As filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on July 11, 2003
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 20-F
[ ] REGISTRATION STATEMENT PURSUANT TO SECTION 12(b) OR (g) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
OR
[x] ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2002
OR
[ ] TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 FOR THE TRANSITION PERIOD FROM TO
COMMISSION FILE NUMBER 33-44756
Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
N/A
(Translation of Registrant’s name into English)
United Mexican States
(Jurisdiction of incorporation or organization)
Av. Revolución No. 780 Módulo 2
Colonia San Juan
03730 México, D.F.
México
(Address of principal executive offices)
Securities registered or to be registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered |
Series B Shares without par value ("B Shares") | New York Stock Exchange (for listing purposes only) |
Series C Shares without par value ("C Shares") | New York Stock Exchange (for listing purposes only) |
Units, each representing three B shares and one C share | New York Stock Exchange (for listing purposes only) |
Global Depositary Shares ("GDSs"), each representing 20 Units | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered or to be registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
(Title of Class)
Securities for which there is a reporting obligation pursuant to Section 15(d) of the Act:
9.375% Senior Notes due 2005
The number of outstanding shares of each of the issuer’s classes of capital or common stock as of December 31, 2002 was:
4,005,551,610 B Shares
338,448,390 C Shares
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (of for such shorter period that he registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes [x] No [ ]
Indicate by check which financial statement item the registrant has elected to follow. Item 17 [x] Item 18 [ ]
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
PART I
Item 1. Identity of Directors, Senior Management and Advisers
Item 2. Offer Statistics and Expected Timetable
Item 3. Key Information
Selected Financial Data
Dividends
Exchange Rate Information
Risk Factors
Forward-Looking Statements
Item 4. Information on the Company
History and Development of the Company
Capital Expenditures
Business Overview
Organizational Structure
Property, Plant and Equipment
Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects
Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees
Board Practices
Item 7. Major Shareholders and Related Party Transactions
Major Shareholders
Related Party Transactions
Item 8. Financial Information
Item 9. Offer and Listing Details
Item 10. Other Information
Bylaws
Material Contracts
Legal Proceedings
Exchange Controls and Restrictions on Foreign Investment
Taxation
Documents on Display
Item 11. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Interest Rate Risk
Foreign Exchange Rate Risk
Item 12. Description of Securities Other than Equity Securities
PART II
Item 13. Defaults, Dividend Arrearages and Delinquencies
Item 14. Material Modifications to the Rights of Security Holders and Use of Proceeds
PART III
Item 15. [Reserved]
Item 16. [Reserved]
PART IV
Item 17. Financial Statements
Item 18. Financial Statements
Item 19. Exhibits
We publish our Financial Statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in Mexico, or Mexican GAAP, which differ in significant respects from generally accepted accounting principles in the United States Of America ("United States"), or U.S. GAAP, and accounting procedures adopted in other countries. The exchange rates used in preparing our Financial Statements are determined by reference as of the specified date to the interbank free market exchange rate, or the Interbank Rate, as reported by Banco Nacional de México, S.A. As of December 31, 2002, the Interbank Rate was Ps. 10.395 to U.S.$1.00. See "Item 3. Key Information Exchange Rate Information." The exchange rates used in translating Pesos into U.S. Dollars elsewhere in this annual report are determined by reference to the Interbank Rate as of December 31, 2002, unless otherwise indicated.
Unless otherwise indicated, (i) information included in this annual report is as of December 31, 2002 and (ii) references to "Ps." or "Pesos" in this annual report are to Mexican Pesos and references to "Dollars," "U.S. Dollars," "U.S. dollars," "$," or "U.S.$" are to United States dollars.
Unless otherwise indicated, (i) operating information contained in this Annual Report regarding our stores relates to all of our stores, which are the Comercial Mexicana, Mega, Bodega, Sumesa, and the Costco membership warehouses (through a joint venture, the Costco Mexico joint venture, or Costco Mexico, with Costco Wholesale Co. (formerly Price/Costco, Inc.), or Costco, of the United States), but not our restaurants, and (ii) information herein regarding same store sales, sales per operating employee and sales per retail square foot is calculated on the basis of 100% of the sales from all of our stores, including those operated through the Costco Mexico joint venture.
As used herein, the term "billion" means one thousand million.
PART I
Item 1. Identity of Directors, Senior Management and Advisers
Not applicable.
Item 2. Offer Statistics and Expected Timetable
Not applicable.
Item 3. Key Information
Selected Financial Data
The following tables present our selected financial data and that of our consolidated subsidiaries. We consolidate our proportionate interest in the results and assets and liabilities of the Costco Mexico joint venture. This data is qualified in its entirety by reference to, and should be read together with, our audited year-end financial statements, or Financial Statements. Our Financial Statements have been prepared in accordance with Mexican GAAP, which differs in significant respects from U.S. GAAP and accounting procedures adopted in other countries. Note 17 to the Financial Statements provides a description of the principal differences between Mexican GAAP and U.S. GAAP as they relate to us and provides a reconciliation to U.S. GAAP of net income for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2000, 2001 and 2002 and total stockholder's equity as of December 31, 2001 and 2002.
In calculating the convenience translations included herein, Pesos are translated into U.S. dollars at an exchange rate of Ps. 10.395 per U.S. dollar, the Representative Rate as of December 31, 2002. These translations should not be construed as a representation that such Peso amounts actually represent U.S. dollar amounts or could be converted into U.S. dollar amounts at the rates indicated.
| Year Ended December 31, |
| | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2002 |
| (Millions of constant Pesos as of December 31, 2002 and millions of U.S. Dollars) (1) |
| Income Statement Data |
| Mexican GAAP: | | | | | | |
| Net sales | 31,770 | 32,659 | 34,883 | 34,948 | 32,053 | 3,084 |
| Gross profit | 6,209 | 6,280 | 6,666 | 6,648 | 6,287 | 605 |
| Selling and administrative | 5,042 | 5,020 | 5,443 | 5,562 | 5,368 | 516 |
| Operating income | 1,167 | 1,259 | 1,223 | 1,086 | 920 | 89 |
| Integral results of financing (2): | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | (400) | (276) | (259) | (272) | (239) | (23) |
| Interest income (3) | 208 | 93 | 58 | 59 | 43 | 4 |
| Foreign-exchange gain (loss), net | (694) | 100 | (57) | 24 | (218) | (21) |
| Loss (gain) in forward agreement | | | | (42) | 49 | 5 |
| Gain from monetary position | 1,077 | 676 | 501 | 242 | 306 | 29 |
| Other income (expense), net (4) | (221) | (166) | (158) | (19) | 5 | |
| Provisions for: | | | | | | |
| Income and asset taxes | (21) | (160) | (145) | (40) | (123) | (12) |
| Employees profit sharing | (4) | (8) | (13) | (2) | (8) | (1) |
| Deferred income tax and gain on monetary position through the initial deferred income tax effect. | | | 74 | (225) | 62 | 6 |
| Interest of minority stockholders in results of subsidiaries | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (7) | (1) |
| Net income | 1,147 | 1,510 | 1,216 | 803 | 789 | 76 |
| Net income per BC Unit and B Unit (5) | 1.06 | 1.40 | 1.12 | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.07 |
| Net income per GDS (7) | 21.30 | 27.89 | 22.51 | 15.14 | 14.64 | 1.41 |
| Dividends per BC Unit and B Unit (5) | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.01 |
| Dividends per GDS (6) | 1.92 | 2.17 | 2.03 | 2.26 | 2.23 | 0.21 |
| Weighted average Units and B Units outstanding (millions)(5) | 1,077 | 1,081 | 1,080 | 1,061 | 1,078 | 104 |
| |
| U.S. GAAP (7): | | | | | | |
| Net sales | 28,439 | 28,694 | 29,913 | 29,325 | 26,116 | 2,512 |
| Net income | 1,370 | 1,553 | 1,320 | 880 | 844 | 81 |
| Net income per BC Unit and B Unit (5) | 1.27 | 1.44 | 1.22 | 0.83 | 0.78 | 0.01 |
| Net income per GDS (6) | 25.49 | 28.58 | 24.44 | 16.59 | 15.66 | 1.51 |
| |
| Balance Sheet Data |
| Mexican GAAP: | | | | | | |
| Cash and temporary investments | 1,027 | 1,181 | 1,415 | 1,253 | 859 | 83 |
| Current assets | 6,286 | 6,930 | 6,811 | 6,472 | 7,389 | 711 |
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 14,504 | 14,537 | 15,030 | 15,545 | 15,334 | 1,475 |
| Total assets | 21,088 | 21,922 | 22,341 | 22,385 | 23,181 | 2,230 |
| Short-term debt (8) | 648 | 376 | | 0 | 158 | 15 |
| Long-term debt (8) | 2,294 | 1,576 | 1,909 | 1,817 | 1,751 | 168 |
| Total liabilities | 9,414 | 8,995 | 11,440 | 10,942 | 11,338 | 1,091 |
| Minority interest | 110 | 111 | 89 | 88 | 85 | 8 |
| Majority stockholders’ equity | 11,563 | 12,815 | 10,813 | 11,355 | 11,758 | 1,131 |
| | | | | | | |
| U.S. GAAP: (7) | | | | | | |
| Total assets | 20,941 | 22,031 | 22,741 | 21,525 | 22,434 | 2,157 |
| Total liabilities | 12,278 | 12,056 | 12,128 | 10,505 | 10,957 | 1,054 |
| Stockholders’ equity | 8,664 | 9,975 | 10,613 | 11,003 | 11,466 | 1,103 |
| |
| Other Data |
| Mexican GAAP: | | | | | | |
| EBITDA (9) | | | 1,902 | 1,808 | 1,645 | 158 |
| Depreciation and amortization | 611 | 604 | 679 | 722 | 725 | 70 |
| Capital expenditures (10) | 2,232 | 1,046 | 1,383 | 1,206 | 742 | 71 |
| Interest expense | (400) | (277) | (259) | (272) | (239) | (23) |
| EBITDA/Interest expense | | | 7.34 | 6.65 | 6.88 | |
| Total debt/EBITDA | | | 1.00 | 1.01 | 1.16 | |
| Net debt/EBITDA (11) | | | 0.27 | 0.31 | 0.63 | |
| Total debt/capitalization | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | |
| Working capital (12) | (801) | (451) | (198) | 160 | (19) | (2) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2002 |
| (Millions of constant Pesos as of December 31, 2001 and millions of U.S.Dollars) (1) |
| Operating Information |
| Store Information (13): | | | | | | |
| Food sales (14) | 64.6% | 64.0% | 63.3% | 63.3% | 64.9% | |
| Non-food sales (14) | 35.4% | 36.0% | 36.7% | 36.7% | 35.1% | |
| Average annual sales per store (millions)(15) | 228 | 228 | 234 | 232 | 220 | 21.2 |
| Sales per retail square foot (thousands)(15) | 3.35 | 3.37 | 3.40 | 3.33 | 3.09 | 0.3 |
| Sales per operating employee (thousands)(15)(16) | 1,253 | 1,311 | 1,270 | 1,473 | 1,339 | 128.8 |
| Same store sales growth (18) | 6.7% | 0.3%. | 2.6% | (3.3)% | (10.3)% | |
| |
| Stores: | | | | | | |
| Operating at end of period | 154 | 158 | 167 | 172 | 170 | |
| Opened | 5 | 5 | 16 | 7 | 3 | |
| Closed | 0 | 1 | 7 | 2 | 5 | |
| Remodeled (18) | 9 | 9 | 10 | 14 | 12 | |
| Total retail square feet at end of period (thousands)(19) | 10,330 | 10,713 | 11,552 | 11,998 | 12,098 | |
| Number of employees (at end of period) | 31,389 | 32,007 | 35,332 | 29,116 | 29,808 | |
| Number of operating employees | 27,616 | 27,581 | 30,946 | 26,828 | 27,947 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Restaurant Information: | | | | | | |
| Restaurants operating at end of period | 35 | 39 | 46 | 50 | 55 | |
| Total restaurant seats at end of period | 7,598 | 8,654 | 10,320 | 11,228 | 12,293 | |
Notes to Selected Consolidated Financial and Operating Information
| (1) | Except Unit and B Unit data and operating information, percentages and ratios. |
| (2) | Integral results of financing include interest expense, interest income, foreign-exchange loss, net, and gain from monetary position. |
| (3) | Interest income includes our income from interest-bearing temporary investments and our net gain or loss on the market value of our temporary investments. In 1998, 1999 and 2000 interest income additionally includes gains of Ps.71.2 million, Ps.1.0 million and Ps.0.3 million respectively (for 2001 there is none) from the repurchase and cancellation of Senior Notes at a discount price. |
| (4) | Includes miscellaneous income, net, revenues received from maintenance income, and negative goodwill from the acquisition of companies under common control, as well as a special item from change in amortization of preopening costs in 1997 and 1998; and in 1998, 1999, 2000 and 2001, write-offs of fixed assets not compliant with the Y2K issue. For the year ended December 31, 2001, also includes gain in permanent investment sales. |
| (5) | After giving effect to the Restructuring, including the split of each B Share into three B Shares and the subsequent distribution of one C Share or one B Share in respect of every three B Shares, as a result of which shareholders now hold Units and B Units. Amounts do not include shares held in treasury. |
| (6) | Each GDS represents 20 Units. |
| (7) | See Note 17 to the Financial Statements. |
| (8) | See Note 7 to the Financial Statements. |
| (9) | EBITDA represents operating income plus depreciation and amortization. We have included EBITDA data as a convenience because such data is used by certain investors to measure a company's ability to service debt. EBITDA is not a measure of financial performance under either Mexican GAAP or U.S. GAAP and should not be considered an alternative to net income as a measure of operating performance or to cash flows from operating activities as a measure of liquidity. |
| (10) | Capital expenditures for all periods exclude amounts contributed by Costco to the Costco de Mexico joint. See "Item 4. Information on the Company." |
| (11) | Net debt is total debt less cash and temporary investments. |
| (12) | Working capital is current assets minus current liabilities. |
| (13) | Store information relates to all of our stores, including those operated through joint ventures (calculated on the basis of 100% of the sales from the Costco de Mexico stores). The information does not include our restaurants. |
| (14) | Food sales include sales of basic groceries and perishables. Non-food sales include sales of general merchandise and clothing. |
| (15) | In computing sales per retail square foot for a period, we divide total store sales for the full period by the aggregate retail square footage at the end of such period. Accordingly, stores that are opened for less than the full period have the effect of decreasing store sales per retail square foot, and stores that are closed prior to the end of the full period have the opposite effect. Similarly, in computing average annual sales per store, we divide total store sales for the full period by the number of stores at the end of the period, and in computing sales per operating employee, we divide total store sales for the full period by the number of operating employees at the end of the period . |
| (16) | Includes all employees at our stores other than administrative employees and employees of our restaurants. |
| (17) | Calculated by comparing sales at stores during a period against sales at the same stores during the prior period, using only those same months in each period during which the same stores were open and using constant Pesos. |
| (18) | Includes conversions of stores from one format to another format. |
| (19) | Retail square feet includes areas for cashiers, which constituted approximately 8.3% of the total selling area of our stores at December 31, 2002. |
Dividends
The table below sets forth the nominal amount of preferential dividends per Unit paid on April 14, 2000 in respect of the fiscal year ended December 31, 1999; paid in April 5, 2001 in respect of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2000; paid on April 11, 2002 in respect of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2001 and paid on April 3, 2003 in respect of the fiscal year ended December 31,2002. Peso amounts have been translated into U.S. dollars at the exchange rate on each of the respective payment dates.
During our last general stockholders meeting on April 3, 2003 our stockholders approved a dividend of Ps.0.107 for each Unit, in a single payment which was made to holders of record on April 15, 2003.
| Dividend |
| In respect of | In nominal pesos per Unit |
| 2000 | Ps.107 |
| 2001 | Ps.107 |
| 2002 | Ps.107 |
Exchange Rate Information
Exchange Rates
Mexico abolished its exchange control system on November 11, 1991. Prior to December 1994, the Mexican central bank, orBanco de México, kept the Peso-U.S. dollar exchange rate within a range prescribed by the government through intervention in the foreign exchange market. On December 21, 1994, the Mexican Government announced its decision to suspend its policy of intervention by Banco de México and to allow the Peso to float freely against the U.S. Dollar. Factors contributing to the decision included the growing size of Mexico's current account deficit, the declining level ofBanco de México's foreign exchange reserves, rising interest rates for other currencies, especially the U.S. dollar, and reduced confidence in the Mexican economy on the part of international investors due to political uncertainty. See "Item 3. Key Information Risk Factors Risk Factors Relating to Mexico" and "Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects." The peso declined sharply in December 1994 and continued to fall under conditions of high volatility in 1995. In 1996 the peso fell more slowly and was less volatile. Relative stability characterized the foreign exchange markets during the first three quarters of 1997. The fall of the Hang Seng Index of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange on October 24, 1997, marked the beginning of a period of increased volatility in the foreign exchange markets with the peso falling over 10% in just a few days. During 1998, the foreign exchange markets experienced volatility as a result of financial crises in Asia and Russia and financial turmoil in countries such as Brazil and Venezuela.
The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, the period-end, average high and low noon buying rate as published by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, or the Noon Buying Rate, expressed in nominal Pesos per U.S. Dollar.
| |
| Year Ended December 31, | Period End | Average (2) | High | Low |
| 1996 | 7.86 | 7.60 | 8.05 | 7.33 |
| 1997 | 8.06 | 7.90 | 8.60 | 7.50 |
| 1998 | 9.90 | 9.29 | 10.54 | 8.04 |
| 1999 | 9.50 | 9.55 | 10.60 | 9.24 |
| 2000 | 9.62 | 9.34 | 10.09 | 9.18 |
| 2001 | 9.16 | 9.34 | 9.97 | 8.95 |
| 2002 | 10.39 | 9.74 | 10.39 | 9.00 |
| Month Ended: December 2002 | 10.39 | 10.22 | 10.39 | 10.10 |
| 2003: January | 10.90 | 10.62 | 10.98 | 10.32 |
| February | 11.03 | 10.94 | 11.06 | 10.77 |
| March | 10.78 | 10.91 | 11.24 | 10.66 |
| April | 10.31 | 10.59 | 10.76 | 10.31 |
| May | 10.34 | 10.25 | 10.42 | 10.11 |
| June (through June 13, 2003) | 10.60 | 10.52 | 10.74 | 10.24 |
(1) As published by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, since November 8, 1993.
(2) Average of end-month rates. Monthly average rates reflect the average of daily rates.
Risk Factors
The following is a discussion of risks associated with our Company and an investment in our securities. Some of the risks of investing in our securities are general risks associated with doing business in Mexico. Other risks are specific to our business. The discussion below contains information about the Mexican government and the Mexican economy obtained from official statements of the Mexican government as well as other public sources. We have not independently verified this information. Any of the following risks, if they actually occur, could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations or the price of our securities.
Risk Factors Relating to Developments in Mexico
Economic and Political Developments in Mexico and Elsewhere May Adversely Affect Our Business. Most of our operations and assets are located in Mexico. As a result, our business may be affected by the general condition of the Mexican economy, the devaluation of the Peso as compared to the U.S. Dollar, Mexican inflation, interest rates and political developments in Mexico and elsewhere.
Mexican Economic Conditions. We are a Mexican company with all our consolidated assets located in Mexico and all our consolidated net sales derived from Mexico. As a result, our business may be affected by the general condition of the Mexican economy, the devaluation of the Peso as compared to the U.S. Dollar, Mexican inflation, interest rates and political developments in Mexico.
The Mexican government has exercised and continues to exercise, significant influence over the Mexican economy. Mexican governmental actions concerning the economy and state-owned enterprises could have a significant impact on Mexican private sector entities, in general, an on us, in particular, and on market conditions, prices, and returns on Mexican securities, including our securities.
The level of manufacturing activity in Mexico has in the past been affected by prevailing conditions in the Mexican economy, and domestic demand (including domestic demand for the Company's products) has been and is, to a significant extent, vulnerable to economic downturns in Mexico. In addition, the Company's financial condition, liquidity (including its ability to obtain financing) and prospects have been and are expected to continue to be affected by prevailing economic conditions in Mexico, particularly downturns in the Mexican economy and changes in government policies, including public spending on infrastructure projects.
In December 1994, Mexico experienced an economic crisis characterized by exchange rate instability and significant devaluation of the peso increased inflation, high domestic interest rates, a substantial outflow of capital, negative economic growth, reduced consumer purchasing power and high unemployment. In addition, the financial crises in 1998 and early 1999 in Asia, Russia and Latin America resulted in instability in the foreign exchange markets and international financial markets. These events resulted in limited liquidity for the Mexican government and for local corporations as well as an increase in interest rates in Mexico.
The recent economic and financial crises in Argentina and recent civil and political unrest in Venezuela could produce similar results. Although the Mexican economy declined by 0.3% in 2001, the Mexican economy grew by 0.9% in 2002 and by 2.3% in the first quarter of 2003. In April 2003, Banco de Mexico decreased the official growth forecast for 2003 to 2.4% from its initial prediction of 3.0%.
Beginning in January 2001, and increasing in the fourth quarter of 2001, amid concerns of a global economic slowdown and a recession in the United States, Mexico began to experience an economic slowdown marked by a decline in GDP. In 2001, Mexico's GDP shrank by 0.3% in real terms while the inflation rate was 4.4%, interest rates on 28-day CETES averaged 11.3% and the peso appreciated 4.6% in value (in nominal terms) relative to the U.S. dollar. During 2002, as the United States and global economic slowdown continued, the Mexican real GDP growth rate was 0.9%, the inflation rate was 5.7%, interest rates on 28 day CETES averaged 11.3% and the peso devalued 13.8% (in nominal terms) relative to the U.S. dollar.
World Economy. In particular, Argentina’s insolvency and recent default on its public debt, which deepened the existing financial, economic and political crises in that country, could adversely affect Mexico, the market value of our securities or our business. The recent Argentine President, Eduardo Duhalde, took office on January 6, 2002 in the midst of significant political unrest after a series of interim presidents and administrations took office following the resignation of President Fernando de la Rúa in December 2001. On May 15, 2003, a new president, Néstor Kirchner, took office in Argentina and is expected to retain the same economy minister and continue the fiscal and monetary policies initiated by President Duhalde The recent devaluation of the Argentine peso will have a material adverse effect on Argentina and presents risks that the Argentine financial system may collapse and that substantial inflation may occur. The rapid and radical nature of changes in the Argentine social, political, economic and legal environment have continued to create significant uncertainty. To the extent that the new Argentine government is unsuccessful in preventing further economic decline via this and other measures, this crisis may adversely affect Mexico, the price of our securities or our business.
In addition, on April 12, 2002, following a week of strikes, demonstrations and riots, Venezuelan President Hugo Chávez was forced to resign from office by Venezuela’s military commanders in an attempted coup d’etat. Although Mr. Chávez was restored to power on April 14, 2002, the political and economic future of Venezuela remains uncertain. More recently, an ongoing nationwide general strike that began in December 2002 has caused a significant reduction in oil production in Venezuela, and has had a material adverse effect on Venezuela’s oil-dependent economy. In response to the general strike and in an effort to shore up the economy and control inflation, in February 2003 Venezuelan authorities imposed foreign exchange and price controls on specified products. We cannot predict what effect, if any, these events will have on the economies of other emerging market countries, Mexico, the price of our securities or our business.
The terrorist attacks on September 11, 2001 depressed economic activity in the U.S. and globally, including the Mexican economy. Since those attacks, there have been terrorist attacks in Indonesia and ongoing threats of future terrorist attacks in the United States and abroad. In response to these terrorist attacks and threats, the United States has instituted several anti-terrorism measures, most notably, the formation of the Office of Homeland Security, a formal declaration of war against terrorism and the war in Iraq. Although it is not possible at this time to determine the long-term effect of these terrorist threats and attacks and the consequent response by the United States, there can be no assurance that there will not be other attacks or threats in the United States or abroad that will lead to a further economic contraction in the United States or any other major markets. In the short term, however, terrorist activity against the United States and the consequent response by the United States has contributed to the uncertainty of the stability of the United States economy as well as global capital markets. It is not certain how long these economic conditions will continue. If terrorist attacks continue or worsen, if the weak economic conditions in the U.S. continue or worsen, or if a global recession materializes, our business, financial condition and results of operations may be materially and adversely affected.
Expansion. Changes in the general business and economic conditions in our operating regions, including the rate of inflation, population growth, and employment and job growth in the markets in which we operate may affect our ability to hire and train qualified employees to operate our stores. This would negatively affect our expected growth. Moreover, General economic changes may also affect the shopping habits of our customers, which could affect our expansion plans for the following years. We currently intend to fund substantially all of our 2003 capital expenditures primarily with cash flows from operations. Although we believe that sufficient financing will be available to us, there can be no assurance that we will have sufficient cash flow from operations to make all of our planned capital expenditures when scheduled or if necessary, that we will be able to obtain, or what the terms may be of, any bank or other financing.
Overview of the Mexican Economy in 2002
Indicators of economic activity suggest that Mexican economy registered a moderate expansion during the second half of 2002. Future development of the economy remains fragile among the different economic sectors. In particular, the rate of growth of the economic sectors closely linked to external markets has been weaker than those sectors associated with domestic sources of demand.
During 2002, Mexico’s Gross Domestic Product increased by 0.9% in real terms, as compared with 2001. The financial services, insurance and real estate sector grew by 4.4%, the electricity, gas and water sector grew by 3.8%, and the transportation, storage and communications sector grew by 2.2%, each in real terms. The construction sector grew by 1.7%, and the community, social and personal services sector grew by 1.3%, each in real terms. The mining, petroleum and gas sector decreased by 0.3%, the agriculture, livestock, fishing and forestry sector and the commerce, hotels and restaurants sector each decreased by 0.4%, and the manufacturing sector decreased by 0.6%, each in real terms. During 2002, the commercial sector (defined by ANTAD as Retailers, Department Stores and other types of stores) grew 1.5%, which was substantially lower than the 6.1% growth predicted at the beginning of 2002.
Inflation during 2002 was 5.70%, as compared to 4.40% during 2001. Inflation during January 2003 was 0.40%, 0.52 percentage points lower than in January 2002.
During 2002, interest rates on 28-day Cetes averaged 7.08% and interest rates on 91-day Cetes averaged 7.44%, as compared with average rates on 28-day and 91-day Cetes of 11.30% and 12.24%, respectively, during 2001.
Last year Mexico registered a trade deficit of US$7,996.8 million, as compared with a trade deficit of US$9,953.6 million for 2001. Merchandise exports increased by 1.4% during 2002, to US$160,682.0 million, as compared with US$158,442.9 million in 2001. During 2002, petroleum exports increased by 13.1% and non-petroleum exports increased by 0.4%, each as compared with 2001. Exports of manufactured goods, which represented 88.4% of total merchandise exports, increased by 0.4% during 2002 as compared with 2001.
Total imports were US $168,678.9 million during 2002, a 0.2% increase as compared to 2001. Imports of intermediate goods increased by 0.3%, imports of capital goods decreased by 6.7% and imports of consumer goods increased by 7.2% during 2002, each as compared with 2001.
As of December 31, 2002, the net internal debt of the Government was US$79.6 billion, as compared with U.S. $75.6 billion outstanding as of December 31, 2001. Gross external debt of the Government totaled US$78.82 billion in 2002. Outstanding gross external debt decreased by approximately US$1.52 billion. Of the total external debt as of December 31, 2002, US$76.03 billion represented long-term debt and US$2.80 billion represented short-term debt.
Mexico’s Economic Outlook for 2003
According to the General Criteria on Economic Policy, the government’s main concern in 2003 will be "to preserve the climate of stability and certainty". This will, in turn, condition its two central objectives: reactivating the economy and reducing poverty. This approach is correct because only with low inflation can economic growth and an increase in social welfare be long lasting.
The government intends to improve its financial situation through a 0.15% reduction in the economic deficit to GDP ratio and no increase in external indebtedness. Furthermore, the government has adopted the 3% inflation target proposed by Banco de México. The signs of fiscal discipline and the support to the central bank’s goal represent the best contribution to economic certainty, among other reasons, because they could reduce the perception of the "country-risk" and lower interest rates.
Currency Fluctuations or the Devaluation and Depreciation of the Peso Could Limit the Ability of Others and Us to Convert Pesos into U.S. Dollars or Other Currencies and/or Adversely Affect Our Financial Condition. Less than half of our indebtedness and some of our costs are U.S. Dollar-denominated, while our revenues are primarily Peso-denominated. As a result, decreases in the value of the Peso against the U.S. Dollar could cause us to incur foreign exchange losses, which would reduce our net income.
Severe devaluation or depreciation of the Peso may also result in governmental intervention, as has resulted in Argentina, or disruption of international foreign exchange markets. This may limit our ability to transfer or convert Pesos into U.S. Dollars and other currencies for the purpose of making timely payments of interest and principal on our indebtedness and adversely affect our ability to obtain imported goods. While the Mexican government does not currently restrict, and for many years has not restricted, the right or ability of Mexican or foreign persons or entities to convert Pesos into U.S. Dollars or to transfer other currencies outside of Mexico, the Mexican government could institute restrictive exchange control policies in the future. Devaluation or depreciation of the Peso against the U.S. Dollar may also adversely affect U.S. Dollar prices for our securities. Such fluctuations also would affect the conversion by the Depositary into U.S. dollars of any cash dividends paid in Pesos on the B Shares and the C Shares comprising the Units.
High Inflation Rates in Mexico May Decrease Consumer Demand for Our Goods While Increasing Our Costs. In recent years, Mexico has experienced high levels of inflation. The annual rate of inflation, as measured by changes in the Mexican National Consumer Price Index, or the NCPI, 9.0% for 2000, 4.4% for 2001 and 5.7% for 2002 and 1.3% for the three month period ended March 31, 2003. High inflation rates can adversely affect our business and results of operations in the following ways:
inflation can adversely affect consumer purchasing power, thereby adversely affecting consumer demand for our products;
to the extent inflation exceeds our price increases, our prices and revenues will be adversely affected in "real" terms; and
if the rate of Mexican inflation exceeds the rate of devaluation of the Peso against the U.S. Dollar, our U.S. Dollar-denominated sales will decrease in relative terms when stated in constant Pesos.
High Interest Rates in Mexico Could Increase Our Financing Costs. Mexico has, and is expected to continue to have, high real and nominal interest rates. The interest rates on 28-day Mexican government treasury securities averaged 15.2%, 11.3%, 7.08% and 8.9% for 2000, 2001, 2002 and the three month period ended March 31, 2003. Accordingly, if we need to incur Peso-denominated debt in the future, it will likely be at high interest rates.
Mexican Antitrust Laws May Limit Our Ability to Expand Through Acquisitions or Joint Ventures. Mexico's federal antitrust laws and regulations may affect some of our activities, including our ability to introduce new products and services, enter into new or complementary businesses or joint ventures and complete acquisitions. In addition, the federal antitrust laws and regulations may adversely affect our ability to determine the rates we charge for our products. Approval of the Mexican Antitrust Commission is required for us to acquire and sell significant businesses or enter into significant joint ventures. The Mexican Antitrust Commission may not approve any proposed future acquisition or joint venture that we may pursue. See "Information on the Company Business Overview."
The Protections Afforded To Minority Shareholders In Mexico Are Different From Those In The United States. In accordance with theLey del Mercado de Valores, or the Mexican Securities Market Law, as amended, we recently amended our bylaws to increase the protections afforded to our minority shareholders in an effort to try to insure that our corporate governance procedures are substantially similar to international standards. See "Other Information Mexican Securities Market Law" and " Bylaws Other Provisions." Notwithstanding these amendments, under Mexican law, the protections afforded to minority shareholders are different from those in the United States. In particular, the law concerning fiduciary duties of directors is not well developed, there is no procedure for class actions or shareholder derivative actions and there are different procedural requirements for bringing shareholder lawsuits. As a result, in practice, it may be more difficult for our minority shareholders to enforce their rights against us or our directors or principal shareholders than it would be for shareholders of an U.S. company.
Risk Factors Relating to the Company
We Participate In A Very Competitive Market And Increased Competition May Adversely Affect Our Business. The retail industry in Mexico is highly competitive. We face strong competition from other national and international operators of supermarket and retail stores, including Walmex (formerly Cifra), Carrefour and Gigante. All of the foregoing stores owned by third parties compete with our stores. The Costco membership warehouses face competition from Sam's Club, a self-service warehouse club owned by Walmex. We expect that other United States and international retailers may enter the market in Mexico in the future either through joint ventures or directly. We also compete with numerous local and regional supermarket and self-service store chains, as well as small, family-owned neighborhood stores and street markets, in each region in which we do business. In addition, certain of our stores, which are located in the same shopping areas, compete with each other. The restaurant business in Mexico is also highly competitive, and Restaurantes California compete with numerous regional and national fast-food restaurant chains, local restaurants and street merchants. There can be no assurance that our performance will not be adversely affected by increased competition, whether resulting from these or other sources. See "Item 4. Information on the Company Business Overview Competition."
Our Growth Strategy is Dependent Upon the Continued Improvement of the Mexican Economy. A major component of our future growth is expected to come from adding new stores (including Costco membership warehouses) and restaurants and remodeling existing stores. Our ability to resume our expansion and remodeling plans as provided in our current business plan and our returns on our investment in expansion and remodeling are dependent to a significant extent on the continued improvement of Mexico's economic performance. Even following the continued recovery of the Mexican economy, there can be no assurance that we will be able to open or remodel the number of stores (including Costco membership warehouses) and restaurants currently intended, whether because of economic conditions, availability of financing, availability of suitable and affordable sites, the ability to attract and retain certain qualified employees or otherwise. See "Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects" and "Item 4. Information on the Company."
Our Joint Venture With Costco Mexico is Jointly Controlled and is Subject to Termination in Certain Circumstances. The Costco Mexico joint venture is managed, on a day-to-day basis, by officers appointed by Costco and approved by us pursuant to certain management agreements between Costco and the Costco Mexico joint venture. In addition, the affirmative vote of at least two of the three directors appointed by each of Costco and us to the Costco Mexico joint venture board of directors is required to approve significant decisions regarding the joint venture, including among other things, certain revisions to the joint venture business plan, obligations or acquisitions of the estate or certain other assets not otherwise provided for in the business plan or the removal of the management personnel appointed by Costco. Furthermore, certain significant decisions also require the approval of both members of an executive committee, which consists of our chief executive officer, and that of Costco. Accordingly, although we expect Costco membership warehouses to be an important part of our future growth, we do not have sole control over the growth and operation of the Costco membership warehouse format. In addition, the Costco Mexico joint venture is subject to termination in certain circumstances. See "Item 4. Business Overview Retail Store Formats."
There Are Differences in Corporate Disclosure and Accounting Standards for Mexican Companies and this May Cause our Financial Statements to Differ in Certain Respects from U.S Issuers. A principal objective of the securities laws of the United States, Mexico and other countries is to promote full and fair disclosure of all material corporate information. However, there may be less publicly available information about foreign issuers of securities listed in the United States than is regularly published by or about domestic issuers of listed securities. In addition, we prepare our Financial Statements in accordance with Mexican GAAP, which differ from U.S. GAAP and accounting procedures adopted in other countries in a number of respects. For example, most Mexican companies, including us, must incorporate the effects of inflation directly in accounting records and in their published Financial Statements. Thus, Mexican financial statements and reported earnings may differ from those of companies in other countries in this and other respects. Note 17 to our Annual Financial Statements describes the principal differences between Mexican GAAP and U.S. GAAP as they relate to us and provides a reconciliation to U.S. GAAP of net income and total stockholders' equity.
The Seasonal Nature of Our Business Affects Our Revenue and a Significant Reduction in Third or Fourth Quarter Net Sales Could Impact Our Results of Operations. Our business reflects seasonal patterns of consumer spending, which is common in the retail industry. We typically recognize a disproportionately large percentage of our overall net sales in the third quarter in connection with the "Julio Regalado" holiday and in the fourth quarter in connection with the Christmas holiday season. Accordingly, a significant reduction in the third or fourth quarter revenue could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We are Controlled by Principal Shareholders. Members of the González family, are included as our Principal Shareholders and own a majority of the outstanding B Shares through B Units and Units. As a result of this majority ownership, the Principal Shareholders are able to elect a majority of the members of the Board and to determine the outcome of the voting on substantially all actions that require shareholder approval. See "Item 7. Major Shareholders and Related Party Transactions."
The Principal Shareholders have advised us that, in connection with any primary sale of equity by us in the future, they may purchase additional B Shares through B Units or Units (through the exercise of pre-emptive rights, if any, or otherwise) so that they will continue to own B Shares representing a majority of the total outstanding B Shares of CCM. The Principal Shareholders have also advised us that they may raise funds for such purchase by selling, borrowing or engaging in other types of financing transactions secured by B Units or Units which they own.
Our Principal Shareholders Have Substantial Influence Over Our Management and the Interests of Our Principal Shareholders May Differ from Those of Other Shareholders. Approximately 69.3% of our outstanding B Units, the class of capital stock that is entitled to elect a majority of our Board of Directors and the only class of capital stock entitled to vote on other general corporate matters, is beneficially owned, directly or indirectly by a trust the beneficiaries of whom are members of the González Family. As our controlling shareholder, this trust controls our business through its power to elect a majority of our Board of Directors and to determine the outcome of almost all actions that require shareholder approval. For example, the trust has the ability to cause us to declare dividends. The principal grantor and beneficiary of this trust is a corporation owned by the González family. For a description of this trust see the section entitled The Scotiabank Trust. In addition to their indirect ownership interest in our company, Mr. Carlos González Nova, Mr. Guillermo González Nova, Mr. Jaime González Nova, Mr. Carlos González Zabalegui, Ms. Elena González Guerra, and Mr. Pablo González Guerra serve as our directors. Mr. Guillermo González Nova also serves as our Chairman of the Board, and Mr. Carlos González Zabalegui serves as our Chief Executive Officer. See "Major Shareholders and Related Party Transactions -Principal Shareholders" and "Directors, Senior Management and Employees."
Forward-Looking Statements
Some written information and oral statements made or incorporated by reference from time to time by CCM, or its representatives in this annual report, other reports, filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, press releases, conferences, or otherwise, are "forward-looking statements" within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Forward-looking statements, which are subject to various risks and uncertainties, include, without limitation, any statement that may predict, forecast, indicate, or imply future results, performance, or achievement, and may contain forward-looking terminology such as "anticipate," "believe," "continue," "expect," "estimate," "project," "will," "will be," "will continue," "will likely result," "may," "plan," or words or phrases of similar meaning. Forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially from the forward-looking statements. The risks and uncertainties are detailed from time to time in reports filed by CCM with the SEC and include, among others, the following:
- Our ability to achieve sales and earnings-per-share goals will be affected primarily by: industry consolidation; pricing and promotional activities of existing and new competitors, including non-traditional competitors.
- Our efforts to meet our working capital reduction targets could be adversely affected by: increases in product costs; our ability to obtain sales growth from new square footage; competitive activity in the markets in which we operate; changes in our product mix; and changes in laws and regulations.
- Our ability to generate operating cash flow to the extent expected could be adversely affected if any of the factors identified above negatively impacts our operations, or if any of our underlying strategies, including those to reduce shrink and SG& A and to increase productivity, are not achieved.
- Consolidation in the retail industry is likely to continue and the effects on our business, favorable or unfavorable, cannot be foreseen.
- The retailing industry continues to experience fierce competition from other retailers, supercenters, clubs or warehouse stores, mom and pop stores and others. Our continued success is dependent upon our ability to compete in this industry and continue to reduce operating expenses, including managing salaries and corporate expenses. While we believe our opportunities for sustained, profitable growth are considerable, unanticipated actions of competitors could impact our sales and net income.
- Changes in laws and regulations, including changes in accounting standards, taxation requirements, and environmental laws may have a material impact on our financial statements.
- Changes in the general business and economic conditions in our operating regions, including the rate of inflation, population growth, and employment and job growth in the markets in which we operate may affect our ability to hire and train qualified employees to operate our stores. This would negatively affect earnings and sales growth. General economic changes may also affect the shopping habits of our customers, which could affect sales and earnings.
- Our capital expenditures could differ from our estimate if we are unsuccessful in acquiring suitable sites for new stores, if development costs vary from those budgeted, or if our logistics and technology projects are not completed in the time frame expected or on budget.
- Depreciation and amortization expenses may vary from our estimates due to the timing of new store openings.
- Interest expense will vary with changes in capital markets and the amount of debt that we have outstanding. Although we use derivative financial instruments to manage our net exposure to financial risks, we are still exposed to interest rate fluctuations and other capital market conditions.
- We cannot fully foresee the effects of the general economic downturn on CCM’s business. We have assumed economic and competitive situations will not change significantly for 2003.
- Other factors and assumptions not identified above could also cause actual results to differ materially from those set forth in the forward-looking information. Accordingly, actual events and results may vary significantly from those included in or contemplated or implied by forward-looking statements made by us or our representatives.
The risks summarized above are not exhaustive. Other sections of this annual report may include additional factors that could adversely impact our business and financial performance. Moreover, we operate in a very competitive and rapidly changing environment. New risk factors emerge from time to time and it is not possible for management to predict all of these risk factors, nor can it assess the impact of all of these risk factors on our business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause actual results to differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statements. Given these risks and uncertainties, investors and analysts should not place undue reliance on forward-looking statements as a prediction of actual results. Accordingly, when considering forward-looking statements, you should keep in mind the factors described in "Item 3. Key Information Risk Factors" and other cautionary statements appearing in "Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects" and elsewhere in this annual report.
The predictive and forward-looking statements in this annual report may not come true and are made under the SEC's disclosure safe harbor. Forward-looking statements speak only as of the date they are made, and we do not undertake any obligation to update them in light of new information or future developments.
Item 4. Information on the Company
History and Development of the Company
Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V., or CCM or the Company, is a limited liability stock company with variable capital (sociedad anónima de capital variable) organized under the laws of Mexico. Our principal offices are located at Av. Revolución No. 780, Módulo 2 Colonia San Juan, C.P. 03730 México, D.F. and our telephone number is (52) 55 5270 9312.
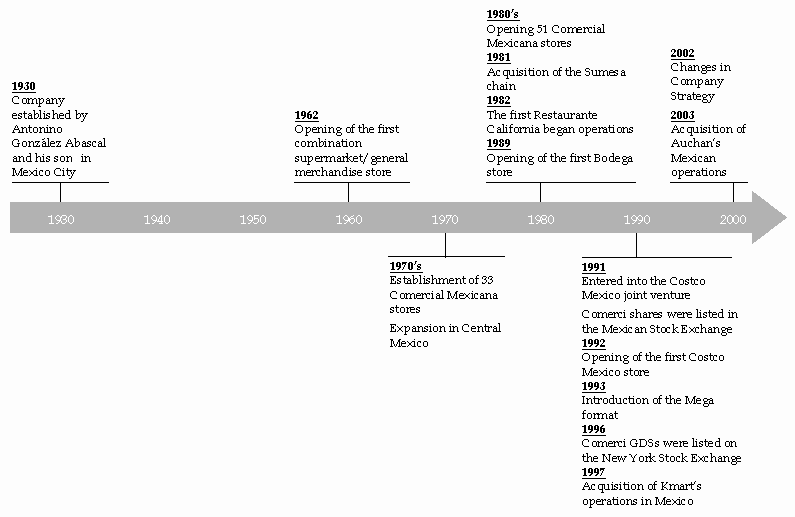
We trace our history to 1944 when Antonino González Abascal and his son founded their first store in Mexico City, which sold primarily textiles. The first combination supermarket/general merchandise store under the name Comercial Mexicana was opened in Mexico City in 1962, and 20 additional stores were established during the 1970's. During the 1980's we continued to expand through the acquisition of the Sumesa chain in 1981 and with 51 Comercial Mexicana store openings. The first Restaurante California commenced operations in 1982, and the first Bodega opened in 1989. We entered into the Costco Mexico joint venture in June 1991, and the initial Costco Mexico opened in February 1992. In 1993, we introduced the Mega format to take advantage of the perceived potential of the supercenter and hypermarket formats. CCM was fully owned by the González family until April 1991, when shares of capital stock of CCM were listed in the Mexican Stock Exchange and offered publicly in Mexico. In 1996, GDSs representing shares of capital stock of CCM were listed on the New York Stock Exchange and the GDSs and the underlying shares were offered publicly in Mexico, the United States and elsewhere outside of Mexico.
Our deed of incorporation was executed on December 9, 1988 and we were registered in the Public Registry of Commerce in Mexico City on February 21, 1989, under the number 60562. The term of the Company is 99 years beginning on May 11, 1989.
