Exhibit 99.2

Rare Disease Development Company BIO - Europe Spring ® 2014 11 March 2014

Forward Looking Statement Statements made in this news release may be forward - looking statements within the meaning of Federal Securities laws that are subject to certain risks and uncertainties and involve factors that may cause actual results to differ materially from those projected or suggested . Factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those in forward - looking statements include, but are not limited to : ( i ) the ability of Marina Biotech to obtain additional funding ; (ii) the ability of Marina Biotech to attract and/or maintain manufacturing, research, development and commercialization partners ; (iii) the ability of Marina Biotech and/or a partner to successfully complete product research and development, including preclinical and clinical studies and commercialization ; (iv) the ability of Marina Biotech and/or a partner to obtain required governmental approvals ; and (v) the ability of Marina Biotech and/or a partner to develop and commercialize products prior to, and that can compete favorably with those of, competitors . Additional factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those projected or suggested in any forward - looking statements are contained in Marina Biotech's most recent filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission . Marina Biotech assumes no obligation to update or supplement forward - looking statements because of subsequent events . 2

Environment is Perfect for Marina’s Emergence in Rare Disease Sector » D EMONSTRATED C LINICAL S AFETY OF N UCLEIC A CID T HERAPEUTICS » All nucleic acid constructs and mechanisms of action available via Marina’s drug discovery platform have reached human clinical development and have been established as safe and well tolerated » I NCREASED P HARMA I NTEREST » Pharma has established rare disease therapeutic areas thus creating single champions for rare disease efforts » S IGNIFICANT I NVESTOR I NTEREST » ~$1 Billion invested in sector since beginning of 2014 » M ARINA P LATFORM F LEXIBILITY » Certain individual nucleic acid approaches will be inadequate in eliciting a therapeutic effect; therefore robust development programs are necessary – clinical programs will likely require more than one nucleic acid modality (lead and back - ups) as part of the clinical package » M ARINA D ELIVERY T ECHNOLOGY » SMARTICLES delivery technology in a Phase 2 and a Phase 1 clinical trial delivering single - AND doubled - stranded oligonucleotides, respectively 3
Unequalled Capability » Novel and proprietary technologies: » Unlocked and locked nucleic acid chemistries » “Tunable” activity/affinity » Multiple delivery technologies » SMARTICLES and DiLA2 lipid based delivery technologies for delivery of both single and double - stranded oligonucleotides via local, I.V. and subq » Bacterial - based system for GI disorders via oral administration » Phage display library for cell - targeting/penetration peptides » A drug discovery platform which can support a robust clinical development program: » Clinical package could contain multiple nucleic acid modalities (leads and back - ups) against therapeutic target(s), via RNAi , steric blocking, exon skipping, mRNA translational inhibition, microRNA antagonism and mimics etc. NOT limited by one approach » Ability to develop diverse compounds to attack multi - system diseases, i.e. different nucleic acid modalities could be applied to muscle, heart and/or CNS in myotonic dystrophy 4

