Table of Contents
UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, DC 20549
Washington, DC 20549
Form 10-K
Annual Report Pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the
Securities Exchange Act of 1934
Securities Exchange Act of 1934
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2009
| Commission File Number: | 1-1063 |
Dana Holding Corporation
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 26-1531856 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (IRS Employer Identification Number) | |
| 3939 Technology Drive, Maumee, OH | 43537 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code:(419) 887-3000
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
| Common Stock, par value $0.01 per share | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
(Title of Class)
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes o No þ
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes þ No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 ofRegulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes o No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 ofRegulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporate by reference in Part III of thisForm 10-K or any amendment to thisForm 10-K. þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” inRule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| Large accelerated filer o | Accelerated filer þ | Non-accelerated filer o | Smaller reporting company o |
(Do not check if a smaller reporting company)
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined inRule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No þ
The aggregate market value of the common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant, computed by reference to the average high and low trading prices of the common stock as of the closing of trading on June 30, 2009, was approximately $128,000,000.
APPLICABLE ONLY TO ISSUERS INVOLVED IN BANKRUPTCY
PROCEEDINGS DURING THE PRECEDING FIVE YEARS:
PROCEEDINGS DURING THE PRECEDING FIVE YEARS:
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed all documents and reports required to be filed by Sections 12, 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 subsequent to the distribution of securities under a plan confirmed by a court. Yesþ Noo
APPLICABLE ONLY TO CORPORATE ISSUERS:
There were 139,421,053 shares of the registrant’s common stock outstanding at February 12, 2010.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the definitive Proxy Statement to be delivered to stockholders in connection with the Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on April 28, 2010 are incorporated by reference into Part III.
DANA HOLDING CORPORATION —FORM 10-K
FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2009
TABLE OF CONTENTS
FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2009
TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
Table of Contents
Forward-Looking Information
Statements in this report (or otherwise made by us or on our behalf) that are not entirely historical constitute “forward-looking” statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Such forward-looking statements are indicated by words such as “anticipates,” “expects,” “believes,” “intends,” “plans,” “estimates,” “projects” and similar expressions. These statements represent the present expectations of Dana Holding Corporation and its consolidated subsidiaries (Dana) based on our current information and assumptions. Forward-looking statements are inherently subject to risks and uncertainties. Our plans, actions and actual results could differ materially from our present expectations due to a number of factors, including those discussed below and elsewhere in this report (our 2009Form 10-K) and in our other filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). All forward-looking statements speak only as of the date made, and we undertake no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statement to reflect events or circumstances that may arise after the date of this report.
3
Table of Contents
PART I
(Dollars in millions, except per share amounts)
| Item 1. | Business |
General
Dana Holding Corporation (Dana), incorporated in Delaware in 2007, is headquartered in Maumee, Ohio. We are a leading supplier of axle, driveshaft, structural, sealing and thermal management products for global vehicle manufacturers. Our people design and manufacture products for every major vehicle producer in the world. At December 31, 2009, we employed approximately 24,000 people in 23 countries and operated 106 major facilities throughout the world.
As a result of the emergence of Dana Corporation (Prior Dana) from operating under Chapter 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code (Chapter 11) on January 31, 2008 (the Effective Date), Dana is the successor registrant to Prior Dana pursuant toRule 12g-3 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. The terms “Dana,” “we,” “our” and “us,” when used in this report with respect to the period prior to Dana Corporation’s emergence from Chapter 11, are references to Prior Dana and, when used with respect to the period commencing after Dana Corporation’s emergence, are references to Dana. These references include the subsidiaries of Prior Dana or Dana, as the case may be, unless otherwise indicated or the context requires otherwise.
The eleven months ended December 31, 2008 and the one month ended January 31, 2008 are distinct reporting periods as a result of our emergence from Chapter 11 on January 31, 2008. References in certain analyses of sales and other results of operations combine the two periods in order to provide additional comparability of such information.
Emergence from Reorganization Proceedings and Related Subsequent Events
Background — Dana and forty of its wholly-owned subsidiaries (collectively, the Debtors) operated their businesses as debtors in possession under Chapter 11 from March 3, 2006 (the Filing Date) until emergence from Chapter 11 on January 31, 2008 pursuant to a plan of reorganization (the Plan). The Debtors’ Chapter 11 cases (collectively, the Bankruptcy Cases) were consolidated in the United States Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York (the Bankruptcy Court) under the captionIn re Dana Corporation, et al.,CaseNo. 06-10354 (BRL). Neither Dana Credit Corporation (DCC) and its subsidiaries nor any of ournon-U.S. affiliates were Debtors.
Claims resolution — On the Effective Date, the Plan was consummated and we emerged from Chapter 11. As provided in the Plan, we issued and set aside approximately 28 million shares of Dana common stock (valued in reorganization at $640) for future distribution to holders of allowed unsecured nonpriority claims in Class 5B under the Plan. These shares are being distributed as the disputed and unliquidated claims are resolved. The claim amount related to the 28 million shares for disputed and unliquidated claims was estimated not to exceed $700. Since emergence, we have issued 23 million of the 28 million shares for allowed claims (valued in reorganization at $540), increasing the total shares issued to 94 million (valued in reorganization at $2,168) for unsecured claims of approximately $2,249. The corresponding decrease in the disputed claims reserve leaves 5 million shares (valued in reorganization at $102). The remaining disputed and unliquidated claims total approximately $96. To the extent that these remaining claims are settled for less than the 5 million remaining shares, additional incremental distributions will be made to the holders of the previously allowed general unsecured claims in Class 5B.
Capitalization at Emergence — Pursuant to the Plan, all of the issued and outstanding shares of Prior Dana common stock, par value $1.00 per share, and any other outstanding equity securities of Prior Dana, including all options and warrants, were cancelled on the Effective Date, and we began the process of issuing 100 million shares of Dana common stock, par value $0.01 per share.
4
Table of Contents
Pursuant to the Plan, we issued 2.5 million shares of 4.0% Series A Preferred Stock, par value $0.01 per share (the Series A Preferred) and 5.4 million shares of 4.0% Series B Preferred Stock, par value $0.01 per share (the Series B Preferred) on the Effective Date. See Note 7 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8 for dividend and conversion terms, dividend payments and an explanation of registration rights with respect to our preferred stock.
We entered into an exit financing facility (the Exit Facility) on the Effective Date. The Exit Facility consisted of a Term Facility Credit and Guaranty Agreement in the amount of $1,430 (the Term Facility) and a $650 Revolving Credit and Guaranty Agreement (the Revolving Facility). In November, 2008 we repaid $150 of the Term Facility and amended the terms of the Exit Facility. See Note 12 for an explanation of our financing activities.
Fresh start accounting — As required by accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (GAAP), we adopted fresh start accounting effective February 1, 2008. The financial statements for the periods ended prior to January 31, 2008 do not include the effect of any changes in our capital structure or changes in the fair value of assets and liabilities as a result of fresh start accounting. See Note 21 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8 for an explanation of the impact of emerging from reorganization and applying fresh start accounting on our financial position.
Overview of our Business
Markets
We serve three primary markets:
| • | Light vehicle market —In the light vehicle market, we design, manufacture and sell light axles, driveshafts, structural products, sealing products, thermal products and related service parts for light trucks, sport utility vehicles (SUVs), crossover utility vehicles, vans and passenger cars. | |
| • | Medium/heavy market —In the medium/heavy vehicle market, we design, manufacture and sell axles, driveshafts, chassis and side rails, ride controls and related modules and systems, engine sealing products, thermal products and related service parts for medium- and heavy-duty trucks, buses and other commercial vehicles. | |
| • | Off-Highway market —In the off-highway market, we design, manufacture and sell axles, transaxles, driveshafts, suspension components, transmissions, electronic controls, related modules and systems, sealing products, thermal products and related service parts for construction machinery and leisure/utility vehicles and outdoor power, agricultural, mining, forestry and material handling equipment and a variety of non-vehicular, industrial applications. |
Segments
Senior management and our Board of Directors review our operations in six operating segments:
| • | Four product-based operating segments sell primarily into the light vehicle market: Light Vehicle Driveline (LVD), Sealing Products (Sealing), Thermal Products (Thermal) and Structural Products (Structures). Sales in this market totaled $3,327 in 2009, with Ford Motor Company (Ford), Toyota Motor Corporation (Toyota), Nissan Motor Company (Nissan), General Motors Corp. (GM) and Hyundai Motor Company (Hyundai) among the largest customers. At December 31, 2009, these segments employed approximately 17,000 people and had 74 major facilities in 21 countries. | |
| • | Two operating segments sell into their respective medium/heavy vehicle markets: Commercial Vehicle and Off-Highway. In 2009, these segments generated sales of $1,901. In 2009, the largest Commercial Vehicle customers were PACCAR Inc (PACCAR), Navistar International Corporation (Navistar), Daimler AG (Daimler) and Oshkosh Corporation. The largest Off-Highway customers included Deere & Company (Deere), AGCO Corporation, Fiat Group and |
5
Table of Contents
| Sandvik Ab. At December 31, 2009, these two segments employed approximately 6,000 people and had 28 major facilities in 14 countries. |
| • | In addition to the segments, two additional major facilities provide administrative services and two engineering facilities support multiple segments. At December 31, 2009, corporate and other support staff totaled approximately 1,000. |
Our operating segments manufacture and market classes of similar products as shown below. See Note 19 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8 for financial information on all of these operating segments.
| Percent of | ||||||||
| Consolidated | ||||||||
Segment | Sales | Products | Market | |||||
| LVD | 39 | % | Front and rear axles, driveshafts, differentials, torque couplings and modular assemblies | Light vehicle | ||||
| Sealing | 10 | Gaskets, cover modules, heat shields and engine sealing systems | Light vehicle, medium/heavy vehicle and off-highway | |||||
| Thermal | 4 | Cooling and heat transfer products | Light vehicle, medium/heavy vehicle and off-highway | |||||
| Structures | 11 | Frames, cradles and side rails | Light and medium/heavy vehicle | |||||
| Commercial Vehicle | 20 | Axles, driveshafts, steering shafts, suspensions and tire management systems | Medium/heavy vehicle | |||||
| Off-Highway | 16 | Axles, transaxles, driveshafts and end-fittings, transmissions, torque converters and electronic controls | Off-highway | |||||
Divestitures
The Board of Directors of Prior Dana approved the divestiture of our engine hard parts, fluid products and pump products operations in 2005 and we reported these businesses as discontinued operations through their respective dates of divestiture. The trailer axle business and the assets of DCC were also approved for divestiture, but did not meet the requirements for treatment as discontinued operations, and their results were included in continuing operations. Substantially all of these operations were sold prior to 2008. See Note 22 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8 for additional information on discontinued operations.
In January 2007, we sold our trailer axle business manufacturing assets for $28 in cash and recorded an after-tax gain of $14. In March 2007, we sold our engine hard parts business, received cash proceeds of $98 and recorded an after-tax loss of $45. We incurred a loss of $5 in January 2008 for a post-closing adjustment to reinstate certain retained liabilities of this business.
In March 2007, we sold our 30% equity interest in GETRAG Getriebe-und Zahnradfabrik Hermann Hagenmeyer GmbH & Cie KG (GETRAG) to our joint venture partner, an affiliate of GETRAG, for $207 in cash. An impairment charge of $58 after tax was recorded in the fourth quarter of 2006 and an additional charge of $2 after tax was recorded in the first quarter of 2007. In August 2007, we executed an agreement relating to our remaining joint ventures with GETRAG. This agreement included the grant of a call option to GETRAG to acquire our interests in these joint ventures for $75 and our payment of GETRAG claims of $11 under certain conditions. We recorded the $11 claim in liabilities subject to compromise and as an expense in other income, net in the second quarter of 2007. In September 2008, we amended our agreement with GETRAG and reduced the call option purchase price to $60, extended the call option exercise period to September 2009 and eliminated the $11 liability. As a result of the reduced call price, we recorded an asset impairment
6
Table of Contents
charge of $15 in the third quarter of 2008 in equity in earnings of affiliates. We are now recognizing the equity in earnings of GETRAG beginning with the expiration of the call in September 2009.
In July and August 2007, we completed the sale of our fluid products hose and tubing business for aggregate cash proceeds of $84 and recorded an aggregate after-tax gain of $32. We recorded an expense of $3 in 2008 associated with a post-closing purchase price adjustment and settlement costs and related expenses. In September 2007, we completed the sale of our coupled fluid products business with the buyer assuming $18 of certain liabilities of the business at closing. We recorded an after-tax loss of $23 in connection with the sale of this business. We completed the sale of a portion of the pump products business in October 2007, generating proceeds of $7 and a nominal after-tax gain. In January 2008, we completed the sale of the remaining assets of the pump products business to Melling Tool Company, generating proceeds of $5 and an after-tax loss of $2.
During the latter part of 2008 and early 2009, we evaluated a number of strategic options in our non-driveline light vehicle businesses. We incurred costs of $18 and $10 during 2009 and 2008 in connection with the evaluation of these strategic options, primarily for professional fees, which we recorded in other income, net.
Structural Products business — In December 2009, we entered into an agreement with Metalsa S.A. de C.V. (Metalsa) to sell substantially all of the assets of our Structural Products business to Metalsa. Dana will retain a facility of this business in Longview, Texas and will continue to produce products for a large customer at this facility. Accordingly, we have not reported the Structures segment as discontinued operations. The parties expect to complete the sale of all but the Venezuelan operations in March 2010, with Venezuela being completed as soon as the necessary governmental approvals are obtained.
As a result of this agreement, we recorded $150 as an impairment of the intangible and long-lived assets in December 2009 and we recorded strategic transaction expenses of $11 associated with the sale in other income, net. The impairment loss was based on expected proceeds of $150 less projected working capital adjustments. Under the terms of our amended Term Facility, we will be required to utilize the proceeds of the sale to pay down our Term Facility debt. For a description of the Term Facility, see Note 12 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8.
Geographic
We maintain administrative and operational organizations in four regions — North America, Europe, South America and Asia Pacific — to facilitate financial and statutory reporting and tax compliance on a worldwide basis and to support our business units with regional market, customer and product strategies, assistance with business plan execution, and management of affiliate relations. Our operations are located in the following countries:
North America | Europe | South America | Asia Pacific | |||||
| Canada | Austria | Italy | Argentina | Australia | ||||
| Mexico | Belgium | Spain | Brazil | China | ||||
| United States | France | Sweden | Colombia | India | ||||
| Germany | United Kingdom | Venezuela | Japan | |||||
| Hungary | South Africa | |||||||
| Taiwan | ||||||||
| Thailand | ||||||||
Ournon-U.S. subsidiaries and affiliates manufacture and sell products similar to those we produce in the U.S. Operations outside the U.S. may be subject to a greater risk of changing political, economic and social environments, changing governmental laws and regulations, currency revaluations and market fluctuations than our domestic operations. See the discussion of risk factors in Item 1A.
7
Table of Contents
Non-U.S. sales comprised $2,826 of our 2009 consolidated sales of $5,228. Our consolidated net loss of $436 included anon-U.S. net loss of $119 in 2009. A summary of sales and long-lived assets by geographic region can be found in Note 19 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8.
Customer Dependence
We have thousands of customers around the world and have developed long-standing business relationships with many of them. Our segments in the automotive markets are largely dependent on light vehicle Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) customers, while our Commercial Vehicle and Off-Highway segments have a broader and more geographically diverse customer base, including machinery and equipment manufacturers in addition to medium- and heavy-duty vehicle OEM customers.
Ford was the only individual customer accounting for 10% or more of our consolidated sales in 2009. As a percentage of total sales from continuing operations, our sales to Ford were approximately 20% in 2009, 17% in 2008 and 23% in 2007, and our sales to Toyota, our second largest customer, were approximately 6% in 2009, 7% in 2008 and 10% in 2007.
PACCAR, GM and Navistar were our third, fourth and fifth largest customers. PACCAR, GM, Navistar, Chrysler Group LLC (Chrysler), Daimler, Hyundai, Nissan and Deere, collectively accounted for approximately 29% of our revenues in 2009.
Loss of all or a substantial portion of our sales to Ford or other large volume customers would have a significant adverse effect on our financial results until such lost sales volume could be replaced and there is no assurance that any such lost volume would be replaced. We continue to work to diversify our customer base and geographic footprint.
Sources and Availability of Raw Materials
We use a variety of raw materials in the production of our products, including steel and products containing steel, stainless steel, forgings, castings and bearings. Other commodity purchases include aluminum, brass, copper and plastics. These materials are usually available from multiple qualified sources in quantities sufficient for our needs. However, some of our operations remain dependent on single sources for certain raw materials.
While our suppliers have generally been able to support our needs, our operations may experience shortages and delays in the supply of raw material from time to time, due to strong demand, capacity limitations and other problems experienced by the suppliers. A significant or prolonged shortage of critical components from any of our suppliers could adversely impact our ability to meet our production schedules and to deliver our products to our customers in a timely manner.
High steel and other raw material costs have had a major adverse effect on our results of operations in recent years. However, during the past few years, we successfully implemented pricing agreements with many of our customers providing adjustments for significant increases or decreases in steel and certain other raw materials costs. Where formal agreements are not in place, we have generally been successful in the past in implementing price adjustments to compensate for inflationary material cost increases. Adjustments may not result in full recovery of cost increases and there may be time lags in recovery of these costs.
Seasonality
Our businesses are generally not seasonal. However, in the light vehicle market, our sales are closely related to the production schedules of our OEM customers and, historically, those schedules have been weakest in the third quarter of the year due to a large number of model year change-overs that occur during this period. Additionally, third-quarter production schedules in Europe are typically
8
Table of Contents
impacted by the summer holiday schedules and fourth-quarter production is affected globally by year end holidays.
Backlog
Our products are generally not sold on a backlog basis since most orders may be rescheduled or modified by our customers at any time. Our product sales are dependent upon the number of vehicles that our customers actually produce as well as the timing of such production. A substantial amount of the new business we are awarded by OEMs is granted well in advance of a program launch. These awards typically extend through the life of the given program. We estimate future revenues from new business on the projected volume under these programs.
Competition
Within each of our markets, we compete with a variety of independent suppliers and distributors, as well as with the in-house operations of certain OEMs. With a renewed focus on product innovation, we differentiate ourselves through: efficiency and performance; materials and processes; sustainability; and product extension.
Light vehicle market —The principal LVD competitors include ZF Friedrichshafen AG (ZF Group), GKN plc, American Axle & Manufacturing (American Axle), Toyota, Magna International Inc. (Magna), Wanxiang Group Corporation (Wanxiang), Unisia Steering Systems (Unisia), IFA Group (acquired Rotarian GmbH), GETRAG and the captive operations of various truck and auto manufacturers (e.g., Chrysler and Ford).
Our principal Structures competitors include Magna, Maxion Sistemas Automotivos Ltda., Metalsa, Tower Automotive Inc. and Martinrea International Inc.
Our principal Sealing competitors include ElringKlinger Ag, Federal-Mogul Corporation and Freudenberg NOK Group.
Thermal competitors include Behr GmbH & Co. KG, Modine Manufacturing Company, Valeo Group and Denso Corporation.
Medium/heavy vehicle market —Our principal Commercial Vehicle competitors include ArvinMeritor, American Axle, Hendrickson (a subsidiary of the Boler Group), Klein Products Inc. and OEMs’ vertically integrated operations. Structures, Sealing and Thermal competitors in this market are the same as in the light vehicle market.
Off-highway market —Our major competitors in the Off-Highway segment include Carraro Group, ZF Group, GKN, Kessler + Co. and certain OEMs’ vertically integrated operations. Sealing and Thermal competition in this market is similar to their competition in the other markets above.
Patents and Trademarks
Our proprietary axle, driveshaft, structural, sealing and thermal product lines have strong identities in the markets we serve. Throughout these product lines, we manufacture and sell our products under a number of patents that have been obtained over a period of years and expire at various times. We consider each of these patents to be of value and aggressively protect our rights throughout the world against infringement. We are involved with many product lines, and the loss or expiration of any particular patent would not materially affect our sales and profits.
We own or have licensed numerous trademarks that are registered in many countries, enabling us to market our products worldwide. For example, our Spicer®, Victor Reinz®, Parish® and Long® trademarks are widely recognized in their market segments.
9
Table of Contents
Research and Development
From our introduction of the automotive universal joint in 1904, we have been focused on technological innovation. Our objective is to be an essential partner to our customers and we remain highly focused on offering superior product quality, technologically advanced products, world-class service and competitive prices. To enhance quality and reduce costs, we use statistical process control, cellular manufacturing, flexible regional production and assembly, global sourcing and extensive employee training.
We engage in ongoing engineering, research and development activities to improve the reliability, performance and cost-effectiveness of our existing products and to design and develop innovative products that meet customer requirements for new applications. We are integrating related operations to create a more innovative environment, speed product development, maximize efficiency and improve communication and information sharing among our research and development operations. At December 31, 2009, we had five major technical centers. Our engineering and research and development costs were $119 in 2009, $193 in 2008 and $189 in 2007. A substantial portion of these costs relates to existing products.
These developments continue to improve customer value. For all of our markets, this means drivelines with higher torque capacity, reduced weight and improved efficiency. End-use customers benefit by having vehicles with better fuel economy and reduced cost of ownership. We are also developing a number of sealing and thermal control products for vehicular and other applications that will assist fuel cell, battery and hybrid vehicle manufacturers in making their technologies commercially viable in mass production.
Employment
Our worldwide employment was approximately 24,000 at December 31, 2009.
Environmental Compliance
We make capital expenditures in the normal course of business as necessary to ensure that our facilities are in compliance with applicable environmental laws and regulations. The cost of environmental compliance has not been a material part of capital expenditures and did not have a materially adverse effect on our earnings or competitive position in 2009.
In connection with our Chapter 11 reorganization, we settled certain pre-petition claims related to environmental matters. See “Contingencies” in Item 7 and the discussion of contingencies in Note 15 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8.
Available Information
Our annual reports onForm 10-K, quarterly reports onForm 10-Q, current reports onForm 8-K and amendments to those reports filed pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (Exchange Act) are available, free of charge, on or through our Internet website(http://www.dana.com/investors) as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such materials with, or furnish them to, the SEC. We also post ourCorporate Governance Guidelines, Standards of Business Conduct for Members of the Board of Directors, Board Committee membership lists and charters,Standards of Business Conductand other corporate governance materials at this website address. Copies of these posted materials are available in print, free of charge, to any stockholder upon request from: Investor Relations, Dana Holding Corporation, P.O. Box 1000, Maumee, Ohio 43537, or via telephone at(419) 887-5159 ore-mail at InvestorRelations@dana.com. The inclusion of our website address in this report is an inactive textual reference only and is not intended to include or incorporate by reference the information on our website into this report.
10
Table of Contents
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors |
We are impacted by events and conditions that affect the light vehicle, medium/heavy vehicle and off-highway markets that we serve, as well as by factors specific to Dana. Among the risks that could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations are the following, many of which are interrelated.
Risk Factors Related to the Markets We Serve
Continuing negative economic conditions in the United States and elsewhere could have a substantial effect on our business.
Our business is tied to general economic and industry conditions as demand for vehicles depends largely on the strength of the economy, employment levels, consumer confidence levels, the availability and cost of credit and the cost of fuel. Current economic conditions have reduced demand for most vehicles. This has had and could continue to have a substantial impact on our business.
While we expect a modest economic recovery in 2010, negative economic conditions could continue to impact our business. The overall market for new vehicle sales in the United States declined significantly in 2009 and while we expect partial recovery in 2010, our customers could reduce their vehicle production in North America and, as a result, demand for our products would continue to be adversely affected.
Demand in ournon-U.S. markets could also decline in response to overall economic conditions, including changes in the global economy, the limited availability of credit and fuel costs.
Our customers and suppliers could experience severe economic constraints in the future, including bankruptcy. Adverse global economic conditions and further deterioration could have a material adverse impact on our financial position and results of operations.
We could be adversely impacted by the loss of any of our significant customers, changes in their requirements for our products or changes in their financial condition.
We are reliant upon sales to several significant customers. Sales to our ten largest customers accounted for 56% of our overall revenue in 2009. In the U.S., the light vehicle industry faces an uncertain future. GM and Chrysler have already required assistance through government loans and other companies in the light vehicle industry may seek government assistance. Changes in our business relationships with any of our large customers or in the timing, size and continuation of their various programs could have a material adverse impact on us.
The loss of any of these customers, the loss of business with respect to one or more of their vehicle models on which we have a high component content, or a further significant decline in the production levels of such vehicles would continue to negatively impact our business, results of operations and financial condition. We are continually bidding on new business with these customers, as well as seeking to diversify our customer base, but there is no assurance that our efforts will be successful. Further, to the extent that the financial condition of our largest customers deteriorates, including possible bankruptcies, mergers or liquidations, or their sales otherwise decline, our financial position and results of operations could be adversely affected.
We may be adversely impacted by changes in international legislative and political conditions.
We operate in 23 countries around the world and we depend on significant foreign suppliers and vendors. Legislative and political activities within the countries where we conduct business, particularly in emerging markets and less developed countries, could adversely impact our ability to operate in those countries. The political situation in some countries creates a risk of the seizure of our assets. The political environment in some of these countries could create instability in our contractual relationships with no effective legal safeguards for resolution of these issues.
11
Table of Contents
We may be adversely impacted by the strength of the U.S. dollar relative to other currencies in the other countries in which we do business.
Approximately 54% of our sales in 2009 were from operations located in countries other than the U.S. Currency variations can have an impact on our results (expressed in U.S. dollars). Currency variations can also adversely affect margins on sales of our products in countries outside of the U.S. and margins on sales of products that include components obtained from affiliates or other suppliers located outside of the U.S. While the U.S. dollar has generally weakened over the past year, strengthening of the U.S. dollar against the euro and many other currencies of countries in which we have operations could adversely affect our results reported in U.S. dollars. We use a combination of natural hedging techniques and financial derivatives to protect against foreign currency exchange rate risks. Such hedging activities may be ineffective or may not offset more than a portion of the adverse financial impact resulting from currency variations.
We may be adversely impacted by new laws, regulations or policies of governmental organizations related to increased fuel economy standards and reduced greenhouse gas emissions, or changes in existing ones.
It is anticipated that the number and extent of governmental regulations related to fuel economy standards and greenhouse gas emissions, and the costs to comply with them, will increase significantly in the future. In the U.S., the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 requires significant increases in the Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) requirements applicable to cars and light trucks beginning with the 2011 model year. In addition, a growing number of states are adopting regulations that establish carbon dioxide emission standards that effectively impose similarly increased fuel economy standards for new vehicles sold in those states. Compliance costs for our customers could require them to alter their spending, research and development plans, curtail sales, cease production or exit certain market segments characterized by lower fuel efficiency. Any of these actions could adversely affect our financial position and results of operations.
Company-Specific Risk Factors
We have taken, and continue to take, cost-reduction actions. Although our process includes planning for potential negative consequences, the cost-reduction actions may expose us to additional production risk and could adversely affect our sales, profitability and ability to attract and retain employees.
We have been reducing costs in all of our businesses and have discontinued product lines, exited businesses, consolidated manufacturing operations and reduced our employee population. The impact of these cost-reduction actions on our sales and profitability may be influenced by many factors including our ability to successfully complete these ongoing efforts, our ability to generate the level of cost savings we expect or that are necessary to enable us to effectively compete, delays in implementation of anticipated workforce reductions, decline in employee morale and the potential inability to meet operational targets due to our inability to retain or recruit key employees.
Our amended Exit Facility contains covenants that may constrain our growth.
The amended financial covenants in our Exit Facility may hinder our ability to finance future operations, make potential acquisitions or investments, meet capital needs or engage in business activities that may be in our best interest such as future issuances of our common stock. These restrictions could hinder us from responding to changing business and economic conditions and from implementing our business plan.
We may be unable to comply with the financial covenants in our amended Exit Facility.
The financial covenants in our amended Exit Facility require us to achieve certain financial ratios based on levels of earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization and certain levels of restructuring and reorganization related costs (Adjusted EBITDA), as defined in the amended Exit
12
Table of Contents
Facility. In November 2008, certain covenants of the Exit Facility were amended to allow for future compliance. A failure to comply with these or other covenants in the amended Exit Facility could, if we were unable to obtain a waiver or another amendment of the covenant terms, cause an event of default that could cause our loans under the amended Exit Facility to become immediately due and payable. In addition, additional waivers or amendments could substantially increase our cost of borrowing.
We operate as a holding company and depend on our subsidiaries for cash to satisfy the obligations of the holding company.
Dana Holding Corporation is a holding company. Our subsidiaries conduct all of our operations and own substantially all of our assets. Our cash flow and our ability to meet our obligations depends on the cash flow of our subsidiaries. In addition, the payments of funds in the form of dividends, intercompany payments, tax sharing payments and otherwise may be subject to restrictions under the laws of the countries of incorporation of our subsidiaries.
Labor stoppages or work slowdowns at Dana, key suppliers or our customers could result in a disruption in our operations and have a material adverse effect on our business.
We and our customers rely on our respective suppliers to provide parts needed to maintain production levels. We all rely on workforces represented by labor unions. Workforce disputes that result in work stoppages or slowdowns could disrupt operations of all of these businesses which in turn could have a material adverse effect on demand for the products we supply our customers.
We could be adversely affected if we are unable to recover portions of our commodity costs (including costs of steel, other raw materials and energy) from our customers.
We continue to work with our customers to recover a greater portion of our material costs. While we have achieved some success in these efforts to date, there is no assurance that commodity costs will not adversely impact our profitability in the future.
We could be adversely affected if we experience shortages of components from our suppliers.
A substantial portion of our annual cost of sales is driven by the purchase of goods and services. To manage and reduce these costs, we have been consolidating our supplier base. As a result, we are dependent on single sources of supply for some components of our products. We select our suppliers based on total value (including price, delivery and quality), taking into consideration their production capacities and financial condition, and we expect that they will be able to support our needs. However, there is no assurance that adverse financial conditions, including bankruptcies of our suppliers, reduced levels of production or other problems experienced by our suppliers will not result in shortages or delays in their supply of components to us or even in the financial collapse of one or more such suppliers. If we were to experience a significant or prolonged shortage of critical components from any of our suppliers, particularly those who are sole sources, and were unable to procure the components from other sources, we would be unable to meet our production schedules for some of our key products and to ship such products to our customers in a timely fashion, which would adversely affect our revenues, margins and customer relations.
We could be adversely impacted by the costs of environmental, health, safety and product liability compliance.
Our operations are subject to environmental laws and regulations in the U.S. and other countries that govern emissions to the air; discharges to water; the generation, handling, storage, transportation, treatment and disposal of waste materials and the cleanup of contaminated properties. Historically, other than the EPA settlement for Hamilton (see Note 15 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8), environmental costs related to our former and existing operations have not been
13
Table of Contents
material. However, there is no assurance that the costs of complying with current environmental laws and regulations, or those that may be adopted in the future will not increase and adversely impact us.
There is also no assurance that the costs of complying with current laws and regulations, or those that may be adopted in the future, that relate to health, safety and product liability matters will not adversely impact us. There is also a risk of warranty and product liability claims, as well as product recalls, in the commercial and automotive vehicle industry if our products fail to perform to specifications or cause property damage, injury or death. (See Note 16 of our consolidated financial statements in Item 8 for additional information on warranties.)
Our ability to utilize our net operating loss carryforwards may be limited.
Net operating tax loss carryforwards (NOLs) approximating $1,600 were available at December 31, 2009 to reduce future U.S income tax liabilities. Our ability to utilize these NOLs may be limited as a result of certain change of control provisions of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code (IRC). We emerged from Chapter 11 with NOLs of approximately $580, which are limited to annual utilization of $85. The additional NOLs accumulated since emergence are not subject to limitation as of the end of 2009. However, there can be no assurance that trading in our shares will not effect another change in control under the IRC which would further limit our ability to utilize our available NOLs. Such limitations may cause us to pay income taxes earlier and in greater amounts than would be the case if the NOLs were not subject to limitation.
Risk Factors Related to our Securities
Volatility is possible in the market price of our common stock.
The market price of our common stock has been and may continue to be volatile. As the price of our common stock on the New York Stock Exchange constantly changes, it is impossible to predict whether the price of our common stock will rise or fall. Trading prices of our common stock will be influenced by our financial condition, operating results and prospects and by economic, financial and other factors, such as prevailing interest rates, interest rate volatility and changes in the automotive industry and competitors. In addition, general market conditions or our issuance of substantial amounts of common stock could affect the price of shares of our common stock.
Provisions in our Restated Certificate of Incorporation, Bylaws and Shareholders Agreement may discourage a takeover attempt.
Certain provisions of our Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Bylaws, as well as the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware, may have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a change in control of Dana. Such provisions, including those regulating the nomination of directors, limiting who may call special stockholders’ meetings and eliminating stockholder action by written consent, together with the terms of our outstanding preferred stock, may make it more difficult for other persons, without the approval of our board of directors, to make a tender offer or otherwise acquire substantial amounts of common stock or to launch other takeover attempts that a stockholder might consider to be in such stockholder’s best interest. In addition, our Shareholders Agreement with the current holders of our Series A Preferred Stock provides that such holders will have approval rights with respect to certain corporate transactions, including certain transactions involving a change of control of Dana. The existence of such approval rights could discourage a takeover attempt.
Holders of our Series A Preferred Stock have limited approval rights with respect to our business and may have conflicts of interest with holders of our common stock in the future.
Under the terms of our Shareholders Agreement, the current holders of our Series A Preferred Stock have limited approval rights with respect to certain corporate transactions, including an issuance of our common stock at a price below the current market price (as defined in the Shareholders
14
Table of Contents
Agreement). There can be no assurance that they will waive their rights or grant approvals in respect of future transactions that may be in the best interests of the holders of our common stock.
Our adoption of fresh start accounting could result in additional asset impairments and may make comparisons of our financial position and results of operations to prior periods more difficult.
As required by GAAP, we adopted fresh start accounting effective February 1, 2008. This adoption increased the value of our long-lived assets. Subsequent developments in our markets resulted in impairments of the fresh start values during 2008 and 2009 and could result in additional impairments in future periods. Since fresh start accounting required us to adjust all of our assets and liabilities to their respective fair values, the consolidated financial statements for periods after the emergence will not be comparable to those of the periods prior to the emergence which are presented on an historical basis. Fresh start accounting may make it more difficult to compare our post-emergence financial position and results of operations to those in the pre-emergence periods which could limit interest and investment in our stock.
| Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments |
-None-
| Item 2. | Properties |
| North | South | Asia/ | ||||||||||||||||||
Type of Facility | America | Europe | America | Pacific | Total | |||||||||||||||
| Administrative Offices | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Engineering — Multiple Groups | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
LVD | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing/Distribution | 17 | 3 | 7 | 12 | 39 | |||||||||||||||
Sealing | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing/Distribution | 8 | 3 | 1 | 12 | ||||||||||||||||
| Engineering | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
Thermal | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing/Distribution | 6 | 2 | 8 | |||||||||||||||||
| Engineering | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
Structures | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing/Distribution | 5 | 4 | 2 | 11 | ||||||||||||||||
Commercial Vehicle | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing/Distribution | 9 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 16 | |||||||||||||||
| Engineering | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
Off-Highway | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing/Distribution | 3 | 7 | 2 | 12 | ||||||||||||||||
Total Dana | 55 | 19 | 12 | 20 | 106 | |||||||||||||||
As of December 31, 2009, we operated in 23 countries and had 106 major manufacturing/ distribution, engineering and office facilities worldwide. While we lease all of 38 and part of five of these manufacturing and distribution operations, we own the remainder of our facilities. We believe that all of our property and equipment is properly maintained. Prior to our emergence from Chapter 11, there was significant excess capacity in our facilities based on our manufacturing and distribution needs, especially in the U.S. As part of our reorganization initiatives, we took significant steps to close facilities and we continued to evaluate capacity requirements in 2009 in light of market conditions.
15
Table of Contents
Our corporate headquarters facilities are located in Maumee, Ohio. This facility and other facilities in the Toledo, Ohio area house functions that have global responsibility for finance and accounting, treasury, risk management, legal, human resources, procurement and supply chain management, communications and information technology. Our obligations under the amended Exit Facility are secured by, among other things, mortgages on all the domestic facilities that we own.
| Item 3. | Legal Proceedings |
As discussed in Notes 20 and 21 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8, we emerged from Chapter 11 on January 31, 2008. Pursuant to the Plan, the pre-petition ownership interests in Prior Dana were cancelled and all of the pre-petition claims against the Debtors, including claims with respect to debt, pension and postretirement healthcare obligations and other liabilities, were addressed in connection with our emergence from Chapter 11.
As previously reported and as discussed in Note 15 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8, we are a party to various pending judicial and administrative proceedings that arose in the ordinary course of business.
After reviewing the currently pending lawsuits and proceedings (including the probable outcomes, reasonably anticipated costs and expenses, availability and limits of our insurance coverage and surety bonds and our established reserves for uninsured liabilities), we do not believe that any liabilities that may result from these proceedings are reasonably likely to have a material adverse effect on our liquidity, financial condition or results of operations.
| Item 4. | Submission of Matters to a Vote of Security Holders |
We did not submit any matters for a stockholder vote in the fourth quarter of 2009.
16
Table of Contents
PART II
| Item 5. | Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
Market Information —Our common stock trades on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol “DAN.” The stock began trading on such exchange on February 1, 2008, in conjunction with our emergence from Chapter 11 proceedings.
Because the value of one share of Prior Dana common stock bears no relation to the value of one share of Dana common stock, only the trading prices of Dana common stock following its listing on the New York Stock Exchange are set forth below. The following table shows the high and low sales prices per share of Dana common stock during 2008 and 2009.
| Quarterly | ||||||||
High and Low Sales Prices per Share of Dana Common Stock | High Price | Low Price | ||||||
| As reported by the New York Stock Exchange: | ||||||||
| First Quarter 2008 (beginning February 1, 2008) | $ | 13.30 | $ | 8.50 | ||||
| Second Quarter 2008 | 12.65 | 5.10 | ||||||
| Third Quarter 2008 | 7.49 | 4.10 | ||||||
| Fourth Quarter 2008 | 4.83 | 0.34 | ||||||
| First Quarter 2009 | 1.16 | 0.19 | ||||||
| Second Quarter 2009 | 2.75 | 0.44 | ||||||
| Third Quarter 2009 | 7.44 | 1.17 | ||||||
| Fourth Quarter 2009 | 11.25 | 5.35 | ||||||
Holders of Common Stock —The number of stockholders of record of our common stock on February 1, 2010 was approximately 5,600.
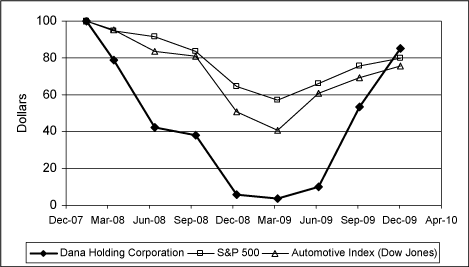
Stockholder Return —The following graph shows the quarterly cumulative total stockholder return for our common stock during the period from February 1, 2008 to December 31, 2009. Five year historical data is not presented since we emerged from Chapter 11 on January 31, 2008 and the stock performance of Dana is not comparable to the stock performance of Prior Dana. The graph also shows the cumulative returns of the S&P 500 Index and the S&P Global Auto Parts Index. The comparison assumes $100 was invested on February 1, 2008 (the date our new common stock began trading on the NYSE). Each of the indices shown assumes that all dividends paid were reinvested.
17
Table of Contents
Performance Chart
Index
| Date | 2/1/08 | 3/31/08 | 6/30/08 | 9/30/08 | 12/31/08 | 3/31/09 | 6/30/09 | 9/30/09 | 12/31/09 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dana Holding Corporation | $ | 100.00 | 78.74 | 42.13 | 38.11 | 5.83 | 3.62 | 10.08 | 53.62 | 85.35 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S&P 500 | $ | 100.00 | 94.79 | 91.73 | 83.58 | 64.73 | 57.18 | 65.88 | 75.75 | 79.91 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Automotive Index (Dow Jones) | $ | 100.00 | 95.13 | 83.58 | 80.69 | 50.83 | 40.54 | 61.09 | 69.46 | 75.84 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends —We did not declare or pay any common stock dividends during 2008 or 2009. The terms of our amended Exit Facility restrict the payment of dividends on shares of common stock, and we do not anticipate paying any such dividends at this time.
Issuer’s Purchases of Equity Securities —The following table presents information with respect to repurchases of common stock made by us during the quarter ended December 31, 2009. These shares were delivered to us by employees as payment for withholding taxes due upon the distribution or exercise of stock awards.
| Total Number of | ||||||||||||||||
| Shares Purchased as | Maximum Number of | |||||||||||||||
| Total Number | Average | Part of Publicly | Shares that May Yet | |||||||||||||
| of Shares | Price Paid | Announced Plans or | be Purchased Under | |||||||||||||
Period | Purchased | per Share | Programs | the Plans or Programs | ||||||||||||
| 10/1/09-10/31/09 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| 11/1/09-11/30/09 | 43,168 | $ | 5.67 | — | — | |||||||||||
| 12/1/09-12/31/09 | 50,931 | $ | 9.26 | — | — | |||||||||||
Annual Meeting —We will hold an annual meeting of stockholders on April 28, 2010.
