequently, the Fairness Opinion has been amended to align with the adjustments made to the original financial projections while maintaining similar conclusions on the valuation outcome.
In our assessment of the fairness of the transaction, we have considered the potential conflicts of interest arising from Global Star’s directors’ and officers’ interests in the Business Combination that are different from the interests of other public stockholders as follows:
Global Star’s Sponsor and officers and directors purchased 2,300,000 shares of GLST Class B Common Stock, which we refer to herein as “Founder Shares,” for an aggregate purchase price of $25,000 and 498,225 Private Units for which they paid an aggregate purchase price of $4,982,250. Specifically: the Sponsor owns 2,798,225 shares of GLST Common Stock; Anthony Ang and Ted Kim beneficially own 1,640,000 shares of GLST Common Stock by virtue of serving as the managing members of the Sponsor, and Mr. Ang also owns 300,000 shares of GLST Common Stock directly; Nicholas Khoo owns 50,000 shares of GLST Common Stock; and Stephen Drew owns 20,000 shares of GLST Common Stock. In addition, on July 12, 2023, the Sponsor sold 160,000 Founder Shares to K Enter for $1,600,000. Thereafter, the Sponsor loaned the $1.6 million to Global Star in exchange for an unsecured, non-interest-bearing promissory note, $1.5 million of which will be converted into 150,000 Global Star Units in connection with the completion of the Business Combination. Stephen Drew, a director of Global Star served as a director of K Enter Holdings, Inc. from January 3, 2023 to April 25, 2023.
Furthermore, we noted that other officers and directors of Global Star also hold shares in K Enter, and Global Star has provided full disclosure regarding these relationships and shareholdings as follows:
Ted Kim, the manager of the Sponsor and a co-founder and director of K Enter, owns 21.3% of the shares of common stock of K Enter through his ownership and control of Global Fund LLC, which owns 12,000 shares, and Lodestar USA, Inc., which owns 8,166 shares. Further, Global Star officers and directors collectively own shares of common stock of K Enter representing approximately 8.9% of the outstanding shares of K Enter. Specifically, Stephen Drew owns 6,000 shares of K Enter common stock, Yang Kan Chong owns 1,337 shares of K Enter common stock, Jukka Rannila, beneficially through Assai OY, owns 600 shares of K Enter common stock. Nicholas Aaron Khoo, the Company’s Chief Operating Officer, owns 600 shares of K Enter common stock, All of such investments will expire worthless if a business combination is not consummated; on the other hand, if a business combination is consummated, such investments could earn a positive rate of return on their overall investment in the combined company, even if other holders of Global Star’s common stock experience a negative rate of return.
We have evaluated these relationships and conclude that they do not present any conflicts of interest that would compromise the fairness of the transaction.
Our assignment was finalized on 12 March 2024, after a period of comments from the management of the SPAC. Any events or information occurring after this date have not been subject to consideration.
EverEdge is retained by the SPAC to provide this Fairness Opinion in connection with the New Proposed Transaction and will receive a total fee of SG$49,500. EverEdge’s fee is not contingent upon, or related to, the size of the Transaction Consideration, or whether the New Proposed Transaction is consummated.
We are providing this Fairness Opinion to the SPAC who may use this document only in its entirety in the communication with the shareholders of the SPAC concerning the New Proposed Transaction. Our opinion expressed below must not be construed as a recommendation as to whether the shareholders of the SPAC should approve the New Proposed Transaction.
Fairness Opinion Conclusion
Based on the work performed by EverEdge, and on the statements above, we are of the opinion that the New Proposed Transaction, on the date of issue of this document, is fair from a financial point of view for the public equity shareholders of Global Star Acquisition Inc.
Yours sincerely,
For further information please contact:
EverEdge Pte. Ltd.
168 Robinson Road,
#20-01, Capital Tower,
Singapore 068912
Revised as of April 29, 2024
| Private and Confidential | 12 March, 2024 |
Opinion of Global Star Acquisition Inc.’s Financial Advisor
Opinion of EverEdge Pte. Ltd.
Pursuant to the engagement proposals dated 12 April 2023 and 12 December 2023, EverEdge Pte. Ltd. (“EverEdge”) was engaged by Global Star Acquisition Inc. (the “SPAC”), to act as its financial advisor in connection with the business combination involving the SPAC and K Enter Holdings Inc. (the “Target”), to evaluate the proposed merger transaction (the “New Proposed Transaction”). As part of this engagement, the SPAC requested that EverEdge evaluate the facts of the New Proposed Transaction and provide an opinion as to whether the purchase consideration of USD 590 million (the “Transaction Consideration”) for 100% of the outstanding equity and equity equivalents of the Target (including its acquisition/merger targets, including options, warrants or other securities that have the right to acquire or convert into equity securities of the Target), is fair and reasonable.
The full text of the EverEdge’s written opinion dated 12 March 2024, as revised on April 29, 2024, which sets forth, among other things, the procedures followed, assumptions made, matters considered, and qualifications and limitations on the scope of review undertaken in rendering its opinion is incorporated by reference in its entirety into this proxy statement. EverEdge’s opinion was addressed to, and provided for the information and benefit of, the relevant officers in the SPAC in connection with their evaluation of the New Proposed Transaction. The opinion does not constitute a recommendation to the relevant officers in the SPAC or to any other persons in respect of the New Proposed Transaction, including as to how any holder of the SPAC’s shares should vote or act in respect of the New Proposed Transaction. EverEdge’s opinion does not address the relative merits of the New Proposed Transaction as compared to other business or financial strategies that might be available to the SPAC, nor does it address the underlying business decision of the SPAC to engage in the New Proposed Transaction.
In connection with rendering its opinion, EverEdge have performed the necessary analyses, giving consideration, to the following information:
| ● | The terms and conditions of the Non-Binding Letter of Intent dated 11 April 2023, the Share Purchase Agreement dated 15 June 2023, the Termination Agreement and Re-Purchase Option Agreement dated 5 March 2024, and the First Amendment to Merger Agreement dated 11 March 2024 (collectively referred to as the “New Proposed Transaction Agreements”); |
| ● | Management financial forecasts for a period of 5 years and provided by the management of K Enter Holdings Inc. (“K Enter Forecasts”); |
| ● | Corporate Presentation Decks of the Target prepared by KPMG Samjong Accounting Corp. (“KPMG”); |
| ● | K Enter Holdings Inc. corporate structure documents including the Articles of Incorporation dated 4 January 2023 and List of Shareholders as of 28 April 2023; |
| ● | Other available public information (i.e., various equity analyst reports, annual reports, and public information about comparable companies), information available from the virtual data room and relevant market data from knowledge databases such as FactSet; |
| ● | Confirmation with Management on key assumptions around discount rate, industry EV/Revenue and EV/EBITDA multiples, and working capital and found them to be reasonable based on industry research; |
| ● | Comparable statistics for companies in segments of the Film entertainment and production industry as well as the Gaming/Webtoons/OTT Platforms industry. |
For purposes of its analysis and opinion, EverEdge assumed and relied upon the accuracy and completeness of the financial and other information publicly available, and all of the information supplied or otherwise made available to, discussed with, or reviewed by EverEdge, without any independent verification of such information (and assumed no responsibility or liability for any independent verification of such information), and further relied upon the assurances of the management of the SPAC that they were not aware of any facts or circumstances that would make such information inaccurate or misleading. With respect to the K Enter Forecasts, EverEdge assumed that they were reasonably prepared on bases reflecting the best currently available estimates and good faith judgments of the management of K Enter Holdings Inc. as to its future financial performance. EverEdge expressed no view as to the K Enter Forecasts nor the assumptions on which they were based.
