UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
| ý | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017
OR
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to .
Commission File Number 001-07845
LEGGETT & PLATT, INCORPORATED
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Missouri | 44-0324630 | |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
No. 1 Leggett Road Carthage, Missouri | 64836 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip code) | |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (417) 358-8131
SECURITIES REGISTERED PURSUANT TO SECTION 12(b) OF THE ACT:
| Title of Each Class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
| Common Stock, $.01 par value | New York Stock Exchange | |
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ý No ¨
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No ý
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ý No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ý No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ý
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer | ý | Accelerated filer ¨ | |
| Non-accelerated filer | ¨ | (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company ¨ |
Emerging growth company ¨ | |||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ¨ No ý
The aggregate market value of the voting stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant (based on the closing price of our common stock on the New York Stock Exchange) on June 30, 2017 was $6,752,500,000.
There were 132,240,307 shares of the registrant’s common stock outstanding as of February 9, 2018.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Part of Item 10, and all of Items 11, 12, 13 and 14 of Part III are incorporated by reference from the Company’s definitive Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on May 15, 2018.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
LEGGETT & PLATT, INCORPORATED—FORM 10-K
FOR THE YEAR ENDED December 31, 2017
Page Number | ||
| PART I | ||
| Item 1. | ||
| Item 1A. | ||
| Item 1B. | ||
| Item 2. | ||
| Item 3. | ||
| Item 4. | ||
| Supp. Item. | ||
| PART II | ||
| Item 5. | ||
| Item 6. | ||
| Item 7. | ||
| Item 7A. | ||
| Item 8. | ||
| Item 9. | ||
| Item 9A. | ||
| Item 9B. | ||
| PART III | ||
| Item 10. | ||
| Item 11. | ||
| Item 12. | ||
| Item 13. | ||
| Item 14. | ||
| PART IV | ||
| Item 15. | ||
| Item 16. | ||
Forward-Looking Statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K and our other public disclosures, whether written or oral, may contain “forward-looking” statements including, but not limited to: projections of revenue, income, earnings, capital expenditures, dividends, capital structure, cash flows, tax impacts or other financial items; possible plans, goals, objectives, prospects, strategies or trends concerning future operations; statements concerning future economic performance, possible goodwill or other asset impairment; and the underlying assumptions relating to the forward-looking statements. These statements are identified either by the context in which they appear or by use of words such as “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “expect,” “intend,” “may,” “plan,” “project,” “should” or the like. All such forward-looking statements, whether written or oral, and whether made by us or on our behalf, are expressly qualified by the cautionary statements described in this provision.
Any forward-looking statement reflects only the beliefs of the Company or its management at the time the statement is made. Because all forward-looking statements deal with the future, they are subject to risks, uncertainties and developments which might cause actual events or results to differ materially from those envisioned or reflected in any forward-looking statement. Moreover, we do not have, and do not undertake, any duty to update or revise any forward-looking statement to reflect events or circumstances after the date on which the statement was made. For all of these reasons, forward-looking statements should not be relied upon as a prediction of actual future events, objectives, strategies, trends or results.
Readers should review Item 1A Risk Factors in this Form 10-K for a description of important factors that could cause actual events or results to differ materially from forward-looking statements. It is not possible to anticipate and list all risks, uncertainties and developments which may affect the future operations or performance of the Company, or which otherwise may cause actual events or results to differ materially from forward-looking statements. However, the known, material risks and uncertainties include the following:
| • | factors that could affect the industries or markets in which we participate, such as growth rates and opportunities in those industries; |
| • | adverse changes in consumer confidence, housing turnover, employment levels, interest rates, trends in capital spending and the like; |
| • | factors that could impact raw materials and other costs, including the availability and pricing of steel scrap and rod and other raw materials, the availability of labor, wage rates and energy costs; |
| • | our ability to pass along raw material cost increases through increased selling prices; |
| • | price and product competition from foreign (particularly Asian and European) and domestic competitors; |
| • | our ability to maintain profit margins if our customers change the quantity and mix of our components in their finished goods; |
| • | our ability to realize 25-35% contribution margin on incremental unit volume produced utilizing spare capacity; |
| • | our ability to achieve expected levels of cash flow; |
| • | our ability to identify and consummate strategically-screened acquisitions; |
| • | our ability to maintain and grow the profitability of acquired companies; |
| • | adverse changes in foreign currency, tariffs, customs, shipping rates, political risk, and U.S. or foreign laws, regulations or legal systems (including the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act and other tax laws); |
| • | our ability to maintain the proper functioning of our internal business processes and information systems through technology failures or otherwise; |
| • | our ability to avoid modification or interruption of our information systems through cyber-security breaches; |
| • | a decline in the long-term outlook for any of our reporting units that could result in asset impairment; |
| • | the amount and timing of share repurchases; |
| • | the loss of one or more of our significant customers; and |
| • | litigation accruals related to various contingencies including vehicle-related personal injury, antitrust, intellectual property, product liability and warranty, taxation, environmental and workers’ compensation expense. |
1
PART I
PART I
Item 1. Business.
Summary
Leggett & Platt, Incorporated was founded as a partnership in Carthage, Missouri in 1883 and was incorporated in 1901. The Company, a pioneer of the steel coil bedspring, has become an international diversified manufacturer that conceives, designs and produces a wide range of engineered components and products found in many homes, offices, automobiles and aircraft. As discussed below, our operations are organized into 14 business units, which are divided into ten groups under our four segments: Residential Products; Industrial Products; Furniture Products; and Specialized Products.
Overview of Our Segments
Residential Products Segment
| BEDDING GROUP |
| U.S. Spring |
| International Spring |
| FABRIC & CARPET CUSHION GROUP |
| Fabric Converting |
| Geo Components |
| Carpet Cushion |
| MACHINERY GROUP |
| Machinery |
Our Residential Products segment began in 1883 with the manufacture of steel coil bedsprings. Today, we supply a variety of components and machinery used by bedding manufacturers in the production and assembly of their finished products. Our range of products offers our customers a single source for many of their component needs. We also produce or distribute carpet cushion, fabric, and geo components.
Innovative proprietary products and low cost have made us the largest U.S. manufacturer in many of these businesses. We strive to understand what drives consumer purchases in our markets and focus our product development activities on meeting end-consumer needs. We attain a cost advantage from efficient manufacturing methods, internal production of key raw materials, purchasing leverage, and large-scale production. Sourcing components from us allows our customers to focus on designing, merchandising and marketing their products.
PRODUCTS
Bedding Group
| • | Innersprings (sets of steel coils, bound together, that form the core of a mattress) | ||
| • | Wire forms for mattress foundations | ||
| • | Machines that we use to shape wire into various types of springs | ||
2
PART I
Fabric & Carpet Cushion Group
| • | Structural fabrics for mattresses, residential furniture and industrial uses | ||
| • | Carpet cushion (made from bonded scrap foam, fiber, rubber and prime foam) | ||
| • | Geo components (synthetic fabrics and various other products used in ground stabilization, drainage protection, erosion and weed control) | ||
Machinery Group
| • | Quilting machines for mattress covers | ||
| • | Industrial sewing/finishing machines | ||
| • | Conveyor lines | ||
| • | Mattress packaging and glue-drying equipment | ||
CUSTOMERS
| • | Manufacturers of finished bedding (mattresses and foundations) | ||
| • | Retailers and distributors of carpet cushion | ||
| • | Contractors, landscapers, road construction companies, and government agencies using geo components | ||
| • | Manufacturers of upholstered furniture, packaging, filtration and draperies | ||
Industrial Products Segment
| WIRE GROUP |
Drawn Wire1 |
| Steel Rod |
1 Drawn Wire includes our former Wire Products business unit effective January 1, 2018.
The quality of our products and service, together with low cost, have made Leggett & Platt the leading U.S. supplier of high-carbon drawn steel wire. Our Wire Group operates a steel rod mill with an annual output of approximately 500,000 tons, of which a substantial majority is used by our own wire mills. We have three wire mills that supply virtually all the wire consumed by our other domestic businesses. We also supply steel wire to trade customers that operate in a broad range of markets.
PRODUCTS
Wire Group
| • | Drawn wire | ||
| • | Steel rod | ||
CUSTOMERS
We use about 70% of our wire output to manufacture our own products, including:
| • | Bedding and furniture components | ||
| • | Automotive seat suspension systems | ||
3
PART I
The Industrial Products segment also has a diverse group of trade customers that include:
| • | Mechanical spring manufacturers | ||
| • | Wire distributors | ||
| • | Packaging and baling companies | ||
Furniture Products Segment
| HOME FURNITURE GROUP |
Home Furniture 1 |
| WORK FURNITURE GROUP |
| Work Furniture |
| CONSUMER PRODUCTS GROUP |
Consumer Products 2 |
1 Home Furniture includes our former Furniture Hardware and Seating & Distribution business units effective January 1, 2018.
2 Consumer Products includes our former Adjustable Bed and Fashion Bed business units effective January 1, 2018.
In our Furniture Products segment, we design, manufacture, and distribute a wide range of components and finished products for the residential furniture, office and commercial furniture, and specialty bedding markets. We supply components used by home and work furniture manufacturers to provide comfort, motion and style in their finished products, as well as select lines of private-label finished furniture. We are also a major supplier of adjustable beds and fashion beds, with domestic manufacturing, distribution, e-commerce fulfillment and global sourcing capabilities.
PRODUCTS
Home Furniture Group
| • | Steel mechanisms and motion hardware (enabling furniture to recline, tilt, swivel, rock and elevate) for reclining chairs, sofas, sleeper sofas and lift chairs | ||
| • | Springs and seat suspensions for chairs, sofas and love seats | ||
Work Furniture Group
| • | Select lines of private-label finished furniture | ||
| • | Bases, columns, back rests, casters and frames for office chairs, and control devices that allow chairs to tilt, swivel and elevate | ||
| • | Molded plywood components | ||
Consumer Products Group
| • | Adjustable beds | ||
| • | Fashion beds and bed frames | ||
4
PART I
CUSTOMERS
| • | Manufacturers of upholstered furniture | ||
| • | Office furniture manufacturers | ||
| • | Mattress and furniture retailers | ||
| • | Department stores and big box retailers | ||
| • | E-commerce retailers | ||
Specialized Products Segment
| AUTOMOTIVE GROUP |
| Automotive |
| AEROSPACE PRODUCTS GROUP |
| Aerospace Products |
HYDRAULIC CYLINDERS GROUP1 |
| Hydraulic Cylinders |
1 Formed January 31, 2018, with the acquisition of a manufacturer of hydraulic cylinders.
Our Specialized Products segment designs, manufactures and sells products including automotive seating components, tubing and fabricated assemblies for the aerospace industry, and hydraulic cylinders for the material handling, construction and transportation industries. Our technical capability and deep customer engagement allows us to compete on critical functionality, such as comfort, size, weight and noise. Our reliable product development and launch capability, coupled with our global footprint, makes us a trusted partner for our Tier 1 and OEM customers.
PRODUCTS
Automotive Group
| • | Mechanical and pneumatic lumbar support and massage systems for automotive seating | ||
| • | Seat suspension systems | ||
| • | Motors and actuators, used in a wide variety of vehicle power features | ||
| • | Cables | ||
Aerospace Products Group
| • | Titanium, nickel and stainless-steel tubing, formed tube and tube assemblies, primarily used in fluid conveyance systems | ||
Hydraulic Cylinders Group
| • | Engineered hydraulic cylinders | ||
5
PART I
CUSTOMERS
| • | Automobile OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers | ||
| • | Aerospace suppliers | ||
| • | Mobile equipment OEMs, primarily serving material handling and construction markets | ||
Segment Financial Information
For information about sales to trade customers, sales by product line, EBIT, and total assets of each of our segments, refer to Note E on page 82 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Our reportable segments are the same as our operating segments, which also correspond with our management organizational structure. In conjunction with the change in executive officers, our management organizational structure and all related internal reporting changed effective January 1, 2017. As a result, the composition of our four segments also changed to reflect the new structure. The new segment structure is largely the same as prior years except the Home Furniture Group moved from Residential Products to Furniture Products (formerly Commercial Products) and the Machinery Group moved from Specialized Products to Residential Products.
In addition, the changes in LIFO reserve are now recognized within the segments to which they relate (primarily Industrial Products). Previously segment EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) reflected the FIFO basis of accounting for certain inventories and an adjustment to the LIFO basis for these inventories was made at the consolidated financial statement level. These changes were retrospectively applied to all periods presented. The methods and assumptions that we use in estimating our LIFO reserve did not change.
Strategic Direction
Key Financial Metric
Total Shareholder Return (TSR), relative to peer companies, is the key financial measure that we use to assess long-term performance. TSR = (Change in Stock Price + Dividends)/Beginning Stock Price. Our goal is to achieve TSR in the top third of the S&P 500 companies over rolling three-year periods through an approach that employs four TSR sources: revenue growth, margin expansion, dividends, and share repurchases.
Our incentive programs reward return generation and profitable growth. Senior executives participate in a TSR-based incentive program (based on our performance compared to a group of approximately 320 peers).
For information about our TSR targets and performance see the discussion under "Total Shareholder Return" in Item 7, Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations on page 28.
Returning Cash to Shareholders
During the past three years, we generated $1.36 billion of operating cash, and we returned much of this cash to shareholders in the form of dividends and share repurchases. Our top priorities for use of cash are organic growth (capital expenditures), dividends, and strategic acquisitions. After funding those priorities, if there is still cash available, we generally intend to repurchase stock.
For information about dividends and share repurchases see the discussion under "Pay Dividends" and "Repurchase Stock" in Item 7, Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations beginning on page 44.
6
PART I
Portfolio Management
We utilize a rigorous strategic planning process to help guide decisions regarding business unit roles, capital allocation priorities, and new areas in which to grow. We review the portfolio classification of each unit on an annual basis to determine its appropriate role (Grow, Core, Fix or Divest). This review includes criteria such as competitive position, market attractiveness, business unit size, and fit within our overall objectives, as well as financial indicators such as business unit return, growth of EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes), EBIT margin, EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization), and operating cash flows. Business units in the Grow category should provide avenues for profitable growth from competitively advantaged positions in attractive markets. Core business units are expected to enhance productivity, improve market share, and generate cash flow from operations while using minimal capital. To remain in the portfolio, business units are expected to consistently generate after-tax returns in excess of our cost of capital. Business units that fail to consistently attain minimum return goals will be moved to the Fix or Divest categories.
Disciplined Growth
We revised our TSR framework in 2016 to moderately increase the expected long-term contribution from revenue growth to 6-9% (from 4-5% previously). Over the last three years, the Company has generated combined unit volume and acquisition growth of 5% per year on average, but this growth was partially offset by divestitures, commodity deflation and currency impact.
Our long-term 6-9% annual revenue growth objective envisions periodic acquisitions. We primarily seek acquisitions within our Grow businesses, and look for opportunities to enter new, higher growth markets (carefully screened for sustainable competitive advantage). We expect all acquisitions to (a) have a clear strategic rationale, a sustainable competitive advantage, a strong fit with the Company, and be in an attractive and growing market; (b) create value by enhancing TSR; (c) for stand-alone businesses: generally possess annual revenue in excess of $50 million, strong management and future growth opportunity with a strong market position in a market growing faster than GDP; and (d) for bolt-on businesses: generally possess annual revenue in excess of $15 million, significant synergies, and a strategic fit with an existing business unit.
Acquisitions
2018
On January 31, 2018, we acquired Precision Hydraulic Cylinders (PHC), a leading global manufacturer of
engineered hydraulic cylinders primarily for the materials handling market. The purchase price was $85 million. This business has current annual revenues of $81 million and represents a new growth platform for the Company. PHC serves a market of mainly large OEM customers utilizing highly engineered, co-designed components with long product life-cycles, yet representing a small percentage of the end product’s cost. PHC will form a new business group titled Hydraulic Cylinders and report in the Specialized Products segment.
2017
We acquired three businesses and the remaining interest in a joint venture for total consideration (including cash and stock) of $56 million. The first was a Canadian geosynthetic products distributor and installer for civil engineering and construction applications. The second was a Michigan-based surface-critical bent tube manufacturer supporting our private-label seating strategy in Work Furniture. We also acquired a North Carolina manufacturer of rebond carpet cushion. Finally, we acquired the remaining 20% ownership in an Asian joint venture in our Work Furniture business.
7
PART I
2016
We acquired three businesses and the remaining interest in a joint venture for total consideration of $65 million. The first was a U.S. manufacturer of aerospace tube assemblies. This business further expands our tube forming and fabrication capabilities, and also adds precision machining to our aerospace platform. We also acquired a distributor of geosynthetic products and a South African producer of mattress innersprings. Finally, we purchased the remaining interest in an Automotive joint venture in China. This business manufactures seat comfort products and lumbar support systems.
2015
We acquired a 70% interest in a European private-label manufacturer of high-end upholstered furniture. This business is complementary to our North American private-label operation and allows us to support our Work Furniture customers as they expand globally. The initial cash outlay for the 70% interest was $12 million and, per the terms of the agreement, we will acquire the remaining 30% in two equal parts, in the second quarters of 2018 and 2020. We have recorded a liability of approximately $14 million for these future payments. The recorded liability is based upon estimates and may fluctuate significantly until the payment dates.
For more information regarding our acquisitions, please refer to Note Q on page 110 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Divestitures
2017
We divested our final Commercial Vehicle Products (CVP) business for total consideration of $9 million. This business unit was engaged in the manufacture of van interiors, including the racks, shelving and cabinets installed in service vans.
2016
We divested four businesses for net consideration of $72 million. We sold two wire operations, one that manufactured wire partitions, perimeter guarding and storage lockers, and another that manufactured automatic wire strapping equipment and related consumable wire products. We also sold a CVP operation that designed and assembled docking stations for mobile computing equipment in vehicles. Finally, we sold a Machinery business that assembled industrial sewing machines.
2015
We sold four operations for total consideration of $36 million. We sold our final two Store Fixtures operations and a small operation within our CVP business. We also sold our Steel Tubing business unit. This business manufactured welded steel tubing and fabricated tube components.
For further information about divestitures and discontinued operations, see Note B on page 77 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
8
PART I
Foreign Operations
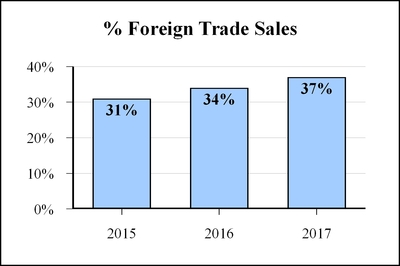
The percentages of our trade sales related to products manufactured outside the United States for the previous three years are shown below. The percentages of foreign trade sales were 31% for 2015, 34% for 2016 and 37% for 2017.
Our international operations are principally located in Europe, China, Canada and Mexico. Our products in these foreign locations primarily consist of:
Europe
| • | Innersprings for mattresses |
| • | Lumbar and seat suspension systems for automotive seating |
| • | Seamless and welded tubing and fabricated assemblies for aerospace applications |
| • | Select lines of private-label finished furniture |
| • | Machinery and equipment designed to manufacture innersprings for mattresses |
China
| • | Lumbar and seat suspension systems for automotive seating |
| • | Cables, motors, and actuators for automotive applications |
| • | Recliner mechanisms and bases for upholstered furniture |
| • | Formed wire for upholstered furniture |
| • | Innersprings for mattresses |
| • | Work furniture components, including chair bases and casters |
Canada
| • | Lumbar supports for automotive seats |
| • | Fabricated wire for the furniture and automotive industries |
| • | Work furniture chair controls, chair bases and table bases |
9
PART I
Mexico
| • | Innersprings and fabricated wire for the bedding industry |
| • | Lumbar and seat suspension systems for automotive seating |
| • | Adjustable beds |
Our international expansion strategy is to locate our operations where we believe we would possess a competitive advantage and where demand for our components is growing. We have also expanded internationally in instances where our customers move the production of their finished products overseas to supply them more efficiently.
Our international operations face the risks associated with any operation in a foreign country. These risks include:
| • | Foreign currency fluctuation |
| • | Foreign legal systems that make it difficult to protect intellectual property and enforce contract rights |
| • | Credit risks |
| • | Increased costs due to tariffs, customs and shipping rates |
| • | Potential problems obtaining raw materials, and disruptions related to the availability of electricity and transportation during times of crisis or war |
| • | Inconsistent interpretation and enforcement, at times, of foreign tax laws |
| • | Political instability in certain countries |
Our Specialized Products segment, which derives roughly 85% of its trade sales from foreign operations, is particularly subject to the above risks. These and other foreign-related risks could result in cost increases, reduced profits, the inability to carry on our foreign operations and other adverse effects on our business.
10
PART I
Geographic Areas of Operation
As of December 31, 2017, we had 121 manufacturing facilities; 73 located in the U.S. and 48 located in 17 foreign countries, as shown below. We also had various sales, warehouse and administrative facilities. However, our manufacturing plants are our most important properties.
| Residential Products | Industrial Products | Furniture Products | Specialized Products | |
| North America | ||||
| Canada | n | n | n | |
| Mexico | n | n | n | n |
| United States | n | n | n | n |
| Europe | ||||
| Austria | n | |||
| Belgium | n | |||
| Croatia | n | |||
| Denmark | n | |||
| France | n | |||
| Hungary | n | |||
| Italy | n | |||
| Poland | n | |||
| Switzerland | n | |||
| United Kingdom | n | n | ||
| South America | ||||
| Brazil | n | |||
| Asia | ||||
| China | n | n | n | |
| India | n | |||
| South Korea | n | |||
| Africa | ||||
| South Africa | n | |||
For further information concerning our trade sales related to products manufactured, and our tangible long-lived assets located outside the United States, refer to Note E on page 82 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
11
PART I
Sales by Product Line
The following table shows our approximate percentage of trade sales by product line for the last three years:
| Product Line | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Bedding Group | 21 | % | 22 | % | 23 | % | ||||
| Automotive Group | 20 | 19 | 16 | |||||||
| Fabric & Carpet Cushion Group | 18 | 18 | 17 | |||||||
| Home Furniture Group | 10 | 11 | 11 | |||||||
| Consumer Products Group | 10 | 8 | 8 | |||||||
Wire Group1 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |||||||
| Work Furniture Group | 7 | 7 | 6 | |||||||
| Aerospace Products Group | 4 | 3 | 3 | |||||||
| Machinery Group | 2 | 2 | 2 | |||||||
Commercial Vehicle Products Group2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||||||
Steel Tubing Group3 | — | — | 2 | |||||||
1Certain operations in the Wire Group were sold in 2016.
2The two remaining Commercial Vehicle Products operations were sold in 2017 and 2016.
3The Steel Tubing Group was sold in 2015.
Distribution of Products
In each of our segments, we sell and distribute our products primarily through our own personnel. However, many of our businesses have relationships and agreements with outside sales representatives and distributors. We do not believe any of these agreements or relationships would, if terminated, have a material adverse effect on the consolidated financial condition, operating cash flows or results of operations of the Company.
Raw Materials
The products we manufacture require a variety of raw materials. We believe that worldwide supply sources are readily available for all the raw materials we use. Among the most important are:
| • | Various types of steel, including scrap, rod, wire, sheet, stainless and angle iron |
| • | Foam scrap |
| • | Woven and non-woven fabrics |
| • | Titanium and nickel-based alloys and other high strength metals |
We supply our own raw materials for many of the products we make. For example, we produce steel rod that we make into steel wire, which we then use to manufacture:
| • | Innersprings and foundations for mattresses |
| • | Springs and seat suspensions for chairs and sofas |
| • | Automotive seating suspension systems |
We supply a substantial majority of our domestic steel rod requirements through our own rod mill. Our wire drawing mills supply nearly all of our U.S. requirements for steel wire.
12
PART I
Customer Concentration
We serve thousands of customers worldwide, sustaining many long-term business relationships. In 2017, our largest customer accounted for approximately 5% of our consolidated revenues. Our top 10 customers accounted for approximately 33% of these consolidated revenues. The loss of one or more of these customers could have a material adverse effect on the Company as a whole, or on the respective segment in which the customer’s sales are reported, including our Residential Products, Specialized Products and Furniture Products segments.
Patents and Trademarks
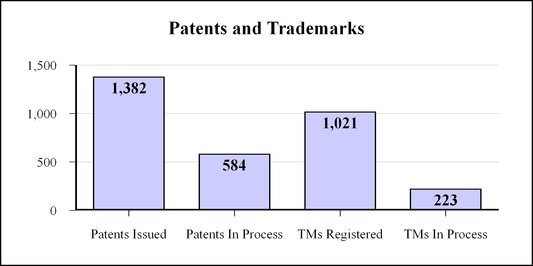
The chart below shows the approximate number of patents issued, patents in process, trademarks registered and trademarks in process held by our continuing operations as of December 31, 2017. No single patent or group of patents, or trademark or group of trademarks, is material to our operations as a whole. Substantially all of our patents relate to products manufactured by the Residential Products, Furniture Products, and Specialized Products segments, while nearly half of our trademarks relate to products manufactured by the Residential Products segment. We had 1,382 patents issued and 584 in process, and 1,021 trademarks registered and 223 in process.
Some of our most significant trademarks include:
| • | ComfortCore®, Mira-Coil®, VertiCoil®, Quantum®, Nanocoil®, Softech®, Lura-Flex®, Superlastic® and Active Support Technology® (mattress innersprings) |
| • | Semi-Flex® (box spring components and foundations) |
| • | Spuhl® (mattress innerspring manufacturing machines) |
| • | Wall Hugger® (recliner chair mechanisms) |
| • | Super Sagless® (motion and sofa sleeper mechanisms) |
| • | No-Sag® (wire forms used in seating) |
| • | LPSense® (capacitive sensing) |
| • | Hanes® (fabric materials) |
| • | Schukra®, Pullmaflex® and Flex-O-Lator® (automotive seating products) |
| • | Gribetz® and Porter® (quilting and sewing machines) |
13
PART I
Product Development
One of our strongest performing product categories across the company is ComfortCore®, our fabric-encased innerspring coils used in hybrid and other mattresses. Our ComfortCore® volume continues to grow, and represented 40% of our total innerspring units by the end of 2017. A growing number of our ComfortCore® innersprings contain a feature we call Quantum® Edge. These are narrow-diameter, fabric-encased coils that form a perimeter around a ComfortCore® innerspring set, replacing foam in a finished mattress. Over 30% of our ComfortCore® innersprings have the Quantum® Edge feature, and the volume of ComfortCore® with Quantum® Edge continues to grow. We are investing in capacity and adding machinery, supplied by our Spuhl® operation, to support the growth in ComfortCore® and Quantum® Edge.
Most of our other businesses are engaged in product development activities to protect our market position and support ongoing growth.
Research and Development
We maintain research, development and testing centers in many locations around the world. We are unable to calculate precisely the cost of research and development because the personnel involved in product and machinery development also spend portions of their time in other areas. However, we estimate our annual cost of research and development to be $25 million each year over the last three years.
Employees
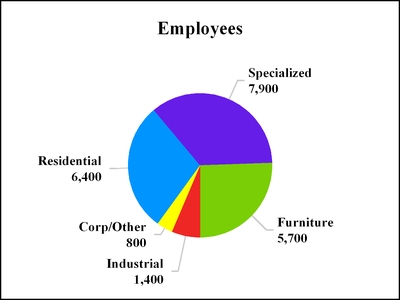
At December 31, 2017, we had approximately 22,200 employees, of which 16,300 were engaged in production. Of the 22,200, approximately 12,700 were international employees (6,400 in China). Approximately 15% of our employees are represented by labor unions that collectively bargain for work conditions, wages or other issues. We did not experience any work stoppage related to contract negotiations with labor unions during 2017. Management is not aware of any circumstances likely to result in a material work stoppage related to contract negotiations with labor unions during 2018. We had approximately 7,900 employees in Specialized Products; 6,400 in Residential Products; 5,700 in Furniture Products; and 1,400 in Industrial Products.
At December 31, 2016, we had approximately 21,300 employees.
14
PART I
Competition
Many companies offer products that compete with those we manufacture and sell. The number of competing companies varies by product line, but many of the markets for our products are highly competitive. We tend to attract and retain customers through innovation, product quality, competitive pricing and customer service. Many of our competitors try to win business primarily on price but, depending upon the particular product, we experience competition based on quality and performance as well. In general, our competitors tend to be smaller, private companies.
We believe we are the largest U.S. manufacturer, in terms of revenue, of the following:
| • | Bedding components |
| • | Automotive seat support and lumbar systems |
| • | Components for home furniture and work furniture |
| • | Carpet cushion |
| • | Adjustable beds |
| • | High-carbon drawn steel wire |
| • | Bedding industry machinery |
We continue to face pressure from foreign competitors as some of our customers source a portion of their components and finished products offshore. In addition to lower labor rates, foreign competitors benefit (at times) from lower raw material costs. They may also benefit from currency factors and more lenient regulatory climates. We typically remain price competitive, even versus many foreign manufacturers, as a result of our efficient operations, low labor content, vertical integration in steel and wire, logistics and distribution efficiencies, and large scale purchasing of raw materials and commodities. However, we have also reacted to foreign competition in certain cases by selectively adjusting prices, and by developing new proprietary products that help our customers reduce total costs.
For information about antidumping duty orders regarding innerspring and steel wire rod imports, please see "Competition" in Item 7, Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations on page 29.
Seasonality
As a diversified manufacturer, we generally have not experienced significant seasonality. However, unusual economic factors in any given year, along with acquisitions and divestitures, can create sales variability and obscure the underlying seasonality of our businesses. Historically, our operating cash flows are stronger in the fourth quarter primarily related to the timing of cash collections from customers and payments to vendors.
Backlog
Our customer relationships and our manufacturing and inventory practices do not create a material amount of backlog orders for any of our segments. Production and inventory levels are geared primarily to the level of incoming orders and projected demand based on customer relationships.
15
PART I
Working Capital Items
For information regarding working capital items, please see the discussion of "Cash from Operations" in Item 7, Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations on page 40.
Government Contracts
The Company does not have a material amount of sales derived from government contracts subject to renegotiation of profits or termination at the election of any government.
Environmental Regulation
Our operations are subject to federal, state, and local laws and regulations related to the protection of the environment. We have policies intended to ensure that our operations are conducted in compliance with applicable laws. While we cannot predict policy changes by various regulatory agencies, management expects that compliance with these laws and regulations will not have a material adverse effect on our competitive position, capital expenditures, financial condition, liquidity or results of operations.
Internet Access to Information
We routinely post information for investors under the Investor Relations section of our website (www.leggett.com). Our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and all amendments to those reports are made available, free of charge, on our website as soon as reasonably practicable after electronically filed with, or furnished to, the SEC. In addition to these reports, the Company’s Financial Code of Ethics, Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, and Corporate Governance Guidelines, as well as charters for the Audit, Compensation, and Nominating & Corporate Governance Committees of our Board of Directors, can be found on our website under the Corporate Governance section. Information contained on our website does not constitute part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Discontinued Operations
For information on discontinued operations, please see Note B on page 77 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Item 1A. Risk Factors.
Investing in our securities involves risk. Set forth below and elsewhere in this report are risk factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from the results contemplated by the forward-looking statements contained in this report. We may amend or supplement these risk factors from time to time by other reports we file with the SEC.
Costs of raw materials could negatively affect our profit margins and earnings.
Raw material cost increases (and our ability to respond to cost increases through selling price increases) can significantly impact our earnings. We typically have short-term commitments from our suppliers; therefore, our raw material costs generally move with the market. When we experience significant increases in raw material costs, we typically implement price increases to recover the higher costs. Inability to recover cost increases (or a delay in the recovery time) can negatively impact our earnings. Conversely, if raw material costs decrease, we generally pass
16
PART I
through reduced selling prices to our customers. Reduced selling prices combined with higher cost inventory can reduce our segment margins and earnings.
Steel is our principal raw material. The global steel markets are cyclical in nature and have been volatile in recent years. This volatility can result in large swings in pricing and margins from year to year. Our operations can also be impacted by changes in the cost of fabrics and foam scrap. We experienced significant fluctuations in the cost of these commodities in past years.
As a producer of steel rod, we are also impacted by volatility in metal margins (the difference between the cost of steel scrap and the market price for steel rod). If market conditions cause scrap costs and rod pricing to change at different rates (both in terms of timing and amount), metal margins could be compressed and this would negatively impact our results of operations.
Higher raw material costs in past years led some of our customers to modify their product designs, changing the quantity and mix of our components in their finished goods. In some cases, higher cost components were replaced with lower cost components. This primarily impacted our Residential Products product mix and decreased profit margins. If this were to occur again it could negatively impact our results of operations.
Competition could adversely affect our market share, sales, profit margins and earnings.
We operate in markets that are highly competitive. We believe that most companies in our lines of business compete primarily on price, but, depending upon the particular product, we experience competition based on quality and performance. We face ongoing pressure from foreign competitors as some of our customers source a portion of their components and finished products from Asia and Europe. In addition to lower labor rates, foreign competitors benefit (at times) from lower raw material costs. They may also benefit from currency factors and more lenient regulatory climates. If we are unable to purchase key raw materials, such as steel, at prices competitive with those of foreign suppliers, our ability to maintain market share and profit margins could be harmed by foreign competitors.
We are exposed to litigation contingencies that, if realized, could have a material negative impact on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Although we deny liability in all currently threatened or pending litigation proceedings and believe that we have valid bases to contest all claims made against us, we have, at December 31, 2017, an aggregate litigation contingency accrual of $.4 million. Based on current facts and circumstances, aggregate reasonably possible (but not probable) losses in excess of the recorded accruals for litigation contingencies (which include Brazilian VAT and other matters) are estimated to be $22 million. If our assumptions or analysis regarding these contingencies is incorrect, or if facts and circumstances change, we could realize loss in excess of the recorded accruals (and in excess of the $22 million referenced above) which could have a material negative impact on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. For more information regarding our legal contingencies, please see Note S on page 115 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
We are exposed to foreign currency risk which may negatively impact our competitiveness, profit margins and earnings.
We expect that international sales will continue to represent a significant percentage of our total sales, which exposes us to currency exchange rate fluctuations. In 2017, 37% of our sales were generated by international operations. The revenues and expenses of our foreign operations are generally denominated in local currencies; however, certain of our operations experience currency-related gains and losses where sales or purchases are denominated in currencies other than their local currency. Further, our competitive position may be affected by the relative strength of the currencies in countries where our products are sold. Foreign currency exchange risks inherent in doing business in foreign countries may have a material adverse effect on our future operations and financial results.
17
PART I
Our goodwill and other long-lived assets are subject to potential impairment which could negatively impact our earnings.
A significant portion of our assets consists of goodwill and other long-lived assets, the carrying value of which may be reduced if we determine that those assets are impaired. At December 31, 2017, goodwill and other intangible assets represented $991 million, or 28% of our total assets. In addition, net property, plant and equipment and sundry assets totaled $793 million, or 22% of total assets. If actual results differ from the assumptions and estimates used in the goodwill and long-lived asset valuation calculations, we could incur impairment charges, which would negatively impact our earnings.
We review our reporting units for potential goodwill impairment in June as part of our annual goodwill impairment testing, and more often if an event or circumstance occurs making it likely that impairment exists. In addition, we test for the recoverability of long-lived assets at year end, and more often if an event or circumstance indicates the carrying value may not be recoverable. We conduct impairment testing based on our current business strategy in light of present industry and economic conditions, as well as future expectations. If we are not able to achieve projected performance levels, future impairments could be possible, which would negatively impact our earnings.
For more information regarding potential goodwill and other long-lived asset impairment, please refer to Note C on page 79 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Technology failures or cyber security breaches could have a material adverse effect on our operations.
We rely on information systems to obtain, process, analyze and manage data, as well as to facilitate the manufacture and distribution of inventory to and from our facilities. We receive, process and ship orders, manage the billing of and collections from our customers, and manage the accounting for and payment to our vendors. We transitioned certain corporate-level shared service systems primarily related to our U.S. operations for general ledger, cash application, purchasing and accounts payable disbursements to a new platform during the first quarter of 2017. Technology failures or security breaches of a new or existing infrastructure could create system disruptions or unauthorized disclosure of confidential information. If this occurs, our operations could be disrupted, or we may suffer financial loss because of lost or misappropriated information. We cannot be certain that advances in criminal capabilities will not compromise our technology protecting information systems. If these systems are interrupted or damaged by these events or fail for any extended period of time, then our results of operations could be adversely affected.
We may not be able to realize deferred tax assets on our balance sheet depending upon the amount and source of future taxable income.
Our ability to realize deferred tax assets on our balance sheet is dependent upon the amount and source of future taxable income. Economic uncertainty or a reduction in the amount of taxable income or a change in the source of taxable income could impact our underlying assumptions on which valuation reserves are established and negatively affect future period earnings and balance sheets.
We have exposure to economic and other factors that affect market demand for our products which may negatively impact our sales, operating cash flows and earnings.
As a supplier of products to a variety of industries, we are adversely affected by general economic downturns. Our operating performance is heavily influenced by market demand for our components and products. Market demand for the majority of our products is most heavily influenced by consumer confidence. To a lesser extent, market demand is impacted by other broad economic factors, including disposable income levels, employment levels, housing turnover and interest rates. All of these factors influence consumer spending on durable goods, and
18
PART I
drive demand for our components and products. Some of these factors also influence business spending on facilities and equipment, which impacts approximately one quarter of our sales.
