- CATX Dashboard
- Financials
- Filings
-
Holdings
- Transcripts
- ETFs
- Insider
- Institutional
- Shorts
-
8-K Filing
Perspective Therapeutics (CATX) 8-KOther Events
Filed: 3 Feb 25, 4:09pm

Corporate Presentation February 2025 NYSE AMERICAN: CATX

This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the United States Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Statements in this presentation that are not statements of historical fact are forward-looking statements. Words such as “may,” “will,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “could,” “intend,” “target,” “project,” “estimate,” “believe,” “predict,” “potential” or “continue” or the negative of these terms or other similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, though not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words. Forward-looking statements in this presentation include statements concerning, among other things, the Company's clinical development plans and the expected timing thereof; the expected timing for availability and release of data; the Company’s timing and expectations regarding regulatory communications, submissions and approvals; expectations regarding the potential market opportunities for the Company’s product candidates; the Company’s expected cash runway; the potential functionality, capabilities and benefits of the Company’s product candidates and the potential application of these product candidates for other disease indications; the potential size of the commercial market for the Company’s product candidates; the Company’s expectations, beliefs, intentions, and strategies regarding the future; the Company’s intentions to improve important aspects of care in cancer treatment; and other statements that are not historical fact. The Company may not actually achieve the plans, intentions or expectations disclosed in the forward-looking statements and you should not place undue reliance on the forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties that could cause the Company’s actual results to differ materially from the results described in or implied by the forward-looking statements, including, without limitation, the potential that regulatory authorities may not grant or may delay approval for the Company’s product candidates; uncertainties and delays relating to the design, enrollment, completion and results of clinical trials; unanticipated costs and expenses; early clinical trials may not be indicative of the results in later clinical trials; clinical trial results may not support regulatory approval or further development in a specified indication or at all; actions or advice of regulatory authorities may affect the design, initiation, timing, continuation and/or progress of clinical trials or result in the need for additional clinical trials; the Company may not be able to maintain regulatory approval for the Company’s product candidates; delays, interruptions or failures in the manufacture and supply of the Company’s product candidates; the size and growth potential of the markets for the Company’s product candidates, and the Company’s ability to service those markets; the Company’s cash and cash equivalents may not be sufficient to support its operating plan for as long as anticipated; the Company’s expectations, projections and estimates regarding expenses, future revenue, capital requirements and the availability of and the need for additional financing; the Company’s ability to obtain additional funding to support its clinical development programs; the availability or potential availability of alternative products or treatments for conditions targeted by the Company that could affect the availability or commercial potential of its product candidates; the ability of the Company to manage growth; whether the Company can maintain its key employees; the ability of the Company to build out its manufacturing facilities and satisfy manufacturing-related regulatory requirements; whether there is sufficient training and use of the Company’s products and product candidates; the market acceptance and recognition of the Company’s products and product candidates; the Company’s ability to maintain and enforce its intellectual property rights; whether the Company can maintain its therapeutic isotope supply agreement with the DOE; the Company’s ability to maintain and increase its supply, manufacturing and distribution capabilities; whether the Company will continue to comply with the procedures and regulatory requirements mandated by the FDA for additional trials, Phase 1 and 2 approvals, Fast Track approvals, and reimbursement codes; and any changes in applicable laws and regulations. Other factors that may cause the Company’s actual results to differ materially from those expressed or implied in the forward-looking statements in this presentation are described under the heading “Risk Factors” in the Company’s most recent Annual Report on Form 10-K and the Company’s most recent Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q, each filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”), in the Company’s other filings with the SEC, and in the Company’s future reports to be filed with the SEC and available at www.sec.gov. Forward-looking statements contained in this presentation are made as of this date, and the Company undertakes no duty to update such information whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required under applicable law. Legal Disclaimers
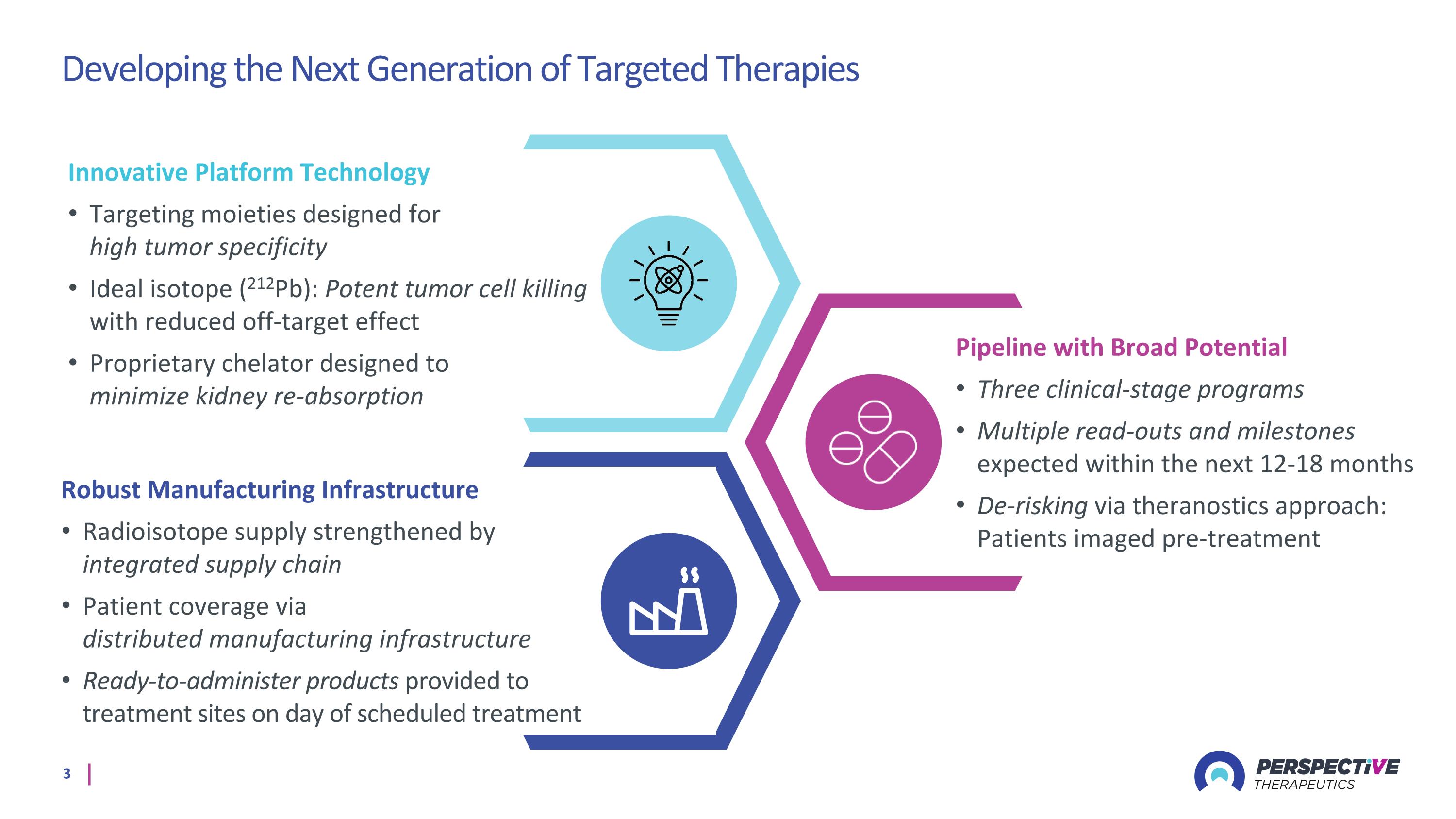
