United States Securities and Exchange Commission
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One) |
☑ Annual Report Pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 |
| For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016 |
or |
☐ Transition Report pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 |
| For the transition period from ___________to ___________ |
| Commission file number 001-00035 |
 |
General Electric Company (Exact name of registrant as specified in charter) |
| New York | 14-0689340 | |||
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |||
| 41 Farnsworth Street, Boston, MA | 02210 | (617) 443-3000 | ||
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | (Telephone No.) | ||
| Securities Registered Pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: | ||||
| Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |||
| Common stock, par value $0.06 per share | New York Stock Exchange | |||
| Securities Registered Pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: |
| (Title of class) |
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☑
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10‑K. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer" and "smaller reporting company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
Large accelerated filer ☑ | Accelerated filer ☐ |
Non-accelerated filer ☐ | Smaller reporting company ☐ |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☑
The aggregate market value of the outstanding common equity of the registrant not held by affiliates as of the last business day of the registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter was at least $279.3 billion. There were 8,724,783,000 shares of voting common stock with a par value of $0.06 outstanding at January 31, 2017.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
The definitive proxy statement relating to the registrant's Annual Meeting of Shareowners, to be held April 26, 2017, is incorporated by reference into Part III to the extent described therein.

GE 2016 FORM 10-K 2

GE 2016 FORM 10-K 3
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 4
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 5
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 6

GE 2016 FORM 10-K 7
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 8
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 10
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 11
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 13
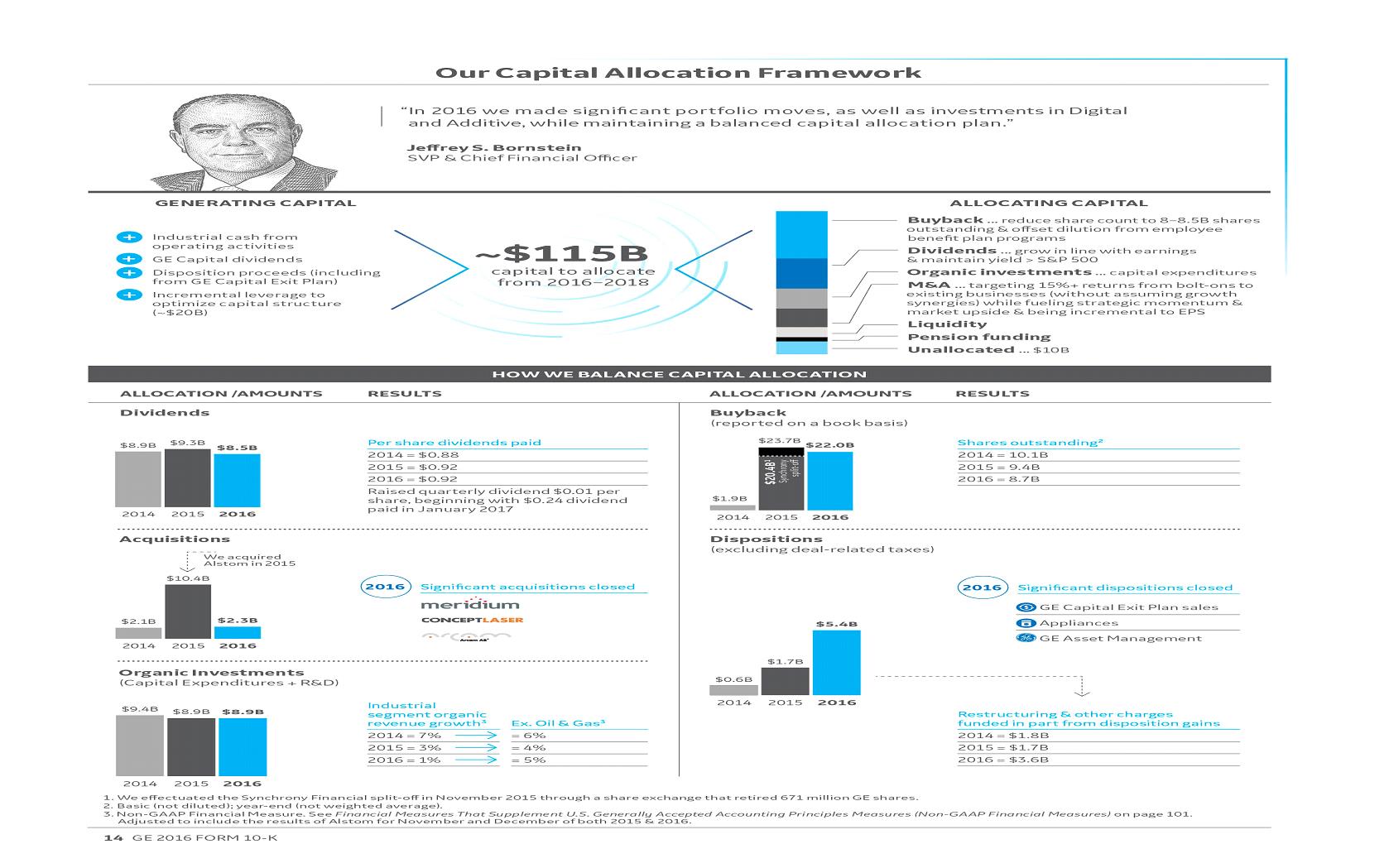
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 15
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 16
FORWARD LOOKING STATEMENTS
This document contains "forward-looking statements" – that is, statements related to future, not past, events. In this context, forward-looking statements often address our expected future business and financial performance and financial condition, and often contain words such as "expect," "anticipate," "intend," "plan," "believe," "seek," "see," "will," "would," "estimate," "forecast" or "target."
Forward-looking statements by their nature address matters that are, to different degrees, uncertain, such as statements about our announced plan to combine our Oil & Gas business with Baker Hughes, including projected revenue and cost synergies, impact on our earnings per share, and the timing and structure of the proposed transaction; the completion of our announced plan to reduce the size of our financial services businesses, including expected cash and non-cash charges associated with this plan and earnings per share of GE Capital's retained businesses (Verticals); expected income; earnings per share, including our 2018 target; revenues; organic growth; growth and productivity associated with our Digital business; margins; cost structure and plans to reduce costs; restructuring charges; transaction-related synergies and gains; cash flows, including the impact of pension funding contributions; returns on capital and investment; capital expenditures; capital allocation, including dividends, share repurchases and acquisitions; or capital structure, including leverage.
For us, particular uncertainties that could cause our actual results to be materially different than those expressed in our forward-looking statements include:
| · | our ability to complete incremental asset sales as we complete our announced plan to reduce the size of our financial services businesses and our ability to reduce costs as we execute that plan; |
| · | changes in law, economic and financial conditions, including interest and exchange rate volatility, commodity and equity prices and the value of financial assets; |
| · | the impact of conditions in the financial and credit markets on the availability and cost of GE Capital Global Holdings, LLC's (GE Capital) funding, and GE Capital's exposure to counterparties; |
| · | pending and future mortgage loan repurchase claims and other litigation claims and investigations in connection with WMC, which may affect our estimates of liability, including possible loss estimates; |
| · | our ability to maintain our current credit rating and the impact on our funding costs and competitive position if we do not do so; |
| · | the amount and timing of our cash flows and earnings and other conditions, which may affect our ability to pay our quarterly dividend at the planned level or to repurchase shares at planned levels; |
| · | GE Capital's ability to pay dividends to GE at the planned level, which may be affected by GE Capital's cash flows and earnings, financial services regulation and oversight, claims and investigations relating to WMC and other factors; |
| · | our ability to launch new products in a cost-effective manner; |
| · | our ability to increase margins through restructuring and other cost reduction measures; |
| · | our ability to convert pre-order commitments/wins into orders/bookings; |
| · | the price we realize on orders/bookings since commitments/wins are stated at list prices; |
| · | customer actions or developments such as early aircraft retirements or reduced energy demand, changes in economic conditions, including oil prices, and other factors that may affect the level of demand and financial performance of the major industries and customers we serve; |
| · | the impact of regulation and regulatory, investigative and legal proceedings and legal compliance risks, including the impact of Alstom investigative and legal proceedings; |
| · | our capital allocation plans, as such plans may change including with respect to the timing and size of share repurchases, acquisitions, joint ventures, dispositions and other strategic actions; |
| · | our success in completing, including obtaining regulatory approvals and satisfying other closing conditions for, announced transactions, such as our announced plans and transactions to combine our Oil & Gas business with Baker Hughes, to reduce the size of our financial services businesses, and to acquire LM Wind Power; |
| · | our success in integrating acquired businesses and operating joint ventures, including Baker Hughes; |
| · | our ability to realize revenue and cost synergies from announced transactions, acquired businesses and joint ventures, including Alstom and Baker Hughes; |
| · | the impact of potential information technology or data security breaches; and |
| · | the other factors that are described in the Risk Factors section of this Form 10-K report. |
These or other uncertainties may cause our actual future results to be materially different than those expressed in our forward-looking statements. We do not undertake to update our forward-looking statements. This document includes certain forward-looking projected financial information that is based on current estimates and forecasts. Actual results could differ materially.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 17
 | ABOUT GENERAL ELECTRIC |
OUR BUSINESS AND HOW WE TALK ABOUT IT
We are a global digital industrial company, transforming industry with software-defined machines and solutions that are connected, responsive and predictive. With products and services ranging from aircraft engines, power generation and oil and gas production equipment to medical imaging, financing and industrial products, we serve customers in approximately 180 countries and employ approximately 295,000 people worldwide. Since our incorporation in 1892, we have developed or acquired new technologies and services that have considerably broadened and changed the scope of our activities.
OUR INDUSTRIAL OPERATING SEGMENTS
 | Power |  | Aviation |  | Energy Connections & Lighting(a) |
 | Renewable Energy |  | Healthcare | ||
 | Oil & Gas |  | Transportation |
OUR FINANCIAL SERVICES OPERATING SEGMENT
 | Capital |
| (a) | Beginning in the third quarter of 2016, the former Energy Connections and Appliances & Lighting segments are presented as one reporting segment called Energy Connections & Lighting. This segment includes historical results of the Appliances business prior to its sale in June 2016. |
Business, operation and financial overviews for our operating segments are provided in the Segment Operations section within the Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (MD&A) section.
COMPETITIVE CONDITIONS AND ENVIRONMENT
In all of our global business activities, we encounter aggressive and able competition. In many instances, the competitive climate is characterized by changing technology that requires continuing research and development. With respect to manufacturing operations, we believe that, in general, we are one of the leading firms in most of the major industries in which we participate. The businesses in which GE Capital engages are subject to competition from various types of financial institutions, including commercial banks, investment banks, leasing companies, independent finance companies, finance companies associated with manufacturers and insurance and reinsurance companies.
As a diverse global company, we are affected by world economies, instability in certain regions, commodity prices, such as the price of oil, and foreign currency volatility. Other factors impacting our business include:
| · | product development cycles for many of our products are long and product quality and efficiency are critical to success, |
| · | research and development expenditures are important to our business and |
| · | many of our products are subject to a number of regulatory standards. |
These factors are discussed throughout MD&A.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 18
OUR EMPLOYEES AND EMPLOYEE RELATIONS
At year-end 2016, General Electric Company and consolidated affiliates employed approximately 295,000 persons, of whom approximately 104,000 were employed in the United States. For further information about employees, see the Other Financial Data section within the MD&A.
Approximately 9,300 GE manufacturing and service employees in the United States are represented for collective bargaining purposes by one of 9 unions (approximately 48 different locals within such unions). A majority of such employees are represented by union locals that are affiliated with the IUE-CWA, The Industrial Division of the Communication Workers of America, AFL-CIO, CLC. In June 2015, we negotiated new four-year collective bargaining agreements with most of our U.S unions. These agreements continue to provide employees with good wages and benefits while addressing competitive realities facing the Company.
Other GE affiliates are parties to labor contracts with various labor unions, also with varying terms and expiration dates that cover approximately 1,700 employees.
PROPERTIES
Manufacturing operations are carried out at 184 manufacturing plants located in 38 states in the United States and Puerto Rico and at 325 manufacturing plants located in 40 other countries.
CORPORATE INFORMATION AND WEBSITES
General Electric's address is 1 River Road, Schenectady, NY 12345-6999; we also maintain executive offices at 41 Farnsworth Street, Boston, MA 02210.
GE's Internet address at www.ge.com, Investor Relations website at www.ge.com/investor-relations and our corporate blog at www.gereports.com, as well as GE's Facebook page, Twitter accounts and other social media, including @GE_Reports, contain a significant amount of information about GE, including financial and other information for investors. GE encourages investors to visit these websites from time to time, as information is updated and new information is posted.
Website references in this report are provided as a convenience and do not constitute, and should not be viewed as, incorporation by reference of the information contained on, or available through, the websites. Therefore, such information should not be considered part of this report.
Our annual report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports are available, without charge, on our website, www.ge.com/investor-relations/events-reports, as soon as reasonably practicable after they are filed electronically with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Copies are also available, without charge, from GE Corporate Investor Communications, 41 Farnsworth Street, Boston, MA 02210.
Reports filed with the SEC may be viewed at www.sec.gov or obtained at the SEC Public Reference Room in Washington, D.C. Information about the operation of the Public Reference Room may be obtained by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 19
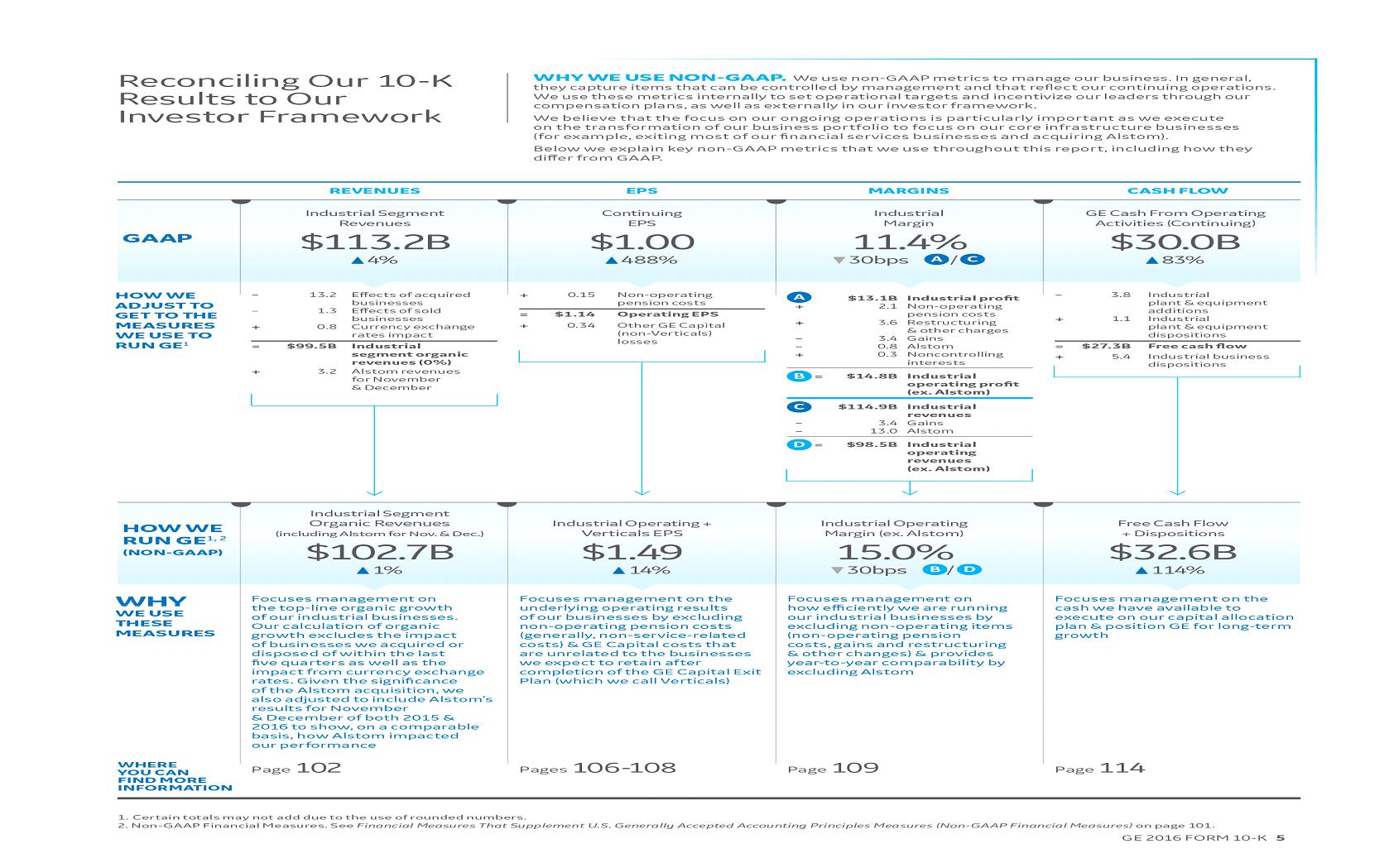
MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS (MD&A)
PRESENTATION
The consolidated financial statements of General Electric Company (the Company) combine the industrial manufacturing and services businesses of General Electric Company (GE) with the financial services businesses of GE Capital Global Holdings, LLC (GE Capital or Financial Services) and its predecessor, General Electric Capital Corporation.
We believe that investors will gain a better understanding of our company if they understand how we measure and talk about our results. Because of the diversity in our businesses, we present our financial statements in a three-column format, which allows investors to see our industrial operations separately from our Financial Services operations. We believe that this provides useful information to investors. When used in this report, unless otherwise indicated by the context, we use the terms to mean the following:
| · | General Electric or the Company – the parent company, General Electric Company. |
| · | GE – the adding together of all affiliates except GE Capital, whose continuing operations are presented on a one-line basis, giving effect to the elimination of transactions among such affiliates. Transactions between GE and GE Capital have not been eliminated at the GE level. We present the results of GE in the center column of our consolidated statements of earnings, financial position and cash flows. An example of a GE metric is GE cash from operating activities (GE CFOA). |
| · | General Electric Capital Corporation or GECC – predecessor to GE Capital Global Holdings, LLC. |
| · | GE Capital Global Holdings, LLC or GECGH – the adding together of all affiliates of GECGH, giving effect to the elimination of transactions among such affiliates. |
| · | GE Capital or Financial Services – refers to GECGH, or its predecessor GECC, and is the adding together of all affiliates of GE Capital giving effect to the elimination of transactions among such affiliates. We present the results of GE Capital in the right-side column of our consolidated statements of earnings, financial position and cash flows. |
| · | GE consolidated – the adding together of GE and GE Capital, giving effect to the elimination of transactions between the two. We present the results of GE consolidated in the left-side column of our consolidated statements of earnings, financial position and cash flows. |
| · | Industrial – GE excluding the continuing operations of GE Capital. We believe that this provides investors with a view as to the results of our industrial businesses and corporate items. An example of an Industrial metric is Industrial CFOA (Non-GAAP), which is GE CFOA excluding the effects of dividends from GE Capital. |
| · | Industrial segment – the sum of our seven industrial reporting segments, without giving effect to the elimination of transactions among such segments and between these segments and our Financial Services segment. This provides investors with a view as to the results of our industrial segments, without inter-segment eliminations and corporate items. An example of an industrial segment metric is industrial segment revenue growth. |
| · | Total segment – the sum of our seven industrial segments and one financial services segment, without giving effect to the elimination of transactions between such segments. This provides investors with a view as to the results of all of our segments, without inter-segment eliminations and corporate items. |
| · | Verticals or GE Capital Verticals – the adding together of GE Capital businesses that we expect to retain, principally its vertical financing businesses—GE Capital Aviation Services (GECAS), Energy Financial Services (EFS) and Industrial Finance (which includes Healthcare Equipment Finance, Working Capital Solutions and Industrial Financing Solutions)—that relate to the Company's core industrial domain and other operations, including our run-off insurance activities, and allocated corporate costs. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 20
We integrate acquisitions as quickly as possible. Revenues and earnings from the date we complete the acquisition through the end of the fourth quarter following the acquisition are considered the acquisition effect of such businesses.
Discussion of GE Capital's total assets includes deferred income tax liabilities, which are presented within assets for purposes of our consolidated statement of financial position presentations for this filing.
Amounts reported in billions in graphs within this report are computed based on the amounts in millions. As a result, the sum of the components reported in billions may not equal the total amount reported in billions due to rounding. Certain columns and rows within the tables may not add due to the use of rounded numbers. Percentages presented are calculated from the underlying numbers in millions.
Discussions throughout this MD&A are based on continuing operations unless otherwise noted.
The MD&A should be read in conjunction with the Financial Statements and Notes to the consolidated financial statements.
OTHER TERMS USED BY GE
| · | Backlog – unfilled customer orders for products and product services (expected life of contract sales for product services). |
| · | Borrowings as a percentage of total capital invested – for GE, the sum of borrowings and mandatorily redeemable preferred stock, divided by the sum of borrowings, mandatorily redeemable preferred stock, redeemable noncontrolling interest, noncontrolling interests and total shareowners' equity. |
| · | Continuing earnings – unless otherwise indicated, we refer to the caption "earnings from continuing operations attributable to GE common shareowners" as continuing earnings or simply as earnings. |
| · | Continuing earnings per share (EPS) – unless otherwise indicated, when we refer to continuing earnings per share, it is the diluted per-share amount of "earnings from continuing operations attributable to GE common shareowners". |
| · | Digital revenues – revenues related to internally developed software (including PredixTM) and associated hardware, and software solutions that improve our customers' asset performance. In 2016, we reassessed the span of our digital product offerings, which now excludes software-enabled product upgrades. These revenues are largely generated from our operating businesses and are included in their segment results. |
| · | Ending Net Investment (ENI) (Non-GAAP) – the total capital we have invested in the Financial Services business. It is the sum of short-term borrowings, long-term borrowings and equity (excluding noncontrolling interests) adjusted for unrealized gains and losses on investment securities and hedging instruments. Alternatively, it is the amount of assets of continuing operations less the amount of non-interest-bearing liabilities. |
| · | Equipment leased to others (ELTO) – rental equipment we own that is available to rent and is stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. |
| · | Free cash flow (Non-GAAP) – GE's cash from operating activities (continuing operations) less GE additions to property, plant and equipment, plus GE dispositions of property, plant and equipment, which are included in cash flows from investing activities. |
| · | GE Capital Exit Plan – our plan, announced on April 10, 2015, to reduce the size of our financial services businesses through the sale of most of the assets of GE Capital, and to focus on continued investment and growth in our industrial businesses. |
| · | Global Growth Organization (GGO) – organization that provides operational processes through a shared services structure for the enabling functions: commercial, enterprise data management, finance, HR, IT, legal, supply chain and tax through a partnership with the businesses and global functions. |
| · | Growth markets – consist of countries/regions which are expected to grow at above average world GDP rates over the long term and typically are resource rich and/or have large infrastructure needs. They encompass the following: Australasia; Canada; Latin America; Middle East, North Africa and Turkey; Russia and CIS; Sub-Saharan Africa; Greater China; South Asia; South East Asia (ASEAN). |
| · | Industrial margin – GE revenues and other income excluding GE Capital earnings (loss) from continuing operations (Industrial revenues) minus GE total costs and expenses less GE interest and other financial charges divided by Industrial revenues. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 21
| · | Industrial operating profit margin (Non-GAAP) – Industrial segment profit plus corporate items and eliminations (excluding gains, restructuring, and pre-tax non-operating pension costs) divided by industrial segment revenues plus corporate items and eliminations (excluding gains and GE-GE Capital eliminations). |
| · | Industrial return on total capital (Industrial ROTC) (Non-GAAP) – earnings from continuing operations attributable to GE common shareowners less GE Capital earnings from continuing operations plus GE after-tax interest, divided by average Industrial shareholders' equity, less average GE Capital's shareholders' equity, plus average debt and other, net. |
| · | Industrial segment gross margin – industrial segment sales less industrial segment cost of sales. |
| · | Industrial shareholders' equity and GE Capital shareholders' equity – for purposes of the Industrial ROTC calculation excludes the effects of discontinued operations and is calculated on an annual basis using a five-point average. |
| · | Net earnings – unless otherwise indicated, we refer to the caption "net earnings attributable to GE common shareowners" as net earnings. |
| · | Net earnings per share (EPS) – unless otherwise indicated, when we refer to net earnings per share, it is the diluted per-share amount of "net earnings attributable to GE common shareowners". |
| · | Non-operating pension cost (Non-GAAP) – comprises the expected return on plan assets, interest cost on benefit obligations and net actuarial gain (loss) amortization for our principal pension plans. |
| · | Operating earnings (Non-GAAP) – GE earnings from continuing operations attributable to common shareowners excluding the impact of non-operating pension costs. |
| · | Operating earnings per share (Non-GAAP) – unless otherwise indicated, when we refer to operating earnings per share, it is the diluted per-share amount of "operating earnings". |
| · | Operating pension cost (Non-GAAP) – comprises the service cost of benefits earned, prior service cost amortization and curtailment gain (loss) for our principal pension plans. |
| · | Organic revenues (Non-GAAP) – revenues excluding the effects of acquisitions, dispositions and translational foreign currency exchange. |
| · | Product services – for purposes of the financial statement display of sales and costs of sales in our Statement of Earnings, "goods" is required by SEC regulations to include all sales of tangible products, and "services" must include all other sales, including other services activities. In our MD&A section of this report, we refer to sales under product services agreements and sales of both goods (such as spare parts and equipment upgrades) and related services (such as monitoring, maintenance and repairs) as sales of "product services," which is an important part of our operations. We refer to "product services" simply as "services" within the MD&A. |
| · | Product services agreements – contractual commitments, with multiple-year terms, to provide specified services for products in our Power, Renewable Energy, Oil & Gas, Aviation and Transportation installed base – for example, monitoring, maintenance, service and spare parts for a gas turbine/generator set installed in a customer's power plant. |
| · | Revenues – unless otherwise indicated, we refer to captions such as "revenues and other income" simply as revenues. |
| · | Segment profit – refers to the operating profit of the industrial segments and the net earnings of the Financial Services segment. See the Segment Operations section within the MD&A for a description of the basis for segment profits. |
| · | Shared Services – sharing of business processes in order to standardize and consolidate services to provide value to the businesses in the form of simplified processes, reduced overall costs and increased service performance. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 22
NON-GAAP FINANCIAL MEASURES
In the accompanying analysis of financial information, we sometimes use information derived from consolidated financial data but not presented in our financial statements prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). Certain of these data are considered "non-GAAP financial measures" under the SEC rules. Specifically, we have referred, in various sections of this report, to:
| · | Industrial segment organic revenues and industrial segment organic revenues excluding Oil & Gas |
| · | Industrial segment organic operating profit |
| · | Oil & Gas organic revenue and operating profit growth |
| · | Operating and non-operating pension cost |
| · | Adjusted corporate costs (operating) |
| · | GE pre-tax earnings from continuing operations, excluding GE Capital earnings (loss) from continuing operations and the corresponding effective tax rates, and the reconciliation of the U.S. federal statutory income tax rate to GE effective tax rate, excluding GE Capital earnings |
| · | Industrial operating earnings and GE Capital earnings (loss) from continuing operations and EPS |
| · | Industrial operating + Verticals earnings and EPS |
| · | Industrial operating profit and operating profit margin (excluding certain items) |
| · | Industrial operating profit + Verticals |
| · | Industrial segment gross margin (excluding Alstom) |
| · | Industrial segment operating profit and operating margin (excluding Alstom) |
| · | Average GE shareowners' equity, excluding effects of discontinued operations |
| · | Average GE Capital shareowners' equity, excluding effects of discontinued operations |
| · | Industrial return on total capital (Industrial ROTC) |
| · | Industrial cash flows from operating activities (Industrial CFOA) and Industrial CFOA excluding taxes related to business sales and principal pension plan funding |
| · | GE cash flows from operating activities (GE CFOA) excluding taxes related to business sales and principal pension plan funding |
| · | Free cash flow (FCF) and FCF plus dispositions |
| · | Ratio of adjusted debt to equity at GE Capital, net of liquidity |
| · | Capital ending net investment (ENI), excluding liquidity |
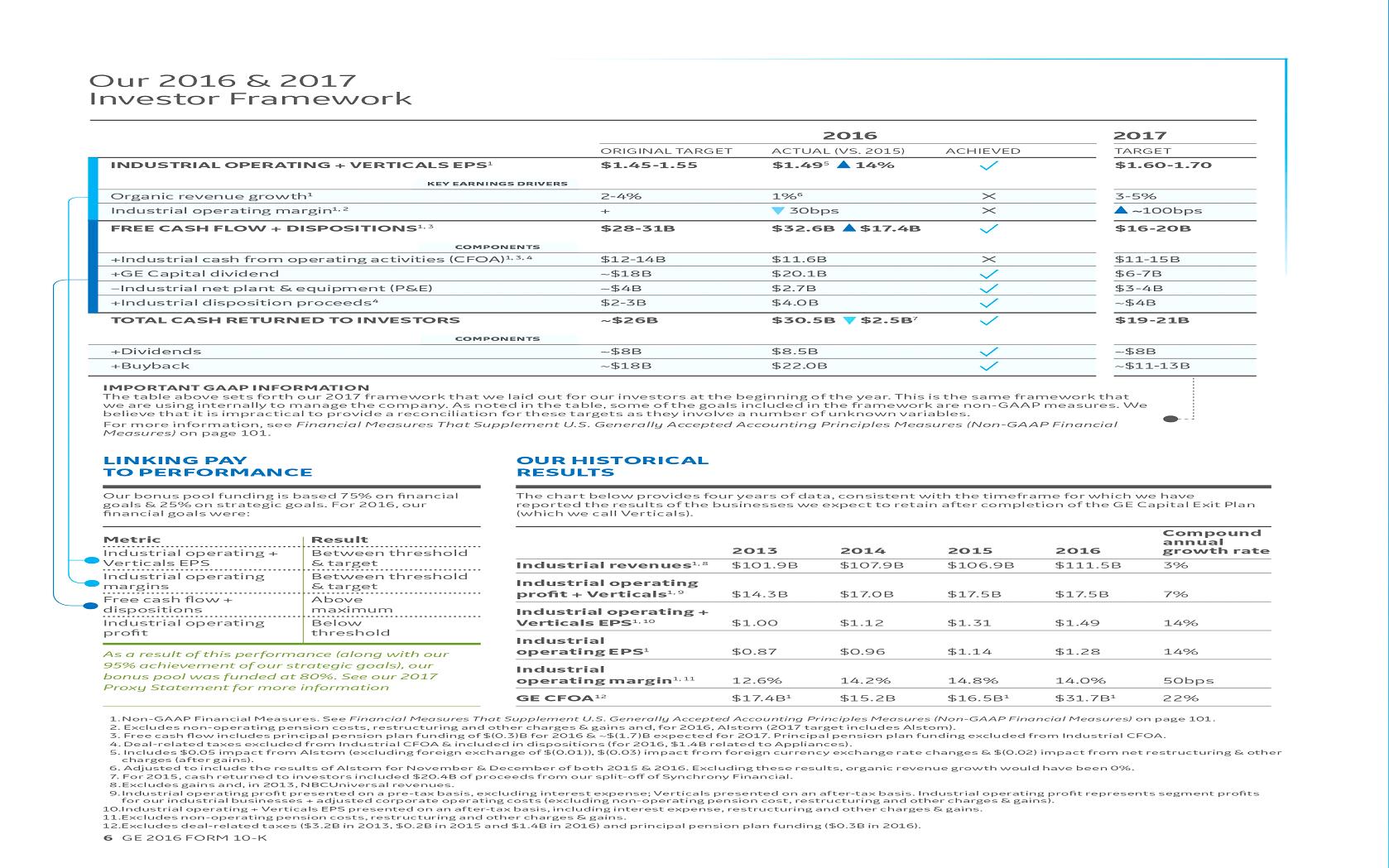
| · | 2017 operating framework including 2017 Industrial operating + Verticals EPS target |
The reasons we use these non-GAAP financial measures and the reconciliations to their most directly comparable GAAP financial measures are included in the Supplemental Information section within the MD&A. Non-GAAP financial measures referred to in this report are either labeled as "non-GAAP" or designated as such with an asterisk (*).
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 23
KEY PERFORMANCE INDICATORS
(Dollars in billions; per-share amounts in dollars)
REVENUES PERFORMANCE | GE CFOA | |||
 |  | GE Capital Dividend Industrial CFOA* | ||
| (a) Including the results of Alstom for November and December of both 2015 and 2016 | (a) Industrial CFOA was $12.2 billion excluding deal taxes of $(0.2) billion related to the sale of our Signaling business (b) Industrial CFOA was $11.6 billion excluding deal taxes of $(1.4) billion related to the sale of our Appliances business and $(0.3) billion of pension funding (c) Included $(0.3) billion related to Alstom in both 2015 and 2016 | |||
INDUSTRIAL ORDERS | INDUSTRIAL BACKLOG | |||
 | Equipment Services |  | Equipment Services | |
(a) Included $2.5 billion related to Alstom (b) Included $17.4 billion related to Alstom | (a) Included $29.2 billion related to Alstom (b) Included $31.2 billion related to Alstom | |||
INDUSTRIAL MARGINS | INDUSTRIAL OPERATING PROFIT MARGINS (NON-GAAP)(a) | |||
 |  | |||
(a) 12.0%, excluding (7.9)% related to Alstom* (b) 12.1%, excluding 5.9% related to Alstom* | (a) Excluded gains, non-operating pension costs, restructuring and other, noncontrolling interests, GE Capital preferred stock dividends, as well as the results of Alstom | |||
*Non-GAAP Financial Measure
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 24
KEY PERFORMANCE INDICATORS
(Dollars in billions; per-share amounts in dollars; attributable to GE common shareowners)
NET EARNINGS (LOSS) | NET EARNINGS (LOSS) PER SHARE | |
 | 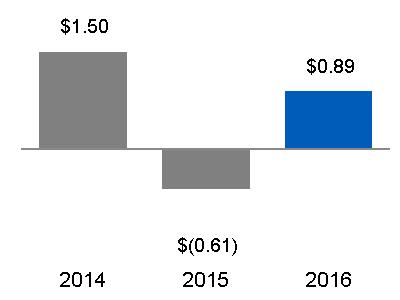 | |
OPERATING EARNINGS (NON-GAAP) | OPERATING EARNINGS PER SHARE (NON-GAAP) | |
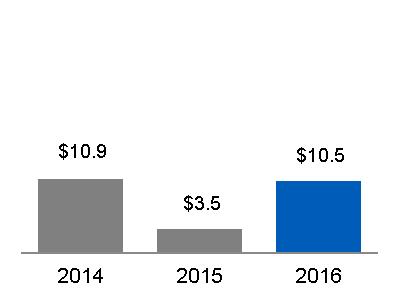 |  | |
INDUSTRIAL OPERATING + VERTICALS EARNINGS (NON-GAAP) | INDUSTRIAL OPERATING + VERTICALS EPS (NON-GAAP) | |
 |  |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 25
KEY PERFORMANCE INDICATORS
(Dollars in billions; per-share amounts in dollars)
| SHAREHOLDER INFORMATION | |
RETURNED $30.5 BILLION TO SHAREOWNERS IN 2016 Dividends $8.5 billion Stock buyback $22.0 billion | ANNUAL MEETING General Electric's 2017 Annual Meeting of Shareowners will be held on April 26, 2017, in Asheville, NC |
FIVE-YEAR PERFORMANCE GRAPH | |
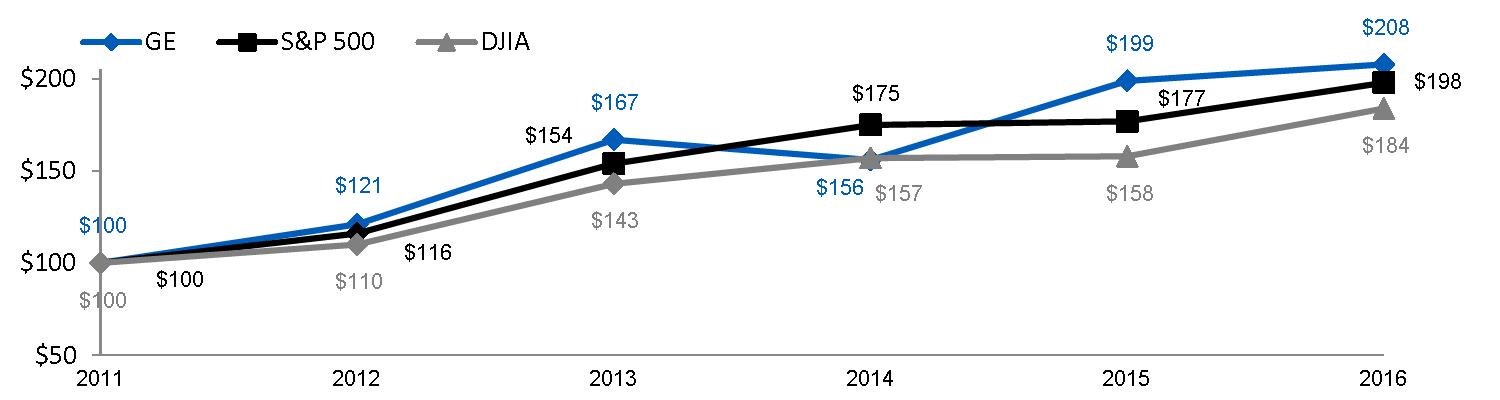 | |
The annual changes for the five-year period shown in the graph on this page are based on the assumption that $100 had been invested in General Electric common stock, the Standard & Poor's 500 Stock Index (S&P 500) and the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) on December 31, 2011, and that all quarterly dividends were reinvested. The cumulative dollar returns shown on the graph represent the value that such investments would have had on December 31 for each year indicated.
| STOCK PRICE RANGE AND DIVIDENDS |
 |
With respect to "Market Information," in the United States, General Electric common stock is listed on the New York Stock Exchange (its principal market). General Electric common stock is also listed on the London Stock Exchange, Euronext Paris, the SIX Swiss Exchange and the Frankfurt Stock Exchange. The chart above shows trading prices, as reported on the New York Stock Exchange, Inc., Composite Transactions Tape.
As of January 31, 2017, there were approximately 440,000 shareowner accounts of record.
On February 10, 2017, our Board of Directors approved a quarterly dividend of $0.24 per share of common stock, which is payable April 25, 2017, to shareowners of record at close of business on February 27, 2017.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 26
CONSOLIDATED RESULTS
| SIGNIFICANT DEVELOPMENTS IN 2016 |
Our consolidated results for 2016 were significantly affected by recent portfolio changes, including the 2015 acquisition of Alstom, the disposal of financial services businesses under the GE Capital Exit Plan initiated in 2015 and the 2016 sale of our Appliances business. |
ALSTOM In 2016, Alstom contributed revenues of $13.0 billion and an operating loss of $0.3 billion, of which $0.8 billion of profit is included in the segment results and $1.0 billion of charges is included in Corporate, primarily related to purchase accounting and acquisition related charges. Including the effects of tax benefits of $0.8 billion, net earnings were $0.4 billion for the year ended December 31, 2016. In addition, Alstom used cash flows from operating activities of $0.3 billion for the year ended December 31, 2016. |
GE CAPITAL EXIT PLAN As of December 31, 2016, we have signed agreements with buyers for $197 billion of GE Capital ending net investment (ENI), excluding liquidity (as originally reported at December 31, 2014), of which $190 billion have closed by the end of 2016. In June 2016, we received approval of our request to the Financial Stability Oversight Council (FSOC) for rescission of GE Capital's designation as a nonbank Systemically Important Financial Institution (SIFI). |
2016 SIGNIFICANT TRANSACTIONS Transactions completed in 2016 included the following. · The June 2016 sale of our Appliances business to Qingdao Haier Co., Ltd. (Haier) for $5.6 billion (including $0.8 billion from sale of receivables originated in our Appliances business and sold from GE Capital to Haier) on which we recognized an after-tax gain of $1.8 billion. · Acquisition of the remaining 74% of software developer Meridium Inc. in September 2016, for $0.4 billion to enhance and accelerate our asset performance-management capabilities across our industrial businesses. · The acquisitions of a 76.2% interest in Arcam AB for $0.5 billion and a 75% interest in Concept Laser GmbH for $0.6 billion, two European 3-D printing companies that print metal parts for aircraft and other industrial components, to expand our additive manufacturing capabilities. |
PLANNED TRANSACTIONS We also announced a number of strategic transactions during 2016 that we expect to complete in 2017, including the following. · In October 2016, we announced an agreement with Baker Hughes Incorporated (Baker Hughes) to combine our Oil & Gas business and Baker Hughes to create a new entity in which GE will hold a 62.5% interest and existing Baker Hughes shareholders will have a 37.5% interest. Baker Hughes shareholders will also receive a cash dividend funded by a $7.4 billion cash contribution by GE. The transaction is subject to the approval of Baker Hughes shareholders, regulatory approvals and other customary closing conditions. · In October 2016, we announced a plan to acquire LM Wind Power, one of the world's largest wind turbine blade manufacturers for $1.7 billion, subject to customary closing conditions. · In October 2016, we also announced our plan to sell our Water & Process Technologies business and in December 2016, we announced our plan to sell our Industrial Solutions business. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 27
(Dollars in billions)
2016 GEOGRAPHIC REVENUES | 2016 SEGMENT REVENUES | ||||||
 |  | ||||||
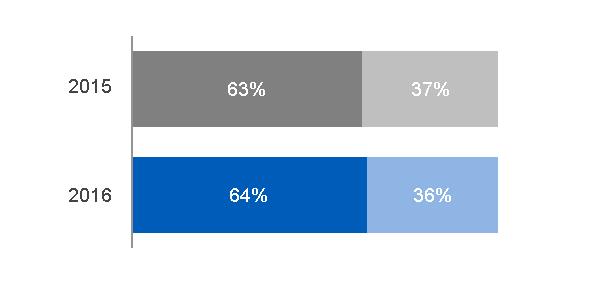
REVENUES | INDUSTRIAL REVENUES | FINANCIAL SERVICES REVENUES | |||||
 | 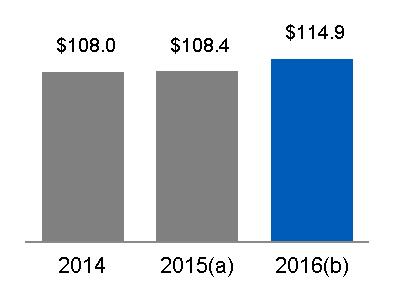 |  | |||||
(a) Includes $2.0 billion related to Alstom (b) Includes $13.0 billion related to Alstom | (a) Includes $2.0 billion related to Alstom (b) Includes $13.0 billion related to Alstom | ||||||
CONTINUING EARNINGS(a) | CONTINUING EARNINGS PER SHARE(a) | ||||||
 |  | ||||||
(a) Attributable to GE common shareowners | |||||||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 28
CONSOLIDATED RESULTS
(Dollars in billions)
REVENUE COMMENTARY: 2016 – 2015 | EARNINGS COMMENTARY: 2016 – 2015 | |
Consolidated revenues increased $6.3 billion, or 5%, primarily driven by increased Industrial revenues of $6.6 billion and increased Financial Services revenues of $0.1 billion, partially offset by an increase in eliminations between Industrial and Financial Services of $0.4 billion. The overall foreign currency impact on consolidated revenues was a decrease of $1.3 billion. · Industrial revenues increased $6.6 billion, or 6% due to increased industrial segment revenues of $4.4 billion, or 4%, as increases at Power, Renewable Energy, Aviation and Healthcare were partially offset by decreases at Oil & Gas, Transportation and Energy Connections & Lighting. This increase in industrial segment revenues was primarily driven by the net effects of acquisitions of $11.2 billion, offset by the net effects of dispositions of $5.6 billion and the effects of a stronger U.S. dollar of $0.8 billion. Excluding the effects of acquisitions, dispositions and translational currency exchange, industrial segment organic revenues* decreased $0.5 billion. Industrial revenues increased an additional $2.2 billion at Corporate as current year gains were $1.9 billion higher than 2015 gains. · Financial Services revenues increased $0.1 billion, or 1%, primarily due to lower impairments, higher gains and the effects of acquisitions, partially offset by organic revenue declines, the effects of dispositions and the effects of translational currency exchange. | Consolidated continuing earnings increased $7.5 billion, primarily driven by decreased Financial Services losses of $6.7 billion, increased Industrial continuing earnings of $0.5 billion and a net decrease of $0.2 billion resulting from income taxes, and interest and other financial charges. The overall foreign currency impact on consolidated earnings was a decrease of $0.3 billion. · Industrial earnings increased $0.5 billion due to increased earnings at Corporate of $0.8 billion, or 17%, as current year gains were $1.9 billion higher and pension costs were $0.7 billion lower than 2015. These increases to earnings were partially offset by $1.8 billion of higher restructuring and other charges. Industrial earnings decreased due to decreased industrial segment earnings of $0.4 billion, or 2%, as decreases at Oil & Gas, Energy Connections & Lighting, and Transportation were partially offset by increases at Aviation, Power, Healthcare and Renewable Energy. This decrease in industrial segment earnings, was primarily driven by decreases in organic operating profit* of $0.8 billion and the net effect of dispositions of $0.5 billion, partially offset by the net effect of acquisitions of $0.9 billion. · Financial Services losses decreased $6.7 billion, or 84%, primarily due to the absence of the 2015 charges associated with the GE Capital Exit Plan. · In addition to the effects on net earnings described above, earnings per share amounts were also positively impacted by the reduction in number of outstanding common shares compared to 2015. The average number of shares outstanding used to calculate 2016 earnings per share amounts was 9% lower than 2015, primarily due to the 2015 Synchrony Financial share exchange and ongoing share buyback activities funded in large part by dividends from GE Capital. |
*Non-GAAP Financial Measure
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 29
CONSOLIDATED RESULTS
(Dollars in billions)
REVENUE COMMENTARY: 2015 – 2014 | EARNINGS COMMENTARY: 2015 – 2014 | |
Consolidated revenues increased $0.2 billion, primarily driven by increased Industrial revenues of $0.4 billion and a decrease in eliminations between Industrial and Financial Services of $0.4 billion, partially offset by decreased Financial Services revenues of $0.5 billion. The overall foreign currency impact on consolidated revenues was a decrease of $4.9 billion. · Industrial revenues increased $0.4 billion due an increase at Corporate of $1.3 billion, or 75%, as 2015 gains were $1.4 billion higher than 2014 year gains. This was offset by decreases in industrial segment revenues of $0.9 billion, or 1%, as decreases at Oil & Gas, Healthcare and Renewable Energy were partially offset by increases at Power, Aviation, Energy Connections & Lighting and Transportation. The $0.9 billion decrease in industrial segment revenues was primarily driven by the translational effects of a stronger U.S. dollar of $4.8 billion and the net effects of dispositions of $1.1 billion, partially offset by the net effects of acquisitions of $2.2 billion. Excluding the effects of acquisitions, dispositions and currency exchange, industrial segment organic revenues* increased by $2.8 billion, or 3%. · Financial Services revenues decreased $0.5 billion, or 5%, primarily due to organic revenue declines, primarily resulting from lower ending net investment (ENI), lower gains and higher impairments, partially offset by the effects of acquisitions and dispositions. | Consolidated continuing earnings decreased $7.9 billion, or 83%, primarily driven by decreased Financial Services net earnings of $9.2 billion, partially offset by an increase in Industrial continuing earnings of $1.3 billion. The overall foreign currency impact on consolidated earnings was a decrease of $0.6 billion. · Industrial earnings increased 1.3 billion, or 11%, due to increased industrial segment earnings of $0.2 billion, or 1%, as increases at Aviation, Energy Connections & Lighting, Transportation and Power were partially offset by decreases at Oil & Gas, Renewable Energy and Healthcare. This increase in industrial segment earnings was primarily driven by increases in organic operating profit* of $1.2 billion, partially offset by the translational currency exchange effects of a stronger U.S. dollar of $0.7 billion, net acquisitions of $0.1 billion and net dispositions of $0.2 billion. Industrial earnings at Corporate increased an additional $1.1 billion, or 18%, as 2015 gains were $1.4 billion higher than 2014 gains, partially offset by $0.5 billion of higher Principal retirement plan costs in 2015. · Financial Services net earnings decreased $9.2 billion, primarily due to 2015 charges associated with the GE Capital Exit Plan. |
See Segment Results and Corporate Items & Eliminations sections within the MD&A for more information.
Also, see the Other Consolidated Information section within the MD&A for a discussion of postretirement benefit plans costs, income taxes and geographic data.
*Non-GAAP Financial Measure
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 30
GE CAPITAL
GE Capital results include continuing operations, which are reported in the Capital segment (see Segment discussion), and discontinued operations (see Discontinued Operations section and Note 2).
THE GE CAPITAL EXIT PLAN
On April 10, 2015, the Company announced a plan (the GE Capital Exit Plan) to create a simple, more valuable company by reducing the size of its financial services businesses through the sale of most of the assets of GE Capital over the following 24 months and aligning a smaller GE Capital with GE's industrial businesses.
Under the GE Capital Exit Plan, the Company is retaining certain GE Capital businesses, principally its vertical financing businesses—GE Capital Aviation Services (GECAS), Energy Financial Services (EFS) and Industrial Finance (which includes Healthcare Equipment Finance, Working Capital Solutions and Industrial Financing Solutions)—that relate to the Company's core industrial domain and other operations, including our run-off insurance activities, and allocated corporate costs (together referred to as GE Capital Verticals or Verticals).
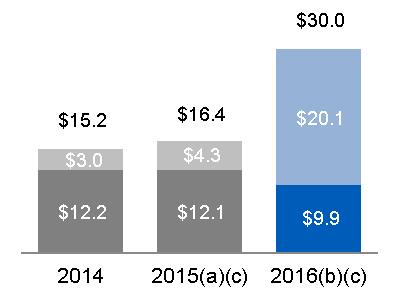
As a result of the GE Capital Exit Plan dispositions, GE Capital has paid $24.4 billion in dividends to GE in 2015 and 2016 ($4.3 billion and $20.1 billion, respectively). We expect GE Capital to release additional dividends of up to approximately $10 billion through the remainder of the plan. In January 2017, GE received an additional $2.0 billion of common dividends from GE Capital. As of December 31, 2016, we are ahead of our plan, having signed agreements with buyers for $197 billion of ending net investment (ENI), excluding liquidity (as originally reported at December 31, 2014), of which $190 billion has closed. As of December 31, 2016, we have substantially completed the dispositions related to the GE Capital Exit Plan. In addition, as part of our initiative to reduce the size of our financial services businesses, we completed the split-off of our remaining interest in GE Capital's North American Retail Finance business, Synchrony Financial, to holders of GE common stock, which resulted in a $20.4 billion buyback of GE common stock (671.4 million shares) in 2015. In connection with the GE Capital Exit Plan, we completed a legal reorganization of GE Capital that included a merger of GE Capital into GE, a guarantee by GE of GE Capital debt, and an exchange of $36 billion of GE Capital debt for new notes guaranteed by GE. The result of all these actions reduced GE Capital's total assets by 63% from $500 billion at December 31, 2014 to $183 billion at December 31, 2016. From inception of plan through December 31, 2016, we incurred charges of $22.0 billion. Due to anticipated tax benefits and gains, we do not expect total after-tax charges through the completion of the GE Capital Exit Plan to exceed our initial $23 billion estimate.
On March 31, 2016, GE filed its request to the Financial Stability Oversight Council (FSOC) for rescission of GE Capital's designation as a nonbank Systemically Important Financial Institution (SIFI). On June 28, 2016, the FSOC rescinded GE Capital's designation as a nonbank SIFI.
SALES AGREEMENTS
During 2016, GE signed agreements to sell approximately $40 billion of ENI, excluding liquidity (as originally reported at December 31, 2014), of which approximately $19 billion, $21 billion and less than $1 billion related to our Commercial Lending and Leasing (CLL), Consumer and Real Estate businesses, respectively.
Sales representing approximately $86 billion of ENI, excluding liquidity (as originally reported at December 31, 2014) closed during 2016, including approximately $70 billion, $16 billion and less than $1 billion related to our CLL, Consumer and Real Estate businesses, respectively.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 31
AFTER-TAX CHARGES RELATED TO THE GE CAPITAL EXIT PLAN
During 2016, GE recorded less than $0.1 billion of after-tax charges related to the GE Capital Exit Plan of which $0.7 billion of net benefits were recorded in continuing operations and $0.7 billion of after-tax charges were recorded in discontinued operations. A description of these after-tax charges for 2016 is provided below.
| · | $1.3 billion of net loss primarily related to the completed and planned dispositions of Consumer and most of the CLL businesses, which was recorded in discontinued operations under the caption "Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes" in the Statement of Earnings. |
| · | $0.3 billion of charges associated with the preferred equity exchange that was completed in January 2016, which was recorded in continuing operations and reported in GE Capital's corporate component under the caption "Preferred stock dividends" in the Statement of Earnings. |
| · | These charges were offset by tax benefits of $1.4 billion primarily related to increased tax efficiency of planned cash repatriations through increased foreign tax credit utilization of $0.8 billion and an IRS tax settlement of $0.6 billion. Of these benefits $1.1 billion was recorded in continuing operations and reported in GE Capital's corporate component under the caption "Benefit (provision) for income taxes" in the Statement of Earnings and $0.2 billion was recorded in discontinued operations under the caption "Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes" in the Statement of Earnings. |
For additional information about the GE Capital Exit Plan 2015 sales agreements and after-tax charges, refer to our Form 8-K filed on June 3, 2016 related to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2015.
In addition to the above charges, during the year ended December 31, 2016, we have incurred other costs related to our ongoing liability management actions, including $0.6 billion of pre-tax losses related to the repurchase of $12.5 billion of long-term unsecured debt and subordinated debentures which were recorded in continuing operations.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 32
SEGMENT CHANGES
| · | Beginning in the third quarter of 2016, the former Energy Connections and Appliances & Lighting segments are presented as one reporting segment called Energy Connections & Lighting. This segment includes historical results of the Appliances business prior to its sale in June 2016. |
REVENUES AND PROFIT
Segment revenues include revenues and other income related to the segment.
Segment profit is determined based on internal performance measures used by the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) to assess the performance of each business in a given period. In connection with that assessment, the CEO may exclude matters such as charges for restructuring; rationalization and other similar expenses; acquisition costs and other related charges; technology and product development costs; certain gains and losses from acquisitions or dispositions; and litigation settlements or other charges, for which responsibility preceded the current management team. For additional information about costs excluded from segment profit, see Corporate Items and Eliminations section within this MD&A.
Segment profit excludes results reported as discontinued operations and material accounting changes. Segment profit also excludes the portion of earnings or loss attributable to noncontrolling interests of consolidated subsidiaries, and as such only includes the portion of earnings or loss attributable to our share of the consolidated earnings or loss of consolidated subsidiaries.
Segment profit excludes or includes interest and other financial charges and income taxes according to how a particular segment's management is measured:
| · | Interest and other financial charges, income taxes and GE preferred stock dividends are excluded in determining segment profit (which we sometimes refer to as "operating profit") for the industrial segments. |
| · | Interest and other financial charges, income taxes and GE Capital preferred stock dividends are included in determining segment profit (which we sometimes refer to as "net earnings") for the Capital segment. |
Certain corporate costs, such as shared services, employee benefits and information technology are allocated to our segments based on usage. A portion of the remaining corporate costs is allocated based on each segment's relative net cost of operations.
With respect to the segment revenue and profit walks, the overall effect of foreign exchange is included within multiple captions as follows:
| · | The translational foreign exchange impact is included within Foreign Exchange. |
| · | The transactional impact of foreign exchange hedging is included in operating cost within Productivity and in other income within Other. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 33
SIGNIFICANT SEGMENT DEVELOPMENTS
ALSTOM ACQUISITION
On November 2, 2015, we completed the acquisition of Alstom's Thermal, Renewables and Grid businesses, resulting in two months of activity in 2015 results and a full year of activity in 2016 results. The completion of the transaction followed the regulatory approval of the deal in over 20 countries and regions including the EU, U.S., China, India, Japan and Brazil. The cash purchase price was €9.2 billion (approximately $10.1 billion), net of cash acquired. The acquisition and alliances with Alstom affected our Power, Energy Connections & Lighting and Renewable Energy segments, and to a lesser extent our Oil & Gas segment.
At year-end 2015, our preliminary allocation of purchase price resulted in recognition of approximately $13.5 billion of goodwill, $5.2 billion of intangible assets, and $1.1 billion of unfavorable customer contract liabilities. The preliminary fair value of the associated noncontrolling interest was approximately $3.6 billion. As of the end of 2016, the amount of goodwill, intangible assets and unfavorable customer contract liabilities recognized was adjusted to approximately $17.3 billion, $4.4 billion, and $2.7 billion, respectively. The adjustments reflected revisions in estimates primarily related to cash flows and other valuation assumptions for customer contracts, increases to legal reserves, and other fair value adjustments related to acquired assets and liabilities. Deferred taxes, unrecognized tax benefits and other tax uncertainties were also adjusted under applicable accounting rules. We finalized our purchase accounting analysis in the fourth quarter of 2016. See Note 8 to the consolidated financial statements for further information.
For the year ended December 31, 2016, Alstom contributed revenues of $13.0 billion and an operating loss of $0.3 billion, of which $0.8 billion of profit is included in the segment results and $1.0 billion of charges is included in Corporate, primarily related to purchase accounting and acquisition related charges. Including the effects of tax benefits of $0.8 billion, net earnings were $0.4 billion for the year ended December 31, 2016. In addition, Alstom used cash flows from operating activities of $0.3 billion for the year ended December 31, 2016. Alstom related revenues and operating profit are presented separately in the segment revenues and profit walks that follow.
SALE OF APPLIANCES
On January 15, 2016, we announced the signing of an agreement to sell our Appliances business to Haier. On June 6, 2016, we completed the sale for proceeds of $5.6 billion (including $0.8 billion from the sale of receivables originated in our Appliances business and sold from GE Capital to Haier) and recognized an after-tax gain of $1.8 billion in 2016.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 34
| SUMMARY OF OPERATING SEGMENTS | ||||||||||||||
| General Electric Company and consolidated affiliates | ||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Revenues | ||||||||||||||
| Power | $ | 26,827 | $ | 21,490 | $ | 20,580 | $ | 19,315 | $ | 20,364 | ||||
| Renewable Energy | 9,033 | 6,273 | 6,399 | 4,824 | 7,373 | |||||||||
| Oil & Gas | 12,898 | 16,450 | 19,085 | 17,341 | 15,539 | |||||||||
| Aviation | 26,261 | 24,660 | 23,990 | 21,911 | 19,994 | |||||||||
| Healthcare | 18,291 | 17,639 | 18,299 | 18,200 | 18,290 | |||||||||
| Transportation | 4,713 | 5,933 | 5,650 | 5,885 | 5,608 | |||||||||
| Energy Connections & Lighting | 15,133 | 16,351 | 15,724 | 15,907 | 15,379 | |||||||||
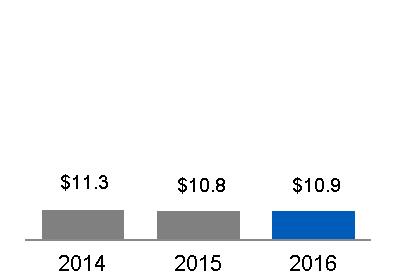
Total industrial segment revenues | 113,156 | 108,796 | 109,727 | 103,383 | 102,548 | |||||||||
| Capital | 10,905 | 10,801 | 11,320 | 11,267 | 11,268 | |||||||||
Total segment revenues | 124,061 | 119,597 | 121,047 | 114,650 | 113,816 | |||||||||
| Corporate items and eliminations | (368) | (2,211) | (3,863) | (1,405) | (1,228) | |||||||||
| Consolidated revenues | $ | 123,693 | $ | 117,386 | $ | 117,184 | $ | 113,245 | $ | 112,588 | ||||
| Segment profit | ||||||||||||||
| Power | $ | 4,979 | $ | 4,502 | $ | 4,486 | $ | 4,328 | $ | 4,368 | ||||
| Renewable Energy | 576 | 431 | 694 | 485 | 914 | |||||||||
| Oil & Gas | 1,392 | 2,427 | 2,758 | 2,357 | 2,064 | |||||||||
| Aviation | 6,115 | 5,507 | 4,973 | 4,345 | 3,747 | |||||||||
| Healthcare | 3,161 | 2,882 | 3,047 | 3,048 | 2,920 | |||||||||
| Transportation | 1,064 | 1,273 | 1,130 | 1,166 | 1,031 | |||||||||
| Energy Connections & Lighting | 311 | 944 | 677 | 491 | 442 | |||||||||
Total industrial segment profit | 17,598 | 17,966 | 17,764 | 16,220 | 15,487 | |||||||||
| Capital | (1,251) | (7,983) | 1,209 | 401 | 1,245 | |||||||||
Total segment profit | 16,347 | 9,983 | 18,973 | 16,621 | 16,731 | |||||||||
| Corporate items and eliminations | (4,226) | (5,108) | (6,225) | (6,002) | (4,719) | |||||||||
| GE interest and other financial charges | (2,026) | (1,706) | (1,579) | (1,333) | (1,353) | |||||||||
| GE provision for income taxes | (967) | (1,506) | (1,634) | (1,667) | (2,013) | |||||||||
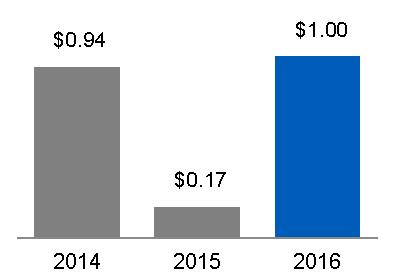
| Earnings from continuing operations | ||||||||||||||
| attributable to GE common shareowners | 9,128 | 1,663 | 9,535 | 7,618 | 8,646 | |||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued | ||||||||||||||
operations, net of taxes | (954) | (7,495) | 5,855 | 5,475 | 5,047 | |||||||||
| Less net earnings (loss) attributable to | ||||||||||||||
| noncontrolling interests, discontinued operations | (1) | 312 | 157 | 36 | 53 | |||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, | ||||||||||||||
| net of taxes and noncontrolling interests | (952) | (7,807) | 5,698 | 5,439 | 4,995 | |||||||||
| Consolidated net earnings (loss) | ||||||||||||||
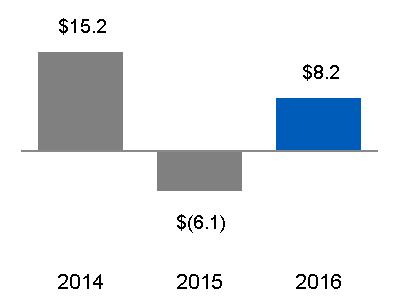
| attributable to GE common shareowners | $ | 8,176 | $ | (6,145) | $ | 15,233 | $ | 13,057 | $ | 13,641 | ||||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 35
SEGMENT RESULTS
(Dollars in billions)
INDUSTRIAL SEGMENT EQUIPMENT & SERVICES REVENUES | INDUSTRIAL SEGMENT PROFIT | |||
 | Equipment(a) Services(b) |  | ||
(a) In 2015, $59.8 billion, excluding $1.1 billion related to Alstom.* In 2016, $52.7 billion, excluding $8.1 billion related to Alstom* (b) In 2015, $47.1 billion, excluding $0.8 billion related to Alstom.* In 2016, $47.5 billion, excluding $4.9 billion related to Alstom* | (a) $18.1 billion, excluding $(0.2) billion related to Alstom* (b) $16.8 billion, excluding $0.8 billion related to Alstom* | |||
2016 – 2015 COMMENTARY | ||||
· Industrial segment revenues increased $4.4 billion, or 4%, primarily driven by increases at Power and Renewable Energy, mainly due to the effects of the Alstom acquisition, and an organic increase at Renewable Energy. This increase in industrial segment revenues was partially offset by lower revenues at Oil & Gas and Transportation, including the effects of foreign currency exchange of $0.3 billion at Oil & Gas. · Industrial segment acquisition revenues, driven by Alstom, also positively affected Energy Connections & Lighting, however, this was mostly offset by the effects of disposition revenues related to the sale of Appliances in the second quarter of 2016 and sales of Meters, Intelligent Platforms Embedded Systems Products and Signaling businesses in 2015. · Industrial segment profit decreased $0.4 billion, or 2%, mainly driven by lower earnings organically at Oil & Gas and Energy Connections & Lighting, as well as an unfavorable impact of foreign exchange, partially offset by higher earnings at Aviation, Power, Healthcare and Renewable Energy. · Industrial segment operating profit margin decreased 90 bps to 15.6%, primarily driven by the effects of Alstom results. Excluding Alstom*, industrial segment operating profit margin was 16.8%, compared with 17.0% in 2015, reflecting core decreases at Power, Oil & Gas and Energy Connections & Lighting, that more than offset increases at Aviation, Healthcare and Transportation. | ||||
| 2015 – 2014 COMMENTARY | |
· Industrial segment revenues decreased $0.9 billion, or 1%, primarily driven by decreases at Oil & Gas, mainly related to the effects of foreign currency exchange and a decrease at Oil & Gas organically. This decrease was partially offset by higher revenues at Power, Energy Connections & Lighting, and Aviation, mainly as a result of organic increases, as well as the effects of the Alstom acquisition at Power and Energy Connections & Lighting, partially offset by the effects of dispositions related to the sale of Intelligent Platforms Embedded Systems Products and Wayne in 2015. · Industrial segment profit increased $0.2 billion, or 1%, mainly driven by higher earnings at Aviation, Energy Connections & Lighting and Transportation, partially offset by lower earnings at Oil & Gas and Renewable Energy, as well as an unfavorable impact of foreign exchange. · Industrial segment operating profit margin increased 30 bps to 16.5% primarily driven by Aviation and Transportation, partially offset by the effects of the Alstom acquisition. Excluding Alstom*, industrial segment operating profit margin was 17.0%, compared with 16.2% in 2014, reflecting core increases at Power and Energy Connections & Lighting. | |
*Non-GAAP Financial Measure
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 36
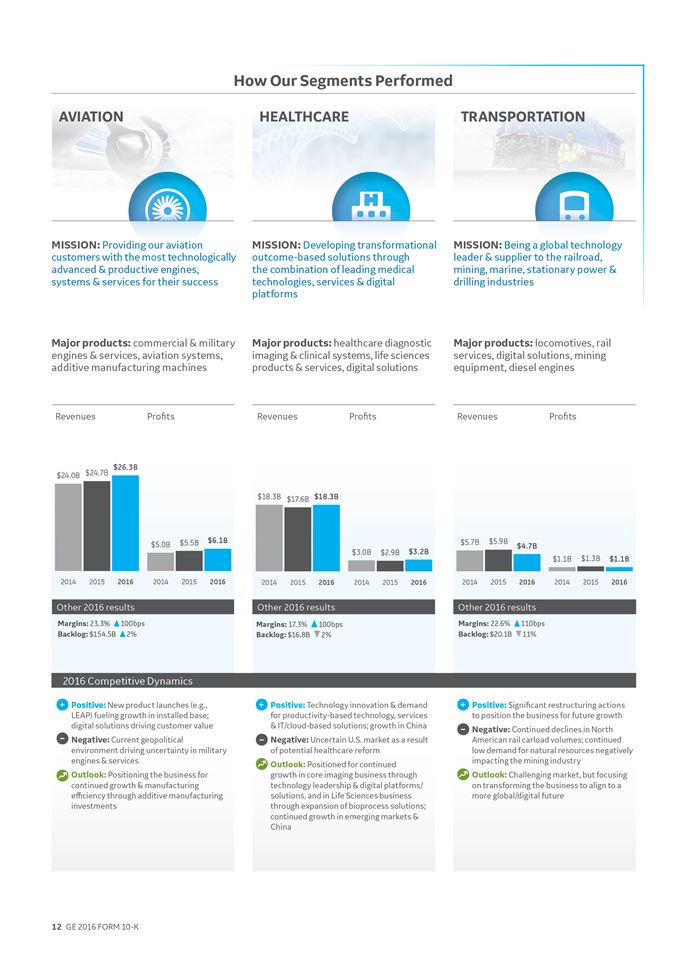
 POWER
POWERBUSINESS OVERVIEW
Leader: Steve Bolze | Headquarters & Operations | |||
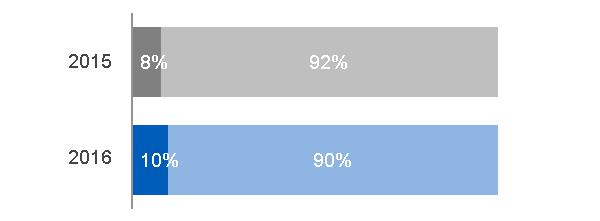
 | · Senior Vice President, GE and President & CEO, GE Power · Over 20 years of service with General Electric |  | · 22% of segment revenues · 24% of industrial segment revenues · 28% of industrial segment profit · Headquarters: Schenectady, NY · Serving customers in 140+ countries · Employees: approximately 57,000 | |
| Products & Services | ||||
 | Power serves power generation, industrial, government and other customers worldwide with products and services related to energy production and water reuse. Our products and technologies harness resources such as oil, gas, coal, diesel, nuclear and water to produce electric power and include gas and steam turbines, full balance of plant, upgrade and service solutions, as well as data-leveraging software. | |||
| · | Gas Power Systems – offers a wide spectrum of heavy-duty and aeroderivative gas turbines for utilities, independent power producers and numerous industrial applications, ranging from small, mobile power to utility scale power plants. |
| · | Steam Power Systems – offers steam power technology for coal and nuclear applications including boilers, generators, steam turbines, and Air Quality Control Systems (AQCS) to help efficiently produce power and provide performance over the life of a power plant. |
| · | Power Services – delivers maintenance, service and upgrade solutions across total plant assets and over their operational lifecycle, leveraging the Industrial Internet to improve the performance of such solutions. |
| · | Distributed Power – provides technology-based products and services to generate reliable and efficient power at or near the point of use. The product portfolio features highly efficient, fuel flexible industrial gas engines, including Jenbacher and Waukesha engines, that generate power for numerous industries globally. |
| · | Water & Process Technologies – provides comprehensive chemical and equipment solutions and services to help manage and optimize water resources across numerous industries and municipalities, including water treatment, wastewater treatment and process system solutions. |
| · | GE Hitachi Nuclear – offers advanced reactor technologies solutions, including reactors, fuels and support services for boiling water reactors, and is offered through joint ventures with Hitachi and Toshiba, for safety, reliability and performance for nuclear fleets. |
| Competition & Regulation |
Worldwide competition for power generation products and services is intense. Demand for power generation is global and, as a result, is sensitive to the economic and political environments of each country in which we do business.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 37
OPERATIONAL OVERVIEW
(Dollars in billions)
| 2016 GEOGRAPHIC REVENUES: $ 26.8 BILLION | ORDERS | ||||
 |  | Equipment Services | |||
(a) Includes $1.0 billion related to Alstom (b) Includes $10.0 billion related to Alstom | |||||
2016 SUB-SEGMENT REVENUES | BACKLOG | ||||
 (a) Includes Water & Process Technologies, Distributed Power and GE Hitachi Nuclear |  | Equipment Services | |||
(a) Includes $15.5 billion related to Alstom (b) Includes $18.3 billion related to Alstom | |||||
EQUIPMENT/SERVICES REVENUES | UNIT SALES | ||||
 |  | ||||
Services Equipment | |||||
| SIGNIFICANT TRENDS & DEVELOPMENTS | |||||
| · | The integration of Alstom's Thermal business has yielded significant efficiencies in supply chain, service infrastructure, new product development and SG&A costs. |
| · | We announced our plan to sell our Water & Process Technologies business that will further position the business for long-term growth. |
| · | We expanded our capabilities surrounding the manufacturing and supply of power plant equipment by acquiring Metem Corporation and a unit of South Korea's Doosan Engineering and Construction Company, which provides Heat Steam Recovery Generators. |
| · | Digital offerings have been developed to further complement our equipment and services business and drive value and better outcomes for our customers. |
| · | The business continues to invest in new product development, such as our new HA-Turbine, reciprocating engines and advanced upgrades, to expand our equipment and services offerings. |
| · | Excess capacity in developed markets, continued pressure in oil and gas applications and macroeconomic and geopolitical environments result in uncertainty for the industry and business. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 38
FINANCIAL OVERVIEW
(Dollars in billions)
| SEGMENT REVENUES | SEGMENT PROFIT | SEGMENT PROFIT MARGIN | ||
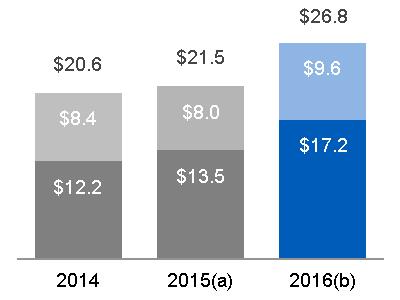 (a) $20.6 billion, excluding $0.9 billion related to Alstom* (b) $20.6 billion, excluding $6.3 billion related to Alstom* | Equipment Services |  (a) $4.6 billion, excluding $(0.1) billion related to Alstom* (b) $4.4 billion, excluding $0.6 billion related to Alstom* |  (a) 22.3%, excluding (8.7)% related to Alstom* (b) 21.5%, excluding 9.0% related to Alstom* |
| SEGMENT REVENUES & PROFIT WALK: | COMMENTARY: | |||||
| 2016 – 2015 | 2016 – 2015 | |||||
Segment revenues up $5.3 billion (25%); Segment profit up $0.5 billion (11%) as a result of: · The increase in revenues was driven primarily by the effects of the Alstom acquisition, including higher sales at Steam Power Systems, as well as higher volume at Power Services, partially offset by the impact of a stronger U.S. dollar and lower other income. Core revenues were flat. · The increase in profit was mainly driven by the effects of the Alstom acquisition, as well as material deflation, partially offset by lower cost productivity and an unfavorable business mix, driven by HA-Turbine shipments in the current year. | ||||||
| Revenues | Profit | |||||
| 2015 | $ | 21.5 | $ | 4.5 | ||
| Volume | 0.1 | - | ||||
| Price | - | - | ||||
| Foreign Exchange | (0.1) | - | ||||
| (Inflation)/Deflation | N/A | 0.1 | ||||
| Mix | N/A | (0.1) | ||||
| Productivity | N/A | (0.1) | ||||
| Other | (0.1) | (0.1) | ||||
| Alstom | 5.3 | 0.6 | ||||
| 2016 | $ | 26.8 | $ | 5.0 | ||
| 2015 – 2014 | 2015 – 2014 | |||||
Segment revenues up $0.9 billion (4%); Segment profit was flat as a result of: · The increase in revenues was mainly driven by higher volume, primarily at Power Services, as well as the effects of the Alstom acquisition, partially offset by the impact of a stronger U.S. dollar. · Profit was flat as higher volume, the effects of deflation, higher prices, and favorable business mix were offset by lower productivity, including an increase in SG&A cost, the impact of a stronger U.S. dollar, and the effects of the Alstom acquisition. | ||||||
| Revenues | Profit | |||||
| 2014 | $ | 20.6 | $ | 4.5 | ||
| Volume | 0.8 | 0.2 | ||||
| Price | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||||
| Foreign Exchange | (0.8) | (0.1) | ||||
| (Inflation)/Deflation | N/A | 0.2 | ||||
| Mix | N/A | 0.1 | ||||
| Productivity | N/A | (0.4) | ||||
| Other | - | - | ||||
| Alstom | 0.9 | (0.1) | ||||
| 2015 | $ | 21.5 | $ | 4.5 | ||
*Non-GAAP Financial Measure
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 39
 RENEWABLE ENERGY
RENEWABLE ENERGYBUSINESS OVERVIEW
Leader: Jérôme Pécresse | Headquarters & Operations | |||
 | · Senior Vice President, GE and President & CEO, GE Renewable Energy · Former Alstom Renewable Power Executive Vice President |  | · 7% of segment revenues · 8% of industrial segment revenues · 3% of industrial segment profit · Headquarters: Paris, France · Serving customers in 80+ countries · Employees: approximately 12,000 | |
Products & Services | ||||
 | GE Renewable Energy makes renewable power sources affordable, accessible, and reliable for the benefit of people everywhere. With one of the broadest technology portfolios in the industry, Renewable Energy creates value for customers with solutions from onshore and offshore wind, hydro, and emerging low carbon technologies. With operations in 40+ countries around the world, Renewable Energy can deliver solutions to where its customers need them most. | |||
| · | Onshore Wind – provides technology and services for the onshore wind power industry by providing wind turbine platforms and hardware and software to optimize wind resources. Wind services help customers improve availability and value of their assets over the lifetime of the fleet. Digital Wind Farm is a site level solution, creating a dynamic, connected and adaptable ecosystem that improves our customers' fleet operations. |
| · | Offshore Wind – offers its high-yield offshore wind turbine, Haliade 150-6MW, which is compatible with bottom fixed and floating foundations. It uses the innovative pure torque design and the Advanced High Density direct-drive Permanent Magnet Generator. Wind services support customers over the lifetime of their fleet. |
| · | Hydro – provides a full range of solutions, products and services to serve the hydropower industry from initial design to final commissioning, from Low Head / Medium / High Head hydropower plants to pumped storage hydropower plants, small hydropower plants, concentrated solar power plants, geothermal power plants and biomass power plants. |
| Competition & Regulation |
Renewable energy is now mainstream and more able to compete with other sources of power generation. While many factors, including government incentives and specific market rules, affect how renewable energy can deliver outcomes for customers in a given region, the point is the same: renewable energy is increasingly able to compete with fossil fuels. That is in large part due to technology. New innovations such as the digitization of renewable energy continue to drive down costs. We are also helping to make renewable energy more competitive through wind turbine product improvements, including larger rotors, taller towers and higher nameplate ratings that continue to drive down the cost of wind energy. As industry models continue to evolve, our digital strategy and investments in technical innovation will position us to add value for customers looking for clean, renewable energy.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 40
OPERATIONAL OVERVIEW
(Dollars in billions)
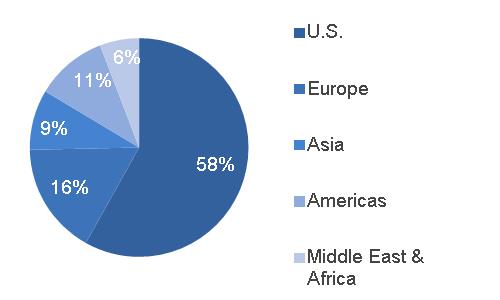
| 2016 GEOGRAPHIC REVENUES: $ 9.0 BILLION | ORDERS | ||||
 |  | Equipment Services | |||
(a) Includes $0.5 billion related to Alstom (b) Includes $1.8 billion related to Alstom | |||||
2016 SUB-SEGMENT REVENUES | BACKLOG | ||||
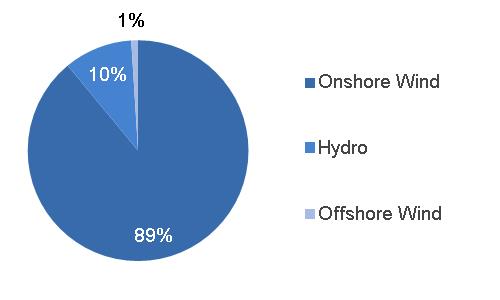 |  | Equipment Services | |||
(a) Includes $5.3 billion related to Alstom (b) Includes $5.5 billion related to Alstom | |||||
EQUIPMENT/SERVICES REVENUES | UNIT SALES | ||||
 |  | ||||
| Services Equipment | |||||
SIGNIFICANT TRENDS & DEVELOPMENTS | |||||
| · | Renewable energy has experienced a surge of development in the last decade. Renewable energy capacity additions account for approximately half of all power plant additions worldwide. |
| · | The market to "repower" existing wind turbines – i.e., upgrade units that have been in service for a number of years to increase their efficiency and performance – is growing as the existing Onshore Wind turbine fleet is aging. Repowering allows customers to increase the annual energy output of their installed base, provide more competitively priced energy, and extend the life of their assets. |
| · | New Product Introductions continue to be a key lever as our customers show a willingness to invest in new technology that decreases the levelized cost of energy. |
| · | The $1.7 billion planned acquisition of LM Wind Power will bolster the ability of the GE Onshore and Offshore wind businesses to add value for customers while in-sourcing production and also better serve the customers of LM Wind Power. |
| · | In 2016, we introduced new software applications suite for the Digital Wind Farm. The new apps, which streamline wind farm operations, are compatible with the company's latest 2 and 3 MW wind turbine platforms and GE's broader Predix software and diagnostics platform. The new applications can reduce maintenance costs by up to 10 percent and deliver one-to-three percent of additional revenue per site. |
| · | The Offshore Wind business supported its customer, Deepwater Wind, in bringing the first ever offshore wind farm – the 30MW Block Island Wind Farm near Rhode Island – into commercial operation in the U.S. |
| · | Continued competitive pressure from other wind turbine producers, as well as from other energy sources such as primarily solar photovoltaic, reinforced by a general move to auction mechanisms, increases price pressure and the need for innovation in the wind market. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 41
FINANCIAL OVERVIEW
(Dollars in billions)
| SEGMENT REVENUES | SEGMENT PROFIT | SEGMENT PROFIT MARGIN | ||
 (a) $6.2 billion, excluding $0.1 billion related to Alstom* (b) $7.9 billion, excluding $1.2 billion related to Alstom* | Equipment Services | 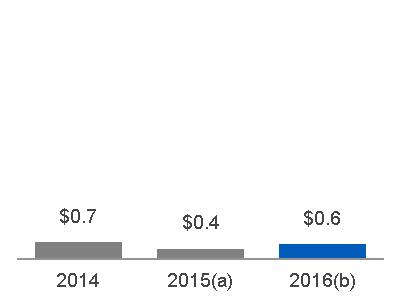 (a) $0.5 billion, excluding $(0.1) billion related to Alstom* (b) $0.5 billion, excluding an insignificant amount related to Alstom* |  (a) 8.1%, excluding (79.3)% related to Alstom* (b) 6.9%, excluding 2.6% related to Alstom* |
| SEGMENT REVENUES & PROFIT WALK: | COMMENTARY: | |||||
| 2016 – 2015 | 2016 – 2015 | |||||
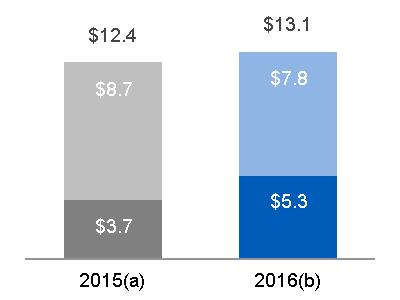
Segment revenues up $2.8 billion (44%); Segment profit up $0.1 billion (34%) as a result of: · The increase in revenues was due to higher volume, mainly driven by higher core equipment sales at Onshore Wind as a result of shipping 420 more onshore wind turbines than in the prior year, as well as higher sales at Hydro, driven by the effects of the Alstom acquisition. The increase was partially offset by lower other income, including negative foreign exchange transactional hedge impacts, and lower prices. · The increase in profit was due to material deflation and higher volume, driven primarily by Onshore Wind, partially offset by lower other income, including negative foreign exchange transactional hedge impacts, lower prices and an unfavorable business mix, driven by low margin projects with higher services margins. | ||||||
| Revenues | Profit | |||||
| 2015 | $ | 6.3 | $ | 0.4 | ||
| Volume | 2.0 | 0.1 | ||||
| Price | (0.1) | (0.1) | ||||
| Foreign Exchange | (0.1) | - | ||||
| (Inflation)/Deflation | N/A | 0.2 | ||||
| Mix | N/A | (0.1) | ||||
| Productivity | N/A | - | ||||
| Other | (0.1) | (0.1) | ||||
| Alstom | 1.1 | 0.1 | ||||
| 2016 | $ | 9.0 | $ | 0.6 | ||
| 2015 – 2014 | 2015 – 2014 | |||||
Segment revenues down $0.1 billion (2%); Segment profit down $0.3 billion (38%) as a result of: · The decrease in revenues was primarily driven by the effects of a stronger U.S. dollar, partially offset by higher volume, driven by the sale of 2 MW onshore units, higher prices, the effects of the Alstom acquisition and other income. · The decrease in profit was due to lower productivity, primarily driven by a shift to new products and technology, the effects of inflation, the effects of the Alstom acquisition and negative business mix, partially offset by higher prices and other income. | ||||||
| Revenues | Profit | |||||
| 2014 | $ | 6.4 | $ | 0.7 | ||
| Volume | 0.3 | - | ||||
| Price | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||||
| Foreign Exchange | (0.6) | - | ||||
| (Inflation)/Deflation | N/A | (0.1) | ||||
| Mix | N/A | (0.1) | ||||
| Productivity | N/A | (0.1) | ||||
| Other | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||||
| Alstom | 0.1 | (0.1) | ||||
| 2015 | $ | 6.3 | $ | 0.4 | ||
*Non-GAAP Financial Measure
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 42
 OIL & GAS
OIL & GASBUSINESS OVERVIEW
Leader: Lorenzo Simonelli | Headquarters & Operations | ||||
 | · Senior Vice President, GE and President & CEO, GE Oil & Gas · Over 20 years of service with General Electric |  | · 10% of segment revenues · 11% of industrial segment revenues · 8% of industrial segment profit · Headquarters: London, UK · Serving customers in 140+ countries · Employees: approximately 34,000 | ||
Products & Services | |||||
 | Oil & Gas serves all segments of the oil and gas industry, from drilling, completion, production and oil field operations, to transportation via liquefied natural gas (LNG) and pipelines. In addition, Oil & Gas provides industrial power generation and compression solutions to the refining and petrochemicals segments. Oil & Gas also delivers pipeline integrity solutions and a wide range of sensing, inspection and monitoring technologies. Oil & Gas exploits technological innovation from other GE segments, such as Aviation and Healthcare, to continuously improve oil and gas industry performance, output and productivity. | ||||
| · | Turbomachinery Solutions (TMS) – provides equipment and related services for mechanical-drive, compression and power-generation applications across the oil and gas industry. Our designs deliver high capacities and efficiencies, increase product flow and decrease both operational and environmental risks in the most extreme conditions, pressures and temperatures. Our portfolio includes drivers (aero-derivative gas turbines, heavy-duty gas turbines and synchronous and induction electric motors), compressors (centrifugal and axial, direct drive high speed, integrated, subsea compressors and turbo expanders), and turn-key solutions (industrial modules and waste heat recovery). |
| · | Subsea Systems & Drilling (SS&D) – provides a broad portfolio of subsea products and services required to facilitate the safe and reliable flow of hydrocarbons from the subsea wellhead to the surface. In addition, the sub-segment designs and manufactures onshore and offshore drilling and production systems and equipment for floating production platforms and provides a full range of services related to onshore and offshore drilling activities. |
| · | Digital Solutions (DS) – provides equipment and services for a wide range of industries, including oil & gas, power generation, aerospace, metals, and transportation. The offerings include sensor-based measurement; non-destructive testing and inspection; turbine, generator and plant controls and condition monitoring, as well as pipeline integrity solutions. |
| · | Surface – provides products and services for onshore oil & gas wells and manufactures artificial lift equipment for extracting crude oil and other fluids from wells. Specific products include downhole tools for well integrity, dry trees and surface wellheads, electric submersible pumps, surface wellheads, wireline logging, artificial lift technologies, drilling pressure control equipment. |
| · | Downstream Technology Solutions (DTS) – provides products and services to serve the downstream segments of the industry including refining, petrochemical, distributed gas, flow and process control and other industrial applications. Products include steam turbines, reciprocating and centrifugal compressors, pumps, valves, and compressed natural gas (CNG) and small-scale LNG solutions used primarily for shale oil and gas field development. |
| Competition & Regulation |
Demand for oil and gas equipment and services is global and, as a result, is sensitive to the economic and political environment of each country in which we do business. We are subject to the regulatory bodies of the countries in which we operate. Our products are subject to regulation by U.S. and non-U.S. energy policies.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 43
OPERATIONAL OVERVIEW
(Dollars in billions)
| 2016 GEOGRAPHIC REVENUES: $ 12.9 BILLION | ORDERS | ||||
 | 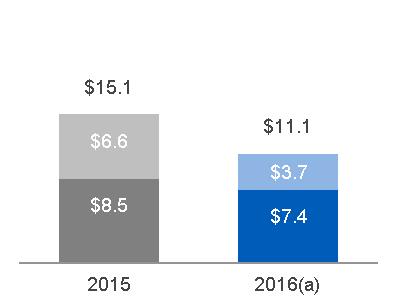 | Equipment Services | |||
| (a) Includes $0.1 billion related to Alstom | |||||
| 2016 SUB-SEGMENT REVENUES | BACKLOG | ||||
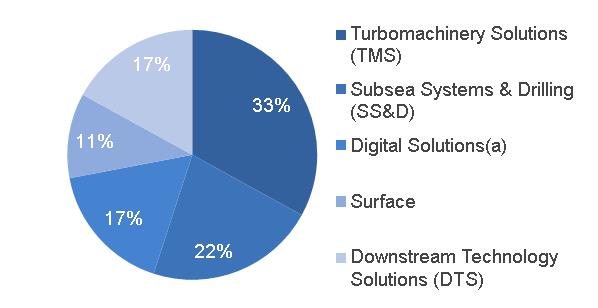 |  | Equipment Services | |||
(a) Previously referred to as Measurement & Controls (M&C) | (a) Includes $0.1 billion related to Alstom | ||||
EQUIPMENT/SERVICES REVENUES | |||||
 | |||||
Services Equipment | |||||
| SIGNIFICANT TRENDS & DEVELOPMENTS | |||||
| · | In October 2016, we announced that our Oil & Gas business would combine with Baker Hughes to create a world-leading oilfield technology provider with mix of service and equipment. The combined businesses will be a leading equipment, technology and services provider in the oil and gas industry. The transaction is subject to the approval of Baker Hughes shareholders, regulatory approvals and other customary closing conditions. |
| · | Lower oil prices leading to reductions in customers' forecasted capital expenditures create industry challenges, the effects of which are uncertain. |
| · | We are impacted by volatility in foreign currency exchange rates mainly due to a high concentration of non-U.S. dollar denominated business as well as long-term contracts denominated in multiple currencies. |
| · | In 2015, a portion of the Distributed Power business that provides turbines for oil and gas applications was realigned from the Power segment to the Oil & Gas segment. |
| · | We continue to take significant cost reduction actions in response to the weakening oil & gas market. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 44
FINANCIAL OVERVIEW
(Dollars in billions)
| SEGMENT REVENUES | SEGMENT PROFIT | SEGMENT PROFIT MARGIN | ||
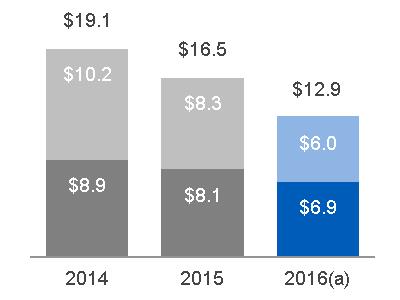 (a) $12.8 billion, excluding $0.1 billion related to Alstom* | Equipment Services | 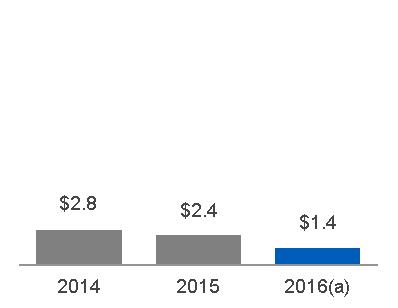 (a) $1.4 billion, excluding an insignificant amount related to Alstom* |  (a) 10.8%, excluding 6.5% related to Alstom* |
| SEGMENT REVENUES & PROFIT WALK: | COMMENTARY: | |||||
| 2016 – 2015 | 2016 – 2015 | |||||
Segment revenues down $3.6 billion (22%); Segment profit down $1.0 billion (43%) as a result of: · The decrease in revenues was mainly due to lower core volume across all sub-segments, primarily Surface and SS&D, due to lower oil prices, as well as the effects of a stronger U.S. dollar, and lower other income, including negative foreign exchange transactional hedge impacts, partially offset by the effects of the Alstom acquisition. · The decrease in profit was primarily market driven, mainly due to lower core volume across all sub-segments due to lower oil prices, which, despite the effects of restructuring actions, drove lower cost productivity. Profit was also adversely impacted by unfavorable foreign exchange transactional hedge impacts in the year. These decreases were partially offset by material deflation. Operating profit excluding the effects of foreign exchange of $0.1 billion was $1.5 billion (down 37% compared with prior year).* | ||||||
| Revenues | Profit | |||||
| 2015 | $ | 16.5 | $ | 2.4 | ||
| Volume | (3.0) | (0.4) | ||||
| Price | (0.3) | (0.3) | ||||
| Foreign Exchange | (0.3) | - | ||||
| (Inflation)/Deflation | N/A | 0.2 | ||||
| Mix | N/A | - | ||||
| Productivity | N/A | (0.5) | ||||
| Other | (0.1) | - | ||||
| Alstom | 0.1 | - | ||||
| 2016 | $ | 12.9 | $ | 1.4 | ||
| 2015 – 2014 | 2015 – 2014 | |||||
Segment revenues down $2.6 billion (14%); Segment profit down $0.3 billion (12%) as a result of: · The decrease in revenues was primarily due to the impact of a stronger U.S. dollar and lower volume at Surface and SS&D, driven by lower oil prices. Organic revenues* were down 5% compared with prior year. · The decrease in profit was primarily due to the impact of a stronger U.S. dollar and lower volume at Surface and SS&D, driven by lower oil prices, partially offset by the effects of deflation and cost productivity. Organic profit* increased 1% compared with prior year. | ||||||
| Revenues | Profit | |||||
| 2014 | $ | 19.1 | $ | 2.8 | ||
| Volume | (1.0) | (0.1) | ||||
| Price | - | - | ||||
| Foreign Exchange | (1.6) | (0.3) | ||||
| (Inflation)/Deflation | N/A | 0.1 | ||||
| Mix | N/A | - | ||||
| Productivity | N/A | 0.1 | ||||
| Other | - | - | ||||
| Alstom | - | - | ||||
| 2015 | $ | 16.5 | $ | 2.4 | ||
*Non-GAAP Financial Measure
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 45
BUSINESS OVERVIEW
Leader: David Joyce | Headquarters & Operations | |||||
 | · Vice Chairman, GE and President & CEO, GE Aviation · Over 30 years of service with General Electric |  | · 21% of segment revenues · 23% of industrial segment revenues · 35% of industrial segment profit · Headquarters: Cincinnati, OH · Serving customers in 120+ countries · Employees: approximately 45,000 | |||
Products & Services | ||||||
 | Aviation designs and produces commercial and military aircraft engines, integrated digital components, electric power and mechanical aircraft systems. We also provide aftermarket services to support our products. | |||||
| · | Commercial Engines – manufactures jet engines and turboprops for commercial airframes. Our commercial engines power aircraft in all categories; regional, narrowbody and widebody. We also manufacture engines and components for business and general aviation segments. |
| · | Commercial Services – provides maintenance, component repair and overhaul services (MRO), including sales of replacement parts. |
| · | Military – manufactures jet engines for military airframes. Our military engines power a wide variety of military aircraft including fighters, bombers, tankers, helicopters and surveillance aircraft, as well as marine applications. We provide maintenance, component repair and overhaul services, including sales of replacement parts. |
| · | Systems – provides components, systems and services for commercial and military segments. This includes avionics systems, aviation electric power systems, flight efficiency and intelligent operation services, aircraft structures and Avio Aero. |
| · | Additive – provides machines for metal additive manufacturing for industry and comprises our existing technologies as well as two new acquisitions, enabling the design and manufacture of complex parts and leverage of technology for improved cost and performance. |
| · | We also produce and market engines through CFM International, a company jointly owned by GE and Snecma, a subsidiary of SAFRAN of France, and Engine Alliance, LLC, a company jointly owned by GE and the Pratt & Whitney division of United Technologies Corporation. New engines are also being designed and marketed in a joint venture with Honda Aero, Inc., a division of Honda Motor Co., Ltd. |
| Competition & Regulation |
The global businesses for aircraft jet engines, maintenance component repair and overhaul services (including parts sales) are highly competitive. Both U.S. and non-U.S. markets are important to the growth and success of the business. Product development cycles are long and product quality and efficiency are critical to success. Research and development expenditures are important in this business, as are focused intellectual property strategies and protection of key aircraft engine design, manufacture, repair and product upgrade technologies. Aircraft engine orders and systems tend to follow civil air travel and demand and military procurement cycles.