For purposes of its analysis and opinion, EverEdge assumed, in all respects material to its analysis, that the representations and warranties of each party contained in the New Proposed Transaction Agreements were true and correct, that each party would perform all of the covenants and agreements required to be performed by it under the New Proposed Transaction Agreements and that all conditions to the consummation of the New Proposed Transaction would be satisfied without waiver or modification thereof. EverEdge further assumed, in all respects material to its analysis, that all governmental, regulatory, or other consents, approvals or releases necessary for the consummation of the New Proposed Transaction would be obtained without any delay, limitation, restriction or condition that would have an adverse effect on the consummation of the New Proposed Transaction or reduce the contemplated benefits to the Target or the Target’s equity holders (including holders of options, warrants, and other convertible securities).
EverEdge did not conduct a physical inspection of the properties nor facilities of the Target. EverEdge did not evaluate the solvency or fair value of the Target under any state or federal laws relating to bankruptcy, insolvency, or similar matters. EverEdge’s opinion is necessarily based upon information made available to EverEdge as of 12 March 2024 and financial, economic, market, and other conditions as they existed and as could be evaluated as of that date. Subsequent developments may affect EverEdge’s opinion and EverEdge does not have any obligation to update, revise, or reaffirm its opinion.
EverEdge was not asked to pass upon, and expressed no opinion with respect to, any matter other than the fairness to the public equity holders (including holders of options, warrants, and other convertible securities) of the SPAC’s shares, from a financial point of view, of the Transaction Consideration. EverEdge did not express any view on, and its opinion does not address, the fairness of the New Proposed Transaction to creditors or other constituencies of the SPAC, nor as to the fairness of the amount or nature of any compensation to be paid or payable to any of the officers, directors, or employees of the Target, or any class of such persons, whether relative to the New Proposed Transaction or otherwise. EverEdge was not asked to, nor did it express any view on, and its opinion does not address, any other term or aspect of the New Proposed Transaction Agreements or the Transaction Consideration, including, without limitation, the structure or form of the New Proposed Transaction, or any term or aspect of any other agreements or instruments contemplated by the New Proposed Transaction Agreements or entered into or amended in connection with the New Proposed Transaction Agreements.
EverEdge’s opinion does not address the relative merits of the New Proposed Transaction as compared to other business or financial strategies that might be available to the SPAC, nor does it address the underlying business decision of the SPAC to engage in the New Proposed Transaction. EverEdge has assumed the accuracy and completeness of assessments by the SPAC and its advisors with respect to legal, regulatory, accounting, and tax matters. The credit, financial, and stock markets have been experiencing unusual volatility and EverEdge expressed no opinion or view as to any potential effects of such volatility on the parties or the New Proposed Transaction.
Set forth below is a summary of the material financial analyses reviewed by EverEdge with the management of the SPAC on 12 March 2024 in connection with rendering its opinion. The following summary, however, does not purport to be a complete description of the analyses performed by EverEdge. The order of the analyses described, and the results of these analyses do not represent relative importance or weight given thereto by EverEdge. Except as otherwise noted, the following quantitative information, to the extent that it is based on market data, is based on market data that existed on or before 12 March 2024, and is not necessarily indicative of current nor future market conditions.
Summary of EverEdge’s Financial Analysis of the Target
The valuation of the financial adequacy of the Transaction Consideration is carried out on a stand-alone basis using different valuation methods. The implied equity value of the Target is calculated as at the date of valuation of 31 December 2023.
The discounted cash flow (“DCF”) method is of key importance in the context of our valuation. The valuation considerations are supplemented by the application of market-based methods based on the trading multiples of comparable companies (Guideline Public Traded Companies Method) and prices paid in past transactions (Guideline Transaction Method). The implied equity value resulting from the DCF method, and from the respective market-based valuations is then compared with the Transaction Consideration. Valuations based on trading and transaction multiples are performed to cross-check against the DCF valuation.
The following provides an overview of the valuation methods used:
Income Approach – Discounted Cash Flow Analysis Method
In general, the value of the company is derived by discounting the expected future free cash flows with the appropriate weighted average cost of capital (“WACC”) at the defined date of valuation. The application of the DCF method to determine enterprise value is the preferred method used by industry practitioners.
EverEdge performed a DCF analysis to calculate the implied enterprise value (and resulting equity value) of the Target, utilizing management estimates of the unlevered, after-tax free cash flows that the Target is expected to generate over the five-year period from FY 2024 to FY 2028 (“Explicit Period”) based on the K Enter Forecasts, approved by the management of the Target. The performance of the Target over the explicit period consolidates the performance of its six subsidiaries and the K Enter Drama team, which forms part of the New Proposed Transaction, under the premise that the SPAC will complete the acquisition of all aforementioned entities. While we assume that significant synergies between subsidiaries will occur post-transaction that will potentially improve Target’s profitability, no explicit values were assigned thereto in the financial analysis and the computation of unlevered free cash flows given the uncertainties around the estimation of any such potential synergies. The consolidation was performed on a sum-of-the-parts basis.
For purposes of its discounted cash flow analyses, unlevered free cash flow is defined as net income after tax, plus depreciation and amortization expenses, plus after-tax interest expenses, less capital expenditures, less working capital investments, and plus/(less) other non-cash expenses/(gains).
The proportion of cash flow that relates to the time after the explicit period into perpetuity (terminal period) is reflected as the terminal value (“TV”). EverEdge calculated the terminal value of the Target using the Gordon Growth Model by applying a stable growth rate of 4.5% to estimate the terminal year unlevered free cash flow reflected in the K Enter Forecasts, for a business in a steady state of growth under the premise of a going concern. The stable growth rate was determined based on the estimated inflation rate and real gross domestic product (GDP) growth rate for South Korea over the terminal period, using the formula:
(1+Terminal Growth) = (1+Inflation rate) x (1+Real GDP growth rate)
The average inflation rate of 2.4% and real GDP growth rate of 2.0% for the period spanning between 2023 to 2028 were used as approximations for the long-term values over the terminal period.
Discounting the unlevered, after-tax free cashflows for the explicit period, as well as the calculated terminal value with a time weighted WACC of 12.6%, in a range between 12.8% to 12.4% from FY2024 to FY2028, gives the present value of free cash flow to firm (“FCFF”). The sum of these present-valued free cash flow to firm results in the enterprise value as at the defined date of valuation. The time-weighted WACC is determined based on EverEdge’s determination of the capital structure and company-specific risk profile of the Target, in conjunction with industry and economic indicators as of the defined date of valuation.
In a final step to derive the equity value from the enterprise value, non-operating assets (mainly cash and cash equivalents) as of 31 December 2023 are added to the enterprise value, and total financial debt and debt equivalents (mainly interest-bearing short-term and long- term financial debt) and non-controlling interests as of 31 December 2023 are deducted from the enterprise value.
This results in the equity value of the Target as of the defined date of valuation.
The underlying financial projections for K Enter Holdings Inc., as well as for each of its subsidiaries, are presented in Supplemental Exhibit A to the proxy statement. The results of the calculations are as follows.
DCF Method
(KRW ‘million) | | Downside
(WACC +50 bp) | | | Base | | | Upside
(WACC - 50 bp) | |
| Net Present Value of FCFF over Forecast Period | | | 748,952 | | | | 167,578 | | | | 172,882 | |
| Net Present Value of Terminal Value | | | 162,496 | | | | 878,262 | | | | 1,047,125 | |
| Total Enterprise Value at Date of Valuation | | | 911,448 | | | | 1,045,840 | | | | 1,220,007 | |
| Add: Non-Operating Assets at Date of Valuation | | | 11,053 | | | | 11,053 | | | | 11,053 | |
| Less: Total Financial Debt at Date of Valuation | | | (7,076 | ) | | | (7,076 | ) | | | (7,076 | ) |
| Less: Non-controlling Interest | | | (269,273 | ) | | | (269,273 | ) | | | (269,273 | ) |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (KRW ‘m) | | | 646,151 | | | | 780,543 | | | | 954,710 | |
| KRW/USD at Date of Valuation | | | 1,300.4 | | | | 1,300.4 | | | | 1,300.4 | |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (USD ‘m) | | | 496.9 | | | | 600.2 | | | | 734.2 | |
EverEdge’s determination of equity value using the DCF method is a median value of USD 600.2 million, in a value range between USD 496.9 million and USD 734.2 million based on a change in WACC by ±50 basis points.
