- SUZ Dashboard
- Financials
- Filings
-
Holdings
- Transcripts
- ETFs
-
Insider
- Institutional
- Shorts
-
6-K Filing
Suzano (SUZ) 6-KCurrent report (foreign)
Filed: 27 Nov 20, 6:30am
Exhibit 99.7
 | (A free translation of the original in Portuguese) FACEPA - Fábrica de Papel da Amazônia S.A. Report on the net book equity value based on the accounting records at August 31, 2020 |
 | (A free translation of the original in Portuguese) Report on the net book equity value based on the accounting records To the Shareholders and Management Fábrica de Papel da Amazônia S.A. Information on the audit firm 1PricewaterhouseCoopers Auditores Independentes, a civil partnership established in the capital city of the state of São Paulo, at Av. Francisco Matarazzo, 1,400, on the 9th, 10th, 13th, 14th, 15th, 16th and 17th floors, Torre Torino, Água Branca, enrolled in the National Corporate Taxpayers' Register of the Ministry of Finance (CNPJ/MF) under no 61.562.112/0001-20, originally enrolled in the Regional Accounting Council (CRC) of the State of São Paulo under no 2SP000160/O-5, with its partnership deed registered at the 4th Registry Office of Deeds and Documents of São Paulo, SP on September 17, 1956, and subsequent amendments registered at the 2nd Registry Office of Deeds and Documents of São Paulo, SP, the last amendment dated November 1st, 2019, having been registered at the 2nd Registry Office of Deeds and Documents of São Paulo, SP, on microfilm under no 152,080, at January 21, 2020, represented by its undersigned partner, Mr. José Vital Pessoa Monteiro Filho, Brazilian, married, accountant, holder of Identity Card no 2.473.821 enrolled in the Individual Taxpayers Register (CPF) under no 856.126.184-68 and the Regional Accounting Council of the State of Pernambuco under no 1PE016700/O-0, resident and domiciled in the State of São Paulo, with office at the same address of the partnership, was appointed as an expert by the management of Suzano S.A. to proceed with the report of the net book equity value of Fábrica de Papel da Amazônia S.A. ("Company") at August 31, 2020, summarized in Attachment I, in accordance with accounting practices adopted in Brazil. The results of this engagement are presented below. The objective of the report 2The objective of the report of the net book equity value at August 31, 2020 of Fábrica de Papel da Amazônia S.A. is its legal merger into Suzano S.A. Management's responsibility for the accounting information 3Management is responsible for the bookkeeping and preparation of the accounting information in accordance with accounting practices adopted in Brazil, and for such internal control as management determines is necessary to enable the preparation of accounting information that is free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error. The main accounting practices adopted by the Company are summarized in Attachment II of the report. 2 of 11 PricewaterhouseCoopers, Av. Francisco Matarazzo 1400, Torre Torino, São Paulo, SP, Brasil, 05001-903, Caixa Postal 60054, T: +55 (11) 3674 2000, www.pwc.com.br |
 | Fábrica de Papel da Amazônia S.A. Scope of the work and responsibility of the independent auditors 4Our responsibility is to express a conclusion on the net book equity value of the Company at August 31, 2020, based on the work performed in accordance with Technical Communication 03/2014 (R1), issued by the Institute of Independent Auditors of Brazil (IBRACON), which establishes that audit procedures be applied to the balance sheet and CTG 2002, issued by the Brazilian Federal Accounting Council, which provides for technical and professional standards to be observed by accountants for issuing report on the net book equity value. Therefore, our audit of the related balance sheet of the Company was conducted in accordance with the Brazilian and International Auditing Standards, which require that we comply with ethical requirements and plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the net book equity value used for the preparation of our report is free from material misstatement. 5An audit involves performing procedures to obtain audit evidence about the amounts recorded. The procedures selected depend on the auditor's judgment, including the assessment of the risks of material misstatement of the shareholders' equity, whether due to fraud or error. In making those risk assessments, the auditor considers internal control relevant to the balance sheet in order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company's internal control. An audit also includes evaluating the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonableness of accounting estimates made by management. We believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our conclusion. Conclusion 6Based on the work performed, we conclude that the amount of R$ 101,203,293.32, according to the balance sheet at August 31, 2020, as stated in the accounting records and summarized in Attachment I, represents, in all material respects, the net book equity value of Fábrica de Papel da Amazônia S.A. according to accounting practices adopted in Brazil. São Paulo, October 6, 2020 PricewaterhouseCoopers Auditores Independentes CRC 2SP000160/O-5 José Vital Pessoa Monteiro Filho Contador CRC 1PE016700/O-0 3 of 11 |