Our product, services and activities are subject to a number of regulators such as by the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) and other regulatory bodies.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 46
OPERATIONAL OVERVIEW
(Dollars in billions)
| 2016 GEOGRAPHIC REVENUES: $ 26.3 BILLION | ORDERS | ||||
 |  | Equipment Services | |||
| 2016 SUB-SEGMENT REVENUES | BACKLOG | ||||
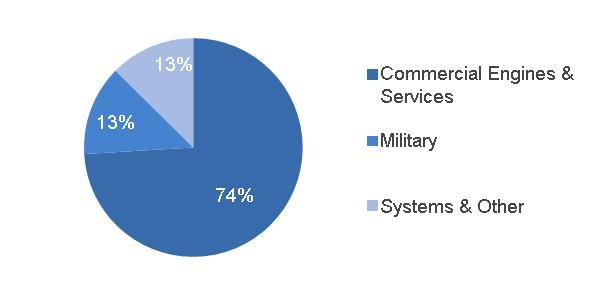 |  | Equipment Services | |||
| EQUIPMENT/SERVICES REVENUES | UNIT SALES | ||||
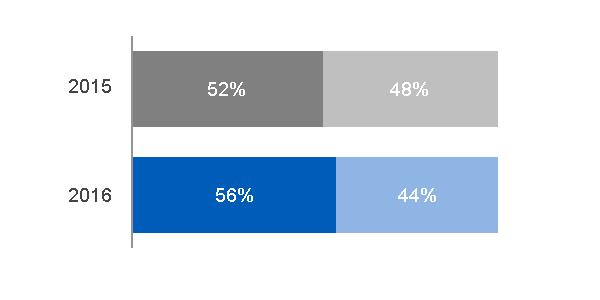 |  (a) GEnx and LEAP engines are a subset of commercial engines (b) Commercial spares shipment rate in millions of dollars per day | ||||
| Services Equipment | |||||
SIGNIFICANT TRENDS & DEVELOPMENTS | |||||
| · | The installed base continues to grow with new product launches. In 2016, through our CFM joint venture, we successfully launched the LEAP engine for application on the Airbus A320 NEO. Another variant of the engine, applied to the Boeing 737 MAX aircraft, is expected to enter in service in 2017. We are also continuing development on the Advanced Turbo Prop program, and the GE9X engine incorporating the latest technologies for application in the widebody aircraft space. |
| · | During the fourth quarter of 2016, Aviation completed its acquisition of a 75% stake in Concept Laser GmbH, a German company specializing in powder bed based laser metal printing, and a 76.2% stake in Arcam AB, a Swedish company specializing in electron beam melting systems. We expect both of these investments in the additive manufacturing space to open a new market segment and also realize manufacturing efficiencies for GE. |
| · | Our digital industrial business is providing insights and operational value for our customers, unlocking opportunities to deliver more productivity beyond our traditional services and becoming a better partner as we work on solving our customers' toughest operational problems. Our digital factory initiatives, including digital design tools, advanced and automated inspection, and advanced manufacturing analytics are enabling our operations, partners and suppliers to dramatically reduce cycle time while improving quality. |
| · | We expect an uptick in military shipments and continue to advance our next generation science and technology programs, two of which were awarded contracts in 2016. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 47
FINANCIAL OVERVIEW
(Dollars in billions)
| SEGMENT REVENUES | SEGMENT PROFIT | SEGMENT PROFIT MARGIN | ||
 | Equipment Services |  |  |
| SEGMENT REVENUES & PROFIT WALK: | COMMENTARY: | |||||
| 2016 – 2015 | 2016 – 2015 | |||||
Segment revenues up $1.6 billion (6%); Segment profit up $0.6 billion (11%) as a result of: · The increase in revenues was primarily due to higher services volume and LEAP engine shipments, partially offset by lower equipment volume driven by lower Military shipments. Revenues also increased as a result of higher engines and services pricing. Prices increased in response to higher material and conversion costs. · The increase in profit was mainly due to higher cost productivity, driven by higher services volume and prices. These increases were partially offset by the effects of inflation, an unfavorable business mix driven by LEAP shipments, and lower other income. | ||||||
| Revenues | Profit | |||||
| 2015 | $ | 24.7 | $ | 5.5 | ||
| Volume | 1.5 | 0.3 | ||||
| Price | 0.2 | 0.2 | ||||
| Foreign Exchange | - | - | ||||
| (Inflation)/Deflation | N/A | (0.2) | ||||
| Mix | N/A | (0.1) | ||||
| Productivity | N/A | 0.5 | ||||
| Other | - | (0.1) | ||||
| 2016 | $ | 26.3 | $ | 6.1 | ||
| 2015 – 2014 | 2015 – 2014 | |||||
Segment revenues up $0.7 billion (3%); Segment profit up $0.5 billion (11%) as a result of: · The increase in revenues was due to higher prices in Commercial Engines and higher services volume, partially offset by decreased equipment sales. · The increase in profit was mainly due to higher prices, favorable business mix and higher cost productivity, partially offset by the effects of inflation and lower other income. | ||||||
| Revenues | Profit | |||||
| 2014 | $ | 24.0 | $ | 5.0 | ||
| Volume | 0.1 | - | ||||
| Price | 0.5 | 0.5 | ||||
| Foreign Exchange | - | - | ||||
| (Inflation)/Deflation | N/A | (0.2) | ||||
| Mix | N/A | 0.2 | ||||
| Productivity | N/A | 0.1 | ||||
| Other | - | (0.1) | ||||
| 2015 | $ | 24.7 | $ | 5.5 | ||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 48
 HEALTHCARE
HEALTHCAREBUSINESS OVERVIEW
Leader: John L. Flannery | Headquarters & Operations | |||||||
 | · Senior Vice President, GE and President & CEO, GE Healthcare · Over 25 years of service with General Electric |  | · 15% of segment revenues · 16% of industrial segment revenues · 18% of industrial segment profit · Headquarters: Chicago, IL · Serving customers in 140+ countries · Employees: approximately 54,000 | |||||
| Products & Services | ||||||||
 | Healthcare provides essential healthcare technologies to developed and emerging markets and has expertise in medical imaging, digital solutions, patient monitoring and diagnostics, drug discovery, biopharmaceutical manufacturing technologies and performance improvement solutions. Products and services are sold worldwide primarily to hospitals, medical facilities, pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, and to the life science research market. | |||||||
| · | Healthcare Systems – provides a wide range of technologies and services that include diagnostic imaging and clinical systems. Diagnostic imaging systems such as X-ray, digital mammography, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance (MR), surgical and interventional imaging and molecular imaging technologies allow clinicians to see inside the human body more clearly. Clinical systems such as ultrasound, electrocardiography (ECG), bone densitometry, patient monitoring, incubators and infant warmers, respiratory care, and anesthesia management that enable clinicians to provide better care for patients every day – from wellness screening to advanced diagnostics to life-saving treatment. Healthcare systems also offers product services that include remote diagnostic and repair services for medical equipment manufactured by GE and by others. |
| · | Life Sciences – delivers products, services and manufacturing solutions for drug discovery, the biopharmaceutical industry and cellular technologies, so scientists and specialists discover new ways to predict, diagnose and treat disease. It also researches, manufactures and markets innovative imaging agents used during medical scanning procedures to highlight organs, tissue and functions inside the human body, to aid physicians in the early detection, diagnosis and management of disease through advanced in-vivo diagnostics. |
| · | Healthcare Digital – provides medical technologies, software, analytics, cloud solutions, implementation and services to drive increased access, enhanced quality and more affordable healthcare around the world. By combining digital and industrial, software and hardware, Healthcare Digital delivers integrated digital solutions that improve outcomes. |
| Competition & Regulation |
Healthcare competes with a variety of U.S. and non-U.S. manufacturers and services providers. Customers require products and services that allow them to provide better access to healthcare, improve the affordability of care, and improve the quality of patient outcomes. Technology and solution innovation to provide products that meet these customer requirements and competitive pricing are among the key factors affecting competition for these products and services. New technologies and solutions could make our products and services obsolete unless we continue to develop new and improved products and services.
Our products are subject to regulation by numerous government agencies, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (U.S. FDA), as well as various laws and regulations that apply to claims submitted under Medicare, Medicaid or other government funded healthcare programs.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 49
OPERATIONAL OVERVIEW
(Dollars in billions)
| 2016 GEOGRAPHIC REVENUES: $ 18.3 BILLION | ORDERS | ||||
 |  | Equipment Services | |||
| 2016 SUB-SEGMENT REVENUES | BACKLOG | ||||
 | 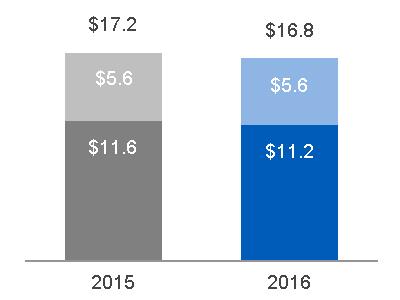 | Equipment Services | |||
| EQUIPMENT/SERVICES REVENUES | |||||
 | |||||
Services Equipment | |||||
| SIGNIFICANT TRENDS & DEVELOPMENTS | |||||
| · | We continue to lead in technology innovation with greater focus on productivity based technology, services, and IT/cloud-based solutions as healthcare providers seek greater productivity and efficiency. |
| · | The U.S. market is facing uncertainty regarding the future of the Affordable Care Act. Emerging markets are expected to grow long-term with short-term volatility. The China market was more robust in 2016 and is expected to be a source of growth. |
| · | Life Sciences is expanding its business through bioprocess market growth and enterprise solutions. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 50
FINANCIAL OVERVIEW
(Dollars in billions)
| SEGMENT REVENUES | SEGMENT PROFIT | SEGMENT PROFIT MARGIN | ||
 | Equipment Services | 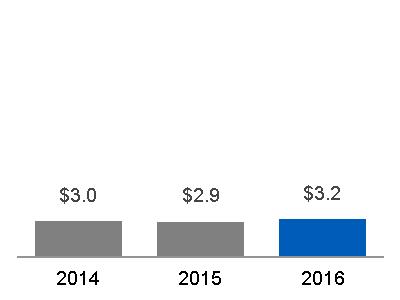 |  |
| SEGMENT REVENUES & PROFIT WALK: | COMMENTARY: | |||||
| 2016 – 2015 | 2016 – 2015 | |||||
Segment revenues up $0.7 billion (4%); Segment profit up $0.3 billion (10%) as a result of: · The increase in revenues was primarily due to higher volume in Life Sciences and Healthcare Systems, as well as higher other income, partially offset by lower prices at Healthcare Systems and the effects of a stronger U.S. dollar. · The increase in profit was primarily driven by higher cost productivity, including the effects of previous restructuring actions and strong volume growth, partially offset by lower prices at Healthcare Systems. | ||||||
| Revenues | Profit | |||||
| 2015 | $ | 17.6 | $ | 2.9 | ||
| Volume | 1.0 | 0.2 | ||||
| Price | (0.3) | (0.3) | ||||
| Foreign Exchange | (0.1) | - | ||||
| (Inflation)/Deflation | N/A | - | ||||
| Mix | N/A | - | ||||
| Productivity | N/A | 0.4 | ||||
| Other | 0.1 | - | ||||
| 2016 | $ | 18.3 | $ | 3.2 | ||
| 2015 – 2014 | 2015 – 2014 | |||||
Segment revenues down $0.7 billion (4%); Segment profit down $0.2 billion (5%) as a result of: · The decrease in revenues was primarily due to the effects of a stronger U.S. dollar, as well as lower prices, mainly at Healthcare Systems, partially offset by higher volume in Life Sciences and Healthcare Systems. · The decrease in profit was primarily due to lower prices, mainly in Healthcare Systems, the effects of inflation and the impact of a stronger U.S. dollar, partially offset by higher productivity, as increased R&D and related costs were more than offset by higher cost productivity, and higher volume. | ||||||
| Revenues | Profit | |||||
| 2014 | $ | 18.3 | $ | 3.0 | ||
| Volume | 0.8 | 0.1 | ||||
| Price | (0.3) | (0.3) | ||||
| Foreign Exchange | (1.1) | (0.1) | ||||
| (Inflation)/Deflation | N/A | (0.2) | ||||
| Mix | N/A | - | ||||
| Productivity | N/A | 0.3 | ||||
| Other | (0.1) | - | ||||
| 2015 | $ | 17.6 | $ | 2.9 | ||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 51
 TRANSPORTATION
TRANSPORTATIONBUSINESS OVERVIEW
Leader: Jamie S. Miller | Headquarters & Operations | |||
 | · Senior Vice President, GE and President & CEO, GE Transportation · 8 years of service with General Electric |  | · 4% of segment revenues · 4% of industrial segment revenues · 6% of industrial segment profit · Headquarters: Chicago, IL · Serving customers in 60+ countries · Employees: approximately 10,000 | |
| Products & Services | |||
 | Transportation is a global technology leader and supplier to the railroad, mining, marine, stationary power and drilling industries. Products and services offered by Transportation include: | ||
| · | Locomotives – we provide freight and passenger locomotives as well as rail services to help solve rail challenges. We manufacture high-horsepower, diesel-electric locomotives including the Evolution SeriesTM, which meets or exceeds the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) Tier 4 requirements for freight and passenger applications. |
| · | Services – we develop partnerships that support advisory services, parts, integrated software solutions and data analytics. Our comprehensive offerings include tailored service programs, high-quality parts for GE and other locomotive platforms, overhaul, repair and upgrade services, and wreck repair. Our portfolio provides the people, partnerships and leading software to optimize operations and asset utilization. |
| · | Digital Solutions – we offer a suite of software-enabled solutions to help our customers lower operational costs, increase productivity and improve service quality and reliability. |
| · | Mining – we provide mining equipment and services. The portfolio includes drive systems for off-highway vehicles, mining equipment, mining power and productivity. |
| · | Marine, Stationary & Drilling – we offer marine diesel engines and stationary power diesel engines and motors for land and offshore drilling rigs. |
| Competition & Regulation |
The competitive environment for locomotives and mining equipment and services consists of large global competitors. A number of smaller competitors compete in a limited-size product range and geographic regions. North America will remain a focus of the industry, due to the EPA Tier 4 emissions standard that went into effect in 2015.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 52
OPERATIONAL OVERVIEW
(Dollars in billions)
| 2016 GEOGRAPHIC REVENUES: $ 4.7 BILLION | ORDERS | ||||
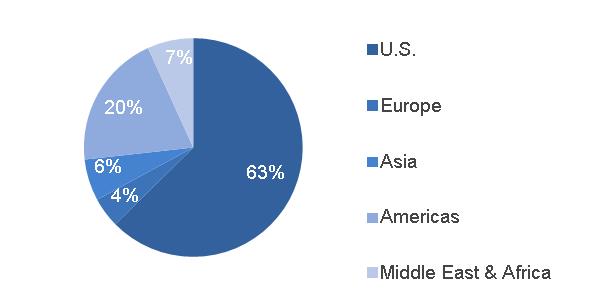 |  | Equipment Services | |||
| 2016 SUB-SEGMENT REVENUES | BACKLOG | ||||
 (a) Includes Digital Solutions and Marine, Stationary & Drilling |  | Equipment Services | |||
EQUIPMENT/SERVICES REVENUES | UNIT SALES | ||||
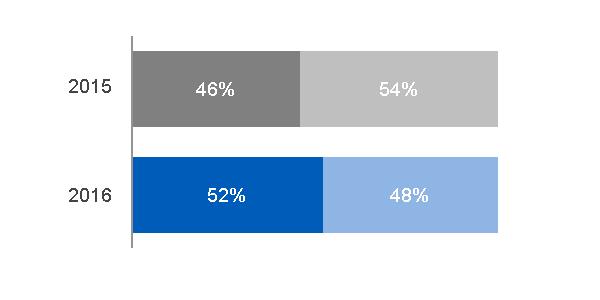 |  | ||||
Services Equipment | |||||
| SIGNIFICANT TRENDS & DEVELOPMENTS | |||||
| · | Rail carload volumes, especially in North America, continue to decline and the number of parked locomotives remained high throughout 2016. |
| · | Demand for natural resources remains low, driving a decline in the overall mining industry. |
| · | Global locomotive deliveries were down from 985 units in 2015 to 749 units in 2016, due to a lower need for power across the railroad industry. |
| · | The Signaling business was sold to Alstom on November 2, 2015 for approximately $0.8 billion, on which we recognized a pre-tax gain of $0.6 billion, which was reported in Corporate. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 53
FINANCIAL OVERVIEW
(Dollars in billions)
| SEGMENT REVENUES | SEGMENT PROFIT | SEGMENT PROFIT MARGIN | ||
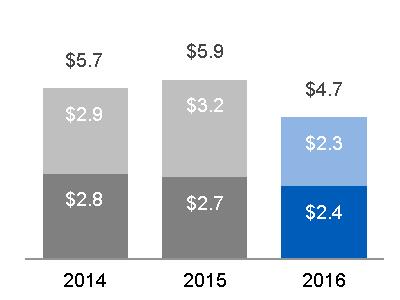 | Equipment Services | 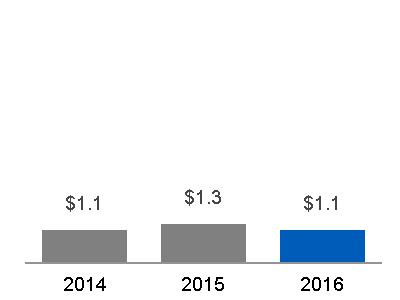 | 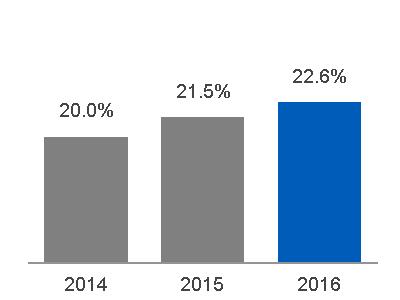 |
| SEGMENT REVENUES & PROFIT WALK: | COMMENTARY: | |||||
| 2016 – 2015 | 2016 – 2015 | |||||
Segment revenues down $1.2 billion (21%); Segment profit down $0.2 billion (16%) as a result of: · The decrease in revenues was primarily driven by lower equipment volume, driven by 236 fewer locomotive shipments than in the prior year, as well as lower services volume due to higher parked locomotives. The decrease in revenues was also impacted by the Signaling business disposition in November 2015. · The decrease in profit was primarily driven by lower volume, partially offset by material deflation and higher cost productivity, as well as the effects of restructuring actions. | ||||||
| Revenues | Profit | |||||
| 2015 | $ | 5.9 | $ | 1.3 | ||
| Volume | (1.2) | (0.2) | ||||
| Price | - | - | ||||
| Foreign Exchange | - | - | ||||
| (Inflation)/Deflation | N/A | 0.1 | ||||
| Mix | N/A | - | ||||
| Productivity | N/A | - | ||||
| Other | - | - | ||||
| 2016 | $ | 4.7 | $ | 1.1 | ||
| 2015 – 2014 | 2015 – 2014 | |||||
Segment revenues up $0.3 billion (5%); Segment profit up $0.1 billion (13%) as a result of: · The increase in revenues was primarily due to higher volume driven by Tier 4 locomotive sales, partially offset by the Signaling disposition. · The increase in profit was primarily due to higher productivity, including a reduction in SG&A cost, and higher volume driven by Tier 4 locomotive sales, partially offset by negative business mix. | ||||||
| Revenues | Profit | |||||
| 2014 | $ | 5.7 | $ | 1.1 | ||
| Volume | 0.3 | 0.1 | ||||
| Price | - | - | ||||
| Foreign Exchange | - | - | ||||
| (Inflation)/Deflation | N/A | - | ||||
| Mix | N/A | (0.2) | ||||
| Productivity | N/A | 0.2 | ||||
| Other | - | - | ||||
| 2015 | $ | 5.9 | $ | 1.3 | ||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 54
 ENERGY CONNECTIONS & LIGHTING
ENERGY CONNECTIONS & LIGHTINGBUSINESS OVERVIEW
Leaders: Russell Stokes, William Lacey & Maryrose Sylvester | Headquarters & Operations | |||||
   | · Senior Vice President, GE and President & CEO, GE Energy Connections · Over 20 years of service with General Electric · Vice President, GE and President & CEO, GE Lighting · 25 years of service with General Electric · Vice President, GE and President & CEO, Current, powered by GE · Over 25 years of service with General Electric |  | · 12% of segment revenues · 13% of industrial segment revenues · 2% of industrial segment profit · Energy Connections HQ: Atlanta, GA · GE Lighting HQ: East Cleveland, OH · Current, powered by GE HQ: Boston, MA · Serving customers in 150+ countries · Employees: approximately 53,000 | |||
Products & Services | ||||||
 | GE Energy Connections designs and deploys industry-leading technologies that transport, convert, automate and optimize energy to ensure safe, efficient and reliable electrical power. Combining all the resources and scale of the world's digital industrial company, we connect brilliant machines, grids, and systems to power utility, oil & gas, marine, mining and renewables customers, that keep our world running. Lighting includes the GE Lighting business, which is primarily focused on consumer lighting applications in the U.S., and Current, powered by GE (Current), which is focused on providing energy efficiency and productivity solutions for commercial and industrial customers. | |||||
Energy Connections
| · | Industrial Solutions – creates advanced technologies that safely, reliably and efficiently distribute and control electricity to protect people, property and equipment. We provide high performance software and control solutions and offer products such as circuit breakers, relays, arresters, switchgear, panel boards and repair for the commercial, data center, healthcare, mining, renewable energy, oil & gas, water and telecommunication markets. |
| · | Grid Solutions – a GE and Alstom joint venture, equips 90% of power utilities worldwide to bring power from the point of generation to end consumers. With over 200 years combined experience in providing advanced energy solutions, our products and services enable more resilient, efficient and reliable power systems. Our products and services, such as high voltage equipment, power electronics, automation and protection equipment, software solutions, in addition to our robust projects and services capabilities modernize the grid. We serve industries such as generation, transmission, distribution, oil & gas, telecommunication, mining and water and our strategic partnership ventures, primarily in Mexico and China, allow us to support our customers through various product and service offerings. |
| · | Power Conversion – applies the science and systems of power conversion to help drive the electric transformation of the world's energy infrastructure. Our product portfolio includes motors, generators, automation and control equipment and drives for energy intensive industries such as marine, oil & gas, renewable energy, mining, rail, metals, test systems and water. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 55
| · | Automation & Controls – serves as the Controls Center of Excellence for GE and is leading the next chapter in GE's digital industrial journey and transformation. In partnership with GE Digital, the Global Research Center, and GE businesses around the world, we are focused on the future of control solutions – helping customers become more productive and efficient. Each year $21 billion of GE equipment is sold with controls inside of them. Controls are critical to keeping industry running and connected. They are the brains of industrial equipment, connecting data and machines. |
Lighting
| · | GE Lighting – focused on driving innovation and growth in light emitting diode (LED) and connected home technology. The business offers LEDs in a variety of shapes, sizes, wattages and color temperatures. It's also investing in the growing smart home category, building a suite of connected lighting products with simple connection points that offer new opportunities to do more at home. |
| · | Current – delivers energy efficiency and productivity solutions for commercial and industrial customers. We combine infrastructure technology like LED and solar with new sensor-enabled data networks and Predix-based digital applications to help our customers reduce energy costs, better predict spend and gain business productivity insights. We partner with a wide variety of digital companies to help expand our application catalog, and we offer flexible financing solutions that help our customers achieve faster payback periods and better long-term value. |
| Competition & Regulation |
Energy Connections & Lighting faces competition from businesses operating with global presence and with deep energy domain expertise. Our products and services sold to end customers are often subject to a number of regulatory specification and performance standards under different federal, state, foreign and energy industry standards. The potential combination of energy technologies like lighting and solar with sensor-based data networks is unlocking new Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities for the commercial and industrial market in which Current operates and introducing new competitors.
SIGNIFICANT TRENDS & DEVELOPMENTS |
Energy Connections
| · | We are continuing to see growth in renewable energy industries, specifically wind & solar industries, which is driving demand in our Power Conversion business for equipment and services. This growth is offset by the decline in the oil & gas industry. |
| · | We see soft demand in the North American and European electrical distribution market, and continued soft demand in other parts of the developed world. There are signs of market improvements in China, but the Asia Pacific region has mixed results. |
| · | The U.S. electrical grid capacity is high and load growth is expected to be slow in the near term; spending by utilities in the U.S. continues to be focused more heavily on sustaining operations versus capital investment. |
| · | Integrating large shares of renewables will require strengthening of the grid and ensuring the availability of power plants to dispatch at short notice; these system integration tools may present further business opportunities, and will be needed to pave the way for further decarbonization. |
| · | In December 2016, we announced our plan to sell our Industrial Solutions business. |
| · | The Intelligent Platforms Embedded Systems Products business of Automation & Control was sold in December 2015 for approximately $0.5 billion and the Electricity Meters business of Grid Solutions was sold in December 2015 for approximately $0.2 billion. |
Lighting
| · | In the last decade, the lighting industry has seen a major technology pivot away from traditional lighting products, including incandescent, halogen and specialty linear fluorescent lamps to energy-saving LEDs. That shift has been supported by the U.S. government phasing out incandescent bulbs and declining prices overall for LEDs. We estimate half of all residential sockets in the U.S. will convert to LED by 2020. This shift aligns with our LED focus. |
| · | In 2016, GE Lighting and Current both made strategic organizational changes to help reduce costs, focus on key markets and simplify the businesses. |
Appliances
| · | In June 2016, we completed the sale of our Appliances business to Haier for $5.6 billion (including $0.8 billion from the sale of receivables originated in our Appliances business and sold from GE Capital to Haier), on which we recognized an after-tax gain of $1.8 billion, which is reported in Corporate. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 56
OPERATIONAL OVERVIEW
(Dollars in billions)
| 2016 GEOGRAPHIC REVENUES: $ 15.1 BILLION | ORDERS | ||
 | 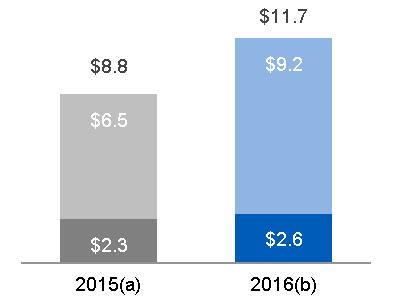 | Equipment Services | |
(a) Includes $1.1 billion related to Alstom (b) Included $5.5 billion related to Alstom | |||
2016 SUB-SEGMENT REVENUES | BACKLOG | ||
 |  | Equipment Services | |
(a) Includes Current, powered by GE (b) Reflects historical results of Appliances prior to its sale in June 2016 | (a) Included $8.4 billion related to Alstom (b) Included $7.9 billion related to Alstom | ||
EQUIPMENT/SERVICES REVENUES | |||
 | |||
| Services Equipment | |||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 57
FINANCIAL OVERVIEW
(Dollars in billions)
| SEGMENT REVENUES | SEGMENT PROFIT | SEGMENT PROFIT MARGIN | ||||||||
 (a) $15.4 billion, excluding $1.0 billion related to Alstom* (b) $9.7 billion, excluding $5.5 billion related to Alstom*, and $7.1 billion, excluding $8.1 billion related to Alstom and Appliances* | Equipment Services |  (a) $0.9 billion, excluding an insignificant amount related to Alstom* (b) $0.1 billion, excluding $0.2 billion related to Alstom*, and $(0.1) billion, excluding $0.4 billion related to Alstom and Appliances* | 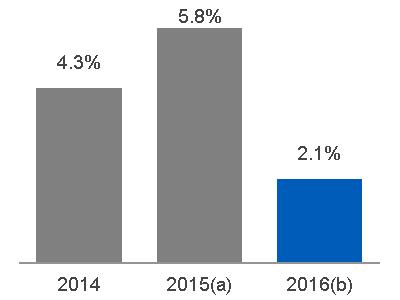 (a) 6.2%, excluding (0.5)% related to Alstom* (b) 1.5%, excluding 3.1% related to Alstom*, and (1.6)%, excluding 5.3% related to Alstom and Appliances* | |||||||
SEGMENT REVENUES & PROFIT WALK: | COMMENTARY: | |||||||||
| 2016 – 2015 | 2016 – 2015 | |||||||||
Segment revenues down $1.2 billion (7%); Segment profit down $0.6 billion (67%) as a result of: · Energy Connections revenues increased driven by the effects of Alstom, including higher equipment sales at Grid, partially offset by core decreases at Industrial Solutions and Power Conversion. The increase in revenues was partially offset by lower prices, the effects of a stronger U.S. dollar, and lower other income, including the negative foreign exchange transactional hedge impacts. Lighting revenues decreased primarily due to lower traditional lighting sales and were partially offset by increases in LED revenues and non-lighting product sales in Current, as well as lower prices. Revenues also decreased as a result of the sale of Appliances in June 2016. · Energy Connections profit decreased primarily as a result of lower cost productivity, driven by core volume decreases, as well as lower other income, including negative foreign exchange transactional hedge impacts, and an unfavorable business mix, partially offset by the effects of Alstom. Lighting profit decreased as a result of the investment in Current, lower other income and lower prices, partially offset by material deflation. Profit also decreased due to the sale of Appliances in June 2016. | ||||||||||
| Revenues | Profit | |||||||||
| 2015 | $ | 16.4 | $ | 0.9 | ||||||
| Volume | (1.7) | (0.1) | ||||||||
| Price | (0.1) | (0.1) | ||||||||
| Foreign Exchange | (0.2) | - | ||||||||
| (Inflation)/Deflation | N/A | - | ||||||||
| Mix | N/A | (0.1) | ||||||||
| Productivity | N/A | (0.2) | ||||||||
| Other | (0.1) | (0.1) | ||||||||
| Alstom | 4.5 | 0.2 | ||||||||
| Appliances | (3.7) | (0.3) | ||||||||
| 2016 | $ | 15.1 | $ | 0.3 | ||||||
*Non-GAAP Financial Measure
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 58
| 2015 – 2014 | 2015 – 2014 | |||||
Segment revenues up $0.6 billion (4%); Segment profit up $0.3 billion (39%) as a result of: · Energy Connections revenues increased primarily due to higher sales at Grid Solutions, driven by the effects of the Alstom acquisition, and a gain on the sale of a meters business, partially offset by the impact of a stronger U.S. dollar and lower volume at Industrial Solutions. Appliance revenues increased as a result of higher volume, partially offset by lower prices. Lighting revenues decreased as lower traditional lighting sales were partially offset by increases in LED revenues, lower prices and the impact of a stronger U.S. dollar, partially offset by gains on asset sales. · Energy Connections profit increased primarily due to higher productivity, including a reduction in SG&A, partially offset by the impact of a stronger U.S. dollar. Appliances profit increased due to improved productivity, including the effects of classifying Appliances as a business held for sale, partially offset by lower prices. Lighting profit decreased as a result of lower prices, partially offset by material deflation. | ||||||
| Revenues | Profit | |||||
| 2014 | $ | 15.7 | $ | 0.7 | ||
| Volume | - | - | ||||
| Price | (0.1) | (0.1) | ||||
| Foreign Exchange | (0.7) | (0.1) | ||||
| (Inflation)/Deflation | N/A | 0.1 | ||||
| Mix | N/A | - | ||||
| Productivity | N/A | 0.1 | ||||
| Other | - | - | ||||
| Alstom | 1.0 | - | ||||
| Appliances | 0.4 | 0.3 | ||||
| 2015 | $ | 16.4 | $ | 0.9 | ||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 59
 CAPITAL
CAPITALBUSINESS OVERVIEW
Leader: Richard Laxer | Headquarters & Operations | |||
 | · Senior Vice President, GE and Chairman & CEO, GE Capital · Over 30 years of service with General Electric |  | · 9% of segment revenues · Headquarters: Norwalk, CT · Employees: approximately 6,000 | |
| Products & Services | ||||
Capital is the financial services division of GE focused on customers and markets aligned with GE's industrial businesses, whether in developed economies or emerging markets. We provide financial products and services around the globe that are geared to utilize GE's industry specific expertise in aviation, energy, infrastructure, and healthcare to capitalize on market-specific opportunities. In addition, we continue to operate our run-off insurance activities as part of our continuing operations. Our expertise, domain knowledge, and deep relationships create an environment for new hospitals to obtain necessary equipment, cities to function more safely, and transportation networks to deliver people, goods, and services on time. We are the Capital in the GE Store. Products and services include: | ||||
| · | Industrial Finance (IF) – provides exclusive equipment financing solutions globally for the GE industrial businesses. In addition, its Working Capital Solutions business provides critical working capital services to GE to help optimize cash management. |
| · | Energy Financial Services (EFS) – a global energy investor that provides world class financial solutions and underwriting capabilities for Power, Renewable Energy, and Oil & Gas to meet rising demand and sustainability imperatives. EFS invests in long-lived, capital intensive energy projects and companies by providing structured equity, debt, leasing, partnership financing, project finance and broad-based commercial finance. |
| · | GE Capital Aviation Services (GECAS) – offers commercial aircraft leasing, financing, services, and consulting with the industry's broadest range of business solutions. |
As a result of the GE Capital Exit Plan, GE Capital's Real Estate business, Consumer business and most of its Commercial Lending and Leasing (CLL) business are classified as discontinued operations and are no longer reported as part of the Capital segment. As such, all comparative prior period information has been reclassified to reflect Real Estate, Consumer and most of CLL as discontinued operations. As of December 31, 2016, we have substantially completed the dispositions related to the GE Capital Exit Plan.
| Competition & Regulation |
The businesses in which we engage are subject to competition from various types of financial institutions, including commercial banks, investment banks, leasing companies, independent finance companies, finance companies associated with manufacturers and insurance and reinsurance companies.
With the rescission of its designation as a nonbank SIFI in June 2016, GE Capital's activities are no longer subject to the consolidated supervision of the Federal Reserve or subject to the enhanced prudential standards set forth in the Dodd Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act and its implementing regulations, including minimum regulatory capital and liquidity requirements, submission of annual resolution plans, the Volcker Rule and regulatory reporting requirements.
GE Capital's international operations are consolidated under GE Capital International Holdings Limited, a wholly owned subsidiary of GE Capital. GE Capital International Holdings Limited continues to maintain its own capital structure and is supervised on a consolidated basis by the U.K. Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA). The PRA's supervision includes capital and liquidity standards that could impact GE Capital's ability to pay dividends to GE. We expect to exit the PRA's consolidated supervision in 2017.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 60
OPERATIONAL OVERVIEW
(Dollars in billions)
| 2016 GEOGRAPHIC REVENUES: $10.9 BILLION | 2016 SUB-SEGMENT REVENUES | |
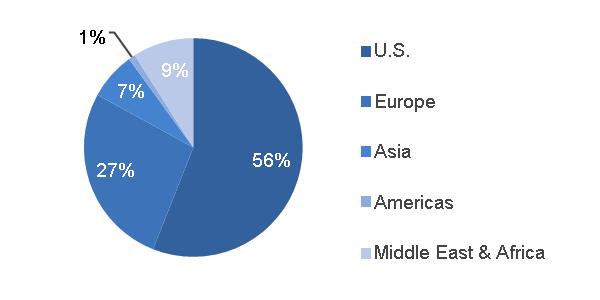 | 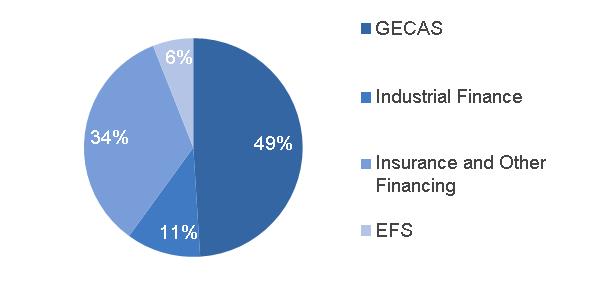 | |
| ENDING NET INVESTMENT, EXCLUDING LIQUIDITY* | SUB-SEGMENT ASSET ALLOCATION AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2016 | |
 |  | |
| (a) $166 billion including discontinued operations (b) $93 billion including discontinued operations |
| SIGNIFICANT TRENDS & DEVELOPMENTS |
| · | The GE Capital Exit Plan – As the GE Capital Exit Plan progresses, we will continue to incur interest on non-Verticals borrowings, restructuring costs and GE and GE Capital headquarters costs that are in excess of those allocated to the Verticals. These costs are recorded within other continuing operations within Capital. |
*Non-GAAP Financial Measure
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 61
FINANCIAL OVERVIEW
(Dollars in billions)
| SEGMENT REVENUES | SEGMENT PROFIT (LOSS)(a) | ||
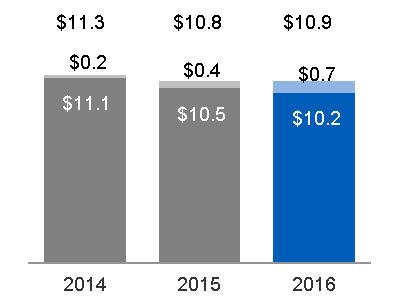 | Total Capital Other Continuing Verticals | 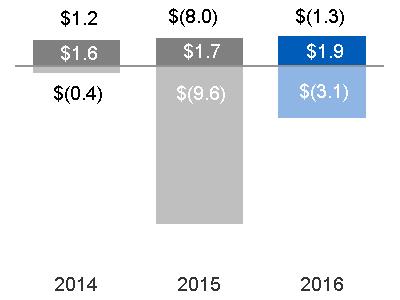 | Total Capital Verticals Other Continuing |
| (a) Interest and other financial charges and income taxes areincluded in determining segment profit for the Capital segment. |
| COMMENTARY: 2016 – 2015 |
Capital revenues increased $0.1 billion, or 1%, primarily due to lower impairments, higher gains and the effects of acquisitions, partially offset by organic revenue declines, the effects of dispositions and the effects of currency exchange.
| · | Within Capital, Verticals revenues decreased by $0.2 billion, or 2%, as a result of organic revenue declines ($0.6 billion) and the effects of dispositions ($0.2 billion), partially offset by higher gains ($0.3 billion), lower impairments ($0.2 billion), and the effects of acquisitions. |
| · | Other Capital revenues increased $0.3 billion, or 99%, as a result of lower impairments ($0.2 billion) and organic revenue growth ($0.2 billion) partially offset by the effects of currency exchange ($0.1 billion). |
Capital net loss decreased by $6.7 billion, or 84%, primarily due to the absence of the 2015 charges associated with the GE Capital Exit Plan.
| · | Within Capital, Verticals net earnings increased by $0.2 billion, or 14%, as a result of higher gains ($0.2 billion) and lower impairments ($0.2 billion), partially offset by the effects of dispositions ($0.1 billion) and core decreases ($0.1 billion). |
| · | Other Capital net loss decreased by $6.5 billion, or 67%, primarily as a result of: |
| · | Lower tax expenses of $6.2 billion primarily related to the absence of the 2015 charges for repatriation of foreign earnings and write-off of deferred tax assets related to the GE Capital Exit Plan. |
| · | 2016 tax benefits of $1.1 billion primarily related to increased tax efficiency of planned cash repatriations through increased foreign tax credit utilization of $0.8 billion and an IRS tax settlement of $0.3 billion. |
| · | Lower impairment expenses of $0.8 billion resulting from the 2015 impairment of a coal-fired power plant in the U.S. |
| · | Higher treasury operation expenses of $1.3 billion reflecting excess interest expense, costs associated with the February and May 2016 debt tenders and derivative activities that reduce or eliminate interest rate, currency or market risk between financial assets and liabilities. We expect to continue to have excess interest costs in 2017. We may engage in liability management actions, such as buying back debt, based on market and economic conditions. |
| · | Charges of $0.3 billion associated with the preferred equity exchange that was completed in January 2016. |
| · | Higher restructuring expenses of $0.2 billion. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 62
| COMMENTARY: 2015 – 2014 |
Capital revenues decreased by $0.5 billion, or 5%, primarily as a result of organic revenue declines, primarily due to lower ENI, lower gains and higher impairments, partially offset by the effects of acquisitions and dispositions.
· Within Capital, Verticals revenues decreased by $0.7 billion, or 6%, as a result of organic revenue declines ($0.9 billion), lower gains ($0.2 billion) and higher impairments ($0.1 billion), partially offset by the effects of acquisitions and dispositions ($0.5 billion).
Capital net earnings decreased by $9.2 billion primarily due to charges associated with the GE Capital Exit Plan.
| · | Within Capital, Verticals net earnings increased by $0.1 billion, or 4%, as a result of lower equipment leased to others (ELTO) impairments ($0.1 billion) related to our operating lease portfolio of commercial aircraft and the effects of acquisitions and dispositions ($0.2 billion), partially offset by lower gains ($0.1 billion) and core decreases ($0.1 billion). |
| · | Other Capital net earnings decreased by $9.3 billion primarily as a result of the GE Capital Exit Plan as follows: |
| · | Higher tax expenses of $7.0 billion primarily related to expected repatriation of foreign earnings and write-off of deferred tax assets related to the GE Capital Exit Plan. |
| · | Higher treasury operation expenses of $1.0 billion reflecting excess interest expense, including costs associated with the debt exchange completed in October 2015 and derivative activities that reduce or eliminate interest rate, currency or market risk between financial assets and liabilities. |
| · | The 2015 $0.8 billion impairment of a coal-fired power plant in the U.S. related to a decision in the fourth quarter to exit the investment over time. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 63
GE CORPORATE ITEMS AND ELIMINATIONS
GE Corporate Items and Eliminations is a caption used in the Segment Operations – Summary of Operating Segment table to reconcile the aggregated results of our segments to the consolidated results of the Company. As such, it includes corporate activities, including certain GE Digital activities, and the elimination of inter-segment activities. Specifically, the GE Corporate Items and Eliminations amounts related to revenues and earnings include the results of disposed businesses, certain amounts not included in GE industrial operating segment results because they are excluded from measurement of their operating performance for internal and external purposes and the elimination of inter-segment activities. In addition, the GE Corporate Items and Eliminations amounts related to earnings include certain costs of our principal retirement plans, restructuring and other costs reported in Corporate, and the unallocated portion of certain corporate costs (such as research and development spending and costs related to our Global Growth Organization).
| REVENUES AND OPERATING PROFIT (COST) | |||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
| Revenues | |||||||||
| Gains (losses) on disposals(a) | $ | 3,444 | $ | 1,047 | $ | 91 | |||
| NBCU settlement | - | 450 | - | ||||||
| Eliminations and other | (3,812) | (3,708) | (3,954) | ||||||
| Total Corporate Items and Eliminations | $ | (368) | $ | (2,211) | $ | (3,863) | |||
| Operating profit (cost) | |||||||||
| Gains (losses) on disposals(a) | $ | 3,444 | $ | 1,047 | $ | 91 | |||
| NBCU settlement | - | 450 | - | ||||||
| Principal retirement plans(b) | (2,044) | (2,760) | (2,313) | ||||||
| Restructuring and other charges | (3,578) | (1,734) | (1,788) | ||||||
| Eliminations and other | (2,048) | (2,111) | (2,215) | ||||||
| Total Corporate Items and Eliminations | $ | (4,226) | $ | (5,108) | $ | (6,225) | |||
| CORPORATE COSTS | |||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
| Total Corporate Items and Eliminations | $ | (4,226) | $ | (5,108) | $ | (6,225) | |||
| Less non-operating pension cost* | (2,052) | (2,764) | (2,120) | ||||||
Total Corporate costs (operating)* | $ | (2,175) | $ | (2,344) | $ | (4,105) | |||
| Less, restructuring and other charges, gains and NBCU settlement | (134) | (237) | (1,697) | ||||||
Adjusted Corporate costs (operating)* | $ | (2,040) | $ | (2,107) | $ | (2,408) | |||
| (a) | Included gains (losses) on disposed or held for sale businesses. |
| (b) | Included non-operating pension cost* of $2.1 billion, $2.8 billion and $2.1 billion in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, which includes expected return on plan assets, interest costs and non-cash amortization of actuarial gains and losses. |
.
*Non-GAAP Financial Measure
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 64
2016 – 2015 COMMENTARY
Revenues and other income increased $1.8 billion, primarily a result of:
| · | $2.4 billion of higher net gains from disposed and held for sale businesses, which included a $3.1 billion gain from the sale of our Appliances business to Haier and a $0.4 billion gain from the sale of GE Asset Management to State Street Corporation in 2016, partially offset by a $0.1 billion impairment charge related to a potential sale of a non-strategic platform in our Aviation business in 2016. Gains on disposed or held for sale businesses in 2015 included a $0.6 billion gain from the sale of our Signaling business, and a $0.2 billion break-up fee paid by Electrolux AB due to the termination of the agreement to acquire the GE Appliances business. |
These increases to revenues and other income was partially offset by the following:
| · | $0.5 billion lower other income from a settlement related to the NBCU transaction in 2015, and |
| · | $0.4 billion of higher inter-segment eliminations. |
Operating costs decreased $0.9 billion, primarily as a result of:
| · | $2.4 billion of higher net gains from disposed and held for sale businesses, which included a $3.1 billion gain from the sale of our Appliances business to Haier and a $0.4 billion gain from the sale of GE Asset Management to State Street Corporation in 2016, partially offset by a $0.1 billion impairment charge related to a potential sale of a non-strategic platform in our Aviation business in 2016. Gains in 2015 included a $0.6 billion gain from the sale of our Signaling business, and a $0.2 billion break-up fee paid by Electrolux AB due to the termination of the agreement to acquire the GE Appliances business, and |
| · | $0.7 billion of lower costs associated with our principal retirement plans including the effects of higher discount rates. |
These decreases to operating costs were partially offset by the following:
| · | $1.8 billion higher restructuring and other charges, which included $0.7 billion of higher restructuring and other charges associated with the Alstom acquisition, and |
| · | $0.5 billion lower other income due to a non-repeat of a settlement related to the NBCU transaction in the second quarter of 2015. |
2015 – 2014 COMMENTARY
Revenues and other income increased $1.7 billion, primarily a result of:
| · | $1.0 billion of higher gains from disposed or held for sale businesses, which included a $0.2 billion break-up fee paid by Electrolux AB due to the termination of the agreement to acquire the GE Appliances business, |
| · | $0.5 billion higher other income from a settlement related to the NBCU transaction in 2015, and |
| · | $0.2 billion of lower eliminations and other, which was driven by $0.4 billion of lower inter-segment eliminations, partially offset by $0.2 billion lower licensing, GE Asset Management fees and other income. |
Operating costs decreased $1.1 billion, primarily as a result of:
| · | $1.0 billion of higher gains from disposed businesses, which included a $0.2 billion break-up fee paid by Electrolux AB due to termination of the agreement to acquire the GE Appliances business, |
| · | $0.5 billion higher other income from a settlement related to the NBCU transaction in 2015, and |
| · | Lower headquarter functional costs offset by higher investment in Information Technology (IT) growth initiatives. |
These decreases to operating costs were partially offset by $0.4 billion of higher costs associated with our principal retirement plans including the effects of lower discount rates and updated mortality assumptions.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 65
Restructuring actions are an essential component of our cost improvement efforts to both existing operations and those recently acquired. Restructuring and other charges relate primarily to workforce reductions, facility exit costs associated with the consolidation of sales, service and manufacturing facilities, the integration of recent acquisitions, including Alstom, and other asset write-downs. We continue to closely monitor the economic environment and may undertake further restructuring actions to more closely align our cost structure with earnings goals.
| RESTRUCTURING & OTHER CHARGES | ||||||||
| (In billions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Workforce reductions | $ | 1.3 | $ | 0.4 | $ | 0.5 | ||
| Plant closures & associated costs and other asset write-downs | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.7 | |||||
| Acquisition/disposition net charges | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.4 | |||||
| Other | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.1 | |||||
| Total | $ | 3.6 | $ | 1.7 | $ | 1.8 | ||
For 2016, restructuring and other charges were $3.6 billion of which approximately $2.3 billion was reported in cost of products/services and $1.2 billion was reported in other costs and expenses (SG&A). These activities were primarily at Power, Oil & Gas and Energy Connections & Lighting. Cash expenditures for restructuring were approximately $1.0 billion in 2016.
For 2015, restructuring and other charges were $1.7 billion of which approximately $1.0 billion was reported in cost of products/services and $0.6 billion was reported in other costs and expenses (SG&A). These activities were primarily at Oil & Gas, Corporate and Energy Connections & Lighting. Cash expenditures for restructuring were approximately $0.4 billion in 2015.
For 2014, restructuring and other charges were $1.8 billion of which approximately $1.0 billion was reported in cost of products/services and $0.5 billion was reported in other costs and expenses (SG&A). These activities were primarily at Power, Corporate and Oil & Gas. Cash expenditures for restructuring were approximately $0.6 billion in 2014.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 66
COSTS AND GAINS NOT INCLUDED IN SEGMENT RESULTS
As discussed in the Segment Operations section within the MD&A, certain amounts are not included in industrial operating segment results because they are excluded from measurement of their operating performance for internal and external purposes. The amount of costs and gains (losses) not included in segment results follows.
| COSTS | ||||||||
| (In billions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Power | $ | 1.2 | $ | 0.3 | $ | 0.5 | ||
| Renewable Energy | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | |||||
| Oil & Gas | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.3 | |||||
| Aviation | 0.1 | - | 0.3 | |||||
| Healthcare | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.5 | |||||
| Transportation | 0.2 | 0.1 | - | |||||
| Energy Connections & Lighting | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |||||
| Total | $ | 3.7 | $ | 1.7 | $ | 2.1 | ||
| GAINS (LOSSES) | ||||||||
| (In billions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Power | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | ||
| Renewable Energy | - | - | - | |||||
| Oil & Gas | - | - | 0.1 | |||||
| Aviation | (0.2) | (a) | - | - | ||||
| Healthcare | - | 0.1 | (c) | - | ||||
| Transportation | - | 0.6 | (d) | - | ||||
| Energy Connections & Lighting | 3.1 | (b) | 0.1 | (e) | - | |||
| Total | $ | 3.0 | $ | 0.9 | $ | 0.1 | ||
| (a) | Largely due to impairment related to a potential sale of a non-strategic platform in our Aviation business. |
| (b) | Related to the sale of our Appliances business in the second quarter of 2016. |
| (c) | Related to the Clarient business disposition in 2015. |
| (d) | Related to the Signaling business disposition in 2015. |
| (e) | Related to the Intelligent Platforms Embedded Systems Products business disposition in 2015. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 67
DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS
Discontinued operations primarily relate to our financial services businesses as a result of the GE Capital Exit Plan and include our Consumer business, most of our CLL business, our Real Estate business and U.S. mortgage business (WMC). All of these operations were previously reported in the Capital segment.
We have entered into Transitional Service Agreements (TSA) with and provided certain indemnifications to buyers of GE Capital's assets. Under the TSAs, GE Capital provides various services for terms generally between 12 and 24 months and receives a level of cost reimbursement from the buyers.
At December 31, 2016, we provided specific indemnifications to buyers of GE Capital's assets that amounted to $2.6 billion, for which we have recognized related liabilities of $0.3 billion. In addition, in connection with the 2015 public offering and sale of Synchrony Financial, GE Capital indemnified Synchrony Financial and its directors, officers, and employees against the liabilities of GECC's businesses other than historical liabilities of the businesses that are part of Synchrony Financial's ongoing operations.
As part of the GE Capital Exit Plan, we entered into hedges (on an after-tax basis) of our net investment in businesses that we plan to dispose. These derivatives are treated as standalone hedges and the mark-to-market valuation changes on the derivatives are recorded in earnings of discontinued operations.
Results of operations, financial position and cash flows for these businesses are separately reported as discontinued operations for all periods presented.
| FINANCIAL INFORMATION FOR DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS | ||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes | $ | (954) | $ | (7,495) | $ | 5,855 | ||
The 2016 loss from discontinued operations, net of taxes, primarily reflected the following:
| · | $1.1 billion after-tax loss at our CLL business (including $0.9 billion after-tax loss on planned disposals), and |
| · | $0.1 billion after-tax loss at our Consumer business (including $0.3 billion after-tax loss on planned disposals). |
| · | 2016 losses were partially offset by a $0.2 billion tax benefit related to an IRS tax settlement in our discontinued insurance operations. |
The 2015 loss from discontinued operations, net of taxes, primarily reflected the following:
| · | $7.9 billion after-tax loss at our CLL business (including $8.7 billion after-tax loss on planned disposals), |
| · | $2.0 billion after-tax loss at our Real Estate business (including $2.0 billion after-tax loss on planned disposals), and |
| · | $0.1 billion after-tax effect of incremental reserves related to retained representation and warranty obligations to repurchase previously sold loans on the 2007 sale of WMC. |
| · | 2015 losses were partially offset by $2.5 billion after-tax earnings at our Consumer business, primarily $3.4 billion after-tax gain on the split-off of Synchrony Financial, $0.5 billion after-tax gain on other transactions closed, partially offset by $0.8 billion after-tax loss on disposals and $0.6 billion after-tax loss from operations. |
The 2014 earnings from discontinued operations, net of taxes, primarily reflected the following:
| · | $3.2 billion of after-tax earnings from operations at our Consumer business, |
| · | $1.8 billion of after-tax earnings from operations at our CLL business, |
| · | $1.0 billion of after-tax earnings from operations at our Real Estate business, and |
| · | $0.1 billion tax benefit related to the extinguishment of our loss-sharing arrangement for excess interest claims associated with the 2008 sale of GE Money Japan. |
| · | 2014 earnings were partially offset by a $0.2 billion after-tax loss on incremental reserves related to retained representation and warranty obligations to repurchase previously sold loans on the 2007 sale of WMC. |
See Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information related to discontinued operations.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 68
OTHER CONSOLIDATED INFORMATION
INTEREST AND OTHER FINANCIAL CHARGES
Interest on borrowings and other financial charges amounted to $5.0 billion, $3.5 billion and $2.7 billion in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The majority of our borrowings are in Financial Services, where interest expense was $3.8 billion, $2.3 billion and $1.6 billion in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Included in interest expense were $0.6 billion, $0.2 billion and an insignificant amount of debt extinguishment costs in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. GE Capital average borrowings were $145.0 billion, $216.8 billion and $266.7 billion in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The GE Capital average composite effective interest rate (including interest allocated to discontinued operations) was 3.0% in 2016, 2.6% in 2015 and 2.6% in 2014. The rate increase from 2015 to 2016 was primarily driven by debt extinguishment costs. Excluding the effect of debt extinguishment costs, the GE Capital average composite effective interest rate (including interest allocated to discontinued operations) was 2.6% in 2016, 2015 and 2014. In 2016, GE Capital average assets continued to decrease in line with the GE Capital Exit Plan. See the Liquidity and Borrowings section within the MD&A for a discussion of liquidity, borrowings and interest rate risk management.
It is our policy to allocate Capital interest expense that is either directly attributable or related to discontinued operations. The allocation is based on a market based leverage ratio, taking into consideration the underlying characteristics of the assets for the specific discontinued operations. Interest expense that is associated with debt that is not assumed by the buyer or required to be repaid as a result of the disposal transaction is reflected in other continuing operations after the disposal occurs.
POSTRETIREMENT BENEFIT PLANS
(Dollars in billions)
| PRINCIPAL PENSION PLANS | ||||
| BENEFIT PLANS COST | DISCOUNT RATES (December 31) | EXPECTED RATE OF RETURN | ||
 |  |  | ||
2016 – 2015 COMMENTARY
| · | Postretirement benefit plans cost decreased $0.9 billion, primarily because of the effects of higher discount rates, lower service cost resulting from fewer active principal pension plans participants and lower loss amortization related to our principal pension plans. |
| · | We updated our mortality assumptions at December 31, 2016 based on guidance issued by the Society of Actuaries to reflect updated rates and methodology for future mortality improvements. The new mortality assumptions decreased our principal pension plans obligations by $0.6 billion at year-end 2016. |
2015 – 2014 COMMENTARY
| · | Postretirement benefit plans cost increased $0.2 billion, primarily because of the effects of lower discount rates and new mortality assumptions, which were partially offset by lower loss amortization related to our principal pension plans and by changes to principal retiree benefit plans. |
| · | In 2015, we amended our principal retiree benefit plans affecting post-65 retiree health and retiree life insurance for certain production participants. These plan amendments reduced our principal postretirement benefit obligations by approximately $3.3 billion. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 69
Looking forward, our key assumptions affecting 2017 postretirement benefits costs are as follows:
| · | Discount rate at 4.11% for our principal pension plans, reflecting current long-term interest rates. |
| · | Assumed long-term return on our principal pension plan assets of 7.5%. |
We expect 2017 postretirement benefit plans cost to be about the same as 2016.
PENSION COSTS
| GAAP AND NON-GAAP PENSION COSTS | ||||||||
| (In billions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| GAAP principal pension plans' cost | $ | 3.6 | $ | 4.5 | $ | 3.6 | ||
| Non-GAAP operating pension cost* | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.5 | |||||
Our operating pension cost for our principal pension plans includes only those components that relate to benefits earned by active employees during the period (service cost, prior service cost amortization and curtailment loss). Non-operating pension cost elements such as interest cost, expected return on plan assets and non-cash amortization of actuarial gains and losses are excluded from this measure. We expect operating pension cost to be approximately $1.4 billion in 2017.
FUNDED STATUS OF PLANS
The table below presents the funded status of our benefit plans. The funded status represents the fair value of plan assets less benefit obligations.
| FUNDED STATUS | |||||
| (In billions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| GE Pension Plan | $ | (19.1) | $ | (16.9) | |
| GE Supplementary Pension Plan | (6.5) | (6.1) | |||
| Other pension plans | (5.5) | (4.3) | |||
| Principal retiree benefit plans | (5.7) | (6.1) | |||
2016 – 2015 COMMENTARY
| · | The GE Pension Plan deficit increased in 2016 primarily due to the growth in pension liabilities and lower discount rates, partially offset by investment performance and changes in mortality assumptions. |
| · | The increase in the underfunding of our other pension plans was primarily attributable to lower discount rates and liability growth, partially offset by investment performance and employer contributions. |
| · | The decrease in principal retiree benefit plans deficit was primarily attributable to employer contributions and lower costs from new healthcare supplier contracts, partially offset by the growth in retiree benefit liabilities. |
The Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) determines minimum pension funding requirements in the U.S. We made a $0.3 billion contribution to the GE Pension Plan in 2016. We did not contribute to the GE Pension Plan in 2015. On an ERISA basis, our preliminary estimate is that the GE Pension Plan was approximately 95% funded at January 1, 2017. The ERISA funded status is higher than the GAAP funded status (71% funded) primarily because the ERISA prescribed interest rate is calculated using an average interest rate. As a result, the ERISA interest rate is higher than the year-end GAAP discount rate. The higher ERISA interest rate lowers pension liabilities for ERISA funding purposes. Our current estimate projects $1.7 billion of pension funding contributions to the GE Pension Plan in 2017 and approximately $1.6 billion in 2018.
*Non-GAAP Financial Measure
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 70
We expect to contribute $0.9 billion to our other pension plans in 2017, as compared to $0.8 billion in 2016 and $0.5 billion in 2015. GE Capital is a member of certain GE pension plans. As a result of the GE Capital Exit Plan, GE Capital will have additional funding obligations for these pension plans. These obligations do not relate to the Verticals and are recognized as an expense in GE Capital's other continuing operations when they become probable and estimable. See the Intercompany Transactions between GE and GE Capital section within the MD&A for further information.
We also expect to contribute $0.5 billion to our principal retiree benefit plans in 2017 as compared to $0.4 billion in 2016 and $0.5 billion in 2015.
The funded status of our postretirement benefit plans and future effects on operating results depend on economic conditions, interest rates and investment performance. See the Critical Accounting Estimates section within the MD&A and Notes 12 and 29 to the consolidated financial statements for further information about our benefit plans and the effects of this activity on our financial statements.
INCOME TAXES
GE pays the income taxes it owes in every country in which it does business. While GE and GE Capital file a consolidated U.S. federal income tax return, many factors impact our income tax expense and cash tax payments. The most significant factor is that we conduct business in approximately 180 countries and more than half of our revenue is earned outside the U.S., often in countries with lower tax rates than in the U.S. We reinvest most of our foreign earnings overseas to be able to fund our active non-U.S. business operations. Our tax liability is also affected by U.S. and foreign tax incentives designed to encourage certain investments, like research and development; and by acquisitions, dispositions and tax law changes. Finally, our tax returns are routinely audited, and settlements of issues raised in these audits sometimes affect our tax rates.
GE and GE Capital file a consolidated U.S. federal income tax return. This enables GE and GE Capital to use tax deductions and credits of one member of the group to reduce the tax that otherwise would have been payable by another member of the group. The effective tax rate reflects the benefit of these tax reductions in the consolidated return. GE makes cash payments to GE Capital for tax reductions and GE Capital pays for tax increases at the time GE's tax payments are due.
