UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2019
or
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from ……………… to ………………
Commission file number 000-03922
PATRICK INDUSTRIES, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Indiana | 35-1057796 | ||
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | ||
| 107 W. FRANKLIN STREET, P.O. BOX 638 | ELKHART, | Indiana | 46515 |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | ||
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (574) 294-7511
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Common stock, without par value | PATK | Nasdaq Stock Market LLC |
| (Title of each class) | (Trading Symbol) | (Name of each exchange on which registered) |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and "emerging growth company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer ☒ Accelerated filer ☐ Non-accelerated filer ☐ Smaller reporting company ☐ Emerging growth company ☐
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
As of June 28, 2019, the last business day of the registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter, the aggregate market value of the common stock of the registrant held by non-affiliates was $1.1 billion. As of February 14, 2020, there were 23,880,778 shares of the registrant’s common stock outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant’s Proxy Statement for its Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on May 14, 2020 are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Form 10-K.
PATRICK INDUSTRIES, INC.
FORM 10-K
FISCAL YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2019
Table of Contents
| ITEM 16. | FORM 10-K SUMMARY | ||
2
FINANCIAL SECTION
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm, Deloitte & Touche LLP | F-2 | |
| F-5 | ||
| F-6 | ||
| F-7 | ||
| Consolidated Statements of Financial Position | F-8 | |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows | F-9 | |
| F-10 | ||
| Exhibits | ||
3
INFORMATION CONCERNING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains certain “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 with respect to financial condition, results of operations, business strategies, operating efficiencies or synergies, competitive position, industry growth and projections, growth opportunities for existing products, plans and objectives of management, markets for the common stock of Patrick Industries, Inc. (the “Company” or “Patrick”) and other matters. Statements in this Form 10-K as well as other statements contained in the annual report and statements contained in future filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) and publicly disseminated press releases, and statements which may be made from time to time in the future by management of the Company in presentations to shareholders, prospective investors, and others interested in the business and financial affairs of the Company, which are not historical facts, are forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those set forth in the forward-looking statements.
There are a number of factors, many of which are beyond the control of the Company, which could cause actual results and events to differ materially from those described in the forward-looking statements. Many of these factors are identified in the “Risk Factors” section of this Form 10-K as set forth in Part I, Item 1A. These factors include, without limitation, the impact of any economic downturns especially in the residential housing market, a decline in discretionary consumer spending, pricing pressures due to competition, costs and availability of raw materials and commodities, the imposition of restrictions and taxes on imports of raw materials and components used in our products, information technology performance and security, the availability of commercial credit, the availability of retail and wholesale financing for recreational vehicles, watercraft, and residential and manufactured homes, the availability and costs of labor, inventory levels of retailers and manufacturers, the financial condition of our customers, retention and concentration of significant customers, the ability to generate cash flow or obtain financing to fund growth, future growth rates in the Company's core businesses, the seasonality and cyclicality in the industries to which our products are sold, realization and impact of efficiency improvements and cost reductions, the successful integration of acquisitions and other growth initiatives, increases in interest rates and oil and gasoline prices, the ability to retain key management personnel, adverse weather conditions impacting retail sales, our ability to remain in compliance with our credit agreement covenants, cyber-related risks and general economic, market and political conditions. In addition, national and regional economic conditions may affect the retail sale of recreational vehicles, watercraft, and residential and manufactured housing. You should consider forward-looking statements, therefore, in light of various important factors, including those set forth in the reports and documents that the Company files with the SEC, including this Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2019.
Any projections of financial performance or statements concerning expectations as to future developments should not be construed in any manner as a guarantee that such results or developments will, in fact, occur. There can be no assurance that any forward-looking statement will be realized or that actual results will not be significantly different from that set forth in such forward-looking statement. Patrick does not undertake to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements, except as required by law. See Part I, Item 1A “Risk Factors” below for further discussion.
PART I
| ITEM 1. | BUSINESS |
Unless the context otherwise requires, the terms “Company,” “Patrick,” “we,” “our,” or “us” refer to Patrick Industries, Inc. and its subsidiaries.
Company Overview
Patrick Industries, Inc. was founded in 1959 and incorporated in the state of Indiana in 1961. Patrick is a major manufacturer and distributor of component and building products and materials serving original equipment manufacturers (“OEMs”) primarily in the recreational vehicle (“RV”), manufactured housing (“MH”) and marine
4
markets. The Company also supplies products to adjacent industrial markets, such as kitchen cabinet, high-rise, office and household furniture, fixtures and commercial furnishings, and other industrial markets.
The Company operates through a nationwide network that includes, as of December 31, 2019, 125 manufacturing plants and 48 warehouse and distribution facilities located in 23 states, China, Canada and the Netherlands. The Company operates within two reportable segments, Manufacturing and Distribution, through a nationwide network of manufacturing and distribution centers for its products, thereby reducing in-transit delivery time and cost to the regional manufacturing footprint of its customers. The Manufacturing and Distribution segments accounted for 70% and 30% of the Company’s consolidated net sales for 2019, respectively. Financial information about these operating segments is included in Note 19 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K (the "Form 10-K") and incorporated herein by reference.
The Company’s strategic and capital allocation strategy is to optimally manage and utilize its resources and leverage its platform of operating brands to continue to grow and reinvest in its business. Through strategic acquisitions, geographic expansion, expansion into new product lines and investment in infrastructure and capital expenditures, Patrick seeks to ensure that its operating network contains capacity, technology and innovative thought processes to support anticipated growth needs, effectively respond to changes in market conditions, inventory and sales levels, and successfully integrate manufacturing, distribution and administrative functions.
Over the last three years, the Company has executed on a number of new product initiatives and invested approximately $651 million in acquisitions, which directly complement our core competencies and existing product lines as well as expand its presence in the marine industry. The combination of improved economic conditions and demographic trends benefiting the RV, MH and marine industries and the execution of the strategic initiatives identified above, among others, resulted in increases in sales, operating income, net income and cash flows over the last several years.
The Company’s principal executive and administrative offices are located at 107 West Franklin Street, Elkhart, Indiana 46515 and the telephone number is (574) 294-7511; Internet website address: www.patrickind.com. The information on Patrick's website is not incorporated by reference into this Form 10-K. The Company makes available free of charge through the website, its Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and all amendments to those reports filed with the SEC as soon as reasonably practicable after such material is electronically filed with or furnished to the SEC.
5
Major Product Lines
Patrick manufactures and distributes a variety of products within its reportable segments including:
| Manufacturing | Distribution |
| Laminated products for furniture, shelving, walls and countertops | Pre-finished wall and ceiling panels |
| Decorative vinyl, wrapped vinyl, paper laminated panels and vinyl printing | Drywall and drywall finishing products |
| Solid surface, granite and quartz countertops | Interior and exterior lighting products |
| Fabricated aluminum products | Wiring, electrical and plumbing products |
| Wrapped vinyl, paper and hardwood profile mouldings | Transportation and logistics services |
| Custom cabinetry | Electronics and audio systems components |
| Electrical systems components including instrument and dash panels | Cement siding |
| Slide-out trim and fascia | Raw and processed lumber |
| Cabinet products, doors, components and custom cabinetry | Fiber reinforced polyester (“FRP”) products |
| Hardwood furniture | Interior passage doors |
| Fiberglass bath fixtures and tile systems | Roofing products |
| Specialty bath and closet building products | Laminate and ceramic flooring |
| Boat covers, towers, tops, and frames | Shower doors |
| Softwoods lumber | Furniture |
| Interior passage doors | Fireplaces and surrounds |
| Wiring and wire harnesses | Appliances |
| CNC molds and composite parts | Tile |
| Aluminum fuel tanks | Other miscellaneous products |
| Slotwall panels and components | |
| RV painting | |
| Thermoformed shower surrounds | |
| Fiberglass and plastic components including front and rear caps and marine helms | |
| Polymer-based flooring | |
| Air handling products | |
| Marine hardware | |
Primary Markets
Patrick manufactures and distributes its building products and interior decorative component products for use in the four primary markets it serves. Operating facilities that supply the Company’s products are strategically located in proximity to the customers they serve. The Company’s sales by market are as follows:
6
| 2019 | 2018 | |||
| RV | 55 | % | 63 | % |
| Marine | 14 | % | 12 | % |
| MH | 19 | % | 12 | % |
| Industrial | 12 | % | 13 | % |
| Total | 100 | % | 100 | % |
Recreational Vehicles
The Company’s RV products are sold primarily to major manufacturers of RVs, smaller OEMs, and to a lesser extent, manufacturers in adjacent industries. The principal types of recreational vehicles include (1) towables: conventional travel trailers, fifth wheels, folding camping trailers, and truck campers; and (2) motorized: motor homes. The RV market is primarily dominated by Thor Industries, Inc. (“Thor”), Forest River, Inc. (“Forest River”) and Winnebago Industries, Inc. ("Winnebago") which combined held 91% of retail market share for towables and 74% for motorized units as reported per Statistical Surveys, Inc. ("SSI") for 2019.
The RV industry experienced a decline in wholesale unit shipments in 2019 and 2018 following eight straight years of growth as RV OEMs continued to adjust their production levels in tandem with the rebalancing of dealer inventories in the retail marketplace. According to the Recreation Vehicle Industry Association ("RVIA"), total RV industry wholesale shipments fell 16% in 2019 compared to 2018, with shipments reaching a total of approximately 406,000 units.
The Company estimates that its mix of RV revenues related to towable units and motorized units is consistent with the overall RV industry production mix. In 2019, towable and motorized unit shipments represented approximately 89% and 11%, respectively, of total RV industry wholesale shipments. The towable sector decreased 16% in 2019 compared to the prior year and the motorized sector decreased 19% per the RVIA.
With estimated retail unit shipments outpacing wholesale unit shipments in 2019, RV dealer inventories declined in 2019. On the retail side, estimated RV retail unit shipments declined 7% in 2019 compared to 2018. For the full year 2019, RV dealer inventories declined by more than 50,000 units, which we believe will position the industry to return to a more direct relationship between wholesale unit shipments and retail unit shipments for the upcoming 2020 selling season.
Recreational vehicle purchases are generally consumer discretionary income purchases, and therefore, any situation which causes concerns related to discretionary income can have a negative impact on this market. The Company believes that industry-wide retail sales and the related production levels of RVs will continue to be dependent on the overall strength of the economy, consumer confidence levels, equity securities market trends, fluctuations in dealer inventories, the level of disposable income, and other demographic trends.
Demographic and ownership trends continue to point to favorable market growth in the long term, as there is a shift toward outdoor, nature-based tourism activities, with a large segment of the population’s “millennials” and "Gen Xers" embracing this outdoor lifestyle and entering into the RV marketplace as well as a large percentage of new campers from increasingly more diverse groups. Per the 2019 KOA North American Camping Report, 41% of all campers and 56% of new campers are millennials, while 36% of all campers and 25% of new campers are Gen Xers.
Detailed narrative information about the Company’s sales to the RV industry is included in Item 7. “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” (the "MD&A") of this Form 10-K.
Marine
The marine industry reflects the similar active, outdoor leisure-based, family-oriented lifestyle that characterizes the RV industry and the Company has increased its focus and expanded its presence in the adjacent marine market through recent acquisitions, particularly within the last three years. Consumer demand in the marine market is generally driven by the popularity of the recreational and leisure lifestyle and by economic conditions.
7
Based on current available data per SSI, within the powerboat sector, fiberglass units accounted for approximately 38% of retail unit sales, aluminum 29%, pontoon 28% and ski & wake 5% for 2019.
According to the National Marine Manufacturers Association ("NMMA"), per its latest available 2018 U.S. Recreational Boating Statistical Abstract, it is estimated that there were approximately 12 million registered boats in the U.S. in 2018. Total U.S. retail expenditures on boats, engines, accessories, and related costs totaled approximately $41.8 billion in 2018, up approximately 7% from 2017. The average age of boats currently in use is approximately 25 years compared to an average useful life of 30 years, and the expected number of boats to be retired over the next four years is approximately 1 million, according to NMMA.
The Company’s sales to the marine industry are primarily focused on the powerboat sector of the market which is comprised of four main categories: fiberglass, aluminum, pontoon and ski & wake. Based on current available data per SSI, marine powerboat retail unit shipments decreased 4% in 2019 compared to 2018, while marine wholesale unit shipments decreased approximately 13% in 2019 compared to 2018, marking the first year of declines in retail and wholesale unit shipments after eight consecutive years of growth in new boat shipments. Detailed narrative information about the Company’s sales to the marine industry is included in the MD&A of this Form 10-K.
Manufactured Housing
The Company’s manufactured housing products are sold primarily to major manufacturers of manufactured homes, other OEMs, and to a lesser extent, to manufacturers in adjacent industries. In the aggregate, the top three manufacturers produced approximately 78% of MH market retail unit shipments in 2019 per SSI.
Although wholesale unit shipments have increased in the MH industry from a low of approximately 49,800 units in 2009 to 94,633 units in 2019, they are still trending well below historical levels. The Company believes there is significant upside potential for this market in the long term driven by pent-up demand, multi-family housing capacity, improving consumer credit and financing conditions, residential housing market conditions, higher consumer confidence levels, increased affordability and quality, demographic trends such as first time home buyers and those looking to downsize, new home pricing, and improved consumer savings levels.
Factors that may favorably impact production levels further in this industry include improving quality credit standards in the residential housing market, new jobs growth, consumer confidence, favorable changes in financing regulations, a narrowing in the difference between interest rates on MH loans and mortgages on traditional residential "stick-built" housing, and any improvement in conditions in the asset-backed securities markets for manufactured housing loans.
In addition, there have been changes in financial regulations, including changes to the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform Act, in efforts to ease the regulatory burden on smaller financial institutions, as well as ongoing MH loan program initiatives by Fannie Mae, which in turn are expected to increase MH loan availability and reduce the total cost of MH borrowing, with a potential resulting increase in MH demand.
Detailed narrative information about the Company’s sales to the MH industry is included in the MD&A of this Form 10-K.
Industrial Markets
The Company estimates that approximately 60% of its industrial net sales in 2019 were associated with the U.S. residential housing market. The Company believes that there is a direct correlation between the demand for its products in this market and new residential housing construction and remodeling activities. Patrick's sales to the industrial market generally lag new housing starts by four to six months and will vary based on differences in regional economic prospects.
Many of Patrick's core manufacturing products are also utilized in the kitchen cabinet, high-rise, office and household furniture, hospitality, and fixtures and commercial furnishings markets. These markets are generally
8
categorized by a more performance-than-price driven customer base, and provide an opportunity for the Company to diversify its customer base. Additionally, other residential and commercial segments have been less vulnerable to import competition, and therefore, provide opportunities for increased sales penetration and market share gains. Over the past three years, the residential housing market in particular has shown signs of improvement across the country and that trend is expected to continue in 2020.
Detailed narrative information about the Company’s sales to the industrial markets is included in the MD&A of this Form 10-K.
Strategic Acquisitions
The Company is focused on driving growth in each of its primary markets through the acquisition of companies with strong management teams having a strategic fit with Patrick’s core values, business model and customer presence, as well as additional product lines, facilities, or other assets to complement or expand its existing businesses. The Company may explore strategic acquisition opportunities that are not directly tied to the four primary markets it serves in order to further leverage its core competencies in manufacturing and distribution and to diversify its end market exposure and presence.
In 2019, the Company invested approximately $56 million in acquisitions and over the last three years has completed approximately $651 million of acquisitions. See Note 4 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for a description of acquisitions completed by the Company in 2019, 2018 and 2017.
Competition
The RV, MH, marine and industrial markets are highly competitive, both among manufacturers and the suppliers of various components. The barriers to entry for each industry are generally low and include compliance with industry standards, codes and safety requirements, and the initial capital investment required to establish manufacturing operations. In addition, the Company competes with manufacturers of manufactured homes with vertically integrated operations. Across the Company’s range of products and services, competition exists primarily on price, product features and innovation, timely and reliable delivery, quality and customer service. Several competitors compete with Patrick in each product line on a regional and local basis. However, in order for a competitor to compete with Patrick on a national basis, the Company believes that a substantial capital commitment and investment in personnel and facilities would be required.
Capacity and Plant Expansions
Patrick has the ability to fulfill demand for certain products in excess of capacity at certain facilities by shifting production to other facilities. Capital expenditures for 2019 consisted of $27.7 million of investments primarily to replace and upgrade production equipment, expand facilities outside of core Midwest markets to align with OEM expansions, increase capacity, and provide more advanced manufacturing automation. Management regularly monitors capacity at its facilities and reallocates existing resources where needed to maintain production efficiencies throughout all of its operations and capitalize on commercial and industrial synergies in key regions to support profitable growth, grow its customer base, and expand its geographical product reach outside its core Midwest market.
Branding
New product development is a key component of the Company’s efforts to grow its market share and revenue base, adapt to changing market conditions, and proactively address customer demand. The Company has expanded its product and service offerings with the integration of new and innovative product lines into its operations that bring additional value to customers and create additional scale advantages.
9
The Studio
The Company's Design/Innovation Center and Showroom, The Studio, is located in Elkhart, Indiana. The Studio presents the latest design trends and products in the markets served by Patrick, and provides a creative environment for customers to design products and enhance their brand. The 45,000 square foot facility includes a 25,000 square foot showroom devoted to the display of products, capabilities and services offered by each of Patrick’s business units, in addition to offices and conference rooms. The Company’s specialized team of designers, engineers and graphic artists works with RV, MH, marine and industrial customers to meet their creative design and product needs, including creating new styles and utilizing new colors, patterns, products, and wood types for panels and mouldings, cabinet doors, furniture, lighting and other products. Other services provided at The Studio include product development, 3D CAD illustration, 3D printing, photography and marketing.
Marine Studio
The Company's Marine Studio, which was opened in February 2020 and is located in Sarasota, Florida, is a comprehensive marine studio showroom, design and engineering center, which provides full engineering and integrated design solutions for our marine customers. The 14,000 square foot facility includes a showroom that displays the Company's marine products as well as the marine design and engineering capabilities and services offered by our marine businesses.
Operating Brands
Through its operating brands, the Company provides customers with specific product knowledge, expertise and support that are tailored to their needs. The Company strives to be the supplier of choice for its customers by elevating the customer purchasing experience with expert product line managers, and support staff and strategic partnerships for each operating brand, which help drive efficiency and maximize value for its customers.
Patrick has no material licenses, franchises, or concessions and does not conduct significant research and development activities.
Marketing and Distribution
As of December 31, 2019, the Company had over 3,100 active customers. Its revenues from the RV market include sales to two major manufacturers of RVs that each account for over 10% of the Company's net sales, Forest River and Thor. Both Forest River and Thor have multiple businesses and brands that operate independently under the parent company and these multiple businesses and brands generally purchase our products independently from one another. The Company’s sales to the various businesses of Forest River and Thor, on a combined basis, accounted for 40%, 49% and 57% of our consolidated net sales, for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
The Company generally maintains supplies of various commodity products in its warehouses to ensure that it has product on hand at all times for its distribution customers. The Company purchases a majority of its distribution segment products in railcar, container, or truckload quantities, which are warehoused prior to their sale to customers. Approximately 12%, 15% and 19% of the Company's distribution segment’s sales were from products shipped directly from the suppliers to Patrick customers in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively. Typically there is a one to two-week period between Patrick receiving a purchase order and the delivery of products to its warehouses or customers and, as a result, the Company has no significant backlog of orders. In periods of declining market conditions, customer order rates can decline, resulting in less efficient logistics planning and fulfillment and thus increasing delivery costs due to increased numbers of shipments with fewer products in each shipment.
Raw Materials
Patrick has arrangements with certain suppliers that specify exclusivity in certain geographic areas, pricing structures and rebate agreements among other terms.
10
Raw materials are primarily commodity products, such as lauan, gypsum, particleboard and other lumber products, aluminum, resin, fiberglass and overlays, among others which are available from many suppliers. Our customers do not maintain long-term supply contracts, and therefore, the Company bears the risk of accurate forecasting of customer orders. Its sales in the short-term could be negatively impacted in the event any unforeseen negative circumstances were to affect its major suppliers. In addition, demand changes in certain market sectors can result in fluctuating costs of certain more commodity-oriented raw materials and other products that are utilized and distributed.
The Company continually explores alternative sources of raw materials and components, both domestically and from outside the U.S. Alternate sources of supply are available for all of its material purchases.
Regulation and Environmental Quality
The Company’s operations are subject to environmental laws and regulations administered by federal, state, and local regulatory authorities including requirements relating to air, water and noise pollution. Additionally, these requirements regulate the Company's use, storage, discharge and disposal of hazardous chemicals used or generated during specific manufacturing processes.
Select products are subject to various legally binding or voluntary standards. For example, the composite wood substrate materials that Patrick uses to produce products for its customers in the RV marketplace have been certified as to compliance with applicable emission standards developed by the California Air Resources Board (“CARB”). All suppliers and manufacturers of composite wood materials are required to comply with the current CARB regulations.
The Company is certified to sell Forestry Stewardship Council (“FSC”) materials to its customers at certain of its manufacturing branches. The FSC certification provides a link between responsible production and consumption of materials from the world’s forests and assists the Company’s customers in making socially and environmentally responsible buying decisions on the products they purchase. Upholstered products and mattresses provided by the Company for RVs must comply with Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards regulated by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration regarding flammability.
The Company also produces and provides products for manufactured homes that must comply with performance and construction regulations promulgated by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (“HUD”).
Seasonality
Manufacturing operations in the RV, marine and MH industries historically have been seasonal and at their highest levels when the weather is moderate. Accordingly, the Company’s sales and profits had generally been the highest in the second quarter and lowest in the fourth quarter. Seasonal industry trends in the past several years have included the impact related to the addition of major RV manufacturer open houses for dealers in the August-September timeframe and marine open houses in the December-February timeframe, resulting in dealers delaying certain restocking purchases until new product lines are introduced at these shows. In addition, recent seasonal industry trends have been, and future trends may be, different than in prior years due to the impact of volatile economic conditions, interest rates, access to financing, cost of fuel, national and regional economic conditions and consumer confidence on retail sales of RVs and marine units and other products for which the Company sells its components, as well as fluctuations in RV and marine dealer inventories, increased volatility in demand from RV and marine dealers, the timing of dealer orders, and from time to time, the impact of severe weather conditions on the timing of industry-wide wholesale shipments.
11
Employees
At December 31, 2019, we had approximately 7,500 employees. The Company believes its relations with its employees are good. The Company is not subject to any collective bargaining agreements with its employees.
Executive Officers of the Company
The following table sets forth our executive officers as of January 1, 2020:
| Officer | Position | Age | ||
| Todd M. Cleveland | Executive Chairman of the Board | 51 | ||
| Andy L. Nemeth | President and Chief Executive Officer | 50 | ||
| Jeffrey M. Rodino | Executive Vice President-Sales and Chief Sales Officer | 49 | ||
| Kip B. Ellis | Executive Vice President-Operations and Chief Operating Officer | 45 | ||
| Joshua A. Boone | Vice President-Finance, Chief Financial Officer and Secretary-Treasurer | 40 | ||
| Courtney A. Blosser | Executive Vice President-Human Resources and Chief Human Resources Officer | 53 | ||
Todd M. Cleveland was appointed Executive Chairman of the Board of the Company in January 2020. Prior to that, Mr. Cleveland was Chairman of the Board from May 2018 to December 2019 and Chief Executive Officer from February 2009 until December 2019. Mr. Cleveland was President of the Company from May 2008 to December 2015, and Chief Operating Officer from May 2008 to March 2013. Prior to that, Mr. Cleveland served as Executive Vice President of Operations and Sales and Chief Operating Officer from August 2007 to May 2008 following the acquisition of Adorn Holdings, Inc. by Patrick in May 2007. Mr. Cleveland has over 29 years of manufactured housing, recreational vehicle, and industrial experience in various leadership capacities.
Andy L. Nemeth was appointed Chief Executive Officer of the Company in January 2020. In addition to this role, Mr. Nemeth serves as President of the Company, a position he has held since January 2016. Mr. Nemeth was the Executive Vice President of Finance and Chief Financial Officer from May 2004 to December 2015, and Secretary-Treasurer from 2002 to 2015. Mr. Nemeth has over 28 years of manufactured housing, recreational vehicle, and industrial experience in various financial and managerial capacities.
Jeffrey M. Rodino was appointed Chief Sales Officer of the Company in September 2016. In addition to this role, Mr. Rodino serves as the Executive Vice President of Sales, a position he has held since December 2011. Prior to that, he was the Chief Operating Officer of the Company from March 2013 to September 2016, and Vice President of Sales for the Midwest from August 2009 to December 2011. Mr. Rodino has over 26 years of experience in serving the recreational vehicle, manufactured housing and industrial markets.
