As filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on April 17, 2018 Registration No. 333-213125
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾
POST-EFFECTIVE AMENDMENT NO. 4
TO
FORM S-1
REGISTRATION STATEMENT
UNDER THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾
Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
Minnesota (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | 6311 (Primary Standard Industrial Classification Code Number) | 41-1366075 (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
5701 Golden Hills Drive
Minneapolis, MN 55416
(800) 950-5872
(Address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of Registrant's principal executive offices)
Stewart D. Gregg, Esq.
Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America
5701 Golden Hills Drive
Minneapolis, MN 55416
(763) 765-2913
(Name, address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of agent for service)
¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾
Approximate date of commencement of proposed sale to the public:
As soon as practicable after this registration statement becomes effective.
As soon as practicable after this registration statement becomes effective.
If any of the securities being registered on this Form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, check the following box. [X]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer" and "smaller reporting company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer [ ] Accelerated filer [ ]
Non-accelerated filer [X] Smaller reporting company [ ]
(Do not check if a smaller reporting company)
The Registrant hereby amends this registration statement on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its effective date until the Registrant shall file a further amendment which specifically states that this registration statement shall thereafter become effective in accordance with Section 8(a) of the Securities Act of 1933 or until the registration statement shall become effective on such date as the Securities and Exchange Commission, acting pursuant to said Section 8(a), may determine.
PART I – PROSPECTUS
SUPPLEMENT DATED MAY 1, 2018
To the following variable annuity prospectuses:
Allianz Index Advantage®
Dated May 1, 2018
Allianz Index Advantage ADVSM
Allianz Index Advantage NFSM
Dated May 1, 2018
ISSUED BY
Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America and Allianz Life Variable Account B
This supplement updates certain information contained in the prospectus and should be
attached to the prospectus and retained for future reference.
Effective June 4, 2018 we are making the Russell 2000® Index, Nasdaq-100® Index and EURO STOXX 50® available under the Index Protection Strategy if your Contract was issued on or after August 24, 2015, has a Contact number starting with AV, and was not issued in Missouri or Washington.
Please discuss with your Financial Professional whether these new Index Protection Strategy Index Options are appropriate for your investment needs. If you would like to include these new Index Protection Strategy Index Options in your future allocation instructions, or your Index Anniversary transfer or optional rebalancing program instructions, you can do so by logging into your online account at allianzlife.com and selecting Index Rebalances under My Contract. You can also change your instructions by contacting your Financial Professional, or calling our Service Center at (800) 624-0197.
PRO-001-0518
ALLIANZ INDEX ADVANTAGE ADVSM VARIABLE ANNUITY CONTRACT
Issued by Allianz Life® Variable Account B and Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America (Allianz Life®, we, us, our)
Prospectus Dated: May 1, 2018
This prospectus describes all material rights and obligations of purchasers under an individual flexible purchase payment variable and index-linked deferred annuity contract (Contract). The Contract is designed to be used by purchasers who are working with a Financial Professional registered or affiliated with an investment adviser registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, as amended, or under state securities law, as applicable. Allianz Life is not an investment adviser, does not provide investment advice with regard to the Contract, and is not a party to any agreement between you and your Financial Professional. The Contract offers both variable investment options (Variable Options) and index-linked investment options (Index Options). (The Variable Options and the Index Options together are referred to as Allocation Options.) You can allocate your money (Purchase Payments) to any or all of the Variable Options or Index Options. The Contract also offers various standard annuity features, including multiple fixed annuitization options (Annuity Options), a free withdrawal privilege, and a guaranteed death benefit (Traditional Death Benefit). For an individually owned Contract, the annuity can be a single or joint annuity. The Contract has a six-year withdrawal charge period applicable only to the Index Options. The Variable Options are not subject to a withdrawal charge. Amounts transferred from the Variable Options to the Index Options and subsequently withdrawn are subject to a Daily Adjustment (which may be negative) and a withdrawal charge. At issue, purchasers can select the optional Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit for an additional fee described in Fee Tables and section 8. The Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit is not available to Contracts issued before the date of this prospectus. The Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit locks in any annual Index Anniversary investment gains (Maximum Anniversary Value) to potentially provide an increased death benefit as described in section 11.
If you allocate Purchase Payments to the Variable Options, the value of your investment (Variable Account Value) increases and decreases based on your selected Variable Options' performance. The Variable Options do not provide any protection against loss of principal. You can lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits) you allocate to the Variable Options.
| Variable Options Currently Available | ||
AZL® MVP Growth Index Strategy Fund | AZL® MVP Balanced Index Strategy Fund | AZL® Government Money Market Fund |
If you allocate Purchase Payments to the Index Options, you receive annual returns (Credits) based on the performance of one or more nationally recognized third-party broad based securities indices (Index or Indices). Unlike the Variable Options, the Index Options do not involve a direct or indirect investment by you in any underlying Index and do not participate directly in the equity market. Instead, Credits are an obligation of Allianz Life, and are subject to the claims paying ability and financial strength of Allianz Life. These Credits are calculated by us based on annual changes in the Index's value.
All Index Credit calculation methods (Crediting Methods) provide a combination of a Credit that is calculated by reference to Index performance, a level of protection against negative Index performance, and a limit or Cap on participation in positive Index performance. The Crediting Methods are described in more detail in section 7, Index Options. The Indices are described in more detail in Appendix A.
| Crediting Methods | Indices |
| Index Protection Strategy | S&P 500® Index |
| Index Performance Strategy | Russell 2000® Index |
| Index Guard Strategy | Nasdaq-100® Index |
| Index Precision Strategy | EURO STOXX 50® |
NOTE:
| ● | The Index Protection Strategy is not available to Contracts issued in Missouri or Washington on or after the date of this prospectus. If in future years the renewal rates for the Index Performance Strategy, Index Guard Strategy or Index Precision Strategy are not acceptable to you, you will not be able to transfer into the Index Protection Strategy and take advantage of its principal protection. This would subject you to ongoing market risk. You could lose money and previously applied positive Credits. |
| ● | Availability restrictions for the Crediting Methods and Indices for Contracts issued before the date of this prospectus are detailed in section 7, Index Options. |
The Index Protection Strategy provides a Declared Protection Strategy Credit (DPSC) if the current Index Value (Index price at the end of the Business Day on the Index Anniversary as provided by Bloomberg or another market source) is equal to or greater than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary. If the current Index Value is less than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary you do not receive the DPSC, but you also do not receive a negative Credit. Amounts withdrawn from the Index Protection Strategy Index Options during the year do not receive the DPSC. We can change the DPSCs at the beginning of each Index Year. An Index Year is a twelve-month period beginning on the Index Effective Date and each subsequent Index Anniversary. An Index Anniversary is a twelve-month anniversary of the Index start date (Index Effective Date) and is the date we apply Credits.
The Index Performance Strategy, Index Guard Strategy, and Index Precision Strategy each provide a different form of Credit calculation. Under the Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy you receive a positive Performance Credit based on positive Index Return (annual percentage change in Index Value from one Index Anniversary to the next) subject to an upper limit called the Cap. If the Index Return is negative you will receive a negative Performance Credit under the Index Performance Strategy if the loss is greater than a specified percentage called the Buffer. Under the Index Guard Strategy, if the Index Return is negative, you will receive a negative Performance Credit down to the amount of a specified percentage called the Floor, but the negative Performance Credit will never exceed the Floor. Under the Index Precision Strategy you receive a positive Performance Credit equal to the Precision Rate if the current Index Value is equal to or greater than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary. This is similar to the DPSCs under the Index Protection Strategy in that positive Performance Credits are equal to the rate set at the beginning of each Index Year. Precision Rates will generally be greater than the DPSCs, though they will generally be less than the Index Performance Strategy Caps. If the current Index Value is less than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary you receive a negative Performance Credit under the Index Precision Strategy if the negative Index Return is greater than the Buffer, which is similar to negative Performance Credits under the Index Performance Strategy. Please note, since the Index Value is priced only on the Index Effective Date and subsequent Index Anniversaries, the Index Return does not account for changes in Index Value during the Index Year. A negative Performance Credit means that you can lose money, including principal and previously applied positive Performance Credits. For more information please see "How Do the Index-Linked Crediting Methods Compare?" on page 16.
We can change the Precision Rates and Caps at the beginning of each Index Year, but we generally establish the Buffers and Floors on the date we issue your Contract (Issue Date). However, if we add a new Index Option to a Contract after the Issue Date, we establish the Buffer or Floor for it on the date we add the Index Option to the Contract. We cannot change Buffers or Floors after they are established. DPSCs, Precision Rates, Caps, Buffers and Floors can all be different. For example, Caps for the Index Performance Strategy can be different between the S&P 500® Index and the Nasdaq-100® Index, and Caps for the S&P 500® Index can be different between the Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy. Amounts allocated to the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Options may fluctuate between Index Anniversaries. We base these interim values on a calculation called the Daily Adjustment, which reflects changes in market value of an Index Option. The Daily Adjustment does not apply to the Index Protection Strategy. You can lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits) that you allocate to the Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy if Index losses are greater than the Buffer, or the Index Guard Strategy for Index losses down to the Floor. This loss could be significant. If money is withdrawn or removed from an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option before the Index Anniversary, you could lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits) even if the Index return is positive on the date of withdrawal due to the application of the Daily Adjustment.
Amounts allocated to the Index Options may also fluctuate based on the Alternate Minimum Value. The Alternate Minimum Value is the guaranteed minimum on the value of each Index Option (Index Option Value) if you take a withdrawal, annuitize the Contract, transfer out of Index Options to the Variable Options, or if we pay a death benefit. The Alternate Minimum Value applies to all Crediting Methods, including the Index Protection Strategy.
The Crediting Methods have different risk and return potentials. The Index Protection Strategy has the lowest return potential, but provides the most protection. Potential returns and risks are higher for the other Crediting Methods.
Positive returns for the Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy are limited by the Caps, and for the Index Precision Strategy by the Precision Rates. The Index Precision Strategy performs best in periods of small market movements because the Precision Rates will generally be greater than the DPSC, though they will generally be less than the Index Performance Strategy Caps. Negative returns are limited for the Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy by the Buffers, and for the Index Guard Strategy by the Floor. The Buffers have protection for smaller negative returns, but also have the potential for the largest loss in any one year. The Index Guard Strategy permits negative Performance Credits down to the Floor, and provides less risk of significant negative returns in any one year than the Buffers.
All guarantees under the Contract are the obligations of Allianz Life and are subject to the claims paying ability and financial strength of Allianz Life.
The Contract involves certain risks, as described in section 1, Risk Factors on page 25 of this prospectus.
Please read this prospectus before investing and keep it for future reference. It contains important information about your annuity and Allianz Life that you ought to know before investing. This prospectus is not an offering in any state, country, or jurisdiction in which we are not authorized to sell the Contracts. You should rely only on the information contained in this prospectus. We have not authorized anyone to give you different information.
Index-linked annuity contracts are complex insurance and investment vehicles. Purchasers should speak with a Financial Professional about the Contract's features, benefits, risks, and fees, and whether the Contract is appropriate based upon the purchaser's financial situation and objectives. The primary purpose of this prospectus is to offer the product for sale; it is not intended to constitute a suitability recommendation or fiduciary advice. Please consult your Financial Professional for a specific recommendation to purchase the Contract.
Allianz Life Variable Account B is the Separate Account that holds the assets allocated to the Variable Options. Additional information about the Separate Account has been filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and is available upon written or oral request without charge, or on the EDGAR database on the SEC's website (www.sec.gov). A Statement of Additional Information (SAI) dated the same date as this prospectus includes additional information about the annuity offered by this prospectus. The SAI is incorporated by reference into this prospectus. The SAI is filed with the SEC on Form N-4 and is available without charge by contacting us at the telephone number or address listed at the back of this prospectus. The SAI's table of contents appears after the Privacy and Security Statement in this prospectus. The prospectus, SAI and other Contract information are also available on the EDGAR database.
The SEC has not approved or disapproved these securities or determined if this prospectus is truthful or complete. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense. An investment in this Contract is not a deposit of a bank or financial institution and is not federally insured or guaranteed by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation or any other federal government agency. An investment in this Contract involves investment risk including the possible loss of principal. Variable and index-linked annuity contracts are complex insurance and investment vehicles. Before you invest, be sure to ask your Financial Professional about the Contract's features, benefits, risks, and fees, and whether the Contract is appropriate for you based upon your financial situation and objectives.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| Glossary | 6 | |
| Summary | 11 | |
| Who Should Consider Purchasing the Contract? | 12 | |
| What Are the Contract's Charges? | 13 | |
| What Are the Contract's Benefits? | 13 | |
| What Are the Index-Linked Crediting Methods and How Do They Work? | 14 | |
| When Do You Establish the Values Used to Determine Index-Linked Credits? | 14 | |
| What Factors Impact the DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps? | 16 | |
| How Do the Index-Linked Crediting Methods Compare? | 16 | |
| How Can I Allocate My Purchase Payments? | 18 | |
| What Are the Different Values Within the Contract? | 18 | |
| How Do We Apply Credits to the Index Options? | 20 | |
| Can My Contract Lose Value Because of Negative Changes in an Index's Value? | 20 | |
| Can I Transfer Index Option Value Between the Allocation Options? | 20 | |
| How Can I Take Money Out of My Contract? | 20 | |
| What Are My Annuity Options? | 21 | |
| Does the Contract Provide a Death Benefit? | 21 | |
| What If I Need Customer Service? | 21 | |
| Fee Tables | 22 | |
| Owner Transaction Expenses | 22 | |
| Owner Periodic Expenses | 22 | |
| Annual Operating Expenses of the Variable Options | 23 | |
| Examples | 24 | |
| Condensed Financial Information | 25 | |
| 1. | Risk Factors | 25 |
| Liquidity Risk | 25 | |
| Risk of Investing in Securities | 26 | |
| Risk of Negative Returns | 27 | |
| Calculation of Credits | 27 | |
| Substitution of an Index | 28 | |
| Changes to Caps, Precision Rates, Declared Protection Strategy Credits (DPSCs), and Notice of Buffers and Floors | 28 | |
| Investment in Derivative Securities | 29 | |
| Variable Option Risk | 30 | |
| Our Financial Strength and Claims-Paying Ability | 30 | |
| Regulatory Protections | 30 | |
| 2. | The Variable Annuity Contract | 30 |
| State Specific Contract Restrictions | 31 | |
| When The Contract Ends | 31 | |
| 3. | Ownership, Annuitants, Determining Life, Beneficiaries, and Payees | 31 |
| Owner | 31 | |
| Joint Owner | 31 | |
| Annuitant | 32 | |
| Determining Life (Lives) | 32 | |
| Beneficiary | 33 | |
| Payee | 33 | |
| Assignments, Changes of Ownership and Other Transfers of Contract Rights | 33 | |
| 4. | Purchasing the Contract | 34 |
| Purchase Requirements | 34 | |
| Applications Sent Electronically | 35 | |
| Allocation of Purchase Payments and Transfers Between the Allocation Options | 35 | |
| Automatic Investment Plan (AIP) | 36 | |
| Free Look/Right to Examine Period | 36 | |
| 5. | Variable Options | 37 |
| Substitution of Variable Options and Limitation on Further Investments | 38 | |
| Transfers Between Variable Options | 39 | |
| Electronic Transfer and Allocation Instructions | 39 | |
| Excessive Trading and Market Timing | 39 | |
| Financial Adviser Fees | 41 | |
| Voting Privileges | 42 | |
| 6. | Valuing Your Contract | 42 |
| Accumulation Units | 42 | |
| Computing Variable Account Value | 43 | |
| 7. | Index Options | 43 |
| Determining Index Option Value for the Index Protection Strategy | 44 | |
| Determining Index Option Values for the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy | 45 | |
| The Alternate Minimum Value | 48 | |
| Optional Rebalancing Program | 49 | |
| 8. | Expenses | 49 |
| Annual Contract Fees: Product Fee and Rider Fee | 49 | |
| Contract Maintenance Charge | 50 | |
| Withdrawal Charge | 50 | |
| Transfer Fee | 53 | |
| Premium Tax | 53 | |
| Income Tax | 53 | |
| Variable Option Expenses | 53 | |
| 9. | Access to Your Money | 53 |
| Free Withdrawal Privilege | 54 | |
| Systematic Withdrawal Program | 55 | |
| Minimum Distribution Program and Required Minimum Distribution (RMD) Payments | 55 | |
| Waiver of Withdrawal Charge Benefit | 56 | |
| Suspension of Payments or Transfers | 56 | |
| 10. | The Annuity Phase | 56 |
| Calculating Your Annuity Payments | 56 | |
| Annuity Payment Options | 57 | |
| When Annuity Payments Begin | 58 | |
| 11. | Death Benefit | 58 |
| Maximum Anniversary Value | 59 | |
| Death of the Owner and/or Annuitant | 60 | |
| Death Benefit Payment Options During the Accumulation Phase | 60 | |
| 12. | Taxes | 61 |
| Qualified and Non-Qualified Contracts | 61 | |
| Taxation of Annuity Contracts | 62 | |
| Tax-Free Section 1035 Exchanges | 62 | |
| 13. | Other Information | 63 |
| The Registered Separate Account | 63 | |
| Our General Account | 63 | |
| Our Unregistered Separate Account | 63 | |
| Distribution | 64 | |
| Additional Credits for Certain Groups | 65 | |
| Administration/Allianz Service Center | 65 | |
| Legal Proceedings | 66 | |
| Status Pursuant to Securities Exchange Act of 1934 | 66 | |
| 14. | Information on Allianz Life | 66 |
| Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance | 66 | |
| Executive Compensation | 71 | |
| Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management | 83 | |
| Transactions with Related Persons, Promoters and Certain Control Persons | 83 | |
| Risks Associated with the Financial Services Industry | 83 | |
| 15. | Financial Statements | 99 |
| Auditor Update | 99 | |
| 16. | Privacy Notice | 100 |
| 17. | Table of Contents of the Statement of Additional Information (SAI) | 101 |
| Appendix A – Available Indices | 102 | |
| Standard & Poor's 500 Index | 102 | |
Russell 2000® Index | 103 | |
Nasdaq-100® Index | 103 | |
EURO STOXX 50® | 104 | |
| Appendix B – Daily Adjustment | 105 | |
| Appendix C – Buffers, Floors and Initial DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps | 107 | |
| Index Protection Strategy | 107 | |
| Index Performance Strategy | 107 | |
| Index Guard Strategy | 108 | |
| Index Precision Strategy | 108 | |
| Appendix D – Annual Contract Fees Calculation Examples | 109 | |
| Traditional Death Benefit | 109 | |
| Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit | 110 | |
| Appendix E – Bar Chart Examples | 110 | |
| Appendix F – Selected Financial Data and Consolidated Financial Statements | 111 | |
| Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (For the 12 month period ended December 31, 2017) | 113 | |
| Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplemental Schedules | 113 | |
| For Service or More Information | 114 | |
| Our Service Center | 114 | |
GLOSSARY
This prospectus is written in plain English. However, there are some technical words or terms that are capitalized and are used as defined terms throughout the prospectus. For your convenience, we included this glossary to define these terms.
Accumulated Alternate Interest – the sum of alternate interest earned for the entire time you own your Contract. The alternate interest for each Index Year is equal to the Alternate Minimum Base multiplied by the alternate interest rate. The alternate interest rate is stated in your Contract and does not change for the entire time you own your Contract. We use the Accumulated Alternate Interest to calculate the Alternate Minimum Value.
Accumulation Phase – the initial phase of your Contract before you apply your Contract Value to Annuity Payments. The Accumulation Phase begins on the Issue Date.
Allocation Options – the Variable Options and Index Options available to you under the Contract.
Alternate Minimum Base – the Index Option Value at the beginning of an Index Year multiplied by the AMB Factor. We use the Alternate Minimum Base to determine the amount of interest earned on the Alternate Minimum Value.
Alternate Minimum Value – the guaranteed minimum Index Option Value we provide for each Crediting Method if you take a withdrawal, annuitize the Contract, transfer out of Index Options to the Variable Options, or if we pay a death benefit.
AMB Factor – the percentage of the Index Option Base that determines the Alternate Minimum Base on the Index Effective Date and each Index Anniversary. The AMB Factor is stated in your Contract and does not change for the entire time you own your Contract. We use the AMB Factor to calculate the Alternate Minimum Value.
AMV Factor – the percentage of the Index Option Base that determines the Alternate Minimum Value on the Index Effective Date and each Index Anniversary. The AMV Factor is stated in your Contract and does not change for the entire time you own your Contract.
Annuitant – the individual upon whose life we base the Annuity Payments. Subject to our approval, the Owner designates the Annuitant, and can add a joint Annuitant for the Annuity Phase. There are restrictions on who can become an Annuitant.
Annuity Date – the date we begin making Annuity Payments to the Payee from the Contract.
Annuity Options – the annuity income options available to you under the Contract.
Annuity Payments – payments made by us to the Payee pursuant to the chosen Annuity Option.
Annuity Phase – the phase the Contract is in once Annuity Payments begin.
Beneficiary – the person(s) the Owner designates to receive any death benefit, unless otherwise required by the Contract or applicable law.
Buffer – under the Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy, this is the negative Index Return that Allianz Life absorbs before applying a negative Performance Credit. We generally establish a Buffer for each Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy Index Option on the Issue Date. However, if we add a new Index Option to a Contract after the Issue Date, we establish the Buffer for it on the date we add the Index Option to your Contract. Buffers are stated in your Contract and do not change after they are established.
Business Day – each day on which the New York Stock Exchange is open for trading, except, with regard to a specific Variable Option, when that Variable Option does not value its shares. Allianz Life is open for business on each day that the New York Stock Exchange is open. Our Business Day closes when regular trading on the New York Stock Exchange closes, which is usually at 4:00 p.m. Eastern Time.
Cap – under the Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy, this is the maximum potential Performance Credit for an Index Option. We set a Cap for each Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Option on the Index Effective Date and each Index Anniversary. The Caps applicable to your Contract are shown on the Index Options Statement.
Charge Base – the Contract Value on the preceding Quarterly Contract Anniversary (or the initial Purchase Payment received on the Issue Date if this is before the first Quarterly Contract Anniversary), adjusted for subsequent Purchase Payments and withdrawals. We use the Charge Base to determine the next product fee and rider fee (if applicable) we deduct.
Contract – the individual flexible purchase payment variable and index-linked deferred annuity contract described by this prospectus.
Contract Anniversary – a twelve-month anniversary of the Issue Date or any subsequent Contract Anniversary.
Contract Value – on any Business Day, the sum of your Index Option Value(s) and Variable Account Value. The Contract Value does not include any currently applicable withdrawal charge, final product fee, final rider fee, or final contract maintenance charge. The Variable Account Value component of the Contract Value fluctuates each Business Day. The Index Option Value component of the Contract Value is adjusted on each Index Anniversary to reflect Credits, which can be negative with the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy. A negative Performance Credit means that you can lose money, including principal and previously applied positive Credits. The Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Option Values also reflect the Daily Adjustment on every Business Day other than the Index Anniversary.
Contract Year – any period of twelve months beginning on the Issue Date or a subsequent Contract Anniversary.
Credit – the annual return you may receive when you allocate money to an Index Option. Credits may be positive, zero, or, in some instances, negative if you select the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy. A negative Credit means that you can lose money, including principal and previously applied positive Credits.
Crediting Method – a method we use to calculate annual Credits if you allocate money to an Index Option.
Daily Adjustment – the change in the market value of an Index Option under the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy as discussed in section 7, Index Options and Appendix B. Each Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Option has a Daily Adjustment. We use the Daily Adjustment to calculate the Index Option Values for these Index Options on each Business Day during the Index Year other than the Index Effective Date or Index Anniversary. The Daily Adjustment can affect the amounts available for withdrawals, annuitizations, death benefits, and the Contract Value used to determine the Charge Base and contract maintenance charge.
Declared Protection Strategy Credit (DPSC) – the positive Credit we apply on an Index Anniversary under the Index Protection Strategy if the current Index Value is equal to or greater than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary (or the Index Effective Date if this is the first Index Anniversary). We set the DPSCs on the Index Effective Date and each Index Anniversary. The DPSCs applicable to your Contract are shown on the Index Options Statement.
Determining Life (Lives) – the person(s) designated at Contract issue and named in the Contract on whose life we base the guaranteed Traditional Death Benefit or Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit.
Financial Professional – the person who advises you regarding the Contract. A Financial Professional may be a registered representative of a broker-dealer and/or an investment adviser representative of a registered investment adviser. However, we do not pay a commission to broker-dealers or their registered representatives in connection with sales of the Contract. The Contracts are intended to be used by purchasers who are working with a Financial Professional registered or affiliated with an investment adviser, offering advisory services for a fee.
Floor – under the Index Guard Strategy, this is the lowest potential negative Performance Credit for an Index Option. We generally establish a Floor for each Index Guard Strategy Index Option on the Issue Date. However, if we add a new Index Option to a Contract after the Issue Date, we establish the Floor for it on the date we add the Index Option to your Contract. Floors are stated in your Contract and do not change after they are established.
Good Order – a request is in "Good Order" if it contains all of the information we require to process the request. If we require information to be provided in writing, "Good Order" also includes providing information on the correct form, with any required certifications, guarantees and/or signatures, and received at our Service Center after delivery to the correct mailing, email, or website address, which are all listed at the back of this prospectus. If you have questions about the information we require, or whether you can submit certain information by fax, email or over the web, please contact our Service Center. If you send information by email or upload it to our website, we send you a confirmation number that includes the date and time we received your information.
Index (Indices) – one (or more) of the nationally recognized third-party broad based securities Indices available to you under the Crediting Methods in your Contract.
Index Anniversary – a twelve-month anniversary of the Index Effective Date or any subsequent Index Anniversary. If an Index Anniversary does not occur on a Business Day, we consider it to occur on the next Business Day for the purposes of determining Index Values and Index Returns, applying Credits, and setting the DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps.
Index Effective Date – the date shown on the Index Options Statement that starts the first Index Year. When you purchase this Contract you select the Index Effective Date as discussed in section 4, Purchasing the Contract – Allocation of Purchase Payments and Transfers Between the Allocation Options.
Index Guard Strategy – one of the Index Crediting Methods described in section 7, Index Options. Section 7 also includes availability restrictions for the Index Guard Strategy. The Index Guard Strategy calculates Performance Credits based on Index Returns subject to a Cap and Floor. You can receive negative Performance Credits under this Crediting Method, which means you can lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits). The Index Guard Strategy is more sensitive to smaller negative market movements that persist over time because the Floor reduces the impact of large negative market movements. In an extended period of smaller negative market returns, the risk of loss is greater with the Index Guard Strategy than with the Index Performance Strategy and Index Precision Strategy.
Index Option – the index-linked investment options to which you can allocate money under the Contract. Each Index Option is the combination of an Index and a Crediting Method.
Index Option Base – an amount we use to calculate Credits and the Daily Adjustment. The Index Option Base is equal to the amounts you allocate to an Index Option adjusted for withdrawals, Contract expenses, transfers into or out of the Index Option, and the application of any Credits.
Index Option Value – on any Business Day it is equal to the value in an Index Option. We establish an Index Option Value for each Index Option you select. Each Index Option Value includes any Credits from previous Index Anniversaries and the deduction of any previously assessed contract maintenance charge, product fee, rider fee, and withdrawal charge. On each Business Day during the Index Year other than the Index Effective Date or an Index Anniversary, each Index Option Value under the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy also includes the Daily Adjustment. If you take a withdrawal, annuitize the Contract, transfer Contract Value out of Index Options, or if we pay a death benefit each Index Option Value for each Crediting Method also includes any increase from the Alternate Minimum Value.
Index Options Statement – an account statement we mail to you on the Index Effective Date and each Index Anniversary thereafter. On the Index Effective Date, the statement shows the initial Index Values, DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps for the Index Options you selected. On each Index Anniversary, the statement shows the new Index Values, Credits received, and renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps that are effective for the next year for the Index Options you selected.
Index Performance Strategy – one of the Index Crediting Methods described in section 7, Index Options. Section 7 also includes availability restrictions for Index Performance Strategy. The Index Performance Strategy calculates Performance Credits based on Index Returns subject to a Cap and Buffer. You can receive negative Performance Credits under this Crediting Method, which means you can lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits). The Index Performance Strategy is more sensitive to large negative market movements because small negative market movements are absorbed by the Buffer. In a period of extreme negative market performance, the risk of loss is greater with the Index Performance Strategy than with the Index Guard Strategy.
Index Precision Strategy – one of the Index Crediting Methods described in section 7, Index Options. Section 7 also includes availability restrictions for Index Precision Strategy. The Index Precision Strategy calculates Performance Credits based on Index Values and Index Returns subject to the Precision Rate and Buffer. You can receive negative Performance Credits under this Crediting Method, which means you can lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits). The Index Precision Strategy performs best in periods of small market movements because the Precision Rates will generally be greater than the DPSCs, though they will generally be less than the Index Performance Strategy Caps. The Index Precision Strategy is more sensitive to large negative market movements because small negative market movements are absorbed by the Buffer. In a period of extreme negative market performance, the risk of loss is greater with the Index Precision Strategy than with the Index Guard Strategy.
Index Protection Strategy – one of the Index Crediting Methods described in section 7, Index Options. Section 7 also includes availability restrictions for Index Protection Strategy. Under the Index Protection Strategy you receive the DPSCs if the current Index Value is equal to or greater than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary (or the Index Effective Date if this is the first Index Anniversary). The Index Protection Strategy provides the most protection because you cannot receive a negative Credit under this Crediting Method.
Index Return – annual percentage change in Index Value on each Index Anniversary we use to determine the Performance Credits under the Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy, and negative Performance Credits under the Index Precision Strategy. The Index Return is an Index's current Index Value, minus its Index Value on the last Index Anniversary (or the Index Effective Date if this is the first Index Anniversary), divided by its Index Value on the last Index Anniversary (or the Index Effective Date if this is the first Index Anniversary).
Index Value – an Index's price at the end of the Business Day on the Index Effective Date and each Index Anniversary as provided by Bloomberg or another market source.
Index Year – any period of twelve months beginning on the Index Effective Date or a subsequent Index Anniversary.
Issue Date – the date shown on the Contract that starts the first Contract Year. Contract Anniversaries and Contract Years are measured from the Issue Date.
Joint Owners – two Owners who own a Contract.
Lock Date – under the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy, this is the Business Day we process your request to lock in an Index Option Value (a Performance Lock) before the Index Anniversary.
Maximum Anniversary Value – the highest Contract Value on any Index Anniversary before age 91, adjusted for subsequent Purchase Payments and withdrawals, used to determine the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit as discussed in section 11. Withdrawals include withdrawals under the free withdrawal privilege, withdrawal charges, but not amounts we withdraw for other Contract expenses.
Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit – an optional benefit described in section 11 that has an additional rider fee and is intended to potentially provide an increased death benefit.
Non-Qualified Contract – a Contract that is not purchased under a pension or retirement plan qualified for special tax treatment under sections of the Internal Revenue Code.
Owner – "you," "your" and "yours." The person(s) or entity designated at Contract issue and named in the Contract who may exercise all rights granted by the Contract.
Payee – the person or entity who receives Annuity Payments during the Annuity Phase.
Performance Lock – a feature under the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy that allows you to lock in each of your current Index Option Values before the Index Anniversary. A Performance Lock applies to the total Index Option Value in an Index Option, and not just a portion of that Index Option Value. After the Lock Date, Daily Adjustments do not apply for the remainder of the Index Year and the Index Option Value will not receive a Performance Credit on the next Index Anniversary.
Performance Credit – the Credit we apply on the Index Anniversary under the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy. We base Performance Credits on Index Values and Index Returns limited by the Precision Rate, Cap, Buffer and Floor. Performance Credits can be negative, which means you can lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits).
Precision Rate – the positive Performance Credit we apply under the Index Precision Strategy if the current Index Value is equal to or greater than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary (or the Index Effective Date if this is the first Index Anniversary). We set a Precision Rate for each Index Precision Strategy Index Option on the Index Effective Date and each Index Anniversary. The Precision Rates applicable to your Contract are shown on the Index Options Statement.
Proxy Investment – an investment tracking mechanism we establish that is structured as a hypothetical set of call and put options designed to provide the same returns as the Performance Credits under the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy on an Index Anniversary. We use the Proxy Investment to calculate the Daily Adjustment between Index Anniversaries. For more information, see Appendix B.
Proxy Value – the value of the Proxy Investment for an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option used to calculate the Daily Adjustment as discussed in Appendix B.
Purchase Payment – the money you put into the Contract.
Qualified Contract – a Contract purchased under a pension or retirement plan qualified for special tax treatment under sections of the Internal Revenue Code (for example, 401(a) and 401(k) plans), Individual Retirement Annuities (IRAs), or Tax-Sheltered Annuities (referred to as TSA or 403(b) contracts). Currently, we issue Qualified Contracts that may include, but are not limited to Roth IRAs, Traditional IRAs and Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRAs. We may also issue an Inherited IRA and Inherited Roth IRA to make any required minimum distribution payments to a beneficiary of a previously held tax-qualified arrangement.
Quarterly Contract Anniversary – the day that occurs three calendar months after the Issue Date or any subsequent Quarterly Contract Anniversary.
Separate Account – Allianz Life Variable Account B is the Separate Account that issues the variable investment portion of your Contract. It is a separate investment account of Allianz Life. The Separate Account holds the Variable Options that underlie the Contracts. The Separate Account is divided into subaccounts, each of which invests exclusively in a single Variable Option. The Separate Account is registered with the SEC as a unit investment trust, and may be referred to as the Registered Separate Account.
Service Center – the area of our company that provides Contract maintenance and routine customer service. Our Service Center address and telephone number are listed at the back of this prospectus. The address for mailing applications and/or checks for Purchase Payments may be different and is also listed at the back of this prospectus.
Traditional Death Benefit – the death benefit provided by the Contract that is equal to the greater of Contract Value (after deduction of the final product fee), or total Purchase Payments adjusted for withdrawals. Withdrawals include withdrawals under the free withdrawal privilege, withdrawal charges, but not amounts we withdraw for other Contract expenses.
Valid Claim – the documents we require to be received in Good Order at our Service Center before we pay any death claim. This includes the death benefit payment option, due proof of death, and any required governmental forms. Due proof of death includes a certified copy of the death certificate, a decree of court of competent jurisdiction as to the finding of death, or any other proof satisfactory to us.
Variable Account Value – on any Business Day, the sum of the values in your selected Variable Options. The Variable Account Value includes the deduction of the Variable Option operating expenses, and any previously assessed transfer fee, contract maintenance charge, product fee, rider fee, and withdrawal charge.
Variable Options – the variable investments available to you under the Contract. Variable Option performance is based on the securities in which they invest.
Withdrawal Charge Basis – the total amount under your Contract that is subject to a withdrawal charge as discussed in section 8, Expenses – Withdrawal Charge.
SUMMARY
The Allianz Index Advantage ADV Variable Annuity is a variable and index-linked deferred annuity product. The product or certain product features may not currently be available in all states or on all Contracts, may vary in your state, or may not be available from all selling firms or from all Financial Professionals. When you purchase a Contract, you tell us how to allocate your money. You can select any or all of the available Variable Options and Index Options. Check with your Financial Professional regarding availability of Allocation Options. Your allocations must be in whole percentages and we only allow allocations to the Index Options once each Index Year. You can only reallocate money from the Index Options to the Variable Options on every sixth Index Anniversary. If you allocate money to the Variable Options offered through the Contract, the value of your investment (Variable Account Value) increases and decreases based on your selected Variable Options performance.
If you allocate money to an Index Option, we calculate an annual return or Credit, on each Index Anniversary. The Credit is based on the change in value of one or more nationally recognized third-party broad based securities Indices. Credits may be positive, zero, or, in some instances, negative, depending on the Index Option you select. Positive Credits are limited by the DPSCs under the Index Protection Strategy, the Precision Rates under the Index Precision Strategy, and the Caps under the Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy. Under the Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy, there are also Buffers on negative Credits, but there is no protection for negative Credits for losses greater than the Buffer. Under the Index Guard Strategy there is a Floor on negative Credits, which determines the minimum Performance Credit you can receive. Once we issue your Contract we can change the DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps annually. We generally establish the Buffers and Floors on the Issue Date. However, if we add a new Index Option to a Contract after the Issue Date, we establish the Buffer or Floor for it on the date we add the Index Option to your Contract. Your Buffers and Floors are stated in your Contract and they cannot change after they are established. We publish any changes to the Buffers and Floors for newly issued Contracts, and changes to initial and renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps at least seven calendar days before they take effect on our website at www.allianzlife.com/indexratesadv.
NOTE:
| ● | You can lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits) that you allocate to the Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy if Index losses are greater than the Buffer, or the Index Guard Strategy for Index losses down to the Floor. You cannot lose money (or previously applied positive Credits) that you allocate to the Index Protection Strategy due to Index losses. The Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy include a risk of potential loss of principal and this loss could be significant. If money is withdrawn or removed from an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option before the Index Anniversary, you could lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits) even if the current Index return is positive on the date of withdrawal. |
| ● | The Index Protection Strategy is not available to Contracts issued in Missouri or Washington on or after the date of this prospectus. If in future years the renewal rates for the Index Performance Strategy, Index Guard Strategy or Index Precision Strategy are not acceptable to you, you will not be able to transfer Index Option Value into the Index Protection Strategy and take advantage of its principal protection. This would subject you to ongoing market risk. You could lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits). |
| ● | Availability restrictions for the Crediting Methods and Indices for Contracts issued before the date of this prospectus are detailed in section 7, Index Options. |
During the Index Year, the Index Protection Strategy Index Option Values do not change for Index performance or the Daily Adjustment. Amounts withdrawn from the Index Protection Strategy during the Index Year will not receive a DPSC. On each Business Day during the Index Year, other than the Index Effective Date or Index Anniversary, the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Option Values change for Index performance through the Daily Adjustment. A Business Day is any day the New York Stock Exchange is open, except, with regard to a specific Variable Option, when that Variable Option does not value its shares. The Daily Adjustment is meant to approximate the Index Option Value on the next Index Anniversary, as adjusted for gains during the Index Year subject to the Precision Rate or Cap and either losses greater than the Buffer for the Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy, or losses down to the Floor for the Index Guard Strategy. Even if the current Index return during the Index Year is positive, the Daily Adjustment may be negative until the Index Anniversary. This means if money is withdrawn or removed from the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy, or Index Guard Strategy, you could lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits) even if the current Index return is positive on that day. If the current Index return during the Index Year is negative, the Daily Adjustment could result in losses greater than the protection provided by the Buffer or the Floor.
The Contract has two phases: the Accumulation Phase and the Annuity Phase. During the Accumulation Phase your Contract Value (the total of your Variable Account Value and all Index Option Values) fluctuates based on the returns of your selected Variable Options and Index Options. During the Accumulation Phase you can add Purchase Payments to your Contract, take withdrawals, and we pay a death benefit if you die.
The Accumulation Phase of your Contract ends and the Annuity Phase starts once you begin Annuity Payments. For an individually owned Contract, Annuity Payments can be either single or joint. You can take Annuity Payments based on your Contract Value as discussed in section 10, The Annuity Phase.
Who Should Consider Purchasing the Contract?
We designed the Contract for people who are looking for a level of protection for their principal while providing potentially higher returns than are available on traditional fixed annuities. This Contract is not intended for someone who is seeking complete protection from downside risk, nor someone who is seeking unlimited investment performance.
We created the Contract for purchasers working with a Financial Professional who is registered as an investment adviser, or is an investment advisory representative of a registered investment adviser, and who is offering advisory services for a fee. A Financial Professional may also be a registered representative of a broker-dealer. However, we do not pay a sales commission to broker-dealers or their registered representatives in connection with sales of the Contract.
Your Financial Professional acts on your behalf, not ours. We are not party to any agreement between you and your Financial Professional, nor are we responsible for your Financial Professional's actions. We do not set your financial adviser's fee or receive any part of it. Any financial adviser fee you pay is in addition to this Contract's fees and expenses. You should ask your Financial Professional about compensation they receive in connection with this Contract. Allianz Life is not an investment adviser, and does not provide investment advice in connection with sales of the Contract. We are not a fiduciary to you, and do not make recommendations or assess suitability.
We do not allow you to instruct us to pay your financial adviser fees from this Contract. If you take withdrawals from this Contract to pay your financial adviser fees, these withdrawals will be subject to any applicable withdrawal charge. Also, if this is a Non-Qualified Contract this will be a taxable withdrawal to the extent that gain exists within the Contract. If any Owner is under age 59½, withdrawals may also be subject to a 10% additional federal tax. You should consult a tax adviser regarding the tax treatment of withdrawals.
We offer other annuity contracts that may address your investment and retirement needs. These contracts include variable annuities, registered index-linked annuities and fixed index annuities. These annuity products may offer different features and benefits more appropriate for your needs, including allocation options, fees and/or charges that are different from those in the Contract offered by this prospectus. Not every contract is offered through every Financial Professional. Some Financial Professionals or selling firms may not offer and/or limit offering of certain features and benefits, as well as limit the availability of the contracts based on criteria established by the Financial Professional or selling firm.
These alternative contracts may have different Index Options, and different rates and minimums for the DPSCs, Precision Rates, Caps, Buffers, and Floors. DPSCs and Caps may also be affected, positively or negatively, by expenses we incur in providing other contract features. For example, a contract that has a product fee may be able to set higher DPSCs, Precision Rates, and Caps than a contract without a product fee. The deduction of the product fee reduces Index Option Values, which may offset the effect of higher DPSCs, Precision Rates, and Caps. For more information about these contracts, please contact your Financial Professional or our Service Center.
What Are the Contract's Charges?
The Contract includes a product fee, contract maintenance charge, transfer fee, and withdrawal charge, and a rider fee if you select the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit. These fees and charges are discussed in more detail in section 8, Expenses.
We assess a 0.25% annualized product fee for the Contract. Contracts with the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit also have an additional annualized rider fee of 0.20%. The product and rider fees are deducted quarterly during the Accumulation Phase while your Contract Value is positive. We calculate and accrue the product and rider fees on a daily basis as a percentage of the Charge Base. The Charge Base is the Contract Value on the preceding Quarterly Contract Anniversary (or the initial Purchase Payment received on the Issue Date if this is before the first Quarterly Contract Anniversary), adjusted for subsequent Purchase Payments and withdrawals. A Quarterly Contract Anniversary is the day that occurs three calendar months after the Issue Date or any subsequent Quarterly Contract Anniversary.
We assess a $50 contract maintenance charge annually, but we waive this charge if your Contract Value is at least $100,000.
We assess a $25 transfer fee for each transfer in excess of 12 between the Variable Options in a Contract Year. A Contract Year is any period of twelve months beginning on the Issue Date or a subsequent Contract Anniversary (a twelve-month anniversary of the Issue Date).
The withdrawal charge is calculated based upon Purchase Payments. The withdrawal charge period applies separately to each Purchase Payment. The withdrawal charge starts at 6.5% and decreases to zero after we have had a Purchase Payment for six complete years. During the period that the withdrawal charge applies, if you withdraw more than is allowed from the Index Options under the free withdrawal privilege, we may deduct a withdrawal charge. The withdrawal charge does not apply to amounts withdrawn from the Variable Options. We only assess the withdrawal charge on and deduct the withdrawal charge from amounts withdrawn from the Index Options. Amounts transferred from the Variable Options to the Index Options and subsequently withdrawn are subject to a Daily Adjustment (which may be negative) and a withdrawal charge. (See section 9, Access to Your Money – Free Withdrawal Privilege.)
Contract charges and pro-rata fees are assessed on any full or partial withdrawal from either the Variable Options or the Index Options as discussed in more detail in section 8, Expenses.
What Are the Contract's Benefits?
The Contract offers a variety of variable and index-linked Allocation Options, each with different return and risk characteristics. The Contract has a free withdrawal privilege that allows you to withdraw up to 10% of your total Purchase Payments from the Index Options each Contract Year during the Accumulation Phase without incurring a withdrawal charge. The Contract includes a waiver of withdrawal charge benefit in most states that allows you to take money out of the Contract without incurring a withdrawal charge if you are confined to a nursing home for a period of time. Keep in mind that if you withdraw money from an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option on any day other than an Index Anniversary, we first calculate the Index Option Value by adding the Daily Adjustment (which can be negative), even if the withdrawal is not subject to a withdrawal charge. The Contract has several Annuity Options which can provide guaranteed income for life, or life and term certain. (For more information see section 9, Access to Your Money and section 10, The Annuity Phase.) We also pay a death benefit to your Beneficiary(s) if you die before Annuity Payments begin.
What Are the Index-Linked Crediting Methods and How Do They Work?
The Contract offers four Index Crediting Methods: the Index Protection Strategy, Index Performance Strategy, Index Precision Strategy and Index Guard Strategy. However, all Crediting Methods may not currently be available in all states or on all Contracts. All of these Crediting Methods are compared as described later in this section under "How Do the Index-Linked Crediting Methods Compare?" A more detailed description of the Crediting Methods, including availability restrictions, is included in section 7, Index Options.
The Index Protection Strategy provides a DPSC on each Index Anniversary if the current Index Value is equal to or greater than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary, regardless of the amount of actual Index Return. If the current Index Value is less than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary you do not receive the DPSC, but you also do not receive a negative Credit.
The Index Performance Strategy provides a positive Performance Credit if the Index Return is positive, adjusted by an upper limit called the Cap. If the Index Return is negative, you will receive a negative Performance Credit if the loss is greater than a specified percentage called the Buffer. A negative Performance Credit means you can lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits). If the Index Return is negative, but the loss is less than or equal to the Buffer, your Performance Credit is zero.
The Index Precision Strategy provides a positive Performance Credit equal to the Precision Rate on each Index Anniversary if the current Index Value is equal to or greater than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary. This is similar to the DPSC under the Index Protection Strategy in that a positive Performance Credit is equal to the rate set at the beginning of each Index Year. Precision Rates will generally be greater than the DPSCs, though they will generally be less than the Index Performance Strategy Caps. If the current Index Value is less than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary you receive a negative Performance Credit if the negative Index Return is greater than the Buffer, which is similar to a negative Performance Credit under the Index Performance Strategy. A negative Performance Credit means you can lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits). If the Index Return is negative, but the loss is less than or equal to the Buffer, your Performance Credit is zero.
The Index Guard Strategy also provides a positive Performance Credit if the Index Return is positive, limited by the Cap. If the Index Return is zero, your Performance Credit is zero. You will receive a negative Performance Credit if the Index Return is negative down to the amount of a specified percentage called the Floor. A negative Performance Credit means you can lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits).
Please note, since the Index Value is priced only on the Index Effective Date and subsequent Index Anniversaries, the Index Return does not account for changes in Index Value during the Index Year.
We cannot eliminate or modify the four Crediting Methods; however, we can adjust the renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps each Index Year. We can replace or substitute an Index either on an Index Anniversary or during the Index Year. If we substitute an Index during an Index Year, we will combine the return of the previously available substituted Index with the return of the new Index. If we substitute an Index during an Index Year, we do not change the Buffers, Floors, current DPSCs, current Precision Rates, or current Caps. Changes to the DPSCs, Precision Rates, or Caps for the new Index, if any, occur at the next regularly scheduled Index Anniversary. For more information see section 1, Risk Factors – Substitution of an Index. We can add new Crediting Methods and Indices to your Contract in the future, and you can select these Crediting Methods and Indices if they are made available to you.
NOTE: For historical information on the Buffers, Floors and initial DPSCs, Caps and Precision Rates that we offered to newly issued Contracts please see Appendix C. This information is for historical purposes only; it is not a representation as to future Buffers, Floors, DPSCs, Precision Rates, or Caps.
When Do You Establish the Values Used to Determine Index-Linked Credits?
We generally establish the Buffers and Floors on the Issue Date. However, the Buffers and Floors we currently offer for newly issued Contracts may change before we issue your Contract. For information on the Buffers and Floors we currently offer for newly issued Contracts, see our website at www.allianzlife.com/indexratesadv. For newly issued Contracts, we publish any changes to the Buffers and Floors on our website at least seven calendar days before they take effect. If we add a new Index Option to a Contract after the Issue Date, we establish the Buffer or Floor for it on the date we add the Index Option to your Contract. Your actual Buffers and Floors are stated in your Contract and cannot change after they are established. The minimum Buffer that we can establish is 5%, and the minimum Floor is -25%. These minimums are the least amount of protection that you could receive from negative Index Returns. Any decline in Index Return in excess of the Buffer reduces your Contract Value. For example, if we set the Buffer at 5% we would absorb the
first 5% of any negative Index Return and you could lose up to 95% of the Contract Value in that Index Option. However, any decline in Index Return in excess of the Floor is absorbed by us. For example, if we set the Floor at ‑25% your maximum loss would be limited to 25% of the Contract Value in that Index Option due to negative Index Returns and we would absorb any remaining loss.
We can change the initial DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps we currently offer for newly issued Contracts frequently at our discretion. However, once these rates are established for your Contract on the Index Effective Date they cannot change until the next Index Anniversary. For information on the initial DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps we currently offer for newly issued Contracts, see our website at www.allianzlife.com/indexratesadv. For newly issued Contracts, we publish any changes to the initial DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps on our website at least seven calendar days before they take effect. These initial DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps may change before your Index Effective Date. The minimum DPSC, Precision Rate and Cap is 1.50% for the entire time you own your Contract. We inform you of the initial DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps for your Contract in the Index Options Statement, which is the account statement we mail to you on the Index Effective Date and each Index Anniversary. The Index Options Statement also includes the Index Values on the Index Effective Date and each subsequent Index Anniversary. We use these Index Values to determine Index Returns and Credits.
DPSCs, Precision Rates, Caps, Buffers and Floors can all be different. For example, Caps for the Index Performance Strategy can be different between the S&P 500® Index and the Nasdaq-100® Index, and Caps for the S&P 500® Index can be different between the Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy.
Once we issue your Contract, we can change the renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps annually on each Index Anniversary, in our discretion. We will send you a letter at least 30 days before each Index Anniversary. This letter advises you that your current DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps are expiring on the upcoming Index Anniversary, and the renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps for the next Index Year will be available for your review in your account on our website at least seven calendar days before the upcoming Index Anniversary. We also have a link to your Contract information with your renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps on our website at www.allianzlife.com/indexratesadv. Your Index Options Statement that we mail on each Index Anniversary will include the actual renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps you received for the current Index Year. The Index Anniversary letter also reminds you of your opportunity to transfer Contract Value from the Variable Options to the Index Options, or rebalance your Index Option Values, on the upcoming anniversary. We must receive your transfer instructions in Good Order at our Service Center by 4 p.m. Eastern Time on the Index Anniversary (or the next Business Day if the Index Anniversary is not a Business Day). If we do not receive transfer instructions from you, your Index Option Value will remain allocated to your existing Index Options at the renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps. A request is in "Good Order" when it contains all the information we require to process it. Our Service Center is the area of our company that issues Contracts and provides Contract maintenance and routine customer service.
NOTE:
| · | The DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps may be different for newly issued Contracts and for inforce Contracts, even if the Contracts have Index Effective Dates with the same month and day. The initial DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps for newly issued Contracts may be higher or lower than the renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps for inforce Contracts. However, all inforce Contracts with Index Effective Dates in the same date range will receive the same renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps. |
For example, if on January 1, 2019 we set initial and renewal Caps for the Index Performance Strategy Index Option using the S&P 500® Index for Contracts with Index Effective Dates of January 7 through February 3, these Caps might hypothetically be as follows: 13% for newly issued Contracts, 14% for inforce Contracts issued in 2018, and 12% for inforce Contracts issued in 2017.
| · | If your Contract is still within its Free Look/Right to Examine period you may be able to take advantage of any increase in initial DPSCs, Precision Rates or Caps for newly issued Contracts by cancelling your existing Contract and purchasing a new Contract. |
What Factors Impact the DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps?
The DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps will vary depending upon a variety of factors, including our hedging strategies and investment performance, your Index Effective Date, and the level of interest rates and volatility on your Index Effective Date and on Index Anniversaries. The DPSCs, Precision Rates, and Caps are also affected by the amount of money available to us through Contract charges to purchase hedging instruments.
While initial and renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps may be affected by a variety of factors (including, a change in the current level of interest rates), the effect of a change in interest rates or other market conditions on the DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps may not be direct or immediate. There may be a lag in changes to DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps. In a rising interest rate environment, increases in Caps, if any, may be substantially slower than increases in interest rates.
(For more information see section 7, Index Options.)
How Do the Index-Linked Crediting Methods Compare?
| Crediting Methods | Indices | Guaranteed Minimum Rates |
| Index Protection Strategy | S&P 500® Index, Russell 2000® Index, Nasdaq-100® Index and EURO STOXX 50® | DPSCs cannot be less than 1.50% |
| Index Performance Strategy | S&P 500® Index, Russell 2000® Index, Nasdaq-100® Index and EURO STOXX 50® | Caps cannot be less than 1.50% Buffers cannot be less than 5% |
| Index Guard Strategy | S&P 500® Index, Russell 2000® Index, Nasdaq-100® Index and EURO STOXX 50® | Caps cannot be less than 1.50% Floors cannot be less than -25% |
| Index Precision Strategy | S&P 500® Index, Russell 2000® Index, Nasdaq-100® Index and EURO STOXX 50® | Precision Rates cannot be less than 1.50% Buffers cannot be less than 5% |
Availability restrictions for the Crediting Methods and Indices are detailed in section 7, Index Options.
Crediting Methods have different risk and return potentials. The Index Protection Strategy has the lowest return potential, but provides the most protection. You cannot lose money (or previously applied positive Credits) that you allocate to the Index Protection Strategy due to negative Index performance. Potential returns and risks are higher for the other Crediting Methods.
Although the Index Performance Strategy, Index Guard Strategy and Index Precision Strategy offer higher potential returns than the Index Protection Strategy, you can lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits) that you allocate to these Crediting Methods due to negative Index performance and these losses could be significant. Positive returns for the Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy are limited by the Caps, and for the Index Precision Strategy by the Precision Rates. The Index Precision Strategy performs best in periods of small market movements because the Precision Rates will generally be greater than the DPSCs, but they will generally be less than the Index Performance Strategy Caps. However, in extreme market environments it is possible that all rates will be equal and reduced to the minimum of 1.50%. Negative returns are limited for the Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy by the Buffers, and for the Index Guard Strategy by the Floor. The Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy Buffers have protection for smaller negative market movements, but also have the potential for the largest loss in any one year that has a significant market decline. The Index Guard Strategy permits negative Performance Credits down to the Floor, and provides less risk of significant negative returns in any one year than the Buffers. The Index Guard Strategy is sensitive to smaller negative market movements that persist over time, but provides more certainty regarding the maximum loss in any one year.
Bar Chart examples depicting how the Crediting Methods perform under different Index Returns are included in Appendix E.
| Comparison of Crediting Methods | ||||
| Index Protection Strategy | Index Precision Strategy | Index Performance Strategy | Index Guard Strategy | |
| What is the growth opportunity? | Offers the least growth opportunity as the DPSCs will generally be less than the Precision Rate and the Index Performance Strategy Cap. You receive the DPSC if the current Index Value is equal to or greater than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary. | Generally offers more growth opportunity than the Index Protection Strategy, but less than the Index Performance Strategy. Growth opportunity may be more or less than what is available with the Index Guard Strategy depending on Precision Rates and Caps. You receive a Performance Credit equal to the Precision Rate if the current Index Value is equal to or greater than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary. | Generally offers more growth opportunity than the Index Protection Strategy or Index Precision Strategy. Growth opportunity may be more or less than what is available with the Index Guard Strategy depending on Caps. Positive Index Returns are limited by the Cap. | Generally offers more growth opportunity than the Index Protection Strategy. Growth opportunity may be more or less than what is available with the Index Precision Strategy or Index Performance Strategy depending on Precision Rates and Caps. Positive Index Returns are limited by the Cap. |
| What is the asset protection? | Offers the most protection. You cannot lose assets based on a loss in Index Value. If the Index loses value, you do not receive a Credit. | Offers protection from smaller negative market movements, but also has the potential for the largest loss in any one year. Asset protection may be more or less than what is available with the Index Performance Strategy depending on Buffers. A percentage of negative Index Return is absorbed by the Buffer, but you will receive a negative Performance Credit for losses greater than the Buffer. | Offers protection from smaller negative market movements, but also has the potential for the largest loss in any one year. Asset protection may be more or less than what is available with the Index Precision Strategy depending on Buffers. A percentage of negative Index Return is absorbed by the Buffer, but you will receive a negative Performance Credit for losses greater than the Buffer. | Offers protection from significant negative market movements, but is sensitive to smaller negative market movements that persist over time. Permits a negative Performance Credit down to the Floor. |
| What can change within a Crediting Method? | The DPSCs are subject to a 1.50% minimum. Initial DPSCs for newly issued Contracts can change frequently. Your initial DPSCs are set on the Index Effective Date. We can change your renewal DPSCs annually on each Index Anniversary. | The Precision Rates are subject to a 1.50% minimum, and the Buffers subject to a 5% minimum. The Buffers and initial Precision Rates for newly issued Contracts can change frequently. Your initial Precision Rates are set on the Index Effective Date. We can change your renewal Precision Rates annually on each Index Anniversary, but we cannot change your Buffers after they are established. | The Caps are subject to a 1.50% minimum, and the Buffers subject to a 5% minimum. The Buffers and initial Caps for newly issued Contracts can change frequently. Your initial Caps are set on the Index Effective Date. We can change your renewal Caps annually on each Index Anniversary, but we cannot change your Buffers after they are established. | The Caps are subject to a 1.50% minimum, and the Floors subject to a -25% minimum. The Floors and initial Caps for newly issued Contracts can change frequently. Your initial Caps are set on the Index Effective Date. We can change your renewal Caps annually on each Index Anniversary, but we cannot change your Floors after they are established. |
NOTE: ● The DPSCs, Precision Rates, and Caps may vary substantially based on market conditions. ● DPSCs, Precision Rates, Caps, Buffers and Floors can all be different. For example, Caps for the Index Performance Strategy can be different between the S&P 500® Index and the Nasdaq-100® Index, and Caps for the S&P 500® Index can be different between the Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy. | ||||
How Can I Allocate My Purchase Payments?
You can allocate your Purchase Payments to any or all of the available Allocation Options in whole percentages. We only allow allocations to the Index Options on the Index Effective Date and on subsequent Index Anniversaries. You can only reallocate money from the Index Options to the Variable Options on every sixth Index Anniversary.
NOTE: If you allocate an additional Purchase Payment to the Index Options, we place that allocation in the AZL Government Money Market Fund until the next Index Anniversary, when we transfer the allocations from the AZL Government Money Market Fund to the Index Options. Additional Purchase Payments that we receive after the Index Effective Date that you allocate to an Index Option are not eligible to receive Credits until the second Index Anniversary after we receive them because they are not applied to the Index Option until the next Index Anniversary.
What Are the Different Values Within the Contract?
The Contract provides the following values.
| · | The Contract Value is the sum of your Variable Account Value and total Index Option Values. Contract Value does not include any currently applicable withdrawal charge, final product fee, final rider fee, or final contract maintenance charge that we assess on a full withdrawal or when you request Annuity Payments. |
| · | The Variable Account Value is the sum of the values in your selected Variable Options. It includes the deduction of Variable Option operating expenses, and any previously assessed transfer fee, contract maintenance charge, product fee and rider fee. Your Variable Account Value changes daily based on the performance of your selected Variable Options. |
| · | The total Index Option Value is the sum of the values in each of your selected Index Options. Each Index Option Value includes any Credits from previous Index Anniversaries and the deduction of any previously assessed contract maintenance charge, product fee, rider fee and withdrawal charge. On each Business Day during the Index Year other than the Index Effective Date or an Index Anniversary, we calculate the current Index Option Value for each Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Option by adding a Daily Adjustment to the Index Option Base (which is the amount you allocate to an Index Option adjusted for withdrawals, Contract expenses, transfers into or out of the Index Option, and the application of any Performance Credits). We calculate the Daily Adjustment before we process any partial withdrawal or deduct any Contract expenses, and the adjustment can be positive or negative. The Daily Adjustment calculation is not affected by any partial withdrawal or the deduction of Contract expenses. Any amounts removed from these Index Options during the Index Year do not receive a Performance Credit on the next Index Anniversary, but the amount remaining does receive a Performance Credit subject to the Precision Rate or Cap and Buffer, or Cap and Floor. If you take a withdrawal, annuitize the Contract, transfer out of Index Options to the Variable Options, or if we pay a death benefit each Index Option Value also includes any increase from the Alternate Minimum Value, if higher. The Alternate Minimum Value applies to all Crediting Methods, including the Index Protection Strategy. If we are determining the Alternate Minimum Value for an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option Value on any day other than an Index Anniversary, we first calculate the Index Option Value by adding the Daily Adjustment, then compare this value to its associated Alternate Minimum Value and we pay the greater of these two amounts. If we are paying a partial withdrawal, we compare the percentage of Index Option Value with an equivalent percentage of its Alternate Minimum Value. We expect that an Alternate Minimum Value generally will not be greater than its Index Option Value. |
During the Index Year the Index Protection Strategy Index Option Values do not change for Index performance. Amounts withdrawn from the Index Protection Strategy during the Index Year will not receive a DPSC. On each Business Day during the Index Year other than the Index Effective Date or Index Anniversary, the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Option Values change for Index performance through the Daily Adjustment. The Daily Adjustment is meant to approximate the Index Option Value on the next Index Anniversary, as adjusted for gains during the Index Year subject to the Precision Rate or Cap and either losses greater than the Buffer for the Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy, or losses down to the Floor for the Index Guard Strategy. The application of the Daily Adjustment is based on your agreement to be exposed to Index Anniversary gains in Index Value subject to the Precision Rate or Cap and losses in Index Value either greater than the Buffer, or losses down to the Floor. The Daily Adjustment does this by tracking the hypothetical value of a Proxy Investment (called the Proxy Value) each Business Day other than an Index Anniversary using the formulas in Appendix B. The Proxy Investment is an investment tracking mechanism designed to return the same amount as the Index Option on an Index Anniversary (an amount equal to the Performance Credit as determined using the applicable Precision Rate or Cap and Buffer, or Cap and Floor). Between Index Anniversaries, the Proxy Investment provides a current estimate of what the Index value gain or loss would be if the investment were held until the Index Anniversary. The Daily Adjustment does not give you the actual Index return on the day of the calculation.
When the Daily Adjustment is positive, your Index Option Value has increased since the beginning of the year; when it is negative, your Index Option Value has decreased (excluding the effect of any partial withdrawal or the deduction of Contract expenses). The Daily Adjustment is generally negatively affected by interest rate decreases, dividend rate increases, poor market performance and the expected volatility of index prices. Increases in the expected volatility of index prices negatively affect the Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy, while decreases in the expected volatility of index prices negatively affect the Index Guard Strategy. All other factors being equal, even if the current Index return during the Index Year is greater than the Precision Rate or Cap, the Daily Adjustment will be lower than the Precision Rate or Cap during the Index Year and will not be equal to the Precision Rate or Cap until the next Index Anniversary.
For more information see section 6, Valuing Your Contract; section 7, Index Options; and Appendix B. The specific details of the Daily Adjustment formula are described in Appendix B and in Exhibit 99(b) of the Form S-1 Registration Statement filed with the SEC, of which this prospectus is a part. This information is incorporated by reference into this prospectus. You can obtain a copy of Exhibit 99(b) by calling (800) 624-0197, or visiting our website at www.allianzlife.com.
How Do We Apply Credits to the Index Options?
We calculate and apply Credits on the Index Anniversary based on the Index Values and the Index Returns. Positive Credits are not guaranteed, and Credits can be zero under all the available Crediting Methods. Credits can be negative after application of the Buffer under the Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy, or negative down to the Floor under the Index Guard Strategy.
Under the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy you can lock in the current Index Option Value on any Business Day during the Index Year by requesting a Performance Lock. You can request a lock once each Index Year for each of your selected Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Options. A Performance Lock applies to the total Index Option Value (including any Daily Adjustment) in an Index Option, and not just a portion of that Index Option Value. After the Business Day we process your request to lock in an Index Option Value (Lock Date), Daily Adjustments do not apply for the remainder of the Index Year and the Index Option Value will not receive a Performance Credit on the next Index Anniversary.
NOTE REGARDING WITHDRAWALS DURING THE INDEX YEAR:
| · | Amounts removed from the Index Options during the Index Year for partial withdrawals and Contract expenses do not receive a Credit on the next Index Anniversary. However, the remaining amount in the Index Options is eligible for a Credit on the next Index Anniversary. Performance Credits under the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy are subject to the Precision Rate or Cap and Buffer, or Cap and Floor. Contract expenses include the product fee, contract maintenance charge and any applicable rider fee or withdrawal charge. |
| · | If you take a partial withdrawal on any day other than an Index Anniversary, we first calculate the Index Option Value (which includes the Daily Adjustment under the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Options), then compare the percentage of Index Option Value withdrawn to an equivalent percentage of its Alternate Minimum Value and pay you the greater of these two amounts. |
Can My Contract Lose Value Because of Negative Changes in an Index's Value?
If you select the Index Protection Strategy, your Contract cannot lose value due to negative Index Returns. However, if you select the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy, your Contract can lose value due to negative Index Returns. These losses could be significant.
Can I Transfer Index Option Value Between the Allocation Options?
On each Index Anniversary you can transfer Variable Account Value to the available Index Options and you can reallocate your Index Option Values. On every sixth Index Anniversary you can transfer Index Option Value to the Variable Options. At the end of the six-year term, we allow you to transfer all of the money in the Index Options to the Variable Options, even if a portion of that money was added after the start of the six-year term, and has been allocated to the Index Options for less than six years.
How Can I Take Money Out of My Contract?
You can take money out of your Contract by taking withdrawals, required minimum distributions or Annuity Payments. You can withdraw money from either the Variable Options or the Index Options. Amounts withdrawn from an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option on any day other than an Index Anniversary do not receive a Performance Credit, but they do receive the Daily Adjustment on the day of the withdrawal. Amounts withdrawn from an Index Protection Strategy Index Option will not receive a DPSC.
A withdrawal before an Index Anniversary from an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option may not receive the full benefit of the Precision Rate, Cap, Buffer or Floor. This occurs because the Daily Adjustment calculation takes into account what may potentially happen between the withdrawal date and the next Index Anniversary. As a result, even if the Index Return is above the Precision Rate or Cap, the Daily Adjustment may be less than the Precision Rate or Cap, because there is a possibility that the Index Return could decrease before the end of the Index Year. Similarly, even though a negative Index Return may be within the amount of the Buffer for the Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy, the Owner (person(s) designated at Contract issue who may exercise all rights granted by the Contract – "you," "your," and "yours") still may receive a negative Daily Adjustment (i.e., lose money, including principal and previously applied positive Credits) because there is a possibility that the Index Return could decrease before the end of the Index Year. Also, a negative Index Return for the Index Guard Strategy may result in you receiving a Daily Adjustment lower than the Floor, because the Daily Adjustment reflects the present value of the Floor and you will not receive the full benefit of the Floor until the Index Anniversary.
If you withdraw more than is allowed by the free withdrawal privilege from the Index Options we may assess a withdrawal charge. Under the waiver of withdrawal charge benefit in most states you can take a one-time withdrawal from your Contract after the first Contract Anniversary without incurring a withdrawal charge if you are confined to a nursing home for a period of at least 90 consecutive days. If you take required minimum distributions from a Contract that qualifies for special tax treatment under sections of the Internal Revenue Code (Qualified Contract) to pay required minimum distribution amounts owing with regard to the Contract, these distributions are not subject to a withdrawal charge. However, required minimum distributions taken from the Index Options reduce the amount available under the free withdrawal privilege.
When we process a withdrawal from an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option on a day other than an Index Anniversary we determine the proper amount to deduct by calculating the Index Option Value using the Daily Adjustment. For more information see section 9, Access to Your Money.
NOTE: Any amount withdrawn from an Index Option is subject to both a Daily Adjustment (which may be negative) and any applicable withdrawal charge.
What Are My Annuity Options?
The Contract includes several Annuity Options that can provide fixed life, or fixed life and term certain Annuity Payments. The designated individual(s) upon whose life we base Annuity Payments are the Annuitant(s). For more information see section 10, The Annuity Phase.
Does the Contract Provide a Death Benefit?
The Contract provides a guaranteed Traditional Death Benefit based on the greater of Contract Value, or total Purchase Payments adjusted for withdrawals. There is no additional charge for the Traditional Death Benefit. Alternatively, you can select at issue the optional Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit for an additional rider fee if all Owners and the Annuitant are age 75 or younger. The Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit is not available to Contracts issued before the date of this prospectus. The Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit provides the greater of Contract Value, or the Maximum Anniversary Value (the highest Contract Value on any Index Anniversary before age 91, adjusted for subsequent Purchase Payments and withdrawals). The Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit cannot be less than the Traditional Death Benefit, but they may be equal. Please discuss this benefit's appropriateness with your Financial Professional.
These death benefits are first-to-die death benefits based on the life of the person(s) designated at Contract issue (Determining Life). The Determining Life (or Lives) is either the Owner(s) or the Annuitant if the Owner is a non-individual. We establish the Determining Lives at Contract issue and they generally do not change unless there is a divorce or you establish a Trust. If you change Owners or the Annuitant after the Issue Date, upon death of the Owner, the person(s) designated to receive the death benefit (Beneficiary(s)) may only receive the Contract Value. For more information see section 3, Ownership, Annuitants, Determining Life, Beneficiaries, and Payees and section 11, Death Benefit.
What If I Need Customer Service?
If you need customer service (for Contract changes, information on Contract Values, requesting a withdrawal or transfer, changing your allocation instructions, etc.) please contact our Service Center at (800) 624-0197. You can also contact us by mail at Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America, P.O. Box 561, Minneapolis, MN 55440-0561.
FEE TABLES
These tables describe the fees and expenses you pay when purchasing, owning and taking a withdrawal from the Contract, or transferring Contract Value between Allocation Options. For more information, see section 8, Expenses.
OWNER TRANSACTION EXPENSES
Withdrawal Charge Applicable to the Index Options During Your Contract's Initial Phase, the Accumulation Phase(1)
(as a percentage of each Purchase Payment withdrawn)(2)
| Number of Complete Years Since Purchase Payment | Withdrawal Charge Amount(3) |
| 0 | 6.5% |
| 1 | 6% |
| 2 | 5% |
| 3 | 4% |
| 4 | 3% |
| 5 | 2% |
| 6 years or more | 0% |
Transfer Fee(4)…………………………………....... …………………………… | $25 |
| (for each transfer between Variable Options after twelve in a Contract Year) | |
Premium Tax(5)…………………………………... ……………………………… | 3.5% |
| (as a percentage of each Purchase Payment) |
OWNER PERIODIC EXPENSES
Contract Maintenance Charge(6)……………………………………………….. | $50 |
| (per Contract per year) |
| (1) | There is no withdrawal charge applicable to amounts withdrawn from the Variable Options. Amounts transferred from the Variable Options to the Index Options and subsequently withdrawn are subject to a Daily Adjustment (which may be negative) and a withdrawal charge. The Contract provides a free withdrawal privilege that allows you to withdraw 10% of your total Purchase Payments annually from the Index Options without incurring a withdrawal charge, as discussed in section 9, Access to Your Money – Free Withdrawal Privilege. |
| (2) | The Withdrawal Charge Basis is the amount subject to a withdrawal charge, as discussed in section 8, Expenses – Withdrawal Charge. |
| (3) | In Florida, the total withdrawal charge on a partial or full withdrawal cannot be greater than 10% of the Contract Value withdrawn. |
| (4) | We count all transfers made in the same Business Day as one transfer, as discussed in section 8, Expenses – Transfer Fee. The transfer fee does not apply to transfers to or from the Index Options and these transfers do not count against your free transfers. Transfers are subject to the market timing policies discussed in section 5, Variable Options – Excessive Trading and Market Timing. |
| (5) | Not currently deducted, but we reserve the right to do so in the future. This is the maximum charge we could deduct if we exercise this right, as discussed in section 8, Expenses – Premium Tax. |
| (6) | Waived if the Contract Value is at least $100,000, as discussed in section 8, Expenses – Contract Maintenance Charge. |
CONTRACT ANNUAL EXPENSES
Annual Contract Fees(7) | |
| (as a percentage of the Charge Base) | |
Product Fee…………………………………......……………………………………………………. | 0.25% |
Rider Fee for the optional Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit…………………… | 0.20% |
Total Contract Fees for Contracts with the optional Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit…………………………………………………………………………………………. | 0.45% |
| (7) | We do not assess the product fee or rider fee during the Annuity Phase. See section 8, Expenses – Annual Contract Fees: Product Fee and Rider Fee. |
ANNUAL OPERATING EXPENSES OF THE VARIABLE OPTIONS
Following are the minimum and maximum total annual operating expenses charged by any of the Variable Options for the period ended December 31, 2017, before the effect of any contractual expense reimbursement or fee waiver. We show the expenses as a percentage of a Variable Option's average daily net assets. The Index Options do not assess any separate operating expenses, and are not included in the following chart.
| Minimum | Maximum | |
Total annual Variable Option operating expenses (including management fees, distribution or 12b‑1 fees, and other expenses) before fee waivers and expense reimbursements | 0.67% | 0.87% |
The table below describes, in detail, the annual expenses of the Variable Options before fee waivers and/or expense reimbursements. We show the expenses as a percentage of a Variable Option's average daily net assets for the most recent calendar year. Expenses may vary in current and future years. See the Variable Options' prospectuses for further information regarding the expenses you may expect to pay. Some of the Variable Options or their affiliates may also pay service fees to us or our affiliates. If these fees are deducted from Variable Option assets, they are reflected in the table below.
| Variable Option | Management fees | Rule 12b‑1 fees | Other expenses | Acquired fund fees and expenses | Total annual fund operating expenses before fee waivers and/or expense reimbursements |
| BLACKROCK | |||||
AZL Government Money Market Fund(1) | .35 | .25 | .27 | – | .87 |
| ALLIANZ FUND OF FUNDS | |||||
AZL MVP Balanced Index Strategy Fund(2) | .10 | – | .03 | .58 | .71 |
AZL MVP Growth Index Strategy Fund(2) | .10 | – | .01 | .56 | .67 |
| (1) | Other Expenses for the AZL Government Money Market Fund include recoupment of prior waived fees in the amount of 0.22%. The Manager and the Fund have entered into a written contract limiting operating expenses, excluding certain expenses (such as interest expense and Acquired Fund Fees and Expenses) to 0.87% through April 30, 2019. After April 30, 2019, the Manager may terminate the expense limitation agreement for any reason on 30 days written notice to the Fund. Amounts contractually waived or reimbursed under the expense limitation agreement in a particular fiscal year may be recouped by the Manager within the next three fiscal years to the extent that recoupment will not cause the Fund's expenses to exceed the stated limit during the respective year. See the Investment Option prospectus for further information. |
| (2) | The underlying funds may pay 12b‑1 fees to the distributor of the Contracts for distribution and/or administrative services. The underlying funds do not pay service fees or 12b‑1 fees to the Allianz Fund of Funds and the Allianz Fund of Funds do not pay service fees or 12b‑1 fees. The underlying funds of the Allianz Fund of Funds may pay service fees to the insurance companies issuing variable contracts, or their affiliates, for providing customer service and other administrative services to contract purchasers. The amount of such service fees may vary depending on the underlying fund. |
EXAMPLES
These examples are intended to help you compare the cost of investing in this Contract's Variable Options with the costs of other variable annuity contracts. These examples assume you make a $10,000 investment and your Variable Options earn a 5% annual return. They are not a representation of past or future expenses. Your Contract expenses may be more or less than the examples below, depending on the Variable Options you select and whether and when you take withdrawals.
We deduct the $50 contract maintenance charge in the examples on each Contract Anniversary during the Accumulation Phase (or the next Business Day if the Contract Anniversary is not a Business Day), and we deduct it from each Annuity Payment during the Annuity Phase. We may waive this charge under certain circumstances, as described in section 8, Expenses – Contract Maintenance Charge. We deduct the annual Contract fees (maximum charge of 0.25% product fee and a 0.20% rider fee for a Contract with the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit) in the examples on each Quarterly Contract Anniversary during the Accumulation Phase, as described in section 8, Expenses – Annual Contract Fees: Product Fee and Rider Fee. A transfer fee may apply, but is not reflected in these examples (see section 8, Expenses – Transfer Fee).
| 1) | If you surrender your Contract (take a full withdrawal) at the end of each time period. The Contract's withdrawal charge does not apply to withdrawals from the Variable Options, and so the withdrawal charge is not reflected in the following example. |
Total annual Variable Option operating expenses before any fee waivers or expense reimbursements of: | 1 Year | 3 Years | 5 Years | 10 Years |
| 0.87% (the maximum Investment Option operating expense) | $184 | $566 | $967 | $2,067 |
| 0.67% (the minimum Investment Option operating expense) | $164 | $504 | $862 | $1,843 |
Because the withdrawal charge does not apply to the Variable Options, we are including an additional example illustrating the expenses associated with transferring all of the Variable Account Value to the Index Options at the end of each time period and then immediately surrendering your Contract (take a full withdrawal) on the same day.
Total annual Variable Option operating expenses before any fee waivers or expense reimbursements of: | 1 Year | 3 Years | 5 Years | 10 Years |
| 0.87% (the maximum Investment Option operating expense) | $834 | $1,066 | $1,267 | $2,067 |
| 0.67% (the minimum Investment Option operating expense) | $814 | $1,004 | $1,162 | $1,843 |
| 2) | If you annuitize your Contract and begin Annuity Payments at the end of each time period. The earliest available Annuity Date (the date we begin making Annuity Payments) is two years after the Issue Date in all states except Florida, which is one year after the Issue Date. |
Total annual Variable Option operating expenses before any fee waivers or expense reimbursements of: | 1 Year | 3 Years | 5 Years | 10 Years |
| 0.87% (the maximum Investment Option operating expense) | - | $566 | $967 | $2,067 |
| 0.67% (the minimum Investment Option operating expense) | - | $504 | $862 | $1,843 |
| 3) | If you do not surrender your Contract. |
Total annual Variable Option operating expenses before any fee waivers or expense reimbursements of: | 1 Year | 3 Years | 5 Years | 10 Years |
| 0.87% (the maximum Investment Option operating expense) | $184 | $566 | $967 | $2,067 |
| 0.67% (the minimum Investment Option operating expense) | $164 | $504 | $862 | $1,843 |
CONDENSED FINANCIAL INFORMATION
The consolidated financial statements of Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America are included in Appendix F of this prospectus, and the financial statements of Allianz Life Variable Account B are included in Part C of the Form N-4 Registration Statement.
Accumulation unit value (AUV) information for the subaccounts offered under the Contract offered by this prospectus (which were previously made available under the Allianz Index Advantage Variable Annuity, File Number 333-185866), as of the end of December 31, 2017, is listed in the table below. This information should be read in conjunction with the financial statements and related notes of the Separate Account included in Part C of the Form N-4 Registration Statement.
(Number of Accumulation Units in thousands)
(Number of Accumulation Units in thousands)
| Period or Year Ended | AUV at Beginning of Period | AUV at End of Period | Number of Accumulation Units Outstanding at End of Period |
| AZL Government Money Market Fund | |||
| 12/31/2013 | NA | 12.754 | 346 |
| 12/31/2014 | 12.754 | 12.755 | 1560 |
| 12/31/2015 | 12.755 | 12.756 | 2726 |
| 12/31/2016 | 12.756 | 12.757 | 5376 |
| 12/31/2017 | 12.757 | 12.763 | 3831 |
| AZL MVP Balanced Index Strategy Fund | |||
| 12/31/2013 | NA | 12.212 | 10 |
| 12/31/2014 | 12.212 | 12.956 | 237 |
| 12/31/2015 | 12.956 | 12.927 | 473 |
| 12/31/2016 | 12.927 | 13.782 | 537 |
| 12/31/2017 | 13.782 | 15.353 | 606 |
| AZL MVP Growth Index Strategy Fund | |||
| 12/31/2013 | NA | 13.412 | 7 |
| 12/31/2014 | 13.412 | 14.280 | 240 |
| 12/31/2015 | 14.280 | 14.165 | 382 |
| 12/31/2016 | 14.165 | 15.128 | 468 |
| 12/31/2017 | 15.128 | 17.543 | 578 |
| 1. | RISK FACTORS |
The Contract involves certain risks that you should understand before purchasing. You should carefully consider your income needs and risk tolerance to determine whether the Contract is appropriate for you. The level of risk you bear and your potential investment performance will differ depending on the Allocation Options you choose.
LIQUIDITY RISK
We designed the Contract to be a long-term investment that you can use to help build and provide income for retirement. The Contract is not suitable for short-term investment. If you need to take money from your Contract during the withdrawal charge period, we deduct a withdrawal charge for amounts withdrawn from the Index Options unless the withdrawal is specifically not subject to this charge (for example, the amount allowed under the free withdrawal privilege). We calculate the withdrawal charge as a percentage of your Purchase Payments, not Contract Value. Consequently, if the Contract Value has declined since you made a Purchase Payment it is possible the percentage of Contract Value withdrawn to cover the withdrawal charge would be greater than the withdrawal charge percentage. For example, assume you buy the Contract with a single Purchase Payment of $1,000 allocated to an Index Option. If your Contract Value in the 5th year is $800 and you take a full withdrawal a 3% withdrawal charge applies. The total withdrawal charge would be $30 (3% of $1,000). This results in you receiving $770.
Deduction of the withdrawal charge, product fee, rider fee (if applicable) and contract maintenance charge may result in loss of principal and Credits. We only apply Credits once each Index Year on the Index Anniversary, rather than on a daily basis. In the interim, we calculate Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Option Values based on the Daily Adjustment, which may result in you not receiving the full benefit of the Index Returns, Precision Rates or Caps and Buffers or Floors if, before the Index Anniversary, you take a withdrawal or annuitize the Contract, or if we pay a death benefit. We do not do an interim calculation for the Index Protection Strategy Index Option Value. While the free withdrawal privilege and required minimum distributions provide liquidity, they permit limited withdrawals and are designed to be used over a number of years. If you need to withdraw most or all of your total Index Option Value in a short period, this will exceed the charge-free amounts available to you and result in a withdrawal charge. Amounts withdrawn from this Contract may also be subject to a 10% additional federal tax if taken before age 59½.
In addition, upon a full withdrawal we assess a withdrawal charge against Purchase Payments that were previously withdrawn as a penalty-free withdrawal if those Purchase Payments are still within their withdrawal charge period. Penalty-free withdrawals include: withdrawals under the free withdrawal privilege and waiver of withdrawal charge benefit; and payments under our minimum distribution program. This means that upon a full withdrawal, we may assess a withdrawal charge on more than the amount you are withdrawing. In addition, if the Contract Value has declined due to poor performance, the withdrawal charge may be greater than the total Contract Value and you will not receive any money.
You can transfer Contract Value from an Index Option to a Variable Option only on every sixth Index Anniversary. At other times, you can only withdraw money from an Index Option by taking partial withdrawals or surrendering the Contract. This may limit your ability to react to changes in market conditions. Amounts withdrawn from an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option before the Index Anniversary may not receive the full benefit of the Buffer or Floor. You should consider whether investing in an Index Option is consistent with your financial needs.
RISK OF INVESTING IN SECURITIES
Returns on securities and securities Indices can vary substantially, which may result in investment losses. The historical performance of the available Allocation Options does not guarantee future results. It is impossible to predict whether underlying investment values will fall or rise. Trading prices of the securities underlying the Allocation Options are influenced by economic, financial, regulatory, geographic, judicial, political and other complex and interrelated factors. These factors can affect capital markets generally and markets on which the underlying securities are traded and these factors can influence the performance of the underlying securities.
If you allocate money to an Index Option, your returns depend on the performance of an Index although you are not directly invested in the Index. Because the S&P 500® Index, Russell 2000® Index, Nasdaq-100® Index and EURO STOXX 50® are each comprised of a collection of equity securities, in each case the value of the component securities is subject to market risk, or the risk that market fluctuations may cause the value of the component securities to go up or down, sometimes rapidly and unpredictably. In addition, the value of equity securities may decline for reasons directly related to the issuers of the securities.
S&P 500® Index. The S&P 500® Index is comprised of equity securities issued by large-capitalization U.S. companies. In general, large-capitalization companies may be unable to respond quickly to new competitive challenges, and also may not be able to attain the high growth rate of successful smaller companies.
Russell 2000® Index. The Russell 2000® Index is comprised of equity securities of small-capitalization U.S. companies. In general, the securities of small-capitalization companies may be more volatile and may involve more risk than the securities of larger companies.
Nasdaq-100® Index. The Nasdaq-100® Index is comprised of equity securities of the largest U.S. and non-U.S. companies listed on The Nasdaq Stock Market, including companies across all major industry groups except the financial industry. To the extent that the Nasdaq-100® Index is comprised of securities issued by companies in a particular sector, that company's securities may not perform as well as companies in other sectors or the market as a whole. Also, any component securities issued by non-U.S. companies (including related depositary receipts) are subject to the risks related to investments in foreign markets (e.g., increased price volatility; changing currency exchange rates; and greater political, regulatory, and economic uncertainty).
EURO STOXX 50®. EURO STOXX 50® is comprised of the equity securities of large-capitalization companies in the Eurozone. The securities comprising EURO STOXX 50® are subject to the risks related to investments in foreign markets (e.g., increased price volatility; changing currency exchange rates; and greater political, regulatory, and economic uncertainty), and are significantly affected by the European markets and actions of the European Union.
RISK OF NEGATIVE RETURNS
If you allocate money to the Variable Options, returns will fluctuate and may be negative. You can lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits).
If you allocate money to the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy, Index fluctuations may cause Performance Credits to be either negative after application of the Buffer, or negative down to the amount of the Floor. You can incur a loss, which could be significant. If money is withdrawn or removed from an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option before the Index Anniversary, you could lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits) because of the Daily Adjustment and Contract fees and expenses (including withdrawal charges that we deduct when amounts are withdrawn before the end of the withdrawal charge period) even if Index performance has been positive. Ongoing Contract fees and expenses associated with investments in the index-linked annuities could also cause amounts available for withdrawal to be less than what you invested, even if Index performance has been positive.
