Exhibit 13
ANNUAL REPORT
OF THE TRUSTEES OF
MESABI TRUST
For The Year Ended January 31, 2010
ADDRESS
Mesabi Trust
c/o Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas
Trust & Securities Services — GDS
60 Wall Street, 27th Floor
New York, NY 10005
(615) 835-2749 (telephone)
www.mesabi-trust.com
REGISTRAR AND TRANSFER AGENT
Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas
LEGAL COUNSEL
Oppenheimer Wolff & Donnelly LLP, General Counsel
REGISTRANT INFORMATION
Mesabi Trust maintains a website that provides access to its annual, quarterly, and other reports it files with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Such reports can be accessed at www.mesabi-trust.com. Mesabi Trust will provide, upon the written request of any Unitholder addressed to the Trustees at the above address and without charge to such Unitholder, (i) a paper copy of Mesabi Trust’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2010 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and (ii) the Trustees Code of Ethics.
Special Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
Certain statements contained in this document are considered “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. All such forward-looking statements, including those statements estimating calendar year 2010 production or shipments, are based on input from the lessee/operator (and its parent corporation) of the mine located on the lands owned and held in trust for the benefit of the holders of units of beneficial interest of Mesabi Trust. These statements may be identified by the use of forward-looking words, such as “may,” “will,” “could,” “project,” “believe,” “anticipate,” “expect,” “estimate,” “continue,” “potential,” “plan,” “forecast” and other similar words. Such forward-looking statements are inherently subject to known and unknown risks and uncertainties. Actual results and future developments could differ materially from the results or developments expressed in or implied by these forward-looking statements. Factors that may cause actual results to differ materially from those contemplated by such forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, volatility of iron ore and steel prices, market supply and demand, regulation or government action, litigation and uncertainties about estimates of reserves, and those described under the caption “Risk Factors” in this annual report. Mesabi Trust undertakes no obligation to make any revisions to the forward-looking statements contained in this filing or to update them to reflect circumstances occurring after the date of this filing.
OVERVIEW
Mesabi Trust (“Mesabi Trust” or the “Trust”), formed pursuant to an Agreement of Trust dated July 18, 1961 (the “Agreement of Trust”), is a trust organized under the laws of the State of New York. Mesabi Trust holds all of the interests formerly owned by Mesabi Iron Company, including all right, title and interest in the Amendment of Assignment, Assumption and Further Assignment of Peters Lease (the “Amended Assignment of Peters Lease”), the Amendment of Assignment, Assumption and Further Assignment of Cloquet Lease (the “Amended Assignment of Cloquet Lease” and together with the Amended Assignment of Peters Lease, the “Amended Assignment Agreements”), the beneficial interest in the Mesabi Land Trust (as such term is defined below) and all other assets and property identified in the Agreement of Trust. The Amended Assignment of Peters Lease relates to an Indenture made as of April 30, 1915 among East Mesaba Iron Company (“East Mesaba”), Dunka River Iron Company (“Dunka River”) and Claude W. Peters (the “Peters Lease”) and the Amended Assignment of Cloquet Lease relates to an Indenture made May 1, 1916 between Cloquet Lumber Company and Claude W. Peters (the “Cloquet Lease”).
The Agreement of Trust specifically prohibits the Trustees from entering into or engaging in any business. This prohibition seemingly applies even to business activities the Trustees may deem necessary or proper for the preservation and protection of the Trust Estate. Accordingly, the Trustees’ activities in connection with the administration of Trust assets are limited to collecting income, paying expenses and liabilities, distributing net income to the holders of Certificates of Beneficial Interest in Mesabi Trust (“Unitholders”) after the payment of, or provision for, such expenses and liabilities, and protecting and conserving the assets held. Because the Units of the Trust are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and are listed on the New York Stock Exchange, the Trustees are also responsible for ensuring that the Trust maintains compliance with all applicable laws, rules and regulations. Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, the Corporate Trustee, performs certain administrative functions for the Trust.
The Trustees do not intend to expand their responsibilities beyond those permitted or required by the Agreement of Trust, the Amendment to the Agreement of Trust dated October 25, 1982 (the “Amendment”), and those required under applicable law. The Trust has no employees, but it engages independent consultants to assist the Trustees in, among other things, monitoring the amount and sales prices of iron ore products shipped from Silver Bay, Minnesota, based on information supplied to the Trustees by Northshore Mining Company (“Northshore”), the lessee/operator of the Mesabi Trust lands, and its parent company Cliffs Natural Resources Inc (“Cliffs”). References to Northshore in this annual report, unless the context requires otherwise, are applicable to Cliffs as well.
The information regarding amounts and sales prices of shipped iron ore products is used to compute the royalties payable to the Trust by Northshore. The Trustees request material information, from time to time, for use in the Trust’s periodic reports and as part of their evaluation of the Trust’s disclosure controls and procedures. The Trustees rely on Northshore to provide accurate and timely information for use in the Trust’s current, periodic and annual reports filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Pursuant to a ruling from the Internal Revenue Service, which ruling was based on the terms of the Agreement of Trust including the prohibition against entering into any business, the Trust is not taxable as a corporation for Federal income tax purposes. Instead, the Unitholders are considered “owners” of the Trust and the Trust’s income is taxable directly to the Unitholders. In accordance with the Agreement of Trust, the Trust will terminate twenty-one years after the death of the survivor of twenty-five persons named in an exhibit to the Agreement of Trust, the youngest of whom is believed to be forty-nine years old.
2
RISK FACTORS
The results of operations and financial condition of the Trust are subject to various risks. Some of these risks are described below, and you should take such risks into account in evaluating the Trust or any investment decision involving the Trust. This section does not describe all risks that may be applicable to the Trust and it is intended only as a summary of certain material risk factors. More detailed information concerning the risk factors described below is contained in other sections of this Annual Report.
The Trustees have no control over the operations and activities of Cliffs or Northshore.
Except within the framework of the Amended Assignment Agreements, neither the Trust nor the Trustees have any control over the operations and activities of Cliffs or its wholly-owned subsidiary, Northshore. Accordingly, the income of the Trust is highly dependent upon the activities and operations of Northshore, and the terms and conditions of the Amended Assignment Agreements. Northshore together with Cliffs, without any influence from the Trust, control: (i) historical operating data, including iron ore production volumes, marketing of iron ore products, operating and capital expenditures as they relate to Northshore, environmental and other liabilities and the effects of regulatory changes; (ii) plans for Northshore’s future production, operations and capital expenditures; (iii) geological data relating to iron ore reserve estimates; (iv) shipments of iron ore products to customers of Cliffs; and (v) the provisions and pricing under the Cliffs Pellet Agreements. Any substantial alteration of Cliffs’ business or the operations, production and shipments by Northshore could adversely affect the income of the Trust.
Price adjustment provisions in the North American supply agreements with Cliffs’ customers can cause significant positive and negative fluctuations in the royalties paid to the Trust.
In Cliffs’ Form 10-K filed February 18, 2010, Cliffs has reported that five customers together accounted for more than 80 percent of its North American iron ore sales revenues. According to the Form 10-K filed by Cliffs, sales volume under these agreements is largely dependent on customer requirements, and in some cases, Cliffs is the sole supplier of iron ore pellets to its customers. Contractual disputes with any of Cliffs’ significant customers could result in lower sales volume or lower sales prices, which could adversely affect the royalties received by the Trust.
Cliffs has also reported that its North American term supply agreements contain a number of price adjustment provisions, including adjustments based on general industrial inflation rates, the price of steel and the international price of iron ore pellets, among other factors, that allow Cliffs to adjust the prices under those agreements generally on an interim and annual basis. Factors that could result in price adjustment include measures of general industrial inflation, steel prices and international pellet prices. These market prices are dependent upon supply and demand relationships and a variety of other factors over which the Trust has no control. Cliffs’ price adjustment provisions are weighted and some are subject to annual collars, which limit Cliffs’ ability to raise prices to match international levels and fully capitalize on strong demand for iron ore. These price adjustments can be positive or negative, and can result in significant variations in royalties received by Mesabi Trust from quarter to quarter and year to year. These variations could adversely affect the royalties received by the Trust and, in turn, the resulting cash available for distribution to Unitholders.
3
Royalties received by the Trust, and distributions paid to Unitholders, in any particular quarter are not necessarily indicative of royalties or distributions that will be paid in any subsequent quarter or for a full year.
Royalties received by the Trust can fluctuate significantly from quarter to quarter and year to year based upon market prices for iron ore products, the level of orders for iron ore products from Cliffs’ customers, the consumption of inventory by Cliffs’ customers, and production decisions made by Northshore. Moreover, because the royalties paid to the Trust in any particular quarter include payments made with respect to pellets shipped and sold at estimated prices that are subject to future interim and final multi-year adjustments in accordance with Cliff’s Customer Agreements, the recent downward trends in demand and market prices for iron and steel products could result in negative adjustments to royalties in future quarters, some of which may be significant. These negative price adjustments could have a material adverse effect on the Trust’s royalty income, which in turn could result in lower quarterly distributions, and possibly reduce or even eliminate funds available for distribution in any quarter and in some quarters may completely offset royalties otherwise payable to the Trust. Because of this, cash available for distribution to Unitholders in future quarters could be reduced, potentially materially, and in some cases, such reduction could result in no cash being available for distribution to Unitholders. As a result, the royalties received by the Trust, and the distributions paid to Unitholders, in any particular quarter are not necessarily indicative of royalties that will be received, or distributions that will be paid, in any subsequent quarter or for a full year. Based on the foregoing and the current uncertainty in the economic environment, the Trust cannot ensure that there will be adequate cash available to make a distribution to Unitholders in any particular quarter.
The Trust does not control the portion of Northshore’s shipments that will come from ore mined from Mesabi Trust lands.
The Trustees do not exert any influence over mining operational decisions and Northshore alone determines whether to mine from lands owned by the Trust or state-owned lands, based on its current production estimates and engineering plan. Northshore’s mining operations (the Peter Mitchell Mine) include mineral-producing land owned by the Trust and the State of Minnesota. Ore mined from state-owned lands by Northshore is processed, along with ore mined from Trust-owned lands, in Northshore-owned crushing, concentrating and pelletizing facilities and is separately accounted for on a periodic basis. Northshore also has the ability to process and ship iron ore products from lands other than Mesabi Trust lands. In certain circumstances, the Trust may be entitled to royalties on those other shipments, but not in all cases. In general, the Trust will receive higher royalties (assuming all other factors are equal) if a higher percentage of shipments are from Mesabi Trust lands. The percentages of shipments from Mesabi Trust lands were 93.6%, 90.2%, 88.2%, 90.9% and 90.1% in calendar years 2009, 2008, 2007, 2006 and 2005, respectively. If Northshore decides to materially reduce the percentage of ore mined, or pellets shipped, from Mesabi Trust lands, the income of the Trust could be adversely affected.
The global economic climate and the recent disruption in the financial and credit markets have created uncertainty and a prolonged downturn in global economic conditions could adversely affect the royalties received by the Trust.
The volatile global economic climate and the recent global financial and credit crisis could have a material adverse effect on the royalties received by the Trust. Financial markets in the United States and elsewhere have been experiencing extreme disruption, including, among other things, extreme volatility in security prices, diminished liquidity and credit availability, ratings downgrades of certain investments and declining values of others. The global economy is struggling to exit a recession. In 2009 Cliffs announced
4
production curtailments, workforce reductions and an extended idling of production at Northshore. Deterioration or worsening of economic conditions, prolonged global, national or regional economic instability or other events could produce major changes in demand patterns and may have a material adverse effect on sales prices of iron ore products shipped by Northshore which would adversely affect the royalties received by the Trust. Moreover, such conditions could impact the international benchmark pellet price, hot band steel prices and various Producer Price Indexes all of which affect the royalties payable to the Trust. The Trustees are not able to predict the impact the volatile global economic climate and the recent global financial and credit crisis will have on future royalties payable to the Trust.
The world price of iron ore and steel are strongly influenced by international demand and global market conditions which are uncertain. Domestic demand for iron ore and steel products, which is influenced by international markets, is also uncertain. In recent years, many major iron ore suppliers increased their capacity to meet the increased demand for iron ore and steel products, particularly from China. Despite some signs that the global economic environment is improving, there is a high degree of uncertainty concerning the overall demand for steel and iron ore products. Reduced demand for iron ore will likely result in decreased sales of products to Cliffs’ customers and decreasing prices, all of which would adversely affect royalties received by the Trust in 2010. Since the Trust is not party to any specific customer contracts that Cliffs has with its customers and because these macroeconomic forces are difficult to forecast, the Trustees are not able to predict the extent to which reduced demand and lower prices for iron ore products will adversely affect royalties payable to the Trust.
The royalties payable to the Trust could be adversely affected by the failure of the Trust’s independent experts to competently perform.
As permitted by the terms of the Agreement of Trust and the Amendment, the Trustees are entitled to, and in fact do rely, upon certain experts to assist the Trustees in carrying out and fulfilling their obligations as Trustees. Independent consultants perform services, render advice and produce reports with respect to monthly production and shipments, which include figures on crude ore production, iron ore pellet production, iron ore pellet shipments, and discussions concerning the condition and accuracy of the scales used to weigh iron ore pellets produced at Northshore’s facilities. The Trustees have also retained an accounting firm to provide non-audit services, including preparing financial statements, reviewing financial data related to shipping and sales reports provided by Northshore and reviewing the schedule of leasehold and fee royalties payable to the Trust. The Trustees believe that the independent experts are qualified to perform the services and functions assigned to them. Nevertheless, any negligence or the failure of any such independent expert to competently perform could adversely affect the royalties received by the Trust.
The Trust relies on Cliffs’ estimates of recoverable reserves and if those estimates are inaccurate the total potential future royalty stream to the Trust and distributions payable to each Unitholder may be adversely affected.
The Trustees do not participate in preparing the ore reserve estimate reported by Cliffs. According to Cliffs’ Form 10-K, Cliffs regularly evaluates its iron ore reserves based on revenues and costs and updates them as required in accordance with Securities Act Industry Guide 7, promulgated by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. In 2010, the Trustees engaged an independent firm of geological experts to evaluate the process Cliffs uses to estimate the mineral reserves at the Peter Mitchell Mine. Still, there are numerous uncertainties inherent in estimating quantities of reserves of mineral producing lands and such estimates necessarily depend upon a number of variable factors and assumptions, such as production capacity, effects of regulations by governmental agencies, future prices for iron ore, future industry conditions and operating costs,
5
severance and excise taxes, development costs and costs of extraction and reclamation costs, all of which may in fact vary considerably from actual results. For these reasons, estimates of the economically recoverable quantities of mineralized deposits attributable to the lands owned by Mesabi Trust and the classifications of such reserves based on the risk of recovery prepared by different engineers or by the same engineers at different times may vary substantially as the criteria change. Cliffs’ estimate of the ore reserves could be negatively affected by future industry conditions, geological conditions and ongoing mine planning at the Peter Mitchell Mine. Actual reserves and therefore actual royalties will likely vary from estimates, and if such variances are negative and material, the expected royalties of the Trust could be adversely affected and the value of the Trust’s Units could decline.