Market Approach – Guideline Public Traded Companies (GPTC) Method
The valuation based on forward trading multiples is used to cross-check the DCF valuation. The GPTC Method is a market indicator used to value a business, based on trading multiples derived from publicly traded companies that are similar to the target company. The significance of the forward trading multiples valuation may be limited as both the business model of the Target and the specific situation of the comparable companies may differ. EverEdge reviewed and compared certain information of the Target (business activity, revenue sources, geography) to the following selected publicly traded companies in selected segments of the Film entertainment and production industry as well as the Gaming/Webtoons/OTT Platforms industry (referred to in this section as the “Comparable Companies”):
Comparable Companies (Film & Entertainment): United States
| ● | AMC Entertainment Holdings Inc. |
| ● | Lions Gate Entertainment |
| ● | Madison Square Garden Entertainment Corp. |
| ● | Warner Music Group Corp. |
| ● | Warner Bros. Discovery, Inc. |
Comparable Companies (Direct Film & Drama Production): South Korea
| ● | ContentreeJoongAng Corp. |
| ● | Wysiwyg Studios Co., Ltd |
| ● | Chorokbaem Media Co., Ltd* |
| ● | Next Entertainment World Co., Ltd |
Comparable Companies (CGI / VFX): South Korea and United States
Comparable Companies (DVD and Merchandise): South Korea
| * | Certain identified comparable companies have been assessed to be outliers and are subsequently excluded from the analysis. |
Comparable Companies (Gaming / Webtoons / OTT Platforms): South Korea
| ● | Barunson Entertainment & Arts Corp. |
| ● | DoubleDown Interactive Co., Ltd* |
Our analysis concentrated on identifying companies with industries closely resembling that of the Target, particularly within the film and/or music production sectors in South Korea or the United States. We emphasize that while none of the Comparable Companies listed above are directly comparable to the Target, EverEdge selected these companies due to the similar operating industries with business characteristics that, for the purposes of its analysis, EverEdge considered as close proxies to the business characteristics of the Target for the business lines presented in the K Enter Forecasts. Despite notable differences in scale and financial standing, these identified companies were deemed relevant for comparison purposes due to their shared industry focus.
Moreover, while the Target may be a newly established entity, the entities to be contracted as subsidiaries of the Target boast a well-established operational history. It is important to also recognize that market capitalization and operating history alone do not necessarily equate direct comparability. Factors such as the industry alignment, business model nuances, geographic focus, and product diversity, which we have considered, also play significant roles in assessing relevance.
Finally, we also exercised discretion in excluding companies with negative operating results or exceptionally high valuation multiples deemed outliers, as these factors could potentially distort the integrity of our analysis
For each of the Comparable Companies identified above, the Enterprise Value-to-EBITDA (EV/EBITDA) multiple as well as an Enterprise-to-Revenue (EV/Revenue) multiple were selected as the comparable valuation metrics to determine the implied enterprise value of the Target, as reflected in the most recent public filings made by the Comparable Companies and consensus estimates obtained from publicly available equity research analysts’ projections made available by FactSet as of the date of valuation. For more details, please refer to Supplemental Exhibit C to the proxy statement for the list of comparable companies.
Based on the compilation of identified Comparable Companies, EverEdge has computed an average EV/EBITDA multiple of 16.4x, in a range between 10.6x to 17.0x, and an average EV/Revenue multiple of 2.4x, in a range between 1.6x to 2.8x. To address the company-specific risk profile and size of the Target in relation to publicly traded Comparable Companies, an additional discount to trading multiples of 20.4% has been applied to both the EV/EBITDA and EV/Revenue multiples. Consequently, the adjusted average EV/EBITDA multiple stands at 13.1x, in a range between 8.4x and 13.5x, while the adjusted average EV/Revenue multiple is 1.9x, in a range between 1.3x to 2.3x.
As a logical continuation of the foregoing analysis, the implied enterprise value of the Target is determined through the application of adjusted trading multiples to the projected FY2026 EBITDA and FY2026 Revenue figures. This calculation operates on the assumption that the Target’s revenue and profitability will exhibit stability from FY2026, a consequence of the business stabilization process occurring post-2023 and the synergistic effects realized among subsidiaries. The valuation methodology employs forward-looking financials representing FY2026 EBITDA and FY2026 Revenue.
As the trading multiples derived from Comparable Companies have generally factored in a discount for lack of control to reflect the fair value of a minority stake in a publicly traded company, a control premium on 26.1% was also applied to adjust the enterprise value from a minority stake perspective of the GPTC method to an enterprise value on a controlling basis.
Subsequently, the resultant forward-looking enterprise values are discounted commensurately with the relevant time horizon, concluding at the defined date of valuation.
In a final step, non-operating assets (mainly cash and cash equivalents) estimated as of 31 December 2023 are added, and total financial debt and debt equivalents (mainly interest-bearing short-term and long-term financial debt) and non-controlling interests as of 31 December 2023 are deducted to derive the equity value from the enterprise value.
| * | Certain identified comparable companies have been assessed to be outliers and are subsequently excluded from the analysis. |
The results of the calculations are as follows:
EV/EBITDA Multiples
(KRW ‘million) | | 25th
Percentile | | | Median | | | 75th
Percentile | |
| FY 2026 EBITDA | | | 58,586 | | | | 58,586 | | | | 58,586 | |
| Unadjusted EV/EBITDA Multiple | | | 10.6 | x | | | 16.4 | x | | | 17.0 | x |
| Minus: Discount to Trading Multiples (%) | | | (20.4 | %) | | | (20.4 | %) | | | (20.4 | %) |
| Adjusted EV/EBITDA Multiple | | | 8.4 | x | | | 13.1 | x | | | 13.5 | x |
| Enterprise Value on a Non-Controlling, Non-Marketable Basis | | | 492,379 | | | | 765,692 | | | | 790,679 | |
| Add: Control Premium (%) | | | 26.1 | % | | | 26.1 | % | | | 26.1 | % |
| Control Premium | | | 128,511 | | | | 199,846 | | | | 206,367 | |
| Enterprise Value on a Controlling, Non-Marketable Basis | | | 620,891 | | | | 965,537 | | | | 997,046 | |
| WACC (%) | | | 12.6 | % | | | 12.6 | % | | | 12.6 | % |
| Discount Factor | | | 0.74 | | | | 0.74 | | | | 0.74 | |
| Enterprise Value at Date of Valuation | | | 460,642 | | | | 716,337 | | | | 739,714 | |
| Add: Non-Operating Assets at Date of Valuation | | | 11,053 | | | | 11,053 | | | | 11,053 | |
| Less: Total Financial Debt at Date of Valuation | | | (7,076 | ) | | | (7,076 | ) | | | (7,076 | ) |
| Less: Non-controlling Interest | | | (269,273 | ) | | | (269,273 | ) | | | (269,273 | ) |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (KRW ‘m) | | | 195,345 | | | | 451,040 | | | | 474,417 | |
| KRW/USD at Date of Valuation | | | 1,300.4 | | | | 1,300.4 | | | | 1,300.4 | |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (USD ‘m) | | | 150.2 | | | | 346.8 | | | | 364.8 | |
EverEdge’s determination of equity value using the forward trading FY2026 EV/EBITDA multiples under the GPTC method results in a median equity value of USD 346.8 million, in a value range between USD 150.2 million and USD 364.8 million.