CONSOLIDATED
(Dollars in billions)
EFFECTIVE TAX RATE (ETR) | PROVISION (BENEFIT) FOR INCOME TAXES | CASH INCOME TAXES PAID(a) | ||
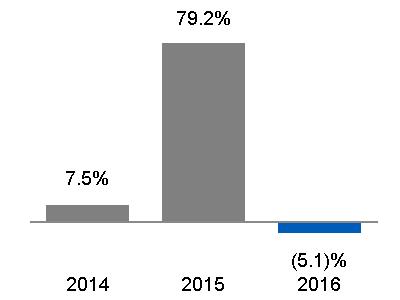 |  |  |
| (a) | Includes taxes paid related to discontinued operations. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 71
2016 – 2015 COMMENTARY
| · | The consolidated income tax rate for 2016 was (5.1)%. The effective tax rate was negative largely because of increased tax benefits from global operations including benefits from the repatriation of GE non-U.S. earnings, benefits of integrating our existing services business with Alstom's services business and foreign tax credit planning at GE Capital to reduce the tax cost of anticipated repatriations of foreign cash. |
| · | The decrease in the consolidated provision for income tax was attributable to the increased benefit from global operations and the non-repeat of the 2015 charges associated with the GE Capital Exit Plan. |
| · | As discussed in Note 14 to the consolidated financial statements, in 2015 in conjunction with the GE Capital Exit Plan, we incurred tax expense of $6.3 billion related to expected repatriation of foreign earnings and write-off of deferred tax assets. |
| · | The consolidated tax provision includes $1.5 billion and $1.0 billion for GE (excluding GE Capital) for 2015 and 2016, respectively. |
2015 – 2014 COMMENTARY
| · | The consolidated income tax rate for 2015 was greater than 35% due to charges associated with the GE Capital Exit Plan. |
| · | The increase in the income tax expense is primarily due to the tax expense incurred as part of the GE Capital Exit Plan. |
| · | The consolidated tax provision includes $1.6 billion and $1.5 billion for GE (excluding GE Capital) for 2014 and 2015, respectively. |
BENEFITS FROM GLOBAL OPERATIONS
Absent the effects of the GE Capital Exit Plan, our consolidated income tax provision is lower because of the benefits of lower-taxed global operations. There is a benefit from global operations as non-U.S. income is subject to local country tax rates that are significantly below the 35% U.S. statutory rate. These non-U.S. earnings have been indefinitely reinvested outside the U.S. and are not subject to current U.S. income tax. Most of these earnings have been reinvested in active non-U.S. business operations and we do not intend to repatriate these earnings to fund U.S. operations. The rate of tax on our indefinitely reinvested non-U.S. earnings is below the 35% U.S. statutory tax rate because we have significant business operations subject to tax in countries where the tax on that income is lower than the U.S. statutory rate and because GE funds certain non-U.S. operations through foreign companies that are subject to low foreign taxes.
A substantial portion of the benefit related to business operations subject to tax in countries where the tax on that income is lower than the U.S. statutory rate is derived from our GECAS aircraft leasing operations located in Ireland, from our Power operations located in Switzerland and Hungary, and our Healthcare operations in Europe.
We expect our ability to benefit from non-U.S. income taxed at less than the U.S. rate to continue, subject to changes in U.S. or foreign law. In addition, since this benefit depends on management's intention to indefinitely reinvest amounts outside the U.S., our tax provision will increase to the extent we no longer indefinitely reinvest foreign earnings.
| BENEFITS FROM LOWER-TAXED GLOBAL OPERATIONS | ||||||||
| (In billions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Benefit of lower foreign tax rate on indefinitely reinvested non-U.S. earnings | $ | 0.9 | $ | 1.1 | $ | 1.2 | ||
| GE Capital Exit Plan | - | (6.1) | - | |||||
| Benefit of audit resolutions | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | |||||
| Other | 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.5 | |||||
| Total | $ | 2.1 | $ | (4.4) | $ | 1.8 | ||
2016 – 2015 COMMENTARY
Our benefit from lower-taxed global operations increased in 2016 because of the non-repeat of the 2015 tax expense associated with the GE Capital Exit Plan and because of benefits from the repatriation of GE non-U.S. earnings, benefits of integrating our existing services business with Alstom's services business and foreign tax credit planning at GE Capital to reduce the tax cost of anticipated repatriations of foreign cash, all of which are included in "other" in the table above.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 72
2015 – 2014 COMMENTARY
Our benefits from lower-taxed global operations decreased in 2015 because of the tax expense associated with the GE Capital Exit Plan.
OTHER INFORMATION
To the extent non-U.S. operating income increases, we would expect tax benefits to increase, subject to management's intention to indefinitely reinvest those earnings. Included in 2015 is a tax expense of $6.1 billion related to the expected repatriation of foreign earnings and write-off of deferred tax assets in conjunction with the GE Capital Exit Plan.
The tax benefit from non-U.S. income taxed at a local country rate rather than the U.S. statutory tax rate is reported in the caption "Tax on global activities including exports" in the effective tax rate reconciliation in Note 14 to the consolidated financial statements.
A more detailed analysis of differences between the U.S. federal statutory rate and the consolidated effective rate, as well as other information about our income tax provisions, is provided in the Critical Accounting Estimates section within the MD&A and Note 14 to the consolidated financial statements. The nature of business activities and associated income taxes differ for GE and for GE Capital; therefore, a separate analysis of each is presented in the paragraphs that follow.
GE EFFECTIVE TAX RATE (EXCLUDING GE CAPITAL EARNINGS)
(Dollars in billions)
We believe that the GE effective tax rate and provision for income taxes are best analyzed in relation to GE earnings before income taxes excluding the GE Capital net earnings from continuing operations, as GE tax expense does not include taxes on GE Capital earnings. For further information on this calculation, see the Supplemental Information section within the MD&A.
GE ETR, EXCLUDING GE CAPITAL EARNINGS* | GE PROVISION FOR INCOME TAXES | |
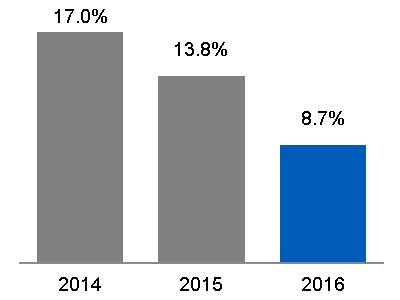 | 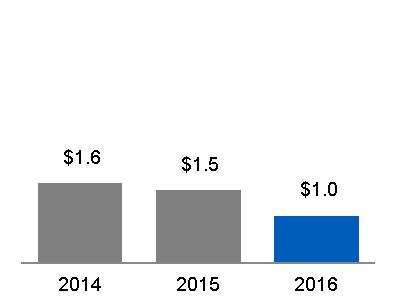 |
2016 – 2015 COMMENTARY
| · | The GE provision for income taxes decreased in 2016 because of increased benefits from lower-taxed global operations ($0.3 billion), including benefits from the repatriation of GE non-U.S. earnings and benefits of integrating our existing services business with Alstom's services business. |
| · | The GE provision for income taxes also decreased due to increases in the benefit from deductible stock losses ($0.4 billion). |
| · | Partially offsetting these decreases was a lower benefit of audit resolutions ($0.1 billion) shown below. |
2015 – 2014 COMMENTARY
| · | The GE provision for income taxes decreased in 2015 because of increased benefits from lower-taxed global operations ($0.2 billion), including benefits from integrating our existing services business with Alstom's services business. |
| · | The GE provision for income taxes also decreased due to increases in the benefit of audit resolutions ($0.2 billion) shown below and deductible stock losses ($0.2 billion). |
| · | Partially offsetting these decreases was an increase in income taxed at rates above the average tax rate ($0.5 billion). |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 73
Resolution of audit matters reduced the GE provision for income taxes by $0.2 billion, $0.3 billion and $0.1 billion in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The effects of such resolutions are included in the following captions in Note 14 to the consolidated financial statements.
| AUDIT RESOLUTIONS - EFFECT ON GE TAX RATE, EXCLUDING GE CAPITAL EARNINGS | ||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||
| Tax on global activities including exports | (1.4) | % | (1.5) | % | (0.2) | % |
| U.S. business credits | - | (0.5) | - | |||
| All other - net | (0.4) | (0.3) | (0.7) | |||
| Total | (1.8) | % | (2.3) | % | (0.9) | % |
GE CAPITAL EFFECTIVE TAX RATE
(Dollars in billions)
GE CAPITAL ETR | GE CAPITAL PROVISION (BENEFIT) FOR INCOME TAXES | ||||
 |  | ||||
2016 – 2015 COMMENTARY
| · | The decrease in the income tax expense for GE Capital from an expense of $5.0 billion to a benefit of $1.4 billion is primarily due to the non-recurrence of the $6.3 billion tax expense, discussed in Note 14 to the consolidated financial statements, related to the GE Capital Exit Plan. |
| · | The GE Capital tax expense also decreased in 2016 due to higher benefits from global operations including foreign tax credit planning to reduce the tax cost of anticipated repatriations of foreign cash. |
2015 – 2014 COMMENTARY
| · | The increase in the income tax expense from a benefit of $0.9 billion for 2014 to an expense of $5.0 billion for 2015 is primarily due to the tax expense, discussed in Note 14 to the consolidated financial statements, related to the GE Capital Exit Plan. |
GEOGRAPHIC DATA
Our global activities span all geographic regions and primarily encompass manufacturing for local and export markets, import and sale of products produced in other regions, leasing of aircraft, sourcing for our plants domiciled in other global regions and provision of financial services within these regional economies. Thus, when countries or regions experience currency and/or economic stress, we often have increased exposure to certain risks, but also often have new opportunities that include, among other things, expansion of industrial activities through purchases of companies or assets at reduced prices and lower U.S. debt financing costs.
Financial results of our non-U.S. activities reported in U.S. dollars are affected by currency exchange. We use a number of techniques to manage the effects of currency exchange, including selective borrowings in local currencies and selective hedging of significant cross-currency transactions. Such principal currencies are the euro, the pound sterling, the Brazilian real and the Chinese renminbi.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 74
REVENUES
Revenues are classified according to the region to which products and services are sold. For purposes of this analysis, the U.S. is presented separately from the remainder of the Americas.
| GEOGRAPHIC REVENUES | ||||||||||||
| V% | ||||||||||||
| (Dollars in billions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016-2015 | 2015-2014 | |||||||
| U.S. | $ | 53.3 | $ | 53.2 | $ | 51.1 | -% | 4 % | ||||
| Non-U.S. | ||||||||||||
| Europe | 21.6 | 16.8 | 18.4 | |||||||||
| Asia | 20.4 | 19.3 | 20.2 | |||||||||
| Americas | 10.5 | 12.0 | 11.8 | |||||||||
| Middle East and Africa | 17.8 | 16.0 | 15.6 | |||||||||
| Total Non-U.S. | 70.4 | 64.1 | 66.0 | 10 % | (3)% | |||||||
| Total | $ | 123.7 | $ | 117.4 | $ | 117.2 | 5 % | -% | ||||
| Non-U.S. Revenues as a % of Consolidated Revenues | 57% | 55% | 56% | |||||||||
NON-U.S. REVENUES AND EARNINGS
The increase in non-US. revenues in 2016 was primarily due to increases of 32% in Europe (primarily due to Alstom), 12% in Middle East, North Africa and Turkey (MENAT) and 35% in India, partially offset by a decrease of 10% in Latin America.
The decrease in non-U.S. revenues in 2015 was primarily due to decreases in growth markets of 11% in Canada and 29% in Australia & New Zealand (ANZ), partially offset by an increase of 2% in Middle East, North Africa and Turkey (MENAT) and 1% in China.
The effects of currency fluctuations on reported results were as follows:
| · | Decreased revenues by $1.3 billion in 2016, primarily driven by the Brazilian real ($0.2 billion), pound sterling ($0.2 billion), euro ($0.1 billion) and the Chinese renminbi ($0.1 billion). |
| · | Decreased revenues by $4.9 billion in 2015, primarily driven by the euro ($2.6 billion), the Brazilian real ($0.9 billion) and the Canadian dollar ($0.2 billion). |
The effects of foreign currency fluctuations decreased earnings by $0.3 billion in 2016. The effects of foreign currency fluctuations decreased earnings in 2015 by $0.7 billion.
ASSETS
We classify certain assets that cannot meaningfully be associated with specific geographic areas as "Other Global" for this purpose.
| TOTAL ASSETS (CONTINUING OPERATIONS) | |||||
| December 31 (In billions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| U.S. | $ | 179.0 | $ | 176.7 | |
| Non-U.S. | |||||
| Europe | 110.8 | 141.9 | |||
| Asia | 24.0 | 22.0 | |||
| Americas | 20.6 | 17.5 | |||
| Other Global | 15.8 | 14.0 | |||
| Total Non-U.S. | 171.4 | 195.4 | |||
| Total | $ | 350.4 | $ | 372.1 |
The decrease in total assets of non-U.S. operations on a continuing basis reflected a decrease primarily in Europe driven by the strengthening of the U.S. dollar against the euro and pound sterling, coupled with a decrease in time deposits in line with debt maturities at GE Capital.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 75
FOREIGN CURRENCY EXPOSURE
As a result of our global operations, we generate and incur a significant portion of our revenues and expenses in currencies other than the U.S. dollar. Such principal currencies are the euro, the pound sterling, the Brazilian real and the Chinese renminbi. The results of operating entities reported in currencies other than U.S. dollar are translated to the U.S. dollar at the applicable exchange rate for inclusion in the financial statements. We use a number of techniques to manage the effects of currency exchange, including selective borrowings in local currencies and selective hedging of significant cross-currency transactions. The foreign currency effect arising from operating activities outside of the U.S., including the remeasurement of derivatives, can result in significant transactional foreign currency fluctuations at points in time, but will generally be offset as the underlying hedged item is recognized in earnings. The effects of foreign currency fluctuations, excluding the earnings impact of the underlying hedged item, decreased net earnings for the year ended December 31, 2016 by $0.3 billion.
On June 23, 2016, a referendum in the United Kingdom (U.K.) was approved to withdraw from the European Union. The referendum was advisory and the terms of any withdrawal are subject to a negotiation period that could last for two years after the U.K. government initiates the withdrawal process. The approval of the referendum had, and may continue to have, an impact on foreign currency exchange rates, among other things. We actively manage our exposure to the U.K. and do not anticipate a material economic impact from our currency exposure as a result of the recent decision by the U.K. to exit the European Union.
See Notes 20 and 29 to the consolidated financial statements for further information about our risk exposures, our use of derivatives, and the effects of this activity on our financial statements.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 76
STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION
Because GE and GE Capital share certain significant elements of their Statements of Financial Position, the following discussion addresses significant captions in the consolidated statement. Within the following discussions, however, we distinguish between GE and GE Capital activities in order to permit meaningful analysis of each individual consolidating statement.
MAJOR CHANGES IN OUR FINANCIAL POSITION DURING 2016
| · | Cash and equivalents decreased $22.4 billion. GE Cash and equivalents increased $0.2 billion due to continuing cash flows from operating activities of $30.0 billion (including common dividends from GE Capital of $20.1 billion), proceeds from the sale of our Appliances business of $4.8 billion and a short-term loan from GE Capital of $1.3 billion. This is partially offset by treasury stock net purchases of $21.4 billion (cash basis), including $11.4 billion paid under ASR agreements, common dividends of $8.5 billion, net PP&E additions of $2.7 billion, business acquisitions of $2.3 billion and software spend of $0.7 billion. GE Capital Cash and equivalents decreased $22.5 billion primarily driven by $58.8 billion net repayments of debt, $20.4 billion in payments of dividends to shareowners and a short-term loan to GE of $1.3 billion, partially offset by $59.9 billion in proceeds from business dispositions and $0.8 billion in proceeds from the sale of receivables originated in our Appliances business and sold to Haier. See the Statement of Cash Flows section of MD&A for additional information. |
| · | Investment securities increased $12.3 billion, primarily driven by investing excess cash in longer term investments to achieve higher yield at GE Capital. See Note 3 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information. |
| · | All other assets decreased $9.6 billion, primarily due to maturities of time deposits in line with debt maturities at GE Capital. See Note 9 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information. |
| · | Assets of discontinued operations decreased $106.1 billion, primarily due to the disposition of CLL businesses of $89.2 billion at GE Capital. See Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information. |
| · | Borrowings decreased $61.4 billion, primarily due to net repayment of debt at GE Capital. See Note 10 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information. |
| · | Liabilities of discontinued operations decreased $42.3 billion, primarily driven by the disposition of CLL businesses of $34.7 billion at GE Capital. See Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information. |
| · | Common stock held in treasury increased $19.5 billion, primarily due to treasury stock purchases of $22.0 billion (book basis), including $11.4 billion repurchased under ASR agreements. This was partially offset by treasury stock issuances of $2.6 billion. See Note 15 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 77
FINANCIAL RESOURCES AND LIQUIDITY
LIQUIDITY AND BORROWINGS
We maintain a strong focus on liquidity. At both GE and GE Capital we manage our liquidity to help provide access to sufficient funding to meet our business needs and financial obligations throughout business cycles.
Our liquidity and borrowing plans for GE and GE Capital are established within the context of our annual financial and strategic planning processes. At GE, our liquidity and funding plans take into account the liquidity necessary to fund our operating commitments, which include primarily purchase obligations for inventory and equipment, payroll and general expenses (including pension funding). We also take into account our capital allocation and growth objectives, including paying dividends, repurchasing shares, investing in research and development and acquiring industrial businesses. At GE, we rely primarily on cash generated through our operating activities, any dividend payments from GE Capital, and also have historically maintained a commercial paper program that we regularly use to fund operations in the U.S., principally within the quarters.
During 2017, GE plans to incur new long-term debt to refinance existing unsecured term debt, finance the Baker Hughes transaction, and for other corporate purposes. This new debt may consist of new unsecured term debt issued by GE or intercompany arrangements between GE and GE Capital utilizing GE Capital's excess unsecured term debt. GE maintains a commercial paper program with a balance of $1.5 billion at December 31, 2016.
Based on asset and liability management actions we have taken, GE Capital does not plan to issue any incremental GE Capital senior unsecured term debt until 2019. GE Capital's global commercial paper issuances total $5.0 billion at December 31, 2016. GE Capital mainly relies on excess cash positions, cash generated through dispositions, and the cash flow from our Verticals to fund our debt maturities, including current portion of long-term debt ($18.2 billion at December 31, 2016), and our operating and interest costs. GE Capital's liquidity position is targeted to meet its obligations under both normal and stressed conditions. We expect to maintain an elevated liquidity position as we generate cash from asset sales, returning to more normalized levels in 2019. During this period we expect to continue to have excess interest costs as asset sales have outpaced our debt maturities. While we maintain elevated liquidity levels, we may engage in liability management actions, such as buying back debt, based on market and economic conditions in order to reduce our excess interest costs. In 2016, we repurchased $6.7 billion of long-term unsecured debt and $5.8 billion of subordinated debentures, resulting in a pre-tax loss of $0.6 billion.
We maintain a detailed liquidity policy for GE Capital that defines GE Capital's liquidity risk tolerance under stress based on its liquidity sources, and a comprehensive framework for managing liquidity risk including metrics to identify and monitor liquidity risk and procedures to escalate and address potential issues.
On December 2, 2015, $87.7 billion of senior unsecured notes and $4.9 billion of commercial paper was assumed by GE upon its merger with GE Capital. On the GE balance sheet, assumed debt is presented in borrowings with an offsetting receivable from GE Capital. On the GE Capital balance sheet, assumed debt is reflected as an intercompany payable to GE presented in borrowings (see Note 10 for additional information). The following table illustrates total GE and GE Capital external debt and debt assumed by GE as of December 31, 2016.
| December 31, 2016 (In billions) | GE | GE Capital | Consolidated(a) | ||||||
| External debt | $ | 79.3 | $ | 58.5 | $ | 136.2 | |||
| Debt assumed by GE from GE Capital | (58.8) | 58.8 | - | ||||||
| Debt adjusted for assumed debt | 20.5 | 117.3 | 136.2 | ||||||
(a) Includes $1.6 billion elimination of intercompany borrowings between GE and GE Capital.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 78
LIQUIDITY SOURCES
In addition to GE cash of $10.5 billion at December 31, 2016, GE Capital maintained liquidity sources of $50.5 billion that consisted of cash and equivalents of $37.6 billion, high-quality investments of $11.5 billion and cash and equivalents of $1.4 billion classified as discontinued operations. Additionally, at December 31, 2016, we have $20.0 billion of committed unused credit lines extended by 36 banks in a syndicated credit facility agreement. GE Capital has the right to compel GE to borrow under such credit lines and transfer the proceeds as loans to GE Capital.
| CASH AND EQUIVALENTS | |||||||
| (In billions) | December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2016 | |||||
| GE(a) | $ | 10.5 | U.S. | $ | 9.6 | ||
| GE Capital(b) | 37.6 | Non-U.S.(c) | 38.6 | ||||
| (a) | At December 31, 2016, $3.5 billion of GE cash and equivalents was held in countries with currency controls that may restrict the transfer of funds to the U.S. or limit our ability to transfer funds to the U.S. without incurring substantial costs. These funds are available to fund operations and growth in these countries and we do not currently anticipate a need to transfer these funds to the U.S. |
| (b) | At December 31, 2016, GE Capital cash and equivalents of about $0.5 billion was primarily in insurance entities and was subject to regulatory restrictions. |
| (c) | Of this amount at December 31, 2016, $3.3 billion is held outside of the U.S. and is available to fund operations and other growth of non-U.S. subsidiaries; it is also available to fund our needs in the U.S. on a short-term basis through short-term loans, without being subject to U.S. tax. Under the Internal Revenue Code, these loans are permitted to be outstanding for 30 days or less and the total of all such loans is required to be outstanding for less than 60 days during the year. If we were to repatriate this cash, we would be subject to additional U.S. income taxes and foreign withholding taxes. |
There were no new senior unsecured debt issuances in 2016.
| COMMERCIAL PAPER | |||||
| (In billions) | GE | GE Capital | |||
| Average commercial paper borrowings during the fourth quarter of 2016 | $ | 13.9 | $ | 5.0 | |
| Maximum commercial paper borrowings outstanding during the fourth quarter of 2016 | 19.5 | 5.1 | |||
GE Capital commercial paper maturities have historically been funded principally through new commercial paper issuances and at GE are substantially repaid before quarter-end using indefinitely reinvested overseas cash, which as discussed above, is available for use in the U.S. on a short-term basis without being subject to U.S. tax.
We securitize financial assets as an alternative source of funding. At December 31, 2016, consolidated non-recourse securitization borrowings were $0.4 billion.
We have two deposit-taking banks outside of the U.S., which are classified as discontinued operations, and neither deposit-taking platform will be retained after the planned completion of the remaining GE Capital Exit Plan dispositions in Europe in 2017. On April 18, 2016, we completed the sale of the deposit-taking bank in the U.S., GE Capital Bank, an industrial bank.
EXCHANGE RATE AND INTEREST RATE RISKS
Exchange rate and interest rate risks are managed with a variety of techniques, including match funding and selective use of derivatives. We use derivatives to mitigate or eliminate certain financial and market risks because we conduct business in diverse markets around the world and local funding is not always efficient. In addition, we use derivatives to adjust the debt we are issuing to match the fixed or floating nature of the assets we are originating. We apply strict policies to manage each of these risks, including prohibitions on speculative activities. Following is an analysis of the potential effects of changes in interest rates and currency exchange rates using so-called "shock" tests that seek to model the effects of shifts in rates. Such tests are inherently limited based on the assumptions used (described further below) and should not be viewed as a forecast; actual effects would depend on many variables, including market factors and the composition of the Company's assets and liabilities at that time.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 79
| · | It is our policy to minimize exposure to interest rate changes. We fund our financial investments using debt or a combination of debt and hedging instruments so that the interest rates of our borrowings match the expected interest rate profile on our assets. To test the effectiveness of our hedging actions, we assumed that, on January 1, 2016, interest rates decreased by 100 basis points across the yield curve (a "parallel shift" in that curve) and further assumed that the decrease remained in place for the next 12 months. Based on the year-end 2016 portfolio and holding all other assumptions constant, we estimated that our consolidated net earnings for the next 12 months, starting in January 2016, would decline by less than $0.1 billion as a result of this parallel shift in the yield curve. |
| · | It is our policy to minimize currency exposures and to conduct operations either within functional currencies or using the protection of hedge strategies. We analyzed year-end 2016 consolidated currency exposures, including derivatives designated and effective as hedges, to identify assets and liabilities denominated in other than their relevant functional currencies. For such assets and liabilities, we then evaluated the effects of a 10% shift in exchange rates between those currencies and the U.S. dollar, holding all other assumptions constant. This analysis indicated that our 2016 consolidated net earnings would decline by less than $0.3 billion as a result of such a shift in exchange rates. This analysis excludes any translation impact from changes in exchange rates on our financial results and any offsetting effect from the forecasted future transactions that are economically hedged. |
DEBT AND DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS, GUARANTEES AND COVENANTS
CREDIT RATINGS
We have relied, and may continue to rely, on the short-term and long-term debt capital markets to fund, among other things, a significant portion of our operations and significant acquisitions. The cost and availability of debt financing is influenced by our credit ratings.
On September 23, 2016, Standard and Poor's Global Ratings (S&P) lowered GE's and GE Capital's long-term unsecured debt ratings to AA- from AA+. The A-1+ short-term funding rating from S&P remained unchanged. On October 31, 2016, GE announced an agreement with Baker Hughes as previously discussed in the Consolidated Results section of MD&A. Moody's, S&P and Fitch Ratings (Fitch) affirmed GE's credit ratings following the announcement. Fitch has published credit ratings for GE and GE Capital since August 2, 2016.
We are disclosing these ratings to enhance understanding of our sources of liquidity and the effects of our ratings on our costs of funds. Although we currently do not expect a downgrade in the credit ratings, our ratings may be subject to a revision or withdrawal at any time by the assigning rating organization, and each rating should be evaluated independently of any other rating. For a description of some of the potential consequences of a reduction in our credit ratings, see "Risk Factors – Financial Risks - Funding access/costs - Failure to maintain our credit ratings, or conditions in the financial and credit markets, could adversely affect our access to capital markets, funding costs and related margins, liquidity and competitive position."
GE's and GE Capital's ratings are set forth in the table below.
| Moody's | S&P | Fitch | |||
| GE | |||||
| Outlook | Stable | Stable | Stable | ||
| Short term | P-1 | A-1+ | F1+ | ||
| Long term | A1 | AA- | AA- | ||
| GE Capital | |||||
| Outlook | Stable | Stable | Stable | ||
| Commercial paper | P-1 | A-1+ | F1+ | ||
| Senior notes | A1 | AA- | AA- | ||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 80
PRINCIPAL DEBT AND DERIVATIVE CONDITIONS
Certain of our derivative instruments can be terminated if specified credit ratings are not maintained and certain debt and derivatives agreements of other consolidated entities have provisions that are affected by these credit ratings.
Fair values of our derivatives can change significantly from period to period based on, among other factors, market movements and changes in our positions. We manage counterparty credit risk (the risk that counterparties will default and not make payments to us according to the terms of our standard master agreements) on an individual counterparty basis. Where we have agreed to netting of derivative exposures with a counterparty, we offset our exposures with that counterparty and apply the value of collateral posted to us to determine the net exposure. We actively monitor these net exposures against defined limits and take appropriate actions in response, including requiring additional collateral.
Swap, forward and option contracts are executed under standard master agreements that typically contain mutual downgrade provisions that provide the ability of the counterparty to require termination if the long-term credit ratings of the applicable GE entity were to fall below A-/A3 or other ratings levels agreed upon with the counterparty. In certain of these master agreements, the counterparty also has the ability to require termination if the short-term ratings of the applicable GE entity were to fall below A-1/P-1. The net derivative liability after consideration of netting arrangements, outstanding interest payments and collateral posted by us under these master agreements was estimated to be $0.4 billion at December 31, 2016.
See Notes 20 and 29 to the consolidated financial statements for further information about our risk exposures, our use of derivatives, and the effects of this activity on our financial statements.
GE GUARANTEE OF CERTAIN GE CAPITAL DEBT
GE provides implicit and explicit support to GE Capital through commitments, capital contributions and operating support. At December 31, 2016, GE debt assumed from GE Capital in connection with the merger of GE Capital into GE was $58.8 billion, and GE guaranteed $47.5 billion of GE Capital debt. See Note 28 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on the guarantor financial statements.
ACCELERATED SHARE REPURCHASE AGREEMENT
During 2016, we repurchased $22.0 billion of our common stock, including $11.4 billion repurchased under accelerated share repurchase (ASR) agreements.
In December 2016, we entered into an ASR agreement with a financial institution that allowed us to repurchase GE common stock at a price below its volume weighted-average price during a given period. During the fourth quarter, we paid $2.2 billion and received and classified as treasury shares an initial delivery of 59,177,215 shares based on then-current market prices. The payment was recorded as a reduction to shareowners' equity, consisting of a $1.9 billion increase in treasury stock, which reflects the value of the shares received upon initial delivery, and a $0.3 billion decrease in other capital, which reflects the value of the stock held back pending final delivery.
We accounted for the ASR as two separate transactions: (i) 59,177,215 shares of common stock initially delivered to GE and $1.9 billion was accounted for as a treasury stock transaction and (ii) the unsettled contract of $0.3 billion was determined to be a forward contract indexed to GE's own common stock. The initial delivery of 59,177,215 shares resulted in an immediate reduction of the outstanding shares used to calculate the weighted-average common shares outstanding for basic and diluted earnings per share. GE has determined that the forward contract, indexed to its own common stock, met all the criteria for equity classification.
In the first quarter of 2017, we received the remaining 10,773,050 shares based on the final volume weighted-average price less the negotiated discount.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 81
CONSOLIDATED CASH FLOWS
We evaluate our cash flows performance by reviewing our industrial (non-GE Capital) businesses and GE Capital businesses separately. Cash from operating activities (CFOA) is the principal source of cash generation for our industrial businesses.
GE CASH FLOWS
(Dollars in billions)
| OPERATING CASH FLOWS | INVESTING CASH FLOWS | FINANCING CASH FLOWS | ||||||||
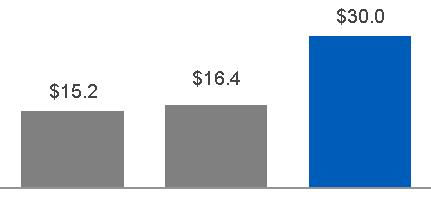 |  | 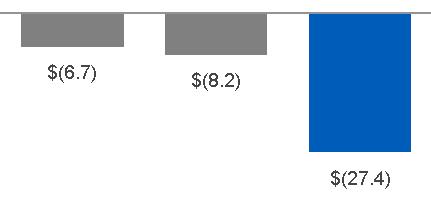 | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | ||
With respect to GE CFOA, we believe that it is useful to supplement our GE Statement of Cash Flows and to examine in a broader context the business activities that provide and require cash.
The most significant source of cash in GE CFOA is customer-related activities, the largest of which is collecting cash resulting from product or services sales. The most significant operating use of cash is to pay our suppliers, employees, tax authorities and others for a wide range of material and services. Dividends from GE Capital represent the distribution of a portion of GE Capital retained earnings, and are distinct from cash from continuing operations within the GE Capital businesses.
All other operating activities reflect cash sources and uses as well as non-cash adjustments to net income including those related to taxes, interest, pension, contract assets and gains (losses) on principal business dispositions. See Note 26 to the consolidated financial statements for further information.
See the Intercompany Transactions between GE and GE Capital section within the MD&A and Notes 4, 22 and 24 to the consolidated financial statements for further information regarding certain transactions affecting our consolidated Statement of Cash Flows.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 82
2016 – 2015 COMMENTARY – CONTINUING OPERATIONS:
GE cash from operating activities-continuing operations increased $13.6 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | GE Capital paid common dividends totaling $20.1 billion and $4.3 billion to GE in 2016 and 2015, respectively. |
| · | Improvement of working capital of $3.6 billion, primarily due to increases in progress collections and accounts payable, partially offset by an increase in inventory build. |
| · | These increases were partially offset by the following decreases: |
| · | $1.0 billion increase in income tax payments, including $1.4 billion in taxes related to the 2016 sale of our Appliances business to Haier. |
| · | Higher restructuring and interest payments of $0.6 billion and $0.4 billion, respectively, when compared to 2015. |
| · | $0.5 billion of 2016 incentive compensation payments due to long-term performance awards. No such payments were made in 2015. |
| · | 2016 GE Pension Trust funding of $0.3 billion representing net sale proceeds associated with the July 1, 2016 sale of GE Asset Management (GEAM) to State Street Corporation. |
| · | The nonrecurrence of settlements related to the NBCU transaction of $0.5 billion and an Electrolux break-up fee of $0.2 billion received in 2015. |
| · | See Note 26 to the consolidated financial statements for further information regarding cash sources and uses as well as non-cash adjustments to net income reported as All other operating activities. |
GE cash used for investing activities-continuing operations decreased $10.8 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | Higher proceeds from principal business dispositions of $3.6 billion, primarily driven by the sale of our Appliances business to Haier for proceeds of $4.8 billion and the sale of GEAM for proceeds of $0.4 billion in 2016, compared to $1.7 billion of total proceeds from principal business dispositions in 2015. |
| · | A decrease in business acquisition activity of $8.1 billion, primarily driven by the acquisition of Alstom for $10.1 billion in 2015. |
| · | These decreases were partially offset by the funding of joint ventures of $0.4 billion in 2016, principally related to our Aviation business (reflected in All other investing activities). |
GE cash used for financing activities-continuing operations increased $19.2 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | Net purchases of GE treasury shares of $21.4 billion, including $11.4 billion paid under ASR agreements compared to $1.1 billion in 2015. |
| · | This increase in cash usage was partially offset by the following decreases: |
| · | A net increase in borrowings of $0.8 billion, primarily driven by a short-term loan from GE Capital to GE with remaining principal of $1.3 billion in 2016 (the loan was fully repaid in January 2017). |
| · | Lower dividends paid to shareowners of $0.8 billion due to lower shares outstanding in 2016 because of on-going repurchases of GE treasury shares. |
2015 – 2014 COMMENTARY – CONTINUING OPERATIONS:
GE cash from operating activities-continuing operations increased $1.2 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | GE Capital paid common dividends totaling $4.3 billion and $3.0 billion to GE in 2015 and 2014, respectively. |
| · | Improvement of working capital of $0.6 billion, primarily related to increased collections on current receivables, partially offset by a decrease in accounts payable and progress collections. |
| · | Settlements related to the NBCU transaction of $0.5 billion and an Electrolux break-up fee of $0.2 billion received in 2015. |
| · | These increases were partially offset by a $0.3 billion increase in income tax payments. |
| · | See Note 26 to the consolidated financial statements for further information regarding cash sources and uses as well as non-cash adjustments to net income reported as All other operating activities. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 83
GE cash used for investing activities-continuing operations increased $6.9 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | Higher business acquisition activity of $8.3 billion primarily driven by the 2015 acquisition of Alstom for $10.1 billion. This compares to the 2014 acquisitions of certain Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. life-sciences business for $1.1 billion, Cameron's Reciprocating Compression Division for $0.6 billion and API Healthcare (API) for $0.3 billion. Partially offset by; |
| · | Higher proceeds from principal business dispositions of $1.1 billion in 2015, primarily relating to Signaling of $0.8 billion and Intelligent Platforms Embedded Systems Products of $0.5 billion in 2015, compared to $0.6 billion of proceeds from principal business dispositions in 2014. |
GE cash used for financing activities-continuing operations increased $1.5 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | The 2015 repayment of $2.0 billion of GE unsecured notes, partially offset by; |
| · | The 2015 issuance of unsecured notes of $3.4 billion compared to $3.0 billion in 2014. |
GE CAPITAL CASH FLOWS
(Dollars in billions)
| OPERATING CASH FLOWS | INVESTING CASH FLOWS | FINANCING CASH FLOWS | ||||||||
 |  | 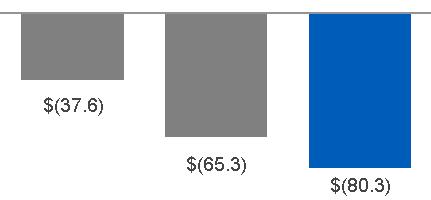 | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | ||
2016 – 2015 COMMENTARY
GE Capital cash from operating activities decreased $3.1 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | Higher net income tax payments of $2.6 billion. |
| · | Higher cash paid for interest reflecting excess interest expense, and costs associated with the February and May 2016 debt tenders. |
| · | These decreases were partially offset by a net increase in cash collateral received from counterparties on derivative contracts of $1.7 billion. |
| · | See Note 26 to the consolidated financial statements regarding All other operating activities. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 84
GE Capital cash from investing activities decreased $12.2 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | Net proceeds from the sales of our CLL, Consumer and Real Estate businesses of $59.9 billion compared to $79.6 billion in 2015. |
| · | Liquidity investments of $11.5 billion purchased in 2016. |
| · | Net cash received from derivative settlements of $0.4 billion compared to $4.4 billion in 2015. |
| · | An increase in net financing receivables of $1.5 billion, including $4.3 billion in additions, partially offset by $2.1 billion received from the refinancing of our Receivables Facility and proceeds from the sale of receivables purchased from our Appliances business of $0.8 billion in 2016. |
| · | A short-term loan from GE Capital to GE with remaining principal of $1.3 billion in 2016 (the loan was fully repaid in January 2017). |
| · | These decreases were partially offset by the following increases: |
| · | Investment and maturity of $20.8 billion related to high quality interest bearing deposits reflecting an investment of $10.4 billion in 2015 that matured in 2016. |
| · | Other investing activities of $3.9 billion, primarily due to a reduction in net additions to property, plant & equipment of $1.6 billion and an increase in aircraft deposits received of $1.5 billion. |
| · | The 2015 acquisition of Milestone Aviation Group resulting in net cash paid of $1.7 billion. |
GE Capital cash used for financing activities increased $15.0 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | GE Capital paid common dividends to GE totaling $20.1 billion compared to $4.3 billion in 2015, partially offset by; |
| · | Lower net repayments of borrowings of $58.8 billion compared to $59.3 billion in 2015, reflecting $2.1 billion of repayments resulting from the refinancing of our Receivables Facility in 2016. |
2015 – 2014 COMMENTARY
GE Capital cash from operating activities decreased $4.7 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | Net decrease in cash collateral received from counterparties on derivative contracts of $3.0 billion. |
| · | A decrease in accounts payable of $0.4 billion. |
| · | See Note 26 to the consolidated financial statements regarding All other operating activities. |
GE Capital cash from investing activities increased $49.1 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | In 2015, we closed the sales of certain of our CLL, Real Estate and Consumer businesses for proceeds of $35.2 billion, $27.7 billion and $16.7 billion, respectively. |
| · | These increases were partially offset by the following decreases: |
| · | 2015 investment of $10.4 billion in high quality interest bearing deposits (with a maturity date of April 2016). |
| · | Aircraft deposits received of $0.1 billion compared to $2.3 billion in 2014. |
| · | The net cash payment of $1.7 billion for the 2015 acquisition of Milestone Aviation Group. |
| · | Net activity from equity method investments of $1.4 billion compared to $0.3 billion in 2014. |
GE Capital cash used for financing activities increased $27.7 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | Higher net repayments of borrowings of $25.7 billion primarily driven by an increase in short-term and long-term debt maturities of $59.3 billion compared to $33.6 billion in 2014. |
| · | GE Capital paid higher common dividends to GE totaling $4.3 billion compared to $3.0 billion in 2014. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 85
GE CAPITAL DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS CASH FLOWS
(Dollars in billions)
OPERATING CASH FLOWS | INVESTING CASH FLOWS | FINANCING CASH FLOWS | ||||||||
 |  | 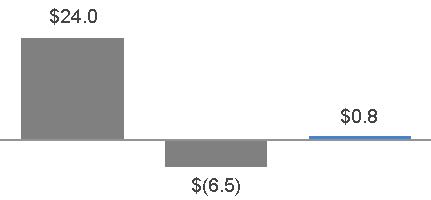 | ||||||||
2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | ||
2016 – 2015 COMMENTARY – DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS:
GE Capital cash from operating activities-discontinued operations decreased $14.3 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | Lower cash generated as a result of certain dispositions in our CLL business of $9.9 billion and Consumer business of $5.9 billion (primarily resulting from the 2015 split-off of Synchrony Financial), partially offset by our Real Estate business of $2.4 billion. In connection with the GE Capital Exit Plan, we closed a vast majority of our Consumer business and substantially all of our CLL and Real Estate business dispositions in 2015 and 2016. |
| · | Lower cash paid for interest, partially offset by higher net income tax payments that are included in the above. |
GE Capital cash used for investing activities-discontinued operations increased $11.4 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | The sale of bank deposits for $16.5 billion in net cash paid in conjunction with the sale of GE Capital Bank's U.S. online deposit platform during 2016. |
| · | The sale of bank deposits and other investments for $1.1 billion in net cash paid related to our Consumer platform during 2016. |
| · | These increases were partially offset by Other investing activities of $6.2 billion, primarily higher net cash received on investment securities of $3.5 billion (including the sale of investment securities resulting from the split-off of Synchrony Financial) and cash generated from 2015 collections of financing receivables and other investing assets prior to disposition of the underlying business. |
GE Capital cash used for financing activities-discontinued operations decreased $7.3 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | Lower repayments of borrowings of $9.3 billion as a result of certain dispositions in our Consumer (including the 2015 split-off of Synchrony Financial), CLL and Real Estate businesses, partially offset by; |
| · | Other financing activities of $2.1 billion primarily newly issued debt of $1.5 billion in 2016. |
2015 – 2014 COMMENTARY – DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS:
GE Capital cash from operating activities-discontinued operations decreased $3.6 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | Lower cash generated as a result of certain dispositions in our Consumer business of $2.4 billion, CLL business of $1.2 billion and our Real Estate business of $0.3 billion. In connection with the GE Capital Exit Plan, we closed a vast majority of our Real Estate business dispositions in 2015 and split-off of Synchrony Financial in 2015. |
| · | Included in the above were lower net income tax payments of $1.0 billion. |
GE Capital cash used for investing activities-discontinued operations decreased $22.1 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | A decrease in net investing activities of $20.0 billion primarily related to decreased financing receivables, a reduction in net additions to property, plant and equipment and decreased investment in other assets (including the 2015 split-off of Synchrony Financial) as a result of certain dispositions in connection with the GE Capital Exit Plan in 2015. |
| · | Lower cash used for purchases of investment securities of $2.1 billion. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 86
GE Capital cash from financing activities-discontinued operations decreased $30.4 billion, primarily due to the following:
| · | Higher net repayments of borrowings of $17.5 billion as a result of certain 2015 dispositions in our Consumer (including the 2015 split-off of Synchrony Financial), CLL and Real Estate businesses in connection with the GE Capital Exit Plan. |
| · | Cash proceeds from bank deposits of $0.5 billion compared to $10.5 billion in 2014 (including the 2015 split-off of Synchrony Financial). |
| · | Proceeds from the initial public offering of Synchrony Financial in 2014 of $2.8 billion. |
INTERCOMPANY TRANSACTIONS BETWEEN GE AND GE CAPITAL
We are repositioning GE to be the world's best infrastructure and technology company, with a smaller financial services division. Our focus is on driving infrastructure leadership, investing in innovation and achieving a culture of simplification to better serve our customers around the world. Over the last decade, we have made significant strides in transforming our portfolio and focusing on our industrial leadership. We have grown our infrastructure platforms with major portfolio moves, investing in adjacencies and pursuing opportunities that are closely related to our core.
In parallel, we have made a concentrated effort to reduce the size of our GE Capital business and align its growth with Industrial earnings. As a result, GE Capital vertical businesses are now focused on investing financial, human and intellectual capital to promote growth for our industrial businesses and their customers. GE Capital accomplishes this in part through related party transactions with GE that are made on an arms-length basis and are reported in the GE and GE Capital columns of our financial statements, but are eliminated in deriving our consolidated financial statements. These transactions include, but are not limited to, the following:
| · | GE Capital dividends to GE, |
| · | GE Capital working capital solutions to optimize GE cash management, |
| · | GE Capital enabled GE industrial orders, and |
| · | Aircraft engines, power equipment and healthcare equipment manufactured by GE that are installed on GE Capital investments, including leased equipment. |
In addition to the above transactions that primarily enable growth for the GE businesses, there are routine related party transactions, which include, but are not limited to, the following:
| · | Expenses related to parent-subsidiary pension plans, |
| · | Buildings and equipment leased between GE and GE Capital, including sale-leaseback transactions, |
| · | Information technology (IT) and other services sold to GE Capital by GE, and |
| · | Various investments, loans and allocations of GE corporate overhead costs. |
CASH FLOWS
GE Capital paid $20.1 billion, $4.3 billion and $3.0 billion of common dividends to GE in the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. In January 2017, GE received an additional $2.0 billion of common dividends from GE Capital.
In order to manage credit exposure, GE sells current receivables to GE Capital and other third parties in part to fund the growth of our industrial businesses. These transactions can result in cash generation or cash use. During any given period, GE receives cash from the sale of receivables to GE Capital and other third parties. GE also leverages GE Capital for its expertise in receivables collection services and sales of receivables to GE Capital are made on an arm's length basis. The incremental amount of cash received from sales of receivables represents the cash generated or used in the period relating to this activity. The incremental cash generated in GE CFOA from current receivables sold to GE Capital, including current receivables subsequently sold to third parties, increased GE's CFOA by $2.1 billion, $2.1 billion and $1.6 billion in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
As of December 31, 2016, GE Capital had approximately $12.3 billion recorded on its balance sheet related to current receivables purchased from GE. Of these amounts, approximately half had been sold by GE to GE Capital with recourse (i.e., the GE business retains the risk of default). The evaluation of whether recourse transactions qualify for accounting derecognition is based, in part, upon the legal jurisdiction of the sale; as such, the majority of recourse transactions outside the U.S. qualify for sale treatment. Claims by GE Capital on receivables sold with recourse to GE have not been significant for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 87
In December 2016, GE Capital entered into a Receivables Facility with members of a bank group, designed to provide extra liquidity to GE. The Receivables Facility allows us to sell eligible current receivables on a non-recourse basis for cash and a deferred purchase price to members of the bank group. The purchase commitment of the bank group at December 31, 2016 was $3.0 billion. See Note 22 to the consolidated financial statements for further information.
ENABLED ORDERS
Enabled orders represent the act of introducing, elevating and influencing customers and prospects that result in an industrial sale, potentially coupled with programmatic captive financing or driving incremental products or services across the GE Store. During the year ended December 31, 2016, GE Capital enabled $13.4 billion of GE industrial orders, primarily with our Power ($6.9 billion), Renewable Energy ($4.8 billion) and Healthcare ($0.9 billion) businesses.
AVIATION
During the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, GE Capital acquired 44 aircraft (list price totaling $6.5 billion) and 56 aircraft (list price totaling $6.4 billion), respectively, from third parties that will be leased to others, which are powered by engines that were manufactured by GE Aviation and affiliates. Additionally, GE Capital had $1.5 billion and $1.1 billion of net book value of engines, originally manufactured by GE Aviation and affiliates and subsequently leased back to GE Aviation and affiliates at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
PENSIONS
GE Capital is a member of certain GE Pension Plans. As a result of the GE Capital Exit Plan, GE Capital will have additional funding obligations for these pension plans. These obligations do not relate to the Verticals and are recognized as an expense in GE Capital's other continuing operations when they become probable and estimable. The additional funding obligations recognized by GE Capital were $0.6 billion and $0.2 billion for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Certain of this additional funding is recorded as a contra expense for GE and GE's related future pension obligations will be paid by GE Capital. For certain other pension plan funding obligations triggered by the GE Capital Exit Plan, GE agreed to assume the funding obligation that would have been triggered by GE Capital at the date of exit from the plan in exchange for an assumption fee that GE recorded as Other income. The total cash transferred to GE for the assumption of these GE Capital funding obligations was $0.2 billion and $0.1 billion for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
On a consolidated basis, the additional required pension funding and any related assumption fees do not affect current period earnings. Any additional required pension funding will be reflected as a reduction of the pension liability when paid.
GE GUARANTEE OF GE CAPITAL THIRD-PARTY TRANSACTIONS
In certain instances, GE provides guarantees to GE Capital transactions with third parties primarily in connection with enabled orders. In order to meet its underwriting criteria, GE Capital may obtain a direct guarantee from GE related to the performance of the third party. GE guarantees can take many forms and may include, but not be limited to, direct performance or payment guarantees, return on investment guarantees, asset value guarantees and loss pool arrangements. As of December 31, 2016, GE had outstanding guarantees to GE Capital on $1.8 billion of funded exposure and $0.5 billion of unfunded commitments. The recorded amount of these contingent liabilities was $0.1 billion as of December 31, 2016 and is dependent upon individual transaction level defaults, losses and/or returns.
GE GUARANTEE OF CERTAIN GE CAPITAL DEBT
GE provides implicit and explicit support to GE Capital through commitments, capital contributions and operating support. As previously discussed, GE debt assumed from GE Capital in connection with the merger of GE Capital into GE was $58.8 billion, and GE guaranteed $47.5 billion of GE Capital debt at December 31, 2016. See Note 24 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information about the eliminations of intercompany transactions between GE and GE Capital.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 88
CONTRACTUAL OBLIGATIONS
As defined by reporting regulations, our contractual obligations for estimated future payments as of December 31, 2016, follow.
| Payments due by period | ||||||||||||||
| 2022 and | ||||||||||||||
| (In billions) | Total | 2017 | 2018-2019 | 2020-2021 | thereafter | |||||||||
| Borrowings (Note 10) | $ | 136.2 | $ | 32.6 | $ | 21.5 | $ | 24.9 | $ | 57.2 | ||||
| Interest on borrowings | 42.5 | 3.7 | 5.9 | 4.8 | 28.1 | |||||||||
| Purchase obligations(a)(b) | 56.8 | 21.3 | 12.8 | 13.5 | 9.2 | |||||||||
| Insurance liabilities (Note 11)(c) | 11.1 | 1.3 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 6.4 | |||||||||
| Operating lease obligations (Note 27) | 4.2 | 0.8 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 1.1 | |||||||||
| Other liabilities(d) | 78.9 | 11.3 | 11.2 | 8.7 | 47.7 | |||||||||
| Contractual obligations of discontinued operations(e) | 4.2 | 4.2 | - | - | - | |||||||||
| (a) | Included all take-or-pay arrangements, capital expenditures, contractual commitments to purchase equipment that will be leased to others, software acquisition/license commitments, contractual minimum programming commitments and any contractually required cash payments for acquisitions. |
| (b) | Excluded funding commitments entered into in the ordinary course of business. See Notes 20 and 23 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on these commitments and other guarantees. |
| (c) | Included contracts with reasonably determinable cash flows such as structured settlements, guaranteed investment contracts, and certain property and casualty contracts, and excluded long-term care, variable annuity and other life insurance contracts. |
| (d) | Included an estimate of future expected funding requirements related to our postretirement benefit plans and included liabilities for unrecognized tax benefits. Because their future cash outflows are uncertain, the following non-current liabilities are excluded from the table above: derivatives, deferred revenue and other sundry items. See Notes 14, 20 and 29 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on certain of these items. |
| (e) | Included payments for other liabilities. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 89
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES
Accounting estimates and assumptions discussed in this section are those that we consider to be the most critical to an understanding of our financial statements because they involve significant judgments and uncertainties. Many of these estimates include determining fair value. All of these estimates reflect our best judgment about current, and for some estimates future, economic and market conditions and their potential effects based on information available as of the date of these financial statements. If these conditions change from those expected, it is reasonably possible that the judgments and estimates described below could change, which may result in future impairments of investment securities, goodwill, intangibles and long-lived assets, incremental losses on financing receivables, increases in reserves for contingencies, establishment of valuation allowances on deferred tax assets and increased tax liabilities, among other effects. Also see Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, which discusses our most significant accounting policies.
REVENUE RECOGNITION ON LONG-TERM PRODUCT SERVICES AGREEMENTS
Revenue recognition on long-term product services agreements requires estimates of profits over the multiple-year terms of such agreements, considering factors such as the frequency and extent of future monitoring, maintenance and overhaul events; the amount of personnel, spare parts and other resources required to perform the services; and future billing rate, cost changes and customers' utilization of assets. We routinely review estimates under product services agreements and regularly revise them to adjust for changes in outlook.
We also regularly assess customer credit risk inherent in the carrying amounts of receivables and contract costs and estimated earnings, including the risk that contractual penalties may not be sufficient to offset our accumulated investment in the event of customer termination. We gain insight into future utilization and cost trends, as well as credit risk, through our knowledge of the installed base of equipment and the close interaction with our customers that comes with supplying critical services and parts over extended periods. Revisions may affect a product services agreement's total estimated profitability resulting in an adjustment of earnings; such adjustments increased earnings by $2.2 billion, $1.4 billion and $1.0 billion in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. We provide for probable losses when they become evident.
See Notes 1 and 9 to the consolidated financial statements for further information.
ASSET IMPAIRMENT
Asset impairment assessment involves various estimates and assumptions as follows:
INVESTMENTS
We regularly review investment securities for impairment using both quantitative and qualitative criteria. For debt securities, if we do not intend to sell the security and it is not more likely than not that we will be required to sell the security before recovery of our amortized cost, we evaluate other qualitative criteria to determine whether a credit loss exists, such as the financial health of and specific prospects for the issuer, including whether the issuer is in compliance with the terms and covenants of the security. Quantitative criteria include determining whether there has been an adverse change in expected future cash flows. For equity securities, our criteria include the length of time and magnitude of the amount that each security is in an unrealized loss position. Our other-than-temporary impairment reviews involve our finance, risk and asset management functions as well as the portfolio management and research capabilities of our internal and third-party asset managers. See Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, which discusses the determination of fair value of investment securities.
See Notes 1 and 3 to the consolidated financial statements for further information about actual and potential impairment losses.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 90
LONG-LIVED ASSETS
We review long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the related carrying amounts may not be recoverable. Determining whether an impairment has occurred typically requires various estimates and assumptions, including determining which undiscounted cash flows are directly related to the potentially impaired asset, the useful life over which cash flows will occur, their amount, and the asset's residual value, if any. In turn, measurement of an impairment loss requires a determination of fair value, which is based on the best information available. We derive the required undiscounted cash flow estimates from our historical experience and our internal business plans. To determine fair value, we use quoted market prices when available, our internal cash flow estimates discounted at an appropriate discount rate and independent appraisals, as appropriate.
Our operating lease portfolio of commercial aircraft is a significant concentration of assets in Capital, and is particularly subject to market fluctuations. Therefore, we test recoverability of each aircraft in our operating lease portfolio at least annually. Additionally, we perform quarterly evaluations in circumstances such as when aircraft are re-leased, current lease terms have changed or a specific lessee's credit standing changes. We consider market conditions, such as global demand for commercial aircraft. Estimates of future rentals and residual values are based on historical experience and information received routinely from independent appraisers. Estimated cash flows from future leases are reduced for expected downtime between leases and for estimated costs required to prepare aircraft to be redeployed. Fair value used to measure impairment is based on management's best estimates which are benchmarked against third-party appraiser current market values for aircraft of similar type and age.
See Notes 7 and 23 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on impairment losses and our exposure to the commercial aviation industry.
GOODWILL AND OTHER IDENTIFIED INTANGIBLE ASSETS
We test goodwill for impairment annually in the third quarter of each year using data as of July 1 of that year. The impairment test consists of two steps: in step one, the carrying value of the reporting unit is compared with its fair value; in step two, which is applied when the carrying value is more than its fair value, the amount of goodwill impairment, if any, is derived by deducting the fair value of the reporting unit's assets and liabilities from the fair value of its equity, and comparing that amount with the carrying amount of goodwill. We determined fair values for each of the reporting units using the market approach, when available and appropriate, or the income approach, or a combination of both. We assess the valuation methodology based upon the relevance and availability of the data at the time we perform the valuation. If multiple valuation methodologies are used, the results are weighted appropriately.
Valuations using the market approach are derived from metrics of publicly traded companies or historically completed transactions of comparable businesses. The selection of comparable businesses is based on the markets in which the reporting units operate giving consideration to risk profiles, size, geography, and diversity of products and services. A market approach is limited to reporting units for which there are publicly traded companies that have the characteristics similar to our businesses.
Under the income approach, fair value is determined based on the present value of estimated future cash flows, discounted at an appropriate risk-adjusted rate. We use our internal forecasts to estimate future cash flows and include an estimate of long-term future growth rates based on our most recent views of the long-term outlook for each business. Actual results may differ from those assumed in our forecasts. We derive our discount rates using a capital asset pricing model and analyzing published rates for industries relevant to our reporting units to estimate the cost of equity financing. We use discount rates that are commensurate with the risks and uncertainty inherent in the respective businesses and in our internally developed forecasts. Discount rates used in our reporting unit valuations ranged from 9.5% to 16.5%.
Estimating the fair value of reporting units requires the use of estimates and significant judgments that are based on a number of factors including actual operating results. It is reasonably possible that the judgments and estimates described above could change in future periods.
During the third quarter of 2016, we performed our annual impairment test of goodwill for all of our reporting units. Based on the results of our step one testing, the fair values of each of the GE reporting units exceeded their carrying values; therefore, the second step of the impairment test was not required to be performed for any of our reporting units and no goodwill impairment was recognized.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 91
We review identified intangible assets with defined useful lives and subject to amortization for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the related carrying amounts may not be recoverable. Determining whether an impairment loss occurred requires comparing the carrying amount to the sum of undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. We test intangible assets with indefinite lives annually for impairment using a fair value method such as discounted cash flows. For our insurance activities remaining in continuing operations, we periodically test for impairment our deferred acquisition costs and present value of future profits.
See Notes 1 and 8 to the consolidated financial statements for further information.
BUSINESSES AND ASSETS HELD FOR SALE
Businesses and assets held for sale represent components that meet the accounting requirements to be classified as held for sale and are presented as single asset and liability amounts in our financial statements with a valuation allowance, if necessary, to recognize the net carrying amount at the lower of cost or fair value, less cost to sell. Financing receivables that no longer qualify to be presented as held for investment must be classified as assets held for sale and recognized in our financial statements at the lower of cost or fair value, less cost to sell, with that amount representing a new cost basis at the date of transfer.
The determination of fair value for businesses and assets held for sale involves significant judgments and assumptions. Development of estimates of fair values in this circumstance is complex and is dependent upon, among other factors, the nature of the potential sales transaction (for example, asset sale versus sale of legal entity), composition of assets and/or businesses in the disposal group, the comparability of the disposal group to market transactions, negotiations with third party purchasers, etc. Such factors bear directly on the range of potential fair values and the selection of the best estimates. Key assumptions were developed based on market observable data and, in the absence of such data, internal information that is consistent with what market participants would use in a hypothetical transaction.
We review all businesses and assets held for sale each reporting period to determine whether the existing carrying amounts are fully recoverable in comparison to estimated fair values.
PENSION ASSUMPTIONS
Pension assumptions are significant inputs to the actuarial models that measure pension benefit obligations and related effects on operations. Two assumptions – discount rate and expected return on assets – are important elements of plan expense and asset/liability measurement. We evaluate these critical assumptions at least annually on a plan and country-specific basis. We periodically evaluate other assumptions involving demographic factors such as retirement age, mortality and turnover, and update them to reflect our experience and expectations for the future. Actual results in any given year will often differ from actuarial assumptions because of economic and other factors.
Projected benefit obligations are measured as the present value of expected payments. We discount those cash payments using the weighted average of market-observed yields for high-quality fixed-income securities with maturities that correspond to the payment of benefits. Lower discount rates increase present values and subsequent-year pension expense; higher discount rates decrease present values and subsequent-year pension expense.
Our discount rates for principal pension plans at December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 were 4.11%, 4.38% and 4.02%, respectively, reflecting market interest rates.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 92
To determine the expected long-term rate of return on pension plan assets, we consider current and target asset allocations, as well as historical and expected returns on various categories of plan assets. In developing future long-term return expectations for our principal benefit plans' assets, we formulate views on the future economic environment, both in the U.S. and abroad. We evaluate general market trends and historical relationships among a number of key variables that impact asset class returns such as expected earnings growth, inflation, valuations, yields and spreads, using both internal and external sources. We also take into account expected volatility by asset class and diversification across classes to determine expected overall portfolio results given current and target allocations. Assets in our principal pension plans earned 6.5% in 2016, and had average annual returns of 7.8%, 4.0%, and 8.0% per year in the 5-, 10- and 25-year periods ended December 31, 2016, respectively. The average historical 10- and 25- year returns were significantly affected by investment losses in 2008. Based on our analysis of future expectations of asset performance, past return results, and our current and target asset allocations, we have assumed a 7.5% long-term expected return on those assets for cost recognition in 2017 the same as 2016 and 2015.
Changes in key assumptions for our principal pension plans would have the following effects.
| · | Discount rate – A 25 basis point increase in discount rate would decrease pension cost in the following year by $0.2 billion and would decrease the pension benefit obligation at year-end by about $2.2 billion. |
| · | Expected return on assets – A 50 basis point decrease in the expected return on assets would increase pension cost in the following year by $0.2 billion. |
See Other Consolidated Information – Postretirement Benefit Plans section within the MD&A and Notes 12 and 29 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on our pension plans.
INCOME TAXES
Our annual tax rate is based on our income, statutory tax rates and tax planning opportunities available to us in the various jurisdictions in which we operate. Tax laws are complex and subject to different interpretations by the taxpayer and respective governmental taxing authorities. Significant judgment is required in determining our tax expense and in evaluating our tax positions, including evaluating uncertainties. We review our tax positions quarterly and adjust the balances as new information becomes available. Our income tax rate is significantly affected by the tax rate on our global operations. In addition to local country tax laws and regulations, this rate depends on the extent earnings are indefinitely reinvested outside the United States. Indefinite reinvestment is determined by management's judgment about and intentions concerning the future operations of the Company. At December 31, 2016 and 2015, approximately $82 billion and $104 billion of earnings, respectively, have been indefinitely reinvested outside the United States. Most of these earnings have been reinvested in active non-U.S. business operations, and we do not intend to repatriate these earnings to fund U.S. operations. Because of the availability of U.S. foreign tax credits, it is not practicable to determine the U.S. federal income tax liability that would be payable if such earnings were not reinvested indefinitely outside the United States.
Deferred income tax assets represent amounts available to reduce income taxes payable on taxable income in future years. Such assets arise because of temporary differences between the financial reporting and tax bases of assets and liabilities, as well as from net operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. We evaluate the recoverability of these future tax deductions and credits by assessing the adequacy of future expected taxable income from all sources, including reversal of taxable temporary differences, forecasted operating earnings and available tax planning strategies. These sources of income rely heavily on estimates. We use our historical experience and our short- and long-range business forecasts to provide insight. Further, our global and diversified business portfolio gives us the opportunity to employ various prudent and feasible tax planning strategies to facilitate the recoverability of future deductions. Amounts recorded for deferred tax assets related to non-U.S. net operating losses, net of valuation allowances, were $3.1 billion and $5.1 billion at December 31, 2016 and 2015, including $0.3 billion and $0.8 billion at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, of deferred tax assets, net of valuation allowances, associated with losses reported in discontinued operations, primarily related to our Real Estate and Consumer businesses and our loss on the sale of GE Money Japan. Such year-end 2016 amounts are expected to be fully recoverable within the applicable statutory expiration periods. To the extent we do not consider it more likely than not that a deferred tax asset will be recovered, a valuation allowance is established.
See Other Consolidated Information – Income Taxes section within the MD&A and Note 14 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on income taxes.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 93
DERIVATIVES AND HEDGING
We use derivatives to manage a variety of risks, including risks related to interest rates, foreign exchange and commodity prices. Accounting for derivatives as hedges requires that, at inception and over the term of the arrangement, the hedged item and related derivative meet the requirements for hedge accounting. The rules and interpretations related to derivatives accounting are complex. Failure to apply this complex guidance correctly will result in all changes in the fair value of the derivative being reported in earnings, without regard to the offsetting changes in the fair value of the hedged item.
In evaluating whether a particular relationship qualifies for hedge accounting, we test effectiveness at inception and each reporting period thereafter by determining whether changes in the fair value of the derivative offset, within a specified range, changes in the fair value of the hedged item. If fair value changes fail this test, we discontinue applying hedge accounting to that relationship prospectively. Fair values of both the derivative instrument and the hedged item are calculated using internal valuation models incorporating market-based assumptions, subject to third-party confirmation, as applicable.
See Notes 1, 9, 20 and 29 to the consolidated financial statements for further information about our use of derivatives.
FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
Assets and liabilities measured at fair value every reporting period include investments in debt and equity securities and derivatives. Other assets and liabilities are subject to fair value measurements only in certain circumstances, including purchase accounting applied to assets and liabilities acquired in a business combination, impaired loans that have been reduced based on the fair value of the underlying collateral, cost and equity method investments and long-lived assets that are written down to fair value when they are impaired. Upon closing an acquisition, we estimate the fair values of assets and liabilities acquired and integrate the acquisition as soon as practicable. The size, scope and complexity of an acquisition will affect the time it takes to obtain the necessary information to record the acquired assets and liabilities at fair value. It may take up to one year to finalize the initial fair value estimates used in the preliminary purchase accounting. Accordingly, it is reasonably likely that our initial estimates will be subsequently revised, which could affect carrying amounts of goodwill, intangibles and potentially other assets and liabilities in our financial statements. Assets that are written down to fair value when impaired are not subsequently adjusted to fair value unless further impairment occurs.
A fair value measurement is determined as the price we would receive to sell an asset or pay to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. In the absence of active markets for the identical assets or liabilities, such measurements involve developing assumptions based on market observable data and, in the absence of such data, internal information that is consistent with what market participants would use in a hypothetical transaction that occurs at the measurement date. The determination of fair value often involves significant judgments about assumptions such as determining an appropriate discount rate that factors in both risk and liquidity premiums, identifying the similarities and differences in market transactions, weighting those differences accordingly and then making the appropriate adjustments to those market transactions to reflect the risks specific to our asset being valued.
See Notes 1, 3, 8, 19, 20 and 29 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on fair value measurements and related matters.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 94
OTHER LOSS CONTINGENCIES
Other loss contingencies are uncertain and unresolved matters that arise in the ordinary course of business and result from events or actions by others that have the potential to result in a future loss. Such contingencies include, but are not limited to environmental obligations, litigation, regulatory proceedings, product quality and losses resulting from other events and developments.
When a loss is considered probable and reasonably estimable, we record a liability in the amount of our best estimate for the ultimate loss. When there appears to be a range of possible costs with equal likelihood, liabilities are based on the low-end of such range. However, the likelihood of a loss with respect to a particular contingency is often difficult to predict and determining a meaningful estimate of the loss or a range of loss may not be practicable based on the information available and the potential effect of future events and decisions by third parties that will determine the ultimate resolution of the contingency. Moreover, it is not uncommon for such matters to be resolved over many years, during which time relevant developments and new information must be continuously evaluated to determine both the likelihood of potential loss and whether it is possible to reasonably estimate a range of possible loss. When a loss is probable but a reasonable estimate cannot be made, disclosure is provided.
Disclosure also is provided when it is reasonably possible that a loss will be incurred or when it is reasonably possible that the amount of a loss will exceed the recorded provision. We regularly review all contingencies to determine whether the likelihood of loss has changed and to assess whether a reasonable estimate of the loss or range of loss can be made. As discussed above, development of a meaningful estimate of loss or a range of potential loss is complex when the outcome is directly dependent on negotiations with or decisions by third parties, such as regulatory agencies, the court system and other interested parties. Such factors bear directly on whether it is possible to reasonably estimate a range of potential loss and boundaries of high and low estimates.
See Note 23 to the consolidated financial statements for further information.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 95
OTHER ITEMS
NEW ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
ASU NO. 2016-16, ACCOUNTING FOR INCOME TAXES: INTRA-ENTITY ASSET TRANSFERS OF ASSETS OTHER THAN INVENTORY
In October 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2016-16, Accounting for Income Taxes: Intra-Entity Asset Transfers of Assets Other than Inventory. The ASU eliminates the deferral of the tax effects of intra-entity asset transfers other than inventory. As a result, the tax expense from the intercompany sale of assets, other than inventory, and associated changes to deferred taxes will be recognized when the sale occurs even though the pre-tax effects of the transaction have not been recognized. The effect of the adoption of the standard will depend on the nature and amount of future transactions.
ASU NO. 2016-02, LEASES
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, Leases. The new standard establishes a right-of-use (ROU) model that requires a lessee to record a ROU asset and a lease liability on the balance sheet for all leases with terms longer than 12 months. Leases will be classified as either finance or operating, with classification affecting the pattern of expense recognition. Similarly, lessors will be required to classify leases as sales-type, finance or operating, with classification affecting the pattern of income recognition. Classification for both lessees and lessors will be based on an assessment of whether risks and rewards as well as substantive control have been transferred through a lease contract. The new standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those fiscal years, with early adoption permitted. A modified retrospective transition approach is required for leases existing at, or entered into after, the beginning of the earliest comparative period presented in the financial statements, with certain practical expedients available. While we continue to evaluate the effect of the standard on our ongoing financial reporting, we anticipate that the adoption of the ASU may materially affect our Statement of Financial Position.
ASU NO. 2014-09, REVENUE FROM CONTRACTS WITH CUSTOMERS
BACKGROUND
In May 2014, the FASB issued a new comprehensive set of revenue recognition principles (ASU No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers) that supersedes most existing U.S. GAAP revenue recognition guidance (including ASC 605-35, Revenue Recognition - Construction-Type and Production-Type Contracts). The new standard will become effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017. We will adopt the standard on January 1, 2018, will apply it retrospectively to all periods presented and will elect the practical expedient for contract modifications. Since the issuance of the new standard by the FASB, we have engaged in a collaborative process with our industry peers and worked with standard setters on important interpretive matters with the objective of ensuring consistency in the application of the standard.
TRANSITION METHOD FOR APPLYING THE NEW STANDARD
Companies can use either a full retrospective or modified retrospective method to adopt the standard. Under the full retrospective method, all periods presented will be updated upon adoption to conform to the new standard and a cumulative adjustment for effects on periods prior to 2016 will be recorded to retained earnings as of January 1, 2016. Under the modified retrospective approach, prior periods are not updated to be presented on an accounting basis that is consistent with 2018. Rather, a cumulative adjustment for effects of applying the new standard to periods prior to 2018 is recorded to retained earnings as of January 1, 2018. Because only 2018 revenues reflect application of the new standard, incremental disclosures are required to present the 2018 revenues under the prior standard.
As noted above, we have elected to apply the full retrospective approach. We chose that approach because we believe that it is the most helpful to our investors. First and foremost, when we adopt the standard in 2018 we will provide investors with a consistent view of historical trends, as 2016 and 2017 will be on a basis consistent with 2018.
As noted above, we have elected to apply the full retrospective approach. We chose that approach because we believe that it is the most helpful to our investors. First and foremost, when we adopt the standard in 2018 we will provide investors with a consistent view of historical trends, as 2016 and 2017 will be on a basis consistent with 2018.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 96
CHANGE IN TIMING AND PRESENTATION, NO IMPACT TO CASH OR ECONOMICS
The new standard requires companies to identify contractual performance obligations and determine whether revenue should be recognized at a point in time or over time based on when control of goods and services transfer to a customer. As a result, we expect significant changes in the presentation of our financial statements, including: (1) timing of revenue recognition, and (2) changes in classification between revenue and costs. The new standard will have no cash impact and, as such, does not affect the economics of our underlying customer contracts. The effect of applying the new guidance to our existing book of contracts will result in lower reported earnings in 2018 (and comparative periods previously reported) and in the early years after adoption. However, we expect to experience an increase in reported earnings, on that existing book of contracts, as they mature. The new standard will provide for a better alignment of cash and earnings for the affected long-term customer contracts and we expect that it will enhance comparability across industry peers.
SPECIFIC EFFECT ON GE BUSINESSES
Power and Aviation Service Agreements - For our long-term product service agreements, primarily in our Power and Aviation businesses, we expect to continue to recognize revenue based on costs incurred plus an estimated margin rate (over time model). However, the new standard provides prescriptive guidance tied to several factors for determining what constitutes the proper scope of a customer contract for accounting purposes. These factors include optional purchases, contract modifications, and termination clauses. For example, under the new standard contract modifications will be accounted for prospectively by recognizing the financial effect of the modification over the remaining life of the contract. Under existing accounting guidance revisions to estimated margin rates resulting from modifications were reflected as cumulative effect adjustments to earnings in the current period.
Aviation Commercial Engines - Consistent with industry peers, the financial presentation of our Aviation Commercial engines business will be significantly affected as they will be accounted for as of a point in time, which is a change from our current long-term contract accounting process. Our current process applies contract-specific estimated margin rates, which include the effect of estimated cost improvements, to costs incurred. This change is required because our commercial engine contracts do not transfer control to the customer during the manufacturing process. Each install and spare engine will be accounted for as a separate performance obligation, reflecting the actual price and manufacturing costs of such engines. We expect that the most significant effect of this change will be reflected when we have new engine launches, where the cost of earlier production units is higher than the cost of later production units because of cost improvements.
All Other Large Equipment - For the remainder of our equipment businesses, the new revenue standard requires emphasis on transfer of control rather than risks and rewards, which may accelerate timing of revenue recognition versus our current practices. For example, in our Renewable Energy business we wait for risk of loss to be assumed by the customer before recognizing revenue, which generally occurs later than when control is transferred.
CURRENT RANGE OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT EFFECT
We will adopt the new standard as of January 1, 2018. When we report our 2018 results, the comparative results for 2017 and 2016 will be updated to reflect the application of the requirements of the new standard to these periods. Based on our assessment and best estimates to date, we expect a non-cash charge to our January 1, 2016 retained earnings balance of approximately $4 billion. We estimate that the charge will comprise approximately $1 billion related to commercial aircraft engines and $3 billion related primarily to our Services businesses (predominately in Power and Aviation). Beyond those effects, we expect application of the new guidance will result in increases and decreases in revenue within our segments, which will largely offset overall and will be immaterial at a total company level. We estimate that our 2016 restated earnings per share will be lower by approximately $0.10. We anticipate that 2018 earnings per share will be lower by approximately $0.05 compared to what our results would be under existing revenue recognition guidance. These amounts include significant estimates and will remain subject to change as we complete our evaluation of the new standard and reflect actual activity for 2017.
To summarize, we will adopt the new standard in 2018, at which time we will update prior periods to be presented on a consistent basis. As discussed above, we anticipate the dilutive effect of the new standard in the year of adoption to be approximately $0.05 EPS and the effect will be less dilutive for years after initial adoption. However, this expectation is based on many variables, which are subject to change. Importantly, application of the new guidance has no effect on the cash we expect to receive nor the economics of these contracts. Rather, it will simply more closely align revenue with cash, which we believe will be helpful to our investors.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 97
In late 2015, we created GE Digital, whose activities are focused on assisting in the market development of our digital product offerings through software design, fulfillment and product management, while also interfacing with our customers. Digital revenues include internally developed software (including Predix) and associated hardware, and software solutions that improve our customers' asset performance. These revenues are largely generated from our operating businesses and are included in their segment results.
GE Digital revenues of $3.6 billion increased $0.5 billion, or 16%, in 2016 and were principally driven by expansion of our Digital offerings in GE's Power, Energy Connections & Lighting and Oil & Gas segments.
GE Digital orders of $4.0 billion increased $0.7 billion, or 22%, in 2016 principally driven by expansion of our Digital offerings in GE's Power, Energy Connections & Lighting, Oil & Gas segments and in Digital Core, partially offset by a market-driven slowdown in Transportation.
One aspect of our Digital transformation includes an initiative to digitize the operations of GE. These investments include applications and analytics that improve the productivity of our internal processes across engineering, services, sourcing, and commercial – collectively referred to as the Digital Thread. During 2016, we internally invested $0.4 billion through various digitally-driven productivity initiatives, yielding $0.7 billion of gross productivity, principally related to our services businesses. Costs associated with revenue-generating activities are recorded within the results of our segments and at Corporate and are reflected in their respective margin rates.
In addition, we made several acquisitions to further enhance and expand our digital capabilities:
| · | On January 10, 2017, we completed the acquisition of ServiceMax, a leader in cloud-based field service management (FSM) solutions, for $0.9 billion. This acquisition is expected to provide enhanced capabilities to advance our Industrial Internet vision, enabling customers to immediately gain more value from their assets and find greater efficiency in their field service processes. |
| · | On November 9, 2016, we acquired the remaining 89% of Bit Stew, a software company specializing in gathering data from connected devices in complex industrial systems to help companies plan predictive maintenance and optimize productivity, for $0.1 billion. |
| · | On October 26, 2016, we acquired Wise.io, a leading machine learning and intelligent systems company, for less than $0.1 billion. This acquisition is expected to further accelerate development of advanced machine learning and data science offerings in the Predix platform. |
| · | On September 14, 2016, we acquired the remaining 74% of the software developer Meridium Inc. for $0.4 billion. The acquisition is expected to enhance and accelerate our Asset Performance Management capabilities across our industrial businesses. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 98
IRAN THREAT REDUCTION AND SYRIA HUMAN RIGHTS ACT OF 2012
The Company is making the following disclosure pursuant to Section 13(r) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
Under Section 13(r) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, enacted in 2012, GE is required to disclose in its periodic reports if it or any of its affiliates knowingly engaged in business activities relating to Iran, even if those activities are conducted in accordance with authorizations subsequently issued by the U.S. Government. Reportable activities include investments that significantly enhance Iran's ability to develop petroleum resources valued at $20 million or more in the aggregate during a twelve-month period. Reporting is also required for transactions related to Iran's domestic production of refined petroleum products or Iran's ability to import refined petroleum products valued at $5 million or more in the aggregate during a twelve-month period.
In January 2016, the U.S. Department of Treasury's Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) issued General License H authorizing U.S.-owned or controlled foreign entities to engage in transactions with Iran if these entities meet the requirements of the general license. Pursuant to this authorization, a non-U.S. affiliate of GE's Power business received a purchase order during the third quarter of 2016 for the sale of spare parts to an Iranian entity to provide electricity and steam to an area of Iran that includes certain oil refineries. During the fourth quarter of 2016, the non-U.S. affiliate received purchase orders directly from one of the end users for €7.1 million ($7.9 million) of the work contemplated under the original purchase order. As a result, the original purchase order will be revised. As of December 31, 2016, gross revenues attributable to these purchase orders was €0.9 million ($1.0 million), and net profits attributable to these transactions was €0.5 million ($0.6 million). The non-U.S. affiliate intends to continue this activity.
