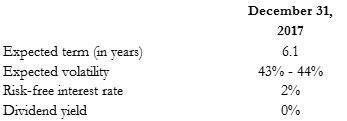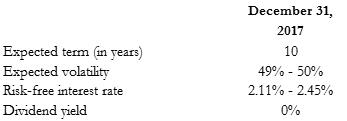Exhibit 99.1
Spinal Kinetics, Inc. And Subsidiaries
___________
Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2017
Spinal Kinetics, Inc. And Subsidiaries
____________
Contents
| | | Page (s) |
Independent Auditors’ Report | | | |
| | | |
| | | |
Financial Statements: | | | 1 |
| | | |
Balance Sheet | | | 2 |
| | | |
Statement of Operations and Comprehensive Loss | | | 3 |
| | | |
Statement of Stockholders’ Deficit | | | 4 |
| | | |
Statement of Cash Flows | | | 5 |
| | | |
Notes to Financial Statements | | | 6–29 |
| | | |
Report of Independent Auditors
Board of Directors
Spinal Kinetics, Inc. and Subsidiaries
We have audited the accompanying consolidated financial statements of Spinal Kinetics, Inc. and subsidiaries, which comprise the consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2017, and the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss, changes in stockholders’ deficit and cash flows for the year then ended, and the related notes to the consolidated financial statements.
Management’s Responsibility for the Financial Statements
Management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of these financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles; this includes the design, implementation and maintenance of internal control relevant to the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements that are free of material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error.
Auditor’s Responsibility
Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit. We conducted our audit in accordance with auditing standards generally accepted in the United States. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement.
An audit involves performing procedures to obtain audit evidence about the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. The procedures selected depend on the auditor’s judgment, including the assessment of the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to fraud or error. In making those risk assessments, the auditor considers internal control relevant to the entity’s preparation and fair presentation of the financial statements in order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the entity’s internal control. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes evaluating the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonableness of significant accounting estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements.
We believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our audit opinion.
Opinion
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of Spinal Kinetics, Inc. and subsidiaries at December 31, 2017, and the consolidated results of their operations and their cash flows for the year then ended in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Dallas, Texas
April 30, 2018
1
Spinal Kinetics, Inc. And Subsidiaries
Consolidated Balance Sheet
December 31, 2017
(In thousands, except for per share and share amounts)
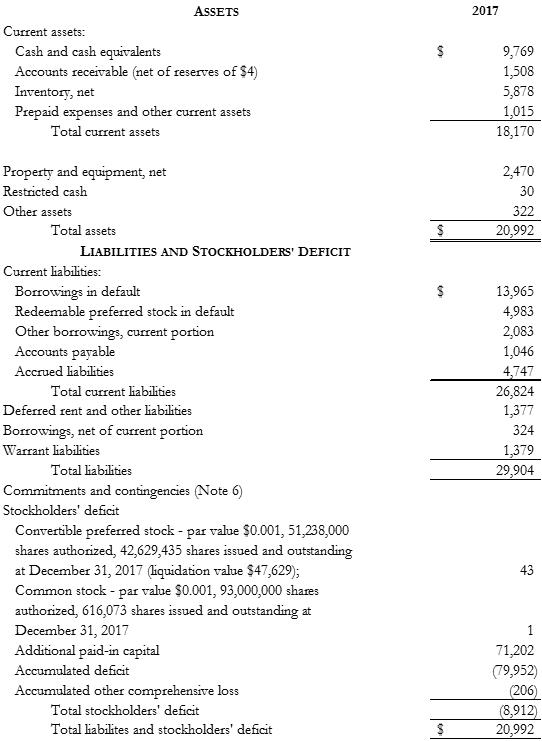
Assets 2017 current assets: cash and cash equivalents accounts receivable (net of reserves of $4) inventory, net prepaid expenses and other current assets property and equipment, net restricted cash other assets total assets liabilities and stockholders' deficit current liabilities: borrowings in default redeemable preferred stock in default other borrowings, current portion accounts payable accrued liabilities total current liabilities deferred rent and other liabilities borrowings, net of current portion warrant liabilities total liabilities commitments and contingencies (Note 6) stockholders' deficit convertible preferred stock - par value $0.001, 51,238,000 shares authorized, 42,629,435 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2017 (liquidation value $47,629); common stock - par value $0.001, 93,000,000 shares authorized, 616,073 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2017 additional paid-in-capital accumulated deficit accumulated other comprehensive loss total stockholders' deficit $ 9,769 1,508 5,878 1,015 18,170 2,470 30 322 $ 20,992 $ 13,965 4,983 2,083 1,046 4,747 26,824 1,377 324 1,379 29,904 43 1 71,202 (79,952) (206) (8,912) $ 20,992
The accompanying notes are an integral
part of these financial statements.
2
Spinal Kinetics, Inc. And Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statement of Operations and comprehensive loss
For the year ended December 31, 2017
(In thousands)
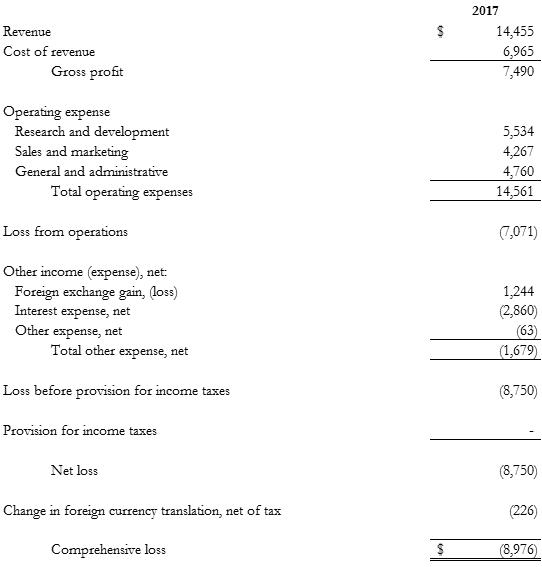
Revenue cost of revenue gross profit operating expense research and development sales and marketing general and administrative total operating expenses loss from operations other income (expense), net: Foreign exchange gain, (loss) interest expense, net other expense, net total other expense, net loss before provision for income taxes provision for income taxes net loss change in foreign currency translation, net of tax comprehensive loss 2017 $ 14,455 6,965 7,490 5,534 4,267 4,760 14,561 (7,071) 1,244 (2,860) (63) (1,679) (8,750) - (8,750) (226) $ (8,976)
The accompanying notes are an integral
part of these financial statements.
3
Spinal Kinetics, Inc. And Subsidiaries
Statement of Stockholders’ deficit
For the year ended December 31, 2017
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
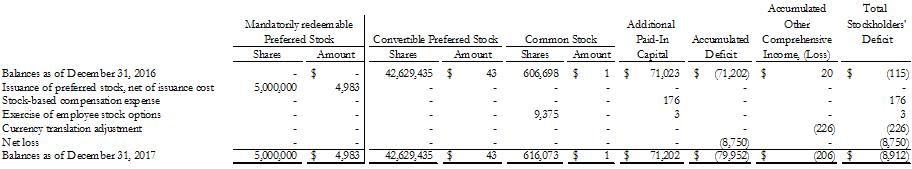
Balances as of December 31, 2016 issuance of preferred stock, net of issuance cost stock-based compensation expense exercise of employee stock options currency translation adjustment net loss balances as of December 31, 2017 mandatorily redeemable preferred stock shares amount convertible preferred stock shares amount common stock shares amount additional paid-in capital accumulated deficit accumulated other comprehensive income, (loss) total stockholders' deficit - 5,000,000 - - - - 5,000,000 $ - 4,983 - - - - $4,983 42,629,435 - - - - - 42,629,435 $ 43 - - - - - $ 43 606,698 - - 9,375 - - 616,073 $ 1 - - - - - $ 1 $ 71,023 - 176 3 - - $ 71,202 $ (71,202) - - - - (8,750) $ (79,952) $ 20 - - - (226) - $ (206) $ (115) - 176 3 (226) (8,750) $ (8,912)
The accompanying notes are an integral
part of these financial statements.