Demand weakness in our markets can lead to lower unit orders, sales and earnings in our businesses. Several factors, including a weak global economy, low consumer confidence, or a depressed housing market could contribute to conservative spending habits by consumers around the world. Short lead times in most of our markets allow for limited visibility into demand trends. If economic and market conditions deteriorate, we may experience material negative impacts on our business, financial condition, operating cash flows and results of operations.
We are exposed to political, regulatory, and legislative risks that may arise from actions by U.S. or foreign governments that could negatively impact our results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
In 2017, 37% of our sales were generated by international operations. Further, many of our businesses obtain products, components and raw materials from global suppliers. Accordingly, our business is subject to the political, regulatory, and legislative risks inherent in operating in numerous countries. These regulations and laws are complex and may change. If the U.S. or foreign governments adopt or change regulations, this could negatively impact our results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
Changes in tax laws or challenges to our tax positions could negatively impact our results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
We are subject to the tax laws and reporting rules of the U.S. (federal, state and local) and several foreign jurisdictions. Current economic and political conditions make these tax rules (and governmental interpretation of these rules) in any jurisdiction, including the U.S., subject to significant change and uncertainty. There have been proposals, most notably by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, the European Union, the U.S., and Canada, to reform tax laws or change interpretations of existing tax rules. Some of these proposals, if adopted, could significantly impact how multinational corporations are taxed on their earnings and transactions. Although we cannot predict whether or in what form these proposals will become law, or how they might be interpreted, such changes could have a material adverse effect on our earnings and cash flows.
On December 22, 2017, the U.S. government enacted comprehensive tax legislation commonly referred to as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), resulting in significant changes to U.S. federal income tax law, including the reduction of the statutory federal income tax rate for corporations and the transition from a worldwide tax system to a territorial system. We are continuing to assess the extensive changes under this legislation and its overall impact on the Company. Based on our current understanding, we expect TCJA to reduce our tax rate in future periods. However, this expectation is based on our current knowledge of the legislation and assumptions we have made. Recognized impacts could differ materially from current estimates based on additional analysis, changes in our interpretation of certain aspects of the legislation, actual financial results for 2018, additional regulatory guidance that might be issued, and other factors, including actions the Company may take as a result of TCJA.
Business disruptions to our steel rod mill, if coupled with an inability to purchase an adequate and/or timely supply of quality steel rod from alternative sources, could have a material negative impact on our Residential Products and Industrial Products segments and Company results of operations.
We purchase steel scrap from third party suppliers. This scrap is converted into steel rod in our mill in Sterling, Illinois. Our steel rod mill has annual output of approximately 500,000 tons, a substantial majority of which is used by our three wire mills. Our wire mills convert the steel rod into drawn steel wire. This wire is used in the production of many of our products, including mattress innersprings.
19
PART I
A disruption to the operation of, or supply of steel scrap to, our steel rod mill could require us to purchase steel rod from alternative supply sources, subject to market availability. Ongoing trade action by domestic rod producers against several foreign suppliers could result in the imposition of additional duties on steel rod imports which could result in reduced market availability and/or higher cost of steel rod.
If we experience a disruption to our ability to produce steel rod in our mill, coupled with a reduction of adequate and/or timely supply from alternative market sources of quality steel rod, we could experience a material negative impact on our Residential Products and Industrial Products segments and Company results of operations.
Inability to identify and consummate acquisitions at a sufficient rate and at appropriate prices could negatively impact our annual revenue growth rate.
Our long-term 6-9% annual revenue growth objective envisions periodic acquisitions. We expect to continue our strategy of seeking acquisitions that have a clear strategic rationale, a sustainable competitive advantage, a strong fit with the Company, are in a growing market, and create value by enhancing total shareholder return. Our ability to grow revenues at 6-9% depends, in part, upon our ability to identify and successfully acquire these businesses at appropriate prices. Because of competition among prospective buyers which often leads to higher valuations, the need to satisfy applicable closing conditions or obtain antitrust and other regulatory approvals on acceptable terms, and accounting, regulatory and tax requirements, we may not be able to identify or consummate these acquisitions at a sufficient rate, which could adversely impact our annual revenue growth rate.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments.
None.
Item 2. Properties.
The Company’s corporate office is located in Carthage, Missouri. As of December 31, 2017 we had 121 manufacturing locations, of which 73 are located across the United States and 48 are located in 17 foreign countries. We also had various sales, warehouse and administrative facilities. However, our manufacturing plants are our most important properties.
Manufacturing Locations by Segment
| Company- Wide | Subtotals by Segment | |||||||||
| Manufacturing Locations | Residential Products | Industrial Products | Furniture Products | Specialized Products | ||||||
| United States | 73 | 38 | 6 | 25 | 4 | |||||
| Europe | 15 | 7 | — | 1 | 7 | |||||
| China | 17 | 2 | — | 5 | 10 | |||||
| Canada | 6 | 1 | — | 2 | 3 | |||||
| Mexico | 6 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||
| Other | 4 | 2 | — | — | 2 | |||||
| Total | 121 | 52 | 7 | 34 | 28 | |||||
For more information regarding the geographic location of our manufacturing facilities refer to “Geographic Areas of Operation” under Item 1 Business on page 11.
20
PART I
Manufacturing Locations Owned or Leased by Segment
| Company- Wide | Subtotals by Segment | |||||||||
| Manufacturing Locations | Residential Products | Industrial Products | Furniture Products | Specialized Products | ||||||
| Owned | 70 | 36 | 7 | 19 | 8 | |||||
| Leased | 51 | 16 | — | 15 | 20 | |||||
| Total | 121 | 52 | 7 | 34 | 28 | |||||
In 2017, 69% of the Company's net sales were produced in these owned facilities. We also lease many of our manufacturing, warehouse and other facilities on terms that vary by lease (including purchase options, renewals and maintenance costs). For additional information regarding lease obligations, see Note J on page 92 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. Of our 121 manufacturing facilities, none are subject to liens or encumbrances that are material to the segment in which they are reported or to the Company as a whole.
None of our physical properties are, by themselves, material to the Company’s overall manufacturing processes, except for our steel rod mill in Sterling, Illinois, which is reported in Industrial Products. The rod mill consists of approximately 1 million square feet of production space, which we own, and has annual output of approximately 500,000 tons of steel rod, of which a substantial majority is used by our own wire mills. Our wire mills convert the steel rod into drawn steel wire. This wire is used in the production of many of our products, including mattress innersprings. A disruption to the operation of, or supply of steel scrap to, our steel rod mill could require us to purchase steel rod from alternative supply sources, subject to market availability. Ongoing trade action by domestic rod producers against several foreign suppliers could result in the imposition of additional duties on steel rod imports which could result in reduced market availability and/or the increase in our cost of steel rod. If we experience a disruption to our ability to produce steel rod in our mill, coupled with a reduction of adequate and/or timely supply from alternative market sources of quality steel rod, we could experience a material negative impact on our Residential Products and Industrial Products segments and Company results of operations.
In the opinion of management, the Company’s owned and leased facilities are suitable and adequate for the manufacture, assembly and distribution of our products. Our properties are located to allow quick and efficient delivery of products and services to our diverse customer base. In certain businesses, productive capacity continues to exceed current operating levels. However, utilization has increased in many of our businesses with improving market demand, and we are investing to support growth in several of our businesses, including Automotive, U.S. Spring, European Spring and Adjustable Bed.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings.
The information in Note S beginning on page 115 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements is incorporated into this section by reference.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures.
Not applicable.
21
PART I
Supplemental Item. Executive Officers of the Registrant.
The following information is included in accordance with the provisions of Part III, Item 10 of Form 10-K and Item 401(b) of Regulation S-K.
The table below sets forth the names, ages and positions of all executive officers of the Company. Executive officers are normally appointed annually by the Board of Directors.
| Name | Age | Position | ||
| Karl G. Glassman | 59 | President and Chief Executive Officer | ||
| Matthew C. Flanigan | 56 | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | ||
| Perry E. Davis | 58 | Executive Vice President, President - Residential Products & Industrial Products | ||
| J. Mitchell Dolloff | 52 | Executive Vice President, President - Specialized Products & Furniture Products | ||
| David M. DeSonier | 59 | Senior Vice President, Strategy & Investor Relations | ||
| Scott S. Douglas | 58 | Senior Vice President, General Counsel & Secretary | ||
| Russell J. Iorio | 48 | Senior Vice President, Corporate Development | ||
| Tammy M. Trent | 51 | Senior Vice President, Chief Accounting Officer | ||
Subject to the severance benefit agreements with Mr. Glassman, Mr. Flanigan, Mr. Davis, Mr. Dolloff and Mr. Douglas listed as exhibits to this Report (and certain other immaterial agreements with other executive officers), the executive officers generally serve at the pleasure of the Board of Directors. Please see Exhibit Index on page 120 for reference to the agreements.
Karl G. Glassman was appointed Chief Executive Officer of the Company in 2016 and President in 2013. He previously served the Company as Chief Operating Officer from 2006 to 2015. He also served as Executive Vice President from 2002 to 2013, President of Residential Furnishings from 1999 to 2006, Senior Vice President from 1999 to 2002 and in various capacities since 1982.
Matthew C. Flanigan was appointed Executive Vice President of the Company in 2013 and has served as Chief Financial Officer since 2003. He previously served as Senior Vice President from 2005 to 2013, Vice President from 2003 to 2005, Vice President and President of the Office Furniture Components Group from 1999 to 2003 and in various capacities since 1997.
Perry E. Davis was appointed Executive Vice President, President - Residential Products & Industrial Products effective January 1, 2017. He previously served as Senior Vice President and President of the Residential Furnishings segment beginning in 2012. He also served as Vice President of the Company, President—Bedding Group from 2006 to 2012, as Vice President of the Company, Executive VP of the Bedding Group and President—U.S. Spring beginning in 2005. He served as Executive VP of the Bedding Group and President—U.S. Spring from 2004 to 2005, President—Central Division Bedding Group from 2000 to 2004, and in various capacities since 1981.
J. Mitchell Dolloff was appointed Executive Vice President, President - Specialized Products & Furniture Products effective January 1, 2017. He previously served as Senior Vice President and President of the Specialized Products segment beginning in 2016. He served the Company as Vice President from 2014 to 2015. He also served as President of Automotive Asia from 2011 to 2013, Vice President of the Specialized Products segment from 2009 to 2013, and Director of Business Development for Specialized Products from 2007 to 2009. He has served the Company in various other capacities since 2000.
22
PART I
David M. DeSonier was appointed Senior Vice President—Strategy & Investor Relations in 2011. He previously served as Vice President—Strategy & Investor Relations from 2007 to 2011. He has served as Assistant Treasurer since 2002. He joined the Company as Vice President—Investor Relations in 2000.
Scott S. Douglas was appointed Senior Vice President and General Counsel in 2011. He was appointed Secretary of the Company in 2016. He previously served as Vice President and General Counsel from 2010 to 2011, as Vice President—Law and Deputy General Counsel from 2008 to 2010, as Associate General Counsel—Mergers & Acquisitions from 2001 to 2007, and as Assistant General Counsel from 1991 to 2001. He has served the Company in various legal capacities since 1987.
Russell J. Iorio was appointed Senior Vice President, Corporate Development in 2016. He previously served the Company as Senior Vice President, Mergers & Acquisitions from 2014 to 2016. He served the Company as Vice President, Mergers & Acquisitions from 2005 to 2014, and Director of Mergers, Acquisitions & Strategic Planning from 2002 to 2005.
Tammy M. Trent was appointed Senior Vice President in 2017 and has served as Chief Accounting Officer since 2015. She served as Staff Vice President, Financial Reporting from 2007 to 2015. She has served the Company in a series of progressively more responsible accounting capacities since 1998.
23
PART II
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities.
Our common stock is traded on the New York Stock Exchange (symbol LEG). The table below highlights quarterly and annual stock market information for the last two years.
| Price Range (1) | Volume of Shares Traded (1) (in Millions) | Dividend Declared | ||||||||||||
| High | Low | |||||||||||||
| 2017 | ||||||||||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 50.89 | $ | 46.24 | 61.1 | $ | 0.34 | |||||||
| Second Quarter | 54.97 | 49.92 | 59.9 | 0.36 | ||||||||||
| Third Quarter | 53.96 | 43.17 | 59.9 | 0.36 | ||||||||||
| Fourth Quarter | 51.99 | 44.76 | 58.2 | 0.36 | ||||||||||
| For the Year | $ | 54.97 | $ | 43.17 | 239.1 | $ | 1.42 | |||||||
| 2016 | ||||||||||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 48.50 | $ | 36.64 | 60.3 | $ | 0.32 | |||||||
| Second Quarter | 51.20 | 47.11 | 50.7 | 0.34 | ||||||||||
| Third Quarter | 54.63 | 45.11 | 55.6 | 0.34 | ||||||||||
| Fourth Quarter | 50.79 | 44.02 | 57.0 | 0.34 | ||||||||||
| For the Year | $ | 54.63 | $ | 36.64 | 223.6 | $ | 1.34 | |||||||
(1) Price and volume data reflect composite transactions; price range reflects intra-day prices; data source is Bloomberg.
Shareholders and Dividends
As of February 9, 2018, we had 8,497 shareholders of record.
Increasing the dividend remains a high priority. In 2017, we increased the quarterly dividend by $.02, or 6% to $.36 per share. In each year for over 25 years, we have generated operating cash in excess of our annual requirement for capital expenditures and dividends. We expect this again to be the case in 2018. We have no restrictions that materially limit our ability to pay such dividends or that we reasonably believe are likely to limit the future payment of dividends.
For more information on dividends see "Pay Dividends" in Item 7, Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations on page 44.
24
PART II
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
The table below is a listing of our purchases of the Company’s common stock during each calendar month of the fourth quarter of 2017.
| Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased (1) | Average Price Paid per Share | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs (2) | Maximum Number of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs (2) | |||||||||
| October 2017 | — | $ | — | — | 7,133,023 | ||||||||
| November 2017 | 5,875 | $ | 46.45 | 3,000 | 7,130,023 | ||||||||
| December 2017 | 6,066 | $ | 48.26 | — | 7,130,023 | ||||||||
| Total | 11,941 | $ | 47.37 | 3,000 | |||||||||
| (1) | This number includes 8,941 shares which were not repurchased as part of a publicly announced plan or program, all of which were shares surrendered in transactions permitted under the Company’s benefit plans. It does not include shares withheld for taxes on option exercises and stock unit conversions, or forfeitures of stock units, all of which totaled 11,852 shares for the fourth quarter. |
| (2) | On August 4, 2004, the Board authorized management to repurchase up to 10 million shares each calendar year beginning January 1, 2005. This standing authorization was first reported in the quarterly report on Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2004, filed August 5, 2004, and will remain in force until repealed by the Board of Directors. As such, effective January 1, 2018, the Company was authorized by the Board of Directors to repurchase up to 10 million shares in 2018. No specific repurchase schedule has been established. |
25
PART II
Item 6. Selected Financial Data.
| (Unaudited) | 2017 1 | 2016 2 | 2015 3 | 2014 4 | 2013 5 | ||||||||||||||
| (Dollar amounts in millions, except per share data) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Summary of Operations | |||||||||||||||||||
| Net Sales from Continuing Operations | $ | 3,944 | $ | 3,750 | $ | 3,917 | $ | 3,782 | $ | 3,477 | |||||||||
| Earnings from Continuing Operations | 294 | 367 | 328 | 225 | 186 | ||||||||||||||
| (Earnings) Attributable to Noncontrolling Interest, net of tax | — | — | (4 | ) | (3 | ) | (2 | ) | |||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from Discontinued Operations, net of tax | (1 | ) | 19 | 1 | (124 | ) | 13 | ||||||||||||
| Net Earnings attributable to Leggett & Platt, Inc. common shareholders | 293 | 386 | 325 | 98 | 197 | ||||||||||||||
| Earnings per share from Continuing Operations | |||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | 2.16 | 2.66 | 2.30 | 1.57 | 1.27 | ||||||||||||||
| Diluted | 2.14 | 2.62 | 2.27 | 1.55 | 1.25 | ||||||||||||||
| Earnings (Loss) per share from Discontinued Operations | |||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | (.01 | ) | .14 | .01 | (.88 | ) | .09 | ||||||||||||
| Diluted | (.01 | ) | .14 | .01 | (.87 | ) | .09 | ||||||||||||
| Net Earnings (Loss) per share | |||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | 2.15 | 2.80 | 2.31 | .69 | 1.36 | ||||||||||||||
| Diluted | 2.13 | 2.76 | 2.28 | .68 | 1.34 | ||||||||||||||
| Cash Dividends declared per share | 1.42 | 1.34 | 1.26 | 1.22 | 1.18 | ||||||||||||||
| Summary of Financial Position | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total Assets | $ | 3,551 | $ | 2,984 | $ | 2,964 | $ | 3,136 | $ | 3,105 | |||||||||
| Long-term Debt, including capital leases | $ | 1,098 | $ | 956 | $ | 942 | $ | 762 | $ | 685 | |||||||||
All amounts are presented after tax.
1 | Net earnings from Continuing Operations for 2017 includes a $50 million charge associated with the TCJA; $13 million of net gains on sales of a business and real estate; an $8 million tax benefit from a divestiture; a $10 million pension settlement charge; and a $3 million charge for an impairment of a wire business. |
2 | Net earnings from Continuing Operations for 2016 includes $16 million of gains on sales of businesses; a $3 million goodwill impairment charge; and a $5 million gain on a foam litigation settlement. Discontinued operations primarily consists of a gain on a foam litigation settlement. |
3 | Net earnings from Continuing Operations for 2015 includes $4 million of impairments; $3 million associated with litigation accruals; and an $8 million pension settlement charge. |
4 | Net earnings from Continuing Operations for 2014 includes $33 million associated with litigation accruals. Discontinued Operations includes the following items: $93 million goodwill impairment; $5 million loss on the sale of the majority of our Store Fixtures unit; and $22 million associated with litigation accruals. |
5 | Net earnings from Continuing Operations for 2013 include charges of $45 million related to the Commercial Vehicle Products group ($43 million goodwill impairment charge and $2 million accelerated amortization of a customer-related intangible asset); and an $8 million bargain purchase gain related to an acquisition. |
26
PART II
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
HIGHLIGHTS
Sales increased 5% in 2017, from growth in volume, raw material-related price inflation and currency impact. Acquisitions added 2% to sales but were offset by divestitures (-2%). Sales growth came primarily from Automotive, reflecting content gains and new program awards, and Adjustable Bed. Several other businesses, including International Spring, Geo Components, Work Furniture and Aerospace, contributed to sales growth this past year.
Earnings from continuing operations decreased significantly from the effects of one-time costs associated with the recently enacted Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA). Other significant factors that reduced earnings include on going steel inflation and the timing lag associated with passing along higher steel costs. These reductions were partially offset by increased sales and lower income taxes.
We continue to optimize our portfolio by increasing investment in those businesses that possess strong competitive advantage and reducing our exposure to businesses and markets that are less attractive. We increased capital expenditures in 2017 to support product categories that are growing. In addition, we acquired three small businesses. We also divested the last remaining operation within the Commercial Vehicle Products group during the year.
Operating cash flow decreased versus 2016, primarily from higher working capital due to sales growth and inflation. However, we once again generated more than enough operating cash flow to comfortably fund dividends and capital expenditures, something we have accomplished each year for more than 25 years.
We raised the quarterly dividend by 6% in 2017 and extended our record of consecutive annual increases to 46 years. We also bought back 3.3 million shares of our stock.
During the year, we issued $500 million of 3.5% notes maturing in 2027. We also extended the term of, and expanded the borrowing capacity under, our revolving credit facility from $750 million to $800 million and correspondingly increased our commercial paper program. We ended 2017 with net debt to net capital at 33%, comfortably within our long-standing targeted range of 30-40%, as discussed on page 47.
We assess our overall performance by comparing our Total Shareholder Return (TSR) to that of peer companies on a rolling three-year basis. We target TSR in the top third of the S&P 500 over the long term. For the three years ended December 31, 2017, we generated TSR of 7% per year on average, placing us just below the midpoint of the S&P 500.
These topics are discussed in more detail in the sections that follow.
27
PART II
INTRODUCTION
Total Shareholder Return
Total Shareholder Return (TSR), relative to peer companies, is the key financial measure that we use to assess long-term performance. TSR is driven by the change in our share price and the dividends we pay: TSR = (Change in Stock Price + Dividends) / Beginning Stock Price. We seek to achieve TSR in the top third of the S&P 500 over the long term through an approach that employs four TSR drivers: revenue growth, margin expansion, dividends, and share repurchases.
We monitor our TSR performance relative to the S&P 500 on a rolling three-year basis. For the three-year measurement period that ended December 31, 2017, we generated TSR of 7% per year on average, just below the midpoint of the S&P 500.
The table below shows the components of our TSR targets. Accomplishing this level of performance over rolling three-year periods should enable us to consistently attain our top-third TSR goal.
| Current Targets | ||
| Revenue Growth | 6-9% | |
| Margin Increase | 1% | |
| Dividend Yield | 3% | |
| Stock Buyback | 1% | |
| Total Shareholder Return | 11-14% | |
Customers
We serve a broad suite of customers, with our largest customer representing approximately 5% of our sales. Many are companies whose names are widely recognized. They include producers of residential furniture and bedding, automotive and office seating manufacturers, and a variety of other companies.
Major Factors That Impact Our Business
Many factors impact our business, but those that generally have the greatest impact are market demand, raw material cost trends, and competition.
Market Demand
Market demand (including product mix) is impacted by several economic factors, with consumer confidence being most significant. Other important factors include disposable income levels, employment levels, housing turnover, and interest rates. All of these factors influence consumer spending on durable goods, and therefore affect demand for our components and products. Some of these factors also influence business spending on facilities and equipment, which impacts approximately one quarter of our sales.
Raw Material Costs
In many of our businesses, we enjoy a cost advantage from being vertically integrated into steel wire and rod. This is a benefit that our competitors do not have. We also experience favorable purchasing leverage from buying large quantities of raw materials. Still, our costs can vary significantly as market prices for raw materials (many of which are commodities) fluctuate.
28
PART II
We typically have short-term commitments from our suppliers; accordingly, our raw material costs generally move with the market. Our ability to recover higher costs (through selling price increases) is crucial. When we experience significant increases in raw material costs, we typically implement price increases to recover the higher costs. Conversely, when costs decrease significantly, we generally pass those lower costs through to our customers. The timing of our price increases or decreases is important; we typically experience a lag in recovering higher costs, and we also realize a lag as costs decline.
Steel is our principal raw material. At various times in past years we have experienced significant cost fluctuations in this commodity. In most cases, the major changes (both increases and decreases) were passed through to customers with selling price adjustments. Throughout 2015, market prices for steel decreased significantly, leading to downward pressure on selling prices. We realized a beneficial pricing lag during 2015, as costs generally decreased at a faster rate than selling prices. In 2016, steel costs once again became volatile. Steel inflation during the first half of 2016 was followed by deflation in the third quarter, and significant inflation late in the year. This steel inflation continued throughout 2017. We implemented price increases to recover most of the higher costs, but with the normal lag in realizing selling price increases, the cost inflation led to margin pressure throughout 2017.
As a producer of steel rod, we are also impacted by changes in metal margins (the difference between the cost of steel scrap and the market price for steel rod). Metal margins within the steel industry have been volatile in past years, were moderately compressed in late 2016, and began to increase modestly in the second half of 2017.
Our other raw materials include woven and non-woven fabrics, foam scrap, and chemicals. We have experienced changes in the cost of these materials in past years and generally have been able to pass them through to our customers.
When we raise our prices to recover higher raw material costs, this sometimes causes customers to modify their product designs and replace higher cost components with lower cost components. We must continue providing product options to our customers that enable them to improve the functionality of their products and manage their costs, while providing higher profits for our operations.
Competition
Many of our markets are highly competitive, with the number of competitors varying by product line. In general, our competitors tend to be smaller, private companies. Many of our competitors, both domestic and foreign, compete primarily on the basis of price. Our success has stemmed from the ability to remain price competitive, while delivering innovation, better product quality, and customer service.
We continue to face pressure from foreign competitors as some of our customers source a portion of their components and finished products offshore. In addition to lower labor rates, foreign competitors benefit (at times) from lower raw material costs. They may also benefit from currency factors and more lenient regulatory climates. We typically remain price competitive in most of our business units, even versus many foreign manufacturers, as a result of our highly efficient operations, low labor content, vertical integration in steel and wire, logistics and distribution efficiencies, and large scale purchasing of raw materials and commodities. However, we have also reacted to foreign competition in certain cases by selectively adjusting prices, and by developing new proprietary products that help our customers reduce total costs.
Since 2009, there have been antidumping duty orders on innerspring imports from China, South Africa and Vietnam, ranging from 116% to 234%. In March 2014, the Department of Commerce (DOC) and the International Trade Commission (ITC) determined that the duties should be continued. In April 2014, the DOC published its final order continuing the duties through February 2019 (for China) and December 2018 (for South Africa and Vietnam).
An antidumping and countervailing duty case filed in January 2014 by major U.S. steel wire rod producers was concluded in December 2014, resulting in the imposition of duties on imports of Chinese steel wire rod. The
29
PART II
antidumping duties range from 106% to 110% and the countervailing duties range from 178% to 193%. Both remain in effect through December 2019. Also, in March 2017 certain U.S. steel wire rod producers filed antidumping and countervailing duty petitions on imports of steel wire rod from Belarus, Italy, Korea, Russia, South Africa, Spain, Turkey, Ukraine, United Arab Emirates, and the United Kingdom. The ITC and the DOC have made final affirmative determinations and imposed antidumping duties on imports from Belarus (280%), Russia (437% to 757%), South Africa (135% to 142%), Ukraine (35% to 44%), and United Arab Emirates (84%). Final antidumping and countervailing duty determinations on the remaining countries are expected in March and April 2018.
Because of the documented evasion of antidumping orders by certain importers, typically shipping goods through third countries and falsely identifying the countries of origin, Leggett and several other U.S. manufacturers formed a coalition to seek stronger enforcement of existing antidumping and/or countervailing duty orders. As a result of these efforts, the U.S. Congress passed the Enforcing Orders and Reducing Customs Evasion (ENFORCE) Act. The ENFORCE Act requires U.S. Customs and Border Protection to implement a transparent, time-limited process to investigate allegations of duty evasion and to assess duties where appropriate.
Change in Segment Reporting in 2017
Our reportable segments are the same as our operating segments, which also correspond with our management organizational structure. In conjunction with a change in executive officers, our management organizational structure and all related internal reporting changed as of January 1, 2017. Effective January 1, 2017, Perry E. Davis became President of the Residential Products and Industrial Products segments, and J. Mitchell Dolloff became President of the Specialized Products and Furniture Products segments.
The composition of our four segments also changed effective January 1, 2017. The table below outlines the new segment structure. We reported under this new structure when we filed our 2017 first quarter 10-Q.
| Residential Products | Industrial Products | Furniture Products | Specialized Products |
| Bedding Group | Wire Group | Work Furniture Group | Automotive Group |
| Fabric & Carpet Cushion Group | Home Furniture Group | Aerospace Products Group | |
| Machinery Group | Consumer Products Group | CVP Group | |
The new structure is largely the same as in prior years except that the Home Furniture Group was moved from Residential Products (formerly Residential Furnishings) to Furniture Products (formerly Commercial Products), and the Machinery Group was moved from Specialized Products to Residential Products. The Industrial Products segment (formerly Industrial Materials) had no changes. Our final CVP operation was sold in 2017.
Prior to January 1, 2017, all of our segments used the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method for valuing inventory. In our consolidated financials, we converted approximately 50% of these inventories (primarily our domestic, steel-related inventories) to the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method, and reported the related LIFO benefit or expense outside of the segments. Effective January 1, 2017, the LIFO benefit or expense was recognized within the segment to which it relates. This change has been retrospectively applied to all prior periods presented.
30
PART II
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS—2017 vs. 2016
Sales increased 5% in 2017, from growth in volume, raw material-related price inflation, and currency impact. Acquisitions added 2% to sales but were offset by divestitures. Sales growth came primarily from Automotive, reflecting content gains and new program awards, and Adjustable Bed. Several other businesses, including International Spring, Geo Components, Work Furniture and Aerospace, contributed to sales growth this year.
Earnings from continuing operations decreased significantly from the effects of one-time costs associated with the recently enacted TCJA. Other significant factors that reduced earnings include ongoing steel inflation and the timing lag associated with passing along higher steel costs. These reductions were partially offset by increased sales and lower income taxes. Further details about our consolidated and segment results are discussed below.
Consolidated Results (continuing operations)
The following table shows the changes in sales and earnings from continuing operations during 2017, and identifies the major factors contributing to the changes.
| (Dollar amounts in millions, except per share data) | Amount | % * | ||||
| Net sales: | ||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2016 | $ | 3,750 | ||||
| Divestitures | (78 | ) | (2 | )% | ||
| 2016 sales excluding divestitures | 3,672 | |||||
| Approximate volume gains | 142 | 4 | % | |||
| Approximate raw material-related inflation and currency impact | 65 | 2 | % | |||
| Same location sales | 207 | 6 | % | |||
| Acquisition sales growth | 65 | 2 | % | |||
| Year ended December 31, 2017 | $ | 3,944 | 5 | % | ||
| Earnings from continuing operations: | ||||||
| (Dollar amounts, net of tax) | ||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2016 | $ | 367 | ||||
| TCJA impact, net | (50 | ) | ||||
| Pension settlement charge | (10 | ) | ||||
| Real estate gain | 15 | |||||
| Divestiture tax benefit | 8 | |||||
| Divestiture loss | (2 | ) | ||||
| Impairment | (3 | ) | ||||
| Non-recurrence of divestiture gains | (17 | ) | ||||
| Non-recurrence of litigation settlement gain | (5 | ) | ||||
| Other, including higher steel costs (and LIFO expense), | ||||||
| partially offset by higher volume and lower income taxes | (9 | ) | ||||
| Year ended December 31, 2017 | $ | 294 | ||||
| Earnings Per Diluted Share (continuing operations)—2016 | $ | 2.62 | ||||
| Earnings Per Diluted Share (continuing operations)—2017 | $ | 2.14 | ||||
* Calculations impacted by rounding
31
PART II
Sales increased 5% from volume growth, raw-material price increases and currency impact. Acquisitions also contributed 2% to sales growth but were offset by divestitures. The growth came primarily from Automotive and Adjustable Bed. Several other businesses, including International Spring, Geo Components, Work Furniture and Aerospace, also contributed to sales growth this past year.
During 2017, we divested the last remaining CVP operation, which had total annual sales of $43 million.
As indicated in the table above, earnings from continuing operations decreased primarily from the impact of the recently enacted TCJA. Operationally, earnings decreased largely from steel inflation, the timing lag associated with passing along these higher steel costs, and several smaller items partially offset by higher volume and lower income taxes.
LIFO Impact
Approximately 50% of our inventories are valued on the LIFO method. These are primarily our domestic, steel-related inventories. In 2017, increasing steel costs over the course of the year resulted in a full-year pretax LIFO expense of $19 million. In 2016, increasing steel costs, particularly in the fourth quarter, resulted in a full-year pretax LIFO expense of $11 million.
For further discussion of inventories, see Note A to the Consolidated Financial Statements on page 71.
Interest and Income Taxes
Net interest expense in 2017 did not appreciably change.
Our tax rate is determined by a combination of items, some recurring and some discrete. Recurring items include income earned in various tax jurisdictions and differences in tax rates in those jurisdictions. These items tend to be relatively stable from year to year. Conversely, discrete items may not be as consistent from year to year.
On December 22, 2017, President Trump signed into law TCJA, enacting significant changes to the U.S. Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, including a reduction in the maximum U.S. federal corporate income tax rate from 35% to 21%, the transition of U.S. taxation from a worldwide tax system to a territorial system, and the imposition of a one-time tax associated with the mandatory deemed repatriation of untaxed foreign earnings. Although these provisions are generally applicable for years after December 31, 2017, several impacted our 2017 earnings, including the one-time deemed repatriation tax, additional taxes for expected foreign cash repatriations, and the revaluation of our U.S. deferred taxes. As a result, we recorded a net tax expense of $50 million in the fourth quarter of 2017 related to these items, which negatively impacted our full year tax rate by 12%. Of this total amount, $67 million is related to the one-time deemed repatriation tax that will be paid on a graduated scale over the next eight years.
The amount recorded is our best estimate and based on our current understanding of TCJA and the guidance currently available, but should be considered provisional. The ultimate impact may differ from the provisional amount and the accounting will be finalized no later than the fourth quarter of 2018.
While the U.S. statutory federal income tax rate was 35% in both years, our worldwide effective income tax rate on continuing operations was 32% in 2017, compared to 25% for 2016. As discussed above, our rate was negatively impacted by 12% in 2017 due to the effect of TCJA (16% associated with the deemed repatriation tax and 2% from tax on expected future foreign cash repatriations, partially offset by a 6% benefit from the revaluation of our U.S. net deferred tax liabilities). In both years our tax rate benefited from earnings in non-U.S. jurisdictions, which reduced our effective tax rate by 8% in 2017 and 6% in 2016. In addition, the 2017 tax rate benefited by 2% related to tax attributes from a divested business, 2% related to the tax effects of stock-based compensation deductions in the year, and 3% from other permanent tax differences.
32
PART II
The 2016 tax rate benefited by 3% related to the tax effects of stock-based compensation deductions in the year and 1% (net) from other items.
We anticipate an effective tax rate for 2018 of approximately 22%, which includes the anticipated tax effects associated with TCJA and certain other expected discrete items, including stock compensation payments. The expected tax impact from stock compensation can fluctuate based on stock price and other factors, and any changes to our 2017 provisional and 2018 expected TCJA amounts could impact our anticipated 2018 tax rate. Our tax rate is also contingent upon other factors such as our overall profitability, the mix of earnings among tax jurisdictions, the type of income earned, business acquisitions and dispositions, the impact of tax audits and other discrete items, and the effect of other tax law changes and prudent tax planning strategies.
33
PART II
Segment Results
In the following section we discuss 2017 sales and EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes) for each of our segments. We provide additional detail about segment results and a reconciliation of segment EBIT to consolidated EBIT in Note E to the Consolidated Financial Statements on page 82. 2016 segment data has been retrospectively adjusted to reflect the change in segment reporting discussed on page 30.
| (Dollar amounts in millions) | 2017 | 2016 | Change in Sales | % Change Same Location Sales (1) | ||||||||||||||||
| $ | % | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sales | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Residential Products | $ | 1,639 | $ | 1,589 | $ | 50 | 3 | % | — | % | ||||||||||
| Industrial Products | 546 | 583 | (37 | ) | (6 | )% | — | % | ||||||||||||
| Furniture Products | 1,113 | 1,048 | 65 | 6 | % | 5 | % | |||||||||||||
| Specialized Products | 943 | 906 | 37 | 4 | % | 8 | % | |||||||||||||
| Total segment sales | 4,241 | 4,126 | 115 | |||||||||||||||||
| Intersegment sales elimination | (297 | ) | (376 | ) | 79 | |||||||||||||||
| Trade sales | $ | 3,944 | $ | 3,750 | $ | 194 | 5 | % | 6 | % | ||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | Change in EBIT | EBIT Margins (2) | |||||||||||||||||
| $ | % | 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||||||||
| EBIT | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Residential Products | $ | 184 | $ | 168 | $ | 16 | 10 | % | 11.2 | % | 10.5 | % | ||||||||
| Industrial Products | 21 | 65 | (44 | ) | (68 | )% | 3.8 | % | 11.2 | % | ||||||||||
| Furniture Products | 81 | 107 | (26 | ) | (24 | )% | 7.3 | % | 10.2 | % | ||||||||||
| Specialized Products | 196 | 181 | 15 | 8 | % | 20.8 | % | 20.0 | % | |||||||||||
| Intersegment eliminations & other | 1 | 1 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Pension settlement charge | (15 | ) | (15 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Total EBIT | $ | 468 | $ | 522 | $ | (54 | ) | (10 | )% | 11.9 | % | 13.9 | % | |||||||
______________________________
| (1) | This is the change in sales not attributable to acquisitions or divestitures. These are sales that come from the same plants and facilities that we operated one year earlier. |
| (2) | Segment margins are calculated on total sales. Overall company margin is calculated on trade sales. |
Residential Products
Residential Products total sales increased 3% in 2017 from acquisitions, net of a small divestiture. Same locations sales were flat, with volume growth and raw material-related price increases offset by lower pass-through sales of adjustable beds (which originate in Furniture Products but are occasionally distributed through Residential Products). Within our U.S. Spring business, total innerspring units decreased 4%, but growth continued in ComfortCore® (our pocketed coil innersprings), with unit volume in that category up 8%. Volume also increased in our International Spring business.
EBIT and EBIT margin increased in 2017 due to the pass-through of raw material cost increases and higher volume, despite the non-recurrence of a $7 million litigation benefit in 2016.
34
PART II
Industrial Products
Total sales in the segment declined 6%, due to divestitures completed in 2016. Same location sales in Industrial Products were flat with steel-related price increases offset by lower volume.
EBIT decreased primarily from the non-recurrence of a $16 million divestiture gain in 2016, higher raw material costs (including LIFO expense), the timing lag associated with passing along inflation, an impairment charge of $5 million, and lower volume.
Furniture Products
Sales in Furniture Products increased 6%, with same location sales up 5% from growth in Adjustable Bed and Work Furniture. A small acquisition in Work Furniture added 1% to sales growth.