Capability Comparison (FTO A gainst Competition) Chemistry Delivery siRNA Anti - sense MicroRNA mimics Antagomirs Lipid Polymer Peptide Bacterial Marina X X X X X X X Alnylam X X X Arrowhead X X X Dicerna X X Rxi X X Silence X X Tekmira X X Isis X Prosensa X Sarepta X Regulus X X Santarus X PhaseRx X 5
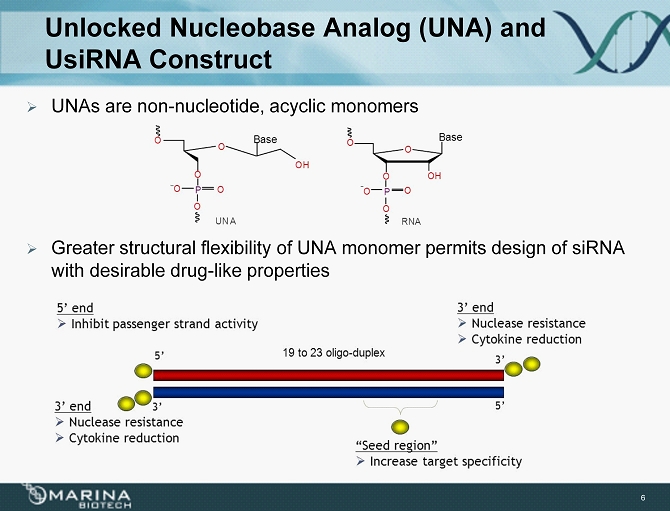
Unlocked Nucleobase Analog (UNA) and UsiRNA Construct » UNAs are non - nucleotide, acyclic monomers » Greater structural flexibility of UNA monomer permits design of siRNA with desirable drug - like properties 6
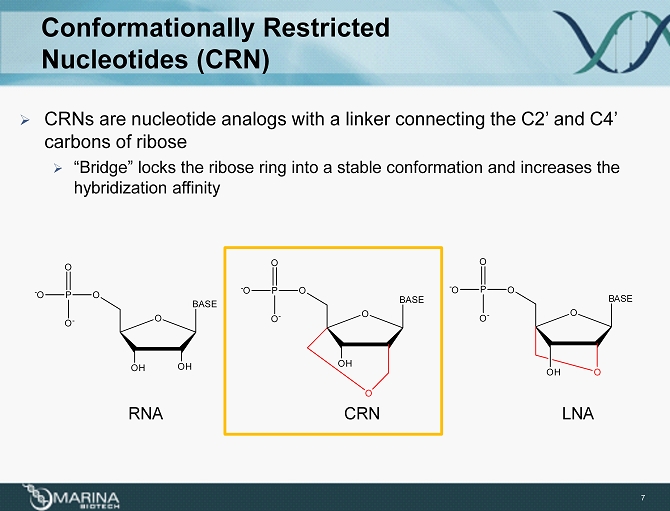
Conformationally Restricted Nucleotides (CRN ) » CRNs are nucleotide analogs with a linker connecting the C2’ and C4’ carbons of ribose » “Bridge” locks the ribose ring into a stable conformation and increases the hybridization affinity RNA CRN LNA O OH BASE OH OP - O O - O OP - O O - O O OH O BASE O P - O O - O O O BASE OH 7

Attributes of UNA and CRN Chemistry » UNA and CRN - substituted oligonucleotides are highly active and well tolerated » UNA/CRN chemistry can be used to develop highly potent and specific nucleic acid - based therapeutics to target mRNA or microRNA » UNA increases target specificity and provides advantages in the development of RNAi - based therapeutics » UNA blocks activity against unintended microRNA targets » CRN - substituted oligonucleotides can be administered via systemic and subcutaneous routes in multiple formulations including normal saline » CRN increases affinity (i.e. potency/efficacy) for catalytic and non - catalytic mechanisms when targeting either coding or non - coding RNA 8

SMARTICLES Clinical Status » ProNAi Therapeutics (PNT2258) » Phase 1 Completed in November 2012 » 30 patients ( dose range 1 - 150 mg/m2 ); (J Clin Oncol 30, 2012 ( suppl ; abstr TPS3110 )) » Reported interim Phase 2 data at American Society of Hematology in December 2013 » 82% of patients had tumor shrinkage when receiving single - agent therapy with PNT2258. » Overall response rate in patients with follicular lymphoma is 40% and in patients with diffuse large B - cell lymphoma is 50%. » Licensed exclusively for ProNAi’s proprietary DNA interference ( DNAi ) technology » Mirna Therapeutics (MRX34) » Initiated Phase 1 clinical testing in May 2013 » Exclusive for six specific microRNA mimics as defined by sequence 9