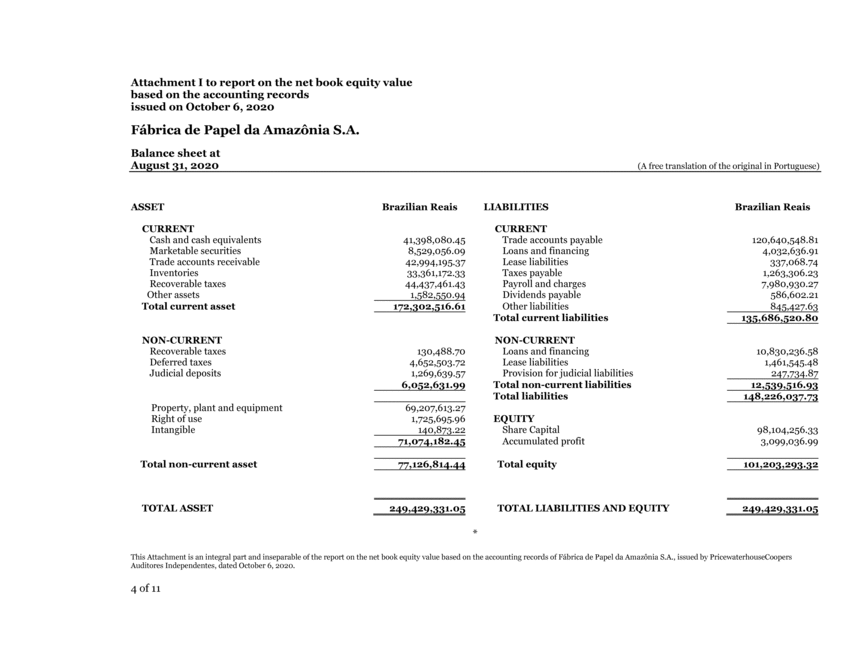 | Attachment I to report on the net book equity value based on the accounting records issued on October 6, 2020 Fábrica de Papel da Amazônia S.A. Balance sheet at August 31, 2020 (A free translation of the original in Portuguese) ASSETBrazilian ReaisLIABILITIESBrazilian Reais TOTAL ASSET249,429,331.05TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY249,429,331.05 * This Attachment is an integral part and inseparable of the report on the net book equity value based on the accounting records of Fábrica de Papel da Amazônia S.A., issued by PricewaterhouseCoopers Auditores Independentes, dated October 6, 2020. |
 | 1.Basis of preparation and summary of the significant accounting policies The balance sheet at August 31, 2020 was prepared with the objective of report of the net book equity value of the Fábrica de Papel da Amazônia S.A, ("Company"), to be used in the merger into Suzano S.A. The balance sheet at August 31, 2020 has been prepared in accordance with accounting practices adopted in Brazil, including the pronouncements issued by the Brazilian Accounting Pronouncements Committee (“CPC”). The preparation of this balance sheet requires the use of certain critical accounting policies. The main accounting policies applied in the preparation of this balance sheet are presented below. 1.1.Cash and cash equivalents Cash and cash equivalents include cash, bank deposits, marketable securities and highly liquid short-term investments, which have original maturities up to 90 days and are readily convertible into a known amount of cash and subject to an immaterial risk of change of value. Marketable securities classified in this group, by their very nature, are measured at fair value through profit or loss. 1.2.Financial assets 1.2.1. Classification Financial assets are classification based on the purpose for which the financial assets were acquired, as set forth below: (i)financial assets at amortized cost; (ii)financial assets at fair value through profit or loss, Regular purchases and sales of financial assets are recognized on the trade date, it means, the date on which the Company commits to purchase or sell the asset, Financial assets are derecognized when the rights to receive cash flows from the investments have expired or have been transferred but only if it has transferred substantially all risks and rewards of ownership. 1.2.1.1. Financial instruments measured at amortized cost Financial assets at amortized cost are financial assets held by the Company (i) in order to receive their contractual cash flow and not to sell to realization a profit or loss and (ii) whose contractual terms give rise, on specified dates, to cash flows that exclusively, payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding, Any changes are recognized under financial income in income statement. |
 | It includes the balance of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable from customers and other assets. 1.2.1.2.Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss are either designated in this category or not classified in any of the other categories, any changes are recognized under financial income (expense) in income statement for non-derivative financial instruments. It includes the balance of marketable securities. 1.2.2. Settlement of financial instruments Financial assets and liabilities are settled, and the net amount is recorded in the balance sheet when there is a (i) legally enforceable right to settle the recognized amounts and (ii) there is an intention to settle on a net basis or realize the asset and settle the liability simultaneously. 1.2.3. Impairment of financial assets 1.2.3.1.Financial instruments measured at amortized cost Annually, the Company assesses if there is evidence that a financial asset is impaired, A financial is impaired only if there is evidence of an impairment as a result of one or more events that occurred after the initial recognition of the asset and that loss event has an impact on the estimated future cash flows of the financial asset that can be reliably estimated. The criteria used to determine if there is evidence of an impairment loss include: (i)significant financial difficulty of the issuer or debtor; (ii)default or late interest or principal payments in the agreement; (iii)where Company, for economic or legal reasons relating to the borrower's financial difficulty, grants to the borrower a concession that the lender would not otherwise receive; (iv)the disappearance of an active market for that financial asset because of financial difficulties; (v)observable data indicating that there is a measurable decrease in the estimated future cash flows from a portfolio of financial assets since the initial recognition of those assets, although the decrease cannot yet be identified with the individual financial assets in the portfolio. |