Kip B. Ellis was appointed Executive Vice President of Operations and Chief Operating Officer of the Company in September 2016. He was elected an officer in September 2016. Mr. Ellis joined the Company as Vice President of Market Development in April 2016. Prior to his role at Patrick, Mr. Ellis served as Vice President of Aftermarket Sales for the Dometic Group from 2015 to 2016. Prior to his tenure at Dometic, Mr. Ellis served as Vice President of Global Sales and Marketing from 2007 to 2015 at Atwood Mobile Products. Mr. Ellis has over 23 years of experience serving the recreational vehicle, manufactured housing, industrial and automotive markets.
Joshua A. Boone was appointed Vice President of Finance, Chief Financial Officer and Secretary-Treasurer of the Company in January 2016. He was elected an officer in May 2016. Mr. Boone joined the Company as its Director of Corporate Finance in July 2014. Prior to his role at Patrick, Mr. Boone served as Chief Financial Officer for Pretzels, Inc. from 2012 to 2014 and served in several leadership positions in finance and accounting at Brunswick Corporation from 2007 to 2012. Mr. Boone has over 15 years of experience serving the manufacturing, industrial and marine industries in various financial and managerial capacities.
12
Courtney A. Blosser was appointed Executive Vice President of Human Resources and Chief Human Resources Officer of the Company in May 2016. Prior to that, Mr. Blosser was the Vice President of Human Resources from October 2009 to May 2016. Prior to his role at Patrick, Mr. Blosser served as the Corporate Director-Human Resources of Whirlpool Corporation from 2008 to 2009. Mr. Blosser has over 31 years of operations and human resource experience in various industries.
Website Access to Company Reports
We make available free of charge through our website, www.patrickind.com, our Annual Report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and all amendments to those reports as soon as reasonably practicable after such material is electronically filed with or furnished to the SEC. The charters of our Audit, Compensation, and Corporate Governance and Nominations Committees, our Corporate Governance Guidelines, our Code of Ethics and Business Conduct, and our Code of Ethics Applicable to Senior Executives are also available on the “Corporate Governance” portion of our website. Our website and the information contained therein or incorporated therein are not intended to be incorporated into this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| ITEM 1A. | RISK FACTORS |
In addition to the other information set forth in this report, you should carefully consider the following factors which could materially affect our business, financial condition or results of operations. The risks described below are not the only risks we face. Additional factors not presently known to us or that we currently deem to be immaterial also may materially adversely affect our business, cash flows, financial condition or results of operations in future periods.
Economic and business conditions beyond Patrick's control, including cyclicality and seasonality in the industries it sells products, could lead to fluctuations in and negatively impact operating results.
The RV, MH, marine and industrial markets in which we operate are subject to cycles of growth and contraction in consumer demand, and volatility in production levels, shipments, sales and operating results, due to external factors such as general economic conditions, consumer confidence, employment rates, financing availability, interest rates, inflation, fuel prices, and other economic conditions affecting consumer demand and discretionary spending. Periods of economic recession and downturns have adversely affected our business and operating results in the past, and have potential to adversely impact our future results. Consequently, the results for any prior period may not be indicative of results for any future period. In addition, fluctuation in demand could adversely affect our management of inventory, which could lead to an inability to meet customer needs or a charge for obsolete inventory.
Manufacturing operations in the RV, marine and MH industries historically have been seasonal and at their highest levels when the weather is moderate. Accordingly, the Company’s sales and profits had generally been the highest in the second quarter and lowest in the fourth quarter. Seasonal industry trends in the past several years have included the impact related to the addition of major RV manufacturer open houses for dealers in the August-September timeframe and marine open houses in the December-February timeframe, resulting in dealers delaying certain restocking purchases until new product lines are introduced at these shows. In addition, recent seasonal industry trends have been, and future trends may be, different than in prior years due to the impact of volatile economic conditions, interest rates, access to financing, cost of fuel, national and regional economic conditions and consumer confidence on retail sales of RVs and marine units and other products for which the Company sells its components, as well as fluctuations in RV and marine dealer inventories, increased volatility in demand from RV and marine dealers, the timing of dealer orders, and from time to time, the impact of severe weather conditions on the timing of industry-wide wholesale shipments.
13
If the financial condition of our customers and suppliers deteriorate, our business and operating results could suffer.
The markets we serve have been highly sensitive to changes in the economic environment. Weakening conditions in the economy, or the lack of available financing in the credit market, could cause the financial condition of our customers and suppliers to deteriorate, which could negatively affect our business through the loss of sales or the inability to meet our commitments. Many of our customers participate in highly competitive markets and their financial condition may deteriorate as a result. In addition, a decline in the financial condition of our customers could hinder our ability to collect amounts owed by customers.
Although we have a large number of customers, our sales are significantly concentrated with two customers, the loss of either of which could have a material adverse impact on our operating results and financial condition.
Two customers in the RV market accounted for a combined 40% of our consolidated net sales in 2019. The loss of either of these customers could have a material adverse impact on our operating results and financial condition. We do not have long-term agreements with our customers and cannot predict that we will maintain our current relationships with these customers or that we will continue to supply them at current levels.
Changes in consumer preferences relating to our products could adversely impact our sales levels and our operating results.
Changes in consumer preferences, or our inability to anticipate changes in consumer preferences for RVs, marine models or manufactured homes, or for the products we make could reduce demand for our products and adversely affect our operating results and financial condition.
A significant percentage of the Company’s sales are concentrated in the RV industry, and declines in the level of RV unit shipments or reductions in industry growth could reduce demand for our products and adversely impact our operating results and financial condition.
In 2019 and 2018, the Company's net sales to the RV industry were approximately 55% and 63%, respectively, of consolidated net sales. While the Company measures its RV segment sales against industry-wide wholesale shipment statistics, the underlying health of the RV industry is determined by retail demand. Retail sales of RVs historically have been closely tied to general economic conditions, and as well to consumer confidence, which has been on an upward trend since 2010. In addition, the recalibration of RV dealer inventory levels contributed to a decline in wholesale unit shipment levels in 2018 and 2019. Declines in RV unit shipment levels or reductions in industry growth could significantly reduce the Company’s revenue from the RV industry and have a material adverse impact on its operating results in 2020 and other future periods.
The RV, MH, marine and industrial industries are highly competitive and some of our competitors may have greater resources than we do.
We operate in a highly competitive business environment and our sales could be negatively impacted by our inability to maintain or increase prices, changes in geographic or product mix, or the decision of our customers to purchase our competitors’ products or to produce in-house products that we currently produce. We compete not only with other suppliers to the RV, MH, marine and industrial producers, but also with suppliers to traditional site-built homebuilders and suppliers of cabinetry and countertops. Sales could also be affected by pricing, purchasing, financing, advertising, operational, promotional, or other decisions made by purchasers of our products. Additionally, we cannot control the decisions made by suppliers of our distributed and manufactured products and therefore, our ability to maintain our distribution arrangements may be adversely impacted.
Although we are one of the largest competitors in our industry, the greater financial resources or the lower levels of debt or financial leverage of certain of our competitors may enable them to commit larger amounts of capital in response to changing market conditions. Competitors may develop innovative new products that could put the Company at a competitive disadvantage. If we are unable to compete successfully against other manufacturers and
14
suppliers to the RV, MH and marine industries as well as to the industrial markets we serve, we could lose customers and sales could decline, or we may not be able to improve or maintain profit margins on sales to customers or be able to continue to compete successfully in our core markets.
Conditions in the credit market could limit the ability of consumers and wholesale customers to obtain retail and wholesale financing for RVs, manufactured homes, and marine products, resulting in reduced demand for our products.
Restrictions on the availability of consumer and wholesale financing for RVs, manufactured homes and marine products and increases in the costs of such financing have in the past limited, and could again limit, the ability of consumers and wholesale customers to purchase such products, which would result in reduced production by our customers, and therefore reduce demand for our products.
Loans used to finance the purchase of manufactured homes usually have shorter terms and higher interest rates, and are more difficult to obtain, than mortgages for site-built homes. Historically, lenders required a higher down payment, higher credit scores and other criteria for these loans. Current lending criteria are more stringent than historical criteria, and many potential buyers of manufactured homes may not qualify.
The availability, cost, and terms of these manufactured housing loans are also dependent on economic conditions, lending practices of financial institutions, government policies, and other factors, all of which are beyond our control. Reductions in the availability of financing for manufactured homes and increases in the costs of this financing have limited, and could continue to limit, the ability of consumers and wholesale customers to purchase manufactured homes, resulting in reduced production of manufactured homes by our customers, and therefore reduced demand for our products. In addition, certain provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act, which regulate financial transactions, could make certain types of loans more difficult to obtain, including those historically used to finance the purchase of manufactured homes.
The manufactured housing industry has experienced a significant long-term decline in shipments, which has led to reduced demand for our products.
The MH industry, which accounted for 19% of the Company's consolidated net sales for 2019, has experienced a significant decline in production of new homes compared to the last peak production level in 1998. The downturn was caused, in part, by limited availability and high cost of financing for manufactured homes and was exacerbated by economic and political conditions during the 2008 financial crisis. Although industry-wide wholesale production of manufactured homes has improved somewhat in recent years, annual production remains well below historical averages and a worsening of conditions in the MH market could have a material adverse impact on our operating results.
Fuel shortages or high prices for fuel could have an adverse impact on our operations.
The products produced by the RV and marine industries typically require gasoline or diesel fuel for their operation, or the use of a vehicle requiring gasoline or diesel fuel for their operation. There can be no assurance that the supply of gasoline and diesel fuel will continue uninterrupted or that the price or tax on fuel will not significantly increase in the future. Shortages of gasoline and diesel fuel, and substantial increases in the price of fuel, have had a material adverse effect on our business and the RV industry as a whole in the past and could have a material adverse effect on our business in the future.
If we cannot effectively manage the challenges and risks associated with doing business internationally, our revenues and profitability may suffer.
We purchase a significant portion of our raw materials and other supplies from suppliers located in Indonesia, China, Malaysia and Canada. As a result, our ability to obtain raw materials and supplies on favorable terms and in a timely fashion are subject to a variety of risks, including fluctuations in foreign currencies, changes in the economic strength of the foreign countries in which we do business, difficulties in enforcing contractual obligations and
15
intellectual property rights, compliance burdens associated with a wide variety of international and U.S. import laws, and social, political, and economic instability. Our business with our international suppliers could be adversely affected by restrictions on travel to and from any of the countries in which we do business due to a health epidemic or outbreak or other event. Additional risks associated with our foreign business include restrictive trade policies, imposition of duties, taxes, or government royalties by foreign governments, and compliance with the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and local anti-bribery laws. Any measures, or proposals to implement such measures, could negatively impact our relations with our international suppliers and the volume of shipments to the U.S. from these countries, which could have a materially adverse effect on our business and operating results. We maintain limited operations in Canada, the Netherlands and China but are nevertheless exposed to risks of operating in those countries associated with: (i) the difficulties and costs of complying with a wide variety of of complex laws, treaties and regulations; (ii) unexpected changes in political or regulatory environments; (iii) earnings and cash flows that may be subject to tax withholding requirements or the imposition of tariffs, exchange controls, or other restrictions; (iv) political, economic, and social instability; (v) import and export restrictions and other trade barriers; (vi) responding to disruptions in existing trade agreements or increased trade tensions between countries or political or economic unions; (vii) maintaining overseas subsidiaries and managing international operations; and (viii) fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates.
We are dependent on third-party suppliers and manufacturers and any increased cost and limited availability of certain raw materials may have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
Prices of certain materials, including gypsum, lauan, particleboard, MDF, aluminum and other commodity products, can be volatile and change dramatically with changes in supply and demand. Certain products are purchased from overseas and their availability is dependent upon weather conditions, seasonal and religious holidays, political unrest, economic conditions overseas, tariffs or other cross-border taxes, natural disasters, vessel shipping schedules and port availability. Further, our commodity product suppliers sometimes operate at or near capacity, resulting in some products having the potential of being put on allocation. We generally have been able to maintain adequate supplies of materials and to pass higher material costs on to our customers in the form of surcharges and base price increases where needed. However, it is not certain future price increases can be passed on to our customers without affecting demand or that limited availability of materials will not impact our production capabilities. Our sales levels and operating results could be negatively impacted by changes in any of these items.
Generally, our raw materials, supplies and energy requirements are obtained from various sources and in the quantities desired. While alternative sources are available, our business is subject to the risk of price increases and periodic delays in delivery. Fluctuations in prices may be driven by the supply/demand relationship for that commodity, governmental regulation, tariffs or other cross-border taxes, economic conditions in other countries, religious holidays, natural disasters, and other events. In addition, if any of our suppliers seek bankruptcy relief or otherwise cannot continue their business as anticipated, the availability or price of these requirements could be adversely affected.
If we are unable to manage our inventory, our operating results could be materially and adversely affected.
Our customers generally do not maintain long-term supply contracts and, therefore, we must bear the risk of certain inventory commitments, based on our projections of future customer orders. We maintain an inventory to support these customers’ needs. Changes in demand, market conditions and/or product specifications could result in material obsolescence and a lack of alternative markets for certain of our customer specific products and could negatively impact operating results.
We could incur charges for impairment of assets, including goodwill and other long-lived assets, due to potential declines in the fair value of those assets or a decline in expected profitability of the Company or individual reporting units of the Company.
Approximately 65% of our total assets as of December 31, 2019 were comprised of goodwill, intangible assets, operating lease right-of-use assets and property, plant and equipment. Under generally accepted accounting principles, each of these assets is subject to periodic review and testing to determine whether the asset is recoverable
16
or realizable. The events or changes that could require us to test our goodwill and intangible assets for impairment include changes in our estimated future cash flows, changes in rates of growth in our industry or in any of our reporting units, and decreases in our stock price and market capitalization.
In the future, if sales demand or market conditions change from those projected by management, asset write-downs may be required. Significant impairment charges, although not always affecting current cash flow, could have a material effect on our operating results and financial position.
Increases in demand for our products could make it more difficult for us to obtain additional skilled labor, which may adversely impact our operating efficiencies.
In certain geographic regions in which we have manufacturing facilities, we have experienced shortages of qualified employees, which negatively impacted our cost of goods sold. Labor shortages and continued competition for qualified employees may increase, especially during improving economic times, the cost of our labor and create employee retention and recruitment challenges, as employees with knowledge and experience have the ability to change employers more easily.
If demand continues to increase, we may not be able to increase production to timely satisfy demand, and may initially incur higher labor and production costs, which could adversely impact our financial condition and operating results.
We may incur significant charges or be adversely impacted by the consolidation and/or closure of all or part of a manufacturing or distribution facility.
We periodically assess the cost structure of our operating facilities to distribute and/or manufacture products in the most efficient manner. We may make capital investments to move, discontinue manufacturing and/or distribution capabilities, or products and product lines, sell or close all or part of additional manufacturing and/or distribution facilities in the future. These changes could result in significant future charges or disruptions in our operations, and we may not achieve the expected benefits from these changes, which could result in an adverse impact on our operating results, cash flows, and financial condition.
We are subject to governmental and environmental regulations, and failure in our compliance efforts, changes to such laws and regulations or events beyond our control could result in damages, expenses or liabilities that individually, or in the aggregate, would have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Some of our manufacturing processes involve the use, handling, storage and contracting for recycling or disposal of hazardous or toxic substances or wastes. Accordingly, we are subject to various governmental and environmental laws and regulations regarding these substances, as well as environmental requirements relating to air, water and noise pollution. The implementation of new laws and regulations or amendments to existing regulations could significantly increase the cost of the Company’s products. We cannot presently determine what, if any, legislation may be adopted by federal, state or local governing bodies, or the effect any such legislation may have on our customers or us. Failure to comply with present or future regulations could result in fines or potential civil or criminal liability. Both scenarios could negatively impact our results of operations or financial condition.
The inability to attract and retain qualified executive officers and key personnel may adversely affect our operations.
While we include succession planning as part of our ongoing talent development and management process to help ensure the continuity of our business model, the loss of any of our executive officers or other key personnel could reduce our ability to manage our business and strategic plan in the short-term and could cause our sales and operating results to decline. In addition, our future success will depend on, among other factors, our ability to attract and retain executive management, key employees, and other qualified personnel.
17
Our ability to integrate acquired businesses may adversely affect operations.
As part of our business and strategic plan, we look for strategic acquisitions to provide shareholder value. Any acquisition will require the effective integration of an existing business and certain of its administrative, financial, sales and marketing, manufacturing, distribution and other functions to maximize synergies. Acquired businesses involve a number of risks that may affect our financial performance, including increased leverage, diversion of management resources, assumption of liabilities of the acquired businesses, and possible corporate culture conflicts. If we are unable to successfully integrate these acquisitions, we may not realize the benefits identified in our due diligence process, and our financial results may be negatively impacted. Additionally, significant unexpected liabilities could arise from these acquisitions.
Our level of indebtedness could limit our operational flexibility and harm our financial condition and results of operations.
As of December 31, 2019, we had $705.0 million of total long-term debt, including current maturities and exclusive of deferred financing costs and debt discount, outstanding under our $650.0 million 2019 Credit Facility, Senior Notes and Convertible Senior Notes (all as defined herein).
Our level of indebtedness could have adverse consequences on our future operations, including making it more difficult for us to meet our payments on outstanding debt, and we may not be able to find alternative financing sources to replace our indebtedness in such an event. Our level of indebtedness could: (i) reduce the availability of our cash flow to fund working capital, capital expenditures, acquisitions and other general corporate purposes, and limit our ability to obtain additional financing for these purposes; (ii) limit our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, and increase our vulnerability to, changes in our business and the industry in which we operate; (iii) place us at a competitive disadvantage compared to our competitors that have less debt or are less leveraged; and (iv) create concerns about our credit quality which could result in the loss of supplier contracts and/or customers. Our ability to satisfy our debt obligations will depend on our future operating performance which may be affected by factors beyond our control.
Our 2019 Credit Agreement contains various financial performance and other covenants. If we do not remain in compliance with these covenants, our 2019 Credit Agreement could be terminated and the amounts outstanding thereunder could become immediately due and payable.
We have debt outstanding that contains financial and non-financial covenants with which we must comply that place restrictions on us. There can be no assurance that we will maintain compliance with the financial covenants under our 2019 Credit Agreement (as defined herein). These covenants require that we comply with a maximum level of a consolidated total leverage ratio and a minimum level of a consolidated fixed charge coverage ratio. If we fail to comply with the covenants contained in our 2019 Credit Agreement, the lenders could cause our debt to become due and payable prior to maturity or it could result in our having to refinance the indebtedness under unfavorable terms. If our debt were accelerated, our assets might not be sufficient to repay our debt in full and there can be no assurance that we would be able to refinance any or all of this indebtedness.
Due to industry conditions and our operating results, there have been times in the past when we have had limited access to sources of capital. If we are unable to locate suitable sources of capital when needed, we may be unable to maintain or expand our business.
We depend on our cash balances, our cash flows from operations, and our 2019 Credit Facility to finance our operating requirements, capital expenditures and other needs. If a significant economic recession occurred, such as the recession that impacted the economy in 2007-2010, production of RVs, marine units and manufactured homes could decline, resulting in reduced demand for our products. A decline in our operating results could negatively impact our liquidity. If our cash balances, cash flows from operations, and availability under our 2019 Credit Facility are insufficient to finance our operations and alternative capital is not available, we may not be able to expand our business and make acquisitions, or we may need to curtail or limit our existing operations.
18
We have letters of credit representing collateral for our casualty insurance programs and for general operating purposes that have been issued under our 2019 Credit Agreement. The inability to retain our current letters of credit, to obtain alternative letter of credit sources, or to retain our 2019 Credit Agreement to support these programs could require us to post cash collateral, reduce the amount of cash available for our operations, or cause us to curtail or limit existing operations.
The conditional conversion feature of the Convertible Notes that we issued in January 2018, if triggered, may adversely affect our financial condition and operating results.
In the event the conditional conversion feature of the Convertible Senior Notes due 2023 (the "Convertible Notes") is triggered, holders of Convertible Notes will be entitled to convert the Convertible Notes at any time during specified periods at their option. If one or more holders elect to convert their Convertible Notes, unless we elect to satisfy our conversion obligation by delivering solely shares of our common stock (other than paying cash in lieu of delivering any fractional share), we would be required to settle a portion or all of our conversion obligation through the payment of cash, which could adversely affect our liquidity. In addition, even if holders do not elect to convert their Convertible Notes, we could be required under applicable accounting rules to reclassify all or a portion of the outstanding principal of the Convertible Notes as a current rather than long-term liability. See Notes 8 and 9 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional details.
The convertible note hedge and warrant transactions may affect the value of the Convertible Notes and our common stock.
In connection with the pricing of the Convertible Notes, we entered into convertible note hedge transactions with certain of the initial purchasers and/or their respective affiliates (the “option counterparties”). At the same time, we entered into warrant transactions with the option counterparties. The convertible note hedge transactions are expected generally to reduce the potential dilution upon conversion of the Convertible Notes and/or offset any cash payments we are required to make in excess of the principal amount of converted notes, as the case may be. However, the warrant transactions could separately have a dilutive effect on our common stock to the extent that the market price per share of our common stock exceeds the strike price of the warrants.
In addition, the option counterparties or their respective affiliates may modify their hedge positions by entering into or unwinding various derivatives with respect to our common stock and/or purchasing or selling our common stock or other securities of ours in secondary market transactions following the pricing of the Convertible Notes and prior to the maturity of the Convertible Notes (and are likely to do so during any observation period related to a conversion of Convertible Notes). This activity could cause or avoid an increase or a decrease in the market price of our common stock or the Convertible Notes, which could affect a holder's ability to convert the Convertible Notes and, to the extent the activity occurs during any observation period related to a conversion of Convertible Notes, it could affect the number of shares and value of the consideration that a holder will receive upon conversion of the Convertible Notes.
A variety of factors, many of which are beyond our control, could influence fluctuations in the market price for our common stock.
The stock market, in general, experiences volatility that has often been unrelated to the underlying operating performance of companies. If this volatility continues, the trading price of our common stock could decline significantly, independent of our actual operating performance. The market price of our common stock could fluctuate significantly in response to a number of factors, many of which are beyond our control, including the following:
| • | variations in our, our customers' and our competitors’ operating results; |
| • | high concentration of shares held by institutional investors; |
| • | announcements by us or our competitors of significant contracts, acquisitions, strategic partnerships, joint ventures or capital commitments; |
| • | announcements by us or our competitors of technological improvements or new products; |
19
| • | the gain or loss of significant customers; |
| • | additions or departures of key personnel; |
| • | events affecting other companies that the market deems comparable to us; |
| • | changes in investor perception of our business and/or management; |
| • | changes in global economic conditions or general market conditions in the industries in which we operate; |
| • | sales of our common stock held by certain equity investors or members of management; |
| • | issuance of our common stock or debt securities by the Company; and |
| • | the occurrence of other events that are described in these risk factors. |
If our information technology systems fail to perform adequately, our operations could be disrupted and could adversely affect our business, reputation and results of operations.
We are increasingly dependent on digital technology, including information systems and related infrastructure, to process and record financial and operating data, manage inventory and communicate with our employees and business partners. We rely on our information technology systems to effectively manage our business data, inventory, supply chain, order entry and fulfillment, manufacturing, distribution, warranty administration, invoicing, collection of payments, and other business processes. Our systems are subject to damage or interruption from power outages, telecommunications or internet failures, computer viruses and malicious attacks, security breaches and catastrophic events. If our systems are damaged or fail to function properly or reliably, we may incur substantial repair or replacement costs, experience data loss or theft and impediments to our ability to manage our business, which could adversely affect our results of operations. At the end of the third quarter of 2019, the Company experienced a highly-sophisticated third-party malware cyberattack that impacted certain of the Company's administrative and production servers and resulted in a disruption of administrative and network operations for approximately two business days. Any such events could result in legal claims or proceedings, liability or penalties under privacy laws, disruption in operations, and damage to our reputation, which could adversely affect our business.
In addition, we may be required to make significant technology investments to maintain and update our existing computer systems. Implementing significant system changes increases the risk of computer system disruption. The potential problems and interruptions associated with implementing technology initiatives could disrupt or reduce our operational efficiency.
A cyber incident or data breach could result in information theft, data corruption, operational disruption, and/or financial loss.