SMARTICLES Status 10 » Demonstrated statistically significant, dose - dependent, and specific knockdown of gene target in a Phase 1 clinical study » Currently in multiple clinical trials with both a single and double - stranded oligonucleotide » Demonstrated anti - tumor efficacy with both single - and double - stranded oligonucleotides in rodent models » Demonstrated delivery to tumor, liver, spleen, kidney and lung tissue in rodent models » Manufactured in large quantities under GMP
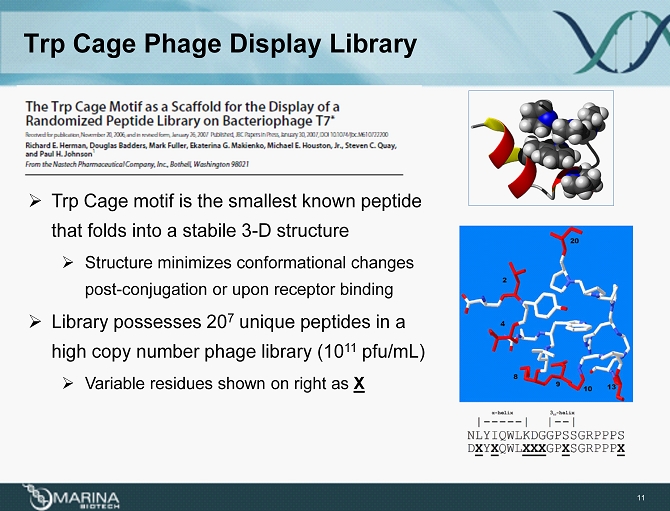
Trp Cage Phage Display Library » Trp Cage motif is the smallest known peptide that folds into a stabile 3 - D structure » Structure minimizes conformational changes post - conjugation or upon receptor binding » Library possesses 20 7 unique peptides in a high copy number phage library (10 11 pfu/mL) » Variable residues shown on right as X 11
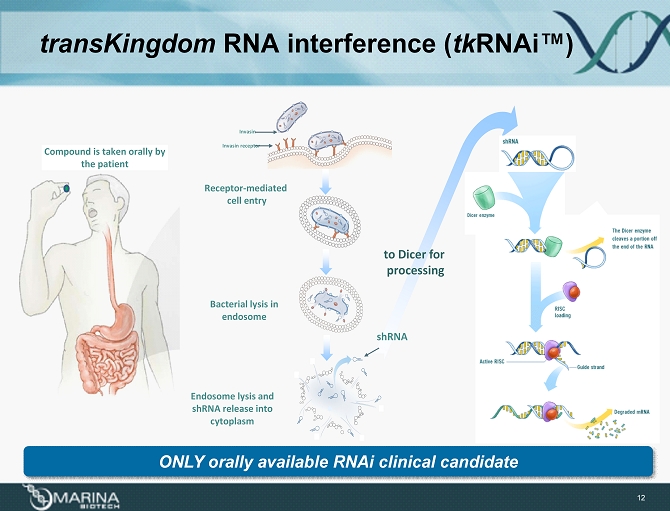
transKingdom RNA interference ( tk RNAi ™) 12 to Dicer for processing Bacterial lysis in endosome Receptor - mediated cell entry Endosome lysis and shRNA release into cytoplasm Invasin receptor Invasin shRNA Compound is taken orally by the patient ONLY orally a vailable RNAi clinical c andidate