Another non-U.S. affiliate of GE's Oil & Gas business received four purchase orders during the fourth quarter of 2016 for the sale of goods pursuant to General License H that could potentially enhance Iran's ability to develop petroleum resources. The purchase orders cover the sale of spare parts for gas turbine equipment for ultimate end use by an Iranian company in gas production projects in Iran and have a total value of €16.8 million ($17.6 million). The non-U.S. affiliate has also begun operational activities related to previously reported contracts. A second non-U.S. affiliate of GE's Oil & Gas business received a purchase order pursuant to General License H valued at €0.2 million ($0.2 million) during the fourth quarter of 2016 for the sale of services associated with the commissioning of gas compressors in Iran. As of December 31, 2016, these non-US affiliates have not recognized any revenue, but have incurred €2.7 million ($2.9 million) in costs. The non-U.S. affiliates intend to continue this activity.
For additional information on business activities related to Iran, please refer to the Other Items section within MD&A of our Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2016.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 99
ENVIRONMENTAL MATTERS
Our operations, like operations of other companies engaged in similar businesses, involve the use, disposal and cleanup of substances regulated under environmental protection laws. We are involved in a number of remediation actions to clean up hazardous wastes as required by federal and state laws. Such statutes require that responsible parties fund remediation actions regardless of fault, legality of original disposal or ownership of a disposal site. Expenditures for site remediation actions amounted to approximately $0.2 billion, $0.3 billion and $0.4 billion for the years 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. We presently expect that such remediation actions will require average annual expenditures of about $0.2 billion in 2017 and about $0.1 billion in 2018.
As previously reported, in 2000, GE and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) entered into a consent decree relating to PCB cleanup of the Housatonic River in Massachusetts. Following EPA's release in September 2015 of an intended final remediation decision, GE and EPA engaged in mediation and the first step of the dispute resolution process contemplated by the consent decree. In October 2016, EPA issued its final remediation decision pursuant to the consent decree. GE and several other interested parties have appealed that decision to EPA's Environmental Appeals Board. A decision of the Board can ultimately be appealed to the United States Court of Appeals for the First Circuit. EPA may not implement any remedy until all appeals are exhausted. As of December 31, 2016, and based on its assessment of current facts and circumstances and its defenses, GE believes that it has recorded adequate reserves to cover future obligations associated with an expected final remedy.
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Total R&D | $ | 5,466 | $ | 5,278 | $ | 5,273 | ||
| Less customer funded R&D (principally the U.S. Government) | (611) | (803) | (721) | |||||
| Less partner funded R&D | (73) | (226) | (319) | |||||
| GE funded R&D | $ | 4,782 | $ | 4,249 | $ | 4,233 | ||
Of the total Research and Development, the segments with the most significant expenditures for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 were: Aviation $1,595 million, $1,893 million and $1,965 million, respectively; Healthcare $938 million, $905 million, and $817 million, respectively; and Power $695 million, $721 million and $641 million, respectively. The remaining segments and Corporate, including Global Research Center, had combined expenditures of $2,238 million, $1,759 million and $1,850 million, for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 respectively.
OTHER
We own, or hold licenses to use, numerous patents. New patents are continuously being obtained through our research and development activities as existing patents expire. Patented inventions are used both within the Company and are licensed to others.
GE is a trademark and service mark of General Electric Company.
Because of the diversity of our products and services, as well as the wide geographic dispersion of our production facilities, we use numerous sources for the wide variety of raw materials needed for our operations. We have not been adversely affected by our inability to obtain raw materials.
Sales of goods and services to agencies of the U.S. Government as a percentage of revenues follow.
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
| Total sales to U.S. Government agencies | 3 | % | 3 | % | 3 | % | ||
| Aviation segment defense-related sales | 2 | 2 | 3 | |||||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 100
FINANCIAL MEASURES THAT SUPPLEMENT U.S. GENERALLY ACCEPTED ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES MEASURES (NON-GAAP FINANCIAL MEASURES)
We sometimes use information derived from consolidated financial information but not presented in our financial statements prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). Certain of these data are considered "non-GAAP financial measures" under U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission rules. Specifically, we have referred, in various sections of this report, to:
| · | Industrial segment organic revenues and industrial segment organic revenues excluding Oil & Gas |
| · | Industrial segment organic operating profit |
| · | Oil & Gas organic revenue and operating profit growth |
| · | Operating and non-operating pension cost |
| · | Adjusted corporate costs (operating) |
| · | GE pre-tax earnings from continuing operations, excluding GE Capital earnings (loss) from continuing operations and the corresponding effective tax rates, and the reconciliation of the U.S. federal statutory income tax rate to GE effective tax rate, excluding GE Capital earnings |
| · | Industrial operating earnings and GE Capital earnings (loss) from continuing operations and EPS |
| · | Industrial operating + Verticals earnings and EPS |
| · | Industrial operating profit and operating profit margin (excluding certain items) |
| · | Industrial operating profit + Verticals |
| · | Industrial segment gross margin (excluding Alstom) |
| · | Industrial segment operating profit and operating margin (excluding Alstom) |
| · | Average GE shareowners' equity, excluding effects of discontinued operations |
| · | Average GE Capital shareowners' equity, excluding effects of discontinued operations |
| · | Industrial return on total capital (Industrial ROTC) |
| · | Industrial cash flows from operating activities (Industrial CFOA) and Industrial CFOA excluding taxes related to business sales and principal pension plan funding |
| · | GE cash flows from operating activities (GE CFOA) excluding taxes related to business sales and principal pension plan funding |
| · | Free cash flow (FCF) and FCF plus dispositions |
| · | Ratio of adjusted debt to equity at GE Capital, net of liquidity |
| · | Capital ending net investment (ENI), excluding liquidity |
| · | 2017 operating framework including 2017 Industrial operating + Verticals EPS target |
The reasons we use these non-GAAP financial measures and the reconciliations to their most directly comparable GAAP financial measures follow.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 101
| INDUSTRIAL SEGMENT ORGANIC REVENUES AND INDUSTRIAL SEGMENT ORGANIC REVENUES EXCLUDING OIL & GAS | ||||||||
| (Dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | V% | |||||
| Industrial segment revenues (GAAP) | $ | 113,156 | $ | 108,796 | 4% | |||
| Adjustments: | ||||||||
| Acquisitions | 13,207 | 1,961 | ||||||
| Business dispositions (other than dispositions of businesses acquired for investment) | 1,256 | 6,838 | ||||||
| Currency exchange rates | (808) | - | ||||||
| Industrial segment organic revenues (Non-GAAP) | $ | 99,501 | $ | 99,997 | -% | |||
| Adjustment: Plus Alstom November and December(a) | 3,202 | 1,812 | ||||||
| Industrial segment organic revenues including Alstom results for November and December | ||||||||
| of both 2015 and 2016 (Non-GAAP) | $ | 102,702 | $ | 101,809 | 1% | |||
| Oil & Gas revenues (GAAP) | $ | 12,898 | $ | 16,450 | (22)% | |||
| Adjustments: | ||||||||
| Acquisitions | 140 | - | ||||||
| Business dispositions (other than dispositions of businesses acquired for investment) | - | 57 | ||||||
| Currency exchange rates | (290) | - | ||||||
| Oil & Gas organic revenues (Non-GAAP) | $ | 13,048 | $ | 16,394 | (20)% | |||
| Adjustment: Plus Alstom November and December(a) | 28 | - | ||||||
| Oil & Gas organic revenues including Alstom results for November and December | ||||||||
| of both 2015 and 2016 (Non-GAAP) | $ | 13,075 | $ | 16,394 | (20)% | |||
| Industrial segment organic revenues including Alstom results for November and December | ||||||||
| of both 2015 and 2016 and excluding Oil & Gas (Non-GAAP) | $ | 89,627 | $ | 85,416 | 5% | |||
| (Dollars in millions) | 2015 | 2014 | V% | |||||
| Industrial segment revenues (GAAP) | $ | 108,796 | $ | 109,727 | (1)% | |||
| Adjustments: | ||||||||
| Acquisitions | 2,204 | 46 | ||||||
| Business dispositions (other than dispositions of businesses acquired for investment) | 108 | 1,224 | ||||||
| Currency exchange rates | (4,791) | - | ||||||
| Industrial segment organic revenues (Non-GAAP) | $ | 111,276 | $ | 108,457 | 3% | |||
| Oil & Gas revenues (GAAP) | $ | 16,450 | $ | 19,085 | (14)% | |||
| Adjustments: | ||||||||
| Acquisitions | 145 | 30 | ||||||
| Business dispositions (other than dispositions of businesses acquired for investment) | 25 | 319 | �� | |||||
| Currency exchange rates | (1,597) | - | ||||||
| Oil & Gas organic revenues (Non-GAAP) | $ | 17,878 | $ | 18,735 | (5)% | |||
| Industrial segment organic revenues excluding Oil & Gas (Non-GAAP) | $ | 93,398 | $ | 89,723 | 4% | |||
| (Dollars in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | V% | |||||
| Industrial segment revenues (GAAP) | $ | 109,727 | $ | 103,383 | 6% | |||
| Adjustments: | ||||||||
| Acquisitions | 2,170 | 463 | ||||||
| Business dispositions (other than dispositions of businesses acquired for investment) | 246 | 1,712 | ||||||
| Currency exchange rates | (545) | - | ||||||
| Industrial segment organic revenues (Non-GAAP) | $ | 107,856 | $ | 101,208 | 7% | |||
| Oil & Gas revenues (GAAP) | $ | 18,676 | $ | 16,975 | 10% | |||
| Adjustments: | ||||||||
| Acquisitions | 1,221 | 319 | ||||||
| Business dispositions (other than dispositions of businesses acquired for investment) | 109 | 726 | ||||||
| Currency exchange rates | (67) | - | ||||||
| Oil & Gas organic revenues (Non-GAAP) | $ | 17,413 | $ | 15,930 | 9% | |||
| Industrial segment organic revenues excluding Oil & Gas (Non-GAAP) | $ | 90,443 | $ | 85,279 | 6% | |||
| (a) | Alstom was acquired in November 2015. This adjustment results in the inclusion of Alstom revenues from November and December of both 2015 and 2016 in the adjusted organic revenue growth measure as described below. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 102
Organic revenue growth measures revenue growth excluding the effects of acquisitions, business dispositions and currency exchange rates. We believe that this measure provides management and investors with a more complete understanding of underlying operating results and trends of established, ongoing operations by excluding the effect of acquisitions, dispositions and currency exchange, which activities are subject to volatility and can obscure underlying trends. We also believe that presenting organic revenue growth separately for our industrial businesses provides management and investors with useful information about the trends of our industrial businesses and enables a more direct comparison to other non-financial businesses and companies. Management recognizes that the term "organic revenue growth" may be interpreted differently by other companies and under different circumstances. Although this may have an effect on comparability of absolute percentage growth from company to company, we believe that these measures are useful in assessing trends of the respective businesses or companies and may therefore be a useful tool in assessing period-to-period performance trends.
We integrate acquisitions as soon as possible. Revenues from the date we complete the acquisition through the end of the fourth quarter following the acquisition are considered the acquisition effect of such business for purposes of calculating organic revenue. As such, organic revenue excludes Alstom revenues from November 3, 2015 through December 31, 2016. However, because of the significance of Alstom to our results and the exclusion of Alstom revenues for more than 12 months in calculating organic revenue growth, we believe investors would also find it helpful to see the revenue growth of the industrial segments adjusted to include Alstom's November and December revenues in an organic measure. As a result, we have also presented an adjusted organic revenue growth measure on that basis.
We also believe that variability in the revenue of our Oil & Gas business may obscure underlying trends of our other industrial businesses. As a result, we have also presented our organic revenue growth measure excluding the revenues of our Oil & Gas business.
| INDUSTRIAL SEGMENT ORGANIC OPERATING PROFIT | ||||||||
| (Dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | V% | |||||
| Industrial segment profit (GAAP) | $ | 17,598 | $ | 17,966 | (2)% | |||
| Adjustments: | ||||||||
| Acquisitions | 739 | (151) | ||||||
| Business dispositions (other than dispositions of businesses acquired for investment) | 181 | 649 | ||||||
| Currency exchange rates | (33) | - | ||||||
| Industrial segment organic operating profit (Non-GAAP) | $ | 16,712 | $ | 17,469 | (4)% | |||
| (Dollars in millions) | 2015 | 2014 | V% | |||||
| Industrial segment profit (GAAP) | $ | 17,966 | $ | 17,764 | 1% | |||
| Adjustments: | ||||||||
| Acquisitions | (132) | (1) | ||||||
| Business dispositions (other than dispositions of businesses acquired for investment) | 3 | 195 | ||||||
| Currency exchange rates | (670) | - | ||||||
| Industrial segment organic operating profit (Non-GAAP) | $ | 18,766 | $ | 17,570 | 7% | |||
Industrial segment organic operating profit growth measures Industrial segment profit excluding the effects of acquisitions, business dispositions and currency exchange rates. We believe that this measure provides management and investors with a more complete understanding of underlying operating results and trends of established, ongoing operations by excluding the effect of acquisitions, dispositions and currency exchange, which activities are subject to volatility and can obscure underlying trends. We also believe that presenting industrial segment organic operating profit growth separately for our industrial businesses provides management and investors with useful information about the trends of our industrial businesses and enables a more direct comparison to other non-financial businesses and companies. Management recognizes that the term "Industrial segment organic operating profit growth" may be interpreted differently by other companies and under different circumstances. Although this may have an effect on comparability of absolute percentage growth from company to company, we believe that these measures are useful in assessing trends of the respective businesses or companies and may therefore be a useful tool in assessing period-to-period performance trends.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 103
| OIL & GAS ORGANIC REVENUE GROWTH | |||||||
| (Dollars in millions) | 2015 | 2014 | V% | ||||
| Oil & Gas segment revenue (GAAP) | $ | 16,450 | $ | 19,085 | (14)% | ||
| Adjustments: | |||||||
| Acquisitions | 145 | 30 | |||||
| Business dispositions (other than dispositions of businesses acquired for investment) | 25 | 319 | |||||
| Currency exchange rates | (1,597) | - | |||||
| Oil & Gas organic revenue (Non-GAAP) | $ | 17,878 | $ | 18,735 | (5)% | ||
| OIL & GAS ORGANIC OPERATING PROFIT GROWTH | |||||||
| (Dollars in millions) | 2015 | 2014 | V% | ||||
| Oil & Gas segment profit (GAAP) | $ | 2,427 | $ | 2,758 | (12)% | ||
| Adjustments: | |||||||
| Acquisitions | 8 | - | |||||
| Business dispositions (other than dispositions of businesses acquired for investment) | 1 | 18 | |||||
| Currency exchange rates | (349) | - | |||||
| Oil & Gas organic profit (Non-GAAP) | $ | 2,768 | $ | 2,739 | 1% | ||
Organic revenue and operating profit growth measure revenue and profit excluding the effects of acquisitions, business dispositions and currency exchange rates. We believe that these measures provide management and investors with a more complete understanding of underlying operating results and trends of established, ongoing operations by excluding the effect of acquisitions, dispositions and currency exchange, which activities are subject to volatility and can obscure underlying trends. Management recognizes that the terms "organic revenue growth" and "organic operating profit growth" may be interpreted differently by other companies and under different circumstances. Although this may have an effect on comparability of absolute percentage growth from company to company, we believe that these measures are useful in assessing trends of the Oil & Gas business and may therefore be a useful tool in assessing period-to-period performance trends.
| OPERATING AND NON-OPERATING PENSION COST | |||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Service cost for benefits earned | $ | 1,237 | $ | 1,424 | $ | 1,205 | $ | 1,535 | |||
| Prior service cost amortization | 303 | 205 | 214 | 246 | |||||||
| Curtailment loss | 31 | 105 | 65 | - | |||||||
| Operating pension cost (Non-GAAP) | 1,571 | 1,734 | 1,484 | 1,781 | |||||||
| Expected return on plan assets | (3,336) | (3,302) | (3,190) | (3,500) | |||||||
| Interest cost on benefit obligations | 2,939 | 2,778 | 2,745 | 2,460 | |||||||
| Net actuarial loss amortization | 2,449 | 3,288 | 2,565 | 3,664 | |||||||
| Non-operating pension cost (Non-GAAP) | 2,052 | 2,764 | 2,120 | 2,624 | |||||||
| Total principal pension plans cost (GAAP) | $ | 3,623 | $ | 4,498 | $ | 3,604 | $ | 4,405 | |||
We have provided the operating and non-operating components of cost for our principal pension plans. Operating pension cost comprises the service cost of benefits earned, prior service cost amortization and curtailment loss for our principal pension plans. Non-operating pension cost comprises the expected return on plan assets, interest cost on benefit obligations and net actuarial loss amortization for our principal pension plans. We believe that the operating components of pension cost better reflect the ongoing service-related cost of providing pension benefits to our employees. We believe that the operating and non-operating components of cost for our principal pension plans, considered along with the corresponding GAAP measure, provide management and investors with additional information for comparison of our pension plan cost and operating results with the pension plan cost and operating results of other companies.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 104
| ADJUSTED CORPORATE COSTS (OPERATING) | |||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Total Corporate Items and Eliminations (GAAP) | $ | (4,226) | $ | (5,108) | $ | (6,225) | $ | (6,002) | |||
| Less: non-operating pension cost (Non-GAAP) | (2,052) | (2,764) | (2,120) | (2,624) | |||||||
| Total Corporate costs (operating) (Non-GAAP) | $ | (2,175) | $ | (2,344) | $ | (4,105) | $ | (3,378) | |||
| Less: restructuring and other charges, gains (losses), | |||||||||||
| NBCU settlement and NBCU LLC | (134) | (237) | (1,697) | (17) | |||||||
| Adjusted total corporate costs (operating) (Non-GAAP) | $ | (2,040) | $ | (2,107) | $ | (2,408) | $ | (3,361) | |||
Operating corporate costs exclude non-service-related pension costs of our principal pension plans, which comprise interest costs, expected return on plan assets and amortization of actuarial gains/losses. Service cost, prior service cost and curtailment loss components of our principal pension plans are included in operating corporate costs. We believe that these components of pension cost better reflect the ongoing service-related costs of providing pension benefits to our employees. Accordingly, we believe that our measure of operating corporate costs provides management and investors with a useful measure of the operational costs incurred outside of our businesses. We believe that this measure, considered along with the corresponding GAAP measure, provides management and investors with additional information for comparison of our operating corporate costs to the operating corporate costs of other companies.
We also believe that adjusting operating corporate costs to exclude the effects of items that are not closely associated with ongoing corporate operations, such as earnings of previously divested businesses, gains and losses on disposed and held for sale businesses, restructuring and other charges, a settlement and NBCU LLC provides management and investors with a meaningful measure that increases the period-to-period comparability of our ongoing corporate costs.
| GE PRE-TAX EARNINGS FROM CONTINUING OPERATIONS, EXCLUDING GE CAPITAL EARNINGS (LOSS) FROM | ||||||||||||
| CONTINUING OPERATIONS AND THE CORRESPONDING EFFECTIVE TAX RATES | ||||||||||||
| (Dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| GE earnings from continuing operations before income taxes (GAAP) | $ | 9,815 | $ | 3,252 | $ | 11,119 | ||||||
| Less: GE Capital earnings (loss) from continuing operations | (1,251) | (7,672) | 1,532 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 11,066 | $ | 10,924 | $ | 9,587 | ||||||
| GE provision for income taxes (GAAP) | $ | 967 | $ | 1,506 | $ | 1,634 | ||||||
| GE effective tax rate, excluding GE Capital earnings (Non-GAAP) | 8.7 % | 13.8 % | 17.0 % | |||||||||
| RECONCILIATION OF U.S. FEDERAL STATUTORY INCOME TAX RATE TO GE EFFECTIVE TAX RATE, | ||||||||||||
| EXCLUDING GE CAPITAL EARNINGS | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| U.S. federal statutory income tax rate | 35.0 % | 35.0 % | 35.0 % | |||||||||
| Reduction in rate resulting from: | ||||||||||||
Tax on global activities including exports | (18.5) | (15.8) | (13.9) | |||||||||
U.S. business credits | (0.8) | (1.2) | (1.1) | |||||||||
| All other – net | (7.0) | (4.2) | (3.0) | |||||||||
| (26.3) | (21.2) | (18.0) | ||||||||||
| GE effective tax rate, excluding GE Capital earnings | 8.7 % | 13.8 % | 17.0 % | |||||||||
We believe that the GE effective tax rate is best analyzed in relation to GE earnings before income taxes excluding the GE Capital net earnings from continuing operations, as GE tax expense does not include taxes on GE Capital earnings. Management believes that in addition to the Consolidated and GE Capital tax rates shown in Note 14 to the consolidated financial statements, this supplemental measure provides investors with useful information as it presents the GE effective tax rate that can be used in comparing the GE results to other non-financial services businesses.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 105
| INDUSTRIAL OPERATING EARNINGS AND GE CAPITAL EARNINGS (LOSS) FROM CONTINUING OPERATIONS AND EPS | |||||||||||
| (Dollars in millions; except per share amounts) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Consolidated earnings from continuing operations attributable | |||||||||||
| to GE common shareowners (GAAP) | $ | 9,128 | $ | 1,663 | $ | 9,535 | $ | 7,618 | |||
| Non-operating pension cost (pre-tax) | 2,052 | 2,764 | 2,120 | 2,624 | |||||||
| Tax effect on non-operating pension cost(a) | (718) | (967) | (742) | (919) | |||||||
| Adjustment: non-operating pension cost (net of tax) | 1,334 | 1,797 | 1,378 | 1,705 | |||||||
| Operating earnings (Non-GAAP) | $ | 10,462 | $ | 3,460 | $ | 10,913 | $ | 9,323 | |||
| Adjustment: GE Capital earnings (loss) from continuing operations | |||||||||||
| attributable to GE common shareowners | (1,251) | (7,983) | 1,209 | 401 | |||||||
| Industrial operating earnings (Non-GAAP) | $ | 11,713 | $ | 11,443 | $ | 9,705 | $ | 8,922 | |||
Earnings (loss) per share (EPS) - diluted(b) | |||||||||||
| Consolidated EPS from continuing operations | |||||||||||
| attributable to GE common shareowners (GAAP) | $ | 1.00 | $ | 0.17 | $ | 0.94 | $ | 0.74 | |||
| Adjustment: non-operating pension cost (net of tax) | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.17 | |||||||
| Operating EPS (Non-GAAP) | 1.14 | 0.35 | 1.08 | 0.90 | |||||||
| GE Capital EPS from continuing operations | |||||||||||
| attributable to GE common shareowners (GAAP) | (0.14) | (0.80) | 0.12 | 0.04 | |||||||
| Industrial operating EPS (Non-GAAP) | $ | 1.28 | $ | 1.14 | $ | 0.96 | $ | 0.87 | |||
| (a) | The tax effect of non-operating pension costs was calculated using a 35% U.S. federal statutory tax rate, based on its applicability to such cost. |
| (b) | Earnings-per-share amounts are computed independently. As a result, the sum of per-share amounts may not equal the total. |
Operating earnings excludes non-service-related pension costs of our principal pension plans comprising interest cost, expected return on plan assets and amortization of actuarial gains/losses. The service cost, prior service cost and curtailment loss components of our principal pension plans are included in operating earnings. We believe that these components of pension cost better reflect the ongoing service-related costs of providing pension benefits to our employees. As such, we believe that our measure of operating earnings provides management and investors with a useful measure of the operational results of our business. Other components of GAAP pension cost are mainly driven by capital allocation decisions and market performance, and we manage these separately from the operational performance of our businesses. Neither GAAP nor operating pension costs are necessarily indicative of the current or future cash flow requirements related to our pension plans. We also believe that this measure, considered along with the corresponding GAAP measure, provides management and investors with additional information for comparison of our operating results to the operating results of other companies. We believe that presenting operating earnings separately for our industrial businesses also provides management and investors with useful information about the relative size of our industrial and financial services businesses in relation to the total company.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 106
| INDUSTRIAL OPERATING + VERTICALS EARNINGS AND EPS | |||||||||||
| (Dollars in millions; except per share amounts) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| GE Capital earnings (loss) from continuing operations attributable | |||||||||||
| to GE common shareowners (GAAP) | $ | (1,251) | $ | (7,983) | $ | 1,209 | $ | 401 | |||
| Adjustment: GE Capital other continuing earnings (loss) (Other Capital) | (3,143) | (9,649) | (399) | (1,009) | |||||||
| Verticals earnings(a) | 1,892 | 1,666 | 1,608 | 1,410 | |||||||
| Industrial operating earnings (Non-GAAP) | $ | 11,713 | $ | 11,443 | $ | 9,705 | $ | 8,922 | |||
| Verticals earnings(a) | 1,892 | 1,666 | 1,608 | 1,410 | |||||||
| Industrial operating earnings + Verticals earnings (Non-GAAP) | $ | 13,605 | $ | 13,109 | $ | 11,313 | $ | 10,332 | |||
| Adjustment: Non-operating pension cost and other Capital | (4,477) | (11,446) | (1,777) | (2,714) | |||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing operations | |||||||||||
| attributable to GE common shareowners (GAAP) | $ | 9,128 | $ | 1,663 | $ | 9,535 | $ | 7,618 | |||
Earnings (loss) per share - diluted(b) | |||||||||||
| Industrial operating EPS (Non-GAAP) | $ | 1.28 | $ | 1.14 | $ | 0.96 | $ | 0.87 | |||
| Verticals EPS | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.14 | |||||||
| Industrial operating + Verticals EPS (Non-GAAP) | $ | 1.49 | $ | 1.31 | $ | 1.12 | $ | 1.00 | |||
| Adjustment: Non-operating pension cost and other Capital | (0.49) | (1.14) | (0.18) | (0.27) | |||||||
| EPS from continuing operations (GAAP) | $ | 1.00 | $ | 0.17 | $ | 0.94 | $ | 0.74 | |||
| (a) | Verticals include businesses expected to be retained (GECAS, Energy Financial Services, Industrial Finance and run-off insurance activities), including allocated corporate costs of $100 million, $133 million, $233 million and $233 million after tax for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. |
| (b) | Earnings-per-share amounts are computed independently. As a result, the sum of per-share amounts may not equal the total. |
As described above, Verticals represents the GE Capital businesses that we expect to retain. We believe that presenting Industrial operating + Verticals earnings-per-share amounts provides management and investors with a useful measure to evaluate the performance of the businesses we expect to retain after the disposition of most of our financial services business.
See below for a graphic presentation of the reconciliation between GAAP EPS from continuing operations to the Industrial operating + Verticals EPS.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 107
| INDUSTRIAL OPERATING + VERTICALS EARNINGS AND EPS(a) | |||||
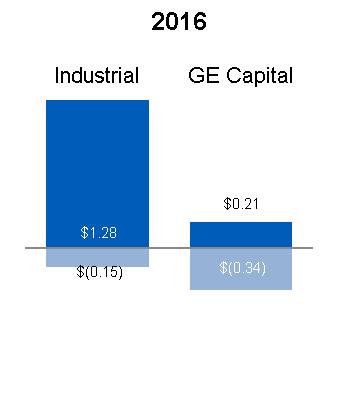 | Industrial operating & Verticals $1.49 Non-operating pension & other Capital $(0.49) |  | Industrial operating & Verticals $1.31 Non-operating pension & other Capital $(1.14) | ||
| GAAP Continuing EPS | $1.00 | $0.17 | |||
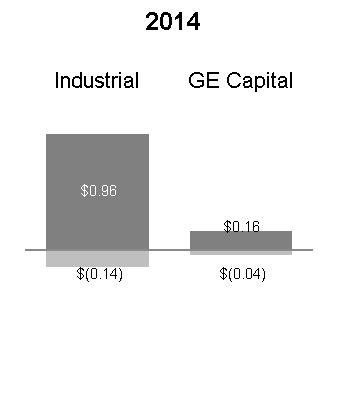 | Industrial operating & Verticals $1.12 Non-operating pension & other Capital $(0.18) |  | Industrial operating & Verticals $1.00 Non-operating pension & other Capital $(0.27) | ||
| GAAP Continuing EPS | $0.94 | $0.74 | |||
| (a) | Earnings-per-share amounts are computed independently. As a result, the sum of per share amounts may not equal the total. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 108
| INDUSTRIAL OPERATING PROFIT AND OPERATING PROFIT MARGIN (EXCLUDING CERTAIN ITEMS) | ||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Revenues | ||||||||||||||
| GE total revenues and other income | $ | 113,676 | $ | 100,700 | $ | 109,546 | $ | 104,599 | $ | 104,900 | ||||
| Less: GE Capital earnings (loss) from | ||||||||||||||
| continuing operations | (1,251) | (7,672) | 1,532 | 699 | 1,368 | |||||||||
| GE revenues and other income excluding GE Capital | ||||||||||||||
| earnings (loss) (Industrial revenues) (GAAP) | $ | 114,927 | $ | 108,371 | $ | 108,014 | $ | 103,900 | $ | 103,532 | ||||
| Less: gains | 3,444 | 1,497 | 91 | 453 | 186 | |||||||||
| Less: NBCU | - | - | - | 1,528 | 1,615 | |||||||||
| Adjusted Industrial revenues (Non-GAAP) | $ | 111,483 | $ | 106,874 | $ | 107,923 | $ | 101,919 | $ | 101,731 | ||||
| Less: Alstom revenues | 13,015 | 1,956 | - | - | - | |||||||||
| Adjusted Industrial revenues ex. Alstom (Non-GAAP) | $ | 98,468 | $ | 104,918 | $ | 107,923 | $ | 101,919 | $ | 101,731 | ||||
| Costs | ||||||||||||||
| GE total costs and expenses | $ | 103,860 | $ | 97,447 | $ | 98,427 | $ | 95,068 | $ | 94,081 | ||||
| Less: GE interest and other financial charges | 2,026 | 1,706 | 1,579 | 1,333 | 1,353 | |||||||||
| Industrial costs excluding interest and other | ||||||||||||||
| financial charges (GAAP) | $ | 101,834 | $ | 95,741 | $ | 96,848 | $ | 93,735 | $ | 92,728 | ||||
| Less: gains (cost basis) | - | - | - | 6 | - | |||||||||
| Less: non-operating pension cost (pre-tax) | 2,052 | 2,764 | 2,120 | 2,624 | 2,132 | |||||||||
| Less: restructuring and other charges | 3,578 | 1,734 | 1,788 | 1,992 | 732 | |||||||||
| Less: noncontrolling interests and 2015 GE Capital | ||||||||||||||
| preferred stock dividends | 279 | 229 | 372 | 53 | (37) | |||||||||
| Adjusted Industrial costs (Non-GAAP) | $ | 95,925 | $ | 91,015 | $ | 92,567 | $ | 89,060 | $ | 89,901 | ||||
| Less: Alstom costs and expenses | 12,243 | 2,110 | - | - | - | |||||||||
| Adjusted Industrial costs ex. Alstom (Non-GAAP) | $ | 83,682 | $ | 88,905 | $ | 92,567 | $ | 89,060 | $ | 89,901 | ||||
| Industrial profit (GAAP) | $ | 13,093 | $ | 12,630 | $ | 11,166 | $ | 10,165 | $ | 10,804 | ||||
| Industrial margins (GAAP) | 11.4% | 11.7% | 10.3% | 9.8% | 10.4% | |||||||||
| Industrial operating profit (Non-GAAP) | $ | 15,558 | $ | 15,859 | $ | 15,356 | $ | 12,859 | $ | 11,831 | ||||
| Industrial operating profit margins (Non-GAAP) | 14.0% | 14.8% | 14.2% | 12.6% | 11.6% | |||||||||
| Industrial operating profit ex. Alstom (Non-GAAP) | $ | 14,786 | $ | 16,013 | $ | 15,356 | $ | 12,859 | $ | 11,830 | ||||
| Industrial operating profit margins ex. Alstom (Non-GAAP) | 15.0% | 15.3% | 14.2% | 12.6% | 11.6% | |||||||||
| . | ||||||||||||||
We have presented our Industrial operating profit and operating profit margin excluding gains, non-operating pension costs (pre-tax), restructuring and other, noncontrolling interests, GE Capital preferred stock dividends, as well as the results of Alstom. We believe that Industrial operating profit and operating profit margin adjusted for these items are meaningful measures because they increase the comparability of period-to-period results.
| INDUSTRIAL OPERATING PROFIT + VERTICALS | |||||||||||
| (Dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Industrial operating profit (Non-GAAP)(a) | $ | 15,558 | $ | 15,859 | $ | 15,356 | $ | 12,859 | |||
| Vertical earnings(b) | 1,892 | 1,666 | 1,606 | 1,410 | |||||||
| Industrial operating profit + Verticals (Non-GAAP) | $ | 17,450 | $ | 17,525 | $ | 16,962 | $ | 14,269 | |||
| . | |||||||||||
| (a) | See Industrial Operating Profit and Operating Profit Margin reconciliation above for computation. |
| (b) | See Industrial Operating + Verticals earnings and EPS reconciliation above for computation. |
We have presented our measure of Industrial operating profit and Vertical earnings, which is the sum of the Industrial operating profit used in measuring the operating margins of our industrial businesses and the net earnings of our Verticals businesses. See the reconciliations for these measures for additional information about the basis for the measures and explanation of why we believe these individual measures are helpful to management and our investors. We also believe that this measure, which combines an industrial business measure with the results of our Vertical financial services business provides management and investors with a measure that is aligned with the way in which we manage these businesses.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 109
| INDUSTRIAL SEGMENT GROSS MARGIN (EXCLUDING ALSTOM) | |||||
| (Dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Industrial Sales | $ | 110,835 | $ | 106,206 | |
| Less: Corporate sales and eliminations | (2,071) | (1,858) | |||
| Industrial segment sales | 112,906 | 108,064 | |||
| Less: Alstom sales | 13,096 | 1,953 | |||
| Industrial segment sales excluding Alstom | $ | 99,810 | $ | 106,111 | |
| Industrial cost of sales | $ | 85,712 | $ | 80,828 | |
| Less: Corporate cost of sales and eliminations | 3,315 | 2,026 | |||
| Industrial segment cost of sales | 82,397 | 78,802 | |||
| Less: Alstom cost of sales | 10,364 | 1,730 | |||
| Industrial segment cost of sales excluding Alstom | $ | 72,033 | $ | 77,072 | |
| Industrial segment gross margin | $ | 30,509 | $ | 29,262 | |
| Industrial segment gross margin percentage | 27.0% | 27.1% | |||
| Industrial segment gross margin excluding Alstom | $ | 27,777 | $ | 29,039 | |
| Industrial segment gross margin percentage excluding Alstom | 27.8% | 27.4% | |||
We have presented our segment gross margin excluding the results of our fourth quarter 2015 Alstom power and grid acquisition. We believe that industrial segment gross margin adjusted for the Alstom impacts is a meaningful measure because it increases the comparability of period-to-period results.
| INDUSTRIAL SEGMENT OPERATING PROFIT AND OPERATING PROFIT MARGIN (EXCLUDING ALSTOM) | |||||||||||||
| (Dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
| Revenues | |||||||||||||
| Total industrial segment revenues (GAAP) | $ | 113,156 | $ | 108,796 | $ | 109,727 | $ | 103,383 | $ | 102,548 | |||
| Less: Alstom revenues | 13,015 | 1,956 | - | - | - | ||||||||
| Total industrial segment operating | |||||||||||||
| revenues excluding Alstom (Non-GAAP) | $ | 100,141 | $ | 106,840 | $ | 109,727 | $ | 103,383 | $ | 102,548 | |||
| Segment profit (loss) | |||||||||||||
| Total industrial segment operating profit (GAAP) | $ | 17,598 | $ | 17,966 | $ | 17,764 | $ | 16,220 | $ | 15,487 | |||
| Total industrial segment operating profit margin (GAAP) | 15.6% | 16.5% | 16.2% | 15.7% | 15.1% | ||||||||
| Less: Alstom profit (loss) | $ | 772 | $ | (154) | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||
| Total industrial segment operating profit | |||||||||||||
| excluding Alstom (Non-GAAP) | $ | 16,826 | $ | 18,120 | $ | 17,764 | $ | 16,220 | $ | 15,487 | |||
| Total industrial segment operating profit margin | |||||||||||||
| excluding Alstom (Non-GAAP) | 16.8% | 17.0% | 16.2% | 15.7% | 15.1% | ||||||||
| . | |||||||||||||
We have presented our segment gross margin excluding the results of our fourth quarter 2015 Alstom power and grid acquisition. We believe that industrial segment gross margin adjusted for the Alstom impacts is a meaningful measure because it increases the comparability of period-to-period results.
We have also presented results of our Power, Renewable Energy and Energy Connections & Lighting segments excluding the effects of the fourth quarter Alstom power and grid acquisition. These measurements included revenues, operating profit and margin excluding Alstom, the reconciliations for which are included in the segment sections within MD&A. We believe that metrics adjusted for the Alstom impacts are meaningful measures because they increase the comparability of period-to-period results.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 110
| AVERAGE GE SHAREOWNERS' EQUITY, EXCLUDING EFFECTS OF DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS(a) | ||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Average GE shareowners' equity(a) (GAAP) | $ | 86,412 | $ | 111,140 | $ | 131,914 | $ | 124,501 | $ | 120,401 | ||||
| Less the effects of the average net investment | ||||||||||||||
in discontinued operations | 2,854 | 27,910 | 45,455 | 44,948 | 41,399 | |||||||||
| Average GE shareowners' equity, excluding | ||||||||||||||
effects of discontinued operations(b) (Non-GAAP) | $ | 83,558 | $ | 83,230 | $ | 86,459 | $ | 79,553 | $ | 79,002 | ||||
| (a) | On an annual basis, calculated using a five-point average. |
| (b) | Used for computing Industrial return on total capital (ROTC). |
Our Industrial ROTC calculation excludes earnings (losses) of discontinued operations from the numerator because GAAP requires us to display those earnings (losses) in the Statement of Earnings. Those earnings (losses) from discontinued operations include an allocation of interest expense either directly attributable or related to discontinued operations. Net investment in discontinued operations is calculated as assets of discontinued operations less liabilities of discontinued operations, including an allocation of GE Capital debt. Our calculation of average GE shareowners' equity may not be directly comparable to similarly titled measures reported by other companies. We believe that it is a clearer way to measure the ongoing trend in return on total capital for the continuing operations of our businesses given the extent that discontinued operations have affected our reported results. We believe that this results in a more relevant measure for management and investors to evaluate performance of our continuing operations, on a consistent basis, and to evaluate and compare the performance of our continuing operations with the ongoing operations of other businesses and companies.
Definitions indicating how the above-named ratios are calculated using average GE shareowners' equity, excluding effects of discontinued operations, can be found in the Other Items and Measures section within the MD&A.
| AVERAGE GE CAPITAL SHAREOWNERS' EQUITY, EXCLUDING EFFECTS OF DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS(a) | |||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Average GE Capital shareowners' equity(a) (GAAP) | $ | 34,382 | $ | 67,930 | $ | 85,370 | $ | 83,358 | $ | 79,873 | |||||
| Less the effects of the average net | |||||||||||||||
| investment in discontinued operations | 2,955 | 28,028 | 45,589 | 45,023 | 41,504 | ||||||||||
| Average GE Capital shareowners' equity, | |||||||||||||||
| excluding effects of discontinued operations(b) (Non-GAAP) | $ | 31,427 | $ | 39,902 | $ | 39,781 | $ | 38,335 | $ | 38,369 | |||||
| (a) | On an annual basis, calculated using a five-point average. |
| (b) | Used for computing Industrial return on total capital (ROTC). |
Our Industrial ROTC calculation excludes earnings (losses) of discontinued operations from the numerator because GAAP requires us to display those earnings (losses) in the Statement of Earnings. Our calculation of average GE Capital shareowners' equity may not be directly comparable to similarly titled measures reported by other companies. We believe that it is a clearer way to measure the ongoing trend in return on total capital for the continuing operations of our businesses given the extent that discontinued operations have affected our reported results. We believe that this results in a more relevant measure for management and investors to evaluate performance of our continuing operations, on a consistent basis, and to evaluate and compare the performance of our continuing operations with the ongoing operations of other businesses and companies.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 111
| INDUSTRIAL RETURN ON TOTAL CAPITAL (INDUSTRIAL ROTC) | ||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Earnings from continuing operations (GAAP) | $ | 9,494 | $ | 1,700 | $ | 9,490 | $ | 7,881 | $ | 8,816 | ||||
| Less: GE Capital earnings (loss) from continuing operations | (606) | (7,718) | 1,537 | 716 | 1,378 | |||||||||
| Plus: GE after-tax interest | 1,499 | 1,262 | 1,026 | 865 | 880 | |||||||||
| Adjusted Industrial return (Non-GAAP) | $ | 11,599 | $ | 10,680 | $ | 8,979 | $ | 8,030 | $ | 8,318 | ||||
| Average GE shareholders' equity, excluding effects | ||||||||||||||
| of discontinued operations(a) | $ | 83,558 | $ | 83,230 | $ | 86,459 | $ | 79,553 | $ | 79,002 | ||||
| Less: average GE Capital's shareholders' equity, | ||||||||||||||
| excluding effects of discontinued operations(a) | 31,427 | 39,902 | 39,781 | 38,335 | 38,369 | |||||||||
| Average Industrial shareholders' equity, excluding | ||||||||||||||
| effects of discontinued operations | 52,131 | 43,328 | 46,678 | 41,218 | 40,633 | |||||||||
| Plus: average debt(a) | 21,491 | 18,411 | 15,724 | 13,652 | 12,899 | |||||||||
| Plus: other, net(b) | 1,924 | 1,486 | 1,743 | 1,367 | (1,106) | |||||||||
| Adjusted Industrial capital (Non-GAAP) | $ | 75,546 | $ | 63,225 | $ | 64,145 | $ | 56,237 | $ | 52,426 | ||||
| Industrial ROTC | 15.4 % | 16.9 % | 14.0 % | 14.3 % | 15.9 % | |||||||||
| (a) | On an annual basis, calculated using a five-point average. |
| (b) | Includes average noncontrolling interests, calculated using a five-point average partially offset by the estimated value of assets held by GE to support GE Capital. |
Our Industrial ROTC calculation excludes earnings (losses) of discontinued operations from the numerator. We believe that this is a clearer way to measure the ongoing trend in return on Industrial capital for the continuing operations of the business to the extent that discontinued operations have affected our reported results. Our Industrial shareowners' equity used in the denominator is adjusted for debt, redeemable noncontrolling interests and noncontrolling interests. We believe that these adjustments provide a more meaningful denominator in measuring the return on our industrial businesses. Industrial ROTC was 15.4% in 2016 versus 16.9% in 2015 and 14.0% in 2014. In 2016, an 8.6% increase in the adjusted Industrial return was combined with a 19.5% increase in the adjusted Industrial capital. This increase in capital was principally driven by increased debt and effects from Alstom redeemable noncontrolling interests. Our calculation of the return on Industrial capital may not be directly comparable to similarly titled measures reported by other companies. We believe that the adjustments described above result in a more relevant measure for management and investors to evaluate performance of our Industrial continuing operations, on a consistent basis, and to evaluate and compare the performance of our Industrial continuing operations with the continuing operations of other businesses and companies.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 112
| INDUSTRIAL CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES (INDUSTRIAL CFOA) AND INDUSTRIAL CFOA | |||||||||||
| EXCLUDING TAXES RELATED TO BUSINESS SALES AND PRINCIPAL PENSION PLAN FUNDING | |||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Cash from GE's operating activities (continuing operations), | |||||||||||
| as reported (GAAP) | $ | 29,960 | $ | 16,354 | $ | 15,171 | $ | 14,255 | |||
| Adjustment: dividends from GE Capital | 20,095 | 4,300 | 3,000 | 5,985 | |||||||
| Industrial CFOA (Non-GAAP) | $ | 9,865 | $ | 12,054 | $ | 12,171 | $ | 8,270 | |||
| Adjustment: taxes related to business sales | 1,398 | 184 | - | 3,184 | |||||||
| Adjustment: Principal pension plan funding | 347 | - | - | - | |||||||
| Industrial CFOA excluding deal-related taxes and | |||||||||||
| Principal pension plan funding (Non-GAAP) | $ | 11,610 | $ | 12,238 | $ | 12,171 | $ | 11,454 | |||
| GE CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES (GE CFOA) EXCLUDING TAXES RELATED TO BUSINESS SALES | |||||||||||
| AND PRINCIPAL PENSION PLAN FUNDING | |||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Cash from GE's operating activities (continuing operations), | |||||||||||
| as reported (GAAP) | $ | 29,960 | $ | 16,354 | $ | 15,171 | $ | 14,255 | |||
| Adjustment: taxes related to business sales | 1,398 | 184 | - | 3,184 | |||||||
| Adjustment: Principal pension plan funding | 347 | - | - | - | |||||||
| GE CFOA excluding deal-related taxes and | |||||||||||
| Principal pension plan funding (Non-GAAP) | $ | 31,705 | $ | 16,538 | $ | 15,171 | $ | 17,439 | |||
We define "Industrial CFOA" as GE's cash from operating activities (continuing operations) less the amount of dividends received by GE from GE Capital. This reflects the effects of intercompany transactions, which include, but are not limited to, the following: GE Capital working capital solutions to optimize GE cash management; GE Capital enabled GE industrial orders; aircraft engines, power equipment and healthcare equipment manufactured by GE that are installed on GE Capital investments, including leased equipment; expenses related to parent-subsidiary pension plans; buildings and equipment leased between GE and GE Capital, including sale-leaseback transactions; information technology (IT) and other services sold to GE Capital by GE; and various investments, loans and allocations of GE corporate overhead costs.
We believe that investors may find it useful to compare GE's operating cash flows without the effect of GE Capital dividends, since these dividends are not representative of the operating cash flows of our industrial businesses and can vary from period to period based upon the results of the financial services businesses. We also believe that investors may find it useful to compare Industrial CFOA and GE CFOA excluding the effects of taxes paid related to the sales of the Appliances, Signaling and NBCU LLC businesses and contributions to our principal pension plans. Management recognizes that these measures may not be comparable to cash flow results of companies which contain both industrial and financial services businesses, but believes that this comparison is aided by the provision of additional information about the amounts of dividends paid by our financial services business and the separate presentation in our financial statements of the GE Capital cash flows. We believe that our measure of Industrial CFOA, and both Industrial CFOA and GE CFOA excluding such sale-related taxes and pension contributions (representing net sale proceeds associated with the July 1, 2016 sale of GEAM to State Street Corporation) provides management and investors with useful measures to compare the capacity of our industrial operations to generate operating cash flow with the operating cash flow of other non-financial businesses and companies and as such provides useful measures to supplement the reported GAAP CFOA measure.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 113
| FREE CASH FLOW (FCF) AND FCF PLUS DISPOSITIONS | ||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Cash from GE's operating activities (continuing operations) (GAAP) | $ | 29,960 | $ | 16,354 | $ | 15,171 | ||
| Less: GE additions to property, plant and equipment | 3,758 | 3,785 | 3,970 | |||||
| Plus: GE dispositions of property, plant and equipment | 1,080 | 939 | 615 | |||||
| Free cash flow (Non-GAAP) | 27,282 | 13,508 | 11,816 | |||||
| Plus: GE proceeds from principal business dispositions | 5,357 | 1,725 | 602 | |||||
| Free cash flow plus dispositions (Non-GAAP) | 32,639 | 15,233 | 12,418 | |||||
We define free cash flow as GE's cash from operating activities (continuing operations) less GE additions to property, plant and equipment and plus GE dispositions of property, plant and equipment, which are included in cash flows from investing activities. We believe that free cash flow is a useful financial metric to assess our ability to pursue opportunities to enhance our growth. We also believe that presenting free cash flow plus proceeds from business dispositions provides investors with useful information about the company's actual performance against performance targets. Management recognizes that the term free cash flow may be interpreted differently by other companies and under different circumstances. Although this may have an effect on comparability of absolute percentage growth from company to company, we believe that these measures are useful in assessing trends of the respective businesses or companies and may therefore be a useful tool in assessing period-to-period performance trends.
| RATIO OF ADJUSTED DEBT TO EQUITY AT GE CAPITAL, NET OF LIQUIDITY | ||||||||||||||
| December 31 (Dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| GE Capital debt | $ | 117,303 | $ | 180,178 | $ | 245,252 | $ | 283,820 | $ | 315,172 | ||||
| Plus: debt of businesses held for sale | ||||||||||||||
| and discontinued operations | 2,076 | 31,075 | 105,687 | 86,546 | 81,229 | |||||||||
| Adjusted GE Capital debt | 119,379 | 211,253 | 350,939 | 370,366 | 396,401 | |||||||||
| Less: liquidity(a) | 49,100 | 70,497 | 54,109 | 65,492 | 52,810 | |||||||||
| Less: cash of businesses held for | ||||||||||||||
| sale and discontinued operations | 1,429 | 20,395 | 22,243 | 9,617 | 9,308 | |||||||||
| $ | 68,849 | $ | 120,361 | $ | 274,587 | $ | 295,256 | $ | 334,283 | |||||
| GE Capital equity | $ | 24,677 | $ | 46,227 | $ | 87,499 | $ | 82,694 | $ | 81,889 | ||||
| Ratio | 2.79:1 | 2.6:1 | 3.14:1 | 3.57:1 | 4.08:1 | |||||||||
| (a) | Liquidity includes cash and equivalents and $11.5 billion of high quality investments at December 31, 2016. |
We have provided the GE Capital ratio of debt to equity on a basis that reflects the use of liquidity as a reduction of debt. For purposes of this ratio, we have also adjusted cash and debt balances to include amounts classified as assets and liabilities of businesses held for sale and discontinued operations. We believe that this is a useful comparison to a GAAP-based ratio of debt to equity because liquidity balances may be used to reduce debt. The usefulness of this supplemental measure may be limited, however, as the total amount of liquidity at any point in time may be different than the amount that could practically be applied to reduce outstanding debt. Despite this potential limitation, we believe that this measure, considered along with the corresponding GAAP measure, provides investors with additional information that may be more comparable to other financial institutions and businesses.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 114
| CAPITAL ENDING NET INVESTMENT (ENI), EXCLUDING LIQUIDITY | ||||||||
| December 31 (In billions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014(a) | |||||
| GE Capital total assets (GAAP) | $ | 183.0 | $ | 311.5 | $ | 500.2 | ||
| Less: assets of discontinued operations | 14.8 | 120.9 | 1.2 | |||||
| Less: non-interest bearing liabilities | 37.4 | 38.8 | 60.5 | |||||
| Capital ENI (Non-GAAP) | 130.7 | 151.8 | 438.5 | |||||
| Less: liquidity(b) | 49.1 | 70.5 | 75.5 | |||||
| Capital ENI, excluding liquidity (Non-GAAP) | $ | 81.6 | $ | 81.3 | $ | 363.0 | ||
| Plus: Discontinued operations ENI | 11.2 | 84.9 | (0.1) | |||||
| Total ENI (excluding liquidity) including discontinued operations (Non-GAAP) | $ | 92.8 | $ | 166.2 | $ | 362.9 | ||
| (a) | As originally reported. |
| (b) | Liquidity includes cash and equivalents and $11.5 billion of high quality investments at December 31, 2016. |
We use ENI to measure the size of our Capital segment. We believe that this measure is a useful indicator of the capital (debt or equity) required to fund a business as it adjusts for non-interest bearing current liabilities generated in the normal course of business that do not require a capital outlay. We also believe that by excluding liquidity, we provide a meaningful measure of assets requiring capital to fund our Capital segment as a substantial amount of liquidity resulted from debt issuances to pre-fund future debt maturities and will not be used to fund additional assets. Liquidity consists of cash and equivalents and certain high quality investments. As a general matter, investments included in liquidity are expected to be highly liquid, giving us the ability to readily convert them to cash. Providing this measure will help investors measure how we are performing against our previously communicated goal to reduce the size of our financial services segment.
| 2017 OPERATING FRAMEWORK INCLUDING 2017 INDUSTRIAL OPERATING + VERTICALS EPS TARGET |
2017 Industrial operating + Verticals EPS Target $1.60-1.70 Items not included in non-GAAP metric: 1) Non-operating pension cost, which we estimate to be approximately $(0.16) – (0.17) per share. 2) Capital Other continuing earnings (excluding Verticals), which we estimate to be approximately $(0.03) – (0.12) per share. This amount is affected by, among other things: • The timing of when, and the amount by which, the Company pays down GE Capital's outstanding debt; and • The timing and magnitude of the remaining costs associated with GE Capital's Exit Plan. |
Note: The company cannot provide an equivalent GAAP EPS guidance range without unreasonable effort because of the uncertainty of the amount and timing of events affecting earnings as we execute the GE Capital Exit Plan. Although we have attempted to estimate GE Capital's Other continuing earnings for the purpose of explaining the probable significance of this component, as described under number 2, this calculation involves a number of unknown variables, resulting in a GAAP range that we believe is too large and variable to be meaningful.
It is also impractical to provide a reconciliation for our organic revenue, Industrial operating margin expansion and Free Cash Flow plus Dispositions targets as these involve a number of unknown variables including the effects of future acquisitions, dispositions, restructuring activities, property plant and equipment purchases and dispositions and currency exchange.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 115
OTHER FINANCIAL DATA
SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
| (Dollars in millions; per-share amounts in dollars) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| General Electric Company and Consolidated Affiliates | |||||||||||||||
Revenues and other income | $ | 123,693 | $ | 117,386 | $ | 117,184 | $ | 113,245 | $ | 112,588 | |||||
| Earnings from continuing operations attributable to the Company | 9,784 | 1,681 | 9,535 | 7,618 | 8,646 | ||||||||||
Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes, | |||||||||||||||
| attributable to the Company | (952) | (7,807) | 5,698 | 5,439 | 4,995 | ||||||||||
Net earnings (loss) attributable to the Company | 8,831 | (6,126) | 15,233 | 13,057 | 13,641 | ||||||||||
Dividends declared(a) | 9,054 | 9,161 | 8,948 | 8,060 | 7,372 | ||||||||||
Return on average GE shareowners' equity | 10.9 | % | 1.6 | % | 10.8 | % | 9.5 | % | 10.9 | % | |||||
Per common share | |||||||||||||||
Earnings from continuing operations – diluted | $ | 1.00 | $ | 0.17 | $ | 0.94 | $ | 0.74 | $ | 0.82 | |||||
Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations – diluted | (0.10) | (0.78) | 0.56 | 0.53 | 0.47 | ||||||||||
Net earnings (loss) – diluted | 0.89 | (0.61) | 1.50 | 1.27 | 1.29 | ||||||||||
Earnings from continuing operations – basic | 1.01 | 0.17 | 0.95 | 0.74 | 0.82 | ||||||||||
Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations – basic | (0.11) | (0.78) | 0.57 | 0.53 | 0.47 | ||||||||||
Net earnings (loss) – basic | 0.90 | (0.62) | 1.51 | 1.28 | 1.29 | ||||||||||
Dividends declared | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.79 | 0.70 | ||||||||||
Stock price range | 33.00 -27.10 | 31.49 -19.37 | 27.94-23.69 | 28.09-20.68 | 23.18-18.02 | ||||||||||
Year-end closing stock price | 31.60 | 31.15 | 25.27 | 28.03 | 20.99 | ||||||||||
| Cash and equivalents | 48,129 | 70,483 | 70,025 | 79,175 | 68,225 | ||||||||||
| Total assets of continuing operations | 350,368 | 372,120 | 330,637 | 332,998 | 338,675 | ||||||||||
| Total assets | 365,183 | 493,071 | 653,931 | 662,202 | 690,415 | ||||||||||
| Long-term borrowings | 105,080 | 144,659 | 185,832 | 216,640 | 228,443 | ||||||||||
| Common shares outstanding – average (in thousands) | 9,025,479 | 9,944,179 | 10,044,995 | 10,222,198 | 10,522,922 | ||||||||||
| Common shareowner accounts – average | 450,000 | 470,000 | 490,000 | 512,000 | 537,000 | ||||||||||
| Employees at year end | |||||||||||||||
| United States | 104,000 | 125,000 | 136,000 | 135,000 | 134,000 | ||||||||||
| Other countries | 191,000 | 208,000 | 169,000 | 172,000 | 171,000 | ||||||||||
| Total employees(c) | 295,000 | 333,000 | 305,000 | 307,000 | 305,000 | ||||||||||
| GE data | |||||||||||||||
Short-term borrowings(d) | $ | 20,482 | $ | 19,792 | $ | 3,872 | $ | 1,841 | $ | 6,041 | |||||
Long-term borrowings(d) | 58,810 | 83,309 | 12,421 | 11,484 | 11,393 | ||||||||||
| Redeemable noncontrolling interests | 3,025 | 2,972 | 98 | 176 | 183 | ||||||||||
Noncontrolling interests | 1,378 | 1,378 | 825 | 835 | 777 | ||||||||||
GE shareowners' equity | 75,828 | 98,274 | 128,159 | 130,566 | 123,026 | ||||||||||
Total capital invested | $ | 159,523 | $ | 205,725 | $ | 145,375 | $ | 144,903 | $ | 141,420 | |||||
Industrial return on total capital(b)* | 15.4 | % | 16.9 | % | 14.0 | % | 14.3 | % | 15.9 | % | |||||
Borrowings as a percentage of total capital invested(b) | 49.7 | % | 50.1 | % | 11.2 | % | 9.2 | % | 12.3 | % | |||||
| GE Capital data | |||||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 10,905 | $ | 10,801 | $ | 11,320 | $ | 11,267 | $ | 11,268 | |||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing operations attributable to GE Capital | (595) | (7,654) | 1,532 | 699 | 1,368 | ||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes, | |||||||||||||||
| attributable to GE Capital | (954) | (7,485) | 5,860 | 5,540 | 4,901 | ||||||||||
| Less net earnings (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests, | |||||||||||||||
| discontinued operations | (1) | 312 | 157 | 36 | 53 | ||||||||||
Net earnings (loss) attributable to GE Capital | (1,548) | (15,450) | 7,234 | 6,204 | 6,216 | ||||||||||
Net earnings (loss) attributable to GE Capital common shareowner | (2,204) | (15,780) | 6,912 | 5,906 | 6,092 | ||||||||||
GE Capital shareowners' equity | 24,677 | 46,227 | 87,499 | 82,694 | 81,889 | ||||||||||
Total borrowings(e) | 117,303 | 180,178 | 245,252 | 283,820 | 315,172 | ||||||||||
Ratio of debt to equity at GE Capital(f) | 4.75:1 | 3.90:1 | 2.80:1 | 3.43:1 | 3.85:1 | ||||||||||
Total assets(g) | $ | 182,970 | $ | 311,508 | $ | 499,614 | $ | 517,717 | $ | 538,802 | |||||
Transactions between GE and GE Capital have been eliminated from the consolidated information.
| (a) | Included $656 million and $18 million of preferred stock dividends in 2016 and 2015, respectively. |
| (b) | Indicated terms are defined in the Other Terms used by GE section within the MD&A. |
| (c) | For 2015, includes 55,500 employees as a result of the Alstom acquisition. |
| (d) | Excluding assumed debt of GE Capital, GE total borrowings is $20,512 million at December 31, 2016. |
| (e) | Included $58,780 million of GE Capital debt assumed by GE and maintained as intercompany payable to GE at December 31, 2016. |
| (f) | Ratios of 2.79:1, 2.6:1, 3.14:1, 3.57:1, and 4.08:1 for 2016, 2015, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively, net of liquidity*. For purposes of these ratios, cash and debt balances have been adjusted to include amounts classified as assets and liabilities of businesses held for sale and discontinued operations. |
| (g) | GE Capital's total assets includes deferred income tax liabilities, which are presented within assets for purposes of our consolidating balance sheet presentation. |
*Non-GAAP Financial Measure
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 116
| PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES BY THE ISSUER AND AFFILIATED PURCHASERS | ||||||||||
| Approximate | ||||||||||
| dollar value | ||||||||||
| Total number | of shares that | |||||||||
| of shares | may yet be | |||||||||
| purchased | purchased | |||||||||
| as part of | under our | |||||||||
| Total number | Average | our share | share | |||||||
| of shares | price paid | repurchase | repurchase | |||||||
| Period | purchased(a) | per share | program(b) | program(b) | ||||||
| (Shares in thousands) | ||||||||||
| 2016 | ||||||||||
| October | 32,338 | $ | 27.39 | 32,265 | ||||||
| November | 20,805 | 30.16 | 20,791 | |||||||
| December(c) | 74,390 | 31.60 | 74,390 | |||||||
| Total | 127,533 | $ | 30.30 | 127,446 | $ | 24.7 | billion | |||
| (a) | This category included 87 thousand shares repurchased from our various benefit plans. |
| (b) | Shares were repurchased through the 2015 GE Share Repurchase Program (the Program). As of December 31, 2016, we were authorized to repurchase up to $50.0 billion of our common stock through 2018 and we had repurchased a total of approximately $25.3 billion under the Program. The Program is flexible and shares will be acquired with a combination of borrowings and free cash flow from the public markets and other sources, including GE Stock Direct, a stock purchase plan that is available to the public. The total amount remaining under our share repurchase program excludes an unsettled amount of $0.3 billion under an accelerated share repurchase (ASR) agreement. |
| (c) | Includes 59,177 thousand shares repurchased at an average price of $31.60 per share pursuant to an ASR agreement. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 117
A disciplined approach to risk is important in a diversified organization like ours to ensure that we are executing according to our strategic objectives and that we only accept risk for which we are adequately compensated. We evaluate risk at the individual transaction level, and evaluate aggregated risk at the customer, industry, geographic and collateral-type levels, where appropriate.
RESPONSIBILITIES
GE BOARD OF DIRECTORS
The GE Board of Directors (Board) has oversight for risk management with a focus on the most significant risks facing the Company, including strategic, operational, financial and legal and compliance risks. Throughout the year, the Board and the committees to which it has delegated responsibility dedicate a portion of their meetings to review and discuss specific risk topics in greater detail.
COMMITTEES
The Board has delegated responsibility for the oversight of specific risks to Board committees as follows:
THE AUDIT COMMITTEE oversees the policies, processes and risks relating to the financial statements, financial reporting processes, regulatory, compliance and litigation risks and auditing. The Audit Committee discusses with management the Company's risk assessment and risk management practices and, when reviewing and approving the annual audit plan for the Company's internal audit function, prioritizes audit focus areas based on their potential risk. The Audit Committee also oversees the Company's financial risk exposures related to GE Capital, following the dissolution of the GE Capital Committee effective December 31, 2016.
THE GOVERNANCE & PUBLIC AFFAIRS COMMITTEE oversees risk related to the Company's governance structure and processes and risks arising from related-person transactions. It also reviews and discusses with management risks related to GE's public policy initiatives and activities and positions on corporate social responsibilities, and it oversees the Company's environmental, health and safety compliance and related risks.
THE MANAGEMENT DEVELOPMENT & COMPENSATION COMMITTEE oversees risk associated with management resources and structure, succession planning and management development and selection processes, and it reviews executive compensation practices at GE to confirm that pay arrangements incentivize leaders to improve the Company's competitive position without encouraging excessive risk taking. The Management Development and Compensation Committee reviews and discusses, at least annually, the relationship between risk management policies and practices, corporate strategy and senior executive compensation.
THE TECHNOLOGY & INDUSTRIAL RISK COMMITTEE oversees the Company's overall strategic direction and investment in research and development and technological and scientific initiatives. It also reviews and identifies specific technology, science and innovation matters and risks, including industrial, product, market and cybersecurity risk, that could have a significant impact on Company operations.
SENIOR MANAGEMENT
The GE Board's risk oversight process builds upon management's risk assessment and mitigation processes, which include standardized reviews of long-term strategic and operational planning; executive development and evaluation; compliance under the Company's The Spirit & The Letter, laws and regulations; the Company's integrity programs; health, safety and environmental compliance; financial reporting and controllership; and information technology and cybersecurity programs.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 118
OPERATING REVIEWS
CORPORATE AUDIT STAFF is responsible for reviewing the governance, processes, controls and accuracy of GE's financial reporting and, in concert with GE's Global Law & Policy function, GE's compliance reporting.
COMPLIANCE RISK REVIEWS are performed by the Policy Compliance Review Board, a management-level committee that assists in assessing and mitigating compliance risk. Members of the Policy Compliance Review Board, which include the Company's general counsel as chair, the Chief Financial Officer and other senior-level functional leaders, participated in ten compliance operating reviews in 2016.
GE BLUEPRINT REVIEWS are integrated business planning reviews across GE that evaluate strategic objectives, operating and organizational performance, and enterprise risks. Blueprint reviews are held at least four times per year and include the most senior GE business leaders.
RISK MANAGERS
Risk assessment and risk management are the responsibility of management and are carried out through risk managers who are operationally integrated into each of our businesses. These risk managers bring deep domain expertise to the businesses' operations and core processes. Both risk managers and the business leadership teams have specific, enterprise risk focused goals and objectives that are aligned with our overall risk framework.
RISK MITIGATION & COMMUNICATION
Risks identified through our risk management processes are prioritized and, depending on the probability and severity of the risk, escalated as appropriate. Senior management discusses these risks periodically and assigns responsibility for them to the businesses. The assigned owners continually monitor, evaluate and report on risks for which they bear responsibility. Enterprise risk leaders within each business and corporate function are responsible to present risk assessments and key risks to senior management at least annually.
Depending on the nature of the risk involved and the particular business or function affected, we use a wide variety of risk mitigation strategies, including delegations of authority, standardized processes and strategic planning reviews, operating reviews, insurance, and hedging. As a matter of policy, we generally hedge the risk of fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates, interest rates and commodity prices. Our service businesses employ a comprehensive tollgate process leading up to and through the execution of a contractual service agreement to mitigate legal, financial and operational risks. Furthermore, we centrally manage some risks by purchasing insurance, the amount of which is determined by balancing the level of risk retained or assumed with the cost of transferring risk to others. We manage the risk of fluctuations in economic activity and customer demand by monitoring industry dynamics and responding accordingly, including by adjusting capacity, implementing cost reductions and engaging in mergers, acquisitions, dispositions and restructuring.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 119
The following discussion of risk factors contains "forward-looking statements," as discussed in the Forward-Looking Statements section. These risk factors may be important to understanding any statement in this Annual Report on Form 10-K or elsewhere. The following information should be read in conjunction with the Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (MD&A) section and the consolidated financial statements and related notes.
We leverage the risk framework in each of our businesses, which have adopted approaches that correspond to the Company's overall risk policies, guidelines and review mechanisms. Our risk framework operates at the business and functional levels and is designed to identify, evaluate and mitigate risks within each of the risk categories below.
Our businesses routinely encounter and address risks, some of which will cause our future results to be different – sometimes materially different – than we presently anticipate. Below, we describe certain important strategic, operational, financial, and legal and compliance risks. Our reactions to material future developments as well as our competitors' reactions to those developments will affect our future results.
STRATEGIC RISKS
Strategic risk relates to the Company's future business plans and strategies, including the risks associated with: the global macro-environment in which we operate; mergers and acquisitions and restructuring activity; intellectual property; and other risks, including the demand for our products and services, competitive threats, the success of investments in our Digital business, technology and other product and service innovations, and public policy.
Global macro-environment - Our growth is subject to global economic and political risks.
We operate in virtually every part of the world and serve customers in approximately 180 countries. In 2016, 57% of our revenue was attributable to activities outside the United States. Our operations and the execution of our business plans and strategies are subject to the effects of global competition and geopolitical risks. They are also affected by local economic environments, including low interest rates, inflation, recession, currency volatility, currency controls and actual or anticipated default on sovereign debt. Political changes and trends such as populism, economic nationalism and sentiment toward multinational companies and resulting changes to trade, tax or other laws and policies may be disruptive, and can interfere with our global operating model, our supply chain, our customers and all of our activities in a particular location. While some global economic and political risks can be hedged using derivatives or other financial instruments and some are insurable, such attempts to mitigate these risks are costly and not always successful, and our ability to engage in such mitigation may decrease or become even more costly as a result of more volatile market conditions.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 120
M&A/restructuring - The success of our business depends on achieving our strategic objectives, including through acquisitions and business integrations, joint ventures, dispositions and restructurings.
With respect to acquisitions, joint ventures and restructuring actions, we may not achieve expected returns and other benefits as a result of various factors, including integration and collaboration challenges, such as personnel and technology. Restructuring actions in connection with acquisitions or otherwise may also give rise to reputational risk, or such actions may not achieve anticipated cost savings and may result in lower margin rates. For example, our anticipated returns from mergers and acquisitions such as the Alstom acquisition in 2015 or the combination of our Oil & Gas business with Baker Hughes that was announced in October 2016 include cost and growth synergy benefits over a multi-year period that we may not fully realize. We also participate in a number of joint ventures with other companies or government enterprises in various markets around the world, including joint ventures where we may have a lesser degree of control over the business operations, which may expose us to additional operational, financial, legal or compliance risks. We have been selling financial assets and businesses in numerous transactions in connection with the GE Capital Exit Plan, and we also continue to evaluate the potential disposition of other assets and businesses that may no longer help us meet our objectives. When we decide to sell assets or a business, we may encounter difficulty in finding buyers or executing alternative exit strategies on acceptable terms in a timely manner, which could delay the accomplishment of our strategic objectives. Alternatively, we may dispose of a business at a price or on terms that are less favorable than we had anticipated, or with the exclusion of assets that must be divested or run off separately. After reaching an agreement with a buyer or seller for the acquisition or disposition of a business, such as the proposed combination of our Oil & Gas business with Baker Hughes, the transaction remains subject to necessary regulatory and governmental approvals on acceptable terms as well as the satisfaction of pre-closing conditions, which may prevent us from completing the transaction. Dispositions may also involve continued financial involvement in the divested business, such as through continuing equity ownership, transition service agreements, guarantees, indemnities or other current or contingent financial obligations. Under these arrangements, performance by the divested businesses or other conditions outside our control could affect our future financial results.
Intellectual property - Our intellectual property portfolio may not prevent competitors from independently developing products and services similar to or duplicative to ours, and the value of our intellectual property may be negatively impacted by external dependencies.
Our patents and other intellectual property may not prevent competitors from independently developing or selling products and services similar to or duplicative of ours, and there can be no assurance that the resources invested by us to protect our intellectual property will be sufficient or that our intellectual property portfolio will adequately deter misappropriation or improper use of our technology. We could also face competition in some countries where we have not invested in an intellectual property portfolio. If we are not able to protect our intellectual property, the value of our brand and other intangible assets may be diminished, and our business may be adversely affected. We also face attempts to gain unauthorized access to our IT systems or products for the purpose of improperly acquiring our trade secrets or confidential business information. The theft or unauthorized use or publication of our trade secrets and other confidential business information as a result of such an incident could adversely affect our competitive position and the value of our investment in research and development. In addition, we may be the target of enforcement of patents by third parties, including aggressive and opportunistic enforcement claims by non-practicing entities. Regardless of the merit of such claims, responding to infringement claims can be expensive and time-consuming. If GE is found to infringe any third-party rights, we could be required to pay substantial damages or we could be enjoined from offering some of our products and services. The value of, or our ability to use, our intellectual property may also be negatively impacted by dependencies on third parties, such as our ability to obtain or renew on reasonable terms licenses that we need in the future, or our ability to secure or retain ownership or rights to use data in certain software analytics or services offerings.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 121
OPERATIONAL RISKS
Operational risk relates to risks arising from systems, processes, people and external events that affect the operation of our businesses. It includes product life cycle and execution; product safety and performance; information management and data protection and security, including cybersecurity; supply chain and business disruption; and other risks, including human resources and reputation.
Operations - We may face operational challenges that could have a material adverse effect on our business, reputation, financial position and results of operations, and we are dependent on the maintenance of existing product lines, market acceptance of new product and service introductions and product and service innovations for continued revenue and earnings growth.
We produce highly sophisticated products and provide specialized services for both our and third-party products that incorporate or use leading-edge technology, including both hardware and software. Many of our products and services involve complex industrial machinery or infrastructure projects, such as commercial jet engines, offshore oil and gas drilling or nuclear power generation, and accordingly the impact of a catastrophic product failure or similar event could be significant. While we have built extensive operational processes to ensure that our product design, manufacture and servicing, and other services that we provide, meet the most rigorous quality standards, there can be no assurance that we or our customers or other third parties will not experience operational process failures or other problems, including through cyber attacks and other intentional acts, that could result in potential product, safety, regulatory or environmental risks. Despite the existence of crisis management or business continuity plans, operational failures or quality issues, including as a result of organizational changes, attrition or labor relations, could have a material adverse effect on our business, reputation, financial position and results of operations. For projects where we take on the full scope of engineering, procurement, construction or other services, the potential risk is greater that operational, quality or other issues at particular projects could adversely affect GE's results of operations. The markets in which we operate are also subject to technological change and require skilled talent. Our long-term operating results and competitive position depend substantially upon our ability to continually develop, introduce, and market new and innovative products and services, to modify existing products and services, to customize products and services, to anticipate and respond to market and technological changes driven by emerging risks and opportunities such as increased digitization or climate change and to deliver products, services and outcomes in line with our projected performance and/or cost estimates.
Cybersecurity - Increased cybersecurity requirements, vulnerabilities, threats and more sophisticated and targeted computer crime could pose a risk to our systems, networks, products, solutions, services and data.
Increased global cybersecurity vulnerabilities, threats and more sophisticated and targeted cyber-related attacks pose a risk to the security of GE's and its customers', partners', suppliers' and third-party service providers' products, systems and networks and the confidentiality, availability and integrity of GE's and its customers' data. While we attempt to mitigate these risks by employing a number of measures, including employee training, monitoring and testing, and maintenance of protective systems and contingency plans, we remain potentially vulnerable to additional known or unknown threats. We also may have access to sensitive, confidential or personal data or information in certain of our businesses that is subject to privacy and security laws, regulations or customer-imposed controls. Despite our efforts to protect sensitive, confidential or personal data or information, we may be vulnerable to material security breaches, theft, misplaced or lost data, programming errors, employee errors and/or malfeasance that could potentially lead to the compromising of sensitive, confidential or personal data or information, improper use of our systems, software solutions or networks, unauthorized access, use, disclosure, modification or destruction of information, defective products, production downtimes and operational disruptions. In addition, a cyber-related attack could result in other negative consequences, including damage to our reputation or competitiveness, remediation or increased protection costs, litigation or regulatory action.
Supply chain - Significant raw material shortages, supplier capacity constraints, supplier production disruptions, supplier quality and sourcing issues or price increases could increase our operating costs and adversely impact the competitive positions of our products.
Our reliance on third-party suppliers, contract manufacturers and service providers, and commodity markets to secure raw materials, parts, components and sub-systems used in our products exposes us to volatility in the prices and availability of these materials, parts, components, systems and services. Some of these suppliers or their sub-suppliers are limited- or sole-source suppliers. A disruption in deliveries from our third-party suppliers, contract manufacturers or service providers, capacity constraints, production disruptions, price increases, or decreased availability of raw materials or commodities, including as a result of catastrophic events, could have an adverse effect on our ability to meet our commitments to customers or increase our operating costs. Quality, capability and sourcing issues experienced by third-party providers can also adversely affect our costs, margin rates and the quality and effectiveness of our products and services and result in liability and reputational harm.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 122
FINANCIAL RISKS
Financial risk relates to our ability to meet financial obligations and mitigate exposure to broad market risks, including volatility in foreign currency exchange rates and interest rates and commodity prices; credit risk; and liquidity risk, including risk related to our credit ratings and our availability and cost of funding. Credit risk is the risk of financial loss arising from a customer or counterparty failure to meet its contractual obligations. We face credit risk in our industrial businesses, as well as in our GE Capital investing, lending and leasing activities and derivative financial instruments activities. Liquidity risk refers to the potential inability to meet contractual or contingent financial obligations (whether on- or off-balance sheet) as they arise, and could potentially impact an institution's financial condition or overall safety and soundness.
Economy/counterparties - A deterioration of conditions in the global economy, the major industries we serve or the financial markets, or the soundness of financial institutions and governments we deal with, may adversely affect our business and results of operations.
The business and operating results of our industrial businesses have been, and will continue to be, affected by worldwide economic conditions, including conditions in the air and rail transportation, power generation, oil and gas, renewables, healthcare and other major industries we serve. Existing or potential customers may delay or cancel plans to purchase our products and services, including large infrastructure projects, and may not be able to fulfill their obligations to us in a timely fashion as a result of business deterioration, cash flow shortages, low oil prices or difficulty obtaining financing due to slow global economic growth and other challenges affecting the global economy. The airline industry, for example, is highly cyclical, and the level of demand for air travel is correlated to the strength of the U.S. and international economies. An extended period of slow growth in the U.S. or internationally that results in the loss of business and leisure traffic could have a material adverse effect on our airline customers and the viability of their business. Service contract cancellations or customer dynamics such as early aircraft retirements, reduced electricity demand in our Power and Renewable Energy businesses or declines in orders, project commencement delays and pricing pressures on our Oil & Gas business from low oil prices could affect our ability to fully recover our contract costs and estimated earnings. Further, our vendors may be experiencing similar conditions, which may impact their ability to fulfill their obligations to us. We may also face greater challenges collecting on receivables with customers that are sovereign governments or located in emerging markets. If slow growth in the global economy continues for a significant period or there is significant deterioration in the global economy, our results of operations, financial position and cash flows could be materially adversely affected.
GE Capital also has exposure to many different industries and counterparties, including sovereign governments, and routinely executes transactions with counterparties in the financial services industry, including brokers and dealers, commercial banks, investment banks and other institutional clients. Many of these transactions expose GE Capital to credit risk in the event of default of its counterparty or client. If conditions in the financial markets deteriorate, they may adversely affect the business and results of operations of GE Capital, as well as the soundness of financial institutions, governments and other counterparties we deal with. In addition, GE Capital's credit risk may be increased when the value of collateral held cannot be realized through sale or is liquidated at prices insufficient to recover the full amount of the loan or derivative exposure due to it. GE Capital also has exposure to these financial institutions in the form of cash on deposit and unsecured debt instruments held in its investment portfolios. GE Capital has policies relating to credit rating requirements and to exposure limits to counterparties (as described in Notes 20 and 29 to the consolidated financial statements), which are designed to limit credit and liquidity risk. There can be no assurance, however, that any losses or impairments to the carrying value of financial assets would not materially and adversely affect GE Capital's business, financial position, results of operations or capacity to provide financing to support orders from GE's industrial businesses.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 123
Funding access/costs - Failure to maintain our credit ratings, or conditions in the financial and credit markets, could adversely affect our access to capital markets, funding costs and related margins, liquidity and competitive position.
