Exhibit VIII
Financial report 2007
Contents
Financial report
Report of the Board of Directors 2007
The year 2007 marked the first full year of NIB operations being guided by its new mission and strategy focusing on competitiveness and the environment. NIB also coped with changing conditions in the financial markets. Whereas the beginning of the year was characterised by rather ample liquidity in the financial markets, the latter part of the year was dominated by increased uncertainty stemming from problems related to the sub-prime market in the US. This gave rise to increased demand for NIB’s loans, especially towards the end of the year. NIB’s lending activities were on the highest level ever in the Bank’s history. Accordingly, the operational results showed steady growth. At the same time, the increase in credit spreads and the general increase in long-term interest rates had a negative effect on the market valuation of the trading portfolio.
Since the establishment of the Bank’s new mission and strategy in 2006, work on streamlining policies and practices has continued. Consequently, the Board of Directors updated and adopted a number of policies in 2007.
The Board of Directors approved the revised Financial Policies for the Bank, which cover NIB’s general operating principles and policies. They also define the Bank’s financial structure and credit policy, including NIB’s policies on funding, liquidity and portfolio management as well as risk management. A revision and update of the Bank’s Financial Policies was called for, given the revisions to the strategy and the changes in the Bank’s organisation and credit process.
After public consultation, the Board of Directors approved NIB’s revised Environmental Policy. The revised environmental policy communicates NIB’s standing on environmental issues in relation to the Bank’s new mission and strategy, as well as harmonises it with the principles of other international financial institutions. Starting from the beginning of 2008, the Bank publishes advance information on all potential investment projects having an extensive environmental impact. The public will have the opportunity to comment on the environmental aspects of the projects before the Bank makes any decisions on financing. As before, NIB conducts an environmental analysis of all loan applications.
As part of NIB’s efforts to promote openness and transparency, the Board of Directors approved a new Disclosure Policy for the Bank. The policy sets rules for the disclosure of the Bank’s administrative and internal processes as well as its operational activities.
Besides the new policies, HR and business development as well as NIB’s mandate rating were central issues on the Board’s agenda in 2007. Arild Sundberg acted as Chairman of the Board during the year.
In 2007, NIB continued to participate in international and regional cooperation, especially regarding environmental issues. The Bank continued to play an active role in the Northern Dimension Environmental Partnership (NDEP) by taking over the rotating chair in July 2007. The aim of the partnership is to coordinate and streamline the financing of environmental projects with cross-border effects in the Baltic Sea region, the Barents region and Northwest Russia.
Strategic focus
The Governors of the Bank decided at their annual meeting that the Bank should identify the areas of activity where NIB could provide the highest added value. Thus four key areas for regional cooperation in the Nordic and Baltic Sea Region were identified: energy, the environment, infrastructure (transport) and innovation. These issues were discussed by the Board of Directors in connection with several of its meetings throughout the year.
The Bank has a long track record as a lender in these areas but additional steps to enhance the proactivity, additionality and visibility of the Bank’s participation are also being considered. The Bank is looking into new modalities of operation and exploring ways to further develop its offering, for example through sector-oriented interventions.
Concerning innovation, the Bank is already today actively financing various segments of the innovation process including research and development in client enterprises. Through the mezzanine financing programme, the Bank supports investments in growth companies.
NIB continued to focus on financing large investments by the corporate sector, as well as on small and medium-sized enterprises via financial intermediaries, to enhance competitiveness and the environment.
| | | | | | | | | |
| Table 1 | | | | | | |
| KEY FIGURES | | | | | | |
| (In EUR million) | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| Net interest income | | | 187 | | | | 179 | |
| Core earnings | | | 161 | | | | 154 | |
| Profit | | | 69 | | | | 137 | |
| Equity | | | 2,037 | | | | 2,021 | |
| Total assets | | | 19,973 | | | | 17,988 | |
| Profit/average equity (%) | | | 3.3 | | | | 6.9 | |
| Solvency ratio (equity/total assets %) | | | 10.2 | | | | 11.2 | |
1 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report
Operations and financial results
The year 2007 was marked by steady growth in core earnings reflecting positive developments in lending and funding activities as well as stability in costs. At the same time, the increase in credit spreads in the financial markets in the latter part of the year had a negative effect on the market valuation of the trading portfolio.
Net interest income grew by EUR 8 million to EUR 187 million during the year as a result of higher market interest rates and a stable level of interest-earning assets.
Loans and guarantees outstanding increased by 7% to EUR 12,316 million, in line with the targets set for 2007 and despite the depreciation of the US dollar. Net interest income from lending operations increased by 3.1%, supported by growth in lending in the Nordic markets and in Europe and Eurasia. Volume growth compensated for the pressure on margins, which was evident, in particular, in the first part of the year.
Loans agreed increased in total by 41% to EUR 2,214 million. NIB experienced further expansion of its lending activities in 2007 and disbursements reached an all-time high of EUR 2,390 million.
Lending activities were focused on the energy and manufacturing sectors, together totalling more than two thirds of all loans agreed. Investments in the energy sector went mainly to power plants and transmission grid expansions, while the dominating industries within manufacturing were machinery and equipment followed by chemicals.
At year-end, NIB had loans agreed or outstanding in 31 countries outside the membership area. The largest borrower regions were Europe and Eurasia, as well as Asia. The Bank was particularly active during the year in its financing of projects in Russia and China. Several projects were also prepared in Romania, India and Ukraine.
In 2007 environmental loans comprised 17% of the total loans agreed. NIB participated in the financing of several projects in the energy sector and in water treatment, for example investments in energy efficiency and emission treatment, geothermal power and wind power, as well as the upgrading of existing hydro power.
NIB’s administrative expenses including depreciations remained unchanged, at EUR 32 million, compared to 2006.
The Bank’s operational results in terms of core earnings (i.e. the profits before adjustments to hedge accounting, fair value adjustments made to the trading portfolio and credit losses and reversals of these) rose to EUR 161 million, compared to EUR 154 million the previous year. Due to the widening of credit spreads following the turbulence on the markets at the end of the year, and the fact that long-term interest rates in general rose during the period, the marked-to-market value of NIB’s trading portfolio fell and reduced the Bank’s results by
EUR 82 million. The general increase in long-term interest rates affected the value of the trading portfolio by EUR -10 million. The widening of credit spreads affected the value of the trading portfolio by EUR -72 million.
NIB’s profit in 2007 was 69 million, corresponding to a return on equity of 3.3% compared to 6.9% the previous year.
Total assets increased by 11%, or EUR 1,985 million, to EUR 19,973 million during 2007. The increase in the balance sheet reflects higher business volumes.
The Bank’s debt issuance increased to EUR 4,288 million, which is the highest amount ever recorded. Debts evidenced by certificates as per 31 December 2007 amounted to EUR 15,023 million in total. During 2007 NIB launched its all-time largest global benchmark issue in the amount of USD 1.5 billion and issued its sixth annual 1 billion US dollar deal.
At year-end, the Bank’s net liquidity was more than ample, standing at EUR 4,039 million. This was well in line with the policy to cover the liquidity requirements for the coming 12 months.
The trading portfolio has been invested, in line with the Bank’s policy, in high credit quality securities such as government bonds, floating rate notes issued by banks with a minimum rating of single A and in high-rated asset-backed securities with triple-A ratings. The interest rate risk was kept low for the portfolio given the low yield environment in the beginning of the year,
NIB Annual Report 2007 2
Financial report
but the yield increases and spread widening have nevertheless led to a negative revaluation of many securities in the portfolio.
The quality of the Bank’s loan portfolio and its financial counterparties remains strong in all markets. No credit losses were recognised during the year. The Board of Directors proposes to the Board of Governors that EUR 25 million be paid as dividends to the Bank’s member countries for the year 2007.
| | | | | | | | | |
| Table 2 | | | | | | |
| LENDING | | | | | | |
| (In EUR million) | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| |
Loans disbursed, total | | | 2,390 | | | | 1,605 | |
| Member countries | | | 1,761 | | | | 991 | |
| Non-member countries | | | 630 | | | | 614 | |
Loans agreed, total | | | 2,214 | | | | 1,575 | |
| Member countries | | | 1,810 | | | | 994 | |
| Non-member countries | | | 404 | | | | 581 | |
Number of loan agreements, total | | | 57 | | | | 64 | |
| Member countries | | | 45 | | | | 41 | |
| Non-member countries | | | 12 | | | | 23 | |
Loans outstanding and guarantees | | | 12,316 | | | | 11,559 | |
| Member countries | | | 9,898 | | | | 9,231 | |
| Non-member countries | | | 2,417 | | | | 2,328 | |
Repayments and prepayments | | | 1,282 | | | | 1,478 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Table 3 | | | | | | |
| FINANCIAL ACTIVITIES | | | | | | |
| (In EUR million) | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| New debt issues | | | 4,288 | | | | 2,689 | |
| Number of borrowing transactions | | | 69 | | | | 66 | |
| Number of borrowing currencies | | | 10 | | | | 11 | |
| Debts evidenced by certificates at year-end | | | 15,023 | | | | 13,622 | |
| Net liquidity at year-end | | | 4,039 | | | | 3,224 | |
| Fixed income portfolio | | | 1,948 | | | | 1,919 | |
Risk management
The quality of the Bank’s portfolios continued to be very high in 2007. The portfolios were well-balanced as regards both geographical and sectoral distribution, as well as the degree of concentration in terms of exposure on individual counterparties.
During 2007, emphasis was put on reviewing and refining various processes to reflect the organisational changes made in the previous year. The rating tools applied in the Bank’s risk assessment process are validated periodically. In 2007 the loss-given-default component, amongst others, was reviewed and refined based on recent developments in this field.
Administration
The process of organisational development continued during the year as a new job evaluation process was introduced and a job satisfaction survey was conducted. NIB’s legal activities were reorganised into a legal department. It was decided to set up a new compliance function for the Bank. A new General Counsel and a new Head of Treasury joined the Management Committee during the year. At year-end the number of employees was 158 (160).
The Board approved amendments to the Rules of Procedure for the Bank’s Committee on Fighting Corruption, as well as amendments to the Resolution on Fighting Corruption. The anti-corruption committee continued its work during the year. Gunnar Okk, Head of Planning and Administration, acted as chairman in 2007. The Board appointed Siv Hellén, Chief Compliance Officer, as chairman of the committee as of
1 January 2008.
During 2007, the policy on NIB’s IT governance model was approved. In addition, a revised Code of Conduct for the Staff was approved by the Board.
Outlook
The uncertainty regarding the economic outlook for 2008 has increased due to the continuing problems in the financial markets. In line with its strategy, NIB will continue to focus on priority sectors and activities in which the Bank can take full advantage of its strengths.
For 2008, the pipeline of upcoming loans suggests stable growth in NIB’s lending operations both in the Bank’s member and non-member countries. Energy, infrastructure and environmental technology will comprise priority areas of the Bank’s activities.
In order to fund its lending operations, NIB will continue its flexible, global borrowing strategy in 2008 through a combination of global benchmark issues of bonds and smaller public and private issues targeting particular market niches in capital markets. In 2007, the uncertainties in the financial markets favoured high-quality issuers such as NIB. This trend can be expected to further improve the Bank’s already good position on the international financial markets. In line with this, core earnings are expected to continue to increase steadily.
3 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report
Proposal by the Board of Directors to the Board of Governors
The Board of Directors’ proposal for the allocation of profits for the year 2007 takes into consideration that the Bank’s operations are carried out with an objective to achieve a reasonable return on the Bank’s paid-in capital and a satisfactory dividend to the member countries. The proposal will facilitate the continuing accumulation of the Bank’s equity and keep its ratio of equity to total assets at a secure level, both of which are prerequisites for maintaining the Bank’s high creditworthiness.
In accordance with section 11 of the Statutes of the Bank, the profit for 2007 of EUR 68,719,366.55 be allocated as follows:
| | • | | no transfer is made to the General Credit Risk Fund as a part of equity; |
| |
| | • | | EUR 43,719,366.55 is transferred to the Special Credit Risk Fund for Project Investment Loans; |
| |
| | • | | no transfer is made to the Statutory Reserve. The Statutory Reserve amounts to EUR 645,612,201.03 or 15.6% of the Bank’s authorised capital stock; and |
| |
| | • | | EUR 25,000,000.00 is made available for distribution as dividends to the Bank’s member countries. |
The income statement, balance sheet, changes in equity and cash flow statement, as well as the notes to the financial statements, are to be found on pages 5 through 39.
Helsinki, 6 March 2008
| | |
| | | |
Arild Sundberg | | 
Ólafur Hjálmarsson |
| | 
Lars Kolte | |

Edmunds Krastiņš | | 
Rolandas Kriščiūnas |
| | 
Kristina Sarjo | |
Madis Üürike | | 
Erik Åsbrink |
Johnny Åkerholm,
President and CEO
NIB Annual Report 2007 4
Financial report
Income statement 1 January – 31 December
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| | | Note | | EUR 1,000 | | | EUR 1,000 | |
| |
| Interest income | | | | | | | 856,280 | | | | 673,197 | |
| Interest expense | | | | | | | -669,155 | | | | -494,390 | |
| |
Net interest income | | | (1), (2), | (22 | ) | | 187,125 | | | | 178,807 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Commission income and fees received | | | | (3 | ) | | 6,135 | | | | 6,821 | |
| Commission expense and fees paid | | | | | | | -2,425 | | | | -1,734 | |
| Net profit/loss on financial operations | | | | (4 | ) | | -89,719 | | | | -14,406 | |
| Foreign exchange gains and losses | | | | | | | -361 | | | | 136 | |
| |
Operating income | | | | | | | 100,755 | | | | 169,624 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| General administrative expenses | | | (5), | (22 | ) | | 27,507 | | | | 27,909 | |
| Depreciation | | | (9), | (10 | ) | | 4,529 | | | | 4,246 | |
| Credit loss/recovery | | | (6), | (8 | ) | | — | | | | — | |
| |
Total expenses | | | | | | | 32,036 | | | | 32,156 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
PROFIT FOR THE YEAR | | | | | | | 68,719 | | | | 137,469 | |
| |
The Nordic Investment Bank’s accounts are kept in euro.
5 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report
Balance sheet at 31 December
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Note | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | EUR 1,000 | | | EUR 1,000 | |
ASSETS | | | | | | | (1), (18), (19), (20), | (21 | ) | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | (17), | (23 | ) | | 4,493,285 | | | | 3,753,444 | |
| |
| Financial placements | | | | | | | (7), | (17 | ) | | | | | | | |
| Placements with credit institutions | | | | | | | | | | | 93,432 | | | | 91,429 | |
| Debt securities | | | | | | | | | | | 1,582,750 | | | | 1,416,378 | |
| Other | | | | | | | | | | | 7,043 | | | | 7,135 | |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | 1,683,225 | | | | 1,514,942 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans outstanding | | | | | | | (8), | (17 | ) | | 12,290,768 | | | | 11,534,229 | |
| |
| Intangible assets | | | | | | | | (9 | ) | | 6,740 | | | | 7,342 | |
| |
| Tangible assets, property and equipment | | | | | | | | (9 | ) | | 36,767 | | | | 35,633 | |
| |
| Other assets | | | | | | | (11), | (17 | ) | | | | | | | |
| Derivatives | | | | | | | | | | | 1,049,725 | | | | 751,036 | |
| Other assets | | | | | | | | (22 | ) | | 1,596 | | | | 12,031 | |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | 1,051,321 | | | | 763,067 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Paid-in capital and payments to the Bank’s reserves, receivable 1) | | | | | | | | | | | 42,713 | | | | 47,494 | |
| |
| Accrued interest and fees receivable | | | | | | | | | | | 368,422 | | | | 331,995 | |
| |
TOTAL ASSETS | | | | | | | | | | | 19,973,242 | | | | 17,988,146 | |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | | | | | (1), (18), (19), (20), | (21 | ) | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amounts owed to credit institutions | | | | | | | (17), | (22 | ) | | | | | | | |
| Short-term amounts owed to credit institutions | | | | | | | | (23 | ) | | 454,498 | | | | 313,025 | |
| Long-term amounts owed to credit institutions | | | | | | | | | | | 91,674 | | | | 90,262 | |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | 546,172 | | | | 403,287 | |
| Repurchase agreements | | | | | | | | | | | — | | | | 216,739 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Debts evidenced by certificates | | | | | | | (12), | (17 | ) | | | | | | | |
| Debt securities issued | | | | | | | | | | | 14,829,821 | | | | 13,367,157 | |
| Other debt | | | | | | | | | | | 192,979 | | | | 254,358 | |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | 15,022,800 | | | | 13,621,516 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other liabilities | | | | | | | (13), | (17 | ) | | | | | | | |
| Derivatives | | | | | | | | | | | 1,999,356 | | | | 1,415,445 | |
| Other liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | 4,496 | | | | 4,331 | |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | 2,003,852 | | | | 1,419,776 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accrued interest and fees payable | | | | | | | | | | | 363,468 | | | | 305,978 | |
| |
Total liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | 17,936,292 | | | | 15,967,296 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Authorised and subscribed capital | | | 4,141,903 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| of which callable capital | | | -3,723,301 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Paid-in capital 1) | | | 418,602 | | | | | (14 | ) | | 418,602 | | | | 418,602 | |
| Reserve funds | | | | | | | | (15 | ) | | | | | | | | |
| Statutory Reserve | | | | | | | | | | | 645,612 | | | | 644,983 | |
| General Credit Risk Fund | | | | | | | | | | | 622,131 | | | | 534,662 | |
| Special Credit Risk Fund PIL | | | | | | | | | | | 238,200 | | | | 238,200 | |
| Fund, HIPC Programme | | | | | | | | | | | — | | | | 629 | |
| Payments to the Bank’s reserves, receivable | | | | | | | | | | | 42,713 | | | | 42,713 | |
| Other value adjustments | | | | | | | | | | | 973 | | | | 3,592 | |
| Profit for the year | | | | | | | | | | | 68,719 | | | | 137,469 | |
| |
Total equity | | | | | | | | | | | 2,036,950 | | | | 2,020,850 | |
| |
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | | | | | | | | | 19,973,242 | | | | 17,988,146 | |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Guarantee commitments | | | | | | | (8), | (16 | ) | | 25,000 | | | | 25,000 | |
| Collateral and commitments | | | | | | | | (16 | ) | | | | | | | | |
| | |
| 1) | | The paid-in capital, EUR 418,602 thousand, has been received in total as of 31 December 2007 (December 2006, EUR 413,821). |
The Nordic Investment Bank’s accounts are kept in euro.