If you select the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy we calculate each of your Index Option Values on each Business Day during the Index Year by adding the Daily Adjustment. The Daily Adjustment affects the calculation of these Index Option Values we use to calculate Contract Value between Index Anniversaries, and it affects the Contract Value available for withdrawal, annuitization, death benefits, and the Contract Value used to determine the Charge Base and contract maintenance charge. The Daily Adjustment may result in a loss even if Index performance has been positive since the beginning of the Index Year. The Contract Value as adjusted by the Daily Adjustment may also be less than you would have received as a Performance Credit on the next Index Anniversary. The Daily Adjustment is generally negatively affected by interest rate decreases, dividend rate increases, poor market performance and the expected volatility of index prices. Increases in the expected volatility of index prices negatively affect the Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy, while decreases in the expected volatility of index prices negatively affect the Index Guard Strategy. All other factors being equal, even if the current Index Return during the Index Year is greater than the Precision Rate or Cap, the Daily Adjustment will frequently be lower than the Precision Rate or Cap during the Index Year and will not be equal to the Precision Rate or Cap until the next Index Anniversary. Even if the current Index return during the Index Year is positive, the Daily Adjustment may be negative until the Index Anniversary. This means if money is withdrawn or removed from the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy, or Index Guard Strategy, you could lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits) even if the current Index return is positive on that day. If the current Index return during the Index Year is negative, the Daily Adjustment could result in losses greater than the protection provided by the Buffer or the Floor.
The Alternate Minimum Value may, in limited instances, mitigate negative return risk associated with the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Options.
CALCULATION OF CREDITS
We calculate Credits each Index Year on the Index Anniversary. If you allocate money to the Index Protection Strategy, positive returns are limited by the amount of the DPSCs. You are not subject, however, to potential negative Credits. The Precision Rates on the Index Precision Strategy and the Caps on the Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy limit upward performance and could cause your returns to be lower than they would otherwise have been if you invested in a mutual fund or exchange traded fund designed to track the performance of the applicable Index, or if you allocated to the Variable Options.
The Index Options do not directly participate in the returns of the Indices' underlying securities, and do not receive any dividends payable on these securities. Index returns would be higher if they included the dividends from the underlying securities. Over the past ten years the actual Index returns without dividends and the returns if dividends for the underlying securities had been included would have been as follows:
| January 1, 2008 through December 31, 2017 | ||||
S&P 500® Index | Nasdaq-100® Index | Russell 2000® Index | EURO STOXX 50® | |
| Returns without dividends | 8.04% | 14.91% | 9.23% | -0.21% |
| Returns with dividends | 10.36% | 16.13% | 10.74% | 3.88% |
DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps may be adjusted annually on the Index Anniversary and may vary significantly from year to year. Changes to DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps may significantly affect the amount of Credit you receive. (For more information, see the "Changes to Caps, Precision Rates, Declared Protection Strategy Credits (DPSCs), and Notice of Buffers and Floors" discussion later in this section.
The Crediting Methods only capture Index Values on one day each year, so you will bear the risk that the Index Value might be abnormally low on these days.
SUBSTITUTION OF AN INDEX
There is no guarantee that the Indices will be available during the entire time that you own your Contract. If we substitute a new Index for an existing Index, the performance of the new Index may be different and this may affect your ability to receive positive Credits. We may substitute a new Index for an existing Index if:
| · | the Index is discontinued, |
| · | we are unable to use the Index because, for example, changes to an Index make it impractical or expensive to purchase derivative securities to hedge the Index, or we are not licensed to use the Index, or |
| · | the method of calculation of the Index Values changes substantially, resulting in significantly different Index Values and performance results. This could occur, for example, if an Index altered the types of securities tracked, or the weighting of different categories of securities. |
If we add or substitute an Index, we first seek any required regulatory approval (from each applicable state insurance regulator) and then provide you with written notice. We also provide you with written notice if an Index changes its name. Substitutions of an Index may occur during an Index Year. If we substitute an Index during an Index Year, we will combine the return of the previously available substituted Index from the prior Index Anniversary to the substitution date with the return of the new Index from the substitution date to the next Index Anniversary. If we substitute an Index during an Index Year, we do not change the Buffers, Floors, current Charge Base, current DPSCs, current Precision Rates, or current Caps. Changes to the DPSCs, Precision Rates, or Caps for the new Index, if any, occur at the next regularly scheduled Index Anniversary. Depending on the constitution of the previously available substituted Index, the volatility of its investments, and our ability to hedge the Index's performance, we may determine for the next Index Year, in our discretion, that a higher or lower Precision Rate, Cap or DPSC may be appropriate for the new Index. However, we would not implement any change to reflect this difference until the next Index Anniversary after the substitution. Under the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy, this may result in an abnormally large change in the Daily Adjustment on the day we substitute the Index.
The selection of a substitution Index is in our discretion; however, it is anticipated that any substitute Index will be substantially similar to the Index it is replacing and we will replace any equity Index with a broad-based equity index.
CHANGES TO CAPS, PRECISION RATES, DECLARED PROTECTION STRATEGY CREDITS (DPSCs), AND NOTICE OF BUFFERS AND FLOORS
NOTE: You can only transfer Contract Value you allocate to an Index Option to a Variable Option on a sixth Index Anniversary.
We generally establish the Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy Buffers and Index Guard Strategy Floors on the Issue Date. However, if an Index Option is added to your Contract after the Issue Date, the Buffer or Floor for that Index Option is established on the date the Index Option is added to your Contract. Buffers and Floors are stated in your Contract and do not change after they are established. We establish the initial DPSCs for the Index Protection Strategy, initial Precision Rates for the Index Precision Strategy and initial Caps for the Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy on the Index Effective Date. We publish the Buffers, Floors, DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps for newly issued Contracts on our website at www.allianzlife.com/indexratesadv at least seven calendar days before they take effect.
We can change the renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps as frequently as annually and they are effective on Index Anniversaries. The renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps may be adjusted up or down or they may stay the same. The Buffers and Floors you receive are stated in your Contract and do not change after they are established. Renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps are available for your review in your account on our website at least seven calendar days before each Index Anniversary. We send you a letter at least 30 days in advance of each Index Anniversary notifying you of your upcoming anniversary. When the renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps are set on the Index Anniversary you have the option of staying in your current Index Option or moving to another permitted Allocation Option, subject to the limitations on transferring from an Index Option to a Variable Option.
If you do not review information regarding renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps when they are published, or take no action to move to another permitted Allocation Option, you stay in your current Index Options and automatically become subject to the renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps until the next Index Anniversary.
You risk the possibility that the renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps you receive may be less than you would find acceptable. If you do not find the renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps acceptable, you must give us notice no later than the Index Anniversary (or the next Business Day if the anniversary is not a Business Day) and request to move your money on the Index Anniversary or you will be subject to these renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps for the next Index Year. Other than on a sixth Index Anniversary when you can move money from the Index Options to the Variable Options, when your renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps change the only option available to you is to move your money between Index Options. We will inform you of the renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps applicable to your Contract in your annual Index Options Statement.
Initial and renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps may vary significantly from year to year. There are a variety of factors that may affect DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps including market volatility, the price and availability of hedging instruments, the level of interest rates, utilization of Contract benefits by Owners, and our profitability goals.
We manage our obligation to provide Credits in part by trading call and put options, and other derivatives on the available Indices. The costs of the call and put options and other derivatives vary based on market conditions, and we may adjust future renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps to reflect these cost changes. The primary factor affecting the differences in the initial DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps for new business and renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps for inforce Contracts is the difference in what we can earn from these investments for new business versus what we are earning on the investments that were made, and are being held to maturity, for inforce Contracts. In some instances we may need to reduce the DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps for new business and inforce Contracts or we may need to replace an Index on the Contract. You bear the risk that we may reduce the DPSCs, Precision Rates and/or Caps, which reduces your opportunity to receive positive Credits. You also bear the risk that the Buffers and Floors for your Contract are small, which increases the risk that you could receive negative Performance Credits and incur losses.
For more information about how we set Buffers, Floors, DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps, see the "What Are the Index-Linked Crediting Methods and How Do They Work?" discussion in the Summary section of this prospectus.
INVESTMENT IN DERIVATIVE SECURITIES
The Index Options are supported by bonds and other fixed income securities used to support the Contract guarantees, cash, and derivative hedging instruments used to hedge the movements of the applicable Index.
At Contract issue, we invest a substantial majority of the initial Contract Value allocated to the Index Options in fixed income securities, with most of the remainder invested in derivative hedging securities. The derivative securities are purchased to track and hedge Index movements and support our obligations with regard to the Index Options. The derivative securities we purchase include put options, call options, futures, swaps, and other derivatives.
We manage the hedging securities used to support the Index Protection Strategy differently than we do the hedging securities used to support the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy. The Index Protection Strategy purchases derivative securities within the general account. In contrast, the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy purchases derivative securities within an unregistered separate account. For these Crediting Methods, we move assets between the general account and the unregistered separate account during the Index Year based on Index performance. We typically transfer assets between these accounts if there is a 10% incremental change in year-to-date Index performance. For these Crediting Methods, this starts at a -10% decrease in the market. We monitor year-to-date Index performance daily and change allocations daily if needed based on this 10% increment. For more information on our unregistered separate account backing the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy, see section 13, Other Information – Our Unregistered Separate Account.
We currently limit our purchase of derivative securities to liquid securities. However, like many types of derivative securities, these securities may be volatile and their price may vary substantially. In addition, because we pay Credits regardless of the performance of derivative securities we purchase, we may incur losses on hedging mismatches or errors in hedging. Our experience with hedging securities may affect new business rates for Buffers, Floors, DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps, and may also affect renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps.
Certain Variable Options may also invest in derivative securities. For more information on these investments, see the Variable Option prospectuses.
VARIABLE OPTION RISK
The Variable Options do not provide any protection against loss of principal. You can lose some or all of the money you allocate to the Variable Options.
OUR FINANCIAL STRENGTH AND CLAIMS-PAYING ABILITY
We make Annuity Payments and apply Credits from our general account. Our general account assets are subject to claims by our creditors, and any payment we make from our general account is subject to our financial strength and claims-paying ability. The assets in our unregistered separate account, Separate Account IANA, that hold a portion of any assets you allocate to the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy are also subject to claims by our creditors. This does not apply to the Texas unregistered separate account, Separate Account IATX. You can obtain information on our financial condition by reviewing our financial statements in this prospectus.
REGULATORY PROTECTIONS
Allianz Life is not an investment company and therefore we are not registered as an investment company under the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended, and the protections provided by this Act are not applicable to the guarantees we provide. The Separate Account is, however, registered as an investment company. Any allocations you make to an Index Option are not part of the Separate Account. Allianz Life is not an investment adviser and so is not subject to the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, and does not provide investment advice to you in connection with your Contract.
Your Contract is registered in accordance with the Securities Act of 1933 and the offering of the Contract must be conducted in accordance with the requirements of this Act. In addition, the offer and sale of the Contract is subject to the provisions of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
The Contract is filed with and approved by each state in which the Contract is offered. State insurance laws provide a variety of regulatory protections.
| 2. | THE VARIABLE ANNUITY CONTRACT |
An annuity is a contract between you as the Owner, and an insurance company (in this case Allianz Life), where you make payments to us and the money is invested in Allocation Options available through the Contract. Depending on market conditions, your Contract may gain or lose value based on the returns of your selected Allocation Options. When you are ready to take money out, we make payments to you according to your instructions and any restrictions associated with the payout option you select that is described in this prospectus. We do not make any changes to your Contract without your permission except as may be required by law.
The Contract has an Accumulation Phase and an Annuity Phase.
The Accumulation Phase is the first phase of your Contract, and it begins on the Issue Date. During the Accumulation Phase, your money is invested in the Allocation Options you select on a tax-deferred basis. Tax deferral means you are not taxed on any earnings or appreciation on the assets in your Contract until you take money out of your Contract. (For more information, see section 12, Taxes.)
During the Accumulation Phase you can take withdrawals (subject to any withdrawal charge) and you can make additional Purchase Payments subject to the restrictions set out in section 4, Purchasing the Contract – Purchase Requirements. The Contract also offers at issue the optional Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit for an additional rider fee (see section 11) if all Owners and the Annuitant are age 75 or younger on the Issue Date. The Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit potentially provides an increased death benefit based on the Maximum Anniversary Value (highest Contract Value on any Index Anniversary before age 91, adjusted for subsequent Purchase Payments and withdrawals).
The Accumulation Phase ends upon the earliest of the following.
| · | The Business Day before the Annuity Date. |
| · | The Business Day we process your request for a full withdrawal. |
| · | Upon the death of any Owner (or the Annuitant if the Contract is owned by a non-individual), the Business Day we first receive the documents we require before we pay any death claim (Valid Claim) from any one Beneficiary, unless the surviving spouse/Beneficiary continues the Contract. If there are multiple Beneficiaries, the remaining Contract Value continues to fluctuate with the performance of the Allocation Options until the complete distribution of the death benefit. |
If you request Annuity Payments, your Contract enters the Annuity Phase. During the Annuity Phase we make regular fixed periodic payments (Annuity Payments) based on the life of a person you choose (the Annuitant), or life and term certain. We send Annuity Payments to you (the Payee). You can choose when Annuity Payments begin, subject to certain restrictions. We base Annuity Payments on your Contract Value and the payout rates for the Annuity Option you select. Your Annuity Payments do not change unless an Annuitant dies. The Annuity Phase ends when we make the last Annuity Payment under your selected Annuity Option. For more information, see section 10, The Annuity Phase.
STATE SPECIFIC CONTRACT RESTRICTIONS
If you purchase a Contract, it is subject to the law of the state in which it is issued. Some of the features of your Contract may differ from the features of a Contract issued in another state because of state-specific legal requirements. Features for which there are state-specific Contract provisions include the following.
| · | Free look/right to examine provisions. |
| · | Availability of Crediting Methods. |
| · | The withdrawal charge. |
| · | Restrictions on additional Purchase Payments, Contract assignments and the earliest Annuity Date. |
| · | The insulation or non-insulation of the unregistered separate account that supports your Contract. |
| · | Availability of the waiver of withdrawal charge benefit. |
All material state variations in the Contract are disclosed in this prospectus. If you would like more information regarding state-specific Contract provisions, you should contact your Financial Professional or contact our Service Center at the toll-free telephone number listed at the back of this prospectus.
WHEN THE CONTRACT ENDS
The Contract ends when:
| · | all applicable phases of the Contract (Accumulation Phase and/or Annuity Phase) have ended, and/or |
| · | if we received a Valid Claim, all applicable death benefit payments have been made. |
For example, if you purchase a Contract and later take a full withdrawal of the total Contract Value, both the Accumulation Phase and the Contract end even though the Annuity Phase never began and we did not make any death benefit payments.
| 3. | OWNERSHIP, ANNUITANTS, DETERMINING LIFE, BENEFICIARIES, AND PAYEES |
OWNER
You, as the Owner, have all the rights under the Contract. The Owner is designated at Contract issue. The Owner may be a non-individual, which is anything other than an individual person, and could be a trust, qualified plan, or corporation. Qualified Contracts and non-individually owned Contracts can only have one Owner.
JOINT OWNER
A Contract that is not qualified pursuant to a specialized provision of the Internal Revenue Code (Non-Qualified Contract) can be owned by up to two individual Owners (Joint Owners). We generally require the signature of both Joint Owners on any forms that are submitted to our Service Center.
ANNUITANT
The Annuitant is the individual on whose life we base Annuity Payments. Subject to our approval, you designate an Annuitant when you purchase a Contract. For Qualified Contracts, before the Annuity Date the Owner must be the Annuitant unless the Contract is owned by a qualified plan or is part of a custodial arrangement. You can change the Annuitant on an individually owned Non-Qualified Contract at any time before the Annuity Date, but you cannot change the Annuitant if the Owner is a non-individual (for example, a qualified plan or trust). Subject to our approval, you can add a joint Annuitant on the Annuity Date. For Qualified Contracts, the ability to add a joint Annuitant is subject to any plan requirements associated with the Contract. For individually owned Contracts, if the Annuitant who is not an Owner dies before the Annuity Date, the sole Owner (or younger Joint Owner) automatically becomes the new Annuitant, but the Owner can subsequently name another Annuitant.
Designating different persons as Owner(s) and Annuitant(s) can have important impacts on whether a death benefit is paid, and on who receives it as indicated below. For more examples, please see the Appendix to the SAI. Use care when designating Owners and Annuitants, and consult your Financial Professional if you have questions.
| UPON THE DEATH OF A SOLE OWNER | |
| Action if the Contract is in the Accumulation Phase | Action if the Contract is in the Annuity Phase |
· We pay a death benefit to the person you designate (the Beneficiary) unless the Beneficiary is the surviving spouse and continues the Contract. · If the deceased Owner was a Determining Life and the surviving spouse Beneficiary continues the Contract: – we increase the Contract Value to equal the guaranteed death benefit value if greater and available, and the death benefit ends, – the surviving spouse becomes the new Owner, – the Accumulation Phase continues, and – upon the surviving spouse's death, his or her Beneficiary(s) receives the Contract Value. (The guaranteed death benefit value is total Purchase Payments adjusted for withdrawals if the Traditional Death Benefit applies, or the Maximum Anniversary Value if the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit applies.) · If the deceased Owner was not a Determining Life, the Traditional Death Benefit or Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit are not available and the Beneficiary(s) receives the Contract Value. | · The Beneficiary becomes the Payee. If we are still required to make Annuity Payments under the selected Annuity Option, the Beneficiary also becomes the new Owner. · If the deceased was not an Annuitant, Annuity Payments to the Payee continue. No death benefit is payable. · If the deceased was the only surviving Annuitant, Annuity Payments end or continue as follows. – Annuity Option 1 or 3, payments end. – Annuity Option 2 or 4, payments end when the guarantee period ends. – Annuity Option 5, payments end and the Payee may receive a lump sum refund. · If the deceased was an Annuitant and there is a surviving joint Annuitant, Annuity Payments to the Payee continue during the lifetime of the surviving joint Annuitant. No death benefit is payable. |
DETERMINING LIFE (LIVES)
The Determining Life (Lives) are the individuals on whose life we base the guaranteed death benefit provided by the Traditional Death Benefit or Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit. We establish the Determining Life (Lives) at Contract issue and they generally do not change. For an individually owned Contract the Determining Life (Lives) are the Owner(s). For a non-individually owned Contract the Determining Life is the Annuitant. After the Issue Date the Determining Life (Lives) only change as follows:
| · | If you remove a Joint Owner due to divorce we also remove that person as a Determining Life, or |
| · | If you establish a jointly owned Non-Qualified Contract and change ownership to a Trust, we remove the prior Owner who is not the Annuitant as a Determining Life. |
BENEFICIARY
The Beneficiary is the person(s) or entity you designate at Contract issue to receive any death benefit. You can change the Beneficiary or contingent Beneficiary at any time before your death unless you name an irrevocable Beneficiary. If a Beneficiary dies before you, or you and a Beneficiary die simultaneously as defined by applicable state law or regulation, that Beneficiary's interest in this Contract ends unless your Beneficiary designation specifies otherwise. If there are no surviving primary Beneficiaries, we pay the death benefit to the contingent Beneficiaries who survive you. If there are no surviving Beneficiaries or if there is no named Beneficiary, we pay the death benefit to your estate or the Owner if the Owner is a non-individual.
NOTE FOR JOINTLY OWNED CONTRACTS: The sole primary Beneficiary is the surviving Joint Owner regardless of any other named primary Beneficiaries. If both Joint Owners die simultaneously as defined by applicable state law or regulation, we pay the death benefit to the named contingent Beneficiaries, or equally to the estate of the Joint Owners if there are no named contingent Beneficiaries.
PAYEE
The Payee is the person or entity who receives Annuity Payments during the Annuity Phase. The Owner receives tax reporting on those payments. Generally we require the Payee to be an Owner. However, we may allow you to name a charitable trust, financial institution, qualified plan, or an individual specified in a court order as a Payee subject to our approval. For Qualified Contracts owned by a qualified plan, the qualified plan must be the Payee.
ASSIGNMENTS, CHANGES OF OWNERSHIP AND OTHER TRANSFERS OF CONTRACT RIGHTS
You can assign your rights under this Contract to someone else during the Accumulation Phase. An assignment may be absolute or limited, and includes changes of ownership, collateral assignments, or any other transfer of specific Contract rights. After an assignment, you may need the consent of the assignee of record to exercise certain Contract rights depending on the type of assignment and the rights assigned.
You must submit your request to assign the Contract in writing to our Service Center and we must approve it in writing. To the extent permitted by state law, we reserve the right to refuse to consent to any assignment at any time on a nondiscriminatory basis. We will not consent if the assignment would violate or result in noncompliance with any applicable state or federal law or regulation.
Upon our consent, we record the assignment. We are not responsible for the validity or effect of the assignment. We are not liable for any actions we take or payments we make before we receive your request in Good Order and record it. Assigning the Contract does not change, revoke or replace the originally named Annuitant or Beneficiary; if you also want to change the Annuitant or Beneficiary you must make a separate request.
An assignment may be a taxable event. In addition, there are other restrictions on changing the ownership of a Qualified Contract and Qualified Contracts generally cannot be assigned absolutely or on a limited basis. You should consult with your tax adviser before assigning this Contract.
NOTE:
| · | An assignment does not change the Determining Life (Lives). |
| · | We cannot restrict assignments for Contracts issued in California, Florida, New Jersey, Ohio, and Wisconsin. For Contracts issued in Connecticut, we can only restrict assignments to settlement companies and institutional investors as described in your Contract. The Traditional Death Benefit and Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit are only available on the death of a Determining Life. If you assign the Contract and the Determining Life (Lives) are no longer an Owner (or Annuitant if the Owner is a non-individual) the Traditional Death Benefit or Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit may not be available and your Beneficiary(s) will only receive the Contract Value. |
| 4. | PURCHASING THE CONTRACT |
PURCHASE REQUIREMENTS
To purchase this Contract, all Owners and the Annuitant must be age 80 or younger on the Issue Date.
The Purchase Payment requirements for this Contract are as follows.
| · | The minimum initial Purchase Payment due on the Issue Date is $10,000. |
| · | You can make additional Purchase Payments of $50 or more during the Accumulation Phase. |
| · | We do not accept additional Purchase Payments on or after the Annuity Date. |
| · | The maximum total Purchase Payments we accept without our prior approval is $1 million. |
We may, at our sole discretion, waive the minimum Purchase Payment requirements.
Once we receive your initial Purchase Payment and all necessary information in Good Order at our Service Center, we issue the Contract within two Business Days and allocate your payment to your selected Allocation Options. If you do not give us all of the information we need, we contact you or your Financial Professional. If for some reason we are unable to complete this process within five Business Days, we either send back your money or get your permission to keep it until we get all of the necessary information. If you make additional Purchase Payments, we add this money to your Contract on the Business Day we receive it in Good Order. Our Business Day closes when regular trading on the New York Stock Exchange closes.
If you submit a Purchase Payment and/or application to your Financial Professional, we do not begin processing the payment and/or application until we receive it. A Purchase Payment is "received" when it arrives at our Service Center from the address for mailing checks listed at the back of this prospectus regardless of how or when you submitted them. We forward Purchase Payments we receive at the wrong address to the last address listed at the back of this prospectus, which may delay processing.
We may terminate your ability to make additional Purchase Payments because we reserve the right to decline any or all Purchase Payments at any time on a nondiscriminatory basis. This applies to Contracts issued in all states except those listed in the following Note. If mandated under applicable law, we may be required to reject a Purchase Payment. If we exercise our right to no longer allow additional Purchase Payments this may limit your ability to fund your Contract's guaranteed benefits such as the Traditional Death Benefit or Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit.
NOTE:
| · | For Contracts issued in Maryland and Florida: We can only decline a Purchase Payment if it would cause total Purchase Payments to be more than $1 million, or if it would otherwise violate the Purchase Payment restrictions of your Contract (for example, we do not allow additional Purchase Payments on or after the Annuity Date). |
| · | For Contracts issued in New Jersey: The maximum total Purchase Payments that we can accept is $1 million. We can only decline a Purchase Payment if it would cause total Purchase Payments to be more than $1 million, or if it would otherwise violate the Purchase Payment restrictions of your Contract (for example, we do not allow additional Purchase Payments on or after the Annuity Date). |
| · | For Contracts issued in Mississippi: We do not accept additional Purchase Payments on or after the first Contract Anniversary. We also limit the amount of additional Purchase Payments you can make on or after the first Quarterly Contract Anniversary to the amount of total Purchase Payments we received before the first Quarterly Contract Anniversary. |
| · | For Contracts issued in Utah: We do not accept additional Purchase Payments on or after the first Contract Anniversary. |
APPLICATIONS SENT ELECTRONICALLY
We accept manually signed applications that are in Good Order and are sent by fax, or email, or uploaded to our website. It is important to verify receipt of any faxed application, or to receive a confirmation number when using email or the web. We are not liable for applications that we do not receive. A manually signed application sent by fax, email or over the web is considered the same as an application delivered by mail. Our electronic systems (fax, email or website) may not always be available; any electronic system can experience outages or slowdowns which may delay application processing. Although we have taken precautions to help our system handle heavy use, we cannot promise complete reliability. If you experience problems, please submit your written application by mail to our Service Center. We reserve the right to discontinue or modify our electronic application policy at any time and for any reason.
ALLOCATION OF PURCHASE PAYMENTS AND TRANSFERS BETWEEN THE ALLOCATION OPTIONS
NOTE: You can only transfer Contract Value you allocate to an Index Option to a Variable Option on a sixth Index Anniversary.
You can allocate your Purchase Payments to the available Allocation Options. At issue we collect Index Effective Date allocation instructions. You must allocate your money to the Allocation Options in whole percentages. If an Index Option is chosen at issue, then the future Purchase Payment allocation instructions for the portion allocated to the Index Options will be to the AZL Government Money Market Fund until the next Index Anniversary unless you give us alternate instructions.
We only allow allocations (both Purchase Payments and transfers of Contract Value) into the Index Options on the Index Effective Date and on subsequent Index Anniversaries. We only allow you to move money between Index Options on an Index Anniversary. You cannot move money from one Index Option to another mid-year. When you purchase this Contract you select the Index Effective Date. The Index Effective Date can be any Business Day from the Issue Date up to and including the first Quarterly Contract Anniversary. However, it cannot be the 29th, 30th or 31st of a month, and it must be a Business Day. If the Index Effective Date would occur on the 29th, 30th or 31st of a month, or on a day that is not a Business Day, we change the Index Effective Date to be the next available Business Day. You can change your Index Effective Date before it occurs by submitting a request. We must receive your request in Good Order at our Service Center no later than the end of the Business Day on which you want the Index Effective Date to occur.
On each Index Anniversary, if we have not received transfer or optional rebalancing program instructions from you, all monies invested in an Index Option continue to be invested in that Index Option at the renewal DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps.
We place any Purchase Payments you allocate to an Index Option that we receive before the Index Effective Date or the next Index Anniversary, as applicable, in the AZL Government Money Market Fund. Then on the Index Effective Date, we rebalance your Contract Value among your selected Allocation Options according to your Index Effective Date allocation instructions. We only allow transfers of Index Option Value from the Index Options to the Variable Options on every sixth Index Anniversary. At the end of the six-year term, we allow you to transfer all of the money in the Index Options to the Variable Options, even if a portion of that money was added after the start of the six-year term, and has been allocated to the Index Options for less than six years. A request to transfer Index Option Value to the Variable Options on a sixth Index Anniversary will automatically cancel any prior transfer instructions you gave to us regarding moving Variable Account Value to the Index Options. We must receive all transfer instructions in Good Order at our Service Center by 4 p.m. Eastern Time on the Index Anniversary (or the next Business Day if the Index Anniversary is not a Business Day).
You can instruct us on how to allocate additional Purchase Payments, but we do not allow you to invest additional Purchase Payments in Index Options until the next Index Anniversary. If you do not instruct us on how to allocate an additional Purchase Payment, we allocate it according to your future Purchase Payment allocation instructions. The allocation instructions you provide us at issue automatically become your future Purchase Payment allocation instructions until you give us different instructions. However, if those instructions include allocations to the Index Options, we place those allocations in the AZL Government Money Market Fund until the next Index Anniversary, when we transfer the allocations from the AZL Government Money Market Fund to the Index Option. We notify you at least 30 days in advance of each Index Anniversary as a reminder that you may transfer Contract Value from the Variable Options to the Index Options on the upcoming anniversary. Contract Value transfers between Allocation Options do not change your future allocation instructions. For more information, see section 5, Variable Options – Electronic Transfer and Allocation Instructions.
You can change your future Purchase Payment allocation instructions at any time without fee or penalty. These changes are effective on the Business Day we receive them in Good Order at our Service Center. We accept changes to future allocation instructions from any Owner unless you instruct otherwise. We may allow you to authorize someone else to change these allocation instructions on your behalf. Changes you make to your future Purchase Payment allocation instructions will not rebalance or transfer Contract Value among your selected Index Options on the next Index Anniversary.
NOTE: Variable Options are subject to market risk and money allocated to them may lose value before it can be transferred into the Index Options. Additional Purchase Payments that we receive after the Index Effective Date that you allocate to an Index Option are not eligible to receive Credits until the second Index Anniversary after we receive them because they are not applied to the Index Option until the next Index Anniversary.
AUTOMATIC INVESTMENT PLAN (AIP)
The AIP makes additional Purchase Payments to the Variable Options during the Accumulation Phase on a monthly or quarterly basis by electronic money transfer from your savings, checking or brokerage account. You can participate in AIP by completing our AIP form. Our Service Center must receive your form in Good Order by the 15th of the month (or the next Business Day if the 15th is not a Business day) in order for AIP to begin that same month. We process AIP Purchase Payments on the 20th of the month, or the next Business Day if the 20th is not a Business Day. We allocate AIP Purchase Payments according to your future allocation instructions which must comply with the allocation requirements and restrictions stated in this section. AIP has a maximum of $1,000 per month. We must receive your request to stop or change AIP at our Service Center by 4 p.m. Eastern Time on the Business Day immediately before the Business Day we process AIP to make the change that month. If you choose to begin Annuity Payments, AIP ends automatically on the Business Day before the Annuity Date. We reserve the right to discontinue or modify AIP at any time and for any reason.
NOTE: For Owners of Qualified Contracts, AIP is not available if your Contract is funding a plan that is tax qualified under Section 401 of the Internal Revenue Code. AIP is also not available if your Contract is an Inherited IRA or Inherited Roth IRA.
FREE LOOK/RIGHT TO EXAMINE PERIOD
If you change your mind about owning the Contract, you can cancel it within ten days after receiving it (or the period required in your state). If you cancel within the allowed period, in most states we return your Contract Value as of the Business Day we receive your cancellation request in Good Order. This may be more or less than your initial Purchase Payment. In states that require us to return Purchase Payments less withdrawals if you cancel your Contract, we return Contract Value less withdrawal charges if greater.
IRA Contracts require us to return Purchase Payments less withdrawals in most states; in these states we return Contract Value less withdrawal charges if greater. Certain states (such as Pennsylvania) require return of Contract Value for IRA Contracts; in these states we return Purchase Payments less withdrawals if greater.
Some states and certain IRA Contracts require return of Purchase Payments. For these Contracts, we reserve the right to allocate your initial Purchase Payment to the AZL Government Money Market Fund until the free look period ends, and then re-allocate your money, less fees and charges, according to your future Purchase Payment allocation instructions. If we allocate your initial Purchase Payment to the AZL Government Money Market Fund during the free look period and:
| · | your requested Index Effective Date would occur during this time, we change your Index Effective Date to the next Business Day after the free look period that is not the 29th, 30th or 31st of the month. |
| · | you cancel your Contract during this time, we return the greater of Purchase Payments less withdrawals, or Contract Value. |
| · | you do not cancel your Contract during this time, we re-allocate your money according to your future Purchase Payment allocation instructions after the free look period as follows: |
| – | if your instructions include the Variable Options, we re-allocate this portion of your money on the next Business Day after the free look period. |
| – | if your instructions include the Index Options, we re-allocate this portion of your money on the Index Effective Date. |
Contract Value includes application of the Alternate Minimum Value if the free look occurs after the Index Effective Date and you selected an Index Option.
In the Contract, the free look provision is also called the right to examine.
NOTE FOR CONTRACTS ISSUED TO PERSONS AGES 60 OR OLDER IN CALIFORNIA: For Owners age 60 or older (or Annuitants age 60 or older for non-individually owned Contracts), we are required to allocate your initial Purchase Payment to the AZL Government Money Market Fund during the 30 day free look period unless you specify otherwise on the appropriate form. If you want to immediately apply your Purchase Payment to the Index Options or other Variable Options you must opt out of this allocation. If you do not opt out of this allocation to the AZL Government Money Market Fund your Index Effective Date cannot occur until the free look period has ended.
| 5. | VARIABLE OPTIONS |
The following table lists this Contract's Variable Options and their associated investment advisers and subadvisers, investment objectives, and principle investment strategies. Depending on market conditions, you can gain or lose value by investing in the Variable Options. In the future, we may add, eliminate or substitute Variable Options to the extent permitted by the federal securities laws and, when required, the SEC.
You should read the Variable Options' prospectuses carefully. The Variable Options invest in different types of securities and follow varying investment strategies. There are potential risks associated with each of these types of securities and investment strategies. The operation of the Variable Options and their various risks and expenses are described in the Variable Options' prospectuses. We send you the current copy of the Variable Options' prospectus when we issue the Contract. (You can also obtain the current Variable Options' prospectus by contacting your Financial Professional or calling us at the toll-free telephone number listed at the back of this prospectus.)
Currently, the Variable Options are not publicly traded mutual funds. They are available only as Variable Options in variable annuity contracts or variable life insurance policies issued by life insurance companies or in some cases, through participation in certain qualified pension or retirement plans. A material conflict of interest may arise between insurance companies, owners of different types of contracts, and retirement plans or their participants. Each Variable Option's Board of Directors monitors for material conflicts, and determines what action, if any, should be taken to address any conflicts.
The names, investment objectives and policies of certain Variable Options may be similar to the names, investment objectives and policies of other portfolios managed by the same investment advisers. Although the names, objectives and policies may be similar, the Variable Options' investment results may be higher or lower than these other portfolios' results. The investment advisers cannot guarantee, and make no representation, that these similar funds' investment results will be comparable even though the Variable Options have the same names, investment advisers, objectives, and policies.
Each Variable Option offered by the Allianz Variable Insurance Products Fund of Funds Trust (Allianz VIP Fund of Funds Trust) is a "fund of funds" and diversifies its assets by investing primarily in shares of several other affiliated mutual funds.
The Variable Options may pay 12b‑1 fees to the Contracts' distributor, our affiliate, Allianz Life Financial Services, LLC, for distribution and/or administrative services. In addition, we may enter into certain arrangements under which we, or Allianz Life Financial Services, LLC, are compensated by the Variable Options' advisers, distributors and/or affiliates for administrative services and benefits we provide to the Variable Options. The compensation amount usually is based on the Variable Options' aggregate assets purchased through contracts we issue or administer. Some advisers may pay us more or less than others. The maximum service fee we currently receive from any variable investment option in any variable annuity contract we offer is 0.35% annually of the average aggregate amount invested by us in the variable investment options.
The Allianz VIP Fund of Funds Trust underlying funds do not pay 12b‑1 fees or service fees to the Trust, and the Trust does not charge 12b‑1 fees or service fees. The Allianz VIP Fund of Funds Trust underlying funds or their advisers may pay service fees to us and our affiliates for providing customer service and other administrative services to you. Service fees may vary depending on the underlying fund.
We offer other variable annuity contracts that may invest in these Variable Options. These contracts may have different charges and may offer different benefits more appropriate to your needs. For more information about these contracts, please contact our Service Center.
Allianz Investment Management LLC is an adviser/subadviser that is a subsidiary of Allianz Life.
VARIABLE OPTIONS
| Investment Management Company and Adviser/Subadviser | Investment Option Name | Asset Class | Investment Objective | Principal Investment Strategies (Normal market conditions) |
| ALLIANZ FUND OF FUNDS | ||||
| Allianz Investment Management LLC | AZL MVP Balanced Index Strategy Fund | A "Fund of Funds" Model Portfolio | Long-term capital appreciation with preservation of capital as an important consideration | Invests primarily (approximately 80% to 100%) in a combination of five underlying index funds (generally allocated 40% to 60% to underlying equity index funds and 40% to 60% to underlying bond index funds), combined with the MVP (Managed Volatility Portfolio) risk management process intended to adjust the risk of the portfolio based on quantitative indicators of market risk. |
| AZL MVP Growth Index Strategy Fund | A "Fund of Funds" Model Portfolio | Long-term capital appreciation | Invests primarily (approximately 80% to 100%) in a combination of five underlying index funds (generally allocated 65% to 85% to underlying equity index funds and 15% to 35% to underlying bond index funds), combined with the MVP (Managed Volatility Portfolio) risk management process intended to adjust the risk of the portfolio based on quantitative indicators of market risk. | |
| BLACKROCK | ||||
| Allianz Investment Management LLC/BlackRock Advisors, LLC | AZL Government Money Market Fund | Cash Equivalent | Current income consistent with stability of principal | Invests at least 99.5% of its total assets in cash, government securities, or repurchase agreements that are collateralized fully. Invests at least 80% in government securities or in repurchase agreements collateralized by government securities. Investments include U.S. Treasury bills, notes and other obligations issued or guaranteed as to principal and interest by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities, and repurchase agreements secured by such obligations. In addition, the Fund may invest in variable and floating rate instruments. During extended periods of low interest rates, and due in part to contract fees and expenses, the yield of the AZL Government Money Market Fund may also become extremely low and possibly negative. |
SUBSTITUTION OF VARIABLE OPTIONS AND LIMITATION ON FURTHER INVESTMENTS
We may substitute another Variable Option for one of your selected Variable Options, for any reason in our sole discretion. To the extent required by the Investment Company Act of 1940 or other applicable law, we do not substitute any shares without SEC approval and providing you notice. We may make substitutions with respect to your existing allocations, future Purchase Payment allocations, or both. New or substitute Variable Options may have different fees and expenses, and their availability may be limited to certain purchaser classes. We may limit further Variable Option allocations if marketing, tax or investment considerations warrant, or for any reason in our sole discretion. We may also close Variable Options to additional allocations. The fund companies that sell Variable Option shares to us, pursuant to participation agreements, may end those agreements and discontinue offering us their shares.
TRANSFERS BETWEEN VARIABLE OPTIONS
You can make transfers between Variable Options, subject to the following restrictions. Currently, there is no maximum number of transfers allowed, but we may change this in the future. Transfers may be subject to a transfer fee, see section 8, Expenses.
The following applies to any transfer.
| · | Your request for a transfer must clearly state the Variable Options involved and how much to transfer. |
| · | Your right to make transfers is subject to the Excessive Trading and Market Timing policy discussed later in this section. |
| · | Variable Account Value transfers between Variable Options do not change your future Purchase Payment allocation instructions. |
We process transfer requests based on prices next determined after we receive your request in Good Order at our Service Center. If we do not receive your transfer request before the end of the current Business Day, even if due to our delay in answering your call or a delay caused by our electronic systems, you receive the next Business Day's prices. For jointly owned Contracts, unless you require us to obtain signatures from both Joint Owners, we accept transfer instructions from any Joint Owner. We may also allow you to authorize someone else to request transfers on your behalf.
ELECTRONIC TRANSFER AND ALLOCATION INSTRUCTIONS
We use reasonable procedures to confirm that electronic transfer and allocation instructions given to us are genuine. If we do not use such procedures, we may be liable for any losses due to unauthorized or fraudulent instructions. We record all telephone instructions and log all fax, email and website instructions. We reserve the right to deny any transfer request or allocation instruction change, and to discontinue or modify our electronic instruction privileges at any time for any reason.
Please note that telephone, fax, email and/or the website may not always be available. Any electronic system, whether it is ours, yours, your service provider's, or your Financial Professional's, can experience outages or slowdowns for a variety of reasons, which may delay or prevent our processing of your transfer request or allocation instruction change. Although we have taken precautions to help our systems handle heavy use, we cannot promise complete reliability. If you are experiencing problems, you should submit your instructions in writing to our Service Center.
By authorizing electronic instructions, you authorize us to accept and act upon these instructions for your Contract. There are risks associated with electronic communications that do not occur with a written request. Anyone authorizing or making such requests bears those risks. You should protect your website password, because the website is available to anyone with your password; we cannot verify that the person providing instructions on the website is you, or is authorized by you.
EXCESSIVE TRADING AND MARKET TIMING
We may restrict or modify your right to make transfers to prevent any use that we consider to be part of a market timing program.
Frequent transfers, programmed transfers, transfers into and then out of a Variable Option in a short period of time, and transfers of large amounts at one time (collectively referred to as "potentially disruptive trading") may have harmful effects for other Owners, Annuitants and Beneficiaries. These risks and harmful effects include the following.
| · | Dilution of the interests of long-term investors in a Variable Option, if market timers or others transfer into a Variable Option at prices that are below their true value, or transfer out at prices above their true value. |
| · | An adverse effect on portfolio management, such as causing a Variable Option to maintain a higher level of cash or causing a Variable Option to liquidate investments prematurely. |
| · | Increased brokerage and administrative expenses. |
We attempt to protect our Owners and the Variable Options from potentially disruptive trading through our excessive trading and market timing policies and procedures. Under these policies and procedures, we could modify your transfer privileges for some or all of the Variable Options. Unless prohibited by your Contract or applicable state law, we may:
| · | Limit transfer frequency (for example, prohibit more than one transfer a week, or more than two a month, etc.). |
| · | Restrict the transfer method (for example, requiring all transfers be sent by first-class U.S. mail and rescinding electronic transfer privileges). |
| · | Require a minimum time period between each transfer into or out of the same Variable Option. Our current policy, which is subject to change without notice, prohibits "round trips" within 14 calendar days. We do not include transfers into and/or out of the AZL Government Money Market Fund when available in your Contract. Round trips are transfers into and back out of the same Variable Option, or transfers out of and back into the same Variable Option. |
| · | Refuse transfer requests made on your behalf by an asset allocation and/or market timing service. |
| · | Limit the dollar amount of any single Purchase Payment or transfer request to a Variable Option. |
| · | Prohibit transfers into specific Variable Options. |
| · | Impose other limitations or restrictions to the extent permitted by federal securities laws. |
We also reserve the right to reject any specific Purchase Payment allocation or transfer request from any person if in the investment adviser's, subadviser's or our judgment, a Variable Option may be unable to invest effectively in accordance with its investment objectives and policies. This could occur, for example, where frequent or rapid trading causes the investment adviser to hold an excess of uninvested cash to meet redemption requests, or to sell investment positions to fund redemptions, thereby affecting Variable Option returns. Similarly, rapid or frequent trading may cause a Variable Option to incur excessive transaction fees, which also could affect performance.
Currently, we attempt to deter disruptive trading as follows. If a transfer(s) is/are identified as potentially disruptive trading, we may (but are not required to) send a warning letter. If the conduct continues and we determine it constitutes disruptive trading, we also impose transfer restrictions. Transfer restrictions may include refusing electronic transfers and requiring all transfers be sent by first-class U.S. mail. We do not enter into agreements permitting market timing and would not permit activities determined to be disruptive trading to continue. We also reserve the right to impose transfer restrictions if we determine, in our sole discretion, that transfers disadvantage other Owners. We notify you in writing if we impose transfer restrictions on you.
We do not include automatic transfers made under any of our programs or Contract features when applying our market timing policy.
We adopted these policies and procedures as a preventative measure to protect all Owners from the potential effects of disruptive trading, while also abiding by your legitimate interest in diversifying your investment and making periodic asset re-allocations based on your personal situation or overall market conditions. We attempt to protect your interests in making legitimate transfers by providing reasonable and convenient transfer methods that do not harm other Owners.
We may make exceptions when imposing transfer restrictions if we determine a transfer is appropriate, although it may technically violate our policies and procedures discussed here. In determining if a transfer is appropriate, we may, but are not required to, take into consideration its relative size, whether it was purely a defensive transfer into the AZL Government Money Market Fund, and whether it involved an error or similar event. We may also reinstate electronic transfer privileges after we revoke them, but we do not reinstate these privileges if we believe they might be used for future disruptive trading.
We cannot guarantee the following.
| · | Our monitoring will be 100% successful in detecting all potentially disruptive trading activity. |
| · | Revoking electronic transfer privileges will successfully deter all potentially disruptive trading. |
In addition, some of the Variable Options are available to other insurance companies and we do not know if they adopted policies and procedures to detect and deter potentially disruptive trading, or what their policies and procedures might be. Because we may not be completely successful at detecting and preventing market timing activities, and other insurance companies that offer the Variable Options may not have adopted adequate market timing procedures, there is some risk that market timing activity may occur and negatively affect other Owners.
We may, without prior notice to any party, take whatever action we deem appropriate to comply with any state or federal regulatory requirement. In addition, purchase orders for a Variable Option's shares are subject to acceptance by that Variable Option's manager. We reserve the right to reject, without prior notice, any Variable Option transfer request or Purchase Payment if the purchase order is rejected by the investment manager. We have entered into agreements required under SEC Rule 22c-2 (Rule 22c-2 agreements) whereby, upon request by an underlying fund or its designee, we must provide information about you and your trading activities to the underlying fund or its designee. Under the terms of the Rule 22c-2 agreements, we are required to: (1) provide details concerning every purchase, redemption, transfer, or exchange of Variable Options during a specified period; and (2) restrict your trading activity if the party receiving the information so requests. Under certain Rule 22c-2 agreements, if we fail to comply with a request to restrict trading activity, the underlying fund or its designee may refuse to accept buy orders from us until we comply.
Variable Options may add or change policies designed to restrict market timing activities. For example, Variable Options may impose restrictions on transfers between Variable Options in an affiliated group if the investment adviser to one or more of the Variable Options determines that the person requesting the transfer has engaged, or is engaging in, market timing or other abusive trading activities. In addition, a Variable Option may impose a short-term trading fee on purchases and sales within a specified period. You should review the Variable Options' prospectuses regarding any applicable transfer restrictions and the imposition of any fee to discourage short-term trading. The imposition of these restrictions would occur as a result of Variable Option restrictions and actions taken by the Variable Options' managers.
NOTE: This Contract is not designed for professional market timing organizations, or other persons using programmed, large, or frequent transfers, and we may restrict excessive or inappropriate transfer activity.
We retain some discretion in determining what actions constitute potentially disruptive trading and in determining when and how to impose trading restrictions. Therefore, persons engaging in potentially disruptive trading may be subjected to some uncertainty as to when and how we apply trading restrictions, and persons not engaging in potentially disruptive trading may not know precisely what actions will be taken against a person engaging in potentially disruptive trading. For example, if we determine a person is engaging in potentially disruptive trading, we may revoke that person's electronic transfer privileges and require all future requests to be sent by first-class U.S. mail. In the alternative, if the disruptive trading affects only a single Variable Option, we may prohibit transfers into or Purchase Payment allocations to that Variable Option. We notify the person or entity making the potentially disruptive trade when we revoke any transfer privileges.
The retention of some level of discretion by us may result in disparate treatment among persons engaging in potentially disruptive trading, and it is possible that some persons could experience adverse consequences if others are able to engage in potentially disruptive trading practices that have negative effects.
FINANCIAL ADVISER FEES
We do not allow you to instruct us to pay your financial adviser fees from this Contract. If you take withdrawals from this Contract to pay your financial adviser fees, these withdrawals will be withdrawn proportionately from each Allocation Option unless you provide us with alternate instructions. Because the withdrawal charge only applies to amounts withdrawn from the Index Options, there is a financial disadvantage to taking a withdrawal from the Index Options, compared to taking a withdrawal from the Variable Options. Withdrawals of adviser fees reduce your total Purchase Payments adjusted for withdrawals if the Traditional Death Benefit applies, or the Maximum Anniversary Value if the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit applies. Please consult with your Financial Professional before taking a withdrawal from this Contract to pay financial adviser fees. When deducting adviser fees from the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Options on any day other than an Index Anniversary we first apply the Daily Adjustment to these Index Option Values and then deduct the adviser fees. If this is a Non-Qualified Contract this will be a taxable withdrawal to the extent that gain exists within the Contract. If any Owner is under age 59½, withdrawals may also be subject to a 10% additional federal tax. You should consult a tax adviser regarding the tax treatment of withdrawals.
Your investment adviser acts on your behalf, not ours. We are not party to any agreement between you and your financial adviser, nor are we responsible for your financial adviser's actions. We do not set your financial adviser's fee or receive any part of it. Any financial adviser fee you pay is in addition to this Contract's fees and expenses. You should ask your financial adviser about compensation they receive for this Contract. Allianz Life is not an investment adviser, and does not provide investment advice in connection with sales of the Contract. We are not a fiduciary to you, and do not make recommendations or assess suitability.
You can submit a written request to our Service Center on a form satisfactory to us to allow your financial adviser to make Variable Option transfers on your behalf. However, we reserve the right to review a financial adviser's trading history before allowing him or her to make transfers. If, in our sole discretion, we believe the financial adviser's trading history indicates excessive trading, we can deny your request. If we approve it, your financial adviser is subject to the same trading restrictions that apply to Owners. We can deny or revoke trading authority in our sole discretion.
VOTING PRIVILEGES
We legally own the Variable Option shares. However, when a Variable Option holds a shareholder vote that affects your investment, we ask you to give us voting instructions. We then vote all of our shares, including any we own on our behalf, in proportion to those instructions. Because most Owners do not give us instructions and we vote shares proportionally, a small number of Owners may determine a vote's outcome. If we determine we no longer need to get your voting instructions, we will decide how to vote the shares. Only Owners have voting privileges. Annuitants, Beneficiaries, Payees and other persons have no voting privileges unless they are also Owners.
We determine your voting interest in a Variable Option as follows.
| · | You can provide voting instructions based on the dollar value of the Variable Option's shares in your Contract's subaccount. We calculate this value based on the number and value of accumulation units for your Contract on the record date. We count fractional units. |
| · | You receive proxy materials and a voting instruction form. |
| 6. | VALUING YOUR CONTRACT |
Your Contract Value increases and decreases based on Purchase Payments, transfers, withdrawals, deduction of fees and charges, and the performance of your selected Allocation Options. Your Contract Value is the total of the Variable Account Value (if you allocate to the Variable Options or for Purchase Payments held in the AZL Government Money Market Fund before we transfer them to the Index Options) and the total Index Option Value (if you allocate to the Index Options). For information on how we calculate your Index Option Values see section 7, Index Options.
ACCUMULATION UNITS
When we receive a Purchase Payment that you allocate to the Variable Options at our Service Center, or for a Purchase Payments held in the AZL Government Money Market Fund before we transfer it to the Index Options, we credit your Contract with accumulation units based on the Purchase Payment amount and daily price (accumulation unit value) for the subaccount of your selected Variable Option. A subaccount's accumulation unit value is based on the price (net asset value) of the underlying Variable Option. A Variable Option's net asset value is typically determined at the end of each Business Day, and any Purchase Payment received at or after the end of the current Business Day receives the next Business Day's price.
We arbitrarily set the initial accumulation unit value for each subaccount. On the Issue Date, the number of accumulation units in each subaccount is equal to the initial Purchase Payment amount allocated to a subaccount, divided by that subaccount's accumulation unit value.
Example
| · | On Wednesday, we receive at our Service Center an additional Purchase Payment of $3,000 from you before the end of the Business Day. |
| · | When the New York Stock Exchange closes on that Wednesday, we determine that the accumulation unit value is $13.25 for your selected Variable Option. |
We then divide $3,000 by $13.25 and credit your Contract on Wednesday night with 226.415094 subaccount accumulation units for your selected Variable Option.
At the end of each Business Day, we adjust the number of accumulation units in each subaccount as follows. Additional Purchase Payments and transfers into a subaccount increase the number of accumulation units. Withdrawals, transfers out of a subaccount, and the deduction of any Contract charge decrease the number of accumulation units.
At the end of each Business Day for each subaccount, we multiply the accumulation unit value at the end of the prior Business Day by the percentage change in value of a Variable Option since the prior Business Day. The percentage change includes the market performance of the Variable Option.
COMPUTING VARIABLE ACCOUNT VALUE
We calculate your Variable Account Value at the end of each Business Day by multiplying each subaccount's accumulation unit value by its number of accumulation units, and then adding those results together for all subaccounts. Allocations (additional Purchase Payments and transfers of Index Option Value to the Variable Options) increase your Variable Account Value, withdrawals, transfers to the Index Options and Contract expenses reduce your Variable Account Value.
| 7. | INDEX OPTIONS |
When you allocate money to the Index Options you earn Credits based on the Index Option you select. The following are the currently available Crediting Methods and Indices. Each Index Option is the combination of a Crediting Method and an Index. The Indices are described in more detail in Appendix A.
| Crediting Methods | Indices |
| Index Protection Strategy | S&P 500® Index |
| Index Precision Strategy | Russell 2000® Index |
| Index Performance Strategy | Nasdaq-100® Index |
| Index Guard Strategy | EURO STOXX 50® |
The following availability restrictions apply to the Crediting Methods and/or Indices:
| Crediting Method / Indices | Not Available To: |
| Index Protection Strategy | - Contracts issued in Missouri or Washington |
Index Protection Strategy with the Russell 2000® Index, Nasdaq-100® Index and EURO STOXX 50® | - All Contracts issued before the date of this prospectus |
If a Crediting Method or Index is not available, you cannot allocate to it unless we make it available to you on a future Index Anniversary. Certain Crediting Methods and/or Indices also may not be available from all selling firms or from all Financial Professionals. Please consult with your Financial Professional for more information.
NOTE TO CONTRACTS THAT DO NOT INCLUDE THE INDEX PROTECTION STRATEGY: If in future years the renewal Cap and Precision Rates for the Index Performance Strategy, Index Guard Strategy and Index Precision Strategy are not acceptable to you, you will not be able to transfer into the Index Protection Strategy and take advantage of its principal protection. This would subject you to ongoing market risk. You could lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits).
The Crediting Methods have different risk and return potentials. The Index Protection Strategy has the lowest return potential, but provides the most protection. You cannot lose money (or previously applied positive Credits) that you allocate to the Index Protection Strategy due to negative Index performance. Potential returns and risks are higher for the other Crediting Methods.
Although the Index Performance Strategy, Index Guard Strategy and Index Precision Strategy offer higher potential returns than the Index Protection Strategy, you can lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits) that you allocate to these Crediting Methods due to negative Index performance and these losses could be significant. Positive returns for the Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy are limited by the Caps, and for the Index Precision Strategy by the Precision Rates. The Index Precision Strategy performs best in periods of small market movements because the Precision Rates will generally be greater than the DPSCs, though they will generally be less than the Index Performance Strategy Caps. Negative returns are limited for the Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy by the Buffers, and for the Index Guard Strategy by the Floor. The Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy Buffers have protection for smaller negative market movements, but also have the potential for the largest loss in any one year that has a significant market decline. The Index Guard Strategy permits negative Performance Credits down to the Floor, and provides less risk of significant negative returns in any one year than the Buffers. The Index Guard Strategy is sensitive to smaller negative market movements that persist over time, but provides more certainty regarding the maximum loss in any one year.
The total Index Option Value is the sum of the values in each of your selected Index Options. Each Index Option Value includes any Credits from previous Index Anniversaries, and the deduction of any previously assessed contract maintenance charge, product fee, rider fee and withdrawal charge during the Index Year. Positive Credits are not guaranteed, and Credits can be zero under all the available Crediting Methods. Credits can be negative after application of the Buffer under the Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy, or negative down to the Floor under the Index Guard Strategy. A negative Performance Credit means that you can lose money (including principal and previously applied positive Credits). We apply Credits on Index Anniversaries. On Index Anniversaries each Index Option Value also increases with any additional Purchase Payment allocated or Contract Value transferred into an Index Option and decreases with any transfer out of an Index Option.
On each Business Day during the Index Year other than the Index Effective Date or an Index Anniversary, each Index Option Value under the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy is valued by using the Daily Adjustment. The Daily Adjustment estimates the present value of positive or negative Performance Credits on the next Index Anniversary. The application of the Daily Adjustment is based on your agreement to be exposed to Index Anniversary gains in Index Value subject to the Precision Rate or Cap and losses in Index Value either greater than the Buffer, or losses down to the Floor. The Daily Adjustment is a calculation mechanism by which Index Option Values are established each Business Day for purposes of computing amounts available for full or partial withdrawals (including withdrawals under the free withdrawal privilege), an annuitization, death benefits, and the Contract Value used to determine the Charge Base and contract maintenance charge. The Daily Adjustment may result in an adjustment up or down from the preceding Index Anniversary or Index Effective Date.
If you take a withdrawal, annuitize the Contract, transfer Contract Value from an Index Option to a Variable Option, or if we pay a death benefit, we calculate the Alternate Minimum Value for each Index Option Value in all Crediting Methods. If we are determining the Alternate Minimum Value for an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option Value on any day other than an Index Anniversary, we first calculate the Index Option Value by adding the Daily Adjustment, then compare this value to its associated Alternate Minimum Value and we pay the greater of these two amounts. If we are paying a partial withdrawal, we compare the percentage of Index Option Value with an equivalent percentage of its Alternate Minimum Value. We expect that an Alternate Minimum Value generally will not be greater than its Index Option Value.
NOTE REGARDING WITHDRAWALS DURING THE INDEX YEAR: Amounts removed from the Index Options during the Index Year for partial withdrawals and Contract expenses do not receive a Credit on the next Index Anniversary. However, the remaining amount in the Index Options is eligible for a Credit on the next Index Anniversary. Performance Credits under Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy are subject to the Precision Rate or Cap and Buffer, or Cap and Floor. Contract expenses include the product fee, the contract maintenance charge and any applicable rider fee or withdrawal charge.
DETERMINING INDEX OPTION VALUE FOR THE INDEX PROTECTION STRATEGY
On any Business Day, each Index Protection Strategy Index Option Value is equal to the amount you allocate to that Index Option adjusted for withdrawals, Contract expenses, transfers into or out of the Index Option, and the Index Option Base. The Daily Adjustment does not apply to the Index Protection Strategy, but the Alternate Minimum Value does.
On the Index Effective Date both the Index Option Value and the Index Option Base for each of your selected Index Protection Strategy Index Options are equal to either:
| · | the amount of your initial Purchase Payment you allocated to the Index Option if the Index Effective Date is the Issue Date, or |
| · | the amount of Variable Account Value you allocated to the Index Option. |
At the end of each Business Day other than the Index Effective Date or Index Anniversary during the Index Year, we reduce each of your selected Index Option Values by the dollar amount withdrawn from the Index Option for partial withdrawals you request and Contract expenses we deduct (any withdrawal charge, product fee, rider fee and/or contract maintenance charge).
| · | We deduct partial withdrawals and Contract expenses from the Allocation Options proportionately based on the percentage of Contract Value in each Allocation Option. |
| - | The percentage is equal to each Index Option Value divided by the Contract Value using values determined at the end of the Business Day before we process the withdrawal or deduct the Contract expense. |
| · | However, if you specifically direct us to take a partial withdrawal from an Index Protection Strategy Index Option we reduce that Index Option Value by the dollar amount you specify, including any applicable withdrawal charge. |
| - | You cannot specify from which Allocation Option we deduct Contract fees and expenses; Contract expenses are deducted from each Allocation Option proportionately. However, you can specify from which Allocation Option we deduct a partial withdrawal. Because the withdrawal charge only applies to amounts withdrawn from the Index Options, there is a financial disadvantage to taking a withdrawal from the Index Options, compared to taking a withdrawal from the Variable Options. |
| · | We then set each Index Option Base equal to its Index Option Value. |
On each Index Anniversary we first determine if you receive a DPSC. If the current Index Value is less than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary (or the Index Effective Date if this is the first Index Anniversary), you do not receive the DPSC. If the current Index Value is equal to or greater than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary, you receive the DPSC as follows.
| · | We multiply each Index Option Base by its DPSC and add this amount to the Index Option Base. |
| · | Then we set each Index Option Value equal to the Index Option Base. |
Then we increase and/or decrease each Index Option Base and Index Option Value on the Index Anniversary for additional Purchase Payments, transfers into or out of the Index Option, partial withdrawals and the deduction of any Contract expenses.
| · | Additional Purchase Payments received and allocated to this Index Option and transfers of Variable Account Value or Index Option Value into this Index Option increase these values by the dollar amount allocated to this Index Option. |
| · | Transfers out of this Index Option reduce these values by the dollar amount removed from the Index Option. |
| · | Partial withdrawals and Contract expenses reduce these values as on any other Business Day. |
Lastly, at the end of each Business Day during the Index Year, we apply the Alternate Minimum Value as discussed later in this section, if you take a withdrawal, annuitize the Contract, transfer Contract Value out of Index Options, or if we pay a death benefit.
DETERMINING INDEX OPTION VALUES FOR THE INDEX PRECISION STRATEGY, INDEX PERFORMANCE STRATEGY AND INDEX GUARD STRATEGY
We use the Index Option Base to determine the Index Option Value. On each Index Anniversary we determine each of your selected Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Option Values by applying its associated Performance Credit to its Index Option Base. On any day other than an Index Anniversary each Index Option Value is equal to the Index Option Base plus the Daily Adjustment as discussed later in this section.
On the Index Effective Date both the Index Option Value and the Index Option Base for each of your selected Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Options are equal to either:
| · | the amount of your initial Purchase Payment you allocated to that Index Option if the Index Effective Date is the Issue Date, or |
| · | the percentage of Variable Account Value you allocated to that Index Option. |
At the end of each Business Day during the Index Year other than the Index Effective Date or Index Anniversary we first add each of these Index Option's Daily Adjustment to its Index Option Base and determine its Index Option Value (as discussed later in this section) before we process any partial withdrawal or deduct any Contract expenses.
At the end of each Business Day during the Index Year we reduce each of these Index Option Values by the dollar amount withdrawn from the Index Option for partial withdrawals you request and Contract expenses we deduct (any withdrawal charge, product fee, rider fee and/or contract maintenance charge).
| · | We deduct partial withdrawals and Contract expenses from the Allocation Options proportionately based on the percentage of Contract Value in each Allocation Option. |
| - | The percentage is equal to each Index Option Value divided by the Contract Value using values determined at the end of the Business Day before we process the withdrawal or deduct the Contract expense. |
| · | However, if you specifically direct us to take a partial withdrawal from an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option we reduce that Index Option Value by the dollar amount you specify, including any applicable withdrawal charge. |
| - | You cannot specify from which Allocation Option we deduct Contract fees and expenses; Contract expenses are deducted from each Allocation Option proportionately. However, you can specify from which Allocation Option we deduct a partial withdrawal. Because the withdrawal charge only applies to amounts withdrawn from the Index Options, there is a financial disadvantage to taking a withdrawal from the Index Options, compared to taking a withdrawal from the Variable Options. |
| · | We then reduce each Index Option Base by the same percentage that the amount withdrawn reduced its associated Index Option Value. |
On each Index Anniversary we first determine your Performance Credit. If you select the EURO STOXX 50®, Performance Credits are based on the Index Returns without any exchange rate adjustment.
| · | If the current Index Value is equal to or greater than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary (or the Index Effective Date if this is the first Index Anniversary) and you selected the Index Precision Strategy, you receive a positive Performance Credit equal to the Precision Rate. |
| · | If the Index Return is positive and you selected the Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy, you receive a positive Performance Credit limited by the Cap. For example if the Cap is 8% and the Index Return is 10%, you receive an 8% Performance Credit. |
| · | If the Index Return is zero and you selected the Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy, the Performance Credit is zero. |
| · | If the Index Return is negative and you selected the Index Precision Strategy or Index Performance Strategy, we apply the Buffer and determine if you receive a negative Performance Credit. For example, if the Buffer is 10% and the Index Return is -8%, we apply a Performance Credit of zero to your Index Option Base. If instead the Index Return is -12%, we apply a -2% Performance Credit to your Index Option Base. |
| · | If the Index Return is negative and you selected the Index Guard Strategy, we apply the Floor and determine the amount of the negative Performance Credit. For example, if the Floor is -10% and the Index Return is -8%, we apply a Performance Credit of -8% to your Index Option Base. If instead the Index Return is -12%, we apply a -10% Performance Credit to your Index Option Base. |
We then apply the Performance Credit to the Index Option as follows:
| · | We multiply each Index Option Base by its Performance Credit and add this amount to its Index Option Base. |
| · | Then we set each Index Option Value equal to its Index Option Base. |
Then we increase and/or decrease each Index Option Base and Index Option Value on the Index Anniversary for additional Purchase Payments, transfers into or out of the Index Option, partial withdrawals and the deduction of any Contract expenses.
| · | Additional Purchase Payments received and allocated to this Index Option and transfers of Variable Account Value or Index Option Value into this Index Option increase these values by the dollar amount allocated to this Index Option. |
| · | Transfers out of this Index Option reduce these values by the dollar amount removed from the Index Option. |
| · | Partial withdrawals and Contract expenses reduce these values as on any other Business Day. |
Lastly, at the end of each Business Day during the Index Year we compare each of these Index Option Values to its Alternate Minimum Value as discussed later in this section, if you take a withdrawal, annuitize the Contract, transfer out of Index Options to the Variable Options, or if we pay a death benefit. If the Alternate Minimum Value calculation occurs on any day other than an Index Anniversary, this comparison occurs after we add the Daily Adjustment, and we pay the greater of these two amounts.
Index Option Value Daily Adjustment for the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy
We designed the Daily Adjustment to provide an Index Option Value during the Accumulation Phase on days other than the Index Effective Date or an Index Anniversary. The Daily Adjustment generally reflects the change in market value of your allocation to an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option. We add a Daily Adjustment to these Index Option Values for purposes of computing amounts available for withdrawal, annuitization, death benefits, and the Contract Value used to determine the Charge Base and contract maintenance charge. The Daily Adjustment directly increases or decreases your Index Option Values. The Daily Adjustment is different from the method we use to apply Performance Credits to an Index Option on an Index Anniversary. The Daily Adjustment is meant to approximate the Index Option Value on the next Index Anniversary, as adjusted for gains during the Index Year subject to the Precision Rate or Cap and either losses greater than the Buffer, or losses down to the Floor. The application of the Daily Adjustment is based on your agreement to be exposed to Index Anniversary gains in Index Value subject to the Precision Rate or Cap and losses in Index Value either greater than the Buffer, or losses down to the Floor. The Daily Adjustment does this by using a Black Scholes model to track the hypothetical value of a Proxy Investment (called the Proxy Value) each Business Day other than an Index Anniversary. The Proxy Investment is designed to return the same amount as the Index Option on an Index Anniversary (an amount equal to the Performance Credit as determined using the applicable Precision Rate or Cap and Buffer, or Cap and Floor). Between Index Anniversaries, the Proxy Investment provides a current estimate of what the Index Value gain or loss would be if the investment were held until the Index Anniversary. The Daily Adjustment does not give you the actual Index return on the day of the calculation.
The Daily Adjustment can be positive or negative. When the Daily Adjustment is positive, an Index Option Value is higher than the Index Option Base. When the Daily Adjustment is negative, an Index Option Value is lower than the Index Option Base. The Daily Adjustment will differ from the current Index return. The Daily Adjustment is affected by the length of time until the next Index Anniversary and it is generally negatively affected by interest rate decreases, dividend rate increases, poor market performance and the expected volatility of index prices. Increases in the expected volatility of index prices negatively affect the Index Precision Strategy and Index Performance Strategy, while decreases in the expected volatility of index prices negatively affect the Index Guard Strategy. All other factors being equal, even if the current Index return during the Index Year is greater than the Precision Rate or Cap, the Daily Adjustment will be lower than the Precision Rate or Cap during the Index Year and will frequently not be equal to the Precision Rate or Cap until the next Index Anniversary. Even if the current Index return during the Index Year is positive, the Daily Adjustment may be negative until the Index Anniversary. This means if money is withdrawn or removed from the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy, or Index Guard Strategy, you could lose money (including principal and previously applied Credits) even if the current Index return is positive on that day. If the current Index return during the Index Year is negative, the Daily Adjustment could result in losses greater than the protection provided by the Buffer or the Floor.
At the end of each Business Day during the Index Year (other than the Index Effective Date or Index Anniversary) we add each Daily Adjustment to its Index Option Base to calculate each Index Option Value before we process any partial withdrawal or deduct any Contract expenses. If there is a system error in calculating your Daily Adjustment, or if the Index Value for a Business Day is not received, we will calculate the Daily Adjustment when corrected or other required information is received, effective as of the original pricing date.
For more information on how we calculate the Daily Adjustment see Appendix B.
Index Option Value Performance Locks for the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy
Under the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy you can lock in a current Index Option Value by requesting a Performance Lock. You can request a lock once each Index Year for each of these Index Options. We must receive your Performance Lock request in Good Order before the end of the Business Day on the Lock Date to lock an Index Option on that Business Day. Otherwise the Lock Date will occur on the next Business Day that your request is in Good Order. For requests submitted in writing, we don't consider the request to be received until it arrives at our Service Center. A Performance Lock applies to the total Index Option Value in an Index Option, and not just a portion of that Index Option Value. After the Lock Date Daily Adjustments do not apply for the remainder of the Index Year and the Index Option Value will not receive a Performance Credit on the next Index Anniversary. However, the Index Option Value does decrease during the remainder of the Index Year for any partial withdrawals and the deduction of any Contract expenses. Beginning on the next Index Anniversary, your locked Index Options will no longer be locked and Daily Adjustments will again apply.
A Performance Lock can help eliminate doubt about future Index performance and possibly limit the impact, or avoid receiving, a negative Performance Credit. The disadvantage of taking a Performance Lock is that the relevant Index Value may increase until the next Index Anniversary, and you will not participate in that increase. In addition, if you exercise a Performance Lock, you may receive less than the full Precision Rate or Cap, or less than the full protection of the Buffer or the Floor that you would have received if you waited for us to apply the Performance Credit on the next Index Anniversary.
THE ALTERNATE MINIMUM VALUE
The Alternate Minimum Value is the guaranteed minimum on each of your Index Option Values if we pay a death benefit, upon annuitization, if you take a withdrawal, or if you transfer Contract Value from an Index Option to a Variable Option. The Alternate Minimum Value applies to all of the Crediting Methods. If we are determining the Alternate Minimum Value for an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option on any day other than an Index Anniversary, we first calculate the Index Option Value and add the Daily Adjustment, then compare this value to its associated Alternate Minimum Value and we pay the greater of these two amounts. On the Index Effective Date the Alternate Minimum Value for each of your Index Options is equal to the Index Option Base multiplied by the AMV Factor. On each day during the Index Year, the Alternate Minimum Value is equal to the Index Option Base on the last Index Anniversary (or the Index Effective Date if this is the first Index Year) (adjusted for any withdrawals, including any withdrawal charge) multiplied by the AMV Factor plus the Accumulated Alternate Interest. We then add the Daily Adjustment if this is an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option.
We establish the Alternate Minimum Base for each of your Index Options. On the Index Effective Date it is equal to the Index Option Base multiplied by the AMB Factor. The Accumulated Alternate Interest is the total interest your Contract has earned under the Alternate Minimum Value. The interest that is added each day to the Accumulated Alternate Interest is equal to the Alternate Minimum Base multiplied by the alternate interest rate, then dividing this result by 365. We set the alternate interest rate on the Issue Date and it does not change during the time you own your Contract
On each Index Anniversary we reset your Alternate Minimum Value to equal the new Index Option Base multiplied by the AMV Factor plus the Accumulated Alternate Interest. We also reset your Alternate Minimum Base to equal the Index Option Base multiplied by the AMB Factor plus the Accumulated Alternate Interest. The Accumulated Alternate Interest does not reset on the Index Anniversary. The Index Option Base is determined at the end of the day on the Index Anniversary after applying any Credit, additional Purchase Payment, transfers into or out of the Index Option, partial withdrawals and Contract expenses. If you receive no Credits, or only modest Credits, over many years the Alternate Minimum Value may be higher than the Index Option Value. However, we expect that an Alternate Minimum Value generally will not be greater than its Index Option Value.
If you take a full withdrawal, annuitize the Contract, or we pay a death benefit we compare each of your Index Option Values (after any applicable withdrawal charge, final product fee, final rider fee and final contract maintenance charge) and its associated Alternate Minimum Value using values determined at the end of the Business Day. If any Index Option Value is less than its Alternate Minimum Value, we increase the Index Option Value to equal its Alternate Minimum Value before we calculate Annuity Payments or pay out any full withdrawal or death benefit.
If you take a partial withdrawal or transfer Index Option Value to a Variable Option, we compare the percentage of Index Option Value withdrawn (including any applicable withdrawal charge) with an equivalent percentage of its Alternate Minimum Value using values determined at the end of the Business Day we process the partial withdrawal or transfer. If the percentage of Index Option Value is less than the equivalent percentage of Alternate Minimum Value, we add the difference to the amount we pay to you as a partial withdrawal or to the amount transferred.
You can find more information about the Alternate Minimum Value at Exhibit 99(a) of the Form S-1 Registration Statement filed with the SEC, of which this prospectus is a part. This information is incorporated by reference into this prospectus. You can obtain a copy of Exhibit 99(a) by calling (800) 624-0197, or visiting our website at www.allianzlife.com.
OPTIONAL REBALANCING PROGRAM
Your selected Index Options' performance may cause the percentage of total Index Option Value in each Index Option to change. Rebalancing can help you maintain your selected Index Option allocation percentages. You can direct us to automatically adjust your Index Option Value on each Index Anniversary (or on the next Business Day if the Index Anniversary is not a Business Day) according to your instructions. We must receive your optional rebalancing program form in Good Order at our Service Center by 4 p.m. Eastern Time on the Business Day we rebalance. We reserve the right to discontinue or modify the optional rebalancing program at any time and for any reason. To end this program, we must receive your request at our Service Center by 4 p.m. Eastern Time on the Business Day immediately before the Index Anniversary.
| 8. | EXPENSES |
Contract fees and expenses reduce your investment return and are described here in detail.
ANNUAL CONTRACT FEES: PRODUCT FEE AND RIDER FEE
The product and rider fees are annualized rates that we calculate and accrue on a daily basis as a percentage of the Charge Base during the Accumulation Phase. The Charge Base is initially equal to the Purchase Payment received on the Issue Date. At the end of each Business Day, we adjust the Charge Base as follows.
| · | We increase it by the amount of any additional Purchase Payments. |
| · | We reduce it by the percentage of any Contract Value withdrawn. Withdrawals include withdrawals under the free withdrawal privilege and all Contract expenses (withdrawal charge, product fee, rider fee, contract maintenance charge, and transfer fee). |
On each Quarterly Contract Anniversary (or on the next Business Day if the Quarterly Contract Anniversary is not on a Business Day) the Charge Base is equal to the Contract Value determined at the end of the Business Day after we process any additional Purchase Payments or withdrawals, and if this is an Index Anniversary, after we apply any Credits.
We begin calculating and accruing the daily product fee amount, and rider fee amount if applicable, on the day after the Issue Date. We calculate the daily product and rider fees before we process any additional Purchase Payments or withdrawals, and if this is also an Index Anniversary, before we apply any Credits. We deduct the product and rider fees on each Quarterly Contract Anniversary (or the next Business Day if the Quarterly Contract Anniversary is not a Business Day) with the following exceptions.
| · | If you withdraw the total Contract Value, we deduct the final product and rider fees (the total of all daily product and rider fees we calculated for the current Contract quarter) before processing the withdrawal. |
| · | If you annuitize the Contract, we deduct the final product and rider fees before calculating Annuity Payments. |
| · | Upon the death of an Owner (or Annuitant if the Owner is a non-individual), we deduct the final rider fee before calculating the death benefit, and we deduct the final product fee before calculating the death benefit if death benefit payment Option A or Annuity Payments under death benefit payment Option C is selected. |
| Annual Contract Fees | |
| (as a percentage of the Charge Base) | |
Product Fee(1)…………………………………......………………………………………………….… | 0.25% |
Rider Fee for the optional Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit(2)………………..… | 0.20% |
Total Contract Fees for Contracts with the optional Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit…………………………………………………………………………………………………….. | 0.45% |
| (1) | Upon the death of the Owner, we continue to assess this product fee under death benefit payment Option B, and with optional payments under death benefit payment Option C, as noted in section 11, Death Benefit. |
| (2) | We no longer assess the 0.20% rider fee for the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit once we receive either the first Valid Claim from any one Beneficiary, or due proof of a Determining Life's death if you and the Determining Life are different individuals and the Determining Life predeceases you. |
We deduct the product and rider fees on a dollar for dollar basis from the Contract Value and we deduct it proportionately from each Allocation Option.
We do not treat the deduction of the product and rider fees as a withdrawal when computing total Purchase Payments adjusted for withdrawals under the Traditional Death Benefit, or the Maximum Anniversary Value under the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit (see section 11). However, if you select the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit we deduct all Contract expenses on the Index Anniversary (including the product and rider fees if this is also a Quarterly Contract Anniversary) before we lock in any annual investment gains to the Maximum Anniversary Value.
If on a Quarterly Contract Anniversary (or the next Business Day if the Quarterly Contract Anniversary is not a Business Day) the Contract Value is less than the product and rider fees, we deduct your total remaining Contract Value to cover the final product and rider fees and reduce your Contract Value to zero. If your selected death benefit has ended and the deduction of the final product and rider fees reduces your Contract Value to zero, we treat this as a full withdrawal and your Contract ends.
Changes to the Charge Base change the product and rider fee amount. For example, if you make an additional Purchase Payment both your Charge Base and daily product and rider fee amount also increase. Similarly, a withdrawal decreases both your Charge Base and daily product and rider fee amount.
The product fee compensates us for providing all your Contract's benefits, including our contractual obligation to make Annuity Payments and certain Contract and distribution expenses. The product fee compensates us for assuming the expense risk that the current charges are less than future Contract administration costs as well as the cost of providing certain features under the Contract. The rider fee compensates us for the benefit provided by the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit, including the benefit's guarantees. If the product and rider fees cover these costs and risks, any excess is profit to us. We anticipate making such a profit.
Examples depicting how we calculate the product and rider fees are included in Appendix D.
CONTRACT MAINTENANCE CHARGE
Your annual contract maintenance charge is $50. This charge is for Contract administration and maintenance expenses. We waive this charge as follows:
| · | During the Accumulation Phase, if the total Contract Value for all Index Advantage ADV Contracts you own is at least $100,000 at the end of the last Business Day before the Contract Anniversary, or if the Contract Value for this single Index Advantage ADV Contract is at least $100,000 on the Contract Anniversary. We determine the total Contract Value for all individually owned Index Advantage ADV Contracts by using the Owner's social security number, and for non-individually owned Index Advantage ADV Contracts we use the Annuitant's social security number. |
| · | During the Annuity Phase if the Contract Value on the last Business Day before the Annuity Date is at least $100,000. |
| · | When paying death benefits under death benefit payment options A, B, or C. |
During the Accumulation Phase, we deduct the contract maintenance charge on a dollar for dollar basis from the Contract Value on the Contract Anniversary (or the next Business Day if the Contract Anniversary is not a Business Day) and we deduct it proportionately from each Allocation Option. If you take a full withdrawal from your Contract (other than on a Contract Anniversary), we deduct the full contract maintenance charge. We do not treat the deduction of the contract maintenance charge as a withdrawal when computing total Purchase Payments adjusted for withdrawals under the Traditional Death Benefit, or the Maximum Anniversary Value under the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit (if applicable). During the Annuity Phase, we deduct the contract maintenance charge proportionately from each Annuity Payment.
WITHDRAWAL CHARGE
You can take withdrawals during the Accumulation Phase. A withdrawal charge applies if any part of a withdrawal comes from a Purchase Payment that is still within the withdrawal charge period that is being withdrawn from an Index Option. There is no withdrawal charge taken from amounts being withdrawn from the Variable Options. We assess the withdrawal charge against the Withdrawal Charge Basis, which is equal to total Purchase Payments, less any Purchase Payments withdrawn (excluding any penalty-free withdrawals), and less any applicable withdrawal charge. We do not reduce the Withdrawal Charge Basis for any amounts withdrawn from the Variable Options or any amounts we deduct to pay other Contract expenses.
We do not assess a withdrawal charge on amounts withdrawn from the Variable Options or on penalty-free withdrawals or on amounts we deduct to pay Contract expenses, other than the withdrawal charge. However, any amounts used to pay a withdrawal charge are subject to a withdrawal charge. Amounts withdrawn from the Index Options to pay investment adviser fees are subject to a withdrawal charge if they exceed the free withdrawal privilege. Penalty-free withdrawals include: withdrawals under the free withdrawal privilege and waiver of withdrawal charge benefit and payments under our minimum distribution program.
For purposes of calculating any withdrawal charge for a withdrawal from the Index Options, we withdraw Purchase Payments on a "first-in-first-out" (FIFO) basis and we process withdrawal requests as follows.
| 1. | First we withdraw from Purchase Payments that we have had for six or more complete years, which is your Contract's withdrawal charge period. This withdrawal is not subject to a withdrawal charge and it reduces the Withdrawal Charge Basis. |
| 2. | Then, if this is a partial withdrawal, we withdraw from the free withdrawal privilege (see section 9, Access to Your Money – Free Withdrawal Privilege). This withdrawal is not subject to a withdrawal charge and it does not reduce the Withdrawal Charge Basis. |
| 3. | Next, on a FIFO basis, we withdraw from Purchase Payments within your Contract's withdrawal charge period and assess a withdrawal charge. Withdrawing payments on a FIFO basis may help reduce the total withdrawal charge because the charge declines over time. We determine your total withdrawal charge by multiplying each payment by its applicable withdrawal charge percentage and then totaling the charges. This withdrawal reduces the Withdrawal Charge Basis. |
| 4. | Finally we withdraw any Contract earnings. This withdrawal is not subject to a withdrawal charge and it does not reduce the Withdrawal Charge Basis. |
The withdrawal charge as a percentage of each Purchase Payment withdrawn is as follows.
| Number of Complete Years Since Purchase Payment | Withdrawal Charge Amount |
| 0 | 6.5% |
| 1 | 6% |
| 2 | 5% |
| 3 | 4% |
| 4 | 3% |
| 5 | 2% |
| 6 years or more | 0% |
Upon a full withdrawal, we first deduct any applicable product fee, rider fee and contract maintenance charge before we calculate the withdrawal charge. We deduct any applicable withdrawal charge from the total Contract Value and send you the remaining amount. For a partial withdrawal we deduct the amount you request, plus any applicable withdrawal charge from the total Contract Value. We apply the withdrawal charge to the amount withdrawn from the Index Options and we pay you the amount you requested. We deduct partial withdrawals proportionately from each Allocation Option unless you provide us with alternate instructions. However, we do not deduct withdrawal charges from the Variable Options. If a partial withdrawal occurs on a day that we also assess the product fee, rider fee and/or contract maintenance charge, we assess these charges in this order after we deduct the withdrawal and any applicable withdrawal charge from the Contract Value. When we deduct the withdrawal charge, we do not assess a withdrawal charge against amounts being withdrawn from the Variable Options. We only deduct the withdrawal charge applicable to amounts being withdrawn from the Index Options.
The withdrawal charge compensates us for expenses associated with selling the Contract.
Example: You make an initial Purchase Payment of $30,000 and make another Purchase Payment in the first month of the second Contract Year of $70,000. All Purchase Payments are allocated to the Index Options. In the third month of the third Contract Year, your Contract Value is $110,000 and you request a $52,000 withdrawal. We withdraw money and compute the withdrawal charge as follows.
| 1) | Purchase Payments beyond the withdrawal charge period. All payments are still within the withdrawal charge period, so this does not apply. |
| 2) | Amounts available under the free withdrawal privilege. You did not take any other withdrawals this year, so you can withdraw up to 10% of your total payments (or $10,000) without incurring a withdrawal charge. |
| 3) | Purchase Payments within the withdrawal charge period on a FIFO basis. The total amount we withdraw from the first Purchase Payment is $30,000, which is subject to a 5% withdrawal charge, and you receive $28,500. We determine this amount as follows: |
(amount withdrawn) x (1 – withdrawal charge) = the amount you receive, or:
$30,000 x 0.95 = $28,500.
$30,000 x 0.95 = $28,500.
Next we withdraw from the second Purchase Payment. So far, you received $38,500 ($10,000 under the free withdrawal privilege and $28,500 from the first Purchase Payment), so we withdraw $13,500 from the second Purchase Payment to equal the $52,000 you requested. The second Purchase Payment is subject to a 6% withdrawal charge. We calculate the total amount withdrawn and its withdrawal charge as follows:
(the amount you receive) ÷ (1 – withdrawal charge) = amount withdrawn, or:
$13,500 ÷ 0.94 = $14,362.
$13,500 ÷ 0.94 = $14,362.
| 4) | Contract earnings. We already withdrew your requested amount, so this does not apply. |
In total we withdrew $54,326 from your Contract, of which you received $52,000 and paid a withdrawal charge of $2,326.
Reduction or Elimination of the Withdrawal Charge
We may reduce or eliminate the withdrawal charge when the Contract is sold under circumstances that reduce its sales expenses. We will implement this withdrawal charge reduction or elimination in a nondiscriminatory manner. For example, if a large group of individuals purchases Contracts or if a prospective purchaser already has a relationship with us. We may choose not to deduct a withdrawal charge under a Contract issued to an officer, director, or employee of Allianz Life or any of its affiliates. Also, we may reduce or eliminate the withdrawal charge when a Contract is sold by a Financial Professional appointed with Allianz Life to any members of his or her immediate family. We must pre-approve any withdrawal charge reduction or elimination. Keep in mind that if you withdraw money from an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option on any day other than an Index Anniversary, we first calculate the Index Option Value by adding the Daily Adjustment (which can be negative), even if the withdrawal is not subject to a withdrawal charge.