Developing the Next Generation of Targeted Therapies Robust Manufacturing Infrastructure Radioisotope supply strengthened by integrated supply chain Patient coverage via distributed manufacturing infrastructure Ready-to-administer products provided to treatment sites on day of scheduled treatment Innovative Platform Technology Targeting moieties designed for high tumor specificity Ideal isotope (212Pb): Potent tumor cell killing with reduced off-target effect Proprietary chelator designed to minimize kidney re-absorption Pipeline with Broad Potential Three clinical-stage programs Multiple read-outs and milestones expected within the next 12-18 months De-risking via theranostics approach: Patients imaged pre-treatment
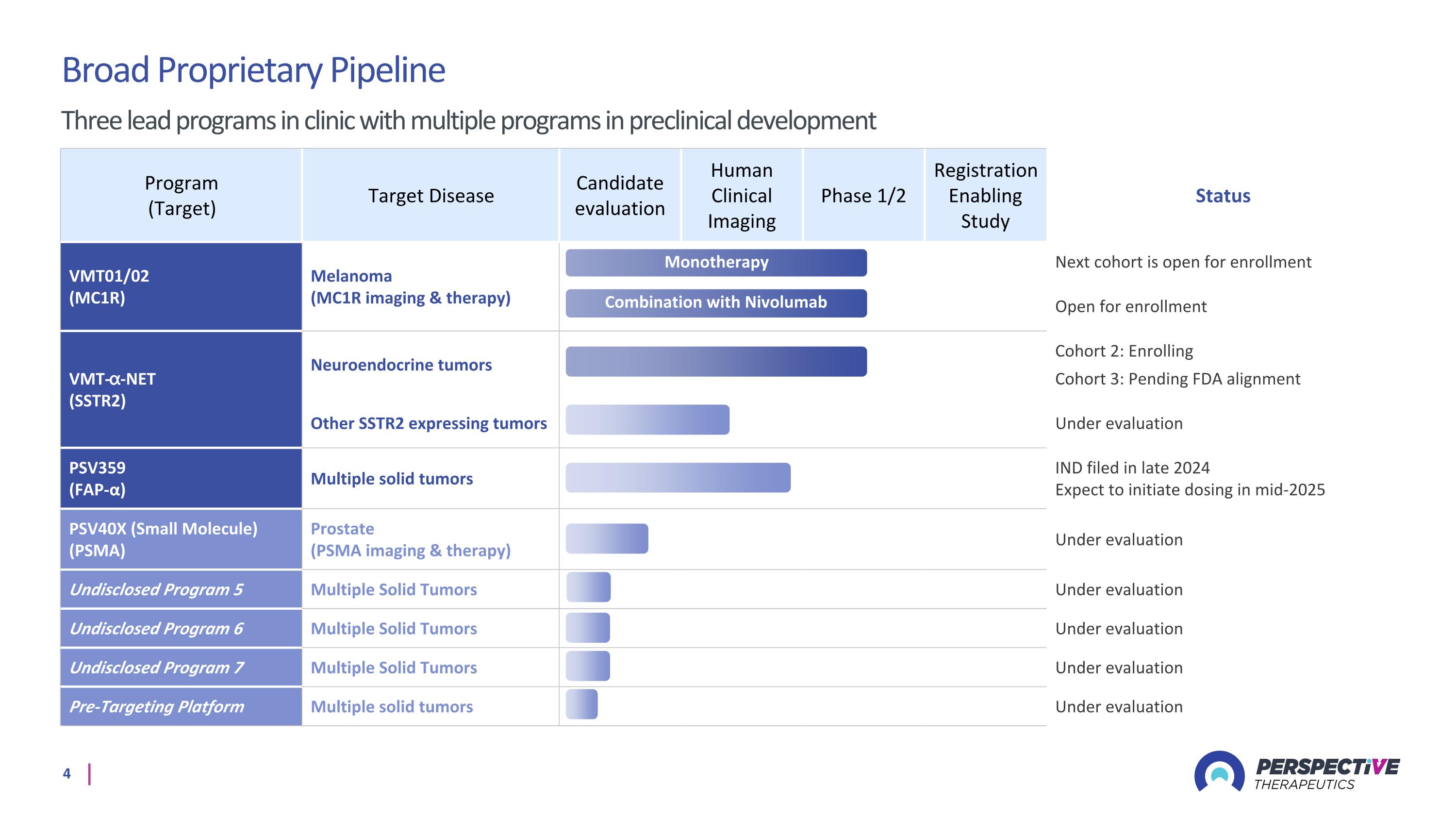
Program (Target) Target Disease Candidate evaluation Human Clinical Imaging Phase 1/2 Registration Enabling Study Status VMT01/02 (MC1R) Melanoma (MC1R imaging & therapy) Next cohort is open for enrollment Open for enrollment VMT-⍺-NET (SSTR2) Neuroendocrine tumors Cohort 2: Enrolling Cohort 3: Pending FDA alignment Other SSTR2 expressing tumors Under evaluation PSV359 (FAP-α) Multiple solid tumors IND filed in late 2024 Expect to initiate dosing in mid-2025 PSV40X (Small Molecule) (PSMA) Prostate (PSMA imaging & therapy) Under evaluation Undisclosed Program 5 Multiple Solid Tumors Under evaluation Undisclosed Program 6 Multiple Solid Tumors Under evaluation Undisclosed Program 7 Multiple Solid Tumors Under evaluation Pre-Targeting Platform Multiple solid tumors Under evaluation Monotherapy Broad Proprietary Pipeline Three lead programs in clinic with multiple programs in preclinical development Combination with Nivolumab
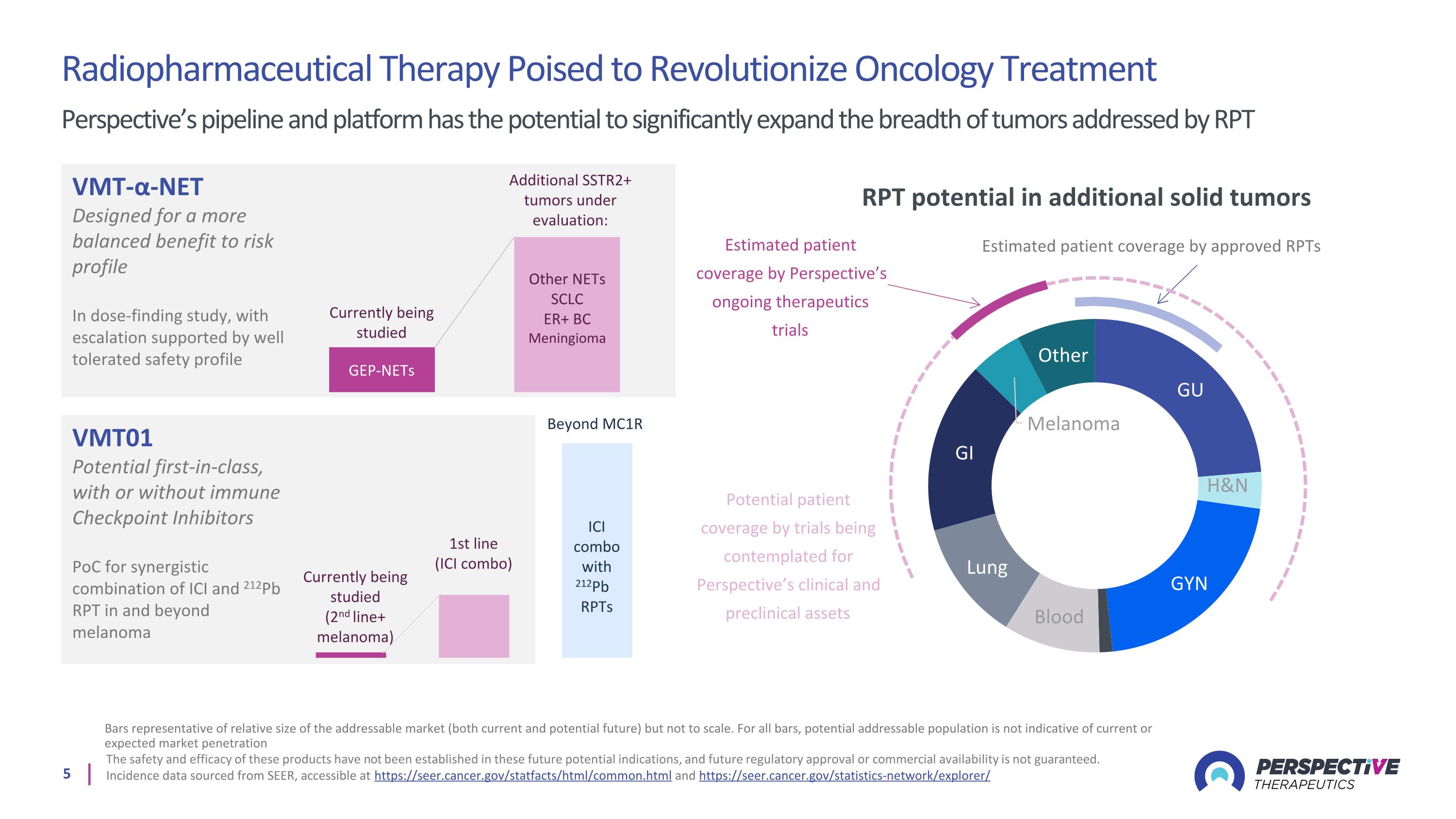
Radiopharmaceutical Therapy Poised to Revolutionize Oncology Treatment Perspective’s pipeline and platform has the potential to significantly expand the breadth of tumors addressed by RPT Bars representative of relative size of the addressable market (both current and potential future) but not to scale. For all bars, potential addressable population is not indicative of current or expected market penetration The safety and efficacy of these products have not been established in these future potential indications, and future regulatory approval or commercial availability is not guaranteed. Incidence data sourced from SEER, accessible at https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/common.html and https://seer.cancer.gov/statistics-network/explorer/ RPT potential in additional solid tumors Estimated patient coverage by approved RPTs Estimated patient coverage by Perspective’s ongoing therapeutics trials Potential patient coverage by trials being contemplated for Perspective’s clinical and preclinical assets VMT-α-NET Designed for a more balanced benefit to risk profile In dose-finding study, with escalation supported by well tolerated safety profile VMT01 Potential first-in-class, with or without immune Checkpoint Inhibitors PoC for synergistic combination of ICI and 212Pb RPT in and beyond melanoma Other NETs SCLC ER+ BC Meningioma GEP-NETs Additional SSTR2+ tumors under evaluation: Currently being studied 1st line (ICI combo) Currently being studied (2nd line+ melanoma) Beyond MC1R ICI combo with 212Pb RPTs
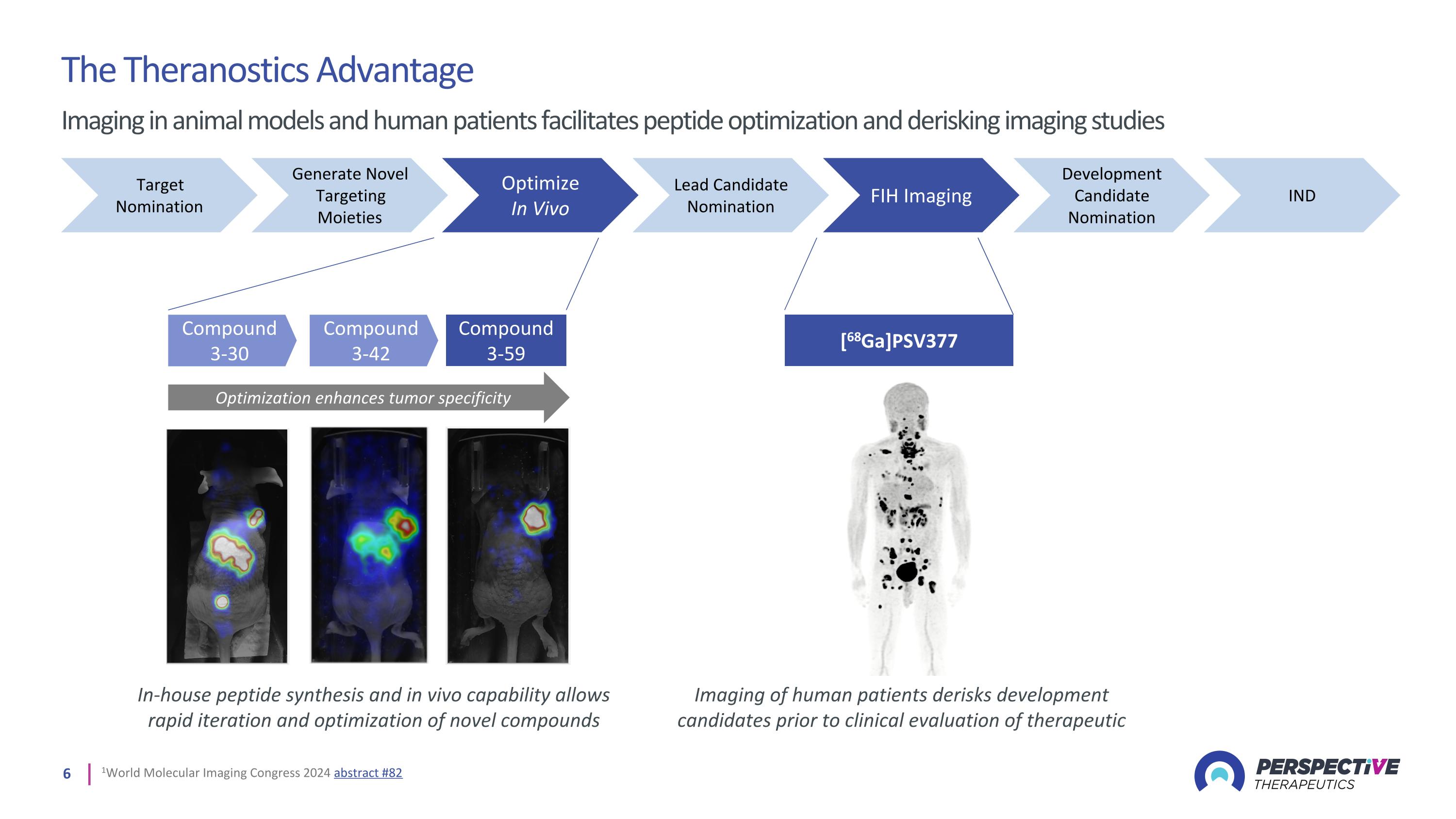
Generate Novel Targeting Moieties Optimize In Vivo Lead Candidate Nomination Development Candidate Nomination IND Target Nomination FIH Imaging Compound 3-30 Compound 3-59 Compound 3-42 Optimization enhances tumor specificity In-house peptide synthesis and in vivo capability allows rapid iteration and optimization of novel compounds 1World Molecular Imaging Congress 2024 abstract #82 The Theranostics Advantage Imaging in animal models and human patients facilitates peptide optimization and derisking imaging studies [68Ga]PSV377 Imaging of human patients derisks development candidates prior to clinical evaluation of therapeutic

Perspective’s Innovative Platform Enabling broad applications in the clinic
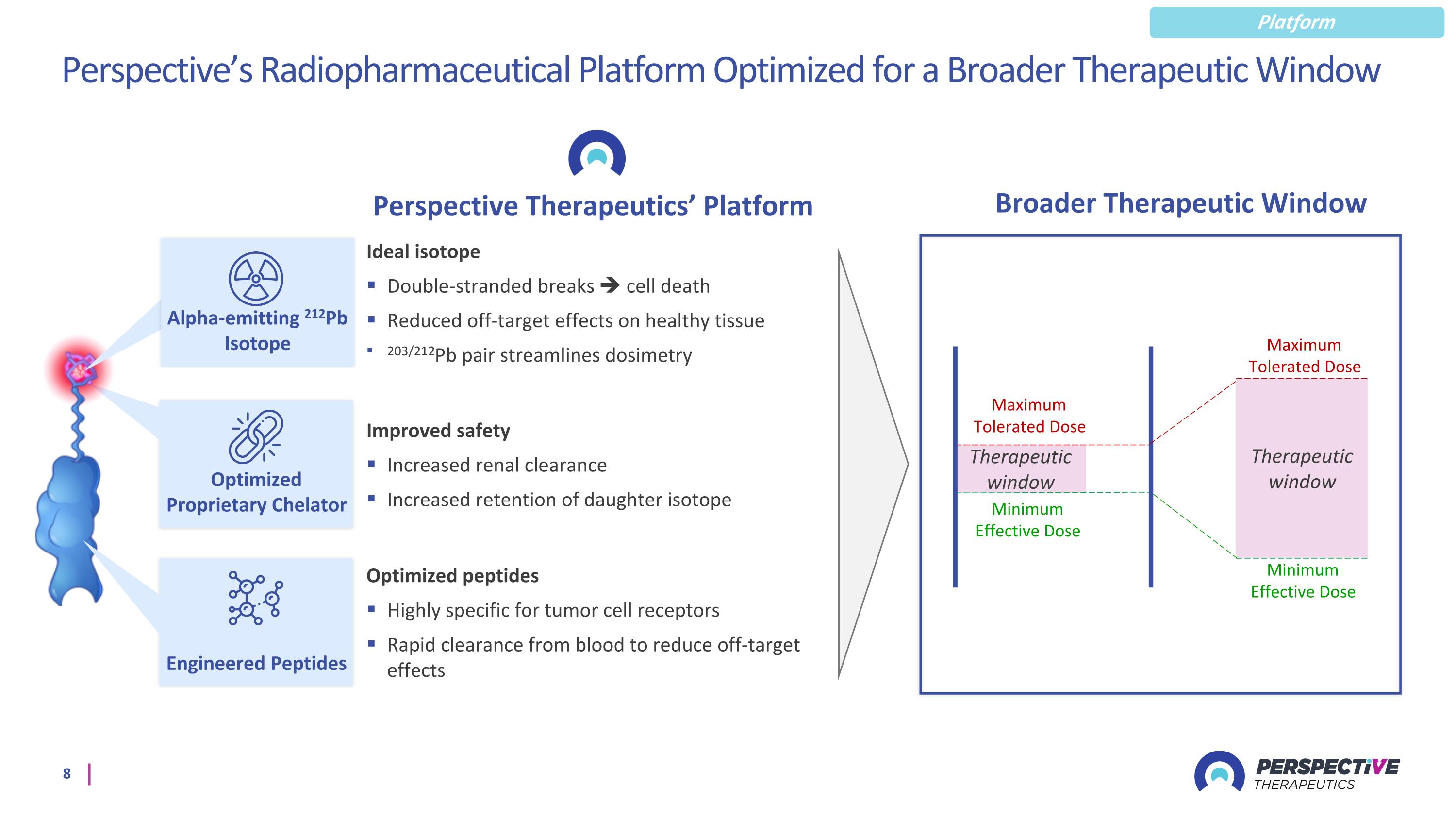
Perspective’s Radiopharmaceutical Platform Optimized for a Broader Therapeutic Window Perspective Therapeutics’ Platform Optimized peptides Highly specific for tumor cell receptors Rapid clearance from blood to reduce off-target effects Ideal isotope Double-stranded breaks cell death Reduced off-target effects on healthy tissue 203/212Pb pair streamlines dosimetry Improved safety Increased renal clearance Increased retention of daughter isotope Minimum Effective Dose Maximum Tolerated Dose Therapeutic window Minimum Effective Dose Maximum Tolerated Dose Therapeutic window Optimized Proprietary Chelator Engineered Peptides Broader Therapeutic Window Platform Alpha-emitting 212Pb Isotope
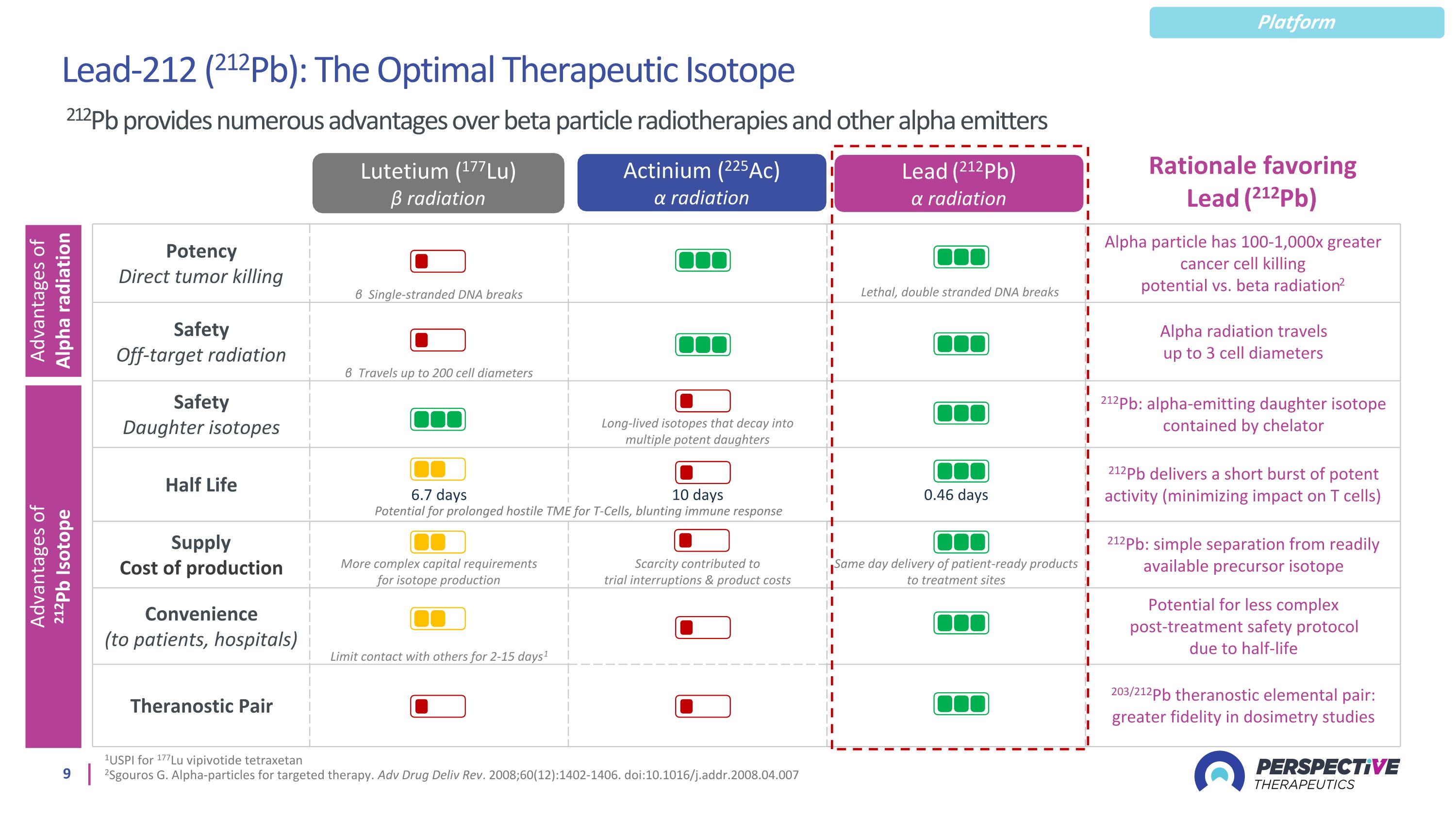
1USPI for 177Lu vipivotide tetraxetan 2Sgouros G. Alpha-particles for targeted therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60(12):1402-1406. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2008.04.007 Lead (212Pb) α radiation Actinium (225Ac) α radiation Lutetium (177Lu) ϐ radiation Potency Direct tumor killing β Single-stranded DNA breaks Alpha particle has 100-1,000x greater cancer cell killing potential vs. beta radiation2 Safety Off-target radiation β Travels up to 200 cell diameters Alpha radiation travels up to 3 cell diameters Safety Daughter isotopes Long-lived isotopes that decay into multiple potent daughters 212Pb: alpha-emitting daughter isotope contained by chelator Half Life 6.7 days 10 days 0.46 days 212Pb delivers a short burst of potent activity (minimizing impact on T cells) Supply Cost of production More complex capital requirements for isotope production Scarcity contributed to trial interruptions & product costs Same day delivery of patient-ready products to treatment sites 212Pb: simple separation from readily available precursor isotope Convenience (to patients, hospitals) Limit contact with others for 2-15 days1 Potential for less complex post-treatment safety protocol due to half-life Theranostic Pair 203/212Pb theranostic elemental pair: greater fidelity in dosimetry studies Advantages of Alpha radiation Advantages of 212Pb Isotope Potential for prolonged hostile TME for T-Cells, blunting immune response Rationale favoring Lead (212Pb) Lead-212 (212Pb): The Optimal Therapeutic Isotope 212Pb provides numerous advantages over beta particle radiotherapies and other alpha emitters Lethal, double stranded DNA breaks Platform