 | The amount of an impairment loss is measured as the difference between the carrying amount of the asset and the present value of estimated future cash flows discounted at the financial asset's original effective interest rate, If the financial asset is impaired the carrying amount of the asset is reduced and a loss is recognized in the income statement. In a subsequent measurement, if there is an improvement in the asset rating, such as an improvement in the debtor's credit rating, the reversal of the previously recognized impairment loss is recognized in the income statement. 1.3.Trade Accounts Receivable They are recorded at the nominal amount billed on the date of the sale, in the normal course of the Company's activities, adjusted for exchange rate variations when denominated in foreign currency and, when applicable, deducted from expected credit losses. The Company uses the matrix of provisions by maturity with the appropriate grouping of its portfolio. When necessary, based on individual analysis, the provision for expected loss is supplemented. The Company adopts procedures and analysis to establish credit limits. The Company examines on a monthly basis the maturity of receivables and identifies those customers with overdue balances assessing the specific situation of each client including the risk of loss, the existence of contracted insurance, letters of credit, collateral and the customer's financial situation. In the event of default, collection attempts are made, which include direct contact with customers and collection through third parties. Should these efforts prove unsuccessful, court measures are considered, and credit expected loss is recognized. The notes are written-off from the credit expected loss when Management considers that they are not recoverable after taking all appropriate measures to collect them. 1.4.Inventories These are evaluated at average acquisition, net of recoverable taxes, not exceeding their net realizable value. Finished products and work-in-process consist of raw materials, direct labor, production costs, freight, storage and general production expenses, which are related to the processes required to make the products available for sale. Provisions for losses, adjustments to net realizable value, impaired items and slow-moving inventories are recorded when necessary. Normal production losses are included in the production cost for the respective month, while abnormal losses, if any, are recorded directly in the cost of products sold without being carried over inventory. |
 | 1.5.Property,plant and equipment Stated at the cost of acquisition, formation, construction or dismantling, net of recoverable taxes. Such cost is deducted of accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment losses, when incurred, at the highest of the value of use and sale, less cost to sell. The borrowing costs are capitalized as a component of construction in progress, considering the weighted average interest rate of the Company's debt at the capitalization date. Depreciation is recognized based on the estimated economic useful life of each asset on a straight-line basis. The estimated useful life, residual values and depreciation methods are annually reviewed and the effects of any changes in estimates are accounted for prospectively. Land is not depreciated. The Company annually performs an analysis of impairment indicators of property, plant and equipment. An impairment for loss for property, plant and equipment, is only recognized if the related cash-generating unit is devalued. Such condition is also applied if the asset's recoverable amount is less than it is carrying amount. The recoverable amount of asset or cash-generating unit is the highest of its value in use and its fair value less cost to sell. The cost of major renovations is capitalized if the future economic benefits exceed the performance standard initially estimated for the asset and are depreciated over the remaining useful life of the related asset. Repairs and maintenance are expensed when incurred. Gains and losses on disposals of property, plant and equipment are measured by comparing the proceeds with the book value and are recognized as other operating income a (expense), net at the disposal date. 1.6.Intangible assets These are measured at cost at the time they are initially recognized, after initial recognition, intangible assets are presented at cost less accumulated amortization and impairment losses, when applicable. The useful life of intangible assets is assessed as finite. Intangible assets with a finite life are amortized over the economic useful life and reviewed for impairment whenever there is an indication that their carrying values may be impaired, The amortization period and method for an intangible asset with a finite useful life are reviewed at least at the end of each fiscal year, The amortization of intangible assets with a finite useful life is recognized in the statement of income as an expense related to its use and consistently with the economic useful life of the intangible asset. |
 | 1.7.Current and deferred income tax and social contribution Income taxes comprise income tax and social contribution on net income, current and deferred. These taxes are recognized in the income statement, except to the extent that they are related to items recognized directly in equity. In this case, they are recognized in equity under the equity adjustment. The current charge is calculated based on the tax laws enacted in the countries in which the Company and its subsidiaries and affiliates operate and generate taxable income. Management periodically evaluates the positions assumed in the income tax returns with respect to situations in which the applicable tax regulations give rise to interpretations and establishes provisions, when appropriate, based on the amounts that must be paid to the tax authorities. Deferred tax and contribution liabilities are recognized on temporary differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their carrying amounts in the financial statements. Deferred taxes and contributions are determined based on the rates in force on the balance sheet date and, which must be applied when they are realized or when they are settled. Deferred tax assets and contributions are recognized to the extent that it is probable that future taxable profit will be available to be used to offset temporary differences, based on projections of future results prepared and based on internal assumptions and future economic scenarios that may, therefore, undergo changes. Deferred taxes and contributions, assets and liabilities, are presented at the net amount in the balance sheet when there is a legal right and the intention to offset them when calculating current taxes, generally related to the same legal entity and the same tax authority. 