The operations at Northshore are largely dependent on a single-source energy supplier.
The operations at Northshore are largely dependent on Silver Bay Power Company, a 115 megawatt power plant, for its electrical supply. Silver Bay Power Company, which is wholly owned by Northshore, has an interconnection agreement with Minnesota Power, Inc. for backup power, and sells 40 megawatts of excess power capacity to Xcel Energy under a contract that extends to 2011. A significant interruption in service from Silver Bay Power Company due to vandalism, terrorism, weather conditions, natural disasters, or any other cause could cause a decrease in production capacity or require a temporary shutdown of Northshore’s operations. In addition, one natural gas pipeline serves all of Cliffs’ Minnesota mines, and a pipeline failure could idle or substantially impair the operations at Northshore. Any substantial interruption of, or material reduction in, Northshore’s operations could adversely affect the royalties received by the Trust.
The mining operations of Northshore are subject to extensive governmental regulation and Northshore is subject to risks related to its compliance with federal and state environmental regulations.
Northshore, as the owner/operator of the Peter Mitchell Mine, is subject to various federal, state and local laws and regulations on matters such as employee health and safety, air quality, water pollution, plant and wildlife protection, reclamation and restoration of mining properties, the discharge of materials into the environment, and the effects that mining has on groundwater quality and availability. Northshore is required to maintain permits and approvals issued by federal and state regulatory agencies and its mining operations are subject to inspection and regulation by the Mine Safety and Health Administration of the United States Department of Labor (“MSHA”) under the provisions of the Mine Safety and Health Act of 1977. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (“OSHA”) also has jurisdiction over safety and health standards not covered by MSHA and the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency (“MPCA”) regulates various aspects of Northshore’s operations. Northshore is involved in litigation with the MPCA over certain air quality permitting matters but because the Trust has no control over Northshore’s operations, the potential impact of these proceedings cannot be determined. Moreover, Northshore is solely responsible for its compliance with any laws, regulations or permits applicable to Northshore’s operations and therefore the Trust cannot determine whether Northshore has been or will continue to be in compliance with such laws and regulations. If Northshore fails to comply with these laws, regulations or permits, it could be subject to fines or other sanctions, any of which could have an adverse effect on its operations and its ability to ship iron ore products from Silver Bay, Minnesota, which could, in turn, have an adverse effect on the royalties paid to the Trust.
Equipment failures and other unexpected events at Northshore may lead to production curtailments or shutdowns.
Interruptions in production capabilities at the mine operated by Northshore may have an adverse impact on the royalties payable to the Trust. In addition to planned production shutdowns and curtailments, equipment
6
failures, the Northshore facilities are also subject to the risk of loss due to unanticipated events such as fires, explosions or extreme weather conditions. The manufacturing processes that take place in Northshore’s mining operations, as well as in its crushing, concentrating and pelletizing facilities, depend on critical pieces of equipment, such as drilling and blasting equipment, crushers, grinding mills, pebble mills, thickeners, separators, filters, mixers, furnaces, kilns and rolling equipment, as well as electrical equipment, such as transformers. It is possible that this equipment may, on occasion, be out of service because of unanticipated failures or unforeseeable acts of vandalism or terrorism. In addition, because the Northshore mine and processing facilities have been in operation for several decades, some of the equipment is aged. Because the Trustees have no control over the operations or maintenance of the equipment at Northshore, a shutdown or reduction in capacity may come with little or no advance warning. The remediation of any interruption in production capability at Northshore could require Cliffs to make large capital expenditures which may take place over an extended period of time. A shutdown or reduction in operations at Northshore could adversely affect the royalties paid to the Trust.
If steelmakers use methods other than blast furnace production to produce steel, shut down or reduce production using blast furnaces, the demand for iron ore pellets may decrease.
Demand for iron ore pellets is determined by the operating rates for the blast furnaces of steel companies. However, not all finished steel is produced by blast furnaces; finished steel also may be produced by other methods that do not require iron ore pellets. For example, steel “mini-mills,” which are steel recyclers, generally produce steel by using scrap steel, not iron ore pellets, in their electric furnaces. North American steel producers also can produce steel using imported iron ore or semi-finished steel products, which eliminates the need for domestic iron ore. Environmental restrictions on the use of blast furnaces also may reduce the use of their blast furnaces in steel production. Because the maintenance of blast furnaces can require substantial capital expenditures, manufacturers may choose not to maintain their blast furnaces, and some of them may not have the resources necessary to adequately maintain their blast furnaces. If steel manufacturers significantly alter the methods they use to produce steel or otherwise substantially reduce their use of iron ore pellets, demand for iron ore pellets will decrease, which could adversely affect the royalties paid to the Trust.
Risk factors affecting Cliffs’ North American Iron Ore Business and Operations at Northshore could have a material adverse effect on the royalties of the Trust.
Because substantially all of the Trust’s revenue is derived from iron ore products shipped by Northshore from Silver Bay, Northshore’s iron ore pellet processing and shipping activities directly impact the Trust’s revenues in each quarter and each year. A number of factors affect Cliffs’ operations, including Northshore’s production and shipment volume. These factors which are described in Cliffs’ Form 10-K filed February 18, 2010 include, among others, the global economic climate and financial market conditions, economic conditions in the iron ore industry, extensive governmental regulation relating to environmental matters and the costs and risks related thereto, availability of substitute materials, pricing by domestic and international competitors, long-term customer contracts or arrangements by Northshore or its competitors, price adjustment provisions in Cliffs’ North American term supply agreements (which take into account various price indexes), availability of ore boats, production at Northshore’s mining operations, natural disasters, shipping conditions in the Great Lakes and production at Northshore’s pelletizing/processing facility. Specifically, if any portion of Northshore’s pelletizing lines becomes idle for any reason, production, shipments and, consequently, the royalties paid to the Trust could be adversely affected.
7
The Trustees are not subject to annual election and, as a result, the ability of the holders of Certificates of Beneficial Interest to influence the policies of the Trust may be limited.
Directors of a corporation are generally subject to election at each annual meeting of stockholders or, in the case of staggered boards, at regular intervals. Under the Agreement of Trust, however, the Trust is not required to hold annual meetings of holders of Certificates of Beneficial Interest to elect Trustees and Trustees generally hold office until their death, resignation or disqualification. As a result, the ability of holders of Certificates of Beneficial Interest to effect changes in the Board of Trustees, and the policies of the Trust, is significantly more limited than that of the stockholders of a corporation.
OVERVIEW OF TRUST’S ROYALTY STRUCTURE
Leasehold royalty income constitutes the principal source of the Trust’s revenue. Royalty rates are determined in accordance with the terms of Mesabi Trust’s leases and assignments of leases. Three types of royalties, as well as royalty bonuses, comprise the Trust’s royalty income:
· Base overriding royalties. Base overriding royalties have historically constituted the majority of Mesabi Trust’s royalty income. Base overriding royalties are determined by both the volume and selling price of iron ore products shipped. Northshore is obligated to pay Mesabi Trust base overriding royalties in varying amounts, based on the volume of iron ore products shipped. Base overriding royalties are calculated as a percentage of the gross proceeds of iron ore products produced at Mesabi Trust lands (and to a limited extent other lands) and shipped from Silver Bay, Minnesota. The percentage ranges from 2-1/2% of the gross proceeds for the first one million tons of iron ore products so shipped annually to 6% of the gross proceeds for all iron ore products in excess of 4 million tons so shipped annually. Base overriding royalties are subject to interim and final price adjustments under the Cliffs Pellet Agreements and, as described elsewhere in this report, such adjustments may be positive or negative.
· Royalty bonuses. The Trust earns royalty bonuses when iron ore products shipped from Silver Bay are sold at prices above a threshold price per ton. The royalty bonus is based on a percentage of the gross proceeds of product shipped from Silver Bay and sold at prices above a threshold price. The threshold price is adjusted (but not below $30.00 per ton) on an annual basis for inflation and deflation (the “Adjusted Threshold Price”). The Adjusted Threshold Price was $47.43 per ton for calendar year 2008, $48.48 per ton for calendar year 2009 and will be $48.81 per ton for calendar year 2010. The royalty bonus percentage ranges from 1/2 of 1% of the gross proceeds (on all tonnage shipped for sale at prices between the Adjusted Threshold Price and $2.00 above the Adjusted Threshold Price) to 3% of the gross proceeds (on all tonnage shipped for sale at prices $10.00 or more above the Adjusted Threshold Price). Royalty bonuses are subject to price adjustments under the Cliffs Pellet Agreements (described elsewhere in this Annual Report); such adjustments may be positive or negative. See the section entitled “Comparison of Financial Results for Fiscal Years ended January 31, 2010 and January 31, 2009” on page 12 of this Annual Report for more information.
· Fee royalties. Fee royalties have historically constituted a smaller component of the Trust’s total royalty income. Fee royalties are payable to the Mesabi Land Trust, a Minnesota land trust, which holds a 20% interest as fee owner in the Amended Assignment of Peters Lease. Mesabi Trust holds the entire beneficial interest in the Mesabi Land Trust for which U.S. Bank N.A. acts as the corporate trustee. Mesabi Trust receives the net income of the Mesabi Land Trust, which is
8
generated from royalties on the amount of crude ore mined after the payment of expenses to U.S. Bank N.A. for its services as corporate trustee. Crude ore is the source of iron oxides used to make iron ore pellets and other products. The fee royalty on crude ore is based on an agreed price per ton, subject to certain indexing.
· Minimum advance royalties. Northshore’s obligation to pay base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses with respect to the sale of iron ore products generally accrues upon the shipment of those products from Silver Bay. However, regardless of whether any shipment has occurred, Northshore is obligated to pay to Mesabi Trust a minimum advance royalty. Each year, the amount of the minimum advance royalty is adjusted (but not below $500,000 per annum) for inflation and deflation. The minimum advance royalty was $790,721 for calendar year 2008, $808,177 for calendar year 2009 and is $813,729 for calendar year 2010. Until overriding royalties (and royalty bonuses, if any) for a particular year equal or exceed the minimum advance royalty for the year, Northshore must make quarterly payments of up to 25% of the minimum advance royalty for the year. Because minimum advance royalties are essentially prepayments of base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses earned each year, any minimum advance royalties paid in a fiscal quarter are recouped by credits against base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses earned in later fiscal quarters during the year.
The current royalty rate schedule became effective on August 17, 1989 pursuant to the Amended Assignment Agreements, which the Trust entered into with Cyprus Northshore Mining Corporation (“Cyprus NMC”). Pursuant to the Amended Assignment Agreements, overriding royalties are determined by both the volume and selling price of iron ore products shipped. In 1994, Cyprus NMC was sold by its parent corporation to Cliffs and renamed Northshore Mining Company. Cliffs now operates Northshore as a wholly owned subsidiary.
Under the relevant agreements, Northshore has the right to mine and ship iron ore products from lands other than Mesabi Trust lands. Northshore alone determines whether to conduct mining operations on Trust and/or such other lands based on its current mining and engineering plan. The Trustees do not exert any influence over mining operational decisions. To encourage the use of iron ore products from Mesabi Trust lands, Mesabi Trust receives royalties on stated percentages of iron ore shipped from Silver Bay, whether or not the iron ore products are from Mesabi Trust lands. Mesabi Trust receives royalties at the greater of (i) the aggregate quantity of iron ore products shipped that were mined from Mesabi Trust lands, and (ii) a portion of the aggregate quantity of all iron ore products shipped from Silver Bay that were mined from any lands, such portion being 90% of the first four million tons shipped from Silver Bay during such year, 85% of the next two million tons shipped during such year, and 25% of all tonnage shipped during such year in excess of six million tons.
Royalty income constitutes the principal source of the Trust’s revenue, which comprised 99.9%, 99.9% and 99.7% of the total revenue of the Trust in fiscal years ended 2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively. A more complete discussion of royalty rates and the manner in which they are determined is set forth under the headings “Leasehold Royalties” and “Land Trust and Fee Royalties,” beginning on pages 25 and 28, respectively, of this Annual Report.
During the course of its fiscal year some portion of royalties expected to be paid to Mesabi Trust is based in part on estimated prices for iron ore products sold under term contracts between Northshore, Cliffs and certain of their customers (the “Cliffs Pellet Agreements”). The Cliffs Pellet Agreements use estimated prices which are subject to interim and final pricing adjustments, which can be positive or negative, and which
9
adjustments are dependent in part on multiple price and inflation index factors that are not known until after the end of a contract year. Even though Mesabi Trust is not a party to the Cliffs Pellet Agreements, these adjustments can result in significant variations in royalties received by Mesabi Trust (and in turn the resulting amount available for distribution to Unitholders by the Trust) from quarter to quarter and on a comparative historical basis, and these variations, which can be positive or negative, cannot be predicted by Mesabi Trust. In either case, these price adjustments will impact future royalties received by the Trust that become available for distribution to Unitholders.
As described elsewhere in this Annual Report, the royalty percentage paid to the Trust increases as the aggregate tonnage of iron ore products shipped, attributable to the Trust, in any calendar year increases past each of the first four one-million ton volume thresholds. Assuming a consistent sales price per ton throughout a calendar year, shipments of iron ore product attributable to the Trust later in the year generate a higher royalty to the Trust, as total shipments for the year exceed increasing levels of royalty percentages and pass each of the first four one-million ton volume thresholds.
As also described elsewhere in this Annual Report, the Trust receives a bonus royalty equal to a percentage of the gross proceeds of iron ore products (mined from Mesabi Trust lands) shipped from Silver Bay and sold at prices above the Adjusted Threshold Price. Although Cliffs was able to sell all of the iron ore products at prices higher than the Adjusted Threshold Price during calendar 2009, the Trustees are unable to project whether Northshore will continue to be able to sell pellets at prices above the applicable Adjusted Threshold Price, entitling the Trust to any future bonus royalty payments.
SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
| | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 | |
Years ended on January 31 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Royalty and interest income | | $ | 13,241,669 | | $ | 35,469,105 | | $ | 18,866,511 | | $ | 17,902,988 | | $ | 21,579,833 | |
Trust expenses | | 818,007 | | 799,320 | | 634,151 | | 756,322 | | 844,956 | |
Net income(1) | | $ | 12,423,662 | | $ | 34,669,785 | | $ | 18,232,360 | | $ | 17,146,666 | | $ | 20,734,877 | |
Net income per Unit(2) | | $ | 0.95 | | $ | 2.64 | | $ | 1.39 | | $ | 1.31 | | $ | 1.58 | |
Distributions declared Per unit(2)(3) | | $ | 1.15 | | $ | 2.48 | | $ | 1.35 | | $ | 1.60 | | $ | 1.53 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Years ended on January 31 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Assets | | $ | 11,199,575 | | $ | 5,346,932 | | $ | 8,488,509 | | $ | 5,414,552 | | $ | 11,328,959 | |
(1) The Trust, as a grantor trust, is exempt from federal and state income taxes.