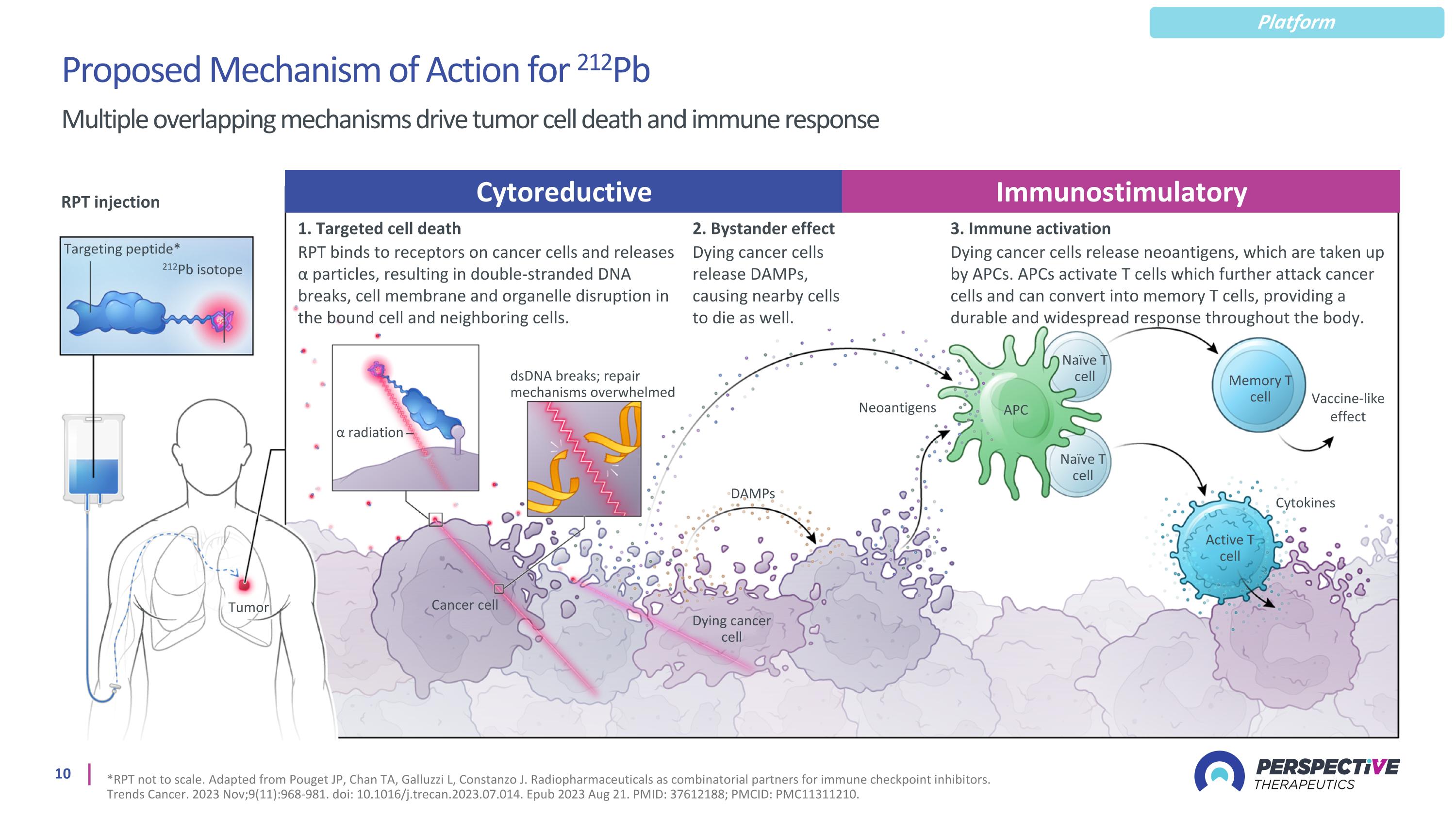
Multiple overlapping mechanisms drive tumor cell death and immune response Proposed Mechanism of Action for 212Pb Platform *RPT not to scale. Adapted from Pouget JP, Chan TA, Galluzzi L, Constanzo J. Radiopharmaceuticals as combinatorial partners for immune checkpoint inhibitors. Trends Cancer. 2023 Nov;9(11):968-981. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2023.07.014. Epub 2023 Aug 21. PMID: 37612188; PMCID: PMC11311210. RPT injection Targeting peptide* 212Pb isotope 1. Targeted cell death RPT binds to receptors on cancer cells and releases α particles, resulting in double-stranded DNA breaks, cell membrane and organelle disruption in the bound cell and neighboring cells. 3. Immune activation Dying cancer cells release neoantigens, which are taken up by APCs. APCs activate T cells which further attack cancer cells and can convert into memory T cells, providing a durable and widespread response throughout the body. α radiation dsDNA breaks; repair mechanisms overwhelmed Neoantigens Tumor Dying cancer cell DAMPs Cancer cell APC Naïve T cell Naïve T cell Memory T cell Active T cell Cytokines Vaccine-like effect Cytoreductive Immunostimulatory 2. Bystander effect Dying cancer cells release DAMPs, causing nearby cells to die as well.
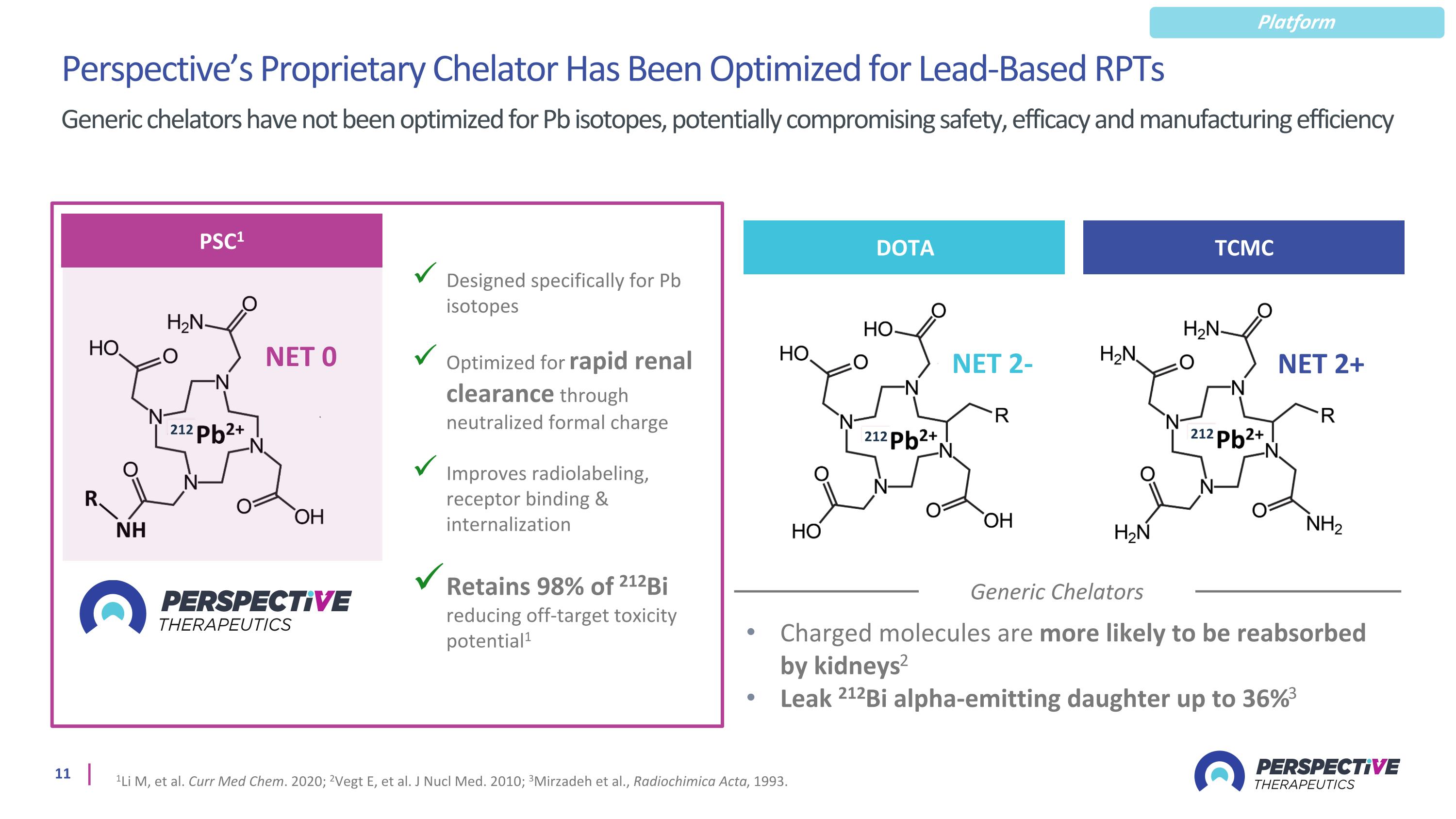
Perspective’s Proprietary Chelator Has Been Optimized for Lead-Based RPTs Generic chelators have not been optimized for Pb isotopes, potentially compromising safety, efficacy and manufacturing efficiency 1Li M, et al. Curr Med Chem. 2020; 2Vegt E, et al. J Nucl Med. 2010; 3Mirzadeh et al., Radiochimica Acta, 1993. Generic Chelators Charged molecules are more likely to be reabsorbed by kidneys2 Leak 212Bi alpha-emitting daughter up to 36%3 Designed specifically for Pb isotopes Optimized for rapid renal clearance through neutralized formal charge Improves radiolabeling, receptor binding & internalization Retains 98% of 212Bi reducing off-target toxicity potential1 PSC1 NET 0 212 DOTA NET 2- 212 TCMC NET 2+ 212 Platform
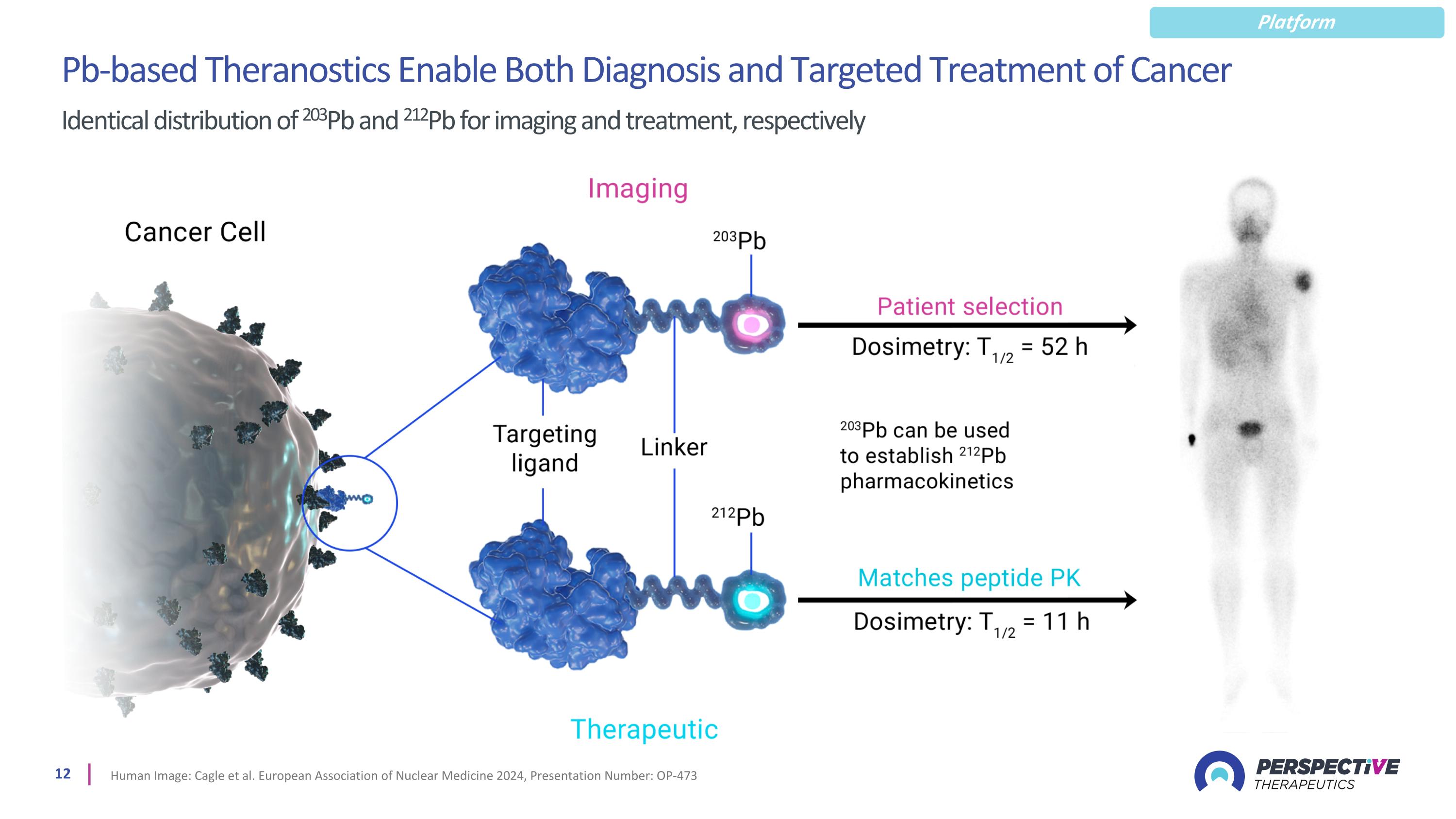
Pb-based Theranostics Enable Both Diagnosis and Targeted Treatment of Cancer Identical distribution of 203Pb and 212Pb for imaging and treatment, respectively Human Image: Cagle et al. European Association of Nuclear Medicine 2024, Presentation Number: OP-473 Platform
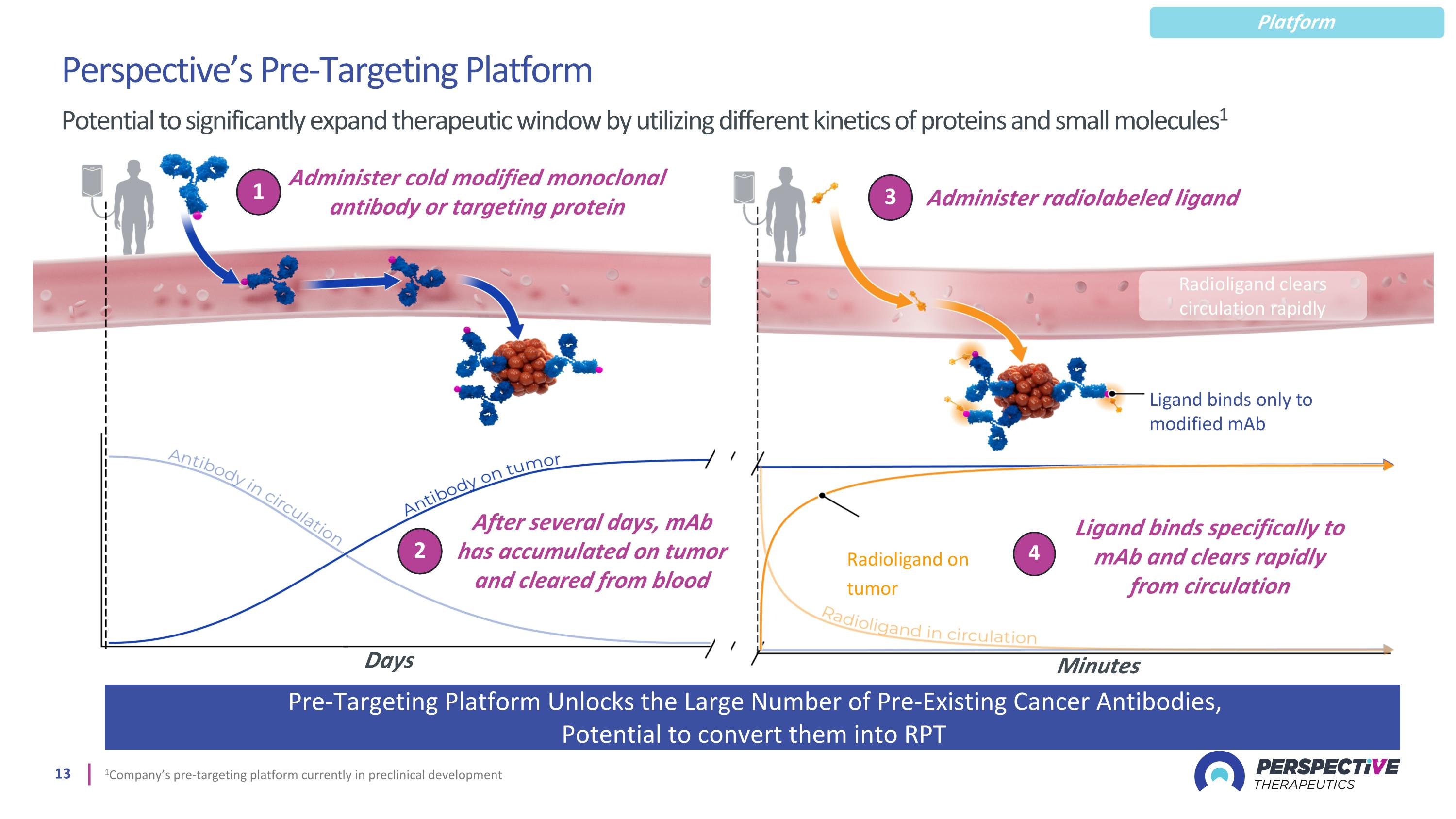
1 Administer cold modified monoclonal antibody or targeting protein Perspective’s Pre-Targeting Platform Potential to significantly expand therapeutic window by utilizing different kinetics of proteins and small molecules1 Minutes 1Company’s pre-targeting platform currently in preclinical development Pre-Targeting Platform Unlocks the Large Number of Pre-Existing Cancer Antibodies, Potential to convert them into RPT 2 After several days, mAb has accumulated on tumor and cleared from blood Ligand binds specifically to mAb and clears rapidly from circulation 3 Administer radiolabeled ligand Minutes Days Platform
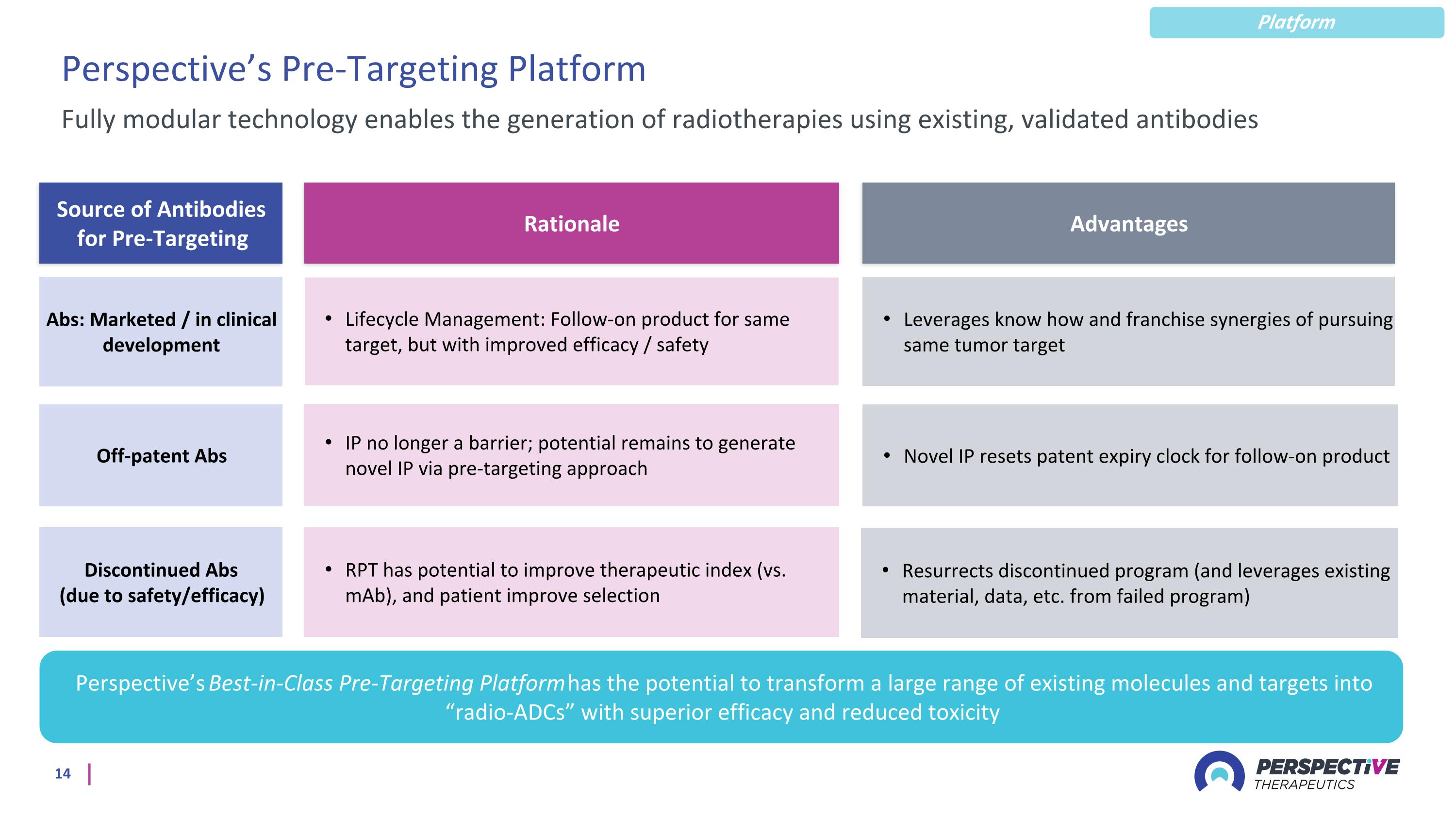
Perspective’s Pre-Targeting Platform Fully modular technology enables the generation of radiotherapies using existing, validated antibodies Abs: Marketed / in clinical development Off-patent Abs Discontinued Abs (due to safety/efficacy) Lifecycle Management: Follow-on product for same target, but with improved efficacy / safety Novel IP resets patent expiry clock for follow-on product RPT has potential to improve therapeutic index (vs. mAb), and patient improve selection Perspective’s Best-in-Class Pre-Targeting Platform has the potential to transform a large range of existing molecules and targets into “radio-ADCs” with superior efficacy and reduced toxicity Leverages know how and franchise synergies of pursuing same tumor target IP no longer a barrier; potential remains to generate novel IP via pre-targeting approach Resurrects discontinued program (and leverages existing material, data, etc. from failed program) Rationale Source of Antibodies for Pre-Targeting Advantages Platform

Supply Chain and Manufacturing Infrastructure Ensuring radioisotope supply and ability to deliver ready-to-administer products to hospitals
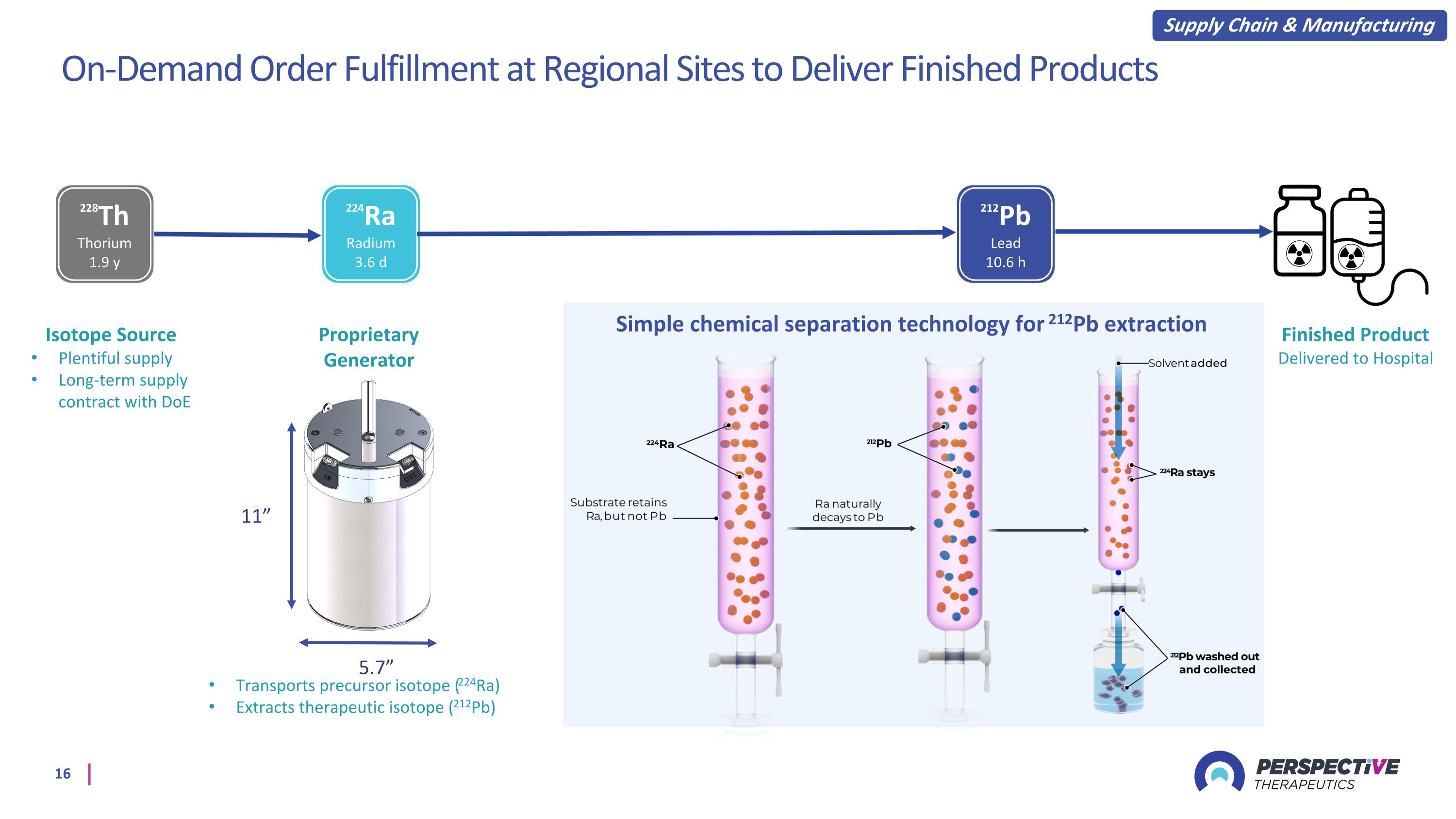
On-Demand Order Fulfillment at Regional Sites to Deliver Finished Products 5.7” 11” Proprietary Generator Simple chemical separation technology for 212Pb extraction 228Th Thorium 1.9 y 224Ra Radium 3.6 d 212Pb Lead 10.6 h Transports precursor isotope (224Ra) Extracts therapeutic isotope (212Pb) Isotope Source Plentiful supply Long-term supply contract with DoE Supply Chain & Manufacturing Finished Product Delivered to Hospital
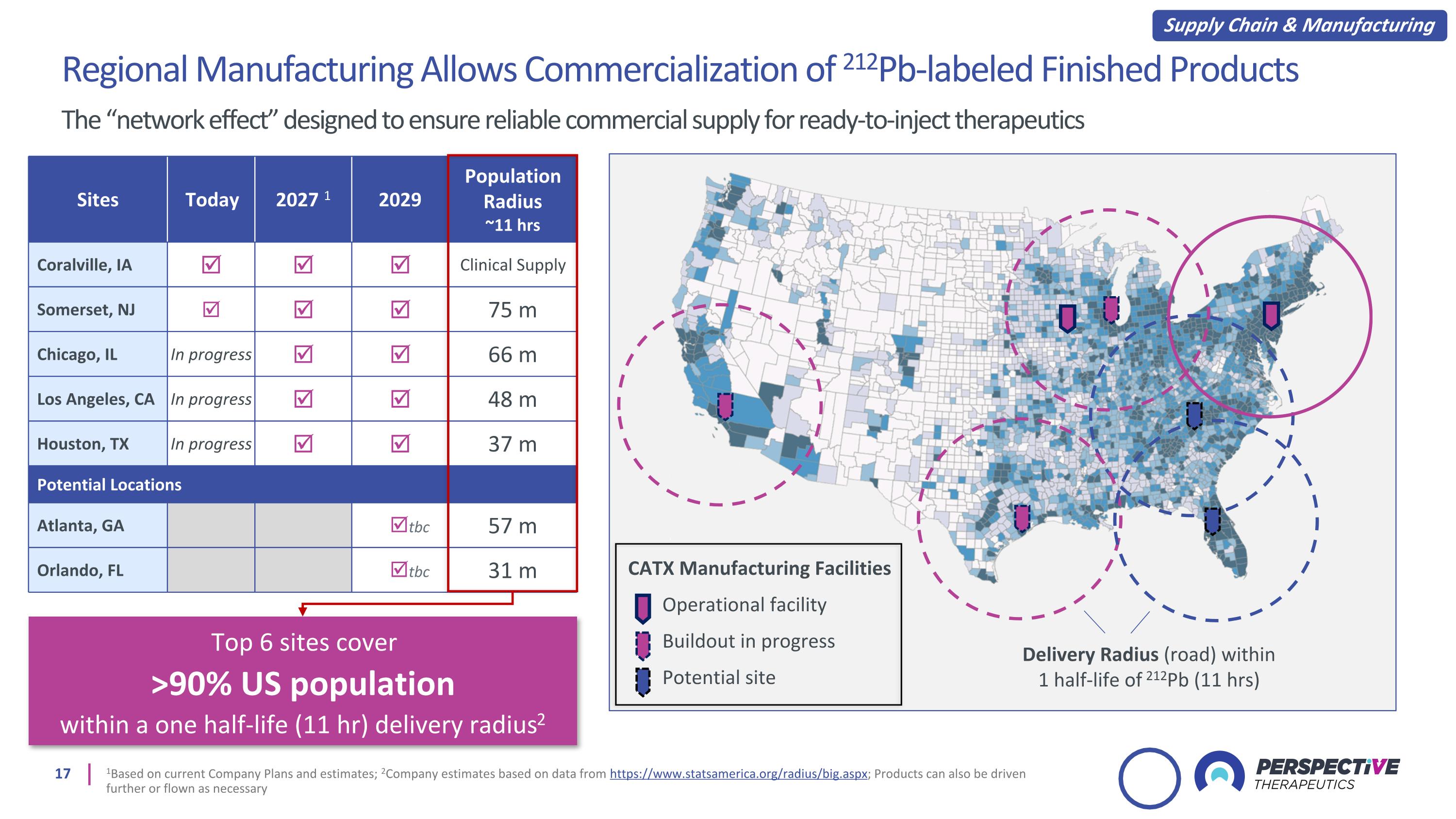
Sites Today 2027 1 2029 Population Radius ~11 hrs Coralville, IA Clinical Supply Somerset, NJ 75 m Chicago, IL In progress 66 m Los Angeles, CA In progress 48 m Houston, TX In progress 37 m Potential Locations Atlanta, GA tbc 57 m Orlando, FL tbc 31 m Top 6 sites cover >90% US population within a one half-life (11 hr) delivery radius2 Regional Manufacturing Allows Commercialization of 212Pb-labeled Finished Products The “network effect” designed to ensure reliable commercial supply for ready-to-inject therapeutics 1Based on current Company Plans and estimates; 2Company estimates based on data from https://www.statsamerica.org/radius/big.aspx; Products can also be driven further or flown as necessary CATX Manufacturing Facilities Operational facility Buildout in progress Potential site Delivery Radius (road) within 1 half-life of 212Pb (11 hrs) Supply Chain & Manufacturing