4
Spinal Kinetics, Inc. And Subsidiaries
Statement of Cash Flows
For the year ended December 31, 2017
(In thousands)

Cash flows from operating activities: net loss adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: depreciation and amortization stock-based compensation expense amortization of debt discount accrued interest on borrowings provision for doubtful accounts change in fair value of warrant liability changes in operating assets and liabilities: trade receivables prepaid expenses and other current assets inventories accounts payable accrued liabilities deferred rent and other liabilities net cash used in operating activities cash flows from investing activities cash flows from investing activities: change in restricted cash proceeds from property and equipment disposals acquisition of property and equipment net cash used in investing activities cash flows from financing activities: proceeds from issuance of series d preferred shares, net of issuance costs proceeds from issuance of term note, net of issuance costs payments on term notes payments on capital lease net cash provided by financing activities effect of foreign exchange rates net increase in cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year cash and cash equivalents at end of year supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: interest paid taxes paid noncash activities: warrants issued in connection with term debt payment in kind interest added to loan principal 2017 $ (8,750) 718 176 319 717 (61) (245) (12) 66 380 78 12 65 (6,537) 76 65 (521) (380) 4,983 14,518 (5,161) (59) 14,281 414 7,778 1,991 $ 9,769 $ 15 $ - $ 922 $ 580
The accompanying notes are an integral
part of these financial statements.
5
SPINAL KINETICS, INC AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2017
1.General
Spinal Kinetics, Inc. (the “Company”) was incorporated in Delaware on July 22, 2003. The Company is a privately-held medical device company that designs and manufactures motion preservation systems for treating degenerative diseases of the spine. The Company offers M6-C Artificial Cervical Disc, which offers an option for artificial cervical disc replacement; and M6-L Artificial Lumbar Disc, which offers an option for artificial lumbar disc replacement. Spinal Kinetics sells its products through a wholly-owned subsidiary in Germany and through distributors in Europe, Asia, Australia, and North and South America. The consolidated financial statements include the financial statements of the Company and its wholly owned subsidiaries. All intercompany accounts and transactions are eliminated in consolidation.
2. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
Liquidity
The consolidated financial statements of the Company were prepared on a going concern basis, which contemplates the realization of assets and the satisfaction of liabilities in the normal course of business. The Company has incurred significant net losses and negative cash flows from operations since inception. At December 31, 2017, the Company has an accumulated deficit of $79,952 and the Company is in default of its secured promissory note (see Note 5) and mandatorily redeemable preferred stock (see Note 7). The Company expects operating losses to continue in the foreseeable future because of additional costs and expenses related to research and development activities and increase its market share. Based on current operating levels and required debt repayments, the Company will need to raise additional funds by selling additional equity or incurring additional debt. To date, the Company has been able to fund its operations through the sale of preferred stock, warrants and debt financings. Additionally, future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including the rate of revenue growth, the selling price of the Company’s products, the expansion of sales and marketing activities, the timing and extent of spending on research and development efforts and the continuing market acceptance of the Company’s products.
On March 15, 2018, the Company entered into a definitive merger agreement (the “Merger Agreement”) with Orthofix International N.V. (“Orthofix”), a global medical device company focused on musculoskeletal healing products and value-added services. As consideration, the Company has agreed to accept an aggregate of $45 million in cash, subject to certain adjustments, upon closing plus potential milestone receipts of up to $60 million in cash. The proceeds from this transaction will be used to pay off all of the Company’s debt obligations. Additionally, all warrants and preferred stock obligations will be settled as part of this transaction.
On April 30, 2018, the Merger Agreement was completed, and the Company became a wholly-owned subsidiary of Orthofix. As a result of the merger with Orthofix, management believes it has sufficient capital to operate beyond the next 12 months.
Concentration of Credit Risk and Other Risks and Uncertainties
The Company is subject to all the risks inherent in an early stage company developing a new medical device. These risks include, but are not limited to raising capital, limited management resources, intense competition, dependence upon consumer acceptance of the product, and the changing nature of the medical device industry. The Company’s operating results may be materially affected by the foregoing factors.
6
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
The Company’s product requires clearance from the Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) prior to commercialize sales in the United States of America. There can be no assurance that the Company’s products will receive any of these required clearances. If the Company was denied such clearances or such clearances were delayed, it would have a materially adverse impact on the Company.
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to significant concentration of credit risk consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents and accounts receivable. Cash and cash equivalents are deposited in demand and money market accounts at two financial institutions.
The Company performs ongoing credit evaluations of its customers' financial condition and generally does not require collateral from its customers. At December 31, 2017, 1 customer accounted for 15% of total revenue and 2 customers accounted for 33% and 13% each of total accounts receivable, respectively.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the financial statements and expenses during the reporting period. Such estimates include the valuation of deferred tax assets and the value of the Company’s stock. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments purchased with original maturities of three months or less to be cash equivalents. The Company maintains deposits with two financial institutions and invests its excess cash primarily in money market funds that bear minimal risk. At times, these balances may exceed the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation insurance limits. While the Company monitors the cash balances at these institutions and adjusts cash balances as appropriate, these cash balances could be impacted if the underlying financial institution fails or is subject to other adverse conditions in the financial markets. To date the Company has experienced no loss or lack of access to its deposits in these institutions.
Restricted Cash
At December 31, 2017, cash of $30 was restricted from withdrawal. Restricted cash of $30 was held by a bank in the form of a certificate of deposit, which collateralizes the Company's available credit for corporate credit cards.
Trade Receivables
Trade receivables are recorded at the invoiced amount and are non-interest-bearing. The Company maintains an allowance for doubtful accounts for estimated losses resulting from customers failing to make required payments. This valuation allowance is reviewed on a periodic basis to determine whether a provision or reversal is required. The review is based on factors including the application of historical collection rates to current receivables and economic conditions. The Company will record an increase or reduction of its allowance for doubtful accounts if collection rates or economic conditions are more or less favorable than it anticipated.
7
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
Inventory
Inventories are valued at the lower of cost or estimated net realizable value, after provisions for excess, obsolete or impaired items, which is reviewed periodically by management. For inventory procured or produced, at our manufacturing facility in Sunnyvale, standard costs, which approximates actual cost on the FIFO method, is used to value inventory. Standard costs are reviewed annually by management, or more often in the event circumstances indicate a change in cost has occurred.
The Company adjusts the value of its inventory to the extent management determines that the cost cannot be recovered due to obsolescence or other factors. In order to make these determinations, management uses estimates of future demand and sales prices for each product to determine the appropriate inventory reserves and to make corresponding adjustments to the carrying value of these inventories to reflect the lower of cost or market value.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization of property and equipment are computed using the straight-line method over their estimated useful lives of the respective assets as follows: computer equipment and software over three years; laboratory equipment and furniture and other equipment over five years. Leasehold improvements are amortized on a straight-line basis over the shorter of the estimated useful life of the asset or the life of the lease. Upon retirement or sale, the cost and related accumulated depreciation are removed from the balance sheet and resulting gain or loss is reflected in operations. Maintenance and repairs are charged to operations as incurred.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Carrying amounts of the Company’s certain financial instruments including cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, prepaid expenses and other current assets, accounts payable, accrued liabilities approximate fair value due to their relatively short maturities, and market interest rates if applicable.
Landlord funded leasehold improvements and deferred rent
In connection with the new office building lease, the Company entered into an agreement with the landlord in which the landlord agreed to pay the cost of certain leasehold improvements. The Company is obligated to repay to the landlord for a portion of the cost of the improvements. The Company has accounted for the net cost of the improvements paid for by the landlord as leasehold improvements in property and equipment and is amortizing the cost over the initial term of the lease. The Company has also recorded a related liability for deferred rent which is being amortized ratably as a reduction in rent expense over the initial term of the lease. The Company records rent expense on a straight-line basis, with a corresponding deferred rent liability recognized in deferred rent and other liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
Foreign Currency Translation
Assets and liabilities of the Company’s foreign subsidiaries are translated into U. S. Dollars from their functional currencies of Euros using the exchange rate in effect at the balance sheet date. Additionally, net sales and expenses are translated using exchange rates approximating average rates prevailing during the fiscal year. Translation
8
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
adjustments that arise from translating the financial statements from local currencies to U. S. Dollars are accumulated and reflected as a separate component of shareholders’ equity (deficit).