EBIT and EBIT margin decreased, with the benefit from sales growth more than offset by higher steel costs (including LIFO expense), production inefficiencies and other smaller items.
Specialized Products
In Specialized Products, total sales increased 4% in 2017, and same location sales increased 8%, with volume gains in Automotive and Aerospace partially offset by lower sales in the former CVP business unit. CVP divestitures reduced sales by 4%.
EBIT and EBIT margin increased primarily from a $23 million gain related to the sale of real estate formerly associated with CVP and higher volume, partially offset by a non-recurring divestiture gain in 2016 ($11 million) and growth-related costs.
Results from Discontinued Operations
Full year earnings from discontinued operations, net of tax, decreased to -$1 million from $19 million in 2016. This decrease is primarily due to the non-recurrence of a litigation gain ($20 million) related to our former Prime Foam business. For further information about discontinued operations, see Note B to the Consolidated Financial Statements on page 77.
35
PART II
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS—2016 vs. 2015
Sales decreased 4% in 2016, with slightly higher unit volume and acquisitions more than offset by divestitures, raw material-related price deflation, and currency impact. Sales growth continued in Automotive, reflecting content gains and new program awards, but several other businesses experienced soft market demand and lower unit volume during the year.
Earnings from continuing operations increased from several factors, including divestiture gains. The benefit from increased unit volume and lower income taxes was partially offset by steel inflation and the non-recurrence of a pricing lag benefit associated with deflation late in 2015. Further details about our consolidated and segment results are discussed below.
Consolidated Results (continuing operations)
The following table shows the changes in sales and earnings from continuing operations during 2016, and identifies the major factors contributing to the changes.
| (Dollar amounts in millions, except per share data) | Amount | % | ||||
| Net sales: | ||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2015 | $ | 3,917 | ||||
| Divestitures | (141 | ) | (4 | )% | ||
| 2015 sales excluding divestitures | 3,776 | |||||
| Approximate volume gains | 58 | 2 | % | |||
| Approximate raw material-related deflation and currency impact | (111 | ) | (3 | )% | ||
| Same location sales | (53 | ) | (1 | )% | ||
| Acquisition sales growth | 27 | 1 | % | |||
| Year ended December 31, 2016 | $ | 3,750 | (4 | )% | ||
| Earnings from continuing operations: | ||||||
| (Dollar amounts, net of tax) | ||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2015 | $ | 328 | ||||
| Divestiture gains | 17 | |||||
| Litigation settlement gain | 5 | |||||
| Non-recurrence of pension settlement charge | 8 | |||||
| Other, including benefit from higher volume and lower income taxes, partially | ||||||
| offset by steel inflation and non-recurrence of prior year pricing lag benefit | 9 | |||||
| Year ended December 31, 2016 | $ | 367 | ||||
| Earnings Per Diluted Share (continuing operations)—2015 | $ | 2.27 | ||||
| Earnings Per Diluted Share (continuing operations)—2016 | $ | 2.62 | ||||
Sales decreased 4%, with unit volume growth and acquisitions more than offset by divestitures, raw material-related price decreases, and currency impact. Strong growth in Automotive was partially offset by soft demand in several other markets, including bedding and home furniture.
During 2016, we divested two wire operations, a CVP business and a Machinery operation. These businesses had total combined annual sales of approximately $100 million.
As indicated in the table above, earnings from continuing operations increased from divestiture gains (related to a CVP business and a wire operation), a litigation settlement gain, and the non-recurrence of the prior year's
36
PART II
pension settlement charge. Operationally, earnings also benefited from higher unit volume and lower income taxes related to a new accounting standard for stock-based compensation. These improvements were partially offset by steel inflation that began to occur in late 2016 and the non-recurrence of the prior year pricing lag benefit (that occurred as steel costs deflated in late 2015).
LIFO Impact
Approximately 50% of our inventories are valued on the LIFO method. These are primarily our domestic, steel-related inventories. In 2016, increasing steel costs, particularly in the fourth quarter, resulted in a full-year pretax LIFO expense of $11 million. In 2015, significant deflation in steel costs, particularly in the fourth quarter, resulted in a full-year pretax LIFO benefit of $46 million.
For further discussion of inventories, see Note A to the Consolidated Financial Statements on page 71.
Interest and Income Taxes
Net interest expense in 2016 decreased slightly due to the repayment of $200 million 5% notes in August 2015.
Our tax rate is determined by a combination of items, some recurring and some discrete. Recurring items include things like income earned in various tax jurisdictions, and differences in tax rates in those jurisdictions. These items tend to be relatively stable from year to year. Conversely, discrete items are things that may not be as consistent from year to year.
While the U.S. statutory federal income tax rate was 35% in both years, our worldwide effective income tax rate on continuing operations was 25% in 2016, compared to 27% for 2015. In both years our tax rate benefited from earnings in non-U.S. jurisdictions, which reduced our effective tax rate by 6% in each year. In addition, the 2016 tax rate benefited by 3% related to the tax effects of stock-based compensation deductions in the year, and 1% (net) from other items. The 2015 tax rate benefited by 1% related to the reduction of a tax accrual for Chinese earnings that we decided to reinvest within China to acquire the remaining interest in a joint venture and 1% (net) from other items.
In the first quarter of 2016 we adopted Accounting Standards Update (ASU) 2016-09, Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting. This ASU provides that the tax effects of stock-based awards must be treated as discrete items affecting the tax rate in the interim reporting period in which the tax deductions occur. Many variables (such as timing of award settlements or expirations, changes in stock price over time, ultimate payout levels for awards with performance contingencies, shares cancelled before vesting, and the tax rules in effect at the time of settlement) will impact both the timing and the amount of the tax deductions. Thus, this ASU is likely to add more volatility to the effective tax rate of companies such as Leggett that use stock-based compensation plans.
37
PART II
Segment Results
In the following section we discuss 2016 sales and EBIT for each of our segments. We provide additional detail about segment results and a reconciliation of segment EBIT to consolidated EBIT in Note E to the Consolidated Financial Statements on page 82. All segment data has been retrospectively adjusted to reflect the change in segment reporting discussed on page 30.
| (Dollar amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | Change in Sales | % Change Same Location Sales (1) | ||||||||||||||||
| $ | % | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sales | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Residential Products | $ | 1,589 | $ | 1,688 | $ | (99 | ) | (6 | )% | (6 | )% | |||||||||
| Industrial Products | 583 | 777 | (194 | ) | (25 | )% | (12 | )% | ||||||||||||
| Furniture Products | 1,048 | 1,072 | (24 | ) | (2 | )% | (3 | )% | ||||||||||||
| Specialized Products | 906 | 847 | 59 | 7 | % | 8 | % | |||||||||||||
| Total segment sales | 4,126 | 4,384 | (258 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Intersegment sales elimination | (376 | ) | (467 | ) | 91 | |||||||||||||||
| Trade sales | $ | 3,750 | $ | 3,917 | $ | (167 | ) | (4 | )% | (1 | )% | |||||||||
| �� | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | Change in EBIT | EBIT Margins (2) | |||||||||||||||||
| $ | % | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||
| EBIT | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Residential Products | $ | 168 | $ | 155 | $ | 13 | 8 | % | 10.5 | % | 9.2 | % | ||||||||
| Industrial Products | 65 | 77 | (12 | ) | (16 | )% | 11.2 | % | 9.9 | % | ||||||||||
| Furniture Products | 107 | 118 | (11 | ) | (9 | )% | 10.2 | % | 11.0 | % | ||||||||||
| Specialized Products | 181 | 150 | 31 | 21 | % | 20.0 | % | 17.7 | % | |||||||||||
| Pension settlement charge | — | (12 | ) | 12 | ||||||||||||||||
| Intersegment eliminations & other | 1 | (1 | ) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total EBIT | $ | 522 | $ | 487 | $ | 35 | 7 | % | 13.9 | % | 12.4 | % | ||||||||
______________________________
| (1) | This is the change in sales not attributable to acquisitions or divestitures. These are sales that come from the same plants and facilities that we operated one year earlier. |
| (2) | Segment margins are calculated on total sales. Overall company margin is calculated on trade sales. |
Residential Products
Residential Products sales decreased 6% in 2016 from a combination of lower unit volume in several product categories, lower pass-through sales of adjustable beds (which originate in Furniture Products but are occasionally distributed through Residential Products), raw material-related price decreases, and currency impact. Within our U.S. Spring business, total innerspring units decreased 6%, but growth continued in ComfortCore® (our pocketed coil innersprings), with unit volume in that category up 4%. Volume also increased in our European Spring business.
EBIT and EBIT margin increased in 2016 due to a litigation gain ($7 million) and non-recurrence of last year's foam litigation expense ($5 million). Operationally, the impact on EBIT from lower unit volume was offset by pricing discipline.
38
PART II
Industrial Products
Same location sales in Industrial Products were down 12% from steel-related price decreases and lower unit volume in Drawn Wire. Total sales in the segment declined 25%, also reflecting the divestitures of the Steel Tubing business in late 2015 and two wire operations in 2016.
EBIT decreased primarily due to higher raw material costs (including LIFO impact) and lower unit volume. The operational impacts were partially offset by a divestiture gain ($16 million) from the sale of one of the Wire Products operations, and the non-recurrence of the prior year's impairment charge ($6 million) and divestiture loss ($3 million), both associated with the sale of the Steel Tubing business.
Furniture Products
Sales in Furniture Products decreased 2%, primarily from lower volume in Home Furniture, steel-related price decreases, and currency impact. These items were partially offset by growth from a Work Furniture acquisition completed in March 2015. Adjustable Bed unit volume increased 1% (versus strong growth in each of the prior two years) as we began ramping up new programs selling directly to major bedding retailers and transitioning away from former programs with bedding manufacturers. The decline in these bedding manufacturer programs also caused the decrease in pass-through sales of adjustable beds discussed in the Residential Products segment above.
EBIT and EBIT margin decreased, primarily from higher raw material costs (including LIFO impact) and lower volume, partially offset by operational improvements, gains from building sales of $3 million, and a favorable sales mix.
Specialized Products
In Specialized Products, sales increased 7% in 2016, with volume gains in Automotive and an Aerospace acquisition completed early in the year, partially offset by divestitures, and currency impact.
EBIT and EBIT margin increased from higher sales, a divestiture gain ($11 million) related to the sale of a CVP operation, and currency impact. These items were partially offset by goodwill impairment of $4 million.
We agreed to sell real estate associated with the CVP business and expected to realize a gain on this transaction in 2017. This property reached held-for-sale status in 2016, causing the fair value of the CVP reporting unit to fall below its carrying value, and triggering the $4 million impairment charge.
Results from Discontinued Operations
Full year earnings from discontinued operations, net of tax, increased to $19 million from $1 million in 2015. This increase is primarily due to a litigation gain ($20 million) related to our former Prime Foam business. For further information about discontinued operations, see Note B to the Consolidated Financial Statements on page 77.
39
PART II
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITALIZATION
Cash from operations decreased in 2017, primarily from working capital increases due to sales growth and inflation. Our operations once again provided more than enough cash to fund both capital expenditures and dividend payments, something we have accomplished each year for over 25 years. We expect this to again be the case in 2018.
We continued to invest in businesses and product categories that are growing. This resulted in higher capital expenditures in 2017. We raised the quarterly dividend by 6% and extended our record of consecutive annual increases to 46 years. We also bought back 3.3 million shares of our stock during the year.
In November 2017, we issued $500 million of 3.5% notes maturing in 2027. We also extended the term of our revolving credit facility to November 2022, expanded the borrowing capacity from $750 million to $800 million and correspondingly increased our commercial paper program. We ended 2017 with net debt to net capital at 33%, comfortably within our long-standing targeted range of 30-40%, as discussed on page 47.
Cash from Operations
Cash from operations is our primary source of funds. Earnings and changes in working capital levels are the two factors that generally have the greatest impact on our cash from operations.
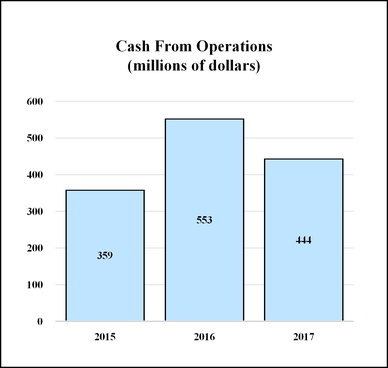
Cash from operations decreased in 2017 primarily from working capital increases due to sales growth and inflation. Cash from operations should approximate $500 million in 2018, with working capital expected to be a smaller use of cash than in 2017.
40
PART II
We closely monitor our working capital levels, and we ended 2017 with adjusted working capital at 10.6% of annualized sales1. The table below explains this non-GAAP calculation. We eliminate cash and current debt maturities from working capital to monitor our operating efficiency and performance related to trade receivables, inventories, and accounts payable. We believe this provides a more useful measurement to investors since cash and current maturities can fluctuate significantly from period to period. As discussed on page 48, a substantial amount of our cash is held by international operations and may not be immediately available to reduce debt on a dollar-for-dollar basis.
| (Dollar amounts in millions) | 2017 | 2016 | |||||
| Current assets | $ | 1,767 | $ | 1,325 | |||
| Current liabilities | (976 | ) | (707 | ) | |||
| Working capital | 791 | 618 | |||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | (526 | ) | (282 | ) | |||
| Current debt maturities | 154 | 4 | |||||
| Adjusted working capital | $ | 419 | $ | 340 | |||
Annualized sales 1 | $ | 3,936 | $ | 3,616 | |||
| Working capital as a percent of annualized sales | 20.1 | % | 17.1 | % | |||
| Adjusted working capital as a percent of annualized sales | 10.6 | % | 9.4 | % | |||
1. | Annualized sales equal 4th quarter sales ($984 million in 2017 and $904 million in 2016) multiplied by 4. We believe measuring our working capital against this sales metric is more useful, since efficient management of working capital includes adjusting those net asset levels to reflect current business volume. |
Three Primary Components of our Working Capital
| Amount (in millions) | Days | |||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||
| Trade Receivables | $ | 522 | $ | 451 | $ | 449 | DSO 1 | 45 | 44 | 43 | ||||||||
| Inventories | $ | 571 | $ | 520 | $ | 505 | DIO 2 | 65 | 66 | 60 | ||||||||
| Accounts Payable | $ | 430 | $ | 351 | $ | 307 | DPO 3 | 46 | 42 | 41 | ||||||||
Calculations of days are as follows:
| 1. | Days sales outstanding: ((beginning of year trade receivables + end of year trade receivables)÷2) ÷ (net trade sales ÷ number of days in the year). |
| 2. | Days inventory on hand: ((beginning of year inventory + end of year inventory)÷2) ÷ (cost of goods sold ÷ number of days in the year). |
| 3. | Days payables outstanding: ((beginning of year accounts payable + end of year accounts payable)÷2) ÷ (cost of goods sold ÷ number of days in the year). |
41
PART II
Trade Receivables - Our trade receivables increased $71 million at December 31, 2017 compared to the prior year primarily due to increased sales and currency fluctuations. Our sales to international customers, which are predominantly in the Specialized Products segment, continue to increase and typically have longer payment terms. We continue to look for ways to improve speed of customer payments, including third party programs with early payment incentives in certain circumstances.
Our provision for losses on accounts receivable has averaged $2 million, and our allowance for bad debt as a percentage of our net receivables has averaged 2% for the last three years. We have experienced favorable trends in the number of accounts monitored for possible loss or written off in the last few years. We obtain credit applications, credit reports, bank and trade references, and periodic financial statements from our customers to establish credit limits and terms as appropriate. In cases where a customer’s payment performance or financial condition begins to deteriorate, we tighten our credit limits and terms and make appropriate reserves when deemed necessary.
Inventories - The increase in inventories of $51 million at December 31, 2017 compared to the prior year primarily reflects higher levels necessary to support sales growth and meet customer delivery requirements, and higher raw material costs.
Days inventory on hand of 65 days at the end of 2017 is within a reasonable historical range. We believe we have established adequate reserves for any slower moving or obsolete inventories. We continuously monitor our slow-moving and potentially obsolete inventory through reports on inventory quantities compared to usage within the previous 120 days. We also utilize cycle counting programs and complete physical counts of our inventory. When potential inventory obsolescence is indicated by these controls, we will take charges for write-downs to maintain an adequate level of reserves. We have averaged inventory obsolescence charges of $8 million annually for the last three years. Our reserve balances (not including our LIFO reserves) as a percentage of our year-end inventory were 6% at the end of 2017, which is consistent with our historical average.
Accounts Payable - The increase in accounts payables of $79 million at December 31, 2017 compared to the prior year is primarily due to increased purchases to support sales growth, a focused effort on optimizing payment terms, and currency fluctuations. We continue to optimize payment terms through our significant purchasing power and also utilize third party services that allow flexible payment options to enhance our DPO.
42
PART II
Uses of Cash
Finance Capital Requirements
Cash is readily available to fund growth.
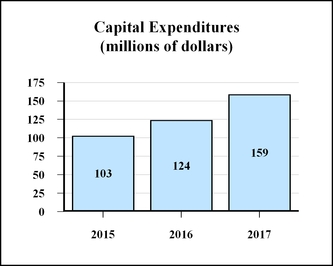
In certain of our businesses and product lines we have minimal excess production capacity, and we are therefore investing to support continued growth. In Automotive, we are expanding capacity to support new programs that will begin production over the next few years. In Bedding, we are investing in equipment to support ongoing growth in ComfortCore® innersprings and newer product features such as Quantum® Edge. We are also investing to support rapid growth in Adjustable Bed.
We will continue to make investments to support expansion in businesses and product lines where sales are growing, and for efficiency improvement and maintenance. We expect capital expenditures to again approximate $160 million in 2018. Our employee incentive plans emphasize returns on capital, which include net fixed assets and working capital. This emphasis focuses our management on asset utilization and helps ensure that we are investing additional capital dollars where attractive return potential exists.
In some of our businesses, we have capacity to accommodate additional volume. For each $10 million of sales from incremental unit volume produced utilizing spare capacity, we expect to generate approximately $2.5 million to $3.5 million of additional pretax earnings. The earnings and margin improvement that we have realized over the past few years reflects, in part, higher utilization in our businesses from market share gains and higher market demand.
Our long-term 6-9% annual growth objective envisions periodic acquisitions. We are seeking acquisitions primarily within our Grow business units, and we are looking for opportunities to enter new growth markets (carefully screened for sustainable competitive advantage).
In 2015, we acquired a 70% interest in a European private-label manufacturer of high-end upholstered furniture for an initial cash outlay of $12 million and will acquire the remaining 30% in two equal parts, in the second quarters of 2018 and 2020, respectively, for a currently estimated amount of $14 million. This business is complementary to our North American private-label operation and allows us to support our Work Furniture customers as they expand globally.
In 2016, we acquired three businesses and the remaining interest in a joint venture for total consideration of $65 million. The first, a U.S. manufacturer of aerospace tube assemblies, expands our tube forming and fabrication
43
PART II
capabilities and adds precision machining to our aerospace platform. The second is a distributor of geosynthetic products, and the third, a South African producer of mattress innersprings. Finally, we purchased the remaining interest in an Automotive joint venture in China. This business manufactures seat comfort products and lumbar support systems.
In 2017, we acquired three businesses and the remaining interest in a joint venture for total consideration of $56 million (cash and stock). The first, a Canadian distributor and installer of geosynthetic products expands the geographic scope and capabilities of our Geo Components business. The second is a U.S. manufacturer of surface-critical bent tube components which supports the private-label finished seating strategy in our Work Furniture business. The third is a U.S. producer of rebond carpet underlay which adds to our production capacity and expands the geographic footprint in our Carpet Cushion business. Finally, we acquired the remaining 20% of an Asian joint venture in our Work Furniture business.
Additional details about acquisitions can be found in Note Q to the Consolidated Financial Statements on page 110.
Pay Dividends
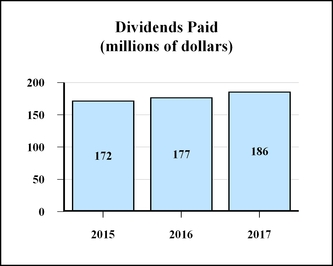

Increasing the dividend remains a high priority. In 2017, we increased the quarterly dividend by $.02, or 6%, to $.36 per share. This extended our record of consecutive annual dividend increases to 46 years. Our targeted dividend payout ratio is 50-60% of continuing operations adjusted EPS (which exclude special items such as significant tax law impacts, divestiture gains, impairment charges, litigation accruals and settlement proceeds). We expect future dividend growth to approximate earnings growth.
44
PART II
Repurchase Stock
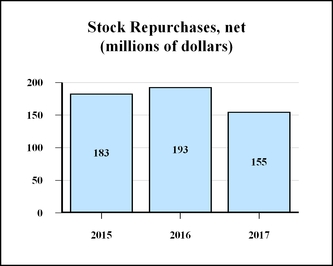
As shown in the chart above, share repurchases were significant in each of the last three years. During that time frame, we repurchased a total of 12.1 million shares of our stock and issued 6.2 million shares (through employee benefit plans and stock option exercises), reducing outstanding shares by 4%. In 2017, we repurchased 3.3 million shares (at an average price of $48.66) and issued 1.7 million shares.
Our top priorities for uses of cash are organic growth (via capital expenditures), dividends, and strategic acquisitions. After funding those priorities, to the extent there is remaining cash available, we generally intend to repurchase stock. We have been authorized by the Board to repurchase up to 10 million shares each year, but we have established no specific repurchase commitment or timetable.
45
PART II
Capitalization
This table presents key debt and capitalization statistics at the end of the three most recent years.
| (Dollar amounts in millions) | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||
| Long-term debt outstanding: | |||||||||||
| Scheduled maturities | $ | 1,098 | $ | 760 | $ | 761 | |||||
Average interest rates (1) | 3.6 | % | 3.7 | % | 3.7 | % | |||||
Average maturities in years (1) | 6.9 | 5.8 | 6.8 | ||||||||
| Revolving credit/commercial paper | — | 196 | 181 | ||||||||
| Average interest rate on year-end balance | — | % | 1.0 | % | .5 | % | |||||
| Average interest rate during the year | 1.4 | % | .8 | % | .5 | % | |||||
| Total long-term debt | 1,098 | 956 | 942 | ||||||||
| Deferred income taxes and other liabilities | 286 | 227 | 223 | ||||||||
| Equity | 1,191 | 1,094 | 1,098 | ||||||||
| Total capitalization | $ | 2,575 | $ | 2,277 | $ | 2,263 | |||||
Unused committed credit: (2) | |||||||||||
| Long-term | $ | 800 | $ | 554 | $ | 419 | |||||
| Short-term | — | — | — | ||||||||
| Total unused committed credit | $ | 800 | $ | 554 | $ | 419 | |||||
| Current maturities of long-term debt | $ | 154 | $ | 4 | $ | 3 | |||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 526 | $ | 282 | $ | 253 | |||||
Ratio of earnings to fixed charges (3) | 8.1 x | 9.6 x | 8.6 x | ||||||||
| (1) | These rates include current maturities, but exclude commercial paper to reflect the averages of outstanding debt with scheduled maturities. The rates also include amortization of interest rate swaps. |
| (2) | The unused credit amount is based upon our revolving credit facility and commercial paper program which, at the end of 2015, had $600 million of borrowing capacity. The credit facility was amended in the second quarter of 2016 to increase the borrowing capacity to $750 million and the commercial paper program was increased to a corresponding amount. The credit facility was amended again in the fourth quarter of 2017 to increase the borrowing capacity to $800 million and the commercial paper program was increased to a corresponding amount. |
| (3) | Fixed charges include interest expense, capitalized interest, plus implied interest included in operating leases. Earnings consist principally of income from continuing operations before income taxes, plus fixed charges. |
46
PART II
The next table shows the ratio of long-term debt to total capitalization at December 31, 2017 and 2016, calculated in two ways:
| • | Long-term debt and total capitalization as reported in the previous table. |
| • | Long-term debt and total capitalization each reduced by total cash and increased by current maturities of long-term debt. |
We believe that adjusting this measure for cash and current maturities allows a more useful comparison to periods during which cash fluctuates significantly. We use these adjusted (non-GAAP) measures as supplemental information to track leverage trends across time periods with variable levels of cash. Our long-term target is to have net debt as a percentage of net capital in the 30-40% range. As discussed on page 48, a substantial amount of cash is held by our international operations. Therefore, we may not be able to use all of our cash to reduce our debt on a dollar-for-dollar basis, as reflected in the net debt to net capital ratio.
| (Dollar amounts in millions) | 2017 | 2016 | |||||
| Long-term debt | $ | 1,098 | $ | 956 | |||
| Current debt maturities | 154 | 4 | |||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | (526 | ) | (282 | ) | |||
| Net debt | $ | 726 | $ | 678 | |||
| Total capitalization | $ | 2,575 | $ | 2,277 | |||
| Current debt maturities | 154 | 4 | |||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | (526 | ) | (282 | ) | |||
| Net capitalization | $ | 2,203 | $ | 1,999 | |||
| Long-term debt to total capitalization | 42.6 | % | 42.0 | % | |||
| Net debt to net capitalization | 33.0 | % | 33.9 | % | |||
Total debt (which includes long-term debt and current debt maturities) increased $292 million in 2017, primarily from the $500 million debt issuance described below, partially offset by a reduction in commercial paper.
In November 2017, we issued $500 million aggregate principal amount of notes that mature in 2027. The notes bear interest at a rate of 3.5% per year, with interest payable semi-annually beginning on May 15, 2018. The net proceeds of these notes were used to pay down commercial paper, which in turn provided borrowing capacity under our commercial paper program for general corporate purposes and the repayment or refinancing of existing indebtedness, at maturity.
47
PART II
Short Term Borrowings
We can raise cash by issuing commercial paper through a program that is backed by our revolving credit facility with a syndicate of 14 lenders. In May 2016, we increased the borrowing capacity under the facility from $600 million to $750 million and extended the term by two years to 2021. In November 2017, we increased the borrowing capacity under the facility from $750 million to $800 million and extended the term by one year to 2022. The credit facility allows us to issue letters of credit totaling up to $250 million. When we issue letters of credit under the facility, we reduce our available credit and commercial paper capacity by a corresponding amount. Amounts outstanding at year-end related to our commercial paper program were:
| (Dollar amounts in millions) | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||
| Total program authorized | $ | 800 | $ | 750 | $ | 600 | |||||
| Commercial paper outstanding (classified as long-term debt) | — | (196 | ) | (181 | ) | ||||||
| Letters of credit issued under the credit facility | — | — | — | ||||||||
| Total program usage | — | (196 | ) | (181 | ) | ||||||
| Total program available | $ | 800 | $ | 554 | $ | 419 | |||||
The average and maximum amounts of commercial paper outstanding during 2017 were $436 million and $625 million, respectively. During the fourth quarter, the average and maximum amounts outstanding were $309 million and $625 million, respectively. At year end, we had no letters of credit outstanding under the credit facility, but we had issued $51 million of stand-by letters of credit under other bank agreements to take advantage of better pricing.
With cash on hand, operating cash flow, our commercial paper program, and our ability to issue debt in the capital markets, we believe we have sufficient funds available to repay maturing debt (including $150 million of 4.4% notes due July 1, 2018), as well as support our ongoing operations, pay dividends, fund future growth, and repurchase stock.
Our revolving credit facility and certain other long-term debt obligations contain restrictive covenants. Based upon our planned use of cash, we could utilize the full $800 million of commercial paper, and we would expect to remain in compliance with all of the covenants. The covenants limit, among other things: a) our total amount of indebtedness to 65% of our total capitalization (each as defined in the revolving credit facility), b) the amount of total secured debt to 15% of our total consolidated assets, and c) our ability to sell, lease, transfer, or dispose of all or substantially all of total consolidated assets. For more information about long-term debt, please see Note I to the Consolidated Financial Statements on page 91.
Accessibility of Cash
At December 31, 2017, we had cash and cash equivalents of $526 million primarily invested in interest-bearing bank accounts and in bank time deposits with original maturities of three months or less. Over 80% of these funds are held in the international accounts of our foreign operations. We do not rely on this foreign cash as a source of funds to support our ongoing U.S. liquidity needs. During 2018, we expect to repatriate approximately $300 million of foreign cash. The timing and exact amounts of these cash repatriations are difficult to predict, and are, among other things, subject to local governmental requirements.
As discussed previously, TCJA enacted at the end of 2017 imposed a one-time U.S. tax on the earnings that produced our foreign cash. This deemed repatriation tax totaled $67 million and will be paid on a graduated scale over the next eight years. We can now bring cash to the U.S. without incurring incremental U.S. federal taxes. There likely will be some state-level income tax; however, we believe any such tax will not be material. As a result, the enactment of TCJA increases the likelihood of repatriating cash from past, current and future foreign earnings.
48
PART II
If we were to bring all our current foreign cash back immediately to the U.S. in the form of dividends, we would pay previously accrued foreign withholding taxes of approximately $21 million, based upon historic foreign withholding tax rates. However, due to statutory requirements in various jurisdictions, approximately $36 million of this cash was inaccessible for repatriation at year end. In 2017, 2016, and 2015, we brought back cash of $116 million, $5 million, and $112 million, respectively, at little to no added tax cost.
CONTRACTUAL OBLIGATIONS
The following table summarizes our future contractual cash obligations and commitments at December 31, 2017:
Payments Due by Period 5 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Contractual Obligations | Total | Less Than 1 Year | 1-3 Years | 3-5 Years | More Than 5 Years | ||||||||||||||
| (Dollar amounts in millions) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt ¹ | $ | 1,246 | $ | 152 | $ | — | $ | 299 | $ | 795 | |||||||||
| Capitalized leases | 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | — | ||||||||||||||
| Operating leases | 130 | 35 | 49 | 31 | 15 | ||||||||||||||
| Purchase obligations ² | 373 | 368 | 3 | 2 | — | ||||||||||||||
| Interest payments ³ | 306 | 43 | 78 | 75 | 110 | ||||||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 83 | — | — | — | 83 | ||||||||||||||
Other obligations (including pensions and net reserves for tax contingencies) 4 | 205 | 2 | 14 | 9 | 180 | ||||||||||||||
| Total contractual cash obligations | $ | 2,349 | $ | 602 | $ | 147 | $ | 417 | $ | 1,183 | |||||||||
1 | The long-term debt payment schedule presented above could be accelerated if we were not able to make the principal and interest payments when due. |
2 | Purchase obligations primarily include open short-term (30-120 days) purchase orders that arise in the normal course of operating our facilities. |
3 | Interest payments are calculated on debt outstanding at December 31, 2017 at rates in effect at the end of the year. |
4 | Other obligations include our net reserves for tax contingencies in the "More Than 5 Years" column because these obligations are long-term in nature and actual payment dates cannot be specifically determined. Other obligations also include a $62 million long-term deemed repatriation tax payable and our current estimate of $2 million for minimum contributions to defined benefit pension plans. |
5 | Less Than 1 Year (due in 2018), 1-3 Years (due in 2019 and 2020), 3-5 Years (due in 2021 and 2022) and More Than 5 Years (due in 2023 and beyond). |
49
PART II
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND ESTIMATES
We prepare our consolidated financial statements in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. To do so, we must make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues, expenses, and disclosures. If we used different estimates or judgments our financial statements would change, and some of those changes could be significant. Our estimates are frequently based upon historical experience and are considered by management, at the time they are made, to be reasonable and appropriate. Estimates are adjusted for actual events, as they occur.
“Critical accounting estimates” are those that are: a) subject to uncertainty and change, and b) of material impact to our financial statements. Listed below are the estimates and judgments which we believe could have the most significant effect on our financial statements.
We provide additional details regarding our significant accounting policies in Note A to the Consolidated Financial Statements on page 71.