NIB Annual Report 2007 6
Financial report
Changes in equity
(Amounts in EUR 1,000)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Payments to the Bank’s | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | General Credit Risk | | | Special Credit Risk | | | Fund, HIPC | | | Statutory Reserve and | | | Appropriation to dividend | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Paid-in capital | | | Statutory Reserve | | | Fund | | | Fund PIL | | | Programme | | | credit risk funds | | | payment | | | Other value adjustments | | | Profit for the year | | | Total | |
Equity at 31 December 2005 | | | 418,602 | | | | 644,983 | | | | 424,367 | | | | 238,200 | | | | 4,300 | | | | 42,713 | | | | 0 | | | | 7,109 | | | | 165,295 | | | | 1,945,569 | |
| Appropriations between reserve funds | | | | | | | | | | | 110,295 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 55,000 | | | | | | | | -165,295 | | | | 0 | |
| Paid-in capital | | | 4,780 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 4,780 | |
| Called in authorised and subscribed capital | | | -4,780 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | -4,780 | |
| Payments to the Bank’s Statutory Reserve and credit risk funds, receivable | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 0 | |
| Dividend payment | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | -55,000 | | | | | | | | | | | | -55,000 | |
| Used fund, HIPC programme | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | -3,671 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | -3,671 | |
| |
| Profit for the period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 137,469 | | | | 137,469 | |
| Available-for-sale portfolio (recognised in equity) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 395 | | | | | | | | 395 | |
Cash flow hedge accounting (recognised in income statement) 1) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | -3,912 | | | | | | | | -3,912 | |
| |
| Total income and expense for the year | | | 0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0 | | | | -3,517 | | | | 137,469 | | | | 133,952 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
EQUITY AT 31 DECEMBER 2006 | | | 418,602 | | | | 644,983 | | | | 534,662 | | | | 238,200 | | | | 629 | | | | 42,713 | | | | 0 | | | | 3,592 | | | | 137,469 | | | | 2,020,850 | |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Appropriations between reserve funds | | | | | | | 629 | | | | 87,469 | | | | | | | | -629 | | | | | | | | 50,000 | | | | | | | | -137,469 | | | | 0 | |
| Paid-in capital | | | 4,780 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 4,780 | |
| Called in authorised and subscribed capital | | | -4,780 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | -4,780 | |
| Payments to the Bank’s Statutory Reserve and credit risk funds, receivable | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 0 | |
| Dividend payment | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | -50,000 | | | | | | | | | | | | -50,000 | |
| Used fund, HIPC programme | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 0 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Profit for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 68,719 | | | | 68,719 | |
| Available-for-sale portfolio (recognised in equity) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | -1,023 | | | | | | | | -1,023 | |
Cash flow hedge accounting (recognised in income statement) 1) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | -1,596 | | | | | | | | -1,596 | |
| |
| Total income and expense for the year | | | 0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0 | | | | -2,619 | | | | 68,719 | | | | 66,101 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
EQUITY AT 31 DECEMBER 2007 | | | 418,602 | | | | 645,612 | | | | 622,131 | | | | 238,200 | | | | 0 | | | | 42,713 | | | | 0 | | | | 973 | | | | 68,719 | | | | 2,036,950 | |
| |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Proposed appropriation of the year’s profit | | 2007 | | 2006 | |
| Appropriation to Statutory Reserve | | | — | | | | 629 | |
| Appropriations to credit risk reserve funds | | | | | | | | |
| General Credit Risk Fund | | | — | | | | 87,469 | |
| Special Credit Risk Fund PIL | | | 43,719 | | | | — | |
| Fund, HIPC Programme | | | — | | | | -629 | |
| Appropriation to dividend payment | | | 25,000 | | | | 50,000 | |
| |
PROFIT FOR THE YEAR | | | 68,719 | | | | 137,469 | |
| |
| | |
| |
| 1) | | No new cash flow hedging swaps were acquired during the year. The decrease in fair value is due to the fact that some of the old cash flow hedging swaps have matured and the maturity of the remaining cash flow hedging swaps is one year shorter. |
The Nordic Investment Bank’s accounts are kept in euro.
7 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report
Cash flow statement 1 January–31 December
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Note | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| | | EUR 1,000 | | EUR 1,000 | |
Cash flows from operating activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Profit from operating activities | | | | | | | 68,719 | | | | 137,469 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjustments: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amortisation of issuing charges | | | | | | | 10,840 | | | | 9,091 | |
| Market value adjustment, trading portfolio | | | | | | | 7,381 | | | | 5,831 | |
| Depreciation and write-down in value of tangible and intangible assets | | | | | | | 4,529 | | | | 4,246 | |
| Change in accrued interest and fees (assets) | | | | | | | -36,427 | | | | -27,430 | |
| Change in accrued interest and fees (liabilities) | | | | | | | 57,489 | | | | 37,147 | |
| Credit loss/recovery | | | | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Adjustment to hedge accounting and changes in fair value of non-hedging derivatives | | | | | | | 10,319 | | | | 7,034 | |
| Other adjustments to the year’s profit | | | | | | | -35 | | | | -56 | |
| |
Adjustments, total | | | | | | | 54,097 | | | | 35,863 | |
Lending 1) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Disbursements of loans | | | | | | | -2,390,392 | | | | -1,605,088 | |
| Repayments of loans | | | | | | | 1,281,546 | | | | 1,477,741 | |
| Capitalisations, redenominations, index adjustments etc. | | | | | | | -338 | | | | -1,070 | |
| Exchange rate adjustments | | | | | | | 331,656 | | | | 260,126 | |
| |
Lending, total | | | | | | | -777,527 | | | | 131,709 | |
Cash flows from operating activities, total | | | | | | | -654,711 | | | | 305,041 | |
| |
Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Placements and debt securities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchase of debt securities | | | | | | | -458,493 | | | | -498,431 | |
| Sold and matured debt securities | | | | | | | 285,238 | | | | 377,582 | |
| Placements with credit institutions | | | | | | | -2,010 | | | | 13,418 | |
| Other financial placements | | | | | | | -931 | | | | 313 | |
| Exchange rate adjustments etc. | | | | | | | -3 | | | | 1,286 | |
| |
Placements and debt securities, total | | | | | | | -176,200 | | | | -105,832 | |
Other items | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Acquisition of intangible assets | | | | | | | -1,799 | | | | -1,905 | |
| Acquisition of tangible assets | | | | | | | -3,262 | | | | -3,010 | |
| Change in other assets | | | | | | | 9,948 | | | | -8,492 | |
| |
Other items, total | | | | | | | 4,886 | | | | -13,407 | |
Cash flows from investing activities, total | | | | | | | -171,314 | | | | -119,239 | |
| |
Cash flows from financing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
Debts evidenced by certificates | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Issues of new debt 2) | | | | | | | 4,278,931 | | | | 2,683,280 | |
| Redemptions | | | | | | | -1,958,157 | | | | -2,039,639 | |
| Exchange rate adjustments | | | | | | | -1,063,724 | | | | -1,025,220 | |
| |
Debts evidenced by certificates, total | | | | | | | 1,257,050 | | | | -381,579 | |
Other items | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Placements from credit institutions | | | | | | | 1,412 | | | | -9,813 | |
Change in swap receivables 3) | | | | | | | -222,019 | | | | 62,699 | |
| Change in swap payables | | | | | | | 649,743 | | | | 320,820 | |
| Change in other liabilities | | | | | | | 165 | | | | -934 | |
| Dividend paid | | | | | | | -50,000 | | | | -55,000 | |
| Paid-in capital | | | | | | | 4,780 | | | | 4,780 | |
| Used fund, HIPC Programme | | | | | | | — | | | | -3,671 | |
| |
Other items, total | | | | | | | 384,081 | | | | 318,881 | |
Cash flows from financing activities, total | | | | | | | 1,641,131 | | | | -62,698 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
CHANGE IN NET LIQUIDITY | | | (23 | ) | | | 815,106 | | | | 123,104 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Opening balance for net liquidity | | | | | | | 3,223,681 | | | | 3,100,576 | |
Closing balance for net liquidity | | | | | | | 4,038,787 | | | | 3,223,681 | |
| |
Additional information to the statement of cash flows | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income received | | | | | | | 892,707 | | | | 700,626 | |
| Interest expense paid | | | | | | | -611,666 | | | | -457,243 | |
The cash flow statement has been prepared using the indirect method and the items of cash flows cannot be directly concluded from the balance sheets.
| | |
| 1) | | Lending activities have been moved from investing activities to operating activities. |
| |
| 2) | | Including issuing charges EUR -9,256 thousand (-5,330). |
| |
| 3) | | Change in swap receivables has been moved from investing activities to financing activities. |
These reclassifications have been made in order to better describe the nature of these activities.
The Nordic Investment Bank’s accounts are kept in euro.
NIB Annual Report 2007 8
Financial report
Notes to the financial statements
ACCOUNTING POLICIES
General operating principles
The operations of the Nordic Investment Bank (hereinafter called the Bank or NIB) are governed by an agreement among the governments of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway and Sweden (hereinafter called the member countries), and the Statutes adopted in conjunction with that agreement.
NIB is a multilateral financial institution that operates in accordance with sound banking principles. NIB finances private and public projects which have high priority with the member countries and the borrowers. NIB finances projects both within and outside the member countries, and offers its clients long-term loans and guarantees on competitive market terms.
NIB acquires the funds to finance its lending by borrowing on international capital markets.
The authorised capital stock of the Bank is subscribed by the member countries. Any increase or decrease in the authorised capital stock shall be decided by the Board of Governors, upon a proposal of the Board of Directors of the Bank.
In the member countries, the Bank is exempt from payment restrictions and credit policy measures, and has the legal status of an international legal person, with full legal capacity. The Agreement concerning NIB contains provisions regarding immunity and privileges accorded to the Bank, e.g. the exemption of the Bank’s assets and income from taxation.
The headquarters of the Bank are located at Fabianinkatu 34 in Helsinki, Finland.
Significant accounting principles
BASIS FOR PREPARING THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The Bank’s financial statements have been prepared in accordance with the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). The Bank’s accounts are kept in euro. With the exceptions noted below, they are based on historical cost.
SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING JUDGEMENTS AND ESTIMATES
As part of the process of preparing the financial statements, the Bank’s management is required to make certain estimates and assumptions that have an effect on the Bank’s profits, its financial position and other information presented in the annual report. These estimates are based on available information and the judgements made by the Bank’s management. Actual outcomes may deviate from the assessments made, and such deviations may at times be substantial.
The Bank uses various valuation models and techniques to estimate fair values of assets and liabilities. There are significant uncertainties related to these estimates in particular when they involve modelling complex financial instruments, such as derivative instruments used for hedging activities related to both borrowing and lending. The estimates are highly dependent on market data, such as the level of interest rates, currency rates and other factors. The uncertainties related to these estimates are reflected mainly in the balance sheet. NIB undertakes continuous development in order to improve the basis for the fair value estimates, both with regard to modelling and market data. Changes in estimates resulting from refinements in assumptions and methodologies are reflected in the period in which the enhancements are first applied.
RECOGNITION AND DERECOGNITION OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
Financial instruments are recognised in the balance sheet on a settlement date basis.
A financial asset is derecognised when the contractual rights to the cash flows from the financial asset expire.
A financial liability is removed from the balance sheet when the obligation specified in the contract is discharged, cancelled or expires.
FOREIGN CURRENCY TRANSLATION
Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are recognised in the accounts at the exchange rate prevailing on the closing date. Non-monetary assets and liabilities are recognised in the accounts at the euro rate prevailing on the transaction date. Income and expenses recognised in currencies other than the euro are converted on a daily basis to the euro, in accordance with the euro exchange rate prevailing each day.
Realised and unrealised exchange rate gains and losses are recognised in the income statement.
The Bank uses the official exchange rates published for the euro by the European Central Bank. See Note 24.
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, NET LIQUIDITY
The item “Cash and cash equivalents” refers to monetary assets and placements with original maturities of 6 months or less, calculated from the date the acquisition and placements were made. The item also includes placements in liquid debt securities at floating interest rates, regardless of original maturity.
Net liquidity in the cash flow statement refers to the net amount of monetary assets, placements and liabilities with original maturities of 6 months or less calculated from the time the transaction was entered into, as well as placements in liquid debt securities at floating interest rates irrespective of original maturity. This corresponds in substance to the Bank’s operational net liquidity.
FINANCIAL PLACEMENTS
Items recognised as financial placements in the balance sheet include placements with credit institutions and in debt securities,
9 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
for example, bonds and other debt certificates, as well as certain placements in instruments with equity features. The placements are initially recognised on the settlement date. Their subsequent accounting treatment depends on the purpose of the placements.
Financial assets held for trading are carried at fair value. Changes in fair value are recognised in the income statement. Held-to-maturity financial investments are carried at amortised cost. These financial assets are assessed on an ongoing basis for impairment.
Available-for-sale financial assets are measured at fair value. Unrealised value changes are recognised in “Equity” under the item “Other value adjustments” until the asset is sold or the unrealised loss is considered to be permanent. When the placement is sold or written down, the accumulated unrealised gain or loss is transferred to the year’s profit or loss, and becomes part of “Net profit on financial operations”.
LENDING
The Bank may grant loans and provide guarantees under its Ordinary Lending or under various special lending facilities. The special lending facilities, which carry member country guarantees, consist of Project Investment Loans (PIL) and Environmental Investment Loans (MIL).
Ordinary Lending includes loans and guarantees within and outside the member countries. The Bank’s Ordinary Lending ceiling corresponds to 250% of its authorised capital and accumulated general reserves and amounts to EUR 13,631 million following the appropriations of the year’s profits in accordance with the Board of Directors’ proposal.
Project Investment Loans are granted for financing creditworthy projects in the emerging markets of Africa, Asia, Europe and Eurasia, Latin America and the Middle East. The Bank’s Statutes permit loans to be granted and guarantees to be issued under the PIL facility up to an amount corresponding to EUR 4,000 million. The member countries guarantee the PIL loans up to a total amount of EUR 1,800 million. The Bank, however, will assume 100% of any losses incurred under an individual PIL loan, up to the amount available at any given time in the Special Credit Risk Fund for PIL. Only thereafter would the Bank be able to call the member countries’ guarantees according to the following principle: the member countries guarantee 90% of each loan under the PIL facility up to a total amount of EUR 1,800 million. Payment under the member countries’ guarantees takes place at the request of the Board of Directors, as provided for under an agreement between the Bank and each individual member country.
The Bank is authorised to grant special Environmental Investment Loans up to the amount of EUR 300 million, for the financing of environmental projects in the areas adjacent to the member countries. The Bank’s member countries guarantee 100% of the MIL facility.
Until 31 December 1999, the Bank granted loans for investments in the Baltic countries within the EUR 60 million Baltic Investment Loan facility. No new loans have been granted under the BIL facility since year-end 1999, when the facility expired. The Nordic countries guaranteed 100% of the BIL facility.
The Bank’s lending transactions are recognised in the balance sheet at the time the funds are transferred to the borrower. Loans are recognised initially at historical cost, which corresponds to the fair value of the transferred funds including transaction costs. Loans outstanding are carried at amortised cost. If the loans are hedged against changes in fair value by using derivative instruments, they are recognised in the balance sheet at fair value, with value changes recognised in the income statement. Changes in fair value are generally caused by changes in market interest rates.
CREDIT LOSSES AND IMPAIRMENT OF RECEIVABLES
Receivables are carried at their estimated recoverable amount. Where the collectability of identified loans is in doubt, specific impairment losses are recognised in the income statement. Impairment is defined as the difference between the carrying value of the asset and the net present value of expected future cash flows, determined using the instrument’s original effective interest rate where applicable. Impairment losses are measured based on individual assessment of the collectable amount for loans and guarantees. The assessment takes into account any costs of administration or realisation of the security.
On the liabilities side, impairment is recognised in respect of the guarantees NIB has issued. The net cost of any calls made under guarantees and other similar commitments issued by NIB is likewise recognised in the income statement.
In the event that payments in respect of an ordinary loan are more than 90 days overdue, all of the borrower’s loans are deemed to be non-performing and consequently the need for impairment is assessed and recognised.
In the event that payments in respect of a PIL loan to a government or guaranteed by a government are more than 180 days overdue, all of the borrower’s loans are deemed to be non-performing. Whenever payments in respect of a PIL loan that is not to a government or guaranteed by a government are more than 90 days overdue, all of the borrower’s loans are deemed to be non-performing. Impairment losses are then recognised in respect of the part of the outstanding loan principal, interest, and fees that correspond to the Bank’s own risk for this loan facility at any given point in time.
NIB Annual Report 2007 10
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Intangible assets mainly consist of investments in software, software licenses and ongoing investments in new IT systems. The investments are carried at historical cost, and are amortised over the assessed useful life of the assets, which is estimated to be between 3 and 5 years. The amortisations are made on a straight-line basis.
TANGIBLE ASSETS
Tangible assets in the balance sheet include land, buildings, office equipment, and other tangible assets owned by the Bank. The assets are recognised at historical cost, less any accumulated depreciation based on their assessed useful life. No depreciations are made for land. The Bank’s office building in Helsinki is depreciated on a straight-line basis over a 40-year period. The Bank’s other buildings are depreciated over a 30-year period. The depreciation period for office equipment and other tangible assets is determined by assessing the individual item. The depreciation period is usually 3 to 5 years. The depreciations are calculated on a straight-line basis.
WRITE-DOWNS AND IMPAIRMENT OF INTANGIBLE AND TANGIBLE ASSETS
The Bank’s assets are reviewed annually for impairment. If there is any objective evidence of impairment, the impairment loss is determined based on the recoverable amount of the assets.
