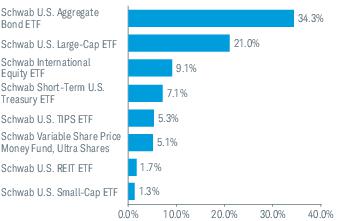
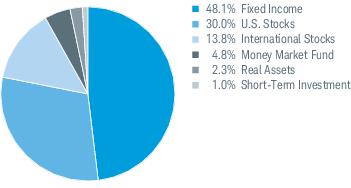
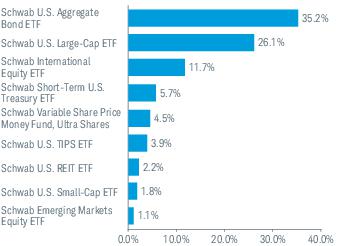
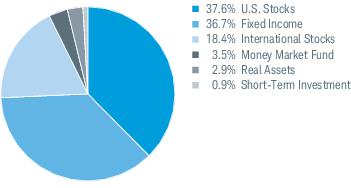
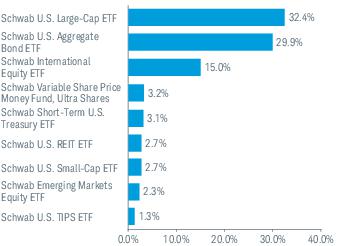
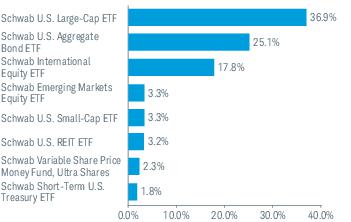
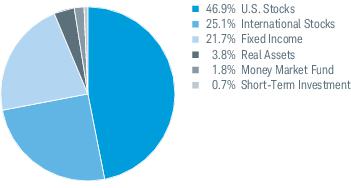
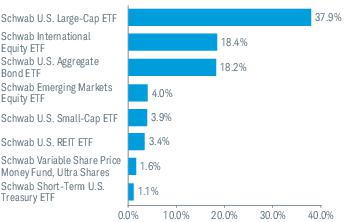
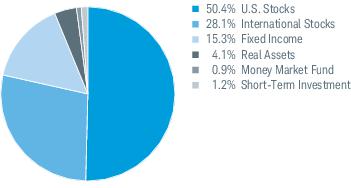
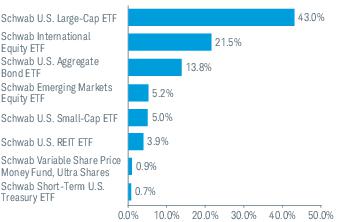
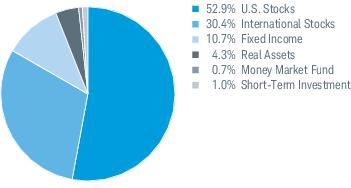
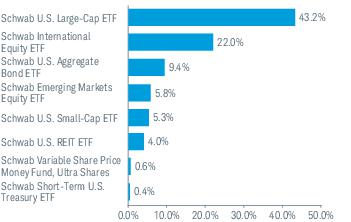
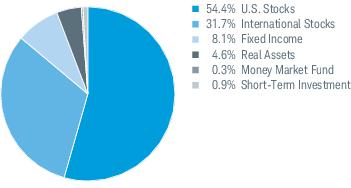
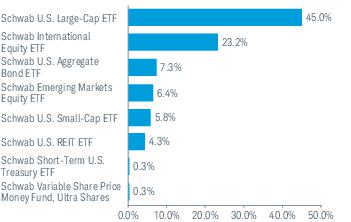
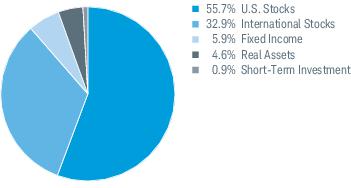
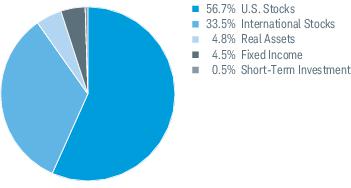
3. Risk Factors (continued):
• Foreign Investment Risk. An underlying fund’s investments in securities of foreign issuers may involve certain risks that may be greater than those associated with investments in securities of U.S. issuers. These include risks of adverse changes in foreign economic, political, regulatory and other conditions; changes in currency exchange rates or exchange control regulations (including limitations on currency movements and exchanges); the imposition of economic sanctions or other government restrictions; differing accounting, auditing, financial reporting and legal standards and practices; differing securities market structures; and higher transaction costs. These risks may negatively impact the value or liquidity of an underlying fund’s investments, and could impair the underlying fund’s ability to meet its investment objective or invest in accordance with its investment strategy. There is a risk that investments in securities denominated in, and/or receiving revenues in, foreign currencies will decline in value relative to the U.S. dollar.