NOTE:
| · | Because there is no withdrawal charge applicable to the Variable Options, there is a financial disadvantage to directing us to withdraw Contract Value only from the Index Options from Purchase Payments within the withdrawal charge period, rather than the Variable Options. |
| · | Any amount withdrawn from an Index Option is subject to both a Daily Adjustment (which may be negative) and any applicable withdrawal charge. |
| · | Because we do not reduce the Withdrawal Charge Basis for penalty-free withdrawals or the deduction of Contract expenses other than the withdrawal charge, we may assess a withdrawal charge on more than the amount you are withdrawing upon a full withdrawal of the total Contract Value. Also, upon full withdrawal, if the Contract Value has declined due to poor performance, the withdrawal charge may be greater than the total Contract Value and you will not receive any money. |
| · | Withdrawals may have tax consequences and, if taken before age 59½, may be subject to a 10% additional federal tax. For tax purposes in most instances, withdrawals from Non-Qualified Contracts are considered to come from earnings first, not Purchase Payments. |
| · | For Contracts issued in Florida: The withdrawal charge cannot exceed 10% of the Contract Value withdrawn. |
TRANSFER FEE
The first twelve transfers between Variable Options every Contract Year are free. After that, we deduct a $25 transfer fee for each additional transfer. We count all transfers made in the same Business Day as one transfer. We do not count transfers between the Variable Options and Index Options or reallocation of Index Option Value among the Index Options against the free transfers we allow and these transfers are not subject to a transfer fee. The transfer fee continues to apply under death benefit payment Option B, and with optional payments under death benefit payment Option C as noted in section 11, Death Benefit.
We deduct the transfer fee on a dollar for dollar basis from the amount of Variable Account Value being transferred before allocating the remaining Variable Account Value to your selected Variable Options. We do not treat the deduction of the transfer fee as a withdrawal when computing total Purchase Payments adjusted for withdrawals under the Traditional Death Benefit.
PREMIUM TAX
Premium tax is based on your state of residence at the time you make each Purchase Payment. In states that assess a premium tax, we do not currently deduct it from the Contract, although we reserve the right to do so in the future. Premium tax normally ranges from 0% to 3.5% of the Purchase Payment, depending on the state or governmental entity.
INCOME TAX
Currently, we do not deduct any Contract related income tax we incur, although we reserve the right to do so in the future.
VARIABLE OPTION EXPENSES
The Variable Options' assets are subject to operating expenses (including management fees). These expenses are described in the Fee Tables and in the Variable Options' prospectuses. These expenses reduce the Variable Options' performance and, therefore, negatively affect your Contract Value and any payments based on Contract Value. The Variable Options' investment advisers provided us with the expense information in this prospectus and we did not independently verify it.
| 9. | ACCESS TO YOUR MONEY |
The money in your Contract is available under the following circumstances:
| · | by withdrawing your Contract Value; |
| · | by taking required minimum distributions (Qualified Contracts only) as discussed in "Minimum Distribution Program and Required Minimum Distribution (RMD) Payments" later in this section; |
| · | by taking Annuity Payments; or |
| · | when we pay a death benefit. |
You can take withdrawals during the Accumulation Phase. We process withdrawal requests based on values next determined after receipt of the request in Good Order at our Service Center. Values are normally determined at the end of each Business Day. Any withdrawal request received at or after the end of the current Business Day receives the next Business Day's values.
Any partial withdrawal must be for at least $100.* The Contract Value after a partial withdrawal must be at least $2,000.* We reserve the right to treat a partial withdrawal that reduces the Contract Value below this minimum as a full withdrawal.
| * | Does not apply to required minimum distributions. |
We deduct partial withdrawals proportionately from each Allocation Option unless you provide us with alternate instructions. However, we do not deduct withdrawal charges from the Variable Options. If you are withdrawing money from an Index Option we also apply any Alternate Minimum Value to the amount we send you as described in section 7, Index Options – The Alternate Minimum Value.
When you take a full withdrawal, we process your request on the Business Day we receive it in Good Order at our Service Center as follows:
| · | total Contract Value, |
| · | less any final product fee, final rider fee and final contract maintenance charge, |
| · | less any withdrawal charge, and |
| · | plus any increase from the application of the Alternate Minimum Value if you selected an Index Option. |
See the Fee Tables and section 8, Expenses for a discussion of these charges. See also section 7, Index Options – The Alternate Minimum Value.
We pay withdrawals promptly, but in no event later than seven days after receipt of your request in Good Order at our Service Center, unless the suspension of payments or transfers provision is in effect (see the discussion later in this section).
NOTE:
| · | Any amount withdrawn from an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option is subject to a Daily Adjustment, which may be negative. |
| · | Ordinary income taxes and tax penalties may apply to any withdrawal you take. |
| · | We may be required to provide information about you or your Contract to government regulators. We may also be required to stop Contract disbursements and thereby refuse any transfer requests, and refuse to pay any withdrawals, surrenders, or death benefits until we receive instructions from the appropriate regulator. If, pursuant to SEC rules, the AZL Government Money Market Fund suspends payment of redemption proceeds in connection with a fund liquidation, we will delay payment of any transfer, partial withdrawal, surrender, or death benefit from the AZL Government Money Market Fund subaccount until the fund is liquidated. |
| · | For Contracts issued in Montana: If you take a partial withdrawal that reduces the Contract Value below $2,000, we contact you by phone and give you the option of modifying your withdrawal request. If we cannot reach you, we process your request as a full withdrawal. |
| · | For Contracts issued in Texas: We only treat a partial withdrawal that reduces the Contract Value below $2,000 as a full withdrawal if you have not made an additional Purchase Payment in the past two calendar years. |
FREE WITHDRAWAL PRIVILEGE
Each Contract Year, you can withdraw up to 10% of your total Purchase Payments from the Index Options without incurring a withdrawal charge (the free withdrawal privilege). Any unused free withdrawal privilege in one Contract Year is not added to the amount available next year. Purchase Payment withdrawals that are outside the six year withdrawal charge period that are taken from the Variable Options are not subject to a withdrawal charge and do not reduce your free withdrawal privilege. Required minimum distribution payments are not subject to a withdrawal charge, but do reduce your free withdrawal privilege.
NOTE: The free withdrawal privilege is not available upon a full withdrawal.
SYSTEMATIC WITHDRAWAL PROGRAM
The systematic withdrawal program can provide automatic withdrawal payments to you. However, if your Contract Value is less than $25,000, we only make annual payments. You can request to receive these withdrawal payments monthly, quarterly, semi-annually or annually. The minimum amount you can withdraw under this program is $100 and there is no maximum. During the withdrawal charge period (if applicable), systematic withdrawals from the Index Options in excess of the free withdrawal privilege are subject to a withdrawal charge. We make systematic withdrawals on the ninth of the month, or the next Business Day if the ninth is not a Business Day. We must receive your systematic withdrawal program form instructions in Good Order at our Service Center by 4 p.m. Eastern Time on the Business Day before we process these withdrawals, or your program does not begin until the next month. This program ends at your request or when you withdraw your total Contract Value. However, we reserve the right to discontinue or modify the systematic withdrawal program at any time and for any reason.
NOTE:
| · | Ordinary income taxes and tax penalties may apply to systematic withdrawals. |
| · | The systematic withdrawal program is not available while you are receiving required minimum distribution payments. |
MINIMUM DISTRIBUTION PROGRAM AND REQUIRED MINIMUM DISTRIBUTION (RMD) PAYMENTS
If you own an IRA or SEP IRA Contract, you can participate in the minimum distribution program during the Accumulation Phase. If you purchase this Contract as an Inherited IRA Contract, we generally require you to participate in the minimum distribution program when you purchase this Contract. Under this program, we make payments to you designed to meet the applicable minimum distribution requirements imposed by the Internal Revenue Code for this Qualified Contract. RMD payments are not subject to a withdrawal charge, but to the extent they are withdrawn from Index Options, they reduce the free withdrawal privilege amount during the Contract Year. We can make payments to you on a monthly, quarterly, semi-annual or annual basis. However, if your Contract Value is less than $25,000, we only make annual payments. You cannot aggregate RMD payments between this Contract and other qualified contracts that you own. We make RMD payments on the ninth of the month, or the next Business Day if the ninth is not a Business Day. We must receive your program form instructions in Good Order at our Service Center by 4 p.m. Eastern Time on the Business Day before we process these payments, or your program does not begin until the next month.
Inherited IRA Contracts. If you (the Owner) were the spouse of the deceased owner of a previous tax-qualified investment and your spouse had not yet reached the date at which he/she was required to begin receiving RMD payments, then you can wait to begin receiving RMD payments until the year that your deceased spouse would have reached age 70½. Alternately, if your deceased spouse had already reached the date at which he/she was required to begin receiving RMD payments, you can begin RMD payments based on your single life expectancy in the year following your deceased spouse's death, or (if longer) your deceased spouse's life expectancy in the year of his/her death reduced by one. You must begin to receive these RMD payments by December 31 of the year following the year of your deceased spouse's death.
NOTE:
| · | You should consult a tax adviser before purchasing a Qualified Contract that is subject to RMD payments. |
| · | The minimum distribution program is not available while you are receiving systematic withdrawals. |
WAIVER OF WITHDRAWAL CHARGE BENEFIT
After the first Contract Year, if any Owner becomes confined to a nursing home for a period of at least 90 consecutive days and a physician certifies that continued confinement is necessary, you can take withdrawals and we waive the withdrawal charge. This waiver is not available if any Owner was confined to a nursing home on the Issue Date. We base this benefit on the Annuitant for non-individually owned Contracts. We must receive proof of confinement in Good Order for each withdrawal before we waive the withdrawal charge.
NOTE FOR CONTRACTS ISSUED IN:
| · | Massachusetts – The waiver of withdrawal charge benefit is not available. |
| · | New Hampshire – The definition of nursing home is an institution operated in accordance with state law. |
| · | Pennsylvania – The waiver is not available if on the Issue Date, an Owner was confined to a nursing home or was already diagnosed with a terminal illness. Also, the nursing home confinement requirement is a total of 90 days within a six month period. These 90 days do not need to be consecutive. |
SUSPENSION OF PAYMENTS OR TRANSFERS
We may be required to suspend or postpone transfers or payments for withdrawals for any period when:
| · | the New York Stock Exchange is closed (other than customary weekend and holiday closings); |
| · | trading on the New York Stock Exchange is restricted; |
| · | an emergency (as determined by the SEC) exists as a result of which disposal of the Variable Option shares is not reasonably practicable or we cannot reasonably value the Variable Option shares; or |
| · | during any other period when the SEC, by order, so permits for the protection of Owners. |
| 10. | THE ANNUITY PHASE |
Prior to annuitization, you can surrender your Contract and receive your total Contract Value (less the final product fee, any final rider fee or contract maintenance charge, and any applicable withdrawal charge). If you surrender your Contract on any day other than an Index Anniversary and you have Contract Value in the Index Performance Strategy, Index Guard Strategy or Index Precision Strategy, we apply the Daily Adjustment to these Index Option Values before we deduct the final Contract fees and charges.
Annuity Payments offer a guaranteed income stream with certain tax advantages and are designed for Owners who are not concerned with continued access to Contract Value.
You can apply your Contract Value to regular periodic fixed annuity payments (Annuity Payments). The Payee receives the Annuity Payments. You receive tax reporting on the payments, whether or not you are the Payee. We may require proof of the Annuitant(s)' age before we make any life contingent Annuity Payment. If you misstate the Annuitant(s)' age or gender, we recalculate the Annuity Payments based on the correct age or gender.
CALCULATING YOUR ANNUITY PAYMENTS
We base Annuity Payments upon the following:
| · | The Contract Value on the Annuity Date. |
| · | The age of the Annuitant and any joint Annuitant on the Annuity Date. |
| · | The gender of the Annuitant and any joint Annuitant where permitted. |
| · | The Annuity Option you select. |
| · | Your Contract's interest rate (or current rates, if higher) and mortality table. |
If the Annuity Date is not an Index Anniversary and you selected the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy, Contract Value includes the Daily Adjustment. If the Annuity Date is not an Index Anniversary and you selected the Index Protection Strategy, Contract Value does not include the DPSC. Contract Value does include any increase from the Alternate Minimum Value if you selected any of the available Index Options. We guarantee the dollar amount of Annuity Payments and this amount remains fixed and does not change during the entire annuity payout option period that you selected, except as provided under Annuity Option 3. The contract maintenance charge is deducted proportionately from each Annuity Payment, unless your Contract Value on the last Business Day before the Annuity Date is at least $100,000.
ANNUITY PAYMENT OPTIONS
You can choose one of the Annuity Options described below or any other payment option to which we agree. Before the Annuity Date, you can select and/or change the Annuity Option with at least 30 days written notice to us. After Annuity Payments begin, you cannot change the Annuity Option.
Option 1. Life Annuity. We make Annuity Payments during the life of the Annuitant, and the last payment is the one that is due before the Annuitant's death. If the Annuitant dies shortly after the Annuity Date, the Payee may receive less than your investment in the Contract.
Option 2. Life Annuity with Payments Over 5, 10, 15 or 20 Years Guaranteed. We make Annuity Payments during the life of the Annuitant, with payments for a guaranteed minimum period that you select.
Option 3. Joint and Last Survivor Annuity. We make Annuity Payments during the lifetimes of the Annuitant and the joint Annuitant. Upon the death of one Annuitant, Annuity Payments to the Payee continue during the lifetime of the surviving joint Annuitant, at a level of 100%, 75% or 50% selected by the Owner when he or she chose this Annuity Payment option. If both Annuitants die shortly after the Annuity Date, the Payee may receive less than your investment in the Contract.
Option 4. Joint and Last Survivor Annuity with Payments Over 5, 10, 15 or 20 Years Guaranteed. We make Annuity Payments during the lifetimes of the Annuitant and the joint Annuitant, with payments for a minimum guaranteed period that you select.
Option 5. Refund Life Annuity. We make Annuity Payments during the lifetime of the Annuitant, and the last payment is the one that is due before the Annuitant's death. After the Annuitant's death, the Payee may receive a lump sum refund. The amount of the refund equals the amount applied to this Annuity Option minus the total paid under this option.
Under Annuity Options 1, 3 and 5, if all Annuitants die on or after the Annuity Date and before we send the first Annuity Payment, we will cancel the Annuity Option that was elected and upon receipt of a Valid Claim, we will pay the amount applied to the selected Annuity Option minus the total paid under the option. If the Owner is an individual we pay the surviving individual Owner, or the Beneficiary(s) if there is no surviving Owner. If the Owner is a non-individual, we pay the Owner.
After the Annuitant's death under Option 2, or the last surviving joint Annuitant's death under Option 4, we make Annuity Payments during the remaining guaranteed period in the following order based on who is still alive: the Payee, any surviving original Owner, the last surviving Owner's Beneficiaries, or to the last surviving Owner's estate if there are no remaining or named Beneficiaries.
Annuity Payments are usually lower if you select an Annuity Option that requires us to make more frequent Annuity Payments or to make payments over a longer period of time. If you choose life contingent Annuity Payments, payout rates for a younger Annuitant are lower than the payout rates for an older Annuitant and payout rates for life with a guaranteed period are typically lower than life only payments. Monthly payout rates are lower than annual payout rates, payout rates for a 20-year guaranteed period are less than payout rates for a 10-year guaranteed period, and payout rates for a 50-year-old Annuitant are less than payout rates for a 70-year-old Annuitant.
NOTE: If you do not choose an Annuity Option before the Annuity Date, we make Annuity Payments to the Payee under Annuity Option 2 with ten years of guaranteed monthly payments.
WHEN ANNUITY PAYMENTS BEGIN
Annuity Payments begin on the Annuity Date. Your scheduled Annuity Date is the first day of the calendar month following the later of: a) the Annuitant's 90th birthday, or b) the tenth Contract Anniversary and is stated in your Contract. An earlier Annuity Date or a withdrawal may be required to satisfy minimum required distribution rules under certain Qualified Contracts. You can make an authorized request for a different, earlier or later Annuity Date after the Issue Date, but any such request is subject to applicable law and our approval. An earlier or later Annuity Date may not be available to you depending on the Financial Professional you purchase your Contract through and your state of residence. Your Annuity Date must be at least two years after the Issue Date.* The Annuity Date cannot be later than what is permitted under applicable law.
| * | In Florida, the earliest acceptable Annuity Date is one year after the Issue Date. |
NOTE: If on the Annuity Date (which may occur as early as age 90 or as late as age 100) your Contract Value is greater than zero, you must annuitize the Contract. We notify you of your available options in writing 60 days in advance, including the option to extend your Annuity Date if available. If on your Annuity Date you have not selected an Annuity Option, we make payments under Annuity Option 2 with ten years of guaranteed monthly payments. Upon annuitization you no longer have Contract Value or a death benefit, and you cannot receive any other periodic withdrawals or payments other than Annuity Payments.
| 11. | DEATH BENEFIT |
"You" in this section refers to the Owner, or the Annuitant if the Contract is owned by a non-individual.
The Contract provides the Traditional Death Benefit. If available, you can instead select the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit at Contract issue for an additional rider fee if all Owners and the Annuitant are age 75 or younger. The Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit is not available to Contracts issued before the date of this prospectus. The Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit cannot be less than the Traditional Death Benefit, but they may be equal. Please discuss this benefit's appropriateness with your Financial Professional.
The death benefit is only available during the Accumulation Phase. If you or the Determining Life (Lives) die during the Accumulation Phase, we process the death benefit using prices determined after we receive the required information, which is either a Valid Claim or due proof of death as stated here. (For information on due proof of death see the Glossary – Valid Claim). If we receive this information after the end of the current Business Day, we use the next Business Day's prices.
If there are multiple Beneficiaries, each Beneficiary receives the portion of the death benefit he or she is entitled to when we receive his or her Valid Claim. If a Beneficiary dies before you or the Designated Life, that Beneficiary's interest in this Contract ends unless your Beneficiary designation specifies otherwise. If there are no remaining Beneficiaries, or no named Beneficiaries, we pay the death benefit to your estate, or if the Owner is a non-individual, to the Owner. Unless you instruct us to pay Beneficiaries a specific percentage of the death benefit, he or she each receives an equal share. Any part of the death benefit that is in the Allocation Options remains there until distribution begins. From the time we determine the death benefit until we make a complete distribution, any amount in the Allocation Options continues to be subject to investment risk that is borne by the recipient(s). Once we receive notification of death, we may no longer accept or process transfer requests. After we receive the first Valid Claim from any Beneficiary we also will not accept additional Purchase Payments or allow any partial or full withdrawals unless the withdrawal is required to comply with federal tax law.
The Contract provides the Traditional Death Benefit based on the greater of:
| · | Contract Value, or |
| · | total Purchase Payments adjusted for withdrawals. Withdrawals reduce total Purchase Payments by the percentage of Contract Value withdrawn, determined at the end of each Business Day. Withdrawals include withdrawals under the free withdrawal privilege, withdrawal charges, but not amounts we withdraw for other Contract expenses. |
If instead you select the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit, the death benefit is the greater of:
| · | the Contract Value, or |
| · | the Maximum Anniversary Value. |
If the date we are determining the death benefit is not an Index Anniversary and you selected the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy, Contract Value includes the Daily Adjustment. Contract Value also includes any increase from the Alternate Minimum Value if you selected any of the available Index Options.
MAXIMUM ANNIVERSARY VALUE
The Maximum Anniversary Value is initially equal to the Purchase Payment received on the Issue Date. At the end of each Business Day, we adjust the Maximum Anniversary Value as follows.
| · | We increase it by the amount of any additional Purchase Payments. |
| · | We reduce it by the percentage of any Contract Value withdrawn. Withdrawals include withdrawals under the free withdrawal privilege, withdrawal charges, but not amounts we withdraw for other Contract expenses. |
If the Index Effective Date occurs after the Issue Date, the Maximum Anniversary Value on the Index Effective Date is calculated in the same way as on an Index Anniversary.
On each Index Anniversary before the end date (or on the next Business Day if the Index Anniversary is not on a Business Day) the Maximum Anniversary Value is equal to the greater of:
| · | its current value after processing any additional Purchase Payments or withdrawals, or |
| · | the Contract Value determined at the end of the Business Day after we process all daily transactions including Credits, any additional Purchase Payments or withdrawals, and amounts we withdraw for Contract expenses. |
On and after the end date, we no longer make this comparison and you will no longer receive lock ins of any annual investment gains to the Maximum Anniversary Value.
The end date occurs on the earliest of:
| · | the older Determining Life's 91st birthday; or |
| · | the end of the Business Day we receive the first Valid Claim from any one Beneficiary. |
What Happens Upon Death?
If you are the Determining Life, or if you and the Determining Life (Lives) are different individuals and die simultaneously as defined by applicable state law or regulation we determine the Traditional Death Benefit or Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit (if applicable) at the end of the Business Day we receive a Valid Claim. For multiple Beneficiaries, each surviving Beneficiary receives the greater of:
| · | their portion of total Purchase Payments adjusted for withdrawals if the Traditional Death Benefit applies (or their portion of the Maximum Anniversary Value if the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit applies) determined at the end of the Business Day we receive the first Valid Claim from any one Beneficiary, or |
| · | their portion of the Contract Value determined at the end of the Business Day during which we receive his or her Valid Claim. |
If you and the Determining Life (Lives) are different individuals and do not die simultaneously, the death benefit is as follows. This can only occur if you change the Owner after the Issue Date.
| · | If a Determining Life dies before you, we do not pay a death benefit to the Beneficiary(s) but we may increase the Contract Value if the Traditional Death Benefit or Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit are still in effect. At the end of the Business Day we receive due proof of a Determining Life's death we increase the Contract Value to equal the guaranteed death benefit value if greater, and your selected death benefit ends. (The guaranteed death benefit value is total Purchase Payments adjusted for withdrawals if the Traditional Death Benefit applies, or the Maximum Anniversary Value if the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit applies.) We allocate any Contract Value increase to the Allocation Options according to future Purchase Payment allocation instructions. |
| · | Upon your death your Beneficiary(s) receive the Contract Value determined at the end of the Business Day during which we receive each Beneficiary's Valid Claim. |
The Traditional Death Benefit and Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit end upon the earliest of the following.
| · | The Business Day before the Annuity Date. |
| · | The Business Day that total Purchase Payments adjusted for withdrawals and Contract Value are both zero if the Traditional Death Benefit applies. |
| · | The Business Day that the Maximum Anniversary Value and Contract Value are both zero if the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit applies. |
| · | Upon the death of a Determining Life, the end of the Business Day we receive a Valid Claim from all Beneficiaries if you and the Determining Life are the same individuals, or if you and the Determining Life (Lives) are different individuals and die simultaneously as defined by applicable state law or regulation. |
| · | Upon the death of a Determining Life, the end of the Business Day we receive due proof of the Determining Life's death if you and the Determining Life (Lives) are different individuals and do not die simultaneously. |
| · | Upon the death of an Owner (or Annuitant if the Owner is a non-individual), the end of the Business Day we receive the first Valid Claim from any one Beneficiary, if the Owner (or Annuitant) is no longer a Determining Life. |
| · | The Business Day the Contract ends. |
NOTE: The Traditional Death Benefit and Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit are first-to-die benefits based on the Determining Life (or Lives). This means that upon the death of an Owner (or Annuitant if the Owner is a non-individual), if a surviving spouse continues the Contract:
| · | the Traditional Death Benefit (or Maximum Anniversary Value Death if applicable) is no longer available, and |
| · | if you selected the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit, we no longer assess the additional 0.20% rider fee for this benefit. |
Also, if you and the Determining Life (Lives) are different individuals and you die first, the Traditional Death Benefit or Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit are not available to your Beneficiary(s).
DEATH OF THE OWNER AND/OR ANNUITANT
The Appendix to the Statement of Additional Information includes tables that are intended to help you better understand what happens upon the death of any Owner and/or Annuitant under the different portions of the Contract.
DEATH BENEFIT PAYMENT OPTIONS DURING THE ACCUMULATION PHASE
If you do not designate a death benefit payment option, a Beneficiary must select one of the options listed below. If a Beneficiary requests a lump sum payment under Option A, we pay that Beneficiary within seven days of receipt of his or her Valid Claim, unless the suspension of payments or transfers provision is in effect. Payment of the death benefit may be delayed, pending receipt of any state forms.
Spousal Continuation: If the Beneficiary is the deceased Owner's spouse, he or she can choose to continue the Contract with the portion of the death benefit the spouse is entitled to in his or her own name. For non-individually owned Contracts, spousal continuation is only available to Qualified Contracts. Spouses must qualify as such under federal law to continue the Contract. Individuals who have entered into a registered domestic partnership, civil union, or other similar relationship that is not considered to be a marriage under state law are also not considered to be married under federal law. An election by the spouse to continue the Contract must be made on the death claim form before we pay the death benefit. If the deceased Owner was a Determining Life and the surviving spouse Beneficiary continues the Contract, at the end of the Business Day we receive his or her Valid Claim we increase the Contract Value to equal the guaranteed death benefit value if greater and available, and the death benefit ends. (The guaranteed death benefit value is total Purchase Payments adjusted for withdrawals if the Traditional Death Benefit applies, or the Maximum Anniversary Value if the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit applies.) We allocate any Contract Value increase to the Allocation Options according to future Purchase Payment allocation instructions. If the surviving spouse continues the Contract:
| · | he or she becomes the new Owner and may exercise all of the Owner's rights, including naming a new Beneficiary or Beneficiaries; |
| · | he or she is subject to any remaining withdrawal charge; and |
| · | upon the surviving spouse's death their Beneficiary(s) receive the Contract Value determined at the end of the Business Day during which we receive a Valid Claim from each Beneficiary. |
Death Benefit Payment Options
Option A: Lump sum payment of the death benefit.
Option B: Payment of the entire death benefit within five years of the date of any Owner's death. The Beneficiary can continue to make transfers between Allocation Options and is subject to a transfer fee and the product fee.
Option C: If the Beneficiary is an individual, payment of the death benefit as Annuity Payments under Annuity Options 1, 2 or 5. With our written consent other options may be available for payment over a period not extending beyond the Beneficiary's life expectancy under which the Beneficiary can continue to make transfers between Allocation Options and is subject to a transfer fee and the product fee.
Distribution must begin within one year of the date of the Owner's death. Any portion of the death benefit not applied to Annuity Payments within one year of the date of the Owner's death must be distributed within five years of the date of death.
If the Contract is owned by a non-individual, then we treat the death of an Annuitant as the death of an Owner for purposes of the Internal Revenue Code's distribution at death rules, which are set forth in Section 72(s) of the Code.
In all events, notwithstanding any provision to the contrary in the Contract or this prospectus, the Contract is interpreted and administered in accordance with Section 72(s) of the Internal Revenue Code.
Other rules may apply to Qualified Contracts.
| 12. | TAXES |
This section provides a summary explanation of the tax ramifications of purchasing a Contract. More detailed information about product taxation is contained in the Statement of Additional Information, which is available by calling the toll-free telephone number at the back of this prospectus. We do not provide individual tax advice. You should contact your tax adviser to discuss this Contract's effects on your personal tax situation.
QUALIFIED AND NON-QUALIFIED CONTRACTS
You can purchase either a Qualified Contract or a Non-Qualified Contract. A Qualified Contract is purchased pursuant to a specialized provision of the Internal Revenue Code (Code). For example, a Contract may be purchased pursuant to Section 408 of the Code as an Individual Retirement Annuity (IRA).
Qualified Contracts are subject to certain restrictions, including restrictions on the amount of annual contributions, restrictions on how much you can earn and still be able to contribute to a Qualified Contract, and specialized restrictions on withdrawals. Qualified Contracts must be purchased from earned income from the relevant year or years, or from a rollover or transfer from a qualified contract. An IRA to IRA indirect rollover can occur only once in any twelve month period from all of the IRAs you currently own. Purchase Payments to Qualified Contracts other than from a qualified transfer may be restricted once the Owner reaches age 70½.
Currently, we offer the following types of Qualified Contracts.
| Type of Contract | Persons and Entities that can buy the Contract |
| IRA | Must have the same individual as Owner and Annuitant. |
| Roth IRA | Must have the same individual as Owner and Annuitant. |
| Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA | Must have the same individual as Owner and Annuitant. |
| Certain Code Section 401 Plans | A qualified retirement plan is the Owner and the Annuitant must be an individual. We may determine which types of qualified retirement plans are eligible to purchase this Contract. |
| Inherited IRA and Inherited Roth IRA | Must have the same individual as Owner and Annuitant. The deceased owner of the previously held tax‑qualified arrangement will also be listed in the titling of the Contract. |
If you purchase a Qualified Contract, you already receive the benefit of tax deferral through the qualified plan, and so you should purchase this Contract for purposes other than tax deferral.
You can instead purchase a Non-Qualified Contract, which is not qualified pursuant to a specialized provision of the Code. There are no Code restrictions on annual contributions to a Non-Qualified Contract or how much you can earn and still contribute to a Contract.
TAXATION OF ANNUITY CONTRACTS
The Contract has the following tax characteristics.
| · | Taxes on earnings are deferred until you take money out. Non-Qualified Contracts owned by corporations or partnerships do not receive income tax deferral on earnings. |
| · | When you take money out of a Non-Qualified Contract, earnings are generally subject to federal income tax and applicable state income tax. All pre-tax money distributed from Qualified Contracts are subject to federal and state income tax, but qualified distributions from Roth IRA Contracts are not subject to federal income tax. This prospectus does not address specific state tax laws. You should discuss state taxation with your tax adviser. |
| · | Taxable distributions are subject to an ordinary income tax rate, rather than a capital gains rate. |
| · | Distributions from Non-Qualified Contracts are considered investment income for purposes of the Medicare tax on investment income. Thus, in certain circumstances, a 3.8% tax may apply to some or all of the taxable portion of distributions (e.g. earnings) to individuals whose income exceeds certain threshold amounts ($200,000 for filing single, $250,000 for married filing jointly and $125,000 for married filing separately.) Please consult a tax advisor for more information. |
| · | If you take partial withdrawals from your Non-Qualified Contract, the withdrawals are generally taxed as though you were paid taxable earnings first, and then as a non-taxable return of Purchase Payments. |
| · | If you annuitize your Non-Qualified Contract and receive a stream of Annuity Payments, you receive the benefit of the exclusion ratio. The exclusion ratio is a calculation that causes a portion of each Annuity Payment to be non-taxable, based upon the percentage of your Contract Value that is from Purchase Payments. Purchase Payments are treated as a non-taxable return of principal, whereas earnings are taxable. |
| · | If you take partial withdrawals or annuitize a Qualified Contract, you will be responsible for determining what portion, if any, of the distribution consists of after-tax money. |
| · | If you take out earnings before age 59½, you may be subject to a 10% additional federal tax, unless you take a lifetime annuitization of your Contract or you take money out in a stream of substantially equal payments over your expected life in accordance with the requirements of the Code. |
| · | A pledge, assignment, or ownership change of a Contract may be treated as a taxable event. You should discuss any pledge, assignment, or ownership change of a Contract with your tax adviser. |
| · | If you purchase multiple non-qualified deferred annuity contracts from an affiliated group of companies in one calendar year, these contracts are treated as one contract for purposes of determining the tax consequences of any distribution. |
| · | Death benefit proceeds from Non-Qualified Contracts are taxable to the beneficiary as ordinary income to the extent of any earnings. Death benefit proceeds must be paid out in accordance with the requirements of the Code. |
| · | Depending upon the type of Qualified Contract you own, required minimum distributions (RMDs) must be satisfied when you reach a certain age. If you enroll in our minimum distribution program, we make RMD payments to you that are designed to meet this Contract's RMD requirements. |
| · | When you take money out of a Contract, we may deduct premium tax that we pay on your Contract. This tax varies from 0% to 3.5%, depending on your state. Currently, we pay this tax and do not pass it on to you. |
TAX-FREE SECTION 1035 EXCHANGES
Subject to certain restrictions, you can make a "tax-free" exchange under Section 1035 of the Internal Revenue Code for all or a portion of one non-qualified annuity contract for another, or all of a life insurance policy for a non-qualified annuity contract. Before making an exchange, you should compare both contracts carefully. Remember that if you exchange a life insurance policy or annuity contract for the Contract described in this prospectus:
| · | you might have to pay a withdrawal charge on your previous contract, |
| · | there is a new withdrawal charge period for this Contract, |
| · | other charges under this Contract may be higher (or lower), |
| · | the benefits may be different, and |
| · | you no longer have access to any benefits from your previous contract. |
If the exchange does not qualify for Section 1035 treatment, you also may have to pay federal income tax, including a possible additional federal tax, on the exchange. You should not exchange an existing life insurance policy or another annuity contract for this Contract unless you determine the exchange is in your best interest and not just better for the person selling you the Contract. You should consult a tax adviser to discuss the potential tax effects before making a 1035 exchange.
| 13. | OTHER INFORMATION |
THE REGISTERED SEPARATE ACCOUNT
We established Allianz Life Variable Account B (the Separate Account) as a separate account under Minnesota insurance law on May 31, 1985. The Separate Account is registered with the SEC as a unit investment trust under the Investment Company Act of 1940. The SEC does not supervise our management of the Separate Account.
The Separate Account holds the shares of the Variable Options that have been purchased with Contract assets. We keep the Separate Account assets separate from the assets of our general account and other separate accounts, including the non-unitized separate accounts we established in connection with the Index Options. The Separate Account is divided into subaccounts, each of which invests exclusively in a single Variable Option.
We own the assets of the Separate Account. We credit gains to or charge losses against the Separate Account, whether or not realized, without regard to the performance of other investment accounts. The Separate Account's assets are insulated, so that the assets cannot be used to pay any of our liabilities, other than those arising from the investment of Contract assets in the Variable Options.
If the Separate Account's assets exceed the required reserves and other liabilities, we may transfer the excess to our general account, to the extent of seed money invested by us or earned fees and charges. The obligations under the Contracts are obligations of Allianz Life.
OUR GENERAL ACCOUNT
Our general account holds all our assets other than assets in our separate accounts. We own our general account assets, and, subject to applicable law, have sole investment discretion over them. The assets are subject to our general business operation liabilities and claims of our creditors and may lose value. We have not registered our general account as an investment company under the Investment Company Act of 1940.
Our general account assets fund guarantees provided in the Contracts, including obligations associated with the Index Options. Contract Value that you apply to Annuity Payments becomes part of our general account. In addition, we place a majority of the assets you allocate to the Index Options in our general account where we primarily invest the assets in a variety of fixed income securities.
OUR UNREGISTERED SEPARATE ACCOUNT
Initially, a substantial majority of the aggregate assets backing the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Options are allocated to our general account. We place all other assets that you allocate to these Index Options in an unregistered, non-unitized, non-insulated separate account (Separate Account IANA), which we established under Minnesota Insurance Law solely for the purpose of supporting our obligations to pay Performance Credits associated with these Index Options. Subsequently, there may be significant transfers of assets between the general account and Separate Account IANA in response to Index performance. We typically transfer assets between these accounts if there is a 10% incremental change in year-to-date Index performance. We examine year-to-date Index performance daily and change the account allocations daily if needed based on this 10% increment.
We invest the assets in Separate Account IANA in hedging instruments, including derivative investments such as put and call options, as well as cash and fixed income securities. Like our general account, the assets in Separate Account IANA are subject to our general business operation liabilities and the claims of our creditors.
An Owner who allocates Contract Value to an Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy or Index Guard Strategy Index Option does not have any interest in or claim on the assets in Separate Account IANA. In addition, neither the Owner nor these Index Options participate in any way in the performance of assets held in Separate Account IANA.
NOTE FOR CONTRACTS ISSUED IN DELAWARE, MISSOURI AND WASHINGTON: All of the assets backing the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Options are allocated to Separate Account IANA. We do not move assets between the general account and Separate Account IANA for the Contracts.
NOTE FOR CONTRACTS ISSUED IN TEXAS: We place all assets that you allocate to the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Options that are not invested in the general account in an unregistered, non-unitized, insulated separate account (Separate Account IATX). Separate Account IATX is structured differently from Separate Account IANA. Unlike Separate Account IANA, Separate Account IATX is for the exclusive benefit of persons purchasing a Contract in the State of Texas. Separate Account IATX is insulated from the claims of creditors and Contract purchasers are given priority with regard to Separate Account IATX's assets over Contract purchasers from other states as well as general creditors. Separate Account IATX was established under Minnesota law for the benefit of Texas Contract purchasers. Separate Account IATX supports our obligations to pay Performance Credits to Texas Contract Owners. Allocations and reallocations to and from the Separate Account IATX are managed in the same manner as Separate Account IANA. Neither Texas Contract purchasers nor these Index Options participate in any way in the performance of assets held in Separate Account IATX.
DISTRIBUTION
Allianz Life Financial Services, LLC (ALFS), a wholly owned subsidiary of Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America, serves as principal underwriter for the Contracts. ALFS is a limited liability company organized in Minnesota, and is located at 5701 Golden Hills Drive, Minneapolis, MN 55416. ALFS is registered as a broker/dealer with the SEC under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as well as with the securities commissions in the states in which it operates, and is a member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA). ALFS is not a member of Securities Investors Protection Corporation. More information about ALFS is available at www.finra.org or by calling 1-800-289-9999. You also can obtain an investor brochure from FINRA describing its Public Disclosure Program.
We have entered into a distribution agreement with ALFS for the distribution of the Contracts. ALFS also may perform various administrative services on our behalf.
We may fund ALFS operating and other expenses, including: overhead; legal and accounting fees; Financial Professional training; compensation for the ALFS management team; and other expenses associated with the Contracts. Financial Professionals and their managers may also be eligible for various benefits, such as production incentive bonuses, insurance benefits, and non-cash compensation items that we may provide jointly with ALFS. Non-cash items include conferences, seminars and trips (including travel, lodging and meals in connection therewith), entertainment, awards, merchandise and other similar items.
ALFS does not itself sell the Contracts to customers. Rather, customers typically are working with a Financial Professional who is registered as an investment adviser, or is an investment advisory representative of a registered investment adviser, and who is offering advisory services for a fee. A Financial Professional may also be a registered representative of a broker-dealer. Investment advisers and broker-dealers involved in selling the Contracts may include Questar Asset Management, Inc., an affiliated investment adviser, or Questar Capital Corporation, an affiliated broker/dealer.
We do not pay sales commissions in connection with sales of the Contracts. Rather, you pay a financial adviser fee to your Financial Professional. We do not set your financial adviser's fee or receive any part of it. You should ask your Financial Professional about compensation they receive in connection with this Contract.
The Variable Options may assess a Rule 12b‑1 fee. These fees are paid to ALFS as consideration for providing certain services and incurring certain expenses permitted under the Investment Option's plan. These fees typically equal 0.25% of an Investment Option's average daily net assets for the most recent calendar year.
In certain instances, an investment adviser and/or subadviser (and/or their affiliates) of an Investment Option may make payments for administrative services to ALFS or its affiliates.
Broker-dealers and investment advisers involved in sales of the Contracts may receive payments from us for administrative and other services that do not directly involve the sale of the Contracts, including payments made for recordkeeping, the recruitment and training of personnel, production of promotional literature and similar services.
We and/or ALFS may pay certain broker-dealer and investment advisory firms additional marketing support allowances for:
| · | marketing services and increased access to their Financial Professionals; |
| · | sales promotions relating to the Contracts; |
| · | costs associated with sales conferences and educational seminars; |
| · | the cost of client meetings and presentations; and |
| · | other sales expenses incurred by them. |
We retain substantial discretion in determining whether to grant a marketing support payment to a particular firm and the amount of any such payment.
We may also make payments for marketing and wholesaling support to broker/dealer affiliates of Variable Options that are available through the variable annuities we offer.
Additional information regarding marketing support payments can be found in the Distributor section of the Statement of Additional Information.
A portion of the payments made to broker-dealer and investment advisory firms may be passed on to their Financial Professionals. Financial Professionals may receive cash and non-cash compensation and other benefits. Ask your Financial Professional for further information about what they and their firm may receive in connection with your purchase of a Contract.
We offer the Contracts to the public on a continuous basis. We anticipate continuing to offer the Contracts but reserve the right to discontinue the offering.
ADDITIONAL CREDITS FOR CERTAIN GROUPS
We may credit additional amounts to a Contract instead of modifying charges because of special circumstances that result in lower sales or administrative expenses or better than expected mortality or persistency experience.
ADMINISTRATION/ALLIANZ SERVICE CENTER
The Allianz Service Center performs certain administrative services regarding the Contracts and is located at 5701 Golden Hills Drive, Minneapolis, Minnesota. The Service Center mailing address and telephone number are listed at the back of this prospectus. The administrative and routine customer services performed by our Service Center include processing and mailing of account statements and other mailings to Owners, responding to Owner correspondence and inquiries. Allianz Life also contracts with Tata Consultancy Services (Tata) located at #42(P) & 45(P), Think Campus, Electronic City, Phase II, Bangalore, Karnataka 560100, India, to perform certain administrative services including:
| · | issuance and maintenance of the Contracts, |
| · | maintenance of Owner records, and |
| · | routine customer service including: |
| – | processing of Contract changes, |
| – | processing withdrawal requests (both partial and total) and |
| – | processing requests for fixed annuity payments. |
Services performed by Tata are overseen and quality control checked by our Service Center.
To reduce expenses, only one copy of most financial reports and prospectuses, including reports and prospectuses for the Variable Options, may be mailed to your household, even if you or other persons in your household have more than one contract issued by us or our affiliate. Call our Service Center at the toll-free telephone number listed at the back of this prospectus if you need additional copies of financial reports, prospectuses, or annual and semiannual reports, or if you would like to receive one copy for each contract in future mailings.
LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
We and our subsidiaries, like other life insurance companies, from time to time are involved in legal proceedings of various kinds, including regulatory proceedings and individual and class action lawsuits. In some legal proceedings involving insurers, substantial damages have been sought and/or material settlement payments have been made. Although the outcome of any such proceedings cannot be predicted with certainty, we believe that, at the present time, there are no pending or threatened legal proceedings to which we, the Separate Account, or ALFS is a party that are reasonably likely to materially affect the Separate Account, our ability to meet our obligations under the Contracts, or ALFS ability to perform its obligations.
STATUS PURSUANT TO SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
Allianz Life hereby relies on the exemption provided by Rule 12h-7 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 from the requirement to file reports pursuant to Section 15(d) of that Act.
| 14. | INFORMATION ON ALLIANZ LIFE |
Allianz Life is a stock life insurance company organized under the laws of the State of Minnesota in 1896. Our address is 5701 Golden Hills Drive, Minneapolis, MN 55416. We are a wholly owned subsidiary of Allianz of America, Inc. (AZOA), a financial holding company. AZOA is a wholly owned subsidiary of Allianz Europe, B.V., which in turn is a wholly owned subsidiary of Allianz SE, which is registered in Munich, Germany. We currently offer fixed index annuities, variable annuities, individual life insurance, and registered index-linked annuities. We are licensed to do direct business in 49 states and the District of Columbia.
DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
BOARD OF DIRECTORS
The Board currently consists of six members, including our Chairman, our President and Chief Executive Officer, our Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer, and three independent members.
The Board holds regular quarterly meetings, generally in February, April/May, July, and October/November of each year, and holds special meetings or takes action by unanimous written consent as circumstances warrant. The Board has standing Executive, Audit, and Nomination, Evaluation and Compensation Committees, described in further detail below. All but one of the directors attended 100% of the Board and committee meetings to which he or she was assigned during 2017. One director was absent from one Board and one committee meeting to which he was assigned in 2017. In 2017, the Board acted one time by unanimous written action.
The current members of our Board are as follows:
Jacqueline Hunt
Director and Chair of the Board
Director and Chair of the Board
Jackie Hunt, age 50, currently serves as Chair of Allianz Life's Board of Directors. She is also Chair of the Board of Management of Allianz Asset Management GmbH and a Member of the Board of Management of Allianz SE, Asset Management, US Life Insurance. Prior to this she was an Executive Director of Prudential plc and the Chief Executive of Prudential UK, Europe and Africa. She joined Prudential from Standard Life plc where she was an Executive Director and Group Chief Financial Officer. Prior to this, Jackie held a number of senior management positions in companies including Norwich Union Insurance, Aviva, Hibernian Group, RSA Insurance and PricewaterhouseCoopers.
Jackie acted as a Commissioner of the Dormant Assets Commission. She was Deputy Chair of the FCA Practitioner Panel, a Non-executive director of TheCityUK, a member of the ABI Board and the Senior Independent Director of National Express Group plc.
Walter R. White
Director, President and Chief Executive Officer
Director, President and Chief Executive Officer
Walter R. White, age 61, joined Allianz Life in 2009, and currently serves as our President and Chief Executive Officer, and a member of the Board of Directors. Mr. White also serves as Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Allianz Life Insurance Company of New York (Allianz Life of New York). Mr. White is responsible for leading and overseeing Allianz Life and Allianz Life of New York and providing strategic management and direction. Mr. White served as Chief Administrative Officer of Allianz Life from 2009 to 2011. Prior to joining Allianz Life, Mr. White held executive roles at Woodbury Financial Services from 2001 to 2009, serving as Chief Operating Officer from 2003 to 2007 and President from 2007 to 2009. Prior to that, Mr. White held senior management roles at Fortis from 1994 to 2001, serving as Senior Vice President of Fortis Investors from 1998 to 2001. Mr. White also held senior management roles at the MONY Group from 1988 to 1994, serving as the President of MONY Brokerage from 1991 to 1994.
Mr. White brings to the Board extensive financial services and brokerage experience as well as key strategic planning and leadership skills developed as the Chief Executive Officer of Allianz Life and President of Woodbury Financial.
William E. Gaumond
Director, Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer
Director, Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer
William E. Gaumond, age 44, joined Allianz Life in 2004 and currently serves as Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer and as a member of the Board of Directors. He also currently serves as Director, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer of Allianz Life of New York. Mr. Gaumond is responsible for all finance and risk management functions, with oversight of the controller, financial planning, treasury and corporate risk management areas. Prior to his current role, Mr. Gaumond spent 12 years in a number of finance and investment-related positions at Allianz Life, including Senior Vice President of the Asset Liability Management and Investment Risk Management department. During this time, Mr. Gaumond also served for two years as a senior member of the Group Planning and Controlling department for Allianz SE in Munich, Germany. Before joining Allianz Life, Mr. Gaumond worked for nine years at PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP. Mr. Gaumond received his Bachelor of Business Administration degree in accounting from the University of Notre Dame, where he graduated summa cum laude.
Mr. Gaumond brings to the Board extensive financial services, investment and insurance industry experience, including serving as Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer of Allianz Life and Allianz Life of New York.
Ronald M. Clark
Director
Director
Ronald M. Clark, age 70, joined Allianz Life's Board of Directors on January 1, 2014 and also serves as Chairman of the Nomination, Evaluation and Compensation Committee. Mr. Clark has over 40 years of experience in investments, having served as the President of Allianz Investment Corporation from 1980 to 1990, Chief Operating Officer of AZOA from 1990 to 2001, and Chief Investment Officer of AZOA from 2002 to 2011. Mr. Clark retired as of December 31, 2011. Mr. Clark also serves on the Board of Directors of Allianz Life of New York and serves as a director and Chair of the Compensation Committee of Manitex International, Inc. Manitex International, Inc. is a leading worldwide provider of highly engineered specialized equipment, including boom trucks, cranes, and other related industrial equipment.
Mr. Clark brings to the Board extensive experience in the financial services and insurance industries as well as extensive experience with investment matters. The Board also benefits from his perspective as a current and former director of other companies.
Udo Frank
Director
Director
Udo Frank, age 58, joined Allianz Life's Board of Directors on May 1, 2015. Mr. Frank has over 30 years of experience in the financial services and insurance industries. Mr. Frank worked with various Allianz SE investment and asset management affiliates from 1994 through 2014, including serving in numerous executive positions. In 2001, Mr. Frank was appointed as the Global Chief Executive Officer of RCM Capital Management LLC. In 2012, he was appointed the Head of Product Management and Chief Marketing Officer of Allianz Global Investors – U.S. Prior to joining Allianz, Mr. Frank worked at both Capital Management International, Deutsche Bank Group, and Allgemeine Deutsche Credit Anstalt in Frankfurt, Germany. Mr. Frank has also served as a director of various insurance industry groups.
Mr. Frank brings to the Board extensive experience in the financial services and insurance industry as well as extensive experience in investments and asset management.
Kevin E. Walker
Director
Director
Kevin E. Walker, age 55, joined Allianz Life's Board of Directors on May 23, 2017. Mr. Walker has over 30 years of insurance and financial services experience. Mr. Walker served at various Allianz affiliates throughout his career, most recently as the President and Chief Executive Officer of San Francisco Reinsurance Company from 2015 through 2016. Prior to that, he was the Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of Fireman's Fund Insurance Company ("FFIC") from 2011 through 2015, and the Senior Vice President, Group Planning and Controlling at Allianz SE from 2006 through 2010. In between, he served as the Senior Vice President & Chief Financial Officer, Retirement and Protection Division at Genworth Financial from 2010 through 2011. From 1995 through 2004, Mr. Walker worked at Allianz Life, serving as the Vice President, Treasurer and Senior Investment Officer, following which he became the Senior Vice President and Senior Financial Officer for all product lines until 2006. Mr. Walker has also served as a director and officer for several other Allianz affiliates.
Mr. Walker brings to the Board extensive experience in the insurance industry as well as extensive experience in finance and operations.
EXECUTIVE OFFICERS
The current executive officers (other than Messrs. White and Gaumond, whose biographies are included above in the Board of Directors information) are as follows:
Thomas P. Burns
Senior Vice President, Chief Distribution Officer
Senior Vice President, Chief Distribution Officer
Thomas P. Burns, age 62, joined Allianz Life in 2006 and currently serves as Senior Vice President, Chief Distribution Officer of Allianz Life, He also serves as Director and President of Allianz Life of New York, and the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Manager of Allianz Life Financial Services, LLC. Mr. Burns is responsible for the development, design and implementation of Allianz Life's and Allianz Life of New York's sales and distribution strategies. Prior to joining Allianz Life, Mr. Burns served as Senior Vice President, Distribution of Securian from 2002 to 2006. Prior to joining Securian, Mr. Burns worked for Prudential for 24 years, from 1978 to 2002, in various managerial capacities.
Gretchen Cepek
Senior Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary
Senior Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary
Gretchen Cepek, age 50, joined Allianz Life in 2009, and currently serves as Senior Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary. She is also Chief Legal Officer and Secretary of Allianz Life of New York. In this role, Ms. Cepek is responsible for the legal and compliance departments as well as government relations and the special investigations unit. Prior to her current role, Ms. Cepek served as Vice President, Legal Business Operations, Distribution and Product Development, of Allianz Life from 2009 to February 2012. Prior to joining Allianz Life, Ms. Cepek served as Counsel at Woodbury Financial Services from 2005 to 2009. Prior to joining Woodbury Financial, Ms. Cepek spent 13 years with the law firm of Querrey & Harlow, Ltd. from 1992 to 2005, where she served as a law clerk, associate attorney and then as a shareholder. Ms. Cepek received her J.D. from Valparaiso University School of Law in 1993.
Nancy E. Jones
Senior Vice President, Chief Marketing Officer
Senior Vice President, Chief Marketing Officer
Nancy E. Jones, age 57, joined Allianz Life in 2008, and currently serves as Senior Vice President, Chief Marketing Officer. Ms. Jones is responsible for new business strategy, product innovation, marketing, and corporate communications. Ms. Jones leads Allianz Life's product strategy and development for its annuity and life insurance product lines. Ms. Jones' team drives the Allianz Life brand through segmentation, customer experience, interactive initiatives, and advanced market insights to create strategies designed to help people reach their retirement income goals. Ms. Jones also leads Allianz Life's digital strategy and oversees public relations, internal communications, and community relations efforts. She is also responsible for the United States regional brand strategy for the United States family of Allianz SE companies. Prior to joining Allianz Life, Ms. Jones served as the Senior Vice President of Client Experience and Marketing Operations at Ameriprise Financial (formerly American Express). Prior to that, Ms. Jones held several senior roles at American Express in the traditional financial advisory business, as well as developing new direct and online businesses. Her career in the financial services industry spans more than 30 years, with roles in business strategy, product development, distribution channel management, and marketing.
Catherine A. Mahone
Senior Vice President, Chief Administrative Officer
Senior Vice President, Chief Administrative Officer
Catherine Mahone, age 53, joined Allianz Life in 2008 and currently serves as Senior Vice President Chief Administrative Officer. Ms. Mahone is responsible for the oversight of enterprise operations, information technology, and other strategic initiatives. Previously, Ms. Mahone was Senior Vice President, Enterprise Operations, a position she held until assuming her current role in 2012. Prior to joining Allianz Life, Ms. Mahone had approximately 20 years of financial services experience with Ameriprise Financial, where she served in several leadership roles, including Vice President of the Operations Project Management Office. In her more than 20-year career with Ameriprise, Ms. Mahone held a variety of leadership positions in operations, distribution and marketing.
Ms. Mahone earned a Bachelor of Arts degree in mass communications from the University of Minnesota and a Master's degree in business communications from the University of St. Thomas. Ms. Mahone also holds her FINRA Series 7 and 24 securities registrations.
Neil H. McKay
Senior Vice President, Chief Actuary
Senior Vice President, Chief Actuary
Neil H. McKay, age 56, joined Allianz Life and Allianz Life of New York in 1999 and currently serves as Senior Vice President, Chief Actuary of Allianz Life, and as Chief Actuary of Allianz Life of New York. Mr. McKay is responsible for all of the actuarial functions of Allianz Life and Allianz Life of New York, including the actuarial assumptions underlying their products and the rate setting associated with existing and new products. Prior to joining Allianz Life, Mr. McKay served in a variety of roles at LifeUSA Holding Company (prior to its merger with Allianz Life) from 1990 to 1999, culminating in the position of Vice President of Finance. Prior to that, Mr. McKay held the position of Assistant Product Actuary from 1984 to 1990 for Security Life of Denver, in Denver, Colorado.
Todd M. Hedtke
Senior Vice President, Chief Investment Officer
Senior Vice President, Chief Investment Officer
Todd M. Hedtke, age 45, joined Allianz Life in 2000 and currently serves as Senior Vice President, Chief Investment Officer. He also currently serves as Chief Investment Officer of Allianz Life of New York. Mr. Hedtke leads the investment management, liquidity planning, hedging, and trading functions at Allianz Life. He is also a member of the global Allianz Investment Management Board, which services the Allianz Group insurance companies. Prior to his current role, Mr. Hedtke spent 15 years in a number of investment-related positions at Allianz Life and its affiliate Allianz Investment Management, LLC, including his prior role as Vice President, Investment Management from October 2010 until August 2015. Prior to joining Allianz Life, Mr. Hedtke held various finance and investment positions at Cargill, EBF & Associates, and American Express. Mr. Hedtke earned his BA from Hamline University and MBA from the University of Minnesota Carlson School of Management. In addition to being a Chartered Financial Analyst, he holds designations as a financial risk manager and Fellow of the Life Management Institute.
Suzanne D. Zeller
Senior Vice President, Human Resources
Senior Vice President, Human Resources
Suzanne D. Zeller, age 64, joined Allianz Life in August 2010 and currently serves as Senior Vice President, Human Resources. In this position, Ms. Zeller is responsible for setting strategy and leading the Human Resources and Facilities departments to improve business results and increase employee engagement. Prior to joining Allianz Life, Ms. Zeller worked in various capacities with The Hartford Financial Services Group from 2003 to 2010, culminating in the position of Vice President of Human Resources for the international wealth management business of Hartford Life, Inc., a subsidiary of The Hartford Financial Services Group. Prior to that, Ms. Zeller ran her own consulting practice that specialized in executive coaching, business strategy planning and leadership development. Ms. Zeller also has held senior human resources and organizational effectiveness positions at a number of insurance and reinsurance companies, including Swiss Re, Met Life, American Re and Chubb Executive Risk.
Robert DeChellis
Field Senior Vice President, Chief Retirement Strategist, Allianz Exchange
Field Senior Vice President, Chief Retirement Strategist, Allianz Exchange
Robert DeChellis, age 51, joined Allianz Life in 2006 and currently serves as Field Senior Vice President, Chief Retirement Strategist, Allianz Exchange. He also serves as Field Senior Vice President, Chief Retirement Strategist, Allianz Exchange of Allianz Life of New York. As Chief Retirement Strategist, Allianz Exchange, Mr. DeChellis is responsible for uniting strategic relationships, technology and intellectual capital to identify uncommon financial solutions and thought leadership. In this role, Mr. DeChellis collaborates with the global family of Allianz companies as well as outside partners to address the growing demand for holistic financial advice. Mr. DeChellis also currently serves as Chairman of the Board of the Insured Retirement Institute, the leading financial services trade association for the retirement income industry. Previously, Mr. DeChellis served as Field Senior Vice President, Broker Dealer Distribution of Allianz Life, and Field Vice President, Broker Dealer Distribution of Allianz Life of New York. He also served as President of Allianz Life Financial Services, LLC. Prior to joining Allianz Life, Mr. DeChellis served as Executive Vice President of the Retail Annuities Division of Travelers Life & Annuity. Prior to that, Mr. DeChellis served as Executive Vice President and national sales manager for Jackson National Life Distributors, Inc. Before joining the annuity industry, Mr. DeChellis spent 13 years in asset management, holding positions with firms such as Goldman Sachs and Lord Abbett.
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Committees of the Board
The Executive Committee of the Board ("Executive Committee") is currently composed of Ms. Hunt (Chair) and Messrs. White and Clark. The function of the Executive Committee is to exercise the authority of the Board between meetings of the Board, with the exceptions set forth in Allianz Life's By-Laws. The Executive Committee did not meet in 2017.
The Audit Committee of the Board is currently composed of Messrs. Frank (Chair), Clark and Walker. Mr. Conway served on the Audit Committee until his resignation on May 22, 2017. On May 23, 2017, Mr. Walker was appointed to the Audit Committee. Mr. Terzariol served on the Audit Committee until his resignation on December 31, 2017. The Audit Committee is responsible for overseeing Allianz Life's accounting and financial reporting and control processes on behalf of the Board, which includes assisting with Board oversight of (1) quality and integrity of Allianz Life's financial statements, (2) Allianz Life's compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, (3) the qualifications, independence and fees of the independent-auditors, (4) Allianz Life's system of internal controls and (5) the performance of Allianz Life's internal audit function. The Board has determined that each member of the Audit Committee is financially literate. The Audit Committee met four times in 2017, and acted zero times by unanimous written action.
The Nomination, Evaluation and Compensation Committee (NEC Committee) is currently composed of Messrs. Clark (Chair), Frank and Walker. Mr. Conway served on the NEC Committee until his resignation on May 22, 2017. On May 23, 2017, Mr. Walker was appointed to the NEC Committee. The NEC Committee's purpose is to (1) nominate candidates for director for election, (2) evaluate the performance of officers deemed to be "principal officers," and (3) recommend to the Board the selection and compensation of the "principal officers." The NEC Committee met two times in 2017, and acted one time by unanimous written action.
Independence of Certain Directors
Allianz Life is not subject to the independence standards of the New York Stock Exchange or any other national securities exchange, but is subject to the independence standards required under the Model Audit Rule. Applying the independence standards of the Model Audit Rule to the current members of the Board, the Board has determined that Messrs. Frank, Clark and Walker, and former director Mr. Conway, are "independent" under the Model Audit Rule.
Code of Ethics
All of our officers and employees, including our Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer and Controller, are subject to the Allianz Life Code of Ethics.
Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance
Not applicable.
EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
Compensation Discussion and Analysis
In this section, we provide an overview of the goals and principal components of our executive compensation program and describe how we determine the compensation of our "Named Executive Officers" or "NEOs." For 2017, our NEOs were:
| · | Walter White, President and Chief Executive Officer |
| · | William Gaumond, Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer |
| · | Thomas Burns, Senior Vice President and Chief Distribution Officer |
| · | Neil McKay, Senior Vice President and Chief Actuary |
| · | Catherine Mahone, Senior Vice President and Chief Administrative Officer |
The details of each NEO's compensation may be found in the Summary Compensation Table and other compensation tables included in this Executive Compensation section.
Executive Summary
Allianz Life's compensation programs are intended to align our NEOs' interests with those of our ultimate stockholder. Our indirect stockholder is Allianz SE, the ultimate parent company of Allianz Life. Allianz Life's compensation programs are designed to reward performance that meets or exceeds the goals established by the Compensation Committee, a management committee of Allianz Life, which is an indirect subsidiary of Allianz SE. Allianz Life is tasked with establishing the executive compensation philosophy. In line with Allianz Life's compensation philosophy described below, the total compensation received by our NEOs will vary based on individual and corporate performance in light of annual and long-term performance goals. Our NEOs' total compensation is composed of a mix of annual base salary, annual cash awards based on corporate objectives and executive performance factors and long-term equity incentive awards in the form of restricted stock units of the equity securities of Allianz SE.
Compensation Philosophy and Strategy
Overview
The overriding goal of Allianz Life's executive compensation programs is to attract, retain and motivate top-performing executive officers who will dedicate themselves to long-term financial and operational success. To this end, Allianz Life has structured the executive compensation programs to foster a pay-for-performance management culture by:
| · | providing total compensation opportunities that are competitive with the levels of total compensation available at the large diversified financial services companies with which Allianz Life most directly competes in the marketplace; |
| · | setting performance metrics and objectives for variable compensation arrangements that reward executives for attaining both annual targets and medium-range and long-term business objectives, thereby providing individual executives with the opportunity to earn above-average compensation by achieving above-average results; |
| · | establishing equity-based arrangements that align executives' financial interests with those of Allianz SE by ensuring executives have a material financial stake in the equity value of Allianz SE and the business success of its affiliates; and |
| · | structuring compensation packages and outcomes to foster internal pay equity. |
Compensation Components
To support this pay-for-performance strategy, Allianz Life's total compensation program provides a mix of compensation components that bases the majority of each executive's compensation on their success and on an assessment of each executive's overall contribution to that success.
| Compensation Element | Description | Objective |
| Base Salary | Fixed rate of pay that compensates employees for fulfilling their basic job responsibilities. For NEOs, increases are generally provided in the case of a significant increase in responsibilities or a significant discrepancy versus the market. | Attract and retain high-caliber leadership. |
| Annual Incentive Plan | Incentive compensation that promotes and rewards the achievement of annual performance objectives through awards under the Allianz Life Annual Incentive Plan ("AIP"). | ▪ Link compensation to annual performance results. ▪ Attract and motivate high-caliber leadership. ▪ Align the interests of NEOs and our stockholder. |
| Long-Term Incentives | Incentive compensation that promotes and rewards the achievement of long-term performance objectives through awards under the Allianz Life Long-Term Performance Unit Plan ("ALTPUP"). Allianz Life's Chief Executive Officer, Walter White, is eligible to receive annual awards through the Allianz SE Mid-Term Bonus Plan instead of the ALTPUP. | ▪ Link compensation to annual and multi-year performance results. ▪ Motivate and retain high-caliber leadership with multi-year vesting. ▪ Align the interests of NEOs and our stockholder. |
| Performance-Based Equity Incentives | Incentive compensation through restricted stock unit awards made under the Allianz Equity Incentive Plan ("AEI") that promotes and rewards the achievement of senior executive officers. The AEI replaced the Allianz Group Equity Incentives Plan 2007 ("GEI"). | ▪ Retain high-caliber leadership with multi-year vesting. ▪ Align the interests of NEOs and our stockholder. |
| Severance Arrangements | Severance payments to employees, including NEOs, under certain company-initiated termination events. | Compensate employees generally for situations where the employee's position is eliminated as a result of outsourcing, merger or other corporate transaction. |
| Perquisites-Benefits | Perquisites provided to our NEOs include employer matching contributions to the NEOs' accounts in the 401(k) plan and may also include the payment of life insurance premiums, relocation reimbursements, and reimbursements for financial planning, tax preparation services, and spousal travel expenses. | Provide market competitive total compensation package. |
In addition, Allianz Life offers all employees, including our NEOs, broad-based benefits, including comprehensive medical, dental and vision insurance, group term life insurance and participation in a 401(k) plan.
How Compensation Decisions Are Made
Role of the Board of Directors and Compensation Committee
The framework governing the executive compensation policies for Allianz Life, except as such policies relate to the compensation for the Chief Executive Officer, is set through the Compensation Committee. Decisions affecting the compensation of the Chief Executive Officer are outside the scope of the Compensation Committee. Any such decisions are made by Allianz SE, subject to review by the NEC Committee, and final approval by Allianz Life's Board of Directors. With respect to the compensation of other "principal officers" selected by the Board for purposes of the duties of the NEC Committee under Minn. Stat. § 60D.20, subd. 3(d), the Compensation Committee's decision are similarly subject to review by the NEC Committee and final approval by the Board. The "principal officers" include the Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer and General Counsel. The Board has delegated the following responsibilities to the Compensation Committee:
| · | In general, establish the compensation philosophy and strategy of Allianz Life and oversee the development and implementation of compensation, benefit and perquisite programs for corporate executives consistent with the principles of ensuring that leadership is compensated effectively in a manner consistent with the stated compensation strategy, internal equity considerations, competitive practices, shareholder interests, and the requirements of any applicable regulatory bodies in order to attract and retain high-quality leadership. |
| · | Review and approve the establishment of, or material modification to, any executive incentive compensation plans or programs for Allianz Life. |
| · | Review and approve any special benefits, perquisites or compensation contracts in effect for, or offered to, any prospective, current or former Allianz Life employee, regardless of the employee's level or assignment within Allianz Life. Such benefits and perquisites are those that are unusual or different than the benefits offered to all similarly-situated employees. |
| · | Review and approve any employment agreements or any severance, change in control or similar termination arrangements or agreements proposed to be made with any prospective, current or former employee of Allianz Life. This does not include special termination agreements, separation or settlement agreements negotiated in connection with and at the time of termination of an executive's employment. |
| · | Review and approve compensation decisions. |
| · | Oversee Allianz Life's compliance with regulations with respect to compensation matters and ensure adherence to the set principles and standards of the Allianz Group Rewards Framework and German regulations. |
The Compensation Committee will at all times be composed of at least five members who are appointed by the full Board of Directors of Allianz Life. The Compensation Committee currently consists of the following members: the Chairman of the Board, the Chief Executive Officer, the Chief Financial Officer, the General Counsel, and the Chief Human Resources Officer. Effective as of February 22, 2018, the composition of the Compensation Committee changed to three members who are appointed by the Board of Directors of Allianz Life, consisting of the Chairman of the Board, the Chief Executive Officer, and the Chief Human Resources Officer. The Compensation Committee also utilizes internal personnel to provide advice to the Compensation Committee regarding market trends in compensation policies at competing companies and on a more macro level.
Following its review and decision, the Compensation Committee produces and submits a report on executive compensation to Allianz Life's Board of Directors at its request. With respect to the compensation of "principal officers" selected by the Board for purposes of the duties of the NEC Committee under Minnesota Statutes § 60D.20, subd. 3(d), the Compensation Committee produces and submits a report on executive compensation proposed for the designated "principal officers", to the NEC Committee for its review and recommendation to the Board for final approval.
Role of the Chief Executive Officer
Our Chief Executive Officer assists the Compensation Committee in its review of the total compensation of all the NEOs except himself. He provides the Compensation Committee with his assessment of their performances relative to the corporate and individual goals and other expectations set for them for the preceding year. He then provides his recommendations for each NEO's total compensation and the appropriate goals for each in the year to come. However, the Compensation Committee is not bound by his recommendations.
Role of Allianz Life's Human Resources
Allianz Life's Human Resources supports the Compensation Committee on executive compensation matters by being responsible for many of the organizational and administrative tasks that underlie the compensation review and determination process and making presentations on various topics. Allianz Life's Human Resources efforts include, among other things:
| · | evaluating the compensation data from industry groups, national executive pay surveys and other sources for the NEOs and other executive officers as appropriate; |
| · | gathering and correlating performance ratings and reviews for individual executive officers, including the NEOs; |
| · | reviewing executive compensation recommendations against appropriate market data and for internal consistency and equity; and |
| · | reporting to, and answering requests for, information from the Compensation Committee. |
Allianz Life's Human Resources officers also coordinate and share information with their counterparts at Allianz SE.
Use of Competitive Compensation Data
Because Allianz Life competes most directly for executive talent with other large diversified financial services companies, we regard it as essential to regularly review the competitiveness of the total compensation programs for executives to ensure that we provide compensation opportunities that compare favorably with the levels of total compensation offered to similarly situated executives by other companies that participate in the compensation surveys in which Allianz Life participates. Allianz Life relies primarily on external market surveys of corporate compensation and benefits published by various national compensation consulting firms, especially salary surveys focusing on insurance companies. In addition, other factors taken into account include the average revenues and number of employees of companies that participate in such surveys.
All these information sources are employed to measure and compare actual pay levels not only on an aggregate, total compensation basis but by breaking down the total compensation program component by component to review and compare specific compensation elements as well as the particular mixes of fixed versus variable, short-term versus long-term and cash versus equity-based compensation at the surveyed companies. This information, as collected and reviewed by Allianz Life's Human Resources, is submitted to the Compensation Committee for review and discussion.
Internal Pay Equity Analysis
Allianz Life's compensation programs are designed with the goal of providing compensation to our NEOs that is fair, reasonable, and competitive. To achieve this goal, Allianz Life believes it is important to compare compensation paid to each NEO not only with compensation paid by the surveyed companies, as discussed above, but also with compensation paid to each of our other NEOs. Such an internal comparison is important to ensure that compensation is equitable among our NEOs.
Components of Total Compensation For Our NEOs
Allianz Life provides total compensation to our NEOs that consists of several components. These components include the three components of the total compensation program (i.e., base salary, annual and multi-year incentives and equity) as well as: (i) retirement, health and other benefit programs, (ii) severance benefits and (iii) perquisites.
Base Salary
Allianz Life's philosophy is to make base salary a relatively small portion of the overall compensation package for our NEOs, which we believe is common in the industry in which we operate. The amount of the base salary awarded to NEOs is based on the position held, the NEO's tenure, the scope of the position's responsibilities and the NEO's own performance, all of which are reviewed with the aid of market survey data. Using this data, Allianz Life maintains a 50th percentile pricing philosophy, comparing base salaries against the median for comparable salaries at surveyed companies, unless exceptional conditions require otherwise.
With respect to the base salary of our Chief Executive Officer, the Chairman of the Board considered the Chief Executive Officer's experience, performance, and contribution to overall corporate performance when determining his base salary for 2017 for recommendation to the NEC Committee. Base salaries for our other NEOs for 2017 were also set by the Compensation Committee based upon each NEO's individual experience and contribution to the overall performance of Allianz Life, and subject to Allianz SE Compensation Committee reviews and, with respect to the base salaries of "principal officers" selected by Allianz Life's Board of Directors for purposes of the duties of the NEC Committee under Minnesota Statutes § 60D.20, subd. 3(d), subject to NEC Committee review and recommendation to the Board for final approval.
AIP
Allianz Life offers annual cash bonuses to certain executive officers under the AIP. The AIP is designed to improve performance and profitability by motivating employees to accomplish organizational objectives and financial goals. Bonus awards that may be paid pursuant to the AIP are within the sole discretion of the Compensation Committee, and with respect to our CEO, the Chairman of the Board, and are intended to:
| · | reward the performance of participants who have made significant contributions to the achievement of annual goals and objectives; |
| · | provide an incentive that will encourage future superior individual performance; and |
| · | encourage the retention of employees who have demonstrated exceptional performance and/or are anticipated to significantly contribute to the long-term success of Allianz Life. |
Following the performance year, the Compensation Committee approved a specific amount of cash awards to be made pursuant to the AIP to executive officers, including our NEOs, for the 2017 operating year. The amount determined to be available for such awards was at the discretion of the Compensation Committee and was dependent upon many factors as outlined previously, including, but not limited to, current financial performance and contributions of our NEOs in achieving performance objectives, and with respect to the awards to the "principal officers" selected by Allianz Life's Board for purposes of the duties of the NEC Committee under Minnesota Statutes § 60D.20, subd. 3(d), subject to NEC Committee review and recommendation to the Board for final approval.
Long-Term Incentives
The purpose of the ALTPUP is to advance the interests of Allianz Life, including Allianz Life of New York, and our indirect stockholder. The ALTPUP seeks to accomplish this purpose by providing an incentive in addition to current compensation to certain individuals within designated classes of employees of Allianz Life who contribute significantly to their company's long-term performance. Such incentive shall be in the form of Long-Term Performance Units ("ALTPUP Units"), which are contingent awards, subject to the terms, conditions and restrictions described in the ALTPUP and the Award Agreement under which such awards are made, by which participants in the ALTPUP may become entitled to receive cash upon the redemption of the ALTPUP Units on the valuation date. The award of ALTPUP Units is discretionary and any payments from the ALTPUP are intended to:
| · | reward the performance of participants who have made significant contributions to the achievement of annual goals and objectives, |
| · | provide an incentive that will encourage future superior individual performance, and |
| · | encourage the retention of employees who have demonstrated exceptional performance and/or are anticipated to significantly contribute to the long-term success of Allianz Life. |
The Compensation Committee (and, with respect to those NEOs that are "principal officers" for purposes of the NEC Committee's duties, the NEC Committee with final approval of Allianz Life's Board of Directors) reviewed the performance of our NEOs following the end of our 2017 fiscal year relative to the ALTPUP.
Targeted levels of bonus awards made pursuant to the ALTPUP for our NEOs were established by the Compensation Committee (or, in the case of those NEOs that are "principal officers" for purposes of the NEC Committee's duties, the NEC Committee with final approval of the Board) based on a number of factors related to the performance of Allianz Life and Allianz Life of New York, and the performance of the NEO. Maximum bonus awards made to our NEOs pursuant to the ALTPUP are set to two times the target amount for each NEO. See footnote (2) to the Summary Compensation Table for the specific amounts awarded to each NEO for the year ended December 31, 2017.
Our Chief Executive Officer receives cash awards pursuant to the terms of the Allianz SE Mid-Term Bonus Plan instead of the ALTPUP. The Allianz SE Mid-Term Bonus Plan covers business performance over a three-year period. The minimum payout is zero and the maximum payout is 165% of the target amount. Target award amounts generally focus on performance of Allianz Life and Allianz Life of New York, including the growth and operating profit and achievement of goals set by Allianz Life. At the end of each three-year period, the performance of Allianz Life is assessed, along with relevant comparable company comparisons. Proposed incentive awards are endorsed by the Allianz SE Board of Management and approved by the respective Compensation Committee and with respect to the "principal officers" for purposes of the NEC Committee's duties, by the NEC Committee for final approval by the Board.
AEI
The AEI is (a) one part of the variable compensation element for senior executives and provided under the Allianz Sustained Performance Plan ("ASPP") or (b) offered by Allianz Life to selected senior employees as an additional part of their variable compensation on a case by case basis. The AEI is granted in the form of restricted stock units of Allianz SE ("RSUs").
Benefit Perquisites
Allianz Life provides our NEOs with certain limited perquisites. All of our employees, including our NEOs, may participate in the qualified 401(k) plan. Allianz Life and Allianz Life of New York generally provide our executive officers, including our NEOs, with a matching contribution up to $20,250 annually. In addition, Allianz Life and Allianz Life of New York provide excess liability insurance coverage to all of our NEOs and provide financial planning and tax preparation services, relocation reimbursements and reimbursements of spousal travel expenses to certain of our NEOs. The incremental costs of perquisites for the NEOs during 2017 are included in the column entitled "All Other Compensation" in the Summary Compensation Table included in this section.
Severance Arrangements
We have entered into an Executive Severance Agreement with our Chief Executive Officer, Walter White, which is described in the "Allianz Life Executive Severance Agreement" discussion later in this section. We have not entered into any other specific severance agreements with any of our NEOs.
The remainder of our NEOs are eligible for severance payments under the Executive Severance Plan if they experience a qualifying termination of employment and otherwise satisfy the conditions set forth in the plan.
Other than the Executive Severance Plan, which is described later in this section, our NEOs (except for Walter White) are not eligible for severance payments. Certain of our executive officers receive offer letters which set forth the terms relating to base salary, sign-on incentives and equity compensation. However, Allianz Life does not view these offer letters as employment agreements as each offer letter states that employment with Allianz Life is "at will."
Other Compensation Policies
Tax and Accounting Implications
Stock-Based Compensation. Stock-based compensation, including Allianz SE stock appreciation rights (SARs) and Allianz SE restricted stock units (RSUs) granted pursuant to the AEI, are accounted for in accordance with the requirements of Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification ("FASB ASC") Topic 718. The fair value of the RSUs at grant is the arithmetic average of the closing prices of an Allianz SE share in the electronic cash market trading system Xetra (or any successor system) on that day and the nine immediately preceding trading days, less the present value of dividends expected to be paid on one Allianz SE share over the vesting period, and less the fair value of payout restrictions deriving from the vesting period and the payout cap.
Summary Compensation Table
The following table sets forth the compensation paid by Allianz Life during the year ended December 31, 2017 to our principal executive officer, our principal financial officer and each of the three highest paid NEOs who are involved in the management and operations of Allianz Life. The executive compensation information in this prospectus is shown for a one-year period, in accordance with Regulation S-K Item 402, Instruction 1 to Item 402(c).
| Name and Principal Position | Year | Salary | Bonus | Stock Awards | Option Awards | Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation | Change in Pension Value and Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Earnings | All Other Compensation | Total |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | (e)(1) | (f) | (g)(2),(3) | (h) | (i)(4) | (j) |
| Walter White | 2017 | $865,100 | N/A | $1,345,231 | N/A | $2,690,461 | N/A | $25,924 | $4,926,716 |
| President and Chief | |||||||||
| Executive Officer | |||||||||
| William Gaumond | 2017 | $425,000 | N/A | $390,150 | N/A | $645,150 | N/A | $25,090 | $1,485,390 |
| Senior Vice President | |||||||||
| and Chief Financial | |||||||||
| Officer | |||||||||
| Thomas Burns | 2017 | $595,000 | N/A | $498,015 | N/A | $855,015 | N/A | $38,044 | $1,986,074 |
| Senior Vice President | |||||||||
| and Chief Distribution | |||||||||
| Officer | |||||||||
| Neil McKay | 2017 | $500,000 | N/A | $421,500 | N/A | $721,500 | N/A | $34,481 | $1,677,481 |
| Senior Vice President | |||||||||
| and Chief Actuary | |||||||||
| Catherine Mahone | 2017 | $400,000 | N/A | $334,800 | N/A | $574,800 | N/A | $20,920 | $1,330,520 |
| Senior Vice President | |||||||||
| and Chief Administrative | |||||||||
| Officer |
| (1) | Represents the grant date fair value of the RSUs issued pursuant to the AEI. The RSUs vest over a four-year period. The RSUs issued in 2018 for the 2017 performance year have a March 2022 exercise date. The grant price of the RSUs was the arithmetic average of the closing prices of an Allianz SE share in the electronic cash market trading system Xetra (or any successor system) on that day and the nine immediately preceding trading days, less the present value of dividends expected to be paid on one Allianz SE share over the vesting period, and less the fair value of the payout restrictions deriving from the vesting period and the payout cap. These numbers show the amount realized for financial reporting purposes as calculated in accordance with the FASB ASC Topic 718. Under FASB ASC Topic 718, the grant date fair value is calculated using the closing market price of the common stock of Allianz SE on the date of grant, which is then recognized over the requisite service period of the award. |
| (2) | Includes the following payments and grants made pursuant to the AIP and the ALTPUP. |
| Name | Year | Payments made pursuant to the AIP | Grants made pursuant to the ALTPUP(3) |
| Walter White | 2017 | $1,345,231 | $1,345,231 |
| William Gaumond | 2017 | $390,150 | $255,000 |
| Thomas Burns | 2017 | $498,015 | $357,000 |
| Neil McKay | 2017 | $421,500 | $300,000 |
| Catherine Mahone | 2017 | $334,800 | $240,000 |
| (3) | Walter White, as Chief Executive Officer, participates in the global Allianz SE Mid-Term Bonus Program rather than the ALTPUP. |
| (4) | The following table provides additional details regarding compensation found in the "All Other Compensation" column. |
| Name | Year | Spousal Travel (5) | Milestone/ Anniversary/ Recognition(6) | Life Insurance Premiums | Employer Match to 401(k) Plan | ASAAP Cont-ribution(7) | ESPP Imputed Income(8) | Total |
| Walter White | 2017 | $4,564 | -- | $1,110 | $20,250 | -- | -- | $25,924 |
| William Gaumond | 2017 | -- | -- | $666 | $18,000 | $2,250 | $4,174 | $25,090 |
| Thomas Burns | 2017 | $15,567 | $1,650 | $577 | $20,250 | -- | -- | $38,044 |
| Neil McKay | 2017 | $7,947 | -- | $888 | $20,250 | -- | $5,396 | $34,481 |
| Catherine Mahone | 2017 | -- | -- | $670 | $20,250 | -- | -- | $20,920 |
| (5) | Represents reimbursement or payments made to defray the costs of a spouse's travel. |
| (6) | Represents Milestone Anniversary Program, which pays a bonus at three and five year anniversaries, and then every five years thereafter. |
| (7) | Represents company matching contribution to the Allianz Supplemental Asset Accumulation Plan for deferrals in excess of IRS compensation limit. |
| (8) | Represents value of the discount associated with stock purchases in the Employee Stock Purchase Plan. |
Performance-Based Incentive Compensation Plans
AIP
The AIP is intended to provide an incentive that will encourage superior individual performance and encourage retention of employees who have demonstrated exceptional performance or who are anticipated to significantly contribute to the long-term success of Allianz Life. The AIP seeks to accomplish this purpose by providing a bonus opportunity to eligible employees who have made significant contributions during the plan year to the achievement of annual goals and objectives. The guidelines for target awards are meant to be illustrative of competitive market bonuses for similar job levels in the marketplace. While the target awards may be used for illustrative, budget planning or distribution scenarios, all bonus awards are discretionary and are in no way guaranteed.
The Compensation Committee or other duly authorized committee determines allocation of bonus awards to employees. With respect to "principal officers" for purposes of the NEC Committee's duties, the NEC Committee recommends to Allianz Life's Board of Directors awards for final approval.
ALTPUP
In order to be eligible for ALTPUP awards, individuals must be nominated by the business unit and approved by the Compensation Committee and with respect to "principal officers" for purposes of the NEC Committee's duties, by the NEC Committee with final approval by the Board. Receipt of an ALTPUP award one year is not a guarantee that an ALTPUP award will be granted in subsequent years. The ALTPUP incentive is in the form of ALTPUP Units, which have a target value of $10. The threshold value is $5 and the maximum value is $20. ALTPUP award periods are three years, with one-third of the ALTPUP Units paying out each year over the three-year award period. The valuation date is December 31 at the end of each performance year, unless the Compensation Committee in its discretion selects an earlier date.
Allianz SE Mid-Term Bonus Plan
Our Chief Executive Officer receives cash awards pursuant to the terms of the Allianz SE Mid-Term Bonus Plan instead of the ALTPUP. The Allianz SE Mid-Term Bonus Plan covers business performance over a three-year period. The minimum payout is zero and the maximum payout is 165% of the target amount. Target award amounts generally focus on company performance, including growth and operating profit and achievement of goals set by Allianz Life. At the end of each three-year period, the performance of Allianz Life is assessed, along with relevant company comparisons. Proposed incentive awards are endorsed by the Allianz SE Board of Management and with respect to the "principal officers" for purposes of the NEC Committee's duties, by the NEC Committee for final approval by the Board.
AEI
The AEI is designed to recognize the participant's continuous employment with Allianz Life over the relevant period and shall be an incentive to continue in employment. Grants under the AEI will generally only be made if the participant is employed with Allianz Life at the date of grant. Payments will be made only if the participant remains employed with Allianz Life during the vesting period of the RSU, or leaves employment under circumstances set out in the AEI, including after retirement or early retirement eligibility, disability, or under certain other circumstances. The securities issuable under the AEI are RSUs. An RSU constitutes the right to receipt of the market value of Allianz SE common stock at the time of exercise. This amount will be paid in cash. RSUs are subject to a four-year vesting period. At the end of the four-year period, the RSUs are exercised uniformly for all participants, provided they remain employed by Allianz Life or terminate after retirement or early retirement eligibility, or under certain other circumstances. Vesting and exercise may accelerate if a participant leaves employment under other "good leaver" circumstances set forth in the AEI. The grant at fair value cannot be greater than 165% of a participant's target amount. The maximum value of an exercise is an increase of 200% over the grant value (i.e., 300% of the grant value).