Matching the Nucleic Acid Construct to the Most Effective Mechanism of Action Chemistry Delivery UNA CRN SMARTICLES DiLA2 Lipo - peptide tkRNAi TrpCage RNAi (mRNA inhibition) X X X X X X X Antisense (mRNA inhibition) X X X X X X Exon - Skipping (Intron - Exon Splice Bias) X X X X X Steric Blocking (Binding site competition) X X microRNA replacement (microRNA mimic) X X X X X X Antagomirs (microRNA inhibition) X X X X X X X mRNA replacement (mRNA) X X 13 CRN - and UNA - Substituted C onstructs S pan E ntire T herapeutic S pectrum
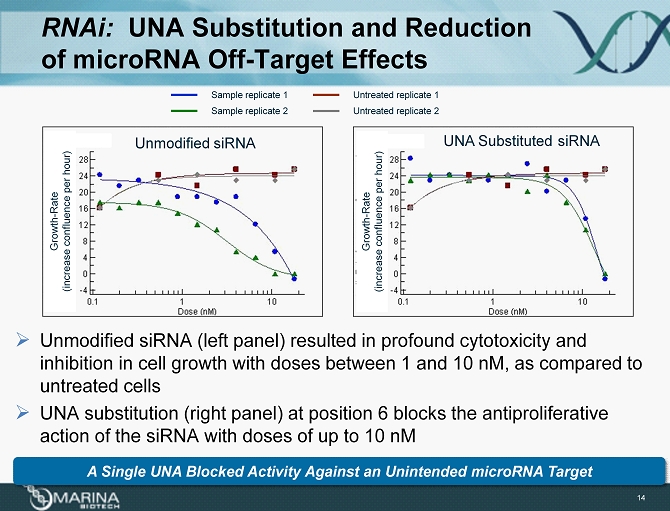
RNAi: UNA Substitution and Reduction of microRNA Off - Target Effects 14 » Unmodified siRNA (left panel) resulted in profound cytotoxicity and inhibition in cell growth with doses between 1 and 10 nM, as compared to untreated cells » UNA substitution (right panel ) at position 6 blocks the antiproliferative action of the siRNA with doses of up to 10 nM Sample replicate 1 Sample replicate 2 Untreated replicate 1 Untreated replicate 2 Unmodified siRNA UNA Substituted siRNA Growth - Rate (increase confluence per hour) Growth - Rate (increase confluence per hour) A Single UNA B locked Activity Against an Unintended microRNA Target

Translational Blocking: Dose - response for CRN - and LNA - Substituted Oligo 15 » Dose - response for each oligo, CRN outperforms LNA 1 CRN - substituted Translational Block Oligo LNA - substituted Translational Block Oligo 1 Data produced by academic laboratory In Vitro Myotonic Dystrophy Assay Measuring CUG Repeat Blocking (Lower % is Better)
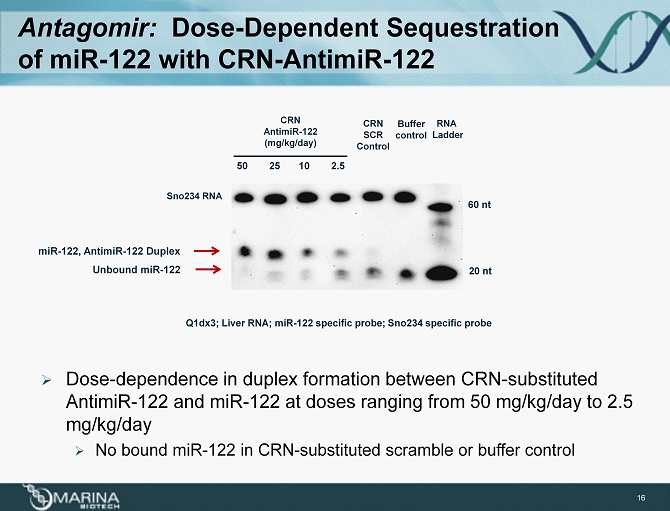
Antagomir : Dose - Dependent Sequestration of miR - 122 with CRN - AntimiR - 122 Sno234 RNA 20 nt 60 nt CRN AntimiR - 122 (mg/kg/day) Buffer control RNA Ladder 50 25 10 2.5 CRN SCR Control Q1dx3; Liver RNA; miR - 122 specific probe; Sno234 specific probe » Dose - dependence in duplex formation between CRN - substituted AntimiR - 122 and miR - 122 at doses ranging from 50 mg/kg/day to 2.5 mg/kg/day » No bound miR - 122 in CRN - substituted scramble or buffer control 16 Unbound miR - 122 miR - 122, AntimiR - 122 Duplex