BORROWING
The Bank’s borrowing transactions are recognised in the balance sheet at the time the funds are transferred to the Bank. The borrowing transactions are recognised initially at a cost that comprises the fair value of the funds transferred, less transaction costs. The Bank uses derivative instruments to hedge the fair value of virtually all its borrowing transactions. In these instances, the borrowing transaction is subsequently recognised in the balance sheet at fair value, with any changes in value recognised in the income statement.
DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS AND HEDGE ACCOUNTING
The Bank’s derivative instruments are initially recognised on a trade-date basis at fair value in the balance sheet as “Other assets” or “Other liabilities”.
During the time the Bank holds a derivative instrument, any changes in the fair value of such an instrument are recognised in the income statement, or directly in “Equity” as part of the item “Other value adjustments”, depending on the purpose for which the instruments were acquired. The value changes of derivative instruments that were not acquired for hedging purposes are recognised in the income statement. The accounting treatment for derivative instruments that were acquired for hedging purposes depends on whether the hedging operation was in respect of cash flow or fair value.
At the time the IAS 39 standard concerning hedge accounting was adopted, the Bank had a portfolio of floating rate assets, which had been converted to fixed rates using derivative contracts (swaps). This portfolio was designated as a cash flow hedge, but this specific type of hedging is no longer used for new transactions. In general, the Bank does not have an ongoing programme for entering into cash flow hedging, although it may choose to do so at any given point in time.
When hedging future cash flows, the change in fair value of the effective portion of the hedging instrument is recognised directly in “Equity” as part of the item “Other value adjustments” until the maturity of the instrument. At maturity, the amount accumulated in “Equity” is included in the income statement in the same period or periods during which the hedged item affects the income statement.
In order to protect NIB from market risks that arise as an inherent part of its borrowing and lending activities, the Bank enters into swap transactions. The net effect of the swap hedging is to convert the borrowing and lending transactions to floating rates. This hedging activity is an integrated part of the Bank’s business process and is designed as a fair value hedge.
When hedging the fair value of a financial asset or liability, the derivative instrument’s change in fair value is recognised in the income statement together with the hedged item’s change in fair value in “Net profit on financial operations”.
Sometimes a derivative may be a component of a hybrid financial instrument that includes both the derivative and a host contract. Such embedded derivative instruments are part of a structured financing transaction that is hedged against changes in fair value by means of matching swap contracts. In such cases, both the hedged borrowing transaction and the hedging derivative instrument are recognised at fair value with changes in fair value in the income statement.
The hedge accounting is based on a clearly documented relationship between the item hedged and the hedging instrument. When there is a high (negative) correlation between the hedging instrument on the one hand and the value change on the hedged item or the cash flows generated by the hedged item on the other, the hedge is regarded as effective. The hedging relationship is documented at the time the hedge transaction is entered into, and the effectiveness of the hedge is assessed continuously.
DETERMINATION OF FAIR VALUE
The fair value of financial instruments, including derivative instruments that are traded in a liquid market, is the bid or offered closing price at balance sheet date. Many of NIB’s financial instruments are not traded in a liquid market, like the Bank’s borrowing transactions with embedded derivative instruments. These are measured at fair value using different
11 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
valuation models and techniques. This process involves determining future expected cash flows, which can then be discounted to the balance sheet date. The estimation of future cash flows for these instruments is subject to assumptions on market data and in some cases, in particular where options are involved, even on the behaviour of the Bank’s counterparties. The fair value estimate may therefore be subject to large variations and may not be realisable in the market. Under different market assumptions the values could also differ substantially.
EQUITY
The Bank’s authorised and subscribed capital is EUR 4,141.9 million, of which the paid-in portion is EUR 418.6 million. Payment of the subscribed, non-paid-in portion of the authorised capital, i.e., the callable capital, will take place at the request of the Bank’s Board of Directors to the extent that the Board deems it necessary for the fulfilment of the Bank’s debt obligations.
The Bank’s reserves have been built up by means of appropriations from the profits of previous accounting periods, and consist of the Statutory Reserve, as well as funds for credit risks: the General Credit Risk Fund, the Special Credit Risk Fund for PIL and the Fund for the HIPC Programme (Debt Initiative for Heavily Indebted Poor Countries).
The Bank’s profits, after allocation to appropriate credit risk funds, are transferred to the Statutory Reserve until it amounts to 10% of NIB’s subscribed authorised capital. Thereafter, the Board of Governors, upon a proposal by the Bank’s Board of Directors, shall decide upon the allocation of the profits between the reserve fund and dividends on the subscribed capital.
The General Credit Risk Fund is designed to cover unidentified exceptional risks in the Bank’s operations. Allocations to the Special Credit Risk Fund for PIL are made primarily to cover the Bank’s own risk in respect of credit losses on PIL loans.
In 2000, the Bank decided to participate in the HIPC Programme initiated by the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund. NIB’s participation in the programme concerned only one borrower country. During 2006, the Bank paid its contribution to the HIPC initiative. See Note 15.
INTEREST
The Bank’s net interest income includes accrued interest on loans as well as accruals of the premium or discount value of financial instruments. Net interest income also includes swap fees that are accrued over the transactions’ lifetimes.
Borrowing costs are recognised as reductions of the borrowing in the balance sheet. They are amortised over the lifetime of the borrowing and included in “Net interest income” in the income statement.
FEES AND COMMISSIONS
Fees collected when disbursing loans are recognised as income at the time of the disbursement, which means that fees and commissions are recognised as income at the same time as the costs are incurred. Commitment fees are charged on loans that are agreed but not yet disbursed, and are accrued in the income statement over the commitment period.
Annually recurrent costs arising as a result of the Bank’s borrowing, investment and payment transactions are recognised under the item “Commission expense and fees paid”.
FINANCIAL TRANSACTIONS
The Bank recognises in “Net profit on financial operations” both realised and unrealised gains and losses on debt securities and other financial instruments. Adjustments for hedge accounting are included.
ADMINISTRATIVE EXPENSES
The Bank provides services to its related parties, the Nordic Development Fund (NDF) and the Nordic Environment Finance Corporation (NEFCO). Payments received by the Bank for providing services at cost to these organisations are recognised as a reduction in the Bank’s administrative expenses.
NIB receives a host country reimbursement from the Finnish Government equal to the tax withheld from the salaries of NIB’s employees. This payment reduces the Bank’s administrative expenses. It is shown in Note 5.
LEASING AGREEMENTS
Leasing agreements are classified as operating leases if the rewards and risks incident to ownership of the leased asset, in all major respects, lie with the lessor. Lease payments under operating leases are recognised on a straight-line basis over the lease term. The Bank’s rental agreements are classified as operating leases.
EMPLOYEES’ PENSIONS AND INSURANCE
The Bank is responsible for arranging pension security for its employees. In accordance with the Headquarters Agreement between the Bank and the Finnish Government and as part of the Bank’s pension arrangements, the Bank has decided to apply the Finnish state pension system. Contributions to this pension system, which are paid to the Finnish State Pension Fund, are calculated as a percentage of salaries. The Finnish Government determines the basis for the contributions, and the Finnish State Treasury establishes the actual percentage of the contributions. See Note 5.
NIB Annual Report 2007 12
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
NIB has also provided its permanent employees with a supplementary pension insurance scheme arranged by a private pension insurance company. This is group pension insurance based on a defined contribution plan. The Bank’s pension liability is completely covered.
In addition to the applicable local social security systems, NIB has taken out a comprehensive accident, life and health insurance policy for its employees in the form of group insurance.
Segment information
Segment information and currency distribution in the notes are presented in nominal amounts. The adjustment to hedge accounting is presented as a separate item (except for Note 1, primary reporting segment).
Reclassifications
Some minor reclassifications have been made. The comparative figures have been adjusted accordingly.
International Financial Reporting Standards
and Interpretations
NEW STANDARDS AND INTERPRETATIONS 2007
The Bank has assessed the relevance of the new standards, amendments and interpretations that are mandatory for the Bank’s accounting periods beginning on or after 1 January 2007. The following standards were implemented in 2007:
| | • | | IFRS 7 Financial Instruments: Disclosures |
| |
| | • | | IAS 1 (Amendment) Presentation of Financial Statements: Capital Disclosures |
The following standards, interpretations or their revisions have been published but are not yet in force, and the Bank has not applied them prior to their mandatory entry into force:
| | • | | IFRS 8 Operating Segments |
| |
| | • | | IAS 23 Borrowing costs, revised |
| |
| | • | | IFRIC 11 IFRS 2 Group and Treasury Share Transactions |
| |
| | • | | IFRIC 12 Service Concession Arrangements |
| |
| | • | | IFRIC 13 Customer Loyalty Programmes |
| |
| | • | | IFRIC 14 The Limit on a Defined Benefit Asset, Minimum Funding Requirements and their Interaction |
The view of the Bank’s management is that the introduction of the above IFRIC interpretations and IFRS standards will have no material effect, if any, on NIB’s financial statements information or accounting policies. IFRIC 11, 12, 13 and 14 are not applicable.
13 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
FINANCIAL GUIDELINES AND RISK MANAGEMENT
NIB assumes a conservative approach to risk-taking. The Bank’s constituent documents require that loans be made in accordance with sound banking principles, that adequate security be obtained for the loans and that the Bank protect itself against the risk of exchange rate losses. The main risks: credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk and operational risk, are managed carefully with risk management closely integrated into the Bank’s business processes. As a multilateral financial institution, NIB is not subject to any national or international banking regulations. However, the Bank’s risk management procedures are reviewed and refined on an ongoing basis in order to comply in substance with what the Bank identifies as the relevant market standards, recommendations and best practices.
Key risk responsibilities
The Board of Directors defines the overall risk profile of the Bank by approving its financial policies and guidelines, maximum limits for exposure as well as individual loans. The business functions, Lending and Treasury, are responsible for managing the risks assumed through their operations and for ensuring that an adequate return for the risks taken is achieved. Risk Management, Credit and Analysis and Internal Audit are independent from the departments carrying out the Bank’s business activities. Risk Management has the overall responsibility for identifying, assessing, monitoring and reporting all types of risk inherent in the Bank’s operations. Credit and Analysis is responsible for assessing and monitoring credit risk in the Bank’s lending operations and it oversees that credit proposals are in compliance with established limits and policies. Internal Audit provides an independent evaluation of the control and risk management processes. Based on regular reporting from the relevant departments, three committees comprising members of the senior management supervise the Bank’s aggregate risk-taking so that it is consistent with its financial resources and risk profile and that risk and return are balanced and appropriate under prevailing market conditions. The Management Committee has the overall responsibility for risk management. The risk management duties of the Credit Committee are focused on credit risk in the Bank’s lending operations and the Finance Committee deals with credit risk and market risk related to the Bank’s treasury operations.
Credit risk
Credit risk is NIB’s main financial risk. Credit risk is the risk that the Bank’s borrowers and other counterparties fail to fulfil their contractual obligations and that any collateral provided does not cover the Bank’s claims. Following from NIB’s mandate and financial structure, most of the credit risk arises in the lending operations. Credit decisions are primarily made by the Board of Directors, with some delegation of credit approval authority to the President for execution in the Credit Committee. The Bank’s credit policy forms the basis for all its lending operations. The credit policy aims at maintaining the Bank’s high quality loan portfolio and ensuring proper risk diversification as well as enhancing the Bank’s mission and strategy. The credit policy sets the basic criteria for acceptable risks and identifies risk areas that require special attention.
The Bank is also exposed to credit risk in its treasury activities, where credit risk derives from the financial assets and derivative instruments that the Bank uses for investing its liquidity and managing currency and interest rate risks as well as other market risks related to structured funding transactions.
CREDIT RISK MANAGEMENT
The Bank’s credit risk management is based on an internal credit risk rating system: a limit system based on the credit risk ratings and on a model for the calculation of economic capital for the management of portfolio-level credit risk. A primary element of the credit approval process is a detailed risk assessment, which also involves a risk-versus-return analysis. The risk assessment concludes with a classification of the risk of the counterparty and the transaction, expressed in terms of a counterparty risk rating and a transaction risk class.
Credit risk ratings. The Bank assesses the creditworthiness of all counterparties that create credit risk exposure. Based on the assessment, a credit risk rating is assigned to each counterparty. The rating process is carried out through functions independent of the business-originating departments.
The Bank’s rating system is based on a quantitative and a qualitative model for estimating the probability of default (PD) of a counterparty and the loss given default (LGD) on a transaction. The PD is assessed using a rating tool comprising quantitative and qualitative factors. Based on the PD, the counterparty is assigned a rating class on a scale from 1 to 20, with class 1 referring to the lowest probability of default and class 20 to the highest probability of default. Furthermore, each transaction is assigned a risk class reflecting the expected loss. The expected loss is the combined effect of the PD of the counterparty and the Bank’s estimate of the portion of the Bank’s claim that would not be recoverable if the counterparty defaults. The non-recoverable portion, i.e. the loss given default (LGD), is determined based on benchmark values for unsecured transactions and by using a security rating tool for secured transactions. The risk classes range from 1 to 20, such that risk class 1 refers to the lowest expected loss and class 20 to the highest expected loss. The counterparty ratings and the transaction risk classes form the basis for setting exposure limits, for the risk-based pricing of loans as well as for monitoring and reporting the Bank’s credit quality.
NIB Annual Report 2007 14
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
Credit limits. NIB applies a limit system in which maximum exposure to a counterparty is determined based on the probability of default and the expected loss. The limits are aligned to the Bank’s equity and to the counterparty’s equity. To reduce large risk concentrations to groups of borrowers and industry sectors, the Bank applies separate portfolio-level limits (country and sector limits). The Board of Directors sets the limits for maximum exposure.
Measurement of credit risk exposure. For loans and capital market investments, credit exposure is measured in terms of gross nominal amounts, without recognising the availability of collateral or other credit enhancement. Exposure to each counterparty is measured on a consolidated group level, i.e. individual counterparties that are linked to one another by ownership or other group affiliation are considered as one counterparty.
The credit risk exposure of swaps is measured as the current market value plus an allowance for potential increases in exposure over the transaction’s lifetime (often referred to as potential exposure). The add-on for potential exposure reflects the fact that significant fluctuations in the swap’s value may occur over time. As a rule, NIB enters into the International Swaps and Derivatives Association (ISDA) contract with swap counterparties. This allows the netting of the obligations arising under all of the derivative contracts covered by the ISDA agreement in case of insolvency and, thus, results in one single net claim on, or payable to, the counter-party. Netting is applied for the measurement of the Bank’s credit exposure only in cases when it is deemed to be legally enforceable in the relevant jurisdiction and against a counter-party. The gross total market value of swaps at year-end 2007 amounted to EUR 1,000 million, compared to a value of EUR 425 million after applying netting.
To further reduce the exposure to derivatives, NIB enters into credit support agreements with its major swap counter-parties. This provides risk mitigation, as the swap transactions are regularly marked-to-market and the party being the net obligor is requested to post collateral. The Bank strives to use one-way credit support agreements, under which the Bank does not have to post collateral. When credit support agreements are in place, NIB does not apply add-ons in the exposure calculation.
Economic capital. Economic capital refers to the amount of capital that the Bank needs in order to be able to absorb severe unexpected losses, with a defined level of certainty. As a multilateral financial institution, the Bank is not subject to regulatory capital requirements. However, the Bank uses standards proposed by the Basel II Capital Accord as a benchmark for its risk management and economic capital framework. The Bank’s policy is to hold a level of capital required to maintain the AAA/Aaa rating.
The overall purpose of the Bank’s economic capital framework is to incorporate risk awareness throughout the business decision process. The economic capital model provides an aggregated view of the Bank’s risk position at a certain point in time, it allows capital to be allocated for the purpose of the risk-based pricing of loans and it is used for measuring the Bank’s risk-adjusted performance.
The Bank estimates its economic capital requirement for each of the main risks: credit risk, market risk and operational risk. When allocating economic capital for credit risk, the model uses the PD and LGD values arrived at in the internal rating process and it recognises correlations between assets in various sectors and geographical regions. When estimating the total economic capital requirement, the model recognises correlations between the different types of risk (credit risk, market risk and operational risk).
CREDIT QUALITY
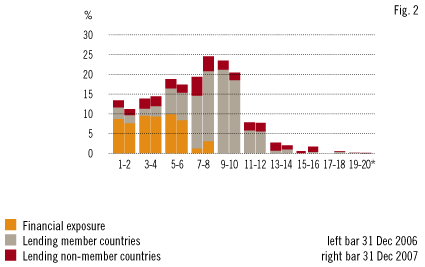
The quality of the Bank’s aggregate credit exposure remained at a high level in 2007. Figure 2, “Total exposure by NIB rating”, compares the quality of the Bank’s credit risks based on the credit risk classification system at year-end 2006 and 2007. The figures for 2006 have been restated due to a re-scaling of the LGD benchmark levels in 2007. Aggregate credit exposure includes lending and treasury exposure. Lending exposure refers to loans outstanding and loans agreed but not yet disbursed.
Lending in member countries. The quality of loans provided in the member countries continued to be healthy. The share of the four weakest credit risk classes was low at 0.6% of the portfolio. Most of the portfolio—almost 80%—was located in the risk classes 5 to 10.
LOANS OUTSTANDING
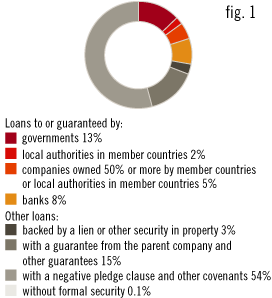
Distribution by type of security
as of 31 Dec 2007
The total amount of the percentage shares may differ from 100% due to rounding.
15 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
TOTAL EXPOSURE BY NIB RATING
*The risk classes range from 1 (highest credit quality) to 20 (lowest credit quality).
Lending in non-member countries. The quality of the loan portfolio comprising non-member countries was slightly weaker than in 2006. The exposure to the four weakest credit risk classes remained low, amounting to 1.4% at year-end 2007.
Financial counterparties. The credit quality of the counterparties in the Bank’s treasury operations remained at a high level. The exposure to the top four classes accounted for close to 60% of the total exposure.
