UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, DC 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
| þ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE |
| | ACT OF 1934 For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2013 |
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE |
| | ACT OF 1934 For the transition period from to |
Commission file number: 001-31343
ASSOCIATED BANC-CORP
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| | |
| Wisconsin | | 39-1098068 |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
| |
433 Main Street Green Bay, Wisconsin | | 54301 |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (920) 491-7000
SECURITIES REGISTERED PURSUANT TO SECTION 12(b) OF THE ACT
| | |
Title of each class | | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| |
Common stock, par value $0.01 per share Depositary Shares, each representing a 1/40th interest in a share of 8.00% Perpetual Preferred Stock, Series B Warrants to purchase shares of Common Stock of Associated Banc-Corp | | The NASDAQ Stock Market LLC The New York Stock Exchange The NASDAQ Stock Market LLC |
SECURITIES REGISTERED PURSUANT TO SECTION 12(g) OF THE ACT
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yes þ No ¨
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes ¨ No þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes þ No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).
Yes þ No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer þ | | Accelerated filer ¨ | | Non-accelerated filer ¨ | | Smaller reporting company ¨ |
| | | | (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | | |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act).
Yes ¨ No þ
As of June 30, 2013, (the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter) the aggregate market value of the voting stock held by nonaffiliates of the registrant was approximately $2,553,187,000. This excludes approximately $25,576,000 of market value representing the outstanding shares of the registrant owned by all directors and officers who individually, in certain cases, or collectively, may be deemed affiliates. This includes approximately $59,221,000 of market value representing 2.30% of the outstanding shares of the registrant held in a fiduciary capacity by the trust company subsidiary of the registrant.
As of January 24, 2014, 161,072,785 shares of common stock were outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
| | |
Document: Proxy Statement for Annual Meeting of Shareholders on April 22, 2014 | | Part of Form 10-K Into Which Portions of Documents are Incorporated: Part III |
ASSOCIATED BANC-CORP
2013 FORM 10-K TABLE OF CONTENTS
Special Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
This document, including the documents that are incorporated by reference, contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”) and Section 21E of the Exchange Act (the “Exchange Act”). You can identify forward-looking statements by words such as “may,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “believe,” “estimate,” “predict,” “potential,” “continue,” “could,” “future,” or the negative of those terms or other words of similar meaning. You should read statements that contain these words carefully because they discuss our future expectations or state other “forward-looking” information. Such forward-looking statements may relate to our financial condition, results of operations, plans, objectives, future performance, or business and are based upon the beliefs and assumptions of our management and the information available to our management at the time these disclosures are prepared. These forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties that we may not be able to accurately predict or control and our actual results may differ materially from those we described in our forward-looking statements. Shareholders should be aware that the occurrence of the events discussed under the heading “Risk Factors” in this document and in the information incorporated by reference herein, could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations, and financial condition. These factors, many of which are beyond our control, include the following:
| • | | credit risks, including changes in economic conditions and risk relating to our allowance for loan losses; |
| • | | liquidity and interest rate risks, including the impact of capital markets conditions and changes in monetary policy on our borrowings and net interest income; |
| • | | operational risks, including processing, information systems, vendor problems, business interruption, and fraud risks; |
| • | | strategic and external risks, including economic, political, and competitive forces impacting our business; |
| • | | legal, compliance, and reputational risks, including regulatory and litigation risks; and |
| • | | the risk that our analyses of these risks and forces could be incorrect and / or that the strategies developed to address them could be unsuccessful. |
For a discussion of these and other risks that may cause actual results to differ from expectations, please refer to the “Risk Factors” section of this document. The forward-looking statements contained or incorporated by reference in this document relate only to circumstances as of the date on which the statements are made. We undertake no obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events, or otherwise.
PART I
General
Associated Banc-Corp (individually referred to herein as the “Parent Company” and together with all of its subsidiaries and affiliates, collectively referred to herein as the “Corporation,” “Associated,” “we,” “us,” or “our”) is a bank holding company registered pursuant to the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956, as amended (the “BHC Act”). Our bank subsidiary traces its history back to the founding of the Bank of Neenah in 1861. We were incorporated in Wisconsin in 1964 and were inactive until 1969 when permission was received from the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (the “Federal Reserve”) to acquire three banks. At December 31, 2013, we owned one nationally chartered commercial bank headquartered in Green Bay, Wisconsin and serving local communities across the upper Midwest, one nationally chartered trust company headquartered in Wisconsin, and 19 limited purpose banking and nonbanking subsidiaries either located in or conducting business primarily in our three-state footprint that are closely related or incidental to the business of banking. Measured by total assets reported at December 31, 2013, we are the largest commercial bank holding company headquartered in Wisconsin and one of the top 50, publicly traded, bank holding companies headquartered in the U.S.
1
Services
Through our banking subsidiary Associated Bank, National Association (“Associated Bank” or the “Bank”), and various nonbanking subsidiaries, we provide a broad array of banking and nonbanking products and services to individuals and businesses through over 200 banking offices serving more than 100 communities, primarily within our three-state branch footprint (Wisconsin, Illinois, and Minnesota). Our business is primarily relationship-driven and is organized into three reportable segments: Commercial Banking, Consumer Banking, and Risk Management and Shared Services. See also Note 20, “Segment Reporting,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements in Part II, Item 8, “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data,” for additional information concerning our reportable segments.
Commercial Banking— The Commercial Banking segment serves a wide range of customers including, businesses, developers, non-profits, municipalities, and financial institutions. Business customers in this segment typically include companies with annual sales over $10 million and delivery of services is provided through our regional and middle market units, our commercial real estate unit, as well as our specialized industries and commercial financial services area. The financial solutions provided to our customers include but are not limited to: (1) Lending solutions, such as business loans and lines of credit, business credit cards, commercial real estate financing, construction loans, letters of credit, leasing, and asset based lending. For our larger clients we also offer syndicated loans to meet their lending needs; (2) Deposit and cash management solutions such as business checking and interest-bearing deposit products, safe deposit and night depository services, liquidity solutions, payables and receivables solutions; and information services; and (3) Specialized financial services such as insurance and benefits related products and services, risk management, and international banking solutions. In serving the commercial banking segment we compete based on an in-depth understanding of our customers’ financial needs, the ability to match market competitive solutions to those needs, and the highest standards of relationship and service excellence in the delivery of these services.
Consumer Banking— The Consumer Banking segment serves individuals and small businesses (typically entities with less than $10 million in annual sales) through our various Retail Banking and Private Client offices, and provides companies of varying sizes with fiduciary services such as administration of pension, profit-sharing and other employee benefit plans, fiduciary and corporate agency services, and institutional asset management. The services provided to our individual and small business customers include but are not limited to: (1) Transactional solutions such as checking, credit, debit and pre-paid cards, online banking and bill pay, and money transfer services; (2) Lending solutions such as residential mortgages, home equity loans and lines of credit, business loans and lines, and personal and installment loans; and (3) Investable funds solutions such as savings, money market deposit accounts, IRA accounts, certificates of deposit, market linked certificates of deposit, fixed and variable annuities, full-service, discount and on-line investment brokerage; as well as trust and investment management accounts. In serving the consumer banking segment we compete based on providing a broad range of solutions to meet the needs of our customers in their entire financial lifecycle, convenient access to our services through multiple channels such as branches, phone based services, online and mobile banking, and a relationship based business model which assists our customers in navigating any changes and challenges in their financial circumstances.
Risk Management and Shared Services —The Risk Management and Shared Services segment includes Corporate Risk Management, Credit Administration, Finance, Treasury, Operations, and Technology, which are key shared functions. The segment also includes Parent Company activity, intersegment eliminations and residual revenue and expenses, representing the difference between actual amounts incurred and the amounts allocated to operating segments, including interest rate risk residuals (funds transfer pricing mismatches) and credit risk and provision residuals (long term credit charge mismatches). The earning assets within this segment include the Corporation’s investment portfolio and capital includes both allocated as well as any remaining unallocated capital.
We are not dependent upon a single or a few customers, the loss of which would have a material adverse effect on us. No material portion of our business is seasonal.
2
Employees
At December 31, 2013, we had approximately 4,600 full-time equivalent employees. None of our employees are represented by unions.
Competition
The financial services industry is highly competitive. We compete for loans, deposits, and financial services in all of our principal markets. We compete directly with other bank and nonbank institutions located within our markets, internet-based banks, out-of-market banks and bank holding companies that advertise or otherwise serve our markets, money market and other mutual funds, brokerage houses, and various other financial institutions. Additionally, we compete with insurance companies, leasing companies, regulated small loan companies, credit unions, governmental agencies, and commercial entities offering financial services products. Competition involves efforts to retain current customers and to obtain new loans and deposits, the scope and type of services offered, interest rates paid on deposits and charged on loans, as well as other aspects of banking. We also face direct competition from subsidiaries of bank holding companies that have far greater assets and resources than ours.
Supervision and Regulation
Overview
Financial institutions are highly regulated both at the federal and state levels. Numerous statutes and regulations affect the business of the Corporation.
Bank Holding Company Act Requirements
As a registered bank holding company under the BHC Act, we are regulated, supervised, and examined by the Federal Reserve. In connection with applicable requirements, bank holding companies file periodic reports and other information with the Federal Reserve. The BHC Act also governs the activities that are permissible to bank holding companies and their affiliates and permits the Federal Reserve, in certain circumstances, to issue cease and desist orders and other enforcement actions against bank holding companies and their non-banking affiliates to correct and curtail unsafe or unsound banking practices. Under the Dodd-Frank Act and longstanding Federal Reserve Policy, bank holding companies are required to act as a source of financial strength to each of their subsidiaries pursuant to which such holding company may be required to commit financial resources to support such subsidiaries in circumstances when, absent such requirements, they might not otherwise do. The BHC Act further regulates holding company activities, including requirements and limitations relating to capital, transactions with officers, directors and affiliates, securities issuances, dividend payments, inter-affiliate liabilities, extensions of credit, and expansion through mergers and acquisitions.
The BHC Act allows certain qualifying bank holding companies that elect treatment as “financial holding companies” to engage in activities that are financial in nature and that explicitly include the underwriting and sale of insurance. The Parent Company thus far has not elected to be treated as a financial holding company. Bank holding companies that have not elected such treatment generally must limit their activities to banking activities and activities that are closely related to banking.
The Dodd-Frank Act
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the “Dodd-Frank Act”), enacted in July 2010, significantly changed the bank regulatory structure and affected the lending, investment, trading and operating activities of financial institutions and their holding companies. The Dodd-Frank Act requires the Federal Reserve to set minimum capital levels for bank holding companies that are as stringent as those required for insured depository institutions. The legislation also establishes a floor for capital of insured depository
3
institutions that cannot be lower than the standards in effect today, and directs the federal banking regulators to implement new leverage and capital requirements. The new leverage and capital requirements must take into account off-balance sheet activities and other risks, including risks relating to securitized products and derivatives. Pursuant to the Dodd-Frank Act, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (the “FDIC”) has backup enforcement authority over a depository institution holding company, such as the Parent Company, if the conduct or threatened conduct of such holding company poses a risk to the Deposit Insurance Fund (“DIF”), although such authority may not be used if the holding company is generally in sound condition and does not pose a foreseeable and material risk to the DIF. In addition, the Dodd-Frank Act contains a wide variety of provisions affecting the regulation of depository institutions, including restrictions related to mortgage originations, risk retention requirements as to securitized loans, the establishment of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (“CFPB”), and restrictions on proprietary trading (the “Volcker Rule”). The Dodd-Frank Act may have a material impact on the Corporation’s and the Bank’s operations, particularly through increased compliance costs resulting from possible future consumer and fair lending regulations. See Part I, Item 1A, “Risk Factors” for a more extensive discussion of this topic.
Regulation of Associated Bank and Trust Company
Associated Bank and our nationally chartered trust subsidiary are regulated, supervised and examined by the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (the “OCC”). The OCC has extensive supervisory and regulatory authority over the operations of the Corporation’s national bank subsidiaries. As part of this authority, the national bank subsidiaries are required to file periodic reports with the OCC and are subject to regulation, supervision and examination by the OCC. Associated Bank, our only subsidiary that accepts insured deposits, is also subject to examination by the FDIC. We are subject to the enforcement and rule-making authority of the CFPB regarding consumer financial products. The CFPB has authority to create and enforce consumer protection rules and regulations and has the power to examine us for compliance with such rules and regulations. The CFPB also has the authority to prohibit “unfair, deceptive or abusive” acts and practices. The CFPB has examination and enforcement authority over all banks with more than $10 billion in assets, such as Associated Bank. The Dodd-Frank Act weakens the federal preemption available for national banks and gives broader rights to state attorney generals to enforce certain federal consumer protection loans.
Banking Acquisitions
We are required to obtain prior Federal Reserve approval before acquiring more than 5% of the voting shares, or substantially all of the assets, of a bank holding company, bank or savings association. In determining whether to approve a proposed bank acquisition, federal bank regulators will consider, among other factors, the effect of the acquisition on competition, the public benefits expected to be received from the acquisition, the projected capital ratios and levels on a post-acquisition basis, and the acquiring institution’s record of addressing the credit needs of the communities it serves, including the needs of low and moderate income neighborhoods, consistent with the safe and sound operation of the bank, under the Community Reinvestment Act.
Banking Subsidiary Dividends
The Parent Company is a legal entity separate and distinct from its banking and other subsidiaries. A substantial portion of our revenue comes from dividends paid to us by Associated Bank. The OCC’s prior approval of the payment of dividends by Associated Bank to the Parent Company is required only if the total of all dividends declared by the Bank in any calendar year exceeds the sum of the Bank’s net profits for that year and its retained net profits for the preceding two calendar years, less any required transfers to surplus. Federal law also prohibits national banks from paying dividends that would be greater than the bank’s undivided profits after deducting statutory bad debt in excess of the bank’s allowance for loan losses.
4
Holding Company Dividends
In addition, we and our banking subsidiary are subject to various general regulatory policies and requirements relating to the payment of dividends, including requirements to maintain adequate capital above regulatory minimums. The appropriate federal regulatory authority is authorized to determine under certain circumstances relating to the financial condition of a bank or bank holding company that the payment of dividends would be an unsafe or unsound practice and to prohibit payment thereof. The appropriate federal regulatory authorities have indicated that paying dividends that deplete a bank’s capital base to an inadequate level would be an unsafe and unsound banking practice and that banking organizations should generally pay dividends only out of current operating earnings.
Capital, Liquidity and Stress Testing Requirements
Capital Requirements
We are subject to various regulatory capital requirements both at the Parent Company and at the Bank level administered by the Federal Reserve and the OCC, respectively. Failure to meet minimum capital requirements could result in certain mandatory and possible additional discretionary actions by regulators that, if undertaken, could have an adverse material effect on our financial statements. Under capital adequacy guidelines and the regulatory framework for prompt corrective action (described below), we must meet specific capital guidelines that involve quantitative measures of our assets, liabilities, and certain off-balance sheet items as calculated under regulatory accounting policies. Our capital amounts and classification are also subject to judgments by the regulators regarding qualitative components, risk weightings, and other factors. We have consistently maintained regulatory capital ratios at or above the well capitalized standards.
The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision has drafted frameworks for the regulation of capital and liquidity of internationally active banking organizations, generally referred to as “Basel III.” In July 2013, the Federal Reserve and the OCC issued final rules establishing a new comprehensive capital framework for U.S. banking organizations that would implement the Basel III capital framework and certain provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act. The final rules seek to strengthen the components of regulatory capital, increase risk-based capital requirements, and make selected changes to the calculation of risk-weighted assets. The final rules, among other things:
| • | | revise minimum capital requirements and adjust prompt corrective action thresholds; |
| • | | revise the components of regulatory capital and create a new capital measure called “Tier 1 Common Equity,” which must constitute at least 4.5% of risk-weighted assets; |
| • | | specify that Tier 1 capital consists only of Tier 1 Common Equity and certain “Additional Tier 1 Capital” instruments meeting specified requirements; |
| • | | increase the minimum Tier 1 capital ratio requirement from 4% to 6%; |
| • | | retain the existing risk-based capital treatment for 1-4 family residential mortgage exposures; |
| • | | permit most banking organizations, including the Parent Company, to retain, through a one-time permanent election, the existing capital treatment for accumulated other comprehensive income; |
| • | | implement a new capital conservation buffer of common equity Tier 1 capital equal to 2.5% of risk-weighted assets, which will be in addition to the 4.5% common equity Tier 1 capital ratio and be phased in over a three year period beginning January 1, 2016 which buffer is generally required to make capital distributions and pay executive bonuses; |
| • | | increase capital requirements for past-due loans, high volatility commercial real estate exposures, and certain short-term loan commitments; |
| • | | require the deduction of mortgage servicing assets and deferred tax assets that exceed 10% of common equity Tier 1 capital in each category and 15% of common equity Tier 1 capital in the aggregate; and |
| • | | remove references to credit ratings consistent with the Dodd-Frank Act and establish due diligence requirements for securitization exposures. |
5
Under the final rules, compliance is required beginning January 1, 2015, for most banking organizations including the Parent Company and Associated Bank, subject to a transition period for several aspects of the final rules, including the new minimum capital ratio requirements, the capital conservation buffer, and the regulatory capital adjustments and deductions. Requirements to maintain higher levels of capital could adversely impact our return on equity. We are still in the process of assessing the impacts of these complex final rules; however, we believe we will continue to exceed all estimated well-capitalized regulatory requirements on a fully phased-in basis. For further detail on capital and capital ratios see discussion under Part II, Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” sections, “Liquidity” and “Capital,” and under Part II, Item 8, Note 18, “Regulatory Matters,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements.
Liquidity Requirements
Historically, regulation and monitoring of bank and bank holding company liquidity has been addressed as a supervisory matter, without required formulaic measures. However, the Basel III liquidity framework requires banks and bank holding companies to measure their liquidity against specific liquidity tests that, although similar in some respects to liquidity measures historically applied by banks and regulators for management and supervisory purposes, going forward would be required by regulation. One test, referred to as the liquidity coverage ratio (“LCR”), is designed to ensure that the banking entity maintains an adequate level of unencumbered high-quality liquid assets equal to the entity’s expected net cash outflow for a 30-day time horizon (or, if greater, 25% of its expected total cash outflow) under an acute liquidity stress scenario. The other, referred to as the net stable funding ratio (“NSFR”), is designed to promote more medium- and long-term funding of the assets and activities of banking entities over a one-year time horizon.
On October 30, 2013, the federal banking agencies published a notice of proposed joint rulemaking (the “LCR Proposal”) that would create standardized minimum liquidity requirements for internationally active banking organizations (those with over $250 billion in total assets or over $10 billion in on-balance sheet foreign exposure), as well as modified liquidity requirements for bank holding companies and depository institutions that have more than $50 billion in total assets but are not internationally active banking organizations. The LCR Proposal is generally consistent with the proposed Basel III framework; however, it is more stringent in certain areas and requires an earlier transition period. The LCR Proposal would require certain banking entities to maintain an adequate level of unencumbered high quality liquid assets (“HQLA”) equal to or greater than its expected net cash outflow during a short-term stress period. For certain banks with more than $50 billion in total assets that are not internationally active banking organizations, the LCR would be calculated using a 21-calendar day stress scenario and would equal HQLA divided by total net cash outflows during this period. The LCR Proposal has a phase-in period that would require a minimum LCR ratio of: 80% beginning January 1, 2015, 90% beginning January 1, 2016 and 100% beginning January 1, 2017. The LCR Proposal is subject to further regulatory action and interpretation as well as a comment period ending January 31, 2014. As of December 31, 2013, the Parent Company had $24 billion of total assets, and therefore, is not specifically within the scope of the LCR Proposal as currently drafted.
Capital Planning and Stress Testing Requirements
On October 12, 2012, the Federal Reserve published two Final Rules implementing the company-run stress test requirements mandated by the Dodd-Frank Act: one for U.S. bank holding companies with total consolidated assets of $10 billion to $50 billion, and one for U.S. bank holding companies with total consolidated assets of $50 billion or more. Under the Rule applicable to the Parent Company, which became effective November 15, 2012, we are required to conduct annual company-run stress tests using data as of September 30 of each year and different scenarios provided by the Federal Reserve. Submissions are due to the Federal Reserve during the first quarter of each following year. We anticipate that our pro forma capital ratios, as reflected in the stress test calculations under the required stress test scenarios, will be an important factor considered by the Federal Reserve Board in evaluating whether proposed payments of dividends or stock repurchases are consistent with its prudential expectations. Requirements to maintain higher levels of capital or liquidity to address potential adverse stress scenarios could adversely impact our net income and our return on equity. The Corporation intends to submit its initial stress test report in March 2014.
6
Enforcement Powers of the Federal Banking Agencies; Prompt Corrective Action
The Federal Reserve, the OCC, and the CFPB have extensive supervisory authority over their regulated institutions, including, among other things, the power to compel higher reserves, the ability to assess civil money penalties, the ability to issue cease-and-desist or removal orders and the ability to initiate injunctive actions. In general, these enforcement actions may be initiated for violations of laws and regulations or for unsafe or unsound banking practices. Other actions or inactions by the Parent Company may provide the basis for enforcement action, including misleading or untimely reports.
Federal banking regulators are authorized and, under certain circumstances, required to take certain actions against banks that fail to meet their capital requirements. The federal banking agencies have additional enforcement authority with respect to undercapitalized depository institutions.
“Well capitalized” institutions may generally operate without supervisory restriction. With respect to “adequately capitalized” institutions, such banks cannot normally pay dividends or make any capital contributions that would leave it undercapitalized; they cannot pay a management fee to a controlling person if, after paying the fee, it would be undercapitalized; and they cannot accept, renew or roll over any brokered deposit unless the bank has applied for and been granted a waiver by the FDIC.
The federal banking agencies are required to take action to restrict the activities of an “undercapitalized,” “significantly undercapitalized,” or “critically undercapitalized” insured depository institution. Any such bank must submit a capital restoration plan that is guaranteed by the parent holding company. Until such plan is approved, it may not increase its assets, acquire another institution, establish a branch or engage in any new activities, and generally may not make capital distributions. In certain situations, a federal banking agency may reclassify a well capitalized institution as adequately capitalized and may require an adequately capitalized or undercapitalized institution to comply with supervisory actions as if the institution were in the next lower category.
Institutions must file a capital restoration plan with the OCC within 45 days of the date it receives a notice from the OCC that it is “undercapitalized,” “significantly undercapitalized,” or “critically undercapitalized.” Compliance with a capital restoration plan must be guaranteed by a parent holding company. In addition, the OCC is permitted to take any one of a number of discretionary supervisory actions, including but not limited to the issuance of a capital directive and the replacement of senior executive officers and directors.
Finally, bank regulatory agencies have the ability to impose higher than normal capital requirements known as individual minimum capital requirement (“IMCR”) for institutions with a high-risk profile.
At December 31, 2013, the Bank satisfied the requirements as “well capitalized”. The imposition of any of the measures described above could have a material adverse effect on the Corporation and on its profitability and operations. The Corporation’s shareholders do not have preemptive rights and, therefore, if the Corporation is directed by the OCC or the FDIC to issue additional shares of common stock, such issuance may result in dilution in shareholders’ percentage of ownership of the Corporation.
Deposit Insurance Premiums
Associated Bank is a member of the FDIC and pays an insurance premium to the FDIC based upon its assessment rates on a quarterly basis. Deposits are insured up to applicable limits by the FDIC and such insurance is backed by the full faith and credit of the United States Government.
Under the Dodd-Frank Act, a permanent increase in deposit insurance was authorized to $250,000. The coverage limit is per depositor, per insured depository institution for each account ownership category.
7
The Dodd-Frank Act also set a new minimum DIF reserve ratio at 1.35% of estimated insured deposits. The FDIC is required to attain this ratio by September 30, 2020. The Dodd-Frank Act also required the FDIC to define the deposit insurance assessment base for an insured depository institution as an amount equal to the institution’s average consolidated total assets during the assessment period minus average tangible equity. The assessment rate schedule for larger institutions like Associated Bank (i.e., institutions with at least $10 billion in assets) differentiates between such large institutions by use of a “scorecard” that combines an institution’s CAMELS ratings with certain forward-looking financial information to measure the risk to the DIF. Pursuant to this “scorecard” method, two scores (a performance score and a loss severity score) will be combined and converted to an initial base assessment rate. The performance score measures an institution’s financial performance and ability to withstand stress. The loss severity score measures the relative magnitude of potential losses to the DIF in the event of the institution’s failure. Total scores are converted pursuant to a predetermined formula into an initial base assessment rate. Assessment rates range from 2.5 basis points to 45 basis points for large institutions. Premiums for Associated Bank are now calculated based upon the average balance of total assets minus average tangible equity as of the close of business for each day during the calendar quarter.
The FDIC has the flexibility to adopt actual rates that are higher or lower than the total base assessment rates adopted without notice and comment, if certain conditions are met.
DIF-insured institutions pay a Financing Corporation (“FICO”) assessment in order to fund the interest on bonds issued in the 1980s in connection with the failures in the thrift industry. For the fourth quarter of 2013, the FICO assessment was equal to 0.640 basis points computed on assets as required by the Dodd-Frank Act. These assessments will continue until the bonds mature in 2019.
The FDIC is authorized to conduct examinations of and require reporting by FDIC-insured institutions. It is also authorized to terminate a depository bank’s deposit insurance upon a finding by the FDIC that the bank’s financial condition is unsafe or unsound or that the institution has engaged in unsafe or unsound practices or has violated any applicable rule, regulation, order or condition enacted or imposed by the bank’s regulatory agency. The termination of deposit insurance for our national bank subsidiary would have a material adverse effect on our earnings, operations and financial condition.
Standards for Safety and Soundness
The federal banking agencies have adopted the Interagency Guidelines for Establishing Standards for Safety and Soundness. The Guidelines establish certain safety and soundness standards for all depository institutions. The operational and managerial standards in the Guidelines relate to the following: (1) internal controls and information systems; (2) internal audit systems; (3) loan documentation; (4) credit underwriting; (5) interest rate exposure; (6) asset growth; (7) compensation, fees and benefits; (8) asset quality; and (9) earnings. Rather than providing specific rules, the Guidelines set forth basic compliance considerations and guidance with respect to a depository institution. Failure to meet the standards in the Guidelines, however, could result in a request by the OCC to one of the nationally chartered banks to provide a written compliance plan to demonstrate its efforts to come into compliance with such Guidelines. Failure to provide a plan or to implement a provided plan requires the appropriate federal banking agency to issue an order to the institution requiring compliance.
Transactions with Affiliates
Transactions between our national banking subsidiary and its related parties or any affiliate are governed by Sections 23A and 23B of the Federal Reserve Act. An affiliate is any company or entity, which controls, is controlled by or is under common control with the bank. In a holding company context, at a minimum, the parent holding company of a national bank and any companies which are controlled by such parent holding company are affiliates of the bank. Generally, Sections 23A and 23B (i) limit the extent to which an institution or its subsidiaries may engage in “covered transactions” with any one affiliate to an amount equal to 10% of such institution’s capital stock and surplus, and contain an aggregate limit on all such transactions with all affiliates to
8
an amount equal to 20% of such capital stock and surplus, and (ii) require that all such transactions be on terms substantially the same, or at least as favorable, to the institution or subsidiary as those provided to a nonaffiliate. The term “covered transaction” includes the making of loans, purchase of assets, issuance of a guarantee and similar types of transactions. Certain types of covered transactions must be collateralized according to a schedule set forth in the statute based on the type of collateral.
Certain transactions with our directors, officers or controlling persons are also subject to conflicts of interest regulations. Among other things, these regulations require that loans to such persons and their related interests be made on terms substantially the same as for loans to unaffiliated individuals and must not create an abnormal risk of repayment or other unfavorable features for the financial institution. See Note 3, “Loans,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements in Part II, Item 8, “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data,” for additional information on loans to related parties.
Community Reinvestment Act Requirements
Our national bank subsidiary, Associated Bank, is subject to periodic Community Reinvestment Act (“CRA”) reviews by the OCC. The CRA does not establish specific lending requirements or programs for financial institutions and does not limit the ability of such institutions to develop products and services believed best-suited for a particular community. An institution’s CRA assessment may be used by its regulators in their evaluation of certain applications, including a merger, acquisition or the establishment of a branch office. An unsatisfactory rating may be used as the basis for denial of such an application.
Associated Bank underwent a CRA examination by the OCC on November 20, 2006, for which it received a Satisfactory rating.
Privacy
Financial institutions, such as our national bank subsidiary, are required by statute and regulation to disclose their privacy policies. In addition, such financial institutions must appropriately safeguard its customers’ nonpublic, personal information.
Bank Secrecy Act / Anti-Money Laundering
The Bank Secrecy Act (“BSA”), which is intended to require financial institutions to develop policies, procedures, and practices to prevent and deter money laundering, mandates that every national bank have a written, board-approved program that is reasonably designed to assure and monitor compliance with the BSA. The program must, at a minimum: (1) provide for a system of internal controls to assure ongoing compliance; (2) provide for independent testing for compliance; (3) designate an individual responsible for coordinating and monitoring day-to-day compliance; and (4) provide training for appropriate personnel. In addition, national banks are required to adopt a customer identification program as part of its BSA compliance program. National banks are also required to file Suspicious Activity Reports when they detect certain known or suspected violations of federal law or suspicious transactions related to a money laundering activity or a violation of the BSA.
On February 23, 2012, Associated Bank entered into a Consent Order with the OCC regarding its BSA compliance. The Consent Order required, among other things, that the Bank: (1) create a Compliance Committee of at least three directors; (2) create a BSA-focused action plan to supplement existing customer due diligence policies and procedures; (3) review, update and implement an ongoing BSA risk assessment; (4) review and update risk-based processes to obtain and analyze appropriate customer due diligence information at the time of account opening and on an ongoing basis; (5) ensure adherence to a written program of policies and procedures to provide compliance with the BSA; (6) complete independent testing; (7) ensure it has a permanent, qualified, and experienced BSA Officer; (8) develop and implement a comprehensive, ongoing BSA and OFAC training program; and (9) submit certain reports to the OCC. The Bank has been working cooperatively with the OCC and believes it is in compliance with all provisions of the Consent Order.
9
In addition to complying with the BSA, the Bank is subject to the Uniting and Strengthening America by Providing Appropriate Tools Required to Intercept and Obstruct Terrorism Act of 2001 (the “Patriot Act”). The Patriot Act is designed to deny terrorists and criminals the ability to obtain access to the United States’ financial system and has significant implications for depository institutions, brokers, dealers, and other businesses involved in the transfer of money. The Patriot Act mandates that financial service companies implement additional policies and procedures and take heightened measures designed to address any or all of the following matters: customer identification programs, money laundering, terrorist financing, identifying and reporting suspicious activities and currency transactions, currency crimes, and cooperation between financial institutions and law enforcement authorities. The Corporation believes it is in compliance with the Patriot Act requirements.
Interstate Branching
Pursuant to the Dodd-Frank Act, national and state-chartered banks may open an initial branch in a state other than its home state (e.g., a host state) by establishing a de novo branch at any location in such host state at which a bank chartered in such host state could establish a branch. Applications to establish such branches must still be filed with the appropriate primary federal regulator.
Volcker Rule
The Dodd-Frank Act prohibits insured depository institutions and their holding companies from engaging in proprietary trading except in limited circumstances, and prohibits them from owning equity interests in excess of three percent (3%) of Tier 1 Capital in private equity and hedge funds (known as the “Volcker Rule”). On December 10, 2013, five U.S. financial regulators, including the Federal Reserve and the OCC, adopted final rules (the “Final Rules”) implementing the Volcker Rule. The Final Rules prohibit banking entities from (1) engaging in short-term proprietary trading for their own accounts, and (2) having certain ownership interests in and relationships with hedge funds or private equity funds. The Final Rules are intended to provide greater clarity with respect to both the extent of those primary prohibitions and of the related exemptions and exclusions. The Final Rules also require each regulated entity to establish an internal compliance program that is consistent with the extent to which it engages in activities covered by the Volcker Rule, which must include (for the largest entities) making regular reports about those activities to regulators. Although the Final Rules provide some tiering of compliance and reporting obligations based on size, the fundamental prohibitions of the Volcker Rule apply to banking entities of any size, including the Parent Company and Associated Bank. The Final Rules are effective April 1, 2014, but the conformance period has been extended from its statutory end date of July 21, 2014 until July 21, 2015. The Corporation has evaluated the implications of the Final Rules on its investments and does not expect any material financial implications.
Under the Final Rules, banking entities would have been prohibited from owning certain Collateralized Debt Obligations (CDOs) backed by Trust Preferred Securities (TruPS) as of July 21, 2015, which could have forced banking entities to recognize unrealized market losses based on the inability to hold any such investments to maturity. However, on January 14, 2014, the U.S. financial regulators issued an interim rule (“Interim Rule”), effective April 1, 2014, exempting TruPS CDOs from the Volcker Rule if (i) the CDO was established prior to May 19, 2010, (ii) the banking entity reasonably believes that the offering proceeds of the CDO were used to invest primarily in TruPS issued by banks with less than $15 billion in assets, and (iii) the banking entity acquired the CDO on or before December 10, 2013. The Corporation currently does not have any impermissible holdings of TruPS CDOs under the Interim Rule, and therefore, will not be required to divest of any such investments or change the accounting treatment. However, regulators are soliciting comments to the Interim Rule, and this exemption could change prior to its effective date.
Incentive Compensation Policies and Restrictions
In July 2010, the federal banking agencies issued guidance that applies to all banking organizations supervised by the agencies (thereby including both the Parent Company and the Bank). Pursuant to the guidance, to be consistent with safety and soundness principles, a banking organization’s incentive compensation arrangements
10
should: (1) provide employees with incentives that appropriately balance risk and reward; (2) be compatible with effective controls and risk management; and (3) be supported by strong corporate governance including active and effective oversight by the banking organization’s board of directors. Monitoring methods and processes used by a banking organization should be commensurate with the size and complexity of the organization and its use of incentive compensation.
In addition, in March 2011, the federal banking agencies, along with the Federal Housing Finance Agency, and the Securities and Exchange Commission, released a proposed rule intended to ensure that regulated financial institutions design their incentive compensation arrangements to account for risk. Specifically, the proposed rule would require compensation practices at the Parent Company and at the Bank to be consistent with the following principles: (1) compensation arrangements appropriately balance risk and financial reward; (2) such arrangements are compatible with effective controls and risk management; and (3) such arrangements are supported by strong corporate governance. In addition, financial institutions with $1 billion or more in assets would be required to have policies and procedures to ensure compliance with the rule and would be required to submit annual reports to their primary federal regulator. The comment period has closed and a final rule has not yet been published; however, the Corporation believes it is in compliance with the rule as currently proposed.
Ability-to-Repay and Qualified Mortgage Rule
Pursuant to the Dodd Frank Act, the CFPB issued a final rule on January 10, 2013 (effective on January 10, 2014), amending Regulation Z as implemented by the Truth in Lending Act, requiring mortgage lenders to make a reasonable and good faith determination based on verified and documented information that a consumer applying for a mortgage loan has a reasonable ability to repay the loan according to its terms. Mortgage lenders are required to determine consumers’ ability to repay in one of two ways. The first alternative requires the mortgage lender to consider the following eight underwriting factors when making the credit decision: (1) current or reasonably expected income or assets; (2) current employment status; (3) the monthly payment on the covered transaction; (4) the monthly payment on any simultaneous loan; (5) the monthly payment for mortgage-related obligations; (6) current debt obligations, alimony, and child support; (7) the monthly debt-to-income ratio or residual income; and (8) credit history. Alternatively, the mortgage lender can originate “qualified mortgages,” which are entitled to a presumption that the creditor making the loan satisfied the ability-to-repay requirements. In general, a “qualified mortgage” is a mortgage loan without negative amortization, interest-only payments, balloon payments, or terms exceeding 30 years. In addition, to be a qualified mortgage the points and fees paid by a consumer cannot exceed 3% of the total loan amount. Qualified mortgages that are “higher-priced” (e.g. subprime loans) garner a rebuttable presumption of compliance with the ability-to-repay rules, while qualified mortgages that are not “higher-priced” (e.g. prime loans) are given a safe harbor of compliance. The Corporation is predominantly an originator of compliant qualified mortgages.
Other Banking Regulations
Our banking subsidiary is also subject to a variety of other regulations with respect to the operation of its businesses, including but not limited to the Dodd-Frank Act, Truth in Lending Act, Truth in Savings Act, Equal Credit Opportunity Act, Electronic Funds Transfer Act, Fair Housing Act, Home Mortgage Disclosure Act, Fair Debt Collection Practices Act, Fair Credit Reporting Act, Expedited Funds Availability (Regulation CC), Reserve Requirements (Regulation D), Insider Transactions (Regulation O), Privacy of Consumer Information (Regulation P), Margin Stock Loans (Regulation U), Right To Financial Privacy Act, Flood Disaster Protection Act, Homeowners Protection Act, Servicemembers Civil Relief Act, Real Estate Settlement Procedures Act, Telephone Consumer Protection Act, CAN-SPAM Act, Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act, and the John Warner National Defense Authorization Act.
The laws and regulations to which we are subject are constantly under review by Congress, the federal regulatory agencies, and the state authorities. These laws and regulations could be changed drastically in the future, which could affect our profitability, our ability to compete effectively, or the composition of the financial services industry in which we compete.
11
Government Monetary Policies and Economic Controls
Our earnings and growth, as well as the earnings and growth of the banking industry, are affected by the credit policies of monetary authorities, including the Federal Reserve. An important function of the Federal Reserve is to regulate the national supply of bank credit in order to combat recession and curb inflationary pressures. Among the instruments of monetary policy used by the Federal Reserve to implement these objectives are open market operations in U.S. government securities, changes in reserve requirements against member bank deposits, and changes in the Federal Reserve discount rate. These means are used in varying combinations to influence overall growth of bank loans, investments, and deposits, and may also affect interest rates charged on loans or paid for deposits. The monetary policies of the Federal Reserve authorities have had a significant effect on the operating results of commercial banks in the past and are expected to continue to have such an effect in the future.
In view of changing conditions in the national economy and in money markets, as well as the effect of credit policies by monetary and fiscal authorities, including the Federal Reserve, it is difficult to predict the impact of possible future changes in interest rates, deposit levels, and loan demand, or their effect on our business and earnings or on the financial condition of our various customers.
Other Regulatory Authorities
In addition to regulation, supervision and examination by federal banking agencies, the Corporation and certain of its subsidiaries, including those that engage in securities brokerage, dealing and investment advisory activities, are subject to other federal and state securities laws and regulations, and to supervision and examination by other regulatory authorities, including the Securities and Exchange Commission, the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (“FINRA”), the NASDAQ Global Select Market and others.
Available Information
We file annual, quarterly, and current reports, proxy statements, and other information with the SEC. These filings are available to the public on the Internet at the SEC’s web site at www.sec.gov. Shareholders may also read and copy any document that we file at the SEC’s public reference rooms located at 100 F Street, NE, Washington, DC 20549. Shareholders may call the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330 for further information on the public reference room.
Our principal internet address is www.associatedbank.com. We make available free of charge on or through our website our annual report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC. In addition, shareholders may request a copy of any of our filings (excluding exhibits) at no cost by writing, telephoning, or e-mailing us using the following information: Associated Banc-Corp, Attn: Shareholder Relations, 433 Main Street, Green Bay, WI 54301; phone 920-491-7059; or e-mail to shareholders@associatedbank.com. Our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, Corporate Governance Guidelines, and committee charters for standing committees of the Board are all available on our website, www.associatedbank.com/About Us/Investor Relations/Corporate Governance. We will disclose on our website amendments to or waivers from our Code of Ethics in accordance with all applicable laws and regulations. Information contained on any of our websites is not deemed to be a part of this Annual Report.
An investment in our common stock is subject to risks inherent to our business. The material risks and uncertainties that management believes affect us are described below. Before making an investment decision, you should carefully consider the risks and uncertainties described below, together with all of the other information included or incorporated by reference herein. The risks and uncertainties described below are not the
12
only ones facing us. Additional risks and uncertainties that management is not aware of or focused on or that management currently deems immaterial may also impair our business operations. This report is qualified in its entirety by these risk factors. See also, “Special Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements.”
If any of the following risks actually occur, our financial condition and results of operations could be materially and adversely affected. If this were to happen, the value of our securities could decline significantly, and you could lose all or part of your investment.
Credit Risks
Changes in economic and political conditions could adversely affect our earnings, as our borrowers’ ability to repay loans and the value of the collateral securing our loans decline. Our success depends, to a certain extent, upon economic and political conditions, local and national, as well as governmental monetary policies. Conditions such as an economic recession, rising unemployment, changes in interest rates, money supply and other factors beyond our control may adversely affect our asset quality, deposit levels and loan demand and, therefore, our earnings. Because we have a significant amount of real estate loans, decreases in real estate values could adversely affect the value of property used as collateral. Adverse changes in the economy may also have a negative effect on the ability of our borrowers to make timely repayments of their loans, which could have an adverse impact on our earnings. Consequently, declines in the economy in our market area could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Our allowance for loan losses may be insufficient. All borrowers have the potential to default and our remedies to recover (seizure and / or sale of collateral, legal actions, guarantees, etc.) may not fully satisfy the debt owed to us. We maintain an allowance for loan losses, which is a reserve established through a provision for loan losses charged to expense, which represents management’s best estimate of probable credit losses that have been incurred within the existing portfolio of loans. The allowance for loan losses, in the judgment of management, is necessary to reserve for estimated loan losses and risks inherent in the loan portfolio. The level of the allowance for loan losses reflects management’s continuing evaluation of industry concentrations; specific credit risks; loan loss experience; current loan portfolio quality; present economic, political, and regulatory conditions; and unidentified losses inherent in the current loan portfolio. The determination of the appropriate level of the allowance for loan losses inherently involves a high degree of subjectivity and requires us to make significant estimates of current credit risks using existing qualitative and quantitative information, all of which may undergo material changes. Changes in economic conditions affecting borrowers, new information regarding existing loans, identification of additional problem loans, and other factors, both within and outside of our control, may require an increase in the allowance for loan losses. In addition, bank regulatory agencies periodically review our allowance for loan losses and may require an increase in the provision for loan losses or the recognition of additional loan charge offs, based on judgments different than those of management. An increase in the allowance for loan losses would result in a decrease in net income, and possibly risk-based capital, and could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
We are subject to lending concentration risks. As of December 31, 2013, approximately 62% of our loan portfolio consisted of commercial and industrial, real estate construction, commercial real estate loans, and lease financing (collectively, “commercial loans”). Commercial loans are generally viewed as having more inherent risk of default than residential mortgage loans or retail loans. Also, the commercial loan balance per borrower is typically larger than that for residential mortgage loans and retail loans, inferring higher potential losses on an individual loan basis. Because our loan portfolio contains a number of commercial loans with balances over $25 million, the deterioration of one or a few of these loans could cause a significant increase in nonaccrual loans. An increase in nonaccrual loans could result in a loss of interest income from these loans, an increase in the provision for loan losses, and an increase in loan charge offs, all of which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
13
Financial services companies depend on the accuracy and completeness of information about customers and counterparties. In deciding whether to extend credit or enter into other transactions, we may rely on information furnished by or on behalf of customers and counterparties, including financial statements, credit reports, and other financial information. We may also rely on representations of those customers, counterparties, or other third parties, such as independent auditors, as to the accuracy and completeness of that information. Reliance on inaccurate or misleading financial statements, credit reports, or other financial information could cause us to enter into unfavorable transactions, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Lack of system integrity or credit quality related to funds settlement could result in a financial loss. We settle funds on behalf of financial institutions, other businesses and consumers and receive funds from clients, card issuers, payment networks and consumers on a daily basis for a variety of transaction types. Transactions facilitated by us include wire transfers, debit card, credit card and electronic bill payment transactions, supporting consumers, financial institutions and other businesses. These payment activities rely upon the technology infrastructure that facilitates the verification of activity with counterparties and the facilitation of the payment. If the continuity of operations or integrity of processing were compromised this could result in a financial loss to us due to a failure in payment facilitation. In addition, we may issue credit to consumers, financial institutions or other businesses as part of the funds settlement. A default on this credit by a counterparty could result in a financial loss to us.
We are subject to environmental liability risk associated with lending activities. A significant portion of our loan portfolio is secured by real property. During the ordinary course of business, we may foreclose on and take title to properties securing certain loans. In doing so, there is a risk that hazardous or toxic substances could be found on these properties. If hazardous or toxic substances are found, we may be liable for remediation costs, as well as for personal injury and property damage. Environmental laws may require us to incur substantial expenses which may materially reduce the affected property’s value or limit our ability to use or sell the affected property. In addition, future laws or more stringent interpretations or enforcement policies with respect to existing laws may increase our exposure to environmental liability. Although we have policies and procedures to perform an environmental review before initiating any foreclosure action on real property, these reviews may not be sufficient to detect all potential environmental hazards. The remediation costs and any other financial liabilities associated with an environmental hazard could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Liquidity and Interest Rate Risks
Liquidity is essential to our businesses. The Corporation requires liquidity to meet its deposit and debt obligations as they come due. Access to liquidity could be impaired by an inability to access the capital markets or unforeseen outflows of deposits. Risk factors that could impair our ability to access capital markets include a downturn in our Midwest markets, difficult credit markets, credit rating downgrades, or regulatory actions against the Corporation. The Corporation’s access to deposits can be impacted by the liquidity needs of our customers as a substantial portion of the Corporation’s liabilities are demand while a substantial portion of the Corporation’s assets are loans that cannot be sold in the same timeframe. Historically, the Corporation has been able to meet its cash flow needs as necessary. If a sufficiently large number of depositors sought to withdraw their deposits for whatever reason, the Corporation may be unable to obtain the necessary funding at terms favorable to the Bank.
We are subject to interest rate risk. Our earnings and cash flows are largely dependent upon our net interest income. Interest rates are highly sensitive to many factors that are beyond our control, including general economic conditions and policies of various governmental and regulatory agencies and, in particular, the Federal Reserve. Changes in monetary policy, including changes in interest rates, could influence not only the interest we receive on loans and investments and the amount of interest we pay on deposits and borrowings, but such changes could also affect (i) our ability to originate loans and obtain deposits; (ii) the fair value of our financial assets and liabilities; and (iii) the average duration of our mortgage portfolio and other interest-earning assets. If
14
the interest rates paid on deposits and other borrowings increase at a faster rate than the interest rates received on loans and other investments, our net interest income, and therefore earnings, could be adversely affected. Earnings could also be adversely affected if the interest rates received on loans and other investments fall more quickly than the interest rates paid on deposits and other borrowings. Our most significant interest rate risk may be further declines in the absolute level of interest rates or the prolonged continuation of the current low rate environment, as this would generally lead to further compression of our net interest margin, reduced net interest income, and devaluation of our deposit base.
Although management believes it has implemented effective asset and liability management strategies, including the potential use of derivatives as hedging instruments, to reduce the potential effects of changes in interest rates on our results of operations, any substantial, unexpected, prolonged change in market interest rates could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations. Also, our interest rate risk modeling techniques and assumptions likely may not fully predict or capture the impact of actual interest rate changes on our balance sheet.
The impact of interest rates on our mortgage banking business can have a significant impact on revenues. Changes in interest rates can impact our mortgage related revenues and net revenues associated with mortgage pipeline derivative activities. A decline in mortgage rates generally increases the demand for mortgage loans as borrowers refinance, but also generally leads to accelerated payoffs. Conversely, in a constant or increasing rate environment, we would expect fewer loans to be refinanced and a decline in payoffs. Although we use models to assess the impact of interest rates on mortgage related revenues, the estimates of revenues produced by these models are dependent on estimates and assumptions of future loan demand, prepayment speeds and other factors which may differ from actual subsequent experience.
Changes in interest rates could reduce the value of our investment securities holdings. The Corporation maintains an investment portfolio consisting of various high quality liquid fixed-income securities. The total book value of the securities portfolio as of December 31, 2013 was $5.4 billion and the duration of the aggregate portfolio was 3.9 years. The nature of fixed-income securities is such that changes in market interest rates impact the value of these assets. Based on the duration of the Corporation’s securities portfolio, one would expect a market value change of approximately $213 million for a one percent change in market rates.
Changes in interest rates could also reduce the value of our residential mortgage-related securities and mortgage servicing rights, which could negatively affect our earnings. We have a portfolio of mortgage servicing rights. A mortgage servicing right (“MSR”) is the right to service a mortgage loan (i.e., collect principal, interest, escrow amounts, etc.) for a fee. We acquire MSRs when we originate mortgage loans and keep the servicing rights after we sell or securitize the loans or when we purchase the servicing rights to mortgage loans originated by other lenders. We carry MSRs at the lower of amortized cost or estimated fair value. Fair value is the present value of estimated future net servicing income, calculated based on a number of variables, including assumptions about the likelihood of prepayment by borrowers.
When interest rates fall, borrowers are more likely to prepay their mortgage loans by refinancing them at a lower rate. As the likelihood of prepayment increases, the fair value of our residential mortgage-related securities and MSRs can decrease. Each quarter we evaluate our residential mortgage-related securities and MSRs for impairment. If temporary impairment exists, we establish a valuation allowance through a charge to earnings for the amount the carrying amount exceeds fair value. We also evaluate our MSRs for other-than-temporary impairment. If we determine that other-than-temporary impairment exists, we will recognize a direct write-down of the carrying value of the MSRs.
We rely on dividends from our subsidiaries for most of our revenue. The Parent Company is a separate and distinct legal entity from its banking and other subsidiaries. A substantial portion of the Parent Company’s revenue comes from dividends from its subsidiaries. These dividends are the principal source of funds to pay dividends on the Parent Company’s common and preferred stock, and to pay interest and principal on the Parent Company’s debt. Various federal and / or state laws and regulations limit the amount of dividends that our
15
national bank subsidiary and certain nonbank subsidiaries may pay to us. Also, our right to participate in a distribution of assets upon a subsidiary’s liquidation or reorganization is subject to the prior claims of the subsidiary’s creditors. In the event our national bank subsidiary is unable to pay dividends to us, we may not be able to service debt, pay obligations, or pay dividends on our common and preferred stock. The inability to receive dividends from our national bank subsidiary could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Operational Risks
We face significant operational risks due to the high volume and the high dollar value nature of transactions we process. We operate in many different businesses in diverse markets and rely on the ability of our employees and systems to process transactions. Operational risk is the risk of loss resulting from our operations, including but not limited to, the risk of fraud by employees or persons outside our company, the execution of unauthorized transactions, errors relating to transaction processing and technology, breaches of our internal control systems, compliance failures, business continuation and disaster recovery issues, and other external events. Insurance coverage may not be available for such losses, or where available, such losses may exceed insurance limits. This risk of loss also includes the potential legal actions that could arise as a result of an operational deficiency or as a result of noncompliance with applicable regulatory standards, adverse business decisions or their implementation, and customer attrition due to potential negative publicity. In the event of a breakdown in the internal control system, improper operation of systems or improper employee actions, we could suffer financial loss, face regulatory action and suffer damage to our reputation.
Our information systems may experience an interruption or breach in security. We rely heavily on communications and information systems to conduct our business. Any failure, interruption, or breach in security or operational integrity of these systems could result in failures or disruptions in our customer relationship management, general ledger, deposit, loan, and other systems. While we have policies and procedures designed to prevent or limit the effect of the failure, interruption, or security breach of our information systems, we cannot completely ensure that any such failures, interruptions, or security breaches will not occur or, if they do occur, that they will be adequately addressed. The occurrence of any failures, interruptions, or security breaches of our information systems could damage our reputation, result in a loss of customer business, subject us to additional regulatory scrutiny, or expose us to civil litigation and possible financial liability, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Unauthorized disclosure of sensitive or confidential client or customer information, whether through a breach of our computer systems or otherwise, could severely harm our business. As part of our business, we collect, process and retain sensitive and confidential client and customer information on our behalf and on behalf of other third parties. Despite the security measures we have in place, our facilities and systems may be vulnerable to security breaches, acts of vandalism, computer viruses, misplaced or lost data, programming and / or human errors, or other similar events. Any security breach involving the misappropriation, loss or other unauthorized disclosure of confidential customer information could severely damage our reputation, expose us to the risk of litigation and liability, disrupt our operations and have a material adverse effect on our business.
We are dependent upon third parties for certain information system, data management and processing services and to provide key components of our business infrastructure. We outsource certain information system and data management and processing functions to third party providers, including, among others, Fiserv, Inc. and its affiliates. These third party service providers are also sources of operational and informational security risk to us, including risks associated with operational errors, information system interruptions or breaches, and unauthorized disclosures of sensitive or confidential client or customer information. If third party service providers encounter any of these issues, or if we have difficulty communicating with them, we could be exposed to disruption of operations, loss of service or connectivity to customers, reputational damage, and litigation risk that could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations or our business.
16
Third party vendors provide key components of our business infrastructure such as internet connections, network access and core application processing. While we have selected these third party vendors carefully, we do not control their actions. Any problems caused by these third parties, including as a result of their not providing us their services for any reason or their performing their services poorly, could adversely affect our ability to deliver products and services to our customers and otherwise to conduct our business. Replacing these third party vendors could also entail significant delay and expense.
The potential for business interruption exists throughout our organization. Integral to our performance is the continued efficacy of our technical systems, operational infrastructure, relationships with third parties and the vast array of associates and key executives in our day-to-day and ongoing operations. Failure by any or all of these resources subjects us to risks that may vary in size, scale and scope. This includes, but is not limited to, operational or technical failures, ineffectiveness or exposure due to interruption in third party support as expected, as well as the loss of key individuals or failure on the part of key individuals to perform properly. Although management has established policies and procedures to address such failures, the occurrence of any such event could have a material adverse effect on our business, which, in turn, could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Changes in our accounting policies or in accounting standards could materially affect how we report our financial results. Our accounting policies are fundamental to understanding our financial results and condition. Some of these policies require use of estimates and assumptions that may affect the value of our assets or liabilities and financial results. Some of our accounting policies are critical because they require management to make difficult, subjective and complex judgments about matters that are inherently uncertain and because it is likely that materially different amounts would be reported under different conditions or using different assumptions. If such estimates or assumptions underlying our financial statements are incorrect, we may experience material losses.
From time to time the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and the SEC change the financial accounting and reporting standards or the interpretation of those standards that govern the preparation of our external financial statements. These changes are beyond our control, can be hard to predict and could materially impact how we report our results of operations and financial condition. We could be required to apply a new or revised standard retroactively, resulting in our restating prior period financial statements in material amounts.
Our internal controls may be ineffective. Management regularly reviews and updates our internal controls, disclosure controls and procedures, and corporate governance policies and procedures. Any system of controls, however well designed and operated, is based in part on certain assumptions and can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurances that the objectives of the controls are met. Any failure or circumvention of our controls and procedures or failure to comply with regulations related to controls and procedures could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
Impairment of investment securities, goodwill, other intangible assets, or deferred tax assets could require charges to earnings, which could result in a negative impact on our results of operations. In assessing whether the impairment of investment securities is other-than-temporary, management considers the length of time and extent to which the fair value has been less than cost, the financial condition and near-term prospects of the issuer, and the intent and ability to retain our investment in the security for a period of time sufficient to allow for any anticipated recovery in fair value in the near term.
Under current accounting standards, goodwill is not amortized but, instead, is subject to impairment tests on at least an annual basis or more frequently if an event occurs or circumstances change that reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying amount. A decline in our stock price or occurrence of a triggering event following any of our quarterly earnings releases and prior to the filing of the periodic report for that period could, under certain circumstances, cause us to perform a goodwill impairment test and result in an impairment charge being recorded for that period which was not reflected in such earnings release. During 2013, the annual impairment test conducted in May indicated that the fair value of all of the Corporation’s reporting units
17
exceeded the fair value of their assets and liabilities. In the event that we conclude that all or a portion of our goodwill may be impaired, a non-cash charge for the amount of such impairment would be recorded to earnings. Such a charge would have no impact on tangible capital. At December 31, 2013, we had goodwill of $929 million, representing approximately 32% of stockholders’ equity.
In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. Assessing the need for, or the sufficiency of, a valuation allowance requires management to evaluate all available evidence, both negative and positive, including the recent trend of quarterly earnings. Positive evidence necessary to overcome the negative evidence includes whether future taxable income in sufficient amounts and character within the carryback and carryforward periods is available under the tax law, including the use of tax planning strategies. When negative evidence (e.g., cumulative losses in recent years, history of operating loss or tax credit carryforwards expiring unused) exists, more positive evidence than negative evidence will be necessary. The Corporation has concluded that based on the level of positive evidence, it is more likely than not that the deferred tax asset will be realized. At December 31, 2013, net deferred tax assets were approximately $46 million. The impact of each of these impairment matters could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
We may not be able to attract and retain skilled people. Our success depends, in large part, on our ability to attract and retain skilled people. Competition for the best people in most activities engaged in by us can be intense, and we may not be able to hire sufficiently skilled people or to retain them. The unexpected loss of services of one or more of our key personnel could have a material adverse impact on our business because of their skills, knowledge of our markets, years of industry experience, and the difficulty of promptly finding qualified replacement personnel.
Loss of key employees may disrupt relationships with certain customers. Our business is primarily relationship-driven in that many of our key employees have extensive customer relationships. Loss of a key employee with such customer relationships may lead to the loss of business if the customers were to follow that employee to a competitor. While we believe our relationship with our key personnel is good, we cannot guarantee that all of our key personnel will remain with our organization. Loss of such key personnel, should they enter into an employment relationship with one of our competitors, could result in the loss of some of our customers.
Revenues from our investment management and asset servicing businesses are significant to our earnings. Generating returns that satisfy clients in a variety of asset classes is important to maintaining existing business and attracting new business. Administering or managing assets in accordance with the terms of governing documents and applicable laws is also important to client satisfaction. Failure in either of the foregoing areas can expose us to liability, and result in a decrease in our revenues and earnings.
Severe weather, natural disasters, acts of war or terrorism, and other external events could significantly impact our business. Severe weather, natural disasters, acts of war or terrorism, and other adverse external events could have a significant impact on our ability to conduct business. Such events could affect the stability of our deposit base, impair the ability of borrowers to repay outstanding loans, impair the value of collateral securing loans, cause significant property damage, result in loss of revenue and / or cause us to incur additional expenses. Although management has established disaster recovery policies and procedures, the occurrence of any such event could have a material adverse effect on our business, which, in turn, could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Strategic and External Risks
Our earnings are significantly affected by the fiscal and monetary policies of the federal government and its agencies. The policies of the Federal Reserve impact us significantly. The Federal Reserve regulates the supply of money and credit in the United States. Its policies directly and indirectly influence the rate of interest earned
18
on loans and paid on borrowings and interest-bearing deposits and can also affect the value of financial instruments we hold. Those policies determine to a significant extent our cost of funds for lending and investing. Changes in those policies are beyond our control and are difficult to predict. Federal Reserve policies can also affect our borrowers, potentially increasing the risk that they may fail to repay their loans. For example, a tightening of the money supply by the Federal Reserve could reduce the demand for a borrower’s products and services. This could adversely affect the borrower’s earnings and ability to repay its loan, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Our financial condition and results of operations could be negatively affected if we fail to grow or fail to manage our growth effectively. Our business strategy includes significant growth plans. We intend to continue pursuing a profitable growth strategy. Our prospects must be considered in light of the risks, expenses and difficulties frequently encountered by companies in significant growth stages of development. We cannot assure you that we will be able to expand our market presence in our existing markets or successfully enter new markets or that any such expansion will not adversely affect our results of operations. Failure to manage our growth effectively could have a material adverse effect on our business, future prospects, financial condition or results of operations and could adversely affect our ability to successfully implement our business strategy. Also, if we grow more slowly than anticipated, our operating results could be materially adversely affected.
We operate in a highly competitive industry and market area. We face substantial competition in all areas of our operations from a variety of different competitors, many of which are larger and may have more financial resources. Such competitors primarily include national, regional, and internet banks within the various markets in which we operate. We also face competition from many other types of financial institutions, including, without limitation, savings and loans, credit unions, finance companies, brokerage firms, insurance companies, and other financial intermediaries. The financial services industry could become even more competitive as a result of legislative, regulatory, and technological changes and continued consolidation. Banks, securities firms, and insurance companies can merge under the umbrella of a financial holding company, which can offer virtually any type of financial service, including banking, securities underwriting, insurance (both agency and underwriting), and merchant banking. Also, technology has lowered barriers to entry and made it possible for nonbanks to offer products and services traditionally provided by banks, such as automatic transfer and automatic payment systems. Many of our competitors have fewer regulatory constraints and may have lower cost structures. Additionally, due to their size, many competitors may be able to achieve economies of scale and, as a result, may offer a broader range of products and services as well as better pricing for those products and services than we can.
Our ability to compete successfully depends on a number of factors, including, among other things:
| | • | | the ability to develop, maintain, and build upon long-term customer relationships based on top quality service, high ethical standards, and safe, sound assets; |
| | • | | the ability to expand our market position; |
| | • | | the scope, relevance, and pricing of products and services offered to meet customer needs and demands; |
| | • | | the rate at which we introduce new products and services relative to our competitors; |
| | • | | customer satisfaction with our level of service; and |
| | • | | industry and general economic trends. |
Failure to perform in any of these areas could significantly weaken our competitive position, which could adversely affect our growth and profitability, which, in turn, could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Our profitability depends significantly on economic conditions in the states within which we do business. Our success depends on the general economic conditions of the specific local markets in which we operate, particularly Wisconsin, Illinois and Minnesota. Local economic conditions have a significant impact on
19
the demand for our products and services, as well as the ability of our customers to repay loans, on the value of the collateral securing loans, and the stability of our deposit funding sources. A significant decline in general local economic conditions, caused by inflation, recession, unemployment, changes in securities markets, changes in housing market prices, or other factors could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
The earnings of financial services companies are significantly affected by general business and economic conditions. Our operations and profitability are impacted by general business and economic conditions in the United States and abroad. These conditions include short-term and long-term interest rates, inflation, money supply, political issues, legislative and regulatory changes, fluctuations in both debt and equity capital markets, broad trends in industry and finance, the strength of the United States economy, and uncertainty in financial markets globally relating to financial crises in the European Union and elsewhere, all of which are beyond our control. A deterioration in economic conditions could result in an increase in loan delinquencies and nonperforming assets, decreases in loan collateral values, and a decrease in demand for our products and services, among other things, any of which could have a material adverse impact on our financial condition and results of operations.
New lines of business or new products and services may subject us to additional risk. From time to time, we may implement new lines of business or offer new products and services within existing lines of business. There are substantial risks and uncertainties associated with these efforts, particularly in instances where the markets are not fully developed. In developing and marketing new lines of business and / or new products and services, we may invest significant time and resources. Initial timetables for the introduction and development of new lines of business and / or new products or services may not be achieved and price and profitability targets may not prove feasible. External factors, such as compliance with regulations, competitive alternatives, and shifting market preferences, may also impact the successful implementation of a new line of business and / or a new product or service. Furthermore, any new line of business and / or new product or service could have a significant impact on the effectiveness of our system of internal controls. Failure to successfully manage these risks in the development and implementation of new lines of business and / or new products or services could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Failure to keep pace with technological change could adversely affect our business. The financial services industry is continually undergoing rapid technological change with frequent introductions of new technology-driven products and services. The effective use of technology increases efficiency and enables financial institutions to better serve customers and to reduce costs. Our future success depends, in part, upon our ability to address the needs of our customers by using technology to provide products and services that will satisfy customer demands, as well as to create additional efficiencies in our operations. Many of our competitors have substantially greater resources to invest in technological improvements. We may not be able to effectively implement new technology-driven products and services or be successful in marketing these products and services to our customers. Failure to successfully keep pace with technological change affecting the financial services industry could have a material adverse impact on our business and, in turn, our financial condition and results of operations.