Neuroendocrine Tumors: VMT-⍺-NET Targeting the somatostatin receptor to treat rare neuroendocrine-type cancers
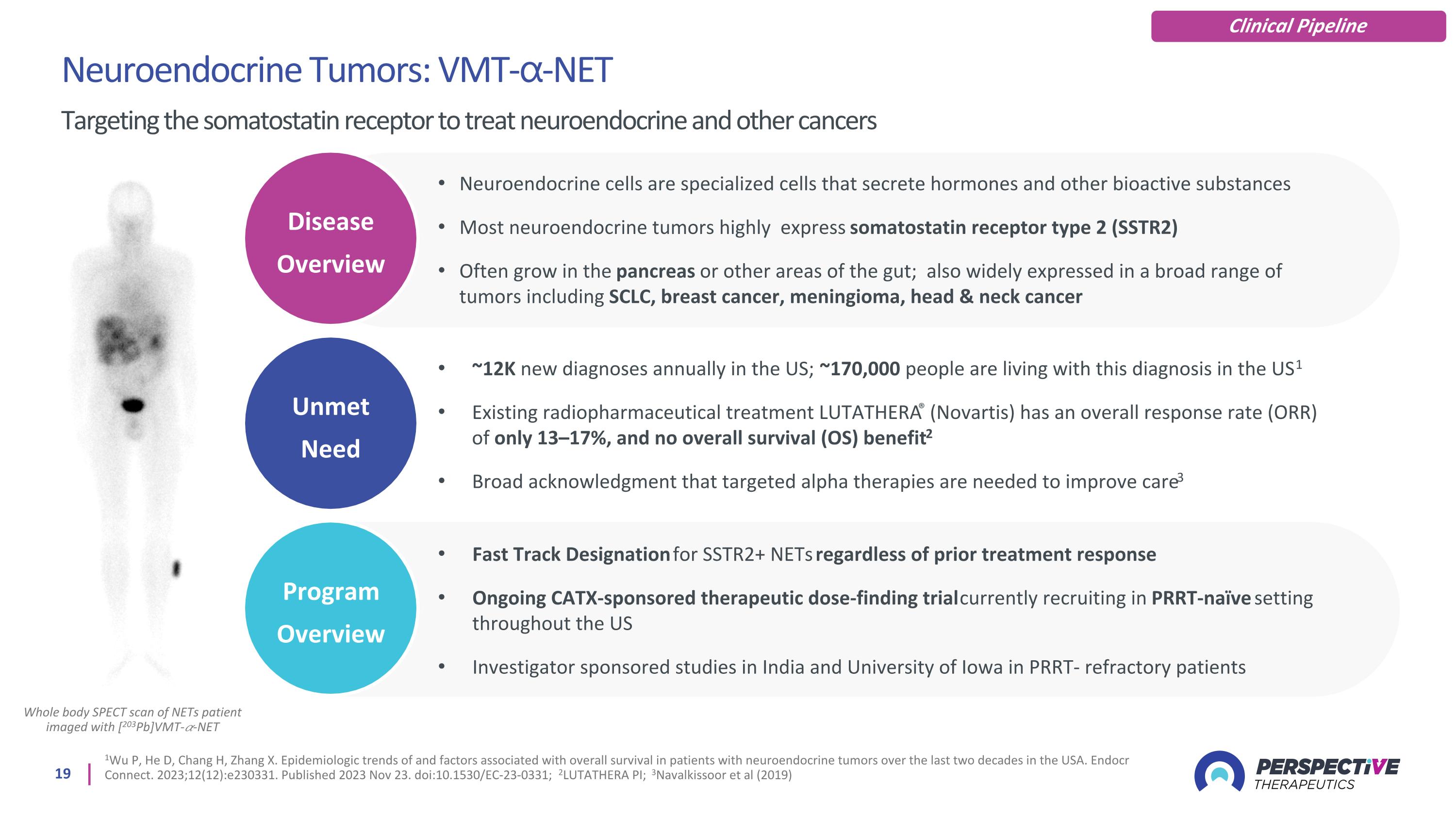
Whole body SPECT scan of NETs patient imaged with [203Pb]VMT-𝛼-NET Neuroendocrine Tumors: VMT-⍺-NET Targeting the somatostatin receptor to treat neuroendocrine and other cancers Clinical Pipeline Unmet Need Disease Overview Program Overview 1Wu P, He D, Chang H, Zhang X. Epidemiologic trends of and factors associated with overall survival in patients with neuroendocrine tumors over the last two decades in the USA. Endocr Connect. 2023;12(12):e230331. Published 2023 Nov 23. doi:10.1530/EC-23-0331; 2LUTATHERA PI; 3Navalkissoor et al (2019) Neuroendocrine cells are specialized cells that secrete hormones and other bioactive substances Most neuroendocrine tumors highly express somatostatin receptor type 2 (SSTR2) Often grow in the pancreas or other areas of the gut; also widely expressed in a broad range of tumors including SCLC, breast cancer, meningioma, head & neck cancer ~12K new diagnoses annually in the US; ~170,000 people are living with this diagnosis in the US1 Existing radiopharmaceutical treatment LUTATHERA® (Novartis) has an overall response rate (ORR) of only 13–17%, and no overall survival (OS) benefit2 Broad acknowledgment that targeted alpha therapies are needed to improve care3 Fast Track Designation for SSTR2+ NETs regardless of prior treatment response Ongoing CATX-sponsored therapeutic dose-finding trial currently recruiting in PRRT-naïve setting throughout the US Investigator sponsored studies in India and University of Iowa in PRRT- refractory patients
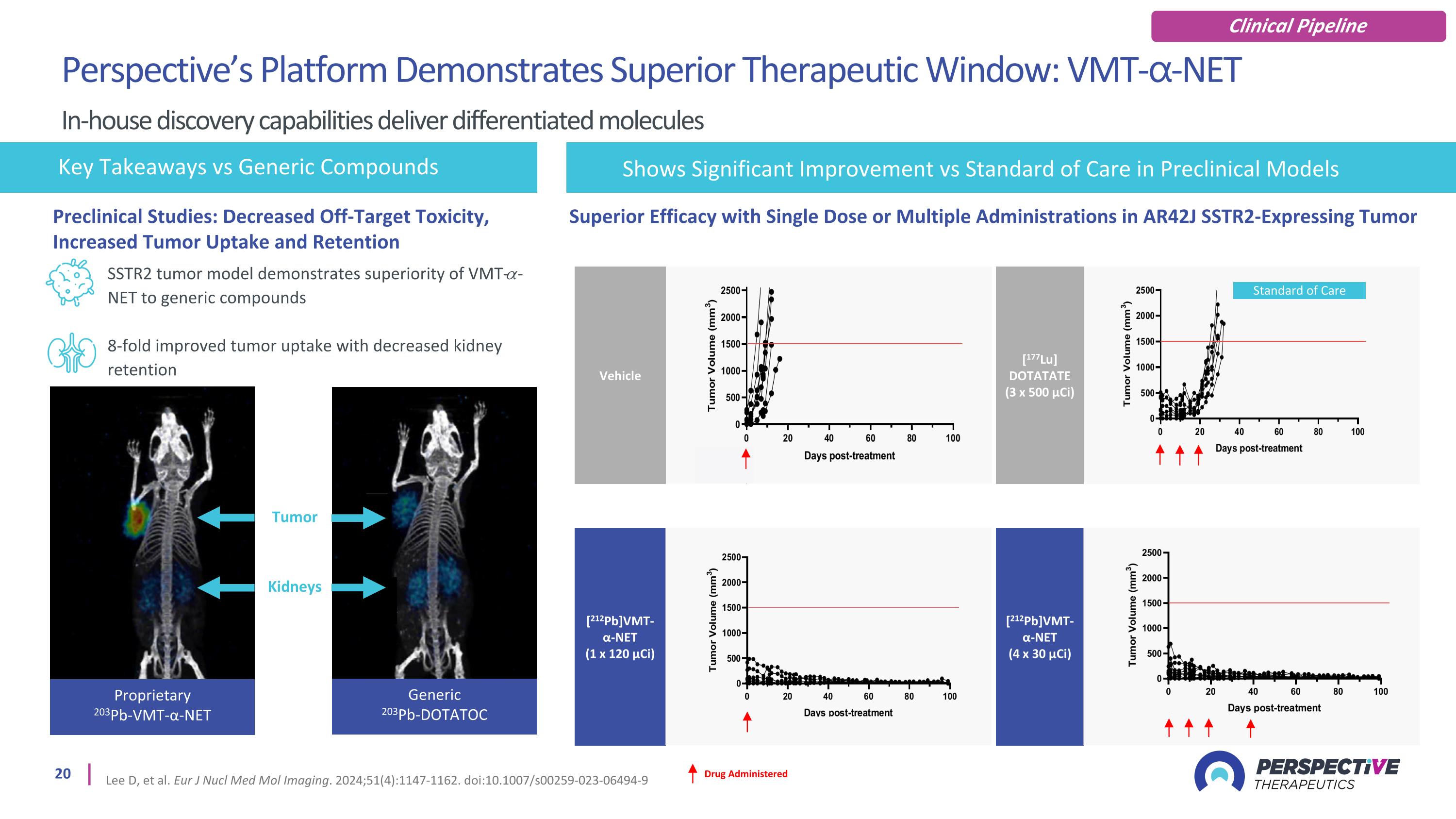
SSTR2 tumor model demonstrates superiority of VMT-𝛼-NET to generic compounds 8-fold improved tumor uptake with decreased kidney retention Key Takeaways vs Generic Compounds Generic 203Pb-DOTATOC Proprietary 203Pb-VMT-α-NET Tumor Kidneys Drug Administered [212Pb]VMT-α-NET (1 x 120 µCi) Vehicle [212Pb]VMT-α-NET (4 x 30 µCi) [177Lu] DOTATATE (3 x 500 µCi) Standard of Care Superior Efficacy with Single Dose or Multiple Administrations in AR42J SSTR2-Expressing Tumor Shows Significant Improvement vs Standard of Care in Preclinical Models Preclinical Studies: Decreased Off-Target Toxicity, Increased Tumor Uptake and Retention Perspective’s Platform Demonstrates Superior Therapeutic Window: VMT-⍺-NET In-house discovery capabilities deliver differentiated molecules Lee D, et al. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024;51(4):1147-1162. doi:10.1007/s00259-023-06494-9 Clinical Pipeline
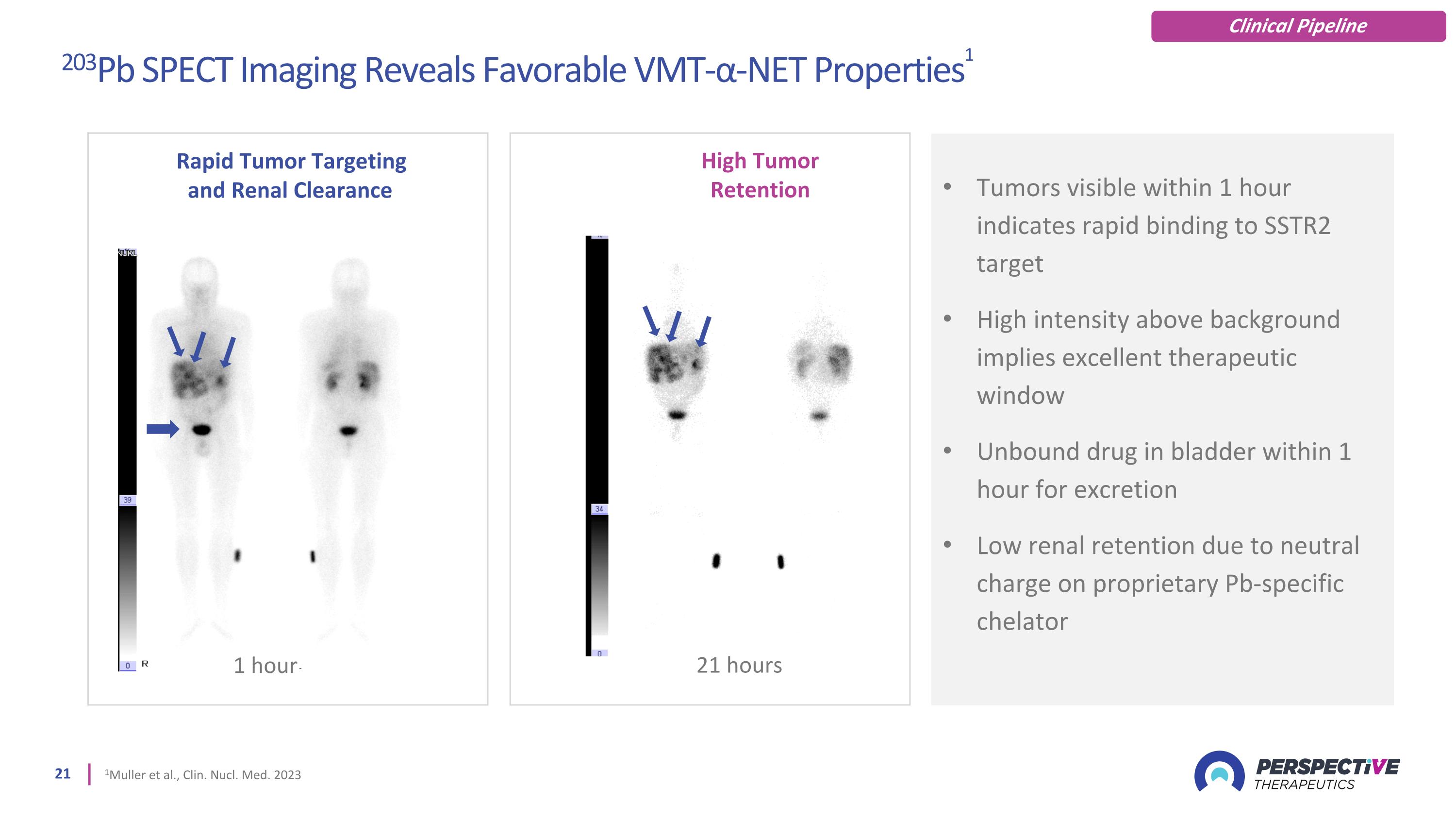
Tumors visible within 1 hour indicates rapid binding to SSTR2 target High intensity above background implies excellent therapeutic window Unbound drug in bladder within 1 hour for excretion Low renal retention due to neutral charge on proprietary Pb-specific chelator 21 hours Rapid Tumor Targeting and Renal Clearance 1 hour High Tumor Retention 203Pb SPECT Imaging Reveals Favorable VMT-α-NET Properties1 1Muller et al., Clin. Nucl. Med. 2023 Clinical Pipeline
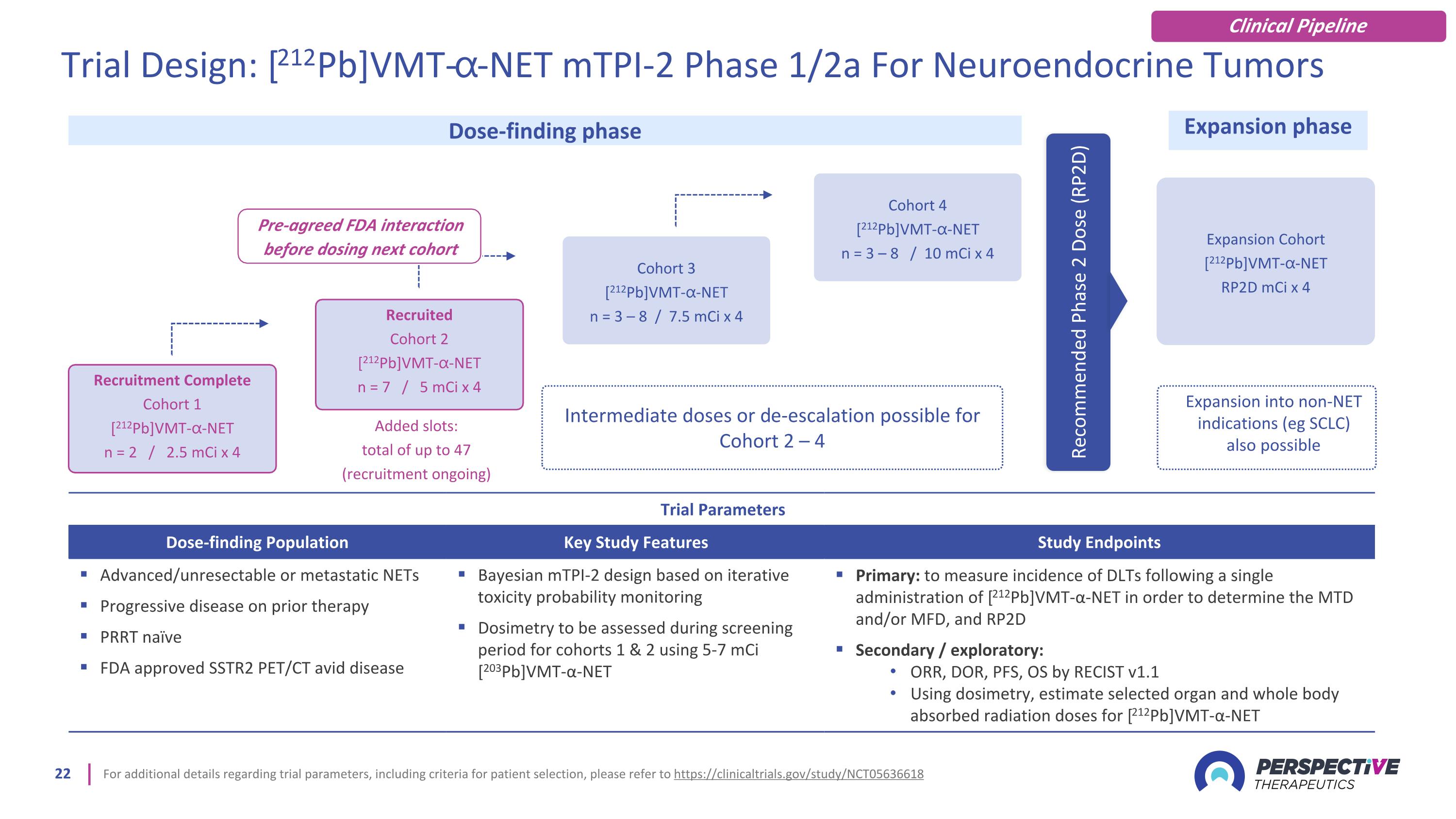
For additional details regarding trial parameters, including criteria for patient selection, please refer to https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05636618 Trial Parameters Dose-finding Population Key Study Features Study Endpoints Advanced/unresectable or metastatic NETs Progressive disease on prior therapy PRRT naïve FDA approved SSTR2 PET/CT avid disease Bayesian mTPI-2 design based on iterative toxicity probability monitoring Dosimetry to be assessed during screening period for cohorts 1 & 2 using 5-7 mCi [203Pb]VMT-α-NET Primary: to measure incidence of DLTs following a single administration of [212Pb]VMT-α-NET in order to determine the MTD and/or MFD, and RP2D Secondary / exploratory: ORR, DOR, PFS, OS by RECIST v1.1 Using dosimetry, estimate selected organ and whole body absorbed radiation doses for [212Pb]VMT-α-NET Expansion Cohort [212Pb]VMT-⍺-NET RP2D mCi x 4 Dose-finding phase Expansion phase Expansion into non-NET indications (eg SCLC) also possible Recommended Phase 2 Dose (RP2D) Recruitment Complete Cohort 1 [212Pb]VMT-⍺-NET n = 2 / 2.5 mCi x 4 Recruited Cohort 2 [212Pb]VMT-⍺-NET n = 7 / 5 mCi x 4 Cohort 3 [212Pb]VMT-⍺-NET n = 3 – 8 / 7.5 mCi x 4 Cohort 4 [212Pb]VMT-⍺-NET n = 3 – 8 / 10 mCi x 4 Intermediate doses or de-escalation possible for Cohort 2 – 4 Added slots: total of up to 47 (recruitment ongoing) Trial Design: [212Pb]VMT-⍺-NET mTPI-2 Phase 1/2a For Neuroendocrine Tumors Pre-agreed FDA interaction before dosing next cohort Clinical Pipeline
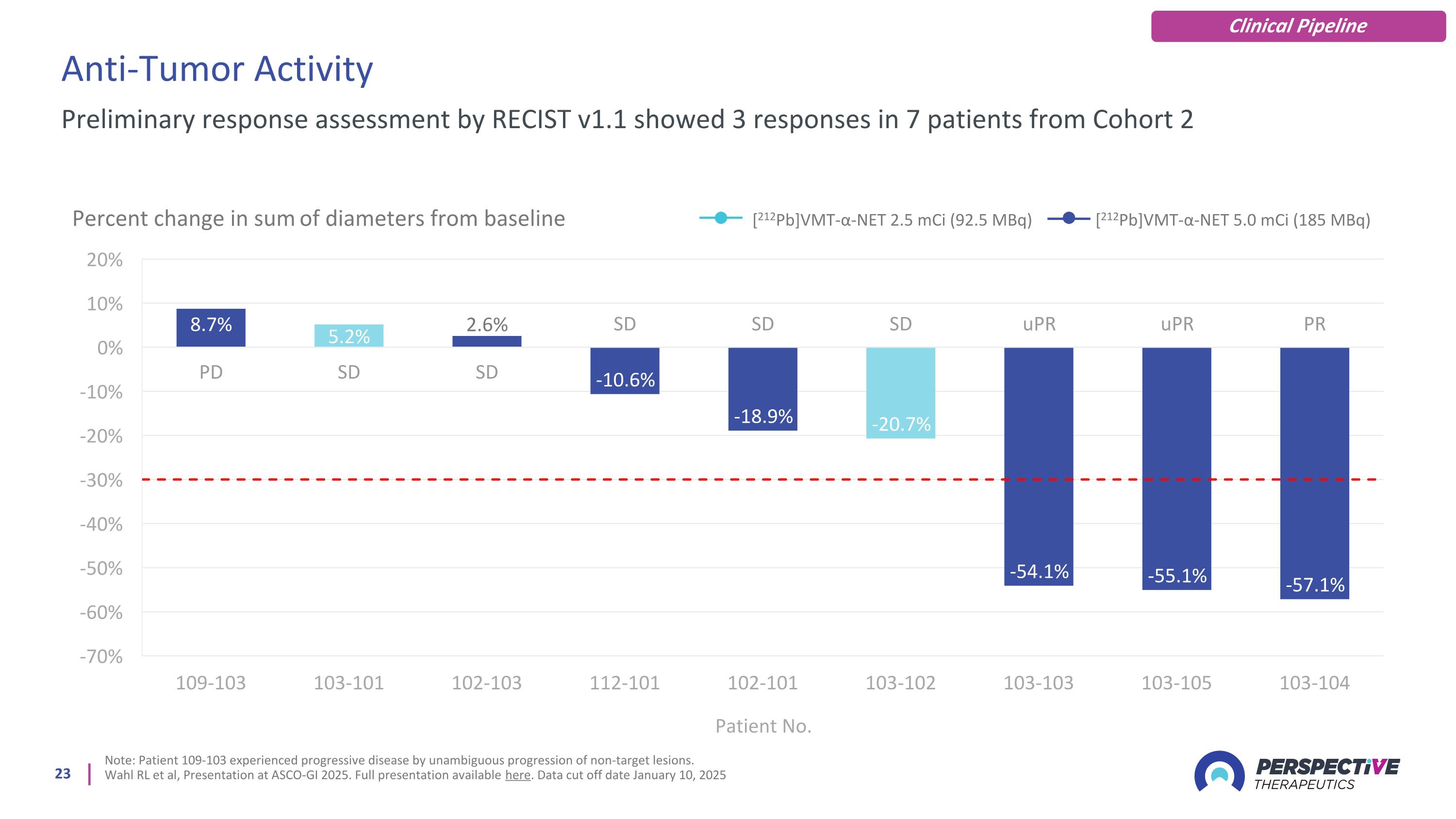
Anti-Tumor Activity Note: Patient 109-103 experienced progressive disease by unambiguous progression of non-target lesions. Wahl RL et al, Presentation at ASCO-GI 2025. Full presentation available here. Data cut off date January 10, 2025 Preliminary response assessment by RECIST v1.1 showed 3 responses in 7 patients from Cohort 2 Clinical Pipeline Percent change in sum of diameters from baseline [212Pb]VMT-α-NET 2.5 mCi (92.5 MBq) [212Pb]VMT-α-NET 5.0 mCi (185 MBq)
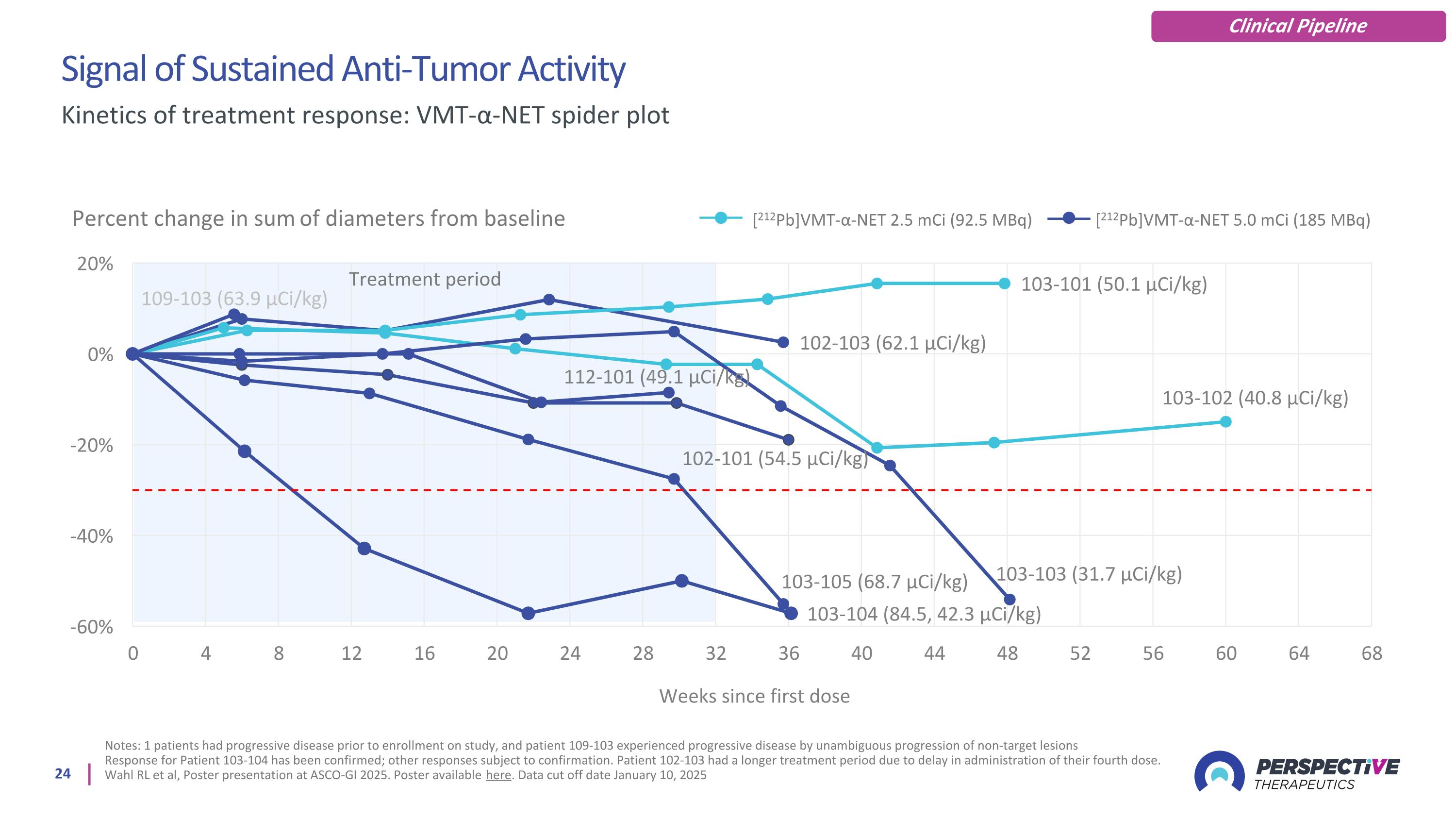