Antagomir : Dose Response of CRN - substituted AntimiR - 122 on ALDOA mRNA » Dose - dependent effect on de - repression of liver AldoA mRNA with CRN - substituted AntimiR - 122 relative to buffer relative to buffer » Up to 5, 3 and 2 - fold increase in AldoA mRNA at 50, 25 and 10 mg/kg respectively; no effect at the lowest dose of 2.5 mg/kg » No effect with CRN - substituted scramble control » Up to 2 to 3 - fold increase in AldoA mRNA with LNA - substituted AntimiR - 122 at all doses except for 2.5 mg/kg relative to buffer 17 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 50 25 10 2.5 50 25 10 2.5 50 50 AmiR-122-16-CRN-8a AmiR-122-16-LNA-8a AmiR-122- 16-CRN- SCR LNA Mismatch control Buffer AldoA mRNA relative to buffer control mg/kg/day Dose Response; AldoA mRNA; Q1dx3; 24 h post last dose; n=5 per group

Antagomir : Tolerability of CRN - substituted AntimiR - 122 in Mouse Model » No change in body weights in CRN - substituted AntimiR - 122 treated animals at any dose level 18 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 50 25 10 2.5 50 25 10 2.5 50 50 AmiR-122-16-CRN8a AmiR-122-16-LNA8a AmiR-122- 16-CRN- SCR LNA Mismatch control Buffer Body Weight (g) mg/kg/day Average Body Weight, Q1dx3; 24 h post last dose, n=5 per group