EV/Revenue Multiples
(KRW ‘million) | | 25th
Percentile | | | Median | | | 75th
Percentile | |
| FY 2026 Revenue | | | 614,805 | | | | 614,805 | | | | 614,805 | |
| Unadjusted EV/Revenue Multiple | | | 1.6 | x | | | 2.4 | x | | | 2.8 | x |
| Minus: Discount to Trading Multiples (%) | | | (20.40 | %) | | | (20.40 | %) | | | (20.40 | %) |
| Adjusted EV/Revenue Multiple | | | 1.3 | x | | | 1.9 | x | | | 2.3 | x |
| Enterprise Value on a Non-Controlling, Non-Marketable Basis | | | 781,854 | | | | 1,170,281 | | | | 1,388,353 | |
| Add: Control Premium (%) | | | 26.1 | % | | | 26.1 | % | | | 26.1 | % |
| Control Premium | | | 204,064 | | | | 305,443 | | | | 362,360 | |
| Enterprise Value on a Controlling, Non-Marketable Basis | | | 985,918 | | | | 1,475,724 | | | | 1,750,714 | |
| WACC (%) | | | 12.6 | % | | | 12.6 | % | | | 12.6 | % |
| Discount Factor | | | 0.74 | | | | 0.74 | | | | 0.74 | |
| Enterprise Value at Date of Valuation | | | 731,457 | | | | 1,094,847 | | | | 1,298,863 | |
| Add: Non-Operating Assets at Date of Valuation | | | 11,053 | | | | 11,053 | | | | 11,053 | |
| Less: Total Financial Debt at Date of Valuation | | | (7,076 | ) | | | (7,076 | ) | | | (7,076 | ) |
| Less: Non-controlling Interest | | | (269,273 | ) | | | (269,273 | ) | | | (269,273 | ) |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (KRW ‘m) | | | 466,161 | | | | 829,551 | | | | 1,033,567 | |
| KRW/USD at Date of Valuation | | | 1,300.4 | | | | 1,300.4 | | | | 1,300.4 | |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (USD ‘m) | | | 358.5 | | | | 637.9 | | | | 794.8 | |
EverEdge’s determination of equity value using the forward trading FY2026 EV/Revenue multiples under the GPTC method results in a median equity value of USD 637.9 million, in a value range between USD 358.5 million and USD 794.8 million.
Market Approach – Guideline Transaction Method (GTM)
EverEdge also used the Guideline Transaction Method (GTM) as a third valuation methodology, to calculate the implied enterprise value (and resulting equity value) of the Target, by analyzing comparable transactions in the marketplace.
EverEdge relied on identifying relevant transactions exhibiting similarities to the Target in terms of industry, size, growth prospects, and other relevant attributes. The implied enterprise value (and resulting equity value) of the Target using this approach was determined by multiplying the forward looking FY2026 EBITDA by the transaction EV/EBITDA multiple. Subsequently, the calculated value was discounted commensurately over the forecast period to the defined date of valuation.
For more details, please refer to Supplemental Exhibit D to the proxy statement for the list of comparable precedent transactions. The results of the calculations are as follows:
Transaction Multiples
(KRW ‘million) | | 25th
Percentile | | | Median | | | 75th
Percentile | |
| FY 2026 EBITDA | | | 58,586 | | | | 58,586 | | | | 58,586 | |
| Transaction EV/EBITDA Multiple | | | 14.3 | x | | | 14.8 | x | | | 15.3 | x |
| Undiscounted Enterprise Value | | | 837,781 | | | | 867,074 | | | | 896,367 | |
| WACC (%) | | | 12.6 | % | | | 12.6 | % | | | 12.6 | % |
| Discount Factor | | | 0.74 | | | | 0.74 | | | | 0.74 | |
| Enterprise Value at Date of Valuation | | | 621,554 | | | | 643,287 | | | | 665,020 | |
| Add: Non-Operating Assets at Date of Valuation | | | 11,053 | | | | 11,053 | | | | 11,053 | |
| Less: Total Financial Debt at Date of Valuation | | | (7,076 | ) | | | (7,076 | ) | | | (7,076 | ) |
| Less: Non-controlling Interest | | | (269,273 | ) | | | (269,273 | ) | | | (269,273 | ) |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (KRW ‘m) | | | 356,258 | | | | 377,990 | | | | 399,723 | |
| KRW/USD at Date of Valuation | | | 1,300.4 | | | | 1,300.4 | | | | 1,300.4 | |
| Equity Value at Date of Valuation (USD ‘m) | | | 274.0 | | | | 290.7 | | | | 307.4 | |
EverEdge’s determination of equity value using the transaction multiples under the GTM method results in a median equity value of USD 290.7 million, in a value range between USD 274.0 million and USD 307.4 million.
Conclusion
Based on the analyses described above and an assessment and evaluation of all the information provided, EverEdge has come to the following conclusion with regard to the financial adequacy of the SPAC’s New Proposed Transaction of the Target.
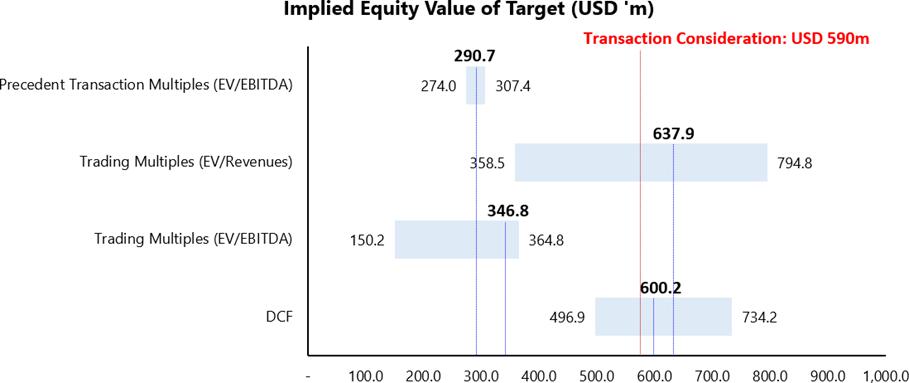
Based on our analyses and value considerations as well as the results presented, EverEdge considers the Transaction Consideration of USD 590 million to be fair from a financial point of view to the public equity holders of Global Star. This conclusion is based on the following considerations:
| 1. | The significance of the valuation range derived from the Precedent Transaction Multiples approach is deemed minimal due to the limited pool of comparable precedent transactions. |
| 2. | While we assume that significant synergies between subsidiaries will occur post-transaction that will potentially improve Target’s profitability, no explicit values were assigned thereto in the financial analysis. Consequently, the valuation range derived from EV/EBITDA trading multiples is assessed to be understated. |
| 3. | The Transaction Consideration is supported by the DCF valuation. |
| 4. | The Transaction Consideration is within the value range resulting from the application of EV/Revenue trading multiples. |
Miscellaneous
The foregoing summary of certain financial analyses does not purport to be a complete description of the analyses or data presented by EverEdge. In connection with the evaluation of the New Proposed Transaction by the SPAC, EverEdge performed a variety of financial and comparative analyses for purposes of rendering its opinion. The preparation of a fairness opinion is a complex process and is not necessarily susceptible to partial analysis or summary descriptions. Selecting portions of the analyses or of the summary described above, without considering the analyses as a whole, may create an incomplete view of the processes underlying EverEdge’s opinion. In arriving at its fairness determination, EverEdge considered the results of all the analyses and did not draw, in isolation, conclusions from or with regard to any one analysis or factor considered by it for purposes of its opinion. Rather, EverEdge made its determination as to fairness on the basis of its experience and professional judgment after considering the results of all the analyses. In addition, EverEdge may have given certain analyses and factors more or less weight than others and may have deemed certain assumptions more or less probable than others. As a result, the range of valuations resulting from any particular analysis or combination of analyses described above should not be taken to be the view of Eve rEdge with respect to the actual value of the Target. Further, Eve rEdge’s analyses involve complex considerations and judgments concerning financial and operating characteristics and other factors that could affect the acquisition, public trading or other values of the companies used, including judgments and assumptions with regard to industry performance, general business, economic, market and financial conditions and other matters, many of which are beyond the control of the SPAC or its advisors.