Revenue Recognition
The Company’s revenue is primarily comprised of the sale of its motion preservation discs that are intended to replicate the anatomic and biomechanical attributes of a natural intervertebral disc. The Company recognizes revenue in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 605 Revenue Recognition. Under this standard, the following four criteria must be met in order to recognize revenue:
| • | Persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists; |
| • | The selling price is fixed or determinable; and |
| • | Collectability is reasonably assured. |
The Company sells to distributors outside of the United States. The Company’s distributors are responsible for all marketing, sales, training and warranty for the Company’s products. The terms and conditions set out in the Company’s agreements with these distributors do not provide price protection or stock rotation rights to any of its distributors. The Company sells direct to hospitals in Germany through its wholly owned subsidiary. Shipping costs are included in cost of sales.
Research and Development
Research and development costs reflect clinical expenditures and product development, which are substantially related to the ongoing development and associated regulatory approvals of the Company’s products and technology. Research and development costs are expensed as incurred.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company accounts for employee stock-based expense in accordance with the provisions of ASC 718, Share Based Payment (“ASC 718”). The employee stock-based expense is based on the fair value of our stock-based awards over their respective vesting periods, which is generally four years. The Company uses the Black-Scholes valuation model and the straight-line method, which allocates expense on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period of the last separately vesting portion of an award.
The Company accounts for equity instruments issued to nonemployees in accordance with the provisions of ASC 505-50, Equity based payments to non-employees. The equity instruments, consisting of stock options, are valued using the Black-Scholes valuation model. The measurement of stock-based compensation is subject to periodic adjustments as the underlying equity instruments vest.
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes under the asset and liability method, which requires, among other things, that deferred income taxes be provided for temporary differences between the tax basis of the Company’s assets and liabilities and their financial statement reported amounts. In addition, deferred tax assets are recorded for the future benefit of utilizing net operating losses and research and development credit carryforwards. A valuation allowance is provided against deferred tax assets unless it is more likely than not they will be realized.
9
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
Recent Accounting Pronouncement
In May 2017, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2017-09, Compensation – Stock Compensation (Topic 718) Scope of Modification Accounting. The amendments in ASU 2017-09 provide guidance about which changes to the terms or conditions of a share-based payment award require an entity to apply modification accounting in Topic 718. The adoption of ASU 2017-09 will become effective for the Company in fiscal year 2018. The Company is in the process of evaluating the impact of this guidance to the consolidated financial statements
In October 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-16, Intra-entity Transfers of Assets Other Than Inventory. The amendments in ASU 2016-16 provide guidance regarding the timing of the recognition of current and deferred income taxes for intra-entity asset transfers (Topic 740). The Board decided that an entity should recognize the income tax consequences of an intra-entity transfer of an asset other than inventory when the transfer occurs rather than after the asset has been sold to an outside party. The guidance is effective for the Company in fiscal year 2019. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is in the process of evaluating the impact of this guidance to the consolidated financial statements.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-15, Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments. Topic 230. This guidance addresses specific cash flow issues with the objective of reducing the diversity in practice for the treatment of these items. In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows, Restricted Cash: Topic 230. This guidance requires that a statement of Cash flows explain the change during the period of total cash, cash equivalents, and amounts generally described as restricted cash or restricted cash equivalents. Amounts described as restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents should be included with cash and cash equivalents when reconciling the beginning of period and end of period to total amounts shown on the statement of cash flows. The guidance for these two ASUs is effective for the Company in fiscal year 2019. The Company is in the process of evaluating the impact of this guidance to the consolidated financial statements.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-09, Compensation - Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvement to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting. The new standard contains several amendments that will simplify the accounting for employee share-based payment transactions, including the accounting for income taxes, forfeitures, statutory tax withholding requirements, classification of awards as either equity or liabilities, and classification on the statement of cash flows. The changes in the new standard eliminate the accounting for excess tax benefits to be recognized in additional paid-in capital and tax deficiencies recognized either in the income tax provision or in additional paid-in capital. The standard is effective for the Company in fiscal year 2019. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is in the process of evaluating the impact of this guidance to the consolidated financial statements.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, Leases. This standard requires management to present all leases greater than one year on the balance sheet. This new standard will be effective for the Company in the fiscal year 2020. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of the adopting of this guidance to the consolidated financial statements.
In August 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-14, Revenue from Contracts With Customers, addressing guidance for revenue from contracts with customers. The guidance outlines a single comprehensive model for entities to use in accounting for revenue arising from contracts with customers and supersedes most current revenue recognition guidance, including industry specific guidance. The guidance also required enhanced disclosures regarding the nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from an entity’s contracts with customers. This new standard will be effective for the Company for the fiscal year 2019, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of adopting this new guidance to the consolidated financial statements.
10
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
In July 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-11, Inventory. This standard requires management to measure inventory at the lower of cost or net realizable value. Net realizable value is the estimated selling prices in the ordinary course of business, less reasonably predictable costs of completion, disposal, and transportation. This new standard is effective for the Company in the fiscal year 2017. The Company implemented ASU No. 2015-11 during the fiscal year 2017, and the impact of the adoption on its consolidated financial statements was immaterial.
3. | Balance Sheet Components |
| The balance sheet items below consist of the following: |
Trade receivables, net

Trade receivables allowance for doubtful accounts December 31, 2017 $ 1,512 (4) $ 1,508
Inventory, net

Production materials work-in-process finished goods December 31, 2017 $ 2,234 423 3,221 $ 5,878
Property and Equipment, Net

Laboratory equipment software computer equipment furniture and other equipment leasehold improvements less: accumulated depreciation and amortization net property and equipment December 31, 2017 $ 5,721 294 184 537 2,846 9,582 (7,112) $ 2,470
11
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
Depreciation and amortization expense for the years ended December 31, 2017 was $712.
Accrued Liabilities

Accrued royalties accrued payroll and bonus accrued professional fees accrued accounts payable accrued clinical trials accrued other total accrued liabilities December 31, 2017 $ 882 $ 599 $ 158 $ 1,350 $ 542 $ 1, 216 $ 4,747
4. | Fair Value Measurements |
We define fair value as the price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Valuation techniques we use to measure fair value maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. We classify the inputs used to measure fair value into the following hierarchy:
Level 1Unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities
Level 2Unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for similar assets or liabilities, or unadjusted quoted
prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active, or inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the asset or liability.