The major debt rating agencies routinely evaluate our debt. This evaluation is based on a number of factors, which include financial strength as well as transparency with rating agencies and timeliness of financial reporting. As of December 31, 2016, GE and GE Capital's long-term unsecured debt credit rating from both Standard and Poor's Ratings Service (S&P) and from Fitch Ratings Service (Fitch) was AA- (the fourth highest of 22 rating categories) with a stable outlook. The long-term unsecured debt credit rating from Moody's Investors Service (Moody's) for GE and for GE Capital was A1 (the fifth highest of 21 credit ratings), both with stable outlooks. As of December 31, 2016, GE and GE Capital's short-term credit rating from S&P was A-1+ (the highest rating category of six categories), from Fitch was F1+ (the highest rating category of six categories) and from Moody's was P-1 (the highest rating category of four categories). There can be no assurance that we will be able to maintain our credit ratings and failure to do so could adversely affect our cost of funds and related margins, liquidity, competitive position and access to capital markets. In addition, various debt and derivative instruments, guarantees and covenants would require posting additional capital or collateral in the event of a ratings downgrade, which, depending on the extent of the downgrade, could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity and capital position.
Furthermore, to the extent that we rely on the availability of the unsecured debt markets to access funding for term and commercial paper maturities for 2017 and beyond, external conditions in the financial and credit markets may limit the availability of funding at particular times or increase the cost of funding, which could affect our overall profitability. Factors that may affect the availability of funding or cause an increase in our funding costs include decreased capacity and increased competition among commercial paper issuers, and potential impacts arising in the United States, Europe or China from developments in sovereign debt situations, currency movements or other potential market disruptions. If GE or GE Capital's cost of funding were to increase, it may adversely affect our competitive position and result in lower net interest margins, earnings and cash flows as well as lower returns on shareowners' equity and invested capital.
Social costs - Sustained increases in pension and healthcare benefits costs may reduce our profitability.
Our results of operations may be positively or negatively affected by the amount of income or expense we record for our defined benefit pension plans. GAAP requires that we calculate income or expense for the plans using actuarial valuations. These valuations reflect assumptions about financial market and other economic conditions, which may change based on changes in key economic indicators. The most significant year-end assumptions we use to estimate pension expense for 2017 are the discount rate and the expected long-term rate of return on the plan assets. In addition, we are required to make an annual measurement of plan assets and liabilities, which may result in a significant reduction or increase to equity. At the end of 2016, the GE Pension Plan was underfunded, on a GAAP basis, by $19.1 billion, and the GE Supplementary Pension Plan, an unfunded plan, had a projected benefit obligation of $6.5 billion. Although GAAP expense and pension funding contributions are not directly related, key economic factors that affect GAAP expense would also likely affect the amount of cash we would contribute to pension plans as required under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA). Failure to achieve expected returns on plan assets driven by various factors, which could include a continued environment of low interest rates or sustained market volatility, could also result in an increase to the amount of cash we would be required to contribute to pension plans. In addition, there may be upward pressure on the cost of providing healthcare benefits to current employees and retirees. Although we have actively sought to control increases in these costs, there can be no assurance that we will succeed in limiting cost increases, and continued upward pressure could reduce our profitability. For a discussion regarding how our financial statements can be affected by our pension and healthcare benefit obligations, see the Other Consolidated Information – Postretirement Benefit Plans section and Notes 12 and 29 to the consolidated financial statements. See also the Critical Accounting Estimates – Pension Assumptions section for a discussion regarding how our financial statements can be affected by our pension plan accounting policies.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 124
LEGAL & COMPLIANCE RISKS
Legal and compliance risk relates to risks arising from the government and regulatory environment and action and from legal proceedings and compliance with integrity policies and procedures, including those relating to financial reporting, environmental health and safety. Government and regulatory risk includes the risk that the government or regulatory actions will impose additional cost on us or require us to make adverse changes to our business models or practices.
Regulatory - We are subject to a wide variety of laws, regulations and government policies that may change in significant ways.
Our businesses are subject to regulation under a wide variety of U.S. federal and state and non-U.S. laws, regulations and policies. There can be no assurance that laws, regulations and policies will not be changed in ways that will require us to modify our business models and objectives or affect our returns on investments by restricting existing activities and products, subjecting them to escalating costs or prohibiting them outright. In particular, legislative, regulatory or other actions that U.S. and non-U.S. governments have undertaken or are considering in areas such data privacy and sovereignty, foreign exchange intervention in response to currency volatility, currency controls that could restrict the movement of liquidity from particular jurisdictions, trade controls or tariffs on imports and exports in the U.S. or other countries, complex economic sanctions and tax reform may have an effect on GE's, GE Capital's or other regulated subsidiaries' structure, operations, sales, liquidity, capital requirements, effective tax rate and performance. For example, efforts by public and private sectors to control the growth of healthcare costs may lead to lower reimbursements and increased utilization controls related to the use of our products by healthcare providers. Continued government scrutiny, including reviews of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (U.S. FDA) medical device pre-market authorization and post-market surveillance processes, may impact the requirements for marketing our products and slow our ability to introduce new products, resulting in an adverse impact on our business. Furthermore, we have been, and expect to continue, participating in U.S. and international governmental programs, which require us to comply with strict governmental regulations. Inability to comply with these regulations could adversely affect our status in these projects and adversely affect our results of operations, financial position and cash flows.
Legal proceedings - We are subject to legal proceedings and legal compliance risks.
We are subject to a variety of legal proceedings and legal compliance risks in virtually every part of the world, including the matters described in the Legal Proceedings section. We, our representatives, and the industries in which we operate are subject to continuing scrutiny by regulators and other governmental authorities in the U.S., the European Union and other jurisdictions, which may, in certain circumstances, lead to enforcement actions, adverse changes to our business practices, fines and penalties or the assertion of private litigation claims and damages that could be material. For example, in connection with our acquisition of Alstom's Thermal, Renewables and Grid businesses in November 2015, we are subject to legacy legal proceedings and legal compliance risks that relate to claimed anti-competitive conduct or improper payments by Alstom in the pre-acquisition period. In addition, our discontinued U.S. mortgage business, WMC, is a defendant in 11 civil lawsuits arising out of its origination and sale of mortgages from 2005 through 2007, and we learned in December 2015 that, as part of continuing industry-wide investigation of subprime mortgages, the Civil Division of the U.S. Department of Justice is investigating potential violations of the Financial Institutions Reform, Recovery, and Enforcement Act of 1989 (FIRREA) by WMC and its affiliates. We have established reserves for these and other legal matters as appropriate; however, the estimation of legal reserves or possible losses involves significant judgment and may not reflect the full range of uncertainties and unpredictable outcomes inherent in litigation and investigations, and the actual losses arising from particular matters may exceed our current estimates and adversely affect our results of operations. Additionally, we and our subsidiaries are subject to remedial actions to clean up contaminated sites as required by federal and state laws, such as the anticipated remediation for a stretch of the Housatonic River in Massachusetts, as described in the Environmental Matters section. While we believe that we have adopted appropriate risk management and compliance programs, the global and diverse nature of our operations and the current enforcement environment mean that legal and compliance risks will continue to exist with respect to our continuing and discontinued operations, and additional legal proceedings and other contingencies, the outcome of which cannot be predicted with certainty, will arise from time to time. Moreover, we are increasingly selling products and services in growth markets where claims arising from a catastrophic product failure, alleged violations of law or other incidents involving our products and services may be adjudicated within legal systems that are less developed and less reliable than those of the U.S. or other more developed markets, and this can create additional uncertainty about the outcome of proceedings before courts or other governmental bodies in such markets. See the Legal Proceedings section and Note 23 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information about legal proceedings and other loss contingencies.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 125
LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
WMC. There are 11 lawsuits in which our discontinued U.S. mortgage business, WMC, is a party. The adverse parties in 10 of these cases are securitization trustees or parties claiming to act on their behalf. While the alleged claims for relief vary from case to case, the complaints and counterclaims in these actions generally assert claims for breach of contract, indemnification, and/or declaratory judgment, and seek specific performance (repurchase) and/or monetary damages. Beginning in the fourth quarter 2013, WMC entered into settlements that reduced its exposure on claims asserted in certain securitizations, and the claim amounts reported herein reflect the effect of these settlements.
Five WMC cases are pending in the United States District Court for the District of Connecticut. Four of these cases were initiated in 2012, and one was initiated in the third quarter 2013. Deutsche Bank National Trust Company (Deutsche Bank) is the adverse party in four cases, and Law Debenture Trust Company of New York (Law Debenture) is the adverse party in one case. The Deutsche Bank complaints assert claims on approximately $4,300 million of mortgage loans and seek to recover damages in excess of approximately $1,800 million. The Law Debenture complaint asserts claims on approximately $800 million of mortgage loans, and alleges losses on these loans in excess of approximately $425 million. In September, WMC and Deutsche Bank agreed to settle all claims arising out of the four securitizations at issue in the Connecticut lawsuits, subject to judicial approvals. In October, Deutsche Bank filed petitions for instruction in California state court seeking judicial instructions that Deutsche Bank's entry into the settlement agreements was a reasonable exercise of its discretion and approving the distribution of settlement proceeds pursuant to the terms of each trust's governing documents.
Four cases are pending against WMC in New York State Supreme Court, all of which were initiated by securitization trustees or securities administrators. These cases involve, in the aggregate, claims involving approximately $4,559 million of mortgage loans. One of these lawsuits was initiated by Deutsche Bank in the second quarter 2013 and names as defendants WMC and Barclays Bank PLC. It involves claims against WMC on approximately $1,000 million of mortgage loans and does not specify the amount of damages sought. In September 2016, WMC and Deutsche Bank agreed to settle all claims arising out of the two securitizations at issue in this lawsuit, subject to judicial approvals. In October 2016, Deutsche Bank filed petitions for instruction in California state court seeking judicial instructions that Deutsche Bank's entry into the settlement agreements was a reasonable exercise of its discretion and approving the distribution of settlement proceeds pursuant to the terms of each trust's governing documents. The second case, in which the plaintiff is The Bank of New York Mellon (BNY), was initiated in the fourth quarter 2012 and names as defendants WMC, J.P. Morgan Mortgage Acquisition Corporation and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. BNY asserts claims on approximately $1,300 million of mortgage loans, and seeks to recover damages in excess of $650 million. The third case was initiated by BNY in November 2013 and names as defendants WMC, J.P. Morgan Mortgage Acquisition Corporation and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. In this case, BNY asserts claims on approximately $1,300 million of mortgage loans, and seeks to recover damages in excess of $600 million. On September 18, 2015, the court granted defendants' motion to dismiss this case on statute of limitations grounds, and the plaintiff filed a notice of appeal on October 21, 2015. The fourth case was filed in October 2014 and names as defendants WMC, J.P. Morgan Mortgage Acquisition Corporation and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. The plaintiff, BNY, asserts claims on approximately $959 million of mortgage loans and seeks to recover damages in excess of $475 million.
One case is pending against WMC in the United States District Court for the Southern District of New York. The case was initiated by the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA) in the fourth quarter 2012. In the second quarter 2013, Deutsche Bank, in its role as securitization trustee, intervened as a plaintiff and filed a complaint relating to approximately $1,300 million of loans and alleging losses in excess of approximately $100 million. In December 2013, the District Court issued an order denying WMC's motion to dismiss but, on its own motion, ordered re-briefing on several issues raised by WMC's motion to dismiss in February 2015. On July 10, 2015, the District Court entered an order dismissing the lawsuit as time-barred under the applicable statute of limitations. Deutsche Bank filed a notice of appeal from this order of dismissal on August 13, 2015, and the United States Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit heard oral argument on June 10, 2016. In September 2016, WMC and Deutsche Bank agreed to settle all claims arising out of the securitization at issue in this lawsuit, subject to judicial approval. In October 2016, Deutsche Bank filed a petition for instruction in California state court seeking judicial instructions that Deutsche Bank's entry into the settlement agreement was a reasonable exercise of its discretion and approving the distribution of settlement proceeds pursuant to the terms of the trust's governing documents. The court has scheduled the initial hearing on this petition, and the other petitions filed by Deutsche Bank referenced above, for April 2017.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 126
The amounts of the claims at issue in these cases (discussed above) reflect the purchase price or unpaid principal balances of the mortgage loans at issue at the time of purchase and do not give effect to pay downs, accrued interest or fees, or potential recoveries based upon the underlying collateral. All of the mortgage loans involved in these lawsuits are included in WMC's reported claims at December 31, 2016. See Note 23 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information.
On January 23, 2017, the ResCap Liquidating Trust, as successor to Residential Funding Company, LLC (RFC), filed a lawsuit seeking unspecified damages against WMC in the United States District Court for the District of Minnesota arising from alleged breaches in representations and warranties made by WMC in connection with the sale of approximately $840 million in loans to RFC over a period of time preceding RFC's filing for bankruptcy protection in May 2012.
In December 2015, we learned that, as part of continuing industry-wide investigation of subprime mortgages, the Civil Division of the U.S. Department of Justice is investigating potential violations of the Financial Institutions Reform, Recovery, and Enforcement Act of 1989 (FIRREA) by WMC and its affiliates arising out of the origination, purchase or sale of residential mortgage loans between January 1, 2005 and December 31, 2007. The Justice Department subsequently issued subpoenas to WMC and GE Capital, and we are cooperating with the Justice Department's investigation.
Alstom legacy matters. In connection with our acquisition of Alstom's Thermal, Renewables and Grid businesses in November 2015, we are subject to legacy legal proceedings and legal compliance risks that relate to claimed anti-competitive conduct or improper payments by Alstom in the pre-acquisition period. See Note 23 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information. As previously reported, in September 2013 the Israeli Antitrust Authority issued a decision whereby Alstom, Siemens AG and ABB Ltd. were held liable for an alleged anti-competitive arrangement in the gas-insulated switchgears market in Israel. While there was no fine in connection with that decision, claimants brought civil actions in 2013 seeking damages of approximately $950 million and $600 million, respectively, related to the alleged conduct underlying the decision that are pending before the Central District Court in Israel. In December 2016, all parties agreed in principle to participate in a formal mediation in 2017 with the goal of reaching a global settlement of the two civil actions.
Environmental matters. As previously reported, in 2000, GE and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) entered into a consent decree relating to PCB cleanup of the Housatonic River in Massachusetts. Following EPA's release in September 2015 of an intended final remediation decision, GE and EPA engaged in mediation and the first step of the dispute resolution process contemplated by the consent decree. In October 2016, EPA issued its final remediation decision pursuant to the consent decree. GE and several other interested parties have appealed that decision to EPA's Environmental Appeals Board. A decision of the Environmental Appeals Board can ultimately be appealed to the United States Court of Appeals for the First Circuit. EPA may not implement any remedy until all appeals are exhausted. As of December 31, 2016, and based on its assessment of current facts and circumstances and its defenses, GE believes that it has recorded adequate reserves to cover future obligations associated with an expected final remedy. See Note 23 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 127
MANAGEMENT AND AUDITOR'S REPORTS
MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION OF FINANCIAL RESPONSIBILITY
We believe that great companies are built on a foundation of reliable financial information and compliance with the spirit and letter of the law. For General Electric Company, that foundation includes rigorous management oversight of, and an unyielding dedication to, controllership. The financial disclosures in this report are one product of our commitment to high-quality financial reporting. In addition, we make every effort to adopt appropriate accounting policies, we devote our full resources to ensuring that those policies are applied properly and consistently and we do our best to fairly present our financial results in a manner that is complete and understandable.
Members of our corporate leadership team review each of our businesses routinely on matters that range from overall strategy and financial performance to staffing and compliance. Our business leaders monitor financial and operating systems, enabling us to identify potential opportunities and concerns at an early stage and positioning us to respond rapidly. Our Board of Directors oversees management's business conduct, and our Audit Committee, which consists entirely of independent directors, oversees our internal control over financial reporting. We continually examine our governance practices in an effort to enhance investor trust and improve the Board's overall effectiveness. The Board and its committees annually conduct a performance self-evaluation and recommend improvements. Our lead director chaired four meetings of our independent directors this year, helping us sharpen our full Board meetings to better cover significant topics. Compensation policies for our executives are aligned with the long-term interests of GE investors.
We strive to maintain a dynamic system of internal controls and procedures—including internal control over financial reporting—designed to ensure reliable financial recordkeeping, transparent financial reporting and disclosure, and protection of physical and intellectual property. We recruit, develop and retain a world-class financial team. Our internal audit function, including members of our Corporate Audit Staff, conducts thousands of financial, compliance and process improvement audits each year. Our Audit Committee oversees the scope and evaluates the overall results of these audits, and in 2016, members of that Committee regularly attended GE Capital Board of Directors, Corporate Audit Staff and Controllership Council meetings. Our global integrity policies—"The Spirit & The Letter"—require compliance with law and policy, and pertain to such vital issues as upholding financial integrity and avoiding conflicts of interest. These integrity policies are available in 35 languages, and are provided to all of our employees, holding each of them accountable for compliance. Our strong compliance culture reinforces these efforts by requiring employees to raise any compliance concerns and by prohibiting retribution for doing so. To facilitate open and candid communication, we have designated ombudspersons throughout the Company to act as independent resources for reporting integrity or compliance concerns. We hold our directors, consultants, agents and independent contractors to the same integrity standards.
We are keenly aware of the importance of full and open presentation of our financial position and operating results, and rely for this purpose on our disclosure controls and procedures, including our Disclosure Committee, which comprises senior executives with detailed knowledge of our businesses and the related needs of our investors. We ask this committee to review our compliance with accounting and disclosure requirements, to evaluate the fairness of our financial and non-financial disclosures, and to report their findings to us. In 2016, we further ensured strong disclosure by holding approximately 140 analyst and investor meetings with GE leadership present.
We welcome the strong oversight of our financial reporting activities by our independent registered public accounting firm, KPMG LLP, engaged by and reporting directly to the Audit Committee. U.S. legislation requires management to report on internal control over financial reporting and for auditors to render an opinion on such controls. Our report and the KPMG LLP report for 2016 follow.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 128
MANAGEMENT'S ANNUAL REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting for the Company. With our participation, an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting was conducted as of December 31, 2016, based on the framework and criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
Based on this evaluation, our management has concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2016.
Our independent registered public accounting firm has issued an audit report on our internal control over financial reporting. Their report follows.
| /s/ Jeffrey R. Immelt | /s/ Jeffrey S. Bornstein | |
| Jeffrey R. Immelt | Jeffrey S. Bornstein | |
Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer February 24, 2017 | Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
DISCLOSURE CONTROLS
Under the direction of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, we evaluated our disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting and concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of December 31, 2016.
Other than as explained below, there have been no changes in the Company's internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2016, that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, its internal control over financial reporting.
On November 2, 2015, we closed the acquisition of Alstom's Thermal, Renewable, and Grid businesses. During 2016, we completed our purchase price allocations and transitioned the acquired businesses to our accounting and reporting policies. We also commenced integrating their systems and processes into our framework of internal controls over financial reporting. As part of this process, we have enhanced and augmented the internal controls of the acquired businesses to raise them to a level that meets U.S. requirements. Efforts to further improve those controls are continuing.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 129
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
The Board of Directors and Shareowners
of General Electric Company:
We have audited the accompanying statement of financial position of General Electric Company and consolidated affiliates (the "Company") as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the related statements of earnings, comprehensive income, changes in shareowners' equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2016. We also have audited the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission ("COSO"). The Company's management is responsible for these consolidated financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management's Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements and an opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the consolidated financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of General Electric Company and consolidated affiliates as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2016, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by COSO.
Our audits of the consolidated financial statements were made for the purpose of forming an opinion on the consolidated financial statements taken as a whole. The accompanying consolidating information appearing on pages 133, 137, and 139 is presented for purposes of additional analysis of the consolidated financial statements rather than to present the financial position, results of operations, and cash flows of the individual entities. The consolidating information has been subjected to the auditing procedures applied in the audits of the consolidated financial statements and, in our opinion, is fairly stated in all material respects in relation to the consolidated financial statements taken as a whole.
| /s/ KPMG LLP |
KPMG LLP
Boston, Massachusetts
February 24, 2017
February 24, 2017
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 130
AUDITED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND NOTES
| Statement of Earnings | 132 | |||
| Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income (Loss) | 134 | |||
| Consolidated Statement of Changes in Shareowners' Equity | 135 | |||
| Statement of Financial Position | 136 | |||
| Statement of Cash Flows | 138 | |||
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | ||||
| 1 | Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies | 140 | ||
| 2 | Businesses Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations | 149 | ||
| 3 | Investment Securities | 153 | ||
| 4 | Current Receivables | 155 | ||
| 5 | Inventories | 156 | ||
| 6 | GE Capital Financing Receivables and Allowance for Losses on Financing Receivables | 156 | ||
| 7 | Property, Plant and Equipment | 157 | ||
| 8 | Acquisitions, Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets | 158 | ||
| 9 | Contract Assets and All Other Assets | 164 | ||
| 10 | Borrowings | 165 | ||
| 11 | Investment Contracts, Insurance Liabilities and Insurance Annuity Benefits | 167 | ||
| 12 | Postretirement Benefit Plans | 167 | ||
| 13 | All Other Liabilities | 172 | ||
| 14 | Income Taxes | 172 | ||
| 15 | Shareowners' Equity | 176 | ||
| 16 | Other Stock-related Information | 181 | ||
| 17 | Other Income | 184 | ||
| 18 | Earnings Per Share Information | 184 | ||
| 19 | Fair Value Measurements | 185 | ||
| 20 | Financial Instruments | 189 | ||
| 21 | Variable Interest Entities | 195 | ||
| 22 | Receivables Facility | 197 | ||
| 23 | Commitments, Guarantees, Product Warranties and Other Loss Contingencies | 198 | ||
| 24 | Intercompany Transactions | 202 | ||
| 25 | Operating Segments | 203 | ||
| 26 | Cash Flows Information | 205 | ||
| 27 | Cost Information | 207 | ||
| 28 | Guarantor Financial Information | 208 | ||
| 29 | Supplemental Information | 215 | ||
| 30 | Quarterly Information (unaudited) | 221 | ||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 131
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| STATEMENT OF EARNINGS | ||||||||
| General Electric Company | ||||||||
| and consolidated affiliates | ||||||||
| For the years ended December 31 (In millions; per-share amounts in dollars) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Revenues and other income | ||||||||
| Sales of goods | $ | 75,414 | $ | 74,510 | $ | 76,568 | ||
| Sales of services | 34,976 | 31,298 | 30,190 | |||||
| Other income (Note 17) | 4,005 | 2,227 | 778 | |||||
| GE Capital earnings (loss) from continuing operations | - | - | - | |||||
| GE Capital revenues from services | 9,297 | 9,350 | 9,648 | |||||
Total revenues and other income | 123,693 | 117,386 | 117,184 | |||||
| Costs and expenses (Note 27) | ||||||||
| Cost of goods sold | 62,440 | 59,905 | 61,257 | |||||
| Cost of services sold | 25,043 | 22,788 | 22,447 | |||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 18,377 | 17,831 | 16,848 | |||||
| Interest and other financial charges | 5,025 | 3,463 | 2,723 | |||||
| Investment contracts, insurance losses and | ||||||||
| insurance annuity benefits | 2,797 | 2,605 | 2,530 | |||||
| Other costs and expenses | 982 | 2,608 | 1,115 | |||||
Total costs and expenses | 114,663 | 109,200 | 106,921 | |||||
| Earnings from continuing operations | ||||||||
| before income taxes | 9,030 | 8,186 | 10,263 | |||||
| Benefit (provision) for income taxes (Note 14) | 464 | (6,485) | (773) | |||||
| Earnings from continuing operations | 9,494 | 1,700 | 9,490 | |||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, | ||||||||
| net of taxes (Note 2) | (954) | (7,495) | 5,855 | |||||
| Net earnings (loss) | 8,540 | (5,795) | 15,345 | |||||
| Less net earnings (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | (291) | 332 | 112 | |||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to the Company | 8,831 | (6,126) | 15,233 | |||||
| Preferred stock dividends | (656) | (18) | - | |||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to GE common shareowners | $ | 8,176 | $ | (6,145) | $ | 15,233 | ||
| Amounts attributable to GE common shareowners | ||||||||
| Earnings from continuing operations | $ | 9,494 | $ | 1,700 | $ | 9,490 | ||
| Less net earnings (loss) attributable to | ||||||||
| noncontrolling interests, continuing operations | (290) | 19 | (45) | |||||
| Earnings from continuing operations attributable | ||||||||
| to the Company | 9,784 | 1,681 | 9,535 | |||||
| Preferred stock dividends | (656) | (18) | - | |||||
| Earnings from continuing operations attributable | ||||||||
| to GE common shareowners | 9,128 | 1,663 | 9,535 | |||||
Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes | (954) | (7,495) | 5,855 | |||||
| Less net earnings (loss) attributable to | ||||||||
| noncontrolling interests, discontinued operations | (1) | 312 | 157 | |||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to GE common shareowners | $ | 8,176 | $ | (6,145) | $ | 15,233 | ||
| Per-share amounts (Note 18) | ||||||||
Earnings from continuing operations | ||||||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | 1.00 | $ | 0.17 | $ | 0.94 | ||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 1.01 | $ | 0.17 | $ | 0.95 | ||
Net earnings (loss) | ||||||||
Diluted earnings (loss) per share | $ | 0.89 | $ | (0.61) | $ | 1.50 | ||
Basic earnings (loss) per share | $ | 0.90 | $ | (0.62) | $ | 1.51 | ||
| Dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.93 | $ | 0.92 | $ | 0.89 | ||
Amounts may not add due to rounding.
See Note 3 for other-than-temporary impairment amounts on investment securities.
See accompanying notes.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 132
| STATEMENT OF EARNINGS (CONTINUED) | |||||||||||||||||
| For the years ended December 31 | GE(a) | Financial Services (GE Capital) | |||||||||||||||
| (In millions; per-share amounts in dollars) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||
| Revenues and other income | |||||||||||||||||
| Sales of goods | $ | 75,580 | $ | 74,565 | $ | 76,715 | $ | 115 | $ | 79 | $ | 121 | |||||
| Sales of services | 35,255 | 31,641 | 30,594 | - | - | - | |||||||||||
| Other income (Note 17) | 4,092 | 2,165 | 707 | - | - | - | |||||||||||
| GE Capital earnings (loss) from continuing operations | (1,251) | (7,672) | 1,532 | - | - | - | |||||||||||
| GE Capital revenues from services | - | - | - | 10,790 | 10,722 | 11,199 | |||||||||||
Total revenues and other income | 113,676 | 100,700 | 109,546 | 10,905 | 10,801 | 11,320 | |||||||||||
| Costs and expenses (Note 27) | |||||||||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold | 62,628 | 59,970 | 61,420 | 93 | 69 | 104 | |||||||||||
| Cost of services sold | 23,084 | 20,858 | 20,456 | 2,238 | 2,273 | 2,394 | |||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 16,123 | 14,914 | 14,972 | 2,947 | 3,512 | 2,689 | |||||||||||
| Interest and other financial charges | 2,026 | 1,706 | 1,579 | 3,790 | 2,301 | 1,638 | |||||||||||
| Investment contracts, insurance losses and | |||||||||||||||||
| insurance annuity benefits | - | - | - | 2,861 | 2,737 | 2,660 | |||||||||||
| Other costs and expenses | - | - | - | 1,013 | 2,647 | 1,159 | |||||||||||
Total costs and expenses | 103,860 | 97,447 | 98,427 | 12,942 | 13,539 | 10,645 | |||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing operations | |||||||||||||||||
| before income taxes | 9,815 | 3,252 | 11,119 | (2,037) | (2,739) | 676 | |||||||||||
| Benefit (provision) for income taxes (Note 14) | (967) | (1,506) | (1,634) | 1,431 | (4,979) | 861 | |||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing operations | 8,849 | 1,746 | 9,485 | (606) | (7,718) | 1,537 | |||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, | |||||||||||||||||
| net of taxes (Note 2) | (952) | (7,807) | 5,698 | (954) | (7,485) | 5,860 | |||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) | 7,896 | (6,061) | 15,182 | (1,560) | (15,202) | 7,397 | |||||||||||
| Less net earnings (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | (279) | 83 | (50) | (12) | 248 | 162 | |||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to the Company | 8,176 | (6,145) | 15,233 | (1,548) | (15,450) | 7,234 | |||||||||||
| Preferred stock dividends | - | - | - | (656) | (330) | (322) | |||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to GE common shareowners | $ | 8,176 | $ | (6,145) | $ | 15,233 | $ | (2,204) | $ | (15,780) | $ | 6,912 | |||||
| Amounts attributable to GE common shareowners: | |||||||||||||||||
Earnings (loss) from continuing operations | $ | 8,849 | $ | 1,746 | $ | 9,485 | $ | (606) | $ | (7,718) | $ | 1,537 | |||||
| Less net earnings (loss) attributable to | |||||||||||||||||
| noncontrolling interests, continuing operations | (279) | 83 | (50) | (10) | (64) | 5 | |||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing operations attributable | |||||||||||||||||
| to the Company | 9,128 | 1,663 | 9,535 | (595) | (7,654) | 1,532 | |||||||||||
| Preferred stock dividends | - | - | - | (656) | (330) | (322) | |||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing operations attributable | |||||||||||||||||
| to GE common shareowners | 9,128 | 1,663 | 9,535 | (1,251) | (7,983) | 1,209 | |||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes | (952) | (7,807) | 5,698 | (954) | (7,485) | 5,860 | |||||||||||
| Less net earnings (loss) attributable to | |||||||||||||||||
| noncontrolling interests, discontinued operations | - | - | - | (1) | 312 | 157 | |||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to GE common shareowners | $ | 8,176 | $ | (6,145) | $ | 15,233 | $ | (2,204) | $ | (15,780) | $ | 6,912 | |||||
| (a) |
Amounts may not add due to rounding.
In the consolidating data on this page, "GE" means the basis of consolidation as described in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements; "GE Capital" means GE Capital Global Holdings, LLC (GECGH) and its predecessor General Electric Capital Corporation (GECC) and all of their affiliates and associated companies. Separate information is shown for "GE" and "Financial Services (GE Capital)." Transactions between GE and GE Capital have been eliminated from the "General Electric Company and consolidated affiliates" columns on the prior page.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 133
| GENERAL ELECTRIC COMPANY AND CONSOLIDATED AFFILIATES | ||||||||
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) | ||||||||
| For the years ended December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Net earnings (loss) | $ | 8,540 | $ | (5,795) | $ | 15,345 | ||
| Less net earnings (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | (291) | 332 | 112 | |||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to the Company | $ | 8,831 | $ | (6,126) | $ | 15,233 | ||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | ||||||||
Investment securities | $ | 203 | $ | (553) | $ | 708 | ||
Currency translation adjustments | (1,311) | (3,137) | (2,730) | |||||
Cash flow hedges | 93 | 99 | 234 | |||||
Benefit plans | (1,068) | 5,165 | (7,278) | |||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | (2,083) | 1,575 | (9,066) | |||||
| Less other comprehensive income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | (14) | (69) | (13) | |||||
Other comprehensive income (loss) attributable to the Company | $ | (2,069) | $ | 1,644 | $ | (9,053) | ||
| Comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 6,457 | $ | (4,220) | $ | 6,278 | ||
| Less comprehensive income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | (305) | 263 | 99 | |||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to the Company | $ | 6,762 | $ | (4,483) | $ | 6,180 | ||
Amounts presented net of taxes. See Note 15 for further information about other comprehensive income (loss) and noncontrolling interests.
Amounts may not add due to rounding.
See accompanying notes.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 134
| GENERAL ELECTRIC COMPANY AND CONSOLIDATED AFFILIATES | |||||||||
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN SHAREOWNERS' EQUITY | |||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
| GE shareowners' equity balance at January 1 | $ | 98,274 | $ | 128,159 | $ | 130,566 | |||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to the Company | 8,831 | (6,126) | 15,233 | ||||||
| Dividends and other transactions with shareowners | (9,054) | (9,155) | (8,948) | ||||||
| Redemption value adjustment for redeemable noncontrolling interests | (266) | (25) | (2) | ||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) attributable to the Company | (2,069) | 1,644 | (9,053) | ||||||
| Net sales (purchases) of shares for treasury(a)(b) | (19,499) | (20,946) | (32) | ||||||
| Changes in other capital | (389) | 4,724 | 396 | ||||||
| Ending balance at December 31 | 75,828 | 98,274 | 128,159 | ||||||
| Noncontrolling interests | 1,663 | 1,864 | 8,674 | ||||||
| Total equity balance at December 31 | $ | 77,491 | $ | 100,138 | $ | 136,833 | |||
| (a) |
| (b) | 2016 included $(11,370) million of GE shares purchased under accelerated share repurchase (ASR) agreements. |
Amounts may not add due to rounding.
See Note 15 for further information about changes in shareowners' equity.
See accompanying notes.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 135
| STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION | |||||
General Electric Company | |||||
| and consolidated affiliates | |||||
| December 31 (In millions, except share amounts) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Assets | |||||
| Cash and equivalents | $ | 48,129 | $ | 70,483 | |
| Investment securities (Note 3) | 44,313 | 31,973 | |||
| Current receivables (Note 4) | 24,076 | 27,022 | |||
| Inventories (Note 5) | 22,354 | 22,515 | |||
| Financing receivables – net (Note 6) | 12,242 | 12,052 | |||
| Other GE Capital receivables | 5,944 | 6,782 | |||
| Property, plant and equipment – net (Note 7) | 50,518 | 54,095 | |||
| Receivable from GE Capital (debt assumption) | - | - | |||
| Investment in GE Capital | - | - | |||
| Goodwill (Note 8) | 70,438 | 65,526 | |||
| Other intangible assets – net (Note 8) | 16,436 | 17,797 | |||
| Contract assets (Note 9) | 25,162 | 21,156 | |||
| All other assets (Note 9) | 27,176 | 36,797 | |||
| Deferred income taxes (Note 14) | 1,833 | 3,105 | |||
| Assets of businesses held for sale (Note 2) | 1,745 | 2,818 | |||
| Assets of discontinued operations (Note 2) | 14,815 | 120,951 | |||
| Total assets(a) | $ | 365,183 | $ | 493,071 | |
| Liabilities and equity | |||||
| Short-term borrowings (Note 10) | $ | 30,714 | $ | 49,860 | |
| Accounts payable, principally trade accounts | 14,435 | 13,680 | |||
| Progress collections and price adjustments accrued | 16,760 | 15,776 | |||
| Dividends payable | 2,107 | 2,167 | |||
| Other GE current liabilities | 17,564 | 23,597 | |||
| Non-recourse borrowings of consolidated securitization entities (Note 10) | 417 | 3,083 | |||
| Long-term borrowings (Note 10) | 105,080 | 144,659 | |||
| Investment contracts, insurance liabilities and insurance annuity benefits (Note 11) | 26,086 | 25,692 | |||
| Non-current compensation and benefits | 43,780 | 40,487 | |||
| All other liabilities (Note 13) | 22,912 | 23,611 | |||
| Liabilities of businesses held for sale (Note 2) | 656 | 861 | |||
| Liabilities of discontinued operations (Note 2) | 4,158 | 46,487 | |||
| Total liabilities(a) | 284,668 | 389,961 | |||
| Redeemable noncontrolling interests (Note 15) | 3,025 | 2,972 | |||
| Preferred stock (5,944,250 shares outstanding at both December 31, 2016 | |||||
| and December 31, 2015) | 6 | 6 | |||
| Common stock (8,742,614,000 and 9,379,288,000 shares outstanding | |||||
| at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively) | 702 | 702 | |||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) – net attributable to GE(b) | |||||
Investment securities | 674 | 460 | |||
Currency translation adjustments | (6,816) | (5,499) | |||
Cash flow hedges | 12 | (80) | |||
Benefit plans | (12,469) | (11,410) | |||
| Other capital | 37,224 | 37,613 | |||
| Retained earnings | 139,532 | 140,020 | |||
| Less common stock held in treasury | (83,038) | (63,539) | |||
| Total GE shareowners' equity | 75,828 | 98,274 | |||
| Noncontrolling interests(c) (Note 15) | 1,663 | 1,864 | |||
| Total equity (Note 15) | 77,491 | 100,138 | |||
| Total liabilities, redeemable noncontrolling interests and equity | $ | 365,183 | $ | 493,071 | |
| (b) |
| (c) |
Amounts may not add due to rounding.
See accompanying notes.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 136
| STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION (CONTINUED) | |||||||||||
| GE(a) | Financial Services (GE Capital) | ||||||||||
| December 31 (In millions, except share amounts) | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Assets | |||||||||||
| Cash and equivalents | $ | 10,525 | $ | 10,372 | $ | 37,604 | $ | 60,111 | |||
| Investment securities (Note 3) | 137 | 151 | 44,180 | 31,827 | |||||||
| Current receivables (Note 4) | 12,715 | 14,707 | - | - | |||||||
| Inventories (Note 5) | 22,263 | 22,449 | 91 | 66 | |||||||
| Financing receivables – net (Note 6) | - | - | 26,041 | 25,003 | |||||||
| Other GE Capital receivables | - | - | 15,576 | 15,455 | |||||||
| Property, plant and equipment – net (Note 7) | 19,103 | 20,145 | 32,225 | 34,781 | |||||||
| Receivable from GE Capital (debt assumption) | 58,780 | 84,704 | - | - | |||||||
| Investment in GE Capital | 24,677 | 46,227 | - | - | |||||||
| Goodwill (Note 8) | 68,070 | 63,157 | 2,368 | 2,370 | |||||||
| Other intangible assets – net (Note 8) | 16,131 | 17,365 | 305 | 435 | |||||||
| Contract assets (Note 9) | 25,162 | 21,156 | - | - | |||||||
| All other assets (Note 9) | 12,007 | 12,813 | 14,608 | 25,081 | |||||||
| Deferred income taxes (Note 14) | 6,666 | 7,666 | (4,833) | (4,561) | |||||||
| Assets of businesses held for sale (Note 2) | 1,629 | 2,818 | - | - | |||||||
| Assets of discontinued operations (Note 2) | 9 | 9 | 14,806 | 120,942 | |||||||
| Total assets | $ | 277,874 | $ | 323,737 | $ | 182,970 | $ | 311,508 | |||
| Liabilities and equity | |||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings(b) (Note 10) | $ | 20,482 | $ | 19,792 | $ | 23,443 | $ | 48,617 | |||
| Accounts payable, principally trade accounts | 20,876 | 19,250 | 1,605 | 1,745 | |||||||
| Progress collections and price adjustments accrued | 16,838 | 15,776 | - | - | |||||||
| Dividends payable | 2,107 | 2,167 | - | - | |||||||
| Other GE current liabilities | 17,564 | 23,595 | - | - | |||||||
| Non-recourse borrowings of consolidated securitization entities (Note 10) | - | - | 417 | 3,083 | |||||||
| Long-term borrowings(b) (Note 10) | 58,810 | 83,309 | 93,443 | 128,478 | |||||||
| Investment contracts, insurance liabilities and insurance annuity benefits (Note 11) | - | - | 26,546 | 26,155 | |||||||
| Non-current compensation and benefits | 42,770 | 39,472 | 1,001 | 1,006 | |||||||
| All other liabilities (Note 13) | 17,506 | 16,217 | 7,430 | 9,351 | |||||||
| Liabilities of businesses held for sale (Note 2) | 656 | 1,409 | - | - | |||||||
| Liabilities of discontinued operations (Note 2) | 35 | 128 | 4,123 | 46,359 | |||||||
| Total liabilities | 197,644 | 221,115 | 158,008 | 264,795 | |||||||
| Redeemable noncontrolling interests (Note 15) | 3,025 | 2,972 | - | - | |||||||
| Preferred stock (5,944,250 shares outstanding at both December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||
| and December 31, 2015) | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |||||||
| Common stock (8,742,614,000 and 9,379,288,000 shares outstanding | |||||||||||
| at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively) | 702 | 702 | - | - | |||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) – net attributable to GE | |||||||||||
Investment securities | 674 | 460 | 656 | 456 | |||||||
Currency translation adjustments | (6,816) | (5,499) | (740) | (898) | |||||||
Cash flow hedges | 12 | (80) | 43 | (112) | |||||||
Benefit plans | (12,469) | (11,410) | (622) | (540) | |||||||
| Other capital | 37,224 | 37,613 | 12,669 | 12,326 | |||||||
| Retained earnings | 139,532 | 140,020 | 12,664 | 34,988 | |||||||
| Less common stock held in treasury | (83,038) | (63,539) | - | - | |||||||
| Total GE shareowners' equity | 75,828 | 98,274 | 24,677 | 46,227 | |||||||
| Noncontrolling interests (Note 15) | 1,378 | 1,378 | 285 | 486 | |||||||
| Total equity (Note 15) | 77,205 | 99,651 | 24,962 | 46,713 | |||||||
| Total liabilities, redeemable noncontrolling interests and equity | $ | 277,874 | $ | 323,737 | $ | 182,970 | $ | 311,508 | |||
| (a) |
Amounts may not add due to rounding.
In the consolidating data on this page, "GE" means the basis of consolidation as described in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements; "GE Capital" means GE Capital Global Holdings, LLC (GECGH) and its predecessor General Electric Capital Corporation (GECC) and all of their affiliates and associated companies. Separate information is shown for "GE" and "Financial Services (GE Capital)." Transactions between GE and GE Capital have been eliminated from the "General Electric Company and consolidated affiliates" columns on the prior page.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 137
| STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS | ||||||||
| General Electric Company | ||||||||
| and consolidated affiliates | ||||||||
| For the years ended December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Cash flows – operating activities | ||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) | $ | 8,540 | $ | (5,795) | $ | 15,345 | ||
| Less net earnings (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | (291) | 332 | 112 | |||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to the Company | 8,831 | (6,126) | 15,233 | |||||
| (Earnings) loss from discontinued operations | 954 | 7,495 | (5,855) | |||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net earnings attributable to the | ||||||||
Company to cash provided from operating activities: | ||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization of property, | ||||||||
| plant and equipment | 4,997 | 4,847 | 4,953 | |||||
Earnings from continuing operations retained by GE Capital | - | - | - | |||||
Deferred income taxes | 814 | 383 | (882) | |||||
Decrease (increase) in GE current receivables | 1,514 | (52) | (1,913) | |||||
Decrease (increase) in inventories | (1,389) | (314) | (872) | |||||
Increase (decrease) in accounts payable | 1,198 | (541) | 565 | |||||
Increase (decrease) in GE progress collections | 1,836 | (996) | (515) | |||||
All other operating activities | (12,655) | 7,160 | 5,318 | |||||
| Cash from (used for) operating activities – continuing operations | 6,099 | 11,856 | 16,033 | |||||
| Cash from (used for) operating activities – discontinued operations | (6,343) | 8,034 | 11,676 | |||||
| Cash from (used for) operating activities | (244) | 19,891 | 27,709 | |||||
| Cash flows – investing activities | ||||||||
| Additions to property, plant and equipment | (7,199) | (7,309) | (7,134) | |||||
| Dispositions of property, plant and equipment | 4,424 | 3,020 | 2,923 | |||||
| Net decrease (increase) in GE Capital financing receivables | 200 | 1,043 | 1,260 | |||||
| Proceeds from sale of discontinued operations | 59,890 | 79,615 | 232 | |||||
| Proceeds from principal business dispositions | 5,357 | 2,283 | 630 | |||||
| Net cash from (payments for) principal businesses purchased | (2,271) | (12,027) | (2,091) | |||||
| All other investing activities | 2,212 | (5,013) | 23,410 | |||||
| Cash from (used for) investing activities – continuing operations | 62,613 | 61,613 | 19,229 | |||||
| Cash from (used for) investing activities – discontinued operations | (13,412) | (2,125) | (24,263) | |||||
| Cash from (used for) investing activities | 49,202 | 59,488 | (5,034) | |||||
| Cash flows – financing activities | ||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in borrowings (maturities of | ||||||||
| 90 days or less) | (1,135) | (24,459) | (6,409) | |||||
| Newly issued debt (maturities longer than 90 days) | 1,492 | 13,951 | 14,629 | |||||
| Repayments and other reductions (maturities longer than 90 days) | (58,768) | (47,038) | (38,410) | |||||
| Net dispositions (purchases) of GE shares for treasury | (21,429) | (1,099) | (1,218) | |||||
| Dividends paid to shareowners | (8,806) | (9,295) | (8,852) | |||||
| All other financing activities | (1,274) | (1,605) | (652) | |||||
| Cash from (used for) financing activities – continuing operations | (89,920) | (69,547) | (40,912) | |||||
| Cash from (used for) financing activities – discontinued operations | 789 | (6,507) | 23,956 | |||||
| Cash from (used for) financing activities | (89,131) | (76,054) | (16,956) | |||||
| Effect of currency exchange rate changes on cash and equivalents | (1,146) | (3,464) | (3,492) | |||||
| Increase (decrease) in cash and equivalents | (41,319) | (138) | 2,224 | |||||
| Cash and equivalents at beginning of year | 90,879 | 91,017 | 88,792 | |||||
| Cash and equivalents at end of year | 49,558 | 90,879 | 91,017 | |||||
| Less cash and equivalents of discontinued operations | ||||||||
| at end of year | 1,429 | 20,395 | 20,991 | |||||
| Cash and equivalents of continuing operations at end of year | $ | 48,129 | $ | 70,483 | $ | 70,025 | ||
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flows information | ||||||||
| Cash paid during the year for interest | $ | (5,779) | $ | (8,764) | $ | (9,539) | ||
| Cash recovered (paid) during the year for income taxes | (7,469) | (2,486) | (2,955) | |||||
Amounts may not add due to rounding.
See accompanying notes.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 138
| STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS (CONTINUED) | |||||||||||||||||
| GE(a) | Financial Services (GE Capital) | ||||||||||||||||
| For the years ended December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||
| Cash flows – operating activities | |||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) | $ | 7,896 | $ | (6,061) | $ | 15,182 | $ | (1,560) | $ | (15,202) | $ | 7,397 | |||||
| Less net earnings (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | (279) | 83 | (50) | (12) | 248 | 162 | |||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to the Company | 8,176 | (6,145) | 15,233 | (1,548) | (15,450) | 7,234 | |||||||||||
| (Earnings) loss from discontinued operations | 952 | 7,807 | (5,698) | 954 | 7,485 | (5,860) | |||||||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net earnings attributable to the | |||||||||||||||||
Company to cash provided from operating activities: | |||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization of property, | |||||||||||||||||
plant and equipment | 2,597 | 2,473 | 2,508 | 2,384 | 2,436 | 2,529 | |||||||||||
Earnings from continuing operations retained by GE Capital(b) | 21,345 | 12,284 | 1,625 | - | - | - | |||||||||||
Deferred income taxes | 1,107 | (1,800) | (476) | (293) | 2,183 | (406) | |||||||||||
Decrease (increase) in GE current receivables | 929 | 666 | (473) | - | - | - | |||||||||||
Decrease (increase) in inventories | (1,337) | (282) | (877) | (10) | (14) | 27 | |||||||||||
Increase (decrease) in accounts payable | 1,716 | 276 | 884 | 17 | (189) | 258 | |||||||||||
Increase (decrease) in GE progress collections | 1,913 | (1,010) | (528) | - | - | - | |||||||||||
All other operating activities | (7,438) | 2,083 | 2,973 | (3,054) | 5,087 | 2,480 | |||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) operating activities – continuing operations | 29,960 | 16,354 | 15,171 | (1,552) | 1,537 | 6,263 | |||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) operating activities – discontinued operations | (90) | (12) | (2) | (6,253) | 8,046 | 11,678 | |||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) operating activities | 29,870 | 16,342 | 15,169 | (7,805) | 9,583 | 17,941 | |||||||||||
| Cash flows – investing activities | |||||||||||||||||
| Additions to property, plant and equipment | (3,758) | (3,785) | (3,970) | (3,769) | (4,237) | (3,818) | |||||||||||
| Dispositions of property, plant and equipment | 1,080 | 939 | 615 | 3,637 | 2,526 | 2,331 | |||||||||||
| Net decrease (increase) in GE Capital financing receivables | - | - | - | (1,279) | 226 | (161) | |||||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of discontinued operations | - | - | - | 59,890 | 79,615 | 232 | |||||||||||
| Proceeds from principal business dispositions | 5,357 | 1,725 | 602 | - | 532 | - | |||||||||||
| Net cash from (payments for) principal businesses purchased | (2,271) | (10,350) | (2,091) | - | (1,677) | - | |||||||||||
| All other investing activities | (2,392) | (1,308) | (1,062) | 1,639 | (4,690) | 24,574 | |||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) investing activities – continuing operations | (1,984) | (12,779) | (5,906) | 60,118 | 72,295 | 23,158 | |||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) investing activities – discontinued operations | 90 | 12 | 2 | (13,501) | (2,137) | (24,263) | |||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) investing activities | (1,894) | (12,767) | (5,905) | 46,617 | 70,158 | (1,105) | |||||||||||
| Cash flows – financing activities | |||||||||||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in borrowings (maturities of | |||||||||||||||||
| 90 days or less) | 1,595 | 603 | 243 | (1,655) | (24,834) | (7,078) | |||||||||||
| Newly issued debt (maturities longer than 90 days) | 5,307 | 3,560 | 3,084 | 1,174 | 10,391 | 11,545 | |||||||||||
| Repayments and other reductions (maturities longer than 90 days) | (4,156) | (2,190) | (323) | (58,285) | (44,848) | (38,087) | |||||||||||
| Net dispositions (purchases) of GE shares for treasury | (21,429) | (1,099) | (1,218) | - | - | - | |||||||||||
| Dividends paid to shareowners | (8,474) | (9,289) | (8,851) | (20,427) | (4,620) | (3,322) | |||||||||||
| All other financing activities | (273) | 203 | 346 | (1,127) | (1,362) | (679) | |||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) financing activities – continuing operations | (27,430) | (8,211) | (6,719) | (80,320) | (65,273) | (37,621) | |||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) financing activities – discontinued operations | - | - | - | 789 | (6,507) | 23,956 | |||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) financing activities | (27,430) | (8,211) | (6,719) | (79,531) | (71,780) | (13,665) | |||||||||||
| Effect of currency exchange rate changes on cash and equivalents | (392) | (908) | (312) | (754) | (2,556) | (3,180) | |||||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in cash and equivalents | 153 | (5,544) | 2,234 | (41,473) | 5,406 | (9) | |||||||||||
| Cash and equivalents at beginning of year | 10,372 | 15,916 | 13,682 | 80,506 | 75,100 | 75,109 | |||||||||||
| Cash and equivalents at end of year | 10,525 | 10,372 | 15,916 | 39,033 | 80,506 | 75,100 | |||||||||||
| Less cash and equivalents of discontinued operations | |||||||||||||||||
| at end of year | - | - | - | 1,429 | 20,395 | 20,991 | |||||||||||
| Cash and equivalents of continuing operations at end of year | $ | 10,525 | $ | 10,372 | $ | 15,916 | $ | 37,604 | $ | 60,111 | $ | 54,109 | |||||
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flows information | |||||||||||||||||
| Cash paid during the year for interest | $ | (1,753) | $ | (1,327) | $ | (1,248) | $ | (4,982) | $ | (8,047) | $ | (8,910) | |||||
| Cash recovered (paid) during the year for income taxes | (2,612) | (1,636) | (1,337) | (4,857) | (850) | (1,618) | |||||||||||
| (a) |
| (b) |
Amounts may not add due to rounding.
In the consolidating data on this page, "GE" means the basis of consolidation as described in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements; "GE Capital" means GE Capital Global Holdings, LLC (GECGH) and its predecessor General Electric Capital Corporation (GECC) and all of their affiliates and associated companies. Separate information is shown for "GE" and "Financial Services (GE Capital)." Transactions between GE and GE Capital have been eliminated from the "Consolidated" columns and are discussed in Note 24.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 139
Our financial statements consolidate all of our affiliates – entities in which we have a controlling financial interest, most often because we hold a majority voting interest. To determine if we hold a controlling financial interest in an entity, we first evaluate if we are required to apply the variable interest entity (VIE) model to the entity, otherwise, the entity is evaluated under the voting interest model.
Where we hold current or potential rights that give us the power to direct the activities of a VIE that most significantly impact the VIE's economic performance, combined with a variable interest that gives us the right to receive potentially significant benefits or the obligation to absorb potentially significant losses, we have a controlling financial interest in that VIE. Rights held by others to remove the party with power over the VIE are not considered unless one party can exercise those rights unilaterally. When changes occur to the design of an entity, we reconsider whether it is subject to the VIE model. We continuously evaluate whether we have a controlling financial interest in a VIE.
We hold a controlling financial interest in other entities where we currently hold, directly or indirectly, more than 50% of the voting rights or where we exercise control through substantive participating rights or as a general partner. Where we are a general partner, we consider substantive removal rights held by other partners in determining if we hold a controlling financial interest. We reevaluate whether we have a controlling financial interest in these entities when our voting or substantive participating rights change.
Associated companies are unconsolidated VIEs and other entities in which we do not have a controlling financial interest, but over which we have significant influence, most often because we hold a voting interest of 20% to 50%. Associated companies are accounted for as equity method investments. Our share of the results of associated companies are presented on a one-line basis. Investments in, and advances to, associated companies are presented on a one-line basis in the caption "All other assets" in our Statement of Financial Position, net of allowance for losses, which represents our best estimate of probable losses inherent in such assets.
We have reclassified certain prior-year amounts to conform to the current-year's presentation. Certain columns and rows may not add due to the use of rounded numbers. Percentages presented are calculated from the underlying numbers in millions.
Upon closing an acquisition, we consolidate the acquired business as soon as practicable. The size, scope and complexity of an acquisition can affect the time necessary to adjust the acquired company's accounting policies, procedures, and books and records to our standards. Accordingly, it is possible that changes will be necessary to the carrying amounts and presentation of assets and liabilities in our financial statements as the acquired company is fully assimilated.
Financial data and related measurements are presented in the following categories:
GE. This represents the adding together of all affiliates except GE Capital, whose continuing operations are presented on a one-line basis, giving effect to the elimination of transactions among such affiliates.
GE Capital. This refers to GE Capital Global Holdings, LLC (GECGH), or its predecessor General Electric Capital Corporation (GECC), and is the adding together of all affiliates of GE Capital giving effect to the elimination of transactions among such affiliates.
Consolidated. This represents the adding together of GE and GE Capital, giving effect to the elimination of transactions between GE and GE Capital.
Operating Segments. These comprise our eight businesses, focused on the broad markets they serve: Power, Renewable Energy, Oil & Gas, Aviation, Healthcare, Transportation, Energy Connections & Lighting and Capital.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 140
Unless otherwise indicated, information in these notes to consolidated financial statements relates to continuing operations. Certain of our operations have been presented as discontinued. See Note 2.
The effects of translating to U.S. dollars the financial statements of non-U.S. affiliates whose functional currency is other than the U.S. dollar are included in shareowners' equity. Asset and liability accounts are translated at year-end exchange rates, while revenues and expenses are translated at average rates for the respective periods.
Preparing financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) requires us to make estimates based on assumptions about current, and for some estimates future, economic and market conditions which affect reported amounts and related disclosures in our financial statements. Although our current estimates contemplate current conditions and how we expect them to change in the future, as appropriate, it is reasonably possible that actual conditions could be worse than anticipated in those estimates, which could materially affect our results of operations and financial position. Among other effects, such changes could result in future impairments of investment securities, goodwill, intangibles and long-lived assets, incremental losses on financing receivables, establishment of valuation allowances on deferred tax assets, incremental fair value marks on businesses and assets held for sale carried at lower of cost or market, and increased tax liabilities and insurance reserves.
Our financial statements are prepared in conformity with GAAP.
We record all sales of goods and services only when a firm sales agreement is in place, delivery has occurred or services have been rendered and collectability of the fixed or determinable sales price is reasonably assured.
Arrangements for the sale of goods and services sometimes include multiple components. Most of our multiple component arrangements involve the sale of goods and services in the Healthcare segment. Our arrangements with multiple components usually involve an upfront deliverable of large machinery or equipment and future service deliverables such as installation, commissioning, training or the future delivery of ancillary products. In most cases, the relative values of the undelivered components are not significant to the overall arrangement and are typically delivered within three to six months after the core product has been delivered. In such agreements, selling price is determined for each component and any difference between the total of the separate selling prices and total contract consideration (i.e., discount) is allocated pro rata across each of the components in the arrangement. The value assigned to each component is objectively determined and obtained primarily from sources such as the separate selling price for that or a similar item or from competitor prices for similar items. If such evidence is not available, we use our best estimate of selling price, which is established consistent with the pricing strategy of the business and considers product configuration, geography, customer type, and other market specific factors.
Except for goods sold under long-term agreements, we recognize sales of goods under the provisions of U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Staff Accounting Bulletin (SAB) 104, Revenue Recognition. In arrangements where we sell products that provide the customer with a right of return, we use our accumulated experience to estimate and provide for such returns when we record the sale. In situations where arrangements include customer acceptance provisions based on seller or customer-specified objective criteria, we recognize revenue when we have reliably demonstrated that all specified acceptance criteria have been met or when formal acceptance occurs, respectively. In arrangements where we provide goods for trial and evaluation purposes, we only recognize revenue after customer acceptance occurs. Unless otherwise noted, we do not provide for anticipated losses before we record sales.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 141
We recognize revenue on agreements for sales of goods and services under power generation unit and uprate contracts, nuclear fuel assemblies, larger oil drilling equipment projects, aeroderivative unit contracts, military development contracts, locomotive production contracts, and long-term construction projects, using long-term construction and production contract accounting. We estimate total long-term contract revenue net of price concessions as well as total contract costs. For goods sold under power generation unit and uprate contracts, nuclear fuel assemblies, aeroderivative unit contracts, military development contracts and locomotive production contracts, we recognize sales as we complete major contract-specified deliverables, most often when customers receive title to the goods or accept the services as performed. For larger oil drilling equipment projects and long-term construction projects, we recognize sales based on our progress toward contract completion measured by actual costs incurred in relation to our estimate of total expected costs. We measure long-term contract revenues by applying our contract-specific estimated margin rates to incurred costs. We routinely update our estimates of future costs for agreements in process and report any cumulative effects of such adjustments in current operations. We provide for any loss that we expect to incur on these agreements when that loss is probable.
We recognize revenue upon delivery for sales of aircraft engines and military propulsion equipment. Delivery of commercial engines and non-U.S. military equipment occurs on shipment; delivery of military propulsion equipment sold to the U.S. government or agencies thereof occurs upon receipt of a Material Inspection and Receiving Report, DD Form 250 or Memorandum of Shipment. Commercial aircraft engines are complex equipment manufactured to customer order under a variety of sometimes complex, long-term agreements. We measure sales of commercial aircraft engines by applying our contract-specific estimated margin rates to incurred costs. We routinely update our estimates of future revenues and costs for commercial aircraft engine agreements in process and report any cumulative effects of such adjustments in current operations. Significant components of our revenue and cost estimates include price concessions and performance-related guarantees as well as material, labor and overhead costs. We measure revenue for military propulsion equipment and spare parts not subject to long-term product services agreements based on the specific contract on a specifically measured output basis. We provide for any loss that we expect to incur on these agreements when that loss is probable; consistent with industry practice, for commercial aircraft engines, we make such provision only if such losses are not recoverable from future highly probable sales of spare parts and services for those engines.
We sell product services under long-term product maintenance or extended warranty agreements in our Aviation, Power, Oil & Gas and Transportation segments, where costs of performing services are incurred on other than a straight-line basis. We also sell similar long-term product services in our Healthcare and Renewable Energy segments, where such costs generally are expected to be incurred on a straight-line basis. For the Aviation, Power, Oil & Gas and Transportation agreements, we recognize related sales based on the extent of our progress toward completion measured by actual costs incurred in relation to total expected costs. We routinely update our estimates of future costs for agreements in process and report any cumulative effects of such adjustments in current operations. For the Healthcare and Renewable Energy agreements, we recognize revenues on a straight-line basis and expense related costs as incurred. We provide for any loss that we expect to incur on any of these agreements when that loss is probable.
We use the interest method to recognize income on loans. Interest on loans includes origination, commitment and other non-refundable fees related to funding (recorded in earned income on the interest method). We stop accruing interest at the earlier of the time at which collection of an account becomes doubtful or the account becomes 90 days past due. Previously recognized interest income that was accrued but not collected from the borrower is reversed, unless the terms of the loan agreement permit capitalization of accrued interest to the principal balance. Payments received on nonaccrual loans are applied to reduce the principal balance of the loan.
We resume accruing interest on nonaccrual, non-restructured commercial loans only when (a) payments are brought current according to the loan's original terms and (b) future payments are reasonably assured. When we agree to restructured terms with the borrower, we resume accruing interest only when it is reasonably assured that we will recover full contractual payments, and such loans pass underwriting reviews equivalent to those applied to new loans.
We recognize financing lease income on the interest method to produce a level yield on funds not yet recovered. Estimated unguaranteed residual values are based upon management's best estimates of the value of the leased asset at the end of the lease term. We use various sources of data in determining these estimates, including information obtained from third parties, which is adjusted for the attributes of the specific asset under lease. Guarantees of residual values by unrelated third parties are included within minimum lease payments. Significant assumptions we use in estimating residual values include estimated net cash flows over the remaining lease term, anticipated results of future remarketing, and estimated future component part and scrap metal prices, discounted at an appropriate rate.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 142
We recognize operating lease income on a straight-line basis over the terms of underlying leases.
Businesses and assets held for sale represent components that meet accounting requirements to be classified as held for sale and are presented as single asset and liability amounts in our financial statements with a valuation allowance, if necessary, to recognize the net carrying amount at the lower of cost or fair value, less cost to sell. Financing receivables that no longer qualify to be presented as held for investment must be classified as assets held for sale and recognized in our financial statements at the lower of cost or fair value, less cost to sell, with that amount representing a new cost basis at the date of transfer.
The determination of fair value for businesses and assets held for sale involves significant judgments and assumptions. Development of estimates of fair values in this circumstance is complex and is dependent upon, among other factors, the nature of the potential sales transaction (for example, asset sale versus sale of legal entity), composition of assets and/or businesses in the disposal group, the comparability of the disposal group to market transactions, negotiations with third party purchasers etc. Such factors bear directly on the range of potential fair values and the selection of the best estimates. Key assumptions were developed based on market observable data and, in the absence of such data, internal information that is consistent with what market participants would use in a hypothetical transaction.
We review all businesses and assets held for sale each reporting period to determine whether the existing carrying amounts are fully recoverable in comparison to estimated fair values.
The cost of GE manufacturing plant and equipment is generally depreciated on a straight-line basis over its estimated economic life.
The cost of GE Capital equipment leased to others on operating leases is depreciated on a straight-line basis to estimated residual value over the lease term or over the estimated economic life of the equipment.
Our financing receivables portfolio consists of a variety of loans and leases, including both larger-balance, non-homogeneous loans and leases and smaller-balance homogeneous loans and leases. We routinely evaluate our entire portfolio for potential specific credit or collection issues that might indicate an impairment.
Losses on financing receivables are recognized when they are incurred, which requires us to make our best estimate of probable losses inherent in the portfolio. The method for calculating the best estimate of losses depends on the size, type and risk characteristics of the related financing receivable. Such an estimate requires consideration of historical loss experience, adjusted for current conditions, and judgments about the probable effects of relevant observable data, including present economic conditions such as delinquency rates, financial health of specific customers and market sectors, collateral values, and the present and expected future levels of interest rates. The underlying assumptions, estimates and assessments we use to provide for losses are updated periodically to reflect our view of current conditions. Changes in such estimates can significantly affect the allowance and provision for losses. It is possible that we will experience credit losses that are different from our current estimates. Write-offs are deducted from the allowance for losses when we judge the principal to be uncollectible and subsequent recoveries are added to the allowance at the time cash is received on a written-off account.
Gains or losses on sales of affiliate shares where we retain a controlling financial interest are recorded in equity. Gains or losses on sales that result in our loss of a controlling financial interest are recorded in earnings along with remeasurement gains or losses on any investments in the entity that we retained.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 143
CASH AND EQUIVALENTS
Debt securities and money market instruments with original maturities of three months or less are included in cash equivalents unless designated as available-for-sale and classified as investment securities.
We report investments in debt and marketable equity securities, and certain other equity securities, at fair value. See Note 19 for further information on fair value. Unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale investment securities are included in shareowners' equity, net of applicable taxes and other adjustments.
We regularly review investment securities for impairment using both quantitative and qualitative criteria. For debt securities, if we do not intend to sell the security or it is not more likely than not that we will be required to sell the security before recovery of our amortized cost, we evaluate other qualitative criteria to determine whether we do not expect to recover the amortized cost basis of the security, such as the financial health of and specific prospects for the issuer, including whether the issuer is in compliance with the terms and covenants of the security. We also evaluate quantitative criteria including determining whether there has been an adverse change in expected future cash flows. If we do not expect to recover the entire amortized cost basis of the security, we consider the security to be other-than-temporarily impaired (OTTI), and we record the difference between the security's amortized cost basis and its recoverable amount in earnings and the difference between the security's recoverable amount and fair value in other comprehensive income. If we intend to sell the security or it is more likely than not we will be required to sell the security before recovery of its amortized cost basis, the security is also considered OTTI and we recognize the entire difference between the security's amortized cost basis and its fair value in earnings. For equity securities, we consider the length of time and magnitude of the amount that each security is in an unrealized loss position. If we do not expect to recover the entire amortized cost basis of the security, we consider the security to be other-than-temporarily impaired, and we record the difference between the security's amortized cost basis and its fair value in earnings.
Realized gains and losses are accounted for on the specific identification method. Unrealized gains and losses on investment securities classified as trading and certain retained interests are included in earnings.
All inventories are stated at the lower of cost or realizable values. Cost for a portion of GE U.S. inventories is determined on a last-in, first-out (LIFO) basis. Cost of other GE inventories is determined on a first-in, first-out (FIFO) basis. LIFO was used for 34% of GE inventories in both 2016 and 2015.
We do not amortize goodwill, but test it at least annually for impairment at the reporting unit level. A reporting unit is the operating segment, or one level below that operating segment (the component level) if discrete financial information is prepared and regularly reviewed by segment management. However, components are aggregated as a single reporting unit if they have similar economic characteristics. We recognize an impairment charge if the carrying amount of a reporting unit exceeds its fair value and the carrying amount of the reporting unit's goodwill exceeds the implied fair value of that goodwill. We use a market approach, when available and appropriate, or the income approach, or a combination of both to establish fair values. When a portion of a reporting unit is disposed, goodwill is allocated to the gain or loss on disposition based on the relative fair values of the business or businesses disposed and the portion of the reporting unit that will be retained.
We amortize the cost of other intangibles over their estimated useful lives unless such lives are deemed indefinite. The cost of intangible assets is generally amortized on a straight-line basis over the asset's estimated economic life, except that individually significant customer-related intangible assets are amortized in relation to total related sales. Amortizable intangible assets are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the related carrying amounts may not be recoverable. In these circumstances, they are tested for impairment based on undiscounted cash flows and, if impaired, written down to fair value based on either discounted cash flows or appraised values. Intangible assets with indefinite lives are tested annually for impairment and written down to fair value as required.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 144
INVESTMENT CONTRACTS, INSURANCE LIABILITIES AND INSURANCE ANNUITY BENEFITS
Our run-off insurance activities include providing insurance and reinsurance for life and health risks and providing certain annuity products. Two primary product types are provided: traditional insurance contracts and investment contracts. Insurance contracts are contracts with significant mortality and/or morbidity risks, while investment contracts are contracts without such risks.
For short-duration insurance contracts, including accident and health insurance, we report premiums as earned income over the terms of the related agreements, generally on a pro-rata basis. For traditional long-duration insurance contracts, including long-term care, term, whole life and annuities payable for the life of the annuitant, we report premiums as earned income when due.
Premiums received on investment contracts (including annuities without significant mortality risk) are not reported as revenues but rather as deposit liabilities. We recognize revenues for charges and assessments on these contracts, mostly for mortality, contract initiation, administration and surrender. Amounts credited to policyholder accounts are charged to expense.
Liabilities for traditional long-duration insurance contracts represent the present value of such benefits less the present value of future net premiums based on mortality, morbidity, interest and other assumptions at the time the policies were issued or acquired. Liabilities for investment contracts equal the account value, that is, the amount that accrues to the benefit of the contract or policyholder including credited interest and assessments through the financial statement date.
Liabilities for unpaid claims and estimated claim settlement expenses represent our best estimate of the ultimate obligations for reported and incurred-but-not-reported claims and the related estimated claim settlement expenses. Liabilities for unpaid claims and estimated claim settlement expenses are continually reviewed and adjusted through current operations.
The following sections describe the valuation methodologies we use to measure financial and non-financial instruments accounted for at fair value including certain assets within our pension plans and retiree benefit plans.
For financial assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis, fair value is the price we would receive to sell an asset or pay to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction with a market participant at the measurement date. In the absence of active markets for the identical assets or liabilities, such measurements involve developing assumptions based on market observable data and, in the absence of such data, internal information that is consistent with what market participants would use in a hypothetical transaction that occurs at the measurement date.
Observable inputs reflect market data obtained from independent sources, while unobservable inputs reflect our market assumptions. Preference is given to observable inputs. These two types of inputs create the following fair value hierarchy:
| Level 1 – | Quoted prices for identical instruments in active markets. |
| Level 2 – | Quoted prices for similar instruments in active markets; quoted prices for identical or similar instruments in markets that are not active; and model-derived valuations whose inputs are observable or whose significant value drivers are observable. |
| Level 3 – | Significant inputs to the valuation model are unobservable. |
We maintain policies and procedures to value instruments using the best and most relevant data available. In addition, we have risk management teams that review valuation, including independent price validation for certain instruments. With regard to Level 3 valuations (including instruments valued by third parties), we perform a variety of procedures to assess the reasonableness of the valuations. Such reviews include an evaluation of instruments whose fair value change exceeds predefined thresholds (and/or does not change) and consider the current interest rate, currency and credit environment, as well as other published data, such as rating agency market reports and current appraisals. These reviews are performed within each business by the asset and risk managers. A detailed review of methodologies and assumptions is performed by individuals independent of the business for individual measurements with a fair value exceeding predefined thresholds. This detailed review may include the use of a third-party valuation firm.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 145
RECURRING FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
The following sections describe the valuation methodologies we use to measure different financial instruments at fair value on a recurring basis.
Investments in Debt and Equity Securities. When available, we use quoted market prices to determine the fair value of investment securities, and they are included in Level 1. Level 1 securities primarily include publicly traded equity securities.
For large numbers of investment securities for which market prices are observable for identical or similar investment securities but not readily accessible for each of those investments individually (that is, it is difficult to obtain pricing information for each individual investment security at the measurement date), we obtain pricing information from an independent pricing vendor. The pricing vendor uses various pricing models for each asset class that are consistent with what other market participants would use. The inputs and assumptions to the model of the pricing vendor are derived from market observable sources including: benchmark yields, reported trades, broker/dealer quotes, issuer spreads, benchmark securities, bids, offers, and other market-related data. Since many fixed income securities do not trade on a daily basis, the methodology of the pricing vendor uses available information as applicable such as benchmark curves, benchmarking of like securities, sector groupings, and matrix pricing. The pricing vendor considers available market observable inputs in determining the evaluation for a security. Thus, certain securities may not be priced using quoted prices, but rather determined from market observable information. These investments are included in Level 2 and primarily comprise our portfolio of corporate fixed income, and government, mortgage and asset-backed securities. In infrequent circumstances, our pricing vendors may provide us with valuations that are based on significant unobservable inputs, and in those circumstances we classify the investment securities in Level 3.
Annually, we conduct reviews of our primary pricing vendor to validate that the inputs used in that vendor's pricing process are deemed to be market observable as defined in the standard. While we are not provided access to proprietary models of the vendor, our reviews have included on-site walk-throughs of the pricing process, methodologies and control procedures for each asset class and level for which prices are provided. Our reviews also include an examination of the underlying inputs and assumptions for a sample of individual securities across asset classes, credit rating levels and various durations. In addition, the pricing vendor has an established challenge process in place for all security valuations, which facilitates identification and resolution of potentially erroneous prices. We believe that the prices received from our pricing vendor are representative of prices that would be received to sell the assets at the measurement date (exit prices) and are classified appropriately in the hierarchy.
We use non-binding broker quotes and other third-party pricing services as our primary basis for valuation when there is limited, or no, relevant market activity for a specific instrument or for other instruments that share similar characteristics. We have not adjusted the prices we have obtained. Investment securities priced using non-binding broker quotes and other third-party pricing services are included in Level 3. As is the case with our primary pricing vendor, third-party brokers and other third-party pricing services do not provide access to their proprietary valuation models, inputs and assumptions. Accordingly, our risk management personnel conduct reviews of vendors, as applicable, similar to the reviews performed of our primary pricing vendor. In addition, we conduct internal reviews of pricing for all such investment securities quarterly to ensure reasonableness of valuations used in our financial statements. These reviews are designed to identify prices that appear stale, those that have changed significantly from prior valuations, and other anomalies that may indicate that a price may not be accurate. Based on the information available, we believe that the fair values provided by the brokers and other third-party pricing services are representative of prices that would be received to sell the assets at the measurement date (exit prices).
Derivatives. We use closing prices for derivatives included in Level 1, which are traded either on exchanges or liquid over-the-counter markets.
The majority of our derivatives are valued using internal models. The models maximize the use of market observable inputs including interest rate curves and both forward and spot prices for currencies and commodities. Derivative assets and liabilities included in Level 2 primarily represent interest rate swaps, cross-currency swaps and foreign currency and commodity forward and option contracts.
Derivative assets and liabilities included in Level 3 primarily represent equity derivatives and interest rate products that contain embedded optionality or prepayment features.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 146
NON-RECURRING FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
Certain assets are measured at fair value on a non-recurring basis. These assets are not measured at fair value on an ongoing basis, but are subject to fair value adjustments only in certain circumstances. These assets can include loans and long-lived assets that have been reduced to fair value when they are held for sale, impaired loans that have been reduced based on the fair value of the underlying collateral, cost and equity method investments and long-lived assets that are written down to fair value when they are impaired and the remeasurement of retained investments in formerly consolidated subsidiaries upon a change in control that results in deconsolidation of a subsidiary, if we sell a controlling interest and retain a noncontrolling stake in the entity. Assets that are written down to fair value when impaired and retained investments are not subsequently adjusted to fair value unless further impairment occurs.
The following sections describe the valuation methodologies we use to measure financial and non-financial instruments accounted for at fair value on a non-recurring basis and for certain assets within our pension plans and retiree benefit plans at each reporting period, as applicable.
Financing Receivables and Loans Held for Sale. When available, we use observable market data, including pricing on recent closed market transactions, to value loans that are included in Level 2. When this data is unobservable, we use valuation methodologies using current market interest rate data adjusted for inherent credit risk, and such loans are included in Level 3. When appropriate, loans may be valued using collateral values (see Long-Lived Assets below).
Cost and Equity Method Investments. Cost and equity method investments are valued using market observable data such as quoted prices when available. When market observable data is unavailable, investments are valued using a discounted cash flow model, comparative market multiples or a combination of both approaches as appropriate and other third-party pricing sources. These investments are generally included in Level 3.
Investments in private equity, real estate and collective funds held within our pension plans, are generally valued using the net asset value (NAV) per share as a practical expedient for fair value provided certain criteria are met. The NAVs are determined based on the fair values of the underlying investments in the funds. On January 1, 2016, we adopted guidance whereby investments that are measured at fair value using the NAV practical expedient are no longer classified in the fair value hierarchy.
Long-lived Assets. Fair values of long-lived assets, including aircraft, are primarily derived internally and are based on observed sales transactions for similar assets. In other instances, for example, collateral types for which we do not have comparable observed sales transaction data, collateral values are developed internally and corroborated by external appraisal information. Adjustments to third-party valuations may be performed in circumstances where market comparables are not specific to the attributes of the specific collateral or appraisal information may not be reflective of current market conditions due to the passage of time and the occurrence of market events since receipt of the information.
Retained Investments in Formerly Consolidated Subsidiaries. Upon a change in control that results in deconsolidation of a subsidiary, the fair value measurement of our retained noncontrolling stake is valued using market observable data such as quoted prices when available, or if not available, an income approach, a market approach, or a combination of both approaches as appropriate. In applying these methodologies, we rely on a number of factors, including actual operating results, future business plans, economic projections, market observable pricing multiples of similar businesses and comparable transactions, and possible control premium. These investments are generally included in Level 1 or Level 3, as appropriate, determined at the time of the transaction.
On September 30, 2016, we adopted ASU 2016-09, Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting, which was intended to simplify several aspects of the accounting for employee share-based payment transactions including the accounting for income taxes, forfeitures, and statutory tax withholding requirements, as well as classification in the statement of cash flows.
We adopted the standard on a prospective basis with the effect of adoption reflected for the interim periods after the year beginning January 1, 2016 as required by the standard. The primary effects of adoption were the recognition of excess tax benefits in our provision for income taxes rather than paid-in capital and the reclassification of cash flows related to excess tax benefits from a financing activity to an operating activity for the periods beginning January 1, 2016. We will continue to estimate the number of awards that are expected to vest in our determination of the related periodic compensation cost.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 147
As a result of the adoption, our provision for income taxes decreased by $97 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016, for the excess tax benefits related to share-based payments in its provision for income taxes. Application of the cash flow presentation requirements from January 1, 2016, resulted in an increase to cash from operating activities and a decrease to cash from financing activities of $137 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016.
On January 1, 2016, we adopted ASU 2015-16, Simplifying the Accounting for Measurement-Period Adjustments, which eliminated the requirement for an acquirer in a business combination to account for measurement-period adjustments retrospectively. See Note 8 for further discussion of the purchase accounting effects of recent acquisitions.
On January 1, 2016, we adopted ASU 2015-03, Simplifying the Presentation of Debt Issuance Costs, which requires that debt issuance costs related to a recognized debt liability to be presented on the balance sheet as a direct deduction from the debt liability, similar to the presentation of debt premiums and discounts. ASU 2015-03 applies retrospectively and does not change the recognition and measurement requirements for debt issuance costs. The adoption of ASU 2015-03 resulted in the reclassification of $674 million of unamortized debt issuance costs related to the Company's borrowings from all other assets to short-term and long-term borrowings within our consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2015.
On January 1, 2016, we adopted ASU 2015-02, Amendments to the Consolidation Analysis. The ASU amended the consolidation guidance for VIEs and general partners' investment in limited partnerships and modified the evaluation of whether limited partnerships and similar legal entities are VIEs or voting interest entities.