18
Table of Contents
| Item 6. | Selected Financial Data |
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 5,228 | $ | 7,344 | $ | 751 | $ | 8,721 | $ | 8,504 | $ | 8,611 | |||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations before income taxes | $ | (454 | ) | $ | (549 | ) | $ | 914 | $ | (387 | ) | $ | (571 | ) | $ | (285 | ) | ||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations | $ | (436 | ) | $ | (667 | ) | $ | 717 | $ | (423 | ) | $ | (611 | ) | $ | (1,169 | ) | ||||||||
| Loss from discontinued operations | (4 | ) | (6 | ) | (118 | ) | (121 | ) | (434 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Effect of change in accounting | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | (436 | ) | (671 | ) | 711 | (541 | ) | (732 | ) | (1,599 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Less: Noncontrolling interests net income (loss) | (5 | ) | 6 | 2 | 10 | 7 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to the parent company | $ | (431 | ) | $ | (677 | ) | $ | 709 | $ | (551 | ) | $ | (739 | ) | $ | (1,605 | ) | ||||||||
| Income (loss) per share from continuing operations available to parent company stockholders | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | (4.19 | ) | $ | (7.02 | ) | $ | 4.77 | $ | (2.89 | ) | $ | (4.11 | ) | $ | (7.86 | ) | ||||||||
| Diluted | $ | (4.19 | ) | $ | (7.02 | ) | $ | 4.75 | $ | (2.89 | ) | $ | (4.11 | ) | $ | (7.86 | ) | ||||||||
| Loss per share from discontinued operations attributable to parent company stockholders | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | — | $ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.79 | ) | $ | (0.81 | ) | $ | (2.90 | ) | ||||||||
| Diluted | $ | — | $ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.79 | ) | $ | (0.81 | ) | $ | (2.90 | ) | ||||||||
| Net income per share from effect of change in accounting attributable to parent company stockholders | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diluted | $ | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) per share available to parent company stockholders | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | (4.19 | ) | $ | (7.06 | ) | $ | 4.73 | $ | (3.68 | ) | $ | (4.92 | ) | $ | (10.73 | ) | ||||||||
| Diluted | $ | (4.19 | ) | $ | (7.06 | ) | $ | 4.71 | $ | (3.68 | ) | $ | (4.92 | ) | $ | (10.73 | ) | ||||||||
| Cash dividends per common share | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 0.37 | |||||||||||||
Common Stock Data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average common shares outstanding (number in millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | 110 | 100 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Diluted | 110 | 100 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 151 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Stock price | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| High | $ | 11.25 | $ | 13.30 | $ | 2.51 | $ | 8.05 | $ | 17.56 | |||||||||||||||
| Low | 0.19 | 0.34 | 0.02 | 0.65 | 5.50 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Note: Information for Prior Dana is not comparable to the information shown for Dana due to our emergence from Chapter 11 on January 31, 2008.
19
Table of Contents
| As of December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | |||||||||||||||||
Summary of Financial Position | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 5,064 | $ | 5,607 | $ | 6,425 | $ | 6,664 | $ | 7,358 | |||||||||||
| Short-term debt | 34 | 70 | 1,183 | 293 | 2,578 | ||||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt | 969 | 1,181 | 19 | 722 | 67 | ||||||||||||||||
| Liabilities subject to compromise | 3,511 | 4,175 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Preferred stock | 771 | 771 | |||||||||||||||||||
Common stock, additionalpaid-in-capital, accumulated deficit and accumulated other comprehensive loss | 908 | 1,257 | (782 | ) | (834 | ) | 545 | ||||||||||||||
| Total parent company stockholders’ equity (deficit) | $ | 1,679 | $ | 2,028 | $ | (782 | ) | $ | (834 | ) | $ | 545 | |||||||||
| Book value per share | $ | 15.24 | $ | 20.28 | $ | (5.22 | ) | $ | (5.55 | ) | $ | 3.63 | |||||||||
Note: Information for Prior Dana is not comparable to the information shown for Dana due to our emergence from Chapter 11 on January 31, 2008.
| Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Dollars in millions) |
Management’s discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with the financial statements and accompanying notes in Item 8.
Management Overview
Dana Holding Corporation (Dana) is a world leader in the supply of axles; driveshafts; and structural, sealing and thermal-management products; as well as genuine service parts. Our customer base includes virtually every major vehicle manufacturer in the global light vehicle, commercial vehicle, and off-highway markets. Headquartered in Maumee, Ohio, Dana was incorporated in Delaware in 2007. As of December 31, 2009, we employed approximately 24,000 people and owned or leased 106 major facilities in 23 countries around the world.
We are committed to continuing to diversify our product offerings, customer base and geographic footprint and minimizing our exposure to individual market and segment declines. In 2009, North American operations accounted for 51% of our revenue, while our operations throughout the rest of the world accounted for 49%. Light vehicle products accounted for 64% of our global revenues, with commercial vehicle and off-highway products representing 36%.
Our Internet address is www.dana.com. The inclusion of our website address in this report is an inactive textual reference only, and is not intended to include or incorporate by reference the information on our website into this report.
Business Strategy
We continue to evaluate the strategy for each of our operating segments and to focus on driving operational improvements and restructuring our operations to improve profitability. In 2008, we began implementing the Dana Operating System — an operational excellence system patterned after the Toyota production system — in our manufacturing facilities. The lean operational standards and global metrics rolled out through this system were instrumental in helping us achieve the significant cost reductions in 2009 that enabled us to largely offset the effects of substantially lower production levels. Driving our cost structure down and improving our manufacturing efficiency will be critical to our future success as lower production levels will continue to be a major challenge affecting our business.
20
Table of Contents
Our business strategies will increasingly be directed at opportunities for profitably growing the business. Over the past two years, we’ve worked with our customers to address program pricing. The improvements on this front, combined with reductions to our cost structure, have improved the underlying profitability of our major customer programs. These operational improvements, along with the actions we took in 2009 to reduce debt and strengthen our cash position through an equity offering, significantly improved our financial position. As a result, we are better positioned today to pursue attractive growth opportunities in a number of our businesses, particularly outside North America. Our growth strategies include reinvigorating our product portfolio and capitalizing on technology advancement opportunities. Material advancements are playing a key role in this endeavor, with an emphasis on research and development of efficient technologies such as lightweight, high-strength aluminum applications currently in demand. Further, we recently announced the consolidation of our Heavy Vehicle products North American engineering centers in Kalamazoo, MI and Statesville, NC with our Light Vehicle engineering center in Maumee, OH. A principal reason for this move was the opportunity to better share technologies among our businesses.
As we drive additional operational improvements, restructure the businesses and pursue growth opportunities, we intend to do so with a discipline that ensures continued improvement in profitability and maintaining a strong balance sheet.
Sale of the Structural Products Business
In keeping with the strategy of continually evaluating our businesses, we announced in December 2009 that we had signed an agreement to sell substantially all of the assets of our Structural Products business to Metalsa, S.A. de C.V., the largest vehicle frame and structures supplier in Mexico. We will retain and continue to operate our Longview, TX Structural Products operation. The parties expect to complete the sale of all but the Venezuelan operations in March 2010, with Venezuela being completed as soon as the necessary governmental approvals are obtained. Our Structural Products business had 2009 external sales of $592 and Segment EBITDA of $35.
Segments
We manage our operations globally through six operating segments. Our products in the light vehicle market primarily support light vehicle original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) with products for light trucks, sport utility vehicles, crossover utility vehicles, vans and passenger cars. The operating segments in the light vehicle markets are: LVD, Structures, Sealing and Thermal. As of January 1, 2009, the Light Axle and Driveshaft segments were combined in line with our new management structure into the LVD segment with certain operations from these former segments moving to our Commercial Vehicle and Off-Highway segments.
Two operating segments, Commercial Vehicle and Off-Highway, support the OEMs of medium-duty(Classes 5-7) and heavy-duty (Class 8) commercial vehicles (primarily trucks and buses) and off-highway vehicles (primarily wheeled vehicles used in construction and agricultural applications).
We revised our definition of segment earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization (Segment EBITDA) in the first quarter of 2009. See Note 19 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8.
Trends in Our Markets
Light Vehicle Markets
Rest of the world — Markets outside of North America will take on increasing importance for us as they experience greater growth. During 2009, overall global economic weakness impacted light vehicle production in these markets, just as it has in North America. Light vehicle production outside of North America of around 48 million units in 2009, was about 8% lower than 2008. Outside of North America, the production decline was most significant in Europe where production levels were down
21
Table of Contents
about 20% from 2008. In South America production was down around 2% and Asia Pacific down about 1%. Signs of improving market conditions were evident in the fourth quarter of 2009. In each of these three regions, fourth quarter production levels were the strongest of any quarter during 2009. For 2010, our current outlook for light vehicle markets outside North America is unit production of around51-54 million. We expect European production in 2010 to be flat to up around 4% as compared to 2009, with the other two regions being somewhat stronger — South America up in the 7-12% range and Asia Pacific 9-16% higher than 2009. (Source: Global Insight and CSM Worldwide).
North America — Production levels in the North American markets were negatively impacted by overall economic conditions beginning in the second half of 2008 and continuing through 2009. Adding to the market challenges were bankruptcy reorganizations by two of the major North American automakers — GM and Chrysler. As a consequence, North American light vehicle production of about 8.5 million units in 2009 was about 32% lower than 2008. In the light truck segment of the market where more of our programs are focused, 2009 production was down about 29%. While down significantlyyear-over-year, production levels increased dramatically during the second half of 2009 as GM and Chrysler both emerged from relatively short bankruptcy reorganizations and improving market and overall economic conditions led to increased vehicle sales. Second half 2009 light vehicle unit production was around 5 million units, nearly 1.5 times first half 2009 production levels. (Source: Global Insight and CSM Worldwide).
North American light vehicle industry inventory levels have improved from the end of 2008. The days supply of total light vehicles in North America was 53 at December 31, 2009, down from 93 at the end of 2008. Light truck inventory was 49 days at December 31, 2009, down from 86 days at December 31, 2008. With the reduction that has occurred, inventory levels at the end of 2009 are more in line with historical norms. As such, near-term production levels are likely to be driven more directly by vehicle sales. (Source: Ward’s Automotive).
While the overall economic environment continues to be somewhat fragile, we expect the improving conditions during the second half of 2009 to carry into 2010. We expect 2010 North American light vehicle production to be around 10.4 to 10.8 million units, an increase of22-26% over 2009. We believe the strongest increases will be in passenger car production levels. As we look at our primarypick-up and SUV light truck programs, we are forecasting production level increases in the11-22% range.
Rapid Technology Changes
On May 19, 2009, the U.S. government announced plans for a new national fuel economy policy. The program, which still requires U.S. Congressional approval, covers model years2012-2016 and would increase Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards by five percent each year through 2016. The proposal requires that passenger vehicles achieve an industry standard of 35.5 miles per gallon by 2016, an average increase of eight miles per gallon per vehicle from the 2011 requirements. While providing the regulatory certainty and predictability of nationwide standards versus previously proposedstate-by-state standards, this change will require a rapid response by automakers. It also represents an opportunity for suppliers that are able to produce highly engineered products that will help OEMs quickly meet these stricter carbon-emission and fuel-economy requirements.
The National Academy of Sciences estimates that fuel economy could be increased by 50 percent without sacrificing vehicle size, performance, or safety. Midsize cars could average 41 miles per gallon and large pickups nearly 30 miles per gallon, all using existing technology to develop new components and applications. Suppliers such as Dana that are able to provide these new components and applications will fare best in this new environment. Our materials and process competencies, product enhancements and new product technologies can provide OEMs with needed vehicle weight reduction, friction management and improved engine performance, assisting them in their efforts to meet the new and more stringent CAFE requirements.
22
Table of Contents
Medium/heavy Vehicle Markets
Rest of the world — Outside of North America, medium- and heavy-duty truck production has been severely impacted by the overall global economic weakness. After increasing to about 2.3 million units in 2008, commercial vehicle production levels outside North America for 2009 declined more than 30% to around 1.5 million units in 2009. Production levels in Europe, particularly, declined about 60% from the previous year. With improving economic conditions, we expect that commercial vehicle production levels outside North America will begin to rebound in 2010 — mostly during the second half of the year. We currently expect production outside North America in 2010 to be around 1.6 to 1.8 million units. (Source: Global Insight and ACT).
North America — Developments in this region have a significant impact on our results as North America accounts for approximately 70% of our sales in the commercial vehicle market. Production of heavy-duty (Class 8) vehicles during 2009 of approximately 116,000 units compares to 196,000 units produced in 2008, a decline of 41%. In the medium-duty(Class 5-7) market, 2009 production of around 97,000 units was down 38% from the prior year’s production of 157,000 units.
The North American medium/heavy truck market is being impacted by many of the same overall economic conditions negatively impacting the light vehicle markets, as customers are being cautious about the economic outlook and, consequently, new vehicle purchases. We have begun to see signs of improving market conditions with new truck orders picking up in recent months, and we expect the strengthening market conditions to continue into 2010. We currently expect 2010 Class 8 production in North America to be around 122,000 to 145,000 units — an increase of 5% to as much as 25% from 2009. On the medium dutyClass 5-7 side, we expect 2010 production of about 106,000 to 129,000 units — a slightly higheryear-over-year increase than for Class 8 (Source: Global Insight and ACT).
Off-Highway Markets
Our off-highway business has become an increasingly more significant component of our total operations over the past few years. Unlike our on-highway businesses, our off-highway business is largely outside of North America, with more than 70% of its sales coming from outside North America. We serve several segments of the diverse off-highway market, including construction, agriculture, mining and material handling. Our largest markets are the European and North American construction and agricultural equipment segments. After being relatively strong through the first half of 2008, customer demand in these markets began softening during the latter part of 2008. During 2009, the adverse effects of a weaker global economy significantly reduced demand levels in these markets. Demand in the construction market was down 70-75% from 2008 while demand in the agricultural market was down 35-40%. Unlike the light vehicle and commercial vehicle markets, we have not seen signs of improvement in this market, and we do not expect to see improving conditions until late 2010. We currently expect that this segment’s primary construction and agriculture markets could be somewhat weaker in 2010 than 2009, or at the top end of our estimates, relatively flatyear-on-year.
Sales, Earnings and Cash Flow Outlook
With the lower level of sales in 2009, we focused on aggressively right sizing our costs. We reduced the work force during 2008 by about 6,000 people and in 2009 we reduced our workforce by another 5,000 people. Additional reductions are expected in 2010 as we complete remaining restructuring actions and continue to identify opportunities to reduce our costs. Further, given the structural cost improvements that we have made, we are not expecting to bring back a large share of the salaried and indirect cost that was eliminated as sales levels improve in 2010. Partially offsetting these expected operational cost improvements will be some higher costs associated with pension benefits and restoration of certain additional compensation programs. We also completed several pricing and material recovery initiatives during the latter part of 2008 and into 2009 that benefited
23
Table of Contents
margins in these years. While certain of these actions will provide additional margin improvement in 2010, on balance we do not expect that pricing will be a significant factor in our 2010 year-over-year profitability.
During 2009, we generated free cash flow (defined as operating cash flow less bankruptcy-related claim payments and capital expenditures) of $109. Improved profitability, reduced working capital and disciplined capital expenditures all contributed to the free cash flow generated. Included in this amount is $138 that was used for right sizing and restructuring the business.
Based on the production outlook in our markets and the addition of some net new business, we currently expect our sales for 2010 to be higher by 5-10%, growing to approximately $5,500 to $5,750. In addition to the margin contribution from higher sales, as indicated above, cost reduction actions are expected to provide incremental profit improvement. Combined, we expect these factors to improve profitability by approximately $175. We expect to again generate positive free cash flow in 2010. These sales, earnings and cash flow projections are before considering the effects of the sale of substantially all of the Structural Products business. A number of factors, including the timing of the sale, the duration of transition services, and our ability to impact retained costs will have an impact on these projections.
Results of Operations — Summary
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 5,228 | $ | 7,344 | $ | 751 | $ | 8,721 | |||||||||
| Cost of sales(1) | 4,985 | 7,113 | 702 | 8,231 | |||||||||||||
| Gross margin(1) | 243 | 231 | 49 | 490 | |||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 313 | 303 | 34 | 365 | |||||||||||||
| Amortization of intangibles | 71 | 66 | |||||||||||||||
| Restructuring charges, net | 118 | 114 | 12 | 205 | |||||||||||||
| Impairment of goodwill | 169 | 89 | |||||||||||||||
| Impairment of intangible assets | 156 | 14 | |||||||||||||||
| Other income, net | 98 | 53 | 8 | 162 | |||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations before interest, reorganization items and income taxes(1) | $ | (317 | ) | $ | (382 | ) | $ | 11 | $ | (7 | ) | ||||||
| Fresh start accounting adjustments | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,009 | $ | — | |||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations(1) | $ | (436 | ) | $ | (667 | ) | $ | 717 | $ | (423 | ) | ||||||
| Loss from discontinued operations | $ | — | $ | (4 | ) | $ | (6 | ) | $ | (118 | ) | ||||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to the parent company(1) | $ | (431 | ) | $ | (677 | ) | $ | 709 | $ | (551 | ) | ||||||
| (1) | In 2009, we changed our method of accounting for U.S. inventories from LIFO to FIFO and retroactively applied this inventory costing from the date of our emergence from Chapter 11. The effect of this change on the 2008 results above was a reduction of $14 in cost of sales and additional earnings of $14 in: gross margin; loss from continuing operations before interest, reorganization items and income taxes; loss from continuing operations and net loss attributable to the parent company. |
As a consequence of our emergence from Chapter 11 on January 31, 2008, the results of operations for 2008 consist of the month of January pre-emergence results of Prior Dana and the
24
Table of Contents
eleven-month results of Dana. Fresh start accounting affects our post-emergence results, but not the pre-emergence January results. Adjustments to adopt fresh start accounting were recorded as of January 31, 2008.
Results of Operations (2009 versus 2008)
Geographic Sales, Segment Sales and Margin Analysis
The tables below show our sales by geographic region and by segment for the year ended December 31, 2009, eleven months ended December 31, 2008 and one month ended January 31, 2008. Certain reclassifications were made to conform 2008 to the 2009 presentation.
Although the eleven months ended December 31, 2008 and one month ended January 31, 2008 are distinct reporting periods as a consequence of our emergence from Chapter 11 on January 31, 2008, the emergence and fresh start accounting effects had negligible impact on the comparability of sales between the periods. Accordingly, references in our analysis to 2008 sales information combine the two periods in order to enhance the comparability of such information for the annual periods.
Geographical Sales Analysis
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | |||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | |||||||||||
| North America | $ | 2,659 | $ | 3,523 | $ | 396 | |||||||
| Europe | 1,190 | 2,169 | 224 | ||||||||||
| South America | 798 | 966 | 67 | ||||||||||
| Asia Pacific | 581 | 686 | 64 | ||||||||||
| Total | $ | 5,228 | $ | 7,344 | $ | 751 | |||||||
Sales in 2009 were $2,867 lower than sales for the combined periods in 2008, a reduction of 35%. Currency movements reduced sales by $190 as a number of currencies in international markets weakened against the U.S. dollar. Exclusive of currency, sales decreased $2,677 or 33%, primarily due to lower production levels in each of our markets. Partially offsetting the effects of lower production was improved pricing.
North American sales for 2009, adjusted for currency, declined approximately 32% due largely to the lower production levels in both the light vehicle and commercial vehicle markets. Light truck production was down about 29% compared to 2008 and medium/heavy truck production was down about 40%. The impact of lower vehicle production levels was partially offset by the impact of higher pricing.
Weaker international currencies decreased 2009 sales by $83 in Europe. Adjusted for currency effects, European sales were 47% lower than 2008. Light vehicle production levels were down about 20% while commercial vehicle sector production was about 60% lower. Our European region has a significant presence in off-highway vehicle markets which also experienced significant year-over-year production declines.
Weaker international currencies reduced 2009 sales by $62 in South America and $22 in Asia Pacific. Exclusive of currency effects, sales were down 17% and 20% in these regions, due largely to reduced production levels.
25
Table of Contents
Segment Sales Analysis
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | |||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | |||||||||||
| LVD | $ | 2,021 | $ | 2,603 | $ | 281 | |||||||
| Sealing | 535 | 641 | 64 | ||||||||||
| Thermal | 179 | 231 | 28 | ||||||||||
| Structures | 592 | 786 | 90 | ||||||||||
| Commercial Vehicle | 1,051 | 1,442 | 130 | ||||||||||
| Off-Highway | 850 | 1,637 | 157 | ||||||||||
| Other Operations | 4 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Total | $ | 5,228 | $ | 7,344 | $ | 751 | |||||||
Our LVD, Sealing, Thermal and Structures segments principally serve the light vehicle markets. Exclusive of currency effects, sales in 2009 declined 28% in LVD, 27% in Thermal and 30% in Structures as compared to the combined periods in 2008, all principally due to lower production levels. The sales decline in Sealing, exclusive of currency effects, was somewhat lower at 22%, in part due to this business having a larger proportionate share of sales to the aftermarket. Improved pricing in our LVD and Structures segments helped offset some of the reduction attributed to lower production.
Our Commercial Vehicle segment is heavily concentrated in the North American market where Class 8 commercial truck production was down about 41% andClass 5-7 commercial truck production was down about 38%. The sales decline in Commercial Vehicle, exclusive of currency effects, was 31% as the volume reduction associated with lower production levels was partially offset by higher pricing under material cost recovery arrangements.
With its significant European presence, our Off-Highway segment was negatively impacted by weaker international currencies. Excluding this effect, sales were down 50% compared to 2008 as demand levels in construction markets were down70-75% and in agriculture markets down35-40%. Increased pricing provided a partial offset.
26
Table of Contents
Margin Analysis
The chart below shows our segment margin analysis for the year ended December 31, 2009, eleven months ended December 31, 2008 and one month ended January 31, 2008.
| As a Percentage of Sales | |||||||||||||
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | |||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | |||||||||||
| Gross margin: | |||||||||||||
| LVD | 3.1 | % | 1.0 | % | 4.1 | % | |||||||
| Sealing | 7.7 | 10.0 | 14.1 | ||||||||||
| Thermal | 3.6 | 0.7 | 9.6 | ||||||||||
| Structures | (2.0 | ) | 1.6 | 1.2 | |||||||||
| Commercial Vehicle | 9.1 | 5.7 | 7.3 | ||||||||||
| Off-Highway | 6.4 | 7.9 | 10.9 | ||||||||||
| Consolidated | 4.7 | % | 3.1 | % | 6.5 | % | |||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses: | |||||||||||||
| LVD | 4.5 | % | 3.2 | % | 4.1 | % | |||||||
| Sealing | 11.2 | 9.2 | 9.1 | ||||||||||
| Thermal | 8.9 | 7.4 | 4.7 | ||||||||||
| Structures | 3.2 | 2.6 | 2.6 | ||||||||||
| Commercial Vehicle | 6.4 | 4.2 | 5.3 | ||||||||||
| Off-Highway | 4.9 | 3.4 | 3.1 | ||||||||||
| Consolidated | 6.0 | % | 4.1 | % | 4.5 | % | |||||||
Gross margin — Consolidated gross margin for the year ended December 31, 2009 was $37 lower than the gross margin for the combined eleven months ended December 31, 2008 and the month of January in 2008. Significantly lower sales levels negatively impacted 2009 margins by more than $500 as compared to 2008, with improved pricing of approximately $200 along with reductions in material, conversion and warranty costs offsetting a substantial portion of the volume related reduction. Year-over-year consolidated gross margins were favorably impacted by reduced costs from the 2008 application of fresh start accounting at emergence from bankruptcy which resulted in astep-up in inventory values. This in turn increased cost of sales by $49 as the inventory was sold in the first half of 2008.
Margin in our LVD segment increased $26 from 2008 as pricing improvement of approximately $100 and margin improvement from cost reductions and other items (primarily conversion cost, material and warranty) more than offset the margin decline of about $150 attributed to lower sales volume. Lower sales-related margin declines drove the gross margin reduction of $33 in our Sealing business, however, margin improved as a percent of sales as cost reduction actions more than offset the effect of lower sales volume. Gross margin in our Thermal segment improved over 2008 as cost reduction efforts, lower warranty expense and other benefits more than offset the reduced sales impact. Our Structures business margin was down $26 from 2008. Lower sales volume resulted in reduced margin of approximately $65. Year-over-year margin was also negatively impacted by a pension settlement gain of $8 in 2008. Pricing improvements of approximately $38 combined with cost reductions provided some offset to these other factors.
In our Commercial Vehicle segment, margins improved as a percent of sales as margin reduction of approximately $75 resulting from lower sales volume was substantially offset by improved pricing and cost reductions. Our Off-Highway segment experienced a gross margin reduction of $93. Lower
27
Table of Contents
sales reduced margins by about $150 while pricing improvement of $25 and cost reductions provided a partial offset.
Selling, general and administrative expenses — With the significant decline in sales, consolidated SG&A and the SG&A of each operating segment increased as a percent of sales. However, for 2009, SG&A was $24 lower than the combined periods in 2008, primarily as a result of the cost reduction actions taken during the last half of 2008 and the first part of 2009 in response to reduced sales levels. The fourth quarter of 2009 includes an expense of $13 for additional compensation to certain employees. No additional compensation expense was accrued for 2008.
Amortization of intangibles — Amortization of customer relationship intangibles resulted from the application of fresh start accounting at the date of emergence from Chapter 11; consequently, there is no expense in the one-month period ended January 31, 2008.
Restructuring charges and impairments — Restructuring charges are primarily costs associated with the workforce reduction actions and facility closures. Restructuring expense of $118 for 2009 represents a decrease from expense of $126 for the combined periods of 2008. Expense in both periods is primarily due to separation costs incurred in connection with workforce reductions.
In connection with the planned divestiture of substantially all of the assets of our Structural Products business, we recorded an impairment charge of $150 in the fourth quarter of 2009 against the definite-lived intangibles and long-lived assets of this segment. Charges for impairment of goodwill and indefinite-lived intangibles of $6 in 2009 and $183 in 2008 were recorded in connection with the new valuations triggered by revised economic outlooks. These charges are recorded as impairment of goodwill and impairment of long-lived assets.
Other income, net — Other income of $98 for the year ended December 31, 2009 was $37 higher than the corresponding periods of 2008. We recognized a net gain on extinguishment of debt of $35 in 2009 whereas repayment of debt in 2008 resulted in a net loss on $10. Contract cancellation income in connection with the early termination of a customer program added $17 over 2008. Net currency transaction gains were $18 favorable to 2008 and interest income was lower by $28.
Interest expense — Interest expense includes the costs associated with the Exit Facility and other debt agreements which are described in Note 12 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8. Interest expense in 2009 includes $14 of amortized OID recorded in connection with the Exit Facility, $13 of amortized debt issuance costs and $6 for debt issuance costs resulting from extinguishment of debt. Also included is $8 of other non-cash interest expense associated primarily with the accretion of certain liabilities that were recorded at discounted values in connection with the adoption of fresh start accounting upon emergence from Chapter 11. For the eleven months ended December 31, 2008, interest expense includes $16 of amortized OID and $8 of amortized debt issuance costs. Non-cash interest expense relating to the accretion of certain liabilities in the eleven months ended December 31, 2008 was $8. In the month of January 2008, a substantial portion of our debt obligations was reported as liabilities subject to compromise. The interest expense not recognized on these obligations during the month of January 2008 was $9.
Reorganization items — Reorganization items were directly attributable to our Chapter 11 reorganization process. See Note 20 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8 for a summary of these costs. During the Chapter 11 process, there were ongoing advisory fees of professionals representing Dana and the other Chapter 11 constituents. Certain of these costs continued subsequent to emergence as there are disputed claims which require resolution, claims which require payment and other post-emergence activities related to emergence from Chapter 11. Reorganization items in 2008 include a gain on the settlement of liabilities subject to compromise and several one-time emergence costs, including the cost of employee stock bonuses, transfer taxes and success fees and other fees earned by certain professionals upon emergence. During the second quarter of 2009, we reduced our vacation benefit liability by $5 to correct the amount accrued in 2008 as union agreements arising
28
Table of Contents
from our reorganization activities were being ratified. We recorded $3 as a reorganization item benefit consistent with the original expense recognition.
Income tax expense — In the U.S. and certain other countries, our recent history of operating losses does not allow us to satisfy the “more likely than not” criterion for recognition of deferred tax assets. Consequently, there is no income tax benefit recognized on the pre-tax losses of these jurisdictions as valuation allowance adjustments offset the associated tax benefit or expense.
During 2009, we recorded a tax benefit of $22 to reduce liabilities previously accrued for expected repatriation of earnings from ournon-U.S. subsidiaries. In the U.S., our projections of other comprehensive income (OCI) for 2009 caused us to record tax expense in OCI and recognize a U.S. tax benefit of $18 in continuing operations during the nine months ended September 30, 2009. Based on our final OCI at December 31, 2009, this amount was reversed in the fourth quarter of 2009. For 2009, the reduction in the liability associated with repatriation ofnon-U.S. subsidiary earnings and valuation allowance impacts are the primary factors which cause the tax benefit of $27 for the year ended December 31, 2009 to differ from an expected tax benefit of $159 at the U.S. federal statutory rate of 35%. For 2008, the valuation allowances, the fresh start adjustments and the impairment of goodwill are the primary factors which caused the tax expense of $107 for the eleven months ended December 31, 2008 and $199 for the month of January 2008 to differ from an expected tax benefit of $192 and tax expense of $320 at the U.S. federal statutory rate of 35%.
Results of Operations (2008 versus 2007)
Geographic Sales, Segment Sales and Margin Analysis
The tables below show our sales by geographic region and by segment for the eleven months ended December 31, 2008, one month ended January 31, 2008 and the year ended December 31, 2007. Certain reclassifications were made to conform 2007 to the 2008 presentation.
Although the eleven months ended December 31, 2008 and one month ended January 31, 2008 are distinct reporting periods as a consequence of our emergence from Chapter 11 on January 31, 2008, the emergence and fresh start accounting effects had negligible impact on the comparability of sales between the periods. Accordingly, references in our analysis to annual 2008 sales information combine the two periods in order to enhance the comparability of such information for the two annual periods.
Geographical Sales Analysis
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||
| Ended | Ended | Year Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||||
| North America | $ | 3,523 | $ | 396 | $ | 4,791 | |||||||
| Europe | 2,169 | 224 | 2,256 | ||||||||||
| South America | 966 | 67 | 914 | ||||||||||
| Asia Pacific | 686 | 64 | 760 | ||||||||||
| Total | $ | 7,344 | $ | 751 | $ | 8,721 | |||||||
Sales for the combined periods of 2008 were $626 lower than sales in 2007. Currency movements generated $256 of increased sales as a number of the major currencies in international markets where we conduct business strengthened against the U.S. dollar. Exclusive of currency, sales decreased $882, or 10%, primarily due to lower production levels in each of our markets. Partially offsetting the effects of lower production was improved pricing, largely for recovery of higher material cost.
29
Table of Contents
Sales for 2008 in North America, adjusted for currency, declined approximately 19% due to the lower production levels in both the light duty and medium/heavy vehicle markets. Light and medium duty truck production was down 25% in 2008 compared to 2007 and the production of Class 8 commercial vehicle trucks was down 4%. The impact of lower vehicle production levels was partially offset by the impact of higher pricing, principally to recover higher material costs.
Sales in Europe, South America and Asia Pacific all benefited from the effects of stronger local currencies against the U.S. dollar. Stronger currencies increased 2008 sales by $163 in Europe, $60 in South America and $11 in Asia Pacific. Exclusive of this currency effect, European sales were down $27 against 2007, principally due to the lower production levels in the second half of 2008. In South America, year-over-year production levels were stronger, leading to increased sales of $59 after excluding currency effects.
Segment Sales Analysis
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||
| Ended | Ended | Year Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||||
| LVD | $ | 2,603 | $ | 281 | $ | 3,476 | |||||||
| Sealing | 641 | 64 | 728 | ||||||||||
| Thermal | 231 | 28 | 293 | ||||||||||
| Structures | 786 | 90 | 1,069 | ||||||||||
| Commercial Vehicle | 1,442 | 130 | 1,531 | ||||||||||
| Off-Highway | 1,637 | 157 | 1,609 | ||||||||||
| Other Operations | 4 | 1 | 15 | ||||||||||
| Total | $ | 7,344 | $ | 751 | $ | 8,721 | |||||||
LVD sales declined 17% due principally to lower light truck production levels in North America and Europe, with increased pricing and favorable currency effects providing a partial offset. Sales in the Sealing segment declined 3%. The Sealing business also supports the medium/heavy vehicle market and has a proportionately larger share of business in Europe where the production declines were lower than in North America and a stronger euro provided favorable currency effect. Thermal sales declined 12%, primarily due to lower North American production levels partially offset by favorable currency effect. Lower North American production was also the primary factor leading to an 18% reduction in sales in the Structures business.
Our Commercial Vehicle segment is heavily concentrated in the North American market. Despite the drop in North American production levels discussed in the regional review above, sales in this segment increased 3% as stronger markets outside North America, pricing improvements and favorable currency effects more than offset the weaker North American production. With its significant European presence, our Off-Highway segment benefited from the stronger euro. Exclusive of favorable currency effects of $105, Off-Highway sales increased 5% due to stronger production levels during the first half of 2008, sales from new programs and increased pricing.
30
Table of Contents
Margin Analysis
The chart below shows our segment margin analysis for the eleven months ended December 31, 2008, one month ended January 31, 2008 and the year ended December 31, 2007.
| As a Percentage of Sales | |||||||||||||
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | Year | |||||||||||
| Ended | Ended | Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||||
| Gross margin: | |||||||||||||
| LVD | 1.0 | % | 4.1 | % | 3.1 | % | |||||||
| Sealing | 10.0 | 14.1 | 12.7 | ||||||||||
| Thermal | 0.7 | 9.6 | 7.9 | ||||||||||
| Structures | 1.6 | 1.2 | 5.0 | ||||||||||
| Commercial Vehicle | 5.7 | 7.3 | 7.3 | ||||||||||
| Off-Highway | 7.9 | 10.9 | 11.1 | ||||||||||
| Consolidated | 3.1 | % | 6.5 | % | 5.6 | % | |||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses: | |||||||||||||
| LVD | 3.2 | % | 4.1 | % | 2.8 | % | |||||||
| Sealing | 9.2 | 9.1 | 8.1 | ||||||||||
| Thermal | 7.4 | 4.7 | 6.2 | ||||||||||
| Structures | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.0 | ||||||||||
| Commercial Vehicle | 4.2 | 5.3 | 3.0 | ||||||||||
| Off-Highway | 3.4 | 3.1 | 3.0 | ||||||||||
| Consolidated | 4.1 | % | 4.5 | % | 4.2 | % | |||||||
Consolidated-gross margin — Margins during the eleven-month period ended December 31, 2008 were adversely impacted by two significant factors — reduced sales levels and higher steel costs. Adjusted for currency effects, sales in 2008 were down from the comparable 2007 period, with most of the reduction occurring in the second half of 2008. As a result, there was a lower sales base relative to our fixed costs, negatively affecting margins in the eleven-month period ended December 31, 2008 as compared to the first month of 2008 and the full previous year. For the combined periods in 2008, lower sales volumes reduced margin by approximately $245. Higher steel costs reduced margin by approximately $140. Gross margins during the eleven-month period ended December 31, 2008 were also reduced by about $73 resulting from the fresh start accounting effects discussed below. Partially offsetting these adverse developments were benefits from the reorganization actions undertaken in connection with the bankruptcy process — customer pricing improvement, labor cost savings, overhead cost reduction and manufacturing footprint optimization. Those customer pricing actions began contributing to gross margins in the first quarter of 2007, with additional pricing improvements being achieved over the course of 2007 and into 2008. The 2008 results reflect a full year of customer pricing improvements while 2007 includes only a portion thereof.
Pricing improvements unrelated to the reorganization process, primarily associated with recovery of higher steel cost, were also achieved, which when combined with the reorganization-related pricing actions increased margin by approximately $140 during the eleven months ended December 31, 2008 and the month of January 2008. We did not begin benefiting significantly from non-union employee benefit plan reductions and other labor savings until the first quarter of 2008 with much of the savings associated with the agreements negotiated with the unions only becoming effective upon our emergence on January 31, 2008. Labor cost savings associated with the reorganization initiatives and other actions added approximately $100 to margin in the eleven months ended December 31, 2008, while overhead reduction, manufacturing footprint and increased pricing actions provided additional margin improvement.
31
Table of Contents
In connection with the application of fresh start accounting, margins were negatively impacted by two factors. At emergence, inventory values were increased in accordance with fresh start accounting requirements. The fresh startstep-up amortization of $49 was recorded as cost of sales in the first and second quarters of 2008 as the inventory was sold. The other factor negatively impacting margins as a result of fresh start accounting was higher depreciation expense on thestepped-up value of fixed assets and amortization expense associated with technology related intangibles recognized at emergence. The higher depreciation and amortization reduced margin for the eleven months ended December 31, 2008 by approximately $24.
In the LVD segment, reduced sales volume led to margin reduction of approximately $131, while higher steel costs resulted in lower margin of about $62. Partially offsetting these effects were customer pricing improvement and labor cost reductions which contributed approximately $128 to 2008 margin and other cost reductions and operational improvements.
In the Sealing segment, the gross margin decline was primarily due to lower sales volume and higher depreciation and amortization resulting from application of fresh start accounting. These effects were partially offset by lower material cost, currency effect and cost reductions. Gross margin in our Thermal segment declined due to lower sales volume, additional warranty cost and higher depreciation and amortization. Our Structures business was significantly impacted by lower sales levels which reduced margin by approximately $72. Mitigating the effects of lower sales were improved pricing and labor savings which improved margin by about $20 and lower depreciation and amortization expense related to fresh start accounting which increased margin by $17.
Gross margin in the Commercial Vehicle segment in 2008 was negatively affected by lower sales volume and higher steel costs which reduced margin by about $13 and $38. Offsetting some of the reduction due to these factors was additional pricing of approximately $34. In the Off-Highway segment, the gross margin decline was primarily due to higher material costs of about $34, increased warranty expense of $10 and increased depreciation and amortization expense of $8. The margin reduction from these and other factors was partially offset by improved pricing of $28.
Corporate and other - gross margin — Consolidated gross margin is impacted by cost of sales activity in corporate and other related to applying LIFO costing to inventory in the U.S. prior to February 1, 2008 and full absorption inventory costing globally. Prior to February 1, 2008, corporate and other margin includes an adjustment to record the U.S. inventory on a LIFO basis. A credit to cost of sales of $3 was recognized in the month of January 2008. During 2007, LIFO-based charges to cost of sales amounted to $7.
The application of full absorption costing consists principally of reclassifying certain expenses to cost of sales that are reported by the operating segments as SG&A. These costs are generally reviewed and adjusted annually. Cost of sales increased and SG&A decreased by $5 for the one month ended January 31, 2008; $59 for the eleven months ended December 31, 2008 and by $56 for the year ended December 31, 2007.
Due to the application of fresh start accounting, corporate and other in the eleven months ended December 31, 2008 also includes a charge of $49 to amortize the fresh startstep-up of our global inventories.
Selling, general and administrative expenses — For the combined periods in 2008, SG&A of $337 is lower by $28 from the 2007 expense. Both the combined 2008 periods and 2007 SG&A expense were 4.2% of sales. The 2008 period expense benefited from certain labor and overhead cost reduction initiatives implemented in connection with the bankruptcy reorganization process as well as additional reductions implemented post-emergence. Additionally, the 2007 expense included a provision for short-term incentive compensation, whereas nothing was provided in 2008 based on that year’s results. Partially offsetting the factors reducing year-over-year SG&A expense was additional costs incurred during 2008 in connection with personnel changes and restoring long-term incentive
32
Table of Contents
plans. Also adversely impacting the year-over-year margin comparison was a reduction in long-term disability accruals in 2007.
Amortization of intangibles — Amortization of customer relationship intangibles recorded in connection with applying fresh start accounting at the date of emergence resulted in expense of $66 for the eleven months ended December 31, 2008.
Restructuring charges and impairments — Restructuring charges are primarily costs associated with the workforce reduction actions and facility closures, certain of which were part of the manufacturing footprint optimization actions that commenced in connection with our bankruptcy plan of reorganization. These actions are more fully described in Note 3 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8. Restructuring charges in 2007 include $136 of cost relating to the settlement of our pension obligations in the United Kingdom, which was completed in April 2007.
We recorded $169 for impairment of goodwill and $14 for impairment of indefinite-lived intangibles during the eleven months ended December 31, 2008. We recorded $89 for impairment of goodwill during 2007 as discussed more fully in Note 6 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8.