Acquisitions may disrupt our business and dilute shareholder value. As part of our announced growth strategy, we regularly evaluate merger and acquisition opportunities and conduct due diligence activities related to possible transactions with other financial institutions and financial services companies. As a result, negotiations may take place and future mergers or acquisitions involving cash, debt, or equity securities may occur at any time. We seek merger or acquisition partners that are culturally similar, have experienced management, and possess either significant market presence or have potential for improved profitability through financial management, economies of scale, or expanded services.
20
Acquiring other banks, businesses, or branches involves potential adverse impact to our financial results and various other risks commonly associated with acquisitions, including, among other things:
| | • | | difficulty in estimating the value of the target company; |
| | • | | payment of a premium over book and market values that may dilute our tangible book value and earnings per share in the short and long term; |
| | • | | potential exposure to unknown or contingent liabilities of the target company, including, without limitation, liabilities for regulatory and compliance issues; |
| | • | | exposure to potential asset quality issues of the target company; |
| | • | | there may be volatility in reported income as goodwill impairment losses could occur irregularly and in varying amounts; |
| | • | | difficulty and expense of integrating the operations and personnel of the target company; |
| | • | | inability to realize the expected revenue increases, cost savings, increases in geographic or product presence, and / or other projected benefits; |
| | • | | potential disruption to our business; |
| | • | | potential diversion of our management’s time and attention; |
| | • | | the possible loss of key employees and customers of the target company; and |
| | • | | potential changes in banking or tax laws or regulations that may affect the target company. |
Consumers may decide not to use banks to complete their financial transactions. Technology and other changes are allowing parties to complete financial transactions through alternative methods that historically have involved banks. For example, consumers can now maintain funds that would have historically been held as bank deposits in brokerage accounts, mutual funds or general-purpose reloadable prepaid cards. Consumers can also complete transactions such as paying bills and / or transferring funds directly without the assistance of banks. The process of eliminating banks as intermediaries, known as “disintermediation,” could result in the loss of fee income, as well as the loss of customer deposits and the related income generated from those deposits. The loss of these revenue streams and the lower cost of deposits as a source of funds could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Legal, Compliance and Reputational Risks
We are subject to increasingly extensive government regulation and supervision. We, primarily through Associated Bank and certain nonbank subsidiaries, are subject to increasingly extensive federal and state regulation and supervision. Banking regulations are primarily intended to protect depositors’ funds, federal deposit insurance funds, and the banking system as a whole, not shareholders. These regulations affect our lending practices, capital structure, investment practices, dividend policy, and growth, among other things. Congress and federal regulatory agencies continually review banking laws, regulations, and policies for possible changes. Changes to statutes, regulations, or regulatory policies, including changes in interpretation or implementation of statutes, regulations, or policies, could affect us in substantial and unpredictable ways. Such changes could subject us to additional costs, limit the types of financial services and products we may offer, and / or increase the ability of nonbanks to offer competing financial services and products, among other things. Failure to comply with laws, regulations, or policies could result in sanctions by regulatory agencies, civil money penalties, and / or reputation damage, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations. While we have policies and procedures designed to prevent any such violations, there can be no assurance that such violations will not occur.
Examples of increasing regulatory oversight include the creation of the CFPB, which now has separate examination and supervision authority over the Bank with respect to consumer financial products and services.
21
Further evidence of this oversight includes the April 2010 Memorandum of Understanding between the Corporation and the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago requiring the Corporation to submit various plans and reports and obtain approval prior to taking specified actions, which was terminated in March 2012, and the February 2012 Consent Order between the Bank and the OCC, which is described in detail under Part 1, Item 1, “Business — Supervision and Regulation — Bank Secrecy Act / Anti-Money Laundering.”
The full impact of the recently enacted Dodd-Frank Act is currently unknown given that many of the details and substance of the new laws will be implemented through agency rulemakings. On July 21, 2010, the Dodd-Frank Act was signed into law. The Dodd-Frank Act represents a comprehensive overhaul of the financial services industry within the United States and requires federal agencies to adopt nearly 250 new rules and conduct more than 60 studies over the course of the next few years, ensuring that the federal regulations and implementing policies in these areas will continue to develop for the foreseeable future.
Significantly, the Dodd-Frank Act includes the following provisions which affect the Corporation or the Bank:
| | • | | It established the CFPB which directly regulates and supervises the Bank for compliance with the CFPB’s regulations and policies. The creation of the CFPB will directly impact the scope and cost of products and services offered to consumers by the Bank and may have a significant effect on its financial performance. |
| | • | | It revised the FDIC’s insurance assessment methodology so that premiums are assessed based upon the average consolidated total assets of the Bank less tangible equity capital. |
| | • | | It permanently increased deposit insurance coverage to $250,000. |
| | • | | It authorized the Federal Reserve to set debit interchange fees in an amount that is “reasonable and proportional” to the costs incurred by processors and card issuers. Under the final rule issued by the Federal Reserve, there is a cap of 21 cents per transaction (with a maximum of 24 cents per transaction permitted if certain requirements are met). Implementation of these caps went into effect on October 1, 2011. |
| | • | | It imposes proprietary trading restrictions on insured depository institutions and their holding companies that prohibit them from engaging in proprietary trading except in limited circumstances, and prevents them from owning equity interests in excess of three percent (3%) of a bank’s Tier 1 capital in private equity and hedge funds. |
| | • | | It requires a phased-in exclusion of trust preferred securities as a component of Tier 1 capital for certain bank holding companies. |
| | • | | Depository institution holding companies must now act as a “source of strength” for their depository institution subsidiaries (previously, this had been limited to regulatory policy). |
| | • | | Pursuant to the Dodd-Frank Act, the CFPB issued a final rule effective January 10, 2014, requiring mortgage lenders to make a reasonable and good faith determination based on verified and documented information that a consumer applying for a mortgage loan has a reasonable ability to repay the loan according to its terms, or to originate “qualified mortgages” that meet specific requirements with respect to terms, pricing and fees. The new rule also contains new disclosure requirements at mortgage loan origination and in monthly statements. These requirements will likely require significant personnel resources and could have a material adverse effect on our operations. |
Based on the text of the Dodd-Frank Act and the implementing regulations (both published and yet-to-be-published), it is anticipated that the costs to banks and their holding companies may increase or fee income may decrease significantly which could adversely affect the Corporation’s results of operations, financial condition or liquidity.
22
The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau may reshape the consumer financial laws through rulemaking and enforcement of the prohibitions against unfair, deceptive and abusive business practices. Compliance withany such change may impact the business operations of depository institutions offering consumer financial products or services, including the Bank. The CFPB has broad rulemaking authority to administer and carry out the provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act with respect to financial institutions that offer covered financial products and services to consumers. The CFPB has also been directed to write rules identifying practices or acts that are unfair, deceptive or abusive in connection with any transaction with a consumer for a consumer financial product or service, or the offering of a consumer financial product or service. The concept of what may be considered to be an “abusive” practice is relatively new under the law. Moreover, the Bank will be supervised and examined by the CFPB for compliance with the CFPB’s regulations and policies. The costs and limitations related to this additional regulatory reporting regimen have yet to be fully determined, although they may be material and the limitations and restrictions that will be placed upon the Bank with respect to its consumer product offering and services may produce significant, material effects on the Bank’s (and the Corporation’s) profitability.
The Bank is periodically examined for mortgage-related issues, including mortgage loan and default services, fair lending, and mortgage banking. In the wake of the mortgage crisis of the last few years, federal and state banking regulators are closely examining the mortgage and mortgage servicing activities of depository financial institutions. Should the OCC or the Federal Reserve have serious concerns with respect to our operations in this regard, the effect of such concerns could have a material adverse effect on our profits.
We may experience unanticipated losses as a result of residential mortgage loan repurchase or reimbursement obligations under agreements with secondary market purchasers. We may be required to repurchase residential mortgage loans, or to reimburse the purchaser for losses with respect to residential mortgage loans, which have been sold to secondary market purchasers in the event there are breaches of certain representations and warranties contained within the sales agreements, such as representations and warranties related to credit information, loan documentation, collateral and insurability. Consequently, we are exposed to credit risk, and potentially funding risk, associated with sold loans. Although we had only seen a limited number of repurchase and reimbursement claims in prior years, this activity has increased and as a result we have established reserves in our consolidated financial statements for potential losses related to the residential mortgage loans we have sold. The adequacy of the reserves and the ultimate amount of losses incurred will depend on, among other things, the actual future mortgage loan performance, the actual level of future repurchase and reimbursement requests, the actual success rate of claimants, actual recoveries on the collateral and macroeconomic conditions. Due to uncertainties relating to these factors, there can be no assurance that the reserves we establish will be adequate or that the total amount of losses incurred will not have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
We are subject to examinations and challenges by tax authorities. We are subject to federal and state income tax regulations. Income tax regulations are often complex and require interpretation. Changes in income tax regulations could negatively impact our results of operations. In the normal course of business, we are routinely subject to examinations and challenges from federal and state tax authorities regarding the amount of taxes due in connection with investments we have made and the businesses in which we have engaged. Recently, federal and state taxing authorities have become increasingly aggressive in challenging tax positions taken by financial institutions. These tax positions may relate to tax compliance, sales and use, franchise, gross receipts, payroll, property and income tax issues, including tax base, apportionment and tax credit planning. The challenges made by tax authorities may result in adjustments to the timing or amount of taxable income or deductions or the allocation of income among tax jurisdictions. If any such challenges are made and are not resolved in our favor, they could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
We are subject to claims and litigation pertaining to fiduciary responsibility. From time to time, customers make claims and take legal action pertaining to the performance of our fiduciary responsibilities. Whether customer claims and legal action related to the performance of our fiduciary responsibilities are founded or
23
unfounded, if such claims and legal actions are not resolved in a manner favorable to us, they may result in significant financial liability and / or adversely affect the market perception of us and our products and services, as well as impact customer demand for those products and services. Any financial liability or reputation damage could have a material adverse effect on our business, which, in turn, could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
We are a defendant in a variety of litigation and other actions, which may have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operation. We may be involved from time to time in a variety of litigation arising out of our business. Our insurance may not cover all claims that may be asserted against us, and any claims asserted against us, regardless of merit or eventual outcome, may harm our reputation. Should the ultimate judgments or settlements in any litigation exceed our insurance coverage, they could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operation for any period. In addition, we may not be able to obtain appropriate types or levels of insurance in the future, nor may we be able to obtain adequate replacement policies with acceptable terms, if at all.
Negative publicity could damage our reputation. Reputation risk, or the risk to our earnings and capital from negative public opinion, is inherent in our business. Negative public opinion could adversely affect our ability to keep and attract customers and expose us to adverse legal and regulatory consequences. Negative public opinion could result from our actual or alleged conduct in any number of activities, including lending or foreclosure practices, corporate governance, regulatory compliance, mergers and acquisitions, and disclosure, sharing or inadequate protection of customer information, and from actions taken by government regulators and community organizations in response to that conduct. Because we conduct most of our business under the “Associated Bank” brand, negative public opinion about one business could affect our other businesses.
Ethics or conflict of interest issues could damage our reputation. We have established a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics and related policies and procedures to address the ethical conduct of business and to avoid potential conflicts of interest. Any system of controls, however well designed and operated, is based, in part, on certain assumptions and can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurances that the objectives of the system are met. Any failure or circumvention of our related controls and procedures or failure to comply with the established Code of Business Conduct and Ethics and Related Party Transaction Policies and Procedures could have a material adverse effect on our reputation, business, results of operations, and / or financial condition.
Risks Related to an Investment in Our Securities
The price of our securities can be volatile. Price volatility may make it more difficult for you to sell your securities when you want and at prices you find attractive. Our securities prices can fluctuate widely in response to a variety of factors including, among other things:
| | • | | actual or anticipated variations in quarterly results of operations or financial condition; |
| | • | | operating results and stock price performance of other companies that investors deem comparable to us; |
| | • | | news reports relating to trends, concerns, and other issues in the financial services industry; |
| | • | | perceptions in the marketplace regarding us and / or our competitors; |
| | • | | new technology used or services offered by competitors; |
| | • | | significant acquisitions or business combinations, strategic partnerships, joint ventures, or capital commitments by or involving us or our competitors; |
| | • | | failure to integrate acquisitions or realize anticipated benefits from acquisitions; |
| | • | | changes in government regulations; |
| | • | | geopolitical conditions such as acts or threats of terrorism or military conflicts; and |
| | • | | recommendations by securities analysts. |
24
General market fluctuations, industry factors, and general economic and political conditions and events, such as economic slowdowns or recessions, interest rate changes, or credit loss trends, could also cause our securities prices to decrease regardless of our operating results.
There may be future sales or other dilution of our equity, which may adversely affect the market price of our securities. We are not restricted from issuing additional securities, including common stock and securities that are convertible into or exchangeable for, or that represent the right to receive, common stock. The issuance of additional shares of common stock or the issuance of convertible securities would dilute the ownership interest of our existing common shareholders. The market price of our common stock could decline as a result of an equity offering, as well as other sales of a large block of shares of our common stock or similar securities in the market after an equity offering, or the perception that such sales could occur. Both we and our regulators perform a variety of analyses of our assets, including the preparation of stress case scenarios, and as a result of those assessments we could determine, or our regulators could require us, to raise additional capital.
In addition, the exercise of the common stock warrants originally issued to the U.S. Department of the Treasury (the “UST”) under TARP, which have been sold by the UST in a public offering, would dilute the ownership interest of our existing shareholders. See also Note 9, “Stockholders’ Equity,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements in Part II, Item 8, “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data,” for additional information on the common stock warrants issued to the UST.
We may eliminate dividends on our common stock. Although we have historically paid a quarterly cash dividend to the holders of our common stock, holders of our common stock are not entitled to receive dividends. Downturns in the domestic and global economies could cause our board of directors to consider, among other things, the elimination of dividends paid on our common stock. This could adversely affect the market price of our common stock. Furthermore, as a bank holding company, our ability to pay dividends is subject to the guidelines of the Federal Reserve regarding capital adequacy and dividends, and we are required to consult with the Federal Reserve before declaring or paying any dividends. Dividends also may be limited as a result of safety and soundness considerations.
Common stock is equity and is subordinate to our existing and future indebtedness and preferred stock and effectively subordinated to all the indebtedness and other non-common equity claims against our subsidiaries. Shares of the common stock are equity interests in us and do not constitute indebtedness. As such, shares of the common stock will rank junior to all of our indebtedness and to other non-equity claims against us and our assets available to satisfy claims against us, including our liquidation. Additionally, holders of our common stock are subject to prior dividend and liquidation rights of holders of our outstanding preferred stock. Our board of directors is authorized to issue additional classes or series of preferred stock without any action on the part of the holders of our common stock, and we are permitted to incur additional debt. Upon liquidation, lenders and holders of our debt securities and preferred stock would receive distributions of our available assets prior to holders of our common stock. Furthermore, our right to participate in a distribution of assets upon any of our subsidiaries’ liquidation or reorganization is subject to the prior claims of that subsidiary’s creditors, including holders of any preferred stock of that subsidiary.
Our articles of incorporation, bylaws, and certain banking laws may have an anti-takeover effect. Provisions of our articles of incorporation and bylaws, and federal banking laws, including regulatory approval requirements, could make it more difficult for a third party to acquire us, even if doing so would be perceived to be beneficial to our shareholders. The combination of these provisions may prohibit a non-negotiated merger or other business combination, which, in turn, could adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
An investment in our common stock is not an insured deposit. Our common stock is not a bank deposit and, therefore, is not insured against loss by the FDIC, any other deposit insurance fund, or by any other public or private entity. An investment in our common stock is inherently risky for the reasons described in this “Risk Factors” section and elsewhere in this report and is subject to the same market forces that affect the price of common stock in any company. As a result, if you acquire our common stock, you may lose some or all of your investment.
25
An entity holding as little as a 5% interest in our outstanding common stock could, under certain circumstances, be subject to regulation as a “bank holding company.” An entity (including a “group” composed of natural persons) owning or controlling with the power to vote 25% or more of our outstanding common stock, or 5% or more if such holder otherwise exercises a “controlling influence” over us, may be subject to regulation as a “bank holding company” in accordance with the BHC Act. In addition, (1) any bank holding company or foreign bank with a U.S. presence may be required to obtain the approval of the Federal Reserve under the BHC Act to acquire or retain 5% or more of our outstanding common stock, and (2) any person not otherwise defined as a company by the BHC Act and its implementing regulations may be required to obtain the approval of the Federal Reserve under the Change in Bank Control Act to acquire or retain 10% or more of our outstanding common stock. Becoming a bank holding company imposes certain statutory and regulatory restrictions and obligations, such as providing managerial and financial strength for its bank subsidiaries. Regulation as a bank holding company could require the holder to divest all or a portion of the holder’s investment in our common stock or such nonbanking investments that may be deemed impermissible or incompatible with bank holding company status, such as a material investment in a company unrelated to banking.
| ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED | STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
During 2013, our corporate headquarters moved to downtown Green Bay. Our corporate headquarters is located at 433 Main Street in Green Bay, Wisconsin, in an owned facility with approximately 118,000 square feet of office space making this our largest owned facility. The Corporation owns two additional large properties located in the Green Bay area and Stevens Point, Wisconsin with approximately 91,000 and 96,000 square feet, respectively. Our largest leased location, at 96,000 square feet, is our Milwaukee corporate site located in downtown Milwaukee. In late 2013, multiple leased Chicago locations relocated into one centralized Chicago location with 35,000 square feet, which is also leased.
At December 31, 2013, our bank subsidiary occupied over 200 banking locations serving more than 100 different communities within Illinois, Minnesota, and Wisconsin. The main office of Associated Bank, National Association, at 200 North Adams Street in Green Bay, Wisconsin, is owned. Most bank subsidiary branch offices are freestanding buildings that provide adequate customer parking, including drive-through facilities of various numbers and types for customer convenience and are mostly owned. Some bank branch offices are in office towers, supermarket locations or in retirement communities; such properties are generally leased. As of December 31, 2013, 65% of our branches were owned and 35% were leased. In addition, we own other real property that, when considered in aggregate, is not material to our financial position.
The following is a description of the Corporation’s material pending legal proceedings.
A class action lawsuit regarding overdraft fees, consolidated intoIn re: Checking Account Overdraft Litigation MDL No. 2036 in the United States District Court for the Southern District of Florida, was settled by the Bank for $13 million for a full and complete release of all claims brought against the Bank. The settlement amount was accrued for in 2011, and, in 2012, the Bank settled with an insurer for a $2.5 million contribution to the settlement amount and partial reimbursement of defense costs of up to $2.1 million.
A lawsuit,R.J. ZAYED v. Associated Bank, N.A., was filed in the United States District Court for the District of Minnesota on January 29, 2013. The lawsuit relates to a Ponzi scheme perpetrated by Oxford Global Partners and related entities (“Oxford”) and individuals and was brought by the receiver for Oxford. Oxford was a depository customer of the Bank. The lawsuit claims that the Bank is liable for failing to uncover the Oxford Ponzi scheme,
26
and specifically alleges the Bank aided and abetted (1) the fraudulent scheme; (2) a breach of fiduciary duty; (3) conversion; and (4) false representations and omissions. The lawsuit seeks unspecified consequential and punitive damages. At this stage of the lawsuit, it is not possible for management to assess the probability of a material adverse outcome or reasonably estimate the amount of any potential loss at this time. The court granted the Bank’s motion to dismiss the complaint on September 30, 2013, and the plaintiff has appealed the dismissal to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Eighth Circuit. The Bank intends to vigorously defend this lawsuit. A lawsuit by investors in the same Ponzi scheme,Herman Grad, et al v. Associated Bank, N.A., brought in Brown County, Wisconsin in October 2009 was dismissed by the circuit court, and the dismissal was affirmed by the Wisconsin Court of Appeals in June 2011 in an unpublished opinion.
The Bank is currently subject to a Consent Order with the OCC relating to its Bank Secrecy Act of 1970 (“BSA”) compliance. The OCC has issued a written notice to the Bank related to the Bank’s past BSA deficiencies. After the OCC’s review of the Bank’s response, the OCC may impose a civil money penalty related to these deficiencies. The Corporation is currently not able to estimate a reasonable range of losses relating to that possibility.
| ITEM 4. | MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES |
Not applicable.
INFORMATION ABOUT THE EXECUTIVE OFFICERS
The following is a list of names and ages of executive officers of Associated indicating all positions and offices held by each such person and each such person’s principal occupation(s) or employment during the past five years. Officers are appointed annually by the Board of Directors at the meeting of directors immediately following the annual meeting of shareholders. There are no family relationships among these officers, nor any arrangement or understanding between any officer and any other person pursuant to which the officer was selected. No person other than those listed below has been chosen to become an executive officer of Associated. The information presented below is as of February 1, 2014.
Philip B. Flynn - Age: 56
Philip B. Flynn has been President and Chief Executive Officer of Associated and a member of the Board of Directors since December 2009. Mr. Flynn has more than 30 years of financial services industry experience. Prior to joining Associated, he served as Vice Chairman and Chief Operating Officer of Union Bank. During his nearly 30-year career with Union Bank, he held a broad range of executive positions, including chief credit officer and head of commercial banking, specialized lending and wholesale banking. He served as a member of Union Bank’s board of directors from 2004 to 2009.
Oliver Buechse - Age: 45
Oliver Buechse has been Executive Vice President, Chief Strategy Officer, of Associated and Associated Bank, National Association since February 2010. He is also a director of Associated Banc-Corp Foundation. From February 2004 to January 2010, he was Senior Vice President, Strategy and Special Projects at Union Bank, and from January 2009 to January 2010, he also served as Senior Vice President, Vision and Strategy, North American Strategy Office at The Bank of Tokyo —Mitsubishi UFJ. He began his career at McKinsey & Company, working in the U.S., Germany, and Austria.
Christopher J. Del Moral-Niles - Age: 43
Christopher J. Del Moral-Niles has been Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer, of Associated and Associated Bank, National Association since March 2012. He joined Associated in July 2010 and previously served as Associated’s Deputy Chief Financial Officer and as Associated’s Corporate Treasurer. From 2006 to
27
2010, he held various leadership roles for The First American Corporation and its subsidiaries, including serving as Corporate Treasurer and as divisional President of First American Trust, FSB. From 2003 to 2006, Mr. Niles held various positions with Union Bank, including serving as Senior Vice President and Director of Liability Management. Prior to his time with Union Bank, Mr. Niles spent a decade as a financial services investment banker supporting mergers and acquisitions of financial institutions, bank and thrift capital issuances, and bank funding transactions.
Patrick J. Derpinghaus - Age: 58
Patrick J. Derpinghaus has been Executive Vice President, Chief Audit Executive, of Associated and Associated Bank, National Association since April 2011. Mr. Derpinghaus has over 34 years of banking experience serving in various executive finance and audit positions. From March 2008 until March 2011, Mr. Derpinghaus served as Audit Director for U.S. Bank in Minneapolis, Minnesota. Prior to his position at U.S. Bank, Mr. Derpinghaus served as Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of The Bankers Bank in Atlanta, Georgia from October 2005 to December 2007.
Judith M. Docter - Age: 52
Judith M. Docter has been Executive Vice President, Chief Human Resources Officer, of Associated and Associated Bank, National Association since November 2005. She is a director of Associated Financial Group, LLC. She was Senior Vice President, Director of Organizational Development, for Associated from May 2002 to November 2005. From March 1992 to May 2002, she served as Director of Human Resources for Associated Bank, National Association, Fox Valley Region and Wealth Management.
Randall J. Erickson - Age: 54
Randall J. Erickson has been Executive Vice President, General Counsel and Corporate Secretary of Associated and Associated Bank, National Association since April 2012. Prior to joining Associated, he served as senior vice president, chief administrative officer and general counsel of Milwaukee-based bank holding company Marshall & Ilsley Corporation from 2002 until it was acquired by BMO Financial in 2011. Upon leaving M&I, he became a member of Milwaukee law firm Godfrey & Kahn’s securities practice group. He had been a partner at Godfrey & Kahn from 1990 to 2002 prior to joining M&I as its general counsel. Mr. Erickson served as a director of Renaissance Learning, Inc., an educational software company, from 2009 until it was acquired by Permira Funds in 2011.
Breck Hanson - Age: 65
Breck Hanson has been the Executive Vice President, Head of Commercial Real Estate, of Associated and Associated Bank, National Association since October 2010. He is also a director of Associated Banc-Corp Foundation. He has more than 30 years of banking experience, including over 20 years of leadership responsibility within the CRE segment. Most recently, he was Executive Vice President, Commercial Real Estate with Bank of America, where he was responsible for all levels of business in the Midwest Commercial Real Estate Group, which included 370 employees and 7 CRE business lines. He spent over two decades in CRE leadership roles with LaSalle Bank prior to its merger with Bank of America.
Arthur G. Heise - Age: 65
Arthur G. Heise has been Executive Vice President, Chief Risk Officer, of Associated and Associated Bank, National Association since April 2011. Mr. Heise brings more than 30 years leadership experience in risk management roles. From October 2007 through March 2011, he held positions of Chief Audit Executive and of Director of Enterprise Risk Services for US Bancorp. Prior to his position at US Bancorp, Mr. Heise served as Director, Business Risk and Control at CitiMortgage from 2004 to 2007.
28
Scott S. Hickey - Age: 58
Scott S. Hickey has been Executive Vice President, Chief Credit Officer, of Associated and Associated Bank, National Association since October 2008. He was with U.S. Bank from 1985 to 2008, and served as Chief Approval Officer from 2002 to 2008.
Timothy J. Lau - Age: 51
Timothy J. Lau has been Executive Vice President, Head of Private Client and Institutional Services, of Associated and Associated Bank, National Association since December 2010. He is President of Associated Trust Company, National Association and oversees Associated’s Private Banking, Trust and Investment Services. He is also a director of Associated Banc-Corp Foundation, Associated Investment Services, Inc. and Associated Financial Group, LLC. He joined Associated in 1989 and has held a number of senior management positions in Consumer and Small Business Banking, Residential Lending, and Commercial Banking.
Donna N. Smith - Age: 62
Donna N. Smith has been Executive Vice President, Head of Commercial Banking, of Associated and Associated Bank, National Association since June 2011. She joined Associated in June 2010, overseeing the commercial and industrial business line for Associated’s southern region, which includes Chicago, southern Illinois, Missouri and Indiana. Prior to joining Associated, she served as a market executive at Bank of America from October 2007 to June 2010 and as a Senior Vice President at one of its predecessors, LaSalle Bank, from March 2003 to October 2007. She has more than 30 years of commercial banking experience, having previously held leadership roles at Bank of America, LaSalle Bank, Harris Bank and Fifth Third.
David L. Stein - Age: 50
David L. Stein has been Executive Vice President, Head of Retail Banking, of Associated and Associated Bank, National Association since June 2007. He is Chairman of Associated Investment Services, Inc. and a director of Associated Financial Group, LLC and Associated Banc-Corp Foundation. He was the President of the Southwest Region of Associated Bank, National Association, from January 2005 until June 2007. He held various positions with J.P. Morgan Chase & Co., and one of its predecessors, Bank One Corporation, from 1989 until joining Associated in 2005.
John A. Utz - Age: 45
John A. Utz has been Executive Vice President, Head of Specialized Financial Services Group, of Associated and Associated Bank, National Association since June 2011. He joined Associated in March 2010 with upwards of 20 years of banking experience, having previously served as President of Union Bank’s UnionBanCal Equities and head of its Capital Markets division from September 2007 to March 2010, and as head of the National Banking and Asset Management teams from October 2002 to September 2007.
James Yee - Age: 61
James Yee has been Executive Vice President, Chief Information and Operations Officer of Associated and Associated Bank, National Association since May 2012. Prior to joining Associated, he was a Senior Executive Vice President and Chief Information Officer at Union Bank, in San Francisco. His experience also includes serving as Chief Information Officer of Banc of America Securities and Stanford University Medical Center.
29
PART II
| ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Information in response to this item is incorporated by reference to the discussion of dividend restrictions in Note 9, “Stockholders’ Equity,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements included under Item 8 of this report. The Corporation’s common stock is traded on the NASDAQ Global Select Market under the symbol ASBC.
The number of shareholders of record of the Corporation’s common stock, $.01 par value, as of January 24, 2014, was approximately 10,200. Certain of the Corporation’s shares are held in “nominee” or “street” name and the number of beneficial owners of such shares is approximately 20,200.
Payment of future dividends is within the discretion of the Board of Directors and will depend, among other factors, on earnings, capital requirements, and the operating and financial condition of the Corporation. The Board of Directors makes the dividend determination on a quarterly basis. The aggregate amount of the quarterly dividends was $0.33 per common share for 2013 and $0.23 per common share for 2012.
Following are the Corporation’s monthly common stock purchases during the fourth quarter of 2013. For a detailed discussion of the common stock repurchases during 2013 and 2012, see section “Capital” included under Part II, Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” of this document and Part II, Item 8, Note 9, “Stockholders’ Equity,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements included under Item 8 of this document.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Period | | Total Number of
Shares Purchased(a) | | | Average Price
Paid per Share | | | Total Number of
Shares Purchased as
Part of Publicly
Announced Plans
or Programs | | | Maximum Number of
Shares that May Yet
Be Purchased Under
the Plans
or Programs(b) | |
October 1 — October 31, 2013 | | | 1,807,618 | | | $ | 16.07 | | | | 1,807,618 | | | | — | |
November 1 — November 30, 2013 | | | 59,429 | | | | 16.07 | | | | 59,429 | | | | — | |
December 1 — December 31, 2013 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | |
Total | | | 1,867,047 | | | $ | 16.07 | | | | 1,867,047 | | | | 5,459,770 | |
| | | | |
| (a) | During the fourth quarter of 2013, the Corporation repurchased 3,275 shares for minimum tax withholding settlements on equity compensation. These purchases are not included in the monthly common stock purchases table above and do not count against the maximum number of shares that may yet be purchased under the Board of Directors’ authorization. |
| (b) | On November 13, 2012, the Board of Directors authorized the Corporation to repurchase up to an aggregate amount of $125 million of common stock, of which none remained available to repurchase as of December 31, 2013. On July 23, 2013, the Board of Directors also authorized the repurchase of up to an additional $120 million of common stock, of which $95 million remained available to repurchase as of December 31, 2013. Using the closing stock price on December 31, 2013 of $17.40, a total of approximately 5.5 million common shares remained available to be repurchased under the July 2013 authorization as of December 31, 2013. |
30
Market Information
The following represents selected market information of the Corporation’s common stock for 2013 and 2012.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | Market Price Range
Closing Sales Prices | |
| | | Dividends Paid | | | Book Value | | | High | | | Low | | | Close | |
2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
4th Quarter | | $ | 0.09 | | | $ | 17.40 | | | $ | 17.56 | | | $ | 15.34 | | | $ | 17.40 | |
3rd Quarter | | | 0.08 | | | | 17.10 | | | | 17.60 | | | | 15.29 | | | | 15.49 | |
2nd Quarter | | | 0.08 | | | | 16.97 | | | | 15.69 | | | | 13.81 | | | | 15.55 | |
1st Quarter | | | 0.08 | | | | 17.13 | | | | 15.30 | | | | 13.46 | | | | 15.19 | |
| | | | |
2012 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
4th Quarter | | $ | 0.08 | | | $ | 16.97 | | | $ | 13.54 | | | $ | 12.19 | | | $ | 13.12 | |
3rd Quarter | | | 0.05 | | | | 16.82 | | | | 13.79 | | | | 12.04 | | | | 13.16 | |
2nd Quarter | | | 0.05 | | | | 16.59 | | | | 13.97 | | | | 11.76 | | | | 13.19 | |
1st Quarter | | | 0.05 | | | | 16.32 | | | | 14.63 | | | | 11.43 | | | | 13.96 | |
| | | | |
31
Total Shareholder Return Performance Graph
Set forth below is a line graph (and the underlying data points) comparing the yearly percentage change in the cumulative total shareholder return (change in year-end stock price plus reinvested dividends) on Associated’s common stock with the cumulative total return of the Nasdaq Bank Index and the S&P 500 Index for the period of five fiscal years commencing on January 1, 2009, and ending December 31, 2013. The Nasdaq Bank Index is prepared for NASDAQ by the Center for Research in Securities Prices at the University of Chicago. The graph assumes that the value of the investment in Common Stock for each index was $100 on December 31, 2008. Historical stock price performance shown on the graph is not necessarily indicative of the future price performance.
5 Year Trend
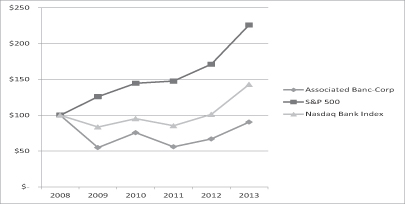
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Source: Bloomberg | | 2008 | | | 2009 | | | 2010 | | | 2011 | | | 2012 | | | 2013 | |
Associated Banc-Corp | | | 100.0 | | | | 54.8 | | | | 75.7 | | | | 56.0 | | | | 66.9 | | | | 90.4 | |
S&P 500 | | | 100.0 | | | | 125.9 | | | | 144.6 | | | | 147.6 | | | | 171.1 | | | | 225.9 | |
Nasdaq Bank Index | | | 100.0 | | | | 83.6 | | | | 95.3 | | | | 85.3 | | | | 101.2 | | | | 143.0 | |
The Total Shareholder Return Performance Graph shall not be deemed incorporated by reference by any general statement incorporating by reference this Annual Report on Form 10-K into any filing under the Securities Act or under the Exchange Act, except to the extent Associated specifically incorporates this information by reference, and shall not otherwise be deemed filed under such Acts.
32
| ITEM 6. SELECTED | FINANCIAL DATA |
TABLE 1: EARNINGS SUMMARY AND SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
(In thousands, except per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | | | 2010 | | | 2009 | |
Interest income | | $ | 708,983 | | | $ | 718,284 | | | $ | 741,622 | | | $ | 806,126 | | | $ | 981,256 | |
Interest expense | | | 63,440 | | | | 92,292 | | | | 128,791 | | | | 172,347 | | | | 255,251 | |
| | | | |
Net interest income | | | 645,543 | | | | 625,992 | | | | 612,831 | | | | 633,779 | | | | 726,005 | |
Provision for loan losses | | | 10,000 | | | | 3,000 | | | | 52,000 | | | | 390,010 | | | | 750,645 | |
| | | | |
Net interest income (loss) after provision for loan losses | | | 635,543 | | | | 622,992 | | | | 560,831 | | | | 243,769 | | | | (24,640 | ) |
Noninterest income | | | 313,099 | | | | 313,290 | | | | 273,119 | | | | 335,462 | | | | 336,573 | |
Noninterest expense | | | 680,749 | | | | 681,823 | | | | 650,523 | | | | 620,259 | | | | 597,032 | |
| | | | |
Income (loss) before income taxes | | | 267,893 | | | | 254,459 | | | | 183,427 | | | | (41,028 | ) | | | (285,099 | ) |
Income tax expense (benefit) | | | 79,201 | | | | 75,486 | | | | 43,728 | | | | (40,172 | ) | | | (153,240 | ) |
| | | | |
Net income (loss) | | | 188,692 | | | | 178,973 | | | | 139,699 | | | | (856 | ) | | | (131,859 | ) |
Preferred stock dividends and discount accretion | | | 5,158 | | | | 5,200 | | | | 24,830 | | | | 29,531 | | | | 29,348 | |
| | | | |
Net income (loss) available to common equity | | $ | 183,534 | | | $ | 173,773 | | | $ | 114,869 | | | $ | (30,387 | ) | | $ | (161,207 | ) |
| | | | |
Earnings (loss) per common share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic(1) | | $ | 1.10 | | | $ | 1.00 | | | $ | 0.66 | | | $ | (0.18 | ) | | $ | (1.26 | ) |
Diluted(1) | | | 1.10 | | | | 1.00 | | | | 0.66 | | | | (0.18 | ) | | | (1.26 | ) |
Cash dividends per share(1) | | | 0.33 | | | | 0.23 | | | | 0.04 | | | | 0.04 | | | | 0.47 | |
Weighted average common shares outstanding:(1): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | | 165,584 | | | | 172,255 | | | | 173,370 | | | | 171,230 | | | | 127,858 | |
Diluted | | | 165,802 | | | | 172,357 | | | | 173,372 | | | | 171,230 | | | | 127,858 | |
SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Year-End Balances: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loans | | $ | 15,896,261 | | | $ | 15,411,022 | | | $ | 14,031,071 | | | $ | 12,616,735 | | | $ | 14,128,625 | |
Allowance for loan losses | | | 268,315 | | | | 297,409 | | | | 378,151 | | | | 476,813 | | | | 573,533 | |
Investment securities | | | 5,425,795 | | | | 4,966,635 | | | | 4,937,483 | | | | 6,101,341 | | | | 5,835,533 | |
Total assets | | | 24,226,920 | | | | 23,487,735 | | | | 21,924,217 | | | | 21,785,596 | | | | 22,874,142 | |
Deposits | | | 17,267,167 | | | | 16,939,865 | | | | 15,090,655 | | | | 15,225,393 | | | | 16,728,613 | |
Short and long-term funding | | | 3,828,193 | | | | 3,342,285 | | | | 3,691,556 | | | | 3,160,987 | | | | 3,180,851 | |
Tier 1 common equity(2) | | | 1,913,320 | | | | 1,875,534 | | | | 1,783,515 | | | | 1,657,505 | | | | 1,202,131 | |
Stockholders’ equity | | | 2,891,290 | | | | 2,936,399 | | | | 2,865,794 | | | | 3,158,791 | | | | 2,738,608 | |
Book value per common share(1) | | | 17.40 | | | | 16.97 | | | | 16.15 | | | | 15.28 | | | | 17.42 | |
Tangible book value per common share(1) | | | 11.62 | | | | 11.39 | | | | 10.68 | | | | 9.77 | | | | 9.93 | |
| | | | |
Average Balances: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loans | | $ | 15,663,145 | | | $ | 14,741,785 | | | $ | 13,278,848 | | | $ | 13,186,712 | | | $ | 15,595,636 | |
Investment securities | | | 4,995,331 | | | | 4,469,541 | | | | 5,497,297 | | | | 5,439,729 | | | | 5,502,786 | |
Earning assets | | | 20,980,128 | | | | 19,613,777 | | | | 19,442,263 | | | | 20,568,495 | | | | 21,337,382 | |
Total assets | | | 23,305,758 | | | | 21,976,357 | | | | 21,588,620 | | | | 22,625,065 | | | | 23,609,471 | |
Deposits | | | 17,438,195 | | | | 15,582,369 | | | | 14,401,127 | | | | 16,946,301 | | | | 15,959,046 | |
Interest-bearing liabilities | | | 15,964,647 | | | | 14,905,735 | | | | 15,120,824 | | | | 16,304,220 | | | | 17,659,282 | |
Stockholders’ equity | | | 2,892,312 | | | | 2,948,988 | | | | 2,997,290 | | | | 3,183,572 | | | | 2,902,911 | |
| | | | |
Financial Ratios: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Return on average assets | | | 0.81 | % | | | 0.81 | % | | | 0.65 | % | | | — | % | | | (0.56 | )% |
Return on average tangible common equity(3) | | | 9.73 | | | | 8.96 | | | | 6.45 | | | | (1.77 | ) | | | (11.25 | ) |
Return on average tier 1 common equity(2) | | | 9.77 | | | | 9.45 | | | | 6.71 | | | | (1.95 | ) | | | (11.89 | ) |
Tangible common equity to tangible assets(3) | | | 8.11 | | | | 8.56 | | | | 8.84 | | | | 8.12 | | | | 5.79 | |
Tier 1 common equity to risk-weighted assets(2) | | | 11.46 | | | | 11.61 | | | | 12.24 | | | | 12.26 | | | | 7.85 | |
| (1) | Share and per share data adjusted retroactively for stock splits and stock dividends. |
| (2) | Tier 1 common equity is Tier 1 capital excluding qualifying perpetual preferred stock and trust preferred securities. |
| (3) | Tangible common equity is common equity excluding goodwill and other intangible assets. Tangible assets is assets excluding goodwill and other intangible assets. |
33
| ITEM 7. | MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
The following discussion is management’s analysis to assist in the understanding and evaluation of the consolidated financial condition and results of operations of the Corporation. It should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and footnotes and the selected financial data presented elsewhere in this report.
The detailed financial discussion that follows focuses on 2013 results compared to 2012. Discussion of 2012 results compared to 2011 is predominantly in section “2012 Compared to 2011.”
Overview
The Corporation is a bank holding company headquartered in Wisconsin, providing a broad array of banking and nonbanking products and services to businesses and consumers primarily within our three-state footprint. The Corporation’s primary sources of revenue, through the Bank, are net interest income (predominantly from loans and investment securities), and noninterest income, principally fees and other revenue from financial services provided to customers or ancillary services tied to loans and deposits. Business volumes and pricing drive revenue potential, and tend to be influenced by overall economic factors, including market interest rates, business spending, consumer confidence, economic growth, and competitive conditions within the marketplace.
2013 was another successful year for the Corporation. Net income available to common equity for 2013 was $184 million, an increase of $10 million from a year ago. Earnings per common share were $1.10 per common share in 2013, an increase of 10% over 2012. Average loan balances increased $921 million (6%) during 2013 with growth in most loan categories, while average deposit balances grew $1.9 billion (12%). The net interest margin for 2013 was 3.17%, while net interest income increased $20 million (3%). Total revenue grew 2% to $959 million and noninterest expense was down slightly from 2012. Credit quality continued to improve with net charge offs, nonaccrual loans, past due loans, and potential problem loans all declining year over year. The Corporation repurchased $120 million, or approximately 7.7 million shares of common stock, at an average cost per share of $15.57 during 2013. Total dividends per common share were $0.33, an increase of 43% from 2012.
Performance Summary
| | • | | Net income available to common equity for 2013 was $184 million (compared to net income available to common equity of $174 million for 2012) or diluted earnings per common share of $1.10 (versus diluted earnings per common share of $1.00 for 2012). |
| | • | | Total loans increased $485 million (3%) between year-end 2013 and 2012, with growth in most loan categories. On average, loans increased $921 million (6%). For 2014, the Corporation expects mid single digit average loan growth. |
| | • | | Total deposits increased $327 million (2%) between year-end 2013 and 2012. On average, total deposits increased $1.9 billion (12%) from 2012. For 2014, the Corporation expects high single digit average deposit and other funding growth. |
| | • | | Credit quality continued to improve during 2013 with net charge offs, nonaccrual loans, past due loans, and potential problem loans all declining year over year. For 2014, the Corporation anticipates the provision for loan losses will grow based on expected loan growth. |
| | • | | The net interest margin for 2013 was 3.17%, 13 bp lower than 3.30% in 2012, while taxable equivalent net interest income was $666 million for 2013, $19 million (3%) higher than 2012. For 2014, the Corporation anticipates continued modest compression on the net interest margin. |
| | • | | Noninterest income was $313 million for 2013, relatively unchanged from 2012. Core fee-based revenues (including trust service fees, service charges on deposit accounts, card-based and other nondeposit fees, |
34
| | insurance commissions, and brokerage and annuity commissions) totaled $224 million for 2013, up $4 million or 2% from $220 million for 2012. Collectively, all remaining noninterest income categories were $89 million, down $4 million compared to 2012. For additional discussion concerning noninterest income see section, “Noninterest Income.” For 2014, the Corporation expects noninterest income to be down slightly with declines in net mortgage banking offset by growth in core fee-based revenues. |
| | • | | Noninterest expense of $681 million decreased $1 million from 2012. Personnel expense was $397 million, up $16 million (4%) versus 2012, while nonpersonnel noninterest expenses on an aggregate basis were down modestly (6%) compared to 2012. The efficiency ratio was 69.57% for 2013 and 69.99% for 2012, respectively. For additional discussion regarding noninterest expense see section, “Noninterest Expense.” For 2014, the Corporation expects flat year over year noninterest expense with continued focus on efficiency initiatives. |
| | • | | Income tax expense for 2013 was $79 million, compared to income tax expense of $75 million for 2012. The effective tax rate was 29.6% for 2013, compared to an effective tax rate of 29.7% for 2012. For additional discussion concerning income tax see section, “Income Taxes.” |
INCOME STATEMENT ANALYSIS
Net Interest Income
Net interest income is the primary source of the Corporation’s revenue. Net interest income is the difference between interest income on interest-earning assets, such as loans and investment securities, and the interest expense on interest-bearing deposits and other borrowings used to fund interest-earning and other assets or activities. Net interest income is affected by changes in interest rates and by the amount and composition of earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities, as well as the sensitivity of the balance sheet to changes in interest rates, including characteristics such as the fixed or variable nature of the financial instruments, contractual maturities, repricing frequencies, loan prepayment behavior, and the use of interest rate derivative financial instruments.
Interest rate spread and net interest margin are utilized to measure and explain changes in net interest income. Interest rate spread is the difference between the yield on earning assets and the rate paid for interest-bearing liabilities that fund those assets. The net interest margin is expressed as the percentage of net interest income to average earning assets. The net interest margin exceeds the interest rate spread because noninterest-bearing sources of funds (“net free funds”), principally noninterest-bearing demand deposits and stockholders’ equity, also support earning assets. To compare tax-exempt asset yields to taxable yields, the yield on tax-exempt loans and investment securities is computed on a taxable equivalent basis. Net interest income, interest rate spread, and net interest margin are discussed on a taxable equivalent basis.
Table 2 provides average balances of earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities, the associated interest income and expense, and the corresponding interest rates earned and paid, as well as net interest income, interest rate spread, and net interest margin on a taxable equivalent basis for the three years ended December 31, 2013. Tables 3 and 4 present additional information to facilitate the review and discussion of taxable equivalent net interest income, interest rate spread, and net interest margin.
Net interest income in the consolidated statements of income (which excludes the taxable equivalent adjustment) was $646 million in 2013 compared to $626 million in 2012. The taxable equivalent adjustments (the adjustments to bring tax-exempt interest to a level that would yield the same after-tax income had that income been subject to a taxation using a 35% tax rate) of $20 million and $21 million for 2013 and 2012, respectively, resulted in fully taxable equivalent net interest income of $666 million in 2013 and $647 million in 2012.
Taxable equivalent net interest income of $666 million for 2013 was $19 million or 3% higher than 2012. The increase in taxable equivalent net interest income was a function of favorable volume variances (as balance sheet
35
changes in both volume and mix increased taxable equivalent net interest income by $53 million) and unfavorable interest rate changes (as the impact of changes in the interest rate environment and product pricing decreased taxable equivalent net interest income by $34 million). See sections “Interest Rate Risk” and “Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk,” for a discussion of interest rate risk and market risk.
The net interest margin for 2013 was 3.17%, compared to 3.30% in 2012. The 13 bp decline in net interest margin was attributable to an 8 bp decrease in interest rate spread (the net of a 30 bp decrease in the yield on earning assets and a 22 bp decrease in the cost of interest-bearing liabilities), and a 5 bp lower contribution from net free funds (due principally to lower rates on interest-bearing liabilities reducing the value of noninterest-bearing deposits and other net free funds).
The Federal Reserve left the targeted Federal funds rate unchanged at 0.25% during 2013 and 2012. In December 2013, the Federal Reserve affirmed that it is unlikely that the short-term interest rates will increase until 2015.
For 2013, the yield on average earning assets of 3.47% was 30 bp lower than 2012. Loan yields decreased 30 bp (to 3.77%), due to the repricing of adjustable rate loans and competitive pricing pressures in a low interest rate environment. The yield on securities and short-term investments decreased 27 bp to 2.59%, and was also impacted by the low interest rate environment and prepayment speeds of mortgage-related securities purchased at a premium.
The cost of average interest-bearing liabilities of 0.40% in 2013 was 22 bp lower than 2012. The average cost of interest-bearing deposits was 0.24% in 2013, 12 bp lower than 2012, reflecting the low rate environment and a reduction of higher cost deposit products. The cost of short and long-term funding decreased 39 bp to 1.16% for 2013, with short-term funding down 13 bp, while long-term funding decreased 62 bp.
Average earning assets of $21.0 billion in 2013 were $1.4 billion (7%) higher than 2012. Average loans increased $921 million (6%), including a $1.0 billion increase in commercial loans and a $384 million increase in residential mortgage loans, partially offset by a $489 million decrease in retail loans. Average securities and short-term investments increased $445 million.
Average interest-bearing liabilities of $16.0 billion in 2013 were up $1.1 billion (7%) versus 2012. On average, interest-bearing deposits increased $1.6 billion, while average noninterest-bearing demand deposits (a principal component of net free funds) increased by $300 million. Average short and long-term funding decreased $496 million, consisting of a $239 million decrease in short-term funding and a $257 million decrease in long-term funding.
36
TABLE 2: Average Balances and Interest Rates (interest and rates on a taxable equivalent basis)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
| | | Average
Balance | | | Interest | | | Average
Rate | | | Average
Balance | | | Interest | | | Average
Rate | | | Average
Balance | | | Interest | | | Average
Rate | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
ASSETS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Earning assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loans:(1)(2)(3) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | $ | 5,809,578 | | | $ | 208,039 | | | | 3.58 | % | | $ | 5,139,155 | | | $ | 202,444 | | | | 3.94 | % | | $ | 4,301,377 | | | $ | 182,362 | | | | 4.24 | % |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 3,705,526 | | | | 149,539 | | | | 4.04 | | | | 3,350,190 | | | | 140,881 | | | | 4.21 | | | | 2,973,351 | | | | 132,789 | | | | 4.47 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 9,515,104 | | | | 357,578 | | | | 3.76 | | | | 8,489,345 | | | | 343,325 | | | | 4.04 | | | | 7,274,728 | | | | 315,151 | | | | 4.33 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 3,714,544 | | | | 123,275 | | | | 3.32 | | | | 3,330,123 | | | | 121,399 | | | | 3.65 | | | | 2,819,702 | | | | 116,207 | | | | 4.12 | |
Retail | | | 2,433,497 | | | | 110,338 | | | | 4.53 | | | | 2,922,317 | | | | 135,094 | | | | 4.62 | | | | 3,184,418 | | | | 154,793 | | | | 4.86 | |
| | | | |
Total loans | | | 15,663,145 | | | | 591,191 | | | | 3.77 | | | | 14,741,785 | | | | 599,818 | | | | 4.07 | | | | 13,278,848 | | | | 586,151 | | | | 4.41 | |
Investment securities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Taxable | | | 4,202,478 | | | | 88,919 | | | | 2.12 | | | | 3,676,914 | | | | 86,945 | | | | 2.36 | | | | 4,701,482 | | | | 123,371 | | | | 2.62 | |
Tax-exempt(1) | | | 792,853 | | | | 43,752 | | | | 5.52 | | | | 792,627 | | | | 45,848 | | | | 5.78 | | | | 795,815 | | | | 47,899 | | | | 6.02 | |
Other short-term investments | | | 321,652 | | | | 5,193 | | | | 1.61 | | | | 402,451 | | | | 6,719 | | | | 1.67 | | | | 666,118 | | | | 5,575 | | | | 0.84 | |
| | | | |
Investments and other | | | 5,316,983 | | | | 137,864 | | | | 2.59 | | | | 4,871,992 | | | | 139,512 | | | | 2.86 | | | | 6,163,415 | | | | 176,845 | | | | 2.87 | |
| | | | |
Total earning assets | | $ | 20,980,128 | | | $ | 729,055 | | | | 3.47 | % | | $ | 19,613,777 | | | $ | 739,330 | | | | 3.77 | % | | $ | 19,442,263 | | | $ | 762,996 | | | | 3.92 | % |
Allowance for loan losses | | | (282,880 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | (342,313 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | (442,034 | ) | | | | | | | | |
Cash and due from banks | | | 354,897 | | | | | | | | | | | | 352,735 | | | | | | | | | | | | 318,650 | | | | | | | | | |
Other assets | | | 2,253,613 | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,352,158 | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,269,741 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 23,305,758 | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 21,976,357 | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 21,588,620 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest-bearing liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Savings deposits | | $ | 1,188,910 | | | $ | 942 | | | | 0.08 | % | | $ | 1,096,692 | | | $ | 851 | | | | 0.08 | % | | $ | 987,198 | | | $ | 1,091 | | | | 0.11 | % |
Interest-bearing demand deposits | | | 2,827,778 | | | | 4,517 | | | | 0.16 | | | | 2,148,459 | | | | 3,741 | | | | 0.17 | | | | 1,947,506 | | | | 3,429 | | | | 0.18 | |
Money market deposits | | | 7,322,476 | | | | 13,702 | | | | 0.19 | | | | 6,148,663 | | | | 15,336 | | | | 0.25 | | | | 5,147,437 | | | | 16,385 | | | | 0.32 | |
Time deposits | | | 1,849,718 | | | | 12,106 | | | | 0.65 | | | | 2,239,709 | | | | 21,503 | | | | 0.96 | | | | 2,937,858 | | | | 44,843 | | | | 1.53 | |
| | | | |
Total interest-bearing deposits | | | 13,188,882 | | | | 31,267 | | | | 0.24 | | | | 11,633,523 | | | | 41,431 | | | | 0.36 | | | | 11,019,999 | | | | 65,748 | | | | 0.60 | |
Federal funds purchased and securities sold under agreements to repurchase | | | 675,574 | | | | 1,322 | | | | 0.20 | | | | 1,177,105 | | | | 2,687 | | | | 0.23 | | | | 1,926,474 | | | | 6,196 | | | | 0.32 | |
Other short-term funding | | | 1,198,264 | | | | 1,519 | | | | 0.13 | | | | 936,376 | | | | 3,294 | | | | 0.35 | | | | 767,230 | | | | 6,215 | | | | 0.81 | |
| | | | |
Total short-term funding | | | 1,873,838 | | | | 2,841 | | | | 0.15 | | | | 2,113,481 | | | | 5,981 | | | | 0.28 | | | | 2,693,704 | | | | 12,411 | | | | 0.46 | |
Long-term funding | | | 901,927 | | | | 29,332 | | | | 3.25 | | | | 1,158,731 | | | | 44,880 | | | | 3.87 | | | | 1,407,121 | | | | 50,632 | | | | 3.60 | |
| | | | |
Total short and long-term funding | | | 2,775,765 | | | | 32,173 | | | | 1.16 | | | | 3,272,212 | | | | 50,861 | | | | 1.55 | | | | 4,100,825 | | | | 63,043 | | | | 1.54 | |
| | | | |
Total interest-bearing liabilities | | $ | 15,964,647 | | | $ | 63,440 | | | | 0.40 | % | | $ | 14,905,735 | | | $ | 92,292 | | | | 0.62 | % | | $ | 15,120,824 | | | $ | 128,791 | | | | 0.85 | % |
Noninterest-bearing demand deposits | | | 4,249,313 | | | | | | | | | | | | 3,948,846 | | | | | | | | | | | | 3,381,128 | | | | | | | | | |
Accrued expenses and other liabilities | | | 199,486 | | | | | | | | | | | | 172,788 | | | | | | | | | | | | 89,378 | | | | | | | | | |
Stockholders’ equity | | | 2,892,312 | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,948,988 | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,997,290 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | | $ | 23,305,758 | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 21,976,357 | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 21,588,620 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
Net interest income and rate spread(1) | | | | | | $ | 665,615 | | | | 3.07 | % | | | | | | $ | 647,038 | | | | 3.15 | % | | | | | | $ | 634,205 | | | | 3.07 | % |
| | | | |
Net interest margin(1) | | | | | | | | | | | 3.17 | % | | | | | | | | | | | 3.30 | % | | | | | | | | | | | 3.26 | % |
| | | | |
Taxable equivalent adjustment | | | | | | $ | 20,072 | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 21,046 | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 21,374 | | | | | |
| | | | |
| (1) | The yield on tax-exempt loans and securities is computed on a taxable equivalent basis using a tax rate of 35% for all periods presented and is net of the effects of certain disallowed interest deductions. |
| (2) | Nonaccrual loans and loans held for sale have been included in the average balances. |
| (3) | Interest income includes net loan fees. |
37
TABLE 3: Rate/Volume Analysis(1)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 Compared to 2012
Increase (Decrease) Due to | | | 2012 Compared to 2011
Increase (Decrease) Due to | |
| | | Volume | | | Rate | | | Net | | | Volume | | | Rate | | | Net | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Interest income: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loans:(2) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | $ | 24,994 | | | $ | (19,399 | ) | | $ | 5,595 | | | $ | 33,726 | | | $ | (13,644 | ) | | $ | 20,082 | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 14,506 | | | | (5,848 | ) | | | 8,658 | | | | 16,186 | | | | (8,094 | ) | | | 8,092 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 39,500 | | | | (25,247 | ) | | | 14,253 | | | | 49,912 | | | | (21,738 | ) | | | 28,174 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 13,307 | | | | (11,431 | ) | | | 1,876 | | | | 19,552 | | | | (14,360 | ) | | | 5,192 | |
Retail | | | (22,208 | ) | | | (2,548 | ) | | | (24,756 | ) | | | (12,350 | ) | | | (7,349 | ) | | | (19,699 | ) |
| | | | |
Total loans | | | 30,599 | | | | (39,226 | ) | | | (8,627 | ) | | | 57,114 | | | | (43,447 | ) | | | 13,667 | |
Investment securities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Taxable | | | 14,737 | | | | (12,763 | ) | | | 1,974 | | | | (30,639 | ) | | | (5,787 | ) | | | (36,426 | ) |
Tax-exempt(2) | | | 13 | | | | (2,109 | ) | | | (2,096 | ) | | | (191 | ) | | | (1,860 | ) | | | (2,051 | ) |
Other short-term investments | | | (1,311 | ) | | | (215 | ) | | | (1,526 | ) | | | (2,832 | ) | | | 3,976 | | | | 1,144 | |
| | | | |
Investments and other | | | 13,439 | | | | (15,087 | ) | | | (1,648 | ) | | | (33,662 | ) | | | (3,671 | ) | | | (37,333 | ) |
| | | | |
Total earning assets(2) | | $ | 44,038 | | | $ | (54,313 | ) | | $ | (10,275 | ) | | $ | 23,452 | | | $ | (47,118 | ) | | $ | (23,666 | ) |
| | | | |
Interest expense: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Savings deposits | | $ | 73 | | | $ | 18 | | | $ | 91 | | | $ | 112 | | | $ | (352 | ) | | $ | (240 | ) |
Interest-bearing demand deposits | | | 1,105 | | | | (329 | ) | | | 776 | | | | 350 | | | | (38 | ) | | | 312 | |
Money market deposits | | | 2,611 | | | | (4,245 | ) | | | (1,634 | ) | | | 2,870 | | | | (3,919 | ) | | | (1,049 | ) |
Time deposits | | | (3,331 | ) | | | (6,066 | ) | | | (9,397 | ) | | | (8,589 | ) | | | (14,751 | ) | | | (23,340 | ) |
| | | | |
Total interest-bearing deposits | | | 458 | | | | (10,622 | ) | | | (10,164 | ) | | | (5,257 | ) | | | (19,060 | ) | | | (24,317 | ) |
Federal funds purchased and securities sold under agreements to repurchase | | | (1,023 | ) | | | (342 | ) | | | (1,365 | ) | | | (2,010 | ) | | | (1,499 | ) | | | (3,509 | ) |
Other short-term funding | | | 742 | | | | (2,517 | ) | | | (1,775 | ) | | | 1,159 | | | | (4,080 | ) | | | (2,921 | ) |
| | | | |
Total short-term funding | | | (281 | ) | | | (2,859 | ) | | | (3,140 | ) | | | (851 | ) | | | (5,579 | ) | | | (6,430 | ) |
Long-term funding | | | (9,021 | ) | | | (6,527 | ) | | | (15,548 | ) | | | (9,429 | ) | | | 3,677 | | | | (5,752 | ) |
| | | | |
Total short and long-term funding | | | (9,302 | ) | | | (9,386 | ) | | | (18,688 | ) | | | (10,280 | ) | | | (1,902 | ) | | | (12,182 | ) |
| | | | |
Total interest-bearing liabilities | | $ | (8,844 | ) | | $ | (20,008 | ) | | $ | (28,852 | ) | | $ | (15,537 | ) | | $ | (20,962 | ) | | $ | (36,499 | ) |
| | | | |
Net interest income(2) | | $ | 52,882 | | | $ | (34,305 | ) | | $ | 18,577 | | | $ | 38,989 | | | $ | (26,156 | ) | | $ | 12,833 | |
| | | | |
| (1) | The change in interest due to both rate and volume has been allocated in proportion to the relationship to the dollar amounts of the change in each. |
| (2) | The yield on tax-exempt loans and securities is computed on a fully taxable equivalent basis using a tax rate of 35% for all periods presented and is net of the effects of certain disallowed interest deductions. |
38
TABLE 4: Interest Rate Spread and Interest Margin (on a taxable equivalent basis)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 Average | | | 2012 Average | | | 2011 Average | |
| | | Balance | | | % of
Earning
Assets | | | Yield /
Rate | | | Balance | | | % of
Earning
Assets | | | Yield /
Rate | | | Balance | | | % of
Earning
Assets | | | Yield /
Rate | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Total loans | | $ | 15,663,145 | | | | 74.7 | % | | | 3.77 | % | | $ | 14,741,785 | | | | 75.2 | % | | | 4.07 | % | | $ | 13,278,848 | | | | 68.3 | % | | | 4.41 | % |
Securities and short-term investments | | | 5,316,983 | | | | 25.3 | % | | | 2.59 | % | | | 4,871,992 | | | | 24.8 | % | | | 2.86 | % | | | 6,163,415 | | | | 31.7 | % | | | 2.87 | % |
| | | | |
Earning assets | | $ | 20,980,128 | | | | 100.0 | % | | | 3.47 | % | | $ | 19,613,777 | | | | 100.0 | % | | | 3.77 | % | | $ | 19,442,263 | | | | 100.0 | % | | | 3.92 | % |
| | | | |
Financed by: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest-bearing funds | | $ | 15,964,647 | | | | 76.1 | % | | | 0.40 | % | | $ | 14,905,735 | | | | 76.0 | % | | | 0.62 | % | | $ | 15,120,824 | | | | 77.8 | % | | | 0.85 | % |
Noninterest-bearing funds | | | 5,015,481 | | | | 23.9 | % | | | | | | | 4,708,042 | | | | 24.0 | % | | | | | | | 4,321,439 | | | | 22.2 | % | | | | |
| | | | |
Total funds sources | | $ | 20,980,128 | | | | 100.0 | % | | | 0.30 | % | | $ | 19,613,777 | | | | 100.0 | % | | | 0.47 | % | | $ | 19,442,263 | | | | 100.0 | % | | | 0.66 | % |
| | | | |
Interest rate spread | | | | | | | | | | | 3.07 | % | | | | | | | | | | | 3.15 | % | | | | | | | | | | | 3.07 | % |
Contribution from net free funds | | | | | | | | | | | 0.10 | % | | | | | | | | | | | 0.15 | % | | | | | | | | | | | 0.19 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net interest margin | | | | | | | | | | | 3.17 | % | | | | | | | | | | | 3.30 | % | | | | | | | | | | | 3.26 | % |
| | | | |
Average prime rate* | | | | | | | | | | | 3.25 | % | | | | | | | | | | | 3.25 | % | | | | | | | | | | | 3.25 | % |
Average effective federal funds rate* | | | | | | | | | | | 0.11 | % | | | | | | | | | | | 0.15 | % | | | | | | | | | | | 0.11 | % |
Average spread | | | | | | | | | | | 314 | bp | | | | | | | | | | | 310 | bp | | | | | | | | | | | 314 | bp |
| | | | |
Provision for Loan Losses
The provision for loan losses in 2013 was $10 million, compared to $3 million in 2012. Net charge offs were $39 million (representing 0.25% of average loans) for 2013, compared to $84 million (representing 0.57% of average loans) for 2012. At December 31, 2013, the allowance for loan losses was $268 million. In comparison, the allowance for loan losses was $297 million at December 31, 2012. The ratio of the allowance for loan losses to total loans was 1.69% and 1.93% at December 31, 2013, and 2012, respectively. Nonaccrual loans at December 31, 2013, were $185 million, compared to $253 million at December 31, 2012, representing 1.17% and 1.64% of total loans, respectively.