EverEdge prepared these analyses for the purpose of providing an opinion to the relevant officers in the SPAC as to the fairness, from a financial point of view, of the Transaction Consideration to the equity holders (including holders of options, warrants, and other convertible securities) of the Target’s shares. These analyses do not purport to be appraisals or to necessarily reflect the prices at which the business or securities may be sold at. Any estimates contained in these analyses are not necessarily indicative of actual future results, which may be significantly more or less favorable than those suggested by such estimates. Accordingly, estimates used in, and the results derived from, EverEdge’s analyses are inherently subject to substantial uncertainty, and EverEdge assumes no responsibility if future results are materially different from those forecasted in such estimates.
The issuance of EverEdge’s fairness opinion was approved by an opinion committee of EverEdge.
Pursuant to the terms of EverEdge’s engagement letter with the SPAC, EverEdge was entitled to receive a total fee of SG$49,500. The SPAC has also agreed to reimburse EverEdge for any reasonable and documented out-of-pocket expenses (including any travel or search costs) and to indemnify EverEdge for certain liabilities arising out of its engagement.
The SPAC engaged EverEdge to act as a supplier of the fairness opinion based on EverEdge’s qualifications, experience, and reputation. EverEdge is a global advisory and transaction firm specializing in intangible assets and is regularly engaged in business valuation practices.
Supplemental Exhibit A: K Enter Forecasts
A summary of the 5-year financial forecasts for the entities contracted to be subsidiaries of the Target are provided below. All figures shown in these exhibits are presented in KRW millions.
Play Company Co., Ltd
| Fiscal Year | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Calendar | | 31-Dec-23 | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | 31-Dec-27 | | | 31-Dec-28 | |
| PlayCo Revenues | | | 76,804 | | | | 105,519 | | | | 164,579 | | | | 228,832 | | | | 283,626 | | | | 312,989 | |
| PlayF&B Revenues | | | 18,390 | | | | 21,841 | | | | 26,712 | | | | 33,574 | | | | 39,099 | | | | 44,560 | |
| Total Revenues | | | 95,194 | | | | 127,361 | | | | 191,291 | | | | 262,405 | | | | 322,725 | | | | 357,548 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | 33.8 | % | | | 50.2 | % | | | 37.2 | % | | | 23.0 | % | | | 10.8 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| PlayCo COGS | | | (62,083 | ) | | | (94,025 | ) | | | (149,760 | ) | | | (205,090 | ) | | | (250,579 | ) | | | (276,478 | ) |
| PlayF&B COGS | | | (18,780 | ) | | | (19,079 | ) | | | (21,483 | ) | | | (24,781 | ) | | | (27,227 | ) | | | (29,507 | ) |
| Total COGS | | | (80,863 | ) | | | (113,104 | ) | | | (171,243 | ) | | | (229,871 | ) | | | (277,806 | ) | | | (305,985 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | 14,331 | | | | 14,256 | | | | 20,048 | | | | 32,534 | | | | 44,919 | | | | 51,564 | |
| GP Margin | | | 15.1 | % | | | 11.2 | % | | | 10.5 | % | | | 12.4 | % | | | 13.9 | % | | | 14.4 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| PlayCo SG&A Expenses | | | (2,957 | ) | | | (3,445 | ) | | | (3,694 | ) | | | (3,991 | ) | | | (4,284 | ) | | | (4,598 | ) |
| PlayF&B SG&A Expenses | | | (1,148 | ) | | | (1,423 | ) | | | (1,547 | ) | | | (1,695 | ) | | | (1,841 | ) | | | (1,998 | ) |
| Total SG&A Expenses | | | (4,105 | ) | | | (4,868 | ) | | | (5,241 | ) | | | (5,686 | ) | | | (6,126 | ) | | | (6,596 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | 4.3 | % | | | 3.8 | % | | | 2.7 | % | | | 2.2 | % | | | 1.9 | % | | | 1.8 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBITDA | | | 10,226 | | | | 9,389 | | | | 14,807 | | | | 26,848 | | | | 38,793 | | | | 44,968 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | 10.7 | % | | | 7.4 | % | | | 7.7 | % | | | 10.2 | % | | | 12.0 | % | | | 12.6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| PlayCo Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (188 | ) | | | (192 | ) | | | (195 | ) | | | (199 | ) | | | (202 | ) | | | (206 | ) |
| PlayF&B Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (1,213 | ) | | | (1,314 | ) | | | (1,411 | ) | | | (1,542 | ) | | | (1,617 | ) | | | (1,668 | ) |
| Adjusted for Consolidation | | | (1,303 | ) | | | (1,303 | ) | | | (1,303 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (2,705 | ) | | | (2,809 | ) | | | (2,910 | ) | | | (1,741 | ) | | | (1,819 | ) | | | (1,875 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBIT | | | 7,521 | | | | 6,580 | | | | 11,897 | | | | 25,106 | | | | 36,974 | | | | 43,093 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | 7.9 | % | | | 5.2 | % | | | 6.2 | % | | | 9.6 | % | | | 11.5 | % | | | 12.1 | % |
Supplemental Exhibit A: K Enter Forecasts (Continued)
The LAMP Pictures Co., Ltd
| Fiscal Year | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Calendar | | 31-Dec-23 | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | 31-Dec-27 | | | 31-Dec-28 | |
| Drama Revenues | | | 4,073 | | | | 8,400 | | | | 17,522 | | | | 19,388 | | | | 42,694 | | | | 46,800 | |
| Film Revenues | | | 11,485 | | | | 16,124 | | | | 16,819 | | | | 25,375 | | | | 27,669 | | | | 45,600 | |
| Total Revenues | | | 15,559 | | | | 24,524 | | | | 34,341 | | | | 44,763 | | | | 70,363 | | | | 92,400 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | 57.6 | % | | | 40.0 | % | | | 30.3 | % | | | 57.2 | % | | | 31.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Drama COGS | | | (3,849 | ) | | | (7,980 | ) | | | (15,750 | ) | | | (16,500 | ) | | | (34,500 | ) | | | (36,000 | ) |
| Film COGS | | | (10,898 | ) | | | (14,762 | ) | | | (15,270 | ) | | | (22,900 | ) | | | (24,590 | ) | | | (40,560 | ) |
| Total COGS | | | (14,747 | ) | | | (22,742 | ) | | | (31,020 | ) | | | (39,400 | ) | | | (59,090 | ) | | | (76,560 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | 812 | | | | 1,782 | | | | 3,321 | | | | 5,363 | | | | 11,273 | | | | 15,840 | |