Rare Disease Drug Development 19
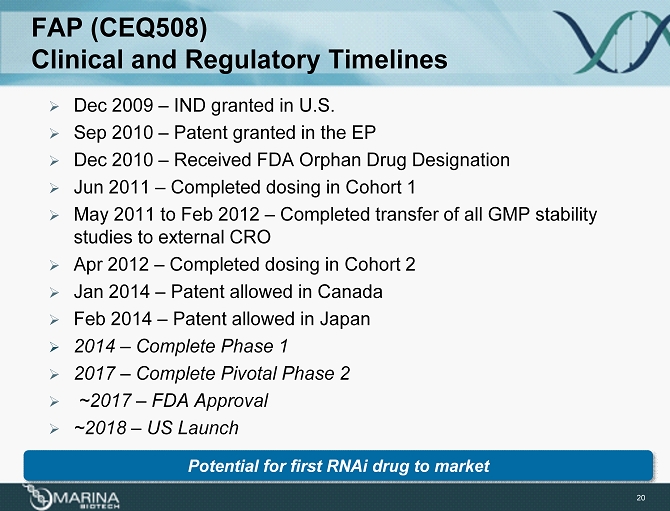
FAP (CEQ508) Clinical and Regulatory Timelines 20 » Dec 2009 – IND granted in U.S. » Sep 2010 – Patent granted in the EP » Dec 2010 – Received FDA Orphan Drug Designation » Jun 2011 – Completed dosing in Cohort 1 » May 2011 to Feb 2012 – Completed transfer of all GMP stability studies to external CRO » Apr 2012 – Completed dosing in Cohort 2 » Jan 2014 – Patent allowed in Canada » Feb 2014 – Patent allowed in Japan » 2014 – Complete Phase 1 » 2017 – Complete Pivotal Phase 2 » ~2017 – FDA Approval » ~2018 – US Launch Potential for first RNAi drug to market
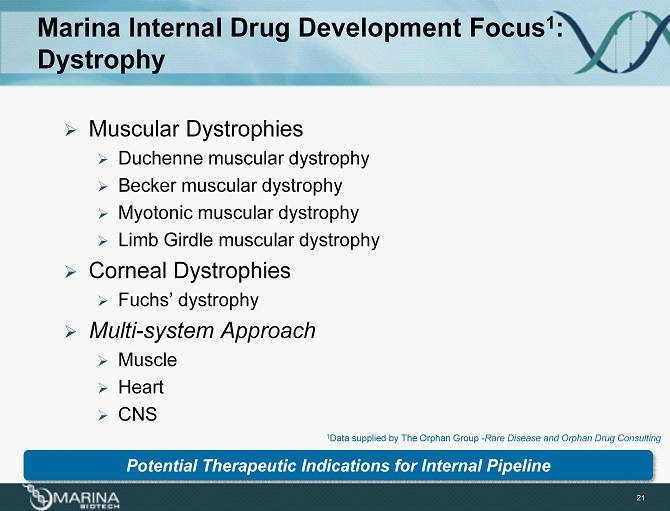
Marina Internal Drug Development Focus 1 : Dystrophy 21 » Muscular Dystrophies » Duchenne muscular dystrophy » Becker muscular dystrophy » Myotonic muscular dystrophy » Limb Girdle muscular dystrophy » Corneal Dystrophies » Fuchs’ dystrophy » Multi - system Approach » Muscle » Heart » CNS Potential Therapeutic Indications for Internal Pipeline 1 Data supplied by The Orphan Group - Rare Disease and Orphan Drug Consulting
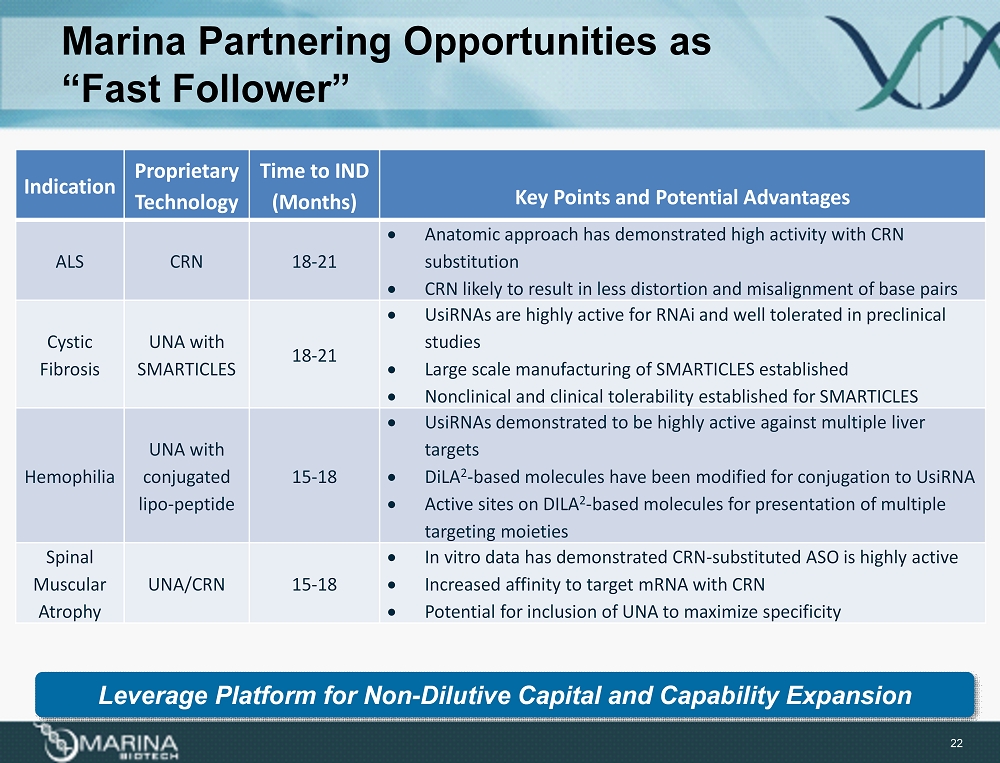
Marina Partnering Opportunities as “Fast Follower” Indication Proprietary Technology Time to IND (Months) Key Points and Potential Advantages ALS CRN 18 - 21 • Anatomic approach has demonstrated high activity with CRN substitution • CRN likely to result in less distortion and misalignment of