Grants of Plan-Based Awards
The following table provides additional information about plan-based compensation disclosed in the Summary Compensation Table. This table includes both equity and non-equity awards granted during the year ended December 31, 2017.
| Name | Grant Date | Estimated Future Payouts Under Non-Equity Incentive Plan Awards(1),(2) | Estimated Future Payouts Under Equity Incentive Plan Awards(3),(4) | ||||
| Threshold ($) | Target ($) | Maximum ($) | Threshold ($) | Target ($) | Maximum ($) | ||
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | (e) | (f) | (g) | (h) |
| Walter White | 3/2/2018 | ||||||
| RSUs (under AEI) | $0 | $865,100 | $4,282,245 | ||||
| AIP Award | $0 | $865,100 | $1,427,415 | ||||
| Midterm Bonus Plan | $0 | $865,100 | $1,427,415 | ||||
| William Gaumond | 3/2/2018 | ||||||
| RSUs (under AEI) | $0 | $255,000 | $1,262,250 | ||||
| AIP Award | $0 | $255,000 | $510,000 | ||||
| ALTPUP Award | $0 | $255,000 | $510,000 | ||||
| Thomas Burns | 3/2/2018 | ||||||
| RSUs (under AEI) | $0 | $357,000 | $1,767,150 | ||||
| AIP Award | $0 | $357,000 | $714,000 | ||||
| ALTPUP Award | $0 | $357,000 | $714,000 | ||||
| Neil McKay | 3/2/2018 | ||||||
| RSUs (under AEI) | $0 | $300,000 | $1,485,000 | ||||
| AIP Award | $0 | $300,000 | $600,000 | ||||
| ALTPUP Award | $0 | $300,000 | $600,000 | ||||
| Catherine Mahone | 3/2/2018 | ||||||
| RSUs (under AEI) | $0 | $240,000 | $1,188,000 | ||||
| AIP Award | $0 | $240,000 | $480,000 | ||||
| ALTPUP Award | $0 | $240,000 | $480,000 | ||||
| (1) | The target and maximum columns show the target award and maximum award for 2017 for each NEO under the AIP. There is no threshold amount for any participant in the AIP. The actual 2017 awards granted to the NEOs are listed in the Non-Equity Incentive Compensation column of the Summary Compensation Table. AIP target and maximum awards are a pre-designated percentage of base salary determined at the executive's level. |
| (2) | The target and maximum columns show the target award and maximum award for 2017 for each NEO under the ALTPUP. Under the ALTPUP, all awards are discretionary. To the extent that awards are made, the minimum amount of an award will equal at least 50% of the target amount as determined by the Compensation Committee (or with respect to "principal officers" for purposes of the NEC Committee's duties, the NEC Committee with final approval of the Board). The actual 2017 awards granted to the NEOs are listed in the Non-Equity Incentive Compensation column of the Summary Compensation Table. ALTPUP target and maximum awards are a pre-designated percentage of base salary determined at the executive's level. |
| (3) | RSUs have a vesting schedule as disclosed in the footnotes to the Summary Compensation Table. See "Outstanding Equity Awards at December 31, 2017" for disclosure regarding the number of RSUs that are unvested as of December 31, 2017. |
| (4) | The target and maximum columns show the target award and maximum award for 2017 for each NEO under the AEI. There is no threshold amount for any participant in the AEI. The actual 2017 awards granted to the NEOs are listed in the Stock Awards column of the Summary Compensation Table. |
Outstanding Equity Awards at December 31, 2017
The following table sets forth the outstanding equity awards at the December 31, 2017 fiscal year-end. The table shows RSUs granted pursuant to the AEI.
| Name | RSUs | |||
| Number of RSUs That Have Not Vested | Market Value of RSUs That Have Not Vested | Equity Incentive Plan Awards: Number of Unearned RSUs That Have Not Vested | Equity Incentive Plan Awards: Market or Payout Value of Unearned RSUs That Have Not Vested | |
| (a) | (g)(1)(2) | (h)(3) | (i) | (j) |
| Walter White | N/A | N/A | ||
| 7,927 | $1,828,204 | |||
| 6,364 | $1,467,729 | |||
| 10,097 | $2,328,671 | |||
| 8,161 | $1,882,171 | |||
| William Gaumond | N/A | N/A | ||
| 1,559 | $359,552 | |||
| 679 | $156,598 | |||
| 721 | $166,284 | |||
| 1,452 | $334,875 | |||
| Thomas Burns | N/A | N/A | ||
| 3,723 | $858,635 | |||
| 3,151 | $726,715 | |||
| 3,714 | $856,560 | |||
| 3,073 | $708,726 | |||
| Neil McKay | N/A | N/A | ||
| 3,180 | $733,403 | |||
| 2,586 | $596,409 | |||
| 3,536 | $815,508 | |||
| 3,073 | $588,107 | |||
| Catherine Mahone | N/A | N/A | ||
| 1,973 | $455,033 | |||
| 1,774 | $409,138 | |||
| 2,320 | $535,062 | |||
| 1,928 | $444,655 | |||
| (1) | Represents unvested RSUs issued pursuant to the AEI. RSUs issued under the AEI during 2017 are subject to a four-year vesting period from the grant date. At the end of the respective vesting period, the RSUs are exercised uniformly for all participants, provided they remain employed by Allianz Life or terminate after retirement or early retirement eligibility, or under certain other circumstances. Vesting and exercise may accelerate if a participant leaves employment under other "good leaver" circumstances set forth in the AEI. |
| (2) | For each of the NEOs, the number of RSUs listed on the first line were exercised in 2018, the RSUs listed on the second line will exercise in 2019, the RSUs listed on the third line will exercise in 2020, and the RSUs listed on the fourth line will exercise in 2021. |
| (3) | Based on an assumed stock price of $230.63 per share, which was the arithmetic average of the closing prices of an Allianz SE share in the electronic cash market trading system Xetra (or any successor system) on December 29, 2017 and the nine immediately preceding trading days, converted from Euros into U.S. dollars. |
Allianz SE Option Exercises and Stock Grants Vested in 2017
The following table summarizes the value received from Allianz SE stock option exercises and stock grants vested during the year ended December 31, 2017.
| Name | Option Awards | Stock Awards | ||
Number of Shares Acquired on Exercise (#) | Value Realized on Exercise ($)(1) | Number of Shares Acquired on Vesting (#) | Value Realized on Vesting ($)(2) | |
| Walter White | 4,160 | $344,995 | 7,930 | $1,388,167 |
| William Gaumond | -- | $0 | 2,234 | $391,067 |
| Thomas Burns | -- | $0 | 3,526 | $617,235 |
| Neil McKay | -- | $0 | 3,264 | $571,372 |
| Catherine Mahone | -- | $0 | 2,220 | $388,617 |
| (1) | Represents Allianz SE SARs that were exercised during 2017 pursuant to the GEI. Amounts realized were paid in cash. |
| (2) | Represents Allianz SE RSUs that were exercised during 2017 pursuant to the GEI and AEI. Amounts realized were paid in cash. |
Allianz Life Executive Severance Agreement
Allianz Life entered into an Executive Severance Agreement with our Chief Executive Officer, Walter White, with an expiration date of December 31, 2020. The severance arrangements for Mr. White are prescribed by the Executive Severance Agreement.
Pursuant to the Executive Severance Agreement, Mr. White is entitled to a lump sum cash payment upon separation of $1,730,200 in the event he is terminated without "cause" as defined in the Executive Severance Agreement. In addition, pursuant to the Executive Severance Agreement, Mr. White is also bound by other restrictive covenants, including covenants relating to confidentiality and non-disparagement. Mr. White would also be entitled to continuation of medical and dental coverage at the employee premium rates for a period of 18 months following termination if Mr. White timely elects continuation and pays the required premiums.
The remainder of our NEOs are eligible for severance payments under the Executive Severance Plan if they experience a qualifying termination of employment and otherwise satisfy the conditions set forth in the applicable plan. The terms of this plan are set forth below.
Executive Severance Plan
Executive officers who have the title of Senior Vice President or above and report directly to a senior executive officer at a specific level are eligible to receive severance benefits under the Executive Severance Plan if they experience a qualifying termination of employment and otherwise satisfy the conditions set forth in the plan. The purpose of the Executive Severance Plan is to provide severance benefits to executive officers whose employment is involuntarily terminated in order to assist with job transition. Pursuant to the Executive Severance Plan, eligible executive officers who are involuntarily terminated will receive a lump sum cash payment equal to one and one-half times their "annual base pay" in effect at the time of termination. Annual base pay, for purposes of this agreement, equals base salary and excludes special payments, such as bonuses, expense reimbursements, living or other allowances. Eligible executive officers would also be entitled to continuation of medical and dental coverage at employee premium rates for a period of 18 months following termination, if the executive officer timely elects continuation coverage and pays the required premiums.
The following table shows the lump sum payments that would have been payable to each of our NEOs had they been terminated on December 31, 2017 and been eligible for severance payments pursuant to the Executive Severance Plan.
| NEOs | Lump Sum Payment |
| Walter White | N/A(1) |
| William Gaumond | $637,500 |
| Thomas Burns | $892,500 |
| Neil McKay | $750,000 |
| Catherine Mahone | $600,000 |
| (1) | Mr. White is not eligible to receive payments pursuant to the Executive Severance Plan. See "Allianz Life Executive Severance Agreement" for information regarding severance payments that Mr. White is eligible to receive upon termination of service. |
Director Compensation
The following table provides information on compensation paid to the directors of Allianz Life for the year ended December 31, 2017.
| Name | Fees Earned or Paid in Cash ($)(1) | Stock Awards ($) | Option Awards ($) | Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation ($) | Change in Pension Value and Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Earnings | All Other Compensation | Total ($) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | (e) | (f) | (g) | (h) |
Jacqueline Hunt(2) Chairman of the Board | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Walter White(3) President and Chief Executive Officer | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
William Gaumond(3) Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Ronald M. Clark Independent Director | $40,000 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | $40,000 |
Kevin E. Walker Independent Director | $30,000 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | $30,000 |
Udo Frank Independent Director | $40,000 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | $40,000 |
| 1 | Represents cash compensation provided to our independent directors for the year ended December 31, 2017. Mr Conway served on the Board until his resignation on May 22, 2017. He received $10,000 in cash compensation for the year ended December 31, 2017. |
| 2 | Ms. Hunt and our former director Mr. Terzariol, who resigned December 31, 2017, did not receive any compensation for their services as a director since they are not independent directors. |
| 3 | As employee directors, Messrs. White and Gaumond do not receive any compensation for their service as directors. The compensation Messrs. White and Gaumond receive as executive officers of Allianz Life is disclosed in the Summary Compensation Table as set forth herein. |
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT
We are an indirect wholly owned subsidiary of Allianz SE. Allianz SE's principal executive offices are located at Königinstrasse 28, 80802 Munich, Germany. As of March 31, 2017, the directors and executive officers of Allianz Life held less than 1% of Allianz SE's ordinary shares issued and outstanding.
We are not aware of any arrangements that may at a later date result in a change in control of Allianz Life.
TRANSACTIONS WITH RELATED PERSONS, PROMOTERS AND CERTAIN CONTROL PERSONS
We are a wholly owned subsidiary of AZOA, which is a wholly owned subsidiary of Allianz Europe, B.V. Allianz Europe, B.V. is a wholly owned subsidiary of Allianz SE, our ultimate parent, which is registered in Munich, Germany.
RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH THE FINANCIAL SERVICES INDUSTRY
There are a number of risks associated with the financial services industry including the insurance industry.
Legal, Regulatory, and Tax Risks
We are heavily regulated by state insurance departments and other regulators, and changes in existing or new laws and regulations may reduce our profitability and limit our growth.
We are subject to detailed and comprehensive regulation and supervision in all the jurisdictions in which we operate. Our insurance operations are subject to insurance laws and regulations, which are generally intended to protect policyholders, not our stockholders or creditors. Changes in existing insurance laws and regulations may materially affect the way in which we conduct our business and the products we offer.
State insurance laws regulate most aspects of our insurance business. We are domiciled in Minnesota and are primarily regulated by the Minnesota Department of Commerce, which regulates insurance companies in the State of Minnesota, and by the states in which we are licensed. State laws in the United States grant insurance regulatory authorities broad administrative powers with respect to, among other things:
| · | licensing companies and agents to transact business; |
| · | calculating the value of assets to determine compliance with statutory requirements; |
| · | regulating unfair trade and claims practices, including through the imposition of restrictions on marketing and sales practices, distribution arrangements and payment of inducements; |
| · | establishing statutory capital and reserve requirements and solvency standards; |
| · | fixing maximum interest rates on insurance policy loans and minimum rates for guaranteed crediting rates on life insurance policies and annuity contracts; |
| · | restricting the payment of dividends and other transactions between insurance subsidiaries and affiliates; and |
| · | regulating the types, amounts, concentrations and valuation of investments. |
Our asset management operations are also subject to extensive regulation in various jurisdictions. These regulations are primarily intended to protect investors in the securities markets or investment advisory clients and generally grant supervisory authorities broad regulatory powers. Changes to these laws and regulations may adversely affect our asset management operations. We are also subject to increasing regulation under various laws and regulations governing the solvency of insurers and other financial institutions. We are also increasingly subject to detailed and comprehensive regulations governing such matters as money laundering, "know your customer," prohibited transactions with countries or counterparties subject to sanctions, and bribery and other anti-corruption measures.
We are faced with significant challenges due to the fact that our regulatory environment is evolving rapidly and supervisory authorities around the country are assuming an increasingly active and aggressive role in interpreting and enforcing regulations governing a variety of business practices, such as the escheatment of unclaimed property, in the jurisdictions where we do business. We have been and may become in the future subject to regulatory investigations and/or examinations which, together with civil actions often following these investigations, may affect our image, brand, relations with regulators and/or results of operations. We cannot predict with any certainty the potential effects that any change in applicable laws or regulations, their interpretation or enforcement, or any enactment of new regulation or legislation in the future may have on our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
Our products are heavily regulated and must be approved by the individual state regulators where such products are sold. State insurance regulators and the National Association of Insurance Commissioners ("NAIC") regularly reexamine existing laws and regulations applicable to insurance companies and their products. Changes in these laws and regulations, or in interpretations thereof, could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and consolidated results of operations. The NAIC continues to change and modernize its financial and solvency requirements and regulations. These changes could have a material adverse effect on our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
For example, in December 2014, the NAIC adopted Actuarial Guideline XLVIII ("AG 48") which established a new regulatory requirement applicable to XXX and AXXX reserve financing transactions ceded to reinsurers, including affiliated reinsurers. AG 48 is an important part of the implementation of the XXX and AXXX reinsurance framework the NAIC adopted in June 2014. As adopted, AG 48 limits the type of assets that may be used as collateral to cover the XXX and AG 38 statutory reserves. In January 2016, the NAIC adopted changes to the Credit for Reinsurance Model Law, giving regulators the authority to pass regulations related to captive reserve financing transactions. In December 2016, the NAIC adopted the Term and Universal Life Insurance Reserve Financing Model Regulation ("XXX/AXXX Model Regulation") codifying the regulatory framework set forth in AG 48. Following adoption of the XXX/AXXX Model Regulation, the NAIC adopted further revisions to AG 48 effective January 1, 2017, in order to make it substantively consistent with the XXX/AXXX Model Regulation as well as to avoid confusion and ensure uniformity of treatment between states, companies, and ceded policies. Generally, AG 48 will cease to be effective, on a state by state basis, as individual states enact the XXX/AXXX Model Regulation, which is likely to become an accreditation standard effective January 1, 2020. Additionally, in May 2015, the NAIC adopted proposed revisions to the preamble to the NAIC accreditation standards, which would require states to apply NAIC accreditation standards to captive reinsurers. The revisions would add captive insurance companies that assume XXX or AXXX business, variable annuities, and long-term care insurance. A state will be deemed in compliance as it relates to XXX or AXXX captives if the applicable reinsurance transaction complies with AG 48 or the XXX/AXXX Model Regulation, as applicable.
In 2015, the NAIC established a variable annuity issues working group to study and address regulatory issues resulting in variable annuity captive reinsurance transactions. The working group developed a draft report that suggests numerous changes to current NAIC rules and regulations that would be designed to decrease incentives for insurers to establish variable annuity captives. This report proposed adoption of changes to current rules and regulations. The draft report was updated in 2017, and NAIC has exposed the proposed changes for comment until March 2, 2018. However, it is unclear whether such changes will be adopted or when they might take effect. If adopted, the changes could have a material adverse effect on our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
In addition, every state has unclaimed property laws which generally treat annuity contracts and life insurance policies as abandoned property if they have remained inactive for a period of three to five years from the date that death benefit proceeds associated with such contracts or policies became due and payable. Life insurance companies are generally required to report and remit such abandoned property to the appropriate state administrators of abandoned property. A number of states have audited life insurance companies for compliance with unclaimed property laws. These audits have focused on maturities of policies or contracts, i.e., policies that have exceeded limiting age with respect to death benefits that companies should treat as unclaimed property and report to the state. A number of life insurers, including Allianz Life, have entered into resolution agreements with states in which the insurers agree to procedures requiring, among other things: (i) comparison of contract owners and policyholders against a death database such as the Social Security Death Master File; (ii) investigation of any potential database matches to confirm a death; (iii) determination whether benefits are due and an attempt to locate the beneficiaries of any benefits that are due; and (iv) reporting abandoned contract of policy proceeds to the state as unclaimed property if no beneficiary can be located. Further, the Uniform Law Commission released its Revised Uniform Unclaimed Property Act in 2016 ("2016 consider adopting similar legislation this year. Additionally, a NAIC working group is developing a model Uniform Act"). Several states adopted the 2016 Uniform Act in 2017, and states in which we conduct business may also unclaimed property law. If states make changes to their unclaimed property laws based on the 2016 Uniform Act or other factors, we cannot predict what impact such changes could have on our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
Our business is subject to significant litigation risks in the various states in which we operate; an adverse outcome in any significant pending or future litigation or regulatory investigation may have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, reputation or image in the marketplace.
We have been named as defendants in lawsuits (both class actions and individual lawsuits) and involved in various regulatory investigations and examinations and may be involved in more in the future. These actions arise in various contexts, including in connection with our activities as an insurer, securities issuer, employer, investment adviser, investor and taxpayer. We cannot predict what impact certain lawsuits or regulatory investigations could have on our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
Certain of these lawsuits and investigations seek significant or unspecified amounts of damages, including punitive damages, and certain of the regulatory authorities involved in these proceedings have substantial powers over the conduct and operations of our business. Due to the nature of certain of these lawsuits and investigations, we cannot make an estimate of loss or predict with any certainty the potential impact of these suits or investigations on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Our products are subject to extensive regulation and failure to meet any of the complex product requirements may reduce profitability.
Our products are subject to a complex and extensive array of state and federal tax, securities, insurance and employee benefit plan laws and regulations, which are administered and enforced by a number of different governmental and self-regulatory authorities, including, among others, state insurance regulators, state securities administrators, state banking authorities, the SEC, FINRA, the Department of Labor ("DOL") and the IRS.
For example, U.S. federal income tax law imposes requirements relating to insurance and annuity product design, administration and investments that are conditions for beneficial tax treatment of such products under the Internal Revenue Code. Additionally, state and federal securities and insurance laws impose requirements relating to insurance and annuity product design, offering and distribution and administration. Failure to administer product features in accordance with contract provisions or applicable law, or to meet any of these complex tax, securities or insurance requirements could subject us to administrative penalties imposed by a particular governmental or self-regulatory authority, unanticipated costs associated with remedying such failure or other claims, litigation, harm to our reputation or interruption of our operations. If this were to occur, it could adversely impact our profitability, business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
Laws and regulations aimed at bank and financial institutions, including the Dodd-Frank Act, could have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Among other things, the Dodd-Frank Act imposes a comprehensive new regulatory regime on the over-the-counter ("OTC") derivatives marketplace and grants new joint regulatory authority to the SEC and the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission ("CFTC") over OTC derivatives. While the SEC and CFTC continue to promulgate rules required by the Dodd-Frank Act, most rules have been finalized and, as a result, certain of the Company's derivatives operations are subject to, among other things, new recordkeeping, reporting and documentation requirements and new clearing requirements for certain swap transactions (currently, certain interest rate swaps and index-based credit default swaps; cleared swaps require the posting of margin to a clearinghouse via a futures commission merchant and, in some case, to the futures commission merchant as well).
In the latter part of 2015, U.S. federal banking regulators and the CFTC adopted regulations that will require swap dealers, security-based swap dealers, major swap participants and major security-based swap participants ("Swap Entities") to post margin to, and collect margin from, their OTC swap counterparties (the "Margin Rules"). Under the Margin Rules, the Company would be considered a "financial end-user" that, when facing a Swap Entity, is required to post and collect variation margin for its non-cleared swaps. In addition, depending on its derivatives exposure, the Company may be required to post and collect initial margin as well. The initial margin requirements of the Margin Rules will be phased-in over a period of five years based on the average aggregate notional amount of the Swap Entity's (combined with all of its affiliates) and its counterparty's (combined with all of its affiliates) swap positions. It is anticipated that the Company will not be subject to the initial margin requirements until September 1, 2020. The variation margin requirement took effect on September 1, 2016, for swaps where both the Swap Entity (and its affiliates) and its counterparty (and its affiliates) have an average daily aggregate notional amount of swaps for March, April and May of 2016 that exceeds $3 trillion. Otherwise, the variation margin requirement, to which we are subject, took effect on March 1, 2017.
Other regulatory requirements may indirectly impact us. For example, non-U.S. counterparties of the Company may also be subject to non-U.S. regulation of their derivatives transactions with the Company. In addition, counterparties regulated by the Prudential Regulators are subject to liquidity, leverage and capital requirements that impact their derivatives transactions with the Company. Collectively, these new requirements have increased the direct and indirect costs of our derivatives activities and may further increase them in the future.
Currently, the U.S. federal government does not directly regulate the business of insurance. While the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the "Dodd-Frank Act") does not remove primary responsibility for the supervision and regulation of insurance from the states, Title V of the Dodd-Frank Act establishes a Federal Insurance Office ("FIO") within the U.S. Treasury Department. The FIO has authority that extends to a wide variety of lines of insurance, including life insurance and annuities. Under the Dodd-Frank Act, the FIO is charged with monitoring all aspects of the insurance industry (including identifying gaps in regulation that could contribute to a systemic crisis), recommending to the Financial Stability Oversight Council the designation of any insurer and its affiliates as a non-bank systemically important financial institution subject to oversight by the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (including the administration of stress testing on capital), assisting the Treasury Secretary in negotiating "covered agreements" with non-U.S. governments or regulatory authorities, and, with respect to state insurance laws and regulation, determining whether such state insurance measures are pre-empted by such covered agreements.
On December 12, 2013, the FIO released a study required by Title V of the Dodd-Frank Act entitled "How to Modernize and Improve the System of Insurance Regulation in the United States" (the "Report"). While the Report reflects extensive study and analysis of the broader issue of the appropriate regulatory framework for insurance, it also reviews some narrower regulatory issues that are current topics of discussion. The Report does not recommend direct federal regulation of insurance, but does recommend significantly greater federal involvement in a number of areas. Some of the recommendations outlined in the Report have been implemented. For example, the National Association of Registered Agents and Brokers Reform Act was signed into law in 2015. The FIO has also engaged with the supervisory colleges to monitor financial stability and identify regulatory gaps for large national and internationally active insurers. We cannot predict what impact these or any other recommendations that stem from the Report could have on our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
In addition, the Dodd-Frank Act otherwise made a number of changes to the regulation of financial services entities, products and markets. For example, under the so-called Volcker Rule established by the Dodd-Frank Act, the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System could impose additional capital requirements and quantitative limits on certain trading and investment activities of a non-bank systemically important financial institution.
Non-bank financial companies such as Allianz Life that are not affiliates with an insured depository institution or otherwise brought within the definition of "banking entity" generally will not be subject to the Volcker Rule's prohibitions. However, the prohibitions of the Volcker Rule could impact financial markets generally, for example, through reduced liquidity in certain markets or the exiting of positions by banking entities as the end of the conformance period approaches.
Non-bank systemically important financial institutions and certain other large financial companies can be assessed under Dodd-Frank for any uncovered costs arising in connection with the resolution of a systemically important financial institution and to cover the expenses of the Office of Financial Research, an agency established by Dodd-Frank to improve the quality of financial data available to policymakers and facilitate more robust and sophisticated analysis of the financial system. To date, Allianz Life has not been designated a non-bank systemically important financial institution. However, as discussed under "Global Initiatives", Allianz SE, the ultimate parent company of Allianz Life, has been designated as a global systematically important insurer.
Additionally, Dodd-Frank created the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau ("CFPB"), an independent division of the Department of Treasury with jurisdiction over credit, savings, payment and other consumer financial products and services other than what is already regulated by the SEC or the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission. The CFPB has issued a rule to bring under its supervisory authority certain non-banks whose activities or products it determines pose risks to consumers. Additionally, the CFPB previously indicated it is exploring the possibility of helping Americans manage their retirement savings and is considering the extent of its authority in that area. We are unable to predict the impact of these or similar activities of the CFPB.
Regulation of Broker-Dealers and Sales of Insurance Products
The sales of our insurance products could also be adversely affected to the extent that some or all of the third-party firms that distribute our products face heightened regulatory scrutiny, increased regulation and potentially heightened litigation risks that cause them to de-emphasize sales of the types of products issued by our insurance companies.
For example, the Dodd-Frank Act provides that the SEC may promulgate rules to provide that the standard of conduct for all broker-dealers, when providing personalized investment advice about securities to retail customers (and any other customers as the SEC may by rule provide) will be the same as the standard of conduct applicable to an investment adviser under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940. Although the full impact of such a provision can only be measured when the implementing regulations are adopted, the intent of this provision is to authorize the SEC to impose a heightened standard of care owed by broker-dealers to their customers, similar to the duties applicable to investment advisers under existing law. SEC Chairman Jay Clayton has publicly stated that SEC staff is working on a rule proposal addressing the standard of care owed by a broker-dealer to its customers. We cannot predict whether any such proposal will be adopted and, if so, what impact it could have on our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
On April 6, 2016, the DOL issued a final rule that significantly expands the definition of "investment advice" and increases the circumstances under which insurance companies, broker-dealers, insurance agencies and other financial institutions that sell our products could be deemed a fiduciary when providing investment advice with respect to plans under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 ("ERISA") or individual retirement accounts ("IRAs"). The DOL also introduced amendments to longstanding exemptions from the prohibited transaction provisions under ERISA that would increase fiduciary requirements in connection with transactions involving ERISA plans, plan participants and IRAs, and that would apply more onerous disclosure and contract requirements to such transactions. While certain parts of the new rule (often referred to as the "impartial conduct standards") and the new prohibited transaction exemptions became effective on June 9, 2017, the potential effective date for compliance with the full conditions of the final rule and the prohibited transaction exemptions have been delayed until July 1, 2019. It is not yet certain whether or how implementation of the currently effective portions of the rule will change our business, results of operations or financial condition.
In addition, other executive, legislative or judicial action could result in the final rule issued by the DOL being further delayed, revised, or repealed. In particular, we are not yet certain how, if at all, these rules might be amended during this extension of the applicability date given the change in presidential administrations following the publication of the final rule. However, if the final rule does become applicable, it may be necessary for us to change sales representative and/or broker compensation, limit the assistance or advice provided to owners of our annuities, or otherwise change the manner of design and sales support of the annuities at that time. These changes could have an adverse impact on the level and type of services provided and compliance with the rule could also increase our overall operational costs for providing some of the services currently provided. Further, these changes may lead to greater exposure to legal claims in certain circumstances, including an increased risk of DOL enforcement actions, and an increased risk of litigation, including class-actions.
There is also a possibility that the various states may develop rules raising the standard of care owed by insurance agents to their customers that may be in harmony or conflict with the DOL rules. For example, the NAIC annuity suitability working group exposed a proposal to add a "best interest" standard to the NAIC's Suitability in Annuity Transactions Model Regulation. In addition, the NYDFS, the regulatory authority for the insurance industry in New York, published a proposal to add a "best interest" standard to Insurance Regulation 187, a regulation that imposes suitability requirements on annuity recommendations by producers and insurers in New York. While these proposals differ to some degree, they generally would require, among other things, that annuity purchase or exchange recommendations be both suitable and in the best interest of the customer. As a result, if these or similar changes were adopted by our state insurance regulator(s) and made applicable to us or the third-party firms that distribute our products, they could have an adverse impact on our business. Whether these or similar proposals will be adopted in their proposed form or at all is uncertain.
Global Initiatives
In addition, regulators and lawmakers in non-U.S. jurisdictions are engaged in addressing the causes of the financial crisis and means of avoiding such crises in the future. On July 18, 2013, the Financial Stability Board ("FSB") published its initial list of nine global systematically important insurers ("G-SIIs"), which includes Allianz SE, our ultimate parent company, based on the assessment methodology of the International Association of Insurance Supervisors (IAIS). In addition to imposition of basic capital requirements (BCR), the IAIS framework of policy measures calls for additional capital requirements (called higher loss absorbency, or HLA) for G-SIIs which engage in activities deemed to be systemically risky. Beginning in 2015, G-SIIs starting reporting BCR on a confidential basis to group-wide supervisors, subject to access by the IAIS. Beginning in 2016, G-SIIs started reporting HLA on the same basis. BCR will continue to be revised by the IAIS, and a final capital framework for G-SIIs is anticipated by 2019. HLA requirements are to be applied in 2019 to companies designated as G-SIIs in 2017. In addition, the IAIS is developing a risk-based global insurance company standard, and released a revised public consultation document on the standard in 2016. The standard will apply to all internationally active insurance groups, including G-SIIs, with final implementation to begin in 2019 following a confidential reporting period that started in 2017. These IAIS policy measures would need to be implemented by legislation or regulation in each applicable jurisdiction, and the precise implications of being designated a G-SII are not yet clear. However, they could have far-reaching regulatory and competitive implications for Allianz SE and adversely impact its capital requirements, profitability, ability to provide capital/financial support for its affiliates, ability to grow through future acquisitions, ability to conduct its business and overall competitive position compared to insurance groups that are not designated G-SIIs. The IAIS has also released an updated report on systemic risks related to insurance product features. Developments related to IAIS activity could affect the way we conduct our business (including, for example, which products we offer) and manage our capital, and could require us to satisfy increased capital requirements, which could materially affect our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
Changes in tax laws and regulations, including elimination of tax benefits for our products, may adversely affect sales of our insurance and investment advisory products, and also impact our deferred tax assets.
Changes to tax laws, including changes resulting from the tax reform legislation commonly referred to as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act that was signed into law on December 22, 2017, may affect the attractiveness of certain of our products, which currently have beneficial tax treatment. From time to time, governments have considered or implemented proposals for changes in tax law that could adversely affect our products. These proposals have included proposals to levy taxes on the undistributed increase in value of life insurance policies or annuities or similar proposals that affect the tax-favored status of life insurance products and annuities in certain jurisdictions as well as other changes that could adversely affect the attractiveness of our products. The enactment of these or other similar types of legislation in the various countries where we operate, including proposals in the U.S. to create or favor alternative tax-favored long-term savings vehicles, could result in a significant decrease in sales of our currently tax-favored products. There is uncertainty as to the impact of these proposals and the December 2017 tax reform legislation on us and the contracts we issue.
In addition, changes in tax laws or regulations (including changes resulting from the December 2017 tax reform legislation) or an operating performance below currently anticipated levels may lead to a significant impairment of deferred tax assets, in which case we could be obligated to write off certain tax assets. Tax assets may also need to be written down if certain assumptions of profitability prove to be incorrect, as losses incurred for longer than expected will make it more unlikely that we would be able to use our tax assets. Any such development may have a material adverse impact on our business or results of operations. We cannot predict what impact any such development could have on our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
Capital, Credit and Investment Risks
The amount of statutory capital that we have and the amount of statutory capital we must hold to meet our statutory capital requirements and our financial strength and credit ratings can vary significantly from time to time.
Statutory accounting standards and capital and reserve requirements are prescribed by the applicable state insurance regulators and the NAIC. State insurance regulators have established regulations that govern reserving requirements and provide minimum capitalization requirements based on risk-based capital ("RBC") ratios for life insurance companies. This RBC formula establishes capital requirements relating to insurance, business, asset and market risks including equity and interest rate risks associated with variable annuities, fixed annuities, life insurance and other insurance businesses. In any particular year, statutory surplus amounts and RBC ratios may increase or decrease depending on a variety of factors, including but not limited to the amount of statutory income or losses we generate (which itself is sensitive to equity market and credit market conditions), changes in reserves, the amount of additional capital we must hold to support business growth, changes in equity market levels, the value of certain fixed-income and equity securities in our investment portfolio, changes in interest rates, and changes to existing RBC formulas. Additionally, state insurance regulators have significant leeway in interpreting existing regulations, which could further impact the amount of statutory capital or reserves that we must maintain. If our primary state regulator were to take more stringent positions than other state insurance regulators on matters affecting, among other things, statutory capital and/or reserves, the effect of these more stringent positions may be that our financial condition appears to be worse than competitors who are not subject to the same stringent standards, which could have a material adverse impact on our competitiveness, results of operations and/or financial condition. Moreover, rating agencies may implement changes to their internal models that have the effect of increasing or decreasing the amount of capital we must hold in order to maintain our current ratings. To the extent that our statutory capital resources are deemed to be insufficient to maintain a particular rating by one or more rating agencies, our financial strength and credit ratings might be downgraded by one or more rating agencies. There can be no assurance that we will be able to maintain our current RBC ratio in the future or that our RBC ratio will not fall to a level that could have a material adverse effect on our business and consolidated results of operations or financial condition.
Changes in statutory reserve or other requirements and/or the impact of adverse market conditions could result in changes to our product offerings that could negatively impact our business.
Changes in statutory reserve or other requirements, increased costs of hedging, other risk mitigation techniques and financing, and other adverse market conditions could result in certain products becoming less profitable or unprofitable. These circumstances could cause modifications and/or the cessation of sales of certain products in the future. Modifications to products that we have made (or make in the future) may result in certain of our products being less attractive and/or competitive. This may adversely impact sales, which could negatively impact our ability to retain our sales personnel and maintain our distribution relationships. This, in turn, may negatively impact our business and our results of operations and financial condition.
Our reserves could be inadequate due to differences between our actual experience and management's estimates and assumptions.
We establish and carry reserves to pay future policyholder benefits and claims. Our reserve requirements for our business are calculated based on a number of estimates and assumptions, including estimates and assumptions related to future mortality, morbidity, interest rates, future equity performance, reinvestment rates, persistency, claims experience, and policyholder elections (i.e., the exercise or non-exercise of rights by policyholders under the contracts). Examples of policyholder elections include, but are not limited to, lapses and surrenders, withdrawals and amounts of withdrawals, and contributions and the allocation thereof. The assumptions and estimates used in connection with the reserve estimation process are inherently uncertain, involve the exercise of significant judgment, and reflect evolving information. For example, the current rates of mortality and morbidity may continue to improve in the future due to medical and technological advancements that have resulted in policyholders living longer than anticipated. We periodically review the adequacy of reserves and the underlying assumptions and make adjustments when appropriate. We cannot, however, determine with precision the amounts that we will pay for, or the timing of payment of, actual benefits and claims or whether the assets supporting the policy liabilities will grow to the level assumed prior to payment of benefits or claims. Our claim costs could increase significantly and our reserves could be inadequate if actual results differ significantly from our estimates and assumptions. If so, we will be required to increase reserves or accelerate amortization of deferred acquisition costs ("DAC"), which could adversely impact our earnings and/or capital.
Our investments are subject to several market risks, including interest rate risk, market price fluctuation risk and counterparty credit risk. These factors may have a material effect on the fair values of our investments.
The fair values of our investments are subject to market risks, including credit risk, interest rate risk and equity price risk.
Credit Risk. Counterparty credit risk is defined as the risk that a third party in a transaction will default on its commitments. Investment portfolios held by our insurance operations (excluding assets backing unit-linked products where the financial risk is borne by policyholders) could give rise to counterparty credit risk through the bonds and derivative products held within them. Credit risk diversification and analysis policies, particularly using credit ratings, are implemented by our investment group and monitored by our risk management group, but these policies may be inadequate or ineffective in protecting us against credit risk.
Interest Rate Risk. The fair values of our fixed maturity investments will fluctuate in response to changes in market interest rates. Increases and decreases in prevailing interest rates generally result in decreases and increases in fair values of those instruments.
Equity Price Risk. The carrying values of investments subject to equity price risk are, in almost all instances, based on quoted market prices as of the balance sheet dates. Market prices are subject to fluctuation and, consequently, the amount realized in the subsequent sale of an investment may differ significantly from the reported market value. Fluctuation in the market price of a security may result from, among other things, perceived changes in the underlying economic characteristics of the investee, the relative price of comparable investments and general market conditions.
Losses due to defaults by financial institution counterparties and other third parties and affiliates, impairment of our investment assets and unrealized losses all could negatively affect the value of our investments and reduce our profitability.
Third parties and affiliates that owe us money, securities or other assets may not perform under their obligations. These parties include issuers whose securities we may hold in our investment portfolios (including mortgage-backed, asset-backed and other types of securities), borrowers under mortgages and other loans that we may hold or extend, customers, trading counterparties, counterparties under swap and other derivative contracts, other counterparties (including brokers and dealers, commercial and investment banks), other investment funds, clearing agents, exchanges, clearing houses and other financial institutions. Many of our transactions with these third parties and affiliates expose us to credit risk in the event of default of our counterparty. In addition, with respect to secured transactions, our credit risk may be exacerbated when the collateral held by us cannot be realized upon or is liquidated at prices not sufficient to cover the full amount of the loan, derivative or other secured obligation. Also, defaults by parties with which we have no direct contractual relation, such as a default by a credit insurer that has insured bonds, structured finance products or other securities we may hold in our investment portfolios, may adversely impact the value of those securities and potentially adversely affect the financial markets more generally. These parties may default on their obligations due to bankruptcy, lack of liquidity, downturns in the economy or real estate market, operational failure or other reasons. Negative trends and investment climates in our major markets may result in an increase in investment impairments on our investment assets. There can be no assurance that any such losses or impairments to the carrying value of these assets would not materially and adversely affect our business and results of operations. The default of a major market participant could disrupt the securities markets or clearance and settlement systems in our major markets, which could in turn cause market declines or volatility. A failure of a major market participant could also cause some clearance and settlement systems to assess members of that system or could lead to a chain of defaults that could adversely affect us.
Some of our investments are relatively illiquid. If we are forced to liquidate these investments, we may be unable to sell them at prices that reflect fair value.
We hold certain investments that may lack liquidity, such as privately placed fixed maturity securities, mortgage loans, collateralized debt obligations, commercial mortgage-backed securities, equity real estate and limited partnership interests. Although we seek to adjust our cash and short-term investment positions to minimize the likelihood that we would need to sell illiquid investments, if we were required to liquidate these investments on short notice, we may have difficulty doing so and be forced to sell them for less than we otherwise would have been able to realize.
Interest rate and credit spread volatility may adversely affect our profitability.
Our exposure to interest rate risk relates primarily to the market price and cash flow variability associated with changes in interest rates.
During periods of declining interest rates, life insurance and annuity products may be relatively more attractive to consumers, resulting in increased premium payments on products with flexible premium features, and a higher percentage of insurance policies remaining in force from year-to-year, creating asset-liability duration mismatches. During a low interest rate period, our investment earnings may be lower because the interest earnings on our fixed income investments will likely have declined in parallel with market interest rates, which would also cause unrealized gains on our assets recorded at fair value under GAAP. In addition, mortgages and fixed maturity securities in our investment portfolios will be more likely to be prepaid or redeemed as borrowers seek to borrow at lower interest rates. Consequently, we may be required to reinvest the proceeds in securities bearing lower interest rates. Accordingly, during periods of declining interest rates, our profitability may suffer as the result of a decrease in the spread between interest rates credited to policyholders and returns on our investment portfolios.
Conversely, in periods of increasing interest rates, surrenders of life insurance policies and fixed annuity contracts may increase as policyholders choose to forgo insurance protection and seek higher investment returns. Obtaining cash to satisfy these obligations may require us to liquidate fixed maturity investments at a time when market prices for those assets are depressed because of increases in interest rates. This may result in realized investment losses. Regardless of whether we realize an investment loss, these cash payments would result in a decrease in total invested assets, and may decrease our net income. Premature withdrawals may also cause us to accelerate amortization of DAC, which would also reduce our net income.
Our mitigation efforts with respect to interest rate risk are primarily focused towards maintaining an investment portfolio with diversified maturities that has a weighted average duration that is approximately equal to the duration of our estimated liability cash flow profile. However, our estimate of the liability cash flow profile may be inaccurate and we may be forced to liquidate investments prior to maturity at a loss in order to cover the liability. Although we take measures to manage the economic risks of investing in a changing interest rate environment, we may not be able to fully mitigate the interest rate risk of our assets relative to our liabilities.
Our exposure to credit spreads primarily relates to market variability associated with changes in credit spreads. A widening of credit spreads will increase the net unrealized loss position of the investment portfolio. Credit spread tightening will reduce net investment income associated with new purchases of fixed maturity securities. Ongoing volatility in interest rates and credit spreads, individually or in tandem with other factors such as lack of pricing transparency, market illiquidity and declines in equity prices, could have a material adverse effect on our consolidated results of operations, financial condition or cash flows through realized losses, impairments, and changes in unrealized loss positions.
Recent periods have been characterized by low interest rates, and the Federal Reserve Board has committed to keeping interest rates low until there is substantial improvement in the labor market. Although the Federal Reserve continues to increase short-term interest rates, medium and long-term interest rates have remained at low levels. A prolonged period during which interest rates remain at levels lower than those anticipated may result in (1) greater costs associated with certain of our product features that guarantee death benefits or income streams for stated periods or for life, (2) higher costs for derivative instruments used to hedge certain of our product risks or (3) shortfalls in investment income on assets supporting policy obligations as our portfolio earnings decline over time, each of which may require us to record charges to increase reserves. In addition to compressing spreads and reducing net investment income, such an environment may cause policies to remain in force for longer periods than we anticipated in our pricing, potentially resulting in greater claims costs than we expected and resulting in lower overall returns on business in force.
Reinsurance may not be available, affordable or adequate to protect us against losses.
As part of our overall risk management strategy, we purchase reinsurance for certain risks underwritten by our various business segments. While reinsurance agreements generally bind the reinsurer for the life of the business reinsured at generally fixed pricing, market conditions beyond our control can determine the availability and cost of the reinsurance protection for new business. In certain circumstances, the price of reinsurance for business already reinsured may also increase. Any decrease in the amount of reinsurance will increase our risk of loss and any increase in the cost of reinsurance will reduce our earnings. Accordingly, we may be forced to incur additional expenses for reinsurance, may not be able to obtain sufficient reinsurance on acceptable terms or may not be able to obtain reinsurance coverage, which could adversely affect our ability to write future business, offer new products or enter new markets, or result in the assumption of more risk with respect to those policies we issue.
Our business is subject to fluctuations in financial markets and our hedging programs may be inadequate to protect us.
Certain types of insurance and investment products that we offer expose us to risks associated with fluctuations in financial markets, including certain types of interest sensitive or variable products such as guaranteed annuities or variable annuities, which have crediting or other guaranteed rates or guaranteed minimum benefits not necessarily related to prevailing market interest rates or investment returns on underlying assets. Although we use hedging techniques to manage our exposure under certain of these guarantees, increased volatility in the financial markets, combined with unanticipated policyholder behavior, may increase the cost of these hedges and/or negatively affect our ability to hedge certain of these risks, which may adversely affect our profitability. Our hedging programs may be inadequate to protect us against the full extent of the exposure or losses we seek to mitigate, which in turn may negatively impact our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
Poor investment performance in our variable products could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
Poor investment performance could result in a reduction in fee income received from our variable annuity products since these products generate fees primarily related to the value of our assets under management. Poor performance also could impair our prospects for growth, because our ability to attract funds from existing and new clients might diminish and existing clients might withdraw assets from our variable products in favor of better performing products of other companies, which would result in lower revenues.
The determination of the amount of allowances and impairments taken on our investments requires use of significant management judgment in certain cases, particularly for debt instruments, and could materially impact our results of operations or financial position.
The determination of the amount of allowances and impairments vary by investment type and is based upon our periodic evaluation and assessment of known and inherent risks associated with each asset class. Such evaluations and assessments are revised as conditions change and new information becomes available. In considering impairments, management considers a wide range of factors and uses its best judgment in evaluating the cause of the decline in the estimated fair value of the security and the prospects for near-term recovery. For certain asset classes, particularly debt instruments, management's evaluation involves a variety of assumptions and estimates about the operations of the issuer and its future earnings potential. Management updates its evaluations regularly and reflects changes in allowances and impairments as such evaluations are revised. There can be no assurance, however, that management has accurately assessed the level of impairments taken and allowances reflected in our financial statements, and any additional impairments and/or allowances may have a material adverse effect on our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
A downgrade or potential downgrade in our financial strength ratings could result in a loss of business.
Claims-paying and financial strength ratings, which various ratings organizations publish as measures of an insurance company's ability to meet contract holder and policyholder obligations, are important to maintaining public confidence in our Company and our products, and the ability to market our products and our competitive position. A downgrade in our financial strength ratings, or the announced potential for a downgrade, could have an adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows in several ways, including:
| · | reducing new sales of insurance products, annuities and other investment products; |
| · | increasing our cost of capital or limiting our access to sources of capital; |
| · | adversely affecting our relationships with our field marketing organizations, agents and other sales specialists; |
| · | materially increasing the number or amount of policy surrenders and withdrawals by contract holders and policyholders; |
| · | requiring us to reduce prices or increase crediting rates for many of our products and services to remain competitive; and |
| · | adversely affecting our ability to obtain reinsurance or obtain reasonable pricing on reinsurance. |
The impairment or negative performance of other financial institutions could adversely affect our business.
We have exposure to many different industries and counterparties, and routinely execute transactions with counterparties in the financial services industry, including broker-dealers, commercial banks, investment banks, insurers, reinsurers and other investment and financial institutions. The operations of U.S. and global financial services institutions are interconnected, and a decline in the financial condition of one or more financial services institutions, or the perceived lack of creditworthiness of such financial institutions, may expose us to credit losses or defaults, limit access to liquidity or otherwise disrupt the operations of our business. While we regularly assess our exposure to different industries and counterparties, the performance and financial strength of specific institutions are subject to rapid change, the timing and extent of which cannot be known.
Many transactions with and investments in the products and securities of other financial institutions expose us to credit risk in the event of default of our counterparty. With respect to secured transactions, our credit risk may be exacerbated when the collateral we hold cannot be realized upon or is liquidated at prices insufficient to recover the full amount of the loan or derivative exposure. We also have exposure to financial institutions in the form of unsecured debt instruments, derivative transactions, repurchase and underwriting arrangements and equity investments. There can be no assurance that any such losses or impairments to the carrying value of these assets would not materially and adversely impact our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
Downgrades in the credit or financial strength ratings assigned to the counterparties with whom we transact business or other adverse reputational impacts to such counterparties could create the perception that our financial condition will be adversely impacted as a result of potential future defaults by such counterparties. Additionally, we could be adversely affected by a general, negative perception of financial institutions caused by the downgrade or other adverse impact to the reputation of other financial institutions.
Business and Operational Risks
Difficult conditions in the global capital markets and the economy could materially adversely affect our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
Our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition are materially affected by conditions in the global capital markets and the economy generally.
Factors such as consumer spending, business investment, government spending, the volatility and strength of the equity markets, interest rates, deflation and inflation all affect the business and economic environment and, ultimately, the profitability of our business. In an economic downturn characterized by higher unemployment, lower family income, lower corporate earnings, lower business investment and lower consumer spending, the demand for our financial and insurance products could be adversely affected. In addition, the levels of surrenders and withdrawals of our annuity contracts we face may be adversely impacted. Our policyholders may choose to defer paying insurance premiums or stop paying insurance premiums altogether. Adverse changes in the economy could affect earnings negatively and could have a material adverse effect on our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
We use numerous assumptions to determine the appropriate level of insurance reserves and DAC and to calculate certain widely used industry measures of value, which involve a significant degree of management judgment and predictions about the future that are inherently uncertain; if these assumptions are not correct, it may have an adverse impact on our results of operations and/or performance indicators.
The establishment of insurance reserves, including the impact of minimum guarantees which are contained within certain of our variable and fixed annuity products, the adequacy test performed on the reserves for life and annuity policies and the establishment of DAC, are inherently uncertain processes involving assumptions about factors such as policyholder behavior (e.g., lapses, persistency and mortality), court decisions, changes in laws and regulations, social, economic and demographic trends, inflation, investment returns and other factors, and in the life insurance and annuity business, assumptions concerning mortality and morbidity trends. The use of different assumptions about these factors could have a material effect on our reserves and underwriting expenses as well as on our DAC. In addition, insurance reserves for minimum guarantees contained within certain of our variable and fixed annuity products may be significantly impacted by the state of the financial markets and significant declines could have a material adverse effect on our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
We face competition from other insurance companies, banks and other financial institutions, which may adversely impact our market share and profitability.
There is strong competition among insurers, banks, brokerage firms and other financial institutions and providers seeking clients for the types of products and services we provide, including insurance, annuity and other investment products and services. Competition is intense among a broad range of financial institutions and other financial service providers for retirement and other savings dollars. This competition makes it especially difficult to provide unique insurance products since once such products are made available to the public, they often are reproduced and offered by our competitors. In addition, this competition may adversely impact our market share and profitability.
Our ability to compete is dependent on numerous factors, including, among others, the successful implementation of our strategy; our financial strength as evidenced, in part, by our financial and claims-paying ratings; our access to diversified sources of distribution; our size and scale; our product quality, range, features/functionality and price; our ability to bring customized products to the market quickly; our ability to explain complicated products and features to our distribution channels and customers; our crediting rates on our fixed products; the visibility, recognition and understanding of our brands in the marketplace; our reputation and quality of service; and (with respect to variable insurance and annuity products, mutual funds and other investment products) our investment options, flexibility and investment management performance.
Consolidation of distributors of insurance products may adversely affect the insurance industry and the profitability of our business.
The insurance industry distributes many of its products through other financial institutions such as banks, broker-dealers and field marketing organizations. Over the last several years, there has been substantial consolidation of these financial institutions, particularly between and among banks and other financial services companies. An increase in consolidation activity with banks and other financial services companies affecting insurance distributors may create firms with even stronger competitive positions and negatively impact the industry's sales. Such consolidation could increase competition for access to distributors, result in greater distribution expenses and impair our ability to market insurance products to our current customer base or expand our customer base. Consolidation of distributors and/or other industry changes may also increase the likelihood that distributors will try to renegotiate the terms of any existing selling agreements to terms less favorable to us.
Inadequate or failed processes or systems, human factors or external events may adversely affect our profitability, reputation or operational effectiveness.
Operational risk is inherent in our business and can manifest itself in various ways, including business interruption, poor vendor performance, information systems malfunctions or failures, regulatory breaches, human errors, employee misconduct, and external fraud. These events can potentially result in financial loss, harm to our reputation and/or hinder our operational effectiveness. Management attempts to control these risks and keep operational risk at low levels by maintaining a sound and well controlled environment in light of the characteristics of our business, markets and regulatory environment in which we operate. Notwithstanding these measures, operational risk is part of the business environment in which we operate, and we may incur losses from time to time due to these types or risks.
The failure to maintain and modernize our information systems could adversely affect our business.
Our business depends significantly on effective information systems, and we have different information systems for our various lines of business. We must commit significant resources to maintain and enhance our existing information systems and develop new ones in order to keep pace with the evolving information technology, industry and regulatory standards and customer preferences. If we do not maintain adequate information systems, we may not be able to gather and rely on adequate information to base our pricing, underwriting and reserving decisions. We may also have difficulties in attracting new customers and preserving our existing customer base. In addition, underperforming information systems could cause us to become subject to a higher number of customer, provider and agent disputes, may increase our litigation and regulatory exposure and may make us incur higher administrative expenses, including remediation costs.
We may not be able to protect our intellectual property and may be subject to infringement claims by a third party.
We rely on a combination of contractual rights, copyright, trademark, and trade secret laws to establish and protect our intellectual property. Although we use a broad range of measures to protect our intellectual property rights, third parties may infringe or misappropriate our intellectual property. The loss of intellectual property protection or the inability to secure or enforce the protection of our intellectual property assets could have a material adverse effect on our business and our ability to compete.
Third parties may have, or may eventually be issued, patents or other protections that could be infringed by our products, methods, processes or services or could limit our ability to offer certain product features. In recent years, there has been increasing intellectual property litigation in the financial services industry challenging, among other things, product designs and business processes. If a third party were to successfully assert an intellectual property infringement claim against us, or if we were otherwise precluded from offering certain features or designs, or utilizing certain processes, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
Changes in and the adoption of accounting standards could have a material impact on our financial statements.
We prepare our financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP. From time to time, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB"), the SEC, and other regulators change the financial accounting and reporting standards governing the preparation of our financial statements. In some cases, we could be required to apply a new or revised standard retrospectively, resulting in the restating of prior period financial statements. The FASB and International Accounting Standards Board ("IASB") have ongoing projects to revise accounting standards for insurance contracts. The FASB has focused on disclosures for short-duration insurance contracts and on targeted improvements to accounting measurements and disclosures for long-duration insurance contracts. The IASB continues to contemplate significant changes to accounting measurements for both short and long duration insurance contracts. While the final resolution of changes to U.S. GAAP and International Financial Reporting Standards pursuant to these projects remains unclear, changes to the manner in which we account for insurance products could have a significant impact on our future financial reports, business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition. Further, the adoption of a new insurance contracts standard as well as other future accounting standards could have a material effect on our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
Our risk management policies and procedures may not be fully effective in identifying or mitigating our risk exposure in all market environments or against all types of risk, including employee misconduct.
We have devoted significant resources to develop our risk management policies and procedures and will continue to do so. Nonetheless, our policies and procedures to identify, monitor and manage risks may not be fully effective in mitigating our risk exposure in all market environments or against all types of risk. Many of our methods of managing risk and exposures are based upon our use of observed historical market behavior or statistics based on historical models. During periods of market volatility or due to unforeseen events, the historically derived correlations upon which these methods are based may not be valid. As a result, these methods may not predict future exposures accurately, which could be significantly greater than what our models indicate. This could cause us to incur investment losses or cause our hedging and other risk management strategies to be ineffective.
Other risk management methods depend upon the evaluation of information regarding markets, clients, catastrophe occurrence or other matters that are publicly available or otherwise accessible to us, which may not always be accurate, complete, up-to-date or properly evaluated. Moreover, we are subject to the risks of errors and misconduct by our employees, such as fraud, non-compliance with policies, recommending transactions that are not suitable, and improperly using or disclosing confidential information. These risks are difficult to detect in advance and deter, and could harm our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
We are also subject to the risk of nonperformance or inadequate performance of contractual obligations by third-party vendors of products and services that are used in our business as well as misconduct by our employees. Past or future misconduct by our employees or employees of our vendors could result in violations of law by us, regulatory sanctions and/or serious reputational or financial harm and the precautions we take to prevent and detect this activity may not be effective in all cases. Policies and procedures designed to mitigate operational, legal and regulatory risks may not be fully effective in mitigating our risk exposure in all market environments or against all types of risk. Insurance and other traditional risk-shifting tools may be held by or available to us in order to manage certain exposures, but they are subject to terms such as deductibles, coinsurance, limits and policy exclusions, as well as risk of counterparty denial of coverage, default or insolvency. We also review our compensation policies and practices as part of our overall risk management program, but it is possible that our compensation policies and practices could inadvertently incentivize excessive or inappropriate risk taking. If our associates take excessive or inappropriate risks, those risks could harm our reputation and have a material adverse effect on our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
Breaches of security, or interference with our technology infrastructure, could harm our business.
Our business is reliant upon technology systems and networks, including systems and networks managed by third parties to process, transmit and store information and to conduct business activities and transactions with clients, distributors, vendors and other third parties. We are also subject to certain federal and state regulations that require us to establish and maintain policies and procedures designed to protect sensitive client information. Maintaining the integrity of our systems is critical to the success of our business operations, including the retention of clients, and to the protection of our clients' personal information. To date, we have not experienced any material breaches of or interference with our systems and networks; however, we routinely encounter and address such threats, including an increasing frequency of phishing scams, introductions of malware and unauthorized payment requests. Any such breaches or interference by third parties or by our employees that may in the future occur could have a material adverse impact on our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
We have implemented and maintain security measures designed to protect against breaches of security and other interference with systems and networks resulting from attacks by third parties, including hackers, and from employee error or malfeasance. We also require third party vendors who, in the provision of services to us, are provided with or process information pertaining to our business or our clients to meet certain information security standards. Changes in our technology platforms, such as an evolution to accommodate mobile computing, may also require corresponding changes in our systems, networks and data security measures. In addition, the increasing reliance on technology systems and networks and the occurrence and potential adverse impact of attacks on such systems and networks, both generally and in the financial services industry, have enhanced government and regulatory scrutiny of the measures taken by companies to protect against cyber-security threats. As these threats, and government and regulatory oversight of associated risks, continue to evolve, we may be required to expend additional resources to enhance or expand upon the security measures we currently maintain. Despite the measures we have taken and may in the future take to address and mitigate these risks, we cannot ensure that our systems and networks will not be subject to breaches or interference. Any such event may result in operational disruptions as well as unauthorized access to or the disclosure or loss of our proprietary information or our clients' personal information, which in turn may result in legal claims, regulatory scrutiny and liability, reputational damage, the incurrence of costs to eliminate or mitigate further exposure, the loss of clients or other damage to our business. In addition, the trend toward broad consumer and general public notification of such incidents could exacerbate the harm to our business, financial condition, or results of operations. Even if we successfully protected our technology infrastructure and the confidentiality of sensitive data, we may incur significant expenses in responding to any such attacks as well as the adoption and maintenance of appropriate security measures. We could also suffer harm to our business and reputation if attempted security breaches are publicized. We cannot be certain that advances in criminal capabilities, discovery of new vulnerabilities, attempts to exploit vulnerabilities in our systems, data thefts, physical system or network break-ins or inappropriate access, or other developments will not compromise or breach the technology or other security measures protecting our networks and systems used in connection with our products and services.
The failure to protect our clients' confidential information and privacy could adversely affect our business.
A number of our businesses are subject to privacy regulations and confidentiality obligations. For example, certain of the activities conducted by our businesses are subject to the privacy regulations of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act and state privacy laws and regulations. We also have contractual obligations to protect certain confidential information we obtain from our existing vendors and clients. These obligations generally include protecting such confidential information in the same manner and to the same extent as we protect our own confidential information. The actions we take to protect confidential information vary by business segment and may include, among other things:
| · | training and educating our employees regarding our obligations relating to confidential information; |
| · | monitoring changes in state or federal privacy and compliance requirements; |
| · | drafting appropriate contractual provisions into any contract that raises proprietary and confidentiality issues; |
| · | maintaining secure storage facilities for tangible records; |
| · | limiting access to electronic information; and |
| · | in the event of a security breach, providing credit monitoring or other services to affected customers. |
In addition, we must develop, implement and maintain a comprehensive written information security program with appropriate administrative, technical and physical safeguards to protect such confidential information. If we do not properly comply with privacy regulations and protect confidential information, we could experience adverse consequences, including regulatory sanctions, such as penalties, fines and loss of license, as well as loss of reputation and possible litigation. This could have an adverse impact on our Company's image and, therefore, result in lower sales or lapses of existing business.
We face intense competition in attracting and retaining key talent.
Our continued success depends to a substantial degree on our ability to attract and retain qualified people. The market for qualified talent is extremely competitive, and we may not be able to attract and retain the employees we need to sustain and grow our business and operations. If we are unable to attract and retain qualified individuals or our recruiting and retention costs increase significantly, our financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely impacted.
Third-party defaults, bankruptcy filings, legal actions and other events may limit the value of or restrict our access to cash and investments.
Capital and credit market volatility can exacerbate, and has exacerbated, the risk of third-party defaults, bankruptcy filings, foreclosures, legal actions and other events that may limit the value of or restrict our access to cash and investments.
We may have contingent liabilities from discontinued, divested and run-off businesses and may incur other off-balance sheet liabilities that could result in charges to the income statement.
We may, from time to time, retain insurance obligations and other contingent liabilities in connection with our liquidation or run-off of various businesses. Our reserves for these types of obligations and liabilities may be inadequate, which could cause us to take additional charges that could be material to our results of operations. We may also, from time to time and in the course of our business, provide guarantees and enter into derivative and other types of off-balance sheet transactions that could result in income statement charges.
Protection from system interruptions and operating errors is important to our business. If we were to experience a sustained interruption to our telecommunications or data processing systems or other failure in operational execution, these events could harm our business.
Operating errors and system or network interruptions could delay and disrupt our ability to develop, deliver or maintain our products and services, causing harm to our business and reputation and resulting in loss of customers or revenue. Interruptions could be caused by operational failures arising from employee error or malfeasance, interference by third parties (including hackers and other cyber-attacks), implementation of new technology, and maintenance of existing technology. Our financial, accounting, data processing or other operating systems and facilities may fail to operate or report data properly, experience connectivity disruptions or otherwise become disabled as a result of events that are wholly or partially beyond our control, adversely affecting our ability to process transactions or provide products and services to customers. The cause of these interruptions can include fires, floods, earthquakes and other natural disasters, power losses, equipment failures, attacks by third parties, failures of internal or vendor software or systems and other events beyond our control.
We rely on third party service providers and vendors for certain communications, technology and business functions and face the risk of operational failure (including, without limitation, failure caused by an inaccuracy, untimeliness or other deficiency in data reporting), termination or capacity constraints of any of the clearing agents, exchanges, clearing houses or other third party service providers that we use to facilitate or are component providers to our transactions and other product manufacturing and distribution activities. These risks are heightened by the evolution in the financial markets of increasingly sophisticated products, by business-driven hedging, by compliance issues and by other risk management or investment or by financial management strategies. Any such failure, termination or constraint could adversely impact our ability to implement transactions, service our clients, manage our exposure to risk or otherwise achieve desired outcomes.
Failures elsewhere in the insurance industry could obligate us to pay assessments through guaranty associations.
When an insurance company becomes insolvent, state insurance guaranty associations have the right to assess other insurance companies doing business in their state for funds to pay obligations to policyholders of the insolvent company, up to the state-specified limit of coverage. The total amount of the assessment is typically based on the number of insured residents in each state, and each company's portion is based on its proportionate share of premium volume in the relevant lines of business. The future failure of a large life, health or annuity insurer could trigger assessments which we would be obligated to pay. Further, amounts for historical insolvencies may be assessed over many years, and there can be significant uncertainty around the total obligation for a given insolvency. In addition, certain states allow us to offset future assessments with premium tax offsets which are estimated and recorded as a corresponding asset. Existing liabilities may not be sufficient to fund the ultimate obligations of a historical insolvency, and we may be required to increase our liability, which could have an adverse effect on our results of operations. In addition, future premium tax offsets may not be realized and we may be required to decrease our assets, which could also have an adverse effect on our business, consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
The occurrence of natural or man-made disasters and catastrophes could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
The occurrence of natural or man-made disasters and catastrophes, including acts of terrorism, pandemics, industrial accident, blackout, cyber-attack, computer virus, insider threat, insurrections and military actions, unanticipated problems with our disaster recovery systems, or a support failure from external providers, could adversely affect our financial condition or results of operations particularly if those events affect our computer-based data processing, transmission, storage, and retrieval systems or destroy data. Such disasters and catastrophes may damage our facilities, preventing our employees from performing their roles or otherwise disturbing our ordinary business operations, and by impacting claims. Such disasters and catastrophes may also impact us indirectly by changing the condition and behaviors of our customers, business counterparties and regulators, as well as by causing declines or volatility in the economic and financial markets.
| 15. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
The financial statements of Allianz Life Variable Account B as of and for the year or period ended December 31, 2017 (including the statements of changes in net assets for each of the years or periods in the two year period then ended and the financial highlights for each of the periods presented), are included in Part C of the Registration Statement filed with the SEC on Form N-4 in reliance upon the report of KPMG LLP, independent registered public accounting firm, and upon the authority of said firm as experts in accounting and auditing.
The consolidated financial statements and supplemental schedules of Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 and for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2017, are included in Appendix F of this prospectus, in reliance upon the report of KPMG LLP, independent registered public accounting firm, and upon the authority of said firm as experts in accounting and auditing.
AUDITOR UPDATE
European regulations that go into effect in 2021 require Allianz SE, Allianz Life's indirect parent, to change auditors. Allianz Life has conducted a 'request for proposal' process with three major accounting firms for the annual independent audit of Allianz Life and its subsidiaries and registered separate accounts.
On May 23, 2017, Allianz Life's Board of Directors approved a decision to change independent auditors. On the same day, the Board appointed PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP ("PwC") as Allianz Life's new independent registered public accounting firm to audit Allianz Life's consolidated financial statements for the fiscal year 2018.
After the issuance of the audited report for the period ended December 31, 2017, the Allianz Life Board of Directors dismissed KPMG ("KPMG") as our independent registered public accounting firm. The reports of KPMG on Allianz Life's consolidated financial statements for the two most recent fiscal years , did not contain any adverse opinion or a disclaimer of opinion and were not qualified or modified as to uncertainty, audit scope or accounting principles.
For the two most recent fiscal years or any subsequent interim period, and through the date of KPMG's report on Allianz Life's consolidated financial statements, there were: (i) no disagreements between Allianz Life and KPMG on any matter of accounting principles or practices, consolidated financial statement disclosure, or auditing scope or procedures, which disagreements, if not resolved to the satisfaction of KPMG, would have caused KPMG to make reference to the subject matter of the disagreements in connection with its report, and (ii) no reportable events within the meaning set forth in Item 304(a)(1)(v) of Regulation S-K.
Allianz Life provided KPMG with a copy of this disclosure before its filing with the SEC and requested that KPMG provide us with a letter addressed to the SEC stating whether or not it agrees with the above statements. A copy of this letter is filed as Exhibit 99 to Allianz Life's registration statement numbers 333-217303, 333-213125, 333-215103, and 333-222817 on Form S-1.
For the two most recent fiscal years, and any subsequent interim period prior to engaging PwC's engagement, we did not consult with PwC regarding (i) the application of accounting principles to a specified transaction, either completed or proposed, or the type of audit opinion that might be rendered on Allianz Life's consolidated financial statements, and PwC did not provide either a written report or oral advice to Allianz Life that was an important factor considered by Allianz Life in reaching a decision as to any accounting, auditing, or financial reporting issue, or (ii) any matter that was either the subject of a disagreement (as defined in Item 304(a)(1)(iv) of Regulation S-K and the related instructions) or a reportable event (as defined in Item 304(a)(1)(v) of Regulation S-K).
| 16. | PRIVACY NOTICE |
Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America
PO Box 1344
Minneapolis, MN 55440-1344
800.328.5600
PO Box 1344
Minneapolis, MN 55440-1344
800.328.5600
Your privacy is a high priority for Allianz ("we" or "our"). This Privacy Notice outlines our principles for collecting, using and protecting information that we maintain about you. This Privacy Notice is also displayed on our website at www.allianzlife.com.
Information about you that Allianz collects
We collect information about you so that we can process the insurance transactions you request and administer or service your policy. We also collect information to inform you of new products and services and to engage in studies or research relating to our business. We limit the information collected to what is needed for our business purposes. We may collect your information from the following sources.
| · | From you, either directly or through our financial professionals. This may include information provided on your insurance application or other forms you may complete. The information we collect includes, but is not limited to, your name, social security number, address, telephone number and e-mail address. |
| · | From others, through the process of issuing a policy or handling a claim. This may include information from consumer reporting agencies and medical or accident reports. |
| · | From your doctor or during a home visit by a health care professional. This may include your health records gathered with your written consent. |
| · | From your relationship with us. For example, this may include the number of years you have been a customer or the types of products you have purchased. |
| · | From data brokers that collect publicly available information about you. This includes household information, financial transactions, and social media activity. |
Information about you that Allianz shares
We do not share information about current or former customers with anyone, except as allowed by law. "Allowed by law" means that we may share the information we collect about you as follows.
| · | With people and entities when we have your consent to share your information. |
| · | With our affiliates and other third parties in order to process your application, or administer or service your policy. |
| · | With consumer reporting agencies to obtain a medical report, credit report, or motor vehicle report. These reports are used to decide eligibility for a policy or to process transactions you request. |
| · | With our financial professionals so that they can service your policy. They may also inform you of other Allianz products and services that may be of interest to you. |
| · | With health care providers in order to process your claim. |
| · | As required or otherwise permitted by law. This may include sharing information with state insurance agencies, law enforcement, and other government officials. We may also share your information to respond to subpoenas, court orders and other legal requests. |
| · | With research groups to conduct studies on our business to improve the products and services we offer. |
| · | To inform you of products and services that may be of interest to you. These communications may be made by us, our financial professionals, or through third parties. |
| · | With our affiliates so they can market their products and services to you. State insurance laws do not allow you to restrict this disclosure. |
Allianz does not sell your information to anyone
We do not sell your information to anyone for their own marketing purposes. For this reason, we are not required to obtain your "opt in election," "opt out election" or authorization.
Allianz policies and practices regarding security of your information
We limit access to your information to those employees, affiliates, and service providers who need it for our business purposes. We protect your information using safeguards that comply with applicable federal and state law. This includes measures that are administrative, physical, and technical in nature. We use reasonable measures to secure our websites and protect the information that may be shared over these sites.
Your ability to access and correct your information
You have the right to access and obtain a copy of your information. You may write to us and ask for a record of any disclosure of your medical information made within the last three (3) years. This does not include the right to access and copy your information related to a claim or civil or criminal proceeding. If you wish to review your information, please write us at the address above. Provide your full name, address and policy number(s). For your protection, please have your request notarized.
Within 30 working days of our receipt of your written request, you may see and get a copy of your information in person. If you prefer, we will send you a copy of your information. If medical information is contained in your file, we may request that you name a medical professional to whom we will send your information.
If you believe any of your information is incorrect, you may write to us at the address above. Within 30 working days, we will let you know if our review has resulted in a correction of your information. If we do not agree there is an error, you may file a statement disputing our finding. We will attach the statement to your file. We will send any corrections we make, or your statement, to anyone we shared your information with over the past two years, and to anyone who may receive your information from us in the future. We do not control the information about you obtained from a consumer reporting agency or a Department of Motor Vehicles. We will provide you with the names and addresses of these agencies so you can contact them directly.
Notification of change
Your trust is one of our most important assets. If we revise our privacy practices in the future, we will notify you prior to implementing any changes.
For more information or if you have questions
If you have any questions or concerns about our privacy practices, please call the Corporate Compliance Privacy Office at 800.328.5600, write us at the address above, or contact us via the secured website.
This Privacy Notice is being provided on behalf of the following companies:
| ● | Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America |
| ● | Allianz Life Financial Services, LLC |
M40018 (R-8/2017)
| 17. | TABLE OF CONTENTS OF THE STATEMENT OF ADDITIONAL INFORMATION (SAI) |
Allianz Life as Custodian………………………… | 2 | Annuity Purchases by Nonresident Aliens and | |
Legal Opinions………………………………..….. | 2 | Foreign Corporations……………………………………. | 9 |
Distributor…………………………………………. | 2 | Income Tax Withholding…………………….……………….. | 9 |
Administrative Service Fees……………………. | 2 | Multiple Contracts……………………………………………. | 9 |
Federal Tax Status…………………………..….… | 3 | Partial 1035 Exchanges……………………………………… | 9 |
| Annuity Contracts in General……………….… | 3 | Assignments, Pledges and Gratuitous Transfers…………. | 9 |
| Taxation of Annuities in General……………… | 3 | Death Benefits………………………………………………… | 10 |
| Qualified Contracts……………………..……… | 3 | Spousal Continuation and the Federal Defense of | |
| Purchasing a Qualified Contract……………… | 5 | Marriage Act (DOMA)…………………………………… | 10 |
| Distributions-Qualified Contracts……………… | 6 | Federal Estate Taxes………………………………………… | 10 |
| Distributions-Non-Qualified Contracts……..… | 7 | Generation-Skipping Transfer Tax…………………………. | 10 |
| Required Distributions………………………..… | 8 | Foreign Tax Credits………………………………………….. | 10 |
| Diversification……………………………………. | 8 | Possible Tax Law Changes…………………………………. | 10 |
| Owner Control……………………………….…. | 8 | Annuity Payments…………………………………………….. | 11 |
| Contracts Owned by Non-Individuals………… | 8 | Annuity Payment Options…………………………………… | 11 |
Appendix – Death of the Owner and/or Annuitant……… | 12 | ||
APPENDIX A – AVAILABLE INDICES
STANDARD & POOR'S 500 INDEX
The S&P 500® Index is comprised of 500 stocks representing major U.S. industrial sectors.
S&P® is a registered trademark of Standard & Poor's Financial Services LLC ("S&P"). This trademark has been licensed for use by S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC. S&P marks are trademarks of S&P. These trademarks have been sublicensed for certain purposes by Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America ("Allianz"). The S&P 500® Index ("the Index") is a product of S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC and/or its affiliates and have been licensed for use by Allianz.
Allianz products are not sponsored, endorsed, sold, or promoted by S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC, Dow Jones, S&P, or any of their respective affiliates (collectively, "S&P Dow Jones Indices"). S&P Dow Jones Indices make no representation or warranty, express or implied, to the owners of the Allianz products or any member of the public regarding the advisability of investments generally or in Allianz products particularly or the ability of the Index and Average to track general market performance. S&P Dow Jones Indices' only relationship to Allianz with respect to the Index and Average is the licensing of the Index and Average and certain trademarks, service marks, and/or trade names of S&P Dow Jones Indices and/or its third-party licensors. The Index and Average are determined, composed, and calculated by S&P Dow Jones Indices without regard to Allianz or the products. S&P Dow Jones Indices have no obligation to take the needs of Allianz or the owners of the products into consideration in determining, composing, or calculating the Index and Average. S&P Dow Jones Indices are not responsible for and have not participated in the design, development, pricing, and operation of the products, including the calculation of any interest payments or any other values credited to the products. S&P Dow Jones Indices have no obligation or liability in connection with the administration, marketing, or trading of products. There is no assurance that investment products based on the Index and Average will accurately track index performance or provide positive investment returns. S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC and its subsidiaries are not investment advisors. Inclusion of a security or futures contract within an index is not a recommendation by S&P Dow Jones Indices to buy, sell, or hold such security or futures contract, nor is it considered to be investment advice. Notwithstanding the foregoing, CME Group Inc. and its affiliates may independently issue and/or sponsor financial products unrelated to products currently being issued by Allianz, but which may be similar to and competitive with Allianz products. In addition, CME Group Inc., an indirect minority owner of S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC, and its affiliates may trade financial products which are linked to the performance of the Index and Average. It is possible that this trading activity will affect the value of the products.
S&P DOW JONES INDICES DO NOT GUARANTEE THE ADEQUACY, ACCURACY, TIMELINESS, AND/OR THE COMPLETENESS OF THE INDEX AND AVERAGE OR ANY DATA RELATED THERETO OR ANY COMMUNICATION, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO, ORAL OR WRITTEN COMMUNICATION (INCLUDING ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATIONS) WITH RESPECT THERETO. S&P DOW JONES INDICES SHALL NOT BE SUBJECT TO ANY DAMAGES OR LIABILITY FOR ANY ERRORS, OMISSIONS, OR DELAYS THEREIN. S&P DOW JONES INDICES MAKE NO EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, AND EXPRESSLY DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR USE OR AS TO RESULTS TO BE OBTAINED BY ALLIANZ, OWNERS OF THE PRODUCTS, OR ANY OTHER PERSON OR ENTITY FROM THE USE OF THE INDEX AND AVERAGE OR WITH RESPECT TO ANY DATA RELATED THERETO. WITHOUT LIMITING ANY OF THE FOREGOING, IN NO EVENT WHATSOEVER SHALL S&P DOW JONES INDICES BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO, LOSS OF PROFITS, TRADING LOSSES, LOST TIME, OR GOODWILL, EVEN IF THEY HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, TORT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR OTHERWISE. THERE ARE NO THIRD-PARTY BENEFICIARIES OF ANY AGREEMENTS OR ARRANGEMENTS BETWEEN S&P DOW JONES INDICES AND ALLIANZ OTHER THAN THE LICENSORS OF S&P DOW JONES INDICES.
RUSSELL 2000® INDEX
The Russell 2000® Index is an equity index that measures the performance of the 2,000 smallest companies in the Russell 3000® Index, which is made up of 3,000 of the biggest U.S. stocks. The Russell 2000® Index is constructed to provide a comprehensive and unbiased small-cap barometer and is completely reconstituted annually to ensure larger stocks do not affect the performance and characteristics of the true small-cap index.
The Russell 2000® Index (the "Index") is a trademark of Frank Russell Company ("Russell") and has been licensed for use by Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America ("Allianz"). Allianz products are not in any way sponsored, endorsed, sold or promoted by Russell or the London Stock Exchange Group companies ("LSEG") (together the "Licensor Parties") and none of the Licensor Parties make any claim, prediction, warranty or representation whatsoever, expressly or impliedly, either as to (i) the results to be obtained from the use of the Index (upon which the Allianz product is based), (ii) the figure at which the Index is said to stand at any particular time on any particular day or otherwise, or (iii) the suitability of the Index for the purpose to which it is being put in connection with the Allianz product. None of the Licensor Parties have provided or will provide any financial or investment advice or recommendation in relation to the Index to Allianz or to its clients. The Index is calculated by Russell or its agent. None of the Licensor Parties shall be (a) liable (whether in negligence or otherwise) to any person for any error in the Index or (b) under any obligation to advise any person of any error therein.
NASDAQ-100® INDEX
The NASDAQ-100 Index® includes 100 of the largest domestic and international non-financial securities listed on The NASDAQ Stock Market® based on market capitalization.
The Product(s) is not sponsored, endorsed, sold or promoted by Nasdaq, Inc. or its affiliates (Nasdaq, with its affiliates, are referred to as the "Corporations"). The Corporations have not passed on the legality or suitability of, or the accuracy or adequacy of descriptions and disclosures relating to, the Product(s). The Corporations make no representation or warranty, express or implied to the owners of the Product(s) or any member of the public regarding the advisability of investing in securities generally or in the Product(s) particularly, or the ability of the Nasdaq-100 Index® to track general stock market performance. The Corporations' only relationship to Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America ("Licensee") is in the licensing of the NASDAQ®, and Nasdaq-100 Index® registered trademarks, and certain trade names of the Corporations and the use of the Nasdaq-100 Index® which is determined, composed and calculated by NASDAQ without regard to Licensee or the Product(s). Nasdaq has no obligation to take the needs of the Licensee or the owners of the Product(s) into consideration in determining, composing or calculating the Nasdaq-100 Index®. The Corporations are not responsible for and have not participated in the determination of the timing of, prices at, or quantities of the Product(s) to be issued or in the determination or calculation of the equation by which the Product(s) is to be converted into cash. The Corporations have no liability in connection with the administration, marketing or trading of the Product(s).
THE CORPORATIONS DO NOT GUARANTEE THE ACCURACY AND/OR UNINTERRUPTED CALCULATION OF THE NASDAQ-100 INDEX® OR ANY DATA INCLUDED THEREIN. THE CORPORATIONS MAKE NO WARRANTY, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, AS TO RESULTS TO BE OBTAINED BY LICENSEE, OWNERS OF THE PRODUCT(S), OR ANY OTHER PERSON OR ENTITY FROM THE USE OF THE NASDAQ-100 INDEX® OR ANY DATA INCLUDED THEREIN. THE CORPORATIONS MAKE NO EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, AND EXPRESSLY DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR USE WITH RESPECT TO THE NASDAQ-100 INDEX® OR ANY DATA INCLUDED THEREIN. WITHOUT LIMITING ANY OF THE FOREGOING, IN NO EVENT SHALL THE CORPORATIONS HAVE ANY LIABILITY FOR ANY LOST PROFITS OR SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, PUNITIVE, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, EVEN IF NOTIFIED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
EURO STOXX 50®
The EURO STOXX 50®, Europe's leading Blue-chip index for the Eurozone, provides a blue-chip representation of supersector leaders in the Eurozone. The index covers 50 stocks from 11 Eurozone countries: Austria, Belgium, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal and Spain.
STOXX Limited, Deutsche Börse Group and their licensors, research partners or data providers have no relationship to Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America ("Allianz"), other than the licensing of the EURO STOXX 50® and the related trademarks for use in connection with Allianz products.
STOXX, Deutsche Börse Group and their licensors, research partners or data providers do not:
| • | sponsor, endorse, sell or promote Allianz products. |
| • | recommend that any person invest in Allianz products or any other securities. |
| • | have any responsibility or liability for or make any decisions about the timing, amount or pricing of Allianz products. |
| • | have any responsibility or liability for the administration, management or marketing of Allianz products. |
| • | consider the needs of Allianz products or the owners of Allianz products in determining, composing or calculating the EURO STOXX 50 or have any obligation to do so. |
STOXX, Deutsche Börse Group and their licensors, research partners or data providers give no warranty, and exclude any liability (whether in negligence or otherwise), in connection with the Allianz products or their performance.
STOXX does not assume any contractual relationship with the purchasers of Allianz products or any other third parties.
Specifically,
| • | STOXX, Deutsche Börse Group and their licensors, research partners or data providers do not give any warranty, express or implied, and exclude any liability about: |
| • | The results to be obtained by Allianz products, the owner of Allianz products or any other person in connection with the use of the EURO STOXX 50 and the data included in the EURO STOXX 50; |
| • | The accuracy, timeliness, and completeness of the EURO STOXX 50 and its data; |
| • | The merchantability and the fitness for a particular purpose or use of the EURO STOXX 50 and its data; |
| • | The performance of Allianz products generally. |
| • | STOXX, Deutsche Börse Group and their licensors, research partners or data providers give no warranty and exclude any liability, for any errors, omissions or interruptions in the EURO STOXX 50 or its data; |
| • | Under no circumstances will STOXX, Deutsche Börse Group or their licensors, research partners or data providers be liable (whether in negligence or otherwise) for any lost profits or indirect, punitive, special or consequential damages or losses, arising as a result of such errors, omissions or interruptions in the EURO STOXX 50 or its data or generally in relation to Allianz products, even in circumstances where STOXX, Deutsche Börse Group or their licensors, research partners or data providers are aware that such loss or damage may occur. |
The licensing Agreement between Allianz and STOXX is solely for their benefit and not for the benefit of the owners of Allianz products or any other third parties.
APPENDIX B – DAILY ADJUSTMENT
We designed the Daily Adjustment to provide an Index Option Value for the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy Index Options on days other than the Index Effective Date or an Index Anniversary. The Daily Adjustment is meant to approximate the Index Option Value on the next Index Anniversary, as adjusted for gains during the Index Year subject to the Precision Rate or Cap and either losses greater than the Buffer, or down to the Floor. The application of the Daily Adjustment is based on your agreement to be exposed to Index Anniversary gains in Index Value subject to the Precision Rate or Cap and losses in Index Value either greater than the Buffer, or down to the Floor. The Daily Adjustment in essence is a proxy for the performance of these Crediting Methods accomplished by investing a portion of the Index Option Value in a set of options and the remaining balance in an interest bearing asset.
The Daily Adjustment has two components, the change in Proxy Value and accumulated proxy interest, both multiplied by the Index Option Base. The change in Proxy Value represents the current market value of the Proxy Investment ("current Proxy Value"), less the cost of the Proxy Investment at the beginning of the Index Year ("beginning Proxy Value"). The proxy interest is an amount of interest that is earned to provide compensation for the cost of the Proxy Investment at the beginning of the Index Year. The proxy interest is approximated by the value of amortizing the cost of the Proxy Investment over the Index Year to zero. The proxy interest may be significantly different from current interest rates available on interest bearing investments. The change in Proxy Value and the proxy interest estimates the present value of positive or negative Performance Credits on the next Index Anniversary. You should note that even if your selected Index(s) experience positive growth, their Daily Adjustments may be negative because of other market conditions, such as the expected volatility of Index prices and interest rates.
The formula for the calculation of the Daily Adjustment is as follows:
Daily Adjustment = (a) change in Proxy Value plus (b) proxy interest
(a) change in Proxy Value = (current Proxy Value – beginning Proxy Value) x Index Option Base
(b) proxy interest = proxy interest rate x (1 - time remaining) x Index Option Base
proxy interest rate = beginning Proxy Value
The current Proxy Value is the Proxy Value calculated on the same day as the Daily Adjustment. The beginning Proxy Value is the Proxy Value calculated on the first day of the current Index Year. The time remaining is equal to the number of days remaining in the Index Year divided by 365.
The Proxy Value is calculated differently for each Crediting Method. We designed the Proxy Value to mimic the market value of your allocation to an Index Option. We calculate a Proxy Value for each of these Index Options you select.
For the Index Precision Strategy, the Proxy Value tracks two hypothetical derivatives:
| · | an at-the-money binary call; and |
| · | an out-of-the-money put. |
An Index Precision Strategy Index Option Proxy Value = Precision Rate x (at-the-money binary call) – (out-of-the-money put)
We designed the at-the-money binary call option to value the potential for gains equal to the Precision Rate if on the next Index Anniversary the Index Value is greater than or equal to the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary (or the Index Effective Date if this is the first Index Anniversary), and the out-of-the-money put option to value the potential for Index losses greater than the Buffer for the Index Precision Strategy. It is important to note that the out-of-the-money put option will almost always reduce the Daily Adjustment, even when the current Index price on a Business Day is higher than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary. This is because the risk that the Index Value could be lower on the next Index Anniversary is present to some extent whether or not the current Index price on a Business Day is lower than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary.
For the Index Performance Strategy, the Proxy Value tracks three hypothetical derivatives:
| · | an at-the-money call; |
| · | an out-of-the-money call; and |
| · | an out-of-the-money put. |
An Index Performance Strategy Index Option Proxy Value = (at-the-money call) – (out-of-the-money call) – (out-of-the-money put)
We designed the at-the-money call option and out-of-the-money call option to value the potential for Index gains up to the Cap, and the out-of-the-money put option to value the potential for Index losses greater than the Buffer for the Index Performance Strategy. Similar to the Index Precision Strategy, it is important to note that the out-of-the-money put option will almost always reduce the Daily Adjustment, even when the current Index price on a Business Day is higher than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary. This is because the risk that the Index Value could be lower on the next Index Anniversary is present to some extent whether or not the current Index price on a Business Day is lower than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary.
For the Index Guard Strategy, the Proxy Value tracks four hypothetical derivatives:
| · | an at-the-money call; |
| · | an at-the-money put; |
| · | an out-of-the-money call; and |
| · | an out-of-the-money put. |
An Index Guard Strategy Index Option Proxy Value = (at-the-money call) – (out-of-the-money call) – (at-the-money put) + (out-of-the-money put)
We designed the at-the-money call option and out-of-the-money call option to value the potential for Index gains up to the Cap and the at-the-money put option to value the potential for Index losses, but add back the out-of-money put option to mimic the protection of the Floor for the Index Guard Strategy. It is important to note that the at-the-money put option will almost always reduce the Daily Adjustment, even when the current Index price on a Business Day is higher than the Index Value on the last Index Anniversary. It is also important to note that the out-of-money put option will almost always reduce, and never exceed, the negative impact of the at-the-money put option for the Index Guard Strategy.
On the Index Anniversary, the current Proxy Value for an Index Option is equal to its Performance Credit as discussed in section 7, Index Options – Determining the Index Option Values for the Index Precision Strategy, Index Performance Strategy and Index Guard Strategy.
You can find a more detailed explanation of the calculation of the Proxy Value, including examples, at Exhibit 99(b) of the Form S-1 Registration Statement filed with the SEC, of which this prospectus is a part. This Exhibit is incorporated by reference into this prospectus. You can obtain a copy of this Exhibit by calling (800) 624-0197, or visiting our website at www.allianzlife.com.
APPENDIX C – BUFFERS, FLOORS AND INITIAL DPSCs, PRECISION RATES AND CAPS
This information regarding the Buffers, Floors and initial DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps is for historical purposes only; it is not a representation as to future Buffers, Floors, DPSCs, Precision Rates or Caps. DPSCs, Precision Rates and Caps may change frequently, and may vary substantially based on market conditions.