| GP Margin | | | 5.2 | % | | | 7.3 | % | | | 9.7 | % | | | 12.0 | % | | | 16.0 | % | | | 17.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total SG&A Expenses | | | (838 | ) | | | (1,035 | ) | | | (1,105 | ) | | | (1,186 | ) | | | (1,341 | ) | | | (1,479 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | 5.4 | % | | | 4.2 | % | | | 3.2 | % | | | 2.7 | % | | | 1.9 | % | | | 1.6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBITDA | | | (26 | ) | | | 747 | | | | 2,216 | | | | 4,176 | | | | 9,932 | | | | 14,361 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | (0.2 | %) | | | 3.0 | % | | | 6.5 | % | | | 9.3 | % | | | 14.1 | % | | | 15.5 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (50 | ) | | | (51 | ) | | | (51 | ) | | | (52 | ) | | | (53 | ) | | | (54 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBIT | | | (75 | ) | | | 696 | | | | 2,164 | | | | 4,124 | | | | 9,879 | | | | 14,307 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | (0.5 | %) | | | 2.8 | % | | | 6.3 | % | | | 9.2 | % | | | 14.0 | % | | | 15.5 | % |
Supplemental Exhibit A: K Enter Forecasts (Continued)
Bidangil Pictures Co., Ltd
| Fiscal Year | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Calendar | | 31-Dec-23 | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | 31-Dec-27 | | | 31-Dec-28 | |
| Drama Revenues | | | 9,000 | | | | 21,000 | | | | 20,460 | | | | 23,100 | | | | 21,347 | | | | 23,400 | |
| Film Revenues | | | 370 | | | | 10,700 | | | | 37,440 | | | | 39,024 | | | | 42,900 | | | | 46,800 | |
| Total Revenues | | | 9,370 | | | | 31,700 | | | | 57,900 | | | | 62,124 | | | | 64,247 | | | | 70,200 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | 238.3 | % | | | 82.7 | % | | | 7.3 | % | | | 3.4 | % | | | 9.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Drama COGS | | | (8,100 | ) | | | (18,900 | ) | | | (18,600 | ) | | | (21,000 | ) | | | (17,250 | ) | | | (18,000 | ) |
| Film COGS | | | (345 | ) | | | (9,520 | ) | | | (34,200 | ) | | | (35,650 | ) | | | (39,270 | ) | | | (42,840 | ) |
| Total COGS | | | (8,445 | ) | | | (28,420 | ) | | | (52,800 | ) | | | (56,650 | ) | | | (56,520 | ) | | | (60,840 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | 924 | | | | 3,280 | | | | 5,100 | | | | 5,474 | | | | 7,727 | | | | 9,360 | |
| GP Margin | | | 9.9 | % | | | 10.3 | % | | | 8.8 | % | | | 8.8 | % | | | 12.0 | % | | | 13.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total SG&A Expenses | | | (1,063 | ) | | | (1,072 | ) | | | (1,095 | ) | | | (1,128 | ) | | | (1,156 | ) | | | (1,186 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | 11.3 | % | | | 3.4 | % | | | 1.9 | % | | | 1.8 | % | | | 1.8 | % | | | 1.7 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBITDA | | | (138 | ) | | | 2,208 | | | | 4,005 | | | | 4,346 | | | | 6,571 | | | | 8,174 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | (1.5 | %) | | | 7.0 | % | | | 6.9 | % | | | 7.0 | % | | | 10.2 | % | | | 11.6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBIT | | | (138 | ) | | | 2,208 | | | | 4,005 | | | | 4,346 | | | | 6,571 | | | | 8,174 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | (1.5 | %) | | | 7.0 | % | | | 6.9 | % | | | 7.0 | % | | | 10.2 | % | | | 11.6 | % |
Supplemental Exhibit A: K Enter Forecasts (Continued)
Apeitda Co., Ltd
| Fiscal Year | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Calendar | | 31-Dec-23 | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | 31-Dec-27 | | | 31-Dec-28 | |
| Drama Revenues | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 19,388 | | | | 21,347 | | | | 46,800 | |
| Film Revenues | | | 329 | | | | 104 | | | | 38,850 | | | | 37,750 | | | | 41,038 | | | | 44,400 | |
| Total Revenues | | | 329 | | | | 104 | | | | 38,850 | | | | 57,138 | | | | 62,384 | | | | 91,200 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | (68.4 | %) | | | 373.1 x | | | | 47.1 | % | | | 9.2 | % | | | 46.2 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Drama COGS | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (16,500 | ) | | | (17,250 | ) | | | (36,000 | ) |
| Film COGS | | | (1 | ) | | | (95 | ) | | | (37,000 | ) | | | (33,900 | ) | | | (36,090 | ) | | | (38,280 | ) |
| Total COGS | | | (1 | ) | | | (95 | ) | | | (37,000 | ) | | | (50,400 | ) | | | (53,340 | ) | | | (74,280 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | 327 | | | | 9 | | | | 1,850 | | | | 6,738 | | | | 9,044 | | | | 16,920 | |
| GP Margin | | | 99.6 | % | | | 8.5 | % | | | 4.8 | % | | | 11.8 | % | | | 14.5 | % | | | 18.6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total SG&A Expenses | | | (287 | ) | | | (292 | ) | | | (299 | ) | | | (308 | ) | | | (316 | ) | | | (324 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | | | | | 281.7 | % | | | 0.8 | % | | | 0.5 | % | | | 0.5 | % | | | 0.4 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBITDA | | | 40 | | | | (284 | ) | | | 1,551 | | | | 6,430 | | | | 8,729 | | | | 16,596 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | 12.3 | % | | | (273.2 | %) | | | 4.0 | % | | | 11.3 | % | | | 14.0 | % | | | 18.2 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (45 | ) | | | (46 | ) | | | (47 | ) | | | (48 | ) | | | (48 | ) | | | (49 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBIT | | | (5 | ) | | | (330 | ) | | | 1,504 | | | | 6,382 | | | | 8,680 | | | | 16,547 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | (1.4 | %) | | | (317.4 | %) | | | 3.9 | % | | | 11.2 | % | | | 13.9 | % | | | 18.1 | % |
Supplemental Exhibit A: K Enter Forecasts (Continued)
Studio Anseillen Co., Ltd
| Fiscal Year | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Calendar | | 31-Dec-23 | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | 31-Dec-27 | | | 31-Dec-28 | |
| Drama Revenues | | | | | | | 17,535 | | | | 39,225 | | | | 66,779 | | | | 86,082 | | | | 119,700 | |
| Film Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Revenues | | | - | | | | 17,535 | | | | 39,225 | | | | 66,779 | | | | 86,082 | | | | 119,700 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | | | | | 123.7 | % | | | 70.2 | % | | | 28.9 | % | | | 39.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Drama COGS | | | | | | | (16,700 | ) | | | (35,000 | ) | | | (56,353 | ) | | | (69,069 | ) | | | (91,890 | ) |
| Film COGS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total COGS | | | - | | | | (16,700 | ) | | | (35,000 | ) | | | (56,353 | ) | | | (69,069 | ) | | | (91,890 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | - | | | | 835 | | | | 4,226 | | | | 10,426 | | | | 17,013 | | | | 27,810 | |
| GP Margin | | | 10.3 | % | | | 4.8 | % | | | 10.8 | % | | | 15.6 | % | | | 19.8 | % | | | 23.2 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total SG&A Expenses | | | - | | | | (1,367 | ) | | | (1,396 | ) | | | (1,436 | ) | | | (1,471 | ) | | | (1,509 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | | | | | 7.8 | % | | | 3.6 | % | | | 2.2 | % | | | 1.7 | % | | | 1.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBITDA | | | - | | | | (532 | ) | | | 2,830 | | | | 8,990 | | | | 15,541 | | | | 26,301 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | | | | | (3.0 | %) | | | 7.2 | % | | | 13.5 | % | | | 18.1 | % | | | 22.0 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBIT | | | - | | | | (532 | ) | | | 2,830 | | | | 8,990 | | | | 15,541 | | | | 26,301 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | | | | | (3.0 | %) | | | 7.2 | % | | | 13.5 | % | | | 18.1 | % | | | 22.0 | % |