Signal of Sustained Anti-Tumor Activity Notes: 1 patients had progressive disease prior to enrollment on study, and patient 109-103 experienced progressive disease by unambiguous progression of non-target lesions Response for Patient 103-104 has been confirmed; other responses subject to confirmation. Patient 102-103 had a longer treatment period due to delay in administration of their fourth dose. Wahl RL et al, Poster presentation at ASCO-GI 2025. Poster available here. Data cut off date January 10, 2025 Kinetics of treatment response: VMT-α-NET spider plot Percent change in sum of diameters from baseline [212Pb]VMT-α-NET 2.5 mCi (92.5 MBq) [212Pb]VMT-α-NET 5.0 mCi (185 MBq) Treatment period Clinical Pipeline
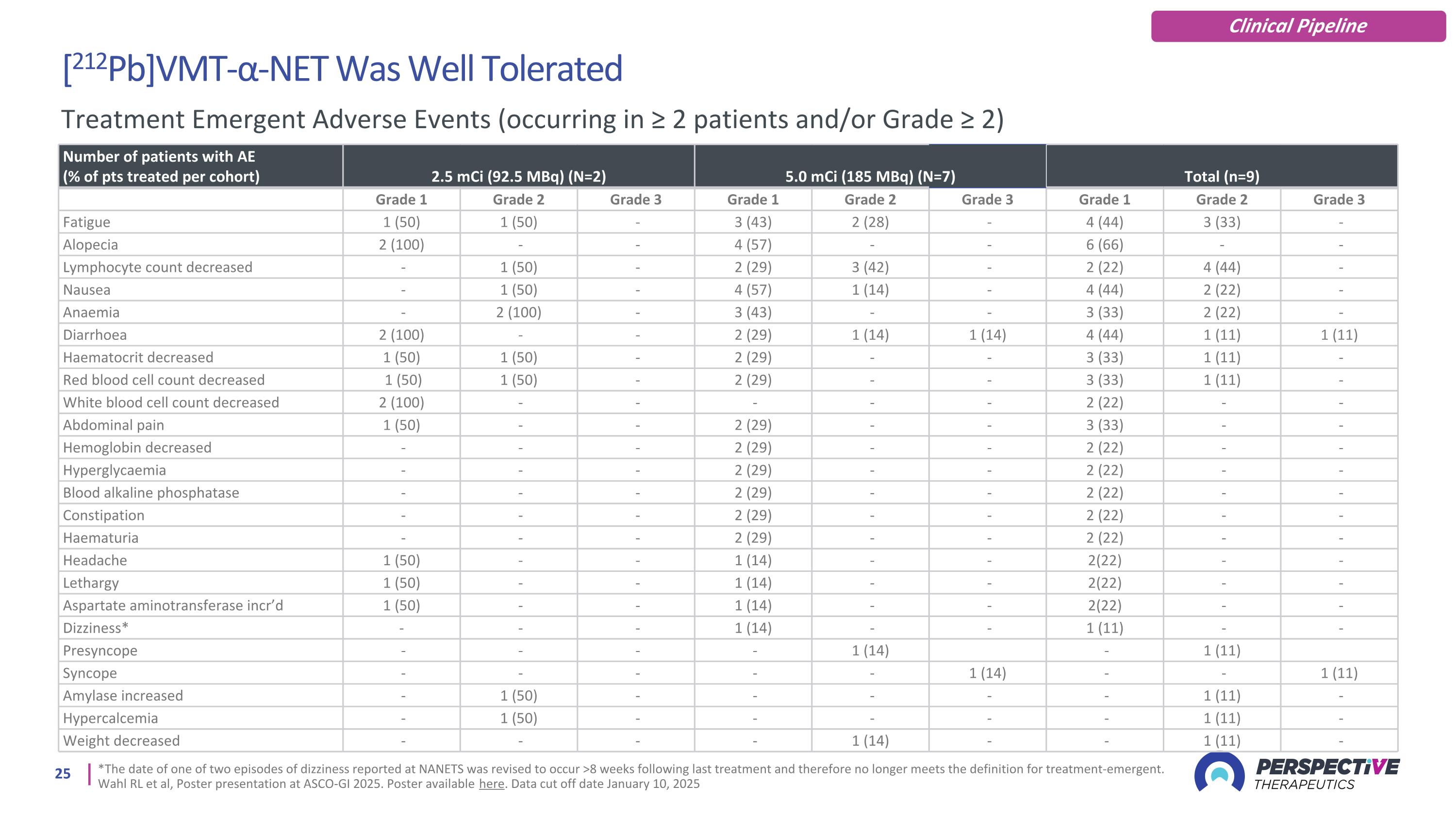
[212Pb]VMT-α-NET Was Well Tolerated *The date of one of two episodes of dizziness reported at NANETS was revised to occur >8 weeks following last treatment and therefore no longer meets the definition for treatment-emergent. Wahl RL et al, Poster presentation at ASCO-GI 2025. Poster available here. Data cut off date January 10, 2025 Number of patients with AE (% of pts treated per cohort) 2.5 mCi (92.5 MBq) (N=2) 5.0 mCi (185 MBq) (N=7) Total (n=9) Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Fatigue 1 (50) 1 (50) - 3 (43) 2 (28) - 4 (44) 3 (33) - Alopecia 2 (100) - - 4 (57) - - 6 (66) - - Lymphocyte count decreased - 1 (50) - 2 (29) 3 (42) - 2 (22) 4 (44) - Nausea - 1 (50) - 4 (57) 1 (14) - 4 (44) 2 (22) - Anaemia - 2 (100) - 3 (43) - - 3 (33) 2 (22) - Diarrhoea 2 (100) - - 2 (29) 1 (14) 1 (14) 4 (44) 1 (11) 1 (11) Haematocrit decreased 1 (50) 1 (50) - 2 (29) - - 3 (33) 1 (11) - Red blood cell count decreased 1 (50) 1 (50) - 2 (29) - - 3 (33) 1 (11) - White blood cell count decreased 2 (100) - - - - - 2 (22) - - Abdominal pain 1 (50) - - 2 (29) - - 3 (33) - - Hemoglobin decreased - - - 2 (29) - - 2 (22) - - Hyperglycaemia - - - 2 (29) - - 2 (22) - - Blood alkaline phosphatase - - - 2 (29) - - 2 (22) - - Constipation - - - 2 (29) - - 2 (22) - - Haematuria - - - 2 (29) - - 2 (22) - - Headache 1 (50) - - 1 (14) - - 2(22) - - Lethargy 1 (50) - - 1 (14) - - 2(22) - - Aspartate aminotransferase incr’d 1 (50) - - 1 (14) - - 2(22) - - Dizziness* - - - 1 (14) - - 1 (11) - - Presyncope - - - - 1 (14) - 1 (11) Syncope - - - - - 1 (14) - - 1 (11) Amylase increased - 1 (50) - - - - - 1 (11) - Hypercalcemia - 1 (50) - - - - - 1 (11) - Weight decreased - - - - 1 (14) - - 1 (11) - Treatment Emergent Adverse Events (occurring in ≥ 2 patients and/or Grade ≥ 2) Clinical Pipeline
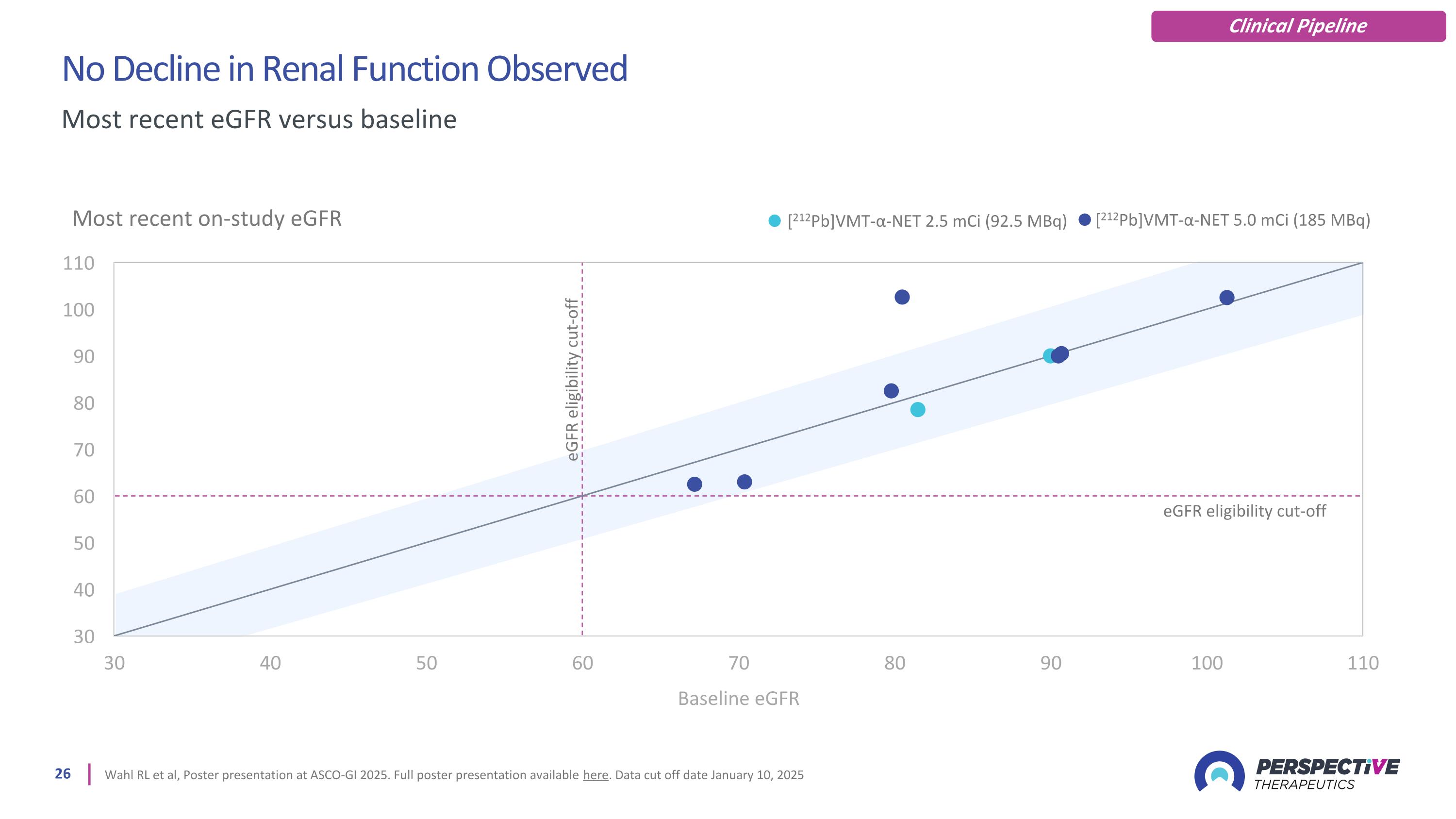
No Decline in Renal Function Observed Wahl RL et al, Poster presentation at ASCO-GI 2025. Full poster presentation available here. Data cut off date January 10, 2025 Most recent eGFR versus baseline Most recent on-study eGFR [212Pb]VMT-α-NET 2.5 mCi (92.5 MBq) [212Pb]VMT-α-NET 5.0 mCi (185 MBq) eGFR eligibility cut-off eGFR eligibility cut-off Clinical Pipeline
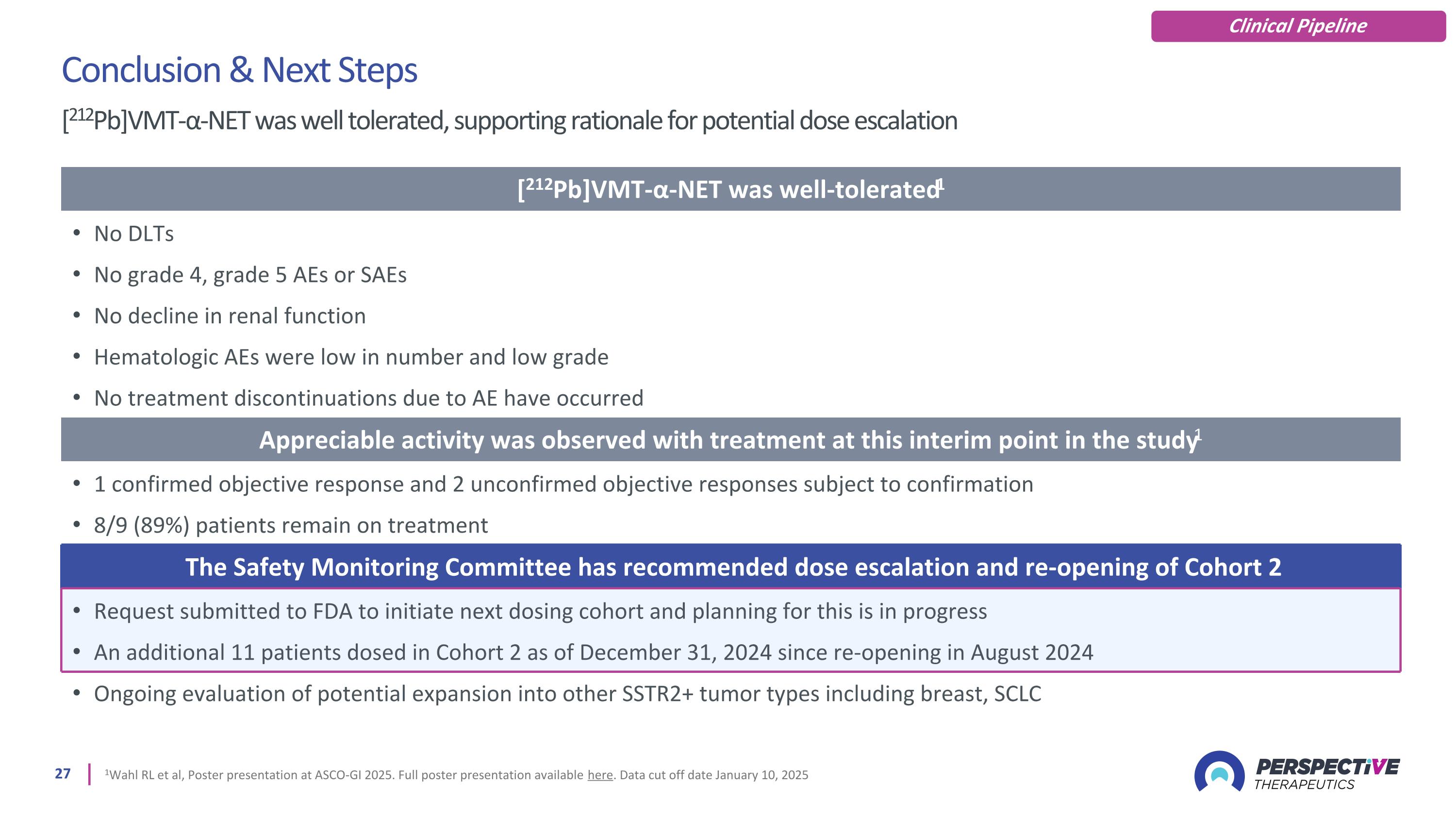
1Wahl RL et al, Poster presentation at ASCO-GI 2025. Full poster presentation available here. Data cut off date January 10, 2025 Conclusion & Next Steps [212Pb]VMT-α-NET was well tolerated, supporting rationale for potential dose escalation Clinical Pipeline [212Pb]VMT-α-NET was well-tolerated1 No DLTs No grade 4, grade 5 AEs or SAEs No decline in renal function Hematologic AEs were low in number and low grade No treatment discontinuations due to AE have occurred Appreciable activity was observed with treatment at this interim point in the study1 1 confirmed objective response and 2 unconfirmed objective responses subject to confirmation 8/9 (89%) patients remain on treatment The Safety Monitoring Committee has recommended dose escalation and re-opening of Cohort 2 Request submitted to FDA to initiate next dosing cohort and planning for this is in progress An additional 11 patients dosed in Cohort 2 as of December 31, 2024 since re-opening in August 2024 Ongoing evaluation of potential expansion into other SSTR2+ tumor types including breast, SCLC
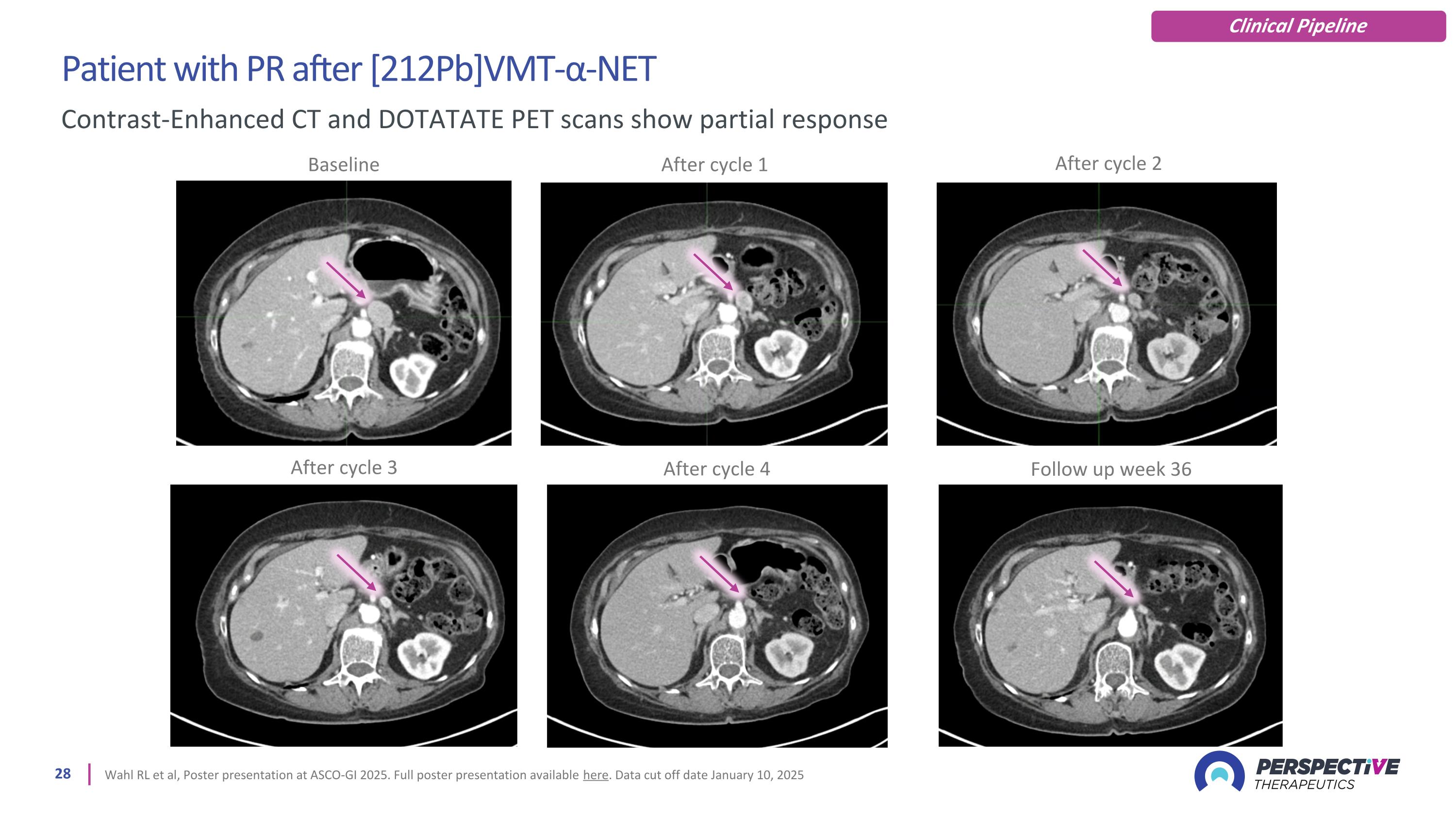
Patient with PR after [212Pb]VMT-α-NET Wahl RL et al, Poster presentation at ASCO-GI 2025. Full poster presentation available here. Data cut off date January 10, 2025 Contrast-Enhanced CT and DOTATATE PET scans show partial response Baseline After cycle 2 After cycle 1 After cycle 3 After cycle 4 Follow up week 36 Clinical Pipeline

Melanoma Program: VMT01/02 Using the melanocortin receptor (MC1R) to target melanoma for imaging and therapy
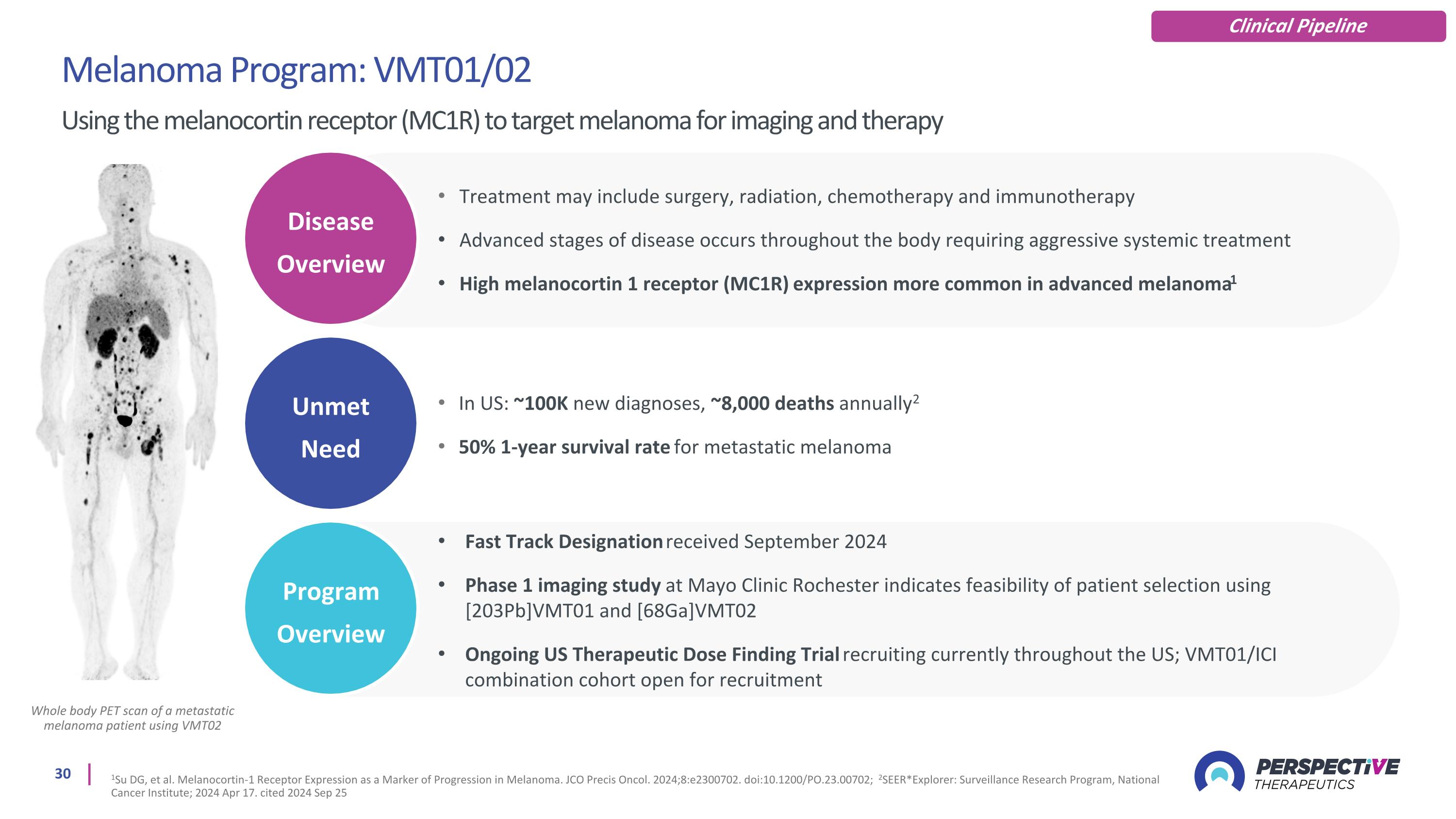
Whole body PET scan of a metastatic melanoma patient using VMT02 Melanoma Program: VMT01/02 Using the melanocortin receptor (MC1R) to target melanoma for imaging and therapy 1Su DG, et al. Melanocortin-1 Receptor Expression as a Marker of Progression in Melanoma. JCO Precis Oncol. 2024;8:e2300702. doi:10.1200/PO.23.00702; 2SEER*Explorer: Surveillance Research Program, National Cancer Institute; 2024 Apr 17. cited 2024 Sep 25 Clinical Pipeline Unmet Need Disease Overview Program Overview Treatment may include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy and immunotherapy Advanced stages of disease occurs throughout the body requiring aggressive systemic treatment High melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) expression more common in advanced melanoma1 In US: ~100K new diagnoses, ~8,000 deaths annually2 50% 1-year survival rate for metastatic melanoma Fast Track Designation received September 2024 Phase 1 imaging study at Mayo Clinic Rochester indicates feasibility of patient selection using [203Pb]VMT01 and [68Ga]VMT02 Ongoing US Therapeutic Dose Finding Trial recruiting currently throughout the US; VMT01/ICI combination cohort open for recruitment
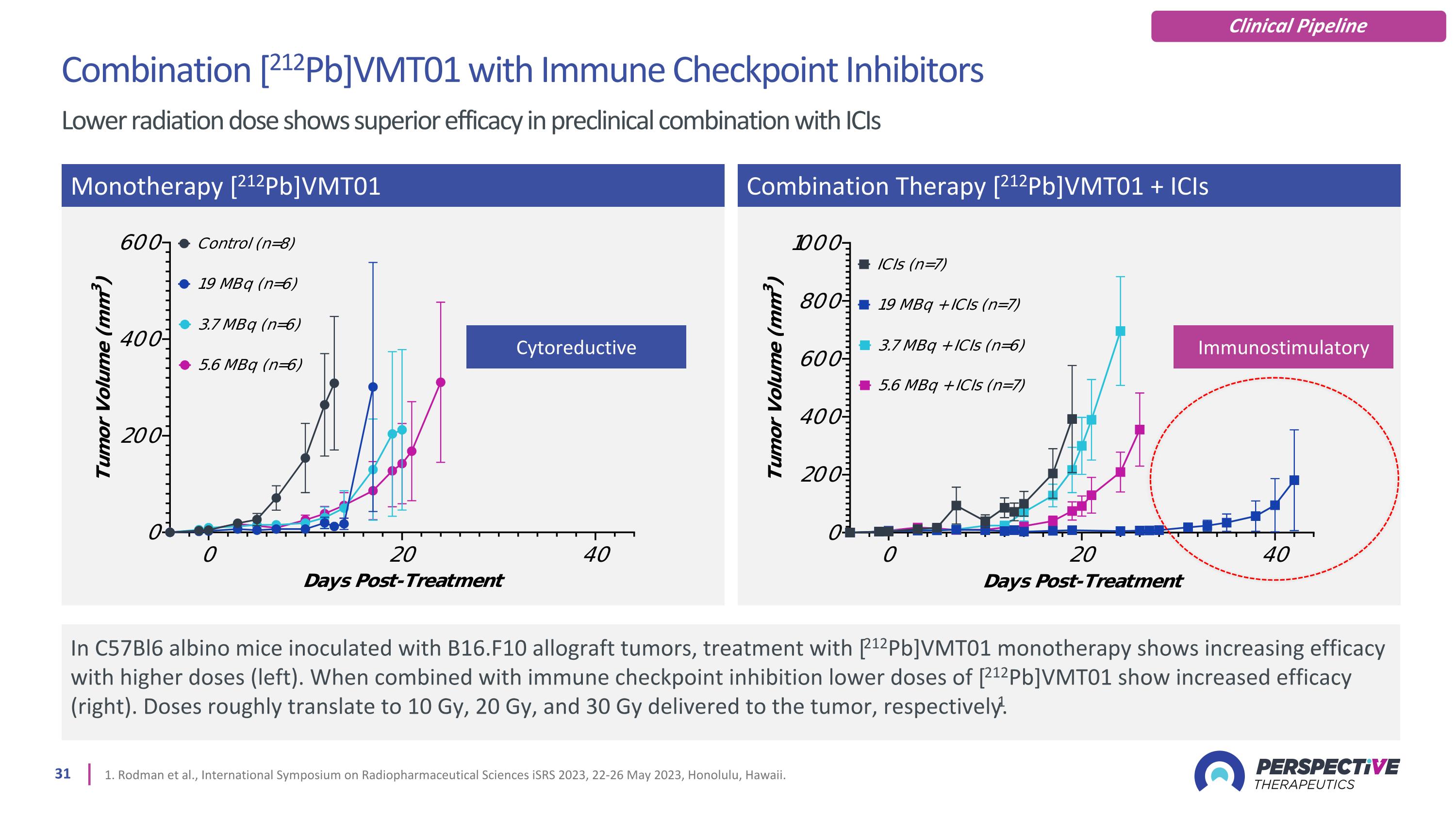