| Description | Judgments and Uncertainties | Effect if Actual Results Differ From Assumptions | ||
| Goodwill | ||||
Goodwill is assessed for impairment annually as of June 30 and as triggering events occur. | Goodwill is evaluated annually for impairment as of June 30 using either a quantitative or qualitative analysis at the reporting unit level, which is one level below our operating segments. We begin with a qualitative assessment of whether it is more likely than not that a reporting unit's fair value is less than its carrying value before applying the two step goodwill impairment model. Judgment is required in the two step model to estimate fair value for the reporting unit. We estimate fair value using a combination of a discounted cash flow model and a market approach using price to earnings ratios for comparable publicly traded companies with characteristics similar to the reporting unit. The cash flow model contains uncertainties related to the forecast of future results as many outside economic and competitive factors can influence future performance. Margins, sales growth, and discount rates are the most critical estimates in determining enterprise values using the cash flow model. The market approach requires judgment to determine the appropriate price to earnings ratio. Ratios are derived from comparable publicly-traded companies that operate in the same or similar industry as the reporting unit. | The June 2017 review indicated no goodwill impairments. However, we exited a few small businesses in each of the years presented and evaluated goodwill for impairment when they were classified as held for sale. We recognized goodwill impairments of less than $5 million in each of the years presented, associated with the exit of these businesses. Information regarding material assumptions used to determine if a goodwill impairment exists can be found in Note C to the Consolidated Financial Statements on page 79. At December 31, 2017, we had $822 million of goodwill. We conduct impairment testing based on our current business strategy in light of present industry and economic conditions, as well as future expectations. If we are not able to achieve projected performance levels, future impairments could be possible. | ||
50
PART II
| Description | Judgments and Uncertainties | Effect if Actual Results Differ From Assumptions | ||
| Other Long-lived Assets | ||||
Other long-lived assets are tested for recoverability at year-end and whenever events or circumstances indicate the carrying value may not be recoverable. For other long-lived assets we estimate fair value at the lowest level where cash flows can be measured (usually at a branch level). | Impairments of other long-lived assets usually occur when major restructuring activities take place, or we decide to discontinue product lines completely. Our impairment assessments have uncertainties because they require estimates of future cash flows to determine if undiscounted cash flows are sufficient to recover carrying values of these assets. For assets where future cash flows are not expected to recover carrying value, fair value is estimated which requires an estimate of market value based upon asset appraisals for like assets. | These impairments are unpredictable. Impairments averaged approximately $2 million per year over the last three years. At December 31, 2017, net property, plant and equipment was $664 million and net intangible assets other than goodwill was $169 million. | ||
| Inventory Reserves | ||||
We reduce the carrying value of inventories to reflect an estimate of net realizable value for obsolete and slow-moving inventory. We value inventory at net realizable value (what we think we will recover). Generally a reserve is not required unless we have more than a one-year's supply of the product. If we have had no sales of a given product for 12 months, those items are generally deemed to have no value and are written down completely. | Our inventory reserve contains uncertainties because the calculation requires management to make assumptions about the value of products that are obsolete or slow-moving (i.e., not selling very quickly). Changes in customer behavior and requirements can cause inventory to quickly become obsolete or slow-moving. The calculation also uses an estimate of the ultimate recoverability of items identified as slow-moving based upon historical experience (65% on average). | At December 31, 2017, the reserve for obsolete and slow-moving inventory was $35 million (approximately 6% of FIFO inventories). This is consistent with the $33 million of reserves at December 31, 2016 and 2015, representing 6% of FIFO inventories. Additions to inventory reserves in 2017 were $5 million, which were lower than 2016 and 2015 amounts of $9 million and $10 million, respectively. We do not expect obsolescence to change from current levels. | ||
51
PART II
| Description | Judgments and Uncertainties | Effect if Actual Results Differ From Assumptions | ||
| Workers’ Compensation | ||||
| We are substantially self-insured for costs related to workers’ compensation, and this requires us to estimate the liability associated with this obligation. | Our estimates of self-insured reserves contain uncertainties regarding the potential amounts we might have to pay. We consider a number of factors, including historical claim experience, demographic factors, and potential recoveries from third party insurance carriers. | Over the past five years, we have incurred, on average, $8 million annually for costs associated with workers’ compensation. Average year-to-year variation over the past five years has been approximately $1 million. At December 31, 2017, we had accrued $34 million to cover future self-insurance liabilities. | ||
| Credit Losses | . | |||
For accounts and notes receivable, we estimate a bad debt reserve for the amount that will ultimately be uncollectible. When we become aware of a specific customer’s potential inability to pay, we record a bad debt reserve for the amount we believe may not be collectible. | Our bad debt reserve contains uncertainties because it requires management to estimate the amount uncollectible based upon an evaluation of several factors such as the length of time that receivables are past due, the financial health of the customer, industry and macroeconomic considerations, and historical loss experience. Our customers are diverse and many are small-to-medium sized companies, with some being highly leveraged. Bankruptcy can occur with some of these customers relatively quickly and with little warning. In cases where a customer’s payment performance or financial condition begins to deteriorate, we tighten our credit limits and terms and make appropriate reserves when deemed necessary. Certain of our customers have from time to time experienced bankruptcy, insolvency and/or an inability to pay their debts to us as they come due. If our customers suffer significant financial difficulty, they may be unable to pay their debts to us timely or at all, they may reject their contractual obligations to us under bankruptcy laws or otherwise, or we may have to negotiate significant discounts and/or extend financing terms with these customers. | A significant change in the financial status of a large customer could impact our estimates. We believe we have established adequate reserves on our riskier customer accounts. We have experienced favorable trends in the number of accounts monitored for possible loss or written off in the last few years. The average annual amount of customer-related bad debt expense was less than $2 million (significantly less than 1% of annual net sales) over the last three years. At December 31, 2017, our allowances for doubtful accounts were less than $5 million (about 1% of our trade accounts and notes receivable of $528 million). | ||
52
PART II
| Description | Judgments and Uncertainties | Effect if Actual Results Differ From Assumptions | ||
| Pension Accounting | ||||
For our pension plans, we must estimate the cost of benefits to be provided (well into the future) and the current value of those benefit obligations. In 2017, we completed an annuity purchase transaction for pensioners that were currently receiving a small monthly benefit, and in 2015 offered a voluntary one-time lump-sum payment option to selected participants. Please see Note L to our Consolidated Financial Statements on page 99. | The pension liability calculation contains uncertainties because it requires management's judgment. Significant assumptions used to measure our pension liabilities and pension expense annually include: - the discount rate used to calculate the present value of future benefits - an estimate of expected return on pension assets based upon the mix of investments held (bonds and equities) - certain employee-related factors, such as turnover, retirement age and mortality. Mortality assumptions represent our best estimate of the duration of future benefit payments at the measurement date. These estimates are based on each plans' demographics and other relevant facts and circumstances - the rate of salary increases where benefits are based on earnings | Each 25 basis point decrease in the discount rate increases pension expense by $.5 million and increases the plans’ benefit obligation by $8 million. A 25 basis point reduction in the expected return on assets would increase pension expense by $.4 million, but have no effect on the plans’ funded status. Assuming a long-term investment horizon, we do not expect a material change to the return on asset assumption. | ||
| Contingencies | ||||
| We evaluate various legal, environmental, and other potential claims against us to determine if an accrual or disclosure of the contingency is appropriate. If it is probable that an ultimate loss will be incurred and reasonably estimable, we accrue a liability for the estimate of the loss. | Our disclosure and accrual of loss contingencies (i.e., losses that may or may not occur) contain uncertainties because they are based on our assessment of the probability that the expenses will actually occur, and our reasonable estimate of the likely cost. Our estimates and judgments are subjective and can involve matters in litigation, the results of which are generally unpredictable. | Legal contingencies are related to numerous lawsuits and claims described in Note S to the Consolidated Financial Statements on page 115. During the three-year period ended December 31, 2017, we recorded expense of $18 million ($13 million for continuing operations and $5 million in discontinued operations). There were no material uninsured individual claims during the three-year period ending December 31, 2017. | ||
53
PART II
| Description | Judgments and Uncertainties | Effect if Actual Results Differ From Assumptions | ||
| Income Taxes | ||||
| In the ordinary course of business, we must make estimates of the tax treatment of many transactions, even though the ultimate tax outcome may remain uncertain for some time. These estimates become part of the annual income tax expense reported in our financial statements. Subsequent to year end, we finalize our tax analysis and file income tax returns. Tax authorities periodically audit these income tax returns and examine our tax filing positions, including (among other things) the timing and amounts of deductions, and the allocation of income among tax jurisdictions. If necessary, we adjust income tax expense in our financial statements in the periods in which the actual outcome becomes more certain. | Our tax liability for unrecognized tax benefits contains uncertainties because management is required to make assumptions and to apply judgment to estimate the exposures related to our various filing positions. Our effective tax rate is also impacted by changes in tax laws, the current mix of earnings by taxing jurisdiction, and the results of current tax audits and assessments. On December 22, 2017, the U.S. enacted comprehensive tax legislation commonly referred to as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), which resulted in significant changes to U.S. federal income tax law affecting the Company. Current and expected impacts are based on our current knowledge of the legislation and certain assumptions we have made. Please see Note M-Income Taxes on page 103 for more information. At December 31, 2017 and 2016, we had $12 million and $26 million, respectively, of net deferred tax assets on our balance sheet related to net operating losses and other tax carryforwards. The ultimate realization of these deferred tax assets is dependent upon the amount, source, and timing of future taxable income. In cases where we believe it is more likely than not that we may not realize the future potential tax benefits, we establish a valuation allowance against them. In addition, assumptions have been made regarding the non-repatriation of earnings from certain subsidiaries. Those assumptions may change in the future, thereby affecting future period results for the tax impact of possible repatriation. | Changes in tax laws could impact assumptions related to the repatriation of certain foreign earnings. Audits by various taxing authorities continue as governments look for ways to raise additional revenue. Based upon past audit experience, we do not expect any material changes to our tax liability as a result of this audit activity; however, we could incur additional tax expense if we have audit adjustments higher than recent historical experience. The likelihood of recovery of net operating losses and other tax carryforwards has been closely evaluated and is based upon such factors as the time remaining before expiration, viable tax planning strategies, and future taxable earnings expectations. We believe that appropriate valuation allowances have been recorded as necessary. However, if earnings expectations or other assumptions change such that additional valuation allowances are required, we could incur additional tax expense. Likewise, if fewer valuation allowances are needed, we could incur reduced tax expense. | ||
54
PART II
LITIGATION CONTINGENCIES
Accruals for Probable Losses
Although the Company denies liability in all currently threatened or pending litigation proceedings in which it is or may be a party and believes that it has valid bases to contest all claims threatened or made against it, we have recorded a litigation contingency accrual for our reasonable estimate of probable loss for pending and threatened litigation proceedings, in aggregate, in millions, as follows:
| Twelve Months Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Litigation contingency accrual - Beginning of period | $ | 3.2 | $ | 8.1 | $ | 83.9 | |||||
| Adjustment to accruals - expense - Continuing operations | .6 | 7.1 | 5.7 | ||||||||
| Adjustment to accruals - expense - Discontinued operations | 1.6 | 2.0 | .7 | ||||||||
| Cash payments | (5.0 | ) | (14.0 | ) | (82.2 | ) | |||||
| Litigation contingency accrual - End of period | $ | .4 | $ | 3.2 | $ | 8.1 | |||||
A large percentage of the accruals and cash payments in 2015 and 2016 were related to antitrust proceedings. The above litigation contingency accruals do not include accrued expenses related to workers' compensation, vehicle-related personal injury, product and general liability claims, taxation issues and environmental matters, some of which may contain a portion of litigation expense. However, any litigation expense associated with these categories is not anticipated to have a material effect on our financial condition, results of operations, or cash flows. For more information regarding accrued expenses, see Note H - Supplemental Balance Sheet Information to the Consolidated Financial Statements under "Accrued expenses" on page 90.
We have relied on several facts and circumstances to conclude that some loss is probable with respect to certain proceedings and matters, and to arrive at a reasonable estimate of loss or range of loss and record the accruals, including: the maturation of the pending proceedings and matters; our experience in settlement negotiations and mediation; comparative settlements of other companies in similar proceedings; discovery becoming or being substantially complete in certain proceedings; certain quantitative metrics used to value probable loss contingencies; and our willingness to settle certain proceedings to forgo the cost and risk of litigation and distraction to our senior executives.
Reasonably Possible Losses in Excess of Accruals
Although there are a number of uncertainties and potential outcomes associated with all of our pending or threatened litigation proceedings, we believe, based on current known facts, that additional losses, if any, are not expected to materially affect our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows. However, based upon current known facts, as of December 31, 2017, aggregate reasonably possible (but not probable, and therefore not accrued) losses in excess of the accruals noted above are estimated to be approximately $22 million, including approximately $21 million for Brazilian VAT matters and $1 million for other matters. If our assumptions or analyses regarding these contingencies are incorrect, or if facts change, we could realize loss in excess of the recorded accruals, and even greater than our estimate of reasonably possible losses in excess of recorded accruals.
For more information regarding litigation contingencies, please refer to Note S on page 115 of the Consolidated Financial Statements, which are incorporated herein by reference.
NEW ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
The FASB has issued accounting guidance effective for current and future periods. See Note A to the Consolidated Financial Statements on page 71 for a more complete discussion.
55
PART II
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
(Unaudited)
(Dollar amounts in millions)
Interest Rates
The table below provides information about the Company’s debt obligations sensitive to changes in interest rates. Substantially all of the debt shown in the table below is denominated in United States dollars. The fair value of fixed rate debt was not materially different from its carrying value at both December 31, 2017 and 2016. The fair value of fixed rate debt was calculated using a Bloomberg secondary market rate, as of December 31, 2017 for similar remaining maturities, plus an estimated “spread” over such Treasury securities representing the Company’s interest costs for its notes. The fair value of variable rate debt is not significantly different from its recorded amount.
| Scheduled Maturity Date | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt as of December 31, | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | Thereafter | 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Principal fixed rate debt | $ | 150.0 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 300.0 | $ | 800.0 | $ | 1,250.0 | $ | 750.0 | |||||||||||||||
Average interest rate 1 | 4.40 | % | — | — | — | 3.40 | % | 3.61 | % | 3.66 | % | 3.76 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Principal variable rate debt | 2.4 | — | — | — | — | 3.8 | 6.2 | 12.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average interest rate | 1.30 | % | — | — | — | — | 1.22 | % | 1.25 | % | .33 | % | |||||||||||||||||||
| Unamortized discounts and deferred loan costs | (10.9 | ) | (4.7 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial Paper 2 | — | 196.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Miscellaneous debt 3 | 6.4 | 6.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total debt | 1,251.7 | 959.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Less: current maturities | (153.8 | ) | (3.6 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total long-term debt | $ | 1,097.9 | $ | 956.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1These rates exclude the amortization of interest rate swap.
2Commercial paper is supported by an $800 revolving credit facility which terminates in 2022. The weighted average interest rate on the balance of commercial paper outstanding at the year ended December 31, 2016 was 1.0%. The weighted average interest rate for the average commercial paper outstanding during the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 was 1.4% and .8%, respectively.
3Miscellaneous debt consists primarily of capitalized leases.
Derivative Financial Instruments
The Company is subject to market and financial risks related to interest rates and foreign currency. In the normal course of business, the Company utilizes derivative instruments (individually or in combinations) to reduce or eliminate these risks. The Company seeks to use derivative contracts that qualify for hedge accounting treatment; however, some instruments may not qualify for hedge accounting treatment. It is the Company’s policy not to speculate using derivative instruments. Information regarding cash flow hedges and fair value hedges is provided in Note R beginning on page 112 to the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements and is incorporated by reference into this section.
56
PART II
Investment in Foreign Subsidiaries
The Company views its investment in foreign subsidiaries as a long-term commitment and does not hedge translation exposures. This investment may take the form of either permanent capital or notes. The Company’s net investment (i.e., total assets less total liabilities subject to translation exposure) in foreign operations with functional currencies other than the U.S. dollar at December 31 is as follows:
| Functional Currency (amounts in millions) | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||
| Chinese Renminbi | $ | 381.1 | $ | 294.6 | ||||
| European Currencies | 364.3 | 292.6 | ||||||
| Canadian Dollar | 260.0 | 185.6 | ||||||
| Mexican Peso | 29.1 | 23.7 | ||||||
| Other | 50.4 | 48.1 | ||||||
| Total | $ | 1,084.9 | $ | 844.6 | ||||
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
The Consolidated Financial Statements and Notes, Financial Statement Schedule and supplementary financial information included in this Report are listed and included in Item 15 on page 63, and are incorporated by reference into this item.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure.
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures.
Effectiveness of the Company’s Disclosure Controls and Procedures
An evaluation as of December 31, 2017, was carried out by the Company’s management, with the participation of the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”)). Based upon this evaluation, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective, as of December 31, 2017, to provide assurance that information required to be disclosed by the Company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported, within the time periods specified by the Securities and Exchange Commission’s rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures, include without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by the Company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to the Company’s management, including its Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, or persons performing similar functions, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
57
PART II
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting and Auditor’s Attestation Report
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting can be found on page 64, and the Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm regarding the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting can be found on page 65 of this Form 10-K. Each is incorporated by reference into this Item 9A.
Changes in the Company’s Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There were no changes during the quarter ended December 31, 2017 that have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect our internal control over financial reporting.
During the first quarter of 2017, we transitioned certain corporate-level shared service systems for general ledger, cash application, purchasing and accounts payable disbursements to a new software platform. The new platform further automates and enhances a number of existing processes and activities primarily related to our domestic U.S. operations. The total capital outlay for this activity approximated $20 million, most of which was recorded in 2015 and 2016.
These improvements were system process enhancements and were not made in response to any control deficiency or weakness. Our internal control over financial reporting has been effective. Implementation risk was controlled through an on-going process of monitoring and evaluation to mitigate potential risk. The system deployments included fully evaluating and updating our internal control over financial reporting, as well as significant testing and training.
Item 9B. Other Information.
None.
58
PART III
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance.
The subsections entitled “Proposal 1—Election of Directors,” “Board & Committee Composition and Meetings,” “Consideration of Director Nominees and Diversity,” “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” and “Director Independence” as well as the introductory paragraph under the "Corporate Governance & Board Matters" section in the Company’s definitive Proxy Statement for the Company’s Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on May 15, 2018, are incorporated by reference.
Directors of the Company
Directors are normally elected annually at the Annual Meeting of Shareholders and hold office until the next annual meeting of shareholders or until their successors are elected and qualified. All current directors have been nominated for re-election at the Company’s Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held May 15, 2018.
In order to be nominated for election as a director, a nominee must submit a contingent resignation to the Nominating & Corporate Governance Committee (N&CG Committee). The resignation will become effective only if (i) the director nominee fails to receive an affirmative majority of the votes cast in the director election; and (ii) the Board accepts the resignation. If a nominee fails to receive an affirmative majority of the votes cast in the director election, the N&CG Committee will make a recommendation to the Board of Directors whether to accept or reject the director’s resignation and whether any other action should be taken. If a director’s resignation is not accepted, that director will continue to serve until the Company’s next annual meeting or until his or her successor is duly elected and qualified. If the Board accepts the director’s resignation, it may, in its sole discretion, either fill the resulting vacancy or decrease the size of the Board to eliminate the vacancy.
Brief biographies of the Company’s Board of Directors are provided below.
Robert E. Brunner, age 60, was the Executive Vice President of Illinois Tool Works (ITW), a Fortune 250 global, multi-industrial manufacturer of advanced industrial technology, from 2006 until his retirement in 2012. He previously served ITW as President—Global Auto beginning in 2005 and President—North American Auto from 2003. Mr. Brunner holds a degree in finance from the University of Illinois and an MBA from Baldwin-Wallace University. He currently serves as the non-executive chair of NN, Inc., a global manufacturer of precision bearings and plastic, rubber and metal components, and as a director of Lindsay Corporation, a global manufacturer of irrigation equipment and road safety products. Mr. Brunner’s experience and leadership with ITW, a diversified manufacturer with a global footprint, provides valuable insight to our Board on strategy, business development, mergers and acquisitions, operations, and international issues. He was first elected as a director of the Company in 2009.
Robert G. Culp, III, age 71, is the co-founder of Culp, Inc., an upholstery and bedding fabrics designer and manufacturer, where he has been the Chairman since 1990 and served as CEO from 1988 to 2007. Mr. Culp holds a degree in economics from the University of North Carolina - Chapel Hill and an MBA from the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania. Mr. Culp is the Chairman of the Board of Culp, Inc. and the lead independent director of Old Dominion Freight Line, Inc., a national motor transportation and logistics company. Mr. Culp's experience in the bedding and furniture industries provides valuable insight into a number of the Company's key markets. Through his leadership of Culp, Inc., a publicly-traded company with an international scope, he understands the complexities of the financial and regulatory requirements facing U.S. companies, as well as the challenges and opportunities of developing global operations. He was first elected as a director of the Company in 2013.
R. Ted Enloe, III, age 79, has been Managing General Partner of Balquita Partners, Ltd., a family securities and real estate investment partnership, since 1996. His former positions include Vice Chairman of the Board and member of the Office of the Chief Executive for Compaq Computer Corporation and President of Lomas Financial Corporation and Liberte Investors. He holds a degree in petroleum engineering from Louisiana Polytechnic
59
PART III
University and a law degree from Southern Methodist University. Mr. Enloe currently serves as a director of Live Nation, Inc., a venue operator, promoter and producer of live entertainment events, and he was previously a director of Silicon Laboratories Inc., a designer of mixed-signal integrated circuits. Mr. Enloe’s professional background and experience, previously held senior-executive level positions, financial expertise and service on other company boards, qualifies him to serve as a member of our Board of Directors. Further, his wide-ranging experience combined with his intimate knowledge of the Company from over 40 years on the Board provides an exceptional mix of familiarity and objectivity. He was first elected as a director of the Company in 1969 and has served as Independent Board Chair since 2016.
Manuel A. Fernandez, age 71, co-founded SI Ventures, a venture capital firm focusing on IT and communications infrastructure, and has served as the managing director since 2000. Previously, he served as the Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer at Gartner, Inc., a research and advisory company, from 1989 to 2000. Prior to Gartner, Mr. Fernandez was President and CEO of three technology-driven companies, including Dataquest, an information services company, Gavilan Computer Corporation, a laptop computer manufacturer, and Zilog Incorporated, a semiconductor manufacturer. Mr. Fernandez was the Executive Chairman of Sysco Corporation, a marketer and distributor of foodservice products, from 2012 until his retirement in 2013, having previously served as Non-executive Chairman from 2009 and as a director from 2006. Mr. Fernandez holds a degree in electrical engineering from the University of Florida, and completed post-graduate work in solid-state engineering at the University of Florida. Mr. Fernandez currently serves as lead independent director of Brunswick Corporation, a market leader in the marine, fitness, and billiards industries, and as a director of Performance Food Group Company, a foodservice products distributor. He was previously a director of Flowers Foods, Inc., a national producer and marketer of packaged bakery foods, Tibco, a global leader in infrastructure and business intelligence software, and Time Inc., a global media company. Mr. Fernandez' venture capital experience, leadership of several technology companies as CEO and service on a number of public company boards offers Leggett outstanding insight into corporate strategy and development, information technology, international growth, and corporate governance. He was first appointed as a director in 2014.
Matthew C. Flanigan, age 56, was appointed Executive Vice President of the Company in 2013 and has served as Chief Financial Officer since 2003. He previously served as Senior Vice President from 2005 to 2013, Vice President from 2003 to 2005, Vice President and President of the Office Furniture Components Group from 1999 to 2003 and in various capacities since 1997. Mr. Flanigan holds a degree in finance and business administration from the University of Missouri. He serves as the lead director of Jack Henry & Associates, Inc., the nation's leading provider of information processing systems for small-to-medium-sized financial institutions. As the Company’s CFO, Mr. Flanigan adds valuable knowledge of the Company’s finance, risk and compliance functions to the Board. In addition, his prior experience as one of the Company’s group presidents provides valuable operations insight. He was first elected as a director of the Company in 2010.
Karl G. Glassman, age 59, was appointed Chief Executive Officer in 2016 and has served as President since 2013. He previously served the Company as Chief Operating Officer from 2006 to 2015, Executive Vice President from 2002 to 2013, President of the Residential Furnishings segment from 1999 to 2006, Senior Vice President from 1999 to 2002, and in various capacities since 1982. Mr. Glassman holds a degree in business management and finance from California State University—Long Beach. He previously served as a director of Remy International, Inc., a leading global manufacturer of alternators, starter motors and electric traction motors. As the Company's CEO, Mr. Glassman provides comprehensive insight to the Board from strategic planning to implementation at all levels of the Company around the world, as well as the Company's relationships with investors, the financial community and other key stakeholders. He also serves on the Board of Directors of the National Association of Manufacturers. Mr. Glassman was first elected as a director of the Company in 2002.
Joseph W. McClanathan, age 65, served as President and Chief Executive Officer of the Household Products Division of Energizer Holdings, Inc., a manufacturer of portable power solutions, from 2007 through his retirement in 2012. Previously, he served Energizer as President and Chief Executive Officer of the Energizer Battery Division from 2004 to 2007, as President—North America from 2002 to 2004, and as Vice President—North America from 2000 to 2002. Mr. McClanathan holds a degree in management from Arizona State University. Through his leadership experience at Energizer and as a former director of the Retail Industry Leaders Association,
60
PART III
Mr. McClanathan offers an exceptional perspective to the Board on manufacturing operations, marketing and development of international capabilities. He was first elected as a director of the Company in 2005.
Judy C. Odom, age 65, served, until her retirement in 2002, as Chief Executive Officer and Board Chair at Software Spectrum, Inc., a global business to business software services company which she co-founded in 1983. Prior to founding Software Spectrum, she was a partner with the international accounting firm, Grant Thornton. Ms. Odom is a licensed Certified Public Accountant and holds a degree in business administration from Texas Tech University. She is a director of Harte-Hanks, a direct marketing service company, and Sabre, Inc., which provides technology solutions for the global travel and tourism industry. Ms. Odom’s director experience with several companies offers a broad leadership perspective on strategic and operating issues. Her experience co-founding Software Spectrum and growing it to a global Fortune 1000 enterprise before selling it to another public company provides the insight of a long-serving CEO with international operating experience. Ms. Odom was first elected as a director of the Company in 2002.
Phoebe A. Wood, age 64, has been a principal in CompaniesWood, a consulting firm specializing in early stage investments, since her 2008 retirement as Vice Chairman and Chief Financial Officer of Brown-Forman Corporation, a diversified consumer products manufacturer, where she had served since 2001. Ms. Wood previously held various positions at Atlantic Richfield Company, an oil and gas company, from 1976 to 2000. She holds a degree in psychology from Smith College and an MBA from UCLA. Ms. Wood is a director of Invesco, Ltd., an independent global investment manager, Pioneer Natural Resources, an independent oil and gas company, and PPL Corporation, a utility and energy services company. She previously served as a director of Coca-Cola Enterprises, Inc., a major bottler and distributor of Coca-Cola products. From her career in business and various directorships, Ms. Wood provides the Board with a wealth of understanding of the strategic, financial, and accounting issues the Board faces in its oversight role. Ms. Wood was first elected as a director of the Company in 2005.
Please see the “Supplemental Item” in Part I hereof, for a listing of and a description of the positions and offices held by the executive officers of the Company.
The Company has adopted a code of ethics that applies to its chief executive officer, chief financial officer, and chief accounting officer called the Leggett & Platt, Incorporated Financial Code of Ethics. The Company has also adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics for directors, officers and employees, and Corporate Governance Guidelines. The Financial Code of Ethics, the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics and the Corporate Governance Guidelines are available on the Company’s website at www.leggett-search.com/governance. Each of these documents is available in print to any person, without charge, upon request. Such requests may be made to the Company’s Secretary at Leggett & Platt, Incorporated, No. 1 Leggett Road, Carthage, Missouri 64836.
On February 20, 2018, the N&CG Committee amended the Company’s procedure for identifying and nominating director candidates to strengthen the Committee's support for diversity. The amended provisions provide that, while nominations for the Board will be based on merit and experience, the Committee recognizes the benefits of a diverse Board and will strive to select director candidates who will maintain and strengthen the Board's diversity. The Committee expanded the list of nondiscriminatory factors in the selection of directors to include ethnicity and age. This process also applies to shareholder recommendations of director nominees. The complete procedure is available at www.leggett-search.com/governance, under Corporate Governance, Director Nomination Procedure.
The Company intends to satisfy the disclosure requirement under Item 5.05 of Form 8-K by posting any applicable amendment or waiver to its Financial Code of Ethics, within four business days, on its website at the above address for at least a 12-month period. We routinely post important information to our website. However, the Company’s website does not constitute part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
61
PART III
Item 11. Executive Compensation.
The subsections entitled “Board’s Oversight of Risk Management,” “Director Compensation,” “Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation” together with the entire section entitled “Executive Compensation Related Matters” in the Company’s definitive Proxy Statement for the Company’s Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on May 15, 2018, are incorporated by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.
The entire sections entitled “Security Ownership” and “Equity Compensation Plan Information” in the Company’s definitive Proxy Statement for the Company’s Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on May 15, 2018, are incorporated by reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
The subsections entitled "Proposal 1 - Election of Directors," “Transactions with Related Persons,” “Director Independence” and “Board & Committee Composition and Meetings” in the Company’s definitive Proxy Statement for the Company’s Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on May 15, 2018, are incorporated by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services.
The subsections entitled “Audit and Non-Audit Fees” and “Pre-Approval Procedures for Audit and Non-Audit Services” in the Company’s definitive Proxy Statement for the Company’s Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on May 15, 2018, are incorporated by reference.
62
PART IV
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules.
(a) Financial Statements and Financial Statement Schedule.
The Reports, Financial Statements and Notes, supplementary financial information and Financial Statement Schedule listed below are included in this Form 10-K:
| Page No. | |
We have omitted other information schedules because the information is inapplicable, not required, or in the financial statements or notes.
(b) Exhibits—See Exhibit Index beginning on page 120.
We did not file other long-term debt instruments because the total amount of securities authorized under all of these instruments does not exceed ten percent of the total assets of the Company and its subsidiaries on a consolidated basis. The Company agrees to furnish a copy of such instruments to the SEC upon request.
63
PART IV
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management of Leggett & Platt, Incorporated is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Exchange Act Rule 13a-15(f). Leggett & Platt’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that:
| • | Pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of Leggett & Platt; |
| • | Provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, and that receipts and expenditures of Leggett & Platt are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of Leggett & Platt; and |
| • | Provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of Leggett & Platt assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements. |
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Under the supervision and with the participation of management (including ourselves), we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of Leggett & Platt’s internal control over financial reporting, as of December 31, 2017, based on the criteria in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on the evaluation under this framework, we concluded that Leggett & Platt’s internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2017.
Leggett & Platt’s internal control over financial reporting, as of December 31, 2017, has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report appearing on page 65 of this Form 10-K.
| /s/ KARL G. GLASSMAN | /s/ MATTHEW C. FLANIGAN | |
Karl G. Glassman President and Chief Executive Officer | Matthew C. Flanigan Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | |
| February 22, 2018 | February 22, 2018 | |
64
PART IV
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of
Leggett & Platt, Incorporated:
Opinions on the Financial Statements and Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Leggett & Platt, Incorporated and its subsidiaries as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income (loss), changes in equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2017, including the related notes and financial statement schedule listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a) (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). We also have audited the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2017 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the COSO.
Basis for Opinions
The Company's management is responsible for these consolidated financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management's Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express opinions on the Company’s consolidated financial statements and on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) ("PCAOB") and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud, and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audits of the consolidated financial statements included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ PRICEWATERHOUSECOOPERS LLP
St. Louis, Missouri
February 22, 2018
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 1991.
65
LEGGETT & PLATT, INCORPORATED
Consolidated Statements of Operations
| Year Ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions, except per share data) | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 3,943.8 | $ | 3,749.9 | $ | 3,917.2 | |||||
| Cost of goods sold | 3,075.9 | 2,850.7 | 2,994.0 | ||||||||
| Gross profit | 867.9 | 899.2 | 923.2 | ||||||||
| Selling and administrative expenses | 403.6 | 396.8 | 416.9 | ||||||||
| Amortization of intangibles | 20.7 | 19.9 | 20.8 | ||||||||
| Impairments | 4.9 | 4.1 | 6.3 | ||||||||
| Gain on sale of assets and businesses | (24.2 | ) | (37.6 | ) | (.5 | ) | |||||
| Other (income) expense, net | (5.0 | ) | (6.0 | ) | (6.8 | ) | |||||
| Earnings from continuing operations before interest and income taxes | 467.9 | 522.0 | 486.5 | ||||||||
| Interest expense | 43.5 | 38.8 | 41.1 | ||||||||
| Interest income | 7.6 | 3.9 | 4.4 | ||||||||
| Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes | 432.0 | 487.1 | 449.8 | ||||||||
| Income taxes | 138.4 | 120.0 | 121.8 | ||||||||
| Earnings from continuing operations | 293.6 | 367.1 | 328.0 | ||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax | (.9 | ) | 19.1 | 1.2 | |||||||
| Net earnings | 292.7 | 386.2 | 329.2 | ||||||||
| (Earnings) attributable to noncontrolling interest, net of tax | (.1 | ) | (.4 | ) | (4.1 | ) | |||||
| Net earnings attributable to Leggett & Platt, Inc. common shareholders | $ | 292.6 | $ | 385.8 | $ | 325.1 | |||||
| Earnings per share from continuing operations attributable to Leggett & Platt, Inc. common shareholders | |||||||||||
| Basic | $ | 2.16 | $ | 2.66 | $ | 2.30 | |||||
| Diluted | $ | 2.14 | $ | 2.62 | $ | 2.27 | |||||
| Earnings (loss) per share from discontinued operations attributable to Leggett & Platt, Inc. common shareholders | |||||||||||
| Basic | $ | (.01 | ) | $ | .14 | $ | .01 | ||||
| Diluted | $ | (.01 | ) | $ | .14 | $ | .01 | ||||
| Net earnings per share attributable to Leggett & Platt, Inc. common shareholders | |||||||||||
| Basic | $ | 2.15 | $ | 2.80 | $ | 2.31 | |||||
| Diluted | $ | 2.13 | $ | 2.76 | $ | 2.28 | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
66
LEGGETT & PLATT, INCORPORATED
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
| Year Ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||
| Net earnings | $ | 292.7 | $ | 386.2 | $ | 329.2 | |||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: | |||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments, including acquisition of non-controlling interest | 79.1 | (33.9 | ) | (92.1 | ) | ||||||
| Cash flow hedges | 6.3 | 10.4 | (8.1 | ) | |||||||
| Defined benefit pension plans | 18.7 | .9 | 11.2 | ||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | 104.1 | (22.6 | ) | (89.0 | ) | ||||||
| Comprehensive income | 396.8 | 363.6 | 240.2 | ||||||||
| Less: comprehensive (income) attributable to noncontrolling interest | (.1 | ) | (.3 | ) | (3.6 | ) | |||||
| Comprehensive income attributable to Leggett & Platt, Inc. | $ | 396.7 | $ | 363.3 | $ | 236.6 | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
67
LEGGETT & PLATT, INCORPORATED
Consolidated Balance Sheets
| December 31 | |||||||
| (Amounts in millions, except per share data) | 2017 | 2016 | |||||
| ASSETS | |||||||
| Current Assets | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 526.1 | $ | 281.9 | |||
| Trade receivables, net | 522.3 | 450.8 | |||||
| Other receivables, net | 72.8 | 35.8 | |||||
| Total receivables, net | 595.1 | 486.6 | |||||
| Inventories | |||||||
| Finished goods | 285.6 | 255.7 | |||||
| Work in process | 53.0 | 52.6 | |||||
| Raw materials and supplies | 283.4 | 245.1 | |||||
| LIFO reserve | (50.9 | ) | (33.8 | ) | |||
| Total inventories, net | 571.1 | 519.6 | |||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 74.2 | 36.8 | |||||
| Total current assets | 1,766.5 | 1,324.9 | |||||
| Property, Plant and Equipment—at cost | |||||||
| Machinery and equipment | 1,210.6 | 1,133.8 | |||||
| Buildings and other | 626.0 | 559.4 | |||||
| Land | 40.6 | 37.7 | |||||
| Total property, plant and equipment | 1,877.2 | 1,730.9 | |||||
| Less accumulated depreciation | 1,213.3 | 1,165.4 | |||||
| Net property, plant and equipment | 663.9 | 565.5 | |||||
| Other Assets | |||||||
| Goodwill | 822.2 | 791.3 | |||||
| Other intangibles, net | 169.1 | 164.9 | |||||
| Sundry | 129.1 | 137.5 | |||||
| Total other assets | 1,120.4 | 1,093.7 | |||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 3,550.8 | $ | 2,984.1 | |||
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | |||||||
| Current Liabilities | |||||||
| Current maturities of long-term debt | $ | 153.8 | $ | 3.6 | |||
| Accounts payable | 430.3 | 351.1 | |||||
| Accrued expenses | 303.4 | 257.7 | |||||
| Other current liabilities | 88.7 | 94.2 | |||||
| Total current liabilities | 976.2 | 706.6 | |||||
| Long-term Liabilities | |||||||
| Long-term debt | 1,097.9 | 956.2 | |||||
| Other long-term liabilities | 202.9 | 173.0 | |||||
| Deferred income taxes | 83.0 | 54.3 | |||||
| Total long-term liabilities | 1,383.8 | 1,183.5 | |||||
| Commitments and Contingencies | |||||||
| Equity | |||||||
| Capital stock: Preferred stock—authorized, 100.0 shares; none issued; Common stock—authorized, 600.0 shares of $.01 par value; 198.8 shares issued | 2.0 | 2.0 | |||||
| Additional contributed capital | 514.7 | 506.2 | |||||
| Retained earnings | 2,511.3 | 2,410.5 | |||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | (9.5 | ) | (113.6 | ) | |||
| Less treasury stock—at cost (66.9 and 65.3 shares at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively) | (1,828.3 | ) | (1,713.5 | ) | |||
| Total Leggett & Platt, Inc. equity | 1,190.2 | 1,091.6 | |||||
| Noncontrolling interest | .6 | 2.4 | |||||
| Total equity | 1,190.8 | 1,094.0 | |||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | $ | 3,550.8 | $ | 2,984.1 | |||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
68
LEGGETT & PLATT, INCORPORATED
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
| Year Ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||
| Operating Activities | |||||||||||
| Net earnings | $ | 292.7 | $ | 386.2 | $ | 329.2 | |||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net earnings to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||||||
| Depreciation | 95.3 | 86.8 | 83.5 | ||||||||
| Amortization of intangibles and debt issuance costs | 30.6 | 28.6 | 29.7 | ||||||||
| Long-lived asset impairments | 3.6 | .4 | 2.4 | ||||||||
| Goodwill impairment | 1.3 | 3.7 | 4.1 | ||||||||
| Provision for losses on accounts and notes receivable | .8 | 1.6 | 2.6 | ||||||||
| Writedown of inventories | 4.9 | 8.9 | 9.8 | ||||||||
| Net gain from sales of assets and businesses | (24.4 | ) | (38.5 | ) | (3.7 | ) | |||||
| Deemed repatriation tax payable | 67.3 | — | — | ||||||||
| Deferred income tax expense | 16.6 | 17.6 | 24.1 | ||||||||
| Stock-based compensation | 36.6 | 37.1 | 45.2 | ||||||||
| Tax benefits from stock-based compensation payments | — | — | (15.7 | ) | |||||||
| Pension expense (benefit), net of contributions | 7.1 | (2.2 | ) | 15.6 | |||||||
| Other, net | (8.5 | ) | 7.3 | 3.1 | |||||||
| Increases/decreases in, excluding effects from acquisitions and divestitures: | |||||||||||
| Accounts and other receivables | (40.6 | ) | 3.4 | (16.4 | ) | ||||||
| Inventories | (48.1 | ) | (33.3 | ) | (49.1 | ) | |||||
| Other current assets | (36.8 | ) | (2.1 | ) | (.4 | ) | |||||
| Accounts payable | 58.8 | 50.8 | (54.3 | ) | |||||||
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | (13.5 | ) | (3.7 | ) | (50.6 | ) | |||||
| Net Cash Provided by Operating Activities | 443.7 | 552.6 | 359.1 | ||||||||
| Investing Activities | |||||||||||
| Additions to property, plant and equipment | (159.4 | ) | (124.0 | ) | (103.2 | ) | |||||
| Purchases of companies, net of cash acquired | (39.1 | ) | (29.5 | ) | (11.1 | ) | |||||
| Proceeds from sales of assets and businesses | 45.2 | 86.1 | 51.4 | ||||||||
| Advance of non-trade note receivable | — | (24.6 | ) | — | |||||||
| Other, net | (11.7 | ) | (10.0 | ) | (6.7 | ) | |||||
| Net Cash Used for Investing Activities | (165.0 | ) | (102.0 | ) | (69.6 | ) | |||||
| Financing Activities | |||||||||||
| Additions to long-term debt | 493.4 | .4 | .4 | ||||||||
| Payments on long-term debt | (9.2 | ) | (5.4 | ) | (205.0 | ) | |||||
| Change in commercial paper and short-term debt | (202.7 | ) | 11.5 | 201.3 | |||||||
| Dividends paid | (185.6 | ) | (177.4 | ) | (171.6 | ) | |||||
| Issuances of common stock | 2.6 | 4.9 | 8.3 | ||||||||
| Purchases of common stock | (157.6 | ) | (198.0 | ) | (191.5 | ) | |||||
| Purchase of remaining interest in noncontrolling interest | (2.6 | ) | (35.2 | ) | — | ||||||
| Tax benefits from stock-based compensation payments | — | — | 15.7 | ||||||||
| Other, net | (2.8 | ) | (3.0 | ) | (6.8 | ) | |||||
| Net Cash Used for Financing Activities | (64.5 | ) | (402.2 | ) | (349.2 | ) | |||||
| Effect of Exchange Rate Changes on Cash | 30.0 | (19.7 | ) | (19.9 | ) | ||||||
| Increase (decrease) in Cash and Cash Equivalents | 244.2 | 28.7 | (79.6 | ) | |||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents—Beginning of Year | 281.9 | 253.2 | 332.8 | ||||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents—End of Year | $ | 526.1 | $ | 281.9 | $ | 253.2 | |||||
| Supplemental Information | |||||||||||
| Interest paid (net of amounts capitalized) | $ | 40.1 | $ | 37.5 | $ | 43.6 | |||||
| Income taxes paid | 90.6 | 112.3 | 91.6 | ||||||||
| Common stock issued for acquired companies | 11.8 | — | — | ||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment acquired through capital leases | 2.4 | 4.7 | 1.6 | ||||||||
| Capital expenditures in accounts payable | 6.7 | 5.1 | 2.5 | ||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
69
LEGGETT & PLATT, INCORPORATED
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity
(Amounts in millions, except per share data) | Common Stock | Additional Contributed Capital | Retained Earnings | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Treasury Stock | Non-controlling Interest | Total Equity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2014 | 198.8 | $ | 2.0 | $ | 502.4 | $ | 2,061.3 | $ | (2.6 | ) | (61.0 | ) | $ | (1,416.6 | ) | $ | 8.4 | $ | 1,154.9 | ||||||||||||||
| Net earnings | — | — | — | 329.2 | — | — | — | — | 329.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Earnings) attributable to noncontrolling interest, net of tax | — | — | — | (4.1 | ) | — | — | — | 4.1 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends declared (A) | — | — | 4.9 | (177.2 | ) | — | — | — | — | (172.3 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock purchased | — | — | — | — | — | (4.3 | ) | (198.2 | ) | — | (198.2 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock issued | — | — | (20.7 | ) | — | — | 2.1 | 50.8 | — | 30.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | — | — | — | — | (91.6 | ) | — | — | (.5 | ) | (92.1 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash flow hedges, net of tax | — | — | — | — | (8.1 | ) | — | — | — | (8.1 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Defined benefit pension plans, net of tax | — | — | — | — | 11.2 | — | — | — | 11.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation, net of tax | — | — | 42.9 | — | — | — | — | — | 42.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition of noncontrolling interest | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | .1 | .1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2015 | 198.8 | $ | 2.0 | $ | 529.5 | $ | 2,209.2 | $ | (91.1 | ) | (63.2 | ) | $ | (1,564.0 | ) | $ | 12.1 | $ | 1,097.7 | ||||||||||||||
| Net earnings | — | — | — | 386.2 | — | — | — | — | 386.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Earnings) attributable to noncontrolling interest, net of tax | — | — | — | (.4 | ) | — | — | — | .4 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends declared (A) | — | — | 5.1 | (184.5 | ) | — | — | — | — | (179.4 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid to noncontrolling interest | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1.6 | ) | (1.6 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock purchased | — | — | — | — | — | (4.5 | ) | (210.9 | ) | — | (210.9 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock issued | — | — | (25.4 | ) | — | — | 2.4 | 61.4 | — | 36.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | — | — | — | — | (34.8 | ) | — | — | (.1 | ) | (34.9 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash flow hedges, net of tax | — | — | — | — | 10.4 | — | — | — | 10.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Defined benefit pension plans, net of tax | — | — | — | — | .9 | — | — | — | .9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation, net of tax | — | — | 24.9 | — | — | — | — | — | 24.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Purchase of remaining interest in non-controlling interest | — | — | (27.9 | ) | — | 1.0 | — | — | (8.4 | ) | (35.3 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2016 | 198.8 | $ | 2.0 | $ | 506.2 | $ | 2,410.5 | $ | (113.6 | ) | (65.3 | ) | $ | (1,713.5 | ) | $ | 2.4 | $ | 1,094.0 | ||||||||||||||
Effect of accounting change on prior years (See Note A) | — | — | — | 1.1 | — | — | — | — | 1.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted beginning balance, January 1, 2017 | 198.8 | 2.0 | 506.2 | 2,411.6 | (113.6 | ) | (65.3 | ) | (1,713.5 | ) | 2.4 | 1,095.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings | — | — | — | 292.7 | — | — | — | — | 292.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Earnings) attributable to noncontrolling interest, net of tax | — | — | — | (.1 | ) | — | — | — | .1 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends declared (A) | — | — | 5.2 | (192.9 | ) | — | — | — | — | (187.7 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock purchased | — | — | — | — | — | (3.3 | ) | (162.1 | ) | — | (162.1 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock issued | — | — | (16.1 | ) | — | — | 1.7 | 47.3 | — | 31.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | — | — | — | — | 78.7 | — | — | — | 78.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash flow hedges, net of tax | — | — | — | — | 6.3 | — | — | — | 6.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Defined benefit pension plans, net of tax | — | — | — | — | 18.7 | — | — | — | 18.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation, net of tax | — | — | 20.0 | — | — | — | — | — | 20.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Purchase of remaining interest in non-controlling interest | — | — | (.6 | ) | — | .4 | — | — | (2.4 | ) | (2.6 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition of noncontrolling interest | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | .5 | .5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2017 | 198.8 | $ | 2.0 | $ | 514.7 | $ | 2,511.3 | $ | (9.5 | ) | (66.9 | ) | $ | (1,828.3 | ) | $ | .6 | $ | 1,190.8 | ||||||||||||||
(A) – Cash dividends declared (per share: 2017—$1.42; 2016—$1.34; 2015—$1.26)
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
70
Leggett & Platt, Incorporated
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollar amounts in millions, except per share data)
December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
A—Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
PRINCIPLES OF CONSOLIDATION: The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Leggett & Platt, Incorporated and its majority-owned subsidiaries (“we” or “our”). Management does not expect foreign exchange restrictions to significantly impact the ultimate realization of amounts consolidated in the accompanying financial statements for subsidiaries located outside the United States. All intercompany transactions and accounts have been eliminated in consolidation.