Our technologies, systems, networks, and those of our business partners have in the past and may in the future become the target of cyber-attacks or information security breaches that could result in the unauthorized release, gathering, monitoring, misuse, loss, or destruction of proprietary and other information, or other disruption of our business operations. A cyber-attack could include gaining unauthorized access to digital systems for purposes of misappropriating assets or sensitive information, corrupting data, or causing operational disruption or destruction due to ransom attacks or malware or result in denial of service on websites. We have programs in place to detect, contain and respond to data security incidents. However, because the techniques used to obtain unauthorized access, disable or degrade service, or sabotage systems change frequently and may be difficult to detect for long periods of time, we may be unable to anticipate these techniques or implement adequate preventive measures. Unauthorized parties may also attempt to gain access to our systems or facilities, or those of third parties with whom we do business, through fraud, trickery, or other forms of deceiving our team members, contractors, vendors, and temporary staff. In addition, hardware, software, or applications we develop or procure from third parties may contain defects in design or manufacture or other problems that could unexpectedly compromise information security. Any cyber-attack on our business could materially harm our business and operating results. The Company currently carries insurance to cover exposure to this type of incident, but this coverage may not be sufficient to cover all potential losses. As cyber threats continue to evolve, we may be required to expend significant additional resources to continue to modify or enhance our protective measures or to investigate and remediate any information security vulnerabilities. At the end of the third quarter of 2019, the Company experienced a highly-sophisticated third-party malware cyberattack that impacted certain of the Company's administrative and production servers and
20
resulted in a disruption of administrative and network operations for approximately two business days. If we or our suppliers experience additional significant data security breaches or fail to detect and appropriately respond to significant data security breaches, we could be exposed to costly government enforcement actions and private litigation and our business and operating results could suffer.
We are required to evaluate our internal controls over financial reporting under Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and any adverse results from such evaluation could result in a loss of investor confidence in our financial reports and could have an adverse effect on our stock price.
Pursuant to Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, we are required to furnish a report by our management on our internal control over financial reporting. Such report contains, among other matters, an assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of the end of our fiscal year, including a statement as to whether or not our internal control over financial reporting is effective. This assessment must include disclosure of any material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting identified by management. Each year we must prepare or update the process documentation and perform the evaluation needed to comply with Section 404. During this process, if our management identifies one or more material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting, we will be unable to assert that such internal control is effective. Ensuring that we have adequate internal financial and accounting controls and procedures in place is a costly and time-consuming effort that needs to be re-evaluated frequently. We and our independent auditors may in the future discover areas of our internal controls that need further attention and improvement, particularly with respect to any businesses that we decide to acquire in the future. Any failure to implement required new or improved controls, or difficulties encountered in their implementation, could harm our operating results or cause us to fail to meet our reporting obligations. Investor perception that our internal controls are inadequate or that we are unable to produce accurate financial statements on a timely, consistent basis may adversely affect our stock price. Failure to comply with Section 404 could also potentially subject us to sanctions or investigations by the SEC, NASDAQ, or other regulatory authorities.
Certain provisions in our Articles of Incorporation and Amended and Restated By-laws may delay, defer or prevent a change in control that our shareholders each might consider to be in their best interest.
Our Articles of Incorporation and Amended and Restated By-laws contain provisions that are intended to deter coercive takeover practices and inadequate takeover bids. These provisions may delay, defer or prevent a change in control that our shareholders might consider to be in their best interest.
Conditions within the insurance markets could impact our ability to negotiate favorable terms and conditions for various liability coverage and could potentially result in uninsured losses.
We generally negotiate our insurance contracts annually for property, casualty, workers compensation, general liability, health insurance, and directors and officers liability coverage. Due to conditions within these insurance markets and other factors beyond our control, future coverage limits, terms and conditions and the amount of the related premiums could have a negative impact on our operating results. While we continually measure the risk/reward of policy limits and coverage, the lack of coverage in certain circumstances could result in potential uninsured losses.
| ITEM 1B. | UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
21
| ITEM 2. | PROPERTIES |
At December 31, 2019, the Company leased approximately 6.9 million square feet of manufacturing, distribution and corporate facilities and owned approximately 2.7 million square feet, as listed below.
| Area Sq. Ft. | |||
| Location | Use | Leased | Owned |
| Alabama | Manufacturing | 10,000 | |
| Alabama | Distribution | 103,000 | |
| Alabama | Manufacturing & Distribution | 94,000 | |
| Arizona | Manufacturing | 22,550 | |
| Arizona | Distribution | 10,600 | |
| California | Manufacturing | 332,404 | |
| California | Manufacturing & Distribution | 193,297 | |
| Canada | Distribution | 9,752 | |
| China | Manufacturing | 6,876 | |
| Colorado | Distribution | 9,918 | |
| Florida | Manufacturing | 316,661 | |
| Florida | Distribution | 60,977 | |
| Georgia | Manufacturing | 150,800 | 50,440 |
| Georgia | Distribution | 75,000 | 31,000 |
| Idaho | Manufacturing | 117,510 | |
| Idaho | Distribution | 16,000 | |
| Illinois | Manufacturing | 54,400 | |
| Indiana | Manufacturing | 2,283,171 | 1,271,761 |
| Indiana | Distribution | 669,653 | 593,733 |
| Indiana | Manufacturing & Distribution | 373,400 | |
| Michigan | Manufacturing | 363,552 | |
| Michigan | Distribution | 22,525 | |
| Minnesota | Distribution | 58,000 | |
| Minnesota | Manufacturing | 19,088 | |
| Mississippi | Manufacturing | 267,250 | |
| Missouri | Manufacturing | 223,000 | 31,250 |
| North Carolina | Manufacturing | 81,950 | |
| North Carolina | Distribution | 104,160 | |
| The Netherlands | Distribution | 1,300 | |
| Nevada | Manufacturing | 8,295 | |
| Nevada | Distribution | 6,720 | |
| Oregon | Manufacturing | 54,600 | |
| Oregon | Distribution | 86,000 | 48,565 |
| Pennsylvania | Manufacturing | 89,000 | |
| Pennsylvania | Distribution | 79,000 | |
| South Carolina | Manufacturing | 57,650 | |
| Tennessee | Manufacturing | 371,837 | |
| Tennessee | Distribution | 67,500 | |
| Texas | Manufacturing | 105,162 | 132,600 |
| Texas | Distribution | 99,510 | |
| Utah | Distribution | 6,000 | |
| Washington | Manufacturing | 64,000 | |
| Wisconsin | Manufacturing | 85,055 | |
| Corporate/Other: | |||
| Indiana | Corporate/Administrative Offices | 35,000 | |
| Indiana | Design Center & Showrooms | 56,200 | |
| Various | Other | 52,137 | 50,925 |
| Total square footage | 6,931,455 | 2,653,279 | |
22
Pursuant to the terms of the Company’s 2019 Credit Agreement, all owned real property subject to the existing security documents is subject to a security interest.
The Company's leased properties have lease expiration dates ranging from 2020 to 2030. Patrick believes the facilities occupied as of December 31, 2019 are adequate for the purposes for which they are currently being used and are well-maintained. The Company may, as part of its strategic operating plan, further consolidate and/or close certain owned facilities and may not renew leases on property with near-term lease expirations. Use of its manufacturing and distribution facilities may vary with seasonal, economic, and other business conditions.
| ITEM 3. | LEGAL PROCEEDINGS |
Patrick is subject to claims and lawsuits in the ordinary course of business. In management's opinion, currently pending legal proceedings and claims against the Company will not, individually or in the aggregate, have a material adverse effect on its financial condition, results of operations, or cash flows.
In August 2019, a group of companies calling itself the Lusher Site Remediation Group (the “Group”) commenced litigation against the Company in Lusher Site Remediation Group v. Sturgis Iron & Metal Co., Inc., et al., Case Number 3:18-cv-00506, pending in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of Indiana. The Group’s Second Amended Complaint, which is the first to assert claims against Patrick, asserts claims under the federal Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (“CERCLA”), 42 U.S.C. § 7601 et seq., an Indiana state environmental statute and Indiana common law. One of the other defendants in the case, Sturgis Iron & Metal Co., Inc. (“Sturgis”) subsequently filed two cross claims against Patrick, one for contribution under CERCLA and one for contractual indemnity. The Company has moved to dismiss the Second Amended Complaint and the Sturgis cross claims, and those motions remain pending. The Company does not currently believe that this matter is likely to have a material adverse impact on its financial condition, results of operations, or cash flows. However, any litigation is inherently uncertain, and any judgment or injunctive relief entered against us or any adverse settlement could materially and adversely impact our business, results of operations, financial condition, and prospects.
| ITEM 4. | MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES |
Not applicable.
PART II
| ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS, AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Market Information
The Company's common stock is listed on The NASDAQ Global Stock MarketSM under the symbol PATK.
Holders of Common Stock
As of February 14, 2020, there were 266 shareholders of record. A number of shares are held in broker and nominee names on behalf of beneficial owners.
Dividends
In December 2019, the Company's Board of Directors (the "Board") adopted a dividend policy under which it plans to declare regular quarterly cash dividends. The Company paid cash dividends of $0.25 per share, or $5.8 million in the aggregate, in 2019. Any future determination to pay cash dividends will be made by the Board in light of the Company’s earnings, financial position, capital requirements, and restrictions under the Company’s 2019 Credit Agreement, and such other factors as the Board deems relevant.
23
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer
| (c) | Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
| Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased (1) | Average Price Paid Per Share (1) | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs (2) | Maximum Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs (2) | |||||||||
| Sep. 30 - Oct. 27, 2019 | — | $ | — | — | $ | 26,722,195 | |||||||
| Oct. 28 - Dec. 1, 2019 | 3,582 | 48.96 | 3,166 | 26,567,451 | |||||||||
| Dec. 2 - Dec. 31, 2019 | 1,565 | 48.68 | 1,565 | 26,491,262 | |||||||||
| Total | 5,147 | 4,731 | |||||||||||
| (1) | Amount includes 416 shares common stock purchased by the Company in November 2019 for the sole purpose of satisfying the minimum tax withholding obligations of employees upon the vesting of stock awards held by the employees. |
| (2) | See Note 14 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information about the Company's stock repurchase program. |
Stock Performance Graph
The following graph compares the cumulative 5-year total return to shareholders of the Company’s common stock relative to the cumulative total returns of the Russell 2000 index and a customized peer group of companies, which includes Brunswick Corporation, Cavco Industries, Inc., LCI Industries, Spartan Motors, Inc., Thor Industries, Inc., Winnebago Industries, Inc., and Wabash National Corporation. This graph assumes an initial investment of $100 (with reinvestment of all dividends) was made in our common stock, in the index and in the peer group on December 31, 2014 and its relative performance is tracked through December 31, 2019.
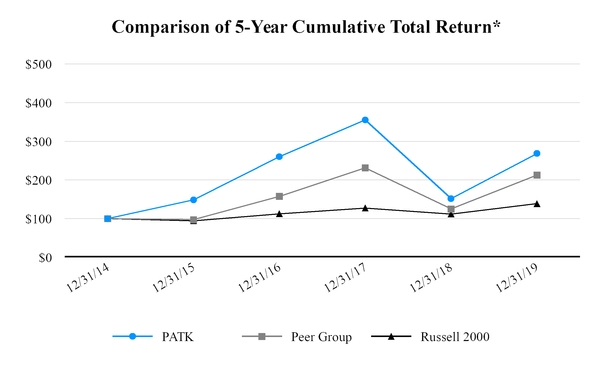
24
| ($) | 12/31/2014 | 12/31/2015 | 12/31/2016 | 12/31/2017 | 12/31/2018 | 12/31/2019 | ||||||
| Patrick Industries, Inc. | 100.00 | 148.36 | 260.23 | 355.30 | 151.48 | 268.23 | ||||||
| Peer Group | 100.00 | 97.15 | 157.74 | 231.50 | 125.10 | 212.63 | ||||||
| Russell 2000 | 100.00 | 94.29 | 112.65 | 127.46 | 111.94 | 138.50 | ||||||
*The stock price performance included in this graph is not necessarily indicative of future stock price performance.
| ITEM 6. | SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA |
| As of or for the Year Ended December 31 | |||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||
| (thousands except per share amounts) | |||||||||||||||
| Operating Data: | |||||||||||||||
Net sales (1) | $ | 2,337,082 | $ | 2,263,061 | $ | 1,635,653 | $ | 1,221,887 | $ | 920,333 | |||||
| Gross profit | 422,871 | 415,866 | 278,915 | 202,469 | 152,279 | ||||||||||
Operating income (1) | 154,442 | 178,415 | 121,900 | 90,837 | 69,918 | ||||||||||
| Net income | 89,566 | 119,832 | 85,718 | 55,577 | 42,219 | ||||||||||
| Basic net income per common share | $ | 3.88 | $ | 4.99 | $ | 3.54 | $ | 2.47 | $ | 1.84 | |||||
| Diluted net income per common share | $ | 3.85 | $ | 4.93 | $ | 3.48 | $ | 2.43 | $ | 1.81 | |||||
| Cash dividends paid per common share | $ | 0.25 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
| Financial Data: | |||||||||||||||
Total assets (1) (2) | $ | 1,470,993 | $ | 1,231,231 | $ | 866,644 | $ | 534,950 | $ | 381,584 | |||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | 139,390 | 6,895 | 2,767 | 6,449 | 87 | ||||||||||
Total short-term and long-term debt (3) | 705,000 | 661,082 | 354,357 | 273,153 | 204,484 | ||||||||||
| Shareholders' equity | 497,481 | 408,754 | 370,685 | 185,448 | 128,597 | ||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities | 192,410 | 200,013 | 99,901 | 97,147 | 66,856 | ||||||||||
(1) See Note 4 to Consolidated Financial Statements for information regarding revenues, operating income and net assets of businesses acquired in fiscal years 2019, 2018 and 2017.
(2) See Note 16 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information regarding operating lease right-of-use assets reflected on the Company's balance sheet with the adoption of a new lease accounting standard in 2019.
(3) Total short-term and long-term debt for each of the periods presented in the table above is not presented net of deferred financing costs or debt discount.
| ITEM 7. | MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
This Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (“MD&A”) should be read in conjunction with the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements and Notes thereto included in Item 8 of this Report. In addition, this MD&A contains certain statements relating to future results that are forward-looking statements as that term is defined in the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. See “Information Concerning Forward-Looking Statements” on page 4 of this Report.
25
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Overview of Markets and Related Industry Performance
Recreational Vehicle ("RV") Industry
The RV industry is our primary market and comprised 55% of the Company’s sales in 2019. Sales from the RV industry decreased 10% in 2019 compared to 2018.
According to the Recreation Vehicle Industry Association (“RVIA”), wholesale industry shipments totaled 406,000 units in 2019, a decline of 16% compared to 484,000 units in 2018. On the retail side, RV industry retail unit shipments declined 7% in 2019. With retail industry unit shipments outpacing wholesale industry unit shipments in 2019, RV industry dealer inventories declined in 2019. For the full year 2019, RV industry dealer inventories declined by more than 50,000 units, which we believe will position the industry to return to a more direct relationship between wholesale unit shipments and retail unit shipments for the upcoming 2020 selling season.
Marine Industry
Sales to the marine industry, which represented approximately 14% of the Company's consolidated net sales in 2019, increased 20% in 2019 compared to 2018. For 2019, overall marine retail industry unit shipments in the powerboat sector, which is the Company's primary marine market, decreased an estimated 4%, with aluminum fishing industry shipments decreasing an estimated 10%; pontoon industry shipments decreasing an estimated 2%; fiberglass industry shipments decreasing an estimated 3%; and ski and wake industry shipments increasing an estimated 4%.
Adverse weather and flooding in certain regions of the country impacted marine retail unit shipments in the first half of 2019, particularly in the pontoon and aluminum fishing categories. Reflecting this retail softness in the first half of 2019, we saw inventory recalibration by marine dealers in the second half of 2019, which we believe contributed to a decline in wholesale unit shipments in the second half of 2019 despite the slight increase in overall retail unit shipments in the second half of 2019. Due to the impact of weather in the first half of 2019 and the related dealer inventory re-calibration, the powerboat sector of this market experienced an estimated wholesale unit percentage decline of 13%.
Manufactured Housing ("MH") Industry
Sales to the MH industry, which represented 19% of the Company’s sales in 2019, increased 59% in 2019 compared to 2018. Based on industry data from the Manufactured Housing Institute, MH wholesale industry unit shipments decreased by 2% in 2019. Manufactured housing was negatively impacted in the first half of 2019 by wet weather conditions in certain regions of the country where moving inventory and setting foundations and houses were difficult.
Industrial Market
The industrial market is comprised primarily of the kitchen cabinet industry, high-rise, hospitality market, retail and commercial fixtures market, office and household furniture market and regional distributors. Sales to this market represented 12% of our consolidated sales in 2019, increasing 2% in 2019 compared to 2018. Overall, our revenues in these markets are focused on the residential housing, hospitality, high-rise housing and office, commercial construction and institutional furniture markets. We estimate that approximately 60% of our industrial business is directly tied to the residential housing market, with the remaining 40% directly tied to the non-residential and commercial markets.
Combined new housing starts increased 3% in 2019 compared to 2018, with single family housing starts increasing 1% and multifamily residential starts increasing 8% for the same period. Our industrial products are generally among the last components installed in new unit construction and as such our related sales typically trail new housing starts by four to six months. Because of this lag in the relationship between new housing starts and our sales of related industrial products, we expect our industrial sales to benefit in 2020 from recent growth in residential housing starts.
26
CONSOLIDATED OPERATING RESULTS
The following table sets forth the percentage relationship to net sales of certain items on the Company’s consolidated statements of income for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017.
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||
| Net sales | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||
| Cost of goods sold | 81.9 | 81.6 | 82.9 | |||||
| Gross profit | 18.1 | 18.4 | 17.1 | |||||
| Warehouse and delivery expenses | 4.2 | 3.3 | 2.9 | |||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 5.8 | 5.7 | 5.6 | |||||
| Amortization of intangible assets | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.2 | |||||
| Operating income | 6.6 | 7.9 | 7.4 | |||||
| Interest expense, net | 1.6 | 1.2 | 0.5 | |||||
| Income taxes | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.7 | |||||
| Net income | 3.8 | 5.3 | 5.2 | |||||
Year Ended December 31, 2019 Compared to 2018
Net Sales. Net sales in 2019 increased approximately $74.0 million or 3%, to $2.34 billion from $2.26 billion in 2018. The increase was attributable to a 59% increase in the Company’s sales from the MH industry, a 20% increase in revenues from the marine industry and a 2% increase in sales from the industrial markets, partly offset by a 10% decrease in sales from the RV industry. The sales increase largely reflected the revenue contribution from the acquisition of LaSalle Bristol ("LaSalle"), completed in the fourth quarter of 2018. The consolidated net sales decrease from the RV industry in 2019 primarily reflected decreases in RV OEM wholesale unit shipments.
In 2019 and 2018, revenue attributable to acquisitions completed in each of those periods was $8.3 million and $249.3 million, respectively.
The Company’s RV content per wholesale unit for 2019 increased 7% to $3,170 from $2,965 in 2018. Marine powerboat content per retail unit for 2019 increased 26% to an estimated $1,581 from $1,256 in 2018. The MH content per wholesale unit for 2019 increased 62% to $4,616 from $2,849 in 2018.
Cost of Goods Sold. Cost of goods sold increased $67.0 million, or 4%, to $1.9 billion in 2019 from $1.8 billion in 2018. As a percentage of net sales, cost of goods sold increased during 2019 to 81.9% from 81.6% in 2018.
Cost of goods sold as a percentage of net sales was impacted during 2019 by: (i) higher overall fixed overhead costs relative to RV and marine revenue and (ii) the lower margin profile of LaSalle, which was acquired in the fourth quarter of 2018. In general, the Company's cost of goods sold percentage can be impacted by demand changes in certain market sectors that can result in fluctuating costs of certain raw materials and commodity-based components that are utilized in the production of our products.
Gross Profit. Gross profit increased $7.0 million or 2%, to $422.9 million in 2019 from $415.9 million in 2018. As a percentage of net sales, gross profit decreased to 18.1% in 2019 from 18.4% in 2018. The decrease in gross profit as a percentage of net sales in 2019 compared to 2018 reflects the impact of the factors discussed above under “Cost of Goods Sold”.
27
Economic or industry-wide factors affecting the profitability of our RV, MH, marine and industrial businesses include the costs of commodities and the labor used to manufacture our products as well as the competitive environment that can cause gross margins to fluctuate from quarter-to-quarter and year-to-year.
Warehouse and Delivery Expenses. Warehouse and delivery expenses increased $23.1 million, or 31%, to $98.1 million in 2019 from $75.0 million in 2018. As a percentage of net sales, warehouse and delivery expenses were 4.2% in 2019 and 3.3% in 2018. The increase in expense 2019 compared to 2018 was primarily attributable to the impact of the LaSalle acquisition that had higher warehouse and delivery expenses as a percentage of net sales when compared to the consolidated percentage. Increased sales volumes in 2019 compared to 2018 also contributed to the increase in warehouse and delivery expense. In addition, the Company's shipments to OEMs in 2019 compared to 2018 were generally lower volume and higher frequency, and as a result transportation costs relative to sales levels of products delivered increased as a percentage of net sales.
Selling, General and Administrative ("SG&A") Expenses. SG&A expenses increased $6.3 million, or 5%, to $134.5 million in 2019 from $128.2 million in 2018. As a percentage of net sales, SG&A expenses were 5.8% in 2019 and 5.7% in 2018. The increase in SG&A expenses in 2019 compared to 2018 is primarily due to: (i) a loss on extinguishment of debt associated with the amendment of the Company's credit facility in 2019 and (ii) the impact of certain acquisitions completed in 2018 that had higher SG&A expenses as a percentage of net sales when compared to the consolidated percentage. Partially offsetting these factors was a decrease in incentive compensation and sales commissions in 2019 compared to 2018.
Amortization of Intangible Assets. Amortization of intangible assets increased $1.7 million, or 5%, in 2019 compared to 2018. The increase in 2019 compared to 2018 primarily reflects the impact of businesses acquired in 2018, partly offset by purchase accounting adjustments to intangible assets and the associated impact to amortization expense.
Operating Income. Operating income decreased $24.0 million, or 13%, to $154.4 million in 2019 from $178.4 million in 2018. Operating income in 2019 and 2018 included $0.9 million and $23.2 million, respectively, from the businesses acquired in each such year. Operating income as a percentage of net sales was 6.6% in 2019 and 7.9% in 2018. The decrease in operating income is primarily attributable to the items discussed above.
Interest Expense, Net. Interest expense, net, increased $10.2 million, or 39%, to $36.6 million in 2019 from $26.4 million in 2018. The increase in net interest expense reflects: (i) increased borrowings related to 2018 acquisitions, (ii) increases in the average interest rate on the variable rate portion of the Company's debt, which reflects a higher weighted average LIBOR in 2019 compared to 2018 and (iii) an increase in the Company's overall average interest rate resulting from the issuance of the Company's 7.5% Senior Notes due 2027 (the "Senior Notes") in the third quarter of 2019.
Income Taxes. Income tax expense decreased $3.8 million, or 12%, to $28.3 million in 2019 from $32.1 million in 2018. For 2019, the effective tax rate was 24.0% compared to 21.2% in 2018. The increase in the effective tax rate in 2019 was mostly attributable to a decrease in excess tax benefits on share-based compensation. For the full year 2020, the Company estimates its effective tax rate to be between 25% and 26%.
See our Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2018 for a discussion of our consolidated operating results for the year ended December 31, 2018 compared to 2017.
Use of Financial Metrics
Our MD&A includes financial metrics, such as RV, marine and MH content per unit, which we believe are important measures of the Company's business performance. Content per unit metrics are generally calculated using our market sales divided by third-party industry volume metrics. These metrics should not be considered alternatives to U.S. GAAP. Our computations of content per unit may differ from similarly titled measures used by others. These metrics should not be considered in isolation or as substitutes for an analysis of our results as reported under U.S. GAAP.
28
BUSINESS SEGMENTS
The Company's reportable segments, manufacturing and distribution, are based on its method of internal reporting. The Company regularly evaluates the performance of the manufacturing and distribution segments and allocates resources to them based on a variety of indicators including sales and operating income. The Company does not measure profitability at the customer market (RV, marine, MH and industrial) level.
| • | Manufacturing – This segment includes the following products: laminated products that are utilized to produce furniture, shelving, walls, countertops and cabinet products; cabinet doors; fiberglass bath fixtures and tile systems; hardwood furniture; vinyl printing; decorative vinyl and paper laminated panels; solid surface, granite, and quartz countertop fabrication; RV painting; fabricated aluminum products; fiberglass and plastic components; fiberglass bath fixtures and tile systems; softwoods lumber; custom cabinetry; polymer-based flooring; electrical systems components including instrument and dash panels; wrapped vinyl, paper and hardwood profile mouldings; interior passage doors; air handling products; slide-out trim and fascia; thermoformed shower surrounds; specialty bath and closet building products; fiberglass and plastic helm systems and components products; wiring and wire harnesses; boat covers, towers, tops and frames; marine hardware; aluminum fuel tanks; CNC molds and composite parts; slotwall panels and components; and other products. |
| • | Distribution – The Company distributes pre-finished wall and ceiling panels; drywall and drywall finishing products; electronics and audio systems components; appliances; wiring, electrical and plumbing products; fiber reinforced polyester products; cement siding; raw and processed lumber; interior passage doors; roofing products; laminate and ceramic flooring; tile; shower doors; furniture; fireplaces and surrounds; interior and exterior lighting products; and other miscellaneous products in addition to providing transportation and logistics services. |
Sales pertaining to the manufacturing and distribution segments as stated in the table below and in the following discussions include intersegment sales. Gross profit includes the impact of intersegment operating activity.