Upon adoption, we deconsolidated three investment funds managed by GE Asset Management (GEAM) that had been accounted for under the guidance prior to the issuance of ASU 2009-17, Improvements to Financial Reporting by Enterprises Involved with Variable Interest Entities, by virtue of the deferral provided by ASU 2010-10, Amendments for Certain Investment Funds. We concluded that GEAM's management contracts were no longer variable interests in the three investment funds and therefore continued consolidation was not appropriate. We deconsolidated net assets and noncontrolling interests of $123 million, respectively.
In addition, many of the limited partnerships in which Energy Financial Services invests became VIEs because the limited partners have no participating rights or substantive removal rights over the general partners. The general partners continue to control these limited partnerships, however, our disclosed exposure to unconsolidated VIEs in Note 21 increased by $6,110 million as a result.
On January 1, 2014, we adopted ASU 2013-11, Presentation of an Unrecognized Tax Benefit When a Net Operating Loss Carryforward, a Similar Tax Loss, or a Tax Credit Carryforward Exists. Under the new guidance, an unrecognized tax benefit is required to be presented as a reduction to a deferred tax asset if the disallowance of the tax position would reduce the available tax loss or tax credit carryforward instead of resulting in a cash tax liability. The ASU applies prospectively to all unrecognized tax benefits that exist as of the adoption date and reduced both deferred tax assets and income tax liabilities (including amounts reported in assets and liabilities of discontinued operations) by $1,224 million as of January 1, 2014.
ACCELERATED SHARE REPURCHASE AGREEMENTS
During 2016, we entered into accelerated share repurchase (ASR) agreements to repurchase shares of GE common stock. Under an ASR agreement, the Company pays a specified amount to a financial institution and receives an initial delivery of shares based on the terms of the agreement. Upon settlement of the agreement, the financial institution delivers additional shares, or the Company returns shares, with the final net number of shares calculated based on the volume-weighted average price of GE common stock over the term of the agreement, less an agreed upon discount. When certain conditions are met, the transaction is accounted for as an equity transaction and the shares are included in treasury stock when received, at which time there is an immediate reduction in the weighted- average number of common shares used in calculating earnings per share. See Note 15 for additional information.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 148
ASSETS AND LIABILITIES OF BUSINESSES HELD FOR SALE
In the fourth quarter of 2016, we classified our Water business within our Power segment with assets of $1,617 million and liabilities of $656 million, as held for sale. We expect to complete a sale of the business within the next twelve months.
In the third quarter of 2016, we classified a business at Aviation with assets of $601 million and liabilities of $58 million, as held for sale and adjusted the carrying value of the business to fair value, which resulted in a $145 million after-tax loss (including a $120 million loss on the planned disposal). In the fourth quarter of 2016, we ceased negotiations with the potential buyer due to economic and strategic reasons, and concluded that a sale of the business within the next twelve months was no longer probable. As a result, we reclassified the business to held and used and reversed through income approximately $50 million of the after-tax loss recorded in the third quarter of 2016 primarily related to allocated goodwill that is not impaired and retained customer contracts.
On March 30, 2016, we announced an agreement to sell GE Asset Management (GEAM), GE's asset management arm with assets under management of approximately $100 billion, to State Street Corporation. On July 1, 2016, we completed the sale for proceeds of $437 million and recognized an after-tax gain of $260 million. During the fourth quarter of 2016, net sale proceeds associated with U.S. pension plans of $330 million were deposited into the GE Pension Trust, increasing trust assets used to pay GE Pension Plan benefits.
On January 15, 2016, we announced the signing of an agreement to sell our Appliances business to Qingdao Haier Co., Ltd. (Haier). On June 6, 2016, we completed the sale for proceeds of $5,568 million (including $773 million from sale of receivables originated in our Appliances business and sold from GE Capital to Haier) and recognized an after-tax gain of approximately $1,825 million in 2016.
| FINANCIAL INFORMATION FOR ASSETS AND LIABILITIES OF BUSINESSES HELD FOR SALE | |||||
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Assets | |||||
| Current receivables | $ | 366 | $ | 79 | |
| Inventories | 211 | 583 | |||
| Property, plant, and equipment – net | 632 | 1,208 | |||
| Goodwill | 212 | 370 | |||
| Other intangible assets – net | 123 | 162 | |||
| Contract assets | 125 | - | |||
| Other | 76 | 416 | |||
| Assets of businesses held for sale | $ | 1,745 | $ | 2,818 | |
| Liabilities | |||||
| Accounts payable(a) | $ | 190 | $ | 503 | |
| Progress collections and price adjustments accrued | 141 | - | |||
| Other current liabilities | 133 | 325 | |||
| Other | 192 | 33 | |||
| Liabilities of businesses held for sale | $ | 656 | $ | 861 | |
NBCU
As previously disclosed, Comcast Corporation was obligated to share with us potential tax savings associated with its purchase of our interest in NBCU LLC. During the second quarter of 2015, we recognized $450 million of pre-tax income related to the settlement of this obligation.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 149
Discontinued operations primarily relate to our financial services businesses as a result of the GE Capital Exit Plan and include our Consumer business, most of our CLL business, our Real Estate business and our U.S. mortgage business (WMC). All of these operations were previously reported in the Capital segment. Results of operations, financial position and cash flows for these businesses are separately reported as discontinued operations for all periods presented.
We have entered into Transitional Service Agreements (TSA) with and provided certain indemnifications to buyers of GE Capital's assets. Under the TSAs, GE Capital provides various services for terms generally between 12 and 24 months and receives a level of cost reimbursement from the buyers. See Note 23 for further information about indemnifications.
| FINANCIAL INFORMATION FOR DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS | ||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Operations | ||||||||
| Total revenues and other income | $ | 2,968 | $ | 23,003 | $ | 31,136 | ||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations before income taxes | $ | (162) | $ | 887 | $ | 6,615 | ||
| Benefit (provision) for income taxes(a) | 460 | (791) | (776) | |||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes | $ | 298 | $ | 96 | $ | 5,839 | ||
| Disposals | ||||||||
| Gain (loss) on disposals before income taxes | $ | (750) | $ | (6,612) | $ | 14 | ||
| Benefit (provision) for income taxes(a) | (502) | (979) | 1 | |||||
| Gain (loss) on disposals, net of taxes | $ | (1,252) | $ | (7,591) | $ | 15 | ||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes(b)(c) | $ | (954) | $ | (7,495) | $ | 5,855 | ||
| (b) | The sum of GE industrial earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes, and GE Capital earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes, after adjusting for earnings (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests related to discontinued operations, is reported within GE industrial earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes, on the Consolidated Statement of Earnings (Loss). |
| (c) | Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations attributable to the Company, before income taxes, was $(911) million, $(6,038) million, and $6,472 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively. |
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Assets | |||||
| Cash and equivalents | $ | 1,429 | $ | 20,395 | |
| Investment securities | 2,626 | 8,478 | |||
| Financing receivables – net | - | 3,205 | |||
| Other receivables | 310 | 1,221 | |||
| Property, plant and equipment – net | 274 | 7,537 | |||
| Goodwill | 67 | 7,764 | |||
| Other intangible assets - net | 5 | 80 | |||
| Deferred income taxes | 487 | 2,447 | |||
| Financing receivables held for sale | 8,547 | 69,847 | |||
| Valuation allowance on disposal group classified as discontinued operations | (726) | (6,374) | |||
| Other | 1,797 | 6,350 | |||
| Assets of discontinued operations | $ | 14,815 | $ | 120,951 | |
| Liabilities | |||||
| Short-term borrowings | $ | 3 | $ | 739 | |
| Accounts payable | 164 | 2,870 | |||
| Non-recourse borrowings | 1,519 | 3,994 | |||
| Bank deposits | 529 | 25,613 | |||
| Long-term borrowings | 25 | 730 | |||
| All other liabilities | 1,652 | 11,053 | |||
| Deferred income taxes | 221 | 1,437 | |||
| Other | 45 | 52 | |||
| Liabilities of discontinued operations | $ | 4,158 | $ | 46,487 | |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 150
In connection with the GE Capital Exit Plan, we announced the planned disposition of our Consumer business (including Synchrony Financial) and classified the business as discontinued operations. We closed a vast majority of our Consumer business dispositions (including the split-off of Synchrony Financial) in 2015 and 2016.
| FINANCIAL INFORMATION FOR CONSUMER | ||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Operations | ||||||||
| Total revenues and other income | $ | 1,168 | $ | 11,690 | $ | 15,023 | ||
| Interest | $ | (180) | $ | (2,081) | $ | (2,611) | ||
| Selling, general, and administrative expenses | (522) | (3,940) | (4,572) | |||||
| Cost of services sold | - | (1) | - | |||||
| Provision for losses on financing receivables | 1 | (5,029) | (3,544) | |||||
| Investment contracts, insurance losses and insurance annuity benefits | (3) | (12) | (18) | |||||
| Other costs and expenses | (89) | (392) | (388) | |||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, | ||||||||
| before income taxes | 375 | 236 | 3,891 | |||||
| Benefit (provision) for income taxes | (171) | (878) | (736) | |||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes | $ | 204 | $ | (642) | $ | 3,155 | ||
| Disposals | ||||||||
| Gain (loss) on disposals before income taxes | $ | 273 | $ | 2,739 | $ | - | ||
| Benefit (provision) for income taxes | (607) | 363 | - | |||||
| Gain (loss) on disposals, net of taxes | $ | (334) | $ | 3,102 | $ | - | ||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes(a) | $ | (130) | $ | 2,460 | $ | 3,155 | ||
In connection with the GE Capital Exit Plan, we announced the planned disposition of most of our CLL business and classified this portion of the business as discontinued operations. We closed substantially all of our CLL business dispositions in 2015 and 2016.
| FINANCIAL INFORMATION FOR COMMERCIAL LENDING AND LEASING | ||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Operations | ||||||||
| Total revenues and other income | $ | 1,732 | $ | 10,580 | $ | 13,413 | ||
| Interest | $ | (518) | $ | (2,365) | $ | (3,069) | ||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | (1,585) | (3,576) | (3,598) | |||||
| Cost of services sold | - | (1,735) | (3,859) | |||||
| Provision for losses on financing receivables | (2) | (1,753) | (456) | |||||
| Other costs and expenses | (89) | (127) | (135) | |||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, before income taxes | (463) | 1,024 | 2,296 | |||||
| Benefit (provision) for income taxes | 319 | (186) | (487) | |||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes | $ | (144) | $ | 838 | $ | 1,808 | ||
| Disposals | ||||||||
| Gain (loss) on disposals before income taxes | $ | (971) | $ | (8,013) | $ | - | ||
| Benefit (provision) for income taxes | 43 | (698) | - | |||||
| Gain (loss) on disposals, net of taxes | $ | (928) | $ | (8,711) | $ | - | ||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes(a) | $ | (1,072) | $ | (7,873) | $ | 1,808 | ||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 151
REAL ESTATE
In connection with the GE Capital Exit Plan, we announced the planned disposition of our Real Estate business and classified the business as discontinued operations. We closed substantially all of our Real Estate business dispositions in 2015 and 2016.
| FINANCIAL INFORMATION FOR REAL ESTATE | ||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Operations | ||||||||
| Total revenues and other income | $ | 79 | $ | 911 | $ | 2,969 | ||
| Interest | $ | (42) | $ | (457) | $ | (1,079) | ||
| Selling, general and administrative | (112) | (444) | (484) | |||||
| Cost of services sold | - | (5) | - | |||||
| Provision for losses on financing receivables | - | 5 | 86 | |||||
| Other costs and expenses | (3) | (158) | (712) | |||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, | ||||||||
| before income taxes | (78) | (149) | 780 | |||||
| Benefit (provision) for income taxes | 70 | 168 | 224 | |||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes | $ | (8) | $ | 19 | $ | 1,003 | ||
| Disposals | ||||||||
| Gain (loss) on disposals before income taxes | $ | (52) | $ | (1,338) | $ | - | ||
| Benefit (provision) for income taxes | 62 | (639) | - | |||||
| Gain (loss) on disposals, net of taxes | $ | 10 | $ | (1,977) | $ | - | ||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes(a) | $ | 2 | $ | (1,958) | $ | 1,003 | ||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 152
Substantially all of our investment securities are classified as available-for-sale and comprise mainly investment-grade debt securities supporting obligations to annuitants and policyholders in our run-off insurance operations. We do not have any securities classified as held-to-maturity.
| 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross | Gross | Gross | Gross | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortized | unrealized | unrealized | Estimated | Amortized | unrealized | unrealized | Estimated | ||||||||||||||||
| December 31 (In millions) | cost | gains | losses | fair value | cost | gains | losses | fair value | |||||||||||||||
| GE | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Debt | |||||||||||||||||||||||
U.S. corporate | $ | 1 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 2 | $ | 2 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 3 | |||||||
Corporate – non-U.S. | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | |||||||||||||||
U.S. government and federal | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| agency | 49 | - | - | 49 | 49 | - | - | 49 | |||||||||||||||
| Equity | 54 | 34 | (1) | 86 | 87 | 13 | (2) | 98 | |||||||||||||||
| 104 | 34 | (1) | 137 | 139 | 14 | (2) | 151 | ||||||||||||||||
| GE Capital | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Debt | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. corporate | 20,048 | 3,081 | (85) | 23,044 | 19,971 | 2,669 | (285) | 22,355 | |||||||||||||||
State and municipal | 3,916 | 412 | (92) | 4,236 | 3,910 | 407 | (73) | 4,245 | |||||||||||||||
Mortgage and asset-backed | 2,787 | 111 | (37) | 2,861 | 2,995 | 157 | (35) | 3,116 | |||||||||||||||
Corporate – non-U.S. | 11,917 | 98 | (27) | 11,987 | 759 | 96 | (9) | 846 | |||||||||||||||
Government – non-U.S. | 1,137 | 127 | (2) | 1,262 | 279 | 136 | - | 415 | |||||||||||||||
U.S. government and federal | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| agency | 656 | 33 | (25) | 664 | 623 | 104 | - | 727 | |||||||||||||||
| Equity | 105 | 22 | (1) | 126 | 112 | 16 | (4) | 123 | |||||||||||||||
| 40,565 | 3,883 | (268) | 44,180 | 28,648 | 3,585 | (407) | 31,827 | ||||||||||||||||
| Eliminations | (4) | - | - | (4) | (4) | - | - | (4) | |||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 40,665 | $ | 3,917 | $ | (269) | $ | 44,313 | $ | 28,783 | $ | 3,599 | $ | (409) | $ | 31,973 | |||||||
Our corporate debt portfolio comprises securities issued by public and private corporations in various industries, mainly in the U.S. Substantially all of our corporate debt securities are rated investment grade by the major rating agencies.
Mortgage and asset-backed securities substantially comprises commercial and residential mortgage-backed securities. Substantially all of these securities have investment-grade credit ratings. Our commercial mortgage-backed securities (CMBS) portfolio is collateralized by both diversified pools of mortgages that were originated for securitization (conduit CMBS) and pools of large loans backed by high-quality properties (large loan CMBS). Our residential mortgage-backed securities (RMBS) portfolio is collateralized primarily by pools of individual, direct mortgage loans, of which substantially all are in a senior position in the capital structure of the deals, not by other structured products such as collateralized debt obligations.
The fair value of investment securities increased to $44,313 million at December 31, 2016, from $31,973 million at December 31, 2015, primarily due to higher net purchases of Corporate – non-U.S. debt securities and higher net unrealized gains in U.S. Corporate.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 153
| ESTIMATED FAIR VALUE AND GROSS UNREALIZED LOSSES OF AVAILABLE-FOR-SALE INVESTMENT SECURITIES | ||||||||||||
| In loss position for | ||||||||||||
| Less than 12 months | 12 months or more | |||||||||||
| Gross | Gross | |||||||||||
| Estimated | unrealized | Estimated | unrealized | |||||||||
| (In millions) | fair value(a) | losses(a) | fair value | losses | ||||||||
| December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||
| Debt | ||||||||||||
U.S. corporate | $ | 1,692 | $ | (55) | $ | 359 | $ | (30) | ||||
State and municipal | 674 | (27) | 158 | (64) | ||||||||
Mortgage and asset-backed | 822 | (21) | 132 | (16) | ||||||||
| Corporate – non-U.S. | 5,352 | (26) | 14 | (1) | ||||||||
| Government - non-U.S. | 313 | (2) | - | - | ||||||||
| U.S. government and federal agency | 236 | (25) | - | - | ||||||||
| Equity | 9 | (1) | - | - | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 9,098 | $ | (157) | $ | 663 | $ | (111) | ||||
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||
| Debt | ||||||||||||
U.S. corporate | $ | 2,966 | $ | (218) | $ | 433 | $ | (67) | ||||
State and municipal | 494 | (20) | 155 | (53) | ||||||||
| Mortgage and asset-backed | 719 | (20) | 84 | (16) | ||||||||
Corporate – non-U.S. | 56 | (4) | 14 | (4) | ||||||||
| Equity | 36 | (6) | - | - | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 4,273 | $ | (269) | $ | 686 | $ | (140) | ||||
| (a) | Includes the estimated fair value of and gross unrealized losses on equity securities held by GE. |
Unrealized losses are not indicative of the amount of credit loss that would be recognized and at December 31, 2016 are primarily due to increases in market yields subsequent to our purchase of the securities. We presently do not intend to sell the vast majority of our debt securities that are in unrealized loss positions and believe that it is not more likely than not that we will be required to sell the vast majority of these securities before anticipated recovery of our amortized cost. The methodologies and significant inputs used to measure the amount of credit loss for our investment securities during 2016 have not changed.
| PRE-TAX, OTHER-THAN-TEMPORARY IMPAIRMENTS ON INVESTMENT SECURITIES | ||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Total recognized | $ | 31 | $ | 64 | $ | 316 | ||
| Recognized in AOCI | - | - | (4) | |||||
| Recognized in earnings(a) | $ | 31 | $ | 64 | $ | 312 | ||
| (a) | Included equity securities of $11 million, $5 million and $219 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. |
| CONTRACTUAL MATURITIES OF INVESTMENT IN AVAILABLE-FOR-SALE DEBT SECURITIES | |||||
| (EXCLUDING MORTGAGE AND ASSET-BACKED SECURITIES) | |||||
| Amortized | Estimated | ||||
| (In millions) | cost | fair value | |||
| Due | |||||
| Within one year | $ | 7,139 | $ | 7,148 | |
| After one year through five years | 7,947 | 8,124 | |||
| After five years through ten years | 4,996 | 5,410 | |||
| After ten years | 17,641 | 20,562 | |||
We expect actual maturities to differ from contractual maturities because borrowers have the right to call or prepay certain obligations.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 154
| GROSS REALIZED GAINS AND LOSSES ON AVAILABLE-FOR-SALE INVESTMENT SECURITIES | ||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| GE | ||||||||
| Gains | $ | 11 | $ | 7 | $ | 3 | ||
| Losses, including impairments | (12) | (36) | (218) | |||||
| Net | (2) | (29) | (215) | |||||
| GE Capital | ||||||||
| Gains | 50 | 121 | 87 | |||||
| Losses, including impairments | (43) | (51) | (104) | |||||
| Net | 7 | 70 | (16) | |||||
| Total | $ | 6 | $ | 41 | $ | (231) | ||
Although we generally do not have the intent to sell any specific securities at the end of the period, in the ordinary course of managing our investment securities portfolio, we may sell securities prior to their maturities for a variety of reasons, including diversification, credit quality, yield and liquidity requirements and the funding of claims and obligations to policyholders.
Proceeds from investment securities sales and early redemptions by issuers totaled $1,718 million, $5,746 million, and $1,898 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively. In 2016 and 2015, investment securities sales were principally of U.S. government and federal agency and mortgage and asset-backed securities.
| Consolidated(a)(b) | GE(c) | ||||||||||
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Power | $ | 7,688 | $ | 6,675 | $ | 3,632 | $ | 4,377 | |||
| Renewable Energy | 1,903 | 2,336 | 1,293 | 1,418 | |||||||
| Oil & Gas | 4,259 | 4,958 | 2,478 | 2,764 | |||||||
| Energy Connections & Lighting | 2,716 | 4,432 | 1,675 | 2,173 | |||||||
| Aviation | 3,542 | 4,133 | 1,731 | 1,876 | |||||||
| Healthcare | 3,996 | 4,022 | 2,068 | 1,943 | |||||||
| Transportation | 377 | 609 | 186 | 193 | |||||||
| Corporate items and eliminations | 454 | 372 | 499 | 464 | |||||||
| 24,935 | 27,538 | 13,562 | 15,209 | ||||||||
| Less Allowance for Losses(d) | (858) | (515) | (847) | (502) | |||||||
| Total | $ | 24,076 | $ | 27,022 | $ | 12,715 | $ | 14,707 | |||
| (b) | In order to manage credit exposure, the Company sells additional current receivables to third parties outside the Receivables Facility described in Note 22. In connection with certain of these sales, we provide servicing activities and limited recourse to the purchasers. At December 31, 2016 and 2015, GE serviced $2,962 million and $2,167 million, respectively, of these receivables that remain outstanding. Of these balances, $458 million and $378 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, were current receivables serviced by GE Capital that GE sold directly to third-parties. At December 31, 2016 and 2015, our maximum exposure to loss under the limited recourse arrangements is $215 million and $154 million, respectively. |
| (c) | GE current receivables of $299 million and $251 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, arose from sales, principally of Aviation goods and services, on open account to various agencies of the U.S. government. As a percentage of GE revenues, approximately 3% of GE sales of goods and services were to the U.S. government in 2016, compared with 4% in 2015 and 3% in 2014. |
| (d) | The 2016 increase in allowance for losses is primarily due to Alstom purchase price adjustments of $263 million. |
GE current receivables balances at December 31, 2016 and 2015, before allowance for losses, included $8,927 million and $10,535 million, respectively, from sales of goods and services to customers. The remainder of the balances primarily relates to supplier advances, revenue sharing programs and other non-income based tax receivables.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 155
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Raw materials and work in process | $ | 12,636 | $ | 13,415 | |
| Finished goods | 8,798 | 8,265 | |||
| Unbilled shipments | 536 | 628 | |||
| 21,971 | 22,308 | ||||
| Revaluation to LIFO | 383 | 207 | |||
| Total inventories | $ | 22,354 | $ | 22,515 | |
| FINANCING RECEIVABLES – NET | |||||
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Loans, net of deferred income | $ | 21,101 | $ | 20,115 | |
| Investment in financing leases, net of deferred income | 4,998 | 4,969 | |||
| 26,099 | 25,084 | ||||
| Allowance for losses | (58) | (81) | |||
| Financing receivables – net | $ | 26,041 | $ | 25,003 | |
| NET INVESTMENT IN FINANCING LEASES | |||||||||||||||||
| Total financing leases | Direct financing leases(a) | Leveraged leases(b) | |||||||||||||||
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||
| Total minimum lease payments receivable | $ | 5,466 | $ | 5,901 | $ | 3,274 | $ | 3,251 | $ | 2,191 | $ | 2,649 | |||||
Less principal and interest on third-party non-recourse debt | (1,053) | (1,482) | - | - | (1,053) | (1,482) | |||||||||||
| Net rentals receivable | 4,412 | 4,419 | 3,274 | 3,251 | 1,138 | 1,167 | |||||||||||
| Estimated unguaranteed residual value of leased assets | 1,985 | 2,057 | 927 | 928 | 1,058 | 1,129 | |||||||||||
| Less deferred income | (1,400) | (1,507) | (909) | (913) | (491) | (593) | |||||||||||
| Investment in financing leases, net of deferred income(c) | $ | 4,998 | $ | 4,969 | $ | 3,292 | $ | 3,266 | $ | 1,706 | $ | 1,703 | |||||
| (b) | Included pre-tax income of $74 million and $61 million and income tax of $28 million and $23 million during 2016 and 2015, respectively. Net investment credits recognized on leveraged leases during 2016 and 2015 were insignificant. |
(c) See Note 14 for deferred tax amounts related to financing leases.
| CONTRACTUAL MATURITIES | ||||||
| Total | Net rentals | |||||
| (In millions) | loans | receivable | ||||
| Due in | ||||||
| 2017 | $ | 12,853 | $ | 851 | ||
| 2018 | 1,718 | 845 | ||||
| 2019 | 2,327 | 685 | ||||
| 2020 | 1,149 | 528 | ||||
| 2021 | 1,114 | 398 | ||||
| 2022 and later | 1,940 | 1,106 | ||||
| Total | $ | 21,101 | $ | 4,412 | ||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 156
We manage our financing receivables portfolio using delinquency and nonaccrual data as key performance indicators. At December 31, 2016, $811 million (3.1%), $407 million (1.6%) and $322 million (1.2%) of financing receivables were over 30 days past due, over 90 days past due and on nonaccrual, respectively. Of the $322 million of nonaccrual financing receivables at December 31, 2016, the vast majority are secured by collateral and $68 million are currently paying in accordance with the contractual terms. At December 31, 2015, $622 million (2.5%), $201 million (0.8%) and $256 million (1.0%) of financing receivables were over 30 days past due, over 90 days past due and on nonaccrual, respectively.
The recorded investment in impaired loans at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015 was $262 million and $175 million, respectively. The method used to measure impairment for these loans is primarily based on collateral value. At December 31, 2016, troubled debt restructurings included in impaired loans were $176 million.
| Depreciable | ||||||||||||||||
| lives-new | Original Cost | Net Carrying Value | ||||||||||||||
| December 31 (Dollars in millions) | (in years) | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||
| GE | ||||||||||||||||
| Land and improvements | 8 | (a) | $ | 932 | $ | 888 | $ | 910 | $ | 870 | ||||||
| Buildings, structures and related equipment | 8-40 | 9,680 | 10,050 | 6,016 | 5,440 | |||||||||||
| Machinery and equipment | 4-20 | 24,596 | 24,515 | 9,369 | 9,986 | |||||||||||
| Leasehold costs and manufacturing plant under construction | 1-10 | 3,407 | 4,359 | 2,809 | 3,849 | |||||||||||
| 38,615 | 39,812 | 19,103 | 20,145 | |||||||||||||
| GE Capital(b) | ||||||||||||||||
| Land and improvements, buildings, structures and related equipment | 1-10 | (a) | 238 | 267 | 68 | 101 | ||||||||||
| Equipment leased to others | ||||||||||||||||
Aircraft(c) | 15-20 | 47,360 | 50,339 | 31,786 | 34,316 | |||||||||||
All other | 3-35 | 587 | 543 | 371 | 364 | |||||||||||
| 48,185 | 51,149 | 32,225 | 34,781 | |||||||||||||
| Eliminations | (925) | (939) | (809) | (831) | ||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 85,875 | $ | 90,022 | $ | 50,518 | $ | 54,095 | ||||||||
| (b) | Included $1,457 million and $1,024 million of original cost of assets leased to GE with accumulated amortization of $147 million and $83 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. |
| (c) | The GECAS business of GE Capital recognized impairment losses of $99 million and $168 million in 2016 and 2015, respectively. These losses are recorded in the caption "Cost of services sold" in the Statement of Earnings to reflect adjustments to fair value based on management's best estimates, which are benchmarked against third-party appraiser current market values for aircraft of similar type and age. |
Consolidated depreciation and amortization related to property, plant and equipment was $4,997 million, $4,847 million and $4,953 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Amortization of GE Capital equipment leased to others was $2,231 million, $2,266 million and $2,386 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
| (In millions) | ||
| Due in | ||
| 2017 | $ | 3,684 |
| 2018 | 3,307 | |
| 2019 | 2,912 | |
| 2020 | 2,575 | |
| 2021 | 2,144 | |
2022 and later | 6,338 | |
| Total | $ | 20,961 |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 157
ACQUISITIONS
In the fourth quarter of 2016, we acquired two European 3-D printing companies in our Aviation segment. On November 17, 2016, we acquired an additional 61.9% of the shares of Arcam AB, a Swedish company specializing in electron beam melting systems, for $422 million to bring our total ownership stake to 76.2%. Upon gaining control, we fair valued the business including our previously held 14.3% equity interest. The preliminary purchase price allocation resulted in goodwill of approximately of $495 million and amortizable intangible assets of approximately $95 million. On December 8, 2016, we acquired 75% of Concept Laser GmbH, a German company specializing in powder-bed based laser metal printing, for $573 million. GE holds a call option on the 25% noncontrolling interest that is exercisable for a one-year period beginning on the third anniversary of the acquisition date. The non-controlling interest holds a put option that is exercisable for a one-year period beginning on the fifth anniversary of the closing date. The preliminary purchase price allocation resulted in goodwill of approximately of $550 million and amortizable intangible assets of approximately $170 million. The allocation of purchase prices will be finalized upon completion of post-closing procedures.
On November 9, 2016, we acquired the remaining 89% of Bit Stew, a software company specializing in gathering data from connected devices in complex industrial systems to help companies plan predictive maintenance and optimize productivity, for $129 million. Upon gaining control, we fair valued the business including our previously held 11% equity interest. The preliminary purchase price allocation resulted in goodwill of approximately $110 million and amortizable intangible assets of approximately $50 million. The allocation of the purchase price will be finalized upon completion of post-closing procedures.
On October 31, 2016, we announced an agreement with Baker Hughes Incorporated (Baker Hughes) to combine GE's Oil & Gas business and Baker Hughes to create a new company. The transaction will be executed using a partnership structure, pursuant to which GE Oil & Gas and Baker Hughes will each contribute their operating assets to a newly formed partnership. GE will have a 62.5% interest in this partnership and existing Baker Hughes shareholders will have a 37.5% interest through a newly NYSE listed corporation. Baker Hughes shareholders will also receive a special one-time cash dividend of $17.50 per share at closing. GE will contribute $7.4 billon to the new partnership to fund the cash dividend to existing Baker Hughes shareholders. The transaction is subject to the approval of Baker Hughes shareholders, regulatory approvals and other customary closing conditions.
On September 14, 2016, we acquired the remaining 74% of the software developer Meridium Inc. for $370 million. Upon gaining control, we fair valued the business including our previously held 26% equity interest. The preliminary purchase price allocation resulted in goodwill of approximately $350 million and amortizable intangible assets of approximately $165 million. The allocation of the purchase price will be finalized upon completion of post-closing procedures.
On May 10, 2016, we announced the pending acquisition of the heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) business from Doosan Engineering & Construction (Doosan) for $250 million. On August 16, 2016, we acquired 80% of the HRSG business for approximately $220 million. The remaining 20% of the HRSG business continues to be subject to local regulatory requirements and we expect a staggered close beginning in the first quarter of 2017 through the first half of 2017. The preliminary purchase price allocation resulted in goodwill of approximately $170 million and amortizable intangible assets of approximately $35 million. The allocation of the purchase price will be finalized upon completion of post-closing procedures.
On January 30, 2015, we acquired Milestone Aviation Group (Milestone Aviation), a helicopter leasing business, for approximately $1,750 million, which is included in our Capital segment. The purchase price allocation resulted in goodwill of approximately $730 million and amortizable intangible assets of approximately $345 million.
On November 2, 2015, we acquired the Thermal, Renewables and Grid businesses from Alstom. The purchase price was €9,200 million ($10,124 million), net of cash acquired of approximately €1,600 million ($1,765 million). In order to obtain approval by the European Commission and the Department of Justice, GE pledged to sell certain of Alstom's gas-turbine assets and its Power Systems Manufacturing subsidiary to Ansaldo Energia SpA (Ansaldo) after the close of the transaction for approximately €120 million. The purchase price will be paid by Ansaldo over a period of five years. The transaction closed on February 25, 2016.
We formed three consolidated joint ventures with Alstom in grid technology, renewable energy, and global nuclear and French steam power. In addition, GE contributed its Digital Energy business to the grid technology joint venture.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 158
Alstom holds redemption rights with respect to its interest in the grid technology and renewable energy joint ventures, which, if exercised, would require us to purchase all of their interest during September 2018 or September 2019. Alstom also holds similar redemption rights for the global nuclear and French steam power joint venture that are exercisable during the first full calendar quarter immediately following the fifth or sixth anniversary of the acquisition date. The redemption price would generally be equal to Alstom's initial investment plus annual accretion of 3% for the grid technology and renewable energy joint ventures and plus annual accretion of 2% for the nuclear and French steam power joint venture, with potential upside sharing based on an EBITDA multiple. Alstom also holds additional redemption rights in other limited circumstances as well as a call option to require GE to sell all of its interests in the renewable energy joint venture at the higher of fair value or Alstom's initial investment plus annual accretion of 3% during the month of May in the years 2016 through 2019 and also upon a decision to IPO the joint venture.
GE holds a call option on Alstom's interest in the global nuclear and French steam power joint venture at the same amount as Alstom's redemption price in the event that Alstom exercises its put option in the grid technology or renewable energy joint ventures. GE also has call options on Alstom's interest in the three joint ventures in other limited circumstances. In addition, the French Government holds a preferred interest in the global nuclear and French steam power joint venture, giving it certain protective rights.
The acquisition and alliances with Alstom will have a significant effect on our Power, Energy Connections and Renewable Energy segments, and to a lesser extent our Oil & Gas segment. The financial impact of acquired businesses on individual segments will be affected by a number of variables, including operating performance, purchase accounting effects and realized synergies. In addition, due to the amount of time that elapsed between signing and closing, the commercial operations of the businesses were negatively affected primarily as a result of uncertainty among Alstom customers regarding the execution of the transaction. This affected the overall valuation of the acquired businesses at the time of close and, accordingly, is reflected among the initial and adjusted amounts assigned to the assets and liabilities recorded in purchase accounting.
The total consideration for the acquired businesses, at the time of close in November 2015 included our purchase price of $10,124 million (net of cash acquired) and a preliminary valuation of noncontrolling interests, of approximately $3,600 million for a total of approximately $13,700 million. In the fourth quarter of 2015, the preliminary allocation of purchase price resulted in goodwill, intangible assets and unfavorable customer contract liabilities of approximately $13,500 million, $5,200 million, and $1,100 million respectively. The amount of goodwill recognized compared with identifiable intangible assets is affected by estimated GE-specific synergies, which are not permitted to be included in the measurement of identifiable intangibles. Such synergies include additional revenue from cross-selling complementary product lines. The preliminary fair value of the associated noncontrolling interests consisted of approximately $2,900 million for Alstom's redeemable noncontrolling interests in the three joint ventures (presented separately from total equity in the consolidated statement of financial position) and $700 million for all other noncontrolling interests.
Through the fourth quarter of 2016, we adjusted the preliminary allocation of purchase price, which has now resulted in goodwill, intangible assets, and unfavorable customer contract liabilities, of $17,304 million, $4,370 million, and $2,720 million, respectively as of the acquisition date. These adjustments, which are necessary to reflect acquired assets and liabilities of the acquired businesses at fair value, reflected revisions in 2016, primarily related to cash flow and other valuation assumptions for customer contracts, increases to legal reserves, and other fair value adjustments related to acquired assets and liabilities. The approximate amounts of significant purchase accounting adjustments recorded since the date of acquisition include a reduction in the book value of assets sold to Ansaldo of $405 million, adjustments to the fair value of derivative contracts of $335 million, decreases in inventory balances of $130 million, increases to legal reserves of $990 million, a reduction in the book value of aged accounts receivable of $175 million and other project related costs such as warranty provisions and liquidating damages of $665 million. In addition, the fair value of all other noncontrolling interests decreased by $55 million.
See Note 23 for further information about legal reserves for Alstom legacy matters.
In addition to purchase price allocation based on the fair value of acquired assets and liabilities, other adjustments were necessary to reflect differences between IFRS and GAAP, as applied to differences in facts and circumstances between those businesses as part of Alstom and as part of GE post acquisition. The table below presents consideration paid, amounts of assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the acquisition date, inclusive of the purchase accounting adjustments and IFRS to GAAP adjustments recorded as of December 31, 2016, and the fair value of the non-controlling interest.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 159
| ASSETS ACQUIRED AND LIABILITIES ASSUMED AT THE ACQUISITION DATE | ||
| Balance at | ||
| (In millions) | December 31, 2016 | |
| Assets | ||
| Cash and equivalents | $ | 1,766 |
| Current receivables | 4,064 | |
| Inventories | 4,663 | |
| Property, plant and equipment | 2,782 | |
| Goodwill | 17,304 | |
| Other intangible assets | 4,370 | |
| All other assets, net(a) | 3,673 | |
| Total Assets | $ | 38,622 |
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts payable | $ | 1,908 |
| Progress collections | 2,919 | |
| Accrued contract liabilities | 10,714 | |
| All other liabilities(b) | 7,658 | |
| Total Liabilities | $ | 23,199 |
| Redeemable noncontrolling interests | 2,921 | |
| Noncontrolling interest | 612 | |
| Total purchase price | 11,890 | |
| Less cash acquired | 1,766 | |
| Total purchase price, net of cash acquired | $ | 10,124 |
| (b) | Included approximately $859 million of liabilities for unrecognized income tax benefits and other uncertain taxes and approximately $772 million of pension and other employee related costs. |
GOODWILL
| CHANGES IN GOODWILL BALANCES | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dispositions, | Dispositions, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| currency | currency | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at | exchange | Balance at | Balance at | exchange | Balance at | ||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | January 1 | Acquisitions | and other | December 31 | January 1 | Acquisitions | and other | December 31 | |||||||||||||||
| Power | $ | 16,736 | $ | 3,347 | $ | (268) | $ | 19,816 | $ | 7,769 | $ | 9,582 | $ | (615) | $ | 16,736 | |||||||
| Renewable Energy | 2,580 | (46) | (27) | 2,507 | 984 | 1,631 | (35) | 2,580 | |||||||||||||||
| Oil & Gas | 10,594 | - | (231) | 10,363 | 10,572 | 22 | - | 10,594 | |||||||||||||||
| Aviation | 8,567 | 1,045 | (158) | 9,455 | 8,952 | - | (385) | 8,567 | |||||||||||||||
| Healthcare | 17,353 | 191 | (120) | 17,424 | 17,532 | 11 | (190) | 17,353 | |||||||||||||||
| Transportation | 851 | 41 | 6 | 899 | 887 | - | (36) | 851 | |||||||||||||||
| Energy Connections & Lighting | 6,441 | 846 | (420) | 6,868 | 4,796 | 2,314 | (669) | 6,441 | |||||||||||||||
| Capital | 2,370 | - | (1) | 2,368 | 1,680 | 728 | (37) | 2,370 | |||||||||||||||
| Corporate | 34 | 487 | 218 | 739 | 34 | - | - | 34 | |||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 65,526 | $ | 5,911 | $ | (1,000) | $ | 70,438 | $ | 53,207 | $ | 14,287 | $ | (1,968) | $ | 65,526 | |||||||
Goodwill balances increased by $4,912 million in 2016, primarily as a result of the Alstom acquisition purchase accounting adjustments and other acquisitions, partially offset by currency exchange effects of a stronger U.S. dollar against other major currencies.
Goodwill balances increased $12,319 million in 2015, primarily as a result of the Alstom and Milestone Aviation acquisitions, partially offset by currency exchange effects of the stronger U.S. dollar and disposals.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 160
We test goodwill for impairment annually in the third quarter of each year using data as of July 1 of that year. The impairment test consists of two steps: in step one, the carrying value of the reporting unit is compared with its fair value; in step two, which is applied when the carrying value is more than its fair value, the amount of goodwill impairment, if any, is derived by deducting the fair value of the reporting unit's assets and liabilities from the fair value of its equity, and comparing that amount with the carrying amount of goodwill. We determined fair values for each of the reporting units using the market approach, when available and appropriate, or the income approach, or a combination of both. We assess the valuation methodology based upon the relevance and availability of the data at the time we perform the valuation. If multiple valuation methodologies are used, the results are weighted appropriately.
Valuations using the market approach are derived from metrics of publicly traded companies or historically completed transactions of comparable businesses. The selection of comparable businesses is based on the markets in which the reporting units operate giving consideration to risk profiles, size, geography, and diversity of products and services. A market approach is limited to reporting units for which there are publicly traded companies that have the characteristics similar to our businesses.
Under the income approach, fair value is determined based on the present value of estimated future cash flows, discounted at an appropriate risk-adjusted rate. We use our internal forecasts to estimate future cash flows and include an estimate of long-term future growth rates based on our most recent views of the long-term outlook for each business. Actual results may differ from those assumed in our forecasts. We derive our discount rates using a capital asset pricing model and analyzing published rates for industries relevant to our reporting units to estimate the cost of equity financing. We use discount rates that are commensurate with the risks and uncertainty inherent in the respective businesses and in our internally developed forecasts. Discount rates used in our reporting unit valuations ranged from 9.5% to 16.5%.
During the third quarter of 2016, we performed our annual impairment test of goodwill for all of our reporting units. Based on the results of our step one testing, the fair values of each of the GE reporting units exceeded their carrying values; therefore, the second step of the impairment test was not required to be performed for any of our reporting units and no goodwill impairment was recognized.
While all of our reporting units passed step one of our annual impairment testing in 2016, we identified four reporting units for which the fair value was not substantially in excess of its carrying value. Due to the continuation of depressed oil and natural gas prices, the fair value of our Energy Financial Services reporting unit, within our Capital operating segment, continues to be impacted and was in excess of its carrying value by approximately 2%. Based on the results of the step one testing, we further substantiated our Energy Financial Services goodwill balance by performing the second step analysis in which the implied fair value of goodwill exceeded its carrying value by approximately $670 million. We continued to monitor the volatility in the oil and gas environment during the fourth quarter and updated our analysis using data as of October 1, 2016. This analysis indicated that the fair value of our Energy Financial Services reporting unit was significantly in excess of its carrying value. The improvement in fair value over its carrying value was driven by higher forecasted investment and return performance, reflecting stabilization in the commodities markets. The estimated fair value of the Energy Financial Services reporting unit is based on a number of assumptions about future business performance and investment, including the performance of our renewable investment portfolio and the expected proceeds and timing of non-strategic investment divestitures. While all reporting units within our Oil & Gas operating segment are significantly in excess of their carrying value, the business continues to experience declines in orders, project commencement delays and pricing pressures, which affect their fair value. While the goodwill of the Energy Financial Services and Oil & Gas reporting units are not currently impaired, we will continue to monitor the oil & gas industry and the impact it may have on these businesses.
In addition, due to a decline in order growth and an increase in the order-to-cash cycle, the fair value of the Power Conversion reporting unit, within our Energy Connections operating segment, was impacted and was in excess of its carrying value by approximately 9%. Due to continued decline in order growth and increase to the order-to-cash cycle, we performed an impairment test in the fourth quarter using data as of December 1, 2016, which resulted in the fair value of our Power Conversion reporting unit to be in excess of its carrying value by approximately 8%. The goodwill associated with our Power Conversion reporting unit was $987 million at December 31, 2016, representing approximately 1% of our total goodwill. While the goodwill of the reporting unit is not currently impaired, there could be an impairment in the future as a result of changes in certain assumptions. For example, the reporting unit's fair value could be adversely affected and result in an impairment of goodwill if actual cash flows are below estimated cash flows, the estimated cash flows are discounted at a higher risk-adjusted rate or market multiples decrease.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 161
Finally, two reporting unit fair values were impacted as a result of the Alstom transaction. Subsequent to the close of the acquisition of Alstom, we formed two new reporting units, Grid Solutions and Hydro. The Alstom Grid business was combined with our Digital Energy business, within our Energy Connections operating segment, to create the new Grid Solutions reporting unit and the Alstom Hydro business is a newly created reporting unit within our Renewable Energy operating segment. Since fair values equaled carrying value at the time of acquisition, this caused the fair values of these reporting units not to be significantly in excess of their carrying values. As the fair values of these reporting units are not significantly in excess of their carrying values, we performed impairment tests in the fourth quarter using data as of December 1, 2016, which resulted in the fair value of the Hydro reporting unit approximating its carrying value and the excess of fair value over carrying value of the Grid Solutions reporting unit being approximately 3%. The goodwill associated with our Hydro and Grid Solutions reporting units was $899 million and $4,405 million, respectively, representing approximately 1% and 6% of our total goodwill at December 31, 2016. While the goodwill of these reporting units are not currently impaired, there could be an impairment in the future as a result of changes in certain assumptions. For example, the fair value of these reporting units could be adversely affected and result in impairments of goodwill if expected synergies of the acquisition with Alstom are not realized or if the reporting units were not able to execute on customer opportunities, the estimated cash flows are discounted at a higher risk-adjusted rate or market multiples decrease.
As of December 31, 2016, we believe that the goodwill is recoverable for all of the reporting units; however, there can be no assurances that the goodwill will not be impaired in future periods.
In 2015, we identified one reporting unit for which the fair value was not substantially in excess of its carrying value. Due to the sharp decline experienced in oil prices and the prospect of a continuation of prevailing oil prices, the fair value of our Energy Financial Services reporting unit, within our Capital operating segment, had been affected and was in excess of its carrying value by approximately 13%. Due to the continued decline in oil prices, we performed an impairment test in the fourth quarter using data as of December 31, 2015, which resulted in the fair value of our Energy Financial Services reporting unit being in excess of its carrying value by approximately 12%. In the current year, the fair value of the Energy Financial Services reporting unit continues to be impacted by the market conditions within the oil & gas industry as discussed above.
In 2015, although not impaired, our Oil & Gas business had also experienced declines in orders, project commencement delays and pricing pressures, which affected the fair value of our Oil & Gas reporting units. Our Oil & Gas business continues to be affected by the overall market conditions as discussed above.
Estimating the fair value of reporting units requires the use of estimates and significant judgments that are based on a number of factors including actual operating results. It is reasonably possible that the judgments and estimates described above could change in future periods.
| OTHER INTANGIBLE ASSETS - NET | |||||
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Intangible assets subject to amortization | $ | 16,336 | $ | 17,688 | |
| Indefinite-lived intangible assets(a) | 100 | 109 | |||
| Total | $ | 16,436 | $ | 17,797 | |
| (a) | Indefinite-lived intangible assets principally comprise trademarks and in-process research and development. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 162
| INTANGIBLE ASSETS SUBJECT TO AMORTIZATION | |||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Gross | Gross | ||||||||||||||||
| carrying | Accumulated | carrying | Accumulated | ||||||||||||||
| December 31 (In millions) | amount | amortization | Net | amount | amortization | Net | |||||||||||
| Customer-related | $ | 9,172 | $ | (2,408) | $ | 6,764 | $ | 9,758 | $ | (2,113) | $ | 7,645 | |||||
| Patents and technology | 8,693 | (3,325) | 5,368 | 8,543 | (3,096) | 5,447 | |||||||||||
| Capitalized software | 7,652 | (4,538) | 3,114 | 7,375 | (4,136) | 3,239 | |||||||||||
| Trademarks | 1,165 | (307) | 858 | 1,337 | (282) | 1,055 | |||||||||||
| Lease valuations | 143 | (59) | 84 | 167 | (22) | 145 | |||||||||||
| Present value of future profits(a) | 684 | (684) | - | 651 | (651) | - | |||||||||||
| All other | 273 | (124) | 149 | 267 | (108) | 159 | |||||||||||
| Total | $ | 27,781 | $ | (11,444) | $ | 16,336 | $ | 28,098 | $ | (10,408) | $ | 17,688 | |||||
GE amortization expense related to intangible assets subject to amortization was $1,704 million, $1,505 million and $1,386 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. GE Capital amortization expense related to intangible assets subject to amortization was $131 million, $148 million and $84 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Estimated GE Consolidated annual pre-tax amortization for intangible assets over the next five calendar years follows.
| ESTIMATED 5 YEAR CONSOLIDATED AMORTIZATION | ||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |||||||||
| Estimated annual pre-tax amortization | $ | 2,058 | $ | 1,947 | $ | 1,846 | $ | 1,666 | $ | 1,519 | ||||
During 2016 we recorded additions to intangible assets subject to amortization of $2,313 million. The components of finite-lived intangible assets acquired during 2016 and their respective weighted-average amortizable periods follow.
| COMPONENTS OF FINITE-LIVED INTANGIBLE ASSETS ACQUIRED DURING 2016 | |||||
| Weighted-average | |||||
| Gross | amortizable period | ||||
| (In millions) | carrying value | (in years) | |||
| Customer-related | $ | 387 | 15.3 | ||
| Patents and technology | 804 | 12.4 | |||
| Capitalized software | 1,107 | 5.0 | |||
| Trademarks | 11 | 7.2 | |||
| All other | 3 | 3.0 | |||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 163
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| GE | |||||
| Revenue in excess of billings | |||||
| Long-term product service agreements(a) | $ | 12,752 | $ | 10,346 | |
| Long-term equipment contract revenue(b) | 5,859 | 5,645 | |||
| Total revenue in excess of billings | 18,611 | 15,991 | |||
| Deferred inventory costs(c) | 3,349 | 2,328 | |||
| Non-recurring engineering costs(d) | 2,185 | 1,790 | |||
| Other | 1,018 | 1,048 | |||
| Contract assets | $ | 25,162 | $ | 21,156 | |
| (a) | Long-term product service agreement balances are presented net of related billings in excess of revenues of $3,750 million and $2,602 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. |
| (b) | Reflects revenues earned in excess of billings on our long-term contracts to construct technically complex equipment (such as gas power systems). |
| (c) | Represents cost deferral for shipped goods (such as components for wind turbine assembly within our Renewable Energy segment) and other costs for which the criteria for revenue recognition has not yet been met. |
| (d) | Included costs incurred prior to production (e.g., requisition engineering) for long-term equipment production contracts, primarily within our Aviation segment, which are allocated ratably to each unit produced. |
Contract assets increased $4,006 million in 2016, which was primarily driven by a change in estimated profitability within our long-term product service agreements resulting in an adjustment of $2,216 million, as well as an increase in deferred inventory costs.
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| GE | |||||
| Investments | |||||
Associated companies | $ | 3,574 | $ | 3,582 | |
Other | 631 | 644 | |||
| 4,205 | 4,226 | ||||
| Long-term receivables, including notes | 2,433 | 2,310 | |||
| Derivative instruments | 313 | 733 | |||
| Other(a) | 5,055 | 5,544 | |||
| 12,007 | 12,813 | ||||
| GE Capital | |||||
| Investments | |||||
Associated companies | 8,124 | 8,373 | |||
Assets held for sale(b) | 2,361 | 857 | |||
| Time deposits(c) | - | 10,386 | |||
Other | 122 | 97 | |||
| 10,607 | 19,713 | ||||
| Derivative instruments | 32 | 549 | |||
| Advances to suppliers | 1,632 | 1,809 | |||
| Other(d) | 2,337 | 3,010 | |||
| 14,608 | 25,081 | ||||
| Eliminations | 561 | (1,097) | |||
| All Other Assets | $ | 27,176 | $ | 36,797 | |
| (b) | Assets were classified as held for sale on the date a decision was made to dispose of them through sale or other means. At December 31, 2016 and 2015, such assets consisted primarily of loans, aircraft and equipment, and were accounted for at the lower of carrying amount or estimated fair value less costs to sell. |
| (c) | Balances at December 31, 2015 included $10,386 million of high quality interest bearing deposits with European branches of global banks, predominantly in the U.K., that matured in April 2016. |
| (d) | Balances at December 31, 2016 and 2015 included deferred acquisition cost adjustments of $558 million and $544 million, respectively, in our run-off insurance operations to reflect the effects that would have been recognized had the related unrealized investment securities holding gains and losses actually been realized. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 164
| December 31 (Dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings | Amount | Average Rate(a) | Amount | Average Rate(a) | ||||||||
| GE | ||||||||||||
| Commercial paper | $ | 1,500 | 0.60 | % | $ | 500 | 0.15 | % | ||||
| Current portion of long-term borrowings | 17,109 | 3.16 | 17,770 | 2.10 | ||||||||
| Other | 1,874 | 1,522 | ||||||||||
| Total GE short-term borrowings(b) | 20,482 | 19,792 | ||||||||||
| GE Capital | ||||||||||||
| Commercial paper | ||||||||||||
U.S. | 5,002 | 0.59 | 650 | 0.46 | ||||||||
Non-U.S. | - | - | 4,351 | 0.01 | ||||||||
| Current portion of long-term borrowings(c) | 6,517 | 1.64 | 24,969 | 4.28 | ||||||||
| Intercompany payable to GE(d) | 11,696 | 17,642 | ||||||||||
| Other | 229 | 1,005 | ||||||||||
| Total GE Capital short-term borrowings | 23,443 | 48,617 | ||||||||||
| Eliminations(d) | (13,212) | (18,549) | ||||||||||
| Total short-term borrowings | $ | 30,714 | $ | 49,860 | ||||||||
| Long-term borrowings | Maturities | Amount | Average Rate(a) | Amount | Average Rate(a) | |||||||
| GE | ||||||||||||
| Senior notes | 2018-2054 | $ | 54,396 | 3.35 | % | $ | 72,471 | 3.23 | % | |||
| Subordinated notes | 2021-2037 | 2,768 | 3.73 | 2,940 | 3.68 | |||||||
| Subordinated debentures(e) | 2067 | 719 | 6.12 | 6,600 | 6.14 | |||||||
| Other | 928 | 1,298 | ||||||||||
| Total GE long-term borrowings(b) | 58,810 | 83,309 | ||||||||||
| GE Capital | ||||||||||||
| Senior notes | 2018-2039 | 44,131 | 2.45 | 59,107 | 2.54 | |||||||
| Subordinated notes | 236 | 251 | - | |||||||||
| Intercompany payable to GE(d) | 47,084 | 67,062 | ||||||||||
| Other(c) | 1,992 | 2,058 | ||||||||||
| Total GE Capital long-term borrowings | 93,443 | 128,478 | ||||||||||
| Eliminations(d) | (47,173) | (67,128) | ||||||||||
| Total long-term borrowings | $ | 105,080 | $ | 144,659 | ||||||||
| Non-recourse borrowings of | ||||||||||||
| consolidated securitization entities(f) | 2017-2018 | $ | 417 | 2.23 | % | $ | 3,083 | 1.00 | % | |||
| Total borrowings | $ | 136,210 | $ | 197,602 | ||||||||
| (a) |
| (b) | Excluding assumed debt of GE Capital, the total amount of GE borrowings was $20,512 million at December 31, 2016. |
| (c) | Included $2,665 million and $2,679 million of funding secured by aircraft and other collateral at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively, of which $1,419 million and $1,534 million is non-recourse to GE Capital at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively. |
| (d) | The amount of the intercompany payable to GE was $58,780 million as of December 31, 2016, which includes a reduction in the short-term intercompany payable to GE for a $(1,329) million loan which bears the right of offset against amounts owed under the assumed debt agreement. The remaining short-term loan balance was paid in January 2017. |
| (e) | Included $719 million and $2,587 million of subordinated debentures at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively, which constitute the sole assets of trusts that have issued trust preferred securities and where GE owns 100% of the common securities of the trusts. Obligations associated with these trusts are unconditionally guaranteed by GE. |
| (f) | Included $320 million and $918 million of current portion of long-term borrowings at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively. See Note 21. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 165
On June 3, 2016, GE commenced an offering to exchange $19.6 billion of all the outstanding, unregistered senior notes that were issued by GE Capital International Funding Company Unlimited Company in a private offering on October 26, 2015, for identical, registered 2.342% Senior Notes due 2020, 3.373% Senior Notes due 2025 and 4.418% Senior Notes due 2035. The exchange offer was completed on July 8, 2016.
As discussed in Note 1, the adoption of ASU 2015-03 resulted in the reclassification of $674 million of unamortized debt issuance costs related to the Company's borrowings, of which $641 million was reclassified in long-term borrowings and $33 million was reclassified in short-term borrowings, within our consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2015.
On April 10, 2015, GE provided a full and unconditional guarantee on the payment of the principal and interest on all tradable senior and subordinated outstanding long-term debt securities and all commercial paper issued or guaranteed by GE Capital. $92,537 million of such debt was assumed by GE on December 2, 2015 upon its merger with GE Capital resulting in an intercompany payable to GE. At December 31, 2016, the amount of the intercompany payable to GE was $58,780 million, which includes a reduction in the short-term intercompany payable to GE for a $(1,329) million loan to GE which bears the right of offset against amounts owed under the assumed debt agreement. The remaining short-term loan balance was paid in January 2017. The Guarantee applies to approximately $47,476 million of GE Capital debt. Prior to the merger $35,999 million (representing $31,154 million of outstanding principal and $4,846 million of premium) of GE Capital debt was exchanged into a new GE Capital international entity, including $16,372 million, which matured on April 15, 2016.
See Notes 20 and 29 for additional information about borrowings and associated swaps.
Liquidity is affected by debt maturities and our ability to repay or refinance such debt. Long-term debt maturities over the next five years follow.
| (In millions) | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |||||||||
| GE(a) | $ | 17,109 | $ | 7,899 | $ | 3,787 | $ | 6,996 | $ | 4,708 | ||||
| GE Capital | 6,517 | (b) | 5,578 | 4,111 | 11,107 | 2,131 | ||||||||
| (a) |
| (b) | Fixed and floating rate notes of $498 million contain put options with exercise dates in 2017, and which have final maturity beyond 2021. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 166
Investment contracts, insurance liabilities and insurance annuity benefits comprise mainly obligations to annuitants and policyholders in our run-off insurance operations.
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Life insurance benefits(a) | $ | 18,741 | $ | 18,555 | |
| Investment contracts | 2,813 | 2,955 | |||
| Other(b) | 4,992 | 4,646 | |||
| 26,546 | 26,155 | ||||
| Eliminations | (460) | (463) | |||
| Total | $ | 26,086 | $ | 25,692 | |
| (a) |
| (b) | Substantially all unpaid claims and claims adjustment expenses and unearned premiums. |
When insurance affiliates cede insurance risk to third parties, such as reinsurers, they are not relieved of their primary obligation to policyholders. When losses on ceded risks give rise to claims for recovery, we establish allowances for probable losses on such receivables from reinsurers as required. Reinsurance recoverables are included in the caption "Other receivables" on our Consolidated Statement of Financial Position, and amounted to $2,038 million and $1,880 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
We recognize reinsurance recoveries as a reduction of the Consolidated Statement of Earnings caption "Investment contracts, insurance losses and insurance annuity benefits." Reinsurance recoveries were $370 million, $351 million and $228 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
ABOUT OUR PLANS
We sponsor a number of pension plans, including our two principal pension plans for certain U.S. employees as well as other affiliate pension plans. Our principal pension plans, the GE Pension Plan and the GE Supplementary Pension Plan, are discussed below. A summary of other postretirement plans is also provided.
The GE Pension Plan is a defined benefit plan that covers 238,000 retirees and beneficiaries, 168,000 vested former employees and 61,000 active employees. This plan is closed to new participants. The GE Supplementary Pension Plan is an unfunded plan that provides supplementary benefits to higher-level, longer-service employees. The GE Supplementary Pension Plan annuity benefit is closed to new participants and has been replaced by an installment benefit. We use a December 31 measurement date for these plans.
On our balance sheet, we measure our plan assets at fair value and the obligations at the present value of the estimated payments to plan participants. Participants earn benefits based on their service and pay. Those estimated payment amounts are determined based on assumptions. Differences between our actual results and what we assumed are recorded in a separate component of equity each period. These differences are amortized into earnings over the remaining average future service of active employees or the expected life of participants, as applicable, who participate in the plan.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 167
THE COST OF OUR PLANS
The amount we report in our earnings as pension cost consists of the following components:
| · | Service cost – the cost of benefits earned by active employees who participate in the plan. |
| · | Prior service cost amortization – the cost of changes to our benefits plans (plan amendments) related to prior service performed. |
| · | Expected return on plan assets – the return we expect to earn on plan investments used to pay future benefits. |
| · | Interest cost – the accrual of interest on the pension obligations due to the passage of time. |
| · | Net actuarial loss (gain) amortization – differences between our estimates, (for example, discount rate, expected return on plan assets) and our actual experience which are initially recorded in equity and amortized into earnings. |
| · | Curtailment loss – earnings effects of amounts previously deferred which have been accelerated because of an event that shortens future service or eliminates benefits (for example, a sale of a business). |
Pension cost components follow.
| COST OF PENSION PLANS | ||||||||
| Principal pension plans | ||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Service cost for benefits earned | $ | 1,237 | $ | 1,424 | $ | 1,205 | ||
| Prior service cost amortization | 303 | 205 | 214 | |||||
| Expected return on plan assets | (3,336) | (3,302) | (3,190) | |||||
| Interest cost on benefit obligations | 2,939 | 2,778 | 2,745 | |||||
| Net actuarial loss amortization | 2,449 | 3,288 | 2,565 | |||||
| Curtailment loss | 31 | 105 | 65 | |||||
| Pension cost | $ | 3,623 | $ | 4,498 | $ | 3,604 | ||
Accounting requirements necessitate the use of assumptions to reflect the uncertainties and the length of time over which the pension obligations will be paid. The actual amount of future benefit payments will depend upon when participants retire, the amount of their benefit at retirement and how long they live. To reflect the obligations in today's dollars, we discount the future payments using a rate that matches the time frame over which the payments will be made. We also need to assume a long-term rate of return that will be earned on investments used to fund these payments.
The assumptions used to measure our pension benefit obligations follow.
| ASSUMPTIONS USED TO MEASURE PENSION BENEFIT OBLIGATIONS | ||||||
| Principal pension plans | ||||||
| December 31 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||
| Discount rate | 4.11 | % | 4.38 | % | 4.02 | % |
| Compensation increases | 3.80 | 3.80 | 4.10 | |||
The discount rate used to measure the pension obligations at the end of the year is also used to measure pension cost in the following year. The assumptions used to measure pension cost follow.
| ASSUMPTIONS USED TO MEASURE PENSION COST | ||||||
| Principal pension plans | ||||||
| December 31 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||
| Discount rate | 4.38 | % | 4.02 | % | 4.85 | % |
| Expected return on assets | 7.50 | 7.50 | 7.50 | |||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 168
We evaluate these assumptions annually. We evaluate other assumptions periodically, such as retirement age, mortality and turnover, and update them as necessary to reflect our actual experience and expectations for the future.
We determine the discount rate using the weighted-average yields on high-quality fixed-income securities that have maturities consistent with the timing of benefit payments. Lower discount rates increase the size of the benefit obligation and pension expense in the following year; higher discount rates reduce the size of the benefit obligation and subsequent-year pension expense.
The expected return on plan assets is the estimated long-term rate of return that will be earned on the investments used to fund the pension obligations. To determine this rate, we consider the current and target composition of plan investments, our historical returns earned, and our expectations about the future.
The compensation assumption is used to estimate the annual rate at which pay of plan participants will grow. If the rate of growth assumed increases, the size of the pension obligations will increase, as will the amount recorded in shareowners' equity and amortized to earnings in subsequent periods.
Further information about our pension assumptions, including a sensitivity analysis of certain assumptions, can be found in the Critical Accounting Estimates – Pension Assumptions within Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (MD&A).
| FUNDED STATUS | |||||
| Principal pension plans | |||||
| December 31 (in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Projected benefit obligations | $ | 71,501 | $ | 68,722 | |
| Fair value of plan assets | 45,893 | 45,720 | |||
| Underfunded | $ | 25,608 | $ | 23,002 | |
| PROJECTED BENEFIT OBLIGATIONS (PBO) | ||||||
| Principal pension plans | ||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 68,722 | $ | 70,735 | ||
| Service cost for benefits earned | 1,237 | 1,424 | ||||
| Interest cost on benefit obligations | 2,939 | 2,778 | ||||
| Participant contributions | 115 | 155 | ||||
| Plan amendments | - | 902 | ||||
| Actuarial loss (gain) | 1,874 | (a) | (4,017) | (b) | ||
| Benefits paid | (3,386) | (3,255) | ||||
| Balance at December 31(c) | $ | 71,501 | $ | 68,722 | ||
| (b) | Principally associated with discount rate changes. |
| (c) | The PBO for the GE Supplementary Pension Plan, which is an unfunded plan, was $6,531 million and $6,099 million at year-end 2016 and 2015, respectively. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 169
THE COMPOSITION OF OUR PLAN ASSETS
The fair value of our pension plans' investments is presented below. The inputs and valuation techniques used to measure the fair value of these assets are described in Note 1 and have been applied consistently.
| Principal pension plans | |||||
| December 31 (in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Equity securities | |||||
U.S. equity securities(a) | $ | 12,130 | $ | 12,447 | |
Non-U.S. equity securities(a) | 9,029 | 9,088 | |||
| Debt securities | |||||
Fixed income and cash investment funds | 4,897 | 3,252 | |||
U.S. corporate(b) | 5,252 | 5,529 | |||
Other debt securities(c) | 5,066 | 5,131 | |||
| Private equities(a) | 4,492 | 4,885 | |||
| Real estate(a) | 3,244 | 3,186 | |||
| Other investments(d) | 1,783 | 2,202 | |||
| Total plan assets | $ | 45,893 | $ | 45,720 | |
| (b) | Primarily represented investment-grade bonds of U.S. issuers from diverse industries. |
| (c) | Primarily represented investments in residential and commercial mortgage-backed securities, non-U.S. corporate and government bonds and U.S. government, federal agency, state and municipal debt. |
(d) Substantially all represented hedge fund investments and net unsettled transaction-related investment activity.
Plan assets valued using NAV as a practical expedient amounted to $16,894 million and $15,430 million as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The percentages of plan assets valued using NAV by investment fund type for equity securities, fixed income and cash, and alternative investments were 12%, 8% and 17% as of December 31, 2016, respectively, and 10%, 7% and 17% as of December 31, 2015, respectively.
Those investments that were measured at fair value using practical expedient were excluded from the fair value hierarchy. The practical expedient was not applied for investments with a fair value of $2,504 million and $2,492 million in 2016 and 2015, respectively and those investments were classified within Level 3. The remaining investments were substantially all considered Level 1 and 2.
| FAIR VALUE OF PLAN ASSETS | |||||
| Principal pension plans | |||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 45,720 | $ | 48,280 | |
| Actual gain on plan assets | 2,892 | 307 | |||
| Employer contributions | 552 | 233 | |||
| Participant contributions | 115 | 155 | |||
| Benefits paid | (3,386) | (3,255) | |||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 45,893 | $ | 45,720 | |
Amounts included in shareowners' equity that will be amortized in future reporting periods follow.
| Principal pension plans | |||||
| December 31 (in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Prior service cost | $ | 1,138 | $ | 1,473 | |
| Net actuarial loss | 16,664 | 16,795 | |||
| Total | $ | 17,802 | $ | 18,268 | |
In 2017, we estimate that we will amortize $295 million of prior service cost and $2,840 million of net actuarial loss from shareowners' equity into pension cost. Comparable amounts amortized in 2016 were $303 million and $2,449 million, respectively.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 170
OTHER PENSION AND POSTRETIREMENT PLANS
We also administer other pension plans, including legacy plans that were part of acquisitions. Other pension plans in 2016 included 49 U.S. and non-U.S. pension plans with assets or obligations greater than $50 million. These other pension plans cover 60,000 retirees and beneficiaries, 59,000 vested former employees and 33,000 active employees. We also sponsor a number of postretirement health and life insurance benefit plans (retiree benefit plans). Principal retiree benefit plans cover approximately 187,000 retirees and dependents.
Summarized information about these plans follows.
| COST OF BENEFIT PLANS | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other pension plans | Principal retiree benefit plans | |||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||
| Benefit plan cost | $ | 374 | $ | 373 | $ | 412 | $ | 115 | $ | 174 | $ | 789 | ||||||
| FUNDED STATUS | |||||||||||
| Principal retiree | |||||||||||
| Other pension plans | benefit plans | ||||||||||
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Benefit obligations | $ | 22,543 | $ | 21,618 | $ | 6,289 | $ | 6,757 | |||
| Fair value of plan assets | 17,091 | 17,368 | 575 | 695 | |||||||
| Underfunded | $ | 5,452 | $ | 4,250 | $ | 5,714 | $ | 6,062 | |||
Amounts included in shareowners' equity that will be amortized in future reporting periods follow.
| Principal retiree | |||||||||||
| Other pension plans | benefit plans | ||||||||||
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Prior service credit | $ | (88) | $ | (29) | $ | (2,975) | $ | (3,132) | |||
| Net actuarial loss (gain) | 4,800 | 3,080 | (682) | (464) | |||||||
| Total | $ | 4,712 | $ | 3,051 | $ | (3,657) | $ | (3,596) | |||
In 2017, we estimate that we will amortize $5 million of prior service credit and $520 million of net actuarial loss for the other pension plans from shareowners' equity into pension cost. For principal retiree benefit plans, the estimated prior service credit and net actuarial gain to be amortized in 2017 will be $170 million and $80 million, respectively. Comparable amounts amortized in 2016, respectively, were $1 million of prior service credit and $256 million of net actuarial loss for the other pension plans and $164 million of prior service credit and $50 million of net actuarial gain for the principal retiree benefit plans.
OUR FUNDING POLICY
Our policy for funding the GE Pension Plan is to contribute amounts sufficient to meet minimum funding requirements under employee benefit and tax laws. We may decide to contribute additional amounts beyond this level. We made a contribution of $330 million to the GE Pension Plan in 2016. We did not make any contributions to the GE Pension Plan in 2015. We expect to contribute approximately $1,720 million to the GE Pension Plan in 2017.
We expect to pay approximately $250 million for benefit payments under our GE Supplementary Pension Plan and administrative expenses of our principal pension plans and expect to contribute approximately $910 million to other pension plans in 2017. In 2016, comparative amounts were $222 million and $795 million, respectively.
We fund retiree health benefits on a pay-as-you-go basis and the retiree life insurance trust at our discretion. We expect to contribute approximately $460 million in 2017 to fund such benefits. In 2016, we contributed $410 million for these plans.
See Note 29 for further information about our pension plans and principal retiree benefit plans.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 171
This caption includes liabilities for various items including deferred income, interest on tax liabilities, unrecognized tax benefits, environmental remediation, legal reserves, asset retirement obligations, derivative instruments, product warranties and a variety of sundry items.
See Note 14 for further information on interest on tax liabilities and unrecognized tax benefits. See Notes 20 and 29 for further information on derivative instruments. See Note 23 for further information on environmental matters, legal reserves and product warranties.
GE and GE Capital file a consolidated U.S. federal income tax return. This enables GE and GE Capital to use tax deductions and credits of one member of the group to reduce the tax that otherwise would have been payable by another member of the group. The effective tax rate reflects the benefit of these tax reductions in the consolidated return. GE makes cash payments to GE Capital for tax reductions and GE Capital pays for tax increases at the time GE's tax payments are due.
Our businesses are subject to regulation under a wide variety of U.S. federal, state and foreign tax laws, regulations and policies. Changes to these laws or regulations may affect our tax liability, return on investments and business operations.
In conjunction with the GE Capital Exit Plan, GE Capital significantly reduced its non-U.S. assets while continuing to operate appropriately capitalized non-U.S. businesses with substantial assets related to GE Capital's vertical financing businesses, including Energy Financial Services, GECAS and Healthcare Equipment Finance. As a result of the GE Capital Exit Plan, GE Capital recognized a tax expense of $6,327 million in continuing operations during 2015. This primarily consisted of $3,548 million of tax expense related to the repatriation of excess foreign cash and the write-off of deferred tax assets of $2,779 million that will no longer be supported under this plan.
The repatriation of cash included approximately $10 billion of foreign earnings that, prior to the approval of the GE Capital Exit Plan, were indefinitely reinvested in GE Capital's international operations. GE Capital's indefinitely reinvested earnings were also reduced by charges recognized in connection with the disposition of international assets. The remainder of the indefinitely reinvested earnings will continue to be reinvested in the significant international base of assets that will remain after the GE Capital Exit Plan is fully executed. The write-off of deferred tax assets largely related to our Treasury operations in Ireland where it was no longer apparent that the tax benefits would be realized upon implementation of the GE Capital Exit Plan. These charges, which increased the 2015 Consolidated effective tax rate by 77.3 percentage points, are reported in the lines "Tax on global activities including exports", and "All other-net" in the Reconciliation of U.S. federal statutory income tax rate to actual income tax rate."
| (BENEFIT) PROVISION FOR INCOME TAXES | ||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| GE | ||||||||
| Current tax expense (benefit) | $ | (140) | $ | 3,307 | $ | 2,110 | ||
| Deferred tax expense (benefit) from temporary differences | 1,107 | (1,800) | (476) | |||||
| 967 | 1,506 | 1,634 | ||||||
| GE Capital | ||||||||
| Current tax expense (benefit) | (1,138) | 2,796 | (455) | |||||
| Deferred tax expense (benefit) from temporary differences | (293) | 2,183 | (406) | |||||
| (1,431) | 4,979 | (861) | ||||||
| Consolidated | ||||||||
| Current tax expense (benefit) | (1,278) | 6,103 | 1,655 | |||||
| Deferred tax expense (benefit) from temporary differences | 814 | 383 | (882) | |||||
| Total | $ | (464) | $ | 6,485 | $ | 773 | ||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 172
| CONSOLIDATED EARNINGS (LOSS) FROM CONTINUING OPERATIONS BEFORE INCOME TAXES | ||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| U.S. earnings | $ | 2,145 | $ | (309) | $ | 3,176 | ||
| Non-U.S. earnings | 6,885 | 8,495 | 7,087 | |||||
| Total | $ | 9,030 | $ | 8,186 | $ | 10,263 | ||
| CONSOLIDATED (BENEFIT) PROVISION FOR INCOME TAXES | |||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
| U.S. Federal | |||||||||
| Current | $ | (2,646) | $ | 1,549 | $ | (122) | |||
| Deferred | (754) | 492 | 261 | ||||||
| Non - U.S. | |||||||||
| Current | 1,730 | 4,867 | 2,035 | ||||||
| Deferred | 1,239 | (121) | (982) | ||||||
| Other | (33) | (302) | (419) | ||||||
| Total | $ | (464) | $ | 6,485 | $ | 773 | |||
| RECONCILIATION OF U.S. FEDERAL STATUTORY INCOME TAX RATE TO ACTUAL INCOME TAX RATE | ||||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated | GE | GE Capital | ||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| U.S. federal statutory income tax rate | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % |
| Increase (reduction) in rate resulting from | ||||||||||||||||||
| inclusion of after-tax earnings of GE Capital in | ||||||||||||||||||
| before-tax earnings of GE | - | - | - | 4.5 | 82.4 | (4.8) | - | - | - | |||||||||
| Tax on global activities including exports | (23.7) | 54.1 | (17.7) | (20.8) | (52.8) | (12.0) | 4.9 | (224.5) | (72.0) | |||||||||
| U.S. business credits(a) | (4.5) | (4.7) | (3.3) | (0.9) | (4.1) | (1.0) | 15.7 | 9.2 | (34.5) | |||||||||
All other – net(b) | (11.9) | (5.2) | (6.5) | (7.9) | (14.2) | (2.5) | 14.7 | (1.5) | (55.9) | |||||||||
| (40.1) | 44.2 | (27.5) | (25.1) | 11.3 | (20.3) | 35.3 | (216.8) | (162.4) | ||||||||||
| Actual income tax rate | (5.1) | % | 79.2 | % | 7.5 | % | 9.9 | % | 46.3 | % | 14.7 | % | 70.3 | % | (181.8) | % | (127.4) | % |
| (a) |
| (b) | Included (7.7)% and (7.1)% in consolidated and GE, respectively, related to deductible stock losses in 2016. Included (4.2)% and (10.6)% in consolidated and GE, respectively, related to deductible stock losses in 2015. Also includes, for each period, the expense or (benefit) for "Other" taxes reported above in the consolidated (benefit) provision for income taxes, net of 35% federal effect. |
Annually, we file over 6,000 income tax returns in over 300 global taxing jurisdictions. We are under examination or engaged in tax litigation in many of these jurisdictions. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is currently auditing our consolidated U.S. income tax returns for 2012-2013. In addition, certain other U.S. tax deficiency issues and refund claims for previous years are still unresolved. It is reasonably possible that a portion of the unresolved items could be resolved during the next 12 months, which could result in a decrease in our balance of "unrecognized tax benefits" – that is, the aggregate tax effect of differences between tax return positions and the benefits recognized in our financial statements. The IRS had disallowed the tax loss on our 2003 disposition of ERC Life Reinsurance Corporation. We contested the disallowance of this loss. In August 2016, the government approved a final settlement of the case and the balance of unrecognized tax benefits and associated interest was adjusted to reflect the agreed settlement. During 2015, the IRS completed the audit of our consolidated U.S. income tax returns for 2010-2011, except for certain issues that were completed in 2016. We believe that there are no other jurisdictions in which the outcome of unresolved issues or claims is likely to be material to our results of operations, financial position or cash flows. We further believe that we have made adequate provision for all income tax uncertainties. Resolution of audit matters, including the IRS audit of our consolidated U.S. income tax returns for 2010-2011 and the resolution of the ERC Life Reinsurance Corporation case, reduced our 2016 consolidated income tax rate by 5.3 percentage points. Resolution of audit matters, including the IRS audit of our consolidated U.S. income tax returns for 2010-2011, reduced our 2015 consolidated income tax rate by 4.4 percentage points.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 173
The balance of unrecognized tax benefits, the amount of related interest and penalties we have provided and what we believe to be the range of reasonably possible changes in the next 12 months were:
| UNRECOGNIZED TAX BENEFITS | |||||
| December 31, (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Unrecognized tax benefits | $ | 4,692 | $ | 6,778 | |
| Portion that, if recognized, would reduce tax expense and effective tax rate(a) | 2,886 | 4,723 | |||
| Accrued interest on unrecognized tax benefits | 615 | 805 | |||
| Accrued penalties on unrecognized tax benefits | 118 | 98 | |||
| Reasonably possible reduction to the balance of unrecognized tax benefits | |||||
| in succeeding 12 months | 0-600 | 0-700 | |||
| Portion that, if recognized, would reduce tax expense and effective tax rate(a) | 0-500 | 0-200 | |||
| UNRECOGNIZED TAX BENEFITS RECONCILIATION | |||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 6,778 | $ | 5,619 | |
| Additions for tax positions of the current year | 248 | 720 | |||
| Additions for tax positions of prior years(a) | 521 | 1,296 | |||
| Reductions for tax positions of prior years | (2,016) | (754) | |||
| Settlements with tax authorities | (823) | (70) | |||
| Expiration of the statute of limitations | (16) | (33) | |||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 4,692 | $ | 6,778 | |
We classify interest on tax deficiencies as interest expense; we classify income tax penalties as provision for income taxes. For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, $(105) million, $48 million and $(68) million of interest expense (income), respectively, and $(4) million, $(4) million and (45) of tax expense (income) related to penalties, respectively, were recognized in the Statement of Earnings.