ESTIMATES: The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America ("GAAP") requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses and the accrual and disclosure of loss contingencies.
CASH EQUIVALENTS: Cash equivalents include cash in excess of daily requirements which is invested in various financial instruments with original maturities of three months or less.
TRADE AND OTHER RECEIVABLES AND ALLOWANCE FOR DOUBTFUL ACCOUNTS: Trade receivables are recorded at the invoiced amount and generally do not bear interest. Credit is also occasionally extended in the form of a note receivable to facilitate our customers’ operating cycles. Other notes receivable are established in special circumstances, such as in partial payment for the sale of a business or to support other business opportunities. Other notes receivable generally bear interest at market rates commensurate with the corresponding credit risk on the date of origination.
The allowance for doubtful accounts is an estimate of the amount of probable credit losses. Interest income is not recognized for nonperforming accounts that are placed on nonaccrual status. Allowances and nonaccrual status designations are determined by individual account reviews by management, and are based on several factors such as the length of time that receivables are past due, the financial health of the companies involved, industry and macroeconomic considerations, and historical loss experience. Interest income is recorded on the date of cash receipt for nonaccrual status accounts. Account balances are charged against the allowance when it is probable the receivable will not be recovered.
INVENTORIES: All inventories are stated at the lower of cost or net realizable value. We generally use standard costs which include materials, labor and production overhead at normal production capacity. The cost for approximately 50% of our inventories is determined by the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method and is primarily used to value domestic inventories with raw material content consisting of steel, wire, chemicals and foam scrap. For the remainder of the inventories, we principally use the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, which is representative of our standard costs. For these inventories, the FIFO cost for the periods presented approximated expected replacement cost.
Inventories are reviewed at least quarterly for slow-moving and potentially obsolete items using actual inventory turnover, and if necessary, are written down to estimated net realizable value. We have had no material changes in inventory writedowns or slow-moving and obsolete inventory reserves in any of the years presented.
The following table presents the activity in our LIFO reserve for each of the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015.
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Balance, beginning of year | $ | 33.8 | $ | 22.6 | $ | 73.0 | |||||
| LIFO expense (benefit) | 18.6 | 10.5 | (46.4 | ) | |||||||
| Allocated to divested businesses | (1.5 | ) | .7 | (4.0 | ) | ||||||
| Balance, end of year | $ | 50.9 | $ | 33.8 | $ | 22.6 | |||||
71
DIVESTITURES: Significant accounting policies associated with a decision to dispose of a business are discussed below:
Discontinued Operations—A business is classified as discontinued operations if the disposal represents a strategic shift that will have a major effect on operations or financial results, meets the criteria to be classified as held for sale, or is disposed of by sale or otherwise. Significant judgments are involved in determining whether a business meets the criteria for discontinued operations reporting and the period in which these criteria are met.
If a business is reported as a discontinued operation, the results of operations through the date of sale, including any gain or loss recognized on the disposition, are presented on a separate line of the income statement. Interest on debt directly attributable to the discontinued operation is allocated to discontinued operations. Gains and losses related to the sale of businesses that do not meet the discontinued operation criteria are reported in continuing operations and separately disclosed if significant.
Assets Held for Sale—An asset or business is classified as held for sale when (i) management commits to a plan to sell and it is actively marketed; (ii) it is available for immediate sale and the sale is expected to be completed within one year; and (iii) it is unlikely significant changes to the plan will be made or that the plan will be withdrawn. In isolated instances, assets held for sale may exceed one year due to events or circumstances beyond our control. Upon being classified as held for sale, the recoverability of the carrying value must be assessed. Evaluating the recoverability of the assets of a business classified as held for sale follows a defined order in which property and intangible assets subject to amortization are considered only after the recoverability of goodwill and other assets are assessed. After the valuation process is completed, the assets held for sale are reported at the lower of the carrying value or fair value less cost to sell, and the assets are no longer depreciated or amortized. An impairment charge is recognized if the carrying value exceeds the fair value less cost to sell. The assets and related liabilities are aggregated and reported on separate lines of the balance sheet.
Assets Held for Use—If a decision to dispose of an asset or a business is made and the held-for-sale criteria are not met, it is considered held for use. Assets of the business are evaluated for recoverability in the following order: (i) assets other than goodwill, property and intangibles; (ii) property and intangibles subject to amortization; and (iii) goodwill. In evaluating the recoverability of property and intangible assets subject to amortization, the carrying value is first compared to the sum of the undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use and eventual disposition. If the carrying value exceeds the undiscounted expected cash flows, then a fair value analysis is performed. An impairment charge is recognized if the carrying value exceeds the fair value.
LOSS CONTINGENCIES: Loss contingencies are accrued when a loss is probable and reasonably estimable. If a range of outcomes are possible, the most likely outcome is used to accrue these costs. If no outcome is more likely, we accrue at the minimum amount of the range. Any insurance recovery is recorded separately if it is determined that a recovery is probable. Legal fees are accrued when incurred.
PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT: Property, plant and equipment is stated at cost, less accumulated depreciation. Assets are depreciated by the straight-line method and salvage value, if any, is assumed to be minimal. The table below presents the depreciation periods of the estimated useful lives of our property, plant and equipment. Accelerated methods are used for tax purposes.
| Useful Life Range | Weighted Average Life | ||
| Machinery and equipment | 3-20 years | 10 years | |
| Buildings | 10-40 years | 28 years | |
| Other items | 3-15 years | 8 years | |
Property is reviewed for recoverability at year end and whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that its carrying value may not be recoverable as discussed above.
GOODWILL: Goodwill results from the acquisition of existing businesses and is not amortized; it is assessed for impairment annually and as triggering events may occur. We perform our annual review in the second quarter of each year. Our nine reporting units are the business groups one level below the operating segment level for which discrete financial information is available.
The Company has the option to first assess qualitative factors to determine whether events and circumstances indicate that it is more likely than not that goodwill is impaired. If after such an assessment, with regard to each reporting unit, we
72
conclude that the goodwill of a reporting unit is not impaired, then no further action is required (commonly referred to as the Step Zero Analysis approach).
For those reporting units where a significant change or event occurs, and where potential impairment indicators exist (based on the Step Zero Analysis approach), recoverability of goodwill is then evaluated using a two-step process. The first step involves a comparison of the fair value of a reporting unit with its carrying value.
If the carrying value of the reporting unit exceeds its fair value, the second step of the process is necessary and involves a comparison of the implied fair value and the carrying value of the goodwill of that reporting unit. If the carrying value of the goodwill of a reporting unit exceeds the implied fair value of that goodwill, an impairment loss is recognized in an amount equal to the excess.
Fair value of reporting units is determined using a combination of two valuation methods: a market approach and an income approach. Each method is generally given equal weight in determining the fair value assigned to each reporting unit. Absent an indication of fair value from a potential buyer or similar specific transaction, we believe that the use of these two methods provides a reasonable estimate of a reporting unit’s fair value. Assumptions common to both methods are operating plans and economic projections, which are used to project future revenues, earnings, and after-tax cash flows for each reporting unit. These assumptions are applied consistently for both methods.
The market approach estimates fair value by first determining price-to-earnings ratios for comparable publicly-traded companies with similar characteristics of the reporting unit. The price-to-earnings ratio for comparable companies is based upon current enterprise value compared to the historical earnings for the past two years. The enterprise value is based upon current market capitalization and includes a control premium. Projected earnings are based upon market analysts’ projections. The earnings ratios are applied to the projected earnings of the comparable reporting unit to estimate fair value. Management believes this approach is appropriate because it provides a fair value estimate using multiples from entities with operations and economic characteristics comparable to our reporting units.
The income approach is based on projected future (debt-free) cash flow that is discounted to present value using factors that consider the timing and risk of future cash flows. Management believes that this approach is appropriate because it provides a fair value estimate based upon the reporting unit’s expected long-term operating cash flow performance. Discounted cash flow projections are based on 10-year financial forecasts developed from operating plans and economic projections noted above, sales growth, estimates of future expected changes in operating margins, terminal value growth rates, future capital expenditures and changes in working capital requirements. There are inherent assumptions and judgments required in the analysis of goodwill impairment. It is possible that assumptions underlying the impairment analysis will change in such a manner that impairment in value may occur in the future.
OTHER INTANGIBLE ASSETS: Substantially all other intangible assets are amortized using the straight-line method over their estimated useful lives and are evaluated for impairment using a process similar to that used in evaluating the recoverability of property, plant and equipment.
| Useful Life Range | Weighted Average Life | ||
| Other intangible assets | 1-40 years | 15 years | |
STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION: The cost of employee services received in exchange for all equity awards granted is based on the fair market value of the award as of the grant date. Expense is recognized net of an estimated forfeiture rate using the straight-line method over the vesting period of the award.
SALES RECOGNITION: We recognize sales when title and risk of loss pass to the customer. The terms of our sales are split approximately evenly between FOB shipping point and FOB destination. The timing of our recognition of FOB destination sales is determined based on shipping date and distance to the destination. We have no significant or unusual price protection, right of return or acceptance provisions with our customers. Sales allowances, discounts and rebates can be reasonably estimated throughout the period and are deducted from sales in arriving at net sales.
SHIPPING AND HANDLING FEES AND COSTS: Shipping and handling costs are included as a component of “Cost of goods sold.”
RESTRUCTURING COSTS: Restructuring costs are items such as employee termination, contract termination, plant closure and asset relocation costs related to exit activities or workforce reductions. Restructuring-related items are inventory writedowns and gains or losses from sales of assets recorded as the result of exit activities. We recognize a liability for costs
73
associated with an exit or disposal activity when the liability is incurred. Certain termination benefits for which employees are required to render service are recognized ratably over the respective future service periods.
INCOME TAXES: The provision for income taxes is determined using the asset and liability approach of accounting for income taxes. Under this approach, deferred taxes represent the future tax consequences expected to occur when the reported amounts of assets and liabilities are recovered or paid. The provision for income taxes represents income taxes paid or payable for the current year plus the change in deferred taxes during the year. Deferred taxes result from differences between the financial and tax basis of our assets and liabilities and are adjusted for changes in tax rates and laws, as appropriate. A valuation allowance is provided to reduce deferred tax assets when management cannot conclude that it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will be realized. A provision is also made for incremental taxes on undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries and related companies to the extent that such earnings are not deemed to be indefinitely invested.
The calculation of our U.S., state, and foreign tax liabilities involves dealing with uncertainties in the application of complex global tax laws. We recognize potential liabilities for anticipated tax issues which might arise in the U.S. and other tax jurisdictions based on management’s estimate of whether, and the extent to which, additional taxes will be due. If payment of these amounts ultimately proves to be unnecessary, the reversal of the liabilities would result in tax benefits being recognized in the period when we determine the liabilities are no longer necessary. Conversely, if the estimate of tax liabilities proves to be less than the ultimate tax assessment, a further charge to tax expense would result.
CONCENTRATION OF CREDIT RISKS, EXPOSURES AND FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS: We manufacture, market, and distribute products for the various end markets described in Note E. Our operations are principally located in the United States, although we also have operations in Europe, China, Canada, Mexico and other various countries.
We maintain allowances for potential credit losses. We perform ongoing credit evaluations of our customers’ financial conditions and generally require no collateral from our customers, some of which are highly leveraged. Management also monitors the financial condition and status of other notes receivable. Other notes receivable have historically primarily consisted of notes accepted as partial payment for the divestiture of a business or to support other business opportunities. Some of these companies are highly leveraged and the notes are not fully collateralized.
We have no material guarantees or liabilities for product warranties which require disclosure.
From time to time, we will enter into contracts to hedge foreign currency denominated transactions, and interest rates related to our debt. To minimize the risk of counterparty default, only highly-rated financial institutions that meet certain requirements are used. We do not anticipate that any of the financial institution counterparties will default on their obligations.
The carrying value of cash and short-term financial instruments approximates fair value due to the short maturity of those instruments.
OTHER RISKS: Although we obtain insurance for workers’ compensation, automobile, product and general liability, property loss and medical claims, we have elected to retain a significant portion of expected losses through the use of deductibles. Accrued liabilities include estimates for unpaid reported claims and for claims incurred but not yet reported. Provisions for losses are recorded based upon reasonable estimates of the aggregate liability for claims incurred utilizing our prior experience and information provided by our third-party administrators and insurance carriers.
DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS: We utilize derivative financial instruments to manage market and financial risks related to foreign currency and interest rates. We seek to use derivative contracts that qualify for hedge accounting treatment; however some instruments that economically manage currency risk may not qualify for hedge accounting treatment. It is our policy not to speculate using derivative instruments.
Under hedge accounting, we formally document our hedge relationships, including identification of the hedging instruments and the hedged items, as well as our risk management objectives and strategies for entering into the hedge transaction. The process includes designating derivative instruments as hedges of specific assets, liabilities, firm commitments or forecasted transactions. We also formally assess both at inception and on a quarterly basis thereafter, whether the derivatives used in hedging transactions are highly effective in offsetting changes in either the fair value or cash flows of the hedged item. If it is determined that a derivative ceases to be highly effective, deferred gains or losses are recorded in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
On the date the contract is entered into, we designate the derivative as one of the following types of hedging instruments and account for it as follows:
74
Cash Flow Hedge—The hedge of a forecasted transaction or of the variability of cash flows to be received or paid related to a recognized asset or liability or anticipated transaction is designated as a cash flow hedge. The effective portion of the change in fair value is recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income. When the hedged item impacts the income statement, the gain or loss included in other comprehensive income is reported on the same line of the Consolidated Statements of Operations as the hedged item to match the gain or loss on the derivative to the gain or loss on the hedged item. Any ineffective portion of the changes in the fair value is immediately reported in the Consolidated Statements of Operations on the same line as the hedged item. Settlements associated with the sale or production of product are presented in operating cash flows and settlements associated with debt issuance are presented in financing cash flows.
Fair Value Hedge—The hedge of a recognized asset or liability or an unrecognized firm commitment is designated as a fair value hedge. For fair value hedges, both the effective and ineffective portions of the changes in fair value of the derivative, along with the gain or loss on the hedged item that is attributable to the hedged risk, are recorded in earnings and reported in the Consolidated Statements of Operations on the same line as the hedged item. Cash flows from settled contracts are presented in the category consistent with the nature of the item being hedged.
FOREIGN CURRENCY TRANSLATION: The functional currency for most foreign operations is the local currency. The translation of foreign currencies into U.S. dollars is performed for balance sheet accounts using current exchange rates in effect at the balance sheet date and for income and expense accounts using monthly average exchange rates. The cumulative effects of translating the functional currencies into the U.S. dollar are included in comprehensive income.
RECLASSIFICATIONS: Certain reclassifications have been made to the prior years’ information in the Consolidated Financial Statements and related notes to conform to the 2017 presentation. These were primarily a result of changes in our management organizational structure and related internal reporting (See Note E - Segment Information).
NEW ACCOUNTING GUIDANCE: The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) regularly issues updates to the FASB Accounting Standards Codification that are communicated through issuance of an Accounting Standards Update (ASU).
Below is a summary of the ASUs, effective for current or future periods, most relevant to our financial statements:
Adopted in 2017:
| • | ASU 2016-16 "Accounting for Income Taxes (Topic 740): Intra-Entity Asset Transfers of Assets Other than Inventory": Eliminates deferral of the tax effects of all intra-entity asset sales other than inventory, resulting in tax expense being recorded on the sale of the asset in the seller's tax jurisdiction when the sale occurs, even though the pretax effects of the transaction are eliminated in consolidation. Any deferred tax asset arising in the buyer's jurisdiction is also recognized at the time of sale. We adopted this guidance in the first quarter of 2017. The modified retrospective approach was required, and as a result, we recorded a $1.1 increase to beginning retained earnings on January 1, 2017. Adoption of this new guidance did not materially impact our 2017 Consolidated Statements of Operations. |
To be adopted in future years:
| • | ASU 2014-09 “Revenue from Contracts with Customers” (Topic 606): Supersedes most of the existing authoritative literature for revenue recognition and prescribes a five-step model for recognizing revenue from contracts with customers. This standard was issued in 2015 and was subsequently amended several times in 2016. We will adopt the standard effective January 1, 2018. |
We do not expect the adoption of this standard to materially impact our future statements of operations, total assets, or cash flows. We will transition to the new standard using the modified retrospective method. Under the modified retrospective method, there will be an adjustment to our January 1, 2018, equity for the cumulative effect of existing contracts. 2017 and earlier years will be presented under legacy GAAP. 2018 will be presented under the new standard for existing and new contracts. The footnotes will disclose existing and new contracts under both the new standard and legacy GAAP.
We disclosed in our September 30, 2017 Form 10-Q that we identified certain contracts containing provisions that will require the recognition of revenue over time. These contracts were for the production of a highly customized good with no alternative use where we had a contractual right to payment (including a normal profit) for goods in a finished goods status in the event of contract termination. In finalizing our interpretation of Topic 606 and a deeper analysis of the termination provisions of these contracts, we have concluded that most of our contracts will not meet the criteria to recognize revenue over time. We have subsequently concluded that the contract duration begins at the point we begin
75
manufacturing. At the work-in-process stage, our contract provisions only provide for a reimbursement of costs. Based on these conclusions, we would lack the contractual right to a payment that includes a normal profit throughout the duration of the contract. Thus, Topic 606 would require revenue to be recognized at the point where the customer obtains control of the goods in most of our contractual arrangements.
We have concluded that our customer obtains control of a good when it has the ability to direct the use of the good, obtain substantially all the remaining benefits of that good, or obtain the right to deploy or restrict another entity from deploying the good. We believe this control transfer will occur upon shipment from our facility or upon delivery to our customer’s facility and will depend on the terms of the contract. We do not believe our control transfer conclusion will have a material impact on our income statement when compared to legacy GAAP.
During the fourth quarter, we concluded our tooling arrangements with our customers are not part of ongoing major or central operations and therefore, do not transfer a good or service to our customers. In these tooling arrangements, we enter into a contract to produce or obtain tooling to be used in production of that customer’s goods, and that customer agrees to reimburse us for the costs of that tooling.
We believe that our tooling arrangements are activities to fulfill our performance obligations to our customers. Under prior accounting standards for the recognition of revenue, we recorded an immaterial amount of revenue related to these reimbursements. Upon adoption of Topic 606, we will account for these tooling costs and reimbursements on a net basis and recognize no revenue related to tooling reimbursements. This change will not materially impact our revenues, cost of sales, net earnings, or our total assets.
| • | ASU 2016-02 “Leases” (Topic 842): Requires that a lessee recognize a right-of-use asset and a lease liability on the balance sheet for most lease arrangements. This ASU will be effective January 1, 2019. We have assembled a cross-functional implementation team and are assessing all potential impacts of the standard. We believe our assets and liabilities will increase for the adoption of this ASU through the recording of these right-of-use assets and corresponding lease liabilities. We continue to evaluate its impact on our statements of operations and cash flows. |
| • | ASU 2017-12 “Derivatives and Hedging (Topic 815): Targeted Improvements to Accounting for Hedging Activities”: This ASU is intended to simplify and clarify the accounting and disclosure requirements for hedging activities by more closely aligning the results of cash flow and fair value hedge accounting with the risk management activities of an entity. The amendments in this ASU are effective for annual periods, and interim periods within those annual periods, beginning after December 15, 2018, with early adoption permitted. We are currently evaluating the effect of the ASU on our results of operations, financial condition or cash flows. |
| • | ASU 2017-04, "Intangibles - Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment": This ASU simplifies the subsequent measurement of goodwill by eliminating Step 2 from the goodwill impairment test. Under this ASU, the annual goodwill impairment test is performed by comparing the fair value of a reporting unit with its carrying amount. An impairment charge would be recognized for the amount by which the carrying amount exceeds the reporting unit's fair value up to the total amount of goodwill for the reporting unit. This ASU will be effective January 1, 2020, with early adoption permitted. We are currently evaluating this guidance, and do not expect it to materially impact our future financial statements. |
| • | ASU 2018-02, “Income Statement - Reporting Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Reclassification of Certain Tax Effects from Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income”: This ASU provides financial statement preparers with an option to reclassify stranded tax effects within accumulated other comprehensive income in each period in which the effect of the change in the U.S. federal corporate income tax rate in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) is recorded. The ASU will be effective for us January 1, 2019. Early adoption is permitted and the amendments should be applied in either the period of adoption or retrospectively to each period in which the effect of the change in federal corporate income tax rate in the TCJA is recognized. We are currently evaluating this guidance. |
| • | ASUs 2016-13 “Financial Instruments - Credit Losses” (Topic 326) and 2016-15 “Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments (a consensus of the Emerging Issues Task Force)” are currently being evaluated; however, we do not expect these updates to materially impact our future financial statements. |
76
The FASB has issued accounting guidance, in addition to the issuance discussed above, effective for current and future periods. This guidance did not have a material impact on our current financial statements, and we do not believe it will have a material impact on our future financial statements.
B—Discontinued Operations, Assets Held for Sale, and Other Divestitures
Discontinued Operations
The table below includes activity related to discontinued operations for the years presented:
| Year Ended | |||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Trade sales: | |||||||||||
| Furniture Products - Store Fixtures (1) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 19.4 | |||||
| Earnings (loss): | |||||||||||
| Furniture Products - Store Fixtures (1) | $ | — | $ | .7 | $ | 3.4 | |||||
| Subsequent activity related to divestitures completed prior to 2015 (2) | (1.4 | ) | 29.4 | (1.5 | ) | ||||||
| Earnings (loss) before interest and income taxes (EBIT) | (1.4 | ) | 30.1 | 1.9 | |||||||
| Income tax (expense) benefit (3) | .5 | (11.0 | ) | (.7 | ) | ||||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax | $ | (.9 | ) | $ | 19.1 | $ | 1.2 | ||||
| (1) | During the fourth quarter of 2014, we divested the majority of our Store Fixtures reporting unit, which was previously part of the Furniture Products segment. We sold the final Store Fixtures business in the fourth quarter of 2015. Total consideration for these businesses was approximately $72.0 during this time period. No significant gains or losses were realized on the sale of these businesses. |
| (2) | Activity is primarily related to two unrelated litigation settlements associated with our former Prime Foam Products unit. This unit was sold in March 2007 and was previously part of the Residential Products segment. During 2016, we received proceeds from an antitrust litigation settlement of approximately $38.0 ($25.0 after-tax) of which $31.4 ($19.8 after-tax) is associated with this unit. Additionally, during 2017 we settled a final antitrust litigation for a cash payment that was not material to the company and was not materially different from the amount previously accrued for the claim. |
| (3) | The 2016 tax expense is primarily related to the antitrust litigation settlement. |
77
Other Divestitures
The following businesses were divested during the periods presented, but did not meet the discontinued operations criteria.
| Date | Year Ended | ||||||||||||
| Divested | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Trade Sales: | |||||||||||||
| Residential Products: | |||||||||||||
| Machinery operation | Fourth quarter 2016 | $ | — | $ | 3.1 | $ | 3.7 | ||||||
| Industrial Products: | |||||||||||||
| Wire operations | Second and fourth quarters 2016 | — | 38.0 | 69.4 | |||||||||
| Steel Tubing business unit | Fourth quarter 2015 | — | — | 88.9 | |||||||||
| Specialized Products: | |||||||||||||
| Commercial Vehicle Products (CVP) operation | Third quarter 2017 | 25.1 | 59.7 | 58.8 | |||||||||
| CVP operation | Second quarter 2016 | — | 15.3 | 27.5 | |||||||||
| CVP operation | Fourth quarter 2015 | — | — | 9.3 | |||||||||
| Total Trade Sales | $ | 25.1 | $ | 116.1 | $ | 257.6 | |||||||
| EBIT: | |||||||||||||
| Residential Products: | |||||||||||||
| Machinery operation | Fourth quarter 2016 | $ | — | $ | (.3 | ) | $ | .1 | |||||
| Industrial Products: | |||||||||||||
| Wire operations | Second and fourth quarters 2016 | — | 1.8 | 3.0 | |||||||||
| Steel Tubing business unit | Fourth quarter 2015 | — | — | .2 | |||||||||
| Specialized Products: | |||||||||||||
| CVP operation | Third quarter 2017 | (2.3 | ) | 3.1 | (.1 | ) | |||||||
| CVP operation | Second quarter 2016 | — | 2.8 | 3.9 | |||||||||
| CVP operation | Fourth quarter 2015 | — | — | (.6 | ) | ||||||||
| Total EBIT | $ | (2.3 | ) | $ | 7.4 | $ | 6.5 | ||||||
The amounts discussed below are not included in the operating results presented in the above table.
In 2017, we realized a pretax loss of $3.3 related to the sale of our remaining CVP operation. We also completed the sale of real estate associated with this operation, realizing a pretax gain of $23.4.
In 2016, we realized gains of $21.2 and $11.2 related to the sale of the wire operations and a CVP operation, respectively. No other material gains or losses were realized on the sale of other businesses.
78
C—Impairment Charges
Pretax impact of impairment charges is summarized in the following table.
The Statements of Operations reflect the following: Goodwill and other long-lived asset impairments are reported in "Impairments"; discontinued operations are reported in “Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax.”
| Year Ended | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Goodwill Impairment | Other Long-Lived Asset Impairments | Total Impairments | Goodwill Impairment | Other Long-Lived Asset Impairments | Total Impairments | Goodwill Impairment | Other Long-Lived Asset Impairments | Total Impairments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Continuing operations: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Residential Products | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | .4 | $ | .4 | $ | — | $ | .7 | $ | .7 | |||||||||||||||||
| Industrial Products: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wire operation | 1.3 | 3.3 | 4.6 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Steel Tubing | — | — | — | — | — | — | 4.1 | 1.4 | 5.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | — | .3 | .3 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specialized Products - CVP | — | — | — | 3.7 | — | 3.7 | — | .1 | .1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total continuing operations | 1.3 | 3.6 | 4.9 | 3.7 | .4 | 4.1 | 4.1 | 2.2 | 6.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discontinued operations | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | .2 | .2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total impairment charges | $ | 1.3 | $ | 3.6 | $ | 4.9 | $ | 3.7 | $ | .4 | $ | 4.1 | $ | 4.1 | $ | 2.4 | $ | 6.5 | |||||||||||||||||
Other Long-Lived Assets
As discussed in Note A, we test other long-lived assets for recoverability at year end and whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value may not be recoverable. Fair value and the resulting impairment charges noted above were based primarily upon offers from potential buyers or third party estimates of fair value less selling costs.
Goodwill
As discussed in Note A, goodwill is required to be tested for impairment at the reporting unit level at least once a year and as triggering events may occur. We perform our annual goodwill impairment review in the second quarter of each year.
2017 Goodwill Impairment Review
The 2017 annual goodwill impairment review indicated no goodwill impairments.
We performed a Step Zero Analysis for our annual goodwill review for each of our reporting units and we considered i) the excess in fair value of the reporting unit over its carrying amount from the most recent quantitative analysis, ii) macroeconomic conditions, iii) industry and market trends, and iv) overall financial performance. We concluded that it was more likely than not that the fair value of all reporting units, except for two, exceeded their carrying values. Because sales and profits for two reporting units were less than expected, we performed a quantitative analysis for our Work Furniture and Aerospace reporting units under the two-step model. These reporting units were determined to have fair values in excess of their carrying amounts of at least 75%. Goodwill associated with these two reporting units was $157.4 at December 31, 2017.
During the third quarter of 2017, a wire operation within the Industrial Products segment reached held-for-sale status. Because fair value less costs to sell had fallen below the carrying amount, we fully impaired $1.3 of goodwill and $3.3 of other long-lived assets.
79
2016 Goodwill Impairment Review
Because all reporting unit fair values exceeded their respective carrying values (fair value over carrying value divided by carrying value) by a range of 115% to 600% during the 2015 testing (performed on a quantitative basis for all reporting units), we performed a qualitative assessment (Step Zero Analysis) for our annual goodwill impairment review in the second quarter of 2016. Among other things, we considered i) the excess in fair value of the reporting unit over its carrying amount from the most recent quantitative analysis, ii) macroeconomic conditions, iii) industry and market trends, and iv) overall financial performance.
Based on the Step Zero Analysis we concluded that it was more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting units exceeded their carrying amount, except for our CVP reporting unit.
With regard to our CVP reporting unit, in the second quarter of 2016 we sold one of our two remaining businesses. Additionally, real estate associated with the remaining CVP business reached held-for-sale status during the second quarter of 2016. As a result of these two events, the fair value of the CVP reporting unit (consisting of one remaining business) had fallen below its carrying amount, and we fully impaired the remaining $3.7 of goodwill for this reporting unit.
2015 Goodwill Impairment Review
The 2015 goodwill impairment review indicated no goodwill impairments.
The Steel Tubing unit met the held-for-sale criteria during the first quarter of 2015. Because fair value less costs to sell had fallen below recorded book value, we fully impaired $4.1 of goodwill and $1.4 of other long-lived assets.
The fair values of reporting units in relation to their respective carrying values and significant assumptions used in the second quarter 2015 review are presented in the table below.
| Fair Value over Carrying Value divided by Carrying Value | December 31, 2015 Goodwill Value | 10-year Compound Annual Growth Rate Range for Sales | Terminal Values Long- term Growth Rate for Debt-Free Cash Flow | Discount Rate Ranges | |||||||||
| Less than 100% | $ | — | — | % | — | % | — | % | |||||
| 101% - 300% | 588.7 | .6% - 7.0% | 3.0 | % | 8.0% - 12.5% | ||||||||
| 301% - 600% | 217.4 | 3.1% - 10.9% | 3.0 | % | 8.0% - 9.0% | ||||||||
| $ | 806.1 | .6% - 10.9% | 3.0 | % | 8.0% - 12.5% | ||||||||
80
D—Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
The changes in the carrying amounts of goodwill are as follows:
Residential Products | Industrial Products | Furniture Products | Specialized Products | Total | |||||||||||||||
| Net goodwill as of January 1, 2016 | $ | 351.2 | $ | 76.7 | $ | 190.0 | $ | 188.2 | $ | 806.1 | |||||||||
| Additions for current year acquisitions | 4.9 | — | — | 3.8 | 8.7 | ||||||||||||||
| Adjustments to prior year acquisitions | — | — | .1 | — | .1 | ||||||||||||||
| Reductions for sale of business | (.1 | ) | (4.3 | ) | — | (8.8 | ) | (13.2 | ) | ||||||||||
| Impairment charge (1) | — | — | — | (3.7 | ) | (3.7 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | (3.2 | ) | (.5 | ) | (2.2 | ) | (.8 | ) | (6.7 | ) | |||||||||
| Net goodwill as of December 31, 2016 | 352.8 | 71.9 | 187.9 | 178.7 | 791.3 | ||||||||||||||
| Additions for current year acquisitions | 7.6 | — | 3.9 | — | 11.5 | ||||||||||||||
| Adjustments to prior year acquisitions | .8 | — | — | — | .8 | ||||||||||||||
| Impairment charge (2) | — | (1.3 | ) | — | — | (1.3 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | 7.0 | .2 | 4.4 | 8.3 | 19.9 | ||||||||||||||
| Net goodwill as of December 31, 2017 | $ | 368.2 | $ | 70.8 | $ | 196.2 | $ | 187.0 | $ | 822.2 | |||||||||
| Net goodwill as of December 31, 2017 is comprised of: | |||||||||||||||||||
| Gross goodwill | $ | 368.2 | $ | 76.2 | $ | 446.8 | $ | 253.7 | $ | 1,144.9 | |||||||||
| Accumulated impairment losses | — | (5.4 | ) | (250.6 | ) | (66.7 | ) | (322.7 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net goodwill as of December 31, 2017 | $ | 368.2 | $ | 70.8 | $ | 196.2 | $ | 187.0 | $ | 822.2 | |||||||||
(1) We recorded a goodwill impairment charge related to the Commercial Vehicle Products unit as outlined in Note C.
(2) We recorded a goodwill impairment charge related to a wire operation as outlined in Note C.