Capital Expenditures
Capital expenditures reflect our strategy of growth through expansion and acquisition as well as our emphasis on self-development and ownership of real estate, and on logistics and technology improvements. Continued capital spending in technology focusing on improved store operations, logistics, manufacturing procurement, category management, merchandising and buying practices, should reduce merchandising costs as a percent of sales. For fiscal 2003, we expect capital spending to be approximately $130 million. We intend to use the combination of cash flow from operations, including reductions in working capital to finance capital expenditure requirements.
The following table sets forth our capital expenditures for each of the three years ended December 31, 2000, 2001, 2002 and the budgeted capital expenditures for 2003:
| Year ended December 31(1), |
| | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 (2) |
| (Millions of constant Pesos as of December 31, 2002, except for 2003 amounts which are in nominal Pesos) |
| Real estate | 500.7 | 590.8 | 315.7 | 526.4 |
| Store fixture (3) | 859.8 | 593.4 | 411.3 | 685.9 |
| Information systems | 22.2 | 21.4 | 15.4 | 25.7 |
| | | | | |
| Total | Ps.1,382.7 | Ps.1,205.6 | Ps. 742.4 | Ps. 1,238.0 |
(1) Capital expenditures exclude Ps.239.9 in 2000, Ps.276.0 in 2001 and Ps. 204.0 in 2002 contributed by Costco to the Costco Mexico joint venture.
(2) Represents budgeted amounts for the year ending December 31, 2003.
(3) Represents store fixtures and other equipment expenditures.
Annually, we invest significant resources in areas such as construction, acquisition of equipment and the remodeling of stores. Since 2000, we have opened 23 stores and 17 restaurants. Additionally, 25 units have been remodeled and 12 units have been reconverted, to better serve the geographic areas where these stores are located. Similarly, we have invested significant resources in the construction of an efficient and reliable merchandise system.
The capital expenditures of Ps. 742.4 million in 2002 were funded with cash generated from operations. Our plans for 2003 are contingent primarily upon the economic situation in Mexico and our ability to generate sufficient cash flow to fund such expenditures. Depending upon these conditions, our goal is to open or commence construction on an aggregate of up to 10 stores and 6 restaurants in 2003, and to remodel 12 units.
We currently intend to fund substantially all of our 2003 capital expenditures primarily with cash flows from operations. Although we believe that sufficient financing will be available to us, there can be no assurance that we will have sufficient cash flow from operations to make all of our planned capital expenditures when scheduled or if necessary, that we will be able to obtain, or what the terms may be of, any bank or other financing. Costco is responsible for funding 50% of the cost of the new Costco membership warehouses. See "Item 4. Information on the Company Property, Plant, and Equipment" and "Item 3. Key Information Risk Factors Factors Relating to the Company Growth Strategy Dependent Upon Continued Improvement of Mexican Economy."
Business Overview
General
CCM is a holding company, which, through its subsidiaries, operates the second largest retail company in Mexico, as measured by net sales in 2002, as well as a chain of family restaurants. In addition, we own a 50% interest in the Costco Mexico joint venture with Costco of the United States, which operates a chain of warehouse clubs in Mexico. Our retail operations sell a wide variety of food items, including basic groceries and perishables, and non-food items, which include general merchandise and clothing, with food items representing 64.9% of our total sales in 2002. At December 31, 2002, we had 170 stores operating under five retailing formats (including stores operated by the Costco Mexico joint venture) with a total selling area of approximately 12.1 million square feet, concentrated primarily in the Mexico City metropolitan area and the central Mexico region, including Guadalajara, or the Central Region.
The Mexican retail sector is fragmented and consumers are served by a number of formats, including traditional formats such as independent grocery stores and food specialists, modern formats such as supermarkets, hypermarkets and department stores, as well as informal outlets such as street vendors and markets. We believe that there is considerable potential for growth as the Mexican retail sector continues its process of modernization. We believe that consumer preferences are shifting away from smaller, traditional and informal outlets toward larger, standardized supermarket and hypermarket chains, which offer consumers superior value through greater merchandise selection, convenience and better prices through the chains' greater purchasing power. Our strategy is designed to capitalize on this trend. Additionally, we believe that the recovery of consumers' purchasing power in Mexico and favorable demographics approximately half of Mexico's population is under 21 years old which will lead to increased numbers of consumers, will benefit the retail sector in the near and long terms.
Strategy
Our strategies are designed to benefit from the modernization of the retail sector, building upon our position as one of Mexico's leading chains and our strong brand franchise. To achieve this goal, we pursue four primary strategies in the Mexican retail market.
Merchandising Strategy. Our merchandising strategy emphasizes competition on the basis of product selection, quality, price and consumer service. We target specific consumer preferences and demographics by using distinct retail formats, which differ in store size, service level and product range. As Mexican consumer preferences have shifted toward large supermarkets and hypermarkets, we have met this demand by introducing our Mega format in 1993. In addition, we have sought partnerships with leading international retailers to introduce innovative formats to the Mexican market. In 1992 our Costco Mexico joint venture opened the first Costco Mexico warehouse club. Currently, we operate five retailing formats:
- Combination Supermarket/General Merchandise Stores. Through our flagship subsidiary "Comercial Mexicana," we operate combination self service supermarket/general merchandise stores under three formats: Comercial Mexicana stores (71 stores), which target middle and upper income segments; Bodega Comercial Mexicana stores (34 stores), which target lower income segments; and Mega (27 stores), super combination stores which carry the broadest line of products and complementary services in the combination store format and target a broad range of income levels.
- Supermarkets. Under the name Sumesa, we currently operate 17 neighborhood supermarkets.
- Membership Warehouse Stores. Through the Costco Mexico joint venture we operate 21 self-service membership warehouse stores, targeting businesses, professionals and upper income customers, which offer members low prices on bulk purchases.
Pricing Strategy. The Company believes that its historical strategy of promotions and deep discounts was effective in the historical Mexican macroeconomic environment, which was characterized by high inflation. As the Mexican economic landscape has become more stable, consumers have become more aware of price differences, and have started comparing them among the different retailers. The introduction of the Walmex strategy of "Every Day Low Prices" has become more attractive to consumers. The "promotion/heavy discount" strategy also attracted wholesale customers (resellers), who only shopped for discounted merchandise, and as a rule do not show any kind of customer loyalty. With the main objective attracting a more loyal customer base, the Company decided to adopt a low prices strategy in the second quarter of 2002. The Company believes that its customer base is adjusting to this change in pricing strategy, and that the Company’s operational results and its ability to forecast and plan its procurement needs are consistently improving, thereby achieving better costs, efficiencies and ultimately higher customer satisfaction. The Company is very optimistic about the final outcome of this strategy.
Operating Strategy. Our operating strategy emphasizes increased productivity and customer service through investment in information technology. From 2000 through December 31, 2002, we invested approximately U.S.$ 5.6 million in computer systems focused primarily on improving inventory efficiency, supply levels and controls. Innovative technologies used by our stores include point of sales systems (including bar code scanners), a unit inventory control system, fiber optic communications networks and an electronic communication system to submit purchase orders to suppliers. We believe that continued upgrading of our systems would allow it to further increase efficiencies, reduce expenses and provide the necessary product and sales information to enhance merchandising decisions at each store.
Growth Strategy. Our growth strategy is intended to take advantage of the fragmented nature of the Mexican retailing market and to strengthen our market penetration. Our growth strategy has two principal components: (i) continued improvements in same-store sales growth through enhanced merchandising techniques, attractive promotions, remodeling and expansion of selling area and (ii) new store openings both in areas where we already have a strong presence and in areas with high potential but which are currently undeserved by modern retail formats. From 2000 and through 2001, we invested Ps.2,588.3 million to open 8 Comercial Mexicana, 5 Mega, 3 Bodega, 12 Restaurantes California, 1 Sumesa store and 3 Costco. During this period we also remodeled 15 units, converted 4 Comercial Mexicana stores into the Mega format and 7 Comercial Mexicana into the Bodega format. In 2002, we invested Ps.742.4 to open 1 Mega, 1 Bodega Comercial Mexicana, 1 Costco membership warehouse, and 5 Restaurantes California. We also remodeled 10 units and converted 1 Comercial Mexicana into the Mega format. We intend to open 10 stores, 6 restaurants and remodel 12 units in 2003. In particular, we intend to continue the growth of the larger formats stores, such as Mega hypermarkets and Costco membership warehouses.
Since December 1994, when Mexico experienced an economic crisis, instability, increased inflation, high domestic interest rates, negative economic growth, increased unemployment, we have implemented a program to streamline operations in order to reduce operating expenses and increase cash flow while taking steps to minimize the effects of reduced purchasing power. During 2003, we expect to continue our aggressive program to reduce expenses at both our branches and at the corporate level in an effort to improve our operating margins. Economic conditions continued to improve in 2000 with gross domestic product increasing by 6.9% in 2000 as compared to 1999, but declined by 0.3% in 2001 as compared to 2000, and increased in 2002 by 0.9% compared to 2002. In 2000, 2001 the retail sector increased by 7.5%, 6.9% and decreased by 1.8% en 2002 respectively, while our total net sales increased by 6.8%, 0.2% and decreased 8.3% during the periods. In response to the improving economic conditions, we resumed our growth strategy, with capital expenditures of Ps.1.401.5 million in 2000 Ps.1,205.6 million in 2001 and Ps. 742.4 million in 2002.
At December 31, 2002, we also operated a chain of 55 family-style restaurants under the name of "Restaurantes California". Restaurantes California provide customers with homemade-style food and high quality service at affordable prices. As part of our growth strategy, we intend to open six new Restaurantes California by the end of 2003.
Location Strategy. In opening new stores, we select the type of retail store and offer the merchandise and service mix which they consider most appropriate for each location's anticipated customer base. The Company determines a location's anticipated customer base by analyzing a number of factors, including the current and expected future population density, income levels and competitive conditions surrounding that location. Decisions with respect to opening new Costco warehouses are made by the Costco Mexico joint venture.
Seasonally
Due to the seasonal nature of the retail industry, where merchandise sales and cash flows from operations are historically higher in the third and fourth quarters than any other period, a disproportionate amount of operating cash flows are generated in the previously mentioned quarters. In preparation for the Julio Regalado and the Holiday seasons, we significantly increase our merchandise inventories, which traditionally have been financed by cash flows from operations, bank lines of credit, trade credit and terms from vendors. Our profitability and cash flows are primarily dependent upon the large sales volume generated during the quarters of our fiscal year.
Sales in our stores typically increase during the "Julio Regalado" special promotion occurring each July, and during the Christmas season. In 2000, 2001 and 2002 approximately 55.1%, 50.9% and 53.6% respectively, of our sales occurred during the last six months of the year, with an average of 27.4% in 2000, 22.7% in 2001 and 27.6% in 2002 of such sales occurring in the last quarter of the year. Although we have recently instituted a year-round "Low-Price" strategy, we currently intend to continue to yearly "Julio Regalado" and Christmas Holidays promotions.
Retail Operations
At December 31, 2002, we had 170 stores operating under five retailing formats with a total selling area of approximately 12.1 million square feet. Although we operate nationwide, our stores are concentrated in the two most populated areas of Mexico, the Mexico City metropolitan area and the Central region. Our stores located in those areas account for approximately 76.6% of our total retail floor space at December 31, 2002.
The percentage breakdown of our total selling area and number of stores by geographic region at December 31, 2002, is set forth in the following table:
| | At December 31, 2002 |
| | Percentage of Total Selling Area | Number of Stores |
| Mexico City metropolitan area | 39.6% | 78 |
| Central region | 37.0 | 57 |
| Northwest region | 9.2 | 13 |
| Northeast region | 2.8 | 4 |
| Southeast region | 6.8 | 10 |
| Southwest region | 4.6 | 8 |
| Total | 100.0% | 170 |
The percentage breakdown of the contribution of our retail formats (including the Costco membership warehouses) and restaurants to total sales is set forth below for each of the three years ended December 31, 2002.
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 |
| Comercial Mexicana | 51.3% | 46.5% | 40.0% |
| Bodega | 13.1 | 13.9 | 14.9 |
| Mega | 17.8 | 19.8 | 22.6 |
| Sumesa | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.3 |
| Costco | 14.3 | 16.1 | 18.5 |
| Restaurantes California | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.5 |
| Miscellaneous Income | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| Total | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% |
Except for Sumesa stores, which offer primarily food items, stores operated by us offer a combination of food and non-food items. Management classifies our sales into four main product lines. The percentage contribution to total sales of each of these product lines is set forth below for each of the three years ended December 31, 2000, 2001 and 2002.
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 |
| Perishables | 26.0% | 25.4% | 26.1% |
| Groceries | 37.3 | 38.0 | 38.8 |
| General Merchandise | 25.2 | 25.3 | 24.7 |
| Clothing | 11.5 | 11.3 | 10.4 |
| Total | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% |
Our management believes that in recent years Mexican consumers have increasingly preferred stores that offer a combination of the wide variety of food items carried by conventional supermarkets as well as a variety of non-food items, such as general merchandise, clothing, household items and home improvement products. In response to this change in consumer preferences, our newer stores offer expanded perishable departments, prepared foods, tortilla presses and bakery goods as well as wider selections of health, beauty and pharmaceutical products.
Multiple Format Strategy. We conduct retail operations through our five retailing store formats: Comercial Mexicana, Bodega, Mega, Sumesa and Costco membership warehouses (through the Costco Mexico joint venture). Through these formats, we are able to target nearly all the population segments in Mexico City and the other areas, which we serve.
In opening new stores, we select the type of retail store and offers the merchandise and service mix which we consider most appropriate for each location's anticipated customer base. We determine a location's anticipated customer base by referring to a number of factors, including the current and expected future population density, income levels and competitive conditions surrounding that location. Decisions with respect to opening new Costco warehouses are made by the Costco Mexico joint venture.
We believe, based on changing demographics and competitive characteristics of the location surrounding an established store, in changing the retailing format of our retail sites when appropriate. For example, in 2001 three Comercial Mexicana were converted into a Mega and another five were converted into Bodega and in 2002 we converted one Comercial Mexicana into a Mega and one Bodega into a Comercial Mexicana. In addition, since acquiring the Sumesa chain in 1981, we have converted six Sumesa stores into other formats. The conversion costs typically ranged from U.S.$2.1 million to U.S.$5.0 million per unit, averaging approximately U.S.$3.1 million per unit.
While we currently expect to continue using our five retailing formats, we may experiment with additional formats in the future.
Retail Store Formats
We currently operate stores in the five retail formats discussed below.
Combination Supermarket/General Merchandise Stores
Comercial Mexicana. At December 31, 2002, we operated 71 Comercial Mexicana stores, including 19 in the Mexico City metropolitan area, 30 in the central region (including Guadalajara), 9 in the Northwest region (including Tijuana), 2 in the Northeast region, 5 in the Southeast region and 6 in the Southwest region. Comercial Mexicana stores are targeted at middle and upper-income customers.
Comercial Mexicana stores carry an extensive line of food items and non-food items. Food items include meats, poultry, fish, fresh fruits and vegetables, dairy products, baked goods, frozen goods, canned goods, prepared foods, delicatessen, wines and liquors and imported foods. Non-food items include men's, women's and children's clothing and shoes, paper products, office supplies, books and magazines, health and beauty products, garden supplies, automotive supplies, photographic supplies, electric appliances, sporting goods, toys and gifts and numerous household items. All Comercial Mexicanas have one or more specialty departments, such as a bakery, tortilla press or video rental shop. Most Comercial Mexicana stores have pharmacies offering prescription and non-prescription medications. A typical Comercial Mexicana offers more than 55,000 products.
Most Comercial Mexicana stores are located in neighborhood shopping centers. Comercial Mexicana stores require large parking lots and access to roads to allow customers to drive to the stores.
Comercial Mexicana stores offer, at competitive prices, locally and nationally advertised and distributed brands of merchandise, together with certain food items, general merchandise and clothing product lines which are sold under our own private label names. Comercial Mexicana stores incorporate merchandising techniques, such as good lighting, wider-than-usual aisles and store layouts, which are designed to encourage greater spending per customer. All Comercial Mexicana stores are identified by an easily recognizable pelican logo.
Comercial Mexicana remodeling generally involves the installation of new services, lighting, decorations, freezers and refrigerators and automated check-out counters, as well as the replacement of fixtures, painting and necessary repairs and changes in the store layout which are intended to make the stores more attractive to customers. At the same time, the store systems are upgraded to improve operating efficiencies and allow the introduction of new services. In 2000, 2001 and 2002, we remodeled three Comercial Mexicana and four for both years 2001 and 2002.
Comercial Mexicana stores generally range in size from approximately 43,000 to 107,000 square feet of selling area, with an average of approximately 68,000 square feet. Comercial Mexicana stores employed 10,566 individuals at December 31, 2002.
Comercial Mexicana stores have experienced a decline in the number of customers in the last three years. The Company believes this is mainly a result of our conversion of eight Comercial Mexicanas into Bodegas or Megas in 2000 and 2001, and increased competition in the market. We have developed several strategies in response to these developments, including reorganization of the Comercial Mexicana employee structure, construction of new a distribution center servicing all store formats, including Comercial Mexicana, and the institution of a new pricing strategy of low prices instead of one-time promotionsand discounts.
Bodega. At December 31, 2002, we operated 34 Bodegas, of which 25 were located in Mexico City and its surrounding suburbs, seven were located in the Central region (including one store in Guadalajara), one was located in the Southeast region and one in the Southwest region. During 2002, we opened one Bodega in the Central Region. Bodegas target lower-income customers.
Bodegas are warehouse stores, which offer more than 30,000 products, mainly food items, pharmaceutical items and general merchandise of the type sold in Comercial Mexicana stores (but with less selection in terms of brands and sizes of items offered).
Bodegas have lower operating costs as a percentage of sales than those of Comercial Mexicana stores. Lower operating costs are obtained primarily because Bodegas use less advertising and a lower level of customer service, fewer amenities, less decoration and reduced storage costs (because items are stocked on display on the sales floor). In addition, Bodegas have fewer promotions and product introductions. Most of the Bodegas have a tortilla press, a bakery and/or other specialty department. Because their customers generally do not have cars, Bodegas are within walking distance of residential areas or accessible by public transportation. Bodegas also are identified by the same easily recognizable pelican logo as Comercial Mexicana stores.
Bodegas range in size from approximately 24,000 to 65,000 square feet of selling area, with an average of approximately 50,600 square feet. Bodegas employed 4,366 individuals at December 31, 2002.
Mega. Under the Mega format, we currently operate our largest combination stores. As of December 31, 2002, we operated 27 Megas, including 14 in Mexico City, 10 in the Central Region, 2 in the North and one in the South Region. The Mega targets a broad range of economic groups.
We introduced the Mega format in 1993 to take advantage of the perceived potential of, and as a competitive response to, the supercenter and hypermarket formats which had begun to appear in Mexico. Prices in Megas are generally lower than those in Comercial Mexicana stores, but not as low as in Bodegas. Megas carry an array of items, which is broader than that offered in Comercial Mexicana stores, offering approximately 60,000 products. The different types of merchandise carried by Megas are separated into distinct areas or departments. Each Mega contains a bakery, a pharmacy and other complementary services operated by us, just as in Comercial Mexicana stores. In addition, Megas contain separate specialty retail facilities leased to and operated by third-party tenants, such as banks, key makers, jewelry shops, shoe repair shops, photo developers and optical centers. Megas contain a wide center aisle that, in connection with the location of most perishables and groceries at the rear of the store, is intended to draw customers into the store past special advertising displays, as well as past the clothing and general merchandise areas.
Megas generally range in size from 110,000 to 140,000 square feet selling area, with an average of approximately 120,000. Megas employed 6,295 individuals at December 31, 2002.
The Company recently acquired Auchan’s operations in Mexico. By acquiring Auchan’s 5 stores, the Company absorbed a competitor, acquired stores with prime locations and a store format that should prove very successful in high density populated areas. The acquisition did not require the incurrence of additional debt, and will be paid in fixed installments through 2008. The payment of these installments is equivalent to opening one Mega per year (similar format as Auchan). With its 5 new stores, Comercial Mexicana has accelerated its growth in this successful format. Due to Auchan’s higher margin sales mix, Comercial Mexicana will be improving its margins in the coming months.
Supermarkets
Sumesa. At December 31, 2002, we had 17 Sumesa in operation. Except for two Sumesa in Cuernavaca, all Sumesa are located in Mexico City. Sumesa stores are targeted from upper to upper-middle income customers.
Sumesa are designed to serve their surrounding neighborhoods, which typically are densely populated. Sumesa are smaller in size than Comercial Mexicana stores and Bodegas. Developed as neighborhood stand-alone supermarkets, Sumesas emphasize sales of quality groceries and perishables and carry more than 8,000 products. All Sumesas include pharmacies, as well as bakeries and tortilla presses.
We intend to remodel the existing Sumesas to update their appearance and, to the extent that space at existing locations permits, to include specialty departments. In 1996, we added specialty departments to four Sumesas. We remodeled one Sumesa store in 1999 and two in 2000. All three remodeled stores are located in Mexico City.
Sumesas generally range in size from approximately 7,000 to 11,800 square feet of selling area, with an average of approximately 8,600 square feet. Sumesa employed 755 individuals at December 31, 2002. Since acquiring Sumesa in 1981, we have closed seven locations, primarily because we were unable to agree to the lease renewal terms and the last one in 2002 to convert it into a Restaurante California.
Membership Warehouse Stores
Costco Membership Warehouses. In June 1991, CCM and Costco formed a joint venture to develop the membership warehouse-style warehouses that are popular in the United States and Canada. The first Costco membership warehouse was opened in a suburb of Mexico City in February 1992. At December 31, 2002, the Costco Mexico joint venture was operating 21 Costco membership warehouses, five of which were located in Mexico City and its surrounding suburbs, eight were located in the Central Region (including one in Guadalajara), three were located in the Northwest Region, one was located in the Northeast Region, three in the Southeast Region and one in the Southwest Region.
Costco membership warehouses are self-service warehouse clubs, which offers members low prices on volume purchases of a limited selection of branded and private label products in a wide range of merchandise categories in order to produce rapid inventory turnover and high sales volumes. This rapid inventory turnover, combined with the operating efficiencies achieved by direct volume purchasing from manufacturers and no-frills merchandise displays, which enables Costco Mexico to operate profitably albeit at lower gross margins than traditional wholesalers, retailers or supermarkets. Costco membership warehouses carry a selection of approximately 3,500 local and imported items, together with general merchandise products, offering a limited selection in each product line and are generally located in easily accessible locations. All of the Costco membership warehouses offer bakeries and a selection of high quality perishables and meats.
Membership is limited to businesses and professionals and members of their families. A primary membership, including one affiliate membership, currently costs Ps.300.0 (approximately U.S.$28.86) per year with one additional membership and each additional affiliate membership costs Ps.100.0 (approximately U.S.$9.62) per year. Costco membership warehouses seek to meet the needs of business customers who might otherwise pay a premium for small purchases or who cannot otherwise obtain the full range of their product requirements from any single source. In addition, these business members often combine personal shopping with their business purchases.
Costco membership warehouses range in size from approximately 90,000 to 120,000 square feet of selling area, with an average of 100,000 square feet, and are designed with minimal amenities and decorations. Floor plans are designed for economical and efficient use of space and inventory control. Members push flatbed carts or large basket-style shopping carts through the warehouses, selecting products for their business or personal use, or for resale. Merchandise is generally offered in case, carton, or multiple-pack quantities or in single, jumbo-sized packages, and is displayed and stored in packing cartons on pallets and steel racks separated by extra-wide aisles. In response to the economic conditions in Mexico, in 1995 the Costco Mexico joint venture reduced the size of certain packages sold at the Costco membership warehouses and substituted imports with national products when available at an acceptable price and quality level. The standard no-frills facility designs, direct manufacturer purchasing and rapid inventory turnover, combined with extensive cost controls and low mark-ups, result in substantial savings to the customer as compared to most other traditional sources of merchandise. Costco membership warehouses employed 5,965 individuals at December 31, 2002.
The Costco Mexico joint venture is a corporation organized under the laws of Mexico and is owned equally by Costco and us. The joint venture is governed by a board of directors consisting of six members, three of whom are appointed by us (including the chairman of the board of the joint venture) and the other three are appointed by Costco. Pursuant to management agreements between Costco and the Costco Mexico joint venture, the joint venture is managed by officers appointed by Costco and approved by us. The management agreements may be terminated by either Costco or the Costco Mexico joint venture at any time, and any termination initiated by the joint venture must be approved by a majority (at least four directors consisting of two representatives of each of CCM and Costco) of its board of directors. The affirmative vote of a majority of the entire board of directors of the joint venture is required to approve certain significant decisions regarding the joint venture, including, among other things, certain revisions to the joint venture business plan, obligations or acquisitions of real estate or certain other fixed assets not otherwise provided for in the business plan, the removal of any of the management personnel appointed by Costco and certain transfers of ownership interests in the joint venture. In addition, the affirmative vote of both members of a two-person executive committee consisting of the chief executive officers of Costco and us is required to approve certain obligations not otherwise provided for in the business plan and other significant decisions regarding the joint venture which are not specially reserved for the board of directors.
Costco and we as determined from time to time by each party share the funding requirements of the joint venture. Each of Costco and CCM contributed U.S.$10.0 million and U.S.$28.5 million in 2000 and 2001 respectively. In the event that either party defaults on its obligations to provide its portion of the funding for the joint venture, the other party, at its option, may, among other things, exercise its right to buy out the defaulting party's interest at fair market value. The joint venture agreement contains certain limitations on competition in the Price Club-style warehouse format by Costco and us. The joint venture has duration of 99 years, ending 2090. However, the joint venture agreement may be terminated and the joint venture dissolved, (i) by mutual agreement of Costco and us, and (ii) upon a sale by either party of its entire interest in the joint venture by written agreement. We or Costco may purchase the other party's interest in the joint venture at a price determined by reference to the fair market value of that interest in the event that the other party (i) fails to provide its portion of the financing to the joint venture, (ii) fails to provide or maintain and guarantee pursuant to the joint venture agreement, (iii) transfers its interest to an unaffiliated third party without the consent of the board of directors of the joint venture, (iv) is unable to resolve with the other party within a prescribed period a deadlock of the board of directors, (v) is in default of its obligations under the joint venture agreement, (vi) is insolvent or bankrupt, or (vii) undergoes a change of control.
Marketing
We seek to attract customers to our store by emphasizing customer service, offering a wide selection of private label goods, facilitating purchase by customers through our own "captive" credit card, vouchers for payment, and a lay-away system under which customers can purchase general merchandise by agreed-upon partial payments and providing customers credit in connection with purchases of big-ticket items. Another marketing initiative includes promotions every Wednesday on fresh fruit and vegetables at Comercial Mexicana, Bodega and Mega stores, which has helped make Wednesday one of the busiest days of the week in our stores. We intend to maintain advertising expenditures in 2003 substantially in line with the amount spent in 2002, which was 1.3 % of our total sales.
We emphasize customer service by (i) offering the product and service mix that we believe customers find most appealing, (ii) maintaining clear, well-lit stores with attractive, modern decor, (iii) training employees to be courteous and helpful, (iv) changing the mix of products to include a variety of imported goods and (v) in recent years, by offering butcher's shops, bakeries, pharmacies, tortilla presses and other specialty departments. Many stores have electric carts to enable elderly or disabled individuals to shop without assistance and shopping carts with infant seats to allow parents to shop with young children. The specialty departments, such as the butcher's shops and bakeries, offer products and individual service comparable to those offered in independent specialty stores. In addition, all stores with bar-code scanners have price verifiers located conveniently throughout the stores to allow customers to check the prices on goods. See "Information Systems."
In recent years, we have begun to emphasize our own private label merchandise, including specialty products prepared by us (such as baked goods, tortillas and prepared foods), and currently offer approximately 419 private label products, principally groceries. In 1999, we introduced a line of generic medicines under the "Farmacom" name, which comply fully with the Ministry of Health regulations. On December 31, 2002 we offered over 150 medicines under this brand name. In addition, we offer private label men's, women's and children's clothing, household, automotive and gardening products. Each of our private label brands reflects a special image and delivers high quality merchandise at prices lower than brand name products. Sales of private label products as percentage of total sales were 11.5% en 2000 and 11.2% en 2001and 11.0% in 2002. Our margins on private label products are similar to those on brand name products, although prices on private label products are lower to the consumer.
Our store sales are paid in either cash, through credit or with vouchers. Credit card terminals are installed at checkout counters in all of our stores (including all Costco membership warehouses). We have our own captive credit card under the name "Comercial Mexicana," which can be used only for purchases at our stores (including Costco membership warehouses). The Comercial Mexicana credit cards are issued, and Banco Nacional de Mexico, S.A., or Banamex extends credit under such cards. In addition, we offer our customers the option to acquire certain big-ticket items on credit through an in-store program known as Credicomer. This program, offered with Banco BBV- Bancomer S.A., or BBV- Bancomer, does not require a down payment and may be paid over a period to 12 months. BBV-Bancomer extends the credit and assumes 100% of the credit risk, and we receive an amount equal to the purchase price from BBV- Bancomer by the end of that same business day. We also established a lay-away system under which customers can purchase general merchandise by paying through installments, without interest. We believe that our relationships and discount arrangements with credit-issuing banks are the best in the market. The vouchers are issued by us and by certain independent companies, and are accepted in all of our stores except for the Costco membership warehouses. Employers distribute vouchers to their employees as a tax-advantaged part of the employee's compensation. The vouchers issued by us are sold at a discount to third party employers and are, in effect, prepaid sales. The vouchers issued by independent companies are honored by us and then collected and presented (usually between one and seven days) to the issuing company for payment. In 2002 we also introduced our "Thirteen Month Interest-Free" promotion which offers customers thirteen months of interest-free credit for certain large purchases when they use participating credit cards. The Company and the supplier share the cost of the program.
As part of our marketing strategy, we promote our stores and the merchandising and services which they offer. Our advertising strategy and campaigns focus on communicating the image of our stores, particularly Comercial Mexicana stores, as being newer, cleaner stores, which offer superior customer service. In addition, advertising is used to publicize the merchandise carried in our stores. We used third-party advertising agencies to formulate and implement our advertising campaigns. The single largest advertising medium used by us is radio, but we also advertise on television and through newspapers and promotional flyers, as well as in our stores at the point of sale. We employ cooperative advertising with suppliers and suppliers participate in special programs with us, particularly in connection with new store openings. Each July, Comercial Mexicana, Bodega and Mega stores run the "Julio Regalado" special promotion to increase sales for that month.
The Costco Mexico joint venture does not generally use media advertising, except newspaper announcements of new Costco membership warehouse openings. When a new warehouse is opened, the Costco Mexico joint venture's marketing efforts include canvassing businesses in the area by marketing teams, and direct mailings to potential members in the area.
Distribution
We currently operate a 377,000 square foot distribution center in Mexico City. We rent a distribution facility of 417,000 square feet located in Mexico City, which we use to distribute primarily private label products and imported merchandise. Merchandise is shipped from the distribution centers to our retail stores primarily by independent shipping companies as well as Company-owned trucks. In 1997, we also opened a 538,000 square foot distribution center for Costco Mexico operations.
Approximately 20% of all goods purchased by us are supplied from the distribution centers operated by us. In the Costco Mexico joint venture, approximately 75% of all the merchandise is supplied from the distribution center. Suppliers and independent distributors directly to our stores deliver the remaining products. We supply some goods through our own distribution system rather than with direct deliveries from suppliers and independent distributors in order to take advantage of quantity discounts for certain products and, in the case of other products, to assure an adequate source of supply.
The Company will be completing a new Distribution Center ("DC") by August 2003 that we started constructing on Third Quarter 2002. The DC will have an storage capacity of 538,196 square feet. The center will increase the Company’s storage capacity by 160.5% from current levels, and will allow the Company to negotiate better prices with suppliers, which can place their products in one centralized location rather than in different locations. At present, 80% of the Company’s products are placed in each store, but with the new DC, 80% of all the Company’s products will be delivered to centralized locations. Suppliers have found it difficult to supply many of the cities in which the Company has stores with the same degree of efficiency than the stores located in Mexico City. The Company believed that this inefficiency has been a cause for certain amount of customer dissatisfaction in its stores located in the interior of the country (due to stock outs of products with higher rotations), and with the implementation of its new distribution strategy the Company will reduce stock outs and thereby increase customer satisfaction and sales in those stores.
Information Systems
We have placed special emphasis in recent years on the development of our management information system, particularly a unitary inventory control system that allows us to track sales, flow and turnover of specific product lines or items. The unitary inventory control system has been installed in all Comercial Mexicana stores, Bodegas and Megas and we plan to implement it in all of our units. As a part of this system, these stores are linked through a common computer network that facilitates the flow of information through fiber optic communications among the stores and to our management. This system provides us with information which enables us to (i) optimize inventory levels by identifying products with low sales volumes and by maintaining perpetual inventory booking, (ii) minimize shrinkage, (iii) reduce out-of-stock products, (iv) allow our buyers to negotiate more effectively with suppliers and (v) otherwise improve operating efficiency. This system is currently being used with all of the suppliers that supply our stores. Related projects have focused on introducing advanced computer technology to the stores (other than, to date, most Sumesas), particularly at the point of sale, and have included the installation of improved cash registers with bar-code scanner systems and electronic scales, state-of-the-art credit card and debit card approval systems to track sales and reduce the check-out time for customers, and, in the stores, state of the art point of sale computers which provide the customers additional information regarding the items being purchased and the relevant promotions and savings, as well as equipping stores with portable scanners to expedite the process of checking shipments from suppliers and to aid in price audits and taking inventory. Costco membership warehouses are linked, and transmit similar information, by satellite to Costco in San Diego, California and Seattle, Washington. Such linkage and transmission, in turn, provide us with information on the operations of Costco membership warehouses.
Capital expenditures for our information systems were Ps.22.2 million in 2000, Ps.21.4 million in 2001 and Ps.15.4 million in 2002.
New Initiatives
"Low Prices" Pricing Strategy. For several years, the Company based its pricing strategy cyclical promotions and discounts offered from time-to-time. This strategy proved successful in a market with high inflation rates. As prices changed often, consumers did not have the opportunity of comparing prices among different retailers.
As the result of the recent decrease in inflation, among other things, the Company has moved away from this strategy toward a strategy of offering consistently low prices, retaining only the most popular promotions, including the "Julio Regalado", in order to attract customer traffic. The new pricing strategy was fully implemented in August 2002.
Since the implementation of the "low prices" strategy, the Company has experienced a drop in number of customers and [tickets] per customer, but key ratios appear to be improving. The Company believes the new pricing strategy will prove successful.
Food Voucher Program. In the fourth quarter of 2002 the Company obtained an important voucher contract from the Government of Mexico City, for a nominal amount of aproximately U.S.$140 million and serving approximately 300,000 local government employees. Pursuant to this contract, the Company offers all program participants a 22.2% discount on all merchandise. The Company believes this contract will result in the growth of our customer base. Also, voucher holders purchase additional full-price items at an average 10% more than their voucher value. The Company recognized an account receivable and a deferred revenue of approximately US$ 109 million. The revenue is recognized when the customers purchases merchandise using the vouchers. As of December 31, 2002, the recognized revenue of this transaction reached US$ 62 million.
Acquisition of Auchan’s Mexican Operations. In February 2003, the Company acquired the Mexican operations of Auchan, consisting of five hypermarket stores located in the central region of Mexico. The Company now operates these stores under the Mega format. The Company will pay a net present value of approximately U.S.$91.0 million in interest free payments over a five-year period.
With these new stores in Mexico, it is the Group’s intention to keep maintaining our long lasted position as the second largest retailer in the country. At the same time, we are buying an international competitor that during its operational time in our country had the economic resources to grow by itself or through the acquisition of medium and large companies similar to ours.
This acquisition appoints directly to the Company’s strategy to focus on large areas like Megas, which is a format with excellent image and acceptance among Mexican customers for its service, convenient locations, nice atmosphere, variety of products and additional services. Actually, we already have converted these stores into Megas.
Additionally, Auchan stores are very well located, two of them are in Mexico City and two are in the metropolitan area, where nowadays is very complicated to get suitable land to build department stores. Nevertheless we consider there is a high potential market in these zones that has not been reached due to the lack of available land and to the complicated authorization process from local authorities that have made it difficult to open new facilities. The fifth store in Puebla, is also well located.
Auchan has an important commercial area at the stores leased and operated to third parties, which is very important since it gives our clients additional services as beauty parlors, banks, dry-cleaners, boutiques etc. that have always been part of Mega’s strategy. With this important addition we would increase approximately 495,140 square feet our present commercial area representing an increase of 37.0% on this concept.
As a result, we foresee this year an increase of sales of approximately 4.8% and 5.0% of floor sales attributable to these new stores.
This operation will not require additional debt since it will be paid with the Company’s five years cash flow. Actually, using those resources from Auchan’s operations and from third parties leasing at the operating commercial stores we may be able to pay the stores in the same period.
In connection with the acquisition, the Company expects the following:
- 4.8% increase in annual sales
- 5.0% increase in sales area
- 37.0% increase in commercial centers area
- 9.0% EBITDA growth
Restaurants
At December 31, 2002, we had 55 Restaurantes California located in 16 cities in Mexico (30 of which are located in the Mexico City metropolitan area), with an average seating capacity of 222 seats per restaurant. Restaurantes California focus on middle- through upper-income customers and tourists.
In 2000 we opened eight Restaurantes California, in 2001, we opened 4 Restaurantes California and in 2002 we opened five Restaurantes California. We intend to open six new Restaurantes California and remodel two additional units by the end of 2003. Our goal is to increase the number of Restaurantes California throughout Mexico.
Restaurantes California are family-style restaurants serving a wide variety of Mexican and continental cuisines for breakfast, lunch and dinner. These restaurants emphasize high quality, homemade-style food with fast service at low prices, with an average lunch costing less than Ps.85.00 (approximately U.S.$8.0).
Meals at Restaurantes California are prepared fresh when ordered. To differentiate ourselves from our competitors, each Restaurante California also has a buffet and salad bar, and we emphasize sales of buffet-style food, and in some stores "super buffet," which generally have higher gross margins. The buffet sales in relation to total restaurant sales have increased from 54.0% for 2000, 56.3% in 2001 and 57.0% in 2002. Restaurantes California are designed and built to a standardized format and compete on the basis of their high-quality food and service, cleanliness, attractive architecture and decorations, hand-painted dishes, colorful menus and innovative promotions (such as free buffets for children accompanied by adult and the "Birthdays Free" campaign).
Restaurantes California have traditionally been located in commercial areas near a Comercial Mexicana store, but are increasingly being operated on a stand-alone basis. In choosing the sites for Restaurantes California, our real estate professionals consider criteria similar to those used in selecting store sites. Suppliers deliver all products used in the operation of Restaurantes California directly to the restaurants. Restaurantes California generally do not use media advertising. At December 31, 2002, Restaurantes California had 2,799 employees.
Suppliers
We purchase the products frequently carried or used by our stores and restaurants from more than 6,050 suppliers. No single supplier or group of related suppliers’ accounts for more than 2.8% of the total products purchased by us. Our management believes that the sources and availability of materials for our retail store and restaurant operations are adequate and will continue to be so for the foreseeable future.
Certain suppliers prepare items for us for sale under our private label brand names, and expect that the source and availability of private label products will be adequate in the foreseeable future. We have not experienced any difficulty in obtaining the types or quantities of the merchandise we require on a timely basis and believe that, if any of our current sources of supply were to become unavailable, alternative sources could be obtained without any material disruption of business.
We maintain a centralized purchasing department that specializes in perishables, groceries, clothing and other merchandise through four principal groups. One group within the purchasing department is responsible for the Comercial Mexicana stores, Megas, Bodegas and Sumesas. A second group is responsible for purchasing the products required by Restaurantes California. A third group, consisting of two separate teams of buyers for Costco membership warehouses, is responsible for determining and purchasing the items carried in the Costco membership warehouses. One Costco Mexico purchasing team is located in Mexico and is responsible for purchasing domestic products. The other Costco Mexico purchasing team is located in San Diego, California, operating with the support of Costco. The separate groups of buyers allow each group to focus on the needs of the target customers for the retailing store formats serviced by that group of buyers. These purchasing groups coordinate with one another, sharing information on suppliers and the terms and conditions on products offered by suppliers. The buyers determine the products that will be stocked in our stores and are responsible for maintaining our relationships with our suppliers and negotiating the prices of all goods stocked in our stores and products required by our restaurants. The centralized purchasing department orders approximately 80% of the goods stocked in our stores and most of the balance is ordered by store managers pursuant to the arrangements (including prices) with suppliers negotiated by the central purchasing department.
We believe that communication through our information systems have allowed us to negotiate more effectively with suppliers and that we conduct business with our suppliers on terms which are not less favorable than those generally available in the retail industry. Domestic suppliers are paid in Pesos on terms that vary with the product being purchased. Foreign suppliers are paid in foreign currencies, primarily U.S. dollars.
In 2000, 2001 and 2002 approximately 16.9%, 16.5%and 17.0% respectively, of our sales consisted of products imported from outside of Mexico. In addition, we sell certain imported products, which we acquire, at prices denominated in Pesos, from multinational corporations, distributors and wholesalers in Mexico.
Competition
The retail industry in Mexico is highly competitive and is characterized by high inventory turnover and small profit margins as a percentage of sales. Earnings primarily depend upon the maintenance of high per-store sales volumes, efficient product purchasing and distribution and cost-effective store operations. Advertising and promotional expenses that are necessary to maintain our competitive position in our major markets affect margins at our stores. We compete with numerous local companies and regional and national supermarket and self-service store chains, including Gigante and Soriana, as well as small family-owned neighborhood stores and street markets, in each region in which we do business. In addition, certain major United States and international retailers have established joint ventures with Mexican companies or have acquired the majority of shares to control businesses which compete with our stores (for example, Wal-Mart Stores, Inc., or Wal-Mart, controls Walmex). The Costco membership warehouses compete with Sam's Club, a self-service warehouse owned by Walmex, and our hypermarkets and other stores face competition from Carrefour. We expect that other United States and international retailers may enter the market in Mexico in the future either through joint ventures or directly. In addition, certain of our stores, which are located in the same shopping areas, compete with each other. We believe that our principal competitive factors for our stores are location, price, cleanliness, promotion, customer service and quality of merchandise. See "Item 3 Key Information Risk Factors Factors Relating to the Company Competition."
In 2002, we were one of the largest retail companies in Mexico as measured by net sales. We have a significant presence in the Mexico City metropolitan area and the Central Region, where approximately 76.1% of the selling area of our stores were located as of December 31, 2002.
The restaurant business in Mexico is also highly competitive. Restaurantes California compete with numerous regional and national fast-food restaurant chains, local restaurants and prepared food establishments and street markets. In addition, certain United States fast-food restaurant chains (such as McDonalds, Burger King, Kentucky Fried Chicken, Dominos Pizza and Pizza Hut) have opened restaurants in Mexico. We believe that Restaurantes California compete on the basis of high-quality food, fast service, cleanliness, attractive architecture and decoration and innovative promotion.
Government Regulation
Aspects of the retail restaurant business, including our Restaurantes California operations, are subject to regulation directly or indirectly by various Mexican federal, state and local governmental agencies. The most significant of these agencies are theSecretaría de Economia, or the Ministry of Economy, and theSecretaría de Salud, or Ministry of Health, of Mexico.
The Ministry of Economy regulates the prices at which we can sell some medicines. The Ministry of Economy also verifies that all imported products have a label in Spanish specifying the products origin and ingredients and the company importing the product. See "Item 3 Key Information Risk Factors Price Controls Relating to Certain of Our Products."
The Ministry of Health establishes minimum standards for cleanliness of our stores and restaurants. We believe that we are in compliance in all material respects with the regulations of the Ministry of Economy and that our operations meet or exceed all requirements imposed by the Ministry of Health.
We maintain licenses, such as licenses to sell liquor, which are granted by governmental agencies and which we consider important to our business.
Our compliance with Mexican federal, state and local provisions that regulate the discharge of materials into the environment has not had and is not expected to have a material effect upon our capital expenditures, earnings or competitive position.
Trademarks
We own and use various trademarks in our business, the most important being "Comercial Mexicana," "Bodega Comercial Mexicana," "Sumesa," "Mega Comercial Mexicana," "Restaurantes California," and the pelican symbol identified with our stores. In addition, the Costco Mexico joint venture has a license from Costco to use in Mexico the service marks "Price Club", "Price Costco" and "Costco". We actively protect our intellectual property rights.