Level 3Unobservable inputs for the asset or liability
At December 31, 2017, the Company’s liabilities measured on a recurring basis were as follows:

Liabilities: warrant liabilities December 31, 2017 Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 $ 1,379 $ - $ 1,379
The following table includes a summary of changes in the fair value of the Company's warrant liabilities measured at fair value using significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) for the years ended December 31, 2017:
12
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)

Beginning balance additions change in fair value ending balance warrant liabilities December 31, 2017 $ 701 923 (245) $ 1,379
| Morgan Stanley Loan and Security Agreement |
| On January 23, 2017, the Company entered into a secured promissory note agreement (“Secured Note”) with Morgan Stanley for $15,000 in secured debt financing. The loan is interest only for 60 months with an interest rate of 10% plus the greater of the three-month LIBOR or 1%. Interest is payable in arrears on a quarterly basis. In addition, fixed secured interest of 4% (the “PIK” interest) is accrued each month, and added to the loan principal. The Secured Note will not be subject to redemption until two years following the Closing Date of the loan, unless there is a change of control. The Company paid to Morgan Stanley on the Closing Date an origination fee equal to 2% of the Secured Note. The Company may repay the loan prior to the five-year maturity date, but the following fees apply. |
| | If the Secured Note is repaid prior to the second anniversary of the Closing Date, the Company will pay to Morgan Stanley an amount equal to 6% of the accreted value at the time of the repayment |
| | If the Secured Note is repaid prior to the third anniversary, but on or after the second anniversary of the Closing Date, the Company will pay to Morgan Stanley an amount equal to 3% of the accreted value at the time of repayment |
| | If the Secured Note is repaid on the third anniversary of the Closing date, there is no fee |
| | If the Secured Note is repaid after the third anniversary and before the fourth anniversary of the Closing Date, then the Company will pay to Morgan Stanley an amount equal to 4% of the accreted value at the time of repayment |
| | If the Secured Note is repaid after the fourth anniversary but prior to the fifth anniversary, the Company will pay to Morgan Stanley an amount equal to 10% of the accreted value at the time of repayment. |
| In connection with the funding of the Secured Note, the Company agreed to issue to Morgan Stanley detachable warrants to purchase Series C Preferred Stock of the Company at a warrant coverage ratio equal to 10% of the Commitment Amount at a price of $1.00 per share. If the Company closes a next round of equity financing of at least $10,000 then the number of warrants granted will be determined by dividing $1,500 by the new (next round) share price. The warrant has a term of 10 years and will survive an Initial Public Offering or acquisition in which the consideration consists exclusively of cash or publicly traded stock. If the Company does not enter into a definitive agreement with a third party to acquire the Company on or prior to June 30, 2017, and if the transaction Closing Date is not on or before September 30, 2017, then the price of the warrants becomes $0.01 per share. The Company did not enter into such a definitive agreement within the required time frame, and accordingly the price of the warrants became $0.01. |
13
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
Upon issuance, the fair value of the warrant was determined to be $922 which in addition to other fees and legal costs to obtain the loan, was originally recorded as a debt discount. At June 30, 2017, the Company revalued the warrants using the Black Scholes option pricing model with a volatility of 49.5%, term of 9.57 years and a risk-free interest rate of 2.29%. The fair value of the warrants was determined to be $722. The liability and debt discount were adjusted, and $75 was recognized as other income. The debt discount is being amortized to interest expense over the repayment period of the loan using the effective interest rate method.
| The Company is responsible for adhering to certain financial covenants as described below: |
| | Measured on a quarterly basis, the Company’s revenue over the previous 12-month period must be a minimum of $12,000. |
| | The Company’s maximum cash usage, measured at the end of each quarter, must not exceed $9,000. |
| | The Company must maintain a minimum cash balance of at least $3,000. |
| | The Company must have closed at least $5,000 of net cash proceeds in equity financing by September 30, 2017, and an additional $15,000 of net proceeds in equity financing by December 31, 2017 for a total of $20,000 in equity financing prior to the end of 2017. |
| As of December 2017, the Company had not raised the required $20,000 in equity financing, thereby violating the financial covenants, and creating an Event of Default. On February 5, 2018, the Company entered into a Forbearance Agreement with Morgan Stanley which for consideration listed below, Morgan Stanley agreed to forbear from exercising rights and remedies under the Secured Note. Until the Forbearance agreement has been terminated, the Company will provide to Morgan Stanley additional consideration and commitments which includes: |
- Forbearance Fee of 1% of the cumulative amount of principal and paid in capital at the time of the default.
- Default Interest of 5% will be paid quarterly, in addition to the existing quarterly interest due on the principal.
- Provide to Morgan Stanley a revised operating plan for the four-year period ending December 31, 2021.
- Develop and present to Morgan Stanley a commercialization plan which outlines the strategy and execution plan to commercialize the Company’s product in the United States.
- Engage a debt advisory firm to assist in developing a refinancing plan.
- Update the Company’s perfection certificate.
- Provide to Morgan Stanley a Certificate of No Event of Default which, except for the provisions of the forbearance agreement, certify the Company is not in default on any other covenants or provisions of the Note.
- Schedule monthly Board meetings.
- Provide weekly updates to Morgan Stanley.
14
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
The Company continued to operate within the provisions set forth in the Forbearance Agreement until it expired March 31, 2018 and was not extended further due to the signing of the definitive merger agreement entered into on March 15, 2018. (See Footnote 10 “Subsequent Events”).
| The Secured Note is senior to all other Company indebtedness except for the Silicon Valley Bank loan (“SVB loan”). The Company agreed to set aside as restricted cash $4,500 of the total $15,000 in debt proceeds to be used to retire the SVB loan. |
Silicon Valley Bank Loan
In August 2015, the Company entered into a $5,000 credit facility with Silicon Valley Bank (" SVB"). The credit facility included an initial $3,000 term loan and $2,000 in commitments for an additional term loan, subject to the satisfaction of certain conditions. The SVB initial term loan was repayable over 36 months commencing April 1, 2016 and bore interest at prime rate plus 0.25%. During January 2016, the Company drew the remaining $2,000 from the $5,000 commitment provided by SVB in 2015. The $2,000 second tranche bore interest at prime rate plus 0.25%. The draw of the second tranche extended the interest-only period through September 20, 2016 for first tranche. Both tranches amortized over 30 months ending with a final maturity date of March 31, 2019. The loan could be prepaid at the Company’s discretion subject to additional fees during the first two years. Under the loan and security agreement with SVB, the Company was required to pay 4.75% of the total amount borrowed under the loan at the maturity date of the loan.
In connection with initial term loan, the Company issued warrants to purchase a total of 60,000 shares of Series C preferred stock. Upon issuance, the fair value of the warrants of $33, in addition to other fees and legal costs to obtain the loan, was recorded as a debt discount. The draw of the second tranche amended the 60,000 warrants to purchase Series C issued to SVB in connection with the first tranche to 80,000 warrants under the same terms as originally granted. Upon issuance, the fair value of the warrants of $12, in addition to other fees and legal costs to obtain the loan, was recorded as a debt discount. The debt discount was being amortized to interest expense over the repayment period of the loan using the effective interest rate method.
Monthly minimum unrestricted cash of $1.5 million was required to be held at the bank at each month-end. Upon the bank's receipt of evidence that the borrower had received a signed term sheet for a bona-fide issuance of new equity with investors satisfactory to bank and on terms satisfactory to bank that would result in net proceeds to the borrower of at least $15 million and, so long as the borrower had complied with the other financial covenants for each fiscal quarter then ended, then the borrower's minimum amount of unrestricted cash held at the bank would be reduced to $1.0 million.
During the year 2016, the Company repaid $500 of the SVB loans and in December 2016 amended the loan and security agreement to borrow an additional $500 with an option to borrow an additional $500 thereafter on or before January 31, 2017. The term loan was repayable over 20 months commencing July 1, 2017 and bore interest at the greater of prime rate plus 0.25% or 3.75%. In connection with the amendment, SVB waived all covenants until January 31, 2017. Under the additional tranche to the loan and security agreement with SVB, the Company was required to pay 4.75% of the total amount borrowed under the loan at the maturity date of the loan. At December 31, 2016, the Company had borrowed $500 under this facility.
As collateral for the term loan, the Company granted SVB a senior, perfected security interest on all assets, with the exception of intellectual property for which there is a negative pledge.
15
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
In May 2015, SVB issued a $750 Letter of Credit in favor of the Company with a maturity of 15 months from date of issuance in compliance with the terms of the building lease. The Company’s letter of credit was retired in January 2017.
| On April 21, 2016, the Company violated the financial covenants of the original loan agreement which violation was waived by Silicon Valley Bank. On August 2, 2016 the bank and the Company agreed to amend the original loan agreement revising the financial covenants. In October 2016, the Company violated the amended financial covenants of the loan agreement which violation was waived by Silicon Valley Bank. |
Early retirement of Silicon Valley Bank Loan
On April 17, 2017, the Company elected to retire the $4,500 of debt provided by SVB. In October of 2016, the Company began the 30-month amortization of the two tranches under the $5,000 debt facility. At the time of the loan repayment in April 2017, the Company had amortized $1,000 of the $5,000, and had a balance of $4,000 on its books as of March 31, 2017. In addition, the Company also repaid the additional $500 it had drawn down in connection with the amended the loan and security agreement which closed in December of 2016.
