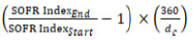Composition and Characteristics of SOFR
On June 22, 2017, the Alternative Reference Rates Committee (“ARRC”) convened by the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System and the Federal Reserve Bank of New York identified the SOFR as the rate that, in the consensus view of the ARRC, represented best practice for use in certain new U.S. dollar derivatives and other financial contracts. SOFR is a broad measure of the cost of borrowing cash overnight collateralized by U.S. treasury securities, and has been published by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York since April 2018. The Federal Reserve Bank of New York has also begun publishing historical indicative SOFR from 2014. Investors should not rely on any historical changes or trends in SOFR as an indicator of future changes in SOFR.
The composition and characteristics of SOFR are not the same as those of the London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”), and SOFR is fundamentally different from LIBOR for two key reasons. First, SOFR is a secured rate, while LIBOR is an unsecured rate. Second, SOFR is an overnight rate, while LIBOR is a forward-looking rate that represents interbank funding over different maturities (e.g., three months). As a result, there can be no assurance that SOFR (including SOFR Average) will perform in the same way as LIBOR would have at any time, including, without limitation, as a result of changes in interest and yield rates in the market, market volatility or global or regional economic, financial, political, regulatory, judicial or other events.
Since the initial publication of SOFR, daily changes in SOFR have, on occasion, been more volatile than daily changes in other benchmark or market rates, such as USD LIBOR. Although changes in SOFR Average generally are not expected to be as volatile as changes in daily levels of SOFR, the return on and value of the notes may fluctuate more than floating rate securities that are linked to less volatile rates. In addition, the volatility of SOFR has reflected the underlying volatility of the overnight U.S. Treasury repurchase agreement (“repo”) market. The Federal Reserve Bank of New York has at times conducted operations in the overnight U.S. Treasury repo market in order to help maintain the federal funds rate within a target range. There can be no assurance that the Federal Reserve Bank of New York will continue to conduct such operations in the future, and the duration and extent of any such operations is inherently uncertain. The effect of any such operations, or of the cessation of such operations to the extent they are commenced, is uncertain and could be materially adverse to investors in the notes.
The Federal Reserve Bank of New York states on its publication page for SOFR that use of SOFR is subject to important disclaimers, limitations and indemnification obligations, including that the Federal Reserve Bank of New York may alter the methods of calculation, publication schedule, rate revision practices or availability of SOFR at any time without notice.
Market Acceptance of SOFR, SOFR Average and SOFR Index
According to the ARRC, SOFR was developed for use in certain U.S. dollar derivatives and other financial contracts as an alternative to USD LIBOR, in part because it is considered a good representation of general funding conditions in the overnight U.S. Treasury repo market. However, as a rate based on transactions secured by U.S. Treasury securities, it does not measure bank-specific credit risk and, as a result, is less likely to correlate with the unsecured short-term funding costs of banks. This may mean that market participants would not consider SOFR a suitable replacement or successor for all of the purposes for which USD LIBOR has historically been used (including, without limitation, as a representation of the unsecured short-term funding costs of banks), which may, in turn, lessen market acceptance of SOFR. Any failure of SOFR to gain market acceptance could adversely affect the return on and value of the notes and the price at which investors can sell the notes in the secondary market.
-8-