The table below presents information about the sales, gross profit, and operating income of the Company’s segments. Reconciliations of the amounts below to consolidated totals are presented in Note 19 to Consolidated Financial Statements.
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| (thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||
| Sales | |||||||||||
| Manufacturing | $ | 1,673,486 | $ | 1,779,048 | $ | 1,368,454 | |||||
| Distribution | 699,159 | 521,235 | 300,447 | ||||||||
| Gross Profit | |||||||||||
| Manufacturing | 307,362 | 337,451 | 232,671 | ||||||||
| Distribution | 110,957 | 81,016 | 48,136 | ||||||||
| Operating Income | |||||||||||
| Manufacturing | 174,913 | 215,246 | 151,635 | ||||||||
| Distribution | 38,953 | 31,491 | 18,858 | ||||||||
29
Year Ended December 31, 2019 Compared to 2018
Manufacturing
Sales. Sales decreased $105.6 million, or 6%, to $1.67 billion from $1.78 billion in 2018. This segment accounted for approximately 70% and 77% of the Company’s consolidated net sales in 2019 and 2018, respectively. The sales decrease primarily reflected a decrease in revenue from of the Company's RV market.
In 2019 and 2018, revenue attributable to acquisitions completed in each of those periods was $8.3 million and $150.9 million, respectively.
Gross Profit. Gross profit decreased $30.1 million, or 9%, to $307.4 million in 2019 from $337.5 million in 2018. As a percentage of sales, gross profit decreased to 18.4% in 2019 from 19.0% in 2018. The overall decrease in gross profit dollars and as a percentage of sales reflected higher overall fixed overhead costs relative to RV and marine revenue in 2019.
Operating Income. Operating income decreased $40.3 million, or 19%, to $174.9 million in 2019 from $215.2 million in 2018. Operating income attributable to acquisitions completed in 2019 and 2018 was $0.9 million and $18.5 million, respectively. The decrease in operating income primarily reflects the decrease in gross profit mentioned above.
Distribution
Sales. Sales increased $178.0 million, or 34%, to $699.2 million in 2019 from $521.2 million in 2018. This segment accounted for approximately 30% and 23% of the Company’s consolidated net sales for 2019 and 2018, respectively. The sales increase largely reflected the revenue contribution from the acquisition of LaSalle. The businesses acquired in 2018 contributed $98.4 million to total sales in the Distribution segment in 2018. There were no Distribution segment acquisitions in 2019.
Gross Profit. Gross profit increased $30.0 million, or 37%, to $111.0 million in 2019 from $81.0 million in 2018. As a percentage of sales, gross profit was 15.9% in 2019 compared to 15.5% in 2018. The increase in gross profit as a percentage of sales for 2019 reflected the contribution of increased sales in our higher margin transportation business and the positive impact of leveraging fixed costs on higher sales volumes in our other distribution businesses, partially offset by the lower gross margin profile of LaSalle, which was acquired in the fourth quarter of 2018, compared to our other distribution businesses.
Operating Income. Operating income in 2019 increased $7.5 million, or 24%, to $39.0 million from $31.5 million in 2018. The businesses acquired in 2018 contributed approximately $4.7 million to operating income in the Distribution segment in 2018. The overall net improvement in operating income in 2019 primarily reflects the items discussed above.
Unallocated Corporate Expenses
As presented in Note 19 to the Consolidated Financial Statements, unallocated corporate expenses in 2019 decreased $10.6 million, or 31%, to $23.5 million from $34.1 million in 2018. The decrease in 2019 was mostly attributed to a decrease in professional fees, administrative wages and incentive compensation.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
The Company's primary sources of liquidity are cash flow from operations, which includes selling its products and collecting receivables, available cash reserves and borrowing capacity available under its credit facility. Principal uses of cash are to support working capital demands, meet debt service requirements and support the Company's capital allocation strategy, which includes acquisitions, capital expenditures, dividends and repurchases of the Company’s common stock, among others.
30
Cash Flows
Year Ended December 31, 2019 Compared to 2018
Operating Activities
Cash flows from operating activities are one of the Company's primary sources of liquidity, representing the net income the Company earned in the reported periods, adjusted for non-cash items and changes in operating assets and liabilities.
Net cash provided by operating activities decreased $7.6 million to $192.4 million 2019 from $200.0 million in 2018 primarily due to: a decrease in net income of $30.2 million, partly offset by (i) an increase of depreciation and amortization of $7.7 million, (ii) an increase in stock based compensation expense, amortization of debt discount and other operating items of $3.8 million, (iii) an increase in deferred income taxes of $4.8 million and (iv) a net source of cash from changes in operating assets and liabilities of $6.3 million. Changes in operating assets and liabilities were mostly attributable to a decrease in inventories due to improved working capital management and a decrease in accounts receivable, net of acquisitions, due to timing of collections, offset partly by an increase in prepaid expenses, mostly attributable to an increase in prepaid income taxes.
Investing Activities
Net cash used in investing activities decreased $292.2 million to $79.2 million in 2019 from $371.4 million in 2018 primarily due to a decrease in cash used in business acquisitions of $287.4 million and a decrease in capital expenditures of $6.8 million, offset slightly by a decrease in proceeds from sale of property, plant, equipment and other investing activities of $2.0 million.
The Company's current operating model forecasts capital expenditures, primarily to enhance and expand our capabilities in our manufacturing facilities, for fiscal 2020 of approximately $30 million.
Financing Activities
Net cash flows provided by financing activities decreased $156.2 million to $19.3 million in 2019 from $175.5 million in 2018 primarily due to: (i) cash used for net repayments on the Company's credit facility of $256.1 million in 2019 compared to a source of cash from net borrowings on the Company's credit facility of $134.2 million in 2018; (ii) gross proceeds of $172.5 million from the third quarter 2018 issuance of 1% Convertible Senior Notes due 2023 (the "Convertible Notes") with no comparable amount in 2019; (iii) a source of cash in 2018 of $18.1 million from the related sale of warrants with no comparable amount in 2019 (iv) a use of cash of $4.4 million in 2019 from payment of contingent consideration resulting from a business acquisition with no comparable amount in 2018 and (v) payment of dividends of $5.8 million in 2019 with no comparable amount in 2018. Partially offsetting these items were: (i) the issuance of $300.0 million of Senior Notes in 2019 with no comparable amount in 2018; (ii) a use of cash in 2018 of $31.5 million from the purchase of Convertible Notes hedges with no comparable amount in 2019 and (iii) a decrease in the use of cash for stock repurchases of $103.8 million in 2019 compared to 2018.
See our Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2018 for a discussion of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2018 compared to 2017.
Summary of Liquidity and Capital Resources
The Company believes that existing cash and cash equivalents, cash generated from operations, and available borrowings under its 2019 Credit Facility (as defined herein) will be sufficient to meet anticipated cash needs for working capital and capital expenditures for at least the next 12 months, exclusive of any acquisitions, based on its current cash flow budgets and forecast of short-term and long-term liquidity needs.
The ability to access unused borrowing capacity under the 2019 Credit Facility as a source of liquidity is dependent on maintaining compliance with the financial covenants as specified under the terms of the credit agreement that
31
established the 2019 Credit Facility (the "2019 Credit Agreement"). In 2019, the Company was in compliance with its financial debt covenants as required under the terms of the 2019 Credit Agreement. The required maximum consolidated total leverage ratio and the required minimum consolidated fixed charge coverage ratio compared to the actual amounts as of December 31, 2019 and for the fiscal period then ended are as follows:
| Required | Actual | |||||
| Consolidated total leverage ratio (12-month period) | 4.00 | 2.27 | ||||
| Consolidated fixed charge coverage ratio (12-month period) | 1.50 | 5.28 | ||||
Working capital requirements vary from period to period depending on manufacturing volumes primarily related to the RV, MH and marine industries as well as the industrial markets we serve, the timing of deliveries, and the payment cycles of customers. In the event that operating cash flow is inadequate and one or more of the Company's capital resources were to become unavailable, the Company would seek to revise its operating strategies accordingly. The Company will continue to assess its liquidity position and potential sources of supplemental liquidity in view of operating performance, current economic and capital market conditions, and other relevant circumstances.
Borrowings under the revolving credit loan (the "2019 Revolver") and the term loan (the "2019 Term Loan" and, together with the 2019 Revolver, the "2019 Credit Facility") established under the 2019 Credit Agreement, which are subject to variable rates of interest, are subject to a maximum total borrowing limit of $650.0 million (effective September 17, 2019). See Note 8 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further information. See Note 9 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for information on interest rate swaps used to partially hedge variable interest rates under the 2019 Revolver and 2019 Term Loan. The unused availability under the 2019 Credit Facility as of December 31, 2019 was $411.1 million.
Contractual Obligations
The following table summarizes the Company's contractual cash obligations at December 31, 2019, and the future periods during which the Company expects to settle these obligations.
| Payments due by period | |||||||||||||||
| (thousands) | 2020 | 2021-2022 | 2023-2024 | Thereafter | Total | ||||||||||
| Long-term debt | $ | 5,000 | $ | 17,500 | $ | 382,500 | $ | 300,000 | $ | 705,000 | |||||
Interest payments on debt (1) | 34,838 | 68,884 | 61,213 | 62,812 | 227,747 | ||||||||||
| Deferred compensation payments | 216 | 309 | 260 | 1,831 | 2,616 | ||||||||||
| Minimum pension contributions | 610 | 1,810 | 1,500 | 1,800 | 5,720 | ||||||||||
Purchase obligations (2) | 210,609 | — | — | — | 210,609 | ||||||||||
Contingent consideration (3) | 2,000 | 8,000 | 1,000 | — | 11,000 | ||||||||||
| Leases payments | 30,443 | 42,765 | 22,553 | 5,867 | 101,628 | ||||||||||
| Total contractual cash obligations | $ | 283,716 | $ | 139,268 | $ | 469,026 | $ | 372,310 | $ | 1,264,320 | |||||
| (1) | Scheduled interest payments on debt obligations are calculated based on interest rates in effect at December 31, 2019 as follows: (a) 2019 Revolver - 4.59%, (b) 2019 Term Loan - 4.53%, (c) Convertible Notes - 1.00% and (d) Senior Notes - 7.50%. The projected interest payments exclude non-cash interest that would normally be included in interest expense on the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Income. |
32
| (2) | The purchase obligations are primarily comprised of purchase orders issued in the normal course of business. |
| (3) | Amount for 2020 represents actual contractual payment in 2020 achieved based on 2019 performance. 2021-2023 amounts represent undiscounted estimated contingent payments. |
We also have commercial commitments as described below (in thousands):
| Other Commercial Commitments | Total Amount Committed | Outstanding at 12/31/19 | Date of Expiration | ||||||
| Letters of Credit | $ | 25,000 | (1) | $ | 3,863 | September 17, 2024 | |||
| (1) | The $25.0 million commitment for the Letters of Credit is a sub-limit contained within the 2019 Revolver as of December 31, 2019. |
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
Other than the commercial commitments set forth above, we have no off-balance sheet arrangements.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the U.S. requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. The SEC has defined a company’s critical accounting policies as those that are most important to the portrayal of its financial condition and results of operations, and which require the Company to make its most difficult and subjective judgments, often as a result of the need to make estimates of matters that are inherently uncertain. Although management believes that its estimates and assumptions are reasonable, they are based upon information available when they are made. Actual results may differ significantly from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions. Other significant accounting policies are described in Notes 1, 3 and 16 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. The Company has identified the following critical accounting policies and estimates:
Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets. The Company’s acquisitions include purchased goodwill and other intangible assets. Goodwill represents the excess of cost over the fair value of the net assets acquired. Other intangible assets acquired are classified as customer relationships, non-compete agreements, patents and trademarks.
Goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets, representing acquired trademarks, are not amortized but are subject to an annual (or under certain circumstances more frequent) impairment test in the fourth quarter based on their estimated fair value. We test more frequently, if there are indicators of impairment, or whenever such circumstances suggest that the carrying value of goodwill or trademarks may not be recoverable. These indicators include a sustained significant decline in our share price and market capitalization, a decline in expected future cash flows, or a significant adverse change in the business climate. A significant adverse change in the business climate could result in a significant loss of market share or the inability to achieve previously projected revenue growth.
Impairment reviews of goodwill are performed at the reporting unit level. The Company’s reporting units are defined as one level below our operating segments, Manufacturing and Distribution, which are the same as our reportable segments. In evaluating goodwill for impairment, either a qualitative or quantitative assessment is performed. If the qualitative assessment indicates it is more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying value, the Company performs a quantitative assessment. When estimating reporting unit fair value with the quantitative assessment, the Company uses a combination of market and income-based methodologies. The market approach includes a comparison of multiples of earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization for the reporting units to similar businesses or guideline companies whose securities are actively traded in public markets. When calculating the present value of future cash flows under the income
33
approach, the Company takes into consideration multiple variables, including forecasted sales volumes and operating income, current industry and economic conditions, and historical results. The income approach fair value estimate also includes estimates of long-term growth rates and discount rates that are commensurate with the risks and uncertainty inherent in the respective reporting units and the internally-developed forecasts.
Impairment reviews of indefinite-lived intangible assets (trademarks) consist of a comparison of the fair value of the trademark to its carrying value. Fair value is measured using a relief-from-royalty approach, a form of discounted cash flow method. Estimated royalty rates applied to projected revenues are based on comparable industry studies and consideration of operating margins. Discount rates are derived in a manner similar to what is done in testing goodwill for impairment.
Based on the results of the Company's analyses, the estimated fair value of each of the Company's reporting units and trademarks was determined to exceed the carrying value for each of the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, and so no impairments were recognized. Further, based on the results of the impairment analyses, none of the Company’s reporting units or trademarks were at risk of failing the impairment assessments discussed above that would have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements for any period presented.
Finite-lived intangible assets that meet certain criteria continue to be amortized over their useful lives and are also subject to an impairment test based on estimated undiscounted cash flows when impairment indicators exist.
Business Combinations. From time to time, we may enter into business combinations. We recognize the identifiable assets acquired and the liabilities assumed at their fair values as of the date of acquisition. We measure goodwill as the excess of consideration transferred, which we also measure at fair value, over the net of the acquisition date fair values of the identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed. The acquisition method of accounting requires us to make significant estimates and assumptions regarding the fair values of the elements of a business combination as of the date of acquisition, including the fair values of identifiable intangible assets and contingent consideration. Significant estimates and assumptions include subjective and/or complex judgments regarding items such as discount rates, customer attrition rates, royalty rates, economic lives and other factors, including estimated future cash flows that we expect to generate from the acquired assets.
The acquisition method of accounting also requires us to refine these estimates over a measurement period not to exceed one year to reflect new information obtained about facts and circumstances that existed as of the acquisition date that, if known, would have affected the measurement of the amounts recognized as of that date. If we are required to adjust provisional amounts that we have recorded for the fair values of assets and liabilities in connection with acquisitions, these adjustments could have a material impact on our financial condition and results of operations. No changes in fiscal 2019 to our fiscal 2018 provisional fair value estimates of assets and liabilities assumed in acquisitions were material. If the subsequent actual results and updated projections of the underlying business activity change compared with the assumptions and projections used to develop the acquisition date fair value estimates, we could record future impairment charges. In addition, we estimate the economic lives of certain acquired assets and these lives are used to calculate depreciation and amortization expense. If our estimates of the economic lives change, depreciation or amortization expenses could be increased or decreased, or the acquired assets could be impaired.
| ITEM 7A. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
Debt Obligations
At December 31, 2019, our total debt obligations under our 2019 Credit Agreement were under LIBOR-based interest rates. A 100 basis point increase in the underlying LIBOR rates would result in additional annual interest cost of approximately $0.3 million, assuming average borrowings, including the Term Loan, subject to variable rates of $33.0 million, which was the amount of such borrowings outstanding at December 31, 2019 subject to variable rates after taking into consideration interest rate swaps with a combined notional principal amount of $200 million.
34
Inflation
The prices of key raw materials, consisting primarily of lauan, gypsum, particleboard, fiberglass and aluminum, and petroleum-based products are influenced by demand and other factors specific to these commodities, such as the price of oil, rather than being directly affected by inflationary pressures. Prices of certain commodities have historically been volatile and continued to fluctuate in 2019. During periods of rising commodity prices, we have generally been able to pass the increased costs to our customers in the form of surcharges and price increases. However, there can be no assurance future cost increases, if any, can be partially or fully passed on to customers, or that the timing of such sales price increases will match raw material cost increases. We do not believe that inflation had a material effect on results of operations for the periods presented.
| ITEM 8. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA |
The information required by this item is set forth in Item 15(a)(1) of Part IV of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| ITEM 9. | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
The information required by this Item 9 was previously reported in the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K that was filed with the SEC on June 7, 2019.
| ITEM 9A. | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Company maintains “disclosure controls and procedures”, as such term is defined under Securities Exchange Act Rule 13a-15(e), that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in our Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”) reports is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow for timely decisions regarding required disclosures. In designing and evaluating the disclosure controls and procedures, the Company’s management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives and the Company’s management necessarily is required to apply its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures.
Under the supervision and with the participation of our senior management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, the Company conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of the end of the period covered by this report (the “Evaluation Date”). Based on this evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded as of the Evaluation Date that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective such that the information relating to the Company, including consolidated subsidiaries, required to be disclosed in our reports filed under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and is accumulated and communicated to Company’s management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We are responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act. Our internal control system was designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the fair and reliable preparation and presentation of our published financial statements. We continually evaluate our system of internal control over financial reporting to determine if changes are appropriate based upon changes in our operations or the business environment in which we operate.
35
All internal control systems, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation.
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, we conducted an assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in the 2013 Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). This assessment included a review of the documentation of controls, an assessment of the design effectiveness of controls, testing of the operating effectiveness of controls, and a conclusion on this evaluation. As permitted under SEC guidance, management’s assessment of and conclusion regarding the design and effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting excluded the internal control over financial reporting of the operations of businesses acquired in 2019, which are described in Note 4 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. Businesses acquired in 2019 represented less than 1% of consolidated net sales for the year ended December 31, 2019 and approximately 5% of consolidated total assets as of December 31, 2019. Based on our assessment, we have concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2019.
The Company’s independent registered public accounting firm, Deloitte & Touche LLP, audited our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, as stated in their report in the section entitled “Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” included elsewhere in this Form 10-K, which expresses an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019.
Changes in internal control over financial reporting
There have been no changes in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the fourth quarter ended December 31, 2019 or subsequent to the date the Company completed its evaluation, that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
| ITEM 9B. | OTHER INFORMATION |
None.
PART III
| ITEM 10. | DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
Directors of the Company
The information required by this item with respect to directors is set forth in our Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on May 14, 2020, under the captions “Election of Directors” and “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance,” which information is hereby incorporated herein by reference.
Executive Officers of the Registrant
The information required by this item is set forth under the caption “Executive Officers of the Company” in Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Audit Committee
Information on our Audit Committee is contained under the caption “Audit Committee” in our Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on May 14, 2020 and is incorporated herein by reference.
36
Code of Ethics and Business Conduct
We have adopted a Code of Ethics and Business Conduct Policy applicable to all employees. Additionally, we have adopted a Code of Ethics Applicable to Senior Executives including, but not limited to, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer of the Company. Our Code of Ethics and Business Conduct, and our Code of Ethics Applicable to Senior Executives are available on the Company’s web site at www.patrickind.com under “Investor Relations”. We intend to post on our web site any substantive amendments to, or waivers from, our Code of Ethics and Business Conduct Policy and our Code of Ethics Applicable to Senior Executives as well as our Corporate Governance Guidelines. We will provide shareholders with a copy of these policies without charge upon written request directed to the Company’s Corporate Secretary at the Company’s address.
Corporate Governance
Information on our corporate governance practices is contained under the caption “Corporate Governance” in our Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on May 14, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference.
| ITEM 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
The information required by this item is set forth in the Company’s Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on May 14, 2020, under the captions “Executive Compensation – Compensation of Executive Officers and Directors,” “Compensation Committee Interlocks and Director Participation,” and “Compensation Committee Report,” and is incorporated herein by reference.
| ITEM 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
The information required by this item is set forth in our Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on May 14, 2020, under the captions “Equity Compensation Plan Information” and “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management,” and is incorporated herein by reference.
| ITEM 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
The information required by this item is set forth in our Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on May 14, 2020, under the captions “Related Party Transactions” and “Independent Directors,” and is incorporated herein by reference.
| ITEM 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES |
The information required by this item is set forth in our Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on May 14, 2020, under the heading “Independent Public Accountants,” and is incorporated herein by reference.
37
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
| (a) | (1) The financial statements listed in the accompanying Index to the Financial Statements on page F-1 of the separate financial section of this Report are incorporated herein by reference. | |
| (3) The exhibits required to be filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K are listed under (c) below. | ||
| (c) | Exhibits | |
| Exhibit Number | Exhibits | |
| 3.1 | ||
| 3.2 | ||
| 3.3 | ||
| 4.1 | ||
| 4.2 | ||
| 4.3** | ||
| 10.1 | ||
| 10.2* | ||
| 10.3* | ||
| 10.4* | ||
| 10.5* | ||
| 10.6* | ||
| 10.7* | ||
| 10.8* | ||
38
| 10.9 | ||
| 10.10 | ||
| 10.11 | ||
| 10.12 | ||
| 10.13 | ||
| 10.14 | ||
| 10.15 | ||
| 10.16 | ||
| 10.17 | ||
| 12** | ||
| 21** | ||
| 16.1 | ||
| 23.1** | ||
| 23.2** | ||
| 31.1** | ||
| 31.2** | ||
| 32** | ||
39
XBRL Exhibits.
Interactive Data Files. The following materials are filed electronically with this Annual Report on Form 10-K:
| 101.INS | XBRL Instance Document |
| 101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Schema Document |
| 101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Calculation Linkbase Document |
| 101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Definition Linkbase Document |
| 101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Label Linkbase Document |
| 101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Presentation Linkbase Document |
Attached as Exhibits 101 to this report are the following financial statements from the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2019 formatted in XBRL (“eXtensible Business Reporting Language”): (i) the Consolidated Statements of Financial Position; (ii) the Consolidated Statements of Income; (iii) the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income; (iv) the Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity; and (v) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, and the related Notes to these financial statements in detail tagging format.
*Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
**Filed herewith.
All other financial statement schedules are omitted because they are not applicable or the required information is immaterial or is shown in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
ITEM 16. FORM 10-K SUMMARY
None.
40
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized
| PATRICK INDUSTRIES, INC. | ||
Date: February 27, 2020 | By: | /s/ Andy L. Nemeth |
| Andy L. Nemeth | ||
| President and Chief Executive Officer | ||
Pursuant to the Requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
| /s/ Andy L. Nemeth | President and Chief Executive Officer | February 27, 2020 | ||
| Andy L. Nemeth | (Principal Executive Officer) | |||
| Director | ||||
| /s/ Joshua A. Boone | Vice President Finance, Chief Financial Officer and | February 27, 2020 | ||
| Joshua A. Boone | Secretary-Treasurer | |||
| (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | ||||
| /s/ Joseph M. Cerulli | Director | February 27, 2020 | ||
| Joseph M. Cerulli | ||||
| /s/ Todd M. Cleveland | Executive Chairman of the Board | February 27, 2020 | ||
| Todd M. Cleveland | ||||
| /s/ John A. Forbes | Director | February 27, 2020 | ||
| John A. Forbes | ||||
| /s/ Michael A. Kitson | Director | February 27, 2020 | ||
| Michael A. Kitson | ||||
| /s/ Pamela R. Klyn | Director | February 27, 2020 | ||
Pamela R. Klyn | ||||
| /s/ Derrick B. Mayes | Director | February 27, 2020 | ||
| Derrick B. Mayes | ||||
| /s/ Denis G. Suggs | Director | February 27, 2020 | ||
Denis G. Suggs | ||||
| /s/ M. Scott Welch | Lead Director | February 27, 2020 | ||
| M. Scott Welch | ||||
41
PATRICK INDUSTRIES, INC.