Pursuant to the retirement of the amounts outstanding under the original debt facility and the amended loan and security agreement, the Company paid to Silicon Valley Bank the following amounts:
Principal$4,500
Interest$ 15
4.75% Final payment$ 261
Prepayment fee$ 50
Total repayment$ 4,826
The principal amount of $4,500 of the total $4,826 paid to Silicon Valley Bank was funded from the $4,500 restricted cash account established by Morgan Stanley for this purpose.
Convertible Promissory Notes
In October, November and December 2016, the Company entered into a convertible promissory note purchase agreement with various investors and certain officers of the Company. Under the agreement, the Company borrowed $1.65 million which was due on demand one year from the date of issuance. In November 2017, the maturity dates of the convertible promissory notes were extended to March 31, 2018 and was not extended further due to the signing of the definitive merger agreement entered into on March 15, 2018. (See Footnote 10 “Subsequent Events”). The notes bear interest at 8% per annum, payable at maturity, are secured and were originally subordinated to SVB debt. In connection with these convertible promissory notes, other fees and legal costs to obtain the loan were recorded as a debt discount, which is being amortized to interest expense over the repayment period of the loan using the effective interest rate method. The notes contain the following prepayment provision and conversion features.
Elective Prepayment Upon a Qualified Financing
In the event of a Qualified Financing that occurs prior to repayment or conversion, the Company will redeem the unpaid principal amount, together with all accrued but unpaid interest, that has not been paid or converted into equity securities, immediately subsequent to the closing of such Qualified Financing, for an amount equal to two hundred percent (200%) of the unpaid principal amount and all accrued but unpaid interest. This elective
16
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
prepayment is at the option of the noteholder, and no such prepayment shall occur without the written consent of the noteholder.
Elective Prepayment Upon a Change of Control
In the event of a Change of Control that occurs prior to repayment or conversion, the Company will redeem the unpaid principal amount, together with all accrued but unpaid interest that has not been paid or converted into equity securities, immediately subsequent to the closing of such Change of Control, for an amount equal to two hundred percent (200%) of the unpaid principal amount and all accrued but unpaid interest. This elective prepayment is at the option of the noteholder, and no prepayment shall occur without the written consent of the noteholder.
Conversion:
Conversion upon a Qualified Financing
If a Qualified Financing occurs on or prior to any repayment of the convertible promissory notes, then the outstanding principal amount and all accrued and unpaid interest, that has not otherwise been redeemed or repaid, shall convert into fully paid and nonassessable shares of the Preferred Stock issued in such Qualified Financing at the Conversion Price equal to the lower of eighty percent (80%) of the price per share paid by the other cash purchasers of the Preferred Stock or $1.00. No conversion shall occur without the written consent of the Investor.
Conversion upon a Change of Control.
If a Change of Control occurs prior to any repayment or conversion, then, the outstanding principal amount and all accrued and unpaid interest, that has not otherwise been redeemed or repaid, shall convert, immediately prior to the Change of Control, into fully paid and nonassessable shares of the Company’s Series C Preferred Stock at the Conversion Price equal to $1.00 per share. No conversion shall occur without the written consent of the Investor.
Conversion upon an Initial Public Offering
If an Initial Public Offering occurs prior to any repayment or conversion, then the outstanding principal amount and all accrued and unpaid interest that has not otherwise been redeemed or repaid, shall convert, immediately prior to such Initial Public Offering, into fully paid and nonassessable shares of the Company’s Common Stock at the Conversion Price equal to $1.00 per share.
De Nova Convertible Promissory Note
In November 2016, the Company entered into a convertible promissory note purchase agreement with an existing investor of the Company. Under the agreement, the Company borrowed $500 which is due on demand one year from the date of issuance or upon a qualified change of control. The note bears interest at 1% per annum, payable at maturity, is secured and was originally subordinated to the SVB debt. In connection with this convertible promissory note, other fees and legal costs to obtain the loan were recorded as a debt discount, which is being amortized to interest expense over the repayment period of the loan using the effective rate method.
This convertible promissory note contains a conversion feature upon the occurrence of a Qualified Financing. If a Qualified Financing occurs on or prior to any repayment, then the outstanding principal amount and all accrued and unpaid interest, that has not otherwise been redeemed or repaid, shall convert into such Equity Securities
17
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
sold in the Qualified Financing at a conversion price equal to the price paid per share for Company Securities by the Investors in the Qualified Financing or into such Convertible Securities at a principal amount equal to the outstanding principal balance and any unpaid interest. No Conversion shall occur without the written consent of the Investor.
Equipment loan
During 2015, the Company entered into a loan agreement to finance the purchase of certain equipment used in its manufacturing process. The loan was collateralized by the equipment and bears interest at 4.2% per annum. Monthly principal and interest payments were due beginning September 30, 2015 and ended on August 31, 2017.
Loan payable to landlord
During 2015, the Company entered into a loan agreement with its landlord to repay the landlord for a portion of the cost of certain leasehold improvements provided by the landlord. The loan bears interest at 9% per annum, monthly principal and interest payments are due beginning January 1, 2016 and ending December 1, 2022. The loan is not collateralized.
The scheduled principal payments for the Company’s borrowings, excluding Series D mandatorily redeemable preferred stock as of December 31, 2017 are as follows:

2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 total less: current portion of borrowings borrowings, net of current portion at December 31, 2017 bank landlord convertible notes payable total $ 15, 00 $ 15,000 (15,000) $ - $65 70 77 84 93 $389 (65) $ 324 $ 2, 150 $ 2,150 (2,150) $ - $ 17,215 70 77 84 93 $ 17,539 (17,215) $ 324
6. | Commitments and Contingencies |
Operating Leases
In April 2015 the Company entered into an agreement to lease a new office building. The operating lease commenced in October 2015 and has a term of 7 years and 3 months. Under the terms of the lease, the Company is responsible for taxes, insurance and maintenance expense. Rent expense for the year ended December 31, 2017 was $790.
Future minimum lease payments under the noncancelable operating leases as of December 31, 2017 are as follows:
18
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)

2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 total minimum future payments operating leases $ 810 815 839 864 890 $ 4,218
Contingencies
In an agreement entered into in 2013 and amended in January 2015, the Company is contingently liable to certain employees in the event there is a sale of the Company or other transaction that results in a change of control as it is defined in the agreement. The agreement is subject to continued employment of the specified employees. This contingent liability is equal to $2,363, and will be paid from sale proceeds received in the sale of the Company, or other available funds.
Litigation
The Company received notice in June of 2016 that legal action had been filed in the United States District Court on behalf of a patient who had received a cervical disc manufactured by Spinal Kinetics during a surgery in 2007, performed by German physicians in Germany. The suit alleges the patient was injured as a result of the disc they received, and is seeking unspecified damages. The receipt of a suit such as this, while not common, is not outside the course of normal business and is not a material event. The Company has sufficient product liability insurance in place to defend itself against claims such as this, and because of the policy deductible, the
Company's maximum exposure is $50.
Mandatorily Redeemable Preferred Stock
During 2017, the Company sold 5,000,000 shares of Series D Mandatorily Redeemable Preferred stock at $1.00 per share raising $5,000 in cash less $17 issuance costs. These shares have a par value $0.001, 5,000,000 shares authorized, issued and outstanding and liquidation value of $5,000 at December 31, 2017. The shares are redeemable following the fifth anniversary of the original issue date, upon receipt by the Company of a redemption request at the option of the holder.
At December 31, 2017, the Company violated the financial covenants of the Morgan Stanley Secured Note, creating an Event of Default with regard to the Series D Mandatorily Redeemable Preferred stock. As a result, the Series D mandatorily redeemable preferred stock has been reclassed to current liabilities. On February 5, 2018, the Company entered into a Forbearance Agreement with Morgan Stanley under which Morgan Stanley agreed to forbear from exercising rights and remedies under the Secured Note. The Forbearance Agreement expired March 31, 2018.