Supplemental Exhibit A: K Enter Forecasts (Continued)
Solaire Partners LLC
| Fiscal Year | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Calendar | | 31-Dec-23 | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | 31-Dec-27 | | | 31-Dec-28 | |
| Commission for fund management | | | 1,742 | | | | 2,850 | | | | 5,746 | | | | 6,857 | | | | 7,636 | | | | 7,867 | |
| Direct Investment | | | 34 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other revenue | | | 25 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Revenues | | | 1,801 | | | | 2,850 | | | | 5,746 | | | | 6,857 | | | | 7,636 | | | | 7,867 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | 58.2 | % | | | 101.6 | % | | | 19.3 | % | | | 11.4 | % | | | 3.0 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total COGS | | | (32 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | 1,770 | | | | 2,850 | | | | 5,746 | | | | 6,857 | | | | 7,636 | | | | 7,867 | |
| GP Margin | | | 98.2 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total SG&A Expenses | | | (1,364 | ) | | | (2,004 | ) | | | (3,217 | ) | | | (3,626 | ) | | | (4,037 | ) | | | (4,475 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | 75.7 | % | | | 70.3 | % | | | 56.0 | % | | | 52.9 | % | | | 52.9 | % | | | 56.9 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBITDA | | | 406 | | | | 846 | | | | 2,528 | | | | 3,231 | | | | 3,600 | | | | 3,392 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | 22.5 | % | | | 29.7 | % | | | 44.0 | % | | | 47.1 | % | | | 47.1 | % | | | 43.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (2 | ) | | | (2 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (3 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBIT | | | 403 | | | | 844 | | | | 2,526 | | | | 3,228 | | | | 3,597 | | | | 3,389 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | 22.4 | % | | | 29.6 | % | | | 44.0 | % | | | 47.1 | % | | | 47.1 | % | | | 43.1 | % |
Supplemental Exhibit A: K Enter Forecasts (Continued)
K Enter Drama Team
| Fiscal Year | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Calendar | | 31-Dec-23 | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | 31-Dec-27 | | | 31-Dec-28 | |
| Drama Revenues | | | | | | | 23,845 | | | | 36,436 | | | | 60,390 | | | | 89,484 | | | | 110,700 | |
| Film Revenues | | | | | | | - | | | | 11,419 | | | | 12,375 | | | | 27,669 | | | | 30,000 | |
| IP Investment (Film) | | | | | | | 11,000 | | | | 12,656 | | | | 28,750 | | | | 32,313 | | | | 54,000 | |
| Additional Business | | | | | | | 10,000 | | | | 11,500 | | | | 13,225 | | | | 15,209 | | | | 17,490 | |
| Total Revenues | | | - | | | | 44,845 | | | | 72,011 | | | | 114,740 | | | | 164,674 | | | | 212,190 | |
| Total Revenue Growth | | | | | | | | | | | 60.6 | % | | | 59.3 | % | | | 43.5 | % | | | 28.9 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Drama COGS | | | | | | | (21,968 | ) | | | (33,375 | ) | | | (50,626 | ) | | | (71,490 | ) | | | (84,780 | ) |
| Film COGS | | | | | | | - | | | | (10,500 | ) | | | (11,000 | ) | | | (24,590 | ) | | | (26,280 | ) |
| IP Investment COGS (Film) | | | | | | | (10,000 | ) | | | (11,250 | ) | | | (25,000 | ) | | | (27,500 | ) | | | (45,000 | ) |
| Additional Business COGS | | | | | | | (8,500 | ) | | | (9,775 | ) | | | (11,241 | ) | | | (12,927 | ) | | | (14,867 | ) |
| Total COGS | | | - | | | | (40,468 | ) | | | (64,900 | ) | | | (97,867 | ) | | | (136,508 | ) | | | (170,927 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Profit | | | - | | | | 4,377 | | | | 7,111 | | | | 16,873 | | | | 28,166 | | | | 41,264 | |
| GP Margin | | | | | | | 9.8 | % | | | 9.9 | % | | | 14.7 | % | | | 17.1 | % | | | 19.4 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total SG&A Expenses | | | (10,494 | ) | | | (11,954 | ) | | | (11,832 | ) | | | (12,307 | ) | | | (12,750 | ) | | | (13,224 | ) |
| SG&A Expenses as % of Revenues | | | | | | | 26.7 | % | | | 16.4 | % | | | 10.7 | % | | | 7.7 | % | | | 6.2 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBITDA | | | (10,494 | ) | | | (7,577 | ) | | | (4,721 | ) | | | 4,566 | | | | 15,417 | | | | 28,040 | |
| EBITDA Margin | | | | | | | (16.9 | %) | | | (6.6 | %) | | | 4.0 | % | | | 9.4 | % | | | 13.2 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Depreciation & Amortization Expenses | | | (115 | ) | | | (235 | ) | | | (238 | ) | | | (243 | ) | | | (247 | ) | | | (252 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EBIT | | | (10,609 | ) | | | (7,812 | ) | | | (4,959 | ) | | | 4,323 | | | | 15,170 | | | | 27,788 | |
| EBIT Margin | | | | | | | (17.4 | %) | | | (6.9 | %) | | | 3.8 | % | | | 9.2 | % | | | 13.1 | % |
Supplemental Exhibit B: Calculation of consolidated unlevered free cash flows for the Target
| Fiscal Year | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | |
| Calendar | | | 31-Dec-24 | | | 31-Dec-25 | | | 31-Dec-26 | | | 31-Dec-27 | | | 31-Dec-28 | |
| PlayCompany CFO | | | | 11,952 | | | | 16,561 | | | | 23,844 | | | | 32,728 | | | | 37,332 | |
| The Lamp CFO | | | | 481 | | | | 1,572 | | | | 3,127 | | | | 7,336 | | | | 11,049 | |
| Bidangil CFO | | | | 2,545 | | | | 772 | | | | 3,144 | | | | 5,275 | | | | 6,152 | |
| Apetida CFO | | | | (302 | ) | | | 2,080 | | | | 5,762 | | | | 7,291 | | | | 14,307 | |
| K-Enter Drama CFO | | | | (10,294 | ) | | | (6,356 | ) | | | 2,734 | | | | 13,261 | | | | 21,711 | |
| Studio Anseillen CFO | | | | 12 | | | | 2,773 | | | | 7,000 | | | | 11,990 | | | | 21,874 | |
| Solaire Partners CFO | | | | 163 | | | | 540 | | | | 2,051 | | | | 2,525 | | | | 2,646 | |
| Consolidated Cash Flow from Operations (CFO) | | | | 4,557 | | | | 17,942 | | | | 47,663 | | | | 80,406 | | | | 115,072 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| PlayCompany CFI | | | | (1,506 | ) | | | (1,606 | ) | | | (1,741 | ) | | | (1,819 | ) | | | (1,875 | ) |
| The Lamp CFI | | | | (51 | ) | | | (51 | ) | | | (52 | ) | | | (53 | ) | | | (54 | ) |
| Bidangil CFI | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Apetida CFI | | | | (46 | ) | | | (47 | ) | | | (48 | ) | | | (48 | ) | | | (49 | ) |
| K-Enter Drama CFI | | | | (235 | ) | | | (238 | ) | | | (243 | ) | | | (247 | ) | | | (252 | ) |
| Studio Anseillen CFI | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Solaire Partners CFI | | | | (2 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (3 | ) |