Organizational Structure
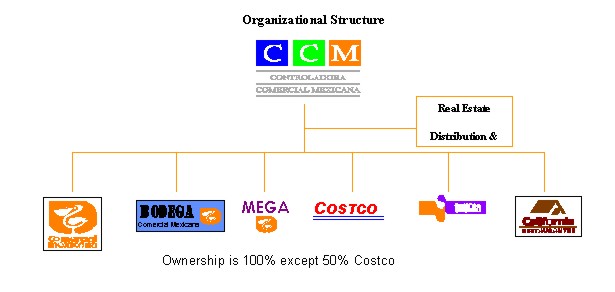
Following is a list of our significant subsidiaries, all of which are incorporated in Mexico:
| | Activity as of December 31, 2002 | Percentage Ownership as of December 31, 2002 |
| Subsidiary holding companies: |
| Comercial Mexicana, S. A. de C.V. | Operate a chain of 132 stores. | 99 % |
| Super Mercados, S. A. de C. V. | Operate a chain of 17 stores. | 99 % |
| Restaurantes California, S.A. de C.V. | Operate a chain of 55 restaurants. | 99% |
| Costco de Mexico, S. A. de C. V. | Operate a chain of 21 membership warehouse stores | 50 % |
| Subsidiary real estate companies: | | |
| Real estate subsidiaries | Operate as a real estate group. | 99 % |
| Subsidiary service companies: | | |
| Subsidiary service companies | Operate as a services group. | 99 % |
The Company consolidates the accounts of all of its majority owned subsidiaries. See Note 2 of our Financial Statements.
The Company's investment in Costco Mexico meets the joint control criteria discussed in International Accounting Standard No. 31. Accordingly, we report under the proportionate consolidation method.
Property, Plant and Equipment
Our properties primarily consist of different store formats, restaurants and distribution centers, most of which are located in Mexico City. In addition, as of December 31, 2002, we had approximately 8.5 million square feet in land reserve. Our principal executive offices are located in Mexico City.
We currently operate a 377,000 square feet distribution center in Mexico City, and we expect to complete a new 538,196 square foot distribution center by August 2003. Since 1994, we have rented a distribution facility of 417,000 square feet located in Mexico City, which we use to distribute primarily private label products and imported merchandise. Merchandise is shipped from the distribution centers to our retail stores primarily by independent shipping companies as well as Company-owned trucks. The Costco Mexico joint venture operates a distribution center of 538,000 square feet for Costco Mexico operations.
We own, develop and lease real estate to support our operations and expansion plans. We continuously study potential new locations and make decisions regarding new stores and restaurant locations based on, among other things, the location's population, income demographics, traffic, public transportation, access to streets, zoning and other services and facilities. The Costco Mexico joint venture uses similar criteria to select suitable real estate for its operation.
On December 9, 2002 and January 1, 2003, we purchased 1,875,945 square feet of real estate located in the Querétaro region of Mexico from certain of our affiliates. We intend to use this property for future store openings in the different formats.
As of December 31, 2002, we owned approximately 77.5% of the land on which our stores are located, and own the land on which 34 of the 55 Restaurantes California are located. Substantially all of the remaining land on which our stores and restaurants are located is leased from independent third parties. Leases generally have a 10 to 15 year term, with one or more options to extend or renew. Approximately 85% of our stores and restaurants which lease land (representing 27% of our total stores and restaurants) have leases which will expire between 2000 and 2010. The lease agreements for the stores and restaurants generally provide for rent payments calculated as a percentage of monthly net sales, ranging from 1.5% to 2.5%, with a minimum guaranteed rental. Given the high cost of property in the Mexico City metropolitan area and the increased availability of leasehold interests, we intend to emphasize renting the properties on which we build new stores and restaurants.
The following table sets forth our owned and rented retail space by total selling area, selling area as percentage of total area and number of our stores at December 31, 2002.
| At December 31, 2002 |
| | Total Selling Area (in sq.ft.) | Percentage Total Area | Number of Stores |
| |
| Owned properties | 9,373,290 | 77.5% | 110 |
| Leased properties | 2,724,516 | 22.5% | 60 |
| Total | 12,097,806 | 100.0% | 170 |
The following table sets forth our owned and leased retail space by store format, number of stores and total area at December 31, 2002.
| At December 31, 2002 |
| Store Format | Owned | Leased | Total | Total Selling Area |
| |
| Comercial Mexicana | 43 | 28 | 71 | 4,796,986 |
| Bodega | 19 | 15 | 34 | 1,969,621 |
| Mega | 24 | 3 | 27 | 2,874,672 |
| Sumesa | 4 | 13 | 17 | 162,815 |
| Costco Mexico | 20 | 1 | 21 | 2,293,712 |
Our real estate subsidiaries have also engaged in the development of shopping centers in which Comercial Mexicana stores have participated as anchor tenants, with the remaining floor space being leased to third parties. Currently we have over 1,356 commercial tenants, with approximately 885,700 square feet under lease, from which we receive income.
Capital expenditures reflect our strategy of growth through expansion and acquisition as well as our emphasis on self-development and ownership of real estate, and on logistics and technology improvements. Continued capital spending in technology focusing on improved store operations, logistics, manufacturing procurement, category management, merchandising and buying practices, should reduce merchandising costs as a percent of sales. For fiscal 2003, we expect capital spending to be approximately Ps.1,238 million. We intend to use the combination of cash flow from operations, including reductions in working capital to finance capital expenditure requirements.
We have a land reserve of unimproved land for future development of approximately 7.8 million square feet the Mexico City metropolitan area and in the Central Region, and other cities in Mexico, which management expects will be sufficient for substantially all of our expansion plans for 2003 and 2004 whether economic conditions in Mexico continue to improve. Because it is increasingly difficult to locate, the larger plots of land suitable for store sites within Mexico City, we are increasingly looking at land outside of Mexico City, primarily in the suburbs of Mexico City and the Central Region.
Insurance
We maintain all risk and first loss insurance policies (including insurance for losses resulting from hurricanes and earthquakes) and business interruption insurance with an insurance value up to Ps.24.3 billion (calculated on the basis of the maximum foreseeable loss) with a maximum per claim of Ps.1.9 billion (calculated on the basis of the maximum foreseeable loss) per location, and a limit up to Ps.5.9 billion per event. The fixed assets at each of our locations are covered on a replacement cost of market value basis. We also maintain a transit insurance policy that protects against loss for shipment up to Ps.8.5 million per shipment. We maintain comprehensive liability insurance policies with an insured limit of up to Ps.300.0 million per event per location.
Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects
For an understanding of the significant factors that influenced our performance during the past three fiscal years, the following discussion should be read in conjunction with the audited consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto and the Cautionary Statement Concerning Forward-Looking Statements presented in this Annual Report. We intend for this discussion to provide you with information that will assist you in understanding our financial statements, the changes in certain key items in those financial statements from year to year, and the primary factors that accounted for those changes, as well as how certain accounting principles affect our financial statements. The discussion also provides information about the financial results of the various segments of our business so that you may better understand how those segments and their results affect the financial condition and results of operations of the Company as a whole.
Preparation of Financial Statements
Our Financial Statements have been prepared in accordance with Mexican GAAP, which differs in significant respects from U.S. GAAP. Note 17 to our Financial Statements provides a description of the relevant differences between Mexican GAAP and U.S. GAAP as they relate to us, and a reconciliation to U.S. GAAP of net income for the years ended December 31, 2000, 2001 and 2002 and stockholders’ equity as of December 31, 2001 and 2002.In addition to the other information in this annual report, investors should consider carefully the following discussion and the information set forth under "Key Information Risk Factors" in evaluating us and our business.
General
CCM is a Mexican company, which maintains its financial records in Pesos. Mexican GAAP requires that all financial information be presented in constant Pesos (having the same purchasing power for each period indicated taking into account inflation) as of the date of the most recent balance sheet. The presentation of financial information in constant Pesos is intended to recognize certain effects of inflation on the Financial Statements and to permit comparisons between comparable periods in comparable monetary units. The result of this adjustment is that growth rates between periods are stated in "real" terms, eliminating the general effects of inflation. Except where otherwise indicated, financial data for all periods in the Financial Statements and throughout this Annual Report have been restated in constant Pesos with purchasing power as of December 31, 2002. See Note 3 to the Financial Statements. References in this Annual Report to "real" amounts are to inflation-adjusted numbers and "nominal" amounts are to unadjusted numbers. Unless otherwise specified, all growth rates in the following discussion are stated in real terms.
Mexico experienced inflation in certain of the periods covered by the Financial Statements. In 2000, 2001 and 2002 the annual rates of inflation in Mexico, as measured by changes in NCPI, were 9.0%, 4.4% and 5.7%, respectively.
Bulletin B-10 requires us to restate non-monetary assets with the exception of inventories and fixed assets of non-Mexican origin, using the National Consumer Price Index (Indice Nacional de Precios al Consumidor), or NCPI. Inventories are stated at cost using the retail method, which is equivalent to replacement cost. The cost of sale is restated using methods that recognize the replacement cost of merchandise at the time of sale (last-in, first-out).
In accordance with Bulletin B-10 we are required to report, as a gain or loss on our net monetary position, the effects of inflation on our monetary assets and liabilities. This net amount reflects the gain or loss arising from holding net monetary liabilities or assets in an inflationary period because over time a monetary liability can be settled for units of less purchasing power whereas a monetary asset decreases in value in real terms.
All amounts in the following discussion include the operations of Restaurantes California and other operations (which represented in the aggregate approximately 1.5% of net sales for the year ended December 31, 2002).
Effects of Devaluation and Inflation
The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, the percentage that the Mexican Peso devalued or appreciated against the U.S. Dollar, the Mexican inflation rate, the U.S. inflation rate, the percentage that Mexican gross domestic product, or GDP, changed as compared to the previous year and the percentage change in the Mexican retail sector as compared to the previous year.
| Year ended December 31, |
| | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 |
| Devaluation (appreciation) of the Mexican Peso as compared to the U.S. Dollar (1) | 1.6% | (5.1)% | 13.5% |
| Mexican inflation rate (2) | 9.0 | 4.4 | 5.7 |
| U.S. inflation rate | 3.4 | 2.9 | 1.6 |
| Increase (decrease) in Mexican gross domestic product | 6.9 | (0.3) | 0.9 |
| Increase (decrease) in the Mexican retail sector (3) | 7.5 | 6.9 | (1.8) |
____________
(1) Based on changes in the Representative Rate, at the beginning of each period, which were as follows: Ps. 9.6500 per U.S. Dollar as of December 31, 2000; Ps.9.1600 per U.S. Dollar as of December 31, 2001 and Ps.10.395 per U.S. Dollar as of December 31, 2002.
(2) Based on changes in the NCPI from the previous period, as reported byBanco de México.
(3) As reported by the National Association of Self-service and Department Stores, or ANTAD.
The general condition of the Mexican economy, inflation and high interest rates have adversely affected, and may in the future adversely affect, our financial conditions and results of operations in the following manner.
Changes in exchange rates or in Mexico’s exchange control laws may hamper the ability of Comercial Mexicana to service its foreign currency debt.
While the Mexican Government does not currently restrict the ability of Mexican companies or individuals to convert pesos into dollars or other currencies, in the future, the Mexican Government could impose a restrictive exchange control policy, as it has done in the past. We cannot assure you that the Mexican Government will maintain its current policies with regard to the peso or that the pesos’s value will not fluctuate significantly in the future. The peso has been subject to significant devaluations against the US Dollar in the past and maybe subjects to significant fluctuations in the future. Mexican Government policies affecting the value of the Peso could prevent us from paying our foreign currency obligations. As of December 31, 2002, approximately U.S.$129.6 million of our outstanding indebtedness was denominated in U.S. Dollars. See "Liquidity and Capital Resources."
Inflation also affects consumer demand, our ability to raise prices, supplier price, employment rates, competitive factors and consumer purchasing power, in addition to the extent inflation exceeds our price increases, our prices and revenues will be adversely affected in "real" terms; and if the rate of Mexican inflation exceeds the rate of devaluation of the Peso against the U.S. Dollar, our U.S. Dollar-denominated sales will decrease in relative terms when stated in constant Pesos.
See "Results of Operations," "Comparison of Fiscal Years Ended December 31, 2002 and December 31, 2001 Net Sales" and "Integral Results of Financing," "Liquidity and Capital Resources" and "Recent Operating Results." See also "Item 3. Key Information Risk Factors Risks Factors Relating to Mexico Mexican Governmental, Political, Economic and Social Factors" and "Currency Fluctuations and Exchange Controls" and "Item 10. Other InformationExchange Controls and Restrictions on Foreign Investment."
Critical Accounting Policies
We prepare our consolidated financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in Mexico, which requires management to make certain estimates and apply judgment. We base our estimates and judgments on historical experience, current trends and other factors that management believes to be important at the time the consolidated financial statements are prepared. On a regular basis, management reviews our accounting policies and how they are applied and disclosed in our consolidated financial statements. We continually evaluate the information used to make these estimates as our business and the economic environment change.
While management believes that the historical experience, current trends and other factors considered support the preparation of our consolidated financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in Mexico, actual results could differ from our estimates, and such differences could be material.
Management believes that these following accounting policies include a higher degree of judgement and/or complexity and, thus, are considered to be critical accounting policies. The critical accounting policies discussed below are applicable to both of our business segments. Management has discussed the development and selection of our critical accounting policies with the Audit Committee of our Board of Directors and the Audit Committee has reviewed the Company’s disclosures relating to them.
Property, plant and equipment
Property, equipment and leasehold improvement are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation of buildings, equipment, and other depreciable assets is primarily determined using the straight-line method. Expenditures that substantially improve and/or increase the useful life of facilities or equipment are capitalized. Maintenance and repair costs are expensed as incurred. Gains and losses on retirements are included in income as they occur.
Property, equipment and leasehold improvement are evaluated for possible impairment on a specific asset basis or in groups of similar assets, as applicable, whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to estimate undiscounted future net cash flows to be generated by the asset. If the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its estimated future cash flows, an impairment loss is recognized for the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the asset. Assets to be disposed of are reported at the lower of the carrying amount or fair value less costs to sell, and depreciation ceases.
The key factors for property, equipment and leasehold improvement policy are the estimation of the useful lives of the Company’s various asset types, the election to primarily utilize the straight-line method for recording depreciation, management’s judgment regarding appropriate capitalization or expensing of costs related to fixed assets, and management’s determination regarding impairment of any Company asset or group of assets. The estimation of useful lives for fixed assets impacts the level of annual depreciation expense recorded. Utilization of the straight-line method for recording depreciation or any of the other acceptable methods for depreciating assets results in the same amount of depreciation over the life of an asset; however, the amount of annual depreciation expense and the resulting carrying amount of net property, equipment and leasehold improvement will vary significantly depending on the method elected. Management feels that the straight-line method results in the most accurate recognition of periodic depreciation expense for all the Company’s assets. Management’s evaluation of whether an expenditure related to property, equipment and leasehold improvement substantially improves and/or increases the useful life of an asset and is appropriately capitalized as an addition to the asset’s cost basis or is expensed as normal maintenance and repair expense also can significantly affect results of operations for a given period, as well as the Company’s financial position. Management has also evaluated any asset or group of assets for which potential impairment might exist and has determined that there are none requiring an impairment write-down. This process requires management s estimate of future cash flows generated by each asset or group of assets. For any instance where this evaluation process might indicate an impairment exists, the appropriate asset’s carrying values would be written down to fair value and the amount of the write-down would be charged against the results of continuing operations.
Inventories
Inventories are valued under the retail inventory method, or RIM. Under RIM, the valuation of inventories at cost and the resulting gross margins are calculated by applying a calculated cost-to retail ratio to the retail value of inventories. RIM is an averaging method that has been widely used in the retail industry due to its practicality. The use of RIM results in an inventory valuation at the lower of cost or market when markdowns are currently taken as a reduction of the retail value of inventories.
Inherent in the RIM calculation are certain significant management judgments and estimates including, among others, merchandise mark-ups, markdowns and shrinkage, which significantly impact the ending inventory valuation at cost as well as resulting gross margins. To reduce the potential for distortion in the valuation of inventory, the Company's RIM utilizes four different categories (Groceries, General Merchandise, Clothing and Perishables) divided into several sections or departments in which similar classes of merchandise inventories are valued under the same standards. Historically, we have rarely experienced significant distortion in the valuation of inventory. However, future changes in circumstances and inappropriate management's estimations could cause to the Company's inventory to be inappropriately valuated and as a consequence, the possible distortion would have to be charged against the cost of sales.
Revenue recognition
Our principle source of income is derived from sales to customers in the self-service supermarket/general merchandise stores. Revenue is recognized at the point of sale, except for the layaway transactions that are recognized when the customer satisfies all payment obligations and takes possession of the merchandise. Defective merchandise returned by customers is either returned to the supplier or is destroyed and reimbursement is sought from the supplier, which, in most of the cases accept our reimbursement claim.
Discounts provided to customers at the point of sale are recognized as a reduction in sales as the products are sold. We monitor our revenue recognition figures using a variety of tools. One of our most important tracking tools is the daily revenue reports received by the stores, which are reconciled with register reports and receipts. This information is gathered at the store level, then combined and reviewed in our central accounting department, in order to identify any possible distortion.
Accounting for income taxes
In the preparation of our consolidated Financial Statements we are required to estimate our expected income taxes. This process involves an estimation of our actual current tax and an assessment of temporary differences resulting from differing treatment of items for tax and accounting purposes. These differences result in deferred asset and liabilities, which are included within our consolidated balance sheet. We must then assess the likelihood that our deferred as assets will be recovered from future taxable income and to the extent we believe that recovery is not likely, we must establish a valuation allowance. To the extent we establish a valuation allowance or increase this allowance in a period, we must include a charge against the tax provision in the statement of operations.
Significant management judgment is required in determining our provision for income taxes, our deferred tax assets and liabilities and any valuation allowance recorded against our net deferred tax asset. The valuation allowance is based on our estimates of taxable income and the period over which our deferred tax asset will be recoverable. In the event that actual results differ from these estimates or we adjust these estimates in future periods we may need to establish an additional valuation allowance which could materially impact our financial position and results of operations.
Results of Operations
General
The following table sets forth income statement data for the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 as presented in our Financial Statements, expressed as a percentage of consolidated net sales.
| Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2002 (1) | 2001 (1) | 2000 (1) |
| Net sales | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Cost of sales | (80.4) | (81.0) | (80.9) |
| Gross profit | 19.6 | 19.0 | 19.1 |
| Operating expenses: | | | |
| Selling (net of depreciation and amortization) | (12.2) | (11.8) | (11.3) |
| Administrative (net of depreciation and amortization) | (2.2) | (2.1) | (2.4) |
| Depreciation and amortization | (2.3) | (2.1) | (1.9) |
| Total operating expenses | 16.7 | 15.9 | 15.6 |
| | | | |
| Operating income | 2.9 | 3.1 | 3.5 |
| Integral results of financing: | | | |
| Interest expense | (0.7) | (0.8) | (0.7) |
| Interest income | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Gain from repurchase of Senior Notes | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Foreign exchange loss, net | (0.7) | 0.1 | (0.2) |
| Gain from monetary position | 1.0 | 0.7 | 1.4 |
| Total integral results of financing | (0.2) | 0.0 | 0.7 |
| | | | |
| Other income (expense) and special item | 0.0 | (0.1) | (0.5) |
| Provisions for: | | | |
| Income tax and asset tax | 0.4 | (0.1) | (0.4) |
| Employees' profit sharing | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Deferred income taxes | (0.2) | (0.6) | (0.4) |
| Income before minority interest | 2.5 | 2.3 | 3.5 |
| Minority interest | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Net income | 2.5% | 2.3% | 3.5% |
___________________
(1) Columns may not add due to rounding.
Segment Disclosures
Our business is operated in three segments: (1) the CCM Group, which includes the Comercial Mexicana, Bodega and Mega supermarkets, and comprises our core business (2) the Costco Mexico Group, which operates Costco Mexico, our joint venture with Costco Wholesale Co., and (3) the Other Group, which includes Restaurantes California and our Sumesa stores. Operating decisions are made separately for Costco Mexico. Under Mexican GAAP, segment disclosure must be made in respect of net sales, revenues from external customers, depreciation and amortization, net income and certain balance sheet items. Information about our reportable segments is provided below.
| As of and for the year ended December 31, 2002 | | CCM Group | | Costco Mexico Group | | Other Group | | Eliminations | | Total |
| |
| Revenue from external customers | | Ps 24,893,276 | | Ps 11,868,009 | | Ps 1,226,031 | | Ps (5,934,005) | | Ps 32,053,311 |
| Inter-segment revenues | | 217,759 | | - | | - | | (217,759) | | - |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 598,456 | | 215,679 | | 18,474 | | (107,840) | | 724,769 |
| Interest expense | | 230,123 | | 16,254 | | 662 | | (8,127) | | 238,912 |
| Interest income | | 22,864 | | 30,141 | | 5,205 | | (15,071) | | 43,139 |
| Income taxes(1) | | 4,054 | | 142,556 | | (5,698) | | (71,278) | | 69,634 |
| Net income | | 583,113 | | 304,251 | | 53,578 | | (152,126) | | 788,816 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-lived assets | | Ps 13,119,578 | | Ps 4,315,179 | | Ps 514,006 | | Ps (2,157,590) | | Ps 15,791,173 |
| Significant liabilities | | 4,767,588 | | 1,550,724 | | 106,725 | | (775,362) | | 5,649,675 |
| Capital expenditures | | 468,033 | | 408,070 | | 70,351 | | (204,035) | | 742,419 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of and for the year ended December 31, 2001 | | CCM Group | | Costco Mexico Group | | Other Group | | Eliminations | | Total |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue from external customers | | Ps 28,137,898 | | Ps 11,244,842 | | Ps 1,187,275 | | Ps (5,622,421) | | Ps 34,947,594 |
| Inter-segment revenues | | 285,260 | | - | | - | | (285,260) | | - |
| Depreciation and Amortization | | 610,777 | | 190,326 | | 16,156 | | (95,163) | | 722,096 |
| Interest expense | | 261,546 | | 17,910 | | 1,257 | | (8,955) | | 271,758 |
| Interest income | | 34,433 | | 35,513 | | 6,523 | | (17,757) | | 58,712 |
| Income taxes(1) | | 194,083 | | 69,787 | | 37,785 | | (34,894) | | 266,761 |
| Net income | | 624,317 | | 306,748 | | 24,836 | | (153,374) | | 802,527 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-lived assets | | Ps 13,416,538 | | Ps 4,060,673 | | Ps 466,346 | | Ps (2,030,336) | | Ps 15,913,221 |
| Significant liabilities | | 4,550,847 | | 1,410,192 | | 123,991 | | (705,096) | | 5,379,934 |
| Capital expenditures | | 910,896 | | 447,405 | | 71,031 | | (223,702) | | 1,205,630 |
| As of and for the year ended December 31, 2000 | | CCM Group | | Costco Mexico Group | | Other Group | | Eliminations | | Total |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue from external customers | | Ps 28,774,261 | | Ps 9,941,048 | | Ps 1,138,066 | | Ps (4,970,523) | | Ps 34,882,852 |
| Inter-segment revenues | | 254,175 | | - | | - | | (254,175) | | - |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 596,579 | | 135,586 | | 14,650 | | (67,793) | | 679,022 |
| Interest expense | | 251,167 | | 15,553 | | 718 | | (7,776) | | 259,662 |
| Interest income | | 43,063 | | 18,943 | | 5,526 | | (9,471) | | 58,061 |
| Income taxes(1) | | 78,935 | | (19,333) | | 13,294 | | 9,666 | | 82,562 |
| Extraordinary gain | | 309 | | - | | - | | - | | 309 |
| Net income | | 983,335 | | 360,138 | | 52,974 | | (180,068) | | 1,216,379 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-lived assets | | Ps 13,481,300 | | Ps 3,616,273 | | Ps 125,924 | | Ps (1,808,136) | | Ps 15,415,361 |
| Significant liabilities | | 5,287,736 | | 1,334,590 | | 75,586 | | (667,295) | | 6,030,617 |
| Capital expenditures | | 1,051,021 | | 479,891 | | 91,698 | | (239,945) | | 1,382,665 |
______________________________
- Amounts include current and deferred income tax, asset tax and employee’s profit sharing.
For an understanding of the significant factors that influenced our performance during the past three fiscal years, the following discussion should be read in conjunction with the audited consolidated financial statements and the notes there to and the Cautionary Statement Concerning Forward-Looking Statements presented in this Annual Report. We intend for this discussion to provide you with information that will assist you in understanding our financial statements, the changes in certain key items in those financial statements from year to year, and the primary factors that accounted for those changes, as well as how certain accounting principles affect our financial statements. The discussion also provides information about the financial results of the various segments of our business so that you may better understand how those segments and their results affect the financial condition and results of operations of the Company as a whole.
Comparison of fiscal years ended December 31, 2002 and December 31, 2001 for CCM Group
At the end of 2002 the Company had 132 stores to 134 stores in 2001.
During 2002 the Company opened one Bodega and one Mega. Ten units were remodeled, one Comercial Mexicana was converted into Mega and one Bodega was converted into Comercial Mexicana. The retail sales area decreased 0.1% from approximately 9,654,949 square feet at the end of 2001 to 9,641,279 square feet at the end of 2002.
Net Sales. Net sales decreased 11.5% from Ps28,137.8 million in 2001 to Ps24,893.3 million during 2002. Comparative store sales are also referred as ’Same Store Sales’ within the retail industry decreased 13.1%.
This decrease was mainly due to a combination of the following factors:
- The first and most important was the change of price strategy we performed during 2002, from our well-known promotions and discounts to a permanent low prices campaign.
- The economy did not show any improvement during 2002 and a very conservative attitude from our clients who simply reduced consumption until the economy recovered.
- 2002 a stronger competition was observed in the Central zone of the country resulting in same store sales decrease.
With regards to our formats, the most affected was Comercial Mexicana. Mega and Bodega had practically a similar performance. We partially attribute this low performance of Comercial Mexicana stores to the fact that it is the format with the highest participation in the most economically affected zones in the country.
General merchandise sales as percentage were 29.6% in 2001 and 33.8% in 2002.
Total sales per square feet decreased 11.4% from Ps2,914.3 per square feet in 2001 to Ps2,581.9 per square feet in 2002. Net sales per operative employee decreased 14.4% from Ps1,369.6 thousand per operative employee in 2001 to Ps 1,172.7 thousand in 2002.
Cost of Sales. Cost of sales decreased 12.5% from Ps22,664.2 million in 2001 to Ps19,826.2 million in 2002 mostly due to the following factors;
- The change of price strategy we performed during 2002 was the most important reason for this reduction because the deflation in prices obtained with this change affected not only sales but also the cost of the good sold.
- Better negotiations with suppliers. The company has been working with a consulting firm in order to improve and make more efficient the purchasing process in the company.
- Better selection of high margin products as a consequence of an improvement in category management.
Gross Profit. The Company’s gross profit expressed as percentage of net sales was 20.4% in 2002 compared to 19.4% in 2001. This increase is due to the efficient change in the commercial strategy performed during the current year by the purchasing area, the improvement in the purchase procurement and also because of better internal practices.
Operating Selling and Administrative Expenses (’SG&A’ expenses). Total SG&A expenses decreased 5.3% from Ps4,611.4 million in 2001 to Ps4,367.8 million in 2002. Operating expenses expressed as percentage of net sales increased from 16.4% in 2001 to 17.5% in 2002 as a result of the sales reduction and with that the impossibility to have a better expense absorption in 2002.
- Selling expenses (net of depreciation and amortization) decreased 6.3% from Ps3,406.0 million in 2001 to Ps3,189.1 million in 2002, representing 12.1% of net sales in 2001 and 12.8% of net sales in 2002. Selling expenses include payroll, publicity, leasing and others. This decrease was mainly due to the downsize in the operations area. Previously, a deep analysis was conducted in order to evaluate all those areas subject to be reduced to avoid any possibility to affect customers service.
- Administrative expenses (net of depreciation and amortization) decrease 2.4% from Ps594.6 million in 2001 to Ps580.2 million in 2002, representing 2.1% of net sales during 2001 and 2.3% in 2002.
Depreciation and amortization expenses decreased 1.8% from Ps610.8 million during 2001 to Ps.598.5 million during 2002, representing 2.2% in 2001 and 2.4% in 2002 of net sales.This decrease was mainly due to the closing of stores during 2002.
Operating Income. As a result of the above, operating income decreased 21.4% from Ps862.2 million in 2001 to Ps699.3 million in 2002, representing 3.1% and 2.8% of net sales in 2001 and 2002, respectively.
Integral Results of Financing
- Decreased of the interest expense was 12.0% from Ps261.6 million in 2001 to Ps230.1 million in 2002. Weighted average effective interest rate on our debt was 7.4% during 2002 compared to 8.0% in 2001 (in both cases the amounts for withholding taxes are included).
- Interest income decreased 33.4% from Ps34.4 million in 2001 to Ps22.9 million in 2002. See’Cash Policy’
- During 2001 the Company recognized a forward exchange foreign gain of Ps17.5 million compared to Ps221.4 million loss in 2002 mainly due to the 13.5% peso devaluation compared to dollar during 2002.
- Gain from monetary position increased 25% from Ps223.5 million in 2001 to Ps279.3 million in 2002. This increase was mainly due to the higher inflation registered during the year compared to 2001.
Integral cost of financing had 320.4.% variation from Ps27.0 million loss in 2001 to Ps113.5 million loss in 2002 due to all those considerations already explained in the previous paragraphs.
Other (expense). Other expense was Ps8.0 million expense in 2001 and Ps8.5 million income in 2002. This variation was mainly due to the amortization in 2002 of the deferred revenue originated by the acquisition of companies with tax carryforwards.
Taxes and employees’ Profit Sharing. In 2002 the Company caused Ps16.5 million in asset taxes and Ps79.7 million in income taxes. Deferred taxes show 160.2% variation from Ps166.2 million loss in 2001 to Ps100.1 million gain in 2002.
As a result of the changes to the Income Tax Law approved on January 1, 2002, the income tax rate will be reduced annually beginning in 2003 until it reaches a nominal rate of 32% in 2005. The effect of this gradual reduction in the tax rate will be to reduce the deferred income tax liability by Ps239,269 in 2002, and increase net income by the same amount..
The Company’s provision for employees’ profit sharing payment was Ps1.2 million in 2001 compared to Ps7.9 million in 2002.
Minority Interest. Participation of minority stockholders in the subsidiaries profits and losses reflects that part of the subsidiaries’ operation losses and profits corresponding to third parties.
Net Profit. As a result, net profit decreased 6.6% from Ps624.3 million during 2001 to Ps583.1 million in 2002. Net profit as percentage of net sales was 2.2% during 2001 compared to 2.3% in 2002.
Comparison of fiscal years ended December 31, 2001 and December 31, 2000 for CCM Group.
As of December 31, 2001, we had 134 stores compared to 131 as of December 31, 2000.
In 2001, we opened one Comercial Mexicana store, one Bodega and three Megas. In addition, five of our retail stores were remodeled and eight Comercial Mexicana stores were converted into five Bodegas and three Mega hypermarkets. The total retail selling area increased 3.2% from 9,361,127 square feet in 2000 to 9,654,949 square feet at the end of 2001. See ’Item 4. - Information on the Company-History and Development of the Company’.
Net Sales. Net sales decreased 2.2% from Ps.28,774.3 in 2000 to Ps. 28,137.8 in 2001. Same store sales decreased 5.1% during 2001.
The Company’s net sales were influenced by an adverse economic environment which resulted in increased unemployment and decreased consumer demand, increased competition and the loss of the contract with the Mexico City government.
Non-food sales as percentage of net sales remained constant at 32.3% in 2000.
Sales per square feet decreased 5.2%, to Ps.2,914.3 per square foot in 2001, from Ps.3,073.8 in 2000. Net sales by operating employee increased 17.7% from Ps 1,163.2 thousand per employee in 2000 to Ps.1,369.6 thousand in 2001. This increase was mainly attributable to a reduction in headcount.
Cost of Sales. Cost of sales decreased 2.2%, from Ps.23,162.3 million in 2000 to Ps.22,664.2 million in 2001 mostly due to the decrease in sales.
Operating Selling and Administrative Expenses (’SG&A’ expenses). Total SG&A expenses increased 0.1%, from Ps.4,606.8 million in 2000 to Ps.4,611.4 million in 2001. Operating costs as a percentage of net sales increased from 16.0% in 2000 to 16.4% in 2001 as a result of salary increases that exceeded the rate of inflation.
- Selling expenses (net of depreciation and amortization) increased 2.4%, to Ps.3,406.0 million in 2001, from Ps.3,326.4 million in 2000, representing 12.1% of net sales in 2001 and 11.6% of net sales in 2000. Selling expenses include mainly salaries, advertising and rents. Selling expenses increased mainly as a result of salary increases and employee bonuses.
- Administrative expenses (net of depreciation and amortization) decreased 13.0%, to Ps.594.6 million in 2001, from Ps.683.8 million in 2000, representing 2.4% of net sales in 2000 and 2.1% of net sales in 2001. Administrative expenses decreased mainly as a result of reductions in salary expenses, which resulted from a reduction in administrative employees, leasing payments, energy and maintenance expenses.
Depreciation and amortization increased 2.4%, to Ps.610.8 million in 2001, from Ps.596.6 million in 2000, representing 2.1% of net sales in 2000 and 2.2% of net sales in 2001, as a result of the new store openings.
As a result of the above, operating income decreased 14.2%, to Ps.862.2million in 2001, from Ps.1,005.2 million in 2000, representing 3.1% and 3.5% of net sales in 2001 and 2000, respectively.
Integral Results of Financing. Interest expense increased 4.1%, to Ps.261.6 million in 2001, from Ps.251.2 million in 2000, mainly as a result of an increase in banking commissions payments we incurred in connection with our ’Seven Months Interest-Free’ promotion as well as the recognition of the interest expense of certain interest rate hedging activities. See ’Business Overview-Marketing’ and ’Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk’. The weighted average effective interest rate on our debt was 8.0% in 2001 compared to 9.0% in 2000 (including, in each case, additional amounts currently payable in respect of certain Mexican withholding taxes).
Interest income decreased 20.2%, to Ps.34.4 million in 2001, from Ps.43.4 million in 2000, despite the decrease in nominal interest rates. Such change was due primarily to better cash flow management. See ’Cash Policy’.
During 2001 we recognized foreign exchange gain of Ps.17.5 million compared to Ps.60.7 million foreign exchange loss in 2000, mainly due to 5.0% appreciation of peso against dollar in 2001 as compared to a 1.6% depreciation in 2000.
Gain from monetary position decreased 52.3% from Ps.453.6 million in 2000 to Ps.223.5 million in 2001 due mainly to a lower inflation rate of 4.4% in 2001 as compared to 8.9% in 2000.
As a result of the above, integral results of financing decreased 85.4% from Ps.185.1 million gain in 2000 to Ps.27.0 million loss in 2001.
Other (Expense). Other expenses decreased 94.0%, from Ps.134.4 million in 2000 to Ps.8.0 million in 2001. This decrease resulted from our sale of certain permanent investments.
Taxes and Employees’ Profit Sharing. In 2001, we caused Ps.11.5 million in asset tax and Ps.15.0 million in income tax as compared to Ps.122.5 million asset tax in 2000 and Ps.11.3 million in income tax in 2000.
Our provision for employees’ profit sharing payment was Ps.1.2 million in 2000 and 2001, representing 0.4% of profit before taxes in 2000 and 2001, as a result of the decrease in net income.
Minority Interest. Participation of minority stockholders in the subsidiaries profits and losses reflects that part of the subsidiaries’ operation losses and profits corresponding to third parties.
Net Income. As a result of the above, net income decreased 35.6% from Ps.968.8 million during 2000 to Ps.624.3 million during 2001. Net income as percentage of net sales was 3.4% during 2000 compared to 2.2% during 2001.
Comparison of fiscal years ended December 31, 2002 and December 31, 2001 for Costco Mexico Group
Figures express in this analysis reflect 100% of Costco’s operation, no matter CCM consolidates only 50% according to the proportionate consolidation method.
As of December 31, 2002 the Company had 21 warehouses located in the principal states of the Mexican Republic compared to 20 warehouses in 2001. Additionally two warehouses are being built which will be opened at the end of 2003.
During 2002 a new warehouse club was opened increasing the sales area from 2,172,790 square feet in 2001 to 2,293,712 square feet in 2002.
Net Sales. Net sales increased 5.6% from Ps.11,233.6 million in 2001 to Ps.11,868.0 million in 2002. Same store sales increased 4.2% during this period.
This increase was practically effective during the first half of 2002 since sales for the second semester decreased mainly by two factors: the country’s uncertainty for the USA’s foreign events and the construction of an internal highway that temporarily affected one important store in Mexico City.
Sales per square feet were Ps. 5.2 thousand in both years. Total sales per operative employee decreased 2.6% from Ps.2,043.2 thousand in 2001 to Ps.1,989.6 thousand in 2002.
Cost of Sales. Percentage of cost of sales with regards to net sales decreased 20 base points that increased 7.4% gross profit compared to 2001. This improvement was mainly due to the strict controls implemented by the Company in order to reduce shrinkage and to the improving negotiations with suppliers.
Gross Profit. The Company’s gross profit expressed as percentage of net sales increased 0.2%. This increase was due to the cost of sales improvement as previously mentioned.
Operating expenses. Total operating expenses increased 5.0% from Ps.1,073.6 million in 2001 to Ps.1,127.1 million in 2002 mainly due to increases in salaries and employees’ benefits (2% increase above inflation), maintenance and store remodeling to standardize equipment and store image, as well as expenses for a new warehouse. On the other hand operating expenses (net of depreciation and amortization) expressed as percentage of sales had a light decrease from 7.8% in 2001 to 7.7% in 2002 mainly due to austere expenses program performed during the year.
Depreciation and amortization expenses increase 7.4% from Ps.200.7 million in 2001 to Ps.215.7 million in 2002. This difference is due to the increase in store and computing equipment depreciation rates once their useful life was revised; this increase was also reflected as percentage with respect to sales from 1.8% in both years.
As a result of above, operating income increased from 2.6% of total sales in 2001 to 2.9% in 2002 representing Ps. 295.1 million in 2001 and Ps. 342.4 million in 2002, that is 16% growth.
Integral Results of Financing. During 2002 the interest average rate had an important decrease with respect to 2001 from 11.9% to 6.5% in 2002 decreasing interest income from 0.32% in 2001 to 0.25% in 2002 from total sales. This 15.1% represents a cash flow decrease of Ps.5.4 million.
On the other hand the Company does not usually use external financing neither for investment plans nor for the operation itself, therefore interest paid come from financial leasing due to some financial strategy. During 2002 interest paid was Ps.1.6 million compared to Ps.0.5 million paid in 2001 representing 262.4% growth.
With regards to banking commissionspaid by the Company for credit cards acceptance at our warehouses decreased 16.1% from one year to another from Ps.17.5 million in 2001 to Ps.14.7 million in 2002.
The Company recognized foreign exchange gain during the last two years with an increase of 15.3% from Ps.28.8 million in 2001 compared to Ps.33.2 million in 2002 mainly due to the fact that the Company buys dollars at a low exchange rate and generates gains when paying debts. Furthermore the operation of some warehouses clubs in the North Zone of Mexico generates dollars cash flow.
Gain from monetary position increased to Ps. 46.8 million in 2001 compared to Ps. 49.3 million in 2002. This increased was mainly due to an inflation rate of 4.4% during 2001, compared to 5.7% rate recorded during 2002.
Taxes. The Company generated Ps.26.9 million on asset taxes in 2001 and Ps.48.7 in 2002. Taxes as percentage of sales were 0.2% for 2001 and 0.4% in 2002.
Deferred taxes increased by 67.7%, from Ps.56.0 million credits in 2001 to Ps.93.9 million credit in 2002. This variation was mainly due to the tax loss carry forward reduction of Ps.187.1 million from one year to another, the tax loss carry forwards helped to reduce the amount of differed taxes.
Net income. All the above explains the decrease in net income as a percentage of sales that in 2001 was 2.7% and 2.6% in 2002. Net income was Ps. 306.8 million in 2001 and Ps. 304.3 millions in 2002.
Comparison of fiscal years ended December 31,2001 and 2000 for Costco Mexico Group
Net sales. Net sales increased 13.1% from Ps.9,931.1 million in 2000 to Ps.11,233.6 in 2001. Same store sales increased 13.7% during this period.
Sales per square increased in 7.0% from Ps.4.9 thousand in 2000 to Ps. 5.2 thousand in 2001. Total sales per operative employee increased 13.7% from Ps. 1,796.5 thousand in 2000 to Ps.2,043.2 thousand in 2001.
Cost of Sales. This amount as percentage of sales decreased 0.36% from 2000 to 2001. This improvement was due because of the company’s strict controls in shrinkage and better negotiations with suppliers.
Gross profit. Gross profit as percentage of sales increased 0.36% during this period, because of the improvement in cost of sales.
Operating expenses. Total operating expenses increased 17.0% from Ps.917.8 million in 2000 to Ps.1,073.6 million in 2001, this variation was mainly because salary increases, employees benefits (2.0% above inflation and increase), maintenance and leases. Operating expenses net of depreciation and amortization as percentage of sales a slightly increased from 7.2% in 2000 to 7.8% in 2001. This benefit is a consequence of the expense control taken by the Company.
Depreciation and amortization expenses remained without change during this period, with Ps.200.7 million for both years, as percentage of sales, the results were 2.0% in 2000 and 1.8% in 2001.
As result of above, operating income increased from Ps. 255.6 million pesos in 2000 to Ps. 295.1 million pesos in 2001, representing a growth of 15.5% in real terms.
Integral Result of Financing. During 2001 the average interest bank rate had an important reduction from 15.4% in 2000 to 11.9% in 2001. However, interest income was not affected and had a considerable increase passing from 0.2% in 2000 to 0.3% in 2001 as percentage of sales. This increased represented a 114.6% growth in cash flow of Ps.19.0 million pesos.
The company does not incur in any external sources financing neither for expansion or operations. The interests paid are from financial leasing agreements as a consequence of a financial strategy. In 2001 and 2000, Ps. 0.4 million were paid as interest .
The bank commissions that the company paid are generated because of the credit cards acceptance in our stores. This commissions increased 15.9% in this period, from Ps.15.1 million in 2000 to Ps. 17.5 million pesos in 2001.
The foreign exchange gains increased 81.0% from Ps.15.9 million gain in 2000 to Ps. 28.8 million gain in 2001, because the company buys US dollars with a low exchange rate generating an income when paying debts, and some of the Costco stores generated a good flow in dollars.
Gain from monetary position increased to Ps10.8 million in 2000 compared to Ps. 46.8 million in 2001.
Taxes. The Company paid asset taxes of Ps.14.3 million pesos in 2000 and Ps.26.9 million pesos in 2001, representing 0.1% and 0.2% as percentage of sales respectively.
Net Income.As a result of above, net profit of the company changed from 2.4% as a percentage of sales in 2000 to 2.7% in 2001 representing Ps.234.2 million in 2000 and Ps.306.8 million in 2001.
Comparison of fiscal years ended December 31, 2002 and December 31, 2001 for Other Group (Sumesa and Restaurantes California).
As of December 31, 2002, we had 17 stores and 55 Restaurantes compared to 18 stores and 50 Restaurantes at the end of 2001.
In 2002, we closed one Sumesa and opened five Restaurantes California.
Net Sales. Net sales increased 3.3% from Ps.1,187.3 in 2001 to Ps. 1,226.0 in 2002 as a result of the opening of five restaurants during the year.
Cost of Sales. Cost of sales increased 3.9% from Ps.712.7 million in 2001 to Ps.740.4 million in 2002 mostly as a direct consequence of a more efficient purchasing process in Sumesa and a deep restructure and rationalization of the raw material in Restaurantes.
Gross Profit. Gross profit expressed as percentage of net sales reduced from 39.6% in 2002 compared to 40.0% in 2001. No matter this decrease in the percentage of sales, the gross profit increased 2.3% in pesos from Ps.474.6 in 2001 to Ps.485.6 in 2002 due to the increase on sales and also because all those changes explained in the previous section.
Comparison of fiscal years ended December 31, 2001 and December 31, 2000 for Other Group (Sumesa and Restaurantes California).
As of December 31, 2001, we had 18 stores and 50 Restaurantes compared to 17 stores and 46 Restaurantes at the end of 2000.
In 2001, we opened four Restaurantes California and one Sumesa.
Net Sales. Net sales increased 4.3% from Ps.1,138.1 in 2000 to Ps. 1,187.3 in 2001 as a result of the opening of restaurants during the year.
Cost of Sales. Cost of sales increased 4.8% from Ps.680.4 million in 2000 to Ps.713.0 million in 2001 mostly as a direct consequence of the opening of new stores during the year.