Deferred income tax balances reflect the effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities and their tax bases, as well as from net operating loss and tax credit carryforwards, and are stated at enacted tax rates expected to be in effect when taxes are actually paid or recovered. Deferred income tax assets represent amounts available to reduce income taxes payable on taxable income in future years. We evaluate the recoverability of these future tax deductions and credits by assessing the adequacy of future expected taxable income from all sources, including reversal of taxable temporary differences, forecasted operating earnings and available tax planning strategies. To the extent we do not consider it more likely than not that a deferred tax asset will be recovered, a valuation allowance is established.
We have not provided U.S. deferred taxes on cumulative earnings of non-U.S. affiliates and associated companies that have been reinvested indefinitely. These earnings relate to ongoing operations and, at December 31, 2016 and 2015, were approximately $82 billion and $104 billion, respectively. Most of these earnings have been reinvested in active non-U.S. business operations and we do not intend to repatriate these earnings to fund U.S. operations. Because of the availability of U.S. foreign tax credits, it is not practicable to determine the U.S. federal income tax liability that would be payable if such earnings were not reinvested indefinitely. Deferred taxes are provided for earnings of non-U.S. affiliates and associated companies when we plan to remit those earnings.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 174
Aggregated deferred income tax amounts are summarized below.
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Assets | |||||
| GE | $ | 21,106 | $ | 20,539 | |
| GE Capital | 5,093 | 4,643 | |||
| 26,199 | 25,182 | ||||
| Liabilities | |||||
| GE | (14,440) | (12,873) | |||
| GE Capital | (9,926) | (9,204) | |||
| (24,366) | (22,077) | ||||
| Net deferred income tax asset (liability) | $ | 1,833 | $ | 3,105 | |
| COMPONENTS OF THE NET DEFERRED INCOME TAX ASSET (LIABILITY) | |||||
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| GE | |||||
| Principal pension plans | $ | 8,963 | $ | 8,051 | |
| Other non-current compensation and benefits | 4,230 | 4,133 | |||
| Provision for expenses | 2,633 | 2,827 | |||
| Retiree insurance plans | 2,000 | 2,122 | |||
| Non-U.S. loss carryforwards(a) | 1,444 | 1,940 | |||
| Contract assets | (6,677) | (5,143) | |||
| Intangible assets | (2,962) | (3,192) | |||
| Depreciation | (1,755) | (1,688) | |||
| Investment in global subsidiaries | (899) | (915) | |||
| Other – net | (311) | (469) | |||
| 6,666 | 7,666 | ||||
| GE Capital | |||||
| Operating leases | (3,582) | (3,863) | |||
| Financing leases | (1,632) | (1,665) | |||
| Energy investments | (1,410) | (1,276) | |||
| Investment in global subsidiaries | (343) | 5 | |||
| Intangible assets | (125) | (103) | |||
| Non-U.S. loss carryforwards(a) | 1,323 | 2,262 | |||
| Other – net | 936 | 79 | |||
| (4,833) | (4,561) | ||||
| Net deferred income tax asset (liability) | $ | 1,833 | $ | 3,105 | |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 175
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Preferred stock issued | $ | 6 | $ | 6 | $ | - | ||
| Common stock issued | $ | 702 | $ | 702 | $ | 702 | ||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | ||||||||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | (16,529) | $ | (18,172) | $ | (9,119) | ||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | (4,602) | (3,312) | (12,088) | |||||
| Reclassifications from other comprehensive income | 2,533 | 4,956 | 3,035 | |||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net, attributable to GE | (2,069) | 1,644 | (9,053) | |||||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | (18,598) | $ | (16,529) | $ | (18,172) | ||
| Other capital | ||||||||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 37,613 | $ | 32,889 | $ | 32,494 | ||
| Gains (losses) on treasury stock dispositions and other(a)(b) | (389) | 4,724 | 396 | |||||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 37,224 | $ | 37,613 | $ | 32,889 | ||
| Retained earnings | ||||||||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 140,020 | $ | 155,333 | $ | 149,051 | ||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to the Company | 8,831 | (6,126) | 15,233 | |||||
| Dividends and other transactions with shareowners | (9,054) | (9,161) | (8,948) | |||||
| Redemption value adjustment on redeemable noncontrolling interests | (266) | (25) | (2) | |||||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 139,532 | $ | 140,020 | $ | 155,333 | ||
| Common stock held in treasury | ||||||||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | (63,539) | $ | (42,593) | $ | (42,561) | ||
| Purchases(c)(d) | (22,073) | (23,762) | (1,950) | |||||
| Dispositions | 2,574 | 2,816 | 1,917 | |||||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | (83,038) | $ | (63,539) | $ | (42,593) | ||
| Total equity | ||||||||
| GE shareowners' equity balance at December 31 | $ | 75,828 | $ | 98,274 | $ | 128,159 | ||
| Noncontrolling interests balance at December 31 | 1,663 | 1,864 | 8,674 | |||||
| Total equity balance at December 31 | $ | 77,491 | $ | 100,138 | $ | 136,833 | ||
| (a) |
| (b) | Included $4,949 million related to issuance of new preferred stock in exchange for existing GE Capital preferred stock in 2015. |
| (c) | Included $(20,383) million related to the split-off of Synchrony Financial from GE, where GE shares were exchanged for shares of Synchrony Financial in 2015. |
| (d) | Included $(11,370) million of GE shares purchased under accelerated share repurchase (ASR) agreements in 2016. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 176
SHARES OF GE PREFERRED STOCK
At December 31, 2014, GECC had outstanding 50,000 shares of non-cumulative A, B and C Series perpetual preferred stock at an average dividend rate of 6.44% with a face value of $5,000 million. In connection with the GE Capital Exit Plan, on December 3, 2015, these shares were converted into a corresponding Series A, B, and C of fixed-to-floating rate non-cumulative perpetual preferred stock issued by GE with face value of $2,778 million, $2,073 million, and $1,094 million, respectively, for a cumulative face value of $5,944 million and an initial average fixed dividend rate of 4.07%. The incremental shares were issued in order to compensate preferred holders for the lower dividend rate. Subsequent to the issuance of the preferred stock on December 3, 2015, in response to investor feedback, GE launched an exchange offer on December 18, 2015 that allowed GE preferred stock investors to exchange their existing Series A, B and C preferred stock into a Series D GE preferred stock. These Series D instruments bear an initial fixed interest rate of 5.00% through January 21, 2021, will bear a floating rate equal to three-month LIBOR plus 3.33% thereafter and are callable on January 21, 2021. On January 20, 2016, $2,687 million of Series A, $2,008 million of Series B and $999 million of Series C were exchanged into $5,694 million Series D GE preferred stock. In addition to interim dividends and accretion of $129 million, a deemed dividend of $232 million was recorded in the year ended December 31, 2016. The deemed dividend included $195 million for the amount by which the fair value of the Series D GE preferred stock exceeded the fair value of the original GECC Series A, B and C preferred stock, and a cash payment of $37 million to the GE Series A and B preferred stockholders who exchanged into the Series D GE preferred stock. Post exchange, $91 million of Series A, $64 million of Series B and $95 million of Series C GE preferred stock remain outstanding. The carrying value of the GE preferred stock at December 31, 2016 was $5,283 million and will increase to $5,944 million through periodic accretion to the respective call dates of each series. Principal and accretion for the preferred stock is recorded in other capital in the consolidated Statement of Financial Position and dividends and accretion are presented under the caption "Preferred stock dividends" in the Statement of Earnings (Loss). Dividends on GE preferred stock are payable semi-annually, in June and December and accretion is recorded on a quarterly basis.
In conjunction with the exchange of the GE Capital preferred stock into GE preferred stock and the exchange of Series A, B and C preferred stock into Series D preferred stock, GE Capital issued preferred stock to GE for which the amount and terms mirror the GE preferred stock held by external investors ($5,283 million carrying value at December 31, 2016).
GE has 50.0 million authorized shares of preferred stock ($1.00 par value). 5,944,250 shares were issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. No shares were issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2014.
SHARES OF GE COMMON STOCK
On April 10, 2015, the GE Board has authorized a new repurchase program of up to $50.0 billion in common stock, excluding the Synchrony Financial exchange we completed in 2015. Under our share purchase programs, on a book basis, we repurchased shares of 725.8 million, 109.8 million and 73.6 million for a total of $22,005 million, $3,320 million and $1,901 million for the years ended 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively. During 2016, we repurchased $11,370 million of our common stock under the accelerated share repurchase (ASR) agreements.
In December 2016, we entered into an ASR agreement with a financial institution which allowed us to repurchase GE common stock at a price below its volume weighted-average price during a given period. During the fourth quarter, we paid $2,200 million and received and classified as treasury shares an initial delivery of 59,177,215 shares based on then-current market prices. The payment was recorded as a reduction to shareowners' equity, consisting of a $1,870 million increase in treasury stock, which reflects the value of the shares received upon initial delivery, and a $330 million decrease in other capital, which reflects the value of the stock held back pending final delivery.
We accounted for the ASR as two separate transactions: (i) 59,177,215 shares of common stock initially delivered to GE and $1,870 million was accounted for as a treasury stock transaction and (ii) the unsettled contract of $330 million was determined to be a forward contract indexed to GE's own common stock. The initial delivery of 59,177,215 shares resulted in an immediate reduction of the outstanding shares used to calculate the weighted-average common shares outstanding for basic and diluted earnings per share. GE has determined that the forward contract, indexed to its own common stock, met all the criteria for equity classification.
In the first quarter of 2017, we received the remaining 10,773,050 shares based on the final volume weighted-average price less the negotiated discount.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 177
On November 17, 2015, we completed the split-off of Synchrony Financial through which we acquired 671,366,809 shares of GE common stock from our shareholders in exchange for 705,270,833 shares of Synchrony Financial stock we held.
GE's authorized common stock consists of 13,200,000,000 shares having a par value of $0.06 each.
Common shares issued and outstanding are summarized in the following table.
| December 31 (In thousands) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||
| Issued | 11,693,841 | 11,693,841 | 11,693,841 | |||
| In treasury(a)(b) | (2,951,227) | (2,314,553) | (1,636,461) | |||
| Outstanding | 8,742,614 | 9,379,288 | 10,057,380 | |||
| (a) |
| (b) | Included (370,824) thousand GE shares purchased under accelerated share repurchase agreements in 2016. |
| ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) | ||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Investment securities | ||||||||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 460 | $ | 1,013 | $ | 307 | ||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) (OCI) before reclassifications – | ||||||||
| net of deferred taxes of $84, $(270) and $352(a) | 170 | (486) | 562 | |||||
| Reclassifications from OCI – net of deferred taxes of $30, $(36) and $85 | 34 | (67) | 146 | |||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss)(b) | 203 | (553) | 708 | |||||
| Less OCI attributable to noncontrolling interests | (11) | (1) | 2 | |||||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 674 | $ | 460 | $ | 1,013 | ||
| Currency translation adjustments (CTA) | ||||||||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | (5,499) | $ | (2,428) | $ | 283 | ||
| OCI before reclassifications – net of deferred taxes of $719, $1,348 and $(129) | (1,606) | (4,932) | (2,600) | |||||
| Reclassifications from OCI – net of deferred taxes of $241, $(1,489) and $213 | 294 | 1,794 | (129) | |||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss)(b) | (1,311) | (3,137) | (2,730) | |||||
| Less OCI attributable to noncontrolling interests | 6 | (66) | (19) | |||||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | (6,816) | $ | (5,499) | $ | (2,428) | ||
| Cash flow hedges | ||||||||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | (80) | $ | (180) | $ | (414) | ||
| OCI before reclassifications – net of deferred taxes of $(41), $(21) and $22 | (234) | (732) | (609) | |||||
| Reclassifications from OCI – net of deferred taxes of $37, $86 and $34 | 327 | 831 | 844 | |||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss)(b) | 93 | 99 | 234 | |||||
| Less OCI attributable to noncontrolling interests | - | - | - | |||||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 12 | $ | (80) | $ | (180) | ||
| Benefit plans | ||||||||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | (11,410) | $ | (16,578) | $ | (9,296) | ||
| Prior service credit (costs) - net of deferred taxes of $46, $859 and $219 | 128 | 1,541 | 396 | |||||
| Net actuarial gain (loss) – net of deferred taxes of $(1,062), $647 and $(5,332) | (3,074) | 1,227 | (9,849) | |||||
| Net curtailment/settlement - net of deferred taxes of $12, $(42) and $41 | 19 | (76) | 72 | |||||
| Prior service cost amortization – net of deferred taxes of $84, $103 and $241 | 62 | 100 | 349 | |||||
| Net actuarial loss amortization – net of deferred taxes of $870, $1,199 and $859 | 1,797 | 2,373 | 1,753 | |||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss)(b) | (1,068) | 5,165 | (7,278) | |||||
| Less OCI attributable to noncontrolling interests | (9) | (3) | 3 | |||||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | (12,469) | $ | (11,410) | $ | (16,578) | ||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) at December 31 | $ | (18,598) | $ | (16,529) | $ | (18,172) | ||
| (a) | Included adjustments of $57 million, $(611) million and $960 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, to deferred acquisition costs, present value of future profits, and investment contracts, insurance liabilities and insurance annuity benefits in our run-off insurance operations to reflect the effects that would have been recognized had the related unrealized investment securities holding gains and losses actually been realized. |
| (b) | Total other comprehensive income (loss) was $(2,083) million, $1,575 million and $(9,066) million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 178
| RECLASSIFICATION OUT OF AOCI | ||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | Statement of earnings caption | ||||||
| Available-for-sale securities | ||||||||||
| Realized gains (losses) on | ||||||||||
| sale/impairment of securities | $ | (63) | $ | 103 | $ | (231) | Total revenues and other income(a) | |||
| Income taxes | 30 | (36) | 85 | Benefit (provision) for income taxes(b) | ||||||
| Net of tax | $ | (34) | $ | 67 | $ | (146) | ||||
| Currency translation adjustments | ||||||||||
| Gains (losses) on dispositions | $ | (535) | $ | (305) | $ | (85) | Total revenues and other income(c) | |||
| Income taxes | 241 | (1,489) | 213 | Benefit (provision) for income taxes(d) | ||||||
| Net of tax | $ | (294) | $ | (1,794) | $ | 129 | ||||
| Cash flow hedges | ||||||||||
Gains (losses) on interest rate derivatives | $ | (79) | $ | (130) | $ | (234) | Interest and other financial charges | |||
| Foreign exchange contracts | (247) | (801) | (666) | (e) | ||||||
| Other | (38) | 13 | 22 | (f) | ||||||
| Total before tax | (364) | (918) | (878) | |||||||
| Income taxes | 37 | 86 | 34 | Benefit (provision) for income taxes | ||||||
| Net of tax | $ | (327) | $ | (831) | $ | (844) | ||||
| Benefit plan items | ||||||||||
| Curtailment gain (loss) | $ | (31) | $ | 118 | $ | (113) | (g) | |||
| Amortization of prior service costs | (146) | (203) | (590) | (g) | ||||||
| Amortization of actuarial gains (losses) | (2,667) | (3,572) | (2,612) | (g) | ||||||
| Total before tax | (2,844) | (3,657) | (3,315) | |||||||
| Income taxes | 966 | 1,260 | 1,141 | Benefit (provision) for income taxes | ||||||
| Net of tax | $ | (1,878) | $ | (2,397) | $ | (2,174) | ||||
| Total reclassification adjustments (net of tax) | $ | (2,533) | $ | (4,956) | $ | (3,035) | ||||
| (a) |
| (b) | Included $32 million, $(30) million and $3 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, in earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes. |
| (c) | Included $(453) million, $(224) million and $(51) million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, in earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes. |
| (d) |
| (e) | Included $(182) million, $(758) million and $(607) million in GE Capital revenues from services and $(65) million, $(43) million and $(59) million in interest and other financial charges in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. |
| (f) | Primarily recorded in costs and expenses. |
| (g) | Curtailment gain (loss), amortization of prior service costs and actuarial gains and losses reclassified out of AOCI are included in the computation of net periodic pension costs. See Notes 12 and 29 for further information. |
Noncontrolling interests in equity of consolidated affiliates includes common shares in consolidated affiliates and preferred stock issued by our affiliates.
Prior to the fourth quarter of 2015, the preferred stock issued by GECC was classified as noncontrolling interests in our consolidated Statement of Financial Position, with dividends presented as noncontrolling interest in our consolidated Statement of Earnings. As discussed previously in this note, this preferred stock was converted to a corresponding series of preferred stock issued by GE and on January 20, 2016 a substantial majority of those shares were exchanged into GE Series D preferred stock. Effective with these changes, the preferred stock issued by GE is reflected in our shareowners' equity and dividends are presented as a reduction of net earnings attributable to GE in the statement of earnings (under the caption "Preferred stock dividends") for the year ended December 31, 2015 and subsequently.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 179
| CHANGES TO NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS | ||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 1,864 | $ | 8,674 | $ | 6,217 | ||
| Net earnings (loss) | (46) | 377 | 183 | |||||
| GECC preferred stock(a) | - | (4,949) | - | |||||
| GECC preferred stock dividend | - | (311) | (322) | |||||
| Dividends | (72) | (43) | (74) | |||||
| Dispositions | (232) | 189 | (81) | |||||
| Synchrony Financial(b) | - | (2,840) | 2,393 | |||||
| Other (including AOCI)(c)(d)(e)(f) | 150 | 767 | 358 | |||||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 1,663 | $ | 1,864 | $ | 8,674 | ||
| (b) | Related to the split-off of Synchrony Financial from GE in 2015, where GE shares were exchanged for shares of Synchrony Financial; related to the Synchrony Financial IPO in 2014. |
| (c) | Included $695 million related to the Alstom acquisition in 2015. |
| (d) | Included $155 million related to Arcam AB acquisition in our Aviation segment in 2016. |
| (e) | Included $(123) million for deconsolidation of investment funds managed by GE Asset Management (GEAM) upon the adoption of ASU 2015-2, Amendments to the Consolidation Analysis in 2016. See Note 1. |
| (f) | Includes research & development partner funding arrangements, acquisitions and eliminations. |
REDEEMABLE NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS
Redeemable noncontrolling interest presented in our Statement of Financial Position includes common shares issued by our affiliates that are redeemable at the option of the holder of those interests.
As part of the Alstom acquisition, we formed three joint ventures in which the noncontrolling interests hold certain redemption rights. These joint ventures and the associated redemption rights are discussed in Note 8. Our retained earnings will be adjusted for subsequent changes in the redemption value of the noncontrolling interest in these entities to the extent that the redemption value exceeds the carrying amount of the noncontrolling interest.
| CHANGES TO REDEEMABLE NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS | ||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 2,972 | $ | 98 | $ | 178 | ||
| Net (loss) | (244) | (46) | (71) | |||||
| Dividends | (17) | (11) | (12) | |||||
| Redemption value adjustment | 266 | 25 | 2 | |||||
| Other(a)(b) | 49 | 2,906 | 1 | |||||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 3,025 | $ | 2,972 | $ | 98 | ||
| (a) | Included $2,875 million related to joint ventures formed by GE and Alstom as part of the Alstom acquisition in 2015. |
| (b) | Included $204 million related to the Concept Laser GmbH acquisition in our Aviation segment in 2016. |
OTHER
Common dividends from GE Capital to GE totaled $20,118 million, $4,311 million and $3,000 million for the years ended 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Dividends on GE preferred stock totaled $656 million and $18 million, including cash dividends of $332 million and $8 million for the years ended 2016 and 2015, respectively. There were no dividends on GE preferred stock in 2014.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 180
SHARE-BASED COMPENSATION
We grant stock options, restricted stock units and performance share units to employees under the 2007 Long-Term Incentive Plan. Grants made under all plans must be approved by the Management Development and Compensation Committee of GE's Board of Directors, which is composed entirely of independent directors.
STOCK OPTIONS
Under our stock option program, an employee receives an award that provides the opportunity in the future to purchase GE shares at the market price of our stock on the date the award is granted (the strike price). The options become exercisable in equal amounts over a five-year vesting period and expire 10 years from the grant date if they are not exercised. Stock options have no financial statement effect on the date they are granted but rather are reflected over time through recording compensation expense and increasing shareowners' equity. We record compensation expense based on the estimated fair value of the awards expected to vest, and that amount is amortized as compensation expense on a straight-line basis over the five-year vesting period. Accordingly, total expense related to the award is reduced by the fair value of options that are expected to be forfeited by employees that leave GE prior to vesting. We estimate forfeitures based on our experience and adjust the expense to reflect actual forfeitures over the vesting period. The offset to the expense we record is reflected as an increase in the "Other capital" component of shareowners' equity.
| (In millions, after tax) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Compensation expense | $ | 207 | $ | 234 | $ | 215 | ||
We estimate the fair value of each stock option award on the date of grant using a Black-Scholes option pricing model. The table below provides the weighted-average grant-date fair values, key assumptions and other inputs into the pricing model. With the exception of the dividend yield assumption, an increase in any individual assumption will increase the estimated fair value of the option, all other things being equal.
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Weighted-average grant-date fair value of stock options | $ | 3.61 | $ | 4.64 | $ | 5.26 | |||
| Stock Option Valuation Assumptions: | |||||||||
| Risk-free interest rate | 1.4 | % | 2.0 | % | 2.3 | % | |||
| Dividend yield | 3.4 | % | 3.4 | % | 3.1 | % | |||
| Expected volatility | 20.0 | % | 25.0 | % | 26.0 | % | |||
| Expected option life (in years) | 6.5 | 6.8 | 7.3 | ||||||
| Other pricing model inputs: | |||||||||
| Weighted-average grant-date market price of GE stock (strike price) | $ | 29.63 | $ | 25.79 | $ | 26.11 | |||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 181
The table below shows the amount and weighted-average strike price of options granted during 2016, as well as those outstanding and exercisable at year-end 2016.
| As of December 31, 2016 unless, otherwise stated (in thousands, except per-share data) | ||
| Stock options granted during 2016 | 30,948 | |
| Weighted-average strike price of awards granted in 2016 | $ | 29.63 |
| Stock options outstanding | 420,303 | |
| Weighted-average strike price of stock options outstanding | $ | 22.29 |
| Stock options exercisable | 301,952 | |
| Weighted-average strike price of stock options exercisable | $ | 20.73 |
When an employee exercises an option, we issue treasury shares to satisfy the requirements of the option.
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Stock options exercised (in thousands) | 56,973 | 65,764 | 30,433 | ||||||
| Cash received from stock options exercised (in millions) | $ | 1,037 | $ | 1,098 | $ | 439 | |||
Outstanding stock option awards may be dilutive to earnings per share when they are in the money (the market price of GE stock is greater than the strike price of the option). When an option is dilutive, it increases the number of shares used in the diluted earnings per share calculation, which will decrease earnings per share. However, the effect stock options have on the number of shares added to the diluted earnings per share calculation is not one-for-one. The average amount of unrecognized compensation expense (the portion of the fair value of these option awards not yet amortized) and the market price of GE stock during the reporting period affect how many of these potential shares are included in the calculation. The calculation assumes that the proceeds received from the exercise and the unrecognized compensation expense are used to buy back shares, which reduces the dilutive impact.
As of December 31, 2016, there was $427 million of unrecognized compensation expense related to unvested options, which will be amortized over the remaining vesting period (the weighted-average period is approximately 2 years). Of that total, approximately $118 million, after tax, is estimated to be recorded as compensation expense in 2017.
The dilutive effect of in-the-money options on our earnings per share from continuing operations has been $0.01 or less per share (1% or less) for the last three years. See Note 18 for additional information about earnings per share.
RESTRICTED STOCK
A restricted stock award provides an employee with the right to receive shares of GE stock when the restrictions lapse, which occurs in equal amounts over the vesting period. Upon vesting, each unit of restricted stock is converted into GE common stock on a one-for-one basis using treasury stock shares. The expense to be recognized on a restricted stock unit is based upon the market price on the grant date (which is its fair value) multiplied by the number of units expected to vest. Accordingly, total expense related to the award is reduced by the fair value of restricted stock units that are expected to be forfeited by employees that leave GE prior to lapse of the restrictions. That amount is amortized as compensation expense on a straight-line basis over a five-year vesting period. We estimate forfeitures based on our experience and adjust the expense to reflect actual forfeitures over the vesting period. The offset to compensation expense is an increase in the "Other capital" component of shareowners' equity.
| (In millions, after tax) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Compensation expense(a) | $ | 90 | $ | 72 | $ | 56 | ||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 182
The fair value of a restricted stock unit at the grant date is equal to the market price of our stock on the grant date.
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Weighted-average grant-date fair value of restricted stock awards | $ | 30.20 | $ | 26.74 | $ | 26.08 | |||
| As of December 31, 2016, unless otherwise stated (in thousands, except per-share data) | ||
| Restricted stock units granted during 2016 | 8,933 | |
| Non-vested restricted stock units outstanding | 17,859 | |
| Weighted-average fair value at grant date of non-vested stock | $ | 27.72 |
| (In thousands) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Restricted stock units vested during the year ended | 4,427 | 3,899 | 3,305 | |||||
As of December 31, 2016, there was $346 million of total unrecognized compensation expense related to unvested restricted stock units, which will be amortized over the remaining vesting period (the weighted-average period is approximately 2 years). Of that total, approximately $75 million, after tax, is estimated to be recorded as compensation expense in 2017.
OTHER INFORMATION
When options are exercised and restricted stock units vest, we issue shares from treasury stock, which increases shares outstanding. The "Other capital" component of shareowners' equity is adjusted for differences between the strike price of GE stock and the average cost of our treasury stock. We also record the difference between the tax benefits assumed (based on the fair value of the award on the grant date) and the actual tax benefit in our provision for income taxes. Any excess tax benefit is recorded as cash flows from operating activities in our Statement of Cash Flows. The table below provides information about tax benefits related to all share-based compensation arrangements.
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
| Income tax benefit recognized in earnings | $ | 274 | $ | 148 | $ | 147 | |||
| Excess of actual tax deductions over amounts assumed recognized in equity(a) | - | 167 | 86 | ||||||
Share-based compensation programs serve as a means to attract and retain talented employees and are an important element of their total compensation. The intrinsic value of a stock option award is the amount by which the award is in the money and represents the potential value to the employee upon exercise of the option. The intrinsic value of restricted stock units is the value of the shares awarded at the current market price. The table below provides information about the intrinsic value of option and restricted stock awards.
| Aggregate | |||
| intrinsic | |||
| As of December 31, 2016, unless otherwise stated (in millions) | value | ||
| Stock options outstanding | $ | 3,984 | |
| Stock options exercised in 2016 | 723 | ||
| Non-vested restricted stock units outstanding | 564 | ||
| Restricted stock units vested in 2016 | 137 | ||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 183
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| GE | ||||||||
| Purchases and sales of business interests(a) | $ | 3,701 | $ | 1,020 | $ | 188 | ||
| Licensing and royalty income | 175 | 168 | 288 | |||||
| Associated companies | 76 | 45 | 176 | |||||
| Net interest and investment income(b) | 167 | 65 | (77) | |||||
| Other items(c) | (27) | 868 | 132 | |||||
| 4,092 | 2,165 | 707 | ||||||
| Eliminations | (87) | 62 | 71 | |||||
| Total | $ | 4,005 | $ | 2,227 | $ | 778 | ||
(b) Included other-than-temporary impairments on investment securities of $(217) million in 2014.
| (c) | In 2015, included a $450 million NBCU tax settlement and a $175 million break-up fee from Electrolux. Included net gains on asset sales of $101 million, $90 million and $127 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. |
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||
| (In millions; per-share amounts in dollars) | Diluted | Basic | Diluted | Basic | Diluted | Basic | |||||||||||
| Amounts attributable to the Company: | |||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing operations for | |||||||||||||||||
per-share calculation(a)(b) | $ | 9,764 | $ | 9,769 | $ | 1,680 | $ | 1,679 | $ | 9,523 | $ | 9,523 | |||||
| Preferred stock dividends declared | (656) | (656) | (18) | (18) | - | - | |||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing operations attributable to | |||||||||||||||||
| common shareowners for per-share calculation(a)(b) | $ | 9,108 | $ | 9,113 | $ | 1,662 | $ | 1,661 | $ | 9,523 | $ | 9,523 | |||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations | |||||||||||||||||
for per-share calculation(a)(b) | (955) | (950) | (7,795) | (7,795) | 5,691 | 5,691 | |||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to GE common | |||||||||||||||||
shareowners for per-share calculation(a)(b) | $ | 8,157 | $ | 8,163 | $ | (6,135) | $ | (6,135) | $ | 15,213 | $ | 15,212 | |||||
| Average equivalent shares | |||||||||||||||||
| Shares of GE common stock outstanding | 9,025 | 9,025 | 9,944 | 9,944 | 10,045 | 10,045 | |||||||||||
| Employee compensation-related shares (including | |||||||||||||||||
stock options) and warrants | 105 | - | 72 | - | 78 | - | |||||||||||
| Total average equivalent shares | 9,130 | 9,025 | 10,016 | 9,944 | 10,123 | 10,045 | |||||||||||
| Per-share amounts | |||||||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing operations | $ | 1.00 | $ | 1.01 | $ | 0.17 | $ | 0.17 | $ | 0.94 | $ | 0.95 | |||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations | (0.10) | (0.11) | (0.78) | (0.78) | 0.56 | 0.57 | |||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) | 0.89 | 0.90 | (0.61) | (0.62) | 1.50 | 1.51 | |||||||||||
Our unvested restricted stock unit awards that contain non-forfeitable rights to dividends or dividend equivalents are considered participating securities and, therefore, are included in the computation of earnings per share pursuant to the two-class method. Application of this treatment had an insignificant effect.
| (a) | Included a dilutive adjustment of an insignificant amount of dividend equivalents in each of the three years presented. |
| (b) | Included in 2016 is a dilutive adjustment for the change in income for forward purchase contracts that may be settled in stock. |
For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, there were approximately 22 million, 97 million and 98 million, respectively, of outstanding stock awards that were not included in the computation of diluted earnings per share because their effect was antidilutive.
In December 2016, we entered into an ASR agreement to repurchase shares of GE common stock. See Note 15 for additional information. The initial delivery of 59,177,215 shares resulted in an immediate reduction of the outstanding shares used to calculate the weighted-average common shares outstanding for basic and diluted earnings per share. GE has determined that the forward contract, indexed to its own common stock, met all the criteria for equity classification. There was no dilutive impact on earnings per share related to the forward contract.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 184
Earnings-per-share amounts are computed independently for earnings (loss) from continuing operations, earnings (loss) from discontinued operations and net earnings (loss). As a result, the sum of per-share amounts from continuing operations and discontinued operations may not equal the total per-share amounts for net earnings.
RECURRING FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
Our assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis include investment securities mainly supporting obligations to annuitants and policyholders in our run-off insurance operations and derivatives.
| ASSETS AND LIABILITIES MEASURED AT FAIR VALUE ON A RECURRING BASIS | ||||||||||||||
| Netting | ||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | Level 1 | (a) | Level 2 | (a) | Level 3 | adjustment | (b) | Net balance | ||||||
| December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||||
| Investment securities | ||||||||||||||
Debt | ||||||||||||||
U.S. corporate | $ | - | $ | 19,647 | $ | 3,399 | $ | - | $ | 23,046 | ||||
State and municipal | - | 4,163 | 73 | - | 4,236 | |||||||||
Mortgage and asset-backed | - | 2,852 | 9 | - | 2,861 | |||||||||
Corporate – non-U.S. | - | 11,299 | 688 | - | 11,987 | |||||||||
Government – non-U.S. | - | 1,262 | - | - | 1,262 | |||||||||
U.S. government and federal agency | - | 482 | 232 | - | 714 | |||||||||
Equity | 188 | 14 | 6 | - | 208 | |||||||||
| Derivatives(c) | - | 5,444 | 23 | (5,121) | 345 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 188 | $ | 45,163 | $ | 4,429 | $ | (5,121) | $ | 44,658 | ||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||||
| Derivatives | $ | - | $ | 4,880 | $ | 2 | $ | (4,449) | $ | 434 | ||||
| Other(e) | - | 1,143 | - | - | 1,143 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | - | $ | 6,024 | $ | 2 | $ | (4,449) | $ | 1,577 | ||||
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||||
| Investment securities | ||||||||||||||
Debt | ||||||||||||||
U.S. corporate | $ | - | $ | 19,351 | $ | 3,006 | $ | - | $ | 22,358 | ||||
State and municipal | - | 4,215 | 30 | - | 4,245 | |||||||||
Mortgage and asset-backed | - | 3,084 | 32 | - | 3,116 | |||||||||
Corporate – non-U.S. | 12 | 544 | 290 | - | 847 | |||||||||
Government – non-U.S. | 5 | 410 | - | - | 415 | |||||||||
U.S. government and federal agency | 49 | 404 | 323 | - | 776 | |||||||||
Equity | 194 | 9 | 13 | - | 216 | |||||||||
| Derivatives(c) | - | 7,312 | 79 | (6,110) | 1,281 | |||||||||
| Other(d) | - | - | 259 | - | 259 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 260 | $ | 35,331 | $ | 4,033 | $ | (6,110) | $ | 33,512 | ||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||||
| Derivatives | $ | - | $ | 5,677 | $ | 4 | $ | (4,968) | $ | 713 | ||||
| Other(e) | - | 1,182 | - | - | 1,182 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | - | $ | 6,860 | $ | 4 | $ | (4,968) | $ | 1,895 | ||||
| (b) | The netting of derivative receivables and payables (including the effects of any collateral posted or received) is permitted when a legally enforceable master netting agreement exists. |
| (c) | The fair value of derivatives includes an adjustment for non-performance risk. At December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, the cumulative adjustment for non-performance risk was $(3) million and insignificant, respectively. See Notes 20 and 29 for additional information on the composition of our derivative portfolio. |
| (d) | Includes private equity investments. |
| (e) | Primarily represents the liabilities associated with certain of our deferred incentive compensation plans. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 185
The majority of our Level 3 balances consist of investment securities classified as available-for-sale with changes in fair value recorded in shareowners' equity.
| CHANGES IN LEVEL 3 INSTRUMENTS FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| change in | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net | Net | unrealized | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| realized/ | realized/ | gains | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| unrealized | unrealized | (losses) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| gains | gains | relating to | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (losses) | (losses) | Transfers | Transfers | instruments | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at | included in | included | into | out of | Balance at | still held at | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | January 1 | earnings(a) | in AOCI | Purchases | Sales | Settlements | Level 3(b) | Level 3(b) | December 31 | December 31(c) | |||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Investment securities | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Debt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
U.S. corporate | $ | 3,006 | $ | 9 | $ | 137 | $ | 468 | $ | (70) | $ | (155) | $ | 32 | $ | (29) | $ | 3,399 | $ | - | |||||||
State and municipal | 30 | - | 1 | 43 | - | (1) | - | - | 73 | - | |||||||||||||||||
Mortgage and | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
asset-backed | 32 | (19) | 1 | - | - | (6) | - | - | 9 | - | |||||||||||||||||
Corporate – non-U.S. | 290 | 28 | - | 461 | (82) | (1) | 2 | (10) | 688 | - | |||||||||||||||||
U.S. government and | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
federal agency | 323 | - | (90) | - | - | (1) | - | - | 232 | - | |||||||||||||||||
Equity | 13 | (7) | 2 | - | (1) | (2) | - | - | 6 | - | |||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives(d)(e) | 88 | (18) | - | 1 | - | (59) | - | 8 | 21 | (21) | |||||||||||||||||
| Other | 259 | - | - | - | - | - | - | (259) | - | - | |||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 4,042 | $ | (7) | $ | 51 | $ | 974 | $ | (152) | $ | (226) | $ | 35 | $ | (290) | $ | 4,427 | $ | (21) | |||||||
| 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Investment securities | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Debt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
U.S. corporate | $ | 3,053 | $ | 3 | $ | (165) | $ | 362 | $ | (80) | $ | (137) | $ | - | $ | (30) | $ | 3,006 | $ | - | |||||||
State and municipal | 58 | - | (2) | - | - | (9) | - | (17) | 30 | - | |||||||||||||||||
Mortgage and | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
asset-backed | 146 | (19) | (9) | - | (32) | (4) | - | (49) | 32 | - | |||||||||||||||||
| Corporate – non-U.S. | 337 | - | (6) | 9 | (49) | (1) | - | - | 290 | - | |||||||||||||||||
| Government – non-U.S. | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | (2) | - | - | |||||||||||||||||
U.S. government and | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
federal agency | 266 | - | 58 | - | - | (1) | - | - | 323 | - | |||||||||||||||||
Equity | 9 | 2 | (5) | - | - | (4) | 10 | - | 13 | - | |||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives(d)(e) | 29 | 25 | - | - | - | (6) | 40 | - | 88 | 22 | |||||||||||||||||
| Other | 277 | 8 | - | - | (26) | - | - | - | 259 | 5 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 4,175 | $ | 19 | $ | (128) | $ | 370 | $ | (187) | $ | (161) | $ | 51 | $ | (98) | $ | 4,042 | $ | 27 | |||||||
| (a) |
| (b) | Transfers in and out of Level 3 are considered to occur at the beginning of the period. Transfers out of Level 3 for the twelve months ended December 31, 2016 were primarily a result of the adoption of ASU 2015-02, Amendments to the Consolidation Analysis. See Note 1. |
| (c) | Represents the amount of unrealized gains or losses for the period included in earnings. |
| (d) | Represents derivative assets net of derivative liabilities and includes cash accruals of none and $13 million not reflected in the fair value hierarchy table for the twelve months ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. |
| (e) | Gains (losses) included in net realized/unrealized gains (losses) included in earnings were offset by the earnings effects from the underlying items that were economically hedged. See Notes 20 and 29. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 186
The following table represents non-recurring fair value amounts (as measured at the time of the adjustment) for those assets remeasured to fair value on a non-recurring basis during the fiscal year and still held at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015.
| Remeasured during the years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| (In millions) | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||
| Financing receivables and financing receivables held for sale | $ | - | $ | 30 | $ | - | $ | 154 | |||
| Cost and equity method investments | - | 103 | 1 | 436 | |||||||
| Long-lived assets | 17 | 1,055 | 2 | 882 | |||||||
| Total | $ | 17 | $ | 1,189 | $ | 3 | $ | 1,471 | |||
The following table represents the fair value adjustments to assets measured at fair value on a non-recurring basis and still held at December 31, 2016 and 2015.
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Financing receivables and financing receivables held for sale | $ | (14) | $ | (69) | |
| Cost and equity method investments | (44) | (506) | |||
| Long-lived assets | (196) | (1,603) | |||
| Total | $ | (254) | $ | (2,177) | |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 187
| LEVEL 3 MEASUREMENTS - SIGNIFICANT UNOBSERVABLE INPUTS | |||||||||
| Range | |||||||||
| (Dollars in millions) | Fair value | Valuation technique | Unobservable inputs | (weighted-average) | |||||
| December 31, 2016 | |||||||||
| Recurring fair value measurements | |||||||||
| Investment securities – Debt | |||||||||
| U.S. corporate | $ | 809 | Income approach | Discount rate(a) | 1.4%-17.4% (8.1%) | ||||
| State and municipal | 20 | Income approach | Discount rate(a) | 3.7%-3.7% (3.7%) | |||||
| Mortgage and asset-backed | 1 | Income approach | Discount rate(a) | 2.7%-6.9% (4.3%) | |||||
| Non-recurring fair value measurements | |||||||||
| Financing receivables and | |||||||||
| financing receivables held for sale | $ | 30 | Income approach | Discount rate(a) | 2.5%-30.0% (20.3%) | ||||
| Cost and equity method investments | 94 | Income approach | Discount rate(a) | 9.0%-30.0% (11.8%) | |||||
| Long-lived assets | 683 | Income approach | Discount rate(a) | 2.5%-20.0% (10.4%) | |||||
| December 31, 2015 | |||||||||
| Recurring fair value measurements | |||||||||
| Investment securities – Debt | |||||||||
| U.S. corporate | $ | 834 | Income approach | Discount rate(a) | 1.7%-14.1% (8.6%) | ||||
| Mortgage and asset-backed | 31 | Income approach | Discount rate(a) | 5.0%-12.0% (10.5%) | |||||
| Corporate – non-U.S. | 236 | Income approach | Discount rate(a) | 6.5%-14.0% (7.5%) | |||||
| Other financial assets | 259 | Income approach, | EBITDA multiple | 6.1X-15.0X (9.9X) | |||||
| Market comparables | Capitalization rate | 7.8%-7.8% (7.8%) | |||||||
| Non-recurring fair value measurements | |||||||||
| Financing receivables and | |||||||||
| financing receivables held for sale | $ | 146 | Income approach | Discount rate(a) | 6.5%-30.0% (10.7%) | ||||
| Cost and equity method investments | 293 | Income approach | Discount rate(a) | 9.5%-35.0% (14.4%) | |||||
| Long-lived assets | 830 | Income approach | Discount rate(a) | 1.8%-11.7% (10.5%) | |||||
At December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, other Level 3 recurring fair value measurements of $3,598 million and $2,637 million, respectively, and non-recurring measurements of $379 million and $122 million, respectively, are valued using non-binding broker quotes or other third-party sources. At December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, other recurring fair value measurements of an insignificant amount and $32 million, respectively, and non-recurring fair value measurements of $2 million and $80 million, respectively, were individually insignificant and utilize a number of different unobservable inputs not subject to meaningful aggregation.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 188
The following table provides information about assets and liabilities not carried at fair value. The table excludes finance leases and non-financial assets and liabilities. Substantially all of the assets discussed below are considered to be Level 3. The vast majority of our liabilities' fair values can be determined based on significant observable inputs and thus considered Level 2. Few of the instruments are actively traded and their fair values must often be determined using financial models. Realization of the fair value of these instruments depends upon market forces beyond our control, including marketplace liquidity.
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||
| Carrying | Carrying | |||||||||||
| amount | Estimated | amount | Estimated | |||||||||
| December 31 (In millions) | (net) | fair value | (net) | fair value | ||||||||
| GE | ||||||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||
Investments and notes receivable | $ | 1,526 | $ | 1,595 | $ | 1,104 | $ | 1,174 | ||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||
Borrowings(a)(b) | 19,184 | 19,923 | 18,397 | 18,954 | ||||||||
| Borrowings (debt assumed)(a)(c) | 60,109 | 66,998 | 84,704 | 92,231 | ||||||||
| GE Capital | ||||||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||
Loans | 21,060 | 20,830 | 20,061 | 19,774 | ||||||||
| Time deposits(d) | - | - | 10,386 | 10,386 | ||||||||
Other commercial mortgages | 1,410 | 1,472 | 1,381 | 1,447 | ||||||||
Loans held for sale | 473 | 473 | 342 | 342 | ||||||||
Other financial instruments(e) | 121 | 150 | 94 | 110 | ||||||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||
Borrowings(a)(f)(g)(h) | 58,523 | 62,024 | 95,474 | 99,396 | ||||||||
Investment contracts | 2,813 | 3,277 | 2,955 | 3,441 | ||||||||
(b) Included $115 million and $116 million of accrued interest in estimated fair value at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively.
| (c) | Included $803 million and $1,006 million of accrued interest in estimated fair value at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively. |
| (d) | Balances at December 31, 2015 comprised high quality interest bearing deposits with European branches of global banks, predominantly in the U.K., that matured in April 2016. |
| (e) | Principally comprises cost method investments. |
| (f) | Fair values exclude interest rate and currency derivatives designated as hedges of borrowings. Had they been included, the fair value of borrowings at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015 would have been reduced by $2,397 million and $3,001 million, respectively. |
| (g) | Included $775 million and $1,103 million of accrued interest in estimated fair value at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively. |
| (h) | Excluded $58,780 million and $84,704 million of intercompany payable to GE at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015 respectively, which includes a reduction in the short-term intercompany payable to GE for a $(1,329) million loan to GE, which bears the right of offset against amounts owed under the assumed debt agreement. The remaining short-term loan balance was paid in January 2017. |
Loans. Based on a discounted future cash flows methodology, using current market interest rate data adjusted for inherent credit risk or quoted market prices and recent transactions, if available.
Borrowings. Based on valuation methodologies using current market interest rate data that are comparable to market quotes adjusted for our non-performance risk.
Investment contracts. Based on expected future cash flows, discounted at currently offered rates for immediate annuity contracts or the income approach for single premium deferred annuities.
Time deposits. Carrying value approximates fair value as these financial instruments have limited credit risk, short-term maturities and interest rates that approximate market.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 189
All other instruments. Based on observable market transactions and/or valuation methodologies using current market interest rate data adjusted for inherent credit risk.
Assets and liabilities that are reflected in the accompanying financial statements at fair value are not included in the above disclosures; such items include cash and equivalents, investment securities and derivative financial instruments.
Additional information about notional amounts of loan commitments follows.
| NOTIONAL AMOUNTS OF LOAN COMMITMENTS | |||||
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Ordinary course of business lending commitments(a) | $ | 687 | $ | 531 | |
| Unused revolving credit lines | 238 | 279 | |||
| (a) | Excluded investment commitments of $522 million and $782 million at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively. |
SECURITIES REPURCHASE AND REVERSE REPURCHASE ARRANGEMENTS
Our issuances of securities repurchase agreements are insignificant. No repurchase agreements were accounted for as off-book financing and we do not engage in securities lending transactions. At December 31, 2016, we were party to no repurchase agreements.
We also enter into reverse securities repurchase agreements, primarily for short-term investment with maturities of 90 days or less. At December 31, 2016, we were party to reverse repurchase agreements totaling $6.9 billion, which were reported in cash and equivalents on the financial statements. Under these reverse securities repurchase agreements, we typically lend available cash at a specified rate of interest and hold U.S. or highly-rated European government securities as collateral during the term of the agreement. Collateral value is in excess of amounts loaned under the agreements.
In this section, we explain how we use derivatives to manage our risks and how these financial instruments are reflected in our financial statements. Our use of derivatives relates solely to risk management; we do not use derivatives for speculation. As discussed elsewhere in this report, we are executing a plan to reduce the size and scope of our financial services business, with the intention of principally retaining those activities that support our industrial businesses. The affected businesses have either been sold or are held for sale and are presented as discontinued operations in our financial statements as of December 31, 2016. As a result of these actions, the significance of financial services hedging activity will diminish significantly in the future.
RISK MANAGEMENT STRATEGY
In our industrial businesses, we buy, manufacture and sell components and products across global markets. These activities expose us to changes in foreign currency exchange rates and commodity prices, which can adversely affect revenues earned and costs of operating our industrial businesses. When the currency in which we sell equipment differs from the primary currency of one of our industrial businesses (known as its functional currency) and the exchange rate fluctuates, it will affect the revenue we earn on the sale. These sales and purchase transactions also create receivables and payables denominated in foreign currencies, which expose us to foreign currency gains and losses based on changes in exchange rates. Changes in the price of a raw material that we use in manufacturing can affect the cost of manufacturing. We use derivatives to mitigate or eliminate these exposures.
With respect to our ongoing financial services activities, our key exposures relate to interest rate and currency risk. To the extent feasible, we seek to ensure that the characteristics of the debt we have issued align with the assets being funded. The form (fixed rate or floating rate) and currency denomination of the debt we issue depends on a number of considerations, the most important of which are market factors (demand, pricing, etc.) that affect the economics of the issuance. If the form and currency denomination of the debt does not match the assets being funded, we typically execute derivatives to meet this objective within defined limits.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 190
FORMS OF HEDGING
In this section we explain the hedging methods we use and their effects on our financial statements.
Cash flow hedges – We use cash flow hedging primarily to reduce or eliminate the effects of foreign exchange rate changes on purchase and sale contracts in our industrial businesses and to convert foreign currency debt that we have issued in our financial services business back to our functional currency. Accordingly, the vast majority of our derivative activity in this category consists of currency exchange contracts. As a result of acquisitions in our industrial businesses, we expect to significantly expand our foreign currency hedging activity related to long-term contracts. We also use commodity derivatives to reduce or eliminate price risk on raw materials purchased for use in manufacturing.
Under hedge accounting, the derivative carrying amount is measured at fair value each period and any resulting gain or loss is recorded in a separate component of shareowners' equity. Differences between the derivative and the hedged item may cause changes in their fair values to not offset completely, which is referred to as ineffectiveness. When the hedged transaction occurs, these amounts are released from shareowners' equity, in order that the transaction will be reflected in earnings at the rate locked in by the derivative. The effect of the hedge is reported in the same financial statement line item as the earnings effects of the hedged transaction. The table below summarizes how the derivative is reflected in the balance sheet and in earnings under hedge accounting. The effect of the hedged forecasted transaction is not presented in this table but offsets the earnings effect of the derivative.
As part of our ongoing effort to reduce borrowings, we may repurchase debt that was in a cash flow hedge accounting relationship. At the time of determining that the debt cash flows are probable of not occurring, any related OCI will be released to earnings.
| FINANCIAL STATEMENT EFFECTS - CASH FLOW HEDGES | |||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Balance sheet changes | |||||
| Fair value of derivatives increase (decrease) | $ | (274) | $ | (911) | |
| Shareowners' equity (increase) decrease | 274 | 913 | |||
| Earnings (loss) related to ineffectiveness | 1 | 2 | |||
| Earnings (loss) effect of derivatives(a) | (364) | (918) | |||
| (a) Offsets earnings effect of the hedged forecasted transaction | |||||
The following table explains the effect of changes in market rates on the fair value of derivatives we use most commonly in cash flow hedging arrangements.
| Interest rate forwards/swaps | Interest rate increases | Interest rate decreases | ||
| Pay fixed rate/receive floating rate | Fair value increases | Fair value decreases | ||
| Currency forwards/swaps | U.S. dollar strengthens | U.S. dollar weakens | ||
| Pay U.S. dollars/receive foreign currency | Fair value decreases | Fair value increases | ||
| Commodity derivatives | Price increases | Price decreases | ||
| Receive commodity/ pay fixed price | Fair value increases | Fair value decreases | ||
Fair value hedges – These derivatives are used to hedge the effects of interest rate and currency exchange rate changes on debt that we have issued. We have issued mostly fixed rate debt that is used to fund both fixed and floating rate assets. In instances where fixed rate debt is funding floating rate assets, we have an exposure to changes in interest rates. We enter into interest rate swaps that receive a fixed rate and pay a floating rate of interest to align with that portion of our debt which funds floating rate assets. These swaps typically match the maturity of the associated debt being hedged.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 191
Under hedge accounting, the derivative is measured at fair value and the carrying amount of the hedged debt is adjusted for the change in value related to the exposure being hedged, with both adjustments offset to earnings as interest expense. For example, the earnings effect of an increase in the fair value of the derivative will be largely offset by the earnings effect of an increase in the carrying amount of the hedged debt. Differences between the terms of the derivative and the hedged debt may cause changes in their fair values to not offset completely, which is referred to as ineffectiveness. The table below summarizes how the derivative and the hedged debt are reflected in the balance sheet and in earnings under hedge accounting. The effect on interest expense of changing from the fixed rate on the debt to the floating rate on the swap is not shown in this table.
| FINANCIAL STATEMENT EFFECTS - FAIR VALUE HEDGES | |||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Balance sheet changes | |||||
| Fair value of derivative increase (decrease) | $ | 170 | $ | (151) | |
| Adjustment to carrying amount of hedged debt (increase) decrease | (433) | 75 | |||
| Earnings (loss) related to hedge ineffectiveness | (263) | (75) | |||
The effect of changes in market interest rates on the fair value of derivatives we use most commonly in fair value hedging arrangements is presented below.
| Interest rate forwards/swaps | Interest rate increases | Interest rate decreases | ||
| Pay floating rate/receive fixed rate | Fair value decreases | Fair value increases | ||
Net investment hedges – We invest in foreign operations that conduct their financial services activities in currencies other than the U.S. dollar. We hedge the currency risk associated with those investments primarily using short-term currency exchange contracts under which we receive U.S. dollars and pay foreign currency and non-derivatives instruments such as debt denominated in a foreign currency.
Under hedge accounting, the portion of the fair value change of the derivative or debt instrument that relates to changes in spot currency exchange rates is offset in a separate component of shareowners' equity. For example, an increase in the fair value of the derivative related to changes in spot exchange rates will be offset by a corresponding increase in the currency translation component of shareowners' equity. The portion of the fair value change of the derivative related to differences between spot and forward rates, which primarily relates to the interest component, is recorded in earnings each period as interest expense. As a result of this hedging strategy, the investments in foreign operations of our financial services business are largely unaffected by changes in currency exchange rates. The amounts recorded in shareowners' equity only affect earnings if the hedged investment is sold, substantially liquidated, or control is lost.
| FINANCIAL STATEMENT EFFECTS - NET INVESTMENT HEDGES | |||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Balance sheet changes | |||||
| Fair value of derivatives increase (decrease) | $ | 639 | $ | 4,871 | |
| Fair value of non-derivatives (increase) decrease | 1,819 | (849) | |||
| Shareowners' equity (increase) decrease | (2,376) | (4,131) | |||
| Earnings (loss) related to spot-forward differences | 82 | (109) | |||
| Earnings (loss) related to reclassification upon sale or liquidation(a) | (528) | 4,547 | |||
| (a) | Included $(529) million and $4,549 million recorded in discontinued operations in the twelve months ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. |
The effect of changes in currency exchange rates on the fair value of derivatives we use in net investment hedging arrangements is presented below.
| Currency forwards/swaps | U.S. dollar strengthens | U.S. dollar weakens | ||
| Receive U.S. dollars/pay foreign currency | Fair value increases | Fair value decreases |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 192
Economic Hedges - These derivatives are not designated as hedges from an accounting standpoint (and therefore we do not apply hedge accounting to the relationship) but otherwise serve the same economic purpose as other hedging arrangements. Economic hedges are used when changes in the carrying amount of the hedged item are already recorded in earnings in the same period as the derivative, making hedge accounting unnecessary. For example, in our industrial businesses we record the effects of spot exchange rate changes on our foreign currency payables and receivables in earnings each period along with the fair value changes on the foreign currency forward contracts used as economic hedges. In these cases, the earnings effects of the derivative and hedged item largely offset. We also use economic hedges when we have exposures to currency exchange risk for which we are unable to meet the requirements for hedge accounting. For example, we use currency forwards as an economic hedge of forecasted foreign currency cash flows under long-term contracts. In this case, the forecast period is so long that it is difficult to meet the hedge accounting requirement that the occurrence of the hedged transactions is probable. For these types of economic hedges, changes in the fair value of the derivative are recorded in earnings currently but changes in the value of the forecasted foreign currency cash flows are only recognized in earnings when they occur. As a result, even though the derivative is an effective economic hedge, there is a net effect on earnings in each period due to differences in the timing of earnings recognition between the derivative and the hedged item.
The table below provides information about the earnings effects of all derivatives that serve as economic hedges. These derivatives are marked to fair value through earnings each period. For our financial services business, these gains and losses are reported in "GE Capital revenues from services". For our industrial businesses, the effects are reported in "Other income" or "Other costs and expenses". The offsetting earnings effects associated with hedged assets and liabilities are also displayed in the table below. In general, the earnings effects of the hedged item are recorded in the same financial statement line as the derivative. The earnings effect of economic hedges, after considering offsets related to earnings effects of hedged assets and liabilities, is substantially offset by changes in the fair value of forecasted transactions that have not yet affected earnings.
| FINANCIAL STATEMENT EFFECTS - ECONOMIC HEDGES | |||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Balance sheet changes | |||||
| Change in fair value of economic hedge increase (decrease) | $ | (2,456) | $ | (2,720) | |
| Change in carrying amount of item being hedged increase (decrease) | 2,107 | 2,543 | |||
| Earnings (loss) effect of economic hedges(a) | (348) | (177) | |||
The table below explains the effects of market rate changes on the fair value of derivatives we use most commonly as economic hedges.
| Interest rate forwards/swaps interest rate | Interest rate increases | Interest rate decreases | ||
| Pay floating rate/receive fixed rate | Fair value decreases | Fair value increases | ||
| Currency forwards/swaps | U.S. dollar strengthens | U.S. dollar weakens | ||
| Pay U.S. dollars/receive foreign currency | Fair value decreases | Fair value increases | ||
| Receive U.S. dollars/pay foreign currency | Fair value increases | Fair value decreases | ||
| Commodity derivatives | Price increases | Price decreases | ||
| Receive commodity/ pay fixed price | Fair value increases | Fair value decreases | ||
The notional amount of a derivative is the number of units of the underlying (for example, the notional principal amount of the debt in an interest rate swap). The notional amount is used to compute interest or other payment streams to be made under the contract and is a measure of our level of activity. We generally disclose derivative notional amounts on a gross basis. A substantial majority of the outstanding notional amount of $181 billion at December 31, 2016 is related to managing interest rate and currency risk between financial assets and liabilities in our financial services business. The remaining derivative notional amount primarily relates to hedges of anticipated sales and purchases in foreign currency, commodity purchases and contractual terms in contracts that are considered embedded derivatives.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 193
The table below provides additional information about how derivatives are reflected in our financial statements. Derivative assets and liabilities are recorded at fair value exclusive of interest earned or owed on interest rate derivatives, which is presented separately on our Statement of Financial Position. Cash collateral and securities held as collateral represent assets that have been provided by our derivative counterparties as security for amounts they owe us (derivatives that are in an asset position).
| CARRYING AMOUNTS RELATED TO DERIVATIVES | |||||
| December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Derivative assets | $ | 5,467 | $ | 7,391 | |
| Derivative liabilities | (4,883) | (5,681) | |||
| Accrued interest | 792 | 1,014 | |||
| Cash collateral & credit valuation adjustment | (672) | (1,141) | |||
| Net Derivatives | 703 | 1,583 | |||
| Securities held as collateral | (442) | (1,277) | |||
| Net amount | $ | 262 | $ | 306 | |
All derivatives are marked to fair value on our balance sheet, whether they are designated in a hedging relationship for accounting purposes or are used as economic hedges. As discussed in the previous sections, each type of hedge affects the financial statements differently. In fair value and economic hedges, both the hedged item and the hedging derivative largely offset in earnings each period. In cash flow and net investment hedges, the effective portion of the hedging derivative is offset in separate components of shareowners' equity and ineffectiveness is recognized in earnings. The table below summarizes these offsets and the net effect on pre-tax earnings.
| (In millions) | Effect on hedging instrument | Effect on underlying | Effect on earnings | |||||
| 2016 | ||||||||
| Cash flow hedges | $ | (274) | $ | 274 | $ | 1 | ||
| Fair value hedges | 170 | (433) | (263) | |||||
| Net investment hedges(a) | 2,458 | (2,376) | 82 | |||||
| Economic hedges(b) | (2,456) | 2,107 | (348) | |||||
| Total | $ | (528) | ||||||
| 2015 | ||||||||
| Cash flow hedges | $ | (911) | $ | 913 | $ | 2 | ||
| Fair value hedges | (151) | 75 | (75) | |||||
| Net investment hedges(a) | 4,022 | (4,131) | (109) | |||||
| Economic hedges(b) | (2,720) | 2,543 | (177) | |||||
| Total | $ | (359) | ||||||
The amounts in the table above generally do not include associated derivative accruals in income or expense.
(b) Net effect is substantially offset by the change in fair value of the hedged item that will affect earnings in future periods.
See Note 15 for additional information about changes in shareowners' equity related to hedging and amounts released to earnings. See Note 29 for other supplemental information about derivatives and hedging.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 194
A VIE is an entity that has one of three characteristics: (1) it is controlled by someone other than its shareowners or partners, (2) its shareowners or partners are not economically exposed to the entity's earnings (for example, they are protected against losses), or (3) it was thinly capitalized when it was formed.
In the normal course of our business we become involved with VIEs either because we help create them or we invest in them. Our VIEs either provide goods and services to customers or provide financing to third parties for the purchase of GE goods and services. If we control the VIE, we consolidate it and provide disclosures below. However, if the VIE is a business and use of its assets is not limited to settling its liabilities, ongoing disclosures are not required.
CONSOLIDATED VARIABLE INTEREST ENTITIES
Our most significant consolidated VIEs are the three joint ventures that were formed as part of the Alstom acquisition. These joint ventures include grid technology, renewable energy, and global nuclear and French steam power and have combined assets, liabilities and redeemable noncontrolling interest as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 of $14,460 million, $9,922 million and $2,709 million and $11,536 million, $8,739 million and $2,859 million, respectively. These joint ventures are considered VIEs because the equity held by Alstom does not participate fully in the earnings of the ventures due to the contractual features allowing Alstom to sell their interests back to GE. We consolidate these ventures because we control all their significant activities. These joint ventures are in all other respects regular businesses and are therefore exempt from ongoing disclosure requirements for VIEs provided below.
The table below provides information about VIEs that are subject to ongoing disclosure requirements. Substantially all of these entities were created to help our customers finance the purchase of GE goods and services or to purchase GE current and customer notes receivable originating from sales of goods and services. These entities have no features that could expose us to losses that would significantly exceed the difference between the consolidated assets and liabilities.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 195
| ASSETS AND LIABILITIES OF CONSOLIDATED VIEs | ||||||||||||||
| GE Capital | ||||||||||||||
| Current | Customer | |||||||||||||
| (In millions) | GE | receivables(a) | Notes receivables(b) | Other | Total | |||||||||
| December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||||
| Financing receivables, net | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 1,035 | $ | 1,035 | ||||
| Current receivables | 57 | - | 670 | - | 727 | |||||||||
| Investment securities | - | - | - | 982 | 982 | |||||||||
| Other assets | 492 | (c) | - | 1,122 | 1,747 | 3,361 | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 549 | $ | - | $ | 1,792 | $ | 3,764 | $ | 6,105 | ||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||||
| Borrowings | $ | 1 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 818 | $ | 819 | ||||
| Non-recourse borrowings | - | - | 401 | 16 | 417 | |||||||||
| Other liabilities | 457 | (c) | - | 1,378 | 1,482 | 3,317 | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 458 | $ | - | $ | 1,779 | $ | 2,316 | $ | 4,553 | ||||
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||||
| Financing receivables, net | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 882 | $ | 882 | ||||
| Current receivables | 385 | 3,506 | - | - | 3,891 | |||||||||
| Investment securities | - | - | - | 1,404 | 1,404 | |||||||||
| Other assets | 2,482 | 24 | - | 1,068 | 3,574 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 2,867 | $ | 3,530 | $ | - | $ | 3,354 | $ | 9,751 | ||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||||
| Borrowings | $ | 221 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 960 | $ | 1,181 | ||||
| Non-recourse borrowings | - | 3,022 | - | 61 | 3,083 | |||||||||
| Other liabilities | 2,289 | 34 | - | 1,234 | 3,557 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 2,510 | $ | 3,056 | $ | - | $ | 2,255 | $ | 7,821 | ||||
In the fourth quarter of 2016, we completed the restructure of our Receivables Facility described in Note 22. The restructured facility does not use a consolidated VIE.
| (b) | In the first quarter of 2016, two funding vehicles were established to purchase customer notes receivable from GE, one of which is partially funded by third-party debt. |
| (c) | In the first quarter of 2016, we purchased the minority interest in an Oil & Gas joint venture and as a result the entity is no longer a VIE. Consolidated VIE assets and liabilities were reduced by $1,240 million and $1,284 million, respectively. |
Total revenues from our consolidated VIEs were $1,141 million, $1,638 million and $1,457 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Related expenses consisted primarily of cost of goods and services of $692 million, $1,232 million and $823 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Where we provide servicing for third-party investors, we are contractually permitted to commingle cash collected from customers on financing receivables sold to third-party investors with our own cash prior to payment to third-party investors, provided our short-term credit rating does not fall below A-1/P1. These third-party investors also owe us amounts for purchased financial assets and scheduled interest and principal payments. At December 31, 2016 and 2015, the amounts of commingled cash owed to the third-party investors were $1,117 million and $1,093 million, respectively, and the amounts owed to us by third-party investors were $5 million and $7 million, respectively.
We become involved with unconsolidated VIEs primarily through assisting in the formation and financing of the entity. We do not consolidate these entities because we do not have power over decisions that significantly affect their economic performance. Our investments in unconsolidated VIEs, at December 31, 2016 and 2015 were $6,346 million and $787 million, respectively. Obligations to make additional investments in these entities are not significant.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 196
Our investments in long-lived, capital-intensive energy limited partnerships through Energy Financial Services became non-consolidated VIEs in accordance with our January 2016 adoption of ASU 2015-2, Amendments to the Consolidated Analysis (see Note 1). In these partnerships we are the sole limited partner and had no participating rights or substantive removal rights over the general partners. The general partners of these entities, who possess the technical and industry expertise necessary to operate and manage their activities, continue to control these limited partnerships. As a result of this accounting change, our disclosed investments in unconsolidated VIEs increased by $6,077 million, without additional funds being advanced to these entities.
Since 2002, the Company, as part of its working capital management, has sold current receivables to trusts in which third-party investors invest (the Receivables Facility). We use the cash generated from those sales to fund GE working capital earlier than we would otherwise receive payment from our customers and to manage credit exposures.
In 2010, we consolidated the trust that existed at that time pursuant to a change in the accounting guidance and subsequently reported both current receivables owned by the trust and the associated non-recourse third-party debt of the trust as assets and liabilities of a consolidated VIE on the Statement of Financial Position. Our economic exposure to the sold receivables remained the same before and after we consolidated the trust.
In the fourth quarter of 2016, we completed a refinancing of the Receivables Facility. The total facility size remained at $3,000 million. As a result of this refinancing, the current receivables are now purchased directly by third-party investors, who make their own arrangements to fund the purchase, and we no longer use the trust we used prior to the refinancing. Upon sale of the receivables, we receive proceeds of cash and a deferred purchase price (DPP). The DPP is an interest in specified assets of the purchasers (the receivables sold by GE Capital) that entitles GE Capital to the residual cash flows of those specified assets. The third-party purchasers have no recourse to other assets of GE Capital in the event of non-payment by the debtors. Where the purchasing entity is a bank multi-seller commercial paper conduit, assets transferred by other parties to that entity form a majority of the entity's assets.
The amount of customer receivables sold and outstanding under the Receivables Facility at December 31, 2016 was $2,575 million, and the consolidated customer receivables financed by third-party investors at December 31, 2015 was $3,506 million.
The amount of DPP due to GE Capital was $483 million at December 31, 2016, and is classified as "Current receivables" in the consolidated column of the Statement of Financial Position and as "Financing receivables" in the GE Capital column of the Statement of Financial Position.
Because of the refinancing, GE Capital's financing receivables decreased by approximately $2,092 million as of December 31, 2016 when compared to December 31, 2015. The Company's economic exposure under the Receivables Facility, represented by the DPP, remained the same before and after we completed the refinancing of the Receivables Facility.
Given the short-term nature of the underlying receivables, discount rates and prepayments are not factors in determining the value of the DPP. Collections on the DPP are presented within Cash flows from operating activities in the consolidated column in the Statement of Cash Flows. As the performance of the transferred current receivables is similar to the performance of our other current receivables, delinquencies are not expected to be significant.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 197
COMMITMENTS
The GE Capital Aviation Services (GECAS) business in GE Capital had placed multiple-year orders for various Boeing, Airbus and other aircraft manufacturers with list prices approximating $32,958 million and secondary orders with airlines for used aircraft of approximately $1,275 million at December 31, 2016. In our Aviation segment, we had committed to provide financing assistance of $2,230 million of future customer acquisitions of aircraft equipped with our engines.
Our guarantees are provided in the ordinary course of business. We underwrite these guarantees considering economic, liquidity and credit risk of the counterparty. We believe that the likelihood is remote that any such arrangements could have a significant adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations or liquidity. We record liabilities for guarantees at estimated fair value, generally the amount of the premium received, or if we do not receive a premium, the amount based on appraisal, observed market values or discounted cash flows. Any associated expected recoveries from third parties are recorded as other receivables, not netted against the liabilities.
At December 31, 2016, we were committed under the following guarantee arrangements beyond those provided on behalf of VIEs. See Note 21.
Credit Support. We have provided $1,352 million of credit support on behalf of certain customers or associated companies, predominantly joint ventures and partnerships, using arrangements such as standby letters of credit and performance guarantees. These arrangements enable these customers and associated companies to execute transactions or obtain desired financing arrangements with third parties. Should the customer or associated company fail to perform under the terms of the transaction or financing arrangement, we would be required to perform on their behalf. Under most such arrangements, our guarantee is secured, usually by the asset being purchased or financed, or possibly by certain other assets of the customer or associated company. The length of these credit support arrangements parallels the length of the related financing arrangements or transactions. The liability for such credit support was $44 million at December 31, 2016.
Indemnification Agreements – Continuing Operations. We have agreements that require us to fund up to $222 million at December 31, 2016 under residual value guarantees on a variety of leased equipment. Under most of our residual value guarantees, our commitment is secured by the leased asset. The liability for these indemnification agreements was $7 million at December 31, 2016.
At December 31, 2016, we also had $973 million of other indemnification commitments, substantially all of which relate to representations and warranties in sales of businesses or assets. The liability for these indemnification commitments was $228 million at December 31, 2016.
Indemnification Agreements – Discontinued Operations. At December 31, 2016, we provided specific indemnifications to buyers of GE Capital's assets that amounted to $2,638 million, for which we have recognized related liabilities of $285 million. In addition, in connection with the 2015 public offering and sale of Synchrony Financial, GE Capital indemnified Synchrony Financial and its directors, officers, and employees against the liabilities of GECC's businesses other than historical liabilities of the businesses that are part of Synchrony Financial's ongoing operations.
Contingent Consideration. These are agreements to provide additional consideration to a buyer or seller in a business combination if contractually specified conditions related to the acquisition or disposition are achieved. Amount of contingent consideration was insignificant at December 31, 2016.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 198
PRODUCT WARRANTIES
We provide for estimated product warranty expenses when we sell the related products. Because warranty estimates are forecasts that are based on the best available information – mostly historical claims experience – claims costs may differ from amounts provided. An analysis of changes in the liability for product warranties follows.
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 1,723 | $ | 1,199 | $ | 1,370 | ||
| Current-year provisions | 791 | 649 | 593 | |||||
| Expenditures | (729) | (718) | (714) | |||||
| Other changes(a) | 135 | 593 | (50) | |||||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 1,920 | $ | 1,723 | $ | 1,199 | ||
OTHER LOSS CONTINGENCIES
LEGAL MATTERS
WMC. During the fourth quarter of 2007, we completed the sale of WMC, our U.S. mortgage business. WMC substantially discontinued all new loan originations by the second quarter of 2007, and is not a loan servicer. In connection with the sale, WMC retained certain representation and warranty obligations related to loans sold to third parties prior to the disposal of the business and contractual obligations to repurchase previously sold loans that had an early payment default. All claims received by WMC for early payment default have either been resolved or are no longer being pursued.
The remaining active claims have been brought by securitization trustees or administrators seeking recovery from WMC for alleged breaches of representations and warranties on mortgage loans that serve as collateral for residential mortgage-backed securities (RMBS). At December 31, 2016, such claims consisted of $1,060 million of individual claims generally submitted before the filing of a lawsuit (compared to $2,887 million at December 31, 2015) and $5,456 million of additional claims asserted against WMC in litigation without making a prior claim (Litigation Claims) (compared to $8,047 million at December 31, 2015). The total amount of these claims, $6,516 million, reflects the purchase price or unpaid principal balances of the loans at the time of purchase and does not give effect to pay downs or potential recoveries based upon the underlying collateral, which in many cases are substantial, nor to accrued interest or fees. WMC believes that repurchase claims brought based upon representations and warranties made more than six years before WMC was notified of the claim would be disallowed in legal proceedings under applicable law and the June 11, 2015 decision of the New York Court of Appeals in ACE Securities Corp. v. DB Structured Products, Inc., on the statute of limitations period governing such claims.
Reserves related to repurchase claims made against WMC were $626 million at December 31, 2016, reflecting a net decrease to reserves in the year ended December 31, 2016 of $249 million due to settlements partially offset by incremental provisions. The reserve estimate takes into account recent settlement activity and is based upon WMC's evaluation of the remaining exposures as a percentage of estimated lifetime mortgage loan losses within the pool of loans supporting each securitization for which timely claims have been asserted in litigation against WMC. Settlements in prior periods reduced WMC's exposure on claims asserted in certain securitizations and the claim amounts reported above give effect to these settlements.
| ROLLFORWARD OF THE RESERVE | |||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | |||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 875 | $ | 809 | |
| Provision | 91 | 212 | |||
| Claim resolutions / rescissions | (340) | (146) | |||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 626 | $ | 875 | |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 199
Given the significant litigation activity and WMC's continuing efforts to resolve the lawsuits involving claims made against WMC, it is difficult to assess whether future losses will be consistent with WMC's past experience. Adverse changes to WMC's assumptions supporting the reserve may result in an increase to these reserves. WMC estimates a range of reasonably possible loss from $0 to approximately $500 million over its recorded reserve at December 31, 2016. This estimate involves significant judgment and may not reflect the range of uncertainties and unpredictable outcomes inherent in litigation, including the matters discussed in Legal Proceedings and potential changes in WMC's legal strategy. This estimate excludes any possible loss associated with an adverse court decision on the applicable statute of limitations or an adverse outcome in the Financial Institutions Reform, Recovery, and Enforcement Act of 1989 (FIRREA) investigation discussed in Legal Proceedings, as WMC is unable at this time to develop such a meaningful estimate.
At December 31, 2016, there were 10 lawsuits involving claims made against WMC arising from alleged breaches of representations and warranties on mortgage loans included in 11 securitizations. The adverse parties in these cases are securitization trustees or parties claiming to act on their behalf. On January 23, 2017, the ResCap Liquidating Trust, as successor to Residential Funding Company, LLC (RFC), filed a lawsuit against WMC in the United States District Court for the District of Minnesota arising from alleged breaches in representations and warranties made by WMC in connection with the sale of approximately $840 million in loans to RFC over a period of time preceding RFC's filing for bankruptcy protection in May 2012. Although the alleged claims for relief vary from case to case, the complaints and counterclaims in these actions generally assert claims for breach of contract, indemnification, and/or declaratory judgment, and seek specific performance (repurchase of defective mortgage loan) and/or money damages. Adverse court decisions, including in cases not involving WMC, could result in new claims and lawsuits on additional loans. However, WMC continues to believe that it has defenses to the claims asserted in litigation, including, for example, based on causation and materiality requirements and applicable statutes of limitations. It is not possible to predict the outcome or impact of these defenses and other factors, any of which could materially affect the amount of any loss ultimately incurred by WMC on these claims.
WMC has also received indemnification demands, nearly all of which are unspecified, from depositors/underwriters/sponsors of RMBS in connection with lawsuits brought by RMBS investors concerning alleged misrepresentations in the securitization offering documents to which WMC is not a party or, in two cases, involving mortgage loan repurchase claims made against RMBS sponsors. WMC believes that it has defenses to these demands.
To the extent WMC is required to repurchase loans, WMC's loss also would be affected by several factors, including pay downs, accrued interest and fees, and the value of the underlying collateral. The reserve and estimate of possible loss reflect judgment, based on currently available information, and a number of assumptions, including economic conditions, claim and settlement activity, pending and threatened litigation, court decisions regarding WMC's legal defenses, indemnification demands, government activity, and other variables in the mortgage industry. Actual losses arising from claims against WMC could exceed these amounts and additional claims and lawsuits could result if actual claim rates, governmental actions, litigation and indemnification activity, adverse court decisions, actual settlement rates or losses WMC incurs on repurchased loans differ from its assumptions.
| FINANCIAL INFORMATION FOR WMC | ||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Total revenues and other income (loss) | $ | (8) | $ | (184) | $ | (291) | ||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes | $ | (52) | $ | (146) | $ | (199) | ||
Alstom legacy matters. On November 2, 2015, we acquired the Thermal, Renewables and Grid businesses from Alstom. Prior to the acquisition, the seller was the subject of two significant cases involving anti-competitive activities and improper payments: (1) in January 2007, Alstom was fined €65 million by the European Commission for participating in a gas insulated switchgear cartel that operated from 1988 to 2004 (that fine was later reduced to €59 million), and (2) in December 2014, Alstom pled guilty in the United States to multiple violations of the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and paid a criminal penalty of $772 million. As part of GE's accounting for the acquisition, we established a reserve amounting to $858 million for legal and compliance matters related to the legacy business practices that were the subject of these and related cases in various jurisdictions.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 200
Regardless of jurisdiction, the allegations relate to claimed anti-competitive conduct or improper payments in the pre-acquisition period as the source of legal violations and/or damages. Given the significant litigation and compliance activity related to these matters and our ongoing efforts to resolve them, it is difficult to assess whether the disbursements will ultimately be consistent with the reserve established. The estimation of this reserve involved significant judgment and may not reflect the full range of uncertainties and unpredictable outcomes inherent in litigation and investigations of this nature. Damages sought may include disgorgement of profits on the underlying business transactions, fines and/or penalties, interest, or other forms of resolution. Factors that can affect the ultimate amount of losses associated with these matters include the way cooperation is assessed and valued, prosecutorial discretion in the determination of damages, formulas for determining fines and penalties, the duration and amount of legal and investigative resources applied, and political and social influences within each jurisdiction, among other considerations. Actual losses arising from claims in these matters could exceed the amount provided. At this time, we are unable to develop a meaningful estimate of the range of reasonably possible additional losses for this exposure.
ENVIRONMENTAL MATTERS
Our operations, like operations of other companies engaged in similar businesses, involve the use, disposal and cleanup of substances regulated under environmental protection laws. We are involved in numerous remediation actions to clean up hazardous wastes as required by federal and state laws. Liabilities for remediation costs exclude possible insurance recoveries and, when dates and amounts of such costs are not known, are not discounted. When there appears to be a range of possible costs with equal likelihood, liabilities are based on the low end of such range. It is reasonably possible that our environmental remediation exposure will exceed amounts accrued. However, due to uncertainties about the status of laws, regulations, technology and information related to individual sites, such amounts are not reasonably estimable. Total reserves related to environmental remediation and asbestos claims, were $1,767 million at December 31, 2016.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 201
Transactions between related companies are made on an arms-length basis and are reported in the GE and GE Capital columns of our financial statements, but are eliminated in deriving our consolidated financial statements. These transactions include, but are not limited to, the following:
| · | GE Capital dividends to GE, |
| · | GE Capital working capital solutions to optimize GE cash management, |
| · | GE Capital enabled GE industrial orders, and |
| · | Aircraft engines, power equipment and healthcare equipment manufactured by GE that are installed on GE Capital investments, including leased equipment. |
In addition to the above transactions that primarily enable growth for the GE businesses, there are routine related party transactions, which include, but are not limited to, the following:
| · | Expenses related to parent-subsidiary pension plans, |
| · | Buildings and equipment leased between GE and GE Capital, including sale-leaseback transactions, |
| · | Information technology (IT) and other services sold to GE Capital by GE, and |
| · | Various investments, loans and allocations of GE corporate overhead costs. |
Presented below is a walk of intercompany eliminations from the unconsolidated GE and GE Capital totals to the consolidated cash flows.