19
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
Dividends
| The holders of shares of Series D preferred stock shall be entitled to receive dividends, out of any assets legally available therefore, prior and in preference to any declaration or payment of any dividend on the common stock. Holders of Series D Preferred stock are entitled to dividends at a rate of 12% per annum of the accrued value, cumulative and payable when, as and if declared by the Board of Directors. |
Liquidation
| In the event of a liquidation of the Company, the funds and assets that may be legally distributed to the Corporation’s stockholders shall be distributed as follows: the holders of each share of Series D Preferred stock are entitled to be paid, on a pro rata basis, out of the available funds and assets, and prior and in preference to any further payment or distribution (or any setting apart of any payment or distribution) of any available funds and assets on any shares of Series C Preferred stock, Series C-l Preferred stock, Common stock or any other class or series of capital stock of the Corporation, an amount per share equal to the Series D Original Issue Price, plus any Series D dividends accrued but unpaid thereon, whether or not declared, together with any dividends declared but unpaid thereon. If the available funds and assets are insufficient to permit the payment to holders of the Series D Preferred stock of their full Series D liquidation amount, then all such remaining available funds and assets shall be distributed among the holders of the then outstanding Series D Preferred stock on a pro rata basis in proportion to the full amounts they would otherwise be entitled to receive. |
The Series D preferred stock does not have voting rights and is not convertible into shares of common stock.
Preferred Stock
The Company Articles of Incorporation, as amended, authorize 51,238,000 shares of convertible preferred stock as indicated in the table below at December 31, 2017:

Series C C-1 shares authorized shares issued and outstanding liquidation value 44,000,000 7,238,000 51,238,000 35,395,332 7,234,103 42,629,435 $ 35,395 7,234 $ 42,629
Dividends
Holders of Series C and C-1 Preferred stock are entitled to dividends at the rate of $0.10 per share per annum on each outstanding share of Series C convertible preferred stock, and at the rate of $0.10 per share per annum on each outstanding share of Series C-1 preferred stock, cumulative and payable when, as and if declared by the Board of Directors. As of December 31, 2017, no dividends have been declared by the Board of Directors.
In the event of a liquidation of the Company, the funds and assets that may be legally distributed to the Corporation’s stockholders shall be distributed as follows:
20
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
| (a) | After the payment or setting aside for the payment specified for the Series D holders, the next $60,000 of funds and assets shall be distributed with equal priority and pro rata among the holders of Series C Preferred stock and Common stock in proportion to the number of shares of Common stock held by them, with the shares of Series C Preferred stock being treated for this purpose on an as-if converted basis. |
| (b) | After the payment or setting aside for the payments specified in paragraphs (a) and (b) above, the holders of each share of Series C Preferred stock and Series C-1 Preferred stock shall be entitled to be paid on a pro rata basis, out of the remaining available funds and assets, and prior and in preference to any further payment or distribution to Common stockholders, an amount per share equal to the original issue price for the Series C Preferred stock and for the Series C-1 Preferred stock, plus all accumulated but unpaid dividends thereon. If after setting aside for the payments specified in paragraphs (a) and (b) above, the remaining funds are insufficient to permit the payment to holders of Series C Preferred stock and Series C-1 Preferred stock their full preferential amount described in this paragraph, then all remaining available funds and assets shall be distributed on a pro rata basis in proportion to the full amounts they would otherwise be entitled to receive. |
| (c) | If there are any available funds and assets after the payment distributions noted in paragraphs (a), (b), and (c) above, then it should be distributed with equal priority and pro rata among the holders of the Series C Preferred stock and Common stock in proportion to the number of shares of Common stock held by them, with the shares of Series C Preferred stock being treated for this purpose on an as-if converted basis. |
A consolidation or merger of the Company with or into any other corporation or corporations, acquisition by any other corporation or corporations, or a sale of all or substantially all the assets or voting control of the Company in which the prior stockholders of the Company do not own a majority of the outstanding shares of the surviving corporation is deemed to be a liquidation.
Voting
Each holder of shares of Common stock shall be entitled to one vote for each share held. Each holder of Series C convertible preferred stock shall be entitled to the number of votes equal to the number of shares of Common stock into which the shares of Series C convertible preferred stock held by such holder could be converted as of the record date. The holders of Series C-1 preferred stock do not have voting rights. The holders of shares of Series C convertible preferred stock shall be entitled to vote on all matters on which the common stock shall be entitled to vote. The holders of Preferred Series C stock as a separate class shall be entitled to elect five directors. The holders of Preferred Series C stock and the holders of Common stock voting together as a single class (on an as-converted basis), shall be entitled to elect the remaining directors of the Corporation.
Conversion
Each share of Series C Preferred stock is convertible into one share of Common stock at the option of the holder at any time, with the conversion being subject to anti-dilution provisions. Each share of Series C Preferred stock shall automatically be converted into Common stock, either immediately prior to the closing of a Qualified IPO or upon the receipt of the written consent of at least 65% of the then outstanding shares of Preferred stock, voting on a combined and as-if converted basis. An amount of 39,060,332 shares of the Company’s Common stock have been reserved for conversion. The Series C-1 Preferred stock is not convertible into shares of common stock.
21
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
Warrants Liability
The Company's outstanding freestanding warrants, related to a line of credit loan that was fully repaid in 2012, are accounted for in accordance with ASC 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity ("ASC 480"). These warrants are able to be exercised into 435,000 shares of the Series C convertible preferred stock at $1.00 per share and expire the later of either 10 years after the issuance date or 5 years after the Company's initial public offering. Under ASC 480, the outstanding freestanding warrants are classified as liability on the consolidated balance sheet at the estimated value on the balance sheet date. These warrants contain a liquidation bonus such that, if the net proceeds from the lender's warrant position are less than $655 in the event of a change of control, the lender shall earn a cash bonus of $655 in lieu of exercising its warrant. However, if the net proceeds from the lender's warrant position would be greater than $655, the bonus provision will be cancelled, and there will be no liquidation bonus. The fair value of the warrants, calculated based on a minimum payout provision, were estimated to be $655 at the date of grant and were recorded as a liability and debt discount. The discount has been fully amortized as interest expense prior to fiscal 2016. As of December 31, 2017, these warrants remain outstanding, and are shown as a liability in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
In connection with the initial term loan in August 2015, the Company issued Silicon Valley Bank warrants to purchase 60,000 shares of Series C at $1.00 per share. Using the Black-Scholes model with a volatility of 43.1 %, term of 10 years and a risk-free interest rate of 2.05%, the fair value of the warrants was determined to be $33. The fair value of the warrants was recorded as a liability and a debt discount.
In connection with Tranche 2 of the term loan in January 2016, the Company issued Silicon Valley Bank a warrant to purchase an additional 20,000 shares of Preferred Series C Stock, with an exercise price of $1.00 per share, exercisable 10 years from date of issue, expiring in August 2025. Using the Black Scholes option pricing model with a volatility of 43.1 %, term of 10 years and a risk-free interest rate of 2.05%, the fair value of the warrants was determined to be $12. The fair value of the warrants was recorded as a liability and a debt discount.
In connection with the Morgan Stanley Loan and Security Agreement, the Company agreed to issue detachable warrants to purchase Series C Preferred Stock of the Company at a warrant coverage ratio equal to 10% of the Commitment Amount at a price of $1.00 per share. If the Company closes a next round of equity financing of at least $10,000 then the number of warrants granted will be determined by dividing $1,500 by the new (next round) share price. The warrant has a term of 10 years and will survive an Initial Public Offering or acquisition in which the consideration consists exclusively of cash or publicly traded stock. If the Company does not enter into a definitive agreement with a third party to acquire the Company on or prior to June 30, 2017, and if the transaction Closing Date is not on or before September 30, 2017, then the price of the warrants becomes $0.01 per share. The Company did not enter into such a definitive agreement within the required time frame, and accordingly the price of the warrants became $0.01.