The provision for loan losses is predominantly a function of the Corporation’s reserving methodology and judgments as to other qualitative and quantitative factors used to determine the appropriate level of the allowance for loan losses which focuses on changes in the size and character of the loan portfolio, changes in levels of impaired and other nonaccrual loans, historical losses and delinquencies on each portfolio category, the level of loans sold or transferred to held for sale, the risk inherent in specific loans, concentrations of loans to specific borrowers or industries, existing economic conditions, the fair value of underlying collateral, and other factors which could affect potential credit losses. See additional discussion under sections, “Allowance for Loan Losses,” and “Nonaccrual Loans, Potential Problem Loans, and Other Real Estate Owned.”
39
Noninterest Income
Noninterest income was $313 million for 2013, relatively flat from 2012. “Fee income” (defined in Table 5 below) as a percentage of “total revenue” (defined as taxable equivalent net interest income plus fee income) was 32% for 2013 compared to 33% for 2012.
TABLE 5: Noninterest Income
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years Ended December 31, | | | Change From Prior Year | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | | | $ Change
2013 | | | % Change
2013 | | | $ Change
2012 | | | % Change
2012 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Trust service fees | | $ | 45,633 | | | $ | 40,737 | | | $ | 39,145 | | | $ | 4,896 | | | | 12.0 | % | | $ | 1,592 | | | | 4.1 | % |
Service charges on deposit accounts | | | 70,009 | | | | 68,917 | | | | 75,908 | | | | 1,092 | | | | 1.6 | | | | (6,991 | ) | | | (9.2 | ) |
Card-based and other nondeposit fees | | | 49,913 | | | | 47,862 | | | | 57,905 | | | | 2,051 | | | | 4.3 | | | | (10,043 | ) | | | (17.3 | ) |
Insurance commissions | | | 44,024 | | | | 47,014 | | | | 45,554 | | | | (2,990 | ) | | | (6.4 | ) | | | 1,460 | | | | 3.2 | |
Brokerage and annuity commissions | | | 14,877 | | | | 15,643 | | | | 17,230 | | | | (766 | ) | | | (4.9 | ) | | | (1,587 | ) | | | (9.2 | ) |
| | | | |
Core fee-based revenue | | | 224,456 | | | | 220,173 | | | | 235,742 | | | | 4,283 | | | | 1.9 | | | | (15,569 | ) | | | (6.6 | ) |
Mortgage banking income | | | 49,772 | | | | 89,231 | | | | 45,956 | | | | (39,459 | ) | | | (44.2 | ) | | | 43,275 | | | | 94.2 | |
Mortgage servicing rights expense | | | 925 | | | | 25,731 | | | | 33,233 | | | | (24,806 | ) | | | (96.4 | ) | | | (7,502 | ) | | | (22.6 | ) |
| | | | |
Mortgage banking, net | | | 48,847 | | | | 63,500 | | | | 12,723 | | | | (14,653 | ) | | | (23.1 | ) | | | 50,777 | | | | N/M | |
Capital market fees, net | | | 13,080 | | | | 14,241 | | | | 8,711 | | | | (1,161 | ) | | | (8.2 | ) | | | 5,530 | | | | 63.5 | |
Bank owned life insurance income | | | 11,855 | | | | 13,952 | | | | 14,896 | | | | (2,097 | ) | | | (15.0 | ) | | | (944 | ) | | | (6.3 | ) |
Other | | | 8,884 | | | | 9,259 | | | | 14,358 | | | | (375 | ) | | | (4.1 | ) | | | (5,099 | ) | | | (35.5 | ) |
| | | | |
Subtotal (“fee income”) | | | 307,122 | | | | 321,125 | | | | 286,430 | | | | (14,003 | ) | | | (4.4 | ) | | | 34,695 | | | | 12.1 | |
Asset gains (losses), net | | | 5,413 | | | | (12,096 | ) | | | (12,199 | ) | | | 17,509 | | | | (144.8 | ) | | | 103 | | | | (0.8 | ) |
Investment securities gains (losses), net | | | 564 | | | | 4,261 | | | | (1,112 | ) | | | (3,697 | ) | | | (86.8 | ) | | | 5,373 | | | | N/M | |
| | | | |
Total noninterest income | | $ | 313,099 | | | $ | 313,290 | | | $ | 273,119 | | | $ | (191 | ) | | | (0.1 | )% | | $ | 40,171 | | | | 14.7 | % |
| | | | |
N/M=not meaningful
Notable contributions to the change in 2013 noninterest income were:
| | • | | Trust service fees for 2013 were $46 million, up $5 million (12%) from 2012, primarily attributable to an increase in personal trust fees and retirement plan services. The market value of assets under management at December 31, 2013, was $7.4 billion compared to $6.5 billion at December 31, 2012. |
| | • | | Card-based and other nondeposit fees were $50 million for 2013, an increase of $2 million (4%) from 2012 primarily attributable to higher commercial loan service charges due to year over year growth in commercial loan balances. Insurance commissions were $44 million for 2013, down $3 million (6%) from 2012, primarily due to a $3 million reserve established in 2013 related to third party insurance products sold in prior years. |
| | • | | Net mortgage banking income for 2013 was $49 million, down $15 million (23%) compared to 2012. Net mortgage banking consists of gross mortgage banking income less mortgage servicing rights expense. Gross mortgage banking income includes servicing fees, the mortgage repurchase reserve provision, and the gain or loss on sales of mortgage loans to the secondary market, related fees and fair value marks on the mortgage derivatives (collectively “gains on sales and related income”) and was $50 million in 2013, a decrease of $39 million (44%) compared to 2012. This decrease was primarily attributable to lower gains on sales and related income (down $38 million) and a $1 million increase in the repurchase reserve provision for losses related to repurchases and loss reimbursements on previously sold mortgage loans (see section “Contractual Obligations, Commitments, Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements, and Contingent Liabilities,” and Note 15, “Commitments, Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements, and Contingent Liabilities,” |
40
| | of the notes to consolidated financial statements for additional information concerning this repurchase reserve). Secondary mortgage production was $2.3 billion for 2013, compared to $2.8 billion for 2012. |
| | • | | Mortgage servicing rights expense includes both the amortization of the mortgage servicing rights asset and changes to the valuation allowance associated with the mortgage servicing rights asset. Mortgage servicing rights expense is affected by the size of the servicing portfolio, as well as the changes in the estimated fair value of the mortgage servicing rights asset. Mortgage servicing rights expense was $1 million for 2013 compared to $26 million for 2012, an improvement of $25 million; with a $17 million favorable change to the valuation reserve (comprised of a $15 million recovery to the valuation reserve in 2013, compared to a $2 million addition to the valuation reserve during 2012) and an $8 million reduction in amortization. Mortgage servicing rights are considered a critical accounting policy given that estimating their fair value involves a discounted cash flow model and assumptions that involve judgment, particularly of estimated prepayment speeds of the underlying mortgages serviced and the overall level of interest rates. See section “Critical Accounting Policies,” as well as Note 1, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” for the Corporation’s accounting policy for mortgage servicing rights, Note 4, “Goodwill and Intangible Assets,” and Note 17, “Fair Value Measurements,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements for additional disclosure. |
| | • | | Net asset gains of $5 million for 2013 were primarily attributable to a $2 million gain on the sale of branches, and a $3 million net gain on the sale of real estate and miscellaneous assets. Net asset losses of $12 million for 2012 were primarily attributable to write-downs of $8 million on impaired and abandoned software during 2012 and $10 million of losses on sales and other write-downs on other real estate owned, partially offset by a $6 million gain on the sale of three retail branches in rural western Illinois. Net investment securities gains were less than $1 million in 2013; while net investment securities gains of $4 million for 2012 were primarily attributable to gains on sales of equity, mortgage-related and trust preferred debt securities. |
Noninterest Expense
Noninterest expense for 2013 was $681 million, a decrease of $1 million from 2012. Personnel expense increased $16 million (4%), while nonpersonnel noninterest expenses decreased $17 million (6%) compared to 2012.
TABLE 6: Noninterest Expense
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years Ended December 31, | | | Change From Prior Year | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | | | $ Change
2013 | | | % Change
2013 | | | $ Change
2012 | | | % Change
2012 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Personnel expense | | $ | 397,015 | | | $ | 381,404 | | | $ | 360,144 | | | $ | 15,611 | | | | 4.1 | % | | $ | 21,260 | | | | 5.9 | % |
Occupancy | | | 59,409 | | | | 60,794 | | | | 55,939 | | | | (1,385 | ) | | | (2.3 | ) | | | 4,855 | | | | 8.7 | |
Equipment | | | 25,351 | | | | 23,566 | | | | 19,873 | | | | 1,785 | | | | 7.6 | | | | 3,693 | | | | 18.6 | |
Technology | | | 49,445 | | | | 43,548 | | | | 32,475 | | | | 5,897 | | | | 13.5 | | | | 11,073 | | | | 34.1 | |
Business development and advertising | | | 23,346 | | | | 21,303 | | | | 23,038 | | | | 2,043 | | | | 9.6 | | | | (1,735 | ) | | | (7.5 | ) |
Other intangible amortization | | | 4,043 | | | | 4,195 | | | | 4,714 | | | | (152 | ) | | | (3.6 | ) | | | (519 | ) | | | (11.0 | ) |
Loan expense | | | 13,162 | | | | 12,285 | | | | 12,008 | | | | 877 | | | | 7.1 | | | | 277 | | | | 2.3 | |
Legal and professional fees | | | 20,226 | | | | 31,232 | | | | 18,205 | | | | (11,006 | ) | | | (35.2 | ) | | | 13,027 | | | | 71.6 | |
Losses other than loans | | | 1,942 | | | | 12,258 | | | | 17,921 | | | | (10,316 | ) | | | (84.2 | ) | | | (5,663 | ) | | | (31.6 | ) |
Foreclosure / OREO expense | | | 10,068 | | | | 15,069 | | | | 21,393 | | | | (5,001 | ) | | | (33.2 | ) | | | (6,324 | ) | | | (29.6 | ) |
FDIC expense | | | 19,461 | | | | 19,478 | | | | 28,484 | | | | (17 | ) | | | (0.1 | ) | | | (9,006 | ) | | | (31.6 | ) |
Other | | | 57,281 | | | | 56,691 | | | | 56,329 | | | | 590 | | | | 1.0 | | | | 362 | | | | 0.6 | |
| | | | |
Total noninterest expense | | $ | 680,749 | | | $ | 681,823 | | | $ | 650,523 | | | $ | (1,074 | ) | | | (0.2 | )% | | $ | 31,300 | | | | 4.8 | % |
| | | | |
Personnel expense to total noninterest expense | | | 58.3 | % | | | 55.9 | % | | | 55.4 | % | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
41
Notable contributions to the change in 2013 noninterest expense were:
| | • | | Personnel expense (which includes salary-related expenses and fringe benefit expenses) was $397 million for 2013, up $16 million (4%) from 2012. Average full-time equivalent employees were 4,728 for 2013, down 5% from 4,968 employees for 2012. Salary-related expenses increased $18 million (6%). This increase was primarily the result of higher compensation (up $16 million or 7%). Fringe benefit expenses decreased $2 million (3%), primarily due to a decrease in health insurance costs. |
| | • | | Nonpersonnel noninterest expenses on a combined basis were $284 million, down $17 million (6%) compared to 2012. Equipment and technology were up $8 million (11%) due to strategic investments in our systems and infrastructure. Business development and advertising expenses increased $2 million (10%) from 2012 as the Corporation increased advertising related to our brand campaign. Legal and professional fees decreased $11 million due to a decrease in consultant costs related to certain BSA compliance issues. Losses other than loans decreased $10 million primarily due to a $7 million decrease in the provision for losses on unfunded commitments and a $3 million decrease in the provision for reinsurance losses. Foreclosure / OREO expenses of $10 million decreased $5 million, primarily attributable to a decline in legal and collection expenses related to the improvement in credit quality. All remaining noninterest expense categories on a combined basis were relatively flat compared to 2012. |
Income Taxes
The Corporation recognized income tax expense of $79 million for 2013 compared to income tax expense of $75 million for 2012. The change in income tax expense was primarily due to the increase in the level of pretax income between the years. The effective tax rate was 29.6% for 2013, compared to an effective tax rate of 29.7% for 2012. During 2013, the Corporation recorded a $6 million net decrease in the reserve for uncertain tax positions related to the settlement of a tax issue and the expiration of various statutes of limitation. During 2012, the Corporation recorded a $5 million net decrease in the reserve for uncertain tax positions related to the settlement of a tax issue and the expiration of various statutes of limitations. Income tax expense is also impacted by ongoing federal and state income tax audits and changes in tax law and rates.
See Note 1, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements for the Corporation’s income tax accounting policy and section “Critical Accounting Policies.” Income tax expense recorded in the consolidated statements of income involves the interpretation and application of certain accounting pronouncements and federal and state tax laws and regulations, and is, therefore, considered a critical accounting policy. The Corporation is subject to examination by various taxing authorities. Examination by taxing authorities may impact the amount of tax expense and / or the reserve for uncertain tax positions if their interpretations differ from those of management, based on their judgments about information available to them at the time of their examinations. See Note 12, “Income Taxes,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements for more information.
BALANCE SHEET ANALYSIS
The Corporation’s balance sheet growth historically was driven by loan growth. See section “Loans.” The Corporation has historically financed its asset growth through increased deposits and issuance of debt (see sections, “Deposits,” “Other Funding Sources,” and “Liquidity”), as well as retention of earnings and the issuance of common and preferred stock (see section “Capital”).
42
TABLE 7: Loan Composition
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | | | 2010 | | | 2009 | |
| | | Amount | | | % of
Total | | | Amount | | | % of
Total | | | Amount | | | % of
Total | | | Amount | | | % of
Total | | | Amount | | | % of
Total | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 4,822,680 | | | | 31 | % | | $ | 4,502,021 | | | | 29 | % | | $ | 3,724,736 | | | | 27 | % | | $ | 3,049,752 | | | | 24 | % | | $ | 3,450,632 | | | | 24 | % |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 1,114,715 | | | | 7 | | | | 1,219,747 | | | | 8 | | | | 1,086,829 | | | | 8 | | | | 1,049,798 | | | | 9 | | | | 1,198,075 | | | | 9 | |
Lease financing | | | 55,483 | | | | — | | | | 64,196 | | | | 1 | | | | 58,194 | | | | — | | | | 60,254 | | | | — | | | | 95,851 | | | | 1 | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 5,992,878 | | | | 38 | | | | 5,785,964 | | | | 38 | | | | 4,869,759 | | | | 35 | | | | 4,159,804 | | | | 33 | | | | 4,744,558 | | | | 34 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 2,939,456 | | | | 18 | | | | 2,906,759 | | | | 19 | | | | 2,563,767 | | | | 18 | | | | 2,339,415 | | | | 18 | | | | 2,618,991 | | | | 18 | |
Real estate construction | | | 896,248 | | | | 6 | | | | 655,381 | | | | 4 | | | | 584,046 | | | | 4 | | | | 553,069 | | | | 4 | | | | 1,397,493 | | | | 10 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 3,835,704 | | | | 24 | | | | 3,562,140 | | | | 23 | | | | 3,147,813 | | | | 22 | | | | 2,892,484 | | | | 22 | | | | 4,016,484 | | | | 28 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 9,828,582 | | | | 62 | | | | 9,348,104 | | | | 61 | | | | 8,017,572 | | | | 57 | | | | 7,052,288 | | | | 55 | | | | 8,761,042 | | | | 62 | |
Home equity revolving lines of credit | | | 874,840 | | | | 5 | | | | 936,065 | | | | 6 | | | | 1,059,865 | | | | 8 | | | | 1,153,406 | | | | 9 | | | | 1,294,154 | | | | 9 | |
Home equity loans first liens | | | 742,120 | | | | 5 | | | | 1,013,757 | | | | 6 | | | | 1,104,674 | | | | 8 | | | | 956,618 | | | | 8 | | | | 721,231 | | | | 5 | |
Home equity loans junior liens | | | 208,054 | | | | 1 | | | | 269,672 | | | | 2 | | | | 340,165 | | | | 2 | | | | 413,033 | | | | 3 | | | | 530,782 | | | | 4 | |
| | | | |
Home equity | | | 1,825,014 | | | | 11 | | | | 2,219,494 | | | | 14 | | | | 2,504,704 | | | | 18 | | | | 2,523,057 | | | | 20 | | | | 2,546,167 | | | | 18 | |
Installment | | | 407,074 | | | | 3 | | | | 466,727 | | | | 3 | | | | 557,782 | | | | 4 | | | | 695,383 | | | | 6 | | | | 873,568 | | | | 6 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 3,835,591 | | | | 24 | | | | 3,376,697 | | | | 22 | | | | 2,951,013 | | | | 21 | | | | 2,346,007 | | | | 19 | | | | 1,947,848 | | | | 14 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 6,067,679 | | | | 38 | | | | 6,062,918 | | | | 39 | | | | 6,013,499 | | | | 43 | | | | 5,564,447 | | | | 45 | | | | 5,367,583 | | | | 38 | |
| | | | |
Total loans | | $ | 15,896,261 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 15,411,022 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 14,031,071 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 12,616,735 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 14,128,625 | | | | 100 | % |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate and Real estate construction loan detail: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Farmland | | $ | 8,591 | | | | — | % | | $ | 17,730 | | | | 1 | % | | $ | 26,221 | | | | 1 | % | | $ | 36,741 | | | | 2 | % | | $ | 47,514 | | | | 2 | % |
Multi-family | | | 951,348 | | | | 33 | | | | 905,372 | | | | 31 | | | | 694,056 | | | | 27 | | | | 485,977 | | | | 21 | | | | 543,936 | | | | 21 | |
Non-owner occupied | | | 1,979,517 | | | | 67 | | | | 1,983,657 | | | | 68 | | | | 1,843,490 | | | | 72 | | | | 1,816,697 | | | | 77 | | | | 2,027,541 | | | | 77 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | $ | 2,939,456 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 2,906,759 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 2,563,767 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 2,339,415 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 2,618,991 | | | | 100 | % |
| | | | |
1-4 family construction | | $ | 259,031 | | | | 29 | % | | $ | 176,874 | | | | 27 | % | | $ | 120,170 | | | | 21 | % | | $ | 96,296 | | | | 17 | % | | $ | 251,307 | | | | 18 | % |
All other construction | | | 637,217 | | | | 71 | | | | 478,507 | | | | 73 | | | | 463,876 | | | | 79 | | | | 456,773 | | | | 83 | | | | 1,146,186 | | | | 82 | |
| | | | |
Real estate construction | | $ | 896,248 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 655,381 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 584,046 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 553,069 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 1,397,493 | | | | 100 | % |
| | | | |
Loans
Total loans were $15.9 billion at December 31, 2013, an increase of $485 million or 3% from December 31, 2012. Commercial and business loans were $6.0 billion, up $207 million (4%) from December 31, 2012, to represent 38% of total loans at December 31, 2013. Commercial real estate totaled $3.8 billion at December 31, 2013 and represented 24% of total loans, an increase of $274 million (8%) from December 31, 2012. Consumer loans were $6.1 billion at December 31, 2013, relatively unchanged from December 31, 2012, and represented 38% of total loans at December 31, 2013.
The Corporation has long-term guidelines relative to the proportion of Commercial and Business, Commercial Real Estate, and Consumer loans within the overall loan portfolio, with each targeted to represent 30-40% of the overall loan portfolio. The targeted long-term guidelines were unchanged during 2012 and 2013. Furthermore, certain sub-asset classes within the respective portfolios were further defined and dollar limitations were placed on these sub-portfolios. These guidelines and limits are reviewed quarterly and approved annually by the Enterprise Risk Committee of the Corporation’s Board of Directors. These guidelines and limits are designed to create balance and diversification within the loan portfolios.
43
The commercial and business lending portfolio, which consists of commercial and business loans and owner occupied commercial real estate loans, was $6.0 billion at December 31, 2013 up $207 million (4%) since year-end 2012. The commercial and business lending classification primarily includes commercial loans to large corporations, middle market companies and small businesses. At December 31, 2013, the largest industry groups within the commercial and business loan category included the manufacturing sector which represented 8% of total loans and 22% of the total commercial and business loan portfolio. The next largest industry group within the commercial and business loan category included the wholesale trade sector, which represented 4% of total loans and 11% of the total commercial and business loan portfolio at December 31, 2013. The remaining portfolio is spread over a diverse range of industries, none of which exceed 5% of total loans. The credit risk related to commercial loans is largely influenced by general economic conditions and the resulting impact on a borrower’s operations or on the value of underlying collateral, if any.
The commercial real estate lending portfolio, which consists of investor commercial real estate and construction loans, totaled $3.8 billion at December 31, 2013, up $274 million (8%) from December 31, 2012. Within the commercial real estate lending portfolio, commercial real estate lending to investors totaled $2.9 billion at December 31, 2013, relatively unchanged from December 31, 2012. Commercial real estate primarily includes commercial-based loans to investors that are secured by commercial income properties or multifamily projects. Commercial real estate loans are typically intermediate to long-term financings. Loans of this type are mainly secured by commercial income properties or multifamily projects. Credit risk is managed in a similar manner to commercial and business loans by employing sound underwriting guidelines, lending primarily to borrowers in local markets and businesses, periodically evaluating the underlying collateral, and formally reviewing the borrower’s financial soundness and relationship on an ongoing basis. Real estate construction loans were $896 million, an increase of $241 million (37%) compared to December 31, 2012. Loans in this classification are primarily short-term or interim loans that provide financing for the acquisition or development of commercial income properties, multifamily projects or residential development, both single family and condominium. Real estate construction loans are made to developers and project managers who are generally well known to the Corporation, and have prior successful project experience. The credit risk associated with real estate construction loans is generally confined to specific geographic areas but is also influenced by general economic conditions. The Corporation controls the credit risk on these types of loans by making loans in familiar markets to developers, reviewing the merits of individual projects, controlling loan structure, and monitoring project progress and construction advances.
The Corporation’s current lending standards for commercial real estate and real estate construction lending are determined by property type and specifically address many criteria, including: maximum loan amounts, maximum loan-to-value (“LTV”), requirements for pre-leasing and / or presales, minimum borrower equity, and maximum loan to cost. Currently, the maximum standard for LTV is 80%, with lower limits established for certain higher risk types, such as raw land which has a 50% LTV maximum. The Corporation’s LTV guidelines are in compliance with regulatory supervisory limits. In most cases, for real estate construction loans, the loan amounts include interest reserves, which are built into the loans and sized to fund loan payments through construction and lease up and / or sell out.
Consumer loans totaled $6.1 billion at December 31, 2013, relatively unchanged from December 31, 2012. Loans in this classification include residential mortgage, home equity and installment loans. Residential mortgage loans totaled $3.8 billion at December 31, 2013, up $459 million (14%) from December 31, 2012. Residential mortgage loans include conventional first lien home mortgages and the Corporation generally limits the maximum loan to 80% of collateral value without credit enhancement (e.g. private mortgage insurance). As part of management’s historical practice of originating and servicing residential mortgage loans, generally the Corporation’s 30-year, fixed-rate residential real estate mortgage loans are sold in the secondary market with servicing rights retained. The Corporation also retains a portion of its 15-year and under, fixed-rate residential real estate mortgages in its loan portfolio. At December 31, 2013, the residential mortgage portfolio was comprised of $1.4 billion of fixed-rate residential real estate mortgages and $2.4 billion of variable-rate residential real estate mortgages, compared to $1.3 billion of fixed-rate mortgages and $2.1 billion variable-rate mortgages at December 31, 2012.
44
The Corporation’s underwriting and risk-based pricing guidelines for residential mortgage loans include minimum borrower FICO and maximum LTV of the property securing the loan. Residential mortgage products generally are underwritten using FHLMC and FNMA secondary marketing guidelines.
Home equity totaled $1.8 billion at December 31, 2013, down $394 million (18%) compared to December 31, 2012, and consists of home equity lines, as well as home equity loans, approximately half of which are first lien positions. Home equity balances declined as customers continued to deleverage and refinance into lower-priced, first lien residential mortgage loans. Loans and lines in a junior position at December 31, 2013 included approximately 35% for which the Corporation also owned or serviced the related first lien loan and approximately 65% where the Corporation did not service the related first lien loan.
The Corporation’s credit risk monitoring guidelines for home equity is based on an ongoing review of loan delinquency status, as well as a semi-annual review of FICO score deterioration and property devaluation. The Corporation does not routinely obtain appraisals on performing loans to update LTV ratios after origination; however, the Corporation monitors the local housing markets by reviewing the various home price indices and incorporates the impact of the changing market conditions in its ongoing credit monitoring process. For second lien home equity loans, the Corporation is unable to track the performance of the first lien loan if it does not own or service the first lien loan. However, the Corporation obtains a refreshed FICO score on a semi-annual basis and monitors this as part of its assessment of the home equity portfolio.
The Corporation’s underwriting and risk-based pricing guidelines for home equity lines and loans consist of a combination of both borrower FICO and the original LTV of the property securing the loan. Currently, for home equity products, the maximum acceptable LTV is 90% for customers with FICO scores exceeding 700. Home equity loans generally have a 20 year term and are fixed rate with principal and interest payments required. As of December 31, 2013, approximately 40% of the home equity loan first liens have a remaining maturity of more than 10 years. Home equity lines are variable rate, interest only lines of credit which do not require the payment of principal during the initial revolving period, after which principal payments are required. Based upon outstanding balances at December 31, 2013, the following table presents the periods when home equity lines of credit revolving periods are scheduled to end.
Table 8: Home Equity Lines of Credit — Revolving Period End Dates
| | | | | | | | |
| | | $ in Thousands | | | % to Total | |
Less than 1 year | | $ | 4,674 | | | | 1 | % |
1 — 3 years | | | 4,242 | | | | 0 | % |
3 — 5 years | | | 6,317 | | | | 1 | % |
5 — 10 years | | | 141,981 | | | | 16 | % |
Over 10 years | | | 717,626 | | | | 82 | % |
| | | | |
Total home equity revolving lines of credit | | $ | 874,840 | | | | 100 | % |
| | | | |
Installment loans totaled $407 million at December 31, 2013 down $60 million (13%) compared to December 31, 2012, and consist of student loans, as well as short-term and other personal installment loans. The Corporation had $330 million and $374 million of student loans at December 31, 2013, and December 31, 2012, respectively, the majority of which are government guaranteed. Credit risk for non-government guaranteed student, short-term and personal installment loans is generally influenced by general economic conditions, the characteristics of individual borrowers, and the nature of the loan collateral. Risks of loss are generally on the smaller average balances per loan spread over many borrowers. Once charged off, there is usually less opportunity for recovery on these smaller retail loans. Credit risk is primarily controlled by reviewing the creditworthiness of the borrowers, monitoring payment histories, and taking appropriate collateral and guaranty positions.
Factors that are important to managing overall credit quality are sound loan underwriting and administration, systematic monitoring of existing loans and commitments, effective loan review on an ongoing basis, early identification of potential problems, and appropriate allowance for loan losses, nonaccrual and charge off policies.
45
An active credit risk management process is used for commercial loans to further ensure that sound and consistent credit decisions are made. Credit risk is controlled by detailed underwriting procedures, comprehensive loan administration, and periodic review of borrowers’ outstanding loans and commitments. Borrower relationships are formally reviewed and graded on an ongoing basis for early identification of potential problems. Further analyses by customer, industry, and geographic location are performed to monitor trends, financial performance, and concentrations.
The loan portfolio is widely diversified by types of borrowers, industry groups, and market areas within our core footprint. Significant loan concentrations are considered to exist when there are amounts loaned to numerous borrowers engaged in similar activities that would cause them to be similarly impacted by economic or other conditions. At December 31, 2013, no significant concentrations existed in the Corporation’s portfolio in excess of 10% of total loans.
TABLE 9: Commercial Loan Maturity Distribution and Interest Rate Sensitivity
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Maturity(1) | |
December 31, 2013 | | Within
1 Year(2) | | | 1-5 Years | | | After
5 Years | | | Total | | | % of Total | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 3,709,379 | | | $ | 832,982 | | | $ | 280,319 | | | $ | 4,822,680 | | | | 49 | % |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 1,049,838 | | | | 1,735,055 | | | | 154,563 | | | | 2,939,456 | | | | 30 | % |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 398,343 | | | | 570,596 | | | | 145,776 | | | | 1,114,715 | | | | 12 | % |
Real estate construction | | | 520,374 | | | | 334,889 | | | | 40,985 | | | | 896,248 | | | | 9 | % |
| | | | |
Total | | $ | 5,677,934 | | | $ | 3,473,522 | | | $ | 621,643 | | | $ | 9,773,099 | | | | 100 | % |
| | | | |
Fixed rate | | $ | 2,359,568 | | | $ | 1,292,253 | | | $ | 345,456 | | | $ | 3,997,277 | | | | 41 | % |
Floating or adjustable rate | | | 3,318,366 | | | | 2,181,269 | | | | 276,187 | | | | 5,775,822 | | | | 59 | % |
| | | | |
Total | | $ | 5,677,934 | | | $ | 3,473,522 | | | $ | 621,643 | | | $ | 9,773,099 | | | | 100 | % |
| | | | |
Percent by maturity distribution | | | 58 | % | | | 36 | % | | | 6 | % | | | 100 | % | | | | |
| (1) | Based upon scheduled principal repayments. |
| (2) | Demand loans, past due loans, and overdrafts are reported in the “Within 1 Year” category. |
The total commercial loans that were floating or adjustable rate was $5.8 billion (59%) at December 31, 2013. Including the $2.4 billion of fixed rate loans due within one year, the total percentage of the commercial loan portfolio noted above that reprices or resets within one year is 83%.
Allowance for Loan Losses
Credit risks within the loan portfolio are inherently different for each loan type. Credit risk is controlled and monitored through the use of lending standards, a thorough review of potential borrowers, and on-going review of loan payment performance. Active asset quality administration, including early problem loan identification and timely resolution of problems, aids in the management of credit risk and minimization of loan losses. Credit risk management for each loan type is discussed briefly in the section entitled “Loans.”
The level of the allowance for loan losses represents management’s estimate of an amount appropriate to provide for probable credit losses in the loan portfolio at the balance sheet date. To assess the appropriateness of the allowance for loan losses, an allocation methodology is applied by the Corporation which focuses on evaluation of many factors, including but not limited to: evaluation of facts and issues related to specific loans, management’s ongoing review and grading of the loan portfolio, consideration of historical loan loss and delinquency experience on each portfolio category, trends in past due and nonaccrual loans, the level of potential problem loans, the risk characteristics of the various classifications of loans, changes in the size and character of
46
the loan portfolio, concentrations of loans to specific borrowers or industries, existing economic conditions, the fair value of underlying collateral, and other qualitative and quantitative factors which could affect potential credit losses. Assessing these factors involves significant judgment. Because each of the criteria used is subject to change, the allowance for loan losses is not necessarily indicative of the trend of future loan losses in any particular category. The total allowance for loan losses is available to absorb losses from any segment of the loan portfolio. Therefore, management considers the allowance for loan losses a critical accounting policy — see section “Critical Accounting Policies” and further discussion in this section. See also management’s allowance for loan losses accounting policy in Note 1, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” and see Note 3, “Loans,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements for additional allowance for loan losses disclosures. Table 7 provides information on loan growth and composition, Tables 10 and 11 provide additional information regarding activity in the allowance for loan losses, and Table 12 provides additional information regarding nonperforming assets.
At December 31, 2013, the allowance for loan losses was $268 million, compared to $297 million at December 31, 2012. The allowance for loan losses to total loans was 1.69% and 1.93% at December 31, 2013, and 2012, respectively, and the allowance for loan losses covered 145% and 118% of nonaccrual loans at December 31, 2013, and 2012, respectively. The provision for loan losses for 2013 was $10 million, compared to a provision for loan losses of $3 million for 2012. Net charge offs were $39 million for 2013 and $84 million for 2012. The ratio of net charge offs to average loans was 0.25% and 0.57% for 2013 and 2012, respectively. Management believes the level of allowance for loan losses to be appropriate at December 31, 2013 and December 31, 2012.
Although improving, the economy remained fragile during 2013, as accelerating real estate values, record high corporate profit margins, and improved (but relatively elevated) levels of unemployment were countered by stagnant growth and public sector fiscal concerns in the United States and lingering European economic concerns.
The national unemployment rate declined to 7.0% at November 2013 versus 7.8% twelve months earlier, though some of the unemployment rate improvement is attributed to the 63% labor force participation rate — the lowest level since 1978. The Midwest jobless rate paralleled that trend in 2013 and remains slightly below the national level, as the Midwest unemployment rate was 6.9% at November 2013 compared with 7.1% at November 2012, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Real GDP growth continued at the disappointing 2% range in 2013, the same pace that has prevailed throughout the recovery since the Great Recession. The economic drag from past fiscal policy was approximated to be a substantial 1.5 percentage points of GDP in 2013, which is expected to dissipate in 2014 and beyond.
Residential real estate markets experienced significant gains both nationally and within the Corporation’s core footprint. Based on the Case Shiller Home Price Index, residential home prices increased nearly 15% across the U.S. and approximately 10% within the core footprint states. Foreclosures remain elevated over pre-recession levels but declined significantly in 2013 which will mitigate the downward price pressure of residential home prices going forward.
Commercial real estate values (based on the Commercial Repeat Sales Index — CCRSI) continued to advance nationally during 2013 as evidenced by growth just shy of 10% for all commercial property types. Likewise to the residential real estate market, the percentage of commercial property selling at distressed price nationally dropped to near 10% at the end of 2013 compared to 24% a year ago. On a regional level, the Midwest still has 23% of property selling at distressed levels although pricing in the region has begun to stabilize after bottoming out in 2012, more than a year later than the other regions. Multifamily and retail commercial property types continue to buoy the Midwest region despite relatively stagnant office type prices and an eroding industrial property sector.
47
In an improving yet challenging real estate market, such as currently exists as described above, the value of the collateral securing the loans continues to be one of the most important factors in determining the appropriate amount of allowance for estimated loan losses to record at the balance sheet date.
Credit quality continued to improve during 2013. Nonaccrual loans declined to $185 million (representing 1.17% of total loans), down 27% from December 31, 2012, due to portfolio improvements, including a lower level of loans moving into the nonaccrual and potential problem loan categories. Accruing loans past due 30-89 days totaled $53 million at December 31, 2013, a decrease of 17% from December 31, 2012, while potential problem loans declined to $235 million, a reduction of 35% from year-end 2012.
48
TABLE 10: Loan Loss Experience
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years Ended December 31, | |
($ in Thousands) | | 2013 | | | | | | 2012 | | | | | | 2011 | | | | | | 2010 | | | | | | 2009 | | | | |
Allowance for loan losses, at beginning of year | | $ | 297,409 | | | | | | | $ | 378,151 | | | | | | | $ | 476,813 | | | | | | | $ | 573,533 | | | | | | | $ | 265,378 | | | | | |
Provision for loan losses | | | 10,000 | | | | | | | | 3,000 | | | | | | | | 52,000 | | | | | | | | 390,010 | | | | | | | | 750,645 | | | | | |
Loans charged off: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | | 35,146 | | | | | | | | 43,240 | | | | | | | | 38,662 | | | | | | | | 121,179 | | | | | | | | 161,260 | | | | | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 6,474 | | | | | | | | 4,080 | | | | | | | | 9,485 | | | | | | | | 20,871 | | | | | | | | 7,889 | | | | | |
Lease financing | | | 206 | | | | | | | | 797 | | | | | | | | 173 | | | | | | | | 11,081 | | | | | | | | 1,575 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 41,826 | | | | | | | | 48,117 | | | | | | | | 48,320 | | | | | | | | 153,131 | | | | | | | | 170,724 | | | | | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 9,846 | | | | | | | | 14,000 | | | | | | | | 29,479 | | | | | | | | 96,530 | | | | | | | | 49,399 | | | | | |
Real estate construction | | | 3,375 | | | | | | | | 3,588 | | | | | | | | 38,222 | | | | | | | | 204,728 | | | | | | | | 157,752 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 13,221 | | | | | | | | 17,588 | | | | | | | | 67,701 | | | | | | | | 301,258 | | | | | | | | 207,151 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 55,047 | | | | | | | | 65,705 | | | | | | | | 116,021 | | | | | | | | 454,389 | | | | | | | | 377,875 | | | | | |
Home equity revolving lines of credit(3) | | | 10,855 | | | | | | | | 18,736 | | | | | | | | 25,679 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Home equity loans first liens(3) | | | 2,759 | | | | | | | | 3,758 | | | | | | | | 1,603 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Home equity loans junior liens(3) | | | 7,015 | | | | | | | | 11,631 | | | | | | | | 15,341 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
Home equity(3) | | | 20,629 | | | | | | | | 34,125 | | | | | | | | 42,623 | | | | | | | | 51,132 | | | | | | | | 49,674 | | | | | |
Installment | | | 1,389 | | | | | | | | 3,057 | | | | | | | | 16,134 | | | | | | | | 9,787 | | | | | | | | 10,364 | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | 10,996 | | | | | | | | 14,159 | | | | | | | | 14,954 | | | | | | | | 13,184 | | | | | | | | 14,293 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 33,014 | | | | | | | | 51,341 | | | | | | | | 73,711 | | | | | | | | 74,103 | | | | | | | | 74,331 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Total loans charged off(1)(2) | | | 88,061 | | | | | | | | 117,046 | | | | | | | | 189,732 | | | | | | | | 528,492 | | | | | | | | 452,206 | | | | | |
Recoveries of loans previously charged off: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | | 28,865 | | | | | | | | 18,363 | | | | | | | | 16,350 | | | | | | | | 20,609 | | | | | | | | 5,583 | | | | | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 339 | | | | | | | | 453 | | | | | | | | 2,509 | | | | | | | | 308 | | | | | | | | 537 | | | | | |
Lease financing | | | 218 | | | | | | | | 1,899 | | | | | | | | 1,955 | | | | | | | | 25 | | | | | | | | 5 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 29,422 | | | | | | | | 20,715 | | | | | | | | 20,814 | | | | | | | | 20,942 | | | | | | | | 6,125 | | | | | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 6,961 | | | | | | | | 4,796 | | | | | | | | 5,666 | | | | | | | | 10,141 | | | | | | | | 512 | | | | | |
Real estate construction | | | 5,511 | | | | | | | | 2,129 | | | | | | | | 7,521 | | | | | | | | 6,040 | | | | | | | | 555 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 12,472 | | | | | | | | 6,925 | | | | | | | | 13,187 | | | | | | | | 16,181 | | | | | | | | 1,067 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 41,894 | | | | | | | | 27,640 | | | | | | | | 34,001 | | | | | | | | 37,123 | | | | | | | | 7,192 | | | | | |
Home equity revolving lines of credit(3) | | | 2,995 | | | | | | | | 2,725 | | | | | | | | 1,867 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Home equity loans first liens(3) | | | 104 | | | | | | | | 58 | | | | | | | | 44 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Home equity loans junior liens(3) | | | 1,113 | | | | | | | | 1,115 | | | | | | | | 1,290 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
Home equity(3) | | | 4,212 | | | | | | | | 3,898 | | | | | | | | 3,201 | | | | | | | | 2,733 | | | | | | | | 884 | | | | | |
Installment | | | 1,633 | | | | | | | | 1,234 | | | | | | | | 1,584 | | | | | | | | 1,669 | | | | | | | | 1,525 | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | 1,228 | | | | | | | | 532 | | | | | | | | 284 | | | | | | | | 237 | | | | | | | | 115 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 7,073 | | | | | | | | 5,664 | | | | | | | | 5,069 | | | | | | | | 4,639 | | | | | | | | 2,524 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Total recoveries(1)(2) | | | 48,967 | | | | | | | | 33,304 | | | | | | | | 39,070 | | | | | | | | 41,762 | | | | | | | | 9,716 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Total net charge offs(1)(2) | | | 39,094 | | | | | | | | 83,742 | | | | | | | | 150,662 | | | | | | | | 486,730 | | | | | | | | 442,490 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Allowance for loan losses, at end of year | | $ | 268,315 | | | | | | | $ | 297,409 | | | | | | | $ | 378,151 | | | | | | | $ | 476,813 | | | | | | | $ | 573,533 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Ratios at end of year: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for loan losses to total loans | | | 1.69 | % | | | | | | | 1.93 | % | | | | | | | 2.70 | % | | | | | | | 3.78 | % | | | | | | | 4.06 | % | | | | |
Allowance for loan losses to net charge offs | | | 6.9x | | | | | | | | 3.6x | | | | | | | | 2.5x | | | | | | | | 1.0x | | | | | | | | 1.3x | | | | | |
| | | | |
Net loan charge offs (recoveries): | | | | | | | (A | ) | | | | | | | (A | ) | | | | | | | (A | ) | | | | | | | (A | ) | | | | | | | (A | ) |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 6,281 | | | | 14 | | | $ | 24,877 | | | | 63 | | | $ | 22,312 | | | | 70 | | | $ | 100,570 | | | | 330 | | | $ | 155,677 | | | | 401 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 6,135 | | | | 53 | | | | 3,627 | | | | 33 | | | | 6,976 | | | | 67 | | | | 20,563 | | | | 183 | | | | 7,352 | | | | 58 | |
Lease financing | | | (12 | ) | | | (2 | ) | | | (1,102 | ) | | | N/M | | | | (1,782 | ) | | | N/M | | | | 11,056 | | | | N/M | | | | 1,570 | | | | 144 | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 12,404 | | | | 21 | | | | 27,402 | | | | 53 | | | | 27,506 | | | | 64 | | | | 132,189 | | | | 310 | | | | 164,599 | | | | 312 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 2,885 | | | | 10 | | | | 9,204 | | | | 33 | | | | 23,813 | | | | 98 | | | | 86,389 | | | | 346 | | | | 48,887 | | | | 197 | |
Real estate construction | | | (2,136 | ) | | | (27 | ) | | | 1,459 | | | | 25 | | | | 30,701 | | | | N/M | | | | 198,688 | | | | N/M | | | | 157,197 | | | | N/M | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 749 | | | | 2 | | | | 10,663 | | | | 32 | | | | 54,514 | | | | 183 | | | | 285,077 | | | | N/M | | | | 206,084 | | | | 468 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 13,153 | | | | 14 | | | | 38,065 | | | | 45 | | | | 82,020 | | | | 113 | | | | 417,266 | | | | 536 | | | | 370,683 | | | | 383 | |
Home equity revolving lines of credit(3) | | | 7,860 | | | | 88 | | | | 16,011 | | | | 159 | | | | 23,812 | | | | 215 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Home equity loans first liens(3) | | | 2,655 | | | | 31 | | | | 3,700 | | | | 34 | | | | 1,559 | | | | 14 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Home equity loans junior liens(3) | | | 5,902 | | | | 250 | | | | 10,516 | | | | 344 | | | | 14,051 | | | | 374 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
Home equity(3) | | | 16,417 | | | | 82 | | | | 30,227 | | | | 125 | | | | 39,422 | | | | 153 | | | | 48,399 | | | | 195 | | | | 48,790 | | | | 181 | |
Installment | | | (244 | ) | | | (6 | ) | | | 1,823 | | | | 36 | | | | 14,550 | | | | 237 | | | | 8,118 | | | | 95 | | | | 8,839 | | | | 103 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 9,768 | | | | 26 | | | | 13,627 | | | | 41 | | | | 14,670 | | | | 52 | | | | 12,947 | | | | 63 | | | | 14,178 | | | | 60 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 25,941 | | | | 42 | | | | 45,677 | | | | 73 | | | | 68,642 | | | | 114 | | | | 69,464 | | | | 129 | | | | 71,807 | | | | 121 | |
| | | | |
Total net charge offs(1)(2) | | $ | 39,094 | | | | 25 | | | $ | 83,742 | | | | 57 | | | $ | 150,662 | | | | 113 | | | $ | 486,730 | | | | 369 | | | $ | 442,490 | | | | 284 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate and Real estate construction net charge off detail: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Farmland | | $ | 366 | | | | 25 | | | $ | (47 | ) | | | (21 | ) | | $ | 704 | | | | 225 | | | $ | 377 | | | | 89 | | | $ | 146 | | | | 28 | |
Multi-family | | | 499 | | | | 5 | | | | 103 | | | | 1 | | | | 4,531 | | | | 77 | | | | 13,516 | | | | 256 | | | | 6,225 | | | | 119 | |
Non-owner occupied | | | 2,020 | | | | 10 | | | | 9,148 | | | | 47 | | | | 18,578 | | | | 103 | | | | 72,496 | | | | 377 | | | | 42,516 | | | | 224 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | $ | 2,885 | | | | 10 | | | $ | 9,204 | | | | 33 | | | $ | 23,813 | | | | 98 | | | $ | 86,389 | | | | 346 | | | $ | 48,887 | | | | 197 | |
| | | | |
1-4 family construction | | $ | (3,796 | ) | | | (163 | ) | | $ | (1,541 | ) | | | N/M | | | $ | 11,888 | | | | N/M | | | $ | 41,748 | | | | N/M | | | $ | 38,662 | | | | N/M | |
All other construction | | | 1,660 | | | | 30 | | | | 3,000 | | | | 66 | | | | 18,813 | | | | N/M | | | | 156,940 | | | | N/M | | | | 118,535 | | | | N/M | |
| | | | |
Real estate construction | | $ | (2,136 | ) | | | (27 | ) | | $ | 1,459 | | | | 25 | | | $ | 30,701 | | | | N/M | | | $ | 198,688 | | | | N/M | | | $ | 157,197 | | | | N/M | |
| | | | |
49
| (A) | Ratio of net charge offs to average loans by loan type in basis points. |
| (1) | Charge offs for the year ended December 31, 2010 include $8 million related to write-downs on loans transferred to held for sale and $189 million related to write-downs of commercial loans sold and charge offs of commercial loans resolved through discounted payoff, comprised of $20 million in commercial and industrial, $66 million in commercial real estate, and $111 million in real estate construction. |
| (2) | Charge offs for the year ended December 31, 2011, include $10 million of write-downs related to installment loans transferred to held for sale. |
| (3) | A break-down between home equity categories is not available for 2010 and 2009. |
TABLE 11: Allocation of the Allowance for Loan Losses
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | | | | 2012 | | | | | | 2011 | | | | | | 2010 | | | | | | 2009 | | | | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Allowance allocation: | | | | | | | (A | ) | | | | | | | (A | ) | | | | | | | (A | ) | | | | | | | (A | ) | | | | | | | (A | ) |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 104,501 | | | | 2.17 | % | | $ | 97,852 | | | | 2.17 | % | | $ | 124,374 | | | | 3.34 | % | | $ | 137,770 | | | | 4.52 | % | | $ | 196,637 | | | | 5.70 | % |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 19,476 | | | | 1.75 | | | | 27,389 | | | | 2.25 | | | | 36,200 | | | | 3.33 | | | | 54,320 | | | | 5.17 | | | | 52,275 | | | | 4.36 | |
Lease financing | | | 1,607 | | | | 2.90 | | | | 3,024 | | | | 4.71 | | | | 2,567 | | | | 4.41 | | | | 7,396 | | | | 12.27 | | | | 8,303 | | | | 8.66 | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 125,584 | | | | 2.10 | | | | 128,265 | | | | 2.22 | | | | 163,141 | | | | 3.35 | | | | 199,486 | | | | 4.80 | | | | 257,215 | | | | 5.42 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 58,156 | | | | 1.98 | | | | 63,181 | | | | 2.17 | | | | 86,689 | | | | 3.38 | | | | 111,264 | | | | 4.76 | | | | 110,162 | | | | 4.21 | |
Real estate construction | | | 23,418 | | | | 2.61 | | | | 20,741 | | | | 3.16 | | | | 21,327 | | | | 3.65 | | | | 56,772 | | | | 10.26 | | | | 118,708 | | | | 8.49 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 81,574 | | | | 2.13 | | | | 83,922 | | | | 2.36 | | | | 108,016 | | | | 3.43 | | | | 168,036 | | | | 5.81 | | | | 228,870 | | | | 5.70 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 207,158 | | | | 2.11 | | | | 212,187 | | | | 2.27 | | | | 271,157 | | | | 3.38 | | | | 367,522 | | | | 5.21 | | | | 486,085 | | | | 5.55 | |
Home equity | | | 32,196 | | | | 1.76 | | | | 56,826 | | | | 2.56 | | | | 70,144 | | | | 2.80 | | | | 55,090 | | | | 2.18 | | | | 43,783 | | | | 1.72 | |
Installment | | | 2,416 | | | | 0.59 | | | | 4,299 | | | | 0.92 | | | | 6,623 | | | | 1.19 | | | | 17,328 | | | | 2.49 | | | | 11,298 | | | | 1.29 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 26,545 | | | | 0.69 | | | | 24,097 | | | | 0.71 | | | | 30,227 | | | | 1.02 | | | | 36,873 | | | | 1.57 | | | | 32,367 | | | | 1.66 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 61,157 | | | | 1.01 | | | | 85,222 | | | | 1.41 | | | | 106,994 | | | | 1.78 | | | | 109,291 | | | | 1.96 | | | | 87,448 | | | | 1.63 | |
| | | | |
Total allowance for loan losses | | $ | 268,315 | | | | 1.69 | % | | $ | 297,409 | | | | 1.93 | % | | $ | 378,151 | | | | 2.70 | % | | $ | 476,813 | | | | 3.78 | % | | $ | 573,533 | | | | 4.06 | % |
| | | | |
| | | (B | ) | | | (C | ) | | | (B | ) | | | (C | ) | | | (B | ) | | | (C | ) | | | (B | ) | | | (C | ) | | | (B | ) | | | (C | ) |
Commercial and industrial | | | 39 | % | | | 31 | % | | | 33 | % | | | 29 | % | | | 33 | % | | | 27 | % | | | 29 | % | | | 24 | % | | | 34 | % | | | 24 | % |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 7 | | | | 7 | | | | 9 | | | | 8 | | | | 10 | | | | 8 | | | | 11 | | | | 9 | | | | 9 | | | | 9 | |
Lease financing | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | 1 | | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2 | | | | — | | | | 2 | | | | 1 | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 47 | | | | 38 | | | | 43 | | | | 38 | | | | 43 | | | | 35 | | | | 42 | | | | 33 | | | | 45 | | | | 34 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 21 | | | | 18 | | | | 21 | | | | 19 | | | | 23 | | | | 18 | | | | 23 | | | | 18 | | | | 19 | | | | 18 | |
Real estate construction | | | 9 | | | | 6 | | | | 7 | | | | 4 | | | | 6 | | | | 4 | | | | 12 | | | | 4 | | | | 21 | | | | 10 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 30 | | | | 24 | | | | 28 | | | | 23 | | | | 29 | | | | 22 | | | | 35 | | | | 22 | | | | 40 | | | | 28 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 77 | | | | 62 | | | | 71 | | | | 61 | | | | 72 | | | | 57 | | | | 77 | | | | 55 | | | | 85 | | | | 62 | |
Home equity | | | 12 | | | | 11 | | | | 19 | | | | 14 | | | | 18 | | | | 18 | | | | 11 | | | | 20 | | | | 7 | | | | 18 | |
Installment | | | 1 | | | | 3 | | | | 2 | | | | 3 | | | | 2 | | | | 4 | | | | 4 | | | | 6 | | | | 2 | | | | 6 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 10 | | | | 24 | | | | 8 | | | | 22 | | | | 8 | | | | 21 | | | | 8 | | | | 19 | | | | 6 | | | | 14 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 23 | | | | 38 | | | | 29 | | | | 39 | | | | 28 | | | | 43 | | | | 23 | | | | 45 | | | | 15 | | | | 38 | |
| | | | |
Total allowance for loan losses | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % |
| | | | |
| (A) | Allowance for loan losses category as a percentage of total loans by category. |
| (B) | Allowance for loan losses category as a percentage of total allowance for loan losses. |
| (C) | Total loans by category as a percentage of total loans. |
The methodology used for the allocation of the allowance for loan losses at December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011 was generally comparable, whereby the Corporation segregated its loss factors (used for both criticized and non-criticized loans) into a component primarily based on historical loss rates and a component primarily based on other qualitative factors that may affect loan collectability. Management allocates the allowance for loan losses by pools of risk within each loan portfolio. The allocation methodology consists of the following components: First, a valuation allowance estimate is established for specifically identified commercial and consumer loans determined by the Corporation to be impaired, using discounted cash
50
flows, estimated fair value of underlying collateral, and / or other data available. Second, management allocates the allowance for loan losses with loss factors, for criticized loan pools by loan type as well as for non-criticized loan pools by loan type, primarily based on historical loss rates after considering loan type, historical loss and delinquency experience, and industry statistics. Loans that have been criticized are considered to have a higher risk of default than non-criticized loans, as circumstances were present to support the lower loan grade, warranting higher loss factors. The loss factors applied in the methodology are periodically re-evaluated and adjusted to reflect changes in historical loss levels or other risks. Lastly, management allocates allowance for loan losses to absorb unrecognized losses that may not be provided for by the other components due to other factors evaluated by management, such as limitations within the credit risk grading process, known current economic or business conditions that may not yet show in trends, industry or other concentrations with current issues that impose higher inherent risks than are reflected in the loss factors, and other relevant considerations. Because each of the criteria used is subject to change, the allocation of the allowance for loan losses is made for analytical purposes and is not necessarily indicative of the trend of future loan losses in any particular loan category. The total allowance is available to absorb losses from any segment of the loan portfolio. The allocation of the Corporation’s allowance for loan losses for the last five years is shown in Table 11.
Consolidated net income and stockholders’ equity could be affected if management’s estimate of the allowance for loan losses is subsequently materially different, requiring additional or less provision for loan losses to be recorded. Management carefully considers numerous detailed and general factors, its assumptions, and the likelihood of materially different conditions that could alter its assumptions. While management uses currently available information to recognize losses on loans, future adjustments to the allowance for loan losses may be necessary based on newly received appraisals, updated commercial customer financial statements, rapidly deteriorating customer cash flow, and changes in economic conditions that affect our customers. Additionally, larger credit relationships do not inherently create more risk, but can create wider fluctuations in net charge offs and asset quality measures. As an integral part of their examination process, various federal and state regulatory agencies also review the allowance for loan losses. These agencies may require additions to the allowance for loan losses or may require that certain loan balances be charged off or downgraded into criticized loan categories when their credit evaluations differ from those of management, based on their judgments about information available to them at the time of their examination.
Nonaccrual Loans, Potential Problem Loans, and Other Real Estate Owned
Management is committed to a proactive nonaccrual and problem loan identification philosophy. This philosophy is implemented through the ongoing monitoring and review of all pools of risk in the loan portfolio to ensure that problem loans are identified quickly and the risk of loss is minimized. Table 12 provides detailed information regarding nonperforming assets, which include nonaccrual loans and other real estate owned.
Nonaccrual Loans
Nonaccrual loans are considered to be one indicator of potential future loan losses. Loans are generally placed on nonaccrual status when contractually past due 90 days or more as to interest or principal payments, unless the loan is well secured and in the process of collection. Additionally, whenever management becomes aware of facts or circumstances that may adversely impact the collectability of principal or interest on loans, it is management’s practice to place such loans on nonaccrual status immediately, rather than delaying such action until the loans become 90 days past due. When a loan is placed on nonaccrual status, previously accrued and uncollected interest is reversed, amortization of related deferred loan fees or costs is suspended, and income is recorded only to the extent that interest payments are subsequently received in cash and a determination has been made that the principal and interest balance of the loan is collectible. If collectability of the principal and interest is in doubt, payments received are applied to loan principal.
51
TABLE 12: Delinquent (Past Due) Loans, Potential Problem Loans, Nonperforming Assets, and Other Real Estate Owned
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | | | 2010 | | | 2009 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Accruing loans past due 90 days or more: | | | | |
Commercial | | $ | 1,199 | | | $ | 1,036 | | | $ | 4,236 | | | $ | 2,096 | | | $ | 9,394 | |
Consumer | | | 1,151 | | | | 1,253 | | | | 689 | | | | 1,322 | | | | 15,587 | |
| | | | |
Total accruing loans past due 90 days or more | | $ | 2,350 | | | $ | 2,289 | | | $ | 4,925 | | | $ | 3,418 | | | $ | 24,981 | |
| | | | |
Restructured loans (accruing): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial | | $ | 94,265 | | | $ | 88,182 | | | $ | 85,084 | | | $ | 48,124 | | | $ | 480 | |
Consumer | | | 29,720 | | | | 32,905 | | | | 28,080 | | | | 31,811 | | | | 18,557 | |
| | | | |
Total restructured loans (accruing) | | $ | 123,985 | | | $ | 121,087 | | | $ | 113,164 | | | $ | 79,935 | | | $ | 19,037 | |
| | | | |
Restructured loans included in nonaccrual loans | | $ | 59,585 | | | $ | 80,590 | | | $ | 87,493 | | | $ | 35,939 | | | $ | 9,393 | |
Ratios at year end: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Nonaccrual loans to total loans | | | 1.17 | % | | | 1.64 | % | | | 2.54 | % | | | 4.55 | % | | | 7.63 | % |
NPAs to total loans plus OREO | | | 1.28 | % | | | 1.86 | % | | | 2.83 | % | | | 4.89 | % | | | 8.07 | % |
NPAs to total assets | | | 0.84 | % | | | 1.23 | % | | | 1.82 | % | | | 2.84 | % | | | 5.01 | % |
AFLL to nonaccrual loans | | | 145 | % | | | 118 | % | | | 106 | % | | | 83 | % | | | 53 | % |
AFLL to total loans at end of year | | | 1.69 | % | | | 1.93 | % | | | 2.70 | % | | | 3.78 | % | | | 4.06 | % |
| | | | |
Nonperforming assets by type: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 37,719 | | | $ | 39,182 | | | $ | 56,075 | | | $ | 99,845 | | | $ | 230,000 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 29,664 | | | | 24,254 | | | | 35,718 | | | | 59,317 | | | | 59,785 | |
Lease financing | | | 69 | | | | 3,031 | | | | 10,644 | | | | 17,080 | | | | 19,506 | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 67,452 | | | | 66,467 | | | | 102,437 | | | | 176,242 | | | | 309,291 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 37,596 | | | | 58,687 | | | | 99,352 | | | | 164,610 | | | | 246,308 | |
Real estate construction | | | 6,467 | | | | 27,302 | | | | 41,806 | | | | 94,929 | | | | 409,289 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 44,063 | | | | 85,989 | | | | 141,158 | | | | 259,539 | | | | 655,597 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 111,515 | | | | 152,456 | | | | 243,595 | | | | 435,781 | | | | 964,888 | |
Home equity revolving lines of credit(A) | | | 11,883 | | | | 20,446 | | | | 27,239 | | | | | | | | | |
Home equity loans first liens(A) | | | 6,135 | | | | 8,717 | | | | 7,452 | | | | | | | | | |
Home equity loans junior liens(A) | | | 7,149 | | | | 10,052 | | | | 12,216 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
Home equity(A) | | | 25,167 | | | | 39,215 | | | | 46,907 | | | | 51,712 | | | | 24,452 | |
Installment | | | 1,114 | | | | 1,838 | | | | 2,715 | | | | 10,544 | | | | 6,648 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 47,632 | | | | 59,359 | | | | 63,555 | | | | 76,319 | | | | 81,811 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 73,913 | | | | 100,412 | | | | 113,177 | | | | 138,575 | | | | 112,911 | |
| | | | |
Total nonaccrual loans | | | 185,428 | | | | 252,868 | | | | 356,772 | | | | 574,356 | | | | 1,077,799 | |
Commercial real estate owned | | | 8,359 | | | | 16,664 | | | | 24,795 | | | | 31,830 | | | | 52,468 | |
Residential real estate owned | | | 5,217 | | | | 12,748 | | | | 13,285 | | | | 9,090 | | | | 11,572 | |
Bank properties real estate owned | | | 4,542 | | | | 5,488 | | | | 3,491 | | | | 3,410 | | | | 4,401 | |
| | | | |
Other real estate owned | | | 18,118 | | | | 34,900 | | | | 41,571 | | | | 44,330 | | | | 68,441 | |
| | | | |
Total nonperforming assets | | $ | 203,546 | | | $ | 287,768 | | | $ | 398,343 | | | $ | 618,686 | | | $ | 1,146,240 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate & Real estate construction nonaccrual loans Detail: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Farmland | | $ | — | | | $ | 803 | | | $ | 1,907 | | | $ | 4,734 | | | $ | 1,524 | |
Multi-family | | | 3,782 | | | | 9,328 | | | | 7,909 | | | | 23,864 | | | | 17,867 | |
Non-owner occupied | | | 33,814 | | | | 48,556 | | | | 89,536 | | | | 136,012 | | | | 226,917 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | $ | 37,596 | | | $ | 58,687 | | | $ | 99,352 | | | $ | 164,610 | | | $ | 246,308 | |
| | | | |
1-4 family construction | | $ | 1,915 | | | $ | 16,639 | | | $ | 21,717 | | | $ | 23,963 | | | $ | 77,645 | |
All other construction | | | 4,552 | | | | 10,663 | | | | 20,089 | | | | 70,966 | | | | 331,644 | |
| | | | |
Real estate construction | | $ | 6,467 | | | $ | 27,302 | | | $ | 41,806 | | | $ | 94,929 | | | $ | 409,289 | |
| | | | |
| (A) | The break-down of home equity categories is not available for the years 2010 and 2009. |
52
TABLE 12: Delinquent (Past Due) Loans, Potential Problem Loans, Nonperforming Assets, and Other Real Estate Owned (continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | | | 2010 | | | 2009 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Accruing loans 30-89 days past due by type: | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 6,826 | | | $ | 11,339 | | | $ | 8,743 | | | $ | 33,013 | | | $ | 64,369 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 3,106 | | | | 11,053 | | | | 7,092 | | | | 9,295 | | | | 30,043 | |
Lease financing | | | — | | | | 12 | | | | 104 | | | | 132 | | | | 823 | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 9,932 | | | | 22,404 | | | | 15,939 | | | | 42,440 | | | | 95,235 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 23,215 | | | | 13,472 | | | | 4,970 | | | | 37,191 | | | | 51,932 | |
Real estate construction | | | 1,954 | | | | 3,155 | | | | 996 | | | | 8,016 | | | | 56,559 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 25,169 | | | | 16,627 | | | | 5,966 | | | | 45,207 | | | | 108,491 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 35,101 | | | | 39,031 | | | | 21,905 | | | | 87,647 | | | | 203,726 | |
Home equity revolving lines of credit(A) | | | 6,728 | | | | 7,829 | | | | 5,059 | | | | | | | | | |
Home equity loans first liens(A) | | | 1,110 | | | | 1,457 | | | | 2,890 | | | | | | | | | |
Home equity loans junior liens(A) | | | 2,842 | | | | 4,252 | | | | 4,240 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
Home equity(A) | | | 10,680 | | | | 13,538 | | | | 12,189 | | | | 13,886 | | | | 14,304 | |
Installment | | | 1,150 | | | | 2,109 | | | | 2,592 | | | | 9,624 | | | | 8,499 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 6,118 | | | | 9,403 | | | | 7,224 | | | | 8,722 | | | | 14,226 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 17,948 | | | | 25,050 | | | | 22,005 | | | | 32,232 | | | | 37,029 | |
| | | | |
Total accruing loans 30-89 days past due | | $ | 53,049 | | | $ | 64,081 | | | $ | 43,910 | | | $ | 119,879 | | | $ | 240,755 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate & real estate construction loans 30-89 days past due: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Farmland | | $ | — | | | $ | 101 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 47 | | | $ | 1,338 | |
Multi-family | | | 14,755 | | | | 1,901 | | | | 407 | | | | 2,758 | | | | 7,669 | |
Non-owner occupied | | | 8,460 | | | | 11,470 | | | | 4,563 | | | | 34,386 | | | | 42,925 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | $ | 23,215 | | | $ | 13,472 | | | $ | 4,970 | | | $ | 37,191 | | | $ | 51,932 | |
| | | | |
1-4 family construction | | $ | 987 | | | $ | 503 | | | $ | 475 | | | $ | 930 | | | $ | 38,555 | |
All other construction | | | 967 | | | | 2,652 | | | | 521 | | | | 7,086 | | | | 18,004 | |
| | | | |
Real estate construction | | $ | 1,954 | | | $ | 3,155 | | | $ | 996 | | | $ | 8,016 | | | $ | 56,559 | |
| | | | |
Potential problem loans by type: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 113,669 | | | $ | 128,434 | | | $ | 153,306 | | | $ | 354,284 | | | $ | 563,836 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 56,789 | | | | 99,592 | | | | 136,366 | | | | 193,819 | | | | 251,312 | |
Lease financing | | | 1,784 | | | | 264 | | | | 158 | | | | 2,617 | | | | 8,367 | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 172,242 | | | | 228,290 | | | | 289,830 | | | | 550,720 | | | | 823,515 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 52,429 | | | | 107,068 | | | | 230,206 | | | | 298,959 | | | | 346,825 | |
Real estate construction | | | 5,263 | | | | 13,092 | | | | 27,649 | | | | 91,618 | | | | 391,105 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 57,692 | | | | 120,160 | | | | 257,855 | | | | 390,577 | | | | 737,930 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 229,934 | | | | 348,450 | | | | 547,685 | | | | 941,297 | | | | 1,561,445 | |
Home equity revolving lines of credit(A) | | | 303 | | | | 520 | | | | 1,291 | | | | | | | | | |
Home equity loans first liens(A) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | | | | | |
Home equity loans junior liens(A) | | | 1,810 | | | | 3,150 | | | | 4,160 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
Home equity(A) | | | 2,113 | | | | 3,670 | | | | 5,451 | | | | 3,057 | | | | 13,400 | |
Installment | | | 50 | | | | 111 | | | | 233 | | | | 703 | | | | 1,524 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 3,312 | | | | 8,762 | | | | 13,037 | | | | 18,672 | | | | 19,150 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 5,475 | | | | 12,543 | | | | 18,721 | | | | 22,432 | | | | 34,074 | |
| | | | |
Total potential problem loans | | $ | 235,409 | | | $ | 360,993 | | | $ | 566,406 | | | $ | 963,729 | | | $ | 1,595,519 | |
| | | | |
53
Nonaccrual loans were $185 million at December 31, 2013, compared to $253 million at December 31, 2012. As shown in Table 12, total nonaccrual loans were down $68 million since year-end 2012, with commercial nonaccrual loans down $41 million and consumer-related nonaccrual loans down $27 million. The ratio of nonaccrual loans to total loans at the end of 2013 was 1.17%, as compared to 1.64% December 31, 2012. The ratio of the Corporation’s allowance for loan losses to nonaccrual loans was 145% at year-end 2013, up from 118% at year-end 2012.