Other income, net — Net currency transaction losses reduced other income by $12 in the eleven months ended December 31, 2008 while net gains of $3 were recognized in the month of January 2008. This compares to $35 of net currency transaction gains in 2007. Dana Credit Corporation (a former financing business of Dana) had asset sales and divestitures that provided other income of $49 in 2007, but only minimal income in 2008. Other income in 2008 also benefited from interest income of $48 in the eleven months ended December 31, 2008 and $4 in the month of January 2008 as compared to $42 in 2007. Other income in the eleven-month period ended December 31, 2008 includes a charge of $10 to recognize the loss incurred in connection with repayment of $150 of our term debt in November 2008. Costs of approximately $10 have been incurred in 2008 in connection with the evaluation of strategic alternatives relating to certain businesses. Other income in 2007 also included a one-time claim settlement charge of $11 representing the cost to settle a contractual matter with an investor in one of our equity investments.
Interest expense — Interest expense includes the costs associated with the Exit Facility and other debt agreements which are described in detail in Note 12 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8. Interest expense in the eleven months ended December 31, 2008 includes $16 of amortized OID recorded in connection with the Exit Facility and $8 of amortized debt issuance costs. Also included is $4 associated with the accretion of certain liabilities that were recorded at discounted values in connection with the adoption of fresh start accounting upon emergence from Chapter 11. During 2007 and the month of January 2008, as a result of the bankruptcy reorganization process, a substantial portion of our debt obligations were reported as liabilities subject to compromise in our consolidated financial statements with no interest expense being accrued on these obligations. The interest expense not recognized on these obligations amounted to $108 in 2007 and $9 during the month of January 2008.
Reorganization items — Reorganization items are expenses directly attributed to our Chapter 11 reorganization process. See Note 20 to our financial statements in Item 8 for a summary of these costs. During the bankruptcy process, there were ongoing advisory fees of professionals representing Dana and the other bankruptcy constituencies. Certain of these costs continued subsequent to emergence as there are disputed claims which require resolution, claims which require payment and other post-emergence activities incident to emergence from Chapter 11. Among these ongoing costs are expenses associated with additional facility unionization under the framework of the global agreements negotiated with the unions as part of our reorganization activities. Reorganization items in the month of January 2008 include a gain on the settlement of liabilities subject to compromise and several one-time emergence costs, including the cost of employee stock bonuses, transfer taxes, and success fees and other fees earned by certain professionals upon emergence.
33
Table of Contents
Income tax expense — In the U.S. and certain other countries, our recent history of operating losses does not allow us to satisfy the “more likely than not” criterion for realization of deferred tax assets. Consequently, there is no income tax benefit against the pre-tax losses of these jurisdictions as valuation allowances are established offsetting the associated tax benefit or expense. In the U.S., the other comprehensive income (OCI) reported for 2007 caused us to record tax expense in OCI and recognize a U.S. tax benefit of $120 in continuing operations. For 2008, the valuation allowance impacts in the above-mentioned countries, the fresh start adjustments and the impairment of goodwill in 2008 and 2007 are the primary factors which cause the tax expense of $107 for the eleven months ended December 31, 2008, $199 for the month of January 2008, and $62 for 2007 to differ from an expected tax benefit of $192, tax expense of $320 and tax benefit of $135 for those periods at the U.S. federal statutory rate of 35%.
Discontinued operations — Our engine hard parts, fluid products and pump products operations had been reported as discontinued operations. The sales of these businesses were substantially completed in 2007, except for a portion of the pump products business that was sold in January 2008. The results for 2007 reflect the operating results of these businesses as well as adjustments to the net assets of these businesses necessary to reflect their fair value less cost to sell based on expected sales proceeds. See Note 22 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8 for additional information relating to the discontinued operations.
Liquidity
Common stock offering and debt reduction —In September 2009, we completed a common stock offering of 34 million shares at a price per share of $6.75, generating net proceeds of $217. The provisions of our Term Facility required that a minimum of 50% of the net proceeds of the equity offering be used to repay outstanding principal of our term loan. As a result of previous debt repurchases, approximately 10% of the outstanding principal amount of the term loan is held by a wholly-ownednon-U.S. subsidiary of Dana. Accordingly, $11 of the $109 term loan repayment made to the lenders was received by this wholly-ownednon-U.S. subsidiary and $98 was used to repay outstanding principal of our term loan held by third parties.
The September 2009 equity offering provided the underwriters with an over-allotment option to purchase an additional 5 million shares. The purchase of these additional shares was completed in October 2009, generating additional net proceeds of $33. Of these proceeds, $15 was used to repay third party debt principal.
Additional debt reduction occurred in the second and third quarters of 2009 when the combination of Dana repayments and purchases of debt by a wholly-ownednon-U.S. subsidiary of Dana reduced our outstanding principal under our Term Facility by $129 (net of OID of $9) with a cash outlay of $86.
Covenants — At December 31, 2009, we were in compliance with our debt covenants under the amended Term Facility with a Leverage Ratio of 3.09 compared to a maximum of 3.80 and an Interest Coverage Ratio of 4.64 compared to a minimum of 2.80. Based on our current forecast assumptions, which include cost reduction actions, and other initiatives, we expect to be able to maintain compliance for the next twelve months and we believe that our overall liquidity and operating cash flow will be sufficient to meet our anticipated cash requirements for capital expenditures, working capital, debt obligations and other commitments during this period. However, there is uncertainty in the current environment and it is possible that the factors affecting our business could result in our not being able to comply with the financial covenants in our debt agreements or to maintain sufficient liquidity.
Based on our financial covenants, we had additional borrowing capacity of $232 at December 31, 2009. The borrowing available from our credit facilities was $224 based on the borrowing base collateral of those lines.
34
Table of Contents
Global liquidity —Our global liquidity at December 31, 2009 was as follows:
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 947 | ||
| Less: Deposits supporting obligations | (43 | ) | ||
| Available cash | 904 | |||
| Additional cash availability from lines of credit in the U.S. and Europe | 224 | |||
| Total global liquidity | $ | 1,128 | ||
As of December 31, 2009, the consolidated cash balance totaled $947, with $524 of this amount located in the U.S. Approximately $43 of our cash balance is in cash deposits that support certain of our obligations, primarily workers compensation. In addition, $91 is held by less than wholly-owned subsidiaries where our access may be restricted. Our ability to efficiently access other cash balances in certain subsidiaries and foreign jurisdictions is subject to local regulatory, statutory or other requirements. Our current credit ratings are B and B3 from Standard and Poor’s and Moody’s.
The principal sources of liquidity for our future cash requirements are expected to be (i) cash flows from operations, (ii) cash and cash equivalents on hand, (iii) proceeds related to our trade receivable securitization and financing programs and (iv) borrowings from the Revolving Facility. Our future ability to borrow the full amount of availability under our revolving credit facilities could be effectively limited by our financial covenants.
At December 31, 2009, there were no borrowings under our European trade receivable securitization program and $63 of availability based on the borrowing base. At December 31, 2009, we had no borrowings under the Revolving Facility but we had utilized $183 for letters of credit. Based on our borrowing base collateral, we had availability at that date under the Revolving Facility of $161 after deducting the outstanding letters of credit.
Cash Flow
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||
| Cash used in reorganization activity | $ | (2 | ) | $ | (882 | ) | $ | (74 | ) | $ | (148 | ) | |||||
| Cash provided by (used for) changes in working capital | 94 | 18 | (61 | ) | 83 | ||||||||||||
| Other cash provided by (used in) operations | 116 | (33 | ) | 13 | 13 | ||||||||||||
| Total cash provided by (used in) operating activities | 208 | (897 | ) | (122 | ) | (52 | ) | ||||||||||
| Cash provided by (used in) investing activities | (98 | ) | (221 | ) | 77 | 348 | |||||||||||
| Cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 32 | (207 | ) | 912 | 166 | ||||||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | $ | 142 | $ | (1,325 | ) | $ | 867 | $ | 462 | ||||||||
Operating activities — The table above summarizes our consolidated statement of cash flows. Exclusive of working capital and reorganization-related activity, other cash provided from operations was $116 during 2009, as compared to a use of $20 for the combined periods of 2008 and cash generation of $13 in 2007. An increased level of operating earnings was the primary factor for the higher level of cash provided in 2009 as compared to the prior periods. As our operational improvements continued, our workforce reduction and other restructuring activities consumed cash of $138 during 2009, an increase of $5 over the combined periods of 2008 and $81 more than was used for such activities in 2007.
35
Table of Contents
Working capital provided cash of $94 in 2009, whereas cash of $43 was used in 2008. In 2007, working capital provided cash of $83. The combination of focused operational initiatives and lower sales levels combined to generate cash of $299 in 2009 from reductions in inventory. During 2008 and 2007, cash of $34 and $5 was used to finance increased inventory. Bringing inventories in line with current requirements caused accounts payable to decrease, using cash of $184 in 2009. Lower sales levels during the latter part of 2008 led to a reduction in accounts payable cash use of $210, while in 2007 cash of $110 was provided from increased accounts payable. Reductions to receivables generated cash of $107 in 2009, $434 in 2008 — again driven heavily by lower sales during the latter part of 2008, and $23 in 2007.
During 2008, cash was used to satisfy various obligations associated with our emergence from Chapter 11. Cash of $733 was used shortly after emergence to satisfy our payment obligation to VEBAs established to fund non-pension benefits of union retirees. We also made a payment of $53 at emergence to satisfy our obligation to a VEBA established to fund non-pension benefits relating to non-union retirees, with a payment of $2 being made under another union arrangement. Payments of reorganization expenses totaled $46 and Chapter 11 emergence-related claim payments totaled $100 during the eleven months ended December 31, 2008.
Investing activities — Expenditures for property, plant and equipment in 2009 of $99 are down from $250 for the combined periods of 2008 and $254 for 2007 as capital expenditures were closely managed and prioritized throughout the past year. DCC cash of $93 that was restricted during Chapter 11 by a forbearance agreement with DCC noteholders was released in January 2008 as payments were made to the noteholders. In 2007, divestitures of our engine hard parts, fluid products and trailer axle businesses, the sale of our investment in GETRAG, proceeds from DCC asset sales and other divestment related actions provided cash of $609.
Financing activities — In September and October of 2009, we completed a common stock offering for 39 million shares at a price per share of $6.75, generating net proceeds of $250. Additional borrowing sources outside the U.S. were accessed to raise $26 of long-term debt, while cash of $214 was used in 2009 to reduce long-term debt and $36 was used to reduce short term borrowings. In 2008, cash was provided by financing activities as proceeds from our Exit Facility and the issuance of preferred stock at emergence exceeded the cash used for the repayment of other debt. During 2007, we borrowed additional amounts under our bankruptcy reorganization credit facility of $200 and utilized other short-term financing sources to raise cash of $98. Our DCC operation repaid $132 of their outstanding debt in 2007 with proceeds from their asset sales.
36
Table of Contents
Contractual Obligations
We are obligated to make future cash payments in fixed amounts under various agreements. These include payments under our long-term debt agreements, rent payments under operating lease agreements and payments for equipment, other fixed assets and certain raw materials under purchase agreements. The following table summarizes our significant contractual obligations as of December 31, 2009
| Payments Due by Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Less than | 2 - 3 | 4 - 5 | After | |||||||||||||||||
Contractual Cash Obligations | Total | 1 Year | Years | Years | 5 Years | |||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt (1) | $ | 1,042 | $ | 17 | $ | 46 | $ | 786 | $ | 193 | ||||||||||
| Interest payments (2) | 217 | 49 | 92 | 75 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Leases (3) | 372 | 50 | 74 | 74 | 174 | |||||||||||||||
| Unconditional purchase obligations (4) | 116 | 104 | 5 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||
| Pension contribution (5) | 13 | 13 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Retiree healthcare benefits (6) | 81 | 7 | 16 | 16 | 42 | |||||||||||||||
| Uncertain income tax positions (7) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total contractual cash obligations | $ | 1,841 | $ | 240 | $ | 233 | $ | 958 | $ | 410 | ||||||||||
Notes:
| (1) | Principal payments on long-term debt. Excludes OID and deferred fees which were prepaid. |
| (2) | These amounts represent future interest payments based on the debt balances at December 31. Payments related to variable rate debt are based on December 31, 2009 interest rates. |
| (3) | Capital and operating leases related to real estate, vehicles and other assets. |
| (4) | The unconditional purchase obligations presented are comprised principally of commitments for procurement of fixed assets and the purchase of raw materials. |
| (5) | These amounts represent estimated 2010 contributions to our global defined benefit pension plans. We have not estimated pension contributions (other than the U.S.) beyond 2010 due to the significant impact that return on plan assets and changes in discount rates might have on such amounts. Our U.S. estimate for 2011 is a contribution of $75 which is not included in the table above. |
| (6) | This amount represents estimated obligations under ournon-U.S. retiree healthcare programs. Obligations under the retiree healthcare programs are not fixed commitments and will vary depending on various factors, including the level of participant utilization and inflation. Our estimates of the payments to be made in the future consider recent payment trends and certain of our actuarial assumptions. |
| (7) | There are no expected payments in 2010 related to the uncertain tax positions as of December 31, 2009. We are not able to reasonably estimate the timing of the FIN 48 liability in individual years beyond 2010 due to uncertainties in the timing of the effective settlement of tax positions. As disclosed in Note 17 of the consolidated financial statements in Item 8, we expect to make a payment of approximately $75 during the first half of 2010 in connection with finalizing the settlement of U.S. income tax audits from 1999 through 2005. |
Dividend obligations of approximately $8 per quarter are accrued while all shares of our preferred stock are outstanding. The payment of preferred dividends was suspended in November 2008 under the terms of our amended Exit Facility. We are permitted under the terms of our amended Exit Facility to resume a dividend when our total leverage ratio as of the most recently completed fiscal quarter is less than or equal to 3.25:1.00. At December 31, 2009 our ratio was 3.09:1.00. Payment of the
37
Table of Contents
dividends accrued but not paid at December 31, 2009 of $42 is at the discretion of the Board of Directors.
At December 31, 2009, we maintained cash balances of $43 on deposit with financial institutions to support surety bonds, letters of credit and bank guarantees and to provide credit enhancements for certain lease agreements. These surety bonds enable us to self-insure our workers compensation obligations. We accrue the estimated liability for workers compensation claims, including incurred but not reported claims. Accordingly, no significant impact on our financial condition would result if the surety bonds were called.
We have agreed, subject to certain conditions, to increase our equity interest in Dongfeng Dana Axle Co., Ltd. from 4% to 50%. Under the agreement, our additional interest is based on a valuation of the business which would result in an additional investment of $54 to $77. The actual investment could vary significantly from this range in the event that the parties mutually agree that the operating results and prospects of the venture at the expected closing date of June 30, 2010 support a higher valuation of the business.
Contingencies
For a summary of litigation and other contingencies, see Note 15 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8. We do not believe that any liabilities that may result from these contingencies are reasonably likely to have a material adverse effect on our liquidity or financial condition.
Critical Accounting Estimates
The preparation of our consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Considerable judgment is often involved in making these determinations. Critical estimates are those that require the most difficult, subjective or complex judgments in the preparation of the financial statements and the accompanying notes. We evaluate these estimates and judgments on a regular basis. We believe our assumptions and estimates are reasonable and appropriate. However, the use of different assumptions could result in significantly different results and actual results could differ from those estimates. The following discussion of accounting estimates is intended to supplement the Summary of Significant Accounting Policies presented as Note 1 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8.
Income taxes — Accounting for income taxes is complex, in part, because we conduct business globally and therefore file income tax returns in numerous tax jurisdictions. Significant judgment is required in determining the income tax provision, uncertain tax positions, deferred tax assets and liabilities and the valuation allowance recorded against our net deferred tax assets. In assessing the recoverability of deferred tax assets, we consider whether it is more likely than not that some or a portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. A valuation allowance is provided when, in our judgment, based upon available information; it is more likely than not that a portion of such deferred tax assets will not be realized. To make this assessment, we consider the historical and projected future taxable income or loss in different tax jurisdictions and we review our tax planning strategies. We have recorded valuation allowances against deferred tax assets in the U.S. and other foreign jurisdictions where realization has been determined to be uncertain. Since future financial results may differ from previous estimates, periodic adjustments to our valuation allowance may be necessary.
In the ordinary course of business, there are many transactions and calculations where the ultimate tax determination is less than certain. We are regularly under audit by the various applicable tax authorities. Although the outcome of tax audits is always uncertain, we believe that we have appropriate support for the positions taken on our tax returns and that our annual tax provisions include amounts sufficient to pay assessments, if any, which may be proposed by the taxing
38
Table of Contents
authorities. Nonetheless, the amounts ultimately paid, if any, upon resolution of the issues raised by the taxing authorities may differ materially from the amounts accrued for each year. See additional discussion of our deferred tax assets and liabilities in Note 17 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8.
Retiree benefits — Accounting for pensions and OPEB involves estimating the cost of benefits to be provided well into the future and attributing that cost over the time period each employee works. These plan expenses and obligations are dependent on assumptions developed by us in consultation with our outside advisors such as actuaries and other consultants and are generally calculated independently of funding requirements. The assumptions used, including inflation, discount rates, investment returns, life expectancies, turnover rates, retirement rates, future compensation levels and health care cost trend rates, have a significant impact on plan expenses and obligations. These assumptions are regularly reviewed and modified when appropriate based on historical experience, current trends and the future outlook. Changes in one or more of the underlying assumptions could result in a material impact to our consolidated financial statements in any given period. If actual experience differs from expectations, our financial position and results of operations in future periods could be affected.
The inflation assumption is based on an evaluation of external market indicators. Retirement, turnover and mortality rates are based primarily on actual plan experience. Health care cost trend rates are developed based on our actual historical claims experience, the near-term outlook and an assessment of likely long-term trends. For our largest plans, discount rates are based upon the construction of a theoretical bond portfolio, adjusted according to the timing of expected cash flows for the future obligations. A yield curve is developed based on a subset of these high-quality fixed-income investments (those with yields between the 40th and 90th percentiles). The projected cash flows are matched to this yield curve and a present value developed which is then calibrated to develop a single equivalent discount rate. Pension benefits are funded through deposits with trustees that satisfy, at a minimum, the applicable funding regulations. For our largest defined benefit pension plans, expected investment rates of return are based upon input from the plan’s investment advisors and actuary regarding our expected investment portfolio mix, historical rates of return on those assets, projected future asset class returns, the impact of active management and long-term market conditions and inflation expectations. We believe that the long-term asset allocation on average will approximate the targeted allocation and we regularly review the actual asset allocation to periodically rebalance the investments to the targeted allocation when appropriate. OPEB benefits are funded as they become due.
Actuarial gains or losses may result from changes in assumptions or when actual experience is different from that expected. Under the applicable standards, those gains and losses are not required to be immediately recognized as expense, but instead may be deferred as part of accumulated other comprehensive income and amortized into expense over future periods.
In 2009 we experienced significant differences between the expected and actual return on plan assets. The most significant of our funded plans exist in the U.S. and Canada. Our U.S. and Canadian pension plans were heavily invested in government securities at the end of 2008. These securities were in great demand at that time due to the global financial crisis. As the global crisis began to ease in 2009, investors started to sell these securities as their appetite for risk and higher yields began to increase. This shift in demand resulted in a declining market value for these securities. A decrease in the fair value of plan assets will increase next year’s pension cost because of the lower expected return on plan assets. Our financial position is also sensitive to changes in the high quality bond yield rates used to determine an appropriate discount rate. Over the later part of 2009 and into 2010, the credit markets have stabilized resulting in a general decline in the yields on high quality corporate bonds of all maturities. A decrease in the discount rate increases the benefit obligation.
39
Table of Contents
As a result, at the end of 2009, we have significant unrecognized net losses in accumulated other comprehensive income, principally in the U.S. The amortization of these unrecognized losses is resulting in increased domestic net periodic pension cost. Our normal net periodic pension cost will change from a benefit of $7 in 2009 (before any curtailment impacts) to a charge of $22 in 2010. No cash contributions are required in 2010. However, we estimate a contribution approximating $75 to our U.S. plans will be required in 2011.
A change in the pension discount rate of 25 basis points would result in a change in our pension obligations of approximately $45 and a change in pension expense of approximately $2. A 25 basis point change in the rate of return would change pension expense by approximately $3.
Restructuring actions involving facility closures and employee downsizing and divestitures frequently give rise to adjustments to employee benefit plan obligations, including the recognition of curtailment or settlement gains and losses. Upon the occurrence of these events, the obligations of the employee benefit plans affected by the action are also re-measured based on updated assumptions as of the re-measurement date. See additional discussion of our pension and OPEB obligations in Note 10 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8.
Long-lived asset impairment — We perform periodic impairment analyses on our long-lived amortizable assets whenever events and circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of such assets may not be recoverable. When indications are present, we compare the estimated future undiscounted net cash flows of the operations to which the assets relate to their carrying amount. If the operations are determined to be unable to recover the carrying amount of their assets, the long-lived assets are written down to their estimated fair value. Fair value is determined based on discounted cash flows, third party appraisals or other methods that provide appropriate estimates of value. A considerable amount of management judgment and assumptions are required in performing the impairment tests, principally in determining whether an adverse event or circumstance has triggered the need for an impairment review of the fair value of the operations. In Structures we have impaired the long-lived assets based on the expected proceeds from the sale of substantially all of the assets of this segment. In all of our other segments, a 50% reduction in either the projected cash flows or the peer multiples would not result in impairment of long-lived assets including the definite lived intangible assets. While we believe our judgments and assumptions were reasonable, changes in assumptions underlying these estimates could result in a material impact to our consolidated financial statements in any given period.
Goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets — We test goodwill and other indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment as of October 31 of each year for all of our reporting units, or more frequently if events occur or circumstances change that would warrant such a review. We make significant assumptions and estimates about the extent and timing of future cash flows, growth rates and discount rates. The cash flows are estimated over a significant future period of time, which makes those estimates and assumptions subject to a high degree of uncertainty. We also utilize market valuation models which require us to make certain assumptions and estimates regarding the applicability of those models to our assets and businesses. We believe that the assumptions and estimates used to determine the estimated fair value of our Off-Highway reporting unit and our intangible assets were reasonable. In addition, a 65% reduction in either the projected cash flows or the peer multiples in the Off-Highway segment would not result in additional impairment in this segment. However, different assumptions could materially affect the results. As described in Note 6 to our consolidated financial statements in Item 8, we recorded goodwill impairment of $169 in 2008 related to our Driveshaft business segment.
Indefinite-lived intangible asset valuations are generally based on revenue streams. We impaired indefinite-lived intangible assets by $35 in 2009 and $14 in the eleven months ended December 31, 2008. Additional reductions in forecasted revenue could result in additional impairment.
Warranty — Costs related to product warranty obligations are estimated and accrued at the time of sale with a charge against cost of sales. Warranty accruals are evaluated and adjusted as appropriate
40
Table of Contents
based on occurrences giving rise to potential warranty exposure and associated experience. Warranty accruals and adjustments require significant judgment, including a determination of our involvement in the matter giving rise to the potential warranty issue or claim, our contractual requirements, estimates of units requiring repair and estimates of repair costs. If actual experience differs from expectations, our financial position and results of operations in future periods could be affected.
Contingency reserves — We have numerous other loss exposures, such as environmental claims, product liability and litigation. Establishing loss reserves for these matters requires the use of estimates and judgment in regards to risk exposure and ultimate liability. We estimate losses under the programs using consistent and appropriate methods; however, changes to our assumptions could materially affect our recorded liabilities for loss.
Fresh start accounting — As required by GAAP, in connection with emergence from Chapter 11, we adopted fresh start accounting effective February 1, 2008. Accordingly, the reorganization value represents the fair value of the entity before considering liabilities and approximates the amount a willing buyer would pay for the assets of Dana immediately after restructuring. The reorganization value is allocated to the respective fair value of assets. The excess reorganization value over the fair value of identified tangible and intangible assets is recorded as goodwill. Liabilities, other than deferred taxes, are stated at present values of amounts expected to be paid.
Fair values of assets and liabilities represent our best estimates based on our appraisals and valuations. Where the foregoing were not available, industry data and trends or references to relevant market rates and transactions were used. These estimates and assumptions are inherently subject to significant uncertainties and contingencies beyond our reasonable control. Moreover, the market value of our common stock may differ materially from the fresh start equity valuation.
| Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk |
We are exposed to various types of market risks including the effects of fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates, adverse movements in commodity prices for products we use in our manufacturing and adverse changes in interest rates. To reduce our exposure to these risks, we maintain risk management controls to monitor these risks and take appropriate actions to attempt to mitigate such forms of market risks.
Foreign currency exchange rate risks — We have global operations and thus make investments and enter into transactions denominated in various foreign currencies. Our operating results are impacted by buying, selling and financing in currencies other than the functional currency of our operating companies. Wherever possible, we mitigate the impact by focusing on natural hedging techniques which include the following: (i) structuring foreign subsidiary balance sheets with appropriate levels of debt to reduce subsidiary net investments and subsidiary cash flow subject to conversion risk; (ii) avoidance of risk by denominating contracts in the appropriate functional currency and (iii) managing cash flows on a net basis (both in timing and currency) to minimize the exposure to foreign currency exchange rates.
After considering natural hedging techniques, some portions of remaining exposure, especially for anticipated inter-company and third party commercial transaction exposure in the short term, may be hedged using financial derivatives, such as foreign currency exchange rate forwards. Some of our foreign entities were party to foreign currency contracts for anticipated transactions in U.S. dollars, British pounds, Swedish krona, euros, South African rand, Indian rupees and Australian dollars at the end of 2009.
In addition to the transactional exposure discussed above, our operating results are impacted by the translation of our foreign operating income into U.S. dollars (translation exposure). We do not enter into foreign exchange contracts to mitigate translation exposure.
Risk from adverse movements in commodity prices — We purchase certain raw materials, including steel and other metals, which are subject to price volatility caused by fluctuations in supply and
41
Table of Contents
demand as well as other factors. To mitigate the impact of higher commodity prices we have consolidated our supply base and negotiated fixed price supply contracts with many of our commodity suppliers. In addition, we continue to negotiate with our customers to provide for the sharing of increased raw material costs. No assurances can be given that the magnitude and duration of increased commodity costs will not have a material impact on our future operating results. We had no derivatives in place at December 31, 2009 to hedge commodity price movements.
Interest rate risk — Our interest rate risk relates primarily to our floating rate exposure on borrowing under the amended Exit Facility. Under the terms of the Exit Facility we were required to enter into interest rate hedge agreements and to maintain agreements covering a notional amount of not less than 50% of the aggregate loans outstanding under the Term Facility until January 2011. We have hedged interest on $702 of the $1,003 outstanding at December 31, 2009 with an interest rate cap on the London Interbank Borrowing Rate (LIBOR) portion of the interest rate.
42
Table of Contents
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Dana Holding Corporation
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(1) present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Dana Holding Corporation (Dana) and its subsidiaries at December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2009 and the period from February 1, 2008 through December 31, 2008 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. In addition, in our opinion, the financial statement schedule listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(3) for the year ended December 31, 2009 and the period from February 1, 2008 through December 31, 2008 presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein when read in conjunction with the related consolidated financial statements. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009, based on criteria established inInternal Control — Integrated Frameworkissued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements and financial statement schedule, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A. Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements, on the financial statement schedule, and on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our integrated audits. We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company changed the manner in which it reports noncontrolling interests in consolidated subsidiaries in 2009. As discussed in Note 4 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company changed the manner in which it accounts for inventory in 2009.
As discussed in Note 21 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company filed a petition on March 3, 2006 with the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York for reorganization under the provisions of Chapter 11 of the Bankruptcy Code. The Company’s Third Amended Joint Plan of Reorganization of Debtors and Debtors in Possession (as modified, the “Plan”) was confirmed on December 26, 2007. Confirmation of the Plan resulted in the discharge of certain claims against the Company that arose before March 3, 2006 and substantially alters rights and interests of equity security holders as provided for in the Plan. The Plan was substantially consummated on January 31, 2008 and the Company emerged from bankruptcy. In connection with its emergence from bankruptcy, the Company adopted fresh start accounting on January 31, 2008.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal
43
Table of Contents
control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
Toledo, Ohio
February 24, 2010
44
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Dana Holding Corporation
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(1) present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Dana Corporation (Prior Dana) and its subsidiaries at December 31, 2007, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for the period from January 1, 2008 through January 31, 2008 and for the year ended December 31, 2007 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. In addition, in our opinion, the financial statement schedule listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(3) for the year ended December 31, 2007 and the period from January 1, 2008 through January 31, 2008 presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein when read in conjunction with the related consolidated financial statements. The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements and financial statement schedule. Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements and on the financial statement schedule based on our audits. We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
As discussed in Note 17 to the consolidated financial statement, the Company changed the manner in which it accounts for uncertain tax positions in 2007.
As discussed in Note 21 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company filed a petition on March 3, 2006 with the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York for reorganization under the provisions of Chapter 11 of the Bankruptcy Code. The Company’s Third Amended Joint Plan of Reorganization of Debtors and Debtors in Possession (as modified, the “Plan”) was confirmed on December 26, 2007. Confirmation of the Plan resulted in the discharge of certain claims against the Company that arose before March 3, 2006 and substantially alters rights and interests of equity security holders as provided for in the Plan. The Plan was substantially consummated on January 31, 2008 and the Company emerged from bankruptcy. In connection with its emergence from bankruptcy, the Company adopted fresh start accounting.
/s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
Toledo, Ohio
March 16, 2009
45
Table of Contents
Dana Holding Corporation
Consolidated Statement of Operations
(In millions except per share amounts)
Consolidated Statement of Operations
(In millions except per share amounts)
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||
Net sales | $ | 5,228 | $ | 7,344 | $ | 751 | $ | 8,721 | |||||||||
| Costs and expenses | |||||||||||||||||
| Cost of sales | 4,985 | 7,113 | 702 | 8,231 | |||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 313 | 303 | 34 | 365 | |||||||||||||
| Amortization of intangibles | 71 | 66 | |||||||||||||||
| Restructuring charges, net | 118 | 114 | 12 | 205 | |||||||||||||
| Impairment of goodwill | 169 | 89 | |||||||||||||||
| Impairment of long-lived assets | 156 | 14 | |||||||||||||||
| Other income, net | 98 | 53 | 8 | 162 | |||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations before interest, reorganization items and income taxes | (317 | ) | (382 | ) | 11 | (7 | ) | ||||||||||
| Interest expense | 139 | 142 | 8 | 105 | |||||||||||||
| Reorganization items | (2 | ) | 25 | 98 | 275 | ||||||||||||
| Fresh start accounting adjustments | 1,009 | ||||||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations before income taxes | (454 | ) | (549 | ) | 914 | (387 | ) | ||||||||||
| Income tax benefit (expense) | 27 | (107 | ) | (199 | ) | (62 | ) | ||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of affiliates | (9 | ) | (11 | ) | 2 | 26 | |||||||||||
Income (loss) from continuing operations | (436 | ) | (667 | ) | 717 | (423 | ) | ||||||||||
Loss from discontinued operations | (4 | ) | (6 | ) | (118 | ) | |||||||||||
Net income (loss) | (436 | ) | (671 | ) | 711 | (541 | ) | ||||||||||
| Less: Noncontrolling interests net income (loss) | (5 | ) | 6 | 2 | 10 | ||||||||||||
Net income (loss) attributable to the parent company | (431 | ) | (677 | ) | 709 | (551 | ) | ||||||||||
Preferred stock dividend requirements | 32 | 29 | |||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) available to common stockholders | $ | (463 | ) | $ | (706 | ) | $ | 709 | $ | (551 | ) | ||||||
Income (loss) per share from continuing operations available to parent company stockholders: | |||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | (4.19 | ) | $ | (7.02 | ) | $ | 4.77 | $ | (2.89 | ) | ||||||
| Diluted | $ | (4.19 | ) | $ | (7.02 | ) | $ | 4.75 | $ | (2.89 | ) | ||||||
Loss per share from discontinued operations attributable to parent company stockholders: | |||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | — | $ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.79 | ) | ||||||
| Diluted | $ | — | $ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.79 | ) | ||||||
Net income (loss) per share available to parent company stockholders: | |||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | (4.19 | ) | $ | (7.06 | ) | $ | 4.73 | $ | (3.68 | ) | ||||||
| Diluted | $ | (4.19 | ) | $ | (7.06 | ) | $ | 4.71 | $ | (3.68 | ) | ||||||
| Average common shares outstanding | |||||||||||||||||
| Basic | 110 | 100 | 150 | 150 | |||||||||||||
| Diluted | 110 | 100 | 150 | 150 | |||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
46
Table of Contents
Dana Holding Corporation
Consolidated Balance Sheet
(In millions)
Consolidated Balance Sheet
(In millions)
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
Assets | ||||||||
| Current assets | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 947 | $ | 777 | ||||
| Accounts receivable | ||||||||
| Trade, less allowance for doubtful accounts of $18 in 2009 and $23 in 2008 | 728 | 764 | ||||||
| Other | 141 | 164 | ||||||
| Inventories | 608 | 869 | ||||||
| Other current assets | 59 | 52 | ||||||
| Current assets held for sale | 99 | 121 | ||||||
Total current assets | 2,582 | 2,747 | ||||||
| Goodwill | 111 | 108 | ||||||
| Intangibles | 438 | 515 | ||||||
| Investments and other assets | 233 | 200 | ||||||
| Investments in affiliates | 112 | 119 | ||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 1,484 | 1,636 | ||||||
| Non-current assets held for sale | 104 | 282 | ||||||
Total assets | $ | 5,064 | $ | 5,607 | ||||
Liabilities and equity | ||||||||
| Current liabilities | ||||||||
| Notes payable, including current portion of long-term debt | $ | 34 | $ | 70 | ||||
| Accounts payable | 601 | 759 | ||||||
| Accrued payroll and employee benefits | 103 | 112 | ||||||
| Accrued restructuring costs | 29 | 65 | ||||||
| Taxes on income | 40 | 93 | ||||||
| Other accrued liabilities | 270 | 258 | ||||||
| Current liabilities held for sale | 79 | 89 | ||||||
Total current liabilities | 1,156 | 1,446 | ||||||
| Long-term debt | 969 | 1,181 | ||||||
| Deferred employee benefits and other non-current liabilities | 1,160 | 845 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 15) | ||||||||
Total liabilities | 3,285 | 3,472 | ||||||
| Parent company stockholders’ equity | ||||||||
| Preferred stock, 50,000,000 shares authorized | ||||||||
| Series A, $0.01 par value, 2,500,000 issued and outstanding | 242 | 242 | ||||||
| Series B, $0.01 par value, 5,400,000 issued and outstanding | 529 | 529 | ||||||
| Common stock, $0.01 par value, 450,000,000 authorized, 139,414,149 issued and outstanding | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 2,580 | 2,321 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (1,169 | ) | (706 | ) | ||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (504 | ) | (359 | ) | ||||
| Total parent company stockholders’ equity | 1,679 | 2,028 | ||||||
| Noncontrolling interests | 100 | 107 | ||||||
Total equity | 1,779 | 2,135 | ||||||
Total liabilities and equity | $ | 5,064 | $ | 5,607 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
47
Table of Contents
Dana Holding Corporation
Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows
(In millions)
Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows
(In millions)
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | �� | Ended | Ended | Year Ended | |||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | $ | (436 | ) | $ | (671 | ) | $ | 711 | $ | (541 | ) | ||||||
| Depreciation | 311 | 269 | 23 | 279 | |||||||||||||
| Amortization of intangibles | 86 | 81 | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of inventory valuation | 49 | ||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of deferred financing charges and original issue discount | 34 | 27 | |||||||||||||||
| Impairment of goodwill, intangibles, investments and other assets | 156 | 183 | 131 | ||||||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | (20 | ) | 22 | 191 | (29 | ) | |||||||||||
| (Gain) loss on extinguishment of debt | (35 | ) | 10 | ||||||||||||||
| Non-cash portion of U.K. pension charge | 60 | ||||||||||||||||
| Unremitted earnings of affiliates, net of dividends received | 11 | 21 | (4 | ) | (26 | ) | |||||||||||
| Reorganization: | |||||||||||||||||
| Reorganization items net of cash payments | (4 | ) | (24 | ) | 79 | 154 | |||||||||||
| Payment of claims | (100 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Payments to VEBAs | (733 | ) | (55 | ) | (27 | ) | |||||||||||
| Gain on settlement of liabilities subject to compromise | (27 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Fresh start adjustments | (1,009 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Pension contributions in excess of expense | (5 | ) | (36 | ) | (2 | ) | |||||||||||
| OPEB — payments made in excess of expense | (1 | ) | (2 | ) | (71 | ) | |||||||||||
| Loss on sale of assets | 9 | 6 | 7 | ||||||||||||||
| Change in accounts receivable | 107 | 512 | (78 | ) | (23 | ) | |||||||||||
| Change in inventories | 299 | (6 | ) | (28 | ) | (5 | ) | ||||||||||
| Change in accounts payable | (184 | ) | (227 | ) | 17 | 110 | |||||||||||
| Change in accrued payroll and employee benefits | (80 | ) | (79 | ) | 12 | 10 | |||||||||||
| Change in accrued income taxes | (41 | ) | (40 | ) | (2 | ) | (6 | ) | |||||||||
| Change in other current assets and liabilities | (7 | ) | (142 | ) | 18 | (3 | ) | ||||||||||
| Change in other non-current assets and liabilities, net | 8 | (19 | ) | 27 | (65 | ) | |||||||||||
Net cash flows provided by (used in) operating activities | 208 | (897 | ) | (122 | ) | (52 | ) | ||||||||||
Cash flows — investing activities | |||||||||||||||||
| Purchases of property, plant and equipment | (99 | ) | (234 | ) | (16 | ) | (254 | ) | |||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of businesses and assets | 3 | 12 | 5 | 421 | |||||||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of DCC assets and partnership interests | 2 | 188 | |||||||||||||||
| Payments received on leases and loans | 11 | ||||||||||||||||
| Change in investments and other assets | (1 | ) | 14 | ||||||||||||||
| Change in restricted cash | 93 | (78 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Other | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | (5 | ) | 46 | ||||||||||
Net cash flows provided by (used in) investing activities | (98 | ) | (221 | ) | 77 | 348 | |||||||||||
Cash flows — financing activities | |||||||||||||||||
| Net change in short-term debt | (36 | ) | (70 | ) | (18 | ) | 98 | ||||||||||
| Proceeds from Exit Facility debt | 80 | 1,350 | |||||||||||||||
| Deferred financing payments | (1 | ) | (26 | ) | (40 | ) | |||||||||||
| Proceeds from long-term debt | 27 | ||||||||||||||||
| Repayment of long-term debt | (214 | ) | (164 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock | 264 | ||||||||||||||||
| Underwriting fee payment | (14 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid to preferred stockholders | (18 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid to noncontrolling interests | (5 | ) | (7 | ) | (1 | ) | (4 | ) | |||||||||
Proceeds from (repayment of)debtor-in-possession facility | (900 | ) | 200 | ||||||||||||||
| Payment of DCC Medium Term Notes | (136 | ) | (132 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Original issue discount payment | (114 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Issuance of Series A and Series B preferred stock | 771 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other | 11 | (2 | ) | 4 | |||||||||||||
Net cash flows provided by (used in) financing activities | 32 | (207 | ) | 912 | 166 | ||||||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 142 | (1,325 | ) | 867 | 462 | ||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents — beginning of period | 777 | 2,147 | 1,271 | 704 | |||||||||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash balances | 28 | (45 | ) | 5 | 104 | ||||||||||||
| Net change in cash of discontinued operations | 4 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents — end of period | $ | 947 | $ | 777 | $ | 2,147 | $ | 1,271 | |||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
48
Table of Contents
Dana Holding Corporation
Consolidated Statement of Stockholders’ Equity and Comprehensive Income (Loss)
(In millions)
Consolidated Statement of Stockholders’ Equity and Comprehensive Income (Loss)
(In millions)
| Parent Company Stockholders | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accumulated Other | Parent | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Company | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Additional | Foreign | Unrealized | Post- | Stockholders’ | Non- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Preferred | Common | Paid-In | Accumulated | Currency | Gains | retirement | Equity | controlling | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock | Stock | Capital | Deficit | Translation | (Losses) | Benefits | (Deficit) | Interests | Equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2006, Prior Dana | $ | — | $ | 150 | $ | 201 | $ | 80 | $ | (188 | ) | $ | — | $ | (1,077 | ) | $ | (834 | ) | $ | 81 | $ | (753 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Adoption of accounting for uncertainty in income tax, January 1, 2007 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | (551 | ) | (551 | ) | 10 | (541 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency translation | 33 | 33 | 18 | 51 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Defined benefit plans | 568 | 568 | 568 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | (2 | ) | (2 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income | 599 | 18 | 617 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive income | 48 | 28 | 76 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of shares for equity compensation plans, net | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | (10 | ) | (10 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid | (4 | ) | (4 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2007, Prior Dana | 150 | 202 | (468 | ) | (155 | ) | (2 | ) | (509 | ) | (782 | ) | 95 | (687 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | 709 | 709 | 2 | 711 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency translation | 3 | 3 | (21 | ) | (18 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Defined benefit plans | 79 | 79 | 3 | 82 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | (6 | ) | (6 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | 76 | (18 | ) | 58 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive income (loss) | 785 | (16 | ) | 769 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cancellation of Prior Dana common stock | (150 | ) | (202 | ) | (352 | ) | (352 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elimination of Prior Dana accumulated deficit and accumulated other comprehensive loss | (241 | ) | 152 | 8 | 430 | 349 | 34 | 383 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance, January 31, 2008, Prior Dana | 112 | 112 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of new equity in connection with emergence from Chapter 11 | 771 | 1 | 2,267 | 3,039 | 3,039 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance, January 31, 2008, Dana | 771 | 1 | 2,267 | 3,039 | 112 | 3,151 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | (677 | ) | (677 | ) | 6 | (671 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency translation | (224 | ) | (224 | ) | (6 | ) | (230 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Defined benefit plans | (84 | ) | (84 | ) | (84 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized investment losses and other | (51 | ) | (51 | ) | (51 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss | (359 | ) | (6 | ) | (365 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss | (1,036 | ) | (1,036 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Additional investment | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid | (7 | ) | (7 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Preferred stock dividends ($3.67 per share) | (29 | ) | (29 | ) | (29 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of additional equity in connection with emergence from Chapter 11 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Employee emergence bonus | 45 | 45 | 45 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock compensation | 7 | 7 | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2008, Dana | 771 | 1 | 2,321 | (706 | ) | (224 | ) | (51 | ) | (84 | ) | 2,028 | 107 | 2,135 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | (431 | ) | (431 | ) | (5 | ) | (436 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency translation | 109 | 109 | 2 | 111 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Defined benefit plans | (317 | ) | (317 | ) | (317 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized investment gains and other | 63 | 63 | 1 | 64 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | (145 | ) | 3 | (142 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss | (576 | ) | (2 | ) | (578 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid | (5 | ) | (5 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Preferred stock dividends ($4.00 per share) | (32 | ) | (32 | ) | (32 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share issuance | 250 | 250 | 250 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock compensation | 9 | 9 | 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2009, Dana | $ | 771 | $ | 1 | $ | 2,580 | $ | (1,169 | ) | $ | (115 | ) | $ | 12 | $ | (401 | ) | $ | 1,679 | $ | 100 | $ | 1,779 | |||||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
49
Table of Contents
Dana Holding Corporation
Index to Notes to Consolidated
Financial Statements
| 1. | Organization and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
| 2. | Acquisitions and Divestitures |
| 3. | Restructuring of Operations |
| 4. | Inventories |
| 5. | Supplemental Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Information |
| 6. | Goodwill, Other Intangible Assets and Long-Lived Assets |
| 7. | Capital Stock |
| 8. | Earnings Per Share |
| 9. | Incentive and Stock Compensation |
| 10. | Pension and Postretirement Benefit Plans |
| 11. | Cash Deposits |
| 12. | Financing Agreements |
| 13. | Fair Value Measurements |
| 14. | Risk Management and Derivatives |
| 15. | Commitments and Contingencies |
| 16. | Warranty Obligations |
| 17. | Income Taxes |
| 18. | Other Income, Net |
| 19. | Segment, Geographical Area and Major Customer Information |
| 20. | Reorganization Items |
| 21. | Emergence from Chapter 11 |
| 22. | Discontinued Operations |
50
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In millions, except share and per share amounts)
| Note 1. | Organization and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
General
Dana Holding Corporation (Dana), incorporated in Delaware in 2007, is headquartered in Maumee, Ohio. We are a leading supplier of axle, driveshaft, structural, sealing and thermal management products for global vehicle manufacturers. Our people design and manufacture products for every major vehicle producer in the world.