Bank level. At an aggregate level, the Bank’s credit quality weakened slightly during the year but continues to be strong. At year-end 2007 one-fourth of the credit exposure was in the categories with the lowest risk (1 to 4) and more than 60% was in the risk categories 5 to 10. The exposure to the classes with the highest risk (17 to 20) was low at 0.6%. The credit exposure continued to be fairly well balanced in respect of the geographical and industrial sector distribution as well as regarding the distribution of the exposure by size.
Market risk
Market risk includes, inter alia, the risk that losses incur as a result of fluctuations in exchange rates and interest rates. NIB’s exposure to exchange rate risk occurs when translating assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies into the functional currency, the euro. The Bank funds its operations by borrowing in the international capital markets and often provides loans in currencies other than those borrowed, which unhedged would create currency mismatches in assets and liabilities. Furthermore, the funds borrowed often have other interest rate structures than those applied in the loans provided to the Bank’s customers. By using derivative instruments, NIB seeks to reduce its exposure to exchange rate risk and interest rate risk created in the normal course of business. The residual risk must be within strictly defined limits. Such limits are kept very narrow to accommodate the Statutes, which stipulate that the Bank is not allowed to bear foreign exchange risks that could affect its financial position and net income, other than to a marginal extent.
EXCHANGE RATE RISK
Exchange rate risk is the impact of unanticipated changes in foreign exchange rates on the Bank’s assets and liabilities and on net interest income. The Bank measures and manages exchange rate risk in terms of the net nominal value of all assets and liabilities per currency on a daily basis (translation risk). The Board of Directors sets the limits for acceptable currency positions, i.e. the difference between assets and liabilities in a specific currency. The overnight exposure to any one currency may not exceed the equivalent of EUR 4 million. The currency positions are monitored against the established limits on a daily basis and reported regularly to the Finance Committee.
The Bank does not have a policy on hedging future net interest income in foreign currency. Loans are provided primarily in euros and US dollars and there is a possibility that interest income in US dollars may cause some fluctuation in the Bank’s future net income in euro terms. However, at present the Bank expects that any such potential fluctuations in the future cash flows from its current portfolio would be minor in relation to the Bank’s total assets and equity.
INTEREST RATE RISK
Interest rate risk is the impact that fluctuations in market interest rates can have on the value of the Bank’s interest-bearing assets and liabilities and on its net interest income. The Bank applies a set of limits and various tools to measure and manage interest rate risk. Maximum exposure limits are set by the Board of Directors. Compliance with these limits is monitored on a daily basis and reported regularly to the Finance Committee.
GAP analysis measures interest rate risk as the sensitivity of the Bank’s interest income to a 1% change in interest rates. A gross total limit is defined for the acceptable interest rate risk, with separate sub-limits for each individual currency. The limits are set in relation to the Bank’s equity and they are adjusted annually. At year-end, the gross total limit was EUR 40 million, which corresponds to approximately 2% of NIB’s equity. Total interest rate risk was approximately EUR 6.6 million, or 16.5% of the limit.
Risk emanating from differences in the maturity profile of assets and liabilities is managed by limits established for refinancing and reinvestment risk. Refinancing risk arises when long-term assets are financed with short-term liabilities. Reinvestment risk occurs when short-term assets are financed with long-term liabilities. The limits for refinancing and reinvestment risk are set in relation to the Bank’s equity. They are reviewed annually and approved by the Board of Directors. At year-end 2007 the maximum limit for refinancing and
NIB Annual Report 2007 16
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
reinvestment risk was EUR 20 million, which is approximately 1% of NIB’s equity. The total exposure under this limit was EUR 18.3 million. Refinancing and reinvestment risk is measured by means of a sensitivity analysis. The analysis captures the impact on the Bank’s net interest income over time of a 0.1% change in the margin on an asset or liability. In addition, a EUR 2,000 million ceiling has been established to limit the difference in the cash flow from assets and liabilities in the course of any given year. This serves to prevent a large concentration of refinancing or reinvestment needs in the capital markets in one single year.
NIB invests an amount corresponding to the size of its equity in a fixed income portfolio denominated in euro. According to a Board of Directors’ decision, a maximum of 35% of the equity may be invested on a marked-to-market basis, while the balance must be invested on a held-to-maturity basis. To measure interest rate risk in this portfolio, the Bank uses a value-at-risk model and modified duration. Value-at-risk estimates the potential future loss (in terms of market value) that will not be exceeded in a defined period of time and with a defined confidence level. For measuring value-at-risk, the Bank applies both a parametric method and the Monte Carlo method. Under the Monte Carlo method, simulations are made to estimate the sensitivity of the portfolio and the individual transactions to changes in the yield curve and exchange rates. The model is based on a 95% confidence level and a holding period of 1 day. The daily value-at-risk may not exceed 0.4% of the marked-to-market portfolio’s value. In 2007 the daily value-at-risk fluctuated in the interval 0.059-0.195%. At year-end 2007 the value-at-risk amounted to 0.095%, or EUR 618,000. Modified duration measures how much the price of a security or portfolio of securities will change for a given change in interest rates. Generally, the shorter the duration, the less interest rate-sensitive the security. The current limit for the maximum modified duration is set at 5.5 years.
NIB’s exposure to credit spread changes is monitored by calculating the impact of a 0.01% change in credit spreads on the value of the bonds held in the Bank’s marked-to-market portfolios. At year-end 2007 this exposure was EUR 1.2 million.
Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk management safeguards the ability of the Bank to meet all payment obligations when they become due. NIB’s policy is to maintain a liquidity corresponding to its net liquidity requirements for 12 months. The liquid assets consist of receivables from banks and high-quality marketable securities denominated primarily in euros and US dollars. Another important element of the liquidity risk management is the Bank’s aim to diversify its funding sources in terms of, inter alia, investor type and geographical region. The Treasury Department is responsible for managing the liquidity. Status reports are submitted to the Finance Committee on a regular basis.
Operational risks—internal control
Operational risk can be broadly defined as any risk which is neither credit risk, liquidity risk nor market risk. More precisely, it is the risk of financial losses or damaged reputation due to failure attributable to technology, employees, procedures or physical arrangements including external events and legal risks.
The Bank’s status as an international organisation with immunities and privileges granted to the Bank and its personnel, and the fact that the Bank is not bound by or under the supervision of any national laws as such, results in a specific need to address potential risks by adopting an extensive set of guidelines, regulations, rules and instructions governing the activities of the Bank and its staff.
The Bank’s operational risk management focuses on proac-tive measures in order to ensure business continuity, the accuracy of information used internally and reported externally, the expertise and integrity of the Bank’s personnel and its adherence to established rules and procedures. Furthermore, security arrangements to protect the physical infrastructure of the Bank are an integral part of its operational risk management. The Bank attempts to mitigate operational risks by following strict rules for the assignment of duties and responsibilities among and within the business and support functions and by following a system of internal control and supervision. The main principle for organising work flows is to segregate business-generating functions from recording and monitoring functions. An important factor in operational risk mitigation is also the continuous development and upgrading of strategic information and communication systems.
The internal audit is part of the Bank’s internal control system. Important focal areas for the internal audit include the efficiency and reliability of the Bank’s individual processes and systems, as well as compliance. The internal audit is carried out in accordance with international standards for professional practice issued by the Institute of Internal Auditors. The annual activity plan for the internal audit is approved by the Board of Directors, and the audit reports are regularly submitted to the Board of Directors and to the Bank’s Control Committee.
17 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
NOTES TO THE INCOME STATEMENT, BALANCE SHEET AND CASH FLOW STATEMENT
| (1) | | SEGMENT INFORMATION |
| |
| | | Primary reporting segment—business operations |
| |
| | | The segment reporting in NIB is based on internal business areas. The segment results in this note are reported in the same form in which they are reported to the management. |
| |
| | | In its segment reporting, NIB divides its operations into two major segments: lending and financial operations. NIB offers long-term loans and guarantees on competitive market terms to its clients in the private and public sectors. Financial operations consist of the management of liquidity and placement of funds in financial investment portfolios. |
| |
| | | (Amounts in EUR 1,000) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Placements | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Placements | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | in financial | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | in financial | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | investment | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | investment | | | | |
| | | Lending | | | Liquidity | | | portfolios | | | Total | | | Lending | | | Liquidity | | | portfolios | | | Total | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2007 | | | 2007 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2006 | | | 2006 | | | 2006 | |
| |
Net interest income | | | 83,308 | | | | 19,790 | | | | 84,026 | | | | 187,125 | | | | 80,777 | | | | 20,194 | | | | 77,837 | | | | 178,807 | |
| Commission income and fees received | | | 5,829 | | | | 306 | | | | — | | | | 6,135 | | | | 6,598 | | | | 222 | | | | — | | | | 6,821 | |
| Commission expense and fees paid | | | — | | | | -2,425 | | | | — | | | | -2,425 | | | | — | | | | -1,734 | | | | — | | | | -1,734 | |
| Net profit on financial operations | | | 2,311 | | | | -68,882 | | | | -23,147 | | | | -89,719 | | | | 776 | | | | -4,771 | | | | -10,411 | | | | -14,406 | |
| Foreign exchange gains and losses | | | — | | | | -361 | | | | — | | | | -361 | | | | — | | | | 136 | | | | — | | | | 136 | |
| Administrative expenses | | | -24,168 | | | | -904 | | | | -2,435 | | | | -27,507 | | | | -23,984 | | | | -1,353 | | | | -2,573 | | | | -27,909 | |
| Depreciation | | | -2,899 | | | | -1,141 | | | | -489 | | | | -4,529 | | | | -2,718 | | | | -1,070 | | | | -458 | | | | -4,246 | |
| Credit loss / recovery | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Profit for the year | | | 64,381 | | | | -53,617 | | | | 57,954 | | | | 68,719 | | | | 61,449 | | | | 11,625 | | | | 64,394 | | | | 137,469 | |
Assets | | | 12,421,919 | | | | 5,514,373 | | | | 2,036,950 | | | | 19,973,242 | | | | 11,642,905 | | | | 4,324,391 | | | | 2,020,850 | | | | 17,988,146 | |
Liabilities and equity | | | 12,421,919 | | | | 5,514,373 | | | | 2,036,950 | | | | 19,973,242 | | | | 11,642,905 | | | | 4,324,391 | | | | 2,020,850 | | | | 17,988,146 | |
| | | Secondary reporting segment—geographical segment |
| |
| | | The table below is based on the region where the borrowers reside, according to the domicile of the borrower’s group headquarters. |
| |
| | | (Amounts in EUR 1,000) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| | | Net interest income | | | Net interest income | |
| |
Member countries |
| Denmark | | | 6,046 | | | | 6,025 | |
| Estonia | | | 976 | | | | 765 | |
| Finland | | | 15,267 | | | | 15,847 | |
| Iceland | | | 3,816 | | | | 3,825 | |
| Latvia | | | 1,000 | | | | 1,059 | |
| Lithuania | | | 243 | | | | 215 | |
| Norway | | | 7,875 | | | | 7,284 | |
| Sweden | | | 22,004 | | | | 21,602 | |
| |
Total, member countries | | | 57,228 | | | | 56,621 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Non-member countries |
| Africa | | | 2,026 | | | | 2,051 | |
| Asia | | | 7,578 | | | | 7,846 | |
| Europe and Eurasia | | | 8,011 | | | | 6,027 | |
| Latin America | | | 7,129 | | | | 6,946 | |
| Middle East | | | 1,336 | | | | 1,286 | |
| |
Total, non-member countries | | | 26,080 | | | | 24,155 | |
| |
Total, net interest income from lending | | | 83,308 | | | | 80,777 | |
| |
NIB Annual Report 2007 18
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
| (2) | | INTEREST INCOME AND INTEREST EXPENSE |
| |
| (Amounts in EUR 1,000) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Interest income | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 197,167 | | | | 136,969 | |
| Placements with credit institutions for more than 6 months | | | 3,726 | | | | 2,881 | |
| Debt securities of more than 6 months | | | 65,998 | | | | 61,159 | |
| Loans outstanding | | | 589,079 | | | | 471,480 | |
| Other interest income | | | 310 | | | | 708 | |
| |
Total, interest income 1) | | | 856,280 | | | | 673,197 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Interest expense |
| Short-term amounts owed to credit institutions | | | 12,235 | | | | 11,553 | |
| Long-term amounts owed to credit institutions | | | 3,593 | | | | 2,728 | |
| Short-term repurchase agreements | | | 8,394 | | | | 6,724 | |
| Debts evidenced by certificates | | | 737,017 | | | | 694,511 | |
| Swap contracts and other interest expenses, net | | | -92,085 | | | | -221,127 | |
| |
Total, interest expense 2) | | | 669,155 | | | | 494,390 | |
| | |
| 1) | | Including interest income of financial assets recognised at amortised cost: EUR 684,823 thousand (539,964). |
| |
| 2) | | Including interest expense of financial liabilities recognised at amortised cost: EUR 660,761 thousand (487,666). |
| (3) | | COMMISSION INCOME AND FEES RECEIVED |
| |
| (Amounts in EUR 1,000) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| Commitment fees | | | 1,547 | | | | 1,823 | |
| Loan disbursement fees | | | 3,445 | | | | 3,232 | |
| Guarantee commissions | | | 139 | | | | 139 | |
| Premiums on prepayments of loans | | | 697 | | | | 1,404 | |
| Commissions on lending of securities | | | 306 | | | | 222 | |
| |
Total, commission income and fees received | | | 6,135 | | | | 6,821 | |
| (4) | | NET PROFIT / LOSS ON FINANCIAL OPERATIONS |
| |
| (Amounts in EUR 1,000) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| Bonds in trading portfolio, realised gains and losses | | | -4,162 | | | | -3,268 | |
| Floating Rate Notes in trading portfolio, realised gains and losses | | | 1,158 | | | | 1,655 | |
| Derivatives in trading portfolio, realised gains and losses | | | -3,561 | | | | -645 | |
| |
Financial instruments in trading portfolio, realised gains and losses, total | | | -6,565 | | | | -2,258 | |
| Bonds in trading portfolio, unrealised gains and losses | | | -6,893 | | | | -6,800 | |
| Floating Rate Notes in trading portfolio, unrealised gains and losses | | | -71,038 | | | | -2,431 | |
| Derivatives in trading portfolio, unrealised gains and losses | | | 2,305 | | | | 1,699 | |
| |
Financial instruments in trading portfolio, unrealised gains and losses, total | | | -75,626 | | | | -7,533 | |
| Adjustment in fair value of hedged loans | | | -21,023 | | | | -50,697 | |
| Adjustment in fair value of derivatives hedging loans | | | 22,650 | | | | 51,035 | |
| Adjustment in fair value of hedged debts evidenced by certificates | | | -133,394 | | | | 461,700 | |
| Adjustment in fair value of derivatives hedging debts evidenced by certificates | | | 123,511 | | | | -467,331 | |
| Adjustment in fair value of asset swaps | | | -382 | | | | -93 | |
| |
Adjustment to hedge accounting, unrealised gains and losses of fair value hedges, total | | | -8,638 | | | | -5,386 | |
| Changes in fair value of non-hedging derivatives, unrealised gains and losses | | | -1,681 | | | | -1,648 | |
| Repurchase of NIB bonds, other items | | | 2,791 | | | | 2,419 | |
| |
Total, net profit/loss on financial operations | | | -89,719 | | | | -14,406 | |
19 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
| (5) | | GENERAL ADMINISTRATIVE EXPENSES |
| |
| (Amounts in EUR 1,000) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| Staff costs | | | 18,512 | | | | 18,032 | |
| Wages and salaries | | | 14,235 | | | | 14,220 | |
| Social security costs | | | 444 | | | | 368 | |
| Other staff costs | | | 3,833 | | | | 3,444 | |
| Pension premiums in accordance with the Finnish state pension system | | | 3,423 | | | | 3,141 | |
| Other pension premiums | | | 1,084 | | | | 1,029 | |
| Office premises costs | | | 1,996 | | | | 2,253 | |
| IT costs | | | 2,295 | | | | 1,974 | |
| Other general administrative expenses | | | 6,844 | | | | 7,407 | |
| Cost coverage, NDF and NEFCO | | | -786 | | | | -843 | |
| Cost coverage, rental income and other administrative income | | | -887 | | | | -645 | |
| |
Total | | | 32,479 | | | | 32,350 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Host country reimbursement according to agreement with the Finnish Government | | | -4,972 | | | | -4,440 | |
| |
Net | | | 27,507 | | | | 27,909 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 2007 | | | | 2006 | |
Remuneration to the auditors |
Audit fee 1) | | | 273 | | | | 168 | |
| Other audit-related service fee | | | 1 | | | | 3 | |
| |
Total remuneration | | | 274 | | | | 171 | |
| | |
| 1) | | The cost of issuing comfort letters and certificates in relation to the borrowing operations of the Bank is included in the audit fee. |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| Average number of employees | | | 156 | | | | 158 | |
| Average age of the employees | | | 44 | | | | 43 | |
| Average period (years) of employment | | | 10 | | | | 9 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Distribution by gender | | | | | | | | |
| All employees | | | | | | | | |
| Females | | | 79 | | | | 77 | |
| Males | | | 79 | | | | 83 | |
| Management Committee (including the President) | | | | | | | | |
| Females | | | 1 | | | | 2 | |
| Males | | | 6 | | | | 5 | |
| Professional staff | | | | | | | | |
| Females | | | 41 | | | | 33 | |
| Males | | | 56 | | | | 60 | |
| Clerical staff | | | | | | | | |
| Females | | | 37 | | | | 42 | |
| Males | | | 17 | | | | 18 | |
| | | Compensation for the Board of Directors, the Control Committee, the President and the Management Committee |
| |
| | | Compensation for the Board of Directors (BoD) and the Control Committee (CC) is set by the Board of Governors (BoG). The compensation consists of a fixed annual remuneration and an attendee allowance. The members of the BoD and the CC are also entitled to reimbursement of travel and accommodation expenses and a daily allowance in accordance with the Bank’s travel policy. |
| |
| | | The BoD makes decisions concerning the employment and the remuneration of the President. The President is appointed on a fixed-term contract for five years at a time. While the BoD decides on the principles for remuneration of the members of the Management Committee (MC), the President decides upon the employment and specific remuneration of the MC. The members of the MC are normally employed for an indefinite period of time. The period of notice varies from three to six months. The remuneration package for the members of the MC includes a fixed base salary and customary taxable benefits, which are in principle the same for all staff on the managerial level. In addition to this remuneration package, the members of the MC enjoy other benefits common to all staff (health care, supplementary group pension, staff loans and insurance coverage). The Bank pays performance bonuses up to one month’s salary for excellent and extraordinary performance within a total of 1.5% of the estimated total staff salary costs for the previous year. All personnel are eligible for bonus awards. |
NIB Annual Report 2007 20
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
Compensation for BoD, the CC, the President and the MC is presented in the table below:
(Amounts in EUR)
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| | | Compensation/ | | | Compensation/ | |
| | | Taxable income | | | Taxable income | |
| Board of Directors | | | | | | | | |
| Chairman | | | | | | | | |
| annual remuneration | | | 12,495 | | | | 12,141 | |
| attendee allowance | | | 1,409 | | | | 1,510 | |
| Other Directors and Alternates (15 persons) | | | | | | | | |
| annual remuneration | | | 71,865 | | | | 70,079 | |
| attendee allowance | | | 11,360 | | | | 10,284 | |
| Control Committee | | | | | | | | |
| Chairman | | | | | | | | |
| annual remuneration | | | 4,207 | | | | 3,488 | |
| attendee allowance | | | 545 | | | | 328 | |
| Other members (9 persons) | | | | | | | | |
| annual remuneration | | | 15,645 | | | | 13,747 | |
| attendee allowance | | | 4,392 | | | | 1,900 | |
| President | | | 424,609 | | | | 418,472 | |
| Members of the Management Committee (6 persons) | | | 1,460,826 | | | | 1,415,717 | |
Pension obligations
NIB is responsible for arranging the pension security for its employees. The current pension arrangement consists of pension based on the Finnish state pension system (VEL Pension) as the basis for the pension benefits. The VEL pension is calculated on the basis of the employee’s annual taxable income and the applicable age-linked pension accrual rate. The employer’s pension contribution in 2007 was 17.98% of the taxable income. The employee’s pension contribution was either 4.88% or 5.98%, depending on the employee’s age. NIB pays this contribution for the permanent staff and it is taxed as a benefit for the employee.