Accruing Loans Past Due 90 Days or More
Loans past due 90 days or more but still accruing interest are classified as such where the underlying loans are both well secured (the collateral value is sufficient to cover principal and accrued interest) and are in the process of collection. At December 31, 2013 accruing loans 90 days or more past due totaled $2 million, relatively unchanged from December 31, 2012.
Troubled Debt Restructurings (“Restructured Loans”)
Loans are considered restructured loans if concessions have been granted to borrowers that are experiencing financial difficulty. The concessions granted generally involve the modification of terms of the loan, such as changes in payment structure or interest rate, which generally would not otherwise be considered. Restructured loans can involve loans remaining on nonaccrual, moving to nonaccrual, or continuing on accrual status, depending on the individual facts and circumstances of the borrower. Nonaccrual restructured loans are included and treated with all other nonaccrual loans. In addition, all accruing restructured loans are reported as troubled debt restructurings, which are considered and accounted for as impaired loans. Generally, restructured loans remain on nonaccrual until the customer has attained a sustained period of repayment performance under the modified loan terms (generally a minimum of six months). However, performance prior to the restructuring, or significant events that coincide with the restructuring, are considered in assessing whether the borrower can meet the new terms and whether the loan should be returned to or maintained on accrual status. If the borrower’s ability to meet the revised payment schedule is not reasonably assured, the loan remains on nonaccrual status.
At December 31, 2013, the Corporation had total restructured loans of $184 million (including $60 million classified as nonaccrual and $124 million performing in accordance with the modified terms), compared to $202 million at December 31, 2012 (including $81 million classified as nonaccrual and $121 million performing in accordance with the modified terms).
Potential Problem Loans
The level of potential problem loans is another predominant factor in determining the relative level of risk in the loan portfolio and in determining the appropriate level of the allowance for loan losses. Potential problem loans are generally defined by management to include loans rated as substandard by management but that are not considered impaired (i.e., nonaccrual loans and accruing troubled debt restructurings); however, there are circumstances present to create doubt as to the ability of the borrower to comply with present repayment terms. The decision of management to include performing loans in potential problem loans does not necessarily mean that the Corporation expects losses to occur, but that management recognizes a higher degree of risk associated with these loans. The loans that have been reported as potential problem loans are predominantly commercial loans covering a diverse range of businesses and real estate property types. At December 31, 2013, potential problem loans totaled $235 million, compared to $361 million at December 31, 2012. The $126 million decrease in potential problem loans since December 31, 2012, was primarily due to a $62 million decrease in commercial real estate lending and a $56 million decrease in commercial and business lending.
Other Real Estate Owned
Other real estate owned decreased to $18 million at December 31, 2013, compared to $35 million at December 31, 2012. Net gains on sales of other real estate owned were $1 million for 2013, while net losses on
54
sales of other real estate owned were $2 million in 2012. Write-downs on other real estate owned were $4 million and $8 million for 2013, and 2012, respectively. Management actively seeks to ensure properties held are monitored to minimize the Corporation’s risk of loss.
The following table shows, for those loans accounted for on a nonaccrual basis and restructured loans for the years ended as indicated, the approximate gross interest that would have been recorded if the loans had been current in accordance with their original terms and the amount of interest income that was included in interest income for the period.
TABLE 13: Foregone Loan Interest
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Interest income in accordance with original terms | | $ | 16,338 | | | $ | 24,644 | | | $ | 31,463 | |
Interest income recognized | | | (10,137 | ) | | | (11,726 | ) | | | (13,414 | ) |
| | | | |
Reduction in interest income | | $ | 6,201 | | | $ | 12,918 | | | $ | 18,049 | |
| | | | |
Investment Securities Portfolio
The investment securities portfolio is intended to provide the Corporation with adequate liquidity, flexibility in asset / liability management, a source of stable income, and is structured with minimal credit exposure to the Corporation. At the time of purchase, the Corporation classifies its investment purchases as available for sale or held to maturity, consistent with these investment objectives, including possible securities sales in response to changes in interest rates or prepayment risk, the need to manage liquidity or regulatory capital, and other factors. Investment securities classified as available for sale are carried at fair value in the consolidated balance sheet, while investment securities classified as held to maturity are shown at amortized cost in the consolidated balance sheet.
At December 31, 2013, the Corporation’s investment securities portfolio did not contain securities of any single issuer that were payable from and secured by the same source of revenue or taxing authority where the aggregate carrying value of such securities exceeded 5% of stockholders’ equity or approximately $145 million.
The Corporation did not recognize any credit-related other-than-temporary impairment write-downs during 2013 or 2012. See Note 1, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” and Note 2, “Investment Securities,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements for additional information.
The Volcker Rule prohibits insured depository institutions and their holding companies from engaging in proprietary trading except in limited circumstances, and prohibits them from owning equity interests in excess of three percent of Tier 1 Capital in private equity and hedge funds. The Volcker Rule will not have a material impact on the Corporation’s investment securities portfolio. See Part I, Item 1, “Business,” for additional information on the Volcker Rule.
55
TABLE 14: Investment Securities Portfolio
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | At December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | % of Total | | | 2012 | | | % of Total | | | 2011 | | | % of Total | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Investment Securities Available for Sale: | | | | |
Amortized Cost: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. Treasury securities | | $ | 1,001 | | | | <1 | % | | $ | 1,003 | | | | <1 | % | | $ | 1,000 | | | | <1 | % |
Federal agency securities | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 24,031 | | | | 1 | |
Obligations of state and political subdivisions | | | 653,758 | | | | 12 | | | | 755,644 | | | | 16 | | | | 797,691 | | | | 17 | |
Residential mortgage-related securities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Government-sponsored enterprise (“GSE”) | | | 3,855,467 | | | | 73 | | | | 3,708,287 | | | | 77 | | | | 3,633,803 | | | | 76 | |
Private-label | | | 3,035 | | | | <1 | | | | 6,002 | | | | <1 | | | | 40,893 | | | | 1 | |
GSE commercial mortgage-related securities | | | 673,555 | | | | 13 | | | | 226,420 | | | | 5 | | | | 16,647 | | | | <1 | |
Asset-backed securities | | | 23,049 | | | | <1 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 188,439 | | | | 4 | |
Other securities (debt and equity) | | | 60,711 | | | | 1 | | | | 90,622 | | | | 2 | | | | 72,896 | | | | 1 | |
| | | | |
Total amortized cost | | $ | 5,270,576 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 4,787,978 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 4,775,400 | | | | 100 | % |
| | | | |
Fair Value: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. Treasury securities | | $ | 1,002 | | | | <1 | % | | $ | 1,004 | | | | <1 | % | | $ | 1,001 | | | | <1 | % |
Federal agency securities | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 24,049 | | | | 1 | |
Obligations of state and political subdivisions | | | 676,080 | | | | 13 | | | | 801,188 | | | | 16 | | | | 847,246 | | | | 17 | |
Residential mortgage-related securities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
GSE | | | 3,838,430 | | | | 73 | | | | 3,798,155 | | | | 77 | | | | 3,745,816 | | | | 77 | |
Private-label | | | 3,014 | | | | <1 | | | | 6,149 | | | | <1 | | | | 39,774 | | | | — | |
GSE commercial mortgage-related securities | | | 647,477 | | | | 12 | | | | 228,166 | | | | 5 | | | | 18,543 | | | | <1 | |
Asset-backed securities | | | 23,059 | | | | <1 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 187,732 | | | | 4 | |
Other securities (debt and equity) | | | 61,523 | | | | 1 | | | | 92,096 | | | | 2 | | | | 73,322 | | | | 1 | |
| | | | |
Total fair value and carrying value | | $ | 5,250,585 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 4,926,758 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 4,937,483 | | | | 100 | % |
| | | | |
Net unrealized holding gains (losses) | | $ | (19,991 | ) | | | | | | $ | 138,780 | | | | | | | $ | 162,083 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Investment Securities Held to maturity: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Amortized Cost: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Obligations of state and political subdivisions | | $ | 175,210 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 39,877 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | — | | | | — | % |
| | | | |
Total amortized cost and carrying value | | $ | 175,210 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 39,877 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | — | | | | — | % |
| | | | |
Fair Value: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Obligations of state and political subdivisions | | $ | 169,889 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 39,679 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | — | | | | — | % |
| | | | |
Total fair value | | $ | 169,889 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 39,679 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | — | | | | — | % |
| | | | |
Net unrealized holding losses | | $ | (5,321 | ) | | | | | | $ | (198 | ) | | | | | | $ | — | | | | | |
| | | | |
56
Available for Sale
At December 31, 2013, the total carrying value of investment securities available for sale was $5.3 billion, up $324 million from December 31, 2012, and represented 22% of total assets, compared to 21% of total assets at December 31, 2012. On average, the investment securities available for sale portfolio was $4.9 billion for 2013, up $446 million (10%) compared to 2012, and represented 23% of average earning assets for both 2013 and 2012.
Obligations of State and Political Subdivisions (Municipal Securities): At December 31, 2013 and 2012, municipal securities were $676 million and $801 million, and represented 13% and 16%, respectively, of total investment securities based on fair value. Municipal bond insurance company downgrades have resulted in credit downgrades in certain municipal securities; however, due to the large number of small investments in these obligations (general obligation, essential services, etc.) the loss exposure on any particular obligation is mitigated. As of December 31, 2013, the total fair value of municipal securities reflected a net unrealized gain of approximately $22 million.
Residential and Commercial Mortgage-related Securities: At both December 31, 2013 and 2012, residential mortgage-related securities (which include predominantly GSE mortgage-backed securities and collateralized mortgage obligations (“CMOs”)) were $3.8 billion and represented 73% and 77%, respectively, of total investment securities based on fair value, while at December 31, 2013 GSE commercial mortgage-related securities were $647 million and represented 12% of total investment securities compared to $228 million and 5% of total investment securities at December 31, 2012. The fair value of mortgage-related securities is subject to inherent risks based upon the future performance of the underlying collateral (i.e. mortgage loans) for these securities, such as prepayment risk and interest rate changes. The Corporation regularly assesses valuation and credit quality underlying these securities.
Asset-backed Securities: Asset-backed securities are largely comprised of senior, floating rate, tranches of student loan securities issued by SLM Corp and guaranteed under the Federal Family Education Loan Program. At December 31, 2013, the asset-backed securities totaled $23 million.
Other Securities (Debt and Equity): At December 31, 2013 and 2012, other securities were $62 million and $92 million, respectively, and were primarily comprised of debt securities. Debt securities primarily include corporate bonds which mature within 3 years and a rating of A or AA, while equity securities include preferred and common equity securities.
Held to Maturity
At December 31, 2013, the total carrying value of investment securities held to maturity was $175 million, an increase of $135 million from December 31, 2012. During the third quarter of 2012, the Corporation began reinvesting the proceeds from the maturities of available for sale municipal securities into purchases of held to maturity municipal securities in anticipation of the new Basel III requirements.
Regulatory Stock
In addition to the available for sale and held to maturity investment securities noted above, the Corporation is also required to hold certain regulatory stock. The Corporation is required to maintain Federal Reserve stock and Federal Home Loan Bank (“FHLB”) stock as a member of both the Federal Reserve System and the FHLB, and in amounts as required by these institutions. At December 31, 2013, and 2012, the Corporation had FHLB stock of $110 million and $96 million, respectively. The Corporation had Federal Reserve Bank stock of $71 million at both December 31, 2013 and 2012.
57
TABLE 15: Investment Securities Portfolio Maturity Distribution (1) — December 31 2013
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Investment Securities Available for Sale - Maturity Distribution and Weighted Average Yield | |
| | | Within one year | | | After one but
within five years | | | After five but
within ten years | | | After ten years | | | Mortgage-related
and equity
securities | | | Total
Amortized Cost | | | Total
Fair Value | |
| | | Amount | | | Yield | | | Amount | | | Yield | | | Amount | | | Yield | | | Amount | | | Yield | | | Amount | | | Yield | | | Amount | | | Yield | | | Amount | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
U. S. Treasury securities | | $ | 1,001 | | | | 0.30 | % | | $ | — | | | | 0.00 | % | | $ | — | | | | — | | | $ | — | | | | — | | | $ | — | | | | — | | | $ | 1,001 | | | | 0.30 | % | | $ | 1,002 | |
Obligations of states and political subdivisions(2) | | | 11,711 | | | | 6.02 | % | | | 189,750 | | | | 5.63 | % | | | 429,242 | | | | 5.34 | % | | | 23,055 | | | | 6.00 | % | | | — | | | | — | | | | 653,758 | | | | 5.46 | % | | | 676,080 | |
Other debt securities | | | 18,692 | | | | 0.83 | % | | | 42,001 | | | | 1.98 | % | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 0.00 | % | | | — | | | | — | | | | 60,693 | | | | 1.63 | % | | | 61,466 | |
Residential mortgage-related securities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
GSE | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 3,855,467 | | | | 2.60 | % | | | 3,855,467 | | | | 2.60 | % | | | 3,838,430 | |
Private-label | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 3,035 | | | | 3.00 | % | | | 3,035 | | | | 3.00 | % | | | 3,014 | |
GSE commercial mortgage-related securities | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 673,555 | | | | 2.10 | % | | | 673,555 | | | | 2.10 | % | | | 647,477 | |
Asset-backed securities | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 23,049 | | | | 0.56 | % | | | 23,049 | | | | 0.56 | % | | | 23,059 | |
Other equity securities | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 18 | | | | 0.00 | % | | | 18 | | | | 0.00 | % | | | 57 | |
| | | | |
Total amortized cost | | $ | 31,404 | | | | 2.75 | % | | $ | 231,751 | | | | 4.97 | % | | $ | 429,242 | | | | 5.34 | % | | $ | 23,055 | | | | 6.00 | % | | $ | 4,555,124 | | | | 2.52 | % | | $ | 5,270,576 | | | | 2.87 | % | | $ | 5,250,585 | |
| | | | |
Total fair value and carrying value | | $ | 31,503 | | | | | | | $ | 240,398 | | | | | | | $ | 441,137 | | | | | | | $ | 25,510 | | | | | | | $ | 4,512,037 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 5,250,585 | |
| | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Investment Securities Held to Maturity - Maturity Distribution and Weighted Average Yield | |
| | | Within one year | | | After one but
within five years | | | After five but
within ten years | | | After ten years | | | Mortgage-related
and equity
securities | | | Total
Amortized Cost | | | Total
Fair Value | |
| | | Amount | | | Yield | | | Amount | | | Yield | | | Amount | | | Yield | | | Amount | | | Yield | | | Amount | | | Yield | | | Amount | | | Yield | | | Amount | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Obligations of states and political subdivisions(2) | | $ | — | | | | — | | | $ | 232 | | | | 1.99 | % | | $ | 68,394 | | | | 3.49 | % | | $ | 106,584 | | | | 4.32 | % | | $ | — | | | | — | | | $ | 175,210 | | | | 3.99 | % | | $ | 169,889 | |
| | | | |
Total amortized cost and carrying value | | $ | — | | | | — | | | $ | 232 | | | | 1.99 | % | | $ | 68,394 | | | | 3.49 | % | | $ | 106,584 | | | | 4.32 | % | | $ | — | | | | — | | | $ | 175,210 | | | | 3.99 | % | | $ | 169,889 | |
| | | | |
Total fair value | | $ | — | | | | | | | $ | 233 | | | | | | | $ | 66,100 | | | | | | | $ | 103,556 | | | | | | | $ | — | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 169,889 | |
| | | | |
| (1) | Expected maturities will differ from contractual maturities, as borrowers may have the right to call or repay obligations with or without call or prepayment penalties. |
| (2) | Yields on tax-exempt securities are computed on a taxable equivalent basis using a tax rate of 35% and have not been adjusted for certain disallowed interest deductions. |
Deposits
Deposits are the Corporation’s largest source of funds. Selected period-end deposit information is detailed in Note 6, “Deposits,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements, including a maturity distribution of all time deposits at December 31, 2013. A maturity distribution of certificates of deposits and other time deposits of $100,000 or more at December 31, 2013 is shown in Table 17. Table 16 summarizes the distribution of average deposit balances. See also section “Liquidity.”
The Corporation competes with other bank and nonbank institutions for deposits, as well as with a growing number of non-deposit investment alternatives available to depositors, such as mutual funds, money market funds, annuities, and other brokerage investment products. Competition for deposits remains high. Challenges to deposit growth include a usual cyclical decline in deposits historically experienced during the first quarter (noted as a challenge since the return of deposit balances may not be timely or by as much as the outflow), price changes on deposit products given movements in the rate environment and other competitive pricing pressures, and customers choosing higher-cost deposit products or non-deposit investment alternatives.
58
At December 31, 2013, deposits were $17.3 billion, up $327 million or 2% from December 31, 2012. The increase in total deposits included a $388 million increase in money market deposits and a $335 million increase in interest-bearing demand deposits, offset by a $337 million decrease in other time deposits. Average deposit balances were $17.4 billion for 2013, up $1.9 billion or 12% from 2012. Similar to period end deposits, the increase in average deposits included a $1.2 billion increase in money market deposits (growing to represent 42% of average deposits for 2013 compared to 39% for 2012) and a $679 million increase in average interest-bearing demand deposits (representing 16% of average deposits for 2013 compared to 14% for 2012), offset by a $390 million decrease in time deposits (declining to 11% of average total deposits in 2013 versus 15% of average total deposits in 2012).
TABLE 16: Average Deposits Distribution
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
| | | Amount | | | % of Total | | | Amount | | | % of Total | | | Amount | | | % of Total | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Noninterest-bearing demand deposits | | $ | 4,249,313 | | | | 24 | % | | $ | 3,948,846 | | | | 25 | % | | $ | 3,381,128 | | | | 23 | % |
Savings deposits | | | 1,188,910 | | | | 7 | % | | | 1,096,692 | | | | 7 | % | | | 987,198 | | | | 7 | % |
Interest-bearing demand deposits | | | 2,827,778 | | | | 16 | % | | | 2,148,459 | | | | 14 | % | | | 1,947,506 | | | | 14 | % |
Money market deposits | | | 7,322,476 | | | | 42 | % | | | 6,148,663 | | | | 39 | % | | | 5,147,437 | | | | 36 | % |
Time deposits | | | 1,849,718 | | | | 11 | % | | | 2,239,709 | | | | 15 | % | | | 2,937,858 | | | | 20 | % |
| | | | |
Total deposits | | | 17,438,195 | | | | 100 | % | | | 15,582,369 | | | | 100 | % | | | 14,401,127 | | | | 100 | % |
Customer repo sweeps | | | 549,029 | | | | | | | | 624,351 | | | | | | | | 860,831 | | | | | |
Customer repo term | | | 16,193 | | | | | | | | 430,264 | | | | | | | | 932,844 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Total customer funding | | | 565,222 | | | | | | | | 1,054,615 | | | | | | | | 1,793,675 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Total deposits and customer funding | | $ | 18,003,417 | | | | | | | $ | 16,636,984 | | | | | | | $ | 16,194,802 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Network transaction deposits included above in interest-bearing demand and money market | | $ | 2,094,984 | | | | | | | $ | 1,343,595 | | | | | | | $ | 952,825 | | | | | |
Brokered certificates of deposit | | | 55,045 | | | | | | | | 55,574 | | | | | | | | 290,226 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Total network and brokered funding | | $ | 2,150,029 | | | | | | | $ | 1,399,169 | | | | | | | $ | 1,243,051 | | | | | |
| | | | |
Net customer deposits and funding | | $ | 15,853,388 | | | | | | | $ | 15,237,815 | | | | | | | $ | 14,951,751 | | | | | |
| | | | |
TABLE 17: Maturity Distribution-Certificates of Deposit and Other Time Deposits of $100,000 or More
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2013 | |
| | | Certificates
of Deposit | | | Other
Time Deposits | | | Total Certificates
of Deposits and Other
Time Deposits | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Three months or less | | $ | 116,706 | | | $ | 34,635 | | | $ | 151,341 | |
Over three months through six months | | | 45,406 | | | | 23,092 | | | | 68,498 | |
Over six months through twelve months | | | 75,319 | | | | 40,195 | | | | 115,514 | |
Over twelve months | | | 101,977 | | | | 40,368 | | | | 142,345 | |
| | | | |
Total | | $ | 339,408 | | | $ | 138,290 | | | $ | 477,698 | |
| | | | |
Other Funding Sources
Other funding sources, including short-term and long-term funding, were $3.8 billion at December 31, 2013 and $3.3 billion at December 31, 2012. See also section “Liquidity.” Long-term funding at December 31, 2013, was $3.1 billion, an increase of $2.1 billion from December 31, 2012. The increase in long-term funding was
59
primarily attributable to the borrowing of $2.5 billion of five year, putable, variable rate FHLB advances, as the Corporation took advantage of favorable interest rates, partially offset by the maturity of $400 million in fixed rate FHLB advances during the first half of 2013. See Note 8, “Long-term Funding,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements for additional information on long-term funding.
Short-term funding is comprised primarily of short-term FHLB advances; securities sold under agreements to repurchase; Federal funds purchased and commercial paper. Short-term funding sources at December 31, 2013 were $741 million, $1.6 billion lower than December 31, 2012. The decrease in short-term funding was primarily due to a $1.3 billion reduction in FHLB advances as the Corporation took advantage of favorable interest rates on long-term FHLB advances, reducing the need for short-term funding. Many short-term funding sources, particularly Federal funds purchased and securities sold under agreements to repurchase, are expected to be reissued and, therefore, do not represent an immediate need for cash. See Note 7, “Short-term Funding,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements for additional information on short-term funding, and Table 18 for specific disclosures required for major short-term funding categories.
On average, short and long-term funding totaled $2.8 billion for 2013, down $496 million or 15% from 2012, including a $239 million decrease in short-term funding and a $257 million decrease in long-term funding. Within the short-term funding categories, average federal funds purchased and securities sold under agreements to repurchase decreased $501 million, while average short-term FHLB advances increased $212 million. Key changes within average long-term funding included a $201 million decrease in FHLB advances and a $157 million decrease in junior subordinated debentures (related to the early retirement of trust preferred securities and the related junior subordinated debentures during 2012), partially offset by a $107 million increase in average senior notes.
TABLE 18: Short-Term Funding
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Securities sold under agreements to repurchase: | | | | |
Balance end of year | | $ | 419,247 | | | $ | 679,070 | | | $ | 1,359,755 | |
Average amounts outstanding during year | | | 565,222 | | | | 1,054,614 | | | | 1,793,675 | |
Maximum month-end amounts outstanding | | | 662,477 | | | | 1,212,100 | | | | 2,078,038 | |
Average interest rates on amounts outstanding at end of year | | | 0.18 | % | | | 0.24 | % | | | 0.28 | % |
Average interest rates on amounts outstanding during year | | | 0.21 | % | | | 0.24 | % | | | 0.34 | % |
FHLB advances | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance end of year | | $ | 200,000 | | | $ | 1,525,000 | | | $ | 1,000,000 | |
Average amounts outstanding during year | | | 1,131,384 | | | | 918,962 | | | | 751,370 | |
Maximum month-end amounts outstanding | | | 2,150,000 | | | | 1,575,000 | | | | 1,150,000 | |
Average interest rates on amounts outstanding at end of year | | | 0.11 | % | | | 0.07 | % | | | 0.36 | % |
Average interest rates on amounts outstanding during year | | | 0.11 | % | | | 0.35 | % | | | 0.83 | % |
Liquidity
The objective of liquidity management is to ensure that the Corporation has the ability to generate sufficient cash or cash equivalents in a timely and cost-effective manner to satisfy the cash flow requirements of depositors and borrowers and to meet its other commitments as they fall due, including the ability to pay dividends to shareholders, service debt, invest in subsidiaries or acquisitions, and satisfy other operating requirements. In addition to satisfying cash flow requirements in the ordinary course of business, the Corporation actively monitors and manages its liquidity position to ensure sufficient resources are available to meet cash flow requirements in adverse situations.
60
The Corporation’s internal liquidity management framework includes measurement of several key elements, such as deposit funding as a percent of total assets and liquid asset levels. Strong capital ratios, credit quality, and core earnings are essential to maintaining cost-effective access to wholesale funding markets. A downgrade or loss in credit ratings could have an impact on the Corporation’s ability to access wholesale funding at favorable interest rates. In addition to static liquidity measures, the Corporation performs dynamic scenario analysis in accordance with industry best practices. Measures have been established to ensure the Corporation has sufficient high quality short-term liquidity to meet cash flow requirements under stressed scenarios. At December 31, 2013, the Corporation was in compliance with its internal liquidity objectives.
While core deposits and loan and investment securities repayments are principal sources of liquidity, funding diversification is another key element of liquidity management. Diversity is achieved by strategically varying depositor type, term, funding market, and instrument. The Parent Company and its subsidiary bank are rated by Moody’s, Standard and Poor’s (“S&P”), Fitch Investors (“Fitch”), and Dominion Bond Rating Service (“DBRS”). Credit ratings by these nationally recognized statistical rating agencies are an important component of the Corporation’s liquidity profile. Credit ratings relate to the Corporation’s ability to issue debt securities and the cost to borrow money, and should not be viewed as an indication of future stock performance or a recommendation to buy, sell, or hold securities. Among other factors, the credit ratings are based on financial strength, credit quality and concentrations in the loan portfolio, the level and volatility of earnings, capital adequacy, the quality of management, the liquidity of the balance sheet, the availability of a significant base of core deposits, and the Corporation’s ability to access a broad array of wholesale funding sources. Adverse changes in these factors could result in a negative change in credit ratings and impact not only the ability to raise funds in the capital markets but also the cost of these funds. Ratings are subject to revision or withdrawal at any time and each rating should be evaluated independently. The senior credit ratings of the Parent Company and its subsidiary bank are displayed below.
TABLE 19: Credit Ratings
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2013 | |
| | | Moody’s | | | S&P | | | Fitch | | | DBRS | |
Bank short-term deposits | | | P2 | | | | — | | | | F2 | | | | R2H | |
Bank long-term | | | A3 | | | | BBB+ | | | | BBB- | | | | BBBH | |
Corporation short-term | | | P2 | | | | — | | | | F3 | | | | R2M | |
Corporation long-term | | | Baa1 | | | | BBB | | | | BBB- | | | | BBB | |
Outlook | | | Stable | | | | Stable | | | | POS | | | | Stable | |
The Corporation also has multiple funding sources that could be used to increase liquidity and provide additional financial flexibility. The Parent Company filed a “shelf” registration in January 2012, under which the Parent Company may offer any combination of the following securities, either separately or in units: debt securities, preferred stock, depositary shares, common stock, and warrants. In September 2012, the Corporation issued $155 million of senior notes due in March 2014 which bear a 1.875% fixed coupon. The Corporation has called the 2012 senior notes for redemption, at par plus accrued interest, in February 2014. The Parent Company also has a $200 million commercial paper program, of which, $65 million was outstanding at December 31, 2013.
While dividends and service fees from subsidiaries and proceeds from issuance of capital are primary funding sources for the Parent Company, these sources could be limited or costly (such as by regulation or subject to the capital needs of its subsidiaries or by market appetite for bank holding company stock). The Parent Company received dividends of $262 million during 2013 from subsidiaries. See Note 18, “Regulatory Matters,” for additional information on regulatory requirements for the Bank.
The Bank has established federal funds lines with counterparty banks and has the ability to borrow from the Federal Home Loan Bank ($2.7 billion of Federal Home Loan Bank advances were outstanding at December 31, 2013). The Bank also has significant excess loan and investment securities collateral which could be pledged to
61
secure additional deposits or to counterparty banks, the Federal Home Loan Bank or other parties as necessary. Associated Bank may also issue institutional certificates of deposit, network transaction deposits, and brokered certificates of deposit.
Investment securities are an important tool to the Corporation’s liquidity objective. As of December 31, 2013, the majority of the investment securities are classified as available for sale, with only a portion of municipal securities (less than 25%) classified as held to maturity. Of the $5.4 billion investment securities portfolio at December 31, 2013, a portion of these securities were pledged to secure collateralized deposits and repurchase agreements and for other purposes as required or permitted by law. The majority of the remaining investment securities of $2.5 billion could be pledged or sold to enhance liquidity, if necessary.
As reflected in Table 20, the Corporation has various financial obligations, including contractual obligations and other commitments, which may require future cash payments. The time deposits with shorter maturities could imply near-term liquidity risk if such deposit balances do not rollover at maturity into new time or non-time deposits at the Corporation. As evidenced in Table 16, average time deposits were 11% of total average deposits for 2013, compared to 15% of total average deposits for 2012. Many short-term borrowings, also shown in Table 20, particularly Federal funds purchased and securities sold under agreements to repurchase, can be reissued and, therefore, do not represent an immediate need for cash. See additional discussion in sections, “Net Interest Income,” “Investment Securities Portfolio,” and “Interest Rate Risk,” and in Note 2, “Investment Securities,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements. As a financial services provider, the Corporation routinely enters into commitments to extend credit. While contractual obligations represent future cash requirements of the Corporation, a significant portion of commitments to extend credit may expire without being drawn upon.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, net cash provided by operating and financing activities was $487 million and $630 million, respectively, while investing activities used net cash of $1.3 billion, for a net decrease in cash and cash equivalents of $136 million since year-end 2012. Generally, during 2013, net assets increased to $24.2 billion (up $739 million or 3%) compared to year-end 2012, primarily due to a $485 million increase in loans and a $459 million increase in investments. On the funding side, deposits increased $327 million and long-term funding increased $2.1 billion, partially offset by a decrease of $1.6 billion in short-term funding.
For the year ended December 31, 2012, net cash provided by operating activities and financing activities was $350 million and $1.4 billion, respectively, while investing activities used net cash of $1.6 billion, for a net increase in cash and cash equivalents of $121 million since year-end 2011. Generally, during 2012, net assets increased to $23.5 billion (up $1.6 billion or 7%) compared to year-end 2011, primarily due to a $1.4 billion increase in loans. On the funding side, deposits increased $1.8 billion while short-term funding decreased $188 million and long-term funding decreased $162 million.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
Market risk and interest rate risk are managed centrally. Market risk is the potential for loss arising from adverse changes in the fair value of fixed income securities, equity securities, other earning assets and derivative financial instruments as a result of changes in interest rates or other factors. Interest rate risk is the potential for reduced net interest income resulting from adverse changes in the level of interest rates. As a financial institution that engages in transactions involving an array of financial products, the Corporation is exposed to both market risk and interest rate risk. In addition to market risk, interest rate risk is measured and managed through a number of methods. The Corporation uses financial modeling simulation techniques that measure the sensitivity of future earnings due to changing rate environments to measure interest rate risk.
Policies established by the Corporation’s Asset / Liability Committee (“ALCO”) and approved by the Board of Directors are intended to limit these risks. The Board has delegated day-to-day responsibility for managing market and interest rate risk to ALCO. The primary objectives of market risk management is to minimize any adverse effect that changes in market risk factors may have on net interest income and to offset the risk of price changes for certain assets recorded at fair value.
62
Interest Rate Risk
In order to measure earnings sensitivity to changing market interest rates, the Corporation uses a simulation model to measure the impact of various interest rate shocks and other yield curve scenarios on earnings and the fair value of the financial assets and liabilities of the Corporation. The Corporation compares earnings between a static balance sheet scenario and balance sheets with projected growth scenarios to quantify the potential impact on such earnings of various balance sheet management and business strategies.
Simulation of earnings: Determining the sensitivity of short-term future earnings is accomplished through the use of simulation modeling. Assumptions involving projected balance sheet growth, market spreads, prepayments of rate-sensitive instruments, and the cash flows from maturing assets and liabilities are incorporated in these simulation analyses. These analyses are designed to project net interest income based on various interest rate scenarios, compared to a baseline scenario. The Corporation runs numerous scenarios including instantaneous and gradual changes to market interest rates as well as yield curve slope changes. It then compares such scenarios to the baseline scenario to quantify its earnings sensitivity.
The resulting simulations for December 31, 2013, and December 31, 2012 projected that net interest income would increase by approximately 0.4% and 3.4%, respectively, if rates rose instantaneously by a 100 bp shock and projected that net interest income would increase by approximately 0.9% and 6.8%, respectively, if rates rose instantaneously by a 200 bp shock. As of December 31, 2013, the simulations of earnings results were within the limits of the Corporation’s interest rate risk policy.
Market value of equity: The Corporation uses the market value of equity as a measure to quantify market risk from the impact of interest rates. The market value of equity is the fair value of assets, liabilities, and off-balance sheet financial instruments derived from the present value of the future cash flows. While the net interest income simulation model highlights exposures over a short time horizon, the market value of equity incorporates all cash flows over all of the balance sheet and derivative positions.
These results are based on multiple path simulations using an interest rate simulation model calibrated to market traded instruments. Sensitivities are measured assuming several factors including immediate and sustained parallel and non-parallel changes in market rates, yield curves and rate indexes. These factors quantify yield curve risk, basis risk, options risk, repricing mismatch risk, and market spread risk. The results are considered to be conservative estimates due to the fact that no management action to mitigate potential income variances is included within the simulation assumption set. These potentially mitigating factors include future balance sheet growth, changes in yield curve relationships, and changing product spreads. As of December 31, 2013, the projected changes for the market value of equity were within the limits of the Corporation’s interest rate risk policy.
The Corporation provides derivative products to commercial customers who use them to manage their own interest rate risk profiles. The Corporation’s market risk from unfavorable movements in interest rates related to these derivative products is hedged by concurrently entering into offsetting derivative contracts. The offsetting derivative contracts have identical notional values, terms, and indices. Derivative financial instruments are further discussed in Note 13, “Derivative and Hedging Activities,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements.
Contractual Obligations, Commitments, Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements, and Contingent Liabilities
Through the normal course of operations, the Corporation has entered into certain contractual obligations and other commitments, including but not limited to those most usually related to funding of operations through deposits or funding, commitments to extend credit, derivative contracts to assist management of interest rate exposure, and to a lesser degree leases for premises and equipment. Table 20 summarizes significant contractual obligations and other commitments at December 31, 2013, at those amounts contractually due to the recipient, including any unamortized premiums or discounts, hedge basis adjustments, or other similar carrying value adjustments. Further discussion of the nature of each obligation is included in the referenced note to the consolidated financial statements.
63
Table 20: Contractual Obligations and Other Commitments
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2013 | | Note
Reference | | | One Year
or Less | | | One to
Three Years | | | Three to
Five Years | | | Over
Five Years | | | Total | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Time deposits | | | 6 | | | $ | 1,155,159 | | | $ | 335,907 | | | $ | 179,845 | | | $ | 14,285 | | | $ | 1,685,196 | |
Short-term funding | | | 7 | | | | 740,926 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 740,926 | |
Long-term funding | | | 8 | | | | 155,001 | | | | 431,974 | | | | 2,500,067 | | | | 225 | | | | 3,087,267 | |
Operating leases | | | 5 | | | | 10,699 | | | | 21,505 | | | | 17,759 | | | | 33,206 | | | | 83,169 | |
Commitments to extend credit | | | 15 | | | | 3,783,255 | | | | 1,478,750 | | | | 1,099,770 | | | | 108,221 | | | | 6,469,996 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total | | | | | | $ | 5,845,040 | | | $ | 2,268,136 | | | $ | 3,797,441 | | | $ | 155,937 | | | $ | 12,066,554 | |
| | | | | | | | |
The Corporation also has obligations under its retirement plans as described in Note 11, “Retirement Plans,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements. To a lesser degree, the Corporation also has commitments to fund various investments and other projects as discussed further in Note 15, “Commitments, Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements, and Contingent Liabilities,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements.
As of December 31, 2013, the net liability for uncertain tax positions, including associated interest and penalties, was $6 million. This liability represents an estimate of tax positions that the Corporation has taken in its tax returns which may ultimately not be sustained upon examination by the tax authorities. Since the ultimate amount and timing of any future cash settlements cannot be predicted with reasonable certainty, this estimated liability has been excluded from Table 20. See Note 12, “Income Taxes,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements for additional information and disclosure related to uncertain tax positions.
The Corporation may have a variety of financial transactions that, under generally accepted accounting principles, are either not recorded on the balance sheet or are recorded on the balance sheet in amounts that differ from the full contract or notional amounts.
The Corporation routinely enters into lending-related commitments, including commitments to extend credit, interest rate lock commitments to originate residential mortgage loans held for sale (discussed further below), commercial letters of credit, and standby letters of credit. Commitments to extend credit are agreements to lend to customers at predetermined interest rates. The Corporation has $6.5 billion of outstanding commitments to extend credit (see Table 20) at December 31, 2013. In addition, the Corporation had a reserve for losses on unfunded loan and letters of credit commitments totaling $22 million at December 31, 2013. Commercial and standby letters of credit are conditional commitments issued to guarantee the performance of a customer to a third party. At December 31, 2013, the Corporation had $133 million and $250 million of commercial and standby letters of credit, respectively. Since most of these commitments, as well as commitments to extend credit, are expected to expire without being drawn upon, the total commitment amounts do not necessarily represent future cash requirements. See section, “Liquidity” and Note 15, “Commitments, Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements, and Contingent Liabilities,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements for further information.
The Corporation’s derivative interest rate-related instruments, under which the Corporation is required to either receive cash from or pay cash to counterparties depending on changes in interest rates applied to notional amounts, are carried at fair value on the consolidated balance sheet. Because neither the derivative assets and liabilities, nor their notional amounts, represent the amounts that may ultimately be paid under these contracts, they are not included in Table 20. The Corporation’s mortgage derivatives included $102 million of interest rate lock commitments to originate residential mortgage loans held for sale (included in Table 20 as part of commitments to extend credit) and forward commitments to sell $135 million of residential mortgage loans to various investors as of December 31, 2013. For further information and discussion of derivative contracts, see section “Interest Rate Risk,” and Note 1, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” and Note 13, “Derivative and Hedging Activities,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements.
64
The Corporation sells residential mortgage loans to investors in the normal course of business. Residential mortgage loans sold to others are predominantly conventional residential first lien mortgages originated under our usual underwriting procedures, and are most often sold on a nonrecourse basis, primarily to the GSEs. The Corporation’s agreements to sell residential mortgage loans in the normal course of business usually require certain representations and warranties on the underlying loans sold. At December 31, 2013, the Corporation had a repurchase reserve for potential claims on loans previously sold of $6 million. The Corporation may also sell residential mortgage loans with limited recourse (limited in that the recourse period ends prior to the loan’s maturity, usually after certain time and / or loan paydown criteria have been met). At December 31, 2013, there were approximately $56 million of residential mortgage loans sold with limited recourse risk. See Note 15, “Commitments, Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements, and Contingent Liabilities,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements for additional information on residential mortgage loans sold.
The Corporation has a subordinate position to the FHLB in the credit risk on residential mortgage loans it sold to the FHLB in exchange for a monthly credit enhancement fee. The Corporation has not sold loans to the FHLB with such credit risk retention since February 2005. At December 31, 2013, there were $233 million of such residential mortgage loans with credit risk recourse, upon which there have been negligible historical losses to the Corporation.
The Corporation has principal investment commitments to provide capital-based financing to private and public companies through either direct investments in specific companies or through investment funds and partnerships. The Corporation also invests in low-income housing, small-business commercial real estate, new market tax credit projects, and historic tax credit projects to promote the revitalization of low-to-moderate-income neighborhoods throughout the local communities of its bank subsidiary. The aggregate carrying value of these investments at December 31, 2013, was $33 million, included in other assets on the consolidated balance sheets. Related to these investments, the Corporation had remaining commitments to fund of $16 million at December 31, 2013. See Note 15, “Commitments, Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements, and Contingent Liabilities,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements for additional information on these investments. The Volcker Rule prohibits insured depository institutions and their holding companies from engaging in proprietary trading except in limited circumstances, and prohibits them from owning equity interests in excess of three percent of Tier 1 capital in private equity and hedge funds. The Volcker Rule will not have a material impact on the Corporation’s investments in such funds. See Part I, Item 1, “Business,” for additional information on the Volcker Rule.
Capital
Stockholders’ equity at December 31, 2013 was $2.9 billion, down slightly ($45 million) from December 31, 2012. Stockholders’ equity is also described in Note 9, “Stockholders’ Equity,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements. Cash dividends paid in 2013 were $0.33 per common share, compared with $0.23 per common share in 2012. At December 31, 2013, stockholders’ equity included $24 million of accumulated other comprehensive loss compared to $49 million of accumulated other comprehensive income at December 31, 2012. The $73 million decrease in accumulated other comprehensive income resulted primarily from the change in the unrealized gain/loss position, net of the tax effect, on investment securities available for sale. Stockholders’ equity to assets at December 31, 2013, was 11.93%, compared to 12.50% at December 31, 2012.
On November 13, 2012, the Board of Directors approved the repurchase of up to an aggregate amount of $125 million of common stock to be made available for reissuance in connection with the Corporation’s employee incentive plans and / or for other corporate purposes. On July 23, 2013, the Board of Directors approved the repurchase of up to an additional $120 million of common stock. At December 31, 2013, $95 million remained authorized for repurchase under the July 2013 Board of Director authorization, while none remained authorized for repurchase under the November 2012 Board of Directors authorization. During 2013, 7.7 million shares were repurchased for $120 million (or an average cost per common share of $15.57), while during 2012, 4.7 million shares were repurchased for $60 million (or an average cost per common share of $12.77). The Corporation also
65
repurchased shares for minimum tax withholding settlements on equity compensation during 2013 and 2012. See Part II, Item 5, “Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities,” for additional information on the common stock repurchased during the fourth quarter of 2013. The repurchase of shares will be based on market opportunities, capital levels, growth prospects, regulatory constraints, and other investment opportunities. Such repurchases may occur from time to time in open market purchases, block transactions, private transactions, accelerated share repurchase programs, or similar facilities.
Basel III Capital Rules. In July 2013, the Federal Reserve and the OCC issued final rules establishing a new comprehensive capital framework for U.S. banking organizations that would implement the Basel III capital framework and certain provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act. See Part I, Item 1, “Business,” for additional information on Basel III and the Dodd-Frank Act.
Management believes that, as of December 31, 2013, the Corporation and the Bank would meet all capital adequacy requirements under the Basel III Capital Rules on a fully phased-in basis if such requirements were currently effective.
66
Management actively reviews capital strategies for the Corporation and each of its subsidiaries in light of perceived business risks, future growth opportunities, industry standards, and compliance with regulatory requirements. The assessment of overall capital adequacy depends on a variety of factors, including asset quality, liquidity, stability of earnings, changing competitive forces, economic condition in markets served, and strength of management. The capital ratios of the Corporation and its banking affiliate were in excess of regulatory minimum requirements. The Corporation’s capital ratios are summarized in Table 21.
Table 21: Capital
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | At or for the Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
| | | (In Thousands, except per share data) | |
Total stockholders’ equity | | $ | 2,891,290 | | | $ | 2,936,399 | | | $ | 2,865,794 | |
Tangible stockholders’ equity(1) | | | 1,950,938 | | | | 1,992,004 | | | | 1,917,204 | |
Tier 1 capital(2) | | | 1,975,182 | | | | 1,938,806 | | | | 2,051,787 | |
Tier 1 common equity(3) | | | 1,913,320 | | | | 1,875,534 | | | | 1,783,515 | |
Tangible common equity(1) | | | 1,889,076 | | | | 1,928,732 | | | | 1,853,932 | |
Total risk-based capital(2) | | | 2,184,884 | | | | 2,167,954 | | | | 2,263,065 | |
Tangible assets(1) | | | 23,286,568 | | | | 22,543,340 | | | | 20,975,627 | |
Risk weighted assets(2) | | | 16,694,148 | | | | 16,149,038 | | | | 14,568,330 | |
Market capitalization | | | 2,829,640 | | | | 2,221,268 | | | | 1,938,833 | |
| | | | |
Book value per common share | | $ | 17.40 | | | $ | 16.97 | | | $ | 16.15 | |
Tangible book value per common share | | | 11.62 | | | | 11.39 | | | | 10.68 | |
Cash dividends per common share | | | 0.33 | | | | 0.23 | | | | 0.04 | |
Stock price at end of period | | | 17.40 | | | | 13.12 | | | | 11.17 | |
Low closing price for the period | | | 13.46 | | | | 11.43 | | | | 8.95 | |
High closing price for the period | | | 17.60 | | | | 14.63 | | | | 15.36 | |
| | | | |
Total stockholders’ equity / assets | | | 11.93 | % | | | 12.50 | % | | | 13.07 | % |
Tangible common equity / tangible assets(1) | | | 8.11 | | | | 8.56 | | | | 8.84 | |
Tangible stockholders’ equity / tangible assets(1) | | | 8.38 | | | | 8.84 | | | | 9.14 | |
Tier 1 common equity / risk-weighted assets(3) | | | 11.46 | | | | 11.61 | | | | 12.24 | |
Tier 1 leverage ratio(2) | | | 8.70 | | | | 8.98 | | | | 9.81 | |
Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio(2) | | | 11.83 | | | | 12.01 | | | | 14.08 | |
Total risk-based capital ratio(2) | | | 13.09 | | | | 13.42 | | | | 15.53 | |
| | | | |
Return on average equity | | | 6.52 | % | | | 6.07 | % | | | 4.66 | % |
Return on average tangible common equity | | | 9.73 | | | | 8.96 | | | | 6.45 | |
Return on average Tier 1 common equity | | | 9.77 | | | | 9.45 | | | | 6.71 | |
Return on average assets | | | 0.81 | | | | 0.81 | | | | 0.65 | |
Dividend payout ratio(4) | | | 30.00 | | | | 23.00 | | | | 6.06 | |
| | | | |
Common shares outstanding (period end) | | | 162,623 | | | | 169,304 | | | | 173,575 | |
Basic common shares outstanding (average) | | | 165,584 | | | | 172,255 | | | | 173,370 | |
Diluted common shares outstanding (average) | | | 165,802 | | | | 172,357 | | | | 173,372 | |
| | | | |
| (1) | Tangible stockholders’ equity, tangible common equity, and tangible assets are non-GAAP financial measures. Additionally, any ratios utilizing these financial measures are non-GAAP measures. These financial measures have been included as they are considered to be critical metrics with which to analyze and evaluate financial condition and capital strength. Tangible stockholders’ equity is defined as stockholders’ equity excluding goodwill and other intangible assets. Tangible common equity is defined as common stockholders’ equity excluding goodwill and other intangible assets. Tangible assets is defined as total assets excluding goodwill and other intangible assets. |
| (2) | The FRB establishes capital adequacy requirements, including well-capitalized standards for the Corporation. The OCC establishes similar capital adequacy requirements and standards for the Bank. Regulatory capital primarily consists of Tier 1 risk-based capital and Tier 2 risk-based capital. The sum of Tier 1 risk-based capital and Tier 2 risk-based capital equals our total risk-based capital. Risk-based capital guidelines require a minimum level of capital as a percentage of risk-weighted assets. Risk-weighted assets consist of total assets plus certain off-balance sheet and market items, subject to adjustment for predefined credit risk factors. |
67
| (3) | Tier 1 common equity, a non-GAAP financial measure, is used by banking regulators, investors and analysts to assess and compare the quality and composition of our capital with the capital of other financial services companies. Management uses Tier 1 common equity, along with other capital measures, to assess and monitor our capital position. Tier 1 common equity is defined as Tier 1 capital excluding qualifying perpetual preferred stock and qualifying trust preferred securities. |
| (4) | Ratio is based upon basic earnings per common share. |
Segment Review
As discussed in Note 20 of the notes to consolidated financial statements, the Corporation’s reportable segments have been determined based upon its internal profitability reporting system, which is organized by strategic business unit. Certain strategic business units have been combined for segment information reporting purposes where the nature of the products and services, the type of customer, and the distribution of those products and services are similar. The reportable segments are Commercial Banking, Consumer Banking and Risk Management and Shared Services.
The financial information of the Corporation’s segments was compiled utilizing the accounting policies described in Note 1, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” and Note 20, “Segment Reporting,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements. The management accounting policies and processes utilized in compiling segment financial information are highly subjective, and unlike financial accounting, are not based on authoritative guidance similar to U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. As a result, reported segments and the financial information of the reported segments are not necessarily comparable with similar information reported by other financial institutions. Furthermore, changes in management structure or allocation methodologies and procedures may result in changes in previously reported segment financial data. During 2013, certain organization and methodology changes were made and, accordingly, 2012 and 2011 results have been restated and presented on a comparable basis.
Segment Review 2013 Compared to 2012
The Commercial Banking segment consists of lending and deposit solutions to businesses, developers, non-profits, municipalities, and financial institutions, and the support to deliver, fund and manage such banking solutions. The Commercial Banking segment had net income of $111 million in 2013, up $22 million compared to $89 million in 2012. The Corporation began providing resources in late 2011 to grow this segment, including investments to expand into new markets (Cincinnati, Indianapolis, and Michigan) and new industry lending segments (power, oil and gas). Primarily as a result of these investments, segment revenue grew $35 million to $413 million in 2013 compared to $378 million in 2012. The credit provision for loans increased $9 million in 2013 due to the growth in the segment’s loan balances, partially offset by improvement in credit quality as compared to 2012. Total noninterest expense in 2013 was $187 million, down $7 million from $194 million in 2012 as higher expenses were more than offset by lower Corporate overhead charges. Average loan balances were $8.4 billion for 2013, up $899 million from an average balance of $7.5 billion for 2012, and average deposit balances were $5.5 billion in 2013, up $866 million from average deposits of $4.6 billion in 2012, reflecting our investments and strategy to expand and grow the Commercial Banking segment. Average allocated capital increased $46 million to $778 million in 2013 reflecting the increase in the segment’s loan balances offset by an improvement in credit quality as compared to 2012.
The Consumer Banking segment consists of lending and deposit solutions to individuals and small businesses and also provides a variety of investment and fiduciary products and services. The Consumer Banking segment had net income of $45 million in 2013, up $13 million compared to $32 million in 2012. Segment revenue grew $10 million to $519 million for 2013 compared to $509 million for 2012, primarily due to higher net interest income as increases in long-term funding rates favorably impacted the credits provided to the Consumer Banking segment for deposit funding sources. The credit provision for loans increased $1 million to $20 million for 2013 due to the growth in the segment’s loan balances, partially offset by an improvement in credit quality as compared to 2012. Total noninterest expense for 2013 was $429 million, down $12 million from $441 million in 2012, as slightly higher direct expenses were more than offset by lower allocated occupancy costs, reflecting a
68
reduction in our branch network from branch closures. Average loan balances were level at $7.2 billion in 2013 and 2012. Average deposits were $9.7 billion in 2013, up $234 million from 2012. Average allocated capital decreased $26 million to $536 million for 2013.
The Risk Management and Shared Services segment had net income of $33 million in 2013, down $25 million compared to $58 million in 2012. The primary components of the decrease were a $24 million decrease in net interest income due to market changes in the long-term funding rates utilized in the funds transfer pricing methodology for allocating net interest income credits to the Commercial and Consumer segments, and an $18 million increase in noninterest expense primarily due to higher unallocated occupancy costs for unused and vacant space as a result of retail branch closures. Average earning asset balances were $5.3 billion for 2013, up $420 million from an average balance of $4.9 billion in 2012. Average deposits were $2.3 billion in 2013, up $756 million from 2012. Average allocated capital increased $20 million to $564 million for 2013.
Segment Review 2012 Compared to 2011
The Commercial Banking segment had net income of $89 million in 2012, up $11 million compared to $78 million in 2011. As a result of investments made in late 2011 to grow this segment through new markets and new industry lending segments, segment revenue grew $27 million to $378 million in 2012 compared to $351 million in 2011. The credit provision for loans increased to $47 million in 2012 due to the growth in the segment’s loan balances, partially offset by improvement in credit quality as compared to 2011. Total noninterest expense in 2012 was $194 million, up $3 million from $191 million in 2011 as the segment hired additional commercial bankers to support new markets and to enhance its presence in existing markets. Average loan balances were $7.5 billion for 2012, up $1.0 billion from an average balance of $6.5 billion for 2011, and average deposit balances were $4.6 billion in 2012, up $928 million from average deposits of $3.7 billion in 2011. Average allocated capital increased $26 million to $732 million in 2012 reflecting the increase in the segment’s loan balances offset by an improvement in credit quality as compared to 2011.
The Consumer Banking segment had net income of $32 million in 2012, up $10 million compared to $22 million in 2011. Segment revenue increased $16 million to $509 million for 2012 compared to $493 million for 2011, primarily due to much higher mortgage banking income, offset by lower net interest income as a result of the lower rate environment and lower service charge and card-based fee income due to changes in customer behavior and regulatory changes. The credit provision for loans increased $1 million to $19 million for 2012 due to the growth in the segment’s loan balances, partially offset by an improvement in credit quality as compared to 2011. Total noninterest expense was level at $441 million for 2012 and 2011. Average loan balances were $7.2 billion in 2012, up $529 million from $6.7 billion in 2011. The segment’s loan growth was primarily in the residential mortgage portfolio. Average deposits were level at $9.4 billion for 2012 and 2011. Average allocated capital increased $39 million to $562 million for 2012 reflecting the increase in the segment’s loan balances and change in loan product mix.
The Risk Management and Shared Services segment had net income of $58 million in 2012, up $18 million compared to $40 million in 2011. The primary components of the increase was a $57 million lower credit provision, reflecting the much lower provision at the consolidated total level, offset by a $29 million increase in noninterest expenses due to unallocated costs incurred to address certain BSA regulatory compliance issues, personnel expense, and other corporate expense items. Average earning asset balances were $4.9 billion for 2012, down $1.4 billion from an average balance of $6.3 billion for 2011, reflecting the reduction in the Corporation’s investment portfolio.
Fourth Quarter 2013 Results
The Corporation recorded net income of $48 million for the fourth quarter of 2013, compared to net income of $47 million for the fourth quarter of 2012. Net income available to common equity for the fourth quarter of 2013 was $46 million, or $0.28 for both basic and diluted earnings per common share. Comparatively, net income available to common equity was $45 million for the fourth quarter of 2012, or $0.26 for both basic and diluted earnings per common share. See Table 22 for selected quarterly information.
69
Taxable equivalent net interest income for the fourth quarter of 2013 was $172 million, $6 million higher than the fourth quarter of 2012. Changes in the balance sheet volume and mix increased taxable equivalent net interest income by $9 million, while changes in the rate environment and product pricing lowered net interest income by $3 million. The Federal funds target interest rate was unchanged for both fourth quarter periods. The net interest margin between the comparable quarters was down 9 bp to 3.23% in the fourth quarter of 2013, comprised of a 4 bp lower interest rate spread (to 3.15%, as the yield on earning assets declined 20 bp and the rate on interest-bearing liabilities fell 16 bp) and a 5 bp lower contribution from net free funds (to 0.08%, as lower rates on interest-bearing liabilities decreased the value of noninterest-bearing funds).
Average earning assets were $21.2 billion for the fourth quarter of 2013, an increase of $1.2 billion from the fourth quarter of 2012, with average loans up $617 million (including increases in commercial and residential mortgages, of $736 million and $371 million, respectively, offset by a decrease of $490 million in retail) and investments up $592 million (primarily in mortgage-related securities). On the funding side, average interest-bearing deposits were up $1.3 billion, while average demand deposits decreased $95 million and average short and long-term funding balances decreased slightly (down $32 million).
Credit quality continued to improve during 2013 with nonaccrual loans declining to $185 million (1.17% of total loans) at December 31, 2013, compared to $253 million (1.64% of total loans) at December 31, 2012. Compared to the fourth quarter of 2012, potential problem loans were down 35% to $235 million. Annualized net charge offs represented 0.14% of average loans for the fourth quarter of 2013, compared to 0.55% for the fourth quarter of 2012. The allowance for loan losses to loans at December 31, 2013 was 1.69%, compared to 1.93% at December 31, 2012. See sections, “Loans,” “Allowance for Loan Losses,” and “Nonaccrual Loans, Potential Problem Loans, and Other Real Estate Owned” for additional discussion.
Noninterest income for the fourth quarter of 2013 decreased $2 million (3%) to $76 million versus the fourth quarter of 2012. Core fee-based revenues of $57 million were up $3 million (5%) versus the comparable quarter in 2012, with increases in most categories. Net mortgage banking decreased $5 million due to the year-over-year slowdown in mortgage loan refinance activity. All remaining noninterest income categories on a combined basis were up 6% from the fourth quarter of 2012.
On a comparable quarter basis, noninterest expense increased $3 million (2%) to $179 million in the fourth quarter of 2013. Personnel expense increased $3 million (3%) from the fourth quarter of 2012, primarily salary-related expenses. Business development and advertising expense increased $2 million (primarily advertising related to our brand campaign), while legal and professional fees decreased $2 million (due to a decrease in consultant costs). All remaining noninterest expense categories on a combined basis were relatively flat compared to the fourth quarter of 2012.
For the fourth quarter of 2013, the Corporation recognized income tax expense of $14 million, compared to income tax expense of $13 million for the fourth quarter of 2012. The change in income tax was primarily due to the level of pretax income between the comparable quarters, as well as a reversal of certain prior years’ tax reserves during both the fourth quarter of 2013 and 2012. The effective tax rate was 22.5% for the fourth quarter of 2013, compared to an effective tax rate of 22.3% for the fourth quarter of 2012.
70
TABLE 22: Selected Quarterly Financial Data
The following is selected financial data summarizing the results of operations for each quarter in the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 Quarter Ended | |
| | | December 31 | | | September 30 | | | June 30 | | | March 31 | |
| | | (In Thousands, except per share data) | |
Interest income | | $ | 181,537 | | | $ | 175,734 | | | $ | 176,360 | | | $ | 175,352 | |
Interest expense | | | 14,338 | | | | 15,225 | | | | 16,178 | | | | 17,699 | |
| | | | |
Net interest income | | | 167,199 | | | | 160,509 | | | | 160,182 | | | | 157,653 | |
Provision for loan losses | | | 2,000 | | | | — | | | | 4,000 | | | | 4,000 | |
Investment securities gains (losses), net | | | (18 | ) | | | 248 | | | | 34 | | | | 300 | |
Income before income taxes | | | 61,605 | | | | 67,054 | | | | 70,496 | | | | 68,738 | |
Net income available to common equity | | | 46,485 | | | | 44,373 | | | | 46,588 | | | | 46,088 | |
| | | | |
Basic earnings per common share | | $ | 0.28 | | | $ | 0.27 | | | $ | 0.28 | | | $ | 0.27 | |
Diluted earnings per common share | | $ | 0.28 | | | $ | 0.27 | | | $ | 0.28 | | | $ | 0.27 | |
Basic weighted average common shares outstanding | | | 162,611 | | | | 164,954 | | | | 166,605 | | | | 168,234 | |
Diluted weighted average common shares outstanding | | | 163,235 | | | | 165,443 | | | | 166,748 | | | | 168,404 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2012 Quarter Ended | |
| | | December 31 | | | September 30 | | | June 30 | | | March 31 | |
| | | (In Thousands, except per share data) | |
Interest income | | $ | 180,470 | | | $ | 178,656 | | | $ | 178,585 | | | $ | 180,573 | |
Interest expense | | | 19,015 | | | | 23,054 | | | | 24,318 | | | | 25,905 | |
| | | | |
Net interest income | | | 161,455 | | | | 155,602 | | | | 154,267 | | | | 154,668 | |
Provision for loan losses | | | 3,000 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Investment securities gains, net | | | 152 | | | | 3,506 | | | | 563 | | | | 40 | |
Income before income taxes | | | 60,032 | | | | 66,887 | | | | 64,188 | | | | 63,352 | |
Net income available to common equity | | | 45,328 | | | | 45,095 | | | | 42,017 | | | | 41,333 | |
| | | | |
Basic earnings per common share | | $ | 0.26 | | | $ | 0.26 | | | $ | 0.24 | | | $ | 0.24 | |
Diluted earnings per common share | | $ | 0.26 | | | $ | 0.26 | | | $ | 0.24 | | | $ | 0.24 | |
Basic weighted average common shares outstanding | | | 170,707 | | | | 171,650 | | | | 172,839 | | | | 173,846 | |
Diluted weighted average common shares outstanding | | | 170,896 | | | | 171,780 | | | | 172,841 | | | | 173,848 | |
2012 Compared to 2011
The Corporation recorded net income available to common equity for 2012 of $174 million, or diluted earnings per common share of $1.00. For 2011, net income available to common equity was $115 million, or net income of $0.66 for diluted earnings per common share. Cash dividends of $0.23 per common share were paid in 2012, compared to cash dividends of $0.04 per common share paid in 2011. Key factors behind these results are discussed below.