As a result of Dana Corporation’s emergence from Chapter 11 of the U.S. Bankruptcy Code (Chapter 11) on January 31, 2008 (the Effective Date), Dana is the successor registrant to Dana Corporation (Prior Dana) pursuant toRule 12g-3 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
The terms “Dana,” “we,” “our” and “us,” when used in this report with respect to the period prior to Dana Corporation’s emergence from Chapter 11, are references to Prior Dana and, when used with respect to the period commencing after Dana Corporation’s emergence, are references to Dana. These references include the subsidiaries of Prior Dana or Dana, as the case may be, unless otherwise indicated or the context requires otherwise.
This report, as discussed in Note 21, includes the results of the 2008 implementation of the Third Amended Joint Plan of Reorganization of Debtors and Debtors in Possession as modified (the Plan) and the effects of the adoption of fresh start accounting. In accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States (GAAP), historical financial statements of Prior Dana are presented separately from Dana results. The implementation of the Plan and the application of fresh start accounting result in financial statements that are not comparable to financial statements in periods prior to emergence.
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of presentation — Our consolidated financial statements include all subsidiaries in which we have the ability to control operating and financial policies and are consolidated in conformity with GAAP. All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. Affiliated companies (20% to 50% ownership) are recorded in the statements using the equity method of accounting. Less than 20%-owned companies are included in the financial statements at the cost of our investment. Dividends, royalties and fees from these cost basis affiliates are recorded in income when received. Certain prior period amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation.
Dana and forty of its wholly-owned subsidiaries (collectively, the Debtors) reorganized under Chapter 11 of the U.S. Bankruptcy Code from March 3, 2006 (the Filing Date) through the Effective Date. The financial statements for periods subsequent to the filing of a Chapter 11 petition distinguish transactions and events that are directly associated with the reorganization and related restructuring of our business from the ongoing operations of the business.
Effective February 1, 2008, we adopted fresh start accounting. Pursuant to the Plan, all outstanding securities of Prior Dana were cancelled and new securities were issued. In addition, fresh start accounting required that our assets and liabilities be stated at fair value upon our emergence from Chapter 11.
On January 1, 2009, we reorganized our operating segments into a new management structure and modified the calculation of segment earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization (Segment EBITDA), our segment measure of profitability (see Note 19). The Light Axle and Driveshaft segments were combined into the Light Vehicle Driveline (LVD) segment with certain operations from these former segments moving to our Commercial Vehicle and Off-Highway segments. Prior period amounts have been revised to conform to the current year’s presentation.
51
Table of Contents
Change in accounting principle — Our inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market. On January 1, 2009, we changed the method of determining the cost basis of inventories for our U.S. operations from thelast-in-first-out (LIFO) basis to thefirst-in-first-out (FIFO) basis. See Note 4 for additional information regarding this change. Ournon-U.S. operations continue to determine cost using an average or a FIFO cost basis.
Estimates — Our consolidated financial statements are prepared in accordance with GAAP, which requires the use of estimates, judgments and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the consolidated financial statements and accompanying disclosures. Some of the more significant estimates include: valuation of deferred tax assets and inventories; restructuring, environmental, product liability, asbestos and warranty accruals; valuation of post-employment and postretirement benefits; valuation, depreciation and amortization of long-lived assets; valuation of non-current notes receivable; valuation of goodwill; and allowances for doubtful accounts. We believe our assumptions and estimates are reasonable and appropriate. However, due to the inherent uncertainties in making estimates, actual results could differ from those estimates.
Noncontrolling interests — Effective January 1, 2009, we adopted the provisions of a new accounting standard which changed the presentation of noncontrolling interests in subsidiaries. The format of our consolidated statement of operations, consolidated balance sheet, consolidated statement of cash flows and consolidated statement of stockholders equity and comprehensive income (loss) have been reclassified to conform to the new presentation which was required to be applied retrospectively.
Discontinued operations — We classify a business component that either has been disposed of or is classified as held for sale as a discontinued operation if the cash flow of the component has been or will be eliminated from our ongoing operations and we will no longer have any significant continuing involvement in the component. The results of operations of our discontinued operations through the date of sale, including any gains or losses on disposition, are aggregated and presented on two lines in the income statement. Amounts presented for prior years are reclassified to reflect their classification as discontinued operations. See Note 22 for additional information regarding discontinued operations.
Cash and cash equivalents — For purposes of reporting cash flows, we consider highly liquid investments with maturities of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents. Marketable securities that satisfy the criteria for cash equivalents are classified accordingly.
The ability to move cash among operating locations is subject to the operating needs of those locations in addition to locally imposed restrictions on the transfer of funds in the form of dividends, cash advances or loans. In addition, we must meet distributable reserve requirements. Restricted net assets related to our consolidated subsidiaries, which totaled $170 as of December 31, 2009, are attributable to our operations in Venezuela and China which are subject to governmental limitations on their ability to transfer funds outside each of those countries. During 2009, 2008 and 2007, the parent company received dividends of $121, $124 and $76 from consolidated subsidiaries. Dividends of $2, $10 and less than $1 were received from less-than-50%-owned affiliates in 2009, 2008 and 2007.
Inventories — Inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market. Cost is generally determined on the average orfirst-in-first-out (FIFO) cost basis. In connection with our adoption of fresh start accounting on February 1, 2008, inventories were revalued using the methodology outlined in Note 21 and increased by $169, including the elimination of theU.S. last-in-first-out (LIFO) reserve of $120 which restored our inventory to a FIFO basis. The remaining valuation increase of $49 was recognized in cost of sales, as the inventory was sold, negatively impacting gross margin primarily in the first quarter with a nominal amount in the second quarter of 2008. On January 1, 2009, we changed our method of accounting for inventory in the U.S. from LIFO to FIFO. The consolidated financial statements include the retroactive application of this change. See Note 4 for additional information regarding inventories.
52
Table of Contents
Property, plant and equipment — As a result of our adoption of fresh start accounting on February 1, 2008, property, plant and equipment was stated at fair value (see Note 21) with useful lives ranging from two to thirty years. Useful lives of newly acquired assets are generally twenty to thirty years for buildings and building improvements, five to ten years for machinery and equipment, three to five years for tooling and office equipment and three to ten years for furniture and fixtures. Depreciation is recognized over the estimated useful lives using primarily the straight-line method for financial reporting purposes and accelerated depreciation methods for federal income tax purposes. Prior to the Effective Date, property, plant and equipment of Prior Dana was recorded at cost. If assets are impaired, their value is reduced via an increase in the depreciation reserve.
Pre-production costs related to long-term supply arrangements — The costs of tooling used to make products sold under long-term supply arrangements are capitalized as part of property, plant and equipment and amortized over their useful lives if we own the tooling or if we fund the purchase but our customer owns the tooling and grants us the irrevocable right to use the tooling over the contract period. If we have a contractual right to bill our customers, costs incurred in connection with the design and development of tooling are carried as a component of other accounts receivable until invoiced. Design and development costs related to customer products are deferred if we have an agreement to collect such costs from the customer; otherwise, they are expensed when incurred. At December 31, 2009, the machinery and equipment component of property, plant and equipment included $12 of our tooling related to long-term supply arrangements and less than $1 of our customers’ tooling which we have the irrevocable right to use, while trade and other accounts receivable included $25 of costs related to tooling that we have a contractual right to collect from our customers.
Impairment of long-lived assets — We review the carrying value of amortizable long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of the assets to the undiscounted future net cash flows expected to be generated by the assets. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying amount of the assets exceeds the fair value of the assets. Assets to be disposed of are reported at the lower of the carrying amount or fair values less costs to sell and are no longer depreciated. See Note 6 for a discussion of long-lived asset impairment.
Goodwill — Goodwill recorded at emergence represented the excess of the reorganization value of Dana over the fair value of specific tangible and intangible assets. We test goodwill for impairment at least annually as of October 31 and more frequently if conditions arise that warrant an interim review. In assessing the recoverability of goodwill, estimates of fair value are based upon consideration of various valuation methodologies, including projected future cash flows and multiples of current earnings. If these estimates or related projections change in the future, we may be required to record goodwill impairment charges. See Note 6 for more information regarding goodwill and a discussion of the impairment of goodwill in the second and third quarters of 2008.
Intangible assets — Intangible assets were recorded at their estimated fair value at emergence and include the value of core technology, trademarks and trade names and customer relationships. Customer contracts and developed technology have finite lives while substantially all of the trademarks and trade names have indefinite lives. Definite-lived intangible assets are amortized over their useful life using the straight-line method of amortization and are periodically reviewed for impairment indicators. Indefinite-lived intangible assets are reviewed for impairment annually or more frequently if impairment indicators exist. Historically, we carried nominal values for acquired patent and trademark intangibles at cost. See Note 6 for more information about intangible assets.
Long-lived assets and liabilities — In connection with the application of fresh start accounting, we discounted our asbestos and worker’s compensation liabilities and the related amounts recoverable from insurers. We discounted the projected cash flows using a risk-free rate of 4.0%, which we
53
Table of Contents
interpolated for the applicable period using U.S. Treasury rates. Use of a risk free rate was considered appropriate given that other risks affecting the volume and timing of payments had been considered in developing the probability-weighted projected cash flows.
Financial instruments — The reported fair values of financial instruments are based on a variety of factors. Where available, fair values represent quoted market prices for identical or comparable instruments. Where quoted market prices are not available, fair values are estimated based on assumptions concerning the amount and timing of estimated future cash flows and assumed discount rates reflecting varying degrees of credit risk. Fair values may not represent actual values of the financial instruments that could be realized as of the balance sheet date or that will be realized in the future.
The carrying values of cash and cash equivalents, trade receivables and short-term borrowings approximate fair value. Foreign currency forward contracts, the interest rate swap contracts and long-term notes receivable are carried at their fair values. Borrowings under our credit facilities are carried at historical cost and adjusted for amortization of premiums or discounts, foreign currency fluctuations and principal payments.
Derivative financial instruments — We enter into forward currency contracts to hedge our exposure to the effects of currency fluctuations on a portion of our projected sales and purchase commitments. The changes in the fair value of these contracts are recorded in cost of sales and are generally offset by exchange gains or losses on the underlying exposures. We may also use interest rate swaps to manage exposure to fluctuations in interest rates and to adjust the mix of our fixed and floating rate debt. We do not use derivatives for trading or speculative purposes, and we do not hedge all of our exposures.
All derivative instruments are recognized on the balance sheet at fair value. Forward currency contracts have not been designated as hedges, and the effect of marking these instruments to market has been recognized in the results of operations.
Environmental compliance and remediation — Environmental expenditures that relate to current operations are expensed or capitalized as appropriate. Expenditures that relate to existing conditions caused by past operations that do not contribute to our current or future revenue generation are expensed. Liabilities are recorded when environmental assessmentsand/or remedial efforts are probable and the costs can be reasonably estimated. We consider the most probable method of remediation, current laws and regulations and existing technology in determining our environmental liabilities.
Pension and other postretirement benefits — We sponsor a number of defined benefit pension plans covering eligible salaried and hourly employees. Benefits are determined based upon employees’ length of service, wages or a combination of length of service and wages. Our practice is to fund these costs through deposits with trustees in amounts that, at a minimum, satisfy the applicable local funding regulations. We also provide other postretirement benefits, including medical and life insurance, for certain eligible employees upon retirement. Benefits are determined primarily based upon employees’ length of service and include applicable employee cost sharing. Our policy is to fund these benefits as they become due.
Annual net pension and postretirement benefits expenses and the related liabilities are determined on an actuarial basis. These plan expenses and obligations are dependent on management’s assumptions developed in consultation with our actuaries. We review these actuarial assumptions at least annually and make modifications when appropriate. With the input of independent actuaries and other relevant sources, we believe that the assumptions used are reasonable; however, changes in these assumptions, or experience different from that assumed, could impact our financial position, results of operations, or cash flows. See Note 10 for additional information about these plans.
Postemployment benefits — Costs to provide postemployment benefits to employees are accounted for on an accrual basis. Obligations that do not accumulate or vest are recorded when payment of
54
Table of Contents
the benefits is probable and the amounts can be reasonably estimated. Our policy is to fund these benefits equal to our cash basis obligation. Annual net postemployment benefits expense and the related liabilities are accrued as service is rendered for those obligations that accumulate or vest and can be reasonably estimated.
Equity-based compensation — We measure compensation cost arising from the grant of share-based awards to employees at fair value. We recognize such costs in income over the period during which the requisite service is provided, usually the vesting period.
Revenue recognition — Sales are recognized when products are shipped and risk of loss has transferred to the customer. We accrue for warranty costs, sales returns and other allowances based on experience and other relevant factors, when sales are recognized. Adjustments are made as new information becomes available. Shipping and handling fees billed to customers are included in sales, while costs of shipping and handling are included in cost of sales. We record taxes collected from customers on a net basis (excluded from revenues).
Supplier agreements with our original equipment manufacturers (OEM) customers generally provide for fulfillment of the customers’ purchasing requirements over vehicle program lives, which generally range from three to ten years. Prices for product shipped under the programs are established at inception, with subsequent pricing adjustments mutually agreed through negotiation. Pricing adjustments are occasionally determined retroactively based on historical shipments and either paid or received, as appropriate, in lump sum to effectuate the price settlement. Proceeds from retroactive price increases are deferred upon receipt and amortized over the remaining life of the appropriate program, unless the retroactive price increase was determined to have been received under contract or legal provisions, in which case revenue is recognized upon receipt.
Foreign currency translation — The financial statements of subsidiaries and equity affiliates outside the U.S. located in non-highly inflationary economies are measured using the currency of the primary economic environment in which they operate as the functional currency, which typically is the local currency. Transaction gains and losses resulting from translating assets and liabilities of these entities into the functional currency are included in other income, net or in equity earnings. When translating into U.S. dollars, income and expense items are translated at average monthly rates of exchange, while assets and liabilities are translated at the rates of exchange at the balance sheet date. Translation adjustments resulting from translating the functional currency into U.S. dollars are deferred and included as a component of comprehensive loss in stockholders’ equity. For operations whose functional currency is the U.S. dollar, non-monetary assets are translated into U.S. dollars at historical exchange rates and monetary assets are translated at current exchange rates.
Income taxes — In the ordinary course of business there is inherent uncertainty in quantifying our income tax positions. We assess our income tax positions and record tax liabilities for all years subject to examination based upon management’s evaluation of the facts and circumstances and information available at the reporting dates. For those tax positions where it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will be sustained, we have recorded the largest amount of tax benefit with a greater-than-50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement with a taxing authority that has full knowledge of all relevant information. For those income tax positions where it is not more likely than not that a tax benefit will be sustained, no tax benefit has been recognized in the financial statements. Where applicable, the related interest cost has also been recognized.
Deferred income taxes are provided for future tax effects attributable to temporary differences between the recorded values of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the basis of such assets and liabilities as measured by tax laws and regulations. Deferred income taxes are also provided for net operating losses (NOLs), tax credit and other carryforwards. Amounts are stated at enacted tax rates expected to be in effect when taxes are actually paid or recovered. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in the results of operations in the period that includes the enactment date.
55
Table of Contents
In each reporting period, we assess whether it is more likely than not that we will generate sufficient future taxable income to realize our deferred tax assets. This assessment requires significant judgment and, in making this evaluation, we consider all available positive and negative evidence. Such evidence includes trends and expectations for future U.S. andnon-U.S. pre-tax operating income, our historical earnings and losses, the time period over which our temporary differences and carryforwards will reverse and the implementation of feasible and prudent tax planning strategies. While the assumptions require significant judgment, they are consistent with the plans and estimates we are using to manage the underlying business.
We provide a valuation allowance against our net deferred tax assets if, based upon available evidence, we determine that it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the recorded net deferred tax assets will not be realized in future periods. Creating a valuation allowance serves to increase income tax expense during the reporting period. Once created, a valuation allowance against net deferred tax assets is maintained until realization of the deferred tax asset is judged more likely than not to occur. Reducing a valuation allowance against net deferred tax assets serves to reduce income tax expense in the reporting period of change unless the reduction occurs due to the expiration of the underlying loss or tax credit carryforward period. See Note 17 for an explanation of the valuation allowance adjustments made for our net deferred tax assets and additional information on income taxes.
Earnings per share — Basic earnings per share is computed by dividing earnings available to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Prior Dana shares were cancelled at emergence and shares in Dana were issued. Therefore the earnings per share information for Dana is not comparable to Prior Dana earnings per share. See Note 8 for details of the shares outstanding.
Subsequent Events — Companies are required to recognize in the financial statements the effects of subsequent events that provide additional evidence about conditions that existed at the date of the balance sheet including the estimates inherent in the process of preparing financial statements. Subsequent events that provide evidence about conditions that did not exist at the balance sheet date but arose before the financial statements are issued are required to be disclosed if significant. We have properly considered subsequent events through February 24, 2010, the date of thisForm 10-K filing and the date of issuance of the financial statements.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In June 2009, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued guidance regarding accounting for transfers of financial assets. The guidance seeks to improve the relevance and comparability of the information that a reporting entity provides in its financial statements about a transfer of financial assets; the effects of a transfer on its financial position, financial performance and cash flows; and a transferor’s continuing involvement, if any, in transferred financial assets. The guidance eliminates the concept of a qualifying special-purpose entity, creates more stringent conditions for reporting a transfer of a portion of a financial asset as a sale, clarifies other sale-accounting criteria and changes the initial measurement of a transferor’s interest in transferred financial assets. The guidance is effective January 1, 2010. The adoption of this guidance is not expected to have a significant impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In June 2009, the FASB issued additional guidance related to Variable Interest Entities (VIEs) and the determination of whether an entity is a VIE. Companies are required to perform an analysis to determine whether the enterprise’s variable interest or interests give it a controlling financial interest in a VIE. The guidance requires ongoing assessments of whether an enterprise is the primary beneficiary of a VIE, requires enhanced disclosures and eliminates the scope exclusion for qualifying special-purpose entities. The guidance is effective January 1, 2010. The adoption of this guidance is not expected to have a significant impact on our consolidated financial statements.
56
Table of Contents
| Note 2. | Divestitures and Acquisitions |
Acquisitions — In June 2007, our subsidiary Dana Mauritius Limited (Dana Mauritius) purchased 4% of the registered capital of Dongfeng Dana Axle Co., Ltd. (Dongfeng Axle, a commercial vehicle axle manufacturer in China formerly known as Dongfeng Axle Co., Ltd.) from Dongfeng Motor Co., Ltd. (Dongfeng Motor) and certain of its affiliates for $5. Dana Mauritius has agreed, subject to certain conditions, to purchase an additional 46% equity interest in Dongfeng Dana Axle Co., Ltd. by June 2010. Under the agreement, our additional interest is based on a valuation of the business which would result in an additional investment of $54 to $77. The actual investment could vary significantly from this range in the event that the parties mutually agree that the operating results and prospects of the venture at the expected closing date of June 30, 2010 support a higher or lower valuation of the business.
Structural Products business — In December 2009, we entered into an agreement with Metalsa S.A. de C.V. (Metalsa) to sell substantially all of our Structural Products business to Metalsa. We had previously evaluated a number of strategic options in our non-driveline light vehicle businesses and had concluded that this product line was not strategic to our core driveline business. Dana will retain a facility of this business in Longview, Texas and will continue to produce products for a large customer at this facility. Accordingly, we have not reported the Structures segment as discontinued operations. The parties expect to complete the sale of all but the Venezuelan operations in March 2010, with Venezuela being completed as soon as the necessary governmental approvals are obtained.
As a result of this agreement we recorded $150 as an impairment of the intangible and long-lived assets in December 2009 and we recorded strategic transaction expenses of $11 associated with the sale in other income, net. The impairment loss was based on expected proceeds of $150 less projected working capital adjustments. Under the terms of our amended Term Facility, we will be required to utilize the proceeds of the sale to pay down our Term Facility debt.
The assets to be sold in this transaction are reported as assets held for sale in our consolidated balance sheet and consist of the following:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
Assets | ||||||||
| Accounts receivable | $ | 62 | $ | 69 | ||||
| Inventories | 34 | 46 | ||||||
| Other current assets | 3 | 6 | ||||||
Current assets held for sale | $ | 99 | $ | 121 | ||||
| Intangibles | 16 | 54 | ||||||
| Investments and other assets | 6 | 7 | ||||||
| Investments in affiliates | 17 | 16 | ||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 65 | 205 | ||||||
Non-current assets held for sale | $ | 104 | $ | 282 | ||||
Liabilities | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 54 | $ | 65 | ||||
| Accrued payroll | 7 | 8 | ||||||
| Other accrued liabilities | 18 | 16 | ||||||
Current liabilities held for sale | $ | 79 | $ | 89 | ||||
Assets held for sale are included in their respective classifications in the detailed explanations of supplemental balance sheet information in Note 5. In the consolidated statement of cash flows, the
57
Table of Contents
cash flows related to assets held for sale have been reported in the respective categories of cash flows, along with those of our continuing operations.
Divestitures — In January 2007, we sold our trailer axle business manufacturing assets for $28 in cash and recorded an after-tax gain of $14. This business did not meet the requirements for treatment as a discontinued operation and its results prior to divestiture were included in continuing operations. See Note 22 for a discussion of the results of discontinued operations.
In March 2007, we sold our 30% equity interest in GETRAG Getriebe-und Zahnradfabrik Hermann Hagenmeyer GmbH & Cie KG (GETRAG) to our joint venture partner, an affiliate of GETRAG, for $207 in cash. An impairment charge of $58 had been recorded in the fourth quarter of 2006 to adjust this equity investment to fair value and an additional charge of $2 after tax was recorded in the first quarter of 2007 based on the value of the investment at closing.
In August 2007, we executed an agreement relating to our two remaining joint ventures with GETRAG. This agreement included the grant of a call option for GETRAG to acquire our interests in these joint ventures for $75 and our payment of GETRAG claims of $11 under certain conditions. We recorded the $11 claim in liabilities subject to compromise and as an expense in other income, net in the second quarter of 2007. In September 2008, we amended our agreement with GETRAG and reduced the call option purchase price to $60, extended the call option exercise period to September 2009 and eliminated the $11 liability. As a result of the reduced call price, we recorded an asset impairment charge of $15 in the third quarter of 2008 in equity in earnings of affiliates. We are now recognizing the equity in earnings of GETRAG beginning with the expiration of the call in September 2009.
| Note 3. | Restructuring of Operations |
Restructuring of our manufacturing operations was an essential component of our Chapter 11 reorganization plans and remains a primary focus of management. We continue to eliminate excess capacity by closing and consolidating facilities and repositioning operations in lower cost facilities or those with excess capacity and focusing on reducing and realigning overhead costs. Restructuring expense includes costs associated with current and previously announced actions including various workforce reduction programs, manufacturing footprint optimization actions and other restructuring activities across our global businesses.
During 2007, we completed the closure of fifteen facilities. Included in 2007 restructuring charges is $69 relating primarily to the ongoing facility closure activities associated with previously announced manufacturing footprint actions and other restructuring or downsizing actions. The remaining $136 represents pension curtailment and settlement costs associated with our restructured U.K. operations (see Note 10).
In response to increased economic and market challenges during 2008, particularly lower production volumes, we initiated additional cost reduction actions, resulting in a reduction of our global workforce by approximately 6,000 employees, including approximately 5,000 in North America. During 2008, we recorded a total of $73 of severance and other related benefit costs and $53 of long-lived asset impairment and exit costs associated with the 2008 actions described below, as well as with other previously announced actions.
Significant 2008 actions included the closure of certain manufacturing facilities, including our Barrie, Ontario facility in our Commercial Vehicle business as well as our Magog, Quebec facility and our Venezuelan foundry operation in our LVD business. Restructuring expense in 2008 included severance and other costs associated with the termination of employees at these facilities, costs incurred to transfer certain manufacturing operations to Mexico, and accelerated depreciation of certain manufacturing equipment.
In the third quarter of 2008, we entered into an agreement to sell our corporate headquarters. The book value in excess of sale proceeds was recognized as accelerated depreciation and recorded as
58
Table of Contents
restructuring expense from the date we entered the agreement through the closing of the agreement in February 2009. Under the terms of the agreement, we received proceeds of $11. Due to the conditions under which we continued to occupy the facility, we deferred the recognition of the sale until June 2009.
During the fourth quarter of 2008, we also offered a voluntary separation program to our salaried workforce, predominantly in the U.S. and Canada and incurred costs of $17 associated with approximately 275 employees who accepted this offer and terminated employment during the fourth quarter of 2008. Certain other employees in North America accepted the offer of voluntary separation but the separation was deferred until a specified date in the first quarter of 2009. An additional charge of $10 for severance and related benefit costs for approximately 125 additional employees was incurred during the first quarter of 2009.
The adverse economic conditions first experienced in 2008 continued into 2009, prompting further cost reduction actions. We reduced our headcount during 2009 from 29,000 at the end of 2008 to 24,000 at the end of 2009. Workforce reductions and other actions in 2009 resulted in a net charge of $83 for severance and other related benefit costs. Our 2009 cost reduction actions included the announced closures of the Mississauga, Ontario facility in our Thermal business; the Brantford, Ontario and Orangeburg, South Carolina facilities in our LVD business; the McKenzie, Tennessee and Calatayud, Spain facilities in our Sealing business and the Beamsville, Ontario and Glasgow, Kentucky facilities supporting our Commercial Vehicle business. In January 2010, we announced our plans to consolidate our Heavy Vehicle operations which will result in the closing of the Kalamazoo, Michigan and Statesville, North Carolina facilities. Certain costs associated with this consolidation were accrued in 2009.
Restructuring charges during 2009 also included $35 of long-lived asset impairments and exit costs incurred for transfers of production activities among facilities and previously announced facility closures.
59
Table of Contents
The following tables show the restructuring charges and related payments and adjustments, including the amounts accrued in January 2008 under fresh start accounting but exclusive of the U.K. pension charges discussed above, recorded in our continuing operations during 2009, 2008 and 2007.
| Employee | Long-Lived | |||||||||||||||
| Termination | Asset | Exit | ||||||||||||||
| Benefits | Impairment | Costs | Total | |||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2006 | $ | 64 | $ | — | $ | 10 | $ | 74 | ||||||||
| Activity during the year: | ||||||||||||||||
| Charged to restructuring | 33 | 18 | 50 | 101 | ||||||||||||
| Adjustments of accruals | (29 | ) | (3 | ) | (32 | ) | ||||||||||
| Non-cash write-off | (18 | ) | (18 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Cash payments | (15 | ) | (42 | ) | (57 | ) | ||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2007 | 53 | 15 | 68 | |||||||||||||
| Activity during the period: | ||||||||||||||||
| Charged to restructuring | 7 | 2 | 3 | 12 | ||||||||||||
| Fresh start adjustment | 32 | 32 | ||||||||||||||
| Non-cash write-off | (2 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Cash payments | (2 | ) | (3 | ) | (5 | ) | ||||||||||
| Balance at January 31, 2008 | 58 | 47 | 105 | |||||||||||||
| Activity during the period: | ||||||||||||||||
| Charged to restructuring | 77 | 14 | 34 | 125 | ||||||||||||
| Adjustments of accruals | (11 | ) | (11 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Non-cash write-off | (14 | ) | (14 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Cash payments | (62 | ) | (66 | ) | (128 | ) | ||||||||||
| Currency impact | (7 | ) | (5 | ) | (12 | ) | ||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2008 | 55 | 10 | 65 | |||||||||||||
| Activity during the year: | ||||||||||||||||
| Charged to restructuring | 91 | 18 | 23 | 132 | ||||||||||||
| Adjustments of accruals | (8 | ) | (6 | ) | (14 | ) | ||||||||||
| Non-cash write-off | (18 | ) | (18 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Cash payments | (114 | ) | (24 | ) | (138 | ) | ||||||||||
| Currency impact | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2009 | $ | 26 | $ | — | $ | 3 | $ | 29 | ||||||||
At December 31, 2009, $29 of restructuring accruals remained in accrued liabilities, including $26 related to continuing benefits and the reduction of approximately 1,000 employees to be completed over the next two years and $3 for lease continuation and other exit costs. The estimated cash expenditures related to these liabilities are projected to approximate $26 in 2010 and $3 thereafter. In addition to the $29 accrued at December 31, 2009, we estimate that another $58 will be expensed in the future to complete previously announced initiatives.
60
Table of Contents
The following table providesproject-to-date and estimated future expenses for completion of our pending restructuring initiatives for our business segments.
| Expense Recognized | Future | |||||||||||||||
| Prior to | Total | Cost to | ||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2009 | to Date | Complete | |||||||||||||
| LVD | $ | 77 | $ | 36 | $ | 113 | $ | 16 | ||||||||
| Structures | 37 | 7 | 44 | 3 | ||||||||||||
| Sealing | 3 | 17 | 20 | 2 | ||||||||||||
| Thermal | 8 | 8 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Off-Highway | 3 | 4 | 7 | 4 | ||||||||||||
| Commercial Vehicle | 42 | 34 | 76 | 32 | ||||||||||||
| Other | 17 | 12 | 29 | |||||||||||||
| Total continuing operations | $ | 179 | $ | 118 | $ | 297 | $ | 58 | ||||||||
The remaining cost to complete includes estimated noncontractual separation payments, lease continuation costs, equipment transfers and other costs which are required to be recognized as closures are finalized or as incurred during the closure.
| Note 4. | Inventories |
The components of inventory at December 31 are as follows:
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
| Raw materials | $ | 300 | $ | 408 | ||||
| Work in process and finished goods | 342 | 507 | ||||||
| Less: assets held for sale | (34 | ) | (46 | ) | ||||
| Total | $ | 608 | $ | 869 | ||||
Our inventory was revalued at emergence from Chapter 11 on January 31, 2008 as described in Note 21 and that valuation became the new book basis for accounting purposes. On January 1, 2009, we changed the method of determining the cost of inventories for our U.S. operations from the LIFO basis to the FIFO basis. Ournon-U.S. operations continue to determine cost using the average or FIFO cost method. We believe the change is preferable as the FIFO method discloses the current value of inventories on the consolidated balance sheet, provides greater uniformity across our operations and enhances our comparability with peers.
We applied the change in accounting method by adjusting the 2008 financial statements for the periods subsequent to our emergence from Chapter 11 on January 31, 2008. As a result of applying fresh start accounting, inventory values at January 31, 2008 had been adjusted to their acquired value which resulted in the LIFO basis equaling the FIFO basis at that date. At December 31, 2008, our FIFO basis exceeded our LIFO basis by $14. The change in accounting from the LIFO to FIFO method for 2008 was recorded as a reduction to cost of sales, resulting in a $14 benefit to operating income from continuing operations for the eleven months ended December 31, 2008. A charge to cost of sales of $34 to amortize the valuationstep-up recorded at January 31, 2008 in connection with fresh start accounting was offset by a $48 reversal of the LIFO provision that had been recorded in that eleven-month period. There is no net effect on income tax expense due to the valuation allowances on U.S. deferred tax assets.
The impacts of this change in costing on the consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2009 and the eleven months ended December 31, 2008 are shown in the table below. We have estimated the 2009 pro forma impact of LIFO using quarterly standard cost
61
Table of Contents
information and our year-end pro forma index calculation due to reduced costs in 2009. On a pro forma basis, the LIFO reserve would have been a debit balance of $1 at the end of 2009.
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Difference | As Reported | As Reported | Adjustments | As Adjusted | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Year | Between | Year | Eleven Months | to Change | Eleven Months | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ended | LIFO | Ended | Ended | from | Ended | |||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, | and | December 31, | December 31, | LIFO | December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 (LIFO) | FIFO | 2009 (FIFO) | 2008 (LIFO) | to FIFO | 2008 (FIFO) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of sales | $ | 4,970 | $ | 15 | $ | 4,985 | $ | 7,127 | $ | (14 | ) | $ | 7,113 | |||||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations before interest, reorganization items and income taxes | (302 | ) | (15 | ) | (317 | ) | (396 | ) | 14 | (382 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations before income taxes | (439 | ) | (15 | ) | (454 | ) | (563 | ) | 14 | (549 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations | (421 | ) | (15 | ) | (436 | ) | (681 | ) | 14 | (667 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | (421 | ) | (15 | ) | (436 | ) | (685 | ) | 14 | (671 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to the parent company | (416 | ) | (15 | ) | (431 | ) | (691 | ) | 14 | (677 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) available to common stockholders | (448 | ) | (15 | ) | (463 | ) | (720 | ) | 14 | (706 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Income (loss) per share from continuing operations attributable to parent company stockholders: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | (4.05 | ) | $ | (0.14 | ) | $ | (4.19 | ) | $ | (7.16 | ) | $ | 0.14 | $ | (7.02 | ) | |||||||
| Diluted | $ | (4.05 | ) | $ | (0.14 | ) | $ | (4.19 | ) | $ | (7.16 | ) | $ | 0.14 | $ | (7.02 | ) | |||||||
| Net income (loss) per share attributable to parent company stockholders: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | (4.05 | ) | $ | (0.14 | ) | $ | (4.19 | ) | $ | (7.20 | ) | $ | 0.14 | $ | (7.06 | ) | |||||||
| Diluted | $ | (4.05 | ) | $ | (0.14 | ) | $ | (4.19 | ) | $ | (7.20 | ) | $ | 0.14 | $ | (7.06 | ) | |||||||
Note: The “as reported” amounts for 2008 are presented after giving effect to the adjustments made to modify the reporting of noncontrolling interests.
The impacts of this change on reported balances at December 31, 2009 and 2008 are as follows:
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Difference | Adjustments | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Between | As Reported | As Reported | to Change | As Adjusted | ||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, | LIFO and | December 31, | December 31, | from LIFO | December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 (LIFO) | FIFO | 2009 (FIFO) | 2008 (LIFO) | to FIFO | 2008 (FIFO) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Inventories | $ | 609 | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 608 | $ | 855 | $ | 14 | $ | 869 | |||||||||||
| Total current assets | 2,583 | (1 | ) | 2,582 | 2,733 | 14 | 2,747 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total assets | 5,065 | (1 | ) | 5,064 | 5,593 | 14 | 5,607 | |||||||||||||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (1,168 | ) | (1 | ) | (1,169 | ) | (720 | ) | 14 | (706 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Total Dana stockholders’ equity | 1,680 | (1 | ) | 1,679 | 2,014 | 14 | 2,028 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total equity | 1,780 | (1 | ) | 1,779 | 2,121 | 14 | 2,135 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total liabilities and equity | 5,065 | (1 | ) | 5,064 | 5,593 | 14 | 5,607 | |||||||||||||||||
Note: The “as reported” amounts for 2008 are presented after giving effect to the adjustments made to modify the reporting of noncontrolling interests.
62
Table of Contents
The impacts of this change on operating cash flow for the year ended December 31, 2009 and eleven months ended December 31, 2008 are as follows:
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjustments | As Reported | As Reported | Adjustments | As Adjusted | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Year | to Change | Year | Eleven Months | to Change | Eleven Months | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ended | from | Ended | Ended | from | Ended | |||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, | LIFO | December 31, | December 31, | LIFO | December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 (LIFO) | to FIFO | 2009 (FIFO) | 2008 (LIFO) | to FIFO | 2008 (FIFO) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | $ | (421 | ) | $ | (15 | ) | $ | (436 | ) | $ | (685 | ) | $ | 14 | $ | (671 | ) | |||||||
| Amortization of inventory valuation | 15 | 34 | 49 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Change in inventory | 284 | 15 | 299 | 42 | (48 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Note: The “as reported” amounts for 2008 are presented after giving effect to the adjustments made to modify the reporting of noncontrolling interests.