Index to the Financial Statements
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm, Deloitte & Touche LLP | F-2 |
| F-5 | |
Financial Statements: | |
| F-6 | |
| F-7 | |
| F-8 | |
| F-9 | |
| F-10 | |
| F-11 | |
F-1
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the shareholders and the Board of Directors of Patrick Industries, Inc.
Opinions on the Financial Statements and Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statement of financial position of Patrick Industries, Inc. and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2019, the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, shareholders' equity, and cash flows, for the year ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the "financial statements"). We also have audited the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019 based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2019, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2019, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also, in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by COSO.
Basis for Opinions
The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements and an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB. As described in Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting, management excluded from its assessment the internal control over financial reporting at the operations of businesses acquired in 2019, which are described in Note 4, whose financial statements constitute less than 1% of consolidated net sales for the year ended December 31, 2019 and approximately 5% of consolidated total assets as of December 31, 2019. Accordingly, our audit did not include the internal control over financial reporting at these businesses.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud, and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit of the financial statements included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures to respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audit also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in
F-2
accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current-period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Goodwill-Refer to Notes 1 and 7 to the financial statements
Critical Audit Matter Description
The Company’s evaluation of goodwill for impairment involves the comparison of the fair value of each reporting unit to its carrying value. The Company uses a combination of market and income-based methodologies. The market approach includes a comparison of multiples of earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization (EBITDA) for the reporting units to similar businesses or guideline companies whose securities are actively traded in public markets. When calculating the present value of future cash flows under the income approach, the Company takes into consideration multiple variables, including forecasted sales volumes and operating income, current industry and economic conditions, and historical results. The income approach fair value estimate also includes estimates of long-term growth rates and discount rates that are commensurate with the risks and uncertainty inherent in the respective reporting units and the internally-developed forecasts. The goodwill balance was $319 million as of December 31, 2019. The estimated fair value of each of the Company's reporting units was determined to exceed the carrying value for the year ended December 31, 2019, and so no impairment was recognized.
Given the significant judgments made by management to estimate the fair value of certain of the Company’s reporting units, performing audit procedures to evaluate the reasonableness of management’s estimates and assumptions related to selection of the discount rates and forecasts of sales and operating income, specifically due to the sensitivity of the Company’s operations to periods of volatility in the Company’s end customer markets, required a high degree of auditor judgment and an increased extent of effort, including the need to involve our fair value specialists.
How the Critical Audit Matter Was Addressed in the Audit
Our audit procedures related to the discount rate and forecasts of sales and operating income used by management to estimate the fair value of certain reporting units included the following, among others:
| • | We tested the effectiveness of controls over management’s goodwill impairment evaluation, including those over the determination of the fair value of the Company’s reporting units, such as controls related to management’s selection of the discount rates and forecasts of sales and operating income. |
F-3
| • | We evaluated management’s ability to accurately forecast sales and operating income by comparing actual results to management’s historical forecasts. |
| • | We evaluated the reasonableness of management’s sales and operating income assumptions included in the income approach model, and extent to which forecast projection risk had been contemplated in the selection of the discount rates, by comparing the forecasts to historical sales and operating income, the strategic plans communicated to the Board of Directors, and forecasted information included in analyst and industry reports. |
| • | With the assistance of our fair value specialists, we evaluated the reasonableness of the valuation methodology and discount rates by testing the source information underlying the determination of the discount rates and the mathematical accuracy of the calculations and developing a range of independent estimates and comparing those to the discount rates selected by management. |
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Chicago, Illinois
February 27, 2020
We have served as the Company's auditor since 2019.
F-4
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Patrick Industries, Inc.
Elkhart, Indiana
Opinions on the Financial Statements and Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of financial position of Patrick Industries, Inc. (the "Company") as of December 31, 2018, the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the two-year period ended December 31, 2018, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the "financial statements"). In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2018 and 2017, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the two-year period ended December 31, 2018 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) ("PCAOB") and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Crowe LLP
We served as the Company's auditor from 2009 to 2018.
Oak Brook, Illinois
February 28, 2019
F-5
PATRICK INDUSTRIES, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
| (thousands except per share data) | Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
| NET SALES | $ | 2,337,082 | $ | 2,263,061 | $ | 1,635,653 | |||||
| Cost of goods sold | 1,914,211 | 1,847,195 | 1,356,738 | ||||||||
| GROSS PROFIT | 422,871 | 415,866 | 278,915 | ||||||||
| Operating Expenses: | |||||||||||
| Warehouse and delivery | 98,055 | 74,996 | 46,905 | ||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative | 134,466 | 128,242 | 90,736 | ||||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets | 35,908 | 34,213 | 19,374 | ||||||||
| Total operating expenses | 268,429 | 237,451 | 157,015 | ||||||||
| OPERATING INCOME | 154,442 | 178,415 | 121,900 | ||||||||
| Interest expense, net | 36,616 | 26,436 | 8,790 | ||||||||
| Income before income taxes | 117,826 | 151,979 | 113,110 | ||||||||
| Income taxes | 28,260 | 32,147 | 27,392 | ||||||||
| NET INCOME | $ | 89,566 | $ | 119,832 | $ | 85,718 | |||||
| BASIC NET INCOME PER COMMON SHARE | $ | 3.88 | $ | 4.99 | $ | 3.54 | |||||
| DILUTED NET INCOME PER COMMON SHARE | $ | 3.85 | $ | 4.93 | $ | 3.48 | |||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding - Basic | 23,058 | 23,995 | 24,230 | ||||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding - Diluted | 23,280 | 24,317 | 24,643 | ||||||||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
F-6
PATRICK INDUSTRIES, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
| (thousands) | Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
| NET INCOME | $ | 89,566 | $ | 119,832 | $ | 85,718 | |||||
| Other comprehensive (loss) income, net of tax: | |||||||||||
| Change in unrealized loss of hedge derivatives | (2,401 | ) | (1,973 | ) | — | ||||||
| Foreign currency translation loss | (22 | ) | (32 | ) | — | ||||||
| Other | (595 | ) | (741 | ) | 39 | ||||||
| Total other comprehensive (loss) income | (3,018 | ) | (2,746 | ) | 39 | ||||||
| COMPREHENSIVE INCOME | $ | 86,548 | $ | 117,086 | $ | 85,757 | |||||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
F-7
PATRICK INDUSTRIES, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
| December 31, | |||||||
| (thousands except share data) | 2019 | 2018 | |||||
| ASSETS | |||||||
| Current Assets | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 139,390 | $ | 6,895 | |||
| Trade receivables, net | 87,536 | 82,499 | |||||
| Inventories | 253,870 | 272,898 | |||||
| Prepaid expenses and other | 36,038 | 22,875 | |||||
| Total current assets | 516,834 | 385,167 | |||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 180,849 | 177,145 | |||||
| Operating lease right-of-use-assets | 93,546 | — | |||||
| Goodwill | 319,349 | 281,734 | |||||
| Intangible assets, net | 357,014 | 382,982 | |||||
| Deferred financing costs, net | 2,978 | 3,688 | |||||
| Other non-current assets | 423 | 515 | |||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 1,470,993 | $ | 1,231,231 | |||
| LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |||||||
| Current Liabilities | |||||||
| Current maturities of long-term debt | $ | 5,000 | $ | 8,750 | |||
| Current operating lease liabilities | 27,694 | — | |||||
| Accounts payable | 96,208 | 89,803 | |||||
| Accrued liabilities | 58,033 | 59,202 | |||||
| Total current liabilities | 186,935 | 157,755 | |||||
| Long-term debt, less current maturities, net | 670,354 | 621,751 | |||||
| Long-term operating lease liabilities | 66,467 | — | |||||
| Deferred tax liabilities, net | 27,284 | 22,699 | |||||
| Other long-term liabilities | 22,472 | 20,272 | |||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | 973,512 | 822,477 | |||||
| COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES | |||||||
| SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |||||||
| Preferred stock, no par value; authorized 1,000,000 shares; none issued | — | — | |||||
| Common stock, no par value; authorized 40,000,000 shares; issued 2019 - 23,753,551 shares; issued 2018 - 23,527,307 shares | 172,662 | 161,436 | |||||
| Additional paid-in-capital | 25,014 | 25,124 | |||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (5,698 | ) | (2,680 | ) | |||
| Retained earnings | 305,503 | 224,874 | |||||
| TOTAL SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | 497,481 | 408,754 | |||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | $ | 1,470,993 | $ | 1,231,231 | |||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
F-8
PATRICK INDUSTRIES, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| (thousands) | Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | |||||||||||
| Net income | $ | 89,566 | $ | 119,832 | $ | 85,718 | |||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 62,795 | 55,052 | 33,541 | ||||||||
| Amortization of convertible notes debt discount | 7,021 | 5,885 | — | ||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense | 15,436 | 13,981 | 10,411 | ||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 5,593 | 759 | (6,477 | ) | |||||||
| Other | (1,661 | ) | (2,841 | ) | 422 | ||||||
| Change in operating assets and liabilities, net of acquisitions of businesses: | |||||||||||
| Trade receivables | 5,768 | 26,680 | (11,152 | ) | |||||||
| Inventories | 19,682 | 92 | (35,270 | ) | |||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | (12,869 | ) | 1,654 | (7,600 | ) | ||||||
| Accounts payable, accrued liabilities and other | 1,079 | (21,081 | ) | 30,308 | |||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 192,410 | 200,013 | 99,901 | ||||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES | |||||||||||
| Capital expenditures | (27,661 | ) | (34,486 | ) | (22,497 | ) | |||||
| Proceeds from sale of property, equipment, facility and other | 4,402 | 6,463 | 1,211 | ||||||||
| Business acquisitions, net of cash acquired | (55,953 | ) | (343,347 | ) | (251,851 | ) | |||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | (79,212 | ) | (371,370 | ) | (273,137 | ) | |||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES | |||||||||||
| Term debt borrowings | 7,500 | 36,981 | — | ||||||||
| Term debt repayments | (6,250 | ) | (7,691 | ) | (15,766 | ) | |||||
| Borrowing on revolver | 653,129 | 1,211,464 | 673,830 | ||||||||
| Repayments on revolver | (910,461 | ) | (1,106,528 | ) | (576,860 | ) | |||||
| Proceeds from senior notes offering | 300,000 | — | — | ||||||||
| Proceeds from convertible notes offering | — | 172,500 | — | ||||||||
| Purchase of convertible notes hedges | — | (31,481 | ) | — | |||||||
| Proceeds from sale of warrants | — | 18,147 | — | ||||||||
| Cash dividends paid to shareholders | (5,798 | ) | — | — | |||||||
| Stock repurchases under buyback program | (3,815 | ) | (107,567 | ) | — | ||||||
| Proceeds from public offering of common stock, net of expenses | — | — | 93,306 | ||||||||
| Payments related to vesting of stock-based awards, net of shares tendered for taxes | (3,380 | ) | (2,698 | ) | (4,821 | ) | |||||
| Payment of deferred financing costs | (7,219 | ) | (7,632 | ) | (997 | ) | |||||
| Payment of contingent consideration from a business acquisition | (4,416 | ) | — | — | |||||||
| Other financing activities | 7 | (10 | ) | 862 | |||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 19,297 | 175,485 | 169,554 | ||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 132,495 | 4,128 | (3,682 | ) | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 6,895 | 2,767 | 6,449 | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 139,390 | $ | 6,895 | $ | 2,767 | |||||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
F-9
PATRICK INDUSTRIES, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
| (thousands except share data) | Common Stock | Additional Paid-in- Capital | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Retained Earnings | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance January 1, 2017 | $ | 63,716 | $ | 8,243 | $ | 27 | $ | 113,462 | $ | 185,448 | |||||||||||
| Net income | — | — | — | 85,718 | 85,718 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income, net of tax | — | — | 39 | — | 39 | ||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of 2,025,000 shares in public offering, net of expenses | 93,306 | — | — | — | 93,306 | ||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of shares upon exercise of common stock options | 926 | — | — | — | 926 | ||||||||||||||||
| Shares used to pay taxes on stock grants | (5,163 | ) | — | — | — | (5,163 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense | 10,411 | — | — | — | 10,411 | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance December 31, 2017 | $ | 163,196 | $ | 8,243 | $ | 66 | $ | 199,180 | $ | 370,685 | |||||||||||
| Net income | — | — | — | 119,832 | 119,832 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | — | — | (2,746 | ) | — | (2,746 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Stock repurchases under buyback program | (12,783 | ) | (646 | ) | — | (94,138 | ) | (107,567 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Issuance of shares upon exercise of common stock options | — | 3 | — | — | — | 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Shares used to pay taxes on stock grants | (2,961 | ) | — | — | — | (2,961 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense | 13,981 | — | — | — | 13,981 | ||||||||||||||||
| Purchase of convertible notes hedges | — | (31,481 | ) | — | — | (31,481 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of warrants | — | 18,147 | — | — | 18,147 | ||||||||||||||||
| Equity component of convertible note issuance | — | 30,861 | — | — | 30,861 | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance December 31, 2018 | $ | 161,436 | $ | 25,124 | $ | (2,680 | ) | $ | 224,874 | $ | 408,754 | ||||||||||
| Net income | — | — | — | 89,566 | 89,566 | ||||||||||||||||
| Dividends declared | — | — | — | (5,938 | ) | (5,938 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | — | — | (3,018 | ) | — | (3,018 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Stock repurchases under buyback program | — | (706 | ) | (110 | ) | (2,999 | ) | (3,815 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Issuance of shares upon exercise of common stock options | 7 | — | — | — | 7 | ||||||||||||||||
| Shares used to pay taxes on stock grants | (3,511 | ) | — | — | — | (3,511 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense | 15,436 | — | — | — | 15,436 | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance December 31, 2019 | $ | 172,662 | $ | 25,014 | $ | (5,698 | ) | $ | 305,503 | $ | 497,481 | ||||||||||
F-10
PATRICK INDUSTRIES, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| 1. | BASIS OF PRESENTATION AND SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES |
Nature of Business
Patrick Industries, Inc. (“Patrick” or the “Company”) operations consist of the manufacture and distribution of component products and materials for use primarily by the recreational vehicle (“RV”), marine, manufactured housing (“MH”) and industrial markets for customers throughout the United States and Canada. At December 31, 2019, the Company maintained 125 manufacturing plants and 48 distribution facilities located in 23 states, China, Canada and the Netherlands. Patrick operates in 2 business segments: Manufacturing and Distribution.
Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared pursuant to the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”). The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Patrick and its wholly owned subsidiaries. All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform with current year presentation and such reclassifications are immaterial.
In preparation of Patrick’s consolidated financial statements as of December 31, 2019, management evaluated all material subsequent events or transactions that occurred after the balance sheet date through the date of issuance of the Form 10-K to determine those requiring recognition or disclosure in the consolidated financial statements.
Financial Periods
The Company maintains its financial records on the basis of a fiscal year ending on December 31, with the fiscal quarters spanning thirteen weeks, with the first, second and third quarters ending on the Sunday closest to the end of the first, second and third 13-week periods, respectively. The first three quarters of fiscal year 2019 ended on March 31, 2019, June 30, 2019 and September 29, 2019. The first three quarters of fiscal year 2018 ended on April 1, 2018, July 1, 2018 and September 30, 2018. The first three quarters of 2017 ended on March 26, 2017, June 25 2017, and September 24, 2017.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. Estimates include the valuation of goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets, the valuation of long-lived assets, the allowance for doubtful accounts, excess and obsolete inventories, the valuation of estimated contingent consideration and deferred tax asset valuation allowances. Actual results could differ from the amounts reported.
Revenue Recognition
See Note 3 for further information on our revenue recognition accounting policies.
Costs and Expenses
Cost of goods sold includes material costs, direct and indirect labor, overhead expenses, inbound freight charges, inspection costs, internal transfer costs, receiving costs, and other costs.
F-11
Warehouse and delivery expenses include salaries and wages, building rent and insurance, and other overhead costs related to distribution operations and delivery costs related to the shipment of finished and distributed products to customers.
Stock Based Compensation
Compensation expense related to the fair value of restricted stock and restricted stock unit ("RSU") awards as of the grant date is calculated based on the Company’s closing stock price on the date of grant. In addition, the Company estimates the fair value of all stock option and stock appreciation rights (“SARS”) awards as of the grant date by applying the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The use of this valuation model involves assumptions that are judgmental and highly sensitive in the determination of compensation expense and include the dividend yield and exercise price. Expected volatilities take into consideration the historical volatility of the Company’s common stock. The expected term of options and SARS represents the period of time that the options and SARS granted are expected to be outstanding based on historical Company trends. The risk free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant for instruments of a similar term.
Income Per Common Share
Basic net income per common share is computed by dividing net income by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding. Diluted net income per common share is computed by dividing net income by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding, plus the dilutive effect of stock options, SARS, and restricted stock and RSU awards (collectively, “Common Stock Equivalents”). The dilutive effect of Common Stock Equivalents is calculated under the treasury stock method using the average market price for the period. Certain Common Stock Equivalents were not included in the computation of diluted net income per common share because the exercise prices of those Common Stock Equivalents were greater than the average market price of the common shares. See Note 15 for the calculation of both basic and diluted net income per common share.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with a maturity of three months or less at the time of purchase to be cash equivalents.
Trade Receivables
Trade receivables consist primarily of amounts due to the Company from its normal business activities. In assessing the carrying value of its trade receivables, the Company estimates the recoverability by making assumptions based on factors such as current overall and industry-specific economic conditions, historical and anticipated customer performance, historical write-off and collection experience, the level of past-due amounts, and specific risks identified in the trade receivables portfolio.
Allowance for doubtful accounts was immaterial at December 31, 2019 and 2018, and changes in the allowance were immaterial for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017.
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out method) and net realizable value. Based on the inventory aging and other considerations for realizable value, the Company writes down the carrying value to net realizable value where appropriate. The Company reviews inventory on-hand and records provisions for excess and obsolete inventory based on current assessments of future demand, market conditions, and related management initiatives. The cost of manufactured inventories includes raw materials, inbound freight, labor and overhead. The Company’s distribution inventories include the cost of materials purchased for resale and inbound freight.
F-12
Prepaid Expenses and Other
The following table summarizes balances in prepaid expenses and other:
| (thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
| Vendor rebates receivable | $ | 11,524 | $ | 10,127 | ||||
| Income tax receivable | 3,895 | 2,030 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses | 7,571 | 8,419 | ||||||
| Deposits | 1,409 | 2,299 | ||||||
| Prepaid income taxes | 11,639 | — | ||||||
| Total | $ | 36,038 | $ | 22,875 | ||||
Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment (“PP&E”) is generally recorded at cost. Depreciation is computed primarily by the straight-line method applied to individual items based on estimated useful lives, which generally range from 10 to 30 years for buildings and improvements, and from three to seven years for machinery, equipment and transportation equipment. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the lesser of their useful lives or the related lease term. The recoverability of PP&E is evaluated whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the assets may not be recoverable, primarily based on estimated selling price, appraised value or projected future cash flows.
Goodwill and Intangible Assets
Goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets are not amortized but are subject to an annual impairment test based on their estimated fair value. The Company performs the required test for goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets impairment in the fourth quarter, or more frequently, if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value may exceed the fair value. Definite-lived intangible assets are amortized over their useful lives, as detailed further in Note 7, and are also subject to an impairment test based on estimated undiscounted cash flows when impairment indicators exist.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
When events or conditions warrant, the Company evaluates the recoverability of long-lived assets other than goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets and considers whether these assets are impaired. The Company assesses the recoverability of these assets based upon several factors, including management's intention with respect to the assets and their projected future undiscounted cash flows. If projected undiscounted cash flows are less than the carrying amount of the assets, the Company adjusts the carrying amounts of such assets to their estimated fair value. A significant adverse change in the Company’s business climate in future periods could result in a significant loss of market share or the inability to achieve previously projected revenue growth and could lead to a required assessment of the recoverability of the Company’s long-lived assets, which may subsequently result in an impairment charge.
Fair Value and Financial Instruments
The Company accounts for certain assets and liabilities at fair value. The fair values are separated into three broad levels (Levels 1, 2 and 3) based on the assessment of the availability of observable market data and the significance of non-observable data used to determine fair value. Each fair value measurement must be assigned to a level corresponding to the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement in its entirety. The three levels are as follows:
| • | Level 1 inputs, which are quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that the reporting entity has the ability to access at the measurement date. |
F-13
| • | Level 2 inputs, which are inputs other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly. If the asset or liability has a specified (contractual) term, a Level 2 input must be observable for substantially the full term of the asset or liability. |
| • | Level 3 inputs, which are unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. These unobservable inputs reflect the entity’s own assumptions about the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability, and are developed based on the best information available in the circumstances (which might include the reporting entity’s own data). |
The carrying amounts of cash equivalents, representing government and other money market funds traded in an active market, are reported on the consolidated statements of financial position as a component of "Cash and cash equivalents". The carrying amount of cash equivalents at December 31, 2019, which approximated fair value because of the relatively short maturities, was approximately $132.6 million, valued using Level 1 inputs, with 0 corresponding amount at December 31, 2018.
The carrying amounts of the 2019 Term Loan and the 2019 Revolver (each as defined herein) and of the 2018 Term Loan and the 2018 Revolver (each as defined herein) approximated fair value as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively, based upon terms and conditions available to the Company at those dates in comparison to the terms and conditions of its outstanding debt. The estimated fair value of the Convertible Notes (as defined herein), calculated using Level 2 inputs, was approximately $162.5 million and $130.3 million as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. The estimated fair value of the Senior Notes (as defined herein), calculated using Level 2 inputs, was approximately $320.3 million as of December 31, 2019. The estimated fair value of the Company's interest rate swaps are valued using Level 2 inputs and discussed in further detail in Note 9. The estimated fair value of the Company's contingent consideration is valued using Level 3 inputs and is discussed further in Note 4.
Income Taxes
Deferred taxes are provided on an asset and liability method whereby deferred taxes are recognized based on temporary differences between the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and their tax basis. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance when it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets may not be realized.
The Company reports a liability, if any, for unrecognized tax benefits resulting from uncertain tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. The Company recognizes interest and penalties, if any, related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense.
2. RECENTLY ISSUED ACCOUNTING PRONOUNCEMENTS
Leases
In February 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2016-02, "Leases (Topic 842)", which requires in part that an entity recognize lease assets and lease liabilities on its statement of financial position for leases that were previously classified as operating leases under U.S. GAAP.
In July 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-11, "Leases (Topic 842): Targeted Improvements", which offered practical expedient alternatives to the modified retrospective adoption of Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 842.
The Company adopted ASC 842 effective January 1, 2019, and recorded approximately $88 million in lease right-of-use assets and corresponding lease liabilities, with no material impact on the consolidated statement of shareholders' equity, income, comprehensive income or cash flows. See Note 16 for further information.
Goodwill Impairment
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-04, "Intangibles-Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment". This ASU simplifies the accounting for goodwill impairments by eliminating step two from the goodwill impairment test. The standard requires that the impairment loss be measured as the excess of the
F-14
reporting unit's carrying amount over its fair value. It eliminates the second step that requires the impairment to be measured between the implied value of a reporting unit's goodwill and its carrying value. The standard is effective for annual and any interim impairment tests for periods beginning after December 15, 2019 and early adoption is permitted. The Company adopted this ASU 2017-04 on January 1, 2020 and the adoption did not have a material effect on its consolidated financial statements.
Credit Losses
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13 “Financial Instruments – Credit Losses: Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments”, which amends certain provisions of ASC 326, “Financial Instruments-Credit Loss”. The ASU changes the impairment model for most financial assets and certain other instruments. For trade and other receivables, held to maturity debt securities, loans and other instruments, entities will be required to use a new forward-looking “expected loss” model that generally will result in the earlier recognition of allowances for losses. Additionally, entities will be required to disclose more information with respect to credit quality indicators, including information used to track credit quality by year of origination for most financing receivables. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, including interim periods within those fiscal years and will be applied as a cumulative effect adjustment to retained earnings as of the beginning of the first reporting period for which the guidance is effective. The Company adopted ASU 2016-13 on January 1, 2020 and the adoption did not have a material effect on its consolidated financial statements.
| 3. | REVENUE RECOGNITION |
The Company is a major manufacturer and distributor of component products and materials serving original equipment manufacturers in the RV, MH, marine, and industrial industries. Revenue is recognized when or as control of the promised goods transfers to the Company's customers in an amount that reflects the consideration the Company expects to be entitled to in exchange for those goods. The Company’s contracts typically consist of a single performance obligation to manufacture and provide the promised goods. To the extent a contract is deemed to have multiple performance obligations, the Company allocates the transaction price of the contract to each performance obligation using the standalone selling price of each distinct good in the contract. The transaction price for contracts may include reductions to the transaction price for estimated volume discounts and rebates and other customer incentives.