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Cash from (used for) operating activities-continuing operations | ||||||||
| Combined | $ | 28,408 | $ | 17,891 | $ | 21,434 | ||
| GE current receivables sold to GE Capital | 697 | (856) | (1,882) | |||||
| GE Capital dividends to GE | (20,095) | (4,300) | (3,000) | |||||
| Other reclassifications and eliminations(a) | (2,911) | (879) | (519) | |||||
| Total cash from (used for) operating activities-continuing operations | $ | 6,099 | $ | 11,856 | $ | 16,033 | ||
| Cash from (used for) investing activities-continuing operations | ||||||||
| Combined | $ | 58,134 | $ | 59,516 | $ | 17,252 | ||
| GE current receivables sold to GE Capital | (230) | 1,261 | 1,730 | |||||
| GE Capital short-term loan to GE | 1,329 | - | - | |||||
| Other reclassifications and eliminations(a) | 3,380 | 836 | 247 | |||||
| Total cash from (used for) investing activities-continuing operations | $ | 62,613 | $ | 61,613 | $ | 19,229 | ||
| Cash from (used for) financing activities-continuing operations | ||||||||
| Combined | $ | (107,750) | $ | (73,484) | $ | (44,340) | ||
| GE current receivables sold to GE Capital | (467) | (405) | 152 | |||||
| GE Capital dividends to GE | 20,095 | 4,300 | 3,000 | |||||
| GE Capital short-term loan to GE | (1,329) | - | - | |||||
| Other reclassifications and eliminations(a) | (469) | 42 | 276 | |||||
| Total cash from (used for) financing activities-continuing operations | $ | (89,920) | $ | (69,547) | $ | (40,912) | ||
| (a) | Includes eliminations of other cash flows activities including those related to GE Capital enabled GE industrial orders, various investments, loans and allocations of GE corporate overhead costs. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 202
BASIS FOR PRESENTATION
Our operating businesses are organized based on the nature of markets and customers. Segment accounting policies are the same as described and referenced in Note 1. Segment results for our financial services businesses reflect the discrete tax effect of transactions.
A description of our operating segments as of December 31, 2016, can be found below, and details of segment profit by operating segment can be found in the Summary of Operating Segments table in "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" section in this Form 10-K Report.
Power plant products and services, including design, installation, operation and maintenance services are sold into global markets. Gas, steam and aeroderivative turbines, nuclear reactors, generators, combined cycle systems, controls and related services, including total asset optimization solutions, equipment upgrades and long-term maintenance service agreements are sold to power generation and other industrial customers. Water treatment services and equipment include specialty chemical treatment programs, water purification equipment, mobile treatment systems and desalination processes.
Renewable Energy makes power from renewable sources affordable, accessible, and reliable for the benefit of people everywhere. With one of the broadest technology portfolios in the industry, Renewable Energy creates value for customers by providing technology and services in the Onshore Wind Power industry, high-yield offshore wind turbines as well as a full range of solutions, products and services to serve the hydropower industry, from initial design to final commissioning.
Oil & Gas supplies mission critical equipment for the global oil and gas industry, used in applications spanning the entire value chain from drilling and completion through production, liquefied natural gas (LNG) and pipeline compression, pipeline inspection, and including downstream processing in refineries and petrochemical plants. The business designs and manufactures surface and subsea drilling and production systems, equipment for floating production platforms, compressors, turbines, turboexpanders, high pressure reactors, industrial power generation and a broad portfolio of auxiliary equipment.
Aviation products and services include jet engines, aerospace systems and equipment, replacement parts and repair and maintenance services for all categories of commercial aircraft; for a wide variety of military aircraft, including fighters, bombers, tankers and helicopters; for marine applications; and for executive and regional aircraft. Products and services are sold worldwide to airframe manufacturers, airlines and government agencies.
Healthcare products include diagnostic imaging systems such as magnetic resonance (MR), computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scanners, X-ray, surgical & interventional imaging, nuclear imaging, digital mammography and molecular imaging technologies. Healthcare-manufactured technologies include patient and resident monitoring, diagnostic cardiology, ultrasound, bone densitometry, anesthesiology and oxygen therapy, and neonatal and critical care devices. Related services include equipment monitoring and repair, digital technologies and customer productivity services. Products also include diagnostic imaging agents used in medical scanning procedures, drug discovery, biopharmaceutical manufacturing and purification, and tools for protein and cellular analysis for pharmaceutical and academic research, including a pipeline of precision molecular diagnostics in development for neurology, cardiology and oncology applications. Products and services are sold worldwide to hospitals, medical facilities, pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, and to the life science research market.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 203
Transportation is a global technology leader and supplier to the railroad, mining, marine and drilling industries. GE provides freight and passenger locomotives, diesel engines for rail, marine and stationary power applications, railway signaling and communications systems, underground mining equipment, motorized drive systems for mining trucks, information technology solutions, high-quality replacement parts and value added services.
Energy Connections is GE's electrification business. Global teams design leading technology solutions for the delivery, management, conversion and optimization of electrical power for customers across multiple energy-intensive industries. GE has invested in our Energy Connections capabilities, with strategic acquisitions and joint ventures that enable GE to increase its offerings to the utility, industrial, renewable energy, oil and gas, marine, metals and mining industries. Plant automation hardware, software and embedded computing systems including controllers, embedded systems, advanced software, motion control, operator interfaces and industrial computers are also provided by Energy Connections.
Lighting includes the GE Lighting and Current, powered by GE (Current) businesses. GE Lighting is focused on driving innovation and growth in light emitting diode (LED) and connected home technology in the U.S. Lighting offers LEDs in a variety of shapes, sizes, wattages and color temperatures. It's also investing in the growing smart home category, building a suite of connected lighting products with simple connection points that offer new opportunities to do more at home. Current delivers energy efficiency and productivity solutions for commercial and industrial customers. We combine infrastructure technology like LED and solar with new sensor-enabled data networks and Predix-based digital applications to help our customers reduce energy costs, better predict spend and gain business productivity insights. We partner with a wide variety of digital companies to help expand our app catalog, and we offer flexible financing solutions that help our customers achieve faster payback periods and better long-term value.
Capital is the financial services division of GE focused on customers and markets aligned with GE's industrial businesses, whether in developed economies or emerging markets. We provide financial products and services around the globe, that are geared to utilize GE's industry specific expertise in aviation, energy, infrastructure, and healthcare to capitalize on market-specific opportunities. In addition, we continue to operate our run-off insurance activities as part of our continuing operations.
| REVENUES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total revenues(a) | Intersegment revenues(b) | External revenues | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||
| Power | $ | 26,827 | $ | 21,490 | $ | 20,580 | $ | 640 | $ | 762 | $ | 778 | $ | 26,187 | $ | 20,728 | $ | 19,802 | ||||||||
| Renewable Energy | 9,033 | 6,273 | 6,399 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 9,022 | 6,261 | 6,386 | |||||||||||||||||
| Oil & Gas | 12,898 | 16,450 | 19,085 | 383 | 387 | 402 | 12,515 | 16,063 | 18,683 | |||||||||||||||||
| Aviation | 26,261 | 24,660 | 23,990 | 730 | 418 | 692 | 25,530 | 24,242 | 23,298 | |||||||||||||||||
| Healthcare | 18,291 | 17,639 | 18,299 | 15 | 7 | 6 | 18,276 | 17,633 | 18,293 | |||||||||||||||||
| Transportation | 4,713 | 5,933 | 5,650 | 1 | 1 | (2) | 4,713 | 5,932 | 5,652 | |||||||||||||||||
| Energy Connections & Lighting | 15,133 | 16,351 | 15,724 | 1,059 | 1,021 | 912 | 14,074 | 15,329 | 14,812 | |||||||||||||||||
Total industrial | 113,156 | 108,796 | 109,727 | 2,839 | 2,608 | 2,801 | 110,316 | 106,188 | 106,926 | |||||||||||||||||
| Capital | 10,905 | 10,801 | 11,320 | 1,288 | 1,151 | 1,037 | 9,617 | 9,650 | 10,283 | |||||||||||||||||
| Corporate items | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
and eliminations | (368) | (2,211) | (3,863) | (4,127) | (3,759) | (3,838) | 3,760 | 1,548 | (25) | |||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 123,693 | $ | 117,386 | $ | 117,184 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 123,693 | $ | 117,386 | $ | 117,184 | ||||||||
| (b) | Sales from one component to another generally are priced at equivalent commercial selling prices. |
Revenues from customers located in the United States were $53,317 million, $53,238 million and $51,147 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Revenues from customers located outside the United States were $70,376 million, $64,148 million and $66,038 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 204
| Property, plant and | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Assets(a) | equipment additions(b) | Depreciation and amortization | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At December 31 | For the years ended December 31 | For the years ended December 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||
| Power | $ | 55,474 | $ | 51,908 | $ | 26,698 | $ | 769 | $ | 2,122 | $ | 578 | $ | 1,130 | $ | 712 | $ | 563 | ||||||||
| Renewable Energy | 8,794 | 9,468 | 3,572 | 166 | 999 | 41 | 37 | 116 | 113 | |||||||||||||||||
| Oil & Gas | 24,615 | 26,126 | 27,329 | 284 | 422 | 656 | 529 | 596 | 585 | |||||||||||||||||
| Aviation | 38,899 | 34,524 | 33,716 | 1,328 | 1,260 | 1,197 | 900 | 855 | 824 | |||||||||||||||||
| Healthcare | 28,639 | 28,162 | 29,227 | 432 | 284 | 405 | 785 | 799 | 843 | |||||||||||||||||
| Transportation | 4,288 | 4,368 | 4,449 | 108 | 202 | 128 | 159 | 179 | 169 | |||||||||||||||||
| Energy Connections & Lighting | 17,858 | 21,587 | 15,536 | 354 | 1,348 | 535 | 441 | 426 | 548 | |||||||||||||||||
| Capital(c) | 187,804 | 316,069 | 502,204 | 3,769 | 7,570 | 3,818 | 2,515 | 2,584 | 2,612 | |||||||||||||||||
| Corporate items | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
and eliminations(d) | (1,187) | 858 | 11,201 | 94 | (297) | (111) | 341 | 231 | 164 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 365,183 | $ | 493,071 | $ | 653,931 | $ | 7,305 | $ | 13,911 | $ | 7,247 | $ | 6,836 | $ | 6,499 | $ | 6,421 | ||||||||
| (b) | Additions to property, plant and equipment include amounts relating to principal businesses purchased. |
| (c) | Includes Capital discontinued operations |
| (d) | Includes deferred income taxes that are presented as assets for purposes of our consolidating balance sheet presentation. |
| Interest and other financial charges | Provision (benefit) for income taxes | ||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||
| Capital | $ | 3,790 | $ | 2,301 | $ | 1,638 | $ | (1,431) | $ | 4,979 | $ | (861) | |||||
| Corporate items and eliminations(a) | 1,234 | 1,162 | 1,085 | 967 | 1,506 | 1,634 | |||||||||||
| Total | $ | 5,025 | $ | 3,463 | $ | 2,723 | $ | (464) | $ | 6,485 | $ | 773 | |||||
Property, plant and equipment – net associated with operations based in the United States were $14,987 million, $14,273 million and $9,868 million at December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Property, plant and equipment – net associated with operations based outside the United States were $35,531 million, $39,822 million and $38,201 million at December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Changes in operating assets and liabilities are net of acquisitions and dispositions of principal businesses.
Amounts reported in the "Proceeds from sales of discontinued operations" and "Proceeds from principal business dispositions" lines in the Statement of Cash Flows are net of cash disposed and included certain deal-related costs. Amounts reported in the "Net cash from (payments for) principal businesses purchased" line is net of cash acquired and included certain deal-related costs and debt assumed and immediately repaid in acquisitions.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 205
Amounts reported in the "All other operating activities" line in the Statement of Cash Flows consist primarily of adjustments to current and noncurrent accruals, deferrals of costs and expenses and adjustments to assets. Certain supplemental information related to our cash flows is shown below.
| For the years ended December 31 (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| GE | ||||||||
| All other operating activities | ||||||||
| (Gains) losses on purchases and sales of business interests(a) | $ | (3,701) | $ | (1,020) | $ | (188) | ||
| Contract assets (net)(b) | (3,929) | (1,919) | (1,572) | |||||
| Income taxes(c) | (2,752) | 1,671 | 773 | |||||
| Interest charges | 275 | 380 | 332 | |||||
| Principal pension plans(d) | 3,071 | 4,265 | 3,368 | |||||
| Other | (402) | (1,294) | 260 | |||||
| $ | (7,438) | $ | 2,083 | $ | 2,973 | |||
| Net dispositions (purchases) of GE shares for treasury | ||||||||
Open market purchases under share repurchase program(e) | $ | (22,581) | $ | (2,709) | $ | (2,211) | ||
Other purchases | (399) | (58) | (49) | |||||
Dispositions | 1,550 | 1,668 | 1,042 | |||||
| $ | (21,429) | $ | (1,099) | $ | (1,218) | |||
| GE Capital | ||||||||
| All other operating activities | ||||||||
| Cash collateral on derivative contracts | (428) | (1,936) | 738 | |||||
| Increase (decrease) in other liabilities | (2,616) | 4,860 | (3,331) | |||||
| Other | (10) | 2,163 | 5,073 | |||||
| $ | (3,054) | $ | 5,087 | $ | 2,480 | |||
| Net decrease (increase) in GE Capital financing receivables | ||||||||
| Increase in loans to customers | $ | (65,055) | $ | (65,306) | $ | (64,843) | ||
| Principal collections from customers - loans | 60,375 | 60,292 | 60,764 | |||||
| Investment in equipment for financing leases | (690) | (417) | (535) | |||||
| Principal collections from customers - financing leases | 856 | 734 | 841 | |||||
| Sales of financing receivables | 3,235 | 4,923 | 3,612 | |||||
| $ | (1,279) | $ | 226 | $ | (161) | |||
| All other investing activities | ||||||||
| Purchases of investment securities | $ | (18,588) | $ | (7,790) | $ | (2,008) | ||
| Dispositions and maturities of investment securities | 7,343 | 9,587 | 2,723 | |||||
| Decrease (increase) in other assets - investments | 9,202 | (1,439) | (287) | |||||
| Other(f) | 3,682 | (5,048) | 24,146 | |||||
| $ | 1,639 | $ | (4,690) | $ | 24,574 | |||
| Repayments and other reductions (maturities longer than 90 days) | ||||||||
| Short-term (91 to 365 days) | $ | (44,519) | $ | (42,110) | $ | (36,919) | ||
| Long-term (longer than one year) | (13,418) | (2,455) | (864) | |||||
| Principal payments - non-recourse, leveraged leases | (348) | (283) | (304) | |||||
| $ | (58,285) | $ | (44,848) | $ | (38,087) | |||
| All other financing activities | ||||||||
| Proceeds from sales of investment contracts | $ | 19 | $ | 163 | $ | 322 | ||
| Redemption of investment contracts | (346) | (1,235) | (1,113) | |||||
| Other | (800) | (290) | 112 | |||||
| $ | (1,127) | $ | (1,362) | $ | (679) | |||
| (a) | Included pre-tax gains on sales of businesses reclassified to Proceeds from principal business dispositions within Cash flows from investing activities of $(3,136) million for Appliances and $(398) million for GE Asset Management in 2016 and $(623) million for Signaling in 2015. See Note 17. |
| (b) | Contract assets are presented net of related billings in excess of revenues on our long-term product service agreements. See Note 9. |
| (c) | Reflected the effects of current tax expense (benefit) of $(140) million, $3,307 million and $2,110 million and net cash paid during the year for income taxes of $(2,612) million, $(1,636) million and $(1,337) million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Cash flows effects of deferred tax provisions (benefits) are shown separately within cash flows from operating activities. See Note 14. |
| (d) | Reflected the effects of pension costs of $3,623 million, $4,498 million and $3,604 million and employer contributions of $(552) million, $(233) million and $(236) million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. 2016 employer contributions included GE Pension Trust funding of $(330) million representing net sale proceeds associated with the sale of GE Asset Management. See Notes 2 and 12. |
| (e) | Included $(11,370) million paid under ASR agreements in 2016. |
| (f) | Other primarily included net activity related to settlements between our continuing operations (primarily our treasury operations) and businesses in discontinued operations. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 206
We conduct research and development (R&D) activities to continually enhance our existing products and services, develop new product and services to meet our customers' changing needs and requirements, and address new market opportunities.
Research and development expenses are classified in cost of goods and services sold in the Statement of Earnings. In addition, research and development funding from customers, principally the U.S. government, is recorded as an offset to such costs. We also enter into research and development arrangements with unrelated investors, which are generally formed through partnerships and consolidated within GE's financial statements. Research and development funded through consolidated partnerships is classified within net earnings/loss attributable to noncontrolling interests.
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Total R&D | $ | 5,466 | $ | 5,278 | $ | 5,273 | ||
| Less customer funded R&D (principally the U.S. Government) | (611) | (803) | (721) | |||||
| Less partner funded R&D | (73) | (226) | (319) | |||||
| GE funded R&D | $ | 4,782 | $ | 4,249 | $ | 4,233 | ||
Of total Research and Development, the segments with the most significant expenditures for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 were: Aviation $1,595 million, $1,893 million and $1,965 million, respectively; Healthcare $938 million, $905 million, and $817 million, respectively; and Power $695 million, $721 million and $641 million, respectively. The remaining segments and Corporate, including Global Research Center, had combined expenditures of $2,238 million, $1,759 million and $1,850 million, for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
COLLABORATIVE ARRANGEMENTS
Our businesses enter into collaborative arrangements primarily with manufacturers and suppliers of components used to build and maintain certain engines, under which GE and these participants share in the risks and rewards of these product programs. GE's payments to participants are recorded as cost of services sold ($1,080 million, $788 million and $873 million for the years 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively) or as cost of goods sold ($2,482 million, $2,736 million and $2,660 million for the years 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively).
RENTAL EXPENSE
Rental expense under operating leases is shown below.
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| GE | $ | 1,528 | $ | 1,258 | $ | 1,356 | ||
| GE Capital | 91 | 107 | 123 | |||||
| 1,619 | 1,365 | 1,479 | ||||||
| Eliminations | (126) | (169) | (223) | |||||
| Total | $ | 1,493 | $ | 1,196 | $ | 1,256 | ||
At December 31, 2016, minimum rental commitments under noncancellable operating leases aggregated $5,172 million and $302 million for GE and GE Capital, respectively. Amounts payable over the next five years follow.
| (In millions) | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |||||||||
| GE | $ | 942 | $ | 854 | $ | 742 | $ | 640 | $ | 537 | ||||
| GE Capital | 27 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | |||||||||
| 969 | 877 | 763 | 661 | 557 | ||||||||||
| Eliminations | (171) | (155) | (143) | (138) | (130) | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 798 | $ | 722 | $ | 621 | $ | 524 | $ | 427 | ||||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 207
On October 26, 2015, GE Capital International Funding Company Unlimited Company, formerly GE Capital International Funding Company (the Issuer), then a finance subsidiary of General Electric Capital Corporation, settled its previously announced private offers to exchange (the Exchange Offers) the Issuer's new senior unsecured notes for certain outstanding debt securities of General Electric Capital Corporation.
The new notes that were issued were composed of $15.3 billion of 0.964% six month notes due April 2016 (which have subsequently been repaid upon maturity), £0.8 billion of 1.363% six month notes due April 2016 (which have subsequently been repaid upon maturity), $6.1 billion of 2.342% notes due 2020, $2.0 billion of 3.373% notes due 2025 and $11.5 billion of 4.418% notes due 2035. These notes were fully and unconditionally, jointly and severally guaranteed by both the Company and GE Capital International Holdings Limited (GECIHL) (each a Guarantor, and together, the Guarantors).
Under the terms of a registration rights agreement entered into in connection with the Exchange Offers, the Issuer and the Company agreed to file a registration statement with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) for an offer to exchange new senior notes of the Issuer registered with the SEC and guaranteed by the Guarantors for certain of the Issuer's outstanding unregistered senior notes. This exchange was completed in July 2016.
PRESENTATION
In connection with the registration of the senior notes, the Company is required to provide certain financial information regarding the Issuer and the Guarantors of the registered securities. Included are the Condensed Consolidating Statements of Earnings and Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, Condensed Consolidating Statements of Financial Position as of December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015 and Condensed Consolidating Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 for:
| · | General Electric Company (the Parent Company Guarantor) - prepared with investments in subsidiaries accounted for under the equity method of accounting and excluding any inter-segment eliminations. The equity basis earnings (losses) of subsidiaries are reflected in the captions "Equity in earnings (losses) of affiliates" and "Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes"; |
| · | GE Capital International Funding Company Unlimited Company (the Subsidiary Issuer) – incorporated in May 2015 as a finance subsidiary for debt and reflects activity subsequent to the issuance of new notes on October 26, 2015; |
| · | GE Capital International Holdings Limited (GECIHL) (the Subsidiary Guarantor) - prepared with investments in non-guarantor subsidiaries accounted for under the equity method of accounting and reflects activity subsequent to the GE Capital Reorganization on December 3, 2015. The equity basis earnings (losses) of subsidiaries are reflected in the captions "Equity in earnings (losses) of affiliates" and "Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes"; |
| · | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries - prepared on an aggregated basis excluding any elimination or consolidation adjustments and includes predominantly all non-cash adjustments for cash flows; |
| · | Consolidating Adjustments - adjusting entries necessary to consolidate the Parent Company Guarantor with the Subsidiary Issuer, the Subsidiary Guarantor and Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries; and |
| · | Consolidated - prepared on a consolidated basis. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 208
| CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF EARNINGS (LOSS) AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) | ||||||||||||
| FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||
| Parent | Non- | |||||||||||
| Company | Subsidiary | Subsidiary | Guarantor | Consolidating | ||||||||
| (in millions) | Guarantor | Issuer | Guarantor | Subsidiaries | Adjustments | Consolidated | ||||||
| Revenues and other income | ||||||||||||
| Sales of goods and services | $ | 40,315 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 152,047 | $ | (81,971) | $ | 110,391 |
| Other income | 10,949 | - | - | 63,363 | (70,308) | 4,005 | ||||||
| Equity in earnings (loss) of affiliates | 1,397 | - | 1,542 | 116,897 | (119,836) | - | ||||||
| GE Capital revenues from services | - | 897 | 1,419 | 12,994 | (6,012) | 9,297 | ||||||
Total revenues and other income | 52,661 | 897 | 2,961 | 345,301 | (278,127) | 123,693 | ||||||
| Costs and expenses | ||||||||||||
| Interest and other financial charges | 3,505 | 831 | 2,567 | 5,429 | (7,308) | 5,025 | ||||||
| Investment contracts, insurance losses and | ||||||||||||
insurance annuity benefits | - | - | - | 2,863 | (67) | 2,797 | ||||||
| Other costs and expenses | 41,972 | - | 143 | 165,382 | (100,656) | 106,842 | ||||||
Total costs and expenses | 45,478 | 831 | 2,711 | 173,674 | (108,030) | 114,663 | ||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing | ||||||||||||
| operations before income taxes | 7,183 | 66 | 250 | 171,627 | (170,097) | 9,030 | ||||||
| Benefit (provision) for income taxes | 2,539 | (10) | (105) | (1,911) | (49) | 464 | ||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing operations | 9,723 | 56 | 145 | 169,717 | (170,146) | 9,494 | ||||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued | ||||||||||||
| operations, net of taxes | (891) | - | (1,927) | 351 | 1,514 | (954) | ||||||
| Net earnings (loss) | 8,831 | 56 | (1,782) | 170,067 | (168,632) | 8,540 | ||||||
| Less net earnings (loss) attributable to | ||||||||||||
| noncontrolling interests | - | - | - | (149) | (142) | (291) | ||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to | ||||||||||||
| the Company | 8,831 | 56 | (1,782) | 170,216 | (168,490) | 8,831 | ||||||
| Other comprehensive income | (2,069) | (12) | 1,126 | (3,393) | 2,279 | (2,069) | ||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable | ||||||||||||
| to the Company | $ | 6,762 | $ | 44 | $ | (657) | $ | 166,823 | $ | (166,211) | $ | 6,762 |
| CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF EARNINGS (LOSS) AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) | |||||||||||||
| FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||
| Parent | Non- | ||||||||||||
| Company | Subsidiary | Subsidiary | Guarantor | Consolidating | |||||||||
| (in millions) | Guarantor | Issuer | Guarantor | Subsidiaries | Adjustments | Consolidated | |||||||
| Revenues and other income | |||||||||||||
| Sales of goods and services | $ | 43,945 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 139,158 | $ | (77,294) | $ | 105,809 | |
| Other income | 2,725 | - | - | 31,146 | (31,644) | 2,227 | |||||||
| Equity in earnings (loss) of affiliates | 1,815 | - | 437 | 389,796 | (392,048) | - | |||||||
| GE Capital revenues from services | - | 250 | (460) | 36,909 | (27,349) | 9,350 | |||||||
Total revenues and other income | 48,485 | 250 | (23) | 597,009 | (528,335) | 117,386 | |||||||
| 4 | |||||||||||||
| Costs and expenses | |||||||||||||
| Interest and other financial charges | 3,127 | 232 | 284 | 9,037 | (9,216) | 3,463 | |||||||
| Investment contracts, insurance losses and | |||||||||||||
insurance annuity benefits | - | - | - | 2,748 | (143) | 2,605 | |||||||
| Other costs and expenses | 45,308 | - | 3 | 160,472 | (102,651) | 103,132 | |||||||
Total costs and expenses | 48,435 | 232 | 287 | 172,257 | (112,011) | 109,200 | |||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing | |||||||||||||
| operations before income taxes | 50 | 18 | (310) | 424,752 | (416,324) | 8,186 | |||||||
| Benefit (provision) for income taxes | 1,314 | (2) | (9) | (11,426) | 3,639 | (6,485) | |||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing operations | 1,364 | 15 | (319) | 413,326 | (412,686) | 1,700 | |||||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued | |||||||||||||
| operations, net of taxes | (7,490) | - | 483 | (738) | 250 | (7,495) | |||||||
| Net earnings (loss) | (6,126) | 15 | 164 | 412,588 | (412,436) | (5,795) | |||||||
| Less net earnings (loss) attributable to | |||||||||||||
| noncontrolling interests | - | - | - | 249 | 82 | 332 | |||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to | |||||||||||||
| the Company | (6,126) | 15 | 164 | 412,339 | (412,518) | (6,126) | |||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | 1,644 | 12 | 1,377 | (4,843) | 3,454 | 1,644 | |||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable | |||||||||||||
| to the Company | $ | (4,483) | $ | 27 | $ | 1,542 | $ | 407,496 | $ | (409,065) | $ | (4,483) | |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 209
| CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF EARNINGS (LOSS) AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) | |||||||||||||
| FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2014 | |||||||||||||
| Parent | Non- | ||||||||||||
| Company | Subsidiary | Subsidiary | Guarantor | Consolidating | |||||||||
| (in millions) | Guarantor | Issuer | Guarantor | Subsidiaries | Adjustments | Consolidated | |||||||
| Revenues and other income | |||||||||||||
| Sales of goods and services | $ | 44,511 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 137,034 | $ | (74,786) | $ | 106,758 | |
| Other income | 1,722 | - | - | 22,416 | (23,360) | 778 | |||||||
| Equity in earnings (loss) of affiliates | 10,510 | - | - | 53,841 | (64,351) | - | |||||||
| GE Capital revenues from services | - | - | - | 50,749 | (41,101) | 9,648 | |||||||
Total revenues and other income | 56,743 | - | - | 264,040 | (203,598) | 117,184 | |||||||
| Costs and expenses | |||||||||||||
| Interest and other financial charges | 3,014 | - | - | 11,395 | (11,686) | 2,723 | |||||||
| Investment contracts, insurance losses and | |||||||||||||
insurance annuity benefits | - | - | - | 2,678 | (148) | 2,530 | |||||||
| Other costs and expenses | 46,128 | - | - | 155,133 | (99,593) | 101,668 | |||||||
Total costs and expenses | 49,142 | - | - | 169,206 | (111,427) | 106,921 | |||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing | |||||||||||||
| operations before income taxes | 7,601 | - | - | 94,833 | (92,171) | 10,263 | |||||||
| Benefit (provision) for income taxes | 1,777 | - | - | (4,181) | 1,631 | (773) | |||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing operations | 9,378 | - | - | 90,652 | (90,540) | 9,490 | |||||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued | |||||||||||||
| operations, net of taxes | 5,855 | - | - | (27) | 27 | 5,855 | |||||||
| Net earnings (loss) | 15,233 | - | - | 90,625 | (90,513) | 15,345 | |||||||
| Less net earnings (loss) attributable to | |||||||||||||
| noncontrolling interests | - | - | - | 2,893 | (2,781) | 112 | |||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to | |||||||||||||
| the Company | 15,233 | - | - | 87,733 | (87,733) | 15,233 | |||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | (9,053) | - | - | (2,787) | 2,787 | (9,053) | |||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable | |||||||||||||
| to the Company | $ | 6,180 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 84,946 | $ | (84,946) | $ | 6,180 | |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 210
| CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION | |||||||||||||
| DECEMBER 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||
| Parent | Non- | ||||||||||||
| Company | Subsidiary | Subsidiary | Guarantor | Consolidating | |||||||||
| (In millions) | Guarantor | Issuer | Guarantor | Subsidiaries | Adjustments | Consolidated | |||||||
| Assets | |||||||||||||
| Cash and equivalents | $ | 2,558 | $ | - | $ | 3 | $ | 46,994 | $ | (1,426) | $ | 48,129 | |
| Investment securities | 1 | - | - | 47,394 | (3,082) | 44,313 | |||||||
| Receivables - net | 63,620 | 17,157 | 30,470 | 79,401 | (148,385) | 42,263 | |||||||
| Inventories | 4,654 | - | - | 21,076 | (3,377) | 22,354 | |||||||
| Property, plant and equipment - net | 5,768 | - | - | 46,366 | (1,615) | 50,518 | |||||||
| Investment in subsidiaries(a) | 272,685 | - | 80,481 | 492,674 | (845,840) | - | |||||||
| Goodwill and intangible assets | 8,128 | - | - | 42,074 | 36,673 | 86,875 | |||||||
| All other assets | 14,692 | 44 | 39 | 201,276 | (160,134) | 55,917 | |||||||
| Assets of discontinued operations | - | - | - | - | 14,815 | 14,815 | |||||||
| Total assets | $ | 372,107 | $ | 17,202 | $ | 110,992 | $ | 977,255 | $ | (1,112,372) | $ | 365,183 | |
| Liabilities and equity | |||||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings | $ | 167,089 | $ | 1 | $ | 46,432 | $ | 25,919 | $ | (208,727) | $ | 30,714 | |
| Accounts payable | 5,412 | - | - | 47,366 | (38,343) | 14,435 | |||||||
| Other current liabilities | 11,072 | 33 | 117 | 25,095 | 114 | 36,431 | |||||||
| Long-term and non-recourse borrowings | 68,983 | 16,486 | 34,389 | 68,912 | (83,273) | 105,496 | |||||||
| All other liabilities | 43,722 | 511 | 481 | 58,376 | (9,656) | 93,434 | |||||||
| Liabilities of discontinued operations | - | - | - | - | 4,158 | 4,158 | |||||||
| Total Liabilities | 296,279 | 17,030 | 81,419 | 225,667 | (335,727) | 284,668 | |||||||
| Redeemable noncontrolling interests | - | - | - | 2,223 | 802 | 3,025 | |||||||
| GE shareowners' equity | 75,828 | 171 | 29,573 | 747,719 | (777,463) | 75,828 | |||||||
| Noncontrolling interests | - | - | - | 1,647 | 16 | 1,663 | |||||||
| Total equity | 75,828 | 171 | 29,573 | 749,366 | (777,447) | 77,491 | |||||||
| Total liabilities, redeemable | |||||||||||||
| noncontrolling interests and equity | $ | 372,107 | $ | 17,202 | $ | 110,992 | $ | 977,255 | $ | (1,112,372) | $ | 365,183 | |
| (a) | Included within the subsidiaries of the Subsidiary Guarantor are cash and cash equivalent balances of $28.5 billion and net assets of discontinued operations of $6.0 billion. |
| CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION | ||||||||||||
| DECEMBER 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||
| Parent | Non- | |||||||||||
| Company | Subsidiary | Subsidiary | Guarantor | Consolidating | ||||||||
| (In millions) | Guarantor | Issuer | Guarantor | Subsidiaries | Adjustments | Consolidated | ||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||
| Cash and equivalents | $ | 4,137 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 86,955 | $ | (20,609) | $ | 70,483 |
| Investment securities | 14 | - | - | 40,886 | (8,927) | 31,973 | ||||||
| Receivables - net | 88,696 | 33,232 | 69,306 | 75,909 | (221,286) | 45,856 | ||||||
| Inventories | 5,447 | - | - | 19,762 | (2,694) | 22,515 | ||||||
| Property, plant and equipment - net | 6,540 | - | - | 56,808 | (9,253) | 54,095 | ||||||
| Investment in subsidiaries(a) | 274,471 | - | 78,505 | 405,686 | (758,662) | - | ||||||
| Goodwill and intangible assets | 7,793 | - | - | 61,412 | 14,118 | 83,323 | ||||||
| All other assets | 15,732 | 11 | 915 | 247,611 | (200,392) | 63,876 | ||||||
| Assets of discontinued operations | - | - | - | - | 120,951 | 120,951 | ||||||
| Total assets | $ | 402,828 | $ | 33,242 | $ | 148,725 | $ | 995,029 | $ | (1,086,754) | $ | 493,071 |
| Liabilities and equity | ||||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings | $ | 145,051 | $ | 16,204 | $ | 71,862 | $ | 60,601 | $ | (243,858) | $ | 49,860 |
| Accounts payable | 6,096 | - | - | 37,636 | (30,052) | 13,680 | ||||||
| Other current liabilities | 14,482 | - | 17 | 34,903 | (7,861) | 41,540 | ||||||
| Long-term and non-recourse borrowings | 97,471 | 16,423 | 46,392 | 105,801 | (118,345) | 147,742 | ||||||
| All other liabilities | 41,455 | 488 | 224 | 57,996 | (9,513) | 90,651 | ||||||
| Liabilities of discontinued operations | - | - | - | - | 46,487 | 46,487 | ||||||
| Total Liabilities | 304,555 | 33,115 | 118,495 | 296,937 | (363,141) | 389,961 | ||||||
| Redeemable noncontrolling interests | - | - | - | 2,888 | 84 | 2,972 | ||||||
| GE shareowners' equity | 98,274 | 127 | 30,230 | 693,589 | (723,946) | 98,274 | ||||||
| Noncontrolling interests | - | - | - | 1,616 | 248 | 1,864 | ||||||
| Total equity | 98,274 | 127 | 30,230 | 695,204 | (723,697) | 100,138 | ||||||
| Total liabilities, redeemable | ||||||||||||
| noncontrolling interests and equity | $ | 402,828 | $ | 33,242 | $ | 148,725 | $ | 995,029 | $ | (1,086,754) | $ | 493,071 |
| (a) | Included within the subsidiaries of the Subsidiary Guarantor are cash and cash equivalent balances of $40.1 billion and net assets of discontinued operations of $58.6 billion. |
| CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS | ||||||||||||
| FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||
| Parent | Non- | |||||||||||
| Company | Subsidiary | Subsidiary | Guarantor | Consolidating | ||||||||
| (In millions) | Guarantor | Issuer | Guarantor | Subsidiaries | adjustments | Consolidated | ||||||
| Cash flows – operating activities | ||||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) operating activities - | ||||||||||||
| continuing operations | $ | (4,966) | $ | (10) | $ | (52) | $ | 162,918 | $ | (151,791) | $ | 6,099 |
| Cash from (used for) operating activities - | ||||||||||||
| discontinued operations | (891) | - | - | (5,039) | (413) | (6,343) | ||||||
| Cash from (used for) operating activities | (5,858) | (10) | (52) | 157,880 | (152,204) | (244) | ||||||
| Cash flows – investing activities | ||||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) investing activities – | ||||||||||||
| continuing operations | 14,158 | 16,384 | 35,443 | 72,205 | (75,577) | 62,613 | ||||||
| Cash from (used for) investing activities – | ||||||||||||
| discontinued operations | - | - | - | (13,412) | - | (13,412) | ||||||
| Cash from (used for) investing activities | 14,158 | 16,384 | 35,443 | 58,794 | (75,577) | 49,202 | ||||||
| Cash flows – financing activities | ||||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) financing activities – | ||||||||||||
| continuing operations | (9,879) | (16,374) | (35,388) | (275,243) | 246,964 | (89,920) | ||||||
| Cash from (used for) financing activities – | ||||||||||||
| discontinued operations | - | - | - | 789 | - | 789 | ||||||
| Cash from (used for) financing activities | (9,879) | (16,374) | (35,388) | (274,454) | 246,964 | (89,131) | ||||||
| Effect of currency exchange rate changes | ||||||||||||
| on cash and equivalents | - | - | - | (1,146) | - | (1,146) | ||||||
| Increase (decrease) in cash and equivalents | (1,578) | - | 3 | (58,927) | 19,183 | (41,319) | ||||||
| Cash and equivalents at beginning of year | 4,137 | - | - | 107,351 | (20,609) | 90,879 | ||||||
| Cash and equivalents at end of year | 2,558 | - | 3 | 48,423 | (1,426) | 49,558 | ||||||
| Less cash and equivalents of discontinued | ||||||||||||
| operations at end of year | - | - | - | 1,429 | - | 1,429 | ||||||
| Cash and equivalents of continuing operations | ||||||||||||
| at end of year | $ | 2,558 | $ | - | $ | 3 | $ | 46,994 | $ | (1,426) | $ | 48,129 |
| CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS | ||||||||||||
| FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||
| Parent | Non- | |||||||||||
| Company | Subsidiary | Subsidiary | Guarantor | Consolidating | ||||||||
| (In millions) | Guarantor | Issuer | Guarantor | Subsidiaries | adjustments | Consolidated | ||||||
| Cash flows – operating activities | ||||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) operating activities - | ||||||||||||
| continuing operations | $ | 13,587 | $ | 68 | $ | 631 | $ | 433,479 | $ | (435,909) | $ | 11,856 |
| Cash from (used for) operating activities - | ||||||||||||
| discontinued operations | (7,490) | - | (30) | 27,533 | (11,979) | 8,034 | ||||||
| Cash from (used for) operating activities | 6,097 | 68 | 601 | 461,013 | (447,888) | 19,891 | ||||||
| Cash flows – investing activities | ||||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) investing activities – | ||||||||||||
| continuing operations | 7,106 | (248) | (601) | (493,933) | 549,289 | 61,613 | ||||||
| Cash from (used for) investing activities – | ||||||||||||
| discontinued operations | - | - | - | 5,854 | (7,979) | (2,125) | ||||||
| Cash from (used for) investing activities | 7,106 | (248) | (601) | (488,079) | 541,310 | 59,488 | ||||||
| Cash flows – financing activities | ||||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) financing activities – | ||||||||||||
| continuing operations | (13,886) | 180 | - | 67,063 | (122,904) | (69,547) | ||||||
| Cash from (used for) financing activities – | ||||||||||||
| discontinued operations | - | - | - | (37,582) | 31,075 | (6,507) | ||||||
| Cash from (used for) financing activities | (13,886) | 180 | - | 29,481 | (91,829) | (76,054) | ||||||
| Effect of currency exchange rate changes | ||||||||||||
| on cash and equivalents | - | - | - | (3,464) | - | (3,464) | ||||||
| Increase (decrease) in cash and equivalents | (683) | - | - | (1,049) | 1,594 | (138) | ||||||
| Cash and equivalents at beginning of year | 4,820 | - | - | 108,400 | (22,203) | 91,017 | ||||||
| Cash and equivalents at end of year | 4,137 | - | - | 107,351 | (20,609) | 90,879 | ||||||
| Less cash and equivalents of discontinued | ||||||||||||
| operations at end of year | - | - | - | 20,395 | - | 20,395 | ||||||
| Cash and equivalents of continuing operations | ||||||||||||
| at end of year | $ | 4,137 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 86,955 | $ | (20,609) | $ | 70,483 |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 213
| CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS | ||||||||||||
| FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||
| Parent | Non- | |||||||||||
| Company | Subsidiary | Subsidiary | Guarantor | Consolidating | ||||||||
| (In millions) | Guarantor | Issuer | Guarantor | Subsidiaries | adjustments | Consolidated | ||||||
| Cash flows – operating activities | ||||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) operating activities - | ||||||||||||
| continuing operations | $ | (2,483) | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 147,449 | $ | (128,933) | $ | 16,033 |
| Cash from (used for) operating activities - | ||||||||||||
| discontinued operations | 5,855 | - | - | 5,794 | 27 | 11,676 | ||||||
| Cash from (used for) operating activities | 3,372 | - | - | 153,243 | (128,906) | 27,709 | ||||||
| Cash flows – investing activities | ||||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) investing activities – | ||||||||||||
| continuing operations | (1,410) | - | - | (403,870) | 424,509 | 19,229 | ||||||
| Cash from (used for) investing activities – | ||||||||||||
| discontinued operations | - | - | - | (24,263) | - | (24,263) | ||||||
| Cash from (used for) investing activities | (1,410) | - | - | (428,133) | 424,509 | (5,034) | ||||||
| Cash flows – financing activities | ||||||||||||
| Cash from (used for) financing activities – | ||||||||||||
| continuing operations | (5,641) | - | - | 272,150 | (307,421) | (40,912) | ||||||
| Cash from (used for) financing activities – | ||||||||||||
| discontinued operations | - | - | - | 23,956 | - | 23,956 | ||||||
| Cash from (used for) financing activities | (5,641) | - | - | 296,106 | (307,421) | (16,956) | ||||||
| Effect of currency exchange rate changes | ||||||||||||
| on cash and equivalents | - | - | - | (3,492) | - | (3,492) | ||||||
| Increase (decrease) in cash and equivalents | (3,679) | - | - | 17,721 | (11,818) | 2,224 | ||||||
| Cash and equivalents at beginning of year | 8,499 | - | - | 90,678 | (10,385) | 88,792 | ||||||
| Cash and equivalents at end of year | 4,820 | - | - | 108,400 | (22,203) | 91,017 | ||||||
| Less cash and equivalents of discontinued | ||||||||||||
| operations at end of year | - | - | - | 20,991 | - | 20,991 | ||||||
| Cash and equivalents of continuing operations | ||||||||||||
| at end of year | $ | 4,820 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 87,408 | $ | (22,203) | $ | 70,025 |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 214
NOTE 29. SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
POSTRETIREMENT BENEFIT PLANS
As discussed in Note 12, we sponsor a number of pension plans which consist of the two principal pension plans for certain U.S. employees as well as other affiliate pension plans. In addition, we sponsor a number of postretirement health and life insurance benefit plans (retiree benefit plans).
The accounting requirements and concepts discussed in Note 12 Postretirement Benefit Plans are the same for other pension plans and principal retiree benefit plans and are consistently applied.
The following disclosures provide additional information with respect to our pension plans and principal retiree benefit plans.
Other pension plans in 2016 included 49 U.S. and non-U.S. pension plans with pension assets or obligations greater than $50 million.
Principal Retiree Benefit Plans provide health and life insurance benefits to eligible participants and these participants share in the cost of healthcare benefits.
| COST OF BENEFIT PLANS | |||||||||||||||||
| Other pension plans | Principal retiree benefit plans | ||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||
| Service cost for benefits earned | $ | 462 | $ | 416 | $ | 403 | $ | 123 | $ | 145 | $ | 164 | |||||
| Prior service cost (credit) amortization | 1 | - | 6 | (164) | (8) | 353 | |||||||||||
| Expected return on plan assets | (1,034) | (881) | (789) | (43) | (48) | (50) | |||||||||||
| Interest cost on benefit obligations | 670 | 555 | 587 | 249 | 335 | 424 | |||||||||||
| Net actuarial loss (gain) amortization | 256 | 289 | 205 | (50) | (25) | (150) | |||||||||||
| Curtailment loss (gain) | 19 | (6) | - | - | (225) | (a) | 48 | ||||||||||
| Benefit plans cost | $ | 374 | $ | 373 | $ | 412 | $ | 115 | $ | 174 | $ | 789 | |||||
ASSUMPTIONS USED IN BENEFIT CALCULATIONS
The accounting assumptions in the table below are those that are significant to the measurement of our benefit obligations.
| ASSUMPTIONS USED TO MEASURE BENEFIT OBLIGATIONS | |||||||||||||
| Other pension plans (weighted average) | Principal retiree benefit plans | ||||||||||||
| December 31 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Discount rate | 2.58 | % | 3.33 | % | 3.53 | % | 3.75 | % | 3.93 | % | 3.89 | % | |
| Compensation increases | 3.48 | 3.32 | 3.60 | 3.80 | 3.80 | 4.10 | |||||||
| Initial healthcare trend rate | N/A | N/A | N/A | 6.00 | (a) | 6.00 | 6.00 | ||||||
The healthcare trend assumptions for 2015 and 2016 apply to our pre-65 retiree medical plans. Our post-65 retiree plan has a fixed subsidy and therefore is not subject to healthcare inflation.
The discount rate used to measure the benefit obligation at the end of the year is also used to measure benefit cost in the following year. The assumptions used to measure benefit cost follow.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 215
| ASSUMPTIONS USED TO MEASURE BENEFIT COST | ||||||||||||||||
| Other pension plans (weighted average) | Principal retiree benefit plans | |||||||||||||||
| December 31 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Discount rate | 3.33 | % | 3.53 | % | 4.39 | % | 3.93 | % | (a) | 3.89 | % | (a) | 4.61 | % | (a) | |
| Expected return on assets | 6.36 | 6.95 | 6.92 | 7.00 | 7.00 | 7.00 | ||||||||||
| (a) | Weighted average discount rates of 3.86%, 3.92% and 4.47% were used for determination of costs in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. |
| BENEFIT OBLIGATIONS | ||||||||||||
| Other pension plans | Principal retiree benefit plans | |||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 21,618 | $ | 15,589 | $ | 6,757 | $ | 10,703 | ||||
| Service cost for benefits earned | 462 | 416 | 123 | 145 | ||||||||
| Interest cost on benefit obligations | 670 | 555 | 249 | 335 | ||||||||
| Participant contributions | 43 | 15 | 51 | 50 | ||||||||
| Plan amendments | (54) | (12) | (7) | (3,291) | (a) | |||||||
| Actuarial loss (gain) | 2,993 | (b) | (406) | (b) | (291) | (c) | (444) | (b) | ||||
| Benefits paid | (842) | (576) | (603) | (691) | ||||||||
| Acquisitions (dispositions)/ other - net | (98) | 6,859 | (d) | 10 | (50) | |||||||
| Exchange rate adjustments | (2,249) | (822) | - | - | ||||||||
| Balance at December 31(e) | $ | 22,543 | $ | 21,618 | $ | 6,289 | $ | 6,757 | ||||
| (a) |
| (b) | Primarily associated with discount rate changes. |
| (c) | Primarily associated with lower costs from new healthcare supplier contracts. |
| (d) | Substantially all related to Alstom acquisition. |
| (e) | The benefit obligation for retiree health plans was $4,366 million and $4,838 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. |
The fair value of other pension plans' and principal retiree benefit plans' investments is presented below. The inputs and valuation techniques used to measure the fair value of the assets are consistently applied and described in Note 1.
| Other pension plans | Principal retiree benefit plans | ||||||||||
| December 31 (in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Equity securities | |||||||||||
U.S. equity securities | $ | 666 | $ | 667 | $ | 187 | $ | 203 | |||
Non-U.S. equity securities | 6,337 | 6,323 | 152 | 162 | |||||||
| Debt securities | |||||||||||
Fixed income and cash investment funds | 6,049 | 6,258 | 30 | 84 | |||||||
U.S. corporate | 319 | 242 | 38 | 52 | |||||||
Other debt securities | 577 | 551 | 82 | 93 | |||||||
| Private equities | 627 | 703 | 61 | 75 | |||||||
| Real estate | 1,449 | 1,358 | 4 | 6 | |||||||
| Other investments | 1,067 | 1,266 | 21 | 20 | |||||||
| Total plan assets | $ | 17,091 | $ | 17,368 | $ | 575 | $ | 695 | |||
Other Pension Plans assets valued using NAV for practical expedient amounted to $4,669 million and $4,213 million as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The percentages of other pension plans assets valued using NAV by investment fund type for equity securities, fixed income and cash, and alternative investments were 7%, 4% and 16% as of December 31, 2016, respectively, and 6%, 3% and 15% as of December 31, 2015, respectively.
The practical expedient was not applied for investments with a fair value of $135 million and $169 million in 2016 and 2015, respectively and those investments were classified within Level 3. The remaining investments were substantially all considered Level 1 and 2.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 216
Principal retiree benefit plan assets valued using NAV for practical expedient amounted to $133 million and $160 million as of December 31, 2016 and 2015. There were no Level 3 investments held in 2016 and 2015. The remaining investments were considered Level 1 or Level 2.
| FAIR VALUE OF PLAN ASSETS | |||||||||||
| Other pension plans | Principal retiree benefit plans | ||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 17,368 | $ | 12,386 | $ | 695 | $ | 813 | |||
| Actual gain on plan assets | 1,743 | 381 | 22 | 22 | |||||||
| Employer contributions | 795 | 549 | 410 | 501 | |||||||
| Participant contributions | 43 | 15 | 51 | 50 | |||||||
| Benefits paid | (842) | (576) | (603) | (691) | |||||||
| Acquisitions (dispositions) / other - net | (81) | 5,207 | (a) | - | - | ||||||
| Exchange rate adjustments | (1,935) | (594) | - | - | |||||||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 17,091 | $ | 17,368 | $ | 575 | $ | 695 | |||
| ASSET ALLOCATION | ||||||||||||
| Other pension plans | Principal retiree | |||||||||||
| Principal pension plans | (weighted average) | benefit plans | ||||||||||
| 2016 | 2016 | 2016 | 2016 | 2016 | 2016 | |||||||
| Target | Actual | Target | Actual | Target | Actual | |||||||
| December 31 | allocation | allocation | allocation | allocation | allocation | allocation | ||||||
| Equity securities | 18 - 58 | % | 46 | % | 39 | % | 41 | % | 35 - 75 | % | 59 | % |
| Debt securities (including cash equivalents) | 11 - 61 | 33 | 30 | 41 | 11 - 46 | 26 | ||||||
| Private equities | 6 - 16 | 10 | 3 | 4 | 0 - 25 | 11 | ||||||
| Real estate | 3 - 13 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 0 - 12 | 1 | ||||||
| Other investments | 3 - 13 | 4 | 19 | 6 | 0 - 10 | 3 | ||||||
Plan fiduciaries of the GE Pension Plan set investment policies and strategies for the GE Pension Trust and oversee its investment allocation, which includes selecting investment managers and setting long-term strategic targets. The primary strategic investment objectives are balancing investment risk and return and monitoring the plan's liquidity position in order to meet the near-term benefit payment and other cash needs. Target allocation percentages are established at an asset class level by plan fiduciaries. Target allocation ranges are guidelines, not limitations, and occasionally plan fiduciaries will approve allocations above or below a target range.
According to statute, the aggregate holdings of all qualifying employer securities (e.g., GE common stock) and qualifying employer real property may not exceed 10% of the fair value of trust assets at the time of purchase. GE securities represented 2.1% and 3.7% of the GE Pension Trust assets at year end 2016 and 2015, respectively.
The GE Pension Plan has a broadly diversified portfolio of investments in equities, fixed income, private equities, real estate and hedge funds; these investments are both U.S. and non-U.S. in nature. As of December 31, 2016, no sector concentration of assets exceeded 15% of total GE Pension Plan assets.
| ESTIMATED FUTURE BENEFIT PAYMENTS | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2022 - | ||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2026 | ||||||||||||
| Principal pension plans | $ | 3,450 | $ | 3,595 | $ | 3,695 | $ | 3,790 | $ | 3,865 | $ | 20,455 | ||||||
| Other pension plans | 785 | 795 | 805 | 815 | 830 | 4,400 | ||||||||||||
| Principal retiree benefit plans | 600 | 580 | 560 | 535 | 520 | 2,245 | ||||||||||||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 217
| 2016 COST OF POSTRETIREMENT BENEFIT PLANS AND CHANGES IN OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME | |||||||||||||
| Principal | |||||||||||||
| Total | Principal | Other | retiree | ||||||||||
| postretirement | pension | pension | benefit | ||||||||||
| (In millions) | benefit plans | plans | plans | plans | |||||||||
| Cost of postretirement benefit plans | $ | 4,112 | $ | 3,623 | $ | 374 | $ | 115 | |||||
| Changes in other comprehensive income | |||||||||||||
Prior service cost (credit) – current year | (61) | - | (54) | (7) | |||||||||
Net actuarial loss (gain) – current year | 4,038 | 2,317 | 1,989 | (268) | |||||||||
| Net curtailment/gain (loss) | (50) | (31) | (19) | - | |||||||||
Prior service credit (cost) amortization | (140) | (303) | (1) | 164 | |||||||||
Net actuarial gain (loss) amortization | (2,655) | (2,449) | (256) | 50 | |||||||||
| Total changes in other comprehensive income | 1,132 | (466) | 1,659 | (61) | |||||||||
| Cost of postretirement benefit plans and | |||||||||||||
changes in other comprehensive income | $ | 5,244 | $ | 3,157 | $ | 2,033 | $ | 54 | |||||
See Note 20 for the primary information related to our derivatives and hedging activity. This section provides certain supplemental information about this topic.
Changes in the fair value of derivatives are recorded in a separate component of equity (referred to below as Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income, or AOCI) and are recorded in earnings in the period in which the hedged transaction occurs. The table below summarizes this activity by hedging instrument.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 218
| FAIR VALUE OF DERIVATIVES | |||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| December 31 (in millions) | Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities | |||||||
| Derivatives accounted for as hedges | |||||||||||
Interest rate contracts | $ | 3,106 | $ | 210 | $ | 4,132 | $ | 158 | |||
Currency exchange contracts | 402 | 624 | 1,109 | 1,383 | |||||||
Other contracts | - | - | - | - | |||||||
| 3,508 | 834 | 5,241 | 1,541 | ||||||||
| Derivatives not accounted for as hedges | |||||||||||
Interest rate contracts | 62 | 20 | 119 | 44 | |||||||
Currency exchange contracts | 1,778 | 4,011 | 1,715 | 4,048 | |||||||
Other contracts | 119 | 17 | 315 | 49 | |||||||
| 1,958 | 4,048 | 2,149 | 4,141 | ||||||||
| Gross derivatives recognized in statement of | |||||||||||
| financial position | |||||||||||
| Gross derivatives | 5,467 | 4,883 | 7,391 | 5,681 | |||||||
| Gross accrued interest | 768 | (24) | 1,001 | (13) | |||||||
| 6,234 | 4,859 | 8,392 | 5,668 | ||||||||
| Amounts offset in statement of financial position | |||||||||||
| Netting adjustments(a) | (3,097) | (3,094) | (4,326) | (4,326) | |||||||
| Cash collateral(b) | (2,025) | (1,355) | (1,784) | (642) | |||||||
| (5,121) | (4,449) | (6,110) | (4,968) | ||||||||
| Net derivatives recognized in statement of | |||||||||||
| financial position | |||||||||||
| Net derivatives | 1,113 | 410 | 2,282 | 700 | |||||||
| Amounts not offset in statement of | |||||||||||
| financial position | |||||||||||
| Securities held as collateral(c) | (442) | - | (1,277) | - | |||||||
| Net amount | $ | 671 | $ | 410 | $ | 1,005 | $ | 700 | |||
Derivatives are classified in the captions "All other assets" and "All other liabilities" and the related accrued interest is classified in "Other GE Capital receivables" and "All other liabilities" in our Statement of Financial Position.
(a) The netting of derivative receivables and payables is permitted when a legally enforceable master netting agreement exists. Amounts include fair value adjustments related to our own and counterparty non-performance risk. At December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, the cumulative adjustment for non-performance risk was $(3) million and insignificant, respectively.
(b) Excluded excess cash collateral received and posted of $6 million and $177 million at December 31, 2016, respectively, and $48 million and $379 million at December 31, 2015, respectively.
(c) Excluded excess securities collateral received of zero and $107 million at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively.
| CASH FLOW HEDGE ACTIVITY | |||||||||||
| Gain (loss) reclassified | |||||||||||
| Gain (loss) recognized in AOCI | from AOCI into earnings | ||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Interest rate contracts | $ | 6 | $ | (1) | $ | (79) | $ | (130) | |||
| Currency exchange contracts | (281) | (907) | (282) | (784) | |||||||
| Commodity contracts | - | (5) | (2) | (4) | |||||||
| Total(a) | $ | (274) | $ | (913) | $ | (364) | $ | (918) | |||
| (a) | Gain (loss) is recorded in "GE Capital revenues from services", "Interest and other financial charges", and "Other costs and expenses" in our Statement of Earnings when reclassified. |
The total pre-tax amount in AOCI related to cash flow hedges of forecasted transactions was a $40 million gain at December 31, 2016. We expect to transfer $83 million loss to earnings as an expense in the next 12 months contemporaneously with the earnings effects of the related forecasted transactions. In both the twelve months ended 2016 and 2015, we recognized insignificant gains and losses related to hedged forecasted transactions and firm commitments that did not occur by the end of the originally specified period. At December 31, 2016 and 2015, the maximum term of derivative instruments that hedge forecasted transactions was 16 years and 17 years, respectively. See Note 15 for additional information about reclassifications out of AOCI.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 219
For cash flow hedges, the amount of ineffectiveness in the hedging relationship and amount of the changes in fair value of the derivatives that are not included in the measurement of ineffectiveness were insignificant for each reporting period.
COUNTERPARTY CREDIT RISK
Fair values of our derivatives can change significantly from period to period based on, among other factors, market movements and changes in our positions. We manage counterparty credit risk (the risk that counterparties will default and not make payments to us according to the terms of our agreements) on an individual counterparty basis. Where we have agreed to netting of derivative exposures with a counterparty, we net our exposures with that counterparty and apply the value of collateral posted to us to determine the exposure. We actively monitor these net exposures against defined limits and take appropriate actions in response, including requiring additional collateral.
As discussed above, we have provisions in certain of our master agreements that require counterparties to post collateral (typically, cash or U.S. Treasury securities) when our receivables due from the counterparties, measured at current market value, exceeds specified limits. The fair value of such collateral was $2,466 million at December 31, 2016, of which $2,025 million was cash and $442 million was in the form of securities held by a custodian for our benefit. Under certain of these same agreements, we post collateral to our counterparties for our derivative obligations, the fair value of which was $1,355 million at December 31, 2016. At December 31, 2016, our exposure to counterparties (including accrued interest), net of collateral we hold, was $496 million. This excludes exposures related to embedded derivatives.
Additionally, our master agreements typically contain mutual downgrade provisions that provide the ability of each party to require termination if the long-term credit rating of the counterparty were to fall below A-/A3 or other ratings levels agreed upon with the counterparty. In certain of these master agreements, each party also has the ability to require termination if the short-term rating of the counterparty were to fall below A-1/P-1. Our master agreements also typically contain provisions that provide termination rights upon the occurrence of certain other events, such as a bankruptcy or events of default by one of the parties. If an agreement was terminated under any of these circumstances, the termination amount payable would be determined on a net basis and could also take into account any collateral posted. The net amount of our derivative liability, after consideration of collateral posted by us and outstanding interest payments was $385 million at December 31, 2016. This excludes exposure related to embedded derivatives.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 220
| First quarter | Second quarter | Third quarter | Fourth quarter | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions; per-share amounts in dollars) | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| Consolidated operations | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing operations | $ | 415 | $ | (4,673) | $ | 3,363 | $ | 1,813 | $ | 2,056 | $ | 1,915 | $ | 3,659 | $ | 2,645 | |||||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued | |||||||||||||||||||||||
operations | (308) | (8,936) | (541) | (2,947) | (105) | 629 | - | 3,758 | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) | 107 | (13,608) | 2,823 | (1,134) | 1,951 | 2,545 | 3,659 | 6,403 | |||||||||||||||
| Less net earnings (loss) attributable to | |||||||||||||||||||||||
noncontrolling interests | (121) | (35) | (86) | 225 | (76) | 39 | (8) | 103 | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to | |||||||||||||||||||||||
the Company | $ | 228 | $ | (13,573) | $ | 2,908 | $ | (1,360) | $ | 2,027 | $ | 2,506 | $ | 3,667 | $ | 6,301 | |||||||
| Per-share amounts – earnings (loss) from | |||||||||||||||||||||||
continuing operations | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Diluted earnings (loss) per share | $ | 0.03 | $ | (0.45) | $ | 0.36 | $ | 0.17 | $ | 0.23 | $ | 0.19 | $ | 0.39 | $ | 0.26 | |||||||
Basic earnings (loss) per share | 0.03 | (0.45) | 0.36 | 0.17 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.40 | 0.26 | |||||||||||||||
| Per-share amounts – earnings (loss) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
from discontinued operations | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Diluted earnings (loss) per share | (0.03) | (0.90) | (0.06) | (0.30) | (0.01) | 0.05 | - | 0.38 | |||||||||||||||
Basic earnings (loss) per share | (0.03) | (0.90) | (0.06) | (0.30) | (0.01) | 0.05 | - | 0.38 | |||||||||||||||
| Per-share amounts – net earnings (loss) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Diluted earnings (loss) per share | (0.01) | (1.35) | 0.30 | (0.13) | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.39 | 0.64 | |||||||||||||||
Basic earnings (loss) per share | (0.01) | (1.35) | 0.30 | (0.13) | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.40 | 0.64 | |||||||||||||||
| Selected data | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| GE | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Sales of goods and services | $ | 25,407 | $ | 23,839 | $ | 28,150 | $ | 26,141 | $ | 26,934 | $ | 25,612 | $ | 30,345 | $ | 30,614 | |||||||
Gross profit from sales | 5,516 | 5,514 | 6,192 | 6,033 | 6,388 | 6,275 | 7,027 | 7,556 | |||||||||||||||
| GE Capital | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Total revenues | 2,885 | 2,866 | 2,771 | 2,690 | 2,600 | 2,660 | 2,649 | 2,585 | |||||||||||||||
Earnings (loss) from continuing operations | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| attributable to the Company | (603) | (5,721) | (448) | (332) | 59 | (154) | 397 | (1,447) | |||||||||||||||
For GE, gross profit from sales is sales of goods and services less costs of goods and services sold.
Earnings-per-share amounts are computed independently each quarter for earnings (loss) from continuing operations, earnings (loss) from discontinued operations and net earnings. As a result, the sum of each quarter's per-share amount may not equal the total per-share amount for the respective year; and the sum of per-share amounts from continuing operations and discontinued operations may not equal the total per-share amounts for net earnings (loss) for the respective quarters.
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 221
DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Executive Officers of the Registrant (As of February 1, 2017)
| Date assumed | ||||||
| Executive | ||||||
| Name | Position | Age | Officer Position | |||
| Jeffrey R. Immelt | Chairman of the Board & Chief Executive Officer | 60 | January 1997 | |||
| Jeffrey S. Bornstein | Senior Vice President & Chief Financial Officer | 51 | July 2013 | |||
| Elizabeth J. Comstock | Vice Chairman, Business Innovations | 56 | April 2013 | |||
| Alexander Dimitrief | Senior Vice President, General Counsel & Secretary | 58 | November 2015 | |||
| Jan R. Hauser | Vice President, Controller & Chief Accounting Officer | 57 | April 2013 | |||
| David L. Joyce | Vice Chairman of General Electric Company; | 60 | September 2016 | |||
| President & CEO, GE Aviation | ||||||
| Susan P. Peters | Senior Vice President, Human Resources | 63 | August 2013 | |||
| John G. Rice | Vice Chairman of General Electric Company; | 60 | September 1997 | |||
President & CEO, Global Growth Organization |
All Executive Officers are elected by the Board of Directors for an initial term that continues until the Board meeting immediately preceding the next annual statutory meeting of shareowners, and thereafter are elected for one-year terms or until their successors have been elected. All Executive Officers have been executives of General Electric Company for the last five years except for Ms. Hauser. Prior to joining GE in April 2013, Ms. Hauser served as a partner, Accounting Services, National Professional Services Group at PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP.
The remaining information called for by this item is incorporated by reference to "Election of Directors," "Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance," "Other Governance Policies and Practices" and "Board Committees" in our definitive proxy statement for our 2017 Annual Meeting of Shareowners to be held April 26, 2017, which will be filed within 120 days of the end of our fiscal year ended December 31, 2016 (the 2017 Proxy Statement).
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 222
EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
(a)1. Financial Statements
Included in the "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" section of this report:
Management's Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Statement of Earnings for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014
Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014
Consolidated Statement of Changes in Shareowners' Equity for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014
Statement of Financial Position at December 31, 2016 and 2015
Statement of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014
Notes to consolidated financial statements
Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Summary of Operating Segments
(a)2. Financial Statement Schedules
The schedules listed in Reg. 210.5-04 have been omitted because they are not applicable or the required information is shown in the consolidated financial statements or notes thereto.
(a)3. Exhibit Index
Exhibit Number | Description | |
| 2(a) | Transaction Agreement and Plan of Merger dated as of October 30, 2016 among General Electric, Baker Hughes Incorporated, Bear Mergersub, Inc. and Bear Newco, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to GE's Current Report on Form 8-K, dated November 3, 2016 (Commission file number 001-00035)). | |
| 3(i) | The Restated Certificate of Incorporation of General Electric Company (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3(i) to GE's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2013), as amended by the Certificate of Amendment, dated December 2, 2015 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to GE's Current Report on Form 8-K, dated December 3, 2015), as further amended by the Certificate of Amendment, dated January 19, 2016 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to GE's Current Report on Form 8-K, dated January 20, 2016) and as further amended by the Certificate of Change of General Electric Company (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3(1) to GE's Current Report on Form 8-K, dated September 1, 2016 (in each case, under Commission file number 001-00035). | |
| 3(ii) | The By-Laws, as amended, of General Electric Company (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3(ii) to GE's Current Report on Form 8-K dated February 11, 2015 (Commission file number 001-00035)). | |
| 4(a) | Amended and Restated General Electric Capital Corporation Standard Global Multiple Series Indenture Provisions dated as of February 27, 1997 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4(a) to General Electric Capital Corporation's Registration Statement on Form S-3, File No. 333-59707 (Commission file number 001-06461)). | |
| 4(b) | Third Amended and Restated Indenture dated as of February 27, 1997, between General Electric Capital Corporation and The Bank of New York Mellon, as successor trustee (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4(c) to General Electric Capital Corporation's Registration Statement on Form S-3, File No. 333-59707 (Commission file number 001-06461)). | |
| 4(c) | First Supplemental Indenture dated as of May 3, 1999, supplemental to Third Amended and Restated Indenture dated as of February 27, 1997 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4(dd) to General Electric Capital Corporation's Post-Effective Amendment No. 1 to Registration Statement on Form S-3, File No. 333-76479 (Commission file number 001-06461)). | |
| 4(d) | Second Supplemental Indenture dated as of July 2, 2001, supplemental to Third Amended and Restated Indenture dated as of February 27, 1997 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4(f) to General Electric Capital Corporation's Post-Effective Amendment No.1 to Registration Statement on Form S-3, File No. 333-40880 (Commission file number 001-06461)). | |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 223
| 4(e) | Third Supplemental Indenture dated as of November 22, 2002, supplemental to Third Amended and Restated Indenture dated as of February 27, 1997 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4(cc) to General Electric Capital Corporation's Post-Effective Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-3, File No. 333‑100527 (Commission file number 001-06461)). | ||
| 4(f) | Fourth Supplemental Indenture dated as of August 24, 2007, supplemental to Third Amended and Restated Indenture dated as of February 27, 1997 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4(g) to General Electric Capital Corporation's Registration Statement on Form S-3, File number 333-156929 (Commission file number 001-06461)). | ||
| 4(g) | Letter from the Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of General Electric to General Electric Capital Corporation dated September 15, 2006, with respect to returning dividends, distributions or other payments to General Electric Capital Corporation in certain circumstances described in the Indenture for Subordinated Debentures dated September 1, 2006, between General Electric Capital Corporation and the Bank of New York, as successor trustee (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4(c) to General Electric Capital Corporation's Post-Effective Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form S-3, File No. 333-132807 (Commission file number 001-06461)). | ||
| 4(h) | Indenture dated as of October 26, 2015, among GE Capital International Funding Company, as issuer, General Electric Company and General Electric Capital Corporation, as guarantors and The Bank of New York Mellon, as trustee (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99 to General Electric's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 26, 2015 (Commission file number 001-00035)). | ||
| 4(i) | Global Supplemental Indenture dated as of April 10, 2015, among General Electric Capital Corporation, General Electric Company and The Bank of New York Mellon, as trustee. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4(i) to GE's Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission file number 001-00035) for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2015). | ||
| 4(j) | Second Global Supplemental Indenture dated as of December 2, 2015, among General Electric Capital Corporation, General Electric Company and The Bank of New York Mellon, as successor trustee (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to General Electric's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 3, 2015 (Commission file number 001-00035)). | ||
4(k) | Agreement to furnish to the Securities and Exchange Commission upon request a copy of instruments defining the rights of holders of certain long-term debt of the registrant and consolidated subsidiaries.* | ||
| (10) | Except for 10(t) below, all of the following exhibits consist of Executive Compensation Plans or Arrangements: | ||
| (a) | General Electric Incentive Compensation Plan, as amended effective July 1, 1991 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(a) to GE's Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission file number 001-00035) for the fiscal year ended December 31, 1991). | ||
| (b) | General Electric Financial Planning Program, as amended through September 1993 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(h) to GE's Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission file number 001-00035) for the fiscal year ended December 31, 1993). | ||
| (c) | General Electric Supplemental Life Insurance Program, as amended February 8, 1991 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(i) to GE's Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission file number 001-00035) for the fiscal year ended December 31, 1990). | ||
| (d) | General Electric Directors' Charitable Gift Plan, as amended through December 2002 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(i) to GE's Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission file number 001-00035) for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2002). | ||
| (e) | General Electric Leadership Life Insurance Program, effective January 1, 1994 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(r) to GE's Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission file number 001-00035) for the fiscal year ended December 31, 1993). | ||
| (f) | General Electric Supplementary Pension Plan, as amended effective July 1, 2015. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(f) to GE's Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission file number 001-00035) for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2015). | ||
| (g) | General Electric 2003 Non-Employee Director Compensation Plan, Amended and Restated as of September 9, 2016 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(a) to GE's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2016 (Commission file number 000-00035)). | ||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 224
| (h) | Amendment to Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Plans, dated as of December 14, 2004 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(w) to the GE's Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission file number 001-00035) for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2004). | ||
| (i) | GE Retirement for the Good of the Company Program, as amended effective January 1, 2009 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(j) to GE's Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission file number 001-00035) for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008). | ||
| (j) | GE Excess Benefits Plan, effective January 1, 2009 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(k) to GE's Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission file number 001-00035) for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008). | ||
| (k) | General Electric 2006 Executive Deferred Salary Plan, as amended January 1, 2009 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(l) to GE's Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission file number 001-00035) for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008). | ||
| (l) | General Electric Company 2007 Long-Term Incentive Plan (as amended and restated April 25, 2012) (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to GE's Registration Statement on Form S-8, dated May 4, 2012, File number 333-181177 (Commission file number 001-00035)). | ||
| (m) | Form of Agreement for Stock Option Grants to Executive Officers under the General Electric Company 2007 Long-Term Incentive Plan, as amended January 1, 2009 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(n) to GE's Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission file number 001-00035) for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008). | ||
| (n) | Form of Agreement for Annual Restricted Stock Unit Grants to Executive Officers under the General Electric Company 2007 Long-Term Incentive Plan, as amended February 7, 2014 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(a) to GE's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2014 (Commission file number 001-00035)). | ||
| (o) | Form of Agreement for Periodic Restricted Stock Unit Grants to Executive Officers under the General Electric Company 2007 Long-Term Incentive Plan, as amended February 7, 2014 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(b) to GE's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2014 (Commission file number 001-00035)). | ||
| (p) | Form of Agreement for Long Term Performance Award Grants to Executive Officers under the General Electric Company 2007 Long-Term Incentive Plan (as amended and restated April 25, 2012) (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(a) to GE's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2016 (Commission file number 001-00035)). | ||
| (q) | Form of Agreement for Performance Stock Unit Grants to Executive Officers under the General Electric Company 2007 Long-Term Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10 (a) to GE's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2015 (Commission file number 001-00035)). | ||
| (r) | First Restatement of the General Electric International Employee Stock Purchase Plan effective May 1, 2002 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to GE's Registration Statement on Form S-8, dated November 13, 2009, File No. 333-163106 (Commission file number 001-00035)). | ||
| (s) | Time Sharing Agreement dated November 22, 2010 between General Electric Company and Jeffrey R. Immelt (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(z) to GE's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2010 (Commission file number 001-00035)). | ||
| (t) | Amended and Restated Agreement, dated April 10, 2015, between General Electric Company and General Electric Capital Corporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10 to GE's Current Report on Form 8-K, dated April 10, 2015 (Commission file number 001-00035)). | ||
| (u) | Early Retirement Agreement & Release between General Electric Company and Keith Sherin effective January 8, 2017.* | ||
| (11) | Statement re Computation of Per Share Earnings.** | ||
| 12(a) | Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges.* | ||
| 12(b) | Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Combined Fixed Charges and Preferred Stock Dividends.* | ||
| (21) | Subsidiaries of Registrant.* | ||
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 225
| (23) | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.* | |
| (24) | Power of Attorney.* | |
| 31(a) | Certification Pursuant to Rules 13a-14(a) or 15d-14(a) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.* | |
| 31(b) | Certification Pursuant to Rules 13a-14(a) or 15d-14(a) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.* | |
| (32) | Certification Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350.* | |
| 99(a) | Undertaking for Inclusion in Registration Statements on Form S-8 of General Electric Company (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99(b) to General Electric Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission file number 001-00035) for the fiscal year ended December 31, 1992). | |
| 99(b) | Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 12(a) to GE Capital's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2014 (Commission file number 001-06461)). | |
| 99(c) | Supplement to Present Required Information in Searchable Format* | |
| (101) | The following materials from General Electric Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016, formatted in XBRL (eXtensible Business Reporting Language); (i) Statement of Earnings for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, (ii) Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, (iii) Consolidated Statement of Changes in Shareowners' Equity for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, (iv) Statement of Financial Position at December 31, 2016 and 2015, (v) Statement of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, and (vi) the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.* | |
| * | Filed electronically herewith. | |
| ** | Information required to be presented in Exhibit 11 is provided in Note 18 to the consolidated financial statements in this Form 10-K Report in accordance with the provisions of Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification 260, Earnings Per Share. | |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 226
FORM 10-K CROSS REFERENCE INDEX
| Item Number | Page(s) | |||
| Part I | ||||
| Item 1. | Business | 18-19, 33-63, 74-75, 98-99 | ||
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors | 120-125 | ||
| Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments | Not applicable | ||
| Item 2. | Properties | 19 | ||
| Item 3. | Legal Proceedings | 126-127 | ||
| Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures | Not applicable | ||
| Part II | ||||
| Item 5. | Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities | 26, 117 | ||
| Item 6. | Selected Financial Data | 116 | ||
| Item 7. | Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | 20-115 | ||
| Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk | 80-81, 118-119 | ||
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data | 131-221 | ||
| Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure | Not applicable | ||
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures | 129 | ||
| Item 9B. | Other Information | Not applicable | ||
| Part III | ||||
| Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance | 222 | ||
| Item 11. | Executive Compensation | (a) | ||
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters | (b), Note 16 | ||
| Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence | (c) | ||
| Item 14. | Principal Accounting Fees and Services | (d) | ||
| Part IV | ||||
| Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules | 223-226 | ||
| Item 16. | Form 10-K Summary | 3-16, (e) | ||
| Signatures | 228 | |||
| (a) | Incorporated by reference to "Compensation" in the 2017 Proxy Statement. |
| (b) | Incorporated by reference to "Stock Ownership Information" and "Key Data About Our Grant Practices" in the 2017 Proxy Statement. |
| (c) | Incorporated by reference to "Related Person Transactions" and "How We Assess Director Independence" in the 2017 Proxy Statement. |
| (d) | Incorporated by reference to "Independent Auditor Information" in the 2017 Proxy Statement. |
| (e) | The Introduction & Summary does not include Part III information because it will be incorporated by reference to the 2017 Proxy Statement. |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 227
| OTHER INFORMATION |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this annual report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016, to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, and in the capacities indicated, thereunto duly authorized in the City of Boston and Commonwealth of Massachusetts on the 24th day of February 2017.
General Electric Company
(Registrant)
(Registrant)
By /s/ Jeffrey S. Bornstein
Jeffrey S. Bornstein
Senior Vice President and
Chief Financial Officer
(Principal Financial Officer)
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signer | Title | Date | |||
| /s/ Jeffrey S. Bornstein | Principal Financial Officer | February 24, 2017 | |||
Jeffrey S. Bornstein Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | |||||
| /s/ Jan R. Hauser | Principal Accounting Officer | February 24, 2017 | |||
Jan R. Hauser Vice President and Controller | |||||
/s/ Jeffrey R. Immelt Jeffrey R. Immelt* Chairman of the Board of Directors | Principal Executive Officer | February 24, 2017 | |||
| Sébastien M. Bazin* | Director | ||||
| W. Geoffrey Beattie* | Director | ||||
| John J. Brennan* | Director | ||||
| Francisco D'Souza* | Director | ||||
| Marijn E. Dekkers* | Director | ||||
| Peter B. Henry* | Director | ||||
| Susan Hockfield* | Director | ||||
| Andrea Jung* | Director | ||||
| Robert W. Lane* | Director | ||||
| Rochelle B. Lazarus* | Director | ||||
| Lowell C. McAdam* | Director | ||||
| Steven M. Mollenkopf* | Director | ||||
| James J. Mulva* | Director | ||||
| James E. Rohr* | Director | ||||
| Mary L. Schapiro* | Director | ||||
| James S. Tisch* | Director | ||||
| A majority of the Board of Directors | |||||
| *By | /s/ Christoph A. Pereira | ||||
Christoph A. Pereira Attorney-in-fact February 24, 2017 |
GE 2016 FORM 10-K 228