| Consolidated Cash Flow from Investments (CFI) | | | | (1,839 | ) | | | (1,945 | ) | | | (2,087 | ) | | | (2,171 | ) | | | (2,232 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Consolidated Unlevered Free Cash Flows to Firm | | | | 2,718 | | | | 15,996 | | | | 45,575 | | | | 78,235 | | | | 112,839 | |
| Cumulative Discount Factor | | | | 0.94 | | | | 0.84 | | | | 0.74 | | | | 0.66 | | | | 0.59 | |
| Present Value of Unlevered Free Cash Flows to Firm | | | | 2,559 | | | | 13,362 | | | | 33,813 | | | | 51,604 | | | | 66,240 | |
Supplemental Exhibit C: Market Approach – Overview of Comparable Companies
| General Information | | | Profitability | | | Valuation Multiples | |
| Company Name | | Country | | Market Cap
(KRW mil.) | | Annual Revenue
(KRW mil.) | | | Gross Profit
Margin | | EBITDA
Margin | | EBIT
Margin | | | EV/
Sales | |
| ContentreeJoongAng corp. | | South Korea | | 320,332 | | 852,051 | | | 12.4% | | 13.2% | | (8.6%) | | | 2.0x | |
| KX Innovation Co., Ltd. | | South Korea | | 230,307 | | 326,266 | | | 41.6% | | 31.5% | | 24.3% | | | 1.2x | |
| Wysiwyg Studios Co., Ltd. | | South Korea | | 497,752 | | 186,345 | | | 4.8% | | (6.4%) | | (13.7%) | | | 2.3x | |
| SHOWBOX Corp. | | South Korea | | 187,914 | | 56,684 | | | 9.3% | | 69.8% | | (5.6%) | | | 3.4x | |
| Astory Co., Ltd. | | South Korea | | 124,115 | | 71,680 | | | 21.2% | | 12.8% | | 12.0% | | | 2.2x | |
| Next Entertainment World Co., Ltd. | | South Korea | | 123,345 | | 155,617 | | | 22.2% | | 6.9% | | 4.7% | | | 1.4x | |
| Dexter Studios Co., Ltd. | | South Korea | | 183,219 | | 65,906 | | | 9.5% | | 5.4% | | (3.8%) | | | 2.2x | |
| Kakao Corp. | | South Korea | | 22,447,047 | | 7,106,837 | | | 54.6% | | 16.2% | | 8.2% | | | 3.2x | |
| Incross Co.,Ltd. | | South Korea | | 132,927 | | 53,308 | | | 52.4% | | 39.4% | | 36.8% | | | 1.0x | |
| AfreecaTV Co., Ltd. | | South Korea | | 766,701 | | 314,977 | | | 55.9% | | 31.5% | | 26.2% | | | 1.3x | |
| Barunson Entertainment & Arts Corp. | | South Korea | | 51,959 | | 26,033 | | | 15.0% | | (25.9%) | | (28.3%) | | | 2.9x | |
| AMC Entertainment Holdings, Inc. Class A | | United States | | 1,701,802 | | 3,911 | | | 18.1% | | 0.2% | | (9.9%) | | | 2.1x | |
| Fox Corporation Class B | | United States | | 17,942,482 | | 14,913 | | | 32.3% | | 21.3% | | 18.5% | | | 1.3x | |
| Lions Gate Entertainment Corp Class A | | United States | | 2,585,406 | | 3,855 | | | 35.0% | | 48.3% | | 0.5% | | | 1.5x | |
| Madison Square Garden Entertainment Corp. | | United States | | 1,873,989 | | 851 | | | 34.2% | | 21.6% | | 13.0% | | | 2.8x | |
| Liberty Media Corp. Series C Liberty SiriusXM | | United States | | 34,418,910 | | 9,003 | | | 47.3% | | 28.9% | | 22.1% | | | 6.0x | |
| Walt Disney Company | | United States | | 218,876,515 | | 88,454 | | | 27.2% | | 16.0% | | 9.9% | | | 2.5x | |
| Warner Bros. Discovery, Inc. Series A | | United States | | 32,876,907 | | 33,817 | | | 18.2% | | 14.4% | | (6.9%) | | | 1.6x | |
| Warner Music Group Corp. Class A | | United States | | 22,041,707 | | 6,037 | | | 41.9% | | 19.6% | | 14.1% | | | 3.4x | |
| Average | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2.4x | |
| Median | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2.2x | |
| 30th Percentile (Low) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 1.6x | |
| 70th Percentile (High) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2.8x | |
Supplemental Exhibit C: Market Approach – Overview of Comparable Companies (Continued)
| General Information | | | Profitability | | | Valuation Multiples | |
| Company Name | | Country | | Market Cap
(KRW mil.) | | EBITDA
(KRW mil.) | | | Gross Profit
Margin | | EBITDA
Margin | | EBIT
Margin | | | EV/
EBITDA | |
| ContentreeJoongAng corp. | | South Korea | | 320,332 | | 112,674 | | | 12.4% | | 13.2% | | (8.6%) | | | 12.4x | |
| SHOWBOX Corp. | | South Korea | | 187,914 | | 39,563 | | | 9.3% | | 69.8% | | (5.6%) | | | 7.6x | |
| Astory Co., Ltd. | | South Korea | | 124,115 | | 9,199 | | | 21.2% | | 12.8% | | 12.0% | | | 27.7x | |
| Dexter Studios Co., Ltd. | | South Korea | | 183,219 | | 3,583 | | | 9.5% | | 5.4% | | (3.8%) | | | 15.1x | |
| Autodesk, Inc. | | United States | | 60,240,185 | | 1,140 | | | 89.5% | | 23.1% | | 20.1% | | | 39.7x | |
| Kakao Corp. | | South Korea | | 22,447,047 | | 1,149,008 | | | 54.6% | | 16.2% | | 8.2% | | | 21.9x | |
| AMC Entertainment Holdings, Inc. Class A | | United States | | 1,701,802 | | 9 | | | 18.1% | | 0.2% | | (9.9%) | | | 14.6x | |
| Fox Corporation Class B | | United States | | 17,942,482 | | 3,175 | | | 32.3% | | 21.3% | | 18.5% | | | 6.1x | |
| Madison Square Garden Entertainment Corp. | | United States | | 1,873,989 | | 184 | | | 34.2% | | 21.6% | | 13.0% | | | 11.6x | |
| Netflix, Inc. | | United States | | 267,637,788 | | 19,996 | | | 39.4% | | 63.2% | | 17.8% | | | 10.3x | |
| Liberty Media Corp. Series C Liberty SiriusXM | | United States | | 34,418,910 | | 2,598 | | | 47.3% | | 28.9% | | 22.1% | | | 29.2x | |
| Walt Disney Company | | United States | | 218,876,515 | | 14,113 | | | 27.2% | | 16.0% | | 9.9% | | | 15.3x | |
| Warner Bros. Discovery, Inc. Series A | | United States | | 32,876,907 | | 4,867 | | | 18.2% | | 14.4% | | (6.9%) | | | 9.9x | |
| Warner Music Group Corp. Class A | | United States | | 22,041,707 | | 1,182 | | | 41.9% | | 19.6% | | 14.1% | | | 17.4x | |
| Average | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 16.4x | |
| Median | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 14.6x | |
| 30th Percentile (Low) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 10.6x | |
| 70th Percentile (High) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 17.0x | |
Supplemental Exhibit D: Market Approach – Overview of Comparable Precedent Transactions
| General Information | | | Profitability | | | Valuation Multiples | |
| Date | | Target | | | Country | | | Industry | | Deal Value
(USD mil.) | | | Enterprise Value
(USD mil.) | | EBITDA
(USD mil.) | | | EV/EBITDA | |
| 3-Jan-2022 | | Warner Music Group Corp. | | | United States | | | Music Entertainment | | 900 | | | 25,514 | | 1,017 | | | 25.1x | |
| 22-Mar-2021 | | Paramount Global | | | United States | | | Broadcasting / Media / Entertainment | | 750 | | | 73,884 | | 5,157 | | | 14.3x | |
| 25-Jan-2021 | | AMC Networks Inc. | | | United States | | | Media / Entertainment | | 994 | | | 4,477 | | 705 | | | 6.4x | |
| Average | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 15.3x | |
| Median | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 14.3x | |