Manufacturing segment revenue is recognized when control of the products transfers to the customer which is the point when the customer gains the ability to direct the use of and obtain substantially all the remaining benefits from the asset, which is generally upon delivery of goods. In limited circumstances, where the products are customer specific with no alternative use to the Company, and the Company has a legally enforceable right to payment for performance to date with a reasonable margin, revenue is recognized over the contract term based on the cost-to-cost method. However, such revenue is not material to the consolidated financial statements.
Distribution segment revenue from product sales is recognized on a gross basis upon shipment or delivery of goods at which point control transfers to the customer. The Company acts as a principal in such arrangements because it controls the promised goods before delivery to the customer. The Company uses direct shipment arrangements with certain vendors and suppliers to deliver products to its customers without having to physically hold the inventory at its warehouses. The Company is the principal in the transaction and recognizes revenue for direct shipment arrangements on a gross basis. Our role as principal in our distribution sales is generally characterized by (i) customers entering into contracts with the Company, not the vendor; (ii) our obligation to pay the vendor irrespective of our ability to collect from the customer; (iii) our discretion in determining the price of the good provided to the customer; (iv) our title to the goods before the customer receives or accept the goods; and (v) our responsibility for the quality and condition of goods delivered to the customer.
F-15
In the following table, revenue from contracts with customers, net of intersegment sales, is disaggregated by market type and by reportable segment, consistent with how the Company believes the nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows are affected by economic factors:
Year Ended December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||
| (thousands) | Manufacturing | Distribution | Total | |||||||||
| Market type: | ||||||||||||
| Recreational Vehicle | $ | 897,848 | $ | 389,345 | $ | 1,287,193 | ||||||
| Manufactured Housing | 176,665 | 260,121 | 436,786 | |||||||||
| Industrial | 250,969 | 33,595 | 284,564 | |||||||||
| Marine | 316,781 | 11,758 | 328,539 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 1,642,263 | $ | 694,819 | $ | 2,337,082 | ||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||
| (thousands) | Manufacturing | Distribution | Total | |||||||||
| Market type: | ||||||||||||
| Recreational Vehicle | $ | 1,069,981 | $ | 364,276 | $ | 1,434,257 | ||||||
| Manufactured Housing | 163,513 | 111,178 | 274,691 | |||||||||
| Industrial | 246,168 | 33,813 | 279,981 | |||||||||
| Marine | 265,805 | 8,327 | 274,132 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 1,745,467 | $ | 517,594 | $ | 2,263,061 | ||||||
Sales and other taxes collected concurrent with revenue-producing activities are excluded from net sales.
The Company records freight billed to customers in net sales. The corresponding costs incurred for shipping and handling related to these customer billed freight costs are accounted for as costs to fulfill the contract and are included in warehouse and delivery expenses.
The Company’s contracts across each of its businesses typically do not result in situations where there is a time period greater than one year between performance under the contract and collection of the related consideration. The Company does not account for a significant financing component when the Company expects, at contract inception, that the period between the Company's transfer of a promised good or service to a customer and the customer’s payment for that good or service will be one year or less.
The Company recognizes the incremental costs of obtaining contracts as an expense when incurred if the amortization period of the incurred costs that the Company otherwise would have capitalized is one year or less. These costs, representing primarily sales commissions, are included in selling, general and administrative expenses.
The Company does not disclose information about the transaction price being allocated to the remaining performance obligations at period end, as the Company does not have material contracts that have original expected durations of more than one year.
Contract Liabilities
Contract liabilities, representing upfront payments from customers received prior to satisfying performance obligations, were immaterial in all periods presented and changes in contract liabilities were immaterial in all periods presented.
F-16
| 4. | ACQUISITIONS |
General
The Company completed the acquisitions discussed below during December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017. The acquisitions were funded through cash on hand or through borrowings under the Company’s credit facility in existence at the time of acquisition. Assets acquired and liabilities assumed in the individual acquisitions were recorded on the Company’s consolidated statements of financial position at their estimated fair values as of the respective dates of acquisition. For each acquisition, the Company completes its allocation of the purchase price to the fair value of acquired assets and liabilities within a one-year measurement period. For those acquisitions where the purchase price allocation is provisional, which includes only those acquisitions completed in 2019, the Company generally is still in the process of finalizing the fair values of acquired intangible assets, fixed assets, and, if applicable, contingent consideration and deferred tax assets and liabilities. In general, the acquisitions described below provided the opportunity for the Company to either establish a new presence in a particular market and/or expand its product offerings in an existing market and increase its market share and per unit content.
For each acquisition, the excess of the purchase consideration over the fair value of the net assets acquired is recorded as goodwill, which generally represents the combined value of the Company’s existing purchasing, manufacturing, sales, and systems resources with the organizational talent and expertise of the acquired companies’ respective management teams to maximize efficiencies, revenue impact, market share growth and net income. The goodwill recognized is expected to be deductible for income tax purposes for each of the acquisitions with the exception of the 2018 acquisition of Marine Accessories Corporation and the 2017 acquisition of Leisure Product Enterprises, LLC, for which goodwill is expected to be partially deductible for income tax purposes, and the 2019 acquisition of G.G. Schmitt & Sons, Inc. and the 2018 acquisition of LaSalle Bristol, for which goodwill is not deductible for income tax purposes. Intangible asset values were estimated using income-based valuation methodologies. See Note 7 for information regarding the amortization periods assigned to acquired definite-lived intangible assets.
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, revenue of approximately $8.3 million, $249.3 million and $109.7 million, respectively, was included in the Company’s consolidated statements of income pertaining to the businesses acquired in each such year.
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, operating income of approximately $0.9 million, $23.2 million and $13.1 million, respectively, was included in the Company’s consolidated statements of income pertaining to the businesses acquired in each such year. Acquisition-related costs associated with the businesses acquired in 2019, 2018 and 2017 were immaterial.
Contingent Consideration
In connection with certain acquisitions, if certain financial targets for the acquired businesses are achieved, the Company is required to pay additional cash consideration. The Company records a liability for the fair value of the contingent consideration related to each of these acquisitions as part of the initial purchase price based on the present value of the expected future cash flows and the probability of future payments at the date of acquisition. The liability for the contingent consideration is measured at fair value in subsequent periods, with the changes in fair value recorded in the consolidated statements of income.
The aggregate fair value of the contingent consideration as of December 31, 2019 was $9.6 million, $2.0 million of which is included in the line item "Accrued liabilities" and $7.6 million is included in “Other long-term liabilities” on the consolidated statement of financial position. At December 31, 2018, the fair value was $13.8 million, $4.4 million of which was included in the line item "Accrued liabilities" and $9.4 million was included in "Other long-term liabilities". The liability for contingent consideration expires at various dates through December 2023. The contingent consideration arrangements are subject to a maximum payment amount of up to $17.2 million in the aggregate as of December 31, 2019. In 2019, the Company recorded a $3.1 million non-cash decrease to accrued liabilities, which is included within selling, general and administrative expense in the consolidated statement of
F-17
income, partly offset by a $0.7 million non-cash accretion of other long term liabilities, representing changes in the amount of consideration expected to be paid. In 2019, the Company made cash payments of approximately $4.4 million related to contingent consideration liabilities, recording a corresponding reduction to accrued liabilities.
2019 Acquisitions
Acquisitions completed in 2019 include previously announced Topline Counters, LLC, a Sumner, Washington-based designer and manufacturer of kitchen and bathroom countertops for residential and commercial markets, and G.G. Schmitt & Sons, Inc. ("G.G. Schmitt"), a Sarasota, Florida-based designer and manufacturer of customized hardware and structural components for the marine industry. The total initial consideration for these acquisitions was $54.3 million, plus contingent consideration over a one-year period based on future performance in connection with the acquisition of G.G. Schmitt. The preliminary purchase price allocations are subject to valuation activities being finalized, and thus all required purchase accounting adjustments are subject to change within the measurement period as the Company finalizes its estimates. These acquisitions are included in the Manufacturing segment.
2018 Acquisitions
Metal Moulding Corporation (“MMC”)
In February 2018, the Company completed the acquisition of the business and certain assets of Madison, Tennessee-based MMC, a manufacturer of custom metal fabricated products, primarily for the marine market, including hinges, arm rests, brackets, panels and trim, as well as plastic products including boxes, inlay tables, steps, and related components, for a net initial purchase price of $19.9 million, plus contingent consideration over a one-year period based on future performance. MMC is included in the Manufacturing segment.
Aluminum Metals Company, LLC (“AMC”)
In February 2018, the Company completed the acquisition of the business and certain assets of Elkhart, Indiana-based AMC, a manufacturer of aluminum products including coil, fabricated sheets and extrusions and roofing products, primarily for the RV, industrial and marine markets, for a net purchase price of $17.8 million. AMC is included in the Manufacturing segment.
IMP Holdings, LLC d/b/a Indiana Marine Products (“IMP”)
In March 2018, the Company completed the acquisition of the business and certain assets of Angola, Indiana-based IMP, a manufacturer of fully-assembled helm assemblies, including electrical wiring harnesses, dash panels, instrumentation and gauges, and other products primarily for the marine market, for a net initial purchase price of $18.6 million, plus contingent consideration over a three-year period based on future performance. IMP is included in the Manufacturing segment.
Collins & Company, Inc. (“Collins”)
In March 2018, the Company completed the acquisition of the business and certain assets of Bristol, Indiana-based Collins, a distributor of appliances, trim products, fuel systems, flooring, tile, and other related building materials primarily to the RV market as well as the housing and industrial markets, for a net purchase price of $40.0 million. Collins is included in the Distribution segment.
Changes from previously reported estimated amounts as of December 31, 2018 include a decrease to intangible assets of $3.6 million and a $3.6 million offsetting increase to goodwill.
Dehco, Inc. (“Dehco”)
In April 2018, the Company completed the acquisition of Dehco, a distributor and manufacturer of flooring, kitchen and bath products, adhesives and sealants, electronics, appliances and accessories, LP tanks, and other related building materials, primarily for the RV market as well as the MH, marine and other industrial markets, for a net purchase price of $52.8 million. Dehco has operating facilities in Indiana, Oregon, Pennsylvania and Alabama. Dehco is included in the Manufacturing and Distribution segments.
F-18
Changes from previously reported estimated amounts as of December 31, 2018 include a decrease to intangible assets of $0.3 million and a $0.3 million offsetting increase to goodwill.
Dowco, Inc. (“Dowco”)
In May 2018, the Company completed the acquisition of Dowco, a designer and manufacturer of custom designed boat covers and bimini tops, full boat enclosures, mounting hardware, and other accessories and components for the marine market, for a net purchase price of $56.3 million, net of cash acquired. Dowco has operating facilities in Wisconsin, Missouri, Indiana, and Minnesota. Dowco is included in the Manufacturing segment.
Changes from previously reported estimated amounts as of December 31, 2018 include a $2.7 million increase to property, plant and equipment and a $3.3 million increase to goodwill, offset by a $5.9 million decrease to intangible assets and a $0.1 million increase in accounts payable and accrued liabilities.
Marine Accessories Corporation (“MAC”)
In June 2018, the Company acquired 100% of the membership interests of Maryville, Tennessee-based MAC, a manufacturer, distributor and aftermarket supplier of custom tower and canvas products and other related accessories to OEMs, dealers, retailers and distributors within the marine market, as well as direct to consumers, for a net purchase price of $57.0 million, net of cash acquired. MAC is included in the Manufacturing and Distribution segments.
Changes from previously reported estimated amounts as of December 31, 2018 include a $6.5 million decrease to intangible assets and a $1.0 million decrease to property, plant and equipment, offset by a decrease in deferred taxes and other liabilities of $1.1 million and an increase to goodwill of $6.4 million.
Engineered Metals and Composites, Inc. (“EMC”)
In September 2018, the Company completed the acquisition of the business and certain assets of West Columbia, South Carolina-based EMC, a designer and manufacturer of custom marine towers, frames, and other fabricated component products for OEMs in the marine industry, for a net initial purchase price of $25.3 million, plus contingent consideration over a three-month period based on future performance. EMC is included in the Manufacturing segment.
After adjusting for a $0.1 million increase to the estimated purchase price reported at December 31, 2018 due to a final working capital adjustment of $0.1 million, changes from previously reported estimated amounts as of December 31, 2018 include an increase to intangible assets of $1.6 million, an increase to inventory of $0.1 million, a decrease to property, plant and equipment of $0.8 million, a decrease to goodwill of $0.6 million and an increase to accounts payable of $0.2 million.
LaSalle Bristol (“LaSalle”)
In November 2018, the Company completed the acquisition of LaSalle, a distributor and manufacturer of plumbing, flooring, tile, lighting, air handling and building products for the MH, RV, and industrial markets, for a net purchase price of $51.5 million, net of cash acquired. LaSalle is headquartered in Elkhart, Indiana and operates a total of 15 manufacturing and distribution centers located in North America. LaSalle is included in the Manufacturing and Distribution segments.
After adjusting for a $1.5 million increase in the estimated purchase price reported at December 31, 2018 due to a final working capital adjustment of $1.5 million, changes from previously reported estimated amounts as of December 31, 2018 are related primarily to a $6.7 million increase to intangible assets, a $0.8 decrease to deferred tax liabilities, a $0.8 million increase to goodwill, a $0.7 million increase to accounts receivable and a $0.3 million increase to prepaid expenses, partly offset by a $6.7 million decrease to inventory, a $0.8 million decrease to property, plant and equipment and a $0.3 million increase in accounts payable and accrued liabilities.
F-19
2017 Acquisitions
Medallion Plastics, Inc. (“Medallion”)
In March 2017, the Company acquired the business and certain assets of Elkhart, Indiana-based Medallion, a designer, engineer and manufacturer of custom thermoformed products and components which include dash and trim panels and fender skirts for the RV market, and complete interior packages, bumper covers, hoods, and trims for the automotive, specialty transportation and other industrial markets, for a net purchase price of $9.9 million. Medallion is included in the Manufacturing segment.
Leisure Product Enterprises, LLC (“LPE”)
In April 2017, the Company acquired 100% of the membership interests of LPE for a net purchase price of approximately $73.3 million. LPE is comprised of 3 complementary manufacturing companies primarily serving the marine and industrial markets: Marine Electrical Products, located in Lebanon, Missouri, supplies marine OEMs with fully-assembled boat dash and helm assemblies, including electrical wire harnesses as well as custom parts and assemblies for the industrial, commercial, and off-road vehicle markets; Florida Marine Tanks, located in Henderson, North Carolina, supplies aluminum fuel and holding tanks for marine and industrial customers; and Marine Concepts/Design Concepts, with facilities located in Sarasota, Florida and Cape Coral, Florida, designs, engineers and manufactures CNC plugs, open and closed composite molds, and CNC molds for fiberglass boat manufacturers. LPE is included in the Manufacturing segment.
Indiana Technologies, Inc. d/b/a Wire Design (“Wire Design”)
In July 2017, the Company acquired the business and certain assets of Elkhart, Indiana-based Wire Design, a manufacturer of wire harnesses for the RV, marine and industrial markets, for a net purchase price of $10.8 million. Wire Design is included in the Manufacturing segment.
Baymont, Inc. (“Baymont”)
In September 2017, the Company acquired the business and certain assets of Baymont, a manufacturer and supplier of fiberglass showers, tubs, and tile systems for the MH and industrial markets, with operating facilities located in Golden, Mississippi and Belmont, Mississippi. The net purchase price was $3.8 million, plus contingent consideration over a six-year period based on future performance. Baymont is included in the Manufacturing segment.
Indiana Transport, Inc. (“Indiana Transport”)
In November 2017, the Company acquired the business and certain assets of Elkhart, Indiana-based Indiana Transport, a transportation and logistics service provider primarily to OEMs and dealers in the RV market, for a net purchase price of $58.8 million. Indiana Transport is included in the Distribution segment.
LMI, Inc. and Related Companies (collectively, “LMI”)
In November 2017, the Company acquired LMI, a designer, fabricator, and installer of specialty glass, mirror, bath and closet building products to residential housing and commercial high-rise builders, general contractors, retailers, and RV manufacturers in the U.S., for a purchase price of $80.3 million, net of cash acquired. LMI is headquartered in Ontario, California and operates 6 manufacturing and distribution centers in California and Nevada and an additional manufacturing facility in China. LMI is included in the Manufacturing segment.
Nickell Moulding Company, Inc. (“Nickell”)
In December 2017, the Company acquired the business and certain assets of Elkhart, Indiana-based Nickell, a manufacturer of hardwood and wrapped mouldings and trim, custom wood frames, and door components for the RV, retail and hospitality, MH, and other markets, for a net purchase price of $12.6 million. Nickell is included in the Manufacturing segment.
F-20
The following table summarizes the fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the date of the acquisition for 2019, 2018 and 2017 acquisitions. As noted above, the purchase price allocations for the 2019 acquisitions are preliminary and subject to finalization:
| (thousands) | Trade receivables | Inventories | Property, plant and equipment | Prepaid expenses & other | Intangible assets | Goodwill | Less: Total liabilities | Less: Deferred taxes | Total net assets acquired | ||||||||||||||||||
2019(1) | $ | 10,115 | $ | 7,257 | $ | 5,200 | $ | 103 | $ | 17,766 | $ | 24,088 | $ | 5,699 | $ | 1,922 | $ | 56,908 | |||||||||
| 2018 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MMC(2) | $ | 1,463 | $ | 2,324 | $ | 2,085 | $ | — | $ | 8,540 | $ | 7,668 | $ | 827 | $ | — | $ | 21,253 | |||||||||
| AMC | 3,942 | 5,623 | 2,321 | 39 | 6,550 | 1,755 | 2,463 | — | 17,767 | ||||||||||||||||||
IMP(3) | 1,943 | 4,286 | 1,463 | 13 | 12,920 | 8,803 | 2,930 | — | 26,498 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Collins | 2,830 | 9,903 | 1,188 | 5 | 18,430 | 10,237 | 2,586 | — | 40,007 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dehco | 4,771 | 16,923 | 13,755 | 208 | 13,950 | 6,580 | 3,392 | — | 52,795 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dowco | 4,053 | 4,498 | 8,566 | 1,240 | 28,435 | 13,732 | 4,178 | — | 56,346 | ||||||||||||||||||
| MAC | 3,054 | 6,815 | 7,003 | 284 | 26,190 | 25,669 | 4,227 | 7,767 | 57,021 | ||||||||||||||||||
EMC(4) | 623 | 1,678 | 1,684 | — | 17,350 | 7,483 | 987 | — | 27,831 | ||||||||||||||||||
| LaSalle | 8,957 | 39,293 | 7,670 | 6,560 | 12,551 | 4,520 | 28,882 | (798 | ) | 51,467 | |||||||||||||||||
| Other | 473 | 329 | 280 | 13 | 1,667 | 919 | 195 | — | 3,486 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2018 Totals | $ | 32,109 | $ | 91,672 | $ | 46,015 | $ | 8,362 | $ | 146,583 | $ | 87,366 | $ | 50,667 | $ | 6,969 | $ | 354,471 | |||||||||
| 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Medallion | $ | 2,233 | $ | 2,605 | $ | 1,713 | $ | 118 | $ | 3,100 | $ | 1,342 | $ | 1,200 | $ | — | $ | 9,911 | |||||||||
| LPE | 5,848 | 5,162 | 9,225 | 337 | 33,275 | 39,945 | 6,358 | 14,140 | 73,294 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Wire Design | 615 | 437 | 555 | 21 | 5,590 | 4,052 | 491 | — | 10,779 | ||||||||||||||||||
Baymont(5) | — | 1,174 | 2,067 | — | 3,166 | 1,502 | 69 | — | 7,840 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Indiana Transport | 6,379 | — | 2,594 | 1,309 | 31,675 | 19,950 | 3,117 | — | 58,790 | ||||||||||||||||||
| LMI | 11,205 | 9,071 | 6,028 | 449 | 32,810 | 29,241 | 8,471 | — | 80,333 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Nickell | 1,784 | 1,547 | 1,240 | — | 6,250 | 2,331 | 556 | — | 12,596 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other | — | 250 | 2,668 | — | — | 668 | 124 | — | 3,462 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 Totals | $ | 28,064 | $ | 20,246 | $ | 26,090 | $ | 2,234 | $ | 115,866 | $ | 99,031 | $ | 20,386 | $ | 14,140 | $ | 257,005 | |||||||||
(1) Total net assets acquired for the 2019 acquisitions reflect the estimated liability of $2.6 million pertaining to the fair value of contingent consideration relating to the acquisition of G.G. Schmitt. The actual net cash paid for 2019 acquisitions of $54.3 million is included in “Cash Flows from Investing Activities - Business Acquisitions” on the consolidated statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2019. None of the 2019 acquisitions were individually material and therefore aggregated information has been presented.
(2) Total net assets acquired for MMC reflect the estimated liability of $1.4 million pertaining to the fair value of the contingent consideration. The actual net cash paid for the MMC acquisition of $19.9 million is included in “Cash Flows from Investing Activities - Business Acquisitions” on the consolidated statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2018.
(3) Total net assets acquired for IMP reflect the estimated liability of $7.9 million pertaining to the fair value of the contingent consideration. The actual net cash paid for the IMP acquisition of $18.6 million is included in “Cash Flows from Investing Activities - Business Acquisitions” on the consolidated statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2018.
(4) Total net assets acquired for EMC reflect the estimated liability of $2.5 million pertaining to the fair value of the contingent consideration. The actual net cash paid for the EMC acquisition of $25.3 million is included in the amount of $25.2 million in “Cash Flows from Investing
F-21
Activities - Business Acquisitions” on the consolidated statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2018 and $0.1 million on the consolidated statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2019.
(5) Total net assets acquired for Baymont include the estimated liability of $4.0 million pertaining to the fair value of the contingent consideration. The actual net cash paid for the Baymont acquisition of $3.8 million is included in "Cash Flows from Investing Activities - Business Acquisitions" on the consolidated statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2017.
Pro Forma Information (Unaudited)
The following pro forma information assumes the 2019 and 2018 acquisitions occurred as of the beginning of the year immediately preceding each such acquisition. The pro forma information contains the actual operating results of each of the 2019 and 2018 acquisitions, combined with the results prior to their respective acquisition dates, adjusted to reflect the pro forma impact of the acquisitions occurring as of the beginning of the year immediately preceding each such acquisition.
The pro forma information includes financing and interest expense charges based on the actual incremental borrowings incurred in connection with each transaction as if it occurred as of the beginning of the year immediately preceding each such acquisition.
In addition, the pro forma information includes amortization expense, in the aggregate, related to intangible assets acquired of $1.3 million and $7.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, in connection with the acquisitions as if they occurred as of the beginning of the year immediately preceding each such acquisition.
| (thousands except per share data) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
| Net sales | $ | 2,397,225 | $ | 2,658,544 | ||||
| Net income | 92,847 | 133,234 | ||||||
| Basic net income per common share | 4.03 | 5.55 | ||||||
| Diluted net income per common share | 3.99 | 5.48 | ||||||
The pro forma information is presented for informational purposes only and is not necessarily indicative of the results of operations that actually would have been achieved had the acquisitions been consummated as of that time, nor is it intended to be a projection of future results.
| 5. | INVENTORIES |
Inventories as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 consist of the following:
| (thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
| Raw materials | $ | 162,238 | $ | 164,408 | ||||
| Work in process | 14,272 | 12,829 | ||||||
| Finished goods | 28,446 | 28,341 | ||||||
| Less: reserve for inventory excess and obsolescence | (10,123 | ) | (5,354 | ) | ||||
| Total manufactured goods, net | 194,833 | 200,224 | ||||||
| Materials purchased for resale (distribution products) | 60,918 | 74,914 | ||||||
| Less: reserve for inventory excess and obsolescence | (1,881 | ) | (2,240 | ) | ||||
| Total materials purchased for resale (distribution products), net | 59,037 | 72,674 | ||||||
| Total inventories | $ | 253,870 | $ | 272,898 | ||||
F-22
| 6. | PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT |
Property, plant and equipment, net, consists of the following at December 31, 2019 and 2018:
| (thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
| Land and improvements | $ | 9,754 | $ | 8,686 | ||||
| Building and improvements | 67,493 | 59,701 | ||||||
| Machinery and equipment | 204,383 | 191,142 | ||||||
| Transportation equipment | 6,640 | 4,972 | ||||||
| Leasehold improvements | 14,738 | 11,873 | ||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, at cost | 303,008 | 276,374 | ||||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization | (122,159 | ) | (99,229 | ) | ||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | $ | 180,849 | $ | 177,145 | ||||
Total depreciation expense for property, plant and equipment for fiscal 2019, 2018, and 2017 was $26.9 million, $20.8 million and $14.2 million, respectively.
| 7. | GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS |
Changes in the carrying amount of goodwill for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 by segment are as follows:
| (thousands) | Manufacturing | Distribution | Total | ||||||
| Balance - January 1, 2018 | $ | 179,471 | $ | 28,573 | $ | 208,044 | |||
| Acquisitions | 56,704 | 17,138 | 73,842 | ||||||
| Adjustment to prior year preliminary purchase price allocation | (830 | ) | 678 | (152 | ) | ||||
| Balance - December 31, 2018 | 235,345 | 46,389 | 281,734 | ||||||
| Acquisitions | 21,488 | — | 21,488 | ||||||
| Adjustment to prior year preliminary purchase price allocation | 11,569 | 4,558 | 16,127 | ||||||
| Balance - December 31, 2019 | $ | 268,402 | $ | 50,947 | $ | 319,349 | |||
Goodwill at December 31, 2019 and 2018 includes $27.4 million of accumulated impairment in the manufacturing segment.