Credit quality continued to improve during 2012. Nonaccrual loans were $253 million at December 31, 2012, a decrease of $104 million (29%) from December 31, 2011. Potential problem loans declined to $361 million, a decrease of $205 million (36%) from December 31, 2011. At December 31, 2012, the allowance for loan losses to total loans ratio was 1.93%, covering 118% of nonaccrual loans, compared to 2.70% at December 31, 2011, covering 106% of nonaccrual loans. The provision for loan losses was $3 million for 2012, with net charge offs to average loans of 0.57% (compared to a provision for loan losses of $52 million and a net charge off ratio of 1.13% for 2011).
71
Taxable equivalent net interest income was $647 million for 2012, $13 million or 2% higher than 2011, including favorable volume variances (increasing taxable equivalent net interest income by $39 million), partially offset by unfavorable rate variances (decreasing taxable equivalent net interest income by $26 million). The net interest margin for 2012 was 3.30%, 4 bp higher than 3.26% in 2011, attributable to an 8 bp increase in interest rate spread, partially offset by a 4 bp lower contribution from net free funds.
Average earning assets of $19.6 billion in 2012 were $172 million or 1% higher than 2011. Average loans increased $1.5 billion or 11%, including a $1.2 billion increase in commercial loans and a $510 million increase in residential mortgage loans, partially offset by a $262 million decrease in retail loans. Average securities and short-term investments decreased $1.3 billion, reflecting the Corporation’s strategy of funding loan growth primarily through investment securities run-off. Average interest-bearing liabilities of $14.9 billion in 2012 were down $215 million (1%) versus 2011. On average, interest-bearing deposits increased $614 million, while average noninterest-bearing demand deposits increased by $568 million. Average short and long-term funding decreased $829 million, consisting of a $580 million decrease in short-term funding and a $249 million decrease in long-term funding.
At December 31, 2012, total loans were $15.4 billion, up 10% from year-end 2011, with growth in most loan categories (commercial and business lending was up $916 million, commercial real estate lending was up $414 million, and residential mortgage loans were up $426 million, while retail loans decreased $376 million). Total deposits at December 31, 2012, were $16.9 billion, up 12% from year-end 2011. Money market deposits and noninterest-bearing demand deposits increased (up 27% and 21%, respectively), while brokered CDs and other time deposits decreased (down 27%).
Noninterest income was $313 million for 2012, $40 million or 15% higher than 2011. Core fee-based revenues totaled $220 million for 2012, down $16 million or 7% from $236 million for 2011. Net mortgage banking income was $64 million for 2012, an increase of $51 million from 2011. Collectively, all remaining noninterest income categories were $30 million, up $5 million compared to 2011.
Noninterest expense for 2012 was $682 million, an increase of $31 million or 5% over 2011. Personnel expense was $381 million, up $21 million (6%) over 2011, while nonpersonnel noninterest expenses on an aggregate basis were up modestly (3%) compared to 2011. The efficiency ratio was 69.99% for 2012 and 70.15% for 2011, respectively.
Income tax expense for 2012 was $75 million, compared to income tax expense of $44 million for 2011. The increase in income tax was primarily due to the increase in pretax income between the years. The effective tax rate was 29.7% for 2012, compared to an effective rate of 23.8% for 2011.
Recent Developments
On January 28, 2014, the Board of Directors declared a regular quarterly cash dividend of $0.09 per common share, payable on March 17, 2014, to shareholders of record at the close of business on March 3, 2014. The Board of Directors also declared a regular quarterly cash dividend of $0.50 per depositary share on Associated Banc-Corp’s 8.00% Series B Perpetual Preferred Stock to shareholders of record at the close of business on March 3, 2014, with a dividend payable date of March 15, 2014, and an actual payment date of March 17, 2014. These cash dividends have not been reflected in the accompanying consolidated financial statements.
On January 17, 2014, the Corporation repurchased approximately 1.6 million shares of common stock under an accelerated share repurchase program. After this common stock repurchase, the Corporation has $65 million remaining under repurchase authorizations previously approved by the Board of Directors.
On January 10, 2014, the Board of Directors approved the early redemption of $155 million of senior notes due March 12, 2014, at par. The $155 million of senior notes will be redeemed in February, 2014.
72
Critical Accounting Policies
In preparing the consolidated financial statements, management is required to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities as of the date of the balance sheet and revenues and expenses for the period. Actual results could differ significantly from those estimates. Estimates that are particularly susceptible to significant change include the determination of the allowance for loan losses, goodwill impairment assessment, mortgage servicing rights valuation, derivative financial instruments and hedging activities, and income taxes.
The consolidated financial statements of the Corporation are prepared in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles and follow general practices within the industries in which it operates. This preparation requires management to make estimates, assumptions, and judgments that affect the amounts reported in the financial statements and accompanying notes. These estimates, assumptions, and judgments are based on information available as of the date of the financial statements; accordingly, as this information changes, actual results could differ from the estimates, assumptions, and judgments reflected in the financial statements. Certain policies inherently have a greater reliance on the use of estimates, assumptions, and judgments and, as such, have a greater possibility of producing results that could be materially different than originally reported. Management believes the following policies are both important to the portrayal of the Corporation’s financial condition and results of operations and require subjective or complex judgments and, therefore, management considers the following to be critical accounting policies. The critical accounting policies are discussed directly with the Audit Committee of the Corporation’s Board of Directors.
Allowance for Loan Losses: Management’s evaluation process used to determine the appropriateness of the allowance for loan losses is subject to the use of estimates, assumptions, and judgments. The evaluation process combines many factors: management’s ongoing review and grading of the loan portfolio, consideration of historical loan loss and delinquency experience, trends in past due and nonaccrual loans, risk characteristics of the various classifications of loans, concentrations of loans to specific borrowers or industries, existing economic conditions, the fair value of underlying collateral, and other qualitative and quantitative factors which could affect probable credit losses. Because current economic conditions can change and future events are inherently difficult to predict, the anticipated amount of estimated loan losses, and therefore the appropriateness of the allowance for loan losses, could change significantly. The Corporation believes the level of the allowance for loan losses is appropriate as recorded in the consolidated financial statements. See Note 1, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” and Note 3, “Loans,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements as well as the “Allowance for Loan Losses” section.
Goodwill Impairment Assessment: Goodwill is not amortized but, instead, is subject to impairment tests on at least an annual basis, and more frequently if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying amount. The impairment testing process is conducted by assigning net assets and goodwill to each reporting unit. See Note 1, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements.
The Corporation conducted its annual impairment testing in May 2013, utilizing a qualitative assessment. Factors that management considered in this assessment included macroeconomic conditions, industry and market considerations, overall financial performance (both current and projected), changes in management strategy, and changes in the composition or carrying amount of net assets. In addition, management considered the significant increases in both the Corporation’s common stock price and in the overall bank common stock index (based on the Nasdaq bank index), as well as the Corporation’s improving earnings per common share trend over the past year. Based on these assessments, management concluded that the 2013 annual qualitative impairment assessment indicated that it is more likely than not that the estimated fair value exceeded the carrying value (including goodwill) for each reporting unit. Therefore, a step one quantitative analysis was not required. The annual impairment testing in prior years was based upon a quantitative measurement of the fair value of the reporting units. There were no impairment charges recorded in 2011, 2012, or 2013, respectively. See also Note 4, “Goodwill and Intangible Assets,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements.
73
Mortgage Servicing Rights Valuation: The fair value of the Corporation’s mortgage servicing rights asset is important to the presentation of the consolidated financial statements since the mortgage servicing rights are carried on the consolidated balance sheet at the lower of amortized cost or estimated fair value. Mortgage servicing rights do not trade in an active open market with readily observable prices. As such, like other participants in the mortgage banking business, the Corporation relies on an independent valuation from a third party which uses a discounted cash flow model to estimate the fair value of its mortgage servicing rights. The use of a discounted cash flow model involves judgment, particularly of estimated prepayment speeds of underlying mortgages serviced and the overall level of interest rates. Loan type and note interest rate are the predominant risk characteristics of the underlying loans used to stratify capitalized mortgage servicing rights for purposes of measuring impairment. The Corporation periodically reviews the assumptions underlying the valuation of mortgage servicing rights. While the Corporation believes that the values produced by the discounted cash flow model are indicative of the fair value of its mortgage servicing rights portfolio, these values can change significantly depending upon key factors, such as the then current interest rate environment, estimated prepayment speeds of the underlying mortgages serviced, and other economic conditions. The proceeds that might be received should the Corporation actually consider a sale of some or all of the mortgage servicing rights portfolio could differ from the amounts reported at any point in time.
Mortgage servicing rights are carried at the lower of amortized cost or estimated fair value and are assessed for impairment at each reporting date. Impairment is assessed based on the fair value at each reporting date using estimated prepayment speeds of the underlying mortgage loans serviced and stratifications based on the risk characteristics of the underlying loans (predominantly loan type and note interest rate). As mortgage interest rates fall, prepayment speeds are usually faster and the value of the mortgage servicing rights asset generally decreases, requiring additional valuation reserve. Conversely, as mortgage interest rates rise, prepayment speeds are usually slower and the value of the mortgage servicing rights asset generally increases, requiring less valuation reserve. However, the extent to which interest rates impact the value of the mortgage servicing rights asset depends, in part, on the magnitude of the changes in market interest rates and the differential between the then current market interest rates for mortgage loans and the mortgage interest rates included in the mortgage servicing portfolio. Management recognizes that the volatility in the valuation of the mortgage servicing rights asset will continue. To better understand the sensitivity of the impact of prepayment speeds and refinance rates on the value of the mortgage servicing rights asset at December 31, 2013, (holding all other factors unchanged), if refinance rates were to decrease 50 bp, the estimated value of the mortgage servicing rights asset would have been approximately $9 million (or 12%) lower. Conversely, if refinance rates were to increase 50 bp, the estimated value of the mortgage servicing rights asset would have been approximately $7 million (or 9%) higher. However, the Corporation’s potential recovery recognition due to valuation improvement is limited to the balance of the mortgage servicing rights valuation reserve, which was $1 million at December 31, 2013. The Corporation believes the mortgage servicing rights asset is properly recorded in the consolidated financial statements. See also Note 1, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” and Note 4, “Goodwill and Intangible Assets,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements and section “Noninterest Income.”
Derivative Financial Instruments and Hedging Activities: In various aspects of its business, the Corporation may use derivative financial instruments to modify exposures to changes in interest rates and market prices for other financial instruments. Derivative instruments are required to be carried at fair value on the balance sheet with changes in the fair value recorded directly in earnings or accumulated other comprehensive income, as appropriate. To qualify for and maintain hedge accounting, the Corporation must meet formal documentation and effectiveness evaluation requirements both at the hedge’s inception and on an ongoing basis. If in the future derivative financial instruments used by the Corporation no longer qualify for hedge accounting, the impact on the consolidated results of operations and reported earnings could be significant. See also Note 1, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” Note 13, “Derivative and Hedging Activities,” and Note 17, “Fair Value Measurements,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements and section “Interest Rate Risk.”
Income Taxes: The assessment of tax assets and liabilities involves the use of estimates, assumptions, interpretations, and judgment concerning certain accounting pronouncements and federal and state tax codes.
74
There can be no assurance that future events, such as court decisions or positions of federal and state taxing authorities, will not differ from management’s current assessment, the impact of which could be significant to the consolidated results of operations and reported earnings. Quarterly assessments are performed to determine if valuation allowances are necessary against any portion of the Corporation’s deferred tax assets. Assessing the need for, or sufficiency of, a valuation allowance requires management to evaluate all available evidence, both positive and negative, including the recent trend of quarterly earnings. Positive evidence necessary to overcome the negative evidence includes whether future taxable income in sufficient amounts and character within the carryback and carryforward periods is available under the tax law, including the use of tax planning strategies. When negative evidence (e.g., cumulative losses in recent years, history of operating loss or tax credit carryforwards expiring unused) exists, more positive evidence than negative evidence will be necessary. The Corporation has concluded that based on the level of positive evidence, it is more likely than not that the deferred tax asset will be realized. However, there is no guarantee that the tax benefits associated with the deferred tax assets will be fully realized. The Corporation believes the tax assets and liabilities are properly recorded in the consolidated financial statements. See Note 1, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” and Note 12, “Income Taxes,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements and section “Income Taxes.”
Future Accounting Pronouncements
New accounting policies adopted by the Corporation during 2013 are discussed in Note 1, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” of the notes to consolidated financial statements. The expected impact of accounting pronouncements recently issued or proposed but not yet required to be adopted are discussed below. To the extent the adoption of new accounting standards materially affects the Corporation’s financial condition, results of operations, or liquidity, the impacts are discussed in the applicable sections of this financial review and the notes to consolidated financial statements.
In January 2014, the FASB issued an amendment to clarify that an in substance repossession or foreclosure occurs, and a creditor is considered to have received physical possession of residential real estate property collateralizing a consumer mortgage loan, upon either (1) the creditor obtaining legal title to the residential real estate property upon completion of a foreclosure or (2) the borrower conveying all interest in the residential real estate property to the creditor to satisfy that loan through completion of a deed in lieu of foreclosure or through a similar agreement. In addition, the amendments require interim and annual disclosure of both the amount of foreclosed residential real estate property held by the creditor and the recorded investment in consumer mortgage loans collateralized by residential real estate property that are in the process of foreclosure in accordance with local requirements of the applicable jurisdiction. This amendment is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2014. An entity can elect to adopt the amendments using either a modified retrospective method or a prospective transition method. Early adoption is permitted. The Corporation intends to adopt the accounting standard during the first quarter of 2015, as required, with no expected material impact on its results of operations, financial position, or liquidity.
In January 2014, the FASB issued an amendment which permits reporting entities to make an accounting policy election to account for their investments in qualified affordable housing projects using the proportional amortization method if certain conditions are met. Under the proportional amortization method, an entity amortizes the initial cost of the investment in proportion to the tax credits and other tax benefits received and recognizes the net investment performance in the income statement as a component of income tax expense (benefit). For those investments in qualified affordable housing projects not accounted for using the proportional method, the investment should be accounted for as an equity method investment or a cost method investment. The decision to apply the proportional amortization method of accounting is an accounting policy decision that should be applied consistently to all qualifying affordable housing project investments rather than a decision to be applied to individual investments. This amendment should be applied retrospectively to all periods presented. A reporting entity that uses the effective yield method to account for its investments in qualified affordable housing projects before the date of adoption may continue to apply the effective yield method for those preexisting investments. This amendment is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years,
75
beginning after December 15, 2014. The Corporation intends to adopt the accounting standard during the first quarter of 2015, as required, with no expected material impact on its results of operations, financial position, or liquidity.
In July 2013, the FASB issued an amendment to clarify the presentation of an unrecognized tax benefit when a net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss, or a tax credit carryforward exists. An unrecognized tax benefit, or a portion of an unrecognized tax benefit, should be presented in the financial statements as a reduction to a deferred tax asset for a net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss, or a tax credit carryforward, except as follows. To the extent a net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss, or a tax credit carryforward is not available at the reporting date under the tax law of the applicable jurisdiction to settle any additional income taxes that would result from the disallowance of a tax position or the tax law of the applicable jurisdiction does not require the entity to use, and the entity does not intend to use, the deferred tax asset for such purpose, the unrecognized tax benefit should be presented in the financial statements as a liability and should not be combined with deferred tax assets. This amendment is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2013 and should be applied prospectively. Early adoption and retrospective application is permitted. The Corporation intends to adopt the accounting standard during the first quarter of 2014, as required, with no expected material impact on its results of operations, financial position, or liquidity.
| ITEM 7A. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
Information required by this item is set forth in Item 7 under the captions “Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk” and “Interest Rate Risk.”
76
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
ASSOCIATED BANC-CORP
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
| | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | (In Thousands, except share and per share data) | |
ASSETS | | | | | | | | |
Cash and due from banks | | $ | 455,482 | | | $ | 563,304 | |
Interest-bearing deposits in other financial institutions | | | 126,018 | | | | 147,434 | |
Federal funds sold and securities purchased under agreements to resell | | | 20,745 | | | | 27,135 | |
Investment securities held to maturity, at amortized cost | | | 175,210 | | | | 39,877 | |
Investment securities available for sale, at fair value | | | 5,250,585 | | | | 4,926,758 | |
Federal Home Loan Bank and Federal Reserve Bank stocks, at cost | | | 181,249 | | | | 166,774 | |
Loans held for sale | | | 64,738 | | | | 261,410 | |
Loans | | | 15,896,261 | | | | 15,411,022 | |
Allowance for loan losses | | | (268,315 | ) | | | (297,409 | ) |
Loans, net | | | 15,627,946 | | | | 15,113,613 | |
Premises and equipment, net | | | 270,890 | | | | 253,958 | |
Goodwill | | | 929,168 | | | | 929,168 | |
Other intangible assets, net | | | 74,464 | | | | 61,176 | |
Trading assets | | | 43,728 | | | | 70,711 | |
Other assets | | | 1,006,697 | | | | 926,417 | |
Total assets | | $ | 24,226,920 | | | $ | 23,487,735 | |
| |
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | | | | | | | |
Noninterest-bearing demand deposits | | $ | 4,626,312 | | | $ | 4,759,556 | |
Interest-bearing deposits | | | 12,640,855 | | | | 12,180,309 | |
Total deposits | | | 17,267,167 | | | | 16,939,865 | |
Federal funds purchased and securities sold under agreements to repurchase | | | 475,442 | | | | 750,455 | |
Other short-term funding | | | 265,484 | | | | 1,576,484 | |
Long-term funding | | | 3,087,267 | | | | 1,015,346 | |
Trading liabilities | | | 46,470 | | | | 76,343 | |
Accrued expenses and other liabilities | | | 193,800 | | | | 192,843 | |
Total liabilities | | | 21,335,630 | | | | 20,551,336 | |
Stockholders’ equity | | | | | | | | |
Preferred equity | | | 61,862 | | | | 63,272 | |
Common stock | | | 1,750 | | | | 1,750 | |
Surplus | | | 1,617,990 | | | | 1,602,136 | |
Retained earnings | | | 1,392,508 | | | | 1,281,811 | |
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | | | (24,244 | ) | | | 48,603 | |
Treasury stock, at cost | | | (158,576 | ) | | | (61,173 | ) |
Total stockholders’ equity | | | 2,891,290 | | | | 2,936,399 | |
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | | $ | 24,226,920 | | | $ | 23,487,735 | |
| |
Preferred shares issued | | | 63,549 | | | | 65,000 | |
Preferred shares authorized (par value $1.00 per share) | | | 750,000 | | | | 750,000 | |
Common shares issued | | | 175,012,686 | | | | 175,012,686 | |
Common shares authorized (par value $0.01 per share) | | | 250,000,000 | | | | 250,000,000 | |
Treasury shares of common stock | | | 10,874,182 | | | | 4,773,146 | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
77
ASSOCIATED BANC-CORP
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
| | | (In Thousands, except per share data) | |
INTEREST INCOME | | | | |
Interest and fees on loans | | $ | 587,526 | | | $ | 595,965 | | | $ | 582,739 | |
Interest and dividends on investment securities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Taxable | | | 88,919 | | | | 86,945 | | | | 123,371 | |
Tax exempt | | | 27,345 | | | | 28,655 | | | | 29,937 | |
Other interest | | | 5,193 | | | | 6,719 | | | | 5,575 | |
Total interest income | | | 708,983 | | | | 718,284 | | | | 741,622 | |
INTEREST EXPENSE | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest on deposits | | | 31,267 | | | | 41,431 | | | | 65,748 | |
Interest on Federal funds purchased and securities sold under agreements to repurchase | | | 1,322 | | | | 2,687 | | | | 6,196 | |
Interest on other short-term funding | | | 1,519 | | | | 3,294 | | | | 6,215 | |
Interest on long-term funding | | | 29,332 | | | | 44,880 | | | | 50,632 | |
Total interest expense | | | 63,440 | | | | 92,292 | | | | 128,791 | |
NET INTEREST INCOME | | | 645,543 | | | | 625,992 | | | | 612,831 | |
Provision for loan losses | | | 10,000 | | | | 3,000 | | | | 52,000 | |
Net interest income after provision for loan losses | | | 635,543 | | | | 622,992 | | | | 560,831 | |
NONINTEREST INCOME | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Trust service fees | | | 45,633 | | | | 40,737 | | | | 39,145 | |
Service charges on deposit accounts | | | 70,009 | | | | 68,917 | | | | 75,908 | |
Card-based and other nondeposit fees | | | 49,913 | | | | 47,862 | | | | 57,905 | |
Insurance commissions | | | 44,024 | | | | 47,014 | | | | 45,554 | |
Brokerage and annuity commissions | | | 14,877 | | | | 15,643 | | | | 17,230 | |
Mortgage banking, net | | | 48,847 | | | | 63,500 | | | | 12,723 | |
Capital market fees, net | | | 13,080 | | | | 14,241 | | | | 8,711 | |
Bank owned life insurance income | | | 11,855 | | | | 13,952 | | | | 14,896 | |
Asset gains (losses), net | | | 5,413 | | | | (12,096 | ) | | | (12,199 | ) |
Investment securities gains (losses), net: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Realized gains (losses), net | | | 564 | | | | 4,261 | | | | (228 | ) |
Other-than-temporary impairments | | | — | | | | (59 | ) | | | (2,417 | ) |
Less: Non-credit portion recognized in other comprehensive income (before taxes) | | | — | | | | 59 | | | | 1,533 | |
Total investment securities gains (losses), net | | | 564 | | | | 4,261 | | | | (1,112 | ) |
Other | | | 8,884 | | | | 9,259 | | | | 14,358 | |
Total noninterest income | | | 313,099 | | | | 313,290 | | | | 273,119 | |
NONINTEREST EXPENSE | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Personnel expense | | | 397,015 | | | | 381,404 | | | | 360,144 | |
Occupancy | | | 59,409 | | | | 60,794 | | | | 55,939 | |
Equipment | | | 25,351 | | | | 23,566 | | | | 19,873 | |
Technology | | | 49,445 | | | | 43,548 | | | | 32,475 | |
Business development and advertising | | | 23,346 | | | | 21,303 | | | | 23,038 | |
Other intangible amortization | | | 4,043 | | | | 4,195 | | | | 4,714 | |
Loan expense | | | 13,162 | | | | 12,285 | | | | 12,008 | |
Legal and professional fees | | | 20,226 | | | | 31,232 | | | | 18,205 | |
Losses other than loans | | | 1,942 | | | | 12,258 | | | | 17,921 | |
Foreclosure / OREO expense | | | 10,068 | | | | 15,069 | | | | 21,393 | |
FDIC expense | | | 19,461 | | | | 19,478 | | | | 28,484 | |
Other | | | 57,281 | | | | 56,691 | | | | 56,329 | |
Total noninterest expense | | | 680,749 | | | | 681,823 | | | | 650,523 | |
Income before income taxes | | | 267,893 | | | | 254,459 | | | | 183,427 | |
Income tax expense | | | 79,201 | | | | 75,486 | | | | 43,728 | |
Net income | | | 188,692 | | | | 178,973 | | | | 139,699 | |
Preferred stock dividends and discount accretion | | | 5,158 | | | | 5,200 | | | | 24,830 | |
Net income available to common equity | | $ | 183,534 | | | $ | 173,773 | | | $ | 114,869 | |
| |
Earnings per common share: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | $ | 1.10 | | | $ | 1.00 | | | $ | 0.66 | |
Diluted | | $ | 1.10 | | | $ | 1.00 | | | $ | 0.66 | |
Average common shares outstanding: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | | 165,584 | | | | 172,255 | | | | 173,370 | |
Diluted | | | 165,802 | | | | 172,357 | | | | 173,372 | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
78
ASSOCIATED BANC-CORP
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Net income | | $ | 188,692 | | | $ | 178,973 | | | $ | 139,699 | |
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Investment securities available for sale: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net unrealized gains (losses) | | | (158,207 | ) | | | (19,042 | ) | | | 71,606 | |
Reclassification adjustment for net (gains) losses realized in net income | | | (564 | ) | | | (4,261 | ) | | | 1,112 | |
Income tax (expense) benefit | | | 61,266 | | | | 9,651 | | | | (28,566 | ) |
Other comprehensive income (loss) on investment securities available for sale | | | (97,505 | ) | | | (13,652 | ) | | | 44,152 | |
Defined benefit pension and postretirement obligations: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Prior service cost, net of amortization | | | 72 | | | | 242 | | | | 467 | |
Net gain (loss), net of amortization | | | 40,148 | | | | (6,941 | ) | | | (14,810 | ) |
Income tax (expense) benefit | | | (15,562 | ) | | | 2,366 | | | | 5,674 | |
Other comprehensive income (loss) on pension and postretirement obligations | | | 24,658 | | | | (4,333 | ) | | | (8,669 | ) |
Derivatives used in cash flow hedging relationships: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net unrealized gains (losses) | | | — | | | | 6 | | | | (557 | ) |
Reclassification adjustment for net losses and interest expense for interest differential on derivatives realized in net income | | | — | | | | 1,954 | | | | 4,708 | |
Income tax expense | | | — | | | | (974 | ) | | | (1,658 | ) |
Other comprehensive income on cash flow hedging relationships | | | — | | | | 986 | | | | 2,493 | |
Total other comprehensive income (loss) | | | (72,847 | ) | | | (16,999 | ) | | | 37,976 | |
Comprehensive income | | $ | 115,845 | | | $ | 161,974 | | | $ | 177,675 | |
| |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
79
ASSOCIATED BANC-CORP
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive
Income (Loss) | | | | | | | |
| | | Preferred Equity | | | Common Stock | | | Surplus | | | Retained
Earnings | | | | Treasury
Stock | | | Total | |
| | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Shares | | | Amount | | | | | | |
| | | (In Thousands, except per share data) | |
Balance, December 31, 2010 | | | 525 | | | $ | 514,388 | | | | 173,887 | | | $ | 1,739 | | | $ | 1,573,372 | | | $ | 1,041,666 | | | $ | 27,626 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 3,158,791 | |
| | | | |
Comprehensive income: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 139,699 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 139,699 | |
Other comprehensive income | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 37,976 | | | | — | | | | 37,976 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 177,675 | |
Common stock issued: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Stock-based compensation plans, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | 704 | | | | 7 | | | | 4,350 | | | | (785 | ) | | | — | | | | 659 | | | | 4,231 | |
Purchase of treasury stock | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (659 | ) | | | (659 | ) |
Cash dividends: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Common stock, $0.04 per share | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (6,977 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (6,977 | ) |
Preferred stock | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (14,218 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (14,218 | ) |
Issuance of preferred stock | | | 65 | | | | 63,272 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 63,272 | |
Redemption of preferred stock | | | (525 | ) | | | (525,000 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (525,000 | ) |
Accretion of preferred stock discount | | | — | | | | 10,612 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (10,612 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Stock-based compensation expense, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 11,024 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 11,024 | |
Tax impact of stock-based compensation | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2,345 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2,345 | ) |
| | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2011 | | | 65 | | | $ | 63,272 | | | | 174,591 | | | $ | 1,746 | | | $ | 1,586,401 | | | $ | 1,148,773 | | | $ | 65,602 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 2,865,794 | |
| | | | |
Comprehensive income: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 178,973 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 178,973 | |
Other comprehensive loss | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (16,999 | ) | | | — | | | | (16,999 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 161,974 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Common stock issued: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Stock-based compensation plans, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | 422 | | | | 4 | | | | 761 | | | | (1,101 | ) | | | — | | | | 481 | | | | 145 | |
Purchase of treasury stock | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (61,654 | ) | | | (61,654 | ) |
Cash dividends: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Common stock, $0.23 per share | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (39,634 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (39,634 | ) |
Preferred stock | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (5,200 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (5,200 | ) |
Stock-based compensation expense, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 15,759 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 15,759 | |
Tax impact of stock-based compensation | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (785 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (785 | ) |
| | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2012 | | | 65 | | | $ | 63,272 | | | | 175,013 | | | $ | 1,750 | | | $ | 1,602,136 | | | $ | 1,281,811 | | | $ | 48,603 | | | $ | (61,173 | ) | | $ | 2,936,399 | |
| | | | |
Comprehensive income: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 188,692 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 188,692 | |
Other comprehensive loss | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (72,847 | ) | | | — | | | | (72,847 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 115,845 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Common stock issued: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Stock-based compensation plans, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 989 | | | | (17,630 | ) | | | — | | | | 25,946 | | | | 9,305 | |
Purchase of treasury stock | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (123,349 | ) | | | (123,349 | ) |
Cash dividends: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Common stock, $0.33 per share | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (54,991 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (54,991 | ) |
Preferred stock | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (5,158 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (5,158 | ) |
Purchase of preferred stock | | | (1 | ) | | | (1,410 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (216 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1,626 | ) |
Stock-based compensation expense, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 14,840 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 14,840 | |
Tax benefit of stock-based compensation | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 25 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 25 | |
| | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2013 | | | 64 | | | $ | 61,862 | | | | 175,013 | | | $ | 1,750 | | | $ | 1,617,990 | | | $ | 1,392,508 | | | $ | (24,244 | ) | | $ | (158,576 | ) | | $ | 2,891,290 | |
| | | | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
80
ASSOCIATED BANC-CORP
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 188,692 | | | $ | 178,973 | | | $ | 139,699 | |
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Provision for loan losses | | | 10,000 | | | | 3,000 | | | | 52,000 | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 49,711 | | | | 43,611 | | | | 33,628 | |
(Recovery of) addition to valuation allowance on mortgage servicing rights, net | | | (14,563 | ) | | | 2,383 | | | | 7,403 | |
Amortization of mortgage servicing rights | | | 15,488 | | | | 23,348 | | | | 25,830 | |
Amortization of other intangible assets | | | 4,043 | | | | 4,195 | | | | 4,714 | |
Amortization and accretion on earning assets, funding, and other, net | | | 44,965 | | | | 55,101 | | | | 65,670 | |
Deferred income taxes | | | 25,920 | | | | 54,294 | | | | 34,742 | |
Tax impact of stock based compensation | | | 25 | | | | (785 | ) | | | (2,345 | ) |
(Gain) loss on sales of investment securities, net, and impairment write-downs | | | (564 | ) | | | (4,261 | ) | | | 1,112 | |
(Gain) loss on sales of assets and impairment write-downs, net | | | (5,413 | ) | | | 12,096 | | | | 12,199 | |
Gain on mortgage banking activities, net | | | (34,268 | ) | | | (60,312 | ) | | | (31,628 | ) |
Mortgage loans originated and acquired for sale | | | (2,304,006 | ) | | | (2,797,431 | ) | | | (1,855,037 | ) |
Proceeds from sales of mortgage loans held for sale | | | 2,516,690 | | | | 2,822,000 | | | | 1,764,801 | |
Pension Contributions | | | (28,000 | ) | | | (40,000 | ) | | | (26,000 | ) |
Decrease in interest receivable | | | 2,078 | | | | 534 | | | | 5,062 | |
Decrease in interest payable | | | (2,214 | ) | | | (5,723 | ) | | | (1,232 | ) |
Net change in other assets and other liabilities | | | 18,679 | | | | 59,461 | | | | 79,169 | |
Net cash provided by operating activities | | | 487,263 | | | | 350,484 | | | | 309,787 | |
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net increase in loans | | | (593,591 | ) | | | (1,637,901 | ) | | | (1,754,499 | ) |
Purchases of: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Available for sale securities | | | (1,954,936 | ) | | | (2,084,500 | ) | | | (777,309 | ) |
Premises, equipment, and software, net of disposals | | | (67,723 | ) | | | (83,973 | ) | | | (76,648 | ) |
FHLB stock | | | (28,399 | ) | | | (6,601 | ) | | | — | |
Held to maturity securities | | | (135,785 | ) | | | (39,925 | ) | | | — | |
Other assets | | | (2,098 | ) | | | (5,968 | ) | | | (3,061 | ) |
Proceeds from: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Available for sale securities | | | 136,152 | | | | 299,782 | | | | 176,267 | |
Prepayments, calls, and maturities of available for sale securities | | | 1,298,077 | | | | 1,692,076 | | | | 1,776,245 | |
Sale of FHLB stock | | | 14,399 | | | | 31,428 | | | | — | |
Prepayments, calls and maturities of other assets | | | 41,668 | | | | 70,920 | | | | 50,417 | |
Sales of loans originated for investment | | | 39,002 | | | | 130,940 | | | | 136,051 | |
Net cash used in investing activities | | | (1,253,234 | ) | | | (1,633,722 | ) | | | (472,537 | ) |
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net increase (decrease) in deposits | | | 394,340 | | | | 1,969,055 | | | | (134,738 | ) |
Net decrease in deposits due to branch sales | | | (65,430 | ) | | | (113,622 | ) | | | — | |
Net increase (decrease) in short-term funding | | | (1,586,013 | ) | | | (187,546 | ) | | | 767,103 | |
Repayment of long-term funding | | | (427,430 | ) | | | (311,621 | ) | | | (670,104 | ) |
Proceeds from issuance of long-term funding | | | 2,500,000 | | | | 154,738 | | | | 432,504 | |
Proceeds from issuance of preferred shares | | | — | | | | — | | | | 63,272 | |
Purchase of preferred stock | | | (1,626 | ) | | | — | | | | (525,000 | ) |
Cash dividends on common stock | | | (54,991 | ) | | | (39,634 | ) | | | (6,977 | ) |
Cash dividends on preferred stock | | | (5,158 | ) | | | (5,200 | ) | | | (14,218 | ) |
Purchase of treasury stock | | | (123,349 | ) | | | (61,654 | ) | | | (659 | ) |
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | | | 630,343 | | | | 1,404,516 | | | | (88,817 | ) |
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | | (135,628 | ) | | | 121,278 | | | | (251,567 | ) |
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | | | 737,873 | | | | 616,595 | | | | 868,162 | |
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | | $ | 602,245 | | | $ | 737,873 | | | $ | 616,595 | |
| |
Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash paid for interest | | $ | 65,552 | | | $ | 97,938 | | | $ | 129,720 | |
Cash paid (received) for income taxes | | | 49,200 | | | | (9,722 | ) | | | (10,839 | ) |
Loans and bank premises transferred to other real estate owned | | | 26,151 | | | | 39,511 | | | | 48,752 | |
Capitalized mortgage servicing rights | | | 18,256 | | | | 23,528 | | | | 17,476 | |
| |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
81
ASSOCIATED BANC-CORP
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011
NOTE 1 SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES:
The accounting and reporting policies of the Corporation conform to U.S. generally accepted accounting principles and to general practice within the financial services industry. The following is a description of the more significant of those policies.
Business
Associated Banc-Corp (individually referred to herein as the “Parent Company” and together with all of its subsidiaries and affiliates, collectively referred to herein as the “Corporation”) is a bank holding company headquartered in Wisconsin. The Corporation provides a full range of banking and related financial services to consumer and commercial customers through its network of bank and nonbank subsidiaries. The Corporation is subject to competition from other financial and non-financial institutions that offer similar or competing products and services. The Corporation is regulated by federal and state agencies and is subject to periodic examinations by those agencies.
Basis of Financial Statement Presentation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Parent Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. Investments in unconsolidated entities (none of which are considered to be variable interest entities in which the Corporation is the primary beneficiary) are accounted for using the cost method of accounting when the Corporation has determined that the cost method is appropriate. Investments not meeting the criteria for cost method accounting are accounted for using the equity method of accounting. Investments in unconsolidated entities are included in other assets, and the Corporation’s share of income or loss is recorded in other noninterest income, while distributions in excess of the investment are recorded in gain on assets.
All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Certain amounts in the consolidated financial statements of prior periods have been reclassified to conform with the current period’s presentation.
In preparing the consolidated financial statements, management is required to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities as of the date of the balance sheet and revenues and expenses for the period. Actual results could differ significantly from those estimates. Estimates that are particularly susceptible to significant change include the determination of the allowance for loan losses, goodwill impairment assessment, mortgage servicing rights valuation, derivative financial instruments and hedging activities, and income taxes. Management has evaluated subsequent events for potential recognition or disclosure.
Investment Securities
Securities are classified as held to maturity or available for sale at the time of purchase. Investment securities classified as held to maturity, which management has the positive intent and ability to hold to maturity, are reported at amortized cost, adjusted for amortization of premiums and accretion of discounts, using a method that approximates level yield. Investment securities classified as available for sale, which management has the intent and ability to hold for an indefinite period of time, but not necessarily to maturity, are carried at fair value, with unrealized gains and losses, net of related deferred income taxes, included in stockholders’ equity as a separate component of other comprehensive income. Any decision to sell investment securities available for sale would be
82
based on various factors, including, but not limited to, asset / liability management strategies, changes in interest rates or prepayment risks, liquidity needs, or regulatory capital considerations. Premiums and discounts are amortized or accreted into interest income over the estimated life (earlier of call date, maturity, or estimated life) of the related security, using a prospective method that approximates level yield. Declines in the fair value of investment securities available for sale (with certain exceptions for debt securities noted below) that are deemed to be other-than-temporary are charged to earnings as a realized loss, and a new cost basis for the securities is established. In evaluating other-than-temporary impairment, management considers the length of time and extent to which the security has been in an unrealized loss position, changes in security ratings, the financial condition and near-term prospects of the issuer, as well as security and industry specific economic conditions. In addition, the Corporation considers the intent and ability to retain its investment in the issuer for a period of time sufficient to allow for any anticipated recovery in fair value in the near term. Declines in the fair value of debt securities below amortized cost are deemed to be other-than-temporary in circumstances where: (1) the Corporation has the intent to sell a security; (2) it is more likely than not that the Corporation will be required to sell the security before recovery of its amortized cost basis; or (3) the Corporation does not expect to recover the entire amortized cost basis of the security. If the Corporation intends to sell a security or if it is more likely than not that the Corporation will be required to sell the security before recovery, an other-than-temporary impairment write-down is recognized in earnings equal to the difference between the security’s amortized cost basis and its fair value. If an entity does not intend to sell the security or it is not more likely than not that it will be required to sell the security before recovery, the other-than-temporary impairment write-down is separated into an amount representing credit loss, which is recognized in earnings, and an amount related to all other factors, which is recognized in other comprehensive income. Realized securities gains or losses on securities sales (using specific identification method) and declines in value judged to be other-than-temporary are included in investment securities gains (losses), net, in the consolidated statements of income. See Note 2 for additional information on investment securities.
Federal Home Loan Bank (“FHLB”) and Federal Reserve Bank Stocks
The Corporation is required to maintain Federal Reserve stock and FHLB stock as a member of both the Federal Reserve System and the FHLB, and in amounts as required by these institutions. These equity securities are “restricted” in that they can only be sold back to the respective institutions or another member institution at par. Therefore, they are less liquid than other marketable equity securities and their fair value is equal to amortized cost. See Note 2 for additional information on the FHLB and Federal Reserve Bank Stocks.
Loans
Loans are classified as held for investment when management has both the intent and ability to hold the loan for the foreseeable future, or until maturity or payoff. Loans are carried at the principal amount outstanding, net of any unearned income and unamortized deferred fees and costs on originated loans. Loan origination fees and certain direct loan origination costs are deferred, and the net amount is amortized into net interest income over the contractual life of the related loans or over the commitment period as an adjustment of yield.
Management considers a loan to be impaired when it is probable that the Corporation will be unable to collect all amounts due according to the original contractual terms of the note agreement, including both principal and interest. Management has determined that commercial and consumer loan relationships that have nonaccrual status or have had their terms restructured in a troubled debt restructuring meet this impaired loan definition.
Interest income on loans is based on the principal balance outstanding computed using the effective interest method. The accrual of interest income for commercial loans is discontinued when there is a clear indication that the borrower’s cash flow may not be sufficient to meet payments as they become due, while the accrual of interest income for consumer loans is discontinued when loans reach specific delinquency levels. Loans are generally placed on nonaccrual status when contractually past due 90 days or more as to interest or principal payments, unless the loan is well secured and in the process of collection. Additionally, whenever management
83
becomes aware of facts or circumstances that may adversely impact the collectability of principal or interest on loans, it is management’s practice to place such loans on a nonaccrual status immediately, rather than delaying such action until the loans become 90 days past due. When a loan is placed on nonaccrual status, previously accrued and uncollected interest is reversed, amortization of related deferred loan fees or costs is suspended, and income is recorded only to the extent that interest payments are subsequently received in cash and a determination has been made that the principal and interest of the loan is collectible. If collectability of the principal and interest is in doubt, payments received are applied to loan principal.
While a loan is in nonaccrual status, some or all of the cash interest payments received may be treated as interest income on a cash basis as long as the remaining recorded investment in the asset (i.e., after charge off of identified losses, if any) is deemed to be fully collectible. The determination as to the ultimate collectability of the asset’s remaining recorded investment must be supported by a current, well documented credit evaluation of the borrower’s financial condition and prospects for repayment, including consideration of the borrower’s sustained historical repayment performance and other relevant factors. A nonaccrual loan is returned to accrual status when all delinquent principal and interest payments become current in accordance with the terms of the loan agreement, the borrower has demonstrated a period of sustained performance and the ultimate collectability of the total contractual principal and interest is no longer in doubt. A sustained period of repayment performance generally would be a minimum of six months. See Allowance for Loan Losses below for further policy discussion and see Note 3 for additional information on loans.
Troubled Debt Restructurings (“Restructured Loans”)
Loans are considered restructured loans if concessions have been granted to borrowers that are experiencing financial difficulty. The concessions granted generally involve the modification of terms of the loan, such as changes in payment schedule or interest rate, which generally would not otherwise be considered. Restructured loans can involve loans remaining on nonaccrual, moving to nonaccrual, or continuing on accrual status, depending on the individual facts and circumstances of the borrower. Nonaccrual restructured loans are included and treated with all other nonaccrual loans. In addition, all accruing restructured loans are reported as troubled debt restructurings which are considered and accounted for as impaired loans. Generally, restructured loans remain on nonaccrual until the customer has attained a sustained period of repayment performance under the modified loan terms (generally a minimum of six months). However, performance prior to the restructuring, or significant events that coincide with the restructuring, are considered in assessing whether the borrower can meet the new terms and whether the loan should be returned to or maintained on accrual status. If the borrower’s ability to meet the revised payment schedule is not reasonably assured, the loan remains on nonaccrual status.
All restructured loans are considered impaired in the calendar year of restructuring. In subsequent years, a restructured loan may cease being classified as impaired if the loan was modified at a market rate and has performed according to the modified terms for at least six months. A loan that has been modified at a below market rate will return to performing status if it satisfies the six month performance requirement; however, it will remain classified as a restructured loan. See Note 3 for additional information on restructured loans.
Loans Held for Sale
Loans held for sale, which consist generally of current production of certain fixed-rate, first-lien residential mortgage loans, are carried at the lower of cost or estimated fair value as determined on an aggregate basis. The amount by which cost exceeds estimated fair value is accounted for as a market valuation adjustment to the carrying value of the loans. Changes, if any, in the market valuation adjustment are included in mortgage banking, net, in the consolidated statements of income. At December 31, 2013 the carrying value of loans held for sale included a market valuation adjustment of $442,000, while at December 31, 2012, there was no market valuation adjustment to loans held for sale. Holding costs are treated as period costs.
84
Allowance for Loan Losses
The allowance for loan losses is a reserve for estimated credit losses on individually evaluated loans determined to be impaired as well as estimated credit losses inherent in the loan portfolio, and is based on quarterly evaluations of the collectability and historical loss experience of loans. Actual credit losses, net of recoveries, are deducted from the allowance for loan losses. A provision for loan losses, which is a charge against earnings, is recorded to bring the allowance for loan losses to a level that, in management’s judgment, is appropriate to absorb probable losses in the loan portfolio.
The allocation methodology applied by the Corporation, designed to assess the appropriateness of the allowance for loan losses, includes an allocation methodology, as well as management’s ongoing review and grading of the loan portfolio into criticized loan categories (defined as specific loans warranting either specific allocation, or a criticized status of special mention, substandard, doubtful, or loss). The allocation methodology focuses on evaluation of several factors, including but not limited to: evaluation of facts and issues related to specific loans, management’s ongoing review and grading of the loan portfolio, consideration of historical loan loss and delinquency experience on each portfolio category, trends in past due and nonaccrual loans, the level of potential problem loans, the risk characteristics of the various classifications of loans, changes in the size and character of the loan portfolio, concentrations of loans to specific borrowers or industries, existing economic conditions, the fair value of underlying collateral, and other qualitative and quantitative factors which could affect potential credit losses. Because each of the criteria used is subject to change, the allocation of the allowance for loan losses is not necessarily indicative of the trend of future loan losses in any particular loan category. The total allowance for loan losses is available to absorb losses from any segment of the portfolio.
Management, judging current information and events regarding the borrowers’ ability to repay their obligations, considers a loan to be impaired when it is probable that the Corporation will be unable to collect all amounts due according to the contractual terms of the note agreement, including both principal and interest. Management has determined that commercial and consumer loan relationships that have nonaccrual status or have had their terms restructured in a troubled debt restructuring meet this impaired loan definition. When an individual loan is determined to be impaired, the allowance for loan losses attributable to the loan is allocated based on management’s estimate of the borrower’s ability to repay the loan given the availability of collateral, other sources of cash flows, as well as evaluation of legal options available to the Corporation. The amount of impairment is measured based upon the present value of expected future cash flows discounted at the loan’s effective interest rate, the fair value of the underlying collateral less applicable selling costs, or the observable market price of the loan. If foreclosure is probable or the loan is collateral dependent, impairment is measured using the fair value of the loan’s collateral, less costs to sell. Large groups of homogeneous loans, such as residential mortgage, home equity and installment loans, are collectively evaluated for impairment. Interest income on impaired loans is recorded only to the extent that interest payments are subsequently received in cash and a determination has been made that the principal and interest of the loan is collectible.
Management believes that the level of the allowance for loan losses is appropriate. While management uses available information to recognize losses on loans, future changes to the allowance for loan losses may be necessary based on changes in economic conditions. In addition, various regulatory agencies, as an integral part of their examination process, periodically review the Corporation’s allowance for loan losses. Such agencies may require additions to the allowance for loan losses or may require that certain loan balances be charged off or downgraded into criticized loan categories when their credit evaluations differ from those of management based on their judgments about information available to them at the time of their examinations. See Loans above for further policy discussion and see Note 3 for additional information on the allowance for loan losses.
Other Real Estate Owned
Other real estate owned is included in other assets in the consolidated balance sheets and is comprised of property acquired through a foreclosure proceeding or acceptance of a deed-in-lieu of foreclosure, and loans classified as in-substance foreclosure. Other real estate owned is recorded at the fair value of the underlying
85
property collateral, less estimated selling costs. This fair value becomes the new cost basis for the foreclosed asset. The initial write-down, if any, will be recorded as a charge off against the allowance for loan losses. Any subsequent write-downs to reflect current fair value, as well as gains and losses on disposition and revenues and expenses incurred in maintaining such properties, are expensed as incurred. Other real estate owned also includes bank premises formerly but no longer used for banking as well as property originally acquired for future expansion but no longer intended to be used for that purpose. Banking premises are transferred at the lower of carrying value or fair value, less estimated selling costs and any write-down is expensed as incurred. Other real estate owned totaled $18 million and $35 million at December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Reserve for Unfunded Commitments
A reserve for unfunded commitments is maintained at a level believed by management to be sufficient to absorb estimated probable losses related to unfunded credit facilities (including unfunded loan commitments and letters of credit) and is included in other liabilities in the consolidated balance sheets. The determination of the appropriate level of the reserve is based upon an evaluation of the unfunded credit facilities, including an assessment of historical commitment utilization experience and credit risk grading of the loan. Net adjustments to the reserve for unfunded commitments are included in losses other than loans in the consolidated statements of income. See Note 15 for additional information on the reserve for unfunded commitments.
Mortgage Repurchase Reserve
The Corporation sells residential mortgage loans to investors in the normal course of business. Residential mortgage loans sold to investors are predominantly conventional residential first lien mortgages originated under the usual underwriting procedures, and are most often sold on a nonrecourse basis. The Corporation’s agreements to sell residential mortgage loans usually require general representations and warranties on the underlying loans sold, related to credit information, loan documentation, collateral, and insurability, which if subsequently untrue or breached, could require the Corporation to indemnify or repurchase certain loans affected. To a much lesser degree, the Corporation may sell residential mortgage loans with limited recourse (limited in that the recourse period ends prior to the loan’s maturity, usually after certain time and / or loan paydown criteria have been met), whereby indemnification or repurchase could be required if the loan had defined delinquency issues during the limited recourse periods. The balance in the repurchase reserve at the balance sheet date reflects the estimated amount of potential loss the Corporation could incur from repurchasing a loan (“put back” requests), as well as loss reimbursements, indemnification, and other settlement resolutions (“make whole” payments). See Note 15 for additional information on the mortgage repurchase reserve.
Premises and Equipment and Software
Premises and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization are computed on the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the related assets or the lease term. Maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as incurred, while additions or major improvements are capitalized and depreciated over the estimated useful lives. Estimated useful lives of the assets range predominantly as follows:
| | | | |
Land Improvements | | | 3 to 15 years | |
Buildings | | | 5 to 39 years | |
Computers | | | 3 to 5 years | |
Furniture, fixtures, and other equipment | | | 3 to 15 years | |
Leasehold improvements are amortized on a straight-line basis over the lesser of the lease terms or the estimated useful lives of the improvements. Software, included in other assets in the consolidated balance sheets, is amortized on a straight-line basis over the lesser of the contract terms or the estimated useful life of the software. See Note 5 for additional information on premises and equipment.
86
Goodwill and Intangible Assets
Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets: The excess of the cost of an acquisition over the fair value of the net assets acquired consists primarily of goodwill, core deposit intangibles, and other identifiable intangibles (primarily related to customer relationships acquired). Core deposit intangibles have estimated finite lives and are amortized on an accelerated basis to expense over a 10-year period. The other intangibles have estimated finite lives and are amortized on an accelerated basis to expense over their weighted average life (a weighted average life of 14 years for both 2013 and 2012). The Corporation reviews long-lived assets and certain identifiable intangibles for impairment at least annually, or whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable, in which case an impairment charge would be recorded.
Goodwill is not amortized but, instead, is subject to impairment tests on at least an annual basis, and more frequently if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying amount. The impairment testing process is conducted by assigning net assets and goodwill to each reporting unit. An initial qualitative evaluation is made to assess the likelihood of impairment and determine whether further quantitative testing to calculate the fair value is necessary. When the qualitative evaluation indicates that impairment is more likely than not, quantitative testing is required whereby the fair value of each reporting unit is calculated and compared to the recorded book value, “step one.” If the calculated fair value of the reporting unit exceeds its carrying value, goodwill is not considered impaired and “step two” is not considered necessary. If the carrying value of a reporting unit exceeds its calculated fair value, the impairment test continues (“step two”) by comparing the carrying value of the reporting unit’s goodwill to the implied fair value of goodwill. The implied fair value is computed by adjusting all assets and liabilities of the reporting unit to current fair value with the offset adjustment to goodwill. The adjusted goodwill balance is the implied fair value of the goodwill. An impairment charge is recognized if the carrying fair value of goodwill exceeds the implied fair value of goodwill. See Note 4 for additional information on goodwill and other intangible assets.
Mortgage Servicing Rights: The Corporation sells residential mortgage loans in the secondary market and typically retains the right to service the loans sold. Upon sale, a mortgage servicing rights asset is capitalized, which represents the then current fair value of future net cash flows expected to be realized for performing servicing activities. Mortgage servicing rights, when purchased, are initially recorded at fair value. As the Corporation has not elected to subsequently measure any class of servicing assets under the fair value measurement method, the Corporation follows the amortization method. Mortgage servicing rights are amortized in proportion to and over the period of estimated net servicing income, and assessed for impairment at each reporting date. Mortgage servicing rights are carried at the lower of the initial capitalized amount, net of accumulated amortization, or estimated fair value, and are included in other intangible assets, net in the consolidated balance sheets.
The Corporation periodically evaluates its mortgage servicing rights asset for impairment. Impairment is assessed based on fair value at each reporting date using estimated prepayment speeds of the underlying mortgage loans serviced and stratifications based on the risk characteristics of the underlying loans (predominantly loan type and note interest rate). As mortgage interest rates fall, prepayment speeds are usually faster and the value of the mortgage servicing rights asset generally decreases, requiring additional valuation reserve. Conversely, as mortgage interest rates rise, prepayment speeds are usually slower and the value of the mortgage servicing rights asset generally increases, requiring less valuation reserve. A valuation allowance is established, through a charge to earnings, to the extent the amortized cost of the mortgage servicing rights exceeds the estimated fair value by stratification. If it is later determined that all or a portion of the temporary impairment no longer exists for a stratification, the valuation is reduced through a recovery to earnings. An other-than-temporary impairment (i.e., recoverability is considered remote when considering interest rates and loan pay off activity) is recognized as a write-down of the mortgage servicing rights asset and the related valuation allowance (to the extent a valuation allowance is available) and then against earnings. A direct write-down permanently reduces the carrying value of the mortgage servicing rights asset and valuation allowance, precluding subsequent recoveries. See Note 4 for additional information on mortgage servicing rights.
87
Income Taxes
Amounts provided for income tax expense are based on income reported for financial statement purposes and do not necessarily represent amounts currently payable under tax laws. Deferred income taxes, which arise principally from temporary differences between the amounts reported in the financial statements and the tax bases of assets and liabilities, are included in the amounts provided for income taxes. In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income and tax planning strategies which will create taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences become deductible. Management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities, the amount of taxes paid in available carryback years, projected future taxable income, and, if necessary, tax planning strategies in making this assessment.
The Corporation files a consolidated federal income tax return and individual or consolidated state income tax returns. Accordingly, amounts equal to tax benefits of those subsidiaries having taxable federal losses or credits are offset by other subsidiaries that incur federal tax liabilities.
It is the Corporation’s policy to provide for uncertain tax positions as a part of income tax expense based upon management’s assessment of whether a tax benefit is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by tax authorities. At December 31, 2013 and 2012, the Corporation believes it has appropriately accounted for any unrecognized tax benefits. To the extent the Corporation prevails in matters for which a liability for an unrecognized tax benefit is established or is required to pay amounts in excess of the liability, the Corporation’s effective tax rate in a given financial statement period may be effected. See Note 12 for additional information on income taxes.
Derivative Financial Instruments and Hedging Activities
Derivative instruments, including derivative instruments embedded in other contracts, are carried at fair value on the consolidated balance sheets with changes in the fair value recorded to earnings or accumulated other comprehensive income, as appropriate. On the date the derivative contract is entered into, the Corporation designates the derivative as a fair value hedge (i.e., a hedge of the fair value of a recognized asset or liability), a cash flow hedge (i.e., a hedge of the variability of cash flows to be received or paid related to a recognized asset or liability), or a free-standing derivative instrument. For a derivative designated as a fair value hedge, the changes in the fair value of the derivative instrument and the changes in the fair value of the hedged asset or liability are recognized in current period earnings as an increase or decrease to the carrying value of the hedged item on the balance sheet and in the related income statement account. For a derivative designated as a cash flow hedge, the effective portions of changes in the fair value of the derivative instrument are recorded in other comprehensive income and the ineffective portions of changes in the fair value of a derivative instrument are recognized in current period earnings as an adjustment to the related income statement account. Amounts within accumulated other comprehensive income are reclassified into earnings in the period the hedged item affects earnings. If a derivative is designated as a free-standing derivative instrument, changes in fair value are reported in current period earnings.
To qualify for and maintain hedge accounting, the Corporation must meet formal documentation and effectiveness evaluation requirements both at the hedge’s inception and on an ongoing basis. The application of the hedge accounting policy requires strict adherence to documentation and effectiveness testing requirements, judgment in the assessment of hedge effectiveness, identification of similar hedged item groupings, and measurement of changes in the fair value of hedged items. If it is determined that a derivative is not highly effective as a hedge or that it has ceased to be a highly effective hedge, the Corporation discontinues hedge accounting prospectively. When hedge accounting is discontinued on a fair value hedge because it is determined that the derivative no longer qualifies as an effective hedge, the Corporation continues to carry the derivative on the consolidated balance sheet at its fair value and no longer adjusts the hedged asset or liability for changes in fair value. The adjustment to the carrying amount of the hedged asset or liability is amortized over the remaining
88
life of the hedged item, beginning no later than when hedge accounting ceases. When hedge accounting is discontinued on a cash flow hedge because it is determined that the derivative no longer qualifies as an effective hedge, the Corporation records the changes in the fair value of the derivative in earnings rather than through accumulated other comprehensive income and when the cash flows associated with the hedged item are realized, the gain or loss is reclassified out of other comprehensive income and included in the same income statement account of the item being hedged.
The Corporation measures the effectiveness of its hedges, where applicable, at inception and each quarter on an on-going basis. For a fair value hedge, the cumulative change in the fair value of the hedge instrument attributable to the risk being hedged versus the cumulative fair value change of the hedged item attributable to the risk being hedged is considered to be the “ineffective” portion, which is recorded as an increase or decrease in the related income statement classification of the item being hedged (i.e., net interest income). For a cash flow hedge, the ineffective portions of changes in the fair value are recognized immediately in the related income statement account. See Note 13 for additional information on derivative financial instruments and hedging activities.
Stock-Based Compensation
The fair value of stock options granted is estimated on the date of grant using a Black-Scholes option pricing model, while the fair value of restricted stock awards is their fair market value on the date of grant. The fair value of stock options and restricted stock awards are amortized as compensation expense on a straight-line basis over the vesting period of the grants. Compensation expense recognized is included in personnel expense in the consolidated statements of income. See Note 10 for additional information on stock-based compensation.
Comprehensive Income
Comprehensive income includes all changes in stockholders’ equity during a period, except those resulting from transactions with stockholders. In addition to net income, other components of the Corporation’s comprehensive income include the after tax effect of changes in net unrealized gain / loss on securities available for sale, changes in net actuarial gain / loss on defined benefit post-retirement plans, and changes in net unrealized gain / loss on effective cash flow hedging instruments. Comprehensive income is reported in the accompanying consolidated statements of changes in stockholder’s equity and consolidated statements of comprehensive income. See Note 21 for additional information on accumulated other comprehensive income (loss).
Fair Value Measurements
Fair value represents the estimated price at which an orderly transaction to sell an asset or to transfer a liability would take place between market participants at the measurement date under current market conditions (i.e., an exit price concept). As there is no active market for many of the Corporation’s financial instruments, estimates are made using discounted cash flow or other valuation techniques. Inputs into the valuation methods are subjective in nature, involve uncertainties, and require significant judgment and therefore cannot be determined with precision. Accordingly, the derived fair value estimates presented herein are not necessarily indicative of the amounts the Corporation could realize in a current market exchange. Assets and liabilities are categorized into three levels based on the markets in which the assets and liabilities are traded and the reliability of the assumptions used to determine fair value. In instances where the determination of the fair value measurement is based on inputs from different levels of the fair value hierarchy, the level in the fair value hierarchy in which the entire fair value measurement falls is based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement in its entirety. The Corporation’s assessment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurement in its entirety requires judgment, and considers factors specific to the asset or liability. See Note 17 for additional information on fair value measurements. Below is a brief description of each fair value level.
Level 1 — Level 1 inputs utilize quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that the Corporation has the ability to access.
89
Level 2 — Level 2 inputs are inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly. Level 2 inputs may include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, as well as inputs that are observable for the asset or liability (other than quoted prices), such as interest rates, foreign exchange rates, and yield curves that are observable at commonly quoted intervals.
Level 3 — Level 3 inputs are unobservable inputs for the asset or liability, which are typically based on an entity’s own assumptions, as there is little, if any, related market activity.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
For purposes of the consolidated statements of cash flows, cash and cash equivalents are considered to include cash and due from banks, interest-bearing deposits in other financial institutions, and federal funds sold and securities purchased under agreements to resell.
Per Share Computations
Earnings per share are calculated utilizing the two-class method. Basic earnings per share are calculated by dividing the sum of distributed earnings to common shareholders and undistributed earnings allocated to common shareholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding. Diluted earnings per share are calculated by dividing the sum of distributed earnings to common shareholders and undistributed earnings allocated to common shareholders by the weighted average number of shares adjusted for the dilutive effect of common stock awards (outstanding stock options, unvested restricted stock, and outstanding stock warrants). Also see Notes 9 and 19.
New Accounting Pronouncements Adopted
In July 2013, the FASB issued an amendment to permit an entity to designate the Fed Funds Effective Swap Rate, also referred to as the overnight index swap rate (“OIS”), as a benchmark interest rate. The OIS will be included as a U.S. benchmark interest rate for hedge accounting purposes. Prior to this amendment, only interest rates on direct treasury obligations of the U.S. government and the London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”) swap rate were considered benchmark interest rates. In addition, the amendment removes the restriction on using different benchmark rates for similar hedges. This amendment can be applied on a prospective basis for qualifying new or redesignated hedging relationships entered into on or after July 17, 2013. The Corporation adopted the accounting standard during the third quarter of 2013, as required, with no material impact on its results of operations, financial position, or liquidity.
In February 2013, the FASB issued an amendment requiring an entity to provide information about the amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income by component. These disclosures may be presented on the face of the income statement or in the notes to consolidated financial statements, depending upon the specific accounting guidance for the reclassification out of accumulated other comprehensive income. The amendments are effective prospectively for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2012 with early adoption permitted. The Corporation adopted the accounting standard during the first quarter of 2013, as required, with no material impact on its results of operations, financial position, or liquidity. See Note 21 for the required new disclosures on accumulated other comprehensive income.
In July 2012, the FASB issued amendments intended to simplify how entities test the decline in the realizable value (impairment) of indefinite-lived intangible assets other than goodwill. The amendments permit an organization to make a qualitative evaluation about the likelihood of impairment of an indefinite-lived intangible asset to determine whether it should apply the quantitative test and calculate the fair value of the indefinite-lived intangible asset. The amendments do not change how an organization measures an impairment loss. Therefore, it is not expected to affect the information reported to users of the financial statements. The amendments are
90
effective for annual and interim impairment tests performed for fiscal years beginning after September 15, 2012. The Corporation adopted the accounting standard during the first quarter of 2013, as required, with no material impact on its results of operations, financial position, or liquidity.
In December 2011, the FASB issued amendments to require an entity to disclose information about offsetting and related arrangements to enable users of its financial statements to understand the effect of those arrangements on its financial position. This information will enable users of an entity’s financial statements to evaluate the effect or potential effect of netting arrangements with certain financial instruments and derivative instruments. The amendments are effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013, with retrospective application to the disclosures of all comparative periods presented. The Corporation adopted the accounting standard during the first quarter of 2013, as required, with no material impact on its results of operations, financial position, or liquidity. See Note 14 for the required new disclosures on balance sheet offsetting.