1.8.Trade accounts payable Corresponds to the obligations payable for goods or services acquired in the normal course of the Company´s business, recognized at fair value and, subsequently, measured at amortized cost using the effective interest rate method, adjusted to present value and exchange rate variation when denominated in foreign currency, when applicable. 1.9.Loans and financing Loans and financing are initially recognized at their fair value, net of costs incurred in the transaction and are subsequently measured at amortized cost. Any difference between the amounts raised and settled is recognized in the statement of income during the period in which the loans and financing are outstanding, using the effective tax rate method. General or specific borrowing costs, directly attributed to the acquisition, construction or production of a qualified asset, are capitalized as a part of the cost of asset when it is probable that they will result in future economic benefits for the entity and that these costs may be measured with reliability, Other loan costs are recognized as expense in the period they are incurred. |
 | 1.10.Lease At the beginning of the agreement, the Company recognizes a right-of-use asset and a lease liability that represents the obligation to make payments related to the underlying asset of the lease, with exemption allowed low-value or to short-term agreements, which refers to, respectively, agreements where the individual value of the assets is lower than U.S.$5 and maturity date is before 12 months. The right-to-use asset is initially measured at cost and comprises the initial amount of the lease liability and if any, adjusted for any payment made on or before the contract start date, plus any direct initial costs incurred and estimated disassembly, removal costs, restoration of the asset in the place where it is located, less any incentive received. The right-to-use asset is subsequently depreciated using the straight-line method based on the lease term. Except for land agreements that are automatically extended for the same period by means of notification to the lessor, for the other agreements are not allowed automatic renewals and for an indefinite period, as well as the exercise of termination is a right of both parties. The lease liability is initially measured at the present value of remaining balances payable of the lease contracts discounted based on the nominal incremental loan rate. The lease liability is measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. It is remeasured when there is a change (i) in future payments resulting from a change in index or rate (ii) in the estimate of the expected amount to be paid in the guaranteed residual value or (iii) in the assessment of whether the Company will exercise the purchase option, extension or termination. When the lease liability is remeasured, the corresponding adjustment amount is recorded in the book value of the right-of-use asset or in the profit and loss statement, if the book value of the right-of-use asset has been reduced to zero. 1.11.Provision for judicial liabilities A provision is recognized to the extent that the Company expects to disburse cash flows, which can be reliably measured. Civil and labor lawsuits are provisioned when losses are assessed as probable and the amounts involved are measurable with enough security. When the expectation of loss in these proceedings is possible, a description of the proceedings and amounts involved is disclosed in the explanatory notes. Tax and civil judicial liabilities assessed as remote losses are not provisioned or disclosed. 1.12.Other assets and liabilities current and non-current Assets are recognized only when it is probable that the economic benefit associated with the transaction will flow to the Company and its cost or value can be measured reliably. |
 | A liability is recognized when the Company has a legal or constructive obligation arising from a past event, and it is probable that an economic resource will be required to settle this liability. 1.13.Dividend payables The distribution of dividends is recognized as a liability, calculated based on corporate law, the bylaws and the dividend policy of the Company. Any excess portion of the minimum mandatory dividends, if declared after the balance sheet date, must be recorded as additional dividends proposed in shareholders' equity, until approved by the shareholders at the general meeting. Upon approval, the reclassification is made to current liabilities. 1.14.Share capital Common and preferred shares are classified in equity, at cost. *** |