During the third quarter of 2009, we reduced inventory and charged cost of sales for $6 to correct an overstatement of inventory related to full absorption costing that arose in 2008. The $6 charge is not included in segment EBITDA, as full absorption adjustments are recorded at the corporate level. This adjustment was not considered material to the current period or the prior periods to which it related.
| Note 5. | Supplemental Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Information |
The following items comprise the amounts indicated in the respective balance sheet captions at December 31:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
Other current assets | ||||||||
| Prepaid expense | $ | 37 | $ | 53 | ||||
| Deferred tax benefits, net | 13 | |||||||
| Other | 12 | 5 | ||||||
| Less: assets held for sale | (3 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||
| Total | $ | 59 | $ | 52 | ||||
Investments and other assets | ||||||||
| Pension assets, net of related obligations | $ | 9 | $ | 23 | ||||
| Amounts recoverable from insurers | 54 | 57 | ||||||
| Deferred financing costs | 37 | 55 | ||||||
| Notes receivable | 94 | 21 | ||||||
| Non-current prepaids | 9 | 7 | ||||||
| Investment in leveraged leases | 4 | 6 | ||||||
| Other | 32 | 38 | ||||||
| Less: assets held for sale | (6 | ) | (7 | ) | ||||
| Total | $ | 233 | $ | 200 | ||||
63
Table of Contents
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
Property, plant and equipment, net | ||||||||
| Land and improvements to land | $ | 284 | $ | 263 | ||||
| Buildings and building fixtures | 439 | 439 | ||||||
| Machinery and equipment | 1,608 | 1,431 | ||||||
| Total cost | 2,331 | 2,133 | ||||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation | (661 | ) | (292 | ) | ||||
| Less: accumulated impairment | (121 | ) | ||||||
| Less: assets held for sale, net | (65 | ) | (205 | ) | ||||
| Net | $ | 1,484 | $ | 1,636 | ||||
Other accrued liabilities (current) | ||||||||
| Warranty reserves, current portion | $ | 56 | $ | 65 | ||||
| Non-income taxes payable | 46 | 25 | ||||||
| Dividends payable | 43 | 11 | ||||||
| Deferred income | 25 | 11 | ||||||
| Environmental | 8 | 8 | ||||||
| Workers compensation obligations | 16 | 23 | ||||||
| Asbestos personal injury liability | 13 | 19 | ||||||
| Accrued interest | 11 | 14 | ||||||
| Accrued legal fees | 10 | 8 | ||||||
| Payable under forward contracts | 4 | 6 | ||||||
| Accrued professional fees | 4 | 3 | ||||||
| Other expense accruals | 52 | 81 | ||||||
| Less: liabilities held for sale | (18 | ) | (16 | ) | ||||
| Total | $ | 270 | $ | 258 | ||||
Deferred employee benefits and other non-current liabilities | ||||||||
| Pension obligations, net of related assets | $ | 643 | $ | 352 | ||||
| Postretirement obligations other than pension | 117 | 94 | ||||||
| Deferred income tax liability | 111 | 100 | ||||||
| Asbestos personal injury liability | 100 | 105 | ||||||
| Non-current income tax liability | 68 | 71 | ||||||
| Workers compensation obligations | 39 | 39 | ||||||
| Warranty reserves | 27 | 35 | ||||||
| Other non-current liabilities | 55 | 49 | ||||||
| Total | $ | 1,160 | $ | 845 | ||||
64
Table of Contents
Supplemental cash flow information —
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||
| Cash paid during the period for: | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest | $ | 99 | $ | 94 | $ | 11 | $ | 51 | |||||||||
| Income taxes | $ | 27 | $ | 89 | $ | 2 | $ | 106 | |||||||||
| Non-cash financing activities: | |||||||||||||||||
| Dividends on preferred stock accrued not paid | $ | 42 | $ | 11 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||
| Per share | $ | 0.38 | $ | 0.11 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||
| Note 6. | Goodwill, Other Intangible Assets and Long-lived Assets |
Goodwill —We test goodwill for impairment on an annual basis unless conditions arise that warrant an interim review. The annual impairment tests are performed as of October 31. In assessing the recoverability of goodwill, estimates of fair value are based upon consideration of various valuation methodologies, including projected future cash flows and multiples of current earnings. If these estimates or related projections change in the future, we may be required to record goodwill impairment charges.
During the second quarter of 2009, our assessment of the effects of the pace of the market recovery on our forecast for the remainder of the year and for future periods led us to conclude that the related reduction in cash flows projected for those periods comprised a triggering event. As a result, we evaluated our Off-Highway goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets of all of our segments to test for impairment using the fair value methodology described in Note 21. For the Off-Highway goodwill evaluation we used the average of a discounted cash flow (DCF) valuation and comparable company multiple valuation. We utilized a discount rate of 12.9% for the DCF analysis and an EBITDA multiple of 7.7 based on comparable companies in similar markets. The updated fair value of the Off-Highway segment supported the carrying value of the net assets of this business at June 30, 2009 and, accordingly, no impairment charge was recorded in the second quarter of 2009.
Our annual assessment of the Off-Highway goodwill was completed as of October 31, 2009. For this valuation, we utilized cash projections based on our current three-year projections. The projections included estimates of changes in production levels, operational efficiencies resulting from our reorganization initiatives, assumptions of commodity costs and assumptions regarding pricing improvements. We utilized a discount rate of 13.3% for the DCF analysis and an EBITDA multiple of 10.9 based on comparable companies in similar markets. This multiple increased from the second quarter analysis due to the stock market recovery in our industry sector. The final valuation was an average of the two methodologies. Our assessment supported the remaining amount of goodwill carried by this segment. However, market conditions or operational execution impacting any of the key assumptions underlying our estimated cash flows could result in future goodwill impairment.
During 2008, we determined that the decline in sales volume and deterioration of margins resulting from higher steel costs in our driveshaft business, along with the related impact on projected cash flows, constituted a triggering event in that reporting unit. As a result, the corresponding goodwill was tested for impairment in the second quarter of 2008. For the June 30, 2008 valuation, we utilized cash projections based on our five-year projections. The projections included estimates of changes in production levels, operational efficiencies resulting from our reorganization initiatives, assumptions of commodity costs and assumptions regarding pricing improvements. We utilized a discount rate of 10.3% for the DCF analysis and an EBITDA multiple of 4.8 based on comparable companies in similar markets. The final valuation was an average of the two methodologies. The updated fair value of the reporting unit did not support the full amount of the recorded goodwill at June 30 and, accordingly, our
65
Table of Contents
results of operations for the second quarter of 2008 included a goodwill impairment charge of $75 to reduce the goodwill recorded in the driveshaft reporting unit.
Fuel and steel costs began to fall in the latter half of the third quarter of 2008, but declines in consumer confidence and economic conditions in general triggered a tightening of credit, causing sales in all of our markets to decline further and the forecast for our driveshaft reporting unit to be revised again. As a result of this triggering event, the goodwill in our driveshaft reporting unit was tested for impairment at the end of the third quarter. For the September 30, 2008 valuation, we utilized cash projections based on updated five-year projections. The projections included estimates of changes in production levels, operational efficiencies resulting from our reorganization initiatives, revised assumptions of commodity costs and updated assumptions regarding pricing improvements. We utilized a discount rate of 10.6% for the DCF analysis and an EBITDA multiple of 3.7 based on comparable companies in similar markets. The final valuation was an average of the two methodologies. The updated fair value of the driveshaft reporting unit did not support any goodwill at September 30, 2008 and, accordingly, we recorded an impairment charge of $105 in the third quarter of 2008 to eliminate the remaining goodwill in the driveshaft reporting unit.
Under the segment structure in place in 2008, the driveshaft reporting unit comprised the Driveshaft reporting segment. As part of the modification of our reporting segment structure in the first quarter of 2009, we have allocated the goodwill associated with the former Driveshaft segment to the LVD (34%) and Commercial Vehicle (66%) segments based on the relative fair values of the underlying operations. The impairment charges identified herein have been allocated to those segments; however, impairment charges are excluded from segment EBITDA as defined in Note 19.
We evaluated goodwill as of October 31, 2008 and no impairment was indicated. Based on market conditions in the Off-Highway segment that had deteriorated in the fourth quarter and resulted in a decline in our projections, we updated the valuation of the goodwill for this segment as of December 31, 2008. We utilized a discount rate of 14.6% for the DCF analysis and an EBITDA multiple of 4.4 based on comparable companies in similar markets. The final valuation was an average of the two methodologies. Our assessment as of December 31, 2008 continued to support the remaining amount of goodwill carried by this segment.
Changes in goodwill during 2008 by segment were as follows:
DANA HOLDING CORPORATION
Goodwill Walkforward
| Commercial | Off- | |||||||||||||||||||||||
2008 | LVD | Sealing | Thermal | Vehicle | Highway | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
Beginning balance | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Goodwill | $ | 59 | $ | 26 | $ | 120 | $ | 114 | $ | 119 | $ | 438 | ||||||||||||
| Impairment | (89 | ) | (89 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Goodwill, net | 59 | 26 | 31 | 114 | 119 | 349 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Adjustments to goodwill | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fresh start | 1 | (26 | ) | (120 | ) | 1 | 5 | (139 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Currency and other | (3 | ) | (3 | ) | (16 | ) | (22 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| (2 | ) | (26 | ) | (120 | ) | (2 | ) | (11 | ) | (161 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Adjustments to impairment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fresh start | 89 | 89 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Goodwill impairment | (57 | ) | (112 | ) | (169 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| (57 | ) | 89 | (112 | ) | (80 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Ending balance | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Goodwill | 57 | 112 | 108 | 277 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Accumulated impairment | (57 | ) | (112 | ) | (169 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Goodwill, net | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 108 | $ | 108 | ||||||||||||
66
Table of Contents
In 2009, the goodwill balance of $108 in the Off-Highway segment increased to $111 as a result of foreign exchange translation.
Goodwill of $173 was reported in our former Driveshaft segment at the end of 2007. The amount was increased to $175 as part of fresh start accounting. In the eleven months ended December 31, 2008 this goodwill was fully impaired. The related impairment charge was reduced by $13 as a result of pre-emergence income tax adjustments that effectively reduced the amount of goodwill. An additional $9 of the pre-emergence tax adjustments reduced Off-Highway goodwill in 2008.
Other intangible assets —Intangible assets include core technology, trademarks and trade names and customer relationships. Core technology includes the proprietary know-how and expertise that is inherent in our products and manufacturing processes. Trademarks and trade names include our trade names related to product lines and the related trademarks including Dana ®, Spicer ®, Victor-Reinz ® and Long ®. Customer relationships include the established relationships with our customers and the related ability of these customers to continue to generate future recurring revenue and income.
Due to the second-quarter 2009 assessment of our forecasted results noted above, we performed impairment testing on our indefinite-lived intangible assets as of June 30, 2009 and determined that the fair value of trademarks and trade names had declined below the carrying value. These valuations resulted in impairments of $4 and $2 in our Commercial Vehicle and Off-Highway segments in the second quarter of 2009 which we reported as impairment of intangible assets. We utilized an income approach, the relief from royalty method, to determine the fair value of our trademarks and trade names. See Note 13 for the fair value of trademarks and trade names.
We completed the annual assessment of our indefinite-lived intangible assets as of October 31, 2009. We used the fair value methodology as described in Note 21. Our assessment supported the carrying amounts of the intangible assets at that time.
In connection with the anticipated divestiture of substantially all of the assets of our Structural Products business, as discussed above, we assessed the recoverability of our definite-lived intangible assets in the Structures segment. Based on the expected selling price of the related assets, we recorded an impairment of $29 to impair the segment’s intangible assets.
During 2008, due to the triggering economic events in our former Driveshaft segment noted above, we performed impairment testing on this segment’snon-amortizable intangible assets as of June 30, 2008 and, based on market declines and revised forecasts, we determined the need to assess the intangible assets in several additional segments at September 30, 2008. We determined that the fair value of these intangible assets had declined in the Driveshaft segment in the second quarter of 2008 resulting in an impairment charge of $7. In the third quarter of 2008, the fair value of a trademark in our Commercial Vehicle segment indicated an impairment of $3. In the fourth quarter, we reviewed valuations as of October 31 and updated those valuations as of December 31, 2008. These valuations resulted in impairments of $1 in the former Driveshaft segment and $3 in the Off-Highway segment in the fourth quarter of 2008.
67
Table of Contents
The following table summarizes the components of other intangible assets:
| Weighted | December 31, 2009 | December 31, 2008 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average | Gross | Accumulated | Net | Gross | Accumulated | Net | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Useful Life | Carrying | Impairment and | Carrying | Carrying | Impairment and | Carrying | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (years) | Amount | Amortization | Amount | Amount | Amortization | Amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortizable intangible assets | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Core technology | 7 | $ | 98 | $ | (31 | ) | $ | 67 | $ | 97 | $ | (14 | ) | $ | 83 | |||||||||||||
| Trademarks and trade names | 17 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Customer relationships | 8 | 483 | (165 | ) | 318 | 476 | (65 | ) | 411 | |||||||||||||||||||
Non-amortizable intangible assets | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Trademarks and trade names | 65 | 65 | 72 | 72 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Less: Assets held for sale | (62 | ) | 46 | (16 | ) | (62 | ) | 8 | (54 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 588 | $ | (150 | ) | $ | 438 | $ | 586 | $ | (71 | ) | $ | 515 | |||||||||||||||
The net carrying amounts of intangible assets attributable to each of our operating segments at December 31, 2009 were as follows: LVD — $23, Sealing — $38, Thermal — $18, Commercial Vehicle — $193, Off-Highway — $166 and Structures — $16. The Structures intangible assets are reported as assets held for sale. Intangible assets in the Structures segment were impaired by $29 in the fourth quarter of 2009 with $1 and $28 included in core technology and customer relationship accumulated impairment and amortization in the table above.
Amortization expense related to intangible assets was $86 and $81 in 2009 and 2008. Amortization of core technology of $15 and $15 was charged to cost of sales and amortization of trademarks and trade names and customer relationships of $71 and $66 was charged to amortization of intangibles.
Estimated aggregate pre-tax amortization expense related to intangible assets for each of the next five years is as follows: 2010 — $64, 2011 — $63, 2012 — $63, 2013 — $62, and 2014 — $60. These amounts exclude the Structures intangibles which are held for sale. Actual amounts may differ from these estimates due to such factors as currency translation, customer turnover, impairments, additional intangible asset acquisitions and other events.
Long-lived assets —With our adoption of fresh start accounting upon emergence, assets were revalued to new carrying values based on our enterprise reorganization value and, in some cases, the appraised values of long-lived assets are higher than their previous net book value. These increased valuations for fresh start accounting purposes subject us to greater risks of future impairment.
Long-lived assets are tested for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that their carrying amounts may not be recoverable. Recoverability of these assets is determined by comparing the forecasted undiscounted net cash flows of the operation in which the assets are utilized to their carrying amount. If those cash flows are determined to be less than the carrying amount of the assets, the long-lived assets of the operation (excluding goodwill) are written down to fair value if the fair value is lower than the carrying amount. We estimate fair value using a DCF approach or appraisal as appropriate.
Asset impairments often result from significant actions like the discontinuance of customer programs, facility closures or other events which result in the assets being held for sale. When this occurs, the specific assets are adjusted to their fair value less cost to sell or dispose. A number of recent restructuring actions have been completed and a few remain in process. Long-lived assets that continue to be used internally are evaluated for impairment, in the aggregate, by business
68
Table of Contents
segment given the global nature of the business segment operation, the interdependency of operations within the segment and the ability to reallocate assets within the segment.
Based on the second-quarter 2009 assessment of our forecasted results noted above, we evaluated our long-lived assets in each segment for impairment. We reviewed the recoverability of these assets by comparing the carrying amount of the assets to the projected undiscounted future net cash flows expected to be generated. These assessments supported the carrying values of the long-lived assets at the end of the second quarter of 2009; however, market conditions or operational execution impacting any of the key assumptions underlying our estimated cash flows could result in future long-lived asset impairment.
In connection with the planned divestiture of substantially all of the assets of our Structural Products business, we assessed the recoverability of our long-lived assets in the Structures segment in the fourth quarter of 2009. We recorded a charge of $150 to impair this segment’s long-lived assets, with $121 related to property, plant and equipment and $29 related to amortizable intangible assets.
We had evaluated the long-lived assets in certain of our light vehicle market businesses as of June 30, 2008 and determined that the projected undiscounted future net cash flows were adequate to recover the carrying value of those assets. During the second half of 2008, consumer interest continued to shift from pickups and SUVs — important vehicle platforms for us — to smaller vehicles in which we have less content. Production levels continued to drop causing our earnings outlook for many of our businesses to decline. As a result of these declines, we evaluated the long-lived assets of five of our segments for potential impairment as of September 30, 2008 and again at December 31, 2008. We reviewed the recoverability of the assets by comparing the carrying amount of the assets to the projected undiscounted future net cash flows expected to be generated. These assessments supported the carrying values of the long-lived assets and no impairment of those assets was recorded in the third or fourth quarter of 2008.
Equity investments — Based on a revised outlook for 2010 and beyond, we reassessed the valuation of our equity investment in Bendix-Spicer Foundation Brakes LLC. We utilized a discount rate of 12.6% for the DCF analysis and an EBITDA multiple of 9.7 based on comparable companies in similar markets. The final valuation was an average of the two methodologies. Our analysis indicated an impairment of $4 which was charged to equity in earnings of affiliates in the fourth quarter of 2009.
| Note 7. | Capital Stock |
Series A and Series B Preferred Stock
Issuance —Pursuant to the Plan, we issued 2.5 million shares of our Series A Preferred and 5.4 million shares of our Series B Preferred on the Effective Date. The Series A Preferred was sold to Centerbridge Partners, L.P. and certain of its affiliates (Centerbridge) for $250, less a commitment fee of $3 and expense reimbursement of $5, resulting in net proceeds of $242. The Series B Preferred was sold to certain qualified investors (as described in the Plan) for $540, less a commitment fee of $11, resulting in net proceeds of $529.
Conversion rights —In accordance with the terms of the preferred stock, all of the shares of preferred stock are, at the holder’s option, convertible into a number of fully paid and non-assessable shares of common stock at the initial conversion price of $13.19. This price is subject to certain adjustments when dilution occurs (based on a formula set forth in the Restated Certificate of Incorporation). Following our issuance of an additional 39 million shares in a common stock offering completed in September and October 2009 (see Note 12), the preferred stock conversion price was lowered to $11.93. At this price, our preferred shares would convert into approximately 66.2 million shares of common stock.
Shares of Series A Preferred having an aggregate liquidation preference of not more than $125 and the Series B Preferred is convertible at any time at the option of the applicable holder after
69
Table of Contents
July 31, 2008. The remaining shares of Series A Preferred are convertible after January 31, 2011. In addition, we will be able to cause the conversion of all, but not less than all, of the preferred stock, if the per share closing price of the common stock exceeds $22.24 for at least 20 consecutive trading days beginning on or after January 31, 2013. This price is subject to adjustment under certain customary circumstances, including as a result of stock splits and combinations, dividends and distributions and certain issuances of common stock or common stock derivatives.
In connection with the issuance of the preferred stock, we entered into certain Registration Rights Agreements and a Shareholders Agreement. The Registration Rights Agreements provide registration rights for the shares of our preferred stock and certain other of our equity securities. On the Effective Date, we also entered into a Shareholders Agreement with Centerbridge containing certain preemptive rights related to approval of Board members and approvals of significant transactions as well as restrictions related to Centerbridge’s ability to acquire additional shares of our common stock.
Centerbridge is limited for ten years from the Effective Date in its ability to acquire additional shares of our common stock, par value $0.01 per share, if it would own more than 30% of the voting power of our equity securities after such acquisition, or to take certain other actions to control us after the Effective Date without the consent of a majority of our Board of Directors (excluding directors elected by the holders of Series A Preferred or nominated by the Series A Nominating Committee for election by the holders of common stock).
Right to select board members —Pursuant to the Shareholders Agreement and our Restated Certificate of Incorporation as long as shares of Series A Preferred having an aggregate Series A Liquidation Preference (as defined in the Shareholders Agreement) of at least $125 are owned by Centerbridge, Centerbridge will be entitled, voting as a separate class, to elect three directors at each meeting of stockholders held for the purpose of electing directors, at least one of whom will be “independent” of both Dana and Centerbridge, as defined under the rules of the New York Stock Exchange. A special committee consisting of two directors designated by Centerbridge and one non-Centerbridge director selected by the board will nominate a fourth director who must be unanimously approved by this committee.
Approval rights —Until January 31, 2011, so long as Centerbridge owns Series A Preferred having a liquidation preference of at least $125, Centerbridge’s approval is required for us to be able to enter into certain material transactions, issue debt or equity below market price, repurchase shares, enter into merger transactions or pay dividends on common stock.
Centerbridge’s approval rights are subject to override by a vote of two-thirds of our voting securities not owned by Centerbridge or any of its affiliates, and its approval rights for dividends and the issuance of senior or pari passu securities will end no later than January 31, 2011.
Dividends —Dividends on the preferred stock have been accrued from the issue date at a rate of 4% per annum and are payable in cash on a quarterly basis as approved by the Board of Directors. The payment of preferred dividends was suspended in November 2008 under the terms of our amended Term Facility and may resume at the discretion of our Board of Directors when our total leverage ratio as of the end of the previous fiscal quarter is less than or equal to 3.25:1.00. See Note 12 for additional information on the amended Term Facility. Preferred dividends accrued but not paid at December 31, 2009 were $42.
Common Stock
On the Effective Date, we began the process of issuing 100 million shares of Dana common stock, par value $0.01 per share, including approximately 70 million shares for allowed unsecured nonpriority claims, approximately 28 million shares for disputed unsecured nonpriority claims in Class 5B under the Plan and approximately 2 million shares to pay bonuses to union employees and non-union hourly and salaried non-management employees. We relied, based on the Confirmation
70
Table of Contents
Order, on Section 1145(a)(1) of the Bankruptcy Code to exempt us from the registration requirements of the Securities Act for the offer and sale of the common stock to the general unsecured creditors.
On September 29, 2009, we completed an underwritten offering of 34 million shares of common stock at $6.75 per share, generating proceeds of $217, net of underwriting commissions and related offering expenses (see Note 12). On October 5, 2009, we completed the sale of an additional 5 million shares, generating net proceeds of $33. At December 31, 2009, we had issued 139,542,825 shares of our common stock, including treasury shares.
Employees have delivered to us shares of Dana common stock in settlement of withholding taxes due upon the payment of stock awards and other taxable distributions of shares. At December 31, 2009, we held $1 in treasury stock (128,676 shares at an average cost per share of $7.26).
| Note 8. | Earnings Per Share |
The following table reconciles the weighted-average number of shares used in the basic earnings per share calculations to the weighted-average number of shares used to compute diluted earnings per share (in millions of shares):
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||
| Weighted-average number of shares outstanding — basic | 110.2 | 100.1 | 149.9 | 149.9 | |||||||||||||
| Employee compensation-related shares, including stock options | 0.5 | ||||||||||||||||
| Weighted-average number of shares outstanding — diluted | 110.2 | 100.1 | 150.4 | 149.9 | |||||||||||||
Basic earnings (loss) per share is calculated by dividing the net income (loss) attributable to parent company stockholders, less preferred stock dividend requirements, by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding. The outstanding common shares computation excludes any shares held in treasury.
In September and October 2009, we issued an additional 39 million shares in a common stock offering (see Note 12). The terms of our Series A and Series B convertible preferred stock allow for adjustments to the conversion price when dilution occurs. The preferred stock conversion price changed from $13.19 to $11.93 and at this price our preferred shares would have converted into approximately 66.2 million shares of common stock at December 31, 2009.
The share count for diluted earnings (loss) per share is computed on the basis of the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding plus the effects of dilutive common stock equivalents (CSEs) outstanding during the period. CSEs, which are securities that may entitle the holder to obtain common stock, include outstanding stock options, restricted stock unit awards, performance share awards and preferred stock. When the average price of the common stock during the period exceeds the exercise price of a stock option, the options are considered potentially dilutive CSEs. To the extent these CSEs are anti-dilutive they are excluded from the calculation of diluted earnings per share. Also, when there is a loss from continuing operations, potentially dilutive shares are excluded from the computation of earnings per share as their effect would be anti-dilutive.
We excluded 4.8 million, 2.5 million and 11.1 million of CSEs from the table above for the year 2009, the eleven months ended December 31, 2008 and for the year 2007 as the effect of including them would have been anti-dilutive. In addition, we excluded CSEs that satisfied the definition of potentially dilutive shares of 2.2 million, 0.4 million and 0.5 million for these same periods due to the dilutive effect of the loss from continuing operations for these periods. Conversion of the preferred stock was also not included in the share count for diluted earnings per share due to the loss from continuing operations.
71
Table of Contents
The calculation of earnings per share is based on the following income (loss) available to the parent company stockholders:
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations | $ | (463 | ) | $ | (702 | ) | $ | 715 | $ | (433 | ) | ||||||
| Loss from discontinued operations | (4 | ) | (6 | ) | (118 | ) | |||||||||||
| Net income (loss) available to the parent company stockholders | $ | (463 | ) | $ | (706 | ) | $ | 709 | $ | (551 | ) | ||||||
Income (loss) per share from continuing operations available to parent company stockholders and net income (loss) available to parent company stockholders both include a charge for the preferred stock dividend requirement. Earnings per share information reported by Prior Dana is not comparable to earnings per share information reported by Dana because all existing equity interests of Prior Dana were eliminated upon the consummation of the Plan.
| Note 9. | Incentive and Stock Compensation |
Upon emergence, all common stock and outstanding common stock equivalents, including but not limited to stock options and restricted stock units of Prior Dana, were cancelled in accordance with the Plan.
2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan
Our 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan authorizes grants of stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock awards, restricted stock units and performance share awards to be made pursuant to the plan. The eligibility requirements and terms governing the allocation of any common stock and the receipt of other consideration under the 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan are determined by the Board of Directorsand/or its Compensation Committee. The number of shares of common stock that may be issued or delivered may not exceed in the aggregate 16.09 million shares. Cash settled awards do not count against the maximum aggregate number.
At December 31, 2009, there were 5,040,721 shares available for future grants of options and other types of awards under the 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan.
The following table summarizes our award activity during 2009 and the eleven months ended December 31, 2008:
| Options | SARs | Restricted Stock Units | Performance Notional Shares | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weighted- | Weighted- | Weighted- | Weighted- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average | Average | Average | Average | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise | Exercise | Grant-Date | Grant-Date | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Outstanding at | Shares | Price | Shares | Price | Shares | Fair Value | Shares | Fair Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| January 31, 2008 | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Granted | 5,795,432 | 8.09 | 17,626 | 0.69 | 860,046 | 5.10 | 598,110 | 4.16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vested | (47,387 | ) | 2.85 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Forfeited or expired | (216,404 | ) | 10.00 | (22,005 | ) | 10.00 | (241,860 | ) | 9.21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2008 | 5,579,028 | 8.01 | 17,626 | 0.69 | 790,654 | 5.10 | 356,250 | 0.74 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Granted | 4,389,500 | 0.90 | 617,200 | 1.00 | 404,488 | 2.33 | 181,146 | 2.49 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercised or vested | (842 | ) | 2.09 | (248,027 | ) | 2.16 | (283,863 | ) | 1.76 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Forfeited or expired | (744,004 | ) | 4.98 | (14,900 | ) | 0.51 | (82,539 | ) | 7.25 | (16,032 | ) | 2.49 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2009 | 9,223,682 | $ | 4.87 | 619,926 | $ | 1.00 | 864,576 | $ | 4.44 | 237,501 | $ | 0.74 | ||||||||||||||||||||
72
Table of Contents
Stock options and stock appreciation rights (SARs) — The exercise price of each option or SAR equals the closing market price of our common stock on the date of grant. Options and SARs generally vest over three years and their maximum term is ten years. Compensation expense is measured based on the fair value at the date of grant and is recognized on a straight-line basis over the vesting period. Shares issued upon the exercise of options are recorded as common stock and additional paid-in capital at the option price. Options to be settled in cash result in the recognition of a liability representing the vested portion of the obligation. SARs are settled in cash for the difference between the market price on the date of exercise and the exercise price. As a result, SARs are recorded as a liability until the date of exercise. The fair value of each SAR award is recalculated at the end of each reporting period and the liability and expense adjusted based on the new fair value. As of December 31, 2009, a liability of $3 for cash options and SARs is recorded as deferred employee benefits in other non-current liabilities.
We calculated a fair value for each option and SAR at the date of the grant using the Black-Scholes valuation model. The weighted-average key assumptions used in the model for options and SARs granted during 2009 and 2008 are summarized in the following table. The dividend yield is assumed to be zero since there are no current plans to pay common stock dividends. We use the simplified method to calculate the expected term because we have insufficient historical exercise data due to the limited period of time our common stock has been publicly traded.
| Options | SARs | |||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||||
| Expected term (in years) | 6.00 | 5.48 | 6.00 | 6.00 | ||||||||||||
| Risk-free interest rate | 2.21 | % | 2.83 | % | 1.87 | % | 1.72 | % | ||||||||
| Expected volatility | 63.08 | % | 42.46 | % | 63.17 | % | 53.40 | % | ||||||||
The following table summarizes information about options and SARs outstanding and exercisable at December 31, 2009:
| Outstanding Options and SARs | Exercisable Options and SARs | |||||||||||||||||||
| Weighted-Average | Weighted- | |||||||||||||||||||
| Remaining | Average | |||||||||||||||||||
| Range of | Contractual | Exercise | Exercise | |||||||||||||||||
Exercise Prices | Number | Life in Years | Price | Number | Price | |||||||||||||||
| $0.51 - $3.33 | 6,125,511 | 8.3 | $ | 1.09 | 531,005 | $ | 1.88 | |||||||||||||
| $5.23 - $7.00 | 285,550 | 9.0 | 6.36 | 54,815 | 6.36 | |||||||||||||||
| $9.19 - $12.75 | 3,432,547 | 7.4 | 10.80 | 1,584,556 | 11.13 | |||||||||||||||
| 9,843,608 | 8.0 | $ | 4.63 | 2,170,376 | $ | 8.74 | ||||||||||||||
The weighted-average fair value at grant date of options and SARs granted during 2009 and 2008 was $0.54 and $3.50 per share. During 2009 and 2008, we recognized $11 and $6 in compensation expense related to options and SARs. The total fair value of options and SARs vested during 2009 and 2008 was $5 and $2.
Restricted stock units and performance shares — Each restricted stock unit or notional performance share granted represents the right to receive one share of Dana common stock or, at the election of Dana (for units awarded to board members) or for certainnon-U.S. employees (for employee awarded units), cash equal to the market value per share. All restricted stock units contain dividend equivalent rights. Restricted stock units granted to non-employee directors vest in three equal annual installments beginning on the first anniversary date of the grant and those granted to employees generally cliff vest fully after three years. Performance shares are awarded if specified performance goals are achieved during the respective performance period. Compensation expense for stock-settled awards expected to vest is measured based on the closing market price of our common stock at the date of grant and is recognized on a straight-line basis over the vesting period. Compensation expense for cash-settled awards expected to vest is measured based on the closing market price of our common stock at the
73
Table of Contents
end of each reporting period and is recognized on a straight-line basis over the vesting period. As of December 31, 2009, the vested portion of cash-settled restricted stock units and performance shares was $1 and is recorded in deferred employee benefits and other non-current liabilities.
During 2009 and 2008, we recognized $1 and $1 of compensation expense related to restricted stock units. Performance goals were established in 2009 for a performance share award and we recognized $1 during 2009 of related compensation expense. No performance shares were awarded in 2008. Accordingly, no expense was recorded in 2008.
The following table summarizes information about unrecognized compensation expense as of December 31, 2009:
| Restricted | Performance | |||||||||||||||
| Stock | Notional | |||||||||||||||
| Options | SARs | Units | Shares | |||||||||||||
| Unrecognized compensation expense | $ | 4 | $ | 4 | $ | 2 | $ | — | ||||||||
| Weighted-average amortization period in years | 0.9 | 1.1 | 0.8 | — | ||||||||||||
Annual Awards
During the fourth quarter of 2009, we accrued $13 of expense for two additional compensation programs. Employees working in countries where pay increases were frozen in 2009 were awarded a one-time payment of 2% of their eligible base salary. Also included was a one-time Special Recognition Bonus awarded to the top 1,000 bonus eligible employees pursuant to the terms and conditions of the 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan. This award was based on each individual’s compensation level and their individual contributions toward achievement of our 2009 objectives.
Executive Incentive Compensation Plan
Five employees participated in the Executive Incentive Compensation (EIC) Plan during 2007, earning $4 which was recognized as compensation expense in 2007. The EIC Plan specified that a portion of each participant’s bonus, depending on the amount earned, could be paid in common stock of the reorganized Dana. Four of the five employees earned amounts totaling approximately $1 in 2007 that required payment in the form of common stock. The number of shares issued in April 2008 as payment was determined based on the average closing price of the stock for the 20 trading days following the filing of Dana’sForm 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2007, resulting in 73,562 shares of common stock being issued in April 2008 at a value of $9.86 per share.
| Note 10. | Pension and Postretirement Benefit Plans |
We have a number of defined contribution and defined benefit, qualified and nonqualified, pension plans for certain employees. Other postretirement benefit plans (OPEB), including medical and life insurance, are provided for certain employees upon retirement.
Under the terms of the qualified defined contribution retirement plans, employee and employer contributions may be directed into a number of diverse investments. None of these qualified defined contribution plans allow direct investment in our stock.
The funded status of each defined benefit pension and OPEB plan is recognized on the balance sheet. The funded status of a plan is measured as the difference between the plan assets at fair value and the benefit obligation. The funded status of all overfunded plans are aggregated and reported in investments and other assets. The funded status of all underfunded or unfunded plans are aggregated and reported in deferred employee benefits and other non-current liabilities. In addition, the portion of the benefits payable in the next year which exceeds the fair value of plan assets is reported in accrued payroll and employee benefits and is determined on aplan-by-plan basis. The measurement date of a plan’s assets and its obligations coincides with our year end. Changes in the funded status of a defined benefit plan are recognized in the year in which the change occurs.
74
Table of Contents
Components of net periodic benefic costs and other amounts recognized in other comprehensive income (OCI) —
| Pension Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. | Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Service cost | $ | — | $ | 6 | $ | — | $ | 8 | $ | 1 | $ | 1 | $ | 15 | $ | 12 | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest cost | 109 | 19 | 101 | 21 | 9 | 2 | 114 | 30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Expected return on plan assets | (116 | ) | (9 | ) | (126 | ) | (14 | ) | (12 | ) | (2 | ) | (142 | ) | (26 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of prior service cost | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recognized net actuarial loss | 2 | 27 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net periodic benefit cost (credit) | (7 | ) | 16 | (25 | ) | 15 | 1 | 15 | 19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Curtailment (gain) loss | 1 | (1 | ) | 4 | (8 | ) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Settlement (gain) loss | 1 | (12 | ) | 19 | 128 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Termination cost | 2 | 7 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net periodic benefit cost (credit) after curtailments and settlements | $ | (4 | ) | $ | 16 | $ | (14 | ) | $ | 3 | $ | — | $ | 1 | $ | 32 | $ | 151 | |||||||||||||||
Recognized in OCI: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount due to net actuarial (gains) losses | $ | 285 | $ | 27 | $ | 102 | $ | (10 | ) | $ | 105 | $ | 28 | $ | (96 | ) | $ | (14 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Prior service cost from plan amendments | (1 | ) | 7 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of prior service cost in net periodic cost | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of net actuarial gains (losses) in net periodic cost | (2 | ) | (27 | ) | (3 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immediate recognition of prior service cost, unrecognized gains (losses) and transition obligation due to divestitures | (7 | ) | (142 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fresh start adjustment | (407 | ) | (78 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total recognized in OCI | 285 | 26 | 102 | (3 | ) | (304 | ) | (50 | ) | (129 | ) | (159 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total recognized in benefit cost and OCI | $ | 281 | $ | 42 | $ | 88 | $ | — | $ | (304 | ) | $ | (49 | ) | $ | (97 | ) | $ | (8 | ) | |||||||||||||
75
Table of Contents
| Other Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dana Non-U.S. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eleven | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year | Months | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ended | Ended | Prior Dana | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| One Month | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ended | December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, | January 31, 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | U.S. | Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Service cost | $ | 1 | $ | 1 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 5 | $ | 2 | |||||||||||||
| Interest cost | 6 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 70 | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of prior service credit | (3 | ) | (29 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Recognized net actuarial loss | 3 | 34 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net periodic benefit cost | 7 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 80 | 11 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Curtailment gain | (2 | ) | (2 | ) | (61 | ) | (8 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Settlement gain | (13 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Termination cost | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net periodic benefit cost (credit) after curtailments and settlements | $ | 5 | $ | 5 | $ | (56 | ) | $ | 1 | $ | 60 | $ | 11 | ||||||||||||
Recognized in OCI: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prior service credit from plan amendments | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (278 | ) | $ | — | $ | (326 | ) | $ | — | |||||||||||
| Amount due to net actuarial (gains) losses | 9 | (15 | ) | 13 | (68 | ) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of prior service credit in net periodic cost | 64 | 29 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of net actuarial gains (losses) in net periodic cost | (3 | ) | (34 | ) | (2 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Fresh start adjustment | 89 | (52 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Total recognized in OCI | $ | 9 | $ | (15 | ) | $ | (115 | ) | $ | (52 | ) | $ | (399 | ) | $ | 2 | |||||||||
Total recognized in benefit cost and OCI | $ | 14 | $ | (10 | ) | $ | (171 | ) | $ | (51 | ) | $ | (339 | ) | $ | 13 | |||||||||
There were no net periodic other benefit costs in the U.S. for the year 2009 or for the eleven months ended December 31, 2008. Our other postretirement benefit costs for all U.S. employees and retirees were eliminated at our emergence from Chapter 11.
The estimated net actuarial loss for the defined benefit pension plans that will be amortized from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) (AOCI) into benefit cost in 2010 is $20 for our U.S. plans and a nominal amount for ournon-U.S. plans. There is a nominal amount of net actuarial loss related to other postretirement benefit plans that will be amortized from AOCI into benefit cost in 2010 for ournon-U.S. plans.
76
Table of Contents
Funded status —The following tables provide a reconciliation of the changes in the plans’ benefit obligations and plan assets for 2009 and 2008 and the funded status and amounts recognized in the consolidated balance sheets at December 31, 2009 and 2008, with continuing and discontinued operations combined.
| Pension Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Eleven Months Ended | One Month Ended | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2009 | December 31, 2008 | January 31, 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. | Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Reconciliation of benefit obligation: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Obligation at beginning of period | $ | 1,777 | $ | 364 | $ | 1,870 | $ | 540 | $ | 1,849 | $ | 529 | |||||||||||||
| Service cost | 6 | 8 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest cost | 109 | 19 | 101 | 21 | 9 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Plan amendments | (1 | ) | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| New plans | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actuarial (gain) loss | 119 | 18 | (50 | ) | (16 | ) | 22 | 11 | |||||||||||||||||
| Benefit payments | (177 | ) | (28 | ) | (157 | ) | (28 | ) | (11 | ) | (4 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Settlements, curtailments and terminations | 3 | (50 | ) | 13 | (114 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Translation adjustments | 18 | (54 | ) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Obligation at end of period | $ | 1,831 | $ | 351 | $ | 1,777 | $ | 364 | $ | 1,870 | $ | 540 | |||||||||||||
| Other Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Dana | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Year | Eleven Months | Prior Dana | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ended December 31, | One Month Ended | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | January 31, 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | |||||||||||||||||
Reconciliation of benefit obligation: | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Obligation at beginning of period | $ | 100 | $ | 752 | $ | 140 | $ | 1,019 | $ | 141 | |||||||||||
| Service cost | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Interest cost | 6 | 6 | 5 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Plan amendments | (278 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Actuarial (gain) loss | 9 | (17 | ) | 13 | |||||||||||||||||
| Benefit payments | (7 | ) | (752 | ) | (5 | ) | (7 | ) | (1 | ) | |||||||||||
| Settlements, curtailments and terminations | (1 | ) | (2 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Translation adjustments | 16 | (23 | ) | (1 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Obligation at end of period | $ | 124 | $ | — | $ | 100 | $ | 752 | $ | 140 | |||||||||||
77
Table of Contents
| Pension Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Eleven Months Ended | One Month Ended | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2009 | December 31, 2008 | January 31, 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. | Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Reconciliation of fair value of plan assets: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fair value at beginning of period | $ | 1,628 | $ | 183 | $ | 1,784 | $ | 338 | $ | 1,865 | $ | 358 | |||||||||||||
| Actual return on plan assets | (50 | ) | (23 | ) | 19 | (71 | ) | (16 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Employer contributions | 13 | 24 | 13 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Benefit payments | (177 | ) | (28 | ) | (157 | ) | (28 | ) | (11 | ) | (4 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Settlements | (49 | ) | (115 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Translation adjustments | 17 | (44 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Fair value at end of period | $ | 1,401 | $ | 136 | $ | 1,628 | $ | 183 | $ | 1,784 | $ | 338 | |||||||||||||
Funded status at end of period | $ | (430 | ) | $ | (215 | ) | $ | (149 | ) | $ | (181 | ) | $ | (86 | ) | $ | (202 | ) | |||||||
| Other Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dana | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year | Eleven Months | Prior Dana | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ended December 31, | One Month Ended | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | January 31, 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | |||||||||||||||||||||
Reconciliation of fair value of plan assets: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fair value at beginning of period | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||||||
| Employer contributions | 7 | 752 | 5 | 7 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Benefit payments | (7 | ) | (752 | ) | (5 | ) | (7 | ) | (1 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Fair value at end of period | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||||||
Funded status at end of period | $ | (124 | ) | $ | — | $ | (100 | ) | $ | (752 | ) | $ | (140 | ) | |||||||||||
Amounts recognized in the balance sheet —
| Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. | Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | Non-U.S. | Non-U.S. | |||||||||||||||||||
Amounts recognized in the consolidated balance sheet: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncurrent assets | $ | — | $ | 9 | $ | 2 | $ | 20 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||
| Current liabilities | (11 | ) | (10 | ) | (7 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Noncurrent liabilities | (430 | ) | (213 | ) | (151 | ) | (191 | ) | (117 | ) | (94 | ) | ||||||||||||
| AOCI | 387 | 23 | 102 | (3 | ) | (6 | ) | (15 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Net amount recognized | $ | (43 | ) | $ | (192 | ) | $ | (47 | ) | $ | (184 | ) | $ | (130 | ) | $ | (115 | ) | ||||||
78
Table of Contents
| Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. | Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | Non-U.S. | Non-U.S. | |||||||||||||||||||
Amounts recognized in AOCI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net actuarial loss (gain) | $ | 387 | $ | 17 | $ | 102 | $ | (10 | ) | $ | (6 | ) | $ | (15 | ) | |||||||||
| Prior service cost | 6 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross amount recognized | 387 | 23 | 102 | (3 | ) | (6 | ) | (15 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Deferred tax benefits | (3 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net amount recognized | $ | 387 | $ | 20 | $ | 102 | $ | (3 | ) | $ | (6 | ) | $ | (15 | ) | |||||||||
In 2009, we recorded a net of less than $1 in pension curtailment costs and $2 in postretirement healthcare curtailment gains related to our workforce reduction actions. These costs were included in restructuring charges. We also announced the anticipated sale of substantially all of the assets of our Structural Products business, which resulted in a termination of pension service. The associated cost of $2 was recorded in other income, net along with other costs associated with the sale.