(2) Based on 13,120,010 Units of Beneficial Interest outstanding during all years.
(3) During the Trust’s fiscal year ended January 31, 2010, the Trustees distributed $0.71 per Unit (including $0.11 per Unit declared in fiscal 2009 but distributed in fiscal 2010 (February 2009)) and in fiscal 2010 declared a distribution of $0.55 per Unit payable in February 2010, the next fiscal year. During the Trust’s fiscal year ended January 31, 2009, the Trustees distributed $2.885 per Unit (including $0.515 per Unit declared in fiscal 2008 but distributed in fiscal 2009 (February 2008)) and in fiscal 2009 declared a distribution of $0.11 per Unit payable in February 2009, the next fiscal year. During the Trust’s fiscal year ended January 31, 2008, the Trustees distributed $1.15 per Unit (including $0.315 per Unit declared in fiscal 2007 but distributed in fiscal 2008 (February 2007)) and in fiscal 2008 declared a distribution of $0.515 per Unit payable in February 2008, the next fiscal year. During the Trust’s fiscal year ended January 31, 2007, the Trustees distributed $1.755 per Unit (including $0.47 per Unit declared in fiscal 2006 but distributed in fiscal 2007 (February 2006)) and in fiscal 2007 declared a distribution of $0.315 per Unit payable in February 2007, the next fiscal year. During the Trust’s fiscal year ended January 31, 2006, the Trustees distributed $1.355 per Unit (including $0.295 per Unit declared in fiscal 2005 but distributed in fiscal 2006 (February 2005)) and in fiscal 2006 declared a distribution of $0.47 per Unit payable in February 2006, the next fiscal year.
10
TRUSTEES’ DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL
CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Results of Operations
Comparison of Iron Ore Pellet Production and Shipments for the Fiscal Years Ended January 31, 2010, January 31, 2009 and January 31, 2008
During fiscal 2010, production attributed to Trust lands totaled approximately 3.14 million tons, a decrease of 34.2% and 33.4% as compared to production for fiscal years 2009 and 2008, respectively. Shipments to Northshore’s customers attributed to the Trust totaled approximately 3.24 million tons during fiscal 2010. This represents a decrease of 37% and 23.7%, respectively, as compared to shipments for fiscal years 2009 and 2008. The table below, which is based on information provided to the Trust by Northshore, shows the total production and total shipments of iron ore pellets from Mesabi Trust lands during the prior three fiscal years.
Fiscal Year Ended | | Pellets Produced from
Trust Lands
(Tons) | | Pellets Shipped from
Trust Lands
(Tons) | |
January 31, 2010 | | 3,141,395 | | 3,241,237 | |
January 31, 2009 | | 4,774,939 | | 5,146,687 | |
January 31, 2008 | | 4,719,005 | | 4,248,785 | |
Production of iron ore pellets was slightly lower for the fourth quarter of fiscal 2010 as compared to the fourth quarter of fiscal 2009, decreasing 2.8%. However, shipments of iron ore pellets by Northshore during the fourth quarter of fiscal 2010 increased 2,504%. The significant increase in shipments in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2010 is due to the return of more robust customer demand in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2010, as compared to the fourth quarter of fiscal 2009, combined with a dramatic decline in shipments in the fourth fiscal quarter of 2009. Notwithstanding the significant increase in shipments in the fourth quarter, as shown in the table below, shipments attributable to the Trust decreased 37% during fiscal 2010, as compared to fiscal 2009.
Three Months Ended | | Pellets Produced from
Trust Lands
(Tons) | | Pellets Shipped from
Trust Lands
(Tons) | |
January 31, 2010 | | 1,059,310 | | 1,417,425 | |
| | | | | |
January 31, 2009 | | 1,089,757 | | 54,429 | |
The table below shows the change in the percentages of production and shipments from lands owned or leased by Mesabi Trust versus the percentages of production and shipments from lands owned by the State of Minnesota for the most recent three fiscal years.
Fiscal Year Ended | | Percentage of
Pellets Produced
From Trust
Lands | | Percentage of
Pellets Produced
From State
Lands | | Percentage of
Pellets
Shipped
From Trust
Lands | | Percentage of
Pellets
Shipped
From State
Lands | |
January 31, 2010 | | 95.9 | % | 4.1 | % | 93.0 | % | 7.0 | % |
January 31, 2009 | | 87.8 | % | 12.2 | % | 90.2 | % | 9.8 | % |
January 31, 2008 | | 91.7 | % | 8.3 | % | 88.2 | % | 11.8 | % |
11
As is the case with the volume of shipments from Silver Bay, Minnesota, the Trustees cannot predict what percentage of production or shipments will be attributable to Mesabi Trust lands in fiscal 2011. However, pursuant to the Amendment, Mesabi Trust will be credited with at least 90% of the first four million tons of iron ore pellets shipped from Silver Bay, Minnesota in each calendar year, at least 85% of the next two million tons of pellets shipped from Silver Bay, Minnesota in each calendar year, and at least 25% of all tons of pellets shipped from Silver Bay, Minnesota in each calendar year in excess of six million tons.
Comparison of Financial Results for Fiscal Years ended January 31, 2010 and January 31, 2009
Royalty Income
As shown in the table below, in fiscal 2010 there was a 64.9% decrease in base royalties and a 60% decrease in bonus royalties, each as compared to fiscal 2009. Accordingly, the Trust’s total royalty income decreased 62.7% in fiscal 2010 as compared to fiscal 2009. The significant decrease in royalties received by the Trust is primarily the result of lower average selling price for each ton of iron ore shipped from Silver Bay, Minnesota in fiscal 2010, as compared to fiscal 2009, and a decrease in shipments in fiscal 2010 as compared to fiscal 2009.
| | Fiscal Years Ended on January 31, | | % increase | |
| | 2010 | | 2009 | | (decrease) | |
Base overriding royalties | | $ | 7,522,767 | | $ | 21,442,218 | | (64.9 | )% |
Bonus royalties | | 5,401,563 | | 13,454,580 | | (60.0 | )% |
Minimum advance royalty paid (recouped) | | — | | — | | | |
Fee royalties | | 305,407 | | 525,851 | | (41.9 | )% |
Total royalty income | | $ | 13,229,737 | | $ | 35,422,649 | | (62.7 | )% |
The royalty amounts set forth in the table above include pricing adjustments made to royalty payments previously received by the Trust based on shipments from Silver Bay, Minnesota during prior calendar years. Depending on the year, the volume of shipments, and the interim and final price paid to the Trust for shipments from Silver Bay, Minnesota, the price adjustments provisions of the Cliffs Pellet Agreements may increase or decrease, in some cases materially, the distributions payable to Unitholders. Because the Trust is not a party to the Cliffs Pellet Agreements, the Trustees are unable to determine the extent of any pricing adjustments that may occur under the Cliffs Pellet Agreements or whether the adjustments will increase or decrease royalties received by the Trust. With the current volatility in demand and prices for iron ore and steel products, the price adjustment provisions in the Cliffs Pellet Agreements may have a significant impact on future royalties received by the Trust and the adjustments, depending on whether they are positive or negative, may increase or decrease the distributions payable to Unitholders.
Gross Income, Expenses, Net Income and Distributions
As set forth in the table below, net income for fiscal 2010 decreased 64.2% as compared to fiscal 2009 primarily due to a decrease in gross income related to the decrease in shipments and selling price of iron ore pellets. Total expenses for fiscal 2010 increased 2.3% as compared to fiscal 2009 due to a slight increase in legal and accounting fees and other fees related to the administration of the Trust. A more detailed summary of the Trust’s expenses, including legal and accounting expenses, is set forth under the heading “Trust Expenses” on page 28 of this Annual Report.
12
| | Fiscal Years Ended on January 31, | | % increase | |
| | 2010 | | 2009 | | (decrease) | |
Gross Income | | $ | 13,241,669 | | $ | 35,469,105 | | (62.8 | )% |
Expenses | | 818,007 | | 799,320 | | 2.3 | % |
Net Income | | $ | 12,423,662 | | $ | 34,669,785 | | (64.2 | )% |
As discussed in the paragraph above, the Trust’s total royalty income and net income for fiscal 2010 decreased 62.8% and 64.2% respectively, due to decreased shipping activity during fiscal 2010 and the lower prices paid to the Trust for shipments, both as compared to fiscal year 2009. The decrease in the Trust’s net income, combined with an increase in the Trust’s cash reserve for unexpected losses, resulted in a 75.4% decrease in total distributions paid to Unitholders in fiscal 2010, as compared to fiscal year 2009.
| | Fiscal Years Ended on January 31, | | % increase | |
| | 2010 | | 2009 | | (decrease) | |
Total Cash Distributions | | $ | 9,315,207 | | $ | 37,851,229 | | (75.4 | )% |
Distributions Paid per Unit | | $ | 0.71 | | $ | 2.885 | | (75.4 | )% |
Unallocated Reserve
As set forth below, the Unallocated Reserve, decreased $2,664,349 or 70.3% to $1,127,832, as of January 31, 2010, as compared to $3,792,181 as of January 31, 2009. As of January 31, 2010, the Unallocated Reserve consisted of $3,023,894 in unallocated cash and U.S. Government securities, $873,938 of accrued income receivable, primarily representing royalties not yet received by the Trust but anticipated to be received in fiscal 2011, less deferred royalty revenue of ($2,770,000). Comparatively, as of January 31, 2009, the Unallocated Reserve consisted of $1,070,203 in unallocated cash and U.S. Government securities and, $2,721,978 of accrued income receivable.
| | Fiscal Years Ended on January 31, | | % increase | |
| | 2010 | | 2009 | | (decrease) | |
Accrued Income Receivable | | $ | 873,938 | | $ | 2,721,978 | | (67.9 | )% |
Deferred Royalty Revenue | | (2,770,000 | ) | — | | 100 | % |
Cash Reserve | | 3,023,894 | | 1,070,203 | | 182.6 | % |
Unallocated Reserve | | $ | 1,127,832 | | $ | 3,792,181 | | (70.3 | )% |
The 70.3% decrease in the Unallocated Reserve is primarily attributable to the Trust’s deferred royalty revenue. In April 2009, the Trust received a payment from Northshore but did not recognize the entire payment as revenue in accordance with the Trust’s revenue recognition policy. Because of declines in the estimated pricing of iron ore pellets subsequent to January 31, 2009, the royalty payment received by the Trust in April 2009 included funds received by the Trust but for which the Trust has not recognized as revenue in accordance with the Trust’s revenue recognition policy which is described in Note 2 to the Trust’s consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report. Depending on future adjustments to iron ore pellet pricing, if any, the deferred royalty revenue could cause a cumulative negative price adjustment related to shipments of pellets during prior periods, which could partially or even completely offset future royalty income to be received by the Trust.
The decrease in the Unallocated Reserve as of January 31, 2010, is also attributable to a $1,848,040, or 67.9%, decrease in the accrued income receivable portion of the Unallocated Reserve which decreased to $873,938 as of January 31, 2010 from $2,721,978 as of January 31, 2009. The decrease in accrued income receivable is the result of fewer positive pricing adjustments for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2010, as
13
compared to the fiscal year ended January 31, 2009. In accordance with the Cliffs Pellet Agreements, there were positive and negative price adjustments that are determined and finalized by Cliffs each calendar year with respect to shipments by the Trust in earlier calendar years. However, these negative pricing adjustments were partially offset due to higher shipments by the Trust during January 2010 and an accrual for positive price adjustments with respect to tonnage shipped by Northshore as of December 31, 2009, that is estimated using current pricing information provided by Northshore.
The Trust’s cash reserve for unexpected losses increased 182.6% to $3,023,894 as of January 31, 2010 from $1,070,203 as of January 31, 2009. The increase in the Trust’s cash reserve is due to the Trustees’ decision to add to the Trust’s cash reserve because of the Trust’s deferred royalty revenue for fiscal 2010, the use of estimates regarding pricing that is potentially subject to negative adjustment in future periods, and as a result of the continuing uncertainty in the economic environment that affects the royalties paid to the Trust by Northshore under Cliffs Pellet Agreements. It is possible that future negative price adjustments could offset, or even eliminate, royalties or royalty income that would otherwise be payable to the Trust in any particular quarter, or at year end, thereby potentially reducing cash available for distribution to the Trust’s Unitholders in future quarters. See discussion under the heading “Risk Factors” beginning on page 3 of this Annual Report.
The Trustees have determined that the unallocated cash and U.S. Government securities portion of the Unallocated Reserve should be maintained at a prudent level, usually within the range of $500,000 to $1,000,000, to meet present or future liabilities of the Trust. As a result of the deferred royalty revenue recorded by the Trust as a liability, the Trustees have determined that it is prudent to increase the unallocated cash and U.S. Government securities portion of the Unallocated Reserve above the range of $500,000 to $1,000,000. See the discussion under the heading “Unallocated Reserve” on page 29 of this Annual Report for more information on the Trust’s policy for maintaining a cash reserve for unexpected losses. The Trustees will continue to monitor the economic circumstances of the Trust to strike a responsible balance between distributions to Unitholders and the need to maintain reserves at a prudent level, given the unpredictable nature of the iron ore industry, the Trust’s dependence on the actions of the lessee/operator, and the fact that the Trust essentially has no other liquid assets.