Gross Profit. Gross profit expressed as percentage of net sales reduced from 40.2% in 2000 compared to 40.0% in 2001. No matter this decrease in the percentage of sales, the gross profit increased 3.7% in pesos from Ps.457.6 in 2000 to Ps.474.6 in 2001.
Liquidity and Capital Resources.
Liquidity. In the past the Company’s liquidity has been provided by the operations flow and, occasionally, by short-tem loans which are paid before year-end. In order to finance its growth the Company has obtained funds through debt and capital markets.
At December 31, 2002, the Company’s total debt of $1,909 million consisted of a bond without specific guaranty of $881.6 million, local debenture bond for $557.7 million, $157.9 million credit at 2.2% annual rate and a credit with Citibank of $311.9 million. Average cost was 7.4% in 2002. The company will determine the type of currency, the termination date and the characteristics of any future loan, taking into consideration the available terms of market including interest and exchange rates, as well as the general economic conditions.
The Company’s payable account administration for suppliers and inventories is also an important source of financing. Accounts payable surplus average days on inventories average days was 4 days for both years 2001 and 2002.
At December 31, 2002, and 2001, the Company had an aggregate of over Ps 4,910 million and Ps 4,679 million of credit available, respectively, through unused uncommitted lines of credit with ten banking institutions in 2002 and nine in 2001, under which the Company may borrow in pesos or, at its option, in U.S. dollars (converted to pesos at the exchange rate in effect at the time of the borrowing). The terms and conditions of such lines of credit will be determined at the time when they are utilized. The Company renews its bank lines of credit on a yearly basis. The bank credit lines do not contain any financial covenants.
Resources obtained from operation activities reached $773.2 million in 2001 compared to those resources in 2002 for $349.9 million. Inventories decreased 4.6% from $4,088.0 million at December 31, 2001 to $3,901.8 million at December 31, 2002. Inventory average days was 51.8 in 2001 and 51.5 days in 2002. Accounts payable average days were 55days in 2002 and 2001.
Cash Policy
Due to the Company’s activity its liquidity is presented on a real and daily basis by means of merchandise payments additionally to a better inventory turnover with respect to suppliers’ accounts payable terms.
Cash resources obtained from the Company’s operation have been similar to years 2001 and 2002. Credit card payments represent 28.3% in 2001 and 28.5% in 2002; voucher payments 7.0% during 2002 and cash payments represented approximately 64.5% of cash resources.
Regarding foreign resources the Company’s operation does not report exportation products, thus our units in Cancun and Tijuana jointly represent a monthly average amount of US$5 to US$6 million, reaching US$71.9 million in 2001 and US$60.2 million in 2002. These resources are used to pay the Company’s importation needs and liabilities in dollars.
The Company focuses and invests cash flow, including that from subsidiaries, in the holding company. In this way Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V. distributes the cash flow to the subsidiaries in order they can bear up their commitments with suppliers and others. It is worth mention that practically all transfers and payments are electronically performed avoiding mistakes and frauds and having a complete control of resources available.
The Company also has external resources from short-term (chirographic) loans (1 year).
Resources are mainly used for asset investment, which represents approximately 72% of EBITDA, such as new stores, remodeling, and land purchasing and information systems. Approximately another 7% of EBITDA is used for dividend payments.
The Company’s operating results continue to enhance its financial position and ability to continue its internal expansion program. Cash flows from operations and available borrowings are adequate to support currently planned business operations, stock repurchases acquisitions and capital expenditures.
Based on current operating results, we believe that cash flow from operations and other sources of liquidity, including borrowings under our commercial paper program and bank credit facilities, will be adequate to meet anticipated requirements for working capital, capital expenditures, interest payments and scheduled principal payments for the foreseeable future. We also believe we have adequate coverage of our debt covenants to continue to respond effectively to competitive conditions.
As of January 30, 2003, the Company's credit ratings were as follows:
| | Standard & Poors | FITCH |
| Long-term debt international | BBB- | BBB- |
| Long-term debt national | AA | AA |
| Short-term debt national | A-1+ | - |
In assessing our credit strength, both Fitch and Standard & Poor s consider our capital structure and financial policies as well as our consolidated balance sheet and other financial information. We do not currently foresee any reasonable circumstances under which we believe we would lose our current investment-grade debt ratings. However, if this were to occur, it could adversely impact, among other things, our future borrowing costs, access to capital markets and there are no payment acceleration provisions in the Company’s fixed-term debt portfolio related to a downgrade in the Company’s credit ratings. Similarly, a downgrade in the Company’s credit ratings would not affect the Company’s ability to borrow amounts under the revolving credit facilities. However, any adverse changes to the Company’s credit ratings could limit the Company's access to the commercial paper market and increase the cost of debt.
Resources in foreign money correspond principally to operations with import suppliers.
EBITDA
Our bank credit facilities and the indentures underlying our publicly issued debt contain various restrictive covenants. Some of these covenants are based on EBITDA, which we historically defined as earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. In prior years, we disclosed and discussed EBITDA accordingly, as we believed it was an important means by which to measure our liquidity or compliance with our debt covenants, and also a measure by which management monitored our operating results. Furthermore, that measure of EBITDA is used, in part, for certain covenants and credits and from this year on to determine incentive compensation.
We will continue to present EBITDA as we continue to believe it is an important means by which to measure our liquidity. However, any future presentation of EBITDA will be in accordance with SEC release No. 33-8176. We do not intend the presentation of EBITDA to be an alternative to any generally accepted accounting principle measure of performance or liquidity.
The following table provides a reconciliation of EBITDA for the fiscal years of 2002, 2001 and 2000 consistent with release No. 33-8176:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| |
| Resources provided by operating activities | 349,945 | 773,186 | 1,855,999 |
| Labor obligations | (14,491) | (11,787) | (20,073) |
| Increase in working capital | 1,123,417 | 996,957 | (6,612) |
| Taxes and profit sharing | 131,412 | 41,819 | 156,813 |
| Integral result of financing | 59,090 | (10,482) | (242,229) |
| Miscellaneous income, net | (4,831) | 18,622 | 157,920 |
| EBITDA | 1,644,542 | 1,808,315 | 1,901,818 |
Liquidity 2002.In the past the cash generated from operations and occasionally by short-term loans that are generally paid before the year-end has generally provided the Company’s liquidity.
| Contractual Obligations (In millions of pesos and Dollars) | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 and thereafter | Total |
| | | | | | | |
| Long-term debt | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Unsecured notes | | | Ps 881.6 | | | Ps 881.6 |
| Direct loan | Ps 157.9 | Ps 311.9 | | | | Ps 469.8 |
| Debenture bonds | | | | | Ps 557.7 | Ps 557.7 |
| Non cancelable operating leases | Ps 175.5 | Ps 175.5 | Ps 175.5 | Ps 175.5 | Ps 359.7 | Ps 1,061.7 |
| Auchan | US$ 14.9 | US$ 20.0 | US$ 25.0 | US$ 20.0 | US$ 40.0 | US$ 119.9 |
During 2002, 2001 and 2000, the Company paid Ps 147,910, Ps 167,125 and Ps 187,368, respectively, of interest on debt.
As of December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 the Company was in compliance with all its payments and its debt covenants.
The management of our trade payables and inventory is also an important source of financing. In 2002 and 2001 the excess of the average length of days payable for our trade payables exceed the average number of days inventory decreased from 5 in 2001 to 4 in 2002.
Assets Investments
The following table sets forth our capital expenditures for each of the three years ended December 31, 2000, 2001, 2002 and the budgeted capital expenditures for 2003:
| | Year ended December 31(1), |
| | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 (2) |
| (Millions of constant Pesos as of December 31, 2002, except for 2003 amounts which are in nominal Pesos) |
| Real estate | 500.7 | 590.8 | 315.7 | 370.4 |
| Store fixtures(3) | 859.8 | 593.4 | 411.3 | 685.9 |
| Information systems | 22.2 | 21.4 | 15.4 | 25.7 |
| Acquisition of Auchan's operations and its hypermarket stores(4) | | | | 156.0 |
| | | | | |
| Total | Ps.1,382.7 | Ps.1,205.6 | Ps. 742.4 | Ps. 1,238.0 |
(1) Capital expenditures exclude Ps.239.9 in 2000, Ps.276.0 in 2001 and Ps. 204.0 in 2002 contributed by Costco to the Costco Mexico joint venture.
(2) Represents budgeted amounts for the year ending December 31, 2003. Includes US$15 million paid for the Auchan’s operation in our country.
(3) Represents store fixtures and other equipment expenditures.
(4) See Note 16 of the Financial Statements
Assets investments for Ps.742.4 million in 2002 were financed with resources obtained from operations. The plans of the Company for 2003 are contingent due to the economic situation of the country and to the Company's potential to generate enough cash flow to finance such investments.
We currently plan to finance our assets investments for 2003 mainly from cash flow from operations. Although we expect that enough financing will be available, we cannot assure you that there will be adequate cash flow from operations in order to accomplish the investments planned. We are also responsible for financing 50% of the new Costco warehouses.
We currently plan to invest U.S.$130 million in new projects during next year. We expect to open 10 units as follows: one Comercial Mexicana, one Bodega, six Megas (including five Auchan stores), two Costco membership warehouses and six Restaurantes California. We intend to continue remodeling units and expect to complete construction on our new state-of-the-art distribution center, which we believe will increase our storage capacity by 160.5%.
Resources used for this expansion program will be obtained exclusively from the cash flow. See "Business Description Description of Principal Assets".
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
New Item 5.E of Form 20-F, which will be applicable to our annual report next year, will require us to disclose certain off-balance sheet arrangements. As of December 31, 2002, we had no such off-balance sheet arrangements.
Significant Subsequent Events
On June 9, 2003, we issued U.S.$100 million of Senior Notes in two series through a private placement with qualified institutional buyers. The 6.10% Series A Notes due 2010, accounted for U.S.$98 million of the aggregate principal, and the 6.7% Series B Notes due 2010, accounted for U.S.$2 million of the aggregate principal. The proceeds from this issuance were used on June 11, 2003 to redeem the outstanding [U.S.$84 million] 9.75% Senior Notes, with the balance of the proceeds used to repay other indebtedness.
New Mexican and U.S. Accounting Standards
In December 2001 the MIPA issued revised Statement C-9, "Liabilities, Provisions, Contingent Assets and Liabitilties and Commitments", which supersedes the original Statements C-9 and C-12, both from 1974, and Circulars 46, 47 and 48. The provisions of this new Statement are effective for years beginning on or after January 1, 2003; however, early adoption is recommended.
The objective of this Statement is to establish rules for valuation and disclosure of liabilities and provisions, to determine particular rules for valuation and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, and to provide rules for disclosure of commitments acquired by an entity as a part of its normal activities.
In February 2002, the MIPA issued revised Statement C-8, "Intangible Assets", which supersedes the current Statement C-8, effective since 1976. The provisions of this new Statement are effective for years commencing on or after January 1, 2003; however, early adoption is recommended.
The significant provisions of this Statement are: (i) it establishes rules and criteria for accounting for research and development costs; (ii) preoperating costs identified with research and development activities are charged to expenses; and (iii) valuation rules are based on a logical sequence of the assets useful life, considering initial recognition and valuation of the intangible asset, recognition of an expense, additional payments and valuation after the initial recognition.
In March 2003, the MIPA issued Bulletin B-5 "Segment Financial Information". ("Bulletin B-5"). The Bulletin B-5 nullifies the application of the IAS No. 14 "Segment reporting" which was applicable to the Mexican companies under Bulletin A-8. The Bulletin B-5 establishes standards for the way that Mexican Companies report information about operating segments in annual financial statements and requires that those enterprises report selected information about operating segments in interim financial reports issued to stockholders. It also establishes standards for related disclosures about economic segments, geographic areas, and major customers. The Bulletin B-5’s framework for segment reporting is referred to as the management approach. It is intended to give analysts and other financial statement users a view of the enterprise through the eyes of management by looking to a company’s internal management reporting structure as the basis for determining the company’s external segments as well as the basis for determining the information that is to be disclosed for those segments. The provisions of the Bulletin B-5 are required to be applied after its publication. The Company is presently evaluating the impact, if any, that these new standards will have on the consolidated financial statements.
The MIPA issued Bulletin C-15, "Impairment and Disposal of Long-Lived Assets", ("Bulletin C-15"), which will be effective as of January 1, 2004, although early adoption is recommended. Bulletin C-15 provides specific criteria in determining when there is impairment in the value of long-lived assets, for both tangible and intangible assets. Furthermore, Bulletin C-15 establishes a methodology for calculating and recording losses arising from the impairment of assets and their reversal. Also, Bulletin C-15 provides guidance as to presentation and disclosure in the case that there is subsequent reversal of the impairment. In addition, Bulletin C-15 provides guidance for the accounting, presentation and disclosure for discontinued operations. The Company is currently evaluating the impact that adoption of this statement will have on its consolidated financial statements.
In June 2002, the FASB issued SFAS No. 146 "Accounting for Costs Associated with Exit or Disposal Activities". SFAS 146 addresses financial accounting and reporting for costs associated with exit or disposal activities and nullifies Emerging Issues Task Force (EITF) Issue No. 94-3, "Liability Recognition for Certain Employee Termination Benefits and Other Costs to Exit an Activity (including Certain Costs Incurred in a Restructuring)." SFAS is effective for exit or disposal activities initiated after December 31, 2002. The Company is presently evaluating the impact, if any, that these new standards will have on its consolidated financial statements.
In December 2002, the FASB issued SFAS No. 148 "Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation- Transition and Disclosure an amendment of FASB Statement No. 123". SFAS 148 amends FASB Statement No. 123; Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation, to provide alternative methods of transition for a voluntary change to the fair value based method of accounting for stock-based employee compensation. In addition, this Statement amends the disclosure requirements of Statement 123 to require prominent disclosures in both annual and interim financial statements about the method of accounting for stock-based employee compensation and the effect of the method used on reported results. SFAS 148 shall be effective for financial statements for fiscal years ending after December 15, 2002. The Company is presently evaluating the impact, if any, that these new standards will have on its consolidated financial statements.
In April 2003, the FASB issued SFAS 149 "Amendment of Statement 133 on Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities". SFAS 149 amends and clarifies financial accounting and reporting for derivative instruments, including certain derivative instruments embedded in other contracts (collectively referred to as derivatives) and for hedging activities under FASB Statement No. 133, Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities. SFAS 149 is effective for contracts entered into or modified after June 30, 2003, except for hedging relationships designated after June 30, 2003. All provisions of SFAS 149 should be applied prospectively. The Company is presently evaluating the impact, if any, that these new standards will have on the consolidated financial statements.
Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees
Directors
Our Bylaws provide that the Board of Directors will consist of the number of directors elected by CCM's shareholders at the annual shareholders' meeting for a renewable term of one year. The Board currently consists of 13 directors, and may consist of a minimum of 5 and up to 20 directors, 3 of who are independent. The Board is responsible for the management of our business.
Each Board member was elected on April 3, 2003 at our annual shareholders meeting, and are elected for a one-year term. The names and positions of the current members of the Board, their dates of birth, and information on their principal business activities outside CCM are as follows:
Carlos González Nova
Honorary Chairman of the Board | Born: August 14, 1917
First elected: 1957
Principal Occupation: Honorary Chairman of the Board
Other directorships and business experience: Chairman of the Board and Member of the Executive Committee of CCM |
Guillermo González Nova
Chairman of the Board | Born: July 2, 1933
First elected: 1957
Principal Occupation: Chairman of the Board
Other directorships
and business experience: Vice Chairman of the Board and Member of the Executive Committee of CCM |
Jaime González Nova
Vice Chairman of the Board | Born: November 13, 1930
First elected: 1957
Principal Occupation: Vice-Chairman of the Board
Other directorships and business experience: Member of the Executive Committee of CCM |
Carlos González Zabalegui
Vice Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer | Born: July 13, 1951
First elected: 1985
Principal Occupation: Vice-Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer
Other directorships and business experience: Executive Vice-President and General Director of CCM |
Elena M. González Guerra
Director | Born: April 7, 1954
First elected: 1990
Principal Occupation: Director |
Pablo J. González Guerra
Director | Born: January 24, 1951
First elected: 1984
Principal Occupation: Director of Inmobiliaria Nova, S.A. de C.V.
Other directorships and business experience: Director of Operadora Vista Hermosa, S.A. de C.V. |
Francisco Martínez de la Vega
Director and Chief Financial and Administrative Officer | Born: December 21, 1956
First elected: 1990
Principal Occupation: Director and Chief Financial and Administrative Officer
Other directorships and business experience: Member of the Executive Committee, the Board of Directors, Treasury Director of CCM and Director of Prestaciones Universales S.A. de C.V. |
Angel Portilla González
Director | Born: September 25, 1943
First elected: 1990
Principal Occupation: Director
Other directorships and business experience: Sumesa Director |
Javier Cantu Charles
Director | Born: December 13, 1940
First elected: 1992
Principal Occupation: Corporate Planning and Development Director
Other directorships and business experience: Former General Director of Sorimex |
Santiago Garcia Garcia
Director | Born: November 26, 1953
First elected: 2002
Principal Occupation: General Director of Comercial Mexicana
Other directorships and business experience: Chief Operating Officer of Palacio de Hierro; Member of the Executive Committee of CCM |
Fermin Sobero San Martin
Director | Born: February 18, 1938
First elected: 2002
Principal Occupation: Director
Other directorships and business experience:Partner in a Mexican accounting firm. |
Jose Luis Rico Maciel
Director and Secretary | Born: September 19, 1926
First elected: 1957
Principal Occupation: Director
Other directorships and business experience: Member of the Executive Committee, Corporate Legal Affairs Director and Corporate Taxes Director of CCM |
Rodolfo Garcia Gomez de Parada
Director and Secretary Pro Term | Born: May 9, 1953
First elected: 1990
Principal Occupation: Director and Secretary Pro Term
Other directorships and business experience: Member of the Executive Committee, Corporate Tax Matters Director of CCM, Director of Industrias CH S.A. de C.V. and Director of Grupo Simec S.A. de C.V. |
Except for Carlos González Nova each Member has an alternate. The alternates are: Gustavo González Fernandez, Luis Felipe González Solana, Jaime González Solana, Luis José Guichard González, Antonino B. González Guerra, Luis Felipe González Zabalegui, Alejandro González Zabalegui, Ignacio Parada Díaz, Miguel Garatea Lerga and Humberto Meléndez Martínez. Our independent directors are Fermín Sobero San Martín, Pablo J. González Guerra and Elena M. González Guerra.
Carlos González Nova, Jaime González Nova and Guillermo González Nova are brothers. Carlos González Zabalegui is the son of Carlos González Nova and the nephew of Jaime González Nova and Guillermo González Nova. Elena M. González Guerra and Pablo J. González Guerra are the niece and nephew, respectively, of Carlos González Nova, Jaime González Nova and Guillermo González Nova.
On June 1, 2001 the Mexican Securities Market Law, or the Mexican Securities Law, was amended. We amended our bylaws on April 11, 2002 to reflect the changes in the Mexican Securities Law. Pursuant to the amendments to the Mexican Securities Law, our bylaws now provide that the Board of Directors must be composed of at least five and no more than twenty members. At least 25% of the members of the Board of Directors must qualify as Independent Directors. The Mexican Securities Law provides that the following persons, among others, do not qualify as independent:
- employees or managers of the issuer;
- controlling shareholders of the issuer; and
- important clients, suppliers, debtors or creditors of the issuer or their employees or officers.
As a result of amendments to the Mexican Securities Law, our bylaws also provide that a specific alternate director must be appointed for each director. The Chairman of the Board of Directors shall have a casting vote. The Board of Directors shall also meet at least on a quarterly basis. The Chairman, 25% of the Board Members or any statutory auditor may call for a Board meeting. The Board of Directors must approve all transactions that are to be entered into between us and any of our shareholders, our managers or other related individuals that deviate from our ordinary course of business. Likewise, the Board of Directors must approve any purchase or sale that represents 10% or more of our assets, the grant by us of guarantees exceeding 30% of our assets and any other transactions representing more than 1% of our assets, in addition to any other shareholder approvals required by our Bylaws or otherwise.
In addition, our bylaws, as amended pursuant to the Mexican Securities Law, provide that each holder or group of holders representing at least 10% of a series of shares has the right to appoint one director and its corresponding alternate director. Ten percent holders of limited voting stock are also entitled to nominate a director and its corresponding alternate director.
Executive Officers
The names and positions of our current executive officers, their dates of birth, and information concerning their prior business experience are as follows:
Carlos González Zabalegui
Chief Executive Officer | Born: July 13, 1951
Appointed: 1978
Business experience: Chief Executive Officer General Director |
Santiago Garcma Garcma
General Director of Comercial Mexicana | Born: November 26, 1953
Appointed: 2002
Business experience: Chief Operating Officer of Palacio de Hierro; Member of the Executive Committee of CCM |
Javier Cantu Charles
Corporate Planning and Development Director | Born: December 13, 1940
Appointed: 2002
Business experience: General Director of Comercial Mexicana;
General Director of Sorimex |
Luis Felipe González Solana
General Director of Restaurantes California | Born: December 5, 1958
Appointed: 1986
Business experience: General Director of Restaurantes California |
Jaime González Solana
General Director of Costco de Mexico | Born: February 26, 1957
Appointed: 1991
Business experience: General Director of Costco de Mexico |
Jose Luis Rico Maciel
Corporate Legal Affairs and Corporate Taxes Director | Born: September 19, 1926
Appointed: 1957
Business experience: Corporate Legal Affairs and Corporate Taxes Director |
Francisco Martínez de la Vega
Chief Financial and Administrative Officer | Born: December 21, 1956
Appointed: 1990
Business experience: Chief Financial and Administrative Officer |
Angel Portilla González
General Director of Sumesa | Born: September 25, 1943
Appointed: 1984
Business experience: Corporate Planning and Development Director |
Statutory Auditors
Our statutory auditors are Rogerio Casas Alatriste Hernández and Manuel Garcia Braña. Under our bylaws, the holders of a majority of the outstanding B Shares voting together may elect one or more statutory auditors(comisarios) and corresponding alternate statutory auditors. In accordance with the amendments to the Securities Market Law, every 10% holder, or group of holders, of a series of our shares may elect a statutory auditor(comisario) and a corresponding alternate statutory auditor at the annual ordinary shareholders' meeting. The primary role of the statutory auditors is to report to our shareholders at the annual ordinary general meeting regarding the accuracy of the financial information presented to such holders by the Board of Directors. Mexican law requires that the statutory auditors receive monthly reports from the Board of Directors regarding material aspects of our affairs, including our financial condition, and that they be invited to attend any meeting of the Board of Directors and the Audit Committee. The statutory auditors are also authorized to:
- call ordinary or extraordinary general meetings,
- place items on the agenda for meetings of shareholders or the Board of Directors,
- attend meetings of shareholders, the Board of Directors, or the Audit Committee, and
- generally monitor our affairs.
The statutory auditors also receive monthly reports from the Board of Directors regarding material aspects of our affairs, including our financial condition.
C.P. Rogerio Casas Alatriste H., a retired partner of PricewaterhouseCoopers, was elected by our shareholders at the annual general ordinary shareholders' meeting in 2003 to serve as our statutory auditor, and C.P. Manuel García Braña was elected to serve as Mr. Casas' alternate, in each case for a renewable term of one year.
Compensation
For the year ended December 31, 2002, the aggregate compensation we paid to our directors and executive officers for services in all capacities, excluding any benefits under our stock purchase plan described below, was approximately Ps.60.6 million.
Options to Purchase Securities From Registrant or Subsidiaries
Under our stock purchase plan, certain key employees are granted the rights to purchase our BC units at no less than the fair market value of these units on the date the options are granted. The rights vest equally over a five-year term, and expire in 2006. Employees selected to participate in the stock purchase plan have the right to receive the fair value appreciation of their allocated units in lieu of exercising their purchase privileges on the planned anniversary dates. During 2002, we granted 1,101,216 rights at Ps.6.60. During 2001, we granted 6,329,495 rights ranging from Ps.7.15 to Ps.8.69. During 2000, 4,558,785 rights range from Ps.9.00 to Ps.8.00. See Note 12 to the Financial Statements.
At December 31, 2002 and 2000, 6,384,196 and 1,095,164 BC units were available for granting to employees. These units were repurchased by us and placed in a trust. At December 31, 2001, no units were available for granting to employees.
Board Practices
In accordance with the Mexican Securities Market Law and our bylaws, we established an Audit Committee consisting of the following members of our Board: Fermín Sobero San Martín, who is the Chairman of this Committee, and Pablo J. González Guerra and Javier Cantú Charles who are examiners. Both the Chairman and a majority of the members of the Audit Committee must be, and are, independent directors.
We are responsible for maintaining a system of internal accounting controls and procedures to provide reasonable assurance, at an appropriate cost/benefit relationship, that assets are safeguarded and that transactions are authorized, recorded and reported properly. Our internal accounting control system is enhanced by periodic reviews by our internal auditors and independent auditors. In addition, we have hired a group of advisors, which performs a separate review of our disclosure controls. In our opinion, our Company s internal accounting controls provide reasonable assurance that assets are safeguarded and that the financial records are reliable for preparing financial statements.
The Audit Committee meets periodically with management, the internal auditors and the independent auditors to review matters relating to the Company s financial reporting, the adequacy of internal accounting controls and the scope and results of audit work. The internal auditors and independent auditors have full and free access to the Audit Committee.
Our statutory auditors must be invited to attend all Audit Committee meetings. Among other duties and responsibilities, the Audit Committee must:
- prepare an annual report regarding its activities for submission to the Board and to our shareholders at our annual shareholders' meeting;
- prepare and render statements to the Board as to the fairness of transactions and arrangements with related parties, which must be approved by our Board of Directors; and
- retain independent experts to render fairness opinions in connection with extraordinary corporate transactions and arrangements with related parties.
Employees and Labor Relations
At December 31, 2002, we employed 32,993 individuals. During the busiest retail months, part-time employees may constitute up to 10% of our workforce. At December 31, 2002, we had 1,861 administrative and managerial, 31,132 operating employees.
We seek to employ store assistants who meet criteria established by us for particular positions. Frequently, however, depending upon conditions prevailing in regional job markets, we are not able to adhere strictly to these criteria. Although we believe that our turnover of store assistants does not exceed the industry average, it nevertheless remains high. We are seeking to reduce turnover by paying higher compensation and providing opportunities for advancement within the Company.
Our store managerial staff is comprised mostly of employees with long tenure with us who have worked their way up to a managerial position, as well as employees with a higher education who have completed a three-month training program which includes some practical experience in our stores. In many cases, our store managerial staff receives further training from a leading Mexican university under a program exclusively available to our employees.
Our senior managerial and administrative employees have semi-annual performance assessments and receive performance-related compensation, including participation in our stock purchase plan. Our management believes that compensation must attract, retain and motivate the best employees available and, therefore, we are willing to compensate employees at levels which management believes are generally higher than those prevailing in the Mexican retail industry.
We are committed to training employees. During 2002 we dedicated approximately 6 days of training per employee. All new employees are provided with training designed to ensure compliance with our policies relating to customer service, prevention of theft and operational procedures. Continuing on-the-job training is provided to our employees, including upon each transfer or promotion of an employee.
Approximately 15.0% of our employees were members of one of 11 labor unions at December 31, 2002. In addition, labor relations in some stores are governed by separate collective bargaining agreements executed between employees of a single store and a union selected by such employees. The economic terms of the collective bargaining are renegotiated on an annual basis. We have not experienced any work stoppages and management believes that we have a good relationship with our employees and unions.
The following table sets forth the number of employees and a breakdown of employees by main category of activity and geographic location as of the end of each year in the three-year period ended December 31, 2002:
| December 31, |
| | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 |
| Number of Employees | 35,332 | 31,955 | 32,993 |
| Category of Activity | | | |
| Operating Employee | 30,946 | 29,344 | 30,746 |
| Administrative employee | 2,063 | 2,611 | 2,247 |
| | | | |
| Geographic Location | | | |
| Metropolitan | 13,921 | 12,766 | 13,065 |
| Central | 13,108 | 11,563 | 12,207 |
| Northwest | 3,180 | 2,964 | 3,035 |
| Northeast | 883 | 986 | 924 |
| Southwest | 1,696 | 1,475 | 1,518 |
| Southeast | 2,544 | 2,201 | 2,244 |
Share Ownership of Directors and Officers
Share ownership of our directors, alternate directors and executive officers is set forth in the table under "Major Shareholders and Related Party Transactions". Except as set forth in this table, none of our directors, alternate directors or executive officers is the beneficial owner of more than 1% of any class of our capital stock or conditional sale agreements or options representing the right to purchase more than 1% of any class of our capital stock.
None of our other directors, alternate directors or executive officers is the beneficial owner of more than 1% of any class of our capital stock.
Item 7. Major Shareholders and Related Party Transactions
Capital Stock
Our common stock consists of 4,005,551,610 B Shares and 338,448,390 C Shares. B Shares, without par value, provide each holder one vote per share, and C Shares, without par value, do not have voting rights.
Each B Unit may at any time be converted into a Unit, by either the Secretary of the Company or by Indeval, S.A. de C.V. Our capital structure as of December 31 of the last three years was as follows:
| Year ended December 31, | Number of BC Units | Number of B Units |
| 2000 | 338,266,861 | 747,733,139 |
| 2001 | 338,288,361 | 747,711,639 |
| 2002 | 338,448,390 | 747,551,610 |
At December 31, 2002, the Principal Shareholders owned 747,431,760 B Units and 5,528,834 BC Units representing in the aggregate 69.3% of the total outstanding capital stock. The Principal Shareholders determine the outcome of substantially all actions requiring shareholder approval, and through their control of the Board of Directors, select executive officers.
Major Shareholders
The following table sets forth certain information with respect to ownership of CCM's capital stock as of December 31, 2002 of (i) each person who is known by CCM to own more than 5% or each executive officer or director who is known by CCM to own more than 1% of either the currently outstanding B Units (consisting of four B Shares, without par value and with one vote per share, or B Shares, which trade together as a single security) and BC Units (consisting of three B Shares and one C Share, without par value and without voting rights, or C Shares, which trade together as a single security) and (ii) all our executive officers and directors as a group.
| B Units and BC Units Owned as of December 31, 2002 |
| | B Units | BC Units | Aggregate Percentage of Outstanding B Units and BC Units (1) | Voting Power |
| Identity of Owner | Number | Percentage of Class | Number | Percentage of Class |
| | | | | | | |
| Scotiabank Trust(2) | 747,431,760 | 99.9% | 5,528,834 | 1.6% | 69.3% | 75.0% |
| All executive officers and directors as a group (20 persons) (3)(4) | 682,616,100 | 91.3% | 25,497,224 | 7.5% | 65.2% | 70.0% |
_________________
- Total outstanding B and BC Units includes treasury stock (6,384,196 Units as of December 31, 2002).
- For a description of this trust and its beneficiaries which indirectly include our Principal Shareholders, see " Our Principal Shareholders."
- Includes 19,968,390 Units that are subject to our stock option plan that certain officers and directors have the right to purchase pursuant to grants received prior to December 31, 2002.
- Including the Principal Shareholders.
As of December 31, 2002, the public float for the Units (including those represented by GDSs) represented approximately 28.8% of the total outstanding capital stock of CCM.
The Principal Shareholders are able to exercise full voting rights with respect to the B Shares that they hold (including B Shares held through B Units representing a majority of the outstanding B shares (the "Control Position") as well as any B Shares held through Units) and may convert each B Unit into one Unit at any time. The Principal Shareholders have informed us that they currently intend to maintain their Control Position and, through this position, will have the power to elect a majority of our directors and determine the outcome of substantially all actions requiring shareholder approval. See "Item 3. Key Information Factors Relating to the Company Control by the Principal Shareholders."
Our Principal Shareholders. Approximately 69% of our B Units are held by the Scotiabank Inverlat Trust, or the Scotiabank Trust. The largest direct beneficiary of this trust is a company owned by members of the González family. Members of this family, including Carlos González Nova, Guillermo González Nova, and Jaime González Nova, own an equity interest in such company which is substantially equivalent to their relative percentage ownership interest in B Units as reported in our Annual Report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2001. The other beneficiaries of this trust 53 of our employees whose percentage interest in the Trust is approximately 1% percent.
Under the terms of the Scotiabank Trust, the company which contributed the B Units into the Trust, and which is controlled by our Principal Shareholders, may at any time transfer its interest in the Trust to members of the González family or a third party. The Principal Shareholders, as indirect beneficiaries, may from time to time contribute additional B Units, Units, and any other Shares of our capital stock that they may receive in the future, into the Scotiabank Trust.
The Technical Committee. Decisions regarding the Trust are made by a majority vote of a four member Technical Committee. The members of the Technical Committee are Carlos González Nova, Carlos González Zabalegui, Guillermo González Nova and Jaime González Nova. Each member of the Technical Committee has one vote. In the event of a tie, the vote of the President of the Technical Committee, Carlos González Nova, will be deemed the deciding vote. The Technical Committee has the exclusive authority to make decisions regarding voting and disposition of the B Units held by the Scotiabank Trust. In the event a member of the Technical Committee resigns or dies, that member’s alternate will become full member. A new alternate will be selected by the new member, subject to Technical Committee approval.
Related Party Transactions
We do not grant personal loans to our employees or shareholders. Employees and our shareholders are permitted to borrow only against our retirement fund or from our annual savings fund.
We currently lease one store located in Puebla from a company controlled by the Principal Shareholders and certain members of the Principal Shareholders' families. We believe that this lease, which expires in 2015, is on terms no less favorable to us than would be obtainable in an arm's-length transaction.
From time to time, in the regular course of business, we deal with Nova Distex, S.A. de C.V., or Nova. Our majority shareholders own a controlling interest in Nova, a textile manufacturer and property management company. We provide management services to Nova and purchase textiles for resale in our stores. We believe that these transactions are on terms no less favorable to us than would be obtainable in an arm's length transaction.
On December 9, 2002 and January 1, 2003, we entered into arrangements with Nova Distex, S.A. de C.V. (successor to Casa Distex S.A. de C.V.) and Indistex, S.A. de C.V for ownership 1,875,945 square feet of real estate located in the Queretaro region of Mexico. Pursuant to these arrangements, for consideration of Ps. 150,000,000, we purchased 100% of the outstanding shares of Almacenes de Queretaro, S.A. de C.V., and a holding company, which held title to the real estate.
Other than in connection with the previously mentioned operations, we do not participate in transactions that generate relationships with unconsolidated entities or financial partnerships, including variable interest entities, nor do we have or guarantee any off-balance sheet debt.
We entered into a Registration Rights Agreement with our principal shareholders. We have agreed to cooperate with the Principal Shareholders in effecting any future secondary stock offering by them, to take, at our expense, any actions, including registration of such offering under the securities laws of any jurisdiction, that the Principal Shareholders may deem necessary or desirable in connection therewith and to indemnify the Principal Shareholders and such other persons as may be necessary or desirable in connection therewith.
For additional information regarding related party transactions, see Note 5 to our Financial Statements.
Item 8. Financial Information
See "Item 17 Financial Statements" and pages F-1 through F-6, which are incorporated herein by reference.
Item 9. Offer and Listing Details
Market Information
The GDSs, each of which represents 20 Units, are listed on the NYSE, and the NYSE symbol for the GDSs is "MCM". B Shares and the C Shares trade on the Mexican Stock Exchange only as Units or B Units, as the case may be. Each B Unit may at any time be converted into one Unit. However, Units may not be converted into B Units. The B Shares and the C Shares comprising the Units and the B Shares comprising the B Units are transferable on the books of CCM only as Units or B Units, as the case may be, and are not separately transferable.
Two persons with United States addresses held 170,343 GDSs we believe that as of June 19, 2002, of record.
The following table shows the high and low sales prices in nominal Pesos (without adjustment for inflation) for the Units and the B Units on the Mexican Stock Exchange for the period from January 1, 1997 to June 13, 2002.
| | Nominal Pesos Per Unit | Nominal Pesos Per B Unit(2) |
| | High | Low | High | Low |
| 1997 | 10.60 | 5.22 | 9.90 | 5.50 |
| 1998 | 11.00 | 4.19 | 10.60 | 6.10 |
| 1999 | 12.90 | 7.40 | 12.00 | 8.70 |
| | | | | |
| 2000 | | | | |
| First Quarter | 12.80 | 8.80 | 11.10 | 9.62 |
| Second Quarter | 12.62 | 7.02 | 12.18 | 8.38 |
| Third Quarter | 12.00 | 9.42 | 12.10 | 9.50 |
| Fourth Quarter | 11.06 | 7.62 | 11.20 | 9.60 |
| | | | | |
| 2001 | | | | |
| First Quarter | 9.22 | 6.51 | 12.00 | 7.50 |
| Second Quarter | 8.99 | 6.73 | 12.00 | 11.89 |
| Third Quarter | 8.69 | 5.50 | 12.00 | 12.00 |
| Fourth Quarter | 7.50 | 5.35 | 16.00 | 12.00 |
| | | | | |
| 2002 | | | | |
| First Quarter | 8.25 | 6.12 | | |
| Second Quarter | 8.40 | 5.30 | | |
| Third Quarter | 6.65 | 4.80 | | |
| Fourth Quarter | 6.60 | 4.95 | | |
| | | | | |
| 2003 | | | | |
| January | 5.48 | 4.80 | | |
| February | 5.19 | 4.85 | | |
| March | 5.18 | 4.90 | | |
| April | 6.25 | 5.13 | | |
| May | 7.00 | 6.25 | | |
| June (through June 13) | 6.95 | 6.66 | | |
_________________
(1) Source: Mexican Stock Exchange.
(2) B Unit was unlisted from the BMV on Oct. 27.2001.
The following table shows the high and low sales prices in U.S. Dollars for the GDSs on the New York Stock Exchange for the period from January 1, 1997 to June 12, 2003.
| | U.S. Dollars per GDSs(1) |
| | High | Low |
| | | |
| 1997 | 26 5/8 | 18 1/4 |
| 1998 | 14 9/16 | 10 1/16 |
| 1999 | 26 1/4 | 15 7/16 |
| | | |
| 2000 | | |
| First Quarter | 27 1/4 | 19 1/8 |
| Second Quarter | 27 | 15 5/16 |
| Third Quarter | 26 | 18 1/2 |
| Fourth Quarter | 23 3/8 | 16 3/8 |
| December | 20 | 16 3/8 |
| | | |
| 2001 | | |
| First Quarter | 19 1/16 | 14 |
| Second Quarter | 19.50 | 14.75 |
| Third Quarter | 18.75 | 11.75 |
| Fourth Quarter | 16.30 | 11.75 |
| December | 16.30 | 13.33 |
| | | |
| 2002 | | |
| First Quarter | 17.90 | 13.20 |
| Second Quarter | 18.15 | 10.90 |
| Third Quarter | 12.92 | 9.93 |
| Fourth Quarter | 11.80 | 9.90 |
| December | 11.20 | 10.00 |
| | | |
| 2003 | | |
| January | 10.20 | 8.89 |
| February | 9.45 | 8.99 |
| March | 9.45 | 8.50 |
| April | 11.85 | 9.46 |
| May | 13.90 | 12.00 |
| June (through June 12) | 13.32 | 12.50 |
__________________
(1) Source: New York Stock Exchange
Debt Securities
On April 14, 1998, we issued, in a private placement, 9.375% Senior Notes due 2005 in an aggregate principal amount of U.S.$130 million. These notes were registered under the Securities Act of 1933 through an exchange offer. Since April 2003, we had the option to call the bond paying a premium of 104.5%. We made the call on June 11, 2003 for U.S. $ 84.81 million, the outstanding amount of the bond (we have bought back U.S. $ 29.99 million in 1998 and US$ 15.2 millions in 2002), resulting in a final payment, including the premium, of U.S. $ 88.63 million.
In order to finance the call of the previous operation, on June 9, 2003, we issued, in a private placement, 6.10% Senior Unsecured Notes due 2010 in an aggregate principal amount of U.S. $ 100 million. These notes are neither listed for trading on any stock exchange nor approved for quotation through any quotation system. These notes are traded over-the-counter; therefore we cannot determine their high and low sales prices.
The Securities described herein are being offered privately to qualified institutional investors who will be required to represent that they are purchasing the Securities for investment. A purchaser of the Securities must bear the risk associated with holding the investment for an indefinite period of time since the Securities will not be registered under the United States Securities Act of 1933, as amended. No government agency will have passed upon the adequacy or use of this Memorandum or approved the sale of the Securities. There will be no undertaking to register the Securities under state, provincial or federal securities law, and the Securities cannot be sold unless they are subsequently registered or an exemption from registration is available.
The most important characteristics of this operation are the following:
| Issue | Senior Unsecured Notes (the "Notes"). |
| Issuer | Controladora Comercial Mexicana S.A. de C.V. (the "Company"). |
| Subsidiary Guarantors | All Guarantors under the Company's principal bank lending arrangements at the time of closing. The Notes shall be guaranteed by Comercial Mexicana S.A. de C.V. and any other wholly owned Material Subsidiary. At all times, total assets of all Subsidiary Guarantors shall sum to an amount equal to 80% of the Company's Consolidated Total Assets less consolidated assets of Costco de Mexico S.A. de C.V. |
| Principal Amount | US$100,000,000. |
| Noteholders | Accredited Institutional Investors. |
| Placement Agent | Merrill Lynch & Co. |
| Final Maturity | Tranche A: 7 years from the date of Takedown.
Tranche B: 7 years from the date of Takedown. |
| Amortization | Tranche A: 5 equal annual principal repayments beginning on the 3rd anniversary of the issuance of the Notes resulting in an average life of 5 years. |
| Interest Rate | Tranche A: 6.10%, a spread of 350 basis points over the 5 year U.S. Treasury Note yield at the time of commitment. Interest will be payable semiannually in arrears.
Tranche B: 6.70%, a spread of 360 basis points over the 7 year U.S. Treasury Note yield at the time of commitment. Interest will be payable semiannually in arrears. |
| Price | 100% of Principal Amount. |
| Use of Proceeds | To refinance existing debt and for general corporate purposes. |
| Ranking | The Notes shall rank pari passu with the Company's other senior unsecured Debt. |
On June 2, 2003, we received the authorization of the Mexican National Bank Commission to emit a local short-term debenture program in pesos. The characteristics of the approval of the Company’s Short-term Local Bond Program are as follows:
| Issuer: | Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V. |
| Issue: | Short-term Local Bonds |
| Type of bonds: | Chirographic |
| Currency: | Mexican pesos |
| Amount: | $1,000'000,000.00 |
| Amount of each issuance: | Will be determined upon each short-term local bond issuance according to the Program. |
| Rated value: | $1,000,000,000.00. Each local bond will have a rated value of multiple $100.00 (HUNDRED PESOS 00/100). |
| Settlement: | Up to 360 days from the issuance date. |
| Currency: | Mexican Pesos or Investment Units. |
| Settlement date: | 360 days from closing date. During this period several issuances may be accomplished but without exceeding the total amount. |
| Taxation: | Interest rate will be determined just before issuance. Issuance will operate on a discount basis. |
| Review and interests payment: | In the event the issuer pays interests these should be previously calculated under the revised and agreed payable interest rate established: weekly, monthly, quarterly, semiannually or other. |
| Place and payment of Amount and interests: | Amount and interests with respect to Local Bonds will be paid on the maturity date through electronic transfer at SD Indeval, S.A. de C.V. |
| Purchasers: | Mexican or foreign individuals or companies; mutualist insurance institutions; guaranty bonds institutions, deposit institutions, leasing financial companies, credit unions, factorage companies and societies of variable income investment and commercial paper. |
| Amortization: | At the maturity date in one payment |
| Grade: | mxA-1+ |
| Qualifying Institution: | Standard & Poor's, S.A. de C.V. |
| Mutual Agent: | BankBoston, S.A., Institucisn de Banca Mzltiple, Divisisn Fiduciaria. |
| Placement Agent: | Scotia Inverlat Casa de Bolsa, S.A. de C.V., Grupo Financiero Scotiabank Inverlat. |
Trading on the Mexican Stock Exchange
The Mexican Stock Exchange, located in Mexico City, is the only stock exchange in Mexico. Operating continuously since 1907, the Mexican Stock Exchange is organized as a corporation with variable capital, orsociedad anónima de capital variable. Securities trading on the Mexican Stock Exchange occur from 8:30 a.m. to 3:00 p.m., Mexico City time, each business day. Since January 1999, all trading on the Mexican Stock Exchange has been effected electronically. The Mexican Stock Exchange operates a system of automatic suspension of trading in shares of a particular issuer as a means of controlling excessive price volatility, but under current trading regulations this system does not apply to the Units because they are traded in the form of GDSs on a stock exchange outside Mexico, the New York Stock Exchange.