NOTE 2 INVESTMENT SECURITIES:
The amortized cost and fair values of securities available for sale and held to maturity were as follows.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2013: | | Amortized
Cost | | | Gross
Unrealized
Gains | | | Gross
Unrealized
Losses | | | Fair
Value | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Investment securities available for sale: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. Treasury securities | | $ | 1,001 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,002 | |
Obligations of state and political subdivisions (municipal securities) | | | 653,758 | | | | 23,855 | | | | (1,533 | ) | | | 676,080 | |
Residential mortgage-related securities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Government-sponsored enterprise (“GSE”) | | | 3,855,467 | | | | 61,542 | | | | (78,579 | ) | | | 3,838,430 | |
Private-label | | | 3,035 | | | | 16 | | | | (37 | ) | | | 3,014 | |
GSE commercial mortgage-related securities | | | 673,555 | | | | 1,764 | | | | (27,842 | ) | | | 647,477 | |
Asset-backed securities(1) | | | 23,049 | | | | 10 | | | | — | | | | 23,059 | |
Other securities (debt and equity) | | | 60,711 | | | | 855 | | | | (43 | ) | | | 61,523 | |
| | | | |
Total investment securities available for sale | | $ | 5,270,576 | | | $ | 88,043 | | | $ | (108,034 | ) | | $ | 5,250,585 | |
| | | | |
Investment securities held to maturity: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Obligations of state and political subdivisions (municipal securities) | | $ | 175,210 | | | $ | 401 | | | $ | (5,722 | ) | | $ | 169,889 | |
| | | | |
Total investment securities held to maturity | | $ | 175,210 | | | $ | 401 | | | $ | (5,722 | ) | | $ | 169,889 | |
| | | | |
| (1) | The asset-backed securities position is largely comprised of senior, floating rate, tranches of student loan securities issued by SLM Corp and guaranteed under the Federal Family Education Loan Program. |
91
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2012: | | Amortized
Cost | | | Gross
Unrealized
Gains | | | Gross
Unrealized
Losses | | | Fair
Value | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Investment securities available for sale: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
U. S. Treasury securities | | $ | 1,003 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,004 | |
Obligations of state and political subdivisions (municipal securities) | | | 755,644 | | | | 45,599 | | | | (55 | ) | | | 801,188 | |
Residential mortgage-related securities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
GSE | | | 3,708,287 | | | | 93,595 | | | | (3,727 | ) | | | 3,798,155 | |
Private-label | | | 6,002 | | | | 147 | | | | — | | | | 6,149 | |
GSE commercial mortgage-related securities | | | 226,420 | | | | 2,809 | | | | (1,063 | ) | | | 228,166 | |
Other securities (debt and equity) | | | 90,622 | | | | 1,549 | | | | (75 | ) | | | 92,096 | |
| | | | |
Total investment securities available for sale | | $ | 4,787,978 | | | $ | 143,700 | | | $ | (4,920 | ) | | $ | 4,926,758 | |
| | | | |
Investment securities held to maturity: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Obligations of state and political subdivisions (municipal securities) | | $ | 39,877 | | | $ | 98 | | | $ | (296 | ) | | $ | 39,679 | |
| | | | |
Total investment securities held to maturity | | $ | 39,877 | | | $ | 98 | | | $ | (296 | ) | | $ | 39,679 | |
| | | | |
The amortized cost and fair values of investment securities available for sale and held to maturity at December 31, 2013, are shown below. Expected maturities will differ from contractual maturities because borrowers may have the right to call or prepay obligations with or without call or prepayment penalties.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Available for Sale | | | Held to Maturity | |
($ in Thousands) | | Amortized
Cost | | | Fair
Value | | | Amortized
Cost | | | Fair
Value | |
Due in one year or less | | $ | 31,404 | | | $ | 31,503 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Due after one year through five years | | | 231,751 | | | | 240,398 | | | | 232 | | | | 233 | |
Due after five years through ten years | | | 429,242 | | | | 441,137 | | | | 68,394 | | | | 66,100 | |
Due after ten years | | | 23,055 | | | | 25,510 | | | | 106,584 | | | | 103,556 | |
| | | | |
Total debt securities | | | 715,452 | | | | 738,548 | | | | 175,210 | | | | 169,889 | |
Residential mortgage-related securities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
GSE | | | 3,855,467 | | | | 3,838,430 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Private-label | | | 3,035 | | | | 3,014 | | | | — | | | | — | |
GSE commercial mortgage-related securities | | | 673,555 | | | | 647,477 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Asset-backed securities | | | 23,049 | | | | 23,059 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Equity securities | | | 18 | | | | 57 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | |
Total investment securities | | $ | 5,270,576 | | | $ | 5,250,585 | | | $ | 175,210 | | | $ | 169,889 | |
| | | | |
For 2013, net investment securities gains of $1 million were primarily attributable to gains on sales of municipal and debt securities. Net investment securities gains of $4 million for 2012, were primarily attributable to gains on sales of equity, mortgage-related, and trust preferred debt securities. Net investment securities losses of $1 million for 2011 were primarily attributable to credit-related other-than-temporary write-downs on the Corporation’s holding of various investment securities (including write-downs on trust preferred debt securities and various equity securities).
92
Total proceeds and gross realized gains and losses from sales and write-downs of investment securities (with other-than-temporary write-downs on securities included in gross losses) for each of the three years ended December 31 were as follows.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Gross gains | | $ | 637 | | | $ | 4,481 | | | $ | — | |
Gross losses | | | (73 | ) | | | (220 | ) | | | (1,112 | ) |
| | | | |
Investment securities gains (losses), net | | $ | 564 | | | $ | 4,261 | | | $ | (1,112 | ) |
Proceeds from sales of investment securities | | | 136,152 | | | | 299,782 | | | | 176,267 | |
Pledged securities with a carrying value of approximately $2.9 billion and $2.6 billion at December 31, 2013, and December 31, 2012, respectively, were pledged to secure certain deposits, FHLB advances, or for other purposes as required or permitted by law.
The following represents gross unrealized losses and the related fair value of investment securities available for sale and held to maturity, aggregated by investment category and length of time individual securities have been in a continuous unrealized loss position, at December 31, 2013.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Less than 12 months | | | 12 months or more | | | Total | |
| | | | |
| December 31, 2013 | | Number
of
Securities | | | Unrealized
Losses | | | Fair Value | | | Number
of
Securities | | | Unrealized
Losses | | | Fair Value | | | Unrealized
Losses | | | Fair Value | |
| |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Investment securities available for sale: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Obligations of state and political subdivisions (municipal securities) | | | 113 | | | $ | (1,525 | ) | | $ | 47,044 | | | | 1 | | | $ | (8 | ) | | $ | 273 | | | $ | (1,533 | ) | | $ | 47,317 | |
Residential mortgage-related securities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
GSE | | | 106 | | | | (57,393 | ) | | | 1,887,784 | | | | 15 | | | | (21,186 | ) | | | 421,082 | | | | (78,579 | ) | | | 2,308,866 | |
Private-label | | | 2 | | | | (37 | ) | | | 2,105 | | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | 35 | | | | (37 | ) | | | 2,140 | |
GSE commercial mortgage-related securities | | | 19 | | | | (23,854 | ) | | | 443,462 | | | | 1 | | | | (3,988 | ) | | | 45,950 | | | | (27,842 | ) | | | 489,412 | |
Other debt securities | | | 5 | | | | (43 | ) | | | 6,452 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (43 | ) | | | 6,452 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | | | | | $ | (82,852 | ) | | $ | 2,386,847 | | | | | | | $ | (25,182 | ) | | $ | 467,340 | | | $ | (108,034 | ) | | $ | 2,854,187 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Investment securities held to maturity: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Obligations of state and political subdivisions (municipal securities) | | | 298 | | | $ | (5,339 | ) | | $ | 124,435 | | | | 10 | | | $ | (383 | ) | | $ | 5,010 | | | $ | (5,722 | ) | | $ | 129,445 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | | | | | $ | (5,339 | ) | | $ | 124,435 | | | | | | | $ | (383 | ) | | $ | 5,010 | | | $ | (5,722 | ) | | $ | 129,445 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The Corporation reviews the investment securities portfolio on a quarterly basis to monitor its exposure to other-than-temporary impairment. A determination as to whether a security’s decline in fair value is other-than-temporary takes into consideration numerous factors and the relative significance of any single factor can vary by security. Some factors the Corporation may consider in the other-than-temporary impairment analysis include, the length of time and extent to which the security has been in an unrealized loss position, changes in security ratings, financial condition and near-term prospects of the issuer, as well as security and industry specific economic conditions. In addition, with regards to its debt securities, the Corporation may also evaluate payment
93
structure, whether there are defaulted payments or expected defaults, prepayment speeds, and the value of any underlying collateral. For certain debt securities in unrealized loss positions, the Corporation prepares cash flow analyses to compare the present value of cash flows expected to be collected from the security with the amortized cost basis of the security.
Based on the Corporation’s evaluation, management does not believe any unrealized loss at December 31, 2013, represents an other-than-temporary impairment as these unrealized losses are primarily attributable to changes in interest rates and the current market conditions, and not credit deterioration. The unrealized losses reported for residential mortgage-related securities relate to private-label residential mortgage-related securities as well as residential mortgage-related securities issued by government agencies such as the Federal National Mortgage Association (“FNMA”) and the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (“FHLMC”). The unrealized losses reported for commercial mortgage related securities relate to government agency mortgage-related securities. The Corporation currently does not intend to sell nor does it believe that it will be required to sell the securities contained in the above unrealized losses table before recovery of their amortized cost basis.
The following is a summary of the credit loss portion of other-than-temporary impairment recognized in earnings on debt securities during 2012 and 2013.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Private-label
Mortgage-Related
Securities | | | Trust Preferred
Debt Securities | | | Total | |
| | | | |
| | | $ in Thousands | |
Balance of credit-related other-than-temporary impairment at December 31, 2011 | | $ | (17,558 | ) | | $ | (10,835 | ) | | $ | (28,393 | ) |
Reduction due to credit impaired securities sold | | | 17,026 | | | | 4,499 | | | | 21,525 | |
| | | | |
Balance of credit-related other-than-temporary impairment at December 31, 2012 | | $ | (532 | ) | | $ | (6,336 | ) | | $ | (6,868 | ) |
Reduction due to credit impaired securities sold | | | 532 | | | | 57 | | | | 589 | |
| | | | |
Balance of credit-related other-than-temporary impairment at December 31, 2013 | | $ | — | | | $ | (6,279 | ) | | $ | (6,279 | ) |
| | | | |
94
For comparative purposes, the following represents gross unrealized losses and the related fair value of investment securities available for sale, aggregated by investment category and length of time that individual securities have been in a continuous unrealized loss position, at December 31, 2012.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Less than 12 months | | | 12 months or more | | | Total | |
| | | | |
| December 31, 2012 | | Number
of
Securities | | | Unrealized
Losses | | | Fair Value | | | Number
of
Securities | | | Unrealized
Losses | | | Fair
Value | | | Unrealized
Losses | | | Fair Value | |
| |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Investment securities available for sale: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Obligations of state and political subdivisions (municipal securities) | | | 15 | | | $ | (42 | ) | | $ | 5,065 | | | | 1 | | | $ | (13 | ) | | $ | 348 | | | $ | (55 | ) | | $ | 5,413 | |
Residential mortgage-related securities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
GSE | | | 30 | | | | (3,727 | ) | | | 892,964 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (3,727 | ) | | | 892,964 | |
Private-label | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | 50 | | | | — | | | | 50 | |
GSE commercial mortgage-related securities | | | 2 | | | | (1,063 | ) | | | 102,474 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1,063 | ) | | | 102,474 | |
Other securities (debt) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1 | | | | (75 | ) | | | 111 | | | | (75 | ) | | | 111 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | | | | | $ | (4,832 | ) | | $ | 1,000,503 | | | | | | | $ | (88 | ) | | $ | 509 | | | $ | (4,920 | ) | | $ | 1,001,012 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Investment securities held to maturity: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Obligations of state and political subdivisions (municipal securities) | | | 56 | | | $ | (296 | ) | | $ | 28,265 | | | | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | (296 | ) | | $ | 28,265 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | | | | | $ | (296 | ) | | $ | 28,265 | | | | | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | (296 | ) | | $ | 28,265 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Federal Home Loan Bank (“FHLB”) and Federal Reserve Bank Stocks: The Corporation is required to maintain Federal Reserve stock and FHLB stock as a member of both the Federal Reserve System and the FHLB, and in amounts as required by these institutions. These equity securities are “restricted” in that they can only be sold back to the respective institutions or another member institution at par. Therefore, they are less liquid than other marketable equity securities and their fair value is equal to amortized cost. At December 31, 2013, and 2012, the Corporation had FHLB stock of $110 million and $96 million, respectively. The Corporation had Federal Reserve Bank stock of $71 million at both December 31, 2013 and 2012.
The Corporation reviewed these securities for impairment, including but not limited to, consideration of operating performance, the severity and duration of market value declines, as well as its liquidity and funding position. After evaluating all of these considerations, the Corporation believes the cost of these investments will be recovered and no impairment has been recorded on these securities during 2013, 2012, or 2011, respectively.
95
NOTE 3 LOANS:
Loans at December 31 are summarized below.
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 4,822,680 | | | $ | 4,502,021 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 1,114,715 | | | | 1,219,747 | |
Lease financing | | | 55,483 | | | | 64,196 | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 5,992,878 | | | | 5,785,964 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 2,939,456 | | | | 2,906,759 | |
Real estate construction | | | 896,248 | | | | 655,381 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 3,835,704 | | | | 3,562,140 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 9,828,582 | | | | 9,348,104 | |
Home equity | | | 1,825,014 | | | | 2,219,494 | |
Installment | | | 407,074 | | | | 466,727 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 3,835,591 | | | | 3,376,697 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 6,067,679 | | | | 6,062,918 | |
| | | | |
Total loans | | $ | 15,896,261 | | | $ | 15,411,022 | |
| | | | |
The Corporation has granted loans to their directors, executive officers, or their related interests. These loans were made on substantially the same terms, including rates and collateral, as those prevailing at the time for comparable transactions with other unrelated customers, and do not involve more than a normal risk of collection. These loans to related parties are summarized below.
| | | | |
| | | 2013 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Balance at beginning of year | | $ | 36,971 | |
New loans | | | 15,887 | |
Repayments | | | (14,219 | ) |
| | | | |
Balance at end of year | | $ | 38,639 | |
| | | | |
A summary of the changes in the allowance for loan losses for the years indicated was as follows.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Balance at beginning of year | | $ | 297,409 | | | $ | 378,151 | | | $ | 476,813 | |
Provision for loan losses | | | 10,000 | | | | 3,000 | | | | 52,000 | |
Charge offs | | | (88,061 | ) | | | (117,046 | ) | | | (189,732 | ) |
Recoveries | | | 48,967 | | | | 33,304 | | | | 39,070 | |
| | | | |
Net charge offs | | | (39,094 | ) | | | (83,742 | ) | | | (150,662 | ) |
| | | | |
Balance at end of year | | $ | 268,315 | | | $ | 297,409 | | | $ | 378,151 | |
| | | | |
The level of the allowance for loan losses represents management’s estimate of an amount appropriate to provide for probable credit losses in the loan portfolio at the balance sheet date. In general, the change in the allowance for loan losses is a function of a number of factors, including but not limited to changes in the loan portfolio, net charge offs, trends in past due and impaired loans, and the level of potential problem loans. Management considers the allowance for loan losses a critical accounting policy, as assessing these numerous factors involves significant judgment.
96
A summary of the changes in the allowance for loan losses by portfolio segment for the year ended December 31, 2013, was as follows.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| $ in Thousands | | Commercial
and
industrial | | | Commercial
real estate
— owner
occupied | | | Lease
financing | | | Commercial
real
estate —
investor | | | Real estate
construction | | | Home
equity | | | Installment | | | Residential
mortgage | | | Total | |
| | | | |
Balance at Dec 31, 2012 | | $ | 97,852 | | | $ | 27,389 | | | $ | 3,024 | | | $ | 63,181 | | | $ | 20,741 | | | $ | 56,826 | | | $ | 4,299 | | | $ | 24,097 | | | $ | 297,409 | |
Provision for loan losses | | | 12,930 | | | | (1,778 | ) | | | (1,429 | ) | | | (2,140 | ) | | | 541 | | | | (8,213 | ) | | | (2,127 | ) | | | 12,216 | | | | 10,000 | |
Charge offs | | | (35,146 | ) | | | (6,474 | ) | | | (206 | ) | | | (9,846 | ) | | | (3,375 | ) | | | (20,629 | ) | | | (1,389 | ) | | | (10,996 | ) | | | (88,061 | ) |
Recoveries | | | 28,865 | | | | 339 | | | | 218 | | | | 6,961 | | | | 5,511 | | | | 4,212 | | | | 1,633 | | | | 1,228 | | | | 48,967 | |
| | | | |
Balance at Dec 31, 2013 | | $ | 104,501 | | | $ | 19,476 | | | $ | 1,607 | | | $ | 58,156 | | | $ | 23,418 | | | $ | 32,196 | | | $ | 2,416 | | | $ | 26,545 | | | $ | 268,315 | |
| | | | |
Allowance for loan losses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Ending balance impaired loans individually evaluated for impairment | | $ | 7,994 | | | $ | 1,019 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 3,932 | | | $ | 254 | | | $ | 123 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 315 | | | $ | 13,637 | |
Ending balance impaired loans collectively evaluated for impairment | | $ | 3,923 | | | $ | 1,936 | | | $ | 29 | | | $ | 3,963 | | | $ | 2,162 | | | $ | 13,866 | | | $ | 487 | | | $ | 11,872 | | | $ | 38,238 | |
| | | | |
Total impaired loans | | $ | 11,917 | | | $ | 2,955 | | | $ | 29 | | | $ | 7,895 | | | $ | 2,416 | | | $ | 13,989 | | | $ | 487 | | | $ | 12,187 | | | $ | 51,875 | |
Ending balance all other loans collectively evaluated for impairment | | $ | 92,584 | | | $ | 16,521 | | | $ | 1,578 | | | $ | 50,261 | | | $ | 21,002 | | | $ | 18,207 | | | $ | 1,929 | | | $ | 14,358 | | | $ | 216,440 | |
| | | | |
Total | | $ | 104,501 | | | $ | 19,476 | | | $ | 1,607 | | | $ | 58,156 | | | $ | 23,418 | | | $ | 32,196 | | | $ | 2,416 | | | $ | 26,545 | | | $ | 268,315 | |
| | | | |
Loans: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Ending balance impaired loans individually evaluated for impairment | | $ | 29,343 | | | $ | 24,744 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 32,367 | | | $ | 3,777 | | | $ | 929 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 10,526 | | | $ | 101,686 | |
Ending balance impaired loans collectively evaluated for impairment | | $ | 40,893 | | | $ | 17,929 | | | $ | 69 | | | $ | 50,175 | | | $ | 6,483 | | | $ | 33,871 | | | $ | 1,360 | | | $ | 56,947 | | | $ | 207,727 | |
| | | | |
Impaired loan subtotal | | $ | 70,236 | | | $ | 42,673 | | | $ | 69 | | | $ | 82,542 | | | $ | 10,260 | | | $ | 34,800 | | | $ | 1,360 | | | $ | 67,473 | | | $ | 309,413 | |
Ending balance all other loans collectively evaluated for impairment | | $ | 4,752,444 | | | $ | 1,072,042 | | | $ | 55,414 | | | $ | 2,856,914 | | | $ | 885,988 | | | $ | 1,790,214 | | | $ | 405,714 | | | $ | 3,768,118 | | | $ | 15,586,848 | |
| | | | |
Total | | $ | 4,822,680 | | | $ | 1,114,715 | | | $ | 55,483 | | | $ | 2,939,456 | | | $ | 896,248 | | | $ | 1,825,014 | | | $ | 407,074 | | | $ | 3,835,591 | | | $ | 15,896,261 | |
| | | | |
The allocation methodology used by the Corporation includes allocations for specifically identified impaired loans and loss factor allocations, (used for both criticized and non-criticized loan categories) with a component primarily based on historical loss rates and a component primarily based on other qualitative factors. Management allocates the allowance for loan losses by pools of risk within each loan portfolio. The allocation of the allowance for loan losses by loan portfolio is made for analytical purposes and is not necessarily indicative of the trend of future loan losses in any particular category. The total allowance for loan losses is available to absorb losses from any segment of the loan portfolio.
97
For comparison purposes, a summary of the changes in the allowance for loan losses by portfolio segment for the year ended December 31, 2012, was as follows.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| $ in Thousands | | Commercial
and
industrial | | | Commercial
real estate
— owner
occupied | | | Lease
financing | | | Commercial
real estate
— investor | | | Real estate
construction | | | Home
equity | | | Installment | | | Residential
mortgage | | | Total | |
| | | | |
Balance at Dec 31, 2011 | | $ | 124,374 | | | $ | 36,200 | | | $ | 2,567 | | | $ | 86,689 | | | $ | 21,327 | | | $ | 70,144 | | | $ | 6,623 | | | $ | 30,227 | | | $ | 378,151 | |
Provision for loan losses | | | (1,645 | ) | | | (5,184 | ) | | | (645 | ) | | | (14,304 | ) | | | 873 | | | | 16,909 | | | | (501 | ) | | | 7,497 | | | | 3,000 | |
Charge offs | | | (43,240 | ) | | | (4,080 | ) | | | (797 | ) | | | (14,000 | ) | | | (3,588 | ) | | | (34,125 | ) | | | (3,057 | ) | | | (14,159 | ) | | | (117,046 | ) |
Recoveries | | | 18,363 | | | | 453 | | | | 1,899 | | | | 4,796 | | | | 2,129 | | | | 3,898 | | | | 1,234 | | | | 532 | | | | 33,304 | |
| | | | |
Balance at Dec 31, 2012 | | $ | 97,852 | | | $ | 27,389 | | | $ | 3,024 | | | $ | 63,181 | | | $ | 20,741 | | | $ | 56,826 | | | $ | 4,299 | | | $ | 24,097 | | | $ | 297,409 | |
| | | | |
Allowance for loan losses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Ending balance impaired loans individually evaluated for impairment | | $ | 8,790 | | | $ | 654 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 5,241 | | | $ | 1,079 | | | $ | 868 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 155 | | | $ | 16,787 | |
Ending balance impaired loans collectively evaluated for impairment | | $ | 4,951 | | | $ | 3,157 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 4,446 | | | $ | 2,332 | | | $ | 23,712 | | | $ | 1,155 | | | $ | 12,751 | | | $ | 52,504 | |
| | | | |
Total impaired loans | | $ | 13,741 | | | $ | 3,811 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 9,687 | | | $ | 3,411 | | | $ | 24,580 | | | $ | 1,155 | | | $ | 12,906 | | | $ | 69,291 | |
Ending balance all other loans collectively evaluated for impairment | | $ | 84,111 | | | $ | 23,578 | | | $ | 3,024 | | | $ | 53,494 | | | $ | 17,330 | | | $ | 32,246 | | | $ | 3,144 | | | $ | 11,191 | | | $ | 228,118 | |
| | | | |
Total | | $ | 97,852 | | | $ | 27,389 | | | $ | 3,024 | | | $ | 63,181 | | | $ | 20,741 | | | $ | 56,826 | | | $ | 4,299 | | | $ | 24,097 | | | $ | 297,409 | |
| | | | |
Loans: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Ending balance impaired loans individually evaluated for impairment | | $ | 27,213 | | | $ | 16,602 | | | $ | 3,024 | | | $ | 48,894 | | | $ | 20,794 | | | $ | 4,671 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 11,330 | | | $ | 132,528 | |
Ending balance impaired loans collectively evaluated for impairment | | $ | 40,109 | | | $ | 21,504 | | | $ | 7 | | | $ | 51,453 | | | $ | 11,038 | | | $ | 44,512 | | | $ | 2,491 | | | $ | 70,313 | | | $ | 241,427 | |
| | | | |
Impaired loan subtotal | | $ | 67,322 | | | $ | 38,106 | | | $ | 3,031 | | | $ | 100,347 | | | $ | 31,832 | | | $ | 49,183 | | | $ | 2,491 | | | $ | 81,643 | | | $ | 373,955 | |
Ending balance all other loans collectively evaluated for impairment | | $ | 4,434,699 | | | $ | 1,181,641 | | | $ | 61,165 | | | $ | 2,806,412 | | | $ | 623,549 | | | $ | 2,170,311 | | | $ | 464,236 | | | $ | 3,295,054 | | | $ | 15,037,067 | |
| | | | |
Total | | $ | 4,502,021 | | | $ | 1,219,747 | | | $ | 64,196 | | | $ | 2,906,759 | | | $ | 655,381 | | | $ | 2,219,494 | | | $ | 466,727 | | | $ | 3,376,697 | | | $ | 15,411,022 | |
| | | | |
The following table presents commercial loans by credit quality indicator at December 31, 2013.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pass | | | Special
Mention | | | Potential
Problem | | | Impaired | | | Total | |
| | | | |
| | | ($ Thousands) | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 4,485,160 | | | $ | 153,615 | | | | 113,669 | | | $ | 70,236 | | | $ | 4,822,680 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 959,849 | | | | 55,404 | | | | 56,789 | | | | 42,673 | | | | 1,114,715 | |
Lease financing | | | 52,733 | | | | 897 | | | | 1,784 | | | | 69 | | | | 55,483 | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 5,497,742 | | | | 209,916 | | | | 172,242 | | | | 112,978 | | | | 5,992,878 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 2,740,255 | | | | 64,230 | | | | 52,429 | | | | 82,542 | | | | 2,939,456 | |
Real estate construction | | | 877,911 | | | | 2,814 | | | | 5,263 | | | | 10,260 | | | | 896,248 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 3,618,166 | | | | 67,044 | | | | 57,692 | | | | 92,802 | | | | 3,835,704 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | $ | 9,115,908 | | | $ | 276,960 | | | $ | 229,934 | | | $ | 205,780 | | | $ | 9,828,582 | |
| | | | |
98
The following table presents commercial loans by credit quality indicator at December 31, 2012.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pass | | | Special
Mention | | | Potential
Problem | | | Impaired | | | Total | |
| | | | |
| | | ($ Thousands) | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 4,208,478 | | | $ | 97,787 | | | | 128,434 | | | $ | 67,322 | | | $ | 4,502,021 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 1,030,632 | | | | 51,417 | | | | 99,592 | | | | 38,106 | | | | 1,219,747 | |
Lease financing | | | 58,099 | | | | 2,802 | | | | 264 | | | | 3,031 | | | | 64,196 | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 5,297,209 | | | | 152,006 | | | | 228,290 | | | | 108,459 | | | | 5,785,964 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 2,634,035 | | | | 65,309 | | | | 107,068 | | | | 100,347 | | | | 2,906,759 | |
Real estate construction | | | 603,481 | | | | 6,976 | | | | 13,092 | | | | 31,832 | | | | 655,381 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 3,237,516 | | | | 72,285 | | | | 120,160 | | | | 132,179 | | | | 3,562,140 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | $ | 8,534,725 | | | $ | 224,291 | | | $ | 348,450 | | | $ | 240,638 | | | $ | 9,348,104 | |
| | | | |
The following table presents consumer loans by credit quality indicator at December 31, 2013.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Performing | | | 30-89 Days
Past Due | | | Potential
Problem | | | Impaired | | | Total | |
| | | | |
| | | ($ Thousands) | |
Home equity | | $ | 1,777,421 | | | $ | 10,680 | | | | 2,113 | | | $ | 34,800 | | | $ | 1,825,014 | |
Installment | | | 404,514 | | | | 1,150 | | | | 50 | | | | 1,360 | | | | 407,074 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 3,758,688 | | | | 6,118 | | | | 3,312 | | | | 67,473 | | | | 3,835,591 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | $ | 5,940,623 | | | $ | 17,948 | | | $ | 5,475 | | | $ | 103,633 | | | $ | 6,067,679 | |
| | | | |
The following table presents consumer loans by credit quality indicator at December 31, 2012.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Performing | | | 30-89 Days
Past Due | | | Potential
Problem | | | Impaired | | | Total | |
| | | | |
| | | ($ Thousands) | |
Home equity | | $ | 2,153,103 | | | $ | 13,538 | | | | 3,670 | | | $ | 49,183 | | | $ | 2,219,494 | |
Installment | | | 462,016 | | | | 2,109 | | | | 111 | | | | 2,491 | | | | 466,727 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 3,276,889 | | | | 9,403 | | | | 8,762 | | | | 81,643 | | | | 3,376,697 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | $ | 5,892,008 | | | $ | 25,050 | | | $ | 12,543 | | | $ | 133,317 | | | $ | 6,062,918 | |
| | | | |
Factors that are important to managing overall credit quality are sound loan underwriting and administration, systematic monitoring of existing loans and commitments, effective loan review on an ongoing basis, early identification of potential problems, and appropriate allowance for loan losses, nonaccrual and charge off policies.
For commercial loans, management has determined the pass credit quality indicator to include credits that exhibit acceptable financial statements, cash flow, and leverage. If any risk exists, it is mitigated by the loan structure, collateral, monitoring, or control. For consumer loans, performing loans include credits that are performing in accordance with the original contractual terms. Loans are considered past due if the required principal and interest payments have not been received as of the date such payments were due. Special mention credits have potential weaknesses that deserve management’s attention. If left uncorrected, these potential weaknesses may result in deterioration of the repayment prospects for the credit. Potential problem loans are considered inadequately protected by the current net worth and paying capacity of the obligor or the collateral pledged. These loans generally have a well-defined weakness, or weaknesses, that may jeopardize liquidation of the debt and are characterized by the distinct possibility that the bank will sustain some loss if the deficiencies are not corrected. Lastly, management considers a loan to be impaired when it is probable that the Corporation will be unable to collect all amounts due according to the original contractual terms of the note agreement, including
99
both principal and interest. Management has determined that commercial and consumer loan relationships that have nonaccrual status or have had their terms restructured in a troubled debt restructuring meet this impaired loan definition. Commercial loans classified as special mention, potential problem, and impaired are reviewed at a minimum on a quarterly basis, while pass and performing rated credits are reviewed on an annual basis or more frequently if the loan renewal is less than one year or if otherwise warranted. See Note 1 for the Corporation’s accounting policy for loans.
The following table presents loans by past due status at December 31, 2013.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 30-59 Days
Past Due | | | 60-89 Days
Past Due | | | 90 Days or More
Past Due * | | | Total Past Due | | | Current | | | Total | |
| | | | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Accruing loans | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 3,390 | | | $ | 3,436 | | | $ | 1,199 | | | $ | 8,025 | | | $ | 4,776,936 | | | $ | 4,784,961 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 1,015 | | | | 2,091 | | | | — | | | | 3,106 | | | | 1,081,945 | | | | 1,085,051 | |
Lease financing | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 55,414 | | | | 55,414 | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 4,405 | | | | 5,527 | | | | 1,199 | | | | 11,131 | | | | 5,914,295 | | | | 5,925,426 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 9,081 | | | | 14,134 | | | | — | | | | 23,215 | | | | 2,878,645 | | | | 2,901,860 | |
Real estate construction | | | 836 | | | | 1,118 | | | | — | | | | 1,954 | | | | 887,827 | | | | 889,781 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 9,917 | | | | 15,252 | | | | — | | | | 25,169 | | | | 3,766,472 | | | | 3,791,641 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 14,322 | | | | 20,779 | | | | 1,199 | | | | 36,300 | | | | 9,680,767 | | | | 9,717,067 | |
Home equity | | | 8,611 | | | | 2,069 | | | | 346 | | | | 11,026 | | | | 1,788,821 | | | | 1,799,847 | |
Installment | | | 885 | | | | 265 | | | | 637 | | | | 1,787 | | | | 404,173 | | | | 405,960 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 5,253 | | | | 865 | | | | 168 | | | | 6,286 | | | | 3,781,673 | | | | 3,787,959 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 14,749 | | | | 3,199 | | | | 1,151 | | | | 19,099 | | | | 5,974,667 | | | | 5,993,766 | |
| | | | |
Total accruing loans | | $ | 29,071 | | | $ | 23,978 | | | $ | 2,350 | | | $ | 55,399 | | | $ | 15,655,434 | | | $ | 15,710,833 | |
| | | | |
Nonaccrual loans | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 998 | | | $ | 1,764 | | | $ | 9,765 | | | $ | 12,527 | | | $ | 25,192 | | | $ | 37,719 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 2,482 | | | | 1,724 | | | | 11,125 | | | | 15,331 | | | | 14,333 | | | | 29,664 | |
Lease financing | | | — | | | | — | | | | 69 | | | | 69 | | | | — | | | | 69 | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 3,480 | | | | 3,488 | | | | 20,959 | | | | 27,927 | | | | 39,525 | | | | 67,452 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 3,408 | | | | 899 | | | | 20,466 | | | | 24,773 | | | | 12,823 | | | | 37,596 | |
Real estate construction | | | 2,376 | | | | — | | | | 2,267 | | | | 4,643 | | | | 1,824 | | | | 6,467 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 5,784 | | | | 899 | | | | 22,733 | | | | 29,416 | | | | 14,647 | | | | 44,063 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 9,264 | | | | 4,387 | | | | 43,692 | | | | 57,343 | | | | 54,172 | | | | 111,515 | |
Home equity | | | 1,725 | | | | 1,635 | | | | 14,331 | | | | 17,691 | | | | 7,476 | | | | 25,167 | |
Installment | | | 129 | | | | 24 | | | | 289 | | | | 442 | | | | 672 | | | | 1,114 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 3,199 | | | | 3,257 | | | | 26,201 | | | | 32,657 | | | | 14,975 | | | | 47,632 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 5,053 | | | | 4,916 | | | | 40,821 | | | | 50,790 | | | | 23,123 | | | | 73,913 | |
| | | | |
Total nonaccrual loans | | $ | 14,317 | | | $ | 9,303 | | | $ | 84,513 | | | $ | 108,133 | | | $ | 77,295 | | | $ | 185,428 | |
| | | | |
Total loans | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 4,388 | | | $ | 5,200 | | | $ | 10,964 | | | $ | 20,552 | | | $ | 4,802,128 | | | $ | 4,822,680 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 3,497 | | | | 3,815 | | | | 11,125 | | | | 18,437 | | | | 1,096,278 | | | | 1,114,715 | |
Lease financing | | | — | | | | — | | | | 69 | | | | 69 | | | | 55,414 | | | | 55,483 | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 7,885 | | | | 9,015 | | | | 22,158 | | | | 39,058 | | | | 5,953,820 | | | | 5,992,878 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 12,489 | | | | 15,033 | | | | 20,466 | | | | 47,988 | | | | 2,891,468 | | | | 2,939,456 | |
Real estate construction | | | 3,212 | | | | 1,118 | | | | 2,267 | | | | 6,597 | | | | 889,651 | | | | 896,248 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 15,701 | | | | 16,151 | | | | 22,733 | | | | 54,585 | | | | 3,781,119 | | | | 3,835,704 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 23,586 | | | | 25,166 | | | | 44,891 | | | | 93,643 | | | | 9,734,939 | | | | 9,828,582 | |
Home equity | | | 10,336 | | | | 3,704 | | | | 14,677 | | | | 28,717 | | | | 1,796,297 | | | | 1,825,014 | |
Installment | | | 1,014 | | | | 289 | | | | 926 | | | | 2,229 | | | | 404,845 | | | | 407,074 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 8,452 | | | | 4,122 | | | | 26,369 | | | | 38,943 | | | | 3,796,648 | | | | 3,835,591 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 19,802 | | | | 8,115 | | | | 41,972 | | | | 69,889 | | | | 5,997,790 | | | | 6,067,679 | |
| | | | |
Total loans | | $ | 43,388 | | | $ | 33,281 | | | $ | 86,863 | | | $ | 163,532 | | | $ | 15,732,729 | | | $ | 15,896,261 | |
| | | | |
| * | The recorded investment in loans past due 90 days or more and still accruing totaled $2 million at December 31, 2013 (the same as the reported balances for the accruing loans noted above). |
100
The following table presents loans by past due status at December 31, 2012.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 30-59 Days
Past Due | | | 60-89 Days
Past Due | | | 90 Days or More
Past Due * | | | Total Past Due | | | Current | | | Total | |
| | | | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Accruing loans | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 9,557 | | | $ | 1,782 | | | $ | 79 | | | $ | 11,418 | | | $ | 4,451,421 | | | $ | 4,462,839 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 10,420 | | | | 633 | | | | 308 | | | | 11,361 | | | | 1,184,132 | | | | 1,195,493 | |
Lease financing | | | — | | | | 12 | | | | — | | | | 12 | | | | 61,153 | | | | 61,165 | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 19,977 | | | | 2,427 | | | | 387 | | | | 22,791 | | | | 5,696,706 | | | | 5,719,497 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 8,424 | | | | 5,048 | | | | 366 | | | | 13,838 | | | | 2,834,234 | | | | 2,848,072 | |
Real estate construction | | | 1,628 | | | | 1,527 | | | | 283 | | | | 3,438 | | | | 624,641 | | | | 628,079 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 10,052 | | | | 6,575 | | | | 649 | | | | 17,276 | | | | 3,458,875 | | | | 3,476,151 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 30,029 | | | | 9,002 | | | | 1,036 | | | | 40,067 | | | | 9,155,581 | | | | 9,195,648 | |
Home equity | | | 10,151 | | | | 3,387 | | | | 96 | | | | 13,634 | | | | 2,166,645 | | | | 2,180,279 | |
Installment | | | 1,300 | | | | 809 | | | | 1,013 | | | | 3,122 | | | | 461,767 | | | | 464,889 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 8,473 | | | | 930 | | | | 144 | | | | 9,547 | | | | 3,307,791 | | | | 3,317,338 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 19,924 | | | | 5,126 | | | | 1,253 | | | | 26,303 | | | | 5,936,203 | | | | 5,962,506 | |
| | | | |
Total accruing loans | | $ | 49,953 | | | $ | 14,128 | | | $ | 2,289 | | | $ | 66,370 | | | $ | 15,091,784 | | | $ | 15,158,154 | |
| | | | |
Nonaccrual loans | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 8,559 | | | $ | 791 | | | $ | 11,962 | | | $ | 21,312 | | | $ | 17,870 | | | $ | 39,182 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 1,489 | | | | 1,749 | | | | 11,819 | | | | 15,057 | | | | 9,197 | | | | 24,254 | |
Lease financing | | | 15 | | | | — | | | | 9 | | | | 24 | | | | 3,007 | | | | 3,031 | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 10,063 | | | | 2,540 | | | | 23,790 | | | | 36,393 | | | | 30,074 | | | | 66,467 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 197 | | | | 3,072 | | | | 30,928 | | | | 34,197 | | | | 24,490 | | | | 58,687 | |
Real estate construction | | | 16 | | | | — | | | | 9,639 | | | | 9,655 | | | | 17,647 | | | | 27,302 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 213 | | | | 3,072 | | | | 40,567 | | | | 43,852 | | | | 42,137 | | | | 85,989 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 10,276 | | | | 5,612 | | | | 64,357 | | | | 80,245 | | | | 72,211 | | | | 152,456 | |
Home equity | | | 1,456 | | | | 2,518 | | | | 28,474 | | | | 32,448 | | | | 6,767 | | | | 39,215 | |
Installment | | | 153 | | | | 141 | | | | 586 | | | | 880 | | | | 958 | | | | 1,838 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 2,135 | | | | 4,321 | | | | 38,739 | | | | 45,195 | | | | 14,164 | | | | 59,359 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 3,744 | | | | 6,980 | | | | 67,799 | | | | 78,523 | | | | 21,889 | | | | 100,412 | |
| | | | |
Total nonaccrual loans | | $ | 14,020 | | | $ | 12,592 | | | $ | 132,156 | | | $ | 158,768 | | | $ | 94,100 | | | $ | 252,868 | |
| | | | |
Total loans | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 18,116 | | | $ | 2,573 | | | $ | 12,041 | | | $ | 32,730 | | | $ | 4,469,291 | | | $ | 4,502,021 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 11,909 | | | | 2,382 | | | | 12,127 | | | | 26,418 | | | | 1,193,329 | | | | 1,219,747 | |
Lease financing | | | 15 | | | | 12 | | | | 9 | | | | 36 | | | | 64,160 | | | | 64,196 | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 30,040 | | | | 4,967 | | | | 24,177 | | | | 59,184 | | | | 5,726,780 | | | | 5,785,964 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 8,621 | | | | 8,120 | | | | 31,294 | | | | 48,035 | | | | 2,858,724 | | | | 2,906,759 | |
Real estate construction | | | 1,644 | | | | 1,527 | | | | 9,922 | | | | 13,093 | | | | 642,288 | | | | 655,381 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 10,265 | | | | 9,647 | | | | 41,216 | | | | 61,128 | | | | 3,501,012 | | | | 3,562,140 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 40,305 | | | | 14,614 | | | | 65,393 | | | | 120,312 | | | | 9,227,792 | | | | 9,348,104 | |
Home equity | | | 11,607 | | | | 5,905 | | | | 28,570 | | | | 46,082 | | | | 2,173,412 | | | | 2,219,494 | |
Installment | | | 1,453 | | | | 950 | | | | 1,599 | | | | 4,002 | | | | 462,725 | | | | 466,727 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 10,608 | | | | 5,251 | | | | 38,883 | | | | 54,742 | | | | 3,321,955 | | | | 3,376,697 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 23,668 | | | | 12,106 | | | | 69,052 | | | | 104,826 | | | | 5,958,092 | | | | 6,062,918 | |
| | | | |
Total loans | | $ | 63,973 | | | $ | 26,720 | | | $ | 134,445 | | | $ | 225,138 | | | $ | 15,185,884 | | | $ | 15,411,022 | |
| | | | |
| * | The recorded investment in loans past due 90 days or more and still accruing totaled $2 million at December 31, 2012 (the same as the reported balances for the accruing loans noted above). |
101
The following table presents impaired loans at December 31, 2013.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Recorded Investment | | | Unpaid Principal Balance | | | Related Allowance | | | Average Recorded Investment | | | Interest Income Recognized* | |
| | | | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Loans with a related allowance | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 57,857 | | | $ | 65,443 | | | $ | 11,917 | | | $ | 61,000 | | | $ | 1,741 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 22,651 | | | | 25,072 | | | | 2,955 | | | | 24,549 | | | | 995 | |
Lease financing | | | 69 | | | | 69 | | | | 29 | | | | 76 | | | | — | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 80,577 | | | | 90,584 | | | | 14,901 | | | | 85,625 | | | | 2,736 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 64,647 | | | | 68,228 | | | | 7,895 | | | | 68,776 | | | | 2,735 | |
Real estate construction | | | 8,815 | | | | 12,535 | | | | 2,416 | | | | 9,796 | | | | 236 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 73,462 | | | | 80,763 | | | | 10,311 | | | | 78,572 | | | | 2,971 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 154,039 | | | | 171,347 | | | | 25,212 | | | | 164,197 | | | | 5,707 | |
Home equity | | | 34,707 | | | | 40,344 | | | | 13,989 | | | | 36,623 | | | | 1,518 | |
Installment | | | 1,360 | | | | 1,676 | | | | 487 | | | | 1,753 | | | | 100 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 60,157 | | | | 69,699 | | | | 12,187 | | | | 62,211 | | | | 1,861 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 96,224 | | | | 111,719 | | | | 26,663 | | | | 100,587 | | | | 3,479 | |
| | | | |
Total loans | | $ | 250,263 | | | $ | 283,066 | | | $ | 51,875 | | | $ | 264,784 | | | $ | 9,186 | |
| | | | |
Loans with no related allowance | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 12,379 | | | $ | 19,556 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 14,291 | | | $ | 306 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 20,022 | | | | 22,831 | | | | — | | | | 20,602 | | | | 315 | |
Lease financing | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 32,401 | | | | 42,387 | | | | — | | | | 34,893 | | | | 621 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 17,895 | | | | 25,449 | | | | — | | | | 19,354 | | | | 130 | |
Real estate construction | | | 1,445 | | | | 1,853 | | | | — | | | | 1,576 | | | | 13 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 19,340 | | | | 27,302 | | | | — | | | | 20,930 | | | | 143 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 51,741 | | | | 69,689 | | | | — | | | | 55,823 | | | | 764 | |
Home equity | | | 93 | | | | 92 | | | | — | | | | 94 | | | | 2 | |
Installment | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Residential mortgage | | | 7,316 | | | | 8,847 | | | | — | | | | 7,321 | | | | 185 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 7,409 | | | | 8,939 | | | | — | | | | 7,415 | | | | 187 | |
| | | | |
Total loans | | $ | 59,150 | | | $ | 78,628 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 63,238 | | | $ | 951 | |
| | | | |
Total | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 70,236 | | | $ | 84,999 | | | $ | 11,917 | | | $ | 75,291 | | | $ | 2,047 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 42,673 | | | | 47,903 | | | | 2,955 | | | | 45,151 | | | | 1,310 | |
Lease financing | | | 69 | | | | 69 | | | | 29 | | | | 76 | | | | — | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 112,978 | | | | 132,971 | | | | 14,901 | | | | 120,518 | | | | 3,357 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 82,542 | | | | 93,677 | | | | 7,895 | | | | 88,130 | | | | 2,865 | |
Real estate construction | | | 10,260 | | | | 14,388 | | | | 2,416 | | | | 11,372 | | | | 249 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 92,802 | | | | 108,065 | | | | 10,311 | | | | 99,502 | | | | 3,114 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 205,780 | | | | 241,036 | | | | 25,212 | | | | 220,020 | | | | 6,471 | |
Home equity | | | 34,800 | | | | 40,436 | | | | 13,989 | | | | 36,717 | | | | 1,520 | |
Installment | | | 1,360 | | | | 1,676 | | | | 487 | | | | 1,753 | | | | 100 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 67,473 | | | | 78,546 | | | | 12,187 | | | | 69,532 | | | | 2,046 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 103,633 | | | | 120,658 | | | | 26,663 | | | | 108,002 | | | | 3,666 | |
| | | | |
Total loans | | $ | 309,413 | | | $ | 361,694 | | | $ | 51,875 | | | $ | 328,022 | | | $ | 10,137 | |
| | | | |
| * | Interest income recognized included $6 million of interest income recognized on accruing restructured loans for the year ended December 31, 2013. |
102
The following table presents impaired loans at December 31, 2012.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Recorded
Investment | | | Unpaid
Principal
Balance | | | Related
Allowance | | | Average
Recorded
Investment | | | Interest
Income
Recognized* | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Loans with a related allowance | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 57,985 | | | $ | 65,521 | | | $ | 13,741 | | | $ | 56,508 | | | $ | 2,187 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 24,600 | | | | 27,700 | | | | 3,811 | | | | 26,531 | | | | 1,043 | |
Lease financing | | | 7 | | | | 7 | | | | — | | | | 120 | | | | — | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 82,592 | | | | 93,228 | | | | 17,552 | | | | 83,159 | | | | 3,230 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 80,766 | | | | 96,581 | | | | 9,687 | | | | 85,642 | | | | 2,891 | |
Real estate construction | | | 16,299 | | | | 22,311 | | | | 3,411 | | | | 19,122 | | | | 437 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 97,065 | | | | 118,892 | | | | 13,098 | | | | 104,764 | | | | 3,328 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 179,657 | | | | 212,120 | | | | 30,650 | | | | 187,923 | | | | 6,558 | |
Home equity | | | 47,113 | | | | 54,456 | | | | 24,580 | | | | 50,334 | | | | 1,962 | |
Installment | | | 2,491 | | | | 2,847 | | | | 1,155 | | | | 2,773 | | | | 172 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 72,408 | | | | 81,959 | | | | 12,906 | | | | 76,989 | | | | 2,211 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 122,012 | | | | 139,262 | | | | 38,641 | | | | 130,096 | | | | 4,345 | |
| | | | |
Total loans | | $ | 301,669 | | | $ | 351,382 | | | $ | 69,291 | | | $ | 318,019 | | | $ | 10,903 | |
| | | | |
Loans with no related allowance | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 9,337 | | | $ | 16,339 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 10,883 | | | $ | 229 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 13,506 | | | | 16,582 | | | | — | | | | 14,425 | | | | 68 | |
Lease financing | | | 3,024 | | | | 3,024 | | | | — | | | | 3,896 | | | | — | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 25,867 | | | | 35,945 | | | | — | | | | 29,204 | | | | 297 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 19,581 | | | | 28,531 | | | | — | | | | 20,490 | | | | 173 | |
Real estate construction | | | 15,533 | | | | 24,724 | | | | — | | | | 18,350 | | | | 109 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 35,114 | | | | 53,255 | | | | — | | | | 38,840 | | | | 282 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 60,981 | | | | 89,200 | | | | — | | | | 68,044 | | | | 579 | |
Home equity | | | 2,070 | | | | 2,269 | | | | — | | | | 2,164 | | | | 36 | |
Installment | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Residential mortgage | | | 9,235 | | | | 12,246 | | | | — | | | | 11,566 | | | | 208 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 11,305 | | | | 14,515 | | | | — | | | | 13,730 | | | | 244 | |
| | | | |
Total loans | | $ | 72,286 | | | $ | 103,715 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 81,774 | | | $ | 823 | |
| | | | |
Total | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 67,322 | | | $ | 81,860 | | | $ | 13,741 | | | $ | 67,391 | | | $ | 2,416 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 38,106 | | | | 44,282 | | | | 3,811 | | | | 40,956 | | | | 1,111 | |
Lease financing | | | 3,031 | | | | 3,031 | | | | — | | | | 4,016 | | | | — | |
| | | | |
Commercial and business lending | | | 108,459 | | | | 129,173 | | | | 17,552 | | | | 112,363 | | | | 3,527 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 100,347 | | | | 125,112 | | | | 9,687 | | | | 106,132 | | | | 3,064 | |
Real estate construction | | | 31,832 | | | | 47,035 | | | | 3,411 | | | | 37,472 | | | | 546 | |
| | | | |
Commercial real estate lending | | | 132,179 | | | | 172,147 | | | | 13,098 | | | | 143,604 | | | | 3,610 | |
| | | | |
Total commercial | | | 240,638 | | | | 301,320 | | | | 30,650 | | | | 255,967 | | | | 7,137 | |
Home equity | | | 49,183 | | | | 56,725 | | | | 24,580 | | | | 52,498 | | | | 1,998 | |
Installment | | | 2,491 | | | | 2,847 | | | | 1,155 | | | | 2,773 | | | | 172 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 81,643 | | | | 94,205 | | | | 12,906 | | | | 88,555 | | | | 2,419 | |
| | | | |
Total consumer | | | 133,317 | | | | 153,777 | | | | 38,641 | | | | 143,826 | | | | 4,589 | |
| | | | |
Total loans | | $ | 373,955 | | | $ | 455,097 | | | $ | 69,291 | | | $ | 399,793 | | | $ | 11,726 | |
| | | | |
| * | Interest income recognized included $6 million of interest income recognized on accruing restructured loans for the year ended December 31, 2012. |
103
Troubled Debt Restructurings (“Restructured Loans”):
Loans are considered restructured loans if concessions have been granted to borrowers that are experiencing financial difficulty. See Note 1 for the Corporation’s accounting policy for troubled debt restructurings. The Corporation had a $64 million recorded investment in loans modified in a troubled debt restructuring during the year ended December 31, 2013, of which, $42 million were in accrual status and $22 million were in nonaccrual status pending a sustained period of repayment. As of December 31, 2013, there were $8 million of commitments to lend additional funds to borrowers with restructured loans. The following table presents nonaccrual and performing restructured loans by loan portfolio.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2013 | | | December 31, 2012 | |
| | | Performing
Restructured
Loans | | | Nonaccrual
Restructured Loans* | | | Performing
Restructured
Loans | | | Nonaccrual
Restructured Loans* | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 32,517 | | | $ | 6,900 | | | $ | 28,140 | | | $ | 12,496 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 13,009 | | | | 10,999 | | | | 13,852 | | | | 11,514 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 44,946 | | | | 18,069 | | | | 41,660 | | | | 25,221 | |
Real estate construction | | | 3,793 | | | | 2,065 | | | | 4,530 | | | | 6,798 | |
Home equity | | | 9,633 | | | | 5,419 | | | | 9,968 | | | | 6,698 | |
Installment | | | 246 | | | | 451 | | | | 653 | | | | 674 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 19,841 | | | | 15,682 | | | | 22,284 | | | | 17,189 | |
| | | | |
| | $ | 123,985 | | | $ | 59,585 | | | $ | 121,087 | | | $ | 80,590 | |
| | | | |
| * | Nonaccrual restructured loans have been included within nonaccrual loans. |
The following table provides the number of loans modified in a troubled debt restructuring by loan portfolio during the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively, and the recorded investment and unpaid principal balance as of December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, 2013 | | | Year Ended December 31, 2012 | |
| | | Number of
Loans | | | Recorded
Investment(1) | | | Unpaid
Principal
Balance(2) | | | Number of
Loans | | | Recorded
Investment(1) | | | Unpaid
Principal
Balance(2) | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Commercial and industrial | | | 48 | | | $ | 11,833 | | | $ | 14,543 | | | | 85 | | | $ | 12,827 | | | $ | 15,834 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 12 | | | | 8,823 | | | | 9,035 | | | | 27 | | | | 11,978 | | | | 12,766 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 25 | | | | 26,480 | | | | 28,516 | | | | 25 | | | | 12,379 | | | | 13,569 | |
Real estate construction | | | 9 | | | | 1,822 | | | | 1,961 | | | | 31 | | | | 2,955 | | | | 3,549 | |
Home equity | | | 88 | | | | 4,642 | | | | 4,958 | | | | 111 | | | | 4,870 | | | | 6,143 | |
Installment | | | 3 | | | | 193 | | | | 200 | | | | 13 | | | | 298 | | | | 302 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 93 | | | | 10,259 | | | | 12,106 | | | | 121 | | | | 14,292 | | | | 16,787 | |
| | | | |
| | | 278 | | | $ | 64,052 | | | $ | 71,319 | | | | 413 | | | $ | 59,599 | | | $ | 68,950 | |
| | | | |
| (1) | Represents post-modification outstanding recorded investment. |
| (2) | Represents pre-modification outstanding recorded investment. |
Restructured loan modifications may include payment schedule modifications, interest rate concessions, maturity date extensions, modification of note structure (A/B Note), non-reaffirmed Chapter 7 bankruptcies, principal reduction, or some combination of these concessions. For the year ended December 31, 2013, restructured loan modifications of commercial and industrial, commercial real estate, and real estate construction loans primarily included maturity date extensions and payment schedule modifications. Restructured loan modifications of home equity and residential mortgage loans primarily included maturity date extensions, interest rate concessions, payment schedule modifications, non-reaffirmed Chapter 7 bankruptcies, or a combination of these concessions for the year ended December 31, 2013.
104
The following table provides the number of loans modified in a troubled debt restructuring during the previous 12 months which subsequently defaulted during the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively, as well as the recorded investment in these restructured loans as of December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, 2013 | | | Year Ended December 31, 2012 | |
| | | Number of
Loans | | | Recorded
Investment | | | Number of
Loans | | | Recorded
Investment | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Commercial and industrial | | | 15 | | | $ | 1,493 | | | | 16 | | | $ | 1,736 | |
Commercial real estate — owner occupied | | | 4 | | | | 542 | | | | 10 | | | | 4,729 | |
Commercial real estate — investor | | | 4 | | | | 1,784 | | | | 13 | | | | 10,854 | |
Real estate construction | | | 4 | | | | 80 | | | | 5 | | | | 1,695 | |
Home equity | | | 14 | | | | 1,220 | | | | 14 | | | | 2,049 | |
Installment | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1 | | | | 12 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 23 | | | | 4,137 | | | | 10 | | | | 1,499 | |
| | | | |
| | | 64 | | | $ | 9,256 | | | | 69 | | | $ | 22,574 | |
| | | | |
All loans modified in a troubled debt restructuring are evaluated for impairment. The nature and extent of the impairment of restructured loans, including those which have experienced a subsequent payment default, is considered in the determination of an appropriate level of the allowance for loan losses.
NOTE 4 GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS:
Goodwill: Goodwill is not amortized but, instead, is subject to impairment tests on at least an annual basis, and more frequently if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying amount. See Note 1 for the Corporation’s accounting policy for goodwill and other intangible assets.
The Corporation conducted its annual impairment testing in May 2013, utilizing a qualitative assessment. Factors that management considered in this assessment included macroeconomic conditions, industry and market considerations, overall financial performance (both current and projected), changes in management strategy, and changes in the composition or carrying amount of net assets. In addition, management considered the significant increases in both the Corporation’s common stock price and in the overall bank common stock index (based on the Nasdaq bank index), as well as the Corporation’s improving earnings per common share trend over the past year. Based on these assessments, management concluded that the 2013 annual qualitative impairment assessment indicated that it is more likely than not that the estimated fair value exceeded the carrying value (including goodwill) for each reporting unit. Therefore, a step one quantitative analysis was not required. The annual impairment testing in prior years was based upon a quantitative measurement of the fair value of the reporting units. There were no impairment charges recorded in 2011, 2012 or 2013. It is possible that a future conclusion could be reached that all or a portion of the Corporation’s goodwill may be impaired, in which case a non-cash charge for the amount of such impairment would be recorded in earnings. Such a charge, if any, would have no impact on tangible capital and would not affect the Corporation’s “well-capitalized” designation.
At December 31, 2013, the Corporation had goodwill of $929 million, including goodwill of $428 million assigned to the Commercial Banking reporting unit and goodwill of $501 million assigned to the Consumer Banking reporting unit. There was no change in the carrying amount of goodwill for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 or 2011.
105
Other Intangible Assets: The Corporation has other intangible assets that are amortized, consisting of core deposit intangibles, other intangibles (primarily related to customer relationships acquired in connection with the Corporation’s insurance agency acquisitions), and mortgage servicing rights. For core deposit intangibles and other intangibles, changes in the gross carrying amount, accumulated amortization, and net book value were as follows.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Core deposit intangibles: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Gross carrying amount | | $ | 36,230 | | | $ | 41,831 | | | $ | 41,831 | |
Accumulated amortization | | | (31,565 | ) | | | (34,044 | ) | | | (30,815 | ) |
| | | | |
Net book value | | $ | 4,665 | | | $ | 7,787 | | | $ | 11,016 | |
| | | | |
Amortization during the year | | $ | 3,122 | | | $ | 3,229 | | | $ | 3,695 | |
Other intangibles: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Gross carrying amount | | $ | 19,283 | | | $ | 19,283 | | | $ | 19,283 | |
Accumulated amortization | | | (12,764 | ) | | | (11,843 | ) | | | (10,877 | ) |
| | | | |
Net book value | | $ | 6,519 | | | $ | 7,440 | | | $ | 8,406 | |
| | | | |
Amortization during the year | | $ | 921 | | | $ | 966 | | | $ | 1,019 | |
The Corporation sells residential mortgage loans in the secondary market and typically retains the right to service the loans sold. Mortgage servicing rights are amortized in proportion to and over the period of estimated net servicing income, and assessed for impairment at each reporting date. See Note 1 for the Corporation’s accounting policy for mortgage servicing rights. See Note 15, for a discussion of the recourse provisions on serviced residential mortgage loans. See Note 17, which further discusses fair value measurement relative to the mortgage servicing rights asset.
A summary of changes in the balance of the mortgage servicing rights asset and the mortgage servicing rights valuation allowance was as follows.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Mortgage servicing rights | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Mortgage servicing rights at beginning of year | | $ | 61,425 | | | $ | 75,855 | | | $ | 84,209 | |
Additions | | | 18,256 | | | | 23,528 | | | | 17,476 | |
Amortization | | | (15,488 | ) | | | (23,348 | ) | | | (25,830 | ) |
Other-than-temporary impairment | | | — | | | | (14,610 | ) | | | — | |
| | | | |
Mortgage servicing rights at end of year | | $ | 64,193 | | | $ | 61,425 | | | $ | 75,855 | |
| | | | |
Valuation allowance at beginning of year | | | (15,476 | ) | | | (27,703 | ) | | | (20,300 | ) |
(Additions) recoveries, net | | | 14,563 | | | | (2,383 | ) | | | (7,403 | ) |
Other-than-temporary impairment | | | — | | | | 14,610 | | | | — | |
| | | | |
Valuation allowance at end of year | | | (913 | ) | | | (15,476 | ) | | | (27,703 | ) |
| | | | |
Mortgage servicing rights, net | | $ | 63,280 | | | $ | 45,949 | | | $ | 48,152 | |
| | | | |
Fair value of mortgage servicing rights | | $ | 74,444 | | | $ | 45,949 | | | $ | 48,152 | |
Portfolio of residential mortgage loans serviced for others (“servicing portfolio”) | | $ | 8,084,000 | | | $ | 7,453,000 | | | $ | 7,321,000 | |
Mortgage servicing rights, net to servicing portfolio | | | 0.78 | % | | | 0.62 | % | | | 0.66 | % |
Mortgage servicing rights expense(1) | | $ | 925 | | | $ | 25,731 | | | $ | 33,233 | |
| 1) | Includes the amortization of mortgage servicing rights and additions / recoveries to the valuation allowance of mortgage servicing rights, and is a component of mortgage banking, net in the consolidated statements of income. |
106
The following table shows the estimated future amortization expense for amortizing intangible assets. The projections of amortization expense for the next five years are based on existing asset balances, the current interest rate environment, and prepayment speeds as of December 31, 2013. The actual amortization expense the Corporation recognizes in any given period may be significantly different depending upon acquisition or sale activities, changes in interest rates, prepayment speeds, market conditions, regulatory requirements, and events or circumstances that indicate the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Estimated Amortization Expense | | Core Deposit Intangibles | | | Other Intangibles | | | Mortgage Servicing Rights | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Year ending December 31, | | | | |
2014 | | $ | 2,868 | | | $ | 879 | | | $ | 10,009 | |
2015 | | | 1,404 | | | | 839 | | | | 8,412 | |
2016 | | | 281 | | | | 803 | | | | 7,058 | |
2017 | | | 112 | | | | 770 | | | | 5,952 | |
2018 | | | — | | | | 740 | | | | 5,033 | |
Beyond 2018 | | | — | | | | 2,488 | | | | 27,729 | |
| | | | |
Total Estimated Amortization Expense | | $ | 4,665 | | | $ | 6,519 | | | $ | 64,193 | |
| | | | |
NOTE 5 PREMISES AND EQUIPMENT:
A summary of premises and equipment at December 31 was as follows.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Estimated
Useful Lives | | | 2013 | | | | | 2012 | |
| | | | Cost | | | Accumulated
Depreciation | | | Net Book
Value | | | | | Net Book
Value | |
| | | | | | ($ in Thousands) | | | | | | |
Land | | | — | | | $ | 50,668 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 50,668 | | | | | $ | 46,378 | |
Land improvements | | | 3 – 15 years | | | | 10,642 | | | | 4,152 | | | | 6,490 | | | �� | | | 6,412 | |
Buildings | | | 5 – 39 years | | | | 248,394 | | | | 117,622 | | | | 130,772 | | | | | | 121,496 | |
Computers | | | 3 – 5 years | | | | 45,532 | | | | 35,135 | | | | 10,397 | | | | | | 11,428 | |
Furniture, fixtures and other equipment | | | 3 – 15 years | | | | 162,746 | | | | 104,487 | | | | 58,259 | | | | | | 57,667 | |
Leasehold improvements | | | 5 – 30 years | | | | 35,829 | | | | 21,525 | | | | 14,304 | | | | | | 10,577 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total premises and equipment | | | | | | $ | 553,811 | | | $ | 282,921 | | | $ | 270,890 | | | | | $ | 253,958 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Depreciation and amortization of premises and equipment totaled $33 million in 2013, $30 million in 2012, and $24 million in 2011.