Comparison of Financial Results for Fiscal Years ended January 31, 2009 and January 31, 2008
Royalty Income
The increase in the volume of shipments and the higher average selling price for each ton of iron ore both contributed to the 101.8% increase in base royalties and the 74.3% increase in bonus royalties for fiscal 2009, both as compared to fiscal 2008. Accordingly, total royalty income increased 88.3% in fiscal 2009 as compared to fiscal 2008. The significant increase in royalties received by the Trust is primarily the result of higher average selling price for each ton of iron ore shipped from Silver Bay, Minnesota in fiscal 2009, as compared to fiscal 2008, and an increase in shipments in fiscal 2009 as compared to fiscal 2008.
| | Fiscal Years Ended on January 31, | | % increase | |
| | 2009 | | 2008 | | (decrease) | |
Base overriding royalties | | $ | 21,442,218 | | $ | 10,624,935 | | 101.8 | % |
Bonus royalties | | 13,454,580 | | 7,717,513 | | 74.3 | % |
Minimum advance royalty paid (recouped) | | — | | — | | | |
Fee royalties | | 525,851 | | 474,094 | | 10.9 | % |
Total royalty income | | $ | 35,422,649 | | $ | 18,816,542 | | 88.3 | % |
14
Gross Income, Expenses, Net Income and Cash Distributions
Net income for fiscal 2009 increased 90.2% as compared to fiscal 2008 primarily due to an increase in gross income related to the increase in shipments and selling price of iron ore pellets. In addition, total expenses for fiscal 2009 increased as compared to fiscal 2008 as a result of increases in legal and accounting fees and other fees related to the administration of the Trust. A summary of the Trust’s expenses is set forth under the heading “Trust Expenses” on page 28 of this Annual Report.
| | Fiscal Years Ended on January 31, | | % increase | |
| | 2009 | | 2008 | | (decrease) | |
Gross Income | | $ | 35,469,105 | | $ | 18,866,511 | | 88.0 | % |
Expenses | | 799,320 | | 634,151 | | 26.1 | % |
Net Income | | $ | 34,669,785 | | $ | 18,232,360 | | 90.2 | % |
The Trust’s gross income and net income for fiscal 2009 increased 88.0% and 90.2% respectively, resulting in an increase in total distributions paid to Unitholders in fiscal 2009 of 150.9% as compared to fiscal 2008. The significant increase in total cash distributions and distributions per unit in fiscal 2009, as compared to fiscal 2008, is primarily due to increased shipping activity in the fourth calendar quarter of 2008 and increased shipping activity at significantly higher prices with respect to shipments during fiscal 2009.
| | Fiscal Years Ended on January 31, | | % increase | |
| | 2009 | | 2008 | | (decrease) | |
Total Cash Distributions | | $ | 37,851,229 | | $ | 15,088,012 | | 150.9 | % |
Distributions Paid per Unit | | $ | 2.885 | | $ | 1.150 | | 150.9 | % |
Unallocated Reserve
The Unallocated Reserve, which is comprised of accrued income receivable and cash reserve for unexpected losses, increased $2,132,160 or 128.4% to $3,792,181, as of January 31, 2009, as compared to $1,660,021 as of January 31, 2008. The increase in the Unallocated Reserve as of January 31, 2009, is primarily due to a $1,762,053, or 183.6%, increase in the accrued income receivable portion of the Unallocated Reserve which increased to $2,721,978 as of January 31, 2009 from $959,925 as of January 31, 2008. The significant increase in accrued income receivable is due to positive pricing adjustments that were determined and finalized under the Cliffs Pellet Agreements with respect to shipments by the Trust in calendar 2007 and calendar 2008.
| | Fiscal Years Ended on January 31, | | % increase | |
| | 2009 | | 2008 | | (decrease) | |
Accrued Income Receivable | | $ | 2,721,978 | | $ | 959,925 | | 183.6 | % |
Cash Reserve | | $ | 1,070,203 | | $ | 700,096 | | 52.9 | % |
Unallocated Reserve | | $ | 3,792,181 | | $ | 1,660,021 | | 128.4 | % |
Liquidity and Capital Resources
The Trust’s activities are limited to the collection of royalty income, payment of expenses and liabilities, distribution of net income to the Trust’s Unitholders and protection and conservation of Trust assets. Distributions of net income to Unitholders are based on the amount of total royalty income after providing for the payment of expenses and, to the extent deemed prudent by the Trustees, reserving funds in the Unallocated
15
Reserve to provide for potential fixed or contingent future liabilities. See the discussion of the Trustees’ management of liquidity set forth under the heading “Unallocated Reserve” beginning on page 29 of this Annual Report.
The Trust’s primary short-term liquidity needs are to fund the distributions to Unitholders following the Trust’s receipt of the royalty payments from Northshore each calendar quarter. After the Trust receives the royalty payments, the Trust’s current assets are invested in U.S. government securities, either through direct purchases of U.S. government securities or through investments in a money market fund that invests its assets in U.S. Treasury securities and securities guaranteed by the U.S. government its agencies or instrumentalities, or the FDIC. Due to the short-term duration and investment grade nature of these investments, the Trustees believe that the Trust’s current assets are adequate to meet the Trust’s currently foreseeable liquidity needs. As of January 31, 2010, the Trust held $8,444,697 in cash and cash equivalents of which $24,788 was invested in a money market fund that exclusively invests in obligations of the U.S. Treasury. In February 2010, the Trust distributed $7,216,005 to Unitholders of record on January 30, 2010.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
The Trust has no off-balance sheet arrangements.
Contractual Obligations
The Trust has no payment obligations under any long-term borrowings, capital lease, operating lease, or purchase agreement.
Critical Accounting Estimates
This “Trustees’ Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” is based upon the Trust’s financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States. The preparation of these financial statements requires the Trustees to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. These estimates form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. The Trustees base their estimates and judgments on historical experience and on various other assumptions that the Trustees believe are reasonable under the circumstances. However, because future events and their effects cannot be determined with certainty, actual results could differ from our assumptions and estimates, and such differences could be material. Critical accounting policies are those that have meaningful impact on the reporting of the Trust’s financial condition and results of operations, and that require significant judgment and estimates. For a complete description of the Trust’s significant accounting policies, please see Note 2 to the financial statements on pages F-9 through F-13.
Revenue Recognition
Royalty income under the amended lease agreements with Northshore is recognized as it is earned. Under such agreements, royalties are earned upon shipment from Silver Bay, Minnesota, regardless of whether the actual sales proceeds for any shipment are received by Northshore. The amount of base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses payable to the Trust are determined based on the volume of iron ore tonnage shipped from Silver Bay, Minnesota during each calendar quarter and the proceeds to Cliffs resulting from shipments by Cliffs to its customers in accordance with the iron ore pellet sales agreements between Cliffs and its customers.
16
The Trust’s royalty income includes accrued income receivable. Accrued income receivable represents royalty income earned but not yet received by the Trust. Accrued income receivable is calculated using estimated prices and includes (i) shipments during the last month of Mesabi Trust’s fiscal year, if any, and (ii) positive price adjustments under the pricing adjustment mechanisms in the iron ore pellet sales agreements between Cliffs and its customers that determine the final sales price of the shipments from Silver Bay, Minnesota.
Deferred royalty revenue represents an estimate of potential decreases in the Trust’s royalty revenue due to negative price adjustments anticipated to be applied to tons of iron ore that were shipped by Northshore, but for which Northshore has indicated that final pricing is not yet known. The royalty revenue received by the Trust for certain tons of iron ore shipped by Northshore is subject to adjustment in accordance with the Trust’s revenue recognition policy each quarter as updated pricing information is received from Northshore. Accordingly, it is possible that changes in iron ore pellet pricing provided to the Trust by Northshore may have a significant impact on the Trust’s deferred royalty revenue.
Adjustments to royalty income may result from changes in final reconciliations of tonnage shipped by Northshore with the final amounts received from Cliffs’ customers. Adjustments may also result from revisions to estimated prices previously used to record revenue for tonnage shipped. Pricing decreases may give rise to negative price adjustments which may be applied against future royalty income recognized by the Trust and changes in iron ore pellet prices may have a significant impact on the revenue recognized by the Trust
During the fourth quarter of fiscal 2009, positive price adjustments were recorded by Mesabi Trust as accrued income receivable due to price adjustment mechanisms in the agreements between Cliffs and its customers that determine the final sales price of the shipments from Northshore with respect to shipments during calendar 2007 and calendar 2008. During the fourth quarter of fiscal 2010, negative price adjustments were recorded by Mesabi Trust as deferred royalty revenue due to price adjustment mechanisms in the agreements between Cliffs and its customers that determine the final sales price of the shipments from Northshore with respect to certain shipments during calendar 2008 and calendar 2009. As of January 31, 2010, the Trust recognized revenue as accrued income receivable related to approximately 1,400,000 tons of iron ore that were shipped by Northshore as of December 31, 2009, but for which Cliffs has indicated that final pricing is not yet known. Pricing related to these tons is expected to be finalized in the first quarter of 2011.
Recent Developments
2010 Estimates. Neither Cliffs nor Northshore has provided the Trust with an estimate for total calendar year 2010 shipments of iron ore pellets or concentrate. During calendar years 2009, 2008, 2007 and 2006, the percentage of shipments of iron ore products from Mesabi Trust lands was approximately 93.0%, 90.2%, 88.2% and 90.9%, respectively, of total shipments. Northshore has not advised the Trustees as to the percentage of iron ore products from Mesabi Trust lands it anticipates shipping in calendar year 2010. See the description of the uncertainty of market conditions in the iron ore and steel industry under the heading “Risk Factors” above.
Iron Ore Pricing and Contract Adjustments. During the course of its fiscal year some portion of the royalties paid to Mesabi Trust are based on estimated prices for iron ore products sold under term contracts between Cliffs and its subsidiaries and certain of their customers (the “Cliffs Pellet Agreements”). Mesabi Trust is not a party to any of the Cliffs Pellet Agreements. These prices are subject to interim and final pricing adjustments, which can be positive or negative, and which adjustments are dependent in part on a variety of price and inflation index factors, including but not limited to the international benchmark pellet price, hot band steel prices and various Producer Price Indexes. Although Northshore makes interim adjustments to the royalty
17
payments on a quarterly basis, these price adjustments cannot be finalized until after the end of a contract year. This may result in significant and frequent variations in royalties received by Mesabi Trust (and in turn the resulting amount of funds available for distribution to Unitholders by the Trust) from quarter to quarter and on a comparative historical basis, and these variations, which can be positive or negative, cannot be predicted by Mesabi Trust. See the description of pricing adjustments in Cliffs’ contracts under the heading “Risk Factors” above.
ArcelorMittal Arbitration with Cliffs. In its Form 10-K filed February 18, 2010 (“Cliffs’ Form 10-K”), Cliffs provided an update to the matters previously reported regarding Cliffs’ arbitration with ArcelorMittal. As previously reported, Northshore, along with The Cleveland-Cliffs Iron Company, Cliffs Mining Company and Cliffs Sales Company, filed two arbitration demands against ArcelorMittal USA Inc., ISG Cleveland Inc., ISG Indiana Harbor Inc. and Mittal Steel USA Weirton Inc. (collectively, “ArcelorMittal”). Cliffs reported that each arbitration demand was filed on September 11, 2009 and related to that certain Umbrella Agreement between Mittal Steel USA and Cleveland-Cliffs Inc, The Cleveland-Cliffs Iron Company, Cliffs Mining Company, Northshore Mining Company, and Cliffs Sales Company, dated as of March 1, 2007 and effective as of April 12, 2006 (the “Umbrella Agreement”). According to Cliffs, the first arbitration, to which ArcelorMittal filed an answer on October 1, 2009, stemmed from attempts by ArcelorMittal to revise the nomination of ArcelorMittal’s pellet requirements and a corresponding shipping schedule for 2009. Cliffs reported that the Umbrella Agreement allows ArcelorMittal to nominate tonnage under the Umbrella Agreement for export out of the U.S. to any facility owned by ArcelorMittal. Cliffs reported that the nomination and shipping schedule were finalized in November 2008, and that ArcelorMittal provided several revised nominations and shipping schedules in 2009. Cliffs reported that in response to the revised nominations, Cliffs filed the arbitration demand to enforce the nomination and shipping schedule finalized in November 2008 for the year 2009. Cliffs further reported that a similar arbitration demand filed by Cliffs in 2008 and related to attempted revisions to ArcelorMittal’s 2008 nomination was successful.
According to Cliffs, the second arbitration demand, to which ArcelorMittal filed an answer and counterclaim on October 1, 2009, related to ArcelorMittal’s attempt to reverse an election to defer certain tonnage for 2009. As Cliffs reports, the Umbrella Agreement permits ArcelorMittal to make a one-time election to defer tons from one calendar year into the next, which then prevents ArcelorMittal from taking anything less than its minimum tonnage for the following calendar year. ArcelorMittal made an election to defer tonnage from 2009 to 2010. Subsequently, ArcelorMittal purported to revoke its election to defer, which would have the effect of increasing the tonnage to be received in 2009 and allowing ArcelorMittal to defer tonnage from 2010 into 2011. Cliffs reported that it filed the arbitration demand to enforce the nomination and the 2009 deferral contained in the nomination. In its Form 10-K, Cliffs’ reported that the two arbitrations had been consolidated and that an arbitration panel had been selected while noting further that the arbitration was in an early phase.
The Trustees are unable to predict what impact, if any, the arbitration proceedings between Cliffs and ArcelorMittal will have on shipments from Northshore or future royalties payable to the Trust.
Northshore Air Permit Matters. In Cliffs’ Form 10-K, Cliffs provided an update to the matters previously reported regarding air permit amendments submitted to the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency (“MPCA”). As previously reported, Northshore submitted an administrative permit amendment application on December 16, 2006 to the MPCA with respect to its Title V operating permit requesting the deletion of a 30 year old “control city” monitoring requirement. The MPCA denied Northshore’s application on February 23, 2007 and Cliffs appealed the denial to the Minnesota Court of Appeals.
18
Cliffs reported that on August 28, 2008 it filed a major permit amendment to remove the control city requirement from its permit. Cliffs also reported that on November 25, 2008, in response to the proposed amendment, MPCA issued an order declaring that Northshore’s request to remove the control city standard from its permit constitutes a “project” for which an Environmental Assessment Worksheet, or EAW, must be completed. According to Cliffs’ Form 10-K, MPCA also stated that it was ceasing all other work on the permit, including its own efforts to create a replacement standard, until the environmental review process was complete. Northshore filed an action to challenge the MPCA’s requirement for an EAW in Minnesota State District Court.
In Cliff’s Form 10-K, Cliffs reported that on January 13, 2010, the Minnesota District Court ruled that Northshore was entitled to judgment in its favor as a matter of law. Cliffs reported further that the District Court specifically ruled that its request to remove the control city standard was not a project under Minnesota law and that MPCA’s determination that Northshore’s application required an EAW was arbitrary and capricious, unsupported by substantial evidence and an error of law. On March 12, 2010, the MPCA appealed the District Court’s decision to the Minnesota Court of Appeals, however, no further information is available about the status of the appeal as of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
The Trustees are unable to predict what impact the proceedings discussed above will have on Northshore’s compliance with its Title V operating permit or on future royalties payable to the Trust.
Securities Regulation. The Trust is a publicly-traded trust with its units of beneficial interest listed on the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) and is therefore subject to extensive regulation under, among others, the Securities Act of 1933, the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (“Sarbanes-Oxley”) and the rules and regulations of the NYSE. Issuers failing to comply with such authorities risk serious consequences, including criminal as well as civil and administrative penalties. In most instances, these laws, rules and regulations do not specifically address their applicability to publicly-traded trusts such as Mesabi Trust. In particular, Sarbanes-Oxley mandated the adoption by the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) and NYSE of certain rules and regulations that are impossible for the Trust to literally satisfy because of its nature as a pass-through trust. Pursuant to NYSE rules the Trust is exempt from many of the corporate governance requirements that apply to other publicly traded corporations. The Trust does not have, nor does the Agreement of Trust, as amended, provide for, a board of directors, an audit committee, a corporate governance committee, a compensation committee or executive officers. The Trustees intend to closely monitor the SEC’s and NYSE’s rulemaking activity and will comply with their rules and regulations to the extent applicable.
Other Information. Mesabi Trust has no employees, but it engages independent consultants to assist the Trustees in monitoring, among other things, the amount and sales prices of iron ore products shipped by Northshore from Silver Bay, Minnesota. As noted above, the information regarding amounts and sales prices of shipped iron ore products is used to compute the royalties payable to Mesabi Trust by Northshore. Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, the Corporate Trustee, also performs certain administrative functions for Mesabi Trust.