During the first quarter of 2009, we settled a portion of the Canadian retiree pension benefit obligations by purchasing non-participating annuity contracts to cover vested benefits. This action necessitated a remeasurement of the assets and liabilities of the affected plans as of February 28, 2009. The discount rate used for remeasurement was 6.39%. As a result of the annuity purchases, we reduced the benefit obligation by $43 and also reduced the fair value of plan assets by $43. We recorded the related settlement loss of $1 in cost of sales.
In 2008, employee acceptances of early retirement incentives in the U.S. generated pension plan special termination costs of $7 in the second quarter which were included in restructuring charges as well as curtailment losses of $3 which were charged against OCI. Similar incentives in the U.S. generated curtailment losses of $2 in the third quarter which were included in restructuring charges. The affected pension plans were remeasured at June 30, 2008 and again at August 31, 2008. The remeasurement at June 30, 2008 increased net assets by $3 and reduced the net defined benefit obligations by $32 with a credit to OCI of $35. The remeasurement at August 31, 2008 increased net assets by $2 and increased the net defined benefit obligations by $72 with a charge to OCI for $70.
Also during the second quarter of 2008, we settled a substantial portion of the Canadian retiree pension benefit obligations by purchasing non-participating annuity contracts to cover vested benefits. This action necessitated a remeasurement of the assets and liabilities of the affected plans as of May 31, 2008. The discount rate used for remeasurement was 5.50%. As a result of the annuity purchases, we reduced the benefit obligation by $114 and also reduced the fair value of plan assets by $114. We recorded the related settlement gain of $12 as a reduction to cost of sales.
Under fresh start accounting we were required to remeasure all defined benefit plan obligations and assets. The discount rates used to measure the U.S. pension and other postretirement benefit obligations were 6.13% and 6.10% at January 31, 2008 compared to 6.26% and 6.24% at December 31, 2007. The weighted-average discount rates used to measure thenon-U.S. pension and other postretirement benefit obligations were both 5.29% at January 31, 2008 compared to 5.27% and 5.29% at December 31, 2007. The generally adverse asset investment performance during the month of January 2008 negatively impacted net obligations. As a result of these changes, a net actuarial loss of $140 adversely affected the funded status of our plans, reducing net assets by $35 and increasing the net defined benefit obligations by $105 with offsets to AOCI. The AOCI balance at January 31, 2008 was eliminated under fresh start accounting.
Certain changes related to our U.S. pension and postretirement benefit plans specific to non-union employees became effective during the bankruptcy process while changes specific to union-represented employees became effective with our emergence from Chapter 11. Credited service and
79
Table of Contents
benefit accruals were frozen for all U.S. employees in defined benefit pension plans. For union-represented employees we agreed to make future contributions, based on a cents per hour formula, to a USW multiemployer pension trust which will provide future pension benefits for covered employees.
Our postretirement healthcare obligations for all U.S. employees and retirees were eliminated as part of the Chapter 11 reorganization. With regard to union-represented employees and retirees, we contributed an aggregate of approximately $733 in cash on February 1, 2008 (which is net of amounts incurred and paid for non-pension retiree benefits, long-term disability and related healthcare claims of retirees between July 1, 2007 and January 31, 2008) to union-administered Voluntary Employee Benefit Associations (VEBAs). As a result of the changes in our U.S. other postretirement benefits that became effective on January 31, 2008 with our emergence from Chapter 11, we recognized a portion of the previously unrecognized prior service credits as a curtailment gain of $61 due to the negative plan amendment and reported it as a component of the gain on settlement of liabilities subject to compromise as of January 31, 2008. The gain was calculated based on the current estimate of the future working lifetime attributable to those participants who will not receive benefits following the estimated exhaustion of funds. The calculation used current plan assumptions and current levels of plan benefits. In connection with the recognition of our obligations to the VEBAs at emergence, the accumulated postretirement benefit obligation (APBO) was reset to an amount equal to the VEBA payments, resulting in a reduction of $278 with an offsetting credit to AOCI.
Postretirement healthcare benefits for active non-union employees in the U.S. were eliminated effective as of April 1, 2007. This action reduced our APBO by $115 in the first quarter of 2007. Because the elimination of these benefits reduced benefits previously earned, it was considered a negative plan amendment. Accordingly, the reduction in the APBO was offset by a credit to AOCI which was amortized to income as a reduction of OPEB expense until the AOCI was eliminated under fresh start accounting.
With regard to non-union retirees, we contributed an aggregate of $78 to a VEBA trust for postretirement healthcare and life insurance benefits in exchange for release from these obligations. We funded our contribution with payments of $25 in June 2007 and $53 in January 2008. In May 2007, we also made a $2 payment to the International Association of Machinists (IAM) to resolve all claims for postretirement non-pension benefits after September 30, 2007 for retirees and active employees represented by the IAM. These actions reduced our APBO by $303 in the second quarter of 2007, with $80 being offset by the payment obligation to the VEBAs and $223 being credited to AOCI which was eliminated under fresh start accounting.
Exercise of employee early retirement incentives generated pension plan curtailment losses of $5 and $2 in the third and fourth quarters of 2007 which were included in reorganization charges. Completion of a facility closure in the third quarter of 2007 resulted in recognition of a postretirement medical plan curtailment gain of $8 which was included in restructuring charges.
Lump sum distributions from one of the pension plans in the U.S. reached a level during the third quarter of 2007 requiring recognition of $12 as pension settlement expense. The portions attributable to divested operations and manufacturing footprint actions amounted to $4 and $5 and were included in discontinued operations and restructuring charges. The lump sum distributions and the reversal of the decision to close a facility required a remeasurement of two plans which reduced our pension obligation by $42 in the third quarter of 2007 and resulted in a credit to OCI. Continuing high levels of lump sum pension fund distributions during the fourth quarter of 2007 triggered $7 of additional pension settlement charges. The portions attributable to divested operations and manufacturing footprint actions amounted to $1 and $3 and were included in discontinued operations and restructuring charges. In the second quarter of 2007, we recorded a pension curtailment gain of $11 related to the reversal of a decision to close a U.S. facility.
Pursuant to a restructuring of our pension liabilities in the U.K. necessitated by the divestiture of several non-core U.K. businesses, we recorded $8 of pension curtailment cost as a restructuring charge in the first quarter of 2007 and a settlement charge of $145 in the second quarter of 2007
80
Table of Contents
($128 as a restructuring charge in continuing operations and $17 in discontinued operations). During the first quarter of 2007, the sale of our engine hard parts business resulted in a postretirement medical plan settlement gain of $12.
Aggregate funding levels —The following table presents information regarding the aggregate funding levels of our defined benefit pension plans at December 31:
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||
| U.S. | Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | |||||||||||||
| Plans with fair value of plan assets in excess of obligations: | ||||||||||||||||
| Accumulated benefit obligation | $ | 14 | $ | 95 | $ | 13 | $ | 134 | ||||||||
| Projected benefit obligation | 14 | 95 | 13 | 151 | ||||||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets | 14 | 104 | 15 | 158 | ||||||||||||
| Plans with obligations in excess of fair value of plan assets: | ||||||||||||||||
| Accumulated benefit obligation | 1,817 | 238 | 1,764 | 208 | ||||||||||||
| Projected benefit obligation | 1,817 | 256 | 1,764 | 213 | ||||||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets | 1,387 | 32 | 1,613 | 25 | ||||||||||||
Benefit obligations of certainnon-U.S. pension plans, amounting to $200 at December 31, 2009, and other postretirement benefit plans of $124 are not funded.
Fair values of plan assets —
| Fair Value Measurements at December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. | Non-U.S. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quoted | Significant | Quoted | Significant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prices in | Other | Significant | Prices in | Other | Significant | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Active | Observable | Unobservable | Active | Observable | Unobservable | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Markets | Inputs | Inputs | Markets | Inputs | Inputs | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Asset Category | Total | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity securities: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. all cap (a) | $ | 86 | $ | 86 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||
| U.S. large cap | 129 | 129 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. small cap | 20 | 20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EAFE composite | 146 | 146 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Emerging markets | 45 | 45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed income securities: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. core bonds (b) | 116 | 116 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate bonds | 307 | 299 | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. treasury strips | 343 | 343 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Non-U.S. government securities | 111 | 111 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Emerging market debt | 38 | 36 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative investments: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hedge fund of funds (c) | 109 | 109 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Insurance contracts (d) | 9 | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 3 | 2 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | 75 | 70 | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 1,537 | $ | 426 | $ | 864 | $ | 111 | $ | — | $ | 127 | $ | 9 | ||||||||||||||
81
Table of Contents
Notes:
(a) This category comprises a combination of small-, mid- and large-cap equity stocks that are allocated at the investment manager’s discretion.
(b) This category represents a combination of investment grade corporate bonds, sovereign bonds, Yankee bonds, asset backed securities and U.S. government bonds.
(c) This category includes fund managers that invest in a well-diversified group of hedge funds where strategies include, but are not limited to, event driven, relative value, long/short market neutral, multistrategy and global macro.
(d) This category comprises contracts placed with insurance companies where the underlying assets are invested in fixed interest securities.
| 2009 | ||||||||||||||||
| U.S. | Non-U.S. | |||||||||||||||
| Hedge | ||||||||||||||||
| fund of | Insurance | |||||||||||||||
Reconciliation of Level 3 Assets | funds | Other | Total | contract | ||||||||||||
| Fair value at beginning of period | $ | 36 | $ | 2 | $ | 38 | $ | 9 | ||||||||
| Unrealized gains relating to Assets still held at the reporting date | 3 | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Purchases | 70 | 70 | ||||||||||||||
| Fair value at end of period | $ | 109 | $ | 2 | $ | 111 | $ | 9 | ||||||||
Plan assets —Target asset allocations of U.S. pension plans are established through an investment policy, which is updated periodically and reviewed by an Investment Committee, comprised of certain company officers and directors. The investment policy allows for a flexible asset allocation mix which is intended to provide appropriate diversification to lessen market volatility while assuming a reasonable level of economic risk.
Our policy recognizes that properly managing the relationship between pension assets and pension liabilities serves to mitigate the impact of market volatility on our funding levels. During 2009 the Investment Committee approved a new asset allocation. Accordingly, the plan’s assets were transitioned to an appropriately balanced allocation between a Growth Portfolio, an Immunizing Portfolio and a Liquidity Portfolio. These threesub-portfolios are intended to balance the generation of incremental returns with the management of overall risk.
The Growth Portfolio is a return-seeking portfolio invested in a diversified pool of assets in order to generate an incremental return with an acceptable level of risk. The Immunizing Portfolio is a hedging portfolio that may be comprised of fixed income securities and overlay positions. This portfolio is designed to offset changes in the value of the pension liability due to changes in interest rates. The Liquidity Portfolio is a cash portfolio designed to meet short term liquidity needs and reduce the plan’s overall risk.
The allocations between portfolios may be adjusted to meet changing objectives and constraints. We expect that as the funded status of the plan changes, we will increase or decrease the size of the Growth Portfolio in order to manage the risk of losses in the plan. As of December 31, 2009, the Growth Portfolio (U.S andnon-U.S. equities, core and high yield fixed income, as well as, hedge fund of funds and emerging market debt) comprises 52% of total assets, the Immunizing Portfolio (long duration U.S. Treasury strips and corporate bonds) comprises 43% and the Liquidity Portfolio (cash and short term securities) comprises 5%. The Growth Portfolio is currently limited to not less than 35% nor more than 65% of total assets, the Immunizing Portfolio is currently limited to not less than 30% nor more than 60% and the Liquidity Portfolio is currently limited to no more than 10%.
82
Table of Contents
Significant assumptions —The significant weighted average assumptions used in the measurement of pension benefit obligations at December 31 of each year and the net periodic benefit cost for each year are as follows:
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. | Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | |||||||||||||||||||
| Benefit obligations: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discount rate | 5.79 | % | 5.36 | % | 6.44 | % | 5.80 | % | 6.26 | % | 5.27 | % | ||||||||||||
| Net periodic benefit cost: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discount rate | 6.44 | % | 5.80 | % | 6.26 | % | 5.27 | % | 5.88 | % | 5.03 | % | ||||||||||||
| Rate of compensation increase | N/A | 3.21 | % | 5.00 | % | 3.11 | % | 5.00 | % | 2.98 | % | |||||||||||||
| Expected return on plan assets | 7.50 | % | 6.03 | % | 8.25 | % | 6.66 | % | 8.25 | % | 6.32 | % | ||||||||||||
The pension plan discount rate assumptions are evaluated annually in consultation with our outside actuarial advisors. Long-term interest rates on high quality corporate debt instruments are used to determine the discount rate. For our largest plans, discount rates are developed using a discounted bond portfolio analysis, with appropriate consideration given to defined benefit payment terms and duration of the liabilities.
The expected rate of return on plan assets was selected on the basis of our long-term view of return and risk assumptions for major asset classes. We define long-term as forecasts that span at least the next ten years. Our long-term outlook is influenced by a combination of return expectations by individual asset class, actual historical experience and our diversified investment strategy. We consult with and consider the opinions of financial professionals in developing appropriate capital market assumptions. Return projections are also validated using a simulation model that incorporates yield curves, credit spreads and risk premiums to project long-term prospective returns. The appropriateness of the expected rate of return is assessed on an annual basis and revised if necessary. We reduced the U.S. rate for 2009 expense purposes based on the volatility experienced in global equity, debt, currency and commodity markets. Also, since the benefit accruals are frozen for all of our U.S. pension plans, we shifted the targeted asset allocation to a higher percentage of fixed income securities.
The significant weighted average assumptions used in the measurement of other postretirement benefit obligations at December 31 of each year and the net periodic benefit cost for each year are as follows:
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||
| Non-U.S. | Non-U.S. | U.S. | Non-U.S. | |||||||||||||
| Benefit obligations: | ||||||||||||||||
| Discount rate | 5.79 | % | 6.33 | % | 6.24 | % | 5.29 | % | ||||||||
| Net periodic benefit cost: | ||||||||||||||||
| Discount rate | 6.33 | % | 5.29 | % | 5.86 | % | 5.04 | % | ||||||||
| Initial healthcare costs trend rate | 7.98 | % | 8.40 | % | 10.00 | % | 8.38 | % | ||||||||
| Ultimate healthcare costs trend rate | 5.03 | % | 4.95 | % | 5.00 | % | 4.94 | % | ||||||||
| Year ultimate reached | 2015 | 2015 | 2013 | 2015 | ||||||||||||
The discount rate selection process was similar to the pension plans. Assumed healthcare cost trend rates have a significant effect on the healthcare obligation. To determine the trend rates, consideration is given to the plan design, recent experience and healthcare economics.
83
Table of Contents
A one-percentage-point change in assumed healthcare costs trend rates would have the following effects for 2009:
| 1% Point | 1% Point | |||||||
| Increase | Decrease | |||||||
| Effect on total of service and interest cost components | $ | 1 | $ | (1 | ) | |||
| Effect on postretirement benefit obligations | 11 | (10 | ) | |||||
Estimated future benefit payments —Expected benefit payments by our pension plans and other postretirement plans for each of the next five years and for the period 2015 through 2019 are as follows:
| Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | |||||||||||
| Year | U.S. | Non-U.S. | Non-U.S. | |||||||||
| 2010 | $ | 148 | $ | 31 | $ | 7 | ||||||
| 2011 | 145 | 100 | 8 | |||||||||
| 2012 | 143 | 15 | 8 | |||||||||
| 2013 | 139 | 15 | 8 | |||||||||
| 2014 | 135 | 15 | 8 | |||||||||
| 2015 to 2019 | 639 | 85 | 42 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 1,349 | $ | 261 | $ | 81 | ||||||
Pension benefits are funded through deposits with trustees that satisfy, at a minimum, the applicable funding regulations. OPEB benefits are funded as they become due. As a result of the closure of several facilities in Canada, we are required to settle the related retiree pension benefit obligations. These settlements are projected to occur in 2011. Projected contributions to be made to the defined benefit pension plans in 2010 are $13 for ournon-U.S. plans and nil for our U.S. plans.
| Note 11. | Cash Deposits |
Cash deposits are maintained to provide credit enhancement for certain agreements and are reported as part of cash and cash equivalents. For most of these deposits, the cash may be withdrawn if comparable security is provided in the form of letters of credit. Accordingly, these deposits are not considered to be restricted.
| December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. | Non-U.S. | Total | U.S. | Non-U.S. | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 517 | $ | 296 | $ | 813 | $ | 280 | $ | 352 | $ | 632 | ||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents held as deposits | 4 | 39 | 43 | 56 | 20 | 76 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents held at less than wholly owned subsidiaries | 3 | 88 | 91 | 69 | 69 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 524 | $ | 423 | $ | 947 | $ | 336 | $ | 441 | $ | 777 | ||||||||||||
A portion of thenon-U.S. cash and cash equivalents is utilized for working capital and other operating purposes. Several countries have local regulatory requirements that significantly restrict the ability of our operations to repatriate this cash. Beyond these restrictions, there are practical limitations on repatriation of cash from certain countries because of the resulting tax withholdings.
84
Table of Contents
| Note 12. | Financing Agreements |
Common Stock Offering and Debt Reduction
In September and October of 2009, we completed a common stock offering for 39 million shares at a price per share of $6.75, generating net proceeds of $250. The provisions of our Term Facility required that a minimum of 50% of the net proceeds of the equity offering be used to repay outstanding principal of our term loan. As a result of previous debt repurchases, approximately 10% of the outstanding principal amount of the term loan is held by a wholly-ownednon-U.S. subsidiary of Dana. Accordingly, $13 of the $126 term loan repayment made to the lenders was received by this wholly-ownednon-U.S. subsidiary and $113 was used to repay outstanding principal of our term loan held by third parties. We recorded a net loss on extinguishment of debt of $8, including the premium of $1 on the prepayment of debt in connection with the equity offering which is included in other income, net. We also charged $3 of deferred financing costs to interest expense in connection with this reduction in debt. This amount is included in the amortization of deferred financing charges in the statement of cash flows.
Additional debt reduction occurred in the second and third quarters of 2009 when the combination of Dana repayments and purchases of debt by a wholly-ownednon-U.S. subsidiary of Dana reduced the outstanding principal under our Term Facility by $138 (offset by original issue discount (OID) reduction of $9 for a net change of $129) with a cash outlay of $86. The resulting gain of $43 was recorded as other income, net. Related debt issuance costs of $3 were charged to interest expense. This amount is included in the amortization of deferred financing charges in the statement of cash flows.
In connection with the planned divestiture of substantially all of the assets of our Structural Products business, we expect to receive approximately $130 of the proceeds of $150 from this sale in the first quarter of 2010. Under the terms of our amended Exit Facility we will be required to apply the proceeds to pay down our Term Facility.
Financing Agreements
Exit financing —On the Effective Date, Dana, as Borrower, and certain of our domestic subsidiaries, as guarantors, entered into an Exit Facility with Citicorp USA, Inc., Lehman Brothers Inc. and Barclays Capital. The Exit Facility consists of a Term Facility in the total aggregate amount of $1,430 and a $650 Revolving Facility. The Term Facility was fully drawn in borrowings of $1,350 on the Effective Date and $80 on February 1, 2008. Net proceeds were reduced by payment of $114 of OID and other customary issuance costs and fees of $40 for net proceeds of $1,276. There were no initial borrowings under the Revolving Facility.
In November 2008, we entered into an amendment to our Term Facility (the Amendment) which, among other changes, revised our quarterly financial covenants. As of December 31, 2009, the financial covenants are as follows:
| • | a maximum leverage ratio of not greater than 3.80:1.00 at December 31, 2009, decreasing in steps to 2.50:1.00 as of September 30, 2012 and thereafter, based on the ratio of consolidated funded debt to the previous twelve month consolidated earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization (EBITDA), as defined in the agreement; and | |
| • | a minimum interest coverage ratio of not less than 2.80:1.00 at December 31, 2009, increasing in steps to 4.50:1.00 as of March 31, 2013 and thereafter, based on the ratio of the previous twelve month EBITDA (as defined in the agreement) to consolidated interest expense for that period. |
The Amendment changed the Credit Agreement’s definition of EBITDA by increasing the amount of restructuring charges that are excluded from EBITDA in 2009 and 2010 from $50 to $100 per year.
85
Table of Contents
After 2010, restructuring charges of up to $50 per year are excluded (up to an aggregate maximum of $100 for periods after 2010). The Amendment also permits us to dispose of certain lines of business.
Under the Amendment, we may not make preferred or common dividend payments and certain other payments until the total leverage ratio as of the end of the preceding fiscal quarter is less than or equal to 3.25:1.00. The Amendment also reduced the net amount of foreign subsidiary permitted indebtedness to an aggregate of $400 outstanding at any time. The Amendment increased the interest rate payable on outstanding advances by 0.50% per annum. We paid an additional $24 of fees to creditors including an amendment fee of 1.50% of outstanding advances under the Term Facility at that time. These fees are amortized to interest expense on a straight-line basis which approximates the effective interest method.
We repaid $150 of the term loan in November 2008. OID reduced the basis of the $150 of debt repaid by $10 resulting in a loss on the repayment of debt of $10 recorded in other income, net. Related deferred financing costs of $3 were charged to interest expense. This amount is included in the amortization of deferred financing charges in the statement of cash flows.
Amounts outstanding under the Revolving Facility may be borrowed, repaid and reborrowed with the final payment due and payable on January 31, 2013. Amounts outstanding under the Term Facility are payable up to January 31, 2014 in equal quarterly amounts on the last day of each fiscal quarter at a rate of 1% per annum of the original principal amount of the Term Facility, adjusted for any prepayments. The remaining balance is due in equal quarterly installments in the final year of the Term Facility with final maturity on January 31, 2015. The amended Exit Facility contains mandatory prepayment requirements in certain other circumstances and certain term loan prepayments are subject to a prepayment call premium prior to the second anniversary of the Term Facility.
The Revolving Facility bears interest at a floating rate based on, at our option, the base rate or LIBOR rate (each as described in the Revolving Facility) plus a margin based on the undrawn amounts available under the Revolving Facility as set forth below:
Remaining Borrowing Availability | Base Rate | LIBOR Rate | ||||||
| Greater than $450 | 1.00 | % | 2.00 | % | ||||
| Greater than $200 but less than or equal to $450 | 1.25 | % | 2.25 | % | ||||
| $200 or less | 1.50 | % | 2.50 | % | ||||
We pay a commitment fee of 0.375% per annum for unused committed amounts under the Revolving Facility. Up to $400 of the Revolving Facility may be applied to letters of credit. Issued letters of credit reduce availability. We pay a fee for issued and undrawn letters of credit in an amount per annum equal to the applicable LIBOR margin based on a quarterly average availability under the Revolving Facility and a per annum fronting fee of 0.25%, payable quarterly.
As amended, the Term Facility interest rate is a floating rate based on, at our option, the base rate or LIBOR rate (each as described in the Term Facility) plus a margin of 3.25% in the case of base rate loans or 4.25% in the case of LIBOR rate loans. Through January of 2010, the LIBOR rates payable with respect to each of the Revolving Facility and the Term Facility could not be less than 3.00%.
Under the amended Exit Facility, Dana (with certain subsidiaries excluded) is required to comply with customary covenants for facilities of this type and we are required to maintain compliance with the financial covenants. The amended Exit Facility and the European Receivables Loan Facility (see below) also include material adverse change provisions. These credit facilities also include customary events of default for facilities of this type. The amended Exit Facility is guaranteed by all of our domestic subsidiaries except for Dana Credit Corporation (DCC), Dana Companies, LLC and their respective subsidiaries (the guarantors). The Revolving Facility Security Agreement grants a first priority lien on Dana’s and the guarantors’ accounts receivable and inventory and a second priority lien on substantially all of Dana’s and the guarantors’ remaining assets, including a pledge of 65% of the stock of our material foreign subsidiaries.
86
Table of Contents
The net proceeds from the Exit Facility were used to repay Dana’s DIP Credit Agreement (which was terminated pursuant to its terms), make other payments required upon exit from bankruptcy protection and provide liquidity to fund working capital and other general corporate purposes.
As of December 31, 2009, we had gross borrowings of $1,003 and unamortized OID of $57 under the amended Term Facility, no borrowings under the Revolving Facility and we had utilized $183 for letters of credit. Based on our borrowing base collateral of $344, we had potential availability at that date under the Revolving Facility of $161 after deducting the outstanding letters of credit.
As market conditions warrant, we, our affiliates, or major equity holders may from time to time repurchase debt securities issued by Dana or its subsidiaries, in privately negotiated or open market transactions, by tender offer, exchange offer or otherwise.
Interest rate agreements —Interest on the amended Term Facility accrues at variable interest rates. Under the amended Term Facility we are required to carry interest rate hedge agreements covering a notional amount of not less than 50% of the aggregate loans outstanding under the amended Term Facility until January 2011. The fair value of these contracts, which effectively cap our interest rate at 10.25% on $702 of debt, was less than $1 as of December 31, 2009.
European receivables loan facility —In July 2007, certain of our European subsidiaries entered into definitive agreements to establish an accounts receivable securitization program. The agreements include a Receivable Loan Agreement (the Loan Agreement) with GE Leveraged Loans Limited (GE) that provides for a five-year accounts receivable securitization facility under which up to the euro equivalent of $243 in financing is available to those European subsidiaries (Sellers) subject to the availability of adequate levels of accounts receivable.
These obligations are secured by a lien on and security interest in all of each Seller’s rights to the transferred accounts receivable, as well as collection accounts and items related to the accounts receivable. The program is accounted for as a secured borrowing with a pledge of collateral. Accordingly, the accounts receivable sold and the loans from GE and the participating lenders are included in our consolidated financial statements. At December 31, 2009, there were no borrowings under this facility although $123 of accounts receivable available as collateral under the program would have supported $63 of borrowings at that date.
Advances bear interest based on the LIBOR applicable to the currency in which each advance is denominated, plus a margin as specified in the Loan Agreement. Advances are to be repaid in full by July 2012. We also pay a fee to the lenders based on any unused amount of the accounts receivable facility. The Loan Agreement contains representations and warranties, affirmative and negative covenants and events of default that are customary for financings of this type.
Other borrowings — Additional short-term borrowings of $15 and $51 at December 31, 2009 and 2008 carry average interest rates of 2.10% and 5.61%.
Covenants — We were in compliance with our debt covenants at December 31, 2009 and, based on our current forecast assumptions, we expect to be able to satisfy our debt covenants during the next twelve months. Based on our financial covenants, we had additional borrowing capacity of $232 at December 31, 2009. The borrowing available from our credit facilities was $224 based on the borrowing base collateral of those lines.
DCC notes — DCC was a non-Debtor subsidiary of Dana. In December 2006, DCC and the holders of most of the DCC Notes executed a forbearance agreement which provided that DCC would sell its asset portfolio and use the proceeds to pay down DCC debt. In January 2008, DCC made a $90 payment to its noteholders and on the Effective Date Dana paid DCC $49, the remaining amount due to DCC noteholders in settlement of DCC’s general unsecured claim of $325 with the Debtors. DCC used these funds to repay the noteholders in full.
87
Table of Contents
Details of consolidated long-term debt at December 31 are as follows:
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||
| Carrying | Carrying | |||||||||||||||
| Value | Fair Value | Value | Fair Value | |||||||||||||
| Term Loan Facility, weighted average rate, 7.25% | $ | 1,003 | $ | 963 | $ | 1,266 | $ | 608 | ||||||||
| Less original issue discount | (57 | ) | (87 | ) | ||||||||||||
| 946 | 963 | 1,179 | 608 | |||||||||||||
| Nonrecourse notes, fixed rates, 5.92%, due 2010 to 2011 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 6 | ||||||||||||
| Other indebtedness | 38 | 35 | 15 | 13 | ||||||||||||
| Total | 988 | 1,002 | 1,200 | 627 | ||||||||||||
| Less: current maturities | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | ||||||||||||
| Total long-term debt | $ | 969 | $ | 983 | $ | 1,181 | $ | 608 | ||||||||
The total maturities of all long-term debt (excluding OID) for the next five years and after are as follows: 2010, $19; 2011, $16; 2012, $32; 2013, $11; 2014, $774 and beyond 2014, $193.
Fees are paid to the banks for providing committed lines, but not for uncommitted lines. We paid fees of $8, $71 and $18 in 2009, 2008 and 2007 in connection with our committed facilities. Bank fees totaling $19, $18 and $13 in 2009, 2008 and 2007 and amortization of OID of $14 and $16 in 2009 and 2008 are included in interest expense.
| Note 13. | Fair Value Measurements |
The fair value framework establishes a three-tier fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value:
| • | Level 1 inputs (highest priority) include unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. | |
| • | Level 2 inputs include other than quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities that are observable either directly or indirectly. | |
| • | Level 3 inputs (lowest priority) include unobservable inputs in which there is little or no market data, which require the reporting entity to develop its own assumptions. |
The FASB has issued several statements which address specific issues related to the accounting and disclosure of certain financial instruments. This guidance covers the determination of fair value of an asset in a market that is not active, when the volume and level of activity for the asset or liability have significantly decreased, and provides additional guidance for estimating fair value for transactions that are not orderly. Also covered is the recognition and presentation ofother-than-temporary impairments. The guidance was amended for debt securities to make the guidance more operational. Disclosure was also expanded about the fair value of financial instruments.
Companies are permitted to choose to measure eligible financial instruments and certain other items at fair value at specified election dates. Entities that elect the fair value option must report unrealized gains and losses on items for which the fair value option has been elected in earnings at each subsequent reporting date. We did not elect to measure any additional financial instruments or other items at fair value.
��
In measuring the fair value of our assets and liabilities, we use market data or assumptions that we believe market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability including assumptions about risk when appropriate. Our valuation techniques include a combination of observable and unobservable inputs.
88
Table of Contents
As of December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, our assets and liabilities that are carried at fair value on a recurring and a non-recurring basis include the following:
| Fair Value Measurements Using | ||||||||||||||||
| Quoted | Significant | |||||||||||||||
| Prices in | Other | Significant | ||||||||||||||
| Active | Observable | Unobservable | ||||||||||||||
| Markets | Inputs | Inputs | ||||||||||||||
| Total | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | |||||||||||||
December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||
| Assets: | ||||||||||||||||
| Trademarks and trade names | $ | 65 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 65 | ||||||||
| Notes receivable | 94 | 94 | ||||||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 159 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 159 | ||||||||
| Liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||
| Currency forward contracts | $ | 4 | $ | — | $ | 4 | $ | — | ||||||||
| Total liabilities | $ | 4 | $ | — | $ | 4 | $ | — | ||||||||
December 31, 2008 | ||||||||||||||||
| Assets: | ||||||||||||||||
| Trademarks and trade names | $ | 72 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 72 | ||||||||
| Notes receivable | 20 | 20 | ||||||||||||||
| Currency forward contracts | 8 | 8 | ||||||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 100 | $ | — | $ | 8 | $ | 92 | ||||||||
| Liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||
| Currency forward contracts | $ | 6 | $ | — | $ | 6 | $ | — | ||||||||
| Total liabilities | $ | 6 | $ | — | $ | 6 | $ | — | ||||||||
The intangible assets and the property plant and equipment of the Structures segment have been impaired by $150 to a Level 3 value. Following impairment, the intangible assets are valued at $16 and the property, plant and equipment at $65.
The fair value of interest rate caps which are measured using Level 1 inputs was less than $1 at December 31, 2009 and 2008.
Trademarks and trade names are measured at October 31 each year but may also be adjusted to fair value on a non-recurring basis if conditions arise that warrant a review and impairment is indicated. Following an assessment of our forecasted results during the second quarter of 2009, we performed impairment testing on our trademarks and trade names as of June 30, 2009 and they were written down to their fair values (see Note 6).
89
Table of Contents
The change in fair value using Level 3 inputs of the notes receivable can be summarized as follows:
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | |||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | |||||||||||
| Beginning of period | $ | 20 | $ | 62 | $ | 67 | |||||||
| Accretion of value (interest income) | 10 | 9 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Unrealized gain (loss) (OCI) | 64 | (51 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||||
| End of period | $ | 94 | $ | 20 | $ | 62 | |||||||
Substantially all of the notes receivable amount consists of one note, due 2019, obtained in connection with a divestiture in 2004. Its carrying amount is adjusted each quarter based on the market value of publicly traded debt of the operating subsidiary of the obligor. At December 31, 2009, the fair value of the note approximates the contractual value and we believe that all contractual payments related to this note will be received. Net changes in the values of the other notes receivable are less than $1.
See Interest Rate Agreements in Note 12 for a discussion of the interest rate caps.
We manufacture and sell our products in a number of countries and, as a result, are exposed to movements in foreign currency exchange rates. From time to time, we enter into forward contracts to manage the exposure on forecasted transactions denominated in foreign currencies and to manage the risk of transaction gains and losses associated with assets and liabilities denominated in currencies other than the functional currency of certain subsidiaries. The changes in the fair value of these forward contracts are recorded in cost of sales for product related hedges and in other income for repatriation hedges.
| Note 14. | Risk Management and Derivatives |
The total notional amount of outstanding foreign currency derivatives as of December 31, 2009 was $86, which is primarily comprised of forward exchange contracts denominated in euros, British pounds and Australian dollars versus the U.S. dollar.
The fair values of derivative instruments included within the consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2009 is less than $1 of receivables under forward contracts reported as part of other current assets and $4 of payables under forward contacts reported in other accrued liabilities. These derivatives are not designated as hedging instruments. Changes in the fair value of these instruments and any gain or loss realized are reported in other income, net or cost of sales for materials purchases (see Note 13).
Hedges of product costs are recorded in cost of sales when the underlying transaction affects net income. No amounts were designated as hedges during 2009. We also carry an interest rate cap on a notional value of $702 of our long-term debt. The fair value of this derivative at December 31, 2009 was less than $1.
| Note 15. | Commitments and Contingencies |
Class action lawsuit and derivative actions — A securities class action entitledHoward Frank v. Michael J. Burns and Robert C. Richterwas originally filed in October 2005 in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of Ohio, naming our former Chief Executive Officer, Michael J. Burns, and former Chief Financial Officer, Robert C. Richter, as defendants. In a consolidated complaint filed in August 2006, lead plaintiffs alleged violations of the U.S. securities laws and claimed that the price at which our stock traded at various times between April 2004 and October 2005 was artificially inflated as a result of the defendants’ alleged wrongdoing. By order dated August 21, 2007, the District Court
90
Table of Contents
granted the defendants’ motion to dismiss the consolidated complaint and entered a judgment closing the case. On November 19, 2008, following briefing and oral argument on the lead plaintiffs’ appeal, the Sixth Circuit vacated the District Court’s judgment of dismissal on the ground that the decision on which it was based misstated the applicable pleading standard. On August 29, 2009, the District Court entered an amended order granting defendants’ renewed motion to dismiss the consolidated complaint and entered a judgment closing the case. On September 23, 2009, lead plaintiffs filed a notice of appeal of the amended order and the judgment entry. The appellate briefs have been filed and we are awaiting the setting of the oral argument date. We do not believe that any liabilities will result from these proceedings.
SEC investigation — We reached a settlement with the SEC in September 2009, bringing to a close the investigation initiated by the SEC in November 2005 of certain matters related to the restatement of the prior Dana financial statements for fiscal year 2004 and the first two quarters of 2005. No fines or penalties were imposed on Dana. In consenting to a cease and desist order, Dana — as successor registrant to Prior Dana — agreed to comply with various provisions of the federal securities laws. We cooperated fully with the SEC throughout its investigation.
Legal proceedings arising in the ordinary course of business — We are a party to various pending judicial and administrative proceedings arising in the ordinary course of business. These include, among others, proceedings based on product liability claims and alleged violations of environmental laws. We have reviewed these pending legal proceedings, including the probable outcomes, our reasonably anticipated costs and expenses, the availability and limits of our insurance coverage and surety bonds and our established reserves for uninsured liabilities.
Further information about some of these legal proceedings follows, including information about our accruals for the liabilities that may arise from such proceedings. We accrue for contingent liabilities at the time we believe they are both probable and estimable. We review our assessments of probability and estimability as new information becomes available and adjust our accruals quarterly, if appropriate. Since we do not accrue for contingent liabilities that we believe are probable unless we can reasonably estimate the amounts of such liabilities, our actual liabilities may exceed the amounts we have recorded. We do not believe that any liabilities that may result from these proceedings are reasonably likely to have a material adverse effect on our liquidity or financial condition.
Asbestos personal injury liabilities — We had approximately 31,000 active pending asbestos personal injury liability claims at December 31, 2009 and at December 31, 2008. For 2009, approximately 11,000 mostly inactive claims have been settled and are awaiting final documentation and dismissal, with or without payment. We have accrued $113 for indemnity and defense costs for settled, pending and future claims at December 31, 2009, compared to $124 at December 31, 2008. We use a fifteen year time horizon for our estimate of this liability.
At December 31, 2009, we had recorded $58 as an asset for probable recovery from our insurers for the pending and projected asbestos personal injury liability claims, compared to $63 recorded at December 31, 2008. The recorded asset reflects our assessment of the capacity of our current insurance agreements to provide for the payment of anticipated defense and indemnity costs for pending claims and projected future demands. The recorded asset does not represent the limits of our insurance coverage, but rather the amount we would expect to recover if we paid the accrued indemnity and defense costs.
As part of our reorganization, assets and liabilities associated with asbestos claims were retained in Prior Dana which was then merged into Dana Companies, LLC, a consolidated wholly-owned subsidiary of Dana. The assets of Dana Companies, LLC include insurance rights relating to coverage against these liabilities and other assets which we believe are sufficient to satisfy its liabilities. Dana Companies, LLC continues to process asbestos personal injury claims in the normal course of business, is separately managed and has an independent board member. The independent board member is required to approve certain transactions including dividends or other transfers of $1 or more of value to Dana.
91
Table of Contents
Other product liabilities — We had accrued $1 for non-asbestos product liability costs at December 31, 2009, compared to $2 at December 31, 2008, with no recovery expected from third parties at either date. The decline in 2009 results from a reduction in the volume of active claims. We estimate these liabilities based on assumptions about the value of the claims and about the likelihood of recoveries against us derived from our historical experience and current information.
Environmental liabilities — Accrued environmental liabilities at December 31, 2009 were $17, compared to $18 at December 31, 2008. We consider the most probable method of remediation, current laws and regulations and existing technology in determining the fair value of our environmental liabilities. As of December 31, 2009, we have also recorded a receivable of $2, representing amounts recoverable from certain of our insurers.
During the second quarter of 2009, we reached agreements with certain of our insurers related primarily to their coverage of previously settled environmental claims. We recorded the aggregate recovery of $12 in other receivables and reduced cost of sales in the consolidated statement of operations. As agreed, we have collected $10 of this receivable as of December 31, 2009.
One of the larger claims at emergence was a claim involving the Hamilton Avenue Industrial Park (Hamilton) site in New Jersey. We had been a potentially responsible party at this site (also known as the Cornell Dubilier Electronics or CDE site) under the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act (CERCLA). This matter had been the subject of an estimation proceeding as a result of our objection to a claim filed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and other federal agencies (collectively, the Government) in connection with this and several other CERCLA sites. Following several months of litigation and settlement discussions, we had concluded there was a probable settlement outcome and adjusted the liability at December 31, 2007 to the tentative $126 settlement amount. In April 2008, we reached a tentative agreement with the Government providing for an allowed general unsecured claim of $126. Following the Government’s comment period we received court approval and satisfied this claim in October 2008 with the distribution of 5.2 million shares of our common stock (valued in reorganization at $23.15 per share) from the disputed claims reserve.
Other liabilities related to asbestos claims — After the Center for Claims Resolution (CCR) discontinued negotiating shared settlements for asbestos claims for its member companies in 2001, some former CCR members defaulted on the payment of their shares of some settlements and some settling claimants sought payment of the unpaid shares from other members of the CCR at the time of the settlements, including from us. We have been working with the CCR, other former CCR members, our insurers and the claimants over a period of several years in an effort to resolve these issues. Through December 31, 2009, we had collected the entire $47 paid to claimants with respect to these claims. Efforts to recover additional CCR-related payments from surety bonds and other claims are continuing. Additional recoveries are not assured and accordingly have not been recorded at December 31, 2009.
Lease Commitments
Cash obligations under future minimum rental commitments under operating leases and net rental expense are shown in the table below. Operating lease commitments are primarily related to facilities.