The Corporation and certain subsidiaries are obligated under noncancelable operating leases for other facilities and equipment, certain of which provide for increased rentals based upon increases in cost of living adjustments and other operating costs. The approximate minimum annual rentals and commitments under these noncancelable agreements and leases with remaining terms in excess of one year are as follows.
| | | | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
2014 | | $ | 10,699 | |
2015 | | | 10,842 | |
2016 | | | 10,663 | |
2017 | | | 9,476 | |
2018 | | | 8,283 | |
Thereafter | | | 33,206 | |
| | | | |
Total | | $ | 83,169 | |
| | | | |
107
Total rental expense under leases, net of sublease income, totaled $14 million in 2013, $15 million in 2012, and $15 million in 2011, respectively.
NOTE 6 DEPOSITS:
The distribution of deposits at December 31 was as follows.
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Noninterest-bearing demand deposits | | $ | 4,626,312 | | | $ | 4,759,556 | |
Savings deposits | | | 1,159,512 | | | | 1,109,861 | |
Interest-bearing demand deposits | | | 2,889,705 | | | | 2,554,479 | |
Money market deposits | | | 6,906,442 | | | | 6,518,075 | |
Brokered certificates of deposit | | | 50,450 | | | | 26,270 | |
Other time deposits | | | 1,634,746 | | | | 1,971,624 | |
| | | | |
Total deposits | | $ | 17,267,167 | | | $ | 16,939,865 | |
| | | | |
Time deposits of $100,000 or more were $478 million and $612 million at December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Aggregate annual maturities of all time deposits at December 31, 2013, are as follows.
| | | | |
Maturities During Year Ending December 31, | | ($ in Thousands) | |
2014 | | $ | 1,155,159 | |
2015 | | | 198,481 | |
2016 | | | 137,426 | |
2017 | | | 120,545 | |
2018 | | | 59,300 | |
Thereafter | | | 14,285 | |
| | | | |
Total | | $ | 1,685,196 | |
| | | | |
NOTE 7 SHORT-TERM FUNDING:
Short-term funding at December 31 was as follows.
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Federal funds purchased | | $ | 56,195 | | | $ | 71,385 | |
Securities sold under agreements to repurchase | | | 419,247 | | | | 679,070 | |
| | | | |
Federal funds purchased and securities sold under agreements to repurchase | | | 475,442 | | | | 750,455 | |
FHLB advances | | | 200,000 | | | | 1,525,000 | |
Commercial paper | | | 65,484 | | | | 51,484 | |
| | | | |
Other short-term funding | | | 265,484 | | | | 1,576,484 | |
| | | | |
Total short-term funding | | $ | 740,926 | | | $ | 2,326,939 | |
| | | | |
Short-term funding includes funding with original contractual maturities of one year or less. The FHLB advances included in short-term funding are those with original contractual maturities of one year or less. The securities sold under agreements to repurchase represent short-term funding which is collateralized by securities of the U.S. Government or its agencies and mature daily.
108
NOTE 8 LONG-TERM FUNDING:
Long-term funding (funding with original contractual maturities greater than one year) at December 31 was as follows.
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
FHLB advances | | $ | 2,500,297 | | | $ | 400,375 | |
Senior notes, at par | | | 585,000 | | | | 585,000 | |
Subordinated debt, at par | | | — | | | | 25,821 | |
Other long-term funding and capitalized costs | | | 1,970 | | | | 4,150 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total long-term funding | | $ | 3,087,267 | | | $ | 1,015,346 | |
| | | | | | | | |
FHLB advances: At December 31, 2013, the long-term FHLB advances had a weighted average interest rate of 0.10%, compared to 1.79% at December 31, 2012. During the fourth quarter of 2013, the Corporation executed $2.5 billion of five year, variable rate FHLB advances that are putable, at our option, without penalty after six months. The FHLB advances are indexed to the FHLB discount note plus 6 basis points and reprice at varying intervals, including $1.0 billion repricing at four week intervals, $750 million repricing at 13 week intervals, and $750 million repricing daily. These advances offer flexible, low cost, long-term funding that improves the Corporation’s liquidity profile.
Senior notes: In March 2011, the Corporation issued $300 million of senior notes at a discount. In September 2011, the Corporation issued an additional $130 million of senior notes at a premium. The 2011 senior note issuances mature on March 28, 2016 and have a fixed coupon interest rate of 5.125%. In September 2012, the Corporation issued $155 million of senior notes at a discount. The 2012 senior note issuance has a fixed coupon interest rate of 1.875%, matures on March 12, 2014, and is callable beginning in February 2014. The Corporation plans to early retire the 2012 senior note issuance at par on the call date in February 2014.
Subordinated debt: In September 2008, the Corporation issued $26 million of 10-year subordinated debt with a 5-year no-call provision. The subordinated debt was issued at a discount, had a fixed coupon interest rate of 9.25%, and was called in September 2013. The Corporation redeemed the outstanding subordinated debt effective October 15, 2013.
The table below summarizes the maturities of the Corporation’s long-term funding at December 31, 2013.
| | | | |
Year | | ($ in Thousands) | |
2014 | | $ | 155,001 | |
2015 | | | 30 | |
2016 | | | 431,944 | |
2017 | | | 67 | |
2018 | | | 2,500,000 | |
Thereafter | | | 225 | |
| | | | |
Total long-term funding | | $ | 3,087,267 | |
| | | | |
Under agreements with the Federal Home Loan Bank of Chicago, FHLB advances (short-term and long-term) are secured by qualifying mortgages of the subsidiary bank (such as residential mortgage, residential mortgage loans held for sale, home equity, and commercial real estate) and by specific investment securities for certain FHLB advances. At December 31, 2013, the Corporation had $3.5 billion of total collateral capacity supported by residential mortgage and home equity loans. Total short-term and long-term FHLB advances outstanding at December 31, 2013, was $2.7 billion.
109
NOTE 9 STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY:
Preferred Equity: On September 14, 2011, the Corporation issued 2,600,000 depositary shares, each representing a 1/40th interest in a share of the Corporation’s 8.00% Perpetual Preferred Stock, Series B, liquidation preference $1,000 per share (the “Series B Preferred Stock”). The Series B Preferred Stock has no stated maturity and will not be subject to any sinking fund or other obligation of the Corporation. Dividends on the Series B Preferred Stock, if declared, will be payable quarterly in arrears at a rate per annum equal to 8.00%. Dividends on the Series B Preferred Stock initially were cumulative because the Corporation’s previous Articles of Incorporation required that preferred stock dividends be cumulative. During the cumulative period, the Corporation had an obligation to pay any unpaid dividends. Dividends on the Series B Preferred Stock became non-cumulative on April 24, 2012 when the Corporation’s shareholders approved an amendment to the Corporation’s Articles of Incorporation to eliminate the requirement that the Corporation’s preferred stock dividends be cumulative. During the non-cumulative dividend period, the Corporation will have no obligation to pay dividends on the Series B Preferred Stock that were undeclared and unpaid during the cumulative dividend period. Shares of the Series B Preferred Stock have priority over the Corporation’s common stock with regard to the payment of dividends and distributions upon liquidation, dissolution or winding up. As such, the Corporation may not pay dividends on or repurchase, redeem, or otherwise acquire for consideration shares of its common stock unless dividends for the Series B Preferred Stock have been declared for that period, and sufficient funds have been set aside to make payment. The Series B Preferred Stock may be redeemed by the Corporation at its option (i) either in whole or in part, from time to time, on any dividend payment date on or after the dividend payment date occurring on September 15, 2016, or (ii) in whole but not in part, at any time within 90 days following certain regulatory capital treatment events, in each case at a redemption price of $1,000 per share (equivalent to $25 per depositary share), plus any applicable dividends. Except in certain limited circumstances, the Series B Preferred Stock does not have any voting rights.
On July 23, 2013, the Board of Directors authorized the purchase of up to $10 million of the Corporation’s 8.00% Perpetual Preferred Stock, Series B. During 2013, the Corporation repurchased approximately 58,000 depository shares for $1.6 million.
Common Stock Warrants: In November 2008, under the Capital Purchase Program, the Corporation issued a 10-year warrant to purchase approximately 4 million shares of common stock. The Common Stock Warrants have a term of 10 years and are exercisable at any time, in whole or in part, at an exercise price of $19.77 per share (subject to certain anti-dilution adjustments). On December 6, 2011, the U.S. Department of Treasury closed an underwritten secondary public offering of the warrants, each representing the right to purchase one share of common stock, par value $0.01 per share, of the Corporation. The public offering price and the allocation of the warrants in the secondary public warrant offering by the U.S. Treasury were determined by an auction process and the Corporation received no proceeds from the public offering.
Subsidiary Equity: At December 31, 2013, subsidiary equity equaled $3.1 billion. See Note 18 for additional information on regulatory requirements for the Bank.
Stock Repurchases: On November 13, 2012, the Board of Directors approved the repurchase of up to an aggregate amount of $125 million of common stock to be made available for reissuance in connection with the Corporation’s employee incentive plans and / or for other corporate purposes. On July 23, 2013, the Board of Directors approved the repurchase of up to an additional $120 million of common stock. At December 31, 2013, $95 million remained authorized for repurchase under the July 2013 Board of Directors authorization, while none remained authorized for repurchase under the November 2012 Board of Directors authorization. During 2013, the Corporation repurchased 7.7 million shares for $120 million (or an average cost per common share of $15.57), while during 2012, the Corporation repurchased 4.7 million shares for $60 million (or an average cost per common share of $12.77). The Corporation also repurchased shares for minimum tax withholding settlements on equity compensation during 2012 and 2013. See Part II, Item 5, “Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities,” for additional information on the common stock repurchased during the fourth quarter of 2013. The repurchase of shares will be based on market
110
opportunities, capital levels, growth prospects, regulatory constraints, and other investment opportunities. Such repurchases may occur from time to time in open market purchases, block transactions, private transactions, accelerated share repurchase programs, or similar facilities.
Other Comprehensive Income: See the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for a summary of activity in other comprehensive income.
NOTE 10 STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION:
At December 31, 2013, the Corporation had one stock-based compensation plan. All stock awards granted under this plan have an exercise price that is equal to the closing price of the Corporation’s stock on the date the awards were granted.
The Corporation may issue restricted common stock and restricted common stock units with restrictions to certain key employees (collectively referred to as “restricted stock awards”). The shares of restricted stock are restricted as to transfer, but are not restricted as to dividend payment or voting rights. Restricted stock units receive dividend equivalents but do not have voting rights. The transfer restrictions lapse over one, two, three, or four years, depending upon whether the awards are service-based or performance-based. Service-based awards are contingent upon continued employment or meeting the requirements for retirement, and performance-based awards are based on earnings per share performance goals and continued employment or meeting the requirements for retirement.
Stock-Based Compensation Plan:
In March 2010, the Board of Directors, with subsequent approval of the Corporation’s shareholders, approved the adoption of the 2010 Incentive Compensation Plan (“2010 Plan”). Under the 2010 Plan, options are generally exercisable up to 10 years from the date of grant and vest ratably over three or four years, while restricted stock awards vest ratably over three or four years. As of December 31, 2013, no shares remained available for grant under the 2010 Plan.
In March 2013, the Board of Directors, with subsequent approval of the Corporation’s shareholders, approved the adoption of the 2013 Incentive Compensation Plan (“2013 Plan”). Under the 2013 Plan, options are generally exercisable up to 10 years from the date of grant and vest ratably over four years, while restricted stock awards vest ratably over four years. As of December 31, 2013, approximately 19 million shares remained available for grant under the 2013 Plan.
Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation:
The fair value of stock options granted is estimated on the date of grant using a Black-Scholes option pricing model, while the fair value of restricted stock awards is their fair market value on the date of grant. The fair value of stock options and restricted stock awards are amortized as compensation expense on a straight-line basis over the vesting period of the grants. Compensation expense recognized is included in personnel expense in the consolidated statements of income.
111
Assumptions are used in estimating the fair value of stock options granted. The weighted average expected life of the stock option represents the period of time that stock options are expected to be outstanding and is estimated using historical data of stock option exercises and forfeitures. The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant. The expected volatility is based on the historical and implied volatility of the Corporation’s stock. The following assumptions were used in estimating the fair value for options granted in 2013, 2012 and 2011.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
Dividend yield | | | 2.00 | % | | | 2.00 | % | | | 2.00 | % |
Risk-free interest rate | | | 0.99 | % | | | 1.20 | % | | | 2.27 | % |
Weighted average expected volatility | | | 34.35 | % | | | 48.94 | % | | | 47.24 | % |
Weighted average expected life | | | 6 years | | | | 6 years | | | | 6 years | |
Weighted average per share fair value of options | | $ | 3.80 | | | $ | 5.03 | | | $ | 5.56 | |
The Corporation is required to estimate potential forfeitures of stock grants and adjust compensation expense recorded accordingly. The estimate of forfeitures will be adjusted over the requisite service period to the extent that actual forfeitures differ, or are expected to differ, from such estimates. Changes in estimated forfeitures will be recognized in the period of change and will also impact the amount of stock compensation expense to be recognized in future periods.
A summary of the Corporation’s stock option activity for 2013, 2012, and 2011, is presented below.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Stock Options | | Shares | | | Weighted Average
Exercise Price | | | | | Weighted Average
Remaining
Contractual Term | | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value (000s) | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2010 | | | 7,301,458 | | | $ | 24.33 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Granted | | | 1,624,369 | | | | 14.20 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Exercised | | | (23,437 | ) | | | 12.66 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Forfeited or expired | | | (1,847,116 | ) | | | 24.51 | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2011 | | | 7,055,274 | | | $ | 21.99 | | | | | | 5.61 | | | $ | 27 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Options exercisable at December 31, 2011 | | | 4,623,935 | | | $ | 26.10 | | | | | | 4.01 | | | $ | 7 | |
| | | | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2011 | | | 7,055,274 | | | $ | 21.99 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Granted | | | 3,060,519 | | | $ | 12.97 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Exercised | | | (11,120 | ) | | $ | 13.16 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Forfeited or expired | | | (1,464,115 | ) | | $ | 21.56 | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2012 | | | 8,640,558 | | | $ | 18.88 | | | | | | 6.40 | | | $ | 570 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Options exercisable at December 31, 2012 | | | 4,603,963 | | | $ | 23.80 | | | | | | 4.37 | | | $ | 43 | |
| | | | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2012 | | | 8,640,558 | | | | 18.88 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Granted | | | 1,020,979 | | | | 14.02 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Exercised | | | (642,202 | ) | | | 13.43 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Forfeited or expired | | | (985,092 | ) | | | 21.49 | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2013 | | | 8,034,243 | | | $ | 18.37 | | | | | | 6.03 | | | $ | 20,838 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Options exercisable at December 31, 2013 | | | 4,923,720 | | | $ | 21.48 | | | | | | 4.62 | | | $ | 8,580 | |
| | | | |
112
The following table summarizes information about the Corporation’s stock options outstanding at December 31, 2013.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Options
Outstanding | | | Weighted Average
Exercise Price | | | Remaining
Life (Years) | | | Options
Exercisable | | | Weighted Average
Exercise Price | | | |
Range of Exercise Prices: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
$0.00 — $10.00 | | | 2,000 | | | $ | 9.26 | | | | 5.56 | | | | 2,000 | | | $ | 9.26 | | | |
$10.01 — $15.00 | | | 5,248,844 | | | | 13.46 | | | | 7.76 | | | | 2,138,321 | | | | 13.45 | | | |
$15.01 — $20.00 | | | 608,806 | | | | 17.42 | | | | 4.83 | | | | 608,806 | | | | 17.42 | | | |
$20.01 — $25.00 | | | 554,576 | | | | 24.89 | | | | 3.84 | | | | 554,576 | | | | 24.89 | | | |
$25.01 — $30.00 | | | 307,172 | | | | 29.03 | | | | 0.21 | | | | 307,172 | | | | 29.03 | | | |
Over $30.00 | | | 1,312,845 | | | | 33.25 | | | | 1.98 | | | | 1,312,845 | | | | 33.25 | | | |
| | | |
Total | | | 8,034,243 | | | $ | 18.37 | | | | 6.03 | | | | 4,923,720 | | | $ | 21.48 | | | |
| | | |
The following table summarizes information about the Corporation’s nonvested stock option activity for 2013, 2012, and 2011.
| | | | | | | | |
Stock Options | | Shares | | | Weighted Average
Grant Date Fair Value | |
Nonvested at December 31, 2010 | | | 2,025,720 | | | $ | 4.09 | |
Granted | | | 1,624,369 | | | | 5.56 | |
Vested | | | (955,454 | ) | | | 3.77 | |
Forfeited | | | (263,296 | ) | | | 4.85 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Nonvested at December 31, 2011 | | | 2,431,339 | | | $ | 5.11 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Nonvested at December 31, 2011 | | | 2,431,339 | | | $ | 5.11 | |
Granted | | | 3,060,519 | | | | 5.03 | |
Vested | | | (1,097,571 | ) | | | 4.88 | |
Forfeited | | | (357,692 | ) | | | 5.12 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Nonvested at December 31, 2012 | | | 4,036,595 | | | $ | 5.11 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Nonvested at December 31, 2012 | | | 4,036,595 | | | $ | 5.11 | |
Granted | | | 1,020,979 | | | | 3.80 | |
Vested | | | (1,680,981 | ) | | | 5.10 | |
Forfeited | | | (266,070 | ) | | | 5.05 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Nonvested at December 31, 2013 | | | 3,110,523 | | | $ | 4.69 | |
| | | | | | | | |
For the year ended December 31, 2013 the intrinsic value of stock options exercised was $2 million. For the years ended December 31, 2012, and 2011, the intrinsic value of stock options exercised was immaterial. (Intrinsic value represents the amount by which the fair market value of the underlying stock exceeds the exercise price of the stock option.) The total fair value of stock options that vested was $9 million, $5 million and $4 million, respectively, for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011. For the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011, the Corporation recognized compensation expense of $8 million, $9 million, and $5 million respectively, for the vesting of stock options. At December 31, 2013, the Corporation had $8 million of unrecognized compensation expense related to stock options that is expected to be recognized over the remaining requisite service periods that extend predominantly through the fourth quarter 2015.
113
The following table summarizes information about the Corporation’s restricted stock activity for 2013, 2012, and 2011.
| | | | | | | | |
| Restricted Stock | | Shares | | | Weighted Average
Grant Date Fair Value | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2010 | | | 772,262 | | | $ | 13.94 | |
Granted | | | 593,437 | | | | 14.27 | |
Vested | | | (169,499 | ) | | | 17.74 | |
Forfeited | | | (182,435 | ) | | | 13.86 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2011 | | | 1,013,765 | | | $ | 13.79 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2011 | | | 1,013,765 | | | $ | 13.79 | |
Granted | | | 506,258 | | | | 13.00 | |
Vested | | | (533,014 | ) | | | 13.38 | |
Forfeited | | | (54,584 | ) | | | 13.73 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2012 | | | 932,425 | | | $ | 13.60 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2012 | | | 932,425 | | | $ | 13.60 | |
Granted | | | 1,276,868 | | | | 14.03 | |
Vested | | | (626,480 | ) | | | 13.68 | |
Forfeited | | | (71,048 | ) | | | 13.92 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2013 | | | 1,511,765 | | | $ | 13.92 | |
| | | | | | | | |
The Corporation amortizes the expense related to restricted stock awards as compensation expense over the vesting period specified in the grant. Restricted stock awards granted during 2013 and 2012 to the executive officers will vest ratably over a three year period. Restricted stock awards granted to non-executives during 2013 will vest ratably over a four year period, while restricted stock awards granted to non-executives during 2012 will vest ratably over a three year period. Expense for restricted stock awards of approximately $7 million, $7 million, and $6 million was recorded for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011, respectively. The Corporation had $13 million of unrecognized compensation expense related to restricted stock awards at December 31, 2013, that is expected to be recognized over the remaining requisite service periods that extend predominantly through fourth quarter 2015.
The Corporation issues shares from treasury, when available, or new shares upon the exercise of stock options or the granting of restricted stock awards. The Board of Directors has authorized management to repurchase shares of the Corporation’s common stock in the market, to be made available for issuance in connection with the Corporation’s employee incentive plans and for other corporate purposes. The repurchase of shares will be based on market and investment opportunities, capital levels, growth prospects, regulatory constraints. Such repurchases may occur from time to time in open market purchases, block transactions, private transactions, accelerated share repurchase programs, or similar facilities.
NOTE 11 RETIREMENT PLANS:
The Corporation has a noncontributory defined benefit retirement plan (the Retirement Account Plan (“RAP”)) covering substantially allfull-time employees. The benefits are based primarily on years of service and the employee’s compensation paid. Employees of acquired entities generally participate in the RAP after consummation of the business combinations. Any retirement plans of acquired entities are typically merged into the RAP after completion of the mergers, and credit is usually given to employees for years of service at the acquired institution for vesting and eligibility purposes. In connection with the First Federal acquisition in October 2004, the Corporation assumed the First Federal pension plan (the “First Federal Plan”). The First Federal Plan was frozen on December 31, 2004, and qualified participants in the First Federal Plan became eligible to participate in the RAP as of January 1, 2005. Additional discussion and information on the RAP and the First Federal Plan are collectively referred to below as the “Pension Plan.”
114
The Corporation also provides healthcare access for eligible retired employees in its Postretirement Plan (the “Postretirement Plan”). Retirees who are at least 55 years of age with 5 years of service are eligible to participate in the Postretirement Plan. The Corporation has no plan assets attributable to the Postretirement Plan. The Corporation reserves the right to terminate or make changes to the Postretirement Plan at any time.
The funded status and amounts recognized in the 2013 and 2012 consolidated balance sheets, as measured on December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively, for the Pension and Postretirement Plans were as follows.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension
Plan | | | Postretirement
Plan | | | Pension
Plan | | | Postretirement
Plan | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2012 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Change in Fair Value of Plan Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year | | $ | 224,426 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 173,422 | | | $ | — | |
Actual return on plan assets | | | 42,400 | | | | — | | | | 20,781 | | | | — | |
Employer contributions | | | 28,000 | | | | 351 | | | | 40,000 | | | | 495 | |
Gross benefits paid | | | (12,826 | ) | | | (351 | ) | | | (9,777 | ) | | | (495 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Fair value of plan assets at end of year | | $ | 282,000 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 224,426 | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | |
Change in Benefit Obligation | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net benefit obligation at beginning of year | | $ | 159,748 | | | $ | 3,935 | | | $ | 136,846 | | | $ | 3,969 | |
Service cost | | | 12,078 | | | | — | | | | 10,287 | | | | — | |
Interest cost | | | 6,237 | | | | 142 | | | | 6,547 | | | | 182 | |
Curtailments, Settlements, Special Termination Benefits | | | — | | | | — | | | | 42 | | | | — | |
Actuarial (gain) loss | | | (10,613 | ) | | | (438 | ) | | | 15,803 | | | | 279 | |
Gross benefits paid | | | (12,826 | ) | | | (351 | ) | | | (9,777 | ) | | | (495 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Net benefit obligation at end of year | | $ | 154,624 | | | $ | 3,288 | | | $ | 159,748 | | | $ | 3,935 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Funded (unfunded) status | | $ | 127,376 | | | $ | (3,288 | ) | | $ | 64,678 | | | $ | (3,935 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Noncurrent assets | | $ | 127,376 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 67,878 | | | $ | — | |
Current liabilities | | | — | | | | (343 | ) | | | — | | | | (458 | ) |
Noncurrent liabilities | | | — | | | | (2,945 | ) | | | (3,200 | ) | | | (3,477 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Asset (Liability) Recognized in the Consolidated Balance Sheets | | $ | 127,376 | | | $ | (3,288 | ) | | $ | 64,678 | | | $ | (3,935 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Amounts recognized in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax, as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 follow.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension
Plan | | | Postretirement
Plan | | | Pension
Plan | | | Postretirement
Plan | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2012 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Prior service cost | | $ | 188 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 232 | | | $ | — | |
Net actuarial gain | | | 12,894 | | | | 235 | | | | 37,240 | | | | 35 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Amount not yet recognized in net periodic benefit cost, but recognized in accumulated other comprehensive income | | $ | 13,082 | | | $ | 235 | | | $ | 37,472 | | | $ | 35 | |
| | | | | | | | |
115
Other changes in plan assets and benefit obligations recognized in other comprehensive income (“OCI”), net of tax, in 2013 and 2012 were as follows.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Plan
2013 | | | Postretirement Plan
2013 | | | Pension Plan
2012 | | | Postretirement Plan
2012 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Net gain (loss) | | $ | 35,366 | | | $ | 438 | | | $ | (9,735 | ) | | $ | (279 | ) |
Amortization of prior service cost | | | 72 | | | | — | | | | 72 | | | | 170 | |
Amortization of actuarial gain | | | 4,344 | | | | — | | | | 3,073 | | | | — | |
Income tax (expense) benefit | | | (15,394 | ) | | | (168 | ) | | | 2,324 | | | | 42 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total Recognized in OCI | | $ | 24,388 | | | $ | 270 | | | $ | (4,266 | ) | | $ | (67 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
The components of net periodic benefit cost for the Pension and Postretirement Plans for 2013, 2012, and 2011 were as follows.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Plan
2013 | | | Postretirement Plan
2013 | | | Pension Plan
2012 | | | Postretirement Plan
2012 | | | Pension Plan
2011 | | | Postretirement Plan
2011 | |
| | | | | | | | | ($ in Thousands) | | | | | | | |
Service cost | | $ | 12,078 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 10,287 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 9,898 | | | $ | — | |
Interest cost | | | 6,237 | | | | 142 | | | | 6,547 | | | | 182 | | | | 6,414 | | | | 198 | |
Expected return on plan assets | | | (17,647 | ) | | | — | | | | (14,713 | ) | | | — | | | | (12,896 | ) | | | — | |
Amortization of: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Prior service cost | | | 72 | | | | — | | | | 72 | | | | 170 | | | | 72 | | | | 395 | |
Actuarial gain | | | 4,344 | | | | — | | | | 2,708 | | | | — | | | | 2,024 | | | | — | |
Settlement charge | | | — | | | | — | | | | 408 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total net pension cost | | $ | 5,084 | | | $ | 142 | | | $ | 5,309 | | | $ | 352 | | | $ | 5,512 | | | $ | 593 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
As of December 31, 2013, the estimated actuarial losses and prior service cost that will be amortized during 2014 from accumulated other comprehensive income into net periodic benefit cost for the Pension Plan are $1 million and $0.1 million, respectively.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Plan
2013 | | | Postretirement Plan
2013 | | | Pension Plan
2012 | | | Postretirement Plan
2012 | |
Weighted average assumptions used to determine benefit obligations: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Discount rate | | | 4.80 | % | | | 4.80 | % | | | 4.00 | % | | | 4.00 | % |
Rate of increase in compensation levels | | | 4.00 | | | | N/A | | | | 4.00 | | | | N/A | |
Weighted average assumptions used to determine net periodic benefit costs: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Discount rate | | | 4.00 | % | | | 4.00 | % | | | 4.90 | % | | | 4.90 | % |
Rate of increase in compensation levels | | | 4.00 | | | | N/A | | | | 4.00 | | | | N/A | |
Expected long-term rate of return on plan assets | | | 7.50 | | | | N/A | | | | 7.50 | | | | N/A | |
The overall expected long-term rates of return on the Pension Plan assets were 7.50% at December 31, 2013 and 2012. The expected long-term (more than 20 years) rate of return was estimated using market benchmarks for equities and bonds applied to the Pension Plan’s anticipated asset allocations. The expected return on equities was computed utilizing a valuation framework, which projected future returns based on current equity valuations rather than historical returns. The actual rate of return for the Pension Plan assets was 18.54% and 12.46% for 2013 and 2012, respectively.
116
The Pension Plan’s investments are exposed to various risks, such as interest rate, market, and credit risks. Due to the level of risks associated with certain investments and the level of uncertainty related to changes in the value of the investments, it is at least reasonably possible that changes in risks in the near term could materially affect the amounts reported. The investment objective for the Pension Plan is to maximize total return with a tolerance for average risk. The plan has a diversified portfolio that will provide liquidity, current income, and growth of income and principal, with anticipated asset allocation ranges of: equity securities 55-65%, debt securities 35-45%, other cash equivalents 0-5%, and alternative securities 0-15%. Given current market conditions, the Corporation could be outside of the allocation ranges for brief periods of time. The asset allocation for the Pension Plan as of the December 31, 2013 and 2012 measurement dates, respectively, by asset category were as follows.
| | | | | | | | |
Asset Category | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
Equity securities | | | 70 | % | | | 66 | % |
Debt securities | | | 27 | | | | 30 | |
Other | | | 3 | | | | 4 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % |
| | | | | | | | |
The Pension Plan assets include cash equivalents, such as money market accounts, mutual funds, and common / collective trust funds (which include investments in equity and bond securities). Money market accounts are stated at cost plus accrued interest, mutual funds are valued at quoted market prices and investments in common / collective trust funds are valued at the amount at which units in the funds can be withdrawn. Based on these inputs, the following table summarizes the fair value of the Pension Plan’s investments as of December 31, 2013 and 2012.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | Fair Value Measurements Using | |
| | | December 31, 2013 | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Pension Plan Investments: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Money market account | | $ | 7,127 | | | $ | 7,127 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Mutual funds | | | 187,958 | | | | 187,958 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Common /collective trust funds | | | 86,915 | | | | — | | | | 86,915 | | | | — | |
| | | | |
Total Pension Plan Investments | | $ | 282,000 | | | $ | 195,085 | | | $ | 86,915 | | | $ | — | |
| | | | |
| | |
| | | | | | Fair Value Measurements Using | |
| | | December 31, 2012 | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Pension Plan Investments: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Money market account | | $ | 9,958 | | | $ | 9,958 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Mutual funds | | | 124,620 | | | | 124,620 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Common /collective trust funds | | | 89,848 | | | | — | | | | 89,848 | | | | — | |
| | | | |
Total Pension Plan Investments | | $ | 224,426 | | | $ | 134,578 | | | $ | 89,848 | | | $ | — | |
| | | | |
The Corporation’s funding policy is to pay at least the minimum amount required by the funding requirements of federal law and regulations, with consideration given to the maximum funding amounts allowed. The Corporation contributed $28 million and $40 million to its Pension Plan during 2013 and 2012, respectively. The Corporation regularly reviews the funding of its Pension Plan. At this time, the Corporation does not expect to make a contribution in 2014.
117
The projected benefit payments for the Pension and Postretirement Plans at December 31, 2013, reflecting expected future services, were as follows. The projected benefit payments were calculated using the same assumptions as those used to calculate the benefit obligations listed above.
| | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Plan | | | Postretirement Plan | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Estimated future benefit payments: | | | | | | | | |
2014 | | $ | 13,408 | | | $ | 343 | |
2015 | | | 14,007 | | | | 330 | |
2016 | | | 13,348 | | | | 313 | |
2017 | | | 13,160 | | | | 279 | |
2018 | | | 13,450 | | | | 255 | |
2019-2023 | | | 73,305 | | | | 1,173 | |
The health care trend rate is an assumption as to how much the Postretirement Plan’s medical costs will increase each year in the future. The health care trend rate assumption for pre-65 coverage is 9.5% for 2013, and 0.5% lower in each succeeding year, to an ultimate rate of 5% for 2022 and future years. The health care trend rate assumption for post-65 coverage is 9.0% for 2013, and 0.5% lower in each succeeding year, to an ultimate rate of 5% for 2021 and future years.
A one percentage point change in the assumed health care cost trend rate would have the following effect.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | 100 bp Increase | | | 100 bp Decrease | | | 100 bp Increase | | | 100 bp Decrease | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Effect on total of service and interest cost | | $ | 14 | | | $ | (12 | ) | | $ | 15 | | | $ | (13 | ) |
Effect on postretirement benefit obligation | | $ | 290 | | | $ | (255 | ) | | $ | 364 | | | $ | (315 | ) |
The Corporation also has a 401(k) and Employee Stock Ownership Plan (the “401(k) plan”). The Corporation’s contribution is determined by the Compensation and Benefits Committee of the Board of Directors. Total expense related to contributions to the 401(k) plan was $11 million, $10 million, and $9 million in 2013, 2012, and 2011, respectively.
NOTE 12 INCOME TAXES:
The current and deferred amounts of income tax expense (benefit) were as follows.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Current: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Federal | | $ | 50,628 | | | $ | 19,724 | | | $ | 9,336 | |
State | | | 2,653 | | | | 1,468 | | | | (350 | ) |
| | | | |
Total current | | | 53,281 | | | | 21,192 | | | | 8,986 | |
Deferred: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Federal | | | 16,409 | | | | 41,908 | | | | 37,553 | |
State | | | 9,511 | | | | 12,386 | | | | (2,811 | ) |
| | | | |
Total deferred | | | 25,920 | | | | 54,294 | | | | 34,742 | |
| | | | |
Total income tax expense | | $ | 79,201 | | | $ | 75,486 | | | $ | 43,728 | |
| | | | |
118
Temporary differences between the amounts reported in the financial statements and the tax bases of assets and liabilities resulted in deferred taxes. Deferred tax assets and liabilities at December 31 were as follows.
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Gross deferred tax assets: | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for loan losses | | $ | 104,944 | | | $ | 115,128 | |
Allowance for other losses | | | 13,790 | | | | 18,205 | |
Accrued liabilities | | | 6,101 | | | | 6,055 | |
Deferred compensation | | | 28,911 | | | | 27,073 | |
Securities valuation adjustment | | | 1,724 | | | | 2,258 | |
Benefit of tax loss and credit carryforwards | | | 32,552 | | | | 46,376 | |
Nonaccrual interest | | | 4,431 | | | | 1,112 | |
Other | | | 9,433 | | | | 8,518 | |
| | | | |
Total gross deferred tax assets | | | 201,886 | | | | 224,725 | |
Gross deferred tax liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
FHLB stock dividends | | | 6,425 | | | | 7,602 | |
Prepaid expenses | | | 61,225 | | | | 55,944 | |
Intangible amortization | | | 28,914 | | | | 28,478 | |
Mortgage banking activities | | | 14,497 | | | | 6,257 | |
Deferred loan fee income | | | 25,480 | | | | 26,800 | |
State income taxes | | | 12,754 | | | | 16,083 | |
Leases | | | 2,525 | | | | 2,269 | |
Depreciation | | | 17,931 | | | | 22,386 | |
Other | | | 1,374 | | | | 2,225 | |
| | | | |
Total gross deferred tax liabilities | | | 171,125 | | | | 168,044 | |
| | | | |
Net deferred tax assets | | | 30,761 | | | | 56,681 | |
| | | | |
Tax effect of unrealized (gain) loss related to available for sale securities | | | 7,685 | | | | (53,579 | ) |
Tax effect of unrealized loss related to pension and postretirement benefits | | | 8,024 | | | | 23,586 | |
| | | | |
| | | 15,709 | | | | (29,993 | ) |
| | | | |
Net deferred tax assets including items with tax effect recorded directly to OCI | | $ | 46,470 | | | $ | 26,688 | |
| | | | |
At December 31, 2013 and 2012, there was no valuation allowance for deferred tax assets.
At December 31, 2013, the Corporation had state net operating losses of $406 million (of which, $35 million was acquired from various acquisitions) that will expire in the years 2024 through 2031. $235 million of these state net operating loss carryforwards do not expire until after 2031.
The effective income tax rate differs from the statutory federal tax rate. The major reasons for this difference were as follows.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
Federal income tax rate at statutory rate | | | 35.0 | % | | | 35.0 | % | | | 35.0 | % |
Increases (decreases) resulting from: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tax-exempt interest and dividends | | | (4.5 | ) | | | (4.9 | ) | | | (7.0 | ) |
State income taxes (net of federal income taxes) | | | 2.9 | | | | 3.6 | | | | 3.8 | |
Bank owned life insurance | | | (1.5 | ) | | | (1.9 | ) | | | (2.8 | ) |
Valuation allowance | | | — | | | | — | | | | (3.3 | ) |
Federal tax credits | | | (1.0 | ) | | | (1.2 | ) | | | (1.7 | ) |
Tax reserve adjustments | | | (1.9 | ) | | | (1.8 | ) | | | (0.6 | ) |
Compensation deduction limitations | | | 0.1 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 0.7 | |
Other | | | 0.5 | | | | 0.5 | | | | (0.3 | ) |
| | | | |
Effective income tax rate | | | 29.6 | % | | | 29.7 | % | | | 23.8 | % |
| | | | |
119
Savings banks acquired by the Corporation in 1997 and 2004 qualified under provisions of the Internal Revenue Code that permitted them to deduct from taxable income an allowance for bad debts that differed from the provision for such losses charged to income for financial reporting purposes. Accordingly, no provision for income taxes has been made for $100 million of retained income at December 31, 2013. If income taxes had been provided, the deferred tax liability would have been approximately $40 million. Management does not expect this amount to become taxable in the future, therefore, no provision for income taxes has been made.
The Corporation and its subsidiaries file income tax returns in the U.S. federal jurisdiction and various state jurisdictions. The Corporation’s federal income tax returns are open and subject to examination from the 2010 tax return year and forward. Generally, tax return years prior to the 2007 tax return year are no longer subject to state and local income tax examination.
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits was as follows.
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | ($ in Millions) | |
Balance at beginning of year | | $ | 13 | | | $ | 21 | |
Changes in tax positions for prior years | | | 1 | | | | — | |
Statute expiration | | | (8 | ) | | | (8 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Balance at end of year | | $ | 6 | | | $ | 13 | |
| | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2013 and 2012, the total amount of unrecognized tax benefits that, if recognized, would affect the effective tax rate was $4 million and $8 million, respectively.
The Corporation recognizes interest and penalties accrued related to unrecognized tax benefits in the income tax expense line of the consolidated statements of income. As of December 31, 2013, the Corporation had $2 million of interest and penalties (including a $3 million net reduction of previously accrued interest and penalties during 2013) on unrecognized tax benefits of which $2 million had an impact on the effective tax rate. As of December 31, 2012, the Corporation had $5 million of interest and penalties (including a $1 million net reduction of previously accrued interest and penalties during 2012) on unrecognized tax benefits of which $3 million had an impact on the effective tax rate. Management does not anticipate significant adjustments to the total amount of unrecognized tax benefits within the next twelve months.
NOTE 13 DERIVATIVE AND HEDGING ACTIVITIES:
The Corporation facilitates customer borrowing activity by providing various interest rate risk management solutions through its capital markets area. To date, all of the notional amounts of customer transactions have been matched with a mirror swap with another counterparty. The Corporation may also use derivative instruments to hedge the variability in interest payments or protect the value of certain assets and liabilities recorded on its consolidated balance sheet from changes in interest rates. The predominant derivative and hedging activities include interest rate-related instruments (swaps, caps, collars, and corridors), foreign currency exchange forwards, written options, purchased options, and certain mortgage banking activities. The contract or notional amount of a derivative is used to determine, along with the other terms of the derivative, the amounts to be exchanged between the counterparties. The Corporation is exposed to credit risk in the event of nonperformance by counterparties to financial instruments. To mitigate the counterparty risk, interest rate-related instruments generally contain language outlining collateral pledging requirements for each counterparty. Collateral must be posted when the market value exceeds certain threshold limits which are determined from the credit ratings of each counterparty. The Corporation was required to pledge $42 million of investment securities as collateral at December 31, 2013, and pledged $70 million of investment securities as collateral at December 31, 2012.
120
The Corporation’s derivative and hedging instruments are recorded at fair value on the consolidated balance sheets. The fair value of the Corporation’s interest rate-related instruments is determined using discounted cash flow analysis on the expected cash flows of each derivative and also includes a nonperformance / credit risk component (credit valuation adjustment). See Note 17 for additional fair value information and disclosures.
The table below identifies the balance sheet category and fair values of the Corporation’s derivative instruments not designated as hedging instruments.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Notional
Amount | | | Fair
Value | | | Balance Sheet
Category | | Weighted Average | |
($ in Thousands) | | | | | Receive Rate(1) | | | Pay Rate(1) | | | Maturity | |
December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest rate-related instruments — customer and mirror | | $ | 1,821,787 | | | $ | 42,980 | | | Trading assets | | | 1.63 | % | | | 1.63 | % | | | 45 months | |
Interest rate-related instruments — customer and mirror | | | 1,821,787 | | | | (45,815 | ) | | Trading liabilities | | | 1.63 | % | | | 1.63 | % | | | 45 months | |
Interest rate lock commitments (mortgage) | | | 102,225 | | | | 416 | | | Other assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Forward commitments (mortgage) | | | 135,000 | | | | 1,301 | | | Other assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Foreign currency exchange forwards | | | 25,747 | | | | 748 | | | Trading assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Foreign currency exchange forwards | | | 24,413 | | | | (655 | ) | | Trading liabilities | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Purchased options (time deposit) | | | 115,953 | | | | 7,328 | | | Other assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Written options (time deposit) | | | 115,953 | | | | (7,328 | ) | | Other liabilities | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | |
December 31, 2012 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest rate-related instruments — customer and mirror | | $ | 1,728,545 | | | $ | 69,370 | | | Trading assets | | | 1.30 | % | | | 1.30 | % | | | 47 months | |
Interest rate-related instruments — customer and mirror | | | 1,728,545 | | | | (75,131 | ) | | Trading liabilities | | | 1.30 | % | | | 1.30 | % | | | 47 months | |
Interest rate lock commitments (mortgage) | | | 351,786 | | | | 7,794 | | | Other assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Forward commitments (mortgage) | | | 520,000 | | | | (147 | ) | | Other liabilities | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Foreign currency exchange forwards | | | 39,763 | | | | 1,341 | | | Trading assets | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Foreign currency exchange forwards | | | 35,745 | | | | (1,212 | ) | | Trading liabilities | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Purchased options (time deposit) | | | 111,262 | | | | 3,620 | | | Other assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Written options (time deposit) | | | 111,262 | | | | (3,620 | ) | | Other liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
| (1) | Reflects the weighted average receive rate and pay rate for the interest rate swap derivative financial instruments only. |
121
The table below identifies the income statement category of the gains and losses recognized in income on the Corporation’s derivative instruments not designated as hedging instruments.
| | | | | | |
| | | Income Statement Category of
Gain / (Loss) Recognized in Income | | Gain / (Loss)
Recognized in Income | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Year ended December 31, 2013 | | | | | | |
Interest rate-related instruments — customer and mirror, net | | Capital market fees, net | | | 2,926 | |
Interest rate lock commitments (mortgage) | | Mortgage banking, net | | | (7,378 | ) |
Forward commitments (mortgage) | | Mortgage banking, net | | | 1,448 | |
Foreign currency exchange forwards | | Capital market fees, net | | | (36 | ) |
| | | |
| | | | | | |
Year ended December 31, 2012 | | | |
Interest rate-related instruments — customer and mirror, net | | Capital market fees, net | | | 1,160 | |
Interest rate lock commitments (mortgage) | | Mortgage banking, net | | | 3,223 | |
Forward commitments (mortgage) | | Mortgage banking, net | | | 4,624 | |
Foreign currency exchange forwards | | Capital market fees, net | | | (59 | ) |
Covered call options | | Interest on investment securities | | | 469 | |
| | | |
Free Standing Derivatives
The Corporation enters into various derivative contracts which are designated as free standing derivative contracts. These derivative contracts are not designated against specific assets and liabilities on the balance sheet or forecasted transactions and, therefore, do not qualify for hedge accounting treatment. Such derivative contracts are carried at fair value on the consolidated balance sheets with changes in the fair value recorded as a component of Capital market fees, net, and typically include interest rate-related instruments (swaps, caps, collars, and corridors).
Free standing derivatives are entered into primarily for the benefit of commercial customers through providing derivative products which enables the customer to manage their exposures to interest rate risk. The Corporation’s market risk from unfavorable movements in interest rates related to these derivative contracts is generally economically hedged by concurrently entering into offsetting derivative contracts. The offsetting derivative contracts have identical notional values, terms and indices.
Mortgage derivatives
Interest rate lock commitments to originate residential mortgage loans held for sale and forward commitments to sell residential mortgage loans are considered derivative instruments, and the fair value of these commitments is recorded on the consolidated balance sheets with the changes in fair value recorded as a component of mortgage banking, net.
Foreign currency derivatives
The Corporation provides foreign exchange services to customers. The Corporation may enter into a foreign currency forward to mitigate the exchange rate risk attached to the cash flows of a loan or as an offsetting contract to a forward entered into as a service to our customer.
Written and purchased option derivatives (time deposit)
The Corporation periodically enters into written and purchased option derivative instruments to facilitate an equity linked time deposit product (the “Power CD”). The Power CD is a time deposit that provides the purchaser a guaranteed return of principal at maturity plus a potential equity return (a written option), while the Corporation
122
receives a known stream of funds based on the equity return (a purchased option). The written and purchased options are mirror derivative instruments which are carried at fair value on the consolidated balance sheets. During September 2013, the Corporation terminated its Power CD product.
Other derivatives
During the second quarter of 2012, the Corporation began entering into covered call options. Under covered call options, the Corporation will sell options to a bank or dealer for the right to purchase certain securities held within the Corporation’s investment securities portfolio. These option transactions are designed primarily to increase the total return associated with the investment securities portfolio. These options do not qualify as hedges, and, accordingly, the changes in fair value of these contracts are recognized in interest income. There were no covered call options outstanding as of December 31, 2013 or December 31, 2012.
NOTE 14: BALANCE SHEET OFFSETTING
Interest Rate-Related Instruments (“Interest Agreements”)
The Corporation enters into interest rate-related instruments to facilitate the interest rate risk management strategies of commercial customers. The Corporation mitigates this risk by entering into equal and offsetting interest rate-related instruments with highly rated third party financial institutions. The interest agreements are free-standing derivatives and are recorded at fair value in the Corporation’s consolidated balance sheet. The Corporation is party to master netting arrangements with its financial institution counterparties; however, the Corporation does not offset assets and liabilities under these arrangements for financial statement presentation purposes. The master netting arrangements provide for a single net settlement of all interest agreements, as well as collateral, in the event of default on, or termination of, any one contract. Collateral, usually in the form of investment securities, is posted by the counterparty with net liability positions in accordance with contract thresholds. See Note 13 for additional information on the Corporation’s derivative and hedging activities.
Securities Sold Under Agreements to Repurchase (“Repurchase Agreements”)
The Corporation enters into agreements under which it sells securities subject to an obligation to repurchase the same or similar securities. Under these arrangements, the Corporation may transfer legal control over the assets but still retain effective control through an agreement that both entitles and obligates the Corporation to repurchase the assets. As a result, these repurchase agreements are accounted for as collateralized financing arrangements (i.e., secured borrowings) and not as a sale and subsequent repurchase of securities. The obligation to repurchase the securities is reflected as a liability in the Corporation’s consolidated balance sheet, while the securities underlying the repurchase agreements remain in the respective investment securities asset accounts (i.e., there is no offsetting or netting of the investment securities assets with the repurchase agreement liabilities). The right of setoff for a repurchase agreement resembles a secured borrowing, whereby the collateral would be used to settle the fair value of the repurchase agreement should the Corporation be in default (e.g., fails to make an interest payment to the counterparty). In addition, the Corporation does not enter into reverse repurchase agreements; therefore, there is no such offsetting to be done with the repurchase agreements.
123
The following table presents the assets and liabilities subject to an enforceable master netting arrangement as of December 31, 2013 and December 31, 2012. The swap agreements we have with our commercial customers are not subject to an enforceable master netting arrangement, and therefore, are excluded from this table.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Gross
amounts
recognized | | | | | | Gross amounts not offset
in the balance sheet | | | | |
| | | | Gross amounts
offset in the
balance sheet | | | Net amounts
presented in
the balance sheet | | | Financial
instruments | | | Collateral | | | Net amount | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | | | | |
December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Derivative assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest rate-related instruments | | $ | 3,084 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 3,084 | | | $ | (3,082 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | 2 | |
Derivative liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest rate-related instruments | | $ | 41,786 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 41,786 | | | $ | (3,082 | ) | | $ | (33,405 | ) | | $ | 5,299 | |
| | | | |
December 31, 2012 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Derivative assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest rate-related instruments | | $ | 66 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 66 | | | $ | (66 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Derivative liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest rate-related instruments | | $ | 73,067 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 73,067 | | | $ | (66 | ) | | $ | (67,331 | ) | | $ | 5,670 | |
| | | | |
NOTE 15 COMMITMENTS, OFF-BALANCE SHEET ARRANGEMENTS, AND CONTINGENT LIABILITIES:
The Corporation utilizes a variety of financial instruments in the normal course of business to meet the financial needs of its customers and to manage its own exposure to fluctuations in interest rates. These financial instruments include lending-related and other commitments (see below) as well as derivative instruments (see Note 13). The following is a summary of lending-related commitments.
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Commitments to extend credit, excluding commitments to originate residential mortgage loans held for sale(1)(2) | | $ | 6,367,771 | | | $ | 5,526,326 | |
Commercial letters of credit(1) | | | 132,777 | | | | 85,689 | |
Standby letters of credit(3) | | $ | 250,030 | | | $ | 303,705 | |
| 1) | These off-balance sheet financial instruments are exercisable at the market rate prevailing at the date the underlying transaction will be completed and, thus, are deemed to have no current fair value, or the fair value is based on fees currently charged to enter into similar agreements and is not material at December 31, 2013 or 2012. |
| 2) | Interest rate lock commitments to originate residential mortgage loans held for sale are considered derivative instruments and are disclosed in Note 13. |
| 3) | The Corporation has established a liability of $4 million at both December 31, 2013 and 2012, as an estimate of the fair value of these financial instruments. |
Lending-related Commitments
As a financial services provider, the Corporation routinely enters into commitments to extend credit. Such commitments are subject to the same credit policies and approval process accorded to loans made by the Corporation, with each customer’s creditworthiness evaluated on a case-by-case basis. The commitments generally have fixed expiration dates or other termination clauses and may require the payment of a fee. The Corporation’s exposure to credit loss in the event of nonperformance by the other party to these financial instruments is represented by the contractual amount of those instruments. The amount of collateral obtained, if deemed necessary by the Corporation upon extension of credit, is based on management’s credit evaluation of the customer. Since a significant portion of commitments to extend credit are subject to specific restrictive loan
124
covenants or may expire without being drawn upon, the total commitment amounts do not necessarily represent future cash flow requirements. For both December 31, 2013 and December 31, 2012, the Corporation had a reserve for losses on unfunded commitments totaling $22 million included in other liabilities on the consolidated balance sheets. See Note 1 for the Corporation’s accounting policy on the reserve for unfunded commitments.
Lending-related commitments include commitments to extend credit, commitments to originate residential mortgage loans held for sale, commercial letters of credit, and standby letters of credit. Commitments to extend credit are agreements to lend to customers at predetermined interest rates, as long as there is no violation of any condition established in the contracts. Interest rate lock commitments to originate residential mortgage loans held for sale and forward commitments to sell residential mortgage loans are considered derivative instruments, and the fair value of these commitments is recorded on the consolidated balance sheets. The Corporation’s derivative and hedging activity is further described in Note 13. Commercial and standby letters of credit are conditional commitments issued to guarantee the performance of a customer to a third party. Commercial letters of credit are issued specifically to facilitate commerce and typically result in the commitment being drawn on when the underlying transaction is consummated between the customer and the third party, while standby letters of credit generally are contingent upon the failure of the customer to perform according to the terms of the underlying contract with the third party.
Other Commitments
The Corporation has principal investment commitments to provide capital-based financing to private and public companies through either direct investments in specific companies or through investment funds and partnerships. The timing of future cash requirements to fund such commitments is generally dependent on the investment cycle, whereby privately held companies are funded by private equity investors and ultimately sold, merged, or taken public through an initial offering, which can vary based on overall market conditions, as well as the nature and type of industry in which the companies operate. The Corporation also invests in low-income housing, small-business commercial real estate, new market tax credit projects, and historic tax credit projects to promote the revitalization of low-to-moderate-income neighborhoods throughout the local communities of its bank subsidiary. As a limited partner in these unconsolidated projects, the Corporation is allocated tax credits and deductions associated with the underlying projects. The aggregate carrying value of these investments at December 31, 2013, was $33 million, included in other assets on the consolidated balance sheets, compared to $35 million at December 31, 2012. Related to these investments, the Corporation had remaining commitments to fund of $16 million at December 31, 2013, and $18 million at December 31, 2012, respectively.
Contingent Liabilities
The Corporation is party to various pending and threatened claims and legal proceedings arising in the normal course of business activities, some of which involve claims for substantial amounts. Although there can be no assurance as to the ultimate outcomes, the Corporation believes it has meritorious defenses to the claims asserted against it in its currently outstanding matters, including the matters described below, and with respect to such legal proceedings, intends to continue to defend itself vigorously. The Corporation will consider settlement of cases when, in management’s judgment, it is in the best interests of both the Corporation and its shareholders.
On at least a quarterly basis, the Corporation assesses its liabilities and contingencies in connection with all pending or threatened claims and litigation, utilizing the most recent information available. On a matter by matter basis, an accrual for loss is established for those matters which the Corporation believes it is probable that a loss may be incurred and that the amount of such loss can be reasonably estimated. Once established, each accrual is adjusted as appropriate to reflect any subsequent developments. Accordingly, management’s estimate will change from time to time, and actual losses may be more or less than the current estimate. For matters where a loss is not probable, or the amount of the loss cannot be estimated, no accrual is established.
Resolution of legal claims is inherently unpredictable, and in many legal proceedings various factors exacerbate this inherent unpredictability, including where the damages sought are unsubstantiated or indeterminate, it is unclear whether a case brought as a class action will be allowed to proceed on that basis, discovery is not
125
complete, the proceeding is not yet in its final stages, the matters present legal uncertainties, there are significant facts in dispute, there are a large number of parties (including where it is uncertain how liability, if any, will be shared among multiple defendants), or there is a wide range of potential results.
A lawsuit,R.J. ZAYED v. Associated Bank, N.A., was filed in the United States District Court for the District of Minnesota on January 29, 2013. The lawsuit relates to a Ponzi scheme perpetrated by Oxford Global Partners and related entities (“Oxford”) and individuals and was brought by the receiver for Oxford. Oxford was a depository customer of the Bank. The lawsuit claims that the Bank is liable for failing to uncover the Oxford Ponzi scheme, and specifically alleges the Bank aided and abetted (1) the fraudulent scheme; (2) a breach of fiduciary duty; (3) conversion; and (4) false representations and omissions. The lawsuit seeks unspecified consequential and punitive damages. At this early stage of the lawsuit, it is not possible for management to assess the probability of a material adverse outcome or reasonably estimate the amount of any potential loss at this time. The court granted the Bank’s motion to dismiss the complaint on September 30, 2013, and the plaintiff has appealed the dismissal to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Eighth Circuit. The Bank intends to vigorously defend this lawsuit. A lawsuit by investors in the same Ponzi scheme,Herman Grad, et al v. Associated Bank, N.A., brought in Brown County, Wisconsin in October 2009 was dismissed by the circuit court, and the dismissal was affirmed by the Wisconsin Court of Appeals in June 2011 in an unpublished opinion.
The Bank is currently subject to a Consent Order with the OCC relating to its Bank Secrecy Act of 1970 (“BSA”) compliance. Please see “Regulatory Matters” below for additional information.
The Corporation sells residential mortgage loans to investors in the normal course of business. Residential mortgage loans sold to others are predominantly conventional residential first lien mortgages originated under our usual underwriting procedures, and are most often sold on a nonrecourse basis, primarily to the government-sponsored enterprises (“GSEs”). The Corporation’s agreements to sell residential mortgage loans in the normal course of business usually require certain representations and warranties on the underlying loans sold, related to credit information, loan documentation, collateral, and insurability. Subsequent to being sold, if a material underwriting deficiency or documentation defect is discovered, the Corporation may be obligated to repurchase the loan or reimburse the GSEs for losses incurred (collectively, “make whole requests”). The make whole requests and any related risk of loss under the representations and warranties are largely driven by borrower performance. See Note 1 for the Corporation’s accounting policy on the mortgage repurchase reserve.
As a result of make whole requests, the Corporation has repurchased loans with principal balances of $3 million and $5 million during the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively, and paid loss reimbursement claims of $3 million and $4 million for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The Corporation had a repurchase reserve for potential claims on loans previously sold of $6 million at December 31, 2013, compared to $3 million at December 31, 2012. Make whole requests during 2012 and 2013 generally arose from loans sold during the period of January 1, 2006 to December 31, 2013, which total $17.6 billion at the time of sale, and consisted primarily of loans sold to GSEs. As of December 31, 2013, approximately $7.5 billion of these sold loans remain outstanding. Management will continue to monitor this activity and its impact on the reserve. The following summarizes the changes in the mortgage repurchase reserve.
| | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended | | | For the Year Ended | |
| | | December 31, 2013 | | | December 31, 2012 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Balance at beginning of year | | $ | 3,300 | | | $ | — | |
Repurchase provision expense | | | 5,909 | | | | 7,109 | |
Charge offs | | | (3,509 | ) | | | (3,809 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Balance at end of year | | $ | 5,700 | | | $ | 3,300 | |
| | | | | | | | |
The Corporation may also sell residential mortgage loans with limited recourse (limited in that the recourse period ends prior to the loan’s maturity, usually after certain time and / or loan paydown criteria have been met), whereby repurchase could be required if the loan had defined delinquency issues during the limited recourse
126
periods. At December 31, 2013, and December 31, 2012, there were approximately $56 million and $79 million, respectively, of residential mortgage loans sold with such recourse risk. There have been limited instances and immaterial historical losses on repurchases for recourse under the limited recourse criteria.
The Corporation has a subordinate position to the FHLB in the credit risk on residential mortgage loans it sold to the FHLB in exchange for a monthly credit enhancement fee. The Corporation has not sold loans to the FHLB with such credit risk retention since February 2005. At December 31, 2013 and December 31, 2012, there were $233 million and $321 million, respectively, of such residential mortgage loans with credit risk recourse, upon which there have been negligible historical losses to the Corporation.
For certain mortgage loans originated by the Corporation, borrowers may be required to obtain Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI) provided by third-party insurers. The Corporation was previously a party to reinsurance treaties with certain PMI carriers which provided, among other things, for a sharing of losses within a specified range of the total PMI coverage in exchange for a portion of the PMI premiums. The reinsurance treaties typically provided that the Corporation will assume liability for losses once they exceed 5% of the aggregate risk exposure up to a maximum of 10% of the aggregate risk exposure. As of January 1, 2009, the Corporation discontinued providing reinsurance coverage for new loans in exchange for a portion of the PMI premium. During the first half of 2013, the Corporation terminated its reinsurance treaties with all third party PMI mortgage reinsurance carriers. As a result, the Corporation’s estimated liability for reinsurance losses was $0 as of December 31, 2013, compared to $8 million at December 31, 2012.
Regulatory Matters
During the first quarter of 2012, the Bank entered into a Consent Order with the OCC regarding its BSA compliance. The Consent Order required the Bank to create a BSA-focused action plan, supplement existing customer due diligence policies and procedures, perform a BSA risk assessment and complete independent testing. The OCC has issued a written notice to the Bank related to the Bank’s past BSA deficiencies. After the OCC’s review of the Bank’s response, the OCC may impose a civil money penalty related to these deficiencies. The Corporation is currently not able to estimate a reasonable range of losses relating to that possibility. The Bank has been working cooperatively with the OCC and management believes it is in compliance with the Consent Order.
127
NOTE 16 PARENT COMPANY ONLY FINANCIAL INFORMATION:
Presented below are condensed financial statements for the Parent Company.
BALANCE SHEETS
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
ASSETS | | | | | | | | |
Cash and due from banks | | $ | 148,327 | | | $ | 159,725 | |
Investment securities available for sale, at fair value | | | 163,679 | | | | 200,800 | |
Notes receivable from subsidiaries | | | 46,594 | | | | 47,455 | |
Investment in subsidiaries | | | 3,161,153 | | | | 3,250,667 | |
Other assets | | | 81,529 | | | | 74,507 | |
| | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 3,601,282 | | | $ | 3,733,154 | |
| | | | |
| | |
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | | | | | | | |
Commercial paper | | $ | 65,484 | | | $ | 51,245 | |
Senior notes, at par | | | 585,000 | | | | 585,000 | |
Subordinated debt, at par | | | — | | | | 25,821 | |
Long-term funding capitalized costs | | | 1,941 | | | | 2,590 | |
| | | | |
Total long-term funding | | | 586,941 | | | | 613,411 | |
Accrued expenses and other liabilities | | | 57,567 | | | | 132,099 | |
| | | | |
Total liabilities | | | 709,992 | | | | 796,755 | |
Preferred equity | | | 61,862 | | | | 63,272 | |
Common equity | | | 2,829,428 | | | | 2,873,127 | |
| | | | |
Total stockholders’ equity | | | 2,891,290 | | | | 2,936,399 | |
| | | | |
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | | $ | 3,601,282 | | | $ | 3,733,154 | |
| | | | |
128
STATEMENTS OF INCOME
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
INCOME | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Dividends from subsidiaries | | $ | 262,000 | | | $ | 169,500 | | | $ | — | |
Management and service fees from subsidiaries | | | — | | | | — | | | | 54,242 | |
Interest income on notes receivable | | | 1,988 | | | | 1,807 | | | | 2,306 | |
Other income | | | 7,742 | | | | 5,762 | | | | 5,289 | |
| | | | |
Total income | | | 271,730 | | | | 177,069 | | | | 61,837 | |
| | | | |
EXPENSE | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest expense on short and long-term funding | | | 26,769 | | | | 37,066 | | | | 39,072 | |
Personnel expense | | | — | | | | 36 | | | | 38,258 | |
Other expense | | | 8,427 | | | | 12,873 | | | | 16,603 | |
| | | | |
Total expense | | | 35,196 | | | | 49,975 | | | | 93,933 | |
| | | | |
Income (loss) before income tax benefit and equity in undistributed net income (loss) of subsidiaries | | | 236,534 | | | | 127,094 | | | | (32,096 | ) |
Income tax benefit | | | (7,086 | ) | | | (17,948 | ) | | | (17,788 | ) |
| | | | |
Income (loss) before equity in undistributed net income (loss) of subsidiaries | | | 243,620 | | | | 145,042 | | | | (14,308 | ) |
Equity in undistributed net income (loss) of subsidiaries | | | (54,928 | ) | | | 33,931 | | | | 154,007 | |
| | | | |
Net income | | | 188,692 | | | | 178,973 | | | | 139,699 | |
Preferred stock dividends and discount accretion | | | 5,158 | | | | 5,200 | | | | 24,830 | |
| | | | |
Net income available to common equity | | $ | 183,534 | | | $ | 173,773 | | | $ | 114,869 | |
| | | | |
129
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 188,692 | | | $ | 178,973 | | | $ | 139,699 | |
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating | | | | | | | | | | | | |
activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(Increase) decrease in equity in undistributed net income (loss) of subsidiaries | | | 54,928 | | | | (33,931 | ) | | | (154,007 | ) |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 63 | | | | 132 | | | | 171 | |
(Gain) loss on sales of investment securities, net of impairment write-downs | | | (456 | ) | | | (530 | ) | | | 81 | |
(Gain) loss on sales of assets, net | | | (1,007 | ) | | | 1,365 | | | | (13 | ) |
Net change in other assets and other liabilities | | | (94,712 | ) | | | 142,900 | | | | 25,356 | |
| | | | |
Net cash provided by operating activities | | | 147,508 | | | | 288,909 | | | | 11,287 | |
| | | | |
INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Proceeds from sales of investment securities | | | 55,445 | | | | 49,819 | | | | 14,667 | |
Purchase of investment securities | | | (23,101 | ) | | | (186,432 | ) | | | (75,221 | ) |
Net (increase) decrease in notes receivable | | | 3,049 | | | | (225 | ) | | | 391,996 | |
Purchase of other assets, net of disposals | | | 2,407 | | | | (7,336 | ) | | | 4,977 | |
| | | | |
Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | | | 37,800 | | | | (144,174 | ) | | | 336,419 | |
| | | | |
FINANCING ACTIVITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net increase in short-term funding | | | 14,239 | | | | 51,245 | | | | — | |
Proceeds from issuance of long-term funding | | | — | | | | 154,738 | | | | 432,504 | |
Repayment of long-term funding | | | (25,821 | ) | | | (211,340 | ) | | | (170,000 | ) |
Proceeds from issuance of preferred stock | | | — | | | | — | | | | 63,272 | |
Purchase of preferred stock | | | (1,626 | ) | | | — | | | | (525,000 | ) |
Cash dividends | | | (60,149 | ) | | | (44,834 | ) | | | (21,195 | ) |
Purchase of treasury stock | | | (123,349 | ) | | | (61,654 | ) | | | (659 | ) |
| | | | |
Net cash used in financing activities | | | (196,706 | ) | | | (111,845 | ) | | | (221,078 | ) |
| | | | |
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | | (11,398 | ) | | | 32,890 | | | | 126,628 | |
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | | | 159,725 | | | | 126,835 | | | | 207 | |
| | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | | $ | 148,327 | | | $ | 159,725 | | | $ | 126,835 | |
| | | | |
NOTE 17 FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS:
Fair value represents the estimated price at which an orderly transaction to sell an asset or to transfer a liability would take place between market participants at the measurement date under current market conditions (i.e., an exit price concept). See Note 1 for the Corporation’s accounting policy for fair value measurements.