NOTE: The Index Protection Strategy with the Russell 2000® Index, Nasdaq-100® Index and EURO STOXX 50® were not available before May 1, 2018. Therefore no DPSCs for these Index Options are included here.
INDEX PROTECTION STRATEGY
Following are the initial DPSCs (offered to newly issued Contracts) from May 23, 2017, the date the Contracts were first issued, to May 1, 2018.
S&P 500® Index
| Index Effective Date | 5/23/2017- 6/5/2017 | 6/6/2017- 7/3/2017 | 7/5/2017- 7/14/2017 | 7/17/2017- 7/31/2017 | 8/1/2017- 9/5/2017 | 9/6/2017- 10/2/2017 | 10/3/2017- 11/6/2017 | 11/7/2017- 12/4/2017 |
| Initial DPSC | 3.75% | 3.75% | 3.75% | 4.75% | 4.75% | 3.75% | 3.75% | 3.75% |
| Index Effective Date | 12/5/2017-1/2/2018 | 1/3/2018- 2/5/2018 | 2/6/2018- 3/5/2018 | 3/6/2018- 4/2/2018 | 4/3/2018- 4/30/2018 | |||
| Initial DPSC | 3.75% | 3.75% | 3.85% | 3.90% | 3.95% |
INDEX PERFORMANCE STRATEGY
Following are the initial Caps (offered to newly issued Contracts) May 23, 2017, the date the Contracts were first issued, to May 1, 2018. During the periods shown below, the Buffer for the Index Performance Strategy with these Indices was 10.00% on all newly issued Contracts.
S&P 500® Index
| Index Effective Date | 5/23/2017- 6/5/2017 | 6/6/2017- 7/3/2017 | 7/5/2017- 7/14/2017 | 7/17/2017- 7/31/2017 | 8/1/2017- 9/5/2017 | 9/6/2017- 10/2/2017 | 10/3/2017- 11/6/2017 | 11/7/2017- 12/4/2017 |
| Initial Cap | 11.75% | 11.50% | 11.50% | 14.50% | 14.50% | 10.25% | 11.25% | 11.50% |
| Index Effective Date | 12/5/2017-1/2/2018 | 1/3/2018- 2/5/2018 | 2/6/2018- 3/5/2018 | 3/6/2018- 4/2/2018 | 4/3/2018- 4/30/2018 | |||
| Initial Cap | 11.50% | 11.50% | 11.50% | 13.75% | 13.25% |
Russell 2000® Index
| Index Effective Date | 5/23/2017- 6/5/2017 | 6/6/2017- 7/3/2017 | 7/5/2017- 7/14/2017 | 7/17/2017- 7/31/2017 | 8/1/2017- 9/5/2017 | 9/6/2017- 10/2/2017 | 10/3/2017- 11/6/2017 | 11/7/2017- 12/4/2017 |
| Initial Cap | 15.75% | 14.75% | 15.50% | 18.50% | 18.50% | 13.50% | 14.50% | 14.00% |
| Index Effective Date | 12/5/2017-1/2/2018 | 1/3/2018- 2/5/2018 | 2/6/2018- 3/5/2018 | 3/6/2018- 4/2/2018 | 4/3/2018- 4/30/2018 | |||
| Initial Cap | 14.50% | 14.25% | 14.25% | 16.25% | 15.50% |
Nasdaq 100® Index
| Index Effective Date | 5/23/2017- 6/5/2017 | 6/6/2017- 7/3/2017 | 7/5/2017- 7/14/2017 | 7/17/2017- 7/31/2017 | 8/1/2017- 9/5/2017 | 9/6/2017- 10/2/2017 | 10/3/2017- 11/6/2017 | 11/7/2017- 12/4/2017 |
| Initial Cap | 11.00% | 10.25% | 11.00% | 14.00% | 14.00% | 10.75% | 12.25% | 11.75% |
| Index Effective Date | 12/5/2017-1/2/2018 | 1/3/2018- 2/5/2018 | 2/6/2018- 3/5/2018 | 3/6/2018- 4/2/2018 | 4/3/2018- 4/30/2018 | |||
| Initial Cap | 11.75% | 12.00% | 12.25% | 14.75% | 14.00% |
EURO STOXX 50®
| Index Effective Date | 5/23/2017- 6/5/2017 | 6/6/2017- 7/3/2017 | 7/5/2017- 7/14/2017 | 7/17/2017- 7/31/2017 | 8/1/2017- 9/5/2017 | 9/6/2017- 10/2/2017 | 10/3/2017- 11/6/2017 | 11/7/2017- 12/4/2017 |
| Initial Cap | 15.75% | 25.00% | 20.00% | 23.00% | 23.00% | 25.00% | 25.50% | 25.00% |
| Index Effective Date | 12/5/2017-1/2/2018 | 1/3/2018- 2/5/2018 | 2/6/2018- 3/5/2018 | 3/6/2018- 4/2/2018 | 4/3/2018- 4/30/2018 | |||
| Initial Cap | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 27.00% | 26.00% |
INDEX GUARD STRATEGY
Following are the initial Caps (offered to newly issued Contracts) May 23, 2017, the date the Contracts were first issued, to May 1, 2018. During the periods shown below, the Floor for the Index Guard Strategy with these Indices was -10.00% on all newly issued Contracts.
S&P 500® Index
| Index Effective Date | 5/23/2017- 6/5/2017 | 6/6/2017- 7/3/2017 | 7/5/2017- 7/14/2017 | 7/17/2017- 7/31/2017 | 8/1/2017- 9/5/2017 | 9/6/2017- 10/2/2017 | 10/3/2017- 11/6/2017 | 11/7/2017- 12/4/2017 |
| Initial Cap | 11.50% | 12.00% | 12.00% | 15.00% | 15.00% | 12.25% | 10.75% | 11.00% |
| Index Effective Date | 12/5/2017-1/2/2018 | 1/3/2018- 2/5/2018 | 2/6/2018- 3/5/2018 | 3/6/2018- 4/2/2018 | 4/3/2018- 4/30/2018 | |||
| Initial Cap | 10.50% | 10.25% | 10.50% | 10.00% | 9.75% |
Russell 2000® Index
| Index Effective Date | 5/23/2017- 6/5/2017 | 6/6/2017- 7/3/2017 | 7/5/2017- 7/14/2017 | 7/17/2017- 7/31/2017 | 8/1/2017- 9/5/2017 | 9/6/2017- 10/2/2017 | 10/3/2017- 11/6/2017 | 11/7/2017- 12/4/2017 |
| Initial Cap | 12.25% | 12.75% | 13.00% | 16.00% | 16.00% | 12.50% | 12.00% | 11.75% |
| Index Effective Date | 12/5/2017-1/2/2018 | 1/3/2018- 2/5/2018 | 2/6/2018- 3/5/2018 | 3/6/2018- 4/2/2018 | 4/3/2018- 4/30/2018 | |||
| Initial Cap | 11.75% | 11.25% | 11.50% | 11.75% | 11.25% |
Nasdaq 100® Index
| Index Effective Date | 5/23/2017- 6/5/2017 | 6/6/2017- 7/3/2017 | 7/5/2017- 7/14/2017 | 7/17/2017- 7/31/2017 | 8/1/2017- 9/5/2017 | 9/6/2017- 10/2/2017 | 10/3/2017- 11/6/2017 | 11/7/2017- 12/4/2017 |
| Initial Cap | 10.75% | 10.75% | 10.50% | 13.50% | 13.50% | 10.50% | 10.00% | 10.25% |
| Index Effective Date | 12/5/2017-1/2/2018 | 1/3/2018- 2/5/2018 | 2/6/2018- 3/5/2018 | 3/6/2018- 4/2/2018 | 4/3/2018- 4/30/2018 | |||
| Initial Cap | 10.25% | 10.00% | 10.50% | 10.75% | 10.50% |
EURO STOXX 50®
| Index Effective Date | 5/23/2017- 6/5/2017 | 6/6/2017- 7/3/2017 | 7/5/2017- 7/14/2017 | 7/17/2017- 7/31/2017 | 8/1/2017- 9/5/2017 | 9/6/2017- 10/2/2017 | 10/3/2017- 11/6/2017 | 11/7/2017- 12/4/2017 |
| Initial Cap | 12.25% | 22.00% | 19.75% | 22.75% | 22.75% | 25.00% | 24.50% | 25.00% |
| Index Effective Date | 12/5/2017-1/2/2018 | 1/3/2018- 2/5/2018 | 2/6/2018- 3/5/2018 | 3/6/2018- 4/2/2018 | 4/3/2018- 4/30/2018 | |||
| Initial Cap | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% |
INDEX PRECISION STRATEGY
NOTE: The Index Precision Strategy was not available before November 14, 2017.
Following are the initial Precision Rates (offered to newly issued Contracts) from November 14, 2017, the date the Index Precision Strategy was first available, through May 1, 2018.
S&P 500® Index
| Index Effective Date | 11/14/2017- 12/4/2017 | 12/5/2017-1/2/2018 | 1/3/2018- 2/5/2018 | 2/6/2018- 3/5/2018 | 3/6/2018- 4/2/2018 | 4/3/2018- 4/30/2018 | ||
| Initial Precision Rate | 7.00% | 7.25% | 7.25% | 7.05% | 8.70% | 8.35% |
Russell 2000® Index
| Index Effective Date | 11/14/2017- 12/4/2017 | 12/5/2017-1/2/2018 | 1/3/2018- 2/5/2018 | 2/6/2018- 3/5/2018 | 3/6/2018- 4/2/2018 | 4/3/2018- 4/30/2018 | ||
| Initial Precision Rate | 8.75% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 8.85% | 10.25% | 9.75% |
Nasdaq 100® Index
| Index Effective Date | 11/14/2017- 12/4/2017 | 12/5/2017-1/2/2018 | 1/3/2018- 2/5/2018 | 2/6/2018- 3/5/2018 | 3/6/2018- 4/2/2018 | 4/3/2018- 4/30/2018 | ||
| Initial Precision Rate | 8.25% | 8.25% | 8.50% | 8.35% | 10.15% | 9.65% |
EURO STOXX 50®
| Index Effective Date | 11/14/2017- 12/4/2017 | 12/5/2017-1/2/2018 | 1/3/2018- 2/5/2018 | 2/6/2018- 3/5/2018 | 3/6/2018- 4/2/2018 | 4/3/2018- 4/30/2018 | ||
| Initial Precision Rate | 10.75% | 10.75% | 10.75% | 11.10% | 12.10% | 11.85% |
APPENDIX D – ANNUAL CONTRACT FEES CALCULATION EXAMPLES
Please note that these examples may differ from your actual results due to rounding.
TRADITIONAL DEATH BENEFIT
You purchase a Contract with the Traditional Death Benefit. On the Quarterly Contract Anniversary your annual product fee is 0.25% and your Contract Value and Charge Base are $100,000. This Contract Value includes any Variable Option gains or losses and any Daily Adjustments or Credits on the Index Options. During the quarter you make no additional Purchase Payments and take no withdrawals. We calculate the daily product fee amount for this quarter as follows:
(the Charge Base) x (annual product fee ÷ 365) = daily product fee amount, or: $100,000 x (0.25% ÷ 365) = $0.68
If there are 89 days in the current quarter (which includes the next Quarterly Contract Anniversary), then the total quarterly product fee is:
(number of days in the current quarter) x (daily product fee amount), or: 89 x $0.68= $60.96
On the next Quarterly Contract Anniversary we would deduct $60.96 from the Contract Value. We first account for any gains/losses on the Variable Options and add any Daily Adjustments or Credits to the Index Option Values, then process any additional Purchase Payments and withdrawals, including deduction of the total quarterly product fee. We then set the Charge Base equal to this new Contract Value. If the Contract Value at the end of the day on the Quarterly Contract Anniversary after all processing is $101,250 we would begin computing the daily product fee for the next quarter on the next day as:
(the Charge Base) x (annual product fee ÷ 365) = daily product fee amount, or: $101,250 x (0.25% ÷ 365) = $0.69
If you make an additional Purchase Payment of $15,000 on the 43rd day of the next quarter, your Charge Base would increase by the amount of the payment to $116,250 ($101,250 + $15,000). We would then use this new Charge Base to begin computing the daily product fee for the remainder of the quarter on the next day as:
(the Charge Base) x (annual product fee ÷ 365) = daily product fee amount, or: $116,250 x (0.25% ÷ 365) = $0.80
If there are 92 days in the current quarter (which includes the next Quarterly Contract Anniversary), then the total quarterly product fee is:
(number of days in the current quarter) x (daily product fee amount), or:
(43 x $0.69) + (49 x $0.80) = $29.82 + $39.02 = $68.84
On the next Quarterly Contract Anniversary we would deduct $68.84 from the Contract Value after we account for any gains/losses on the Variable Option and add any Daily Adjustments or Credits to the Index Option Values. We would then process any additional Purchase Payments and any other withdrawals and set the Charge Base equal to this new Contract Value and begin computing the daily product fee for the next quarter on the next day.
MAXIMUM ANNIVERSARY VALUE DEATH BENEFIT
You purchase a Contract with the Maximum Anniversary Value Death Benefit. On the Quarterly Contract Anniversary your total annual Contract fees are 0.45% (0.25% product fee and a 0.20% rider fee) and your Contract Value and Charge Base are $100,000. This Contract Value includes any Variable Option gains or losses and any Daily Adjustments or Credits on the Index Options. During the quarter you make no additional Purchase Payments and take no withdrawals. We calculate the daily product fee amount for this quarter as follows:
(the Charge Base) x (total annual Contract fees ÷ 365) = daily Contract fee amount, or: $100,000 x (0.45% ÷ 365) = $1.23
If there are 89 days in the current quarter (which includes the next Quarterly Contract Anniversary), then the total quarterly Contract fees are:
(number of days in the current quarter) x (daily Contract fee amount), or: 89 x $1.23 = $109.73
On the next Quarterly Contract Anniversary we would deduct $109.73 from the Contract Value. We first account for any gains/losses on the Variable Options and add any Daily Adjustments or Credits to the Index Option Values, then process any additional Purchase Payments and withdrawals, including deduction of the total quarterly product fee. We then set the Charge Base equal to this new Contract Value. If the Contract Value at the end of the day on the Quarterly Contract Anniversary after all processing is $101,250, we would begin computing the daily Contract fee for the next quarter on the next day as:
(the Charge Base) x (total annual Contract fees ÷ 365) = daily Contract fee amount, or: $101,250 x (0.45% ÷ 365) = $1.25
If you make an additional Purchase Payment of $15,000 on the 43rd day of the next quarter, your Charge Base would increase by the amount of the payment to $116,250 ($101,250 + $15,000). We would then use this new Charge Base to begin computing the daily product fee for the remainder of the quarter on the next day as:
(the Charge Base) x (total annual Contract fees ÷ 365) = daily Contract fee amount, or: $116,250 x (0.45% ÷ 365) = $1.43
If there are 92 days in the current quarter (which includes the next Quarterly Contract Anniversary), then the total quarterly Contract fees are:
(number of days in the current quarter) x (daily Contract fee amount), or:
(43 x $1.25) + (49 x $1.43) = $53.68 + $70.23 = $123.91
On the next Quarterly Contract Anniversary we would deduct $123.91 from the Contract Value after we account for any gains/losses on the Variable Option and add any Daily Adjustments or Credits to the Index Option Values. We would then process any additional Purchase Payments and any other withdrawals and set the Charge Base equal to this new Contract Value and begin computing the daily Contract fee for the next quarter on the next day.
APPENDIX E – BAR CHART EXAMPLES
These hypothetical examples show conceptually how the Crediting Methods might work in different market environments and assume no change in the hypothetical DPSC, Caps or Precision Rate. They do not predict or project the actual performance of the Allianz Index Advantage ADV Variable Annuity. Although an Index or Indices will affect your Index Option Values, the Index Options do not directly participate in any stock or equity investment and are not a direct investment in an Index. The Index Value does not include the dividends paid on the stocks underlying a stock index. An allocation to an Index Option is not a purchase of shares of any stock or index fund. These examples do not reflect deduction of the Contract expenses.
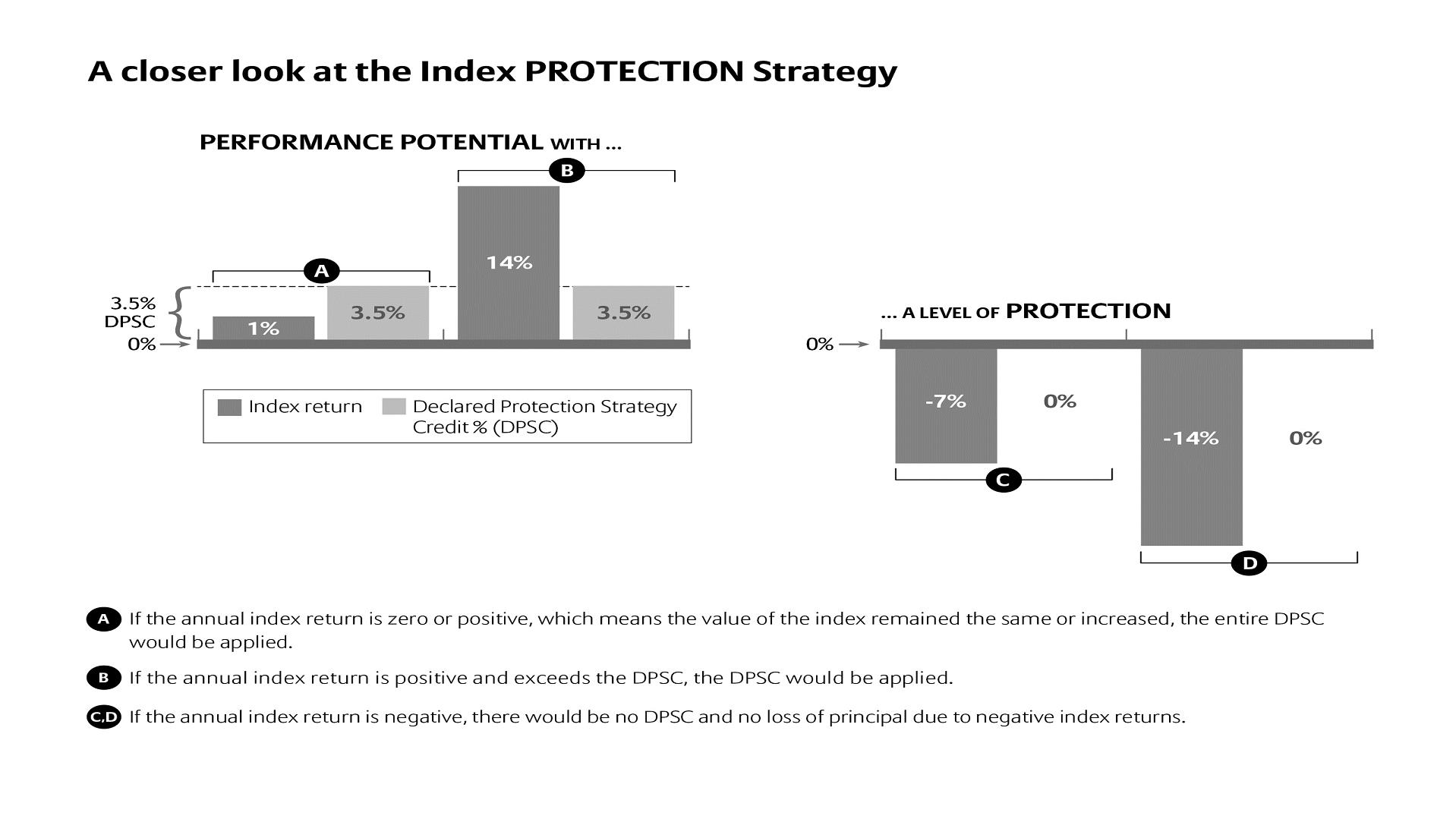

Allianz Index Advantage ADVSM Variable Annuity Prospectus – May 1, 2018
APPENDIX F – SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA AND CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS (FOR THE 12 MONTH PERIOD ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2017)
The following discussion of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and notes to those statements included in this Appendix. The discussion and analysis in this Appendix includes certain forward-looking statements that are subject to risks, uncertainties and other factors, as described in "Risk Factors" and elsewhere in this prospectus, that could cause our actual growth, results of operations, performance, financial position and business prospects and opportunities in 2018 and beyond to differ materially from those expressed in, or implied by, those forward-looking statements. See "Forward-Looking Statements."
CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTAL SCHEDULES
The following consolidated financial statements and supplemental schedules of Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 and for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2017, are included in this Appendix in reliance upon the report of KPMG LLP, independent registered public accounting firm, and upon the authority of said experts in accounting and auditing. The principal business address of KPMG LLP is 4200 Wells Fargo Center, 90 South Seventh Street, Minneapolis, MN.
Part I
Item 11(f).
Selected Financial Data
(dollars in thousands, unless otherwise stated)
The following table sets forth the Company’s selected historical consolidated financial data. The selected financial data has been derived from the audited U.S. generally accepted auditing principles (GAAP) Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this prospectus, and should be read in conjunction with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and the Company’s audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements.
These historical results are not necessarily indicative of results to be expected for any future period.
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Selected income data | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||
| Premiums and policy fees, net | $ | 1,605,227 | $ | 1,407,279 | $ | 1,449,591 | $ | 1,408,097 | $ | 1,288,373 | ||||||||||
| Interest and similar income, net | 4,522,219 | 4,325,737 | 4,175,469 | 3,955,659 | 3,587,373 | |||||||||||||||
| Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 3,602,468 | (178,238 | ) | (532,720 | ) | 1,841,989 | 921,265 | |||||||||||||
| Realized investment gains (losses), net | 83,622 | (49,325 | ) | 94,413 | 77,762 | 188,297 | ||||||||||||||
| Fee, commission, and other revenue | 324,730 | 309,854 | 303,399 | 311,820 | 306,779 | |||||||||||||||
| Total revenue | 10,138,266 | 5,815,307 | 5,490,152 | 7,595,327 | 6,292,087 | |||||||||||||||
| Total benefits and expenses | 9,215,746 | 4,671,973 | 4,646,790 | 7,415,139 | 5,547,609 | |||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) | 208,557 | 355,156 | 243,066 | 24,723 | 203,292 | |||||||||||||||
| Net income | $ | 713,963 | $ | 788,178 | $ | 600,296 | $ | 155,465 | $ | 541,186 | ||||||||||
| As of December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Selected balance sheet data | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||
| Total investments | $ | 113,183,598 | $ | 100,199,823 | $ | 91,030,336 | $ | 88,992,022 | $ | 75,459,751 | ||||||||||
| Deferred acquisition costs | 3,850,840 | 5,246,343 | 6,283,236 | 4,362,771 | 4,820,215 | |||||||||||||||
| Separate account assets | 28,192,877 | 27,733,261 | 28,243,123 | 30,789,371 | 30,747,777 | |||||||||||||||
| Total assets | 158,183,050 | 145,589,400 | 137,717,795 | 135,107,955 | 121,124,973 | |||||||||||||||
| Total policyholder liabilities | 116,837,774 | 106,395,800 | 98,282,760 | 92,264,270 | 78,949,169 | |||||||||||||||
| Separate account liabilities | 28,192,877 | 27,733,261 | 28,243,123 | 30,789,371 | 30,747,777 | |||||||||||||||
| Total liabilities | 150,223,344 | 138,514,733 | 131,201,469 | 127,331,605 | 114,028,449 | |||||||||||||||
| Total stockholder’s equity | 7,959,706 | 7,074,667 | 6,516,326 | 7,776,350 | 7,096,524 | |||||||||||||||
Item 11(h).
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following discussion and analysis provides an assessment by management of the Company’s financial condition as of December 31, 2017, compared with December 31, 2016, and its results of operations for each of the three years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, 2015, respectively. The information contained herein should be read in conjunction with the Company’s 2017 and 2016 audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements . The information contained below includes certain forward-looking statements that are subject to risks, uncertainties and other factors, as described in “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this prospectus, that could cause actual growth, results of operations, performance, financial position and business prospects and opportunities in 2018 and beyond to differ materially from those expressed in, or implied by, those forward-looking statements. See “Forward-Looking Statements.”
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 1 of 27
Company Overview
Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America (hereafter referred to as “the Company”, “we”, “our” and “us”) is a life insurance company with one wholly-owned life insurance company subsidiary, Allianz Life Insurance Company of New York (Allianz Life of NY) . The Company is domiciled in the State of Minnesota, and is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Allianz of America, Inc. (AZOA or parent company), which is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Allianz Europe, B.V. Allianz Europe, B.V. is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Allianz SE. Allianz SE is a European company registered in Munich, Germany, and is the Company’s ultimate parent.
The Company offers a portfolio of individual annuities and individual life insurance products and is licensed to sell in the United States, Canada, and several U.S. territories. We also maintain a legacy portfolio of individual long-term care (LTC), individual and group life, individual and group annuity, and individual and group accident and health policies, but do not actively issue new policies related to these products. Our products are either sold through licensed independent agents, contracted with a field marketing organization or insurance agency, or through licensed registered representatives that are contracted with a broker-dealer or associated with a banking institution.
The Company has organized its principal operations into the following segments: Individual Annuities, Life, Questar, and Legacy.
Individual Annuities
The Individual Annuities segment provides tax-deferred investment growth and lifetime income opportunities for our customers through fixed, fixed-indexed, variable, and variable-indexed annuities. The “fixed” and “variable” classifications describe whether we or the contractholders bear the investment risk of the assets supporting the contract. We are one of the largest sellers of fixed-indexed annuity products and also offer a number of variable and variable-indexed products. Fixed and variable annuities provide for both asset accumulation and asset distribution needs.
Fixed and fixed-indexed annuities provide guarantees related to the preservation of principal and interest credited. In 2017, sales were lower than the prior year due to changes in the regulatory and compensation environment after the implementation of the Department of Labor (DOL) Fiduciary Rule. In addition, favorable equity market performance created more demand for products with uncapped growth. In 2016, sales were higher than the prior year due to the Allianz 222 FIA sales promotion which offered contract holders certain bonus enhancements.
Variable annuities allow the contractholder to make deposits into various investment options and also have unique product features that allow for guaranteed minimum income benefits, guaranteed minimum accumulation benefits, guaranteed minimum death benefits, and guaranteed minimum withdrawal benefits. The variable annuity products with guaranteed minimum benefits which provide a minimum return based on their initial deposit may be increased by additional deposits, bonus amounts, or other account crediting features. The income and accumulation benefits shift a portion of the investment risk from the contractholder back to the Company. In 2017, sales of the variable-indexed annuity continued to gain momentum and were positively impacted by a sales campaign which offered enhanced crediting rates. This product combines a separate account option with a general account option that is similar to a fixed-indexed annuity. Our Individual Annuity products are sold through both independent and wholly-owned distribution channels made up of agents and registered representatives.
Life
Our life insurance products provide flexibility and control over a person’s assets, providing the assurance that the beneficiaries will be protected after the insured is gone and, in certain cases, to add cash value accumulation potential. The sales focus of our Life segment is our fixed-indexed universal life (FIUL) insurance products. Deposits are credited to an account maintained for the policyholder. Our individual life products are sold through independent distribution channels made up of agents and registered representatives.
Questar
The Questar segment consists of two wholly-owned subsidiaries, Questar Capital Corporation (Questar Capital) and Questar Asset Management, Inc. (QAM). Questar Capital is registered as a broker-dealer under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and operates as a retail broker-dealer. Questar Capital distributes a full range of securities products, including mutual funds, variable life insurance, and annuity contracts. Questar Capital also processes general securities transactions through a clearing arrangement with a third-party provider. QAM provides portfolio management for clients and revenue is driven by fees received based on assets under management.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 2 of 27
Legacy
The Legacy business consists of closed blocks of LTC and Special Markets products. The Special Markets products include individual and group annuity and life products, including universal life and term life insurance. Although Legacy products are part of the consolidated results, the Company does not allocate additional resources to these areas other than to maintain the operational support to its current customers. The Company enters into reinsurance agreements to manage risk resulting from businesses we have chosen to exit. The performance of these product lines is not material enough to warrant discussion as separate operating segments.
Refer to Application of Critical Accounting Policies section for information related to the allocation of income and expense to our segments.
Basis of Presentation
The audited Consolidated Financial Statements have been prepared in accordance with GAAP, which vary in certain respects from accounting practices permitted or prescribed by state insurance regulatory authorities. The accounts of the Company’s primary subsidiary, Allianz Life Insurance Company of New York (AZNY), and all other subsidiaries have been consolidated. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make certain estimates and assumptions that affect reported amounts of assets and liabilities, including reporting or disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Future events, including changes in mortality, morbidity, interest rates, capital markets, and asset valuations could cause actual results to differ from the estimates used within the Consolidated Financial Statements. Such changes in estimates are recorded in the period they are determined.
Application of Critical Accounting Policies
The preparation of the Financial Statements in conformance with GAAP requires us to adopt accounting policies and make certain estimates and assumptions, which affect amounts reported in the Consolidated Financial Statements. Our critical accounting policies are summarized in “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies” included in the accompanying notes to the audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements and require the use of judgments related to a variety of assumptions and estimates, in particular expectations of current and future mortality, persistency, investment returns, equity market performance, expenses, and interest rates. Our most critical accounting policies include those policies related to the Company’s accounting for (i) Valuation of Investments, (ii) Other-than-temporary Impairments (OTTI), (iii) Derivatives and Hedging, (iv) Deferred Acquisition Costs (DAC) and Deferred Sales Inducements (DSI), (v) Account Balances and Future Policy Benefit Reserves, (vi) Income Taxes, and (vii) Income and Expense allocation. Due to the inherent uncertainty of assumptions and estimates, the effect of certain accounting policies under different conditions or assumptions could be materially different from that reported in the audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements. A discussion of the various critical accounting policies is presented below.
Valuation of Investments
We have portfolios of certain fixed-maturity securities and equity securities classified as available-for-sale, at fair value. The related unrealized gains and losses are credited or charged directly to accumulated other comprehensive income (AOCI) in stockholder’s equity, net of tax and related shadow adjustments. The adjustments to DAC, DSI, and value of business acquired (VOBA) represent the change in amortization that would have been required as a charge to operations had such unrealized amounts been realized. The adjustment to reserves represents the increase or decrease in the reserve balance that would have been required as a charge to operations had such unrealized amounts been realized. We use a significant amount of judgment to determine the fair value of these investments.
We also have portfolios of certain fixed-maturity securities and equity securities classified as “trading”. These securities are carried at fair value, and related unrealized and realized gains and losses are reflected in Change in fair value of assets and liabilities within the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
The Fair Value Measurement Topic of the Accounting Standards Codification (Codification) establishes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs used in the valuation techniques to measure fair value.
Level 1 – Unadjusted quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets that the Company has the ability to access at the measurement date.
Level 2 – Valuations derived from techniques that utilize observable inputs, other than quoted prices included in Level 1, which are observable for the asset or liability either directly or indirectly, such as:
(a) Quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 3 of 27
(b) Quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active.
(c) Inputs other than quoted prices that are observable.
(d) Inputs that are derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data by correlation or other means.
Level 3 – Valuations derived from techniques in which the significant inputs are unobservable. Level 3 fair values reflect the Company’s own assumptions about the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability (including assumptions about risk).
The fair value of fixed-maturity securities and equity securities is based on quoted market prices in active markets when available. Based on the market data, the securities are categorized into asset class, and based on the asset class of the security, appropriate pricing applications, models and related methodology, and standard inputs are utilized to determine what a buyer in the marketplace would pay for the security in a current sale. When quoted prices are not readily available or in an inactive market, standard inputs used in the valuation models, listed in approximate order of priority, include, but are not limited to, benchmark yields, reported trades, Municipal Securities Rulemaking Board reported trades, Nationally Recognized Municipal Securities Information Repository material event notices, broker-dealer quotes, issuer spreads, two-sided markets, benchmark securities, bids, offers, reference data, and industry and economic events. In some cases, including private placement securities and certain difficult-to-price securities, internal pricing models may be used that are based on market proxies.
Generally, U.S. Treasury securities and exchange-traded stocks are included in Level 1. Most bonds for which prices are provided by third-party pricing sources are included in Level 2, because the inputs used are market observable. Bonds for which prices were obtained from broker quotes, certain bonds without active trading markets and private placement securities that are internally priced are included in Level 3.
See Note 6 of the audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding fair value of investments, including management’s process related to review of third-party pricing services.
Other-than-temporary Impairments
The Company reviews the available-for-sale and held-to-maturity fixed-maturity investment portfolios to determine whether or not declines in fair value are other-than-temporary. In addition, the Company continually evaluates average amortized cost, fair value, credit quality, extent and duration of the decline, market analysis, current events, recent price declines, changes in risk-free interest rates, and likelihood of recovery in a reasonable period of time. Based on this evaluation, management determines whether fixed-income securities are considered other-than-temporarily impaired.
When the fair value of a fixed-maturity security is less than its amortized cost, the Company assesses whether or not (i) it has the intent to sell the security or (ii) it is more likely than not that we will be required to sell the security before its anticipated recovery. We evaluate these factors to determine whether the Company or any of its internal and external investment managers have the intent to sell a security or a group of securities. We perform a cash flow projection for several years into the future to determine whether cash needs would require the sale of any securities in an unrealized loss position. If either of these conditions are met, we must recognize an other-than-temporary impairment (OTTI) for the difference between the investment’s amortized cost basis and its fair value through earnings. For securities that do not meet the above criteria and we do not expect to recover a security’s amortized cost basis, the security is also considered other-than-temporarily impaired. For these securities, we separate the total impairment into the credit loss component and the amount of the loss related to other factors. The amount of the total impairment related to credit loss is considered an OTTI and is recognized in Realized investment gains (losses), net on the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The amount of the total impairment related to other factors is recognized in other comprehensive income, net of impacts to DAC, DSI, VOBA, reserves, and deferred income taxes.
See Note 2 and 4 of the audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding other-than-temporary impairment losses.
Derivatives and Hedging
The Company utilizes derivatives within certain actively managed investment portfolios. Within these portfolios, derivatives can be used for hedging, replication, and income generation only. The financial instruments are carried at fair value and the unrealized gains and losses are reflected in Change in fair value of assets and liabilities in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 4 of 27
The Company utilizes foreign currency swaps to hedge cash flows and applies hedge accounting treatment. Specifically, the Company uses foreign currency swaps to hedge foreign currency and interest rate fluctuations on certain underlying foreign currency denominated fixed-maturity securities. The foreign currency swaps are reported at fair value in Derivative assets and Derivative liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The fair value of the foreign currency swaps are derived using a third-party vendor software program and deemed by management to be reasonable. Interest income generated from the foreign currency swaps is recorded in Interest and similar income, net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
We utilize over-the-counter (OTC) and exchange-traded interest rate swaps (IRS) to economically hedge certain variable annuity and fixed-indexed guarantee benefits. We can receive the fixed or variable rate. The IRS are traded in varying maturities. We will only enter into OTC IRS contracts with counterparties rated BBB+ or better. IRS are centrally cleared through an exchange. The IRS are subject to rules of the International Swaps and Derivatives Association, Inc. and associated Credit Support Annex agreements.
We utilize OTC options and exchange-traded options (ETO) with the objective to economically hedge certain variable annuity guaranteed benefits as well as fixed-indexed annuity, variable-indexed annuity and life products tied to certain indices. These options are not used for speculative or income generating purposes. The ETO provide us with the flexibility to use instruments that are exchange-cleared to mitigate counterparty credit risk. These options are cleared through the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC), which operates under the jurisdiction of both the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Commodities Futures Trading Commission. The credit rating on the OCC is currently AA+ from S&P.
We utilize exchange-traded futures to economically hedge fixed-indexed annuity, life, and variable annuity guarantees. The futures contracts did not require an initial investment, for the period ended December 31, 2017 and 2016.
We issue certain variable annuity products with guaranteed minimum benefit riders, including the guaranteed minimum withdrawal benefit (GMWB) and the guaranteed minimum accumulation benefit (GMAB), which are measured at fair value separately from the host variable annuity contract, with changes in fair value reported in Change in fair value of annuity and life embedded derivatives on the Consolidated Statements of Operations. These embedded derivatives are classified within Account balances and future policy benefit reserves on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Certain fixed-indexed annuity products, variable annuity riders, and fixed universal life policies include a market value liability option (MVLO), which is an embedded derivative with equity-indexed features. This embedded derivative is reported within Account balances and future policy benefit reserves on the Consolidated Balance Sheets with changes in fair value reported in Change in fair value of annuity and life embedded derivatives on the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
See Note 5 of the audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding derivatives and hedging instruments.
Deferred Acquisition Costs and Deferred Sales Inducements
Acquisition costs consist of commissions and other incremental costs that are directly related to the successful acquisition of insurance contracts. Acquisition costs are deferred to the extent recoverable from future policy revenues and gross profits. However, acquisition costs associated with insurance contracts recorded under the fair value option are not deferred as guidance related to the fair value option requires that transaction costs are recorded immediately as an expense. For life and annuity products, with the exception of variable annuity contracts issued prior to 2010, acquisition costs are amortized in relation to the present value of expected future gross profits from investments and mortality, morbidity, and expense charges. For variable annuity contracts issued prior to 2010, acquisition costs are amortized in relation to the present value of estimated gross revenues from investments and mortality, morbidity, and expense charges.
Acquisition costs for accident and health insurance policies are amortized over the lives of the policies in the same manner as premiums are earned. For traditional life and group life products, such costs are amortized over the projected earnings pattern of the related policies using the same actuarial assumptions used in computing future policy benefit reserves.
DAC are reviewed for recoverability and loss recognition, at least annually, and adjusted when necessary. The evaluation is a two-step process where current policy year issues are evaluated for recoverability, and then in-force policies are evaluated for loss recognition. Before assessing recoverability and loss recognition, DAC are capped, if necessary, such that the balance cannot exceed the original capitalized costs plus interest.
Sales inducements are product features that enhance the investment yield to the contractholder on the contract. The Company offers an immediate bonus on certain annuity contracts which increases the account value at inception.
These annuity sales inducements are deferred when credited to contractholders. DSI are reported in Other assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. They are amortized over the expected life of the contract in a manner similar to DAC and are reviewed annually for recoverability. DSI amortization is recorded in Policyholder benefits, net of recoveries within the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 5 of 27
We review our best-estimate assumptions and record “unlocking” on an annual basis. These reviews are based on recent changes in the organization and businesses of the Company, and actual and expected performance of in-force policies. Our review includes all assumptions, including mortality, lapses, expenses, and separate account returns. The revised best estimate assumptions are applied to the current in-force policies to project future gross profits.
See Note 9 and 10 of the audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding DAC and DSI.
Account Balances and Future Policy Benefit Reserves
We calculate and maintain reserves for the estimated future payment of claims to policyholders based on actuarial assumptions and in accordance with industry practice. Many factors can affect these reserves, including economic and social conditions, as well as inflation. The reserves we establish are policy and contract account balances for interest-sensitive products, which include fixed deferred annuities and fixed life contracts and are generally carried at accumulated contract values. For fixed-indexed annuity products, the policyholder obligation is divided into two parts – one part representing the value of the underlying base contract (host contract) and the second part representing the fair value of the expected index benefit over the life of the contract. The value of the host contract accrues to guaranteed minimum amounts of the base policy. The index benefit is valued at fair value using current capital market assumptions, such as market index and volatility, to estimate future index levels. The index benefit valuation is also dependent upon estimates of future policyholder behavior. We must include provisions for our own credit risk and for risk that our assumptions about policyholder activity could differ from actual experience. The fair value determination of the index benefit is sensitive to the economic market and interest rate environment, as it is discounted at current market interest rates. There is volatility in this liability due to these external market sensitivities.
Certain two-tier fixed annuity products provide additional benefits payable upon annuitization for period-certain and life-contingent payout options. An additional annuitization reserve is accrued using assumptions consistent with those used in estimating gross profits for purposes of amortizing DAC.
We issue variable annuity contracts through our separate accounts for which investment income and investment gains and losses accrue directly to, and investment risk is borne by, the contractholder. We recognize gains or losses on transfers from the general account to the separate accounts at fair value to the extent of contractholder interests in separate accounts, which are offset by changes in contractholder liabilities. We also issue variable annuity contracts through our separate accounts where we provide certain contractual guarantees to the contractholder. These guarantees are in the form of a guaranteed minimum death benefit (GMDB), a guaranteed minimum income benefit (GMIB), a GMAB, and a GMWB. These guarantees provide for benefits that are payable to the contractholder in the event of death, annuitization, or at specified dates during the accumulation period.
Changes in GMDB and GMIB are calculated in accordance with the Financial Services – Insurance Topic of the Codification and are included in Policyholder benefits, net of recoveries, on the Consolidated Statements of Operations. GMAB and GMWB are considered to be embedded derivatives under the Derivatives and Hedging Topic of the Codification, and the changes in these embedded derivatives are included in Change in fair value of annuity and life embedded derivatives on the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The GMDB provides a specified minimum return upon death. The survivor has the option to terminate the contract or continue it and have the death benefit paid into the contract. The GMIB is a living benefit that provides the contractholder with a guaranteed annuitization value. The GMDB and GMIB liabilities are determined each period by estimating the expected future claims in excess of the associated account balances. We regularly evaluate estimates used and adjust the additional liability balance, with a related charge or credit to Policyholder benefits, net of recoveries, on the Consolidated Statements of Operations if actual experience or other evidence suggests that earlier assumptions should be revised. The GMAB is a living benefit that provides the contractholder with a guaranteed value that was established at least five years prior at each contract anniversary. The GMWB is a living benefit that provides the contractholder with a guaranteed amount of income in the form of partial withdrawals.
Contract account balances for variable annuity products are carried at accumulated contract values. Future policy benefit reserves for any death and income benefits that may exceed the accumulated contract values are established using a range of economic scenarios and are accrued for using assumptions consistent with those used in estimating gross profits or gross revenues for purposes of amortizing DAC. Future policy benefit reserves for accumulation and withdrawal benefits that may exceed account values are established using capital market assumptions, such as market index and volatility, along with estimates of future contractholder behavior.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 6 of 27
Contract account balances for variable-indexed annuity products are measured at fair value, floored at the current contract value. The fair value measurement uses current capital market assumptions, such as market index and volatility, to estimate future index levels. The contract valuation is also dependent upon estimates of future contractholder behavior. The Company must include provisions for the Company’s own credit risk and for risk that the Company’s assumptions about contractholder activity could differ from actual experience. The fair value determination of the index benefit is sensitive to the economic market and interest rate environment, as it is discounted at current market interest rates. There is volatility in this liability due to these external market sensitivities. However, if the accumulated contract account value exceeds the calculated fair value, the Company records the contract account balances at their current contract value.
See Note 2 of the audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding Account Balances and Future Policy Benefit Reserves.
Income Taxes
We file a consolidated federal income tax return with AZOA and all of its wholly-owned subsidiaries. The consolidated tax allocation agreement stipulates that each company participating in the return will bear its share of the tax liability pursuant to certain tax allocation elections under the Internal Revenue Code and its related regulations and reimbursement will be in accordance with an intercompany tax reimbursement arrangement. We provide for federal income taxes based on amounts we believe are ultimately owed. Inherent in the provision for federal income taxes are estimates regarding the deductibility of certain items and the realization of certain tax credits. In the event the ultimate deductibility of certain items or the realization of certain tax credits differs from estimates, we may be required to significantly change the provision for federal income taxes recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Any such change could significantly affect the amounts reported within the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Management uses best estimates to establish reserves based on current facts and circumstances regarding tax exposure items where the ultimate deductibility is open to interpretation. Quarterly, we evaluate the appropriateness of such reserves based on any new developments specific to their fact patterns. Information considered includes results of completed tax examinations, Technical Advice Memorandums, and other rulings issued by the Internal Revenue Service or the tax courts.
We utilize the asset and liability method of accounting for income tax. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in operations in the period that includes the enactment date. Subsequent changes in deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized in operations or OCI, depending on the nature of the underlying temporary difference. Valuation allowances are established when it is determined that it is more likely than not that the deferred tax asset will not be fully realized or that the related temporary differences, such as OTTI, will not reverse over time.
See Note 11 of the audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding income tax estimates and assumptions.
Income and Expense Allocation
The Company maintains segregated investment portfolios at the subsidiary level but does not maintain segregated portfolios for each segment. All Interest and similar income, net and Realized investment gains (losses), net are allocated to the segments. Assets are only monitored at the total Company level, and as such, asset disclosures by segment are not included herein.
Income and expense related to assets backing policyholder reserves are allocated to the segments based on policyholder statutory reserve levels. The results of our segments also reflect allocation of income and expense related to assets backing surplus. Income and expense related to assets backing surplus are allocated to the segments based on required capital levels for each segment and are excluded from estimated gross profits used in reserve and DAC model projections.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 7 of 27
Consolidated Results of Operations
| Year ended December 31, | Increase (decrease) and % change | Increase (decrease) and % change | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2017 - 2016 | 2016 - 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Premiums and policy fees, net | $ | 1,605,227 | $ | 1,407,279 | $ | 1,449,591 | $ | 197,948 | 14.1 | % | $ | (42,312 | ) | (2.9 | )% | ||||||||||
| Interest and similar income, net | 4,522,219 | 4,325,737 | 4,175,469 | 196,482 | 4.5 | % | 150,268 | 3.6 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 3,602,468 | (178,238 | ) | (532,720 | ) | 3,780,706 | NM* | 354,482 | 66.5 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Realized investment gains (losses), net | 83,622 | (49,325 | ) | 94,413 | 132,947 | 269.5 | % | (143,738 | ) | (152.2 | )% | ||||||||||||||
| Fee, commission, and other revenue | 324,730 | 309,854 | 303,399 | 14,876 | 4.8 | % | 6,455 | 2.1 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Total revenue | 10,138,266 | 5,815,307 | 5,490,152 | 4,322,959 | 74.3 | % | 325,155 | 5.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Benefits and expenses: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net benefits and expenses | 7,129,239 | 2,383,178 | 2,603,094 | 4,746,061 | 199.1 | % | (219,916 | ) | (8.4 | )% | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative and commission | 1,812,144 | 2,029,388 | 1,804,437 | (217,244 | ) | (10.7 | )% | 224,951 | 12.5 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Change in deferred acquisition costs, net | 274,363 | 259,407 | 239,259 | 14,956 | 5.8 | % | 20,148 | 8.4 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Total benefits and expenses | 9,215,746 | 4,671,973 | 4,646,790 | 4,543,773 | 97.3 | % | 25,183 | 0.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Pretax income | 922,520 | 1,143,334 | 843,362 | (220,814 | ) | (19.3 | )% | 299,972 | 35.6 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) | 208,557 | 355,156 | 243,066 | (146,599 | ) | (41.3 | )% | 112,090 | 46.1 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Net income | $ | 713,963 | $ | 788,178 | $ | 600,296 | $ | (74,215 | ) | (9.4 | )% | $ | 187,882 | 31.3 | % | ||||||||||
| *Not meaningful | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2017 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2016
Overview
| • | Net income: For the Company, the decrease in net income was primarily due to our Individual Annuity segment driven by unfavorable net hedging and reserve movements due to the increase in equity markets. This was partially offset by the passing of the H.R.1, commonly referred to as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 (Tax Act of 2017), which reduced the corporate tax rate from 35% to 21% for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017. As a result, the deferred taxes recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheets were revalued and the total impact was $118,343. |
Revenue
Premiums and policy fees, net: Net premiums consist primarily of premiums for term life insurance, and LTC, net of reinsurance. Policy fees represent asset fees, cost of insurance charges, administrative fees, charges for guarantees on investment products, and surrender charges for investment products and universal life insurance.
| • | Premiums and policy fees increased primarily due to the Individual Annuity segment due to the favorable fixed-indexed annuity surrender margin and higher variable-indexed annuity product fee income. The Life segment also had favorable impacts from higher premium and expense fees as a result of the continued growth of the block of business. |
Interest and similar income, net: Interest and similar income primarily includes interest income on fixed-maturity securities.
| • | Interest and similar income increased primarily due to an increase in average invested assets backing policyholder liabilities and an increase in the general account balance. |
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 8 of 27
Change in fair value of assets and liabilities: Change in fair value of assets and liabilities primarily represents the changes in fair value and the realized gains and losses from derivative instruments driven by interest rate and equity market movement. It also includes gains and losses and changes in fair value on equity security investments classified as trading or fair value through income or for which we have elected the fair value option. We utilize derivatives within certain actively managed investment portfolios to manage the risk associated with variability in cash flows or changes in fair values related to financial assets and liabilities. See Application of Critical Accounting Policies section for additional information. The derivative results economically hedge reserve changes related to embedded derivatives in Net benefits and expenses line.
| • | The Change in fair value of assets and liabilities increase is driven by gains on derivative assets within our Individual Annuity segment mainly due to the favorable equity market movements in 2017. This was partially offset by the change in the fair value option due to the continued growth of the variable-indexed annuity product. |
Realized investment gains (losses), net: Realized investment gains consist of gains (losses) from the sale or impairment of investments.
| • | The increased realized investment gains in 2017 were primarily due to sales activity and lower credit impairments. The prior year credit impairments were driven by energy sector impairments which have since recovered and have been sold. |
Fee, commission, and other revenue: Fee, commission and other revenue relate primarily to annual marketing or distribution fees on investment options (12B-1 fees) and investment advisory fees earned on assets under management by fund companies within Individual Annuity and Questar, and gross dealer concessions from sales of products within Questar. This also includes the change in cash surrender value for our corporate-owned life insurance (COLI) policies.
| • | Fee, commission, and other revenue increased driven by higher revenue in our Questar segment due to an increase in first year concessions and higher registered investment advisor fees due to higher assets under management and favorable COLI impacts due to the 2017 equity market increase. This was offset by lower variable annuity investment advisory fees and 12B-1 revenue within our Individual Annuity segment due to the change in investment strategy from actively to passively managed funds. |
Benefits and Expenses
Net benefits and expenses: Net benefits and expenses consist of amounts paid to policyholders and changes in liabilities held for anticipated future benefit payments under insurance policies and annuity contracts. Amounts are net of benefit payments recovered or expected to be recovered under reinsurance contracts. The index benefit under fixed-indexed annuities and FIUL, and the accumulation and withdrawal benefits under variable annuity guarantees include the change in fair value for these embedded derivatives. The derivatives economically hedge these benefits and changes are included in revenue under Change in fair value of assets and liabilities. Net benefits and expenses also include amortization of DSI.
| • | Net benefits and expenses increased driven by the Individual Annuity products which reflect an unfavorable change in reserves primarily due to the increase in equity markets in 2017. The equity markets had significant gains in 2017 compared to 2016. This was partially offset by favorable impacts from unlocking in our Life segment. |
General and administrative and commission: General and administrative and commission includes compensation, commissions paid to sales force, consultant fees and information technology (IT) expenses, facilities and equipment, advertising and marketing, legal and regulatory, and corporate related expenses. Commissions and other incremental acquisition costs, which are directly related to the successful acquisition of insurance contracts, are capitalized in Change in deferred acquisition costs, net.
| • | General and administrative and commission decreased primarily due to lower fixed annuity commissions, consistent with the decrease in deposits. This was partially offset by the Life segment due to higher commissions driven by the increase in production. |
Change in deferred acquisition costs, net: Change in deferred acquisition costs, net represents the capitalization of acquisition costs reported in general and administrative and commission expenses, and amortization of DAC. Impacts due to changes in assumptions are recorded as amortization through the unlocking process.
| • | The change in DAC reflects an unfavorable change primarily due to lower DAC capitalization partially offset by lower DAC amortization. The lower capitalization is driven by the decrease in production in 2017 within our fixed-indexed annuities due to the higher demand for products with uncapped growth largely impacted by 2017 equity market conditions. In addition, sales were lower than the prior year due to changes in the regulatory and compensation environment after the implementation of the DOL Fiduciary Rule. The lower amortization is due to the change in estimated gross profits (EGP) and the favorable impacts of unlocking in the Individual Annuity segment. |
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 9 of 27
Income tax expense
| • | Income tax expense: The decrease in the 2017 Income tax expense is the result of a deferred tax benefit as a result of the enacted tax rate changes for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017. The change required the Company to revalue the deferred taxes as of the enactment date of the new tax law, December 22, 2017, on its Consolidated Balance Sheets from the current rate of 35% to the new 21% rate which is recorded in Income tax expense. |
Year Ended December 31, 2016 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2015
Overview
| • | Net income: The increase in net income was driven by our Individual Annuity segment due to the favorable impacts from the change in the equity markets, increase in interest rates, and positive unlocking. This was partially offset by Questar due to lower revenue, higher IT expenses, and consulting fees due to anticipated Department of Labor (DOL) regulations. We also had higher claims and a model adjustment in our LTC business within the Legacy Segment . |
Revenue
| • | Premiums and policy fees, net: Premium and policy fee revenue decreased primarily due to the unfavorable impacts of unlocking within our Life segment and lower variable product maintenance and expense (M&E) fees due to the lower Separate Account balance in our Individual Annuity segment. This was partially offset by the variable product increase in rider charges due to the higher benefit base and higher variable-indexed annuity product fee income driven by the growth of this product in 2016. |
| • | Interest and similar income, net: Interest and similar income increased primarily due to an increase in average invested assets backing policyholder liabilities, higher cash flows, and an increase in the general account balance. |
| • | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities: Change in fair value of assets and liabilities increased driven by favorable results in the Individual Annuity segment driven by gains on fixed annuity derivative assets due to the equity market gains in 2016 compared to losses in 2015. The positive variance also is driven by the interest rate impacts on derivatives backing variable annuity products (2016 interest rate increase compared to declines in 2015). The Individual Annuity and Life derivative results economically hedge reserve changes in net benefits and expenses. |
| • | Realized investment gain (losses), net: Realized investment gains (losses) , net decreased in 2016 primarily related to higher credit impairments driven by the energy sector and lower realized gains due to normal sale activity. |
| • | Fee, commission, and other revenue: Fee, commission, and other revenue increased driven by favorable COLI results and offset by lower variable investment advisory fees and 12B-1 revenue within our Individual Annuity segment and lower revenue and higher IT expenses and consulting fees in our Questar segment. This was partially offset by the lower variable investment advisory fees and 12b-1 revenue due to the decline in the asset base in 2016. |
Benefits and Expenses
| • | Net benefits and expenses: Net benefits and expenses decreased in 2016 primarily due to the Individual Annuity products which reflect a favorable change in reserves driven by the change in interest rates and positive impacts of unlocking. There was a favorable variance for both fixed and variable annuity products due to the increase in interest rates in 2016. This was partially offset by the change in reserves due to the change in equity markets. |
| • | General and administrative and commission: General and administrative and commission increased primarily due to higher fixed annuity commissions, consistent with the increase in deposits, an Allianz SE IT initiative expense, and legal accrual activity. |
| • | Change in deferred acquisition costs, net: The change in DAC reflects an unfavorable change primarily due to higher DAC amortization partially offset by higher DAC capitalization. The higher amortization is due to the impacts of unlocking. This partially offset by the change in EGPs and impacts from fixed-indexed annuities within the Individual Annuity segment, and favorable impacts of unlocking within the Life segment. The higher capitalization is driven by increased production in 2016 which is the result of the fixed-indexed annuity sales promotion. |
Income tax expense
| • | Income tax expense: The increased pretax income, with minimal variance in deductions, resulted in an increased effective tax rate of 31.1% compared to an effective tax rate of 28.8% in 2015. |
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 10 of 27
Individual Annuities
Segment Results of Operations
| Year ended December 31, | Increase (decrease) and % change | Increase (decrease) and % change | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2017 - 2016 | 2016 - 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Premiums and policy fees, net | $ | 1,249,793 | $ | 1,117,580 | $ | 1,133,285 | $ | 132,213 | 11.8 | % | $ | (15,705 | ) | (1.4 | )% | ||||||||||
| Interest and similar income, net | 4,301,602 | 4,133,359 | 3,999,693 | 168,243 | 4.1 | % | 133,666 | 3.3 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 3,368,121 | (218,922 | ) | (492,479 | ) | 3,587,043 | NM* | 273,557 | 55.5 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Realized investment gains (losses), net | 80,111 | (49,126 | ) | 90,948 | 129,237 | 263.1 | % | (140,074 | ) | (154.0 | )% | ||||||||||||||
| Fee, commission, and other revenue | 249,280 | 243,789 | 236,454 | 5,491 | 2.3 | % | 7,335 | 3.1 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Total revenue | 9,248,907 | 5,226,680 | 4,967,901 | 4,022,227 | 77.0 | % | 258,779 | 5.2 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Benefits and expenses: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net benefits and expenses | 6,570,915 | 1,982,879 | 2,296,057 | 4,588,036 | 231.4 | % | (313,178 | ) | (13.6 | )% | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative and commission | 1,486,314 | 1,774,740 | 1,549,692 | (288,426 | ) | (16.3 | )% | 225,048 | 14.5 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Change in deferred acquisition costs, net | 313,504 | 315,760 | 279,582 | (2,256 | ) | (0.7 | )% | 36,178 | 12.9 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Total benefits and expenses | 8,370,733 | 4,073,379 | 4,125,331 | 4,297,354 | 105.5 | % | (51,952 | ) | (1.3 | )% | |||||||||||||||
| Pretax income | $ | 878,174 | $ | 1,153,301 | $ | 842,570 | $ | (275,127 | ) | (23.9 | )% | $ | 310,731 | 36.9 | % | ||||||||||
| *Not meaningful | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Selected Operating Performance Measures
| Year ended December 31, | Increase (decrease) and % change | Increase (decrease) and % change | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2017 - 2016 | 2016 - 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Individual Annuity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deposits | $ | 9,952,793 | $ | 12,254,785 | $ | 10,784,423 | $ | (2,301,992 | ) | (18.8 | )% | $ | 1,470,362 | 13.6 | % | ||||||||||
| In-force | 118,409,012 | 109,698,006 | 103,222,981 | 8,711,006 | 7.9 | % | 6,475,025 | 6.3 | % | ||||||||||||||||
Deposits and in-force amounts in the table above are for direct and assumed business. Deposits reflect amounts collected on both new and renewal business. In-force represents account values of the annuity contracts for our fixed, fixed-indexed, variable, and variable-indexed annuity contracts. In 2017, sales were lower than the prior year due to changes in the regulatory and compensation environment after the implementation of the DOL Fiduciary Rule. In 2016, sales of our fixed-indexed annuity products were higher than the prior year due to the Allianz 222 FIA sales promotion which offered policyholders certain bonus enhancements.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 11 of 27
Change in Key Market Factors
Our Individual Annuity segment is impacted by various market impacts and movements which are summarized below:
| Year ended December 31, | % change | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2017 - 2016 | 2016 - 2015 | |||||
| Stock Index | |||||||||
| S&P 500 | 19.42% | 9.54% | (0.73)% | 9.88% | 10.27% | ||||
| NASDAQ 100 | 31.52% | 5.89% | 8.43% | 25.63% | (2.54)% | ||||
| BUDBI | 15.94% | 4.83% | (2.00)% | 11.11% | 6.83% | ||||
| BUDBI II | 14.31% | 4.25% | (1.33)% | 10.06% | 5.58% | ||||
| Year ended December 31, | Basis point (bps) change | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2017 - 2016 | 2016 - 2015 | |||||
| Interest Rates | |||||||||
| LIBOR 10yr | 2.40% | 2.34% | 2.20% | 6 bps | 14 bps | ||||
| LIBOR 20yr | 2.53% | 2.56% | 2.50% | (3) bps | 6 bps | ||||
Year Ended December 31, 2017 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2016
Overview
Our Individual Annuity segment pretax income decreased due to net hedging and reserve movements primarily driven by the increase in equity markets partially offset by the fixed-indexed favorable surrender margin and higher variable-indexed annuity fee income, and higher realized gains.
Revenue
| • | Premiums and policy fees. net: Premiums and policy fees increased primarily due to the favorable fixed-indexed annuity surrender margin and higher variable-indexed annuity product fee income driven by continued growth of this product in 2017. |
| • | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities: The increase in Change in fair value of assets and liabilities is driven by gains on derivative assets mainly due to the equity market movements in 2017. This was partially offset by the change in the fair value option due to the continued growth of the variable-indexed annuity product. The derivative results economically hedge reserve changes on embedded derivatives in Net benefits and expenses line. |
| • | Realized investment gains (losses) , net: The increased realized investment gains in 2017 were primarily due to sales activity and lower credit impairments. The prior year credit impairments were driven by energy sector impairments which have since recovered and have been sold. |
Benefits and Expenses
| • | Net benefits and expenses: The Net benefits and expenses reflect an unfavorable change in reserves primarily driven by the increase in equity markets in 2017. The equity markets had significant gains in 2017 compared to 2016. Reserve movements on embedded derivatives are economically hedged in Change in fair value of assets and liabilities, however, the mismatch between the economic and accounting reserve calculations cause income volatility year over year. |
| • | General and administrative and commission: The General, administrative and commission expense decreased primarily due to lower fixed-indexed annuity commissions consistent with the decrease in deposits. |
Year Ended December 31, 2016 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2015
Overview
Our Individual Annuity segment pretax income increase is primarily driven by equity market and interest rate movements partially offset by higher realized losses and impairments, an Allianz SE IT initiative expense, and lower legal accrual reserve releases in 2016 compared to 2015.
Revenue
| • | Premiums and policy fees, net: Premiums and policy fees decreased primarily due to lower M&E fees due to the lower Separate Account balance partially offset by increases in rider charges due to the higher benefit base and higher variable-indexed annuity product fee income driven by continued growth of this product in 2016. |
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 12 of 27
| • | Interest and similar income, net: The increase in interest and similar income is primarily due to an increase average invested assets backing policyholder liabilities, more favorable cash flows, and a higher general account balance. |
| • | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities: Change in fair value of assets and liabilities favorable change is driven by gains on derivative assets mainly due to the market movements in 2016 compared to 2015. This was partially offset by unfavorable interest rate impacts on derivatives backing variable annuity products and the change in the fair value option due to growth of the variable-indexed annuity product in 2016. The derivative results economically hedge reserve changes related to embedded derivatives in net benefits and expenses. |
| • | Realized investment gains (losses) , net: The increased realized investment losses in 2016 were primarily due to higher credit impairments within the energy sector and lower realized gains due to normal sale activity. |
Benefits and Expenses
| • | Net benefits and expenses: The Individual Annuity products reflect a favorable change in reserves primarily driven by the increase in interest rates partially offset by the change in equity markets. Interest rates increased in 2016 compared to interest rate declines in 2015. The equity markets had gains in 2016 compared to losses in 2015. Reserve movements related to embedded derivatives are economically hedged in Change in fair value of assets and liabilities. Net benefits and expenses include a favorable impact of $376,513 from unlocking in 2016 compared to $138,580 in the prior year. |
| • | General and administrative and commission: The General, administrative and commission expense increased primarily due to higher fixed-indexed annuity commissions consistent with the increase in deposits. The gross written premium increase is driven by the 2016 Allianz 222 sales promotion. We also incurred an Allianz SE IT initiative expense and had lower legal accrual releases in 2016 compared to 2015. |
| • | Change in deferred acquisition costs, net: The change in DAC within the Individual Annuity products reflect an unfavorable change primarily due to higher DAC amortization offset by higher DAC capitalization. The higher amortization is due to the impacts of unlocking and partially offset by the change in EGPs. The higher capitalization is driven by the increase in production in 2016 due to the fixed-annuity sales promotion. The change in DAC unfavorable unlocking impacts were $246,681 in 2016 compared to the unfavorable impact of $76,604 in 2015. |
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 13 of 27
Life
Segment Results of Operations
| Year ended December 31, | Increase (decrease) and % change | Increase (decrease) and % change | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2017 - 2016 | 2016 - 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Premiums and policy fees, net | $ | 204,920 | $ | 147,013 | $ | 172,660 | $ | 57,907 | 39.4 | % | $ | (25,647 | ) | (14.9 | )% | ||||||||||
| Interest and similar income, net | 135,346 | 113,465 | 103,326 | 21,881 | 19.3 | % | 10,139 | 9.8 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 233,840 | 40,600 | (38,553 | ) | 193,240 | 476.0 | % | 79,153 | 205.3 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Realized investment gains (losses), net | 2,272 | 623 | 1,597 | 1,649 | 264.7 | % | (974 | ) | (61.0 | )% | |||||||||||||||
| Fee, commission, and other revenue | 1,485 | 747 | 186 | 738 | 98.8 | % | 561 | 301.6 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Total revenue | 577,863 | 302,448 | 239,216 | 275,415 | 91.1 | % | 63,232 | 26.4 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Benefits and expenses: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net benefits and expenses | 350,354 | 194,667 | 114,377 | 155,687 | 80.0 | % | 80,290 | 70.2 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative and commission | 219,519 | 159,455 | 165,386 | 60,064 | 37.7 | % | (5,931 | ) | (3.6 | )% | |||||||||||||||
| Change in deferred acquisition costs, net | (59,168 | ) | (69,477 | ) | (53,642 | ) | 10,309 | 14.8 | % | (15,835 | ) | (29.5 | )% | ||||||||||||
| Total benefits and expenses | 510,705 | 284,645 | 226,121 | 226,060 | 79.4 | % | 58,524 | 25.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Pretax income | $ | 67,158 | $ | 17,803 | $ | 13,095 | $ | 49,355 | 277.2 | % | $ | 4,708 | 36.0 | % | |||||||||||
Selected Operating Performance Measures
| Year ended December 31, | Increase (decrease) and % change | Increase (decrease) and % change | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2017 - 2016 | 2016 - 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Life | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deposits and Gross premiums written | $ | 758,469 | $ | 627,563 | $ | 574,388 | $ | 130,906 | 20.9 | % | $ | 53,175 | 9.3 | % | |||||||||||
| In-force | 33,783,904 | 30,026,514 | 26,838,320 | 3,757,390 | 12.5 | % | 3,188,194 | 11.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||
Deposits and gross premiums written and in-force amounts in the table above are for direct and assumed business. Deposits reflect amounts collected on our FIUL business, and gross premiums written reflect premiums collected on our term business. In-force amounts represent life insurance in-force on our FIUL, older universal life, and term life business. The increase in deposits in 2017 and 2016 was driven by an increase in renewal deposits and new gross premiums written as a result of product changes made in 2016. The movement of in-force, year over year, is primarily driven by policyholder activity. Increases are driven by deposits and new business, and decreases are driven by policyholder charges, surrenders, and claims.
Year Ended December 31, 2017 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2016
Overview
The Life segment pretax income increased primarily due to the favorable impacts of unlocking, higher premium loads and allocated investment income due to the overall growth of the block of business partially offset by higher legal expenses.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 14 of 27
Revenue
| • | Premiums and policy fees, net: Premiums and policy fees increased primarily due to the favorable impacts of the unearned revenue reserve (URR) and higher premium and expense fees driven by increased deposits as a result of the continued growth of the Life segment. |
| • | Interest and similar income, net: Interest and similar income increased primarily due to an increase in average invested assets. |
| • | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities: Derivative income increased due to derivative results primarily driven by change in fair value of futures and options, which are intended to economically hedge reserve changes in net benefits and expenses. |
Benefits and Expenses
| • | Net benefits and expenses: Net benefits and expenses increased primarily due to unfavorable reserve movements driven by the change in equity markets partially offset by favorable impacts from unlocking. Equity market returns were more favorable in 2017 which had negative impacts on the reserves. The Life fair value reserve movement is economically hedged in Change in fair value of assets and liabilities. |
| • | General and administrative and commission: The expenses increased primarily due to higher commissions driven by the increase in production, higher allocated expenses due to the growing block of Life business, and higher product litigation expenses. |
| • | Change in deferred acquisition costs, net: The unfavorable change in DAC is driven by higher amortization and partially offset by higher capitalization. The higher amortization is driven by the change in EGP and the higher capitalization is due to the increase in first year premium in 2017. |
Year Ended December 31, 2016 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2015
Overview
The Life segment pretax income increased primarily due to the increase in interest and similar income due the growing and maturing block of business. This was partially offset by a universal life (UL) secondary guarantee reserve accrual adjustment recorded in 2016 and a 2015 premium bonus reserve adjustment, and unfavorable impacts of unlocking.
Revenue
| • | Premium and policy fees, net: Premiums and policy fees decreased primarily due to the unfavorable impacts of unlocking on URR which was partially offset by higher premium and expense fees driven by increased deposits as a result of the continued growth of the Life Segment. |
| • | Interest and similar income, net: Interest and similar income increased primarily due to an increase in Life average invested assets. |
| • | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities: Derivative income increased due to derivative results primarily driven by change in fair value of futures and options, which are intended to economically hedge reserve changes on embedded derivatives in net benefits and expenses. |
Benefits and Expenses
| • | Net benefits and expenses: Net benefits and expenses increased primarily driven by the change in the equity market in 2016 and the impacts of reserve adjustments recorded in 2016 and 2015. Market returns were more favorable in 2016 which had negative impacts on the reserves. The reserve adjustment is related to an additional UL secondary guarantee reserve accrual recorded in 2016 and impacts from the 2015 premium bonus modeling adjustments. The Life fair value reserve movement is economically hedged in Change in fair value of assets and liabilities. |
| • | General and administrative and commission: The expenses decreased primarily due to lower commissions driven by the mix of premium partially offset by higher allocated expenses due to the growing block of Life business. |
| • | Change in deferred acquisition costs, net: The favorable change in DAC is driven by lower amortization and partially offset by lower capitalization. The lower amortization is driven by the impacts of unlocking and the lower capitalization is due to decline in first year premium production in 2016. |
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 15 of 27
Questar
Segment Results of Operations
| Year ended December 31, | Increase (decrease) and % change | Increase (decrease) and % change | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2017 - 2016 | 2016 - 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest and similar income, net | $ | 68 | $ | 32 | $ | 3 | $ | 36 | 112.5 | % | $ | 29 | NM | ||||||||||||
| Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 2 | 2 | — | — | — | % | 2 | — | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Realized investment gains (losses), net | 3 | — | — | 3 | — | % | — | — | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Fee, commission, and other revenue | 110,989 | 101,432 | 105,830 | 9,557 | 9.4 | % | (4,398 | ) | (4.2 | )% | |||||||||||||||
| Total revenue | 111,062 | 101,466 | 105,833 | 9,596 | 9.5 | % | (4,367 | ) | (4.1 | )% | |||||||||||||||
| Benefits and expenses: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative and commission | 122,989 | 114,009 | 110,624 | 8,980 | 7.9 | % | 3,385 | 3.1 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Total benefits and expenses | 122,989 | 114,009 | 110,624 | 8,980 | 7.9 | % | 3,385 | 3.1 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Pretax income | $ | (11,927 | ) | $ | (12,543 | ) | $ | (4,791 | ) | $ | 616 | 4.9 | % | $ | (7,752 | ) | (161.8 | )% | |||||||
Fee, Commission and Other Revenue
| Year ended December 31, | Increase (decrease) and % change | Increase (decrease) and % change | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2017 - 2016 | 2016 - 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross dealer concessions | $ | 61,117 | $ | 54,811 | $ | 59,578 | $ | 6,306 | 11.5 | % | $ | (4,767 | ) | (8.0 | )% | ||||||||||
| Allianz Life production | 32,464 | 31,583 | 32,308 | 881 | 2.8 | % | (725 | ) | (2.2 | )% | |||||||||||||||
| Registered investment advisor fees and other revenue | 17,407 | 15,038 | 13,944 | 2,369 | 15.8 | % | 1,094 | 7.8 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Total Fee, commission and other revenue: | $ | 110,988 | $ | 101,432 | $ | 105,830 | $ | 9,556 | 9.4 | % | $ | (4,398 | ) | (4.2 | )% | ||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2017 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2016
Overview
Our Questar segment pretax loss is in line with prior year results.
Revenue
Fee, commission and other revenue: Revenue increase driven by higher gross dealer concessions revenue due to an increase in first year concessions and higher registered investment advisor fees due to higher assets under management.
Benefits and Expenses
General and administrative and commission: Expenses increased primarily due to higher general and administrative expenses driven by higher commission expenses due to the increase in production and higher legal expenses related to product litigation.
Year Ended December 31, 2016 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2015
Overview
Our Questar segment pretax loss increased compared to the prior year and is primarily due to lower revenue, the rebate of certain 12B-1 fees, higher IT expenses and consulting fees due to the anticipated DOL regulations.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 16 of 27
Revenue
Fee, commission and other revenue: Revenue decreased driven by lower gross dealer concessions revenue due to a decrease in first year concessions and partially offset by higher registered investment advisor fees due to higher assets under management.
Benefits and Expenses
General and administrative and commission: Expenses increased primarily due to higher general and administrative expenses due to higher IT expenses and consulting fees due to anticipated DOL regulations, and rebate of certain 12B-1 fees.
Legacy
Segment Results of Operations
| Year ended December 31, | Increase (decrease) and % change | Increase (decrease) and % change | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2017 - 2016 | 2016 - 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Premiums and policy fees, net | $ | 150,514 | $ | 142,686 | $ | 143,646 | $ | 7,828 | 5.5 | % | $ | (960 | ) | (0.7 | )% | ||||||||||
| Interest and similar income, net | 85,203 | 78,881 | 72,447 | 6,322 | 8.0 | % | 6,434 | 8.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 505 | 82 | (1,688 | ) | 423 | 515.9 | % | 1,770 | 104.9 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Realized investment gains (losses), net | 1,236 | (822 | ) | 1,868 | 2,058 | 250.4 | % | (2,690 | ) | (144.0 | )% | ||||||||||||||
| Fee, commission, and other revenue | 1,380 | 1,191 | 253 | 189 | 15.9 | % | 938 | 370.8 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Total revenue | 238,838 | 222,018 | 216,526 | 16,820 | 7.6 | % | 5,492 | 2.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Benefits and expenses: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net benefits and expenses | 207,970 | 205,632 | 192,660 | 2,338 | 1.1 | % | 12,972 | 6.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative and commission | 21,726 | 18,489 | 18,059 | 3,237 | 17.5 | % | 430 | 2.4 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Change in deferred acquisition costs, net | 20,027 | 13,124 | 13,319 | 6,903 | 52.6 | % | (195 | ) | (1.5 | )% | |||||||||||||||
| Total benefits and expenses | 249,723 | 237,245 | 224,038 | 12,478 | 5.3 | % | 13,207 | 5.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Pretax income | $ | (10,885 | ) | $ | (15,227 | ) | $ | (7,512 | ) | $ | 4,342 | 28.5 | % | $ | (7,715 | ) | (102.7 | )% | |||||||
Selected Operating Performance Measures
| Year ended December 31, | Increase (decrease) and % change | Increase (decrease) and % change | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2017 - 2016 | 2016 - 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Legacy Products | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross premiums written | $ | 261,258 | $ | 260,649 | $ | 264,274 | $ | 609 | 0.2 | % | $ | (3,625 | ) | (1.4 | )% | ||||||||||
| In-force | 3,459,361 | 3,721,992 | 3,973,990 | (262,631 | ) | (7.1 | )% | (251,998 | ) | (6.3 | )% | ||||||||||||||
Gross premiums written and in-force amounts in the table above are for direct and assumed business. Gross premiums written reflect premiums collected on renewal business. There are no new premiums as these are closed blocks of business. In-force amounts represent gross life insurance within our Special Markets products. The increase in gross premiums written in 2017 compared to 2016 was due to a rate increase implemented in the LTC block of business. The decrease in gross premiums written in 2016 compared to 2015 was partially driven by an increase in LTC experience refund in 2016 which decreased assumed premiums due to the change in claim activity. The continued decline in in-force volume is attributable to the Legacy segment being a closed block of business.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 17 of 27
Year Ended December 31, 2017 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2016
Overview
The Legacy segment favorable change in pretax income was driven by positive reserve impacts due to lower reserves on future losses driven by enhancements made to the reserve calculations partially offset by higher claims.
Revenue
| • | Premiums and policy fees, net: Premiums and policy fees increased primarily due to a LTC rate increase implemented in 2017 and favorable reserve changes due to model updates implemented in 2016. |
| • | Interest and similar income, net: LTC reflects higher investment income due to growth in reserves driven by an aging block of business. |
| • | Realized investment (losses) gains, net: The realized investment gains increased due to investment activity in 2017 compared to higher impairments in 2016. |
Benefits and Expenses
| • | Net benefits and expenses: Net benefits and expenses increased primarily due to overall higher LTC claim activity in 2017 and was partially offset by the impact of lower reserve charges on future losses. |
| • | General and administrative and commission: The unfavorable change in general and administrative is driven by higher LTC commissions and an increase in allocated investment expenses. |
| • | Change in deferred acquisition costs, net: The unfavorable change in DAC is driven by policyholder activity due to the rate increase which allows for a higher rate of amortization based upon the change in the benefits elected by the policyholder. |
Year Ended December 31, 2016 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2015
Overview
Our Legacy segment pretax loss increased due to a Special Markets unclaimed property assessment accrual release in 2015 and higher LTC incurred claims and the implementation of a new reserving model in 2016.
Revenue
| • | Interest and similar income, net: LTC reflects higher investment income due to higher allocated interest and similar income due to growth in reserves driven by an aging block of business. |
| • | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities: The change in fair value of assets and liabilities increased due to lower allocated losses relating to investments not backing policyholder assets in 2016. |
| • | Realized investment (losses) gains, net: The realized investment loss increased due to higher impairments and allocated losses in 2016 primarily driven by normal investment activity. |
Benefits and Expenses
| • | Net benefits and expenses: Net benefits and expenses increased primarily due to overall higher LTC claim activity in 2016, impact of the implementation of a new LTC reserving model in 2016, and an unclaimed property assessment accrual release recorded in 2015. |
Financial Condition
Investment Strategy
Our investment strategy focuses on diversification by asset class. We seek to achieve economic diversification, while reducing overall credit and liquidity risks. We attempt to mitigate these credit and liquidity risks by adhering to investment policies that provide portfolio diversification on an asset class, creditor, and industry basis, and by complying with investment limitations governed by state insurance laws and regulations, as applicable. We also consider all relevant objective information available in estimating the cash flows related to structured securities. We actively monitor and manage exposures, and determine whether any securities are impaired. The aggregate credit risk taken in the investment portfolio is influenced by our risk/return preferences, the economic and credit environment, and the ability to manage this risk through liability portfolio management. We also have an asset-liability management strategy to align cash flows and duration of the investment portfolio with contractholder liability cash flows and duration.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 18 of 27
The following table presents the investment portfolio at December 31:
| 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||
| Carrying value | % of total | Carrying value | % of total | ||||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities | $ | 98,841,507 | 87.3 | % | $ | 87,584,050 | 87.4 | % | |||||
| Mortgage loans on real estate | 11,761,939 | 10.4 | % | 10,351,741 | 10.3 | % | |||||||
| Derivative assets | 1,388,190 | 1.2 | % | 1,059,031 | 1.1 | % | |||||||
| Equity securities | 586,279 | 0.5 | % | 637,659 | 0.6 | % | |||||||
| Policy loans | 184,409 | 0.2 | % | 171,012 | 0.2 | % | |||||||
| Other invested assets | 382,154 | 0.3 | % | 357,210 | 0.4 | % | |||||||
| Loans to affiliates | 39,120 | 0.1 | % | 39,120 | 0.0 | % | |||||||
| Total investments | $ | 113,183,598 | 100.0 | % | $ | 100,199,823 | 100.0 | % | |||||
Fixed-Maturity Securities
Refer to Note 4 of the audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements for information regarding the nature of our portfolio of fixed-maturity securities for information regarding the nature of our portfolio of fixed-maturity securities. Securities by quality rating category were as follows at December 31, 2017 and 2016.
| 2017 | |||||||||||||
| Fair Value | % of Total | Amortized Cost | % of Total | ||||||||||
| AAA | $ | 9,742,628 | 9.9 | % | $ | 9,536,784 | 10.3 | % | |||||
| AA | 23,809,251 | 24.1 | % | 22,599,765 | 24.4 | % | |||||||
| A | 27,800,022 | 28.1 | % | 25,351,066 | 27.4 | % | |||||||
| BBB | 36,290,582 | 36.7 | % | 34,073,361 | 36.8 | % | |||||||
| BB | 703,396 | 0.7 | % | 656,707 | 0.7 | % | |||||||
| B and below | 459,409 | 0.5 | % | 397,478 | 0.4 | % | |||||||
| Total | $ | 98,805,288 | 100.0 | % | $ | 92,615,161 | 100.0 | % | |||||
| 2016 | |||||||||||||
| Fair Value | % of Total | Amortized Cost | % of Total | ||||||||||
| AAA | $ | 8,528,225 | 9.7 | % | $ | 8,389,899 | 10.0 | % | |||||
| AA | 20,269,321 | 23.2 | % | 19,495,026 | 23.2 | % | |||||||
| A | 23,976,680 | 27.4 | % | 22,496,241 | 26.8 | % | |||||||
| BBB | 32,545,459 | 37.2 | % | 31,404,065 | 37.4 | % | |||||||
| BB | 1,599,321 | 1.8 | % | 1,614,331 | 1.9 | % | |||||||
| B and below | 627,965 | 0.7 | % | 630,083 | 0.7 | % | |||||||
| Total | $ | 87,546,971 | 100.0 | % | $ | 84,029,645 | 100.0 | % | |||||
Sub-prime and Alt-A Mortgage Exposure
We do not originate or purchase whole-loan mortgages with sub-prime or Alt-A. Sub-prime lending is the origination of loans to customers with weaker credit profiles. Due to the high quality of our mortgaged-backed securities, and the lack of sub-prime loans in the securities, we do not have a material exposure to sub-prime mortgages in those holdings. Alt-A loans are defined as any security backed by residential mortgage collateral which is not clearly identifiable as prime or sub-prime; we do not have a material exposure to Alt-A mortgages.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 19 of 27
Commercial Mortgage-backed, Residential Mortgage-backed, and Other Asset-backed Securities
Commercial mortgage-backed securities (CMBS) represent pools of commercial mortgages that are broadly diversified across property types and geographical areas. The following table summarizes our exposure to CMBS holdings by credit quality and vintage year as of December 31:
| 2017 | ||||||||||||
| % of total CMBS | Vintage | |||||||||||
| AAA | $ | 7,452,888 | 87.5 | % | 2017 | $ | 1,933,390 | 22.7 | % | |||
| AA | 1,067,808 | 12.5 | % | 2016 | 1,930,802 | 22.6 | % | |||||
| A | 2,919 | 0.0 | % | 2015 | 2,156,241 | 25.3 | % | |||||
| BBB | 1,140 | 0.0 | % | 2014 | $ | 1,672,205 | 19.6 | % | ||||
| BB and below | 1,180 | 0.0 | % | 2013 and prior | 833,297 | 9.8 | % | |||||
| $ | 8,525,935 | 100.0 | % | $ | 8,525,935 | 100.0 | % | |||||
| 2016 | ||||||||||||
| % of total CMBS | Vintage | |||||||||||
| AAA | $ | 6,699,139 | 89.5 | % | 2016 | $ | 1,724,742 | 22.9 | % | |||
| AA | 740,389 | 9.9 | % | 2015 | 2,002,009 | 26.9 | % | |||||
| A | 37,949 | 0.5 | % | 2014 | 1,557,726 | 20.8 | % | |||||
| BBB | 1,270 | 0.0 | % | 2013 | 15,308 | 0.2 | % | |||||
| BB and below | 4,870 | 0.1 | % | 2012 and prior | 2,183,832 | 29.2 | % | |||||
| $ | 7,483,617 | 100.0 | % | $ | 7,483,617 | 100.0 | % | |||||
Asset backed security (ABS) holdings consist primarily of aircraft leases, credit card receivables and other asset-backed securities that meet specific criteria, such as credit quality, insurance requirements, or limits on these types of investments.