1. Rodman et al., International Symposium on Radiopharmaceutical Sciences iSRS 2023, 22-26 May 2023, Honolulu, Hawaii. In C57Bl6 albino mice inoculated with B16.F10 allograft tumors, treatment with [212Pb]VMT01 monotherapy shows increasing efficacy with higher doses (left). When combined with immune checkpoint inhibition lower doses of [212Pb]VMT01 show increased efficacy (right). Doses roughly translate to 10 Gy, 20 Gy, and 30 Gy delivered to the tumor, respectively.1 Monotherapy [212Pb]VMT01 Combination Therapy [212Pb]VMT01 + ICIs Combination [212Pb]VMT01 with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Lower radiation dose shows superior efficacy in preclinical combination with ICIs Cytoreductive Immunostimulatory Clinical Pipeline
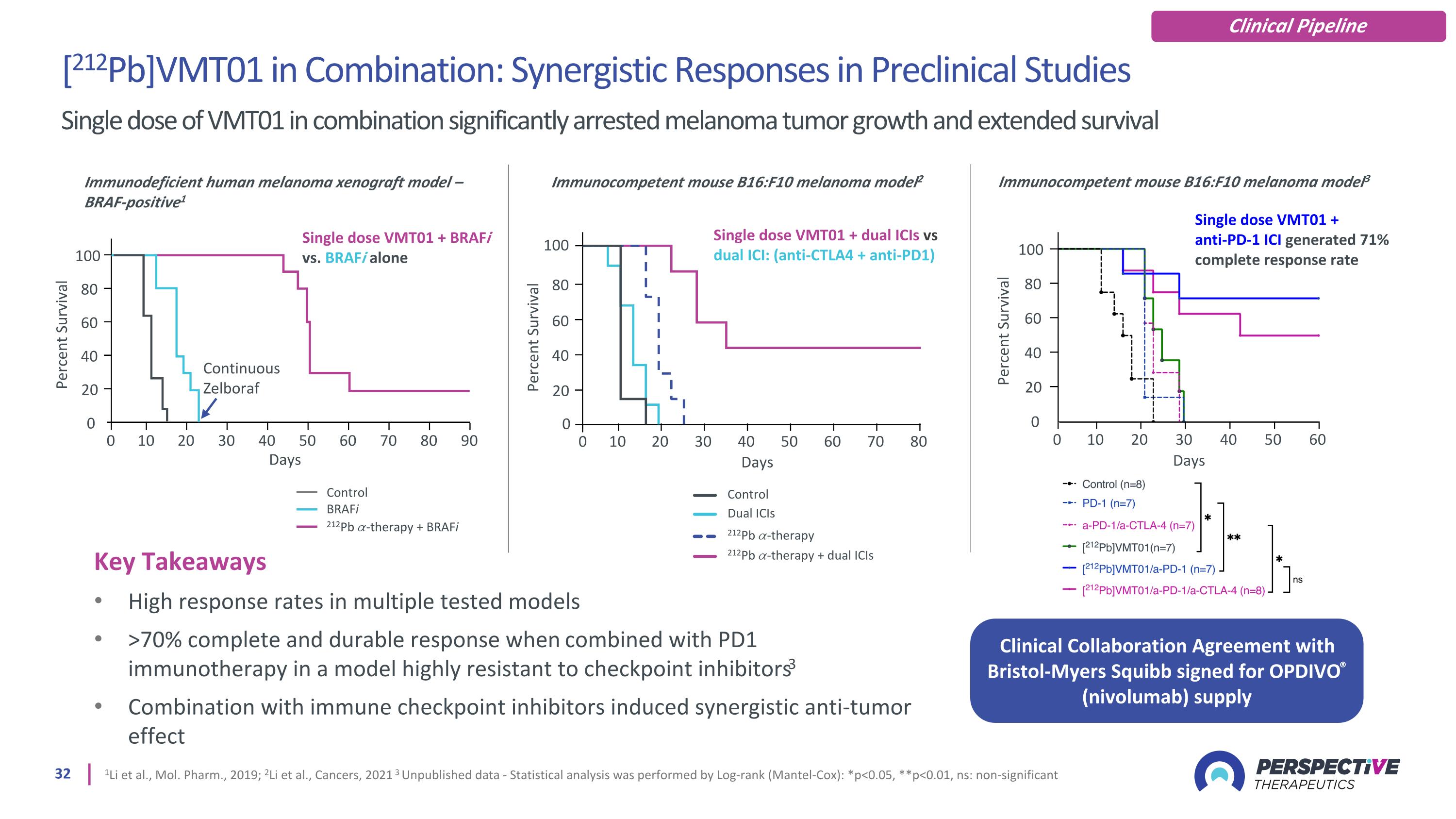
Key Takeaways High response rates in multiple tested models >70% complete and durable response when combined with PD1 immunotherapy in a model highly resistant to checkpoint inhibitors3 Combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors induced synergistic anti-tumor effect 1Li et al., Mol. Pharm., 2019; 2Li et al., Cancers, 2021 3 Unpublished data - Statistical analysis was performed by Log-rank (Mantel-Cox): *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ns: non-significant Immunodeficient human melanoma xenograft model – BRAF-positive1 Single dose VMT01 + BRAFi vs. BRAFi alone 0 0 Percent Survival Continuous Zelboraf Days 80 60 40 20 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Control BRAFi 212Pb 𝛼-therapy + BRAFi Percent Survival Days 0 100 Immunocompetent mouse B16:F10 melanoma model2 Single dose VMT01 + dual ICIs vs dual ICI: (anti-CTLA4 + anti-PD1) Dual ICIs 212Pb 𝛼-therapy 212Pb 𝛼-therapy + dual ICIs Control 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 80 60 40 20 [212Pb]VMT01 in Combination: Synergistic Responses in Preclinical Studies Single dose of VMT01 in combination significantly arrested melanoma tumor growth and extended survival 0 0 Percent Survival Days 80 60 40 20 10 20 30 40 50 60 100 Immunocompetent mouse B16:F10 melanoma model3 Single dose VMT01 + anti-PD-1 ICI generated 71% complete response rate Clinical Collaboration Agreement with Bristol-Myers Squibb signed for OPDIVO® (nivolumab) supply Clinical Pipeline
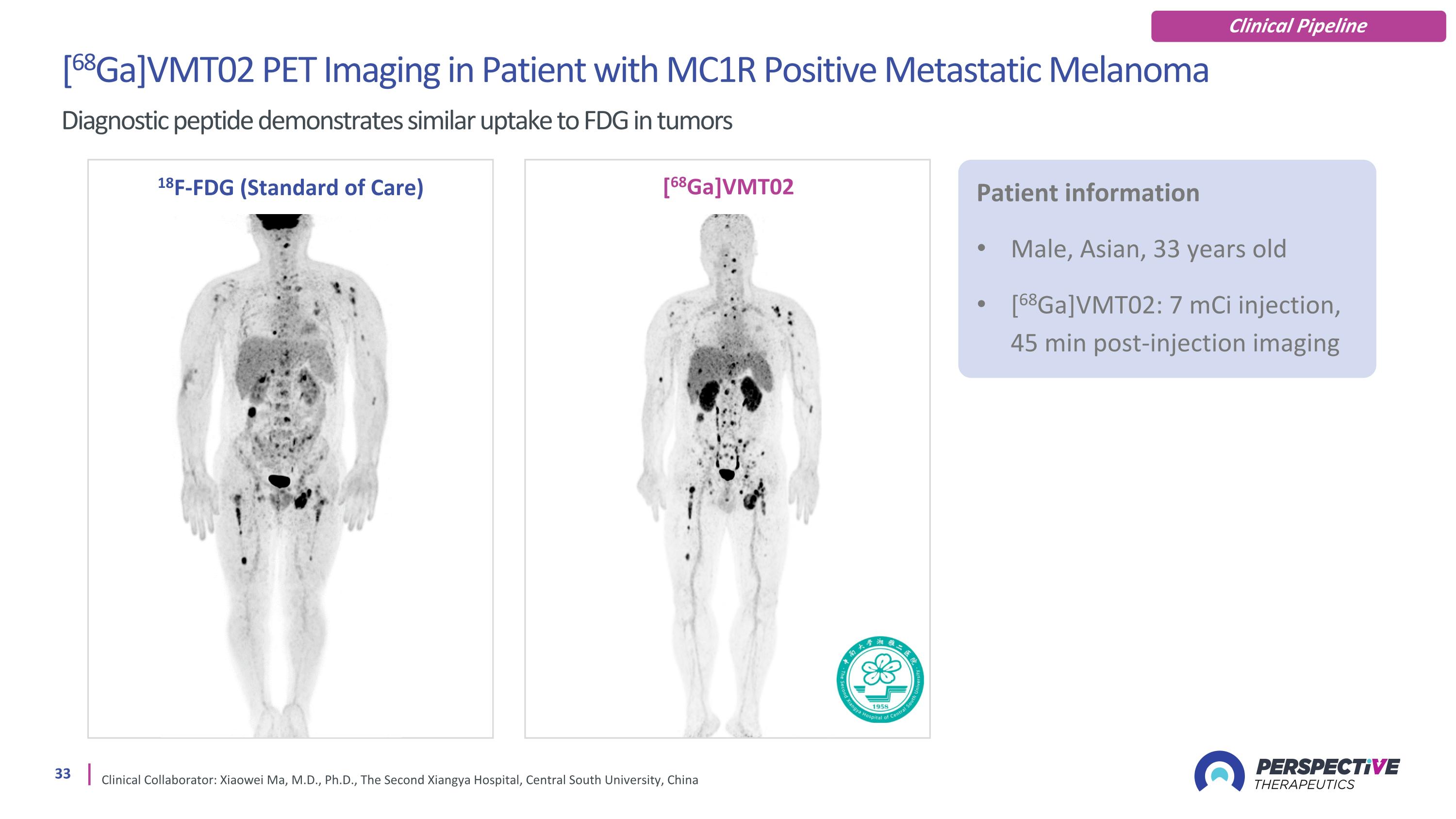
[68Ga]VMT02 PET Imaging in Patient with MC1R Positive Metastatic Melanoma Diagnostic peptide demonstrates similar uptake to FDG in tumors Clinical Collaborator: Xiaowei Ma, M.D., Ph.D., The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, China 18F-FDG (Standard of Care) [68Ga]VMT02 Patient information Male, Asian, 33 years old [68Ga]VMT02: 7 mCi injection, 45 min post-injection imaging Clinical Pipeline
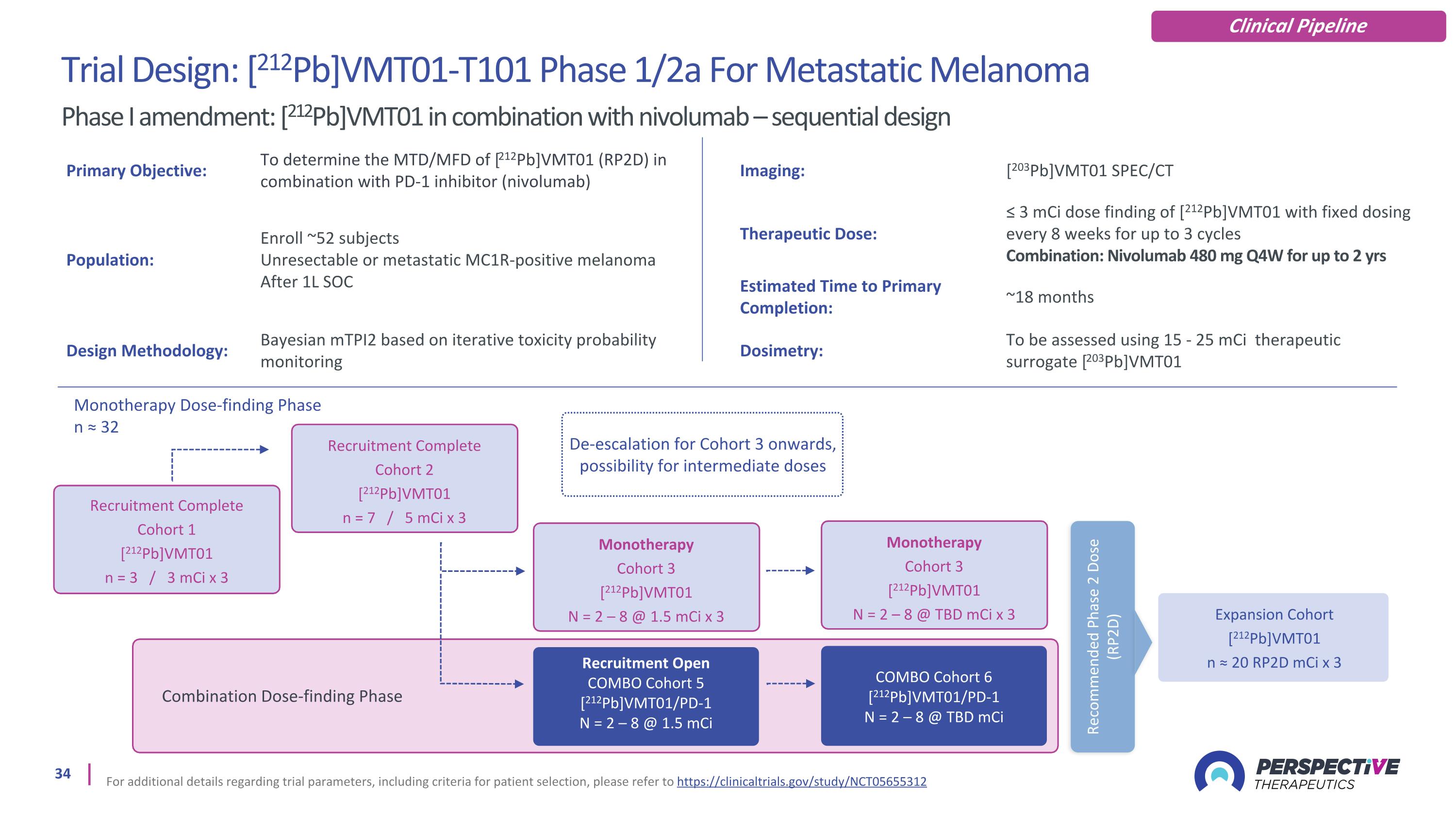
De-escalation for Cohort 3 onwards, possibility for intermediate doses For additional details regarding trial parameters, including criteria for patient selection, please refer to https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05655312 Monotherapy Dose-finding Phase n ≈ 32 Recruitment Complete Cohort 1 [212Pb]VMT01 n = 3 / 3 mCi x 3 Recruitment Complete Cohort 2 [212Pb]VMT01 n = 7 / 5 mCi x 3 Trial Design: [212Pb]VMT01-T101 Phase 1/2a For Metastatic Melanoma Recruitment Open COMBO Cohort 5 [212Pb]VMT01/PD-1 N = 2 – 8 @ 1.5 mCi COMBO Cohort 6 [212Pb]VMT01/PD-1 N = 2 – 8 @ TBD mCi Combination Dose-finding Phase Recommended Phase 2 Dose (RP2D) Expansion Cohort [212Pb]VMT01 n ≈ 20 RP2D mCi x 3 Phase I amendment: [212Pb]VMT01 in combination with nivolumab – sequential design Primary Objective: To determine the MTD/MFD of [212Pb]VMT01 (RP2D) in combination with PD-1 inhibitor (nivolumab) Imaging: [203Pb]VMT01 SPEC/CT Population: Enroll ~52 subjects Unresectable or metastatic MC1R-positive melanoma After 1L SOC Therapeutic Dose: ≤ 3 mCi dose finding of [212Pb]VMT01 with fixed dosing every 8 weeks for up to 3 cycles Combination: Nivolumab 480 mg Q4W for up to 2 yrs Estimated Time to Primary Completion: ~18 months Design Methodology: Bayesian mTPI2 based on iterative toxicity probability monitoring Dosimetry: To be assessed using 15 - 25 mCi therapeutic surrogate [203Pb]VMT01 Monotherapy Cohort 3 [212Pb]VMT01 N = 2 – 8 @ 1.5 mCi x 3 Monotherapy Cohort 3 [212Pb]VMT01 N = 2 – 8 @ TBD mCi x 3 Clinical Pipeline
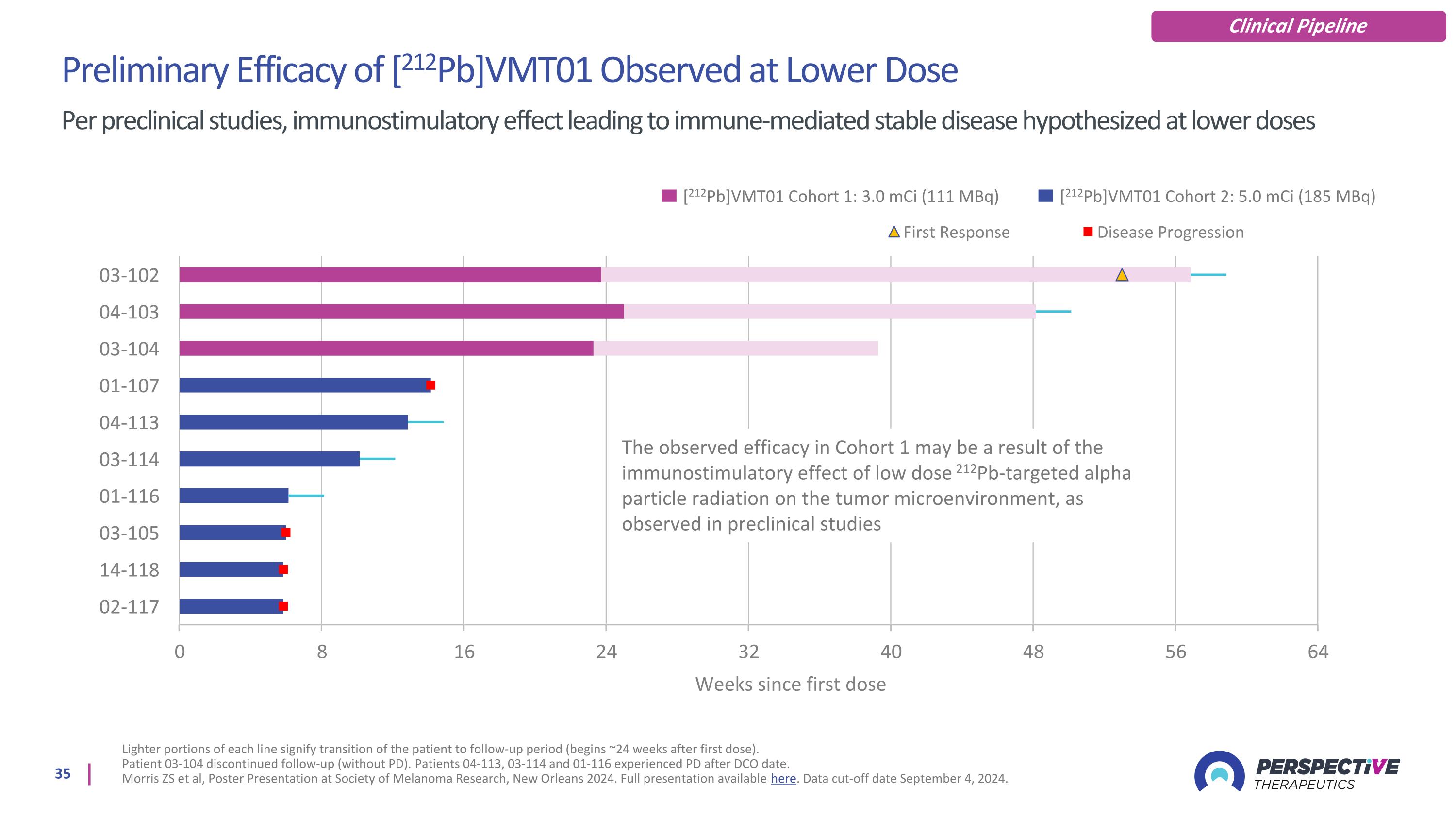
Preliminary Efficacy of [212Pb]VMT01 Observed at Lower Dose Per preclinical studies, immunostimulatory effect leading to immune-mediated stable disease hypothesized at lower doses Lighter portions of each line signify transition of the patient to follow-up period (begins ~24 weeks after first dose). Patient 03-104 discontinued follow-up (without PD). Patients 04-113, 03-114 and 01-116 experienced PD after DCO date. Morris ZS et al, Poster Presentation at Society of Melanoma Research, New Orleans 2024. Full presentation available here. Data cut-off date September 4, 2024. Clinical Pipeline [212Pb]VMT01 Cohort 1: 3.0 mCi (111 MBq) [212Pb]VMT01 Cohort 2: 5.0 mCi (185 MBq) The observed efficacy in Cohort 1 may be a result of the immunostimulatory effect of low dose 212Pb-targeted alpha particle radiation on the tumor microenvironment, as observed in preclinical studies
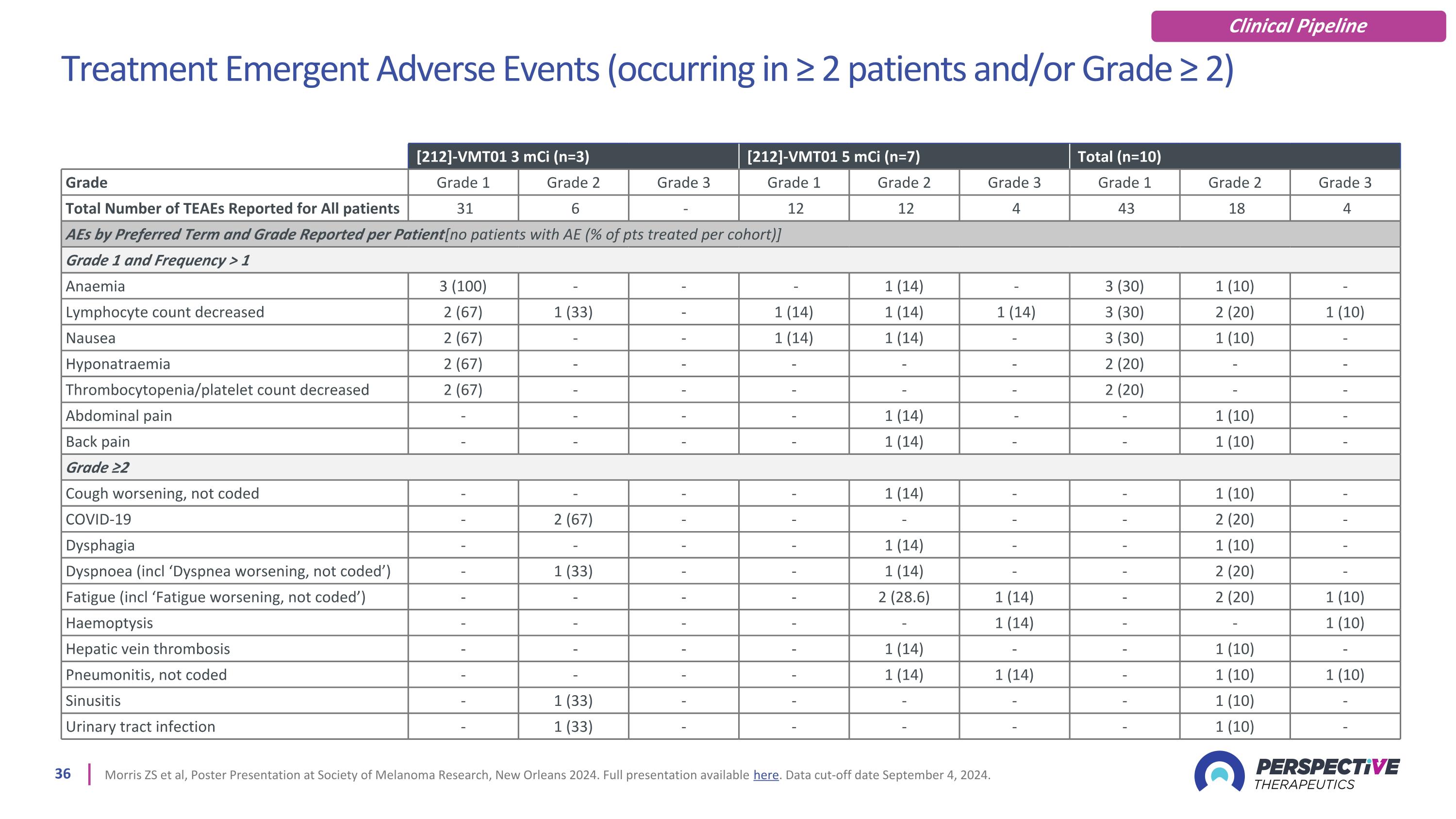
Treatment Emergent Adverse Events (occurring in ≥ 2 patients and/or Grade ≥ 2) Morris ZS et al, Poster Presentation at Society of Melanoma Research, New Orleans 2024. Full presentation available here. Data cut-off date September 4, 2024. [212]-VMT01 3 mCi (n=3) [212]-VMT01 5 mCi (n=7) Total (n=10) Grade Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Total Number of TEAEs Reported for All patients 31 6 - 12 12 4 43 18 4 AEs by Preferred Term and Grade Reported per Patient [no patients with AE (% of pts treated per cohort)] Grade 1 and Frequency > 1 Anaemia 3 (100) - - - 1 (14) - 3 (30) 1 (10) - Lymphocyte count decreased 2 (67) 1 (33) - 1 (14) 1 (14) 1 (14) 3 (30) 2 (20) 1 (10) Nausea 2 (67) - - 1 (14) 1 (14) - 3 (30) 1 (10) - Hyponatraemia 2 (67) - - - - - 2 (20) - - Thrombocytopenia/platelet count decreased 2 (67) - - - - - 2 (20) - - Abdominal pain - - - - 1 (14) - - 1 (10) - Back pain - - - - 1 (14) - - 1 (10) - Grade ≥2 Cough worsening, not coded - - - - 1 (14) - - 1 (10) - COVID-19 - 2 (67) - - - - - 2 (20) - Dysphagia - - - - 1 (14) - - 1 (10) - Dyspnoea (incl ‘Dyspnea worsening, not coded’) - 1 (33) - - 1 (14) - - 2 (20) - Fatigue (incl ‘Fatigue worsening, not coded’) - - - - 2 (28.6) 1 (14) - 2 (20) 1 (10) Haemoptysis - - - - - 1 (14) - - 1 (10) Hepatic vein thrombosis - - - - 1 (14) - - 1 (10) - Pneumonitis, not coded - - - - 1 (14) 1 (14) - 1 (10) 1 (10) Sinusitis - 1 (33) - - - - - 1 (10) - Urinary tract infection - 1 (33) - - - - - 1 (10) - Clinical Pipeline