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | Thereafter | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lease Commitments | $ | 48 | $ | 39 | $ | 33 | $ | 29 | $ | 45 | $ | 174 | $ | 368 | ||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
| Rental Expense | $ | 71 | $ | 89 | $ | 105 | ||||||
92
Table of Contents
| Note 16. | Warranty Obligations |
We record a liability for estimated warranty obligations at the dates our products are sold. We record the liability based on our estimate of costs to settle future claims. Adjustments are made as new information becomes available.
Changes in our warranty liabilities are summarized below:
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | |||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | |||||||||||
| Balance, beginning of period | $ | 100 | $ | 93 | $ | 92 | |||||||
| Amounts accrued for current period sales | 34 | 62 | 4 | ||||||||||
| Adjustments of prior accrual estimates | 3 | 10 | |||||||||||
| Settlements of warranty claims | (56 | ) | (61 | ) | (3 | ) | |||||||
| Foreign currency translation and other | 2 | (4 | ) | ||||||||||
| Balance, end of period | $ | 83 | $ | 100 | $ | 93 | |||||||
We have been notified by two of our larger customers that quality issues allegedly relating to products supplied by us could result in warranty claims. We have been engaged in discussions with both Toyota Motor Corporation and a tier one supplier to the Volkswagen Group regarding the technical aspects of the root causes of the vehicle performance issues. Our technical analysis and discussions with these customers are ongoing. Based on the information currently available to us, we do not believe that either of these matters will result in a material liability to Dana.
| Note 17. | Income Taxes |
Continuing operations — Income tax expense (benefit) attributable to continuing operations can be summarized as follows:
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||||||
Expense (benefit) | 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||||||
| Current | |||||||||||||||||
| U.S. federal and state | $ | (15 | ) | $ | 19 | $ | 14 | $ | 52 | ||||||||
| Non-U.S. | 8 | 66 | (6 | ) | 39 | ||||||||||||
| Total current | (7 | ) | 85 | 8 | 91 | ||||||||||||
| Deferred | |||||||||||||||||
| U.S. federal and state | 1 | (8 | ) | 27 | (106 | ) | |||||||||||
| Non-U.S. | (21 | ) | 30 | 164 | 77 | ||||||||||||
| Total deferred | (20 | ) | 22 | 191 | (29 | ) | |||||||||||
| Total expense (benefit) | $ | (27 | ) | $ | 107 | $ | 199 | $ | 62 | ||||||||
Net interest expense (income) of $4, ($10) and $9 was recognized as part of the provision for income taxes in the year ended December 31, 2009, the eleven months ended December 31, 2008 and the year ended December 31, 2007.
93
Table of Contents
Income tax expense was calculated based upon the following components of income (loss) from continuing operations before income tax:
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||
| U.S. operations | $ | (322 | ) | $ | (618 | ) | $ | 429 | $ | (406 | ) | ||||||
| Non-U.S. operations | (132 | ) | 69 | 485 | 19 | ||||||||||||
| Total income (loss) from continuing | |||||||||||||||||
| operations before income taxes | $ | (454 | ) | $ | (549 | ) | $ | 914 | $ | (387 | ) | ||||||
The interplay of OCI recorded for our U.S. operations and the related taxable loss projected for 2009 resulted in the recording of tax expense of $25 in OCI and the recognition of a tax benefit of $18 in continuing operations through the first three quarters of 2009. The actuarial loss resulting from the 2009 year-end valuation of our defined benefit pension plans caused the OCI recorded for our U.S. operations to be a loss for the full year. Accordingly, the tax expense of $25 in OCI and the tax benefit of $18 in continuing operations were both reversed in the fourth quarter.
Effective tax rate —The effective income tax rate for continuing operations differs from the U.S. federal statutory income tax rate for the following reasons:
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||
| U.S. federal income tax rate | (35 | )% | (35 | )% | 35 | % | (35 | )% | |||||||||
| Adjustments resulting from: | |||||||||||||||||
| Non-deductible items, including reorganization expense | 14 | ||||||||||||||||
| State and local income taxes, net of federal benefit | 1 | 2 | (1 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Non-U.S. income | (2 | ) | 14 | (4 | ) | 1 | |||||||||||
Non-U.S. withholding taxes on undistributed earnings ofnon-U.S. operations | (4 | ) | (1 | ) | 1 | 10 | |||||||||||
| Goodwill impairment | 10 | 8 | |||||||||||||||
| Settlement and return adjustments | (2 | ) | 5 | ||||||||||||||
| Fresh start accounting adjustments | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Effect of gain on settlement of liabilities subject to compromise | 66 | ||||||||||||||||
| Miscellaneous items | 1 | 4 | 4 | ||||||||||||||
| Impact on continuing operations before valuation allowance adjustments on effective tax rate | (42 | ) | (7 | ) | 101 | 6 | |||||||||||
| Valuation allowance adjustments | 36 | 26 | (79 | ) | 10 | ||||||||||||
| Effective income tax rate for continuing operations | (6 | )% | 19 | % | 22 | % | 16 | % | |||||||||
Generally, the discharge of a debt obligation for an amount less than the adjusted issue price creates cancellation of indebtedness income (CODI), which must be included in the obligor’s taxable income. However, recognition of CODI is limited for a taxpayer that is a debtor in a reorganization
94
Table of Contents
case if the discharge is granted by the court or pursuant to a plan of reorganization approved by the court. In our case, the Plan enabled the Debtors to qualify for this bankruptcy exclusion rule. The CODI triggered by discharge of debt under the Plan affected the taxable income of the Debtors for the stub period tax return (January 2008) by reducing certain income tax attributes otherwise available in the following order: (i) net operating losses (NOLs) for the year of discharge and net operating loss carryforwards; (ii) most credit carryforwards, including the general business credit and the minimum tax credit; (iii) net capital losses for the year of discharge and capital loss carryforwards; and (iv) the tax basis of the Debtors’ assets.
Through further evaluation and audit adjustment, our estimated pre-emergence U.S. NOLs approximate $580. The Internal Revenue Code (IRC) annual limitation on our use of these pre-emergence NOLs is estimated to be $85. The deferred tax assets related to our pre-emergence U.S. NOLs, including those remaining post-emergence, have a full valuation allowance. The additional NOLs accumulated since emergence are not subject to limitation as of the end of 2009. However, there can be no assurance that trading in our shares will not effect another change in control under the IRC which would further limit our ability to utilize our available NOLs.
We paid approximately $733 following emergence to fund two VEBAs for certain union employee benefit obligations. In July 2009, we finalized an agreement with the IRS confirming our treatment of the amount paid as a deductible cost in the 2008 post-emergence period. This amount did not increase the $580 of pre-emergence NOLs that are subject to the limitations imposed by the IRC. Offsetting this deduction in 2008 was additional CODI generated by the amendment of our Exit Facility in November 2008. Under IRS regulations, this amendment is treated as a reissuance of debt at fair value for tax purposes. The difference between the fair market value of the debt at that time and the face value becomes an original issue discount for tax purposes generating CODI of approximately $550. We believe that the full amount of this discount will be deductible over the remaining term of the loan. The net deferred tax assets related to these issues have a full valuation allowance.
Valuation allowance adjustments — We periodically assess the need to establish valuation allowances against our net deferred tax assets. Based on this analysis and our history of losses and our near-term profit outlook, we have established 100% valuation allowances against our U.S. deferred tax assets. Similar valuation allowances are recorded in other countries where, based on the profit outlook, realization of the deferred tax asset does not satisfy the more likely than not recognition criterion. Consequently, there is no income tax benefit recognized on the pre-tax losses of these jurisdictions as valuation allowances are established, offsetting the associated tax benefit. During 2009, we determined that certain deferred tax assets in Spain required a valuation allowance and we recorded a charge to tax expense of $8. During 2008, we determined that our deferred tax assets in Canada required a full valuation allowance and we recorded a charge to tax expense of $34. We will maintain full valuation allowances against our net deferred tax assets in the U.S. and other applicable countries until sufficient positive evidence exists to reduce or eliminate the valuation allowance.
95
Table of Contents
Deferred tax assets and liabilities — Temporary differences and carryforwards give rise to the following deferred tax assets and liabilities:
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||
| December 31, | January 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | |||||||||||
| Net operating loss carryforwards | $ | 869 | $ | 624 | $ | 336 | |||||||
| Expense accruals | 247 | 335 | 174 | ||||||||||
| Pension accruals | 180 | 46 | 35 | ||||||||||
| Research and development costs | 124 | 155 | 184 | ||||||||||
| Foreign tax credits recoverable | 111 | 111 | 107 | ||||||||||
| Other tax credits recoverable | 72 | 69 | 61 | ||||||||||
| Postretirement benefits other than pensions | 36 | 32 | 156 | ||||||||||
| Capital loss carryforward | 31 | 12 | 82 | ||||||||||
| Postemployment benefits | 13 | (3 | ) | 14 | |||||||||
| Inventory reserves | 2 | (22 | ) | (51 | ) | ||||||||
| Other employee benefits | 2 | 4 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Other | 33 | 54 | 30 | ||||||||||
| Total | 1,720 | 1,417 | 1,129 | ||||||||||
| Valuation allowance | (1,409 | ) | (1,137 | ) | (710 | ) | |||||||
Deferred tax assets | 311 | 280 | 419 | ||||||||||
| Unremitted earnings | (202 | ) | (81 | ) | (104 | ) | |||||||
| Intangibles | (149 | ) | (199 | ) | (234 | ) | |||||||
| Depreciation - non-leasing | (45 | ) | (124 | ) | (181 | ) | |||||||
| Leasing activities | 3 | (6 | ) | ||||||||||
| Goodwill | (4 | ) | 5 | (2 | ) | ||||||||
| Other | (8 | ) | |||||||||||
Deferred tax liabilities | (408 | ) | (396 | ) | (527 | ) | |||||||
Net deferred tax liabilities | $ | (97 | ) | $ | (116 | ) | $ | (108 | ) | ||||
Our deferred tax assets include benefits expected from the utilization of NOLs, capital loss and credit carryforwards in the future. The following table identifies the various deferred tax asset components and the related allowances that existed at December 31, 2009. Due to time limitations
96
Table of Contents
on the ability to realize the benefit of the carryforwards, additional portions of these deferred tax assets may become unrealizable in the future.
| Deferred | Earliest | |||||||||||
| Tax | Valuation | Carryforward | Year of | |||||||||
| Asset | Allowance | Period | Expiration | |||||||||
| Net operating losses | ||||||||||||
| U.S. federal | $ | 563 | $ | (563 | ) | 20 | 2023 | |||||
| U.S. state | 116 | (116 | ) | Various | 2010 | |||||||
| Luxembourg | 59 | (59 | ) | Unlimited | ||||||||
| Brazil | 41 | (35 | ) | Unlimited | ||||||||
| France | 27 | Unlimited | ||||||||||
| Australia | 16 | (16 | ) | Unlimited | ||||||||
| Venezuela | 15 | (8 | ) | 3 | 2011 | |||||||
| U.K. | 12 | (12 | ) | Unlimited | ||||||||
| Argentina | 5 | (5 | ) | 5 | 2011 | |||||||
| Mexico | 5 | (5 | ) | 10 | 2017 | |||||||
| Spain | 5 | (4 | ) | 15 | 2024 | |||||||
Othernon-U.S. | 5 | (1 | ) | Various | 2014 | |||||||
| Total | 869 | (824 | ) | |||||||||
| Capital losses | 31 | (31 | ) | |||||||||
| Other credits | 183 | (183 | ) | 10 - 20 | 2010 | |||||||
| Total | $ | 1,083 | $ | (1,038 | ) | |||||||
Foreign income repatriation — We provide for U.S. federal income andnon-U.S. withholding taxes on the projected future repatriations of the earnings from ournon-U.S. operations. During 2009, we continued to modify our forecast for future repatriations due to the current market conditions. Accordingly, we adjusted the future income andnon-U.S. withholding tax liabilities for these repatriations and recognized a net benefit of $22 in 2009.
The earnings of ournon-U.S. subsidiaries will likely be repatriated to the U.S. in the form of repayments of intercompany borrowings and distributions from earnings. Certain of our international operations had intercompany loan obligations to the U.S. totaling $285 at the end of 2009. Of this amount, intercompany loans with an equivalent value of $156 are denominated in a foreign currency and are not considered to be permanently invested as they are expected to be repaid in the near term.
Income tax audits — We conduct business globally and, as a result, file income tax returns in multiple jurisdictions that are subject to examination by taxing authorities throughout the world. With few exceptions, we are no longer subject to U.S. federal, state and local or foreign income tax examinations for years before 1999. The U.S. federal income tax audits for 1999 through 2005 are settled subject to finalization of the closing agreements. Upon finalization of the closing agreements in the first half of 2010, we expect to make a payment of $75 and adjust our reserves for uncertain tax benefits as appropriate. We are under audit in the U.S. for 2006 — 2008, but we do not expect to incur any additional tax liability for that period.
We are currently under audit by foreign authorities for certain taxation years. When these issues are settled the total amounts of unrecognized tax benefits for all open tax years may be modified. Audit outcomes and the timing of the audit settlements are subject to uncertainty and we cannot make an estimate of the impact on our financial position at this time.
Unrecognized tax benefits — We adopted the guidance for accounting for uncertain income tax positions on January 1, 2007 and credited retained earnings for the initial impact of $3. As of the
97
Table of Contents
adoption date, we had gross unrecognized tax benefits of $137, of which $112 could be reduced by NOL carryforwards, and other timing adjustments. The net amount of $25, if recognized, would affect our effective tax rate. Unrecognized tax benefits are the difference between a tax position taken, or expected to be taken, in a tax return and the benefit recognized for accounting purposes. Interest income or expense, as well as penalties relating to income tax audit adjustments and settlements are recognized as components of income tax expense or benefit. Interest of $7, $5 and $8 was accrued on the uncertain tax positions as of December 31, 2009 and 2008 and January 31, 2008.
A reconciliation of the beginning to ending amount of gross unrecognized tax benefits is as follows:
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 44 | $ | 57 | ||||
| Decreases related to prior year tax positions | (11 | ) | ||||||
| Balance at January 31 | 44 | 46 | ||||||
| Decrease related to expiration of statute of limitations | (3 | ) | 8 | |||||
| Decreases related to prior years tax positions | (7 | ) | (27 | ) | ||||
| Increases related to current year tax positions | 7 | 17 | ||||||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 41 | $ | 44 | ||||
As at December 31, 2009, the total amount of gross unrecognized tax benefits was $41, all of which, if recognized, would impact the effective tax rate. If open matters are settled with the IRS, the total amounts of unrecognized tax benefits for open tax years may be modified.
Note 18. Other Income, Net
Other income, net included:
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||
| Interest income | $ | 24 | $ | 48 | $ | 4 | $ | 42 | |||||||||
| Gain (loss) on extinguishment of debt | 35 | (10 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Contract cancellation income | 17 | ||||||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange gain (loss) | 9 | (12 | ) | 3 | 35 | ||||||||||||
| Exports and other credits | 19 | 11 | 1 | 17 | |||||||||||||
| Strategic transaction expenses | (16 | ) | (10 | ) | |||||||||||||
| DCC other income (loss), net | 2 | (1 | ) | 38 | |||||||||||||
| Divestiture gains (costs) | 11 | ||||||||||||||||
| Claim settlement | (11 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Other, net | 10 | 24 | 1 | 30 | |||||||||||||
| Other income, net | $ | 98 | $ | 53 | $ | 8 | $ | 162 | |||||||||
As discussed in Note 12 above, the net gain (loss) on extinguishment of debt resulted from the repurchase and repayment of Term Facility debt in 2008 and 2009.
Dana and its subsidiaries enter into foreign exchange forward contracts to hedge currency exposure on certain intercompany loans and accrued interest balances as well as to reduce exposure in cross-currency transactions in the normal course of business. At December 31, 2009, these foreign exchange forward contracts had a total notional amount of $86. These contracts are marked to
98
Table of Contents
market, with the gain or loss recorded in cost of sales for material purchase transactions and in other income, net for intercompany accounts. Foreign exchange gains and losses on cross-currency intercompany loan balances that are not considered permanently invested are included in foreign exchange gain (loss) above. Foreign exchange gains and losses on loans that are permanently invested are reported in OCI.
The contract cancellation income of $17 represents recoveries in connection with early cancellation of certain customer programs during 2009.
Strategic transaction expenses relate primarily to costs incurred in connection with evaluating alternative opportunities for certain of our businesses. Included in this amount is $11 which has been recorded in connection with the pending sale of substantially all of the assets of our Structural Products business (Note 2).
Other recoveries — During 2009, we agreed on remuneration for early termination of a customer program in mid-2010. Since this program was not immediately cancelled and is continuing in full production through mid-2010, the remuneration received for early cancellation is being reported in sales over the remainder of the program. Program cancellation income of $10 was recognized as revenue in 2009 and $2 remains deferred at December 31, 2009.
Note 19. Segment, Geographical Area and Major Customer Information
The components that management establishes for purposes of making decisions about an enterprise’s operating matters are referred to as “operating segments.”
We manage our operations globally through six operating segments with four operating segments — LVD, Sealing, Thermal and Structures — focused on specific products for the light vehicle market and two operating segments — Commercial Vehicle and Off-Highway — focused on specific medium-duty and heavy-duty vehicle markets. The former Light Axle and Driveshaft segments were generally combined in the first quarter of 2009 in line with our internal management structure into the LVD segment but certain operations of those segments were moved into the Commercial Vehicle and Off-Highway segments. Prior period amounts have been retrospectively adjusted for these changes.
We report the results of our operating segments and related disclosures about each of our segments on the basis that is used internally for evaluating segment performance and deciding how to allocate resources to those segments.
The primary measure of operating results is Segment EBITDA which is closely aligned with the definition of EBITDA in our debt agreements. We use this adjusted EBITDA to enhance the comparability and usefulness of our operating segment results after the application of fresh start accounting upon emergence from bankruptcy. The following items are excluded from our covenant calculation of EBITDA and are shown separately in the reconciliation of Segment EBITDA to the consolidated income (loss) from continuing operations before income taxes: gain or loss on reductions in debt, strategic transaction expenses, loss on sale of assets, stock compensation expense, unrealized foreign exchange gains or losses on intercompany loans and market value adjustments on currency forward contracts. We allocate the costs of corporate administrative services other than executive activities and shared service centers to our segments based on segment sales, operating assets and headcount. We do not allocate trailing costs of previously divested businesses and other non-administrative costs that are not directly attributable to the operating segments. The corporate costs allocated to the operating segments are $111, $110, $10 and $129 for 2009, the eleven months ended December 31, 2008, the one month ended January 31, 2008 and the full year 2007. Prior period segment results presented below have been adjusted to conform to the 2009 presentation.
Our adjusted EBITDA, as defined for both internal performance measurement and debt covenant compliance also excludes equity in earnings of affiliates, noncontrolling interest net income, restructuring charges (capped at $100 in 2009 for cash charges), reorganization items, asset impairment, amortization of the fresh start inventorystep-up and divestiture gains and losses.
99
Table of Contents
Segment Information
We used the following information to evaluate our operating segments:
| Dana | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2009 | December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inter- | 2009 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| External | Segment | Segment | Capital | Depreciation/ | Net | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | Sales | Sales | EBITDA | Spend | Amortization | Assets | ||||||||||||||||||
| LVD | $ | 2,021 | $ | 104 | $ | 131 | $ | 32 | $ | 134 | $ | 966 | ||||||||||||
| Sealing | 535 | 11 | 21 | 24 | 35 | 458 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal | 179 | 5 | 8 | 5 | 16 | 112 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Structures | 592 | 9 | 35 | 9 | 44 | 151 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Vehicle | 1,051 | 38 | 81 | 20 | 44 | 721 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Off-Highway | 850 | 26 | 38 | 4 | 29 | 572 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Eliminations and other | (193 | ) | 5 | 9 | 12 | |||||||||||||||||||
| �� | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 5,228 | $ | — | $ | 314 | $ | 99 | $ | 311 | $ | 2,992 | ||||||||||||
| Dana | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eleven Months Ended December 31, 2008 | December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inter- | 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| External | Segment | Segment | Capital | Depreciation/ | Net | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 | Sales | Sales | EBITDA | Spend | Amortization | Assets | ||||||||||||||||||
| LVD | $ | 2,603 | $ | 158 | $ | 79 | $ | 69 | $ | 120 | $ | 1,116 | ||||||||||||
| Sealing | 641 | 17 | 44 | 30 | 32 | 372 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal | 231 | 6 | 3 | 10 | 15 | 119 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Structures | 786 | 10 | 37 | 43 | 36 | 352 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Vehicle | 1,442 | 43 | 50 | 57 | 33 | 754 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Off-Highway | 1,637 | 43 | 102 | 25 | 25 | 595 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Eliminations and other | 4 | (277 | ) | 8 | 94 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 7,344 | $ | — | $ | 315 | $ | 234 | $ | 269 | $ | 3,402 | ||||||||||||
| Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| One Month Ended January 31, 2008 | January 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inter- | 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| External | Segment | Segment | Capital | Depreciation/ | Net | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 | Sales | Sales | EBITDA | Spend | Amortization | Assets | ||||||||||||||||||
| LVD | $ | 281 | $ | 15 | $ | 10 | $ | 8 | $ | 10 | $ | 1,007 | ||||||||||||
| Sealing | 64 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 292 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal | 28 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 126 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Structures | 90 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 329 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Vehicle | 130 | 6 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 620 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Off-Highway | 157 | 4 | 14 | 2 | 469 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Eliminations and other | 1 | (27 | ) | 518 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 751 | $ | — | $ | 43 | $ | 16 | $ | 23 | $ | 3,361 | ||||||||||||
100
Table of Contents
| Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2007 | December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inter- | 2007 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| External | Segment | Segment | Capital | Depreciation/ | Net | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | Sales | Sales | EBITDA | Spend | Amortization | Assets | ||||||||||||||||||
| LVD | $ | 3,476 | $ | 145 | $ | 112 | $ | 87 | $ | 116 | $ | 1,195 | ||||||||||||
| Sealing | 728 | 22 | 62 | 27 | 25 | 285 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal | 293 | 6 | 17 | 15 | 11 | 117 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Structures | 1,069 | 18 | 86 | 38 | 58 | 373 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Vehicle | 1,531 | 67 | 78 | 47 | 40 | 568 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Off-Highway | 1,609 | 42 | 142 | 30 | 21 | 434 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Eliminations and other | 15 | (300 | ) | 8 | 7 | 531 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 8,721 | $ | — | $ | 497 | $ | 252 | $ | 278 | $ | 3,503 | ||||||||||||
The net assets of the Structures segment include the assets held for sale related to the planned divestiture of substantially all of the assets of the segment and are net of the impairment recorded in the fourth quarter of 2009. See Note 2.
The following table reconciles Segment EBITDA to the consolidated income (loss) from continuing operations before income taxes:
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||
| Segment EBITDA | $ | 314 | $ | 315 | $ | 43 | $ | 497 | |||||||||
| Shared services and administrative | (22 | ) | (23 | ) | (3 | ) | (14 | ) | |||||||||
| Other income (expense) not in segments | 33 | 22 | (2 | ) | (27 | ) | |||||||||||
| Foreign exchange not in segments | 1 | (3 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation | (311 | ) | (269 | ) | (23 | ) | (279 | ) | |||||||||
| Amortization of intangibles | (86 | ) | (81 | ) | |||||||||||||
Amortization of fresh start inventorystep-up | (49 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Restructuring | (118 | ) | (114 | ) | (12 | ) | (205 | ) | |||||||||
| DCC EBIT | (2 | ) | 39 | ||||||||||||||
| Impairment of goodwill | (169 | ) | (89 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Impairment of long-lived assets | (156 | ) | (14 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Reorganization items, net | 2 | (25 | ) | (98 | ) | (275 | ) | ||||||||||
| Gain (loss) on extinguishment of debt | 35 | (10 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Strategic transaction expenses | (16 | ) | (10 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Loss on sale of assets, net | (8 | ) | (10 | ) | (9 | ) | |||||||||||
| Stock compensation expense | (13 | ) | (6 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange on intercompany loans and market value adjustments on forwards | 6 | (7 | ) | 4 | 44 | ||||||||||||
| Interest expense | (139 | ) | (142 | ) | (8 | ) | (105 | ) | |||||||||
| Interest income | 24 | 48 | 4 | 42 | |||||||||||||
| Fresh start accounting adjustments | 1,009 | ||||||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations before income taxes | $ | (454 | ) | $ | (549 | ) | $ | 914 | $ | (387 | ) | ||||||
101
Table of Contents
Net assets at the segment level are intended to correlate with invested capital. The amount includes accounts receivable, inventories, prepaid expenses (excluding taxes), goodwill, investments in affiliates, net property, plant and equipment, accounts payable and certain accrued liabilities.
Net assets differ from consolidated total assets as follows:
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
| Net assets | $ | 2,992 | $ | 3,402 | ||||
| Accounts payable and other current liabilities | 1,043 | 1,205 | ||||||
| Other current and long-term assets | 1,029 | 1,000 | ||||||
| Consolidated total assets | $ | 5,064 | $ | 5,607 | ||||
Although accounting for discontinued operations does not result in the reclassification of prior balance sheets, our segment reporting excludes the assets of our discontinued operations for all periods presented based on the treatment of these items for internal reporting purposes. The differences between operating capital spending and depreciation shown by segment and purchases of property, plant and equipment and depreciation shown on the cash flow statement result from the exclusion from the segment table of the amounts related to discontinued operations.
Geographic Information
Of our consolidated net sales, no country other than the U.S. accounts for more than 10% and only Brazil, Germany and Italy are between 5% and 10%. Sales are attributed to the location of the product entity recording the sale. Long-lived assets include property, plant and equipment; goodwill and equity investments in joint ventures. They do not include certain other non-current assets.
| Net Sales | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dana | Prior Dana | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | Long-Lived Assets | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | Year Ended | December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | Dana | Prior Dana | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| North America | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| United States | $ | 2,402 | $ | 3,016 | $ | 333 | $ | 4,000 | $ | 522 | $ | 790 | $ | 1,070 | ||||||||||||||||
| Canada | 137 | 319 | 46 | 536 | 71 | 80 | 113 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mexico | 120 | 188 | 17 | 255 | 110 | 109 | 41 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total North America | 2,659 | 3,523 | 396 | 4,791 | 703 | 979 | 1,224 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Europe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Italy | 378 | 838 | 85 | 821 | 191 | 199 | 86 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Germany | 333 | 442 | 45 | 459 | 156 | 153 | 196 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other Europe | 479 | 889 | 94 | 976 | 187 | 211 | 303 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Europe | 1,190 | 2,169 | 224 | 2,256 | 534 | 563 | 585 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| South America | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brazil | 426 | 578 | 47 | 527 | 160 | 125 | 112 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other South America | 372 | 388 | 20 | 387 | 129 | 132 | 81 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total South America | 798 | 966 | 67 | 914 | 289 | 257 | 193 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Asia Pacific | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Australia | 157 | 188 | 14 | 250 | 48 | 49 | 97 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other Asia Pacific | 424 | 498 | 50 | 510 | 231 | 236 | 185 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Asia Pacific | 581 | 686 | 64 | 760 | 279 | 285 | 282 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 5,228 | $ | 7,344 | $ | 751 | $ | 8,721 | $ | 1,805 | $ | 2,084 | $ | 2,284 | ||||||||||||||||
Long-lived assets include the assets held for sale in the Structures segment.
102
Table of Contents
Sales to Major Customers
Ford is the only large customer whose sales have exceeded 10% of our consolidated sales in the past three years. Sales to Ford for the three most recent years were $1,058 (20%) in 2009, $1,399 (17%) in 2008 and $1,991(23%) in 2007.
Export sales from the U.S. tonon-U.S. locations were $228, $345 and $314 in 2009, 2008 and 2007.
Note 20. Reorganization Items
Professional advisory fees and other costs directly associated with our reorganization are reported separately as reorganization items. Post-emergence professional fees relate to claim settlements, plan implementation and other transition costs attributable to the reorganization. Reorganization items of Prior Dana include provisions and adjustments to record the carrying value of certain pre-petition liabilities at their estimated allowable claim amounts, as well as the costs incurred by non-Debtor companies as a result of the Debtors’ Chapter 11 proceedings.
The reorganization items in the consolidated statement of operations consisted of the following items:
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Ended | Ended | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||
| Professional fees | $ | 1 | $ | 19 | $ | 27 | $ | 131 | |||||||||
| Contract rejections and claim settlements prior to emergence | 134 | ||||||||||||||||
| Employee emergence bonus | 47 | ||||||||||||||||
| Foreign tax costs due to reorganization | 33 | ||||||||||||||||
| Interest income | (1 | ) | (15 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Other | (3 | ) | 6 | 19 | 25 | ||||||||||||
| Total reorganization items | (2 | ) | 25 | 125 | 275 | ||||||||||||
| Gain on settlement of liabilities subject to compromise | (27 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Reorganization items, net | $ | (2 | ) | $ | 25 | $ | 98 | $ | 275 | ||||||||
During the second quarter of 2009, we reduced our vacation benefit liabilities by $5 to correct the amount accrued in 2008 as union agreements arising from our reorganization activities were being ratified. We recorded $3 as a reorganization item benefit consistent with the original expense recognition. This adjustment is not material to the current year or to the prior periods to which it relates.
The gain on settlement of liabilities subject to compromise resulted from the satisfaction of these liabilities at emergence through issuance of Dana common stock or cash payments. The $125 of reorganization items for the one month ended January 31, 2008 included $104 of costs incurred as a direct consequence of emergence from Chapter 11. These costs included an accrual for stock bonuses for certain union and non-union employees of $47, transfer taxes and other tax charges to effectuate the emergence and new legal organization, success fee obligations to certain professional advisors and other parties contributing to the Chapter 11 reorganization and other costs relating directly to emergence.
103
Table of Contents
Note 21. Emergence from Chapter 11
Background — The Debtors operated their businesses as debtors in possession under Chapter 11 of the Bankruptcy Code from the Filing Date until emergence from Chapter 11 on January 31, 2008. The Debtors’ Chapter 11 cases (collectively, the Bankruptcy Cases) were consolidated in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York (the Bankruptcy Court) under the captionIn re Dana Corporation, et al., CaseNo. 06-10354 (BRL). Neither DCC and its subsidiaries nor any of ournon-U.S. affiliates were Debtors.
Liabilities subject to compromise —Liabilities that were being addressed through the bankruptcy process (i.e., general unsecured nonpriority claims) were reported as liabilities subject to compromise and adjusted to the allowed claim amount as determined through the bankruptcy process, or to the estimated claim amount if determined to be probable and estimable. Certain of these claims were resolved and satisfied on or before our emergence on January 31, 2008, while others have been or will be resolved subsequent to emergence. Although the allowed amount of certain disputed claims has not yet been determined, our liability associated with these disputed claims was discharged upon our emergence. Except for certain specific priority claims (see below), most of the allowed unsecured nonpriority claims in Class 5B were or will be satisfied by distributions from the previously funded reserve holding shares of Dana common stock. Therefore, the future resolution of these disputed claims will not have an impact on our post-emergence results of operations or financial condition. Liabilities subject to compromise in the consolidated balance sheet shown below include those of our discontinued operations.
On the Effective Date, the Plan required that certain liabilities previously reported as liabilities subject to compromise be retained by Dana. Accordingly, at December 31, 2007, we reclassified approximately $213 of liabilities, including $145 of asbestos liabilities, $27 of pension liabilities and $41 of other liabilities from liabilities subject to compromise to current or long-term liabilities of Dana. Liabilities subject to compromise declined further, by $128, in January 2008 as a result of the retention of additional liabilities including $111 of priority tax claim liabilities, $9 of other tax liabilities and $8 of other liabilities. The remaining liabilities subject to compromise were discharged at January 31, 2008 under the terms of the Plan.
Claims resolution — On the Effective Date, the Plan was consummated and we emerged from Chapter 11. As provided in the Plan, we issued and distributed approximately 70 million shares of Dana common stock (valued in reorganization at $1,628) on the Effective Date to holders of allowed general unsecured claims in Class 5B totaling approximately $2,050. Pursuant to the Plan, we also issued and set aside approximately 28 million shares of Dana common stock (valued in reorganization at $640) for future distribution to holders of allowed unsecured nonpriority claims in Class 5B under the Plan. These shares are being distributed as the disputed and unliquidated claims are resolved. The claim amount related to the 28 million shares for disputed and unliquidated claims was estimated not to exceed $700. Since emergence, we have issued 23 million of the 28 million shares for allowed claims (valued in reorganization at $540), increasing the total shares issued to 94 million (valued in reorganization at $2,168) for unsecured claims of approximately $2,249. The corresponding decrease in the disputed claims reserve leaves 5 million shares (valued in reorganization at $102). The remaining disputed and unliquidated claims total approximately $96. To the extent that these remaining claims are settled for less than the 5 million remaining shares, additional incremental distributions will be made to the holders of the previously allowed general unsecured claims in Class 5B.
Under the provisions of the Plan, approximately two million shares of common stock (valued in reorganization at $45) have been issued and distributed since the Effective Date to pay emergence bonuses to union employees and non-union hourly and salaried non-management employees. The original accrual of $47 on the Effective Date included approximately 65,000 shares (valued in reorganization at $2) that were not utilized for these bonuses. These shares will be distributed instead to the holders of allowed general unsecured claims in Class 5B as provided in the Plan.
104
Table of Contents
Settlement obligations relating to non-pension retiree benefits and long-term disability (LTD) benefits for union claimants and non-pension retiree benefits for non-union claimants were satisfied with cash payments of $788 to VEBAs established for the benefit of the respective claimant groups. Additionally, we paid DCC $49, the remaining amount due to DCC noteholders, thereby settling DCC’s general unsecured claim of $325 against the Debtors. DCC, in turn, used these funds to repay the noteholders in full. Since emergence, payments of $100 have been made for administrative claims, priority tax claims, settlement pool claims and other classes of allowed claims. Additional cash payments of $75, related primarily to federal, state, and local tax claims, are expected to be paid in the first half of 2010.
Fresh start accounting — As required by GAAP, we adopted fresh start accounting effective February 1, 2008. The financial statements for the periods ended prior to January 31, 2008 do not include the effect of any changes in our capital structure or changes in the fair value of assets and liabilities as a result of fresh start accounting.
The timing of the availability of funds for our post-reorganization financing resulted in a January 31, 2008 consummation of the Plan. We selected February 1, 2008 for adoption of fresh start accounting. Accordingly, the results of operations of Dana for January 2008 include charges of $21 incurred during the month of January plus one-time reorganization costs incurred at emergence of $104 offset by a pre-emergence gain of $27 resulting from the discharge of liabilities under the Plan. In addition, we recorded a credit to earnings of $1,009 ($831 after tax) resulting from the aggregate changes to the net carrying value of our pre-emergence assets and liabilities to record their fair values under fresh start accounting.
GAAP provides, among other things, for a determination of the value to be assigned to the equity of the emerging company as of a date selected for financial reporting purposes. Dana’s compromise total enterprise value was determined to be $3,563. This value represents the amount of resources available for the satisfaction of post-petition liabilities and allowed claims, as negotiated between the Debtors and their creditors. This value, along with other terms of the Plan, was determined after extensive arms-length negotiations with the claimholders. Dana developed its view of what the value should be based upon expected future cash flows of the business after emergence from Chapter 11, discounted at rates reflecting perceived business and financial risks (the discounted cash flows or DCF). This valuation and a valuation using market value multiples for peer companies were blended to arrive at the compromise valuation. This value is the enterprise value of the entity and, after adjusting for certain liabilities and debt as explained below and summarized in explanatory note (5) to the reorganized consolidated balance sheet, is intended to approximate the amount a willing buyer would pay for the assets and liabilities of Dana immediately after restructuring.
The basis for the DCF was the projections published in the Plan. These five-year estimates included projected changes associated with our reorganization initiatives, anticipated changes in general market conditions, including variations in market regions and known new business gains and losses, as well as other factors considered by Dana management. We completed the DCF analysis by operating segment in late 2007 using discount rates ranging from 10.5% to 11.5% based on a capital asset pricing model which utilized weighted-average cost of capital relative to certain light vehicle and heavy vehicle reference group companies. The estimated enterprise value and the resulting equity value were highly dependent on the achievement of the future financial results contemplated in the projections that were published in the Plan.
The estimates and assumptions made in our valuation were inherently subject to significant uncertainties, many of which are beyond our control, and there was no assurance that these results could be achieved. The primary assumptions for which there is a reasonable possibility of the occurrence of a variation that would have significantly affected the measurement value included the revenue assumptions, anticipated levels of commodity costs, achievement of the cost reductions outlined in our 2007Form 10-K, the discount rate utilized, expected foreign exchange rates, the demand for pickup trucks and SUVs and the overall strength of the U.S. light vehicle markets. The
105
Table of Contents
primary assumptions for conditions expected to be different from conditions in late 2007 were stronger light vehicle and off-highway markets outside North America and a peak in demand for Class 8 trucks in North America in 2009 related to stricter U.S. emission standards that become effective in 2010.
Based on conditions in the automotive industry and general economic conditions, we used the low end of the range of valuations to determine the enterprise reorganization value.
For the DCF portion of the valuation, we utilized the average of two DCF methodologies to derive the enterprise value of Dana:
| • | Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization (EBITDA) multiple method —The sum of the present values of the unlevered free cash flows was added to the present value of the terminal value of Dana, computed using EBITDA exit multiples by segment ranging from 3.8 to 9.0 based in part on the range of multiples calculated in using a comparable public company methodology, to arrive at an implied enterprise value for Dana’s operating assets (excluding cash). | |
| • | Perpetuity growth method — The sum of the present values of the unlevered free cash flows was added to the present value of the terminal value of Dana, which was computed using the perpetuity growth method based in part on industry growth prospects and our business plans, to arrive at an implied enterprise value for Dana’s operating assets (excluding cash). |
We also utilized a comparable companies methodology which identified a group of publicly traded companies whose businesses and operating characteristics were similar to those of Dana as a whole, or similar to significant portions of Dana’s operations, and evaluated various operating metrics, growth characteristics and valuation multiples for equity and net debt for each of the companies in the group. We then developed a range of valuation multiples to apply to our projections to derive a range of implied enterprise values for Dana. The multiples ranged from 3.8 to 9.0 depending on the comparable company.
The final valuation range was an average of the DCF valuation ranges and the comparable company multiples range. This amount was also adjusted for the fair value of unconsolidated subsidiaries, the residual value of DCC’s assets, the fair value of our net operating losses and a note receivable obtained in connection with a divestiture in 2004.
Under fresh start accounting, this compromise total enterprise value was adjusted for Dana’s available cash and was allocated to our assets based on their respective fair values in conformity with the purchase method of accounting for business combinations. Available cash was determined by adjusting actual cash at emergence for emergence-related cash activity expected to occur after January 31, 2008. The valuations required to determine the fair value of certain of Dana’s assets as presented below represent the results of valuation procedures we performed. The enterprise reorganization value, after adjustments for available cash, is reduced by debt, noncontrolling interests and preferred stock with the remainder representing the value to common stockholders.
The significant assumptions related to the valuations of our assets in connection with fresh start accounting included the following:
Inventory — The value of inventory for fresh start accounting was based on the following:
| • | The fair value of finished goods was calculated as the estimated selling price of the finished goods on hand, less the costs to dispose of that inventory (i.e., selling costs) and a reasonable profit margin for the selling effort. | |
| • | The fair value of work in process was calculated as the selling price less the sum of costs to complete the manufacturing process, selling costs and a reasonable profit on the remaining manufacturing effort and the selling effort based on profits for similar finished goods. | |
| • | The fair value of raw material inventory was its current replacement cost. |
106
Table of Contents
Fixed assets — Except for specific fixed assets identified as held for sale, which were valued at their estimated net realizable value, fixed assets were valued at fair value. In establishing fair value, three approaches were utilized to ensure that all market conditions were considered:
| • | The market or comparison sales approach uses recent sales or offerings of similar assets currently on the market to arrive at a probable selling price. In applying this method, aligning adjustments were made to reconcile differences between the comparable sale and the appraised asset. | |
| • | The cost approach considers the amount required to construct or purchase a new asset of equal utility, then adjusts the value in consideration of all forms of depreciation as of the appraisal date as described below: |
Physical deterioration — the loss in value or usefulness attributable solely to physical causes such as wear and tear and exposure to the elements.
Functional obsolescence — a loss in value due to factors inherent in the property itself and due to changes in design or process resulting in inadequacy, overcapacity, excess construction, lack of functional utility or excess operation costs.
Economic obsolescence — loss in value by unfavorable external conditions such as economics of the industry, loss of material and labor sources or change in ordinances.
| • | The income approach considers value in relation to the present worth of future benefits derived from ownership and is usually measured through the capitalization of a specific level of income. |
Useful lives were assigned to applicable appraised assets based on estimates of economic future usefulness in consideration of all forms of depreciation.