In addition to the VEL Pension, the Bank has taken out a supplementary group pension insurance policy for all its permanently employed staff including the President. This pension insurance is based on the principle of a defined contribution. The insurance premium, 6.5%, is calculated on the basis of the employee’s taxable income and paid until the age of 63.
Pension premiums paid for the President amounted to EUR 200,505 of which EUR 101,232 comprised supplementary pension premiums. The corresponding figures for the MC were EUR 486,911 and EUR 155,936.
Staff loans
Staff loans can be granted to permanently employed staff members who have been employed by the Bank for a period of at least one year. The President is granted staff loans subject to a recommendation from the BoD, and the members of the MC are granted staff loans subject to a recommendation from the President. The staff loans are granted by a commercial bank, subject to a recommendation from NIB. Staff loans are granted for the financing of, for example, a permanent residence, other accommodation and motor vehicles.
The total loan amount cannot exceed the amount equivalent to the employee’s base salary for twenty months, the maximum loan amount being EUR 100,000. The employee pays interest on the loan in accordance with the official base rate established by the Ministry of Finance in Finland (4.25% in July–December 2007). The same interest rates, terms and conditions are applicable to all the employees of the Bank, including the President and MC members.
As of 31 December 2007, the total amount outstanding of staff loans to the MC was EUR 29,577 (EUR 57,071 in 2006).
Additional benefits to expatriates
Professional staff (including Management Committee members) who move to Finland for the sole purpose of taking up employment in the Bank, are entitled to certain expatriate benefits, such as an expatriate allowance and a spouse allowance. In addition, NIB assists the expatriate, e.g., in finding accommodation, usually by renting a house or a flat in its own name. The staff member reimburses the Bank a part of the rent, which equals at least the tax value of the accommodation benefit established annually by the Finnish National Board of Taxes.
Rental agreement
NIB owns its headquarters office building in Helsinki. The building’s total area is 18,500 m2. The Bank rents office space totalling 1,723 m2 adjacent to its main office building. Furthermore, the Bank rents office space totalling 353 m2 in the Nordic countries and in Singapore. A total of 1,734 m2 is rented to other parties.
21 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
| (6) | | CREDIT LOSS / RECOVERY |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| Credit losses covered by previously recognised credit losses | | | — | | | | — | |
| Credit losses recognised during the year | | | — | | | | — | |
| Reversals of previously recognised credit losses | | | — | | | | — | |
| |
Credit loss / recovery, net | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | The debt securities were issued by the following counterparties: |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| Governments | | | 396 | | | | 455 | |
| Public institutions | | | 84 | | | | 96 | |
| Other | | | 1,103 | | | | 865 | |
| |
Total, debt securities | | | 1,583 | | | | 1,416 | |
| | | These debt securities are at fixed interest rates. |
| | | The distribution of the Bank’s debt security portfolios was as follows: |
| |
| (Amounts in EUR million) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Book value | | | | Fair value | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| Trading portfolio | | | 373 | | | | 253 | | | | 373 | | | | 253 | |
| Held-to-maturity portfolio | | | 1,210 | | | | 1,164 | | | | 1,181 | | | | 1,171 | |
| |
Total, debt securities | | | 1,583 | | | | 1,416 | | | | 1,554 | | | | 1,424 | |
(8) LOANS OUTSTANDING AND GUARANTEE COMMITMENTS
| | | Loans outstanding were distributed as follows over the Bank’s four loan facilities: |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Ordinary Loans | | | | | | | | |
| Investment loans in the member countries | | | 9,882 | | | | 9,190 | |
| Investment loans in other countries | | | 294 | | | | 196 | |
| Regional loans in the Nordic countries | | | 17 | | | | 23 | |
Adjustment to hedge accounting | | | -31 | | | | -12 | |
| |
Total | | | 10,161 | | | | 9,397 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Project Investment Loans (PIL) | | | | | | | | |
| Africa | | | 235 | | | | 235 | |
| Asia | | | 772 | | | | 802 | |
| Europe and Eurasia | | | 444 | | | | 335 | |
| Latin America | | | 478 | | | | 536 | |
| Middle East | | | 111 | | | | 123 | |
Adjustment to hedge accounting | | | -5 | | | | -3 | |
| |
Total | | | 2,034 | | | | 2,028 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Environmental Investment Loans (MIL) | | | 95 | | | | 105 | |
Baltic Investment Loans (BIL) | | | — | | | | 4 | |
| |
Total, loans outstanding | | | 12,291 | | | | 11,534 | |
The figure for loans outstanding, EUR 12,291 million (11,534), includes medium-term notes (MTN) of EUR 2,342 million (2,137). These are held at amortised cost unless they form a part of a qualifying hedging relationship with a derivative. In a hedge accounting relationship, the MTNs are recognised at fair value.
Loans outstanding at floating interest rates amounted to EUR 10,990 million (10,265), while those at fixed interest rates amounted to EUR 1,336 million (1,284). The nominal amount of the guarantee commitments under Ordinary Lending totalled EUR 25.0 million (25.0) as of 31 December 2007.
NIB Annual Report 2007 22
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
Credit losses
A total of EUR 0.3 million (0.4) has been deducted from the Bank’s loans outstanding for impairment losses on loans. This amount was comprised only of impairment losses on Project Investment Loans. The following changes were recognised in the balance sheet in respect of impairment losses:
(Amounts in EUR million)
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| Impairment losses as of 1 January | | | 0.4 | | | | 0.5 | |
| Impairment losses recognised during the year | | | — | | | | — | |
| Reversals of previously recognised impairment losses | | | — | | | | — | |
| Exchange rate adjustments, impairment accrued | | | -0.1 | | | | -0.1 | |
| |
Impairment losses as of 31 December | | | 0.3 | | | | 0.4 | |
See also Note 6.
The distribution of impairment losses was as follows:
(Amounts in EUR million)
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Distribution by loan facility | | | | | | | | |
| Ordinary Loans | | | — | | | | — | |
| Project Investment Loans (PIL) |
| Africa | | | — | | | | — | |
| Asia | | | — | | | | — | |
| Europe and Eurasia | | | — | | | | — | |
| Latin America | | | 0.3 | | | | 0.4 | |
| Middle East | | | — | | | | — | |
| |
Total, impairment losses | | | 0.3 | | | | 0.4 | |
As of 31 December 2007, all of the Bank’s loans were performing.
As of 31 December 2007, loans agreed but not yet disbursed amounted to the following:
(Amounts in EUR million)
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Loans agreed but not yet disbursed | | | | | | | | |
| Ordinary Loans | | | 577 | | | | 658 | |
| Project Investment Loans | | | 616 | | | | 717 | |
| Environmental Investment Loans | | | 6 | | | | 129 | |
| |
Total, loans agreed but not yet disbursed | | | 1,200 | | | | 1,503 | |
The amounts set forth above for loans agreed but not yet disbursed include loans in considerable amounts, where certain conditions, primarily interest rate conditions, may not yet have been finally approved.
Currency distribution of loans outstanding
(Nominal amounts, in EUR million)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Currency | | Ordinary Loans | | PIL loans | | Total 1) |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| Nordic currencies | | | 3,419 | | | | 3,082 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 3,419 | | | | 3,083 | |
| EUR | | | 5,671 | | | | 5,193 | | | | 571 | | | | 435 | | | | 6,316 | | | | 5,706 | |
| USD | | | 958 | | | | 1,037 | | | | 1,440 | | | | 1,570 | | | | 2,420 | | | | 2,639 | |
| Other currencies | | | 144 | | | | 96 | | | | 28 | | | | 26 | | | | 172 | | | | 122 | |
| |
Total | | | 10,192 | | | | 9,408 | | | | 2,039 | | | | 2,031 | | | | 12,326 | | | | 11,549 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjustment to hedge accounting | | | -31 | | | | -11 | | | | -5 | | | | -3 | | | | -36 | | | | -15 | |
| |
Total, loans outstanding | | | 10,161 | | | | 9,397 | | | | 2,034 | | | | 2,028 | | | | 12,291 | | | | 11,534 | |
| | |
| 1) | | The total amount also includes EUR 95 million (105) in Environmental Investment Loans (MIL) and EUR 0.0 million (4) in Baltic Investment Loans (BIL). |
23 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
Sectoral distribution
(Amounts in EUR million)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans outstanding as of 31 December | | 2007 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2006 | |
| Manufacturing | | | 4,607 | | | | 37 | % | | | 4,287 | | | | 37 | % |
| Energy | | | 3,297 | | | | 27 | % | | | 2,998 | | | | 26 | % |
| Transport and communications | | | 1,666 | | | | 14 | % | | | 1,684 | | | | 15 | % |
| Trade and services | | | 842 | | | | 7 | % | | | 816 | | | | 7 | % |
Banking and finance 2) | | | 999 | | | | 8 | % | | | 959 | | | | 8 | % |
| Regional loans | | | 17 | | | | 0 | % | | | — | | | | 0 | % |
| Other | | | 898 | | | | 7 | % | | | 805 | | | | 7 | % |
Adjustment to hedge accounting | | | -36 | | | | 0 | % | | | -15 | | | | 0 | % |
| |
Total | | | 12,291 | | | | 100 | % | | | 11,534 | | | | 100 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans disbursed | | 2007 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2006 | |
| Manufacturing | | | 1,027 | | | | 43 | % | | | 362 | | | | 23 | % |
| Energy | | | 600 | | | | 25 | % | | | 389 | | | | 24 | % |
| Transport and communications | | | 237 | | | | 10 | % | | | 348 | | | | 22 | % |
| Trade and services | | | 192 | | | | 8 | % | | | 127 | | | | 8 | % |
Banking and finance 2) | | | 175 | | | | 7 | % | | | 157 | | | | 10 | % |
| Regional loans | | | — | | | | 0 | % | | | — | | | | 0 | % |
| Other | | | 160 | | | | 7 | % | | | 223 | | | | 14 | % |
| |
Total | | | 2,390 | | | | 100 | % | | | 1,605 | | | | 100 | % |
| | |
| 2) | | Including the Bank’s financial intermediaries. |
Distribution of loans outstanding and guarantees by various types of security
The following table shows loans outstanding, including guarantee commitments, distributed by type of security:
(Amounts in EUR million)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of 31 December 2007 | | Amount | | | Total amount | | | Share, in % | |
| Loans to or guaranteed by governments | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans to or guaranteed by member countries | | | 204 | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans to or guaranteed by other countries | | | 1,456 | | | | 1,660 | | | | 13.5 | |
| Loans to or guaranteed by local authorities in member countries | | | | | | | 273 | | | | 2.2 | |
Loans to or guaranteed by companies owned 50% or more by member countries or
local authorities in member countries | | | | | | | 578 | | | | 4.7 | |
| Loans to or guaranteed by banks | | | | | | | 980 | | | | 7.9 | |
| Other loans | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Backed by a lien or other security in property | | | 371 | | | | | | | | | |
| With a guarantee from the parent company and other guarantees | | | 1,854 | | | | | | | | | |
| With a negative pledge clause and other covenants | | | 6,620 | | | | | | | | | |
| Without formal security | | | 16 | | | | 8,862 | | | | 71.7 | |
| |
Total | | | | | | | 12,351 | | | | 100.0 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjustment to hedge accounting | | | | | | | -36 | | | | | |
| |
Total, loans outstanding (including guarantees) | | | | | | | 12,316 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of 31 December 2006 | | Amount | | | Total amount | | | Share, in % | |
| Loans to or guaranteed by governments | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans to or guaranteed by member countries | | | 200 | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans to or guaranteed by other countries | | | 1,510 | | | | 1,710 | | | | 14.7 | |
| Loans to or guaranteed by local authorities in member countries | | | | | | | 315 | | | | 2.7 | |
Loans to or guaranteed by companies owned 50% or more by member countries or
local authorities in member countries | | | | | | | 607 | | | | 5.2 | |
| Loans to or guaranteed by banks | | | | | | | 836 | | | | 7.2 | |
| Other loans | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Backed by a lien or other security in property | | | 393 | | | | | | | | | |
| With a guarantee from the parent company and other guarantees | | | 1,817 | | | | | | | | | |
| With a negative pledge clause and other covenants | | | 5,869 | | | | | | | | | |
| Without formal security | | | 28 | | | | 8,107 | | | | 70.0 | |
| |
Total | | | | | | | 11,574 | | | | 100.0 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjustment to hedge accounting | | | | | | | -15 | | | | | |
| |
Total, loans outstanding (including guarantees) | | | | | | | 11,559 | | | | | |
NIB Annual Report 2007 24
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
According to NIB’s Statutes, the member countries shall cover the Bank’s losses arising from failure of payment in connection with PIL loans up to the following amounts:
(Amounts in EUR 1,000)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | 2007 | | | | | | | 2006 | |
| Member country | | Amount of guarantee | | | Share, in % | | | Amount of guarantee | | | Share, in % | |
| Denmark | | | 377,821 | | | | 21.0 | | | | 377,821 | | | | 21.0 | |
| Estonia | | | 13,139 | | | | 0.7 | | | | 13,139 | | | | 0.7 | |
| Finland | | | 344,860 | | | | 19.2 | | | | 344,860 | | | | 19.2 | |
| Iceland | | | 15,586 | | | | 0.9 | | | | 15,586 | | | | 0.9 | |
| Latvia | | | 19,058 | | | | 1.1 | | | | 19,058 | | | | 1.1 | |
| Lithuania | | | 29,472 | | | | 1.6 | | | | 29,472 | | | | 1.6 | |
| Norway | | | 329,309 | | | | 18.3 | | | | 329,309 | | | | 18.3 | |
| Sweden | | | 670,755 | | | | 37.3 | | | | 670,755 | | | | 37.3 | |
| |
Total | | | 1,800,000 | | | | 100.0 | | | | 1,800,000 | | | | 100.0 | |
According to NIB’s Statutes, the member countries shall cover 100% of the Bank’s losses arising from failure of payment in connection with MIL loans up to the following amounts:
(Amounts in EUR 1,000)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | 2007 | | | | | | | 2006 | |
| Member country | | Amount of guarantee | | | Share, in % | | | Amount of guarantee | | | Share, in % | |
| Denmark | | | 70,113 | | | | 23.4 | | | | 70,113 | | | | 23.4 | |
| Estonia | | | 2,190 | | | | 0.7 | | | | 2,190 | | | | 0.7 | |
| Finland | | | 51,377 | | | | 17.1 | | | | 51,377 | | | | 17.1 | |
| Iceland | | | 3,187 | | | | 1.1 | | | | 3,187 | | | | 1.1 | |
| Latvia | | | 3,176 | | | | 1.1 | | | | 3,176 | | | | 1.1 | |
| Lithuania | | | 4,912 | | | | 1.6 | | | | 4,912 | | | | 1.6 | |
| Norway | | | 61,324 | | | | 20.4 | | | | 61,324 | | | | 20.4 | |
| Sweden | | | 103,720 | | | | 34.6 | | | | 103,720 | | | | 34.6 | |
| |
Total | | | 300,000 | | | | 100.0 | | | | 300,000 | | | | 100.0 | |
In addition, the Nordic countries guaranteed loans outstanding under the BIL facility at 100%. No new loans have been granted under the BIL facility since year-end 1999, when it expired. BIL loans outstanding totalled EUR 0.0 million (4) at year-end 2007.
| (9) | | INTANGIBLE ASSETS, TANGIBLE ASSETS (PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT) |
| |
| | | The Bank’s intangible assets amounted to EUR 6.7 million (7.3). |
2007
(Amounts in EUR 1,000)
| | | | | |
| | | Computer software | |
| Intangible assets | | development costs, total | |
| Acquisition value at the beginning of the year | | | 11,593 | |
| Acquisitions during the year | | | 1,799 | |
| Sales/disposals during the year | | | — | |
Acquisition value at the end of the year | | | 13,392 | |
| | | | | |
| Accumulated amortisation at the beginning of the year | | | 4,251 | |
| Amortisation according to plan for the year | | | 2,401 | |
| Accumulated amortisation on sales/disposals during the year | | | — | |
Accumulated amortisation at the end of the year | | | 6,652 | |
| |
Net book value | | | 6,740 | |
As of 31 December 2007, the historical cost of buildings and land was recognised in the balance sheet (net of depreciation on the buildings in accordance with the depreciation plan) at EUR 27.6 million (28.3).