19
TO THE HOLDERS OF
CERTIFICATES OF BENEFICIAL INTEREST IN
MESABI TRUST
THE TRUST ESTATE
The principal assets of Mesabi Trust consist of two different interests in certain properties in the Mesabi Iron Range: (i) Mesabi Trust’s interest as assignor in the Amended Assignment of Peters Lease and the Amended Assignment of Cloquet Lease, which together cover properties aggregating approximately 9,750 largely contiguous acres in St. Louis County, Minnesota (the “Peters Lease Lands” and the “Cloquet Lease Lands,” respectively), and (ii) Mesabi Trust’s ownership of the entire beneficial interest in the Mesabi Land Trust, which has a 20% interest as fee owner in the Peters Lease Lands and a 100% fee ownership in certain non-mineral-bearing lands adjacent to the Peters and Cloquet Lease Lands (the “Mesabi Lease Lands,” together with the Peters Lease Lands and the Cloquet Lease Lands, the “Trust Estate”). The map below shows the approximate location of the Trust Estate.
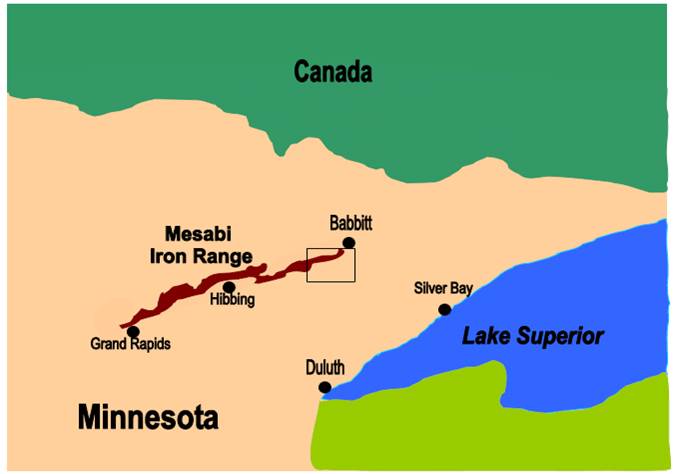
o The boxed area indicates the approximate location of Mesabi Trust’s Trust Estate (not drawn to scale), as defined above under “The Trust Estate,” which is a small part of the region known as the Mesabi Iron Range. The Mesabi Trust does not own any property interests other than in the Trust Estate.
Under the Amended Assignment Agreements, Northshore produces iron ore from the Trust Estate for the manufacture of iron ore products to be sold to various customers of Cliffs. Mesabi Trust receives royalties
20
on the crude ore extracted from such Lands and the pellets produced from such crude ore, and in each case the royalties are based upon the volume of iron ore products shipped and the prices charged to Cliffs’ customers.
The largest component of the Trust Estate is the Peters Lease Lands. The Peters Lease provides that each leasehold estate will continue until the reserves of iron ore, taconite and other minerals or materials on the land subject to the Peters Lease are exhausted. The Mesabi Lease terminates when the Peters Lease terminates. The Cloquet Lease, executed in 1916, terminates in the year 2040. If Northshore decides to terminate or surrender one or more of these leases, it must first give Mesabi Trust at least six months’ notice of its intention to do so and, at Mesabi Trust’s request, reassign all of such leases to Mesabi Trust. If any such reassignment occurs, Northshore must transfer the lease interests to Mesabi Trust free and clear of liens, except public highways. In return, Mesabi Trust must assume Northshore’s future obligations as lessee under the reassigned leases.
The Peters Lease Lands and the Cloquet Lease Lands are located at the northeastern end of the Mesabi Iron Range and contain mineral deposits consisting of a sedimentary bed of banded magnetite in siliceous gangue, a form of low-grade iron ore known as taconite, approximately three tons of which must be beneficiated to produce one ton of high-grade pellets. The Mesabi Lease Lands contain substantially no commercial ore deposits and have been used principally in connection with mining the taconite from other parts of the Trust Estate, such as the provision of an area for location of service roads, supporting plants and equipment and dump sites for overburden.
Because the Trust is not involved with the mining operations at Northshore, the Trust relies on the ore reserve estimate reported in Cliffs’ Form 10-K each year. In Cliff’s most recent Form 10-K, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, which was for the year ended December 31, 2009, the following information was provided by Cliffs regarding the estimated ore reserves at Northshore.
| | | | Tons in Millions (1) | | | | | |
| | Current | | Mineral Reserves (2) | | | | Method of | |
Iron Ore | | Annual | | Current Year | | Previous | | Reserve | |
Mineralization | | Capacity | | Proven | | Probable | | Total | | Year | | Estimation | |
Biwabik Iron Formation (Magnetite) | | 5.7 | | 304 | | 16 | | 320 | | 308 | | Geologic - Block Model | |
(1) Tons are long tons of pellets of 2,240 pounds.
(2) Estimated standard equivalent pellets, including both proven and probable reserves based on life-of-mine operating schedules.
In 2010, the Trustees engaged an independent geological consulting firm, Scott Wilson Roscoe Postle Associates, Inc. (“Scott Wilson RPA”), to confirm that the process used by Cliffs to estimate the ore reserve in the mine at Northshore is reasonable. In its report to the Trustees, Scott Wilson RPA summarized its review and evaluation of Cliffs’ ore reserve estimation process. Scott Wilson RPA reported to the Trustees that the reserve estimation process used by Cliffs is reasonable and complies with the reporting standards set forth in Securities Act Industry Guide 7. Based on the report of Scott Wilson RPA, the Trustees estimate that at least 90% of the ore reserve in the mine at Northshore, as reported by Cliffs, is attributable to the Trust Estate.
21
HISTORY OF THE TRUST’S ACQUISITION OF THE TRUST ESTATE
Prior to the creation of the Mesabi Trust and the Mesabi Land Trust on July 18, 1961, Mesabi Iron Company (“MIC”), the Trust’s predecessor in interest, owned the interests in the Peters, Cloquet and Mesabi Lease Lands. MIC obtained its interests as follows:
Peters Lease Lands. MIC owned a 20% interest in the fee ownership in the Peters Lease Lands. Originally, the Peters Lease Lands were owned by East Mesaba and Dunka River which were wholly owned subsidiaries of Dunka-Mesaba Security Company (“Dunka-Mesaba”). In August 1951, East Mesaba and Dunka River conveyed the Peters Lease Lands to their parent company, Dunka-Mesaba, which in turn conveyed to each of its stockholders an undivided interest in the Peters Lease Lands in proportion to each stockholder’s ownership in the parent company. Accordingly, MIC, which had been the owner of 20% of the outstanding capital stock of Dunka-Mesaba, acquired a 20% undivided interest in the Peters Lease Lands and the right to receive a 20% fee royalty under the Peters Lease.
By an instrument dated October 1, 1917, as of April 30, 1915, East Mesaba and Dunka River leased their properties to Claude W. Peters. (This instrument, as modified by instruments dated February 3, 1921, July 17, 1939 and July 31, 1951, is known as the “Peters Lease.”) Claude W. Peters acquired the Peters Lease on behalf of MIC and an assignment of the Peters Lease from Claude W. Peters to MIC was recorded in 1919. In 1939, MIC assigned the Peters Lease to Reserve Mining Company (“Reserve”) in consideration for which Reserve agreed to pay MIC a percentage of its net profits. Later, these payments were changed to royalty payments.
Cloquet Lease Lands. MIC held a leasehold interest in the Cloquet Lease Lands pursuant to the Indenture of Lease dated May 1, 1916. In 1939, MIC assigned its interest in the Cloquet Lease as lessee to Reserve.
Mesabi Lease Lands. MIC held a fee interest in the Mesabi Lease Lands, subject to earlier grants of mineral rights to other parties. In 1939, MIC leased its interest in the Mesabi Lease Lands to Reserve. One 40-acre parcel of the Mesabi Lease Lands was forfeited in the 1980s to the State of Minnesota and subsequently sold to the United States government, excluding the mineral rights granted to other parties. Further, another 40-acre parcel of the Mesabi Lease Lands, for which the Trust owns only surface rights, is currently being explored for non-ferrous deposits by the holder of the mineral rights to the parcel. The Trustees do not believe that either parcel was ever involved in, or otherwise material to, Northshore’s mining operations.
Acquisition of Interests from MIC. MIC had not engaged in actual mining operations since 1939, with all of its ownership of land in fee having been leased out and its leaseholds in land assigned to Reserve in exchange for royalty payments. Because MIC’s activities in connection with the administration of its assets were limited to the collection of income, the payment of expenses and liabilities, the distribution of the net income and the protection and conservation of the assets held, in July 1961 its board of directors proposed, and its stockholders subsequently approved, to adopt a plan of complete liquidation as a result of which MIC’s assets were transferred to and administered by two trust entities.
To comply with the law of the State of Minnesota, which requires that a trust holding real property located in that state must be administered under Minnesota law, the Mesabi Land Trust was created under Minnesota law on July 18, 1961 pursuant to an Agreement of Trust of even date. MIC transferred to the Mesabi Land Trust its 20% interest as fee owner in the Peters Lease and the Peters Lease Lands and its interest as 100%
22
fee owner in the Mesabi Lease Lands and as lessor of the Mesabi Lease (subject to the reservation of mineral rights described above).
Also pursuant to an Agreement of Trust, the Mesabi Trust was created under New York law on July 18, 1961. MIC transferred to the Mesabi Trust instruments assigning the Amended Assignment of Peters Lease and the Amended Assignment of Cloquet Lease (covering its interest as assignor of the entire leasehold interest in the Peters Lease Lands and the Cloquet Lease Lands), together with cash, marketable securities and other assets. The Mesabi Trust also received all of the beneficial interest in the Mesabi Land Trust.
Reserve, the original lessee, operated the mine until it closed on July 31, 1986. Cyprus Minerals Company (“Cyprus”) purchased substantially all of Reserve’s assets on August 17, 1989 and resumed operations as Cyprus NMC. On September 30, 1994, Cliffs purchased all of Cyprus NMC’s capital stock from Cyprus. Cliffs renamed the operation Northshore Mining Corporation.
Since the creation of the Mesabi Land Trust and the Mesabi Trust, although the mining operators have changed and the Peters Lease, the Cloquet Lease and the Mesabi Lease have been further amended and assigned, the Trust Estate has not changed beyond the forfeiture of one parcel of the Mesabi Lease Lands described above.
The diagram below illustrates the relationships of the various parties that own the lands and have interests in the lands the Trust has interests in:

23
DESCRIPTION OF THE MINERAL PROPERTIES AND NORTHSHORE’S MINING OPERATIONS
Mine and Rock Formation. The Mesabi Trust properties, including the ore mine, are located in northeastern Minnesota, approximately two miles south of Babbitt, Minnesota. The ore mine on the Mesabi Trust properties is called the Peter Mitchell mine, an open pit mine consisting of a 10-mile long segment of a host rock called the Biwabik Iron Formation, which is a very hard cherty rock containing magnetite as the ore mineral. The Biwabik Iron Formation extends west and southwest for over 100 miles and constitutes the Mesabi Iron Range. Recoverable iron grades range from 21% in the west end of the mine open pit to 26% in the central portion and east end, with 22.5% as the cut off grade. The ore body dips south under the hanging wall called the Virginia Formation. To date, the Mesabi Trust properties have been explored for their iron ore potential. To the knowledge of the Mesabi Trustees, no other minerals have been explored on the Mesabi Trust properties.
Mining Properties. As disclosed elsewhere in this Annual Report, Northshore, a wholly owned subsidiary of Cliffs, currently conducts the mining operation upon the Mesabi Trust properties. The main entrance to the Northshore mine is accessed by means of a gravel road and is located off County Road 70. Northshore’s processing facilities are located in Silver Bay, Minnesota, near Lake Superior, on U.S. Highway 61. Each year, the Trustees visit the Northshore mine in Babbitt, Minnesota and the processing plant in Silver Bay, Minnesota. During such visits, the Trustees inspect the condition of the mining properties as well as mining equipment and facilities. Based on information provided to the Trustees’ during the most recent inspection trip in October 2009, the mining properties and facilities at Northshore were in good operating condition.
Northshore’s Operations. Because the Mesabi Trust is not involved in Northshore’s mining operations, the Trustees do not have detailed firsthand information relating to such operations or the equipment and facilities used by Northshore. Therefore, the Trustees rely on information provided by Northshore personnel, disclosed by Cliffs in its periodic reports filed with the SEC or provided in other reports published by independent organizations, such as Skillings Mining Review, in providing the information relating to Northshore’s mining operations, its equipment and facilities.
· Mining and Railroad: Drilling at the Northshore mine is conducted with two P&H 120, one P&H 320XPC and one Gardner Denver 120 rotary units with 16-inch diameter holes on 28- to 30-foot spacing. The drilling is followed with blasts using heavy ANFO (which stands for ammonium nitrate and fuel oil) and emulsion which break an average of 700,000 to 1,200,000 tons of crude taconite. After blasts, taconite is then removed by a loading fleet consisting of three P&H 2800XPC shovels with 37 cubic-yard buckets, one P&H 2800 shovel with a 28 cubic-yard bucket, one LeTourneau L1850 loader with a 28 cubic yard bucket and a Cat 994D loader with a 19 cubic-yard bucket. A haulage fleet of three 250-ton Terex Model 4400AC and four 200-ton Komatsu 730E production trucks carry crude taconite to the primary and secondary crushers located about two miles away. At the crushers, taconite is emptied from the end-dump trucks into a 60 inch primary gyratory unit and four 30-inch by 70-inch secondary crushers for reduction to a nominal 4 inch size. Coarse ore is then fed into 90-ton capacity ore cars for transportation to Silver Bay via a 47 mile long, single track railroad owned by Northshore. Each train is pulled by three or four diesel electric locomotives.
· Concentrating and Pelletizing Process. Upon arrival at the pelletizing facility in Silver Bay, the coarse taconite ore first passes through a fine crushing stage where it is reduced in size to approximately 0-3/4” and then the non-magnetic material is rejected through a dry cobber magnetic separation stage. The non-magnetic material is rail hauled seven miles to the Mile Post 7 disposal site. The magnetic
24
material is then fed into one of the fourteen active grinding lines. Each line includes one 10-1/2-foot by 18-foot rod mill and two 10-foot by 16-foot (14-foot in west plant) ball mills. The final grinding of the crude taconite is reduced to 90% minus 325 mesh.
During the concentrating process, ore concentrate is separated by a two-stage magnetic separation, which removes low grade tailings from the ore concentrate. The tailings are pumped uphill to the Mile Post 7 disposal site. The concentrate is then fed into hydro-separators followed by a final flotation upgrading accomplished with two 500 cubic foot flotation cells per grinding line. Next, the concentrate proceeds to a central filtering facility of nine 9-foot diameter vacuum filters, during which process the moisture content in the concentrate is reduced and the final concentrate is ready for pelletizing. The pelletizing process first feeds the ore concentrate, to which bentonite and starch has been added as a binder, into a balling drum 14 feet long and 7 feet in diameter. The revolving action of the drum causes the concentrate to build up into green balls. Next, the green balls with a target size of plus 0-1/4” and minus 0-1/2” in diameter are conveyed to one of four moving grates and enter into an accompanying high temperature furnace where they are heated to over 2400° F. and are hardened into the final pellet product. From the four furnaces the pellets are conveyed to a dockside storage area with a 5-million ton storage capacity. Northshore’s sheltered harbor at Silver Bay can handle lake-going vessels with capacities up to 55,000 tons.