Upon issuance, the Company estimated the fair value of the warrants using the Black Scholes option pricing model with a volatility of 49.1%, term of 10 years and a risk-free interest rate of 2.47%. The fair value of the warrants was determined to be $922, which was recorded as a liability and a debt discount.
At June 30, 2017, the Company revalued the warrants using the Black Scholes option pricing model with a volatility of 49.5%, term of 9.57 years and a risk-free interest rate of 2.29%. The fair value of the warrants was determined to be $722. The liability and debt discount were adjusted, and $75 was recognized as other income.
At December 31, 2017, the Company estimated the fair value of the warrants using the Black Scholes option pricing model with a volatility of 49.23%, term of 9.17 years and a risk-free interest rate of 2.29%. The fair value of the warrants was determined to be $722, and no adjustment was required.
22
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
Common Stock
The Articles of Incorporation, as amended, authorize the Company to issue 93,000,000 shares of $.001 per value common stock. Common stockholders are entitled to dividends as and when declared by the Board of Directors, subject to the rights of holders of all classes of stock outstanding having priority rights to dividends. There have been no dividends declared to date. The holder of each share of common stock is entitled to one vote.
Stock Option Plan
During fiscal 2014, the Company’s 2003 Stock Option Plan expired and was replaced with the Company’s 2014 Equity Incentive Plan (“the Plan”).
The Company has reserved 8,169,785 shares of its common stock under its 2014 Stock Option Plan for issuance of non-statutory and incentive stock options to employees, directors and consultants of the Company. Options granted under the Plan may be either incentive stock options or nonqualified stock options. Incentive stock options (“ISO”) may be granted only to Company employees (including officers and directors). Nonqualified stock options (“NSO”) may be granted to Company employees and consultants.
Options to purchase the Company’s common stock may be granted at a price not less than 85% of the fair market value in the case of non-statutory stock options, and at a price not less than fair market value in the case of incentive stock options, except for an employee or nonemployee with options who owns more than 10% of the voting power of all classes of stock of the Company in which case the exercise price shall be no less than 110% of the fair market value per share on the grant date. Fair market value is determined by the Board of Directors. Options become exercisable as determined by the Board of Directors but in no case at a rate less than 20% per annum over five years from the grant date. Options expire as determined by the Board of Directors but not more than ten years after the date of grant.
Options generally vest after the date of the grant and monthly over the next 12 months to four years. Options granted to nonemployees generally vest over the term of the related service contract. Options granted under the 2003 Stock Option Plan included provisions permitting exercise of the option prior to full vesting. Any unvested shares so purchased were subject to repurchase by the Company at the original exercise price of the option. At December 31, 2017 there were no shares of common stock outstanding that were subject to repurchase. Cash received from employees for early exercise of unvested options is treated as a liability. Amounts so recorded are transferred into common stock and additional paid-in capital as the shares vest.
Activity under the Plan is as follows:
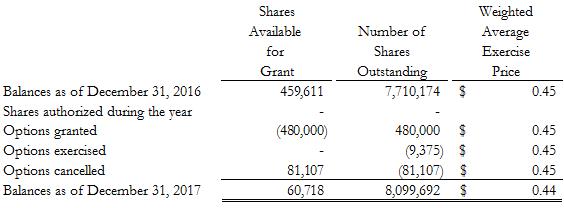
Balances as of December 31, 2016 shares authorized during the year options granted options exercised options cancelled balances as of December 31, 2017 shares available for grant number of shares outstanding weighted average exercise price 459,611 - (480,000) - 81,107 60,718 7,710,174 - 480,000 (9,375) (81,107) 8,099,692 $ 0.45 $ 0.45 $ 0.45 $ 0.45 $ 0.44
23
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
The options vested and vested and expected to vest under the 2014 Plan as of December 31, 2017 are as follows:
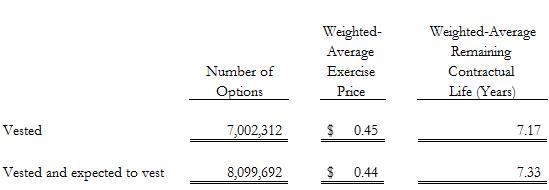
Vest vested and expected to vest number of options weighted-average exercise price weighted-average remaining contractual life (year) 7,002,312 8,099,692 $ 0.45 $0.44 7.17 7.33
Under the 2014 Plan, the options outstanding and currently exercisable by exercise price at December 31, 2017, are as follows:
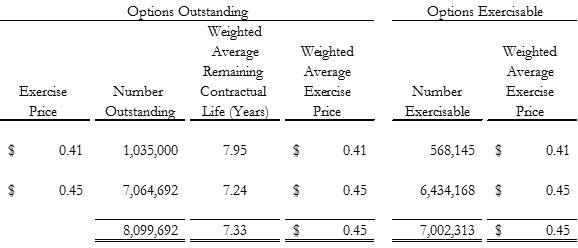
Options outstanding options exercisable exercise price number outstanding weighted average remaining contractual life (years) weighted average exercise price number exercisable weighted average exercise price $ 0.41 $ 0.45 1,035,000 7,064,692 8,099,692 7.95 7.24 7.33 $ 0.41 $ 0.45 $ 0.45 568,145 6,434,168 7,002,313 $ 0.41 $ 0.45 $0.45
Under the expired 2003 Plan, only 24,787 options remain outstanding and exercisable, having a weighted average exercise price of $6.34.
Stock-Based Compensation Associated with Awards to Employees
Under ASC 718, compensation cost for employee stock-based awards is based on the estimated grant-date fair value and is recognized over the vesting period of the applicable award on a straight-line basis. There were 425,000 options granted to employees in 2017.
The Company uses the Black-Scholes pricing model to determine the fair value of stock options. The valuation model for stock compensation expense requires the Company to make assumptions and judgments about the variables used in the calculation including the expected term (weighted average period of time that the options granted are expected to be outstanding), volatility of the Company’s common stock, assumed risk free interest rate and the estimated forfeitures of unvested stock options.
24
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
Weighted-Average Expected Term
The Company derives the expected term based on expected terms for industry peers as the Company does not have sufficient historical information to develop reasonable expectations about future exercise patterns and post vesting employment termination behavior.
Volatility
Since the Company is a private entity with no historical data regarding the volatility of its common stock, the expected volatility is based on volatilities of similar public companies. In evaluating similarity, the Company considers factors such as industry, stage of life cycle and size.
Risk-Free Interest Rate
The risk-free rate is based on U.S. Treasury zero-coupon issues with remaining terms similar to the expected term on the options.
Dividend Yield
The Company has never declared or paid any cash dividends and does not plan to pay cash dividends in the foreseeable future, and, therefore, used an expected dividend yield of zero in the valuation model.
Forfeitures
ASC 718 also requires the Company to estimate forfeitures at the time of grant, and to revise those estimates in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates. The Company uses historical data to estimate pre-vesting option forfeitures and record stock-based compensation expense only for those awards that are expected to vest. To the extent actual forfeitures differ from the estimates, the differences will be recorded as a cumulative adjustment in the period estimates are revised.
The weighted-average grant date fair value of employee stock options granted during the year ended December 31, 2017 was $0.20 per share. As of December 31, 2017, there was $198 in unrecognized compensation expense, net of estimated forfeitures, related to unvested stock options, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 2.3 years.
The awards granted to employees during 2017 were valued using the following assumptions:
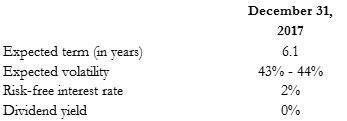
Expected term (in years) expected volatility risk-free interest rate dividend yield December 31, 2017 6.4 43% - 44% 2% 0%
Stock-Based Compensation for Non-employees
During 2017, the Company granted 55,000 options to non-employees. The weighted-average grant date fair value of non- employee stock options granted during the year ended December 31, 2017 was $0.27 per share. As of December 31, 2017, there was $11 in unrecognized compensation expense, net of estimated forfeitures, related to unvested stock options, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.0 years.