81
The gross carrying amount and accumulated amortization by intangible asset class and intangible assets acquired during the period presented included in "Other intangibles" on the Consolidated Balance Sheets are as follows:
Debt Issuance Costs | Patents and Trademarks | Non-compete Agreements | Customer- Related Intangibles | Supply Agreements and Other | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross carrying amount | $ | 3.7 | $ | 65.3 | $ | 14.2 | $ | 210.1 | $ | 27.5 | $ | 320.8 | |||||||||||
| Accumulated amortization | 1.9 | 30.9 | 6.7 | 96.9 | 15.3 | 151.7 | |||||||||||||||||
| Net other intangibles as of December 31, 2017 | $ | 1.8 | $ | 34.4 | $ | 7.5 | $ | 113.2 | $ | 12.2 | $ | 169.1 | |||||||||||
| Acquired during 2017: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acquired related to business acquisitions | $ | — | $ | 8.7 | $ | .4 | $ | 11.2 | $ | — | $ | 20.3 | |||||||||||
| Acquired outside business acquisitions | .6 | 1.4 | — | .2 | 4.5 | 6.7 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total acquired in 2017 | $ | .6 | $ | 10.1 | $ | .4 | $ | 11.4 | $ | 4.5 | $ | 27.0 | |||||||||||
| Weighted average amortization period in years for items acquired in 2017 | 5.0 | 2.7 | 6.9 | 16.4 | 3.0 | 8.6 | |||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross carrying amount | $ | 3.1 | $ | 58.0 | $ | 13.9 | $ | 200.9 | $ | 26.0 | $ | 301.9 | |||||||||||
| Accumulated amortization | 1.6 | 30.8 | 4.4 | 87.9 | 12.3 | 137.0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Net other intangibles as of December 31, 2016 | $ | 1.5 | $ | 27.2 | $ | 9.5 | $ | 113.0 | $ | 13.7 | $ | 164.9 | |||||||||||
| Acquired during 2016: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acquired related to business acquisitions | $ | — | $ | 1.9 | $ | 2.8 | $ | 7.6 | $ | — | $ | 12.3 | |||||||||||
| Acquired outside business acquisitions | .9 | 2.4 | — | — | 2.1 | 5.4 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total acquired in 2016 | $ | .9 | $ | 4.3 | $ | 2.8 | $ | 7.6 | $ | 2.1 | $ | 17.7 | |||||||||||
| Weighted average amortization period in years for items acquired in 2016 | 5.0 | 9.6 | 5.2 | 12.0 | 3.5 | 9.0 | |||||||||||||||||
Estimated amortization expense for items included in our December 31, 2017 balance sheet in each of the next five years is as follows:
| Year ended December 31 | |||
| 2018 | $ | 23.0 | |
| 2019 | 21.0 | ||
| 2020 | 19.0 | ||
| 2021 | 13.0 | ||
| 2022 | 12.0 | ||
E—Segment Information
Our reportable segments are the same as our operating segments, which also correspond with our management structure. In conjunction with a change in executive officers, our management structure and all related internal reporting changed as of January 1, 2017. As a result, the composition of our four segments also changed to reflect the new structure.
The new structure is largely the same as prior years except the Home Furniture Group moved from Residential Products to Furniture Products (formerly Commercial Products) and the Machinery Group moved from Specialized Products to Residential Products. In addition, the changes in LIFO reserve are now recognized within the segments to which they relate (primarily Industrial Products). Previously segment EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) reflected the FIFO basis of
82
accounting for certain inventories and an adjustment to the LIFO basis for these inventories was made at the consolidated financial statement level. These changes were retrospectively applied to all prior periods presented. The methods and assumptions that we use in estimating our LIFO reserve did not change (See Note A - Summary of Significant Accounting Policies).
We have four operating segments that supply a wide range of products:
| • | Residential Products: This segment supplies a variety of components and machinery used by bedding manufacturers in the production and assembly of their finished products. We also produce or distribute carpet cushion, fabric, and geo components. |
| • | Industrial Products: These operations primarily supply steel rod and drawn steel wire to our other operations and to external customers. This wire is used to make bedding, mechanical springs, and many other end products. |
| • | Furniture Products: Operations in this segment supply a wide range of components for residential and work furniture manufacturers, as well as select lines of private-label finished furniture, adjustable bed bases, fashion beds, and bed frames. |
| • | Specialized Products: From this segment we supply lumbar support systems, seat suspension systems, motors and actuators, and control cables used by automotive manufacturers. We also produce and distribute tubing and tube assemblies for the aerospace industry. |
Each reportable segment has an executive vice president that reports to the chief executive officer, who is the chief operating decision maker (CODM). The operating results and financial information reported through the segment structure are regularly reviewed and used by the CODM to evaluate segment performance, allocate overall resources and determine management incentive compensation.
Separately, we also utilize a role-based approach (Grow, Core, Fix or Divest) as a supplemental management tool to ensure capital (which is a subset of the overall resources referred to above) is efficiently allocated within the reportable segment structure.
The accounting principles used in the preparation of the segment information are the same as those used for the consolidated financial statements. We evaluate performance based on EBIT. Intersegment sales are made primarily at prices that approximate market-based selling prices. Centrally incurred costs are allocated to the segments based on estimates of services used by the segment. Certain of our general and administrative costs and miscellaneous corporate income and expenses are allocated to the segments based on sales or other appropriate metrics. These allocated corporate costs include depreciation and other costs and income related to assets that are not allocated or otherwise included in the segment assets.
83
A summary of segment results for the periods presented are as follows:
| Year Ended December 31 | |||||||||||||||
Trade Sales | Inter- Segment Sales | Total Segment Sales | EBIT | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | |||||||||||||||
| Residential Products | $ | 1,620.2 | $ | 18.6 | $ | 1,638.8 | $ | 184.0 | |||||||
| Industrial Products | 291.7 | 253.9 | 545.6 | 21.0 | |||||||||||
| Furniture Products | 1,096.4 | 16.8 | 1,113.2 | 81.5 | |||||||||||
| Specialized Products | 935.5 | 7.1 | 942.6 | 195.6 | |||||||||||
| Intersegment eliminations and other (1) | (14.2 | ) | |||||||||||||
| $ | 3,943.8 | $ | 296.4 | $ | 4,240.2 | $ | 467.9 | ||||||||
| 2016 | |||||||||||||||
| Residential Products | $ | 1,571.4 | $ | 17.2 | $ | 1,588.6 | $ | 167.5 | |||||||
| Industrial Products | 289.4 | 293.1 | 582.5 | 65.3 | |||||||||||
| Furniture Products | 989.3 | 59.3 | 1,048.6 | 106.6 | |||||||||||
| Specialized Products | 899.8 | 6.5 | 906.3 | 181.4 | |||||||||||
| Intersegment eliminations and other | 1.2 | ||||||||||||||
| $ | 3,749.9 | $ | 376.1 | $ | 4,126.0 | $ | 522.0 | ||||||||
| 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| Residential Products | $ | 1,666.1 | $ | 21.9 | $ | 1,688.0 | $ | 154.7 | |||||||
| Industrial Products | 427.6 | 349.0 | 776.6 | 76.8 | |||||||||||
| Furniture Products | 982.7 | 89.1 | 1,071.8 | 118.1 | |||||||||||
| Specialized Products | 840.8 | 6.4 | 847.2 | 150.2 | |||||||||||
| Intersegment eliminations and other (1) | (13.3 | ) | |||||||||||||
| $ | 3,917.2 | $ | 466.4 | $ | 4,383.6 | $ | 486.5 | ||||||||
(1) Intersegment eliminations and other includes $15.3 and $12.1 of pension settlements in years ended December 31, 2017 and 2015, respectively (See Note L).
84
Average assets for our segments are shown in the table below and reflect the basis for return measures used by management to evaluate segment performance. These segment totals include working capital (all current assets and current liabilities) plus net property, plant and equipment. Segment assets for all years are reflected at their estimated average for the year. Acquired companies’ long-lived assets as disclosed below include property, plant and equipment and other long-term assets.
| Year Ended December 31 | |||||||||||||||
| Assets | Additions to Property, Plant and Equipment | Acquired Companies’ Long-Lived Assets | Depreciation And Amortization | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | |||||||||||||||
| Residential Products | $ | 554.6 | $ | 60.5 | $ | 33.6 | $ | 45.8 | |||||||
| Industrial Products | 150.0 | 14.3 | — | 10.2 | |||||||||||
| Furniture Products | 245.7 | 20.2 | 14.3 | 16.2 | |||||||||||
| Specialized Products | 271.7 | 51.7 | — | 31.2 | |||||||||||
| Average current liabilities included in segment numbers above | 557.0 | — | — | — | |||||||||||
| Unallocated assets and other (1) | 1,693.1 | 12.7 | — | 22.5 | |||||||||||
| Difference between average assets and year-end balance sheet | 78.7 | — | — | — | |||||||||||
| $ | 3,550.8 | $ | 159.4 | $ | 47.9 | $ | 125.9 | ||||||||
| 2016 | |||||||||||||||
| Residential Products | $ | 527.2 | $ | 32.4 | $ | 11.2 | $ | 42.9 | |||||||
| Industrial Products | 147.4 | 10.1 | — | 11.8 | |||||||||||
| Furniture Products | 219.4 | 16.6 | — | 14.4 | |||||||||||
| Specialized Products | 248.7 | 42.2 | 13.7 | 29.7 | |||||||||||
| Average current liabilities included in segment numbers above | 495.9 | — | — | — | |||||||||||
| Unallocated assets and other (1) | 1,378.5 | 22.7 | — | 16.6 | |||||||||||
| Difference between average assets and year-end balance sheet | (33.0 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||
| $ | 2,984.1 | $ | 124.0 | $ | 24.9 | $ | 115.4 | ||||||||
| 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| Residential Products | $ | 548.2 | $ | 36.1 | $ | .2 | $ | 42.5 | |||||||
| Industrial Products | 186.7 | 12.5 | — | 14.2 | |||||||||||
| Furniture Products | 212.0 | 13.9 | 25.4 | 13.7 | |||||||||||
| Specialized Products | 230.1 | 31.1 | — | 28.2 | |||||||||||
| Average current liabilities included in segment numbers above | 516.6 | — | — | — | |||||||||||
| Unallocated assets and other (1) | 1,393.3 | 9.6 | — | 14.6 | |||||||||||
| Difference between average assets and year-end balance sheet | (123.2 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||
| $ | 2,963.7 | $ | 103.2 | $ | 25.6 | $ | 113.2 | ||||||||
(1) Unallocated assets consist primarily of goodwill, other intangibles, cash, businesses sold and deferred tax assets. Unallocated depreciation and amortization consists primarily of depreciation of non-operating assets and amortization of debt issue costs.
85
Revenues from trade customers, by product line, are as follows:
| Year Ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Residential Products | |||||||||||
| Bedding group | $ | 837.2 | $ | 831.8 | $ | 918.3 | |||||
| Fabric & Carpet Cushion group | 720.1 | 666.8 | 675.0 | ||||||||
| Machinery group | 62.9 | 72.8 | 72.8 | ||||||||
| 1,620.2 | 1,571.4 | 1,666.1 | |||||||||
| Industrial Products | |||||||||||
| Wire group (1) | 291.7 | 289.4 | 338.6 | ||||||||
| Steel Tubing group (1) | — | — | 89.0 | ||||||||
| 291.7 | 289.4 | 427.6 | |||||||||
| Furniture Products | |||||||||||
| Consumer Products group | 413.3 | 327.2 | 305.6 | ||||||||
| Home Furniture group | 410.2 | 413.3 | 442.9 | ||||||||
| Work Furniture group | 272.9 | 248.8 | 234.2 | ||||||||
| 1,096.4 | 989.3 | 982.7 | |||||||||
| Specialized Products | |||||||||||
| Automotive group | 772.5 | 695.0 | 621.9 | ||||||||
| Aerospace Products group | 137.9 | 129.7 | 123.2 | ||||||||
| Commercial Vehicle Products group (1) | 25.1 | 75.1 | 95.7 | ||||||||
| 935.5 | 899.8 | 840.8 | |||||||||
| $ | 3,943.8 | $ | 3,749.9 | $ | 3,917.2 | ||||||
(1) Our two remaining CVP operations were sold in 2017 and 2016. Certain operations in the Wire group were sold in 2016. The Steel Tubing group was sold in 2015. See Note B.
86
Trade sales and tangible long-lived assets are presented below, based on the geography of manufacture.
| Year Ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Trade sales | |||||||||||
| Foreign sales | |||||||||||
| Europe | $ | 475.3 | $ | 445.2 | $ | 426.8 | |||||
| China | 481.6 | 420.0 | 392.0 | ||||||||
| Canada | 265.1 | 215.1 | 203.1 | ||||||||
| Mexico | 148.5 | 132.8 | 117.3 | ||||||||
| Other | 85.5 | 69.4 | 74.3 | ||||||||
| Total foreign sales | 1,456.0 | 1,282.5 | 1,213.5 | ||||||||
| United States | 2,487.8 | 2,467.4 | 2,703.7 | ||||||||
| Total trade sales | $ | 3,943.8 | $ | 3,749.9 | $ | 3,917.2 | |||||
| Tangible long-lived assets | |||||||||||
| Foreign tangible long-lived assets | |||||||||||
| Europe | $ | 157.4 | $ | 128.6 | $ | 123.6 | |||||
| China | 54.7 | 45.5 | 41.8 | ||||||||
| Canada | 39.9 | 29.6 | 23.0 | ||||||||
| Mexico | 6.5 | 6.3 | 7.6 | ||||||||
| Other | 13.0 | 12.7 | 8.0 | ||||||||
| Total foreign tangible long-lived assets | 271.5 | 222.7 | 204.0 | ||||||||
| United States | 392.4 | 342.8 | 336.8 | ||||||||
| Total tangible long-lived assets | $ | 663.9 | $ | 565.5 | $ | 540.8 | |||||
87
F—Earnings Per Share
Basic and diluted earnings per share were calculated as follows:
| Year Ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Earnings: | |||||||||||
| Earnings from continuing operations | $ | 293.6 | $ | 367.1 | $ | 328.0 | |||||
| (Earnings) attributable to noncontrolling interest, net of tax | (.1 | ) | (.4 | ) | (4.1 | ) | |||||
| Net earnings from continuing operations attributable to Leggett & Platt common shareholders | 293.5 | 366.7 | 323.9 | ||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax | (.9 | ) | 19.1 | 1.2 | |||||||
| Net earnings attributable to Leggett & Platt common shareholders | $ | 292.6 | $ | 385.8 | $ | 325.1 | |||||
| Weighted average number of shares (in millions): | |||||||||||
| Weighted average number of common shares used in basic EPS | 136.0 | 137.9 | 140.9 | ||||||||
| Dilutive effect of equity-based compensation | 1.3 | 2.1 | 2.0 | ||||||||
| Weighted average number of common shares and dilutive potential common shares used in diluted EPS | 137.3 | 140.0 | 142.9 | ||||||||
| Basic and Diluted EPS: | |||||||||||
| Basic EPS attributable to Leggett & Platt common shareholders | |||||||||||
| Continuing operations | $ | 2.16 | $ | 2.66 | $ | 2.30 | |||||
| Discontinued operations | (.01 | ) | .14 | .01 | |||||||
| Basic EPS attributable to Leggett & Platt common shareholders | $ | 2.15 | $ | 2.80 | $ | 2.31 | |||||
| Diluted EPS attributable to Leggett & Platt common shareholders | |||||||||||
| Continuing operations | $ | 2.14 | $ | 2.62 | $ | 2.27 | |||||
| Discontinued operations | (.01 | ) | .14 | .01 | |||||||
| Diluted EPS attributable to Leggett & Platt common shareholders | $ | 2.13 | $ | 2.76 | $ | 2.28 | |||||
| Other information: | |||||||||||
| Anti-dilutive shares excluded from diluted EPS computation | — | — | — | ||||||||
88
G—Accounts and Other Receivables
Accounts and other receivables at December 31 consisted of the following:
| 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||||
| Current | Long-term | Current | Long-term | ||||||||||||
| Trade accounts receivable | $ | 526.1 | $ | — | $ | 456.5 | $ | — | |||||||
| Trade notes receivable | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.5 | .7 | |||||||||||
| Total trade receivables | 527.1 | 1.2 | 458.0 | .7 | |||||||||||
| Other notes receivable | — | 24.7 | — | 24.6 | |||||||||||
| Insurance receivables | 43.0 | — | — | — | |||||||||||
| Taxes receivable, including income taxes | 15.0 | — | 20.8 | — | |||||||||||
| Other receivables | 14.8 | — | 15.0 | — | |||||||||||
| Subtotal other receivables | 72.8 | 24.7 | 35.8 | 24.6 | |||||||||||
| Total trade and other receivables | 599.9 | 25.9 | 493.8 | 25.3 | |||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts: | |||||||||||||||
| Trade accounts receivable | (4.7 | ) | — | (7.1 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Trade notes receivable | (.1 | ) | (.1 | ) | (.1 | ) | (.2 | ) | |||||||
| Total trade receivables | (4.8 | ) | (.1 | ) | (7.2 | ) | (.2 | ) | |||||||
| Other notes receivable | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||
| Total allowance for doubtful accounts | (4.8 | ) | (.1 | ) | (7.2 | ) | (.2 | ) | |||||||
| Total net receivables | $ | 595.1 | $ | 25.8 | $ | 486.6 | $ | 25.1 | |||||||
Notes that were past due more than 90 days or had been placed on non-accrual status were not significant for the periods presented.
Activity related to the allowance for doubtful accounts is reflected below:
| Balance at December 31, 2015 | Add: Charges | Less: Charge-offs, Net of Recoveries | Balance at December 31, 2016 | Add: Charges | Less: Charge-offs, Net of Recoveries | Balance at December 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Trade accounts receivable | $ | 9.2 | $ | 1.8 | $ | 3.9 | $ | 7.1 | $ | .9 | $ | 3.3 | $ | 4.7 | |||||||||||||
| Trade notes receivable | .3 | (.2 | ) | (.2 | ) | .3 | (.1 | ) | — | .2 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total trade receivables | 9.5 | 1.6 | 3.7 | 7.4 | .8 | 3.3 | 4.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Other notes receivable | .4 | — | .4 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total allowance for doubtful accounts | $ | 9.9 | $ | 1.6 | $ | 4.1 | $ | 7.4 | $ | .8 | $ | 3.3 | $ | 4.9 | |||||||||||||
89
H—Supplemental Balance Sheet Information
Additional supplemental balance sheet details at December 31 consisted of the following:
| 2017 | 2016 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | |||||||
| Prepaid income taxes | $ | 28.5 | $ | 1.3 | |||
| Other | 45.7 | 35.5 | |||||
| $ | 74.2 | $ | 36.8 | ||||
| Sundry assets | |||||||
Deferred taxes (see Note M) | $ | 21.4 | $ | 23.9 | |||
Assets held for sale (see Note B) | 2.6 | 11.0 | |||||
Diversified investments associated with stock-based compensation plans (see Note K) | 31.6 | 25.0 | |||||
| Investment in associated companies | 7.1 | 7.1 | |||||
Pension plan assets (see Note L) | 2.2 | 1.1 | |||||
Brazilian VAT deposits (see Note S) | 12.2 | 12.5 | |||||
| Net long-term notes receivable | 25.8 | 25.1 | |||||
| Other | 26.2 | 31.8 | |||||
| $ | 129.1 | $ | 137.5 | ||||
| Accrued expenses | |||||||
Litigation contingency accruals (see Note S) | $ | .4 | $ | 3.2 | |||
| Wages and commissions payable | 70.6 | 76.8 | |||||
Workers’ compensation, vehicle-related and product liability, medical/disability (see Note S) | 90.3 | 48.7 | |||||
| Sales promotions | 47.2 | 35.2 | |||||
Liabilities associated with stock-based compensation plans (see Note K) | 15.7 | 19.0 | |||||
| Accrued interest | 10.9 | 8.8 | |||||
| General taxes, excluding income taxes | 19.1 | 16.0 | |||||
| Environmental reserves | 3.0 | 3.5 | |||||
| Other | 46.2 | 46.5 | |||||
| $ | 303.4 | $ | 257.7 | ||||
| Other current liabilities | |||||||
| Dividends payable | $ | 47.5 | $ | 45.4 | |||
| Customer deposits | 12.7 | 14.4 | |||||
| Sales tax payable | 4.0 | 5.2 | |||||
Derivative financial instruments (see Note R) | 1.8 | 4.1 | |||||
Liabilities associated with stock-based compensation plans (see Note K) | 2.4 | 1.8 | |||||
| Outstanding checks in excess of book balances | 11.0 | 17.8 | |||||
| Other | 9.3 | 5.5 | |||||
| $ | 88.7 | $ | 94.2 | ||||
| Other long-term liabilities | |||||||
Liability for pension benefits (see Note L) | $ | 57.6 | $ | 79.6 | |||
Liabilities associated with stock-based compensation plans (see Note K) | 36.4 | 31.2 | |||||
Deemed repatriation tax payable (see Note M) | 61.9 | — | |||||
| Net reserves for tax contingencies | 12.3 | 15.1 | |||||
Deferred compensation (see Note K) | 17.1 | 18.0 | |||||
| Other | 17.6 | 29.1 | |||||
| $ | 202.9 | $ | 173.0 | ||||
90
I—Long-Term Debt
Long-term debt, interest rates and due dates at December 31 are as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||||||
Year-end Interest Rate | Due Date Through | Balance | Year-end Interest Rate | Due Date Through | Balance | ||||||||||||
| Term notes (1) | 3.7 | % | 2027 | $ | 1,239.1 | 3.8 | % | 2024 | $ | 745.3 | |||||||
| Industrial development bonds, principally variable interest rates | 1.3 | % | 2030 | 6.2 | .9 | % | 2030 | 12.5 | |||||||||
| Commercial paper (2) | 2022 | — | 2021 | 195.9 | |||||||||||||
| Capitalized leases (primarily machinery, vehicle and office equipment) | 5.7 | 5.7 | |||||||||||||||
| Other, partially secured | .7 | .4 | |||||||||||||||
| 1,251.7 | 959.8 | ||||||||||||||||
| Less current maturities | 153.8 | 3.6 | |||||||||||||||
| $ | 1,097.9 | $ | 956.2 | ||||||||||||||
Maturities of long-term debt are as follows (1):
| Year ended December 31 | |||
| 2018 | $ | 153.8 | |
| 2019 | 1.3 | ||
| 2020 | 1.3 | ||
| 2021 | 1.5 | ||
| 2022 | 298.5 | ||
| Thereafter | 795.3 | ||
| $ | 1,251.7 | ||
(1) Includes unamortized discounts and deferred loan costs.
(2) There was no outstanding commercial paper at December 31, 2017. The weighted average interest rate on the balance of commercial paper outstanding at December 31, 2016 was 1.0%. The weighted average interest rate for the net commercial paper activity during the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 was 1.4% and .8%, respectively.
We can raise cash by issuing up to $800 of commercial paper through a program that is backed by a $800 revolving credit facility with a syndicate of 14 lenders. In November 2017, we increased the borrowing capacity under the facility from $750 to $800 and extended the term by one year to 2022. The credit facility allows us to issue total letters of credit up to $250. When we issue letters of credit in this manner, our capacity under the facility, and consequently, our ability to issue commercial paper, is reduced by a corresponding amount. We had no outstanding letters of credit under the facility at year end for the periods presented.
91
Amounts outstanding at December 31 related to our commercial paper program were:
| 2017 | 2016 | ||||||
| Total program authorized | $ | 800.0 | $ | 750.0 | |||
| Commercial paper outstanding (classified as long-term debt) | — | (195.9 | ) | ||||
| Letters of credit issued under the credit facility | — | — | |||||
| Total program usage | — | (195.9 | ) | ||||
| Total program available | $ | 800.0 | $ | 554.1 | |||
The revolving credit facility and certain other long-term debt contain restrictive covenants which, among other things, limit a) the total amount of indebtedness to 65% of our total capitalization (each as defined in the revolving credit facility), b) the amount of our total secured debt to 15% of our total consolidated assets, and c) our ability to sell, lease, transfer or dispose of all or substantially all of total consolidated assets. We have remained well within compliance with all such covenants.
Generally we may elect one of four types of borrowing under the revolving credit facility, which determines the rate of interest to be paid on the outstanding principal balance. The interest rate would typically be commensurate with the currency borrowed and the term of the borrowing, as well as either i.) a competitive variable or fixed rate, or ii.) various published rates plus a pre-defined spread.
We are required to periodically pay accrued interest on any outstanding principal balance under the revolving credit facility at different time intervals based upon the elected interest rate and the elected interest period. Any outstanding principal under this facility will be due upon the maturity date. We may also terminate or reduce the lending commitments under this facility, in whole or in part, upon three business days’ notice.
J—Lease Obligations
We lease certain operating facilities, most of our automotive and trucking equipment and various other assets. Lease terms, including purchase options, renewals and maintenance costs, vary by lease.
Total rental expense for the periods presented was as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Continuing operations | $ | 51.3 | $ | 51.2 | $ | 51.4 | |||||
| Discontinued operations | $ | — | $ | — | $ | .5 | |||||
Future minimum rental commitments for all long-term non-cancelable operating leases are as follows:
| Year ended December 31 | |||
| 2018 | $ | 34.5 | |
| 2019 | 27.1 | ||
| 2020 | 22.0 | ||
| 2021 | 18.4 | ||
| 2022 | 13.0 | ||
| Thereafter | 15.3 | ||
| $ | 130.3 | ||
The above lease obligations expire at various dates through 2025. Aggregate rental commitments above include renewal amounts where it is our intention to renew the lease.
K—Stock-Based Compensation
We use various forms of share-based compensation which are summarized below. One stock unit is equivalent to one common share for accounting and earnings per share purposes. Shares are issued from treasury for the majority of our stock plans’ activity. All share information is presented in millions.
92
Stock options and stock units are granted pursuant to our Flexible Stock Plan (the "Plan"). Each option counts as one share against the shares available under the Plan, but each share granted for any other awards will count as three shares against the Plan.
At December 31, 2017, the following common shares were authorized for issuance under the Plan:
| Shares Available for Issuance | Maximum Number of Authorized Shares | ||||
| Unexercised options | 1.9 | 1.9 | |||
| Outstanding stock units—vested | 3.7 | 7.6 | |||
| Outstanding stock units—unvested | .7 | 1.9 | |||
| Available for grant | 8.5 | 8.5 | |||
| Authorized for issuance at December 31, 2017 | 14.8 | 19.9 | |||
The following table recaps the impact of stock-based compensation (including discontinued operations) on the results of operations for each of the periods presented:
| Year Ended December 31 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| To Be Settled With Stock | To Be Settled In Cash | To Be Settled With Stock | To Be Settled In Cash | To Be Settled With Stock | To Be Settled In Cash | ||||||||||||||||||
| Options (1): | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of the grant date fair value | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1.0 | $ | — | $ | .2 | $ | — | |||||||||||
| Cash payments in lieu of options | — | — | — | 1.0 | — | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based retirement plans contributions (2) | 5.5 | 1.2 | 6.7 | 1.3 | 7.0 | 1.3 | |||||||||||||||||
| Discounts on various stock awards: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred Stock Compensation Program (1) | 2.1 | — | 2.0 | — | 1.9 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based retirement plans (2) | 1.4 | — | 1.5 | — | 1.4 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Discount Stock Plan (6) | 1.1 | — | 1.0 | — | 1.0 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Performance Stock Unit (PSU) awards (3) (7) | 5.4 | (1.4 | ) | 4.8 | 6.5 | 8.3 | 10.6 | ||||||||||||||||
| Profitable Growth Incentive (PGI) awards (4) (7) | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.0 | 6.0 | 5.9 | |||||||||||||||||
| Restricted Stock Units (RSU) awards (5) | 2.5 | — | 2.8 | — | 3.5 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Other, primarily non-employee directors restricted stock | .9 | — | 1.0 | — | 1.2 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Total stock-related compensation expense | 20.3 | $ | 1.2 | 22.2 | $ | 9.8 | 30.5 | $ | 18.8 | ||||||||||||||
| Employee contributions for above stock plans | 16.3 | 14.9 | 14.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total stock-based compensation | $ | 36.6 | $ | 37.1 | $ | 45.2 | |||||||||||||||||
| Tax benefits on stock-based compensation expense | $ | 7.3 | $ | 8.1 | $ | 11.6 | |||||||||||||||||
| Tax benefits on stock-based compensation payments * | 9.9 | 18.2 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total tax benefits associated with stock-based compensation | $ | 17.2 | $ | 26.3 | $ | 11.6 | |||||||||||||||||
* In the first quarter of 2016 we adopted ASU 2016-09, Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting. This ASU provides that the tax effects of stock-based awards must be treated as discrete items affecting the tax rate in the interim reporting period in which the tax deductions occur.
93
The following table recaps the impact of stock-based compensation on assets and liabilities for each of the periods presented:
| 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current | Long-term | Total | Current | Long-term | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
| Assets: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diversified investments associated with the Executive Stock Unit Program (2) | $ | 2.4 | $ | 31.6 | $ | 34.0 | $ | 1.8 | $ | 25.0 | $ | 26.8 | |||||||||||
| Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive Stock Unit Program (2) | $ | 2.4 | $ | 32.0 | $ | 34.4 | $ | 1.8 | $ | 23.8 | $ | 25.6 | |||||||||||
| Performance Stock Unit award (3) | 6.7 | 1.9 | 8.6 | 9.7 | 5.6 | 15.3 | |||||||||||||||||
| Profitable Growth Incentive award (4) | 2.0 | 2.5 | 4.5 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 3.4 | |||||||||||||||||
| Other - primarily timing differences between employee withholdings and related employer contributions to be submitted to various plans' trust accounts | 7.0 | — | 7.0 | 7.7 | — | 7.7 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total liabilities associated with stock-based compensation | $ | 18.1 | $ | 36.4 | $ | 54.5 | $ | 20.8 | $ | 31.2 | $ | 52.0 | |||||||||||
(1) Stock Option Grants
We have historically granted stock options in the following areas:
| • | On a discretionary basis to a broad group of employees |
| • | In conjunction with our Deferred Compensation Program |
| • | As compensation to outside directors |
Options granted to a broad group of employees on a discretionary basis
Options are now offered only in conjunction with the Deferred Compensation Program discussed below, and for a few key executive awards. Prior to 2013, we granted stock options annually on a discretionary basis to a broad group of employees. Options generally become exercisable in one-third increments at 18 months, 30 months and 42 months after the date of grant. Options have a maximum term of ten years and the exercise prices are equal to Leggett’s closing stock price on the grant date.
Grant date fair values are calculated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model and are amortized by the straight-line method over the options’ total vesting period, except for employees who are retirement eligible. Expense for employees who are retirement eligible is recognized immediately. A person is retirement eligible if the employee is age 65, or age 55 with 20 years of Company service.
Deferred Compensation Program
We offer a Deferred Compensation Program under which key managers and outside directors may elect to receive stock options, stock units or interest-bearing cash deferrals in lieu of cash compensation:
| • | Stock options under this program are granted in the last month of the year prior to the year the compensation is earned. The number of options granted equals the deferred compensation times five, divided by the stock’s market price on the date of grant. The option has a 10-year term. It vests as the associated compensation is earned and becomes exercisable beginning 15 months after the grant date. Stock is issued when the option is exercised. |
| • | Deferred stock units (DSU) under this program are acquired every two weeks (when the compensation would have otherwise been paid) at a 20% discount to the market price of our common stock on each acquisition date, and they vest immediately. Expense is recorded as the compensation is earned. Stock units earn dividends at the same rate as cash dividends paid on our common stock. These dividends are used to acquire stock units at a 20% discount. Stock units are |
94
converted to common stock and distributed in accordance with the participant’s pre-set election. However, stock units may be settled in cash at our discretion. Participants must begin receiving distributions no later than ten years after the effective date of the deferral and installment distributions cannot exceed ten years.
| • | Interest-bearing cash deferrals under this program are reported in Other long-term liabilities on the balance sheet and are disclosed in Note H. |
| Options | Units | Cash | |||||||||
| Aggregate amount of compensation deferred during 2017 | $ | .4 | $ | 9.3 | $ | .8 | |||||
Stock Option Summary
Stock option information for the plans discussed above for the periods presented is as follows:
Employee Stock Options | Deferred Compensation Options | Other-Primarily Outside Directors' Options * | Total Options | Weighted Average Exercise Price per Share | Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life in Years | Aggregate Intrinsic Value | |||||||||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2016 | 2.1 | .2 | — | 2.3 | $ | 23.13 | |||||||||||||||
| Granted** | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Exercised | (.4 | ) | — | — | (.4 | ) | 18.64 | ||||||||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2017 | 1.7 | .2 | — | 1.9 | $ | 24.08 | 3.5 | $ | 45.0 | ||||||||||||
| Vested or expected to vest | 1.9 | $ | 24.08 | 3.5 | $ | 45.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Exercisable (vested) at December 31, 2017 | 1.8 | $ | 22.93 | 3.2 | $ | 44.7 | |||||||||||||||
* A small number of options related to this plan (less than .1) were outstanding at December 31, 2017.
** A small number of options (less than .1) were granted for the deferred compensation program during 2017.
Additional information related to stock option activity for the periods presented is as follows:
| Year Ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Total intrinsic value of stock options exercised | $ | 11.7 | $ | 27.7 | $ | 17.1 | |||||
| Cash received from stock options exercised | 2.6 | 4.9 | 8.3 | ||||||||
| Total fair value of stock options vested | 1.2 | .1 | 1.3 | ||||||||
The following table summarizes fair values calculated (and assumptions utilized) using the Black-Scholes option pricing model.
| Year Ended December 31 | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Aggregate grant date fair value | $ | — | $ | 1.4 | $ | .9 | ||||||
| Weighted-average per share grant date fair value | $ | 9.21 | $ | 10.79 | $ | 10.06 | ||||||
| Risk-free interest rate | 2.3 | % | 2.2 | % | 2.1 | % | ||||||
| Expected life in years | 6.0 | 7.9 | 7.5 | |||||||||
| Expected volatility (over expected life) | 19.8 | % | 30.0 | % | 30.5 | % | ||||||
| Expected dividend yield (over expected life) | 3.1 | % | 3.0 | % | 3.0 | % | ||||||
The risk-free rate is determined based on U.S. Treasury yields in effect at the time of grant for maturities equivalent to the expected life of the option. The expected life of the option (estimated average period of time the option will be outstanding) is estimated based on the historical exercise behavior of employees, with executives displaying somewhat longer holding periods than other employees. Expected volatility is based on historical volatility through the grant date, measured daily for a time period equal to the option’s expected life. The expected dividend yield is estimated based on the dividend yield at the time of grant.
95
(2) Stock-Based Retirement Plans
We have two stock-based retirement plans: the tax-qualified Stock Bonus Plan (SBP) for non-highly compensated employees, and the non-qualified Executive Stock Unit Program (ESUP) for highly compensated employees. We make matching contributions to both plans. In addition to the automatic 50% match, we will make another matching contribution of up to 50% of the employee’s contributions for the year if certain profitability levels, as defined in the SBP and the ESUP, are obtained.
| • | Participants in the SBP may contribute up to 6% of their compensation above a certain threshold to purchase Leggett stock or other investment alternatives at market prices. Employees are allowed to fully diversify their employee deferral accounts immediately and their employer matching accounts after three years of service. Dividends earned on Company stock held in the SBP are reinvested or paid in cash at the participant’s election. |
| • | Participants in the ESUP may contribute up to 10% (depending upon salary level) of their compensation above the same threshold applicable to the SBP. Participant contributions are credited to a diversified investment account established for the participant, and we make premium contributions to the diversified investment accounts equal to 17.65% of the participant’s contribution. A participant’s diversified investment account balance is adjusted to mirror the investment experience, whether positive or negative, of the diversified investments selected by the participant. Participants may change investment elections in the diversified investment accounts, but cannot purchase Company common stock or stock units. The diversified investment accounts consist of various mutual funds and retirement target funds and are unfunded, unsecured obligations of the Company that will be settled in cash. Both the assets and liabilities associated with this program are presented in the table above and are adjusted to fair value at each reporting period. |
Company matching contributions to the ESUP, including dividend equivalents, are used to acquire stock units at 85% of the common stock market price on the acquisition date. Stock units are converted to common stock at a 1-to-1 ratio upon distribution from the program and may be settled in cash at our discretion.
Company matches in the SBP and ESUP fully vest upon three and five years, respectively, of cumulative service, subject to certain participation requirements. Distributions under both plans are triggered by an employee’s retirement, death, disability or separation from Leggett.
Information for employee contributions the year ended December 31 for these plans was as follows. See the stock-based compensation table above for information regarding employer contributions.
| SBP 2017 | ESUP 2017 | ||||||
| Employee contributions | $ | 3.3 | $ | 4.5 | |||
| Less diversified contributions | .7 | 4.5 | |||||
| Total employee stock contributions | $ | 2.6 | $ | — | |||
| Employer premium contribution to diversified investment accounts | $ | .8 | |||||
| Shares purchased by employees and company match | .1 | ||||||
Details regarding stock unit activity for the ESUP plan are reflected in the stock units summary table below.
(3) Performance Stock Unit Awards
We also grant PSU awards in the first quarter of each year to selected officers and other key managers. These awards contain the following conditions:
| • | A service requirement—Awards generally “cliff” vest three years following the grant date; and |
| • | A market condition—Awards are based on our Total Shareholder Return [TSR = (Change in Stock Price + Dividends) / Beginning Stock Price] as compared to the TSR of a group of peer companies. The peer group consists of all the companies in the Industrial, Materials and Consumer Discretionary sectors of the S&P 500 and S&P Midcap 400 (approximately 320 companies). Participants will earn from 0% to 175% of the base award depending upon how our TSR ranks within the peer group at the end of the 3-year performance period. |
Grant date fair values are calculated using a Monte Carlo simulation of stock and volatility data for Leggett and each of the comparator companies. Grant date fair values are amortized using the straight-line method over the three-year vesting period.