· Capital Expenditures. During calendar year 2009, Northshore continued to modernize and improve the operations at the Peter Mitchell Mine in Babbitt and Northshore’s pelletizing facility in Silver Bay, Minnesota. Toward that end, Cliffs implemented the following capital expenditures:
· Completed commissioning the third of four P&H 2800-XPC shovels. The final shovel is scheduled for delivery in late calendar 2010.
· Continued a program to improve the railroad locomotive fleet for the ore haul between the Peter Mitchell Mine and Northshore’s pelletizing facility.
· Continued investments in projects for safety (primarily mill liner handler and mine cable handler) and environment (primarily dust control) to protect employees and improve air and water quality.
LEASEHOLD ROYALTIES
Northshore is obligated to pay to Mesabi Trust base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses on all pellets (and other iron ore products) produced from the Peters Lease Lands and the Cloquet Lease Lands (“Mesabi Ore”) and shipped from Silver Bay in each calendar year. The royalties are based on prices per unit of product, volumes of product shipped and where on the escalating scale of royalties—2-1/2% on the first million tons to 6% on shipments above four million long tons per calendar year—each shipment falls.
Base overriding royalties. Base overriding royalties are calculated on the basis of an escalating scale of percentages of gross sales proceeds of iron ore shipped. The applicable percentage is determined by reference to the tonnage of pellets previously shipped in the then current calendar year, as follows:
25
Tons of iron ore products
shipped in calendar year | | Applicable royalty
(expressed as a percentage
of gross sales proceeds
within each tranche) | |
| | | |
one million or less | | 2-1/2% | |
more than one but not more than two million | | 3-1/2% | |
more than two but not more than three million | | 5% | |
more than three but not more than four million | | 5-1/2% | |
more than four million | | 6% | |
Royalty bonuses. Royalty bonuses are payable on all iron ore products produced from Mesabi Ore shipped from Silver Bay during a calendar quarter and sold at prices above the Adjusted Threshold Price. The Adjusted Threshold Price was $47.43 for calendar year 2008, $48.48 for calendar year 2009 and will be $48.81 for calendar year 2010. The Adjusted Threshold Price is subject to adjustment (but not below $30 per ton) for inflation and deflation and is determined each year on the basis of the change in the Gross Domestic Product Implicit Price Deflator, a broad based index of inflation and deflation published quarterly by the U.S. Department of Commerce.
The amount of royalty bonuses payable for any calendar quarter is calculated on the basis of an escalating scale of percentages of the gross sales proceeds to Northshore of pellets produced from Mesabi Ore that are sold at prices above the Adjusted Threshold Price. The applicable percentage is determined by reference to the amount by which the sales prices for a particular quantity of pellets exceeds the Adjusted Threshold Price, as follows:
Amount by which sales price per ton
exceeds Adjusted Threshold Price | | Applicable
Percentage | |
| | | |
$2 or less | | 1/2 of 1% | |
more than $2 but not more than $4 | | 1% | |
more than $4 but not more than $6 | | 1-1/2% | |
more than $6 but not more than $8 | | 2% | |
more than $8 but not more than $10 | | 2-1/2% | |
more than $10 | | 3% | |
Leasehold royalty example. To illustrate the calculation of base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses, assume that no shipments of iron ore products were made during the first calendar quarter of 2010, and further assume that pellets were shipped from Silver Bay in the second and third calendar quarters of 2010 in the following tonnage quantities and rendering the following gross proceeds:
| | Tonnage | | Sales Price per Ton | | Gross Proceeds | |
2nd Quarter: | | 500,000 | | $ | 42.00 | | $ | 21,000,000 | |
3rd Quarter: | | 500,000 | | $ | 44.00 | | $ | 22,000,000 | |
| | 1,000,000 | | $ | 46.00 | | $ | 46,000,000 | |
| | 1,000,000 | | $ | 48.00 | | $ | 48,000,000 | |
| | 1,000,000 | | $ | 50.00 | | $ | 50,000,000 | |
| | 1,500,000 | | $ | 52.00 | | $ | 78,000,000 | |
In this example, the base overriding royalties payable in respect of the second and third calendar quarters of 2010 would be as follows:
26
2nd Quarter: | | $21,000,000 x 2-1/2% | | = | | $ | 525,000 | |
3rd Quarter: | | $22,000,000 x 2-1/2% | | = | | $ | 550,000 | |
| | $46,000,000 x 3-1/2% | | = | | $ | 1,610,000 | |
| | $48,000,000 x 5% | | = | | $ | 2,400,000 | |
| | $50,000,000 x 5-1/2% | | = | | $ | 2,750,000 | |
| | $78,000,000 x 6% | | = | | $ | 4,680,000 | |
Based on the same example, the base overriding royalty percentage applicable for all iron ore products shipped in the fourth calendar quarter of 2010 would be 6%, because more than four million tons were shipped during the first three quarters.
Further, the royalty bonuses payable in respect of the second and third calendar quarters of 2010 would be as follows (with reference to the Adjusted Threshold Price (“ATP”) of $48.81:
2nd Quarter: | | $42.00/ton falls below ATP: no bonus payable | | = | | None | |
3rd Quarter: | | $44.00/ton falls below ATP: no bonus payable | | = | | None | |
| | $46.00/ton falls below ATP: no bonus payable | | = | | None | |
| | $48.00/ton falls below ATP: no bonus payable | | = | | None | |
| | $50,000,000 x 1/2 of 1% | | = | | $ | 250,000 | |
| | $78,000,000 x 1% | | = | | $ | 780,000 | |
The above figures are provided only to illustrate the method for calculating base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses and do not indicate the amount of base overriding royalties or royalty bonuses the Trustees expect Mesabi Trust to earn in calendar 2010 or any other calendar or fiscal year. Accordingly, the foregoing example illustrating the calculation of base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses should not be considered a prediction of the amount of base overriding royalties or royalty bonuses Mesabi Trust will receive.
Bonuses on other ore. Northshore also must pay base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses on pellets produced from lands other than Mesabi Lease Lands (“Other Ore”) to the extent necessary to assure payment of base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses on at least 90% of the first four million tons of pellets shipped from Silver Bay in each calendar year, at least 85% of the next two million tons of pellets shipped therefrom in each calendar year, and at least 25% of all tonnage of pellets shipped therefrom in each calendar year in excess of six million tons. Base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses payable on Other Ore can be recouped by Northshore out of base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses paid on Mesabi Ore. The amount of Other Ore royalties and Other Ore royalty bonuses which can be recouped on any payment date cannot, however, exceed 20% of the amount of Mesabi Ore royalties and royalty bonuses which are otherwise payable on that payment date.
Advance royalties. Northshore is obligated to pay Mesabi Trust advance royalties in equal quarterly installments. The advance royalty was $790,721 for calendar year 2008, $808,177 for calendar year 2009 and is $813,729 for calendar year 2010. The amount of advance royalties payable is subject to adjustment (but not below $500,000 per annum) for inflation and deflation and is determined each year in the same manner as the Adjusted Threshold Price. All payments of advance royalties are credited against payments of base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses payable on Mesabi Ore until fully recouped by Northshore. The amount of advance royalties payable in respect of each calendar quarter constitutes the minimum overriding royalty amount payable by Northshore in respect of that calendar quarter.
27
Other leasehold royalty information. Base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses are payable quarterly and accrue upon shipment, whether or not the actual sales proceeds for any shipment are received by Northshore. The amount of base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses payable with respect to the first three quarters in any calendar year are determined on the basis of tonnage shipped during each such calendar quarter and the actual sales proceeds of such shipments, with an adjustment made to the royalties payable with respect to the last quarter in any calendar year to account for adjustments.
LAND TRUST AND FEE ROYALTIES
Mesabi Land Trust holds a 20% interest as fee owner in the Peters Lease Lands and a 100% interest as fee owner in the Mesabi Lease Lands as lessor of the Mesabi Lease. Mesabi Trust holds the entire beneficial interest in Mesabi Land Trust and is entitled to receive the net income of Mesabi Land Trust after payment of expenses. Northshore is not obligated to pay royalties or rental to Mesabi Land Trust as fee owner of the non-mineral bearing Mesabi Lease Lands, a consideration having been paid in that respect at the inception of the Mesabi Lease.
Northshore is required to pay a base royalty to the fee owners in an amount which, at its option, is either (a) 11-2/3¢ per gross ton of crude ore it mines from the Peters Lease Lands, or (b) $0.0056 for each 1% of metallic iron ore natural contained in each gross ton of pellets it produces from the Peters Lease Lands and ships. The base fee royalty rate is adjusted up or down each quarter (but not below the base royalty specified above) by adding or subtracting an amount to be determined by reference to changes in Lower Lake Mesabi Range pellet prices and the All Commodities Producer Price Index. The adjustment factor is computed by multiplying the base fee royalty rate specified above by a percentage that is the sum of (a) one-half of the percentage change, if any, by which the then prevailing price per iron unit of Mesabi Range taconite pellets delivered by rail or vessel at Lower Lake Erie ports exceeds 80.5¢ (the price per iron unit in effect in January 1982), plus (b) one-half of the percentage change, if any, by which the All Commodities Producer Price Index exceeds 295.8 (the level of the Index for December 1981). Fee royalties aggregating $305,407 with respect to crude ore mined by Northshore were earned by Mesabi Land Trust during the fiscal year ended January 31, 2010.
TRUST EXPENSES
Total Trust Expenses
Total Trust expenses for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2010 were $818,007, representing an increase of 2.3% from the $799,320 of total Trust expenses in fiscal 2009. For the fiscal year ended January 31, 2009, total Trust expenses increased 26.0% to $799,320, as compared to $634,151 for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2008.
Trust Legal Expenses
Mesabi Trust paid Oppenheimer Wolff & Donnelly LLP (“Oppenheimer”) $224,796 for legal services provided to the Trust during the fiscal year ended January 31, 2010. Comparatively, Mesabi Trust paid Oppenheimer $219,389 and $160,780 for legal services provided to the Trust during fiscal years ended January 31, 2009 and January 31, 2008, respectively.
In each of the last three fiscal years, Oppenheimer represented the Trust and assisted the Trustees in the preparation and filing of the Trust’s current, periodic and annual reports with the SEC and related securities law
28
compliance. Oppenheimer also advised the Trust on various other legal matters related to inquiries from third parties in the ordinary course of the Trust’s administration. The total amount of Oppenheimer’s legal fees for services rendered during fiscal 2010 increased approximately $5,400, or 2.5%, as compared to fiscal 2009. The increase in legal fees in fiscal 2010, as compared to fiscal 2009, resulted primarily from Oppenheimer providing the Trust with services related to the preparation of the proxy statement and the proxy solicitation to appoint Robert C. Berglund as an individual trustee of the Trust, legal review of real estate matters and cost of living increases in the billing rates of Oppenheimer attorneys who provide services to the Trust.
The total amount of Oppenheimer’s legal fees for services rendered during fiscal 2009 increased approximately $58,000, or 36%, as compared to fiscal 2008. The increase in legal fees in fiscal 2009, as compared to fiscal 2008, resulted primarily from Oppenheimer providing the Trust with services related to the Trust’s change of its independent certified public accounting firm, responding to comments received from the SEC staff under the disclosure review program, additional third party inquiries made to the Trust, and cost of living increases in the billing rates of Oppenheimer attorneys who provide services to the Trust.
Total Trust expenses by category for fiscal 2010, 2009 and 2008 are set forth in the table below.
| | Fiscal Year ended on January 31, | |
| | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | | | | | | |
Compensation of Trustees | | $ | 178,581 | | $ | 228,053 | | $ | 181,700 | |
Corporate Trustee’s Administrative Fees | | 62,500 | | 62,500 | | 62,500 | |
Professional fees and expenses | | | | | | | |
Legal | | 224,796 | | 219,389 | | 160,780 | |
Accounting | | 125,009 | | 109,268 | | 60,324 | |
Mining consultant and field representatives | | 22,908 | | 22,617 | | 52,242 | |
Insurance | | 66,492 | | 52,518 | | 37,195 | |
Annual stock exchange fee | | 38,000 | | 38,000 | | 38,000 | |
Transfer agent’s and registrar’s fees | | 9,974 | | 10,273 | | 12,694 | |
Other Trust Expenses | | 89,747 | | 56,702 | | 28,716 | |
| | $ | 818,007 | | $ | 799,320 | | $ | 634,151 | |
UNALLOCATED RESERVE
The Trustees have determined that a portion of the Unallocated Reserve, usually within the range of $500,000 to $1,000,000 or such other amount as the Trustees may deem prudent, should be maintained as a cash reserve for unexpected losses. The actual amount of the Unallocated Reserve will fluctuate from time to time and may increase or decrease from its current level. Future distributions will be highly dependent upon royalty income as it is received, changes in estimated pricing, potential for future price adjustments and the level of Trust expenses. Although the actual amount of the Unallocated Reserve will fluctuate from time to time and may increase or decrease from its current level, it is currently intended that future distributions will be highly dependent upon royalty income as it is received and the level of Trust expenses. The amount of future royalty income available for distribution will be subject to the volume of iron ore product shipments and the dollar level of sales by Northshore.
29
As a result of the $2,770,000 deferred royalty revenue recorded by the Trust, the unpredictable nature of the current economic conditions, and the potential for future negative price adjustments under the long-term customer contracts between Northshore, Cliffs and certain customers, the Trustees have determined that it is prudent to increase the cash and U.S. Government securities portion of the Unallocated Reserve above the range of $500,000 to $1,000,000. The amount of future royalty income available for distribution will be subject to the volume of iron ore product shipments and the dollar level of sales by Northshore. Shipping activity is greatly reduced during the winter months and economic conditions, particularly those affecting the steel industry, may adversely affect the amount and timing of such future shipments and sales. It is possible that future negative price adjustments could offset, or even eliminate, royalties or royalty income that would otherwise be payable to the Trust in any particular quarter, or at year end, thereby potentially reducing cash available for distribution to the Trust’s Unitholders in future quarters. See discussion under the heading “Risk Factors” beginning on page 3 of this Annual Report.
The Trustees will continue to monitor the economic circumstances of the Trust to strike a responsible balance between distributions to Unitholders and the need to maintain reserves at a prudent level, given the unpredictable nature of the iron ore industry, the Trust’s dependence on the actions of the Cliffs and Northshore, and the fact that the Trust essentially has no other liquid assets.