For the definite-lived intangible assets attributable to the 2019 acquisitions, the useful life pertaining to non-compete agreements was three years, and the useful life pertaining to customer relationships for 2019 acquisitions was 10 years.
Intangible assets, net consist of the following at December 31, 2019 and 2018:
F-23
| (thousands) | 2019 | Weighted Average Useful Life (years) | 2018 | Weighted Average Useful Life (years) | |||||||
| Customer relationships | $ | 357,513 | 10.1 | $ | 366,228 | 10.1 | |||||
| Non-compete agreements | 16,202 | 5.0 | 19,159 | 4.9 | |||||||
| Patents | 16,495 | 14.6 | 1,048 | 8.9 | |||||||
| Trademarks | 88,524 | Indefinite | 82,358 | Indefinite | |||||||
| 478,734 | 468,793 | ||||||||||
| Less: accumulated amortization | (121,720 | ) | (85,811 | ) | |||||||
| Intangible assets, net | $ | 357,014 | $ | 382,982 | |||||||
Changes in the carrying value of intangible assets for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 by segment are as follows:
| (thousands) | Manufacturing | Distribution | Total | ||||||||
| Balance - January 1, 2018 | $ | 220,540 | $ | 42,927 | $ | 263,467 | |||||
| Acquisitions | 112,517 | 42,085 | 154,602 | ||||||||
| Amortization | (27,413 | ) | (6,800 | ) | (34,213 | ) | |||||
| Adjustment to prior year preliminary purchase price allocation | (1,159 | ) | 285 | (874 | ) | ||||||
| Balance - December 31, 2018 | 304,485 | 78,497 | 382,982 | ||||||||
| Acquisitions | 17,922 | — | 17,922 | ||||||||
| Amortization | (29,457 | ) | (6,451 | ) | (35,908 | ) | |||||
| Adjustment to prior year preliminary purchase price allocation | (10,827 | ) | 2,845 | (7,982 | ) | ||||||
| Balance - December 31, 2019 | $ | 282,123 | $ | 74,891 | $ | 357,014 | |||||
Amortization expense for the next five fiscal years ending December 31 related to definite-lived intangible assets as of December 31, 2019 is estimated to be (in thousands): 2020 - $38,208; 2021 - $37,669; 2022 - $36,844; 2023 - $35,640; and 2024 - $34,045.
F-24
| 8. | DEBT |
A summary of total debt outstanding at December 31, 2019 and 2018 is as follows:
| (thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
| Long-term debt: | ||||||||
| Revolver | $ | 135,000 | $ | 392,332 | ||||
| Term Loan | 97,500 | 96,250 | ||||||
| Senior Notes | 300,000 | — | ||||||
| Convertible Notes | 172,500 | 172,500 | ||||||
| Total long-term debt | 705,000 | 661,082 | ||||||
| Less: Convertible Notes discount and deferred financing costs, net | (23,260 | ) | (30,125 | ) | ||||
| Less: Senior Notes deferred financing costs, net | (5,844 | ) | — | |||||
| Less: Current maturities of long-term debt | (5,000 | ) | (8,750 | ) | ||||
| Less: Term Loan deferred financing costs, net | (542 | ) | (456 | ) | ||||
| Total long-term debt, less current maturities, net | $ | 670,354 | $ | 621,751 | ||||
Senior Notes
On September 17, 2019, the Company issued $300 million aggregate principal amount of 7.50% Senior Notes due 2027 (the “Senior Notes”). The Senior Notes will mature on October 15, 2027. Interest on the Senior Notes will accrue from September 17, 2019 and is payable semi-annually in cash in arrears on April 15 and October 15 of each year, beginning on April 15, 2020. The effective interest rate on the Senior Notes, which includes debt issuance costs, was 7.83%. In connection with the issuance of the Senior Notes, the Company incurred and capitalized as a reduction of the principal amount of the Senior Notes approximately $6.0 million in deferred financing costs which will be amortized using the effective interest rate over the term of the Senior Notes.
The Senior Notes are senior unsecured indebtedness of the Company and are guaranteed by each of the Company’s subsidiaries that guarantee the obligations of the Company under the 2019 Credit Facility (as defined herein). The Company may redeem the Senior Notes, in whole or in part, at any time (a) prior to October 15, 2022, at a price equal to 100% of the principal amount thereof, plus the applicable premium described in the associated indenture and accrued and unpaid interest and (b) on or after October 15, 2022 at specified redemption prices set forth in the indenture, plus accrued and unpaid interest. In addition, prior to October 15, 2022, the Company may redeem, in one or more transactions, up to an aggregate of 40% of the original principal amount of the Senior Notes at a redemption price equal to 107.5% of the principal amount thereof, plus accrued and unpaid interest, with the net cash proceeds of one or more equity offerings. If the Company experiences specific kinds of changes of control, the Company must offer to repurchase all of the Senior Notes (unless otherwise redeemed) at a price equal to 101% of the aggregate principal amount thereof, plus accrued and unpaid interest.
2019 Credit Facility
Simultaneously with the issuance of the Senior Notes, the Company entered into the Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement (the “2019 Credit Agreement”). The 2019 Credit Agreement amended and extended the Company’s 2018 Credit Agreement (as defined herein) and consists of a $550 million senior secured revolver (the “2019 Revolver”) and a $100 million senior secured term loan (the “2019 Term Loan” and together with the 2019 Revolver, the “2019 Credit Facility”). The maturity date for borrowings under the 2019 Credit Agreement is September 17, 2024. Upon the satisfaction of certain conditions, and obtaining incremental commitments from its lenders, the Company may be able to increase the borrowing capacity of the 2019 Credit Facility by up to $250 million.
F-25
Borrowings under the 2019 Credit Facility are secured by substantially all personal property assets of the Company and any domestic subsidiary guarantors. Pursuant to the 2019 Credit Agreement:
| • | The 2019 Term Loan is due in consecutive quarterly installments in the following amounts: (i) beginning September 30, 2019, through and including June 30, 2021, $1,250,000 and (ii) beginning September 30, 2021, and each quarter thereafter, $2,500,000, with the remaining balance due at maturity; |
| • | The interest rates for borrowings under the 2019 Revolver and the 2019 Term Loan are the Prime Rate or LIBOR plus a margin, which ranges from 0.00% to 0.75% for Prime Rate loans and from 1.00% to 1.75% for LIBOR loans depending on the Company’s consolidated total leverage ratio, as defined below. The Company is required to pay fees on unused but committed portions of the 2019 Revolver, which range from 0.15% to 0.225%; and |
| • | Covenants include requirements as to a maximum consolidated total net leverage ratio (4.00:1.00, increasing to 4.50:1.00 in certain circumstances in connection with Company acquisitions) and a minimum consolidated fixed charge coverage ratio (1.50 :1.00) that are tested on a quarterly basis, a minimum liquidity requirement applicable during the six-month period preceding the maturity of the Convertible Notes, and other customary covenants. |
At December 31, 2019, the Company had $97.5 million outstanding under the 2019 Term Loan under the LIBOR-based option, and borrowings outstanding under the 2019 Revolver of $135.0 million under the LIBOR-based option. The interest rate for incremental borrowings at December 31, 2019 was LIBOR plus 1.5% (or 3.31%) for the LIBOR-based option. The fee payable on committed but unused portions of the 2019 Revolver was 0.20% at December 31, 2019. The weighted average interest rate for 2019 borrowings under the 2018 Revolver and 2019 Revolver was 4.59%, and 4.53% for 2019 borrowings under the 2018 Term Loan and 2019 Term Loan.
2018 Credit Facility
The 2018 Credit Agreement was amended by the 2019 Credit Agreement on September 17, 2019 as discussed above. The Company recorded a $0.7 million loss on extinguishment of debt in the third quarter of 2019 in connection with the replacement of the 2018 Credit Facility with the 2019 Credit Facility. The Company's previous credit agreement (the "2018 Credit Agreement") consisted of an $800 million revolving credit loan (the “2018 Revolver”) and a $100 million term loan (the “2018 Term Loan” and, together with the 2018 Revolver, the “2018 Credit Facility”). At December 31, 2018, the Company had $96.3 million outstanding under the 2018 Term Loan under the LIBOR-based option, and borrowings outstanding under the 2018 Revolver of: (i) $388.0 million under the LIBOR-based option and (ii) $4.3 million under the Base Rate-based option. The interest rate for incremental borrowings at December 31, 2018 was the Prime Rate plus 1.00% (or 6.50%) for the Base Rate-based option, or LIBOR plus 2.00% (or 4.56%) for the LIBOR-based option. The weighted average interest rate on borrowings in 2018 was 4.05% for the 2018 Term Loan and 4.20% for the 2018 Revolver.
2015 Credit Facility
Prior to June 5, 2018, the Company's credit facility was established under its Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated April 28, 2015, with Wells Fargo Bank, National Association (“Wells Fargo”), as Administrative Agent and a lender, and the lenders party thereto, as amended (the “2015 Credit Agreement”). The 2015 Credit Agreement consisted of a $417.3 million revolving credit loan (the “2015 Revolver”) and up to an $82.7 million term loan (the “2015 Term Loan” and, together with the Revolver, the “2015 Credit Facility”). The 2015 Credit Facility had a maturity date of March 17, 2022 and was replaced by the 2018 Credit Facility.
F-26
Convertible Senior Notes
In January 2018, the Company issued $172.5 million aggregate principal amount of 1.00% Convertible Senior Notes due 2023 (the “Convertible Notes”). The total debt discount of $36.0 million at issuance consisted of two components: (i) the conversion option component, recorded to shareholders' equity, in the amount of $31.9 million, representing the difference between the principal amount of the Convertible Notes upon issuance less the present value of the future cash flows of the Convertible Notes and (ii) debt issuance costs of $4.1 million. The unamortized portion of the total debt discount is being amortized to interest expense over the life of the Convertible Notes. The effective interest rate on the Convertible Notes, which includes the non-cash interest expense of debt discount amortization and debt issuance costs, was 5.25% as of December 31, 2019 and 2018.
The net proceeds from the issuance of the Convertible Notes were approximately $167.5 million, after deducting the initial purchasers’ discounts and commissions and offering expenses payable by the Company, but before deducting the net cost of the Convertible Note Hedge Transactions and the Warrant Transactions (each as defined herein) described in Note 9. The Convertible Notes are senior unsecured obligations of the Company and pay interest semi-annually in arrears on February 1 and August 1 of each year at an annual rate of 1.00% beginning August 1, 2018. The Convertible Notes will mature on February 1, 2023 unless earlier repurchased or converted in accordance with their terms. The Convertible Notes are convertible by the noteholders, in certain circumstances and subject to certain conditions, into cash, shares of common stock of the Company, or a combination thereof, at the Company’s election. The initial conversion rate for the Convertible Notes is 11.3785 shares of the Company's common stock per $1,000 principal amount of the Convertible Notes (or 1,962,790 shares in the aggregate) and is equal to an initial conversion price of approximately $87.89 per share. If an event of default on the Convertible Notes occurs, the principal amount of the Convertible Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest (including additional interest, if any) may be declared immediately due and payable, subject to certain conditions.
Convertible Notes holders can convert their Convertibles Notes on or after August 1, 2022 at any time at their option. Holders may convert Convertible Notes prior to August 1, 2022, only under the following circumstances: (i) during any calendar quarter commencing after the calendar quarter ending on June 30, 2018, if the last reported sale price of the Company's common stock for at least 20 trading days (whether or not consecutive) during a period of 30 consecutive trading days ending on the last trading day of the immediately preceding calendar quarter is greater than or equal to 130% of the conversion price on each applicable trading day, (ii) during the 5 business day period after any 5 consecutive trading day period in which the trading price per $1,000 principal amount of notes for each trading day of the measurement period was less than 98% of the product of the last reported sale price of our common stock and the conversion rate on each such trading day and (iii) upon the occurrence of certain specified distributions or corporate events.
Debt Maturities
As of December 31, 2019, the aggregate maturities of total long-term debt for the next five fiscal years and thereafter are as follows (in thousands):
| 2020 | $ | 5,000 | |
| 2021 | 7,500 | ||
| 2022 | 10,000 | ||
| 2023 | 182,500 | ||
| 2024 | 200,000 | ||
| Thereafter | 300,000 | ||
| Total | $ | 705,000 | |
Five standby letters of credit totaling $3.9 million were outstanding at December 31, 2019 that exist to meet credit requirements for the Company’s insurance providers.
F-27
Cash paid for interest for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 was $22.1 million, $18.4 million and $8.6 million, respectively.
| 9. | DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS |
Convertible Note Hedge Transactions and Warrant Transactions
In January 2018, in connection with the Convertible Notes offering, the Company entered into privately negotiated convertible note hedge transactions (together, the “Convertible Note Hedge Transactions”) with each of Bank of America, N.A. and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association (together, the “Hedge Counterparties”). Pursuant to the Convertible Note Hedge Transactions, the Company acquired options to purchase the same number of shares of the Company's common stock (or 1,962,790 shares) initially underlying the Convertibles Notes at an initial strike price equal to the initial strike price of the Convertible Notes of approximately $87.89 per share, subject to customary anti-dilution adjustments. The options expire on February 1, 2023, subject to earlier exercise.
At the same time, the Company also entered into separate, privately negotiated warrant transactions (the “Warrant Transactions”) with each of the Hedge Counterparties, pursuant to which the Company sold warrants to purchase the same number of shares of the Company’s common stock (or 1,962,790 shares) underlying the Convertible Notes, at an initial strike price of approximately $113.93 per share, subject to customary anti-dilution adjustments. The warrants have a final expiration date of September 20, 2023.
The Company paid $31.5 million associated with the cost of the Convertible Note Hedge Transactions and received proceeds of $18.1 million related to the Warrant Transactions. The Convertible Note Hedge Transactions are expected generally to reduce potential dilution to the Company’s common stock upon any conversion of the Convertible Notes and/or offset any cash payments the Company is required to make in excess of the principal amount of converted Convertible Notes. However, the Warrant Transactions could separately have a dilutive effect on the Company's common stock to the extent that the market price per share of the common stock exceeds the strike price of the warrants.
As these transactions meet certain accounting criteria, the Convertible Note Hedges Transactions and Warrant Transactions are recorded in stockholders’ equity and are not accounted for as derivatives.
Interest Rate Swaps
The Company's credit facility exposes the Company to risks associated with the variability in interest expense associated with fluctuations in LIBOR. To partially mitigate this risk, the Company entered into interest rate swaps. As of December 31, 2019, the Company had a combined notional principal amount of $200.0 million of interest rate swap agreements, all of which are designated as cash flow hedges. These swap agreements effectively convert the interest expense associated with a portion of the Company's variable rate debt from variable interest rates to fixed interest rates and have maturities ranging from February 2022 to March 2022.
The following table summarizes the fair value of derivative contracts included in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet (in thousands):
| Fair value of derivative liabilities | ||||||||||
| Derivatives accounted for as cash flow hedges | Balance sheet location | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||
| Interest rate swap agreements | Other long-term liabilities | $ | 5,868 | $ | 2,652 | |||||
The interest rate swaps are comprised of over-the-counter derivatives, which are valued using models that primarily rely on observable inputs such as yield curves, and are classified as Level 2 in the fair value hierarchy.
F-28
| 10. | ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE LOSS |
Accumulated other comprehensive loss primarily includes unrealized gains and losses on derivatives that qualify as hedges of cash flows and cumulative foreign currency translation adjustments. The activity in accumulated other comprehensive loss was as follows:
| (thousands) | Cash Flow Hedges | Other | Foreign Currency Items | Total | |||||||||||
| Balance at January 1, 2018 | $ | — | $ | 66 | $ | — | $ | 66 | |||||||
| Other comprehensive loss (net of tax benefit of $679, $254 and $0) | (1,973 | ) | (741 | ) | (32 | ) | (2,746 | ) | |||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | $ | (1,973 | ) | $ | (675 | ) | $ | (32 | ) | $ | (2,680 | ) | |||
| Other comprehensive loss (net of tax benefit of $816, $204 and $0) | (2,401 | ) | (595 | ) | (22 | ) | (3,018 | ) | |||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2019 | $ | (4,374 | ) | $ | (1,270 | ) | $ | (54 | ) | $ | (5,698 | ) | |||
| 11. | ACCRUED LIABILITIES |
Accrued liabilities as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 include the following:
| (thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
| Employee compensation and benefits | $ | 28,717 | $ | 31,898 | ||||
| Property taxes | 3,657 | 3,405 | ||||||
| Customer incentives | 12,297 | 10,318 | ||||||
| Accrued interest | 7,460 | 1,232 | ||||||
| Other | 5,902 | 12,349 | ||||||
| Total accrued liabilities | $ | 58,033 | $ | 59,202 | ||||
| 12. | INCOME TAXES |
On December 22, 2017, the U.S. government enacted comprehensive tax legislation commonly referred to as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “TCJA”). The TCJA makes broad and complex changes to the U.S. tax code, including, but not limited to: (1) reducing the U.S. federal corporate tax rate from 35% to 21% for tax years ending after December 31, 2017; (2) bonus depreciation that will allow for full expensing in the year placed in service of qualified property acquired and placed in service after September 27, 2017; (3) repealing the Domestic Production Activities Deduction for years beginning after December 31, 2017; and (4) requiring a current inclusion in U.S. federal taxable income of certain earnings of controlled foreign corporations.
The Company has accounted for in its 2019 and 2018 income tax provision the impact of Global Intangible Low-Taxed Income, base-erosion anti-abuse tax, interest expense limitations under Section 163(j), and foreign-derived intangible income deductions, although such provisions were either not applicable or resulted in a zero or immaterial impact to the consolidated financial statements.
F-29
The provision for income taxes for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 consists of the following:
| (thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
| Current: | ||||||||||||
| Federal | $ | 17,587 | $ | 22,578 | $ | 27,833 | ||||||
| State | 5,019 | 8,725 | 6,036 | |||||||||
| Foreign | 61 | 85 | — | |||||||||
| Total current | 22,667 | 31,388 | 33,869 | |||||||||
| Deferred: | ||||||||||||
| Federal | 4,529 | 1,529 | (6,289 | ) | ||||||||
| State | 1,064 | (770 | ) | (188 | ) | |||||||
| Total deferred | 5,593 | 759 | (6,477 | ) | ||||||||
| Income taxes | $ | 28,260 | $ | 32,147 | $ | 27,392 | ||||||
A reconciliation of the differences between the actual provision for income taxes and income taxes at the federal statutory income tax rate of 21% for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 and at the federal statutory income tax rate of 35% for the year ended December 31, 2017 is as follows:
| (thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||||||||
| Rate applied to pretax income | $ | 24,744 | 21.0 | % | $ | 31,916 | 21.0 | % | $ | 39,588 | 35.0 | % | ||||||
| State taxes, net of federal tax effect | 5,147 | 4.4 | % | 6,427 | 4.2 | % | 4,060 | 3.6 | % | |||||||||
| Remeasurement of net deferred tax liabilities | — | — | % | — | — | % | (7,699 | ) | (6.8 | )% | ||||||||
| Excess tax benefit on stock-based compensation | (833 | ) | (0.7 | )% | (6,685 | ) | (4.4 | )% | (6,009 | ) | (5.3 | )% | ||||||
| Other | (798 | ) | (0.7 | )% | 489 | 0.4 | % | (2,548 | ) | (2.3 | )% | |||||||
| Income taxes | $ | 28,260 | 24.0 | % | $ | 32,147 | 21.2 | % | $ | 27,392 | 24.2 | % | ||||||
F-30
The composition of the deferred tax assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 is as follows:
| (thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | |||||
| Long-term deferred income tax assets (liabilities): | |||||||
| Trade receivables allowance | $ | 417 | $ | 418 | |||
| Inventory capitalization | 2,226 | 2,591 | |||||
| Accrued expenses | 5,987 | 6,123 | |||||
| Deferred compensation | 413 | 462 | |||||
| Inventory reserves | 4,651 | 1,278 | |||||
| Federal NOL carryforwards | 1,113 | 1,607 | |||||
| State NOL carryforwards | 953 | 2,060 | |||||
| Valuation allowance - NOL | (872 | ) | (649 | ) | |||
| Share-based compensation | 7,221 | 5,848 | |||||
| Operating lease right-of-use assets | (23,910 | ) | — | ||||
| Operating lease liabilities | 24,160 | — | |||||
| Other | 2,015 | 1,432 | |||||
| Intangibles | (28,160 | ) | (26,419 | ) | |||
| Depreciation expense | (22,368 | ) | (16,562 | ) | |||
| Prepaid expenses | (1,130 | ) | (888 | ) | |||
| Net deferred tax liabilities | $ | (27,284 | ) | $ | (22,699 | ) | |
The Company paid income taxes of $36.1 million, $28.2 million and $38.6 million in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
As of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Company had gross federal, state, and foreign net operating losses, of approximately $24.5 million and $53.9 million, respectively. These loss carryforwards generally expire between tax years ending December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2037. The components of the valuation allowance relate to certain acquired federal, state and foreign net operating loss carryforwards that the Company anticipates will not be utilized prior to their expiration, either due to income limitations or limitations under Section 382. The tax effected values of these net operating losses are $2.0 million and $3.7 million at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, exclusive of valuation allowances of $0.9 million and $0.6 million at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
The Company is subject to periodic audits by domestic tax authorities. For the majority of tax jurisdictions, the U.S. federal statute of limitations remains open for the years 2015 and later. The Company is currently under audit by the Internal Revenue Service for the 2015 and 2016 tax years. Uncertain tax benefits were immaterial at December 31, 2019 and 2018 and activity related to uncertain tax benefits was immaterial for all periods presented.
| 13. | SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
Preferred Stock
The Company has 1,000,000 shares of preferred stock authorized, without par value, the issuance of which is subject to approval by the Board of Directors (the “Board”). The Board has the authority to fix the number, rights, preferences and limitations of the shares, subject to applicable laws and the provisions of the Articles of Incorporation.
F-31
Common Stock
In May 2017, the Company's shareholders approved an amendment to the Articles of Incorporation to increase the number of shares of common stock authorized, without par value, from 20,000,000 shares to 40,000,000 shares, of which 23,753,551 and 23,527,307 shares were issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
The Company issued 428,852 shares in 2019, 226,595 shares in 2018 and 411,212 shares in 2017 related to stock-based compensation plans and for the exercise of stock options and SARS. The Company made repurchases of 83,512 shares in 2019, 43,900 shares in 2018 and 82,970 shares in 2017 for the sole purpose of satisfying the minimum tax withholding obligations of employees upon the vesting of stock awards held by the employees.
In addition, in 2019 and 2018, the Company repurchased 102,932 shares and 1,984,095 shares, respectively, of its common stock through a stock repurchase program. There were 0 shares repurchased under a stock repurchase program in 2017. See Note 14 for further details.
On March 14, 2017, the Company completed a public offering of 2,025,000 shares of its common stock at a price of $48.67 per share for gross proceeds of $98.6 million. The net proceeds from the offering of $93.3 million were used to pay down a portion of the Company's outstanding indebtedness.
| 14. | STOCK REPURCHASE PROGRAMS |
In January 2018, the Board approved a stock repurchase program that authorized the repurchase of up to $50.0 million of the Company's common stock over a 24-month period (the "2018 Repurchase Plan") to replace a 2016 Repurchase Plan that expired in January 2018.
In May 2018, the Board approved an increase in the amount of the Company's common stock that may be acquired over 24 months under the current stock repurchase program to $50.0 million, which included $8.5 million remaining under the original $50.0 million authorization announced in January 2018.
In October 2018, the Board approved an increase in the amount of the Company's common stock that may be acquired over 24 months under the current stock repurchase program to $50.0 million, which included $3.6 million remaining under the $50.0 million authorization announced in May 2018. In 2018, the Company repurchased 1,984,095 shares under the 2018 repurchase program at an average price of $54.21 per share for a total cost of $107.6 million.