Settlement is effected two business days after a share transaction on the Mexican Stock Exchange. Deferred settlement, even by mutual agreement, is not permitted without the approval of the CNBV. Most securities traded on the Mexican Stock Exchange, including the CPOs, are on deposit withS.D. Indeval, S.A. de C.V., Institución para el Depósito de Valores, S.A. de C.V., or Indeval, a privately owned securities depositary that acts as a clearinghouse, depositary and custodian, as well as a settlement, transfer and registration agent for Mexican Stock Exchange transactions, eliminating the need for physical transfer of securities.
Although the Mexican Securities Market Law provides for the existence of an over-the-counter market, no such market for securities in Mexico currently exists.
Market Regulation and Registration Standards
In 1946, theComisión Nacional de Valores, or the National Securities Commission, commonly known as the CNV, was established to regulate stock market activity. In 1995, the CNV and theComisión Nacional Bancaria, or the National Banking Commission, were merged to form the CNBV. The Mexican securities market law, which took effect in 1975, introduced important structural changes to the Mexican financial system, including the organization of brokerage firms as corporations. The Mexican securities market law sets standards for the registration of brokerage firms in the intermediaries’ section of the registry. Registration of brokerage firms, which is a prerequisite to becoming a member of the Mexican Stock Exchange, is granted by the Ministry of Finance upon the recommendation of the CNBV. In addition to setting standards for brokerage firms, the Mexican securities market law empowers the CNBV to regulate the public offering and trading of securities and to impose sanctions for the illegal use of insider information. The CNBV regulates the Mexican securities market, the Mexican Stock Exchange and brokerage firms through a board of governors composed of thirteen members, five of which are appointed by the Ministry of Finance.
To offer securities to the public in Mexico, an issuer must meet specific qualitative and quantitative requirements, and only securities for which an application for registration in the National Registry of Securities maintained by the CNBV has been approved by the CNBV may be listed on the Mexican Stock Exchange. This approval does not imply any kind of certification or assurance related to the merits or the quality of the securities or the solvency of the issuer.
In 1993, the CNBV established an intermediate securities market, which was also operated by the Mexican Stock Exchange, in order to permit less-liquid issues and issuers with lower capitalization to participate in a public securities market. In essence, the general rules divided the securities section of the registry into two subsections, subsection A and subsection B. In addition to trading regularly in the auction process, registration of securities in subsection A enabled those securities to be eligible for transactions for which only securities classified as high liquidity issues by the Mexican Stock Exchange were eligible.
To be registered and maintain registration in subsection A of the registry, an issuer was usually required to meet more stringent qualitative and quantitative requirements than for subsection B. The CNBV adopted regulations that became effective on January 1, 2001 that eliminate subsection B and impose additional requirements to those currently applicable to subsection A. Accordingly, as of January 1, 2001, in order to be registered in subsection A, an issuer must or must have, among other things:
- at least three years of operating history, or if an issuer is a holding company, it must present three years of operating history for its principal subsidiaries; if the issuer is a newly created entity as a result of a merger or spin-off, the three year requirement must be evidenced through any of the entities involved in such merger or spin-off, as the case may be;
- shareholders’ equity of at least 20 millionunidades de inversión, or UDIs, which are inflation indexed currency units, equivalent to Ps. 58.2 million as of December 31, 2000;
- profits for the last three years of operation taken as a whole;
- conduct a public offering of at least 15% of the issuer’s paid-in capital stock or, if the offering exceeds 160,000,000 UDIs, it represents at least 7% of the issuer’s paid-in capital stock;
- offer at least 10,000,000 shares at a price per share of at least one UDI; and
- conduct a public offering with the potential to reach at least 200 stockholders.
To maintain its registration, an issuer must have:
- stockholders’ equity of at least 15 million UDIs;
- at least 36 trades in its securities every six months through the Mexican Stock Exchange;
- an average prices of its securities greater than Ps.1.00 during any six-month period;
- at least 100 stockholders;
- a public float of at least 8,000,000 shares; and
- a public float of at least 12% of the issuer’s paid-in capital stock or at least 5% of the issuer’s paid-in capital stock if the initial public offering exceeded 160,000,000 UDIs.
The CNBV has the authority to waive some of these requirements in some circumstances. Also, some of these requirements are applicable for each series of shares of the relevant issuer.
As of June 1, 2001, the Ley del Mercado de Valores, or Securities Market Law, was amended to increase the protection given to minority shareholders and to bring corporate governance procedures of Mexican issuers up to international standards. Such amendments implemented through governmental regulations. Accordingly, we amended our bylaws at our annual shareholders’ meeting held on April 11, 2002, to reflect some of these amendments, including amendments that:
- established a Board with at least five and not more than twenty members and alternate members, of which 25% must qualify as "independent directors" under Mexican law;
- adopted specified corporate governance measures, which require us to establish, among other things, an audit committee, as well as more stringent procedures for the approval of transactions and arrangements with related parties and extraordinary corporate transactions; and
- provide additional protections for minority shareholders.
There are several requirements that have to be met by Mexican issuers in order to continue listed in the Mexican Stock Exchange and registered in the RNVI. Both the Mexican Stock Exchange and the CNBV will review issuers annually to verify the compliance with the foregoing requirements. Some of these requirements may be further reviewed by the CNBV on a quarterly basis. The Mexican Stock Exchange must inform the CNBV of the results of its review. If an issuer fails to comply with any of the foregoing requirements, the Mexican Stock Exchange will request that the issuer propose a plan to cure the violation. If the issuer fails to propose such plan, or if its plan is not acceptable to the Mexican Stock Exchange, trading of its shares on the Mexican Stock Exchange will be temporarily suspended until the situation is corrected. In addition, if the issuer fails to propose the plan or ceases to follow such plan once proposed, the CNBV might suspend or cancel the registration of the shares. In such event, the issuer must evidence the mechanisms to protect the rights of public investors and market in general. In the event the CNBV determines to cancel the registration of our shares, our controlling Shareholder is obligated to conduct a tender offer at a price equal to the higher of (i) the average closing price of the last thirty trading days of our stock or (ii) the book value of such shares, in accordance with our latest quarterly reports filed with the CNBV before such tender offer is to be conducted.
Issuers of listed securities are required to file unaudited quarterly financial statements and audited annual financial statements as well as various periodic reports with the CNBV and the Mexican Stock Exchange. Recently, the internal regulations of the Mexican Stock Exchange were amended to implement the EMISNET, an automated system for the electronic transfer of the information required to be filed with the Mexican Stock Exchange and the CNBV. Issuers of listed securities must prepare and disclose their financial information by a Mexican Stock Exchange-approved system known as the Sistema de Información Financiera Computarizada, or Computerized Financial Information System, commonly known as the SIFIC. Immediately upon its receipt, the Mexican Stock Exchange makes that information available to the public.
Circular 11-28 of the CNBV and the internal regulations of the Mexican Stock Exchange require issuers of listed securities to file through the EMISNET information on the occurrence of material events affecting the relevant issuer. Material events include, but are not limited to:
- the entering into or termination of joint venture agreements or agreements with key suppliers;
- the creation of new lines of businesses or services;
- significant deviations in expected or projected operating performance;
- the restructuring or payment of significant indebtedness;
- material litigation or labor conflicts;
- changes in dividend policy;
- the commencement of any insolvency, suspension or bankruptcy proceedings;
- changes in the directors; and
- any other event that may have a material adverse effect on the results, financial condition or operations of the relevant issuer.
If the Mexican Stock Exchange deems it necessary, it may request additional information regarding material events affecting the issuer.
The CNBV and the Mexican Stock Exchange may suspend the dealing in securities of an issuer as a result of the disclosure of material events if:
- the information filed by the issuer requires further clarifications; or
- the Mexican Stock Exchange determines that the public should be aware of that information before a trade may take place.
In these cases, trading may resume if the Mexican Stock Exchange determines that:
- the additional information provided by the issuer is sufficient and not misleading; or
- the public has had the opportunity to access that information.
Likewise, if the securities of an issuer are traded on both the Mexican Stock Exchange and a foreign securities market, that issuer must file simultaneously with the CNBV and the Mexican Stock Exchange a Spanish version of the information that it is required to file pursuant to the laws and regulations of the relevant jurisdiction.
Pursuant to the Securities Market Law, as amended, the CNBV must be notified by the shareholder of a company listed on the Mexican Stock Exchange before any such shareholder effects one or more simultaneous or successive transactions outside the Mexican Stock Exchange that result in a transfer of 10% or more of that company’s capital stock. The holders of the shares being transferred must also inform the CNBV of the results of such transactions within three days of the completion, or otherwise, the non-completion, of the transaction. The CNBV will notify the Mexican Stock Exchange of these transactions, without disclosing the names of the parties involved. Under the amendments to the Securities Market Law, the CNBV may determine the cases in which the purchaser thereof shall complete such transactions through a tender offer, as well as the minimum and maximum percentages of stock of an issuer that that may be purchased through the tender offer.
Also, the Law states that a shareholder holding 10% or more of the capital stock of a company listed in the registry, is required to notify the CNBV of any ownership changes in shares of such company that results in a transfer of shares representing a beneficial ownership interest of 10% or more, within ten business days following the transfer transaction. The amendments to the Securities Market Law expressly permit Mexican issuers to include in their bylaws anti-takeover defenses.
Item 10. Other Information
Bylaws
Below is a brief summary of some significant provisions of our bylaws and Mexican law. This description does not purport to be complete, and is qualified by reference in its entirety to our bylaws, which have been filed as an exhibit to this annual report and Mexican law. For a description of the provisions of our bylaws relating to our Board of Directors, Executive Committee and statutory auditors, see "Directors, Senior Management and Employees."
Purpose
Article 2 of our bylaws defines our purpose as the promotion, organization, management and participation in the capital stock of all types of commercial companies, partnerships, associations or industrial, trading, services or any other type of company, both domestic and foreign, as well as participation in the administration thereof, as well as other purposes related thereto.
Duration
The Bylaws provide that the duration of CCM is 99 years, which term expires on January 28, 2043.
Registration and Transfer
Share certificates in registered form, which may, evidence our shares or may not have dividend coupons attached. We maintain a stock registry, and in accordance with Mexican law only those holders listed in the stock registry are recognized as our shareholders. We will register B Shares and C Shares in our stock registry only as a part of BC Units or B Units, as the case may be. Shareholders may hold their BC Units or B Units in the form of physical certificates or through book-entries with institutions that have accounts with Indeval. Indeval is the holder of record in respect of such BC Units or B Units held in book-entry form. Brokers, banks and other entities approved by the CNBV may maintain accounts at Indeval.
Voting Rights and Shareholders' Meetings
Board of Directors. The management of our business is vested in our Board of Directors. Article 19 of our bylaws, amended pursuant to the June 2001 amendments to the Mexican Securities Market Law, currently provide for a Board of Directors of a minimum of five and no more than twenty members, at least 25% of which must be "independent directors" under Mexican law, and the same number of alternate directors. The Board currently consists of 13 members. Under Mexican law, as recently amended, a shareholder or group of shareholders owning 10% or more of the capital stock of a company has the right to elect one regular and the corresponding alternate director.
The holders of C Shares will generally not be entitled to vote, or to attend or address meetings of shareholders at which they are not entitled to vote. However, under Mexican law, classes of shareholders (including holders of non-voting stock such as the C Shares) are entitled to vote as a class in a special meeting governed by the same rules that apply to extraordinary general meetings, as described below, on any action that would prejudice the rights of holders of shares of other series, and a holder of shares of such series would be entitled to judicial relief against any such action taken without such a vote. The determination whether an action requires a class vote on these grounds would initially be made by the Board. In certain cases, the Board, the statutory auditors or a Mexican court could call a special meeting. A negative determination would be subject to judicial challenge by an affected shareholder and a court would ultimately determine the necessity for a class vote. There are no other procedures for determining whether a particular proposed shareholder action requires a class vote, and Mexican law does not provide extensive guidance on the criteria to be applied in making such a determination.
Holders of GDSs are entitled to instruct the Depositary how to vote the shares comprising the Units represented by their respective GDSs, subject to the terms of the Deposit Agreement.
General shareholders' meetings may be ordinary general meetings or extraordinary general meetings. Extraordinary general meetings are those called to consider certain matters specified in the Mexican Companies Law and the Bylaws including, principally, amendments of the Bylaws, liquidation, dissolution, merger and transformation from one form of company to another and increases and reductions of the fixed portion of the capital stock. General meetings called to consider all other matters are ordinary meetings. An ordinary general meeting of the holders of B Shares must be held at least once each year within the first four months following the end of the preceding fiscal year to consider the approval of the financial statements of CCM and certain of its subsidiaries for the preceding fiscal year, to elect directors for holders of B Shares and statutory auditors, to determine the compensation of all directors or statutory auditors, and to determine the allocation of the profits or losses of the preceding year.
The quorum for an ordinary general meeting of the B Shares on first call is 50% plus one of such shares, and action may be taken by 50% plus one of the outstanding B Shares. If a quorum is not available, a second meeting may be called at which action may be taken by a majority of the B Shares present, regardless of the number of such shares.
The quorum for an extraordinary general meeting is at least75%and a majority of all of the outstanding shares that are entitled to vote on first and successive calls, respectively, and action may be taken by a vote of 50% plus one of the outstanding shares that are entitled to vote.
Holders of GDRs will be entitled to instruct the Depositary as to the exercise of the voting rights pertaining to the B Shares and the limited voting rights pertaining to the C Shares forming the Units represented by their GDSs.
Under Mexican law, holders of 33% of our outstanding shares may have any shareholder action suspended pending final judicial resolution by filing a complaint with a Mexican court of competent jurisdiction within 15 days after the close of the meeting at which such action was taken, by showing that the challenged action violates Mexican law or the By-laws. Relief under these provisions is only available to holders (i) who were entitled to vote on the challenged shareholder action and (ii) whose shares were not represented when the action was taken or, if represented, were voted against it.
Shareholders' meetings may be called by the Board, our statutory auditors or a Mexican court. The Board or the statutory auditors may be required to call a meeting of the shareholders at the written request of the holders of 33% of the B Shares or, in the case of a meeting at which holders of C Shares would be entitled to vote, at the written request of the holders of 33% of the outstanding C Shares. In the event that a meeting is not called within 15 days following the date of such request, a Mexican court may require such meeting to be called. Notices of meetings and agendas therefor must be published in theDiario Oficial de la Federaciónor a newspaper of general circulation in Mexico City at least 15 days prior to the date set for the meeting. Meetings may be held without such publication, provided that 100% of the shares entitled to vote are represented. To attend a meeting, shareholders must deposit their shares prior to such meeting as indicated in the notice. If entitled to attend the meeting, a shareholder may be represented by an attorney-in-fact.
Dividends and Distributions
At the annual ordinary general meeting of holders of B Shares, the Board submits our financial statements for the previous fiscal year together with a report thereon by the Board and the report of the statutory auditor, to the holders of B Shares for approval. The holders of B Shares, once they have approved the financial statements, determine the allocation of our net profits for the preceding year. They are required by law to allocate at least 5% of such net profits to a legal reserve, which is not thereafter available for distribution except as a stock dividend, until the amount of the legal reserve equals 20% of historical capital stock (before effect of restatement). See Note 11 to our Annual Financial Statements. Thereafter, the shareholders may determine and allocate a certain percentage of net profits to any general or special reserve, including a reserve for open-market purchases of our shares. The remainder of net profits is available for distribution in the form of dividends to the shareholders, subject to the terms of certain restrictive covenants contained in certain of our indebtedness. See "Item 3 Key Information Dividends.
Holders of the B Shares and C Shares and, accordingly, holders of BC Units and B Units, will have equal rights, on a per share basis, to dividends and other distributions, including any distributions upon our liquidation.
Capital Variations
The fixed portion of our capital stock may only be increased or decreased by resolution of an extraordinary general meeting of shareholders, subject to the exception that we may decrease our fixed capital stock under certain circumstances without such a resolution if we, in accordance with the Securities Market Law, repurchase our shares, whereas the variable portion of our capital stock may be increased or decreased by resolution of an ordinary or extraordinary general meeting of shareholders (except in connection with repurchases of shares where no shareholders meeting is required). Increases and decreases in our capital stock must be recorded in our book of capital variations. Any increase or decrease in our capital stock is subject to the limitations that the variable portion of the capital stock may not exceed the equivalent of 10 times the fixed portion of the capital stock and that the C Shares may not at any time represent more than 25% of our capital stock.
Pre-emptive Rights
Except in certain circumstances involving a public offering and requiring prior CNBV approval (including the Offerings) or in connection with the placement of our shares which were previously repurchased, in the event of a capital increase, a holder of existing shares of a given series has a preferential right to subscribe for a sufficient number of shares of the same series to maintain the holder's existing proportionate holdings of shares of that series. For example, subject to certain exceptions, if we issued B Shares and C Shares in the form of Units and B Shares in the form of B Units in the future, pursuant to and subject to applicable Mexican law, each holder of Units and B Units would be entitled to subscribe for a sufficient number of Units and/or B Units, as the case may be, to maintain such holder's then-existing proportionate holdings of B Shares and C Shares, and the Principal Shareholders would be entitled to subscribe for a sufficient number of B Units and Units to maintain their proportionate holdings of B Shares and C Shares with respect thereto. Pre-emptive rights must be exercised during a term fixed by the shareholders at the meeting declaring such capital increase, which term may not end before at least 15 days following the publication of notice of the capital increase in the official gazette of the corporate domicile. Under Mexican law, pre-emptive rights cannot be waived in advance and cannot be represented by an instrument that is negotiable separately from the corresponding share. Holders of GDSs may be restricted in their ability to participate in the exercise of such pre-emptive rights.
The Principal Shareholders have advised us that they may exercise their pre-emptive rights to subscribe for a sufficient number of B Shares so that they will own B Shares, including the Control Position, representing a majority of the outstanding B Shares, in connection with any primary sale of equity by us in the future. See "Item 3. Key Information Risk factors."
Other Provisions
Redemption. The B Shares and the C Shares are subject to redemption in connection with either (i) a reduction of share capital or (ii) a redemption with retained earnings, which, in either case, must be approved by our shareholders at an extraordinary general shareholders' meeting. The shares subject to any such redemption would be selected by us by lot or in the case of redemption with retained earnings, by purchasing shares on the Mexican Stock Exchange, in accordance with the Mexican Companies Law, provided that in no case can shares be redeemed in such a way that the number of currently outstanding C Shares represents more than 25%of our capital stock.
Fixed and Variable Capital. We are permitted to issue shares constituting fixed capital and shares constituting variable capital. The fixed minimum part without right to withdrawal of our capital amounts to the sum of Ps.1,000,000,000.00 and it is represented by 1,000,000,000 shares. The issuance of variable-capital shares, unlike the issuance of fixed-capital shares, does not require an amendment of the Bylaws, although it does require a vote of 50% plus one of the B Shares at an ordinary general meeting of shareholders. Under Mexican law and the Bylaws, if we issued variable capital shares, any holder of such shares would be entitled to redeem them at the holder's option at any time at a redemption price equal to the lower of (i) 95% of the average market value of such shares on the Mexican Stock Exchange for 30 trading days on which the shares were quoted preceding the date on which the exercise of the option is effective and (ii) the book value of such shares at the end of the fiscal year in which the exercise of the option is effective. If the option is exercised during the first three-quarters of a fiscal year, it is effective at the end of that fiscal year, but if it is exercised during the fourth quarter, it is effective at the end of the next succeeding fiscal year. The redemption price would be payable following the annual ordinary general meeting of holders of B Shares at which the relevant annual financial statements were approved.
Forfeiture of Shares. As required by Mexican law, the Bylaws provide that non-Mexican holders of B Shares, C Shares, BC Units and B Units formally agree with the Foreign Affairs Ministry (i) to be considered as Mexicans with respect to the B Shares, the C Shares, the BC Units and the B Units that they acquire or hold as well as the property, rights, concessions, participation or interests owned by us or to the rights and obligations derived from any agreements the Company has with the Mexican government and (ii) not to invoke the protection of their own governments. Failure to comply may result in a penalty of forfeiture of such a shareholder's capital interests in favor of Mexico. In the opinion of Santamarina y Steta, S.C., our Mexican counsel, under this provision a non-Mexican shareholder (including non-Mexican holders of GDSs) is deemed to have agreed not to invoke the protection of his own government by asking such government to interpose a diplomatic claim against the Mexican government with respect to the shareholder's rights as a shareholder, but is not deemed to have waived any other rights it may have, including any rights under the United States securities laws, with respect to its investment in us. If the shareholder should invoke governmental protection in violation of this agreement, its shares could be forfeited to the Mexican government.
Exclusive Jurisdiction. The Bylaws provide that legal actions relating to our relationship and the shareholders may be brought only in courts in the Federal District of Mexico City.
Purchase by CCM of itsShares. We generally may not repurchase our shares, subject to certain exceptions. First, we may repurchase shares for cancellation with distributable earnings pursuant to a decision of an extraordinary general meeting of shareholders. Second, pursuant to judicial adjudication, we may acquire the shares of a shareholder in satisfaction of a debt owned by such shareholder to us, we must sell any shares so acquired within three months, otherwise our capital stock will be reduced and such shares canceled. Third, in accordance with the Securities Market Law and our Bylaws, we may repurchase our shares representing our capital on the Mexican Stock Exchange at any time at the then-prevailing market price. The Board of Directors must approve any such repurchase. Our capital stock would be reduced automatically in an amount equal to the theoretical value of each repurchased share (determined by dividing the outstanding capital stock of CCM by the number of shares outstanding immediately prior to such repurchase); in the event that the purchase price of such shares exceeded the theoretical value, the difference would be paid for with amounts allocated from net earnings to a special reserve created for the repurchase of shares. We would hold repurchased shares as treasury stock, pending future placements thereof which could be effected on the Mexican Stock Exchange. Our capital stock would be automatically increased upon the resale of shares in an amount equal to their theoretical value; any excess amount would be allocated to the special reserve referred to above. The economic and voting rights corresponding to such repurchased shares may not be exercised during the period in which such shares are owned by us and such shares would not be deemed to be outstanding for purposes of calculating any quorum or vote at any shareholder's meeting during such period. In no event may such repurchase result in a percentage of C Shares in excess of that permitted by the Bylaws or applicable law.
Obligation of Majority Shareholders. In accordance with the Mexican Securities Market Law, persons deemed to control us, including the Principal Shareholders, will be required to make a public offer to repurchase any shares held by minority shareholders (at the higher of the average market price during the 30 preceding days or at book value) in the event that either us or the CNBV cancels the registration of such shares with the National Register of Intermediaries and Securities, or RNVI.
Conflict of interest. Any shareholder that has a direct interest with respect to a certain transaction shall abstain from voting with respect to such transaction at the relevant shareholders' meeting. A shareholder that votes on a business transaction in which its interest conflicts with that of CCM may be liable for damages, but only if the transaction would not have been approved without our vote.
Appraisal rights. Whenever the shareholders approve a change of corporate purposes, change of nationality of the corporation or transformation from one form of company to another, any shareholder entitled to vote on such change that has voted against it may withdraw from us and receive the amount calculated as specified under Mexican law attributable to its shares, provided that it exercises its right within 15 days following the adjournment of the meeting at which the change was approved. Because the C Shares may not vote on these matters, such appraisal rights are not available to such holders of C Shares, including C Shares underlying the Units.
Actions against Directors. Action for civil liabilities against the directors may be initiated by resolution of an ordinary shareholders' meeting. In the event the ordinary shareholders' meeting decides to bring such action, the directors against whom such action is to be brought will immediately cease to be directors. Additionally, shareholders representing not less than 15%of the outstanding shares may directly exercise such action against the directors, provided that (i) such shareholders shall not have voted in favor of not exercising such action at the relevant shareholders' meeting, and (ii) the claim covers all the damages alleged to have been caused to us and not only the portion corresponding to such shareholders. Any recovery of damages with respect to such action will be for the benefit of us and not for the shareholders bringing this action.
Material Contracts
In June 1991, we entered into a joint venture with Costco. This joint venture is governed by a board of directors consisting of six members, three of who are appointed by us (including the chairman of the board of the joint venture) and Costco appoints the other three. The management agreements may be terminated by either Costco or the Costco Mexico joint venture at any time, and any termination initiated by the joint venture must be approved by a majority (at least four directors consisting of two representatives of each of CCM and Costco) of its board of directors. The affirmative vote of a majority of the entire board of directors of the joint venture is required to approve certain significant decisions regarding the joint venture, including, among other things, certain revisions to the joint venture business plan, obligations or acquisitions of real estate or certain other fixed assets not otherwise provided for in the business plan, the removal of any of the management personnel appointed by Costco and certain transfers of ownership interests in the joint venture. In addition, the affirmative vote of both members of a two-person executive committee consisting of the chief executive officers of both Costco and us is required to approve certain obligations not otherwise provided for in the business plan and other significant decisions regarding the joint venture which are not specially reserved for the board of directors.
The joint venture has duration of 99 years, ending in the year 2090. However, the joint venture agreement may be terminated and the joint venture dissolved, (i) by mutual agreement of Costco and us, and (ii) upon a sale by either party of its entire interest in the joint venture by written agreement. We or Costco may purchase the other party’s interest in the joint venture at a price determined by reference to the fair market value of that interest in the event that the other party (i) fails to provide its portion of the financing to the joint venture, (ii) fails to provide or maintain and guarantee pursuant to the joint venture agreement, (iii) transfers its interest to an unaffiliated third party without the consent of the board of directors of the joint venture, (iv) is unable to resolve with the other party within a prescribed period a deadlock of the board of directors, (v) is in default of its obligations under the joint venture agreement, (vi) is insolvent or bankrupt, or (vii) undergoes a change of control.
During 2001 and 2000, each of Costco and CCM contributed U.S$ 10.0 million and U.S. $28.5 million, respectively, to the joint venture.
Legal Proceedings
We are involved in certain legal proceedings incidental to the normal conduct of our business, which management does not believe will, in the aggregate, be material to our consolidated financial condition.
Exchange Controls and Restrictions on Foreign Investment
Exchange Rates and Controls
The Mexican economy has suffered balance of payments deficits and shortages in foreign exchange reserves. While the Mexican Government does not currently restrict the ability of Mexican or foreign persons or entities to convert Pesos to U.S. Dollars, no assurance can be given that the Mexican Government will not institute a restrictive exchange control policy in the future (as has been the case in the past). Any such restrictive exchange policy could have a material adverse effect on our business and financial condition. See "Item 3. Key Information Risk Factors Currency Fluctuations and Exchange Controls".
Except for the period from September through December 1982, during the Mexican liquidity crisis, Banco de Mexico consistently has made foreign currencies available to Mexican private sector entities (such as the Company) to meet their foreign currencies obligations. Nevertheless, in the event of renewed shortages of foreign currencies there can be no assurance that Banco de Mexico would continue to make foreign currencies available to private sector companies or that foreign currencies needed by us to service foreign currency obligations could be purchased in the open market without substantial additional cost.
Fluctuations in the exchange rate between the Peso and the U.S. dollar will affect the U.S. dollar equivalent of the Peso price of the securities on the Mexican Stock Exchange, including the Units and, as a result, will likely affect the market price of the GDSs. Such fluctuations also would affect the conversion by the Depositary into U.S. dollars of any cash dividends paid in Pesos on the B Shares and the C Shares comprising the Units.
Foreign Investment Legislation
Ownership by non-Mexicans of shares of Mexican enterprises is regulated by the 1993Ley de Inversión Extranjera, or the Foreign Investment Law, and the 1998Reglamento de la Ley de Inversión Extranjera, or the Foreign Investment Regulations. TheComisión Nacional de Inversiones Extranjeras, or National Foreign Investment Commission, administers the Foreign Investment Law and Regulations. To comply with the restrictions on percentages of capital stock that may be owned by non-Mexicans, Mexican companies typically limit the ownership of particular classes of their capital stock to Mexicans.
The Foreign Investment Law reserves certain economic activities exclusively for the Mexican State, certain other activities exclusively for Mexican individuals or Mexican corporations and limits the participation of non-Mexican investors to certain percentages in regard to enterprises engaged in activities specified therein. Foreign investors may freely participate in up to 100% of the capital stock of Mexican companies or entities except for those existing companies (i) engaged in reserved activities as referred to above and (ii) with assets exceeding the amount to be established annually by the Foreign Investment Commission (which has been set at Ps.85 million) in which case an approval from the Foreign Investment Commission will be necessary in order for foreign investment to exceed 49% of the capital stock. The Principal Shareholders have advised us that they intend to maintain the Control Position directly in the form of B Units. Pursuant to the Foreign Investment Law, unless appropriate authorization is obtained, the Control Position may be transferred only to Mexican nationals.
Mexican and non-Mexican nationals are entitled to hold, and to exercise the rights of a holder of, the Units, the B Units, the B Shares and the C Shares. The C Shares may not represent more than 25% of our capital stock.
Taxation
United States Taxes
General. The following is a summary of the anticipated material U.S. federal income tax consequences of the ownership and disposition of Units and GDSs except as otherwise noted, by U.S. Holders, as defined below. This discussion does not address all aspects of U.S. federal income taxation that may be relevant to a particular holder based on the holder’s particular circumstances. For example, with respect to U.S. Holders, the following discussion does not address the U.S. federal income tax consequences to a U.S. Holder:
- that owns, directly, indirectly or through attribution, 2% or more of the total voting power or value of our shares;
- that is a dealer in securities, insurance company, financial institution, tax-exempt organization, U.S. expatriate, broker-dealer or trader in securities; or
- whose functional currency is not the U.S. dollar.
Also, this discussion does not consider:
- the tax consequences for the shareholders, partners or beneficiaries of a U.S. holder; or
- special tax rules that may apply to a U.S. holder that holds Units or GDSs as part of a "straddle," "hedge," "conversion transaction," "synthetic security" or other integrated investment.
In addition, the following discussion does not address any aspect of state, local or non-U.S. tax laws, other than Mexican tax laws. Further, this discussion generally applies only to U.S. Holders that hold the Units or GDSs as capital assets within the meaning of Section 1221 of the Internal Revenue Code. This summary does not constitute, and should not be considered as legal or tax advice to holders.
The description set forth below is based on the U.S. federal income tax laws as in force on the date of this annual report, including:
- the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, applicable Treasury Regulations and judicial and administrative interpretations; and
- the convention between the Government of the United States of America and the Government of the United Mexican States for the Avoidance of Double Taxation and the Prevention of Fiscal Evasion with Respect to Taxes on Income, including the applicable protocol, which we refer to as the tax treaty;
- and is subject to changes to those laws and the tax treaty subsequent to the date of this annual report, which changes could be made on a retroactive basis; and
- is also based in part on the representations of the Citibank, N.A. as depositary and on the assumption that each obligation in the deposit agreement relating to the Units and GDSs and any related agreement will be performed in accordance with its terms.
Holders should consult their own tax advisors as to the particular United States, Mexican or other tax consequences of the ownership and disposition of Units and GDSs which may be applicable to them.
As used in this section, the term "U.S. Holder" means a beneficial owner Units or GDSs that is, for U.S. federal income tax purposes:
- a citizen or individual resident of the U.S.;
- a corporation or partnership created or organized in or under the laws of the United States or of any political subdivision of the United States, other than a partnership treated as foreign under U.S. Treasury regulations;
- an estate the income of which is included in gross income for U.S. federal income tax purposes regardless of source; or
- a trust, in general, if a U.S. court is able to exercise primary supervision over its administration and one or more U.S. persons have the authority to control all of its substantial decisions.
An individual may be treated as a resident of the United States in any calendar year for U.S. federal income tax purposes by being present in the United States on at least 31 days in that calendar year and for an aggregate of at least 183 days during a three-year period ending at the close of that year. For purposes of this calculation, all of the days present in the current year, one-third of the days present in the immediately preceding year and one-sixth of the days present in the second preceding year would be counted. Residents are taxed for U.S. federal income purposes as if they were U.S. citizens.
The application of the tax treaty to U.S. Holders is conditioned upon, among other things, the assumptions that the U.S. Holder:
- is not a resident of Mexico for purposes of the tax treaty;
- is an individual who has a substantial presence in the United States;
- is entitled to the benefits of the tax treaty under the limitation on benefits provision contained in Article 17 of the tax treaty; and
- does not have a fixed place of business or a permanent establishment in Mexico with which its ownership of CPOs, GDSs or underlying A Shares, L Shares and D Shares is effectively connected.
Ownership of Units and Shares. In general, for the United States federal income tax purposes, U.S. Holders of GDSs will be treated as the owners of Units (and the shares comprising such Units (the "Shares")) represented by those GDSs.
Taxation of Dividends and Stock Distributions. Dividends paid out of current or accumulated earnings and profits (computed based on United States federal income tax principles) with respect to the Shares will be includible in the gross income of a U.S. Holder as ordinary income when the dividends are received by the U.S. Holder or the custodian on behalf of the U.S. Holder and will not be eligible for any dividends received deduction otherwise allowable to corporations under Section 243 of the Code. A U.S. Holder who is an individual may be eligible for reduced rates of taxation on such dividends. Such dividends paid in Pesos will be includible in the income of a U.S. Holder in a U.S. dollar amount calculated by reference to the exchange rate in effect on the day the pesos are received by the U.S. Holder or the custodian on behalf of the U.S. Holder. U.S. Holders should consult their own tax advisor regarding the treatment of any foreign currency gain or loss on any Pesos received by the U.S. Holder or the custodian on behalf of the U.S. Holder which are not converted into U.S. dollars on the day the Pesos are received.
A U.S. Holder may, subject to certain limitations, be eligible to claim as a credit or deduction, for purposes of computing such holder’s United States federal income tax liability, any Mexican withholding tax paid in respect of dividends paid by the Company. Such dividends will generally constitute foreign-source income and will generally be classified as "passive income" or, in the case of certain U.S. Holders, "financial services income" for purposes of determining the United States foreign tax credit limitation. The calculation of United States foreign tax credits and, in the case of a U.S. Holder that elects to deduct foreign taxes, the availability of deductions, involves the application of complex rules that depend on a U.S. Holder’s particular circumstances. U.S. Holders should consult their own tax advisors regarding the availability of foreign tax credits and deductions for such Mexican withholding tax.
Under rules enacted by the United States Congress in 1997 and other guidance released by the United States Department of the Treasury, foreign tax credits will not be allowed for withholding taxes imposed in respect of certain short-term or hedged positions in stock or in respect of arrangements in which a U.S. Holder’s expected economic profit, after non-United States taxes, is insubstantial. U.S. Holders should consult their own tax advisers concerning the implications of these rules in light of their particular circumstances.
Distributions of additional Shares of the Company to U.S. Holders with respect to the Shares (and accompanying distributions with respect to Units and GDSs) that are made as part of a pro rata distribution to all shareholders of the Company generally will not be subject to United States federal income tax.
A holder of Units or GDSs that is with respect to the United States, not a U.S. Holder, or non-U.S. Holder will not be subject to United States federal income or withholding tax on dividends paid with respect to the Shares (or with respect to Units or GDSs), unless such income is effectively connected with the conduct by the Holder of a trade or business in the United States.
Taxation of Capital Gains. Gain or loss recognized by a U.S. Holder on the sale or other taxable disposition of Units or GDSs will be subject to United States federal income taxation as capital gain or loss in an amount equal to the difference (if any) between such U.S. Holder’s tax basis in the Units or GDSs and the amount realized on the sale or other taxable disposition. Such capital gain or loss will be long-term capital gain or loss if the Units or GDSs have been held for more than one year at the time of the disposition. The deductibility of capital losses is subject to limitations. Capital gains recognized on a sale or other taxable disposition of Units or GDSs by a U.S. Holder generally will be treated as United States source income, unless such gains are subject to Mexican taxation under the Tax Treaty, in which case, a U.S. Holder generally will be permitted to elect to treat such gains as foreign source income for United States foreign tax credit purposes. Capital losses recognized on the sale or taxable disposition of Units or GDSs by a U.S. Holder generally will be allocated to reduce income from United States sources for United States foreign tax credit purposes. U.S. Holders should consult their tax advisors concerning the United States foreign tax credit implications of a disposition of Units or GDSs. Deposits and withdrawals of Units or GDSs by U.S. Holders will not be subject to United States federal income tax.
A non-U.S. Holder of Units or GDSs will not be subject to United States federal income or withholding tax on gain realized on the sale or other taxable disposition of Units or GDSs, unless
- such gain is effectively connected with the conduct by the holder of a trade or business in the United States, or
- in the case of gain realized by an individual holder, the holder is present in the United States for 183 days or more in the taxable year of the sale or other taxable disposition and certain other conditions are met.
Backup Withholding and Information Reporting. A U.S. Holder may be subject to U.S. information reporting and U.S. backup withholding at a rate of up to 30% for dividends paid on the Units or GDSs, or proceeds from the sale or other disposition of Units or GDSs unless the U.S. Holder:
- is a corporation or comes within an exempt category; or
- provides a taxpayer identification number, certifies as to no loss of exemption from backup withholding tax and otherwise complies with the applicable requirements of the backup withholding rules.
The amount of any backup withholding will be allowed as a credit against the U.S. Holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability and may entitle such holder to a refund provided that certain required information is furnished to the U.S. Internal Revenue Service.
A Non-U.S. Holder may be required to comply with certification and identification procedures in order to establish its exemption from backup withholding.
Mexican Taxes
General. The following is a general summary of the anticipated material Mexican tax consequences of the purchase, ownership and disposition of Units and GDSs to a person who is not a resident of Mexico for Mexican tax purposes as defined below.
An income tax treaty between the United States and Mexico is in effect (the "Tax Treaty"). Except as indicated below under "Taxation of Capital Gains," the Tax Treaty will not have any material effect on the Mexican tax consequences described herein.
This summary is based upon the tax laws of Mexico as in effect on the date of this Annual Report, which are subject to change. Holders should consult their own tax advisors as to the particular United States, Mexican or other tax consequences of the purchase, ownership and disposition of Units or GDSs which may be applicable to them and as to their entitlement to the benefits afforded by the Tax Treaty or other income tax treaty to which Mexico is a party.
For purposes of Mexican taxation, an individual is a resident of Mexico if he has established his home in Mexico, unless he has resided in another country for more than 183 calendar days, whether consecutive or not, during a year and can demonstrate that he had become a resident of that country for tax purposes, and a legal entity is a resident of Mexico if its principal administrative body is located in Mexico. A Mexican citizen or a legal entity with its corporate domicile in Mexico and established under Mexican law is presumed to be a resident of Mexico unless such person or entity can demonstrate otherwise. If a legal entity is deemed to have a permanent establishment or fixed base in Mexico for tax purposes, all income attributable to such permanent establishment or fixed base shall be required to pay taxes in Mexico in accordance with applicable law.
Taxation of Dividends. Dividends, either in cash or in any form, paid with respect to Shares underlying the Units, including those represented by GDSs, will be subject to a Mexican withholding tax that is calculated on a gross-up basis. Under the Tax Treaty, the current withholding tax rate is 5%. Holders should consult their tax advisors for a determination of the applicable withholding rate and of their possible eligibility for a reduced rate under any of the other applicable treaties currently in effect. The Company will be required to pay 35% tax on the dividend multiplied by 1.5385 if the dividend is not paid from earnings which have already been subject to income taxation, as shown in the required record of such earnings called "cuenta de utilidad neta" or "previously taxed net earnings".
Taxation of Capital Gains. The sale or other disposition of GDSs will not be subject to Mexican tax. Deposits and withdrawals of Units for GDSs will not give rise to Mexican tax or transfer duties.
The sale or other disposition of Units will not be subject to any Mexican tax if the sale is carried out through the Mexican Stock Exchange or other recognized securities market, as determined by Mexican tax authorities under general rules. Sales or other dispositions of Units made in other circumstances would be subject to Mexican income tax. Under the Tax Treaty, gains on the disposition of Units by less than 25% U.S. Holders eligible for benefits under the Tax Treaty will not be subject to Mexican tax, unless (i) 50% or more of the fair market value of the Company's assets consist of "immovable property" (as defined in the treaty) situated in Mexico, or (ii) such gains are attributable to a permanent establishment or fixed base of such U.S. Holder in Mexico. Because of uncertainty regarding the interpretation of the relevant provision of the Tax Treaty there can be no assurance that 50% or more of the fair market value of CCM's assets do not or will not consist of "immovable property" situated in Mexico. Gains of a non-U.S. Holder eligible for benefits under a treaty to which Mexico is a party may be exempt (in whole or in part) from Mexican tax under such treaty. Holders should consult with their tax advisors as to their entitlement to benefits afforded by an applicable income tax treaty.
Other Mexican Taxes. There are no Mexican inheritance or succession taxes applicable to the ownership, transfer or disposition of Units or GDSs. There are no Mexican stamp, issuer, registration or similar taxes or duties payable by holders of Units or GDSs.
Documents on Display
For further information about us and our securities, we refer you to the filings we have made with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, or the SEC.
We are subject to the informational requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and, in accordance with these requirements, file reports and other information with the SEC. These reports and other information, as well as any related exhibits and schedules, may be read and copied at the SEC's public reference facility at Room 1024, Judiciary Plaza, 450 Fifth Street, N.W., Washington, D.C. 20549. Please call the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330 for further information on the public reference rooms and their copy charges. These reports and other information may also be inspected at the offices of the New York Stock Exchange, 20 Broad Street, New York, New York 10005. As a foreign private issuer, we are not required to furnish proxy statements to holders of our GDSs.
As an issuer of securities listed on the Mexican Stock Exchange, we are required to file unaudited quarterly financial statements and audited annual financial statements as well as various periodic reports with the CNBV and the Mexican Stock Exchange. Recently, the internal regulations of the Mexican Stock Exchange were amended to implement the EMISNET. Issuers of listed securities must prepare and disclose their financial information by a Mexican Stock Exchange-approved system known as theSistema de Información Financiera Computarizada, or Computerized Financial Information System, commonly known as the SIFIC. Immediately upon its receipt, the Mexican Stock Exchange makes that information available to the public. In addition, as a Mexican listed company, we must file through the EMISNET, an automated system for the electronic transfer of the information required to be filed with the Mexican Stock Exchange and the CNBV, information regarding the occurrence of material events specified in Mexican Securities regulations.
Item 11. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
We are exposed to market risks, including adverse changes in interest rates and foreign currency exchange rates as discussed below:
Interest Rate Risk
We are exposed to market risk from changes in interest rates, which may adversely affect our financial position, results of operations and cash flows. In seeking to minimize the risks from interest rate fluctuations, we manage exposures through our regular operating and financing activities. We are subject to interest rate risk through our borrowing activities which include U.S. dollar-denominated Senior Notes having an aggregate principal amount of U.S.$84.8 million, and an indexed peso denominated fixed rate debenture instrument for a principal amount of 172.9 million UDIs. Except as set forth below, we currently do not enter into interest rate derivative instruments for hedging or trading purposes. To discuss. See "Foreign Exchange Rate Risk". Further details on the derivative instruments are disclosed in Note 7 to the Financial Statements.
The table below provides information about our financial instruments that are sensitive to changes in interest rates. For each instrument the table presents annual amortization of notional amounts and weighted average interest rates by contractual maturity dates. The fair value of each of the items below is based on the current rates available to us for the remaining outstanding debt of the same remaining maturity.
| |
| | Expected maturity date | | |
| | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | Thereafter | Total notional amount | Fair value |
| Long-term debt: | - | Ps.311,850 | Ps.881,600 (1) | Ps.557,737 (2) | Ps.1,751,187 | Ps.1,863,533 |
| Interest rate | | Libor + 1.75% | 9.375% | 8.0% | 7.97% | 7.97% |
During 2002 and 2001, we engaged in the following transactions:
- (1) Interest rate swap, CCM receives 9.375% fixed rate and pays a six months LIBOR rate plus 5.38%, payable semi-annually on a US$30 million base, maturing on April 2005, and an option for CCM with a limit in the LIBOR rate plus 4.38% if the LIBOR rate exceed 7%.
Interest rate swap, CCM pays LIBOR rate plus 3.5% and receives a fixed rate of 9.375%, payable semi-annually on a US$10 million base, and an option for CCM that limits the payment to 5.10% and expires when LIBOR rate exceed 7.10%.
- (2) Interest rate swap, CCM pays a six months LIBOR rate plus 4.29% and receives a fixed rate of 8.0%, payable semi-annually on a 100 million Investments Units (UDIs) base, maturing on December 2007.