base pairs Cystic Fibrosis UNA with SMARTICLES 18 - 21 • UsiRNAs are highly active for RNAi and well tolerated in preclinical studies • Large scale manufacturing of SMARTICLES established • Nonclinical and clinical tolerability established for SMARTICLES Hemophilia UNA with conjugated lipo - peptide 15 - 18 • UsiRNAs demonstrated to be highly active against multiple liver targets • DiLA 2 - based molecules have been modified for conjugation to UsiRNA • Active sites on DILA 2 - based molecules for presentation of multiple targeting moieties Spinal Muscular Atrophy UNA/CRN 15 - 18 • In vitro data has demonstrated CRN - substituted ASO is highly active • Increased affinity to target mRNA with CRN • Potential for inclusion of UNA to maximize specificity 22 Leverage Platform for Non - Dilutive Capital and Capability Expansion
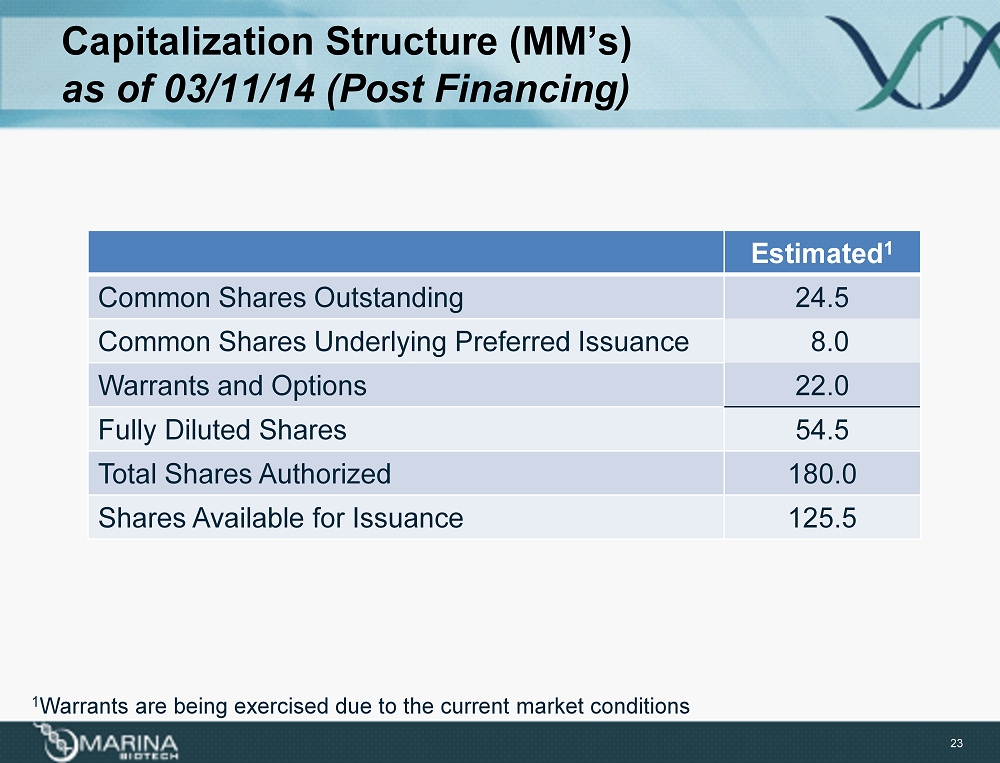
Capitalization Structure (MM’s) as of 03/11/14 (Post Financing) Estimated 1 Common Shares Outstanding 24.5 Common Shares Underlying Preferred Issuance 8.0 Warrants and Options 22.0 Fully Diluted Shares 54.5 Total Shares Authorized 180.0 Shares Available for Issuance 125.5 23 1 Warrants are being exercised due to the current market conditions

Key Value Drivers (through 3Q2014) 24 » Regain SEC compliance » Restart FAP Clinical Trial » Conduct in vivo animal PoC in myotonic dystrophy » Establish a pharma R&D collaboration

Thank You 25
