• Emerging Markets Risk. Emerging market countries may be more likely to experience political turmoil or rapid changes in market or economic conditions than more developed countries. Emerging market countries often have less uniformity in accounting and reporting requirements and greater risk associated with the custody of securities. In addition, the financial stability of issuers (including governments) in emerging market countries may be more precarious than in developed countries. As a result, there may be an increased risk of illiquidity and price volatility associated with an underlying fund’s investments in emerging market countries, which may be magnified by currency fluctuations relative to the U.S. dollar, and, at times, it may be difficult to value such investments.
• Derivatives Risk. An underlying fund may use derivatives to enhance returns or hedge against market declines. Examples of derivatives are options, futures, options on futures and swaps. An option is the right to buy or sell an instrument at a specific price before a specific date. A future is an agreement to buy or sell a financial instrument at a specific price on a specific day. A swap is an agreement whereby two parties agree to exchange payment streams calculated in relation to a rate, index, instrument or certain securities and a predetermined amount. A credit default swap is an agreement in which the seller agrees to make a payment to the buyer in the event of a specified credit event in exchange for a fixed payment or series of fixed payments.
An underlying fund’s use of derivative instruments involves risks different from or possibly greater than the risks associated with investing directly in securities and other traditional investments. Certain of these risks, such as credit risk, leverage risk, liquidity risk, market risk and management risk, are discussed elsewhere in this section. An underlying fund’s use of derivatives is also subject to lack of availability risk, valuation risk, correlation risk and tax risk. Lack of availability risk is the risk that suitable derivative transactions may not be available in all circumstances for risk management or other purposes. Valuation risk is the risk that a particular derivative may be valued incorrectly. Correlation risk is the risk that changes in the value of the derivative may not correlate perfectly with the underlying asset, rate or index. Tax risk is the risk that the use of derivatives may cause an underlying fund to realize higher amounts of short-term capital gains. An underlying fund’s use of derivatives could reduce the underlying fund’s performance, increase its volatility, and could cause the fund to lose more than the initial amount invested. The use of derivatives that are subject to regulation by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) by an underlying fund could cause a fund to become a commodity pool, which would require the fund to comply with certain CFTC rules.
• Leverage Risk. Certain underlying fund transactions, such as derivatives transactions, short sales, reverse repurchase agreements, and mortgage dollar rolls, may give rise to a form of leverage and may expose an underlying fund to greater risk. Leverage tends to magnify the effect of any decrease or increase in the value of an underlying fund’s portfolio securities, which means even a small amount of leverage can have a disproportionately large impact on the underlying fund.
• Concentration Risk. To the extent that an underlying fund’s portfolio is concentrated in the securities of issuers in a particular market, industry, group of industries, sector or asset class, the underlying fund may be adversely affected by the performance of those securities, may be subject to increased price volatility and may be more vulnerable to adverse economic, market, political or regulatory occurrences affecting that market, industry, group of industries, sector or asset class.
• Investment Style Risk. Certain underlying funds seek to track the performance of various segments of the stock market, as measured by their respective indices. Such underlying funds follow these stocks during upturns as well as downturns. Because of their indexing strategy, these underlying funds do not take steps to reduce market exposure or to lessen the effects of a declining market. In addition, because of an underlying fund’s expenses, the underlying fund’s performance is normally below that of the index.
• Liquidity Risk. An underlying fund may be unable to sell certain securities, such as illiquid securities, readily at a favorable time or price, or an underlying fund may have to sell them at a loss.
• Portfolio Turnover Risk. Certain of the underlying funds may buy and sell portfolio securities actively. If they do, their portfolio turnover rate and transaction costs will rise, which may lower the underlying fund’s performance and may increase the likelihood of capital gains distributions.
Please refer to the funds’ prospectus for a more complete description of the principal risks of investing in the funds.