The value of office equipment and other tangible assets is recognised at EUR 9.1 million (7.3).
25 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
2007
(Amounts in EUR 1,000)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Office equipment | | | | |
| | | | | | | and other | | | | |
| Tangible assets | | Buildings | | | tangible assets | | | Total | |
| Acquisition value at the beginning of the year | | | 33,704 | | | | 12,099 | | | | 45,803 | |
| Acquisitions during the year | | | — | | | | 3,316 | | | | 3,316 | |
| Sales/disposals during the year | | | — | | | | -178 | | | | -178 | |
Acquisition value at the end of the year | | | 33,704 | | | | 15,237 | | | | 48,941 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accumulated depreciation at the beginning of the year | | | 5,398 | | | | 4,771 | | | | 10,170 | |
| Depreciation according to plan for the year | | | 670 | | | | 1,458 | | | | 2,128 | |
| Accumulated depreciation on sales/disposals during the year | | | — | | | | -124 | | | | -124 | |
Accumulated depreciation at the end of the year | | | 6,069 | | | | 6,105 | | | | 12,174 | |
| |
Net book value | | | 27,635 | | | | 9,132 | | | | 36,767 | |
The impairment tests conducted in 2007 did not indicate any need for impairment.
2006
(Amounts in EUR 1,000)
| | | | | |
| | | Computer software | |
| Intangible assets | | development costs, total | |
| Acquisition value at the beginning of the year | | | 9,681 | |
| Acquisitions during the year | | | 1,912 | |
| Sales/disposals during the year | | | — | |
Acquisition value at the end of the year | | | 11,593 | |
| | | | | |
| Accumulated amortisation at the beginning of the year | | | 2,259 | |
| Amortisation according to plan for the year | | | 1,986 | |
| Accumulated amortisation on sales/disposals during the year | | | 6 | |
Accumulated amortisation at the end of the year | | | 4,251 | |
| |
Net book value | | | 7,342 | |
2006
(Amounts in EUR 1,000)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Office equipment | | | | |
| | | | | | | and other | | | | |
| Tangible assets | | Buildings | | | tangible assets | | | Total | |
| Acquisition value at the beginning of the year | | | 33,704 | | | | 9,341 | | | | 43,045 | |
| Acquisitions during the year | | | — | | | | 3,024 | | | | 3,024 | |
| Sales/disposals during the year | | | — | | | | -266 | | | | -266 | |
Acquisition value at the end of the year | | | 33,704 | | | | 12,099 | | | | 45,803 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accumulated depreciation at the beginning of the year | | | 4,728 | | | | 3,433 | | | | 8,161 | |
| Depreciation according to plan for the year | | | 670 | | | | 1,590 | | | | 2,260 | |
| Accumulated depreciation on sales/disposals during the year | | | — | | | | -252 | | | | -252 | |
Accumulated depreciation at the end of the year | | | 5,398 | | | | 4,771 | | | | 10,170 | |
| |
Net book value | | | 28,305 | | | | 7,328 | | | | 35,633 | |
NIB Annual Report 2007 26
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
| (10) | | DEPRECIATION |
| |
| (Amounts in EUR 1,000) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| Intangible assets | | | 2,401 | | | | 1,986 | |
| Tangible assets | | | 2,128 | | | | 2,260 | |
| Buildings | | | 670 | | | | 670 | |
| Office equipment | | | 1,458 | | | | 1,590 | |
| |
Total | | | 4,529 | | | | 4,246 | |
| (11) | | OTHER ASSETS |
| |
| | | Derivatives are included in “Other assets”. |
| |
| (Amounts in EUR million) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Interest rate swaps 1) | | | 9,842 | | | | 7,760 | |
Currency swaps 2) | | | 14,468 | | | | 13,383 | |
| |
Total, nominal amount | | | 24,310 | | | | 21,143 | |
| Netting of nominal amount per derivative | | | -23,563 | | | | -20,618 | |
| |
Derivative receivables, net | | | 747 | | | | 525 | |
Adjustment to hedge accounting and changes in fair value of non-hedging derivatives | | | 303 | | | | 226 | |
| |
Derivative instruments | | | 1,050 | | | | 751 | |
| Other | | | 2 | | | | 12 | |
| |
Total | | | 1,051 | | | | 763 | |
| | |
| 1) | | Interest rate swaps at floating interest rates EUR 2,377 million (1,318) and fixed interest rates EUR 7,465 million (6,422). |
| |
| 2) | | Currency swaps at floating interest rates EUR 8,278 million (7,540) and fixed interest rates EUR 6,191 million (5,843). |
| | | Derivatives are carried at fair value in the balance sheet net per contract. Thus, swap contracts with a positive net fair value are recognised in the balance sheet under “Other assets”, while swap contracts with a negative net fair value are recognised under “Other liabilities”. |
27 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
| (12) | | DEBTS EVIDENCED BY CERTIFICATES AND SWAPS |
| |
| | | At year-end, the Bank’s borrowings evidenced by certificates were distributed among the currencies shown in the table below. The table also demonstrates the distribution of borrowings by currency on an after-swap nominal basis. |
| |
| (Amounts in EUR million) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Swap contracts | | | | |
| | | Borrowing | | | payable/receivable | | | Net currency | |
| Currency | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| Nordic currencies | | | 688 | | | | 588 | | | | 2,745 | | | | 2,504 | | | | 3,433 | | | | 3,092 | |
| EUR | | | 676 | | | | 777 | | | | 7,760 | | | | 6,845 | | | | 8,436 | | | | 7,623 | |
| USD | | | 6,862 | | | | 5,736 | | | | -2,969 | | | | -2,362 | | | | 3,893 | | | | 3,373 | |
| JPY | | | 1,547 | | | | 1,507 | | | | -1,512 | | | | -1,466 | | | | 34 | | | | 40 | |
| GBP | | | 2,026 | | | | 1,961 | | | | -2,005 | | | | -1,939 | | | | 21 | | | | 22 | |
| HKD | | | 263 | | | | 416 | | | | -264 | | | | -416 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Other currencies | | | 2,861 | | | | 2,671 | | | | -2,774 | | | | -2,622 | | | | 87 | | | | 49 | |
| |
Total | | | 14,924 | | | | 13,656 | | | | 981 | | | | 543 | | | | 15,905 | | | | 14,199 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjustments to hedge accounting and changes in fair value of non-hedging derivatives | | | 99 | | | | -34 | | | | -130 | | | | 13 | | | | -31 | | | | -21 | |
| Swap fees | | | — | | | | — | | | | 98 | | | | 109 | | | | 98 | | | | 109 | |
| |
Total, borrowings outstanding | | | 15,023 | | | | 13,622 | | | | 950 | | | | 664 | | | | 15,972 | | | | 14,286 | |
| | | The table set forth above includes 276 (279) borrowing transactions in the equivalent amount of EUR 8,268 million (8,813) entered into under the Bank’s euro medium-term note programme, 1 (4) borrowing transactions in the equivalent amount of EUR 53 million (177) under the Bank’s Swedish medium-term note programme, 10 (4) borrowing transactions in the equivalent amount of EUR 7,235 million (3,037) under the Bank’s US medium-term note programmes and 5 (4) borrowing transactions in the equivalent amount of
EUR 597 million (599) under the Bank’s Australian medium-term note programme. The Bank has established a USD 600 million commercial paper programme in Europe and another USD 600 million programme in the United States. |
| |
| | | Of debt securities issued, the amount of EUR 1,590 million (1,579) is at floating interest rates, while EUR 13,139 million (11,825) is at fixed interest rates. Other borrowing transactions, amounting to EUR 194 million (251), are at fixed interest rates. |
| |
| (13) | | OTHER LIABILITIES |
| |
| | | Derivatives are included in “Other liabilities”. |
| |
| (Amounts in EUR million) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 2007 | | | | 2006 | |
Interest rate swaps 1) | | | 9,812 | | | | 7,727 | |
Currency swaps 2) | | | 15,475 | | | | 13,959 | |
| |
Total, nominal amount | | | 25,287 | | | | 21,686 | |
| Netting of nominal amount per derivative | | | -23,461 | | | | -20,509 | |
| |
Derivative payables, net | | | 1,826 | | | | 1,177 | |
Adjustment to hedge accounting and changes in fair value of non-hedging derivatives | | | 173 | | | | 239 | |
| |
Derivative instruments | | | 1,999 | | | | 1,415 | |
| Other | | | 4 | | | | 4 | |
| |
Total | | | 2,004 | | | | 1,420 | |
| | |
| 1) | | Interest rate swaps at floating interest rates EUR 8,684 million (6,666) and fixed interest rates EUR 1,128 million (1,061). |
| |
| 2) | | Currency swaps at floating interest rates EUR 15,153 million (13,662) and fixed interest rates EUR 323 million (297). |
| | | Derivatives are carried at fair value in the balance sheet net per contract. Thus, swap contracts with a positive net fair value are recognised in the balance sheet under “Other assets”, while swap contracts with a negative net fair value are recognised under “Other liabilities”. |
NIB Annual Report 2007 28
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
| (14) | | AUTHORISED CAPITAL—PAID-IN CAPITAL |
| |
| | | The member countries’ portions of authorised capital are as follows: |
| |
| (Amounts in EUR million) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Member country | | 2007 | | | Share, in % | | | 2006 | | | Share, in % | |
| Denmark | | | 881.1 | | | | 21.3 | | | | 881.1 | | | | 21.3 | |
| Estonia | | | 30.2 | | | | 0.7 | | | | 30.2 | | | | 0.7 | |
| Finland | | | 765.8 | | | | 18.5 | | | | 765.8 | | | | 18.5 | |
| Iceland | | | 38.6 | | | | 0.9 | | | | 38.6 | | | | 0.9 | |
| Latvia | | | 43.9 | | | | 1.1 | | | | 43.9 | | | | 1.1 | |
| Lithuania | | | 67.8 | | | | 1.6 | | | | 67.8 | | | | 1.6 | |
| Norway | | | 793.1 | | | | 19.1 | | | | 793.1 | | | | 19.1 | |
| Sweden | | | 1,521.4 | | | | 36.7 | | | | 1,521.4 | | | | 36.7 | |
| |
Total | | | 4,141.9 | | | | 100.0 | | | | 4,141.9 | | | | 100.0 | |
| | | The member countries’ portions of paid-in capital are as follows: |
| |
| (Amounts in EUR million) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Member country | | 2007 | | | Share, in % | | | 2006 | | | Share, in % | |
| Denmark | | | 89.2 | | | | 21.3 | | | | 89.2 | | | | 21.3 | |
| Estonia | | | 3.1 | | | | 0.7 | | | | 3.1 | | | | 0.7 | |
| Finland | | | 74.4 | | | | 17.8 | | | | 74.4 | | | | 17.8 | |
| Iceland | | | 3.9 | | | | 0.9 | | | | 3.9 | | | | 0.9 | |
| Latvia | | | 4.4 | | | | 1.1 | | | | 4.4 | | | | 1.1 | |
| Lithuania | | | 6.9 | | | | 1.6 | | | | 6.9 | | | | 1.6 | |
| Norway | | | 77.1 | | | | 18.4 | | | | 77.1 | | | | 18.4 | |
| Sweden | | | 159.5 | | | | 38.1 | | | | 159.5 | | | | 38.1 | |
| |
Total | | | 418.6 | | | | 100.0 | | | | 418.6 | | | | 100.0 | |
| | | The new member countries have made their payments of the paid-in portion pursuant to an agreed schedule of payments in three annual instalments, the last of which was made on 31 March 2007. |
| |
| (15) | | STATUTORY RESERVE AND CREDIT RISK FUNDS |
| |
| | | At the end of 2007, the Statutory Reserve amounted to EUR 645.6 million, or 15.6% of the Bank’s authorised capital of
EUR 4,141.9 million. |
| |
| | | The General Credit Risk Fund recognised in “Equity” is built up by means of allocations from prior years’ profits. This fund is established to cover unidentified, exceptional credit losses. The Statutory Reserve and the General Credit Risk Fund together constitute the Bank’s general reserves. The General Credit Risk Fund amounted to EUR 622.1 million in 2007. |
| |
| | | In accordance with its Statutes, the Bank has a Special Credit Risk Fund for the Project Investment Loan facility. This fund is primarily designed to cover the Bank’s own risk in respect of this loan facility, guaranteed by the member countries. In 2007, the fund amounted to EUR 238.2 million. The Bank assumes 100% of any losses under individual PIL loans, up to the amount available at any given time in the Special Credit Risk Fund for PIL. Only after this fund has been fully used, can the Board of Directors call the member country guarantees. |
| |
| | | In addition, the Bank had established a EUR 4.3 million fund in “Equity” for the HIPC Programme (Debt Initiative for Heavily Indebted Poor Countries), which was used to pay the Bank’s contribution to the HIPC Programme in 2006. |
| |
| | | Taken together, these credit risk funds (General Credit Risk Fund and Special Credit Risk Fund PIL) amounted to EUR 860.3 million as of 31 December 2007. |
| |
| | | As part of the terms and conditions of membership, Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania have, as of 1 January 2005, agreed to pay to the Bank’s reserves altogether the amount of EUR 42.7 million in the same proportion as their share of the subscribed capital. Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania will make their payments in semi-annual instalments in accordance with individual payment agreements during the period from 31 March 2008 to 30 September 2012. |
29 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
| | | |
(16) | | COLLATERAL AND COMMITMENTS |
| |
| (Amounts in EUR million) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| Guarantees issued at nominal amount (Note 8) | | | 25 | | | | 25 | |
| Loans agreed but not yet disbursed (Note 8) | | | 1,200 | | | | 1,503 | |
| Borrowing commitments | | | 275 | | | | 20 | |
| Collateral provided for staff loans | | | — | | | | — | |
| |
Securities as collateral for repurchase agreements 1) | | | — | | | | 205 | |
| Callable commitments in financial placements | | | 19 | | | | 13 | |
| Collateral with respect to derivatives exposure | | | | | | | | |
Collateral received 2) | | | 250 | | | | 270 | |
Collateral given 1) | | | — | | | | — | |
| | |
| 1) | | Book value |
| |
| 2) | | Fair value |
| | | |
(17) | | FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS |
| |
| (Amounts in EUR million) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | 2006 |
| | | Carrying | | Fair | | | | | | Carrying | | Fair | | |
| | | amount | | value | | Difference | | amount | | value | | Difference |
| |
Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash accounts with banks 1) | | | 4 | | | | 4 | | | | — | | | | 2 | | | | 2 | | | | — | |
Cash equivalents at fair value through profit or loss 2) | | | 3,286 | | | | 3,286 | | | | — | | | | 3,504 | | | | 3,504 | | | | — | |
Other cash and cash equivalents, held-to-maturity 2) | | | 1,203 | | | | 1,203 | | | | — | | | | 248 | | | | 248 | | | | — | |
| |
Cash and cash equivalents, total | | | 4,493 | | | | 4,493 | | | | — | | | | 3,753 | | | | 3,753 | | | | — | |
Placements with credit institutions 1) | | | 93 | | | | 93 | | | | — | | | | 91 | | | | 91 | | | | — | |
Debt securities at fair value through profit or loss, held for trading 2) | | | 373 | | | | 373 | | | | — | | | | 253 | | | | 253 | | | | — | |
Other debt securities, held-to-maturity 2) | | | 1,210 | | | | 1,181 | | | | -29 | | | | 1,164 | | | | 1,171 | | | | 7 | |
| |
Debt securities, total | | | 1,583 | | | | 1,554 | | | | -29 | | | | 1,416 | | | | 1,424 | | | | 7 | |
Other financial placements available for sale 2) | | | 7 | | | | 7 | | | | — | | | | 7 | | | | 7 | | | | — | |
Hedged loans outstanding in fair value hedging relationships 1) | | | 1,288 | | | | 1,288 | | | | — | | | | 1,250 | | | | 1,250 | | | | — | |
Loans outstanding, other 1) | | | 11,003 | | | | 11,007 | | | | 5 | | | | 10,284 | | | | 10,264 | | | | -21 | |
| |
Loans outstanding, total | | | 12,291 | | | | 12,296 | | | | 5 | | | | 11,534 | | | | 11,513 | | | | -21 | |
Hedging derivatives at fair value 1) | | | 1,032 | | | | 1,032 | | | | — | | | | 744 | | | | 744 | | | | — | |
Other derivatives at fair value 1) | | | 17 | | | | 17 | | | | — | | | | 7 | | | | 7 | | | | — | |
| |
Derivatives at fair value, total | | | 1,050 | | | | 1,050 | | | | — | | | | 751 | | | | 751 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | -24 | | | | | | | | | | | | -13 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Short-term amounts owed to credit institutions 1) | | | 454 | | | | 454 | | | | — | | | | 313 | | | | 313 | | | | — | |
Long-term amounts owed to credit institutions 1) | | | 92 | | | | 92 | | | | — | | | | 90 | | | | 90 | | | | — | |
Repurchase agreements 1) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 217 | | | | 217 | | | | — | |
Hedged debt securities issued in fair value hedging relationships 1) | | | 14,821 | | | | 14,821 | | | | — | | | | 13,351 | | | | 13,351 | | | | — | |
Other debt securities issued 1) | | | 9 | | | | 6 | | | | 3 | | | | 16 | | | | 12 | | | | 4 | |
| |
Debt securities issued, total | | | 14,830 | | | | 14,827 | | | | 3 | | | | 13,367 | | | | 13,364 | | | | 4 | |
Hedged other debt in fair value relationships 1) | | | 193 | | | | 193 | | | | — | | | | 254 | | | | 254 | | | | — | |
Hedging derivatives at fair value 1) | | | 663 | | | | 663 | | | | — | | | | 583 | | | | 583 | | | | — | |
Other derivatives at fair value 1) | | | 1,341 | | | | 1,341 | | | | — | | | | 832 | | | | 832 | | | | — | |
| |
Derivatives at fair value, total | | | 2,004 | | | | 2,004 | | | | — | | | | 1,415 | | | | 1,415 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | 3 | | | | | | | | | | | | 4 | |
| | | | | |
Net | | | | | | | | | | | -21 | | | | | | | | | | | | -10 | |
| |
| | |
| 1) | | The fair value is determined using valuation techniques with observable market inputs. |
| |
| 2) | | The fair value is determined according to market quotes. |
NIB Annual report 2007 30
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
| | | |
(18) | | MATURITY PROFILE |
| | | |
| | | The table set forth below presents assets and liabilities according to their remaining maturities, calculated from closing date to maturity date. The possibility of prepayments is taken into consideration regarding derivative contracts and borrowing transactions. Loans outstanding, however, are reported according to the latest possible repayment date. Those assets and liabilities that do not have a contractual maturity date, as well as all value adjustments, are recognised in the “Undefined” column. See also Notes 11 and 13 and Financial Guidelines and Risk Management, Market Risk, page 16. |
| | | |
| | | 2007 |
| |
| (Amounts in EUR million) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Over 3 | | Over 6 | | Over 1 | | Over 5 | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | months | | months | | year | | years | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | and up | | and up | | and up | | and up | | | | | | |
| | | Up to and | | to and | | to and | | to and | | to and | | | | | | |
| | | including | | including | | including | | including | | including | | Over | | | | |