Intangible assets — The financial information used to determine the fair value of intangible assets was consistent with the information used in estimating the enterprise value of Dana. Following is a summary of each category considered in the valuation of intangible assets:
| • | Core technology — An income approach, the relief from royalty method, was used to value developed technology at $99 as of January 31, 2008. Significant assumptions included development of the forecasted revenue streams for each technology category by geographic region, estimated royalty rates for each technology category, applicable tax rates by geographic region and appropriate discount rates which considered variations among markets and geographic regions. | |
| • | Trademarks and trade names — Four trade names/trademarks were identified as intangible assets: Dana®, Spicer®, Victor-Reinz® and Long®. An income approach, the relief from royalty method, was used to value trademarks and trade names at $90 as of January 31, 2008. Significant assumptions included the useful life, the forecasted revenue streams for each trade name/trademark by geographic region, estimated applicable royalty rate for each technology category, applicable tax rates by geographic region and appropriate discount rates. For those indefinite-lived trade names/trademarks (Dana® and Spicer®), terminal growth rates were also estimated. | |
| • | Customer contracts and related relationships — Customer contracts and related relationships were valued by operating segment utilizing an income approach, the multi-period excess earnings method, which resulted in a valuation of $491. Significant assumptions included the forecasted revenue streams by customer by geographic region, the estimated contract renewal probability for each operating segment, estimated profit margins by customer by region, estimated charges for contributory assets for each customer (fixed assets, net working capital, assembled workforce, trade names/trademarks and developed technology), estimated tax rates by geographic region and appropriate discount rates. |
107
Table of Contents
The adjustments presented below were made to our January 31, 2008 balance sheet. The balance sheet reorganization and fresh start adjustments presented below summarize the impact of the adoption of the Plan and the fresh start accounting entries as of the Effective Date.
DANA HOLDING CORPORATION
REORGANIZED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET
REORGANIZED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET
| January 31, 2008 | ||||||||||||||||
| Prior | Reorganization | Fresh Start | ||||||||||||||
| Assets | Dana | Adjustments(1) | Adjustments | Dana | ||||||||||||
| Current assets | ||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 1,199 | $ | 948 | (2) | $ | — | $ | 2,147 | |||||||
| Accounts receivable | ||||||||||||||||
| Trade, less allowance for doubtful accounts | 1,255 | 1 | (6) | 1,256 | ||||||||||||
| Other | 316 | (1 | )(6) | 315 | ||||||||||||
| Inventories | 843 | 169 | (6) | 1,012 | ||||||||||||
| Other current assets | 127 | (32 | )(6) | 95 | ||||||||||||
Total current assets | 3,740 | 948 | 137 | 4,825 | ||||||||||||
| Goodwill | 352 | (50 | )(6) | 302 | ||||||||||||
| Intangibles | 1 | 679 | (6) | 680 | ||||||||||||
| Investments and other assets | 294 | 40 | (2) | (35 | )(6) | 299 | ||||||||||
| (18 | )(3) | (35 | )(7) | (53 | ) | |||||||||||
| As adjusted | 294 | 22 | (70 | ) | 246 | |||||||||||
| Investments in affiliates | 172 | 9 | (6) | 181 | ||||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 1,763 | 278 | (6) | 2,041 | ||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 6,322 | $ | 970 | $ | 983 | $ | 8,275 | ||||||||
108
Table of Contents
| January 31, 2008 | ||||||||||||||||
| Prior | Reorganization | Fresh Start | ||||||||||||||
| Liabilities and Equity | Dana | Adjustments(1) | Adjustments | Dana | ||||||||||||
| Current liabilities | ||||||||||||||||
| Notes payable, including current portion of long-term debt | $ | 177 | $ | (49 | )(2) | $ | 128 | |||||||||
| 15 | (2) | $ | 15 | |||||||||||||
| As adjusted | 177 | (34 | ) | 143 | ||||||||||||
Debtor-in-possession financing | 900 | (900 | )(2) | |||||||||||||
| Accounts payable | 1,094 | 1,094 | ||||||||||||||
| Accrued payroll and employee benefits | 267 | 1 | (6) | 268 | ||||||||||||
| Taxes on income including current deferred | 132 | 132 | ||||||||||||||
| Other accrued liabilities (including VEBA paid on February 1) | 436 | 815 | (3) | 21 | (6) | 1,272 | ||||||||||
| 86 | (3) | 86 | ||||||||||||||
| (15 | )(2) | (15 | ) | |||||||||||||
| As adjusted | 436 | 886 | 21 | 1,343 | (2) | |||||||||||
Total current liabilities | 3,006 | (48 | ) | 22 | 2,980 | |||||||||||
| Liabilities subject to compromise | 3,382 | (3,327 | )(3) | 55 | ||||||||||||
| (55 | )(2) | (55 | ) | |||||||||||||
| As adjusted | 3,382 | (3,382 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Deferred employee benefits and other non-current liabilities | 650 | (29 | )(6) | 621 | ||||||||||||
| 105 | (7) | 105 | ||||||||||||||
| 178 | (6) | 178 | ||||||||||||||
| As adjusted | 650 | 254 | 904 | |||||||||||||
| Long-term debt | 19 | 19 | ||||||||||||||
| Term loan facility | 1,221 | (2) | 1,221 | |||||||||||||
Total liabilities | 7,057 | (2,209 | ) | 276 | 5,124 | |||||||||||
| Parent company stockholders’ equity | ||||||||||||||||
| Series A preferred stock | 242 | (2) | 242 | |||||||||||||
| Series B preferred stock | 529 | (2) | 529 | |||||||||||||
| Common stock – successor | 1 | (3)(5) | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital – successor | 2,267 | (3)(5) | 2,267 | |||||||||||||
| Common stock – predecessor | 150 | (150 | )(4) | |||||||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital – predecessor | 202 | (202 | )(4) | |||||||||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (515 | ) | 27 | (3) | 831 | (6) | 343 | |||||||||
| (104 | )(3) | (591 | )(8) | (695 | ) | |||||||||||
| 352 | (4) | 352 | ||||||||||||||
| As adjusted | (515 | ) | 275 | 240 | ||||||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (668 | ) | 278 | (3) | 591 | (8) | 201 | |||||||||
| (61 | )(3) | (140 | )(7) | (201 | ) | |||||||||||
| As adjusted | (668 | ) | 217 | 451 | ||||||||||||
| Total parent company stockholders’ equity (deficit) | (831 | ) | 3,179 | 691 | 3,039 | |||||||||||
| Noncontrolling interests | 96 | 16 | (6) | 112 | ||||||||||||
Total equity (deficit) | (735 | ) | 3,179 | 707 | 3,151 | |||||||||||
Total liabilities and equity | $ | 6,322 | $ | 970 | $ | 983 | $ | 8,275 | ||||||||
109
Table of Contents
Explanatory Notes
| (1) | Represents amounts recorded on the Effective Date for the implementation of the Plan, including the settlement of liabilities subject to compromise and related payments, the issuance of new debt and repayment of old debt, distributions of cash and new shares of common and preferred stock, and the cancellation of Prior Dana common stock. |
| (2) | Cash proceeds at emergence (net of cash payments): |
| Amount borrowed under the Exit Facility | $ | 1,350 | ||
| Original issue discount (OID) | (114 | ) | ||
| Exit Facility, net of OID ($15 current, $1,221 to long-term debt) | 1,236 | |||
| Less: deferred issuance fees | (40 | ) | ||
| Exit Facility net proceeds | 1,196 | |||
| Preferred stock issuance, net of fees and expenses — Series A | 242 | |||
| Preferred stock issuance, net of fees and expenses — Series B | 529 | |||
| Repayment of DIP lending facility | (900 | ) | ||
| Non-union retiree VEBA obligation payment | (55 | ) | ||
| Fees paid at emergence (including $10 previously accrued) | (15 | ) | ||
| Payment to DCC bondholders | (49 | ) | ||
| Net cash | $ | 948 | ||
This entry records our exit financing, the issuance of new Series A and Series B Preferred Stock and the payment of certain bankruptcy obligations on January 31, 2008. An additional $80 of the term loan portion of the Exit Facility was borrowed by Dana on February 1, 2008 and is not included in the January balance sheet above. Debt issuance costs of $40 are recorded in Investments and other assets and OID of $114 is presented net with the debt balance. Both of these are being deferred and amortized over the term of the facility. The $790 of preferred stock is recorded at the net proceeds of $771.
| (3) | Retirement of liabilities subject to compromise (LSTC): |
| Liabilities subject to compromise | $ | 3,382 | ||
| APBO reduction charged to LSTC and credited to Accumulated other comprehensive loss (See Note 10) | (278 | ) | ||
| Non-union retiree VEBA obligation payment | (55 | ) | ||
| New common stock and paid-in capital issued to satisfy allowed and disputed claims | (2,268 | ) | ||
| Claims to be satisfied in cash transferred to Other accrued liabilities at January 31, 2008 (includes $733 union VEBA obligation paid on February 1) | (815 | ) | ||
| Prior service credits recognized (See Note 10) | 61 | |||
| Gain on settlement of liabilities subject to compromise | $ | 27 | ||
| Deferred tax assets not realizable due to emergence | $ | (18 | ) | |
| Reorganization costs accrued at emergence (includes $47 of emergence bonuses) | (86 | ) | ||
| Total reorganization costs incurred at emergence (See Note 3) | $ | (104 | ) | |
This entry records reorganization costs of $104 incurred as a result of emergence and a gain of $27 on extinguishment of the obligations pursuant to implementation of the Plan.
Other accrued liabilities include a $733 liability to the union VEBAs. On February 1, 2008, Dana paid this obligation and borrowed the remaining $80 of the Term loan commitment in
110
Table of Contents
(2) above. Payments after January 31, under the terms of the Plan, were expected to include approximately $212 of administrative claims, priority tax claims and other classes of allowed claims, and were also included in other accrued liabilities of Dana at January 31, 2008.
| (4) | Closes Prior Dana capital stock and paid-in capital to accumulated deficit. |
| (5) | Reconciliation of enterprise value to the reorganization value of Dana assets, determination of goodwill and allocation of compromise enterprise value to common stockholders: |
| Compromise total enterprise value | $ | 3,563 | ||
| Plus: cash and cash equivalents | 2,147 | |||
| Less: adjustments to cash assumptions used in valuation and emergence related cash payments | (1,129 | ) | ||
| Plus: liabilities (excluding debt and liability for emergence bonuses) | 3,694 | |||
| Reorganization value of Dana assets | 8,275 | |||
| Fair value of Dana assets (excluding goodwill) | 7,973 | |||
| Reorganization value of Dana assets in excess of fair value (goodwill) | $ | 302 | ||
| Reorganization value of Dana assets | $ | 8,275 | ||
| Less: liabilities (excluding debt and the liability for emergence bonuses) | (3,694 | ) | ||
| Less: debt | (1,383 | ) | ||
| Less: noncontrolling interests | (112 | ) | ||
| Less: preferred stock (net of issuance costs) | (771 | ) | ||
| Less: liability for emergence bonus shares not issued at January 31, 2008 | (47 | ) | ||
| New common stock ($1) and paid-in capital ($2,267) | $ | 2,268 | ||
| Shares outstanding at January 31, 2008 | 97,971,791 | |||
| Per share value | $ | 23.15 |
The per share value of $23.15 was utilized to record the shares issued for allowed claims, the shares issued for the disputed claims reserve and the liability for shares issued to employees subsequent to January 31, 2008 as emergence bonuses. The $1,129 in the caption “Adjustments to cash assumptions used in valuation and emergence-related cash payments” in the table above represents adjustments to cash on hand for the then estimated amounts expected to be paid for bankruptcy claims and fees after emergence of $962 (VEBA payments of $733, remaining administrative claims, priority tax claims, settlement pool claims and other classes of allowed claims of $212 and settlements (cures) for contract rejections of $17). In addition, consistent with assumptions made in the determination of enterprise value, available cash was reduced by $56 for DCC settlements and $111 for cash deposits which support letters of credit, a number of self-insured programs and lease obligations, all of which were deemed to be unavailable to Dana.
111
Table of Contents
The following table summarizes the allocation of fair values of the assets and liabilities at emergence as shown in the reorganized consolidated balance sheet as of January 31, 2008:
| Cash | $ | 2,147 | ||
| Current assets | 2,678 | |||
| Goodwill | 302 | |||
| Intangibles | 680 | |||
| Investments and other assets | 246 | |||
| Investments in affiliates | 181 | |||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 2,041 | |||
| Total assets | 8,275 | |||
| Less current liabilities (including notes payable and current portion of long-term debt) | (3,016 | ) | ||
| Less long-term debt | (1,240 | ) | ||
| Less long-term liabilities and noncontrolling interests | (980 | ) | ||
| Net assets acquired | $ | 3,039 | ||
| (6) | This entry records the adjustments for fresh start accounting including thewrite-up of inventory and the adjustment of property, plant and equipment to its appraised value. Fresh start adjustments for intangible assets are also included and are based on valuations discussed above. The adjustments required to report assets and liabilities at fair value under fresh start accounting resulted in a pre-tax adjustment of $1,009, which was reported as fresh start accounting adjustments in the consolidated statement of operations for January 2008. Income tax expense for January included $178 of tax expense related to these adjustments, reducing to $831 the impact of fair value adjustments on net income for the month and on the accumulated deficit at January 31, 2008. |
The $29 reduction in deferred employee benefits and other non-current liabilities resulted from adjustments to the asbestos liability, discounting of workers’ compensation liabilities and reductions in certain tax liabilities.
The fresh start adjustment to other accrued liabilities included restructuring-related exit costs of $32 consisting of $10 of projected maintenance, security and taxes on assets held for sale, $9 of costs to be incurred in preparing these assets for sale and $13 of obligations under lease contracts related to facilities and equipment that were in use at January 31, 2008 but scheduled to cease operations in 2008 as part of restructuring plans approved prior to Dana’s emergence from bankruptcy. Charges to liability accounts, primarily to write off deferred revenue, reduced the total fresh start adjustment to other accrued liabilities to $21.
| (7) | Charge to accumulated other comprehensive loss for the remeasurement of retained employee benefit plans. See Note 10. |
| Reduction of pension plan net assets | $ | (35 | ) | |
| Increase in deferred employee benefits and other non-current liabilities | (105 | ) | ||
| Charge to accumulated other comprehensive loss | $ | (140 | ) | |
| (8) | Adjusts accumulated other comprehensive loss to zero. |
112
Table of Contents
Debtor in Possession Financial Information
Aggregate financial information of the Debtors is presented below for the year ended December 31, 2007. Intercompany balances between Debtors and non-Debtors are not eliminated. The investment in non-Debtor subsidiaries is accounted for on an equity basis and, accordingly, the net loss reported in thedebtor-in-possession statement of operations is equal to the consolidated net loss.
DANA CORPORATION
DEBTOR IN POSSESSION
STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS
(Non-Debtor entities, principallynon-U.S. subsidiaries, reported as equity earnings)
DEBTOR IN POSSESSION
STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS
(Non-Debtor entities, principallynon-U.S. subsidiaries, reported as equity earnings)
| Year Ended | ||||
| December 31, | ||||
| 2007 | ||||
Net sales | ||||
| Customers | $ | 3,975 | ||
| Non-Debtor subsidiaries | 254 | |||
| Total | 4,229 | |||
| Costs and expenses | ||||
| Cost of sales | 4,243 | |||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 226 | |||
| Realignment and impairment | 102 | |||
| Other income, net | 227 | |||
| Loss from continuing operations before interest, reorganization items and income taxes | (115 | ) | ||
| Interest expense (contractual interest of $180 for the year ended December 31, 2007) | 72 | |||
| Reorganization items, net | 265 | |||
| Loss from continuing operations before income taxes | (452 | ) | ||
| Income tax benefit | 55 | |||
| Equity in earnings of affiliates | 3 | |||
Loss from continuing operations | (394 | ) | ||
Loss from discontinued operations | (186 | ) | ||
| Equity in earnings of non-Debtor subsidiaries | 27 | |||
Net loss | (553 | ) | ||
| Less: Noncontrolling interests net income | 2 | |||
Net loss available to common stockholders | $ | (551 | ) | |
113
Table of Contents
DANA CORPORATION
DEBTOR IN POSSESSION
CASH FLOW
(Non-Debtor entities, principallynon-U.S. subsidiaries, reported as equity investments)
DEBTOR IN POSSESSION
CASH FLOW
(Non-Debtor entities, principallynon-U.S. subsidiaries, reported as equity investments)
| Year Ended | ||||
| December 31, | ||||
| 2007 | ||||
Operating activities | ||||
| Net loss | $ | (553 | ) | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 136 | |||
| Loss on sale of assets | 105 | |||
| Deferred income taxes | (106 | ) | ||
| Impairment and divestiture-related charges | 94 | |||
| Reorganization items, net of payments | 154 | |||
| Equity in losses of non-Debtor subsidiaries, net of dividends | 49 | |||
| Payment to VEBAs for postretirement benefits | (27 | ) | ||
| OPEB payments in excess of expense | (76 | ) | ||
| Intercompany settlements | 135 | |||
| Changes in working capital | 62 | |||
| Other | 120 | |||
Net cash flows provided by operating activities | 93 | |||
Investing activities | ||||
| Purchases of property, plant and equipment | (81 | ) | ||
| Proceeds from sale of businesses | 42 | |||
| Other | 42 | |||
Net cash flows provided by investing activities | 3 | |||
Financing activities | ||||
Proceeds fromdebtor-in-possession facility | 200 | |||
| Payments on long-term debt | (2 | ) | ||
Net cash flows provided by financing activities | 198 | |||
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | 294 | |||
| Cash and cash equivalents — beginning of period | 216 | |||
Cash and cash equivalents — end of period | $ | 510 | ||
114
Table of Contents
| Note 22. | Discontinued Operations |
In 2005, the Board of Directors of Prior Dana approved the divestiture of our engine hard parts, fluid products and pump products operations and we have reported these businesses as discontinued operations through their respective dates of divestiture. Substantially all of these operations were sold prior to 2008.
The results of the discontinued operations were as follows:
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||
| Ended | Ended | Year Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||||
| Sales | $ | — | $ | 6 | $ | 495 | |||||||
| Cost of sales | 6 | 500 | |||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative | 26 | ||||||||||||
| Restructuring and other expense, net | 4 | 8 | 61 | ||||||||||
| Loss before income taxes | (4 | ) | (8 | ) | (92 | ) | |||||||
| Income tax benefit (expense) | 2 | (26 | ) | ||||||||||
| Loss from discontinued operations | $ | (4 | ) | $ | (6 | ) | $ | (118 | ) | ||||
During 2007, we recorded pre-tax losses of $16 upon completion of the sales of businesses, charges of $17 for settlement of pension obligations in the U.K. (see Note 10) relating to discontinued operations and $20 for a bankruptcy claim settlement with the purchaser of a previously sold discontinued business.
The sales and net loss of our discontinued operations consisted of the following:
| Dana | Prior Dana | ||||||||||||
| Eleven Months | One Month | ||||||||||||
| Ended | Ended | Year Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, | January 31, | December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2008 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||||
| Sales | |||||||||||||
| Engine | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 131 | |||||||
| Fluid | 276 | ||||||||||||
| Pump | 6 | 88 | |||||||||||
| Total discontinued operations | $ | — | $ | 6 | $ | 495 | |||||||
| Net loss | |||||||||||||
| Engine | $ | (1 | ) | $ | (4 | ) | $ | (68 | ) | ||||
| Fluid | (2 | ) | (1 | ) | (6 | ) | |||||||
| Pump | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | (23 | ) | |||||||
| Other | (21 | ) | |||||||||||
| Total discontinued operations | $ | (4 | ) | $ | (6 | ) | $ | (118 | ) | ||||
There were no assets or liabilities of discontinued operations as of December 31, 2008. In the consolidated statement of cash flows, the cash flows of discontinued operations have been reported in the respective categories of cash flows, along with those of our continuing operations.
In March 2007, we sold our engine hard parts business to MAHLE GmbH (MAHLE) and received cash proceeds of $98. We recorded an after-tax loss of $45 in connection with this sale. We incurred a loss of $5 in the month of January 2008 associated with a post-closing adjustment to reinstate certain retained liabilities of this business.
115
Table of Contents
In July and August 2007, we completed the sale of our fluid products hose and tubing business to Orhan Holding A.S. and certain of its affiliates. Aggregate cash proceeds of $84 were received from these transactions, and an aggregate after-tax gain of $32 was recorded. Additional adjustments to this sale were made during 2008, when we recorded an expense of $3 associated with a post-closing purchase price adjustment and settlement costs and related expenses.
In September 2007, we completed the sale of our coupled fluid products business to Coupled Products Acquisition LLC by having the buyer assume $18 of certain liabilities of the business at closing. We recorded an after-tax loss of $23 in connection with the sale of this business. We completed the sale of a portion of the pump products business in October 2007, generating proceeds of $7 and a nominal after-tax gain.
In January 2008, we completed the sale of the remaining assets of the pump products business to Melling Tool Company, generating proceeds of $5 and an after-tax loss of $2.
Quarterly Results (Unaudited)
| Dana | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For the 2009 Quarters Ended | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| As Reported | As Adjusted | As Reported | As Adjusted | As Reported | As Reported | |||||||||||||||||||
| March 31 | March 31 (1) | June 30 | June 30 (1) | September 30 | December 31 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 1,216 | $ | 1,216 | $ | 1,190 | $ | 1,190 | $ | 1,329 | $ | 1,493 | ||||||||||||
| Gross margin | $ | (17 | ) | $ | (12 | ) | $ | 62 | $ | 67 | $ | 82 | $ | 116 | ||||||||||
| Net income | $ | (160 | ) | $ | (160 | ) | $ | (3 | ) | $ | (3 | ) | $ | (38 | ) | $ | (235 | ) | ||||||
| Net loss attributable to the parent company | $ | (157 | ) | $ | (157 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (38 | ) | $ | (236 | ) | ||||||||
| Net loss per share available to parent company stockholders | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | (1.64 | ) | $ | (1.64 | ) | $ | (0.08 | ) | $ | (0.08 | ) | $ | (0.45 | ) | $ | (2.02 | ) | ||||||
| Diluted | $ | (1.64 | ) | $ | (1.64 | ) | $ | (0.08 | ) | $ | (0.08 | ) | $ | (0.45 | ) | $ | (2.02 | ) | ||||||
Note (1) During the third quarter of 2009, ayear-to-date adjustment was made related to the classification of full absorption inventory costing between cost of sales and selling, general and administrative expenses. The classification was reported correctly in the third quarter of 2009 and has been adjusted in the first and second quarters of 2009 above.
| Prior Dana | Dana | ||||||||||||||||||||
| One Month | For the 2008 Periods Ended | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ended | Two Months | Quarter | Quarter | Quarter | |||||||||||||||||
| January 31, | Ended | Ended | Ended | Ended | |||||||||||||||||
| 2008 | March 31 | June 30 | September 30 | December 31 | |||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 751 | $ | 1,561 | $ | 2,333 | $ | 1,929 | $ | 1,521 | |||||||||||
| Gross margin | $ | 49 | $ | 58 | $ | 145 | $ | 48 | $ | (20 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net income | $ | 711 | $ | (48 | ) | $ | (119 | ) | $ | (255 | ) | $ | (249 | ) | |||||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to the parent company | $ | 709 | $ | (50 | ) | $ | (122 | ) | $ | (256 | ) | $ | (249 | ) | |||||||
| Net income (loss) per share available to parent company stockholders | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | 4.73 | $ | (0.55 | ) | $ | (1.28 | ) | $ | (2.66 | ) | $ | (2.57 | ) | |||||||
| Diluted | $ | 4.71 | $ | (0.55 | ) | $ | (1.28 | ) | $ | (2.66 | ) | $ | (2.57 | ) | |||||||
The fourth quarter of 2009 includes pre-tax impairments of $150 related to the planned sale of substantially all of our Structural Products business.
The second quarter of 2008 included a pre-tax impairment of goodwill of $75. The third quarter of 2008 included a pre-tax impairment of goodwill of $105. The fourth quarter of 2008 included an $11 reduction in goodwill impairment as a result of income tax adjustments being credited to goodwill.
116
Table of Contents
DANA HOLDING CORPORATION AND CONSOLIDATED SUBSIDIARIES
SCHEDULE II
VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS AND RESERVES
| Adjustments | ||||||||||||||||||||
| arising | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Amounts | from change | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at | charged | in currency | Balance at | |||||||||||||||||
| beginning | (credited) | Allowance | exchange rates | end of | ||||||||||||||||
| of period | to income | utilized | and other items | period | ||||||||||||||||
| Dana | ||||||||||||||||||||
For the Year Ended December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Amounts deducted from assets | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful receivables | $ | 23 | $ | 2 | $ | (7 | ) | $ | — | $ | 18 | |||||||||
| Valuation allowance for deferred tax assets | 1,137 | 268 | (64 | ) | 68 | 1,409 | ||||||||||||||
| Total allowances deducted from assets | $ | 1,160 | $ | 270 | $ | (71 | ) | $ | 68 | $ | 1,427 | |||||||||
For the Eleven Months Ended December 31, 2008 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Amounts deducted from assets | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful receivables | $ | 23 | $ | 5 | $ | (4 | ) | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 23 | ||||||||
| Valuation allowance for deferred tax assets | 710 | 266 | 161 | 1,137 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total allowances deducted from assets | $ | 733 | $ | 271 | $ | (4 | ) | $ | 160 | $ | 1,160 | |||||||||
| Prior Dana | ||||||||||||||||||||
For the Month Ended January 31, 2008 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Amounts deducted from assets | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful receivables | $ | 20 | $ | — | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 4 | $ | 23 | |||||||||
| Valuation allowance for deferred tax assets | 1,609 | (723 | ) | (176 | ) | 710 | ||||||||||||||
| Total allowances deducted from assets | $ | 1,629 | $ | (723 | ) | $ | (1 | ) | $ | (172 | ) | $ | 733 | |||||||
For the Year Ended December 31, 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Amounts deducted from assets | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful receivables | $ | 23 | $ | (1 | ) | $ | (2 | ) | $ | — | $ | 20 | ||||||||
| Valuation allowance for deferred tax assets | 1,971 | (57 | ) | (3 | ) | (302 | ) | 1,609 | ||||||||||||
| Total allowances deducted from assets | $ | 1,994 | $ | (58 | ) | $ | (5 | ) | $ | (302 | ) | $ | 1,629 | |||||||
117
Table of Contents
| Item 9. | Changes In and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
None.
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures |
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, has evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as such term is defined inRules 13a-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the Exchange Act)) as of the end of the period covered by this report. Based on such evaluations, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that, as of the end of such period, our disclosure controls and procedures are effective.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Exchange ActRule 13a-15(f). Management, with the participation of the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, has evaluated the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on this evaluation, management has concluded that, as of December 31, 2009, our internal control over financial reporting was effective.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, has audited the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009, as stated in their report which is included herein.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There has not been any change in our internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2009, that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
| Item 9B. | Other Information |
None.
118
Table of Contents
PART III
| Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance |
Dana has adopted Standards of Business Conduct that apply to all of its officers and employees worldwide. Dana also has adopted Standards of Business Conduct for the Board of Directors. Both documents are available on Dana’s website at www.dana.com.
The remainder of the response to this item will be included under the sections captioned “Corporate Governance,” “Selection of Chairman and Chief Executive Officer Succession Planning,” “Information About the Nominees and Series A Preferred Directors,” “Risk Oversight,” “Committees and Meetings of Directors,” “Executive Officers” and “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” of Dana’s definitive Proxy Statement relating to the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on April 28, 2010, which sections are hereby incorporated herein by reference.
| Item 11. | Executive Compensation |
The response to this item will be included under the sections captioned “Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation,” “Compensation of Executive Officers,” “Compensation Discussion and Analysis,” “Compensation of Directors,” “Officer Stock Ownership Guidelines,” ���Compensation Committee Report,” “Summary Compensation Table,” “Grants of Plan-Based Awards,” “Outstanding Equity Awards at Fiscal Year End,” “Option Exercises and Stock Vested,” “Pension Benefits,” “Executive Agreements” and “Potential Payments Upon Termination or Change in Control” of Dana’s definitive Proxy Statement relating to the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on April 28, 2010, which sections are hereby incorporated herein by reference.
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
The response to the remaining requirements of this item will be included under the sections captioned “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” of Dana’s definitive Proxy Statement relating to the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on April 28, 2010, which sections are hereby incorporated herein by reference.
119
Table of Contents
Equity Compensation Plan Information
The following table contains information as of December 31, 2009 about shares of stock which may be issued under our equity compensation plans, all of which have been approved by our shareholders.
| Number of Securities to | ||||||||||||
| be Issued Upon | Weighted Average | |||||||||||
| Exercise of | Exercise Price of | Number of Securities | ||||||||||
| Outstanding Options, | Outstanding Options, | Remaining Available | ||||||||||
Plan Category(1) | Warrants and Rights(2) | Warrants and Rights(3) | for Future Issuance | |||||||||
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | 10,132,214 | $ | 4.88 | 5,040,721 | ||||||||
| Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | ||||||||||||
| Total | 10,132,214 | $ | 4.88 | 5,040,721 | ||||||||
| (1) | As a result of our emergence from bankruptcy on January 31, 2008, all unexercised Prior Dana stock options, unvested restricted shares and restricted stock units and unvested equity incentive plan awards were cancelled with no consideration. All amounts shown relate to the period following emergence. | |
| (2) | In addition to stock options, restricted stock units and performance shares have been awarded under Dana’s equity compensation plans and were outstanding at December 31, 2009. | |
| (3) | Calculated without taking into account the 955,032 shares of common stock subject to outstanding restricted stock units and performance shares that become issuable as those units vest since they have no exercise price and no cash consideration or other payment is required for such shares. |
| Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
The response to this item will be included under the sections captioned “Director Independence and Transactions of Directors with Dana,” “Transactions of Executive Officers with Dana” and “Information about the Nominees and Series A Preferred Directors” of Dana’s definitive Proxy Statement relating to the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on April 28, 2010, which sections are hereby incorporated herein by reference.
| Item 14. | Principal Accountant Fees and Services |
The response to this item will be included under the section captioned “Independent Auditors” of Dana’s definitive Proxy Statement relating to the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on April 28, 2010, which section is hereby incorporated herein by reference.
120
PART IV
| Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules |
| 10-K Pages | ||||||||||
| (a) List of documents filed as a part of this report: | ||||||||||
| 1. | Consolidated Financial Statements: | |||||||||
| Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | 43 | |||||||||
| Consolidated Statement of Operations | 46 | |||||||||
| Consolidated Balance Sheet | 47 | |||||||||
| Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows | 48 | |||||||||
| Consolidated Statement of Shareholders’ Equity | 49 | |||||||||
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | 51 | |||||||||
| 2. | Unaudited Quarterly Financial Information | 116 | ||||||||
| 3. | Financial Statement Schedule: | |||||||||
| Valuation and Qualifying Accounts and Reserves (Schedule II) | 117 | |||||||||
| All other schedules are omitted because they are not applicable or the required information is shown in the financial statements or notes thereto | ||||||||||
| 4. | Exhibits listed in the Exhibit Index | 123 | ||||||||
121
Table of Contents
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, hereunto duly authorized.
DANA HOLDING CORPORATION
Date: February 24, 2010
By:
/s/ James E. Sweetnam
James E. Sweetnam
President and Chief Executive Officer
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below on this 24th day of February 2010 by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities indicated, including a majority of the directors.
Signature | Title | |||
/s/ John M. Devine John M. Devine | Executive Chairman | |||
/s/ James E. Sweetnam James E. Sweetnam | President and Chief Executive Officer, Director (Principal Executive Officer) | |||
/s/ James A. Yost James A. Yost | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) | |||
/s/ Richard J. Dyer Richard J. Dyer | Vice President and Chief Accounting Officer (Principal Accounting Officer) | |||
/s/ Mark T. Gallogly Mark T. Gallogly | Director | |||
/s/ Terrence J. Keating Terrence J. Keating | Director | |||
/s/ Mark A. Schulz Mark A. Schulz | Director | |||
/s/ David P. Trucano David P. Trucano | Director | |||
/s/ Keith E. Wandell Keith E. Wandell | Director | |||
/s/ Jerome B. York Jerome B. York | Director | |||
122
Table of Contents
EXHIBIT INDEX
All documents referenced below were filed by Dana Corporation or Dana Holding Corporation (as successor registrant), file number001-01063, unless otherwise indicated.
No. | Description | |||
| 3 | .1 | Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Dana Holding Corporation. Filed as Exhibit 3.1 to Registrant’s Registration Statement onForm 8-A dated January 31, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 3 | .2 | Bylaws of Dana Holding Corporation. Filed as Exhibit 3.2 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K/A dated February 4, 2009, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 4 | .1 | Registration Rights Agreement dated as of January 31, 2008, by and among the Company and Centerbridge Capital Partners, L.P., Centerbridge Capital Partners Strategic, L.P. and Centerbridge Capital Partners SBS, L.P. Filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated February 6, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 4 | .2 | Shareholders Agreement dated as of January 31, 2008, by and among the Company and Centerbridge Capital Partners, L.P., Centerbridge Capital Partners Strategic, L.P. and Centerbridge Capital Partners SBS, L.P. Filed as Exhibit 10.3 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated February 6, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 4 | .3 | Specimen Common Stock Certificate. Filed as Exhibit 4.1 to Registrant’s Registration Statement onForm 8-A dated January 31, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 4 | .4 | Specimen Series A Preferred Stock Certificate. Filed as Exhibit 4.5 to Registrant’s Annual Report onForm 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2007, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 4 | .5 | Specimen Series B Preferred Stock Certificate. Filed as Exhibit 4.6 to Registrant’s Annual Report onForm 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2007, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .1** | Executive Employment Agreement dated December 16, 2008 and effective January 1, 2009 by and between John M. Devine and Dana Holding Corporation. Filed as Exhibit 10.6 to Registrant’s Annual Report onForm 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008, and as amended as set forth in Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated December 18, 2009 and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .2** | Executive Employment Agreement dated December 16, 2008 and effective January 1, 2009 by and between Gary L. Convis and Dana Holding Corporation. Filed as Exhibit 10.4 to Registrant’s Annual Report onForm 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .3** | Executive Employment Agreement dated December 16, 2008 and effective January 1, 2009 by and between Robert H. Marcin and Dana Holding Corporation. Filed as Exhibit 10.7 to Registrant’s Annual Report onForm 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .4** | Employment Agreement dated May 13, 2008 by and between Dana Holding Corporation and James A. Yost. Filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated May 13, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .5** | Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan for James A. Yost dated May 22, 2008. Filed as Exhibit 10.2 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated May 13, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .6** | Executive Employment Agreement dated May 22, 2009 by and between Dana Holding Corporation and James E. Sweetnam. Filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Quarterly Report onForm 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2009. | ||
| 10 | .7** | Separation Agreement dated August 6, 2009 by and between Nick Stanage and Dana Holding Corporation. Filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated August 6, 2009, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .8** | Dana Holding Corporation 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan. Filed as Exhibit 10.10 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated February 6, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
123
Table of Contents
No. | Description | |||
| 10 | .9** | Form of Stock Option Nonqualified Stock Option Agreement. Filed as Exhibit 10.14 to Registrant’s Annual Report onForm 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2007, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .10** | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement. Filed as Exhibit 10.15 to Registrant’s Annual Report onForm 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2007, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .11** | Form of Indemnification Agreement. Filed as Exhibit 10.4 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated February 6, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .12** | Dana Holding Corporation Summary of Non-Employee Director Compensation Package and Stock Ownership Guidelines. Filed as Exhibit 10.21 to Registrant’s Annual Report onForm 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2007, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .13** | Form of Option Right Agreement For Non-Employee Directors. Filed as Exhibit 10.22 to Registrant’s Annual Report onForm 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2007, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .14** | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement for Non-Employee Directors. Filed as Exhibit 10.23 to Registrant’s Annual Report onForm 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2007, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .15** | Form of Option Agreement under the Dana Holding Corporation 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan, as in use through August 1, 2008. Filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated April 18, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .16** | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement under the Dana Holding Corporation 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan, as in use through August 1, 2008. Filed as Exhibit 10.2 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated April 18, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .17** | Form of Performance Share Agreement under the Dana Holding Corporation 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan, as in use through August 1, 2008. Filed as Exhibit 10.3 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated April 18, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .18** | Form of Option Agreement under the Dana Holding Corporation 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan. Filed as Exhibit 10.38 to Registrant’s Annual Report onForm 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .19** | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement under the Dana Holding Corporation 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan. Filed as Exhibit 10.39 to Registrant’s Annual Report onForm 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .20** | Form of Performance Share Agreement under the Dana Holding Corporation 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan. Filed as Exhibit 10.40 to Registrant’s Annual Report onForm 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .21** | Form of Share Appreciation Rights Agreement under the Dana Holding Corporation 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan. Filed as Exhibit 10.41 to Registrant’s Annual Report onForm 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .22** | Dana Holding Corporation Executive Perquisite Plan. Filed as Exhibit 10.4 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated April 18, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .23** | Dana Holding Corporation Executive Severance Plan. Filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated June 24, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .24** | Letter Agreement effective January 1, 2010 between Dana Holding Corporation and Gary L. Convis. Filed with this report. | ||
| 10 | .25 | Receivables Loan Agreement dated 18 July 2007, between Dana Europe Financing (Ireland) Limited, as Borrower; Dana International Luxembourg SARL, as Servicer and as Performance Undertaking Provider; the persons from time to time party thereto as Lenders; and GE Leveraged Loans Limited, as Administrative Agent. Filed asExhibit 10-Z(1) to Registrant’s Quarterly Report onForm 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2007, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
124
Table of Contents
No. | Description | |||
| 10 | .26 | Master Schedule of Definitions, Interpretation and Construction dated 18 July 2007, between Dana Europe Financing (Ireland) Limited; Dana International Luxembourg SARL; the Originators; GE Leveraged Loans Limited; GE FactorFrance SNC; Dana Europe S.A., the Lenders; and certain other parties. Filed asExhibit 10-Z(2) to Registrant’s Quarterly Report onForm 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2007, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .27 | Performance and Indemnity Deed dated 18 July 2007, between Dana International Luxembourg SARL, as Performance Undertaking Provider; the Intermediate Transferor; Dana Europe Financing (Ireland) Limited, as Borrower; GE Leveraged Loans Limited, as Administrative Agent; and other secured parties. Filed asExhibit 10-Z(3) to Registrant’s Quarterly Report onForm 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2007 and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .28 | Term Facility Credit and Guaranty Agreement, dated as of January 31, 2008, among Dana Holding Corporation, as Borrower, the guarantors party thereto, Citicorp USA, Inc., as administrative agent and collateral agent, Citigroup Capital Markets, Inc., as joint lead arranger and joint bookrunner, Lehman Brothers Inc., as joint lead arranger, joint bookrunner and syndication agent, Barclays Capital, as joint bookrunner and documentation agent and the lenders and other financial institutions party thereto. Filed as Exhibit 10.5 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated February 6, 2008 and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .29 | Revolving Credit and Guaranty Agreement, dated as of January 31, 2008, among Dana Holding Corporation, as Borrower, the guarantors party thereto, Citicorp USA, Inc., as administrative agent and collateral agent, Citigroup Capital Markets, Inc., as joint lead arranger and joint bookrunner, Lehman Brothers Inc., as joint lead arranger, joint bookrunner and syndication agent, Barclays Capital, as joint bookrunner and documentation agent, and the lenders and other financial institutions party thereto. Filed as Exhibit 10.6 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated February 6, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .30 | Term Facility Security Agreement, dated as of January 31, 2008, among Dana Holding Corporation, the guarantors party thereto and Citicorp USA, Inc., as collateral agent. Filed as Exhibit 10.7 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated February 6, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .31 | Revolving Facility Security Agreement, dated as of January 31, 2008, among Dana Holding Corporation, the guarantors party thereto and Citicorp USA, Inc., as collateral agent. Filed as Exhibit 10.8 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated February 6, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .32 | Intercreditor Agreement, dated as of January 31, 2008, among Dana Holding Corporation, Citicorp USA, Inc., as collateral and administrative agents under the Term Facility Credit and Guaranty Agreement and the Revolving Credit and Guaranty Agreement. Filed as Exhibit 10.9 to Registrant’s Current Report onForm 8-K dated February 6, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 10 | .33 | Amendment No. 1 to the Term Facility Credit and Guaranty Agreement dated as of November 21, 2008. Filed as Exhibit 10.74 to Registrant’s Annual Report onForm 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008, and incorporated herein by reference. | ||
| 21 | List of Subsidiaries of Dana Holding Corporation. Filed with this Report. | |||
| 23 | Consent of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP. Filed with this Report. | |||
| 24 | Power of Attorney. Filed with this Report. | |||
| 31 | .1 | Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a) Certification by Chief Executive Officer. Filed with this Report. | ||
| 31 | .2 | Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a) Certification by Chief Financial Officer. Filed with this Report. | ||
| 32 | Section 1350 Certification of Periodic Report (pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes Oxley Act of 2002). Filed with this Report. | |||
** Management contract or compensatory plan required to be filed as part of an exhibit pursuant to Item 15(b) ofForm 10-K.
125