Foreign Exchange Rate Risk
We have U.S. dollar-denominated long-term debt and are subject to foreign currency exchange rate risk on cash flows related to interest and principal payments. From time to time, the Company enters into certain derivative transactions allowed by the Company's risk management policy. The Company uses derivatives primarily as cash flow hedges to set interest rates for forecasted debt issuances, such as interest rate locks. We use derivative financial instruments for purposes other than trading to reduce our exposure to fluctuations in foreign currencies and to minimize the risk and cost associated with financial and global operating activities. Generally, the contract terms of hedge instruments closely mirror those of the item being hedged, providing a high degree of risk reduction and correlation. Contracts that are highly effective at meeting the risk reduction and correlation criteria are recorded using hedge accounting.
Currency swap to realize on April 2005, CCM pays on Mexican Pesos the equivalent to 74,004,278 (UDIs) at that date receives US$20 million, with an option that requires CCM to pay in case of currency exchange exceed $18.6 Mexican Pesos per US Dollar.
The fair values are based on the rates at which we could borrow funds with similar terms and remaining maturities at the dates presented.
Item 12. Description of Securities Other than Equity Securities
Not applicable.
PART II
Item 13. Defaults, Dividend Arrearages and Delinquencies
Not applicable.
Item 14. Material Modifications to the Rights of Security Holders and Use of Proceeds
Not applicable.
PART III
Item 15.
Within the 90 days prior to the date of this annual report, we carried out an evaluation under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures. Based upon and as of the date of that evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures are effective in all material respects to ensure that information required to be disclosed in the reports we file and submit under the U.S. Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is recorded, processed, summarized and reported as and when required. There were no significant changes in our internal controls or in other factors that could significantly affect these controls subsequent to the date of such evaluation.
Item 16. [Reserved]
Not applicable.
PART IV
Item 17. Financial Statements
See pages F-1 through F-6, which are incorporated herein by reference.
Item 18. Financial Statements
We have responded to Item 17 in lieu of Item 18.
Item 19. Exhibits
(a) List of Financial Statements
Report of Independent Accountants
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2001 and 2002
Consolidated Statements of Income for the Years Ended December 31, 2000, 2001 and 2002.
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders' Equity for the Years ended December 31, 2000, 2001 and 2002
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Financial Position for the Years ended December 31, 2000, 2001 and 2002
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
All other schedules relating to us are omitted because they are not required or because the required information is contained in our Financial Statements or Notes thereto.
(b) List of Exhibits
3.1 Amended and Restated Bylaws (Estatutos Sociales) of the Registrant.1
4.1 Indenture, dated as of April 14, 1998, for the Senior Notes between the Registrant and IBJ Schroder Bank & Trust Company as Trustee.2
10.1 Form of Indemnity Agreement between the Registrant and its directors and its executive officers.3
10.2 Restated Corporate Joint Venture Agreement dated February 15, 1995, between the Price Company and Price Venture Mexico and CCM.3
10.3 Credit Agreement, dated as of May 24, 1996, among CCM, Comerical Mexicana S.A. de C.V., the Banks listed therein and Morgan Guaranty Trust Company of New York, as Agent.3
10.4 Form of Share Purchase Agreement between us and certain employees.3
10.5 Form of Registration Rights Agreement between the Company and each of Messrs. Carlos González Nova, Jamie González Nova and Guillermo González Nova.3
12.1 Certification pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
12.2 Certification pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
1 Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant's Amendment No. 1 to its Registration Statement on Form F-1 (File No. 333-5564).
2 Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 20-F for the fiscal year ended December 31, 1997.
3 Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibits 10.2 through 10.5 to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 20-F for the fiscal year ended December 31, 1996.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 12 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant certifies that it meets all of the requirements for filing on Form 20-F and has duly caused this Annual Report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
CONTROLADORA COMERCIAL MEXICANA, S.A. DE C.V.
Registrant
By: /s/ Francisco Martínez de la Vega
Francisco Martínez de la Vega
Chief Financial and Administrative Officer
Dated: July 11, 2003
CERTIFICATION
I, Carlos González Zabalegui, certify that:
1. I have reviewed this annual report on Form 20-F of Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V.;
2. Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3. Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4. The registrant’s other certifying officers and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-14 and 15d-14) for the registrant and we have:
a. designed such disclosure controls and procedures to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared;
b. evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures as of a date within 90 days prior to the filing date of this report (the "Evaluation Date"); and
c. presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures based on our evaluation as of the Evaluation Date;
5. The registrant’s other certifying officers and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation, to the registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent function):
a. all significant deficiencies in the design or operation of internal controls which could adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial data and have identified for the registrant’s auditors any material weaknesses in internal controls; and
b. any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal controls; and
6. The registrant’s other certifying officers and I have indicated in this report whether or not there were significant changes in internal controls or in other factors that could significantly affect internal controls subsequent to the date of our most recent evaluation, including any corrective actions with regard to significant deficiencies and material weaknesses.
Date: July 11, 2003
/s/ CARLOS GONZALEZ ZABALEGUI
Carlos González Zabalegui
Chief Executive Officer
CERTIFICATION
I, Francisco Martínez de la Vega, certify that:
1. I have reviewed this annual report on Form 20-F of Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V.;
2. Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3. Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4. The registrant’s other certifying officers and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-14 and 15d-14) for the registrant and we have:
a. designed such disclosure controls and procedures to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared;
b. evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures as of a date within 90 days prior to the filing date of this report (the "Evaluation Date"); and
c. presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures based on our evaluation as of the Evaluation Date;
5. The registrant’s other certifying officers and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation, to the registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent function):
a. all significant deficiencies in the design or operation of internal controls which could adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial data and have identified for the registrant’s auditors any material weaknesses in internal controls; and
b. any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal controls; and
6. The registrant’s other certifying officers and I have indicated in this report whether or not there were significant changes in internal controls or in other factors that could significantly affect internal controls subsequent to the date of our most recent evaluation, including any corrective actions with regard to significant deficiencies and material weaknesses.
Date: July 11, 2003
/s/ FRANCISCO MARTÍNEZ DE LA VEGA
Francisco Martínez de la Vega
Chief Financial Officer
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO
18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350,
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO
SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with the Annual Report of Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V. (the "Company") on Form 20-F for the period ended December 31, 2002 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the "Report"), I, Carlos González Zabalegui, Chief Executive Officer of the Company, certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. 1350, as adopted pursuant to 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that:
(1) The Report fully complies with the requirements of Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and
(2) The information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company.
| Dated: | July 11, 2003 | | /s/ CARLOS GONZALEZ ZABALEGUI |
| | | Name: | Carlos González Zabalegui |
| | | Title: | Chief Executive Officer |
Dated: July 11, 2003
A signed original of this written statement required by Section 906 has been provided to Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V.. and will be retained by Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V. and furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission or its staff upon request.
In accordance with the interim guidance for Section 906 certification issued by the United States Securities and Exchange Commission on March 21, 2003 in Release No.33-8212, this certification will not be deemed "filed" for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, or otherwise subject to the liability of that section. Such certification will not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into any filing under the Securities Act of 1933 or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, except to the extent that Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V. specifically incorporates it by reference.
Exhibit 12.2
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO
18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350,
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO
SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with the Annual Report of Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V. (the "Company") on Form 20-F for the period ended December 31, 2002 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the "Report"), I, Francisco Martínez De La Vega, Chief Financial Officer of the Company, certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. 1350, as adopted pursuant to 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that:
(1) The Report fully complies with the requirements of Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and
(2) The information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company.
| Dated: | July 11, 2003 | | /s/ FRANCISCO MARTINEZ DE LA VEGA |
| | | Name: | Francisco Martínez de la Vega |
| | | Title: | Chief Financial Officer |
Dated: July 11, 2003
A signed original of this written statement required by Section 906 has been provided to Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V.. and will be retained by Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V. and furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission or its staff upon request.
In accordance with the interim guidance for Section 906 certification issued by the United States Securities and Exchange Commission on March 21, 2003 in Release No.33-8212, this certification will not be deemed "filed" for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, or otherwise subject to the liability of that section. Such certification will not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into any filing under the Securities Act of 1933 or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, except to the extent that Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V. specifically incorporates it by reference.
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
CONTROLADORA COMERCIAL MEXICANA, S.A. DE C.V.
| Report of Independent Accountants | F-1 |
| | |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2002 and 2001 | F-2 |
| | |
| Consolidated Statements of Income for the Years Ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 | F-3 |
| | |
| Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders' Equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 | F-4 |
| | |
| Consolidated Statements of Changes in Financial Position for the Years Ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 | F-5 |
| | |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | F-6 |
| | |
| Costco de México, S.A. de C.V. Report of Independent Accountants | F-40 |
| | |
| Costco de México, S.A. de C.V. Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2002 and 2001 | F-41 |
| | |
| Costco de México, S.A de C.V. Consolidated Statements of Income for the Years Ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 | F-42 |
| | |
| Costco de México, S.A. de C.V. Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 | F-43 |
| | |
| Costco de México, S.A de C.V. Consolidated Statements of Changes in Financial Position for the Years Ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 | F-44 |
| | |
| Costco de México, S.A. de C.V. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | F-45 |
| | |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT ACCOUNTANTS
To the Stockholders of
Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V.
We have audited the consolidated balance sheets of Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V. and its subsidiaries as of December 31, 2002 and 2001, and the related consolidated statements of income, changes in stockholders equity and changes in financial position for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2002. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with auditing standards generally accepted in Mexico and the United States of America. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V. and its subsidiaries as of December 31, 2002 and 2001, and the results of their operations and their changes in stockholders equity and their changes in financial position for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2002, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in Mexico.
Accounting principles generally accepted in Mexico vary in certain significant respects from accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. The application of the latter would have affected the determination of consolidated net income for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2002 and the determination of consolidated stockholders equity at December 31, 2002 and 2001 to the extent summarized in Note 17 to the consolidated financial statements.
PricewaterhouseCoopers
Manuel García Braña
Mexico, D.F., February 28, 2003 (except as to Note 16, for wich the date is June 2, 2003)
CONTROLADORA COMERCIAL MEXICANA S.A. DE C.V. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET
At December 31, 2002 and 2001
(In thousands of Mexican pesos of constant purchasing power
as of December 31, 2002.) |
| | | |
| ASSETS | 2002 | 2001 |
| | | |
| Current assets: | | |
| Cash | Ps 452,316 | Ps 447,756 |
| Temporary investments | 406,575 | 805,013 |
| Trade accounts receivable | 321,705 | 360,530 |
| Other accounts and notes receivable (Note 4) | 2,269,895 | 660,509 |
| Accounts receivable from affiliated companies, net (Note 5) | 4,221 | 4,766 |
| Inventories | 3,901,808 | 4,087,976 |
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | 32,957 | 105,281 |
| | 7,389,477 | 6,471,831 |
| Property, equipment and leasehold improvements, net (Note 6) | 15,334,079 | 15,545,311 |
| Other assets | 457,094 | 367,910 |
| | | |
| Total assets | Ps 23,180,650 | Ps 22,385,052 |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY |
| Current liabilities: | | |
| Trade payables | Ps 5,649,675 | Ps 5,379,934 |
| Taxes payable | 192,191 | 169,618 |
| Financial instruments (Note 8) | - | 41,991 |
| Short-term debt (Note 7) | 157,900 | - |
| Deferred revenue (Notes 4 and 14) | 944,999 | - |
| Other accrued liabilities | 463,313 | 719,866 |
| | 7,408,078 | 6,311,409 |
| Long-term liabilities: | | |
| Long-term debt (Note 7) | 1,751,187 | 1,817,043 |
| Labor obligations (Note10) | 110,426 | 122,814 |
| Deferred income taxes (Note 14) | 2,067,846 | 2,690,414 |
| Total liabilities | 11,337,537 | 10,941,680 |
| | | |
| Stockholders' equity (Note 11): | | |
| Contributed capital: | | |
| Capital stock | 1,737,600 | 1,737,600 |
| Restatement | 5,226,107 | 5,226,107 |
| | 6,963,707 | 6,963,707 |
| Paid in-capital, net | 926,596 | 924,279 |
| | 7,890,303 | 7,887,986 |
| Earned capital: | | |
| Legal reserve | 532,089 | 492,723 |
| Retained earnings | 4,895,827 | 4,789,741 |
| Reserve for repurchase of units | 1,044,073 | 510,065 |
| Units repurchased for stock purchase plan | (34,433) | - |
| Result from holding nonmonetary assets | (3,358,475) | (3,127,530) |
| Net income for the year | 788,816 | 802,527 |
| Total earned capital | 3,867,897 | 3,467,526 |
| Total majority stockholders' equity | 11,758,200 | 11,355,512 |
| Minority interest | 84,913 | 87,860 |
| Total stockholders' equity | 11,843,113 | 11,443,372 |
| | | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | Ps 23,180,650 | Ps 22,385,052 |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
CONTROLADORA COMERCIAL MEXICANA S.A. DE C.V. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF INCOME
For the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000
(In thousands of Mexican pesos of constant purchasing power as of December 31, 2002, except for unit amounts) |
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| | | | |
| Net sales | Ps 32,053,311 | Ps 34,947,594 | Ps 34,882,852 |
| Cost of sales | 25,765,913 | 28,299,464 | 28,216,941 |
| Gross profit | 6,287,398 | 6,648,130 | 6,665,911 |
| | | | |
| Operating expenses: | | | |
| Selling | 4,633,901 | 4,831,990 | 4,603,250 |
| Administrative | 733,724 | 729,921 | 839,865 |
| | 5,367,625 | 5,561,911 | 5,443,115 |
| Operating income | 919,773 | 1,086,219 | 1,222,796 |
| | | | |
| Integral result of financing: | | | |
| Interest expense | (230,713) | (271,758) | (259,662) |
| Gain (loss) from forward agreements | 49,524 | (41,991) | - |
| Interest income | 43,139 | 58,712 | 58,061 |
| (Loss) gain from repurchase of notes | (8,199) | - | 309 |
| Foreign-exchange gain (loss) , net | (218,416) | 23,641 | (57,484) |
| Gain from monetary position | 305,575 | 241,878 | 501,005 |
| | (59,090) | 10,482 | 242,229 |
| | | | |
| Income after integral result of financing | 860,683 | 1,096,701 | 1,465,025 |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Miscellaneous income, (expense), net | 4,831 | (18,622) | (157,920) |
| | | | |
| Income before provisions for income taxes and employee statutory profit sharing | 865,514 | 1,078,079 | 1,307,105 |
| | | | |
| Provisions for income taxes and employee statutory profit sharing (Note 14) | 69,634 | 266,761 | 82,562 |
| | | | |
| Income before minority interest | 795,880 | 811,318 | 1,224,543 |
| | | | |
| Interest of minority stockholders in the results of subsidiaries | (7,064) | (8,791) | (8,164) |
| | | | |
| Net income for the year | Ps 788,816 | Ps 802,527 | Ps 1,216,379 |
| | | | |
| Average number of units | 1,078,225,000 | 1,061,260,000 | 1,079,537,000 |
| | | | |
| Net income per units: | | | |
| Before minority interest | Ps 0.73 | Ps 0.76 | Ps 1.12 |
| Minority interest | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| After minority interest | Ps 0.73 | 0.76 | Ps 1.12 |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
CONTROLADORA COMERCIAL MEXICANA S.A. DE C.V. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS EQUITY
For the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000
(In thousands of Mexican pesos of constant purchasing power as of December 31, 2002, except for unit amounts) |
| | Capital stock | Paid-in capital, net | Legal reserve | Retained earnings | Reserve for repurchases of units | Units repurchased for stock purchase plan | Result from holding non-monetary assets | Net income for the year | Majority stock-holders' equity | Minority interest | Total stock- holders' equity |
| | Ps | Ps | Ps | Ps | Ps | Ps | Ps | Ps | Ps | Ps | Ps |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balances as of December 31, 1999 | 6,963,707 | 1,012,432 | 359,872 | 5,108,237 | 445,214 | (6,361) | (2,577,565) | 1,509,775 | 12,815,311 | 111,941 | 12,927,252 |
| Resolutions of the General Ordinary Stockholders' Meeting held on April 14, 2000: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Transfer to retained earnings | | | | 1,436,767 | | | | (1,436,767) | | | |
| Increase legal reserve | | | 73,008 | | | | | (73,008) | | | |
| Dividends paid (Ps 0.092 per unit) | | | | (116,071) | | | | | (116,071) | | (116,071) |
| Repurchase of units for stock purchase plan, net | | | | | | (589) | | | (589) | | (589) |
| Repurchase of units for treasury stock, net | | | | | (212,365) | | | | (212,365) | | (212,365) |
| Initial effects of deferred taxes | | | | (2,580,048) | | | | | (2,580,048) | | (2,580,048) |
| Decrease in minority interest | | | | | | | | | | (23,750) | (23,750) |
| Comprehensive income (Note 2 .p.) | | | | | | | (309,687) | 1,216,379 | 906,692 | | 906,692 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balances as of December 31, 2000 | 6,963,707 | 1,012,432 | 432,880 | 3,848,885 | 232,849 | (6,950) | (2,887,252) | 1,216,379 | 10,812,930 | 88,191 | 10,901,121 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Resolutions of the General Ordinary Stockholders' Meeting held on April 5, 2001: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Transfer to retained earnings | | | | 1,156,536 | | | | (1,156,536) | | | |
| Increase legal reserve | | | 59,843 | | | | | (59,843) | | | |
| Dividends paid (Ps 0.107 per unit) | | | | (122,882) | | | | | (122,882) | | (122,882) |
| Increase in the reserve for repurchase of units | | | | (92,798) | 92,798 | | | | | | |
| Reissuance of units for stock purchase plan, net | | | | | | 6,950 | | | 6,950 | | 6,950 |
| Reissuance of units for treasury stock, net | | (88,153) | | | 184,418 | | | | 96,265 | | 96,265 |
| Decrease in minority interest | | | | | | | | | | (331) | (331) |
| Comprehensive income (Note 2 .p.) | | | | | | | (240,278) | 802,527 | 562,249 | | 562,249 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balances as of December 31, 2001 | 6,963,707 | 924,279 | 492,723 | 4,789,741 | 510,065 | - | (3,127,530) | 802,527 | 11,355,512 | 87,860 | 11,443,372 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Resolutions of the General Ordinary Stockholders' Meeting held on April 11, 2002: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Transfer to retained earnings | | | | 763,161 | | | | (763,161) | | | |
| Increase legal reserve | | | 39,366 | | | | | (39,366) | | | |
| Dividends paid (Ps 0.107 per unit) | | | | (120,489) | | | | | (120,489) | | (120,489) |
| Increase in the reserve for repurchase of units | | | | (536,586) | 536,586 | | | | | | |
| Repurchase of units for stock purchase plan, net | | 2,317 | | | | (34,433) | | | (32,116) | | (32,116) |
| Repurchase of units for treasury stock, net | | | | | (2,578) | | | | (2,578) | | (2,578) |
| Decrease in minority interest | | | | | | | | | | (2,947) | (2,947) |
| Comprehensive income (Note 2 .p.) | | | | | | | (230,945) | 788,816 | 557,871 | | 557,871 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balances as of December 31, 2002 | 6,963,707 | 926,596 | 532,089 | 4,895,827 | 1,044,073 | (34,433) | (3,358,475) | 788,816 | 11,758,200 | 84,913 | 11,843,113 |
The accompanying notes are integral part of these financial statements.
CONTROLADORA COMERCIAL MEXICANA S.A. DE C.V. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN FINANCIAL POSITION
For the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000
(In thousands of Mexican pesos of constant purchasing power as of December 31, 2002) |
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Operating activities: | | | |
| Net income | Ps 788,816 | Ps 802,527 | Ps 1,216,379 |
| Items applied to income not requiring | | | |
| the use (providing) of funds: | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 724,769 | 722,096 | 679,022 |
| Provision for deferred taxes | (61,778) | 224,942 | (74,251) |
| Labor obligations | 14,491 | 11,787 | 20,073 |
| Minority interest | 7,064 | 8,791 | 8,164 |
| | 1,473,362 | 1,770,143 | 1,849,387 |
| | | | |
| (Increase) decrease in: | | | |
| Accounts receivable | (1,570,016) | (225,801) | 212,937 |
| Inventories | (44,777) | (23,099) | (202,263) |
| Prepaid and other expenses | 84,832 | (2,650) | (8,691) |
| Increase (decrease) in: | | | |
| Trade payables | 269,741 | (650,683) | (113,022) |
| Taxes payable | 22,573 | (90,832) | 32,993 |
| Other accrued liabilities | 114,230 | (3,892) | 84,658 |
| Resources provided by operating activities | 349,945 | 773,186 | 1,855,999 |
| | | | |
| Financing activities: | | | |
| Increase in short-term debt | 157,900 | - | - |
| Decrease in long-term debt | (65,856) | (91,824) | (45,001) |
| (Decrease) increase in financial instruments | (41,991) | 41,991 | - |
| Paid in-capital | 2,317 | (88,153) | - |
| Minority interest | (10,011) | (9,122) | (31,913) |
| Dividends paid | (120,489) | (122,882) | (116,071) |
| (Repurchase) reissuance of units for treasury stock, net | (2,578) | 184,418 | (212,365) |
| Units (repurchased) reissued for stock purchase plan | (34,433) | 6,950 | (589) |
| | | | |
| Resources used in financing activities | (115,141) | (78,622) | (405,939) |
| | | | |
| Investing activities: | | | |
| (Increase) decrease in other assets | (115,145) | 114,367 | - |
| Acquisitions of property and equipment, | | | |
| leasehold improvements and other assets | (742,419) | (1,205,630) | (1,382,665) |
| Disposition of property and equipment | 228,882 | 234,762 | 165,934 |
| | | | |
| Resources used in investing activities | (628,682) | (856,501) | (1,216,731) |
| | | | |
| Net (decrease) increase in cash and temporary investments | (393,878) | (161,937) | 233,329 |
| Cash and temporary investments at beginning of year | 1,252,769 | 1,414,706 | 1,181,377 |
| Cash and temporary investments at end of year | Ps 858,891 | Ps 1,252,769 | Ps 1,414,706 |
| | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
1.ORGANIZATION AND BACKGROUND:
Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V. (CCM, and together with its consolidated subsidiaries, "the Company") was founded as a partnership on January 28, 1944, under the name of Antonino González e hijo. On July 1, 1957, it was incorporated under the name of Comercial Mexicana; on March 5, 1982, it became a limited liability company with variable capital (Sociedad Anónima de Capital Variable). On December 9, 1988, the Company changed its name to Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V., and modified its corporate by-laws, effective January 1, 1989, to enable it to engage in the business of leasing personal property and real estate, and investing in companies engaged in the purchase, sale and distribution of groceries and general merchandise in the Mexican Republic.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES:The principal accounting policies followed by the Company, which are in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in Mexico, are summarized below:
a)Revenue Recognition
Revenue from product sales is recognized at the point of sale, except for the layaway transactions that are recognized when the customer satisfies all payment obligations and takes possession of the merchandise; revenues from membership fees are recognized when they are collected.
b)Consolidation
The percentage investment in significant subsidiary companies is 99.99%, except Costco de México with 50%.
| Subsidiary | Activity |
| Comercial Mexicana, S.A. de C.V. | Operated of a chain of 132 stores (134 in 2001). |
| Super Mercados, S.A. de C.V. | Operated of a chain of 17 stores (18 in 2001). |
| Restaurantes California, S.A. de C.V. | Operated of a chain of 55 restaurants (50 in 2001). |
| Costco de Mexico, S.A. de C.V. | Operated of a chain of 21 membership warehouse stores (20 in 2001). |
| Subsidiary real estate companies | Group of real estate companies. |
| Subsidiary service companies | Group of services companies. |
The Company consolidates the accounts of all majority-owned subsidiaries. The investment in subsidiary companies and the transactions and balances between them have been eliminated from these financial statements.
The Company’s investment in the Costco de Mexico Group joint venture with Costco Wholesale Corporation, meets the joint control criteria discussed in International Accounting Standard No. 31. Accordingly, the Company reports its investment under the proportionate consolidation method.
c)Temporary investments
Temporary investments are recorded at market value as of the balance sheet date. Unrealized gains and losses are included in interest income.
d)Inventories and cost of sales
Inventories and cost of sales are initially recorded using the retail method, which is equivalent to replacement cost and due to the high inventory turnover, amounts so determined do not exceed the market value.
e)Advertising cost
Advertising consists primarily of print, radio and television advertisements. Advertising Costs are expensed as incurred; for the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 advertisement expense amounted to $414 million, $492 million and $494 million , respectively.
f)Vendor discounts
The Company receives discounts from many of the vendors whose products the Company buys for resale in its stores. These vendor discounts are provided to increase the sell-through of the related products. The Company receives discounts for a variety of merchandising activities: placement of the vendor's products in the Company's advertising; placement of the vendor's products in prominent locations in the Company's stores; and to compensate for temporary price reductions offered to customers on products held for sale at retail stores. The Company also receives vendor discounts for buying activities; such as volume commitment rebates. The Company recognized vendor discounts for merchandising activities as an offset to cost of sales when the merchandising activity is performed in accordance with the underlying agreements.
g)Property, equipment and leasehold improvements
The Company restates the amounts of property, equipment and leasehold improvements according to changes in the Nacional Consumer Price Index ("NCPI"), in compliance with the Bulletin B-10 and its amendments.
Depreciation and amortization are calculated by the straight-line method based on the useful lives of the assets, on acquisition cost and restatement. (See Note 6).
h)Long-lived assets
The Company evaluates potential impairment losses to long-lived assets by assessing whether the unamortized carrying amount can be recovered over the remaining life of the assets through undiscounted future expected cash flows generated by the assets and without interest charges. If the sum of the expected future undiscounted cash flow is less than the carrying amount of the assets, a loss is recognized for the difference between the fair value and carrying value of the assets. Long-lived assets are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount may not be recoverable. Long-lived assets for which management has committed to a plan of disposal are recorded at the lower of the unamortized carrying amount or fair value less disposal cost.
i)Segment reporting
In August 1997, the International Accounting Standards Committee issued revised IAS No. 14, "Segment Reporting" ("IAS 14"), which is applicable to Mexican companies under Bulletin A-8. IAS 14, which is effective for years beginning after June 30, 1998, requires companies to look at their internal organizational structure and internal reporting system for the purpose of identifying segments. (See Note 15).
j)Pre-opening costs
Costs associated with the opening of new stores are expensed in the same fiscal year in which such stores start operations.
k)Stock purchase plan
The Company has established a stock purchase plan in which the Company purchases its own units and grants key personnel the right to purchase units on an installment basis. The units are sold to employees at the fair market value on the day granted. The employees pay for their stock purchases ratably over a nine-year period. Accounts receivable from employees for the short-term purchase of units are recorded as other accounts and notes receivable. On the other hand, those maturing longer than a year are recorded under other assets. At December 31,2002, the short-term and long-term units assigned to employees amount approximately to 44,809,924.
l)Income tax
Income tax is recorded by the comprehensive asset-and-liability method, which consists of recognizing deferred tax on all temporary differences between the book and tax values of assets and liabilities. (See Note 14).
Deferred employees’ statutory profit sharing is recorded only in respect of those temporary differences between book income and income adjusted for profit sharing purposes which reasonably be presumed to result in a future liability or benefit.
m)Pension plans, seniority premiums and indemnities
In accordance with Mexican Federal Labor Law, the Company’s Mexican employees are entitled to seniority premiums after 15 years of service or upon dismissal, disability or death. Under Bulletin D-3, "Labor Obligations", the actuarially determined projected benefit obligation is computed using estimates of salaries that would be in effect at the time of payment. Employees not yet eligible for seniority premiums are also included in the determination of the obligation with necessary adjustments made in accordance with the probability that these employees will reach the required seniority. The cost of past service is amortized over the average period required for workers to reach their retirement age. The cost of the employee retirement plans (pensions and seniority premiums), both formal and informal, is recognized as expense in the years in which the services are rendered, in accordance with studies performed by independent actuaries using the projected unit credit method. (See Note 10).
In accordance with Mexican Federal Labor Law, other compensation, based on length of service, to which employees may be entitled in the event of dismissal or death, are charged to income in the year in which they become payable.
n)Foreign currency transactions
Transactions in foreign currencies are recorded at the rates of exchange prevailing on the dates they are entered into and/or settled. Assets and liabilities denominated in such currencies are stated at the Mexican peso equivalents resulting from applying the rates prevailing on the balance sheet dates. Exchange differences arising from fluctuations in the exchange rates between the transaction and settlement dates, or the balance sheet date, are charged or credited to income. (See Note 13).
o)Financial instruments
Effective on January 1, 2001, the Company adopted the guidelines of amended Bulletin C-2, "Financial Instruments" ("Bulletin C-2"), which gives new guidelines for the recognition and disclosure of derivative financial instruments. Bulletin C-2 requires, for instruments not designated as a hedge, the recognition of asset or liability derived from the difference between acquisition cost and fair value of these instruments. Subsequent fair value adjustments are reflected in the statement of income. Upon adoption, the most significant effect of this new accounting bulletin was for the accounting of equity swap share ("Equity Swap") transactions.
Derivative financial instruments are used by the Company primarily to manage its (i) interest rate risk and (ii) foreign exchange rate risk. Interest rate swaps are employed to achieve the Company’s interest rate objectives.
p)Comprehensive income
As of January 1, 2001, Bulletin B-4, "Comprehensive Income", entered into effect. This bulletin requires that the various components of stockholders’ equity resulting from non-owner transactions be shown in the statement of changes in stockholders’ equity under the item of comprehensive income.
Comprehensive income is represented by the net income plus the gain or loss from holding non-monetary assets, and items required by specific accounting standards to be reflected in stockholders’ equity but which do not constitute capital contributions, reductions or distributions. It is restated on the basis of NCPI factors.
q)Use of estimates
The preparation of the financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles, requires Management to make estimates that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the dates of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods. Therefore, actual results could differ from those estimates.
r)Earning per unit
Earning per unit is computed by dividing the net income by the weighted average number of unit outstanding during 2002 and 2001.
s)New accounting standards
In December 2001 the Mexican Institute of Public Accountants ("MIPA") issued revised Statement C-9, "Liabilities, Provisions, Contingent Assets and Liabilities and Commitments", which supersedes the original Statements C-9 and C-12, both from 1974, and Circulars 46, 47 and 48. The provisions of this new Statement are effective for years beginning on or after January 1, 2003; however, early adoption is recommended.
The objective of this Statement is to establish rules for valuation and disclosure of liabilities and provisions, to determine particular rules for valuation and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, and to provide rules for disclosure of commitments acquired by an entity as a part of its normal activities.
In February 2002, the MIPA issued revised Statement C-8, "Intangible Assets", which supersedes the current Statement C-8, effective since 1976. The provisions of this new Statement are effective for years commencing on or after January 1, 2003; however, early adoption is recommended.
The significant provisions of this Statement are: (i) it establishes rules and criteria for accounting for research and development costs; (ii) pre-operating costs identified with research and development activities are charged to expenses; and (iii) valuation rules are based on a logical sequence of the assets’ useful life, considering initial recognition and valuation of the intangible asset, recognition of an expense, additional payments and valuation after the initial recognition.
In March 2003, the MIPA issued Bulletin B-5 "Segment Financial Information". The Bulletin B-5 nullifies the application of the IAS No. 14 "Segment reporting" which was applicable to the Mexican companies under Bulletin A-8. The Bulletin B-5 establishes standards for the way that Mexican Companies report information about operating segments in annual financial statements and requires that those enterprises report selected information about operating segments in interim financial reports issued to stockholders. It also establishes standards for related disclosures about economic segments, geographic areas, and major customers. The Bulletin B-5’s framework for segment reporting is referred to as the management approach. It is intended to give analysts and other financial statement users a view of the enterprise through the eyes of management by looking to a company’s internal management reporting structure as the basis for determining the company’s external segments as well as the basis for determining the information that is to be disclosed for those segments. The provisions of the Bulletin B-5 are required to be applied after its publication. The Company is presently evaluating the impact, if any, that these new standards will have on the consolidated financial statements.
The MIPA issued Bulletin C-15, "Impairment and Disposal of Long-Lived Assets", ("Bulletin C-15"), which will be effective as of January 1, 2004, although early adoption is recommended. Bulletin C-15 provides specific criteria in determining when there is impairment in the value of long-lived assets, for both tangible and intangible assets. Furthermore, Bulletin C-15 establishes a methodology for calculating and recording losses arising from the impairment of assets and their reversal. Also, Bulletin C-15 provides guidance as to presentation and disclosure in the case that there is subsequent reversal of the impairment. In addition, Bulletin C-15 provides guidance for the accounting, presentation and disclosure for discontinued operations. The Company is currently evaluating the impact that adoption of this statement will have on its consolidated financial statements.
3. EFFECTS OF INFLATION ON THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:
The consolidated financial statements of the Company have been prepared in accordance with Bulletin B-10, "Recognition of the Effects of Inflation on Financial Information," as amended, issued by the MIPA. The financial statements have been presented in pesos of constant purchasing power as of December 31, 2002 to be comparable to financial information as of that date, as follows:
The balance sheets have been restated at constant pesos as of December 31, 2002 using the NCPI as of that date.
The statements of income have been restated at constant pesos as of December 31, 2002 using the NCPI for the month in which the transactions were executed.
NCPI used to restate prior years financial statements are as follows:
| | Inflation for the period | Cumulative inflation as for December 31, 2002 |
| | | |
| 2000 | 8.96% | 20.24% |
| 2001 | 4.40% | 10.35% |
| 2002 | 5.70% | 5.70% |
The following items are the result of the recognition of the effects of inflation on the financial information.
Capital stock and earned capital
Capital stock, capital reserves and retained earnings represent the value of these items stated in purchasing power as of the most recent balance sheet date, and are determined by applying factors derived from the NCPI to the historical amounts.
Paid in-capital
The unit premiums represent the difference between the payment for the units subscribed and the nominal value of those units, which is restated by applying NCPI factors.
Deficit in the restatement of capital
The deficit in the restatement of capital is composed mainly of the initial cumulative effects of inflation and of the loss from holding non-monetary assets of property, equipment, leasehold improvements and inventories, restated in Mexican pesos of purchasing power as of the most recent balance sheet date.
During 2002 and 2001 the deficit is due to the fact that inventories are valued at reposition cost instead of the restatement they should have under the change method at general price level.
Gain from monetary position
The gain from monetary position represents the inflation gain, measured in terms of the NCPI, on net monthly monetary assets and liabilities for the year, expressed in pesos of purchasing power as of the most recent balance sheet date.
4. OTHER ACCOUNTS AND NOTES RECEIVABLE:
At December 31, other accounts and notes receivable consist of the following:
| | | 2002 | | 2001 |
| Government of Distrito Federal (1) | Ps | 1,177,826 | Ps | - |
| Lease receivables | | 8,462 | | 5,950 |
| Receivables from employees (2) | | 49,979 | | 38,772 |
| Value- added tax and income tax receivables | | 836,110 | | 431,196 |
| Others | | 197,518 | | 184,591 |
| | Ps | 2,269,895 | Ps | 660,509 |
(1) During the fourth quarter of 2002 the Company participated in a public auction and obtained an important voucher contract from the Government of Mexico City. This contract accounted for approximately US$140 million and benefited around 300,000 local employees. Pursuant to this contract, the Company offers all program participants a 22% of discount on all the merchandise. The Company recognized an account receivable and a deferred revenue of approximately US$ 109 million. The revenue is recognized when the customers purchase merchandise using the vouchers. As of December 31, 2002, the recognized revenue of this transaction reached US$ 62 million.
(2) Primarily receivables arising from installment sales under the employees stock purchase plan. The non-current portion of receivables from the stock purchase plan amounts Ps 90,189 and Ps 115,947 in 2002 and 2001, respectively, and are included in other assets.
5. RELATED PARTIES:
The Company’s majority stockholders own a controlling interest in Nova Distex, S.A. de C.V. (Nova Distex), a textile manufacturer and property management company. The Company provides management services to Nova Distex and purchases textiles for resale in its stores.
At December 31, accounts receivable and payable consist of the following:
| | 2002 | 2001 |
| Accounts receivable: | | |
| Nova Distex, S. A. de C. V. | Ps 5,343 | Ps 1,628 |
| Compania Industrial Distex, S. A. de C. V. | - | 267 |
| Other | - | 3,380 |
| | Ps 5,343 | Ps 5,275 |
| | | |
| Accounts payable: | | |
| Nova Distex, S. A. de C. V. | Ps 269 | Ps 77 |
| Operadora Polynova, S. A. de C. V. | 409 | 432 |
| Other | 444 | - |
| | Ps 1,122 | Ps 509 |
| Net | Ps 4,221 | Ps 4,766 |
The following table summarizes the amounts recorded in the Company’s accounts, which relate to transactions with Nova Distex.
| | | 2002 | | 2001 | | 2000 |
| Costs and expenses: | | | | | | |
| Purchases | Ps | 75,598 | Ps | 85,553 | Ps | 95,000 |
| Purchase of fixed assets and others | | 121,920 | | 6,997 | | 45,929 |
| Sale of fixed assets | | 40,000 | | - | | - |
6. PROPERTY, EQUIPMENT AND LEASEHOLD IMPROVEMENTS:
Property, equipment and leasehold improvements consist of the following at December 31:
| | | 2002 | | 2001 | | Average Depreciation Rate |
| Buildings | Ps | 6,209,453 | Ps | 6,142,972 | | 2 % |
| Store fixtures | | 3,256,247 | | 3,506,568 | | 10 % |
| Electronic equipment | | 840,355 | | 846,706 | | 25 % |
| Office fixtures | | 75,986 | | 87,470 | | 10 % |
| Leasehold improvements | | 2,392,256 | | 2,243,638 | | 5 % |
| | | 12,774,297 | | 12,827,354 | | |
| Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization | | 5,038,915 | | 4,887,247 | | |
| | | 7,735,382 | | 7,940,107 | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Land | | 7,460,658 | | 7,467,245 | | |
| Construction in progress and advances for purchase of fixed assets | | 138,039 | | 137,959 | | |
| | Ps | 15,334,079 | Ps | 15,545,311 | | |
Depreciation expense amounted to Ps 724,769, Ps 722,096 and Ps 679,022, for the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000, respectively.
7. DEBT:
Total debt as of December 31, consists of the following obligations:
| | | 2002 | | 2001 |
| Unsecured notes of US$84.8 million (US$100 million in 2001) maturing in 2005, at a fixed interest rate of 9.375% payable semi-annually. (1) | Ps | 881,600 | Ps | 968,212 |
| Direct loan of US$30 million, maturing in 2004; at a fixed interest rate LIBOR plus 1.75 | | 311,850 | | 290,464 |
| Debenture bonds of 172.9 million Investment Units (UDIs) Maturing in 2010 at a fixed interest rate of 8%, payable semi-annually.(2) | | 557,737 | | 558,367 |
| Direct loan of US$15.2 million, maturing in 2003, at a fixed interest rate of 2.19% | | 157,900 | | - |
| | | 1,909,087 | | 1,817,043 |
| Less: | | | | |
| Short-term debt | | 157,900 | | - |
| Total long-term debt | Ps | 1,751,187 | Ps | 1,817,043 |
(1) In April 1998, CCM issued US$130 million Series B unregistered bonds at a fixed interest rate of 9.375% . Interest on this bond is payable semi-annually in April and October of every year beginning October 1998. Beginning April 2003, CCM has the option to repurchase these bonds, partially or fully, at 104.5% of their nominal value, and 102.25% twelve months after that date. The agreement for this bond has certain covenants that, among other things, limit the ability of CCM and its Restricted Subsidiaries (as defined) to: (i) incur additional indebtedness; (ii) make certain restricted payments (iii) allow restrictions on distributions from Restricted Subsidiaries; (iv) incur liens; (v) enter into certain transactions with affiliates; (vi) sell, assign, transfer, lease, convey or otherwise dispose of all or substantially all of the assets of the Company; (vii) enter into sale and leaseback transactions; (viii) issue capital stock of its Restricted Subsidiaries; and (ix) merge or consolidate with any other entity. Additionally CCM will be required to make an offer to purchase the Notes at a price equal to 100% of the principal amount thereof, plus accrued and unpaid interest to the date of the purchase with the proceeds of certain asset sales. During 2002 and 2000, CCM repurchased US$15.2, and US$1.5 million Notes (fair value), which were cancelled in 2002 and 2000, respectively. In June 2003 CCM exercised the option to repurchase these bonds (See Note 16).
(2) In December 2000, CCM subscribed a program of debentures in an amount up to Ps 1.5 billion. CCM further issued 1,729,000 debenture bonds with a face value of 100 Investment Units (UDIs) each and amounts to an equivalent of 172.9 million Investment Units (UDIs) over a ten year term with a fixed interest rate of 8.45%, plus the increase in the NCPI issued by Banco de Mexico in the value of each UDI. Interest accrued on the debenture bonds will be liquidated every semester on the eighth of June and December every year. The contract has certain financial restrictive covenants that limit the ability of the Company and its subsidiaries (as defined): (i) limit to acquire additional debt; (ii) limitations on encumbrances; (iii) conditions for mergers, spin-offs or sale of assets; (iv) limitation on dividends paid; (v) maintaining a certain degree of priority.
At December 31, 2002, and 2001, the Company had an aggregate of over Ps 4,910 million and Ps 4,679 million of credit available, respectively, through unused uncommitted lines of credit with ten banking institutions in 2002 and nine in 2001, under which the Company may borrow in pesos or, at its option, in U.S. dollars (converted to pesos at the exchange rate in effect at the time of the borrowing). The terms and conditions of such lines of credit will be determined at the time when they are utilized. The Company renews its bank lines of credit on a yearly basis. The bank credit lines do not contain any financial covenants.
During 2002, 2001 and 2000, CCM paid Ps 147,910, Ps 167,125 and Ps 187,368, respectively, of interest on debt.
8. FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS:
At December 31, 2002 and 2001, CCM has financial derivative instruments agreements as follows:
| | Fair Value |
| | 2002 | 2001 |
| Interest rate swap, CCM receives 9.375% fixed rate and pays a six months LIBOR rate plus 5.38%, payable semi-annually on a US$30 million base, maturing on April 2005, and an option for CCM with a limit in the LIBOR rate plus 4.38% if the LIBOR rate exceed 7%. | Ps 14,192 | Ps - |
| | | |
| Interest rate swap, CCM pays LIBOR rate plus 3.5% and receives a fixed rate of 9.375%, payable semi-annually on a US$10 million base, and an option for CCM that limits the payment to 5.10% and expires when LIBOR rate exceed 7.10%. | 11,121 | - |
| | | |
| Interest rate swap, CCM pays a six months LIBOR rate plus 4.29% and receives a fixed rate of 8.0%, payable semi-annually on a 100 million Investments Units (UDIs) base, maturing on December 2007. | 3,500 | - |
| | | |
| Currency swap to realize on April 2005, CCM pays on Mexican Pesos the equivalent to 74,004,278 (UDIs) at that date receives US$20 million, with an option that requires CCM to pay in case of currency exchange exceed $18.6 Mexican Pesos per US Dollar. | (21,280) | (32,587) |
| | | |
| Currency swap for the acquisition of US$30 million at a currency exchange of $9.85 Mexican Pesos per US Dollar, maturing on December 2002. | - | (9,404) |
| | | |
| Fair value effect | Ps 7,533 | Ps (41,991) |
9. LEASES:
The Company leases certain retail locations, warehouse and distribution space under operating leases. Some leases require that the fixed portion of the rent be negotiated annually. Certain leases also provide for contingent rentals based on the sales revenue of the individual stores or restaurants. As leases expire, it can be expected that in the normal course of business, they will be renewed or replaced.
Total rent expense for operating leases for each of the three years ended December 31, is as follows:
| | | 2002 | | 2001 | | 2000 |
| Base rent | Ps | 175,492 | Ps | 191,086 | Ps | 159,186 |
| Contingent rent | | 77,970 | | 99,198 | | 115,657 |
| | | | | | | |
| Total rent expense | Ps | 253,462 | Ps | 290,284 | Ps | 274,843 |
Minimum rental commitments under non-cancelable operating leases at December 31, 2002, are as follows:
| | | Amount |
| 2003 | Ps | 175,492 |
| 2004 | | 175,492 |
| 2005 | | 175,492 |
| 2006 | | 175,492 |
| 2007 and thereafter | | 359,721 |
| | | |
| | Ps | 1,061,689 |
10. SOCIAL WELFARE AND LABOR OBLIGATIONS:
An irrevocable trust fund has been set up for voluntary retirement, death, permanent total disability, hospital medical services and disability payments to which administrative employees are entitled in accordance with the rules of the plan established for that purpose. The Company makes contributions of between 20% and 24% of the principal employees’ salaries to the trust. The Company has no obligation to the employees for benefits in addition to the contributions made. The trust maintains the plan and handles all payments made to the employees covered under the plan. During the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000, contributions were made amounting to Ps 222,290, Ps 227,870 and Ps 209,460,respectively.