CERTIFICATES OF BENEFICIAL INTEREST
The Mesabi Trust’s Certificates of Beneficial Interest are traded on the New York Stock Exchange. Distributions paid to Unitholders during the fiscal year ended January 31, 2010 totaled $9,315,207 as compared to $37,851,229 during fiscal year ended January 31, 2009, and $15,088,011 during the fiscal year ended January 31, 2008. Unitholders received distributions of $0.71 per Unit for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2010, compared with distributions of $2.885 and $1.150 per Unit for the fiscal years ended January 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
During the past two fiscal years, the market ranges of the certificates for each quarterly period and the distributions declared for such quarterly periods were as follows:
Fiscal Quarter Ended | | High | | Low | | Distribution
Declared | | Distribution
Per Unit | |
April 30, 2009 | | $ | 9.75 | | $ | 5.30 | | $ | 4,985,604 | | $ | 0.38 | |
July 31, 2009 | | $ | 13.09 | | $ | 9.50 | | 0 | | 0.00 | |
October 31, 2009 | | $ | 11.22 | | $ | 8.60 | | 2,886,402 | | 0.22 | |
January 31, 2010 | | $ | 15.60 | | $ | 9.65 | | 7,216,005 | | 0.55 | |
| | | | | | $ | 15,088,012 | | $ | 1.15 | |
Fiscal Quarter Ended | | High | | Low | | Distribution
Declared | | Distribution
Per Unit | |
April 30, 2008 | | $ | 28.20 | | $ | 21.36 | | $ | 1,574,401 | | $ | 0.12 | |
July 31, 2008 | | $ | 30.80 | | $ | 24.31 | | 13,120,010 | | 1.00 | |
October 31, 2008 | | $ | 27.65 | | $ | 11.34 | | 16,400,013 | | 1.25 | |
January 31, 2009 | | $ | 12.96 | | $ | 6.98 | | 1,443,201 | | 0.11 | |
| | | | | | $ | 32,537,625 | | $ | 2.48 | |
As of the close of business on April 6, 2010, the beneficial interest in Mesabi Trust was represented by 13,120,010 Units registered in the names of approximately 1,250 individuals holding of record approximately 864,749 Units, and in the names of approximately 115 brokers, nominees, or fiduciaries holding of record approximately 12,255,261 Units.
30
THE TRUSTEES
The name and address of each Trustee and the principal occupation of each individual Trustee are as follows:
Name and Address of Trustee | | Principal Occupation |
| | |
Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas
Corporate Trustee
60 Wall Street
27th Floor
New York, New York 10005 | | New York banking corporation |
| | |
Robert C. Berglund PO Box 351 Corona, New Mexico 88318 | | Retired Mining Engineer |
| | |
James A. Ehrenberg
Individual Trustee
295 Kopp Drive
West St. Paul, Minnesota 55118 | | Until April 2005, Senior Vice
President, Corporate Trust Services,
U.S. Bank, N.A. |
| | |
Richard G. Lareau
Individual Trustee
Oppenheimer Wolff & Donnelly LLP
Plaza VII, Suite 3300
45 South Seventh Street
Minneapolis, Minnesota 55402 | | Senior Partner in the law firm of
Oppenheimer Wolff & Donnelly
LLP |
| | |
Norman F. Sprague III
Individual Trustee
11726 San Vicente Blvd.
Suite 625
Los Angeles, California 90049 | | Private investor; orthopedic surgeon |
| | |
New York, New York
April 15, 2010 | | Respectfully submitted, DEUTSCHE BANK TRUST
COMPANY AMERICAS ROBERT C. BERGLUND JAMES A. EHRENBERG
RICHARD G. LAREAU
NORMAN F. SPRAGUE III |
31
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Trustees’ Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting | | Page F-2 |
| | |
Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firms | | Pages F-3 and F-4 |
| | |
Balance Sheets as of January 31, 2010 and 2009 | | Page F-5 |
| | |
Statements of Income for the years ended January 31, 2010, 2009, and 2008 | | Page F-6 |
| | |
Statements of Unallocated Reserve and Trust Corpus for the years ended January 31, 2010, 2009, and 2008 | | Page F-7 |
| | |
Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended January 31, 2010, 2009, and 2008 | | Page F-8 |
| | |
Notes to Financial Statements | | Pages F-9 – F-16 |
F-1
TRUSTEES’ REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
The Mesabi Trustees are responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting for Mesabi Trust. The Trust’s internal control system was designed to provide reasonable assurance to the Trustees regarding the preparation and fair presentation of published financial statements.
All internal control systems, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation.
The Mesabi Trustees assessed the effectiveness of the Trust’s internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2010. In making this assessment, they used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in Internal Control — Integrated Framework. Based on their assessment, the Trustees believe that, as of January 31, 2010, the Trust’s internal control over financial reporting is effective, based on those criteria.
Wipfli LLP, the Trust’s independent registered public accounting firm, has issued an audit report on its assessment of the Trust’s internal control over financial reporting. This report appears immediately below.
F-2

REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Trustees
Mesabi Trust
New York, New York
We have audited the accompanying balance sheets of Mesabi Trust (the “Trust”) as of January 31, 2010 and 2009, and the related statements of income, unallocated reserve and trust corpus, and cash flows for the years then ended. We also have audited Mesabi Trust’s internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2010, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). Mesabi Trust’s trustees are responsible for these financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for their assessment of the effectiveness of the Trust’s internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Trustees’ Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements and an opinion on the Trust’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audits. The financial statements of Mesabi Trust as of January 31, 2008 were audited by other auditors whose report dated April 8, 2008 expressed an unqualified opinion on those statements.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by the Trustees, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
An organization’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. An organization’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that 1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the organization; 2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the organization are being made only in accordance with authorizations of the Trustees; and 3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the organization’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Mesabi Trust as of January 31, 2010 and 2009, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the years then ended in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, Mesabi Trust maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2010, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
/s/ WIPFLI LLP
St. Paul, Minnesota
April 15, 2010
F-3
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Trustees
MESABI TRUST
New York, New York
We have audited the accompanying statements of income, unallocated reserve and trust corpus, and cash flows of MESABI TRUST (the “Trust”) for the year ended January 31, 2008. We also have audited MESABI TRUST’S internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2008, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Trustees are responsible for these financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for their assessment of the effectiveness of the Trust’s internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Trustees’ Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements and an opinion on the Trust’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by the Trustees, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
An organization’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. An organization’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that 1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the organization; 2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the organization are being made only in accordance with authorizations of the Trustees; and 3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the organization’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the results of operations of MESABI TRUST and cash flows for the year ended January 31, 2008 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, MESABI TRUST maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2008, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
/s/ Gordon, Hughes & Banks, LLP
Greenwood Village, Colorado
April 8, 2008
F-4
MESABI TRUST
BALANCE SHEETS
YEARS ENDED JANUARY 31, 2010 AND 2009
| | 2010 | | 2009 | |
| | | | | |
ASSETS | | | | | |
| | | | | |
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | | $ | 8,444,697 | | $ | 2,254,107 | |
U.S. GOVERNMENT SECURITIES, at amortized cost (which approximates market) | | 1,850,515 | | 340,421 | |
ACCRUED INCOME RECEIVABLE | | 873,938 | | 2,721,978 | |
PREPAID EXPENSE | | 30,422 | | 30,423 | |
| | 11,199,572 | | 5,346,929 | |
| | | | | |
FIXED PROPERTY, including intangibles, at nominal values | | | | | |
Assignments of leased property | | | | | |
Amended assignment of Peters Lease | | 1 | | 1 | |
Assignment of Cloquet Leases | | 1 | | 1 | |
Certificate of beneficial interest for 13,120,010 units of Land Trust | | 1 | | 1 | |
| | 3 | | 3 | |
| | | | | |
| | $ | 11,199,575 | | $ | 5,346,932 | |
| | | | | |
LIABILITIES, UNALLOCATED RESERVE AND TRUST CORPUS | | | | | |
| | | | | |
DISTRIBUTION PAYABLE | | $ | 7,216,005 | | $ | 1,443,201 | |
ACCRUED EXPENSES | | 85,735 | | 111,547 | |
DEFERRED ROYALTY REVENUE | | 2,770,000 | | — | |
| | 10,071,740 | | 1,554,748 | |
| | | | | |
UNALLOCATED RESERVE | | 1,127,832 | | 3,792,181 | |
| | | | | |
TRUST CORPUS | | 3 | | 3 | |
| | | | | |
| | $ | 11,199,575 | | $ | 5,346,932 | |
See Notes to Financial Statements
F-5
MESABI TRUST
STATEMENTS OF INCOME
YEARS ENDED JANUARY 31, 2010, 2009, AND 2008
| | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | | | | | | |
REVENUES | | | | | | | |
Royalties under amended lease agreements | | $ | 12,924,330 | | $ | 34,896,798 | | $ | 18,342,448 | |
Royalties under Peters Lease fee | | 305,407 | | 525,851 | | 474,094 | |
Interest | | 11,932 | | 46,456 | | 49,969 | |
| | | | | | | |
Total revenues | | 13,241,669 | | 35,469,105 | | 18,866,511 | |
| | | | | | | |
EXPENSES | | | | | | | |
Compensation of Trustees | | 178,581 | | 228,053 | | 181,700 | |
Corporate Trustee’s administrative fees | | 62,500 | | 62,500 | | 62,500 | |
Professional fees and expenses: | | | | | | | |
Legal | | 224,796 | | 219,389 | | 160,780 | |
Accounting | | 125,009 | | 109,268 | | 60,324 | |
Mining consultant and field representatives | | 22,908 | | 22,617 | | 52,242 | |
Insurance | | 66,492 | | 52,518 | | 37,195 | |
Annual stock exchange fee | | 38,000 | | 38,000 | | 38,000 | |
Transfer agent’s and registrar’s fees | | 9,974 | | 10,273 | | 12,694 | |
Other Trust expenses | | 89,747 | | 56,702 | | 28,716 | |
| | | | | | | |
Total expenses | | 818,007 | | 799,320 | | 634,151 | |
| | | | | | | |
NET INCOME | | $ | 12,423,662 | | $ | 34,669,785 | | $ | 18,232,360 | |
| | | | | | | |
WEIGHTED AVERAGE NUMBER OF UNITS OUTSTANDING | | 13,120,010 | | 13,120,010 | | 13,120,010 | |
| | | | | | | |
NET INCOME PER UNIT | | $ | 0.947 | | $ | 2.643 | | $ | 1.390 | |
See Notes to Financial Statements
F-6
MESABI TRUST
STATEMENTS OF UNALLOCATED RESERVE AND TRUST CORPUS
YEARS ENDED JANUARY 31, 2010, 2009, AND 2008
| | Unallocated Reserve | | | |
| | Number of | | | | Trust | |
| | Units | | Amount | | Corpus | |
| | | | �� | | | |
BALANCE, JANUARY 31, 2007 | | 13,120,010 | | 1,139,674 | | 3 | |
| | | | | | | |
Net income | | — | | 18,232,360 | | — | |
Distribution paid May 20, 2007, $.045 per unit | | — | | (590,400 | ) | — | |
Distribution paid August 20, 2007, $.310 per unit | | — | | (4,067,203 | ) | — | |
Distribution paid November 20, 2007, $.480 per unit | | — | | (6,297,605 | ) | — | |
Distribution declared January 11, 2008, paid February 20, 2008, $.515 per unit | | — | | (6,756,805 | ) | — | |
| | | | | | | |
BALANCE, JANUARY 31, 2008 | | 13,120,010 | | 1,660,021 | | 3 | |
| | | | | | | |
Net income | | — | | 34,669,785 | | — | |
Distribution paid May 20, 2008, $.12 per unit | | — | | (1,574,401 | ) | — | |
Distribution paid August 20, 2008, $1.00 per unit | | — | | (13,120,010 | ) | — | |
Distribution paid November 20, 2008, $1.25 per unit | | — | | (16,400,013 | ) | — | |
Distribution declared January 16, 2009, paid February 20, 2009, $.11 per unit | | — | | (1,443,201 | ) | — | |
| | | | | | | |
BALANCE, JANUARY 31, 2009 | | 13,120,010 | | $ | 3,792,181 | | $ | 3 | |
| | | | | | | |
Net income | | — | | 12,423,662 | | — | |
Distribution paid May 20, 2009, $.38 per unit | | — | | (4,985,604 | ) | — | |
Distribution paid November 20, 2009, $.22 per unit | | — | | (2,886,402 | ) | — | |
Distribution declared January 15, 2010, paid February 20, 2010, $.55 per unit | | — | | (7,216,005 | ) | — | |
| | | | | | | |
BALANCE, JANUARY 31, 2010 | | 13,120,010 | | $ | 1,127,832 | | $ | 3 | |
See Notes to Financial Statements
F-7
MESABI TRUST
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
YEARS ENDED JANUARY 31, 2010, 2009, AND 2008
| | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | | | | | | |
OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | | | | | |
Royalties received | | $ | 17,841,808 | | $ | 33,658,880 | | $ | 18,265,935 | |
Interest received | | 17,901 | | 48,173 | | 50,415 | |
Expenses paid | | (843,818 | ) | (765,190 | ) | (710,529 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
NET CASH FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | 17,015,891 | | 32,941,863 | | 17,605,821 | |
| | | | | | | |
INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | | | | | |
Maturities of U.S. Government securities | | 329,000 | | 586,953 | | 9,464,477 | |
Purchases of U.S. Government securities | | (1,839,094 | ) | (383,181 | ) | (9,280,787 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
NET CASH FROM (USED FOR) INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | (1,510,094 | ) | 203,772 | | 183,690 | |
| | | | | | | |
FINANCING ACTIVITY | | | | | | | |
Distributions to unitholders | | (9,315,207 | ) | (37,851,229 | ) | (15,088,011 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
NET CHANGE IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | | 6,190,590 | | (4,705,594 | ) | 2,701,500 | |
| | | | | | | |
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF YEAR | | 2,254,107 | | 6,959,701 | | 4,258,201 | |
| | | | | | | |
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, END OF YEAR | | $ | 8,444,697 | | $ | 2,254,107 | | $ | 6,959,701 | |
| | | | | | | |
RECONCILIATION OF NET INCOME TO NET CASH FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 12,423,662 | | $ | 34,669,785 | | $ | 18,232,360 | |
Decrease (increase) in accrued income receivable | | 1,848,040 | | (1,762,053 | ) | (550,161 | ) |
Decrease (increase) in prepaid expense | | 1 | | (5,736 | ) | (5,986 | ) |
Increase (decrease) in accrued expenses | | (25,812 | ) | 39,867 | | (70,392 | ) |
Increase in deferred royalty revenue | | 2,770,000 | | — | | — | |
| | | | | | | |
NET CASH FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | $ | 17,015,891 | | $ | 32,941,863 | | $ | 17,605,821 | |
| | | | | | | |
NON CASH FINANCING ACTIVITY | | | | | | | |
Distributions declared | | $ | 7,216,005 | | $ | 1,443,201 | | $ | 6,756,805 | |
See Notes to Financial Statements
F-8
MESABI TRUST
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JANUARY 31, 2010, 2009 AND 2008
NOTE 1 - NATURE OF BUSINESS AND ORGANIZATION
Nature of Business
Mesabi Trust was created in 1961 upon the liquidation of Mesabi Iron Company. The sole purpose of the Trust, as set forth in the Agreement of Trust dated as of July 18, 1961, is to conserve and protect the Trust Estate and to collect and distribute the income and proceeds there from to the Trust’s certificate holders after the payment of, or provision for, expenses and liabilities. The Agreement of Trust prohibits the Trust from engaging in any business. In accordance with the Agreement of Trust, the Trust will terminate twenty-one years after the death of the survivor of twenty-five persons named in an exhibit to the Agreement of Trust, the youngest of whom is believed to be forty-eight years old.