1Morris ZS et al, Poster Presentation at Society of Melanoma Research, New Orleans 2024. Full presentation available here. Data cut-off date September 4, 2024. Conclusion & Next Steps Activity seen in 3 mCi dose cohort supports dose reduction and nivolumab combination Clinical Pipeline [212Pb]VMT01 was safe at doses studied1 At 3 mCi and 5 mCi activity levels, [212Pb]VMT01 was safe and no DLTs were observed Dosimetry demonstrates high kidney estimates limiting monotherapy escalation SMC recommendation included dose reduction to 1.5 mCi for both monotherapy and the upcoming combination cohort with nivolumab Objective response at lower dose cohort in line with preclinical data An objective response and prolonged PFS was observed at the 3 mCi activity level The observed efficacy in Cohort 1 may be a result of the immunostimulatory effect of low dose 212Pb-targeted alpha particle radiation on the TME, as observed in preclinical studies Lower dose and nivolumab combo cohorts open Monotherapy cohort is open for enrollment The combination cohort with nivolumab is active and now open for enrollment

Pan-Cancer Target: PSV359 Preclinical Efficacy and First in Human Images of Novel Peptide Targeting Fibroblast Activation Protein alpha (FAPɑ)
Pan-Cancer Program: PSV359 Novel peptide targeting fibroblast activation protein alpha (FAP-ɑ) 1Su DG, et al. Melanocortin-1 Receptor Expression as a Marker of Progression in Melanoma. JCO Precis Oncol. 2024;8:e2300702. doi:10.1200/PO.23.00702; 2SEER*Explorer: Surveillance Research Program, National Cancer Institute; 2024 Apr 17. cited 2024 Sep 25; Whole body PET image of colorectal cancer patient using [68Ga]PSV377 Clinical Pipeline Unmet Need Disease Overview Program Overview FAP-ɑ is expressed in the tumor stroma of many epithelial cancers and on the cell surface of other tumor types FAP Expression on Tumor Stroma: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Pancreatic, Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Colorectal Cancer, Breast Cancer, Ovarian Cancer, Others FAP Expression on Tumor Cells: Sarcoma, Mesothelioma, Others The stroma, a connective tissue that supports organs and tissues, is involved in tumorigenesis, metastasis, and drug resistance A high proportion of stroma in cancer tissues is associated with poorer survival Preclinical data indicates potential superiority of therapeutic effect vs. other FAP-targeted therapeutics IND-enabling studies complete; IND for US Therapeutic Dose-finding Trial under preparation Imaging with [68Ga]PSV377 and [203Pb]PSV359 in multiple tumor types suggests rapid uptake, tumor retention and fast clearance
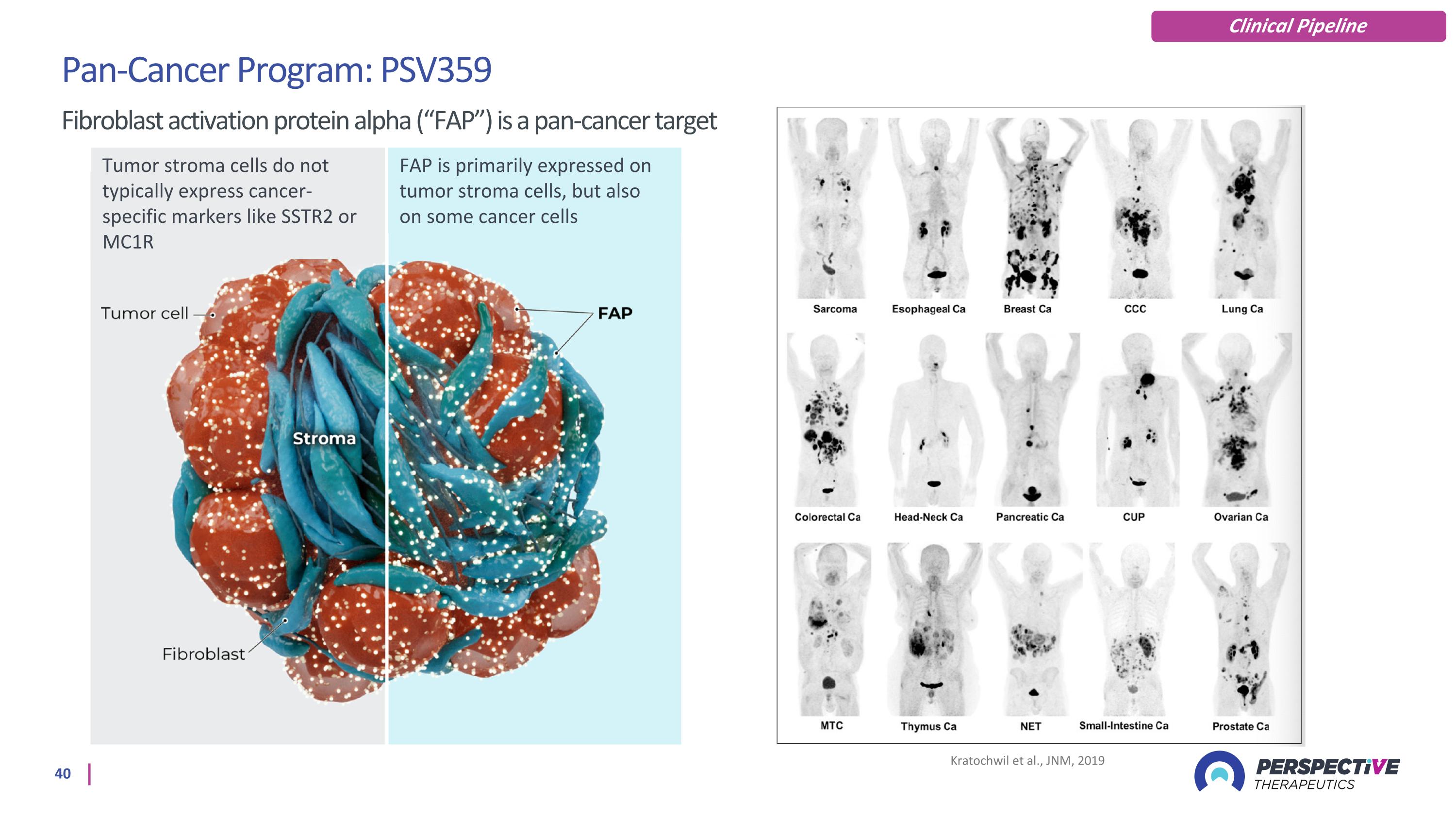
Kratochwil et al., JNM, 2019 FAP is primarily expressed on tumor stroma cells, but also on some cancer cells Tumor stroma cells do not typically express cancer-specific markers like SSTR2 or MC1R Pan-Cancer Program: PSV359 Fibroblast activation protein alpha (“FAP”) is a pan-cancer target Clinical Pipeline
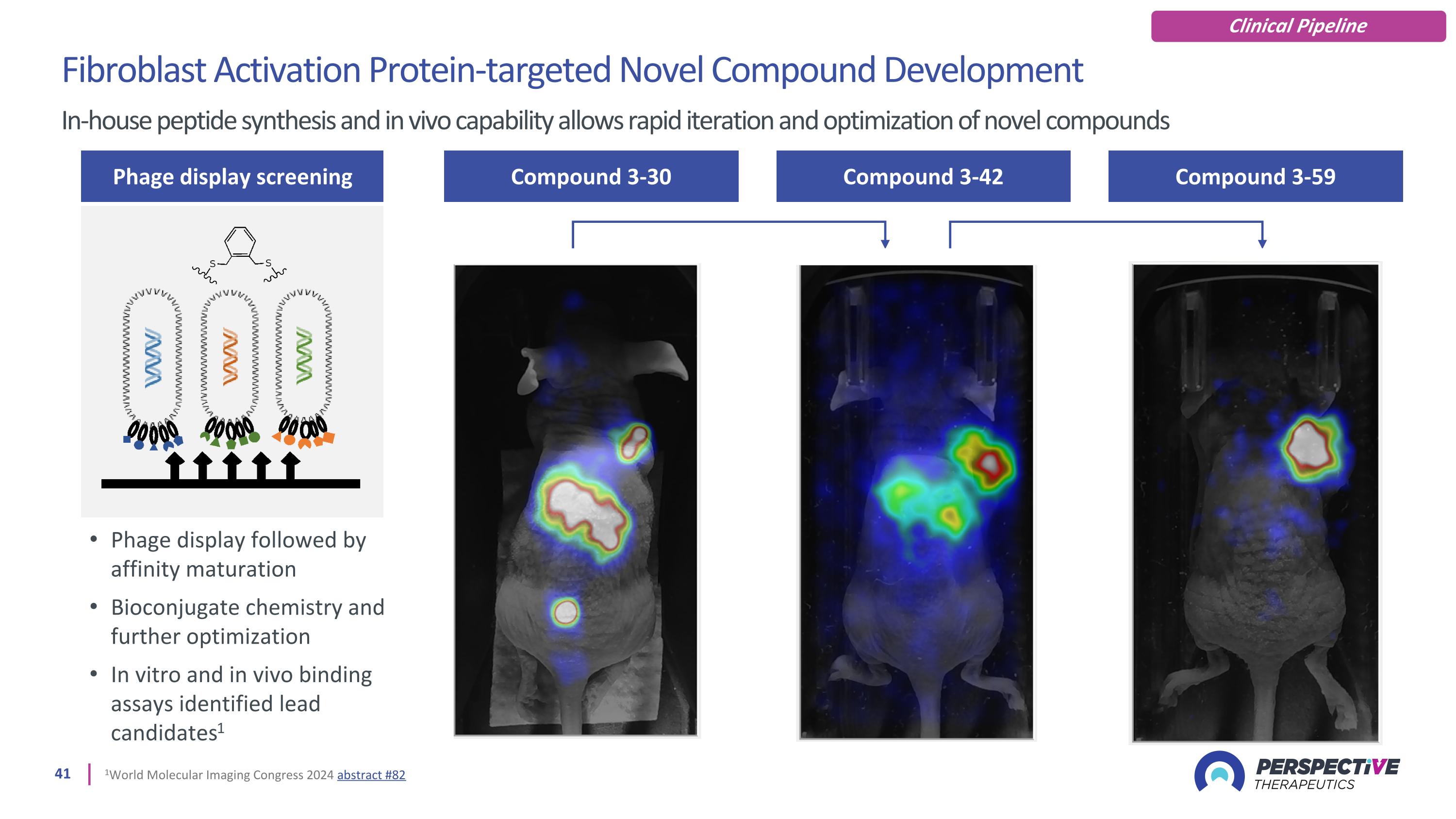
Compound 3-30 Compound 3-42 Compound 3-59 Fibroblast Activation Protein-targeted Novel Compound Development In-house peptide synthesis and in vivo capability allows rapid iteration and optimization of novel compounds Phage display screening Phage display followed by affinity maturation Bioconjugate chemistry and further optimization In vitro and in vivo binding assays identified lead candidates1 1World Molecular Imaging Congress 2024 abstract #82 Clinical Pipeline
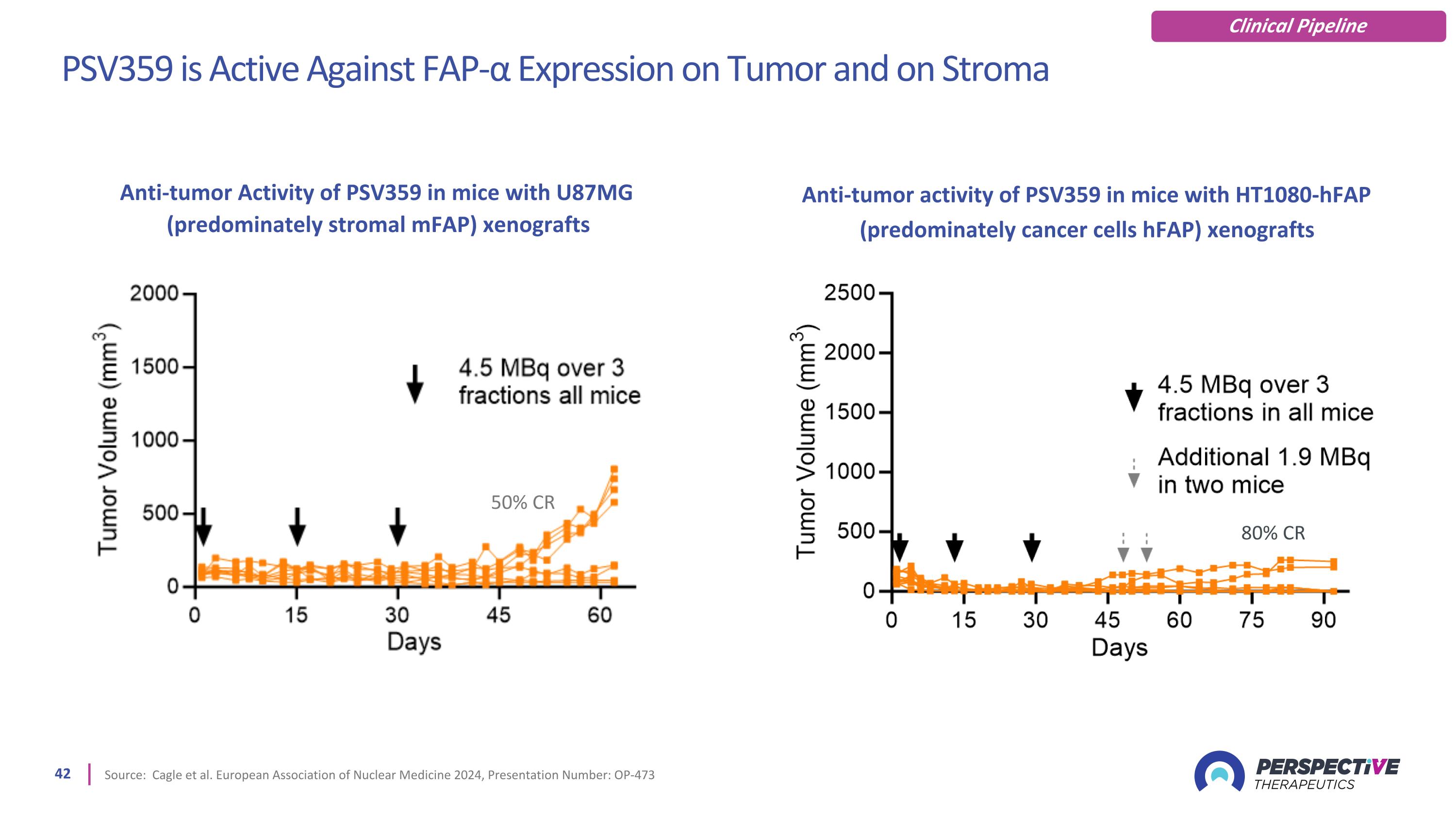
PSV359 is Active Against FAP-α Expression on Tumor and on Stroma Source: Cagle et al. European Association of Nuclear Medicine 2024, Presentation Number: OP-473 80% CR 50% CR Anti-tumor Activity of PSV359 in mice with U87MG (predominately stromal mFAP) xenografts Anti-tumor activity of PSV359 in mice with HT1080-hFAP (predominately cancer cells hFAP) xenografts Clinical Pipeline
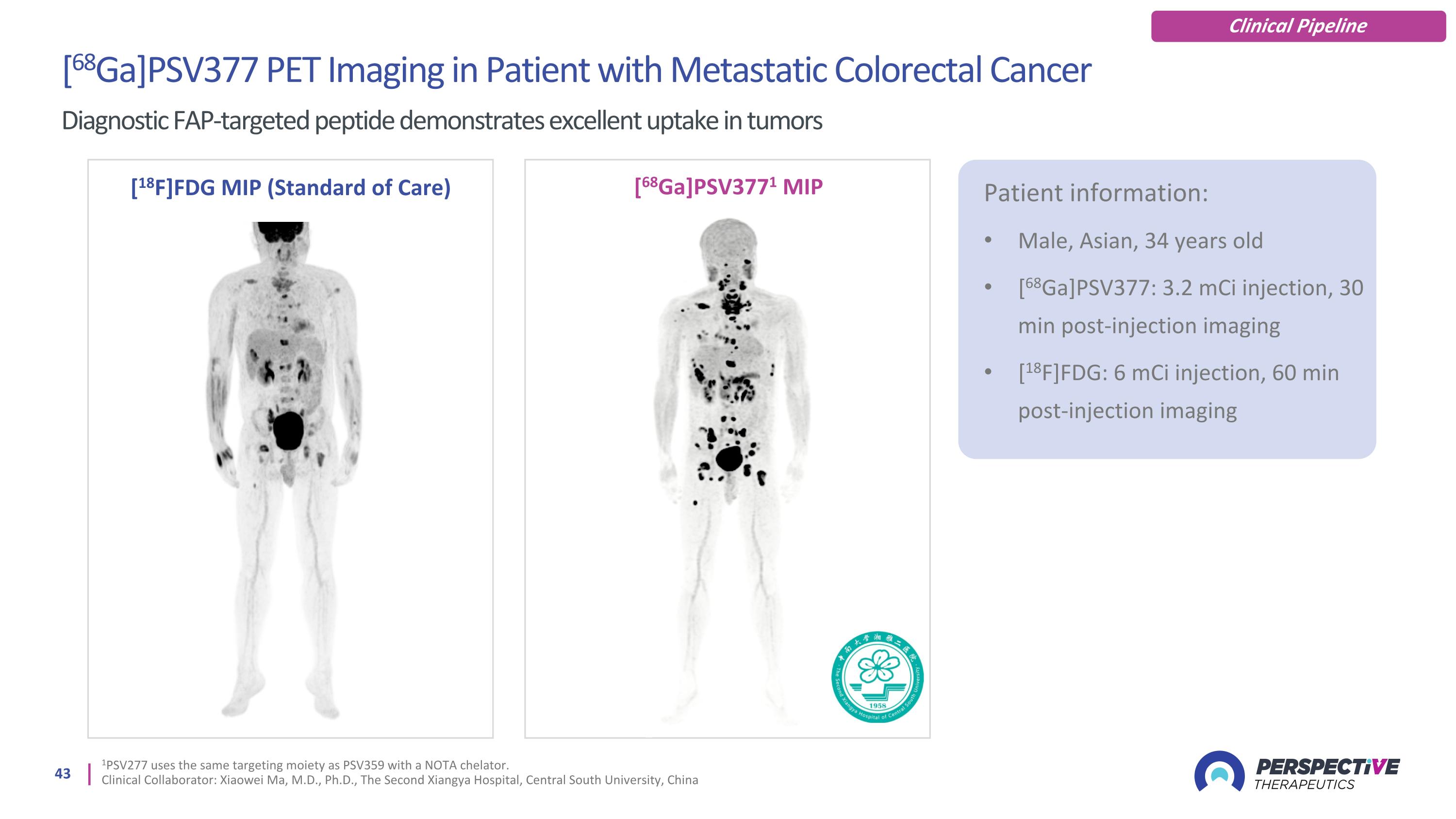
[68Ga]PSV377 PET Imaging in Patient with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Diagnostic FAP-targeted peptide demonstrates excellent uptake in tumors [18F]FDG MIP (Standard of Care) [68Ga]PSV3771 MIP Patient information: Male, Asian, 34 years old [68Ga]PSV377: 3.2 mCi injection, 30 min post-injection imaging [18F]FDG: 6 mCi injection, 60 min post-injection imaging Clinical Pipeline 1PSV277 uses the same targeting moiety as PSV359 with a NOTA chelator. Clinical Collaborator: Xiaowei Ma, M.D., Ph.D., The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, China
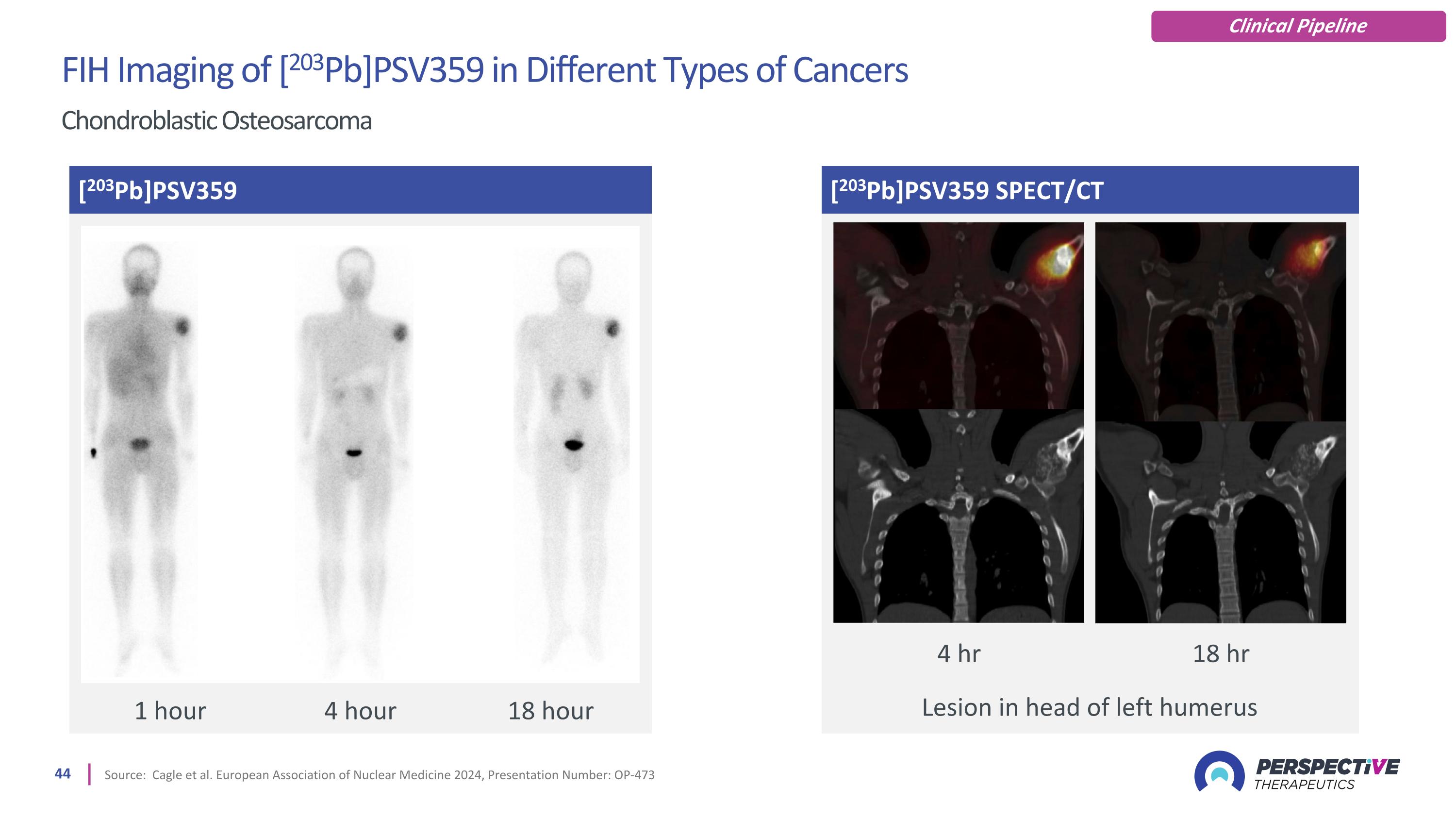
[203Pb]PSV359 SPECT/CT Source: Cagle et al. European Association of Nuclear Medicine 2024, Presentation Number: OP-473 [203Pb]PSV359 Lesion in head of left humerus 1 hour 4 hour 18 hour 4 hr 18 hr FIH Imaging of [203Pb]PSV359 in Different Types of Cancers Chondroblastic Osteosarcoma Clinical Pipeline