| | | 3 months | | 6 months | | 1 year | | 5 years | | 10 years | | 10 years | | Undefined | | Total |
| |
Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 1,100 | | | | 317 | | | | 206 | | | | 2,316 | | | | 559 | | | | 68 | | | | -71 | | | | 4,493 | |
| Financial placements Placements with credit institutions | | | — | | | | — | | | | 34 | | | | 58 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2 | | | | 93 | |
| Investment securities | | | 123 | | | | 26 | | | | 58 | | | | 513 | | | | 562 | | | | 312 | | | | -11 | | | | 1,583 | |
| Other | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7 | | | | 7 | |
| | | |
| | | | 123 | | | | 26 | | | | 92 | | | | 571 | | | | 562 | | | | 312 | | | | -2 | | | | 1,683 | |
| Loans outstanding | | | 258 | | | | 246 | | | | 670 | | | | 5,359 | | | | 4,684 | | | | 1,110 | | | | -36 | | | | 12,291 | |
| Intangible assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7 | | | | 7 | |
| Tangible assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 37 | | | | 37 | |
| Other assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivatives | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Receivables | | | 813 | | | | 668 | | | | 541 | | | | 4,157 | | | | 2,030 | | | | 908 | | | | 303 | | | | 9,421 | |
| Payables | | | -772 | | | | -567 | | | | -514 | | | | -3,959 | | | | -1,773 | | | | -786 | | | | — | | | | -8,371 | |
| | | |
| | | | 42 | | | | 101 | | | | 27 | | | | 198 | | | | 258 | | | | 122 | | | | 303 | | | | 1,050 | |
| Other assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2 | | | | 2 | |
| Paid-in capital and payments to the Bank’s reserves, receivable | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 43 | | | | 43 | |
| Accrued interest and fees receivable | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 368 | | | | 368 | |
| |
Total assets | | | 1,522 | | | | 689 | | | | 994 | | | | 8,444 | | | | 6,062 | | | | 1,612 | | | | 650 | | | | 19,973 | |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities and equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amounts owed to credit institutions | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term | | | 454 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 454 | |
| Long-term | | | — | | | | — | | | | 34 | | | | 58 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 92 | |
| | | |
| | | | 454 | | | | — | | | | 34 | | | | 58 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 546 | |
| Repurchase agreements | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Debts evidenced by certificates | | | 1,107 | | | | 1,332 | | | | 838 | | | | 8,289 | | | | 2,427 | | | | 930 | | | | 99 | | | | 15,023 |
| Other liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivatives | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Receivables | | | -531 | | | | -1,235 | | | | -1,065 | | | | -8,816 | | | | -2,839 | | | | -608 | | | | 178 | | | | -14,916 | |
| Payables | | | 623 | | | | 1,434 | | | | 1,197 | | | | 9,668 | | | | 3,241 | | | | 754 | | | | — | | | | 16,916 | |
| | | |
| | | | 92 | | | | 199 | | | | 132 | | | | 851 | | | | 401 | | | | 146 | | | | 178 | | | | 1,999 | |
| Other liabilities | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 4 | | | | 4 | |
| Accrued interest and fees payable | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 363 | | | | 363 | |
| |
Total liabilities | | | 1,654 | | | | 1,532 | | | | 1,004 | | | | 9,198 | | | | 2,828 | | | | 1,076 | | | | 645 | | | | 17,936 | |
| |
Equity | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,037 | | | | 2,037 | |
| |
Total liabilities and equity | | | 1,654 | | | | 1,532 | | | | 1,004 | | | | 9,198 | | | | 2,828 | | | | 1,076 | | | | 2,682 | | | | 19,973 | |
| |
| |
| Net during the period | | | -132 | | | | -843 | | | | -10 | | | | -754 | | | | 3,234 | | | | 536 | | | | -2,031 | | | | — | |
| Cumulative net during the period | | | -132 | | | | -974 | | | | -984 | | | | -1,738 | | | | 1,495 | | | | 2,031 | | | | — | | | | — | |
31 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
2006
(Amounts in EUR million)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Over 3 | | Over 6 | | Over 1 | | Over 5 | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | months | | months | | year | | years | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | and up | | and up | | and up | | and up | | | | | | |
| | | Up to and | | to and | | to and | | to and | | to and | | | | | | |
| | | including | | including | | including | | including | | including | | Over | | | | |
| | | 3 months | | 6 months | | 1 year | | 5 years | | 10 years | | 10 years | | Undefined | | Total |
| |
Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 280 | | | | 5 | | | | 13 | | | | 2,671 | | | | 715 | | | | 69 | | | | — | | | | 3,753 | |
| Financial placements | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Placements with credit institutions | | | 22 | | | | 29 | | | | 38 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2 | | | | 91 | |
| Investment securities | | | 71 | | | | 45 | | | | — | | | | 565 | | | | 441 | | | | 298 | | | | -4 | | | | 1,416 | |
| Other | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7 | | | | 7 | |
| | | |
| | | | 93 | | | | 74 | | | | 38 | | | | 565 | | | | 441 | | | | 298 | | | | 5 | | | | 1,515 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans outstanding | | | 232 | | | | 311 | | | | 524 | | | | 5,138 | | | | 4,206 | | | | 1,138 | | | | -15 | | | | 11,534 | |
| Intangible assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7 | | | | 7 | |
| Tangible assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 36 | | | | 36 | |
| Other assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivatives | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Receivables | | | 557 | | | | 401 | | | | 356 | | | | 3,312 | | | | 1,540 | | | | 800 | | | | 226 | | | | 7,192 | |
| Payables | | | -533 | | | | -381 | | | | -337 | | | | -3,161 | | | | -1,344 | | | | -684 | | | | — | | | | -6,441 | |
| | | |
| | | | 24 | | | | 19 | | | | 19 | | | | 150 | | | | 196 | | | | 117 | | | | 226 | | | | 751 | |
| Other assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 12 | | | | 12 | |
| Paid-in capital and payments to the Bank’s reserves, receivable | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 47 | | | | 47 | |
| Accrued interest and fees receivable | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 332 | | | | 332 | |
| |
Total assets | | | 630 | | | | 410 | | | | 594 | | | | 8,524 | | | | 5,558 | | | | 1,622 | | | | 651 | | | | 17,988 | |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities and equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amounts owed to credit institutions | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term | | | 308 | | | | 5 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 313 | |
| Long-term | | | 23 | | | | 29 | | | | 39 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 90 | |
| | | |
| | | | 330 | | | | 34 | | | | 39 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 403 | |
| Repurchase agreements | | | 217 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 217 | |
| Debts evidenced by certificates | | | 1,197 | | | | 447 | | | | 874 | | | | 8,380 | | | | 1,675 | | | | 1,083 | | | | -34 | | | | 13,622 | |
| Other liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivatives | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Receivables | | | -705 | | | | -247 | | | | -618 | | | | -9,777 | | | | -1,874 | | | | -848 | | | | 239 | | | | -13,830 | |
| Payables | | | 762 | | | | 334 | | | | 635 | | | | 10,428 | | | | 2,126 | | | | 960 | | | | — | | | | 15,245 | |
| | | |
| | | | 57 | | | | 88 | | | | 17 | | | | 651 | | | | 252 | | | | 112 | | | | 239 | | | | 1,415 | |
| Other liabilities | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 4 | | | | 4 | |
| Accrued interest and fees payable | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 306 | | | | 306 | |
| |
Total liabilities | | | 1,800 | | | | 569 | | | | 929 | | | | 9,031 | | | | 1,927 | | | | 1,196 | | | | 515 | | | | 15,967 | |
| |
Equity | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,021 | | | | 2,021 | |
| |
Total liabilities and equity | | | 1,800 | | | | 569 | | | | 929 | | | | 9,031 | | | | 1,927 | | | | 1,196 | | | | 2,536 | | | | 17,988 | |
| |
| |
| Net during the period | | | -1,170 | | | | -159 | | | | -336 | | | | -507 | | | | 3,631 | | | | 426 | | | | -1,885 | | | | — | |
| Cumulative net during the period | | | -1,170 | | | | -1,329 | | | | -1,665 | | | | -2,172 | | | | 1,459 | | | | 1,885 | | | | — | | | | — | |
NIB Annual Report 2007 32
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
| (19) | | INTEREST RATE RISK |
| |
| | | Interest rate risk is the impact that fluctuations in market interest rates can have on the value of the Bank’s interest-bearing assets and liabilities and on the interest income recognised in the income statement. The table below provides information on the extent of the Bank’s interest rate exposure. The assets and liabilities are grouped into buckets defined by their time to maturity or the date of the interest rate adjustment. The difference, or gap, between assets and liabilities in each time bucket makes the Bank sensitive to interest rate fluctuations. See also Financial Guidelines and Risk Management, Market Risk, page 16. |
| |
| | | 2007 |
| |
| (Amounts in EUR million) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Over 3 | | | Over 6 | | | Over 1 | | | Over 5 | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | months | | | months | | | year | | | years | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | and up | | | and up | | | and up | | | and up | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Up to and | | | to and | | | to and | | | to and | | | to and | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | including | | | including | | | including | | | including | | | including | | | Over | | | | | | | |
| | | 3 months | | | 6 months | | | 1 year | | | 5 years | | | 10 years | | | 10 years | | | Undefined | | | Total | |
| |
Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 4,297 | | | | 268 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | -71 | | | | 4,493 | |
| Financial placements | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Placements with credit institutions | | | — | | | | — | | | | 34 | | | | 58 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2 | | | | 93 | |
| Investment securities | | | 123 | | | | 26 | | | | 58 | | | | 513 | | | | 562 | | | | 312 | | | | -11 | | | | 1,583 | |
| Other | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7 | | | | 7 | |
| | | |
| | | | 123 | | | | 26 | | | | 92 | | | | 571 | | | | 562 | | | | 312 | | | | -2 | | | | 1,683 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans outstanding | | | 4,292 | | | | 6,690 | | | | 190 | | | | 516 | | | | 494 | | | | 145 | | | | -36 | | | | 12,291 | |
| Intangible assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7 | | | | 7 | |
| Tangible assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 37 | | | | 37 | |
| Other assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivatives | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Receivables 1) | | | 6,130 | | | | 6,621 | | | | 781 | | | | 7,886 | | | | 2,246 | | | | 549 | | | | 303 | | | | 24,515 | |
| Other assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2 | | | | 2 | |
| Paid-in capital and payments to the Bank’s reserves, receivable | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 43 | | | | 43 | |
| Accrued interest and fees receivable | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 368 | | | | 368 | |
| |
Total assets | | | 14,841 | | | | 13,604 | | | | 1,063 | | | | 8,972 | | | | 3,302 | | | | 1,006 | | | | 650 | | | | 43,438 | 1) |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities and equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amounts owed to credit institutions | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term | | | 454 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 454 | |
| Long-term | | | — | | | | — | | | | 34 | | | | 58 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 92 | |
| | | |
| | | | 454 | | | | — | | | | 34 | | | | 58 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 546 | |
| Repurchase agreements | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Debts evidenced by certificates | | | 1,885 | | | | 1,695 | | | | 781 | | | | 7,772 | | | | 2,248 | | | | 544 | | | | 99 | | | | 15,023 | |
| Other liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivatives | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Payables 1) | | | 12,394 | | | | 11,586 | | | | 110 | | | | 530 | | | | 500 | | | | 168 | | | | 178 | | | | 25,465 | |
| Other liabilities | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 4 | | | | 4 | |
| Accrued interest and fees payable | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 363 | | | | 363 | |
| |
Total liabilities | | | 14,733 | | | | 13,281 | | | | 925 | | | | 8,360 | | | | 2,748 | | | | 711 | | | | 645 | | | | 41,402 | |
| |
Equity | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,037 | | | | 2,037 | |
| |
Total liabilities and equity | | | 14,733 | | | | 13,281 | | | | 925 | | | | 8,360 | | | | 2,748 | | | | 711 | | | | 2,682 | | | | 43,438 | 1) |
| |
| |
| Net during the period | | | 109 | | | | 323 | | | | 138 | | | | 612 | | | | 554 | | | | 295 | | | | -2,031 | | | | — | |
| Cumulative net during the period | | | 109 | | | | 432 | | | | 570 | | | | 1,182 | | | | 1,736 | | | | 2,031 | | | | — | | | | — | |
33 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
2006
(Amounts in EUR million)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Over 3 | | | Over 6 | | | Over 1 | | | Over 5 | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | months | | | months | | | year | | | years | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | and up | | | and up | | | and up | | | and up | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Up to and | | | to and | | | to and | | | to and | | | to and | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | including | | | including | | | including | | | including | | | including | | | Over | | | | | | | |
| | | 3 months | | | 6 months | | | 1 year | | | 5 years | | | 10 years | | | 10 years | | | Undefined | | | Total | |
| |
Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 3,708 | | | | 45 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 3,753 | |
| Financial placements | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Placements with credit institutions | | | 22 | | | | 29 | | | | 38 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2 | | | | 91 | |
| Investment securities | | | 71 | | | | 45 | | | | — | | | | 565 | | | | 441 | | | | 298 | | | | -4 | | | | 1,416 | |
| Other | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7 | | | | 7 | |
| | | |
| | | | 93 | | | | 74 | | | | 38 | | | | 565 | | | | 441 | | | | 298 | | | | 5 | | | | 1,515 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans outstanding | | | 3,958 | | | | 6,328 | | | | 155 | | | | 538 | | | | 429 | | | | 141 | | | | -15 | | | | 11,534 | |
| Intangible assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7 | | | | 7 | |
| Tangible assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 36 | | | | 36 | |
| Other assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivatives | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Receivables 1) | | | 4,524 | | | | 5,712 | | | | 880 | | | | 7,805 | | | | 1,499 | | | | 616 | | | | 226 | | | | 21,261 | |
| Other assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 12 | | | | 12 | |
| Paid-in capital and payments to the Bank’s reserves, receivable | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 47 | | | | 47 | |
| Accrued interest and fees receivable | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 332 | | | | 332 | |
| |
Total assets | | | 12,284 | | | | 12,159 | | | | 1,073 | | | | 8,907 | | | | 2,369 | | | | 1,055 | | | | 651 | | | | 38,498 | 1) |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities and equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amounts owed to credit institutions | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term | | | 308 | | | | 5 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 313 | |
| Long-term | | | 23 | | | | 29 | | | | 39 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 90 | |
| | | |
| | | | 330 | | | | 34 | | | | 39 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 403 | |
| Repurchase agreements | | | 217 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 217 | |
| Debts evidenced by certificates | | | 2,010 | | | | 937 | | | | 893 | | | | 7,700 | | | | 1,500 | | | | 615 | | | | -34 | | | | 13,622 | |
| Other liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivatives | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Payables 1) | | | 9,317 | | | | 11,098 | | | | 78 | | | | 627 | | | | 426 | | | | 140 | | | | 239 | | | | 21,925 | |
| Other liabilities | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 4 | | | | 4 | |
| Accrued interest and fees payable | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 306 | | | | 306 | |
| |
Total liabilities | | | 11,875 | | | | 12,069 | | | | 1,010 | | | | 8,327 | | | | 1,926 | | | | 755 | | | | 515 | | | | 36,477 | |
| |
Equity | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,021 | | | | 2,021 | |
| |
Total liabilities and equity | | | 11,875 | | | | 12,069 | | | | 1,010 | | | | 8,327 | | | | 1,926 | | | | 755 | | | | 2,536 | | | | 38,498 | 1) |
| |
| |
| Net during the period | | | 409 | | | | 89 | | | | 63 | | | | 580 | | | | 443 | | | | 300 | | | | -1,885 | | | | — | |
| Cumulative net during the period | | | 409 | | | | 498 | | | | 562 | | | | 1,142 | | | | 1,585 | | | | 1,885 | | | | — | | | | — | |
NIB Annual Report 2007 34
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
| (20) | | CURRENCY RISK |
| |
| | | NIB’s operations are mostly in euros and US dollars. The table below shows the net currency positions of the major currencies. The net currency positions show how sensitive NIB is to the currency risk. See also Financial Guidelines and Risk Management, Market Risk, page 16.