The lessee/operator of Mesabi Trust’s mineral interests is Northshore Mining Corporation (NMC), a subsidiary of Cliffs Natural Resources Inc (Cliffs). Cliffs is among the world’s largest producers of iron ore products. Prior to September 30, 1994, the lessee/operator had been a subsidiary of Cyprus Amax Minerals Company and was named Cyprus Northshore Mining Corporation (Cyprus NMC).
Organization
The beneficial interest in Mesabi Trust is represented by 13,120,010 transferable units distributed on July 27, 1961 to shareholders of Mesabi Iron Company.
The Trust’s status as a grantor trust was confirmed by letter ruling addressed to Mesabi Iron Company from the Internal Revenue Service in 1961. As a grantor trust, Mesabi is exempt from Federal income taxes and its income is taxable directly to the Unitholders.
NOTE 2 - SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Trust considers all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. As of January 31, 2010 and 2009, the Trust held $24,788 and $390,661, respectively, in a money market fund that invests primarily in obligations of the U.S. Treasury, which it considers to be cash and cash equivalents.
Investments
The Trust invests solely in U.S. Government securities. Management determines the appropriate classifications of the securities at the time they are acquired and evaluates the appropriateness of such classifications as of each balance sheet date.
The U.S. Government securities are classified as held-to-maturity securities as the Trust has the positive intent and ability to hold to maturity and are therefore stated at amortized cost.
F-9
MESABI TRUST
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JANUARY 31, 2010, 2009 AND 2008
Revenue Recognition
Royalty income under the amended lease agreements with NMC is recognized as it is earned. Under such agreements, royalties are earned upon shipment from Silver Bay, Minnesota (NMC’s location), regardless of whether the actual sales proceeds for any shipment are received by NMC. The amount of base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses payable are determined on the volume of tonnage shipped from Silver Bay, Minnesota during each calendar quarter and the actual proceeds to Cliffs resulting from such shipments.
Royalty income includes accrued income receivable. Accrued income receivable represents royalty income earned but not yet received by the Trust under the royalty agreements described elsewhere in these notes. Accrued income receivable is calculated based on (i) shipments during the last month of Mesabi Trust’s fiscal year, if any, and (ii) positive price adjustment mechanisms in the agreements between Cliffs and its customers that determine the final sales price of the shipments from Silver Bay, Minnesota.
Adjustments to royalty income may result from changes in final reconciliations of tonnage shipped by NMC with the final amounts received from NMC customers. Adjustments may also result from revisions to estimated prices previously used to record revenue for tonnage shipped. Pricing decreases may give rise to negative price adjustments which may be applied against future royalty income recognized by the Trust.
During the fourth quarter of fiscal 2009, positive price adjustments were recorded by Mesabi Trust as accrued income receivable due to price adjustment mechanisms in the agreements between Cliffs and its customers that determine the final sales price of the shipments from NMC with respect to shipments during calendar 2007 and calendar 2008. During the fourth quarter of fiscal 2010, negative price adjustments were recorded by Mesabi Trust as deferred royalty revenue due to price adjustment mechanisms in the agreements between Cliffs and its customers that determine the final sales price of the shipments from NMC with respect to certain shipments during calendar 2008 and calendar 2009. As of January 31, 2010, the Trust recognized revenue as accrued income receivable related to approximately 1,400,000 tons of iron ore that were shipped by NMC as of December 31, 2009, but for which Cliffs has indicated that final pricing is not yet known. Pricing related to these tons is expected to be finalized in the first quarter of 2011.
Royalty income under the Peters Lease fee agreement also is recognized quarterly as it is earned. Under such agreement, however, royalties are earned at the option of NMC either upon mining of crude ore from Peters Lease lands or upon shipment from Silver Bay of iron ore product produced from Peters Lease lands.
Fixed Property, Including Intangibles
The Trust’s fixed property, including intangibles, is recorded at nominal values and includes the following:
1. The entire beneficial interest as assignor in the Amended Peters Lease Assignment and the Amended Cloquet Lease Assignment covering taconite properties in Minnesota which are leased to NMC.
F-10
MESABI TRUST
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JANUARY 31, 2010, 2009 AND 2008
2. The entire beneficial interest in Mesabi Land Trust which owns a 20% fee interest in the lands subject to the Peters Lease and the entire fee interest in other properties in Minnesota.
Deferred Royalty Revenue
Deferred royalty revenue represents an estimate of decreases in pellet revenue related to tons of iron ore that were shipped by Northshore, but for which Northshore has indicated that final pricing is not yet known and is adjusted in accordance with the Trust’s revenue recognition policy each quarter as updated pricing information is received.
Reclassifications
Certain reclassifications have been made to facilitate comparability with current presentation. Such reclassifications have no effect on the statement of income.
Net Income Per Unit
Net income per unit is computed by dividing net income available to Unitholders by the weighted average number of units outstanding.
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments which potentially subject the Trust to concentrations of credit risk consist primarily of cash that is maintained at an FDIC insured financial institution. At times during the year the Trust’s cash balance may exceed insured limits.
As further described in Note 1, NMC is the lessee/operator of the Mesabi Trust land. All royalty income earned by the Trust is received from NMC, and accordingly, the entire accrued income receivable is also due from NMC.
Accounting Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States requires the Trustees to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates. Specifically, the accrued income receivable, deferred royalty revenue and related royalty revenue is a significant estimate which is subject to change in the near term, and changes to this estimate could have a material effect on the Trust’s financial statements.
Fair Value Measures
Valuation Hierarchy
ASC 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures, establishes a three-level valuation hierarchy for classification of fair value measurements. The valuation hierarchy is based upon the transparency of inputs to the valuation of an asset or liability as of the measurement date.
F-11
MESABI TRUST
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JANUARY 31, 2010, 2009 AND 2008
· Level 1 — Valuation is based upon quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
· Level 2 — Valuation is based upon quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, or other inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument.
· Level 3 — Valuation is based upon other unobservable inputs that are significant to the fair value measurement.
The classification of assets and liabilities within the valuation hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement in its entirety.
The carrying amounts of financial instruments including investments, accrued income receivable, distributions payable, accrued expenses and deferred royalty revenue approximated fair value as of January 31, 2010 and 2009, because of the relative short maturity of these instruments.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Effective July 1, 2009, the Trust adopted the FASB Accounting Standards Codification™ (“Codification”). The Codification is the source of authoritative U.S. GAAP recognized by the FASB to be applied by nongovernmental entities. The content of the Codification carries the same level of authority, thereby modifying the previous GAAP hierarchy to include only two levels of GAAP: authoritative and nonauthoritative. The Codification is effective for financial statements issued for interim and annual periods ending after September 15, 2009. Adoption of the Codification did not result in a change in current accounting practice.
In April 2009, the FASB updated ASC 820 to provide additional guidance for estimating fair value when the volume and level of activity for an asset or liability have significantly decreased, including guidance on identifying circumstances that indicate a transaction is not orderly. The updated guidance emphasizes that the objective of a fair value measurement remains the same even if there has been a significant decrease in the volume and level of activity for the asset or liability and amends certain reporting requirements for interim and annual periods related to disclosure of major security types and the inputs and valuation techniques used in determining fair value. The amendment is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009, with early adoption permitted for periods ending after March 15, 2009. The adoption of this amendment did not have a material impact the Trust’s financial statements.
In August 2009, the FASB issued ASU No. 2009-05 which amends ASC 820-10-35 to provide further guidance concerning the measurement of a liability at fair value when there is a lack of observable market information, particularly in relation to a liability whose transfer is contractually restricted. The amendment provides additional guidance on the use of an appropriate valuation technique that reflects the quoted price of an identical or similar liability when traded as an asset and clarifies the circumstances under which adjustments to such price may be required in estimating the fair value of the liability. The guidance provided in this update is effective for the first reporting period beginning after issuance, with early application permitted. The amendment was adopted for the annual reporting period ended January 31, 2010 and did not have a material
F-12
MESABI TRUST
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JANUARY 31, 2010, 2009 AND 2008
impact on the Trust’s financial statements.
In January 2010, the FASB issued ASU 2010-06, which amends the guidance on fair value to add new requirements for disclosures about transfers into and out of Levels 1 and 2 and separate disclosures about purchases, sales, issuances, and settlements relating to Level 3 measurements. It also clarifies existing fair value disclosures about the level of disaggregation and about inputs and valuation techniques used to measure fair value. The new guidance is effective for the first reporting period beginning after December 15, 2009, except for the requirement to provide the Level 3 activity of purchases, sales, issuances, and settlements on a gross basis, which will be effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2010, and for interim periods within those fiscal years. The Trust will adopt this amendment upon its effective date and will report the required disclosures beginning with the interim period ended April 30, 2010.
NOTE 3 - U. S. GOVERNMENT SECURITIES
U.S. government securities at January 31, 2010 and 2009 are classified as held-to-maturity and mature as follows:
| | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | Carrying | | | | Carrying | | | |
| | Value | | Fair Value | | Value | | Fair Value | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Due within one year | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 340,421 | | $ | 335,254 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Due after one year through three years | | 1,850,515 | | 1,855,546 | | — | | — | |
| | $ | 1,850,515 | | $ | 1,855,546 | | $ | 340,421 | | $ | 335,254 | |
NOTE 4 - ROYALTY AGREEMENT
The current royalty rate schedule became effective on August 17, 1989, which was established pursuant to certain agreements (the “Amended Assignment Agreements”) the Trust entered into with Cyprus Northshore Mining Corporation (“Cyprus NMC”). Pursuant to the Amended Assignment Agreements, overriding royalties are determined by both the volume and selling price of iron ore products shipped.
Pursuant to the Amended Assignment Agreements, NMC is obligated to pay Mesabi Trust base overriding royalties, in varying amounts constituting a percentage of the gross proceeds of shipments, from Silver Bay, Minnesota, of iron ore product produced from Mesabi Trust lands or, to a limited extent, other lands. NMC is obligated to make payments of overriding royalties on product shipments within 30 days following the calendar quarter in which such shipments occur. NMC resumed mining operations and shipping product from Silver Bay in the second calendar quarter of 1990, and the first payment of overriding royalties was made in July 1990.
F-13
MESABI TRUST
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JANUARY 31, 2010, 2009 AND 2008
Royalty bonuses are payable on all iron ore products produced from Mesabi Ore shipped from Silver Bay during a calendar quarter and sold at prices above the Adjusted Threshold Price. The Adjusted Threshold Price was $47.43 (per ton) for calendar year 2008, $48.48 (per ton) for calendar year 2009 and will be $48.81 (per ton) for calendar year 2010. The Adjusted Threshold Price is subject to adjustment (but not below $30 per ton) for inflation and deflation and is determined each year on the basis of the change in the Gross Domestic Product Implicit Price Deflator, a broad based index of inflation and deflation published quarterly by the U.S. Department of Commerce.
NMC also is obligated to pay to Mesabi Trust a minimum advance royalty of $500,000 per annum, subject to adjustment for inflation and deflation (but not below $500,000), which is credited against base overriding royalties and royalty bonuses. NMC is obligated to make quarterly payments of the minimum advance royalty in January, April, July and October of each year. For the calendar year ending December 31, 2010, the minimum advance royalty is $813,729. The minimum annual advance royalty was $808,177 and $790,721, for the calendar years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
NOTE 5 - UNALLOCATED RESERVE AND DISTRIBUTIONS
The Trustees have determined that the unallocated cash and U.S. Government securities portion of the Unallocated Reserve should be maintained at a prudent level, usually within the range of $500,000 to $1,000,000, to meet present or future liabilities of the Trust. The actual amount of the unallocated cash and U.S. Government securities portion of the Unallocated Reserve will fluctuate from time to time, and it may increase or decrease from its current level.
The Trustees determine the level of distributions on a quarterly basis after receiving notification from NMC as to the amount of royalty income that will be received and after determination of any known or anticipated expenses, liabilities and obligations of the Trust. As a result of fluctuations in the accrued income receivable portion of the Unallocated Reserve, future distributions may vary depending upon the adjustments to royalty income, which are determined by NMC, and the level of Trust expenses that the Trustees anticipate occurring in subsequent quarters.
During the fiscal years ended January 31, 2010, 2009, and 2008, the Trustees distributed cash payments totaling $9,315,207 ($.71 per Unit), $37,851,229 ($2.89 per Unit), and $15,088,011 ($1.15 per Unit), respectively. In addition, in January 2010 the Trustees declared a distribution of $.55 per Unit of beneficial interest, which was paid in February 2010.
F-14
MESABI TRUST
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JANUARY 31, 2010, 2009 AND 2008
NOTE 6 - SUMMARY OF QUARTERLY EARNINGS (UNAUDITED)
The quarterly results of operations for the two years ended January 31, 2010 and 2009 are presented below:
| | 2010 | |
| | First | | Second | | Third | | Fourth | |
| | Quarter | | Quarter | | Quarter | | Quarter | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Revenue | | $ | 1,024,881 | | $ | 422,936 | | $ | 5,042,739 | | $ | 6,751,113 | |
Expenses | | 223,835 | | 201,925 | | 141,870 | | 250,377 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 801,046 | | $ | 221,011 | | $ | 4,900,869 | | $ | 6,500,736 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Net income per unit | | $ | 0.061 | | $ | 0.017 | | $ | 0.374 | | $ | 0.495 | |
| | 2009 | |
| | First | | Second | | Third | | Fourth | |
| | Quarter | | Quarter | | Quarter | | Quarter | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Revenue | | $ | 3,861,807 | | $ | 16,771,803 | | $ | 11,796,116 | | $ | 3,039,379 | |
Expenses | | 222,154 | | 201,486 | | 138,805 | | 236,875 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 3,639,653 | | $ | 16,570,317 | | $ | 11,657,311 | | $ | 2,802,504 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Net income per unit | | $ | 0.277 | | $ | 1.263 | | $ | 0.889 | | $ | 0.214 | |
F-15
NOTE 7 — SUBSEQUENT EVENT
In April 2010, the Trust received customary quarterly payment notification from NMC, which indicated that the Trust was credited a royalty payment of approximately $1.77 million. The Trust will receive only the minimum advance royalty payment of approximately $203,000 on April 30, 2010 because NMC applied negative pricing adjustments of approximately $2.8 million against the $1.77 million royalty payment credited to the Trust for shipments during the three months ended March 31, 2010. This resulted in a carry forward negative pricing adjustment of approximately $1.1 million. The Trust anticipates that NMC will offset the $1.1 million carry forward negative price adjustment against royalties that will be payable to the Trust in future periods.
F-16