96
Below is a summary of the number of shares and related grant date fair value of PSU’s for the periods presented:
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Total shares base award | .1 | .1 | .2 | ||||||||
| Grant date per share fair value | $ | 50.75 | $ | 40.16 | $ | 42.22 | |||||
| Risk-free interest rate | 1.5 | % | 1.3 | % | 1.1 | % | |||||
| Expected life in years | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | ||||||||
| Expected volatility (over expected life) | 19.5 | % | 19.2 | % | 19.8 | % | |||||
| Expected dividend yield (over expected life) | 2.8 | % | 3.1 | % | 2.9 | % | |||||
| Three-Year Performance Cycle | ||||||||||||||
| Award Year | Completion Date | TSR Performance Relative to the Peer Group (1%=Best) | Payout as a Percent of the Base Award | Number of Shares Distributed | Cash Portion | Distribution Date | ||||||||
| 2013 | December 31, 2015 | 27 | 165.4% | .4 million | $ | 8.5 | First quarter 2016 | |||||||
| 2014 | December 31, 2016 | 10 | 175.0% | .4 million | $ | 9.8 | First quarter 2017 | |||||||
| 2015 | December 31, 2017 | 57 | 61.0% | — | $ | 6.9 | First quarter 2018 | |||||||
We intend to pay out 65% of awards in shares of our common stock and 35% in cash, although we reserve the right to pay up to 100% in cash. We elected to pay 100% of the 2015 award (paid in first quarter 2018) in cash. The cash portion is recorded as a liability and is adjusted to fair value at each reporting period.
(4) Profitable Growth Incentive Awards
The PGI awards are issued to certain key management employees as growth performance stock units (GPSUs). The GPSUs vest (0% to 250%) at the end of a two-year performance period. Vesting is based on the Company's or applicable profit center's revenue growth (adjusted by a GDP factor when applicable) and EBITDA margin over a two-year performance period. The 2015 through 2017 base target PGI awards were less than .1 shares each year. If earned, we intend to pay half in shares of our common stock and half in cash, although we reserve the right to pay up to 100% in cash. Both components are recorded as liabilities and adjusted to fair value at each reporting period. We elected to pay 100% of the 2016 award (to be paid in March 2018) in cash.
| Two-Year Performance Cycle | ||||||||||||
| Award Year | Completion Date | Average Payout as a Percent of the Base Award | Estimated Number of Shares | Cash Portion | Expected Distribution Date | |||||||
| 2014 | December 31, 2015 | 224.7% | .2 million | $ | 6.7 | First quarter 2016 | ||||||
| 2015 | December 31, 2016 | 36.0% | < .1 million | $ | .8 | First quarter 2017 | ||||||
| 2016 | December 31, 2017 | 44.0% | — | $ | 2.0 | First quarter 2018 | ||||||
(5) Restricted Stock Unit Awards
RSU awards are generally granted as follows:
| • | Annual awards to selected managers, and |
| • | On a discretionary basis to selected employees |
| • | As compensation for outside directors, who have a choice to receive RSUs or restricted stock |
The value of these awards is determined by the stock price on the day of the award, and expense is recognized over the vesting period.
97
Stock Units Summary
As of December 31, 2017, the unrecognized cost of non-vested stock units that is not adjusted to fair value was $8.7 with a weighted-average remaining contractual life of 1 year.
Stock unit information for the plans discussed above is presented in the table below.
| DSU | ESUP | PSU* | RSU | PGI** | Total Units | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value per Unit | Aggregate Intrinsic Value | ||||||||||||||||||
| Non-vested at December 31, 2016 | — | — | .9 | .1 | .2 | 1.2 | $ | 20.30 | |||||||||||||||||
| Granted based on current service | .2 | .2 | — | .1 | — | .5 | 48.12 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Granted based on future conditions | — | — | .2 | — | .1 | .3 | 24.97 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vested | (.2 | ) | (.2 | ) | (.4 | ) | (.1 | ) | — | (.9 | ) | 31.57 | |||||||||||||
| Difference between maximum and actual payout | — | — | — | — | (.1 | ) | (.1 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Award elected to be paid in cash | — | — | (.3 | ) | — | (.1 | ) | (.4 | ) | 19.32 | |||||||||||||||
| Total non-vested at December 31, 2017 | — | — | .4 | .1 | .1 | .6 | $ | 19.56 | $ | 30.8 | |||||||||||||||
| Fully vested shares available for issuance at December 31, 2017 | 3.7 | $ | 178.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| * | PSU awards are presented at 175% (i.e., maximum) payout |
** PGI awards are presented at 250% (i.e., maximum) payout
| Year Ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Total intrinsic value of vested stock units converted to common stock | $ | 22.7 | $ | 24.8 | $ | 27.7 | |||||
(6) Discount Stock Plan
Under the Discount Stock Plan (DSP), a tax-qualified §423 stock purchase plan, eligible employees may purchase shares of Leggett common stock at 85% of the closing market price on the last business day of each month. Shares are purchased and issued on the last business day of each month and generally cannot be sold or transferred for one year.
| Average 2017 purchase price per share (net of discount) | $ | 41.75 | |
| 2017 number of shares purchased by employees | .1 | ||
| Shares purchased since inception in 1982 | 23.0 | ||
| Maximum shares under the plan | 27.0 | ||
(7) Adoption of New Performance Stock Unit Forms of Award
In November 2017, the Compensation Committee approved changes to merge the PSU and PGI Award programs for the 2018 award.
The new awards will vest at the end of a 3-year performance period based upon the following:
| • | Relative TSR - 50% of each PSU award will vest based upon on the Company’s TSR compared to a peer group with conditions similar to the previous years’ grants discussed above. |
| • | EBIT CAGR - 50% of each PSU award will vest based upon the Company’s or applicable Segments’ compound annual growth rate of EBIT in the third fiscal year of the performance period compared to the applicable EBIT in the fiscal year immediately preceding the performance period. |
98
50% of the vested PSU award will be paid out in cash, and the Company intends to pay out the remaining 50% in shares of the Company’s common stock, although the Company reserves the right to pay up to 100% in cash. The maximum payout is 200% of the base awards.
In connection with the decision to move a significant portion of the long-term incentive opportunity from a 2-year to a 3-year performance period by eliminating PGI awards, we will also grant participants a one-time transition PSU award in 2018 based upon EBIT CAGR over a two-year performance period.
L—Employee Benefit Plans
The Consolidated Balance Sheets reflect a net liability for the funded status of our domestic and foreign defined benefit pension plans. Our U.S. plans (comprised primarily of three significant plans) represent approximately 87% of our pension benefit obligation in each of the periods presented. Participants in one of the significant domestic plans have stopped earning benefits; this plan is referred to as "frozen" in the following narrative.
A summary of our pension obligations and funded status as of December 31 is as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Change in benefit obligation | |||||||||||
| Benefit obligation, beginning of period | $ | 293.0 | $ | 290.3 | $ | 343.0 | |||||
| Service cost | 4.6 | 4.4 | 4.3 | ||||||||
| Interest cost | 10.9 | 11.3 | 12.6 | ||||||||
| Plan participants’ contributions | .7 | .7 | .7 | ||||||||
| Actuarial loss (gain) | 4.0 | 9.8 | (17.4 | ) | |||||||
| Benefits paid | (15.2 | ) | (19.1 | ) | (13.9 | ) | |||||
| Settlements | (59.8 | ) | — | (35.7 | ) | ||||||
| Foreign currency exchange rate changes | 3.3 | (4.4 | ) | (3.3 | ) | ||||||
Benefit obligation, end of period 1 | 241.5 | 293.0 | 290.3 | ||||||||
| Change in plan assets | |||||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets, beginning of period | 214.1 | 207.5 | 258.9 | ||||||||
| Actual return on plan assets | 28.3 | 18.9 | (1.7 | ) | |||||||
| Employer contributions | 14.9 | 9.8 | 1.8 | ||||||||
| Plan participants’ contributions | .7 | .7 | .7 | ||||||||
| Benefits paid | (15.2 | ) | (19.1 | ) | (13.9 | ) | |||||
| Settlements | (59.8 | ) | — | (35.7 | ) | ||||||
| Foreign currency exchange rate changes | 2.7 | (3.7 | ) | (2.6 | ) | ||||||
| Fair value of plan assets, end of period | 185.7 | 214.1 | 207.5 | ||||||||
| Net funded status | $ | (55.8 | ) | $ | (78.9 | ) | $ | (82.8 | ) | ||
| Funded status recognized in the Consolidated Balance Sheets | |||||||||||
| Other assets—sundry | $ | 2.2 | $ | 1.1 | $ | 1.3 | |||||
| Other current liabilities | (.4 | ) | (.4 | ) | (.4 | ) | |||||
| Other long-term liabilities | (57.6 | ) | (79.6 | ) | (83.7 | ) | |||||
| Net funded status | $ | (55.8 | ) | $ | (78.9 | ) | $ | (82.8 | ) | ||
1 The benefit obligation at December 31, 2017, decreased as compared to December 31, 2016, primarily due to the settlement of $59.8 of pension obligations for our U.S. plans through our annuity purchase transaction as discussed in more detail below.
Our accumulated benefit obligation was not materially different from our projected benefit obligation for the periods presented.
99
Included in the above plans is a subsidiary’s unfunded supplemental executive retirement plan. This is a non-qualified plan, and these benefits are secured by insurance policies that are not included in the plan’s assets. Cash surrender values associated with these policies were approximately $2.0 at December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015.
Comprehensive Income
Amounts and activity included in accumulated other comprehensive income associated with pensions are reflected below:
| December 31, 2016 | 2017 Amortization 1 | 2017 Net Actuarial loss | 2017 Foreign currency exchange rates change | 2017 Income tax change | December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss (gain) (before tax) | $ | 90.6 | $ | (19.9 | ) | $ | (10.9 | ) | $ | .7 | $ | (6.9 | ) | $ | 53.6 | ||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | (33.4 | ) | — | — | — | 18.3 | (15.1 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (net of tax) | $ | 57.2 | $ | (19.9 | ) | $ | (10.9 | ) | $ | .7 | $ | 11.4 | $ | 38.5 | |||||||||
1 Includes a $15.3 settlement loss, discussed in more detail below.
Of the amounts in accumulated other comprehensive income as of December 31, 2017, the portions expected to be recognized as components of net periodic pension cost in 2018 are as follows:
| Net loss | $ | 2.7 | |
Net Pension (Expense) Income
Components of net pension (expense) income for the years ended December 31 were as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Service cost | $ | (4.6 | ) | $ | (4.4 | ) | $ | (4.3 | ) | ||
| Interest cost | (10.9 | ) | (11.3 | ) | (12.6 | ) | |||||
| Expected return on plan assets | 13.4 | 12.9 | 16.5 | ||||||||
| Recognized net actuarial loss | (4.6 | ) | (4.5 | ) | (5.2 | ) | |||||
| Settlements | (15.3 | ) | — | (12.1 | ) | ||||||
| Net pension (expense) income | $ | (22.0 | ) | $ | (7.3 | ) | $ | (17.7 | ) | ||
| Weighted average assumptions for pension costs: | |||||||||||
| Discount rate used in net pension costs | 3.8 | % | 4.1 | % | 3.8 | % | |||||
| Rate of compensation increase used in pension costs | 3.5 | % | 3.5 | % | 3.5 | % | |||||
| Expected return on plan assets | 6.5 | % | 6.5 | % | 6.6 | % | |||||
| Weighted average assumptions for benefit obligation: | |||||||||||
| Discount rate used in benefit obligation | 3.4 | % | 3.8 | % | 4.1 | % | |||||
| Rate of compensation increase used in benefit obligation | 3.0 | % | 3.5 | % | 3.5 | % | |||||
Assumptions used for U.S. and international plans were not significantly different.
We use the average of the Citigroup Pension Discount Curve rate and Merrill Lynch AA-AAA 10-year Bond Index rate to determine the discount rate used for our significant pension plans (rounded to the nearest 25 basis points). The Citigroup Pension Discount Curve rate is a calculated rate using yearly spot rates matched against expected future benefit payments. The Merrill Lynch Index rate is based on the weighted average yield of a portfolio of high grade Corporate Bonds with an average duration approximating the plans’ projected benefit payments, adjusted for any callable bonds included in the portfolio. The discount rates used for our other, primarily foreign, plans are based on rates appropriate for the respective country and the plan obligations.
The overall, expected long-term rate of return is based on each plan’s historical experience and our expectations of future returns based upon each plan’s investment holdings, as discussed below.
100
Pension Plan Assets
The fair value of our major categories of pension plan assets is disclosed below using a three level valuation hierarchy that separates fair value valuation techniques into the following categories:
| • | Level 1: Quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets. |
| • | Level 2: Other significant inputs observable either directly or indirectly (including quoted prices for similar securities, interest rates, yield curves, credit risk, etc.). |
| • | Level 3: Unobservable inputs that are not corroborated by market data. |
Presented below are our major categories of investments for the periods presented:
| Year Ended December 31, 2017 | Year Ended December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Assets Measured at NAV1 | Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Assets Measured at NAV1 | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mutual and pooled funds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed income | $ | 38.2 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 38.2 | $ | 46.4 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 46.4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Equities | 103.2 | — | — | — | 103.2 | 120.6 | — | — | — | 120.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stable value funds | — | 25.8 | — | — | 25.8 | — | 35.1 | — | — | 35.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Money market funds, cash and other | — | — | — | 18.5 | 18.5 | — | — | — | 12.0 | 12.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total investments at fair value | $ | 141.4 | $ | 25.8 | $ | — | $ | 18.5 | $ | 185.7 | $ | 167.0 | $ | 35.1 | $ | — | $ | 12.0 | $ | 214.1 | |||||||||||||||||||
1Certain investments that are measured at fair value using the net asset value (NAV) per share (or its equivalent) practical expedient have not been classified in the fair value hierarchy.
Plan assets are invested in diversified portfolios of equity, debt and government securities, as well as a stable value fund. The aggregate allocation of these investments is as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | ||||
| Asset Category | |||||
| Equity securities | 55 | % | 56 | % | |
| Debt securities | 21 | 22 | |||
| Stable value funds | 14 | 16 | |||
| Other, including cash | 10 | 6 | |||
| Total | 100 | % | 100 | % | |
Our investment policy and strategies are established with a long-term view in mind. We strive for a sufficiently diversified asset mix to minimize the risk of a material loss to the portfolio value due to the devaluation of any single investment. In determining the appropriate asset mix, our financial strength and ability to fund potential shortfalls that might result from poor investment performance are considered. Approximately 50% of our significant plans (the "frozen plans") are employing a Liability Driven Investment strategy and have a target allocation of 60% fixed income and 40% equities. The remaining significant plans (the "active" plans) have a target allocation of 75% equities and 25% fixed income, as historical equity returns have tended to exceed bond returns over the long term.
Assets of our domestic plans represent the majority of plan assets and are allocated to seven different investments.
Six are mutual funds, all of which are passively managed low-cost index funds, and include:
| • | U.S. Total Stock Market Index: Large-, mid-, and small-cap equity diversified across growth and value styles. |
| • | U.S. Large-Cap Index: Large-cap equity diversified across growth and value styles. |
| • | U.S. Small-Cap Index: Small-cap equity diversified across growth and value styles. |
101
| • | World ex US Index: International equity; broad exposure across developed and emerging non-US equity markets around the world. |
| • | Long-term Bond Index: Diversified exposure to the long-term, investment-grade U.S. bond market. |
| • | Extended Duration Treasury Index: Diversified exposure to U.S. treasuries with maturities of 20-30 years. |
The Stable value fund consists of a fixed income portfolio offering consistent return and protection against interest rate volatility.
Settlements
In December 2017, to reduce the size of our pension benefit obligation, reduce volatility of contribution requirements in future years, and also reduce pension-related operational expenses over the long-term, we completed an annuity purchase transaction for pensioners that were currently receiving a small monthly benefit. As part of this annuity purchase, we settled $59.8 of pension obligations for U.S. retirees. This was paid from plan assets and did not require a cash contribution from the Company. As a result of these settlements, we recorded settlement losses of $15.3 ($9.5 net of tax) reflecting the accelerated recognition of unamortized losses in the plan proportionate to the obligation that was settled. These settlement charges were recorded in "Cost of goods sold" and "Selling and administrative expenses" with a corresponding balance sheet reduction in "Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss)" for the year ended December 31, 2017.
In October 2015, we offered a voluntary one-time lump-sum payment option to certain eligible terminated vested participants in our U.S. defined benefit pension plans that, when accepted, settled our obligation to them. The program provided participants with a one-time choice to receive a lump-sum settlement of their remaining pension benefit. As part of this voluntary lump-sum program, we settled $35.7 of pension obligations for U.S. retirees in 2015. This was paid from plan assets and did not require a cash contribution from the company. As a result of these settlements, we recorded settlement losses of $12.1 ($7.5 net of tax) reflecting the accelerated recognition of unamortized losses in the plan proportionate to the obligation that was settled. These settlement charges were recorded in "Cost of goods sold" and "Selling and administrative expenses" with a corresponding balance sheet reduction in "Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss)" for the year ended December 31, 2015.
Future Contributions and Benefit Payments
We expect to contribute approximately $21.0 to our defined benefit pension plans in 2018, some of which are discretionary contributions.
Estimated benefit payments expected over the next ten years are as follows:
| 2018 | $ | 11.2 | |
| 2019 | 11.6 | ||
| 2020 | 11.9 | ||
| 2021 | 12.1 | ||
| 2022 | 12.3 | ||
| 2023-2027 | 66.5 | ||
The December 2017 annuity purchase transaction (discussed above) reduced the amount of estimated benefit payments expected over the next ten years as of December 31, 2017 as compared to the total reported at December 31, 2016.
Other Benefit Plans
Total expense for defined contribution plans was as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Defined contribution plans | $ | 6.3 | $ | 6.1 | $ | 6.8 | |||||
We have limited participation in two union-sponsored, defined benefit, multi-employer pension plans. These plans are not administered by us, and contributions are determined in accordance with provisions of negotiated labor contracts. Aggregate contributions to these plans were less than $.8 for each of the years presented.
102
In addition to regular contributions, we could be obligated to pay additional contributions (known as complete or partial withdrawal liabilities) if a plan has unfunded vested benefits. Factors that could impact the funded status of these plans include investment performance, changes in the participant demographics, financial stability of contributing employers and changes in actuarial assumptions. Withdrawal liability triggers could include a plan's termination, a withdrawal of substantially all employers, or our voluntary withdrawal from the plan (such as decision to close a facility or the dissolution of a collective bargaining unit). We have a very small share of the liability among the participants of these plans. Based upon the information available from plan administrators, both of the multi-employer plans in which we participate are underfunded and estimate our aggregate share of potential withdrawal liability for both plans to be $19.3. We have not recorded any material withdrawal liabilities for the years presented.
M—Income Taxes
On December 22, 2017, President Trump signed into law the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), enacting significant changes to the U.S. Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, including a reduction in the maximum U.S. federal corporate income tax rate from 35% to 21%, the transition of U.S. taxation from a worldwide tax system to a territorial system, various anti-avoidance tax provisions including a potential "global intangible low-taxed income" (GILTI) inclusion, and the imposition of a one-time tax associated with the mandatory deemed repatriation of foreign earnings not previously taxed by the U.S. Although these provisions are generally applicable for years after December 31, 2017, several impacted our 2017 earnings, including the one-time deemed repatriation tax, additional foreign withholding taxes for expected future cash repatriations, and the revaluation of our U.S. deferred taxes at the new, lower, federal tax rate. Accordingly, we recorded a provisional $50.4 net tax charge in the fourth quarter of 2017 related to these items.
The amount recorded is our best estimate, based on our current understanding of TCJA and the guidance currently available, but should be considered provisional in accordance with Staff Accounting Bulletin (SAB) 118, which addresses the application of U.S. GAAP where a registrant does not have the necessary information available, prepared, or analyzed (including computations) in reasonable detail to complete the accounting for certain income tax effects related to TCJA. We have elected to apply the provisions of SAB 118 related to our continued analysis of the impacts from TCJA including, but not limited to, the deemed repatriation tax, the revaluation of our U.S. deferred taxes, the taxes provided for expected foreign cash repatriations, and the ongoing evaluation of our permanently reinvested earnings (discussed below). The ultimate impact may differ from the provisional amounts we have recorded, possibly materially, due to, among other things, additional analysis, changes in interpretations and assumptions, additional regulatory guidance that may be issued, and actions we may take as a result of TCJA. Our accounting will be finalized no later than the fourth quarter of 2018.
Additionally, because of the complexity of the new GILTI rules, we are continuing to evaluate this provision and the application of ASC 740. We have not yet made any adjustments related to potential GILTI tax in our financial statements, nor have we made any policy decision regarding whether to record deferred taxes on GILTI. We will do so no later than the fourth quarter of 2018.
The 2017 impact from TCJA is presented below as an increase or (decrease) in the noted line items from our Consolidated Statements of Operations and Consolidated Balance Sheets:
| Consolidated Statements of Operations | Year Ended December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | U.S. Deferred Tax Revaluation | Deemed Repatriation Tax | Additional Foreign Withholding Taxes | Other Items, net | Total | ||||||||||
| Income taxes | $ | (26.1 | ) | $ | 67.3 | $ | 9.0 | $ | .2 | $ | 50.4 | ||||
| Impact on effective tax rate | (6.0 | )% | 15.6 | % | 2.1 | % | — | % | 11.7 | % | |||||
| Consolidated Balance Sheets | December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | U.S. Deferred Tax Revaluation | Deemed Repatriation Tax | Additional Foreign Withholding Taxes | Other Items, net | Total | ||||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | $ | — | $ | (5.4 | ) | $ | — | $ | 27.4 | $ | 22.0 | ||||
| Deferred income taxes | (26.1 | ) | — | 9.0 | 27.6 | 10.5 | |||||||||
| Other long-term liabilities | — | 61.9 | — | — | 61.9 | ||||||||||
103
The components of earnings from continuing operations before income taxes are as follows:
| Year Ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Domestic | $ | 188.6 | $ | 267.7 | $ | 254.2 | |||||
| Foreign | 243.4 | 219.4 | 195.6 | ||||||||
| $ | 432.0 | $ | 487.1 | $ | 449.8 | ||||||
Income tax expense from continuing operations is comprised of the following components:
| Year Ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Current | |||||||||||
| Federal | $ | 76.0 | $ | 55.7 | $ | 63.1 | |||||
| State and local | 3.8 | 4.1 | 7.6 | ||||||||
| Foreign | 43.2 | 42.5 | 40.0 | ||||||||
| 123.0 | 102.3 | 110.7 | |||||||||
| Deferred | |||||||||||
| Federal | 5.8 | 13.1 | 9.6 | ||||||||
| State and local | (2.6 | ) | 2.3 | .1 | |||||||
| Foreign | 12.2 | 2.3 | 1.4 | ||||||||
| 15.4 | 17.7 | 11.1 | |||||||||
| $ | 138.4 | $ | 120.0 | $ | 121.8 | ||||||
Income tax expense from continuing operations, as a percentage of earnings before income taxes, differs from the statutory federal income tax rate as follows:
| Year Ended December 31 | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Statutory federal income tax rate | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | ||
| Increases (decreases) in rate resulting from: | ||||||||
| State taxes, net of federal benefit | .9 | .9 | 1.6 | |||||
| Tax effect of foreign operations | (8.0 | ) | (6.0 | ) | (5.8 | ) | ||
| Deferred tax on undistributed foreign earnings | 2.8 | .5 | (1.0 | ) | ||||
| Deemed repatriation of foreign earnings | 15.6 | — | — | |||||
| Deferred tax revaluation | (6.0 | ) | — | — | ||||
| Stock-based compensation | (2.0 | ) | (3.4 | ) | — | |||
| Tax benefit for outside basis in subsidiary | (1.8 | ) | — | — | ||||
| Change in valuation allowance | (.4 | ) | .2 | — | ||||
| Change in uncertain tax positions, net | (.6 | ) | (.6 | ) | (.5 | ) | ||
| Domestic production activities deduction | (1.2 | ) | (1.2 | ) | (1.2 | ) | ||
| Other permanent differences, net | (1.6 | ) | (.6 | ) | (1.0 | ) | ||
| Other, net | (.7 | ) | (.2 | ) | — | |||
| Effective tax rate | 32.0 | % | 24.6 | % | 27.1 | % | ||
For all periods presented, the tax rate benefited from income earned in various foreign jurisdictions at rates lower than the U.S. federal statutory rate, primarily related to China, Croatia, and Luxembourg. Other significant items impacting each year's tax rate are:
In 2017, we recognized a net tax expense totaling $50.4 related to the impact of TCJA, as discussed above. We also recognized tax benefits totaling $28.9, including those associated with tax attributes from a divested business and the impact of stock-based compensation.
We recognized net tax benefits in 2016 totaling $21.4, including a tax benefit related to stock-based compensation from the first quarter adoption of ASU 2016-09, "Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting".
104
In 2015, we recognized net tax benefits totaling $9.4, including a reduction in deferred taxes on undistributed foreign earnings associated with a planned reinvestment in China, and a deferred tax benefit related to our Australian operations.
Prior to the adoption of ASU 2016-09 in 2016, all net excess tax benefits related to stock plan activity were recorded to additional contributed capital, which totaled $15.4 in 2015.
We file tax returns in each jurisdiction where we are required to do so. In these jurisdictions, a statute of limitations period exists. After a statute period expires, the tax authorities can no longer assess additional income tax for the expired period. In addition, once the statute expires we are no longer eligible to file claims for refund for any tax that we may have overpaid.
Unrecognized Tax Benefits
The total amount of our gross unrecognized tax benefits at December 31, 2017, is $13.6, of which $8.8 would impact our effective tax rate, if recognized. A reconciliation of the beginning and ending balance of our gross unrecognized tax benefits for the periods presented is as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Gross unrecognized tax benefits, January 1 | $ | 12.1 | $ | 15.5 | $ | 19.8 | |||||
| Gross increases—tax positions in prior periods | .1 | .3 | .3 | ||||||||
| Gross decreases—tax positions in prior periods | (.4 | ) | (1.0 | ) | (.5 | ) | |||||
| Gross increases—current period tax positions | 1.5 | 1.1 | 1.3 | ||||||||
| Change due to exchange rate fluctuations | .3 | — | (1.3 | ) | |||||||
| Settlements | (.9 | ) | (.9 | ) | (1.5 | ) | |||||
| Lapse of statute of limitations | (2.6 | ) | (2.9 | ) | (2.6 | ) | |||||
| Gross unrecognized tax benefits, December 31 | 10.1 | 12.1 | 15.5 | ||||||||
| Interest | 3.0 | 4.0 | 6.0 | ||||||||
| Penalties | .5 | .6 | .6 | ||||||||
| Total gross unrecognized tax benefits, December 31 | $ | 13.6 | $ | 16.7 | $ | 22.1 | |||||
We recognize interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits as part of income tax expense in the Consolidated Statements of Operations, which is consistent with prior reporting periods.
As of December 31, 2017, four tax years were subject to audit by the United States Internal Revenue Service (IRS), covering the years 2014 through 2017. In 2015 and 2017, the IRS examined our 2013 and 2015 tax returns, respectively, for a U.S. non-consolidated filing entity, L&P Financial Services Co., and both audits were concluded with no adjustments. There are no current IRS examinations in process, nor are we aware of any forthcoming.
Additionally, at December 31, 2017, eight tax years were either subject to or undergoing audit by the Canada Revenue Agency, covering the periods 2010 through 2017. The examinations in process are at various stages of completion, but to date we are not aware of any likely material adjustments. In 2016, we settled an appeal with the Canada Revenue Agency relative to our 2007 and 2008 tax years related to transfer pricing issues. The net impact of this settlement on our financial statements was not material.
Various state and other foreign jurisdiction tax years also remain open to examination, though we believe any assessments would not be material to our Consolidated Financial Statements.
It is reasonably possible that the resolution of certain tax audits could reduce our unrecognized tax benefits within the next 12 months, as certain tax positions may either be sustained on audit or we may agree to certain adjustments, or resulting from the expiration of statutes of limitations in various jurisdictions. It is not expected that any change would have a material impact on our Consolidated Financial Statements.
105
Deferred Income Taxes
Deferred income taxes are provided for the temporary differences between the financial reporting basis and the tax basis of our assets and liabilities. The major temporary differences and their associated deferred tax assets or liabilities are as follows:
| December 31 | |||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||||
| Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities | ||||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment | $ | 19.8 | $ | (53.5 | ) | $ | 5.9 | $ | (57.3 | ) | |||||
| Inventories | 1.9 | (14.0 | ) | 3.3 | (22.1 | ) | |||||||||
| Accrued expenses | 59.1 | (.2 | ) | 93.3 | (.3 | ) | |||||||||
| Net operating losses and other tax carryforwards | 35.0 | — | 48.2 | — | |||||||||||
| Pension cost and other post-retirement benefits | 11.9 | (.6 | ) | 31.4 | (.9 | ) | |||||||||
| Intangible assets | 1.2 | (77.3 | ) | 1.1 | (107.6 | ) | |||||||||
| Derivative financial instruments | 5.3 | (1.7 | ) | 9.9 | (1.7 | ) | |||||||||
| Tax on undistributed earnings | — | (21.4 | ) | — | (9.2 | ) | |||||||||
| Uncertain tax positions | 3.5 | — | 5.3 | — | |||||||||||
| Other | .7 | (7.1 | ) | 2.9 | (9.7 | ) | |||||||||
| Gross deferred tax assets (liabilities) | 138.4 | (175.8 | ) | 201.3 | (208.8 | ) | |||||||||
| Valuation allowance | (24.2 | ) | — | (22.9 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Total deferred taxes | $ | 114.2 | $ | (175.8 | ) | $ | 178.4 | $ | (208.8 | ) | |||||
| Net deferred tax (liability) asset | $ | (61.6 | ) | $ | (30.4 | ) | |||||||||
Many of the decreases in our deferred tax categories from 2016 to 2017 relate to the revaluation of our deferred tax assets and liabilities resulting from the U.S. tax rate reduction included in TCJA, discussed above. These changes decreased our overall net deferred tax liability by $26.1 in 2017, as discussed above. Other changes increased our net deferred tax liability by $57.3 from 2016 to 2017, and include:
| • | A reduction of $17.1 in our "Net operating losses and other tax carryforwards" deferred tax asset, primarily related to the 2017 utilization of our foreign tax credit carryover from the TCJA one-time tax on mandatory deemed repatriation and utilization of Canadian net operating losses during the year; |
| • | An increase of $12.2 associated with our "Tax on undistributed earnings" deferred tax liability, primarily associated with additional foreign withholding taxes from TCJA; and |
| • | A $14.5 decrease in the deferred tax asset associated with "Pension cost and other post-retirement benefits", primarily related to the pension settlement charge (Note L), and the acceleration of tax deductions and other planning associated with TCJA. |
The valuation allowance primarily relates to net operating loss, tax credit, and capital loss carryforwards for which utilization is uncertain. Cumulative tax losses in certain state and foreign jurisdictions during recent years, limited carryforward periods in certain jurisdictions, future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences, and reasonable tax planning strategies were among the factors considered in determining the valuation allowance. Individually, none of these tax carryforwards presents a material exposure.
Most of our tax carryforwards have expiration dates that vary generally over the next 20 years, with no amount greater than $10 expiring in any one year.
Deferred income and withholding taxes have been provided on earnings of our foreign subsidiaries to the extent it is anticipated that the earnings will be remitted in the future as dividends. Due to the recently enacted TCJA, we no longer asserted permanent reinvestment on $835.0 of earnings, and accrued provisional deferred taxes of $8.3 in 2017 related to certain earnings under our Canadian ownership structure, and an additional $0.7 in China. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, we have accrued a total of $12.5 and $9.2, respectively, of deferred taxes related to incremental withholding taxes in China.
106
Foreign withholding taxes have not been provided on certain foreign earnings which are indefinitely reinvested outside the U.S. The cumulative undistributed earnings which are indefinitely reinvested as of December 31, 2017, are $410.3. If such earnings were repatriated to the U.S. through dividends, the resulting provisional incremental tax expense would be approximately $26.7, based on present income tax laws and after consideration of the tax we have already accrued for the mandatory deemed repatriation of our foreign earnings (as referenced above).
Deferred tax assets (liabilities) included in the consolidated balance sheets are as follows:
| December 31 | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | ||||||
| Sundry | $ | 21.4 | $ | 23.9 | |||
| Deferred income taxes | (83.0 | ) | (54.3 | ) | |||
| $ | (61.6 | ) | $ | (30.4 | ) | ||
N—Other (Income) Expense
The components of other (income) expense from continuing operations were as follows:
| Year Ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Restructuring charges | $ | .8 | $ | .8 | $ | 1.6 | |||||
| Currency (gain) loss | 1.5 | (2.1 | ) | (2.1 | ) | ||||||
| Royalty income | — | (.3 | ) | (.9 | ) | ||||||
(Gain) loss from diversified investments associated with Executive Stock Unit Program (See Note K) | (4.5 | ) | (2.2 | ) | .3 | ||||||
| Other income | (2.8 | ) | (2.2 | ) | (5.7 | ) | |||||
| $ | (5.0 | ) | $ | (6.0 | ) | $ | (6.8 | ) | |||
107
O—Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss)
The following table sets forth the changes in each component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss):
Foreign Currency Translation Adjustments | Cash Flow Hedges | Defined Benefit Pension Plans | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | ||||||||||||
| Balance January 1, 2015 | $ | 86.8 | $ | (20.1 | ) | $ | (69.3 | ) | $ | (2.6 | ) | ||||
| Other comprehensive income | (88.5 | ) | (13.1 | ) | .1 | (101.5 | ) | ||||||||
| Reclassifications, pretax (1) | (3.6 | ) | 3.5 | 17.3 | 17.2 | ||||||||||
| Income tax effect | — | 1.5 | (6.2 | ) | (4.7 | ) | |||||||||
| Attributable to noncontrolling interest | .5 | — | — | .5 | |||||||||||
| Balance December 31, 2015 | (4.8 | ) | (28.2 | ) | (58.1 | ) | (91.1 | ) | |||||||
| Other comprehensive income | (33.2 | ) | (.9 | ) | (3.0 | ) | (37.1 | ) | |||||||
| Reclassifications, pretax (2) | (1.7 | ) | 15.3 | 4.5 | 18.1 | ||||||||||
| Income tax effect | — | (4.0 | ) | (.6 | ) | (4.6 | ) | ||||||||
| Attributable to noncontrolling interest | 1.1 | — | — | 1.1 | |||||||||||
| Balance December 31, 2016 | (38.6 | ) | (17.8 | ) | (57.2 | ) | (113.6 | ) | |||||||
| Other comprehensive income | 78.7 | 1.6 | 10.2 | 90.5 | |||||||||||
| Reclassifications, pretax (3) | — | 7.2 | 19.9 | 27.1 | |||||||||||
| Income tax effect | — | (2.5 | ) | (11.4 | ) | (13.9 | ) | ||||||||
| Attributable to noncontrolling interest | .4 | — | — | .4 | |||||||||||
| Balance December 31, 2017 | $ | 40.5 | $ | (11.5 | ) | $ | (38.5 | ) | $ | (9.5 | ) | ||||
| (1) 2015 pretax reclassifications are comprised of: | |||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | — | $ | (.6 | ) | $ | — | $ | (.6 | ) | |||||
| Cost of goods sold; selling and administrative expenses | — | — | 17.3 | 17.3 | |||||||||||
| Interest expense | — | 4.1 | — | 4.1 | |||||||||||
| Other (income) expense, net | (3.6 | ) | — | — | (3.6 | ) | |||||||||
| Total 2015 reclassifications, pretax | $ | (3.6 | ) | $ | 3.5 | $ | 17.3 | $ | 17.2 | ||||||
| (2) 2016 pretax reclassifications are comprised of: | |||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | — | $ | 10.6 | $ | — | $ | 10.6 | |||||||
| Cost of goods sold; selling and administrative expenses | — | .5 | 4.5 | 5.0 | |||||||||||
| Interest expense | — | 4.2 | — | 4.2 | |||||||||||
| Other (income) expense, net | (1.7 | ) | — | — | (1.7 | ) | |||||||||
| Total 2016 reclassifications, pretax | $ | (1.7 | ) | $ | 15.3 | $ | 4.5 | $ | 18.1 | ||||||
| (3) 2017 pretax reclassifications are comprised of: | |||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | — | $ | 2.3 | $ | — | $ | 2.3 | |||||||
| Cost of goods sold; selling and administrative expenses | — | .7 | 19.9 | 20.6 | |||||||||||
| Interest expense | — | 4.2 | — | 4.2 | |||||||||||
| Other (income) expense, net | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||
| Total 2017 reclassifications, pretax | $ | — | $ | 7.2 | $ | 19.9 | $ | 27.1 | |||||||
108
P—Fair Value
We utilize fair value measures for both financial and non-financial assets and liabilities.
Items measured at fair value on a recurring basis
The areas in which we utilize fair value measures of financial assets and liabilities are presented in the table below.