Under Federal Labor Law in Mexico, the Company is liable for payments to employees terminated under certain circumstances. In the Company’s main subsidiaries, trust funds have been established to cover incurred and contingent obligations for seniority premiums that are derived from the application of Federal Labor Law.
The cost of these seniority premiums and pension plan is computed based on actuarial calculations using the projected unit credit method. This method establishes the procedures for measuring the expenses and liabilities for the pension plan and seniority premiums.
The net cost of this period amounted to Ps 14,491, Ps 18,438 and Ps 20,073 in 2002, 2001 and 2000, respectively.
The amounts of projected benefits for labor obligations at December 31, 2002 and 2001 (See Note 2.m.) are as follows:
| | | 2002 | | 2001 |
| Accumulated benefit obligation | Ps | (115,520) | Ps | (120,871) |
| Additional projected benefits | | (17,839) | | (21,667) |
| Projected benefit obligation | | (133,359) | | (142,538 |
| Less: | | | | |
| Plan assets | | 35,088 | | 29,301 |
| | | | | |
| Projected benefit obligation in excess of plan assets | | (98,271) | | (113,237) |
| Net transition assets, changes in assumption and adjustments based on experience | | (12,155) | | (9,577) |
| Accrued liabilities | Ps | (110,426) | Ps | (122,814) |
11. STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY:
The authorized capital stock is comprised of 1,086,000,000 B and BC related unit with no stated value. At December 31, 2002, subscribed and paid B and BC units are 747,551,610 and 338,448,390, respectively (747,711,639 and 338,288,361, respectively in 2001).
Each stockholder owns either one BC unit consisting of three B shares and one C share or one B unit consisting of four B shares, both of which trade on the Mexican Stock Exchange.
The nominal capital stock, with Ps1,737,600 stated value, consists of Ps298,258 cash contributions, Ps909,632 of capitalized profits and Ps529,710 of capitalized effects of restatement.
At the General Ordinary Stockholders’ Meeting held on March 31, 1992, a resolution was passed approving the creation of a reserve for the temporary repurchase for the purposes of acquiring the Company’s units. Later on, at the General Ordinary Stockholders’ Meeting held on April 11, 2002 it was approved to increase this reserve up to Ps1,000,000. The amount of this reserve fluctuates as CCM purchases and sales its own units in the stock market. During 2002 and 2001, transactions were held in the net amounts of Ps(2,578) and Ps184,418, respectively, against this reserve.
The profit for the period is subject to the legal disposition requiring at least 5% of the profit for each period to be set aside to increase the legal reserve until it reaches an amount equivalent to 20% of the capital stock.
Dividends paid are not subject to income tax if paid from the Net Tax Profit Account. Any excess over this account is subject to a tax equivalent to 53.85%, which is payable by CCM and may be credited against its income tax in the following three years. Dividends paid are not subject to tax withholding.
At December 31, 2002, cumulative earnings that have been subject to income tax and can be distributed by CCM free of Mexican withholding tax were approximately Ps 3,481 ($84,503 in 2001).
In the event of a capital reduction, any excess of stockholders’ equity over capital contributions, the latter restated in accordance with the provisions of the Income Tax Law, is accorded the same tax treatment as dividends.
12. STOCK PURCHASE PLAN:
CCM has a stock purchase plan under which key employees are granted rights to purchase the Company’s common stock at no less than 100% of the market price on the date the options are granted. The rights vest equally over a five-year. Beginning in 1999, this term was extended for four additional years. Employees selected to participate in the stock purchase plan have the right to receive the fair value appreciation of their allocated units in lieu of exercising their purchase privileges on the planned anniversary dates.
At December 31, 2002 there were 6,384,196 units available for granting to employees. At December 31, 2000, 1,095,164 units were available for granting to employees. These units have been repurchased by CCM and placed in a trust.
A summary of changes in the stock purchase plan during 2002, 2001 and 2000, is as follows:
| | Number of Units | Weighted Average Exercise Price |
| | | |
| Outstanding at January 1, 2000 | 14,329,986 | Ps 6.10 |
| Granted | 4,558,785 | 8.29 |
| Exercised | (1,360,426) | 10.85 |
| Cancelled | (1,006,510) | 6.55 |
| | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2000 | 16,521,835 | Ps 6.77 |
| Granted | 6,329,495 | 7.49 |
| Exercised | (977,794) | 8.17 |
| Cancelled | (1,108,104) | 7.78 |
| | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2001 | 20,765,432 | Ps 7.05 |
| Granted | 1,101,216 | 6.60 |
| Exercised | (218,779) | 7.49 |
| Cancelled | (1,679,479) | 7.41 |
| | | |
| Outstanding (held by 311 employees) at December 31, 2002 | 19,968,390 | Ps 7.00 |
| | | |
| Units exercisable at: | | |
| December 31, 2000 | 3,525,840 | Ps 5.37 |
| December 31, 2001 | 5,340,040 | Ps 5.60 |
| December 31, 2002 | 7,528,008 | Ps 5.64 |
Outstanding stock options at December 31, 2002, are as follows:
| | Outstanding | | Exercisable |
| Exercise Price Range | BC Units | Average Life (a) | Average Exercise Price | BC Units | Average Exercise Price |
| Ps 3.54-5.00 | 6,863,335 | 3.51 | Ps 7.23 | 6,074,941 | Ps 5.13 |
| 7.00-9.58 | 13,105,055 | 6.51 | 6.88 | 1,453,067 | 7.45 |
| Total | 19,968,390 | 5.48 | Ps 7.00 | 7,528,008 | Ps 5.64 |
Outstanding stock options at December 31,2001, are as follows:
| | Outstanding | | Exercisable |
| Exercise Price Range | BC Units | AverageLife (a) | Average Exercise Price | BC Units | Average Exercise Price |
| Ps 3.54-5.00 | 7,408,020 | 4.53 | Ps 4.99 | 4,532,181 | Ps 4.99 |
| 7.00-9.58 | 13,357,412 | 7.70 | 8.19 | 807,859 | 8.45 |
| Total | 20,765,432 | 6.57 | Ps 7.05 | 5,340,040 | Ps 5.60 |
(a) Average contractual life remaining in years
Additionally, during 2001 CCM has established a long-term option plan of units to key personnel, which purchase his/her own units grants under certain circumstances. This units are sold to employees at the fair market value on the day granted; at December 31, 2002 and 2001, 24,841,534 units were granted to employees at the exercise price of Ps 6.13.
13. FOREIGN CURRENCY POSITION:
The foreign currency position as of December 31, is as follows:
| | | | | Year-end Exchange Rates (1) | |
| | 2002 | 2002 | 2001 | 2002 | 2001 |
| Assets: | | | | | |
| US Dollars: | | | | | |
| Investments in securities | Ps 311,257 | US$ 29,943 | US$ 23,193 | Ps 10.395 | Ps 9.16 |
| Liabilities: | | | | | |
| US Dollars: | | | | | |
| Debt and other liabilities | Ps 1,847,628 | US$ 177,742 | US$ 155,376 | Ps 10.395 | Ps 9.16 |
(1) In pesos per US dollar. The assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currency are translated in the financial statements at the exchange rates mentioned above.
As of December 31, 2002 and 2001, the Company had foreign non-monetary assets or whose replacement cost is determined in foreign currency, as detailed below:
| | | 2002 | | 2002 | | 2001 |
| | | | | | | |
| Computer equipment | Ps | 691,621 | US$ | 66,534 | US$ | 56,925 |
| Inventories | | 286,673 | | 27,578 | | 24,113 |
| | Ps | 978,294 | US$ | 94,112 | US$ | 81,038 |
Other transactions carried out in US dollars, for the years ended December 31, are summarized below:
| | | 2002 | | 2001 | | 2000 |
| | | | | | | |
| Net export and import of goods and services | Ps | 2,024,717 | US$ | 194,778 | US$ | 169,262 |
| Technical advice | | 19,678 | | 1,893 | | 1,647 |
| Interest payments | | 112,807 | | 10,852 | | 10,960 |
| | | | | | | |
| | Ps | 2,157,202 | US$ | 207,523 | US$ | 181,869 |
As of February 28, 2003, issuance date of the independent auditors report, the US dollar exchange rate is Ps 11.022 per US dollar as published by brokerage houses.
14. INCOME TAX:
At December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000, income tax and employees’ profit sharing provision are summarized as shown below:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| | | | |
| Income tax due | Ps 82,198 | Ps 15,032 | Ps 11,354 |
| Deferred income tax | 83,306 | 328,851 | 144,108 |
| Assets tax | 40,843 | 25,117 | 132,677 |
| Employees statutory profit sharing | 8,371 | 1,670 | 12,782 |
| Gain on monetary position through the initial deferred income tax effect | (145,084) | (103,909) | (218,359) |
| | Ps 69,634 | Ps 266,761 | Ps 82,562 |
For both Mexican and US GAAP purposes, the financial statement carrying amounts utilized in the determination of the deferred tax assets and liabilities include the inflation adjustment described in Note 3, and their respective tax bases also include the effects of inflation based on tax regulations.
The Company from 1989 obtained authorization from the Mexican Treasury Department to consolidate its tax result with those of its controlled companies.
As of December 31, 2002, the Company had consolidated losses for tax purposes amounting approximately Ps 1,252,576, which will reduce, consolidated taxable income in future years until 2011. In addition, the Company has operating loss carryforwards, which have been generated by subsidiary companies prior to their inclusion in the consolidated income tax calculation. Accordingly, the individual subsidiary companies must generate taxable income for the group to utilize such losses.
Tax loss carryforwards will expire as follows:
| Years ended December 31 | |
| 2003 | Ps 37,626 |
| 2004 | 158,924 |
| 2005 | 535,446 |
| 2006 | 62,318 |
| 2007 and Thereafter | 458,262 |
| | |
| | Ps 1,252,576 |
The assets tax paid may be utilized as a credit against future income taxes during the years in which the Company generates an income tax in excess of the assets tax. The assets tax is available as a carryforward for up to ten years and is subject to restatement based on the NCPI when utilized. As of December 31, 2002 the assets tax is available as a tax loss carryforward in the amount of Ps 445,136 and expires in the years 2004 to 2011.
At December 31, the main temporary differences on which deferred income tax is recognized are summarized as shown below:
| | | 2002 | | 2001 |
| | | | | |
| Inventories | Ps | (1,267,499) | Ps | (1,430,781) |
| Fixed assets | | (1,718,274) | | (1,981,269) |
| Tax loss carryforwards | | 423,393 | | 179,835 |
| Other net items | | 49,398 | | 38,479 |
| | | (2,512,982) | | (3,193,736) |
| | | | | |
| Assets tax carryforwards | | 445,136 | | 503,322 |
| | | | | |
| Deferred income tax payable | Ps | (2,067,846) | Ps | (2,690,414) |
As a result of the changes to the Income Tax Law approved on January 1, 2002, the income tax rate will be reduced annually beginning in 2003 until it reaches a nominal rate of 32% in 2005. The effect of this gradual reduction in the tax rate will be to reduce the deferred income tax liability by Ps 239,269 in 2002, and increase net income by the same amount.
The following is a reconciliation of the statutory income tax rate of the actual effective income tax rate for the year ended December 31:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| | | | |
| Income tax computed at statutory tax rate | 35% | 35% | 35% |
| Depreciation and amortization | (19%) | 2% | 18% |
| Inventories | (6%) | (1%) | (42%) |
| Inflationary interest adjustment and net | | | |
| monetary gain (B-10) | (24%) | (6%) | (16%) |
| Provisions | 19% | 13% | 5% |
| Other | 14% | 3% | (20%) |
| Tax loss carryforwards | (17%) | (24%) | 15% |
| Provision for income tax and deferred tax | 2% | 22% | (5%) |
15. SEGMENT INFORMATION:
Business segments integrating the Company are revealed in compliance with revised International Accounting Standard No.14, "Segment Information".
The Company’s main activity is the operation of supermarkets and mass merchandising store in Mexico.
The Company operates in three segments: (1) the CCM Group, which includes the Comercial Mexicana, Bodega and Mega supermarkets, and comprises our core business (2) the Costco de Mexico Group, which operates Costco de Mexico, our joint venture with Costco Wholesale Corporation, and (3) the Other Group, which includes Restaurantes California and our Sumesa stores. These segments consider organizational structures, administration and financial information separate from the rest the group when decisions are taken.
The balances corresponding to segment information as of December 31, are shown below:
| | Self-service | | Joint venture and others |
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 | | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Revenue from external customers | Ps 24,893,276 | Ps 28,137,898 | Ps 28,774,261 | | Ps 7,160,036 | Ps 6,809,696 | Ps 6,108,591 |
| Depreciation and amortization | 598,456 | 610,777 | 596,579 | | 126,314 | 111,319 | 82,443 |
| Net income | 583,113 | 624,317 | 983,336 | | 205,704 | 178,210 | 233,043 |
| Long-term assets | 13,119,578 | 13,416,538 | 13,481,300 | | 2,671,596 | 2,496,683 | 1,934,061 |
| Material liabilities | 4,767,588 | 4,550,847 | 5,287,736 | | 882,087 | 829,087 | 742,882 |
| Capital expenditures | Ps 468,033 | Ps 910,896 | Ps 1,051,022 | | 274,836 | 294,734 | 331,643 |
16. SUBSEQUENT EVENT:
Acquisition of Auchan’s Mexican operations.
In February 2003, the Company acquired Auchan Mexican operations. Auchan was a company that operated five hypermarket stores. As a part of the agreement CCM commit to acquire the above mentioned hypermarket stores located in the central region of Mexico. Since March 2003 the Company operates these stores under the Mega format.
The payment for this operation will be done in six annual payments without interests from the "Closing" contract conditions as follow:
| February 27, 2003 | US$14,999,000 |
| February 28, 2004 | 20,000,000 |
| February 28, 2005 | 25,000,000 |
| February 28, 2006 | 20,000,000 |
| February 28, 2007 | 20,000,000 |
| February 28, 2008 | 20,000,000 |
| | |
| TOTAL | US$119,999,000 |
Under this commitment, the Company must perform all the above mentioned payments in order to get the ownership of the all five hypermarket stores.
Private placement:
On April 14, 1998, CCM issued, in a private placement, 9.375% Senior Notes due 2005 in an aggregate principal amount of US$130 million. These notes were registered under the Securities Act of 1933 through an exchange offer. Since April 2005, CCM had the option to call the bond paying a premium of 104.5%. CCM made the call on June 11, 2003 for US$ 84.81 million, the outstanding amount of the bond (CCM has bought back US$ 45.19 million since 1998), resulting in a final payment, including the premium, of US$ 88.63 million.
In order to finance the call of the previous operation, on June 9, 2003, CCM issued, in a private placement, 6.10% Senior Unsecured Notes due 2010 in an aggregate principal amount of US$ 100 million. These notes are neither listed for trading on any stock exchange nor approved for quotation through any quotation system.
Short term debenture to program
On June 2, 2003, CCM received the authorization of the Mexican National Bank Commission to emit a local short-term debenture program in pesos. The characteristics of the approval of the Company ’s Short-term Local Bond Program are as follows:
| Type of bonds: | Chirographic |
| Amount: | Ps 1,000,000 |
| Settlement: | Up to 360 days from the issuance date. |
| Review and interests payment | In the event the issuer pays interests these should be previously calculated under the revised and agreed payable interest rate established: weekly, monthly, quarterly, semiannually or other. |
17. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MEXICAN GAAP AND U.S. GAAP:
The Company’s consolidated financial statements are prepared in accordance with Mexican GAAP, which differ in certain significant respects from U.S. GAAP.
The reconciliation to U.S. GAAP does not include the reversal of the adjustments to the financial statement for the effects of inflation required under Bulletin B-10 and Mexican National Banking and Securities Commission ("CNBV") requirements, as amended. The application of Bulletin B-10 represents a comprehensive measure of the effects of price level changes in the inflationary Mexican economy and, as such, is considered a more meaningful presentation than historical cost-based financial reporting for both Mexican and U.S. accounting purposes. The application of Bulletin B-10 to the U.S. GAAP adjustments follows the methodology discussed in Note 3.
The principal differences other than inflation accounting, between Mexican GAAP and U.S. GAAP are presented below together with an explanation, where appropriate, of the adjustments that affect the determination of the consolidated results of operations (net of effects of minority interest), for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 and stockholders’ equity at December 31, 2002 and 2001.
Reconciliation of Net Income
Net income is reconciled as follows:
| | | Year ended December 31, |
| | | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| | | | | |
| Net income reported under Mexican GAAP | | Ps 788,816 | Ps 802,527 | Ps 1,216,379 |
| | | | | |
| U.S. GAAP adjustments: | | | | |
| Deferred income taxes | a. | 26,984 | 67,169 | 67,160 |
| Deferred employee profit sharing | a. | (2,277) | 9,389 | (3,116) |
| Loss (gain) of repurchase of Senior Notes | b. | - | - | (309) |
| Seniority premiums | c. | - | - | 12,190 |
| Unrealized gain on valuation of investments | h. | - | 16,398 | - |
| Compensation gain from stock purchase plan | d. | 16,446 | 25,871 | 31,038 |
| Impact of U.S. GAAP adjustments on minority interest | f. | 2,299 | (6,188) | 1,890 |
| Equity in losses of affiliates | g. | 11,046 | (53,116) | (22,888) |
| Effect of inflation accounting on U.S. GAAP Adjustments | e. | 433 | 18,718 | 17,430 |
| | | | | |
| Total U.S. GAAP adjustments | | 54,931 | 78,241 | 103,395 |
| | | | | |
| Net income before extraordinary items under U.S. GAAP | | 843,747 | 880,768 | 1,319,774 |
| | | | | |
| Extraordinary item- gain on repurchase of notes | b. | - | - | 309 |
| Net income under U.S. GAAP | | Ps 843,747 | Ps 880,768 | Ps 1,320,083 |
| Weighted average units outstanding (thousands) | | 1,078,225 | 1,061,260 | 1,079,537 |
| Outstanding units under stock purchase plans | | 44,810 | 45,607 | 16,522 |
| Diluted weighted average units outstanding (thousands) | | 1,123,035 | 1,106,867 | 1,096,059 |
| | | | | |
| Basic income per unit before extraordinary item | | Ps 0.78 | Ps 0.83 | Ps 1.22 |
| Basic income per unit per extraordinary item | | - | - | - |
| Basic income per unit under U.S. GAAP | | Ps 0.78 | Ps 0.83 | Ps 1.22 |
| Diluted net income per unit under U.S. GAAP | | Ps 0.75 | Ps 0.80 | Ps 1.20 |
Comprehensive Income
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards ("SFAS") No. 130, "Reporting Comprehensive Income" establishes rules for the reporting of comprehensive income and its components. Comprehensive income includes net income, loss from holding non-monetary assets and unrealized gains (losses) from available for sale securities, net. The following table summarizes the components of comprehensive income under U.S. GAAP for the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000.
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2002 | | 2001 | | 2000 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Net income | Ps 843,747 | | Ps 880,768 | | Ps 1,320,083 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Loss from holding non-monetary assets | (230,945) | | (261,505) | (1) | (369,799) | (1) |
| Unrealized gains of available for sale securities, net | - | | (16,398) | | 25,932 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Comprehensive income | Ps 612,802 | | Ps 602,865 | | Ps 976,216 | |
| Accumulated comprehensive income at end of year | Ps 4,278,575 | | Ps 3,665,773 | | Ps 3,062,908 | |
(1) Partial effect of inflation accounting on U.S. GAAP.
Reconciliation of Stockholders’ Equity
Stockholder’s equity is reconciled as follows:
| | | December 31, |
| | | 2002 | 2001 |
| | | | |
| Stockholders equity under Mexican GAAP | | Ps 11,843,113 | Ps 11,443,372 |
| | | | |
Approximate U.S. GAAP adjustments:
Minority interest | f. | (84,913) | (87,860) |
| Impact of U.S. GAAP adjustments on minority interests | | 2,856 | 702 |
| Deferred income taxes | a. | 56,870 | 29,917 |
| Deferred employee profit sharing | a. | (2,213) | - |
| Equity in earnings of affiliates | g. | (33,848) | (44,894) |
| Accrued liability under stock purchase plan | d. | (1,152) | (19,148) |
| Receivable under stock purchase plan | d. | (314,452) | (318,754) |
| Total U.S. GAAP adjustments | | (376,852) | (440,037) |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Stockholders equity under U.S. GAAP | | Ps 11,466,261 | Ps 11,003,335 |
Analysis of changes in Stockholders Equity under U.S. GAAP
| | | 2002 | 2001 |
| | | | |
| Stockholders equity at beginning of year | | Ps 11,003,335 | Ps 10,613,450 |
| Net income | | 843,747 | 880,768 |
| Dividends paid | | (120,489) | (122,882) |
| Reissuance of shares for stock | | | |
| purchase plan, net | | (32,116) | 6,950 |
| (Repurchase) reissuance of treasury stock | | (2,578) | 96,265 |
| Loss from holding non-monetary assets | | (230,945) | (261,505) |
| Change in receivable under stock purchase plan | d. | 4,301 | (195,381) |
| Payments to employees under stock purchase plan | d. | 1,006 | 2,068 |
| Change in unrealized gains on valuation of investments | h. | - | (16,398) |
| Stockholders equity at end of year | | Ps 11,466,261 | Ps 11,003,335 |
a. Deferred Income Taxes and Employee Profit Sharing
Prior to December 31,1999, Under Mexican GAAP, deferred taxes are provided only for the identifiable, non-recurring temporary differences, (i.e., those that are expected to reverse over a definite period of time). Effective January 1, 2000, the Company adopted the provisions of the revised Bulletin D-4, "Accounting Treatment of Income Tax, Asset Tax, and Employee Profit Sharing". The new D-4 changes the accounting treatment from the partial liability method to the full asset and liability method, requiring the recognition of the deferred tax effects for the temporary differences between accounting and tax values of assets and liabilities. For U.S. GAAP purposes, in 1991 the Company adopted SFAS No. 109, "Accounting for Income Taxes," ("SFAS 109") which requires an asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes. Under the asset and liability method, deferred income taxes are recognized for the tax consequences of all temporary differences, both recurring and non-recurring, between the financial statement carrying amounts and the tax basis of existing assets and liabilities. Under SFAS 109, the effect on deferred taxes of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date.
At December 31, the primary components of net deferred tax liability under U.S. GAAP consists of the following:
| | 2002 | 2001 |
| | SFAS No.109 Applied to Mexican GAAP Balances | SFAS No. 109 Applied to U.S. GAAP Adjustments | SFAS No. 109 Total | SFAS No. 109 Total |
Deferred income taxes:
Short-term:
Inventories |
Ps (1,046,779) |
Ps - |
Ps (1,046,779) |
Ps (1,228,329) |
| Accrued vacations | 7,134 | - | 7,134 | 11,275 |
| Tax loss carryforwards | 371,178 | - | 371,178 | 88,026 |
| Prepaid expenses | - | - | - | (15,903) |
| | | | | |
| Total short-term | (668,467) | - | (668,467) | (1,144,931) |
| | | | | |
Long-term:
Fixed assets |
(1,616,090) |
- |
(1,616,090) |
(1,869,368) |
| Equity investments | - | (192,779) | (192,779) | (170,284) |
| Seniority premiums | 21,224 | - | 21,224 | 20,719 |
| Asset tax credit carryforwards | 445,136 | - | 445,136 | 503,322 |
| | | | | |
| Total long-term | (1,149,730) | (192,779) | (1,342,509) | (1,515,611) |
| | | | | |
| Net deferred income tax liabilities | Ps (1,818,197) | Ps (192,779) | Ps (2,010,976) | Ps (2,660,542) |
| | | | | |
For the year ended December 31, 2002 and 2001, the difference in net deferred tax liabilities between Mexican and US GAAP was as follows:
| | Mexican GAAP | U.S.GAAP | Difference |
| Deferred tax liability: | | | |
| | | | |
| At December 31, 2001 | Ps (2,690,414) | Ps (2,660,542) | Ps 29,872 |
| At December 31, 2002 | (2,067,846) | (2,010,976) | 56,870 |
| Net Change | Ps 622,568 | Ps 649,566 | Ps 26,998 |
| | Mexican GAAP | U.S.GAAP | Difference |
| Deferred tax liability: | | | |
| | | | |
| At December 31,2000 | Ps (2,465,472) | Ps (2,515,086) | Ps (49,614) |
| At December 31,2001 | (2,690,414) | (2,660,542) | 29,872 |
| Net Change | Ps (224,942) | Ps (145,456) | Ps 79,486 |
The net change in the deferred tax liabilities during the year ended December 31, 2002 and 2001, was allocated to the following components:
| | Mexican GAAP 2002 | U.S. GAAP
2002 | Difference | |
| | | | | |
| Deferred tax expense : | Ps (83,306) | Ps (56,322) | Ps 26,984 | |
| Monetary gain (1) | 145,084 | 145,098 | 14 | (1) |
| | 61,778 | 88,776 | 26,998 | |
| Gain (loss) from holding non-monetary assets | - | - | - | |
| | Ps 61,778 | Ps 88,776 | Ps 26,998 | |
(1) Amount included in the "Effect of inflation accounting on U.S. GAAP adjustments".
| | Mexican GAAP 2001 | U.S. GAAP 2001 | Difference | |
| | | | | |
| Deferred tax expense : | Ps (328,850) | Ps (261,681) | Ps 67,169 | |
| Monetary gain (1) | 103,908 | 111,531 | 7,623 | (1) |
| | (224,942) | (150,150) | 74,792 | |
| Gain (loss) from holding non-monetary assets | - | 4,694 | 4,694 | |
| | Ps (224,942) | Ps (145,456) | Ps 79,486 | |
(1) Amount included in the "Effect of inflation accounting on U.S. GAAP adjustments".
During, 2002 CCM acquired some companies with tax loss carryforwards. Under Mexican GAAP there is no specific accounting pronouncement that address this type of transaction, therefore; CCM accounted this transaction under EITF 98-11, "Accounting for Acquired Temporary Differences in Certain Purchase Transactions That Are Not Accounted for as Business Combinations", for both Mexican and US GAAP purposes. As of December 31, 2002 CCM recognized a tax asset of Ps371,178 and a deferred credit of Ps291,588.
Under Mexican law, employees’ profit sharing is computed at 10% of the individual income of each of the Company’s subsidiaries. The calculation is based on taxable income adjusted to exclude the effects of inflation and asset restatement. While the employee profit sharing provision is calculated in a similar manner as income taxes, it is classified as an operating expense under U.S. GAAP.
The components of net deferred employee profit sharing liability under U.S. GAAP consist of the following :
| | December 31, | |
| | 2002 | 2001 |
Deferred employee profit sharing:
Short-term:
Inventories |
Ps (10,914) |
Ps (8,294) |
| Accrued vacations | 2,229 | 3,221 |
| | | |
| Total short-term | Ps (8,685) | Ps (5,073) |
Long-term:
Fixed assets |
(161) |
(285) |
| Seniority premiums | 6,633 | 5,920 |
| | | |
| Total long-term | 6,472 | 5,635 |
| Total deferred employee profit sharing before reserve | 2,213 | 562 |
| Reserve for employee profit sharing | - | (562) |
| Total deferred employee profit sharing | Ps 2,213 | Ps - |
The distribution of the net change in deferred employee profit sharing under U.S. GAAP for the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 is provided below:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| | | | |
| Deferred profit sharing income | Ps (2,277) | Ps 9,389 | Ps (3,116) |
| Monetary gain | 64 | 203 | 721 |
| Gain (loss) from holding non-monetary assets | - | 44 | (97) |
| | Ps (2,213) | Ps 9,636 | Ps (2,492) |
b. Extinguishment of Debt
In 2000 under Mexican GAAP, gain or loss from an extinguishment of debt is recognized in the period of the extinguishment in a separate caption of the income statement of current operations, whereas, under U.S. GAAP, gain or loss from an extinguishment is an extraordinary item.
c. Seniority Premiums and Pension Plan
Under Mexican GAAP, the Company used Bulletin D-3 for measuring the expenses and liabilities for pension plans and seniority premiums for the year 1999. During 2000, the Company adopted SFAS No. 87, "Employer’s Accounting for Pensions" ("SFAS 87") to account for the seniority premium expense.
For US GAAP, SFAS 87 is used to account for the seniority premium and pension plan expenses. The difference between the Company’s application of Bulletin D-3 and SFAS 87 consist of different date of adoption. See Note 10 for further information.
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Service cost | Ps 11,855 | Ps 13,001 | Ps 8,467 |
| Interest cost | 3,118 | 4,970 | 2,000 |
| Actual return on plan assets | (1,039) | (372) | (3,355) |
| Net amortization and deferral | 557 | 690 | 1,566 |
| Settlement loss | - | 149 | 24 |
| | | | |
| Net cost under U.S. GAPP | 14,491 | 18,438 | 8,702 |
| Net cost under Mexican GAAP | (14,491) | (18,438) | (20,892) |
| Difference to be recognized under U.S. GAAP | Ps - | Ps - | Ps (12,190) |
Assumptions used in the calculations of net cost under U.S. GAAP as of December 31, are:
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Weighted average discount rates | 3.5 % | 4.0 % | 4.0 % |
| Rates of increase in compensation levels | 1.0 % | 1.0 % | 1.0 % |
| Expected long-term return on assets | 5.0 % | 6.5 % | 6.5 % |
The seniority premium and pension plan liabilities as of December 31, 2002 and 2001, under SFAS 87 is as follows:
| | 2002 | 2001 |
| Actuarial present value benefit obligations: | | |
| Vested benefit obligations | Ps (29,341) | Ps (60,033) |
| Non-vested benefit obligations | (86,179) | (60,838) |
| Accumulated benefit obligations | (115,520) | (120,871) |
| Fair value of plan assets | 35,088 | 29,302 |
| Accumulated benefit obligations in excess of plan assets | Ps (80,432) | Ps (91,569) |
| Projected benefit obligations | Ps (133,359) | Ps (142,538) |
| Plan assets | 35,088 | 29,301 |
| Unfunded projected benefit obligations | (98,271) | (113,237) |
| Unfunded projected benefit obligation to be recognized in future years: | | |
| Unrecognized net gain | (12,155) | (9,577) |
| Unfunded projected benefit obligations to be recognized in the consolidated balance sheet under U.S. GAAP | (110,426) | (122,814) |
| Accrued cost recognized in the consolidated balance sheet under Mexican GAAP | 110,426 | 122,814 |
| Additional liability under U.S. GAAP | Ps - | Ps - |
The assets of the seniority premium and pension plan trusts are invested in equity securities and corporate and government bonds.
The actual investment return of the seniority premium trusts based on fair market values is Ps (1,039) and Ps ( 372 ) as of December 31, 2002 and 2001, respectively.
Changes in the plan’s funded status and plan assets during the year ended December 31, 2002 and 2001 were as follows:
| | 2002 | 2001 |
| Change in benefit obligation: | | |
| Benefit obligation at beginning of year | Ps 142,538 | Ps 129,874 |
| Service cost | 14,100 | 13,001 |
| Interest cost | 5,045 | 4,970 |
| Actuarial losses | (15,955) | 3,897 |
| Benefits paid | (12,369) | (9,204) |
| Benefit obligation at end of year | Ps 133,359 | Ps 142,538 |
| | | |
| Change in plan assets: | | |
| Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year | Ps 29,301 | Ps 16,027 |
| Creation of a new plan | - | 10,514 |
| Actual return on plan assets | 2,857 | 372 |
| Company s contribution | 8,263 | 6,652 |
| Benefits paid | (5,333) | (4,264) |
| Fair value of plan assets at end of year | Ps 35,088 | Ps 29,301 |
d. Stock Purchase Plan
The Company has a stock purchase plan for key employees as described in Note 12. The Company purchases the required number of shares granted under the terms of the plan in the stock market and deposits them into an employee trust. When the options are exercised the employees may pay the Company an amount based on the exercise price of the option and receive the stock certificates from the employee trust or they may elect to receive the appreciation of the units in cash. At December 31, 2002 and 2001, Ps 314,452 and Ps 315,754, respectively, was recorded under Mexican GAAP reflecting the receivable due from the employee trust for outstanding units under the stock purchase plan. Under U.S. GAAP, this receivable would have been reflected as a reduction in stockholder’s equity as additional treasury stock.
Based on the options available to the Company’s employees and the experience in recent years, the stock purchase plan has characteristics which are in substance similar to stock appreciation rights under U.S. GAAP. Compensation expense for stock appreciation rights is measured at the end of each period as the amount by which the quoted market value of the shares of the Company’s stock covered by a grant exceeds the option price or value specified under the plan and is accrued as a charge to expense over the periods the employee performs the related services. Changes in the quoted market value are reflected as an adjustment of accrued compensation and compensation gain (expense) in the periods in which the changes occur until the exercise date. During the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000, compensation benefit related to the stock purchase plan under U.S. GAAP would have amounted to Ps 16,446, Ps 25,871 and Ps 31,038 respectively.
Amounts paid to employees upon exercise of the stock appreciation rights amounted to Ps 1,007 and Ps 2,067 during the years ended December 31, 2002 and 2001, respectively.
The following table summarizes the activity in treasury stock, under U.S. GAAP, for the three years in the period ended December 31, 2002.
| | Units | Ps (Thousands) |
| | | |
| Balance at January 1, 2000 | 742,376 | Ps 6,361 |
| | | |
| Purchases | 4,261,573 | 36,618 |
| Issuance of shares upon exercise of options | (3,908,785) | (36,029) |
| Balance at December 31, 2000 | 1,095,164 | 6,950 |
| | | |
| Purchases | - | - |
| Issuance of shares upon exercise of options | (1,095,164) | (6,950) |
| Balance at December 31, 2001 | - | - |
| | | |
| Purchases | 6,384,196 | 34,433 |
| Issuance of shares upon exercise of options | - | - |
| Balance at December 31, 2002 | 6,384,196 | Ps 34,433 |
e. Effects of Inflation on U.S. GAAP Adjustments
This item represents the inflation adjustment calculated under Bulletin B-10 applied to the changes in monetary assets and liabilities generated by the application of U.S. GAAP to the Company’s financial statements.
Effect of inflation accounting on U.S. GAAP adjustments for the years ended December 31,
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Adjustment relating to: | | | |
| Deferred income taxes | Ps 14 | Ps 7,623 | Ps 3,428 |
| Deferred employee profit sharing | 64 | 203 | 721 |
| Receivable under stock purchase plan and accrued liability under stock purchase plan | 355 | 10,892 | 13,281 |
| | | | |
| | Ps 433 | Ps 18,718 | Ps 17,430 |
f. Minority Interest
Under Mexican GAAP, the minority interest in consolidated subsidiaries is presented as a separate component within the stockholders’ equity section in the consolidated balance sheet. For U.S. GAAP purposes, the minority interest is not included in stockholders’ equity.
g. Equity in Earnings of Affiliates
For Mexican GAAP, the Company accounts for its 50% joint venture in Costco de Mexico by the proportional consolidation method. For U.S. GAAP purposes, this investment is treated as an equity investee.
The Company’s net investment in the Costco de Mexico Joint Venture under U.S. GAAP differs from that recorded under Mexican GAAP due to the method of accounting for pre-opening costs and revenue recognition related to membership fees as summarized below:
| | December 31, |
| | 2002 | 2001 |
| Investment in Costco de Mexico joint venture: | | |
| | | |
| Mexican GAAP | Ps 2,315,558 | Ps 2,210,694 |
| U.S. GAAP | 2,281,710 | 2,165,800 |
| Adjustment | Ps (33,848) | Ps (44,894) |
Condensed financial information for the Costco de Mexico joint venture in accordance with U.S. GAAP is presented below.
| | December 31, |
| | 2002 | 2001 |
| Current assets | Ps 2,603,358 | Ps 2,297,269 |
| Non-current assets | 4,444,602 | 4,349,267 |
| Total assets | Ps 7,047,960 | Ps 6,646,536 |
| Current liabilities | Ps 1,780,604 | Ps 1,639,938 |
| Non-current liabilities | 703,937 | 674,997 |
| Stockholders equity | 4,563,419 | 4,331,602 |
| Total liabilities and stockholders equity | Ps 7,047,960 | Ps 6,646,537 |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Revenues | Ps 11,859,184 | Ps 11,215,714 | Ps 9,907,413 |
| Comprehensive income | 326,343 | 200,514 | 314,363 |
h. Basic Income Per Unit and Diluted Net Income Per Unit
In accordance with SFAS No. 128, "Earnings per Share" U.S. GAAP requires disclosures of basic earnings per share by using the weighted average number of units outstanding. Diluted net income per unit differs from basic net income per unit since the weighted average number of units is adjusted to include potential number of additional units that would have been outstanding under the stock purchase plan.
i. Cash Flow Information
Under Mexican GAAP, the Company presents statements of changes in financial position. The changes in the financial statement balances included in this statement constitute the generation and application of resources stated in Pesos of constant purchasing power as of December 31, 2002.
The changes in the financial statement balances included in this statement constitute cash flow activities stated in Mexican Pesos in purchasing power as of December 31, 2002 (including monetary and foreign exchange gains and losses, which are considered cash gains and losses in the constant Mexican Peso financial statements). Under Mexican GAAP, the effect of restatement of prior year’s balance sheet balances to Mexican Pesos of constant purchasing power are reflected in the stated change of the asset or liability in the statements of changes in financial position and the gain from monetary position is presented as a component of operating activities. Included within financing activities in the statements of changes in financial position for notes payable and long-term debt securities are the effects of restating the prior year notes payable and debt securities balances to constant Mexican Pesos.
Under Mexican GAAP, foreign exchange gains or losses are included in the net change in the respective assets and liabilities within resources provided by or used for operating and financing activities. Under U.S. GAAP, foreign exchange gains or losses are presented as an adjustment to reconcile net income to net cash provided by or used for operating activities.
The statement of cash flow presented below is in accordance with SFAS No. 95, "Statement of Cash Flows" ("SFAS 95") and includes the effect of the U.S. GAAP difference for the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000.
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| | | | |
| Net income | Ps 843,747 | Ps 880,768 | Ps 1,320,083 |
| Operating activities: | | | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to resources Provided by (used for) operating activities: | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 616,481 | 625,000 | 609,295 |
| Seniority premiums | 13,515 | 4,430 | 8,702 |
| Minority interest | (2,760) | 5,603 | (6,191) |
| Deferred income taxes | (88,776) | 145,456 | (144,839) |
| Deferred employee profit sharing | 2,213 | (9,389) | 3,116 |
| Equity in earnings of affiliates | (163,173) | (100,258) | (157,182) |
| Monetary gain | (293,075) | (227,240) | (476,872) |
| Extraordinary item-gain on extinguishment of debt | - | - | (309) |
| Unrealized exchange gains | 171,362 | (25,089) | 47,858 |
| Accrued Interest | 33,068 | 22,705 | 26,820 |
| Unrealized loss on valuation of investments | - | (16,398) | - |
| Write off of fixed assets | 193,689 | 181,098 | 133,119 |
| (Benefit) compensation expense of stock purchase plan | (16,446) | (24,470) | (31,039) |
| | 1,309,845 | 1,462,216 | 1,332,561 |
| | | | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | |
| (Increase) decrease in: | | | |
| Trade accounts receivable | 38,958 | 33,947 | 9,227 |
| Inventories | 7,436 | (25,991) | (159,241) |
| Other accounts and notes receivable | (1,599,261) | (310,032) | 96,336 |
| Affiliated companies | 906 | 11,666 | (2,438) |
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | 68,762 | (64,782) | (89,035) |
| Increase (decrease) in: | | | |
| Trade payables | 464,610 | (462,288) | 237,754 |
| Taxes payable | 28,959 | (80,685) | 216,093 |
| Other accrued liabilities | 77,146 | (58,847) | 80,438 |
| | (912,484) | (957,012) | 389,134 |
| | | | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 397,361 | 505,204 | 1,721,695 |
| | | | |
| Financing activities: | | | |
| Short terms bank loans | 157,900 | 332,455 | 666,606 |
| Repayment of bank loans | (107,847) | (276,748) | (598,504) |
| Paid in capital from reissuance of treasury stock | 2,317 | (88,153) | - |
| Reissuance (repurchase) of treasury stock | (2,578) | 184,418 | (212,365) |
| Repurchase of shares for stock purchase plan, net | (34,433) | 6,950 | (589) |
| Dividends paid | (120,489) | (122,882) | (116,071) |
| Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (105,130) | 36,040 | (260,923) |
| | | | |
| Investing Activities: | | | |
| Other assets | (115,145) | (249,671) | (109,054) |
| Decrease in permanent investments | | 114,367 | - |
| Acquisition of property and equipment, additions to real estate, leasehold improvements and other assets | (537,889) | (871,900) | (1,142,112) |
| Proceeds from sales of property and equipment | - | 38,512 | 6,340 |
| | | | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (653,034) | (968,692) | (1,244,826) |
| | | | |
| Net (decrease) increase in cash and temporary investments | (360,803) | (427,448) | 215,946 |
| Effects of inflation on cash at beginning of the year | (98,640) | 31,617 | (74,439) |
| Cash and temporary investments at beginning of the year | 753,684 | 1,149,514 | 1,008,007 |
| | | | |
| Cash and temporary investments at end of the year | Ps 294,241 | Ps 753,683 | Ps 1,149,514 |
Net resources provided by operating activities reflect cash payments for interest and income taxes as follows:
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| | | | |
| Interest | Ps 147,910 | Ps 167,125 | Ps 187,368 |
| Income taxes | 119,605 | 148,918 | 67,673 |
j. Disclosure About Concentration of Credit Risk
The Company’s financial statements do not include any financial instruments that represent a significant concentration of credit risk.
k. Disclosure About Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Effective January 1, 2001, for U.S. GAAP purposes, CCM adopted Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 133, "Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities" ("SFAS No. 133"), as amended by SFAS No. 137 and SFAS No. 138 and as interpreted by the Derivative Implementation Group (DIG). SFAS No. 133 establishes accounting and reporting standards for derivative instruments, including certain derivative instruments embedded in other contracts (collectively referred to as derivatives) and for hedging activities. SFAS No. 133 requires that an entity recognize all derivatives as either assets or liabilities in the consolidated balance sheet and measure those instruments at fair value. SFAS No. 133 prescribes requirements for designation and documentation of hedging relationships and ongoing assessments of effectiveness in order to qualify for hedge accounting.
If a derivative instrument qualifies as a fair value hedge under the applicable guidance and is documented as such, the change in the fair value of the derivative and the change in the fair value of the hedged item that is due to the hedged risk(s) is recorded in earnings based on the income classification of the item being hedged. These hedges also adjust the book values of the derivatives and hedged item. If a derivative instrument qualifies as a cash flow hedge under the applicable guidance and is documented as such, the effective portion of the hedging instrument’s gain or loss is reported in stockholders’ equity (as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income) and is reclassified into earnings in the period during which the transaction being hedged affects earnings. Gains or losses reclassified from stockholders’ equity to earnings are classified in accordance with earnings treatment of the hedged transaction. The ineffective portion of a hedging derivative’s fair value change, where that derivative is used in a cash flow hedge, is recorded in current earnings. Classification in the statement of operations of the ineffective portion of the hedging instrument’s gain or loss is based on the income statement classification of the transaction being hedged. If a derivative instrument does not qualify as a cash flow hedge under the applicable guidance, the change in the fair value of the derivative is immediately recognized in the statements of operations.
The following methods and assumptions are used to estimate the fair value of financial instruments:
Receivables, Temporary Investments and Short Term Borrowings: The carrying amounts approximate fair value because of the short maturity of those instruments. Values for temporary investments are obtained from quoted market values.
As of December 31, the estimated fair values of CCM’s unsecured notes are as follows:
| | 2002 | | 2001 |
| | Fair value | Carrying Amount | | Fair value | Carrying Amount |
| Unsecured notes | Ps 925,570 | Ps 881,600 | | Ps 1,055,351 | Ps 968,212 |
Rates currently available to CCM for debt with similar terms and remaining maturities are used to estimate fair value of existing debt.