The following table summarizes our exposure to other ABS holdings by credit quality and vintage year as of December 31:
| 2017 | ||||||||||||
| % of total other ABS | Vintage | |||||||||||
| AAA | $ | 126,336 | 12.3 | % | 2017 | $ | 171,346 | 16.7 | % | |||
| AA | 261,660 | 25.5 | % | 2016 | 211,593 | 20.6 | % | |||||
| A | 340,716 | 33.1 | % | 2015 | 221,517 | 21.6 | % | |||||
| BBB | 299,284 | 29.1 | % | 2014 | 35,497 | 3.5 | % | |||||
| BB and below | — | — | % | 2013 and prior | 388,043 | 37.6 | % | |||||
| $ | 1,027,996 | 100.0 | % | $ | 1,027,996 | 100.0 | % | |||||
| 2016 | ||||||||||||
| % of total other ABS | Vintage | |||||||||||
| AAA | $ | 366,852 | 36.2 | % | 2016 | $ | 145,767 | 14.3 | % | |||
| AA | 142,659 | 14.0 | % | 2015 | 226,450 | 22.3 | % | |||||
| A | 220,805 | 21.7 | % | 2014 | 8,239 | 0.8 | % | |||||
| BBB | 266,701 | 26.3 | % | 2013 | 26,408 | 2.6 | % | |||||
| BB and below | 19,467 | 1.8 | % | 2012 and prior | 609,620 | 60.0 | % | |||||
| $ | 1,016,484 | 100.0 | % | $ | 1,016,484 | 100.0 | % | |||||
Non-agency residential mortgage-backed securities (NA RMBS) are backed by pools of residential mortgage loans made to non-prime borrowers, diversified across geographies.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 20 of 27
The following table summarizes our exposure NA RMBS holdings by credit quality and vintage year as of December 31:
| 2017 | ||||||||||||
| % of total NA RMBS | Vintage | |||||||||||
| AAA | $ | 51,266 | 16.2 | % | 2017 | $ | — | — | % | |||
| AA | 8,410 | 2.7 | % | 2016 | — | — | % | |||||
| A | 6,305 | 2.0 | % | 2015 | — | — | % | |||||
| BBB | 19,360 | 6.1 | % | 2014 | — | — | % | |||||
| BB and below | 230,489 | 73.0 | % | 2013 and prior | 315,830 | 100.0 | % | |||||
| $ | 315,830 | 100.0 | % | $ | 315,830 | 100.0 | % | |||||
| 2016 | ||||||||||||
| % of total NA RMBS | Vintage | |||||||||||
| AAA | $ | 2,851 | 10.0 | % | 2016 | $ | — | — | % | |||
| AA | 4,773 | 16.7 | % | 2015 | — | — | % | |||||
| A | 14,918 | 52.3 | % | 2014 | — | — | % | |||||
| BBB | 1,542 | 5.4 | % | 2013 | — | — | % | |||||
| BB and below | 4,434 | 15.6 | % | 2012 and prior | 28,518 | 100.0 | % | |||||
| $ | 28,518 | 100.0 | % | $ | 28,518 | 100.0 | % | |||||
Unrealized investment losses of fixed-maturity securities, for investment grade (IG) and below investment grade (BIG) securities by duration are as follows at December 31:
| 2017 | |||||||||||||
| IG | % of IG and BIG | BIG | % of IG and BIG | ||||||||||
| Twelve months or less below amortized cost | $ | 72,497 | 22.2 | % | $ | 2,562 | 0.8 | % | |||||
| More than twelve months below amortized cost | 231,068 | 70.6 | % | 21,051 | 6.4 | % | |||||||
| Total | $ | 303,565 | 92.8 | % | $ | 23,613 | 7.2 | % | |||||
| 2016 | |||||||||||||
| IG | % of IG and BIG | BIG | % of IG and BIG | ||||||||||
| Twelve months or less below amortized cost | $ | 639,126 | 75.5 | % | $ | 12,984 | 1.6 | % | |||||
| More than twelve months below amortized cost | 123,925 | 14.7 | % | 70,215 | 8.2 | % | |||||||
| Total | $ | 763,051 | 90.2 | % | $ | 83,199 | 9.8 | % | |||||
Unrealized investment losses of fixed-maturity securities, for instances in which fair value declined below amortized cost by greater than or less than 20% for consecutive periods as indicated in the tables below, were as follows at December 31:
| 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Fair Value | Unrealized Capital Loss | Number of Securities | |||||||||||||||||||
| < 20% | > 20% | < 20% | > 20% | < 20% | > 20% | ||||||||||||||||
| Twelve months or less below amortized cost | $ | 9,379,369 | $ | — | $ | 75,059 | $ | — | 515 | — | |||||||||||
| More than twelve months below amortized cost | 7,028,503 | 28,844 | 244,492 | 7,627 | 345 | 5 | |||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 16,407,872 | $ | 28,844 | $ | 319,551 | $ | 7,627 | 860 | 5 | |||||||||||
| 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Fair Value | Unrealized Capital Loss | Number of Securities | |||||||||||||||||||
| < 20% | > 20% | < 20% | > 20% | < 20% | > 20% | ||||||||||||||||
| Twelve months or less below amortized cost | $ | 19,950,380 | $ | 72,821 | $ | 636,932 | $ | 15,178 | 938 | 3 | |||||||||||
| More than twelve months below amortized cost | 2,006,954 | 138,123 | 151,323 | 42,817 | 132 | 15 | |||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 21,957,334 | $ | 210,944 | $ | 788,255 | $ | 57,995 | 1,070 | 18 | |||||||||||
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 21 of 27
OTTI, by market sector, for impairments included in the Consolidated Statements of Operations, were as follows at December 31:
| 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||
| Impairment | No. of Securities | Impairment | No. of Securities | ||||||||||
| States and political subdivisions | $ | — | — | $ | 2,866 | 1 | |||||||
| Corporate securities | 48,574 | 14 | 171,957 | 49 | |||||||||
| $ | 48,574 | 14 | $ | 174,823 | 50 | ||||||||
Refer to Note 4 of the audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements for information regarding our cumulative impairments on fixed-maturity securities.
Financial instruments are carried at fair value on a recurring basis in the Company’s audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements. We have analyzed the valuation techniques and related inputs, evaluated its assets and liabilities reported at fair value, and determined an appropriate fair value hierarchy level based upon trading activity and the observability of market inputs. Based on the results of this evaluation and investment class analysis, each valuation was classified into Level 1, 2, or 3. See Note 6 of the audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information.
| Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | |||||||||||||||
| Assets | |||||||||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale: | $ | 98,805,288 | $ | 2,441,454 | $ | 85,318,631 | $ | 11,045,203 | |||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, trading | 36,219 | 30,901 | 5,168 | 150 | |||||||||||
| Derivative assets | 1,388,190 | 48,177 | 1,327,638 | 12,375 | |||||||||||
| Equity securities, available-for-sale | 271,909 | 258,095 | — | 13,814 | |||||||||||
| Equity securities, fair value option and trading | 314,370 | 288,098 | 26,272 | — | |||||||||||
| Separate account assets | 28,192,877 | 28,192,877 | — | — | |||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 129,008,853 | $ | 31,259,602 | $ | 86,677,709 | $ | 11,071,542 | |||||||
| Liabilities | |||||||||||||||
| Derivative liabilities | $ | 915,147 | $ | 27,678 | $ | 887,469 | $ | — | |||||||
Reserves at fair value (1) | 27,387,975 | — | — | 27,387,975 | |||||||||||
| Total liabilities | $ | 28,303,122 | $ | 27,678 | $ | 887,469 | $ | 27,387,975 | |||||||
| Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | |||||||||||||||
| Assets | |||||||||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale: | $ | 87,546,971 | $ | 1,736,523 | $ | 77,136,330 | $ | 8,674,118 | |||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, trading | 37,051 | 36,901 | — | 150 | |||||||||||
| Derivative assets | 1,059,031 | 42,400 | 1,010,805 | 5,826 | |||||||||||
| Equity securities, available-for-sale | 320,166 | 320,166 | — | — | |||||||||||
| Equity securities, fair value option and trading | 317,493 | 298,481 | 19,012 | — | |||||||||||
| Separate account assets | 27,733,261 | 27,733,261 | — | — | |||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 117,013,973 | $ | 30,167,732 | $ | 78,166,147 | $ | 8,680,094 | |||||||
| Liabilities | |||||||||||||||
| Derivative liabilities | $ | 635,634 | $ | 27,345 | $ | 604,587 | $ | 3,702 | |||||||
Reserves at fair value (1) | 20,152,641 | — | — | 20,152,641 | |||||||||||
| Total liabilities | $ | 20,788,275 | $ | 27,345 | $ | 604,587 | $ | 20,156,343 | |||||||
(1) Reserves at fair value are reported in Account balances and future policy benefit reserves on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. | |||||||||||||||
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 22 of 27
Mortgage Loans on Real Estate
We evaluate the mortgage loan allowance for loan loss quarterly, which resulted in a change of the provision of $(11,400) and $11,000 for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. In 2017, the decrease to the mortgage loan allowance is driven by a reduction in expected losses and reserves based on the improving credit quality of our portfolio and industry analysis showing improving market conditions. The increase to the allowance for loan loss in 2016 was a result of the growing asset base of the mortgage loan portfolio partially offset by improving quality indicators.
We analyze loan impairment quarterly when assessing the valuation allowance. We consider recent trends in the Company’s loan portfolio and information on current loans, such as loan-to-value ratios and debt service coverage, which could impact a loan’s credit quality. We also evaluate the valuation allowance to ensure that the estimate is based on the most recent available industry default and loss studies and historical default rates for the Company as compared with default rates for the industry group. We do not accrue interest on defaulted loans.
Loan-to-value (LTV) and debt service coverage (DSC) ratios are common measurements used to assess the risk and quality of mortgage loans. The LTV ratio, calculated at the time of origination, is the percentage of the loan amount relative to the value of the underlying property. The DSC ratio, based upon the most recently received financial statements from the debtor, is calculated as the amount of the property’s net income divided by the debt service payments.
See Note 7 of the audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information relating to LTV and DSC ratios.
Properties collateralizing mortgage loans are geographically dispersed throughout the United States as follows at December 31:
| 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| Gross Carry Value | % of Total | Gross Carry Value | % of Total | ||||||||
| Mortgage loans by region | |||||||||||
| East North Central | $ | 1,587,527 | 13.5 | % | $ | 1,465,654 | 14.1 | % | |||
| East South Central | 166,898 | 1.4 | % | 56,310 | 0.5 | % | |||||
| Middle Atlantic | 922,054 | 7.8 | % | 617,117 | 5.9 | % | |||||
| Mountain | 770,569 | 6.5 | % | 663,095 | 6.4 | % | |||||
| New England | 847,927 | 7.2 | % | 862,994 | 8.3 | % | |||||
| Pacific | 3,435,323 | 29.1 | % | 3,250,895 | 31.3 | % | |||||
| South Atlantic | 2,709,281 | 23.0 | % | 2,270,291 | 21.8 | % | |||||
| West North Central | 661,284 | 5.6 | % | 589,021 | 5.7 | % | |||||
| West South Central | 698,076 | 5.9 | % | 624,764 | 6.0 | % | |||||
| Total | $ | 11,798,939 | 100.0 | % | $ | 10,400,141 | 100.0 | % | |||
Properties collateralizing mortgage loans are diversified by property type are as follows at December 31:
| 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| Gross Carry Value | % of Total | Gross Carry Value | % of Total | ||||||||
| Mortgage loans by property type | |||||||||||
| Industrial | $ | 2,597,438 | 22.0 | % | $ | 2,274,055 | 21.9 | % | |||
| Retail | 2,580,479 | 21.9 | % | 2,313,307 | 22.1 | % | |||||
| Office | 3,623,345 | 30.7 | % | 3,370,449 | 32.5 | % | |||||
| Apartments | 2,997,677 | 25.4 | % | 2,442,330 | 23.5 | % | |||||
| Total | $ | 11,798,939 | 100.0 | % | $ | 10,400,141 | 100.0 | % | |||
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Overview
Liquidity and Capital Resources represent our overall financial strength and ability to generate cash flows from the business. The liquidity requirements are generally met through funds provided by investment income, receipt of insurance premiums, M&E fees and benefit rider income, maturities and sales of investments, reinsurance recoveries, and capital contributions from Allianz SE as needed.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 23 of 27
We hold membership stock of the Federal Home Loan Bank (FHLB) of Des Moines which provides access to collateralized borrowings. Funding from the FHLB of Des Moines is collateralized with fixed-maturity securities from our general account investment portfolio. In addition, we also participate in securities lending arrangements whereby specific securities are loaned to other institutions. We receive collateral from these arrangements including cash and cash equivalents, which can be reinvested based on the Company's discretion, and noncash collateral, which may not be sold or re-pledged unless the counterparty is in default. See Note 2 of the audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding these agreements.
Reinsurance may play a key role in funding our continued growth, and is utilized for any new line of business for which there is significant uncertainty related to future claims experience. Moreover, we are generally risk adverse for our smaller lines of business, and predictability of future profitability takes precedence over retaining a large percentage of risk.
We do not utilize the capital markets as a source of capital. Should the need for capital arise, we may obtain capital contributions from our ultimate parent, Allianz SE, as an alternative source of funding. The primary uses of funds are policy benefits, commissions, other product-related acquisition costs, investment purchases, operating expenses, and dividends to AZOA. We routinely review our source and use of funds in order to meet our ongoing obligations.
Financial Ratings and Strength
We received the following financial strength ratings as of December 31, 2017:
| • | AM Best A+ (Superior) |
| • | S&P AA (Very Strong) |
| • | Moody's A1 |
The financial strength ratings are influenced by many factors including the operating and financial performance, asset quality, liquidity, asset/liability management, overall portfolio mix, financial leverage, relationship to Allianz SE, and exposure to risks.
Cash Flows
The following table sets forth information from our Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31:
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| Consolidated Cash Flows | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 6,784,624 | $ | 2,644,667 | $ | 2,413,324 | ||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | (8,872,517 | ) | (6,926,348 | ) | (7,144,829 | ) | ||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 2,375,269 | 4,374,483 | 3,588,070 | |||||||||
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | $ | 287,376 | $ | 92,802 | $ | (1,143,435 | ) | |||||
We have the funds necessary to meet the capital requirements of all states in which we do business, and to support our operations.
The increase in net cash provided by operating activities in 2017 as compared to 2016 is primarily a result of derivative impacts due to the increase in equity markets. The increase in net cash provided by operating activities in 2016 as compared to 2015 is a result of the increase in the sale of trading securities, lower realized investment gains offset by the purchase of trading securities.
The increase in cash flows used in investing activities in 2017 as compared to 2016 is a result of higher net purchases of fixed-maturity securities partially offset by higher sales of derivative securities. The 2016 increase in cash flows used in investing activities was primarily related to higher sales of available-for-sale fixed-maturity securities partially offset by higher purchases of fixed-maturity securities.
The decrease in cash flows from financing activities in 2017 as compared to 2016 was driven by lower deposits and higher withdrawals from account balances partially offset by payback of 2016 FHLB advance. The 2016 increase in cash flows from financing activities was driven by higher deposits in our Individual Annuity segment offset by the payback of the FHLB advance and higher dividend payments in 2016 compared to 2015.
Risk-Based Capital
An insurance enterprise’s state of domicile imposes minimum risk based capital (RBC) requirements that were developed by the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC). The formulas for determining the amount of RBC specify various weighting factors that are applied to financial balances or various levels of activity based on the perceived degree of risk. Regulatory compliance is determined by a ratio of an enterprise’s regulatory total adjusted capital to its authorized control level RBC, as defined by the NAIC. Companies below specific trigger points or ratios are classified within certain levels, each of which requires specified corrective action. This ratio for the Company significantly exceeded required minimum thresholds as of December 31, 2017 and 2016.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 24 of 27
Statutory Surplus and Dividends
Statutory accounting practices prescribed or permitted by the Company’s state of domicile are directed toward insurer solvency and protection of policyholders. Accordingly, certain items recorded in financial statements prepared under GAAP are excluded or vary in calculation in determining statutory policyholders’ surplus and gain from operations. Currently, these items include, among others, DAC, deferred taxes, receivables (which are more than 90 days past due), reinsurance, and certain investments. Additionally, account balances and future policy benefit reserves calculated for statutory reporting do not include provisions for withdrawals.
We are also required to meet minimum statutory capital and surplus requirements. Our statutory capital and surplus as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, were in compliance with these requirements. The maximum amount of ordinary dividends that can be paid by Minnesota insurance companies to the stockholder without prior approval of the Department is subject to restrictions relating to statutory earned surplus, also known as unassigned funds. Unassigned funds are determined in accordance with the accounting procedures and practices governing preparation of the statutory annual statement. In accordance with Minnesota Statutes, the Company may declare and pay from its Unassigned surplus cash dividends of not more than the greater of 10% of its prior year-end statutory surplus, or the net gain from operations of the insurer, not including realized gains, for the 12-month period ending the 31st day of the next preceding year. Based on these limitations, ordinary dividends of $601,124 can be paid in 2018 without prior approval of the Commissioner of Commerce.
We paid dividends of $780,000 to our parent, AZOA during the year ended December 31, 2017 compared to $894,165, which represented $861,000 cash and $33,165 related to the AMOSA loan and accrued interest, in the prior year.
Commitments
The following table summarizes certain contractual obligations and the Company’s commitments by period as of December 31, 2017:
| In 1 year | after 1 year | After 3 years | After | ||||||||||||||||
| Total | or less | up to 3 years | up to 5 years | 5 Years | |||||||||||||||
| Payments due | |||||||||||||||||||
| Policyholder liabilities | $ | 128,827,443 | $ | 8,334,074 | $ | 18,253,969 | $ | 18,805,087 | $ | 83,434,313 | |||||||||
| Mortgage notes payable | $ | 68,628 | 8,758 | 19,032 | 21,250 | 19,588 | |||||||||||||
| Operating leases | $ | 6,778 | 2,027 | 3,047 | 1,256 | 448 | |||||||||||||
| Total payments due | $ | 128,902,849 | $ | 8,344,859 | $ | 18,276,048 | $ | 18,827,593 | $ | 83,454,349 | |||||||||
Policyholder liabilities include estimated claim and benefit, policy surrender and commission obligations offset by expected future deposits and premiums on in-force insurance policies and investment contracts in the Individual Annuity and Life segments. We have excluded the separate account liabilities as these obligations are legally insulated from general account obligations and will be fully funded by cash flows from separate account assets. The obligations have not been discounted to present value. Estimated claim and benefit obligations are based upon mortality, morbidity and lapse assumptions comparable to historical experience. The results are based on assuming market growth and interest crediting consistent with other valuation assumptions. In contrast to this table, the majority of our obligations are recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheets at current account values or other GAAP prescribed measurements that are not directly related to liability cash flows. These obligations do not incorporate an expectation on future market growth, interest crediting, or future deposits. Therefore, due to the significance of the assumptions used, the amounts presented could materially differ from actual results.
Operating leases include non-cancelable obligations on certain office space and equipment.
Mortgage notes payable includes contractual principal and interest payments and therefore exceeds the amount shown in the Consolidated Balance Sheet. See Notes 16 and 17of the audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 25 of 27
Contingencies
We are named as defendants in various pending or threatened legal proceedings on an ongoing basis, including three putative class action proceedings, arising from the conduct of business: Sanchez v. Allianz Life Ins. Co. of North America (Superior Court of California, L.A. County, BC594715), Berthiaume et al. v. Allianz Life Ins. Co. of North America et al (Minnesota District Court, Henn. County), and Thompson v. Allianz Life Ins. Co. of North America (United Stated District Court, District of Minnesota, Case No. 0:17-cv00096). None of these putative class actions has been certified. The Company generally intends to vigorously contest the lawsuits, but may pursue settlement negotiations in some cases, if appropriate. The outcome of the cases is uncertain at this time, and there can be no assurance that such litigation, or any future litigation, will not have a material adverse effect on the Company and/or its subsidiaries. The Company recognizes legal costs as incurred.
The Company is contingently liable for possible future assessments under regulatory requirements pertaining to insolvencies and impairments of unaffiliated insurance companies. Provision has been made for assessments currently received and assessments anticipated for known insolvencies.
The financial services industry, including mutual funds, variable and fixed annuities, life insurance, distribution companies, and broker-dealers, is subject to close scrutiny by regulators, legislators, and the media.
Federal and state regulators, such as state insurance departments, state securities departments, the SEC, the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, and other regulatory bodies regularly make inquiries and conduct examinations or investigations concerning various selling practices, including suitability reviews, product exchanges, sales to seniors, and compliance with, among other things, insurance and securities law. The Company is subject to ongoing market conduct examinations and investigations by regulators, which may have a material adverse effect on the Company.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We do not have any off-balance sheet transactions, arrangements or other relationships that we believe would be reasonably likely to have a material effect on our liquidity or the requirements for capital resources.
We utilize exchange-traded futures to economically hedge certain product liabilities. Under this kind of transaction, we agree to purchase a specified number of contracts and settle the variation margin with the counterparty on a daily basis in an amount equal to the change in the market value of the underlying contracts from the close of the previous trading day. The parties with whom we enter into the exchange-traded futures contracts are regulated futures commissions merchants who are members of a trading exchange.
We are exposed to credit-related losses in the event of non-performance by counterparties under the terms of the futures contracts. We minimize counterparty credit risk by establishing relationships only with counterparties rated BBB+ and higher. Given the credit ratings of the counterparties with which we transact, we do not expect any counterparties to fail to meet their obligations. We also execute Credit Support Annexes (CSA) with all active and new counterparties which further limits credit risk by requiring counterparties to post collateral to a segregated account to cover any counterparty exposure. As our futures transactions are executed through a regulated exchange, positions are marked-to-market and settled on a daily basis, and collateral is posted prior to execution of a transaction, we have minimal exposure to credit-related losses in the event of non-performance.
We are also required to post collateral for any futures and options contracts that are executed. The amount of collateral required is determined by the exchange on which the contract is traded. We generally post U.S. Government and acceptable corporate securities to satisfy this collateral requirement. Refer to Note 5 in the audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplemental Schedules for additional information regarding derivative collateral posted.
Forward-looking Statements
This report reviews the Company’s financial condition and results of operations. Where appropriate, factors that may affect future financial performance are also identified and discussed. Certain statements made in this report include “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Forward-looking statements include any statement that may predict, forecast, indicate or imply future results, performance or achievements instead of historical facts, and may contain words like “believe,” “expect,” “estimate,” “project,” “budget,” “forecast,” “anticipate,” “plan,” “will,” “shall,” “may,” and other words, phrases or expressions with similar meaning. Forward-looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties. Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on forward-looking statements as a prediction of actual results. We undertake no obligation to update publicly or revise any forward-looking statements.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 26 of 27
Item 11(j).
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
Market risk is the risk of the loss of fair value resulting from adverse changes in market rates and prices, such as interest rates and equity prices. Market risk is directly influenced by the volatility and liquidity in the markets in which the related underlying financial instruments are traded. Reference Note 3 of the audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements for additional details on how we mitigate our market exposure risk and our overall risk management practices.
Sensitivity Analysis
To assess the impact of changes in interest rate and equity markets, we perform sensitivity tests. Sensitivity tests measure the instantaneous impact of a single hypothetical interest rate or equity price change on our pre-tax income, or fair value of an asset or liability, while holding all other rates or prices constant. To assess interest rate risk, we perform a sensitivity test which instantaneously shocks interest rates across all maturities by a hypothetical 50 basis points (bps). To assess equity risk, we perform a sensitivity test which instantaneously shocks all equity prices by a hypothetical 15%.
Interest Rate Risk
One means of assessing exposure to interest rate changes is to measure the potential change in fair value of an asset due to a hypothetical change in interest rates of 50 bps across all maturities. We noted that under this model, with all other factors remaining constant, a 50 bps increase in interest rates would result in the decrease in the fair value of our fixed income assets of $4,630,042 based on our asset positions as of December 31, 2017.
We also examined the impact on pre-tax income due to a hypothetical decrease in interest rates of 50 bps across all maturities. Note that all impacts referenced below reflect reserve changes net of economic hedge impact and DAC changes unless otherwise noted. Under this model, with all other factors being constant, we estimated that such a decline as of December 31, 2017, would cause our pre-tax income to decrease by $523,459 for the period ended December 31, 2017.
Equity Market Risk
One means of assessing exposure to changes in equity market prices is to estimate the potential changes in pre-tax income from a hypothetical change in equity market prices of 15% at December, 31, 2017. Under this model, with all other factors constant, we estimated that a decrease in equity market prices would cause our pre-tax income to increase by $30,851, while an increase in equity market prices would cause our pre-tax income to decrease by $96,103 based on our equity exposure for the period ended December 31, 2017.
Adoption of New Financial Accounting Standards
See Note 2 – “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies” of the Company’s audited GAAP Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 8 – Financial Statements of this prospectus for information related to recent accounting pronouncements.
Selected Financial Data and Management's Discussion and Analysis
Page 27 of 27
Item 11(e).
Financial Statements meeting the requirements of S-X
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY
OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Financial Statements
and Supplemental Schedules
and Supplemental Schedules
December 31, 2017 and 2016
(With Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm Thereon)
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholder and Board of Directors
Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America:
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income (loss), stockholder’s equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2017, and the related notes and financial statement schedules I, III, and IV (collectively, the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the three‑year period ended December 31, 2017, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ KPMG LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 1980.
Minneapolis, Minnesota
March 29, 2018
Page 1 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Balance Sheets
December 31, 2017 and 2016
(In thousands, except share data)
| Assets | 2017 | 2016 | ||||
| Investments: | ||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities: | ||||||
| Available-for-sale, at fair value (amortized cost of $92,615,161 and $84,029,645, respectively) | $ | 98,805,288 | 87,546,971 | |||
| Trading, at fair value (amortized cost of $35,982 and $36,504, respectively) | 36,219 | 37,051 | ||||
| Held-to-maturity, at amortized cost (fair value of $0 and $3,630, respectively) | — | 28 | ||||
| Mortgage loans on real estate (net allowance for loan loss of $37,000 and $48,400, respectively) | 11,761,939 | 10,351,741 | ||||
| Derivative assets | 1,388,190 | 1,059,031 | ||||
| Loans to affiliates | 39,120 | 39,120 | ||||
| Policy loans | 184,409 | 171,012 | ||||
| Equity securities: | ||||||
| Available-for-sale, at fair value (cost of $261,073 and $316,541, respectively) | 271,909 | 320,166 | ||||
| Fair value option and trading, at fair value (cost of $289,217 and $312,592, respectively) | 314,370 | 317,493 | ||||
| Other invested assets | 382,154 | 357,210 | ||||
| Total investments | 113,183,598 | 100,199,823 | ||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | 1,507,360 | 1,219,984 | ||||
| Accrued investment income | 1,096,862 | 1,095,038 | ||||
| Receivables (net allowance for uncollectible accounts of $4,363 and $4,959, respectively) | 410,296 | 566,088 | ||||
| Reinsurance and investment contract recoverables | 5,295,486 | 4,687,918 | ||||
| Deferred acquisition costs | 3,850,840 | 5,246,343 | ||||
| Net deferred tax asset | — | 388,009 | ||||
| Collateral held from securities lending agreements | 2,657,046 | 2,561,219 | ||||
| Other assets | 1,988,685 | 1,891,717 | ||||
| Assets, exclusive of separate account assets | 129,990,173 | 117,856,139 | ||||
| Separate account assets | 28,192,877 | 27,733,261 | ||||
| Total assets | $ | 158,183,050 | 145,589,400 | |||
Page 2 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Balance Sheets (continued)
December 31, 2017 and 2016
(In thousands, except share data)
| Liabilities and Stockholder’s Equity | 2017 | 2016 | ||||
| Policyholder liabilities: | ||||||
| Account balances and future policy benefit reserves (includes $5,064,282 and $2,611,562 measured at fair value under the fair value option at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively) | $ | 115,774,156 | 105,354,460 | |||
| Policy and contract claims | 696,697 | 620,743 | ||||
| Unearned premiums | 98,272 | 145,335 | ||||
| Other policyholder funds | 268,649 | 275,262 | ||||
| Total policyholder liabilities | 116,837,774 | 106,395,800 | ||||
| Derivative liabilities | 915,147 | 635,634 | ||||
| Mortgage notes payable | 68,628 | 76,916 | ||||
| Net deferred tax liability | 176,416 | — | ||||
| Other liabilities | 4,032,502 | 3,673,122 | ||||
| Liabilities, exclusive of separate account liabilities | 122,030,467 | 110,781,472 | ||||
| Separate account liabilities | 28,192,877 | 27,733,261 | ||||
| Total liabilities | 150,223,344 | 138,514,733 | ||||
| Stockholder’s equity: | ||||||
| Class A, Series A preferred stock, $1 par value. Authorized, issued, and outstanding, 8,909,195 shares; liquidation preference of $1,779 and $2,084 at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively | 8,909 | 8,909 | ||||
| Class A, Series B preferred stock, $1 par value. Authorized, 10,000,000 shares; issued and outstanding, 9,994,289 shares; liquidation preference of $4,060 and $4,283 at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively | 9,994 | 9,994 | ||||
| Common stock, $1 par value. Authorized, 40,000,000 shares; issued and outstanding, 20,000,001 shares at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively | 20,000 | 20,000 | ||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 4,053,371 | 4,053,371 | ||||
| Retained earnings | 1,763,078 | 1,829,115 | ||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income, net of tax | 2,104,354 | 1,153,278 | ||||
| Total stockholder’s equity | 7,959,706 | 7,074,667 | ||||
| Total liabilities and stockholder’s equity | $ | 158,183,050 | 145,589,400 | |||
See accompanying Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
Page 3 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Operations
Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015
(In thousands)
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Revenue: | |||||||||
| Premiums and policy fees, net | $ | 1,605,227 | 1,407,279 | 1,449,591 | |||||
| Interest and similar income, net | 4,522,219 | 4,325,737 | 4,175,469 | ||||||
| Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 3,602,468 | (178,238 | ) | (532,720 | ) | ||||
| Realized investment gains (losses), net | 83,622 | (49,325 | ) | 94,413 | |||||
| Fee and commission revenue | 266,602 | 274,562 | 293,333 | ||||||
| Other revenue | 58,128 | 35,292 | 10,066 | ||||||
| Total revenue | 10,138,266 | 5,815,307 | 5,490,152 | ||||||
| Benefits and expenses: | |||||||||
| Policyholder benefits, net of recoveries | 361,285 | 472,611 | 531,615 | ||||||
| Change in fair value of annuity and life embedded derivatives | 4,962,770 | 275,808 | 588,595 | ||||||
| Net interest credited to account values | 1,805,184 | 1,634,759 | 1,482,884 | ||||||
| Net benefits and expenses | 7,129,239 | 2,383,178 | 2,603,094 | ||||||
| Commissions and other agent compensation | 1,084,430 | 1,333,439 | 1,167,109 | ||||||
| General and administrative expenses | 727,714 | 695,949 | 637,328 | ||||||
| Change in deferred acquisition costs, net | 274,363 | 259,407 | 239,259 | ||||||
| Total benefits and expenses | 9,215,746 | 4,671,973 | 4,646,790 | ||||||
| Income (loss) from operations before income taxes | 922,520 | 1,143,334 | 843,362 | ||||||
| Income tax expense | 208,557 | 355,156 | 243,066 | ||||||
| Net income | $ | 713,963 | 788,178 | 600,296 | |||||
| Supplemental disclosures: | |||||||||
| Realized investment gains (losses), net: | |||||||||
| Total credit-related other-than-temporary impairment losses on securities | $ | (48,574 | ) | (174,823 | ) | (58,975 | ) | ||
| Other net realized gains | 132,196 | 125,498 | 153,388 | ||||||
| Realized investment gains (losses), net | $ | 83,622 | (49,325 | ) | 94,413 | ||||
See accompanying Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
Page 4 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015
(In thousands)
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Net income | $ | 713,963 | 788,178 | 600,296 | |||||
| Net unrealized gain (loss) on investments, net of shadow adjustments and deferred taxes | 958,313 | 693,289 | (1,293,230 | ) | |||||
| Net (loss) gain on cash flow hedging instruments | (8,090 | ) | (29,614 | ) | 8,933 | ||||
| Unrealized (loss) gain on postretirement obligation, net of tax | (4 | ) | (39 | ) | 111 | ||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments, net of tax | 857 | 692 | (4,009 | ) | |||||
| Total other comprehensive income (loss) | 951,076 | 664,328 | (1,288,195 | ) | |||||
| Total comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 1,665,039 | 1,452,506 | (687,899 | ) | ||||
See accompanying Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
Page 5 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Stockholder's Equity
Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015
(In thousands)
| Preferred stock | Common stock | Additional paid-in capital | Retained earnings | Accumulated other comprehensive income | Total stockholder's equity | |||||||||||||
| 2015: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, beginning of year | $ | 18,903 | 20,000 | 4,053,371 | 1,906,931 | 1,777,145 | 7,776,350 | |||||||||||
| Comprehensive loss: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | — | — | — | 600,296 | — | 600,296 | ||||||||||||
| Net unrealized loss on investments, net of shadow adjustments and deferred taxes | — | — | — | — | (1,293,230 | ) | (1,293,230 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net gain on cash flow hedging instruments | — | — | — | — | 8,933 | 8,933 | ||||||||||||
| Net unrealized gain on postretirement obligation, net of deferred taxes | — | — | — | — | 111 | 111 | ||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of deferred taxes | — | — | — | — | (4,009 | ) | (4,009 | ) | ||||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss | (687,899 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Dividend to parent | — | — | — | (572,125 | ) | — | (572,125 | ) | ||||||||||
| Balance, end of year | $ | 18,903 | 20,000 | 4,053,371 | 1,935,102 | 488,950 | 6,516,326 | |||||||||||
| 2016: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, beginning of year | $ | 18,903 | 20,000 | 4,053,371 | 1,935,102 | 488,950 | 6,516,326 | |||||||||||
| Comprehensive income: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | — | — | — | 788,178 | — | 788,178 | ||||||||||||
| Net unrealized gain on investments, net of shadow adjustments and deferred taxes | — | — | — | — | 693,289 | 693,289 | ||||||||||||
| Net loss on cash flow hedging instruments | — | — | — | — | (29,614 | ) | (29,614 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net unrealized loss on postretirement obligation, net of deferred taxes | — | — | — | — | (39 | ) | (39 | ) | ||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of deferred taxes | — | — | — | — | 692 | 692 | ||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive income | 1,452,506 | |||||||||||||||||
| Dividend to parent | — | — | — | (894,165 | ) | — | (894,165 | ) | ||||||||||
| Balance, end of year | $ | 18,903 | 20,000 | 4,053,371 | 1,829,115 | 1,153,278 | 7,074,667 | |||||||||||
| 2017: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, beginning of year | $ | 18,903 | 20,000 | 4,053,371 | 1,829,115 | 1,153,278 | 7,074,667 | |||||||||||
| Comprehensive income: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | — | — | — | 713,963 | — | 713,963 | ||||||||||||
| Net unrealized gain on investments, net of shadow adjustments and deferred taxes | — | — | — | — | 958,313 | 958,313 | ||||||||||||
| Net loss on cash flow hedging instruments | — | — | — | — | (8,090 | ) | (8,090 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net unrealized loss on postretirement obligation, net of deferred taxes | — | — | — | — | (4 | ) | (4 | ) | ||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of deferred taxes | — | — | — | — | 857 | 857 | ||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive income | 1,665,039 | |||||||||||||||||
| Dividend to parent | — | — | — | (780,000 | ) | — | (780,000 | ) | ||||||||||
| Balance, end of year | $ | 18,903 | 20,000 | 4,053,371 | 1,763,078 | 2,104,354 | 7,959,706 | |||||||||||
See accompanying Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
Page 6 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015
(In thousands)
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Cash flows provided by operating activities: | |||||||||
| Net income | $ | 713,963 | 788,178 | 600,296 | |||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||||
| Realized investment gains (losses), net | (85,171 | ) | 47,558 | (80,225 | ) | ||||
| Purchase of trading fixed-maturity securities | (10,207 | ) | (150 | ) | (4,819 | ) | |||
| Sale, maturity, and other redemptions of trading fixed-maturity securities | 10,702 | — | 8,700 | ||||||
| Purchase of fair value option and trading equity securities | (742,825 | ) | (1,371,832 | ) | (497,657 | ) | |||
| Sale and other redemptions of fair value option and trading equity securities | 774,632 | 1,355,529 | 503,912 | ||||||
| Change in annuity-related options, derivatives, and gross reserves | 4,360,198 | 172,780 | 109,763 | ||||||
| Deferred income tax expense (benefit) | 125,443 | (202,860 | ) | (307,986 | ) | ||||
| Charges to policy account balances | (274,975 | ) | (222,131 | ) | (187,637 | ) | |||
| Gross interest credited to account balances | 2,016,226 | 1,760,900 | 1,618,376 | ||||||
| Amortization, depreciation, and change in fair value | (21,880 | ) | 115,328 | 60,857 | |||||
| Change in: | |||||||||
| Accrued investment income | (1,824 | ) | (51,730 | ) | (124,230 | ) | |||
| Receivables | 155,792 | (164,182 | ) | (251,059 | ) | ||||
| Reinsurance and investment contract recoverables | (607,568 | ) | (254,419 | ) | (227,639 | ) | |||
| Deferred acquisition costs | 274,363 | 259,407 | 239,259 | ||||||
| Future policy benefit reserves | 26,260 | 328,295 | 1,218,582 | ||||||
| Policy and contract claims | 75,954 | 102,818 | 74,481 | ||||||
| Other policyholder funds | (6,613 | ) | (20,960 | ) | (35,142 | ) | |||
| Unearned premiums | (11,388 | ) | 21,540 | (20,157 | ) | ||||
| Other assets and liabilities | 14,587 | (19,822 | ) | (278,427 | ) | ||||
| Other, net | (1,045 | ) | 420 | (5,924 | ) | ||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 6,784,624 | 2,644,667 | 2,413,324 | |||||
Page 7 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows (continued)
Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015
(In thousands)
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Cash flows used in investing activities: | |||||||||
| Purchase of available-for-sale fixed-maturity securities | $ | (16,212,518 | ) | (14,962,344 | ) | (15,028,477 | ) | ||
| Sale and other redemptions of available-for-sale and held-to-maturity fixed-maturity securities | 6,469,905 | 8,405,110 | 7,224,211 | ||||||
| Matured available-for-sale and held-to-maturity fixed-maturity securities | 1,512,015 | 1,585,456 | 1,767,133 | ||||||
| Funding of mortgage loans on real estate | (2,292,432 | ) | (2,249,020 | ) | (2,281,527 | ) | |||
| Repayment/disposal of mortgage loans on real estate | 893,634 | 674,296 | 673,278 | ||||||
| Purchase of derivative securities | (202,269 | ) | (423,397 | ) | (512,523 | ) | |||
| Sale of derivative securities | 1,206,462 | 415,794 | 242,298 | ||||||
| Purchase of available-for-sale equity securities | (77,209 | ) | (376,145 | ) | (143,684 | ) | |||
| Sale of available-for-sale equity securities | 136,911 | 152,821 | 58,858 | ||||||
| Purchase of interest in equity method investments | (116,542 | ) | (53,952 | ) | (19,777 | ) | |||
| Sale of real estate | — | — | 5,929 | ||||||
| Net change in short-term securities | (196,672 | ) | 4,454 | 43,443 | |||||
| Purchase of home office property and equipment | (1,040 | ) | (1,794 | ) | (7,486 | ) | |||
| Goodwill and intangible acquisition | — | (7,801 | ) | — | |||||
| Change in loan to affiliate | — | (39,115 | ) | 817,110 | |||||
| Change in loan to non affiliate | — | (43,075 | ) | 19,343 | |||||
| Other, net | 7,238 | (7,636 | ) | (2,958 | ) | ||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | $ | (8,872,517 | ) | (6,926,348 | ) | (7,144,829 | ) | ||
| Cash flows provided by financing activities: | |||||||||
| Cash (paid to) received from FHLB advance | $ | — | (500,000 | ) | 500,000 | ||||
| Policyholders’ deposits to account balances | 10,426,708 | 12,299,879 | 10,035,234 | ||||||
| Policyholders’ withdrawals from account balances | (7,113,663 | ) | (6,601,844 | ) | (6,485,558 | ) | |||
| Policyholders’ net transfers between account balances | (119,732 | ) | 56,943 | 101,897 | |||||
| Change in amounts drawn in excess of bank balances | (29,756 | ) | (11,650 | ) | 16,045 | ||||
| Dividend paid to parent company | (780,000 | ) | (861,000 | ) | (572,125 | ) | |||
| Repayment of mortgage notes payable | (8,288 | ) | (7,845 | ) | (7,423 | ) | |||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | $ | 2,375,269 | 4,374,483 | 3,588,070 | |||||
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | 287,376 | 92,802 | (1,143,435 | ) | |||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 1,219,984 | 1,127,182 | 2,270,617 | ||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 1,507,360 | 1,219,984 | 1,127,182 | |||||
| Note: Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information for non-cash distribution - non-cash dividend payment to affiliate (see note 19 for further discussion) | $ | — | (33,165 | ) | — | ||||
See accompanying Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
Page 8 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (1) | Organization |
Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America (the Company) is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Allianz of America, Inc. (AZOA or parent company), which is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Allianz Europe, B.V. Allianz Europe, B.V. is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Allianz SE. Allianz SE is a European company registered in Munich, Germany, and is the Company’s ultimate parent.
The Company is a life insurance company licensed to sell annuity, group and individual life, and group and individual accident and health policies in the United States, Canada, and several U.S. territories. Based on statutory net premium written, the Company's business is predominately annuity. The annuity business consists of fixed-indexed, variable, variable-indexed, and fixed annuities. The life business consists of both individual and group life. Life business includes products with guaranteed premiums and benefits and consists principally of universal life policies, fixed-indexed universal life policies, term insurance policies, and limited payment contracts. Accident and health business is primarily comprised of closed blocks of long-term care (LTC) insurance. The Company’s primary distribution channels are through independent agents, broker-dealers, banks, and third-party marketing organizations.
| (2) | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
| (a) | Basis of Presentation |
The Consolidated Financial Statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). The accounts of the Company’s primary subsidiary, Allianz Life Insurance Company of New York (AZNY), and all other subsidiaries have been consolidated. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
| (b) | Use of Estimates |
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make certain estimates and assumptions that affect reported amounts of assets and liabilities, including reporting or disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Future events, including changes in mortality, morbidity, interest rates, capital markets, and asset valuations could cause actual results to differ from the estimates used within the Consolidated Financial Statements. Such changes in estimates are recorded in the period they are determined.
| (c) | Investment Products and Universal Life Business |
Investment products consist primarily of fixed and variable annuity products. Premium receipts are reported as deposits to the contractholders’ accounts or an establishment of future policy benefit reserves. Premiums and policy fees, net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations represent asset fees, cost of insurance charges, administrative fees, charges for guarantees on investment products, and surrender charges for investment products and universal life insurance, all of which is net of reinsurance. These fees have been earned and assessed against contractholders on a daily or monthly basis throughout the contract period and are recognized as revenue when assessed and earned. Amounts assessed that represent compensation to the Company for services to be provided in future periods are not earned in the period assessed. Such amounts are reported as unearned revenue, which include unearned revenue reserves (URR), and are recognized in operations over the period benefited using the same assumptions and factors used to amortize capitalized acquisition costs. Unearned revenue is reported in Unearned premiums on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Surrender charges are recognized upon surrender of a contract in accordance with contractual terms. Derivatives embedded in fixed-indexed, variable, and certain life products are recorded at fair value and changes in value are included in Change in fair value of annuity and life embedded derivatives in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Benefits consist of interest credited to contractholders’ accounts and claims incurred in excess of the contractholders’ account balance, net of reinsurance, and are included in Net interest credited to account values and Policyholder benefits, net of recoveries, respectively, within the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Page 9 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The Company offers a variable-indexed annuity product that combines a separate account option with a general account option that is similar to a fixed-indexed annuity. The Company has elected the fair value option to account for the entire insurance contract liability and the variable investment option assets in the separate account. The insurance contracts’ reserves are reported in Account balances and future policy benefit reserves and the variable investment option assets within the separate account are reported in Equity securities, fair value option and trading on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Assets backing the general account are primarily reported in Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Electing the fair value option for an insurance contract liability requires that the Company account for that liability as a financial instrument at fair value through profit and loss and also requires that acquisition costs be recognized immediately in expense. See note 6 for further details regarding the valuation methodology of the variable-indexed annuity product.
| (d) | Life and Accident and Health Insurance |
Premiums on traditional life products are recognized as revenue over the premium-paying periods of the contracts when due from contractholders. Premium revenue generally exceeds expected policy benefits in the early years of the contracts and a reserve liability is established for costs and benefits that are expected to be paid in the later years of the contracts.
Accident and health premiums are recognized as earned on a pro rata basis over the risk coverage periods. Benefits and expenses are recognized as incurred.
| (e) | Investments |
Fixed-Maturity Securities and Equity Securities
The Company has portfolios of fixed-maturity securities and equity securities classified as “available-for-sale.” Accordingly, these securities are carried at fair value, and related unrealized gains and losses are credited or charged directly to accumulated other comprehensive income (AOCI) in stockholder’s equity, net of tax and related shadow adjustments. The adjustments to deferred acquisition costs (DAC), value of business acquired (VOBA), and deferred sale inducements (DSI) represent the change in amortization that would have been required as a charge or credit to operations had such unrealized amounts been realized. The adjustment to reserves represents the increase or decrease in the reserve balance that would have been required as a charge or credit to operations had such unrealized amounts been realized.
Included in the Company’s portfolios of fixed-maturity securities classified as “available-for-sale” are fixed-maturity securities acquired with deteriorated credit quality. On a quarterly basis, the Company estimates the future cash flows for these securities and records any changes as adjustments to accretable yield. Accretable yield refers to the amount of undiscounted cash flows expected in excess of the carrying amount. This amount is converted into a rate and accreted into Interest and similar income, net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Interest is recorded as received on certain securities acquired that do not have reasonably estimable cash flows. If, subsequently, it is probable that there is a significant change in cash flows expected to be collected or if actual cash flows are significantly greater than cash flows previously expected to be collected, the effective yield is recalculated prospectively.
Page 10 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The Company has portfolios of certain fixed-maturity securities and equity securities classified as “trading”. These securities are carried at fair value, and related unrealized and realized gains and losses are reflected in Change in fair value of assets and liabilities within the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Additionally, the Company has a portfolio of mutual fund seed money investments and restricted stock units (RSU) for which the fair value option was elected and is included within Equity securities, fair value option and trading on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The fair value option was elected for the mutual fund seed money investments because the portfolio is managed based on the fair values and ultimately sold to other investors at fair value. For RSU, the fair value option was elected as RSU are tied to the share price of Allianz SE stock, which constitutes a fair value, and more accurately reflects the underlying obligation owed to certain employees. In addition, the Company had portfolios of certain fixed-maturity securities classified as “held-to-maturity” carried at amortized cost on the Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2016. During 2017, the Company sold one portfolio of held-to-maturity fixed-maturity securities for which the Company had collected a substantial portion of the principal outstanding and the remaining portfolio of held-to-maturity fixed-maturities matured. Dividends are accrued on the date they are declared and interest is accrued as earned. Premiums or discounts on fixed-maturity securities are amortized using the constant yield method. Realized gains and losses are computed based on the average amortized cost basis of all lots owned of each security.
The Company has portfolios of structured securities which include mortgage-backed securities, collateralized debt obligations (CDO), collateralized loan obligations (CLO), and other asset-backed securities. Mortgage-backed securities and CDO are presented separately while CLO and other asset-backed securities are included within 'Corporate securities' within the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. Structured securities are amortized using, among other assumptions, anticipated prepayments. Prepayment assumptions for structured securities are obtained from various external sources or internal estimates. The Company believes these assumptions are consistent with those a market participant would use. The Company recognizes income using a constant effective yield method based on prepayment assumptions and the estimated economic life of the securities. For all structured securities without expected credit deterioration, when actual prepayments differ significantly from anticipated prepayments, the effective yield is recalculated to reflect actual payments to date and anticipated future payments retrospectively. Any resulting adjustment is included in Interest and similar income, net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. For structured securities with expected credit deterioration, when adjustments are made to assumptions for prepayments and other future cash flows, the effective yield is recalculated prospectively.
The fair value of fixed-maturity securities and equity securities is obtained from third-party pricing sources whenever possible. Management completes its own independent price verification (IPV) process, which ensures security pricing is obtained from a third-party source other than the sources used by the Company's internal and external investment managers. The IPV process supports the reasonableness of price overrides and challenges by the internal and external investment managers and reviews pricing for appropriateness. Results of the IPV process are reviewed by the Company’s Pricing Committee.
Page 11 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The Company reviews the available-for-sale and held-to-maturity fixed-maturity investment portfolios to determine whether or not declines in fair value are other-than-temporary. In addition, the Company continually evaluates average amortized cost, fair value, credit quality, extent and duration of the decline, market analysis, current events, recent price declines, changes in risk-free interest rates, and likelihood of recovery in a reasonable period of time. Based on this evaluation, the Company determines whether fixed-income securities are considered other-than-temporarily impaired. When the fair value of a fixed-maturity security is less than its amortized cost, the Company assesses whether or not (i) it has the intent to sell the security or (ii) it is more likely than not that the Company will be required to sell the security before its anticipated recovery. The Company evaluates these factors to determine whether the Company or any of its internal and external investment managers have the intent to sell a security or a group of securities. The Company performs a cash flow projection for several years into the future to determine whether cash needs would require the sale of any securities in an unrealized loss position. If either of these conditions are met, the Company must recognize an other-than-temporary impairment (OTTI) for the difference between the investment’s amortized cost basis and its fair value through earnings. For securities that do not meet the above criteria and the Company does not expect to recover a security’s amortized cost basis, the security is also considered other-than-temporarily impaired. For these securities, the Company separates the total impairment into the credit loss component and the amount of the loss related to other factors. The amount of the total impairment related to credit loss is considered an OTTI and is recognized in Realized investment gains (losses), net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The amount of the total impairment related to other factors is recognized in other comprehensive income (OCI), net of impacts to DAC, DSI, VOBA, reserves, and deferred income taxes. For available-for-sale and held-to-maturity securities that have recognized an OTTI through earnings, if through subsequent evaluation there is a significant increase in the cash flow expected, the difference between the amortized cost basis and the discounted cash flows expected to be collected is accreted as interest income. Subsequent increases and decreases not related to additional credit losses in the fair value of available-for-sale securities are included in the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss).
The Company evaluates whether a credit loss exists by considering primarily the following factors: (a) the length of time and extent to which the fair value has been less than the amortized cost of the security; (b) changes in the financial condition, credit rating, and near-term prospects of the issuer; (c) whether the issuer is current on contractually obligated interest and principal payments; (d) changes in the financial condition of the security’s underlying collateral, if any; and (e) the payment structure of the security. The Company uses a probability-weighted cash flow model for fixed-maturity securities to determine the credit loss amount. This measurement is a quantitative and qualitative process that incorporates information received from third-party sources along with certain internal assumptions and significant judgments regarding the future performance of the security. The Company’s probability-weighted cash flow model involves assumptions including, but not limited to, various performance indicators, such as historical and projected default and recovery rates, credit ratings, and current delinquency rates.
The Company provides a supplemental disclosure within the Consolidated Statements of Operations that presents the total OTTI losses recognized in earnings during the period. The supplemental disclosure excludes subsequent increases and decrease in the fair value of these securities.
The Company evaluates whether equity securities are other-than-temporarily impaired through a review process which includes, but is not limited to, market analysis, analyzing current events, assessing recent price declines, and management’s judgment related to the likelihood of recovery within a reasonable period of time.
Impairments in the value of securities held by the Company considered to be other-than-temporary are recorded as a reduction of the cost of the security, and a corresponding realized loss is recognized in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The Company adjusts DAC, VOBA, and DSI for impairments on securities, as discussed in their respective sections of this note.
Page 12 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Mortgage Loans on Real Estate
Mortgage loans on real estate are reflected at unpaid principal balances adjusted for an allowance for uncollectible balances. Interest on mortgage loans is accrued on a monthly basis and recorded in Interest and similar income, net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The Company analyzes loan impairment quarterly when assessing the adequacy of the allowance for uncollectible balances. The Company considers recent trends in the Company’s loan portfolio and information on current loans, such as loan-to-value ratios and debt service coverage, which could impact a loan’s credit quality. The Company also evaluates the allowance for uncollectible balances to ensure that the estimate is based on appropriate market assumptions to reflect default and loss rates. The Company does not accrue interest on delinquent loans. When the Company discontinues accruing interest on delinquent loans, interest is recorded on a cash basis. The Company will begin accruing interest again on a loan once all delinquent interest and principal payments are brought current.
Loans to Affiliates
The Company has a note receivable from a related party and has recorded it in Loans to affiliates on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Loans to affiliate are carried at amortized cost on the Consolidated Balance Sheets and interest is accrued on a monthly basis. Interest payments are received annually.
Policy Loans
Policy loans are supported by the underlying cash value of the policies. Policy loans are carried at unpaid principal balances plus accrued interest income on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Other Invested Assets
Other invested assets include short-term securities, loans to non-affiliates, equity securities carried at cost, investments in limited partnerships, and investments in limited liability companies. Short-term securities are comprised of fixed-maturity securities with an original maturity of twelve months or less and greater than three months when purchased. Short-term securities are carried at amortized cost, which approximates fair value due to their short-term nature. Loans to non-affiliates are carried at amortized cost, and interest is accrued monthly. The Company invests in low income housing limited partnerships and limited liability companies (LIH investments) for tax benefits. The LIH investments are carried at cost, adjusted for amortization based on the proportion of total tax credits and other tax benefits expected to be received over the life of the investments. The investments in the LIH investments were $63,407 and $46,727 as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. The LIH investments are individually evaluated for impairment based on the recoverability of each investment's amortized cost. The Company records a liability and corresponding asset for the discounted future commitment, which decreases as the Company provides capital to fund. The tax benefit is recognized within Income tax expense in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The Company has recognized tax credits related to the LIH investments of $13,651, $7,125, and $2,793 for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, and 2015, respectively.
Investments in limited partnerships and limited liability companies (other than LIH investments) are accounted for using the equity method of accounting. Undistributed limited partnership and limited liability company profits and losses are recorded in Interest and similar income, net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Distributions in excess of cost and impairments of investments in limited partnerships and limited liability companies are recognized within Realized investment gains (losses), net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Investments in limited partnerships and limited liability companies are individually evaluated for impairment based upon the recoverability of the each investment's cost.
Page 13 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The Company is a member of the Federal Home Loan Bank of Des Moines (FHLB), primarily for the purpose of participating in the FHLB’s mortgage collateralized loan advance program with short-term and long-term funding facilities. Members are required to purchase and hold a minimum amount of FHLB capital stock plus additional stock based on outstanding advances. The equity security investment is carried at cost, which approximates fair value, and is reported in Other invested assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The Company held FHLB stock of $30,000 at December 31, 2017 and 2016. Advances are in the form of short-term or long-term notes or funding agreements issued to FHLB. Advances received from FHLB are recorded in Account balances and future policy benefit reserves on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The investment is evaluated for impairment based on the ultimate recoverability of its par value.
The Company has a fully collateralized funding agreement with a balance of $500,000 at December 31, 2017 and 2016. In 2015, the Company obtained a cash advance from FHLB which had a balance of $500,000 as of December 31, 2015. The cash advance was recorded in Other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets and was subsequently paid off in 2016.
Variable Interest Entities
In the normal course of business, the Company enters into relationships with various entities that are deemed to be variable interest entities. A variable interest entity (VIE) is an entity that either (1) has equity investors that lack certain essential characteristics of a controlling financial interest (including the ability to control activities of the entity, the obligation to absorb the entity’s expected losses, and the right to receive the entity’s expected residual returns) or (2) lacks sufficient equity to finance its own activities without financial support provided by other entities, which in turn would be expected to absorb at least some of the expected losses of the VIE. The Company consolidates a VIE if it is determined to be the primary beneficiary. Those entities which do not meet the requirements to be a VIE are voting interest entities (VOEs). The Company consolidates a VOE if it holds a voting interest that is greater than 50%.
| (f) | Derivatives |
The Company utilizes derivatives within certain actively managed investment portfolios. Within these portfolios, derivatives can be used for hedging, replication, and income generation only. The financial instruments are carried at fair value and the unrealized gains and losses are reflected in Change in fair value of assets and liabilities in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Hedge Accounting
To qualify for hedge accounting treatment, a derivative must be highly effective in mitigating changes in the cash flows or fair value of the hedged item due to the designated risk hedged. The documentation process involves defining the Company’s risk management objective, strategy for undertaking each hedge transaction, linking specific derivatives to specific assets or liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets, and defining the effectiveness testing methods to be used. The Company also formally assesses, at inception and on a quarterly basis, whether the derivatives used in hedging transactions have been and are expected to continue to be highly effective in offsetting changes in the cash flows or fair value of hedged items based on the designated risk hedged.
Hedge effectiveness is assessed on a prospective and retrospective basis using quantitative methods. Since the inception of the hedge accounting program, on both a prospective and retrospective basis, changes in the cash flows or fair value of the hedging instrument are expected to offset the changes in the cash flows of the hedged item as the key terms match for both instruments. The cumulative effective amount of unrealized gains and losses of the hedging instrument is recognized in AOCI, net of tax on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The ineffective portion of the change in the fair value of the hedging instrument is recognized in Change in fair value of assets and liabilities in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Page 14 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Foreign Currency Swaps
The Company utilizes foreign currency swaps to hedge cash flows and applies hedge accounting treatment. Specifically, the Company uses foreign currency swaps to hedge foreign currency and interest rate fluctuations on certain underlying foreign currency denominated fixed-maturity securities. The foreign currency swaps are reported at fair value in Derivative assets and Derivative liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The fair value of the foreign currency swaps are derived using a third-party vendor software program and deemed by management to be reasonable. Interest income generated from the foreign currency swaps is recorded in Interest and similar income, net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
The Company has a timing difference between the purchase of the foreign currency swap and settlement of the hedged foreign currency denominated fixed-maturity security. Any changes in value of the foreign currency swap between the purchase and settlement date are recorded in Change in fair value of assets and liabilities in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. After the hedged foreign currency denominated fixed-maturity security is settled, the Company completes documentation and designates hedge accounting.
Nonqualifying hedging
Futures and Options Contracts
The Company provides benefits through certain life and annuity products which are linked to the fluctuation of various market indices, and certain variable annuity contracts that provide minimum guaranteed benefits. The Company has analyzed the characteristics of these benefits and has entered into over-the-counter (OTC) option contracts, exchange-traded option (ETO) contracts, and exchange-traded futures contracts tied to an underlying index with similar characteristics with the objective to economically hedge these benefits. In addition, the Company uses futures contracts to hedge the investment risk associated with seed money. Management monitors in-force amounts and option and futures contract values to ensure satisfactory matching and to identify unsatisfactory mismatches. If actual persistency deviated, management would purchase or sell option and futures contracts as deemed appropriate or take other actions.
The OTC option contracts and ETO contracts are reported at fair value in Derivative assets and Derivative liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The fair value of the OTC options is derived internally and deemed by management to be reasonable via performing an IPV process. The process of deriving internal derivative prices requires the Company to calibrate Monte Carlo scenarios to actual market information. The calibrated scenarios are applied to derivative cash flow models to calculate fair value prices for the derivatives. The fair value of the ETO contacts is based on quoted market prices. Changes in unrealized gains and losses on the OTC option contracts and ETO contracts and incremental gains and losses from expiring contracts are recorded within Change in fair value of assets and liabilities in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Futures contracts do not require an initial cash outlay, and the Company has agreed to daily net settlement based on movements of the representative index. Therefore, no asset or liability is recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Gains and/or losses on futures contracts are included in Change in fair value of assets and liabilities in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Interest Rate Swaps, Credit Default Swaps, Total Return Swaps, and To Be Announced Securities
The Company utilizes interest rate swaps (IRS), credit default swaps (CDS), total return swaps (TRS), and To Be Announced (TBA) securities, which do not meet the regular-way security trade scope exception, to economically hedge market risks embedded in certain life and annuity products. The IRS, CDS, TRS, and TBA securities are reported at fair value in Derivative assets and Derivative liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The fair value of the IRS, CDS, and TBA securities are derived using a third-party vendor software program and deemed by management to be reasonable. Centrally cleared IRS fair values are obtained from the exchange on which they are traded. The fair value of the TRS is based on counterparty pricing and deemed by management to be reasonable. The unrealized gains and losses as well as investment income and expenses on these derivatives are recorded in Change in fair value of assets and liabilities in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Page 15 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Stock Appreciation Rights
The Company enters into contracts with Allianz SE with the objective to economically hedge risk associated with the Allianz SE stock-based compensation plan, which awards certain employees stock appreciation rights (SAR). The contracts are recorded at fair value within Derivative assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The change in fair value for SAR are recorded in Change in fair value of assets and liabilities and General and administrative expenses within the Consolidated Statements of Operations, respectively. See further discussion of the stock-based compensation plan in note 18.
| (g) | Cash and Cash Equivalents |
Cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand, demand deposits, short-term government money market funds, overnight commercial paper, overnight reverse repurchase agreements, and highly liquid debt instruments purchased with an original maturity of three months or less.
In the normal course of business, the Company enters into overnight bilateral and tri-party reverse repurchase agreements, whereby the Company purchases securities and simultaneously agrees to resell the same securities at a stated price on a specified date in the future, for the purpose of earning a specified rate of return. An affiliate of the Company serves as the agent in the bilateral agreements and an unaffiliated bank serves as the custodian in the tri-party agreements. The bilateral agreements require purchases of specifically identified securities. If at any time the fair value of those purchased securities falls below the purchase price, additional collateral in the form of cash or additional securities is required to be transferred to ensure margin maintenance. The tri-party agreements allow for the purchase of certain bonds and structured securities, and require a minimum of 102% of fair value of the securities purchased to be maintained as collateral. Due to the short-term nature of these investments, the carrying value is deemed to approximate fair value.
| (h) | Securities Lending |
The Company participates in securities lending arrangements whereby specific securities are loaned to other institutions. The Company receives collateral from these arrangements including cash and cash equivalents, which can be reinvested based on the Company's discretion, and noncash collateral, which may not be sold or re-pledged unless the counterparty is in default. The Company accounts for its securities lending transactions as secured borrowings, in which the cash collateral received and the related obligation to return the cash collateral are recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheets as Collateral held from securities lending agreements and Other liabilities, respectively. Noncash collateral received is not reflected on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Securities on loan remain on the Consolidated Balance Sheets as Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale, and interest income earned by the Company on loaned securities is recognized in Interest and similar income, net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Company policy requires a minimum of 102% of fair value of securities loaned under securities lending agreements to be maintained as collateral.
| (i) | Receivables |
Receivable balances (contractual amount less allowance for doubtful accounts) are based on pertinent information available to management as of year-end, including the financial condition and creditworthiness of the parties underlying the receivables. Receivable balances are monitored and the allowance for doubtful accounts is maintained based on the nature of the receivables, and the Company’s assessment of the ability to collect. The allowance is estimated by aging the balances due from individual parties and generally setting up an allowance for any balances that are more than 90 days old.
Page 16 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (j) | Reinsurance |
The Company assumes and cedes business with other insurers. Reinsurance premium and benefits paid or provided are accounted for in a manner consistent with the basis used in accounting for original policies issued and the terms of the reinsurance contracts and are included in Premiums and policy fees, net, and Policyholder benefits, net of recoveries, respectively, in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Insurance liabilities are reported before the effects of reinsurance. Account balances and future policy benefit reserves and policy and contract claims covered under reinsurance contracts are recorded in Reinsurance and investment contract recoverables on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Amounts paid or deemed to have been paid for claims covered by reinsurance contracts are recorded as Receivables on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Reinsurance and investment contract recoverables are recognized in a manner consistent with the liabilities related to the underlying reinsured contracts. Amounts due to other insurers on assumed business are recorded as a reinsurance payable, and are included in Other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
A gain recognized when the Company enters into a coinsurance agreement with a third-party reinsurer is deferred and recorded in Other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Such gains are amortized into operations over the revenue-producing period or the claims run-off period of the related reinsured policies. These amortized gains are recorded in Other revenue in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
| (k) | Deferred Acquisition Costs |
Acquisition costs consist of commissions and other incremental costs that are directly related to the successful acquisition of insurance contracts. Acquisition costs are deferred to the extent recoverable from future policy revenues and gross profits. However, acquisition costs associated with insurance contracts recorded under the fair value option are not deferred as guidance related to the fair value option requires that transaction costs are recorded immediately as an expense. For life and annuity products, with the exception of variable annuity contracts issued prior to 2010, acquisition costs are amortized in relation to the present value of expected future gross profits from investments and mortality, morbidity, and expense charges. For variable annuity contracts issued prior to 2010, acquisition costs are amortized in relation to the present value of estimated gross revenues from investments and mortality, morbidity, and expense charges.
Acquisition costs for accident and health insurance policies are amortized over the lives of the policies in the same manner as premiums are earned. For traditional life and group life products, such costs are amortized over the projected earnings pattern of the related policies using the same actuarial assumptions used in computing future policy benefit reserves.
DAC are reviewed for recoverability and loss recognition, at least annually, and adjusted when necessary. The evaluation is a two-step process where current policy year issues are evaluated for recoverability, and then in-force policies are evaluated for loss recognition. Before assessing recoverability and loss recognition, DAC are capped, if necessary, such that the balance cannot exceed the original capitalized costs plus interest.
Changes in assumptions can have an impact on the amount of DAC reported for annuity and life insurance products and their related amortization patterns. In the event experience differs from assumptions or assumptions are revised, the Company is required to record an increase or decrease in DAC amortization expense, which is referred to as DAC unlocking. In general, increases in the estimated investment spreads and fees result in increased expected future profitability and may decrease the rate of DAC amortization, while increases in costs of product guarantees, and lapse/surrender and mortality assumptions reduce the expected future profitability of the underlying business and may increase the rate of DAC amortization.
The Company formally evaluates the appropriateness of the best-estimate assumptions on an annual basis. If the economic environment or policyholder behavior changes quickly and substantially, assumptions will be reviewed more frequently to affirm best estimates. Any resulting DAC unlocking is reflected prospectively in Change in deferred acquisition costs, net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Page 17 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Adjustments to DAC are made to reflect the corresponding impact on the present value of expected future gross profits and revenues from unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale investments used to support policyholder liabilities (commonly known as shadow DAC). These adjustments are included in AOCI and are explained further in the Investments section of this note.
Adjustments may also be made to DAC that correspond to deferred annuities and universal life products for investment activity, such as write-downs on other-than-temporarily impaired fixed-maturity securities and realized gains and losses. Management action may result in assumption changes in the DAC models, such as adjustments to future estimated gross profits (EGP) and estimated gross revenues used, as well as in-force management action such as crediting rate changes or index rate cap adjustments. See further discussion of DAC unlocking in note 9.
The Company assesses internal replacements on insurance contracts to determine whether such modifications significantly change the contract terms. An internal replacement represents a modification in product benefits, features, rights, or coverages that occurs by the exchange of an in-force insurance contract for a new insurance contract, or by amendment, endorsement, or rider to a contract. If the modification substantially changes the contract, the remaining DAC on the original contract are immediately expensed and any new DAC on the replacement contract are deferred. If the contract modification does not substantially change the contract, DAC amortization on the original contract continues and any new acquisition costs associated with the modification are immediately expensed.
| (l) | Deferred Sales Inducements |
Sales inducements are product features that enhance the investment yield to the contractholder on the contract. The Company offers an immediate bonus on certain annuity contracts which increases the account value at inception. These annuity sales inducements are deferred when credited to contractholders. DSI are reported in Other assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. They are amortized over the expected life of the contract in a manner similar to DAC and are reviewed annually for recoverability. DSI amortization is recorded in Policyholder benefits, net of recoveries within the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Adjustments to DSI are made to reflect the estimated corresponding impact on the present value of expected future gross profits and revenues from unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale investments used to support policyholder liabilities (commonly known as shadow DSI). These adjustments are included in AOCI and are explained further in the Investments section of this note.
Adjustments may also be made to DSI for investment activity, such as write-downs on other-than-temporarily impaired fixed-maturity securities, and realized gains and losses. Management action may result in assumption changes in the DSI models, such as adjustments to future EGP used, as well as policyholder changes, such as credited rate changes.
| (m) | Income Taxes |
The Company and its subsidiaries file a consolidated federal income tax return with AZOA and all of its wholly-owned subsidiaries. The consolidated tax allocation agreement stipulates that each company participating in the return will bear its share of the tax liability pursuant to certain tax allocation elections under the Internal Revenue Code (IRC) and its related regulations and reimbursement will be in accordance with an intercompany tax reimbursement arrangement. The Company, and its insurance subsidiaries, generally will be paid for the tax benefit on their losses and any other tax attributes to the extent they could have obtained a benefit against their post-1990 separate return tax liability.
Page 18 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The Company provides for federal income taxes based on amounts the Company believes it ultimately will owe. Inherent in the provision for federal income taxes are estimates regarding the deductibility of certain items and the realization of certain tax credits. In the event the ultimate deductibility of certain items or the realization of certain tax credits differs from estimates, the Company may be required to significantly change the provision for federal income taxes recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Any such change could significantly affect the amounts reported within the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Management uses best estimates to establish reserves based on current facts and circumstances regarding tax exposure items where the ultimate deductibility is open to interpretation. Quarterly, management evaluates the appropriateness of such reserves based on any new developments specific to their fact patterns. Information considered includes results of completed tax examinations, Technical Advice Memorandums, and other rulings issued by the Internal Revenue Service or the tax courts.
The Company utilizes the asset and liability method of accounting for income tax. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized within operations in the period that includes the enactment date. Subsequent changes in deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized in operations or OCI, depending on the nature of the underlying temporary difference. Valuation allowances are established when it is determined that it is more likely than not that the deferred tax asset will not be fully realized or that the related temporary differences will not reverse over time. See note 11 for further details.
| (n) | Goodwill and Intangible Assets |
Goodwill is the excess of the amount paid to acquire a company over the fair value of its tangible net assets, VOBA, other identifiable intangible assets, and valuation adjustments (such as impairments), if any. Goodwill is reported in Other assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Goodwill is evaluated annually for impairment at the reporting unit level, which is one level below an operating segment. Goodwill of a reporting unit is also tested for impairment on an interim basis if a triggering event occurs, such as a significant adverse change in the business climate or a decision to sell or dispose of a business unit.
Intangible assets are required to be recognized apart from goodwill when they arise from contractual or legal rights or are capable of being separated and valued when sold, transferred, licensed, rented, or exchanged. The Company determines the useful life and amortization period for each intangible asset identified at acquisition, and continually monitors these assumptions. An intangible asset with a determinable life is amortized over that period, while an intangible asset with an indefinite useful life is not amortized.
The Company’s intangible assets are reported in Other assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. These intangible assets were assigned values using the present value of projected future cash flows and are generally amortized over five years using the straight-line method.
Recoverability of the value of the determinable-lived intangible assets is assessed whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying amount may not be recoverable. Recoverability of the value of the indefinite-lived intangible assets is assessed annually or earlier if events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying amount may not be recoverable.
| (o) | Value of Business Acquired |
The value of insurance in-force purchased is recorded as VOBA and reported in Other assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The initial value was determined by an actuarial study using the present value of future profits in calculating the value of the insurance in-force purchased. An accrual of interest is added to the unamortized balance using the rates credited to the policyholder accounts. The balance is amortized in relation to the present value of future EGP in the same manner as DAC. The amortization period is expected to be approximately 20 years from the date the business was acquired; however, the Company continually monitors this assumption. If actual EGP differ from expectations, the amortization of VOBA is adjusted on a retrospective or prospective basis, as appropriate.
Page 19 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Adjustments to VOBA are made to reflect the estimated corresponding impact on the present value of future EGP from unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale investments used to support policyholder liabilities (commonly known as shadow VOBA). These adjustments are included in AOCI and are explained further in the Investments section of this note.
The recoverability of VOBA is evaluated annually, or earlier if factors warrant, based on estimates of future earnings related to the insurance in-force purchased. If the existing insurance liabilities, together with the present value of future net cash flows from the blocks of business acquired, are not sufficient to recover VOBA, the difference, if any, is charged to expense through General and administrative expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
| (p) | Held-for-sale Assets and Liabilities |
The Company reported a subsidiary as held-for-sale as of December 31, 2016. The subsidiary's assets of $13,615 were reclassified to held-for-sale and recorded in Other assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2016. The subsidiary's liabilities of $2,754 were reclassified to held-for-sale and recorded in Other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2016. Income and expenses generated from the subsidiary were reclassified and recorded in Other revenue in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
On June 30, 2017, the subsidiary was sold through a stock purchase agreement. See further discussion in note 19.
| (q) | Home Office Property and Equipment |
Home office property consists of buildings and land. Equipment consists of furniture, office equipment, leasehold improvements, and computer hardware and software. Both are reported at cost, net of accumulated depreciation, in Other assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Major upgrades and improvements are capitalized, while maintenance and repairs are expensed when incurred. Depreciation is computed over the estimated useful lives of depreciable assets using the straight-line method. The estimated useful lives used for home office property and equipment are 39 years and 2 - 7 years, respectively. The cost and accumulated depreciation for home office property and equipment sold, retired, or otherwise disposed of are relieved from the accounts, and resulting gains or losses are reflected in General and administrative expenses within the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The home office property and equipment balance was $166,260, net of accumulated depreciation of $170,150, as of December 31, 2017 and $180,328, net of accumulated depreciation of $94,395, as of December 31, 2016. Pre-operating and start-up costs incurred in connection with the construction of the Company’s headquarters were capitalized until the facility became operational. Interest was also capitalized in connection with the construction and recorded as part of the asset. These costs are being amortized, using the straight-line method, over a 39-year period. Amortization of the the Company's headquarters, including capitalized costs and interest, was $4,394, $4,394, and $4,393 during 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively.
| (r) | Corporate-Owned Life Insurance |
Corporate-owned life insurance (COLI) is recognized initially as the amount of premiums paid. Subsequent measurement of the contract is based upon the amount that could be realized assuming the surrender of an individual-life policy (or certificate in a group policy), otherwise known as the cash surrender value. Changes in the cash surrender value are recognized in Other revenue in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The COLI policies are reported in Other assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. There are no contractual restrictions on the ability to surrender the COLI policies held by the Company.
Page 20 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (s) | Separate Accounts and Annuity Product Guarantees |
The Company issues variable annuity and maintains variable life contracts through its separate accounts for which investment income and investment gains and losses accrue directly to, and investment risk is borne by, the contractholder. The Company also issues variable-indexed annuity contracts to its customers. These products have investment options similar to fixed-indexed annuities, but allow contractholders to invest in a variety of variable separate account investment options. The Company recognizes gains or losses on transfers from the general account to the separate accounts at fair value to the extent of contractholder interests in separate accounts, which are offset by changes in contractholder liabilities. The Company issues variable annuity and previously issued life contracts through its separate accounts where the Company provides certain contractual guarantees to the contractholder. These guarantees are in the form of a guaranteed minimum death benefit (GMDB), a guaranteed minimum income benefit (GMIB), a guaranteed minimum accumulation benefit (GMAB), and a guaranteed minimum withdrawal benefit (GMWB). The investments backing the guarantees are held in the general account. These guarantees provide for benefits that are payable to the contractholder in the event of death, annuitization, exercise of the living withdrawal benefit, or at specified dates during the accumulation period.
Separate account assets supporting variable annuity contracts represent funds for which investment income and investment gains and losses accrue directly to contractholders. Each fund has specific investment objectives and the assets are carried at fair value. The assets of each account are legally segregated and are not subject to claims that arise out of any other business of the Company. Separate account assets and liabilities are reported as summary totals on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Amounts charged to the contractholders for mortality and contract maintenance are included in Premiums and policy fees, net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Administrative and other services are included in Fee and commission revenue in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. These fees have been earned and assessed against contractholders on a daily or monthly basis throughout the contract period and are recognized as revenue when assessed and earned. Changes in GMDB and GMIB are calculated in accordance with the Financial Services – Insurance Topic of the Accounting Standards Codification (Codification) and are included in Policyholder benefits, net of recoveries in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. GMAB and GMWB are considered to be embedded derivatives under the Derivatives and Hedging Topic of the Codification, and the changes in these embedded derivatives are included in Change in fair value of annuity and life embedded derivatives in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
The GMDB net amount at risk is defined as the guaranteed amount that would be paid upon death, less the current accumulated contractholder account value. The GMIB net amount at risk is defined as the current amount that would be needed to fund expected future guaranteed payments less the current contractholder account value, assuming that all benefit selections occur as of the valuation date. The GMAB net amount at risk is defined as the current guaranteed value amount that would be added to the contracts less the current contractholder account value. The GMWB net amount at risk is defined as the current accumulated benefit base amount less the current contractholder account value.
The GMDB provides a specified minimum return upon death. The survivor has the option to terminate the contract or continue it and have the death benefit paid into the contract. The Company’s GMDB options have the following features:
| • | Return of Premium – Provides the greater of account value or total deposits made to the contract, less any partial withdrawals and assessments. |
| • | Reset – Provides the greater of a return of premium death benefit or the most recent five-year anniversary account value (prior to age 81), adjusted for withdrawals. |
| • | Ratchet – Provides the greater of a return of premium death benefit or the highest specified anniversary account value (prior to age 81), adjusted for withdrawals. Currently, there are three versions of ratchet, with the difference based on the definition of anniversary: quarterly – evaluated quarterly, annual – evaluated annually, and six-year – evaluated every sixth year. |
Page 21 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| • | Rollup – Provides the greater of a return of premium death benefit or premiums adjusted for withdrawals accumulated with a compound interest rate. There are two variations of rollup interest rates: 5% with no cap and 3% with a cap of 150% of premium. This GMDB locks in at age 81. |
| • | Earnings Protection Rider – Provides the greater of a return of premium death benefit or a death benefit equal to the contract value plus a specified percentage of the earnings on the contract at the date of death. |
The GMIB is a living benefit that provides the contractholder with a guaranteed annuitization value. The GMIB features are:
| • | Return of Premium – Provides the greater of account value or total deposits made to the contract less any partial withdrawals and assessments. |
| • | Ratchet – Provides an annuitization value equal to the greater of account value, net premiums, or the highest one-year anniversary account value (prior to age 81), adjusted for withdrawals. |
| • | Rollup – Provides an annuitization value equal to the greater of account value or premiums adjusted for withdrawals accumulated with a compound interest rate, which is subject to a cap for certain interest rates and products. |
The GMDB and GMIB liabilities are determined each period by estimating the expected future claims in excess of the associated account balances. The Company regularly evaluates estimates used and adjusts the additional liability balance, with a related charge or credit to Policyholder benefits, net of recoveries in the Consolidated Statements of Operations, if actual experience or other evidence suggests that earlier assumptions should be revised.
The GMAB is a living benefit that provides the contractholder with a guaranteed value that was established at least five years prior at each contract anniversary. This benefit is first available at the fifth contract anniversary, seventh contract anniversary, or tenth contract anniversary depending on the type of contract. Depending on the contractholder’s selection at issue, this value may be either a return of premium or may reflect market gains, adjusted at least proportionately for withdrawals. The contractholder also has the option to reset this benefit.
The GMWB is a living benefit that provides the contractholder with a guaranteed amount of income in the form of partial withdrawals. The benefit is payable provided the covered person is between the specified ages in the contract. The benefit is a fixed rate (depending on the age of the covered person) multiplied by the benefit base in the first year the benefit is taken and contract value in following years. The benefit does not decrease if the contract value decreases due to market losses. The benefit can decrease if the contract value is reduced by withdrawals. The benefit base used to calculate the initial benefit is the maximum of the contract value, the quarterly anniversary value, or the guaranteed annual increase of purchase payments (either simple or compound interest, depending on the contract). Additionally, there is a GMWB living benefit where the benefit is an initial payment percentage established at issue, based on issue age. For each year there is a year-over-year contract value increase, the payment percentage will increase by 1.0% (up to age 91). This payment percentage is applied against total purchase payments instead of a benefit base value.
The GMAB and GMWB liabilities are determined each period as the difference between the present value of the expected future claims and the expected future profits. One result of this calculation is that these liabilities can be negative (contra liability). If the sum of the total embedded derivative balance is negative, the Company will reclassify the balance as an asset on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. This methodology will also be applied to the fixed-indexed benefit. The Company regularly evaluates estimates used and adjusts the additional liability balance, with a related charge or credit to Change in fair value of annuity and life embedded derivatives in the Consolidated Statements of Operations, if actual experience or other evidence suggests that earlier assumptions should be revised.
GMAB cash flows are discounted using a rate equal to current month’s London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR) plus a Company specific spread. The expected life-contingent GMWB payments are discounted using a blend of short and long term rates to the date the account value is expected to be exhausted. These obligations and all cash flows are then discounted to the current date using LIBOR plus a Company specific spread.
Page 22 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The Company issues fixed-indexed annuities with a GMWB as an optional rider. The GMWB has a roll-up feature. The net amount at risk is partially limited, because the contractholder account value has an annual credit that is floored at zero. Since the account value cannot decrease, in contrast to a variable annuity, the difference between the withdrawal value and the account value will not diverge to the degree that is possible in a variable annuity.
| (t) | Account Balances and Future Policy Benefit Reserves |
The Company establishes liabilities for amounts payable to policyholders associated with annuity, life insurance, and LTC policies sold. Policy and contract account balances for universal life products are carried at accumulated contract values. For fixed-indexed annuity products, the policyholder obligation is divided into two parts – one part representing the value of the underlying base contract (host contract); and the second part representing the fair value of the expected index benefit over the life of the contract. The host contract is accounted for as an interest-bearing debt instrument. The index benefit is valued at fair value using current capital market assumptions, such as market index and volatility, to estimate future index levels. The index benefit valuation is also dependent upon assumptions of future policyholder behavior. The Company must include provisions for the Company’s own credit risk and for risk that the Company’s assumptions about policyholder activity could differ from actual experience. The fair value determination of the index benefit is sensitive to the economic market and interest rate environment, as it is discounted at current market interest rates. There is volatility in this liability due to these external market sensitivities.
Certain two-tier fixed annuity products provide additional benefits payable upon annuitization for period-certain and life-contingent payout options. An additional annuitization reserve is accrued using assumptions consistent with those used in estimating gross profits for purposes of amortizing DAC.
Contract account balances for variable annuity products are carried at accumulated contract values. Future policy benefit reserves for any death and income benefits that may exceed the accumulated contract values are established using a range of economic scenarios and are accrued for using assumptions consistent with those used in estimating gross profits or gross revenues for purposes of amortizing DAC. Future policy benefit reserves for accumulation and withdrawal benefits that may exceed account values are established using capital market assumptions, such as market index and volatility, along with estimates of future contractholder behavior.
Contract account balances for variable-indexed annuity products are measured at fair value, floored at the current contract value. The fair value measurement uses current capital market assumptions, such as market index and volatility, to estimate future index levels. The contract valuation is also dependent upon estimates of future contractholder behavior. The Company must include provisions for the Company’s own credit risk and for risk that the Company’s assumptions about contractholder activity could differ from actual experience. The fair value determination of the index benefit is sensitive to the economic market and interest rate environment, as it is discounted at current market interest rates. There is volatility in this liability due to these external market sensitivities. However, if the accumulated contract account value exceeds the calculated fair value, the Company records the contract account balances at their current contract value.
Future policy benefit reserves on traditional life products are computed by the net level premium method based upon estimated future investment yield, mortality, and withdrawal assumptions, commensurate with the Company’s experience, modified as necessary to reflect anticipated trends, including possible unfavorable deviations. Most life reserve interest assumptions range from 2.3% to 6.0%.
Future policy benefit reserves on LTC products are computed using a net level reserve method. Reserves are determined as the excess of the present value of future benefits over the present value of future net premiums and are based on best estimate assumptions at the time of issue for morbidity, mortality, lapse, and interest with provisions for adverse deviation. Most LTC reserve interest assumptions range from 5.0% to 6.0%.
An additional LTC reserve has been established to provide for future expected losses that are anticipated to occur after a period of profits. The reserve accrual will be over the profit period and is based on best estimate assumptions as of the current accrual period without provisions for adverse deviation.
Page 23 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (u) | Policy and Contract Claims |
Policy and contract claims include the liability for claims reported but not yet paid, claims incurred but not yet reported (IBNR), and claim settlement expenses on the Company’s accident and health business. Actuarial reserve development methods are generally used in the determination of IBNR liabilities. In cases of limited experience or lack of credible claims data, loss ratios are used to determine an appropriate IBNR liability. Claim and IBNR liabilities of a short-term nature are not discounted, but those claim liabilities resulting from disability income or LTC benefits include interest and mortality discounting.
| (v) | Stockholder’s Equity, Accumulated Unrealized Foreign Currency Translation |
Foreign currency translation adjustments are related to the conversion of foreign currency upon the consolidation of a foreign branch (see further discussion in note 23). The net assets of the Company’s foreign operations are translated into U.S. dollars using exchange rates in effect at each year-end. Translation adjustments arising from differences in exchange rates from period to period are included in Foreign currency translation adjustments, net of tax, reported as a separate component of comprehensive income within the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss).
| (w) | Prescribed and Permitted Statutory Accounting Practices |
The Company is required to file annual statements with insurance regulatory authorities, which are prepared on an accounting basis permitted or prescribed by such authorities. Prescribed statutory accounting practices include state laws, regulations, and general administrative rules, as well as a variety of publications of the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC). Permitted statutory accounting practices encompass all accounting practices that are not prescribed; such practices differ from state to state, may differ from company to company within a state, and may change in the future. The Company and its subsidiaries did not have any permitted practices in effect as of December 31, 2017.
The Company’s subsidiary, Allianz Life Insurance Company of Missouri (AZMO), has adopted an accounting practice that is prescribed by the Department of Insurance, Financial Institutions, and Professional Registration of the State of Missouri (the Missouri Department). The effect of the accounting practice allows a letter of credit to be carried as an admitted asset. Under NAIC statutory accounting principles (SAP), this letter of credit would not be allowed as an admitted asset. This prescribed practice does not impact the net income of AZMO and results in a $103,530 increase to statutory surplus as of December 31, 2017.
The Company and its subsidiaries do not have any other prescribed practices that had an impact on net income or statutory surplus as of December 31, 2017.
| (x) | Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements – Adopted |
In October 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) 2016-17, Consolidation: Interests Held through Related-Parties that are under Common Control, to require a reporting entity to include all of its direct variable interests in a VIE, and on a proportionate basis, its indirect variable interests in a VIE held through related parties, including related parties that are under common control with the reporting entity, when determining whether the reporting entity is the primary beneficiary of the VIE, and therefore required to consolidate the VIE. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The amendments in this update do not have an impact on the Consolidated Financial Statements.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-09, Compensation - Stock Compensation, to update share-based payment accounting for income tax consequences and classification of awards on the balance sheet and statement of cash flows. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The amendments in this update do not have an impact on the Consolidated Financial Statements, other than disclosing the entity-wide election to continue estimating forfeitures for share-based payments as included in note 18.