|
| |
| | | Net currency position as of 31 December 2007 is as follows: |
| |
| (Amounts in EUR million) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Fair value | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | adjust- | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Other | | | ments | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | curren- | | | and swap | | | | |
| | | EUR | | | USD | | | GBP | | | JPY | | | SEK | | | cies | | | netting | | | Total | |
| |
Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 2,844 | | | | 1,586 | | | | 21 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 42 | | | | — | | | | 4,493 | |
| Financial placements | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Placements with credit institutions | | | 93 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 93 | |
| Debt securities | | | 1,582 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | 1,583 | |
| Other financial placements | | | 7 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7 | |
| | | |
| | | | 1,682 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | 1,683 | |
| Loans outstanding | | | 6,316 | | | | 2,420 | | | | 6 | | | | 49 | | | | 1,907 | | | | 1,629 | | | | -36 | | | | 12,291 | |
| Intangible assets | | | 7 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7 | |
| Tangible assets | | | 37 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 37 | |
| Other assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivatives | | | -7,760 | | | | 2,969 | | | | 2,005 | | | | 1,512 | | | | -1,856 | | | | 2,153 | | | | 2,026 | | | | 1,050 | |
| Other assets | | | 2 | | | | — | | | | 4 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | -5 | | | | 2 | |
| | | |
| | | | -7,758 | | | | 2,969 | | | | 2,009 | | | | 1,512 | | | | -1,856 | | | | 2,153 | | | | 2,021 | | | | 1,051 | |
| Paid-in capital and payments to the | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Bank’s reserves, receivable | | | 43 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 43 | |
| Accrued interest and fees receivable | | | 156 | | | | 232 | | | | 41 | | | | 36 | | | | 19 | | | | 108 | | | | -223 | | | | 368 | |
| |
Total assets | | | 3,325 | | | | 7,206 | | | | 2,078 | | | | 1,597 | | | | 71 | | | | 3,933 | �� | | | 1,763 | | | | 19,973 | |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities and equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amounts owed to credit institutions | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term amounts owed to credit institutions | | | 399 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 14 | | | | — | | | | 42 | | | | — | | | | 454 | |
| Long-term amounts owed to credit institutions | | | 92 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 92 | |
| | | |
| | | | 491 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 14 | | | | — | | | | 42 | | | | — | | | | 546 | |
| Repurchase agreements | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Debts evidenced by certificates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Debt securities issued | | | 641 | | | | 6,794 | | | | 2,026 | | | | 1,456 | | | | 53 | | | | 3,760 | | | | 100 | | | | 14,830 | |
| Other debt | | | 35 | | | | 68 | | | | — | | | | 91 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | -1 | | | | 193 | |
| | | |
| | | | 676 | | | | 6,862 | | | | 2,026 | | | | 1,547 | | | | 53 | | | | 3,760 | | | | 99 | | | | 15,023 | |
| Other liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivatives | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,999 | | | | 1,999 | |
| Other liabilities | | | 8 | | | | 72 | | | | 10 | | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | 17 | | | | -103 | | | | 4 | |
| | | |
| | | | 8 | | | | 72 | | | | 10 | | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | 17 | | | | 1,896 | | | | 2,004 | |
| Accrued interest and fees payable | | | 116 | | | | 269 | | | | 42 | | | | 36 | | | | 16 | | | | 107 | | | | -223 | | | | 363 | |
| |
Total liabilities | | | 1,290 | | | | 7,203 | | | | 2,078 | | | | 1,597 | | | | 69 | | | | 3,926 | | | | 1,772 | | | | 17,936 | |
| |
Equity | | | 1,967 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2 | | | | 1,968 | |
| |
Total liabilities and equity | | | 3,257 | | | | 7,203 | | | | 2,078 | | | | 1,597 | | | | 69 | | | | 3,926 | | | | 1,774 | | | | 19,905 | |
| |
| |
| Currency position as of 31 Dec 2007 | | | 68 | | | | 3 | | | | -1 | | | | — | | | | 1 | | | | 7 | | | | -11 | | | | 69 | |
35 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
Net currency position as of 31 December 2006:
(Amounts in EUR million)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Fair value | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | adjust- | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Other | | | ments | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | curren- | | | and swap | | | | |
| | | EUR | | | USD | | | GBP | | | JPY | | | SEK | | | cies | | | netting | | | Total | |
| |
Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 2,810 | | | | 841 | | | | 13 | | | | 5 | | | | 34 | | | | 51 | | | | — | | | | 3,753 | |
| Financial placements | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Placements with credit institutions | | | 87 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 5 | | | | — | | | | 91 | |
| Debt securities | | | 1,415 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | 1,416 | |
| Other | | | 7 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7 | |
| | | |
| | | | 1,509 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 6 | | | | — | | | | 1,515 | |
| Loans outstanding | | | 5,706 | | | | 2,639 | | | | 7 | | | | 36 | | | | 1,785 | | | | 1,377 | | | | -15 | | | | 11,534 | |
| Intangible assets | | | 7 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7 | |
| Tangible assets | | | 36 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 36 | |
| Other assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivatives | | | -6,845 | | | | 2,363 | | | | 1,944 | | | | 1,466 | | | | -1,570 | | | | 2,099 | | | | 1,294 | | | | 751 | |
| Other assets | | | 12 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 11 | | | | -11 | | | | 12 | |
| | | |
| | | | -6,833 | | | | 2,363 | | | | 1,944 | | | | 1,466 | | | | -1,570 | | | | 2,111 | | | | 1,283 | | | | 763 | |
| Paid-in capital and payments to the Bank’s reserves, receivable | | | 47 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 47 | |
| Accrued interest and fees receivable | | | 127 | | | | 193 | | | | 58 | | | | 41 | | | | 17 | | | | 72 | | | | -175 | | | | 332 | |
| |
Total assets | | | 3,409 | | | | 6,035 | | | | 2,022 | | | | 1,548 | | | | 266 | | | | 3,616 | | | | 1,093 | | | | 17,988 | |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities and equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amounts owed to credit institutions | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term amounts owed to credit institutions | | | 216 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 23 | | | | 74 | | | | — | | | | 313 | |
| Long-term amounts owed to credit institutions | | | 85 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 5 | | | | — | | | | 90 | |
| | | |
| | | | 301 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 23 | | | | 79 | | | | — | | | | 403 | |
| Repurchase agreements | | | 217 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 217 | |
| Debts evidenced by certificates | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Debt securities issued | | | 743 | | | | 5,660 | | | | 1,961 | | | | 1,366 | | | | 227 | | | | 3,448 | | | | -38 | | | | 13,367 | |
| Other debt | | | 35 | | | | 76 | | | | — | | | | 140 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 3 | | | | 254 | |
| | | |
| | | | 778 | | | | 5,736 | | | | 1,961 | | | | 1,507 | | | | 227 | | | | 3,448 | | | | -34 | | | | 13,622 | |
| Other liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivatives | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,415 | | | | 1,415 | |
| Other liabilities | | | 8 | | | | 88 | | | | 13 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 15 | | | | -120 | | | | 4 | |
| | | |
| | | | 8 | | | | 88 | | | | 13 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 15 | | | | 1,296 | | | | 1,420 | |
| Accrued interest and fees payable | | | 93 | | | | 211 | | | | 48 | | | | 41 | | | | 16 | | | | 74 | | | | -175 | | | | 306 | |
| |
Total liabilities | | | 1,397 | | | | 6,035 | | | | 2,021 | | | | 1,547 | | | | 265 | | | | 3,616 | | | | 1,086 | | | | 15,967 | |
| |
Equity | | | 1,880 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 3 | | | | 1,883 | |
| |
Total liabilities and equity | | | 3,277 | | | | 6,035 | | | | 2,021 | | | | 1,547 | | | | 265 | | | | 3,616 | | | | 1,089 | | | | 17,851 | |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Currency position as of
31 Dec 2006 | | | 132 | | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | 4 | | | | 137 | |
NIB Annual Report 2007 36
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
| (21) | | AVERAGE BALANCE SHEET |
(Amounts in EUR million)
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Assets | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 4,168 | | | | 3,697 | |
| Financial placements | | | | | | | | |
| Placements with credit institutions | | | 94 | | | | 103 | |
| Debt securities | | | 1,519 | | | | 1,358 | |
| Other | | | 8 | | | | 7 | |
| |
| | | | 1,621 | | | | 1,468 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Loans outstanding | | | 11,920 | | | | 11,520 | |
| Intangible assets | | | 7 | | | | 7 | |
| Tangible assets | | | 37 | | | | 35 | |
| Other assets | | | | | | | | |
| Derivatives | | | 832 | | | | 983 | |
| Other assets | | | 4 | | | | 4 | |
| |
| | | | 836 | | | | 987 | |
| |
| Paid-in capital and payments to the Bank’s reserves, receivable | | | 44 | | | | 49 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Accrued interest and fees receivable | | | 345 | | | | 326 | |
| |
Total assets | | | 18,977 | | | | 18,089 | |
| |
| | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities and equity | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | |
| Amounts owed to credit institutions | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term amounts owed to credit institutions | | | 333 | | | | 372 | |
| Long-term amounts owed to credit institutions | | | 93 | | | | 99 | |
| |
| | | | 426 | | | | 471 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Repurchase agreements | | | 205 | | | | 228 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Debts evidenced by certificates | | | | | | | | |
| Debt securities issued | | | 14,129 | | | | 13,804 | |
| Other debt | | | 210 | | | | 244 | |
| |
| | | | 14,339 | | | | 14,048 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Other liabilities | | | | | | | | |
| Derivatives | | | 1,637 | | | | 1,064 | |
| Other liabilities (incl. exchange rate adjustments) | | | 6 | | | | 7 | |
| |
| | | | 1,643 | | | | 1,071 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Accrued interest and fees payable | | | 312 | | | | 289 | |
| |
Total liabilities | | | 16,926 | | | | 16,108 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Equity | | | 2,051 | | | | 1,981 | |
| |
Total liabilities and equity | | | 18,977 | | | | 18,089 | |
| |
The average balance sheet is calculated on a monthly basis.
37 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
| (22) | | RELATED PARTY DISCLOSURES |
The Bank provides services to and enters into transactions with the Nordic Development Fund (NDF) and the Nordic Environment Finance Corporation (NEFCO), which have for the most part the same owners as NIB. The following table shows the outstanding balance of amounts owed to NDF and NEFCO and the interest paid during the year. The interest paid to these institutions is at normal commercial rates. Information regarding key personnel is presented in Note 5.
(Amounts in EUR 1,000)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Amounts owed by | | | Amounts owed to | |
| | | Interest from | | | Interest to | | | related parties | | | related parties | |
| | | related parties | | | related parties | | | as of 31 Dec | | | as of 31 Dec | |
2007 | | | — | | | | 6,101 | | | | 228 | | | | 145,758 | |
| 2006 | | | — | | | | 4,830 | | | | 324 | | | | 152,430 | |
Rental income (NDF, NEFCO)
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | NDF | | | NEFCO | |
2007 | | | 55 | | | | 90 | |
| 2006 | | | 120 | | | | 88 | |
(Amounts in EUR 1,000)
Specification of the change in net liquidity on 31 December:
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Cash and balances with banks 1) | | | 13,077 | | | | 7,802 | |
| Short-term placements with credit institutions | | | 1,187,733 | | | | 257,355 | |
| Liquid debt securities at floating interest rates | | | 3,292,475 | | | | 3,488,287 | |
| |
Cash and cash equivalents | | | 4,493,285 | | | | 3,753,444 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Short-term amounts owed to credit institutions | | | -454,498 | | | | -313,025 | |
| Short-term repurchase agreements | | | | | | | -216,739 | |
| |
Net liquidity | | | 4,038,786 | | | | 3,223,680 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Change in net liquidity | | | 815,106 | | | | 123,104 | |
| | |
| 1) | | Including EUR 2,176 thousand (378) initial margin requirement for futures on 31 December. |
NIB Annual Report 2007 38
Financial report: Notes to the financial statements
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | EUR rate on | | EUR rate on |
| | | | | | | 31 Dec 2007 | | 29 Dec 2006 |
| |
| DKK | | Danish Krone | | | 7.4583 | | | | 7.456 | |
| EEK | | Estonian Kroon | | | 15.6466 | 1) | | | 15.6466 | 1) |
| ISK | | Icelandic Króna | | | 91.90 | | | | 93.13 | |
| LVL | | Latvian Lats | | | 0.6964 | | | | 0.6972 | |
| NOK | | Norwegian Krone | | | 7.958 | | | | 8.238 | |
| SEK | | Swedish Krona | | | 9.4415 | | | | 9.0404 | |
| AUD | | Australian Dollar | | | 1.6757 | | | | 1.6691 | |
| CAD | | Canadian Dollar | | | 1.4449 | | | | 1.5281 | |
| CHF | | Swiss Franc | | | 1.6547 | | | | 1.6069 | |
| CZK | | Czech Koruna | | | 26.628 | | | | 27.485 | |
| GBP | | Pound Sterling | | | 0.73335 | | | | 0.6715 | |
| HKD | | Hong Kong Dollar | | | 11.4800 | | | | 10.2409 | |
| JPY | | Japanese Yen | | | 164.93 | | | | 156.93 | |
| MXN | | Mexican Peso | | | 16.0778 | 2) | | | 14.291 | 3) |
| NZD | | New Zealand Dollar | | | 1.9024 | | | | 1.8725 | |
| PLN | | Polish Zloty | | | 3.5935 | | | | 3.831 | |
| RUB | | Russian Rouble | | | 35.986 | | | | 34.68 | |
| SDR | | Special Drawing Right | | | 0.931563 | 2) | | | 0.87543 | 3) |
| SGD | | Singapore Dollar | | | 2.1163 | | | | 2.0202 | |
| SKK | | Slovak Koruna | | | 33.583 | | | | 34.435 | |
| TRY | | New Turkish Lira | | | 1.717 | | | | 1.864 | |
| TWD | | New Taiwan Dollar | | | 47.73431 | 2) | | | 42.83543 | 3) |
| USD | | United States Dollar | | | 1.4721 | | | | 1.317 | |
| ZAR | | South African Rand | | | 10.0298 | | | | 9.2124 | |
| | |
| 1) | | Fixed exchange rate in Currency Board arrangement with regard to the euro. |
| |
| 2) | | The exchange rate is calculated by using the market rate for USD/relevant currency, as of 31 December 2007, which then provides the EUR/relevant currency rate. |
| |
| 3) | | The exchange rate is calculated by using the market rate for USD/relevant currency, as of 29 December 2006, which then provides the EUR/relevant currency rate. |
| (25) | | POST-BALANCE SHEET EVENTS |
There have been no material post-balance sheet events that would require disclosure or adjustment to these financial statements. On 6 March 2008, the Board of Directors reviewed and signed the financial statements. These financial statements will be submitted for approval to the Annual Meeting of the Board of Governors to be held on 9 April 2008.
39 NIB Annual Report 2007
Financial report
Auditors’ reports
Independent Auditors’ Report
To the Control Committee of the Nordic Investment Bank
In our capacity as auditors appointed by the Control Committee of the Nordic Investment Bank we have audited the accompanying Financial Statements of the Bank, which comprise the balance sheet as at December 31, 2007, and the income statement, statement of changes in equity and cash flow statement for the year then ended, and a summary of significant accounting policies and other explanatory notes.
The Board of Directors’ and the President’s Responsibility for the Financial Statements
The Board of Directors and the President are responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of these financial statements in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards. This responsibility includes: designing, implementing and maintaining internal control relevant to the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error; selecting and applying appropriate accounting policies; and making accounting estimates that are reasonable in the circumstances.
Auditor’s Responsibility
Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit. We conducted our audit in accordance with International Standards on Auditing. Those standards require that we comply with ethical requirements and plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance whether the financial statements are free from material misstatement.
An audit involves performing procedures to obtain audit evidence about the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. The procedures selected depend on the auditor’s judgment, including the assessment of the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to fraud or error. In making those risk assessments, the auditor considers internal control relevant to the entity’s preparation and fair presentation of the financial statements in order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the entity’s internal control. An audit also includes evaluating the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonableness of accounting estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements.
We believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our audit opinion.
Opinion
In our opinion the Financial Statements give a true and fair view of the financial position of the Nordic Investment Bank as of 31 December 2007, and of its financial performance and its cash flows for the year then ended in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
Report on Other Requirements
Our audit also included a review of whether the Board of Directors’ and the President’s administration have complied with the Statutes of the Bank. It is also our opinion that the administration of the Board of Directors and the President complied with the Statutes of the Bank.
Helsinki, 7 March 2008
Per-Olof Johansson
Authorised Public Accountant
Ernst & Young, Helsinki
Erik Mamelund
State Authorised Public Accountant
Ernst & Young, Oslo
Statement by the Control Committee of the Nordic Investment Bank on the audit of the administration and accounts of the Bank
To the Board of Governors of the Nordic Investment Bank
In accordance with section 17 of the Statutes of the Nordic Investment Bank we have been appointed to control the operations of the Bank and to be responsible for the auditing of the Bank’s accounts. After having completed our assignment for the year 2007, we hereby submit the following report.
The Control Committee met during the fiscal year as well as after the Bank’s Financial Statements had been prepared. Control and examination measures considered necessary were then performed. The Annual Report of the Bank was examined at a meeting in Helsinki on 7 March 2008. In carrying out its tasks, the Control Committee received such information and carried out such examination measures as it deemed necessary to assess the Bank’s position in regard to its risks. We have also received the Independent Auditors’ Report, submitted on 7 March 2008 by the authorised public accountants appointed by the Control Committee.
Following our audit, we note that:
| | | The Bank’s operations during the financial year have been conducted in accordance with the Statutes, and that |
| |
| | | The Financial Statements give a true and fair view of the financial position of the Bank as at 31 December 2007 and of its results and financing in 2007. The Income statement shows a profit of EUR 68,719,366.55 for the financial period. |
NIB Annual Report 2007 40
We recommend to the Board of Governors that:
| | | The appropriation of the Bank’s profits for the financial period, as proposed by the Board of Directors, be approved; |
| |
| | | The Income statement and the Balance Sheet be adopted; |
| |
| | | The proposal by the Board of Directors regarding distribution of dividends to the Bank’s owners be approved; and |
| |
| | | The Board of Directors and the President be discharged from liability for the administration of the Bank’s operations during the accounting period examined by us. |
Helsinki, 7 March 2008
Alexander G. Eðvardsson
Meelis Atonen
Sigita Burbienė
Trond Helleland
Per Kaalund
Johan Linander
Darius Matusevičius
Steingrímur J. Sigfússon
Tuula Peltonen
Viesturs Silenieks
41 NIB Annual Report 2007