In 2019, the Company repurchased 102,932 shares under the 2018 repurchase program at an average price of $37.06 per share for a total cost of $3.8 million.
The Company’s common stock does not have a stated par value. As a result, repurchases of common stock have been reflected, using an average cost method, as a reduction of common stock, additional paid-in-capital and retained earnings in the Company’s consolidated statements of financial position.
F-32
| 15. | NET INCOME PER COMMON SHARE |
Income per common share is calculated for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 as follows:
| (thousands except per share data) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
| Net income | $ | 89,566 | $ | 119,832 | $ | 85,718 | ||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding - basic | 23,058 | 23,995 | 24,230 | |||||||||
| Effect of potentially dilutive securities | 222 | 322 | 413 | |||||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding - diluted | 23,280 | 24,317 | 24,643 | |||||||||
| Basic net income per common share | $ | 3.88 | $ | 4.99 | $ | 3.54 | ||||||
| Diluted net income per common share | $ | 3.85 | $ | 4.93 | $ | 3.48 | ||||||
| Cash dividends paid per common share | $ | 0.25 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
The impact on diluted net income per common share from antidilutive securities excluded from the calculation was immaterial for all periods presented.
On February 25, 2020, the Company’s Board of Directors declared a cash dividend of $0.25 per share of common stock. The dividend will be payable on March 23, 2020 to shareholders of record at the close of business on March 9, 2020.
| 16. | LEASES |
As discussed in Note 2, the Company adopted the provisions of ASC 842 on January 1, 2019 using the modified retrospective approach as of the effective date of ASC 842. Accordingly, financial results in periods reported prior to 2019 are unchanged.
As a result of the adoption of ASC 842, operating leases for certain warehouses, buildings, forklifts, trucks, trailers and other equipment are now recognized as right-of-use assets and corresponding short-term and long-term lease liabilities. The Company utilized a package of available practical expedients in the adoption of ASC 842, which, among them, does not require the reassessment of operating versus capital lease classification.
Leases with an initial term of 12 months or less are not recorded on the balance sheet and expense related to these short term leases was immaterial for fiscal 2019. Lease and non-lease components in the fixed base rent of facility and equipment leases are included as a single component and accounted for as a lease. Pursuant to ASC 842, the Company elected to use the remaining non-cancellable lease term as of January 1, 2019 in determining the lease term at the date of adoption and the corresponding incremental borrowing rate for such leases. Variable lease expense, principally related to trucks, forklifts, and index-related facility rent escalators, was immaterial for the year ended December 31, 2019. Leases have remaining lease terms of one year to eleven years. Certain leases include options to renew for an additional term. Where there is reasonable certainty to utilize a renewal option, we include the renewal option in the lease term used to calculate operating lease right-of-use assets and lease liabilities.
F-33
Lease expense, supplemental cash flow information, and other information related to leases were as follows:
| Year Ended | |||
| (thousands) | December 31, 2019 | ||
| Operating lease cost | $ | 31,653 | |
| Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities: | |||
| Operating cash flows for operating leases | $ | 30,677 | |
| Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for lease obligations: | |||
| Operating leases | $ | 37,112 | |
Balance sheet information related to leases was as follows:
| (thousands, except lease term and discount rate) | December 31, 2019 | ||
| Assets | |||
| Operating lease right-of-use assets | $ | 93,546 | |
| Liabilities | |||
| Operating lease liabilities, current portion | $ | 27,694 | |
| Long-term operating lease liabilities | 66,467 | ||
| Total lease liabilities | $ | 94,161 | |
| Weighted average remaining lease term, operating leases (in years) | 4.2 | |
| Weighted average discount rate, operating leases | 3.7 | % |
F-34
Maturities of operating lease liabilities were as follows at December 31, 2019:
| (thousands) | |||
| 2020 | $ | 30,443 | |
| 2021 | 24,300 | ||
| 2022 | 18,465 | ||
| 2023 | 13,481 | ||
| 2024 | 9,072 | ||
| Thereafter | 5,867 | ||
| Total lease payments | 101,628 | ||
| Less imputed interest | (7,467 | ) | |
| Total | $ | 94,161 | |
Disclosures related to periods prior to the adoption of ASC 842:
Future minimum lease payments were as follows at December 31, 2018:
| (thousands) | |||
| 2019 | $ | 29,345 | |
| 2020 | 23,344 | ||
| 2021 | 16,165 | ||
| 2022 | 9,602 | ||
| 2023 | 5,357 | ||
| Thereafter | 4,883 | ||
| Total | $ | 88,696 | |
| 17. | COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES |
The Company is subject to proceedings, lawsuits, audits, and other claims arising in the normal course of business. All such matters are subject to uncertainties and outcomes that are not predictable with assurance. Accruals for these items, when applicable, have been provided to the extent that losses are deemed probable and are reasonably estimable. These accruals are adjusted from time to time as developments warrant.
Although the ultimate outcome of these matters cannot be ascertained, on the basis of present information, amounts already provided, availability of insurance coverage and legal advice received, it is the opinion of management that the ultimate resolution of these proceedings, lawsuits, and other claims will not have a material adverse effect on the Company’s consolidated financial position, results of operations, or cash flows.
| 18. | COMPENSATION PLANS |
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company has various stock option and stock-based incentive plans and various agreements whereby stock options, restricted stock awards, and SARS were made available to certain key employees, directors, and others based upon meeting various individual, divisional or company-wide performance criteria and time-based criteria. All such awards qualify and are accounted for as equity awards. Equity incentive plan awards, which are granted under
F-35
the Company's 2009 Omnibus Incentive Plan (the "2009 Plan"), are intended to retain and reward key employees for outstanding performance and efforts as they relate to the Company’s short-term and long-term objectives and its strategic plan.
The Company recorded compensation expense of $15.4 million, $14.0 million and $10.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively, on the consolidated statements of income for its stock-based compensation plans. As of December 31, 2019, there was approximately $19.8 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to share-based compensation arrangements granted under incentive plans. That cost is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of approximately 15 months.
Stock Options:
Stock options vest ratably over either three or four years and have nine-year contractual terms.
On January 17, 2017, the Company’s Compensation Committee of the Board (the "Compensation Committee") approved the grant of 340,110 stock options under the 2009 Plan at an exercise price per share of $53.83. The stock options vest pro-rata over four years, commencing on January 17, 2018, and have nine-year contractual terms. There were 0 stock options granted in 2018 and 2019.
The following table summarizes the Company’s option activity during the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017:
| Years ended December 31 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||||
| (shares in thousands) | Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price | |||||||||
| Outstanding beginning of year | 545 | $ | 44.35 | 548 | $ | 44.07 | 288 | $ | 23.59 | ||||||
| Granted during the year | — | — | — | — | 340 | 53.83 | |||||||||
| Forfeited during the year | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||
| Exercised during the year | (9 | ) | 0.67 | (3 | ) | 0.78 | (80 | ) | 11.62 | ||||||
| Outstanding end of year | 536 | $ | 45.11 | 545 | $ | 44.35 | 548 | $ | 44.07 | ||||||
| Vested Options: | |||||||||||||||
| Vested during the year | 115 | $ | 50.46 | 115 | $ | 50.46 | 30 | $ | 40.95 | ||||||
| Eligible end of year for exercise | 336 | $ | 41.07 | 230 | $ | 34.72 | 118 | $ | 18.36 | ||||||
| Aggregate intrinsic value ($ in thousands): | |||||||||||||||
| Total options outstanding | $ | 4,398 | $ | 1,570 | $ | 13,932 | |||||||||
| Options exercisable | $ | 4,051 | $ | 1,570 | $ | 6,037 | |||||||||
| Options exercised | $ | 381 | $ | 195 | $ | 2,601 | |||||||||
| Weighted average fair value of options granted during the year | N/A | N/A | $ | 17.76 | |||||||||||
The aggregate intrinsic value (excess of market value over the option exercise price) in the table above is before income taxes, and assuming the Company’s closing stock price of $52.43, $29.61 and $69.45 per share as of December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively, is the price that would have been received by the option holders had those option holders exercised their options as of that date.
The cash received from the exercise of stock options was immaterial in 2019 and 2018, and approximately $0.9 million in 2017. The income tax benefit related to the stock options exercised in 2019 and 2018 was immaterial and
F-36
was approximately $0.9 million in 2017. The grant date fair value of stock options vested in 2019, 2018 and 2017 was $5.8 million, $5.8 million and $1.2 million, respectively.
A summary of options outstanding and exercisable at December 31, 2019 is as follows:
| (shares in thousands) | Options Outstanding | Options Exercisable | |||||||||
| Shares Outstanding | Remaining Contractual Life (years) | Exercise Price | Shares Exercisable | Exercise Price | |||||||
| 2013 Grant: | |||||||||||
| Exercise price - $12.30 | 75 | 3.0 | $ | 12.30 | 75 | $ | 12.30 | ||||
| 2016 Grant: | |||||||||||
| Exercise price - $40.95 | 121 | 5.8 | $ | 40.95 | 91 | $ | 40.95 | ||||
| 2017 Grant: | |||||||||||
| Exercise price - $53.83 | 340 | 6.0 | $ | 53.83 | 170 | $ | 53.83 | ||||
The following table presents assumptions used in the Black-Scholes model for the stock options granted in 2017. There were 0 stock options granted in 2019 and 2018.
| 2017 | ||
| Dividend rate | — | |
| Risk-free interest rate | 2.00 | % |
| Expected option life (years) | 5.75 | |
| Price volatility | 30.84 | % |
As of December 31, 2019, there was approximately $1.9 million of total unrecognized compensation expense related to the stock options, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average remaining life of approximately 12.2 months.
Stock Appreciation Rights (SARS):
On January 17, 2017, the Compensation Committee approved the grant of 340,128 SARS under the 2009 Plan divided into 4 tranches of 85,032 shares each, at strike prices of $53.83, $60.03, $66.93 and $74.63 per share. The SARS vest pro-ratably over four years from the grant date and have nine-year contractual terms. The SARS are to be settled in shares of common stock, or at the sole discretion of the Board in cash. The grant date fair value of these awards totaled $5.0 million and this amount is being amortized over the four-year vesting period. There were 0 SARS granted in 2018 and 2019.
F-37
The following table summarizes the Company’s SARS activity during the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017:
| Years ended December 31 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||||
| (shares in thousands) | Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price | |||||||||
| Total SARS: | |||||||||||||||
| Outstanding beginning of year | 535 | $ | 54.53 | 535 | $ | 54.53 | 270 | $ | 32.29 | ||||||
| Granted during the year | — | — | — | — | 340 | 63.85 | |||||||||
| Forfeited during the year | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||
| Exercised during the year | — | — | — | — | (75 | ) | 16.50 | ||||||||
| Outstanding end of year | 535 | $ | 54.53 | 535 | $ | 54.53 | 535 | $ | 54.53 | ||||||
| Vested SARS: | |||||||||||||||
| Vested during the year | 115 | $ | 60.71 | 115 | $ | 60.71 | 30 | $ | 51.87 | ||||||
| Eligible end of year for exercise | 336 | $ | 50.04 | 220 | $ | 44.46 | 105 | $ | 26.66 | ||||||
| Aggregate intrinsic value ($ in thousands): | |||||||||||||||
| Total SARS outstanding | $ | 3,190 | $ | 983 | $ | 8,458 | |||||||||
| SARS exercisable | $ | 3,066 | $ | 983 | $ | 4,521 | |||||||||
| SARS exercised | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 3,822 | |||||||||
| Weighted average fair value of SARS granted during the year | N/A | N/A | $ | 14.66 | |||||||||||
The aggregate intrinsic value (excess of market value over the SARS exercise price) in the table above is before income taxes, and assuming the Company’s closing stock price of $52.43, $29.61 and $69.45 per share as of December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively, is the price that would have been received by the SARS holder had that SARS holder exercised the SARS as of that date.
F-38
A summary of SARS outstanding and exercisable at December 31, 2019 is as follows:
| SARS Outstanding | SARS Exercisable | ||||||||||
| (shares in thousands) | Shares Outstanding | Remaining Contractual Life (years) | Exercise Price | Shares Exercisable | Exercise Price | ||||||
| 2013 Grant: | |||||||||||
| Exercise price - $12.30 | 18 | 3.0 | $ | 12.30 | 18 | $ | 12.30 | ||||
| Exercise price - $14.75 | 19 | 3.0 | 14.75 | 19 | 14.75 | ||||||
| Exercise price - $17.71 | 19 | 3.0 | 17.71 | 19 | 17.71 | ||||||
| Exercise price - $21.25 | 19 | 3.0 | 21.25 | 19 | 21.25 | ||||||
| 2016 Grant: | |||||||||||
| Exercise price - $40.95 | 30 | 5.8 | $ | 40.95 | 22 | $ | 40.95 | ||||
| Exercise price - $47.51 | 30 | 5.8 | 47.51 | 23 | 47.51 | ||||||
| Exercise price - $55.11 | 30 | 5.8 | 55.11 | 22 | 55.11 | ||||||
| Exercise price - $63.93 | 30 | 5.8 | 63.93 | 23 | 63.93 | ||||||
| 2017 Grant: | |||||||||||
| Exercise price - $53.83 | 85 | 6.0 | $ | 53.83 | 42 | $ | 53.83 | ||||
| Exercise price - $60.03 | 85 | 6.0 | 60.03 | 43 | 60.03 | ||||||
| Exercise price - $66.93 | 85 | 6.0 | 66.93 | 42 | 66.93 | ||||||
| Exercise price - $74.63 | 85 | 6.0 | 74.63 | 43 | 74.63 | ||||||
The following table presents assumptions used in the Black-Scholes model for the SARS granted in 2017. There were 0 SARS granted in 2019 and 2018.
| 2017 | ||
| Dividend rate | — | |
| Risk-free interest rate | 2.00 | % |
| Expected option life (years) | 5.75 | |
| Price volatility | 30.84 | % |
As of December 31, 2019, there was approximately $1.6 million of total unrecognized compensation expense related to the SARS which is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average remaining life of approximately 12.3 months.
Restricted Stock:
The Company’s stock-based awards include restricted stock awards. As of December 31, 2019, there was approximately $16.3 million of total unrecognized compensation expense related to restricted stock, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average remaining life of approximately 15.7 months.
Restricted stock awards possess voting rights, are included in the calculation of actual shares outstanding, and include both performance- and time-based contingencies. The grant date fair value of the awards is expensed over the related service or performance period. Time-based shares cliff vest at the conclusion of the required service period, which ranges from one to three years. The performance contingent shares are earned based on the achievement of a cumulative financial performance target, which ranges from a one to five-year period and vest at the conclusion of the measurement period.
F-39
The following table summarizes the activity for restricted stock for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017:
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||||||
| (shares in thousands) | Shares | Weighted-Average Grant Date Stock Price | Shares | Weighted-Average Grant Date Stock Price | Shares | Weighted-Average Grant Date Stock Price | |||||||||
| Unvested beginning of year | 606 | $ | 48.56 | 634 | $ | 35.68 | 644 | $ | 22.15 | ||||||
| Granted during the year | 378 | 39.74 | 182 | 65.35 | 233 | 54.46 | |||||||||
| Vested during the year | (230 | ) | 30.46 | (209 | ) | 23.98 | (240 | ) | 17.49 | ||||||
| Forfeited during the year | (16 | ) | 50.49 | (1 | ) | 57.93 | (3 | ) | 46.64 | ||||||
| 738 | $ | 49.65 | 606 | $ | 48.56 | 634 | $ | 35.68 | |||||||
| 19. | SEGMENT INFORMATION |
The Company has 2 reportable segments, Manufacturing and Distribution, which are based on its method of internal reporting, which segregates its businesses based on the way in which its chief operating decision maker allocates resources, evaluates financial results, and determines compensation.
A description of the Company’s reportable segments is as follows:
Manufacturing – This segment includes the following products: laminated products that are utilized to produce furniture, shelving, walls, countertops and cabinet products; cabinet doors; fiberglass bath fixtures and tile systems; hardwood furniture; vinyl printing; decorative vinyl and paper laminated panels; solid surface, granite, and quartz countertop fabrication; RV painting; fabricated aluminum products; fiberglass and plastic components; fiberglass bath fixtures and tile systems; softwoods lumber; custom cabinetry; polymer-based flooring; electrical systems components including instrument and dash panels; wrapped vinyl, paper and hardwood profile mouldings; interior passage doors; air handling products; slide-out trim and fascia; thermoformed shower surrounds; specialty bath and closet building products; fiberglass and plastic helm systems and components products; wiring and wire harnesses; boat covers, towers, tops and frames; marine hardware; aluminum fuel tanks; CNC molds and composite parts; slotwall panels and components; and other products.
Distribution – The Company distributes pre-finished wall and ceiling panels; drywall and drywall finishing products; electronics and audio systems components; appliances; wiring, electrical and plumbing products; fiber reinforced polyester products; cement siding; raw and processed lumber; interior passage doors; roofing products; laminate and ceramic flooring; tile; shower doors; furniture; fireplaces and surrounds; interior and exterior lighting products; and other miscellaneous products in addition to providing transportation and logistics services.
The accounting policies of the segments are the same as those described in Note 1, except that segment data includes intersegment sales. Assets are identified to the segments except for cash, prepaid expenses, land and buildings, and certain deferred assets, which are identified with the corporate division. The corporate division charges rents to the segments for use of the land and buildings based upon estimated market rates. The Company accounts for intersegment sales similar to third party transactions, which reflect current market prices. The Company also records certain income from purchase incentive agreements at the corporate division. The Company evaluates the performance of its segments and allocates resources to them based on a variety of indicators including but not limited to sales and operating income as presented in the tables below.
The tables below present information that is provided to the chief operating decision maker of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 and for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 (in thousands):
F-40
| 2019 | |||||||||||
| Manufacturing | Distribution | Total | |||||||||
| Net outside sales | $ | 1,642,263 | $ | 694,819 | $ | 2,337,082 | |||||
| Intersegment sales | 31,223 | 4,340 | 35,563 | ||||||||
| Total sales | 1,673,486 | 699,159 | 2,372,645 | ||||||||
| Operating income | 174,913 | 38,953 | 213,866 | ||||||||
| Total assets | 990,692 | 304,230 | 1,294,922 | ||||||||
| Capital expenditures | 25,291 | 1,973 | 27,264 | ||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 52,036 | 7,534 | 59,570 | ||||||||
| 2018 | |||||||||||
| Manufacturing | Distribution | Total | |||||||||
| Net outside sales | $ | 1,745,467 | $ | 517,594 | $ | 2,263,061 | |||||
| Intersegment sales | 33,581 | 3,641 | 37,222 | ||||||||
| Total sales | 1,779,048 | 521,235 | 2,300,283 | ||||||||
| Operating income | 215,246 | 31,491 | 246,737 | ||||||||
| Total assets | 948,557 | 240,499 | 1,189,056 | ||||||||
| Capital expenditures | 31,152 | 1,852 | 33,004 | ||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 44,747 | 7,613 | 52,360 | ||||||||
| 2017 | |||||||||||
| Manufacturing | Distribution | Total | |||||||||
| Net outside sales | $ | 1,337,785 | $ | 297,868 | $ | 1,635,653 | |||||
| Intersegment sales | 30,669 | 2,579 | 33,248 | ||||||||
| Total sales | 1,368,454 | 300,447 | 1,668,901 | ||||||||
| Operating income | 151,635 | 18,858 | 170,493 | ||||||||
| Capital expenditures | 21,204 | 309 | 21,513 | ||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 27,481 | 3,521 | 31,002 | ||||||||
F-41
A reconciliation of certain line items pertaining to the total reportable segments to the consolidated financial statements as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 and for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 is as follows (in thousands):
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
| Net sales: | |||||||||||
| Total sales for reportable segments | $ | 2,372,645 | $ | 2,300,283 | $ | 1,668,901 | |||||
| Elimination of intersegment sales | (35,563 | ) | (37,222 | ) | (33,248 | ) | |||||
| Consolidated net sales | $ | 2,337,082 | $ | 2,263,061 | $ | 1,635,653 | |||||
| Operating income: | |||||||||||
| Operating income for reportable segments | $ | 213,866 | $ | 246,737 | $ | 170,493 | |||||
| Unallocated corporate expenses | (23,516 | ) | (34,109 | ) | (29,219 | ) | |||||
| Amortization | (35,908 | ) | (34,213 | ) | (19,374 | ) | |||||
| Consolidated operating income | $ | 154,442 | $ | 178,415 | $ | 121,900 | |||||
| Total assets: | |||||||||||
| Identifiable assets for reportable segments | $ | 1,294,922 | $ | 1,189,056 | |||||||
| Corporate assets unallocated to segments | 36,681 | 35,280 | |||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | 139,390 | 6,895 | |||||||||
| Consolidated total assets | $ | 1,470,993 | $ | 1,231,231 | |||||||
| Depreciation and amortization: | |||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization for reportable segments | $ | 59,570 | $ | 52,360 | $ | 31,002 | |||||
| Corporate depreciation and amortization | 3,225 | 2,692 | 2,539 | ||||||||
| Consolidated depreciation and amortization | $ | 62,795 | $ | 55,052 | $ | 33,541 | |||||
| Capital expenditures: | |||||||||||
| Capital expenditures for reportable segments | $ | 27,264 | $ | 33,004 | $ | 21,513 | |||||
| Corporate capital expenditures | 397 | 1,482 | 984 | ||||||||
| Consolidated capital expenditures | $ | 27,661 | $ | 34,486 | $ | 22,497 | |||||
Amortization expense related to intangible assets in the Manufacturing segment for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 was $29.5 million, $27.4 million and $16.2 million, respectively. Intangible assets amortization expense in the Distribution segment was $6.4 million, $6.8 million and $3.1 million in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
Unallocated corporate expenses include corporate general and administrative expenses comprised of wages, insurance, taxes, supplies, travel and entertainment, professional fees and other.
Major Customers
One RV customer accounted for approximately 14% and 12% of the trade receivables balance at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. In addition, a second RV customer accounted for approximately 13% of the trade receivables balance at December 31, 2018.
One RV customer accounted for approximately 23%, 29% and 32% of consolidated net sales in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively. In addition, a second RV customer accounted for approximately 17%, 20% and 25% of consolidated net sales in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
F-42
| 20. | QUARTERLY FINANCIAL DATA (UNAUDITED) |
Selected quarterly financial data for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 is as follows:
| (thousands except per share data) | 1Q | 2Q | 3Q | 4Q | 2019 | ||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 608,218 | $ | 613,218 | $ | 566,186 | $ | 549,460 | $ | 2,337,082 | |||||
| Gross profit | 106,548 | 112,661 | 104,335 | 99,327 | 422,871 | ||||||||||
| Net income | 20,849 | 27,416 | 21,317 | 19,984 | 89,566 | ||||||||||
Net income per common share(1) | |||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | 0.90 | $ | 1.19 | $ | 0.92 | $ | 0.87 | $ | 3.88 | |||||
| Diluted | 0.90 | 1.18 | 0.92 | 0.86 | 3.85 | ||||||||||
| Cash dividends paid per common share | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 0.25 | $ | 0.25 | |||||
| (thousands except per share data) | 1Q | 2Q | 3Q | 4Q | 2018 | ||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 551,832 | $ | 604,879 | $ | 575,139 | $ | 531,211 | $ | 2,263,061 | |||||
| Gross profit | 97,754 | 114,792 | 106,655 | 96,665 | 415,866 | ||||||||||
| Net income | 30,068 | 34,860 | 27,934 | 26,970 | 119,832 | ||||||||||
Net income per common share(1) | |||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | 1.22 | $ | 1.44 | $ | 1.17 | $ | 1.17 | $ | 4.99 | |||||
| Diluted | 1.20 | 1.42 | 1.15 | 1.15 | 4.93 | ||||||||||
(1) Basic and diluted net income per common share are computed independently for each of the quarters presented. Therefore, the sum of quarterly basic and diluted net income per common share information may not equal annual basic and diluted net income per common share.
| 21. | RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS |
During 2019, 2018, and 2017, the Company entered into transactions with companies affiliated with three of its independent Board members. The Company purchased approximately $1.1 million, $1.1 million, and $1.0 million in fiscal years 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively, of corrugated packaging materials from Welch Packaging Group, an independently owned company established by M. Scott Welch who serves as its President and CEO. The Company sold approximately $0.4 million, $0.6 million and $0.4 million in fiscal years 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively, of RV component products to DNA Enterprises, Inc. ("DNA"). Walter E. Wells, whose son is affiliated with DNA, retired from Patrick's Board on May 15, 2019. In addition, in 2017 the Company sold approximately $1.1 million of various fiberglass and plastic components and wood products to a company with which John A. Forbes was formerly affiliated. Mr. Forbes was not affiliated with this company during 2019 or 2018.
F-43