As of December 31, the estimated fair values of the CCM’s financial instruments are as follows:
| | 2002 | | |
| | Fair Value | Notional Amount | | | |
| Rate swaps | Ps (28,813) | Ps 738,378 | | | |
| | 2002 | | 2001 |
| | Fair Value | Notional Amount | | Fair Value | Notional Amount |
| Currency swaps | Ps 21,280 | Ps 207,900 | | Ps 41,991 | Ps 484,106 |
As of December 31, the estimated fair values of the CCM’s debenture bonds are as follows:
| | 2002 | | 2001 |
| | Fair Value | Carrying Amount | | Fair Value | Carrying Amount |
| Debenture bonds | Ps 626,113 | Ps 557,737 | | Ps 598,454 | Ps 558,367 |
For the years ended December 31, 2002 and 2001, CCM recognized a net gain and a loss of Ps. 49,524 and Ps. 41,991, respectively, reported as "interest net" in the consolidated Statements of Income.
l. Accounting for Debt and Equity Investments
Under Mexican GAAP, temporary investments are carried at market value with unrealized gains or losses recognized in income. Permanent investments are carried at original cost restated utilizing the National Consumer Price Index.
In accordance with SFAS No. 115, "Accounting for Certain Debt and Equity Securities", the Company has determined that its equity securities should be classified as "available for sale" securities and reported at fair value, with unrealized gains or losses excluded from earnings and reported as a separate component of stockholders equity.
During 2002 and 2001, all the available for sale securities were sold at market value. The difference between the Mexican GAAP and US GAAP results is presented as a reconciliation item of Reconciliation of the Net Income.
m. Lease Revenue
The Company leases retail space in its stores to outside parties under non-cancelable operating leases.
Total rentals included in income for the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 were Ps 131,120, Ps 119,622 and Ps 111,988 respectively.
n. Segment Information
The Company is principally engaged in the operation of supermarkets and mass merchandising stores in Mexico. In addition, the Company also operates Costco de Mexico, a warehouse membership club, as a joint venture with Costco Wholesale Co. (Costco de Mexico Joint Venture).
The Company is in the retail industry. However, operating decisions are made separately for Costco de Mexico and the rest of the Company. The basis on which the Company identifies its segments are as follow: The Comercial Mexicana (CCM group) segment including the Comercial Mexicana supermarket, the Bodega warehouse style stores and the Mega hyper-markets. The Costco Mexico Joint Venture segment includes the Costco de Mexico warehouse membership club and the Other segment includes the Restaurantes California, a restaurant chain, and Sumesa, a mini-mart chain.
The measurement of profit or loss for each segment is net income. Information under Mexican GAAP on the Company’s reportable segments is provided below:
As of and for the year ended
December 31, 2002 | CCM group | Costco de Mexico Joint Venture | Other | Eliminations | Total |
| | | | | | |
| Revenue from external customers | Ps 24,893,276 | Ps 11,868,009 | Ps 1,226,031 | Ps (5,934,005) | Ps 32,053,311 |
| Inter-segment revenues | 217,759 | - | - | (217,759) | - |
| Depreciation and Amortization | 598,456 | 215,679 | 18,474 | (107,840) | 724,769 |
| Interest expense | 230,123 | 16,254 | 662 | (8,127) | 238,912 |
| Interest income | 22,864 | 30,141 | 5,205 | (15,071) | 43,139 |
| Income taxes(1) | 4,054 | 142,556 | (5,698) | (71,278) | 69,634 |
| Net income | 583,113 | 304,251 | 53,578 | (152,126) | 788,816 |
| | | | | | |
| Long-lived assets | Ps 13,119,578 | Ps 4,315,179 | Ps 514,006 | Ps (2,157,590) | Ps 15,791,173 |
| Significant liabilities | 4,767,588 | 1,550,724 | 106,725 | (775,362) | 5,649,675 |
| Capital expenditures | 468,033 | 408,070 | 70,351 | (204,035) | 742,419 |
As of and for the year ended
December 31, 2001 | CCM group | Costco de Mexico Joint Venture | Other | Eliminations | Total |
| | | | | | |
| Revenue from external customers | Ps 28,137,898 | Ps 11,244,842 | Ps1,187,275 | Ps (5,622,421) | Ps 34,947,594 |
| Inter-segment revenues | 285,260 | - | - | (285,260) | - |
| Depreciation and amortization | 610,777 | 190,326 | 16,156 | (95,163) | 722,096 |
| Interest expense | 261,546 | 17,910 | 1,257 | (8,955) | 271,758 |
| Interest income | 34,433 | 35,513 | 6,523 | (17,757) | 58,712 |
| Income taxes(1) | 194,083 | 69,787 | 37,785 | (34,894) | 266,761 |
| Net income | 624,317 | 306,748 | 24,836 | (153,374) | 802,527 |
| | | | | | |
| Long-lived assets | Ps 13,416,538 | Ps 4,060,673 | Ps 466,346 | Ps (2,030,336) | Ps 15,913,221 |
| Significant liabilities | 4,550,847 | 1,410,192 | 123,991 | (705,096) | 5,379,934 |
| Capital expenditures | 910,896 | 447,405 | 71,031 | (223,702) | 1,205,630 |
As of and for the year ended
December 31, 2000 | CCM group | Costco de Mexico Joint Venture | Other | Eliminations | Total |
| | | | | | |
| Revenue from external customers | Ps 28,774,261 | Ps 9,941,048 | Ps 1,138,067 | Ps (4,970,524) | Ps 34,882,852 |
| Inter-segment revenues | 254,175 | - | - | (254,175) | - |
| Depreciation and amortization | 596,579 | 135,586 | 14,650 | (67,793) | 679,022 |
| Interest expense | 251,167 | 15,553 | 718 | (7,776) | 259,662 |
| Interest income | 43,063 | 18,943 | 5,526 | (9,471) | 58,061 |
| Income taxes(1) | 78,935 | (19,333) | 13,294 | 9,666 | 82,562 |
| Extraordinary gain | 309 | - | - | - | 309 |
| Net income | 983,336 | 360,138 | 52,974 | (180,069) | 1,216,379 |
| | | | | | |
| Long-lived assets | Ps 13,481,300 | Ps 3,616,273 | Ps 125,924 | Ps (1,808,136) | Ps 15,415,361 |
| Significant liabilities | 5,287,736 | 1,334,590 | 75,586 | (667,295) | 6,030,617 |
| Capital expenditures | 1,051,022 | 479,890 | 91,698 | (239,945) | 1,382,665 |
(1) Amounts include current and deferred income tax, asset tax and employee’s profit sharing.
Significant liabilities comprise of trade payables. Long-lived assets consist of property, plant and equipment and other assets. The eliminations column refers to the inter-segment lease revenues of the real estate subsidiaries of CCM and the 50% of Costco de Mexico Joint Venture not owned by the Company. No single customer accounts for more than ten percent of the consolidated revenues.
The Company operates in only one geographic segment, Mexico.
o. Condensed Financial Information
The condensed balance sheet and income statement presented below reflect the Costco de Mexico Joint Venture as an equity investment and include the effects of all U.S. GAAP adjustments.
| ASSETS |
| | December 31 |
| | 2002 | 2001 |
| Current assets: | | |
| Cash and temporary investments | Ps 286,708 | Ps 753,683 |
| Inventories | 3,271,183 | 3,509,564 |
| Other current assets | 2,831,947 | 1,097,622 |
| | 6,389,838 | 5,360,869 |
| | | |
| | | |
| Non current assets | 13,818,637 | 14,053,684 |
| Equity in affiliates | 2,225,842 | 2,110,216 |
| | | |
| Total assets | Ps 22,434,317 | Ps 21,524,769 |
| | | |
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS EQUITY |
| | 2002 | 2001 |
| Current liabilities | Ps 7,579,938 | Ps 6,738,683 |
| Long-term liabilities | 3,377,448 | 3,765,931 |
| | | |
| Total liabilities | 10,957,386 | 10,504,614 |
| | | |
| Minority interest | 10,670 | 16,820 |
| Stockholders equity | 11,466,261 | 11,003,335 |
| Total liabilities and stockholders equity | Ps 22,434,317 | Ps 21,524,769 |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| | | | |
| Net sales | Ps 26,115,554 | Ps 29,325,173 | Ps 29,912,328 |
| | | | |
| Operating income | 692,792 | 852,473 | 948,631 |
| | | | |
| Comprehensive financing results | (82,935) | (10,074) | 207,342 |
| Equity in earnings of affiliates | 163,172 | 100,257 | 157,181 |
| Other income | 75,955 | 121,223 | - |
| | | | |
| Income before taxes | 848,984 | 1,063,879 | 1,313,154 |
| | | | |
| Income tax | (6,929) | (174,013) | 6,567 |
| Minority interest | 1,692 | (9,098) | 53 |
| Extraordinary item-extinguishment of debt | - | - | 309 |
| | | | |
| Net income | Ps 843,747 | Ps 880,768 | Ps 1,320,083 |
p. New Accounting Pronouncements
In June 2002, the FASB issued SFAS No. 146 "Accounting for Costs Associated with Exit or Disposal Activities". SFAS 146 addresses financial accounting and reporting for costs associated with exit or disposal activities and nullifies Emerging Issues Task Force (EITF) Issue No. 94-3, "Liability Recognition for Certain Employee Termination Benefits and Other Costs to Exit an Activity (including Certain Costs Incurred in a Restructuring)." SFAS is effective for exit or disposal activities initiated after December 31, 2002. The Company is presently evaluating the impact, if any, that these new standards will have on its consolidated financial statements.
In December 2002, the FASB issued SFAS No. 148 "Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation- Transition and Disclosure an amendment of FASB Statement No. 123". SFAS 148 amends FASB Statement No. 123; Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation, to provide alternative methods of transition for a voluntary change to the fair value based method of accounting for stock-based employee compensation. In addition, this Statement amends the disclosure requirements of Statement 123 to require prominent disclosures in both annual and interim financial statements about the method of accounting for stock-based employee compensation and the effect of the method used on reported results. SFAS 148 shall be effective for financial statements for fiscal years ending after December 15, 2002. The Company is presently evaluating the impact, if any, that these new standards will have on its consolidated financial statements.
In April 2003, the FASB issued SFAS 149 "Amendment of Statement 133 on Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities". SFAS 149 amends and clarifies financial accounting and reporting for derivative instruments, including certain derivative instruments embedded in other contracts (collectively referred to as derivatives) and for hedging activities under FASB Statement No. 133, Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities. SFAS 149 is effective for contracts entered into or modified after June 30, 2003, except for hedging relationships designated after June 30, 2003. All provisions of SFAS 149 should be applied prospectively. The Company is presently evaluating the impact, if any, that these new standards will have on the consolidated financial statements.
Independent Auditors’ Report
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
Costco de México, S. A. de C. V.:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of Costco de México, S. A. de C. V. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2002, and the related consolidated statements of income, stockholders’ equity and changes in financial position for the year then ended. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with auditing standards generally accepted in the United States of America. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Costco de México, S. A. de C. V. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2002, and the results of its operations, the changes in its stockholders’ equity and the changes in its financial position for the year then ended in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in Mexico.
Accounting principles generally accepted in Mexico vary in certain significant respects from accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Application of accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America would have affected stockholders’ equity as of December 31, 2002 and results of operations for the year then ended, to the extent summarized in note 15 to the consolidated financial statements.
KPMG CARDENAS DOSAL, S. C.
José Manuel González Garnica
México, D.F., México
February 17, 2003
| COSTCO DE MEXICO, S. A. DE C. V. AND SUBSIDIARIES |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets |
| December 31, 2002 and 2001 |
| (unaudited with respect to amounts as of |
| and for the year ended December 31, 2001) |
| (Thousand of constant Mexican pesos as of December 31, 2002) |
| Assets | | 2002 | 2001 | | Liabilities and Stockholders Equity | | 2002 | 2001 |
| Current assets: | | | | | Current liabilities: | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 1,109,051 | 993,546 | | Trade accounts payable | $ | 1,221,457 | 1,102,387 |
| Related parties (note 4) | | 9,042 | 11,663 | | Costco Wholesale, Co. | | 329,267 | 280,235 |
| Other receivables (note 5) | | 169,881 | 118,579 | | Other liabilities | | 101,271 | 131,122 |
| Inventories (note 6) | | 1,299,269 | 1,156,836 | | Accruals (note 9) | | 116,363 | 97,266 |
| Prepaid expenses | | 14,002 | 1,871 | | Related parties (note 4) | | 12,246 | 14,150 |
| Total current assets | | 2,601,245 | 2,282,495 | | Total current liabilities | | 1,780,604 | 1,625,160 |
| Property and equipment, net (note 7) | | 4,303,635 | 4,166,566 | | Pension and seniority premium plans (note 10) | | 5,410 | 4,067 |
| Other non-current assets, net (note 8) | | 11,544 | 6,976 | | Deferred income taxes (note 11) | | 499,295 | 405,382 |
| | | | | | Total liabilities | | 2,285,309 | 2,034,609 |
| | | | | | Stockholders equity (note 12): | | | |
| | | | | | Capital stock | | 3,369,269 | 3,369,269 |
| | | | | | Retained earnings | | 1,702,973 | 1,398,722 |
| | | | | | Cumulative deferred income taxes | | (128,209) | (128,209) |
| | | | | | Effect from acquisition of shares of subsidiaries | | 934,395 | 934,395 |
| | | | | | Equity adjustment for non-monetary assets | | (1,247,313) | (1,152,749) |
| | | | | | Total stockholders equity | | 4,631,115 | 4,421,428 |
| | | | | | Contingent liabilities (note 13) | | | |
| | $ | 6,916,424 | 6,456,037 | | | $ | 6,916,424 | 6,456,037 |
| See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements. |
| COSTO DE MEXICO, S. A. DE C. V. AND SUBSIDIARIES |
| Consolidated Statements of Income |
| Years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 |
| (unaudited with respect to amounts as of |
| and for the years ended December 31, 2001 and 2000) |
| (Thousand of constant Mexican pesos as of December 31, 2002) |
| | | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Net sales (note 4) | $ | 11,676,959 | 11,066,570 | 9,796,315 |
| Membership income | | 191,050 | 167,067 | 134,748 |
| Total income | | 11,868,009 | 11,233,637 | 9,931,063 |
| Cost of goods sold (note 4) | | 10,398,497 | 9,864,975 | 8,757,701 |
| Gross profit | | 1,469,512 | 1,368,662 | 1,173,362 |
| Operating expenses (note 4) | | 1,127,118 | 1,073,572 | 917,790 |
| Operating income | | 342,394 | 295,090 | 255,572 |
| Comprehensive financial results: | | | | |
| Interest income, net | | 13,887 | 17,605 | 1,004 |
| Foreign exchange gain, net | | 33,244 | 28,756 | 15,890 |
| Monetary position gain | | 49,322 | 46,835 | 10,804 |
| Comprehensive financial results, net | | 96,453 | 93,196 | 27,698 |
| Other income, net | | 7,960 | 1,330 | 1,907 |
| Income before taxes | | 446,807 | 389,616 | 285,177 |
| Income and asset taxes (note 11): | | | | |
| Current | | 48,643 | 26,857 | 14,260 |
| Deferred | | 93,913 | 56,009 | 36,742 |
| Total income and asset taxes | | 142,556 | 82,866 | 51,002 |
| Net income | $ | 304,251 | 306,750 | 234,175 |
| See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements. |
| COSTCO DE MEXICO, S. A. DE C. V. AND SUBSIDIARIES |
| Consolidated Statements of Stockholders Equity |
| Years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 |
| (unaudited with respect to amounts as of |
| and for the years ended December 31, 2001 and 2000) |
| (Thousand of constant Mexican pesos as of December 31, 2002) |
| | | | | | Effect from | Equity | |
| | | | | Cumulative | acquisition | adjustment | Total |
| | | Capital | Retained | deferred | of shares of | for non-monetary | stockholders |
| | | stock | earnings | income taxes | subsidiaries | assets | equity |
| Balances at December 31, 1999 | $ | 1,199,809 | 857,797 | - | - | (872,856) | 1,184,750 |
| Capital contribution resulting from acquisition | | | | | | | |
| of shares (note 1) | | - | - | - | 934,395 | - | 934,395 |
| Cumulative effect of deferred income taxes | | - | - | (128,209) | - | - | (128,209) |
| Increase in capital stock (note 12) | | 218,122 | - | - | - | - | 218,122 |
| Net comprehensive income (note 12) | | - | 234,175 | - | - | (175,551) | 58,624 |
| Balances at December 31, 2000 | | 1,417,931 | 1,091,972 | (128,209) | 934,395 | (1,048,407) | 2,267,682 |
| Increase in capital stock (note 12) | | 1,951,338 | - | - | - | - | 1,951,338 |
| Net comprehensive income (note 12) | | - | 306,750 | - | - | (104,342) | 202,408 |
| Balances at December 31, 2001 | | 3,369,269 | 1,398,722 | (128,209) | 934,395 | (1,152,749) | 4,421,428 |
| Net comprehensive income (note 12) | | - | 304,251 | - | - | (94,564) | 209,687 |
| Balances at December 31, 2002 | $ | 3,369,269 | 1,702,973 | (128,209) | 934,395 | (1,247,313) | 4,631,115 |
| See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements. |
| COSTCO DE MEXICO, S. A. DE C. V. AND SUBSIDIARIES |
| Consolidated Statements of Changes in Financial Position |
| Years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 |
| (unaudited with respect to amounts as of |
| and for the years ended December 31, 2001 and 2000) |
| (Thousand of constant Mexican pesos as of December 31, 2002) |
| | | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Operating activities: | | | | |
| Net income | $ | 304,251 | 306,750 | 234,175 |
| Add charges to operations not requiring funds: | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 215,679 | 200,742 | 44,142 |
| Accrual for pension, seniority premium and other post | | | | |
| retirement benefits | | 1,399 | 1,113 | 835 |
| Deferred income taxes | | 93,913 | 56,009 | 36,741 |
| Funds provided by operations | | 615,242 | 564,614 | 315,893 |
| Net (investing) financing from operating accounts | | (142,365) | 160,573 | (42,394) |
| Funds provided by (used in) operating activities | | 472,877 | 725,187 | (273,499) |
| Financing activities: | | | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock | | - | 1,951,339 | 218,122 |
| Related parties | | - | (1,449,488) | 1,449,488 |
| Pension and seniority premium plans | | (56) | - | - |
| Funds (used in) provided by financing activities | | (56) | 501,851 | 1,667,610 |
| Investing activities: | | | | |
| Capital expenditures | | (323,958) | (672,239) | (1,613,036) |
| Other assets | | (33,358) | (86,129) | (46,065) |
| Funds used in investing activities | | (357,316) | (758,368) | (1,659,101) |
| Increase in cash and cash equivalents | | 115,505 | 468,670 | 282,008 |
| Cash and cash equivalents: | | | | |
| At beginning of year | | 993,546 | 524,876 | 242,868 |
| At end of year | $ | 1,109,051 | 993,546 | 524,876 |
| See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements. |
COSTCO DE MEXICO, S. A. DE C. V. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000
(unaudited with respect to amounts as of
and for the years ended December 31, 2001 and 2000)
(Thousand of constant Mexican pesos as of December 31, 2002)
(1) Description of business and significant transactions-
Description of business-
The Company is a subsidiary of Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S. A. de C. V. (a company incorporated in Mexico) and Costco Wholesale Co. (a company incorporated in the United States of America). The Company is the shareholder of a group of service and real estate companies. The main activity of these companies is the management of stores under the commercial name of "Costco". These store chains execute membership agreements, which allow members to access these stores.
Significant transactions-
On December 28, 2000 an agreement for the acquisition of investment in shares of certain subsidiaries of Controladora Costco, S. A. de C. V., an entity under common control by the Company’s stockholders, was entered into in the amount of $1,390,641 ($1,260,200 in nominal value), which generated a capital contribution from the acquisition of shares of subsidiaries of $934,386 ($846,713 in nominal value) for the difference between the cash paid by the Company and the carrying cost of the net asset acquired.
Also on January 18, 2001, the Company acquired from Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S. A. de C. V. the capital stock of Centro Comercial Orbita, S. A. de C. V. amounting to US$23.5 million representing the fair value of the acquired net assets.
(2) Summary of significant accounting policies-
(a) Financial statement presentation-
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in Mexico (Mexican GAAP), which require the recognition of the effects of inflation on the financial information, and are expressed in Mexican pesos of constant purchasing power, based on the Mexican National Consumer Price Index (NCPI) published by Banco de México (central bank).
The indexes used in recognizing inflation were as follows:
| December 31 | NCPI | Inflation |
| 2002 | 102.9040 | 5.70% |
| 2001 | 97.3543 | 4.40% |
| 2000 | 93.2482 | 8.96% |
| 1999 | 85.5807 | 12.32% |
For purposes of disclosure thousand of pesos or "$" means thousand of Mexican pesos, and dollars means U.S. dollars.
Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform to the 2002 presentation.
(b) Principles of consolidation-
The consolidated financial statements include the financial statements of Costco de México, S. A. de C. V. and those subsidiary companies in which it holds a majority interest (over 50%) and/or has control. All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. The consolidation was based on the audited financial statements of the issuing companies, which were prepared under Mexican GAAP.
The principal subsidiaries are the following:
| Ownership |
| Inmobiliaria Costco Metropolitana, S. A. de C. V. | 99.99% |
| Inmobiliaria Costco de Queretaro, S. A. de C. V. | 99.99% |
| Inmobiliaria Costco de Mexicali, S. A. de C. V. | 99.99% |
| Inmobiliaria Costco de Jalisco, S. A. de C. V. | 99.99% |
| Inmobiliaria Costco de Leon, S. A. de C. V. | 99.99% |
| Inmobiliaria Costco de Mixcoac, S. A. de C. V. | 99.99% |
| Inmobiliaria Costco de Acapulco, S. A. de C. V. | 99.99% |
| Inmobiliaria CWM, S. A. de C. V. | 99.99% |
| Prestadora de Servicios Costco, S. A. de C. V. | 99.99% |
| Costco Corporativo, S. A. de C. V. | 99.99% |
| Centro Comercial Orbita, S. A. de C. V. | 99.99% |
(c) Cash equivalents-
Cash equivalents consist of checking accounts, foreign currency and other highly liquid instruments with original maturities of three months or less. At the date of the financial statements, interest income and expense and foreign exchange gains and losses are included in the results of operations, under comprehensive financial results.
(d) Inventories and cost of sales-
Inventories are initially recorded at cost using the retail inventory method, and subsequently adjusted to replacement value, in accordance with Mexican GAAP inflation accounting, not to exceed realizable value.
Cost of goods represents the replacement cost of inventories at the time of sale, increased when applicable for reductions in the replacement cost or net realizable value of inventories during the year, expressed in constant pesos as of the most recent year-end.
(e) Property and equipment-
Property and equipment is initially recorded at acquisition cost and adjusted for inflation by applying NCPI factors.
Depreciation on property and equipment is calculated on the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets, determined by management. The annual depreciation rates of the principal asset classes are as follows:
| | 2002 | 2001
(unaudited) | 2000
(unaudited) |
| Buildings | 3% | 3% | 3% |
| Leasehold improvements | 5% | 5% | 5% |
| Store equipment | 10% | 10% | 10% |
| Office equipment | 20% | 10% | 17% |
| Telecommunication equipment | 30% | 30% | 11% |
| Computer equipment | 30% | 30% | 22% |
| Transportation equipment | 30% | 30% | 15% |
Minor repairs and maintenance costs are expensed as incurred
(f) Other assets-
Other assets include mainly installation, pre-operating, fixture expenses and are stated at cost, adjusted for inflation based on NCPI factors. Amortization is computed on adjusted asset-values using the straight-line method, over the estimated useful lives of each store.
(g) Pension and seniority premium plans-
Pension and seniority premium benefits to which employees are entitled in accordance with the labor law are charged to operations for the year based on actuarial computations of the present value of this obligation. Amortization of prior service cost is based on the estimated service lives of existing personnel. At December 31, 2002, the estimated service life of employees entitled to plan benefits approximates 11 years.
Other compensations to which employees may be entitled, mainly severance, are charged to operations as incurred.
(h) Income (IT) and asset (AT) taxes, and employee statutory profit sharing (ESPS)-
The Company does not consolidate for tax purposes, accordingly the subsidiaries of the Company file separate tax returns. Income taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and operating loss and tax credit (AT) carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date.
Deferred ESPS is recognized only for timing differences arising from the reconciliation of book income to income for profit sharing purposes, on which it may be reasonably estimated that a future liability or benefit will arise and there is no indication that the liabilities or benefits will not materialize.
(i) Inflation adjustment of capital stock, other stockholder contributions and retained earnings-
This adjustment is determined by multiplying stockholder contributions and retained earnings (deficit) by factors derived from the NCPI, which measure accumulated inflation from the dates of origin through the most recent year end. The resulting amounts represent the constant value of stockholders’ equity.
(j) Cumulative deferred income taxes-
Represents the cumulative effect of the adoption of the deferred taxes accounting principle.
(k) Equity adjustment for non-monetary assets-
Represents the difference between the specific price level of inventories and the values determined using factors derived from the NCPI.
(l) Comprehensive financial results (CFR)-
The CFR includes interest income and expense, foreign exchange gains and losses, monetary position gains and losses.
Transactions in foreign currency are recorded at the exchange rate prevailing on the date of execution or settlement. Foreign currency assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rate in force at the balance sheet date. Exchange differences arising from assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are reported in operations for the year.
Monetary position gains and losses are determined by multiplying the difference between monetary assets and liabilities at the beginning of each month, including deferred taxes, by inflation factors through year end. The aggregate of these results represents the monetary gain or loss for the year arising from inflation, which is reported in operations for the year.
(m) Revenue recognition-
Revenues from the sale of goods are generally recognized upon delivery of the products to the members when the risk of loss is transferred to the customer. Revenues from the memberships are recognized at the time such memberships are sold. The Company deducts returns and discounts from sales.
(n) Business concentration-
The Company’s products are sold to a large number of members without significant concentration with any specific member. The Company provides for an allowance for doubtful accounts based on analyses and estimates made by management.
(o) Contingencies-
Liabilities for loss contingencies are recorded when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount thereof can be reasonably estimated. When a reasonable estimation can not be made, qualitative disclosure is provided in the notes to the consolidated financial statements. Contingent revenues, earnings or assets are not recognized until their realization is virtually assured.
(p) Impairment of property and equipment and other non-current assets-
The Company evaluates periodically the adjusted values of its property and equipment and other non-current assets, to determine whether there is an indication of potential impairment. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to future net revenues expected to be generated by the asset. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment is measured by the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds discounted cash flows of the asset. Assets to be disposed of are reported at the lower of the carrying amount or realizable value.
(q)Use of estimates-
The preparation of financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions affecting the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates and assumptions.
(3) Foreign currency exposure-
Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in dollars as of December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 were as follows:
| | Thousands of Dollars |
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Current assets | 49,461 | 40,272 | 19,653 |
| Current liabilities | (42,587) | (33,213) | (24,330) |
| Net assets (liabilities) | 6,874 | 7,059 | (4,677) |
The exchange rate of the peso to the dollar, as of December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000, was $10.40, $9.17 and $9.60, respectively. At February 17, 2003, the exchange rate was $11.05.
Below is a summary of transactions carried out with foreign entities, for the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000, excluding imports and exports of equipment:
| | Thousands of Dollars |
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Purchases | 262,517 | 289,218 | 176,833 |
| Administrative services | 3,787 | 3,540 | 3,375 |
| Technical assistance | 1,172 | 1,096 | 904 |
| Royalties | 14 | 14 | - |
| | 267,490 | 293,868 | 181,112 |
(4) Related-party transactions and balances-
Transactions carried out with related parties during the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 were as follows:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Sales | $4,792 | 7,881 | - |
| Purchases | 2,595,427 | 2,742,901 | 1,950,085 |
| Fees on administrative services received | 36,833 | 513,508 | 422,367 |
| Fees on technical assistance received | 11,883 | 11,076 | 9,822 |
| Other | 1,081 | 965 | 319 |
Balances receivable from and payable to related parties as of December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 are as follows:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Receivable: | | | |
| Inmobiliaria Gleznova, S. A. de C. V. | $8,200 | 433 | 351 |
| Comercial Mexicana, S. A. de C. V. | 657 | 477 | 773 |
| Importadora Primex, S. A. de C. V. | 185 | - | - |
| Serecor, S. A. de C. V. | - | 10,753 | - |
| | $9,042 | 11,663 | 1,124 |
| Payable: | | | |
| Controladora Comercial Mexicana, S. A. de C. V. | $12,246 | 14,150 | 12,588 |
| Serecor, S. A. de C. V. | - | - | 3,696 |
| Importadora Primex, S. A. de C. V. | - | - | 93 |
| Others | - | - | 128 |
| | $12,246 | 14,150 | 16,505 |
(5) Other receivables-
Other receivables consist of the following:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Debtors | $34,748 | 63,588 | 56,068 |
| Recoverable taxes | 135,133 | 54,991 | 119,746 |
| | $169,881 | 118,579 | 175,814 |
(6) Inventories-
Inventories are comprised as follows:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Finished goods | $1,242,769 | 1,099,976 | 1,121,083 |
| Advances to custom agents | 8,601 | 16,958 | 10,891 |
| Goods in transit | 47,899 | 39,902 | 30,636 |
| | $1,299,269 | 1,156,836 | 1,162,610 |
(7) Property and equipment-
Property and equipment comprise the following:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Buildings | $2,211,752 | 2,101,630 | 1,874,545 |
| Store equipment | 942,999 | 897,949 | 832,836 |
| Computer equipment | 147,216 | 116,691 | 126,217 |
| Carried forward | $3,301,967 | 3,116,270 | 2,833,598 |
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Brought forward | $3,301,967 | 3,116,270 | 2,833,598 |
| Telecommunication equipment | 45,257 | 46,632 | 45,440 |
| Leasehold improvements | 39,664 | 36,566 | 36,817 |
| Office equipment | 11,809 | 12,010 | 11,913 |
| Transportation equipment | 10,896 | 10,330 | 9,123 |
| | 3,409,593 | 3,221,808 | 2,936,891 |
| Less accumulated depreciation | 975,288 | 782,485 | 597,154 |
| | 2,434,305 | 2,439,323 | 2,339,737 |
| Land | 1,750,105 | 1,703,500 | 1,243,821 |
| Construction in progress | 119,225 | 23,743 | 22,186 |
| | $4,303,635 | 4,166,566 | 3,605,744 |
(8) Other non-current assets-
Other non-current assets consist of:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Pre-operating expenses | $145,243 | 139,993 | 136,388 |
| Guarantee deposits | 3,742 | 2,554 | 3,242 |
| Software and other | 826 | 1,446 | 911 |
| | 149,811 | 143,993 | 140,541 |
| Less accumulated amortization | 138,267 | 137,017 | 132,973 |
| | $11,544 | 6,976 | 7,568 |
(9) Accruals-
Accruals at December 31, 2002 include the following:
| Bonuses |
| Balances at December 31, 2001 (unaudited) | $97,266 |
| Increases charged to operations | 48,552 |
| Payments | 29,455 |
| Balances at December 31, 2002 | $116,363 |
(10) Pension and seniority premium plans-
Costco Corporativo, S. A. de C. V. has a defined benefit pension plan covering substantially all of its employees. The benefits are based on years of service and the employees individual compensation during the five years prior to retirement. The Company makes annual contributions to the plan equal to the maximum amount that can be deducted for income tax purposes. Plan contributions during 2002 amounted to $262.
The cost, obligations and other elements of the pension and seniority premium plans, mentioned in note 2(g), have been determined based on computations prepared by independent actuaries at December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000.
The components of the net periodic cost for the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 are as follows:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Net periodic cost: | | | |
| Service cost | $1,301 | 1,017 | 781 |
| Interest cost | 116 | 92 | 73 |
| Variances in assumptions and experience adjustments | (38) | (41) | (28) |
| Amortization of transition asset | 20 | 10 | 10 |
| Net periodic cost | $1,399 | 1,078 | 836 |
The actuarial present value of benefit obligations is as follows:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Accumulated benefit obligation | $4,463 | 3,162 | 2,414 |
| Projected benefit obligation (PBO) | $4,489 | 3,365 | 2,426 |
| Plan assets at fair value | (262) | - | - |
| Projected benefit obligation over plan assets | 4,227 | 3,365 | 2,426 |
| Unrecognized items: | | | |
| Additional liability | 295 | - | - |
| Variances in assumptions and experience adjustments | 1,078 | 763 | 698 |
| Unamortized transition asset | (345) | (61) | (71) |
| | 5,255 | 4,067 | 3,053 |
| Liability in excess | 155 | - | - |
| Net projected liability recorded at balance sheets | $5,410 | 4,067 | 3,053 |
Assumptions used in determining the net periodic cost of the plan are as follows:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Discount real rate (i.e., net of inflation) | 3.5% | 3.5% | 4% |
| Real rate of compensation increase | 1% | 1% | 1% |
| Expected return on plan assets | 5% | 6.5% | 6.5% |
| Amortization period of asset liability | 11 years | 11 years | 11 years |
Plan assets consist of fixed and variable rate instruments under a trust fund managed by a committee appointed by the Company.
(11) Income (IT) and asset (AT) taxes, employee statutory profit sharing (ESPS) and tax loss carryforwards-
Under Mexican tax law, companies must pay the greater of IT or AT, of which AT may be recovered over the following ten years. Net tax operating losses may be carried forward for ten years.
At December 31, 2002, income tax attributable to income from continuing operations before IT differed from the amounts computed by applying the Mexican rate of 35% for income tax, as a result of the following:
| Computed (expected) tax expense | $156,382 |
| Increase (decrease) resulting from: | |
| Effects of inflation, net | (61,839) |
| Non-deductible expenses | 4,450 |
| Increase in valuation allowance | 47,743 |
| Other, net | (4,180) |
| IT expense | $142,556 |
For the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000, the Company did not incur an expense or benefit for employee statutory profit sharing.
The tax effects of temporary differences that give rise to significant portions of the deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities, at December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000, are presented as shown in the next page.
| | IT |
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | |
| Accruals | $42,082 | 43,335 | 31,191 |
| Net operating tax loss carryforwards | 104,429 | 179,578 | 287,442 |
| Recoverable AT | 138,528 | 90,785 | - |
| Total gross deferred tax assets | 285,039 | 323,016 | 318,633 |
| Less valuation allowance | 138,528 | 90,785 | - |
| Net deferred tax assets | $146,511 | 222,913 | 318,633 |
| Deferred tax liabilities: | | | |
| Inventories | 441,438 | 404,892 | 406,886 |
| Equipment | 200,149 | 221,526 | 155,808 |
| Other | 4,219 | 1,877 | 9,063 |
| Total gross deferred tax liabilities | 645,806 | 628,295 | 571,757 |
| Net deferred tax liability | $499,295 | 405,382 | 253,124 |
The valuation allowance for deferred tax assets as of January 1, 2002 amounted to $90,785. The net change in the total valuation allowance for the years ended December 31, 2002 and 2001 was an increase of $47,743 and $90,785, respectively. In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences become deductible. Management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income, and tax planning strategies in making this assessment.
At December 31, 2002, operating tax loss carryforwards and recoverable AT expire as follows (unaudited):
| | Inflation adjusted through June 30,2002 |
| Expiring Year | Operating tax loss carryforwards | Recoverable AT |
|
| 2003 | $ 6,038 | 1,392 |
| 2004 | 8,611 | 3,717 |
| 2005 | 3,885 | 8,493 |
| 2006 | 8,351 | 3,462 |
| 2007 | 29,101 | 6,672 |
| 2008 | 135,119 | 7,261 |
| 2009 | 28,253 | 13,684 |
| 2010 | 8,687 | 16,367 |
| 2011 | 8,135 | 30,134 |
| 2012 | 62,409 | 47,346 |
| | $298,589 | 138,528 |
A new Income Tax Law was enacted on January 1, 2002. This law provides for a 1% annual reduction in the income tax rate beginning in 2003 to 34% and ending in a rate of 32% in 2005.
(12) Stockholders’ equity-
The principal characteristics of stockholders’ equity are described below:
(a) Structure of capital stock-
At the General Extraordinary Shareholders’ Meetings held on February 3, 1999, the shareholders approved an increase in the variable capital stock of the Company of $132,583 ($102,000 in nominal value).
At the General Extraordinary Shareholders’ Meetings held on May 22 and September 19, 2000, the shareholders approved an increase in the variable capital stock of the Company of $218,122 ($190,370 in nominal value).
At the General Extraordinary Shareholders’ Meetings held on January, 18 and 19, 2001, the shareholders approved an increase in the variable capital stock of $1,441,356 ($1,313,342 in nominal value) and $509,982 ($464,690 in nominal value), respectively.
At the General Extraordinary Stockholders’ meeting held on December 3, 2001, the stockholders agreed to merge Arrendadora Costco S. A. de C. V. (formerly Arrendadora Price Club, S. A. de C. V.) and Costco de México, S. A. de C. V., with the latter being the subsisting entity. This merger was effective as of December 31, 2001.
After the above activity, the Company’s capital stock at December 31, 2002 was represented by 2,522,380,882 common shares fully subscribed and paid with a par value of one peso each, of which 1,000 are classified as fixed capital and 2,522,379,882 as variable capital.
According to the Company’s articles of incorporation, the shares are divided into two Series, "A" and "B". Series "A" shares may be owned only by Mexican entities with majority Mexican ownership. Series "B" shares may be acquired by foreign corporations or individuals.
(b) Comprehensive income-
The Components of Comprehensive income reported in the statements of stockholders’ equity, in accordance with Mexican GAAP, are as follows:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Net income | $304,251 | 306,750 | 234,175 |
| Results from holding non-monetary assets | (94,564) | (104,342) | (175,551) |
| Comprehensive income | $209,687 | 202,408 | 58,624 |
(c) Restrictions on stockholders’ equity-
Five percent of net income for the year must be appropriated to the statutory reserve, until it reaches one-fifth of capital stock. As of December 31, 2002, the statutory reserve amounts to $11,611 ($2,372 historical).
Stockholder contributions restated as provided for by the tax law may be refunded to stockholders tax-free, to the extent that the tax such contributions equal or exceed stockholders’ equity.
Retained earnings and other stockholders’ equity accounts on which no income taxes have been paid, are subject to income taxes in the event of distribution, at the rate of 34%, payable by the Company; consequently, the stockholders may only receive 66% of such amounts.
(13) Contingent liabilities-
- The five-year period prior to the most recent income tax return filed is open to governmental tax examination.
- In accordance with the Income Tax Law, companies carrying out transactions with related parties are subject to certain requirements as to the determination of prices, since such prices must be similar to those that would be used in arm’s-length transactions.
Should the tax authorities examine the transactions and reject the related-party prices, they could assess additional taxes plus the related inflation adjustment and interest, in addition to penalties of up to 100% of the omitted taxes.- There is a contingent liability arising from the labor obligations mentioned in note 2(g).
(14) New accounting pronouncements-
(a) Liabilities, accruals, contingent assets and liabilities, and commitments-
In December 2001, the Mexican Institute of Public Accountants issued the new Bulletin C-9, "Liabilities, Accruals, Contingent Assets and Liabilities, and Commitments". New Bulletin C-9, effective for fiscal years beginning after December 31, 2002, supersedes former Bulletins C-9, "Liabilities," and C-12, "Contingencies and Commitments". New Bulletin C-9 establishes additional guidance clarifying the accounting for liabilities, accruals, and contingent assets and liabilities, and establishes new standards for the use of present value techniques to measure liabilities, and accounting for the early settlement of liabilities and convertible debt. Additionally, new Bulletin C-9 establishes new rules for disclosing commitments arising from current business operations.
(b) Intangible assets-
In January 2002, the Mexican Institute of Public Accountants issued the new Bulletin C-8, "Intangible Assets," effective for fiscal years beginning after December 31, 2002. New Bulletin C-8 supersedes former Bulletin C-8, "Intangibles," and establishes that qualifying project development costs be capitalized as intangible assets if the criteria for intangible assets recognition are met. The principal criteria are that these costs be identifiable, that there is reasonable certainty that these costs will generate future benefits to the Company, and that the Company has control over such benefits. Other costs, not meeting the new criteria and incurred after the effective date of new Bulletin C-8, should be expensed as incurred. Pre-operating expenses previously recognized under former Bulletin C-8 will continue to be amortized, subject to periodic impairment evaluations. Development costs incurred in a pre-operating stage may be capitalized after meeting certain conditions under new Bulletin C-8.
This Bulletin also requires that intangibles acquired in a business combination be accounted for at fair value at the date of purchase and be separately reported, unless their cost can not be reasonably determined, in which case, they should be reported as goodwill. Intangible assets and goodwill assets are also subject to periodic impairment evaluations. Amortization of goodwill should be reported in operating expenses in the statements of income.
The Company estimates that the adoption of the new Bulletins C-8 and C-9 will not have a material effect on its financial statements or results of operations.
(15) Differences between Mexican and United States Accounting Principles (US GAAP)-
The consolidated financial statements of the Company, as discussed in note 2, are presented on the basis of accounting principles generally accepted in Mexico (Mexican GAAP). This reconciliation to US GAAP does not include the reversal of the effects of inflation. The application of Bulletin B-10 represents a comprehensive measure of the effects of price level changes in the Mexican economy and, as such, is considered a more meaningful presentation than historical cost financial reporting for both Mexican and US GAAP purposes.
The principal differences between Mexican GAAP and US GAAP are described below together with an explanation, where appropriate, of the method used in the determination of the adjustments than affect net income and stockholders’ equity.
Reconciliation of consolidated stockholders’ equity as of December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000, is as follows:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Stockholders’ equity reported under Mexican GAAP | $4,631,115 | 4,421,428 | 2,267,682 |
| Approximate US GAAP adjustments for: | | | |
| Preoperating expenses (a) | (7,766) | (3,813) | (4,285) |
| Membership fees (b) | (94,803) | (85,978) | (72,038) |
| Effect on deferred income taxes of US GAAP adjustments (c) | 34,873 | 31,427 | 26,713 |
| Total approximate stockholders’ equity under US GAAP | $4,563,419 | 4,363,064 | 2,218,072 |
Reconciliation of consolidated net income for the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 is as follows:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Net income as reported under Mexican GAAP | $304,251 | 306,750 | 234,175 |
| Approximate US GAAP adjustments for: | | | |
| Preoperating expenses (a) | (3,953) | 472 | (16) |
| Membership fees (b) | (8,825) | (13,940) | (20,937) |
| Effect on deferred income taxes of US GAAP adjustments (c) | 3,446 | 4,714 | 7,334 |
| Approximate net income under US GAAP | $294,919 | 297,996 | 220,556 |
| Weighted average shares (in thousands) | 2,522,381 | 2,438,295 | 639,529 |
| Basic and diluted income per share under US GAAP (in Mexican Pesos) | $0.11 | 0.12 | 0.34 |
An analysis of the changes in stockholders’ equity under US GAAP is as follows:
| | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Balance at beginning of year | $4,363,064 | 2,218,072 | 1,020,510 |
| Increase in capital stock | - | 1,951,338 | 218,122 |
| Capital contribution resulting from acquisition of shares of subsidiaries | - | - | 934,395 |
| Results of holding non-monetary assets | (94,564) | (104,342) | (175,511) |
| Net income under US GAAP | 294,919 | 297,996 | 220,556 |
| Balance at end of year | $4,563,419 | 4,363,064 | 2,218,072 |
(a) Preoperating expenses-
Under Mexican GAAP preoperating expenses are capitalized until facilities are completed and operations begin. Under US GAAP, such costs are expensed as incurred.
(b) Membership fees-
Under Mexican GAAP, membership payments are generally recognized as income in the period in which payments are received. Under US GAAP, membership fees are amortized to income during the membership term.
(c)Deferred income taxes-
The Company accounts for income taxes under Bulletin D-4 for Mexican GAAP purposes, requiring the determination of deferred income taxes under the asset and liability method of accounting, which is consistent to that of US GAAP under Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (SFAS) No. 109, "Accounting for Income Taxes". Amounts included in the reconciliations represent the recognition of deferred income taxes on the US GAAP adjustments.
Additionally, under US GAAP, the deferred amounts for ESPS purposes should be recognized under SFAS 109 using the asset and liability method at the statutory rate of 10% and the related deferred amounts are considered compensation expense for US GAAP. Deferred ESPS effects were not significant.
(d) Supplemental cash flow information under US GAAP-
Under Mexican GAAP, the statement of changes in financial position, which identifies the sources and uses of resources based upon the differences between beginning and ending financial statements captions in constant pesos, requires that the monetary position result and unrealized foreign exchange result be treated as cash items in the determination of resources provided by operations. US GAAP, under SFAS 95, requires a statement of cash flow presenting only cash items and excluding non-cash items. SFAS 95 does not provide any guidance with respect to inflation-adjusted financial statements.
The application of the company’s US GAAP adjustment would not have a material effect on net funds provided by (used in) operating activities, taxes paid during the years ended December 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000 amounted to $494,325, $105,167, $78,533, respectively.