Fair value measurements are established using a three level valuation hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value into the following categories:
| • | Level 1: Quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets. |
| • | Level 2: Inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability either directly or indirectly. Short-term investments in this category are valued using discounted cash flow techniques with all significant inputs derived from or corroborated by observable market data. Derivative assets and liabilities in this category are valued using models that consider various assumptions and information from market-corroborated sources. The models used are primarily industry-standard models that consider items such as quoted prices, market interest rate curves applicable to the instruments being valued as of the end of each period, discounted cash flows, volatility factors, current market and contractual prices for the underlying instruments, as well as other relevant economic measures. Substantially all of these assumptions are observable in the marketplace, can be derived from observable data or are supported by observable levels at which transactions are executed in the marketplace. |
| • | Level 3: Unobservable inputs that are not corroborated by market data. |
| As of December 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | ||||||||||||
| Assets: | |||||||||||||||
| Cash equivalents: | |||||||||||||||
| Bank time deposits with original maturities of three months or less | $ | — | $ | 236.4 | $ | — | $ | 236.4 | |||||||
Derivative assets * (see Note R) | — | 3.9 | — | 3.9 | |||||||||||
Diversified investments associated with the ESUP * (see Note K) | 34.0 | — | — | 34.0 | |||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 34.0 | $ | 240.3 | $ | — | $ | 274.3 | |||||||
| Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||
Derivative liabilities * (see Note R) | $ | — | $ | 1.9 | $ | — | $ | 1.9 | |||||||
Liabilities associated with the ESUP * (see Note K) | 34.4 | — | — | 34.4 | |||||||||||
| Total liabilities | $ | 34.4 | $ | 1.9 | $ | — | $ | 36.3 | |||||||
| As of December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | ||||||||||||
| Assets: | |||||||||||||||
| Cash equivalents: | |||||||||||||||
| Bank time deposits with original maturities of three months or less | $ | — | $ | 145.8 | $ | — | $ | 145.8 | |||||||
Derivative assets (see Note R) | — | .8 | — | .8 | |||||||||||
Diversified investments associated with the ESUP * (see Note K) | 26.8 | — | — | 26.8 | |||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 26.8 | $ | 146.6 | $ | — | $ | 173.4 | |||||||
| Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||
Derivative liabilities * (see Note R) | $ | — | $ | 4.1 | $ | — | $ | 4.1 | |||||||
Liabilities associated with the ESUP * (see Note K) | 25.6 | — | — | 25.6 | |||||||||||
| Total liabilities | $ | 25.6 | $ | 4.1 | $ | — | $ | 29.7 | |||||||
* Includes both current and long-term amounts combined.
109
The fair value for fixed rate debt (Level 2) was not materially different from its carrying value of $1,250.0 and $750.0 at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Items measured at fair value on a non-recurring basis
The primary areas in which we utilize fair value measures of non-financial assets and liabilities are allocating purchase price to the assets and liabilities of acquired companies as discussed in Note Q and evaluating long-term assets (including goodwill) for potential impairment as discussed in Note C. Determining fair values for these items requires significant judgment and includes a variety of methods and models that utilize significant Level 3 inputs.
Long-lived assets, acquisitions and the second step of a goodwill impairment test utilize the following methodologies in determining fair value: (i) Buildings and machinery are valued at an estimated replacement cost for an asset of comparable age and condition. Market pricing of comparable assets are used to estimate replacement cost where available. (ii) The most common identified intangible assets are customer relationships and tradenames. Customer relationships are valued using an excess earnings method, using various inputs such as the estimated customer attrition rate, future earnings forecast, the amount of contributory asset charges, and a discount rate. Tradenames are valued using a relief from royalty method, which is based upon comparable market royalty rates for tradenames of similar value. (iii) Inventory is valued at current replacement cost for raw materials, with a step-up for work in process and finished goods items that reflects the amount of ultimate profit earned as of the valuation date. (iv) Other working capital items are generally recorded at face value, unless there are known conditions that would impact the ultimate settlement amount of the particular item.
Q—Acquisitions
The following table contains the estimated fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the date of acquisition for all acquisitions during the periods presented, and any additional consideration paid for prior years’ acquisitions. A portion of the goodwill included in the table below is expected to provide an income tax benefit.
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Accounts receivable | $ | 10.5 | $ | 5.3 | $ | 3.7 | |||||
| Inventory | 6.2 | 5.8 | 4.8 | ||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment | 15.7 | 3.7 | 2.7 | ||||||||
Goodwill (see Note D) | 11.5 | 8.7 | 7.9 | ||||||||
Other intangible assets (see Note D) | 20.3 | 12.3 | 14.9 | ||||||||
| Other current and long-term assets | .8 | — | .1 | ||||||||
| Current liabilities | (4.6 | ) | (4.2 | ) | (8.1 | ) | |||||
| Long-term liabilities | (6.3 | ) | (.5 | ) | (3.3 | ) | |||||
| Non-controlling interest | (.5 | ) | — | — | |||||||
| Fair value of net identifiable assets | 53.6 | 31.1 | 22.7 | ||||||||
| (Plus)/Less: Additional consideration for prior years’ acquisitions | — | (.3 | ) | 1.2 | |||||||
| Less: Additional consideration payable | 2.7 | 1.9 | 10.4 | ||||||||
| Less: Common stock issued for acquired companies | 11.8 | — | — | ||||||||
| Net cash consideration | $ | 39.1 | $ | 29.5 | $ | 11.1 | |||||
The following table summarizes acquisitions for the periods presented.
| Year Ended | Number of Acquisitions | Segment | Product/Service | |||
| December 31, 2017 | 3 | Residential Products; Furniture Products | Distributor and installer of geosynthetic products; Carpet cushion; Surface-critical bent tube components | |||
| December 31, 2016 | 3 | Residential Products; Specialized Products | Distributor of geosynthetic products; Innersprings; Fabricated aerospace tubing and pipe assemblies | |||
| December 31, 2015 | 1 | Furniture Products | Upholstered office furniture | |||
110
We are finalizing all of the information required to complete the purchase price allocations related to the most recent acquisitions and do not anticipate any material modifications.
The results of operations of the above acquired companies have been included in the consolidated financial statements since the dates of acquisition. The unaudited pro forma consolidated net sales, net earnings and earnings per share as though the 2017 and 2016 acquisitions had occurred on January 1 of each year presented are not materially different from the amounts reflected in the accompanying financial statements.
Certain of our acquisition agreements provide for additional consideration to be paid in cash at a later date and are recorded as a liability at the acquisition date. At December 31, 2017 and Decembers 31, 2016 our liability for these future payments was $16.5 ($8.9 current and $7.6 long-term) and $14.5 ($2.4 current and $12.1 long-term), respectively. Components of the liability are based on estimates and future events and the amounts may fluctuate significantly until the payment date.
A brief description of our acquisition activity by year is included below.
2017
In 2017, we acquired three businesses:
•A distributor and installer of geosynthetic products, expanding the geographic scope and capabilities of our Geo Components business.
•A manufacturer of surface-critical bent tube components in support of the private-label finished seating strategy in our Work Furniture business.
•A carpet underlay manufacturer, providing additional production capacity in our Carpet Cushion business.
These businesses broaden our geographic scope, capabilities, and product offerings, and added $11.5 ($7.6 to Residential Products and $3.9 to Furniture Products) of goodwill. We also acquired the remaining 20% ownership in an Asian joint venture in our Work Furniture business for $2.6.
2016
We acquired three small businesses for a total purchase price of $29.2. The first, a U.S. manufacturer of aerospace tube assemblies, expands our tube forming and fabrication capabilities and adds precision machining to our aerospace platform. The second is a distributor of geosynthetic products, and the third, a South African producer of mattress innersprings. In addition to these acquisitions, we purchased the remaining interest in an Automotive joint venture in China for $35.2.
2015
We acquired a 70% interest in a European private-label manufacturer of high-end upholstered furniture. This business is complementary to our North American private-label operation and allows us to support our Work Furniture customers as they expand globally. The initial cash outlay for the 70% interest was $12.3 and per the terms of the agreement, we will acquire the remaining 30% interest in two equal parts, in the second quarters of 2018 and 2020, respectively. We have recorded a liability of approximately $14.0 for these future payments. Future payments are estimated based upon a calculation that incorporates EBITDA and the recorded liability may fluctuate significantly until the payment dates. Any changes in this liability will be reflected in interest income or expense on the Consolidated Statement of Operations.
111
R—Derivative Financial Instruments
Cash Flow Hedges
Derivative financial instruments that we use to hedge forecasted transactions and anticipated cash flows are as follows:
Currency Cash Flow Hedges - The foreign currency hedges manage risk associated with exchange rate volatility of various currencies.
We have also occasionally used interest rate cash flow hedges to manage interest rate risks.
The effective changes in fair value of unexpired contracts are recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income and reclassified to income or expense in the period in which earnings are impacted. Cash flows from settled contracts are presented in the category consistent with the nature of the item being hedged. (Settlements associated with the sale or production of product are presented in operating cash flows and settlements associated with debt issuance are presented in financing cash flows.)
Fair Value Hedges and Derivatives not Designated as Hedging Instruments
These derivatives typically manage foreign currency risk associated with subsidiaries’ assets and liabilities, and gains or losses are recognized currently in earnings. Cash flows from settled contracts are presented in the category consistent with the nature of the item being hedged.
Hedge Effectiveness
We have deemed ineffectiveness to be immaterial, and as a result, have not recorded any amounts for ineffectiveness. If a hedge was not highly effective, the portion of the change in fair value considered to be ineffective would be recognized immediately in the consolidated statements of operations.
We have recorded the following assets and liabilities representing the fair value for our most significant derivative financial instruments. The fair values of the derivatives reflect the change in the market value of the derivative from the date of the trade execution and do not consider the offsetting underlying hedged item.
112
| Expiring at various dates through: | Total USD Equivalent Notional Amount | As of December 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives Designated as Hedging Instruments | Assets | Liabilities | |||||||||||||||||||||
Other Current Assets | Sundry | Other Current Liabilities | Other Long-Term Liabilities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash flow hedges: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency hedges: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Future USD sales of Canadian, Chinese, European and Swiss subsidiaries | Mar 2019 | $ | 144.1 | $ | 2.2 | $ | .2 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||
| Future USD purchases of European and Korean subsidiaries | Mar 2019 | 14.0 | — | — | .5 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Future MXN purchases of a USD subsidiary | Mar 2019 | 6.6 | — | — | .5 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Future JPY sales of Chinese subsidiary | Dec 2018 | 11.2 | .1 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Future DKK sales of Polish subsidiary | Dec 2018 | 16.0 | .6 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Future EUR Sales of Chinese, Swiss and UK subsidiaries | Mar 2019 | 38.8 | 38.8 | — | — | .3 | .1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total cash flow hedges | 2.9 | .2 | 1.3 | .1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Fair value hedges: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| DKK inter-company note receivable on a USD subsidiary | May 2018 | 3.5 | — | — | .1 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| USD inter-company note receivable on a CAD subsidiary | Feb 2018 | 8.0 | .1 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| EUR receivables on a USD subsidiary | Dec 2018 | 4.8 | — | — | .1 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| USD receivables on a EUR subsidiary | Jan 2018 | 5.0 | .1 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| ZAR inter-company note receivable on a USD subsidiary | Dec 2018 | 1.9 | — | — | .1 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| USD inter-company note receivable on a Swiss subsidiary | Aug 2018 | 12.7 | — | — | .2 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Total fair value hedges | .2 | — | .5 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-deliverable hedge on USD exposure to CNY | Nov 2018 | 15.0 | .2 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Non-deliverable hedge on JPY exposure to CNY | Sep 2018 | 2.0 | .1 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Hedge of USD Receivable on CAD Subsidiary | Jan 2018 | 19.0 | .3 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Total derivatives not designated as hedging instruments | .6 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 3.7 | $ | .2 | $ | 1.8 | $ | .1 | ||||||||||||||||
113
| Expiring at various dates through: | Total USD Equivalent Notional Amount | As of December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||
| Derivatives Designated as Hedging Instruments | Assets | Liabilities | ||||||||||||
Other Current Assets | Other Current Liabilities | |||||||||||||
| Cash flow hedges: | ||||||||||||||
| Currency hedges: | ||||||||||||||
| Future USD sales of Canadian, Chinese and Swiss subsidiaries | Dec 2017 | $ | 80.4 | $ | — | $ | 2.4 | |||||||
| Future USD purchases of European subsidiaries | Dec 2017 | 3.8 | .1 | — | ||||||||||
| Future MXN purchases of USD subsidiary | Dec 2017 | 5.8 | — | .9 | ||||||||||
| Future JPY sales of Chinese subsidiary | Dec 2017 | 3.5 | .3 | — | ||||||||||
| Future DKK sales of Polish subsidiary | Mar 2017 | 10.1 | .1 | — | ||||||||||
| Future EUR Sales of Chinese, Swiss and UK subsidiaries | Dec 2017 | 6.4 | — | .2 | ||||||||||
| Total cash flow hedges | .5 | 3.5 | ||||||||||||
| Fair value hedges: | ||||||||||||||
| USD inter-company note receivable on a CAD subsidiary | Jan 2017 | 24.0 | .2 | .1 | ||||||||||
| PLN inter-company note receivable on a GBP subsidiary | Jun 2017 | 2.3 | .1 | — | ||||||||||
| ZAR inter-company note receivable on a USD subsidiary | Dec 2017 | 2.3 | — | .1 | ||||||||||
| Total fair value hedges | .3 | .2 | ||||||||||||
| Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments | ||||||||||||||
| Non-deliverable hedge on USD exposure to CNY | Dec 2017 | 19.0 | — | .3 | ||||||||||
| Hedge of EUR cash on UK Subsidiary | Jan 2017 | 5.9 | — | .1 | ||||||||||
| Total derivatives not designated as hedging instruments | — | .4 | ||||||||||||
| $ | .8 | $ | 4.1 | |||||||||||
The following table sets forth the pretax (gains) losses for our hedging activities for the years presented. This schedule includes reclassifications from accumulated other comprehensive income as well as derivative settlements recorded directly to income or expense.
Income Statement Caption | Amount of (Gain) Loss Recorded in Income for the Year Ended December 31 | |||||||||||||
| Derivatives Designated as Hedging Instruments | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||
| Interest rate cash flow hedges | Interest expense | $ | 4.2 | $ | 4.2 | $ | 4.1 | |||||||
| Currency cash flow hedges | Net sales | (1.4 | ) | 10.8 | 3.2 | |||||||||
| Currency cash flow hedges | Cost of goods sold | .4 | 1.1 | (1.3 | ) | |||||||||
| Currency cash flow hedges | Other (income) expense, net | .6 | .4 | — | ||||||||||
| Total cash flow hedges | 3.8 | 16.5 | 6.0 | |||||||||||
| Fair value hedges | Other (income) expense, net | (.2 | ) | (1.3 | ) | 1.2 | ||||||||
| Derivatives Not Designated as Hedging Instruments | Other (income) expense, net | (1.7 | ) | (.1 | ) | 2.6 | ||||||||
| Total derivative instruments | $ | 1.9 | $ | 15.1 | $ | 9.8 | ||||||||
114
S—Contingencies
We are a party to various proceedings and matters involving employment, antitrust, intellectual property, environmental, taxation, vehicle-related personal injury and other laws. When it is probable, in management's judgment, that we may incur monetary damages or other costs resulting from these proceedings or other claims, and we can reasonably estimate the amounts, we record appropriate accruals in the financial statements and make charges against earnings. For all periods presented, we have recorded no material charges against earnings other than as indicated below. Also, when it is reasonably possible that we may incur additional loss in excess of recorded accruals and we can reasonably estimate the additional losses or range of losses, we disclose such additional reasonably possible losses in these notes.
For specific information regarding accruals, cash payments to settle litigation contingencies, and reasonably possible losses in excess of accruals please see “Accruals and Reasonably Possible Losses in Excess of Accruals” below.
Vehicle-Related Personal Injury Claim
In July 2016, a Company driver was involved in a traffic accident that resulted in two deaths and injury to other vehicle occupants. In the third quarter of 2016, the Company accrued a liability that it believed to be probable in an immaterial, estimated amount based upon known facts, opinion of counsel, as well as comparative settlements of the Company and other companies in similar proceedings. The accrual did not take into account applicable insurance coverage.
The Company received information regarding the events surrounding the accident and preliminary expert reports from one family's attorney at the end of November 2017. No legal proceedings have been filed, no discovery has been taken, and investigation of the facts of the accident remains in its early stages. The Company and its insurance carriers attended a pre-litigation mediation conference regarding this matter on January 8, 2018, with a subsequent meeting on February 14, 2018, in Chicago, Illinois. At the mediation conference, the attorneys representing these claimants alleged the Company's driver was at fault and made a demand for monetary damages. Until the initial mediation session, no demand had been made against the Company.
Based on facts received from the investigation and mediation processes, the Company, through cooperation and consent of its insurance carriers, reached a settlement with these claimants on February 14, 2018. The Company will pay the $5.0 self-insured retention amount and the remainder of the $48.0 settlement is the responsibility of the insurance carriers. The settlement is subject to contingencies, including approval by the Cook County, Illinois, Circuit Court, Probate Division. In the fourth quarter of 2017, the Company recorded a $43.0 receivable from the insurance carriers and a $43.0 liability related to this matter, that is included in current assets and current liabilities, respectively, in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The amount of self-insured retention to be paid by the Company had previously been accrued in the third quarter of 2016, and, therefore, the settlement had no impact on the Company's 2017 earnings. No other material claims have been asserted against the Company related to this accident. Management does not believe the settlement or the outcome of the claim will have a material effect on the Company’s financial condition, cash flows or results of operations.
Brazilian Value-Added Tax Matters
All dollar amounts (in millions) presented in this section have been updated since our last filing to reflect the U.S. Dollar (USD) equivalent of Brazilian Real (BRL).
We deny all allegations in the below Brazilian actions. We believe that we have valid bases to contest such actions and will vigorously defend ourselves. However, these contingencies are subject to uncertainties, and based on current facts, we believe that it is reasonably possible (but not probable) that we may incur losses of approximately $21.0 including interest and attorney fees with respect to these assessments. Therefore, because it is not probable we will incur a loss, no accrual has been recorded for Brazilian VAT matters. For specific information regarding accruals, and reasonably possible losses in excess of accruals please see "Accruals and Reasonably Possible Losses in Excess of Accruals" below.
We have $12.2 on deposit with the Brazilian government to partially mitigate interest and penalties that may accrue while we work through these matters. If we are successful in our defense of these assessments, the deposits are refundable with interest. These deposits are recorded as a long-term asset on our balance sheet.
Brazilian Federal Cases. On December 22 and December 29, 2011, and December 17, 2012, the Brazilian Finance Ministry, Federal Revenue Office issued a notice of violation against our wholly-owned subsidiary, Leggett & Platt do Brasil Ltda. (“L&P Brazil”) in the amount of $2.3, $.1 and $4.1, respectively. The Federal Revenue Office claimed that for the periods beginning November 2006 and continuing through 2011, L&P Brazil used an incorrect tariff code for the collection and
115
payment of value-added tax primarily on the sale of mattress innerspring units in Brazil. L&P Brazil has denied the violations. On December 4, 2015, we filed an Annulment Action related to the $4.1 assessment (for which a $5.1 cash bond was posted, accounting for updated interest), in Camanducaia Judicial District Court seeking to annul the entire assessment. We are awaiting the first level decision.
In addition, L&P Brazil received assessments on December 22, 2011, and June 26, July 2 and November 5, 2012, and September 13, 2013, from the Brazilian Federal Revenue Office where the Federal Revenue Office challenged L&P Brazil’s use of tax credits in years 2005 through 2010. Such credits are generated based upon the tariff classification and rate used by L&P Brazil for value-added tax on the sale of mattress innersprings. On September 4, 2014, the Federal Revenue Office issued five additional assessments regarding this same issue (use of credits), covering certain periods of 2011 and 2012. L&P Brazil filed its defense denying these assessments. Combined with the prior assessments, L&P Brazil has received assessments and penalties totaling $2.9 on the same or similar denial of tax credit matters. L&P Brazil has denied the violations. On September 11, 2017, L&P Brazil received an "isolated penalty" from the Federal Revenue Office in the amount of $.2 regarding the use of certain of these credits.
On February 1, 2013, the Brazilian Finance Ministry filed a Tax Collection action against L&P Brazil in the Camanducaia Judicial District Court, alleging the untimely payment of $.1 of social contributions (social security and social assistance payments) for the period September to October 2010. L&P Brazil argued the payments were not required to be made because of the application of tax credits that were generated by L&P Brazil's use of a correct tariff code for the classification of value-added tax on the sale of mattress innersprings (i.e., the same underlying issue at stake in the other Brazilian matters). On June 26, 2014, the Brazilian Revenue Office issued a new notice of violation against L&P Brazil in the amount of $.8 covering the period from 2011 through 2012 on the same subject matter. L&P Brazil has filed its defense denying the assessments.
On July 1, 2014, the Brazilian Finance Ministry rendered a preliminary decision to reject certain offsetting requests presented by L&P Brazil. The Brazilian Finance Ministry alleges that L&P Brazil improperly offset $.1 of social contributions otherwise due in 2011. L&P Brazil filed its response denying the allegations. L&P Brazil is defending on the basis that the social contribution debts were correctly offset with tax credits generated by L&P Brazil's use of a correct tariff code classification for value-added tax on the sale of mattress innersprings (i.e., the same underlying issue at stake in the other Federal Brazilian matters). On December 15, 2015, the Brazilian Federal Revenue issued an assessment against L&P Brazil in the amount of $.1 for the period of August 2010 through May 2011, as a penalty for L&P Brazil's requests to offset tax credits. We filed our defense denying the assessment.
State of São Paulo, Brazil Cases. The State of São Paulo, Brazil, on April 16, 2009, issued a Notice of Tax Assessment and Imposition of Fine to L&P Brazil originally seeking $1.8 for the tax years 2006 and 2007. The State of São Paulo argued that L&P Brazil was using an incorrect tariff code for the collection and payment of value-added tax on sales of mattress innerspring units in the State of São Paulo. L&P Brazil denied the allegations. On April 17, 2014, the Court of Tax and Fees ruled in the State's favor upholding the original assessment of $1.8. On July 31, 2014, L&P Brazil filed an annulment action in the Sorocaba State Court, seeking to have the Court of Tax and Fees ruling annulled for an updated assessment amount of $3.6 (which included interest from the original assessment date). The Court issued a ruling in our favor on October 27, 2017, nullifying the $3.6 in assessments against L&P Brazil. This ruling has not yet been appealed to second judicial level.
On October 4, 2012, the State of São Paulo issued a Tax Assessment against L&P Brazil in the amount of $1.9 for the tax years 2009 through 2011. Similar to the 2009 assessment (referenced above), the State of São Paulo argues that L&P Brazil was using an incorrect tax rate for the collection and payment of value-added tax on sales of mattress innerspring units in the State of São Paulo. On June 21, 2013, the State of São Paulo converted the Tax Assessment to a tax collection action against L&P Brazil in the amount of $2.5 in Sorocaba Judicial District Court. L&P Brazil has denied all allegations.
L&P Brazil also received a Notice of Tax Assessment and Imposition of a Fine from the State of São Paulo dated March 27, 2014, in the amount of $.9 (currently secured with a $1.2 bond to update for interest) for tax years January 2011 through August 2012 regarding the same subject matter (i.e., the correct tax rate for the collection and payment of value-added tax on mattress innerspring units). L&P filed its response denying the allegations, but the tax assessment was maintained at the administrative level. On June 9, 2016, L&P Brazil filed an annulment action in Sorocaba State Court to annul the entire $1.2 assessment. The Court ruled against L&P Brazil on the assessment, but lowered the interest amount. We filed a motion for clarification. The Court upheld its ruling, and we filed an appeal to the Court of Appeals on May 15, 2017. The Court of Appeals upheld the unfavorable Sorocaba State Court ruling, and we filed a Special and Extraordinary appeal to the High Court on October 10, 2017, and this final appeal remains pending.
State of Minas Gerais, Brazil Cases. On December 18, 2012, the State of Minas Gerais, Brazil issued a tax assessment to L&P Brazil relating to L&P Brazil's classifications of innersprings for the collection and payment of value-added tax on the sale of mattress innersprings in Minas Gerais from March 2008 through August 2012 in the amount of $.5. L&P Brazil filed its response denying any violation. The Minas Gerais Taxpayer's Council ruled against us, and on June 5, 2014, L&P Brazil filed a
116
Motion to Stay the Execution of the Judgment in Camanducaia Judicial District Court alleging the same tax assessment in the amount of $.6. The motion remains pending.
Accruals and Reasonably Possible Losses in Excess of Accruals
Accruals for Probable Losses
Although the Company denies liability in all currently threatened or pending litigation proceedings in which it is or may be a party and believes that it has valid bases to contest all claims threatened or made against it, we have recorded a litigation contingency accrual for our reasonable estimate of probable loss for pending and threatened litigation proceedings, in aggregate, in millions, as follows:
| Twelve Months Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Litigation contingency accrual - Beginning of period | $ | 3.2 | $ | 8.1 | $ | 83.9 | |||||
| Adjustment to accruals - expense (income) - Continuing operations | .6 | 7.1 | 5.7 | ||||||||
| Adjustment to accruals - expense (income) - Discontinued operations | 1.6 | 2.0 | .7 | ||||||||
| Cash payments | (5.0 | ) | (14.0 | ) | (82.2 | ) | |||||
| Litigation contingency accrual - End of period | $ | .4 | $ | 3.2 | $ | 8.1 | |||||
A large percentage of the accruals and cash payments in 2015 and 2016 were related to antitrust proceedings. The above litigation contingency accruals do not include accrued expenses related to workers compensation, vehicle-related personal injury, product and general liability claims, taxation issues and environmental matters, some of which may contain a portion of litigation expense. However, any litigation expense associated with these categories is not anticipated to have a material effect on our financial condition, results of operations or cash flows. For more information regarding accrued expenses, see Note H - Supplemental Balance Sheet Information under "Accrued expenses" on page 90.
We have relied on several facts and circumstances to conclude that some loss is probable with respect to certain proceedings and matters, and to arrive at a reasonable estimate of loss or range of loss and record the accruals, including: the maturation of the pending proceedings and matters; our experience in settlement negotiations and mediation; comparative settlements of other companies in similar proceedings; discovery becoming or being substantially complete in certain proceedings; certain quantitative metrics used to value probable loss contingencies; and our willingness to settle certain proceedings to forgo the cost and risk of litigation and distraction to our senior executives.
Reasonably Possible Losses in Excess of Accruals
Although there are a number of uncertainties and potential outcomes associated with all of our pending or threatened litigation proceedings, we believe, based on current known facts, that additional losses, if any, are not expected to materially affect our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows. However, based upon current known facts, as of December 31, 2017, aggregate reasonably possible (but not probable, and therefore not accrued) losses in excess of the accruals noted above are estimated to be approximately $22.0, including approximately $21.0 for Brazilian VAT matters disclosed above and $1.0 for other matters. If our assumptions or analyses regarding these contingencies are incorrect, or if facts change, we could realize loss in excess of the recorded accruals, and even greater than our estimate of reasonably possible losses in excess of recorded accruals.
117
Leggett & Platt, Incorporated
Quarterly Summary of Earnings
(Unaudited)
(Dollar amounts in millions, except per share data)
| Year ended December 31 | First | Second 3 | Third 1 | Fourth 2,4 | Total | ||||||||||||||
| 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 960.3 | $ | 989.3 | $ | 1,009.7 | $ | 984.5 | $ | 3,943.8 | |||||||||
| Gross profit | 226.0 | 230.1 | 215.8 | 196.0 | 867.9 | ||||||||||||||
| Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes | 107.3 | 113.4 | 100.7 | 110.6 | 432.0 | ||||||||||||||
| Earnings from continuing operations | $ | 86.1 | $ | 87.6 | $ | 83.5 | $ | 36.4 | $ | 293.6 | |||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax | — | — | (.9 | ) | — | (.9 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Net earnings | 86.1 | 87.6 | 82.6 | 36.4 | 292.7 | ||||||||||||||
| (Earnings) attributable to noncontrolling interest, net of tax | — | — | — | (.1 | ) | (.1 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to Leggett & Platt, Inc. common shareholders | $ | 86.1 | $ | 87.6 | $ | 82.6 | $ | 36.3 | $ | 292.6 | |||||||||
| Earnings per share from continuing operations attributable to Leggett & Platt, Inc. common shareholders | |||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | .63 | $ | .64 | $ | .62 | $ | .27 | $ | 2.16 | |||||||||
| Diluted | $ | .62 | $ | .64 | $ | .61 | $ | .27 | $ | 2.14 | |||||||||
| Earnings (loss) per share from discontinued operations attributable to Leggett & Platt, Inc. common shareholders | |||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (.01 | ) | $ | — | $ | (.01 | ) | |||||||
| Diluted | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (.01 | ) | $ | — | $ | (.01 | ) | |||||||
| Net earnings per share attributable to Leggett & Platt, Inc. common shareholders | |||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | .63 | $ | .64 | $ | .61 | $ | .27 | $ | 2.15 | |||||||||
| Diluted | $ | .62 | $ | .64 | $ | .60 | $ | .27 | $ | 2.13 | |||||||||
| 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 938.4 | $ | 958.9 | $ | 948.9 | $ | 903.7 | $ | 3,749.9 | |||||||||
| Gross profit | 233.6 | 234.0 | 227.4 | 204.2 | 899.2 | ||||||||||||||
| Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes | 118.7 | 137.2 | 121.2 | 110.0 | 487.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Earnings from continuing operations | $ | 91.0 | $ | 99.5 | $ | 93.6 | $ | 83.0 | $ | 367.1 | |||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax | .1 | 20.3 | — | (1.3 | ) | 19.1 | |||||||||||||
| Net earnings | 91.1 | 119.8 | 93.6 | 81.7 | 386.2 | ||||||||||||||
| (Earnings) attributable to noncontrolling interest, net of tax | (1.6 | ) | 1.4 | (.1 | ) | (.1 | ) | (.4 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to Leggett & Platt, Inc. common shareholders | $ | 89.5 | $ | 121.2 | $ | 93.5 | $ | 81.6 | $ | 385.8 | |||||||||
| Earnings per share from continuing operations attributable to Leggett & Platt, Inc. common shareholders | |||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | .64 | $ | .73 | $ | .68 | $ | .61 | $ | 2.66 | |||||||||
| Diluted | $ | .63 | $ | .72 | $ | .67 | $ | .60 | $ | 2.62 | |||||||||
| Earnings (loss) per share from discontinued operations attributable to Leggett & Platt, Inc. common shareholders | |||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | — | $ | .15 | $ | — | $ | (.01 | ) | $ | .14 | ||||||||
| Diluted | $ | — | $ | .15 | $ | — | $ | (.01 | ) | $ | .14 | ||||||||
| Net earnings per share attributable to Leggett & Platt, Inc. common shareholders | |||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | .64 | $ | .88 | $ | .68 | $ | .60 | $ | 2.80 | |||||||||
| Diluted | $ | .63 | $ | .87 | $ | .67 | $ | .59 | $ | 2.76 | |||||||||
All below amounts are shown pretax with the exception of fourth quarter 2017 tax reform item discussed below.
| 1. | Third quarter 2017 Earnings from continuing operations include a charge of $5 associated with a small Wire Products business impairment (Note C); $3 charge associated with the sale of a business |
| 2. | Fourth quarter 2017 Earnings from continuing operations include a gain of $23 associated with the sale of real estate; $15 pension settlement charge; $50 charge associated with the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) |
| 3. | Second quarter 2016 Earnings from continuing operations include a gain of $7 associated with litigation accruals; $11 gain associated with the sale of a business; and a $4 charge from CVP impairment (Note C); Discontinued operations earnings primarily consists of a gain associated with litigation accruals |
| 4. | Fourth quarter 2016 Earnings from continuing operations include $16 associated with the gain on sale of a business |
118
LEGGETT & PLATT, INCORPORATED
SCHEDULE II—VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS AND RESERVES
(Amounts in millions)
| Column A | Column B | Column C | Column D | Column E | |||||||||||
| Description | Balance at Beginning of Period | Additions Charged to Cost and Expenses | Deductions | Balance at End of Period | |||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful receivables | $ | 7.4 | $ | .8 | $ | 3.3 | (1) | $ | 4.9 | ||||||
| Excess and obsolete inventory reserve, LIFO basis | $ | 27.1 | $ | 4.9 | $ | 5.6 | $ | 26.4 | |||||||
| Tax valuation allowance | $ | 22.9 | $ | 1.3 | $ | — | $ | 24.2 | |||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful receivables | $ | 9.9 | $ | 1.6 | $ | 4.1 | (1) | $ | 7.4 | ||||||
| Excess and obsolete inventory reserve, LIFO basis | $ | 24.7 | $ | 8.9 | $ | 6.5 | $ | 27.1 | |||||||
| Tax valuation allowance | $ | 26.6 | $ | .8 | $ | 4.5 | $ | 22.9 | |||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful receivables | $ | 17.2 | $ | 2.6 | $ | 9.9 | (1) | $ | 9.9 | ||||||
| Excess and obsolete inventory reserve, LIFO basis | $ | 21.9 | $ | 9.8 | $ | 7.0 | $ | 24.7 | |||||||
| Tax valuation allowance | $ | 27.1 | $ | (.4 | ) | $ | .1 | $ | 26.6 | ||||||
| (1) | Uncollectible accounts charged off, net of recoveries. |
119
EXHIBIT INDEX
| Exhibit No. | Document Description | |
| 3.1 | ||
| 3.2 | ||
| 4.1 | ||
| 4.2 | ||
| 4.2.1 | ||
| 4.3 | ||
| 4.3.1 | ||
| 4.4 | ||
| 4.5 | ||
| 4.6 | ||
| 4.7 | ||
120
| Exhibit No. | Document Description | |
| 4.8 | ||
| 10.1* | ||
| 10.2* | ||
| 10.3* | ||
| 10.4* | ||
| 10.5* | ||
| 10.6* | ||
| 10.7*,** | ||
| 10.8* | ||
| 10.9* | ||
| 10.10*,** | ||
| 10.11* | ||
| 10.12* | ||
| 10.12.1* | ||
| 10.12.2* | ||
121
| Exhibit No. | Document Description | |
| 10.12.3* | ||
| 10.12.4* | ||
| 10.12.5* | ||
| 10.12.6* | ||
| 10.12.7* | ||
| 10.12.8* | ||
| 10.12.9* | ||
| 10.12.10* | ||
| 10.12.11* | ||
| 10.12.12* | ||
| 10.12.13* | ||
| 10.12.14* | ||
| 10.12.15* | ||
| 10.12.16* | ||
122
| Exhibit No. | Document Description | |
| 10.13* | ||
| 10.13.1* | ||
| 10.13.2* | ||
| 10.14* | ||
| 10.15* | ||
| 10.16* | ||
| 10.17* | ||
| 10.18* | ||
| 10.19* | ||
| 10.20* | ||
| 10.21* | ||
| 10.22 | ||
| 10.23 | ||
123
| Exhibit No. | Document Description | |
| 10.24 | ||
| 10.24.1 | ||
| 12** | ||
| 21** | ||
| 23** | ||
| 24** | ||
| 31.1** | ||
| 31.2** | ||
| 32.1** | ||
| 32.2** | ||
| 101.INS*** | XBRL Instance Document. | |
| 101.SCH*** | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema. | |
| 101.CAL*** | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase. | |
| 101.DEF*** | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase. | |
| 101.LAB*** | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase. | |
| 101.PRE*** | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase. | |
______________________________
| * | Denotes management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
| ** | Denotes filed or furnished herewith. |
| *** | Exhibit 101 to this report includes the following formatted in XBRL (eXtensible Business Reporting Language): (i) Consolidated Statements of Operations for each year in the three year period ended December 31, 2017; (ii) Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss) for each year in the three year period ended December 31, 2017; (iii) Consolidated Balance Sheets at December 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016; (iv) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for each year in the three year period ended December 31, 2017; (v) Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity for each year in the three year period ended December 31, 2017; and (vi) Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
124
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary.
None.
125
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| LEGGETT & PLATT, INCORPORATED | ||
| By: | /s/ KARL G. GLASSMAN | |
| Karl G. Glassman | ||
| President and Chief Executive Officer | ||
Date: February 22, 2018
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
| (a) Principal Executive Officer: | ||||
/s/ KARL G. GLASSMAN | President and Chief Executive Officer and Director | February 22, 2018 | ||
| Karl G. Glassman | ||||
| (b) Principal Financial Officer: | ||||
/S/ MATTHEW C. FLANIGAN | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Director | February 22, 2018 | ||
| Matthew C. Flanigan | ||||
| (c) Principal Accounting Officer: | ||||
/S/ TAMMY M. TRENT | Senior Vice President and Chief Accounting Officer | February 22, 2018 | ||
| Tammy M. Trent | ||||
| (d) Directors: | ||||
ROBERT E. BRUNNER* | Director | |||
| Robert E. Brunner | ||||
ROBERT G. CULP, III* | Director | |||
| Robert G. Culp, III | ||||
126
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
R. TED ENLOE, III* | Director | |||
| R. Ted Enloe, III | ||||
MANUEL A. FERNANDEZ* | Director | |||
| Manuel A. Fernandez | ||||
JOSEPH W. MCCLANATHAN* | Director | |||
Joseph W. McClanathan | ||||
JUDY C. ODOM* | Director | |||
| Judy C. Odom | ||||
PHOEBE A. WOOD* | Director | |||
| Phoebe A. Wood | ||||
| *By: | /s/ SCOTT S. DOUGLAS | February 22, 2018 | |
| Scott S. Douglas | |||
Attorney-in-Fact Under Power-of-Attorney dated February 20, 2018 | |||
127