Source: Cagle et al. European Association of Nuclear Medicine 2024, Presentation Number: OP-473 Conclusion & Next Steps Preclinical data and first-in-human imaging data supportive of FIH therapeutic study in 2025 Clinical Pipeline Strong scientific rationale FAP-ɑ is a pan-cancer target that is abundantly expressed in certain cancer cells as well as cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumor lesions and involved in promoting disease progression Perspective’s in-house discovery team has developed an optimized peptide with potential best-in-class characteristics as demonstrated in preclinical models Imaging agent has favorable characteristics First-in-human clinical SPECT/CT imaging revealed strong tumor uptake, fast clearance through the renal system, low accumulation in normal organs, and long tumor retention in three patients with FAP-expressing cancer Therapeutic agent will be dosed in patients in 2025 IND for US therapeutic dose-finding trial filed First-in-human therapeutic studies are expected by mid-2025

General Corporate Information

Deeply Experienced Management Team in Radiopharmaceuticals and Oncology Drug Development Michael Schultz, PHD Chief Science Officer Thijs Spoor Chief Executive Officer Jonathan Hunt Chief Accounting Officer Markus Puhlmann, MD MBA Chief Medical Officer Amos Hedt Chief Business Strategy Officer 20+ years of expertise in biotechnology companies; public and private companies; oncology and nuclear pharmacy 20+ years of oncology drug development across all phases, experience coordinating multiple regulatory filings 20+ years industry and research experience in radiopharmaceuticals; co-founder Viewpoint MT & inventor of Perspective products 20+ years of expertise in financial controls and public accounting for large and small companies across multiple industries 20+ years of expertise in early-stage pharmaceutical and biotech drug development; 10+ years in radiopharmaceuticals 20+ years of experience in life sciences globally, including as CFO of an emerging growth biopharmaceutical company after nearly two decades in Big Pharma Juan Graham Chief Financial Officer

7 Issued Patents (Expiry in 2037 and 2040, with potential PTE) Composition of matter for melanoma targeted radiopharmaceutical compounds; methods of combination therapies; methods of creating radiopharmaceutical compounds using Pb-specific chelators 2 Allowed AU and EP Patent Applications (Expiry in 2039) methods of creating radiopharmaceutical compounds using Pb-specific chelator 54 pending patent applications (including 10 PCT, 38 national, and 6 provisional) Composition of matter and method of use on: Radiometal separation technology Chelators SSTR2, MC1R, FAP, and PSMA targeting radiopharmaceuticals Pre-targeting technology platforms Methods of imaging and treatment Perspective-owned/Exclusively-licensed IP IP Portfolio covers all aspects of radiopharmaceutical value chain Potential for Orphan Drug Designation Potential for U.S. FDA Priority Review Voucher: VMT-𝛼-NET is a candidate for pediatric neuroblastoma indication Strong Intellectual Property Portfolio

Funding into late 20261 Strong Financial Position Preliminary cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments as of December 31, 2024 $227 million Based on our current plans, which include advancing current clinical programs based on readout, progressing multiple pre-IND assets towards clinical trials, as well as developing several regional manufacturing sites, we expect to have sufficient funding into late 2026.1 1As of January 13, 2025 (the date of the Company’s release of certain preliminary financial information as of December 31, 2024), based on cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments as of December 31, 2024 The Company has not yet completed its financial close processes for fiscal year 2024. Therefore, the Company’s statements regarding its expectations for its cash balance as of December 31, 2024 included in this presentation are based on preliminary unaudited estimates only and should not be viewed as a substitute for full audited financial statements prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP. They reflect management’s estimates based solely upon information available to management as of January 13, 2025. Further information learned during the financial close processes and audit may alter the final results. The Company cautions you that actual results which are prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP and are subject to audit may differ materially from the preliminary results described in this presentation. Accordingly, you should not place undue reliance upon this preliminary financial and operating information.

Abbreviations AE: adverse event APC: antigen-presenting cell ASCO-GI: ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium DAMPs: damage-associated molecular patterns DLT: dose limiting toxicities dsDNA: double-stranded DNA EANM: European Association of Nuclear Medicine eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate ER+ BC: estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer FDA: U.S. Food and Drug Administration GEP-NETs: gastroenteropancreatic-NETs GI: gastrointestinal GU: genitourinary GYN: gynecology H&N: head and neck ICI: immune checkpoint inhibitor IND: investigational new drug mAB: monoclonal antibodies MC1R: melanocortin 1 receptor MIP: maximum Intensity Projection mTPI-2: modified toxicity probability index NANETS: North American Neuroendocrine Tumor Society NETs: neuroendocrine tumor PD: progressive disease PoC: proof of concept PR: partial response PRRT: peptide receptor radionuclide therapy PSMA: prostate specific membrane antigen RPT: radiopharmaceutical therapies SAE: serious adverse event SCLC: small cell lung cancer SD: stable disease SMC: safety monitoring committee SNMMI: Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging SSTR2: somatostatin receptor type 2 TEAE: treatment emergent adverse events TME: tumor microenvironment TRAE: treatment related adverse events