Page 24 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-07, Simplifying the Transition to the Equity Method of Accounting, which eliminates the requirement that, upon equity method qualification due to an increase in ownership interest, an investor must adjust the investment, results of operations, and retained earnings retroactively. The entity must recognize the unrealized holding gain or loss currently in AOCI through earnings at the date of qualification. The amendments in this update are effective for all fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The amendments in this update are prospective and do not have an impact on the Consolidated Financial Statements.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-06, Contingent Put and Call Options in Debt Instruments, to provide clarifying guidance regarding the assessment of whether contingent call or put options on debt instruments are clearly related to their debt hosts. The amendments in this update eliminate diversity in practice in assessing embedded contingent call and put options in debt instruments by requiring an entity to make the assessment solely with the four-step decision process. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The amendments in this update do not have an impact on the Consolidated Financial Statements.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-05, Effect of Derivative Contract Novations on Existing Hedge Accounting Relationships, which adds guidance to clarify that in the event of a change in counterparty to the derivative instrument designated as a hedging instrument, the change will not require dedesignation unless other criteria are also present. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The amendments in this update are prospective and do not have a material impact on the Consolidated Financial Statements.
| (y) | Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements – To Be Adopted |
The FASB issued the following updates as part of their comprehensive new revenue recognition standard:
| • | ASU 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. This update defines the new standard for recognizing revenue from contracts when goods and services are transferred to a customer in exchange for payment. The model requires 1) identifying contracts with a customer; 2) identifying separate performance obligations; 3) determining the transaction price; 4) allocating the transaction price to the separate performance obligations; and 5) recognizing revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation. The revenue recognition standard does not apply to financial instruments or to insurance contracts. However, the standard will require significantly more disclosures about items that are recorded under the new revenue recognition model. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017. |
| • | ASU 2016-08, Revenue Recognition - Principal versus Agent (reporting revenue gross versus net). This update adds clarifications to the principal versus agent guidance contained within ASU 2014-09 and provides guidance to aid in the assessment of control. Under the new guidance, an entity that controls the specified good or services before it is transferred to a customer is considered a principal and will recognize revenue on a gross basis. The amendments in this update are effective concurrently with ASU 2014-09. |
| • | ASU 2016-12, Revenue Recognition - Narrow-scope Improvements and Practical Expedients. This update provides clarifying guidance impacting several areas of the new standard, including noncash consideration and assessing collectibility. The amendments in this update are effective concurrently with ASU 2014-09. |
| • | ASU 2016-20, Technical Corrections and Improvements to Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. This update makes various minor clarifications to the guidance issued in ASU 2014-09. The amendments in this update are effective concurrently with ASU 2014-09. |
Page 25 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Currently, fee and commission income is recognized upon completion of the service and is recorded in Fee and commission revenue in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Management and advisory fees are currently recognized periodically as income over the respective investment period for which services have been performed; and fund administrative fees are recognized as the services are performed. Management, advisory, and fund administrative fees are recorded in Other revenue in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Previous guidance requires revenue recognition when it is earned and realized/realizable including consideration of when it is fixed or determinable. Under the new standard, the Company will be required to recognize fee and commission income when the intermediary has satisfied its performance obligation (provision of placement services) and the customer has contractually agreed to the terms of the insurance policy so long as it is probable that the agreement will not be subject to reversal. Similar to previous guidance, management and advisory fees, and fund administrative fees are recognized periodically as income over the period for which services have been performed (usually less than one year) so long as it is probable that the contract will not be subject to clawback. The new standard has not resulted in acceleration in revenue recognition for certain fees and commissions compared to the current method, as anticipated. Rather, recognition of fee and commission income, management and advisory fees, and fund administrative fees has remained relatively unchanged. Further, revenue is currently recognized on a gross basis as earned since the Company maintains control of the good or service before it is transferred. The amendments related to principal versus agent considerations do not impose a change to this recognition. The Company has evaluated the impact of the new standard, and has determined no further impacts on the recognition and presentation of revenue.
In February 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-02, Reclassification of Certain Tax Effects from Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income, which permits stranded tax effects resulting from the passing of H.R.1, commonly referred to as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 (Tax Act of 2017), to be reclassified to retained earnings. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2018, with early adoption permitted. Upon adoption, the Company expects the amendments in this update will decrease Retained earnings as of January 1, 2018 by approximately $393,559 with a corresponding increase to AOCI.
In August 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-12, Targeted Improvements to Accounting for Hedging Activities. The amendments in this update improve presentation of the Company’s risk management activities in its financial statements and simplify application of current hedge accounting guidance. The amendments in this update require presentation of the derivative and hedged item in the same income statement line item, eliminate reporting and measurement of hedge ineffectiveness, and simplify hedge effectiveness testing. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is currently assessing the impact of the amendments in this update.
In March 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-08, Premium Amortization on Purchased Callable Debt Securities. The amendments in this update shorten the amortization period for certain callable debt securities held at a premium. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The Company does not expect the amendments in this update to have a material impact on the Consolidated Financial Statements upon adoption.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-04, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment. The amendments within this update eliminate step two of the current two-step goodwill impairment test. The new guidance will only require a one-step quantitative impairment test where the goodwill impairment loss is measured as the excess reporting unit’s carrying amount over its fair value (but not to exceed the total goodwill allocated to the reporting unit). The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The amendments in this update are not expected to have an impact on the Consolidated Financial Statements.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-01, Business Combinations (Topic 805): Clarifying the Definition of a Business. The amendments within this update clarify the guidance for determining what constitutes a business to help entities evaluate whether transactions shall be accounted for as acquisitions (or disposals) of businesses. The amendments in this update are for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company does not expect the amendments in this update to have an impact on the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Page 26 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows: Restricted Cash, to require that a statement of cash flows explain the change during the period in the total of cash, cash equivalents, and amounts generally described as restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company does not expect the amendments in this update to have an impact on the Consolidated Financial Statements.
In October 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-16, Income Taxes: Intra-Entity Transfers of Assets Other than Inventory, to require entities to recognize the income tax consequences of an intra-entity transfer of an asset other than inventory when the transfer occurs, rather than when it is sold externally. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company does not expect the amendments in this update to have an impact on the Consolidated Financial Statements.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-15, Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments, to clarify or provide additional guidance regarding eight specific cash flow issues. These issues address the following topics: 1) debt prepayment or debt extinguishment costs; 2) settlement of zero-coupon debt instruments or other debt instruments with coupon interest rates that are insignificant in relation to the effective interest rate of the borrowing; 3) contingent consideration payments made after a business combination; 4) proceeds from the settlement of insurance claims; 5) proceeds from the settlement of corporate-owned life insurance policies, including bank-owned life insurance policies; 6) distributions received from equity method investees; 7) beneficial interests in securitization transactions; and 8) separately identifiable cash flows and application of the predominance principle. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company will elect to apply the cumulative earnings approach in recording distributions from equity method investments in the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows upon adopting the amendments in this update. The Company does not expect the amendments in this update to have a material impact on the Consolidated Financial Statements.
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments, to replace the existing incurred loss impairment model with a new methodology that reflects expected credit losses and requires the entity to consider more information to develop credit loss estimates. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted after December 15, 2018. The Company is currently assessing the impact of the amendments in this update.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, Leases, to require that the lessee recognize a right-of-use asset and a lease liability for all leases. There continues to be a distinction between finance leases and operating leases; however, operating leases will now require that the lease assets and liabilities be recognized in the statement of financial position. Lessor accounting remains largely unchanged. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is currently assessing the impact of the amendments in this update. The Company does not anticipate a material impact as it does not hold material leases as a lessee; however, it does anticipate that currently held leases would require recognition of a right-of-use asset and lease liability in accordance with the update.
In January 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-01, Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities, to make various targeted improvements to the accounting for financial instruments, especially equity investments. In particular, the amendments in this update provide improvements to recognition, measurement, presentation and disclosure guidance. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company reclassified $10,836 from AOCI to Retained earnings on January 1, 2018 as a result of changing available-for-sale equity security measurement from fair value through other comprehensive income to fair value through profit and loss upon adoption of the amendments in this update.
Page 27 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (z) | Accounting Changes |
There were no accounting changes made by the Company during the year ended December 31, 2017.
(aa) Reclassifications
Certain amounts in the prior years' Consolidated Financial Statements and related footnotes thereto have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation.
| (3) | Risk Disclosures |
The following is a description of the significant risks facing the Company and how it attempts to mitigate those risks:
| (a) | Credit Risk |
Credit risk is the risk that issuers of fixed-rate and variable-rate income securities, mortgages on commercial real estate, or other parties with whom the Company has transactions, such as reinsurers and derivative counterparties, default on their contractual obligations, resulting in unexpected credit losses.
The Company mitigates this risk by adhering to investment policies and limits that provide portfolio diversification on an asset class, asset quality, creditor, and geographical basis, and by complying with investment limitations from applicable state insurance laws and regulations. The Company considers all relevant objective information available in estimating the cash flows related to structured securities. The Company actively monitors and manages exposures, and determines whether any securities are impaired. The aggregate credit risk is influenced by management’s risk/return preferences, the economic and credit environment, and the ability to manage this risk through liability portfolio management.
For derivative counterparties, the Company mitigates credit risk by tracking and limiting exposure to each counterparty through limits that are reported regularly and, once breached, restricts further trades; establishing relationships with counterparties rated BBB+ and higher; and monitoring the credit default swap of each counterparty as an early warning signal to cease trading when credit default swap spreads imply severe impairment in credit quality.
The Company executes Credit Support Annexes (CSA) with all active and new counterparties which further limits credit risk by requiring counterparties to post collateral to a segregated account to cover any counterparty exposure.
| (b) | Credit Concentration Risk |
Credit concentration risk is the risk of increased exposure to significant asset defaults (of a single security issuer or class of security issuers); economic conditions (if business is concentrated in a certain industry sector or geographic area); or adverse regulatory or court decisions (if concentrated in a single jurisdiction) affecting credit. Concentration risk exposure is monitored regularly.
The Company’s Finance Committee, responsible for asset/liability management (ALM) issues, recommends an investment policy to the Company’s Board of Directors (BOD) and approves the strategic asset allocation and accompanying investment mandates for an asset manager with respect to asset class. The investment policy and accompanying investment mandates specify asset allocation among major asset classes and the degree of asset manager flexibility for each asset class. The investment policy complies, at a minimum, with state statutes. Compliance with the policy is monitored by the Finance Committee who is responsible for implementing internal controls and procedures. Deviations from the policy are monitored and addressed. The Finance Committee and, subsequently, the BOD review the investment policy at least annually.
To further mitigate this risk, internal concentration limits based on credit rating and sector are established and are monitored regularly. Any ultimate obligor group exceeding these limits is placed on a restricted list to prevent further purchases, and the excess exposure may be actively sold down to comply with concentration limit guidelines. Any exceptions require Chief Risk Officer approval and monitoring by the Risk Committee. Further, the Company performs a quarterly concentration risk calculation to ensure compliance with certain state insurance regulations.
Page 28 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (c) | Liquidity Risk |
Liquidity risk is the risk that unexpected timing or amounts of cash needed will require liquidation of assets in a market that will result in a realized loss or an inability to sell certain classes of assets such that an insurer will be unable to meet its obligations and contractual guarantees. Liquidity risk also includes the risk that in the event of a company liquidity crisis, refinancing is only possible at higher interest rates. Liquidity risk can be affected by the maturity of liabilities, the presence of withdrawal penalties, the breadth of funding sources, and terms of funding sources. It can also be affected by counterparty collateral triggers as well as whether anticipated liquidity sources, such as credit agreements, are cancelable.
The Company manages liquidity within four specific domains: (1) monitoring product development, product management, business operations, and the investment portfolio; (2) setting ALM strategies; (3) managing the cash requirements stemming from the Company’s derivative dynamic economic hedging activities; and (4) establishing liquidity facilities to provide additional liquidity. The Company has established liquidity risk limits, which are approved by the Company’s Risk Committee, and the Company monitors its liquidity risk regularly. The Company also sets target levels for the liquid securities in its investment portfolio.
| (d) | Interest Rate Risk |
Interest rate risk is the risk that movements in interest rates or interest rate volatility will cause a decrease in the value of an insurer’s assets relative to the value of its liabilities and/or an unfavorable change in prepayment activity resulting in compressed interest margins.
The Company has an ALM strategy to align cash flows and duration of the investment portfolio with policyholder liability cash flows and duration. The Company further limits interest rate risk on variable annuity guarantees through economic interest rate hedges.
| (e) | Equity Market Risk |
Equity market risk is the risk that movements in equity prices or equity volatility will cause a decrease in the value of an insurer’s assets relative to the value of its liabilities.
The policy value of the fixed-indexed universal life, fixed-indexed annuity, and variable-indexed annuity products is linked to equity market indices. The Company economically hedges this exposure with derivatives.
Variable annuity products may provide a minimum guaranteed level of benefits irrespective of market movements. The Company has adopted an economic hedging program to manage the equity risk of these products.
The Company monitors the impacts of equity stress scenarios on assets and liabilities regularly.
Basis risk is the risk that variable annuity hedge asset value changes unexpectedly relative to the value of the underlying separate account funds of the variable annuity contracts. Basis risk may arise from the Company’s inability to directly hedge the underlying investment options of the variable annuity contracts. The Company mitigates this risk through regular review and synchronization of fund mappings, product design features, and hedge design.
| (f) | Operational Risk |
Operational risk is the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes and systems, from human misbehavior or error, or from external events. Operational risk is comprised of the following seven risk categories: (1) external fraud; (2) internal fraud; (3) employment practices and workplace safety; (4) clients/third-party, products and business practices; (5) damage to physical assets; (6) business disruption and system failure; and (7) execution, delivery, and process management. Operational risk is comprehensively managed through a combination of core qualitative and quantitative activities.
The Operational Risk Management framework includes the following key activities: (1) loss data capture identifies historical operational events that meet a designated threshold to ensure transparency and remediation of each event; (2) an integrated risk and control system is performed to proactively manage significant operational risk scenarios throughout the organization; and (3) scenario analyses are conducted to quantify operational risk capital.
Page 29 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (g) | Legal/Regulatory Risk |
Legal/regulatory risk is the risk that changes in the legal or regulatory environment in which the Company operates may result in reduced demand for its products or additional expenses not assumed in product pricing. Additionally, the Company is exposed to risk related to how the Company conducts itself in the market and the suitability of its product sales to contract holders.
The Company mitigates this risk by offering a broad range of products and by operating throughout the United States. The Company actively monitors all market-related exposure and participates in national and international discussions relating to legal, regulatory, and accounting changes that may impact the business. A formal process exists to assess the Company’s risk exposure to changes in regulation including monitoring by the Compliance and Legal departments and regular reporting to the BOD of all known compliance risks and the effectiveness of the approach used to mitigate such risks. In addition, the Company has implemented suitability standards to mitigate suitability risk.
| (h) | Ratings Risk |
Ratings risk is the risk that rating agencies change their outlook or rating of the Company or a subsidiary of the Company. The rating agencies generally utilize proprietary capital adequacy models in the process of establishing ratings for the Company. The Company is at risk of changes in these models and the impact that changes in the underlying business that it is engaged in can have on such models. To mitigate this risk, the Company maintains regular communications with the rating agencies and evaluates the impact of significant transactions on such capital adequacy models and considers the same in the design of transactions to minimize the adverse impact of this risk. Rating agency capital is calculated and analyzed regularly. Stress tests are performed regularly to assess how rating agency capital adequacy models would be impacted by severe economic events.
| (i) | Mortality/Longevity Risk |
Mortality/longevity risk is the risk that mortality experience is different than the life expectancy assumptions used by the Company to price its products.
The Company mitigates mortality risk primarily through reinsurance, whereby the Company cedes a significant portion of its mortality risk to third parties. The Company also manages mortality risk through the underwriting process. Both mortality and longevity risks are managed through the review of life expectancy assumptions and experience in conjunction with active product management.
| (j) | Lapse Risk |
Lapse risk is the risk that actual lapse experience evolves differently than the assumptions used for pricing and valuation exercises leading to a significant loss in Company value and/or income.
The Company mitigates this risk by performing sensitivity analysis at the time of pricing to affect product design, regular ALM analysis and exercising management levers at issue, as well as post-issue as experience evolves. The Company quantifies lapse risk regularly.
| (k) | Cyber Security Risk |
Cyber security risk is the risk of losses due to external and/or internal attacks impacting the confidentiality, integrity, and/or availability of key systems, data, and processes reliant on digital technology. The Company has implemented preventative, detective, response, and recovery measures including firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention, advanced malware detection, spyware and anti-virus software, email protection, email and laptop encryption, web content filtering, web application firewalls, and regular scanning of all servers and network devices to identify vulnerabilities. Controls are implemented to prevent and review unauthorized access.
| (l) | Reinsurance Risk |
Reinsurance risk is the risk that reinsurance companies default on their obligation where the Company has ceded a portion of its insurance risk. The Company uses reinsurance to limit its risk exposure to certain business lines and to enable better capital management.
Page 30 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Reinsurance contracts do not relieve the Company from its obligations to policyholders. Failure of reinsurers to honor their obligations could result in losses to the Company.
The Company mitigates this risk by requiring certain counterparties to meet thresholds related to the counterparty’s credit rating, exposure, or other factors. If the thresholds are not met by those counterparties, they are required to establish a trust or letter of credit backed by assets meeting certain quality criteria. All arrangements are regularly monitored to determine whether trusts or letters of credit are sufficient to support the ceded liabilities and that their terms are being met. Also, the Company reviews the financial standings and ratings of its reinsurance counterparties and monitors concentrations of credit risk to minimize its exposure to significant losses from reinsurer insolvencies regularly.
| (4) | Investments |
| (a) | Fixed-Maturity Securities and Equity Securities |
At December 31, 2017 and 2016, the amortized cost or cost, gross unrealized gains, gross unrealized losses, and fair values of available-for-sale and held-to-maturity securities are as shown in the following tables:
| Amortized cost or cost | Gross unrealized gains | Gross unrealized losses | Fair value | |||||||||
| 2017: | ||||||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale: | �� | |||||||||||
| U.S. government | $ | 2,449,361 | 15,159 | 23,066 | 2,441,454 | |||||||
| Agencies not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government | 6,692 | 232 | 107 | 6,817 | ||||||||
| States and political subdivisions | 10,177,673 | 1,154,762 | 14,709 | 11,317,726 | ||||||||
| Foreign government | 523,356 | 19,773 | 2,516 | 540,613 | ||||||||
| Corporate securities | 65,145,715 | 5,068,907 | 169,349 | 70,045,273 | ||||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities | 14,297,121 | 246,150 | 117,431 | 14,425,840 | ||||||||
| CDO | 15,243 | 12,322 | — | 27,565 | ||||||||
| Total fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale | 92,615,161 | 6,517,305 | 327,178 | 98,805,288 | ||||||||
| Equity securities, available-for-sale: | ||||||||||||
| Common stock | 259,573 | 10,836 | — | 270,409 | ||||||||
| Preferred stock | 1,500 | — | — | 1,500 | ||||||||
| Total equity securities, available-for-sale | 261,073 | 10,836 | — | 271,909 | ||||||||
| Total available-for-sale securities | $ | 92,876,234 | 6,528,141 | 327,178 | 99,077,197 | |||||||
Page 31 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| Amortized cost or cost | Gross unrealized gains | Gross unrealized losses | Fair value | |||||||||
| 2016: | ||||||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale: | ||||||||||||
| U.S. government | $ | 1,712,400 | 41,003 | 16,880 | 1,736,523 | |||||||
| Agencies not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government | 8,766 | 113 | 22 | 8,857 | ||||||||
| States and political subdivisions | 9,379,273 | 612,248 | 36,908 | 9,954,613 | ||||||||
| Foreign government | 426,724 | 21,006 | 8,803 | 438,927 | ||||||||
| Corporate securities | 60,668,745 | 3,489,117 | 617,795 | 63,540,067 | ||||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities | 11,824,876 | 189,019 | 165,842 | 11,848,053 | ||||||||
| CDO | 8,861 | 11,070 | — | 19,931 | ||||||||
| Total fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale | 84,029,645 | 4,363,576 | 846,250 | 87,546,971 | ||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, held-to-maturity: | ||||||||||||
| Corporate securities | 28 | 5 | — | 33 | ||||||||
| CDO | — | 3,597 | — | 3,597 | ||||||||
| Total fixed-maturity securities, held-to-maturity | 28 | 3,602 | — | 3,630 | ||||||||
| Equity securities, available-for-sale: | ||||||||||||
| Common stock | 316,541 | 3,625 | — | 320,166 | ||||||||
| Total available-for-sale and held-to-maturity securities | $ | 84,346,214 | 4,370,803 | 846,250 | 87,870,767 | |||||||
At December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company did not have any OTTI losses in AOCI.
The net unrealized gains (losses) on available-for-sale securities, held-for-sale securities and effective portion of cash flow hedges consist of the following at December 31:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Available-for-sale securities: | |||||||||
| Fixed-maturity | $ | 6,190,127 | 3,517,326 | 1,553,935 | |||||
| Equity | 10,836 | 3,625 | (2,394 | ) | |||||
| Held-for-sale securities | — | 614 | 798 | ||||||
| Cash flow hedges | (41,993 | ) | (29,547 | ) | 16,013 | ||||
| Adjustments for: | |||||||||
| Shadow adjustments | (3,007,245 | ) | (1,728,234 | ) | (825,607 | ) | |||
| Deferred taxes | (1,055,043 | ) | (617,324 | ) | (259,961 | ) | |||
| Net unrealized gains (losses) | $ | 2,096,682 | 1,146,460 | 482,784 | |||||
The unrealized gain on held-for-sale securities in 2016 and 2015 relates to fixed-maturity securities that were transferred from available-for-sale due to the expected sale of a subsidiary. The subsidiary was subsequently sold in 2017. See note 19 for further details.
Page 32 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The amortized cost and fair value of available-for-sale fixed-maturity securities at December 31, 2017, by contractual maturity, are shown below:
| Amortized cost | Fair value | |||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale: | ||||||
| Due in one year or less | $ | 2,218,716 | 2,249,030 | |||
| Due after one year through five years | 13,236,678 | 13,781,829 | ||||
| Due after five years through ten years | 21,315,386 | 21,909,438 | ||||
| Due after ten years | 40,556,205 | 45,411,155 | ||||
| Structured securities | 15,288,176 | 15,453,836 | ||||
| Total fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale | $ | 92,615,161 | 98,805,288 | |||
Expected maturities will differ from contractual maturities because borrowers may have the right to call or prepay obligations with or without call or prepayment penalties. Fixed-maturity securities not due at a single maturity date have been presented in the year of final contractual maturity. Structured securities are shown separately, as they are not due at a single maturity.
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, investments with a fair value of $24,179 and $28,098, respectively, were held on deposit with various insurance departments and in other trusts as required by statutory regulations.
The Company’s fixed-maturity security portfolios include mortgage-backed securities. Due to the high quality of these investments and the lack of subprime loans within the securities, the Company does not have a material exposure to subprime mortgages.
| (b) | Unrealized Investment Losses |
The following table summarizes the fair value and related unrealized losses on available-for-sale securities that have been in a continuous loss position for the respective years ended December 31 are shown below:
| 12 months or less | Greater than 12 months | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Fair value | Unrealized losses | Fair value | Unrealized losses | Fair value | Unrealized losses | |||||||||||||
| 2017: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale: | ||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. government | $ | 1,583,775 | 9,319 | 472,276 | 13,747 | 2,056,051 | 23,066 | |||||||||||
| Agencies not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government | 4,357 | 107 | — | — | 4,357 | 107 | ||||||||||||
| States and political subdivisions | 221,614 | 2,612 | 250,963 | 12,097 | 472,577 | 14,709 | ||||||||||||
| Foreign government | 81,717 | 830 | 35,805 | 1,686 | 117,522 | 2,516 | ||||||||||||
| Corporate securities | 4,053,797 | 37,776 | 3,507,087 | 131,573 | 7,560,884 | 169,349 | ||||||||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities | 3,434,109 | 24,415 | 2,791,216 | 93,016 | 6,225,325 | 117,431 | ||||||||||||
| Total temporarily impaired securities | $ | 9,379,369 | 75,059 | 7,057,347 | 252,119 | 16,436,716 | 327,178 | |||||||||||
Page 33 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| 12 months or less | Greater than 12 months | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Fair value | Unrealized losses | Fair value | Unrealized losses | Fair value | Unrealized losses | |||||||||||||
| 2016: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale: | ||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. government | $ | 691,559 | 16,880 | — | — | 691,559 | 16,880 | |||||||||||
| Agencies not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government | 3,332 | 22 | — | — | 3,332 | 22 | ||||||||||||
| States and political subdivisions | 1,587,063 | 30,524 | 103,316 | 6,384 | 1,690,379 | 36,908 | ||||||||||||
| Foreign government | 99,527 | 6,634 | 10,383 | 2,169 | 109,910 | 8,803 | ||||||||||||
| Corporate securities | 12,637,792 | 433,682 | 2,000,338 | 184,113 | 14,638,130 | 617,795 | ||||||||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities | 5,003,928 | 164,368 | 31,040 | 1,474 | 5,034,968 | 165,842 | ||||||||||||
| Total temporarily impaired securities | $ | 20,023,201 | 652,110 | 2,145,077 | 194,140 | 22,168,278 | 846,250 | |||||||||||
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, there were 865 and 1,088 available-for-sale fixed-maturity security holdings that were in an unrealized loss position, respectively.
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, of the total amount of unrealized losses, $303,565 or 92.8% and $763,051 or 90.2%, respectively, are related to unrealized losses on investment grade securities. Investment grade is defined as a security having a credit rating of Aaa, Aa, A, or Baa from Moody’s or a rating of AAA, AA, A, or BBB from Standards and Poor’s (S&P), or a NAIC rating of 1 or 2 if a Moody’s or S&P rating is not available. Unrealized losses on securities are principally related to changes in interest rates or changes in sector spreads from the date of purchase. As contractual payments continue to be met, management continues to expect all contractual cash flows to be received and does not consider these investments to be other-than-temporarily impaired.
| (c) | OTTI Losses |
The following table presents a rollforward of the Company’s cumulative credit impairments on fixed-maturity securities held at December 31:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||
| Balance as of January 1 | $ | 115,430 | 59,365 | |||
| Additions for credit impairments recognized on: | ||||||
| Securities not previously impaired | 48,574 | 174,823 | ||||
| Reductions for credit impairments previously on: | ||||||
| Securities that matured, were sold, or were liquidated during the period | (111,956 | ) | (118,758 | ) | ||
| Balance as of December 31 | $ | 52,048 | 115,430 | |||
Page 34 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (d) | Realized Investment Gains (Losses) |
Gross and net realized investment gains (losses) for the years ended December 31 are summarized as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Available-for-sale: | |||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities: | |||||||||
| Gross gains on sales and exchanges | $ | 151,815 | 198,851 | 108,094 | |||||
| Gross losses on sales and exchanges | (37,415 | ) | (71,002 | ) | (15,272 | ) | |||
| OTTI | (48,574 | ) | (172,530 | ) | (57,598 | ) | |||
| Net gains (losses) on fixed-maturity securities | 65,826 | (44,681 | ) | 35,224 | |||||
| Equity securities: | |||||||||
| Gross gains on sales | 5,289 | 3,109 | 2 | ||||||
| Gross losses on sales | (1,054 | ) | (897 | ) | (184 | ) | |||
| Net gains (losses) on equity securities | 4,235 | 2,212 | (182 | ) | |||||
| Net gains (losses) on available-for-sale securities | 70,061 | (42,469 | ) | 35,042 | |||||
| Held-to-maturity securities: | |||||||||
| Gross gains on sales and exchanges | 4,244 | — | 31,832 | ||||||
| Gross losses on sales and exchanges | (11 | ) | (11 | ) | (11 | ) | |||
| Net gains (losses) on held-to-maturity securities | 4,233 | (11 | ) | 31,821 | |||||
| Gain on real estate sales | — | — | 5,929 | ||||||
| Other | 9,328 | (6,845 | ) | 21,621 | |||||
| Net realized investment gains (losses) | $ | 83,622 | (49,325 | ) | 94,413 | ||||
The 2015 realized gain on real estate sales is related to the recognition of a contingent gain as part of the terms of the 2011 sale of the Company’s real estate portfolio. The gross gain in held-to-maturity securities relates primarily to the impact of consolidating a CDO investment in 2015, which was subsequently sold in 2017. See note 4(j) for further discussion regarding the consolidation and sale of the CDO investment.
Proceeds from sales of available-for-sale securities for the years ended December 31 are presented in the following table:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Available-for-sale securities: | |||||||||
| Fixed-maturity | $ | 2,567,050 | 2,177,408 | 996,801 | |||||
| Equity | 136,911 | 152,821 | 58,858 | ||||||
Page 35 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (e) | Trading Gains and Losses |
The portion of trading gains and losses for the year ended December 31 related to trading securities still held at the reporting date is shown below:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Net gains (losses) recognized during the period on trading securities | $ | 21,109 | 12,133 | (17,268 | ) | ||||
| Less: Net gains (losses) recognized during the period on trading securities sold during the period | 7,738 | (2,205 | ) | 576 | |||||
| Unrealized gains (losses) recognized during the reporting period on trading securities still held at the reporting date | $ | 13,371 | 14,338 | (17,844 | ) | ||||
| (f) | Interest and Similar Income |
Major categories of Interest and similar income, net, for the respective years ended December 31 are shown below:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Interest and similar income: | |||||||||
| Available-for-sale fixed-maturity securities | $ | 3,968,147 | 3,847,272 | 3,752,867 | |||||
| Held-to-maturity fixed-maturity securities | 58 | 1,012 | 5,746 | ||||||
| Mortgage loans on real estate | 559,236 | 470,547 | 413,103 | ||||||
| Derivative assets | 13,622 | 11,121 | 5,197 | ||||||
| Loans to affiliates | 625 | 384 | 516 | ||||||
| Policy loans | 9,794 | 10,015 | 9,834 | ||||||
| Available-for-sale equity securities | 6,752 | 11,314 | 1,416 | ||||||
| Fair value option and trading equity securities | 10,647 | 6,814 | 11,838 | ||||||
| Other invested assets | 13,977 | 32,857 | 32,618 | ||||||
| Short-term securities and cash and cash equivalents | 27,878 | 13,896 | 8,761 | ||||||
| Total | 4,610,736 | 4,405,232 | 4,241,896 | ||||||
| Less: Investment expenses | 88,517 | 79,495 | 66,427 | ||||||
| Total interest and similar income, net | $ | 4,522,219 | 4,325,737 | 4,175,469 | |||||
| (g) | Fixed-Maturity Securities Purchased with Deteriorated Credit Quality |
The Company acquired fixed-maturity securities for which there was evidence of credit quality deterioration since origination and for which it was probable at the acquisition date that the Company would be unable to collect all contractually required payments.
The outstanding balance and carrying amount of the fixed-maturity securities purchased with deteriorated credit quality at December 31 are shown below:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale: | ||||||
| Outstanding balance | $ | 301,715 | 261,260 | |||
| Carrying amount | 183,045 | 139,863 | ||||
Page 36 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The following table presents activity for the accretable yield on fixed-maturity securities purchased with deteriorated credit quality:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale: | ||||||
| Balance, beginning of year | $ | 102,221 | 135,075 | |||
| Additions | 11,487 | — | ||||
| Accretion | (11,687 | ) | (19,798 | ) | ||
| Reclassifications from nonaccretable difference | (4,024 | ) | (4,805 | ) | ||
| Disposals | — | (8,251 | ) | |||
| Balance, end of year | $ | 97,997 | 102,221 | |||
Fixed-maturity securities acquired each year for which it was probable at acquisition that all contractually required payments would not be collected are as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale: | |||||||||
| Contractually required payments receivable | $ | 69,695 | — | 99,975 | |||||
| Cash flows expected to be collected | 55,425 | — | 65,489 | ||||||
| Basis in acquired securities | 43,938 | — | 39,823 | ||||||
| (h) | Mortgage Loans on Real Estate |
The Company's investment in mortgage loans on real estate at December 31, 2017 and 2016 was entirely comprised of commercial loans. At December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company's mortgage loans on real estate portfolio include concentrations exceeding 10% for the following states:
| 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||
| Concentration Amount | Concentration % | Concentration Amount | Concentration % | ||||||||||
| California | $ | 2,951,697 | 25.0 | % | $ | 2,925,356 | 28.1 | % | |||||
Illinois (1) | — | — | 1,085,445 | 10.4 | |||||||||
(1) Mortgage loans on real estate in Illinois did not exceed 10% of the Company's mortgage loan portfolio in 2017. | |||||||||||||
The maximum lending rates for mortgage loans made during 2017 and 2016 were 4.9% and 4.6%, respectively. The minimum lending rates for mortgage loans made during 2017 and 2016 were 3.4% and 3.0%, respectively.
Credit quality indicators and allowance for loan loss for mortgage loans on real estate is discussed further at note 7.
| (i) | Securities Lending and Reverse Repurchase Agreements |
The Company had fair value of securities on loan of $2,613,073 and $2,798,597 with associated collateral received of $2,675,912 and $2,888,157, as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Of the total collateral received from the respective counterparties, noncash collateral was $18,866 and $326,938 and cash collateral was $2,657,046 and $2,561,219 as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Page 37 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The collateral received by loaned security type at December 31 is as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||
| Remaining contractual maturity of the agreements | Remaining contractual maturity of the agreements | |||||
Open (1) | Open (1)(2) | |||||
| Foreign government | $ | 25,788 | 10,551 | |||
| Corporate securities | 2,650,124 | 2,877,606 | ||||
| Total | $ | 2,675,912 | 2,888,157 | |||
(1) There is no contractual maturity on the lending agreements. The related loaned security could be returned to the Company on the next business day with notice from the counterparty and the Company would be required to return the collateral immediately. | ||||||
(2) The previously issued 2016 Consolidated Financial Statements disclosed only the cash collateral received by loaned security type. These amounts have been updated to conform with current year presentation to include noncash and cash collateral received by loaned security type. | ||||||
Reinvested collateral is recorded in Collateral held from securities lending agreements on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The amount and type of reinvested collateral at December 31 is as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 1,668,868 | 1,445,249 | |||
| Short-term investments | 988,178 | 1,115,970 | ||||
| Total | $ | 2,657,046 | 2,561,219 | |||
In the normal course of business, the Company enters into overnight reverse repurchase agreements which are used to earn spread income. As part of the reverse repurchase agreements, the Company lends cash and receives U.S. Government securities as collateral. The Company had fair value of reverse repurchase agreements of $860,800 and $100,000 recorded in Cash and cash equivalents on the Consolidated Balance Sheets with associated collateral received of $864,279 and $100,000 as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
| (j) | Variable Interest Entities |
The Company invests in structured securities and limited partnerships which represent interests in VIEs. The Company has carefully analyzed the VIEs to determine whether the Company is the primary beneficiary, taking into consideration whether the Company, or the Company together with its affiliates, has the power to direct the activities of the VIE, that most affect its economic performance and whether the Company has the right to benefits from the VIE. The Company has concluded that it is not the primary beneficiary for any of the VIEs invested in by the Company as of December 31, 2017. As of December 31, 2016, the Company determined it was the primary beneficiary for one of the VIEs invested in by the Company and, as such, only one VIE was consolidated in the Consolidated Financial Statements.
In 2015, a triggering event for consolidation occurred for one VIE when the Company entered into an agreement with the collateral manager to liquidate some or all of the collateral underlying several classes of notes within one of the CDOs. Creditors of the consolidated VIE do not have any recourse on the Company. The Company does not have any implicit or explicit arrangements to provide financial support to the consolidated VIE. Upon initial consolidation, the Company recorded the underlying assets at fair value, generating a gain of $31,832 in Realized investment (losses) gains, net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Page 38 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Subsequent to the consolidation of the CDO, at the Company’s direction, the collateral manager liquidated assets at auction, of which a portion were purchased by the Company. The assets purchased at auction were reported at amortized cost as Other invested assets and at fair value as Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. As of December 31, 2016, the Company held $43,640 as Other invested assets and $10,604 as Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. As of December 31, 2016, the Company also held $19,833 of consolidated assets that are reported at fair value as Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. In addition, the Company had recorded liabilities of $565 as of December 31, 2016 related to the consolidation of this entity. The liabilities are reported in Other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
In February 2017, the Company sold its interest for $16,540 and deconsolidated the VIE. The sale generated a loss of $1,541 which is recorded in Realized investment (losses) gains, net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
The carrying amount and maximum exposure to loss relating to VIEs in which the Company is not deemed to be the primary beneficiary as of December 31 were as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||
| Carrying amount | Maximum exposure to loss (1) | Carrying amount | Maximum exposure to loss (1) | |||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale: | ||||||||||||
| Corporate securities | $ | 1,000,431 | 1,000,431 | 981,066 | 981,066 | |||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities | 14,425,840 | 14,425,840 | 11,823,561 | 11,823,561 | ||||||||
| CDO | 27,565 | 27,565 | 19,931 | 19,931 | ||||||||
| Total fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale | 15,453,836 | 15,453,836 | 12,824,558 | 12,824,558 | ||||||||
| Other invested assets | 78,230 | 387,639 | 205,302 | 487,711 | ||||||||
| Total investments | $ | 15,532,066 | 15,841,475 | 13,029,860 | 13,312,269 | |||||||
(1) The maximum exposure to loss is equal to the carrying amount for Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale. The maximum exposure to loss related to Other invested assets is equal to the carrying amount plus any unfunded commitments. | ||||||||||||
| (5) | Derivatives and Hedging Instruments |
Derivatives held by the Company are designated as either a cash flow hedging instrument (cash flow hedge) or nonqualified hedging instrument (nonqualifying strategies).
Cash Flow Hedges
IRS were used by the Company to hedge against the changes in cash flows associated with variable interest rates on certain underlying fixed-maturity securities until January 2015 when the Company exited these positions. Foreign currency swaps have notional amounts and maturity dates equal and offsetting to the underlying fixed-maturity securities and are determined to be highly effective as of December 31, 2017 and 2016.
On March 31, 2017, the Company changed its retrospective hedge effectiveness test methodology and moved to a regression model. Regression testing utilizes statistical analysis to assess the correlation of the changes in cash flows between the hedging instrument and the hedged item through the use of a hypothetical derivative. In order to change the retrospective test methodology, the Company redesignated all qualifying hedge relationships. The dedesignation and subsequent redesignation occurred contemporaneously.
Page 39 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The following table presents the components of the unrealized gains and losses on the effective portion of the derivatives that qualify as cash flow hedges recorded within the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss):
| Amount of gains (losses) recognized in AOCI at December 31, | |||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Interest rate swaps, net of tax benefit of $0, $0, and $332, at December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively | $ | — | — | (617 | ) | ||||
| Foreign currency swaps, net of tax benefit (expense) of $37,215, ($12,355), and ($15,550), at December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively | (69,113 | ) | 22,945 | 28,879 | |||||
| Total | $ | (69,113 | ) | 22,945 | 28,262 | ||||
The following tables presents the amount of gains reclassified from AOCI into earnings on the effective and ineffective portion of the derivatives that qualify as cash flow hedges:
| Amount of gains reclassified from AOCI into earnings for the years end December 31 (effective portion): | Location in the Consolidated Statements of Operations | ||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Foreign currency swaps, net of tax expense of $4,768, $3,892, and $1,819, at December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively | $ | 8,854 | 7,229 | 3,378 | Interest and similar income, net | ||||||
| Total | $ | 8,854 | 7,229 | 3,378 | |||||||
| Amount of gains reclassified from AOCI into earnings for the years end December 31 (ineffective portion): | Location in the Consolidated Statements of Operations | ||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Foreign currency swaps, net of tax expense of $247, $85, and $0, at December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively | $ | 459 | 158 | — | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | ||||||
| Total | $ | 459 | 158 | — | |||||||
Using December 31, 2017 values, it is estimated that a post-tax gain of approximately $11,813 will be reclassified from AOCI into earnings during the subsequent twelve months ending December 31, 2018. The maximum amount of time for which these cash flows are hedged is 16 years.
See note 22 for a rollforward of cash flow hedges in AOCI.
Nonqualifying Strategies
Futures and Options Contracts
OTC options and ETO are cleared through the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC), which operates under the jurisdiction of both the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Commodities Futures Trading Commission. The fair values of the collateral posted for futures, OTC options, and ETO are discussed in the derivative collateral management section below.
Interest Rate Swaps
The Company can receive the fixed or variable rate and are traded in varying maturities. The fair values of the collateral posted and variation margin for OTC and centrally cleared IRS are discussed in the derivative collateral management section below.
Page 40 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Credit Default Swaps
The CDS within the investment portfolios assume credit risk from a single entity or referenced index for the purpose of synthetically replicating investment transactions. The Company can be required to pay or be the net receiver on the contract depending on the net position. Credit events include bankruptcy of the reference and failure to pay by the reference. The notional amount is equal to the maximum potential future loss amount. The fair value of the collateral posted for centrally cleared CDS is discussed in the derivative collateral management section below.
The following table presents the notional amount, fair value, weighted average years to maturity, underlying referenced credit obligation type, and average credit ratings for the credit derivatives in which the Company was assuming credit risk as of December 31:
| Credit Derivative type by derivative risk exposure and reference type | Notional amount | Fair value | Weighted average years to maturity | Average credit rating | |||||||
| 2017: | |||||||||||
| Basket credit default swaps | |||||||||||
| Investment grade risk exposure U.S. corporate credit | $ | 175,800 | (1,498 | ) | 6 years | BBB+ | |||||
| Total | $ | 175,800 | (1,498 | ) | |||||||
| 2016: | |||||||||||
| Basket credit default swaps | |||||||||||
| Investment grade risk exposure U.S. corporate credit | $ | 331,400 | 367 | 6 years | BBB+ | ||||||
| Total | $ | 331,400 | 367 | ||||||||
Total Return Swaps
The Company engages in the use of OTC TRS, which allow the parties to exchange cash flows based on a variable reference rate such as the three-month LIBOR and the return of an underlying index. The fair value of the collateral posted for OTC TRS is discussed in the derivative collateral management section below.
To Be Announced Securities
The Company uses OTC TBA forward contracts to gain exposure to the investment risk and return of mortgage-backed securities. Typically, the price is agreed upon at the time of the contract and payment for such a contract is made at a specified future date. The fair value of the collateral posted for OTC TBA securities is discussed in the derivative collateral management section below.
Page 41 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The following table presents a summary of the aggregate notional amounts and fair values of the Company’s freestanding derivative instruments reported on the Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31:
| 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Fair Value | Gross Fair Value | ||||||||||||||||||
Notional (1) | Assets | Liabilities | Notional (1) | Assets | Liabilities | ||||||||||||||
| Cash flow hedging instruments | |||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency swaps | $ | 899,000 | $ | 38,939 | (68,354 | ) | 676,000 | 96,975 | (11,731 | ) | |||||||||
| Total cash flow hedging instruments | 38,939 | (68,354 | ) | 96,975 | (11,731 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Nonqualifying hedging instruments | |||||||||||||||||||
| Futures | 27,891,125 | — | — | 17,574,373 | — | — | |||||||||||||
| OTC options | 119,817,491 | 1,156,749 | (815,960 | ) | 77,973,809 | 766,205 | (514,758 | ) | |||||||||||
| ETO | 17,033,569 | 48,177 | (27,678 | ) | 11,109,074 | 42,400 | (27,345 | ) | |||||||||||
| IRS | 3,763,500 | 130,476 | (162 | ) | 7,227,500 | 144,384 | (77,799 | ) | |||||||||||
| TRS | 2,944,000 | 12,375 | — | 7,154,000 | 5,826 | (3,702 | ) | ||||||||||||
| TBA securities | 1,474,100 | 4 | (953 | ) | 693,900 | 833 | (299 | ) | |||||||||||
| SAR | — | — | — | 7,422 * | 545 | — | |||||||||||||
| Total nonqualifying hedging instruments | 1,347,781 | (844,753 | ) | 960,193 | (623,903 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Total freestanding derivative instruments | $ | 1,386,720 | (913,107 | ) | 1,057,168 | (635,634 | ) | ||||||||||||
(1) Notional amounts are presented on a gross basis. | |||||||||||||||||||
| * The notional amount for SAR is equal to the number of contracts outstanding. | |||||||||||||||||||
Derivative Collateral Management
The Company manages separate collateral for exchange-traded and OTC derivatives. The total collateral posted for exchange-traded derivatives at December 31, 2017 and 2016, had a fair value of $2,029,211 and $1,447,970, respectively, and is included in Fixed-maturity securities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The Company retains ownership of the exchange-traded collateral, but the collateral resides in an account designated by the exchange. The collateral is subject to specific exchange rules regarding rehypothecation. The total collateral posted for OTC derivatives at December 31, 2017 and 2016, had a fair value of $137,383 and $49,133, respectively, and is included in Fixed-maturity securities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The Company posts collateral to OTC counterparties based upon exposure amounts. The Company retains ownership of the OTC collateral.
Embedded Derivatives
The Company issues certain variable annuity products with guaranteed minimum benefit riders, including GMWB and GMAB, which are measured at fair value separately from the host variable annuity contract, with changes in fair value reported in Change in fair value of annuity and life embedded derivatives within the Consolidated Statements of Operations. These embedded derivatives are classified within Account balances and future policy benefit reserves on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Certain fixed-indexed annuity products and universal life policies include equity-indexed features, which are separated as an embedded derivative, and referred to as a market value liability option (MVLO). This embedded derivative is reported within Account balances and future policy benefit reserves on the Consolidated Balance Sheets with changes in fair value reported in Change in fair value of annuity and life embedded derivatives within the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Page 42 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Additionally, the Company bifurcated and separately recorded embedded derivatives related to modified coinsurance reinsurance agreements. The embedded derivatives are recorded within Derivative assets and Derivative liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets, with changes in fair value reported in Change in fair value of assets and liabilities within the Consolidated Statements of Operations. See note 19 for further detail regarding the modified coinsurance reinsurance agreement entered into by the Company with an affiliate.
The following table presents a summary of the fair values of the Company’s embedded derivative instruments reported on the Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||
| GMWB | $ | (2,004,918 | ) | (2,156,234 | ) | |
| GMAB | (181,348 | ) | (243,363 | ) | ||
| MVLO | (20,137,427 | ) | (15,141,482 | ) | ||
| Other embedded derivatives, net | (570 | ) | 1,863 | |||
| Total embedded derivative instruments | $ | (22,324,263 | ) | (17,539,216 | ) | |
The following table presents the gains or losses recognized in income on the various nonqualifying freestanding derivative instruments and embedded derivatives:
| Amount of gain (loss) on derivatives recognized for the years ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| Location in the Consolidated Statements of Operations | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||
| GMWB | Change in fair value of annuity and life embedded derivatives | $ | 151,177 | 14,235 | (679,259 | ) | |||||
| GMAB | Change in fair value of annuity and life embedded derivatives | 61,658 | 96,666 | (122,094 | ) | ||||||
| MVLO | Change in fair value of annuity and life embedded derivatives | (5,175,605 | ) | (386,709 | ) | 212,758 | |||||
| Total change in fair value of annuity and life embedded derivatives | (4,962,770 | ) | (275,808 | ) | (588,595 | ) | |||||
| Futures | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 2,362,617 | (287,724 | ) | (423,134 | ) | |||||
| OTC options | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 1,375,643 | 182,882 | (361,419 | ) | ||||||
| ETO | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 54,103 | 13,055 | 291 | |||||||
| IRS | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 127,777 | 87,380 | 279,158 | |||||||
| CDS | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 2,074 | 4,689 | (2,220 | ) | ||||||
| TRS | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 48,228 | (37,143 | ) | 4,093 | ||||||
| TBA securities | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 4,078 | (2,837 | ) | 330 | ||||||
| SAR | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 100 | (54 | ) | 630 | ||||||
| Other embedded | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | (8,120 | ) | (1,234 | ) | 1,235 | |||||
| Total change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 3,966,500 | (40,986 | ) | (501,036 | ) | ||||||
| MVLO | Premiums and policy fees, net | 9,911 | (398,942 | ) | 79,951 | ||||||
| MVLO | Policyholder benefits, net of recoveries | 169,749 | 139,481 | 115,737 | |||||||
| Total derivative gain (loss), net | $ | (816,610 | ) | (576,255 | ) | (893,943 | ) | ||||
Page 43 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Offsetting Assets and Liabilities
Certain financial instruments and derivative instruments are eligible for offset on the Consolidated Balance Sheets under GAAP. The Company’s derivative instruments are subject to master netting arrangements and collateral arrangements. A master netting arrangement with a counterparty creates a right of offset for amounts due to and from that same counterparty that is enforceable in the event of a default or bankruptcy. The Company’s policy is to recognize amounts subject to master netting arrangements on a gross basis on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
The following tables present additional information about derivative assets and liabilities subject to an enforceable master netting arrangement as of the dates indicated:
| December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gross amounts not offset in the Balance Sheet | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gross amounts recognized | Gross amounts offset in the Balance Sheet | Net amounts presented in the Balance Sheet | Financial instruments (1) | Collateral (received) / pledged | Net amounts | |||||||||||||
| Derivative assets | $ | 1,386,720 | — | 1,386,720 | (855,461 | ) | (485,646 | ) | 45,613 | |||||||||
| Derivative liabilities | (913,107 | ) | — | (913,107 | ) | 855,461 | 134,000 | 76,354 | ||||||||||
| Net derivatives | $ | 473,613 | — | 473,613 | — | (351,646 | ) | 121,967 | ||||||||||
| December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gross amounts not offset in the Balance Sheet | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gross amounts recognized | Gross amounts offset in the Balance Sheet | Net amounts presented in the Balance Sheet | Financial instruments (1) | Collateral (received) / pledged | Net amounts | |||||||||||||
| Derivative assets | $ | 1,056,623 | — | 1,056,623 | (615,349 | ) | (395,913 | ) | 45,361 | |||||||||
| Derivative liabilities | (635,634 | ) | — | (635,634 | ) | 615,349 | 37,092 | 16,807 | ||||||||||
| Net derivatives | $ | 420,989 | — | 420,989 | — | (358,821 | ) | 62,168 | ||||||||||
(1) Represents the amount of assets or liabilities that could be offset by liabilities or assets with the same counterparty under master netting or similar arrangements that management elects not to offset on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. | ||||||||||||||||||
In the tables above, the gross amounts of assets or liabilities as presented on the Consolidated Balance Sheets are offset first by financial instruments that have the right of offset under master netting or similar arrangements, then any remaining amount is reduced by the amount of cash and securities collateral.
| (6) | Fair Value Measurements |
The Fair Value Measurement Topic of the Codification establishes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs used in the valuation techniques to measure fair value.
Level 1 – Unadjusted quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets that the Company has the ability to access at the measurement date.
Level 2 – Valuations derived from techniques that utilize observable inputs, other than quoted prices included in Level 1, which are observable for the asset or liability either directly or indirectly, such as:
(a) Quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets.
(b) Quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active.
Page 44 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
(c) Inputs other than quoted prices that are observable.
(d) Inputs that are derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data by correlation or other means.
Level 3 – Valuations derived from techniques in which the significant inputs are unobservable. Level 3 fair values reflect the Company’s own assumptions about the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability (including assumptions about risk).
The Company has analyzed the valuation techniques and related inputs, evaluated its assets and liabilities reported at fair value, and determined an appropriate fair value hierarchy level based upon trading activity and the observability of market inputs. Based on the results of this evaluation and investment class analysis, each financial asset and liability was classified into Level 1, 2, or 3.
The following presents the assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis and their corresponding level in the fair value hierarchy at December 31:
| 2017 | ||||||||||||
| Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale: | ||||||||||||
| U.S. government | $ | 2,441,454 | 2,441,454 | — | — | |||||||
| Agencies not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government | 6,817 | — | 6,817 | — | ||||||||
| States and political subdivisions | 11,317,726 | — | 11,276,965 | 40,761 | ||||||||
| Foreign government | 540,613 | — | 507,166 | 33,447 | ||||||||
| Corporate securities | 70,045,273 | — | 59,074,307 | 10,970,966 | ||||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities | 14,425,840 | — | 14,425,811 | 29 | ||||||||
| CDO | 27,565 | — | 27,565 | — | ||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, trading | 36,219 | 30,901 | 5,168 | 150 | ||||||||
| Derivative assets | 1,388,190 | 48,177 | 1,327,638 | 12,375 | ||||||||
| Equity securities, available-for-sale | 271,909 | 258,095 | — | 13,814 | ||||||||
| Equity securities, fair value option and trading | 314,370 | 288,098 | 26,272 | — | ||||||||
| Separate account assets | 28,192,877 | 28,192,877 | — | — | ||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 129,008,853 | 31,259,602 | 86,677,709 | 11,071,542 | |||||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||
| Derivative liabilities | $ | (915,147 | ) | (27,678 | ) | (887,469 | ) | — | ||||
Reserves at fair value (1) | (27,387,975 | ) | — | — | (27,387,975 | ) | ||||||
| Total liabilities | $ | (28,303,122 | ) | (27,678 | ) | (887,469 | ) | (27,387,975 | ) | |||
Page 45 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| 2016 | ||||||||||||
| Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale: | ||||||||||||
| U.S. government | $ | 1,736,523 | 1,736,523 | — | — | |||||||
| Agencies not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government | 8,857 | — | 8,857 | — | ||||||||
| States and political subdivisions | 9,954,613 | — | 9,925,338 | 29,275 | ||||||||
| Foreign government | 438,927 | — | 404,687 | 34,240 | ||||||||
| Corporate securities | 63,540,067 | — | 54,990,599 | 8,549,468 | ||||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities | 11,848,053 | — | 11,806,849 | 41,204 | ||||||||
| CDO | 19,931 | — | — | 19,931 | ||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, trading | 37,051 | 36,901 | — | 150 | ||||||||
| Derivative assets | 1,059,031 | 42,400 | 1,010,805 | 5,826 | ||||||||
| Equity securities, available-for-sale | 320,166 | 320,166 | — | — | ||||||||
| Equity securities, fair value option and trading | 317,493 | 298,481 | 19,012 | — | ||||||||
| Separate account assets | 27,733,261 | 27,733,261 | — | — | ||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 117,013,973 | 30,167,732 | 78,166,147 | 8,680,094 | |||||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||
| Derivative liabilities | $ | (635,634 | ) | (27,345 | ) | (604,587 | ) | (3,702 | ) | |||
Reserves at fair value (1) | (20,152,641 | ) | — | — | (20,152,641 | ) | ||||||
| Total liabilities | $ | (20,788,275 | ) | (27,345 | ) | (604,587 | ) | (20,156,343 | ) | |||
(1) Reserves at fair value are reported in Account balances and future policy benefit reserves on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. | ||||||||||||
The following is a discussion of the methodologies used to determine fair values for the assets and liabilities listed in the above table. These fair values represent an exit price (i.e., what a buyer in the marketplace would pay for an asset in a current sale or charge to transfer a liability).
| (a) | Valuation of Fixed-Maturity Securities and Equity Securities |
The fair value of fixed-maturity securities and equity securities is based on quoted market prices in active markets when available. Based on the market data, the securities are categorized into asset class, and based on the asset class of the security, appropriate pricing applications, models and related methodology, and standard inputs are utilized to determine what a buyer in the marketplace would pay for the security in a current sale. When quoted prices are not readily available or in an inactive market, standard inputs used in the valuation models, listed in approximate order of priority, include, but are not limited to, benchmark yields, reported trades, Municipal Securities Rulemaking Board reported trades, Nationally Recognized Municipal Securities Information Repository material event notices, broker-dealer quotes, issuer spreads, two-sided markets, benchmark securities, bids, offers, reference data, and industry and economic events. In some cases, including private placement securities and certain difficult-to-price securities, internal pricing models may be used that are based on market proxies.
Generally, U.S. Treasury securities and exchange-traded stocks are included in Level 1. Most bonds for which prices are provided by third-party pricing sources are included in Level 2, because the inputs used are market observable. Bonds for which prices were obtained from broker quotes, certain bonds without active trading markets and private placement securities that are internally priced are included in Level 3.
At December 31, 2017 and 2016, private placement securities of $11,045,203 and $8,509,548, respectively, were included in Level 3. Internal pricing models based on market proxy spread and U.S. Treasury rates are used to value these holdings.
Page 46 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (b) | Valuation of Derivatives |
Active markets for OTC options do not exist. The fair value of OTC options is derived internally, by calculating their expected discounted cash flows, using a set of calibrated, risk-neutral stochastic scenarios, including a market data monitor, a market data model generator, a stochastic scenario calibrator, and the actual asset pricing calculator. The valuation results are reviewed by Management via the Pricing Committee. OTC options that are internally priced, foreign currency swaps, CDS, TBA securities, and IRS are included in Level 2, because they use market observable inputs. TRS are included in Level 3 because they use valuation techniques in which significant inputs are unobservable. The fair value of ETOs are based on quoted market prices and are generally included in Level 1.
Certain derivatives are priced using external third-party vendors. The Company has controls in place to monitor the valuations of these derivatives. Using market observable inputs, IRS prices are derived from a third-party source and are independently recalculated internally and reviewed for reasonableness at the position level on a monthly basis. TRS prices are obtained from the respective counterparties. These prices are also internally recalculated and reviewed for reasonableness at the position level on a monthly basis.
The Company also has embedded derivatives related to modified coinsurance reinsurance agreements. The fair value of the agreements are calculated either as a CDS or TRS, depending on the nature of the agreement. The derivatives are included in Level 2 as the valuations use market observable inputs. See note 19 for further detail regarding the modified coinsurance reinsurance agreement entered into by the Company with an affiliate.
The Company participates in a stock-based compensation plan sponsored by Allianz SE, which awards certain employees SAR that are tied to Allianz SE stock. Allianz SE provides the valuation on a monthly basis to each operating entity. Although these contracts are tied to Allianz SE stock which is actively traded, the exit market is not the same, so they have been included in Level 2.
| (c) | Valuation of Separate Account Assets |
Separate account assets are carried at fair value, which is based on the fair value of the underlying assets. Funds in the separate accounts are primarily invested in variable investment option funds with the following investment types: bond, domestic equity, international equity, or specialty. Variable investment option funds are included in Level 1 because their fair value is based on net asset values that are quoted as prices (unadjusted) in an active, observable market. Additionally, the separate accounts hold certain money market funds which are also included in Level 1 because their fair value is based on quoted prices (unadjusted) in an active, observable market.
| (d) | Valuation of Reserves at Fair Value |
Reserves at fair value principally include the equity-indexed features contained in fixed-indexed annuity and life products, certain variable annuity riders and variable-indexed annuity products. Fair values of the embedded derivative liabilities are calculated based on internally developed models, because active, observable markets do not exist for these liabilities. The fair value is derived from techniques in which one or more significant inputs are unobservable and are included in Level 3. These fair values represent the Company’s best estimate of an amount that could be realized in a current market exchange absent actual market exchanges.
The fair value of the embedded derivative contained in the fixed-indexed annuity products is the sum of the current year’s option value projected stochastically, the projection of future index growth at the option budget, and the historical interest/equity-indexed credits. The valuation of the embedded derivative includes an adjustment for the Company’s own credit standing and a risk margin for noncapital market inputs.
The fair value of the embedded derivative contained in the fixed-indexed universal life insurance products is the amount of the current year’s option value in excess of a fixed crediting valuation over the remainder of the policy year. The valuation of the embedded derivative includes an adjustment for the Company’s own credit standing and a risk margin for noncapital market inputs.
Page 47 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The Company issues certain variable annuity products with GMWB and GMAB riders. The fair value for these riders is estimated using the present value of future benefits minus the present value of future fees using actuarial and capital market assumptions related to the projected cash flows over the expected lives of the contracts. A risk neutral valuation methodology is used under which the cash flows from the riders are projected under multiple capital market scenarios using observable market interest rates. The valuation of these riders includes an adjustment for the Company’s own credit standing and a risk margin for noncapital market inputs.
The Company’s own credit adjustment is determined by taking into consideration publicly available information on industry default risk with considerations for the Company’s own credit profile. Risk margin is incorporated into the valuation model to capture the noncapital market risks of the instrument, which represent the additional compensation a market participant would require to assume the risks related to the uncertainties of certain actuarial assumptions including surrenders, annuitization, premium persistency, and future equity index caps or participation rates. The establishment of the risk margin requires the use of significant management judgment. Market conditions including, but not limited to, changes in interest rates, equity indices, market volatility, changes in the Company’s own credit standing, and variations in actuarial assumptions regarding contractholder behavior and risk margins related to noncapital market inputs may result in significant fluctuations in the fair value of embedded derivatives that could materially affect net income.
The Company elected the fair value option for insurance contracts related to the variable-indexed annuity product. The fair value is calculated internally using the present value of future expected cash flows, floored at the current contract value. Future expected cash flows are generated using contractual features, actuarial assumptions, and market emergence over a complete set of market consistent scenarios. Cash flows are then averaged over the scenario set and discounted back to the valuation date using the appropriate discount factors adjusted for nonperformance risk on the noncollateralized portions of the contract.
| (e) | Level 3 Rollforward |
The following table provides a reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances for the Company’s Level 3 assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis:
| 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities | ||||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale | Trading | |||||||||||||||||
| States and political subdivisions | Foreign government | Corporate securities | Mortgage-backed securities | CDO | Corporate securities | |||||||||||||
| Balance, beginning of year | $ | 29,275 | 34,240 | 8,549,468 | 41,204 | 19,931 | 150 | |||||||||||
| Total realized/unrealized gains (losses) included in: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | — | — | (9,227 | ) | 678 | 11,139 | — | |||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | 1,482 | (793 | ) | 310,320 | 1,279 | (11,070 | ) | — | ||||||||||
| Purchases and issuances | 10,004 | — | 2,660,329 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Sales and settlements | — | — | (444,638 | ) | (24,556 | ) | (20,000 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Transfer out of Level 3 | — | — | (95,286 | ) | (18,576 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Balance, end of year | $ | 40,761 | 33,447 | 10,970,966 | 29 | — | 150 | |||||||||||
| Gains (losses) included in net income related to financial instruments still held at the end of the year | $ | — | — | 956 | — | — | — | |||||||||||
Page 48 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities | ||||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale | Trading | |||||||||||||||||
| States and political subdivisions | Foreign government | Corporate securities | Mortgage-backed securities | CDO | Corporate securities | |||||||||||||
| Balance, beginning of year | $ | 499 | 33,373 | 7,021,597 | 54,906 | 21,164 | — | |||||||||||
| Total realized/unrealized gains (losses) included in: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | — | — | (86,539 | ) | 1,393 | — | — | |||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | 790 | 867 | 272,556 | 302 | (503 | ) | — | |||||||||||
| Purchases and issuances | 27,986 | — | 2,054,111 | 730 | — | 150 | ||||||||||||
| Sales and settlements | — | — | (428,407 | ) | (16,127 | ) | (730 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Transfer out of Level 3 | — | — | (283,850 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||
| Balance, end of year | $ | 29,275 | 34,240 | 8,549,468 | 41,204 | 19,931 | 150 | |||||||||||
| Gains (losses) included in net income related to financial instruments still held at the end of the year | $ | — | — | (80,134 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity securities, Available-for-sale | Derivative assets | Derivative liabilities | Reserves at fair value (1) | Derivative assets | Derivative liabilities | Reserves at fair value (1) | |||||||||||||||
| Balance, beginning of year | $ | — | 5,826 | (3,702 | ) | (20,152,641 | ) | 2,350 | (33,812 | ) | (18,096,009 | ) | |||||||||
| Total realized/unrealized gains (losses) included in: | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | — | 188,230 | (101,030 | ) | (5,550,779 | ) | 553,778 | (583,731 | ) | (649,516 | ) | ||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | 1,496 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Purchases and issuances | 12,318 | — | — | (3,186,229 | ) | — | — | (2,805,725 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Sales and settlements | — | (181,681 | ) | 104,732 | 1,501,674 | (550,302 | ) | 613,841 | 1,398,609 | ||||||||||||
| Balance, end of year | $ | 13,814 | 12,375 | — | (27,387,975 | ) | 5,826 | (3,702 | ) | (20,152,641 | ) | ||||||||||
| Gains (losses) included in net income related to financial instruments still held at the end of the year | $ | — | 6,549 | 3,702 | (5,550,779 | ) | 3,476 | (30,111 | ) | (649,516 | ) | ||||||||||
(1) The Company classifies realized and unrealized gains (losses) on Reserves at fair value as unrealized gains (losses) for purposes of disclosure in this table because the Company monitors Reserves at fair value as a whole unit and does not track realized gains (losses) on a contract-by-contract basis. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (f) | Transfers |
The Company reviews its fair value hierarchy classifications annually. Transfers between levels occur when there are changes in the observability of inputs and market activity. Transfers into and/or out of Levels 1, 2, and 3 are reported as of the end of the period in which the change occurs.
Page 49 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
In 2017, transfers into Level 3 were $0 and transfers out of Level 3 were $113,862. In 2016, transfers into Level 3 were $0 and transfers out of Level 3 were $283,850. All transfers out of Level 3 were recategorized as Level 2 as quoted market prices for similar securities became available, were considered reliable, and could be validated against an alternative source.
There were no transfers between Level 1 and Level 2 for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016.
| (g) | Assets and Liabilities Measured at Fair Value Using Significant Unobservable Inputs |
The following table provides a summary of the significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurements developed by the Company or reasonably available to the Company of Level 3 assets and liabilities on a recurring basis at December 31:
| 2017 | |||||||||
| Fair value | Valuation technique | Unobservable input | Range (weighted average) | ||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities: | |||||||||
| Available-for-sale: | |||||||||
| States and political subdivisions | $ | 40,761 | Discounted cash flow | Option adjusted spread* | 161 (161) | ||||
| Foreign government | 33,447 | Discounted cash flow | Option adjusted spread | 42 - 50 (48) | |||||
| Corporate securities | 10,970,966 | Discounted cash flow | Option adjusted spread | 27 - 515 (130) | |||||
| Mortgage-backed securities | 29 | Third-party vendor | Default and discount rates | ** | |||||
| Trading: | |||||||||
| Corporate securities | 150 | Cost | N/A | N/A | |||||
| Equity securities: | |||||||||
| Available-for-sale: | |||||||||
| Common stock | 12,314 | Consensus pricing | Indicative quotes ($ per share)* | $23.65 ($23.65) | |||||
| Preferred stock | 1,500 | Cost | N/A | N/A | |||||
| Derivative assets: | |||||||||
| TRS | 12,375 | Third-party vendor | Spread and discount rates | ** | |||||
| Derivative liabilities: | |||||||||
| TRS | — | Third-party vendor | Spread and discount rates | ** | |||||
| Reserves at Fair Value: | |||||||||
| MVLO | (20,137,427 | ) | Discounted cash flow | Annuitizations | 0 - 25% | ||||
| Surrenders | 0 - 25% | ||||||||
| Mortality*** | 0 - 100% | ||||||||
| Withdrawal benefit election | 0 - 50% | ||||||||
| GMWB and GMAB | (2,186,266 | ) | Discounted cash flow | Surrenders | 0.5% - 35% | ||||
| Mortality*** | 0% - 100% | ||||||||
| Variable-indexed annuity | (5,064,282 | ) | Contract value | N/A**** | N/A**** | ||||
Page 50 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| 2016 | |||||||||
| Fair value | Valuation technique | Unobservable input | Range (weighted average) | ||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities: | |||||||||
| Available-for-sale: | |||||||||
| States and political subdivisions | $ | 29,275 | Discounted cash flow | Option adjusted spread* | 166 (166) | ||||
| Foreign government | 34,240 | Discounted cash flow | Option adjusted spread | 62 - 75 (70) | |||||
| Corporate securities | 8,549,468 | Discounted cash flow | Option adjusted spread | -214 - 2,112 (147) | |||||
| CDO | 19,931 | Third-party vendor | Default and discount rates | ** | |||||
| Mortgage-backed securities | 41,204 | Third-party vendor | Default and discount rates | ** | |||||
| Trading: | |||||||||
| Corporate securities | 150 | Cost | N/A | N/A | |||||
| Derivative assets: | |||||||||
| TRS | 5,826 | Third-party vendor | Spread and discount rates | ** | |||||
| Derivative liabilities: | |||||||||
| TRS | (3,702 | ) | Third-party vendor | Spread and discount rates | ** | ||||
| Reserves at Fair Value: | |||||||||
| MVLO | (15,141,482 | ) | Discounted cash flow | Annuitizations | 0 – 25% | ||||
| Surrenders | 0 – 25% | ||||||||
| Mortality*** | 0 – 100% | ||||||||
| Withdrawal benefit election | 0 – 50% | ||||||||
| GMWB and GMAB | (2,399,597 | ) | Discounted cash flow | Surrenders | 0.5 – 35% | ||||
| Mortality*** | 0 – 100% | ||||||||
| Variable-indexed annuity | (2,611,562 | ) | Contract value | N/A**** | N/A**** | ||||
| * No range is applicable due to only one security within classification. | |||||||||
| ** Management does not have insight into the specific assumptions used. See narrative below for qualitative discussion. | |||||||||
| *** Mortality assumptions are derived from the Annuity 2000 Mortality Table. See note 14 for further discussion. | |||||||||
| **** Unobservable inputs are not applicable as the fair value of the variable-indexed annuity reserve is floored at contract value. | |||||||||
| (h) | Sensitivity of Fair Value Measurements to Changes in Unobservable Inputs |
Fixed-maturity securities: The primary unobservable input used in the discounted cash flow models for states and political subdivisions, foreign government, and corporate fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale is a corporate index option adjusted spread (OAS). The corporate index OAS used is based on a security's sector, rating, and average life. A significant increase (decrease) of the corporate index OAS in isolation could result in a decrease (increase) in fair value.
CDO and mortgage-backed securities are priced by a third-party vendor and the Company internally reviews the valuation for reasonableness. The Company does not have insight into the specific inputs used; however, the key unobservable inputs would generally include default rates. A significant increase (decrease) in default rates in isolation could result in an decrease (increase) in fair value.
Equity securities: The primary unobservable input used to value common stock are indicative quotes received from third-party vendors. A significant increase (decrease) in the indicative quotes in isolation could result in a decrease (increase) in fair value.
Derivative assets and liabilities: The TRS are priced by a third-party vendor and the Company internally reviews
Page 51 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
the valuation for reasonableness. The Company does not have insight into the specific inputs used; however, the key unobservable input would generally include the spread. For a long position, a significant increase (decrease) in the spread used in the fair value of the TRS in isolation could result in higher (lower) fair value. For a short position, a significant increase (decrease) in the spread used in the fair value of the TRS in isolation could result in lower (higher) fair value.
Reserves at fair value: A significant increase (decrease) in the utilization of annuitization benefits could result in a higher (lower) fair value. A significant decrease (increase) in mortality rates, surrender rates, or utilization of lifetime income benefits could result in a higher (lower) fair value.
| (i) | Nonrecurring Fair Value Measurements |
Occasionally, certain assets and liabilities are measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis. There were no nonrecurring fair value adjustments recorded in 2017, 2016, or 2015.
| (j) | Fair Value of Financial Instruments Carried at Other Than Fair Value |
The following table presents the carrying amount and fair value of certain financial instruments that are not reported at fair value at December 31:
| 2017 | |||||||||||||||
| Carrying | Fair value | ||||||||||||||
| amount | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||
| Financial assets | |||||||||||||||
| Mortgage loans on real estate | $ | 11,761,939 | — | — | 12,372,775 | 12,372,775 | |||||||||
| Loans to affiliates | 39,120 | — | — | 39,120 | 39,120 | ||||||||||
| Policy loans | 184,409 | — | 184,409 | — | 184,409 | ||||||||||
| Other invested assets | 302,216 | 196,672 | — | 105,544 | 302,216 | ||||||||||
| Cash equivalents | 1,442,057 | 581,257 | 860,800 | — | 1,442,057 | ||||||||||
| Receivables | 123,110 | — | — | 123,110 | 123,110 | ||||||||||
| Reinsurance and investment contract recoverables | 1,248,634 | — | — | 1,298,499 | 1,298,499 | ||||||||||
| Collateral held from securities lending agreements | 2,657,046 | — | 2,657,221 | — | 2,657,221 | ||||||||||
| COLI | 578,951 | — | 578,951 | — | 578,951 | ||||||||||
| Financial liabilities | |||||||||||||||
| Investment contracts | $ | (79,019,361 | ) | — | — | (79,519,680 | ) | (79,519,680 | ) | ||||||
| Mortgage notes payable | (68,628 | ) | — | — | (77,637 | ) | (77,637 | ) | |||||||
| Securities lending payable | (2,657,046 | ) | — | (2,657,046 | ) | — | (2,657,046 | ) | |||||||
| Other liabilities | (123,110 | ) | — | — | (123,110 | ) | (123,110 | ) | |||||||
| Separate account liabilities | (28,192,877 | ) | (28,192,877 | ) | — | — | (28,192,877 | ) | |||||||
Page 52 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| 2016 | |||||||||||||||
| Carrying | Fair value | ||||||||||||||
| amount | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||
| Financial assets | |||||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity fixed-maturity securities | $ | 28 | — | — | 3,630 | 3,630 | |||||||||
| Mortgage loans on real estate | 10,351,741 | — | — | 10,900,205 | 10,900,205 | ||||||||||
| Loans to affiliates | 39,120 | — | — | 39,120 | 39,120 | ||||||||||
| Policy loans | 171,012 | — | 171,012 | — | 171,012 | ||||||||||
| Other invested assets | 357,210 | — | — | 426,137 | 426,137 | ||||||||||
| Cash equivalents | 1,250,015 | 1,150,015 | 100,000 | — | 1,250,015 | ||||||||||
| Receivables | 144,180 | — | — | 144,180 | 144,180 | ||||||||||
| Reinsurance and investment contract recoverables | 933,074 | — | — | 987,327 | 987,327 | ||||||||||
| Collateral held from securities lending agreements | 2,561,219 | — | 2,561,985 | — | 2,561,985 | ||||||||||
COLI (1) | 338,092 | — | 338,092 | — | 338,092 | ||||||||||
| Financial liabilities | |||||||||||||||
| Investment contracts | $ | (77,305,738 | ) | — | — | (78,018,770 | ) | (78,018,770 | ) | ||||||
| Mortgage notes payable | (76,916 | ) | — | — | (87,981 | ) | (87,981 | ) | |||||||
| Securities lending payable | (2,561,219 | ) | — | (2,561,219 | ) | — | (2,561,219 | ) | |||||||
| Other liabilities | (144,180 | ) | — | — | (144,180 | ) | (144,180 | ) | |||||||
Separate account liabilities (1) | (27,733,261 | ) | (27,733,261 | ) | — | — | (27,733,261 | ) | |||||||
(1) The previously issued 2016 Consolidated Financial Statements improperly disclosed COLI and Separate account liabilities as financial instruments measured at fair value on a recurring basis. These financial instruments have been corrected in the above table to conform with current year presentation as they are carried at other than fair value. | |||||||||||||||
The fair value of fixed-maturity securities classified as “held-to-maturity” is calculated internally with cash flow models using unobservable inputs.
The fair value of mortgage loans on real estate is calculated by analyzing individual loans and assigning ratings to each loan based on a combination of loan-to-value ratios and debt service coverage ratios. Default rates and loss severity factors are then applied to each loan and a fair value is determined based on these factors as well as the contractual cash flows of each loan and the current market interest rates for similar loans.
Loans to affiliates are carried at cost. Due to the lack of an active market, the current carrying value is the only market price at which the transaction could be settled, the Company believes cost approximates fair value.
Policy loans are supported by the underlying cash value of the policies and are carried at unpaid principal balances plus accrued investment income. As policy loans function like demand deposits, the current carrying value is the only market price at which the transaction could be settled. Due to the lack of an active market and uncertainty on receiving contractual cash flows, the Company believes the carrying value approximates fair value.
Page 53 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Other invested assets primarily include short-term securities, FHLB stock, loans to non-affiliates, and LIH investments. The carrying value of the Company's short-term securities is considered a reasonable estimate of fair value due to their short-term maturities and are included in Level 1. The investments in FHLB stock and loans to non-affiliates are carried at cost, which is deemed to approximate fair value as the current carrying value is the only market price at which the transaction could be settled due to the lack of an active market. The fair value of LIH investments is calculated internally by calculating the expected discounted cash flows utilizing the respective funding and benefits schedule for each investment using unobservable inputs. The investments in FHLB stock, loans to non-affiliates, and LIH investments are included in Level 3 due to the use of unobservable inputs.
Cash equivalents include short-term, highly liquid debt instruments purchased with an original maturity of three months or less, short-term government money market funds, overnight commercial paper, and overnight reverse-repurchase agreements. Due to the short-term nature of these investments, carrying value is deemed to approximate fair value. Of the cash equivalents held, the fair value of short-term, highly liquid debt instruments, short-term government money market funds, and overnight commercial paper is based on quoted market prices and these investments are included in Level 1. Overnight reverse-repurchase agreements are included Level 2 due to the use of quoted prices for similar assets in active markets.
Included in Receivables and Other liabilities is the LIH investments unfunded commitment asset and liability. The fair value is calculated internally by discounting the expected future commitments based upon the respective funding schedule for each investment using unobservable inputs.
Collateral held from securities lending agreements is primarily comprised of cash and cash equivalents and highly liquid fixed-maturity securities. Fair values are determined and classified within the fair value hierarchy in a manner consistent with the method utilized to determine the fair value of similar securities held within the Company’s general account investment portfolio.
The COLI policies held by the Company are carried at their respective cash surrender values, which approximates fair value. The cash surrender value of the policies is based on the value of the underlying assets, which are regularly priced utilizing observable inputs.
Investment contracts include certain reserves related to annuity and life products. These reserves are included in Account balances and future policy benefit reserves on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The fair values of the investment contracts are determined by testing amounts payable on demand against discounted cash flows using market interest rates commensurate with the risks involved, including consideration of the Company’s own credit standing and a risk margin for noncapital market inputs.
Reinsurance and investment contracts recoverable represent the ceded portions of investment contracts. The methods and assumptions used to determined the fair value are consistent with those used to value investment contracts.
The fair value of mortgage notes payable is the sum of the outstanding balance of the note payable plus the expected prepayment penalty due to the lender if the Company were to prepay the mortgage. The Company believes this approximates fair value, as the calculation of the prepayment penalty is based on current market interest rates and represents lost interest to the lender and is an exit price. The penalty is based on specific provisions provided by the lender, which is an unobservable input.
Securities lending payable is set equal the to the cash collateral received. Due to the short-term nature of these loans, the carrying value is deemed to approximate fair value.
Separate account liabilities are recorded at the amount credited to the contractholder, which reflects the change in fair value of the corresponding separate account assets including contractholder deposits less withdrawals and fees. As such, the carrying value is deemed to approximate fair value.
Page 54 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (7) | Financing Receivables |
The Company’s financing receivables are comprised of mortgage loans, nontrade receivables, loans to affiliates, and loans to non-affiliates. Mortgage loans consist of the unpaid balance of mortgage loans on real estate. Nontrade receivables are amounts for policy or contract premiums due from the agents and broker-dealers, or amounts due from reinsurers. Loans to affiliates include loans to related parties to fund certain companywide projects. Loans to non-affiliates are loans that are intended to meet certain financial objectives of the Company, AZOA, and Allianz SE. The mortgage loans and nontrade receivables are evaluated on a collective basis for impairment unless circumstances arise that warrant individual evaluation. The loans to affiliates and loans to non-affiliates are evaluated individually and did not require an allowance as of December 31, 2017 and 2016. For additional information, see note 2 for receivables, note 4 for mortgage loans, and note 19 for loans to affiliates.
Credit Quality Indicators
The Company analyzes certain financing receivables for credit risk by using specific credit quality indicators. The Company has determined the loan-to-value ratio and the debt service coverage ratio are the most reliable indicators in analyzing the credit risk of its mortgage loan portfolio. The loan-to-value ratio is based on the Company’s internal valuation methodologies, including discounted cash flow analysis and comparative sales, depending on the characteristics of the property being evaluated. The debt service coverage ratio analysis is normalized to reflect a 25 year amortization schedule.
The credit quality as of December 31 is shown below:
| Debt Service Coverage Ratios | ||||||||||||||||||
| Greater than 1.4x | 1.2x – 1.4x | 1.0x – 1.2x | Less than 1.0x | Total | Percent of Total | |||||||||||||
| 2017: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Loan-to-value ratios: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Less than 50% | $ | 3,742,536 | 52,805 | 64,700 | 66,486 | 3,926,527 | 33.3 | % | ||||||||||
| 50% – 60% | 4,205,942 | 225,433 | 62,516 | 14,315 | 4,508,206 | 38.2 | ||||||||||||
| 60% – 70% | 2,449,915 | 597,222 | 72,784 | — | 3,119,921 | 26.4 | ||||||||||||
| 70% – 80% | 74,854 | 169,431 | — | — | 244,285 | 2.1 | ||||||||||||
| 80% – 90% | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| 90% – 100% | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Greater than 100% | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 10,473,247 | 1,044,891 | 200,000 | 80,801 | 11,798,939 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||
| Debt Service Coverage Ratios | ||||||||||||||||||
| Greater than 1.4x | 1.2x – 1.4x | 1.0x – 1.2x | Less than 1.0x | Total | Percent of Total | |||||||||||||
| 2016: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Loan-to-value ratios: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Less than 50% | $ | 3,694,757 | 133,289 | 53,761 | — | 3,881,807 | 37.3 | % | ||||||||||
| 50% – 60% | 3,740,956 | 173,453 | 23,378 | 18,930 | 3,956,717 | 38.0 | ||||||||||||
| 60% – 70% | 1,442,783 | 502,746 | 26,005 | 43,607 | 2,015,141 | 19.4 | ||||||||||||
| 70% – 80% | 198,103 | 153,481 | 24,086 | — | 375,670 | 3.6 | ||||||||||||
| 80% – 90% | 57,439 | 83,046 | 27,384 | 2,937 | 170,806 | 1.7 | ||||||||||||
| 90% – 100% | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Greater than 100% | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 9,134,038 | 1,046,015 | 154,614 | 65,474 | 10,400,141 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||
Page 55 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The Company’s nontrade receivables are analyzed for credit risk based upon the customer classification of the agent or reinsurer. The nontrade receivable and allowance for credit losses by customer classification as of December 31 are shown below:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||||||||
| Agent | Reinsurer | Total | Agent | Reinsurer | Total | |||||||||||||
| Nontrade receivables | $ | 14,167 | 27,710 | 41,877 | 11,860 | 20,963 | 32,823 | |||||||||||
| Allowance for credit losses | (4,301 | ) | — | (4,301 | ) | (4,876 | ) | — | (4,876 | ) | ||||||||
| Net nontrade receivables | $ | 9,866 | 27,710 | 37,576 | 6,984 | 20,963 | 27,947 | |||||||||||
Rollforward of Allowance for Credit Losses
The allowances for credit losses and recorded investment in financing receivables as of December 31 are shown below:
| Mortgage loans | Nontrade receivables | Loans to affiliates | Loans to non-affiliates | Total | |||||||||||
| 2017: | |||||||||||||||
| Financing receivables, gross | $ | 11,798,939 | 41,877 | 39,120 | 10,137 | 11,890,073 | |||||||||
| Allowance for credit losses: | |||||||||||||||
| Beginning balance | 48,400 | 4,876 | — | — | 53,276 | ||||||||||
| Provision / (benefit) | (11,400 | ) | (575 | ) | — | — | (11,975 | ) | |||||||
| Ending balance | 37,000 | 4,301 | — | — | 41,301 | ||||||||||
| Financing receivables ending balance net of valuation allowance | $ | 11,761,939 | 37,576 | 39,120 | 10,137 | 11,848,772 | |||||||||
| Mortgage loans | Nontrade receivables | Loans to affiliates | Loans to non-affiliates | Total | |||||||||||
| 2016: | |||||||||||||||
| Financing receivables, gross | $ | 10,400,141 | 32,823 | 39,120 | 10,145 | 10,482,229 | |||||||||
| Allowance for credit losses: | |||||||||||||||
| Beginning balance | 37,400 | 5,525 | — | — | 42,925 | ||||||||||
| Provision / (benefit) | 11,000 | (649 | ) | — | — | 10,351 | |||||||||
| Ending balance | 48,400 | 4,876 | — | — | 53,276 | ||||||||||
| Financing receivables ending balance net of valuation allowance | $ | 10,351,741 | 27,947 | 39,120 | 10,145 | 10,428,953 | |||||||||
The Company evaluates the mortgage loan allowance for loan loss quarterly, which resulted in a change of the provision of $(11,400) and $11,000 for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. In 2017, the decrease to the mortgage loan allowance is driven by a reduction in expected losses and reserves based on the improving credit quality of our portfolio and industry analysis showing improving market conditions. The increase to the allowance for loan loss in 2016 was a result of the growing asset base of the mortgage loan portfolio partially offset by improving quality indicators.
Page 56 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Past-Due Aging Analysis
Aging analysis of past-due financing receivables as of December 31 is shown below:
| 31-60 days past due | 61-90 days past due | Greater than 90 days past due | Total past due | Current | Total | |||||||||||||
| 2017: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mortgage loans | $ | — | — | — | — | 11,798,939 | 11,798,939 | |||||||||||
| Nontrade receivables | 9,955 | 1,279 | 8,200 | 19,434 | 22,443 | 41,877 | ||||||||||||
| Loans to affiliates | — | — | — | — | 39,120 | 39,120 | ||||||||||||
| Loans to non-affiliates | — | 18 | 481 | 499 | 9,638 | 10,137 | ||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 9,955 | 1,297 | 8,681 | 19,933 | 11,870,140 | 11,890,073 | |||||||||||
| 31-60 days past due | 61-90 days past due | Greater than 90 days past due | Total past due | Current | Total | |||||||||||||
| 2016: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mortgage loans | $ | — | — | — | — | 10,400,141 | 10,400,141 | |||||||||||
| Nontrade receivables | 7,590 | 1,662 | 6,712 | 15,964 | 16,859 | 32,823 | ||||||||||||
| Loans to affiliates | — | — | — | — | 39,120 | 39,120 | ||||||||||||
| Loans to non-affiliates | 109 | 10 | 71 | 190 | 9,955 | 10,145 | ||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 7,699 | 1,672 | 6,783 | 16,154 | 10,466,075 | 10,482,229 | |||||||||||
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company’s financing receivables did not include any balances which are on a nonaccrual status, classified as a troubled debt restructuring, or impaired without a corresponding allowance for credit loss.
| (8) | Reinsurance |
The Company primarily enters into reinsurance agreements to manage risk resulting from its life, annuity, and accident and health businesses, as well as businesses the Company has chosen to exit.
In the normal course of business, the Company seeks to limit its exposure to loss by ceding risks under yearly renewal term, coinsurance, and modified coinsurance. The Company generally retained between $1,000 and $5,000 coverage per individual life depending on the type of policy for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016.
The Company monitors the financial exposure and financial strength of the reinsurers on an ongoing basis. The Company attempts to mitigate risk by securing recoverable balances with various forms of collateral, including arranging trust accounts and letters of credit with certain reinsurers. Reinsurance and investment contract recoverables at December 31, 2017 and 2016 are secured by collateral of $3,970,978 and $3,419,252, respectively.