25
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
The following assumptions were used in the estimated grant date fair value calculations for options granted to non-employees during the year ended December 31, 2017:
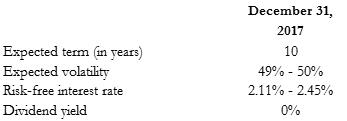
Expected term (in years) expected volatility risk-free interest rate dividend yield December 31, 2017 10 49% - 50% 2.11% - 2.45% 0%
Stock-based compensation expense related to stock options granted to non-employees is recognized as the stock options are earned. The Company believes that the fair value of the stock options is more reliably measurable than the fair value of the services received. The fair value of the stock options granted is calculated at each reporting date using the Black-Scholes option pricing model.
Total stock-based compensation expense recorded under ASC 718 and ASC 505-50 related to options granted to employees and non-employees was allocated to cost of goods sold, research and development, sales and marketing, and general and administrative expense as follows:
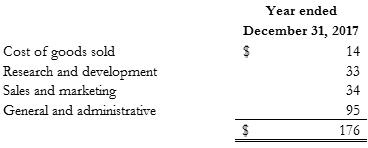
Cost of goods sold research and development sales and marketing general and administrative year ended December 31, 2017 $ 14 33 34 95 $ 176
The Company has not recorded an income tax expense. The Company has a net operating loss and has provided a valuation allowance against net deferred tax assets due to uncertainties regarding the Company's ability to realize these assets.
Significant components of the Company's net deferred tax assets for federal and state income taxes at December 31, 2017 consist of:
26
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)

Net operating loss carryforwards research and development tax credits stock compensation capitalized organization costs accruals and reserves deferred tax assets less: valuation allowance net deferred tax assets December 31, 2017 $ 7,144 1,502 40 85 890 9,661 (9,661) $ -
The Company has established a full valuation allowance against its deferred tax assets due to the uncertainty surrounding realization of assets. The valuation allowance decreased by $4,405 for the year ended December 31, 2017.
As of December 31, 2017, the Company had net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $24,125 and $29,756 respectively, available to reduce future taxable income, if any, for federal and California state income tax purposes, respectively. The net operating loss carry forwards expire between 2024 and 2018, and valuation allowances have been reserved, where necessary.
As of December 31, 2017, the Company had research and development credit carryforwards of approximately $1,594 and $492 respectively, available to reduce future taxable income, if any, for federal and California state income tax purposes. The federal credit carryforwards begin expiring in 2024, and the California credit carryforwards have no expiration date.
The Tax Reform Act of 1986 limits the use of net operating loss carry-forwards in certain situations where changes occur in the stock ownership of a company. In the event the Company has undergone or undergoes a change in ownership, utilization of the carry-forwards could be limited.
The Company has not been audited by the Internal Revenue Service or any state income or franchise tax agency.
As of December 31, 2017, its federal returns for the years ended 2006 through the current period and most state returns for the years ended 2004 through the current period are still open to examination. In addition, all of the net operating losses and research and development credit carry-forwards that may be used in future years are still subject to inquiry given that the statute of limitation for these items would begin in the year of the utilization. The balance of gross unrecognized tax benefits as of December 31, 2017 is approximately $521, all of which would affect the Company's income tax expense if recognized, before consideration of the Company's valuation allowance. The Company does not expect its unrecognized tax benefits to change significantly over the next 12 months. The Company recognizes interest and penalties accrued on any unrecognized tax benefits as a component of income tax expense.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act ("the Act") was enacted on December 22, 2017. The Act reduces the US federal corporate tax rate from 35% to 21%, requires companies to pay a one-time transition tax on earnings of certain foreign subsidiaries that were previously tax deferred and creates new taxes on certain foreign sourced earnings. At December 31, 2017, we have not completed our accounting for the tax effects of enactment of the Act; however, in certain cases, as described below, we have made a reasonable estimate of the effects on our existing deferred tax balances. In other cases, we have not been able to make a reasonable estimate and continue to
27
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
account for those items based on our existing accounting under ASC 740, Income Taxes, and the provisions of the tax laws that were in effect immediately prior to enactment. In all cases, we will continue to make and refine our calculations as additional analysis is completed. In addition, our estimates may also be affected as we gain a more thorough understanding of the tax law.
We are required to recognize the effect of the tax law changes in the period of enactment, such as determining the estimated transition tax, re-measuring our U.S. deferred tax assets and liabilities at a 21% rate as well as reassessing the net realizability of our deferred tax assets and liabilities.
We re-measured certain deferred tax assets and liabilities based on the rates at which they are expected to reverse in the future. The provisional amount related to the re-measurement of our deferred tax balance is a reduction of approximately $3,764,000. Due to the corresponding valuation allowance fully offsetting deferred taxes, there is no income statement impact.
In December 2017, the SEC staff issued Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 118, Income Tax Accounting Implications of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (SAB 118) which allows us to record provisional amounts during a measurement period not to extend beyond one year of the enactment date. Since the Act was passed late in the fourth quarter of 2017, and ongoing guidance and accounting interpretation are expected over the next 12 months, we consider the accounting of the transition tax and deferred tax re-measurements to be incomplete due to the forthcoming guidance and our ongoing analysis of final year-end data and tax positions. We expect to complete our analysis within the measurement period in accordance with SAB 118.
The Company’s tax years 2004-2017 will remain open for examination by the federal and state authorities for three and four years, respectively, from the date of utilization of any net operating loss credits.
The Company started a 401(k) Profit Sharing Plan (the "Plan"), for employees who are 21 years of age or older. According to the terms of the Plan, the Company may make a discretionary contribution to the Plan each year, allocable to all Plan participants. The Company made no contributions to the Plan for the year ended December 31, 2017, and administrative expenses were not significant in either the year.
In connection with the preparation of the financial statements, the Company evaluated subsequent events after the balance sheet date of December 31, 2017 through the financial statement issuance on April 30, 2018. No events have occurred since December 31, 2017, other than the following and as disclosed elsewhere within these financial statements.
On March 15, 2018, the Company, entered into a definitive merger agreement (the “Merger Agreement”) with Orthofix, a global medical device company focused on musculoskeletal healing products and value-added services.
Summary of the terms of the Merger Agreement:
Form of Transaction. The Company will merge with and into a wholly owned subsidiary of Orthofix, with Orthofix remaining as the surviving corporation and a wholly owned subsidiary of Spinal Kinetics
28
Spinal Kinetics, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share and share amounts)
Merger Consideration. All outstanding shares of the Company’s capital stock will be converted into the right to receive at the closing an aggregate of $45 million in cash, subject to certain adjustments including the escrow fund described below, plus milestone payments of up to $60 million in cash. The milestone payments include (i) up to $15 million if the U.S. Food and Drug Administration grants market clearance or approval of the Company’s M6-C artificial cervical disc and (ii) revenue-based milestone payments of up to $45 million in connection with future sales of the M6-C artificial cervical disc and the M6-L artificial lumbar disc. Milestones must be achieved within five years of closing to trigger applicable payments. The Company expects to make the closing payments from cash on hand or available borrowing capacity.
Indemnification and Escrow. The Merger Agreement provides that the Company will indemnify Orthofix for breaches of representations and warranties as well as certain other specified matters in the Merger Agreement, subject to certain limitations in the Merger Agreement. At closing, $4.5 million of the closing merger consideration will be held in escrow to fund this indemnification obligations payable during the first two years after closing. In addition, the Company has agreed that Orthofix, generally, will be entitled to offset losses against contingent milestone payments after all monies on deposit in the escrow fund have been paid out or released or are the subject of pending or unresolved indemnification claims.
Spinal Kinetics Stockholder Approval. The Merger Agreement required the approval of the Company’s stockholders, which was obtained by written consent promptly following the parties entering into the Merger Agreement.
On April 30, 2018, the Merger Agreement was completed.
29