Following is a description of the valuation methodologies used for the Corporation’s more significant instruments measured on a recurring basis at fair value, including the general classification of such instruments pursuant to the valuation hierarchy.
Investment securities available for sale: Where quoted prices are available in an active market, investment securities are classified in Level 1 of the fair value hierarchy. Level 1 investment securities primarily include U.S. Treasury, certain Federal agency, and exchange-traded debt and equity securities. If quoted market prices are not available for the specific security, then fair values are estimated by using pricing models, quoted prices of
130
securities with similar characteristics or discounted cash flows, with consideration given to the nature of the quote and the relationship of recently evidenced market activity to the fair value estimate, and are classified in Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy. Examples of these investment securities include certain Federal agency securities, obligations of state and political subdivisions (municipal securities), mortgage-related securities, asset-backed securities, and other debt securities. Lastly, in certain cases where there is limited activity or less transparency around inputs to the estimated fair value, securities are classified within Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy. Level 3 securities primarily include pooled trust preferred debt securities. To validate the fair value estimates, assumptions, and controls, the Corporation looks to transactions for similar instruments and utilizes independent pricing provided by third party vendors or brokers and relevant market indices. While none of these sources are solely indicative of fair value, they serve as directional indicators for the appropriateness of the Corporation’s fair value estimates. The Corporation has determined that the fair value measures of its investment securities are classified predominantly within Level 1 or 2 of the fair value hierarchy. See Note 2 for additional disclosure regarding the Corporation’s investment securities.
Derivative financial instruments (interest rate-related instruments): The Corporation uses interest rate swaps to manage its interest rate risk. In addition, the Corporation offers customer interest rate-related instruments (swaps, caps, collars, and corridors) to service our customers’ needs, for which the Corporation simultaneously enters into offsetting derivative financial instruments (i.e., mirror interest rate-related instruments) with third parties to manage its interest rate risk associated with these financial instruments. The valuation of the Corporation’s derivative financial instruments is determined using discounted cash flow analysis on the expected cash flows of each derivative and, also includes a nonperformance / credit risk component (credit valuation adjustment). See Note 13 for additional disclosure regarding the Corporation’s derivative financial instruments.
The discounted cash flow analysis component in the fair value measurements reflects the contractual terms of the derivative financial instruments, including the period to maturity, and uses observable market-based inputs, including interest rate curves and implied volatilities. More specifically, the fair values of interest rate swaps are determined using the market standard methodology of netting the discounted future fixed cash receipts (or payments), with the variable cash payments (or receipts) based on an expectation of future interest rates (forward curves) derived from observable market interest rate curves. Likewise, the fair values of interest rate options (i.e., interest rate caps, collars, and corridors) are determined using the market standard methodology of discounting the future expected cash receipts that would occur if variable interest rates fall below (or rise above) the strike rate of the floors (or caps), with the variable interest rates used in the calculation of projected receipts on the floor (or cap) based on an expectation of future interest rates derived from observable market interest rate curves and volatilities.
As of January 1, 2013, the Corporation changed its valuation methodology for interest-rate related derivative financial instruments to discount cash flows based on Overnight Index Swap (“OIS”) rates. Fully collateralized trades are discounted using OIS with no additional economic adjustments to arrive at fair value. Under-collateralized or partially collateralized trades are also discounted at OIS, but include appropriate economic adjustments for funding costs (i.e., a LIBOR-OIS basis adjustment to approximate uncollateralized cost of funds) and credit risk. The Corporation is making the changes to better align its inputs, assumptions, and pricing methodologies with those used in its principal market by most dealers and major market participants. The changes in valuation methodology are immaterial to the Corporation’s results of operations, financial position, and liquidity.
The Corporation also incorporates credit valuation adjustments to appropriately reflect both its own nonperformance risk and the respective counterparty’s nonperformance risk in the fair value measurements. In adjusting the fair value of its derivative financial instruments for the effect of nonperformance risk, the Corporation has considered the impact of netting and any applicable credit enhancements, such as collateral postings, thresholds, mutual puts, and guarantees. In conjunction with the FASB’s fair value measurement guidance, the Corporation made an accounting policy election to measure the credit risk of its derivative financial instruments that are subject to master netting agreements on a net basis by counterparty portfolio.
131
While the Corporation has determined that the majority of the inputs used to value its derivative financial instruments fall within Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy, the credit valuation adjustments utilize Level 3 inputs, such as estimates of current credit spreads to evaluate the likelihood of default by itself and its counterparties. The Corporation has assessed the significance of the impact of the credit valuation adjustments on the overall valuation of its derivative positions as of December 31, 2013, and 2012, and has determined that the credit valuation adjustments are not significant to the overall valuation of its derivative financial instruments. Therefore, the Corporation has determined that the fair value measures of its derivative financial instruments in their entirety are classified within Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy.
Derivative financial instruments (foreign currency exchange forwards): The Corporation provides foreign currency exchange services to customers. In addition, the Corporation may enter into a foreign currency exchange forward to mitigate the exchange rate risk attached to the cash flows of a loan or as an offsetting contract to a forward entered into as a service to our customer. The valuation of the Corporation’s foreign currency exchange forwards is determined using quoted prices of foreign currency exchange forwards with similar characteristics, with consideration given to the nature of the quote and the relationship of recently evidenced market activity to the fair value estimate, and are classified in Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy. See Note 13 for additional disclosures regarding the Corporation’s foreign currency exchange forwards.
Derivative financial instruments (mortgage derivatives): Mortgage derivatives include interest rate lock commitments to originate residential mortgage loans held for sale to individual customers and forward commitments to sell residential mortgage loans to various investors. The Corporation relies on an internal valuation model to estimate the fair value of its interest rate lock commitments to originate residential mortgage loans held for sale, which includes grouping the interest rate lock commitments by interest rate and terms, applying an estimated pull-through rate based on historical experience, and then multiplying by quoted investor prices determined to be reasonably applicable to the loan commitment groups based on interest rate, terms, and rate lock expiration dates of the loan commitment groups.
The Corporation also relies on an internal valuation model to estimate the fair value of its forward commitments to sell residential mortgage loans (i.e., an estimate of what the Corporation would receive or pay to terminate the forward delivery contract based on market prices for similar financial instruments), which includes matching specific terms and maturities of the forward commitments against applicable investor pricing available. While there are Level 2 and 3 inputs used in the valuation models, the Corporation has determined that the majority of the inputs significant in the valuation of both of the mortgage derivatives fall within Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy. See Note 13 for additional disclosure regarding the Corporation’s mortgage derivatives.
Following is a description of the valuation methodologies used for the Corporation’s more significant instruments measured on a nonrecurring basis at the lower of amortized cost or estimated fair value, including the general classification of such instruments pursuant to the valuation hierarchy.
Loans Held for Sale: Loans held for sale, which consist generally of current production of certain fixed-rate, first-lien residential mortgage loans, are carried at the lower of cost or estimated fair value. The estimated fair value of the residential mortgage loans held for sale was based on what secondary markets are currently offering for portfolios with similar characteristics, which the Corporation classifies as a Level 2 nonrecurring fair value measurement.
Impaired Loans: The Corporation considers a loan impaired when it is probable that the Corporation will be unable to collect all amounts due according to the original contractual terms of the note agreement, including both principal and interest. Management has determined that commercial and consumer loan relationships that have nonaccrual status or have had their terms restructured in a troubled debt restructuring meet this impaired loan definition. For individually evaluated impaired loans, the amount of impairment is based upon the present value of expected future cash flows discounted at the loan’s effective interest rate, the estimated fair value of the underlying collateral for collateral-dependent loans, or the estimated liquidity of the note.
132
Mortgage servicing rights: Mortgage servicing rights do not trade in an active, open market with readily observable prices. While sales of mortgage servicing rights do occur, the precise terms and conditions typically are not readily available to allow for a “quoted price for similar assets” comparison. Accordingly, the Corporation utilizes an independent valuation from a third party which uses a discounted cash flow model to estimate the fair value of its mortgage servicing rights. The valuation model incorporates prepayment assumptions to project mortgage servicing rights cash flows based on the current interest rate scenario, which is then discounted to estimate an expected fair value of the mortgage servicing rights. The valuation model considers portfolio characteristics of the underlying mortgages, contractually specified servicing fees, prepayment assumptions, discount rate assumptions, delinquency rates, late charges, other ancillary revenue, costs to service, and other economic factors. The Corporation periodically reviews and assesses the underlying inputs and assumptions used in the model. In addition, the Corporation compares its fair value estimates and assumptions to observable market data for mortgage servicing rights, where available, and to recent market activity and actual portfolio experience. Due to the nature of the valuation inputs, mortgage servicing rights are classified within Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy. The Corporation uses the amortization method (i.e., lower of amortized cost or estimated fair value measured on a nonrecurring basis), not fair value measurement accounting, for its mortgage servicing rights assets. See Note 4 for additional disclosure regarding the Corporation’s mortgage servicing rights.
The table below presents the Corporation’s investment securities available for sale and derivative financial instruments measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2013 and 2012, aggregated by the level in the fair value hierarchy within which those measurements fall.
Assets and Liabilities Measured at Fair Value on a Recurring Basis
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2013 | | | Fair Value Measurements Using | |
| | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Investment securities available for sale: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. Treasury securities | | $ | 1,002 | | | $ | 1,002 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Obligations of state and political subdivisions (municipal securities) | | | 676,080 | | | | — | | | | 676,080 | | | | — | |
Residential mortgage-related securities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Government-sponsored enterprise (GSE) | | | 3,838,430 | | | | — | | | | 3,838,430 | | | | — | |
Private-label | | | 3,014 | | | | — | | | | 3,014 | | | | — | |
GSE commercial mortgage-related securities | | | 647,477 | | | | — | | | | 647,477 | | | | — | |
Asset-backed securities | | | 23,059 | | | | — | | | | 23,059 | | | | — | |
Other securities (debt and equity) | | | 61,523 | | | | 3,238 | | | | 57,986 | | | | 299 | |
| | | | |
Total investment securities available for sale | | $ | 5,250,585 | | | $ | 4,240 | | | $ | 5,246,046 | | | $ | 299 | |
Derivatives (trading and other assets) | | | 52,773 | | | | — | | | | 51,056 | | | | 1,717 | |
Liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Derivatives (trading and other liabilities) | | $ | 53,798 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 53,798 | | | $ | — | |
133
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2012 | | | Fair Value Measurements Using | |
| | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Investment securities available for sale: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. Treasury securities | | $ | 1,004 | | | $ | 1,004 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Obligations of state and political subdivisions (municipal securities) | | | 801,188 | | | | — | | | | 801,188 | | | | — | |
Residential mortgage-related securities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
GSE | | | 3,798,155 | | | | — | | | | 3,798,155 | | | | — | |
Private-label | | | 6,149 | | | | — | | | | 6,149 | | | | — | |
GSE commercial mortgage-related securities | | | 228,166 | | | | — | | | | 228,166 | | | | — | |
Other securities (debt and equity) | | | 92,096 | | | | 2,841 | | | | 88,775 | | | | 480 | |
| | | | |
Total investment securities available for sale | | $ | 4,926,758 | | | $ | 3,845 | | | $ | 4,922,433 | | | $ | 480 | |
Derivatives (trading and other assets) | | | 82,125 | | | | — | | | | 74,331 | | | | 7,794 | |
Liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Derivatives (trading and other liabilities) | | $ | 80,110 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 79,963 | | | $ | 147 | |
The table below presents a rollforward of the balance sheet amounts for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, for financial instruments measured on a recurring basis and classified within Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy.
| | | | | | | | |
| | | Investment Securities
Available for Sale | | | Derivative Financial
Instruments | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Balance December 31, 2011 | | $ | 856 | | | $ | (200 | ) |
Total net gains included in income: | | | | | | | | |
Mortgage derivative gains | | | — | | | | 7,847 | |
Total net gains included in other comprehensive income: | | | | | | | | |
Unrealized investment securities gains | | | 49 | | | | — | |
Sales of investment securities | | | (425 | ) | | | — | |
| | | | |
Balance December 31, 2012 | | $ | 480 | | | $ | 7,647 | |
| | | | |
Total net losses included in income: | | | | | | | | |
Mortgage derivative loss | | | — | | | | (5,930 | ) |
Total net losses included in other comprehensive income: | | | | | | | | |
Unrealized investment securities losses | | | (70 | ) | | | — | |
Sales of investment securities | | | (111 | ) | | | — | |
| | | | |
Balance December 31, 2013 | | $ | 299 | | | $ | 1,717 | |
| | | | |
For Level 3 assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring or nonrecurring basis as of December 31, 2013, the Corporation utilized the following valuation techniques and significant unobservable inputs.
Investment securities available for sale — other securities (debt and equity): In valuing the investment securities available for sale classified within Level 3, the Corporation utilized a discounted cash flow model and incorporated its own assumptions about future cash flows and discount rates adjusting for credit and liquidity factors. The Corporation also reviewed the underlying collateral and other relevant data in developing the assumptions for these investment securities.
Derivative financial instruments (mortgage derivative — interest rate lock commitments to originate residential mortgage loans held for sale): The significant unobservable input used in the fair value measurement of the Corporation’s mortgage derivative interest rate lock commitments (“IRLC”) is the closing ratio, which represents the percentage of loans currently in a lock position which management estimates will ultimately close. Typically
134
the higher the closing ratio on the IRLC’s will result in an increase in the fair value if in a gain position or a decrease in fair value if in a loss position. The closing ratio calculation takes into consideration historical data and loan-level data, (particularly the change in the current interest rates from the time of initial rate lock). The closing ratio is periodically reviewed for reasonableness and reported to the Mortgage Risk Management Committee. At December 31, 2013, the closing ratio was 91%.
Impaired loans: For individually evaluated impaired loans, the amount of impairment is based upon the present value of expected future cash flows discounted at the loan’s effective interest rate, the estimated fair value of the underlying collateral for collateral-dependent loans, or the estimated liquidity of the note, resulting in an average discount of 25% to 30%.
Mortgage servicing rights: The discounted cash flow analyses that generate expected market prices utilize the observable characteristics of the mortgage servicing rights portfolio, as well as certain unobservable valuation parameters. The significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurement of the Corporation’s mortgage servicing rights are the weighted average constant prepayment rate and weighted average discount rate, which were 12.7% and 10.1% at December 31, 2013, respectively. Significant increases (decreases) in any of those inputs in isolation could result in a significantly lower (higher) fair value measurement. Although the prepayment rate and discount rate are not directly interrelated, they will generally move in opposite directions.
These parameter assumptions fall within a range that the Corporation, in consultation with an independent third party, believes purchasers of servicing would apply to such portfolios sold into the current secondary servicing market. Discussions are held with members from Treasury and Consumer Banking to reconcile the fair value estimates and the key assumptions used by the respective parties in arriving at those estimates. The Associated Mortgage Group Risk Committee is responsible for providing control over the valuation methodology and key assumptions. To assess the reasonableness of the fair value measurement, the Corporation also compares the fair value and constant prepayment rate to a value calculated by an independent third party on an annual basis.
The table below presents the Corporation’s loans held for sale, impaired loans, and mortgage servicing rights measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis as of December 31, 2013 and 2012, aggregated by the level in the fair value hierarchy within which those measurements fall.
Assets and Liabilities Measured at Fair Value on a Nonrecurring Basis
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2013 | | | Fair Value Measurements Using | |
| | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Assets: | | | | |
Loans held for sale | | $ | 64,738 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 64,738 | | | $ | — | |
Impaired loans(1) | | | 88,049 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 88,049 | |
Mortgage servicing rights | | | 74,444 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 74,444 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2012 | | | Fair Value Measurements Using | |
| | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Assets: | | | | |
Loans held for sale | | $ | 261,410 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 261,410 | | | $ | — | |
Impaired loans(1) | | | 115,741 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 115,741 | |
Mortgage servicing rights | | | 45,949 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 45,949 | |
| (1) | Represents individually evaluated impaired loans, net of the related allowance for loan losses. |
135
Certain nonfinancial assets measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis include other real estate owned (upon initial recognition or subsequent impairment), nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities measured at fair value in the second step of a goodwill impairment test, and intangible assets and other nonfinancial long-lived assets measured at fair value for impairment assessment.
During 2013 and 2012, certain other real estate owned, upon initial recognition, was re-measured and reported at fair value through a charge off to the allowance for loan losses based upon the estimated fair value of the other real estate owned, less estimated selling costs. The fair value of other real estate owned, upon initial recognition or subsequent impairment, was estimated using appraised values, which the Corporation classifies as a Level 2 nonrecurring fair value measurement. Other real estate owned measured at fair value upon initial recognition totaled approximately $29 million and $47 million for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively. In addition to other real estate owned measured at fair value upon initial recognition, the Corporation also recorded write-downs to the balance of other real estate owned for subsequent impairment of $4 million and $8 million to asset losses, net for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
136
Fair Value of Financial Instruments:
The Corporation is required to disclose estimated fair values for its financial instruments. Fair value estimates, methods, and assumptions are set forth below for the Corporation’s financial instruments.
The estimated fair values of the Corporation’s financial instruments were as follows.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2013 | |
| | | Carrying
Amount | | | Fair Value | | | Fair Value Measurements Using | |
| | | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Financial assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and due from banks | | $ | 455,482 | | | $ | 455,482 | | | $ | 455,482 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Interest-bearing deposits in other financial institutions | | | 126,018 | | | | 126,018 | | | | 126,018 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Federal funds sold and securities purchased under agreements to resell | | | 20,745 | | | | 20,745 | | | | 20,745 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Investment securities held to maturity | | | 175,210 | | | | 169,889 | | | | — | | | | 169,889 | | | | — | |
Investment securities available for sale | | | 5,250,585 | | �� | | 5,250,585 | | | | 4,240 | | | | 5,246,046 | | | | 299 | |
FHLB and Federal Reserve Bank stocks | | | 181,249 | | | | 181,249 | | | | — | | | | 181,249 | | | | — | |
Loans held for sale | | | 64,738 | | | | 64,738 | | | | — | | | | 64,738 | | | | — | |
Loans, net | | | 15,627,946 | | | | 15,599,094 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 15,599,094 | |
Bank owned life insurance | | | 568,413 | | | | 568,413 | | | | — | | | | 568,413 | | | | — | |
Accrued interest receivable | | | 66,308 | | | | 66,308 | | | | 66,308 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Interest rate-related instruments | | | 42,980 | | | | 42,980 | | | | — | | | | 42,980 | | | | — | |
Foreign currency exchange forwards | | | 748 | | | | 748 | | | | — | | | | 748 | | | | — | |
Interest rate lock commitments to originate residential mortgage loans held for sale | | | 416 | | | | 416 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 416 | |
Forward commitments to sell residential mortgage loans | | | 1,301 | | | | 1,301 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,301 | |
Purchased options (time deposit) | | | 7,328 | | | | 7,328 | | | | — | | | | 7,328 | | | | — | |
Financial liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Noninterest-bearing demand, savings, interest-bearing demand, and money market deposits | | $ | 15,581,971 | | | $ | 15,581,971 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 15,581,971 | |
Brokered CDs and other time deposits | | | 1,685,196 | | | | 1,687,198 | | | | — | | | | 1,687,198 | | | | — | |
Short-term funding | | | 740,926 | | | | 740,926 | | | | — | | | | 740,926 | | | | — | |
Long-term funding | | | 3,087,267 | | | | 3,085,893 | | | | — | | | | 3,085,893 | | | | — | |
Accrued interest payable | | | 7,994 | | | | 7,994 | | | | 7,994 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Interest rate-related instruments | | | 45,815 | | | | 45,815 | | | | — | | | | 45,815 | | | | — | |
Foreign currency exchange forwards | | | 655 | | | | 655 | | | | — | | | | 655 | | | | — | |
Standby letters of credit(1) | | | 3,754 | | | | 3,754 | | | | — | | | | 3,754 | | | | — | |
Written options (time deposit) | | | 7,328 | | | | 7,328 | | | | — | | | | 7,328 | | | | — | |
| | | | |
137
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2012 | |
| | | Carrying
Amount | | | Fair Value | | | Fair Value Measurements Using | |
| | | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | |
| | | ($ in Thousands) | |
Financial assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and due from banks | | $ | 563,304 | | | $ | 563,304 | | | $ | 563,304 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Interest-bearing deposits in other financial institutions | | | 147,434 | | | | 147,434 | | | | 147,434 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Federal funds sold and securities purchased under agreements to resell | | | 27,135 | | | | 27,135 | | | | 27,135 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Investment securities held to maturity | | | 39,877 | | | | 39,679 | | | | — | | | | 39,679 | | | | — | |
Investment securities available for sale | | | 4,926,758 | | | | 4,926,758 | | | | 3,845 | | | | 4,922,433 | | | | 480 | |
FHLB and Federal Reserve Bank stocks | | | 166,774 | | | | 166,774 | | | | — | | | | 166,774 | | | | — | |
Loans held for sale | | | 261,410 | | | | 265,914 | | | | — | | | | 265,914 | | | | — | |
Loans, net | | | 15,113,613 | | | | 14,873,851 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 14,873,851 | |
Bank owned life insurance | | | 556,556 | | | | 556,556 | | | | — | | | | 556,556 | | | | — | |
Accrued interest receivable | | | 68,386 | | | | 68,386 | | | | 68,386 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Interest rate-related instruments | | | 69,370 | | | | 69,370 | | | | — | | | | 69,370 | | | | — | |
Foreign currency exchange forwards | | | 1,341 | | | | 1,341 | | | | — | | | | 1,341 | | | | — | |
Interest rate lock commitments to originate residential mortgage loans held for sale | | | 7,794 | | | | 7,794 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7,794 | |
Purchased options (time deposit) | | | 3,620 | | | | 3,620 | | | | — | | | | 3,620 | | | | — | |
Financial liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Noninterest-bearing demand, savings, interest-bearing demand, and money market deposits | | $ | 14,941,971 | | | $ | 14,941,971 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 14,941,971 | |
Brokered CDs and other time deposits | | | 1,997,894 | | | | 1,997,894 | | | | — | | | | 1,997,894 | | | | — | |
Short-term funding | | | 2,326,939 | | | | 2,326,939 | | | | — | | | | 2,326,939 | | | | — | |
Long-term funding | | | 1,015,346 | | | | 1,041,550 | | | | — | | | | 1,041,550 | | | | — | |
Accrued interest payable | | | 10,208 | | | | 10,208 | | | | 10,208 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Interest rate-related instruments | | | 75,131 | | | | 75,131 | | | | — | | | | 75,131 | | | | — | |
Foreign currency exchange forwards | | | 1,212 | | | | 1,212 | | | | — | | | | 1,212 | | | | — | |
Standby letters of credit(1) | | | 3,811 | | | | 3,811 | | | | — | | | | 3,811 | | | | — | |
Forward commitments to sell residential mortgage loans | | | 147 | | | | 147 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 147 | |
Written options (time deposit) | | | 3,620 | | | | 3,620 | | | | — | | | | 3,620 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (1) | The commitment on standby letters of credit was $250 million and $304 million at December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively. See Note 15 for additional information on the standby letters of credit and for information on the fair value of lending-related commitments. |
Cash and due from banks, interest-bearing deposits in other financial institutions, federal funds sold and securities purchased under agreements to resell, and accrued interest receivable—For these short-term instruments, the carrying amount is a reasonable estimate of fair value.
Investment securities (held to maturity and available for sale)—The fair value of investment securities is based on quoted prices in active markets, or if quoted prices are not available for a specific security, then fair values are estimated by using pricing models, quoted prices of securities with similar characteristics, or discounted cash flows.
FHLB and Federal Reserve Bank stocks—The carrying amount is a reasonable fair value estimate for the Federal Reserve Bank and Federal Home Loan Bank stocks given their “restricted” nature (i.e., the stock can only be sold back to the respective institutions (Federal Home Loan Bank or Federal Reserve Bank) or another member institution at par).
138
Loans held for sale—The estimated fair value of the residential mortgage loans held for sale was based on what secondary markets are currently offering for portfolios with similar characteristics.
Loans, net—The fair value estimation process for the loan portfolio uses an exit price concept and reflects discounts the Corporation believes are consistent with liquidity discounts in the market place. Fair values are estimated for portfolios of loans with similar financial characteristics. Loans are segregated by type such as commercial and industrial, real estate construction, commercial real estate (owner occupied and investor), lease financing, residential mortgage, home equity, and other installment. The fair value of loans is estimated by discounting the future cash flows using the current rates at which similar loans would be made to borrowers with similar credit ratings and for similar maturities. The fair value analysis also included other assumptions to estimate fair value, intended to approximate those a market participant would use in an orderly transaction, with adjustments for discount rates, interest rates, liquidity, and credit spreads, as appropriate.
Bank owned life insurance—The fair value of bank owned life insurance approximates the carrying amount, because upon liquidation of these investments, the Corporation would receive the cash surrender value which equals the carrying amount.
Deposits—The fair value of deposits with no stated maturity such as noninterest-bearing demand deposits, savings, interest-bearing demand deposits, and money market accounts, is equal to the amount payable on demand as of the balance sheet date. The fair value of Brokered CDs and other time deposits is based on the discounted value of contractual cash flows. The discount rate is estimated using the rates currently offered for deposits of similar remaining maturities. However, if the estimated fair value of Brokered CDs and other time deposits is less than the carrying value, the carrying value is reported as the fair value.
Accrued interest payable and short-term funding—For these short-term instruments, the carrying amount is a reasonable estimate of fair value.
Long-term funding—Rates currently available to the Corporation for debt with similar terms and remaining maturities are used to estimate the fair value of existing long-term funding.
Interest rate-related instruments—The fair value of interest rate-related instruments is determined using discounted cash flow analysis on the expected cash flows of each derivative. The Corporation also incorporates credit valuation adjustments to appropriately reflect both its own nonperformance risk and the respective counterparty’s nonperformance risk in the fair value measurements.
Foreign currency exchange forwards—The fair value of the Corporation’s foreign currency exchange forwards is determined using quoted prices of foreign currency exchange forwards with similar characteristics, with consideration given to the nature of the quote and the relationship of recently evidenced market activity to the fair value estimate.
Standby letters of credit—The fair value of standby letters of credit represent deferred fees arising from the related off-balance sheet financial instruments. These deferred fees approximate the fair value of these instruments and are based on several factors, including the remaining terms of the agreement and the credit standing of the customer.
Interest rate lock commitments to originate residential mortgage loans held for sale—The Corporation relies on an internal valuation model to estimate the fair value of its interest rate lock commitments to originate residential mortgage loans held for sale, which includes grouping the interest rate lock commitments by interest rate and terms, applying an estimated pull-through rate based on historical experience, and then multiplying by quoted investor prices determined to be reasonably applicable to the loan commitment groups based on interest rate, terms, and rate lock expiration dates of the loan commitment groups.
139
Forward commitments to sell residential mortgage loans—The Corporation relies on an internal valuation model to estimate the fair value of its forward commitments to sell residential mortgage loans (i.e., an estimate of what the Corporation would receive or pay to terminate the forward delivery contract based on market prices for similar financial instruments), which includes matching specific terms and maturities of the forward commitments against applicable investor pricing available.
Purchased and written options—The fair value of the Corporation’s purchased and written options is determined using quoted prices of the underlying stocks.
Limitations—Fair value estimates are made at a specific point in time, based on relevant market information and information about the financial instrument. These estimates do not reflect any premium or discount that could result from offering for sale at one time the Corporation’s entire holdings of a particular financial instrument. Because no market exists for a significant portion of the Corporation’s financial instruments, fair value estimates are based on judgments regarding future expected loss experience, current economic conditions, risk characteristics of various financial instruments, and other factors. These estimates are subjective in nature and involve uncertainties and matters of significant judgment and, therefore, cannot be determined with precision. Changes in assumptions could significantly affect the estimates.
NOTE 18 REGULATORY MATTERS:
Restrictions on Cash and Due From Banks
The Corporation’s bank subsidiary is required to maintain certain vault cash and reserve balances with the Federal Reserve Bank to meet specific reserve requirements. These requirements approximated $45 million at December 31, 2013.
Regulatory Capital Requirements
The Corporation and its subsidiary bank are subject to various regulatory capital requirements administered by the federal banking agencies. Failure to meet minimum capital requirements can initiate certain mandatory and possible additional discretionary actions by regulators that, if undertaken, could have a direct material effect on the Corporation’s financial statements. Under capital adequacy guidelines and the regulatory framework for prompt corrective action, the Corporation must meet specific capital guidelines that involve quantitative measures of the Corporation’s assets, liabilities, and certain off-balance sheet items as calculated under regulatory accounting practices. The Corporation’s capital amounts and classification are also subject to qualitative judgments by the regulators about components, risk weightings, and other factors.
Quantitative measures established by regulation to ensure capital adequacy require the Corporation to maintain minimum amounts and ratios (set forth in the table below) of total and Tier 1 capital (as defined in the regulations) to risk-weighted assets (as defined), and of Tier 1 capital (as defined) to average assets (as defined). Management believes, as of December 31, 2013 and 2012, that the Corporation meets all capital adequacy requirements to which it is subject.
In July 2013, the Federal Reserve and the OCC, the primary federal regulators for the Corporation and the Bank, respectively, published final rules (the “Basel III Capital Rules”) establishing a new comprehensive capital framework for U.S. banking organizations. The rules implement the Basel Committee’s December 2010 framework known as “Basel III” for strengthening international capital standards as well as certain provisions of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act. For additional information on Basel III and the Dodd-Frank Act, see Part I, Item 1.
140
As of December 31, 2013 and 2012, the most recent notifications from the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency and the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation categorized the subsidiary bank as well capitalized under the regulatory framework for prompt corrective action. To be categorized as well capitalized, the subsidiary bank must maintain minimum total risk-based, Tier 1 risk-based, and Tier 1 leverage ratios as set forth in the table. There are no conditions or events since that notification that management believes have changed the institution’s category. The actual capital amounts and ratios of the Corporation and its significant subsidiary are presented below. No deductions from capital were made for interest rate risk in 2013 or 2012.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Actual | | | For Capital Adequacy
Purposes | | | To Be Well Capitalized
Under Prompt Corrective
Action Provisions:(2) | |
($ in Thousands) | | Amount | | | Ratio(1) | | | Amount | | | Ratio(1) | | | Amount | | | Ratio(1) | |
As of December 31, 2013: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Associated Banc-Corp | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Capital | | $ | 2,184,884 | | | | 13.09 | % | | $ | 1,335,532 | | | ³ | 8.00 | % | | | | | | | | |
Tier 1 Capital | | | 1,975,182 | | | | 11.83 | | | | 667,766 | | | ³ | 4.00 | % | | | | | | | | |
Leverage | | | 1,975,182 | | | | 8.70 | | | | 907,937 | | | ³ | 4.00 | % | | | | | | | | |
Associated Bank, N.A. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Capital | | $ | 2,425,188 | | | | 14.70 | % | | $ | 1,319,765 | | | ³ | 8.00 | % | | $ | 1,649,707 | | | ³ | 10.00 | % |
Tier 1 Capital | | | 2,217,987 | | | | 13.44 | | | | 659,883 | | | ³ | 4.00 | % | | | 989,824 | | | ³ | 6.00 | % |
Leverage | | | 2,217,987 | | | | 9.90 | | | | 896,419 | | | ³ | 4.00 | % | | | 1,120,524 | | | ³ | 5.00 | % |
As of December 31, 2012: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Associated Banc-Corp | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Capital | | $ | 2,167,954 | | | | 13.42 | % | | $ | 1,291,923 | | | ³ | 8.00 | % | | | | | | | | |
Tier 1 Capital | | | 1,938,806 | | | | 12.01 | | | | 645,962 | | | ³ | 4.00 | % | | | | | | | | |
Leverage | | | 1,938,806 | | | | 8.98 | | | | 863,674 | | | ³ | 4.00 | % | | | | | | | | |
Associated Bank, N.A. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Capital | | $ | 2,448,280 | | | | 15.34 | % | | $ | 1,277,222 | | | ³ | 8.00 | % | | $ | 1,596,527 | | | ³ | 10.00 | % |
Tier 1 Capital | | | 2,247,307 | | | | 14.08 | | | | 638,611 | | | ³ | 4.00 | % | | | 957,916 | | | ³ | 6.00 | % |
Leverage | | | 2,247,307 | | | | 10.53 | | | | 853,553 | | | ³ | 4.00 | % | | | 1,066,941 | | | ³ | 5.00 | % |
| 1) | Total Capital ratio is defined as Tier 1 capital plus Tier 2 capital divided by total risk-weighted assets. The Tier 1 Capital ratio is defined as Tier 1 capital divided by total risk-weighted assets. The leverage ratio is defined as Tier 1 capital divided by the most recent quarter’s average total assets. |
| 2) | Prompt corrective action provisions are not applicable at the bank holding company level. |
141
NOTE 19 EARNINGS PER COMMON SHARE:
Earnings per share are calculated utilizing the two-class method. Basic earnings per share are calculated by dividing the sum of distributed earnings to common shareholders and undistributed earnings allocated to common shareholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding. Diluted earnings per share are calculated by dividing the sum of distributed earnings to common shareholders and undistributed earnings allocated to common shareholders by the weighted average number of shares adjusted for the dilutive effect of common stock awards (outstanding stock options, unvested restricted stock, and outstanding stock warrants). Presented below are the calculations for basic and diluted earnings per common share.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | |
| | | (In thousands, except per share data) | |
Net income | | $ | 188,692 | | | $ | 178,973 | | | $ | 139,699 | |
Preferred stock dividends and discount accretion | | | (5,158 | ) | | | (5,200 | ) | | | (24,830 | ) |
| | | | |
Net income available to common equity | | $ | 183,534 | | | $ | 173,773 | | | $ | 114,869 | |
| | | | |
Common shareholder dividends | | | (54,505 | ) | | | (39,462 | ) | | | (6,935 | ) |
Unvested share-based payment awards | | | (486 | ) | | | (172 | ) | | | (42 | ) |
| | | | |
Undistributed earnings | | $ | 128,543 | | | $ | 134,139 | | | $ | 107,892 | |
| | | | |
Undistributed earnings allocated to common shareholders | | | 127,592 | | | | 133,549 | | | | 107,231 | |
Undistributed earnings allocated to unvested share-based payment awards | | | 951 | | | | 590 | | | | 661 | |
| | | | |
Undistributed earnings | | $ | 128,543 | | | $ | 134,139 | | | $ | 107,892 | |
| | | | |
Basic | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Distributed earnings to common shareholders | | $ | 54,505 | | | $ | 39,462 | | | $ | 6,935 | |
Undistributed earnings allocated to common shareholders | | | 127,592 | | | | 133,549 | | | | 107,231 | |
| | | | |
Total common shareholders earnings, basic | | $ | 182,097 | | | $ | 173,011 | | | $ | 114,166 | |
| | | | |
Diluted | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Distributed earnings to common shareholders | | $ | 54,505 | | | $ | 39,462 | | | $ | 6,935 | |
Undistributed earnings allocated to common shareholders | | | 127,592 | | | | 133,549 | | | | 107,231 | |
| | | | |
Total common shareholders earnings, diluted | | $ | 182,097 | | | $ | 173,011 | | | $ | 114,166 | |
| | | | |
Weighted average common shares outstanding | | | 165,584 | | | | 172,255 | | | | 173,370 | |
Effect of dilutive common stock awards | | | 218 | | | | 102 | | | | 2 | |
| | | | |
Diluted weighted average common shares outstanding | | | 165,802 | | | | 172,357 | | | | 173,372 | |
Basic earnings per common share | | $ | 1.10 | | | $ | 1.00 | | | $ | 0.66 | |
| | | | |
Diluted earnings per common share | | $ | 1.10 | | | $ | 1.00 | | | $ | 0.66 | |
| | | | |
Options to purchase approximately 3 million, 9 million, and 8 million shares were outstanding at December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011, respectively, but excluded from the calculation of diluted earnings per common share as the effect would have been anti-dilutive.
NOTE 20 SEGMENT REPORTING:
The Corporation utilizes a risk-based internal profitability measurement system to provide strategic business unit reporting. The profitability measurement system is based on internal management methodologies designed to produce consistent results and reflect the underlying economics of the units. Certain strategic business units have been combined for segment information reporting purposes where the nature of the products and services, the type of customer and the distribution of those products and services are similar. The three reportable segments are Commercial Banking, Consumer Banking, and Risk Management and Shared Services, with no segment representing more than half of the assets, liabilities or Tier 1 common equity of the Corporation as a whole.
142
The financial information of the Corporation’s segments has been compiled utilizing the accounting policies described in Note 1, with certain exceptions. The more significant of these exceptions are described herein. The Corporation allocates interest income or interest expense using a funds transfer pricing methodology that charges users of funds (assets) interest expense and credits providers of funds (liabilities, primarily deposits) with income based on the maturity, prepayment and / or repricing characteristics of the assets and liabilities. The net effect of this allocation is recorded in the Risk Management and Shared Services segment. A credit provision is allocated to segments based on long-term annual net charge off rates attributable to the credit risk of loans managed by the segment during the period. In contrast, the level of the consolidated provision for loan losses is determined using the methodologies described in Note 1 to assess the overall appropriateness of the allowance for loan losses. The net effect of the credit provision is recorded in Risk Management and Shared Services. Indirect expenses incurred by certain centralized support areas are allocated to segments based on actual usage (for example, volume measurements) and other criteria. Certain types of administrative expense and bank-wide expense accruals (including amortization of core deposit and other intangible assets associated with acquisitions) are generally not allocated to segments. Income taxes are allocated to segments based on the Corporation’s estimated effective tax rate, with certain segments adjusted for any tax-exempt income or non-deductible expenses. Equity is allocated to the segments based on regulatory capital requirements and in proportion to an assessment of the inherent risks associated with the business of the segment (including interest, credit and operating risk).
The management accounting policies and processes utilized in compiling segment financial information are highly subjective and, unlike financial accounting, are not based on authoritative guidance similar to U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. As a result, reported segments and the financial information of the reported segments are not necessarily comparable with similar information reported by other financial institutions. Furthermore, changes in management structure or allocation methodologies and procedures may result in changes in previously reported segment financial data. During 2013, certain organization and methodology changes were made and, accordingly, 2012 and 2011 results have been restated and presented on a comparable basis.
A description of each business segment is presented below.
Commercial Banking — The Commercial Banking segment serves a wide range of customers including, businesses, developers, non-profits, municipalities, and financial institutions. Business customers in this segment typically include companies with annual sales over $10 million and delivery of services is provided through our regional and middle market units, our commercial real estate unit, as well as our specialized industries and commercial financial services area. The financial solutions provided to our customers include but are not limited to: (1) Lending solutions, such as business loans and lines of credit, business credit cards, commercial real estate financing, construction loans, letters of credit, leasing, and asset based lending. For our larger clients we also offer syndicated loans to meet their lending needs; (2) Deposit and cash management solutions such as business checking and interest-bearing deposit products, safe deposit and night depository services, liquidity solutions, payables and receivables solutions; and information services; and (3) Specialized financial services such as insurance and benefits related products and services, risk management, and international banking solutions. In serving the commercial banking segment we compete based on an in-depth understanding of our customers’ financial needs, the ability to match market competitive solutions to those needs, and the highest standards of relationship and service excellence in the delivery of these services.
Consumer Banking— The Consumer Banking segment serves individuals and small businesses (typically entities with less than $10 million in annual sales) through our various Retail Banking and Private Client offices, and provides companies of varying sizes with fiduciary services such as administration of pension, profit-sharing and other employee benefit plans, fiduciary and corporate agency services, and institutional asset management. The services provided to our individual and small business customers include but are not limited to: (1) Transactional solutions such as checking, credit, debit and pre-paid cards, online banking and bill pay, and money transfer services; (2) Lending solutions such as residential mortgages, home equity loans and lines of credit, business loans and lines, and personal and installment loans; and (3) Investable funds solutions such as
143
savings, money market deposit accounts, IRA accounts, certificates of deposit, market linked certificates of deposit, fixed and variable annuities, full-service, discount and on-line investment brokerage; as well as trust and investment management accounts. In serving the consumer banking segment we compete based on providing a broad range of solutions to meet the needs of our customers in their entire financial lifecycle, convenient access to our services through multiple channels such as branches, phone based services, online and mobile banking, and a relationship based business model which assists our customers in navigating any changes and challenges in their financial circumstances.
Risk Management and Shared Services —The Risk Management and Shared Services segment includes Corporate Risk Management, Credit Administration, Finance, Treasury, Operations, and Technology, which are key shared functions. The segment also includes Parent Company activity, intersegment eliminations and residual revenue and expenses, representing the difference between actual amounts incurred and the amounts allocated to operating segments, including interest rate risk residuals (funds transfer pricing mismatches) and credit risk and provision residuals (long term credit charge mismatches). The earning assets within this segment include the Corporation’s investment portfolio and capital includes both allocated as well as any remaining unallocated capital.
Information about the Corporation’s segments is presented below.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Segment Income Statement Data | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ($ in Thousands) | | Commercial
Banking | | | Consumer
Banking | | | Risk Management
and Shared Services | | | Consolidated
Total | |
2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net interest income | | $ | 318,377 | | | $ | 317,016 | | | $ | 10,150 | | | $ | 645,543 | |
Noninterest income | | | 94,450 | | | | 201,634 | | | | 17,015 | | | | 313,099 | |
| | | | |
Total revenue | | | 412,827 | | | | 518,650 | | | | 27,165 | | | | 958,642 | |
Credit provision* | | | 55,198 | | | | 20,122 | | | | (65,320 | ) | | | 10,000 | |
Noninterest expense | | | 187,277 | | | | 428,591 | | | | 64,881 | | | | 680,749 | |
Income before income taxes | | | 170,352 | | | | 69,937 | | | | 27,604 | | | | 267,893 | |
Income tax expense (benefit) | | | 59,623 | | | | 24,478 | | | | (4,900 | ) | | | 79,201 | |
Net income | | $ | 110,729 | | | $ | 45,459 | | | $ | 32,504 | | | $ | 188,692 | |
Return on average allocated capital (ROT1CE)** | | | 14.2 | % | | | 8.5 | % | | | 4.8 | % | | | 9.8 | % |
| | | | |
2012 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net interest income | | $ | 290,594 | | | $ | 301,807 | | | $ | 33,591 | | | $ | 625,992 | |
Noninterest income | | | 86,912 | | | | 207,234 | | | | 19,144 | | | | 313,290 | |
| | | | |
Total revenue | | | 377,506 | | | | 509,041 | | | | 52,735 | | | | 939,282 | |
Credit provision* | | | 46,563 | | | | 19,419 | | | | (62,982 | ) | | | 3,000 | |
Noninterest expense | | | 194,327 | | | | 440,611 | | | | 46,885 | | | | 681,823 | |
Income before income taxes | | | 136,616 | | | | 49,011 | | | | 68,832 | | | | 254,459 | |
Income tax expense | | | 47,816 | | | | 17,154 | | | | 10,516 | | | | 75,486 | |
Net income | | $ | 88,800 | | | $ | 31,857 | | | $ | 58,316 | | | $ | 178,973 | |
Return on average allocated capital (ROT1CE)** | | | 12.1 | % | | | 5.7 | % | | | 9.8 | % | | | 9.5 | % |
| | | | |
2011 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net interest income | | $ | 264,728 | | | $ | 317,020 | | | $ | 31,083 | | | $ | 612,831 | |
Noninterest income | | | 86,087 | | | | 176,236 | | | | 10,796 | | | | 273,119 | |
| | | | |
Total revenue | | | 350,815 | | | | 493,256 | | | | 41,879 | | | | 885,950 | |
Credit provision* | | | 40,259 | | | | 17,988 | | | | (6,247 | ) | | | 52,000 | |
Noninterest expense | | | 191,038 | | | | 441,468 | | | | 18,017 | | | | 650,523 | |
Income before income taxes | | | 119,518 | | | | 33,800 | | | | 30,109 | | | | 183,427 | |
Income tax expense (benefit) | | | 41,831 | | | | 11,830 | | | | (9,933 | ) | | | 43,728 | |
Net income | | $ | 77,687 | | | $ | 21,970 | | | $ | 40,042 | | | $ | 139,699 | |
Return on average allocated capital (ROT1CE)** | | | 11.0 | % | | | 4.2 | % | | | 3.1 | % | | | 6.7 | % |
| | | | |
144
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Segment Balance Sheet Data | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ($ in Thousands) | | Commercial
Banking | | | Consumer
Banking | | | Risk Management
and Shared Services | | | Consolidated
Total | |
2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Average earning assets | | $ | 8,443,203 | | | $ | 7,225,943 | | | $ | 5,310,982 | | | $ | 20,980,128 | |
Average loans | | | 8,433,389 | | | | 7,225,943 | | | | 3,813 | | | | 15,663,145 | |
Average deposits | | | 5,479,567 | | | | 9,675,302 | | | | 2,283,326 | | | | 17,438,195 | |
Average allocated capital (T1CE)** | | $ | 778,098 | | | $ | 535,783 | | | $ | 564,490 | | | $ | 1,878,371 | |
| | | | |
2012 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Average earning assets | | $ | 7,540,502 | | | $ | 7,182,766 | | | $ | 4,890,509 | | | $ | 19,613,777 | |
Average loans | | | 7,534,026 | | | | 7,182,766 | | | | 24,993 | | | | 14,741,785 | |
Average deposits | | | 4,613,215 | | | | 9,441,330 | | | | 1,527,824 | | | | 15,582,369 | |
Average allocated capital (T1CE)** | | $ | 731,943 | | | $ | 562,125 | | | $ | 544,356 | | | $ | 1,838,424 | |
| | | | |
2011 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Average earning assets | | $ | 6,498,071 | | | $ | 6,653,451 | | | $ | 6,290,741 | | | $ | 19,442,263 | |
Average loans | | | 6,494,133 | | | | 6,653,451 | | | | 131,264 | | | | 13,278,848 | |
Average deposits | | | 3,685,191 | | | | 9,446,488 | | | | 1,269,448 | | | | 14,401,127 | |
Average allocated capital (T1CE)** | | $ | 705,775 | | | $ | 523,168 | | | $ | 484,212 | | | $ | 1,713,155 | |
| | | | |
| * | The consolidated credit provision is equal to the actual reported provision for loan losses. |
| ** | ROT1CE reflects return on average allocated Tier 1 common equity (“T1CE”). The ROT1CE for the Risk Management and Shared Services segment and the Consolidated Total is inclusive of the annualized effect of the preferred stock dividends. |
145
Note 21: ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
The following table summarizes the components of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) at December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011, changes during the years then ended, and reclassifications out of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) during the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011, respectively. The amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income for the investment securities available for sale are included in investment securities gains, net on the consolidated statements of income, while the amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income for the defined benefit pension and post retirement obligations are a component of personnel expense on the consolidated statements of income.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Investments
Securities
Available
For Sale | | | Defined Benefit
Pension and
Post Retirement
Obligations | | | Cash Flow
Hedging
Relationships | | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive
Income (Loss) | |
Balance December 31, 2010 | | $ | 55,609 | | | $ | (24,504 | ) | | $ | (3,479 | ) | | $ | 27,626 | |
Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | | | 71,606 | | | | (16,834 | ) | | | (557 | ) | | | 54,215 | |
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | | | 1,112 | | | | 2,491 | | | | 4,708 | | | | 8,311 | |
Income tax (expense) benefit | | | (28,566 | ) | | | 5,674 | | | | (1,658 | ) | | | (24,550 | ) |
| | | | |
Net other comprehensive income (loss) during period | | | 44,152 | | | | (8,669 | ) | | | 2,493 | | | | 37,976 | |
| | | | |
Balance December 31, 2011 | | $ | 99,761 | | | $ | (33,173 | ) | | $ | (986 | ) | | $ | 65,602 | |
| | | | |
Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | | | (19,042 | ) | | | (10,014 | ) | | | 6 | | | | (29,050 | ) |
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | | | (4,261 | ) | | | 3,315 | | | | 1,954 | | | | 1,008 | |
Income tax (expense) benefit | | | 9,651 | | | | 2,366 | | | | (974 | ) | | | 11,043 | |
| | | | |
Net other comprehensive income (loss) during period | | | (13,652 | ) | | | (4,333 | ) | | | 986 | | | | (16,999 | ) |
| | | | |
Balance December 31, 2012 | | $ | 86,109 | | | $ | (37,506 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | 48,603 | |
| | | | |
Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | | | (158,207 | ) | | | 35,804 | | | | — | | | | (122,403 | ) |
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | | | (564 | ) | | | 4,416 | | | | — | | | | 3,852 | |
Income tax (expense) benefit | | | 61,266 | | | | (15,562 | ) | | | — | | | | 45,704 | |
| | | | |
Net other comprehensive income (loss) during period | | | (97,505 | ) | | | 24,658 | | | | — | | | | (72,847 | ) |
| | | | |
Balance December 31, 2013 | | $ | (11,396 | ) | | $ | (12,848 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | (24,244 | ) |
| | | | |
146
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
Associated Banc-Corp:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Associated Banc-Corp and subsidiaries (the Company) as of December 31, 2013 and 2012, and the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, changes in stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in thethree-year period ended December 31, 2013. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Associated Banc-Corp and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2013 and 2012, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the years in thethree-year period ended December 31, 2013, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), Associated Banc-Corp’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013, based on criteria established inInternal Control — Integrated Framework(1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO), and our report dated February 5, 2014 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
KPMG LLP
Chicago, Illinois
February 5, 2014
147
| ITEM 9. | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
None.
| ITEM 9A. CONTROLS | AND PROCEDURES |
The Corporation maintains disclosure controls and procedures as required under Rule 13a-15(e) andRule 15d-15(e) promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in our Exchange Act reports is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to the Corporation’s management, including its Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
As of December 31, 2013, the Corporation’s management carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of the Corporation’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of its disclosure controls and procedures. Based on the foregoing, its Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that the Corporation’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of December 31, 2013. No changes were made to the Corporation’s internal control over financial reporting (as defined Rule 13a-15(f) and Rule 15d-15(f) promulgated under the Exchange Act) during the last fiscal quarter that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Corporation’s internal control over financial reporting.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management of Associated Banc-Corp is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. The Corporation’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of the Corporation’s financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. Internal control over financial reporting is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”).
As of December 31, 2013, management assessed the effectiveness of the Corporation’s internal control over financial reporting based on criteria for effective internal control over financial reporting established in “Internal Control — Integrated Framework,” issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organization of the Treadway Commission (COSO). Based on this assessment, management has determined that the Corporation’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013, was effective.
KPMG LLP, the independent registered public accounting firm that audited the consolidated financial statements of the Corporation included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, has issued an attestation report on the effectiveness of the Corporation’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013. The report, which expresses an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Corporation’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013, is included below under the heading “Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.”
148
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
Associated Banc-Corp:
We have audited Associated Banc-Corp’s (the Company) internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework(1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanyingManagement’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, Associated Banc-Corp maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013, based on criteria established inInternal Control — Integrated Framework(1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of Associated Banc-Corp and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2013 and 2012, and the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, changes in stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2013, and our report dated February 5, 2014 expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial statements.
KPMG LLP
Chicago, Illinois
February 5, 2014
149
| ITEM 9B. OTHER | INFORMATION |
None.
PART III
| ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, | EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
The information in the Corporation’s definitive Proxy Statement, prepared for the 2014 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which contains information concerning this item under the captions “Election of Directors” and “Information About the Board of Directors”; and information concerning Section 16(a) compliance under the caption “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” is incorporated herein by reference. Information relating to the Corporation’s executive officers is set forth in Part I of this report.
| ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE | COMPENSATION |
The information in the Corporation’s definitive Proxy Statement, prepared for the 2014 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which contains information concerning this item, under the captions “Executive Compensation,” “Director Compensation,” and “Compensation and Benefits Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation,” is incorporated herein by reference.
| ITEM 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
The information in the Corporation’s definitive Proxy Statement, prepared for the 2014 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which contains information concerning this item, under the caption “Stock Ownership,” is incorporated herein by reference.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Plan Category | | (a)
Number of
Securities to be
Issued Upon
Exercise of
Outstanding
Options, Warrants
and Rights | | | (b)
Weighted-Average
Exercise Price of
Outstanding
Options, Warrants
and Rights | | | (c)
Number of Securities
Remaining Available
for Future Issuance
Under Equity
Compensation Plans
(excluding securities
reflected in column (a)) | |
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | | | 8,034,243 | | | $ | 18.37 | | | | 18,844,283 | |
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | |
Total | | | 8,034,243 | | | $ | 18.37 | | | | 18,844,283 | |
| | | | |
| ITEM 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
The information in the Corporation’s definitive Proxy Statement, prepared for the 2014 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which contains information concerning this item under the captions “Related Party Transactions,” and “Information about the Board of Directors,” is incorporated herein by reference.
| ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL | ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES |
The information in the Corporation’s definitive Proxy Statement, prepared for the 2014 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which contains information concerning this item under the caption “Fees Paid to Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm,” is incorporated herein by reference.
150
PART IV
| ITEM | 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES |
(a) 1 and 2 Financial Statements and Financial Statement Schedules
The following financial statements and financial statement schedules are included under a separate caption “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” in Part II, Item 8 hereof and are incorporated herein by reference.
Consolidated Balance Sheets — December 31, 2013 and 2012
Consolidated Statements of Income — For the Years Ended December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income — For the Years Ended December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity — For the Years Ended December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows — For the Years Ended December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
151
(a) 3 Exhibits Required by Item 601 of Regulation S-K
| | | | |
Exhibit
Number | | Description | | |
| | |
| (3)(a) | | Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation | | Exhibit (3) to Report on Form 10-Q filed on May 8, 2006 |
| | |
| (3)(b) | | Articles of Amendment to the Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation of Associated Banc-Corp with respect to its 8.00% Perpetual Preferred Stock, Series B, dated September 12, 2011 | | Exhibit (3.1) to Report on Form 8-K filed on September 15, 2011 |
| | |
| (3)(c) | | Articles of Amendment to the Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation of Associated Banc-Corp regarding the rights and preferences of preferred stock, effective April 25, 2012 | | Exhibit (3.1, 4.1) to Report on Form 8-K filed on April 25, 2012 |
| | |
| (3)(d) | | Amended and Restated Bylaws | | Exhibit (3) to Report on Form 10-Q filed on November 1, 2013 |
| | |
| (4) | | Instruments Defining the Rights of Security Holders, Including Indentures | | |
| | |
| | The Parent Company, by signing this report, agrees to furnish the SEC, upon its request, a copy of any instrument that defines the rights of holders of long-term debt of the Corporation and its consolidated and unconsolidated subsidiaries for which consolidated or unconsolidated financial statements are required to be filed and that authorizes a total amount of securities not in excess of 10% of the total assets of the Corporation on a consolidated basis | | |
| | |
| (4)(b) | | Indenture, dated as of March 14, 2011, between Associated Banc-Corp and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A. | | Exhibit (4.1) to Report on Form 8-K filed on March 28, 2011 |
| | |
| (4)(c) | | Global Note dated as of March 28, 2011 representing $300,000,000 5.125% Senior Notes due 2016 | | Exhibit (4.2) to Report on Form 8-K filed on March 28, 2011 |
| | |
| (4)(d) | | Global Note dated as of September 13, 2011 representing $130,000,000 5.125% Senior Notes due 2016 | | Exhibit (4.4) to Report on Form 8-K filed on September 15, 2011 |
| | |
| (4)(e) | | Deposit Agreement, dated September 14, 2011, among Associated Banc-Corp, Wells Fargo Bank, N.A. and the holders from time to time of the Depositary Receipts described therein, and Form of Depositary Receipt | | Exhibit (4.2) to Report on Form 8-K filed on September 15, 2011 |
| | |
| (4)(f) | | Warrant Agreement for 3,983,308 Warrants, dated as of November 30, 2011, between Associated Banc-Corp and Wells Fargo Bank, N.A. | | Exhibit (4.1) to Report on Form 8-A filed on December 1, 2011 |
152
| | | | |
Exhibit
Number | | Description | | |
| | |
| (4)(g) | | Specimen Warrant for 3,983,308 Warrants | | Exhibit (4.2) to Report on Form 8-A filed on December 1, 2011 |
| | |
| (4)(h) | | Global Note dated as of September 12, 2012 representing $155,000,000 1.875% Senior Notes due 2014 | | Exhibit (4.1) to Report on Form 8-K filed on September 13, 2012 |
| | |
| *(10)(a) | | Associated Banc-Corp 1987 Long-Term Incentive Stock Plan, Amended and Restated Effective January 1, 2008 | | Exhibit (10)(a) to Report on Form 10-K filed on February 26, 2009 |
| | |
| *(10)(b) | | Associated Banc-Corp 1999 Long-Term Incentive Stock Plan, Amended and Restated Effective January 1, 2008 | | Exhibit (10)(b) to Report on Form 10-K filed on February 26, 2009 |
| | |
| *(10)(c) | | Associated Banc-Corp 2003 Long-Term Incentive Stock Plan, Amended and Restated Effective January 1, 2008 | | Exhibit (10)(c) to Report on Form 10-K filed on February 26, 2009 |
| | |
| *(10)(d) | | Associated Banc-Corp Deferred Compensation Plan | | Exhibit (10)(h) to Report on Form 10-K filed on February 26, 2009 |
| | |
| *(10)(e) | | Associated Banc-Corp Directors’ Deferred Compensation Plan, Restated Effective January 1, 2008 | | Exhibit (10)(i) to Report on Form 10-K filed on February 26, 2009 |
| | |
| *(10)(f) | | Amendment to Associated Banc-Corp 2003 Long-Term Incentive Stock Plan effective November 15, 2009 | | Exhibit (99.2) to Report on Form 8-K filed on November 16, 2009 |
| | |
| *(10)(g) | | Associated Banc-Corp 2010 Incentive Compensation Plan | | Exhibit (99.1) to Report on Form 8-K filed on April 29, 2010 |
| | |
| *(10)(h) | | Associated Banc-Corp 2013 Incentive Compensation Plan | | Appendix A to Definitive Proxy Statement filed on March 14, 2013 |
| | |
| *(10)(i) | | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement Pursuant to Associated Banc-Corp 2010 Incentive Compensation Plan | | Exhibit (99.6) to Report on Form 8-K filed on April 29, 2010 |
| | |
| *(10)(j) | | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement | | Exhibit (99.2) to Report on Form 8-K filed on January 27, 2012 |
| | |
| *(10)(k) | | Form of Non-Qualified Stock Option Agreement | | Exhibit (99.3) to Report on Form 8-K filed on January 27, 2012 |
| | |
| *(10)(l) | | Associated Banc-Corp Change of Control Plan, Restated Effective September 28, 2011 | | Exhibit (10.1) to Report on Form 8-K filed on September 30, 2011 |
| | |
| *(10)(m) | | Associated Banc-Corp Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan for Philip B. Flynn | | Exhibit (99.2) to Report on Form 8-K filed on December 23, 2011 |
| | |
| *(10)(n) | | Form of Performance-Based Restricted Stock Unit Agreement | | Exhibit (99.1) to Report on Form 8-K filed on January 27, 2012 |
| | |
| *(10)(o) | | Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan, restated as of January 22, 2013 | | Exhibit (99.1) to Report on Form 8-K filed on January 22, 2013 |
153
| | | | |
Exhibit
Number | | Description | | |
| | |
| (11) | | Statement Re Computation of Per Share Earnings | | See Note 19 in Part II Item 8 |
| | |
| (21) | | Subsidiaries of Associated Banc-Corp | | Filed herewith |
| | |
| (23) | | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | | Filed herewith |
| | |
| (24) | | Powers of Attorney | | Filed herewith |
| | |
| (31.1) | | Certification Under Section 302 of Sarbanes-Oxley by Philip B. Flynn, Chief Executive Officer | | Filed herewith |
| | |
| (31.2) | | Certification Under Section 302 of Sarbanes-Oxley by Christopher J. Del Moral-Niles, Chief Financial Officer | | Filed herewith |
| | |
| (32) | | Certification by the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of Sarbanes-Oxley. | | Filed herewith |
| | |
| (101) | | Interactive data files pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T: (i) Consolidated Balance Sheets, (ii) Consolidated Statements of Income, (iii) Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income, (iv) Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity, (v) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, and (vi) Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. | | Filed herewith |
| * | Management contracts and arrangements. |
Schedules and exhibits other than those listed are omitted for the reasons that they are not required, are not applicable or that equivalent information has been included in the financial statements, and notes thereto, or elsewhere within.
154
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| | | | | | |
| | | | ASSOCIATED BANC-CORP |
| | | |
| Date: February 5, 2014 | | | | By: | | /s/ Philip B. Flynn |
| | | | | | Philip B. Flynn |
| | | | | | President and Chief Executive Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | |
Signature | | Title | | Date |
| | |
/s/ Philip B. Flynn Philip B. Flynn | | President and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | | February 5, 2014 |
| | |
/s/ Christopher J. Del Moral-Niles | | Chief Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer | | February 5, 2014 |
| Christopher J. Del Moral-Niles | | |
Directors: John F. Bergstrom, Ruth M. Crowley, Philip B. Flynn, Ronald R. Harder, William R. Hutchinson, Robert A. Jeffe, Eileen A. Kamerick, Richard T. Lommen, Cory L. Nettles, J. Douglas Quick, Karen T. van Lith and John B. Williams
| | |
| By: | | /s/ Randall J. Erickson |
| | Randall J. Erickson |
| | As Attorney-In-Fact* |
| * | Pursuant to authority granted by powers of attorney, copies of which are filed herewith. |
155