The effect of reinsurance on premiums is disclosed in Schedule IV in the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Page 57 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The effect of reinsurance on benefits for the respective years ended December 31 is shown below:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Direct benefits | |||||||||
| Life | $ | 425,845 | 263,594 | 175,293 | |||||
| Annuities | 6,601,650 | 2,015,225 | 2,333,922 | ||||||
| Accident and health | 566,988 | 630,148 | 590,984 | ||||||
| Total direct benefits | 7,594,483 | 2,908,967 | 3,100,199 | ||||||
| Less: Ceded to other companies | |||||||||
| Life | 73,471 | 67,801 | 65,118 | ||||||
| Annuities | 33,230 | 33,024 | 39,481 | ||||||
| Accident and health | 376,797 | 427,153 | 395,226 | ||||||
| Total ceded to other companies | 483,498 | 527,978 | 499,825 | ||||||
| Plus: Assumed from other companies | |||||||||
| Life | 127 | 650 | 1,057 | ||||||
| Annuities | 1,701 | 1,520 | 1,663 | ||||||
| Accident and health | 16,426 | 19 | — | ||||||
| Total assumed from other companies | 18,254 | 2,189 | 2,720 | ||||||
| Total benefits | $ | 7,129,239 | 2,383,178 | 2,603,094 | |||||
Components of the Company's reinsurance and investment contract recoverables as of December 31 are shown below:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||
| Life | $ | 986,636 | 1,031,953 | |||
| Annuities | 1,275,293 | 890,709 | ||||
| Accident and health | 3,033,557 | 2,765,256 | ||||
| Total reinsurance and investment contract recoverables | $ | 5,295,486 | 4,687,918 | |||
The Life, Annuities, and Accident and health categories presented in the tables above are prescribed splits based on product and will differ from the results of the segments disclosed within note 24.
The Company did not write off any uncollectible recoverables during 2017 or 2016.
| (9) | Deferred Acquisition Costs |
DAC at December 31 and the changes in the balance for the years then ended are as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Balance, beginning of year | $ | 5,246,343 | 6,283,236 | 4,362,771 | |||||
| Capitalization | 730,825 | 1,006,773 | 911,425 | ||||||
| Interest | 239,127 | 172,195 | 181,239 | ||||||
| Amortization | (1,244,315 | ) | (1,438,375 | ) | (1,331,923 | ) | |||
| Change in shadow DAC | (1,121,140 | ) | (777,486 | ) | 2,159,724 | ||||
| Balance, end of year | $ | 3,850,840 | 5,246,343 | 6,283,236 | |||||
Page 58 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The Company reviews its best-estimate assumptions each year and records “unlocking” as appropriate. These reviews are based on recent changes in the operations of the Company and actual and expected performance of in-force policies. The reviews include all assumptions, including mortality, lapses, expenses, and separate account returns. The revised best estimate assumptions were applied to the current in-force policies to project future gross profits.
The pretax impact on the Company’s assets and liabilities as a result of the unlocking during the years ended December 31 is as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Assets: | |||||||||
| DAC | $ | (177,274 | ) | (246,669 | ) | (109,797 | ) | ||
| DSI | (35,266 | ) | (51,156 | ) | (32,400 | ) | |||
| VOBA | — | (212 | ) | (180 | ) | ||||
| Reinsurance and investment contract recoverables | (7,645 | ) | 2,934 | 5,471 | |||||
| Total increase (decrease) in assets | (220,185 | ) | (295,103 | ) | (136,906 | ) | |||
| Liabilities: | |||||||||
| Account balances and future policy benefit reserves | (330,853 | ) | (412,959 | ) | (154,064 | ) | |||
| Unearned premiums | (7,070 | ) | (1,787 | ) | (48,369 | ) | |||
| Total increase (decrease) in liabilities | (337,923 | ) | (414,746 | ) | (202,433 | ) | |||
| Net increase (decrease) in income before taxes | $ | 117,738 | 119,643 | 65,527 | |||||
| (10) | Deferred Sales Inducements |
DSI at December 31 and the changes in the balance for years then ended are as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Balance, beginning of year | $ | 764,554 | 1,110,192 | 847,000 | |||||
| Capitalization | 14,726 | 29,176 | 48,546 | ||||||
| Amortization | (207,629 | ) | (277,616 | ) | (284,883 | ) | |||
| Interest | 23,107 | 28,569 | 33,927 | ||||||
| Change in shadow DSI | (163,440 | ) | (125,767 | ) | 465,602 | ||||
| Balance, end of year | $ | 431,318 | 764,554 | 1,110,192 | |||||
See note 9 for impacts of unlocking relating to DSI.
Page 59 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (11) | Income Taxes |
| (a) | Income Tax Expense (Benefit) |
Total income tax expense for the years ended December 31 is as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) attributable to operations: | |||||||||
| Current tax expense (benefit) | $ | 83,114 | 558,016 | 551,052 | |||||
| Deferred tax expense (benefit) | 125,443 | (202,860 | ) | (307,986 | ) | ||||
| Total income tax expense (benefit) attributable to net income (loss) | 208,557 | 355,156 | 243,066 | ||||||
| Income tax effect on AOCI: | |||||||||
| Attributable to unrealized gain (loss) on: | |||||||||
| Investments | 437,719 | 357,363 | (691,519 | ) | |||||
| Postretirement obligations | (2 | ) | 36 | — | |||||
| Foreign exchange | 461 | 373 | (2,159 | ) | |||||
| Total income tax effect on equity | $ | 646,735 | 712,928 | (450,612 | ) | ||||
| (b) | Components of Income Tax Expense (Benefit) |
Income tax expense computed at the statutory rate of 35% varies from Income tax expense reported in the Consolidated Statements of Operations for the respective years ended December 31 as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Income tax expense computed at the statutory rate | $ | 322,882 | 400,167 | 295,177 | |||||
| Dividends-received deductions and tax-exempt interest | (38,369 | ) | (40,326 | ) | (40,687 | ) | |||
| State income tax | (2,074 | ) | 11,266 | 4,642 | |||||
Accrual (release) of LIH tax credits and benefits (1) | 11,691 | (5,819 | ) | (1,284 | ) | ||||
| Accrual (release) of tax contingency reserve | 522 | 373 | (10,701 | ) | |||||
| Foreign tax, net | (3,410 | ) | (3,587 | ) | (3,143 | ) | |||
| COLI | (14,301 | ) | (7,833 | ) | (2,285 | ) | |||
| Penalties | 232 | (47 | ) | 529 | |||||
Deferred tax revaluation due to tax rate change (2) | (70,281 | ) | — | — | |||||
| Other | 1,665 | 962 | 818 | ||||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) as reported | $ | 208,557 | 355,156 | 243,066 | |||||
(1) The Company recognized impairments on LIH investments of $18,351 during 2017 due to the tax rate change enacted in the United States. | |||||||||
(2) On December 22, 2017, the United States passed the Tax Act of 2017 which reduced the corporate tax rate from 35% to 21% for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017. As a result, the deferred taxes recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheets were revalued to reflect the reduction in the future corporate tax rate. | |||||||||
Page 60 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (c) | Components of Deferred Tax Assets and Liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets |
Tax effects of temporary differences giving rise to the significant components of the net deferred tax asset (liability). The net deferred tax asset (liability) on the Consolidated Balance Sheets at December 31 is as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||
| Deferred tax assets: | ||||||
| Policy reserves | $ | 2,793,209 | 3,326,409 | |||
| Expense accruals | 5,569 | 40,792 | ||||
| Other-than-temporarily impaired assets | 11,352 | 40,821 | ||||
| Provision for postretirement benefits | 32,490 | 49,437 | ||||
| Other | 1,148 | 3,267 | ||||
| Total deferred tax assets | 2,843,768 | 3,460,726 | ||||
| Deferred tax liabilities: | ||||||
| Policy reserves | (795,733 | ) | — | |||
| Deferred acquisition costs | (589,011 | ) | (1,533,188 | ) | ||
| Investment income | (303,537 | ) | (253,987 | ) | ||
| Depreciation and amortization | (36,005 | ) | (59,822 | ) | ||
| Net unrealized gains on investments and foreign exchange | (1,295,898 | ) | (1,225,720 | ) | ||
| Total deferred tax liabilities | (3,020,184 | ) | (3,072,717 | ) | ||
| Net deferred tax asset (liabilities) | $ | (176,416 | ) | 388,009 | ||
As a result of the enactment of the Tax Act of 2017, the Company was required to revalue the deferred taxes for Policy reserves held. As the effect from the Policyholder reserves revaluation will be recognized in taxable income on a straight-line basis over the next eight year period beginning January 1, 2018, a deferred tax liability is recognized in the same amount as the deferred tax asset. Both the deferred tax asset and liability are recorded as of December 31, 2017 and are presented on a gross basis in the table above.
Although realization is not assured, the Company believes it is not necessary to establish a valuation allowance for ordinary deferred tax assets, as it is more likely than not the deferred tax assets will be realized principally through future reversals of existing ordinary taxable temporary differences and future ordinary taxable income. For deferred tax assets that are capital in nature, considering all objective evidence and the available tax planning strategy, it is more likely than not the deferred tax assets that are capital in nature will be realized and no valuation allowance is required. The amount of the ordinary and capital deferred tax assets considered realizable could be reduced in the near term if estimates of future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences and future ordinary and capital taxable income are reduced.
Income taxes (received)/paid by the Company were $267,668, $914,413, and $329,563 in 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively. At December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, the Company had a tax (receivable)/payable from AZOA of $(309,694) and $(89,111), reported in Other assets or Other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
At December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company had a tax payable separate from the agreement with AZOA in the amount of $100 and $18, respectively, reported in Other Liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. These amounts are for foreign taxes.
Page 61 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The Company is included in the consolidated group for which AZOA files a federal income tax return on behalf of all group members. As a member of the AZOA consolidated group, the Company is no longer subject to U.S. federal and non-U.S. income tax examinations for years prior to 2014, though examinations of combined returns filed by AZOA, which include the Company by certain U.S. state and local tax authorities, may still be conducted for 2008 and subsequent years. The last Internal Revenue Service examination of AZOA involved amended returns filed by AZOA for the 2011 tax year. This examination concluded in October 2017 with the Internal Revenue Service accepting the amended returns as filed. The Internal Revenue Service has also initiated examinations of AZOA’s 2015 and 2016 income tax returns.
In accordance with the Income Taxes Topic of the Codification, the Company recognizes liabilities for certain unrecognized tax benefits. Reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits is as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 1,697 | 1,367 | |||
| Additions based on tax positions related to the current year | 845 | 330 | ||||
| Amounts released related to tax positions taken in prior years | (386 | ) | — | |||
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 2,156 | 1,697 | |||
The balance at December 31, 2017, consists of tax positions for which the deductibility is more likely than not. The disallowance would affect the annual effective tax rate. The Company does not expect any significant changes related to unrecognized tax benefits during the next 12 months.
The Company recognizes the changes in unrecognized tax benefits and related accrued interest and penalties in federal income tax expense. The Company had $2,326 and $1,805 for the unrecognized tax benefits and related accrued interest at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, in Other Liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
| (12) | Goodwill and Intangible Assets |
Goodwill at December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the changes in the balance for the years then ended are as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||
| Balance, beginning of year | $ | 487,834 | 482,905 | |||
Increase in goodwill due to acquisition (1) | — | 4,929 | ||||
| Balance, end of year | $ | 487,834 | 487,834 | |||
The goodwill balance at December 31, 2017 and 2016, relates to the Individual Annuity segment. See note 24 for further discussion regarding the operating segments.
Intangible assets at December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the changes in the balance for the years then ended are as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||
| Balance, beginning of year | $ | 2,496 | — | |||
Increase in intangibles due to acquisition (1) | — | 2,872 | ||||
| Amortization | (410 | ) | (376 | ) | ||
| Balance, end of year | $ | 2,086 | 2,496 | |||
(1) The increase in goodwill and intangible assets relates to the acquisition of a Field Marketing Office (FMO). See note 19 for further details regarding the acquisition.
Page 62 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The net amortization of the intangible assets in each of the next five years is as follows:
| 2018 | $ | 410 | |
| 2019 | 410 | ||
| 2020 | 410 | ||
| 2021 | 410 | ||
| 2022 | 410 | ||
| 2023 and beyond | 36 | ||
| Total | $ | 2,086 | |
Accumulated amortization of intangible assets is $15,279 and $14,869 as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Goodwill and intangible assets are reviewed on an annual basis and impairment considerations are made depending on economic market conditions. There were no impairments to goodwill or intangible assets in 2017 or 2016.
| (13) | Value of Business Acquired |
VOBA at December 31 and the changes in the balance for the years then ended are as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Balance, beginning of year | $ | — | — | — | |||||
| Interest | 64 | 127 | 210 | ||||||
| Amortization | (1,857 | ) | (1,619 | ) | (2,950 | ) | |||
| Change in shadow VOBA | 1,793 | 1,492 | 2,740 | ||||||
| Balance, end of year | $ | — | — | — | |||||
The net amortization of the VOBA in each of the next five years is expected to be as follows:
| 2018 | $ | 1,923 | |
| 2019 | 785 | ||
| 2020 and beyond | — | ||
| Total | $ | 2,708 | |
Accumulated amortization of VOBA is $244,692 and $242,835 as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
| (14) | Separate Accounts and Annuity Product Guarantees |
The following assumptions were used to determine the GMDB and GMIB liabilities as of December 31, 2017 and 2016:
| • | 100 stochastically generated investment performance scenarios. |
| • | Mean investment performance assumption of 6.5% in 2017 and 2016. |
| • | Volatility assumption of 13.4% in 2017 and 2016. |
| • | For 2017 and 2016, the mortality assumption is based on the Annuity 2000 mortality table for all variable products. The past mortality improvement is based on gender distinct mortality loads varying by attained age, and future mortality improvement factors are based on gender distinct projection scales varying by attained age and subject to grading factors. |
| • | Lapse rates vary by contract type and duration. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, spike rates could approach 60% and 40%, respectively, with an ultimate rate around 15%. |
| • | Discount rates vary by contract type and equal an assumed long-term investment return (see mean investment performance assumption above), less the applicable mortality and expense rate. |
Page 63 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| • | GMIB contracts contain a dynamic lapse assumption. For example, if the contract is projected to have a large additional benefit, then it becomes less likely to lapse. |
The following assumptions were used to determine the GMAB and GMWB liabilities as of December 31, 2017 and 2016:
| • | 1000 stochastically generated investment performance scenarios. |
| • | Market volatility assumptions vary by fund type and grade from a current volatility number to long-term assumptions over one year as shown below: |
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||
| Fund index type | Current volatility | Long-term forward volatility | Current volatility | Long-term forward volatility | ||||||||
| Large cap | 13.4 | % | 18.0 | % | 16.3 | % | 18.1 | % | ||||
| Bond | 3.4 | 3.9 | 3.4 | 3.9 | ||||||||
| International | 13.7 | 21.2 | 16.8 | 21.4 | ||||||||
| Small cap | 17.4 | 21.5 | 20.3 | 21.5 | ||||||||
| • | For 2017 and 2016, the mortality assumption is based on the Annuity 2000 mortality table for all variable products. The past mortality improvement is based on gender distinct mortality loads varying by attained age, and future mortality improvement factors are based on gender distinct projection scales varying by attained age and subject to grading factors. |
| • | Lapse rates vary by contract type and duration. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, spike rates could approach 60% and 40%, respectively, with an ultimate rate around 15%. |
Page 64 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Guaranteed minimum benefits for the respective years ended December 31 are summarized as follows (note that the amounts listed are not mutually exclusive, as many products contain multiple guarantees):
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||||||
| Account value | Net amount at risk | Weighted age (years) | Account value | Net amount at risk | Weighted age (years) | |||||||||||
| GMDB: | ||||||||||||||||
| Return of premium | $ | 26,092,333 | 25,909 | 64 | 23,400,820 | 73,163 | 64 | |||||||||
| Ratchet and return of premium | 4,555,502 | 26,368 | 68 | 4,602,792 | 142,357 | 68 | ||||||||||
| Ratchet and rollup | 3,598,920 | 365,871 | 72 | 3,602,988 | 484,301 | 71 | ||||||||||
| Ratchet and earnings protection rider | 2,902 | 624 | 86 | 3,072 | 885 | 84 | ||||||||||
| Reset | 81,771 | 475 | 77 | 84,191 | 692 | 76 | ||||||||||
| Earnings protection rider | 236,407 | 26,865 | 70 | 235,360 | 22,383 | 69 | ||||||||||
| Total | $ | 34,567,835 | 446,112 | 31,929,223 | 723,781 | |||||||||||
| GMIB: | ||||||||||||||||
| Return of premium | $ | 88,576 | 265 | 74 | 92,121 | 325 | 73 | |||||||||
| Ratchet and return of premium | 1,728,722 | 446 | 71 | 1,885,185 | 4,526 | 70 | ||||||||||
| Ratchet and rollup | 4,603,105 | 453,715 | 68 | 4,653,568 | 723,893 | 68 | ||||||||||
| Total | $ | 6,420,403 | 454,426 | 6,630,874 | 728,744 | |||||||||||
| GMAB: | ||||||||||||||||
| Five years | $ | 2,489,002 | 1,185 | 71 | 2,738,307 | 10,160 | 70 | |||||||||
| Ten years | 2,994 | 1 | 84 | 3,212 | 1 | 82 | ||||||||||
| Target date retirement-7 year | 578,324 | 447 | 65 | 613,746 | 1,218 | 64 | ||||||||||
| Target date retirement-10 year | 235,167 | 534 | 62 | 250,033 | 4,559 | 61 | ||||||||||
| Target date with management levers | 3,201,192 | 11,720 | 63 | 3,332,790 | 73,070 | 62 | ||||||||||
| Total | $ | 6,506,679 | 13,887 | 6,938,088 | 89,008 | |||||||||||
| GMWB: | ||||||||||||||||
| No living benefit | $ | 762,569 | — | 69 | 707,212 | — | 69 | |||||||||
| Life benefit with optional reset | 927,637 | 145,062 | 69 | 921,876 | 171,135 | 69 | ||||||||||
| Life benefit with automatic reset | 1,521,855 | 133,182 | 66 | 1,471,419 | 194,438 | 65 | ||||||||||
| Life benefit with 8% rollup | 27,283 | 4,380 | 72 | 28,562 | 6,286 | 70 | ||||||||||
| Life benefit with 10% rollup | 1,141,470 | 291,570 | 65 | 1,109,985 | 348,423 | 65 | ||||||||||
| Life benefit with management levers | 12,111,092 | 1,912,242 | 62 | 11,579,110 | 2,307,239 | 61 | ||||||||||
| Total | $ | 16,491,906 | 2,486,436 | 15,818,164 | 3,027,521 | |||||||||||
The growth in account values has outpaced the growth in the net amount at risk in 2017 due to the increased market performance of the separate accounts.
Page 65 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
At December 31, variable annuity account balances were invested in separate account funds with the following investment objectives. Balances are presented at fair value:
| Investment type | 2017 | 2016 | |||||
| Bond | $ | 3,303,084 | 3,484,805 | ||||
| Domestic equity | 14,506,783 | 13,959,524 | |||||
| International equity | 1,387,275 | 1,308,840 | |||||
| Specialty | 8,484,888 | 8,320,880 | |||||
| Money market | 439,587 | 585,039 | |||||
| Other | 71,260 | 74,173 | |||||
| Total | $ | 28,192,877 | 27,733,261 | ||||
The following table summarizes the liabilities for variable contract guarantees that are reflected in the general account and shown in Account balances and future policy benefit reserves on the Consolidated Balance Sheets:
| GMDB | GMIB | GMAB | GMWB | Totals | |||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2015 | $ | 97,027 | 176,465 | 374,857 | 2,170,539 | 2,818,888 | |||||||||
| Incurred guaranteed benefits | 9,845 | (17,290 | ) | (96,596 | ) | (14,236 | ) | (118,277 | ) | ||||||
| Paid guaranteed benefits | (17,598 | ) | (13,942 | ) | (34,898 | ) | (69 | ) | (66,507 | ) | |||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2016 | 89,274 | 145,233 | 243,363 | 2,156,234 | 2,634,104 | ||||||||||
| Incurred guaranteed benefits | 5,492 | (35,136 | ) | (61,660 | ) | (151,177 | ) | (242,481 | ) | ||||||
| Paid guaranteed benefits | (12,789 | ) | (9,999 | ) | (355 | ) | (139 | ) | (23,282 | ) | |||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2017 | $ | 81,977 | 100,098 | 181,348 | 2,004,918 | 2,368,341 | |||||||||
| (15) | Accident and Health Claim Reserves |
Accident and health claim reserves are based on estimates that are subject to uncertainty. Uncertainty regarding reserves of a given accident year is gradually reduced as new information emerges each succeeding year, thereby allowing more reliable reevaluations of such reserves. While management believes that reserves as of December 31, 2017 are appropriate, uncertainties in the reserving process could cause reserves to develop favorably or unfavorably in the near term as new or additional information emerges. Any adjustments to reserves are reflected in the operating results of the periods in which they are made. Movements in reserves could significantly impact the Company’s future reported earnings.
Page 66 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Activity in the accident and health claim reserves is summarized as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Balance at January 1, net of reinsurance and investment contract recoverables of $396,850, $340,048, and $283,252, respectively | $ | 196,603 | 157,321 | 135,168 | |||||
| Adjustment primarily related to commutation and assumption reinsurance on blocks of business | 242 | 34 | 323 | ||||||
| Incurred related to: | |||||||||
| Current year | 105,873 | 93,844 | 71,378 | ||||||
| Prior years | (5,496 | ) | 789 | (4,275 | ) | ||||
| Total incurred | 100,377 | 94,633 | 67,103 | ||||||
| Paid related to: | |||||||||
| Current year | 6,451 | 5,829 | 4,331 | ||||||
| Prior years | 61,917 | 49,556 | 40,942 | ||||||
| Total paid | 68,368 | 55,385 | 45,273 | ||||||
| Balance at December 31, net of reinsurance and investment contract recoverables of $447,140, $396,850, and $340,048, respectively | $ | 228,854 | 196,603 | 157,321 | |||||
Prior year incurred claim reserves for 2017 were favorable as a result of re-estimation of unpaid claims and claim adjustment expenses, principally on individual LTC line of business.
Prior year incurred claim reserves for 2016 were unfavorable as a result of re-estimation of unpaid claims and claim adjustment expenses, principally on individual LTC and group health lines of business. In 2015, prior year incurred claim reserves reflect favorable claim development primarily within the individual LTC line of business. This favorable development is partially due to an update to claim continuance assumptions.
| (16) | Mortgage Notes Payable |
In 2004, the Company obtained an $80,000 mortgage loan from an unrelated third-party for the Company’s headquarters. In 2005, the Company agreed to enter into a separate loan agreement with the same counterparty in conjunction with the construction of an addition to the Company’s headquarters of $65,000. This loan was funded in 2006 and combined with the existing mortgage. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the combined loan had a balance of $68,628 and $76,916, respectively. This 20 year, fully amortizing loan has an interest rate of 5.52%, with a maturity date of August 1, 2024. The level principal and interest payments are made monthly. The loan allows for prepayment; however, it is accompanied by a make-whole provision. The proceeds of this mortgage were used to pay off a floating rate construction loan that the Company used to finance the acquisition of property for, and construction of, the Company’s headquarters.
Interest expense for all loans is $4,002, $4,449, and $4,871 in 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively, and is presented in General and administrative expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
The future principal payments required under the loan are as follows:
| 2018 | $ | 8,758 | |
| 2019 | 9,254 | ||
| 2020 | 9,778 | ||
| 2021 | 10,332 | ||
| 2022 | 10,918 | ||
| 2023 and beyond | 19,588 | ||
| Total | $ | 68,628 | |
Page 67 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (17) | Commitments and Contingencies |
The Company and its subsidiaries are named as defendants in various pending or threatened legal proceedings on an ongoing basis, including three putative class action proceedings, arising from the conduct of business: Sanchez v. Allianz Life Ins. Co. of North America (Superior Court of California, L.A. County, BC594715), Berthiaume et al. v. Allianz Life Ins. Co. of North America et al (Minnesota District Court, Henn. County), and Thompson v. Allianz Life Ins. Co. of North America (United Stated District Court, District of Minnesota, Case No. 0:17-cv00096). None of these putative class actions has been certified. The Company generally intends to vigorously contest the lawsuits, but may pursue settlement negotiations in some cases, if appropriate. The outcome of the cases is uncertain at this time, and there can be no assurance that such litigation, or any future litigation, will not have a material adverse effect on the Company and/or its subsidiaries. The Company recognizes legal costs as incurred.
The Company is contingently liable for possible future assessments under regulatory requirements pertaining to insolvencies and impairments of unaffiliated insurance companies. Provision has been made for assessments currently received and assessments anticipated for known insolvencies.
The financial services industry, including mutual funds, variable and fixed annuities, life insurance, distribution companies, and broker-dealers, is subject to close scrutiny by regulators, legislators, and the media.
Federal and state regulators, such as state insurance departments, state securities departments, the SEC, the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, and other regulatory bodies regularly make inquiries and conduct examinations or investigations concerning various selling practices, including suitability reviews, product exchanges, sales to seniors, and compliance with, among other things, insurance and securities law. The Company is subject to ongoing market conduct examinations and investigations by regulators, which may have a material adverse effect on the Company.
It can be expected that annuity and life product designs and sales practices will be an ongoing source of regulatory scrutiny and enforcement actions, litigation, and rulemaking. Private litigation regarding sales practices is ongoing against a number of insurance companies.
These matters could result in legal precedents and new industry-wide legislation, rules, and regulations that could significantly affect the financial services industry, including life insurance and annuity companies. It is unclear at this time whether any such litigation or regulatory actions will have a material adverse effect on the Company in the future.
When evaluating litigation, claims, and assessments, management considers the nature of the litigation, progress of the case, opinions and views of legal counsel, as well as prior experience in similar cases. Management uses this information to assess whether a loss is probable and if the amount of loss can be reasonably estimated prior to making any accruals.
The Company has the following investments that require a commitment of capital for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||
Limited partnerships (1) | $ | 320,123 | 187,484 | |||
| Private placements | 383,675 | 448,351 | ||||
| Mortgage loans | 458,573 | 414,360 | ||||
| Total | $ | 1,162,371 | 1,050,195 | |||
(1) Included within this caption are limited partnership investments managed by affiliates of the Company. See note 19 for additional details regarding these investments. | ||||||
In addition to the amounts above, the Company has LIH investments that require a commitment of capital. The Company has open capital commitments of $132,954 and $153,887 at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. The Company has recorded an unfunded commitment liability of $123,110 and $144,180, as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, within Other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The liability represents the discounted present value of the expected payments.
Page 68 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The Company leases office space and certain furniture and equipment pursuant to operating leases with some leases containing renewal options and escalation clauses. The expense for all operating leases was $4,083, $3,729, and $3,155 in 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively. The future minimum lease payments required under operating leases are as follows:
| 2018 | $ | 2,027 | |
| 2019 | 1,737 | ||
| 2020 | 1,310 | ||
| 2021 | 777 | ||
| 2022 | 479 | ||
| 2023 and beyond | 448 | ||
| Total | $ | 6,778 | |
The Company has a service agreement (the agreement) with certain unrelated broker-dealers for a marketing support program related to the distribution of select variable insurance products. Under the agreement, the Company pays a base service fee of 0.10% on the amount of variable insurance products under management at the commencement of the agreement. An additional service fee of 0.15% is calculated on the total variable insurance products under management held in excess of this base amount. The fee is calculated on a monthly basis and is paid quarterly. Either party may terminate the agreement with a 90-day notice. Upon termination, the service fee continues to be paid from the date of termination for a period of ten years provided that the broker-dealer is not in material breach of the contract. The Company has calculated this termination commitment at December 31, 2017, to be $5,965 annually with a total commitment of $59,654. The calculation was based on the total variable insurance products under management as of December 31, 2017, due to the variability in estimating future assets under management (such as sales, lapse rate, and fund performance). Total expense under the agreement amounted to $5,736, $6,641, and $6,677 in 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively.
| (18) | Employee Benefit Plans |
The Company participates in the Allianz Asset Accumulation Plan (AAAP), a defined contribution plan sponsored by Allianz of America Corporation (AZOAC). Eligible employees are immediately enrolled in the AAAP on their first day of employment. The AAAP will accept participants’ pretax, Roth 401(k), and/or after-tax contributions up to 80% of the participants’ eligible compensation, although contributions remain subject to annual limitations set by the Internal Revenue Service. The Company matches up to a maximum of 7.5% of the employees’ eligible compensation. Participants are 100% vested in the Company’s matching contribution after three years of service.
The AAAP administration expenses and the trust fund, including trustee fees, investment manager fees, and audit fees, are payable from the trust fund but may, at the Company’s discretion, be paid by the Company. All legal fees are paid by the Company. It is the Company’s policy to fund the AAAP costs as incurred. The Company has expensed $16,317, $15,044, and $14,204, in 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively, toward the AAAP matching contributions and administration expenses.
A defined group of highly compensated employees is eligible to participate in the AZOAC Deferred Compensation Plan. The purpose of the plan is to provide tax planning opportunities, as well as supplemental funds upon retirement. The plan is unfunded, meaning no assets of the Company have been segregated or defined to represent the liability for accrued assets under the plan. Employees are 100% vested upon enrollment in the plan for funds they have deferred. Employees’ funds are invested on a pay period basis and are immediately vested. Participants and the Company share the administrative fee. The accrued liability of $33,682 and $26,358 as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, is recorded in Other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
The Company sponsors a nonqualified deferred compensation plan for a defined group of agents. The Company can make discretionary contributions to the plan in the form and manner the Company determines reasonable. Discretionary contributions are currently determined based on production. The accrued liability of $92,314 and $64,738 as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, is recorded in Other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Page 69 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The Company participates in a stock-based compensation plan sponsored by Allianz SE, which awards certain employees SAR and RSU that are tied to Allianz SE stock. Allianz SE determines the number of SAR and RSU granted to each participant. The Company records expense equal to the change in fair value of the units during the reporting period, which includes the Company's estimate of the number of awards expected to be forfeited. A change in value of $9,223, $3,983, and $9,820 was recorded in 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively, and is included in General and administrative expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The related liability of $18,243 and $13,983 as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, is recorded in Other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
The Company participates in the Employee Stock Purchase Plan sponsored by AZOAC that is designed to provide eligible employees with an opportunity to purchase American Depository Shares of Allianz SE at a discounted price. An aggregate amount of 250,000 ordinary shares is reserved for this plan. Allianz SE determines the purchase price of the share-based on the closing price of an ordinary share of Allianz SE on the Frankfurt stock exchange on the date of each purchase. Employees are given the opportunity to purchase these shares quarterly on predetermined dates set by Allianz SE. Employees are not allowed to sell or transfer the shares for a one-year period following the purchase settlement date. The difference between the market price and the discount price, or the discount, is paid by the Company and amounted to $1,020, $946, and $754 in 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively, and is recorded in General and administrative expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The discount is reflected as taxable income in the year of purchase to employees.
The Company participates in the AZOAC Severance Allowance Plan. Under the AZOAC Severance Allowance Plan, all employees who are involuntarily terminated due to job elimination are eligible to receive benefits. The Company expensed $2,839, $983, and $1,079 in 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively, toward severance payments. This expense is recorded in the General and administrative expenses in the Consolidated Statement of Operations.
The Company offers a life insurance benefit to eligible employees hired prior to January 1, 1993, who retire under the employer sponsored retirement program provided they are age 65 or age 55 with 10 or more years of service. The Company’s plan obligation at December 31, 2017 and 2016, was $1,164 and $1,105, respectively. This liability is included in Other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
The Company closed the Welfare Benefit Trust (Trust) in 2017. The Trust’s assets were used to prefund the Company’s self-insured medical plan. The balance was $0 at December 31, 2017 and 2016.
| (19) | Related-Party Transactions |
| (a) | Loans to Affiliates |
In 2015, the Company entered into an agreement to lend Allianz Technology of America (formerly known as Allianz Managed Operations and Services of America) $33,000. The interest rate was a fixed rate of 2.03%. Interest of $488 was earned during 2015 and is included in Interest and similar income, net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. In March 2016, the $33,000 loan and accrued interest of $165 was assigned to AZOA through a dividend.
In 2016, the Company entered into an agreement to lend AZOA $39,120. The remaining loan balance was $39,120 as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 and is included in Loans to affiliates on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Repayment of this loan will begin in 2021 and has a final maturity date of August 31, 2021. The interest rate is a fixed rate of 1.61%. Interest of $630 and $214 was earned during 2017 and 2016 and is included in Interest and similar income, net in the Consolidated Statement of Operations. The Company had accrued interest of $214 as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, and is recorded in Accrued investment income on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Page 70 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (b) | Investments in Limited Partnerships |
In 2016, the Company made an investment in a limited partnership that is managed by its affiliate, Pacific Investment Management Company (PIMCO). Subsequently, in 2017, the Company made another investment in a different limited partnership also managed by PIMCO. The total committed capital for the limited partnership investments is $70,000 and $50,114, of which $57,000 and $44,000 was unfunded as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. During 2016, the Company received distributions in excess of cost of $413 which is included in Realized investment (losses) gains, net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the fair value of the investments was $14,649 and $6,365 and is recorded in Other invested assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
In 2017, the Company made an investment in a limited partnership that is managed by its affiliate, Allianz Global Investors. The Company committed capital of $35,000 of which $32,788 is unfunded as of December 31, 2017. As of December 31, 2017, no distributions have been received. The fair value of the investment was $2,084 as of December 31, 2017 and is recorded in Other invested assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
| (c) | Real Estate |
The Company has agreements to sublease office space to related parties wholly-owned by the same parent company, AZOA. The Company earned rental income of $990, $909, and $1,065 in 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively, which is included in Other revenue on the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Related to this agreement, the Company had a receivable balance of $282 and $152 at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. In addition, the Company leases office space from Allianz Global Corporate and Specialty, an affiliate, pursuant to a sublease agreement. In connection with this agreement, the Company has incurred rent expense of $28, $27, and $27, in 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively, which is included in General and administrative expenses within the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
| (d) | Service Fees |
The Company incurred fees for services provided by affiliated companies of $104,074, $100,689, and $63,530 in 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively. The Company’s liability for these expenses was $30,462 and $40,267 at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, and is included in Other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. On a quarterly basis, the outstanding amount is settled in cash.
The Company earned revenues for various services provided to affiliated companies of $27,183, $21,568, and $6,305, in 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively. The receivable for these revenues was $8,153 and $8,260 at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, and is included in Receivables on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. On a quarterly basis, the outstanding amount is settled in cash.
The Company has agreements with its affiliates PIMCO, Oppenheimer Capital LLC (OpCap), and with certain other related parties whereby (1) specific investment options managed by PIMCO and OpCap are made available through the Company's separate accounts to holders of the Company's variable annuity products, and (2) the Company receives compensation for providing administrative and recordkeeping services relating to the investment options managed by PIMCO and OpCap. Income recognized by the Company from these affiliates for distribution and in-force related costs as a result of providing investment options to the contractholders was $11,986, $12,771, and $14,102 during 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively, which is included in Fee and commission revenue in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. At December 31, 2017 and 2016, $979 and $2,022, respectively, were included for these fees in Receivables on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Expenses incurred to these affiliates for management of sub-advised investment options were $0, $441, and $732 during 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively, which are included in General and administrative expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
| (e) | Dividends to Parent |
The Company paid cash dividends to AZOA of $780,000 in 2017. In 2016, the Company paid dividends to AZOA of $894,165, which represented $861,000 cash and $33,165 related to the AMOSA loan and accrued interest. In 2015, the Company paid dividends to AZOA of $572,125.
Page 71 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (f) | Subsidiary Transactions |
On July 1, 2015, The Annuity Store Financial and Insurance Services (TAS), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Allianz Individual Insurance Group LLC (AIIG), which is a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company, purchased a 100% interest in Life Sales, a FMO, from Fireman’s Fund Insurance Company (FFIC), a subsidiary of AZOA, for $2,617. TAS recorded the assets and liabilities of Life Sales at the historical cost recorded by FFIC. An excess of $2,125 was paid over the basis and charged to equity as a dividend paid to AZOA. The dividend paid as the result of the sale is included in the dividend paid to parent listed above.
On February 1, 2016, Allegiance Marketing Group, LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of AIIG, merged with and into GamePlan Financial Marketing (GamePlan), another wholly-owned subsidiary of AIIG. GamePlan was the surviving entity.
On February 2, 2016, GamePlan purchased a 100% interest in an independent FMO for a purchase price of $7,710. GamePlan recorded these assets and liabilities of the entity at fair value. As a result of the purchase, Goodwill in the amount of $4,929 and Intangible assets of $2,872 were recorded in Other assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The intangible assets will be amortized over a period of seven years. During 2017 and 2016, the Company recorded amortization expense of $410 and $376 for the intangible assets acquired.
On November 1, 2016, Roster Financial LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of AIIG, merged with and into GamePlan. GamePlan was the surviving entity.
AZL PF Investments, Inc. (AZLPF), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company, issued redeemable preferred stock as a result of a prepaid forward agreement. AZLPF's Board of Directors approved the redemption of the preferred stock in November 2016. The preferred stock liability and related accrued interest of $32,195 was recorded at December 31, 2016 and was reported in Other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The preferred stock and related accrued interest was mandatorily redeemed on January 9, 2017 for $32,244.
On June 30, 2017, Allianz Life and Annuity Company (ALAC), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company, was sold to an unrelated third-party. The sale of the subsidiary generated a realized gain of $1,440 which was recorded in Realized investment gains (losses), net in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. ALAC entered into a modified coinsurance reinsurance agreement with the Company effective May 1, 2017. Under the reinsurance agreement, all liabilities and risk associated with ALAC's contractholders were assumed by the Company.
On November 1, 2017, 3 Mentors, Inc., a wholly-owned subsidiary of GamePlan, merged with and into GamePlan. GamePlan was the surviving entity.
On December 1, 2017, Personalized Brokerage Service, LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of AIIG, merged with and into American Financial Marketing, LLC (AFM), another wholly-owned subsidiary of AIIG. AFM was the surviving entity.
| (g) | Reinsurance |
The Company wholly-owns Allianz Annuity Company of Missouri (AAMO), a special purpose life reinsurance captive insurance company (SPLRC) domiciled in Missouri. Prior to December 2015, the Company ceded to AAMO, and AAMO provided indemnity reinsurance on a combined funds withheld coinsurance and modified coinsurance basis, a 20% quota share of the Company’s net liability of variable annuity policies written directly by the Company starting with 2010 policies for a particular product. The impact of this reinsurance agreement is eliminated through consolidation.
In December 2015, the Company recaptured all risks ceded to AAMO under the reinsurance agreement and terminated the reinsurance agreement. Following the recapture and termination, AAMO maintained its license to act as a Missouri SPLRC under Missouri SPLRC Law. Upon recapture, the liabilities were incorporated into the Company’s general account liabilities and the modified coinsurance and funds withheld trust agreements were terminated. As part of the recapture, bonds and IRS were sold by AAMO which generated realized gains of $3,806. After intercompany balances were settled, AAMO paid a dividend to the Company in the amount of $455,843. The Company received approval from the Department of Insurance, Financial Institutions, and Professional Registration of the State of Missouri for all transactions noted above.
Page 72 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The Company wholly-owns AZMO, a SPLRC domiciled in Missouri. The Company cedes to AZMO, and AZMO provides reinsurance on a coinsurance basis and modified coinsurance basis, a 100% quota share of the Company’s net liability of level term life insurance policies and certain universal life insurance policies written directly by the Company. A letter of credit was issued under an existing letter of credit facility in which Allianz SE is the applicant and the face amount of the letter of credit is in a qualifying trust established by AZMO. The impact of this reinsurance agreement is eliminated through consolidation.
In July 2017, the Company entered into a reinsurance agreement with an affiliate, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Allianz SE. The Company cedes on a combined funds withheld coinsurance and modified coinsurance basis, a 60% quota share of the Company's net liability of certain fixed-indexed annuity policies written directly by the Company. The Company ceded premiums of $429,756 during 2017. The Company recorded a reinsurance recoverable and modified coinsurance payable of $436,298 and $396,562 as of December 31, 2017, respectively. The reinsurance recoverable and modified coinsurance payable are included in Reinsurance and investment contract recoverables and Other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets, respectively.
Excluding the reinsurance agreement mentioned above, the Company has reinsurance and investment contract recoverables and payables due to or from reinsurance agreements with other affiliated entities. Total affiliated net reinsurance recoverable was $423 as of December 31, 2017 and is included in Reinsurance and investment contract recoverables on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Total affiliated net reinsurance payable was $79 as of December 31, 2016, and is included in Other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
| (h) | Line of Credit Agreement |
The Company has a line of credit agreement with its subsidiary, AZNY, to provide liquidity, as needed. The Company’s lending capacity under the agreement is limited to 5% of the general account admitted assets of AZNY as of the preceding year end. No amounts have been borrowed during the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016.
| (20) | Statutory Financial Data and Dividend Restrictions |
Statutory accounting practices prescribed or permitted by the Company’s state of domicile are directed toward insurer solvency and protection of policyholders. Accordingly, certain items recorded in financial statements prepared under GAAP are excluded or vary in calculation in determining statutory policyholders’ surplus and gain from operations. Currently, these items include, among others, DAC, deferred taxes, receivables (which are more than 90 days past due), reinsurance, and certain investments. Additionally, account balances and future policy benefit reserves calculated for statutory reporting do not include provisions for withdrawals.
The Company’s statutory capital and surplus reported in the statutory annual statement filed with the State of Minnesota as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, was $6,011,236 and $6,165,279, respectively. The Company’s net (loss) gain from operations reported in the statutory annual statement filed with the State of Minnesota for the years end December 31, 2017 and 2016, was $(2,849,638) and $1,497,192, respectively.
The Company is required to meet minimum statutory capital and surplus requirements. The Company’s statutory capital and surplus as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, were in compliance with these requirements. The maximum amount of ordinary dividends that can be paid by Minnesota insurance companies to the stockholder without prior approval of the Department is subject to restrictions relating to statutory earned surplus, also known as unassigned funds. Unassigned funds are determined in accordance with the accounting procedures and practices governing preparation of the statutory annual statement. In accordance with Minnesota Statutes, the Company may declare and pay from its Unassigned surplus cash dividends of not more than the greater of 10% of its prior year-end statutory surplus, or the net gain from operations of the insurer, not including realized gains, for the 12-month period ending the 31st day of the next preceding year. Based on these limitations, ordinary dividends of $601,124 can be paid in 2018 without prior approval of the Commissioner of Commerce.
Page 73 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Regulatory Risk-Based Capital
An insurance enterprise’s state of domicile imposes minimum risk-based capital requirements that were developed by the NAIC. The formulas for determining the amount of risk-based capital specify various weighting factors that are applied to financial balances or various levels of activity based on the perceived degree of risk. Regulatory compliance is determined by a ratio of an enterprise’s regulatory total adjusted capital to its authorized control level risk-based capital, as defined by the NAIC. Companies below specific trigger points or ratios are classified within certain levels, each of which requires specified corrective action. This ratio for the Company significantly exceeds required minimum thresholds as of December 31, 2016 and 2017.
| (21) | Capital Structure |
The Company is authorized to issue three types of capital stock, as outlined in the table below:
| Authorized, issued, and outstanding | Par value, per share | Redemption rights | Voluntary or involuntary liquidation rights | |||||
| Common stock | 40,000,000 | $1.00 | None | None | ||||
| 20,000,001 | ||||||||
| 20,000,001 | ||||||||
| Preferred stock: | ||||||||
| Class A | 200,000,000 | $1.00 | Designated by Board for each series issued | Designated by Board for each series issued | ||||
| 18,903,484 | ||||||||
| 18,903,484 | ||||||||
| Class A, Series A | 8,909,195 | $1.00 | $35.02 per share plus an amount to yield a compounded annual return of 6%, after actual dividends paid | $35.02 per share plus an amount to yield a compounded annual return of 6%, after actual dividends paid | ||||
| 8,909,195 | ||||||||
| 8,909,195 | ||||||||
| Class A, Series B | 10,000,000 | $1.00 | $35.02 per share plus an amount to yield a compounded annual return of 6%, after actual dividends paid | $35.02 per share plus an amount to yield a compounded annual return of 6%, after actual dividends paid | ||||
| 9,994,289 | ||||||||
| 9,994,289 | ||||||||
| Class B | 400,000,000 | $1.00 | Designated by Board for each series issued | Designated by Board for each series issued | ||||
| 400,000,000 | ||||||||
| 400,000,000 | ||||||||
Holders of Class A preferred stock and of common stock are entitled to one vote per share with respect to all matters presented to or subject to the vote of shareholders. Holders of Class B preferred stock have no voting rights. All issued and outstanding shares are owned by AZOA. See note 1 for further discussion.
Each share of Class A preferred stock is convertible into one share of the Company’s common stock. The Company may redeem any or all of the Class A preferred stock at any time. Dividends will be paid to each class of stock only when declared by the BOD. In the event a dividend is declared, dividends must be paid to holders of Class A preferred stock, Class B preferred stock, and common stock, each in that order.
As discussed in notes 2 and 19, the Company carried out various capital transactions with related parties during 2017, 2016, and 2015.
Page 74 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| (22) | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income |
Changes in AOCI, net of tax, by component consist of the following at December 31:
| 2017 | |||||||||||||||
| Net unrealized gain (loss) on securities | Net gain (loss) on cash flow hedging (1) | Foreign currency translation adjustments | Pension and postretirement plan adjustments | Total AOCI | |||||||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | 1,165,665 | (19,206 | ) | 6,923 | (104 | ) | 1,153,278 | |||||||
| OCI before reclassifications | 1,001,398 | 1,223 | 857 | (12 | ) | 1,003,466 | |||||||||
| Amounts reclassified from AOCI | (43,085 | ) | (9,313 | ) | — | 8 | (52,390 | ) | |||||||
| Net OCI | 958,313 | (8,090 | ) | 857 | (4 | ) | 951,076 | ||||||||
| Ending balance | $ | 2,123,978 | (27,296 | ) | 7,780 | (108 | ) | 2,104,354 | |||||||
| 2016 | |||||||||||||||
| Net unrealized gain (loss) on securities | Net gain (loss) on cash flow hedging (1)(2) | Foreign currency translation adjustments | Pension and postretirement plan adjustments | Total AOCI | |||||||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | 472,376 | 10,408 | 6,231 | (65 | ) | 488,950 | ||||||||
| OCI before reclassifications | 667,048 | (22,227 | ) | 692 | (42 | ) | 645,471 | ||||||||
| Amounts reclassified from AOCI | 26,241 | (7,387 | ) | — | 3 | 18,857 | |||||||||
| Net OCI | 693,289 | (29,614 | ) | 692 | (39 | ) | 664,328 | ||||||||
| Ending balance | $ | 1,165,665 | (19,206 | ) | 6,923 | (104 | ) | 1,153,278 | |||||||
| 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| Net unrealized gain (loss) on securities | Net gain (loss) on cash flow hedging (1)(2) | Foreign currency translation adjustments | Pension and postretirement plan adjustments | Total AOCI | |||||||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | 1,765,606 | 1,475 | 10,240 | (176 | ) | 1,777,145 | ||||||||
| OCI before reclassifications | (1,263,867 | ) | 12,311 | (4,009 | ) | 95 | (1,255,470 | ) | |||||||
| Amounts reclassified from AOCI | (29,363 | ) | (3,378 | ) | — | 16 | (32,725 | ) | |||||||
| Net OCI | (1,293,230 | ) | 8,933 | (4,009 | ) | 111 | (1,288,195 | ) | |||||||
| Ending balance | $ | 472,376 | 10,408 | 6,231 | (65 | ) | 488,950 | ||||||||
(1) Includes cumulative foreign currency translation losses on the hedged items of $18,704, $79,727, and $27,168 at December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively. | |||||||||||||||
(2) The previously issued 2016 Consolidated Financial Statements improperly disclosed OCI before reclassifications as $(29,614) and $8,933 for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. OCI before reclassifications previously included amounts that were reclassified from AOCI of $(7,387) and $(3,378) for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The December 31, 2016 and 2015 amounts have been corrected to conform with current year presentation. | |||||||||||||||
Page 75 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
Reclassifications from AOCI, net of tax, consist of the following:
| Amounts reclassified from AOCI | Affected line item | |||||||||||
| December 31, | in the Consolidated | |||||||||||
| AOCI | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | Statements of Operations | ||||||||
| Net unrealized gain (loss) on securities: | ||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale securities | $ | 66,284 | (40,370 | ) | 45,174 | Realized investment gains (losses), net | ||||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) | 23,199 | (14,129 | ) | 15,811 | Income tax expense (benefit) | |||||||
| Total | 43,085 | (26,241 | ) | 29,363 | ||||||||
| Net gain on cash flow hedging: | ||||||||||||
| Effective portion of gains | 13,622 | 11,121 | 5,197 | Interest and similar income, net | ||||||||
| Ineffective portion of gains | 706 | 243 | — | Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | ||||||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) | 5,015 | 3,977 | 1,819 | Income tax expense (benefit) | ||||||||
| Total | 9,313 | 7,387 | 3,378 | |||||||||
| Pension and other postretirement plan adjustments: | ||||||||||||
| Amortization of actuarial losses | (12 | ) | (5 | ) | (25 | ) | General and administrative expenses | |||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) | (4 | ) | (2 | ) | (9 | ) | Income tax expense (benefit) | |||||
| Total | (8 | ) | (3 | ) | (16 | ) | ||||||
| Total amounts reclassified from AOCI | $ | 52,390 | (18,857 | ) | 32,725 | Net income | ||||||
| (23) | Foreign Currency Translation |
An analysis of foreign currency translation, net of tax for the respective years ended December 31 is as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Beginning amount of cumulative translation adjustments | $ | 6,923 | 6,231 | 10,240 | |||||
| Aggregate adjustment for the period resulting from translation adjustments | 1,318 | 1,065 | (6,168 | ) | |||||
| Amount of income tax expense for the period related to aggregate adjustment | (461 | ) | (373 | ) | 2,159 | ||||
| Net aggregate translation included in equity | 857 | 692 | (4,009 | ) | |||||
| Ending amount of cumulative translation adjustments | $ | 7,780 | 6,923 | 6,231 | |||||
| Canadian dollar to United States dollar foreign exchange rate at end of year | 0.79812 | 0.74568 | 0.71989 | ||||||
| (24) | Segment Information |
The Company has organized its principal operations into the following segments: Individual Annuities, Life, Questar, and Legacy.
The Individual Annuities segment consists of fixed, fixed-indexed, variable, and variable-indexed annuities that are provided through independent distribution channels made up of agents and registered representatives. Revenues for the Company’s fixed annuity products are primarily earned as net investment income on invested assets supporting fixed account balances, with profitability driven by the spread between net investment income earned and interest credited to account balances. Revenues for the Company’s variable annuity products are primarily earned as management and expense fees charged on underlying account balances.
Page 76 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
The Life segment issues fixed-indexed universal life insurance products, as well as maintains term and whole life in-force blocks that the Company no longer sells or distributes. The primary sources for revenue for this segment are premiums, fees, and charges that the Company receives to assume insurance related risk, in addition to earning a spread on net investment income on invested assets.
The Questar segment consists of two wholly-owned subsidiaries, Questar Capital Corporation (Questar Capital) and Questar Asset Management, Inc. (QAM). Questar Capital is registered as a broker-dealer under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and operates as a retail broker-dealer. Questar Capital distributes a full range of securities products, including mutual funds, variable life insurance, and annuity contracts. Questar Capital also processes general securities transactions through a clearing arrangement with a third-party provider. QAM provides portfolio management for clients and revenue is driven by fees received based on assets under management.
The Legacy business consists of closed blocks of LTC and Special Markets products. The Special Markets products include individual and group annuity and life products, including universal life and term life insurance. Although Legacy products are part of the consolidated results, the Company does not allocate additional resources to these areas other than to maintain the operational support to its current customers.
The Company does not maintain segregated investment portfolios for each segment. All Interest and similar income, net and Realized investment (losses) gains, net are allocated to the segments. Assets are only monitored at the individual company level, and as such, asset disclosures by segment are not included herein.
Income and expense related to assets backing policyholder reserves are allocated to the segments based on policyholder reserve levels. The results of the Individual Annuity, Life, and Legacy segments also reflect allocation of income and expense related to assets backing surplus. Income and expense related to assets backing surplus are allocated to the segments based on required capital levels for each segment and are excluded from EGP used in calculating reserves and DAC.
Unconsolidated segment results are reconciled to the Consolidated Statements of Operations amounts in the tables below:
| Year ended December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Individual annuities | Life | Questar | Legacy | Eliminations | Consolidated | |||||||||||||
| Revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Premiums and policy fees, net | $ | 1,249,793 | 204,920 | — | 150,514 | — | 1,605,227 | |||||||||||
| Interest and similar income, net | 4,301,602 | 135,346 | 68 | 85,203 | — | 4,522,219 | ||||||||||||
| Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | 3,368,121 | 233,840 | 2 | 505 | — | 3,602,468 | ||||||||||||
| Realized investment gains (losses), net | 80,111 | 2,272 | 3 | 1,236 | — | 83,622 | ||||||||||||
| Fee, commission, and other revenue | 249,280 | 1,485 | 110,989 | 1,380 | (38,404 | ) | 324,730 | |||||||||||
| Total revenue | 9,248,907 | 577,863 | 111,062 | 238,838 | (38,404 | ) | 10,138,266 | |||||||||||
| Benefits and expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net benefits and expenses | 6,570,915 | 350,354 | — | 207,970 | — | 7,129,239 | ||||||||||||
| General and administrative and commission | 1,486,314 | 219,519 | 122,989 | 21,726 | (38,404 | ) | 1,812,144 | |||||||||||
| Change in deferred acquisition costs, net | 313,504 | (59,168 | ) | — | 20,027 | — | 274,363 | |||||||||||
| Total benefits and expenses | 8,370,733 | 510,705 | 122,989 | 249,723 | (38,404 | ) | 9,215,746 | |||||||||||
| Pretax income (loss) | $ | 878,174 | 67,158 | (11,927 | ) | (10,885 | ) | — | 922,520 | |||||||||
Page 77 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
| Year ended December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Individual annuities | Life | Questar | Legacy | Eliminations | Consolidated | |||||||||||||
| Revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Premiums and policy fees, net | $ | 1,117,580 | 147,013 | — | 142,686 | — | 1,407,279 | |||||||||||
| Interest and similar income, net | 4,133,359 | 113,465 | 32 | 78,881 | — | 4,325,737 | ||||||||||||
| Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | (218,922 | ) | 40,600 | 2 | 82 | — | (178,238 | ) | ||||||||||
| Realized investment gains (losses), net | (49,126 | ) | 623 | — | (822 | ) | — | (49,325 | ) | |||||||||
| Fee, commission, and other revenue | 243,789 | 747 | 101,432 | 1,191 | (37,305 | ) | 309,854 | |||||||||||
| Total revenue | 5,226,680 | 302,448 | 101,466 | 222,018 | (37,305 | ) | 5,815,307 | |||||||||||
| Benefits and expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net benefits and expenses | 1,982,879 | 194,667 | — | 205,632 | — | 2,383,178 | ||||||||||||
| General and administrative and commission | 1,774,740 | 159,455 | 114,009 | 18,489 | (37,305 | ) | 2,029,388 | |||||||||||
| Change in deferred acquisition costs, net | 315,760 | (69,477 | ) | — | 13,124 | — | 259,407 | |||||||||||
| Total benefits and expenses | 4,073,379 | 284,645 | 114,009 | 237,245 | (37,305 | ) | 4,671,973 | |||||||||||
| Pretax income (loss) | $ | 1,153,301 | 17,803 | (12,543 | ) | (15,227 | ) | — | 1,143,334 | |||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Individual annuities | Life | Questar | Legacy | Eliminations | Consolidated | |||||||||||||
| Revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Premiums and policy fees, net | $ | 1,133,285 | 172,660 | — | 143,646 | — | 1,449,591 | |||||||||||
| Interest and similar income, net | 3,999,693 | 103,326 | 3 | 72,447 | — | 4,175,469 | ||||||||||||
| Change in fair value of assets and liabilities | (492,479 | ) | (38,553 | ) | — | (1,688 | ) | — | (532,720 | ) | ||||||||
| Realized investment gains (losses), net | 90,948 | 1,597 | — | 1,868 | — | 94,413 | ||||||||||||
| Fee, commission, and other revenue | 236,454 | 186 | 105,830 | 253 | (39,324 | ) | 303,399 | |||||||||||
| Total revenue | 4,967,901 | 239,216 | 105,833 | 216,526 | (39,324 | ) | 5,490,152 | |||||||||||
| Benefits and expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net benefits and expenses | 2,296,057 | 114,377 | — | 192,660 | — | 2,603,094 | ||||||||||||
| General and administrative and commission | 1,549,692 | 165,386 | 110,624 | 18,059 | (39,324 | ) | 1,804,437 | |||||||||||
| Change in deferred acquisition costs, net | 279,582 | (53,642 | ) | — | 13,319 | — | 239,259 | |||||||||||
| Total benefits and expenses | 4,125,331 | 226,121 | 110,624 | 224,038 | (39,324 | ) | 4,646,790 | |||||||||||
| Pretax income (loss) | $ | 842,570 | 13,095 | (4,791 | ) | (7,512 | ) | — | 843,362 | |||||||||
Page 78 of 82
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except share data and security holdings quantities)
(25) Subsequent Events
No material subsequent events have occurred since December 31, 2017 through March 29, 2018, the date at which the financial statements were issued, that would require adjustment to the financial statements.
On January 22, 2018, the Company formed TruChoice Financial Group, LLC (TruChoice), a noninsurance subsidiary. TruChoice is a wholly-owned subsidiary of AIIG and was capitalized through an initial cash contribution of $1,716 from AIIG. In addition, AIIG contributed 100% of the membership interests it held in the following FMOs: AFM, GamePlan, TAS, and Ann Arbor Annuity Exchange, LLC, in exchange for 100% of the membership interest of TruChoice.
Page 79 of 82
SCHEDULE I
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Summary of Investments - Other than Investments in Related Parties
December 31, 2017
(In thousands)
| Type of investment | Cost (1) | Fair value | Amount at which shown in the Consolidated Balance Sheets | |||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities: | ||||||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale: | ||||||||||
| U.S. government | $ | 2,449,361 | 2,441,454 | 2,441,454 | ||||||
| Agencies not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government | 6,692 | 6,817 | 6,817 | |||||||
| States and political subdivisions | 10,177,673 | 11,317,726 | 11,317,726 | |||||||
| Foreign government | 523,356 | 540,613 | 540,613 | |||||||
| Corporate securities | 65,145,715 | 70,045,273 | 70,045,273 | |||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities | 14,297,121 | 14,425,840 | 14,425,840 | |||||||
| CDO | 15,243 | 27,565 | 27,565 | |||||||
| Total fixed-maturity securities, available-for-sale | 92,615,161 | 98,805,288 | 98,805,288 | |||||||
| Fixed-maturity securities, trading: | ||||||||||
| U.S. government | 30,578 | 30,901 | 30,901 | |||||||
| Agencies not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government | 5,254 | 5,168 | 5,168 | |||||||
| Corporate securities | 150 | 150 | 150 | |||||||
| Total fixed-maturity securities, trading | 35,982 | 36,219 | 36,219 | |||||||
| Total fixed-maturity securities | 92,651,143 | 98,841,507 | 98,841,507 | |||||||
| Equity securities: | ||||||||||
| Equity securities, available-for-sale: | ||||||||||
| Common stocks: | ||||||||||
| Industrial and miscellaneous | 259,573 | 270,409 | 270,409 | |||||||
| Preferred stocks: | ||||||||||
| Industrial and miscellaneous | 1,500 | 1,500 | 1,500 | |||||||
| Total equity securities, available-for-sale | 261,073 | 271,909 | 271,909 | |||||||
| Equity securities, fair value option and trading: | ||||||||||
| Common stocks: | ||||||||||
| Industrial and miscellaneous | 289,217 | 314,370 | 314,370 | |||||||
| Total equity securities, fair value option and trading | 289,217 | 314,370 | 314,370 | |||||||
| Total equity securities | 550,290 | 586,279 | 586,279 | |||||||
| Other investments: | ||||||||||
| Mortgage loans on real estate, net | 11,761,939 | 12,372,775 | 11,761,939 | |||||||
| Derivative assets | 1,388,190 | 1,388,190 | 1,388,190 | |||||||
| Loans to affiliates | 39,120 | 39,120 | 39,120 | |||||||
| Policy loans | 184,409 | 184,409 | 184,409 | |||||||
| Other invested assets | 382,154 | 382,154 | 382,154 | |||||||
| Total other investments | 13,755,812 | 14,366,648 | 13,755,812 | |||||||
| Total investments | $ | 106,957,245 | 113,794,434 | 113,183,598 | ||||||
(1) The original cost of equity securities and other investments is reduced by impairments. The original cost of fixed-maturity securities is reduced by repayments and impairments adjusted for amortization of premiums and accrual discounts. | ||||||||||
See accompanying Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
Page 80 of 82
SCHEDULE III
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Supplementary Insurance Information
As of and for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015
(In thousands)
| As of December 31 | Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred acquisition costs | Deferred sales inducements (1) | Account balances and future policy reserves | Unearned premiums | Policy and contract claims | Net premium and policy fees | Interest and similar income, net | Net benefits (2) | Net change in deferred sale inducements (3) | Net change in deferred acquisition costs (4) | Other operating expenses | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Annuities | $ | 3,352,997 | 431,318 | 107,307,376 | 117 | — | 1,249,793 | 4,301,602 | 6,402,287 | 168,628 | 313,504 | 1,447,911 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Life | 499,742 | — | 3,930,018 | 35,824 | 3,121 | 204,920 | 135,346 | 349,186 | 1,168 | (59,168 | ) | 219,519 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Questar | — | — | — | — | — | — | 68 | — | — | — | 122,990 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Legacy | (1,899 | ) | — | 4,536,762 | 62,331 | 693,576 | 150,514 | 85,203 | 207,970 | — | 20,027 | 21,724 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 3,850,840 | 431,318 | 115,774,156 | 98,272 | 696,697 | 1,605,227 | 4,522,219 | 6,959,443 | 169,796 | 274,363 | 1,812,144 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Annuities | $ | 4,704,646 | 763,386 | 97,927,975 | 5,864 | 1,731 | 1,117,580 | 4,133,359 | 1,763,154 | 219,725 | 315,760 | 1,737,434 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Life | 523,701 | 1,168 | 3,172,139 | 77,790 | 4,438 | 147,013 | 113,465 | 194,521 | 146 | (69,477 | ) | 159,455 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Questar | — | — | — | — | — | — | 32 | — | — | — | 114,009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Legacy | 17,996 | — | 4,254,346 | 61,681 | 614,574 | 142,686 | 78,881 | 205,632 | — | 13,124 | 18,490 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 5,246,343 | 764,554 | 105,354,460 | 145,335 | 620,743 | 1,407,279 | 4,325,737 | 2,163,307 | 219,871 | 259,407 | 2,029,388 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Annuities | $ | 5,766,176 | 1,108,877 | 90,734,164 | 25,620 | — | 1,133,285 | 3,999,693 | 2,095,788 | 200,269 | 279,582 | 1,510,369 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Life | 486,195 | 1,315 | 2,678,431 | 70,621 | 3,335 | 172,660 | 103,326 | 112,236 | 2,141 | (53,642 | ) | 165,385 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Questar | — | — | — | — | — | — | 3 | — | — | — | 110,624 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Legacy | 30,865 | — | 3,901,902 | 57,875 | 514,590 | 143,646 | 72,447 | 192,660 | — | 13,319 | 18,059 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 6,283,236 | 1,110,192 | 97,314,497 | 154,116 | 517,925 | 1,449,591 | 4,175,469 | 2,400,684 | 202,410 | 239,259 | 1,804,437 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
(1) Deferred sales inducements is located in Other assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(2) Excludes net change in deferred sales inducements. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(3) See note 10 for aggregate gross amortization of deferred sales inducements. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(4) See note 9 for aggregate gross amortization of deferred acquisition costs. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See accompanying Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
Page 81 of 82
SCHEDULE IV
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA AND SUBSIDIARIES
Reinsurance
For the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015
(In thousands)
| Years ended | Direct amount | Ceded to other companies | Assumed from other companies | Net Amount | Percentage of amount assumed to net | ||||||||||
| December 31, 2017: | |||||||||||||||
| Life insurance face amount in force | $ | 37,365,340 | 24,877,754 | 48,647 | 12,536,233 | 0.4 | % | ||||||||
| Premiums and policy fees: | |||||||||||||||
| Life | $ | 275,152 | 68,432 | 686 | 207,406 | 0.3 | % | ||||||||
| Annuities | 1,229,815 | (18,268 | ) | (402 | ) | 1,247,681 | — | ||||||||
| Accident and health | 182,351 | 76,260 | 44,049 | 150,140 | 29.3 | ||||||||||
| Total premiums and policy fees | $ | 1,687,318 | 126,424 | 44,333 | 1,605,227 | 2.8 | % | ||||||||
| December 31, 2016: | |||||||||||||||
| Life insurance face amount in force | $ | 33,748,978 | 23,377,514 | 23,086 | 10,394,550 | 0.2 | % | ||||||||
| Premiums and policy fees: | |||||||||||||||
| Life | $ | 207,771 | 59,071 | 746 | 149,446 | 0.5 | % | ||||||||
| Annuities | 1,111,894 | (4,514 | ) | (425 | ) | 1,115,983 | — | ||||||||
| Accident and health | 184,915 | 78,426 | 35,361 | 141,850 | 24.9 | ||||||||||
| Total premiums and policy fees | $ | 1,504,580 | 132,983 | 35,682 | 1,407,279 | 2.5 | % | ||||||||
| December 31, 2015: | |||||||||||||||
| Life insurance face amount in force | $ | 30,774,840 | 21,809,292 | 60,469 | 9,026,017 | 0.7 | % | ||||||||
| Premiums and policy fees: | |||||||||||||||
| Life | $ | 219,959 | 45,746 | 683 | 174,896 | 0.4 | % | ||||||||
| Annuities | 1,130,514 | (1,447 | ) | (442 | ) | 1,131,519 | — | ||||||||
| Accident and health | 188,885 | 80,987 | 35,278 | 143,176 | 24.6 | ||||||||||
| Total premiums and policy fees | $ | 1,539,358 | 125,286 | 35,519 | 1,449,591 | 2.5 | % | ||||||||
| The Life and Annuities categories above are prescribed splits based on product and will differ from the results of the Life and Individual Annuity segments. | |||||||||||||||
See accompanying Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
Page 82 of 82
FOR SERVICE OR MORE INFORMATION
You can review and copy information about us, the Separate Account, the prospectus and the SAI at the SEC's Public Reference Room in Washington, D.C. You may obtain information about the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling (202) 551-8090.
The SEC also maintains a website (www.sec.gov). The prospectus, the SAI and other information about the Contract are available on the EDGAR database on the SEC's website. If you do not have access to the website, you can get copies of information from the website upon payment of a duplication fee by writing to:
Public Reference Section of the Commission
100 F Street, NE
Washington, DC 20549
OUR SERVICE CENTER
If you need customer service (for Contract changes, information on Contract Values, requesting a withdrawal or transfer, changing your allocation instructions, etc.) please contact our Service Center at (800) 624-0197.
To send an application, a check for an additional Purchase Payment, or for general customer service, please mail to the appropriate address as follows:
Send an application or additional Purchase Payment with a check: | Send an application or general customer service without a check: |
| REGULAR MAIL | REGULAR MAIL |
| Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America | Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America |
| NW5989 | P.O. Box 561 |
| P.O. Box 1450 | Minneapolis, MN 55440-0561 |
| Minneapolis, MN 55485-5989 | |
| OVERNIGHT, CERTIFIED, OR REGISTERED MAIL | OVERNIGHT, CERTIFIED, OR REGISTERED MAIL |
| Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America | Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America |
| NW5989 | 5701 Golden Hills Drive |
| 1801 Parkview Drive | Golden Valley, MN 55416-1297 |
| Shoreview, MN 55126 |
NOTE: Checks sent to the wrong address for applications or additional Purchase Payments are forwarded to the 1801 Parkview Drive address listed above, which may delay processing.
To send information by email, please use this address: variableannuity@send.allianzlife.com. To send information over the web, please upload to your account on our website at: www.allianzlife.com. If you have questions about whether you can submit certain information by email or over the web, please contact our Service Center.
Until May 1, 2019, all dealers that effect transactions in these securities may be required to deliver a prospectus.
PART II - INFORMATION NOT REQUIRED IN PROSPECTUS
ITEM 13. OTHER EXPENSES OF ISSUANCE AND DISTRIBUTION.
| Securities and Exchange Commission Registration Fee | $ 52,139 |
| ---------------- | |
| Estimated Printing and Filing Costs: | $ 30,000 |
| ---------------- | |
| Estimated Accounting Fees: | $ 75,000 |
| ----------------- | |
| Estimated Legal Fees: | $ N/A |
| ----------------- | |
| Estimated Miscellaneous Fees: | $ N/A |
---------------- |
ITEM 14. INDEMNIFICATION OF OFFICERS AND DIRECTORS.
| The Bylaws of the Insurance Company provide: | ||
| ARTICLE XI. INDEMNIFICATION OF DIRECTORS, OFFICERS AND EMPLOYEES | ||
| SECTION 1. RIGHT TO INDEMNIFICATION: | ||
| (a) | Subject to the conditions of this Article and any conditions or limitations imposed by applicable law, the Corporation shall indemnify any employee, director or officer of the Corporation (an "Indemnified Person") who was, is, or in the sole opinion of the Corporation, may reasonably become a party to or otherwise involved in any Proceeding by reason of the fact that such Indemnified Person is or was: | |
| (i) | a director of the Corporation; or | |
| (ii) | acting in the course and scope of his or her duties as an officer or employee of the Corporation; or | |
| (iii) | rendering Professional Services at the request of and for the benefit of the Corporation; or | |
| (iv) | serving at the request of the Corporation as an officer, director, fiduciary or member of another corporation, association, committee, partnership, joint venture, trust, employee benefit plan or other enterprise (an "Outside Organization"). | |
| (b) | Notwithstanding the foregoing, no officer, director or employee shall be indemnified pursuant to these bylaws under the following circumstances: | |
| (i) | in connection with a Proceeding initiated by such person, in his or her own personal capacity, unless such initiation was authorized by the Board of Directors; | |
| (ii) | if a court of competent jurisdiction finally determines that any indemnification hereunder is unlawful; | |
| (iii) | for acts or omissions involving intentional misconduct or knowing and culpable violation of law; | |
| (iv) | for acts or omissions that the Indemnified Person believes to be contrary to the best interests of the Corporation or its shareholders or that involve the absence of good faith on the part of the Indemnified Person; | |
| (v) | for any transaction for which the Indemnified Person derived an improper personal benefit; | |
| (vi) | for acts or omissions that show a reckless disregard for the Indemnified Person's duty to the Corporation or its shareholders in circumstances in which the Indemnified Person was aware or should have been aware, in the ordinary course of performing the Indemnified Person's duties, of the risk of serious injury to the Corporation or its shareholders; | |
| (vii) | for acts or omissions that constitute an unexcused pattern of inattention that amounts to an abdication of the Indemnified Person's duties to the Corporation or its shareholders; | |
| (viii) | in circumstances where indemnification is prohibited by applicable law; | |
| (ix) | in the case of service as an officer, director, fiduciary or member of an Outside Organization, where the Indemnified Person was aware or should have been aware that the conduct in question was outside the scope of the assignment as contemplated by the Corporation. | |
| SECTION 2. SCOPE OF INDEMNIFICATION: | |
| (a) | Indemnification provided pursuant to Section 1(a)(iv) shall be secondary and subordinate to indemnification or insurance provided to an Indemnified Person by an Outside Organization or other source, if any. |
| (b) | Indemnification shall apply to all reasonable expenses, liability and losses, actually incurred or suffered by an Indemnified Person in connection with a Proceeding, including without limitation, attorneys' fees and any expenses of establishing a right to indemnification or advancement under this article, judgments, fines, ERISA excise taxes or penalties, amounts paid or to be paid in settlement and all interest, assessments and other charges paid or payable in connection with or in respect of such expense, liability and loss. |
| (c) | Such indemnification shall continue as to any Indemnified Person who has ceased to be an employee, director or officer of the Corporation and shall inure to the benefit of his or her heirs, estate, executors and administrators. |
| SECTION 3. DEFINITIONS: | |
| (a) | "Corporation" for the purpose of Article XI shall mean Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America and all of its subsidiaries. |
| (b) | "Proceeding" shall mean any threatened, pending, or completed action, suit or proceeding whether civil, criminal, administrative, investigative or otherwise, including actions by or in the right of the Corporation to procure a judgment in its favor. |
| (c) | "Professional Services" shall mean services rendered pursuant to (i) a professional actuarial designation, (ii) a license to engage in the practice of law issued by a State Bar Institution or (iii) a Certified Public Accountant designation issued by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants. |
| Insofar as indemnification for liability arising under the Securities Act of 1933 may be permitted for directors and officers or controlling persons of the Insurance Company pursuant to the foregoing, or otherwise, the Insurance Company has been advised that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Act and, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the Insurance Company of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the Insurance Company in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the Company will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Act and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue. | |
ITEM 15. RECENT SALES OF UNREGISTERED SECURITIES.
NOT APPLICABLE.
ITEM 16. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES.
(a) Exhibits.
| 1.(a) | Principal Underwriter Agreement by and between North American Life and Casualty Company on behalf of NALAC Financial Plans, Inc. dated September 14, 1988 incorporated by reference as exhibit EX-99.B3.a. from Pre-Effective Amendment No.1 to Form N-4 (File Nos. 333-06709 and 811-05618), electronically filed on December 13, 1996. (North American Life and Casualty Company is the predecessor to Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America. NALAC Financial Plans, Inc., is the predecessor to USAllianz Investor Services, LLC, which is the predecessor to Allianz Life Financial Services, LLC.) |
| (b) | Broker-Dealer Agreement (amended and restated) between Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America and Allianz Life Financial Services, LLC, dated June 1, 2010 incorporated by reference as exhibit EX-99B3b. from Pre-Effective Amendment No. 1 to Form N-4 (File Nos. 333-166408 and 811-05618), electronically filed on September 24, 2010. |
| (c) | The current specimen of the selling agreement between Allianz Life Financial Services, LLC, the principal underwriter for the Contracts, and retail brokers which offer and sell the Contracts to the public is incorporated by reference as exhibit EX-99.B3.b. from the initial filing on Form N-4 (File Nos. 333-134267 and 811-05618), electronically filed on May 19, 2006.The underwriter has executed versions of the agreement with approximately 2,100 retail brokers. |
2. Not applicable
| 3. (a) | Articles of Incorporation, as amended and restated August 1, 2006, of Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America, filed on January 3, 2013 as Exhibit 3(a) to Registrant's initial registration on Form S-1 (File No. 333-185864), is incorporated by reference. |
| (b) | Bylaws, as amended and restated August 1, 2006, of Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America, filed on January 3, 2013 as Exhibit 3(b) to Registrant's initial registration on Form S-1 (File No. 333-185864), is incorporated by reference. |
| 4.(a) | Individual Variable Annuity Contract-L40538 incorporated by reference as Exhibit 4(a) from Pre-Effective Amendment No. 1 to Registrant's Form S-1 (File No. 333-185864), electronically filed on April 17, 2013. | ||||
| (b) | Revised Contract Schedule Page S40877-01, including Guard Strategy, incorporated by reference as Exhibit 4(b) from Registrant's Pre-Effective Amendment No. 1 on Form S-1 (File No. 333-213125), electronically filed on October 26, 2016. Contract Schedule Page S40877-01, incorporated by reference as Exhibit 4(b) from Post-Effective Amendment No. 1 to Registrant's Form S-1 (File No. 333-195462), electronically filed on December 8, 2014. Contract Schedule Page S40876 incorporated by reference as Exhibit 4(b) from Pre-Effective Amendment No. 1 to Registrant's Form S-1 (File No. 333-185864), electronically filed on April 17, 2013. | ||||
| (c)* | Index Options Contract Schedule Page, S40895-ADV, filed herewith. Contract Schedule page, S40875-01-ADV, including Precision Strategy, incorporated by reference as Exhibit 4(c) from Post-Effective Amendment No. 1 to Registrant's Form S-1 (File No. 333-213125), electronically filed on January 17, 2017. Contract Schedule Page S40875-ADV, incorporated by reference as Exhibit 4(c) from Registrant's initial registration on Form S-1 (File No. 333-213125), electronically filed on August 15, 2016. | ||||
| (d)* | |||||
| (e) | Index Performance Strategy Crediting Rider-S40878 incorporated by reference as Exhibit 4(d) from Pre-Effective Amendment No. 1 to Registrant's Form S-1 (File No. 333-185864), electronically filed on April 17, 2013. | ||||
| (f) | Index Protection Strategy Crediting Rider-S40879 incorporated by reference as Exhibit 4(e) from Pre-Effective Amendment No. 1 to Registrant's Form S-1 (File No. 333-185864), electronically filed on April 17, 2013. | ||||
| (g) | Index Guard Strategy Crediting Rider-S40889, incorporated by reference as Exhibit 4(g) from Post-Effective Amendment No. 1 to Registrant's Form S-1 (File No. 333-195462), electronically filed on December 8, 2014. | ||||
| (h) | Index Precision Strategy Crediting Rider, S40891, incorporated by reference as Exhibit 4(h) from Post-Effective Amendment No. 1 to Registrant's Form S-1 (File No. 333-213125), electronically filed on January 17, 2017. | ||||
| (i) | Traditional Death Benefit Rider-S40880 incorporated by reference as Exhibit 4(f) from Pre-Effective Amendment No. 1 to Registrant's Form S-1 (File No. 333-185864), electronically filed on April 17, 2013. | ||||
| (j) | Waiver of Withdrawal Charge Rider-S40749 incorporated by reference as exhibit EX-99.B4.f. from Pre-Effective Amendment No. 1 to Registrant's Form N-4 (File Nos. 333-139701 and 811-05618), electronically filed on April 9, 2007. | ||||
| (k) | Inherited IRA/Roth IRA Endorsement-S40713 incorporated by reference as exhibit EX-99.B4.q. from Pre-Effective Amendment No. 1 to Registrant's Form N-4 (File Nos. 333-134267 and 811-05618), electronically filed on September 25, 2006. | ||||
| (l) | Roth IRA Endorsement-S40342 incorporated by reference as exhibit EX-99.B4.l. from Pre-Effective Amendment No. 1 to Registrant's Form N-4 (File Nos. 333-134267 and 811-05618), electronically filed on September 25, 2006. | ||||
| (m) | IRA Endorsement-S40014 incorporated by reference as exhibit EX-99.B4.g. from Pre-Effective Amendment No.1 to Registrant's Form N-4 (File Nos. 333-82329 and 811-05618), electronically filed on December 30, 1999. | ||||
| (n) | Unisex Endorsement-(S20146) incorporated by reference as exhibit EX-99.B4.h. from Pre-Effective Amendment No.1 to Registrant's Form N-4 (File Nos. 333-82329 and 811-05618), electronically filed on December 30, 1999. | ||||
| (o) | Maximum Anniversary Death Benefit Rider- S40897 and MAV Contract Schedule S40898-ADV, incorporated by reference as Exhibit 4(o) from Post-Effective Amendment No. 3 to Registrant's form S-1 (File No. 333-213125), electronically filed on December 15, 2017. | ||||
5. Opinion re Legality - not applicable
8. Opinion re Tax Matters - not applicable
9. Not applicable
10. Material Contracts – not applicable
11. Not applicable
12. Not applicable
15. Not applicable
16. Not applicable
21. Not applicable.
23. (a)* Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm – KPMG LLP, filed herewith.
(b)* Consent of Counsel, filed herewith.
| 24. | (a) | Board Resolution, effective December 11, 2012, of the Board of Directors of Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America, filed on January 3, 2013 as Exhibit 24(b) to Registrant's Initial Registration on Form S-1 (File No. 333-185864), is incorporated by reference. |
(b) Form of Board Resolution of the Board of Directors of Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America, effective April 14, 2014, filed on April 14, 2014 as Exhibit 24 (d) to Registrant's Post-Effective Amendment No. 2 to Form S-1 (File No. 333-185864), is incorporated by reference. |
| (c) | Powers of Attorney, incorporated by reference as Exhibit 24(c) from Registrant's initial registration on form S-1 (File No. 333-222817), electronically filed on February 1, 2018. |
25. Not applicable
26. Not applicable
| 99. | (a) | Alternative Minimum Value Exhibit - IXA-032 (04/2018), incorporated by reference as Exhibit 99(a) from Registrant's initial registration on form S-1 (File No. 333-222817), electronically filed on February 1, 2018. |
| (b) | Appendix B Exhibit – Daily Adjustment Calculation, incorporated by reference as Exhibit 99(b) to Registrant's initial registration on form S-1 (File No. 333-217303), electronically filed on April 13, 2017. |
| (c)* | Transition Representation Letter - Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm, pursuant to S-K, item 304, filed herewith. |
101.INS* XBRL Instance Document, filed herewith.
101.SCH* XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document, filed herewith.
101.CAL* XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase, filed herewith.
101.DEF* XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase, filed herewith.
101.LAB* XBRL Taxonomy Extension Labels Linkbase, filed herewith.
101.PRE* XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase, filed herewith.
* Filed herewith
(b) Financial Statement Schedules
All required financial statement schedules of Allianz Life Insurance Company of North America are included in Part I of this registration statement.
ITEM 17. UNDERTAKINGS.
The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes pursuant to Item 512 of Regulation S-K:
| (1) | To file, during any period in which offers or sales are being made, a post-effective amendment to this registration statement: | |
| (i) | To include any prospectus required by section 10(a)(3) of the Securities Act of 1933; | |
| (ii) | To reflect in the prospectus any facts or events arising after the effective date of the registration statement (or the most recent post-effective amendment thereof) which, individually or in the aggregate, represent a fundamental change in the information set forth in the registration statement. Notwithstanding the foregoing, any increase or decrease in volume of securities offered (if the total dollar value of securities offered would not exceed that which was registered) and any deviation from the low or high end of the estimated maximum offering range may be reflected in the form of prospectus filed with the Commission pursuant to Rule 424(b) if, in the aggregate, the changes in volume and price represent no more than a 20% change in the maximum aggregate offering price set forth in the "Calculation of Registration Fee" table in the effective registration statement. | |
| (iii) | To include any material information with respect to the plan of distribution not previously disclosed in the registration statement or any material change to such information in the registration statement. | |
| (2) | That, for the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each such post-effective amendment shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof. | |
| (3) | To remove from registration by means of a post-effective amendment any of the securities being registered which remain unsold at the termination of the offering. | |
| (4) | That, for the purpose of determining liability under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser, each prospectus filed pursuant to Rule 424(b) as part of a registration statement relating to an offering, other than registration statements relying on Rule 430B or other than prospectuses filed in reliance on Rule 430A, shall be deemed to be part of and included in the registration statement as of the date it is first used after effectiveness. Provided, however, that no statement made in a registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement or made in a document incorporated or deemed incorporated by reference into the registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement will, as to a purchaser with a time of contract of sale prior to such first use, supersede or modify any statement that was made in the registration statement or prospectus that was part of the registration statement or made in any such document immediately prior to such date of first use. | |
| (5) | That, for the purpose of determining liability of the registrant under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser in the initial distribution of the securities: The undersigned registrant undertakes that in a primary offering of securities of the undersigned registrant pursuant to this registration statement, regardless of the underwriting method used to sell the securities to the purchaser, if the securities are offered or sold to such purchaser by means of any of the following communications, the undersigned registrant will be a seller to the purchaser and will be considered to offer or sell such securities to such purchaser: | |
| (i) | Any preliminary prospectus or prospectus of the undersigned registrant relating to the offering required to be filed pursuant to Rule 424; | |
| (ii) | Any free writing prospectus relating to the offering prepared by or on behalf of the undersigned registrant or used or referred to by the undersigned registrant; | |
| (iii) | The portion of any other free writing prospectus relating to the offering containing material information about the undersigned registrant or its securities provided by or on behalf of the undersigned registrant; and | |
| (iv) | Any other communication that is an offer in the offering made by the undersigned registrant to the purchaser. | |
| (6) | Insofar as indemnification for liability arising under the Securities Act of 1933 may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the Registrant pursuant to the foregoing provisions, or otherwise, the registrant has been advised that, in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission, such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Act and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the registrant in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the registrant will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Act and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue. | |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, the registrant has duly caused this registration statement to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the City of Minneapolis, State of Minnesota, on this 17th day of April, 2018.
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA
By: Walter R. White*
Walter R. White
Chief Executive Officer, President, and Director
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, this registration statement has been signed by the following persons in the capacities indicated on April 17, 2018.
| Signature | Title |
Jacqueline Hunt(1) | Director and Chairman of the Board |
Walter R. White(1) | Director, President & Chief Executive Officer |
Giulio Terzariol(1) | Director |
Ronald M. Clark(1) | Director |
Udo Frank(1) | Director |
William E. Gaumond(1) | Director, Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer |
Kevin E. Walker(1) | Director |
| (1) | By Power of Attorney, incorporated by reference as Exhibit 24(c) from Registrant's initial registration on form S-1 (File No. 333-222817), electronically filed on February 1, 2018. |
BY: /s/ Stewart D. Gregg
Stewart D. Gregg, Senior Counsel
POST-EFFECTIVE AMENDMENT NO. 4
TO
FORM S-1
ALLIANZ LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF NORTH AMERICA
INDEX TO EXHIBITS
| Exhibit | Description of Exhibit |
| 4(c) | Index Options Contract Schedule Page, S40895-ADV |
| 4(d) | Application for Individual Variable Annuity Contract – IXA-APP-01-ADV |
| 23(a) | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm – KPMG LLP |
| 23(b) | Consent of Counsel |
| 99(c) | Transition Representation Letter - Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm |
| 101.INS | XBRL Instance Document |
| 101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
| 101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase |
| 101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase |
| 101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Labels Linkbase |
| 101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase |

