UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 20-F
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended DECEMBER 31, 2020 |
Commission file number 001-38755
| Suzano S.A. |
| (Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter) |
| |
| Suzano Inc. |
| (Translation of Registrant’s name into English) |
| |
| Federative Republic of Brazil |
| (Jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
| |
Av. Professor Magalhães Neto, 1,752 10th Floor, Rooms 1010 and 1011 Salvador, Brazil 41810-012 |
| (Address of principal executive offices) |
| |
Marcelo Feriozzi Bacci Chief Financial and Investor Relations Officer Telephone: +55 11 3503-9000 Email: ri@suzano.com.br Av. Faria Lima, 1,355 – 7th Floor São Paulo, Brazil, 01452-919 |
| (Name, Telephone, E-mail and/or Facsimile number and Address of Company Contact Person) |
Securities registered or to be registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act.
Title of each class: | Trading Symbol | Name of each exchange on which registered: |
| Common Shares, without par value | | New York Stock Exchange* |
| American Depositary Shares (as evidenced by American Depositary Receipts), each representing two Common Shares | — | New York Stock Exchange |
| 4.000% Notes due 2025, issued by Fibria Overseas Finance Ltd. | FBR/25 | New York Stock Exchange |
| 5.500% Notes due 2027, issued by Fibria Overseas Finance Ltd. | FBR/27 | New York Stock Exchange |
| 5.250% Notes due 2024, issued by Fibria Overseas Finance Ltd. | FBR/24 | New York Stock Exchange |
| 6.000% Notes due 2029, issued by Suzano Austria GmbH | SUZ/29 | New York Stock Exchange |
| 5.000% Notes due 2030, issued by Suzano Austria GmbH | SUZ/30 | New York Stock Exchange |
| 3.750% Notes due 2031, issued by Suzano Austria GmbH | SUZ/31 | New York Stock Exchange |
* Not for trading purposes but only in connection with the registration on the New York Stock Exchange of American Depositary Shares representing those common shares.
Securities registered or to be registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Securities for which there is a reporting obligation pursuant to Section 15(d) of the Act: None
The number of outstanding shares of stock of Suzano S.A. as of December 31, 2020 was:
1,361,263,584 common shares, without par value
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
☒ Yes ☐ No
If this report is an annual or transition report, indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
☐ Yes ☒ No
Note — Checking the box above will not relieve any registrant required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 from their obligations under those Sections.
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
☒ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files).
☒ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or an emerging growth company. See definition of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer ☒ | | Accelerated filer ☐ | | Non-accelerated filer ☐ | | Emerging growth company ☐ |
If an emerging growth company that prepares its financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards† provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
†The term “new or revised financial accounting standard” refers to any update issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board to its Accounting Standards Codification after April 5, 2012.
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report
☒ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark which basis of accounting the registrant has used to prepare the financial statements included in this filing:
| U.S. GAAP ☐ | | International Financial Reporting Standards as issued
by the International Accounting Standards Board ☒ | | Other ☐ |
If “Other” has been checked in response to the previous question, indicate by check mark which financial statement item the registrant has elected to follow.
If this is an annual report, indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act).
☐ Yes ☒ No
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This annual report includes forward-looking statements, mainly in “Item 3. Key Information — Risk Factors,” “Item 4. Information on Suzano — Business Overview” and “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects.” We have based these forward-looking statements largely on our current expectations about future events and financial trends affecting our business. These forward-looking statements are subject to risks, uncertainties and assumptions, including among other things:
| • | the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic and its impacts on the sanitary and health conditions in Brazil and in our principal export markets, as well as any impact on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects, including impacts in the demand for printing and writing papers, and any further actions that alter our business operations, as may be required by local authorities, or that we determine are in the best interests of our employees, communities and clients; |
| • | our management and future operation; |
| • | the implementation of our main operational strategies, including our potential participation in acquisitions, joint venture transactions or other investment opportunities; |
| • | general economic, political and business conditions, both in Brazil and in our principal export markets; |
| • | industry trends and the general level of demand for, and change in the market prices of, our products; |
| • | existing and future governmental regulation, including tax, labor, pension and environmental laws and regulations and import tariffs in Brazil and in other markets in which we operate or to which we export our products; |
| • | the competitive nature of the industries in which we operate; |
| • | our level of capitalization, including the levels of our indebtedness and overall leverage; |
| • | the cost and availability of financing; |
| • | our compliance with the covenants contained in the instruments governing our indebtedness; |
| • | the implementation of our financing strategy and capital expenditure plans; |
| • | inflation and fluctuations in currency exchange rates, including the Brazilian real and the U.S. dollar; |
| • | legal and administrative proceedings to which we are or may become a party; |
| • | the volatility of the prices of the raw materials we sell or purchase to use in our business; |
| • | other statements included in this annual report that are not historical; and |
| • | other factors or trends affecting our financial condition or results of operations, including those factors identified or discussed in “Item 3. Key Information — Risk Factors.” |
The words “anticipate,” “believe,” “continue,” “could,” “estimate,” “expect,” “hope,” “intend,” “may,” “might,” “should,” “would,” “will,” “understand” and similar words are intended to identify forward-looking statements. We undertake no obligation to update publicly or revise any forward- looking statements because of new information, future events or otherwise. In light of these risks and uncertainties, forward-looking information, events and circumstances discussed in this annual report might not occur and are not guarantees of future performance. Our actual results and performance may differ substantially from the forward-looking statements included in this annual report.
GLOSSARY OF CERTAIN TERMS USED IN THIS ANNUAL REPORT
Herein, “Suzano”, the “Company”, “we”, “us” and “our” refer to Suzano and its consolidated subsidiaries, unless the context otherwise requires. References to “Fibria” refer to former “Fibria Celulose S.A.”. All references herein to the “real,” “reais” or “R$” are to the Brazilian real, the official currency of Brazil. All references to “U.S. dollars,” “dollars” or “US$” are to United States dollars, the official currency of the United States.
| ADENE | Agency for the Development of the Northeastern Brazil, or Agência de Desenvolvimento do Nordeste. |
| ADR | American Depositary Receipts. |
| ADS | American Depositary Shares. |
| ANTAQ | Brazilian regulatory agency regulating aquatic transportation, or Agência Nacional de Transportes Aquaviários. |
| B3 | B3 S.A. – Brasil, Bolsa, Balcão, the São Paulo Stock Exchange. |
| BNDES | The Brazilian Development Bank, or Banco Nacional de Desenvolvimento Econômico e Social. |
| BNDESPAR | BNDES Participações S.A. |
| Brazilian Corporation Law | Brazilian Law No. 6.404/76, as amended. |
| CADE | Brazilian antitrust authority, or Conselho Administrativo de Defesa Econômica. |
| COFINS | Contribution for the Financing of Social Security, or Contribuição para o Financiamento da Seguridade Social. |
| CONFAZ | National Board of Financial Policy, or Conselho Nacional de Política Fazendária. |
| CSLL | Social Contribution on Net Income, or Contribuição Social Sobre o Lucro Líquido. |
| CVM | Brazilian Securities Commission, or Comissão de Valores Mobiliários. |
| Exchange Act | U.S. Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. |
| FGTS | Government Severance Indemnity Fund for Employees, or Fundo de Garantia do Tempo de Serviço. |
| GHG | Greenhouse gas. |
| IBÁ | Brazilian Tree Industry, or Indústria Brasileira de Árvores. |
| IBAMA | Brazilian Federal Environmental Agency, or Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis. |
| ICMS | Tax on Sale of Goods and Services, or Imposto sobre Circulação de Mercadorias e Serviços. |
| IFC | International Finance Corporation. |
| INCRA | Brazilian Institute for Land Reform, or Instituto Nacional de Colonização e Reforma Agrária. |
| INPI | National Industrial Property Institute, or Instituto Nacional da Propriedade Industrial |
| INSS | Social Security Contributions, or Instituto Nacional do Seguro Social. |
| IPCA | Inflation Rate Index for Consumer Goods, or Índice Nacional de Preços ao Consumidor Amplo |
| IPI | Tax on Manufactured Products, or Imposto sobre Produtos Industrializados. |
| IRPJ | Corporate Income Taxes, or Imposto de Renda Pessoa Jurídica. |
| ISS | Tax on Services, or Imposto Sobre Serviços. |
| PIS | Social Integration Program, or Programa de Integração Social. |
| PPPC | Pulp and Paper Products Council. |
| RFB | Brazilian Internal Revenue, or Receita Federal do Brasil. |
| Securities Act | U.S. Securities Act of 1933, as amended. |
| SUDENE | Superintendence for Development of the Northeast, or Superintendência do Desenvolvimento do Nordeste. |
| TJLP | Brazilian Long-Term Interest Rate, or Taxa de Juros de Longo Prazo. |
PRESENTATION OF FINANCIAL AND OTHER INFORMATION
We have prepared our consolidated financial statements as of December 31, 2020 and 2019 and for each of the three years ended December 31, 2020, included herein, in compliance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”). The selected financial information should be read together with our consolidated financial statements, including the notes thereto.
Our functional currency and that of all our subsidiaries is the real, which is also the currency used for the preparation and presentation of our consolidated financial statements, except for investments in associates abroad related to Ensyn Corporation, F&E Technologies LLC and Spinnova OY. See note 3.2.5. to our audited consolidated financial statements.
We make statements in this annual report about our competitive position and our market share in, and the market size of, the market pulp and paper industry. We have made these statements on the basis of statistics and other information from third-party sources that we believe are reliable.
The financial information and certain other information presented in a number of tables in this annual report have been rounded to the nearest whole number or the nearest decimal. Therefore, the sum of the numbers in a column may not conform exactly to the total figure given for that column. In addition, certain percentages presented in the tables in this annual report reflect calculations based upon the underlying information prior to rounding and, accordingly, may not conform exactly to the percentages that would be derived if the relevant calculations were based on the rounded numbers.
Given that the merger of shares (incorporação de ações) (the “Merger”), set forth in the Merger Agreement entered into by Suzano and Fibria on July 26, 2018 (the “Merger Agreement”) was consummated in January 2019, our results of operations and financial condition for some historical periods discussed in this section do not reflect or include the results of operations or any assets or liabilities of Fibria. We began consolidating Fibria and its subsidiaries as from January 1, 2019, and, accordingly, our results of operations and financial condition in future periods may not necessarily be comparable to our results of operations and financial condition for historical periods, including those discussed below. For information on Fibria’s results of operations and financial condition for these periods, see Fibria’s audited consolidated statements as of December 31, 2018 and 2017 and for the years ended December 31, 2018, 2017 and 2016 that were submitted by Fibria to the SEC on Form 6-K on February 22, 2019. In this section, we include, solely for convenience purposes, certain information on Fibria’s results of operations, cash flows and financial condition, including indebtedness and other contractual liabilities, that was extracted from Fibria’s audited consolidated financial statements. However, this information is not indicative of any future results of operations or financial condition of Fibria, or of our company and Fibria operating on a combined basis.
PART I
ITEM 1. IDENTITY OF DIRECTORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT AND ADVISERS
Not applicable.
ITEM 2. OFFER STATISTICS AND EXPECTED TIMETABLE
Not applicable.
ITEM 3. KEY INFORMATION
A. Selected Financial Data
For a discussion of our financial and operating data for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, see “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects.”
OTHER FINANCIAL DATA
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2020 | | | 2019 | | | 2018 | | | 2017 | | | 2016 | |
| | | (in thousands of R$, unless otherwise indicated) | |
| Gross margin (1) | | | 37.7 | % | | | 20.3 | % | | | 48.5 | % | | | 38.6 | % | | | 33.3 | % |
| Operating margin (2) | | | 27.7 | % | | | 10.1 | % | | | 37.3 | % | | | 31.0 | % | | | 13.0 | % |
| Capital expenditures (3) | | | 4,897,860 | | | | 4,868,427 | | | | 2,423,698 | | | | 1,780,302 | | | | 2,324,338 | |
| Depreciation, amortization and depletion (4) | | | 6,772,781 | | | | 5,844,855 | | | | 1,563,223 | | | | 1,402,778 | | | | 1,403,518 | |
| Cash flow provided by (used in): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | | | 13,124,636 | | | | 7,576,437 | | | | 5,169,448 | | | | 3,067,332 | | | | 3,075,539 | |
| Investing activities | | | (736,417 | ) | | | (11,695,019 | ) | | | (21,961,310 | ) | | | (1,007,807 | ) | | | (3,342,484 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | (9,785,139 | ) | | | 3,141,809 | | | | 20,035,049 | | | | (2,612,089 | ) | | | 566,082 | |
| (1) | The gross margin calculation consists of dividing gross profit by net revenues. |
| (2) | The operating margin calculation consists of dividing operating profit before net financial income (expenses) by net revenues. |
| (3) | Relates to capital expenditures cash invested for the acquisition of property, plant and equipment and intangible assets and biological assets. |
| (4) | Solely for the year ended December 31, 2019, depreciation, amortization and depletion includes the amortization of fair value adjustment on the business combination with Fibria/Facepa/Ibema, except for the fair value amortization of inventories and contingencies related to the business combination with Fibria. Solely for the year ended December 31, 2020, depreciation, amortization and depletion includes subleasing of ships. |
OPERATIONAL DATA
| | | As at and for the year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2020 | | | 2019 | | | 2018 | | | 2017 | | | 2016 | |
| Number of employees | | | 15,653 | | | | 14,534 | | | | 9,385 | | | | 7,830 | | | | 7,483 | |
| Nominal production (millions of tons) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pulp | | | 9.8 | | | | 9.4 | | | | 3.5 | | | | 3.5 | | | | 3.5 | |
| Paper | | | 1.2 | | | | 1.2 | | | | 1.3 | | | | 1.2 | | | | 1.2 | |
| Nominal production capacity (millions of tons) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pulp | | | 10.9 | | | | 10.9 | | | | 3.6 | | | | 3.6 | | | | 3.6 | |
| Paper | | | 1.4 | | | | 1.4 | | | | 1.4 | | | | 1.4 | | | | 1.3 | |
| Sales volumes (thousand metric tons) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic market pulp | | | 786,621 | | | | 830,962 | | | | 298,005 | | | | 376,502 | | | | 410,564 | |
| Export market pulp | | | 10,036,495 | | | | 8,580,691 | | | | 2,927,714 | | | | 3,255,329 | | | | 3,117,814 | |
| Total market pulp | | | 10,823,116 | | | | 9,411,653 | | | | 3,225,719 | | | | 3,631,831 | | | | 3,528,378 | |
| Sales volumes (thousand metric tons) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic market paper | | | 801,819 | | | | 853,412 | | | | 878,374 | | | | 815,917 | | | | 826,408 | |
| Export market paper | | | 375,062 | | | | 403,051 | | | | 377,263 | | | | 374,190 | | | | 361,996 | |
| Total market paper | | | 1,176,881 | | | | 1,256,463 | | | | 1,255,637 | | | | 1,190,108 | | | | 1,188,404 | |
| Total sales volumes market paper and pulp | | | 11,999,997 | | | | 10,668,116 | | | | 4,481,356 | | | | 4,821,938 | | | | 4,716,782 | |
Special Note Regarding Non-IFRS Financial Measures
A non-IFRS financial measure is any financial measure that is presented other than in accordance with all relevant accounting standards under IFRS. We disclose EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA for Suzano in this annual report, which are considered to be non-IFRS financial measures. EBITDA is calculated as Net income (loss) plus Net financial result, Income and social contribution taxes, and Depreciation, amortization and depletion. Adjusted EBITDA for Suzano is defined as EBITDA as further adjusted to add or exclude: (i) exceptional adjustments as defined by management are those with no impact on Suzano’s ongoing business, such as Expenses with Fibria’s transaction, Amortization of fair value adjustment on business combination with Fibria, Indemnity – FACEPA, Contract renegotiation, Losango Project Adjustments, COVID-19 - Social actions, COVID-19 - Operating expenses, Fair value adjustment (others), ITBI Provision and fees, Sale of judicial credits, Shut down – 5.1 Project Mucuri facility, Non-Compete Executives, Fees of counsel, Tax credits - gains in tax lawsuit (ICMS from the PIS/COFINS calculation basis) and Agreement White Martins and (ii) non-cash adjustments are those adjustments that have impacted the income statements without a cash impact on Suzano, such as Accrual (reversal) of losses on ICMS credits, Impairment of non-financial assets, Accruals for losses on PIS and COFINS credits, Labor lawsuits provision, Fair value adjustment of biological assets, Result from sale and disposal of property, plant and equipment and biological assets, Income from associates and joint ventures, Reconciliation adjustments and Write-off of physical inventory.
The non-IFRS financial measures described in this annual report are not a substitute for the IFRS measures of net income or other performance measures.
Our management believes that disclosure of our EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA provide useful information to investors, financial analysts and the public in their review of our operating performance and their comparison of our operating performance to the operating performance of other companies in the same industry and other industries.
For example, interest expense is dependent on the capital structure and credit rating of a company. However, debt levels, credit ratings and, therefore, the impact of interest expense on earnings vary significantly between companies. Similarly, the tax positions of individual companies can vary because of their differing abilities to take advantage of tax benefits and the differing jurisdictions in which they transact business. Finally, companies differ in the age and method of acquisition of productive assets, and thus the relative costs of those assets, as well as in the depreciation method (straight-line, accelerated or units of production), which can result in considerable variation in depreciation and amortization expenses between companies. Therefore, for comparison purposes, our management believes that our EBITIDA and Adjusted EBITDA are useful measures of operating profitability because they exclude these elements of earnings that do not provide information about the current operations of existing assets.
Moreover, other companies may calculate EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA differently, and therefore our presentation of EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA may not be comparable to other similarly titled measures used by other companies. Each of these non-IFRS financial measures are important measures to assess our financial and operating performance. We believe that the disclosure of EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA provides useful supplemental information to investors and financial analysts in their review of our operating performance and in the comparison of such operating performance to the operating performance of other companies in the same industry or in other industries that have different capital structures, debt levels and/or income tax rates. The presentation of non-IFRS financial information is not meant to be considered in isolation or as a substitute for the directly comparable financial measures prepared in accordance with IFRS.
See below for a reconciliation of our net income (loss) to EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA.
| Adjusted EBITDA (R$ million) | | 2020 | | | 2019 | |
| EBITDA Reconciliation | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | | | (10,714.9 | ) | | | (2,814.7 | ) |
| (+/–) Net financial result | | | 26,085.5 | | | | 6,725.8 | |
| (+/–) Income and social contribution taxes | | | (6,927.2 | ) | | | (1,282.5 | ) |
| (+) Depreciation, amortization and depletion (1) | | | 6,772.8 | | | | 5,844.8 | |
| EBITDA | | | 15,216.2 | | | | 8,473.4 | |
| Expenses with Fibria’s Transaction(2) | | | 1.0 | | | | 79.9 | |
| Amortization of fair value adjustment on business combination with Fibria(3) | | | — | | | | 2,247.1 | |
| Indemnity – FACEPA(4) | | | — | | | | 4.1 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA (R$ million) | | 2020 | | | 2019 | |
| Accrual (reversal) of losses on ICMS credits(5) | | | (79.0 | ) | | | 181.1 | |
| Contract renegotiation(6) | | | 6.7 | | | | 45.7 | |
| Losango Project Adjustments(7) | | | — | | | | 57.8 | |
| Impairment of non-financial assets(5) | | | 45.4 | | | | — | |
| COVID-19 - Social actions(8) | | | 48.6 | | | | — | |
| COVID-19 - Operating expenses(9) | | | 136.1 | | | | — | |
| Fair value adjustment (others)(10) | | | — | | | | (32.7 | ) |
| ITBI provision and fees(11) | | | 10.5 | | | | — | |
| Accruals for losses on PIS and COFINS credits(5) | | | 11.1 | | | | 21.1 | |
| Labor lawsuits provision(5) | | | — | | | | 32.2 | |
| Fair value adjustment of biological assets(5) | | | (466.5 | ) | | | (185.4 | ) |
| Sale of judicial credits(12) | | | — | | | | (86.6 | ) |
| Result from sale and disposal of property, plant and equipment and biological assets(5) | | | 25.5 | | | | 42.7 | |
| Shut down – 5.1 Project Mucuri facility(13) | | | 29.7 | | | | — | |
| Income from associates and joint ventures(5) | | | (36.1 | ) | | | (32.0 | ) |
| Non-Compete Executives(14) | | | — | | | | 3.8 | |
| Fees of counsel(15) | | | — | | | | 2.4 | |
| Reconciliation adjustments(5) | | | — | | | | (3.0 | ) |
| Tax credits - gains in tax lawsuit (ICMS from the PIS/COFINS calculation basis)(16) | | | — | | | | (128.1 | ) |
| Agreement White Martins(17) | | | 0.4 | | | | — | |
| Write-off of physical inventory(5) | | | — | | | | 0.1 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | | | 14,949.6 | | | | 10,723.6 | |
| (1) | Solely for the year ended December 31, 2019, depreciation, amortization and depletion includes the amortization of fair value adjustment on the business combination with Fibria/Facepa/Ibema, except for the fair value amortization of inventories and contingencies related to the business combination with Fibria. Solely for the year ended December 31, 2020, depreciation, amortization and depletion includes subleasing of ships. |
| (2) | Exceptional: Expenses incurred due to the business combination with Fibria. |
| (3) | Exceptional: Amortization of fair value adjustment on business combination with Fibria related to contingencies and inventory. |
| (4) | Exceptional: expenses related to the dismantling of machinery at Facepa. |
| (6) | Exceptional: Penalties on contractual terminations with some suppliers due to operational synergies arising from business combination with Fibria. |
| (7) | Exceptional: Provisions related to the Losango project, mainly, write-off of advances of forestry development program and write-off of wood stock in the field. |
| (8) | Exceptional: Disbursements made for carrying out the social actions implemented by Suzano. |
| (9) | Exceptional: Includes, mainly, expenses in the facilities units for the upgrading of cafeterias and workplaces, expansion of the frequency of conservation, cleaning, hygiene and maintenance of common areas, public transport with more space between passengers, distribution of masks and realization rapid tests on employees working in facilities units. |
| (10) | Exceptional: Bargain purchase Spinnova. In 2019, the Company revaluated the investment, previously classified as financial investment measured through other comprehensive income. |
| (11) | Exceptional: Provision for Property Transfer Tax ("ITBI") payments and fees referring to the regularization of land acquired prior to 2015. |
| (12) | Exceptional: The amount refers to the sale of credits related to a lawsuit against Centrais Elétricas Brasileiras S.A. (Eletrobrás). |
| (13) | Exceptional: Refers to a 2016 project of the Mucuri facility that was discontinued. |
| (14) | Exceptional: Non-compete payment made to an executive of the Company. |
| (15) | Exceptional: Fees of legal counsel arising from successful causes related to exceptional events. |
| (16) | Exceptional: For certain tax credits to be recovered, the Company has received final favorable court decisions in 2019 and recorded an asset of R$128.1 relating to PIS and COFINS tax credits within recoverable taxes and a gain in the statement of income (loss) within other operational results, regarding certain claims for the calculation period from 2006 to July 2018. |
| (17) | Exceptional: Fine for termination due to supply incidents. |
B. Capitalization and Indebtedness
Not applicable.
C. Reasons for the Offer and Use of Proceeds
Not applicable.
D. Risk Factors
We are subject to various risks and uncertainties resulting from changing competitive, economic, political, environmental and social conditions that could harm our business, results of operations or financial condition. The risks described below, although not being the only ones we face are the most important ones according to our ability to identify material risks. Other risks that we presently believe are not material could also adversely affect us.
Risks Relating to the Pulp and Paper Industry
Our products’ prices are greatly affected by international market prices, which vary depending on a number of factors that are beyond our control and could adversely affect our results of operations and financial conditions and our ability to operate our plants in an economically viable manner.
Pulp markets are typically cyclical, and our pulp prices follow international market prices, which are determined by supply and demand, global pulp production capacity and global economic conditions. Such prices can also be affected by exchange rate fluctuations between the currencies of main producing and consuming countries, movement of inventories, diverging price expectations, business strategies adopted by other producers and availability of substitutes for our products, among others. All of these factors are beyond our control and may have a significant impact on the prices for pulp and, consequently, on our operational margins, profitability and ROIC. Fluctuations in pulp price may lead us to adopt changes in our commercial strategy or production, which also may adversely affect our financial condition and results of operation.
Paper prices are also determined by supply and demand conditions in the markets in which they are sold, and are affected by various factors, including the fluctuation in pulp prices and the specific characteristics of the markets in which we operate.
We cannot assure that pulp and paper market prices and demand for our products will remain favorable to us, and any adverse price or demand fluctuations, which may occur rapidly in our markets, could adversely affect our results of operations and financial conditions and our ability to operate our plants in an economically viable manner.
We are highly dependent on our planted forest areas for the supply of wood, which is essential to our production processes, and any damage to our forest areas or impact on prices of land we seek to purchase for our forests may adversely affect us.
Most of the wood used in our production processes is supplied by our own forestry operations, which include planted forest areas located in close proximity to our production facilities. The wood market in Brazil is very regional and limited in wood availability, as most pulp and paper producers are integrated and utilize wood grown in their own planted forests to meet their wood requirements.
Our planted forests are subject to natural threats, such as drought, fire, pests and diseases, which may reduce our supply of wood or increase the price of wood we acquire. Our planted areas are also subject to other threats, considering their wide territorial coverage and proximity to a significant number of neighbors and local communities, including loss of possession due to social unrest or squatter invasion, land title disputes, wood theft, or arson, which may result in real damage to our planting and transit areas and may adversely affect our results.
In addition, the physical effects of climate change may materially and adversely affect our operations, for example by changing air temperature and water levels, and subjecting us to unusual or different weather-related risks. Any climate changes that negatively affect the favorable climate conditions in Brazil may adversely affect the growth rate and quality of our plantations, or our production costs. Although we cannot predict the impact of changing global climate conditions, any such occurrences may increase our liabilities and capital expenditures and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Additionally, in acquiring land for our timber plantations, we compete with other crops, as well as with cattle breeders, which could ultimately raise land prices or make it more difficult for us to contract independent third parties to cultivate eucalyptus.
Drought in some regions of Brazil, resulting in water scarcity and related rationing, may adversely affect our business and results of operations.
In Brazil, some regions might have drought conditions during some seasons of the year, which could result in acute shortages of water and/or implementation of rationing to restrict usage. Some of our units are located in the affected areas and we cannot assure that our processes for efficient use of water and contingency plans will be able to avoid impacts from severe droughts or governmental measures to address drought conditions on our units’ operations, which could have an adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
We face significant operational risks that can result in the shutdown of our operations, which may adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
We face operational risks that may result in partial or temporary suspension of our operations and in loss of production. Such outages may be caused by factors associated with equipment failure, information system disruptions or failures (including due to cyber-attacks), accidents, fires, strikes, invasions, weather, exposure to natural disasters, regional water crisis, electricity power outages and chemical product spills, accidents involving water reservoirs, landfills, revocation of licenses, among other operational and environmental hazards. The occurrence of these events may, among other impacts, result in serious damage to our property, assets and reputation, liability for damages to the environment and third parties, a decrease in production or an increase in production costs, any of which may adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
During the normal course of our business, we depend on the continuous availability of logistics and transportation networks, including roads, railways, warehouses and ports, among others. Such operations may be disrupted by factors beyond our control, such as social movements, natural disasters, electricity shortages and labor strikes. For example, the general strike of truck drivers in May 2018 throughout Brazil resulted in a temporary suspension of our production operations over some days, which in turn caused losses in production of our pulp and paper products. In order to end the strike, the Brazilian federal government made several concessions to the truck drivers, which may have an adverse effect on our costs of inbound and outbound logistics. Any interruption in the supply of inputs for the operation of our industrial and forestry units or in the delivery of our finished products to clients could cause a material adverse impact on our results of operations.
We have entered into contracts with third parties to provide transportation and logistics services. The early termination of these contracts or our inability to renew them or negotiate new contracts with other service providers with similar conditions could adversely affect our financial and operating condition. In addition, the majority of our suppliers of transportation operate under concessions granted by the Brazilian government. The loss or non- renewal of such concessions without timely replacement for new concessions to third parties that are capable of continuing the services provided and willing to do so on similar terms as the previous service providers may also adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Additionally, we are subject to quality control risks associated with our products, which may affect our consumer market and customers. In this sense, we note that our products have several properties that influence the processes of our customers, as well as the quality of the products they produce. Accordingly, we are also subject to any potential claims relating to the quality of our products, which may have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
We depend on third-party suppliers for a material portion of our wood requirements and also depend on few suppliers for certain raw materials. Significant reductions in supply or increases in price of these materials could adversely affect our production, products’ mix, margin or availability and, consequently, our results of operations.
Our wood resources are not sufficient to satisfy our production needs, and accordingly we seek additional wood supply from third parties through agreements to purchase standing forests or for purchases of wood delivered to our factories. Medium- and long-term supply agreements with wood suppliers may vary between one to three forest cycles, each cycle lasting approximately seven years. Lease agreements or forest partnerships have an average term of 14 to 15 years. Wood price conditions are subject to cyclical and circumstantial variations of wood demand in the different regions where we operate. A material failure to obtain wood from third party suppliers or a material interruption in our current supply arrangements may result in a significant reduction in available wood for processing at our plants, which may adversely affect our production and, accordingly, our results of operations and financial condition.
In addition, we have few sources for certain raw materials that are essential for the production of pulp and paper, including fuel oil, bleached chemo thermo mechanical pulp, natural gas and third-party industry technology (maintenance). We enter into medium and long term supply agreements with such suppliers. Any significant reduction in the supply or increase in prices, on behalf of the relevant supplier, of any of these raw materials, as well as our inability to maintain the relationship or find suitable substitutes for these suppliers, could adversely affect our products’ mix, margin or availability and, consequently, our results of operations.
Investments by us or our competitors to enhance pulp and paper production capacity in the future may adversely affect the market price for our products.
New capacity projects developed by us or our competitors may create an imbalance between supply and demand of pulp and paper, which may cause a reduction in pulp and paper prices. Investments in new capacity may have a negative impact on pulp and paper prices and, consequently, on our financial condition or results of operations.
We face significant competition in some of our lines of business, which may adversely affect our market share in the pulp and paper industries and our profitability.
The pulp and paper markets are extremely competitive. We face substantial competition in both domestic and international markets from a large number of companies, some of which have extensive access to financial resources and low capital costs. In the domestic market, we face competition from national products, produced by companies of Brazilian and international groups, and imported products. In the international market, we compete against companies with large production and distribution capacities, significant consumer base and great variety of products.
In addition, the oversupply of coated paper in the world market, the antidumping measures adopted in other countries and the use of imported coated paper for alternative purposes, especially during periods of prolonged appreciation of the real against the U.S. dollar, may increase competition in Brazil from producers of imported paper. Moreover, if the Brazilian federal government were to decrease import taxes, or in the event of sustained appreciation of the real against the U.S. dollar, competition in Brazil from international producers may increase. The occurrence or continuation of any of the foregoing events could adversely affect us.
Additionally, the pulp and paper markets are served by numerous companies located in different countries. If we are unable to remain competitive against these producers in the future, our market share may be adversely affected. Other companies operating in the same segments may compete with us for acquisition and alliance opportunities. Strategic acquisitions or alliances by our competitors could affect our ability to enter into or consummate acquisitions and alliances that are necessary to expand our business. Further, we may face elevated costs associated with restructuring and/or financing in relation to acquisitions or strategic partnerships in comparison to our competitor companies. Companies that are better positioned to enter into acquisitions or alliances may benefit from preferable production costs, which may affect our competitiveness and market share.
Other factors affecting our ability to compete include the entry of new competitors into the markets we serve, increased competition from overseas producers, our competitors’ pricing strategies, the introduction by our competitors of new technologies and equipment, our ability to anticipate and respond to changing customer preferences and our ability to maintain the cost-efficiency of our facilities. In addition, changes within these industries, including the consolidation of our competitors and our customers, may impact competitive dynamics.
Liquidity restriction periods may increase our financial costs, limit the terms or even preclude the funding in the market, which may adversely affect our operations.
Brazilian paper and pulp companies have made significant investments during the last few years in order to compete more efficiently and on a larger scale in the international market. This trend towards consolidation has enhanced the need for resources and diversification of financing sources among national and foreign financial institutions.
In this context, we depend on third-party capital to conduct our business, by means of financing transactions to support our investments and working capital. We cannot assure that our current sources of funds will be sufficient or that they will remain available to meet our capital needs, which may require us to seek additional funds in the financial and capital markets. In liquidity restriction periods, such as the ones of 2008 and 2009 that occurred due to the international financial crisis, credit lines may become excessively short, expensive or even unavailable. Under these circumstances, there is a higher risk of not achieving success in financing and refinancing transactions, meaning that there is a higher possibility of failure in obtaining financing in the market in order to pay down existing indebtedness, as well as a higher risk of raising these funds at an elevated cost or subject to posting collateral, which may adversely affect our results of operations or financial condition.
More stringent environmental regulation could increase our expenditures and noncompliance with such regulation may result in administrative, civil and criminal liability, which may adversely affect us, our results of operations or financial condition.
Our activities are subject to extensive environmental regulation, including in relation to gas emissions, liquid effluents and solid waste management, reforestation and odor control, as well as maintenance of land reserve and permanent preservation areas. Furthermore, our activities, both industrial and forestry, require periodic renewal of environmental permits.
Environmental standards that are applicable to us are issued at the federal, state and municipal levels, and changes in the laws, rules, policies or procedures adopted in the enforcement of the current laws may adversely affect us. In Brazil, violations of environmental laws, regulations and authorizations could result in administrative, civil or criminal penalties for us, our management and our employees, including fines, imprisonment, interruption of our activities and dissolution of our corporate entity.
Governmental agencies or other competent authorities may provide new rules or additional regulations even stricter than the ones in force, or they may pursue a stricter interpretation of the existing laws and regulations, which could require us to invest additional resources in environmental compliance or to restrict our ability to operate as currently done. Additionally, noncompliance with or a violation of any such laws and regulations could result in the revocation of our licenses and suspension of our activities or in our liability for environmental remediation costs, which could be substantial. Moreover, failure to comply with environmental laws and regulations could restrict our ability to obtain financing from financial institutions.
In December 2015, several countries (including Brazil) signed the Paris Agreement, a new global environmental agreement adopting the Intended Nationally Determined Contributions, or “INDCs”, as the measures taken to reduce its emissions after 2020. The INDC that applies to Brazil provides for an increase in the share of sustainable biofuels and other sources of renewable energy in the Brazilian national energy mix, as well as zero deforestation, reforestation, forest restoration and enhancement of the native forest management. We may be materially affected by more restrictive environmental laws and regulations related to greenhouse gases and climate change, to the extent that such new laws or regulations may cause an increase in capital expenditures and investments to comply with such laws, and indirectly, by changes in prices for transportation, energy and other inputs. Both the regulations related to climate change and the changes in existing regulations, as well as the physical effects of climate change generally, could result in increased liabilities and capital expenditures, all of which could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
Failure to obtain, timely renew or maintain permits, licenses and concessions, grants and registrations necessary to develop our activities, as well as any cancellation thereof, could adversely affect our operations.
We depend on the issuance of permits, licenses, concessions, grants and registrations from various governmental agencies in order to undertake certain operational activities. Moreover, in order to obtain licenses for certain activities that are expected to have a significant environmental impact, certain investments in conservation are required to offset such impact. Furthermore, we have permits, licenses, grants and registrations that are necessary to operate our plants, which are usually valid for five years from the date of issuance and may be timely renewed. Certain of these operational licenses require, among other things, that we periodically report our compliance with emissions standards set by environmental agencies. In addition, the expansion of our operations and/or changes in the applicable legislation may require that new licenses, permits and registrations be obtained from the competent authorities, and we cannot guarantee that we will be able to obtain them or obtain them in a timely manner, which cause delays in our deployment of new activities, increased costs, monetary fines or sentences to pay compensation. In case we are fined and/or penalized for a failure to obtain, timely renew or for the cancellation of our permits, licenses, grants and registrations, as well as for noncompliance with environmental legislation, our financial and operating results and image may be adversely affected. In addition, non-compliance with applicable environmental legislation may result in partial or total shutdowns of our operating activities, which may also adversely affect our financial position and image.
Global or regional economic conditions and events may adversely affect the demand for and the price of our products.
Demand for pulp and paper is directly related to the growth of the world economy and economic conditions. Currently, Europe, China and North America are the main consumer markets of the industry. Fluctuations in the value of local currency versus the U.S. dollar, downturns in economic activity, nationalization or any change in social, political or labor conditions in any of these countries or regions impacting matters such as sustainability, environmental regulations and trade policies and agreements, could negatively affect our financial results. Any slowing of economic growth in Europe, China and North America could adversely affect the price and volume of our exports and thus impact our operating performance.
According to market statistics (PPPC), Chinese demand represented 39% of the global market pulp demand in 2020 (versus 37% in 2019 and 33% in 2018), and this demand has increased at a compound annual growth rate of 9.4% since 2005, above the global average of 2.5%. The recent investments in paper and board machines in China have been boosting pulp demand in China; however, the volatility of Chinese demand due to speculative buying movement is a key risk for any short-term demand forecast. Such behavior was experienced during the year of 2019 when, according to the PPPC’s Chinese Demand report, demand for hardwood in China fell by 3.5% in the first 6 months of 2019 vs. the same period of the previous year. However, in the year-to-date analysis (FY 2019 vs FY 2018), there was an increase of 16.7%. In 2020, the speculative buying movement was not largely noticed with similar demand growth throughout the year.
The outbreak of coronavirus or other diseases may adversely affect our operations and financial results.
In light of our activities in the foreign market, our operations and results may be negatively impacted by the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak. Global or national health concerns, including the outbreak of pandemic or contagious disease, such as the COVID-19, may adversely affect us. Since December 2019, COVID-19 has spread in China and other countries, which continues to adversely impact global commercial activity and has contributed to significant volatility in the market. Such events or potential reactions and mandates from government authorities could cause disruption of regional or global supply chains and economic activity, including significant volatility in demand, which could adversely affect our operations and financial results. Prolonged closures, stoppages and shutdowns, if continuing, may disrupt our operations and the operations of our suppliers, service providers and customers and could materially, adversely affect our revenues, financial condition, profitability, and cash flows. The extent to which the coronavirus and/or other diseases impact our results will depend on future developments, which are highly uncertain and cannot be predicted in light of the rapid development and fluidity of this situation, including new information which may emerge concerning the severity of the coronavirus and/or other diseases and the actions to contain the or treat their impact, among others.
Our exports are subject to special risks that may adversely affect our business.
We export to different regions of the world, which makes us subject to special political and regulatory risks, including currency controls in countries where we have payments receivable, possible formal or informal trade barriers and incentive policies and subsidies favoring local producers in many regions.
Thus, our future financial performance will depend on the economic, political, environmental and social conditions of our main export markets (Europe, Asia and North America). As a result, factors that are beyond our control include:
| • | imposition of barriers to trade by certain countries to limit the access of Brazilian companies to their markets or even to subsidize local producers, particularly with respect to paper products, or the granting of commercial incentives in favor of local producers; |
| • | changes in economic policies and/or conditions of the countries to which we export, which may affect our export capacity and, consequently, our business and operating results; |
| • | logistics costs, including disruptions in shipping or reduced availability of freight transportation; |
| • | significant fluctuations in global demand for pulp products, which could impact our sales, operating income and cash flows; |
| • | the deterioration of global economic conditions, which could impair the financial condition of some of our customers or foreign suppliers, thereby increasing bad debts or non-performance by our foreign suppliers, as well as increasing our costs for financing and refinancing; |
| • | changes in revenues due to variations in foreign currency exchange rates; |
| • | controls on currency exchange; and |
| • | adverse consequences deriving from the need to comply with more stringent regulatory requirements in foreign countries, including environmental rules, regulations and certification requirements. |
Risks Relating to Our Company
We pursue certain transactions from time to time and we may not be able to achieve the expected benefits of such transactions or manage potential risks related to such transactions, which may adversely affect our business and growth prospects, as well as our results of operations and financial condition and the trading price for our securities.
In the course of our business, we analyze, pursue and carry out acquisitions, strategic alliances and divestitures, and, as part of our business strategy, we may acquire other assets or businesses or enter into further strategic partnerships in Brazil or other countries.
Disagreements with our joint operation partners, unexpected events or changes in market conditions, as well as the failure to successfully integrate new businesses or manage strategic alliances, could adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition or prevent us from realizing expected gains of these acquisitions or alliances. For example, we (as successor to Fibria) hold a 50% interest in Veracel, a joint operation with Stora Enso for the production of pulp, and a 51% interest in Portocel, our subsidiary (former subsidiary of Fibria) in which Celulose Nipo-Brasileira S.A. – CENIBRA holds the remaining 49% interest stake. In May 2014, Fibria (Stora Enso’s former partner in the joint operation) commenced an arbitration against Stora Enso for alleged breach of its obligations under certain provisions of the joint operation shareholders’ agreement. For further information on the arbitral proceeding, see Item 8. “Financial Information—Consolidated Statements and Other Financial Information—Civil Proceedings.”
If we attempt to engage in future acquisitions, we would be subject to additional risks, including that we could fail to select the best partners or fail to effectively plan and manage any strategic alliance. Moreover, any significant acquisition may be subject to regulatory approval in Brazil and abroad and, as a result, may not be consummated, which may have an adverse effect on the trading price of our securities.
The expected synergies from operating as a combined company with other companies that merge into and with us may not be achieved.
We cannot provide any assurance as to the extent to which the synergies anticipated or expected from eventual future mergers, or as to the timing for their realization, or as to the expenses that will be incurred in connection with realizing synergic benefits. In particular, we may not be able to realize anticipated cost savings from combination of companies’ production facilities, or anticipated synergic benefits from joint acquisitions of raw materials, sharing of improved production techniques and integration of administrative departments.
If we are not able to achieve the synergies from eventual future mergers, our results of operations and financial condition and the trading price for our securities may be adversely affected. Even if we achieve the expected synergies eventual future mergers, we may not be able fully realize them within the anticipated timeframe.
We recorded a significant amount of goodwill and other intangible assets with determined useful life as a result of the Merger, which may be subject to impairment charges under certain circumstances in future periods in accordance with applicable accounting regulations and adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations or the trading price of our securities.
As of December 31, 2020, the value of our goodwill and other intangible assets with determined useful life relating to the Merger with Fibria were R$7,897.1 million and R$8,303.7 million, respectively. For further information, see notes 16 to our audited consolidated financial statements. Under IFRS, goodwill and intangible assets with undetermined useful life are not subject to amortization and are tested annually to identify possible need for impairment, or more often if any event or circumstance indicates that an impairment loss may have been incurred. Other intangible assets that have determined useful lives are amortized on a straight-line basis over their estimated useful lives and reviewed for impairment whenever there is an indication of impairment. In addition, under IFRS we are required to perform an impairment analysis of assets with undetermined useful life when the book value of our net assets exceeds our market capitalization. As a result, we may be required to record an impairment charge for goodwill or other intangible assets in future periods if required under IFRS, which could lead to decreased assets and reduced net income. If a significant write down were required, the charge could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations or the trading price of our securities.
The level of our indebtedness could adversely affect our financial condition and a material portion of our cash flow may need to be used to service our debt obligations, which could impair our ability to operate our business.
As of December 31, 2020, we had R$72.9 billion of total consolidated outstanding indebtedness (which includes current and non-current loans, financing and debentures). We are subject to the risks normally associated with significant amounts of debt, which could have important consequences to investors. Our indebtedness could, among other things: (i) require us to use a substantial portion of our cash flow from operations to pay our obligations, thereby reducing the availability of our cash flow to fund working capital, operations, capital expenditures, dividend payments, strategic acquisitions, expansion of our operations and other business activities; (ii) increase our vulnerability to a downturn in general economic and industry conditions, and may make us unable to carry out capital spending that is important to our growth; (iii) limit, along with financial and other restrictive covenants in our debt instruments, our ability to incur additional debt or equity financing or dispose of assets; and (iv) decrease our ability to deleverage and place us at a competitive disadvantage compared to our competitors that have less debt.
In addition, we are subject to agreements governing our indebtedness that require us to meet and maintain certain covenants and financial ratios. A significant or prolonged downturn in general business and economic conditions, or other significant adverse developments with respect to our results of operations or financial condition, may affect our ability to comply with these covenants or meet those financial ratios and tests and could require us to take action to reduce our debt or to act in a manner contrary to our current business objectives. Moreover, the restrictions associated with these covenants and financial ratios may prevent us from taking actions that we believe would be in the best interest of our business and may make it difficult for us to execute our business strategy successfully or effectively compete with companies that are not similarly restricted. Additionally, despite these restrictions, we may be able to incur substantial additional indebtedness in the future, which might subject us to additional restrictive covenants that could affect our financial and operational flexibility and otherwise increase the risks associated with our indebtedness as noted above. We may also need to refinance all or a portion of our debt on or before maturity, and we may not be able to do this on commercially reasonable terms or at all.
Additionally, a default under our financial agreements that is not waived by the relevant creditors may result in an acceleration of the maturity of the outstanding balance of such debt, and may also accelerate the maturity of other debt that benefits from cross-default or cross-acceleration provisions. For more information, see Item 5. “Operating and Financial Review and Prospects —Indebtedness.” If such events were to occur, our financial condition and share price could be adversely affected.
We operate under certain tax regimes in Brazil and abroad that may be suspended, cancelled or not renewed, any of which may adversely affect our financial condition and free cash flow generation.
We receive certain tax benefits by virtue of our investment projects in underdeveloped regions in Brazil, which are covered by the SUDENE and the RFB. We also benefit from tax incentives granted by states based on state laws. The program PROMARANHAO in the state of Maranhão and the program Desenvolve in the state of Bahia, published through Ordinance-GABIN nº 435/18 and Decree No. 18.270/18, respectively, are the most relevant ones for our operations. We cannot assure you that the tax incentives we currently benefit from will be maintained or renewed, particularly, but not exclusively, in light of deteriorating macroeconomic conditions that may lead to changes in current material incentives, such as the exemption of export revenues from social security contributions, the Regime Especial de Aquisição de Bens de Capital para Empresas Exportadoras, which is a special regime for the acquisition of capital goods by exporting companies, and Preponderante Exportador, among others. If such tax benefits are not effectively renewed, this could have a material adverse effect on our generation of net cash flow. In the event of constitutional challenges or if we fail to comply with specific obligations to which we are subject in connection with the tax benefits described above, such benefits may be suspended or cancelled, and we may be required to pay the taxes due in the last five years in full, plus penalties and interest, which may adversely affect us.
Our exports and international trading activities are also conducted under certain tax regimes, including rulings and incentives in some foreign countries, including Austria. These the tax rulings or benefits expire and have to be renewed from time to time. We cannot assure you that the tax regimes and incentives from which we currently benefit will be renewed or maintained in the future. In addition, we also benefit from provisions of international treaties entered into by the Brazilian federal government in order to avoid double taxation, such as the non-double taxation treaty between Brazil and Austria, pursuant to which profit earned by our wholly-owned subsidiary in Austria is not subject to double-taxation in Brazil. Although we believe in the validity of the provisions of international treaties, we brought a claim with judicial courts and are currently guaranteeing the enforceability of the Brazilian-Austria treaty by means of a preliminary injunction. If the Brazil-Austria treaty in deemed unenforceable, we may be materially adversely affected.
Fluctuations in interest rates, as well as our inability to manage risks associated with the replacement of benchmark indices, could increase the cost of servicing our debt and negatively affect our overall financial performance.
Our financial results are affected by changes in interest rates, such as the London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”), the Brazilian Interbank Deposit Certificate Rate (Certificado de Depósito Interbancário, or “CDI”) and the Brazilian Long-Term Interest Rate (Taxa de Juros de Longo Prazo, or “TJLP”). The CDI rate has fluctuated significantly in the past in response to the expansion or contraction of the Brazilian economy, as it is an instrument for Brazilian Central Bank to manage inflation and pursuit its policies targets. The CDI rate was 1.90% p.a. as of December 31, 2020, while it was 4.40% p.a. and 6.40% p.a. as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. The TJLP rate was 4.55% p.a., 5.57% p.a. and 6.98% p.a. as of December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
Although the CDI rate has declined, we cannot guarantee that rates will continue to decrease. A significant increase in interest rates may impact our ability to secure financing in acceptable terms and an increase in interest rates, particularly TJLP, CDI or LIBOR, or the inflation rate index for consumer goods, or IPCA, could have a material adverse effect on our financial expenses since a significant part of our debt (BNDES loans, Agribusiness Credit Receivable Certificates - CRA and Export Prepayment Facilities) is linked to these rates. On the other hand, a significant reduction in the CDI rate could adversely impact our financial revenues derived from investment activities, since a material portion of our cash is invested in Brazilian money market instruments that are linked to the CDI rate.
On March 5, 2021 the head of the United Kingdom Financial Conduct Authority (“FCA”) announced in a public statement the date of extinction of Libor 3-months (term to which Suzano's contracts are linked) for June 30th, 2023. Considering the extinction of LIBOR over the next few years, the Company is evaluating its contracts with clauses that envisage the discontinuation of the interest rate. Most debt contracts linked to LIBOR have a clause to replace this rate with a reference index or equivalent interest rate and, for contracts that do not have a specific clause, a renegotiation will be carried out between the parties. Derivative contracts linked to LIBOR provide for a negotiation between the parties to define a new rate or an equivalent rate will be provided by the Calculation Agent.
The Company identified all of its contracts subject to LIBOR reform that have not yet been subject to the transition to an alternative reference rate and has already started contacting the respective counterparties of each contract to ensure that the best market practices will be adopted at the time of transition of the index, these terms are still under negotiation between the parties. We cannot predict how the (i) provisions relating to the discontinuation of LIBOR we have been including in our contracts, (ii) negotiations with other parties for definition of new applicable rates, or (iii) determination of an equivalent fee by a calculation agent will be implemented in practice, and can give no assurance that such implementation will not have a material effect on our financing costs.
A failure or interruption of our third-party suppliers’ or our information technology systems or automated machinery may impact or paralyze our business and negatively impact our operations. Our third-party suppliers’ and our information technology system may also be vulnerable to external actions such as cyber-attacks, which can have a negative impact on our operations, reputation, improper access of confidential information and disruption of our systems integrity as well as result in fines, obligations to clients or legal litigation and have an adverse effect on the results of our business.
Our operations are heavily reliant on information technology systems to efficiently manage business processes. Therefore, disruptions to these systems may impact or even paralyze our business and negatively impact our operations. In addition, we collect and store data, including proprietary business information, and may have access to confidential or personal information in certain of our businesses that is subject to privacy and security laws, regulations and customer-imposed controls. Moreover, any failure of our third-party suppliers’ or our systems related to confidential information, caused by external cyber-attacks or internal actions, including negligence and/or misconduct of our employees, can have a negative impact on our reputation against competitors and external agents (government, regulators, suppliers and others).
Our third-party suppliers’ and our information technology systems may be vulnerable to external actions such as natural disasters, viruses, cyber- attacks, and other security breaches. Any damage or interruption may cause a negative adverse effect on the results of our business, including fines, obligations to clients or legal litigation.
We and our third-party suppliers may be subject to breaches of automation systems causing partial and/or temporary shutdowns of operations and/or improper access to strategic information, in addition to change or loss of relevant data. Costs to address the vulnerability and/or problems mentioned may be significant and may temporarily affect our operations.
While these measures are designed to deterrent, prevent, detect, and respond to unauthorized activities in our systems, we cannot assure that these, or the procedures adopted by third- party suppliers, would be to protect us from certain types of attacks, which may have a material adverse effect on our business and reputation.
Furthermore, any changes to existing safety regulations may impose additional obligations on us and result in an increase in our expenses with respect to safety equipment and procedures. For instance, changes imposing a reduced workday for safety reasons may result in reduced productivity, forcing us to hire additional staff. Similarly, provisions requiring us to install or buy additional safety equipment could increase our labor-related costs and adversely affect our operating costs and results.
Any failure to adapt to or comply with recent Brazilian regulations on data privacy may adversely affect our results and reputation.
On August 15, 2018, the Brazilian General Data Protection Law (Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados – LGPD) came into force. The LGPD regulates the use of personal data in Brazil. The LGPD significantly transformed the data protection system in Brazil and is in line with recent European legislation (the General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR). The LGPD establishes detailed rules for the collection, use, processing and storage of personal data. It will affect all economic sectors, including the relationship between customers and suppliers of goods and services, employees and employers and other relationships in which personal data is collected, both in the digital and physical environment. Pursuant to the LGPD, security breaches that may result in significant risk or damage to personal data must be reported to the National Authority on Data Protection (Autoridade Nacional de Proteção de Dados – ANPD), the data protection regulatory body, within a reasonable time period. In light of the LGPD, our practices related to the treatment of personal data, including digital advertising, may undergo significant changes, generating additional costs to us due to the need to adapt such practices to the LGPD.
Failure to comply with the LGPD may result in formal warnings, public sanctions, the deletion of data, or the suspension of data processing activities. Furthermore, a company may be subject to a fine equal to up to 2% of its gross sales, or the gross sales of its economic group in Brazil, in the preceding fiscal year, excluding taxes, but limited to a total of R$50 million per violation. As a result, failure by us to adhere to the LGPD and any additional privacy laws or regulations enacted or approved in Brazil or in other jurisdictions in which we operate could adversely impact our business, financial condition or results of operations.
We cannot guarantee that our data protection program will be deemed sufficient by the ANPD to meet the provisions of the LGPD, nor that such program will prevent any failures in the protection of personal data processed by us, including with respect to cybersecurity incidents.
A downgrade in our credit ratings may increase our borrowing costs and/or restrict the availability of new capital or financings and have a material adverse effect on us.
The ratings address the likelihood, according to the respective evaluation methodology of each rating agency, of payment of our debt and obligations at their maturity. The ratings also address the timely payment of interest and other costs on each interest payment date. The assigned ratings to us may be raised, lowered or held constant depending, among other factors, on the rating agencies’ respective assessment of our financial strength or a change in methodology of credit assessment adopted by the credit risk agencies. We cannot assure you that our rating will remain for any given period of time or that the rating will not be lowered or withdrawn.
If our credit ratings are downgraded and the market were to perceive any such downgrade as a deterioration of our financial strength, our cost of borrowing would likely increase and our net income could decrease and our ability to obtain new financing may be adversely affected, all of which could have a material adverse effect on us.
In addition, credit rating is sensitive to any change in Brazilian sovereign credit ratings. The credit ratings of the Brazilian sovereign were downgraded in 2016 and 2018, and are no longer investment grade according to the methodologies of the major global rating agencies. Any further decrease in Brazilian sovereign credit ratings may have additional adverse consequences on our ability to obtain financing or our cost of financing and, consequently, on our results of operations and financial condition.
Unfavorable outcomes in litigation may negatively affect our results of operations, cash flows and financial condition.
In the ordinary course of our business dealings, we and our officers are, and may become, party to numerous tax, civil (including environmental) and labor disputes involving, among other remedies, significant monetary claims. An unfavorable outcome against us may result in our being required to pay substantial amounts of money, which could materially adversely affect our reputation, results of operations, cash flows and financial condition. Additionally, the amounts provisioned for legal proceedings may increase and existing provisions may become insufficient due to unfavorable outcomes in disputes against us. For more information on tax, civil (including environmental), labor and other proceedings, see Item 8. “Financial Information—Consolidated Statements and Other Financial Information—Legal and Administrative Proceedings.”
Changes in the credit risk of customers and suppliers to whom we have made advances, sales through credit lines or loans may adversely affect us.
In the markets in which we operate, it is typical, and often a condition for competitive participation, for pulp and paper producers to make advances to suppliers or to make sales to customers on credit. When we make advances, sales on credit or loans to our suppliers or customers, we assume their credit risk. Additionally, we assume additional risks when using debt instruments to make advances and sales on credit to our customers, such as credit letters. Therefore, changes in the macroeconomic environment or the market conditions under which our suppliers and our customers operate, in addition to problems related to the management of our suppliers and clients, may significantly affect their ability to make payments to us, directly impacting our assets and working capital.
These practices also expose us to the risk of a significant divergence between the rates under which we obtain financing from third parties and the rates that we grant to our customers and suppliers. We cannot assure you that we will always be able to match the terms under which we provide financing to our customers and suppliers with the terms of financing provided to us. Any increase in our customers’ and suppliers’ credit risk or divergence between their and our capital costs may materially adversely affect our shareholders’ equity and results of operations.
Social crisis in the relationship with communities and class entities, as well as, expropriation of any of our properties by the government affect the regular use, cause damage, or deprive us of the use of or fair value compensation of our properties.
Organized social movements in Brazil defend agrarian reform and the redistribution of property, with irregular occupations in rural areas being the best known form of action. Such occupations when in areas of the company may interrupt our forestry or industrial activities and, consequently, negatively affect our productive and operational results.
In addition to stoppages, land conflicts can cause a series of risks to the integrity of our employees who work in the field, possible damage to areas of high environmental value such as Permanent Preservation Areas and buffer zones of Environmental Conservation Units, in addition to reputational damage.
An alternative to this scenario is the negotiation with state governments or the federal government and social movements aiming to definitively solve occupations already installed, and to avoid new occupations. According to Brazilian law, governments can act directly on the expropriation of areas, as long as they are in legal and environmental compliance. If the Brazilian government expropriates any property used by us for developing our activities, the results of our operations may be adversely affected. Moreover, if a property owned by us is expropriated, our equity may be adversely affected because it is not possible to guarantee that the compensation paid by the government will be adequate to the losses borne by us. The risk associated with this alternative is that the financial compensation offered by the governments proves to be insufficient or until the compensation via public debt securities, which have limited liquidity, is forced.
Any changes in collective bargaining agreements or safety and outsourcing regulations could increase our labor-related costs or deteriorate labor relations with our employees, which could adversely affect us.
We depend on intensive use of labor in our activities. Most of our employees are represented by unions, and their employment contracts are regulated by collective bargaining agreements. New collective bargaining agreements may have shorter terms than our previous agreements, and, if we are not able to negotiate collective bargaining agreements on acceptable terms to us, we may be subject to a significant increase in labor costs, deterioration of employee relations, slowdowns or work stoppages, which could have a material adverse effect on us.
Additionally, changes in safety and outsourcing regulations may result in an increase in our labor-related costs. We may be considered secondarily liable for any employment obligations relating to such employees or a direct employment relationship may be established by the labor courts with the outsourced employees and us, according to the current regulation in force.
The introduction of a stricter legal framework regarding the use of outsourced employees or third-party subcontractors, and/or the imposition of additional obligations on the contractor of outsourced services, may increase our labor-related costs and may adversely affect our business and operations.
In accordance with existing labor laws and regulations, we are required to provide and ensure the proper use of safety equipment for our employees and other individuals working on our worksites. If we fail to provide all necessary safety equipment and ensure the proper use of the safety equipment, or if we work with companies that are not sufficiently committed to ensuring the safety of their own employees, we may be held liable for any accidents that take place at our worksites. Any accidents at our worksites may expose us to the payment of indemnifications, fines and penalties.
In addition, any changes to existing safety regulations may impose additional obligations on us and result in an increase in our expenses with respect to safety equipment and procedures. For instance, changes imposing a reduced workday for safety reasons may result in reduced productivity, forcing us to hire additional staff. Similarly, provisions requiring us to install or buy additional safety equipment could increase our labor-related costs and adversely affect our operating costs and results.
Our hedging activities may expose us to losses due to fluctuations in currency exchange rates or interest rates, which could have a material adverse effect on our results and financial condition.
We regularly enter into currency, interest rate, commodity price and inflation hedging transactions using financial derivatives instruments, such as future contracts, options and swaps, in accordance with our policies. We have traditionally used hedging transactions to, among others, (1) protect our revenue (which is primarily denominated in U.S. dollars) when converted to reais (our functional currency), (2) convert part of our debt which is denominated in reais into U.S. dollars, (3) swap floating interest rates of our debt to fixed interest rates, (4) swap floating monetary variation of our debt to fixed rate, and swap part of our IPCA indexed debt to CDI.
We account for our derivative instruments at fair value, in accordance with IFRS. The fair value of such instruments may increase or decrease due to fluctuations in currency exchange rates or interest rates, among others, prior to their settlement date. The recent devaluation of the real against the U.S. dollar has led to the increase of the negative fair value of such instruments. We may incur losses due to these market risk factors. Fluctuations may also result from changes in economic conditions, investor sentiment, monetary and fiscal policies, the liquidity of global markets, international and regional political events, acts of war, terrorism, among others.
In the event that we cease to undertake hedging transactions to the extent necessary, we may be exposed to currency exchange, interest rate and inflation risks, which could materially adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Delays in the expansion of our facilities, building new facilities or the ramp up of new or expanded facilities may increase our costs and adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
As part of our strategy, we may decide to expand our existing production facilities or build new production facilities. The expansion or construction of a production facility involves various risks, such as engineering, construction, operational systems, integration with the existing mill on brownfield projects, regulatory and other expected or unexpected significant challenges. These risks delay or prevent the successful operation of the project or significantly increase our costs. Our ability to complete successfully any expansion or new construction project subject to risks, including:
| • | we may either not be able to complete any expansion or new construction project on time or within the expected budget or be required by market conditions or other factors to delay the initiation of construction or the timetable to complete new projects or expansions, including adverse weather conditions, natural disasters, pandemics, fires, delays in supply, inputs or labor and accidents that impair or prevent the development of ongoing projects; |
| • | our new or modified facilities may not operate at designed capacity, ramp up its learning curve as planned or may cost more to operate than we expect; |
| • | we may not be able to sell our additional production at competitive prices; |
| • | we may not have cash, or be able to acquire financing, to implement our growth plans; |
| • | variations on exchange rate or product price may decrease significantly generated value by expansion project or new facilities; |
| • | climate changes could affect our forest base for new projects or brownfield, and significantly increase our wood cost; |
| • | we may have a negative impact on existing mills that can result on operational instability; |
Any of the above events could have a negative impact in our business and financial and operating results.
Our insurance coverage may be insufficient to cover our losses, especially in case of damage to our planted forests, which may cause a material adverse effect on our results and financial condition.
Our insurance coverage may be insufficient to cover losses to our forests, mills, dams, hydroelectric plants and other operating facilities caused by general third party liability for accidents, operational risks and international and domestic transportation if we suffer any catastrophic claim or if there is a particular clause excluding the coverage. In addition, we do not maintain insurance coverage against wars, unforeseeable fortuitous events, force majeure, interruption of certain activities, including due pandemics such as the current COVID-19 pandemic, as well as fire, thefts, pests, diseases, droughts and other risks to our forests. The incurrence of losses or other liabilities that are not covered by insurance, due to the limited extent of the insurance coverage, losses that exceed the limits of our insurance coverage or any other reason that prevents reimbursement or indemnification, could result in significant and unexpected additional costs, our ability to operate and/or shortage of wood supply, which may affect our production. Moreover, the terms and conditions for the renewal of our insurance policies may change in the future depending upon market circumstances and the type and amount of risks insured. See Item 4. “Information on the Company—Business Overview—Insurance.”
Risks Relating to Brazil
The Brazilian government has exercised, and continues to exercise, significant influence over the Brazilian economy. This influence, as well as Brazilian political and economic conditions, may materially and adversely affect us, our activities and the trading prices of our shares.
We conduct a substantial amount of our operations in Brazil, and we sell part of our products to customers in the Brazilian market. For the year ended December 31, 2020, 16.3% of our net revenues were derived from Brazil. Accordingly, our financial condition and results of operations are substantially dependent on economic conditions in Brazil. Future developments in the Brazilian economy may affect Brazil’s growth rates and, consequently, the consumption of our products. As a result, these developments could impair our business strategies, results of operations or financial condition.
The Brazilian economy has been characterized by frequent, and occasionally drastic, interventions by the Brazilian federal government, which have often changed monetary, credit and other policies to influence Brazil’s economy. The Brazilian federal government’s actions to control inflation and other policies have often involved wage and price controls, depreciation of the real, changes in tax policies, controls on remittances abroad, fluctuations of the Central Bank of Brazil’s base interest rate, as well as other measures. We have no control over, nor can we foresee, any measures or policies that the Brazilian federal government may adopt in the future. We may be materially adversely affected by changes in the policies of the Brazilian federal government, in addition to other general economic factors, including, without limitation:
| • | political, economic and social instability; |
| • | exchange rate fluctuations; |
| • | exchange controls and restrictions on remittances abroad; |
| • | tax policy and amendments to the tax legislation; |
| • | liquidity of domestic and foreign capital and lending markets; |
| • | government control of the production of our products; |
| • | restrictive environmental and real estate laws and regulations; and |
| • | other political, social and economic policies or developments in or affecting Brazil. |
Uncertainty as to whether the Brazilian federal government will implement changes in policy or regulations affecting these or other factors in the future may contribute to economic uncertainty in Brazil and to heightened volatility in the Brazilian securities markets and the securities issued by Brazilian companies, including us. Accordingly, such uncertainties and other future developments in the Brazilian economy nay adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operation, negatively impacting our available cash flows for payment, and the trading price of our common shares.
Changes in Brazilian fiscal policies and tax laws may adversely affect us.
The Brazilian federal government has indicated its willingness to implement a tax reform agenda, including to (i) revoke the income tax exemption over the distribution of dividends, which, if promulgated, would increase tax expenses associated with any dividends or distributions, and (ii) decrease import tax (which would increase competition and the role of international competitors), both of which could impact our ability to pay future dividends. Any purported tax reform or change in fiscal policies, if proposed and implemented, may also significantly impact our business. If there is a tax reform or any changes in applicable laws and regulations that alter the applicable taxes or tax incentives/special regimes, either during or after their terms of validity, our business and results may be directly or indirectly affected.
Indeed, the Brazilian federal government has frequently implemented, and may continue to implement, changes in its fiscal policies, including, but not limited to, changes to tax rates, fees, sectorial charges and occasionally the collection of temporary contributions. Some of these measures may result in tax hikes that may negatively affect our business. Increases in taxes could also materially adversely impact industry profitability and the prices of our services, restrict our ability to do business in our existing and target markets and cause our financial results to be negatively impacted. If we are unable to pass on the additional costs associated with such fiscal policy changes to our clients through the prices we charge for our services, we may be adversely affected.
Uncertainty over whether the acting Brazilian federal government will implement changes in policy or regulation affecting these or other factors in the future may contribute to economic uncertainty in Brazil and to heightened volatility in the securities issued abroad by Brazilian companies.
Significant fluctuations in the exchange rate of the real against the value of the U.S. dollar may adversely affect our business, financial conditions or results of operations.
Our export revenues are directly affected by exchange rate variation. Depreciation of the real against the U.S. dollar will increase such revenues when denominated in reais, while appreciation of the real against the U.S. dollar will decrease such export revenues. Our revenues in the domestic market are also affected by exchange rate fluctuation, to the extent that imported products quoted in U.S. dollars become more or less competitive in the domestic market depending on the exchange rate variation.
Furthermore, some of our costs and operating expenses are also affected by fluctuations in the value of the real against the U.S. dollar, including export insurance, freight costs and the cost of certain chemicals we use as raw materials. Depreciation of the real against the U.S. dollar will increase such costs, while appreciation of the real against the U.S. dollar will reduce these costs.
Additionally, we may be adversely affected by depreciation of the real against the U.S. dollar, since a significant portion of our debt is expressed in U.S. dollars. Depreciation or appreciation of the real against the U.S. dollar may increase or decrease, as applicable, our financial expenses arising from these debt and other obligations in U.S. dollars, as well as adversely affect our ability to comply with certain covenants under financing agreements, which require us to maintain specific financial ratios. On the other hand, a significant appreciation of the real against the U.S. dollar or an appreciation during an extended period of time may significantly affect our cost structure and negatively affect our competitiveness in export markets.
As a result of inflationary pressures in recent years, the Brazilian real has been periodically devalued in relation to the U.S. dollar and other foreign currencies. The Brazilian federal government has in the past implemented various economic plans and utilized a number of exchange rate policies, including sudden devaluations, periodic mini-devaluations during which the frequency of adjustments has ranged from daily to monthly, floating exchange rate systems, exchange controls and dual exchange rate markets. From time to time, there have been significant fluctuations in the exchange rate between the Brazilian real, the U.S. dollar and other currencies. There can be no assurance that the real will not depreciate or be devalued again against the U.S. dollar or against any other foreign currency.
Devaluations of the real relative to the U.S. dollar could create additional inflationary pressures in Brazil, lead to increases in interest rates, further limit our access to foreign financial markets and prompt the adoption of recessionary policies by the Brazilian federal government. Conversely, the depreciation of the real against the U.S. dollar may lead to a further deterioration of Brazil’s current account and balance of payments and cause a decrease in Brazilian exports. Any of the foregoing developments may negatively affect the Brazilian economy as a whole, and, consequently, our results. In recent years, the Central Bank of Brazil has occasionally intervened to control unstable movements in the foreign exchange rate. We cannot predict whether the Central Bank of Brazil will continue to let the real float freely. Accordingly, it is not possible to predict what impact the Brazilian federal government’s exchange rate policies may have on us. We cannot assure that in the future the Brazilian federal government will not impose a currency band within which the real U.S. dollar-real exchange rate could fluctuate or set fixed exchange rates, nor can we predict what impact such an event might have on our business, financial position or operating results.
Economic and market conditions in other countries, including in the United States and emerging market countries, may materially and adversely affect the Brazilian economy and, therefore, our financial condition.
The market for securities issued by Brazilian companies is influenced by economic and market conditions in Brazil, and, to varying degrees, market conditions in other countries, whether emerging market countries or not. Although economic conditions are different in each country, the reaction of investors to developments in one country may cause the domestic or international capital markets prices to fluctuate. Developments or conditions in other countries, including non-recurrent events such as US-China trade war, have at times significantly affected the availability of credit in the Brazilian economy and resulted in considerable outflows of funds and reductions in the amount of foreign currency invested in Brazil, as well as limited access to international capital markets, all of which may materially and adversely affect our ability to borrow funds at an acceptable interest rate or to raise equity capital when and if we should have such a need.
Additionally, we depend on third-party financing to carry out our activities, especially to finance our capital expenditures and working capital. In circumstances of limited liquidity, credit availability may be scarce, expensive or nonexistent, and we may face difficulties in our regular activities and in honoring our financial commitments.
Risks Relating to Our Shares and ADSs
Exchange controls and restrictions on remittances abroad may adversely affect holders of ADSs.
Brazilian laws provide that whenever a serious imbalance in Brazil’s balance of payments exists or is anticipated, the Brazilian federal government may impose temporary restrictions on the repatriation by foreign investors of the proceeds of their investment in Brazil and on the conversion of Brazilian currency into foreign currency. For example, for six months in 1989 and early 1990, the Brazilian federal government restricted all fund transfers that were owed to foreign equity investors and held by the Central Bank of Brazil, in order to preserve Brazil’s foreign currency reserves. These amounts were subsequently released in accordance with Brazilian federal government directives. Although the Brazilian federal government has never exercised such a prerogative since, we cannot guarantee that the Brazilian federal government will not take similar actions in the future.
You may be adversely affected if the Brazilian federal government imposes restrictions on the remittance to foreign investors of the proceeds of their investments in Brazil and, as it has done in the past, on the conversion of the real into foreign currencies. These restrictions could hinder or prevent the conversion of dividends, distributions or the proceeds from any sale of shares, as the case may be, into U.S. dollars and the remittance of U.S. dollars abroad. We cannot assure that the government will not take this measure or similar measures in the future. Holders of ADSs could be adversely affected by delays in, or a refusal to grant, any required governmental approval for conversion of real payments and remittances abroad in respect of the shares, including the shares underlying the ADSs. In such a case, the ADS depositary will distribute reais or hold the reais it cannot convert for the account of the ADS holders who have not been paid.
Holders of ADSs may face difficulties in serving process on or enforcing judgments against us and other persons, as well as may face difficulties in protecting their interests because we are subject to different corporate rules and regulations than a U.S. company.
We are organized under and are subject to the laws of Brazil and all our directors and executive officers and our independent registered public accounting firm reside or are based in Brazil. Substantially all of our assets and those of these other persons are located in Brazil. Moreover, our corporate affairs are governed by our bylaws and Brazilian Corporate Law, which differ from the legal principles that would apply if we were incorporated in a jurisdiction in the United States or elsewhere outside Brazil. In addition, the rights of an ADS holder, which are derivative of the rights of holders of our common shares, to protect their interests are different under Brazilian Corporate Law than under the laws of other jurisdictions. Rules against insider trading and self-dealing and the preservation of shareholder interests may also be different in Brazil than in the United States. Furthermore, the structure of a class action in Brazil is different from that in the US, and under Brazilian law, shareholders in Brazilian companies do not have standing to bring a class action, and under our by-laws must, generally with respect to disputes concerning rules regarding the operation of the capital markets, arbitrate any such disputes.
As a result, it may not be possible for holders of the ADSs to effect service of process upon us or these other persons within the United States or other jurisdictions outside Brazil or to enforce against us or these other persons judgments obtained in the United States or other jurisdictions outside Brazil. Because judgments of U.S. courts for civil liabilities based upon the U.S. federal securities laws may only be enforced in Brazil if certain conditions are met, the ADS holders may face greater difficulties in protecting their interests due to actions by us, our directors or executive officers than would shareholders of a U.S. corporation.
The relative volatility and lack of liquidity of the markets for our securities may adversely affect holders of our shares and the ADSs.
Investments in securities, such as our common shares or ADSs, of issuers from emerging market countries, including Brazil, involve a higher degree of risk than investments in securities of issuers from more developed countries. The Brazilian securities market is substantially smaller, less liquid, more concentrated and more volatile than major securities markets in the United States and other jurisdictions, and may be regulated differently from the ways familiar to U.S. investors. There is also significantly greater concentration in the Brazilian securities market than in major securities markets in the United States. These features may substantially limit the ability to sell our shares, including our shares underlying the ADSs, at a price and time at which holders wish to do so and, as a result, could negatively impact the market price of these securities.
In addition, although our public float represented 53.4% (excluding Treasury Shares) of our total capital float as of December 31, 2020, only 3.1% were represented by ADSs. Moreover, our controlling shareholders (including related parties and management) hold 45.8% of our stock. Any potential sale by these shareholders could adversely affect the market price of our securities.
Holders of ADSs may find it difficult to exercise voting rights at our shareholders’ meetings.
Holders of ADSs do not have the same voting rights as holders of our shares. Holders of ADSs will not be our direct shareholders and will be unable to enforce directly the rights of shareholders under our bylaws and Brazilian Corporate Law, they are entitled to the contractual rights set forth for their benefit under the deposit agreement. Holders of ADSs will face practical limitations in exercising their voting rights because of the additional steps involved in our communications with ADS holders. For example, we are required to publish a notice of our shareholders’ meetings in specified newspapers in Brazil. Holders of our shares will be able to exercise their voting rights by attending a shareholders’ meeting in person or voting by proxy. By contrast, ADS holders will receive notice of a shareholders’ meeting by mail from The Bank of New York Mellon, as our depositary, following our notice to the depositary requesting the depository to do so. To exercise their voting rights, ADSs holders have to provide instructions to the depositary on a timely basis on how they wish to vote. In practice, the ability of a holder of ADSs to instruct the depositary as to voting will depend on the timing and procedures for providing instructions to the depositary, either directly or through the holder’s custodian and clearing system and this voting process necessarily will take longer for holders of ADSs than for holders of our shares.
Holders of ADSs also may not receive the voting materials in time to instruct the depositary to vote the shares underlying their ADSs. In addition, the depositary and its agents are not responsible for failing to carry out voting instructions of the holders of ADSs or for the manner of carrying out those voting instructions. Accordingly, holders of ADSs may not be able to exercise voting rights, and they will have little, if any, recourse if the units underlying their ADSs are not voted as requested.
If holders of ADSs exchange their ADSs for underlying shares, they risk losing the ability to timely remit foreign currency abroad and other related advantages.
The ADSs benefit from the certificate of foreign capital registration, which permits our depositary to convert dividends and other distributions with respect to common shares into foreign currency, and to remit the proceeds abroad. The conversion of ADSs directly into ownership of the underlying shares is governed by CMN Resolution No. 4,373/2014, and foreign investors who intend to proceed with such conversion are required to appoint a representative in Brazil for purposes of Annex I of CMN Resolution No. 4,373/2014, who will be in charge of keeping and updating the investors’ certificates of registrations with the Central Bank of Brazil, which entitles registered foreign investors to buy and sell directly on the B3. These arrangements may require additional expenses from the foreign investor. Moreover, if such representatives fail to obtain or update the relevant certificates of registration, investors may incur additional expenses or be subject to operational delays which could affect their ability to receive dividends or distributions relating to the shares or the return of their capital in a timely manner.
If holders of ADSs do not qualify under CMN Resolution No. 4,373/2014, they will generally be subject to less favorable tax treatment on distributions with respect to our common shares. There can be no assurance that the certificate of registration of our depositary, or any certificate of foreign capital registration obtained by holders of ADSs, will not be affected by future legislative or regulatory changes, or that additional Brazilian law restrictions applicable to their investment in the ADSs may not be imposed in the future.
Holders of our shares will be subject to, and holders of the ADSs could be subject to, Brazilian income tax on capital gains from sales of shares or ADSs. Brazilian Law No. 10,833/03 provides that gains on the disposition of assets located in Brazil by non-residents of Brazil, whether to other non- residents or to Brazilian residents, will be subject to Brazilian taxation. Our shares are expected to be treated as assets located in Brazil for purposes of the law, and gains on the disposition of our shares, even by non-residents of Brazil, are expected to be subject to Brazilian taxation. In addition, the ADSs may be treated as assets located in Brazil for purposes of the law, and therefore gains on the disposition of the ADSs by non-residents of Brazil may be subject to Brazilian taxation. Although the holders of ADSs outside Brazil may have grounds to assert that Law No. 10,833/00 does not apply to sales or other dispositions of ADSs, it is not possible to predict whether that understanding will ultimately prevail in the courts of Brazil given the general and unclear scope of Law No. 10,833/03 and the absence of judicial court rulings in respect thereof.
Holders of ADSs may be unable to exercise the preemptive rights relating to our shares underlying the ADSs.
Holders of ADSs may not be able to exercise the preemptive rights relating to our shares underlying their ADSs unless a registration statement under the Securities Act, is effective with respect to the rights or an exemption from the registration requirements of the Securities Act is available. We are not obligated to file a registration statement with respect to the shares or other securities relating to these preemptive rights, and we cannot assure holders of ADSs that we will file any such registration statement. Unless we file a registration statement or an exemption from registration applies, holders of ADSs may receive only the net proceeds from the sale of their preemptive rights by the depositary or, if the preemptive rights cannot be sold, the rights will be allowed to lapse.
We may issue new shares, including in the form of ADSs, which may result in a dilution of our current shareholders’ stake.
We may seek to raise additional capital in the future through public or private issuances of shares or securities convertible into shares. According to article 172 of Brazilian Corporation Law, we may not be required to grant preemptive rights to our shareholders in the event of a capital increase through a public offering of shares or securities convertible into shares, which may result in a dilution of our current shareholders’ stake in our company.
The holders of our shares (including our shares underlying the ADSs) may not receive dividends or interest on net equity.
According to our bylaws, our shareholders are entitled to receive a mandatory minimum annual dividend of the lower of (i) 25% of our annual net profit, calculated and adjusted under the terms of the Brazilian Corporation Law, or (ii) 10% of our operating cash generation in the corresponding fiscal period, which is calculated by subtracting the amount of the investments in maintenance of the respective fiscal year from the Adjusted EBITDA, as defined in our bylaws. Our bylaws allow for the payment of interim dividends, to the retained earnings account or the existing earnings reserves in the last yearly or six- month balance, by means of the annual dividend. We may also pay interest on net equity, as described by Brazilian law. The interim dividends and the interest on net equity declared in each fiscal year may be imputed as the mandatory dividend that results from the fiscal year in which they are distributed. At the general shareholders meeting, shareholders may decide on the capitalization, on the offset of our losses or on the net income retention, as provided for in the Brazilian Corporation Law, with the aforementioned net income not being made available for the payment of dividends or interest on own capital. Additionally, Brazilian Corporate Law allows a publicly traded company, like ours, to suspend the mandatory distribution of dividends and interest on net equity in any particular year if our board of directors informs our shareholders that such distribution would be inadvisable in view of our financial condition or cash availability.
Our management is strongly influenced by our controlling shareholders and their interests may conflict with the interests of our other shareholders.
Our controlling shareholders have the power to, among other things, appoint a majority of the members of our board of directors and to decide any matters requiring shareholder approval, including related-party transactions, corporate reorganizations and disposals, and the timing and payment of any future dividends, subject to the requirements of mandatory dividends under the Brazilian Corporation Law.
Our controlling shareholders may have an interest in making acquisitions, disposals of assets, partnerships, seeking financing or making other decisions that may conflict with the interests of the other shareholders.
Additionally, any of our controlling shareholders may opt to sell significant part or the totality of their respective equity to third parties. In case we cease to have controlling shareholders, the remaining shareholders may no longer have the right to the same protection granted by the Brazilian Corporation Law against the abuses practiced by other shareholders and, as consequence, they may face difficulty in the compensation for damages suffered.
Any unexpected change in our management, in our business strategy and policies, tentative of control acquisition or any dispute among shareholders regarding their rights, may adversely affect our business and operational results.
In case a group of shareholders arises acting together or bounded by a voting agreement, and such group cause to hold the decision control, we may suffer unexpected changes in our business strategy and policies, including through the mechanism of the replacement of the board of directors and statutory offices. In addition, we may turn more vulnerable to hostile takeovers attempts and conflicts arising from such attempts.
Judgments of Brazilian courts with respect to our shares and the ADSs will be payable only in reais
Our bylaws provide that we, our shareholders, our directors and officers and the members of our fiscal council shall submit to arbitration any and all disputes or controversies that may arise amongst ourselves relating to, or originating from, the application, validity, effectiveness, interpretation, violations and effects of violations of the provisions of Brazilian Corporate Law, our bylaws, the rules and regulations of the CMN, the Brazilian Central Bank and the CVM, as well as other rules and regulations applicable to the Brazilian capital markets and the rules and regulations of the Arbitration Regulation of the Market Arbitration Chamber. However, in specific situations, including whenever precautionary motions are needed for protection of rights, the dispute or controversy may have to be brought to a Brazilian court. If proceedings are brought in the courts of Brazil seeking to enforce our obligations in respect of our shares or the ADSs, we will not be required to discharge our obligations in a currency other than reais. Under Brazilian exchange control limitations, an obligation in Brazil to pay amounts denominated in a currency other than reais may only be satisfied in Brazilian currency at the exchange rate, as determined by the Central Bank of Brazil, in effect on the date the judgment is obtained, and such amounts are then adjusted to reflect exchange rate variations through the effective payment date. The then-prevailing exchange rate may not afford non-Brazilian investors with full compensation for any claim arising out of or related to our obligations under our shares and ADSs.
As a foreign private issuer, we have different disclosure and other requirements than U.S. domestic registrants.
As a foreign private issuer, we may be subject to different disclosure and other requirements than domestic U.S. registrants. For example, as a foreign private issuer, in the United States, we are not subject to the same disclosure requirements as a domestic U.S. registrant under the Exchange Act, including the requirements to prepare and issue quarterly reports on Form 10-Q or to file current reports on Form 8-K upon the occurrence of specified significant events, the proxy rules applicable to domestic U.S. registrants under Section 14 of the Exchange Act or the insider reporting and short swing profit rules applicable to domestic U.S. registrants under Section 16 of the Exchange Act. In addition, we rely on exemptions from certain U.S. rules which will permit us to follow Brazilian legal requirements rather than certain of the requirements that are applicable to U.S. domestic registrants.
Furthermore, foreign private issuers are required to file their annual report on Form 20-F within 120 days following the end of each fiscal year, while U.S. domestic issuers that are accelerated filers are required to file their annual report on Form 10-K within 75 days following the end of each fiscal year. As a result of the above, even though, following the declaration of effectiveness of the registration to which this prospectus is attached, we will be required to make submissions on Form 6-K disclosing the information that we have made or are required to make public pursuant to Brazilian law, or are required to distribute to shareholders generally, and that is material to us, you may not receive information of the same type or amount that is required to be disclosed to shareholders of a U.S. company.
ITEM 4. INFORMATION ON THE COMPANY
A. History and Development of the Company
We, Suzano S.A., were incorporated as a corporation on December 8, 1987 under the laws of Brazil. We have the legal status of a sociedade por ações, or a stock corporation, under the Brazilian Corporation Law. Our principal place of business is located at Avenida Brigadeiro Faria Lima, 1355, 7th floor, São Paulo, SP, 01452-919, Brazil (telephone: +55 11 3503-9000). Our shares are traded on the special listing segment of the B3 (Brasil, Bolsa, Balcão), which provides for the highest level of corporate governance in the Brazilian market, and our ADSs are traded on the New York Stock Exchange.
We are subject to reporting requirements under the Exchange Act and are required to file with the SEC, or furnish to the SEC, reports and other information. The SEC maintains a website at www.sec.gov that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding registrants that make electronic filings with the SEC using its EDGAR system. We also make available on our website’s investor relations page, free of charge, our annual report and the text of our reports on Form 6-K, including any amendments to these reports, as well as certain other SEC filings, as soon as reasonably practicable after they are electronically filed with or furnished to the SEC. Our website address is http://ir.suzano.com.br, and investor information can be found therein under the caption “Investor Relations.” Information contained on our website is, however, not incorporated by reference in, and should not be considered a part of this annual report.
Our activities began in 1924, when Leon Feffer, our founder, first entered the paper business to resell national and imported paper used for business cards, writing pads and stationery. In the late 1930s, with the purchase of its first machine, the Suzano Group began to produce its own paper. In the 1950s, Companhia Suzano was formed, becoming what we believe to be the first global industrial-scale producer of eucalyptus pulp. In the mid-1960s, Companhia Suzano became the first paper producer to use 100% eucalyptus pulp in the production of printing and writing paper, according to “The History of the Pulp and Paper Industry in Brazil” (“A História da Indústria de Celulose e Papel no Brasil”), published by the Brazilian Technical Association of Paper and Pulp (Associação Brasileira Técnica de Papel e Celulose), or the ABTCP, in 2004.
On December 8, 1987, we were incorporated under the name Bahia Sul Celulose S.A., or Bahia Sul, as a joint venture between Companhia Vale do Rio Doce – CVRD (currently Vale S.A.), or Vale, and Companhia Suzano. In 2001, Companhia Suzano acquired all of the shares of Bahia Sul that were previously held by Vale, increasing its ownership interest to 100% of our voting stock and 73% of our total stock. In 2002, Companhia Suzano held an exchange offer of preferred shares without voting rights issued by Bahia Sul for new preferred shares without voting rights issued by us, in order to acquire all outstanding preferred shares of Bahia Sul. Upon completion of the exchange offer, Companhia Suzano’s share in Bahia Sul’s capital stock increased to 93.9%.
In 2004, Companhia Suzano merged into Bahia Sul, with the resulting entity named Suzano Bahia Sul Papel e Celulose S.A. In the same year, we listed our shares on the Level 1 segment of the BM&FBOVESPA (former name of B3), thus guaranteeing transparency in our operations and accountability to our shareholders. In July 2006, our corporate name was changed to our former name, Suzano Papel e Celulose S.A.
In 2012, we completed a R$1.5 billion capital increase through a public offering of new shares in the market. The proceeds of the capital increase were used, in part, to finance the construction of our new pulp production unit in the state of Maranhão, which began operations in March 2013.
In 2015, we announced a new three-pillar business strategy: structural competitiveness, adjacent businesses and reshaping the industry. As part of our structural competitiveness strategy, we announced investments to modernize and increase the capacity of our mills and to increase and locate the forest base closer to our mills. In addition to an expected increase in total production capacity, we believe that these projects have been contributing to an approach focused on cost structure optimization. Our adjacent businesses strategy seeks new uses of our asset base and diversification of our products. In 2015, we commenced the production of fluff pulp and announced investments in lignin and the tissue segment. As part of our strategy to reshape the industry, we explore new paths and seek opportunities for reducing our business exposure to market volatility.
In September 2017, we approved the admission of our shares for trading on the listing segment called Novo Mercado of B3, followed by the conversion of the preferred shares issued by us into common shares at the ratio of one preferred share, class “A” or class “B”, for one common share. In addition, we also approved the restatement of our bylaws to adapt them to Novo Mercado rules and a change of our methodology to calculate mandatory dividends, also reflecting best corporate governance practices. We concluded the migration to Novo Mercado segment of B3 in November 2017.
On March 15, 2018, each of Suzano Holding S.A., David Feffer, Daniel Feffer, Jorge Feffer and Ruben Feffer, on one hand, and Votorantim and BNDESPAR, on the other hand, along with Suzano, as intervening party, entered into a voting agreement (Compromisso de Voto e Assunção de Obrigações) (the “Voting Agreement”), pursuant to which the parties agreed on the terms and conditions of a merger of shares (incorporação de ações) of Fibria Celulose S.A. (“Fibria”) and Suzano (the “Merger”), and agreed to exercise their respective voting rights in favor of the Merger. On July 26, 2018, Suzano and Fibria entered into a merger agreement (the “Merger Agreement”), substantially in the form attached to the Voting Agreement, for the combination of the operations and shareholder bases of Fibria and Suzano through a corporate reorganization.
On December 10, 2018, we started trading our Level II ADRs, in accordance with the program approved by the CVM. The Bank of New York Mellon is acting as our depositary bank in the United States, responsible for issuing the respective depositary shares, at the ratio of one ADS for each two common shares. The ADR Program did not require any capital increase or issue of new shares. Its goal is to expand access by foreign investors to our company and increase our stock’s liquidity.
On January 14, 2019, following receipt of all required corporate and regulatory approvals, the Merger was consummated, and Fibria became our wholly owned subsidiary. On such date, holders of all of the issued and outstanding shares and ADSs of Fibria at the record date set in accordance with the Merger Agreement, received shares and ADSs of our company, plus an amount of cash per share of Fibria (R$50.20) calculated pursuant to the Merger Agreement. Upon completion of the Merger, we became the world’s largest producer of market pulp, with an aggregate installed capacity of 10.9 million metric tons of eucalyptus pulp per year and a broad and diversified forest base. Furthermore, on April 1, 2019, Fibria merged with and into Suzano. As a result, the separate corporate existence of Fibria ceased, and Suzano continued as the surviving entity under the laws of Brazil. Accordingly, title to and possession of all property, interests, assets, rights, privileges, immunities, powers and franchises of Fibria vested in Suzano and all debt, liabilities, duties and obligations of Fibria became debt, liabilities, duties and obligations of Suzano.
On April 1, 2019, our shareholders approved our name change from Suzano Papel e Celulose S.A. to Suzano S.A. at our extraordinary shareholders’ meeting. The change of our name was approved by the CVM on April 18, 2019 and became effective with retroactive effect to the date of approval by our shareholders.
On October 6, 2020, BNDES Participações SA – BNDESPAR concluded the public offering for the secondary sale of its 150,217,425 shares held in Suzano, including 13,180,000 Shares in the form of American Depositary Shares , at a price per share of R$46.00, totaling R$6.9 billion, and ceased to be a shareholder.
B. Business Overview
Industry
Pulp can be either recycled or virgin pulp. Recycled pulp is made from used materials, such as printing and writing papers, newsprint, packaging and other types of carton board, and then processed by chemicals in order to remove printing inks and other elements. Virgin pulp can be manufactured from a number of raw materials, such as wood, bagasse and bamboo, and it is classified based on the type of wood or fiber derived from the corresponding raw material as well as the processing system used and whether the pulp will be bleached. Bleached pulp is used for several purposes, including printing and writing, specialty, packaging paperboard and tissue papers. Unbleached pulp has a brown color and is used in the production of packages, corrugated board, paperboard, packaging papers, bags and tissue.
The most common raw material that we use to produce paper is wood pulp. Different tree species yield different fiber characteristics and, consequently, different paper attributes such as strength, softness and opacity.
There are two types of wood pulp: hardwood pulp and softwood pulp. Hardwood pulp is produced using hardwood trees, such as eucalyptus, aspen, birch, acacia, maple, oaks, beech trees and poplars, which have shorter fibers. Short fiber is generally best suited for the manufacture of products that require smoothness, brightness, uniformity an absorption properties, such as coated and uncoated printing and writing paper, tissue paper, specialty papers as image paper and décor laminate paper as well as packaging paperboard. Softwood pulp is produced using softwood trees (e.g. pine, spruce and fir) and is generally best suited for the manufacture of products that require greater durability and strength, such as kraftliner, newsprint, catalogues, boards, lightweight coated paper and tissue. However, paper producers may also substitute fibers used in the paper manufacturing process according to market availability by applying further processing, as refining mechanical treatment. The substitution depends on the raw materials and equipment available and the specifications of the final product.
Pulp can be produced by integrated paper producers or by market pulp producers who sell the pulp to nonintegrated or semi-integrated paper producers. In 2019, approximately 38% of global pulp virgin fiber production was “market pulp” (Hawkins Wright – The Outlook for Market Pulp (August 2020)); that is, pulp sold by pulp mills and bought by paper mills. We produce pulp for our own paper production (integrated pulp) and to sell to other papermakers (market pulp). We produce only hardwood pulp from our renewable forests of planted eucalyptus trees. Eucalyptus pulp is widely accepted among producers of printing and writing paper, specialty papers and tissue papers worldwide because of its properties and cash production cost, and it has represented an increasing percentage of the world production of hardwood pulp. Eucalyptus trees in Brazil have a shorter growth cycle than other hardwood trees (approximately seven years in Brazil) and higher yield per planted hectare.
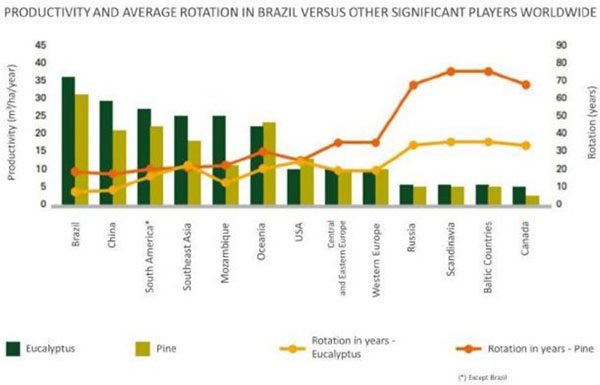
Source: IBÁ (Brazilian Tree Industry - Indústria Brasileira de Árvores) – Annual Report 2019.
Brazil’s competitive advantage is driven by the fact that Brazil has the fastest tree growth rates in the world and the highest productivity rate. Thus, we believe that we are among Brazilian pulp producers that have the lowest production cost in the global market.
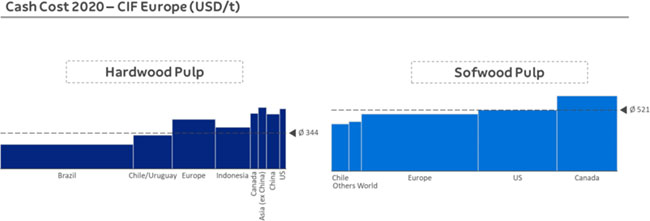
Source: Hawkins Wright, 2020.
The key drivers of global virgin pulp demand growth are packaging, tissue and special paper. These grades presented a production compound annual growth rate (“CAGR”) from 2009 to 2020 of 1.6%, 3.4% and 1.2% respectively, according to AFRY.
Paper consumption in China has been the main driver of demand growth over the past years. According to PPPC, global demand for pulp (including softwood pulp and hardwood pulp) and for tissue is expected to continue increasing in the following years.

Source: Pulp and Paper Products Council – PPPC S&D (2020).

Source: Pulp and Paper Products Council – PPPC S&D (2020).
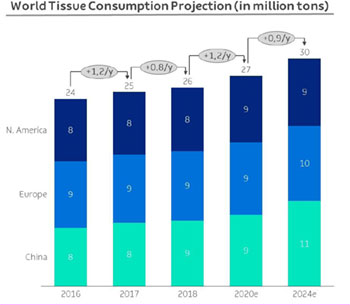
Source: Pulp and Paper Products Council – PPPC (2020).
According to Hawkins Wright, in 2020, we were among the top 10 market pulp producers in terms of capacity, with a combined 14% market share of chemical market pulp capacity. Globally, there is no major project confirmed to increase capacity of chemical market pulp until 2021, and thus, nominal capacity increased slightly during 2020 in light of residual ramp-up and debottlenecking projects.

Source: Hawkins Wright, 2020.
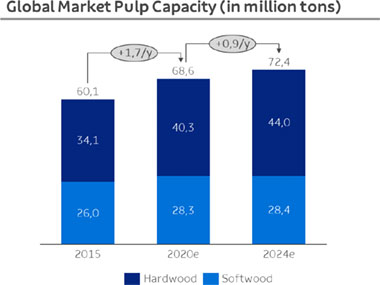
Source: Pulp and Paper Products Council – PPPC S&D (2020).
Our Company
With more than 90 years of experience, we operate mainly in the pulp (paper grade and fluff) and paper (paperboard, printing and writing and tissue) segments. We believe that we are one of the largest vertically integrated producers of pulp and paper in Latin America and, according to Hawkins Wright, we were the largest producer of eucalypt pulp in the world and virgin market pulp in the world in 2020. As other Brazilian eucalyptus pulp producers, we have the lowest cost of pulp production in the world. We believe our modern technology of plantation and harvesting and our strategic location for plantation facilities are among our competitive strengths.
We believe we are one of Brazil’s largest paper producers, and based on data from IBÁ, we accounted for nearly 40% of the printing and writing paper and 25% of the paperboard produced in Brazil in 2020.
Our structure includes administrative offices in Salvador and São Paulo, two integrated pulp and paper production facilities in the state of São Paulo (Suzano and Limeira units), a non-integrated paper production facility in the state of São Paulo (Rio Verde unit), an integrated pulp, paper and tissue facility in the state of Bahia (Mucuri unit), an integrated pulp and tissue facility in the state of Maranhão (Imperatriz unit), two paper facilities in the states of Pará and Ceará (Facepa), and FuturaGene, a biotechnology research and development unit. We own one of the largest distribution structures for paper and graphic products in South America. Following the Merger, we also own pulp production facilities in the state of Espírito Santo (Aracruz unit), in the state of São Paulo state (Jacareí Unit), one unit with two production lines in Três Lagoas (in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul) and 50% equity participation in Veracel together with Stora Enso, an industrial unit located in Eunápolis (in the state of Bahia). On December 31, 2020, subsidiaries Facepa, and FuturaGene Brasil Tecnologia Ltda. were merged into Suzano.
Our eucalyptus pulp production satisfies 100% of our requirements for paper production, and we sell the remaining production as market pulp. As of December 31, 2020, our total eucalyptus pulp installed production capacity was 11.9 million tons per year, and our total production volume was 10.8 million tons, of which 9.8 million tons were produced as market pulp and the remainder was used for the production of 1.2 million tons of paper and paperboard.
The scale of our production capacity, the proximity of our planted forests to our mills and the integration of our pulp and paper production process allow us to benefit from substantial economies of scale and low production costs.
Our Limeira, Suzano, Rio Verde and Jacareí mills are located near the city of São Paulo, the largest consumer market in Brazil according to data from IBÁ and RISI. These mills are located approximately 90 km from the port of Santos, an important export hub, and approximately 190 km from our planted forests. They can supply both domestic and international markets in a competitive manner.
Our Mucuri and Aracruz units are focused primarily on export markets. Mucuri is located approximately 250 km from Portocel, a port specialized in exporting pulp located in the state of Espírito Santo, in which Suzano holds a 51% stake, while Aracruz is located only 3 km from Portocel.
The Imperatriz unit, in Maranhão, is also focused primarily on export markets. Its gateway for the external market is the Port of Itaqui, 600 km far from Imperatriz. Exports are carried from our mill to the ports by train, which allows for very competitive transportation costs.
The Três Lagoas unit, in Mato Grosso do Sul, is focused on export markets, and most of its volume is transported by train to the Port of Santos, where all exporting volumes are shipped. The relatively short distances between our planted forests, our mills and most of our Brazilian customers or export facilities provide us with relatively low transportation costs.
Pulp and Paper
We produce a variety of eucalyptus pulp and paper products, including pulp used in our paper production processes, as well as market pulp. We sell pulp to the Brazilian market and to the export market. We produce coated and uncoated printing and writing paper, paperboard, tissue paper, market pulp and fluff pulp. Within the printing and writing paper category, we produce products of different sizes and shapes, such as cut paper for general purposes (cut-size), folio size and reels. Our sales are not concentrated in any specific customer, in either the Brazilian or the export markets. For the year ended December 31, 2020, no single customer accounted for more than 10.0% of our consolidated net sales revenue.
Pulp and Paper Production Process
Our production process comprises the three main stages: (i) planting and harvesting forests; (ii) pulp manufacturing; and (iii) paper manufacturing. Consistent with our strategy of conducting our business in accordance with the highest environmental standards, we use plantation and harvesting techniques that are environmentally friendly and sustainable, such as minimum-impact cultivation and soil preparation techniques that avoid erosion, maintain soil fertility along generations and promote high levels of efficiency and productivity.
Planting and Harvesting Forests
The development of our planted forests starts in our nurseries, where we use the most modern cloning technology available, and in third-party nurseries that use our genetic materials. The saplings we produce in our nurseries are a variety of eucalyptus that increases the production of pulp and are well suited for the climate and other geographic aspects of the micro-regions in which they will be planted. A harvester is used to cut, de-limb and de-bark the trees, and to cut them into logs. Part of the bark and leaves of the harvested trees is left in the planted forests. A forwarder carries the logs to the edge of the planting area, where a loader loads the logs onto a truck for transportation to the mill.
The management of our forests is the base that sustains our business, based on the planting and management of renewable forests, targeting of a competitive supply of wood through long-term planning and development and application of genetic improvements. As of December 31, 2020, we owned or leased approximately 2.5 million hectares of land, of which approximately 1.3 million hectares were used for eucalyptus cultivation and 1 million for forestry reserves, ensuring compliance with Brazilian law that determines the percentage of area required for legal and permanent preservation reserves, located mainly along the rivers. Remaining 0.2 million hectares are related to other uses such as roads. Our production units are in compliance with or exceed environmental standards – both Brazilian and international – for the production of pulp and paper.
Given the high degree of integration between the production of pulp and paper, we have a low conversion cost of pulp to paper.
Several factors account for our competitive advantage with regard to the cost of wood for the production of pulp: favorable topographic, climate and soil conditions in the regions of Brazil where we operate; advanced genetic improvement and harvesting technology; low average distances between our planted forests and mills, which are among the shortest in the world; our clone selection system, which improves our forests’ yield and industrial performance, integrating our forestry and industrial activities; and our advanced techniques to maximize soil potential, such as mosaic plantation and minimum environmental impact cultivation techniques. Together, these factors enable us to enjoy: a high and increasing average volume of wood per planted hectare; a higher concentration of fibers per ton of harvested wood; the sustainable development of our operations; relatively low operating costs; and eucalyptus tree harvest rotations of approximately seven years, a period shorter than the harvest rotation periods in other regions of the world.
Pulp Manufacturing
The pulp manufacturing process takes place in two stages:
The “Kraft” Cooking Process. The logs received in our pulp mills are first de-barked, if not already de-barked in the field, and chipped in small pieces. The wood chips are screened by size and then transferred with conveyors to the impregnation stage followed by a pressurization and feeding system to the digester where they are “cooked” with sodium sulfide and caustic soda. This “kraft” cooking process is known for minimizing damage to the pulp fibers and allows the recovery of chemicals, thereby preserving high uniformity and strength of the fibers for subsequent paper production or other uses. During the cooking process, the cellulose fibers are separated from lignin and resins to produce unbleached pulp fibers. The unbleached pulp is screened and washed and then submitted to a pre-bleaching stage where oxygen delignification takes place. The Kraft cooking combined with the pre-bleaching removes approximately 95.0% of the lignin. At this point, the pulp can already be used to make certain types of paperboard like in one of the paper machines of the Suzano mill. Although not our main product, unbleached pulp grades can be commercialized or used for specialty of packaging papers or boards. The lignin and by- products of the Kraft process form a substance known as “black liquor” that are separated and piped to evaporators, to increase the concentration of solids. Thereafter, the concentrated black liquor is burned in recovery boilers. In the recovery boilers, the black liquor is the main source of fuel to produce steam and electricity for the whole production process. Also, approximately 99.0% of the chemicals used in the kraft cooking process are recovered for reuse in a closed chemical recovery process loop. Only make up chemicals are required to recover losses.
Bleaching. To produce bleached pulp the unbleached pulp is submitted to a chemical bleaching process. The bleaching process promotes further selective delignification and increases brightness of the fibers. This process consists of a series of medium-consistency bleaching stages in towers. In each bleaching tower a different mixture of bleaching agents is applied and after each stage, the pulp is washed. Three or four bleaching stages are required to obtain a fully bleached pulp. Our modern and low environmental impact bleaching processes are elemental chlorine free (ECF). The bleaching process is designed to be harmless and utilizes chlorine-dioxide, sulfuric acid, caustic soda and oxygen peroxide and does not use elemental chlorine. At the end of the bleaching stages, the diluted bleached pulp, in its fluid state, is pumped to storage towers. Thereafter, the bleached pulp may be transferred directly to integrated operations in our own paper production or tissue paper facilities. Suzano produces paper in the Mucuri, Suzano and Limeira mills and also supplies slushed pulp to integrated paper producing customers in Jacarei (Ahlstrom Munksjö) or Três Lagoas (International Paper). The tissue paper production takes place in the Mucurí and Imperatriz mills. The majority bleached pulp is though sold as raw material after drying in big capacity drying machines and converted to bales. In the Suzano mill we are also producing dried pulp in rolls for fluff applications.
Paper and Tissue Paper Manufacturing
We produce (i) uncoated woodfree printing and writing paper at our Mucuri unit, Limeira unit, Suzano unit and Rio Verde unit; (ii) coated woodfree printing and writing paper at our Suzano unit and Limeira unit; (iii) paperboard at our Suzano unit and (iv) tissue papers at Mucurí, Imperatriz and Belém. We start the paper production process by sending the pulp to refiners, which increases the fibers’ resistance. The pulp slurry is then fed into the paper mill, where it is mixed with fillers and additives to provide the necessary properties required by paper grade and the end users. These additives include synthetic sizing, precipitated calcium carbonate, optical dyes, and others. During the paper and paperboard production, the sheet is formed, pressed and dried in a continuous process. At the end of the process, jumbo rolls are obtained and then converted into reels, folio sheets or cut-size paper. In the case of coated paper, the paper receives additional surface treatments with coating and additional drying before converting to reels or sized papers. Tissue papers are produced in dedicated tissue machines, different from other paper machines and seek for other characteristics like softness, volume and absorbance. Tissue paper production requires very little additives and mechanical preparation of the fibers (refining). The produced tissue paper mother rolls can be converted on site, converted in dedicated conversion units or sold.
Computerized systems control or monitor all process stages. The marketing, sales and production, personnel work close together to manage the programming and control of our paper production process. In this manner, we are able to plan, optimize and customize different product runs and to anticipate, respond and adapt to seasonal variations and customer preferences.
Pulp and Paper Production Schedule
Our integrated pulp and paper mills operate three shifts, 24 hours a day, every day of the year, with the exception of scheduled maintenance periods. The dates of these maintenance periods are flexible and may be moved as a result of factors such as production, market conditions and supply of materials. We keep an inventory of certain spare parts that we consider critical to the production process or that are difficult to replace. We have also developed a close relationship with our suppliers to ensure access to spare parts.
Pulp Production and Sales
Pulp Production
We produce eucalyptus pulp to supply our paper production operations and for sale as market pulp. We describe below our pulp production recorded for the years ended on December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, as well as Fibria’s pulp production for the years ended on December 31, 2018, which information dates as of before the Merger, and is therefore not consolidated in our financial statements for such period.
We produced 9.8 million tons, 8.8 million tons and 3.5 million tons of market pulp in each of 2020, 2019 and 2018 fiscal years. Our pulp production in the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 accounted for 46.8%, 44.5%, and 16.6%, respectively, of the total pulp produced in Brazil during these periods, according to IBÁ.
The following table sets forth our total eucalyptus pulp production, total Brazilian pulp production and our eucalyptus pulp production as a percentage of total Brazilian pulp production for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018.
| | | For the year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2020 | | | 2019 | | | 2018 | |
| | | (in thousands of tons, except %) | |
| Suzano’s total pulp production | | | 9,800 | | | | 8,757 | | | | 3,501 | |
| Total Brazilian pulp production | | | 20,953 | | | | 19,691 | | | | 21,085 | |
| Total Brazilian production (%) | | | 46.8 | | | | 44.5 | | | | 16.6 | |
Fibria for the year ended December 31, 2018 (before the Merger)
Fibria produced 6.8 million tons of pulp in 2018 (including 50.0% of the pulp production of Veracel).
Fibria’s pulp production in the years ended December 31, 2018 accounted for 32.1%, of the total pulp produced in Brazil during these periods, according to IBÁ.
Fibria’s total eucalyptus pulp production was 6,758 thousand tons, which represented 32.1% of the, total Brazilian pulp production for the years ended December 31, 2018.
Pulp Sales
In the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, we sold 10.8 million tons, 9.4 million tons and 3.2 million tons of pulp as market pulp respectively, of which 7.3%, 8.8% and 9.2% was sold in the Brazilian domestic market and 92.7%, 91.2% and 90.8% was sold in the export market.
The following table sets forth our Brazilian domestic and export sales of pulp for the periods indicated.
| | | For the year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2020 | | | 2019 | | | 2018 | |
| | | (in tons) |
| Suzano’s pulp sales volume | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Brazilian | | | 786,621 | | | | 830,962 | | | | 298,005 | |
| International | | | 10,036,495 | | | | 8,580,691 | | | | 2,927,714 | |
| Total | | | 10,823,116 | | | | 9,411,653 | | | | 3,225,719 | |
Fibria for the year ended December 31, 2018 (before the Merger)
In the years ended December 31, 2018, Fibria sold 6.8 million tons of pulp as market pulp, of which 10.4% was sold in the Brazilian market and 89.6% was sold in the export market.
The following table sets forth Fibria’s Brazilian and export sales of pulp for the periods indicated.
Pulp Exports
The table below sets forth our pulp net sales by geographic region for the periods indicated.
| | | For the year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2020 | | | 2019 | | | 2018 | |
| Pulp net sales by geographic region | | R$ (million) | | | Total (%) | | | R$ (million) | | | Total (%) | | | R$ (million) | | | Total (%) | |
| Brazil | | | 1,609.4 | | | | 6.3 | | | | 1,833.9 | | | | 8.7 | | | | 744.6 | | | | 8.5 | |
| Asia | | | 12,921.1 | | | | 50.5 | | | | 9,605.8 | | | | 45.7 | | | | 3,838.0 | | | | 43.7 | |
| Europe | | | 6,409.9 | | | | 25.1 | | | | 5,950.8 | | | | 28.3 | | | | 2,810.9 | | | | 32.0 | |
| North America | | | 4,341.0 | | | | 17.0 | | | | 3,592.6 | | | | 17.1 | | | | 1,340.9 | | | | 15.3 | |
| Others | | | 296.9 | | | | 1.2 | | | | 44.6 | | | | 0.2 | | | | 48.9 | | | | 0.5 | |
| Exports | | | 23,968.9 | | | | 93.7 | | | | 19,193.8 | | | | 91.3 | | | | 8,038.7 | | | | 91.5 | |
| Total | | | 25,578.3 | | | | 100.0 | | | | 21,027.7 | | | | 100.0 | | | | 8,783.3 | | | | 100.0 | |
Fibria for the years ended December 31, 2018 (before the Merger)
The table below sets forth Fibria’s pulp net sales by geographic region for the periods indicated.
| | | For the year ended December 31, 2018 | |
| Pulp net sales by geographic region | | R$ (million) | | | Total (%) | |
| Brazil and others (1) | | | 1,733.7 | | | | 9.5 | |
| Asia | | | 7,384.6 | | | | 40.4 | |
| Europe | | | 6,005.3 | | | | 32.9 | |
| North America | | | 3,140.9 | | | | 17.2 | |
| Exports | | | 16,530.8 | | | | 90.5 | |
| Total | | | 18,264.5 | | | | 100.0 | |
| (1) | Includes Portocel’s services revenue. |
Pulp Customers
In 2020, most of our sales were made under contracts to customers with whom we have a long-term relationship in the Brazilian and export markets. Most of our customers are tissue, printing and writing and specialty paper producers that value the high-quality pulp produced and the reliability of supply provided by us. The majority of deliveries to final customers during last year were made from our overseas terminals in the United States, Europe, Mediterranean and Asia.
Prices may vary among the different geographic regions in which our customers are located. For a specific region, usually the price arrangements under our sales contracts are consistent with each customer profile, varying according to volume negotiated, regularity of purchase and our commercial strategy. Our sales contracts provide for early termination in the event of a material breach, insolvency of one of the parties or a force majeure event of an extended duration.
Our customers generally purchase its products using credit provided by us, which has a diversified customer base for its pulp products. We believe we have a good knowledge base to manage our credit risk portfolio through financial (letters of credit and insurance) and non-financial instruments (guarantees).
Fibria
On May 4, 2015, Fibria (as intervening party and guarantor), Fibria International Trade GmbH and Klabin S.A. entered into a Eucalyptus Pulp Offtake Agreement (the “Offtake Agreement”) for the supply of hardwood pulp produced at the Klabin plant in the state of Paraná (Puma Project), which had its operational startup in 2016. The agreement established a firm commitment for acquisition by Fibria or its subsidiaries of a minimum of 900,000 tons per year of hardwood pulp, for exclusive sale by Fibria or its subsidiaries in countries outside South America. The additional volume produced by the new plant was being sold by Klabin directly as follows: (i) hardwood pulp in Brazil and South America, and (ii) softwood pulp and fluff in the global market. Although the original term of the Offtake Agreement was six years, following the Merger the parties thereto and Suzano entered into a termination agreement pursuant to which the parties agreed to terminate the Offtake Agreement prior to its term after a transitional period of five months starting in April 2019. This termination agreement was signed as part of the commitments submitted to the European Commission in order to receive the approval of the merger between Suzano and Fibria. As part of the agreement, the latest pulp purchase we made from Klabin took place in August 2019 and we sold the last volumes therefrom in the first half of 2020.
Paper Production and Sales
We sell our paper products in Brazil and abroad. The markets we seek to serve are large and very competitive. Although price is very important in these markets, we believe that customers that have high-quality standards prefer our products due to the value and quality our paper imparts to their final products. This preference is shared among customers of all segments, from producers of notebooks and non-promotional materials, to more sophisticated customers, such as producers of promotional materials, high-quality packaging and art books.
The table below sets forth our paper net revenues by geographic region for the periods indicated.
| | | For the year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2020 | | | 2019 | | | 2018 | |
| Paper net revenues by geographic region | | R$ (million) | | | Total (%) | | | R$ (million) | | | Total (%) | | | R$ (million) | | | Total (%) | |
| Brazil | | | 3,358.2 | | | | 68.8 | | | | 3,480.3 | | | | 69.8 | | | | 3,307.1 | | | | 71.0 | |
| Central and South America (1) | | | 723.6 | | | | 14.8 | | | | 710.1 | | | | 14.2 | | | | 774.7 | | | | 16.6 | |
| North America | | | 263.3 | | | | 5.4 | | | | 382.6 | | | | 7.7 | | | | 210.8 | | | | 4.5 | |
| Europe | | | 262.9 | | | | 5.4 | | | | 221.7 | | | | 4.4 | | | | 225.1 | | | | 4.8 | |
| Others | | | 274.0 | | | | 5.6 | | | | 190.6 | | | | 3.8 | | | | 142.4 | | | | 3.1 | |
| Exports | | | 1,523.8 | | | | 31.2 | | | | 1,505.0 | | | | 30.2 | | | | 1,353.0 | | | | 29.0 | |
| Total | | | 4,882.0 | | | | 100.0 | | | | 4,985.3 | | | | 100.0 | | | | 4,660.1 | | | | 100.0 | |
Paper Customers
Our customers generally purchase our products using commercial credit provided by our company. We have a diversified customer base for our paper products. We believe we have a good knowledge base to manage our credit risk portfolio through financial (letters of credit and insurance) and non- financial (guarantees) instruments. Additionally, we believe that our strategy to diversify our portfolio of paper clients improves our credit risk performance due to lower correlation between large, medium, small and micro sized clients.
Seasonality
Forest products, such as pulp and paper products, are typically cyclical. Changes in inventories are usually important in price determination. Furthermore, paper demand depends largely on general economic conditions, since production capacity slowly adjusts to changes in demand. Therefore, we can expect seasonal changes in paper net revenues in Brazil depending on such factors. Changes in production capacity may also affect prices.
Similarly, the pulp industry seasonality pattern has been historically correlated with that of paper production. World paper production normally increases by the end of the summer vacations in the northern hemisphere, as well as during the Christmas and New Year holidays. In Brazil, specifically, paper demand increases in the second half of the year, mainly due to the production of notebooks and books for the beginning of a new school year, which begins in February, and governmental programs such as the National Didactic Book Program (Programa Nacional do Livro Didático).
Compared to the pulp market, the market for paper has a larger number of producers and consumers and greater product differentiation. Although the price of paper is cyclical and historically tied to the price of pulp, with a slight time difference, it is generally considered less volatile than the price of pulp. The main factors affecting the price of paper are economic activity, ability to expand production and fluctuation in exchange rates.
Due to specific factors, including pulp and paper machine closures, start-up of new capacities, changes in the cost structure of the industry and the increase of global pulp demand, the seasonality trends observed in the past for the pulp industry may be subject to changes in the future. Nevertheless, seasonality has not caused significant impacts on us over the last three years. For this reason, we do not measure the impacts of seasonality in our results.
Raw Materials
The main raw materials used in pulp and paper production are described below.
Wood
We use fibers from three primary sources for the production of our paper: (i) our pulp; (ii) recycled paper; and (iii) mechanical pulp. Recycled paper and mechanical pulp are used in the interior layers of certain types of paperboard. We use eucalyptus trees for the production of all of our pulp.
The management of our planted forests is a key resource for wood. For further information, see “—Business Overview—Our Company—Pulp and Paper—Planting and Harvesting Forests.”
Recycled Paper and Mechanical Pulp
Pre- and post-consumption recycled paper and mechanical pulp are used in the production of the middle layers of certain types of paperboard. Recycled paper is also the raw material used in the production of our Reciclato® paper, which, when production began in 2001, was the first recycled uncoated printing and writing paper produced on an industrial scale in Brazil.
Energy
Our primary source of energy, biomass (classified as an energy resource in the categories of forest energy biomass), is applied in our pulp and paper production processes and is generated by burning black liquor in the recovery boiler. See “—Pulp and Paper Production Process—Pulp.”
In addition to the black liquor, a fuel effluent inherent in the cellulose manufacturing process, a secondary source of energy, applied in our processes are bark, wood chips and waste, which are used as complementary fuels to meet the energy needs of the process, burned in auxiliary boilers.
In order to reduce own consumption and be self-sufficient in energy, a large part of the energy load is supplied by own generation, either through energy facilities within each plant, or by allocating energy from self-producing plants in another location to Suzano plants with energy deficits, thru CCEE (Brazilian Energy Clearing House).
At our units in Mucuri, Imperatriz, Três Lagoas and Veracel, we produce 100% of the energy consumed, mostly by means of renewable sources including wood waste reuse. This is possible because of the kraft chemical recovery process adopted in our mills, which allows us to recover chemicals used in the pulp production process and to use the wood residues from wood cooking to generate power. See “—Pulp Manufacturing—The “Kraft” Cooking Process.” At a later stage, the chemical recovery process is completed with quicklime that along with sodium sulphate and caustic soda form green liquor and white liquor, which is then reapplied to the wood cooking process with minimum make up. Therefore, our chemical recovery process allows us to generate power in an environmentally friendly manner.
Chemicals
A variety of chemicals, including sodium sulphate, sodium hydroxide (caustic soda), sodium chlorate, chloride, hydrogen peroxide and oxygen, are utilized in the paper production process, mainly in the pulp production phase. In the production of coated paper, we use various additives, primarily kaolin, calcium carbonate, latex, starch, bleaches and binders. The chemicals used in the pulp production process are recovered and recycled within our pulp mills.
All chemical waste is treated in order to conform to the most current standards and practices of the pulp and paper industry worldwide. The chemicals used in the pulp and paper industry are commonly used in a variety of other industrial activities and do not present a uniquely hazardous threat. Notwithstanding this fact, we strictly adhere to all safety rules and regulations related to the transport, storage and production of chemical products. In addition, we maintain an insurance policy to cover liability in the event of an accident in the transportation, storage or production of chemical products.
Transportation
The cost of transportation of pulp and paper products to the consumer market is an important component of our competitiveness. In the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, logistics costs accounted for 23.7%, 15.0% and 17.8% of our cost of goods sold and selling expenses, respectively.
Our scale of production, the proximity of planted forests to our pulp mills and planted forests in relation to our factories and the integration of the processes of pulp and paper production gives us substantial economies of scale and lower production costs. Suzano and Rio Verde units, in the state of São Paulo, are strategically located near our major customers for paper products and approximately 90 kilometers from the port of Santos, and are located at an average distance of 190 kilometers from our planted forests. The Limeira unit also has these advantages. The Mucuri unit, which primarily services the external market, is strategically located at an average distance of 74 kilometers from our planted forests and is approximately 250 kilometers from Portocel, a port that specializes in the exportation of paper and pulp, and approximately 320 kilometers from the port of Vitória. The Imperatriz unit, in Maranhão, which also primarily services the external market, is located approximately 600 kilometers from the port of Itaquí, and the associated planted forests are located an average of 184 kilometers from the port. The proximity of our forests, factories, Brazilian clients and ports allows us to enjoy relatively low transportation costs, which, in turn, provides a competitive cost structure for exports.
In addition, the Brazilian market may take advantage of Jacareí mill’s proximity to São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro, while the Aracruz mill has the one of the best logistics in the industry with a distance of approximately 3 kilometers to the Portocel port facility. The Tres Lagoas mill is located between two important railways in the southeast of Brazil, ensuring the cost competitiveness of this mill, although distance from the port is over 700 km.
Port Operations
The pulp produced for export is shipped on dedicated vessels or partial-service vessels by carriers hired through long-term or spot contracts to our terminals overseas, and is then delivered to our customers.
We conduct operations in the port of Itaquí, (state of Maranhão), port of Santos (state of São Paulo) and port of Barra do Riacho (namely, Portocel - state of Espírito Santo).
Port of Itaqui
The port of Itaqui is located on the coast of the state of Maranhão. From this port, we exported in 2019 pulp produced at the Imperatriz mill, which is located approximately 700km away from the port of Itaquí. Since 2014 we operate warehouse within the port area to guarantee the continuity of its operations with Empresa Maranhense de Administraçao Portuária (EMAP), a public company held by the state government of Maranhão.
On July 27, 2018, we participated in a public auction conducted by ANTAQ for the concession of public areas and infrastructure for general cargo, especially pulp and paper in the port of Itaquí, for an initial period of 25 years. We were awarded the contract due to our proposal for Itaquí General Cargo Terminal (IQI18), in the amount of R$0.1 million. In 2020, we hired the companies responsible for building a warehouse of 73,000 tons and a berth to support long-term planning of Imperatriz mill at the port of Itaquí, with a construction deadline by 2022.
Port of Santos
The port of Santos is located on the coast of the state of São Paulo. From this port, we export pulp produced at the Jacareí and Três Lagoas, which are located approximately 150 and 750 kilometers away from the port of Santos, respectively. Through a concession, we operate terminals 13/14/15 (T13/14/15) and terminal 32 (T32) of the port of Santos.
In order to facilitate exports from Três Lagoas, we had a port services operation contract with a terminal operator called terminal 31 (Gearbulk Terminal) for an additional storage capacity of 40,000 metric tons of pulp at a specialized terminal where rail connection and vessel berth priority were also taken into consideration. We renewed this agreement with Gearbulk for two more years starting in May of 2019, but rescinded it free of charge in August 2020 as allowed by the agreement. We opted to end the agreement as the terminal was no longer needed due to the beginning of the operation at Vertere (DP World Santos).
Although the concession of T13/14/15 expired in September 2017, we timely requested its renewal before the Infrastructure Ministry, which has been approved under a temporary contract. We continued to operate T13/14/15 from May 2020 until October 2020, when the Company stopped operating at these terminals, also as a result of the beginning of the operation at Vertere.
Paper produced by us for exports is mainly shipped out of the port of Santos, which is located approximately 80 kilometers from the Suzano unit and about 250 km from the Limeira unit, where most of the paper production designated to export markets comes from. We also operate with containers at the port of Santos, mainly used in the paper and fluff business.
DP World Santos
On January 29, 2018, we contracted logistic operations services for transporting pulp, with a take-or-pay condition. These services are rendered by Empresa Brasileira de Terminais Portuários S.A. (Embraport), which has adopted the brand DP World Santos in its private use terminal (TUP) located at the left bank of the Santos estuary, in the state of São Paulo, where a logistic port installation dedicated to warehousing, handling and shipping pulp will be constructed. We invested R$187.8 million in 2018 and are investing approximately R$400 million until 2020. DP World Santos is wholly owned by global trade enabler DP World, one of the largest container port operators in the world, recognized in the industry for its efficiency.
The port operations started since the construction of a new warehouse, two berths and other harbor-logistics structures was completed, and the licenses were released in April 2020. Throughout 2020 we started the operation following the curve of the volume of the ramp up, gradually achieve the full capacity by the beginning of 2021. The port services will be conducted by DP World Santos until 2039, which term may be extended to 2042 subject to the renewal of the port authorization, as applicable.
Portocel
The pulp produced for export at the Aracruz and Veracel pulp mills is shipped out of the port of Barra do Riacho (Portocel), which is located approximately 3 kilometers away from Aracruz and 260 nautical miles from Veracel’s barge terminal. We own 51% of Portocel, the company that operates the port terminal of Aracruz. The remaining 49% of Portocel is owned by Cenibra, another pulp manufacturer.
The Portocel is a modern facility that has the capacity to handle approximately 7.5 million metric tons of pulp and wood per year, from their owners and other players, and different type of material like aluminum, steel coils, granite and project cargo. Warehouse facilities at Portocel are capable of storing approximately 220,000 metric tons of pulp (static storage).
Marketing and Distribution
We have our own sales teams for our pulp and paper business units, which sell our products in both the Brazilian and international markets, to final consumer or distribution intermediaries. We sell our products in both the Brazilian and export markets. In the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, 83.7%, 79.6% and 69.9%, respectively, of our net sales revenue from market pulp and paper products was attributable to sales made outside of Brazil. In the year ended December 31, 2018, 90.5% of Fibria’s net sales revenue was attributable to sales made outside of Brazil. Domestically in Brazil, we have a sales staff consisting of employees operating in various regions of Brazil.
Pulp
Our pulp business unit’s commercial strategy is based on three pillars: strong relationships, long-term partnerships and differentiated services. To ensure proximity with our national and international customers and to ensure that our products are tailored to their needs, we use a Brazilian sales team, which services Latin America, and local sales teams in the United States, Switzerland, Austria and China. In Brazil and in each of our international offices, we have technical assistance departments that focus on our customers’ needs, with the purpose of providing our customers with smart technical solutions for their transition from other types of fiber to eucalyptus fiber. We organize annual technical workshops, in Brazil and in each of the countries where we operate, to share with our customers and international offices our innovative initiatives, technical developments and market strategy.
Paper
In 2020, 68.8% of our paper sales were made in Brazil. In order to better serve this market, we have divided it into seven segments, designing different commercial and marketing strategies for each segment:
| • | Packaging: this is the main end use of our paperboard sales and involves production of packaging for the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, tobacco, toys, clothing, shoes, food, beverage, hygiene and cleaning industries; |
| • | Promotional: this segment mainly involves coated paper sales and production of promotional flyers, catalogues, displays and signs; |
| • | Editorial: this segment accounts for the production of books, magazines and newspapers and involves the sale of all of the paper types that we produce (coated, uncoated and paperboard); |
| • | Notebooks: this segment involves the production of notebooks and diaries in both the local and export markets, and uses uncoated paper and paperboard; |
| • | Mailing: this segment mainly involves the production of forms and invoices, which use uncoated paper; |
| • | Office: this segment encompasses three sub-segments (copying, competition and corporate) and involves the commercialization of uncoated paper in cut-size format, mainly A4; and |
| • | Retail: this segment involves the commercialization of uncoated paper in cut-size format, mainly A4, in stationery stores, self-service businesses and convenience stores. |
In order to serve the first five segments listed above, we combine different distribution channels: large paper volumes are sold directly to publishers and converters and small paper volumes are sold through publishing distributors. In the office and retail segments, sales are made indirectly, through paper distributors and directly through our call center and e-commerce.
We own distributors for our paper and graphic products, one in Brazil and one in Argentina, Stenfar S.A.I.C. Importadora y Exportadora and Stenfar. For Brazilian distribution, we rely on four regional distribution centers: two in São Paulo, one in Serra (Espírito Santo) and one in São José dos Pinhais (Paraná), as well as our local distribution centers, in the cities of Campinas and Ribeirão Preto (state of São Paulo), Belém (state of Pará), Brasília (federal district), Campo Grande (state of Mato Grosso do Sul), Londrina (state of Paraná), Fortaleza (State of Ceará), Goiânia (State of Goiás), Manaus (State of Amazonas), Porto Alegre (State of Rio Grande do Sul), Recife (state of Pernambuco), Rio de Janeiro (state of Rio de Janeiro), Salvador (state of Bahia) and Uberlândia (state of Minas Gerais).
Other than distributing our own line of paperboard and printing and writing paper, we also distribute other product lines to reach the graphics, editorial and consumer segments and to public agencies. Stenfar is a company-owned distributor of paper and computer supplies operating in Argentina through which we conduct such distribution operations. Stenfar has been operating for more than 58 years and has an important and active presence in the market. Stenfar has three subsidiaries in Buenos Aires, Córdoba and Mar del Plata. Stenfar services the graphics, editorial and consumer segments and public agencies, working with printing and writing paper, paperboard and computer supplies. According to market estimates on paper and computer supplies distribution, we believe Stenfar is one of the largest distributors in its market in the area.
In addition to providing our customers a more complete portfolio of services and products, our distribution operations in Brazil and Stenfar’s distribution operations in Argentina reinforce our commitment to strengthen our distribution channels, enlarging our network and directly benefiting our clients through greater proximity and agility in serving them.
In addition to our own lines of paperboard and writing and printing paper, we also distribute other product lines, for the graphics, publishing, consumer, converter and government entities segments.
Competition
The pulp industry is highly competitive. The top 20 producers currently supply approximately 74.0% of the global virgin market pulp capacity according to Hawkins Wright. We face substantial competition from numerous producers of paper and hardwood market pulp, including major Brazilian producers, such as Eldorado, CMPC and Celulose Nipo Brasileira S.A. (Cenibra). Many factors influence competitive position, including mill efficiency and operating rates and the availability, quality and cost of wood, energy, water, chemicals, logistics and labor, and exchange rate fluctuations. Latin American pulp producers have structural cost advantages over other global competitors, mainly in North America and Europe, due to their shorter harvest periods and higher land productivity, which is only partially offset by geographical distance from the end markets. Many of our Latin America competitors enjoy cost advantages similar to ours, including low production costs, and have access to similar sources of funding to finance their expansion projects.
The international pulp and paper markets are highly competitive and involve a large number of producers worldwide. As a vertically integrated pulp and paper producer, we compete not only with other vertically integrated pulp and paper producers, but also with companies that produce only pulp or paper. Many of these producers have greater financial resources than we do and enjoy lower financing costs. However, as the largest producer of eucalyptus pulp in 2020, according to Hawkins Wright, we maintain our competitive advantage by keeping production costs low, maintaining long-term contracts with our customers and vertically integrating our operations.
Environmental Matters
General
We are committed to produce pulp and paper with a minimum of waste production and with the lowest impact on natural resources and the environment. Our continuing goal is to avoid and mitigate adverse impacts on the environment by controlling our emissions into the air and water, preserving biodiversity and by fully complying with Brazilian environmental regulations and recognized international environmental standards.
Our industrial units are ISO 14001 certified, which attests our environmental management system, where our Mucuri unit was the first in the pulp and paper sector globally to obtain this certification in 1996. We also have received other certifications, including ISO 9001 and ISO 45001. Our environmental protection investments in 2020 totaled R$195.3 million in respect of our industrial units.
Our forests units are certified by the Forest Stewardship Council (“FSC”) and the Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (“PEFC”), which attests that our forest management is environmentally correct and socially just. The FSC seal, created by different multisector international organizations, has strong international recognition and it is also labeled in several of our products and our clients’ products. We operate, therefore, under strict compliance with environmental laws and regulations. Our environmental protection investments in 2020 totaled R$30.2 million in respect of our industrial units.
We are committed to respect and preserve the environment, through reducing our consumption of natural resources and mitigating the impacts of our activities. Our environmental policy and environmental management system are aligned with the most advanced international standards and seeks to:
| • | Use natural resources in a balanced way, such as water, soil and inputs; |
| • | Conserve ecosystems and biodiversity; |
| • | Ensure efficiency in the treatment of atmospheric emissions and effluents; |
| • | Promote de reuse of waste and the reduction of its sending to landfills; |
| • | Optimize energy performance; |
| • | Help to combat climate change; |
| • | Respect all environmental legislation applicable to our operations. |
Suzano reinforces its commitment to establish its plantations exclusively in areas previously anthropized by other uses, whose conversion has not occurred under its direct or indirect responsibility, committing itself to a zero deforestation policy.
At the forestry, R$53.8 million have been invested in monitoring and conserving natural resources and biodiversity, habitat restoration projects and implementation, sustainable development of local communities, meeting certification demands, environmental education programs, among others.
In addition, costs incurred to compliance with environmental law were approximately R$7.2 million.
Our environmental commitments are also supported and monitored by relevant organizations and coalitions, including the Global Pact for the Environment, the Fundação Getulio Vargas /Centro de Estudos em Sustentabilidade (FGV-CES) and Coalizão Brasil Clima, Floresta e Agricultura (Climate, Forest and Agriculture Brazilian Coalition). In addition, we maintain a strong partnership with recognized forums and organizations to discuss and share knowledge on sustainability, including the World Wildlife Fund-Brazil, the World Wildlife Fund / New Generation Plantation, The Nature Conservancy, CI (International Conservation), The Forest Dialogue, Diálogos Florestais Nacionais (Brazilian Forest Dialogue), Fórum Florestal (Forest Forum), IBÁ, the Brazilian Corporate Council for Sustainable Development (Conselho Empresarial Brasileiro para o Desenvolvimento Sustentável) and the GHG Protocol Brazil.
Furthermore, we also have a strong commitment to community service and participate in and fund a variety of projects, including projects supported by the Instituto Ecofuturo, a non-governmental organization that we have created and sponsor, whose purpose is to generate and share knowledge and practices that contribute to creating a culture of sustainability. In 2020, we invested R$3.9 million on its maintenance.
Water
After the disclosure of Suzano's Long Term Goals – MLPs in February 2020, we deployed the goal of reducing specific water withdrawal by 15% by 2030, linked to SDG 12 – sustainable consumption and production, for each Industrial Mill and governance has been integrated into Suzano's management routine.
Considering the expected curve until 2030, we defined the annual and monthly targets for each Mill. The results of each Mill in relation to the intermediate targets are monitored monthly in a meeting with the Executive Officer of Pulp Operations, together with representatives of all Mills, integrating them with the governance of safety, production, quality and cost indicators.
Taking into consideration the Suzano governance model, the industrial directors, industrial managers and executives monitor the indicators of each Mill weekly. Any deviations are treated according to the management tools adopted in Suzano's Operational Excellence model.
The results are disclosed to all Suzano employees at the monthly results meetings of each Mill, engaging people in relation to the topic.
At the Units, the targets were stratified by consumer sector and sector performance is monitored at routine Production Meetings.
Also in 2020, improvement projects were identified for each Mill to be implemented by 2030 to achieve the goal. For the construction of this material, research was carried out on best practices adopted in the group, water balance sheets, management tools (such as Six Sigma and PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle)) and innovation projects, through the “i9 focus on water” Program (I9 focus is an incentive Innovation Program, where a theme and several challenges are established, with Soft Money recognition for people with more innovative ideas), encouraging the operational team to insert ideas that may imply in reducing water consumption.
Solid Waste and Wastewater
Waste management is present in our processes and operations, both industrial and forestry. The treatment of effluents in all industrial units is carried out in our own Effluent Treatment Plants and includes primary (physical) and secondary (biological) treatment, a stage in which oxygen and nutrients are added and the pH is controlled. At Limeira, Jacareí, Três Lagoas and Maranhão Mills, the activated sludge technology is used for secondary treatment, while aerated lagoons are used at the Suzano and Aracruz Mills. The Mucuri Mill has used both technologies. The biological sludge generated at the effluent treatment plants has been treated in different eco-efficient ways, such as composting plants at the Limeira Mill, drying and burning at the Jacareí, Imperatriz and Três Lagoas Mills.
In addition to complying with the applicable rules on solid waste, our Mills have a waste management plan and operational procedures. Waste management includes daily monitoring and forums focused on reducing solid waste generation, increased recycling and internal reuse and reduction of shipment to landfills. The Mills also receive internal and external audits.
We also announced in February 2020 a very challenging goal of reducing 70% of waste sent to landfill by 2030.
In the Limeira and Jacareí Industrial Mills, in 2020 we reached the level of ZERO WASTE TO LANDFILLS. In the Três Lagoas Unit, in 2020 we completed the expansion of the Waste Treatment Plant where now including the treatment of organic and inorganic waste generated in the 2 Production Lines.
At the Imperatriz Mill we invested in 2020 in the construction of the Waste Treatment Plant, whose start-up is scheduled for the first quarter of 2021.
The soil acidity corrective program, applied at the Jacareí, Três Lagoas and Imperatriz Mills, consists of the transformation of inorganic residues generated in our industrial process, such as lime mud, dregs, grits and ashes, into soil pH correctors. With this product we stopped buying limestone on the market, benefiting forestry, reinforcing our commitment to the Circular Economy. Another advantage is that the surplus of this solution can be sold on the market in accordance with the rules of the Ministry of Agriculture
Biodiversity
Our forestry practices reflect our concern for the biodiversity conservation, from planning to implementation. Today we plan and implement our forest management operations using the mosaic landscapes approach, where eucalyptus stands are intermingled with native vegetation. We seek to connect the main native fragments, forming ecological corridors, contributing to the preservation of fauna and flora.
Furthermore, we also work with minimal cultivation, where planting is done with low soil interference (crop residues – twigs, leaves and bark – are kept on the ground, contributing to fertility and protecting against erosion). This model provides a suitable environment for conserving and maintaining biodiversity.
We maintain approximately 40% of our total land, or one million hectares for biodiversity conservation. This total includes permanent preservations areas (i.e. riparian forests), legal reserves, high-value conservation areas, and other natural areas dedicated to environmental preservation, where we carry out periodic monitoring of fauna and flora in order to ensure its perpetuity. This monitoring has occurred since 2008 in Bahia and Mato Grosso do Sul, 2009 in São Paulo, 2012 with new methodology in Espírito Santo and Minas Gerais, and since 2013 in Maranhão.
Our biodiversity management and the environmental practices related to the operational activities is monitored through external audits, according to responsible forest management standards of the FSC® (Forest Stewardship Council®) and PEFC / CERFLOR® (Brazilian Forest Certification Program).
Climate Change
Our approach towards climate change incorporates continued investigation, as well as the adoption of best practices, including research and development regarding GHG emissions in our industrial, forest and logistics operations and carbon removals in our plantations and native forests. We undertake these initiatives in order to maintain and improve our performance by considering climate change scenarios, adopting mitigating and adapting strategies and reducing emissions throughout our value chain.
The management of climate change related risks is integrated into our overall risk management, which follows the guidelines defined in our integrated risk management policy with respect to the process of communicating, prioritizing, treating, monitoring and analyzing risks. Priority risks associated with climate change are managed by certain internal departments in charge of monitoring the risk and are periodically monitored by our risk management department through an integrated multi-disciplinary ERM (Enterprise Risk Management) process. In addition, Suzano is a supporter of the Climate Related Financial Disclosures Task Force (TCFD) and was the first company in the pulp and paper sector to be the protagonist of a case study published in the TCFD Knowledge Hub in which it released the Indicators Center - digital platform with Suzano’s information related to climate change, in line with the measurement and transparency recommendations proposed by TCFD.
In 2008, we began a partnership with FGV as one of the founding members of the Brazilian GHG Protocol program, which aims to identify and account for emissions from the production process considering the direct emissions from our operational control sources (scope 1), indirect emissions from electricity consumption (scope 2) and indirect emissions associated with the production chain that are not directly controlled by us (scope 3). This tool is designed in accordance with the World Resource Initiative’s GHG Protocol methodology.
In 2010, we were the first pulp and paper company in Brazil to calculate our carbon footprint by measuring the emissions throughout our products’ entire life cycle, from raw materials production and distribution through their sale, use and disposal, which has a broader scope than the GHG inventory undertaken since 2003. With the goal to build on these studies and seek to measure and understand the impact of our production and the opportunities for improvement, we developed new life cycle analysis studies for some of our products, including Eucafluff, which comparative assessment expresses better performance in key impact categories.
In February 2020, we launched two public targets focused on climate change. First, we expect to remove 40 million tons of GHG from the atmosphere between 2020 and 2030. This number considers the net difference between carbon removal from eucalyptus plantations and native forests and emissions scopes 1, 2 and 3. Second, we plan to reduce by 15% our emission intensity (tCO2e/adt) including scopes 1 and 2 (baseline 2015). Both targets require systemic improvements and technological investments along our production chain and are necessary to ensure the Paris Agreement.
Furthermore, Suzano reuse the biomass and wood residues from the production process to generate a significant portion of their energy requirements. Approximately 86% of this energy comes from renewable fuels (such as black liquor and biomass), and the remaining 14% from non-renewable resources (such as natural gas and fuel oil). We are self-sufficient on Mucuri, Imperatriz and Três Lagoas units in terms of energy needs and some mills are even selling surplus energy back to the grid. In 2020, 193 MW of renewable electric energy were supplied to the public grid. This is aligned with another long-term goal to increase renewable energy exports by 50%, until 2030 (baseline 2018).
Furthermore, our industrial units produce renewable energy that supplies approximately 86% of the mill’s energy needs. Our Mucuri, Imperatriz and Três Lagoas units are almost self-sufficient in terms of energy needs and some mills are even selling surplus energy back to the grid. In 2020, 177.8 MW were supplied to the public grid. This is aligned with another long-term goal to increase renewable energy exports by 50%, until 2030 (baseline 2018).
We have also adopted a policy to reuse the energy resulting from our production process. Our industrial units produce a significant portion of their energy matrix requirements, and currently approximately 85% comes from renewable fuels (such as black liquor and biomass), and the remaining 15% from non-renewable resources (such as natural gas and fuel oil). We are self-sufficient in energy. In fact, we are currently selling energy to the grid. In 2020, we added 604,058.7 MWh to the public grid.
Sustainability Strategy
We believe sustainability is a core component of our corporate strategy and have implemented corporate governance practices, which seek to align our sustainability strategy with our business model. We have a sustainability committee that advises our board of directors. Our sustainability committee is led by the chairman of our board of directors and includes several independent members with diverse backgrounds. It meets three times a year to deliberate and evaluate the construction and implementation of our sustainability strategy.
For us, sustainability involves incorporating social and environmental aspects, long-term value generation strategies and stakeholder views into our business strategy and management. We are part of a value chain that gives importance to numerous aspects beyond traditional operations, such as developing a skilled and engaged workforce, managing and promoting projects that consider the growth and welfare of neighboring communities, preserving and recovering native forests, sequestering carbon, reducing waste, managing with transparency, and strengthening communication channels with civil society, the government and media. Sustainability embodies the recognition of public opinion, customer loyalty, employee pride and trust of partners and neighbors. Furthermore, investing in sustainability may decrease the risks we bear, create opportunities and make us stronger to meet the needs of an increasingly demanding market concerned about sustainable matters.
We seek to be a leader and agent of transformation with respect to sustainability. In 2019, we carried out a broad consultation process with over 90 organizations in Brazil, Europe, North America and Asia, 700 employees in regional workshops and over 200 respondents in an online survey. Desk research was also conducted including institutional risk matrices, materiality assessments, sector reports and benchmarks. This exercise resulted in the development of long-term goals that were approved by our board of executive officers, our sustainability committee and our board of directors, which we list below.
2030 Sustainability Goals:
| • | Even more climate positive: Remove 40 million tons of carbon from the atmosphere (capture – emissions scope 1, 2 and 3). |
| • | Mitigate income inequality: Zero people below the poverty threshold in our area of influence (200,000 people). |
| • | Substitute plastics and petroleum by-products: Offer 10 million tons of renewable products. |
Long-term Goals:
| • | Water in the forest: Increase water availability in 100% of critical watersheds until 2030. |
| • | Water in industrial operations: Reduce water withdrawal by 15% until 2030. |
| • | Energy: Increase renewable energy exports by 50% until 2030. |
| • | Emissions: Reduce specific emissions by 15% (Scope 1 and 2) until 2030. |
| • | Waste: Reduce waste sent to landfill by 70%, until 2030. |
| • | Diversity and inclusion: |
| o | PWDs – Guarantee 100% accessibility and inclusive environment and zero prejudice against people with disabilities, until 2025. |
| o | Women – Reach 30% minimum of women in leadership roles (managers, directors and board), until 2025. |
| o | Blacks - Reach 30% minimum of blacks in leadership roles (managers, directors and board), until 2025. |
| o | LGBTI+ - Guarantee 100% inclusive environment and zero prejudice against LGBTI+, until 2025. |
| • | Education: Increase the Brazilian Education Index (IDEB) by 40% in our area of influence, until 2030. |
The variable remuneration of 100% of the executive board is linked to at least one ESG related target. Since 2020, the board has a collective goal related to diversity and inclusion and individual goals linked to the performance of the long-term goals mentioned above.
Our sustainability strategy also identifies the most relevant issues for us and society, taking internal priorities and the stakeholder perceptions, the themes identified are incorporated in our internal strategy and guides our external disclosures. The process defined the following material themes: (i) climate change; (ii) ethics, governance and transparency; (iii) financial management; (iv) forest management; (v) human capital; (vi) innovation and technology; (vii) operational excellence and ecoefficiency; (viii) social development; (ix) value chain (suppliers and customers; and (x) water.
Our sustainability annual report adheres to the Global Reporting Initiative Standards guidelines for disclosure core level, as well as the framework of the International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC) and in line with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Through these initiatives, we seek to annually account for how we address challenges and achieve results relating to our sustainability strategy and with respect to our role in society. Our sustainability annual report, developed on a voluntary basis, includes details of commitments and performance on the governance, economic, financial, social and environmental aspects of our business following the principles of materiality, stakeholder inclusiveness, sustainability context, completeness, balance, comparability, accuracy, timeliness, clarity and reliability. Our sustainability annual report is publicly disclosed in our website.
Brazilian Environmental Regulation
The Brazilian federal constitution assigns to the Brazilian federal government, the states, the federal district and the municipalities the authority to enact laws and issue regulations regarding environmental protection and preservation of Brazilian fauna and flora, as well as the power to enforce such laws. States can only enact laws and issue regulations to supplement federal law, exerting full legislative power only in the absence of federal regulations. The municipalities have authority to enact laws and issue regulations only with respect to matters of local interest or to supplement federal and state laws.
The Brazilian environmental policy establishes that activities (i) considered actually or potentially polluting; (ii) that use natural resources; or (iii) that, in any manner, may result in environmental degradation, are subject to prior environmental licensing. This procedure is necessary both for the initial installation or expansion of any facility that meets any of those characteristics. The environmental licensing process generally follows three consecutive stages: preliminary license, installation license and operating license.
Regarding licensing procedures, municipalities have the jurisdiction to license facilities that only have a local environmental impact, pursuant to definitions issued by the State Environmental Council. The Brazilian federal government is responsible for the environmental licensing of projects and activities: (i) within the Brazilian inland borders; (ii) located in the Brazilian territorial sea, continental platform or exclusive economic zone (which term is defined under Brazilian law); (iii) located in indigenous lands; (iv) located in national parks or other federal conservation areas; (v) between two or more Brazilian states; (vi) of military nature; (vii) regarding radioactive material and/or nuclear power; (viii) of national interest, as defined in the Executive Order No. 8,437/ 2015. Finally, the states are responsible for the environmental licensing of all the other activities located within their borders.
The preparation of an environmental impact study and its corresponding environmental impact report, or EIA/RIMA, is required for purposes of licensing activities with significant environmental impact. In any such event, the company is required to pay a compensation fee for negative environmental impacts caused by the relevant project. This fee can amount to up to 0.5% of the total cost of the project. Since most of our main activities began before the enacting of the law that established the environmental compensation fee, we were not required to pay such compensation in those cases (projects performed before the year 2000). However, the activities started after the enactment of the National System of Conservation Units – SNUC’s law are subject to the obligation to pay environmental compensation. Therefore, new projects may require additional investments to compensate for the environmental impact.
We have licenses for the operation of our plants, which are generally valid for five years from date of issuance and may be renewed for additional five-year periods. The operating permits require, among other things, that we periodically report our compliance with environmental laws, regulations and standards. With regard to our plans, we are currently either (i) in compliance with all operating and environmental licenses or (ii) in the process of renewing these licenses.
Our forestry activities are regulated by the Brazilian federal government and the state governments of the states of São Paulo, Bahia, Espírito Santo, Minas Gerais, Rio Grande do Sul, Mato Grosso do Sul, Piauí, Tocantins and Maranhão. The planting and harvesting of trees can only be done in accordance with a project previously approved by the state agencies, except for the States of São Paulo and Mato Grosso do Sul, where a forestry license is not required. Furthermore, in observance of the new Forestry Code (Federal Law n. 12,651/2012), we must keep at least 20% of our rural landholdings covered with native forests or replanted with native plant species as a legal reserve (reserva legal). Legal reserves must be registered with a new registry system named the Rural Environmental Registration (CAR – Cadastro Ambiental Rural). In such system, the land owners shall provide information on all the environmentally protected areas to the supervisory agency. However, this restriction increases to 35% in the Cerrado biome and up to 80% in the Amazon forest biome. Also, according to federal law, native vegetation from areas along rivers and other water bodies as well as steep slopes and hilltops are to be treated as permanent preservation areas, which are essential to the conservation of water resources, scenery, animal, human and plant health, biodiversity and soil in the area. Our forestry operations are in compliance with all applicable laws and regulations. See “─Environmental Matters.”
Our operations are subject to various environmental laws and regulations, including those relating to air emissions, effluent discharges, solid waste, odor and reforestation. In Brazil, individuals or legal entities that violate environmental laws can be punished by criminal sanctions that range from fines, imprisonment and confinement, in the case of individuals, to fines, restriction orders or dissolution, in the case of legal entities. In addition, administrative sanctions that can be imposed include, among others:
| • | fines that may reach up to R$10 million if operating without a license and R$50 million in the case of severe environmental damages; |
| • | partial or total suspension of activities; |
| • | forfeiture or restriction of tax incentives or benefits; and |
| • | forfeiture or suspension of participation in credit lines with official credit establishments. |
In addition to criminal and administrative sanctions, pursuant to Brazilian environmental laws, the violator must also provide compensation and reimbursement for the damage that was caused to the environment and third parties. At the civil level, there is joint and strict liability for environmental damages. This means that the obligation to compensate for the damage caused to the environment may affect each and every individual or legal entity directly or indirectly involved, regardless of the existence of actual fault by the agents involved. Therefore, the engagement of third parties to carry out any intervention in our operations, such as the final disposal of waste, does not exempt the contracting party from eventual damages to the environment caused by the contractor. In addition, environmental laws provide for the possibility of piercing the corporate veil, in relation to the controlling shareholder, whenever such corporate veil is an obstacle for the reimbursement of damages caused to the environment.
Using advanced technology, our operations comply with all applicable Brazilian laws and regulations, and we believe that we also meet all recognized international standards determined by institutions and agreements to which we or Brazil are signatories. In the past five years, we have not received any administrative penalties or warnings that might be considered relevant or material fines that might be considered relevant in respect of violations of Brazil’s environmental laws or policies.
Insurance
We believe that we maintain adequate insurance coverage for our facilities with respect to our operational and commercial risks. Consistent with industry norms and practice in Brazil, we do not maintain insurance coverage for fire and other risks to our planted forests. Nonetheless, we adopt a series of measures, such as, maintenance of a firefighting brigade and keeping the lanes between our production units of eucalyptus trees unobstructed, which historically has significantly prevented the spread of fires. We use the amounts we would otherwise pay as premiums for fire insurance to implement preventive and safety measures, such as installing fire towers and fire control equipment and training firefighting personnel. It is our policy to maintain insurance coverage for our inventory of wood.
Organizational Structure
The following chart shows our corporate structure as of December 31, 2020.
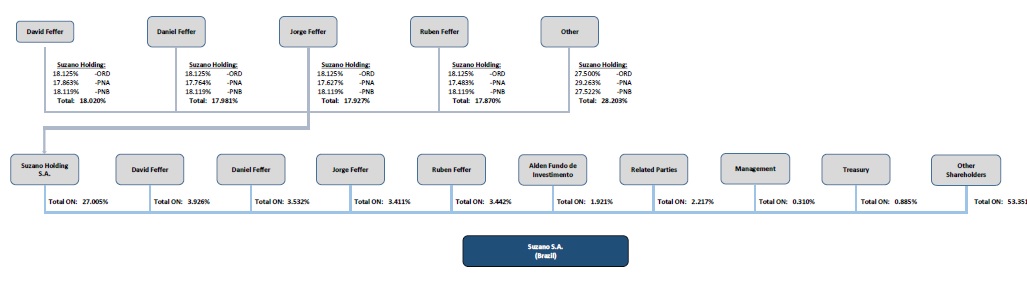

Property, Plant and Equipment
Eucalyptus Planted Forests
General
One of our greatest strengths is that it is a fully integrated low-cost producer of pulp and paper. That is due, in part, to the low cost of cultivating and processing eucalyptus trees compared to other species. As shown in the illustration below, the short growth cycle of our eucalyptus trees — seven years — presents a significant competitive advantage in relation to the costs associated with other fibers. For more information about our low wood costs, see “—Raw Materials—Wood.”
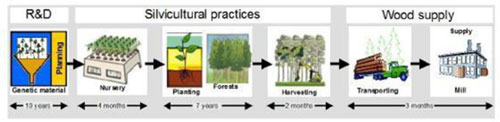
Our planted forests along with those of our partners are concentrated in the south of the State of Bahia, in the state of Espírito Santo, in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul, in the state of São Paulo, in the east of the state of Minas Gerais, in the states of Rio de Janeiro and Rio Grande do Sul, in the states of Tocantins, Pará and in southwest of the state of Maranhão, and in north and east of the state of Maranhão and Piauí.
The table and chart below set forth the location and capacity of our planted eucalyptus forests as of December 31, 2020:
| State | | Planted Area (thousand
hectares) | | | Conservation
Area (thousand
hectares) | | | Other (thousand
hectares) | | | Total (thousand
hectares) | |
| São Paulo | | | 225 | | | | 126 | | | | 17 | | | | 368 | |
| Minas Gerais | | | 23 | | | | 38 | | | | 2 | | | | 64 | |
| Rio de Janeiro | | | 2 | | | | 1 | | | | 0 | | | | 3 | |
| Mato Grosso do Sul | | | 346 | | | | 162 | | | | 64 | | | | 572 | |
| Bahia(1) | | | 247 | | | | 195 | | | | 64 | | | | 464 | |
| Espírito Santo | | | 145 | | | | 109 | | | | 23 | | | | 269 | |
| Rio Grande do Sul | | | 441 | | | | 1 | | | | 0 | | | | 2 | |
| Tocantins, Maranhão, Pará, and Piauí | | | 288 | | | | 382 | | | | 92 | | | | 762 | |
| Total(2) | | | 1,276 | | | | 1,015 | | | | 215 | | | | 2,505 | |
| (1) | Includes the forests associated with the production facility of Veracel. Excludes forest base linked to the sale of forest assets in Southern Bahia State. |
| (2) | Excludes forestry partnership program of 138 thousand hectares. |
Map of location of eucalyptus planted forests
Assisted Growth
For new plantings, we use both seeds and clones selected for their characteristics, such as height and diameter, productivity per hectare, lack of branches below the crown, suitability to local soil and climate conditions, and resistance to disease. Saplings grown from selected seeds and clones are initially cultivated inside climate-controlled greenhouses for 30 days. These saplings are then transferred to outdoor nurseries, where they are allowed to grow for another 70 to 90 days, after which they are moved to be planted.
We conduct research specific to each of our growing regions, utilizing general concepts of plant physiology and genetics. In the future, our productivity may increase through cloned hybrid cuttings or selected seeds. The research program also continues to seek ways to improve the uniformity of wood quality and maintain ecological balance by studying the soil, plant nutrition and pest control.
Harvesting
Eucalyptus trees are harvested by our employees and by independent contractors through an automated system and, in some cases, manually. Logs are generally transported to our pulp mills as needed and we store small amounts of logs at all of our production facilities. Logs to be used in our production facilities in São Paulo are currently stored in the forests for an average of two to five months to allow them to dry before transportation. In Bahia, logs are transferred to the mill 40 days after harvesting.
Plant Locations and Capacity
We produce pulp and paper products from nine modern operating facilities consisting of: (i) two integrated pulp and paper production facilities in the state of São Paulo (the Suzano and Limeira units) including fluff production, (ii) a non-integrated paper production facility in the state of São Paulo (the Rio Verde unit), and a Market Pulp production in the state of São Paulo (Jacareí unit), (iii) an integrated pulp, paper and tissue facility in the state of Bahia (the Mucuri unit), (iv) an integrated pulp and tissue facility in the state of Maranhão (the Imperatriz unit), (v) a market pulp production in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul (Três Lagoas unit), (vi) a market pulp production in the state of Espírito Santo (Aracruz unit) and (vii) two non-integrated tissue paper (Facepa) production in the states of Pará and Ceará (Belém unit and Fortaleza unit). The following table identifies our pulp and paper mills and sets forth the nominal total volume of the production capacity at each mill, as of December 31, 2020.
| | | | Production Capacity | |
| Unit/Location | | Major Products | | (in thousand tons per year) | |
| Mucuri unit — Bahia | | Integrated Pulp | | 200 | |
| | | Market Pulp | | 1,480 | |
| | | Paper | | 250 | |
| | | Tissue | | 60 | |
| Suzano unit — São Paulo | | Integrated Pulp | | 450 | |
| | | Market Pulp | | 70 | |
| | | Fluff(1) | | 100 | |
| | | Paper(1) | | 550 | |
| Limeira – São Paulo | | Integrated Pulp | | 290 | |
| | | Market Pulp | | 400 | |
| | | Paper | | 400 | |
| Rio Verde — São Paulo | | Non-integrated Pulp | | — | |
| | | Market Pulp | | — | |
| | | Paper | | 50 | |
| Imperatriz unit | | Integrated Pulp | | 60 | |
| | | Market Pulp | | 1,590 | |
| | | Paper | | — | |
| | | Tissue | | 60 | |
| Tissue Facepa (Belém & Fortaleza) | | Non-integrated Pulp | | — | |
| | | Market Pulp | | — | |
| | | Tissue | | 50 | |
| Aracruz – Espírito Santo | | Market Pulp | | 2,340 | |
| Três Lagoas – Mato Grosso do Sul | | Market Pulp | | 3,250 | |
| Jacareí – São Paulo | | Market Pulp | | 1,100 | |
| Veracel (2) – Bahia | | Market Pulp | | 560 | |
| (1) | Flexibility to produce either fluff pulp or printing and writing paper. |
| (2) | Represents 50% of the annual production capacity and production of Veracel’s pulp mill. |
For the year ended on December 31, 2020, our facilities had produced 9.8 million tons of total market pulp and approximately 1.2 million tons of paper. The following table sets forth our total pulp and paper production for the periods indicated:
| Production | | 2020 | | | 2019 | | | 2018 | |
| | | (in thousand tons/year) | |
| Market Pulp | | | 9,800 | | | | 8,757 | | | | 3,501 | |
| Paper | | | 1,184 | | | | 1,240 | | | | 1,265 | |
| Total production | | | 10,984 | | | | 9,996 | | | | 4,767 | |
ITEM 4. A. INFORMATION ON THE COMPANY
Not applicable.
ITEM 5. OPERATING AND FINANCIAL REVIEW AND PROSPECTS
The following discussion of our financial condition and operating results should be read in conjunction with our audited consolidated financial statements as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, and for each of the three years ended December 31, 2020, and the accompanying notes thereto, which have been prepared in accordance with IFRS as issued by the IASB, as well as with the information presented under “Presentation of Financial and Other Data”. and “Item 3. Key Information — A. Selected Financial Data.”
The following discussion contains forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. Our actual results may differ significantly from those discussed in the forward-looking statements for several reasons, including, without limitation, the risks described in “Forward-Looking Statements”. and Item 3. “Key Information – Risk Factors.”
Overview
With more than 90 years of experience, we operate mainly in the pulp (paper grade and fluff) and paper (paperboard, printing and writing and tissue) segments. We believe that we are one of the largest vertically integrated producers of pulp and paper in Latin America and, according to Hawkins Wright, Suzano was the largest producer of eucalypt pulp and virgin market pulp in the world in 2020. As other Brazilian eucalyptus pulp producers, we have the lowest cost of pulp production in the world. We believe our modern technology of plantation and harvesting and our strategic location for plantation facilities are among our competitive strengths.
We believe we are one of Brazil’s largest paper producers, and based on data from IBÁ, we accounted for nearly 40% of the printing and writing paper and 25% of the paperboard produced in Brazil in 2020.
On July 26, 2018, Suzano and Fibria entered into the Merger Agreement for the combination of the operations and shareholder bases of Fibria and Suzano through a corporate reorganization. On January 14, 2019, following receipt of all required corporate and regulatory approvals, the Merger was consummated, and Fibria became our wholly owned subsidiary. Upon completion of the Merger, we became the world’s largest producer of market pulp, with an aggregate installed capacity of 10.9 million metric tons of eucalyptus pulp per year and a broad and diversified forest base.
Furthermore, on April 1, 2019, Fibria merged with and into Suzano. As a result, the separate corporate existence of Fibria ceased, and Suzano continued as the surviving entity under the laws of Brazil. Accordingly, title to and possession of all property, interests, assets, rights, privileges, immunities, powers and franchises of Fibria vested in Suzano and all debt, liabilities, duties and obligations of Fibria became debt, liabilities, duties and obligations of Suzano.
With respect to the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, since the beginning we have adopted preventive and mitigating measures in line with the guidelines established by Brazilian and international authorities, Such measures are aimed at minimizing, to the extent possible, the harmful effects from the COVID-19 pandemic on the safety of our employees and the continuity of our businesses.
Our initiatives are based on three pillars:
| (i) | Protection for people: in order to provide security to our employees and third parties who are involved in our operations, we adopted a series of measures aimed at minimizing the exposure of our team and / or mitigating exposure risks. |
| (ii) | Protection of society: one of our three cultural drivers is: “It is only good for us, if it is good for the world”. Therefore, from the beginning of the pandemic to the present, we have adopted a series of measures to protect society, including: |
| • | Donations of personal hygiene products produced by the us (e.g. toilet paper, napkins and disposable diapers) to vulnerable areas; |
| • | Donations of 159 respirators and approximately one million hospital masks to the Federal and State Governments; |
| • | Partnerships with Positivo Tecnologia, Klabin, Flextronics and Embraer, to support Brazilian company Magnamed, in the production and delivery of respirators to the Federal Government. Our disbursement in this action was R$9.6 million; |
| • | Construction, together with Veracel, of a field hospital in the city of Teixeira de Freitas, State of Bahia, which was handed over to the state government and opened in July 2020; |
| • | Partnership with Fatec university of the city of Capão Bonito for the production of alcohol gel; |
| • | Lending of forklifts to move donations received by the Red Cross; |
| • | Maintenance of all direct jobs; |
| • | Support to payroll costs of service providers’ for 90 days (from March to June 2020); |
| • | Support programs to small suppliers and customers, as well as indigenous, quilombola and other communities. |
The disbursements made to carry out the social actions implemented by us totaled R$48.6million through December 31, 2020.
| (i) | Protection for business: to date, we have continued with our normal operations and a crisis management committee has been implemented. |
The World Health Organization (WHO) and several countries recognized the paper and pulp sector as a producer of essential goods, and therefore we have taken measures to ensure, to the greatest extent possible, operational normality and full service to its customers. Such measures include increasing the level of wood and raw material inventories in the factories and advancing its inventories of finished goods product, bringing them closer to their customers to mitigate possible risks of disruption in the factories' supply chain and the sale of products.
The current situation resulting from the COVID-19 also implies a higher credit risk, especially for its customers in the paper business. Thus, we have also been monitoring the evolution of this risk and implementing measures to mitigate it, and so far, there has been no significant financial impact.
Due to quarantine and isolation measures adopted globally, as well as school and office closures and switch to remote work, the demand for printing and writing papers was reduced. In light of this, Suzano and several other paper producers around the world temporarily reduced its paper production volume by means of temporary stoppage at paper production lines. Suzano temporarily suspended the paper production lines of the Mucuri and Rio Verde units, having resumed the activities at the beginning of July 2020.
Finally, it is worth noting that, as a result of the current scenario, the Company has made and maintained a vast communication effort to further increase the interaction with its main stakeholders, with the objective of guaranteeing the adequate transparency and flow of information with the them in a timely manner to the dynamics of the social and economic conjuncture.
We have activated our crisis management team to guarantee coordinated actions for risk mitigation and for contingency and business continuity plans. To date, our operations in Brazil and abroad have not been materially impacted. Nevertheless, given the operational risks arising from the health conditions of our own and third-party employees, as well as the potential legal restrictions that might be imposed due to the COVID-19 pandemic, we cannot assure that our operations and financial condition will not be impacted. For information on how the outbreak of the COVID-19 may affect our operations and financial results, see “Item 3. Key Information — Risk Factors — The outbreak of coronavirus or other diseases may adversely affect our operations and financial results.”
Foreign Currency Impact in Our Operations
As a predominantly exporting company, our results are exposed to exchange variations. As such, fluctuations in the exchange rate, especially with regards to the U.S. dollars, may impact our operating results. We issue debt securities in the international markets as an important part of the capital structure that is also exposed to fluctuations in the exchange rate. The mitigation of these risks comes from our own exports, which creates a natural hedge. Furthermore, we employ U.S. dollar sales, in futures markets, including strategies with options, as a way to ensure attractive levels of operating margins for a portion of our income. The sales in future markets are limited to a percent of the currency over the 18-month horizon and, as such, are dependent on the availability of exchange ready for sale in the short-term.
Pulp Business Unit
The global pulp markets in 2020 were heated throughout the year, despite the negative impacts of pandemic in the main economies worldwide. Changes in consumer behavior supported the strong increase of tissue and packaging papers demand, while the graphic paper consumption was hardly impacted by the economic slowdown and social isolation measures.
On the supply side, pulp availability remained relatively balanced, with over 2 million tons of pulp unexpectedly withdrawn from the market offsetting the increase in production by some producers and temporary conversions of integrated capacities of dissolving pulp to market pulp.
Our pulp production volume increased 12%, from 8.8 million tons in 2019 to 9.8 million tons in 2020. Our sales volume in 2020 increased 15%, from 9.4 million tons in 2019 to 10.8 million tons in 2020. The higher sales volume during the year was supported by the market fundamentals mentioned above.
Net revenue from pulp sales totaled R$25,578.3 million in 2020 (an increase of 21.6% compared to 2019), mainly due to (i) higher sale volume and (ii) the depreciation of the Brazilian real against the U.S. dollar. The share of pulp revenue from exports was 94%, while the domestic market accounted for 6%. With regard to distribution for end use, 64% of pulp sales went to sanitary paper production, 16% to printing and writing paper, 12% to special papers and 7% to packaging.
The average net pulp selling price was US$458/ton in 2020 (a decrease of 19% compared to 2019), while average net price in reais stood at R$2,363/ton (an increase of 5.8% compared to 2019). This divergence in prices in different currencies are related to lower pulp prices in the international markets on an annual average basis that were offset by a stronger Brazilian real against the U.S. dollar. Pulp cash cost ex-downtime was R$604/ton, 9% lower than in the previous year, due to lower wood and input costs (which were offset by the increase in average USD vs. BRL) as well as fixed costs.
Paper Business Unit
According to the IBÁ, domestic sales of printing & writing paper and paperboard contracted 12% in 2020 compared to 2019, while imports decreased 39%.
Our paper production decreased 5%, from 1.23 million tons in 2019 to 1.18 million tons in 2020. This decrease is explained by the reduction in printing and writing, which was offset by the COVID-19 pandemic effects. However, the decrease in printing and writing was partially counterbalanced by tissue production, positively affected by the pandemic. Paper sales stood 1.2 million tons in 2020 to 1.3 million tons in 2019.
In 2020, our net revenue from paper sales totaled R$4,882 million, decreasing 2.1% from the previous year. Net revenue from the domestic and export markets decreased 3.5% and increased 1.2%, respectively, with 68.8% coming from domestic sales and 31.2% from exports. The breakdown of our total revenue from paper sales in 2020 was: 83.6% in Latin America (including Brazil), 5.4% in North America and 11.0% in other regions. Average net paper price in 2020 was R$4.148/ton, 5% higher than in 2019.
In the domestic market, average net paper price was R$4.188/ton, increasing 3% in relation to 2019. In the international market, average price was US$788/ton, down 17% from 2019. In Brazilian real, the average price in the international market was R$4.063/ton, 9% higher than in 2019.
New Accounting Policies and Changes in the Accounting Policies Adopted
Change in the functional currency
Due to the Merger, we experienced several changes in our structure, activities and operations during the year of 2019 that led management to conclude that they needed to reassess the functional currency of our subsidiaries whose functional currency was different from Brazilian Reais.
Those facts resulted in the corporate reorganization, as well as impacted how management conducted our business in order to achieve the alignment between the cultures of the two companies, the unification of processes, operating, systems, tax strategies and synergy gains arising from the business combination. In this process some of our wholly-owned subsidiaries were considered an extension of the activities of the parent company.
These circumstances collectively justify the change in the functional currency to Brazilian Real and they have occurred gradually during 2019, therefore it was not practicable to determine the date of the change at a precise point during the reporting period. Thus, we changed the functional currency of those wholly-owned subsidiaries as of January 1, 2020.
The cumulative translation adjustment (“CTA”) arising from the translation of a foreign operation previously recognized in other comprehensive income will not be reclassified from equity to profit or loss until the disposal of the operations. The total or partial disposal of interest in wholly-owned subsidiaries occurs through sale or dissolution, of all or part of operation.
Therefore, the financial statements of foreign subsidiaries, whose functional currency are different from Brazilian Reais, were translated using the criteria established below:
| (i) | assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rate in effect at period end; |
| (ii) | revenues and expenses are translated based on the monthly average rate; |
| (iii) | the cumulative effects of gains or losses upon translation are recognized as accumulated foreign currency translation adjustments component of other comprehensive income. |
And as from January 1, 2020, the financial statements of foreign subsidiaries, whose functional currency became the Brazilian Real, are converted using the criteria established below:
| (i) | monetary assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rate in effect at period-end; |
| (ii) | non-monetary assets and liabilities are translated at the historical rate of the transaction; |
| (iii) | revenues and expenses are translated based on monthly average rate; |
| (iv) | the cumulative effects of gains or losses on the conversion of the above items are recorded in the financial result of the year. |
Interest rate reform – IAS 39 / IFRS 7 and IFRS 9 - Phase 1 (Applicable on/or after January 1, 2020)
The above mentioned pronouncements were amended by the IASB in response to the ongoing reform of the Interbank offered rates (“Ibor”) and other reference interest rates, issuing a package of amendments to IFRS standards. According to the IASB, the changes are aimed at helping companies provide investors with useful information about the effects of the reform on its financial statements.
The changes made by the IASB in 2020 complement those issued in 2019 and consider the effects, in the financial statements, when a company substitutes, as a result of the reform, the old reference interest rate with an alternative.
The adoption of this pronouncement is divided into 2 (two) phases:
| • | Phase 1: the changes to this phase were issued in September 2019 and provided temporary exemptions from the application of specific hedge accounting requirements for relationships affected by uncertainties that arise as a result of the IBOR reform (exemptions from Phase 1). We assessed the amendments and did not identify any impacts; and |
| • | Phase 2: the changes to this phase were issued in August 2020 and can be summarized as follows: changes in contractual cash flows, hedge accounting requirements and disclosures, as further discussed in Note 3.3.1 to our financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2020. |
New standards, revisions and interpretations not yet in force
Interest Rate Reform – IAS 39 / IFRS 7 and IFRS 9 – Phase 2 (Applicable on / or after January 1, 2021, early adoption permitted)
The new and changed standards and interpretations have been issued, but are not yet in force. We intend to adopt these new standards, changes and interpretations, if applicable, when they come into force and we do not expect them to have a material impact on the financial statements.
| (i) | changes in contractual cash flows: Practical expedient that allows to replace, as a consequence of the reform, the effective interest rate of a financial asset or financial liability with a new economically equivalent rate, without derecognition of the contract; |
| (ii) | hedge accounting requirements: End of exemptions for evaluating the effectiveness of hedge accounting relationships (Phase 1); and |
| (iii) | disclosure: Requirements about the disclosure of risks to which the entity is exposed by the reform, risk management and evolution of the IBORs transition. |
Accounting Judgments, Estimates and Assumptions
This section focuses on critical accounting estimates and assumptions where the nature of the estimates or assumptions is material due to the levels of subjectivity and judgment necessary to account for highly uncertain matters or the susceptibility of such matters to change; and the impact of the estimates and assumptions on our financial condition or operating performance.
Our management has used estimates, judgments and accounting assumptions regarding the future that affect the application of our accounting practices and the amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
See below information on judgments and assumptions used while applying accounting policies that have significant effects on the amounts recognized in our audited consolidated financial statements and which have significant risk of causing material adjustments:
| (i) | control, significant influence and consolidation (see note 1.1 to our audited consolidated financial statements); |
| (ii) | share-based payment transactions (see note 22 to our audited consolidated financial statements); |
| (iii) | transfer of control for revenue recognition (see note 28 to our audited consolidated financial statements); |
| (iv) | fair value of financial instruments (see note 4 to our audited consolidated financial statements); |
| (v) | annual analysis of the impairment of non-financial assets (see notes 15 and 16 to our audited consolidated financial statements); |
| (vi) | expected credit losses (see note 7 to our audited consolidated financial statements); |
| (vii) | net realizable value provision for inventories (see note 8 to our audited consolidated financial statements); |
| (viii) | annual analysis of recoverability of taxes (see notes 9 and 12 to our audited consolidated financial statements); |
| (ix) | fair value of biological assets (see note 13 to our audited consolidated financial statements); |
| (x) | useful life of property, plant and equipment and intangible assets with defined useful life (see notes 15 and 16 to our audited consolidated financial statements); |
| (xi) | annual analysis of recoverable amount of goodwill (see note 16 to our audited consolidated financial statements); |
| (xii) | provision for legal liabilities (see note 20 to our audited consolidated financial statements); |
| (xiii) | pension and post-employment plans (see note 21 to our audited consolidated financial statements); and |
For more information, see note 3 to our audited consolidated financial statements.
A. Operating Results
Results of operations
The following discussion of our results of operations is based on our audited consolidated financial statements as of December 31, 2020 and 2019 and for the three years ended December 31, 2020. For a discussion of our results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to the year ended December 31, 2018, please see “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—A. Operating Results—Results of Operations— Year ended December 31, 2019 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2018” of our annual report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2019.
References to increases or decreases in any year or period are made by comparison with the corresponding prior year or period, except as the context otherwise indicates.
| | | | | | For the year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2020 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | | | 2018 | |
| | | US$ (3) | | | (in thousands of R$), except per share data | |
| Net sales | | | 5,861,465 | | | | 30,460,277 | | | | 26,012,950 | | | | 13,443,376 | |
| Cost of sales | | | (3,649,687 | ) | | | (18,966,331 | ) | | | (20,743,482 | ) | | | (6,922,331 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 2,211,778 | | | | 11,493,946 | | | | 5,269,468 | | | | 6,521,045 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating income (expenses) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Selling | | | (418,468 | ) | | | (2,174,652 | ) | | | (1,905,279 | ) | | | (598,726 | ) |
| General and administrative | | | (277,713 | ) | | | (1,443,192 | ) | | | (1,173,358 | ) | | | (825,209 | ) |
| Income from associates and joint ventures | | | 6,955 | | | | 36,142 | | | | 31,993 | | | | 7,576 | |
| Other, net | | | 102,209 | | | | 531,150 | | | | 405,754 | | | | (96,875 | ) |
| Operating profit before net financial income (expenses) | | | 1,624,761 | | | | 8,443,394 | | | | 2,628,578 | | | | 5,007,811 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net financial income (expenses) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial expenses | | | (858,126 | ) | | | (4,459,425 | ) | | | (4,178,848 | ) | | | (1,500,374 | ) |
| Financial income | | | 63,016 | | | | 327,475 | | | | 493,246 | | | | 459,707 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | (1,813,205 | ) | | | (9,422,682 | ) | | | (1,075,252 | ) | | | (2,735,196 | ) |
| Monetary and exchange variations, net | | | (2,411,317 | ) | | | (12,530,891 | ) | | | (1,964,927 | ) | | | (1,066,650 | ) |
| Net income (loss) before taxes | | | (3,394,872 | ) | | | (17,642,129 | ) | | | (4,097,203 | ) | | | 165,298 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Income taxes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current | | | (35,008 | ) | | | (181,926 | ) | | | (246,110 | ) | | | (586,568 | ) |
| Deferred | | | 1,368,007 | | | | 7,109,120 | | | | 1,528,571 | | | | 741,084 | |
| Net income (loss) for the period | | | (2,061,873 | ) | | | (10,714,935 | ) | | | (2,814,742 | ) | | | 319,814 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Result of the period attributed to the controlling shareholders | | | (2,063,777 | ) | | | (10,724,828 | ) | | | (2,817,518 | ) | | | 319,693 | |
| Result of the period attributed to non-controlling shareholders | | | 1,904 | | | | 9,893 | | | | 2,776 | | | | 121 | |
| Earnings (loss) per share | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic (1) | | | (1.52961 | ) | | | (7.94890 | ) | | | (2.08825 | ) | | | 0.29236 | |
| Diluted (2) | | | (1.52961 | ) | | | (7.94890 | ) | | | (2.08825 | ) | | | 0.29199 | |
| (1) | Basic earnings per share is calculated using the income attributable to controlling shareholders divided by the weighted average number of outstanding common shares. |
| (2) | Diluted earnings per share is calculated based on the results attributable to the controlling shareholders divided by the weighted average number of outstanding common shares, subtracted from the potential dilutive effect generated by the conversion of all common shares. Due to the loss recorded in the period, we do not consider the dilution effect in the calculation |
| (3) | In thousands of US$, except per share data. For convenience purposes only, amounts in reais in the year ended December 31, 2020 have been translated to U.S. dollars using a rate of R$5.1967 to US$1.00, the commercial selling rate for U.S. dollars at December 31, 2020 as reported by the Central Bank of Brazil. These translations should not be considered representations that any such amounts have been, could have been or could be converted into U.S. dollars at that or at any other exchange rate. |
Year ended December 31, 2020 compared to year ended December 31, 2019
Net sales revenue
Our net sales revenue increased 17.1%, or R$4,447.3 million, from R$26,013.0 million in the year ended December 31, 2019 to R$30,460.3 million in the corresponding period in 2020, mainly due to (i) depreciation of the average real against the U.S. dollar, and (ii) a 15.0% increase in pulp sales volume when compared to the volume in the year ended December 31, 2019, partially offset by a 19.1% decrease in pulp prices in U.S. dollars.
Our net sales revenue from pulp increased 21.6%, or R$4,550.6 million, from R$21,027.7 million in the year ended December 31, 2019 to R$25,578.3 million in the corresponding period in 2020, mainly due to (i) depreciation of the average real against the U.S. dollar, and (ii) a 15.0% increase in pulp sales volume when compared to the volume in the year ended December 31, 2019, partially offset by a 19.1% decrease in pulp prices in U.S. dollars. Our net sales revenue from pulp represented 80.8% of total net sales revenue in the year ended December 31, 2019, compared to 84.0% in the corresponding period in 2020.
Our net sales revenue from pulp exports increased 24.9%, or R$4,775.1 million in 2020, from R$19,193.8 million in the year ended December 31, 2019 to R$23,968.8 million in the corresponding period in 2020, mainly due to (i) depreciation of the average real against the U.S. dollar, and (ii) a 17.0% increase in pulp export sales volume when compared to the volume in the year ended December 31, 2019, partially offset by a 18.3% decrease in pulp export prices in U.S. dollars. Net revenues from pulp exports represented 78.7% of total net revenues in the year ended December 31, 2020 (42.4% from Asia, 21.0% from Europe, 14.3% from North America and 1.0% from South and Central America).
Our average international net sales price of pulp in the year ended December 31, 2020 decreased 18.3%, or US$104/ton, from US$567/ton in the year ended December 31, 2019 to US$463/ton in the corresponding period in 2020. In the domestic market, our average net pulp sales price decreased 7%, or R$161/ton, from R$2,207/ton in the year ended December 31, 2019 to R$2,046/ton in the corresponding period in 2020.
Our net sales revenue from paper decreased 2.1%, or R$103.2 million, from R$4,985.3 million in the year ended December 31, 2019 to R$4,882.0 million in the corresponding period in 2020. Net sales revenue from paper represented 19.2% of total net sales in the year ended December 31, 2019, compared to 16.0% in the corresponding period in 2020. The decrease in net sales revenue from paper in the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the corresponding period in 2019 is due to lower sales volume. Net revenues from paper exports represented 5.0% of total net revenues in the year ended December 31, 2020 (2.4% from South and Central America, 0.9% from North America, 0.9% from Europe, 0.6% from Asia and 0.3% from Africa). Our net sales revenue from paper in the domestic market decreased 3.5%, or R$122.1 million, from R$3,480.3 million in the year ended December 31, 2019 to R$3,358.2 million in the corresponding period in 2020, impacted mainly by sales volume decrease.
The average international net paper sales price in 2020 decreased 16.7%, or US$158/ton, from US$946/ton in the year ended December 31, 2019 to US$788/ton in the corresponding period in 2020. In the domestic market, the average net paper sales price increased 3%, or R$110/ton, from R$4,078/ton in the year ended in December 31, 2019 to R$4,188/ton in the corresponding period in 2020.
Cost of sales
Our total cost of sales decreased 8.6%, or R$1,777.2 million, from R$20,743.5 million in the year ended December 31, 2019 to R$18,966.3 million in the corresponding period in 2020, mainly due to (i) decrease of R$2,534.6 million in variable cost, (ii) decrease of R$1,362.0 in depreciation, depletion and amortization, partially offset by the depreciation of the average real against the U.S. dollar and higher sales volumes.
Gross profit
Our gross profit increased 118.1%, or R$6,224.4 million, from R$5,269.5 million in the year ended December 31, 2019 to R$11,493.9 million in the corresponding period in 2020, due to the factors mentioned above. Our gross margin in the year ended December 31, 2019 was 20.3% compared to 37.7% in the corresponding period in 2020. This increase is mainly due to the depreciation of the average real against the U.S. dollar benefiting net revenues and the decrease in cost of sales as explained above.
Selling, general and administrative
Our selling expenses increased 14.1%, or R$269.4 million, from R$1,905.3 million in the year ended December 31, 2019 to R$2,174.7 million in the corresponding period in 2020. The main variation is due to (i) the impact of the depreciation of the average real against the U.S. dollar on logistics cost, and (ii) higher sales volumes in the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the same period in 2019.
Our general and administrative expenses increased 23.0%, or R$269.8 million, from R$1,173.4 million in the year ended December 31, 2019 to R$1,443.2 million in the corresponding period in 2020. The variation is due to (i) an increase of R$219.8 million in personnel expenses, (ii) expenses of R$89.7 million related to the COVID-19 pandemic occurred in 2020, and (iii) an increase of R$52.1 million in depreciation, amortization and depletion in the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the same period in 2019.
Other, net
Our other operating income (expenses), increased R$125.4 million, from a gain of R$405.8 million in the year ended December 31, 2019 to a gain of R$531.2 million in the corresponding period in 2020. The increase is mainly due to: (i) an increase in the amount of R$281.1 million in the result on fair value adjustment of biological assets, (ii) increase of R$120.4 million on the sale and disposal of property, plant and equipment and biological assets and, (iii) increase of R$41.6 million on the sale of other products.
Operating profit before net financial income (expenses)
Our operating profit before net financial income (expense) increased 221.2%, or R$5,814.8 million, from a profit of R$2,628.6 million in the year ended December 31, 2019 to a profit of R$8,443.4 million in the corresponding period in 2020, due to the facts mentioned above. Our operating margin in the year ended December 31, 2019 was 10.1% compared to 27.7% in the corresponding period in 2020. This increase is mainly due to the depreciation of the average real against the U.S. dollar benefiting net revenues and the decrease in cost of sales as explained above.
Net financial income (expenses)
Our net financial income (expenses) decreased 287.8% or R$19,359.7 million, from a loss of R$6,725.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 to a loss of R$26,085.5 million in the corresponding period in 2020. This decrease was largely due to (i) an increase in expenses (income) from monetary and exchange rate variation, net of R$10,566.0 million, and (ii) an increase in expenses (income) from derivative financial instruments of R$8,347.4 million in the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the same period of 2019 as described in note 27 to our audited consolidated financial statements.
Net income (loss) before taxes
Our net income (loss) before taxes decreased 330.6% or R$13,544.9 million, from a loss of R$4,097.2 million in the year ended December 31, 2019 to a loss of R$17,642.1 million in the same period in 2020. This result was largely impacted by the factors mentioned above.
Income taxes
Our income taxes increased 440.1% or R$5,644.7 million, from an income tax gain of R$1,282.5 million in the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to an income tax gain of R$6,927.2 million during the corresponding period in 2020. This increase was largely due to the fact that in the year ended December 31, 2020 the effective rate of income and social contribution tax expenses was 39.3% compared to 31.3% in the same period of 2019. The increase in the effective rate of income and social contribution tax expenses is mainly due to the increase of the tax effect on permanent differences in the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the corresponding period in 2019, as follows (i) a decrease of R$1,398.8 million on Taxation (difference) on profit of wholly-owned subsidiaries abroad; (ii) an increase of R$580.4 million on intercompany transaction (Thin Capitalization – for further details, please refer to Financial Statements – note 12.2), (iii) a decrease of R$72.9 million on the offset of income taxes abroad, (iv) a decrease of R$67.3 million related to merged subsidiaries.
Net income (loss) for the year
Our net income decreased 280.7% or R$7,900.2 million, from a loss of R$2,814.7 million in the year ended December 31, 2019 to a net loss of R$10,714.9 million during the corresponding period in 2020. This result was mainly due to the factors mentioned above.
B. Liquidity and Capital Resources
Sources and Uses of Funds
Our cash flow from operating, investing and financing activities is affected by various factors. The key factors that affect our cash flow from operations are (i) the volume of product sold and the market price of pulp, (ii) the exchange rate between reais and U.S. dollars and (iii) the cost of our raw materials. Investing activities are mainly affected by (i) our capital expenditure program and (ii) our decision to divest some of our assets, such as fixed assets and biological assets. Finally, our cash flow from financing activities is directly related to the level of new debt we have incurred and on the repayment of existing debt.
In our opinion, we believe that our working capital is sufficient for our present requirements. Our primary sources of liquidity have historically been cash flows from operating and financing activities and short-term and long-term borrowings.
Our material cash requirements have historically included the following:
Long-term borrowings have generally been used to finance our major capital expenditure projects and have historically been sourced principally by either export prepayment contracts under which we, or one of our wholly owned subsidiaries, borrow funds by offering the guarantee of export contracts, issuance of Agribusiness Receivables Certificates (“CRA”), or capital expenditures acquisition financing programs offered by BNDES. The scheduled maturities of these long-term loans have been structured to match the expected cash flow from the conclusion of the related capital expenditure projects and, as a result, reduce the risk of any significant deterioration of our liquidity position. We also rely on bonds or notes issued in the international markets either by wholly-owned subsidiaries, mainly domiciled in other countries.
As of December 31, 2020 and 2019, our cash and cash equivalents were R$6,835.1 million and R$3,249.1 million, respectively. Of our cash and cash equivalents and marketable securities held as of December 31, 2020, 5% was denominated in reais invested in both public and private financial investments. The remaining 95% of our cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities was denominated in U.S. dollars.
If necessary, we also have access to an RCF (Revolving Credit Facility) up to 2024 in the total amount of US$500 million. The RFC funds are available to the us at any moment upon a notice of borrowing 3 business day prior to the disbursement.
The fair value of derivative financial instruments represented a net liability balance of R$6,776.0 million as of December 31, 2020.
As of December 31, 2020, our balance sheet presented a positive working capital balance (current assets less current liabilities) of R$9,785.2 million compared to R$7,405.0 million on December 31, 2019. Our current assets as of December 31, 2020 were equivalent to 2.2 times our current liabilities.
For 2021, we have already announced to the market, as approved by our Board of Directors, the intention to invest R$4.9 billion as maintenance capex (for further information please see “─Capital Expenditures” below). This will primarily be financed by the cash and cash equivalents and cash generation for 2021.
For the year of 2021, we also believe that we will be able to access either capital or banking markets, if necessary.
With respect to long term capital needs, we use a model of ten years to monitor our needs in a series of scenarios and variables, including currency exchange rates and commodity prices, with the intention to preserve the liquidity and improve the capital structure. In this context, we work to anticipate exercises of liability management to improve liquidity or if conditions are favorable.
All of our future liquidity conditions rely on a series of scenarios and may be adversely affected depending on market and other conditions. Actual liquidity may differ significantly for several reasons, including, without limitation, the risks described in “Forward-Looking Statements” and Item 3. “Key Information – Risk Factors.”
Operating Activities
Our net cash provided by operating activities totaled R$13,124.6 million in the year ended December 31, 2020, compared to net cash provided in operating activities of R$7,576.4 million in the year ended December 31, 2019. This increase of R$5,548.2 million was primarily due to higher operating cash generation.
Investing Activities
Our net cash used in investing activities totaled R$736.4 million during the year ended December 31, 2020, compared to net cash used in investing activities of R$11,695.0 million in the year ended December 31, 2019. During the year ended December 31, 2020 investing activities for which our used cash primarily consisted of (i) R$1,503.3 million used in additions to property, plant and equipment and (ii) R$3,392.3 million used in additions to biological assets and (iii) cash provided by marketable securities net in the amount of R$3,841.5 million.
Financing Activities
Our financing activities used net cash of R$9,785.1 million during the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to net cash provide in financing activities of R$3,141.8 million in the year ended December 31, 2019. During the year ended December 31, 2020, our principal sources of financing were (i) R$14,761.8 million in loans and financing and debentures, which mainly consisted of R$6,640.3 in Senior Notes (bonds), R$4,899.1 million in export pre-payment transactions (EPP), R$2,638.2 million in revolving credit facility and R$531.7 million in contracts with BNDES (Brazilian National Bank of Social and Economic Development). During the year ended December 31, 2020, our principal uses of financing included (i) repayment of R$19,092.8 million of loans, financing and debentures, (ii) payment of R$4,465.6 million of derivative transactions.
Capital Expenditures
Our capital expenditures (capital expenditures incurred – cash basis) totaled R$4,897.9 million (without projects from ICMS credit ES) in the year ended December 31, 2020, R$4,868.4 million in the in the year ended December 31, 2019. In the year ended December 31, 2020, the amount of R$3,406.2 million was allocated to industrial and forestry maintenance. Investments in projects related to structural competitiveness and adjacent businesses projects amounted to R$727.8 million and were allocated mainly to the expansion in port logistics, expansion and modernizations projects. Other investments amounted to R$91.0 million.
The approved budget of our capital expenditures for 2021, amounting to R$4,935 million (without projects from ICMS credit ES), encompasses remaining investments in projects previously disclosed to the market, such as investment in port logistics assets and potential new investments in lands and forests that may increase our future competitiveness and maintain options for the future growth of our business.
Indebtedness
As of December 31, 2020, our total consolidated outstanding indebtedness (which includes current and non-current loans, financing and debentures) was R$72,899.9 million, of which R$2,043.4 million represented current indebtedness (R$2,035.8 million refers to loans and financing and R$7.6 million refers to debentures) and R$70,856.5 million represented non-current indebtedness (R$65,441.4 million refers to loans and financing and R$5,415.1 million refers to debentures). The description of our consolidated financings and loans is presented below:
| | | | | | | | Current | | | Non-current | | | Total | |
Type | | Interest
rate | | Average
annual
interest
rate - % | | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | | | December 31,
2020 (1) | | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| | | | | | | | (in thousands of R$) | | | (in thousands of R$) | | | (in thousands of US$) | | | (in thousands of R$) | |
| In foreign currency | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BNDES | | UMBNDES | | | 4.8 | | | | 2,506 | | | | 26,307 | | | | 24,486 | | | | 27,620 | | | | 5,194 | | | | 26,992 | | | | 53,927 | |
| Bonds | | Fixed | | | 5.3 | | | | 779,046 | | | | 640,177 | | | | 37,232,554 | | | | 27,375,673 | | | | 7,314,565 | | | | 38,011,600 | | | | 28,015,850 | |
| Export credits (Pre-payment / ACC) | | Libor/Fixed | | | 1.6 | | | | 718,623 | | | | 1,994,868 | | | | 19,400,208 | | | | 15,431,478 | | | | 3,871,463 | | | | 20,118,831 | | | | 17,426,346 | |
| Others | | | | | | | | | 2,516 | | | | 3,481 | | | | | | | | | | | | 484 | | | | 2,516 | | | | 3,481 | |
| | | | | | | | | | 1,502,691 | | | | 2,664,833 | | | | 56,657,248 | | | | 42,834,771 | | | | 11,191,706 | | | | 58,159,939 | | | | 45,499,604 | |
| In local currency | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BNDES | | TJLP | | | 6.8 | | | | 276,441 | | | | 283,658 | | | | 1,254,222 | | | | 1,517,649 | | | | 294,545 | | | | 1,530,663 | | | | 1,801,307 | |
| BNDES | | TLP | | | 10.0 | | | | 25,535 | | | | 18,404 | | | | 522,367 | | | | 441,233 | | | | 105,433 | | | | 547,902 | | | | 459,637 | |
| BNDES | | Fixed | | | 4.9 | | | | 29,115 | | | | 39,325 | | | | 47,177 | | | | 77,333 | | | | 14,681 | | | | 76,292 | | | | 116,658 | |
| BNDES | | SELIC | | | 5.5 | | | | 98,531 | | | | 78,458 | | | | 1,068,959 | | | | 718,017 | | | | 224,660 | | | | 1,167,490 | | | | 796,475 | |
| FINAME | | Fixed | | | | | | | | | | | 4,781 | | | | | | | | 9,564 | | | | | | | | | | | | 14,345 | |
| BNB | | Fixed | | | | | | | | | | | 37,815 | | | | | | | | 156,904 | | | | | | | | | | | | 194,719 | |
| CRA (“Agribusiness Receivables Certificates”) | | CDI/IPCA | | | 7.6 | | | | 32,156 | | | | 2,860,938 | | | | 3,025,527 | | | | 2,952,451 | | | | 588,389 | | | | 3,057,683 | | | | 5,813,389 | |
| Export credit note | | CDI | | | 5.5 | | | | 15,184 | | | | 131,914 | | | | 1,275,045 | | | | 1,270,065 | | | | 248,279 | | | | 1,290,229 | | | | 1,401,979 | |
| Rural producer certificate | | CDI | | | 7.8 | | | | 2,738 | | | | 5,840 | | | | 273,578 | | | | 273,303 | | | | 53,171 | | | | 276,316 | | | | 279,143 | |
| Export credits (“Pre-payment”) | | Fixed | | | 7.6 | | | | 77,570 | | | | 77,694 | | | | 1,313,661 | | | | 1,312,586 | | | | 267,714 | | | | 1,391,231 | | | | 1,390,280 | |
| FCO (“Central West Fund”), FDCO (“Central West Development Fund”) and FINEP | | Fixed | | | | | | | | | | | 76,596 | | | | | | | | 475,905 | | | | | | | | | | | | 552,501 | |
| Others (revolving cost, working capital, FDI and fair value adjustment on business combination) | | Fixed | | | 0.4 | | | | (24,165 | ) | | | (62,302 | ) | | | 3,651 | | | | 4,559 | | | | (3,948 | ) | | | (20,514 | ) | | | (57,743 | ) |
| Debentures | | CDI | | | | | | | 7,590 | | | | 9,997 | | | | 5,415,061 | | | | 5,412,035 | | | | 1,043,480 | | | | 5,422,651 | | | | 5,422,032 | |
| | | | | | | | | | 540,695 | | | | 3,563,118 | | | | 14,199,248 | | | | 14,621,604 | | | | 2,836,404 | | | | 14,739,943 | | | | 18,184,722 | |
| | | | | | | | | | 2,043,386 | | | | 6,227,951 | | | | 70,856,496 | | | | 57,456,375 | | | | 14,028,110 | | | | 72,899,882 | | | | 63,684,326 | |
| Interest on financing | | | | | | | | | 935,010 | | | | 886,886 | | | | | | | | 136,799 | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,023,685 | |
| Non-current funding | | | | | | | | | 1,108,376 | | | | 5,341,065 | | | | 70,856,496 | | | | 57,319,576 | | | | 14,028,110 | | | | 72,899,882 | | | | 62,660,641 | |
| | | | | | | | | | 2,043,386 | | | | 6,227,951 | | | | 70,856,496 | | | | 57,456,375 | | | | 14,028,110 | | | | 72,899,882 | | | | 63,684,326 | |
Notes:
(1) For convenience purposes only, amounts in reais for the year ended December 31, 2020 have been translated to U.S. dollars using a rate of R$5.1967 to US$1.00, the commercial selling rate for U.S. dollars at December 31, 2020 as reported by the Central Bank of Brazil. These translations should not be considered representations that any such amounts have been, could have been or could be converted into U.S. dollars at that or at any other exchange rate.
Debt
Our major categories of long-term indebtedness are described below. The total amounts given below include accrued interest.
| • | Export financing lines in the total outstanding amount of US$4,387.5 million (equivalent to R$22,800.3 million as of December 31, 2020). This category includes export credits (syndicated and bilateral loans), export credit note and export credits (“Pre-payment”). |
| • | U.S. dollar-denominated fixed rate notes in the total outstanding amount of US$7,314.6 million (equivalent to R$38,011.6 million as of December 31, 2020). We have issued in public offerings several series of fixed-rate debt securities, through our subsidiaries, guaranteed by us. |
| • | Certificates of Agribusiness Receivables in the total outstanding amount of US$588.4 million (equivalent to R$3,057.7 million as of December 31, 2020). |
| • | Debentures in the total outstanding amount of US$ 1,043.5 million (equivalent to R$ 5,422.7 million as of December 31, 2020). |
We have a variety of credit lines available, as of December 31, 2020, including two revolving credit facilities with national and international banks, which will mature in 2021 and 2024, respectively. The revolving credit lines allow more efficient cash management, consistent with our strategic focus on cost of capital reduction. As of December 31, 2020, we had no outstanding drawn amounts under these facilities, and the total amount available under these facilities was US$692.4 million (R$3,598.3 million). On April 2, 2020, in order to increase our cash position, we withdrew the amount of US$500.0 and repaid in August 20, 2020.
Export Prepayment Agreements (EPP)
On February 14, 2020, the Company, through its subsidiary Suzano Pulp and Paper Europe S.A., Suzano Austria GmbH and Fibria Overseas Finance Ltd., signed an export prepayment agreement in the amount of US$850.0 million (equivalent at the transaction date to R$3,672.2 million) maturing in February of 2026, with quarterly interest payments of 1.15% per year plus the quarterly LIBOR.
On December 17, 2020, the Company, through its subsidiary Suzano International Trade GmbH, signed a bilateral export prepayment agreement in the amount of US$100.0 million (equivalent on the transaction date to R$517.4 million) maturing in one year, with annual interest rate of 1.3825%.
On December 23, 2020, the Company, through its subsidiary Suzano Pulp and Paper Europe SA, signed a bilateral export prepayment agreement in the amount of US$140.0 million (equivalent on the transaction date to R$709.4 million) maturing in one year, with annual interest rate of 1.35%.
On February 10, 2021, the Company, through its subsidiary Suzano Pulp and Paper Europe SA, signed a sustainability-linked export prepayment agreement in the amount of US$1.570.0 million (equivalent on the transaction date to R$8,481.8 million) maturing in six years, with quarterly interest rate payment of Libor plus 1.15%, which may be subject to positive or negative adjustments ranging from -2bps/+2bps per year depending on our progress in achieving certain milestones towards satisfying key performance metrics (KPIs) related to our industrial water withdrawals and greenhouse gas emissions, as confirmed by an independent external verifier.
All of the operations above are fully guaranteed by Suzano S.A.
Revolving credit facility
On April 02, 2020, the Company, through its subsidiary Suzano Pulp and Paper Europe S.A., withdrew the amount of US$500.0 million (equivalent on the transaction date to R$2,638.2 million) from its credit limit (revolving credit facility) maintained with certain financial institutions, with quarterly payments of LIBOR plus 1.30%, maturing in February 2024. On August 20, 2020 the Company repaid the full amount and the credit returned to be fully available until final maturity.
Banco Nacional de Desenvolvimento Econômico e Social (BNDES)
On June 29, 2020, the Company signed with BNDES a financing agreement in the amount of R$400.0 million, indexed by Selic interest rate plus 1.96% per year, maturing in February 2040, following the strategy of reducing the average cost of debt.
On December 22, 2020, the Company signed with the BNDES a financing agreement in the amount of R$131.8 million, which R$100.0 million refers to a second disbursement from the financing agreement above and R$31.8 million indexed by the long-term interest rate (TLP) plus 1.77% per year, maturing in November 2034.
On February 9, 2021, the Company early settled a financing agreement with BNDES in the principal amount of R$1,453.8 million, with original maturity in May 2026 and monthly interest rate indexed by Selic interest rate plus 3% per year and the long-term interest rate (TJLP) plus 2% per year, with a transaction cost in the amount of R$30,000.
Sustainability-linked Notes 2031 (Senior Notes 2031)
On September 14, 2020, the Company, through its subsidiary Suzano Austria GmbH, issued a principal amount of US$750.0 million in 3.750% Senior Notes due 2031 (equivalent to R$3,973.8 million on the transaction date) with a coupon of 3.750%, with semi-annual interest payments, maturing in 2031.
On November 19, 2020, we issued additional 3.750% Senior Notes due 2031, in the principal amount of US$500.0 million (equivalent to R$2,666.5 million on the transaction date).
These notes are linked to our ability to achieve, by December 31, 2025, a specified target reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions, as confirmed by an independent external verifier, under our new Sustainability-Linked Securities Framework adopted in September 2020. If we do not satisfy the Sustainability Performance Target and provide confirmation thereof to the Trustee together with a related confirmation by the external verifier at least 30 days prior to July 16, 2026, the coupon rate on the bonds will automatically step up by 25 bps to 4.000% per annum.
Fundo de Desenvolvimento do Centro Oeste (FDCO)
On December 28, 2020, the Company prepaid the financing agreement signed with the FDCO in the amount total R$512.0 million, with original maturity date in December in 2027 and semi-annual interest payment of 8.00% per year. It follows the Company strategy to reduce the average cost of debt.
Prepayment of Export Prepayment Agreements (EPP)
On February 14, 2020, the Company, through its subsidiary Suzano Pulp and Paper Europe S.A., prepaid an export prepayment agreement in the amount of US$755.9 million (equivalent on the transaction date to R$3,240.2 million), with original maturity in February 2023 and quarterly interest payments of 1.15% per year plus quarterly LIBOR.
On December 07, 2020, the Company, through its subsidiary Suzano Pulp and Paper Europe S.A., partially prepaid the export prepayment agreement in the total amount of US$300.0 million (equivalent on the transaction date to R$1,355.4 million), with original maturity in December 2023 and quarterly interest payment of 1.15% per year plus quarterly LIBOR.
On March 8, 2021, the Company, through its subsidiary Suzano Pulp and Paper Europe S.A., prepaid a portion of the export prepayment agreement in the principal amount of US$1,666.8 million (equivalent on the transaction date to R$9,558.2 million), with original maturity in December 2023 and quarterly interest payments of 1.15% per year plus quarterly LIBOR.
Senior Notes Partial Repurchases (Notes 2024, 2025 and 2026)
The resources obtained with the September 2020 issuance of 2031 Senior Notes were used to repurchase part of the Senior Notes issued by Fibria Overseas Finance Ltd. and Suzano Austria GmbH in concurrent tender offers, as follows (i) US$247.2 million (equivalent on the transaction date to R$1,303.5 million) with the price of 110.8% over the emission value plus the proportional interest of the Senior Notes issued by Fibria Overseas with coupon of 5.25% per year and maturity in May 2024 (Notes 2024); (ii) US$260.3 million (equivalent on the transaction date to R$1,372.8 million) with the price of 106.6% over the emission value plus proportional interest of the Senior Notes issued by Fibria Overseas with coupon of 4.00% per year and maturity in January 2025 (Notes 2025); and (iii) US$183.4 million (equivalent on the transaction date to R$967.1 million) with the price of 115.2% over the emission value plus proportional interest of the Senior Notes issued by Suzano Austria, with coupon of 5 75% per year and maturing in July 2026 (Notes 2026). The tender offers settled on September 15, 2020.
Covenants
Currently, we have no financial covenants. On December 31, 2020, we were in compliance with all other no financial covenants, which are required under certain long-term borrowings.
C. Research and development, patents and licenses, etc.
Research and Development
Our research, development and innovation (“R&D&I”) efforts are organized under a Chief Technology and Innovation Officer. This initiative aims to increase synergy between areas, accelerating innovation that generates gains throughout the entire value chain. The integration is extended to all of our industrial and forestry areas in close collaboration with production, marketing and sales personnel.
Our technology and innovation facilities are spread to meet the demands and particularities of all of our mills and forest units. The technology centers, where there are the main assets and laboratories, are located in:
| • | Aracruz – state of Espírito Santo, Brazil – where efforts are towards the main business – pulp and forest development; |
| • | Itapetininga – state of São Paulo, Brazil – which concentrates biotechnology activities of Suzano and Futuragene; |
| • | Jacareí – state of São Paulo, Brazil – dedicated to work on activities related to our Eucalyptus Breeding Program; |
| • | Limeira – state of São Paulo, Brazil – focused on biorefinery and paper developments; |
| • | Burnaby – Canada – dedicated to biorefinery research; and |
| • | Rehovoth – Israel – where concentrates developments of Futuragene’s biotechnology. |
In addition to the main technology centers, R&D&I is also present in all forest units: São Paulo, Mato Grosso do Sul, Espírito Santo, Bahia, and Maranhão. The efforts in R&D&I are conducted not only within our research facilities, but also in partnership with various universities, suppliers and private research institutes in Brazil and abroad.
By attempting to improve our processes to develop innovative and higher quality products in a sustainable way, our research and development activities are principally directed at increasing forestry productivity, reducing the operational costs and optimizing industrial processes, making our production more efficient and developing new products through (i) forest management with optimization of natural resources and costs; (ii) robust eucalyptus breeding program; (iii) improving the use of eucalyptus fiber in the manufacture of pulp, paper and paperboard; (iv) developing new applications for eucalyptus fiber including nanomaterials; and (v) developing a eucalyptus bio refinery to obtain renewable base chemicals.
With respect to forest technology and innovation, our efforts are targeted to eucalyptus breeding, biotechnology, forest management, soil nutrition and forest protection. Our goal is to continue improving our planted forest productivity and quality in a sustainable manner. With this purpose, our research group is selecting new eucalyptus clones based on growth, cellulose content and wood quality, making use of state of art techniques like genetic recombination through controlled pollination, use of genomic tools in the selection of new clones, extensive field evaluation (700 ongoing experiments) and laboratory analysis.
In 2020, our Forestry Breeding and Digital teams developed a system – called Tetrys – to help the silviculture team allocate the clones more precisely in available areas for planting.
Tetrys is an initiative to optimize MAIcel (adt/ha.year) in our plantation areas. Using the power of Machine Learning algorithms combined with Forest Inventory and Research data, this system defines the best clone(s) to be planted in a specific planting unit. The models used internally can therefore capitalize on the Genotypes by Environmental interaction. In addition, the system predicts the risk of productivity loss for each clone, considering both biotic and abiotic stress factors. Tetrys allowed the robust elaboration of plantation program for 2021, with more than 90 thousand hectares, and it helped the planning of our operational nurseries and the maximization of productivity.
Others important results are:
| (i) | Eucalyptus Breeding Population: we initiated the strategy defined last year. The parents of each population were selected and established. In several Forestry Units, we initiated the installation of experimental field trials with descendants from these populations, which will guarantee the generation of the clones for the next 10 years. |
| (ii) | Molecular Markers (MM): the use of MM was validated for important traits related to biotic and abiotic stresses in the Eucalyptus breeding program. More than 500 genetic materials were genotyped and associated with phenotype. As result, the data generated was used to validate the MM. Now, these MM are helping us screen our germplasm to assist the identification of potential individuals for cloning. |
| (iii) | Clonal Nursery: a process for production of genetically certified seedlings, which is also free of pathogens, was implemented. In this process, our micropropagation laboratory is responsible for producing seedlings of operational clones, which are planted and propagated from safe sources of specific clones and then it is used to form the new operational mini gardens. |
Biotechnology. We invest in innovation in biotechnology through our subsidiary FuturaGene, which aims at increasing the productivity of its eucalyptus plantations in a sustainable manner, increasing wood quality, insect and disease resistance and resilience. FuturaGene develops biotechnology solutions to improve plantation productivity by enhancing and protecting yield thus optimizing natural resource use efficiency. The aim of FuturaGene’s yield enhancement program is to produce wood using less land, therefore making land available for other uses such as for food production or biodiversity conservation. The yield protection program aims to lower chemical inputs and to enhance the resistance of trees to pests, diseases and the effects of climate change. The wood modification program also aims to produce feedstocks that reduce energy demand and lower chemical load in our mills.
FuturaGene’s first yield enhanced genetically modified eucalyptus variety that produces more wood when compared to conventional clones, approved for commercial use in Brazil in 2015. This variety has been crossed with leading eucalyptus parent varieties from our different operating forest geographies and the derivative varieties are being extensively tested in these different geographies, prior to commercialization. The potential future use of such high yield trees will form part of the solution to meet increasing global wood demand, which is expected to triple by 2050, whilst minimizing the need to irreversibly extract wood from natural forests, thus helping to mitigate the impact of forest destruction on climate change.
FuturaGene has made significant advances in its yield protection platform, which is focused on tackling threats to plant productivity, such as new pests and disease infestations that are increasing in amplitude as a result of climate change. FuturaGene’s program for developing herbicide resistance in trees, which will allow more efficient weed control with lowered chemical load and improved worker conditions, is in advanced regulatory field trials prior to submission of a dossier for commercial release. In developing these traits, FuturaGene utilizes a panoply of technologies including genetic modification, RNA interference (RNAi) and various state-of-the-art gene editing technologies, inter alia. These tools present a powerful armamentarium for selecting, identifying and modulating genes of interest.
In parallel, FuturaGene has been actively developing and enhancing its capabilities in bioinformatics and genomics. These tools both facilitate and guide FuturaGene’s work in biotechnology and are increasingly providing immediate assistance to our breeders for validating their genetic materials and guiding their breeding programs. The increased availability of genetic markers developed in these programs is expected to significantly reduce the development time for new conventional varieties for commercial deployment as well as to prevent the planting of new susceptible tree varieties, which can be pre-tested for disease and pest sensitivity. The first markers developed in this program are advancing to operational testing stage.
We remain open to share the technologies and tools developed by FuturaGene through business relationships or at no additional cost to its partner small growers in Brazil. In addition, FuturaGene has already provided technology on a royalty-free basis for the development of improved subsistence crops for food-insecure regions by academic partners.
Besides efforts in genetic field, we have sought innovations to ensure greater efficiency in forest management processes, aiming at greater productivity per planted area and cost reduction, while seeking to reduce the use of natural resources in this type of operation.
To achieve greater efficiency, in 2020 our entire forest base was reclassified based on environmental parameters and climate risk. Based on this new classification, it will be possible to generate management recommendations, clonal allocation and forest-based repositioning with important gains for productivity and optimization in the use of resources.
The topic of climate change is complex and strategic for us. Climate change is one of the main risks identified according to the Enterprise Risk Management methodology. From the point of view of forestry technology, after a comprehensive review of the theme, a technological roadmap will be prepared with actions to quantify the risk and impacts on forest productivity, with a focus on actions to form resilient forests and reposition the forest base.
In addition to the 2020 advances mentioned, four work fronts are particularly highlighted:
| (i) | Water resources – The risk of water availability is one of the highest priority issues for us. This is because, in addition to assuming a public goal related to the use of water, eucalyptus culture requires a series of precautions in the correct use of this resource. By 2030, we will manage 100% of the hydrographic basins considered critical in our studies, that is, those most demanded by us and also by our neighbors, which, therefore require greater attention. Currently, 40 hydrographic basins are classified as critical, in a total of 2006 basins with the presence of company plantations, that is, 2% of the total. We have the technology to make recommendations for reducing the use of water in critical areas and, mainly, to certify, based on remote sensing, the effectiveness of these recommendations in the regions where we are present; |
| (ii) | Biological pest control – A pioneer in the use of biological control techniques, we are one of the companies that most invests in this subject. In 2020, we reached the production of 49 million natural pest enemies, which were released on 56,376 hectares, exceeding R$ 14 million in net avoided cost in the 2019/2020 biennium. In 2021 we will expand the biological control technique, through the installation of laboratories in Mato Grosso do Sul and Maranhão, in addition to those already existing in São Paulo and Espirito Santo; |
| (iii) | The coppice (regrowth) management – It is the main alternative to reduce the costs of forest formation, but in order to generate productive forests, a lot of technology is needed in the entire process. In 2020, we consolidated the model for selecting areas with greater potential, based on technical premises; we designed the quality control of the forest in two phases; and we innovated with the anticipation of deforestation, which already produces in all units forests of higher quality and productive potential, in addition to providing fertilization recommendations for approximately 150 thousand hectares for all management regimes; |
| (iv) | FenomicS Project – We introduced technologies for large-scale evaluation of our genetic materials, aiming to identify characteristics of resistance and tolerance to biotic and abiotic stresses. Fundamental to mitigate risks related to forest productivity, enhance the useful life of the recommended genetic materials and support the Suzano Genomics program. |
Our R&D&I team continued the work towards the development of solutions that are innovative and sustainable – Innovability is the concept that guides our efforts to offer society new materials. 2020 challenged our team to deliver premium pulp in the challenging pandemic scenario. Meeting regulatory requirements, we developed pulp products to meet Chinese specification for the tissue market. We also offered the unbleached pulp, premium, that can be used in different paper grades. Also, on the product development, Suzano engaged in an effort to develop products for the packaging segment. The effort seeks to offer pulp to the packaging segment, developing new paper packaging, challenging the current furnishes and increasing the amount of eucalyptus in traditional packaging paper.
We have advanced in process optimization. We tested virtual sensors and develop machine learning models and entered the digital area in the production. In agreement with Suzano’s long term goals, we have mapped technologies of low and high technology readiness level (TRL) to repurpose industrial residues and reduce, therefore our residues disposal.
The year of 2020 marked the beginning of a new phase for the biorefinery. The partnership with Spinnova for textile production with MFC evolved, we are on the project phase of MFC pilot production specifically for this application that will start up in 2021. Other MFC applications like fiber cement and paper application were tested in industrial scale with results that shows we are on the right path. We also started the commissioning industrial phase and the commercial production of lignin in the end of 2020 at Limeira mill. Lignin is being currently used in wood board production in replacement of phenol-based resins and new applications were started in 2020 to increase the use of our bio based, renewable material in other value chains. Bio oil produced from our forests biomass initiative developed and we found higher added value fractions to be used besides biofuel.
The biggest challenge for the Paper, Consumer Goods and Fluff R&D team is to develop products capable to address the needs and most particular necessities of our customers, without forgetting to give proper attention to sustainability and all the legal requirements (national and international ones, depending on the product).
As a result, during 2020 the Paper R&D team launched 4 new products: Greenbag (paper for shopping bags), TPCycle (paperboard containing recycled fibers, post-consumption), Coated Blue Cup (paper for cups with waterproof coating) and the reshaped Blue Cup PE, offering to the market a product with better performance and more competitive costs (compared to the last version). We also made significant advances Flexible Packaging. In the search for sustainable solutions to replace plastic used in the cup and flexible packaging sector, we have been developing innovative solutions that are based on improving the physical-mechanical properties of the base paper and applying recyclable and biodegradable barriers on the surface of the paper. These barriers give to the paper properties of resistance to water, grease, water vapor, oxygen transmission and are also heat sealable. This replacement requires technical and economic challenges and for this reason, in 2020, several laboratory and industrial tests were carried out to approve a technology in different market players. Advances have been made, validating not only the performance and machinability of the products but also meeting the strict standards established by Organs regulatory agencies.
The Consumer Goods and Fluff R&D team also achieved important milestones during 2020. In this year the Consumer Goods innovation pipeline had focus on two strategic pillars: product competitiveness, bringing a higher differentiation for our tissue products on national market and allowing a better market positioning of our brand and an improved version of our kitchen towel. The second pillar is about portfolio expansion focusing on products where natural fibers are already used or can be introduced in the future.
The Fluff R&D 2020 pipeline had 2 important projects: Pulp Analysis, which focused on understand, among all the different Eucalyptus fibers that we produce in Brazilian territory, which one could bring the best quality for our fluff; and Process Modeling, focusing on a deep dive of our actual production process and understanding since the wood receiving until the final packaging, what are the main raw material and process variables that affect the fluff performance/quality. Both projects allowed R&D team to construct a solid know how about eucalyptus fluff, since the forest pool of genetic material until the product performance in our clients.
Intellectual Property
Suzano, Futuragene and Portocel currently have, in total, 400 granted patents and patent applications, 49 protected varieties of eucalyptus and more than 150 potential new eucalyptus varieties, which is under evaluation by Forestry Breeding Program.
Achievements during 2020 in the intellectual property field include filing of 11 new technologies were filed as patent and identification of 6 new variety of Eucalyptus for protection. The patents applications filed in 2020 is covering the following main topics:
| • | process to produce microfibrillated cellulose and its uses in products compositions; |
| • | different methods to improve kraft process focused in pulp quality; and |
| • | use of lignin in plant nutrition. |
Due to our investments in research and development activities, we are not dependent on any third party’s patent or trademark, license, royalty agreement, industrial agreement or new production process.
Trademarks
We have registered many of our trademarks, including, as the case may be, our multipurpose corporate trademark Suzano®, in countries across five continents, including, among others, the United States and Canada, countries of the European Union, and countries located in Latin America, Africa, Asia and Oceania.
In 2020, we requested the registration of the new corporate trademark in some strategic countries, 45 trademark renewals and received 23 approvals of different trademarks, including Blue Cup®, Blue Cup Bio®, Loop®, Ecolig®, Lignew®, Ligseal®, Ligflex®, Ligflow®, Ligsperse®, Paperfect®, TP White®, Report®, Report Multiuso®, Supremo Alta Alvura® and Suzano®, in countries across five continents.
D. Trend Information
The primary trends which influence our sales and production and inventory levels are the patterns and cycles of pulp purchases by paper producers, pulp and paper prices, the level of pulp inventory in the hands of pulp producers in the global market, global economic conditions and the effect of currency fluctuations.
More recently, we have been subject to significant volatility in these trends due to the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on global trade, foreign exchange and macroeconomic conditions. See “—Overview” for a discussion of the potential effects of the pandemic on our business.
E. Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We participate in a number of off-balance sheet arrangements, mainly related to guarantees and take or pay contracts. We also have a number of swap transactions as described in “Item 11. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk.” All of these transactions are further described elsewhere in this annual report. See notes 4 and 24 to our audited consolidated financial statements.
ITEM 6. DIRECTORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT AND EMPLOYEES
A. Directors and Senior Management
We are managed by our board of directors and by our executive officers. The address of our management is Avenida Brigadeiro Faria Lima, 1355, 7th Floor, São Paulo, State of São Paulo, Brazil.
Board of Directors
Our board of directors is the decision-making body responsible for determining general guidelines and policies for our business, including our overall long-term strategies, as well as the control and oversight of our performance. Our board of directors is also responsible for, among other things, supervising our executive officers’ actions. It holds meetings whenever called by its chairman, any of its vice-chairmen or our chief executive officer. Currently, our board of directors consists of ten members, seven of which are independent members. Under the provisions of the Novo Mercado, at least two or 20% of the members of our board of directors (whichever is the greater) must be independent directors, as defined under Brazilian law. The following table sets forth the name, age, position, date of election and term expiration of each of the members of our board of directors:
Name | | Age | | Position | | Date of Election | | Term of Expiration |
| David Feffer | | 64 | | Chairman | | May 22, 2020 | | May 22, 2022 |
| Claudio Thomaz Lobo Sonder | | 79 | | Vice Chairman | | May 22, 2020 | | May 22, 2022 |
| Daniel Feffer | | 61 | | Vice Chairman | | May 22, 2020 | | May 22, 2022 |
| Nildemar Secches | | 72 | | Member | | May 22, 2020 | | May 22, 2022 |
| Rodrigo Kede de Freitas Lima | | 49 | | Member | | May 22, 2020 | | May 22, 2022 |
| Maria Priscila Rodini Vansetti Machado | | 62 | | Member | | May 22, 2020 | | May 22, 2022 |
| Ana Paula Pessoa | | 54 | | Member | | May 22, 2020 | | May 22, 2022 |
| Rodrigo Calvo Galindo | | 44 | | Member | | May 22, 2020 | | May 22, 2022 |
| Paulo Rogerio Caffarelli | | 55 | | Member | | May 22, 2020 | | May 22, 2022 |
| Hélio Lima Magalhães | | 69 | | Member | | May 22, 2020 | | May 22, 2022 |
The following is a summary of the business experience of our current directors:
David Feffer. Mr. Feffer has served as chief executive officer of Suzano Holding S.A. since 2003, and currently serves as the chairman of our board of directors. In 2001, Mr. Feffer became a member of the board of directors and chief executive officer of Polpar S.A. and holds the following positions in other companies: (i) chief executive officer of IPLF Holding S.A. since 2004; and (ii) vice chief executive officer of Premesa S.A., a subsidiary company of Suzano Holding S.A., from 2001 to 2015 and chief executive officer of the company since April 2015. He is also a member of the following social and cultural organizations: chairman of the directors’ committee of the School ALEF Peretz, member of the decision making committee of the Israelita Albert Einstein Hospital (Associação Beneficiente Israelita Brasileira Hospital Albert Einstein); vice chairman of the directors’ committee and chairman of the senior board of Ecofuturo Institute – Future for Sustainable Development (Instituto Ecofuturo – Futuro para o Desenvolvimento Sustentável); and coordinator of the Nominating Committee of the executive board of the Arymax Foundation (Fundação Arymax). Mr. Feffer attended specialization courses at Harvard Business School, Columbia University, the Aspen Institute, Singularity University, Stanford University and IMD in Switzerland.
Claudio Thomaz Lobo Sonder. Mr. Sonder currently serves as vice chief executive officer since 2010 and chairman of the board of directors of Suzano Holding S.A. since 2018, member of the board of directors of the company since 2002, being its vice-chief since 2013. Since 2018, Mr. Sonder has also acted as the chairman of the board of directors and vice chief executive officer of IPLF Holding S.A. since 2010. From 2010 to May 2015, he was chief and in April 2015 he was appointed as vice chairman of the board of directors of Polpar S.A. Mr. Sonder also holds the following positions in other companies: (i) executive officer of Alden Desenvolvimento Imobiliário Ltda. since 2011; (ii) member of the directors’ committee and member of the senior board of Ecofuturo Institute – Future for Sustainable Development (Instituto Ecofuturo – Futuro para o Desenvolvimento Sustentável) since 2010; (iii) member of the board of directors of MDS, SGPS, S.A. since 2010 and its chairman of the board of directors since March 2018; (iv) executive officer of Premesa S.A. since April 2015; and (v) member of the board of curators since 2011 and member of the executive board of Fundação Arymax since 2013. Mr. Sonder is a former chairman of the board of directors and chief executive officer of Hoechst do Brasil Química e Farmacêutica S.A. (1983 1993). Mr. Sonder holds a degree in chemical engineering and economics from Mackenzie University and specializations obtained in Munich, Germany, and Boston, United States.
Daniel Feffer. Mr. Feffer currently serves as vice chairman of our board of directors and as a member of our sustainability and strategy committee. Mr. Feffer also holds the following positions in other companies: (i) chairman of the board of ICC Brasil; (ii) chairman of the board of curators of the Arymax Foundation (Fundação Arymax); (iii) chairman of the directors’ committee and vice chairman of the senior board of the Ecofuturo Institute – Future for Sustainable Development (Instituto Ecofuturo – Futuro para o Desenvolvimento Sustentável); (iv) member of the advisory board of IBÁ; (v) member of the board of IEDI – Instituto Econômico para Desenvolvimento Industrial; (vi) founding member of the board of Compromisso Todos Pela Educação; (vii) member of the strategy board of FIESP; (viii) member of the board of MBC – Movimento Brasil Competitivo; (ix) executive member of the board of ICC – Global; and (x) chairman of ITTI – Intelligent Tech & Trade Initiative. Mr. Feffer graduated from Mackenzie Law School and holds specializations from FGV in Brazil; Harvard University, and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the United States; IMD in Switzerland; and London Business School in England (LBS).
Nildemar Secches. Mr. Secches currently serves as a member of our board of directors and member of our sustainability and strategy committee since 2008. Mr. Secches also holds the following positions in other companies: (i) vice chairman of the board of directors of WEG S.A.; (ii) vice chairman of the board of directors of Iochpe Maxion S.A. since 1998; (iii) member of the board of directors of Ultrapar Participações S.A. since 2002; and (iv) vice-chief of the board of directors of Iochpe Maxion S.A. He served as a member of the board of directors of Itaú Unibanco between 2002 and 2017. From 1972 to 1990, Mr. Secches worked at BNDES, where he was a director from 1987 to 1990. From 1990 to 1994, Mr. Secches was the managing corporate officer of the Iochpe Maxion Industrial Holding Group and from 1995 to 2008 he was the president of Perdigão S.A., which specializes in the production of food. From 2007 to 2013, Mr. Secches was the chairman of the board of directors of BRFBRF - Brasil. He holds an undergraduate degree in mechanical engineering from the University of São Paulo, a graduate degree in finance from the Pontifical Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro and a doctoral degree in economy from UNICAMP (Campinas).
Rodrigo Kede de Freitas Lima. Mr. Kede currently serves as a member of our board of directors and audit committee. He is also the chief service officer of IBM in New York and a member of the advisory board of the FDC (Fundação Dom Cabral). Beginning in 1993, Mr. Kede has held the following positions during his time at IBM: (i) chief executive officer of IBM Latin America until 2017, (ii) chief executive officer of IBM Brasil until 2014, (iii) vice chief executive officer of IBM Service Unit – Brazil; global vice chief executive officer of strategy and processing of IBM Brasil; (iv) chief financial officer of IBM Latin America; and (v) chief financial officer for IBM Brasil. Mr. Kede has also served as chief executive officer and a member of the board of directors of TOTVS on 2015. Until 2017, he served as the chairman of the board of directors of the Brazilian Institute of Finance Executives (Instituto Brasileiro de Executivos Financeiros – IBEF) and AmCham (American Chamber of Commerce). Mr. Kede holds an undergraduate degree in mechanical and production engineering from the Pontifical Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro and an MBA from Instituto Brasileiro de Mercados de Capital, currently INSPER, and Harvard Business School.
Maria Priscila Rodini Vansetti Machado. Mrs. Vansetti currently serves as a member of our board of directors. In 2017, she was appointed global chief strategy and business development officer of Corteva Agrisciences, the agricultural division of DowDuPont. Mrs. Vansetti started at DuPont Brasil in 1981, beginning in the agricultural division and going on to hold leadership positions in the Regulatory, Institutional Relations and Research & Development areas. She transferred to Wilmington, Delaware in 1996, where she specialized in Development and Marketing, and in 2008 she was appointed business director of DuPont Canada. Mrs. Vansetti previously held the following positions: (i) global chief strategic planning officer of DuPont Crop Protection from September 2014 to September 2015; (ii) chief executive officer of DuPont Brasil; and (iii) vice chief executive officer of DuPont Crop Protection for DuPont Brazil and DuPont Latin America. Mrs. Vansetti currently serves as a member of the board of directors of the International Center in Indianapolis, Indiana, and of the Inter American Dialogue, in Washington, D.C. She has also been a member of the following social and cultural organizations: (i) member of the board of directors of AmCham (American Chamber of Commerce); (ii) member of the board of directors of the Brazilian Association of Chemical Industry (Associação Brasileira da Indústria Química – ABIQUIM); (iii) member of the agribusiness board of FIESP; and (iv) member of the board of directors of CropLife Canada. Mrs. Vansetti holds an undergraduate degree in agronomic engineering from Escola Superior de Agricultura “Luiz de Queiróz” of the University of São Paulo (ESALQ/USP) and a specialization in executive management and global strategy leadership from the Wharton School (University of Pennsylvania).
Ana Paula Pessoa. Ms. Pessoa currently serves as a member of our board of directors and audit committee. Ms. Pessoa is currently a partner, investor and board chairwoman at Kunumi AI, a leading artificial intelligence start-up in Brazil. She also holds the following positions in other companies: (i) independent board member and member of the audit committee of News Corporation, NY, since 2013, (ii) independent board member and member of the investment and corporate social responsibility committee of Vinci Group, Paris, since 2015, (iii) member of the innovation committee of Credit Suisse AG, Zurich, since 2018, (iv) board member of the board representing IFC at Aegea Saneamento, São Paulo, since 2018, (v) member of Global Advisory Council at Stanford University, California, since 2018, (vi) member of the consulting board of The Nature Conservancy Brazil since 2014, (vii) member of the audit committee for Fundação Roberto Marinho since 2007, and (viii) member of consulting board for Casa FIRJAN since 2018. Ms. Pessoa previously held the following positions: (a) CFO of the Rio 2016 Olympic and Paralympic Games from 2015 to 2017, (b) founder and managing director of Brunswick São Paulo from 2012 to 2015, (c) CFO of Infoglobo Comunicações from 2001 to 2011, and (d) several executive positions at the Globo Organizations since 1993. Additionally, Ms. Pessoa founded and was chair of Neemu Internet, which was sold in 2015 to Linx SA. Ms. Pessoa worked for the World Bank in D.C. and The United Nations Development Programme in New York and Benin, West Africa. Ms. Pessoa holds a bachelor in arts degree in economics and international relations with honors from Stanford University and master in arts degree in development economics also from Stanford University.
Rodrigo Calvo Galindo. Mr. Galindo currently serves as a member of our board of directors. Rodrigo Calvo Galindo has been the Chief Executive Officer of COGNA EDUCAÇÃO S.A. since 01.01.2011. He has been managing educational institutions for over 28 years. He was CEO of Kroton Educacional, Director of Operations and Director of College Education at Kroton Educacional, CEO of Grupo Educacional IUNI, Administrative Dean of the University of Cuiabá and responsible for the management, accreditation and implementation of college education institutions in Bahia, Mato Grosso, Amapá, Acre and Rondônia. Rodrigo Calvo Galindo is currently a member of the Board of Directors of Cogna, Burger King Brasil, Clínica SIM and Endeavor and was a member of the Board of Directors of Arezzo.
Paulo Rogerio Caffarelli. Mr. Caffarelli currently serves as a member of our board of directors. Graduated in Law at PUC / Curitiba, with specialization in Foreign Trade (FAE / CDE Curitiba) and Law in International Trade (IBEJ Curitiba), he has an MBA in Corporate Law and Finance (FGV / RJ) and a master's degree in Business Management and Economics ( University of Brasilia). Since 11/2018 he is President of Cielo SA Joined Banco do Brasil in 1995 becoming Vice President of Wholesale, International Business and Private Banking and Capital Markets (BB BI) from 2011 to 2014 and serving as President of 05 / 2016 to 10/2018. He was Executive Secretary at the Ministry of Finance from 02/2014 to 02/2015 and also worked at Companhia Siderúrgica Nacional as Executive Corporate Director. In the last 5 years, he served, for a certain period, on the Board of Directors of the following companies: Banco do Brasil S.A.; Brasilprev; Elo Participações S.A.; Banco Votorantim; CBSS Visavale (Alelo); Valley; Brasilcap Capitalização and Banco Votorantim; he was also a member of the Advisory Board of Febraban – Brazilian Federation of Banks. He is currently a member of the Board of Directors of Cateno Gestão de Contas S.A.
Hélio Lima Magalhães. Mr. Magalhães currently serves as a member of our board of directors. Graduated in Electrical Engineering and Computer Science from The George Washington University (Washington DC / USA) and post-graduated in Computer Science from the Pontifical Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro. He is currently Chairman of the Independent Board of Directors of Banco do Brasil SA, appointed by the Ministry of Economy since June 2019, member of the Independent Board of Directors of Eletropaulo Metropolitana Eletricidade de São Paulo SA and Companhia Melhoramentos de São Paulo, and member and ex-President (from 2012 to 2017) of the Board of Directors of the American Chamber of Commerce - AMCHAM Brasil (São Paulo). He served as President of Citibank Brasil (São Paulo) from 2012 to 2017. He was also (i) Member of the Board of Directors of Grupo Melhoramentos, (ii) member of the Board of Directors of IRB RE Brasil from 2017 to 2019, (iii ) Member of the Board of Directors of the Credit Guarantee Fund from 2018 to 2019, (iv) Member of the Board of Directors of the Brazilian Federation of Banks (FEBRABAN) from 2012 to 2017, (v) member of the Board of Directors and member of the Executive Committee of Brasil US Business Council (Washington / US) from 2012 to 2017; (vi) Chairman of the Board of Directors of Elavon do Brasil (Means of Payment Company) from 2014 to 2016.
Executive Officers
Our executive officers are responsible for executing general business and all related and necessary or advisable measures, except for those matters attributed to our shareholders’ meeting or our board of directors, pursuant to applicable law and/or our bylaws. Our executive officers consist of a chief executive officer and four to nine executive officers, each of whom must be a Brazilian resident, with recognized technical and administrative experience. Our executive officers are appointed by our board of directors for one-year term and are eligible for re-election. Currently, our board of executive officers consists of seven executive officers. The following table sets forth selected information regarding the current members of our board of executive officers:
Name | | Age | | Position | | Date of Election | | Term of Expiration |
| Walter Schalka | | 60 | | Chief Executive Officer | | February 10, 2021 | | February 10, 2022 |
| Marcelo Feriozzi Bacci | | 51 | | Chief Financial Officer and Investor Relations and Legal Director | | February 10, 2021 | | February 10, 2022 |
| Aires Galhardo | | 43 | | Executive Officer – Pulp Operation | | February 10, 2021 | | February 10, 2022 |
| Carlos Aníbal Fernandes De Almeida Jr | | 51 | | Executive Officer – Forestry, Logistics and Procurement | | February 10, 2021 | | February 10, 2022 |
| Leonardo Barretto De Araujo Grimaldi | | 46 | | Executive Officer – Commercial Pulp, People & Management | | February 10, 2021 | | February 10, 2022 |
| Christian Orga Orglmeister | | 47 | | Executive Officer – New Businesses, Strategy, IT, Digital and Communication | | February 10, 2021 | | February 10, 2022 |
| Fernando de Lellis Garcia Bertolucci | | 55 | | Executive Officer – Research & Development | | February 10, 2021 | | February 10, 2022 |
The following is a summary of the business experience of our current executive officers who are not members of the board of directors or related committees:
Walter Schalka. Mr. Schalka is an engineer and graduated from Instituto Tecnológico da Aeronáutica (ITA) and has a post graduate degree in administration from FGV, and executive programs at IMD and Harvard Business School. Mr. Schalka joined us in January 2013 and has served as our chief executive officer since then. Mr. Schalka started his career at Citibank. In 1989, Mr. Schalka joined Dixie-Toga, where he became CEO in 1991, participating in the company’s expansion, merger of Toga and Dixie-Lalek in 1995 and transfer of control. In 1997, Mr. Schalka became chairman of Dixie-Toga. In 2005, he joined Grupo Votorantim as president of Votorantim Cimentos, being responsible for their operations in Brazil and 14 other countries.
��
Marcelo Feriozzi Bacci. Mr. Bacci Holds a B.A. in Public Administration from the Getulio Vargas Foundation (FGV) and an MBA from Stanford University Graduate School of Business. Currently he is the Chief Financial and Investor Relations Officer of Suzano Pulp and Paper. He also serves as a member of the Board of Ibema Papelcartão and Veracel. At Suzano, he is responsible for the Treasury, M&A, Credit, Investor Relations, Controllership, Shared Services, Taxes, Planning, Risk Management and Compliance and Procurement departments. He began his career at Unibanco in 1991 and later served as executive officer at Promon, as chief financial officer at Louis Dreyfus Company and as Vice-CEO of Suzano Holding.
Carlos Anibal de Almeida Jr. Mr. Almeida currently serves as the executive officer responsible for our pulp commercial and logistics unit. Before Suzano, Mr. Almeida worked for General Electric, where he ultimately held the position of sales general manager for the Latin American division of GE Industrial Systems. Mr. Almeida holds an electrical engineering degree from the Federal University of Minas Gerais and a master’s degree in business administration from IBMEC (São Paulo).
Leonardo Barretto de Araujo Grimaldi. Mr. Grimaldi currently serves as the executive officer for our paper business unit. Mr. Grimaldi joined us in 2000, having occupied different positions in our Marketing and Commercial areas until he became commercial operating officer in 2011. He is responsible for our global paper sales and has led the Suzano Mais initiative. Mr. Grimaldi holds a degree in business administration from FGV and has attended graduate programs at the Wharton School of Business and the Singularity University in Silicon Valley.
Aires Galhardo. Mr. Galhardo currently serves as our executive officer for pulp industrial, energy and engineering unit. Mr. Galhardo worked for Fibria Celulose S.A. as their forest manager from 2011 to January 2019. From 2005 to 2011, he was the general manager of forest and manager of forestry logistics at Votorantim Celulose e Papel S.A. and from 2000 to 2005 he was the logistics manager of Companhia de Bebidas das Américas – Ambev.
Fernando de Lellis Garcia Bertolucci. Fernando Bertolucci is Chief Technology & Innovation Officer at Suzano, responsible for leading the technological innovation process across the company. He holds a bachelor’s degree in Agronomy Engineering and a master’s degree in Genetic Improvement of Plants from the Federal University of Lavras, Higher School of Agriculture (ESAL/UFLA), and has 31 years of experience in the forestry products industry. He is currently responsible for technological development in the areas of Genetic Improvement, Biotechnology, Forest Management, Process Development, Pulp and Paper Products, Consumer Goods and Biorefinery and Biomaterials. He has a graduate degree and has completed specialization programs in Forest Management (UFLA), Corporate Management (Dom Cabral Foundation), Product Development (University of Cambridge), Strategic Innovation (IMD, Switzerland) and Global Executive Academy (MIT, USA).
Christian Orglmeister. Mr. Orglmeister currently serves as our executive officer – people & management. Mr. Orglmeister is responsible for the human resources, communication, strategy, information technology and digital areas. He started his career at Armazéns Gerais Columbia and joined the international consulting Arthur D. Little later. From 2000 to 2002 he worked at the logistics start up Intecom, then joined the operations area of A.T.Kearney. In 2006 he joined The Boston Consulting Group leading people, organization and governance practices and the family business practices on South America. Mr. Orglmeister became the managing director of BCG offices in Brazil in 2015. Since 2016 he is an independent member of our personnel committee. Mr. Orglmeister holds a degree in engineering from FEI, has a post graduate degree from FGV and master’s degree from TRIUM (LSE, HEC, e NYU).
Fiscal Council
Our fiscal council is a non-permanent corporate body comprised of three members, with an equal number of alternates, in case our shareholders request it to be convened at the annual general shareholders’ meeting. Under our bylaws, the members of our fiscal council must sign, before taking office, a compliance statement in accordance with the Novo Mercado rules.
Pursuant to the Brazilian Corporation Law, our fiscal council is independent from our management and our external auditors. In case our fiscal council is installed, members of our fiscal council serve a one-year term that ends at the shareholders’ meeting the year following their election. The fiscal council is primarily responsible for reviewing management’s activities, our audited consolidated financial statements and for reporting its findings to our shareholders.
The following table sets forth the name, position, date of appointment and term expiration for each member of our fiscal council, which has been convened as requested in the annual general shareholders’ meeting held on May 22, 2020:
Name | | Age | | Position | | Date of Election | | Term of Expiration (1) |
| Eraldo Soares Peçanha | | 69 | | Member | | April 27, 2021 | | 2022 |
| Luiz Augusto Marques Paes | | 59 | | Member | | April 27, 2021 | | 2022 |
| Rubens Barletta | | 74 | | Member | | April 27, 2021 | | 2022 |
| Kurt Janos Toth | | 73 | | Alternate | | April 27, 2021 | | 2022 |
| Roberto Figueiredo Mello | | 72 | | Alternate | | April 27, 2021 | | 2022 |
| Luiz Gonzaga Ramos Schubert | | 84 | | Alternate | | April 27, 2021 | | 2022 |
| (1) | The term of the mandates of the members of our fiscal council shall terminate on the date of our annual general shareholders’ meeting in charge of evaluating our audited consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2021. |
The following is a summary of the business experience of the current members of our fiscal council:
Eraldo Soares Peçanha. Mr. Peçanha currently serves as a member of our fiscal council. Mr. Peçanha has previously held the following positions in other companies: (i) internal audit and controller manager of Aracruz Celulose S.A. (1974 to 1996); (ii) controlling company and computing director of CSN Cia. Siderúrgica Nacional (1996 2003); (iii) controlling officer and executive director of corporate governance of Embratel SA (2003 2008); and (iv) executive director of customer services of Icatu Seguros S.A. (2008 2011). He is permanent member at Cadam S.A. since January 2017 and was at Vale, Net Serviços de Comunicação, Ideiasnet and JBS (December 2016 to a September 2017) and is also an alternate member at CCR, Tupy e Ouro Fino Saúde Animal, Ferrovia Centro Atlântica, Itá Energética e Officer Distribuidora Prod. Tecnologia. Since November 2018 he is member of the executive board of My News Channel. Since 2012, he has been working as a consultant in the fields of corporate governance, controlling and processes and accounting and financial systems. Mr. Peçanha holds a degree in accounting and business administration from Cândido Mendes University.
Luiz Augusto Marques Paes. Mr. Paes has been a permanent member of our fiscal council since 1991. He is the managing partner of Paes e Colauto – Sociedade de Advogados, where he provides legal advice and tax and corporate consulting. Mr. Paes is also a permanent member of the fiscal council of JSL S.A., Movida Participações S.A. and Cyrela Brazil Realty S.A. Empreendimentos e Participações. Mr. Paes holds a law degree from the University of São Paulo.
Rubens Barletta. Mr. Barletta is a permanent member of our fiscal council. Mr. Barletta is also a permanent member of the fiscal councils of the following companies: (i) Banco Alfa de Investimento S.A.; and (ii) Alfa Holdings S.A. From 1999 to 2010 he served as a permanent member of the fiscal council of Financeira Alfa S.A. – Crédito, Financiamento e Investimentos. Mr. Barletta has been a partner at Barletta, Schubert e Luiz Sociedade de Advogados, a firm specializing in private law, since 2009. From 1961 to 2008 he was an employee, intern and then partner at Escritório de Advocacia Augusto Lima S.C. Mr. Barletta holds a law degree from São Bernardo do Campo Law School.
Kurt Janos Toth. Mr. Toth currently serves as an alternate member of our fiscal council. Mr. Toth previously enjoyed a long tenure at BNDES, having occupied the following positions: (i) economist in the Internal Control Department(2006-2008); (ii) chief of the Credit Department (1988-2006); (iii) chief of the Industrial Projects Department – Capital Assets and Traditional Industries (1984-1986); (iv) manager of the Industrial Projects Department – Capital Assets and Traditional Industries (1978-1984); (v) economist in the Industrial Projects Department – Capital Assets and Traditional Industries (1973-1978); and intern (1971-1973). Mr. Toth is a permanent member of the fiscal councils of Tupy S.A. since 2017 and Brasiliana Participações S.A. since 2018. He has served as member of the fiscal councils of the following companies: (a) Eletropaulo Metropolitana Eletricidade de São Paulo S.A. (2015 2017); (b): AES Tietê S.A. (2008-2015); (c) AES Elpa S.A. (2012-2014); (d) Eletropaulo Comunicações Ltda. (2010-2011); (e) AES Communications Rio de Janeiro S.A. (2010-2011); (f) Centrais Elétricas Brasileiras S.A. – ELETROBRÁS (2003-2006); and (g) Companhia Vale do Rio Doce (1993/1994). Mr. Toth holds a degree in economics from the Universidade Federal Fluminense and post graduate degree from Pontifícia Universidade Católica – Rio de Janeiro.
Roberto Figueiredo Mello. Mr. Mello currently serves as an alternate member of our fiscal council and has been a partner at Pacaembu Serviços e Participações Ltda. since 1988. Mr. Mello has been a member of the fiscal council of Barclay’s Bank (1995-2002), an officer of Vocal Comércio Veículos Ltda. (1989-1998) and an officer of SPP – Nemo S.A. Coml. Exportadora (1986-1998). Mr. Mello holds a degree in law from the University of São Paulo.
Luiz Gonzaga Ramos Schubert. Mr. Schubert currently serves as an alternate member of our fiscal council. He is also a permanent member of the fiscal council of Financeira Alfa S.A. – Crédito, Financiamento e Investimentos and an alternate member of the fiscal council of Consórcio Alfa de Administração S.A. From 1999 to 2010, he held the position of permanent member of the fiscal council of Bank Alfa de Investimento S.A. Mr. Schubert is a partner at Barleta e Schubert Sociedade de Advogados, a firm specializing in private law, since 2009. From 1972 to March 2009, Mr. Schubert participated as an intern and then a member of the Law Offices of Augusto Lima S.C. Mr. Schubert holds a law degree from São Bernardo do Campo Law School.
Audit Committee
In 2011, the CVM approved an Instruction (No. 509/2011) governing the comitê de auditoria estatutário (statutory audit committee), an audit committee established under the bylaws of the issuer and subject to certain requirements under the CVM rules. Effective January 2018, the B3 listing rules for its Novo Mercado segment require that a company listed on the Novo Mercado (such as ours) create and implement an audit committee in accordance with the CVM rules. The Novo Mercado segment of B3 is a premium listing segment for Brazilian companies that meet the highest standards of corporate governance. For further information on the Novo Mercado listing segment, see Item 9. “The Offer and Listing–Markets–São Paulo Stock Exchange Corporate Governance Standards.”
On April 1, 2019, our shareholders approved an amendment to our bylaws requiring us to establish a statutory audit committee in accordance with CVM Instruction No. 509/2011. Our statutory audit committee is an advisory committee of our board of directors, and provides assistance in matters involving our accounting, internal controls, financial reporting and compliance. Our statutory audit committee also recommends the appointment of our independent auditors to our board of directors and evaluates the effectiveness of our internal financial and legal compliance controls. According to CVM Instruction No. 509/2011, our statutory audit committee must have at least three members, and not more than five members, which must be independent in accordance with the independence requirements of the CVM and at least one of whom must have recognized experience in corporate accounting. Additionally, CVM Instruction No. 509/2011 and the B3 Novo Mercado listing rules both require that at least one member of the audit committee be a board member, but they permit the appointment of other members who are not members of the board of directors provided such other members meet the independence requirements of the CVM. Our bylaws expressly require that our statutory audit committee consist of one or more persons who are members of our board of directors and one or more persons who are not members of our board of directors.
Our statutory audit committee is not equivalent to or comparable with a U.S. audit committee. Pursuant to Exchange Act Rule 10A-3(c)(3), which provides for an exemption under the rules of the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC, regarding the audit committees of listed companies, a foreign private issuer is not required to have an audit committee equivalent to or comparable with a U.S. audit committee if the foreign private issuer has a body established and selected pursuant to home country legal or listing provisions expressly requiring or permitting such a body, and if the body meets the requirements that (i) it be separate from the full board, (ii) its members not be elected by management, (iii) no executive officer be a member of the body, and (iv) home country legal or listing provisions set forth standards for the independence of the members of the body. We believe that our statutory audit committee complies with these requirements, and we rely on the exemption provided by Rule 10A-3(c)(3) under the Exchange Act. The following table sets forth the name, position, date of appointment and term expiration for each of the members of our audit committee:
| Name | | Position | | Date of
Election | | Term Expiration |
| Ana Paula Pessoa | | Chairperson | | April 29, 2019 | | 2021 |
| Carlos Biedermann | | Financial Expert | | April 29, 2019 | | 2021 |
| Marcelo Moses de Oliveira Lyrio | | Member | | April 29, 2019 | | 2021 |
| Rodrigo Kede de Freitas Lima | | Member | | April 29, 2019 | | 2021 |
The following is a summary of the business experience of the current members of our audit committee who are not members of our board of directors:
Carlos Biedermann. Mr. Biedermann currently serves as a member of our audit committee. Mr. Biedermann holds a B.A. in Business Administration and a B.A. in Public Administration from the Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS) and a graduate degree in Capital Markets from the Getulio Vargas Foundation (FGV). Currently he is (i) a member of our audit committee; (ii) a member of the audit committee of the Algar Group, a Brazilian holding company whose core business is information technology and telecommunications, agribusiness, construction, services and tourism; (iii) coordinator of the audit committee of the Cornélio Brennand Group, which operates in the real estate development, energy, glass and cement industries; (iv) a member of the audit committee of Grupo Solar, a manufacturing branch of the Coca-Cola System in Brazil; (v) a member of the board of the American Chamber of Commerce (AmCham) of Rio Grande do Sul; of the Association of Marketing and Sales Executives of Brazil (ADVB), and of Agenda 2020; (vi) chairman of the deliberative board of Grêmio FBPA; (vii) a member of the Advisory Board of Lojas Lebes; (viii) a member of the Audit Committee of Moinho Paulista S.A.; and (ix) a member of the board of directors of Maiojama. Previously, Mr. Biedermann was (a) a lead partner of PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC) from 2002 to 2015; (b) chairman of the audit committee for five years and vice-president from 2013 to 2014 of the Brazilian Corporate Governance Institute (IBGC), a non-profit organization that works to promote best corporate governance practices; (c) a member of the board of directors for six years and director for two years of the Young Presidents Organization (YPO/WPO), a global network of executive officers; (d) the first independent member of the board of directors of Calçados Azaleia, a Brazilian footwear company; (e) a member of the administrative board for 15 years of Santa Casa de Misericórdia de Porto Alegre, a group of seven hospitals of various specialties located in Porto Alegre, Rio Grande do Sul; (f) a member of the audit committee of BB Seguridade, a Brazilian insurer of Banco do Brasil engaged in insurance products, private pension plans, capitalization and brokerage services; (g) a member of the board of directors of Valmont, a company operating in the agribusiness sector; and (h) chairman of the board of Porto Alegre Health Care, a non-profit group composed of public and private players focused on promoting the city of Porto Alegre and medical tourism.
Marcelo Moses de Oliveira Lyrio. Mr. Lyrio currently serves as a member of our audit committee. He has served as the chairman of the board of directors of Braskem S.A since April 2018, and is a founding partner of Prêncipio Assessoria Empresarial. Mr. Lyrio was a partner and co-founder of Signatura Lazard and Managing Director (MD) for Lazard in Brazil from 2004 to 2016, during which he worked as an advisor to large Brazilian and foreign business groups in connection with their local and international investments. Prior to Lazard, he worked from 1990 to 2004 at ING Bank and ING Barings in several areas of the institution, including as President for ING Brazil from 2001 through 2004. Mr. Lyrio holds a degree in economic sciences from the Pontifical Catholic University - PUC of Rio de Janeiro.
As of April 23, 2021, the members of our audit committee, on an individual basis and as a group, directly owned less than 1.0% of our common shares.
B. Compensation
Aggregate compensation for the members of our board of directors and our executive officers is determined annually at our shareholders’ meeting, in accordance with our bylaws. Our board of directors is responsible for the distribution of such amount between its members and the members of our board of executive officers. Our shareholders’ meeting held on April 18, 2019 approved the global compensation for the members of our board of directors, fiscal council and board of executive officers for the fiscal year of 2019 in the amount of up to R$150 million.
For the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019, and 2018, the aggregate compensation of all of our directors, officers and members of our fiscal council was R$133.7 million, R$93.2 million and R$119.2 million, respectively, which includes bonuses in the aggregate amount of R$10.7 million, R$6.7 million and R$33.0 million, respectively. In addition, for 2020, 2019 and 2018 we paid an aggregate of R$0.522 million, R$0.516 million and R$0.415 million into our pension plan on behalf of our directors.
Information on elements of compensation for the year ended December 31, 2020 is detailed in the table below (the percentages reflect the percentage of total remuneration represented by the category)
| Elements of Remuneration | | Board of Directors | | | Board of Executive
Officers
(Statutory) | | | Fiscal Council | |
| Fixed Remuneration | | | 83.0 | % | | | 19.7 | % | | | 83.3 | % |
| Benefits | | | 0.2 | % | | | 0.7 | % | | | 0.0 | % |
| Social Contribution | | | 16.8 | % | | | 4.3 | % | | | 16.7 | % |
| Variable Remuneration | | | 0.0 | % | | | 9.4 | % | | | 0.0 | % |
| Long Term Incentive Plan | | | 0.0 | % | | | 65.9 | % | | | 0.0 | % |
| TOTAL | | | 100.0 | % | | | 100.0 | % | | | 100.0 | % |
In addition to receiving a fixed salary, our entire board of executive officers participate in a profit- sharing program based on the achievement of certain personal and corporate goals. We also provide the following benefits, among others, to certain members of our board of directors and our entire board of executive officers: life insurance, health care plans, dental care, meal vouchers, transport, payroll loans and private pension plans. In addition to the benefits, we offer our management team long-term incentive programs. A quick overview of such programs follows below.
Phantom Shares Plan
Our phantom shares plan is settled in cash and based on the market price of our shares. We grant the phantom shares in addition to the salaries of beneficiaries. The phantom shares vest within three years of working at Suzano and, after such period they can be redeemed by the beneficiary at an exercise price corresponding to a given percentage over the average market price of our shares at closing in the 90 trading days prior to the exercise date.
Phantom shares are granted to the eligible beneficiaries in accordance with general conditions established in specific regulations managed by the (non-statutory) people committee, under the guidelines and conditions defined thereby. Every year, the people committee establishes the corporate performance indicators (condition for acquisition) which, if achieved, entitle beneficiaries to receive phantom shares.
Annually, if certain performance targets are met, our main executives and certain non-executive employees who are beneficiaries are granted “phantom shares” in an amount determined by dividing the number of salaries paid and the arithmetic mean of the closing prices of our shares in the last 90 trading sessions. The number of salaries paid is determined based on (i) the achievement of targets; and (ii) the discretionary quantities attributed by the people committee with regard to the level of achievement of the corporate indicators.
After they are granted, the phantom shares may be redeemed in cash by the beneficiaries provided they fulfill the stipulated vesting period (3 years at the Company).
Stock Option Plan
On August 29, 2008, our shareholders approved our stock option plan, establishing the main terms regarding stock options for the acquisition of our class A preferred shares for our officers, directors and other employees. The terms and conditions to grant such stock options were approved by the board of directors, assisted by a special committee. The options granted under such plan may not exceed 2% of our paid-in capital stock.
On January 18, 2013, 9 million stock options were granted, divided into five tranches of 1,800,000 options each. The vesting period for each of the tranches depends on the performance of the beneficiary during the vesting period, meaning that such vesting period can be anticipated if the relevant performance goals are achieved.
The options were vested as follows: (i) the first tranche was vested within 24 months, and could have been reduced to 12 months; (ii) the second tranche was vested within 36 months, and could have been vesting reduced to 24 months; (iii) the third tranche was vested within 60 months, and could have been vesting reduced to 36 months; (iv) the fourth tranche was vested within 72 months, and could have been vesting reduced to 48 months; and (v) the fifth tranche is vested within 84 months, and could have been vesting reduced to 60 months. Once the options were vested, the beneficiary had 90 days to exercise the options. As the goals were reached, the fifth tranche was anticipated from 84 months to 60 months as provided in the related agreement.
On January 1, 2018, we established a restricted shares plan based on our performance. The plan associated the number of restricted shares granted to our performance in relation to the ROIC goal. The size of the restricted stock grant was defined in financial terms and is subsequently converted into shares based on the last 60 pre-announcements on December 31 of our shares at the B3. The target was reached, and the shares will be transferred after the applicable 36-month lock-up period.
On January 1, 2019, we established a new restricted shares plan based on our performance, which associated the number of restricted shares granted to our performance in relation to our EBITDA goal. The size of the restricted stock grant was defined in financial terms and is subsequently converted into shares based on the last 60 pre-announcements on December 31 of our shares at the B3. The target was not achieved.
On January 1, 2020, we established a new restricted shares plan based on our performance, which associated the number of restricted shares granted to our performance in relation to our OCG (Operating Cash Generation). The size of the restricted stock grant was defined in financial terms and is subsequently converted into shares based on the last 60 pre-announcements on December 31 of our shares at the B3. The target was reached, and the shares will be transferred after the applicable 36-month lock-up period.
At the end of the vesting period, this strategic financial metric is evaluated and the number of shares acquired is determined. However, the beneficiaries must comply with a lockup period of 36 months, during which they are able to negotiate the shares in the market. If beneficiaries leave Suzano before the end of the reference fiscal year for the measurement of Operating Cash Generation (OCG), they will lose the right to the next grant of restricted shares.
Share Appreciation Rights Plan
Since 2014, we make available to certain of our executives and employees a Share Appreciation Rights Plan, under which the payment, in cash, is linked to the price of our shares and, for a group of executives, is also linked to the performance of our shares in relation to our competitors. The difference between this plan and the phantom shares plan is the fact that there is a minimum appreciation requirement for vesting.
The options have an exercise price (or minimum level of share appreciation) that represents the average of the last 90 trading days prior to the grant date. The plan is composed of one tranche with a vesting period ending three years after the grant and maturing six months after the end of the vesting period. After 5 years, the options are exercised automatically.
The beneficiary is invited to participate in the plan. The acceptance by the beneficiary requires the investment of an amount equivalent to 5% of the grant at the date of the grant, and 20% at the end of the vesting period, which must be deposited in our bank account.
The beneficiary’s gain varies depending on the performance of our shares and may vary up to 25% more depending of the relative performance of our shares and the competing shares. This percentage is calculated based on our performance for the relevant period in comparison with our competitors’ performance and may vary between 75% and 125%.
Maximum, Minimum and Average Individual Remuneration of our Board of Directors, Board of Executive Officers and Fiscal Council
Year 2020 | | Number of
Members | | | Number of
Remunerated
Members | | | Highest
Remuneration
(in reais) | | | Lowest
Remuneration
(in reais) | | | Average
Remuneration
(in reais) | |
| Board of Directors | | | 9.58 | | | | 9.58 | | | | 8,247,042.26 | | | | 960,004.80 | | | | 1,965,928.69 | |
| Board of Executive Officers | | | 8 | | | | 8 | | | | 22,112,160.86 | | | | 6,071,057.78 | | | | 14,241,022.26 | |
| Fiscal Council | | | 3 | | | | 3 | | | | 317,280.00 | | | | 317,280.00 | | | | 317,280.00 | |
Note on Calculations:
| • | The average annual remuneration of each body was calculated by dividing the total amount of annual compensation (fixed, variable and indirect benefits, including social contribution) for each body by the number of remunerated members in the respective body. |
| • | The lowest annual individual remuneration (fixed, variable and indirect benefits, including social contribution) of each body excludes all members of the respective body who have held the position for less than 12 months. |
| • | The highest annual individual remuneration (fixed, variable and indirect benefits, including social contribution) of each body makes no exclusions, considering all remuneration received by the respective member for functions exercised in the last 12 months. |
Employee compensation policies
Policy on salaries and variable compensation
The Company ensures a competitive compensation policy, conducting an annual survey of positions and salaries among the biggest and best companies in diverse various segments, at its discretion. The compensation consists of a fixed monthly salary, which is related to the level of complexity of the position, and an annual share in the Company’s results through the variable compensation program.
The variable compensation program mostly aims at leveraging business and results, encouraging employees to effectively contribute to the Company’s growth, strengthening the commitment to sustainable results, while making the short- and long-term visions compatible, enabling that the Company’s growth results in a financial compensation, as well as retaining employees.
Short-Term Variable Compensation Programs
We have two variable compensation programs based on the definition of group and individual targets. These targets are cascaded across all hierarchical levels.
Long-Term Variable Compensation Programs
We have share-based compensation plans for certain non-management employees within our two Long-Term Incentive (LTI) plans linked to the price our stock, paid in local currency. These are the Phantom Shares Plan and the Share Appreciation Right (SAR) plan, described above. Both plans depend on the stock price, and the SAR plan also depends on the performance of our shares in relation to our main competitors.
On November 10, 2017, we migrated our class “A” preferred shares (SUZB5) to common shares (SUZB3). Since then, our common shares have become the underlying asset of our LTI plans.
Benefits policy
Below is a list of some of the benefits offered to employees:
Dental Care: we offer dental care to employees from certain units, which also covers their dependents. At the Mucuri unit, the benefit also covers the parents of employees.
Health Insurance Plan: we offer medical assistance to employees through health insurance plans managed by third-parties, according to the relevant work location. Employees, their dependents (i.e., spouse or partner, children younger than 21 and single, children younger than 24 who are students, and children with disabilities in any age) and interns are entitled to health insurance. The health insurance offered by us has a copayment model, i.e., the employee copays a percentage of the costs of medical procedures, following the rules of the insurance plan and applicable regulations. No monthly fixed contribution is paid. There is an accredited network in all locations to serve employees and their dependents. In addition, employees are entitled to reimbursement of expenses incurred at non-accredited locations, in accordance with the rules of the plan.
Meal Voucher: Credit provided on the last business day of each month, to a prepaid meal card, at locations that do not have a cafeteria.
Cafeteria: Outsourced restaurants that offer meals at manufacturing units, distribution centers and logistic centers (breakfast, lunch, dinner and supper).
Food Voucher: Credit provided on the last business day of each month, to a prepaid food card.
Transportation Voucher: Benefit intended to cover expenses with daily commute to and from work.
Christmas Basket: All employees are eligible for this benefit, which is delivered in December through a prepaid Christmas card.
Toy and/or Toy Check: All employees with children aged up to 12 years are entitled to this benefit. Employees receive a prepaid toy card, which is always delivered in December.
Studying is Growing Program: In partnership with employees who are parents, this benefit aims to improve the academic performance of their children through cash prizes to students who obtain good grades at the end of the academic year. These prizes are paid in accordance with predefined criteria and analysis of the student’s report card by the 1st quarter of the subsequent year, and are deposited into the employee’s account.
School Supplies Kit: Every year, we deliver school supplies to the children of employees, according to the level enrolled. Employees’ children older than 5 (completed by January 31 of a given year) who are in pre-school, primary or secondary education are eligible for this benefit.
Child Care Assistance: Benefit envisaged in the collective bargaining agreement, by which expenses with day care or babysitter services are reimbursed. All female employees who are mothers, male employees who are widowers or legally separated and who hold custody of their children aged 0 to 72 months (depending on the location where the employee works) are entitled to this benefit. The benefit amount is credited to the employee’s payroll. For this, the employee must submit monthly proof of the expenses to the HR department at their unit and there is no deductible.
Allowance for Child with Disability: This benefit is envisaged in the collective bargaining agreement, by which expenses with specialized treatment and education of employees’ children with disabilities are reimbursed. All employees who have children with disabilities or who hold legal custody of a person with disabilities are entitled to this benefit. The benefit is granted upon submission of the respective medical certificate attesting to the disability. The benefit amount is credited in the payroll and the employee must submit monthly proof of expenses to the HR department at the unit. There is no age limit for dependents to receive this benefit. There is no deductible for the employee.
Tribute for Time of Service: At the end of each year, employees completing their 10, 20, 30 and 40 –year anniversary of service at Suzano are honored. Watches and certificates are offered according to their time with us.
Life Insurance: This benefit insures the employee and their dependents in case of death and/or disability. The amount insured corresponds to 36 times the employee’s salary (capped at R$1.2 million).
Payroll Loans: This benefit is offered to active employees and is governed by the Brazilian Labor Code (CLT) (employees on INSS leave, interns and contractors are not eligible). To obtain the benefit, employees must have been working at the Company for at least six months. The loan is repayable in up to 36 months with a maximum monthly installment up to 30% of available compensation. Total deductions (including the loan installment, to be deducted from payroll) cannot exceed 40% of available compensation.
Private Pension Plan: Suzano Prev is our supplementary pension plan, managed by BrasilPrev. All employees aged between 14 and 89 are entitled to this benefit.
C. Board Practices
Our board of directors meets at least four times per year and whenever necessary, according to our interest or when called by its chairman or by the majority of its members. Our board of directors is responsible for, among other things, establishing our general business policies and for electing our executive officers and supervising their activities. Our board of executive officers meets periodically to review our production, commercial and financial operations. Our board of directors and our board of executive officers is governed by each of their respective internal rules, which have been approved by our board of directors in 2019 and 2018, respectively. These rules set forth the structure and functioning, as well as rights and obligations of the members of our board of directors and board of executive officers.
According to the Brazilian Corporation Law and our by-laws, the members of our board of directors are elected by the holders of our common shares at the general shareholders meeting. The members of our board of directors serve two-year terms. In May 2020, the sitting and alternate members of our board of directors were elected to serve a two-year mandate starting on May 22, 2020. In February 2021 the members of our board of executive officers, were elected to serve a one-year mandate starting on February 10, 2021.
D. Employees
As of December 31, 2020, we employed a total of 15,653 employees (Suzano + Portocel + Ecofuturo + Futuragene + 50% Veracel), distributed as follows:
| | | | As of December 31, 2020 | |
| Management | | | | 1,111 | |
| Specialists/Engineers | | | | 58 | |
| Administrative | | | | 3,807 | |
| Operations | | | | 10,678 | |
| Total | | | | 15,653 | |
The increase in the number of employees (1,119 people) compared to 2019 results from the recomposition of the workforce in forestry operations and the internalization of outsourced employees in the area of industrial maintenance.
On December 31, 2020, 22,672 workers (Suzano = 21,508 + 50% Veracel = 1,164) employed by outsourced subcontractors and service providers were used. This scenario represents a 5,6% reduction in outsourced subcontractors and service providers compared to the previous year, equivalent to a reduction of 1337 employees. The workforce is mostly allocated in forestry operations and logistics with 42% of workers, followed by 32% of workers distributed in industrial operations and 26% of workers in support and administrative activities.
In the years of 2020, 2019 and 2018, the number of accidents in our facilities were 146, 195 and 103, respectively.
Our relationship with our employees is subject to the terms and conditions set forth in each of the collective labor agreements executed by us with the local unions to which our employees belong.
E. Share Ownership
As of April 23, 2021 the members of our board of directors and our executive officers, other than members of the Feffer family, as a group, directly owned less than 1.0% of our common shares. See Item 7. “Major Shareholders and Related Party Transactions.”
ITEM 7. MAJOR SHAREHOLDERS AND RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
A. Major Shareholders
As of April 23, 2021, our capital stock fully subscribed and paid in was [R$9,235.5 million] divided into [1,361,263,584] common shares.
The table below presents certain information as of April 23, 2021, regarding (i) any person known to us as the owner of 5% or more of our outstanding common stock, (ii) total amount of the common stock owned by the members of our board of directors, executive officers and fiscal council; and (iii) total amount of the common stock owned by our related parties.
| Shareholder | | Number of Common Shares | | | Total Capital (%) | |
| Suzano Holding S.A (1) | | | 367,612,329 | | | | 27.0 | % |
| David Feffer | | | 53,443,764 | | | | 3.9 | % |
| Daniel Feffer | | | 48,077,095 | | | | 3.5 | % |
| Ruben Feffer | | | 46,856,578 | | | | 3.4 | % |
| Jorge Feffer | | | 46,432,360 | | | | 3.4 | % |
| Alden Fundo de Investimento em Ações | | | 26,154,744 | | | | 1.9 | % |
| Other Related Parties (2) | | | 30,137,921 | | | | 2.2 | % |
| Board of Directors, Executive Officers and Fiscal Council | | | 3,727,508 | | | | 0.3 | % |
| (Other Shareholders) Public Float: | | | 726,779,281 | | | | 53.4 | % |
| Treasury Shares | | | 12,042,004 | | | | 0.9 | % |
| Total | | | 1,361,263,584 | | | | 100.0 | % |
| (1) | The controlling shareholders of Suzano Holding S.A. are David Feffer, Daniel Feffer, Jorge Feffer and Ruben Feffer. |
| (2) | Includes other relatives of the Feffer family. |
In addition, as of April 23, 2021, 3.3% of our common shares were held in the form of ADSs. Our major shareholders do not have different voting rights from other shareholders.
Shareholders’ Agreements
Feffer Voting Agreement
David Feffer, Daniel Feffer, Jorge Feffer, Ruben Feffer, Suzano Holding S.A. and Alden Fundo de Investimento em Ações (“Fundo Alden”), as well as their stocks, their successors and permitted assignees, as the case may be, are parties to a voting agreement dated September 28, 2017 relating to their respective stakes in our company. The voting agreement became effective on November 10, 2017 and shall be in force for an initial 10-year term, which will be automatically renewed for another 10-year period unless any shareholder provides notice of non-renewal two years prior to the initial expiration. The voting agreement (a) will terminate automatically if the shareholders’ agreement of Suzano Holding is terminated, and (b) may be terminated at any time by any two of David Feffer, Daniel Feffer, Jorge Feffer, Ruben Feffer and any of their successors or permitted assignees. The shareholders’ agreement Suzano Holding was entered into on September 28, 2017 and similarly will be in force for an initial 10-year term, which will automatically renew for another 10-year term unless a shareholder provides notice of non-renewal two years prior to the initial expiration.
Pursuant to the voting agreement, the parties are required to vote as a block at our shareholders’ meetings. Prior to each of our shareholders’ meetings, the parties are required to hold a meeting to determine the vote to be cast by each party with respect to all matters submitted for voting at such shareholders’ meeting. Each party is entitled to one vote at such preliminary meetings, and decisions are taken by vote of the majority of the shares bound by the agreement.
Feffer Stock Transfer Agreement
David Feffer, Daniel Feffer, Jorge Feffer and Ruben Feffer are parties to a stock transfer agreement dated as of, and effective on, September 28, 2017, which will be in force for an initial 10-year term, to be automatically renewed for an additional 10-year period unless any party provides notice of non- renewal during the year prior to the year of expiration.
Pursuant to the stock transfer agreement, each party and its successors agrees to not transfer, sell, assign or encumber shares subject to the stock transfer agreement (including through market transactions on an exchange), subject to certain exceptions, without the prior written consent of the other parties.
The stock transfer agreement also includes customary rights of first offer and rights of first refusal to all parties in the event of a sale or transfer of one of the parties. Moreover, the stock transfer agreement prohibits the transfer of shares to a third party that, directly or indirectly, engages in a competing activity, or that presents a common interest with whom engages in a competing activity, in each case with respect to our company.
B. Related-Party Transactions
For transactions with related parties, we shall observe the usual market prices and conditions, as well as the corporate governance practices adopted by us and those recommended and/or required by the legislation.
Transactions with Suzano Holding S.A.
The transactions with our controlling shareholder, Suzano Holding S,A, in the year ended December 31, 2020, totaled R$5.0 million, mainly related to administrative expenses sharing and, to a lesser extent, to guarantees provided by Suzano Holding S.A.
Other transactions
We are currently engaged in commercial pulp transactions with Ibema Companhia Brasileira de Papel (“Ibema”) that is a joint venture between us and Ibema Participações S.A. (“Ibemapar”) concluded in January 2016. Currently, we hold 49.9% of Ibema’s share capital and Ibemapar holds the remaining 50.1%. In the year ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, our net revenues from these transactions was R$117.3 million, R$111.3 million and R$107.3 million, respectively.
We also enter into expense sharing with certain other parties controlled by some of our controlling shareholders in the ordinary course of business.
C. Interests of Experts and Counsel
Not applicable.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL INFORMATION
A. Consolidated Statements and Other Financial Information
See Item 18. “Financial Statements.”
Legal Proceedings
We are currently party to numerous legal proceedings in Brazil relating to civil, administrative, tax, labor, environmental and corporate issues arising in the normal course of our business. Our audited consolidated financial statements only include provisions for probable and reasonably estimable losses and expenses we may incur in connection with pending proceedings. The roll forward of provisions according to the nature of each lawsuit is set forth below:
| | | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| | | | Judicial deposits | | | Provision | | | Provision, net | | | Provision, net | |
| | | | (in thousands of R$) | |
| Tax | | | | (135,641 | ) | | | 2,984,230 | | | | 2,848,589 | | | | 3,052,370 | |
| Labor | | | | (57,780 | ) | | | 217,180 | | | | 159,400 | | | | 176,675 | |
| Civil | | | | (3,495 | ) | | | 251,461 | | | | 247,966 | | | | 283,432 | |
| | | | | (196,916 | ) | | | 3,452,871 | | | | 3,255,955 | | | | 3,512,477 | |
Although the amounts of any liability that could arise against us with respect to these actions cannot be accurately predicted, in our opinion, except as described below, such actions, if decided adversely to us, would not, individually or in the aggregate, have a material adverse effect on our financial condition. The amount of the legal cases assessed as reasonably possible, as of December 31, 2020, is R$7,145.1 million for tax proceedings, R$264.0 million for labor proceedings and R$3,068.9 million for civil proceedings.
Tax Proceedings
As of December 31, 2020, we were involved as the defendant in approximately 51 administrative and judicial proceedings of tax and welfare nature, which likelihood of loss is probable, involving a plurality of taxes, such as corporate income tax (“IRPJ”), social contribution on net income (“CSLL”), retained income tax (“IRRF”), social integration program (“PIS”), social contribution on revenue (“COFINS”), tax on industrialized products (“IPI”), social contribution, tax on rural real estate (“ITR”), value added tax on goods and services (“ICMS”), tax on services (“ISS”) and real estate tax (“IPTU”).
As of December 31, 2020, we had provisions, net of judicial deposits, of R$2,848.6 million related to tax claims for which our legal counsel considers that the likelihood of loss is probable. In addition, the total amount related to proceedings in which we are defendants, and for which our legal counsel considers the likelihood of loss possible, is R$7,145.1 million. As of December 31, 2020, we had no provision accrued for claims which likelihood of loss is possible.
The remaining tax and welfare proceedings refer to other taxes, such as social contribution, IRPJ, CSLL, ITR, ICMS, ISS, IRRF, PIS and COFINS, mainly due to divergences on the interpretation of applicable tax rules and ancillary tax obligations.
We list below our liabilities (i) individually classified as possible losses deemed relevant by us or (ii) which updated value involves, individually, an amount higher than R$100 million:
Tax Assessment – IRPJ/CSLL – exchange of industrial and forestry assets: In December 2012, a tax assessment was issued by the Brazilian Federal Revenue (“RFB”) against us, with respect to IRPJ and CSLL under the allegation that there was no taxed capital gain in February 2007, when we finalized an exchange of industrial and forestry assets with International Paper.
In January 2016, the Tax Federal Administrative Court (“CARF”) rejected the appeal filed by us. The appeal was rejected as per the casting vote of CARF’s President. After notification of the decision, in May 2016, since no new appeal at the administrative level is permitted, we filed a complaint with the judicial courts and are currently awaiting the defendant´s response (Brazilian federal government). We presented judicial guarantee, which was accepted. We continued not provisioning this matter, given that, based on the opinion of our internal and external legal counsel, the likelihood of loss is possible. In the year ended December 31, 2020 the amount is R$2,296.0 million (R$2,251.5 million as of December 31, 2019).
| (i) | Tax Assessment – IRPJ/CSLL – disallowance of depreciation, amortization and depletion expenses – 2010: In December 2015, a tax assessment was issued by the RFB against us, with respect to IRPJ and CSLL. The main argument of the assessment is the non-deductibility of depreciation, amortization and depletion expenses, during the fiscal year of 2010. We filed an administrative appeal, which was judged partially valid. We filed an appeal against this decision in November 2017. On October 16, 2018, the trial was converted into diligence, through resolution n. 1402-000723. Currently, the resolution is expected to be formalized. In the year ended December 31, 2020 the amount is R$712.5 million (R$695.7 million as of December 31, 2019). |
| (ii) | IRPJ/CSLL – partial approval – 1997: we requested approval to offset 1997 tax losses with amounts owed to the tax authorities. In March 2009, the authorities approved only R$83.0 million, which generated a difference of R$51.0 million. We are still awaiting the conclusion of the analysis of the credits discussed at the administrative level following a favorable decision of CARF in August 2019, which granted the Voluntary Appeal filed by us. For the remaining credit, we have appealed the rejection of the tax credits and obtained a partially favorable decision and the final decision is under discussion in the judicial level. Shortly after, an appeal was filed, which was judged in session, determining the conversion of the trial in diligence. On November 6, 2018, a decision was filed reinforcing the tax authorities’ conclusion at the first approval and our arguments. In the year ended December 31, 2020 the amount is R$104.9 million (R$254.1 million as of December 31, 2019). |
| (iii) | Tax Incentive — Agency for the Development of the Northeastern Brazil (ADENE): in 2002 the RFB granted our request to benefit from reductions in corporate income tax and nonrefundable surcharges calculated on operating profits (as defined) for Aracruz facilities A and B (period from 2003 to 2013) and plant C (period from 2003 to 2012), when the qualification reports for the tax reductions are approved by SUDENE. In 2004, we were served an Official Notice by the liquidator of the former Superintendence for the Development of the Northeast (“SUDENE”), who reported that the right to use the benefit previously granted is unfounded and would be cancelled. In 2005, the RFB served us an assessment notice requiring the payment of the amounts of the tax incentive used, plus interest. After administrative discussions, the assessment notice was partially upheld and recognized our right to the tax incentive through 2003. Our management, supported by our legal counsel, believes that the decision to cancel the tax benefits is erroneous and should not prevail, either with respect to benefits already used, or with respect to benefits not used until the corresponding final periods. In the year ended December 31, 2020 the amount is R$127.4 million (R$125.2 million as of December 31, 2019). |
| (iv) | PIS/COFINS – Goods and Services – 2009 to 2011: in December 2013, the RFB issued an assessment against us demanding the collection of PIS and COFINS credits disallowed because they were allegedly not linked to our operating activities. In the first instance, the objection filed by us was dismissed. After the Voluntary Appeal was filed, it was partially provided in April 2016. From this decision, the National Treasury filed a Special Appeal to the Superior Chamber and we filed a Statement of Appeal, which are still pending judgment. The updated amount involved up to December 31, 2020 is R$166.4 million (R$162.8 million as of December 31, 2019). |
| (v) | Compensation – IRRF – period 2000: We filed a lawsuit requesting the compensation of IRRF credits originated in the year ended December 31, 2000 regarding debts owed to the RFB. In April 2008, the RFB partially recognized the credit in our favor. From this decision, we filed a Voluntary Appeal with CARF, which is pending judgment. In the year ended December 31, 2020 the amount is R$109.9 million (R$108.3 million as of December 31, 2019). |
| (vi) | Tax assessment – Corporate Income Tax and Social Contribution: on October 5, 2020, we were notified about the tax assessment issued by the RFB claiming the payment of Corporate Income Tax and Social Contribution, in the total amount of R$454.9 million, resulting from the remeasurement of profit of our wholly-owned subsidiary Suzano Trading Ltd in the years ended December 31, 2014, 2015 and 2016. In addition to us, certain Statutory Executive Officers’ (“Officers”) from Suzano Trading were also included as co-responsible. The legal counsel considered the risk of loss as possible in regards to us and, in reference to the Officers, also possible but with greater chances of success (possible to remote). |
| (vii) | Tax assessment – taxation on a universal basis – year 2015: on November 3, 2020, we received a tax assessment for the collection of income tax and social contribution, alleging unpaid tax related to the year ended December 31, 2015, due to the absence of profits earned by subsidiaries abroad in the determination of taxable income and social contribution calculation basis. The legal advisors hired by us classify the prognosis as a possible loss. Currently, the defense presented at the administrative level is awaiting judgment. In the year ended December 31, 2020 the amount is R$145.0 million. |
Labor Proceedings
As of December 31, 2020, we were involved in 1,010 labor proceedings assessed as reasonably probable, representing a contingency provision, net of judicial deposit, of R$159.4 million duly provisioned in our audited consolidated financial statements. In addition, we are involved in 1,653 labor proceedings assessed as reasonably possible, with a total amount under dispute totaling R$264.0 million. We are also party to several disputes involving unions located in the states of Bahia, Espírito Santo, São Paulo and Mato Grosso do Sul.
The labor claims involving us involve the usual matters under dispute in other agroindustrial companies, such as overtime and termination payments, additional compensation for allegedly unsafe/unhealthy labor conditions, in addition to lawsuits filed by outsourced and third-party employees claiming that we are secondarily or jointly liable for compensation owed to them by their original employers.
Civil and Environmental Proceedings
As of December 31, 2020, we were involved in 58 judicial civil and environmental proceedings assessed as reasonably probable, representing a contingency provision, net of judicial deposits, of R$248.0 million duly provisioned in our audited consolidated financial statements .. In addition, we have 324 civil and environmental proceedings assessed as reasonably possible, amount under dispute totaling R$3,068.9 million.
The civil judicial proceedings refer mainly to indemnification claims, real estate possession challenges, claims for the revision of contractual provisions, bankruptcy, reimbursement of funds claimed from landowners and land lawsuits. The environmental judicial proceedings involving us mainly relate to licensing issues and environmental impacts of our activities. We are also a party in several administrative civil proceedings (inquéritos civis) discussing our obligations to restore native forest in the state of São Paulo. Material claims are outlined below.
Environmental Matters
We currently have three relevant public civil claims (ação civil pública) filed by the Federal Public Prosecution Office in the north and northeast regions of Brazil, which challenge the jurisdiction of the state’s environmental agency to grant environmental licenses. The Federal Public Prosecution Office alleges that the environmental licensing proceedings related to the forest formation and installation of our industrial plant in the state of Maranhão should be carried out by the Brazilian Federal Environmental Agency – IBAMA. The risks involved in such proceedings include delays in our plantation schedule and the suspension of the activities carried out in our Maranhão unit until a new permit is issued. Although an injunction was granted for one of these claims suspending the forest formation in a certain region of the state of Maranhão, we believe there are good grounds underlying our defense, since the IBAMA does not acknowledge having jurisdiction to conduct the related licensing proceedings, and there is no clear legal ground to sustain such jurisdiction. The superior court is still to rule on an appeal against the injunction granted against us, and the other claims are still pending judgement by the trial judge.
In addition, we are involved in a dispute related to possible environmental damages in Cubatão (a city in the state of São Paulo), allegedly caused by Cia Santista de Papel, a company that was acquired by Ripasa S.A. Celulose e Papel, which in turn was acquired by us in 2008. This lawsuit is ongoing for over thirty years and involves more than twenty other companies. Claimants in this lawsuit seek reparation for the environmental damage allegedly caused to Serra do Mar’s State Park (an area under environmental protection) by several companies that maintained activities in the industrial district of Cubatão until the 1990s.
On September 2017, the lawsuit was ruled in favor of the plaintiff, sentencing the defendant companies to recover the damages allegedly caused or, should the environment be already recovered, to pay a compensation of equal value of the cost of the recovery. This compensation would be allocated to expand Serra do Mar’s State Park. The ruling, however, did not determined the amount that should be paid as compensation, leaving the definition of this value to a latter procedural stage.
This ruling was contested by the companies in an appeal, and a decision by the State Supreme Court is still pending.
In December 2020 the Prosecutors Office of the State of Bahia served us in a public civil claim (ação civil pública) questioning the applicability of the concept of “Consolidated Rural Areas”, established by Federal Law No. 12.651 / 2012, in the areas inserted in the Mata Atlântica Biome. The process is still in a preliminary stage awaiting the judge's decision of injunction.
Civil Matters
Regarding civil matters, we are involved in two public civil claims (ação civil pública) filed by the Federal Public Prosecution Office requesting (i) a preliminary injunction to prohibit our trucks from transporting wood in federal highways above legal weight restrictions, (ii) an increase in the amount of fines for cases of overweight, and (iii) compensation for damages to property allegedly caused to federal highways, the environment and the economic order, and compensation for moral damages. One of these claims was ruled against us. We presented an appeal to the Court of Appeals, requesting an interim relief to stay the effects of such ruling until a final decision is reached. We are currently waiting for the ruling on the interim relief by the 1st Regional Federal Court Appeals.
We were served in March 2014 in a public civil claim (ação civil pública) filed by the Federal Prosecutor’s Office regarding real property acquired by us in the northern part of the state of Espírito Santo. The Federal Prosecutor requested the nullity of the deeds, compensation for moral damages and suspension of financing for our operations in the municipalities of São Mateus and Conceição da Barra, both located in the state of Espírito Santo. A preliminary injunction was granted, which blocked around 6,000 hectares of our land in such municipalities and suspended any financing for us by BNDES for either production or planting of eucalyptus pulp on the properties relating to the public civil claim.
In September 2015, we were served a notice of another public civil claim (ação civil pública) filed by the same Federal Prosecutor’s Office, requesting the nullity of the deeds of other certain proprieties acquired in the northern part of the state of Espírito Santo. A preliminary injunction was granted blocking around 5,601 hectares of our land in the same municipalities of São Mateus and Conceição da Barra. We filed our judicial defense and an appeal against such injunction, which is still pending judgment.
Both cases involving the State of Espírito Santo mentioned above are pending ruling by the Federal District Court of São Mateus and remain in pre-trial phase. We believe that there are good grounds for our defense since the acquisition of land discussed in both Public Civil Claims was made in accordance with applicable laws and practices applicable at the time of purchase.
In November 2020, a sea logistic supplier initiated an arbitration proceeding against us due to the early termination of the agreement. The counterparty seeks to enforce a put provision (imposing the ownership and acquisition of barges) allegedly foreseen in the agreement as a penalty for the early termination, and the payment of purported losses and damages suffered because of termination. Our position is that the put is not due, and, even if it was due, the put provision is abusive under the economic ratio of the contract. The case is still in the preliminary stage, pending the indication of the presiding arbitrator for constitution of the arbitral tribunal and signing of the Terms of Reference.
Administrative and Other Proceedings
There have been news reports in the Brazilian press alleging that certain contracts of Argeplan Arquitetura e Engenharia, a Brazilian engineering company unrelated to us, were under investigation, including a wood supply contract entered into with Fibria in September 2005. Following such news reports, we performed a review and concluded that there were no irregularities in connection with the signing of this contract, and that the contract (which is one of many third-party wood supply contracts that we enter into) is on market terms and is in line with industry practices in the pulp sector. Furthermore, official reports prepared by the competent authorities do not indicate any irregularities relating to such contract or the relationship between Suzano and Argeplan Arquitetura e Engenharia. This contract expired in August 2019.
Land Disputes
In April and October 2006, and in December 2009, the Brazilian Institute for Land Reform – INCRA, published a public notice informing that certain reports issued by commissions created by INCRA concluded that approximately 34,430 hectares of land located in the state of Espírito Santo should belong to certain quilombola communities (comunidades quilombolas de Linharinho, São Jorge e São Domingos). From that total area, approximately 25,330 hectares corresponded to property owned by us. The issues raised by INCRA reports are still underway, and there is no final decision by the INCRA. We are confident that the acquisition of this area by us complied with the applicable legislation and was duly registered with the appropriate governmental offices.
Dividends
General
The Brazilian Corporation Law and our bylaws require that we distribute annually to our shareholders a mandatory minimum dividend, which we refer to as the mandatory dividend, equal to at least 25% of our net income after taxes, after certain deductions, including accumulated losses and any amounts allocated to employee and management participation, any amount allocated to our legal reserve, and any amount allocated to the contingency reserve and any amount written off in respect of the contingency reserve accumulated in previous fiscal years, in each case in accordance with Brazilian law.
In accordance with article 26 of our bylaws, the minimum mandatory dividend corresponds to the lower of: (i) 25% of the adjusted annual net profits, and (ii) 10% of the Operating Cash Flow Generation in the relevant fiscal year. The Operating Cash Flow Generation (“GCO”) is calculated using the following formula: GCO = Adjusted EBITDA – Maintenance Capex, where “GCO” means the consolidated Generation of Operational Cash of the Fiscal Year, expressed in national currency, “EBITDA” means our net profit of the fiscal year expressed in national currency, before the income tax and social contribution on net income, financial income and expenses, depreciation, amortization and depletion. “Adjusted EBITDA” means the EBITDA excluding items not recurrent and/or not cash and gains (losses) arising from changes in fair value of sale of the biological assets.
Dividends must be distributed within 60 days from the annual shareholders’ meeting in which the distribution was approved, unless a shareholders’ resolution determines another date, not later than the end of the fiscal year in which such dividend was declared. The Brazilian Corporation Law permits, however, a company to suspend the mandatory distribution of dividends if its board of directors reports to the shareholders’ meeting that the distribution would be incompatible with the financial condition of the company, subject to approval by the shareholders’ meeting and review by the fiscal council. Net income not distributed due to the suspension mentioned here must be attributed to a special reserve and, if not absorbed by subsequent losses, must be paid as dividends as soon as the financial situation of the company permits.
The amounts available for distribution are determined on the basis of financial statements prepared in accordance with the requirements of the Brazilian Corporation Law. In addition, amounts arising from tax incentive benefits or rebates are appropriated to a separate capital reserve in accordance with the Brazilian Corporation Law. This investment incentive reserve is not normally available for distribution, although it can be used to absorb losses under certain circumstances or be capitalized. Amounts appropriated to this reserve are not available for distribution as dividends.
The Brazilian Corporation Law permits a company to pay interim dividends out of preexisting and accumulated profits for the preceding fiscal year or semester, based on financial statements approved by its shareholders. We may prepare financial statements semiannually or for shorter periods. Our board of directors may declare a distribution of dividends based on the profits reported in semiannual financial statements. Our board of directors may also declare a distribution of interim dividends based on profits previously accumulated or in profits reserve, which are reported in such financial statements or in the last annual financial statement approved by resolution taken at a shareholders’ meeting.
In general, shareholders who are not Brazilian residents must register their equity investment with the Central Bank of Brazil to have dividends, sales proceeds or other amounts with respect to their shares eligible to be remitted outside of Brazil. The common shares underlying the ADSs are held in Brazil by Banco Itaú S.A., also known as the custodian, as agent for the depositary, which is the registered owner on the records of the registrar for our shares.
Payments of cash dividends and distributions, if any, are made in reais to the custodian on behalf of the depositary, which then converts such proceeds into U.S. Dollars and causes such U.S. Dollars to be delivered to the depositary for distribution to holders of ADSs. In the event that the custodian is unable to convert immediately the foreign currency received as dividends into U.S. Dollars, the amount of U.S. Dollars payable to holders of ADSs may be adversely affected by devaluations of the Brazilian currency that occur before the dividends are converted. Under the Brazilian Corporation Law, dividends paid to persons who are not Brazilian residents, including holders of ADSs, will not be subject to Brazilian withholding tax.
Payment of dividends
In accordance with the Brazilian Corporation Law and our bylaws, our shareholders approved that there would be no distribution of dividends for the fiscal year of 2020 and 2019, given that there was no net profit for each of such year, and the payment of R$600.0 million in dividends for the fiscal year of 2018, (equivalent to US$115.5 million based on an exchange rate of R$5.1967 to US$1.00, the commercial selling rate for U.S. dollars at December 31, 2020 as reported by the Central Bank of Brazil). We paid no dividends during 2020, in comparison to R$606.6 million and R$210.2 million paid in 2019 and 2018, respectively.
B. Significant Changes
Significant changes or events have occurred after the close of the balance sheet at December 31, 2020. For further information on such events, please see note 32 to our audited consolidated financial statements.
ITEM 9. THE OFFER AND LISTING
A. Offer and Listing Details
Our ADSs are listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the trading symbol “SUZ.” Our common shares trade on the São Paulo Stock Exchange under the symbol “SUZB3.” On December 31, 2020, we had approximately 57,000 shareholders of record at the B3.
B. Plan of Distribution
Not applicable.
C. Markets
Trading on the São Paulo Stock Exchange
Settlement of transactions conducted on the B3 becomes effective two business days after the trade date. Delivery of, and payment for, shares is made through the facilities of separate clearinghouses for each exchange, which maintain accounts for member brokerage firms. The seller is ordinarily required to deliver the shares to the clearinghouse on the second business day following the trade date. The clearinghouse for the B3 is Companhia Brasileira de Liquidação e Custódia, or CBLC.
In order to better control volatility, the B3 has adopted a “circuit breaker” system pursuant to which trading sessions may be suspended for a period of 30 minutes or one hour whenever the indices of these stock exchanges fall below the limits of 10% and 15%, respectively, in relation to the index registered in the previous trading session.
The B3 is less liquid than the New York Stock Exchange or other major exchanges in the world. At December 31, 2020, the aggregate market capitalization of the 77 companies listed on the São Paulo Stock Exchange Index (Ibovespa) was equivalent to approximately US$926 million. Although any of the outstanding shares of a listed company may trade on a Brazilian stock exchange, in most cases fewer than half of the listed shares are actually available for trading by the public, the remainder being held by small groups of controlling persons, governmental entities or one principal shareholder.
Trading on the B3 by non-residents of Brazil is subject to certain limitations under Brazilian foreign investment and tax legislation. See Item 10. “Additional Information — Taxation” and Item 10. “Additional Information — Exchange Controls.”
B3 Corporate Governance Standards
The B3 has three listing segments:
| • | Novo Mercado (New Market) |
These listing segments have been designed for the trading of shares issued by companies that voluntarily undertake to abide by corporate governance practices and disclosure requirements in addition to those already required under the Brazilian Corporation Law. The inclusion of a company in any of these listing segments requires adherence to a series of corporate governance rules. These rules are designed to increase shareholders’ rights and enhance the quality of information provided by Brazilian corporations.
In 2004, we listed our shares on the Level 1 segment of the BM&FBOVESPA (former name of the B3), thus guaranteeing transparency in our operations and accountability to our shareholders. In September 2017, we approved the admission of our shares for trading on the listing segment called Novo Mercado of B3, followed by the conversion of the preferred shares issued by us into common shares at the ratio of one preferred share, class “A” or class “B”, for one common share. In addition, we also approved the restatement of our bylaws to adapt them to Novo Mercado rules and a change of our methodology to calculate mandatory dividends, also reflecting best corporate governance practices. We concluded the migration to Novo Mercado segment of B3 in November 2017.
As a result, in addition to the disclosure obligations imposed by the Brazilian Corporation Law and the CVM, we also must comply with the following additional disclosure requirements set forth by the Novo Mercado rules:
| • | no later than six months following our listing on the Novo Mercado, we must disclose financial statements and consolidated financial statements at the end of each quarter (except the last quarter of the year) and at the end of each fiscal year, including a statement of cash flows which must indicate, at a minimum, the changes in our cash and cash equivalents, divided into operating, financing and investing activities; |
| • | from the date on which we release our financial statements relating to the second fiscal year following our listing on the Novo Mercado we must, no later than four months after the end of the fiscal year: (i) prepare our annual financial statements and consolidated financial statements, if applicable, in accordance with U.S. GAAP or IFRS, in reais or U.S. dollars, in the English language, together with |
| • | management reports, (b) notes to the financial statements, including information on net income and shareholders’ equity calculated at the end of such fiscal year in accordance with Brazilian GAAP, as well as management proposals for allocation of net income, and (c) our independent auditors’ report; or (ii) disclose, in the English language, complete financial statements, management reports and notes to the financial statements, prepared in accordance with the Brazilian Corporation Law, accompanied by (a) an additional note regarding the reconciliation of year-end net income and shareholders’ equity calculated in accordance with Brazilian GAAP to U.S. GAAP or IFRS, as the case may be, which must include the main differences between the accounting principles used, and (b) the independent auditors’ report; and |
| • | from the date on which we release our first financial statement prepared as provided above, no more than 15 days following the term established by law for the publication of quarterly financial information, we must: (i) disclose, in its entirety, our quarterly financial information translated into the English language or (ii) disclose our financial statements and consolidated financial statements in accordance with Brazilian GAAP, U.S. GAAP or IFRS as provided above, accompanied by the independent auditors’ report. |
No later than six months following the listing of our common shares on the Novo Mercado, we must disclose the following information together with our ITR:
| • | our consolidated balance sheet, consolidated income statement and a discussion and analysis of our consolidated performance, if we are obliged to disclose consolidated financial statements at year-end; |
| • | any direct or indirect ownership interest exceeding 5.0% of our capital stock, considering any ultimate individual beneficial owner; |
| • | the number and characteristics, on a consolidated basis, of our common shares held directly or indirectly by any controlling shareholders, members of our board of directors, board of executive officers and fiscal committee; |
| • | changes in the numbers of our common shares held by any controlling shareholders, members of our board of directors, board of executive officers and fiscal committee in the immediately preceding 12 months; |
| • | in an explanatory note, our statement of cash flows and consolidated statement of cash flows, which should indicate the cash flows changes in cash balance and cash equivalent, separated into operating, financing and investing activities; and |
| • | the number of free-float shares, and their percentage in relation to the total number of issued shares. |
The following information must also be included in our formulário de referência within seven business days of the occurrence of the following events, among others:
| • | change in management or of an audit committee member; |
| • | change in capital stock; |
| • | issuance of new securities even if for private subscription; |
| • | change in the rights of the securities issued; |
| • | change in direct or indirect holdings by controlling shareholders or variations in their share positions equal to or greater than 5% of the same types or class of stocks of the issuer; |
| • | when any natural or legal person, or a group of persons representing the same interest, has a direct or indirect share that is equal to or higher than 5% of the same type or class of stocks of the issuer, provided that the issuer is aware of such change; |
| • | any change in the share position held by the persons mentioned in the two preceding items, in an amount greater than 5% of the same types or class of stocks of the issuer, provided that the issuer is aware of such change; |
| • | merger, merger of shares, or spin-off; |
| • | change in the projections or estimates or disclosure of new projections or estimates; |
| • | execution, amendment or termination of a shareholders’ agreement filed at the company’s headquarters or to which the controlling shareholder is party that provides for the exercise of voting rights or the control of the company; and |
| • | bankruptcy, judicial recovery, liquidation, or court approval of an extrajudicial recovery. |
All members of our board of directors, our board of executive officers and our fiscal council have signed a management compliance statement (Termo de Anuência dos Administradores) under which they take personal responsibility for compliance with the Novo Mercado listing agreement, the rules of the Market Arbitration Chamber and the regulations of the Novo Mercado.
Additionally, pursuant to the Novo Mercado rules, we must, by December 10 of each year, publicly disclose and send to the B3 an annual calendar with a schedule of our corporate events. Any subsequent modification to such schedule must be immediately and publicly disclosed and sent to B3.
Significant Differences between our Corporate Governance Practices and NYSE Corporate Governance Standards
See Item 16G. “Corporate Governance — Significant Differences between our Corporate Governance Practices and NYSE Corporate Governance Standards.”
D. Selling Shareholders
Not applicable.
E. Dilution
Not applicable.
F. Expenses of the Issue
Not applicable.
ITEM 10. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
A. Share Capital
As of the date hereof, our outstanding, fully paid-in share capital is R$ 9,269.2 million, comprised of 1.361.263.584 registered, book-entry common shares, with no par value. There has been one increase in the total amount of our share capital in January 10, 2019, with the issuance of 255.437.439 common shares, with no par value. In September, 2017, we approved the admission of our shares for trading on the listing segment called Novo Mercado of B3, followed by the conversion of the preferred shares issued by us into common shares at the ratio of one preferred share, class “A” or class “B”, for one common share. In addition, we also approved the restatement of our bylaws to adapt them to Novo Mercado rules and the change of the methodology to calculate mandatory dividends, also reflecting best corporate governance practices. We concluded the migration to Novo Mercado segment of B3 in November 2017 and the conversion of the preferred shares issued by us into common shares became effective.
The rights attributed to the new common shares (converted from our preferred shares) are identical to the rights previously granted to our then existing common shares. The rights attributed to the new common shares include: (i) the right to vote in our shareholders’ meetings; (ii) the right to receive 100% of the amount paid per voting share in the controlling block in the event our control is sold; (iii) the right to receive dividends and interest on own capital declared by us. For further information, see Item 10.B below and Exhibit 2.1 to this annual report, “Description of Securities Registered under Section 12 of the Exchange Act—I. Common Shares”.
B. Memorandum and Articles of Association
Our bylaws, approved by our shareholders at our general meeting held on April 27, 2021, are filed as Exhibit 1.1 to this annual report. The information otherwise contemplated by this Item has previously been reported in our registration statement on Form F-4 filed with the Commission on August 6, 2018 (Reg. No. 333-226596). This description does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by reference to our Bylaws, the Brazilian corporation law and the rules and regulations of the CVM and the Novo Mercado.
Voting Rights
Each common share entitles its holder to one vote at the matters of the shareholders’ meetings, in accordance with the Brazilian Corporation Law, our bylaws and the Novo Mercado regulation.
Shareholders’ Meetings
According to Brazilian Corporation Law, shareholders must be previously notified through a notice published three times in Brazilian official gazettes in order for an annual or extraordinary shareholders’ meeting to be held. The notification must occur at least 30 days prior to the meeting scheduled date, pursuant to Provisional Presidential Decree No. 1,040, dated March 29th, 2021 (in case such Provisional Decree is not converted into law until July 27th, 2021, the notification deadline will be changed from 30 to 15 days prior to the meeting scheduled date). If the meeting so noticed is not held for any reason on first notice, a second notification must be published at least eight days before the second meeting date.
On the first notice, meetings may be held only if shareholders holding at least one-fourth of voting shares are represented. Extraordinary meetings for the amendment of the bylaws may be held on the first notice only if shareholders holding at least two thirds of the voting capital are represented. On a second call, the meetings are held regardless of quorum.
Pursuant to our bylaws and Brazilian Corporation Law, shareholders at our annual shareholders’ meeting, which is required to be held within the first four months following the end of the fiscal year, will convene to: (i) take the management accounts; examine, discuss and vote on the financial statements; (ii) decide on the uses to which the net income of the fiscal year should be put and on the distribution of dividends; and (iii) elect the members of the Fiscal Council and, when applicable, the members of the Board of Directors.
An Extraordinary Shareholders’ Meeting shall be convened whenever the Company interests so require, and/or to resolve on following matters pursuant to the Brazilian Corporation Law and Provisional Presidential Decree No. 1,040, dated March 29th, 2021: (i) amend our bylaws; (ii) elect or dismiss members of the Board of Directors (Conselho de Administração), at any time; (iii) install our fiscal council and elect its members, if such body was not installed in the annual shareholders’ meeting; (iv) authorize the issuance of debentures; (v) suspend the rights of a shareholder in the event such shareholder does not comply with obligations imposed by law or our bylaws; (vi) accept or reject in-kind contributions offered by a shareholder in consideration for issuance of capital stock; (v) pass resolutions to reorganize the legal form of, merge, consolidate or split the company, to dissolve and liquidate the company, to elect and dismiss our liquidators and to examine their accounts; (ix) authorize management to declare us insolvent and to request a judicial recovery (recuperação judicial, a procedure involving protection from creditors available under Brazilian law); (x) authorize the sale or the contribution, to another company, of assets representing, at least, 50% of the company´s total assets, according to the previous financial statement approved by the shareholders; (xi) the execution of transactions with related parties that meet the criteria of relevance to be defined by the Brazilian Securities and Exchanges Commission (CVM) (in case the Provisional Decree is not converted into law until July 27th, 2021, items (ix), (x) and (xi) will be removed from the list of matters on which the Shareholders’ Meeting shall be convened to resolve).
Still according to our bylaws, the Shareholders Meeting which has as a matter of its agenda the resolution over the change or the exclusion of Article 30 regarding the tender offer in case of acquisition of relevant interest, shall be called, with at least, sixty (60) days in advance.
Dividends
The Brazilian Corporation Law and our bylaws require that we distribute annually to our shareholders a mandatory minimum dividend, which we refer to as the mandatory dividend, after certain deductions, including accumulated losses and any amounts allocated to employee and management participation, any amount allocated to our legal reserve, and any amount allocated to the contingency reserve and any amount written off in respect of the contingency reserve accumulated in previous fiscal years, in each case in accordance with Brazilian law.
In accordance with article 26 of our bylaws, the minimum mandatory dividend corresponds to the lower of: (i) 25% of the adjusted net profits, and (ii) 10% of the Operating Cash Flow Generation in the relevant fiscal year. The Operating Cash Flow Generation (“GCO”) is calculated using the following formula: GCO = Adjusted EBITDA – Maintenance Capex, where “EBITDA” means the net profit of the fiscal year of the Company expressed in national currency, before the income tax and social contribution on net income, financial income and expenses, depreciation, amortization and depletion. “Adjusted EBITDA” means EBITDA excluding items not recurrent and/or not cash and gains (losses) arising from changes in fair value of sale of the biological assets. “Maintenance Capex” means the amount, expressed in national currency, of the investments in maintenance executed in the fiscal year.
Acquisition of a Relevant Interest
Any person, including, without limitation, any natural or legal person, investment fund, condominium, securities portfolio, universality of rights, or other form of organization, resident, domiciled or headquartered in Brazil or abroad solely or jointly with another bound person(s) (person or group of persons bound by a voting agreement or similar agreement, or acting jointly representing the same interests), shareholder(s) or not of the Company, which subscribes, acquires or, in any other form, including, without limitation, by means of exchange, conversion, corporate reorganization (including, but not limiting to the merger of the Company and/or of its shares or the merger by the Company of other company or the shares thereof), or even upon acquisition of preemptive rights and/or subscription of shares or other securities issued by the Company convertible into shares or which give the right to its subscription or purchase of shares of the Company, becomes holder, directly or indirectly, in Brazil or offshore, of any percentage equal to or greater than twenty percent (20%) of the total shares issued by the Company shall, within the maximum term of thirty (30) days counting from the date of the event which results in the ownership of the relevant interest, launch or, in the case of a registered tender offer in the terms of CVM Rule 361/02, file a registry request before CVM of, a tender offer for the acquisition of the totality of the shares issued by the Company, which shall be liquidated in the maximum term of (a) forty eight (48) days counting from the launch of the offer not subject to registration, and (b) one hundred and eighty (180) days counting from the date of registry filing, in the case of an offer subject to registration, in the terms of the law and applicable legislation, except for certain delays which do not arise from any act or omission of the offeror.
Disclosure of Significant Interest
CVM rules provides that all shareholders or groups of shareholders will be required to disclose, through notice to us and to the stock exchanges on which our securities are traded, the negotiation of securities that results in the shareholder surpassing or decreasing the thresholds of 5%, 10%, 15%, and so on, of participation in a certain class or type of share representative of a company’s capital stock.
Pursuant to our bylaws, any person who holds Outstanding Shares in an amount greater than five percent (5%) of the total shares issued by us, and that wishes to carry out a new acquisition of shares issued by us (“New Acquisition”), shall be obliged, prior to each New Acquisition, to communicate in writing to our Investor Relations Officer, at least three (3) business days prior to the date of the New Acquisition: (i) the number of Outstanding Shares that it intends to acquire; (ii) the intention to acquire; (iii) if it has an interest to appoint a member to the Board of Directors or to the Audit Committee; (iv) the source of the resources that will be used for such acquisition; and (v) the strategic plans related to its investment in the Company. By “Outstanding Shares” we mean all shares issued by us, except those (i) owned, directly or indirectly, by the controlling shareholder or persons related thereto; (ii) in the Company's treasury; (iii) held by a company controlled by us; and (iv) directly or indirectly held by our directors, officer or other members of our management.
In the event that the person does not comply with such obligations, the provisions regarding the tender offer for the acquisition of the totality of the shares shall be observed.
Sale of Control
In the event of a direct or indirect sale of our shareholding control, through a single or series of transactions, the acquirer must conduct a public tender offer for all shares held by the remaining shareholders in order to ensure equal treatment of all shareholders (tag-along right). The tender offer is subject to applicable laws and regulations, our bylaws and the rules of the Novo Mercado.
Delisting from the Novo Mercado
According to the new Novo Mercado Listing Rules – applicable as of January 2, 2018 – the withdrawal from the Novo Mercado may be: (i) voluntary; or (ii) mandatory, as a result of the violation of any the rules of the Novo Mercado or the deregistration as publicly-held company.
The withdrawal, however, shall only occur after the launching of a public tender offer for our outstanding shares, which shall (i) follow, as applicable, the CVM regulation that rules that the mandatory tender offer for the deregistration as publicly held company (including the abovementioned possibility to request a second valuation report); and (ii) be launched at a fair price, as appointed in the appraisal report issued by a specialized institution with proven experience for the purposes of the tender offer; and (iii) be approved by at least one third (1/3) of the shareholders representing the free float that participate in the tender offer auction (whether by selling its shares or expressly agreeing with the withdrawal from the Novo Mercado).
The obligation to launch such public tender offer, however, may be waived by the majority of the shareholders representing our free float present at the shareholders’ meeting convened to resolve on that matter. Such shareholders’ meeting may be held on first call with the attendance of shareholders representing two thirds (2/3) of the free float or, on second call, with the attendance of any number of shareholders representing the free float.
The withdrawal from the Novo Mercado does not necessarily result in our deregistration as a publicly-held company on the B3. If we participate in a corporate reorganization involving the transfer of our shareholders’ base to a company that is not listed in the Novo Mercado, such resulting company or companies must apply for listing on Novo Mercado within one hundred and twenty (120) days from the date of the general shareholders meeting that approved the reorganization, unless the majority of the shareholders representing our free float present at such shareholders’ meeting agrees with the non-listing of the resulting company.
Pursuant to the new rules of the Novo Mercado, the voluntary withdrawal shall be preceded by a public tender offer at fair market value. For the withdrawal to move forward, shareholders representing more than one third (1/3) of the outstanding shares shall need to accept the tender offer or expressly agree to delist without selling the shares.
According to the rules of the Novo Mercado, in the event of a transfer of our shareholding control within 12 months following our delisting from the Novo Mercado, the selling controlling shareholder(s) and the acquirer must offer to acquire the remaining shares for the same price and terms offered to the selling controlling shareholders, duly updated, or pay the difference, if any, between the tender offer price accepted by the former shareholders, duly updated, and the price obtained by the controlling shareholder in selling its shares.
Delisting as Publicly-Held Company
Our delisting as publicly-held company shall be conditioned to: (i) the launching of a public tender offer for the acquisition of all of our outstanding shares in accordance with the provisions of Brazilian Corporation Law, the CVM rules and regulations, by us, our controlling shareholders or a group of controlling shareholders and (ii) the acceptance of at least two thirds (2/3) of the shareholders representing the free float that show up at the tender offer auction (whether by selling its shares or expressly agreeing with the delisting), in which case we would become a privately-held company. The price offered for such outstanding shares must at least correspond to the fair value of such shares as set forth in the respective appraisal report issued by a specialized institution with proven experience hired by the offeror for the purposes of the tender offer.
Shareholders holding at least ten percent of the free float of our shares may require our management to call a special shareholders’ meeting to determine whether to perform another valuation using the same or a different valuation method. This request must be made within 15 days following the disclosure of the price to be paid for the shares in the public tender offer. If the new valuation price is equal to or lower than the original valuation price, the shareholders making such request as well as those who vote in its favor must reimburse the Company for any costs incurred in preparing the new appraisal report. If the new valuation price is higher than the original valuation price, the offeror shall then decide whether to proceed with the public tender offer observing the new price or withdraw the tender offer, in which case the Company will continue to be registered as a publicly-held company.
Preemptive Rights
Each of our shareholders has a general preemptive right to subscribe for shares or convertible securities in any capital increase, in proportion to its shareholding, except (i) (i) in case of sale on a stock exchange or by public subscription, (ii) pursuant to an exchange for shares in a public offer for the acquisition of control, in accordance with the Brazilian Corporate Law, (iii) for subscription of shares in accordance with the special law for tax incentives,
| (i) | conversion of debentures and other securities into shares, since, in these cases, the preemptive right must be exercised when the security is issued, (v) in the event of the grant and exercise of any stock option to acquire or subscribe for shares of our capital stock; and (vi) in the context of a capital increase derived from merger, merger of shares and/or spin-off implemented according to Brazilian Corporation Law. A minimum period of 30 days following the publication of notice of the issuance of shares or convertible securities is allowed for exercise of the right, and the right is negotiable. However, according to our bylaws, our board of Directors can eliminate this preemptive right or reduce the 30-day period in case we issue debentures that are convertible into shares, warrants (bônus de subscrição) or shares within the limits authorized by the bylaws and the Brazilian Corporate Law: (i) through a stock exchange or through a public offering or (ii) through an exchange of shares in a public offering to acquire control of another publicly-held company. |
You may not be able to exercise the preemptive rights relating to the common shares underlying your ADSs unless a registration statement under the Securities Act is effective with respect to the shares to which the rights relate or an exemption from the registration requirements of the Securities Act is available and our ADS depositary determines to make the rights available to you. See Item 3. “Key Information — Risk Factors —Holders of ADSs may be unable to exercise the preemptive rights relating to our shares underlying the ADSs.”
Right of Withdrawal
The Brazilian Corporation Law provides that, under certain circumstances, a shareholder has the right to withdraw its equity interest from the company and to receive payment for the portion of shareholders’ equity attributable to its equity interest. Withdrawal rights may be exercised by dissenting or non-voting shareholders, if a vote of at least 50% of voting shares authorizes us:
| • | to establish new shares or to disproportionately increase an existing class of preferred shares relative to the other classes of shares, unless such action is provided for or authorized by the bylaws; |
| • | to modify a preference, privilege or condition of redemption or amortization conferred on one or more classes of preferred shares, or to create a new class with greater privileges than the existing classes of preferred shares; |
| • | to reduce the mandatory distribution of dividends; |
| • | to merge with another company (including if we are merged into one of our controlling companies) or to consolidate, except as described in the fourth paragraph following this list; |
| • | to approve our participation in a centralized group of companies, as defined under the Brazilian Corporation Law, and subject to the conditions set forth therein, except as described in the fourth paragraph following this list; |
| • | to change our corporate purpose; |
| • | to terminate a state of liquidation of the corporation; |
| • | to dissolve the corporation; |
| • | to transfer all of our shares to another company or in order to make us a wholly owned subsidiary of such company, known as a merger of shares (incorporação de ações), except as described in the fourth paragraph following this list; |
| • | to approve the acquisition of control of another company at a price which exceeds certain limits set forth in the Brazilian Corporation Law, except as described in the fourth paragraph following this list; or |
| • | to conduct a spin-off that results in (a) a change of our corporate purposes, except if the assets and liabilities of the spinoff company are contributed to a company that is engaged in substantially the same activities, (b) a reduction in the mandatory dividend or (c) any participation in a centralized group of companies, as defined under the Brazilian Corporation Law. |
In addition, in the event that the entity resulting from incorporação de ações, or a merger of shares, a consolidation or a spinoff of a listed company fails to become a listed company within 120 days of the shareholders’ meeting at which such decision was taken, the dissenting or non-voting shareholders may also exercise their withdrawal rights.
Only holders of shares adversely affected by the changes mentioned in the first and second items above may withdraw their shares. The right of withdrawal lapses 30 days after publication of the minutes of the relevant shareholders’ meeting. In the first two cases mentioned above, however, the resolution is subject to confirmation by the preferred shareholders, which must be obtained at a special meeting held within one year. In those cases, the 30- day term is counted from the date the minutes of the special meeting are published. We would be entitled to reconsider any action giving rise to withdrawal rights within 10 days following the expiration of such rights if the withdrawal of shares of dissenting shareholders would jeopardize our financial stability.
The Brazilian Corporation Law allows companies to redeem their shares at their economic value, subject to certain requirements. Since our bylaws currently do not provide that our shares be subject to withdrawal at their economic value, our shares would be subject to withdrawal at their book value, determined on the basis of the last balance sheet approved by the shareholders. If the shareholders’ meeting giving rise to withdrawal rights occurs more than 60 days after the date of the last approved balance sheet, a shareholder may demand that its shares be valued on the basis of a new balance sheet that is of a date within 60 days of such shareholders’ meeting.
Pursuant to the Brazilian Corporation Law, in events of consolidation, merger, incorporação de ações, participation in a group of companies, and acquisition of control of another company, the right to withdraw does not apply if the shares meet certain tests relating to liquidity and dispersal of the type or class of shares on the market. In such cases, shareholders will not be entitled to withdraw their shares if the shares are a component of a general securities index in Brazil or abroad admitted to trading on the securities markets, as defined by the CVM, and the shares held by persons unaffiliated with the controlling shareholder represent more than half of the outstanding shares of the relevant type or class.
Arbitration
We, our shareholders, managers and members of the Audit Committee, whether sitting or alternate members, if any, undertake to resolve, through arbitration, before the Market Arbitration Chamber (Câmara de Arbitragem do Mercado), pursuant to its regulations, any controversies that may arise between them, relating to or arising from their respective condition as an issuer, shareholder, administrator and/or member of the Audit Committee, in particular, of the provisions contained in Law No. 6,385/76, the Brazilian Corporations Law, our bylaws, in the rules issued by the National Monetary Council, by the Central Bank of Brazil and by the Brazilian Securities and Exchanges Commission (CVM), as well as in the other rules applicable to the operation of the capital markets in general, in addition to those contained in the Novo Mercado Rules, the other regulations of B3 and the Novo Mercado Listing Agreement.
C. Material Contracts
Financing Agreements
For a description of the main agreements comprising our short and long-term indebtedness as of December 31, 2020, see Item 5. “Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—B. Liquidity and Capital Resources—Sources and Uses of Funds—Indebtedness.”
D. Exchange Controls
There are no restrictions on ownership of our common shares by individuals or legal entities domiciled outside Brazil. However, the right to convert dividend payments and proceeds from the sale of common shares into foreign currency and to remit such amounts outside Brazil is subject to exchange control restrictions and foreign investment legislation, which generally require, among other things, obtaining an electronic registration with the Central Bank of Brazil.
Under Resolution No. 4.373/2014, foreign investors may invest in almost all financial assets and engage in almost all transactions available in the Brazilian financial and capital markets, provided that some requirements are fulfilled. In accordance with Resolution No. 4.373/2014, the definition of foreign investor includes individuals, legal entities, mutual funds and other collective investment entities that are domiciled or headquartered abroad.
Investors under Resolution No. 4.373/2014, who are not a Tax Haven Holder or a country that does not impose income tax or in which the maximum income tax rate is lower than 20%, are entitled to favorable tax treatment. See “Taxation—Material Brazilian Tax Considerations.”
Resolution No. 1,927 provides for the issuance of depositary receipts in foreign markets in respect of shares of Brazilian issuers. An application was filed to have the ADSs approved by the Central Bank of Brazil and the CVM under Annex V, and we received final approval before the ADSs Offering.
An electronic registration, which replaced the amended Certificate of Registration, was issued in the name of the depositary with respect to the ADSs and is maintained by the Custodian on behalf of the Depositary. This electronic registration was carried on through the SISBACEN. Pursuant to the electronic registration, the Custodian and the Depositary are able to convert dividends and other distributions with respect to the common shares represented by the ADSs into foreign currency and remit the proceeds outside Brazil. In the event that a holder of ADSs exchanges the ADSs for common shares, the holder will be entitled to continue to rely on the Depositary’s electronic registration for only five business days after the exchange. Thereafter, a holder must seek to obtain its own electronic registration. Unless the common shares are held pursuant to Resolution No. 4.373/2014 by a duly registered investor or a holder of common shares, who applies for and obtains a new electronic registration, that holder may not be able to obtain and remit abroad U.S. Dollars or other foreign currencies upon the disposition of the common shares, or distributions with respect thereto. In addition, if the foreign investor resides in a tax haven jurisdiction or is not an investor registered pursuant to Resolution No. 4.373/2014, the investor will also be subject to less favorable tax treatment.
E. Taxation Brazilian Tax Considerations
The following discussion contains a description of the material Brazilian income tax consequences of the purchase, ownership and disposition of shares or ADSs by a holder which is non-resident or not domiciled in Brazil for Brazilian tax purposes (“Non-Brazilian Holder”). It does not purport to be a comprehensive description of all Brazilian tax considerations that may be applicable to any particular Non-Brazilian Holder.
This summary is based upon tax laws of Brazil and administrative and judicial decisions as in effect on the date of this annual report, which are subject to changes (possibly with retroactive effect) and to differing interpretations. You should consult your own tax advisors as to the Brazilian tax consequences of the purchase, ownership and sale of our common shares or ADSs.
Although there is no treaty for the avoidance of double taxation between Brazil and the United States, the tax authorities of the two countries have been having discussions that may culminate in such a treaty. No assurance can be given, however, as to whether or when a treaty will enter into force or how it will affect the U.S. holders of our common shares or ADSs.
For purposes of Brazilian taxation, there are two types of Non-Brazilian Holders of common shares or ADSs: (a) Non-Brazilian Holders registered before the Central Bank of Brazil and the CVM to invest in Brazil in accordance with Central Bank of Brazil Resolution No. 4,373/14 (“4,373/2014 Holders”); and (b) other Non-Brazilian Holders, which include Non-Brazilian Holders who invest in Brazilian companies under Law No. 4,131/1962. As a general rule, 4,373/2014 Holders are subject to a favorable tax regime in Brazil, as described below.
Central Bank of Brazil Resolution No. 4,373/2014 permits foreign investors, defined to include individuals, legal entities, mutual funds and other collective investment entities, domiciled or headquartered abroad to invest in almost all financial assets and to engage in almost all transactions available in the Brazilian financial and capital markets, provided that certain legal and regulatory requirements are fulfilled. The foreign investors must (a) appoint at least one representative in Brazil with powers to perform actions relating to the foreign investment; (b) file the appropriate foreign investor registration form; (c) obtain the register as a foreign investor before the Brazilian securities commission; and (d) obtain the register of the foreign investment before the Central Bank of Brazil.
U.S. Federal Income Tax Considerations
This summary describes certain U.S. federal income tax considerations that are likely to be relevant to the purchase, ownership and disposition of our common shares or ADSs by a U.S. holder (as defined below). This summary is based on the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 (the “Code”), as amended, its legislative history, existing and proposed regulations promulgated thereunder, published rulings and court decisions, all as currently in effect. These authorities are subject to change, possibly on a retroactive basis. In addition, this summary assumes the deposit agreements governing our shares and ADSs, and all other related agreements, will be performed in accordance with their terms.
This summary is not a comprehensive discussion of all of the tax considerations that may be relevant to a particular investor’s decision to purchase, hold, or dispose of our shares or ADSs. In particular, this summary is directed only to U.S. holders that hold our shares or ADSs as capital assets and does not address tax consequences to U.S. holders who may be subject to special tax rules, such as banks, brokers or dealers in securities or currencies, traders in securities electing to mark to market, financial institutions, life insurance companies, tax exempt entities, regulated investment entities, entities that are treated as partnerships for U.S. federal income tax purposes (or partners therein), holders that own or are treated as owning 10% or more of our shares, by vote or value, persons holding our shares or ADSs as part of a hedging or conversion transaction or a straddle, persons whose functional currency is not the U.S. dollar, or U.S. expatriates. Moreover, this summary does not address state, local or foreign taxes, the U.S. federal estate and gift taxes, or the Medicare contribution tax applicable to net investment income of certain non-corporate U.S. holders, or alternative minimum tax consequences of acquiring, holding or disposing of our shares or ADSs.
As used below, a “U.S. holder” is a beneficial owner of our shares or ADSs that is, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, a citizen or individual resident of the United States or a U.S. domestic corporation or that otherwise is subject to U.S. federal income taxation on a net income basis in respect of such shares or ADSs.
You should consult your own tax advisors about the consequences of the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of our shares or ADSs, including the relevance to your particular situation of the considerations discussed below and any consequences arising under foreign, state, local or other tax laws.
Treatment of our ADSs for U.S. Federal Income Tax Purposes
In general, a holder of our ADSs will be treated, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, as the beneficial owner of the underlying shares that are represented by those ADSs.
Taxation of Dividends
Subject to the discussion below under “—Passive Foreign Investment Company Status,” the gross amount of any distribution of cash or property with respect to our shares or ADSs that is paid out of our current or accumulated earnings and profits (as determined for United States federal income tax purposes) will generally be includible in your taxable income as ordinary dividend income on the day on which you receive the dividend, in the case of our shares, or the date the depositary receives the dividends, in the case of our ADSs, and will not be eligible for the dividends-received deduction allowed to corporations under the Code. We do not expect to maintain calculations of our earnings and profits in accordance with U.S. federal income tax principles. U.S. holders therefore should expect that distributions generally will be treated as dividends for U.S. federal income tax purposes.
If you are a U.S. holder, dividends paid in a currency other than U.S. dollars generally will be includible in your income in a U.S. dollar amount calculated by reference to the exchange rate in effect on the day you receive the dividends, in the case of our shares, or the date the depositary receives the dividends, in the case of our ADSs. U.S. holders should consult their own tax advisers regarding the treatment of foreign currency gain or loss, if any, on any foreign currency received that is converted into U.S. dollars after it is received.
Subject to certain exceptions for short-term positions, the U.S. dollar amount of dividends received by an individual with respect to our shares or ADSs will be subject to taxation at a preferential rate if the dividends are “qualified dividends.” Dividends paid on the our shares or ADSs will be treated as qualified dividends if:
| • | our shares and ADSs are readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States; and |
| • | we were not, in the year prior to the year in which the dividend was paid, and are not, in the year in which the dividend is paid, a passive foreign investment company (a “PFIC”). |
Our ADSs are listed on the NYSE, effective as of December 10, 2018, and our ADSs should qualify as readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States so long as they are so listed. As described in more detail under “—Passive Foreign Investment Company Status,” below, based on our audited financial statements and relevant market and shareholder data, we believe that we were not treated as a PFIC for U.S. federal income tax purposes with respect to our 2019 and 2020 taxable years and will not be a PFIC in our current taxable year. Holders should consult their own tax advisers regarding the availability of the reduced dividend tax rate in light of their own particular circumstances.
Because our shares are not themselves listed on a U.S. exchange, dividends received with respect to our shares that are not represented by ADSs may not be treated as qualified dividends. U.S. holders should consult their own tax advisors regarding the potential availability of the reduced dividend tax rate in respect of our shares.
Dividend distributions with respect to our shares or ADSs generally will be treated as “passive category” income from sources outside the United States for purposes of determining a U.S. holder’s U.S. foreign tax credit limitation. Subject to the limitations and conditions provided in the Code and the applicable U.S. Treasury Regulations, a U.S. holder may be able to claim a foreign tax credit against its U.S. federal income tax liability in respect of any Brazilian income taxes withheld at the appropriate rate applicable to the U.S. holder from a dividend paid to such U.S. holder. Alternatively, the U.S. holder may deduct such Brazilian income taxes from its U.S. federal taxable income, provided that the U.S. holder elects to deduct rather than credit all foreign income taxes for the relevant taxable year. The rules with respect to foreign tax credits are complex and involve the application of rules that depend on a U.S. holder’s particular circumstances. Accordingly, U.S. holders are urged to consult their tax advisors regarding the availability of the foreign tax credit under their particular circumstances.
U.S. holders that receive distributions of additional shares or ADSs or rights to subscribe for our shares or ADSs as part of a pro rata distribution to all our shareholders generally will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax in respect of the distributions, unless the U.S. holder has the right to receive cash or property, in which case the U.S. holder will be treated as if it received cash equal to the fair market value of the distribution.
Taxation of Dispositions of our Shares or ADSs
Subject to the discussion below under “—Passive Foreign Investment Company Status,” if a U.S. holder realizes gain or loss on the sale, exchange or other taxable disposition of our shares or ADSs, that gain or loss will be capital gain or loss and generally will be long-term capital gain or loss if the shares or ADSs have been held for more than one year. Long-term capital gain realized by a U.S. holder that is an individual generally is subject to taxation at a preferential rate. The deductibility of capital losses is subject to limitations.
Gain, if any, realized by a U.S. holder on the sale or other disposition of our shares or ADSs generally will be treated as U.S. source income for U.S. foreign tax credit purposes. Consequently, if a Brazilian withholding tax is imposed on the sale or disposition of the shares, a U.S. holder that does not receive significant foreign source income from other sources may not be able to derive effective U.S. foreign tax credit benefits in respect of such Brazilian taxes.
U.S. holders should consult their own tax advisors regarding the application of the foreign tax credit rules to their investment in, and disposition of, our shares or ADSs.
If a U.S. holder sells or otherwise disposes of our shares or ADSs in exchange for currency other than U.S. dollars, the amount realized generally will be the U.S. dollar value of the currency received at the spot rate on the date of sale or other disposition (or, if the shares or ADSs are traded on an established securities market at such time, in the case of cash basis and electing accrual basis U.S. holders, the settlement date). An accrual basis U.S. holder that does not elect to determine the amount realized using the spot exchange rate on the settlement date will recognize foreign currency gain or loss equal to the difference between the U.S. dollar value of the amount received based on the spot exchange rates in effect on the date of the sale or other disposition and the settlement date. A U.S. holder generally will have a tax basis in the currency received equal to the U.S. dollar value of the currency received at the spot rate on the settlement date. Any currency gain or loss realized on the settlement date or the subsequent sale, conversion, or other disposition of the non-U.S. currency received for a different U.S. dollar amount generally will be U.S.-source ordinary income or loss, and will not be eligible for the reduced tax rate applicable to long-term capital gains. If an accrual basis U.S. holder makes the election described in the first sentence of this paragraph, it must be applied consistently from year to year and cannot be revoked without the consent of the IRS. A U.S. holder should consult its own tax advisors regarding the treatment of any foreign currency gain or loss realized with respect to any currency received in a sale or other disposition of the shares or ADSs. Deposits and withdrawals of shares by U.S. holders in exchange for ADSs will not result in the realization of gain or loss for U.S. federal income tax purposes.
Passive Foreign Investment Company Status
Special U.S. tax rules apply to companies that are considered to be PFICs. We will be classified as a PFIC in a particular taxable year if, either:
| • | 75 percent or more of our gross income for the taxable year is passive income; or |
| • | the average percentage of the value of our assets that produce or are held for the production of passive income is at least 50 percent. |
For this purpose, passive income generally includes dividends, interest, gains from certain commodities transactions, rents, royalties and the excess of gains over losses from the disposition of assets that produce passive income.
We believe, and the following discussion assumes, that we were not a PFIC for our taxable year ending December 31, 2020 and that, based on the present composition of our income and assets and the manner in which we conduct our business, we will not be a PFIC in our current taxable year. However, the determination of whether we are a PFIC is a factual determination made annually, and our status could change depending, among other things, upon changes in the composition of our gross income and the relative quarterly average value of our assets. Accordingly, we cannot be certain that we will not be a PFIC in the current year or in future years. If we were a PFIC for any taxable year in which you hold our shares or ADSs, you generally would be subject to additional taxes on certain distributions and any gain realized from the sale or other taxable disposition of our shares or ADSs regardless of whether we continued to be a PFIC in any subsequent year, unless you elect to mark your shares or ADSs to market for tax purposes on an annual basis. You are encouraged to consult your own tax advisor as to our status as a PFIC and the tax consequences to you of such status.
Foreign Financial Asset Reporting
Certain U.S. holders that own “specified foreign financial assets” with an aggregate value in excess of US$50,000 on the last day of the taxable year or US$75,000 at any time during the taxable year are generally required to file an information statement along with their tax returns, currently on Form 8938, with respect to such assets. “Specified foreign financial assets” include any financial accounts held at a non-U.S. financial institution, as well as securities issued by a non-U.S. issuer that are not held in accounts maintained by financial institutions. The understatement of income attributable to “specified foreign financial assets” in excess of US$5,000 extends the statute of limitations with respect to the tax return to six years after the return was filed. U.S. holders who fail to report the required information could be subject to substantial penalties. Holders are encouraged to consult with their own tax advisors regarding the possible application of these rules, including the application of the rules to their particular circumstances.
Backup Withholding and Information Reporting
Dividends paid on, and proceeds from the sale or other disposition of, our shares or ADSs to a U.S. holder generally may be subject to the information reporting requirements of the Code and may be subject to backup withholding unless the U.S. holder provides an accurate taxpayer identification number and makes any other required certification or otherwise establishes an exemption. Backup withholding is not an additional tax. The amount of any backup withholding from a payment to a U.S. holder will be allowed as a refund or credit against the U.S. holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability, provided the required information is furnished to the IRS in a timely manner.
A holder that is a foreign corporation or a non-resident alien individual may be required to comply with certification and identification procedures in order to establish its exemption from information reporting and backup withholding.
ITEM 11. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
We are exposed to various market risks, including changes in foreign currency exchange rates, interest rates, correction indexes and prices of commodities that may affect the financial results of Suzano. In order to manage the impacts in the results in adverse scenarios, we have provided procedures for the monitoring of political exposure for the implementation of risk management.
The policies establish the limits and instruments to be implemented with the goal of: (i) protection of cash flow due to currency devaluation, (ii) interest rate exposure mitigation, (iii) reduction in the impacts of commodity price fluctuation and (iv) exchange of debt indexes.
In the process of market risk management, the identification, evaluation and implementation, as well as the contracting of financial instruments for risk protection are performed. The development management area accompanies the fulfillment of the limits established in our policies.
Exchange Rate Risk
As a predominantly exporting company, our results are exposed to exchange variations. As such, fluctuations in the exchange rate, especially with regards to the U.S. dollars, may impact our results.
We issue debt securities in the international markets as an important part of the capital structure that is also exposed to fluctuations in the exchange rate. The mitigation of these risks comes from our own exports, which creates a natural hedge. Furthermore, we enter in derivatives transactions in the financial markets, including using strategies with options, as a way to ensure attractive levels of operating margins for a portion of our income. The foreign exchange hedging strategy follows our financial policies.
The net exposure of assets and liabilities in foreign currency, which is substantially in U.S dollars, is set forth below:
| | | December 31, | |
| | | 2020 | | | 2019 | | | 2018 | |
| | | | | (in millions of R$) | | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 6,370.2 | | | | 2,527.8 | | | | 1,144.0 | |
| Trade accounts receivable | | | 1,938.6 | | | | 2,027.0 | | | | 1,661.1 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | 621.4 | | | | 9,440.1 | | | | 493.7 | |
| | | | 8,930.2 | | | | 13,994.9 | | | | 3,298.8 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade accounts payables | | | (492.6 | ) | | | (1,085.2 | ) | | | (72.7 | ) |
| Loans and financing | | | (58,145.1 | ) | | | (45,460.1 | ) | | | (26,384.7 | ) |
| Liabilities for asset acquisitions and subsidiaries | | | (313.0 | ) | | | (288.2 | ) | | | (333.0 | ) |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | (6,994.4 | ) | | | (11,315.9 | ) | | | (1,464.6 | ) |
| | | | (65,945.1 | ) | | | (58,149.4 | ) | | | (28,255.0 | ) |
| Liability exposure | | | (57,014.9 | ) | | | (44,154.5 | ) | | | (24,956.2 | ) |
Sensitivity Analysis – Foreign Exchange Exposure
For purposes of risk analysis, we use scenarios to evaluate the sensitivity that the variations in long and short positions, indexed in foreign currency, may suffer. We take as a base case the values recognized in accounting on December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019 and, from there onwards, appreciations and depreciations are simulated, between 25% and 50%, of the real compared to other foreign currencies. The following table shows the probable values and the variations based on them.
| | | December 31, 2020 | |
| | | As of | | | Effect on income and equity | |
| | | Probable | | | Possible Increase (∆25%) | | | Remote Increase (∆50%) | |
| | | | | (in millions of R$) |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 6,370.2 | | | | 1,592.5 | | | | 3,185.1 | |
| Trade accounts receivable | | | 1,938.6 | | | | 484.6 | | | | 969.3 | |
| Trade accounts payables | | | (492.6 | ) | | | (123.2 | ) | | | (246.3 | ) |
| Loans and financing | | | (58,145.1 | ) | | | (14,536.3 | ) | | | (29,072.5 | ) |
| Liabilities for assets acquisitions and subsidiaries | | | (313.0 | ) | | | (78.2 | ) | | | (156.5 | ) |
| Derivatives Non-deliverable forward (“NDF”) | | | 7.9 | | | | (102.8 | ) | | | (205.5 | ) |
| Derivatives Options | | | (780,9 | ) | | | (3,386.1 | ) | | | (7,232.4 | ) |
| Derivatives Swap | | | (6,503.9 | ) | | | (4,436.5 | ) | | | (8,873.1 | ) |
| | | | (57,918.75 | ) | | | (20,585.95 | ) | | | (41,631.9 | ) |
| | | December 31, 2019 | |
| | | As of | | Effect on income and equity | |
| | | Probable | | | Possible Increase (∆25%) | | | Remote Increase (∆50%) | |
| | | | | | (in millions of R$) | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 2,527.8 | | | | 632.0 | | | | 1,263.9 | |
| Trade accounts receivable | | | 2,027.0 | | | | 506.8 | | | | 1,013.5 | |
| Trade accounts payables | | | (1,085.2 | ) | | | (271.3 | ) | | | (542.6 | ) |
| Loans and financing | | | (45,460.1 | ) | | | (11,365.0 | ) | | | (22,730.1 | ) |
| Liabilities for assets acquisitions and subsidiaries | | | (288.2 | ) | | | (72.1 | ) | | | (144.1 | ) |
| Derivatives Options | | | (2,198.8 | ) | | | (4,087.5 | ) | | | (8,175.0 | ) |
| Derivatives Swap | | | 67.0 | | | | (2,710.5 | ) | | | (6,048.3 | ) |
| | | | (44,410.5 | ) | | | (17,367.6 | ) | | | (35,362.7 | ) |
Commodity Price Risk
We are exposed to commodity prices reflected primarily in the sale price of pulp in the international market. Increases and decreases in production capacities in the global market, as well as the macroeconomic conditions may impact our operational results.
It is not possible to guarantee that prices will remain at levels that are beneficial to our results. We may use financial instruments to mitigate the sales price of part of the production, but in certain cases the employment of price protection for pulp may not be available.
We are also exposed to international oil prices, reflected in the logistical costs of transportation and commercialization.
On December 31, 20120 the Company held a long position in VLSFO (very-low sulfur fuel oil) in the notional amount of US$37.6 million to hedge its logistics costs.
| | | December 31, 2020 | |
| | | As of | | | Effect on income | |
| | | Probable | | | Possible
Increase
(∆25%) | | | Remote
Increase
(∆50%) | |
| | | (in millions of R$) | |
| Oil Derivatives | | | (15.8 | ) | | | 43.6 | | | | 87.2 | |
| | | | (15.8 | ) | | | 43.6 | | | | 87.2 | |
Sensitivity Analysis – Exposure to Commodity Prices
We did not have open assets indexed to commodities in 2020.
Derivatives by Contract Type
As of December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, the open positions of derivatives negotiated in the over-the-counter market, grouped by class of asset and reference index, are represented below.
| | | Notional value in US$ millions | | | | | | Fair value in millions of R$ | |
| | | 2020 | | | 2019 | | | 2018 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | | | 2018 | |
Instruments contracted with protection strategy Operational hedge | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Zero-cost collar (R$ vs. US$) | | | 3,212.3 | | | | 3,425.0 | | | | 3,040.0 | | | | (780.5 | ) | | | 67.1 | | | | (134.8 | ) |
| NDF (R$ x US$) | | | 80.0 | | | | — | | | | 150.0 | | | | 7.9 | | | | — | | | | 17.0 | |
| Fixed Swap (US$) vs. CDI | | | - | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Fixed Swap CDI vs. (US$) | | | - | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Subtotal | | | 3,292.3 | | | | 3,425.0 | | | | 3,190.0 | | | | (772.6 | ) | | | 67.1 | | | | (117.8 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Commodity hedge | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Swap VLSFO/Brent (oil) | | | 37.8 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 5.3 | | | | 15.8 | | | | (0.1 | ) | | | (1.1 | ) |
| Swap US-CPI standing wood (U.S.$) | | | 646.1 | | | | 679.5 | | | | — | | | | 354.9 | | | | 268.5 | | | | — | |
| Subtotal | | | 683.9 | | | | 679.9 | | | | 5.3 | | | | 370.7 | | | | 268.4 | | | | (1.1 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Debt hedge Interest rate hedge | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Swap LIBOR vs. Fixed (US$) | | | 3,683.3 | | | | 2,750.0 | | | | 2,757.1 | | | | | | | | (444.9 | ) | | | (170.7 | ) |
| Swap IPCA vs. CDI (R$) | | | 843.8 | | | | 843.8 | | | | — | | | | | | | | 233.3 | | | | — | |
| Swap IPCA vs. Fixed (US$) | | | 121.0 | | | | 121.0 | | | | — | | | | | | | | 30.5 | | | | — | |
| Swap CDI vs. Fixed (US$) | | | 2,267.1 | | | | 3,115.6 | | | | 2,402.1 | | | | | | | | (1,940.4 | ) | | | (853.1 | ) |
| Swap Fixed (R$) vs. Fixed (US$) | | | 350.0 | | | | 350.0 | | | | — | | | | | | | | (33.0 | ) | | | — | |
| Subtotal | | | 7,265.2 | | | | 7,180.4 | | | | 5,159.2 | | | | (6,374.1 | ) | | | (2,154.5 | ) | | | (1,023.8 | ) |
| Total in derivatives | | | 11,241.4 | | | | 11,285,3 | | | | 8,354.5 | | | | (6,776.0 | ) | | | (1,818.9 | ) | | | (1,142.8 | ) |
| Current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 484 | | | | 260.3 | | | | 352.5 | |
| Non-current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 857,4 | | | | 838.7 | | | | 141.5 | |
| Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (1,991.1 | ) | | | (893.4 | ) | | | (596.5 | ) |
| Non-current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (6,126.3 | ) | | | (2,024.5 | ) | | | (1,040.2 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (6,776.0 | ) | | | (1,818.9 | ) | | | (1,142.8 | ) |
ITEM 12. DESCRIPTION OF SECURITIES OTHER THAN EQUITY SECURITIES
The Bank of New York Mellon, as depositary, has agreed to reimburse us for expenses it incurs that are related to the establishment and maintenance of our ADS program. The depositary has agreed to reimburse us for our continuing and annual stock exchange listing fees. It has also agreed to pay the standard out-of-pocket maintenance costs for the ADRs, and to reimburse us annually for certain investor relations programs or special promotional activities. In certain instances, the depositary has agreed to provide additional payments to us based on any applicable performance indicators relating to the ADR facility. There are limits on the amount of expenses for which the depositary will reimburse us, but the amount of reimbursement available to us is not necessarily tied to the amount of fees the depositary collects from investors.
The depositary collects its fees for delivery and surrender of ADSs directly from investors depositing shares or surrendering ADSs for the purpose of withdrawal or from intermediaries acting for them. The depositary collects fees for making distributions to investors by deducting those fees from the amounts distributed or by selling a portion of distributable property to pay the fees. The depositary may collect is annual fee for depositary services by deduction from cash distributions or by directly billing investors or by charging the book-entry system accounts of participants acting for them.
PART II
ITEM 13. DEFAULTS, DIVIDEND ARREARAGES AND DELINQUENCIES
See discussion at Item 5. “Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Covenants.”
ITEM 14. MATERIAL MODIFICATIONS TO THE RIGHTS OF SECURITY HOLDERS AND USE OF PROCEEDS
None.
ITEM 15. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Disclosure Controls and Procedures: Our management, with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer, after evaluating the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in the Exchange Act under Rule 13a-15(e)) as of the end of the period covered in this annual report, has concluded that, as of that date, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective to provide reasonable assurance that the information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act was being recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the applicable rules and forms, and was accumulated for and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, to allow for timely decisions regarding the required disclosure.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting: Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Exchange Act Rule 13a-15(f) and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting. Our internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by the Company’s Statutory Audit Committee, the Company’s Board of Directors, management, and other personnel to provide reasonable assurances regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with and in compliance with the International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”).
Our internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (a) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of our assets; (b) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with and in compliance with IFRS as issued by the IASB, and that our receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with authorizations of our management and directors; and (c) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of our assets that could have a material effect on our audited consolidated financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with our policies or procedures may deteriorate.
The effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020 is based on the criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013), issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). Based on that assessment, management has concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2020.
Audit of the Effectiveness of Internal Control over Financial Reporting: Our independent registered public accounting firm, PriceWaterhouseCoopers Auditores Independentes, has audited the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting, as stated in their report as of December 31, 2020, which is included herein.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting: There was no change in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred in the period covered by this annual report that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 16. A. AUDIT COMMITTEE FINANCIAL EXPERT
Our board of directors has determined that Mr. Carlos Biedermann, a member of our audit committee, is an audit committee financial expert within the meaning of Sarbanes-Oxley and related regulations.
ITEM 16. B. CODE OF ETHICS
Our board of directors has adopted a code of conduct (“Code of Conduct”) that applies to all of our board members, suppliers and employees, including the members of our financial department, our chief executive officer, our chief financial officer and our chief accounting officer. No waiver, either express or implied, of provisions of our Code of Conduct was granted to our chief executive officer, chief financial officer or chief accounting officer in 2020. A copy of our Code of Conduct has been filed as Exhibit 11.1 to this annual report.
Our Code of Conduct addresses, among others, the following topics:
| • | honest and ethical conduct, treating conflicts and misconduct with absolute secrecy; |
| • | full, fair, accurate, timely, and understandable disclosure in reports and documents that we file with, or submit to public communications made by us; |
| • | compliance with laws, internal procedures and rules and also rules established by Brazilian and international capital market regulatory agencies; and |
| • | the prompt internal reporting of breaches related to our Code to the Ombudsman. |
In order to keep the highest governance standards, every two years we review our Code of Conduct to assure that the document is up-to-date and follows best practices and regulations. In 2019, we approved the last revision of our Code of Conduct. All of our employees confirmed their commitment with our Code of Conduct and to undertake to comply with its principles and guidelines while performing their professional activities by performing mandatory training
Additionally, we have conducted awareness actions in order to enforce the importance of business integrity, compliance and the governance instruments – our Code of Conduct and the Ombudsman. Video-learning format regarding the anti-corruption policy and our Code of Conduct have been given to all employees in 2019, in order to reinforce the main guidelines and practices established by our Code of Conduct. This training program was mandatory for all of our employees and at the end of the training each employee signs the training electronically.
ITEM 16. C. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
The following table sets forth by category of service the total fees for services performed by PricewaterhouseCoopers during the fiscal years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019.
Year Ended December 31 | | 2020 (In thousands of reais) | | | 2019 (In thousands of reais) | |
| Audit Fees | | | 23,083.4 | | | | 21,281.0 | |
| Tax Fees | | | — | | | | 74.7 | |
| Audit Related Fees | | | — | | | | — | |
| All Other Fees | | | — | | | | — | |
| Total | | | 23,083.4 | | | | 21,355.7 | |
Audit Fees
Audit fees in 2020 and 2019 consisted of the aggregate fees billed by PricewaterhouseCoopers Auditores Independentes in connection with the audit of our annual financial statements, the reviews of our quarterly financial statements, and the audit of the statutory financial statements of our subsidiaries. Audit fees also include fees for services that can only be reasonably provided by our independent auditors, such as the issuance of comfort and consent letters and the review of periodic documents filed with the SEC.
Tax Fees
Tax fees consisted of the aggregate fees billed by PricewaterhouseCoopers Auditores Independentes in connection with the consulting services for recovery of tax credits abroad and others.
Pre-Approval Policies and Procedures
Neither our board of directors nor our audit committee has established pre-approval policies and procedures for the engagement of our registered public accounting firm for services. Our board of directors expressly approves on a case-by-case basis any engagement of our registered public accounting firm for audit and non-audit services provided to us or our subsidiaries. Any services provided by PriceWaterhouseCoopers Auditores Independentes that are not specifically included within the scope of the audit must be pre-approved by our board of directors in advance of any engagement. It is within the scope of our audit committee to provide recommendations to our board of directors regarding any such engagement.
ITEM 16. D. EXEMPTIONS FROM THE LISTING STANDARDS FOR AUDIT COMMITTEES
Under the listed company audit committee rules of the NYSE and the SEC, we must comply with Rule 10A-3 under the Exchange Act, which requires that we establish an audit committee composed of members of the board of directors that meets specified requirements. Pursuant to Exchange Act Rule 10A-3(c)(3), a foreign private issuer is not required to have an audit committee equivalent to or comparable with a U.S. audit committee if the foreign private issuer has a body established and selected pursuant to home country legal or listing provisions expressly requiring or permitting such a body, and if the body meets the requirements that (i) it be separate from the full board, (ii) its members not be elected by management, (iii) no executive officer be a member of the body, and (iv) home country legal or listing provisions set forth standards for the independence of the members of the body. We believe that our statutory audit committee complies with these requirements, and we rely on the exemption provided by Rule 10A-3(c)(3) under the Exchange Act. See Item 6.A. “Directors and Senior Management—Audit Committee” for a description of our statutory audit committee.
ITEM 16. E. PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES BY THE ISSUER AND AFFILIATED PURCHASERS
During the fiscal year ended December 31, 2020, neither any “affiliated purchaser,” as defined in Rule 10b-18(a)(3) under the Exchange Act, nor we have purchased any of our equity securities.
ITEM 16. F. CHANGES IN REGISTRANT’S CERTIFYING ACCOUNTANT
Not applicable.
ITEM 16. G. CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Significant Differences between our Corporate Governance Practices and NYSE Corporate Governance Standards
We are subject to the NYSE corporate governance listing standards. As a foreign private issuer, the standards applicable to us are considerably different than the standards applied to U.S. listed companies. Under the NYSE rules, we are required only to: (i) have an audit committee or audit board, pursuant to an applicable exemption available to foreign private issuers, that meets certain requirements, as discussed below, (ii) provide prompt certification by our chief executive officer of any material noncompliance with any corporate governance rules, and (iii) provide a brief description of the significant differences between our corporate governance practices and the NYSE corporate governance practice required to be followed by U.S. listed companies. The significant differences between our corporate governance practices and those required for U.S. listed companies follows below.
Majority of Independent Directors
The NYSE rules require that a majority of a company’s board of directors must consist of independent directors. Independence is defined by various criteria, including the absence of a material relationship between the director and the listed company. Under Brazilian law, according to the provisions of the Novo Mercado, at least 20% or two of the members of our board of directors (whichever is the greater) must be independent directors, as defined under Brazilian law. Currently, our board of directors consists of nine members, six of which are independent members.
Executive Sessions
NYSE rules require that the non-management directors must meet at regularly scheduled executive sessions without management. The Brazilian Corporation Law does not have a similar provision. According to the Brazilian Corporation Law, up to one third of the members of a company’s board of directors can be elected by management. In our case, none of our directors serve both as executive officer and director, simultaneously. There is no requirement under Brazilian law that our directors meet regularly in the absence of our executive officers. As a result, our directors do not typically meet in executive sessions.
Nominating/Corporate Governance Committee
NYSE rules require that listed companies have a nominating/corporate governance committee composed entirely of independent directors and governed by a written charter addressing the committee’s purpose and detailing its responsibilities, which include, among others, identifying and selecting qualified board member nominees and developing a set of corporate governance principles applicable to a company. We are not required under applicable Brazilian law to have a nominating committee/corporate governance committee, and accordingly, to date, we have not established such a committee. Our directors are elected by our shareholders at a general shareholders’ meeting. Our corporate governance practices are adopted by all members of our board directors.
Compensation Committee
NYSE rules require that listed companies have a compensation committee composed entirely of independent directors and governed by a written charter addressing the committee’s required purpose and detailing its required responsibilities, which include, among other things, reviewing corporate goals relevant to CEO compensation, evaluating CEO performance and approving CEO compensation levels and recommending to the board non CEO compensation, incentive compensation and equity based plans. We are not required under applicable Brazilian law to have a compensation committee, although we have established an advisory committee, comprised of board members and independent members, to advise on certain of these matters. Under the Brazilian Corporation Law, the total amount available for compensation of our directors and executive officers and for profit sharing payments to our executive officers must be established by our shareholders at the annual general meeting. Our board of directors, based on recommendations and analysis of the compensation committee, is responsible for determining the compensation and profit-sharing of our executive officers, as well as the compensation of our board and committee members, which is established according to market standards and internal rules of compensation
Audit Committee
Under NYSE Rule 303A.06 and the requirements of Rule 10A-3 of the SEC, domestic listed companies are required to have an audit committee consisting entirely of independent directors that otherwise complies with Rule 10A-3. In addition, a company’s audit committee must have a written charter that addresses the matters outlined in NYSE Rule 303.A.06(c), have an internal audit function and otherwise fulfill the requirements of the NYSE and Rule 10A-3. Under the B3 listing rules for its Novo Mercado segment, we are required to have a “statutory audit committee” that complies with the CVM rules. The statutory audit committee is an advisory committee of the board of directors, and provides assistance in matters involving accounting, internal controls, financial reporting and compliance. The statutory audit committee also recommends the appointment of our independent auditors to our board of directors and evaluates the effectiveness of internal financial and legal compliance controls. The statutory audit committee is not equivalent to or comparable with a U.S. audit committee. Pursuant to Exchange Act Rule 10A-3(c)(3), which provides for an exemption under the rules of the SEC regarding the audit committees of listed companies, a foreign private issuer is not required to have an audit committee equivalent to or comparable with a U.S. audit committee if the foreign private issuer has a body established and selected pursuant to home country legal or listing provisions expressly requiring or permitting such a body, and if the body meets the requirements that (i) it be separate from the full board, (ii) its members not be elected by management, (iii) no executive officer be a member of the body, and (iv) home country legal or listing provisions set forth standards for the independence of the members of the body. See Item 6.A, “Directors and Senior Management—Audit Committee” for a description of our statutory audit committee.
Shareholder Approval of Equity Compensation Plans
NYSE rules require that shareholders be given the opportunity to vote on all equity compensation plans and material revisions thereto, with limited exceptions. Under Brazilian corporate law, shareholders must approve all stock option plans. In addition, any issuance of new shares that exceeds our authorized share capital is subject to shareholder approval.
Corporate Governance Guidelines
NYSE rules require that listed companies adopt and disclose corporate governance guidelines. We have not adopted any formal corporate governance guidelines beyond those required by applicable Brazilian law. We believe that the corporate governance guidelines applicable to us under Brazilian corporate law are consistent with the guidelines established by the NYSE.
Code of Business Conduct and Ethics
NYSE rules require that listed companies adopt and disclose a code of business conduct and ethics for directors, officers and employees, and promptly disclose any waivers of the code for directors or executive officers. Applicable Brazilian law does not have a similar requirement. We believe our code substantially addresses the matters required to be addressed by the NYSE rules. A copy of our Code of Conduct has been filed as Exhibit 11.1 to this annual report. For a further discussion of our Code of Conduct, see Item 16.B “Code of Ethics.”
Internal Audit Function
NYSE rules require that listed companies maintain an internal audit function to provide management and the audit committee with ongoing assessments of the company’s risk management processes and system of internal control. Brazilian law does not require that companies maintain an internal audit function. However, as an issuer on the New York Stock Exchange, we maintain an internal audit function. Our internal audit function is under the supervision of our statutory audit committee and is responsible for independently evaluating corporate, forest and industrial processes, verifying compliance with standards and policies adopted by us and analyzing possible cases of irregularities, such as fraud, bribery, corruption, conflicts of interest, insider information, embezzlement and damage to property.
The internal audit considers a risk-based approach and the views of our management and members of our audit committee. The audit results are reported to our chief executive officer and our statutory audit committee.
ITEM 16. H. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURE
Not applicable.
PART III
ITEM 17. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Not applicable.
ITEM 18. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
See pages F-1 through F-108, included herein.
ITEM 19. EXHIBITS
No. Description
1.1 Bylaws of Suzano, dated as of April 27, 2021.
2.1 Description of Securities.
3.1 English translation of the Suzano Shareholders’ Agreement dated as of September 28, 2017, by and among the Suzano Controlling Shareholders (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of Registration Statement on Form F-4 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on August 6, 2018 (File No. 333-226596)).
3.2 English translation of the Suzano Share Transfer Agreement dated as of September 28, 2017, by and among certain of the controlling shareholders of Suzano (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 of Registration Statement on Form F-4 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on August 6, 2018 (File No. 333-226596)).
8.1 List of Subsidiaries.
11.1 Code of Ethics.
12.1 Certifications Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
13.1 Certifications Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
15.1 Consent Letter of PricewaterhouseCoopers Auditores Independentes.
101.INS XBRL Instance Document
101.SCH XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document
101.CAL XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document
101.DEF XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document
101.LAB XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document
101.PRE XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document
The amount of our long-term debt securities or our subsidiaries authorized under any individual outstanding agreement does not exceed 10% of our total assets on a consolidated basis. We hereby agree to furnish the SEC, upon its request, a copy of any instruments defining the rights of holders of our long-term debt or of our subsidiaries for which consolidated or unconsolidated financial statements are required to be filed.
SIGNATURES
The registrant hereby certifies that it meets all the requirements for filing on Form 20-F and has duly caused this annual report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the city of São Paulo, on April 29, 2021.
| | Suzano S.A. |
| | | |
| | By: | /s/ Walter Schalka |
| | Name: Walter Schalka |
| | Title: Chief Executive Officer |
| | | |
| | By: | /s/ Marcelo Feriozzi Bacci |
| | Name: Marcelo Feriozzi Bacci |
| | Title: Chief Financial Officer and |
| | Investor Relations Director |
Report of independent registered public accounting firm
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders
Suzano S.A.
Opinions on the financial statements and internal control over financial reporting
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Suzano S.A. and its subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, and the related consolidated statements of income (loss), of comprehensive income (loss), of changes in equity and of cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2020, including the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). We also have audited the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2020 in conformity with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the COSO.
Change in Accounting Principle
As discussed in Notes 3.2.17 and 19 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company changed the manner in which it accounts for leases in 2019.
Basis for opinions
The Company’s management is responsible for these consolidated financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express opinions on the Company’s consolidated financial statements and on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the US federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud, and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audits of the consolidated financial statements included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
Definition and limitations of internal control over financial reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Critical audit matters
The critical audit matters communicated below are matters arising from the current period audit of the consolidated financial statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (i) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the consolidated financial statements and (ii) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matters below, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matters or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
Goodwill impairment test - Pulp Cash-Generating Unit
As described in Notes 3.2.18 and 16.1 to the consolidated financial statements, the goodwill associated with the Pulp Cash-Generating unit (“CGU”) was R$ 7,897,051 thousand as of December 31, 2020, arising from Fibria acquisition. Potential impairment is identified by comparing the value in use of the CGU to its carrying amount, including goodwill. Value in use is estimated by management using a discounted cash flow model. Management’s cash flow projections for Pulp CGU included significant judgments and assumptions relating to net average pulp prices and the discount rate.
The principal considerations for our determination that performing procedures relating to the goodwill impairment test of Pulp CGU is a critical audit matter are there was the significant judgment by management when developing the value in use measurement for the CGU. This in turn led to a high degree of auditor judgment, subjectivity, and effort in performing procedures to evaluate management’s cash flow projections and the significant assumptions net average pulp prices and discount rate. In addition, professionals with specialized skill and knowledge were used to assist in performing these procedures and evaluating the audit evidence obtained regarding the estimated discounted cash flow model and discount rate.
Addressing the matter involved performing procedures and evaluating audit evidence in connection with forming our overall opinion on the consolidated financial statements. These procedures included testing the effectiveness of controls relating to management’s goodwill impairment test, including controls over the valuation of the Company’s Pulp CGU. These procedures also included, among others, testing management’s process for developing the value in use estimate; evaluating the appropriateness of the discounted cash flow model; testing the completeness, accuracy, and relevance of underlying data used in the model; and evaluating the significant assumptions used by management, related to the net average pulp prices and the discount rate. Evaluating management’s assumptions relating to net average pulp prices involved evaluating whether the assumptions used by management were reasonable considering; (i) the current and past performance of the CGU, (ii) the consistency with external market and industry data, and (iii) whether these assumptions were consistent with evidence obtained in other areas of the audit. Professionals with specialized skill and knowledge were used to assist in the evaluation of the Company’s discounted cash flow model and the discount rate.
Deferred tax assets
As described in Notes 3.2.19 and 12 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company’s consolidated deferred tax assets balance recorded in non-current assets was R$ 8,677,002 thousand as of December 31, 2020, arising from tax loss carryforwards, negative tax base and temporary differences. Deferred tax assets are recognized to the extent that it is probable that future taxable profit will be available to be used to offset tax loss carryforwards, negative tax base and temporary differences, based on projections of future results. Management’s cash flow projections included significant judgments and assumptions relating to net average pulp and paper prices and the transfer price with the subsidiary based in Austria.
The principal considerations for our determination that performing procedures relating to the deferred tax assets is a critical audit matter are there was the significant judgment by management when estimating the recoverable amount of deferred tax assets and the timing when tax loss carryforwards, negative tax base and temporary differences will occur. This in turn led to a high degree of auditor judgment, subjectivity, and effort in performing procedures to evaluate management’s cash flow projections and significant assumptions, related to the net average pulp and paper prices and the transfer price with the subsidiary based in Austria. In addition, professionals with specialized skill and knowledge were used to assist in performing these procedures and evaluating the audit evidence obtained regarding the estimated cash flow model.
Addressing the matter involved performing procedures and evaluating audit evidence in connection with forming our overall opinion on the consolidated financial statements. These procedures included testing the effectiveness of controls relating to management’s projections, including controls over the valuation of the recoverable amount of deferred tax assets. These procedures also included, among others, testing management’s process for estimating the recoverable amount; evaluating the appropriateness of the cash flow model; testing the completeness, accuracy, and relevance of underlying data used in the model; and evaluating the significant assumptions used by management, related to the net average pulp and paper prices and the transfer price with the subsidiary based in Austria. Evaluating management’s assumptions relating to net average pulp and paper prices involved evaluating whether the assumptions used by management were reasonable considering; (i) the current and past performance of the Company, (ii) the consistency with external market and industry data, and (iii) whether these assumptions were consistent with evidence obtained in other areas of the audit.
Provision for judicial liabilities relating to tax
As described in Notes 3.2.22 and 20 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company’s consolidated provision for judicial liabilities relating to tax was R$ 2,848,589 (net of judicial deposits) thousand as of December 31, 2020. The Company recognizes liabilities in the consolidated financial statements for the resolution of pending litigation when management determines that a loss is probable and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. No liability for an estimated loss is accrued in the consolidated financial statements for unfavorable outcomes when, after assessing the information available, (i) management concludes that it is not probable that a loss will be incurred in any of the pending litigation; or (ii) management is unable to estimate the loss for any of the pending matters.
The principal considerations for our determination that performing procedures relating to provision for judicial liabilities relating to tax is a critical audit matter are there was significant judgement by management when assessing the likelihood of a loss being incurred and when determining whether a reasonable estimate of the loss for each claim can be made, which in turn led to a high degree of auditor judgment and effort in evaluating management’s assessment of the loss contingencies associated with litigation claims. Professionals with specialized skill and knowledge were used to assist in the evaluation of the likelihood of loss being incurred.
Addressing the matter involved performing procedures and evaluating audit evidence in connection with forming our overall opinion on the consolidated financial statement. These procedures included testing the effectiveness of controls relating to management’s evaluation of tax litigation claims, including controls over determining whether a loss is probable and whether the amount of loss can be reasonably estimated. These procedures also included, among others, obtaining and evaluating the letters of audit inquiry with internal and external legal counsel, evaluating the reasonableness of management’s assessment regarding whether an unfavorable outcome is reasonably possible or probable and reasonably estimable, and evaluating the sufficiency of the Company’s litigation contingency disclosures. Professionals with specialized skill and knowledge were used to assist in the evaluation of the likelihood of loss being incurred.
Valuation of biological assets
As described in Notes 3.2.15 and 13 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company’s consolidated biological assets balance was R$ 11,161,210 thousand at December 31, 2020 and are measured at fair value, less estimated costs to sell. Fair value is estimated by management using a discounted cash flow model. Management’s cash flow projections included significant judgments and assumptions relating to gross average sale price of eucalyptus and the average annual growth (IMA) of biological assets.
The principal considerations for our determination that performing procedures relating to the valuation of biological assets is a critical audit matter are (i) there was a high degree of auditor subjectivity in applying our procedures relating to the fair value measurement of the biological assets due to the significant amount of judgment required by management when developing these estimates; (ii) significant audit effort was required in assessing the significant assumptions relating to biological assets, average annual growth (IMA) and gross average sale price of eucalyptus and (iii) professionals with specialized skill and knowledge were used to assist in performing these procedures and evaluating the audit evidence obtained regarding the estimated discount cash flow model and discount rate.
Addressing the matter involved performing procedures and evaluating audit evidence in connection with forming our overall opinion on the consolidated financial statements. These procedures included testing the effectiveness of controls relating to the completeness of data and the model used to measure the fair value of the biological assets. Our procedures also included, among others, testing management’s process for developing the fair value estimate; evaluating the appropriateness of the discounted cash flow model; testing the completeness, accuracy, and relevance of underlying data used in the model; and evaluating the significant assumptions used by management, related to the average annual growth (IMA) and the gross average eucalyptus sale price. Evaluating management’s assumptions relating to average annual growth (IMA) and gross average eucalyptus sale price involved evaluating whether the assumptions used by management were reasonable considering; (i) the consistency with external market and industry data; and (ii) whether these assumptions were consistent with evidence obtained in other areas of the audit. Professionals with specialized skill and knowledge were used to assist in the evaluation of the Company’s discounted cash flow model and the discount rate.
São Paulo, Brazil
February 10, 2021
/s/PricewaterhouseCoopers
Auditores Independentes
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2017.

Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
1 The management of Suzano S.A. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting.
2 The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by the Company’s Statutory Audit Committee, the Company’s Board of Directors, management, and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with and in compliance with the International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”). The Company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (a) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; (b) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with and in compliance with IFRS as issued by the IASB, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and (c) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements.
3 Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
4 The effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020, is based on the criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). Based on that assessment, management has concluded that, as of December 31, 2020, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting is effective.
São Paulo, February 10, 2021
| /s/ Walter Schalka | | /s/ Marcelo Feriozzi Bacci |
| Walter Schalka | | Marcelo Feriozzi Bacci |
| Chief Executive Officer | | Chief Financial Officer and Investor Relations Officer |
Suzano S.A. Consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| | |
| (In thousands of R$, unless otherwise stated) | |
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
| ASSET | | Note | | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| CURRENT | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 5 | | | | 6,835,057 | | | | 3,249,127 | |
| Marketable securities | | | 6 | | | | 2,212,079 | | | | 6,150,631 | |
| Trade accounts receivable | | | 7 | | | | 2,915,206 | | | | 3,035,817 | |
| Inventories | | | 8 | | | | 4,009,335 | | | | 4,685,595 | |
| Recoverable taxes | | | 9 | | | | 406,850 | | | | 997,201 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | 4.5 | | | | 484,043 | | | | 260,273 | |
| Advances to suppliers | | | 10 | | | | 43,162 | | | | 170,481 | |
| Other assets | | | | | | | 738,924 | | | | 335,112 | |
| | | | | | | | 17,644,656 | | | | 18,884,237 | |
| Assets held for sale | | | 1.2.2 | | | | 313,338 | | | | | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | | 17,957,994 | | | | 18,884,237 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| NON-CURRENT | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Marketable securities | | | 6 | | | | 184,778 | | | | 179,703 | |
| Recoverable taxes | | | 9 | | | | 834,575 | | | | 708,914 | |
| Deferred taxes | | | 12 | | | | 8,677,002 | | | | 2,134,040 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | 4.5 | | | | 857,377 | | | | 838,699 | |
| Advances to suppliers | | | 10 | | | | 1,015,115 | | | | 1,087,149 | |
| Judicial deposits | | | | | | | 257,789 | | | | 268,672 | |
| Other assets | | | | | | | 235,341 | | | | 228,881 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Biological assets | | | 13 | | | | 11,161,210 | | | | 10,571,499 | |
| Investments | | | 14 | | | | 359,071 | | | | 322,446 | |
| Property, plant and equipment | | | 15 | | | | 39,156,890 | | | | 41,120,945 | |
| Right of use | | | 19.1 | | | | 4,344,078 | | | | 3,850,237 | |
| Intangible | | | 16 | | | | 16,759,528 | | | | 17,712,803 | |
| Total non-current | | | | | | | 83,842,754 | | | | 79,023,988 | |
| TOTAL ASSET | | | | | | | 101,800,748 | | | | 97,908,225 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of this consolidated financial statements.
Suzano S.A. Consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| | |
| (In thousands of R$, unless otherwise stated) | |
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
| LIABILITIES | | Note | | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| CURRENT | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade accounts payable | | | 17 | | | | 2,361,098 | | | | 2,376,459 | |
| Loans, financing and debentures | | | 18.1 | | | | 2,043,386 | | | | 6,227,951 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | 19.2 | | | | 620,177 | | | | 656,844 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | 4.5 | | | | 1,991,118 | | | | 893,413 | |
| Taxes payable | | | | | | | 170,482 | | | | 307,639 | |
| Payroll and charges | | | | | | | 492,728 | | | | 400,435 | |
| Liabilities for assets acquisitions and subsidiaries | | | 23 | | | | 101,515 | | | | 94,414 | |
| Dividends payable | | | | | | | 6,232 | | | | 5,720 | |
| Advance from customers | | | | | | | 25,171 | | | | 59,982 | |
| Other liabilities | | | | | | | 360,916 | | | | 456,338 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | | 8,172,823 | | | | 11,479,195 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| NON-CURRENT | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans, financing and debentures | | | 18.1 | | | | 70,856,496 | | | | 57,456,375 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | 19.2 | | | | 4,571,583 | | | | 3,327,226 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | 4.5 | | | | 6,126,282 | | | | 2,024,500 | |
| Liabilities for assets acquisitions and subsidiaries | | | 23 | | | | 400,713 | | | | 447,201 | |
| Provision for judicial liabilities | | | 20.1 | | | | 3,255,955 | | | | 3,512,477 | |
| Employee benefit plans | | | 21.2 | | | | 785,045 | | | | 736,179 | |
| Deferred taxes | | | 12 | | | | 570 | | | | 578,875 | |
| Share-based compensation plans | | | 22.3 | | | | 195,135 | | | | 136,505 | |
| Other liabilities | | | | | | | 98,768 | | | | 121,723 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | | | | | 86,290,547 | | | | 68,341,061 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | | | | | | | 94,463,370 | | | | 79,820,256 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EQUITY | | | 25 | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital | | | | | | | 9,235,546 | | | | 9,235,546 | |
| Capital reserves | | | | | | | 10,612 | | | | 6,416,864 | |
| Treasury shares | | | | | | | (218,265 | ) | | | (218,265 | ) |
| Retained earnings reserves | | | | | | | | | | | 317,144 | |
| Other reserves | | | | | | | 2,129,944 | | | | 2,221,341 | |
| Retained loss | | | | | | | (3,926,015 | ) | | | | |
| Controlling shareholder´s | | | | | | | 7,231,822 | | | | 17,972,630 | |
| Non-controlling interest | | | | | | | 105,556 | | | | 115,339 | |
| Total equity | | | | | | | 7,337,378 | | | | 18,087,969 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | | | | | 101,800,748 | | | | 97,908,225 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of this consolidated financial statements.
Suzano S.A. Consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 |  |
| | |
| (In thousands of R$, unless otherwise stated) | |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME (LOSS)
| | | | | | 12 months YTD | |
| | | Note | | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | | | December 31,
2018 | |
| NET SALES | | 28 | | | | 30,460,277 | | | | 26,012,950 | | | | 13,443,376 | |
| Cost of sales | | 30 | | | | (18,966,331 | ) | | | (20,743,482 | ) | | | (6,922,331 | ) |
| GROSS PROFIT | | | | | | 11,493,946 | | | | 5,269,468 | | | | 6,521,045 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| OPERATING INCOME (EXPENSES) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Selling | | 30 | | | | (2,174,652 | ) | | | (1,905,279 | ) | | | (598,726 | ) |
| General and administrative | | 30 | | | | (1,443,192 | ) | | | (1,173,358 | ) | | | (825,209 | ) |
| Income from associates and joint ventures | | 14 | | | | 36,142 | | | | 31,993 | | | | 7,576 | |
| Other, net | | 30 | | | | 531,150 | | | | 405,754 | | | | (96,875 | ) |
| OPERATING PROFIT BEFORE NET FINANCIAL INCOME (EXPENSES) | | | | | | 8,443,394 | | | | 2,628,578 | | | | 5,007,811 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| NET FINANCIAL INCOME (EXPENSES) | | 27 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial expenses | | | | | | (4,459,425 | ) | | | (4,178,848 | ) | | | (1,500,374 | ) |
| Financial income | | | | | | 327,475 | | | | 493,246 | | | | 459,707 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | | | | (9,422,682 | ) | | | (1,075,252 | ) | | | (2,735,196 | ) |
| Monetary and exchange variations, net | | | | | | (12,530,891 | ) | | | (1,964,927 | ) | | | (1,066,650 | ) |
| NET INCOME (LOSS) BEFORE TAXES | | | | | | (17,642,129 | ) | | | (4,097,203 | ) | | | 165,298 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Income and social contribution taxes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current | | 12 | | | | (181,926 | ) | | | (246,110 | ) | | | (586,568 | ) |
| Deferred | | 12 | | | | 7,109,120 | | | | 1,528,571 | | | | 741,084 | |
| NET INCOME (LOSS) FOR THE YEAR | | | | | | (10,714,935 | ) | | | (2,814,742 | ) | | | 319,814 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Attributable to | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Controlling shareholders’ | | | | | | (10,724,828 | ) | | | (2,817,518 | ) | | | 319,693 | |
| Non-controlling interest | | | | | | 9,893 | | | | 2,776 | | | | 121 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Earnings (loss) per share | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic | | 26.1 | | | | (7.94890 | ) | | | (2.08825 | ) | | | 0.29236 | |
| Diluted | | 26.2 | | | | (7.94890 | ) | | | (2.08825 | ) | | | 0.29199 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of this consolidated financial statements.
Suzano S.A. Consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 |  |
| | |
| (In thousands of R$, unless otherwise stated) | |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | | | December 31, 2018 | |
| Net income (loss) for the year | | | (10,714,935 | ) | | | (2,814,742 | ) | | | 319,814 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Exchange rate variation and fair value investments in equity measured at fair value through other comprehensive income | | | 6,290 | | | | 3,576 | | | | | |
| Tax effect of the above items | | | (2,139 | ) | | | (1,216 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Actuarial gain on post-employment plans of the subsidiaries | | | 3,522 | | | | 2,749 | | | | | |
| Tax effect of the above item | | | (1,015 | ) | | | (935 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Actuarial loss on post-employment plans of the subsidiaries | | | (37,188 | ) | | | (147,640 | ) | | | (69,305 | ) |
| Tax effect of the above item | | | 12,644 | | | | 50,198 | | | | 23,564 | |
| Items with no subsequent effect on income | | | (17,886 | ) | | | (93,268 | ) | | | (45,741 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Exchange rate variation on conversion of financial statements of the subsidiaries abroad (1) | | | (2,857 | ) | | | 45,819 | | | | 137,546 | |
| Items with subsequent effect on income | | | (2,857 | ) | | | 45,819 | | | | 137,546 | |
| | | | (10,735,678 | ) | | | (2,862,191 | ) | | | 411,619 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Attributable to | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Controlling shareholders’ | | | (10,745,571 | ) | | | (2,864,967 | ) | | | 411,498 | |
| Non-controlling interest | | | 9,893 | | | | 2,776 | | | | 121 | |
| 1) | As of December 31, 2020 includes the exchange variation related to investments abroad of wholly-owned subsidiaries whose functional currencies are different from the Brazilian Real (notes 3.1.1 and 3.2.5). |
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018 includes the (i) exchange variation related to investments abroad of wholly-owned subsidiaries and (ii) hyperinflation referring to the wholly owned subsidiary Stenfar (note 3.2.6).
The accompanying notes are an integral part of this consolidated financial statements.
Suzano S.A. Consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 |  |
| | |
| (In thousands of R$, unless otherwise stated) | |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
| | | Attributed to of controlling shareholders | | | | | |
| | | Share Capital | | Capital reserves | | | | Retained earnings reserves | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Share
Capital | | Share issuance costs | | Tax
incentives | | Stock options granted | | Share issuance costs | | Other | | Treasurys
shares | | Tax incentives | | Legal
Reserve | | Reserve for capital increase | | Special statutory reserve | | Dividends proposed | | Other
reserves | | Retained earnings (losses) | | Total | | Non-
controlling interest | | Total equity | |
| Balances at December 31, 2017 | | | 6,241,753 | | | | | | 396,006 | | | 14,237 | | | (15,442 | ) | | | | | (241,088 | ) | | | | | 406,897 | | | 2,281,319 | | | 234,602 | | | | | | 2,298,327 | | | | | | 11,616,610 | | | | | | 11,616,610 | |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 319,693 | | | 319,693 | | | 121 | | | 319,814 | |
| Actuarial gain (loss) net of deferred taxes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (45,741 | ) | | | | | (45,741 | ) | | | | | (45,741 | ) |
| Exchange variation on conversion of financial statements of foreign subsidiaries | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 137,546 | | | | | | 137,546 | | | | | | 137,546 | |
| Transactions with shareholders: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Stock options granted | | | | | | | | | | | | 5,170 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 5,170 | | | | | | 5,170 | |
| Sale of treasury shares to meet stock-based compensation plan | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 8,516 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 8,516 | | | | | | 8,516 | |
| Non-controlling interest arising on business combination | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 13,807 | | | 13,807 | |
| Reversal of time-barred dividends | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 66 | | | | | | | | | | | | 66 | | | | | | 66 | |
| Internal changes in equity: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Realization of deemed cost, net of deferred taxes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (68,424 | ) | | 68,424 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Stock options granted | | | | | | | | | | | | (14,307 | ) | | | | | | | | 14,307 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Reserve for tax incentives Sudene-reduction of 75% | | | | | | | | | 288,557 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (288,557 | ) | | | | | | | | | |
| Dividends distributed | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Constitution of special statutory reserve | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 7,882 | | | | | | | | | (7,882 | ) | | | | | | | | | |
| Constitution of the legal reserve | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 15,917 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (15,917 | ) | | | | | | | | | |
| Constitution of a reserve for capital increase | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 70,940 | | | | | | | | | | | | (70,940 | ) | | | | | | | | | |
| Dividends | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (29,976 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (29,976 | ) | | | | | (29,976 | ) |
| Unclaimed dividends forfeited | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (596,534 | ) | | | | | 596,534 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Dividends subject to approval | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Minimum mandatory dividends | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (3,466 | ) | | (3,466 | ) | | | | | (3,466 | ) |
| Unrealized net revenue of 2017 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 4,880 | | | 62 | | | | | | | | | (1,355 | ) | | 3,588 | | | | | | 3,588 | |
| Balances at December 31, 2018 | | | 6,241,753 | | | | | | 684,563 | | | 5,100 | | | (15,442 | ) | | | | | (218,265 | ) | | | | | 422,814 | | | 1,730,629 | | | 242,612 | | | 596,534 | | | 2,321,708 | | | | | | 12,012,006 | | | 13,928 | | | 12,025,934 | |
| Total comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net (loss) for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (2,817,518 | ) | | (2,817,518 | ) | | 2,776 | | | (2,814,742 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (47,449 | ) | | | | | (47,449 | ) | | | | | (47,449 | ) |
| Transactions with shareholders | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss absorption | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (684,563 | ) | | (105,670 | ) | | (1,730,629 | ) | | (242,612 | ) | | | | | | | | 2,763,474 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital increase | | | 3,027,528 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 3,027,528 | | | | | | 3,027,528 | |
| Share issuance costs | | | | | | (33,735 | ) | | | | | | | | 15,442 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (18,293 | ) | | | | | (18,293 | ) |
| Stock options granted | | | | | | | | | | | | 879 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 879 | | | | | | 879 | |
| Non-controlling interest arising from business combination | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 98,635 | | | 98,635 | |
| Unclaimed dividends forfeited | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,126 | | | 1,126 | | | | | | 1,126 | |
| Dividends paid | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (596,534 | ) | | | | | | | | (596,534 | ) | | | | | (596,534 | ) |
| Internal changes in equity | | | | | | | | | (684,563 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 684,563 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Transfers of tax incentives | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Realization of deemed cost, net of taxes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (52,918 | ) | | 52,918 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Issue of common shares related to business combination | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 6,410,885 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 6,410,885 | | | | | | 6,410,885 | |
| Balances at December 31, 2019 | | | 9,269,281 | | | (33,735 | ) | | | | | 5,979 | | | | | | 6,410,885 | | | (218,265 | ) | | | | | 317,144 | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,221,341 | | | | | | 17,972,630 | | | 115,339 | | | 18,087,969 | |
| Total comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net (loss) for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (10,724,828 | ) | | (10,724,828 | ) | | 9,893 | | | (10,714,935 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (20,743 | ) | | | | | (20,743 | ) | | | | | (20,743 | ) |
| Transactions with shareholders | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss absorption (note 25.6) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (6,410,885 | ) | | | | | | | | (317,144 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 6,728,029 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Stock options granted | | | | | | | | | | | | 4,633 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 4,633 | | | | | | 4,633 | |
| Realization of fair value attributable to non-controlling interest | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (19,676 | ) | | (19,676 | ) |
| Unclaimed dividends forfeited | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 130 | | | 130 | | | | | | 130 | |
| Internal changes in equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Partial Realization of deemed cost, net of taxes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (70,654 | ) | | 70,654 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balances at December 31, 2020 | | | 9,269,281 | | | (33,735 | ) | | | | | 10,612 | | | | | | | | | (218,265 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,129,944 | | | (3,926,015 | ) | | 7,231,822 | | | 105,556 | | | 7,337,378 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of this consolidated financial statements.
Suzano S.A. Consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 |  |
| | |
| (In thousands of R$, unless otherwise stated) | |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | | | December 31,
2018 | |
| OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) for the year | | | (10,714,935 | ) | | | (2,814,742 | ) | | | 319,814 | |
| Adjustment to | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Depreciation, depletion and amortization (Notes 27 and 30)(1) | | | 6,565,441 | | | | 7,898,775 | | | | 1,563,223 | |
| Amortization of right of use (Note 19.1) | | | 186,768 | | | | 154,217 | | | | | |
| Sublease of ships | | | (35,841 | ) | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense on lease liabilities | | | 397,746 | | | | 226,103 | | | | | |
| Results from sale, disposals and provision for losses (impairment) of property, plant and equipment and biological assets, net (Note 30) | | | (53,807 | ) | | | 77,930 | | | | 13,580 | |
| Income (loss) from associates and joint ventures (Note 14.2) | | | (36,142 | ) | | | (31,993 | ) | | | (7,576 | ) |
| Exchange rate and monetary variations, net (Note 27) | | | 12,530,891 | | | | 1,964,927 | | | | 1,446,207 | |
| Interest expenses with financing, loans and debentures, net (Note 27) | | | 3,286,254 | | | | 3,363,019 | | | | 872,208 | |
| Premium expenses with repurchase of bonds (Note 27) | | | 391,390 | | | | | | | | | |
| Capitalized interest (Note 27) | | | (10,636 | ) | | | (4,213 | ) | | | | |
| Accrual of interest on marketable securities | | | (94,868 | ) | | | (392,018 | ) | | | (127,037 | ) |
| Amortization of fundraising costs (Note 27) | | | 101,741 | | | | 185,807 | | | | 44,499 | |
| Derivative (gains) losses, net (Note 27) | | | 9,422,682 | | | | 1,075,252 | | | | 2,735,196 | |
| Fair value adjustment of biological assets (Note 13) | | | (466,484 | ) | | | (185,399 | ) | | | 129,187 | |
| Deferred income tax and social contribution (Note 12.3) | | | (7,109,120 | ) | | | (1,528,571 | ) | | | (741,084 | ) |
| Tax credits - gains in tax lawsuit (ICMS from the PIS/COFINS calculation basis) (note 9) | | | | | | | (128,115 | ) | | | | |
| Interest on employee benefits (Note 21.2) | | | 53,092 | | | | 44,496 | | | | 35,920 | |
| Provision for (reversal of) judicial liabilities, net (Note 20.1) | | | 1,288 | | | | 26,807 | | | | 13,285 | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts, net (Note 7.3) | | | 6,022 | | | | (12,286 | ) | | | 6,450 | |
| Provision for (reversal of) inventory losses, net (Note 8.1) | | | 65,675 | | | | 107,269 | | | | (25,096 | ) |
| Provision for loss of ICMS credits, net (Note 9.1) | | | (82,293 | ) | | | 129,283 | | | | | |
| Impairment of non-financial assets (Note 16.1) | | | 45,435 | | | | | | | | | |
| Other | | | 35,451 | | | | (56,517 | ) | | | 235,081 | |
| Decrease (increase) in assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade accounts receivables | | | 884,451 | | | | 991,476 | | | | (186,026 | ) |
| Inventories | | | 651,203 | | | | 873,420 | | | | (622,151 | ) |
| Recoverable taxes | | | 659,930 | | | | 241,934 | | | | 50,960 | |
| Other assets | | | 54,651 | | | | (26,478 | ) | | | (12,720 | ) |
| Increase (decrease) in liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade accounts payables | | | 140,480 | | | | (1,555,697 | ) | | | 1,473 | |
| Taxes payable | | | 47,212 | | | | 240,871 | | | | 432,603 | |
| Payroll and charges | | | 92,278 | | | | (234,948 | ) | | | (100,124 | ) |
| Other liabilities | | | (266,546 | ) | | | (62,294 | ) | | | 225,616 | |
| Cash provided by operations, net | | | 16,749,409 | | | | 10,568,315 | | | | 6,303,488 | |
| Payment of interest with financing, loans and debentures (Note 18.2) | | | (3,244,949 | ) | | | (2,977,957 | ) | | | (806,758 | ) |
| Payment of premium with repurchase of bonds (Note 18.2) | | | (378,381 | ) | | | | | | | | |
| Interest received from marketable securities | | | 186,853 | | | | 377,804 | | | | | |
| Payment of income taxes | | | (188,296 | ) | | | (391,725 | ) | | | (327,282 | ) |
| Cash provided by operating activities | | | 13,124,636 | | | | 7,576,437 | | | | 5,169,448 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Additions to property, plant and equipment (Note 15) | | | (1,503,255 | ) | | | (2,001,674 | ) | | | (1,251,486 | ) |
| Additions to intangible assets (Note 16) | | | (2,307 | ) | | | (17,715 | ) | | | (7,217 | ) |
| Additions to biological assets (Note 13) | | | (3,392,298 | ) | | | (2,849,038 | ) | | | (1,164,995 | ) |
| Proceeds from sale of property, plant and equipment | | | 183,504 | | | | 198,644 | | | | 95,481 | |
| Increase of capital in subsidiaries and associates (Note 14.3) | | | | | | | (45,856 | ) | | | | |
| Marketable securities, net | | | 3,841,493 | | | | 19,378,893 | | | | (19,340,022 | ) |
| Advance for acquisition of wood from operations with development | | | 135,693 | | | | (355,447 | ) | | | 1,402 | |
| Acquisition of subsidiaries, net cash | | | | | | | (26,002,540 | ) | | | (294,473 | ) |
| Dividends received | | | 753 | | | | | | | | | |
| Other investments | | | | | | | (286 | ) | | | | |
| Cash (used) in investing activities, net | | | (736,417 | ) | | | (11,695,019 | ) | | | (21,961,310 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FINANCING ACTIVITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from loans, financing and debentures (note 18.2) | | | 14,761,796 | | | | 18,993,837 | | | | 25,645,822 | |
| Payment of derivative transactions (note 4.5.4) | | | (4,465,640 | ) | | | (135,449 | ) | | | (1,586,415 | ) |
| Payment of loans, financing and debentures (note 18.2) | | | (19,092,810 | ) | | | (13,994,708 | ) | | | (3,738,577 | ) |
| Payment of leases (note 19.2) | | | (824,245 | ) | | | (645,071 | ) | | | | |
| Payment of dividends | | | | | | | (606,632 | ) | | | (210,205 | ) |
| Sale of treasury shares to meet stock-based compensation plan | | | | | | | (879 | ) | | | 8,514 | |
| Liabilities for assets acquisitions and subsidiaries | | | (164,240 | ) | | | (479,480 | ) | | | (84,090 | ) |
| Other financing | | | | | | | 10,191 | | | | | |
| Cash provided (used) by financing activities | | | (9,785,139 | ) | | | 3,141,809 | | | | 20,035,049 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EXCHANGE VARIATION ON CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | | | 982,850 | | | | (161,553 | ) | | | 67,433 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Increase (reduction) in cash and cash equivalents, net | | | 3,585,930 | | | | (1,138,326 | ) | | | 3,310,620 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning for the year | | | 3,249,127 | | | | 4,387,453 | | | | 1,076,833 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the end for the year | | | 6,835,057 | | | | 3,249,127 | | | | 4,387,453 | |
| Increase (reduction) in cash and cash equivalents, net | | | 3,585,930 | | | | (1,138,326 | ) | | | 3,310,620 | |
| 1) | In the year ended December 31, 2019 includes the full amortization of the inventories step up, resulting from the business combination with Fibria, in the amount of R$2,178,903. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of this consolidated financial statements.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
1. COMPANY´S OPERATIONS
Suzano S.A., together with its subsidiaries (“Suzano” or collectively “Company”), is a public company with its headquarters office in Brazil, at Avenida Professor Magalhaes Neto, no. 1,752 - 10th floor, rooms 1010 and 1011, Bairro Pituba, in the city of Salvador, State of Bahia, and the main business office in the city of São Paulo.
Suzano owns shares traded in B3 S.A. (“Brasil, Bolsa, Balcão - “B3”), listed on the New Market under the ticker SUZB3 and American Depositary Receipts (“ADRs”) in a ratio of 1 (one) common share, Level II, traded in the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) under the ticker SUZ.
The Company holds 11 industrial units, located in the cities of Aracruz (Espírito Santo, State), Belém (Pará, State), Eunápolis and Mucuri (Bahia, State), Maracanaú (Ceará, State), Imperatriz (Maranhão, State), Jacareí, Limeira, Rio Verde and Suzano, being 2 units (São Paulo, State) and Três Lagoas (Mato Grosso do Sul, State).
These units produce hardwood pulp from eucalyptus, paper (coated paper, paperboard, uncoated paper and cut size paper) and packages of sanitary paper (consumer goods - tissue) to serve the domestic and foreign markets.
Pulp and paper are sold in the foreign market directly by Suzano, as well as through its wholly-owned subsidiaries in Austria, the United States of America, Switzerland, Argentina and sales offices in China.
The Company’s corporate purpose also includes the commercial operation of eucalyptus forest for its own use, the operation of port terminals, and the holding of interest, as partner or shareholder, in any other company or project, and the generation and sale of electricity.
The Company is controlled by Suzano Holding S.A., through a Voting Agreement whereby it holds 45.77% of the common shares of its share capital.
These consolidated financial statements was approved by Board of Directors on February 10, 2021.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The Company holds equity interest in the following entities:
| | | | | | | | | | | % equity interest | |
| Entity | | Main activity | | Country | | Type of
investment | | Accounting method | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| AGFA – Com. Adm. e Participações Ltda. (1) | | Holding | | Brazil | | Direct | | Consolidated | | | | 100.00 | % |
| Asapir Produção Florestal e Comércio Ltda. (1) | | Eucalyptus cultivation | | Brazil | | Direct | | Consolidated | | | | 100.00 | % |
| Celluforce Inc. | | Nanocrystalline pulp research and development | | Canada | | Direct | | Fair value through other comprehensive income | | 8.30 | % | | 8.30 | % |
| Comercial e Agrícola Paineiras Ltda. (1) | | Lease of reforestation land | | Brazil | | Direct | | Consolidated | | | | 99.99 | % |
| Ensyn Corporation | | Biofuel research and development | | United States of America | | Direct | | Equity | | 25.30 | % | | 25.30 | % |
| F&E Technologies LLC | | Biofuel production, except alcohol | | United States of America | | Direct | | Equity | | 50.00 | % | | 50.00 | % |
| F&E Tecnologia do Brasil S.A. (2) | | Biofuel production, except alcohol | | Brazil | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Facepa - Fábrica de Papel da Amazônia S.A. (1) | | Industrialization and commercialization of tissue paper | | Brazil | | Direct /Indirect | | Consolidated | | | | 92.80 | % |
| Fibria Celulose (USA) Inc. | | Business office | | United States of America | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Fibria Overseas Finance Ltd. | | Financial fundraising | | Cayman Island | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Fibria Terminais Portuários S.A. (1) | | Port operation | | Brazil | | Direct | | Consolidated | | | | 100.00 | % |
| Fibria Terminal de Celulose de Santos SPE S.A. | | Port operation | | Brazil | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| FuturaGene AgriDev Xinjiang Company Ltd. | | Biotechnology research and development | | China | | Indirect | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| FuturaGene Biotechnology Shangai Company Ltd. | | Biotechnology research and development | | China | | Indirect | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| FuturaGene Brasil Tecnologia Ltda. (1) | | Biotechnology research and development | | Brazil | | Direct /Indirect | | Consolidated | | | | 100.00 | % |
| FuturaGene Delaware Inc. | | Biotechnology research and development | | United States of America | | Indirect | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| FuturaGene Hong Kong Ltd. | | Biotechnology research and development | | Hong Kong | | Indirect | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| FuturaGene Inc. | | Biotechnology research and development | | United States of America | | Indirect | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| FuturaGene Israel Ltd. | | Biotechnology research and development | | Israel | | Indirect | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| FuturaGene Ltd. | | Biotechnology research and development | | England | | Indirect | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Gansu FuturaGene Biotech Co. Ltd. (3) | | Biotechnology research and development | | China | | Indirect | | Consolidated | | | | 100.00 | % |
| Ibema Companhia Brasileira de Papel | | Industrialization and commercialization of paperboard | | Brazil | | Direct | | Equity | | 49.90 | % | | 49.90 | % |
| Itacel - Terminal de Celulose de Itaqui S.A. | | Port operation | | Brazil | | Indirect | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Maxcel Empreendimentos e Participações S.A. | | Holding | | Brazil | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Mucuri Energética S.A. | | Power generation and distribution | | Brazil | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Ondurman Empreendimentos Imobiliários Ltda. (1) | | Lease of reforestation land | | Brazil | | Direct /Indirect | | Consolidated | | | | 100.00 | % |
| Paineiras Logística e Transportes Ltda. | | Road freight transport | | Brazil | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Portocel - Terminal Espec. Barra do Riacho S.A. | | Port operation | | Brazil | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 51.00 | % | | 51.00 | % |
| Projetos Especiais e Investimentos Ltda. | | Commercialization of equipment and parts | | Brazil | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Rio Verde Participações e Propriedades Rurais S.A. (4) | | Forest assets | | Brazil | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| SFBC Participações Ltda. (5) | | Packaging production | | Brazil | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | |
| Spinnova OY (6) | | Research and development of sustainable raw materials (wood) for the textile industry | | Finland | | Direct | | Equity | | 23.44 | % | | 24.06 | % |
| Stenfar S.A. Indl. Coml. Imp. Y. Exp. (7) | | Commercialization of computer paper and materials | | Argentina | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Suzano Austria GmbH. | | Business office | | Austria | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Suzano Canada Inc. | | Lignin research and development | | Canada | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Suzano International Trade GmbH. | | Business office | | Austria | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Suzano Operações Industriais e Florestais S.A. (8) | | Industrialization, commercialization and exportation of pulp | | Brazil | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | |
| Suzano Participações do Brasil Ltda. (9) | | Holding | | Brazil | | Direct | | Consolidated | | | | 100.00 | % |
| Suzano Pulp and Paper America Inc. | | Business office | | United States of America | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Suzano Pulp and Paper Europe S.A. | | Business office | | Switzerland | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Suzano Shanghai Ltd. (10) | | Business office | | China | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | |
| Suzano Trading International KFT | | Business office | | Hungary | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Suzano Trading Ltd. | | Business office | | Cayman Island | | Direct | | Consolidated | | 100.00 | % | | 100.00 | % |
| Veracel Celulose S.A. (11) | | Industrialization, commercialization and exportation of pulp | | Brazil | | Direct | | Proportional Consolidated | | 50.00 | % | | 50.00 | % |
| 1) | On December 31, 2020, merger of the entity by Suzano S.A. |
| 2) | On May 31, 2020, reorganization of equity interest as a result of the merger of Suzano Participações do Brasil Ltda. by Suzano S.A. Previously, the participation of this entity was directly held by Suzano Participações do Brasil Ltda. and indirectly by Suzano S.A. After the merger, it was held wholly-owned by Suzano S.A. |
| 3) | On April 8, 2020, disposal of equity interest. |
| 4) | On May 31, 2020 reorganization of equity interest as a result of the merger of Suzano Participações do Brasil Ltda. by Suzano S.A. Previously, the participation of this entity was directly held by Suzano Participações do Brasil Ltda. and indirectly by Suzano S.A. After the merger, it was held wholly-owned by Suzano S.A. |
| 5) | On August 31, 2020, entity established as a result of corporate restructuring. On December 31, 2020, reorganization of equity interest as a result of the merger of Facepa - Fábrica de Papel da Amazônia S.A. by Suzano S.A. Previously, the participation of this entity was wholly-owned held by Facepa - Fábrica de Papel da Amazônia S.A. and indirectly by Suzano S.A. After the merger, it was held directly by Suzano S.A. |
| 6) | On January 29, 2020, dilution of equity interest due to the acquisition of interest by another investor. |
| 7) | On December 31, 2020, reorganization of equity interest as a result of the merger of Comercial e Agrícola Paineiras Ltda. by Suzano S.A. Previously, the participation of this entity was 90% held by Suzano S.A and 10% by Comercial e Agrícola Paineiras Ltda. After the merger, it was held wholly-owned by Suzano S.A. |
| 8) | On December 02, 2020, establishment of legal entity arising from corporate reorganization. |
| 9) | On May 31, 2020, merger of the entity by Suzano S.A. |
| 10) | On February 26, 2020, establishment of legal entity arising from corporate reorganization. |
| 11) | Joint operation with Stora Enso, a company located in Finland. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 1.2. | Major events in the year ended |
| 1.2.1. | Effects arising from COVID 19 |
With the advent of the pandemic COVID-19, Suzano has adopted and has maintained preventive and mitigating measures, in compliance with the rules and policies established by national and international health authorities, in order to minimize as far as possible, the harmful effects of the pandemic of COVID-19, popularly known as the new coronavirus, referring to the safety of people, society and their businesses.
Thus Company’s initiatives are based on three pillars:
| (i) | Protection for people: in order to provide security to its employees and third parties who in its operations, Suzano adopted a series of measures aimed at minimizing the exposure of its team and / or mitigating exposure risks. |
| (ii) | Protection of society: one of Suzano’s three cultural drivers is: “It is only good for us, if it is good for the world”. Therefore, from the beginning of the pandemic to the present, the Company has adopted a series of measures to protect society, including: |
| • | Donation of toilet paper, napkins and disposable diapers produced by the Company for needy regions. |
| • | Acquisition of 159 respirators and 1,000,000 hospital masks for donation to the Federal and State Governments. |
| • | Participation in joint action with Positivo Tecnologia, Klabin, Flextronics and Embraer, to support the Brazilian company Magnamed, in the production of respirators to deliver to the Federal Government. Suzano’s disbursement in this action was R$9,584. |
| • | Construction of a field hospital in Teixeira de Freitas (BA) in conjunction with Veracel, which has already been handed over to the state government and opened in July 2020. |
| • | Establishement a partnership with Fatec of Capão Bonito for the production of gel alcohol. |
| • | Loan of forklifts to move donations received by the Red Cross. |
| • | Maintenance of all direct jobs. |
| • | Maintenance, for 90 days (until the end of June 2020) of payment of 100% of the cost of the payroll of service providers’ workers who had their activities suspended due to the pandemic, aiming at the consequent preservation of jobs. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| • | Creation of the a support program for small suppliers, a social support program for small farmers to sell their products through the home delivery system in 38 communities supported by Suzano’s Rural and Territorial Development Program (“PDRT”) in 5 states and social program with the objective of provide 125,000 masks in communities for donation in 5 states. |
| • | Launch a program to support its portfolio of small and medium-sized paper customers entitled “Tamo Junto” with the objective of ensuring that these companies have the financial and management capacity to resume activities. |
The disbursements made for carrying out the social actions implemented by Suzano, totaled R$48,590 through December 31, 2020 (Note 30).
| (iii) | Protection for business: to date, the Company continues with its normal operations and a crisis management committee has been implemented. |
The paper and pulp sector were recognized by the World Health Organization (“WHO”), as well as by several countries, as a producer of goods essential to society. Therefore, in order to fulfill the responsibility arising from the essentiality of the business, Suzano has taken measures to ensure, to the greatest extent possible, operational normality and full service to its customers, increasing the level of wood and raw material inventories in the factories and has been advancing its inventories of finished goods product bringing them closer to their customers to mitigate possible risks of disruption in the factories’ supply chain and the sale of their products.
The current situation resulting from the COVID-19 also implies a higher credit risk, especially for its customers in the paper business. Thus, the Company has also been monitoring the evolution of this risk and implementing measures to mitigate it, and so far, there has been no significant financial impact.
Due to the social isolation measures adopted in Brazil and in several countries around the world, causing schools and offices to close, for example, the demand for printing and writing papers was reduced. In light of this situation, as announced by paper producers in several countries around the world, Suzano decided to temporarily reduce its paper production volume. As previously disclosed in the quarterly information for the period ended March 31, 2020, the Company temporarily stopped the production at the paper production lines of the Mucuri and Rio Verde units, however, the activities of the factories were resumed at normal level at the beginning of July 2020.
Finally, it is worth noting that, as a result of the current scenario, the Company has made and maintained a vast communication effort to further increase the interaction with its main stakeholders, with the objective of guaranteeing the adequate transparency and flow of information with the them in a timely manner to the dynamics of the social and economic conjuncture.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 1.2.2. | Sale of rural properties and forests (“Transaction”) |
On November 20, 2020, the Company announced that it entered into an agreement for purchase and sale of forests , commitment to purchase and sale rural properties and other covenants, with Bracell SP Celulose Ltda. (“BSP”) and Turvinho Participações Ltda. (“Turvinho”, and in conjunction with BSP, “Buyers”), for which the Company sold and Buyers (i) acquired 21,066 hectares of rural property located in the central region of the State of São Paulo, partly through sale and partly by transfer of Suzano’s lease agreement to the Buyers; (ii) acquired mature and immature forests and (iii) committed to purchase an additional volume of wood, for the price of R$1,056,756, whose composition of the consideration corresponds to:
| (i) | Sale of rural properties: R$680,895 |
| (ii) | Sale of eucalyptus forests (mature) and forests in formation (immature): R$375,860 |
| (iii) | Transfer of lease agreements: R$1 |
The Administrative Council for Economic Defense (“CADE”) analyzed the conditions applicable to this type of operation and approved the transaction, without restrictions, on December 8, 2020. On December 29, 2020, the process was completed and filed, issuing the Transit Certificate in Transaction Judgment.
The closing of the transaction, as established in the contract, took place on the 5th business day following the issuance of the CADE Certificate of Approval, with the transaction completion date, January 5, 2021, as described in Note 32.1.
For the year ended December 31, 2020, in compliance with IFRS 5 Non-Current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations, the Company reclassified to the item of non-current assets held for sale, the assets available immediately and under current conditions (rural properties and mature eucalyptus forests), in the total amount of R$ 313,338, of which:
| (iv) | Property, plant and equipment: referring to rural properties in the amount of R$289,867, corresponding to the book value and deemed cost; and |
| (v) | Biological Assets: referring to mature eucalyptus forests (over 7 years of planting) in the amount of R$23,471, corresponding to the book value of the formation cost. |
For rural properties that have eucalyptus forests in formation (immature), the Company and Turvinho signed a lending agreement on the date of completion of the transaction (“Closing”). The contract will remain in effect until the biological assets reaches the cut-off point (mature), when the wood will be delivered to Bracell. The projection of wood delivery will occur during the period from the year ended in 2021 to 2027.
The biological assets corresponding to eucalyptus forests in formation (immature), in the amount of R$140,142, remains classified in biological assets, until its formation and delivery of the wood to Bracell.
| 1.2.3. | Approval of the legal merger of Facepa |
On December 28, 2020, the Company approved in the Extraordinary Shareholders Meeting of Suzano the legal merger of Facepa, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Suzano, with the transfer of all its equity to Suzano and its consequent winding up (“Legal Merger”), provided that the share capital of the Company not changed due to the Legal Merger. Because of the Legal Merger, Suzano succeeded Facepa in all its rights and obligations.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The following table summarizes, the balance sheet of Facepa as of December 31, 2020:
| ASSET | | | |
| CURRENT | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalentes | | | 47,397 | |
| Trade accounts receivable | | | 53,777 | |
| Inventories | | | 34,977 | |
| Recoverable taxes | | | 45,738 | |
| Other assets | | | 1,845 | |
| Total current asset | | | 183,734 | |
| | | | | |
| NON-CURRENT | | | | |
| Recoverable taxes | | | 183 | |
| Deferred taxes | | | 4,498 | |
| Judicial deposits | | | 1,231 | |
| | | | 5,912 | |
| | | | | |
| Investment | | | 15,839 | |
| Property, plant and equipment | | | 65,487 | |
| Right of use | | | 1,389 | |
| Intangible | | | 120 | |
| | | | 82,835 | |
| Total non-current asset | | | 88,747 | |
| TOTAL ASSET | | | 272,481 | |
| | | | |
| LIABILITIES | | | |
| CURRENT | | | |
| Trade accounts payable | | | 219,578 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | 451 | |
| Taxes payable | | | 1,813 | |
| Payroll and charge | | | 7,064 | |
| Dividends payable | | | 8,004 | |
| Other liabilities | | | 4,515 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 241,425 | |
| | | | | |
| NON-CURRENT | | | | |
| Loans and financing | | | 3,650 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | 1,011 | |
| Provision for judicial liabilities | | | 7 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | 4,668 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | | | 246,093 | |
| | | | | |
| EQUITY | | | | |
| Share capital | | | 24,713 | |
| Accumulated profit | | | 1,675 | |
| Total equity | | | 26,388 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | 272,481 | |
| 1.3. | Major events in the year ended |
| 1.3.1. | Business combination with Fibria |
On January 3, 2019, acquisition date of control by Suzano, after all fulfilled conditions for the conclusion of business combination and shareholding base, Fibria’s shares were exchanged for Suzano’s shares and on January 14, 2019, Suzano concluded the corporate reorganization process, following the terms of the Agreement signed by both entities on March 15, 2018.
Suzano performed a valuation analysis of the fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed of Fibria and, using the total transferred consideration for the Merger, and allocated for such assets and liabilities.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The following table summarizes the final purchase price allocation based on the appraisal report prepared by an independent and specialized entity:
| Cash consideration | | | 27,797,441 | |
| Issuance of shares by Suzano | | | 9,438,413 | |
| Total consideration | | | 37,235,854 | |
| | | | | |
| Book value of Fibria’s shareholders’ equity | | | 14,149,004 | |
| Write-off of the book value of existing goodwill, net of the deferred income taxes | | | (3,495,077 | ) |
| Mandatory minimum dividends (eliminated from the balance sheet at the date of acquisition) | | | 724,829 | |
| Book value of Fibria’s shareholders’ equity, net of goodwill | | | 11,378,756 | |
| | | | | |
| Fair value adjustment on business combination with Fibria (assets and liabilities): | | | | |
| Inventories | | | 2,178,903 | (1) |
| Property, plant and equipment | | | 9,362,315 | (2) |
| Customer relationship | | | 9,030,779 | (3) |
| Port assets | | | 749,060 | (4) |
| Contingent liabilities | | | (2,970,546 | )(5) |
| Loans and financing | | | (59,921 | )(6) |
| Taxes recoverable | | | (235,843 | )(7) |
| Other assets and liabilities, net | | | 451,624 | (8) |
| Deferred taxes, net | | | (546,324 | )(9) |
| Total impact of fair value | | | 17,960,047 | |
| Goodwill on the expectation of future profitability | | | 7,897,051 | (10) |
| 1) | Measured considering the balance of finished products based on selling price, net of selling expenses and an accepted margin based on the results achieved in 2018. |
| 2) | Determined based on the analysis of market data on comparable transactions and cost quantification, based on the estimate of replacement or replacement value of the assets. |
| 3) | In order to determine the fair value adjustment in the customer portfolio, the income approach and the method were used to measure the present value of the income that will be generated during the remaining useful life of the asset. Considering the 5-year history of Fibria’s sales data and the churn rate that measures customer satisfaction and customer permanence in the portfolio, the adjustment was measured using estimated discounted cash flows. |
| 4) | Fibria has concession contracts and port assets to assist in port operations in Brazil. For fair value measurement of these assets was considered the income approach, the Multi Period Excess Earnings Method (“MPEEM”) that measures the present value of the income that will be generated during the remaining useful life of the asset and method of direct cost differential. |
| 5) | In the business combination, for the contingencies fair value measurement, whose chances of loss were classified as possible and remote, Fibria’s Management and its external and independent advisors were considered for their fair values, whose amounts were measured based on the analyzes of Company’s external lawyers. |
| 6) | The adjustment to fair value of loans and financing was measured based on the fair value of the Bonds, based on the quotation of the security in the secondary market, and the adjustment to present value considering the market rate at the base date on December 31, 2018. |
| 7) | For the measurement of the fair value of the taxes to be recovered, the amount to be recovered, discounted to the present value considering the expected Selic rate for the tax period, was considered. |
| 8) | In other net assets and liabilities, including supply contracts, accounts receivable and advances to suppliers, the income evaluation methodology, the present value and the direct cost differential were used. |
| 9) | Deferred asset on income tax on fair value adjustments of assets of Veracel and Portocel. For the remaining fair value, we did not recognize deferred liability on income taxes liabilities due to Fibria’s Legal Merger in April 2019. |
| 10) | Goodwill is attributable to the strong market position and expected future profitability of Fibria in negotiations in the eucalyptus pulp market. |
| 1.3.2. | Approval of the legal merger of Fibria |
On April 1st, 2019, the Company approved in the Extraordinary Shareholders Meeting of Suzano the legal merger of Fibria, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Suzano, with the transfer of all its equity to Suzano and its consequent winding up (“Legal Merger”), provided that the share capital of the Company not changed due to the Legal Merger. Because of the Legal Merger, the Suzano succeeded Fibria in all its rights and obligations.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The following table summarizes, the main items balance sheet of Fibria as of March 31, 2019.
| ASSETS | | | |
| CURRENT | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 29,086 | |
| Marketable securities | | | 2,734,027 | |
| Trade accounts receivable | | | 3,572,059 | |
| Inventories | | | 1,714,560 | |
| Recoverable taxes | | | 768,439 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | 256,675 | |
| Other assets | | | 161,238 | |
| Total current assets | | | 9,236,084 | |
| | | | | |
| NON-CURRENT | | | | |
| Marketable securities | | | 175,559 | |
| Recoverable taxes | | | 546,234 | |
| Deferred taxes | | | 1,364,363 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | 723,084 | |
| Advances to suppliers | | | 696,767 | |
| Judicial deposits | | | 190,533 | |
| Other assets | | | 100,877 | |
| | | | | |
| Biological assets | | | 4,355,102 | |
| Investments | | | 9,481,900 | |
| Property, plant and equipment | | | 14,633,114 | |
| Right of use | | | 2,301,427 | |
| Intangible assets | | | 118,920 | |
| Total non-current | | | 34,687,880 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | | | 43,923,964 | |
| | | | |
| LIABILITIES | | | |
| CURRENT | | | |
| Trade accounts payable | | | 955,210 | |
| Loans and financing | | | 816,180 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | 420,241 | |
| Taxes payable | | | 36,057 | |
| Payroll and charges | | | 104,246 | |
| Related parties | | | 1,179,254 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | 254,444 | |
| Dividends payable | | | 4,015 | |
| Other liabilities | | | 946,099 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 4,715,746 | |
| | | | | |
| NON-CURRENT | | | | |
| Loans and financing | | | 8,139,390 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | 678,833 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | 1,972,531 | |
| Related parties | | | 16,305,560 | |
| Employee benefits | | | 144,557 | |
| Provision for judicial liabilities | | | 190,698 | |
| Other liabilities | | | 175,934 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | 27,607,503 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | | | 32,323,249 | |
| | | | | |
| EQUITY | | | 11,600,715 | |
| TOTAL EQUITY AND LIABILITIES | | | 43,923,964 | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
2. BASIS OF PREPARATION AND PRESENTATION OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The Company’s consolidated financial statements are prepared in accordance with and in compliance with the International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”) and disclose all the applicable significant information related to the financial statements, which is consistent with the information utilized by Management in the performance of its duties.
The Company’s consolidated financial statements are expressed in thousands of Brazilian Reais (“R$”), as well as the amounts of other currencies disclosed in the financial statements, when applicable, were also expressed in thousands, unless otherwise stated.
The preparation of consolidated financial statements requires Management to make judgments, use estimates and adopt assumptions in the process of applying accounting practices, that affect the disclosed amounts of revenues, expenses, assets and liabilities, including contingent liabilities. The accounting practices requiring a higher level of judgment and which are more complex, as well as areas in which assumptions and estimates are significant, are disclosed in note 3.2.34.
The consolidated financial statements were prepared on the historical cost basis, except for the following material items recognized:
| (i) | derivative and non-derivative financial instruments measured at fair value; |
| (ii) | share-based payments and employee benefits measured at fair value; |
| (iii) | biological assets measured at fair value; and |
| (iv) | deemed cost of property, plant and equipment. |
The main accounting polices applied in the preparation of these consolidated financial statements are presented in note 3.
The consolidated financial statements were prepared under the going concern assumption.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
3. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The consolidated financial statements were prepared in accordance with information from Suzano and its subsidiaries on the same base date, as well as consistent accounting policies and practices.
The accounting policies have been consistently applied to all consolidated companies.
There was no change in relation to such policies and methods for calculating estimates, except for the new accounting policies presented in note 3.1, adopted as of January 1, 2020 and whose estimated impact was disclosed in the annual financial statements of December 31, 2019.
| 3.1. | New accounting policies and changes in the accounting policies adopted |
| 3.1.1. | Change in the functional currency |
Due to the merger with Fibria, the Company had several changes in the structure, activities and operations during the year of 2019 that led management to conclude that they needed to reassess the functional currency of its subsidiaries whose functional currency was different from Brazilian Reais.
Those facts resulted in the corporate reorganization, as well as, it has impacted how management conducted the Company’s business in order to achieve the alignment between the cultures of the two Companies, the unification of processes, operating, systems, tax strategies and synergy gains arising from the business combination. In this process some of Company’s wholly-owned subsidiaries were considered an extension of the activities of the parent company.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
These circumstances collectively justify the change in the functional currency to Brazilian Real and they have occurred gradually during 2019, therefore it was not practicable to determine the date of the change at a precise point during the reporting period. Thus, the Company changed the functional currency of those wholly-owned subsidiaries as of January 1, 2020.
The cumulative translation adjustment (“CTA”) arising from the translation of a foreign operation previously recognized in other comprehensive income will not be reclassified from equity to profit or loss until the disposal of the operations. The total or partial disposal of interest in wholly-owned subsidiaries occurs through sale or dissolution, of all or part of operation.
Therefore, the financial statements of foreign subsidiaries, whose functional currency are different from Brazilian Reais, were translated using the criteria established below:
| (i) | assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rate in effect at period end; |
| (ii) | revenues and expenses are translated based on the monthly average rate; |
| (iii) | the cumulative effects of gains or losses upon translation are recognized as accumulated foreign currency translation adjustments component of other comprehensive income. |
And as from January 1, 2020, the financial statements of foreign subsidiaries, whose functional currency became the Brazilian Real, are converted using the criteria established below:
| (iv) | monetary assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rate in effect at period-end; |
| (v) | non-monetary assets and liabilities are translated at the historical rate of the transaction; |
| (vi) | revenues and expenses are translated based on monthly average rate; |
| (vii) | the cumulative effects of gains or losses on the conversion of the above items are recorded in the financial result of the year. |
| 3.1.2. | Business combination – IFRS 3 |
This pronouncement was amended and clarifies definition of a “business”. It is also permitted a simplified assessment of whether an acquired set of activities and assets is a group of assets rather than a business. The Company assessed the content of this pronouncement and did not identify any impacts.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 3.1.3. | Presentation of financial statements – IAS 1 and Accounting policies, changes in accounting estimates and errors – IAS 8 |
This pronouncement was amended and clarifies definition of a “material” and how it should be applied by (i) including in the definition guidance that until now has featured elsewhere in IFRS Standards, (ii) improving the explanations accompanying the definition and, (iii) ensuring that the definition of material is consistent across all IFRS Standards. The Company assessed the content of this pronouncement and did not identify any impacts.
| 3.1.4. | Conceptual framework for financial reporting |
This pronouncement was changed and includes new concepts on the presentation, measurement and disclosure of the financial statements, the main highlights being:
| (i) | the objective of the financial report; |
| (ii) | the qualitative characteristics of useful financial information; |
| (iii) | the description of the reporting entity and its limit; |
| (iv) | definitions of assets, liabilities, equity, income and expenses; |
| (v) | criteria for the inclusion of assets and liabilities in the financial statements (recognition) and guidance on when to remove them (derecognition); |
| (vi) | measurement bases and guidance on when to use them; |
| (vii) | concepts and guidelines on presentation and disclosure. |
These changes help to ensure that accounting standards are conceptually consistent and that similar transactions are treated in the same way, in order to provide useful information for investors and creditors.
The Company assessed the content of this pronouncement and did not identify any impacts.
This pronouncement was changed as a result of benefits related to COVID-19 granted to lessee under lease agreements. The Company assessed the content of this pronouncement and did not identify any impacts, for the clauses of the current lease agreements remained unchanged.
| 3.1.6. | Interest rate reform – IAS 39 / IFRS 7 and IFRS 9 - Phase 1 (Applicable on/or after January 1, 2020) |
These pronouncements were amended by the IASB in response to the ongoing reform of the Interbank offered rates (“Ibor”) and other reference interest rates, issuing a package of amendments to IFRS standards. According to the IASB, the changes are aimed at helping companies to provide investors with useful information about the effects of the reform on its financial statements.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The changes made by the IASB, in 2020, complement the issued in 2019 and considers the effects, in the financial statements, when a company substitutes, as a result of the reform, the old reference interest rate with an alternative.
The adoption of this pronouncement is divided into 2 (two) phases, being:
| (i) | Phase 1: the changes to this phase were issued in September 2019 and provided temporary exemptions from the application of specific hedge accounting requirements for relationships affected by uncertainties that arise as a result of the IBOR reform (exemptions from Phase 1). The Company assessed the amendments and did not identify any impacts; and |
| (ii) | Phase 2: the changes to this phase were issued in August 2020 and can be summarized as follows: changes in contractual cash flows, hedge accounting requirements and disclosures (Note 3.3.1). |
| 3.2. | Accounting policies adopted |
| 3.2.1. | Consolidated financial statements |
The consolidated financial statements were prepared based on the information of Suzano and its subsidiaries in the year ended December 31, 2020, as well as in accordance with consistent accounting practices and policies, except to Futuragene PLC, which period end is November 30, 2020, however, has no material impact in the consolidated financial statements, and if there is any significant event up to December 31, 2020, it is adjusted in the consolidated financial statement. The Company consolidates all subsidiaries over which it has direct or indirect control, that is, when it is exposed or has rights to variable returns on its investment with the investee and has the capacity and ability to direct the relevant activities of the investee and has the ability to direct the investee’s relevant activities.
Additionally, all transactions and balances between Suzano and its subsidiaries, associates and joint ventures are eliminated in the consolidated financial statements, as well as unrealized gains or losses arising from these transactions, net of tax effects. Non-controlling interest is highlighted.
These all entities over which the Company has the power to govern the financial and operating policies of the entity, generally through a majority voting rights. The Company controls an entity when the Company is exposed to, or has rights to, variable returns on its investment with the investee and has the ability to affect those returns through its power over the entity.
Subsidiaries are consolidated from the date on which control is obtained and de-consolidated from the date that control ceases.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
These are all entities in which the Company maintains the contractually established control over its economic activity and exists only when the strategic, financial and operational decisions regarding the activity require the unanimous consent of the parties sharing the control.
In the consolidated financial statements, the balance of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses are recognized proportionally to the interest in joint operation.
| 3.2.4. | Associated and joint ventures |
These are all entities are initially recognized at cost and adjusted thereafter for the equity method, being increased or reduced from its interest in the investee’s income after the acquisition date.
In the investments in associates, the Company must have significant influence, which is the power to participate in the financial and operating policy decisions of the investee, without having its control or joint control of those policies. In investments in joint ventures there is a contractually agreed sharing of control through an arrangement, which exists only when decisions about the relevant activities require the unanimous consent of the parties sharing control.
In the consolidated financial statements, the balance of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses are eliminated, as well as unrealized gains and losses and investments in these entities and their respective equity accounting results.
In relation to associates Ensyn and Spinnova, which period end is November 30, 2020 for their financial statements, they have no material impact in the consolidated financial statement and, if any significant event had occurred until December 31, 2020, it would be adjusted in the consolidated financial statement.
| 3.2.5. | Translation of financial statements to functional and presentation currency |
The Company defined that for all its wholly owned subsidiaries, the functional and presentation currency is the Real. Except for investments in associates abroad related to Ensyn Corporation, F&E Technologies LLC and Spinnova OY, the functional currencies are different from the Real, whose accumulated gain or loss effects on the conversion of financial statements, are recorded in other comprehensive income, in equity.
The individual financial statements of each foreign subsidiaries included in the consolidated financial statement, are prepared in accordance with local currency of the subsidiary operates and translated into Company’s functional and presentation currency.
| 3.2.5.1. | Transactions and balances in foreign currency |
These are translated using the following criteria:
| (i) | monetary assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rate in effect at year-end; |
| (ii) | non-monetary assets and liabilities are translated at the historical rate of the transaction; |
| (iii) | revenues and expenses are translated based on monthly average rate; and |
| (iv) | the cumulative effects of gains or losses upon translation are recognized in the other comprehensive income. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 3.2.6. | Hyperinflationary economies |
Entities based in Argentina, a country considered to have a hyperinflationary economy, are subject to the requirements of IAS 29 - Financial Reporting in Hyperinflationary Economies.
Non-monetary items, as well as incomes and expenses, are adjusted by the changes in the inflation index between the initial recognition and the closing date, so that the balances are stated at current value.
However, the Company’s wholly-owned subsidiary based in Argentina, the functional currency has been the Real since January 1, 2020, as disclosed in note 3.2.7.1 of the financial statements ended on December 31, 2019, therefore it is no longer an entity with hyperinflationary currency and discontinued the preparation and presentation of its individual financial statement in accordance with IAS 29 - Financial Reporting in Hyperinflationary Economies.
The amounts in the financial statements on that date were considered as historical cost, being the basis of the book values of the subsequent financial statements, that is, the updated values are the cost bases of the non-monetary items in the subsequent financial statements, being subject to the requirements of the note 3.2.7.1 above disclosed.
| 3.2.7. | Business combinations |
These are accounted for using the acquisition method when control is transferred to acquirer. The cost of an acquisition is the sum of the consideration paid, evaluated based on the fair value at acquisition date, and the amount of any non-controlling interests in the acquire. For each business combination, the Company recognizes any non-controlling interest in the acquire either at fair value or at the non-controlling interest’s proportionate share of the acquirer’s net assets. The costs directly attributable to the acquisition are recorded as expense when incurred, except for costs related to the issuance of debt instruments or equity instruments, which are presented as debt reduction or equity, respectively.
In a business combination, assets acquired and liabilities assumed are evaluate in order to classify and allocate them assessing the terms of the agreement, economic circumstances and other conditions at the acquisition date.
Goodwill is initially measured as the excess of the consideration paid over the fair value of the net assets acquired. After initial recognition, goodwill is measured at cost, net of any accumulated impairment losses. For purposes of impairment testing, the goodwill recognized in a business combination, as from the acquisition date, is allocated to each of the Company’s cash generating units.
Gains on an advantageous purchase are recognized immediately in the result. The borrowing costs are recorded in the income statement as incurred.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
Contingent liabilities related to tax, civil and labor classified in the acquired company as possible and remote risk is recognized by the acquirer, at its fair values.
Transactions in the acquisition of shares with shared control over the net assets traded apply complementary guidance to IFRS 3 - Business Combination, IFRS 11 and IAS 28 - Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures. Based on the equity method, investment is initially recognized at cost. The carrying amount of the investment is adjusted for recognition of changes in the Company’s share in the acquirer’s Shareholders’ equity as of the acquisition date. Goodwill is segregated from carrying amount of the investment. Other intangible assets identified in the transaction shall be allocated in proportion to the interest acquired by the Company, by the difference between the carrying amounts recorded in the acquired entity and its fair value assets, which may be amortized.
| 3.2.8. | Segment information |
An operating segment is a component of the Company that carries out business activities from which it can obtain revenues and incur expenses. The operating segments reflect how the Company’s management reviews financial information to make decisions. The Company’s management has identified reportable segments, which meet the quantitative and qualitative disclosure requirements. The segments identified for disclosure represent mainly sales channels.
| 3.2.9. | Cash and cash equivalents |
Include cash on hand, bank deposits and highly liquid short-term investments with maturities, upon acquisition, of 90 days or less, which are readily convertible into known amounts of cash and subject to insignificant risk of change in value. The investments classified in this group, due to their nature, are measured at fair value through the profit or loss.
Financial assets are classification based on the purpose for which the financial assets were acquired, as set forth below:
| (i) | financial assets at amortized cost; |
| (ii) | financial assets at fair value through other comprehensive income; |
| (iii) | financial assets at fair value through profit or loss. |
Regular purchases and sales of financial assets are recognized on the trade date, it means, the date on which the Company commits to purchase or sell the asset. Financial assets are derecognized when the rights to receive cash flows from the investments have expired or have been transferred but only if Fibria has transferred substantially all risks and rewards of ownership.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 3.2.10.1.1. | Financial instruments measured at amortized cost |
Financial assets at amortized cost are financial assets held by the Company (i) in order to receive their contractual cash flow and not to sell to realization a profit or loss and (ii) whose contractual terms give rise, on specified dates, to cash flows that exclusively, payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. Any changes are recognized under financial income (expense) in income statement.
It includes the balance of cash and cash equivalents, trade accounts receivable and other assets.
| 3.2.10.1.2. | Financial assets at fair value through other comprehensive income |
Financial assets at fair value through other comprehensive income are financial assets held by the Company (i) either to receive their contractual cash flow as the for sale with realization of profit or loss and (ii) whose contractual terms give rise on specified dates, to cash flows constituting, exclusively, payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. In addition, investments in equity instruments where, on initial recognition, the Company elected to present subsequent changes in its fair value to other comprehensive income, are classified in this category. Any changes are recognized under net financial income (expense) in income statement, except for the fair value of investment in equity instruments, which are recognized in other comprehensive income.
This category includes the balance of other investments (Note 14).
| 3.2.10.1.3. | Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss |
Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss are either designated in this category or not classified in any of the other categories. .. Any changes are recognized under financial income (expense) in income statement for non-derivative financial instruments and for financial derivative instruments under income from derivative financial instruments.
This category includes the balance of marketable securities, financial assets at fair value through profit or loss are the balance of derivative financial instruments, including embedded derivatives, stock options and other securities.
| 3.2.10.2. | Settlement of financial instruments |
Financial assets and liabilities are settled and the net amount is recorded in the balance sheet when there is a (i) legally enforceable right to settle the recognized amounts and (ii) there is an intention to settle on a net basis or realize the asset and settle the liability simultaneously.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 3.2.10.3. | Impairment of financial assets |
| 3.2.10.3.1. | Financial instruments measured at amortized cost |
Annually, the Company assesses if there is evidence that a financial asset is impaired. A financial is impaired only if there is evidence of an impairment as a result of one or more events that occurred after the initial recognition of the asset and that loss event has an impact on the estimated future cash flows of the financial asset that can be reliably estimated.
The criteria that the Company uses to determine if there is evidence of an impairment loss include:
| (i) | significant financial difficulty of the issuer or debtor; |
| (ii) | default or late interest or principal payments in the agreement; |
| (iii) | where Company, for economic or legal reasons relating to the borrower’s financial difficulty, grants to the borrower a concession that the lender would not otherwise receive; |
| (iv) | it becomes probable that the borrower will enter bankruptcy or other financial reorganization; |
| (v) | the disappearance of an active market for that financial asset because of financial difficulties; |
| (vi) | observable data indicating that there is a measurable decrease in the estimated future cash flows from a portfolio of financial assets since the initial recognition of those assets, although the decrease cannot yet be identified with the individual financial assets in the portfolio. |
The amount of an impairment loss is measured as the difference between the carrying amount of the asset and the present value of estimated future cash flows discounted at the financial asset’s original effective interest rate. If the financial asset is impaired the carrying amount of the asset is reduced and a loss is recognized in the income statement.
In a subsequent measurement, if there is an improvement in the asset rating, such as an improvement in the debtor’s credit rating, the reversal of the previously recognized impairment loss is recognized in the income statement.
| 3.2.10.3.2. | Financial assets at fair value through other comprehensive income |
Annually, the Company evaluate if there is evidence that a financial asset is impaired.
For such financial assets, a significant or prolonged decrease in the fair value of the security below its cost is an evidence that the assets are impaired. If any such evidence exists, impairment loss is measured by the difference between the acquisition cost and the current fair value, less any loss previously recognized in other comprehensive income, shall be recognized in the income statement.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 3.2.11. | Derivative financial instruments and hedging activities |
Derivatives financial instruments are recognized at fair value on the date the derivative agreement is entered into and are subsequently remeasured at fair value. Changes in fair value are recorded in under result of derivative financial instruments in the income statement.
Embedded derivatives in non-derivative main contracts are required to be separated when their risks and characteristics are not-closely related to those of main contracts and these are not measured at fair value through profit or loss.
Non-option embedded derivatives are separated from the main contracts in accordance with its stated or implied substantive terms, so that they have zero fair value on initial recognition.
| 3.2.12. | Trade accounts receivables |
These are recorded at the invoiced amount, in the normal course of the Company´s business, adjusted to exchange rate variation when denominated in foreign currency and, if applicable, net of expected credit losses.
The Company applies the aging-based provision matrix with the appropriate grouping of your portfolio. When necessary, based on individual analysis, the provision for expected loss is supplemented.
The Company adopts procedures and analysis to establish credit limits.
The Company examines on a monthly basis the maturity of receivables and identifies those customers with overdue balances assessing the specific situation of each client including the risk of loss, the existence of contracted insurance, letters of credit, collateral and the customer’s financial situation. In the event of default, collection attempts are made, which include direct contact with customers and collection through third parties. Should these efforts prove unsuccessful, court measures are considered and credit expected loss is recognized. The notes are written-off from the credit expected loss when Management considers that they are not recoverable after taking all appropriate measures to collect them.
These are evaluated at average acquisition or formation cost of finished products, net of recoverable taxes, not exceeding their net realizable value.
Finished products and work-in-process consist of raw materials, direct labor, production costs, freight, storage and general production expenses, which are related to the processes required to make the products available for sale.
Imports in transit are presented at the cost incurred until the balance sheet date.
The raw materials derived from biological assets are measured based on their fair value less cost to sell at the point of harvest and freight costs.
Provisions for obsolescence, adjustments to net realizable value, impaired items and slow-moving inventories are recorded when necessary. Usual production losses are recorded and are an integral part of the production cost of the respective month, whereas abnormal losses, if any, are recorded directly as cost of sales.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 3.2.14. | Non-current assets held for sale |
These are measured at carrying amount or fair value less costs to sell, whichever is lower, and are not depreciated or amortized. Such items are only classified under this account when the sale is highly probable and they are available for immediate sale under their current conditions.
The biological assets for production (mature and immature forests) are reforestation eucalyptus forests, with a formation cycle between planting until the harvest of approximately 7 (seven) years, measured at fair value. Depletion is measured by the amount of biological assets depleted (harvested) and measured at fair value less estimated costs to sell.
For the determination of the fair value, the income approach technique was applied using the discounted cash flow model, according to the projected productivity cycle for these assets. The assumptions used to measure the fair value are reviewed every six months, as the Company considers that this interval is sufficient so that there is no significant gap in the fair value balance of biological assets booked. Significant assumptions are presented in note 13.
The gain or loss on the assessment of fair value is recognized in the operating income (expenses), net.
Biological assets in formation under the age of 2 (two) years, accounted for at the formation cost and the areas of permanent environmental preservation, which are not recorded, and it is not included in the measurement at fair value, because it is not characterized as biological assets.
| 3.2.16. | Property, plant and equipment |
Stated at the cost of acquisition, formation, construction or dismantling, net of recoverable taxes. Such cost is deducted of accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment losses, when incurred, at the highest of the value of use and sale, less cost to sell. The borrowing costs are capitalized as a component of construction in progress, pursuant to with IAS 23, considering the weighted average interest rate of the Company’s debt at the capitalization date.
Depreciation is recognized based on the estimated economic useful life of each asset on a straight-line basis. The estimated useful life, residual values and depreciation methods are annually reviewed and the effects of any changes in estimates are accounted for prospectively. Land is not depreciated.
The Company annually performs an analysis of impairment indicators of property, plant and equipment. An impairment for loss for property, plant and equipment, is only recognized if the related cash-generating unit is devalued. Such condition is also applied if the asset’s recoverable amount is less than it is carrying amount. The recoverable amount of asset or cash-generating unit is the highest of its value in use and its fair value less cost to sell.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The cost of major renovations is capitalized if the future economic benefits exceed the performance standard initially estimated for the asset and are depreciated over the remaining useful life of the related asset.
Repairs and maintenance are expensed when incurred.
Gains and losses on disposals of property, plant and equipment are measured by comparing the proceeds with the book value and are recognized as other operating income a (expense), net at the disposal date.
The Company adopted IFRS 16 as of January 1, 2019. This standard determines that lessees must recognize future liabilities in their liabilities and their right to use the leased asset for all lease agreements, with exemption allowed to short-term or low-value contracts. Short-term or low-value contracts for the exemption of the standard refers to contracts where the individual value of the assets is lower than U.S.$5 and maturity date is before 12 months, represented, mainly, by equipment of technology and vehicles. The Company adopted the standard using a modified retrospective approach that does not require the restatement of the comparative balances, before the leases were recognized under IAS 17 - Leases.
In adopting IFRS 16, the Company recognized the lease liabilities in relation to the agreements that meet the definition of lease, whose liabilities were measured at the present value of the remaining lease payments, discounted based on the incremental loan nominal rate. Assets associated with the right of use were measured at the amount equal to the lease liability on January 1st, 2019, with no impact on retained earnings.
The Company used the following practical expedients allowed by the standard:
| (i) | the use of a single discount rate for a portfolio of leases with similar characteristics; |
| (ii) | leases whose maturity will occur within 12 months of the date of initial adoption of the standard, accounting was as short-term leases directly in the income statement; |
| (iii) | the accounting of lease payments as expenses in the case of leases for which the underlying asset is of low value; |
| (iv) | the use of hindsight in determining the lease term, when the agreement contains options to extend or terminate the lease; and |
| (v) | the Company excluded initial direct costs of measuring the right to use asset at the date of initial adoption. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
A contract is, or contains a lease, if the contract transfers the right to control the use of an identified asset for a period in exchange for consideration, for which it is necessary to assess whether:
| (i) | the contract involves the use of an identified asset, which may be explicit or implicit, and may be physically distinct or represent substantially the entire capacity of a physically distinct asset. If the supplier has a substantial right to replace the asset, then the asset is not identified; |
| (ii) | the Company has the right to obtain substantially all the economic benefits from using the asset during the contract period; and |
| (iii) | the Company has the right to direct the use of the asset. The Company has the right to decide to change how and for what purpose the asset is used, if: |
| • | has the right to operate the asset, or |
| • | designed the asset, in a way that predetermines how and for what purpose it will be used. |
At the beginning of the contract, the Company recognizes a right-of-use asset and a lease liability that represents the obligation to make payments related to the underlying asset of the lease.
The right-to-use asset is initially measured at cost and comprises the initial amount of the lease liability adjusted for any payment made on or before the contract start date, plus any direct initial costs incurred and estimated disassembly, removal costs, restoration of the asset in the place where it is located, less any incentive received.
The right-to-use asset is subsequently depreciated using the straight-line method from the start date to the end of the useful life of the right to use or the end of the lease term. Except for land agreements that are automatically extended for the same period by means of notification to the lessor, for the other agreements are not allowed automatic renewals and for an indefinite period, as well as the exercise of termination is a right of both parties.
The lease liability is initially measured at the present value of the payments not made, less the incremental loan rate.
The lease liability is measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. It is remeasured when there is a change:
| (i) | in future payments resulting from a change in index or rate; |
| (ii) | in the estimate of the expected amount to be paid in the guaranteed residual value; or |
| (iii) | in the assessment of whether the Company will exercise the purchase option, extension or termination. |
When the lease liability is remeasured, the corresponding adjustment amount is recorded in the book value of the right-of-use asset or in the profit and loss statement, if the book value of the right-of-use asset has been reduced to zero.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The Company does not have lease agreements with clauses of:
| (i) | variable payments that are based on the performance of the leased assets; |
| (ii) | guarantee of residual value; |
| (iii) | restrictions, such as, for example, obligation to maintain financial ratios. |
Short-term or low-value contracts for the exemption of the standard refers to contracts where the individual value of the assets is lower than U.S.$5 and maturity date is before 12 months, are expensed as incurred.
These are measured at cost at the time they are initially recognized. The cost of intangible assets acquired in a business combination corresponds to the fair value at the acquisition date. After initial recognition, intangible assets are presented at cost less accumulated amortization and impairment losses, when applicable.
The useful life of intangible assets is assessed as finite or indefinite.
Intangible assets with a finite life are amortized over the economic useful life and reviewed for impairment whenever there is an indication that their carrying values may be impaired. The amortization period and method for an intangible asset with a finite useful life are reviewed at least at the end of each fiscal year. The amortization of intangible assets with a finite useful life is recognized in the statement of income as an expense related to its use and consistently with the economic useful life of the intangible asset.
Intangible assets with indefinite useful lives are not amortized, but are tested annually for impairment losses, individually or at the level of the CGU. The allocation is made to the CGU or group of CGUs that represents the lowest level within the entity, in which the goodwill is monitored for management’s internal purposes, and that has benefited from the business combination. The Company records in this subgroup mainly goodwill for expected future profitability (goodwill) and easement of passage.
Such test involved the adoption of assumptions and judgments, disclosed in Note 16.
| 3.2.19. | Current and deferred income tax and social contribution |
Income taxes comprise income tax and social contribution on net income, current and deferred. These taxes are recognized in the income statement, except to the extent that they are related to items recognized directly in equity. In this case, they are recognized in equity under the equity adjustment.
The current charge is calculated based on the tax laws enacted in the countries in which the Company and its subsidiaries and affiliates operate and generate taxable income. Management periodically evaluates the positions assumed in the income tax returns with respect to situations in which the applicable tax regulations give rise to interpretations and establishes provisions, when appropriate, based on the amounts that must be paid to the tax authorities.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
Deferred tax and contribution liabilities are recognized on temporary differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their carrying amounts in the financial statements. Deferred taxes and contributions are determined based on the rates in force on the balance sheet date and, which must be applied when they are realized or when they are settled.
Deferred tax assets and contributions are recognized to the extent that it is probable that future taxable profit will be available to be used to offset temporary differences, based on projections of future results prepared and based on internal assumptions and future economic scenarios that may, therefore, undergo changes.
The projection for realization of deferred tax assets was prepared based on Management’s estimates that are based on significant judgments and assumptions relating to net average pulp and paper prices and the transfer price with the subsidiary based in Austria. However, there are other assumptions that are not under the control of the Company, such as inflation rates, exchange rates, pulp prices practiced in the international market and other economic uncertainties in Brazil, future results may differ from those considered in the preparation of the consolidated projection.
Deferred income tax and social contribution are recognized on temporary differences arising from investments in subsidiaries and associates, except when the timing of the reversal of temporary differences is controlled by the Company, and if it is probable that the temporary difference will not be reversed in a foreseeable future.
Deferred taxes and contributions, assets and liabilities, are presented at the net amount in the balance sheet when there is a legal right and the intention to offset them when calculating current taxes, generally related to the same legal entity and the same tax authority.
| 3.2.20. | Trade accounts payable |
Corresponds to the obligations payable for goods or services acquired in the normal course of the Company´s business, recognized at fair value and, subsequently, measured at amortized cost using the effective interest rate method, adjusted to present value and exchange rate variation when denominated in foreign currency, when applicable.
| 3.2.21. | Loans and financing |
Loans and financing are initially recognized at their fair value, net of costs incurred in the transaction and are subsequently stated at amortized cost. Any difference between the amounts raised and settled is recognized in the statement of income during the period in which the loans and financing are outstanding, using the effective tax rate method.
General or specific borrowing costs, directly attributed to the acquisition, construction or production of a qualified asset, are capitalized as a part of the cost of asset when it is probable that they will result in future economic benefits for the entity and that these costs may be measured with reliability. Other loan costs are recognized as expense in the period they are incurred.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 3.2.22. | Provision, contingent assets and liabilities |
Contingent assets are not recorded. The recognition is only performed when are guarantees or judicial decisions favorable and the amount can be measured with safety. Contingent assets, for which such conditions are not met, are only disclosed in the notes to the financial statements when material.
The provisions are provided to the extent that the Company expects that is probable that it will disburse cash and the amount can be reliably estimated. Tax, civil, environment and labor proceedings are accrued when losses are assessed as probable and the amounts involved can be reliably measured. When the expectation of loss is possible, a description of the processes and amounts involved is disclosed in the notes to the financial statements. Contingent liabilities assessed as remote losses are neither accrued nor disclosed.
A contingent liabilities of business combinations are recognized if they arise from a present obligation that arose from past events and if their fair value can be measured reliably and subsequently are measured at the higher of:
| (i) | the amount that would be recognized in accordance with the accounting policy for the provisions above that comply with IAS 37; or |
| (ii) | the amount initially recognized less, where appropriate, of recognized revenue in accordance with the policy of recognizing revenue from customer contracts IFRS 15. |
| 3.2.23. | Asset retirement obligations |
These primarily relate to future costs for the decommissioning of industrial landfill and related assets. A provision is recorded as a long-term obligation against property, plant and equipment. The provision and the corresponding property, plant and equipment are initially recorded at fair value, based on the present value of estimated cash flows for future cash payments discounted by an adjusted risk-free rate. The long-term obligation accrues interest using a long-term discount rate. The property, plant and equipment are depreciated on a straight-line basis over the useful life of the principal against to cost of sales of the income statement.
| 3.2.24. | Share based payments |
The Company’s executives and managers receive their compensation partially as share-based payment plans to be settled in cash and shares, and alternatively in cash.
Plan-related expenses are recognized in the income statement as a corresponding entry to financial liabilities during the vesting period when services will be rendered. The financial liability is measured by its fair value every balance sheet date and its variation is recorded in the income statement as administrative expenses.
At the option exercise date, if such options are exercised by executive in order to receive Company’s shares, financial liabilities are reclassified under stock options granted in shareholders’ equity. In case of option exercise paid in cash, the Company settles the financial liability in favor to the Company’s executives.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The Company offers benefits related to supplementary contribution plan to all employees and medical assistance and insurance life for a determined group of former employees, and for the last two benefits an actuarial appraisal is annually prepared by an independent actuary and are reviewed by Management.
Actuarial gains and losses are recognized in other reserves when incurred. The interest incurred, resulting from changes in the present value of the actuarial liability, is recorded in income statement under the financial expenses.
| 3.2.26. | Other assets and liabilities current and non-current |
Assets are recognized only when it is probable that the economic benefit associated with the transaction will flow to the entity and its cost or value can be measured reliably.
A liability is recognized when the Company has a legal or constructive obligation arising from a past event, and it is probable that an economic resource will be required to settle this liability.
| 3.2.27. | Government grants and assistance |
Government grants and assistance are recognized at fair value when it is reasonably certain that the conditions established by the granting Governmental Authority were observed and that these subsidies will be obtained. These are recorded as revenue or expense deduction in the income statement for the period of enjoyment of benefit and subsequently are allocated to the tax incentives reserve under shareholders’ equity.
| 3.2.28. | Dividend and interest on own capital |
The distribution of dividends or interest on shareholders’ equity is recognized as a liability, calculated based on Corporate Law, the bylaws and the Company’s Dividend Policy, which establishes that the minimum annual dividend is the lowest amount between (i) 25% of adjusted net income or (ii) the consolidated operating cash flow for the year and, provided they are declared before the end of the year. Any portion in excess of the minimum mandatory dividends, if declared after the balance sheet date, must be recorded under the additional dividends proposed in shareholders’ equity, until approved by the shareholders at the General Assembly. After approval, reclassification to current liabilities is made.
The tax benefit of interest on equity is recognized in the income statement.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
Common shares are classified under shareholders’ equity. Incremental costs directly attributable to a public offer are stated under shareholders’ equity as a deduction from the amount raised, net of taxes.
In 2019, the Company reclassified the share issuance costs from capital reserve to share capital.
| 3.2.30. | Revenue recognition |
Revenue from contracts with customers are recognized as at which the products to customers transfer of control, represented by the ability to determine the use of products and obtain substantially all the remaining benefits from the products.
The Company follows the five-step model: (i) identification of contracts with customers; (ii) identification of performance obligations under contracts; (iii) determining the transaction price; (iv) allocation of the transaction price to the performance obligation provided for in the contracts and (v) recognition of revenue when the performance obligation is met.
For operating segment Pulp, revenue recognition is based on the parameters provided by (i) International Commercial Terms (“Incoterms”), when destined for the foreign market and (ii) lead time, when destined for the internal market.
For operating segment Paper and Consumer Goods, revenue recognition is based on the parameters provided by (i) the corresponding International Commercial Terms (“Incoterms”) and (ii) lead time and are products destined for external and internal market.
Are measured at the fair value of the consideration received or receivable, net of taxes, returns, rebates and discounts and recognized in accordance with the accrual basis of accounting, when the amount is reliably measured.
Accumulated experience is used to estimate and provide for the rebates and discounts, using the expected value method, and revenue is only recognized to the extent that it is highly probable that a significant reversal will not occur. A refund liability (included in trade accounts receivable) is recognized for expected rebates and discounts payable to customers in relation to sales made until the end of the reporting period. No significant element of financing is deemed present as the sales are made with a short credit term.
| 3.2.31. | Financial income and expenses |
Include interest income on financial assets, at the effective interest rate that includes the amortization of funding raising costs, gains and losses on derivative financial instruments, interest on loans and financing, exchange variations on loans and financing and other assets and financial liabilities and monetary variations on other assets and liabilities. Interest income and expenses are recognized in the income statement using the effective interest method.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 3.2.32. | Earnings (losses) per share |
Basic earnings (losses) per share are calculated by dividing the net profit (loss) attributable to the holders of ordinary shares of the Company by (losses) the weighted average number of ordinary shares during the year.
Diluted earnings per share are calculated by dividing the net profit (loss) attributable to the holders of ordinary shares of the Company by the weighted average number of ordinary shares, during the year, plus the weighted average number of ordinary shares that would be issued when converting all dilutive potential ordinary shares into ordinary shares.
| 3.2.33. | Employee and management profit sharing |
Employees are entitled to profit sharing based on certain goals agreed annually. For the Administrators, the statutory provisions proposed by the Board of Directors and approved by the shareholders are used as a basis. Provisions for participation are recognized in the administrative expense, during the period in which the targets are attained.
| 3.2.34. | Accounting judgments, estimates and assumptions |
As disclosed in note 2, Management used judgments, estimates and accounting assumptions regarding the future, whose uncertainty may lead to results that require a significant adjustment to the book value of certain assets, liabilities, income and expenses in future years, are presented below:
| • | control, significant influence and consolidation (Note 1.1); |
| • | share-based payment transactions (Note 22); |
| • | transfer to control for revenue recognition (Note 28); |
| • | fair value of financial instruments (Note 4); |
| • | annual analysis of the impairment of non-financial assets (Notes 15 and 16); |
| • | expected credit losses (Note 7); |
| • | net realizable value provision for inventories (Note 8); |
| • | annual analyses of recoverability of taxes (Notes 9 e 12); |
| • | fair value of biological assets (Note 13); |
| • | useful life of property, plant and equipment and intangible assets with defined useful life (Notes 15 and 16); |
| • | annual analysis recoverable amount of goodwill (Note 16); |
| • | provision for legal liabilities (Note 20); |
| • | pension and post-employment plans (Note 21); |
The Company reviews the estimates and underlying assumptions used in its accounting estimates on annual basis. Revisions to accounting estimates are recognized in the period in which the estimates are revised.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 3.3. | New standards, revisions and interpretations not yet in force |
The new and changed standards and interpretations issued, but not yet in force until the issuance of the Company’s consolidated financial statements, are described below. The Company intends to adopt these new standards, changes and interpretations, if applicable, when it come into force and does not expect to have a material impact on the financial statements.
3.3.1. Interest Rate Reform – IAS 39 / IFRS 7 and IFRS 9 - Phase 2 (Applicable on / or after January 1, 2021, early adoption permitted)
In continuity with that disclosed in note 3.1.6 about phase 2, it is summarized as follows:
| (i) | changes in contractual cash flows: Practical expedient that allows to replace, as a consequence of the reform, the effective interest rate of a financial asset or financial liability with a new economically equivalent rate, without derecognition of the contract; |
| (ii) | hedge accounting requirements: End of exemptions for evaluating the effectiveness of hedge accounting relationships (Phase 1); and |
| (iii) | disclosure: Requirements about the disclosure of risks to which the entity is exposed by the reform, risk management and evolution of the IBORs transition. |
The Company assessed the phase 2 amendments and does not expect to have significant impacts on its debts and derivatives linked to LIBOR (note 4.4.2).
3.3.2. IAS 37 - Onerous contracts: Cost to fulfill an onerous contract (Applicable for annual periods on/or after January 1, 2022, early adoption permitted)
The amendments to IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets clarify what “costs to fulfill a contract” represent when a onerous contract is assessed. Some entities that apply the “incremental cost” approach may have the value of their provisions increased, or new provisions recognized for onerous contracts as a result of the new definition.
The need for clarification was caused by the introduction of IFRS 15, which replaced the existing requirements related to revenue, including guidelines contained in IAS 11, which dealt with construction contracts. While IAS 11 specified which costs were included as costs to fulfill a contract, IAS 37 did not do, generating a diversity of practice. The amendment aims to clarify which costs should be included in the assessment.
3.3.3. Property, plant and equipment - IAS 16 – Revenue earned before an asset is ready for its intended use (Applicable for annual periods beginning on/or after January 1, 2022, early adoption permitted)
In the process of building an item of property, plant and equipment for its intended use, an entity may in the same time produce and sell products generated in the process of construction of the item of property, plant and equipment. Before the change proposed by the IASB, in practice, several ways of accounting for such revenues were found. The IASB has amended the standard to provide guidance on accounting for such revenues and related production costs.
With the new proposal, the sale revenue is no longer deducted from the cost of property, plant and equipment, but is recognized in the income statement together with the production costs of these items. IAS 2 Inventories must be applied in the identification and measurement of production costs.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 3.3.4. | Business Combination IFRS 3 - Reference to the conceptual framework |
The amendments update IFRS 3 so that it refers to the 2018 Conceptual Framework instead of the 1989 Structure. It also include in IFRS 3 the requirement that, for obligations within the scope of IAS 37, the buyer applies IAS 37 to determine whether there is a present obligation on the acquisition date due to past events. For a tax within the scope of IFRIC 21 - Levies, the buyer applies IFRIC 21 to determine whether the event that resulted in the obligation to pay the tax occurred up to the date of acquisition.
The amendments add an explicit statement that the buyer does not recognize contingent assets acquired in a business combination.
The changes are applicable to business combinations whose acquisition date occurs on or after the beginning of the first reporting period beginning on/or after January 1, 2022. Early adoption is permitted if the entity also adopts all other updated references (published together with the updated Conceptual Framework) on the same date or earlier.
3.3.5. Presentation of the financial statements – IAS 1 – Classification of liabilities as current and non-current (Applicable for annual periods beginning on/or after January 1, 2023, early adoption permitted)
The amendments to IAS 1 affect only the presentation of liabilities as current or non-current in the balance sheet and not the amount or the time of recognition of any asset, liability, income or expense, or the information disclosed about these items.
The amendments clarify that the classification of liabilities as current or non-current is based on the rights existing at the balance sheet date, specify that the classification is not affected by expectations about whether an entity will exercise its right to postpone the settlement of the liability, explain that the rights exist if restrictive clauses are complied with at the balance sheet date, and introduce the definition of ‘settlement’ to clarify that refers to the transfer to a counterparty; a cash value, equity instruments, other assets or services.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
4. FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS AND RISKS MANAGEMENT
| 4.1. | Financial risks management |
The Company’s Financial Policies were reviewed and approved at the Board of Directors’ meeting held on August 13, 2020. During the review (i) a new Financial Risk Management Policy, which includes concepts, roles and general limits applicable to all other policies was prepared (ii) a new Counterparty and Issuer Risk Policy was prepared (iii) the Debt, Derivative and Cash Management Policies was revised. The purpose of this review is to improve the governance of financial issues and clarify the understanding of concepts and rules by the different target groups for these policies.
As a result of its activities, the Company is exposed to several financial risks, the main factors considered by management are set forth below:
| (v) | fluctuations of commodity prices; and |
The Management is focused on generating consistent and sustainable results over time, however, arising from external risk factors, unintended level of volatility can influence the Company’s cash flows and income statement.
The Company has policies and procedures for managing market risk which aims:
| (i) | reduce, mitigate or transfer exposure aiming to protect the Company’s cash flows and assets against fluctuations of market prices of raw material and products, exchange rates and interest rates, price and adjustment index (“market risk”) or other assets or instruments traded in liquid markets or not to which the value of the assets, liabilities and cash flows are exposed; |
| (ii) | establish limits and instruments with the purpose of allocating the Company’s cash within acceptable credit risk exposure parameters of financial institutions; and |
| (iii) | optimize the process of hiring financial instruments for protection against exposure to risk, drawing on natural hedges and correlations between the prices of different assets and markets, avoiding any waste of funds used to hiring inefficient transactions. All financial transactions entered into by the Company aim to protect existing exposures, with the assumption of new risks prohibited, except those arising from its operating activities. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
Hedging instruments are hired exclusively for hedging purposes and are based on the following terms:
| (i) | cash flow protection against currency mismatch; |
| (ii) | revenue flow protection for debt settlement and interest to fluctuation of interest rate and currencies; and |
| (iii) | fluctuation in pulp price and other supplies related to production. |
Treasury team is responsible for identification, evaluating and seeking protection against possible financial risk. Board of Directors approves the financial policies that establish the principles and guidance for global risk management, the areas involved in these activities, the use of derivative and non-derivative financial instruments and the allocation of cash surplus.
The Company uses the most liquid financial instruments, and:
| (i) | does not hired leveraged transactions or with other forms of embedded options that change its purpose of protection (hedge); |
| (ii) | does not have double indexed debt or other forms of implied options; and |
| (iii) | does not have any transaction that require margin deposits or other forms of collateral for counterparty credit risk. |
The Company does not adopt hedge accounting. Therefore, gains and losses from derivative operations are fully recognized in the statements of income, as disclosed in Note 27.
All transactions with financial instruments are recognized for accounting purposes and classified in the following categories:
| | | Note | | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amortized cost | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 5 | | | | 6,835,057 | | | | 3,249,127 | |
| Trade accounts receivable | | | 7 | | | | 2,915,206 | | | | 3,035,817 | |
| Other assets | | | | | | | 974,265 | | | | 563,993 | |
| | | | | | | | 10,724,528 | | | | 6,848,937 | |
| Fair value through other comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other investments | | | 14 | | | | 26,338 | | | | 20,048 | |
| | | | | | | | 26,338 | | | | 20,048 | |
| Fair value through profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | 4.5.1 | | | | 1,341,420 | | | | 1,098,972 | |
| Marketable securities | | | 6 | | | | 2,396,857 | | | | 6,330,334 | |
| | | | | | | | 3,738,277 | | | | 7,429,306 | |
| | | | | | | | 14,489,143 | | | | 14,298,291 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amortized cost | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans, financing and debentures | | | 18.1 | | | | 72,899,882 | | | | 63,684,326 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | 19.2 | | | | 5,191,760 | | | | 3,984,070 | |
| Liabilities for assets acquisitions and subsidiaries | | | 23 | | | | 502,228 | | | | 541,615 | |
| Trade accounts payable | | | 17 | | | | 2,361,098 | | | | 2,376,459 | |
| Other liabilities | | | | | | | 459,684 | | | | 578,061 | |
| | | | | | | | 81,414,652 | | | | 71,164,531 | |
| Fair value through profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | 4.5.1 | | | | 8,117,400 | | | | 2,917,913 | |
| | | | | | | | 8,117,400 | | | | 2,917,913 | |
| | | | | | | | 89,532,052 | | | | 74,082,444 | |
| | | | | | | | 75,042,909 | | | | 59,784,153 | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 4.1.3. | Fair value of loans and financing |
The financial instruments are recognized at their contractual amounts. Derivative financial instrument agreements, used exclusively for hedging purposes, are measured at fair value.
In order to determine the market values of financial instruments traded in public and liquid markets, the market closing prices were used at the balance sheet dates. The fair value of interest rate and indexes swaps is calculated as the present value of their future cash flows discounted at the current interest rates available for operations with similar remaining terms and maturities. This calculation is based on the quotations of B3 and ANBIMA for interest rate transactions in Brazilian Reais and the British Bankers Association and Bloomberg for London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”) rate transactions. The fair value of forward or forward exchange agreements is determined using the forward exchange rates prevailing at the balance sheet dates, in accordance with B3 prices.
In order to determine the fair value of financial instruments traded in over-the-counter or unliquidated markets, a number of assumptions and methods based on normal market conditions and not for liquidation or forced sale, are used at each balance sheet date, including the use of option pricing models such as Garman-Kohlhagen, and estimates of discounted future cash flows. The fair value of agreements for the fixing of oil bunker prices is obtained based on the Platts index.
The result of the trading of financial instruments is recognized at the closing or hiring dates, where the Company undertakes to buy or sell these instruments. The obligations arising from the hiring of financial instruments are eliminated from our financial statements only when these instruments expire or when the risks, obligations and rights arising there from are transferred.
The estimated fair values of loans and financing are set forth below:
| | | Yield used
to discount | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Quoted in the secondary market | | | | | | | | | | |
| In foreign currency | | | | | | | | | | |
| Bonds | | Secondary Market | | | 43,703,482 | | | | 30,066,087 | |
| Estimated to present value | | | | | | | | | | |
| In foreign currency | | | | | | | | | | |
| Export credits (“Pre-payment”) | | LIBOR | | | 20,546,778 | | | | 17,213,963 | |
| Export credits (“ACC/ACE”) | | DDI | | | | | | | 575,521 | |
| In local currency | | | | | | | | | | |
| BNP – Forest Financing | | DI 1 | | | | | | | 193,646 | |
| BNDES – TJLP | | DI 1 | | | 1,399,177 | | | | 1,895,959 | |
| BNDES – TLP | | DI 1 | | | 647,235 | | | | 535,812 | |
| BNDES – Fixed | | DI 1 | | | 76,732 | | | | 113,979 | |
| BNDES – Selic (“Special Settlement and Custody System”) | | DI 1 | | | 960,215 | | | | 693,969 | |
| BNDES - Currency basket | | DI 1 | | | 27,239 | | | | 54,420 | |
| CRA (“Agribusiness Receivables Certificate”) | | DI 1/IPCA | | | 3,286,792 | | | | 6,039,983 | |
| Debentures | | DI 1 | | | 5,498,793 | | | | 5,534,691 | |
| FINAME (“Special Agency of Industrial Financing”) | | DI 1 | | | | | | | 14,168 | |
| FINEP (“Financier of Studies and Projects”) | | DI 1 | | | | | | | 5,138 | |
| NCE (“Export Credit Notes”) | | DI 1 | | | 1,322,813 | | | | 1,445,383 | |
| NCR (“Rural Credit Notes”) | | DI 1 | | | 283,702 | | | | 288,122 | |
| Export credits (“Pre-payment”) | | DI 1 | | | 1,490,242 | | | | 1,464,798 | |
| FDCO (“West Center Development Fund”) | | DI 1 | | | | | | | 571,904 | |
| | | | | | 79,243,200 | | | | 66,707,543 | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The Management considers that for its other financial liabilities measured at amortized cost, its book values approximate to their fair values and therefore the information on their fair values is not being presented.
The Company’s guidance is to maintain a strong cash and marketable securities position to meet its financial and operating obligations. The amount kept as cash is used for payments expected in the normal course of its operations, while the cash surplus amount is invested in highly liquid financial investments according Cash Management Policy.
The cash position is monitored by the Company’s senior management, by means of management reports and participation in performance meetings with determined frequency. In the year ended December 31, 2020, the impacts in cash and marketable securities were as expected and the Company believes that, even with the impact of the devaluation of the real against the U.S. Dollars caused by the pandemic of COVID-19, payments of derivative instruments that matured in this period were offset by higher generation of operating cash.
As material fact disclosed to the market on February 14, 2020, the Company, voluntarily prepaid the principal amount of U.S.$750,000 (equivalent, on the transaction date, to R$3,240,229), related to an export prepayment, with quarterly interest payments of 1.15% p.a. plus quarterly LIBOR, which was scheduled to mature in February 14, 2023. At the same time, the Company entered into a new transaction related to an export prepayment in the amount of U.S.$850,000 (equivalent, on the transaction date, to R$3,672,259), of 1.15% p.a. plus quarterly LIBOR, which was scheduled to mature in February 13, 2026. Furthermore, as material fact disclosed to the market on February 28, 2020, the Company through its wholly-owned subsidiary Suzano Trading Ltd. (“Suzano Trading”) exercised its right to redeem all of the outstanding aggregate principal amount of the 5.875% p.a. senior notes issued by it and guaranteed by Suzano due January 2021 (“2021 Notes”) currently outstanding, in the total aggregate principal amount of U.S.$189,630.
Such transactions were performed under market conditions, considered attractive by the Company, and even though they were carried out before the crisis caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, they were in line with the debt management strategy based on cost reduction and extension of the term portfolio, thus reinforcing our liquidity position.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
In line with the announcement to the market on March 30, 2020, there was a disbursement of U.S.$500,000 (equivalent to R$2,638,221 on the transaction date) of its revolving credit facility maintained with certain financial institutions, of 1.30% plus quarterly LIBOR and maturity in February 2024. The disbursement is in line with the preventive measures that the Company has been taking to mitigate eventual impacts resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic and to bring even more strength to the liquidity position of the Company. On August 13, 2020, the Company announcement the market that returned in advance this revolving credit facility and such resources are fully available as a source of additional liquidity for the Company, if necessary.
All derivatives financial instruments were in the over-the-counter derivatives and do not require deposit of guarantee margins.
The remaining contractual maturities of financial liabilities are disclosed at the date of this financial information reporting date. The amounts as set forth below, consist in the undiscounted cash flows and include interest payments and exchange rate variation, and therefore may not be reconciled with the amounts disclosed in the balance sheet.
| | | December 31, 2020 | |
| | | Total book
value | | | Total future
value | | | Up to 1
year | | | 1 - 2
years | | | 2 - 5
years | | | More than
5 years | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade accounts payables | | | 2,361,098 | | | | 2,361,098 | | | | 2,361,098 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans, financing and debentures (1) | | | 72,899,882 | | | | 101,540,320 | | | | 4,034,595 | | | | 6,619,518 | | | | 36,751,023 | | | | 54,135,184 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | 5,191,760 | | | | 9,552,075 | | | | 620,177 | | | | 806,560 | | | | 2,198,419 | | | | 5,926,919 | |
| Liabilities for asset acquisitions and subsidiaries | | | 502,228 | | | | 573,920 | | | | 116,376 | | | | 112,155 | | | | 253,419 | | | | 91,970 | |
| Derivative financial instruments (1) | | | 8,117,400 | | | | 10,868,858 | | | | 1,999,811 | | | | 1,296,199 | | | | 4,133,320 | | | | 3,439,528 | |
| Other liabilities | | | 459,684 | | | | 459,684 | | | | 360,916 | | | | 98,768 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 89,532,052 | | | | 125,355,955 | | | | 9,492,973 | | | | 8,933,200 | | | | 43,336,181 | | | | 63,593,601 | |
| 1) | The variation is due to the increase in the exchange rate variation in the year ended December 31, 2020. |
| | | December 31, 2019 | |
| | | Total book
value | | | Total future
value | | | Up to 1
year | | | 1 - 2
years | | | 2 - 5
years | | | More than
5 years | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade accounts payables | | | 2,376,459 | | | | 2,376,459 | | | | 2,376,459 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans, financing and debentures | | | 63,684,326 | | | | 89,708,210 | | | | 8,501,278 | | | | 5,692,149 | | | | 29,088,292 | | | | 46,426,491 | |
| Lease liabilities | | | 3,984,070 | | | | 7,109,966 | | | | 559,525 | | | | 1,426,011 | | | | 1,186,386 | | | | 3,938,044 | |
| Liabilities for asset acquisitions and subsidiaries | | | 541,615 | | | | 618,910 | | | | 103,132 | | | | 101,149 | | | | 315,989 | | | | 98,640 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | 2,917,913 | | | | 8,299,319 | | | | 1,488,906 | | | | 415,791 | | | | 1,258,200 | | | | 5,136,422 | |
| Other liabilities | | | 578,061 | | | | 578,061 | | | | 456,338 | | | | 121,723 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 74,082,444 | | | | 108,690,925 | | | | 13,485,638 | | | | 7,756,823 | | | | 31,848,867 | | | | 55,599,597 | |
| 4.3. | Credit risk management |
It is related to the possibility of non-compliance with the counterparty commitment in an operation. Credit risk is managed on a group and arises from cash equivalents, marketable securities, derivative financial instruments, bank deposits, Bank Deposit Certificates (“CDB”), fixed income box, repurchase agreements, letters of credit, insurance, receivable terms of customers, advances to suppliers for new projects, among others.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 4.3.1. | Trade accounts receivable and advances to supplier |
As a result of the crisis caused by COVID-19, the Company started to accept requests for the extension of customer invoices, limiting these postponements to those invoices close to maturity, with due interest charges. However, in July 2020, the Company began to receive fewer requests for extensions, returning to levels prior to the crisis.
Most of the customers who requested extension are related to the domestic market in the paper segment and do not represent a significant amount compared to the Company’s total accounts receivable.
The internal analyzes and credit metrics do not demonstrate that these delays may have a significant impact on the Company’s liquidity position. There was also an increase in delays in Latin America, however, for this region, the Company has credit insurance policies that mitigate most of the risks arising from the default of its customers.
The Company has commercial and credit policies aimed at mitigating any risks arising from its customers’ default, mainly through hiring of credit insurance policies, bank guarantees provided by first-tier banks and collaterals according to liquidity. Moreover, portfolio customers are subject to internal credit analysis aimed at assessing the risk regarding payment performance, both for exports and for domestic sales.
For customer credit assessment, the Company applies a matrix based on the analysis of qualitative and quantitative aspects to determine individual credit limits to each customer according to the identified risk. Each analyze is submitted for approval according to established hierarchy and, if applicable, to approval from the Management’s meeting and the Credit Committee.
The risk classification of trade accounts receivable is set forth below:
| | | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Low (1) | | | | 2,813,038 | | | | 2,775,364 | |
| Average (2) | | | | 54,115 | | | | 168,836 | |
| High (3) | | | | 89,942 | | | | 133,613 | |
| | | | | 2,957,095 | | | | 3,077,813 | |
| 1) | Current and overdue to 30 days. |
| 2) | Overdue between 30 and 90 days. |
| 3) | Overdue more than 90 days. |
Part of the amounts above does not consider the expected credit losses calculated based on the provision matrix of R$41,889 and R$41,996 as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 4.3.2. | Banks and financial institutions |
The Company, in order to mitigate credit risk, maintains its financial operations diversified among banks, with a main focus on first-tier financial institutions classified as high-grade by the main risk rating agencies.
The book value of financial assets representing the exposure to credit risk is set forth below:
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 6,835,057 | | | | 3,249,127 | |
| Marketable securities | | | 2,396,857 | | | | 6,330,334 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | 986,526 | | | | 830,426 | |
| | | | 10,218,440 | | | | 10,409,887 | |
The counterparties, substantially financial institutions, in which transactions are performed classified under cash and cash equivalents, marketable securities and derivatives financial instruments, are rated by the rating agencies. The risk rating is set forth below:
| | | Cash and cash equivalents and
marketable securities | | | Derivative financial instruments | |
| | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Risk rating (1) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| AAA | | | | | | | 190,360 | | | | 17,412 | | | | | |
| AA- | | | | | | | 56,388 | | | | 417,510 | | | | | |
| A+ | | | | | | | 606,757 | | | | 1,617 | | | | 27,363 | |
| A | | | | | | | 188,458 | | | | 73,135 | | | | 165,851 | |
| A- | | | | | | | 211,238 | | | | 130,546 | | | | 222,761 | |
| brAAA | | | 7,704,501 | | | | 7,153,079 | | | | 305,311 | | | | 404,693 | |
| brAA+ | | | 163,955 | | | | 745,177 | | | | 32 | | | | 9,758 | |
| brAA | | | 836,546 | | | | 372,188 | | | | 40,963 | | | | | |
| brAA- | | | 278,712 | | | | 23,050 | | | | | | | | | |
| brA | | | 240,382 | | | | 17,847 | | | | | | | | | |
| Others | | | 7,818 | | | | 14,919 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 9,231,914 | | | | 9,579,461 | | | | 986,526 | | | | 830,426 | |
| 1) | We use the Brazilian Risk Rating and the rating is given by agencies Fitch Ratings, Standard & Poor’s and Moody’s. |
| 4.4. | Market risk management |
The Company is exposed to several market risks, mainly, related to fluctuations in exchange rate variation, interest rates, inflation rates and commodity prices that may affect its results and financial situation.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
To mitigate the impacts, the Company has processes to monitor exposures and policies that support the implementation of risk management.
The policies establish the limits and the instruments to be implemented for the purpose of:
| (i) | protecting cash flow due to currency mismatch; |
| (ii) | mitigating exposure to interest rates; |
| (iii) | reducing the impacts of fluctuation in commodity’s prices; and |
| (iv) | change of debt indexes. |
The market risk management comprises the identification, the assessment and the implementation of the strategy, with the effective hiring of adequate financial instruments.
| 4.4.1. | Exchange rate risk management |
The fundraising financing and the currency hedge policy of the Company are guided considering substantial part of net revenue arises from exports with prices negotiated in U.S.Dollar, while substantial part of the production costs is attached to the Brazilian Real. This structure allows the Company to hired export financing in U.S.Dollar and to reconcile financing payments with the cash flows of receivables from sales in foreign market, using the international bond market as an important portion of its capital structure, and providing a natural cash hedge for these commitments.
Moreover, the Company hires U.S.Dollar selling transactions in the futures markets, including strategies involving options, to ensure attractive levels of operating margins for a portion of revenue. Such transactions are limited to a percentage of the net surplus foreign currency over an 18-months’ time horizon and therefore, are matched to the availability of currency for sale in the short term.
The net exposure of assets and liabilities in foreign currency which is substantially in U.S. Dollars, is set forth below:
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 6,370,201 | | | | 2,527,834 | |
| Trade accounts receivables | | | 1,938,614 | | | | 2,027,018 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | 621,385 | | | | 9,440,141 | |
| | | | 8,930,200 | | | | 13,994,993 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | |
| Trade accounts payables | | | (492,617 | ) | | | (1,085,207 | ) |
| Loans and financing | | | (58,145,087 | ) | | | (45,460,138 | ) |
| Liabilities for asset acquisitions and subsidiaries | | | (313,022 | ) | | | (288,172 | ) |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | (6,994,363 | ) | | | (11,315,879 | ) |
| | | | (65,945,089 | ) | | | (58,149,396 | ) |
| Net liability exposure | | | (57,014,889 | ) | | | (44,154,403 | ) |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 4.4.1.1. | Sensitivity analysis – foreign exchange rate exposure – except financial instruments derivatives |
For market risk analysis, the Company uses scenarios to jointly evaluate assets and liabilities positions in foreign currency, and the possible effects on its results. The probable scenario represents the amounts recognized, as they reflect the translation into Brazilian Reais on the base date of the balance sheet (R$ to U.S.$ = R$5.1967).
This analysis assumes that all other variables, particularly, the interest rates, remains constant. The other scenarios considered the appreciation/depreciation of the Brazilian real against the U.S.$. at the rates of 25% and 50%, before taxes.
The following table set forth the potential impacts in absolute amounts:
| | | December 31, 2020 | |
| | | | Effect on profit or loss and equity | |
| | | | Probable (base value) | | | | Possible (25%) | | | | Remote (50%) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 6,370,201 | | | | 1,592,550 | | | | 3,185,101 | |
| Trade accounts receivable | | | 1,938,614 | | | | 484,654 | | | | 969,307 | |
| Trade accounts payable | | | (492,617 | ) | | | (123,154 | ) | | | (246,309 | ) |
| Loans and financing | | | (58,145,087 | ) | | | (14,536,272 | ) | | | (29,072,544 | ) |
| Liabilities for asset acquisitions and subsidiaries | | | (313,022 | ) | | | (78,256 | ) | | | (156,511 | ) |
| 4.4.1.2. | Sensitivity analysis – foreign exchange rate exposure – financial instruments derivatives |
The Company contracts sales operations of U.S. Dollar in the futures markets, including strategies with options, in order to ensure attractive levels of operating margins for a portion of revenue. These operations are limited to a percentage of the net foreign exchange surplus over the 18-month horizon and, therefore, are attached to the availability of ready-to-sell foreign exchange in the short term.
Due to pandemic COVID-19 and the effects on all global economies over the past 12 months, financial markets have experienced volatility throughout the period with a strong sense of aversion to risk, with a consequent substantial devaluation of the Real against the U.S. Dollars.
For the calculation of mark-to-market (“MtM”) the PTAX of the penultimate business day of the quarter was used, in December 2019 it was R$4.0307 and in December 2020 it was R$5.1967, with an increase of 29%. These market movements caused a negative impact on the mark-to-market hedge position entered by the Company.
This analysis assumes that all other variables, particularly, the interest rates, remains constant. The other scenarios considered the appreciation/depreciation of the Brazilian real against the U.S.$. at the rates of 25% and 50%, before taxes, from the base scenario of December 31, 2020.
It is important to mention that the impact caused by fluctuations in the exchange rate, whether positive or negative, will also affect the hedged asset. Therefore, even though there was a negative impact on the fair value of derivative transactions in the year due to the COVID-19 pandemic, this impact was partially offset by the positive effect on the Company’s cash flow. In addition, considering that hedge contracts are limited by the policy in a maximum of 75% of the total exposure in U.S. Dollars, the exchange rate devaluation will always benefit, in a net way, the Company’s cash generation in the long run.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The following table set forth the potential impacts assuming these scenarios:
| | | December 31, 2020 | |
| | | | Effect on profit or loss and equity | |
| | | | Probable (base value) | | | | Possible (+25%) | | | | Remote
(+50%) | | | | Possible (-25%) | | | | Remote (-50%) | |
| | | | 5.1967 | | | | 6.4959 | | | | 7.7951 | | | | 3.8975 | | | | 2.5984 | |
| Financial instruments derivatives | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivative Non-Deliverable Forward (‘NDF’) | | | 7,948 | | | | (102,756 | ) | | | (205,512 | ) | | | 102,756 | | | | 205,512 | |
| Derivative options | | | (780,896 | ) | | | (3,386,080 | ) | | | (7,232,365 | ) | | | 3,253,805 | | | | 7,301,982 | |
| Derivative swaps | | | (6,503,859 | ) | | | (4,436,537 | ) | | | (8,873,083 | ) | | | 4,436,554 | | | | 8,873,100 | |
| 4.4.2. | Interest rate risk management |
Fluctuations in interest rates may imply effects of increased or reduced costs on new loans and operations already contracted.
The Company is constantly looking for alternatives for the use of financial instruments in order to avoid negative impacts on its cash flow.
Considering the extinction of LIBOR over the next few years, the Company is evaluating its contracts with clauses that envisage the discontinuation of the interest rate. Most debt contracts linked to LIBOR have some clause to replace this rate with a reference index or equivalent interest rate and, for contracts that do not have a specific clause, a renegotiation will be carried out between the parties. Derivative contracts linked to LIBOR provide for a negotiation between the parties for the definition of a new rate or an equivalent rate will be provided by the calculation agent.
It is worth mentioning that the clauses related to replacement of the indexes in the Company’s debt contracts indexed to LIBOR, establish that any replacement of the indexation rate in the contracts can only be evaluated in two circumstances (i) after the communication from an official government entity with formalization of the replacement/extinguishment of the effective rate of the contract, and this communication must define the exact date on which LIBOR will be extinguished and / or (ii) syndicated operations begin to be executed at a rate indexed to the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (“SOFR”). Therefore, the negotiation of debt contracts and its related derivatives will be started after these events.
The Company has mapped all contracts subject to IBOR reform that have yet to transition to an alternative benchmark rate and as of December 31, 2020 the Company has R$20,118,831 related to loan and financing contracts and R$1,567,520 related to derivative contracts and so far, it awaits the event of official extinction of LIBOR to start negotiating its contracts with counterparties.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The Company understands that it will not be necessary to change the risk management strategy due to the change in the indexes of the financial contracts linked to LIBOR.
The Company believes it is reasonable to assume that the negotiation of the indexes in its contracts, when the official trigger allows, will move towards to the replacement of LIBOR by SOFR, because the available information indicates that SOFR will be the new interest rate adopted by the capital market. Based on the information available, the Company does not expect to have significant impact on its debts and derivatives linked to LIBOR.
| 4.4.2.1. | Sensitivity analysis – exposure to interest rates – except financial instruments derivatives |
For market risk analysis, the Company uses scenarios to evaluate the sensitivity that variations in operations impacted by the rates: Interbank Deposit Rate (“CDI”), Long Term Interest Rate (“TJLP”), Special System for Settlement and Custody (“SELIC”) and the London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”) which may impact the results. The probable scenario represents the amounts already booked, as they reflect the best estimate of the Management.
This analysis assumes that all other variables, particularly exchange rates, remain constant. The other scenarios considered appreciation/depreciation of 25% and 50% in the market interest rates.
The following table set forth the potential impacts in absolute amounts:
| | | December 31, 2020 | |
| | | | Effect on profit or loss and equity | |
| | | | Probable | | | | Possible (25%) | | | | Remote (50%) | |
| CDI/SELIC | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 115,032 | | | | 546 | | | | 1,093 | |
| Marketable securities | | | 2,396,857 | | | | 11,385 | | | | 22,770 | |
| Loans and financing | | | 9,715,511 | | | | 46,149 | | | | 92,297 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| TJLP | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans and financing | | | 1,553,635 | | | | 17,673 | | | | 35,345 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| LIBOR | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans and financing | | | 18,923,543 | | | | 11,277 | | | | 22,555 | |
| 4.4.2.2. | Sensitivity analysis – exposure to interest rates – financial instruments derivatives |
This analysis assumes that all other variables remain constant. The other scenarios considered appreciation/depreciation of 25% and 50% in the market interest rates.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The following table set forth the potential impacts assuming these scenarios:
| | | December 31, 2020 | |
| | | | Effect on profit or loss and equity | |
| | | | Probable | | | | Probable
(+25%) | | | | Remote
(+50%) | | | | Probable
(-25%) | | | | Remote (-50%) | |
| CDI | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial instruments derivatives | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivative Non-Deliverable Forward (‘NDF’) | | | 7,948 | | | | (2,409 | ) | | | (4,786 | ) | | | 2,442 | | | | 4,916 | |
| Derivative options | | | (780,896 | ) | | | (43,105 | ) | | | (85,545 | ) | | | 43,800 | | | | 88,323 | |
| Derivative swaps | | | (6,503,859 | ) | | | (22,941 | ) | | | (45,441 | ) | | | 23,367 | | | | 47,086 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| LIBOR | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial instruments derivatives | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivative swaps | | | (6,503,859 | ) | | | 45,349 | | | | 90,699 | | | | (45,364 | ) | | | (90,726 | ) |
| 4.4.2.3. | Sensitivity analysis for changes in the consumer price index of the US economy |
For the measurement of the probable scenario, the United States Consumer Price Index (US-CPI) was considered on December 31, 2020. The probable scenario was extrapolated considering an appreciation/depreciation of 25% and 50% in the US-CPI to define the possible and remote scenarios, respectively, in absolute amounts.
| | | December 31, 2020 | |
| | | Impact of an increase/decrease of
US-CPI on the fair value | |
| | | Probable (base value) | | | Possible (25%) | | | Remote (50%) | |
| | | | 2.16 | % | | | 2.70 | % | | | 3.24 | % |
| Embedded derivative in forestry partnership and standing wood supply agreements | | | 354,900 | | | | (158,373 | ) | | | (324,287 | ) |
| 4.4.3. | Commodity price risk management |
The Company is exposed to commodity prices that reflect mainly on the pulp sale price in the foreign market. The dynamics of opening and closing production capacities in the global market and the macroeconomic conditions may have an impact on the Company´s operating results.
Through a specialized team, the Company monitors the pulp price and analyses future trends, adjusting the forecast that aims to assisting preventive measures to properly conduct the different scenarios. There is no liquid financial market to sufficiently mitigate the risk of a material portion of the Company’s operations. Pulp price protection operations available on the market have low liquidity and low volume and large distortion in price formation. No relevant changes were observed in relation to pulp prices and future markets related to this index due to the crisis caused by the pandemic of COVID-19.
The Company is also exposed to international oil prices, which is reflected on logistical costs for selling to the export market. In this case, the Company assess, when comprehend necessary, hiring derivative financial instruments to set marine fuel price. The crisis caused by the COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted the global demand for oil and its derivatives, which caused a substantial devaluation of the prices of these assets in the spot and future markets, during the first quarters of 2020. In this context, and considering attractive market conditions, the Company increased its marine fuel hedge position in line with its hedge strategy and policies and set a good part of its exposure at levels below the estimated price levels for the 2020 budget.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
In the year ended December 31, 2020, the contracted position to hedge its logistics costs was purchased in the amount of US$37,757 (US$0.3645 as of December 31, 2019).
| 4.4.3.1. | Commodity price risk management |
This analysis assumes that all other variables, except price risk, remain constant. The other scenarios considered appreciation/depreciation of 25% and 50% of oil price in the market.
The following table set forth the potential impacts assuming these scenarios:
| | | December 31, 2020 | |
| | | Impact of an increase/decrease of price risk | |
| | | Probable (base value) | | | Possible (25%) | | | Remote (50%) | |
| VLSFO/Brent derivative | | | 15,759 | | | | 43,614 | | | | 87,227 | |
| 4.5. | Derivative financial instruments |
The Company determines the fair value of derivative contracts, which differ from the amounts realized in the event of early settlement due to bank spreads and market factors at the time of quotation. The amounts presented by the Company are based on an estimate using market factors and use data provided by third parties, measured internally and compared to calculations performed by external consultants.
Fair value does not represent an obligation for immediate disbursement or cash receipt, given that such effect will only occur on the dates of contractual fulfillment or on the maturity of each transaction, when the result will be determined, depending on the case and market conditions on the agreed dates.
A summary of the methodologies used for purposes of determining fair value by type of instrument is presented below:
| (i) | Swap: the future value of the asset and liability are estimated by the cash flows projected by the market interest rate of the currency in which the tip of the swap is denominated. The present value of the US dollar-denominated tip is measured using the discount using the exchange coupon curve (the remuneration, in US dollars, of the Reais invested in Brazil) and in the case of the BRL-denominated tip, the discount is made using Brazil’s interest curve, being the future curve of the DI, considering both the credit risk of the Company and the counterparty. The exception is pre-fixed contracts x US$ where the present value at the tip denominated in US$ is measured through the discount using the LIBOR curve, disclosed by Bloomberg. The fair value of the contract is the difference between these two points. Interest rate curves were obtained from B3. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| (ii) | Options (Zero Cost Collar): the fair value was calculated based on the Garman-Kohlhagen model, considering both Company’s and the counterparty credit risk. Volatility information and interest rates are observable and obtained from B3 exchange information to calculate the fair values. |
| (iii) | Non-deliverable forward (NDF): a projection of the future currency quote is made, using the exchange coupon curves and the future DI curve for each maturity. Next, it is verified the difference between this quotation obtained and the rate that was contracted for the operation, considering the credit risk of the Company and the counterparty. This difference is multiplied by the notional value of each contract and brought to present value by the future DI curve. Interest rate curves were obtained from B3. |
| (iv) | Swap US-CPI: liability cash flows are projected by the US inflation curve US-CPI, obtained by the implicit rates for inflation-linked US securities (“Treasury Protected against Inflation - TIPS”), disclosed by Bloomberg. Cash flows from the asset components are projected at the fixed rate implicit in the embedded derivative. The fair value of the embedded derivative is the difference between the two components, adjusted to present value by the curve of the exchange coupon obtained from B3. |
| (v) | Swap VLSFO/Brent (marine fuel): a future projection of the asset price is made, using the future price curve disclosed by Bloomberg. Next, it is verified the difference between this projection obtained and the rate that the operation was contracted, considering both of Company’s and counterpart’s credit risk. This difference is multiplied by the notional value of each contract and adjusted to present value by the LIBOR curve disclosed by Bloomberg. |
The yield curves used to calculate the fair value in December 31, 2020, are as set forth below:
| Interest rate curves | | |
| Term | | Brazil | | United States of America | | Dollar coupon | |
| 1 month | | 1.92 % p.a. | | 0.14 % p.a. | | 4.95 % p.a. | |
| 6 months | | 2.11 % p.a. | | 0.20 % p.a. | | 1.56 % p.a. | |
| 1 year | | 2.86 % p.a. | | 0.19 % p.a. | | 1.20 % p.a. | |
| 2 years | | 4.19 % p.a. | | 0.20 % p.a. | | 1.01 % p.a. | |
| 3 years | | 5.08 % p.a. | | 0.25 % p.a. | | 0.99 % p.a. | |
| 5 years | | 6.05 % p.a. | | 0.44 % p.a. | | 1.16 % p.a. | |
| 10 years | | 7.20 % p.a. | | 0.95 % p.a. | | 1.56 % p.a. | |
| | | | | | | | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 4.5.1. | Outstanding derivatives by type of contract, including embedded derivatives |
The positions of outstanding derivatives are set forth below:
| | | Notional value in U.S.$ | | | Fair value | |
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Instruments contracted with protection strategy | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operational Hedge | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Zero Cost Collar (1) | | | 3,212,250 | | | | 3,425,000 | | | | (780,457 | ) | | | 67,078 | |
| NDF (R$ x US$) | | | 80,000 | | | | | | | | 7,948 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Debt hedge | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate hedge | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Swap LIBOR to Fixed (U.S.$) (1) | | | 3,683,333 | | | | 2,750,000 | | | | (1,059,192 | ) | | | (444,910 | ) |
| Swap IPCA to CDI (notional in Reais) | | | 843,845 | | | | 843,845 | | | | 285,533 | | | | 233,255 | |
| Swap IPCA to Fixed (U.S.$) | | | 121,003 | | | | 121,003 | | | | (114,834 | ) | | | 30,544 | |
| Swap CDI x Fixed (U.S.$) (1) | | | 2,267,057 | | | | 3,115,614 | | | | (4,977,309 | ) | | | (1,940,352 | ) |
| Pre-fixed Swap to U.S.$ (U.S.$) | | | 350,000 | | | | 350,000 | | | | (508,328 | ) | | | (33,011 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Commodity Hedge | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Swap US-CPI standing wood (U.S.$) (2) | | | 646,068 | | | | 679,485 | | | | 354,900 | | | | 268,547 | |
| Swap VLSFO/Brent | | | 37,757 | | | | 365 | | | | 15,759 | | | | (92 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | (6,775,980 | ) | | | (1,818,941 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current assets | | | | | | | | | | | 484,043 | | | | 260,273 | |
| Non-current assets | | | | | | | | | | | 857,377 | | | | 838,699 | |
| Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | (1,991,118 | ) | | | (893,413 | ) |
| Non-current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | (6,126,282 | ) | | | (2,024,500 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | (6,775,980 | ) | | | (1,818,941 | ) |
| 1) | The variation is due to the increase in the exchange rate in the year ended December 31, 2020. |
| 2) | The embedded derivative refers to swap contracts for the sale of US-CPI variations within the term of the forest partnership and standing wood supply contracts. |
The current contracts and the respective protected risks are set forth below:
| (i) | Swap CDI x Fixed US$: positions in conventional swaps exchanging the variation in the Interbank Deposit rate (“DI”) for a fixed rate in United States Dollars (“US$”). The objective is to change the debt index in Reais to US$, in compliance with the Company’s natural exposure of receivables in US$. |
| (ii) | Swap IPCA x CDI: positions in conventional swaps exchanging variation of the Amplified Consumer Price Index (“IPCA”) for DI rate. The objective is to change the debt index in Reais, in compliance with the Company’s cash position in Reais, which is also indexed to DI. |
| (iii) | IPCA swap x Fixed US$: positions in conventional swaps exchanging variation of the IPCA for a fixed rate in US$. The objective is to change the debt index in Reais to US$, in compliance with the Company’s natural exposure of receivables in US$. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| (iv) | Swap LIBOR x Fixed US$: positions in conventional swaps exchanging post-fixed rate (LIBOR) for a fixed rate in US$. The objective is to protect the cash flow from changes in the US interest rate. |
| (v) | Pre Fixed Swap R$ x Fixed US$: positions in conventional swaps a fixed rate in Reais for a fixed rate in US$. The objective is to change the exposure of debts in Reais to US$, in compliance with the Company’s natural exposure of receivables in US$. |
| (vi) | Zero-Cost Collar: positions in an instrument that consists of the simultaneous combination of purchase of put options and sale of call options of US$, with the same principal and maturity value, with the objective of protecting the cash flow of exports. In this strategy, an interval is established where there is no deposit or receipt of financial margin on position adjustments. The objective is to protect the cash flow of exports against decrease Real. |
| (vii) | NDF - Non Deliverable Forward: positions sold in futures contracts of US$ with the objective of protecting the cash flow of exports against the decrease in the Real. |
| (viii) | Swap Very Low Sulphur Fuel Oil (“VLSFO”)/Brent(oil): oil purchase positions, with the objective of protecting logistical costs related to ocean freight contracts, against the increase in oil prices. |
| (ix) | Swap US-CPI: The embedded derivative refers to sale swap contracts of variations of US-CPI within the terms of the forest partnership and standing wood supply contracts. |
The COVID-19 pandemic negatively impacted the financial markets and, consequently, caused increased volatility throughout the year, devaluing the Real against the US Dollar by 40%, as previously mentioned. The variation in the fair value of derivatives for the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the fair value measured on December 31, 2019 is explained substantially by this significant devaluation of the local currency. There were also less significant impacts caused by the variation in the Pre, Foreign Exchange Coupon and LIBOR curves in transactions.
It is important to highlight that, the outstanding agreements in the year ended December 31, 2020, are over-the-counter market, without any kind of guarantee margin or early settlement clause forced by changes from mark to market, including possible variations caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
| 4.5.2. | Fair value by maturity schedule |
| | | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| 2020 | | | | | | | | (633,644 | ) |
| 2021 | | | | (1,507,075 | ) | | | 98,850 | |
| 2022 | | | | (918,030 | ) | | | (154,734 | ) |
| 2023 | | | | (433,195 | ) | | | 185,209 | |
| 2024 | | | | (705,859 | ) | | | (197,718 | ) |
| 2025 | | | | (1,684,124 | ) | | | (606,827 | ) |
| 2026 onwards | | | | (1,527,697 | ) | | | (510,077 | ) |
| | | | | (6,775,980 | ) | | | (1,818,941 | ) |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 4.5.3. | Outstanding of assets and liabilities derivatives positions |
The outstanding derivatives positions are set forth below:
| | | | | | Notional value | | | Fair value | |
| | | Currency | | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Debt hedge | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Swap CDI x Fixed (U.S.$) | | | R$ | | | | 8,594,225 | | | | 11,498,565 | | | | 719 | | | | 11,673,117 | |
| Swap Pre-Fixed to U.S.$ (U.S.$) | | | R$ | | | | 1,317,226 | | | | 1,317,226 | | | | 136,192 | | | | 1,478,336 | |
| Swap LIBOR x Fixed (U.S.$) | | | US$ | | | | 3,683,333 | | | | 2,750,000 | | | | 61,120 | | | | 11,063,970 | |
| Swap IPCA x CDI | | | IPCA | | | | 974,102 | | | | 933,842 | | | | 285,533 | | | | 1,093,067 | |
| Swap IPCA x U.S.$ | | | IPCA | | | | 520,973 | | | | 499,441 | | | | | | | | 579,307 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 483,564 | | | | 25,887,797 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Swap CDI x Fixed (U.S.$) | | | US$ | | | | 2,267,057 | | | | 3,115,614 | | | | (4,978,028 | ) | | | (13,613,469 | ) |
| Swap LIBOR x Fixed (U.S.$) | | | US$ | | | | 350,000 | | | | 350,000 | | | | (644,520 | ) | | | (1,511,347 | ) |
| Swap LIBOR x Fixed (U.S.$) | | | US$ | | | | 3,683,333 | | | | 2,750,000 | | | | (1,120,312 | ) | | | (11,508,880 | ) |
| Swap IPCA x CDI | | | R$ | | | | 843,845 | | | | 843,845 | | | | | | | | (859,812 | ) |
| Swap IPCA x U.S.$ | | | US$ | | | | 121,003 | | | | 121,003 | | | | (114,834 | ) | | | (548,763 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (6,857,694 | ) | | | (28,042,271 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (6,374,130 | ) | | | (2,154,474 | ) |
| Operational hedge | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Zero cost collar (U.S.$ x R$) | | | US$ | | | | 3,212,250 | | | | 3,425,000 | | | | (780,457 | ) | | | 67,078 | |
| NDF (R$ x U.S.$) | | | US$ | | | | 80,000 | | | | | | | | 7,948 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (772,509 | ) | | | 67,078 | |
| Commodity hedge | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Swap US-CPI (standing wood) | | | US$ | | | | 646,068 | | | | 679,485 | | | | 354,900 | | | | 268,547 | |
| Swap VLSFO/Brent | | | US$ | | | | 37,757 | | | | 365 | | | | 15,759 | | | | (92 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 370,659 | | | | 268,455 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (6,775,980 | ) | | | (1,818,941 | ) |
| 4.5.4. | Fair value settled amounts |
The settled derivatives positions are set forth below:
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Operational hedge | | | | | | | | |
| Zero cost collar (R$ x U.S.$) | | | (2,268,158 | ) | | | (104,040 | ) |
| NDF (R$ x U.S.$) | | | (60,815 | ) | | | 63,571 | |
| | | | (2,328,973 | ) | | | (40,469 | ) |
| Commodity hedge | | | | | | | | |
| Swap Bunker (oil) | | | (85,468 | ) | | | 3,804 | |
| | | | (85,468 | ) | | | 3,804 | |
| Debt hedge | | | | | | | | |
| Swap CDI x Fixed (U.S.$) | | | (1,888,906 | ) | | | (68,362 | ) |
| Swap IPCA x CDI | | | 10,601 | | | | 23,024 | |
| Swap IPCA x USD | | | 10,054 | | | | | |
| Swap Pre-Fixed to U.S.$ (U.S.$) | | | 59,351 | | | | (26,358 | ) |
| Swap LIBOR x Fixed (U.S.$) | | | (242,299 | ) | | | (27,088 | ) |
| | | | (2,051,199 | ) | | | (98,784 | ) |
| | | | (4,465,640 | ) | | | (135,449 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
For the year ended on December 31, 2020, there were no changes between the 3 (three) levels of hierarchy and no transfers between levels 1, 2 and 3 during the periods disclosed.
| | | December 31, 2020 | |
| | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fair value through profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | | | | | 1,341,420 | | | | | | | | 1,341,420 | |
| Marketable securities | | | 444,712 | | | | 1,952,145 | | | | | | | | 2,396,857 | |
| | | | 444,712 | | | | 3,293,565 | | | | | | | | 3,738,277 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fair value through other comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other investments - CelluForce | | | | | | | | | | | 26,338 | | | | 26,338 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | 26,338 | | | | 26,338 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Biological assets | | | | | | | | | | | 11,161,210 | | | | 11,161,210 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | 11,161,210 | | | | 11,161,210 | |
| Total assets | | | 444,712 | | | | 3,293,565 | | | | 11,187,548 | | | | 14,925,825 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fair value through profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | | | | | 8,117,400 | | | | | | | | 8,117,400 | |
| | | | | | | | 8,117,400 | | | | | | | | 8,117,400 | |
| Total liabilities | | | | | | | 8,117,400 | | | | | | | | 8,117,400 | |
| | | December 31, 2019 | |
| | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fair value through profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | | | | | 1,098,972 | | | | | | | | 1,098,972 | |
| Marketable securities | | | 1,631,319 | | | | 4,699,015 | | | | | | | | 6,330,334 | |
| | | | 1,631,319 | | | | 5,797,987 | | | | | | | | 7,429,306 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fair value through other comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other investments - CelluForce | | | | | | | | | | | 20,048 | | | | 20,048 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | 20,048 | | | | 20,048 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Biological assets | | | | | | | | | | | 10,571,499 | | | | 10,571,499 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | 10,571,499 | | | | 10,571,499 | |
| Total assets | | | 1,631,319 | | | | 5,797,987 | | | | 10,591,547 | | | | 18,020,853 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fair value through profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | | | | | 2,917,913 | | | | | | | | 2,917,913 | |
| | | | | | | | 2,917,913 | | | | | | | | 2,917,913 | |
| Total liabilities | | | | | | | 2,917,913 | | | | | | | | 2,917,913 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The main objective is to strengthen its capital structure, aiming to maintain an adequate financial leverage, and to mitigate risks that may affect the availability of capital in business development.
The Company monitors constantly significant indicators, such as, consolidated financial leverage, which is the ratio of total net debt to its adjusted Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization (“Adjusted EBITDA”).
| 5. | CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
| | | Average yield
p.a. % | | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Cash and banks | | | 0.41 | | | | 6,212,318 | | | | 2,464,097 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash equivalents | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Local currency | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fixed-term deposits (1) | | | 70.45 of CDI | | | | 115,032 | | | | 630,075 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Foreign currency | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fixed-term deposits (1) | | | 0.43 | | | | 507,707 | | | | 154,955 | |
| | | | | | | | 6,835,057 | | | | 3,249,127 | |
| | 1) | Refers to Time Deposit and Sweep Account applications, maturing up to 90 days. |
| | | Time Deposit is a remunerated bank deposit with a specific maturity period. |
| | | Sweep Account: is a paid sweep account. At the end of the day, the balance remaining in the account is automatically applied and automatically made available the next business day in the morning. |
| | | Average yield
p.a. % | | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| In local currency | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Investment funds | | | 133.36 of CDI | | | | 6,445 | | | | 6,683 | |
| Private funds | | | 157.67 of CDI | | | | 175,317 | | | | 1,431,303 | |
| Public titles measured at fair value through profit or loss | | | 157.67 of CDI | | | | 444,712 | | | | 1,631,319 | |
| Private Securities (Compromised) | | | 102.42 of CDI | | | | 1,585,605 | | | | 3,081,326 | |
| Private Securities (Compromised) - Escrow Account (1) | | | 102.00 of CDI | | | | 184,778 | | | | 179,703 | |
| | | | | | | | 2,396,857 | | | | 6,330,334 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current | | | | | | | 2,212,079 | | | | 6,150,631 | |
| Non-Current | | | | | | | 184,778 | | | | 179,703 | |
| 1) | Refers to the guarantee account, which will be released only after obtaining the applicable governmental approvals and compliance by the Company with the precedent conditions to the conclusion of the Losango Project provided for in the agreement entered with CMPC Celulose Riograndense SA (“CMPC”). The Losango Project was a transaction to buy and sell lands and forests involving Fibria and CMPC, entered into in December 2012. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 7. | TRADE ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE |
| 7.1. | Breakdown of balances |
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Domestic customers | | | | | | | | |
| Third parties | | | 970,796 | | | | 1,027,035 | |
| Related parties (Note 11) (1) | | | 47,685 | | | | 23,760 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Foreign customers | | | | | | | | |
| Third parties | | | 1,938,614 | | | | 2,027,018 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| (-) Expected credit losses | | | (41,889 | ) | | | (41,996 | ) |
| | | | 2,915,206 | | | | 3,035,817 | |
| 1) | The balance refers to transactions with Ibema, an entity that is not consolidated by the Company. |
The Company performs factoring transactions for certain customers’ receivables where, substantially all risks and rewards related to these receivables are transferred to the counterpart, so that these receivables are derecognized from accounts receivable in the balance sheet. This transaction refers to an additional cash generation opportunity and may be discontinued at any time without significant impact on the Company’s operation and is therefore classified as a financial asset measured at amortized cost. The impact of these factoring transactions on the accounts receivable in the balance sheet for the year ended December 31, 2020, is R$5,388,370 (R$3,544,625 as of December 31, 2019).
| 7.2. | Breakdown of trade accounts receivable by maturity |
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Current | | | 2,603,229 | | | | 2,552,459 | |
| Overdue | | | | | | | | |
| Up to 30 days | | | 209,210 | | | | 180,909 | |
| From 31 to 60 days | | | 51,420 | | | | 148,388 | |
| From 61 to 90 days | | | 2,062 | | | | 20,448 | |
| From 91 to 120 days | | | 6,665 | | | | 20,680 | |
| From 121 to 180 days | | | 8,618 | | | | 17,899 | |
| More than 180 days | | | 34,002 | | | | 95,034 | |
| | | | 2,915,206 | | | | 3,035,817 | |
| 7.3. | Rollforward of the expected credit losses |
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Beginning balance | | | (41,996 | ) | | | (37,179 | ) |
| Business combination | | | | | | | (5,947 | ) |
| Addition | | | (9,350 | ) | | | (18,650 | ) |
| Reversal | | | 3,328 | | | | 6,364 | |
| Write-off | | | 7,737 | | | | 13,383 | |
| Exchange rate variation | | | (1,608 | ) | | | 33 | |
| Ending balance | | | (41,889 | ) | | | (41,996 | ) |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The Company maintains guarantees for overdue securities in its commercial operations, through credit insurance policies, letters of credit and other guarantees. These guarantees avoid the need to recognize expected credit losses, in accordance with the Company’s credit policy.
The Company has no customer responsible for more than 10% of net sales of pulp segment for the year ended December 31, 2020. As of December 31, 2019, only 1 (one) customer was responsible for 10% of net sales of pulp segment.
| | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Finished goods | | | | | | | | |
| Pulp | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic (Brazil) | | | 553,229 | | | | 575,335 | |
| Foreign | | | 1,102,994 | | | | 2,229,206 | |
| Paper | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic (Brazil) | | | 225,058 | | | | 199,635 | |
| Foreign | | | 87,638 | | | | 70,199 | |
| Work in process | | | 81,465 | | | | 75,377 | |
| Raw material | | | 1,450,507 | | | | 1,047,433 | |
| Spare parts and other | | | 508,444 | | | | 488,410 | |
| | | | 4,009,335 | | | | 4,685,595 | |
Inventories are shown net of estimated losses.
| 8.1. | Rollforward of estimated losses |
| | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Beginning balance | | | (106,713 | ) | | | (33,195 | ) |
| Business combination | | | | | | | (11,117 | ) |
| Addition (1) | | | (77,173 | ) | | | (111,077 | ) |
| Reversal | | | 11,498 | | | | 9,734 | |
| Write-off (2) | | | 92,503 | | | | 38,942 | |
| Ending balance | | | (79,885 | ) | | | (106,713 | ) |
| 1) | The addition of inventory in the year ended December 31, 2020, refers substantially to the raw material in the amount of R$56,305 (R$57,384 as of December 31, 2019). |
| 2) | The write-off of inventory, in the year ended December 31, 2020, refers mainly to the amounts of (i) finished pulp product of R$32,018 (R$666 as of December 31, 2019) and (ii) raw material of R$49,550 (R$26,083 as of December 31, 2019). |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
For the year ended December 31, 2020, and 2019 there were no inventory items pledged as collateral.
| | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| IRPJ/CSLL – prepayments and withheld taxes | | | 223,754 | | | | 575,351 | |
| PIS/COFINS – on acquisition of property, plant and equipment (1) | | | 126,990 | | | | 61,376 | |
| PIS/COFINS – operations | | | 287,206 | | | | 507,919 | |
| PIS/COFINS – exclusion ICMS (2) | | | 128,115 | | | | 128,115 | |
| ICMS – on acquisition of property, plant and equipment (3) | | | 112,672 | | | | 115,560 | |
| ICMS – operations (4) | | | 1,393,260 | | | | 1,515,840 | |
| Reintegra program (5) | | | 110,121 | | | | 108,657 | |
| Other taxes and contributions | | | 24,089 | | | | 18,758 | |
| Provision for loss of ICMS credits (6) | | | (1,164,782 | ) | | | (1,304,329 | ) |
| Provision for loss of PIS/COFINS credits | | | | | | | (21,132 | ) |
| | | | 1,241,425 | | | | 1,706,115 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Current | | | 406,850 | | | | 997,201 | |
| Non-current | | | 834,575 | | | | 708,914 | |
| 1) | Social Integration Program (“PIS”) and Social Security Funding Contribution (“COFINS”): Credits whose realization is in connection with depreciation year of the corresponding asset. |
| 2) | The Company filed legal actions claiming the exclusion of ICMS from the PIS and COFINS contribution tax basis, in relation to certain operations for certain periods starting from March 1992. Regarding this subject, the Federal Supreme Court (“STF”) initially decided on March 15th, 2017, that ICMS is not included in the tax basis of the aforementioned contributions. The Federal Government made an appeal (“Embargos de Declaração”) in October 2017, requesting the reversal of the Supreme Court’s initial decision among other items. The appeal has yet to be judged. |
| | |
| | Based on the Supreme Court’s initial decision and the legal opinion provided by external legal consultants, the Company believes that the probability of the Supreme Court altering its decision is remote. The Company thus started to exclude the ICMS from the tax basis of the referred contributions since August 2018, a practice also supported by court decisions. For certain PIS and COFINS credits to be recovered, the Company has received final favorable court decisions. The balance recognized in the statement of income (loss) in 2019 within other operational results, regarding certain claims for the calculation period from 2006 to July 2018. The Company has estimated the amount attributable to these claims based on the available relevant fiscal documents, and this amount is subject to adjustments to be recorded by management in the future periods. The Company has additional claims for which a final decision has not been received and for which no asset or gain have been recorded (Note 20.3.1). |
| 3) | Tax on Sales and Services (“ICMS”): Credits from the acquisition of property, plant and equipment are recovered on a linear basis over a four period, from the acquisition date, in accordance with the relevant regulation, ICMS Control on Property, Plant and Equipment (“CIAP”). |
| 4) | ICMS credits accrued due to the volume of exports and credit generated in operations of entry of products: Credits are concentrated in the state of Espírito Santo, Maranhão, Mato Grosso do Sul, São Paulo and Bahia, where the Company realizes the credits through sale of credits to third parties, after approval from the State Ministry of Finance. Credits are also being realized through consumption in its consumer goods (tissue) operations in the domestic market that are already operational in Maranhão. |
| 5) | Special Regime of Tax Refunds for Export Companies (“Reintegra”): Reintegra is a program that aims to refund the residual costs of taxes paid throughout the exportation chain to taxpayers, to make them more competitive in foreign markets. |
| 6) | Includes the provision for discount on sale to third parties of the accumulated ICMS credit in Maranhão and the provision for full loss of the low probability of realization of the units of Espírito Santo, Mato Grosso do Sul and Bahia due to the difficulty of its realization. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 9.1. | Rollforward of provision for loss |
| | | ICMS | | | PIS/COFINS | | | Total | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2018 | | | (10,792 | ) | | | | | | | (10,792 | ) |
| Business combination with Fibria | | | (1,211,109 | ) | | | | | | | (1,211,109 | ) |
| Addition | | | (82,428 | ) | | | (21,132 | ) | | | (103,560 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2019 | | | (1,304,329 | ) | | | (21,132 | ) | | | (1,325,461 | ) |
| Addition | | | (64,107 | ) | | | | | | | (64,107 | ) |
| Write-off | | | 57,254 | | | | 21,132 | | | | 78,386 | |
| Reversal (1) | | | 146,400 | | | | | | | | 146,400 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2020 | | | (1,164,782 | ) | | | | | | | (1,164,782 | ) |
| 1) | Refers to the reversal of the provision for loss resulting from the recovery of ICMS credits from the State of Espírito Santo through sale to third parties. |
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Forestry development program | | | 1,015,115 | | | | 1,087,149 | |
| Advance to suppliers | | | 43,162 | | | | 170,481 | |
| | | | 1,058,277 | | | | 1,257,630 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Current | | | 43,162 | | | | 170,481 | |
| Non-current | | | 1,015,115 | | | | 1,087,149 | |
The forestry development program consists of an incentive partnership for regional forest production, where independent producers plant eucalyptus in their own land to supply the agricultural product wood to Company. Suzano provides eucalyptus seedlings, input subsidies and cash advances, and the latter are not subject to valuation at present value since they will be settled, preferably, in forests. In addition, the Company supports producers through technical advice on forest management but does not have joint control over decisions effectively implemented. At the end of the production cycles, the Company has contractually guaranteed the right to make an offer to purchase the forest and/or wood for market value, however, this right does not prevent producers from negotiating the forest and / or wood with other market participants, provided that the incentive amounts are fully paid.
The Company’s commercial and financial operations with controlling shareholder and Companies owned by controlling shareholder Suzano Holding S.A. (“Suzano Group”). For transactions with related parties, it is determined that the usual market prices and conditions for these transactions are observed, as well as the corporate governance practices adopted by the Company and those recommended and/or required by the legislation.
For the year ended December 31, 2020, there were no material changes in the terms of the agreements, deal and transactions entered into, nor were there any new contracts, agreements or transactions of different natures entered into between the Company and its related parties.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 11.1. | Balances recognized in assets and liabilities |
| | | | | Balances receivable (payable) | |
| | | Nature | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Transactions with controlling shareholders | | | | | | | | | | |
| Suzano Holding S.A. | | Granting of guarantees and administrative expenses | | | 3 | | | | 3 | |
| | | | | | 3 | | | | 3 | |
| Transactions with companies of the Suzano Group and other related parties | | | | | | | | | | |
| Management | | Reimbursement for expenses | | | (5 | ) | | | (1 | ) |
| Bexma Participações Ltda. | | Reimbursement for expenses | | | 1 | | | | 1 | |
| Bizma Investimentos Ltda. | | Reimbursement for expenses | | | 1 | | | | 1 | |
| Ensyn Technologies | | Reimbursement for expenses | | | 2,829 | | | | | |
| Ibema Companhia Brasileira de Papel | | Sale of pulp | | | 47,685 | | | | 23,755 | |
| Ibema Companhia Brasileira de Papel | | Sale of other products | | | 695 | | | | | |
| Ibema Companhia Brasileira de Papel | | Purchase of products | | | (2,834 | ) | | | (2,467 | ) |
| Ibema Companhia Brasileira de Papel | | Dividends receivable | | | 6,415 | | | | | |
| Ibema Companhia Brasileira de Papel | | Interest on shareholders’ equity | | | 1,218 | | | | | |
| Instituto Ecofuturo - Futuro Para o Desenvolvimento Sustentável | | Social services | | | 1 | | | | (9 | ) |
| Nemonorte Imóveis e Participações Ltda. | | Consultori imobiliária | | | (15 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | 55,991 | | | | 21,280 | |
| | | | | | 55,994 | | | | 21,283 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade accounts receivable | | | | | 47,685 | | | | 23,760 | |
| Other accounts receivable | | | | | 11,163 | | | | | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade accounts payable | | | | | (2,849 | ) | | | (2,477 | ) |
| Other accounts payable | | | | | (5 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | 55,994 | | | | 21,283 | |
| 11.2. | Amounts transacted in the year |
| | | | | Expenses (income) | |
| | | Nature | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | | | December 31, 2018 | |
| Transactions with controlling shareholders | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Suzano Holding S.A. | | Granting of guarantees and administrative expenses | | | (5,029 | ) | | | (5,945 | ) | | | (12,723 | ) |
| | | | | | (5,029 | ) | | | (5,945 | ) | | | (12,723 | ) |
| Transactions with companies of the Suzano Group and other related parties | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Management | | Reimbursement for expenses | | | (392 | ) | | | (8,415 | ) | | | 541 | |
| Bexma Participações Ltda. | | Reimbursement for expenses | | | 11 | | | | 11 | | | | 10 | |
| Bizma Investimentos Ltda. | | Reimbursement for expenses | | | 12 | | | | 10 | | | | | |
| Ensyn Corporation | | Loan charges | | | 689 | | | | | | | | | |
| Ficus Empreendimentos e Participações Ltda. | | Reimbursement for expenses | | | (655 | ) | | | (763 | ) | | | | |
| Fundação Arymax | | Reimbursement for expenses | | | 2 | | | | | | | | | |
| Ibema Companhia Brasileira de Papel | | Sale of paper | | | 117,305 | | | | 111,325 | | | | 107,252 | |
| Ibema Companhia Brasileira de Papel | | Purchase of products | | | (5,464 | ) | | | (7,744 | ) | | | 16 | |
| Instituto Ecofuturo - Futuro para o Desenvolvimento Sustentável | | Social services | | | (4,168 | ) | | | (5,272 | ) | | | (4,184 | ) |
| IPFL Holding S.A. | | Reimbursement for expenses | | | 5 | | | | 4 | | | | 4 | |
| Lazam MDS Corretora e Adm. Seguros S.A. | | Sale of paper | | | 3 | | | | 7 | | | | (31 | ) |
| Mabex Representações e Participações Ltda. | | Aircraft services | | | (50 | ) | | | (100 | ) | | | (390 | ) |
| Nemonorte Imóveis e Participações Ltda. | | Real estate advisory | | | (191 | ) | | | (330 | ) | | | (491 | ) |
| | | | | | 107,107 | | | | 88,733 | | | | 102,727 | |
| | | | | | 102,078 | | | | 82,788 | | | | 90,004 | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 11.3. | Management compensation |
Expenses related to the compensation of key management personnel, which include the Board of Directors, Fiscal Council and Board of Statutory Executive Officers, recognized in the statement of income for the year, are set for the below:
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | | | December 31, 2018 | |
| Short-term benefits | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Salary or compensation | | | 47,089 | | | | 39,459 | | | | 48,663 | |
| Direct and indirect benefits | | | 852 | | | | 1,747 | | | | 2,828 | |
| Bonus | | | 11,326 | | | | 8,007 | | | | 16,752 | |
| | | | 59,267 | | | | 49,213 | | | | 68,243 | |
| Long-term benefits | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share-based compensation plan | | | 75,022 | | | | 45,739 | | | | 62,150 | |
| | | | 75,022 | | | | 45,739 | | | | 62,150 | |
| | | | 134,289 | | | | 94,952 | | | | 130,393 | |
Short-term benefits include fixed compensation (salaries and fees, vacation, mandatory bonus and “13th salary” bonus), payroll charges (Company share of contributions to social security – INSS) and variable compensation such as profit sharing, bonus and benefits (company car, health plan, meal voucher, market voucher, life insurance and private pension plan).
Long-term benefits include the stock option plan and phantom shares for executives and key members of the Management, in accordance with the specific regulations as disclosed in Note 22.
| 12. | INCOME AND SOCIAL CONTRIBUTION TAXES |
The Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries located in Brazil are subject to the tax regime based on taxable income. The wholly-owned subsidiaries located abroad are taxed in their respective jurisdictions, according to local regulations.
In Brazil, the Law nº. 12,973/14 revoked article 74 of Provisional Measure nº.2,158/01 and determines that the parcel of the adjustment of the value of the investment in wholly-owned subsidiary, direct and indirect, located abroad, equivalent to the profit earned by it before income tax, except for exchange rate variation, must be added in the determination of taxable income and the social contribution calculation basis of the controlling entity located in Brazil, at the each year ended.
Management’s Company believes on the validity of the provisions of international treaties entered into Brazil to avoid double taxation. In order to guarantee its right to non-double taxation, the Company filed a lawsuit in April 2019, which aims at a non-double taxation, in Brazil, of profit earned by its wholly-owned subsidiary located in Austria, according to Law n°. 12,973/14. Due to the preliminary injunction granted in favor of the Company in the records of the aforementioned lawsuit, the Company decided not to add the profit from Suzano International Trading GmbH, located in Austria, in determining of taxable income and social contribution basis of the net profit of the Company for the year ended December 31, 2020. There is no provision for tax related to the profit of such wholly-owned subsidiary in 2020.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 12.1. | Deferred income and social contribution taxes |
| | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Tax loss carryforwards | | | 1,013,008 | | | | 600,249 | |
| Negative tax base | | | 329,412 | | | | 146,346 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Assets temporary differences | | | | | | | | |
| Provision for judicial liabilities | | | 233,100 | | | | 265,571 | |
| Operating provisions and other losses | | | 1,051,096 | | | | 914,696 | |
| Exchange rate variation (1) | | | 6,112,906 | | | | 2,001,942 | |
| Losses on derivatives (“MtM”) (1) | | | 2,303,833 | | | | 618,427 | |
| Fair value adjustment on business combination – Amortization | | | 718,645 | | | | 713,656 | |
| Unrealized profit on inventories | | | 176,847 | | | | 293,322 | |
| Lease | | | 287,066 | | | | 22,044 | |
| Provision of deferred taxes on results of subsidiaries abroad | | | 33,893 | | | | | |
| Other temporary differences (3) | | | 158,172 | | | | | |
| | | | 12,417,978 | | | | 5,576,253 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Liabilities temporary differences | | | | | | | | |
| Goodwill - Tax benefit on unamortized goodwill | | | 469,875 | | | | 216,857 | |
| Property, plant and equipment - deemed cost adjustment | | | 1,385,642 | | | | 1,506,220 | |
| Accelerated tax depreciation | | | 1,025,136 | | | | 1,113,200 | |
| Borrowing cost | | | 110,036 | | | | 104,549 | |
| Fair value of biological assets | | | 237,879 | | | | 53,502 | |
| Tax provision on results of subsidiaries abroad (2) | | | | | | | 463,850 | |
| Fair value adjustment on business combination – Deferred taxes, net | | | 469,419 | | | | 502,347 | |
| Tax credits - gains in tax lawsuit (ICMS from the PIS/COFINS calculation basis) | | | 43,559 | | | | 43,559 | |
| Other temporary differences | | | | | | | 17,004 | |
| | | | 3,741,546 | | | | 4,021,088 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Non-current assets | | | 8,677,002 | | | | 2,134,040 | |
| Non-current liabilities | | | 570 | | | | 578,875 | |
| 1) | The variation is due to the increase in the exchange rate in the year ended December 31, 2020. |
| 2) | Amount reversed as a result of a favorable judgement entered for Company, which ensured Company’s right to calculate and pay the Corporate Income Tax and Social Contribution on Net Income due in Brazil, without adding to its taxable base the profit earned as of January 2019 by its wholly-owned subsidiary Suzano International Trade GmbH (former Fibria International Trade GmbH), in accordance with the terms of the Brazil-Austria Double Taxation Treaty, either with regard to the merged company Fibria Celulose SA (wholly-owned subsidiary merged on April 1, 2019) in relation to the 1st quarter 2019 base period early terminated due to the merger, either with respect to the subsequent calculation base periods when Suzano International Trade GmbH was already a subsidiary of the Company. |
| 3) | On December 29, 2020, with the final decision of CADE’s approval related to the purchase and sale agreement of rural property (note 1.2.2), Management and legal advisors understand that all conditions suspensive were implemented, with the tax recognition of capital gain being required, pursuant to art. 117 of the National Taxation Code. As the accounting recognition will only occur at the Closing of the Transaction, on January 5, 2021 (note 32.1) with the fulfillment of the performance obligation and delivery of the ownership of the properties to the client, there was a need to establish the deferred tax asset on this difference temporary, in the amount of R$175,202. |
Except for tax loss carryforwards, the negative basis of social contribution and accelerated depreciation are only achieved by the Income Tax (“IRPJ”), other tax bases were subject to both taxes.
The breakdown of accumulated tax losses and social contribution tax loss carryforwards is set forth below:
| | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Tax loss carry forward | | | 4,052,013 | | | | 2,400,998 | |
| Social contribution tax loss carryforward | | | 3,660,133 | | | | 1,626,064 | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The rollforward of net balance of deferred income tax is set for the below:
| | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Beginning balance | | | 1,555,165 | | | | (1,029,135 | ) |
| Tax loss | | | 412,759 | | | | 270,559 | |
| Tax loss carryforwards | | | 183,066 | | | | 139,719 | |
| (Reversal) provision for judicial liabilities | | | (32,471 | ) | | | 31,262 | |
| Operating provision (reversal) and other losses | | | 136,400 | | | | (21,757 | ) |
| Exchange rate variation (1) | | | 4,110,964 | | | | 552,421 | |
| Derivative losses (“MtM”)(1) | | | 1,685,406 | | | | 319,860 | |
| Fair value adjustment on business combination – Amortization | | | 37,917 | | | | 699,527 | |
| Unrealized profit on inventories | | | (116,475 | ) | | | 65,492 | |
| Lease | | | 265,022 | | | | (3,274 | ) |
| Tax benefit on unamortized goodwill | | | (253,018 | ) | | | (203,696 | ) |
| Property, plant and equipment - Deemed cost | | | 120,578 | | | | 46,359 | |
| Accelerated depreciation | | | 88,064 | | | | 82,982 | |
| Borrowing cost | | | (5,487 | ) | | | 44,727 | |
| Fair value of biological assets | | | (184,377 | ) | | | (60,778 | ) |
| Reversal/(provision) of deferred taxes on the result of subsidiaries abroad (2) | | | 497,743 | | | | (351,485 | ) |
| Business combination | | | | | | | 1,034,842 | |
| Tax credits - gains in tax lawsuit (ICMS from the PIS/COFINS calculation basis) | | | | | | | (43,559 | ) |
| Other temporary differences | | | 175,176 | | | | (18,901 | ) |
| Ending balance | | | 8,676,432 | | | | 1,555,165 | |
| 1) | The variation is due to the increase in the exchange rate in the year ended December 31, 2020. |
| 2) | On December 29, 2020, with the final decision of CADE’s approval related to the purchase and sale agreement of rural property (note 1.2.2), Management and legal advisors understand that all conditions suspensive were implemented, with the tax recognition of capital gain being required, pursuant to art. 117 of the National Taxation Code. As the accounting recognition will only occur at the Closing of the Transaction, on January 5, 2021 (note 32.1) with the fulfillment of the performance obligation and delivery of the ownership of the properties to the client, there was a need to establish the deferred tax asset on this difference temporary, in the amount of R$175,202. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 12.2. | Reconciliation of the effects of income tax and social contribution on profit or loss |
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Loss before taxes | | | (17,642,129 | ) | | | (4,097,203 | ) |
| Income tax and social contribution benefit (expense) at statutory nominal rate of 34% | | | 5,998,324 | | | | 1,393,049 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Tax effect on permanent differences | | | | | | | | |
| Taxation (difference) on profit of wholly-owned subsidiaries abroad (1) | | | 1,373,845 | | | | (24,933 | ) |
| Equity method | | | 12,288 | | | | 10,878 | |
| Thin capitalization (2) | | | (675,356 | ) | | | (95,003 | ) |
| Credit related to Reintegra Program | | | 6,278 | | | | 4,515 | |
| Tax incentives applicable to income tax (3) | | | 10,668 | | | | 18,919 | |
| Director bonus | | | (7,677 | ) | | | (43,913 | ) |
| Offset income tax abroad | | | 72,890 | | | | | |
| Merger of subsidiaries (4) | | | 67,311 | | | | | |
| Donations / Fines - Other | | | 68,623 | | | | 18,949 | |
| | | | 6,927,194 | | | | 1,282,461 | |
| Income tax | | | | | | | | |
| Current | | | (173,322 | ) | | | (220,311 | ) |
| Deferred | | | 5,225,655 | | | | 1,093,200 | |
| | | | 5,052,333 | | | | 872,889 | |
| Social Contribution | | | | | | | | |
| Current | | | (8,604 | ) | | | (25,799 | ) |
| Deferred | | | 1,883,465 | | | | 435,371 | |
| | | | 1,874,861 | | | | 409,572 | |
| Income and social contribution benefits (expenses) on the year | | | 6,927,194 | | | | 1,282,461 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Effective rate of income and social contribution tax expenses | | | 39.27 | % | | | 31.30 | % |
| 1) | The effect of the difference in taxation of subsidiaries is substantially due to the difference between the nominal rates of Brazil and subsidiaries abroad. |
| 2) | The Brazilian thin capitalization rules establish that interest paid or credited by a Brazilian entity to a related party abroad may only be deducted for income tax and social contribution purposes if the interest expense is viewed as necessary for the activities of the local entity and when determined limits and requirements are met. On December 31, 2020 the Company did not meet all limits and requirements, therefore a provision for tax payment was recorded. |
| 3) | Tax incentives applicable to ICMS, which is deducted from the calculation basis of Income Tax and Social Contribution. |
| 4) | Merger of legal entities (note 1.1). |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
Company has a tax incentive for the partial reduction of the income tax obtained by the operations carried out in areas of the Northeast Development Superintendency (“SUDENE”) in the Mucuri (BA), Eunápolis – Veracel (BA) and Imperatriz (MA) regions. The IRPJ reduction incentive is calculated based on the activity profit (exploitation profit) and considers the allocation of the operating profit by the incentive production levels for each product. The incentive of lines 1 and 2 of Mucuri (BA) facility expire, respectively, in 2024 and 2027, Imperatriz facility expire in 2024 and Eunápolis – Veracel (BA) facility expire in 2025.
The rollforward of biological assets is set forth below:
| Balances on December 31, 2018 | | | 4,935,905 | |
| Business combination | | | 4,579,526 | |
| Addition | | | 2,849,039 | |
| Depletion | | | (1,905,118 | ) |
| Gain on fair value adjustment | | | 185,399 | |
| Disposal | | | (23,764 | ) |
| Other write-offs | | | (49,488 | ) |
| Balances on December 31, 2019 | | | 10,571,499 | |
| Addition | | | 3,392,975 | |
| Depletion | | | (3,094,742 | ) |
| Transfers (1) | | | (23,471 | ) |
| Gain on fair value adjustment | | | 466,484 | |
| Disposal | | | (93,847 | ) |
| Other write-offs | | | (57,688 | ) |
| Balances on December 31, 2020 | | | 11,161,210 | |
| 1) | Includes transfer to assets held for sale as disclosed in note 1.2.2. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The calculation of fair value of the biological assets falls under Level 3 in the hierarchy set forth in IFRS 13 — Measurement of Fair Value, due to the complexity and structure of calculation.
The main assumptions, Average annual growth (“IMA”), discount rate, and average gross selling price of eucalyptus, stand out as being the most sensitive where increases or reductions in these assumptions generate significant gains or losses in the measurement of fair value.
The assumptions used in measurement of the fair value of biological assets were:
| (i) | Average cycle of forest formation of 6 and 7 years; |
| (ii) | Effective area of forest from the 3rd year of planting; |
| (iii) | IMA consists of the estimated volume of production of wood with bark in m3 per hectare, ascertained based on the genetic material used in each region, silvicultural practices and forest management, production potential, climate factors and ground conditions; |
| (iv) | The estimated average standard cost per hectare includes expenses on silvicultural and forest management applied to each year of formation of the biological cycle of forests, plus costs of land lease agreements and opportunity cost of own land; |
| (v) | The average gross selling prices of eucalyptus were based on specialized research on transactions carried out by the Company with independent third parties; and |
| (vi) | The discount rate used in cash flows is measured based on capital structure and other economic assumptions in an independent market participant in the sale of standing wood (forests). |
The following table discloses the measurement of the premises adopted:
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Planted useful area (hectare) | | | 1,020,176 | | | | 988,720 | |
| Mature assets | | | 111,866 | | | | 86,352 | |
| Immature assets | | | 908,310 | | | | 902,368 | |
| Average annual growth (IMA) – m3/hectare/year | | | 38.43 | | | | 38.34 | |
| Average gross sale price of eucalyptus – R$/m3 | | | 70.22 | | | | 66.81 | |
| Discount rate - % | | | 8.9 | % | | | 8.4 | % |
The pricing model considers net cash flows, after deduction of taxes on profit at the applicable rates.
The fair value adjustment justified by variation of indicators mentioned above, which combined, resulted in a positive variation of R$466,484 recognized under other operating income (expense), net.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Physical changes | | | 156,906 | | | | (347,409 | ) |
| Price | | | 309,578 | | | | 532,808 | |
| | | | 466,484 | | | | 185,399 | |
The Company manages the financial risks related to agricultural activities in a preventive manner. To reducing risks from edaphoclimatic factors, the weather is monitored through meteorological stations and, in the event of pests and diseases, our Department of Forestry Research and Development, an area specialized in physiological and phytosanitary aspects, has procedures to diagnose and act rapidly against any occurrences and losses.
On December 31, 2020, the Company has R$140,142 of biological assets in formation pledged related to the sale of forests to Bracell, as disclosed in the notes 1.2.2 and 32.1.The Company has no biological assets pledged as of December 31, 2019.
| 14.1. | Investments breakdown |
| | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Investments in associates and joint ventures | | | 96,373 | | | | 140,936 | |
| Goodwill | | | 236,360 | | | | 161,462 | |
| Other investments evaluated at fair value through other comprehensive income | | | 26,338 | | | | 20,048 | |
| | | | 359,071 | | | | 322,446 | |
Investments are shown net of estimated losses.
| 14.2. | Investments in associates and joint ventures |
| | | Information of joint ventures as of | | | Company Participation | |
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | In equity | | | In the income of the year | |
| | | Equity | | | Income of the year | | | Participation equity (%) | | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Associate | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Ensyn Corporation | | | 21,629 | | | | (30,153 | ) | | | 25.30 | % | | | 5,472 | | | | 21,437 | | | | (7,629 | ) | | | 12,860 | |
| Spinnova Oy | | | 65,643 | | | | (25,183 | ) | | | 23.44 | % | | | 15,387 | | | | 86,969 | | | | (5,903 | ) | | | (1,332 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 20,859 | | | | 108,406 | | | | (13,532 | ) | | | 11,528 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Joint ventures | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Ibema Companhia Brasileira de Papel | | | 140,893 | | | | 99,547 | | | | 49.90 | % | | | 70,305 | | | | 28,489 | | | | 49,674 | | | | 20,307 | |
| F&E Technologies LLC | | | 10,419 | | | | | | | | 50.00 | % | | | 5,209 | | | | 4,041 | | | | | | | | 158 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 75,514 | | | | 32,530 | | | | 49,674 | | | | 20,465 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 96,373 | | | | 140,936 | | | | 36,142 | | | | 31,993 | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 15. | PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT |
| | | Lands | | | Buildings | | | Machinery, equipment and
facilities | | | Work in
progress | | | Other (1) | | | Total | |
| Average rate % | | | | | | | 3.52 | | | | 5.77 | | | | | | | | 15.76 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cost | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2018 | | | 5,104,717 | | | | 3,058,520 | | | | 16,441,031 | | | | 466,156 | | | | 332,089 | | | | 25,402,513 | |
| Additions | | | 337,932 | | | | 1,943 | | | | 136,855 | | | | 1,477,420 | | | | 47,524 | | | | 2,001,674 | |
| Write-offs | | | (92,705 | ) | | | (36,276 | ) | | | (172,458 | ) | | | (1,462 | ) | | | (34,858 | ) | | | (337,759 | ) |
| Business combination | | | 2,151,338 | | | | 3,918,552 | | | | 20,255,811 | | | | 425,868 | | | | 454,759 | | | | 27,206,328 | |
| Fair value adjustment - Fibria | | | 2,637,671 | | | | 1,502,021 | | | | 5,109,939 | | | | | | | | 195,684 | | | | 9,445,315 | |
| Fair value adjustment – Facepa | | | | | | | | | | | 3,072 | | | | (883 | ) | | | (111 | ) | | | 2,078 | |
| Fair value adjustment – Ibema | | | | | | | | | | | 5,448 | | | | | | | | | | | | 5,448 | |
| Transfer and other (2) | | | 182,621 | | | | 323,029 | | | | 740,879 | | | | (1,397,398 | ) | | | (61,761 | ) | | | (212,630 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2019 | | | 10,321,574 | | | | 8,767,789 | | | | 42,520,577 | | | | 969,701 | | | | 933,326 | | | | 63,512,967 | |
| Additions | | | 2,274 | | | | 2,825 | | | | 194,086 | | | | 1,289,738 | | | | 14,332 | | | | 1,503,255 | |
| Write-offs | | | (213,399 | ) | | | (26,564 | ) | | | (92,915 | ) | | | (18,853 | ) | | | (25,189 | ) | | | (376,920 | ) |
| Transfer and other (2) | | | (198,144 | ) | | | 459,084 | | | | 562,747 | | | | (1,357,202 | ) | | | 137,126 | | | | (396,389 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2020 | | | 9,912,305 | | | | 9,203,134 | | | | 43,184,495 | | | | 883,384 | | | | 1,059,595 | | | | 64,242,913 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Depreciation | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2018 | | | | | | | (906,616 | ) | | | (7,248,143 | ) | | | | | | | (227,495 | ) | | | (8,382,254 | ) |
| Additions | | | | | | | (255,888 | ) | | | (2,123,193 | ) | | | | | | | (91,170 | ) | | | (2,470,251 | ) |
| Write-offs | | | | | | | 26,886 | | | | 115,732 | | | | | | | | 13,944 | | | | 156,562 | |
| Business combination | | | | | | | (1,804,967 | ) | | | (9,552,825 | ) | | | | | | | (249,087 | ) | | | (11,606,879 | ) |
| Additions - Fair value adjustment from business combination – Fibria | | | | | | | (63,495 | ) | | | (543,468 | ) | | | | | | | (17,364 | ) | | | (624,327 | ) |
| Fair value adjustment from business combination – Facepa | | | | | | | (5,742 | ) | | | (6,481 | ) | | | | | | | (95 | ) | | | (12,318 | ) |
| Fair value adjustment from business combination - Ibema | | | | | | | | | | | (593 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | (593 | ) |
| Transfer and other (2) | | | | | | | 29,906 | | | | 508,585 | | | | | | | | 9,547 | | | | 548,038 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2019 | | | | | | | (2,979,916 | ) | | | (18,850,386 | ) | | | | | | | (561,720 | ) | | | (22,392,022 | ) |
| Additions | | | | | | | (291,862 | ) | | | (2,390,583 | ) | | | | | | | (110,012 | ) | | | (2,792,457 | ) |
| Write-offs | | | | | | | 25,992 | | | | 64,397 | | | | | | | | 8,067 | | | | 98,456 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2020 | | | | | | | (3,245,786 | ) | | | (21,176,572 | ) | | | | | | | (663,665 | ) | | | (25,086,023 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Book value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2019 | | | 10,321,574 | | | | 5,787,873 | | | | 23,670,191 | | | | 969,701 | | | | 371,606 | | | | 41,120,945 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2020 | | | 9,912,305 | | | | 5,957,348 | | | | 22,007,923 | | | | 883,384 | | | | 395,930 | | | | 39,156,890 | |
| 1) | Includes vehicles, furniture and utensils and computer equipment. |
| 2) | Includes transfers carried out between the items of property, plant and equipment, intangible assets, inventories and non-current assets held for sale as disclosed in note 1.2.2 (On December 31, 2019 includes right of use). |
For the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company did not identify any indicators of impairment of property, plant and equipment.
| 15.1. | Items pledged as collateral |
For the year ended December 31, 2020, property, plant and equipment items that are pledge as collateral for loans transactions and lawsuits, consisting substantially of the units of, Imperatriz, Limeira, Mucuri, Suzano and Três Lagoas totaled R$20,903,151 (R$24,985,741 consisting substantially of the units of Aracruz, Imperatriz, Limeira, Mucuri, Suzano and Três Lagoas as of December 31, 2019).
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 15.2. | Capitalized expenses |
For the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company capitalized interest in the amount of R$10,636 (R$4,213 as of December 31, 2019). The weighted average interest rate utilized to determine the capitalized amount was 9.06% p.a. (9.50% p.a. as of December 31, 2019).
| 16.1. | Goodwill and intangible assets with indefinite useful life |
| | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Vale Florestar (1) | | | | | | | 45,435 | |
| Facepa | | | 119,332 | | | | 119,332 | |
| Fibria (2) | | | 7,897,051 | | | | 7,897,051 | |
| Other (3) | | | 1,196 | | | | 1,196 | |
| | | | 8,017,579 | | | | 8,063,014 | |
| 1) | Vale Florestar’s main asset is eucalyptus forests planted in leased areas, in the State of Pará, which were acquired for the purpose of supplying wood to the Maranhão Unit. On December 31, 2020, the Company tested goodwill on expected future profitability arising from business combinations with Vale Florestar and identified an impairment of R$45,435 recognized in other operating results. |
| 2) | Amount arising from the business combination with Fibria, held on January 3, 2019, when the Company acquired the net assets of Fibria for total consideration of R$37,235,854 (note 1.3.1). |
| 3) | Refer to other intangible assets with indefinite useful life such as servitude and electricity. |
The goodwill is based on expected future profitability supported by valuation reports, after purchase price allocation.
Goodwill are allocated to cash-generating units as presented in Note 29.4.
The calculation of the value in use of non-financial assets is done annually using the discounted cash flow method. In 2020, the Company used the strategic plan and annual budget with growing projections until 2025 and the average perpetuity of the cash generating units considering a nominal rate of 3.27% p.a. from this date, based on historical information of previous years, economic and financial projections from each specific market that the Company has operations and additionally include official information disclosed by independent institutions and government agencies.
The discount rate, after taxes, adopted by the Management was 9.19% p.a., calculated based on weighted average cost of capital (“WACC”). The assumptions in the table set forth below were also adopted:
| | | 2021 | | | 2022 | | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2025 | |
| Net average pulp price – Foreign market (USD/t) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Asia | | | 495,0 | | | | 651,7 | | | | 457,5 | | | | 492,5 | | | | 502,4 | |
| Europa | | | 490,5 | | | | 640,1 | | | | 504,7 | | | | 505,9 | | | | 516,1 | |
| North America | | | 535,9 | | | | 647,9 | | | | 510,9 | | | | 512,0 | | | | 522,4 | |
| Latin America | | | 511,3 | | | | 637,6 | | | | 502,8 | | | | 503,9 | | | | 514,1 | |
| Net average pulp price – Internal market (USD/t) | | | 421,6 | | | | 641,4 | | | | 505,7 | | | | 506,9 | | | | 517,1 | |
| Average exchange rate (R$/U.S.$) | | | 5,01 | | | | 4,82 | | | | 4,81 | | | | 4,82 | | | | 4,88 | |
| Discount rate (pos-tax) | | | 9.19% p.a. | | | | 9.19% p.a. | | | | 9.19% p.a. | | | | 9.19% p.a. | | | | 9.19% p.a | |
| Discount rate (pre-tax) | | | 13.0% p.a. | | | | 13.0% p.a. | | | | 13.0% p.a. | | | | 13.0% p.a. | | | | 13.0% p.a. | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The recoverability of property, plant and equipment was tested in 2020 and no impairment loss was identified.
| 16.2. | Intangible assets with determined useful life |
| | | | | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Beginning balance | | | | | | | 9,649,789 | | | | 180,311 | |
| Business combination | | | | | | | | | | | 308,681 | |
| Additions | | | | | | | 2,307 | | | | 17,715 | |
| Fair value adjustment on business combination | | | | | | | | | | | 702 | |
| Amortization | | | | | | | (980,385 | ) | | | (74,332 | ) |
| Fair value adjustment on business combination | | | | | | | | | | | 10,159,550 | |
| Port concession | | | | | | | | | | | 54,470 | |
| Lease agreements | | | | | | | | | | | 44,371 | |
| Supplier agreements | | | | | | | | | | | 172,094 | |
| Port services agreements | | | | | | | | | | | 694,590 | |
| Cultivars | | | | | | | | | | | 142,744 | |
| Customer portfolio | | | | | | | | | | | 9,030,779 | |
| Software | | | | | | | | | | | 20,502 | |
| Fair value adjustment on business combination – Amortization (Fibria) | | | | | | | | | | | (956,577 | ) |
| Port concession | | | | | | | | | | | (2,147 | ) |
| Lease agreements | | | | | | | | | | | (7,499 | ) |
| Supplier agreements | | | | | | | | | | | (72,097 | ) |
| Port services agreements | | | | | | | | | | | (29,362 | ) |
| Cultivars | | | | | | | | | | | (20,392 | ) |
| Customer portfolio | | | | | | | | | | | (820,980 | ) |
| Software | | | | | | | | | | | (4,100 | ) |
| Fair value adjustment on business combination – Amortization (Facepa and Ibema) | | | | | | | | | | | (15,454 | ) |
| Exchange rate variation | | | | | | | | | | | 2,930 | |
| Transfers and others | | | | | | | 70,238 | | | | 26,263 | |
| Ending balance | | | | | | | 8,741,949 | | | | 9,649,789 | |
| Represented by | | | Average
rate % | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-compete agreement | | | 46.1 and 5 | | | | 5,706 | | | | 2,150 | |
| Research and development agreement | | | 5.4 | | | | 66,272 | | | | 74,643 | |
| Ports concession | | | 4.3 | | | | 209,506 | | | | 219,256 | |
| Lease agreements | | | 16.9 | | | | 29,373 | | | | 36,871 | |
| Supplier agreements | | | 12.9 | | | | 85,182 | | | | 99,997 | |
| Port service contracts | | | 4.2 | | | | 639,275 | | | | 665,228 | |
| Cultivars | | | 14.3 | | | | 101,960 | | | | 122,352 | |
| Development and implementation of systems | | | 11.2 | | | | 1,392 | | | | 1,687 | |
| Trademarks and patents | | | 10.0 | | | | 16,627 | | | | 20,649 | |
| Customer portfolio | | | 9.1 | | | | 7,388,820 | | | | 8,217,192 | |
| Supplier agreements | | | 17.6 | | | | 41,250 | | | | 51,562 | |
| Software | | | 20.0 | | | | 123,788 | | | | 135,668 | |
| Others | | | 5.0 | | | | 32,798 | | | | 2,534 | |
| | | | | | | | 8,741,949 | | | | 9,649,789 | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 17. | TRADE ACCOUNTS PAYABLE |
| | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| In local currency | | | | | | | | |
| Related party (note 11.1) (1) | | | 2,849 | | | | 2,477 | |
| Third party | | | 1,865,632 | | | | 1,288,775 | |
| In foreign currency | | | | | | | | |
| Third party (2) | | | 492,617 | | | | 1,085,207 | |
| | | | 2,361,098 | | | | 2,376,459 | |
| 1) | The balance refers to transactions with Ibema and Nemonorte, entities that are not consolidated by the Company. |
| 2) | The Company had a take or pay agreement with Klabin S.A., following the requirements imposed by the European Union’s competition authority, this contract expired in July 2019. On December 31, 2019, the amount of R$936,887 in the consolidated refers to purchases of Klabin’s pulp. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 18. | LOANS, FINANCING AND DEBENTURES |
| | | | | | | | Current | | | Non-current | | | Total | |
| Type | | Interest rate | | Average
annual
interest rate -
% | | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| In foreign currency | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BNDES | | UMBNDES | | 4.84 | | | | 2,506 | | | | 26,307 | | | | 24,486 | | | | 27,620 | | | | 26,992 | | | | 53,927 | |
| Bonds (1) | | Fixed | | 5.33 | | | | 779,046 | | | | 640,177 | | | | 37,232,554 | | | | 27,375,673 | | | | 38,011,600 | | | | 28,015,850 | |
| Export credits (ACC - pre-payment) | | LIBOR/Fixed | | 1.64 | | | | 718,623 | | | | 1,994,868 | | | | 19,400,208 | | | | 15,431,478 | | | | 20,118,831 | | | | 17,426,346 | |
| Others | | | | | | | | 2,516 | | | | 3,481 | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,516 | | | | 3,481 | |
| | | | | | | | | 1,502,691 | | | | 2,664,833 | | | | 56,657,248 | | | | 42,834,771 | | | | 58,159,939 | | | | 45,499,604 | |
| In local currency | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BNDES | | TJLP | | 6.77 | | | | 276,441 | | | | 283,658 | | | | 1,254,222 | | | | 1,517,649 | | | | 1,530,663 | | | | 1,801,307 | |
| BNDES | | TLP | | 10.04 | | | | 25,535 | | | | 18,404 | | | | 522,367 | | | | 441,233 | | | | 547,902 | | | | 459,637 | |
| BNDES | | Fixed | | 4.94 | | | | 29,115 | | | | 39,325 | | | | 47,177 | | | | 77,333 | | | | 76,292 | | | | 116,658 | |
| BNDES | | SELIC | | 5.50 | | | | 98,531 | | | | 78,458 | | | | 1,068,959 | | | | 718,017 | | | | 1,167,490 | | | | 796,475 | |
| FINAME | | TJLP/Fixed | | | | | | | | | | 4,781 | | | | | | | | 9,564 | | | | | | | | 14,345 | |
| BNB | | Fixed | | | | | | | | | | 37,815 | | | | | | | | 156,904 | | | | | | | | 194,719 | |
| CRA (“Agribusiness Receivables Certificates”) | | CDI/IPCA | | 7.59 | | | | 32,156 | | | | 2,860,938 | | | | 3,025,527 | | | | 2,952,451 | | | | 3,057,683 | | | | 5,813,389 | |
| NCE (Export credit note) | | CDI | | 5.52 | | | | 15,184 | | | | 131,914 | | | | 1,275,045 | | | | 1,270,065 | | | | 1,290,229 | | | | 1,401,979 | |
| Rural producer Certificate | | CDI | | 7.81 | | | | 2,738 | | | | 5,840 | | | | 273,578 | | | | 273,303 | | | | 276,316 | | | | 279,143 | |
| Export credits (“Pre payment”) | | Fixed | | 7.62 | | | | 77,570 | | | | 77,694 | | | | 1,313,661 | | | | 1,312,586 | | | | 1,391,231 | | | | 1,390,280 | |
| FCO (“Central West Fund”), FDCO (“Central West Development Fund”) and FINEP | | Fixed | | | | | | | | | | 76,596 | | | | | | | | 475,905 | | | | | | | | 552,501 | |
| Debentures | | CDI | | 6.12 | | | | 7,590 | | | | 9,997 | | | | 5,415,061 | | | | 5,412,035 | | | | 5,422,651 | | | | 5,422,032 | |
| Others (Revolving Cost, Working capital and Industrial Development Fund (“FDI”) and fair value adjustment on business combination | | Fixed | | 0.40 | | | | (24,165 | ) | | | (62,302 | ) | | | 3,651 | | | | 4,559 | | | | (20,514 | ) | | | (57,743 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | 540,695 | | | | 3,563,118 | | | | 14,199,248 | | | | 14,621,604 | | | | 14,739,943 | | | | 18,184,722 | |
| | | | | | | | | 2,043,386 | | | | 6,227,951 | | | | 70,856,496 | | | | 57,456,375 | | | | 72,899,882 | | | | 63,684,326 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest on financing | | | | | | | | 935,010 | | | | 886,886 | | | | | | | | 136,799 | | | | 935,010 | | | | 1,023,685 | |
| Non-current funding | | | | | | | | 1,108,376 | | | | 5,341,065 | | | | 70,856,496 | | | | 57,319,576 | | | | 71,964,872 | | | | 62,660,641 | |
| | | | | | | | | 2,043,386 | | | | 6,227,951 | | | | 70,856,496 | | | | 57,456,375 | | | | 72,899,882 | | | | 63,684,326 | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 18.2. | Rollforward in loans, financing and debentures |
| | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Beginning balance | | | 63,684,326 | | | | 35,737,509 | |
| Amounts from the business combination | | | | | | | 20,667,096 | |
| Reclassification - accounts payable from lease operations | | | | | | | (18,225 | ) |
| Fundraising | | | 14,761,796 | | | | 18,993,837 | |
| Interest accrued | | | 3,286,254 | | | | 3,362,250 | |
| Premium with repurchase of bonds | | | 391,390 | | | | | |
| Exchange rate variation, net | | | 13,365,471 | | | | 1,781,562 | |
| Settlement of principal | | | (19,092,810 | ) | | | (13,994,708 | ) |
| Settlement of interest | | | (3,244,949 | ) | | | (2,977,957 | ) |
| Settlement of premium with repurchase of bonds | | | (378,381 | ) | | | | |
| Amortization of fundraising costs | | | 87,959 | | | | 185,807 | |
| Other | | | 38,826 | | | | (52,845 | ) |
| Ending balance | | | 72,899,882 | | | | 63,684,326 | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 18.3. | Breakdown by maturity – non current |
| | | | 2022 | | 2023 | | 2024 | | 2025 | | 2026 | | 2027
onwards | | Total |
| In foreign currency | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BNDES - Currency basket | | | 13,356 | | 11,130 | | | | | | | | | | 24,486 |
| Bonds | | | | | | | 1,823,773 | | 1,741,909 | | 2,707,642 | | 30,959,230 | | 37,232,554 |
| Export credits (ACC pre-payment) | | | 1,576,020 | | 9,549,933 | | 4,555,079 | | 3,250,602 | | 468,574 | | | | 19,400,208 |
| | | | 1,589,376 | | 9,561,063 | | 6,378,852 | | 4,992,511 | | 3,176,216 | | 30,959,230 | | 56,657,248 |
| In local currency | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BNDES – TJLP | | | 269,029 | | 268,272 | | 240,281 | | 292,870 | | 169,102 | | 14,668 | | 1,254,222 |
| BNDES – TLP | | | 18,866 | | 18,866 | | 18,866 | | 17,618 | | 21,161 | | 426,990 | | 522,367 |
| BNDES – Fixed | | | 24,558 | | 18,606 | | 4,013 | | | | | | | | 47,177 |
| BNDES – Selic | | | 97,511 | | 121,202 | | 113,061 | | 238,538 | | 200,697 | | 297,950 | | 1,068,959 |
| CRA (“Agribusiness Receivables Certificates”) | | | 1,512,680 | | 1,512,847 | | | | | | | | | | 3,025,527 |
| Export credit note | | | | | | | | | 640,800 | | 634,245 | | | | 1,275,045 |
| Rural producer certificate | | | | | | | | | 137,500 | | 136,078 | | | | 273,578 |
| Export credits (“Pre payment”) | | | | | | | 1,313,661 | | | | | | | | 1,313,661 |
| Debentures | | | | | | | | | 2,340,550 | | 2,327,011 | | 747,500 | | 5,415,061 |
| Others (Revolving costs, working capital, FIDC and FDI) | | | 3,651 | | | | | | | | | | | | 3,651 |
| | | | 1,926,295 | | 1,939,793 | | 1,689,882 | | 3,667,876 | | 3,488,294 | | 1,487,108 | | 14,199,248 |
| | | | 3,515,671 | | 11,500,856 | | 8,068,734 | | 8,660,387 | | 6,664,510 | | 32,446,338 | | 70,856,496 |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 18.4. | Breakdown by currency |
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Brazilian Reais | | | 14,727,803 | | | | 18,170,261 | |
| U.S. Dollar | | | 58,145,087 | | | | 45,460,138 | |
| Currency basket | | | 26,992 | | | | 53,927 | |
| | | | 72,899,882 | | | | 63,684,326 | |
The fundraising costs are amortized based on terms agreements and effective interest rate.
| | | | | | | | | Balance to be amortized | |
| Type | | Cost | | | Amortization | | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Bonds | | | 390,104 | | | | 151,536 | | | | 238,568 | | | | 201,467 | |
| CRA and NCE | | | 125,222 | | | | 92,848 | | | | 32,374 | | | | 47,443 | |
| Export credits (ACC pre-payment) | | | 102,769 | | | | 46,741 | | | | 56,028 | | | | 40,382 | |
| Debentures | | | 24,467 | | | | 8,428 | | | | 16,039 | | | | 19,065 | |
| BNDES (“IOF”) (1) | | | 62,658 | | | | 22,047 | | | | 40,611 | | | | 38,447 | |
| Others | | | 18,147 | | | | 16,725 | | | | 1,422 | | | | 4,590 | |
| | | | 723,367 | | | | 338,325 | | | | 385,042 | | | | 351,394 | |
| 1) | Tax on Financial Operations |
| 18.6. | Relevant transactions entered into the year |
| 18.6.1. | Export Prepayment Agreements (“EPP”) |
On February 14, 2020, Suzano, through its wholly-owned subsidiaries Suzano Pulp and Paper Europe S.A., Suzano Austria GmbH and Fibria Overseas Finance Ltd., entered into a syndicated export prepayment agreement in the amount of US$850,000 (equivalent, on the transaction date, to R$3,672,259), with a term of six years and maturity in February 2026, grace period of 4 years, quarterly interest payments of 1.15% p.a. plus LIBOR 3M. This transaction is fully and unconditionally guaranteed by Suzano S.A.
On December 17, 2020, the Company, through its wholly-owned subsidiary Suzano International Trade GmbH, signed in a bilateral export prepayment contract with Banco Santander, in the amount of US$100,000 (equivalent on the transaction date to R$517,402) with a term of one year and with an interest rate of 1.3825% p.a.
On December 23, 2020, the Company, through its wholly-owned subsidiary Suzano Pulp and Paper Europe SA, signed in a bilateral export prepayment contract with the bank Rabobank in the amount of US$140,000 (equivalent on the transaction date to R$709,444) with a term of one year and an interest rate of 1.35% p.a.
All the above operations are fully guaranteed by Suzano S.A.
| 18.6.2. | Revolving credit facility |
On April 2, 2020, the Company through its wholly-owned subsidiary Suzano Pulp and Paper Europe S.A, disbursement of US$500,000 (equivalent, on the transaction date, to R$2,638,221) of its revolving credit facility maintained with certain financial institutions with quarterly payments of 1.30% plus quarterly LIBOR and maturity in February 2024.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 18.6.3. | Brazilian National Bank for Economic and Social Development (BNDES) |
On June 29, 2020, the Company raised with BNDES the amount of R$400,000 indexed to the Selic interest rate, plus fixed interest of 1.96% p.a., with an average term of 124 months, maturing in February 2040. This funding is in line with the company’s strategy of lengthening of the average of its obligations and efficiency in servicing its debt (cost of debt).
On December 22, 2020, the Company raised with BNDES the amount of R$131,774, of which R$ 100,000 referring to a second release of the contract raised above and R$31,774 indexed to the long-term interest rate (“TLP”), plus fixed interest of 1.77% p.a., with an average term of 121 months, maturing in November 2034.
| 18.6.4. | Issuance of Sustainability-linked Notes 2031 (“Notes 2031”) |
On September 14, 2020, the Company, through its wholly-owned subsidiary Suzano Austria GmbH (“Suzano Austria”), issued Senior Notes totaling US$ 750,000 (R$ equivalent to R$3,973,831 on the transaction date) with yield of 3.950% per annum, with a coupon of 3.750% p.a., to be paid semi-annually as of January 15, 2021 and with the principal amount due on January 15, 2031.
The Notes have environmental performance indicators (“KPIs”) associated with a goal of reducing GHG emissions by the Company by 2025, evidencing Suzano’s commitment as part of the solution to the global climate crisis and in convergence to the implementation of its Long Term Goal. Under the terms of the Notes, if the Company does not satisfy the Sustainability Performance Target and provide confirmation thereof to the Trustee together with a related confirmation by the External Verifier at least 30 days prior to July 16, 2026, the interest rate payable on the Notes will be increased by 25 basis points from July 16, 2026 to the Maturity Date. Additionally, pursuant to the Sustainability-Linked Securities Framework, the Company has committed to publish annually a Sustainability Report, together with a verification assurance report issued by the External Verifier. Thus, the new debt securities are characterized as sustainability-linked bonds, according to the principles promulgated by the Capital Markets Association.
| 18.6.5. | Sustainability-Linked Notes 2031 (“Notes 2031”) |
On November 19, 2020, the Company, through its wholly-owned subsidiary Suzano Austria GmbH (“Suzano Austria”), made an additional issue of debt securities under Senior Notes 2031, in the principal amount of US$500,000 (equivalent to R$2,666,484 on the transaction date) coupon of 3.750% p.a. (yield to maturity of 3.100% p.a.), to be paid semi-annually as of January 15, 2021 and with the principal amount due on January 15, 2031.
| 18.7. | Relevant transactions settled in the year |
| 18.7.1. | Export Prepayment Agreements (“EPP”) |
On February 14, 2020, Suzano, through its wholly-owned subsidiary Suzano Pulp and Paper Europe S.A., voluntarily prepaid the export prepayment agreement in the amount of U.S.$755,864 (equivalent, on the transaction date, to R$3,240,229), with quarterly interest payments of 1.15% p.a. plus quarterly LIBOR, which was scheduled to mature in February 2023.
On December 7, 2020, the Company, through its subsidiary Suzano Pulp and Paper Europe S.A., partially settled the export prepayment agreement in the total amount of US$300,000 (equivalent on the transaction date to R$1,355,362), with original maturity in December 2023 and quarterly interest rate of 1.15% p.a. plus quarterly LIBOR.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 18.7.2. | Make-whole Senior Notes (“Notes 2021”) |
On March 31, 2020, the Company through its wholly-owned subsidiary Suzano Trading Ltd., redeem all of the outstanding of Senior Notes 2021 in the total amount of US$199,864 (equivalent, on the transaction date, to R$1,039,032) considering redemption price of 104.287% plus interest proportional to the period.
| 18.7.3. | Agribusiness Receivables Certificates (“CRA”) |
On April 13, 2020, the Company disbursed the total amount of R$612,779, from this amount R$600,000 was related to the payment of principal and R$12,779 of interest of the Agribusiness Receivables Certificate issued in April 2016, with interest of 98% of the CDI, this payment was made due to the normal maturity of the CRA.
On June 22, 2020, the single installment of the CRA principal of R$880,155, issued in June 2016, with 97% interest on the CDI, matured. The company disbursed R$895,655 as principal (R$880,155) and interest (R$15,500).
On November 14, 2020, the single installment of the CRA principal in the amount of R$1,000,000, issued in November 2016, with interest of 96% of the CDI, matured. The Company disbursed the amount of R$1,009,068, considering the last installment of interest on the operation.
| 18.7.4. | Revolving credit facility |
On August 13, 2020, in accordance with the announced to the market made on March 30, 2020, the Company announced the early return of the revolving credit facility in the amount of US$ 500,000 (equivalent to R$2,638,221 on the date of the transaction) hired on April 1, 2020, at LIBOR + 1.30% p.a., with an average term of 47 months and final maturity in February 2024. The settlement was on August 20, 2020 in the amount of R$ 2,848,097 (principal and interest) and, once realized, these funds became fully available as a source of additional liquidity for the Company, if necessary.
| 18.7.5. | Notes Tender Offer (“Notes 2024, 2025 e 2026”) |
The proceeds obtained from the issuance of Notes 2031, detailed in note 18.6.4., were used for the partial repurchase of Senior Notes issued by Fibria Overseas Finance Ltd and Suzano Austria GmbH, Suzano’s wholly-owned subsidiaries, as follows (i) partial settlement of US$247,207 (equivalent to R$1,303,473) at a price of 110.8% of the issue value plus the proportional interest of Senior Notes issued by Fibria Overseas currently in circulation with a coupon (interest) of 5.25% p.a. and maturity in May 2024 (“Notes 2024”); (ii) partial settlement of US$260,348 (equivalent to R$1,372,763) at the price of 106.6% of the issue value plus the proportional interest of Senior Notes issued by Fibria Overseas currently in circulation with a coupon (interest) of 4.00% p.a. and maturity in January 2025 (“Notes 2025”); and (iii) partial settlement of US$183,419 (equivalent to R$967,138 on the payment date) at a price of 115.2% of the issue value plus the proportional interest of Senior Notes issued by Suzano Austria, with a coupon (interest) of 5.75% p.a. and maturity in July 2026 (“Notes 2026”).
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
In the execution of the partial repurchase, premium payments were made in the amounts of US$26,698 (equivalent to R$140,775 on the transaction date), US$17,183 (equivalent to R$90,602 on the transaction date) and US$25,506 (equivalent to R$134,488 on the transaction date) to the bondholders of Notes 2024, 2025 and 2026, respectively, recognized in the financial result.
In the partial repurchase of Notes 2026, the Company determined that there was no substantial change under of the existing bonds, therefore, this transaction was recorded as a modification of the financial liability. The amount of US$2,374 (equivalent R$ 12,518 on the transaction date) paid for the exchange will be amortized over the term of Notes 2031, in accordance with the requirements of IFRS 9.
The settlement of the process of repurchase occurred on September 15, 2020.
| 18.7.6. | Central West Development Fund (“FDCO”) |
On December 28, 2020, the Company prepaid the financing credit agreement raised with the Midwest development Fund in the amount of R$512,012, with original maturity in December 2027 and semiannual interest rate of 8.00% p.a.
Some loan and financing agreements have guarantees clauses, in which the financed equipment or other property, plant and equipment are offered by the Company, as disclosed in Note 15.1.
The Company does not have contracts with restrictive financial clauses (financial covenants) to be complied with.
The rollforward of year ended December 31, 2020 is set forth below:
| | | | Lands and
Farms | | | Machines and
Equipment’s | | | Buildings | | | Ships and
boats | | | Vehicles | | | Total | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2018 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Initial adoption on January 1, 2019 | | | | 1,762,943 | | | | 143,685 | | | | 41,570 | | | | 1,408,640 | | | | 1,012 | | | | 3,357,850 | |
| Additions | | | | 260,982 | | | | 1,529 | | | | 39,794 | | | | 612,022 | | | | | | | | 914,327 | |
| Amortization (1) | | | | (254,280 | ) | | | (15,163 | ) | | | (35,365 | ) | | | (116,207 | ) | | | (925 | ) | | | (421,940 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2019 | | | | 1,769,645 | | | | 130,051 | | | | 45,999 | | | | 1,904,455 | | | | 87 | | | | 3,850,237 | |
| Additions | | | | 858,085 | | | | 45,624 | | | | 90,616 | | | | 95,768 | | | | 2,675 | | | | 1,092,768 | |
| Amortization (1) | | | | (265,091 | ) | | | (18,078 | ) | | | (43,903 | ) | | | (122,904 | ) | | | (313 | ) | | | (450,289 | ) |
| Write-offs (2) | | | | (74,578 | ) | | | (72,332 | ) | | | (1,728 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | (148,638 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2020 | | | | 2,288,061 | | | | 85,265 | | | | 90,984 | | | | 1,877,319 | | | | 2,449 | | | | 4,344,078 | |
| 1) | On December 31, 2020, the amount of R$263,613 (R$268,081 as of December 31, 2019) related to land was reclassified to biological assets to compose the formation cost. |
| 2) | Lands and Farms, write-off due to the incorporation of legal entities (note 1.1) and machines and equipment, write-off due to the cancellation of contracts. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
For the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company is not committed to lease agreements not yet in force.
The balance of lease payables for the year ended December 31, 2020, measured at present value and discounted by the respective discount rates are set forth below:
| Nature of agreement | | Average rate - % p.a. (1) | | | Maturity (2) | | | Present value of liabilities | |
| Lands and farms | | 11.45 | | | | July 2048 | | | | 2,361,538 | |
| Machines and Equipment’s | | 10.62 | | | | July 2032 | | | | 189,061 | |
| Buildings | | 9.80 | | | | December 2030 | | | | 81,144 | |
| Ships and boats | | 11.39 | | | | February 2039 | | | | 2,557,824 | |
| Vehicles | | 10.04 | | | | October 2023 | | | | 2,193 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | 5,191,760 | |
| 1) | To determine the discount rates, quotes were obtained from financial institutions for agreements with characteristics and average terms similar to the lease agreements. |
| 2) | Refers to the original maturities of the agreements and, therefore, do not consider eventual renewal clause. |
On March 12 and April 12, 2020, for a period of 10 months, two of the ships leased by the Company were made available for chartering from third parties. In the amount of US$7,500 (equivalent, on the transaction date, to R$35,841). In the year ended December 31, 2020, this transaction is effective. Additionally, the Company is evaluating the renewal of this transaction under the same conditions as before, only replacing the ships, due to the need for planned operational maintenance.
The rollforward in the balances in the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 are as follows:
| Balance as of December 31, 2018 | | | |
| Initial adoption on January 1, 2019 | | | 3,428,897 | |
| Additions | | | 914,327 | |
| Payments | | | (646,487 | ) |
| Accrual of financial charges | | | 275,404 | |
| Exchange rate variation | | | 11,929 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2019 | | | 3,984,070 | |
| Additions | | | 1,092,768 | |
| Write-offs | | | (148,638 | ) |
| Payments | | | (824,245 | ) |
| Accrual of financial charges (1) | | | 486,286 | |
| Exchange rate variation | | | 601,519 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2020 | | | 5,191,760 | |
| | | | | |
| Current | | | 620,177 | |
| Non-current | | | 4,571,583 | |
| 1) | On December 31, 2020, the amount of R$88,540 related to interest expenses on leased lands was capitalized to biological assets to compose the formation cost (R$50,795 as of December 31, 2019). |
The maturity schedule of future payment not discounted to present value related to lease liabilities is disclosed in Note 4.2.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 19.2.1. | Amounts recognized in the statement of income for the year |
In the year ended December 31, 2020, and 2019 are set for the below:
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Expenses relating to short-term assets | | | 7,365 | | | | 37,007 | |
| Expenses relating to low-value assets | | | 12,182 | | | | 14,349 | |
| | | | 19,547 | | | | 51,356 | |
| 20. | PROVISION FOR JUDICIAL LIABILITIES |
The Company is involved in certain legal proceedings arising from the normal course of business, which include tax, labor, civil and environment risks.
The Company classifies the risk of unfavorable decisions in the legal proceedings, based on legal advice, which reflect the estimated probable losses. Contingencies classified as possible loss are disclosed based on reasonably estimated amounts.
The Company’s management believes that, based on the elements existing at the base date of these unaudited condensed consolidated interim financial information, its provision for tax, civil, environment and labor risks, accounted for according to IAS 37 is sufficient to cover estimated losses related to its legal proceedings, as set forth below:
| 20.1. | Rollforward of provisions for probable losses, net of judicial deposits |
| | | December 31, 2020 | |
| Nature of provisions | | Judicial
deposits | | | Provision | | | Provision, net | |
| Taxes and social security | | | (135,641 | ) | | | 2,984,230 | | | | 2,848,589 | |
| Labor | | | (57,780 | ) | | | 217,180 | | | | 159,400 | |
| Civil and environment | | | (3,495 | ) | | | 251,461 | | | | 247,966 | |
| | | | (196,916 | ) | | | 3,452,871 | | | | 3,255,955 | |
| | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Nature of provisions | | Judicial
deposits | | | Provision | | | Provision, net | |
| Taxes and social security | | | (124,133 | ) | | | 3,176,503 | | | | 3,052,370 | |
| Labor | | | (50,464 | ) | | | 227,139 | | | | 176,675 | |
| Civil and environment | | | 273 | | | | 283,159 | | | | 283,432 | |
| | | | (174,324 | ) | | | 3,686,801 | | | | 3,512,477 | |
| 20.1.1. | Changes in the provision according to the nature of the proceedings for probable losses |
| | | December 31, 2020 | |
| | | Tax and social
security | | | Labor | | | Civil and
environment | | | Contingent
liabilities (1) (2) | | | Total | |
| Beginning balance | | | 492,413 | | | | 227,139 | | | | 64,897 | | | | 2,902,352 | | | | 3,686,801 | |
| Payments | | | (23,162 | ) | | | (43,783 | ) | | | (14,618 | ) | | | | | | | (81,563 | ) |
| Write-off | | | (23,106 | ) | | | (52,333 | ) | | | (25,223 | ) | | | (193,099 | ) | | | (293,761 | ) |
| Additions | | | 20,560 | | | | 64,053 | | | | 17,337 | | | | | | | | 101,950 | |
| Monetary adjustment | | | 9,365 | | | | 22,104 | | | | 7,975 | | | | | | | | 39,444 | |
| Ending balance | | | 476,070 | | | | 217,180 | | | | 50,368 | | | | 2,709,253 | | | | 3,452,871 | |
| 1) | Amounts arising from lawsuits with probability of loss possible and remote, of tax nature in the amount of R$2,508,162 and civil in the amount of R$201,091, measured and recorded at the estimated fair value resulting from the business combination with Fibria, in accordance with paragraph 23 of IFRS 3 – Business Combination. |
| 2) | Reversal due to a change in prognosis and/or settlement. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| | | December 31, 2019 | |
| | | Tax and social
security | | | Labor | | | Civil and
environment | | | Contingent
liabilities (1) | | | Total | |
| Beginning balance | | | 296,869 | | | | 50,869 | | | | 3,532 | | | | | | | | 351,270 | |
| Business combination | | | 139,462 | | | | 185,157 | | | | 64,974 | | | | | | | | 389,593 | |
| Payments | | | (34 | ) | | | (34,794 | ) | | | (5,532 | ) | | | | | | | (40,360 | ) |
| Write-off | | | (3,875 | ) | | | (55,730 | ) | | | (13,434 | ) | | | | | | | (73,039 | ) |
| Additions | | | 46,603 | | | | 50,521 | | | | 10,100 | | | | 2,902,352 | | | | 3,009,576 | |
| Monetary adjustment | | | 13,388 | | | | 31,116 | | | | 5,257 | | | | | | | | 49,761 | |
| Ending balance | | | 492,413 | | | | 227,139 | | | | 64,897 | | | | 2,902,352 | | | | 3,686,801 | |
| 1) | Amounts arising from lawsuits with probability of loss possible and remote, measured and recorded at the estimated fair value resulting from the business combination with Fibria, in accordance with paragraph 23 of IFRS 3 – Business Combination. |
| 20.1.2. | Tax and social security |
For the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company was a defendant in 51 (fifty-one) administrative proceedings as well as tax lawsuits in which the disputed matters related, CSLL, IRRF, PIS, COFINS, Social Security Contribution, ICMS, among others whose amounts are provisioned for when the likelihood of loss is deemed probable by the Company’s external legal counsel and the Management.
For the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company was a defendant in 1,010 (one thousand and ten) labor lawsuits.
In general, labor lawsuits are related primarily to matters frequently contested by employees in agribusiness companies, such as certain wages and/or severance payments, in addition to suits filed by outsourced employees of the Company.
| 20.1.4. | Civil and environment |
For the year ended December, 2020, the Company is a defendant in approximately in 58 (fifty eight) civil and environmental lawsuits.
Civil proceedings are related primarily to payment of damages, such as those resulting from contractual obligations, traffic-related injuries, possessory actions, environmental restoration obligations, claims and others.
| 20.2. | Provisions for possible losses |
The Company is involved in tax, civil and labor lawsuits, for which losses have been assessed as possible by management with the support from legal counsel and therefore no provision was recorded:
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Taxes (1) | | | 7,145,147 | | | | 7,504,398 | |
| Labor | | | 263,971 | | | | 279,934 | |
| Civil and environment (1) | | | 3,068,884 | | | | 2,995,576 | |
| | | | 10,478,002 | | | | 10,779,908 | |
| 1) | The amounts above does not include the fair value adjustment allocated to probable contingencies of R$2,677,970, which were recorded at fair value resulting from business combinations with Fibria, in accordance with paragraph 23 of IFRS 3 – Business Combination, as presented in note 20.1.1. above. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 20.2.1. | Tax and social securities |
The Company is a defendant in 782 (seven hundred eighty two ) tax proceedings whose likelihood of loss is considered possible, in the total amount of R$7,145,147 for which there is no provision was recorded.
The other tax and social security lawsuits refer to various taxes, such as IRPJ, CSLL, PIS, COFINS, ICMS, ISS, Withholding Income Tax (“IRRF”), PIS and COFINS, mainly due to differences in interpretation of applicable tax rules and information provided in accessory obligations.
The most relevant tax cases are set forth below:
| (i) | Income tax assessment - IRPJ/CSLL - Swap of industrial and forestry assets: in December 2012, the Company received a tax assessment for the collection of income tax and social contribution, alleging unpaid tax on a capital gain in February 2007, closing of the transaction, when the Company executed an agreement with International Paper for the swap of industrial and forestry assets. |
On January 19, 2016, the Tax Federal Administrative Court (“CARF - Conselho Administrativo de Recursos Fiscais”) rejected as per the casting vote of CARF’s President, the appeal filed by the Company in the administrative process. The Company was notified of the decision on May 25, 2016 and due to the impossibility of new appeal and the consequent closure of the case at the administrative level, decided to continue the discussion with the Judiciary. The Company presented judicial guarantee, which was accepted, and is now awaiting the judgement of the case. We maintain our position to not constitute provisions for contingencies, based on the Company’s and its external legal advisors’ opinion that the probability of loss on this case is possible. The documents have been concluded for judgment since November 25, 2017. In the year ended December 31, 2020 the amount is R$2,296,032 (R$2,251,462 as of December 31, 2019).
| (ii) | Income tax assessment - IRPJ/CSLL - disallowance of depreciation, amortization and depletion expenses – 2010: in December 2015, we received a tax assessment requiring the payment of IRPJ and CSLL, questioning the deductibility of depreciation, amortization and depletion expenses of 2010 included by us in the calculation of income tax expense. We present administrative appeal on the legal period, judged partially valid. The decision was object of voluntary recourse, presented by us in November 2017. On October 16, 2018, the judgement was converted into a diligence, through resolution n. 1402-000723. Currently, the resolution is expected to be formalized. In the year ended December 31, 2020 the amount is R$712,531 (R$695,679 as of December 31, 2019). |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| (iii) | IRPJ/CSLL - partial approval: the Company requested approval to offset 1997 tax losses with amounts owed to the tax authorities. The authorities approved in March 2009, only R$83,000, which generated a difference of R$51,000. The Company is still awaiting the conclusion of the analysis of the credits discussed at the administrative level following a favorable decision of CARF in August 2019, which granted the Voluntary Appeal filed by the Company. For the remaining credit, the Company has appealed the rejection of the tax credits and obtained a partially favorable decision and the final decision is under discussion in the judicial level. Shortly after, an appeal was filed, which was judged in session, it was determined the conversion of the done in diligence. On November 6, 2018, a decision was filed reinforcing the tax authorities’ conclusion at the first approval and our arguments. In the year ended December 31, 2020 the amount is R$104,873 (R$254,081 as of December 31, 2019). |
| (iv) | Tax incentive - Agency for the Development of Northeastern Brazil (“ADENE”): in 2002 the Company was granted its request by the Brazilian Federal Revenue Service (“Receita Federal do Brasil”) to benefit from reductions in corporate income tax and non-refundable surcharges calculated on operating profits (as defined) for Aracruz facilities A and B (period from 2003 to 2013) and plant C (period from 2003 to 2012), when the qualification reports for the tax reductions are approved by SUDENE. |
In 2004, the Company was served an Official Notice by the liquidator of the former Superintendence for the Development of the Northeast (“SUDENE”), who reported that, the right to use the benefit previously granted is unfounded and would be cancelled. In 2005, the Brazilian Federal Revenue Service served the Company an assessment notice requiring the payment of the amounts of the tax incentive used, plus interest. After administrative discussion, the assessment notice was partially upheld and recognized the Company’s right to the tax incentive through 2003.
The Company’s Management, supported by its legal counsel, believes that the decision to cancel the tax benefits is erroneous and should not prevail, either with respect to benefits already used, or with respect to benefits not used until the corresponding final periods. In the year ended December 31, 2020 the amount is R$127,391 (R$125,191 as of December 31, 2019).
| (v) | PIS/COFINS – Goods and services – 2009 to 2011: in December 2013, the Company was assessed by the Brazilian Federal Revenue Service demanding the collection of PIS and COFINS credits disallowed because they are not allegedly linked to its operating activities. In the first instance, the objection filed by the Company was dismissed. After the Voluntary Appeal was filed, it was partially provided in April 2016. From this decision, the National Treasury filed a Special Appeal to the Superior Chamber and the Company filed a Statement of Appeal, which are still pending judgment. The updated amount involved up to December 31, 2020 is R$166,355 (R$162,750 as of December 31, 2019). |
| (vi) | Offsetting - IRRF - period 2000: the Company filed a lawsuit for offsetting IRRF credits measured in the year ended December 31, 2000 with debts owed to the Brazilian Federal Revenue Service. In April 2008, the Brazilian Federal Revenue Service partially recognized the credit in favor of the Company. From this decision, the Company filed a Voluntary Appeal with CARF, which is pending judgment. In the year ended December 31, 2020 the amount is R$109,903 (R$108,320 as of December 31, 2019). |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| (vii) | Tax assessment - Corporate Income Tax and Social Contribution: on October 5, 2020, the Company was notified about the tax assessment issued by the Brazilian Internal Revenue Service claiming the payment of Corporate Income Tax and Social Contribution, in the total amount of R$454,898, resulting from the remeasurement of profit of its wholly-owned subsidiary Suzano Trading Ltd in the years ended December 31, 2014, 2015 and 2016. Besides the Company, Statutory Executive Officers’ (“Officers”) from Suzano Trading were also included as co-responsible. The legal counsel considered the risk of loss as possible in regards to the Company and, in reference to the Officers, also possible but with more chances of winning (possible to remote). |
| (viii) | Tax assessment - taxation on a universal basis - year 2015: on November 3, 2020, the Company received a tax assessment for the collection of income tax and social contribution, alleging unpaid tax on calendar year 2015, due to the lack of addition, in determining taxable income and the social contribution calculation basis, of profits earned by subsidiaries abroad. The legal advisors hired by the Company classify the prognosis as a possible loss. Currently, the defense presented at the administrative level is awaiting judgment. In the year ended December 31, 2020 the amount is R$145,026. |
On December 31, 2020, the Company was a defendant in 1,653 (one thousand, six hundred and fifty-three) labor lawsuits, totaling R$263,971.
The Company also has several lawsuits in which employees’ unions in the states of Bahia, Espírito Santo, Maranhão, São Paulo and Mato Grosso do Sul are included.
| 20.2.3. | Civil and environmental |
On December 31, 2020, the Company is a defendant in approximately 324 (three hundred and twenty-four) civil and environmental lawsuits, totaled the amount of R$3,068,884. Most of these civil lawsuits refers to claims for compensation by former employees or third parties for alleged occupational illnesses and workers’ compensation, collection lawsuits and bankruptcy situations, reimbursement of funds claimed from delinquent landowners and possessory actions filed in order to protect the Company’s equity. The Company has insurance for public liability that covers, within the limits set in the policy, unfavorable sentences in the civil courts for claims for compensation of losses.
Regarding civil matters, we are involved in 2 (two) Public Civil Claims (“Ação Civil Pública”) filed by the Federal Public Prosecution Office requesting (i) a preliminary injunction to prohibit Company’s trucks from transporting wood in federal highways above legal weight restrictions (ii) an increase in the fine for cases of overweight and (iii) compensation for damages to property allegedly caused to federal highways, the environment and the economic order, and compensation for moral damages. One of the Claims was ruled against the Company. Suzano presented an appeal to the Court of Appeals, requesting an interim relief to stay the effects of such ruling until a final decision is reached. We are currently waiting for the ruling on the interim relief by the 1st Regional Federal Court Appeals.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The Company is still defendant in a 2 (two) Public Civil Claim filed by the Federal Prosecutor’s Office regarding real properties acquired by Company in the northern region of the state of Espírito Santo. In the 1st. the Federal Prosecutor requested (i) the nullity of the deeds (ii) compensation for moral damages and (iii) suspension of financing for Company’s operations in the municipalities of São Mateus and Conceição da Barra, both located in the state of Espírito Santo. A preliminary injunction was granted, which blocked around 6,000 hectares of Company’s land in such municipalities and suspended any financing for Suzano by BNDES for either production or planting of eucalyptus pulp on the properties relating to the Public Civil Claim. In the 2nd, the Federal Prosecutor’s Office, requesting the nullity of the deeds of some other proprieties acquired in the northern of the state of Espírito Santo. A preliminary injunction was granted blocking around 5,601 hectares of Company’s lands in the same municipalities of São Mateus and Conceição da Barra. Suzano presented its judicial defense and an appeal against such injunction, which is still pending decision. Both cases are pending ruling by the Federal District Court of São Mateus and remain in pre-trial phase. The Company believes that are good grounds for our defense since the acquisition of the lands discussed in both Public Civil Claims was made in accordance with applicable laws and practices applicable at the time of purchase.
Regarding environmental matters, we are involved in 3 (three) relevant Public Civil Claims filed by the Federal Public Prosecution Office in the northeast region of Brazil challenging the State’s environmental agency’s jurisdiction to grant environmental licenses. The Federal Public Prosecution Office alleges that the environmental licensing proceedings related to the forest formation and installation of our industrial plant in the state of Maranhão should be carried out by the Brazilian Federal Environmental Agency (“Agência Federal do Meio Ambiente - IBAMA”). The risks involved in such cases are delays in our plantation schedule and the suspension of the Maranhão unit activities until new permit is issued. Although an injunction was granted on one of this claims suspending the forest formation in a certain region of the State of Maranhão, we believe there are good grounds for our defense, since IBAMA does not acknowledge having jurisdiction to perform the licensing proceedings and there is no clear legal ground to sustain such jurisdiction. Superior court’s is still to rule on an appeal against the injunction granted against Suzano and the other claims are still pending a decision by the trial judge.
In addition, we are involved in a dispute related to possible environmental damage in Cubatão city located in the State of São Paulo), allegedly caused by Companhia Santista, a company that was acquired by Ripasa, which in turn was acquired by Suzano in 2008. This lawsuit is ongoing for over 30 (thirty) years and involves more than 20 (twenty) other companies. The lawsuit seeks reparation for the environmental damage allegedly caused in area under environmental protection of Serra do Mar’s State Park by several companies that maintained activities in the industrial district of Cubatão until the 1990s. On September 2017, the lawsuit was ruled in favor of the plaintiff, sentencing the defendant companies to recover the damages allegedly caused or, should the environment be already recovered, to pay a compensation of equal value of the cost of the recovery. This compensation is to be allocated to expand Serra do Mar’s State Park. The ruling, however, did not determined the amount that should be paid as compensation, leaving the definition of this value to a latter procedural stage. This ruling was contested by the companies on an appeal and a decision by the State Supreme Court is still pending.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 20.3.1. | Exclusion of VAT (ICMS) from PIS and COFINS tax base |
The Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries have filed lawsuits to discuss their rights to exclude ICMS from the PIS and COFINS tax basis, comprising periods since March 1992 and comprising, eventual amendments in the regulation after the issuance of Law nº 12,973/2014.
Regarding this matter, the Federal Supreme Court (“STF”) ruled on March 15, 2017, at first without the possibility of reversing the understanding on the merits, that the ICMS does not part of the calculation basis of relating contributions. The Federal Government filed an amendment of judgment in October 2017 aiming, among other requests, to modulate the effects of related decision based on the judgment of said amendment of judgment, which are still pending judgment.
Based on the decision of the Supreme Court and the legal opinions of its legal advisors, the Company understands that a change in the outcome of the Supreme Court judgment is unlikely. Accordingly, the ICMS was excluded from the calculation basis of such contributions as from August 2018, based on a favorable decision rendered by the Company, still pending final judgment.
| 21. | EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLANS |
The Company offers supplementary pension plan and defined benefit plan, such as medical assistance and life insurance, as set forth below:
The Company has two current supplementary retirement plans, as disclosed below.
| 21.1.1. | Pension plan – Suzano Prev |
In 2005, the Company established the Suzano Prev pension plan managed by BrasilPrev, an open private pension entity, which serves employees of Suzano Group Companies, in the defined contribution plan.
Under the terms of the benefit plan agreement, for employees who have a salary above 10 URS’s, in addition to the 0.5% contribution, the contributions of the company follow the employees’ contributions and affect on the portion of the salary that exceeds the 10 URS’s, which can vary from 1% to 6% of the nominal salary. This plan is called Basic Contribution1.
The Company’s contributions to the employee are 0.5% of the nominal salary that does not exceed 10 Suzano reference units (“URS”), even though there is no contribution from the employee. This plan is called Basic Contribution 2.
From August 2020, for employees who have a salary lower than 10 URS’s, they will be able to invest 0.5 or 1.0% of the nominal salary and the Company will monitor the employee’s contributions. The employee can choose to invest up to 12% of the salary in the Suzano Prev pension plan, and the excess of Basic Contribution 1 or 2 may be invested in the supplementary contribution, where there is no counterpart from the Company and the employee must consider the two contributions to limit 12% of the salary.
Contributions made by the Company for the year ended December 31, 2020 totaled R$9,388 (R$5,993 as of December 31, 2019) recognized in under employee benefits.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 21.1.2. | Pension plan – FUNSEJEM |
Entities from the business combination with Fibria, managed by a private pension entity, which provide post-employment benefits to employees, under defined contribution plans. In this type of plan participants and sponsor contribute to the formation of an individual savings. In 2000, the Company became a sponsor of the Senador José Ermírio de Moraes Foundation (FUNSEJEM), a not-for-profit pension fund for the employees of the Votorantim Group. Under the fund’s regulations, employees’ contributions to FUNSEJEM, which may range from 0.5% to 6% of nominal salary.
Contributions made by the Company, for Senador José Ermírio de Moraes Foundation (“FUNSEJEM”) pension plan, for the year ended December 31, 2020 amounted to R$5,071 (R$9,920 as of December 31, 2019), recognized under cost of sales, selling and general and administrative expenses.
In July 2020, the Company terminated its relationship with FUNSEJEM. On the occasion that the amounts contributed by employees are released by FUNSEJEM, employees will choose for portability to the Suzano Prev pension plan, to the private pension plan or request the total redemption of the constituted balance. This action is still due to the harmonization of practices arising from the business combination with Fibria.
| 21.2. | Defined benefits plan |
The Company offers the following post-employment in addition to the pension plans, which are measured by actuarial calculation and recognized in the financial statement.
| 21.2.1. | Medical assistance |
The Company guarantees health care program cost coverage for a group of former employees who retired until 1998 and until 2003 at the Suzano, São Paulo administrative office and Limeira and until 2007 at the Jacareí unit, as well as their spouses for life and dependents while they are underage.
For other group of former employees, who exceptionally, according to the Company’s criteria and resolution or according with rights related to the compliance with pertinent legislation, the Company ensures the healthcare program.
Main actuarial risks related are (i) lower interest rates (ii) longer than expected mortality tables, (iii) higher than expected turnover and (iv) higher than expected medical costs growth.
The Company offers the life insurance benefit to the group of former employees who retired until 2005 at Suzano and São Paulo administrative office and did not choose for the supplementary retirement plan.
Main actuarial risks related are (i) lower interest rates and (ii) higher than expected mortality.
| 21.2.3. | Rollforward of actuarial liability |
The rollforward of actuarial liability prepared based on actuarial report, are set forth below:
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | | | 430,427 | |
| Business combination | | | 147,877 | |
| Interest on employee benefits | | | 44,496 | |
| Actuarial loss | | | 147,640 | |
| Benefits paid in the year | | | (34,261 | ) |
| Balance on December 31, 2019 | | | 736,179 | |
| Interest on employee benefits | | | 53,092 | |
| Actuarial loss/gain | | | 33,843 | |
| Employee contribution | | | (88 | ) |
| Exchange rate variation | | | 487 | |
| Benefits paid in the year | | | (38,468 | ) |
| Balance on December 31, 2020 | | | 785,045 | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 21.2.4. | Economic actuarial assumptions and biometric data |
The main economic actuarial assumptions and biometric data used in the actuarial calculations are set forth below:
| | | December 31,
2020 | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Economic | | | | | |
| Discount rate – medical assistance and life insurance | | 4.39% p.a. | | 3.56% p.a. | |
| Medical cost growth rate | | 3.25% p.a. | | 3.25% p.a. | |
| Nominal inflation | | 3.25% p.a. | | 3.50% p.a. | |
| Aging factor | | 0 to 24 years: 1.50% p.a. 25 to 54 years: 2.50% p.a. 55 to 79 years: 4.50% p.a. Above 80 years: 2.50% p.a. | | 0 to 24 years: 1.50% p.a.
25 to 54 years: 2.50% p.a.
55 to 79 years: 4.50% p.a.
Above 80 years: 2.50% p.a. | |
| Biometric | | | | | |
| Table of general mortality | | AT-2000 | | AT-2000 | |
| Table of mortality of disable persons | | IAPB 57 | | IAPB 57 | |
| Table of entry of disable | | Mercer Disability | | Mercer Disability | |
| Turnover | | 1.00% p.a. | | 1.00% p.a. | |
| Other | | | | | |
| Retirement age | | 65 years | | 65 years | |
| | | 90% married | | 90% married | |
| Family composition | | Men 4 years + old | | Men 4 years + old | |
| Permanency in the plan | | 100% | | 100% | |
| 21.2.5. | Sensitivity analysis |
The Company made the sensitivity analysis regarding the relevant assumptions of the plans on December 31, 2020, as set forth below:
| Relevant assumptions | | Changes in
premise | | | Increase in present
value, net | | Decrease in present
value, net | |
| Discount rate | | | 0.50 | % | | Decrease of R$729,203 | | Increase of R$824,894 | |
| Medical costs growth rate | | | 1.00 | % | | Increase of R$876,554 | | Decrease of 689,324 | |
| 21.2.6. | Forecast and average duration of payments of obligations |
The following amounts represent the expected benefit payments for future years (10 years), from the obligation of benefits granted and the average duration of the plan obligations:
| Payments | | | Medical
assistance and
life insurance | |
| 2021 | | | | 35,658 | |
| 2022 | | | | 38,228 | |
| 2023 | | | | 40,886 | |
| 2024 | | | | 43,640 | |
| 2025 | | | | 46,409 | |
| 2026 on onwards | | | | 274,822 | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 22. | SHARE-BASED COMPENSATION PLAN |
For year ended December 31, 2020, the Company had 3 (three) share-based, long-term compensation plans, (i) Phantom stock option plan (“PS”) and (ii) Share Appreciation Rights (“SAR”), both settled in local currency and (iii) common stock options, settled in shares.
| 22.1. | Long term compensation plans (“PS and SAR”) |
Certain executives and key members of the Management have a long-term compensation plan linked to the share price with payment in cash.
Throughout 2020, the Company granted the SAR and PLUS (Share Appreciation Rights) (“SAR”) plans of phantom stock options. In this plan, the beneficiaries should invest 5% of the total amount corresponding to the number of options of phantom shares at the grant date and 20% after 3 (three) years to acquire the option. The Company also granted long-term incentive plans to its key members as part of its retention policy. In this program, the beneficiary does not make any investment.
The vesting period of options may vary from 3 (three) to 5 (five) years, as of the grant date, in accordance with the characteristics of each plan.
The price of the share is calculated based on the average share quote of the 90 previous trading sessions starting from the closing quote on the last business day of the month prior to the month of the grant. The installments of these programs will be adjusted by the variation in the price of the SUZB3 at B3, between the granting and the payment period. On dates when the SUZB3 shares is not traded, the quote of the previous trading session will be considered.
The phantom share options will only be due if the beneficiary is an employee of the Company on the payment date. In case of termination of the employment by initiative of the Company or by initiative of the beneficiary, before the vesting period is completed, the executive will not be entitled to receive all benefits, unless otherwise established in the agreements.
The rollforward is set forth below:
| | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | | | December 31,
2018 | |
| | | Number of shares | |
| Beginning balance | | | 5,996,437 | | | | 5,045,357 | | | | 5,055,519 | |
| Granted during of the year | | | 1,770,384 | | | | 2,413,038 | | | | 1,415,476 | |
| Exercised (1) | | | (1,789,413 | ) | | | (827,065 | ) | | | (751,859 | ) |
| Exercised due to resignation (1) | | | (21,253 | ) | | | (106,983 | ) | | | (153,601 | ) |
| Abandoned / prescribed due to resignation | | | (183,799 | ) | | | (527,910 | ) | | | (520,178 | ) |
| Ending balance | | | 5,772,356 | | | | 5,996,437 | | | | 5,045,357 | |
| 1) | The average price for share options exercised and exercised due to termination of employment, for the year ended December 31, 2020 was R$43.14 (forty-three Brazilian Reais and fourteen cents) (R$31.75 (thirty-one Brazilian Reais and seventy-five cents) as of December 31, 2019). |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
On December 31, 2020, the consolidated outstanding phantom shares option plans are as set forth below:
| | | December 31, 2020 | |
| Plan | | Grant date | | Exercise date | | | Fair value on grant
date (1) | | Quantity of
outstanding options
granted | |
| SAR 2016 | | April 1, 2016 | | | April 1, 2021 | | | R$15.96 | | | 6,972 | |
| PLUS 2016 | | April 1, 2016 | | | April 1, 2021 | | | R$15.96 | | | 4,177 | |
| SAR 2017 | | April 3, 2017 | | | April 3, 2022 | | | R$13.30 | | | 121,555 | |
| PLUS 2017 | | April 3, 2017 | | | April 3, 2022 | | | R$13.30 | | | 25,061 | |
| ILP 2017 - 48 | | April 3, 2017 | | | April 3, 2021 | | | R$13.30 | | | 304,512 | |
| ILP 2017 - 60 | | April 3, 2017 | | | April 3, 2022 | | | R$13.30 | | | 304,512 | |
| Deferral 2017 | | March 1, 2018 | | | March 1, 2021 | | | R$19.88 | | | 162,887 | |
| Deferral 2017 | | March 1, 2018 | | | March 1, 2022 | | | R$19.88 | | | 162,887 | |
| SAR 2018 | | April 2, 2018 | | | April 2, 2023 | | | R$21.45 | | | 677,627 | |
| PLUS 2018 | | April 2, 2018 | | | April 2, 2023 | | | R$21.45 | | | 74,592 | |
| ILP 2019 - 24 | | March 1, 2019 | | | March 1, 2024 | | | R$41.10 | | | 520,000 | |
| ILP 2019 - 36 | | March 1, 2019 | | | March 1, 2024 | | | R$41.10 | | | 520,000 | |
| Deferral 2018 | | March 1, 2019 | | | March 1, 2022 | | | R$41.10 | | | 88,632 | |
| Deferral 2018 | | March 1, 2019 | | | March 1, 2023 | | | R$41.10 | | | 88,632 | |
| ILP 2019 - 36 H | | March 25, 2019 | | | March 25, 2024 | | | R$42.19 | | | 7,500 | |
| ILP 2019 - 48 H | | March 25, 2019 | | | March 25, 2024 | | | R$42.19 | | | 7,500 | |
| ILP 2019 - 24 Apr | | 01/ April, 2019 | | | 01/ April, 2024 | | | R$42.81 | | | 20,000 | |
| ILP 2019 - 36 Apr | | 01/ April, 2019 | | | 01/ April, 2024 | | | R$42.81 | | | 20,000 | |
| SAR 2019 | | 01/ April, 2019 | | | 01/ April, 2024 | | | R$42.81 | | | 747,848 | |
| PLUS 2019 | | 01/ April, 2019 | | | 01/ April, 2024 | | | R$42.81 | | | 15,572 | |
| ILP - Retention 2019 - 24 | | October 1, 2019 | | | October 1, 2021 | | | R$31.86 | | | 93,518 | |
| ILP 2019 - 24 Oct | | October 1, 2019 | | | October 1, 2021 | | | R$31.75 | | | 7,800 | |
| ILP 2019 - 36 Oct | | October 1, 2019 | | | October 1, 2022 | | | R$31.75 | | | 19,500 | |
| ILP 2019 - 48 Oct | | October 1, 2019 | | | October 1, 2023 | | | R$31.75 | | | 11,700 | |
| ILP 2020 - 36 Apr | | April 1, 2020 | | | April 1, 2023 | | | R$38.50 | | | 43,705 | |
| ILP 2020 - 12 Apr | | April 1, 2020 | | | April 1, 2021 | | | R$38.50 | | | 25,500 | |
| ILP 2020 - 24 Apr | | April 1, 2020 | | | April 1, 2022 | | | R$38.50 | | | 21,250 | |
| SAR 2020 | | April 1, 2020 | | | April 1, 2025 | | | R$38.50 | | | 729,421 | |
| ILP 2020 - 36 Apr | | April 1, 2020 | | | April 1, 2023 | | | R$38.50 | | | 38,961 | |
| ILP 2020 - 12 Jul | | July 1, 2020 | | | July 1, 2021 | | | R$37.74 | | | 1,060 | |
| ILP 2020- 48 Condition A | | May 1, 2020 | | | April 30, 2024 | | | R$38.34 | | | 595,000 | |
| ILP 2020- 48 Condition B | | May 1, 2020 | | | April 30, 2024 | | | R$38.34 | | | 127,500 | |
| ILP 2020- 48 Condition C | | May 1, 2020 | | | April 30, 2024 | | | R$38.34 | | | 127,500 | |
| ILP - Retention 2020 - 36 Oct 1 | | October 1, 2020 | | | October 1, 2023 | | | R$38.79 | | | 36,650 | |
| ILP - Retention 2020 - 36 Oct 2 | | October 1, 2020 | | | October 1, 2023 | | | R$43.14 | | | 5,871 | |
| ILP Hiring/Retention Bonus 2020 - 36 Oct | | October 1, 2020 | | | October 1, 2023 | | | R$43.14 | | | 6,954 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | 5,772,356 | |
| (1) | Amounts expressed in Reais. |
| 22.2. | Common stock option plan |
Additionally, in 2020 the Company established a Restricted Shares plan based on the Company’s performance (Program 6). The Plan associates the quantity of Restricted Shares granted to the Company’s performance in relation to the operating cash generation target. The quantity of the restricted stock granted is defined in financial terms and is subsequently converted into shares based on the last 60 (sixty) stock exchange trading days on December 31, 2020 of SUZB3 at B3.
After measurement of operating cash generation 2020, the Restricted Shares will be granted immediately, as they not have to comply to the vesting period. However, the beneficiaries of the grant must comply to the lockup period of thirty-six (36) months during which they will not be able to market the shares.
In the event that the beneficiaries leave the Company before the end of the fiscal year for the measurement of operating cash generation, they will lose the right to the grant of Restricted Share.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The position is set forth below:
| Program | | | Date of grant | | | Deadline for the
options to become
exercisable | | Price on
grant date | | Shares Granted | | | Restricted year for
transfer of shares |
| Program 4 | | | | 01/02/2018 | | | 01/02/2019 | | R$39.10 | | | 130,435 | | | 01/02/2022 |
| 22.3. | Measurement assumptions |
In the case of the phantom shares plan, since the settlement is in cash, the fair value of options is remeasured at the end of each period based on the Monte Carlo Method (“MMC”), which is multiplied by the Total Shareholder Return (“TSR”) in the period (which varies between 75% and 125%, depending on the performance of SUZB3 in relation to its peers in Brazil).
The fair value of the plan of common shares of Program 6, was estimated based on the binomial probability model, which considers the dividends distribution rate and the following assumptions:
| (i) | the expectation of volatility was calculated for each exercise date, considering the remaining time to complete the vesting year, as well as the historical volatility of returns, using the GARCH model for calculating volatility; |
| (ii) | the expectation of average life of phantom stocks and stock options was defined by the remaining term until the limit exercise date; |
| (iii) | the expectation of dividends was defined based on historical earnings per share of the Suzano; |
| (iv) | risk-free weighted average interest rate used was the Brazilian Reais yield curve (DI expectation) observed on the open market, which is the best comparison basis with the Brazilian market risk-free interest rates. The rate used for each exercise date changes according to the vesting year. |
The amounts corresponding to the services received and recognized are set forth below:
| | | | Liabilities and equity | | | | Income statement | |
| | | | December 31,
2020 | | | | December 31,
2019 | | | | December 31,
2020 | | | | December 31,
2019 | | | | December 31,
2018 | |
| Non-current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Provision for phantom stock plan | | | 195,135 | | | | 136,505 | | | | (151,985 | ) | | | (46,389 | ) | | | (126,439 | ) |
| Shareholders’ equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Stock option granted | | | 10,612 | | | | 5,979 | | | | (4,632 | ) | | | (879 | ) | | | (5,170 | ) |
| Total general and administrative expenses from share-based transactions | | | | | | | | | | | (156,617 | ) | | | (47,268 | ) | | | (131,609 | ) |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 23. | LIABILITIES FOR ASSETS ACQUISITIONS AND SUBSIDIARIES |
| | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Lands and forests acquisition | | | | | | | | |
| Real estate receivables certificates (1) | | | 37,104 | | | | 78,345 | |
| | | | 37,104 | | | | 78,345 | |
| Business combination | | | | | | | | |
| Facepa (2) | | | 41,721 | | | | 42,533 | |
| Vale Florestar Fundo de Investimento em Participações (“VFFIP”) (3) | | | 423,403 | | | | 420,737 | |
| | | | 465,124 | | | | 463,270 | |
| | | | 502,228 | | | | 541,615 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Current | | | 101,515 | | | | 94,414 | |
| Non-current | | | 400,713 | | | | 447,201 | |
| 1) | Refers to obligations with the acquisition of land, farms, reforestation and houses built in Maranhão, updated by IPCA. |
| 2) | Acquired in March 2018, for the amount of R$307,876, upon payment of R$267,876 and the remaining updated at IPCA, adjusted by possible losses incurred up to the payment date, with maturities in March 2023 and March 2028. |
| 3) | On August 2014, the Company acquired the Vale Florestar S.A. through VFFIP, for the total amount of R$528,941 with a upon payment of R$44,998 and remaining with maturity to August 2029. The monthly settlements are subject to interest and updated by the variation of the U.S. Dollar exchange rate and partially updated by the IPCA. |
The Company entered into long-term take-or-pay agreements with chemicals, electricity transportation and natural gas suppliers. These agreements contain termination and supply interruption clauses in the event of default of certain essential obligations. Generally, the Company purchases the minimum agreed under the agreements, hence there is no liability recorded at December 31, 2019. The total contractual obligations assumed at December 31, 2020 equivalent to R$12,429,229 per year (R$7,335,609 at December 31, 2019).
On December 31, 2020, the Suzano’s share capital is R$9,269,281 divided into 1,361,263,584 common shares, all nominative, book-entry shares without par value. The share capital is net of the public offering expenses of R$33,735. The breakdown of the share capital is set forth below:
| | | Ordinary | |
| Shareholder | | Quantity | | | (%) | |
| Controlling Shareholders | | | | | | |
| Suzano Holding S.A. | | | 367,612,329 | | | | 27.01 | |
| Controller | | | 194,809,797 | | | | 14.31 | |
| Managements | | | 34,400,167 | | | | 2.53 | |
| Alden Fundo de Investimento em Ações | | | 26,154,741 | | | | 1.92 | |
| | | | 622,977,034 | | | | 45.77 | |
| Treasury | | | 12,042,004 | | | | 0.88 | |
| Votorantim S.A. | | | 50,180,059 | | | | 3.69 | |
| Other shareholders | | | 676,064,487 | | | | 49.66 | |
| | | | 1,361,263,584 | | | | 100.00 | |
On October 6, 2020 the Company closed, the secondary public offering of 150,217,425 common shares, without par value, of Suzano held by BNDES Participações S.A. – BNDESPAR, including 13,180,000 securities in the form of American Depositary Shares (“ADSs”), at a price per Security to the public of R$46.00 (forty-six Brazilian Reais), resulting in an aggregate sale price of R$6,910,002. The ADSs were offered and sold to the public at a price of U.S.$8.15 (eight U.S. Dollars and fifteen cents) per ADS. The price per security in the form of ADS corresponds to the price per security translated into U.S. Dollars, based on the selling exchange rate for U.S. Dollars (PTAX).
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
By resolution of the Board of Directors, the share capital may be increased, irrespective of any amendment to the Bylaws, up to the limit of 780,119,712 common shares, all exclusively book-entry shares.
For the year ended December 31, 2020, SUZB3 common shares ended the year quoted at R$58.54 (fifty-eight Brazilian Reais and fifty-four cents) (R$39.68 (thirty-nine Brazilian Reais and sixty-eight cents) on December 31, 2019).
The Company´s bylaws establishes that the minimum annual dividend is the lowest value between:
| (i) | 25% of adjusted net income for the year pursuant to Article 202 of Brazilian Law nº.6,404/76, or |
| (ii) | 10% of the Company’s consolidated operating cash generation for the year. |
In the year ended December 31, 2020, and 2019 no dividends were distributed, due to the loss in both year.
They are constituted by the allocation of the Company’s profits, after the allocation for the payment of the minimum mandatory dividends and after the allocation to the various profit reserves, as set forth below:
| (i) | legal: it is measured based on 5% (five percent) of net profit of each fiscal year as specified in article 193 of Brazilian Law nº.6,404/76, which shall not exceed 20% (twenty percent) of the share capital, whereas in the year in which the balance of the legal reserve plus the capital reserve amounts exceeds 30% (thirty percent) of the share capital, the allocation of part of the profit will not be mandatory. The use of this reserve is restricted to loss compensation and capital increase and aims to ensure the integrity of the share capital. On December 31, 2020, the reserve of R$317,144 was fully absorbed by the loss of the year. |
| (ii) | capital increase: it is measured basis of up to 90% (ninety percent) of the remaining balance of net income for the year and limited to 80% (eighty percent) of the share capital, pursuant to the Company’s Bylaws, after the allocation to the legal reserve and minimum mandatory dividends. The constitution of this reserve aims to ensure to the Company adequate operating conditions. This reserve was absorbed in full in 2019. |
| (iii) | special statutory: it is measured basis of up to 10% (ten percent) of the remaining balance of net income for the year and aims to ensure the continuity of the semiannual distribution of dividends, up to the limit of 20% (twenty percent) of the share capital. This reserve was absorbed in full in 2019. |
| (iv) | tax incentives: it is measured as specified in article 195-A of the Brazilian Law No. 6,404/76, modified by Brazilian Law nº.11,638/07, based on donation or the amounts of government grants for investment. This reserve was absorbed in full in 2019. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
They consist of amounts received by the Company arising from transactions with shareholders that do not pass through the income statement and may be used to absorb losses when they exceed profit reserves and redemption, reimbursement and purchase of shares.
The breakdown of capital reserves is arising from stock options in the amount of R$10,612 and the issuance of shares related to the business combination with Fibria in the amount of R$6,410,885. As of December 31, 2020, this reserve absorbed R$6,410,885 due to the loss for the year and the balance corresponded to 0.11% of the share capital.
These are changes that occur in shareholders’ equity arising from transactions and other events that do not originate with shareholders and are disclosed net of tax effects, as set forth below:
| | | Debenture
conversion
5th issue | | | Actuarial loss | | | Exchange
variation
and fair
value of
financial
assets | | | Exchange
variation on
conversion of
financial
statements of
foreign
subsidiaries | | | Deemed cost | | | Total | |
| Balances at December 31, 2018 | | | (45,746 | ) | | | (98,490 | ) | | | | | | | 164,168 | | | | 2,301,776 | | | | 2,321,708 | |
| Actuarial loss | | | | | | | (95,628 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (95,628 | ) |
| Gain on conversion of financial asset and fair value | | | | | | | | | | | 2,360 | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,360 | |
| Gain on conversion of financial statements and on foreign investments | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 45,819 | | | | | | | | 45,819 | |
| Realization of deemed cost, net of taxes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (52,918 | ) | | | (52,918 | ) |
| Balances at December 31, 2019 | | | (45,746 | ) | | | (194,118 | ) | | | 2,360 | | | | 209,987 | | | | 2,248,858 | | | | 2,221,341 | |
| Actuarial loss | | | | | | | (22,037 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (22,037 | ) |
| Gain on conversion of financial asset and fair value | | | | | | | | | | | 4,151 | | | | | | | | | | | | 4,151 | |
| Loss on conversion of financial statements and on foreign investments | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (2,857 | ) | | | | | | | (2,857 | ) |
| Partial realization of deemed cost, net of taxes | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (70,654 | ) | | | (70,654 | ) |
| Balances at December 31, 2020 | | | (45,746 | ) | | | (216,155 | ) | | | 6,511 | | | | 207,130 | | | | 2,178,204 | | | | 2,129,944 | |
| | | | Quantity | | | Average cost per share | | | Historical value | | | Market value | |
| Balances at December 31, 2018 | | | | 12,042,004 | | | | 18.13 | | | | 218,265 | | | | 458,560 | |
| Balances at December 31, 2019 | | | | 12,042,004 | | | | 18.13 | | | | 218,265 | | | | 477,827 | |
| Balances at December 31, 2020 | | | | 12,042,004 | | | | 18.13 | | | | 218,265 | | | | 704,939 | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| | Limit on share capital% | | | Result absorption | | | Reserve balances | |
| | | | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | | | December 31,
2020 | | | December 31,
2019 | |
| Realization of deemed cost, net of taxes | | | | | | | (70,654 | ) | | | (52,918 | ) | | | | | | | | |
| Tax incentive reserve | | | | | | | | | | | (684,563 | ) | | | | | | | | |
| Special statutory reserve | | | | | | | | | | | (242,612 | ) | | | | | | | | |
| Legal reserve | | | 20 | % | | | (317,144 | ) | | | (105,670 | ) | | | | | | | 317,144 | |
| Capital increase reserve | | | 80 | % | | | | | | | (1,730,629 | ) | | | | | | | | |
| Capital reserve | | | | | | | (6,410,885 | ) | | | | | | | 10,612 | | | | 6,416,864 | |
| Unclaimed dividends forfeited | | | | | | | (130 | ) | | | (1,126 | ) | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | (6,798,813 | ) | | | (2,817,518 | ) | | | 10,612 | | | | 6,734,008 | |
| 26. | EARNINGS (LOSS) PER SHARE |
The basic (loss) earnings per share is measured by dividing the profit attributable to the Company’s shareholders by the weighted average common shares issued during the year, excluding the common shares acquired by the Company and held as treasury shares.
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | | | December 31, 2018 | |
| Resulted of the year attributable for controlling shareholders’ | | | (10,724,828 | ) | | | (2,817,518 | ) | | | 319,693 | |
| Weighted average number of shares in the year | | | 1,361,264 | | | | 1,361,264 | | | | 1,105,826 | |
| Weighted average treasury shares | | | (12,042 | ) | | | (12,042 | ) | | | (12,333 | ) |
| Weighted average number of outstanding shares | | | 1,349,222 | | | | 1,349,222 | | | | 1,093,493 | |
| Basic loss per common share - R$ | | | (7.94890 | ) | | | (2.08825 | ) | | | 0.29236 | |
The diluted earnings per share is measured by adjusting the weighted average of outstanding common shares, assuming the conversion of all common shares that would cause dilution.
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | | | December 31, 2018 | |
| Resulted of the year attributed to controlling shareholders’ | | | (10,724,828 | ) | | | (2,817,518 | ) | | | 319,693 | |
| Weighted average number of shares in the year (except treasury shares) | | | 1,349,222 | | | | 1,349,222 | | | | 1,093,493 | |
| Adjustment by stock options | | | | | | | | | | | 1,386 | |
| Weighted average number of shares (diluted) | | | 1,349,222 | | | | 1,349,222 | | | | 1,094,879 | |
| Diluted loss per common share - R$ | | | (7.94890 | ) | | | (2.08825 | ) | | | 0.29199 | |
Due to the loss in the year, the Company does not consider the dilution effect in the measurement.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | | | December 31, 2018 | |
| Financial expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest on loans, financing and debentures (1) | | | (3,275,618 | ) | | | (3,358,806 | ) | | | (1,033,485 | ) |
| Premium with repurchase of bonds | | | (391,390 | ) | | | | | | | | |
| Amortization of fundraising costs (2) | | | (101,741 | ) | | | (220,642 | ) | | | (44,499 | ) |
| Amortization of fair value adjustment on business combination | | | (38,826 | ) | | | 1,548 | | | | | |
| Adjustment to present value - lease | | | (486,286 | ) | | | (275,404 | ) | | | | |
| Other financial expenses | | | (165,564 | ) | | | (325,544 | ) | | | (422,390 | ) |
| | | | (4,459,425 | ) | | | (4,178,848 | ) | | | (1,500,374 | ) |
| Financial income | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents and marketable securities | | | 146,930 | | | | 392,018 | | | | 442,378 | |
| Amortization of fair value adjustment on business combination | | | 95,238 | | | | 37,412 | | | | | |
| Other financial income | | | 85,307 | | | | 63,816 | | | | 17,329 | |
| | | | 327,475 | | | | 493,246 | | | | 459,707 | |
| Income from derivative financial instruments | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Income | | | 7,283,864 | | | | 2,711,394 | | | | 588,049 | |
| Expenses | | | (16,706,546 | ) | | | (3,786,646 | ) | | | (3,323,245 | ) |
| | | | (9,422,682 | ) | | | (1,075,252 | ) | | | (2,735,196 | ) |
| Monetary and exchange rate variation, net | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Exchange rate variation on loans, financing and debentures | | | (13,365,471 | ) | | | (1,781,562 | ) | | | (1,311,061 | ) |
| Lease | | | (601,519 | ) | | | (19,327 | ) | | | | |
| Other assets and liabilities (3) | | | 1,436,099 | | | | (164,038 | ) | | | 244,411 | |
| | | | (12,530,891 | ) | | | (1,964,927 | ) | | | (1,066,650 | ) |
| | | | (26,085,523 | ) | | | (6,725,781 | ) | | | (4,842,513 | ) |
| 1) | Does not include the amount of R$10.636 arising from capitalized interest in the year ended on December 31, 2002 (R$4,213 in the year ended on December 31, 2019). |
| 2) | Includes an expense of R$13,783 arising from transaction costs with loans and financing that were recognized directly to the income statement (R$34,836 as of December 31, 2019). |
| 3) | Includes effects of exchange rate variations of trade accounts receivable, trade account payable, cash and cash equivalents, marketable securities and other. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | | | December 31, 2018 | |
| Gross sales | | | 35,663,758 | | | | 31,395,955 | | | | 14,802,821 | |
| Sales deductions | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Adjustment to present value | | | | | | | (5,316 | ) | | | (4,984 | ) |
| Returns and cancelations | | | (68,367 | ) | | | (109,641 | ) | | | (75,477 | ) |
| Discounts and rebates | | | (3,830,267 | ) | | | (3,835,140 | ) | | | (15,695 | ) |
| | | | 31,765,124 | | | | 27,445,858 | | | | 14,706,665 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Taxes on sales | | | (1,304,847 | ) | | | (1,432,908 | ) | | | (1,263,289 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net sales | | | 30,460,277 | | | | 26,012,950 | | | | 13,443,376 | |
| 29.1. | Criteria for identifying operating segments |
The Company evaluates the performance of its business segments through the operating result. The information disclosed under “Not Segmented” is related to income statement and balance sheet items not directly attributed to the pulp and paper segments, such as, net financial result and income and social contribution taxes expenses, in addition to the balance sheet classification items of assets and liabilities.
The operating segments defined by Management are set forth below:
| (i) | Pulp: comprises production and sale of hardwood eucalyptus pulp and fluff pulp mainly to supply the foreign market, with any surplus sold in the domestic market. |
| (ii) | Paper: comprises production and sale of paper to meet the demands of both domestic and foreign markets. Consumer goods (tissue) sales are classified under this segment due to its immateriality. |
Information related to total assets by reportable segment is not disclosed, as it is not included in the set of information made available to the Company’s administration, which makes investment decisions and determine allocation of resources on a consolidated basis.
In addition, with respect to geographical information related to non-current assets, the Company does not disclose such information, as all of our property, plant and equipment, biological and intangible assets are located in Brazil.
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| 29.2. | Information of operating segments |
| | | December 31, 2020 | |
| | | Pulp | | | Paper | | | Not segmented | | | Total | |
| Net sales | | | 25,578,265 | | | | 4,882,012 | | | | | | | | 30,460,277 | |
| Domestic market (Brazil) | | | 1,609,449 | | | | 3,358,186 | | | | | | | | 4,967,635 | |
| Foreign market | | | 23,968,816 | | | | 1,523,826 | | | | | | | | 25,492,642 | |
| Asia | | | 12,921,081 | | | | 196,266 | | | | | | | | 13,117,347 | |
| Europe | | | 6,409,879 | | | | 262,924 | | | | | | | | 6,672,803 | |
| North America | | | 4,340,956 | | | | 263,328 | | | | | | | | 4,604,284 | |
| South and Central America | | | 184,590 | | | | 723,603 | | | | | | | | 908,193 | |
| Africa | | | 112,310 | | | | 77,705 | | | | | | | | 190,015 | |
| Cost of sales | | | (15,754,930 | ) | | | (3,211,401 | ) | | | | | | | (18,966,331 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 9,823,335 | | | | 1,670,611 | | | | | | | | 11,493,946 | |
| Gross margin (%) | | | 38.4 | % | | | 34.2 | % | | | | | | | 37.7 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating income (expenses) | | | (2,409,483 | ) | | | (641,069 | ) | | | | | | | (3,050,552 | ) |
| Selling | | | (1,770,036 | ) | | | (404,616 | ) | | | | | | | (2,174,652 | ) |
| General and administrative | | | (1,016,093 | ) | | | (427,099 | ) | | | | | | | (1,443,192 | ) |
| Other operating, net | | | 390,178 | | | | 140,972 | | | | | | | | 531,150 | |
| Income(loss) from associates and joint ventures | | | (13,532 | ) | | | 49,674 | | | | | | | | 36,142 | |
| Operating profit before net financial income (“EBIT”) (1) | | | 7,413,852 | | | | 1,029,542 | | | | | | | | 8,443,394 | |
| Operating margin (%) | | | 29.0 | % | | | 21.1 | % | | | | | | | 27.7 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial result, net | | | | | | | | | | | (26,085,523 | ) | | | (26,085,523 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) before taxes | | | 7,413,852 | | | | 1,029,542 | | | | (26,085,523 | ) | | | (17,642,129 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Income taxes | | | | | | | | | | | 6,927,194 | | | | 6,927,194 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) for the year | | | 7,413,852 | | | | 1,029,542 | | | | (19,158,329 | ) | | | (10,714,935 | ) |
| Profit (loss) margin for the year (%) | | | 29.0 | % | | | 21.1 | % | | | | | | | (35.2 | )% |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Result of the year attributable to controlling Shareholders | | | 7,413,852 | | | | 1,029,542 | | | | (19,168,222 | ) | | | (10,724,828 | ) |
| Result of the year attributed to non-controlling shareholders | | | | | | | | | | | 9,893 | | | | 9,893 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Depreciation, depletion and amortization | | | 6,232,376 | | | | 540,404 | | | | | | | | 6,772,780 | |
| 1) | Earnings before interest and tax. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| | | December 31, 2019 | |
| | | Pulp | | | Paper | | | Not segmented | | | Total | |
| Net sales | | | 21,027,686 | | | | 4,985,264 | | | | | | | | 26,012,950 | |
| Domestic market (Brazil) | | | 1,833,936 | | | | 3,480,279 | | | | | | | | 5,314,215 | |
| Foreign market | | | 19,193,750 | | | | 1,504,985 | | | | | | | | 20,698,735 | |
| Asia | | | 9,605,799 | | | | 136,882 | | | | | | | | 9,742,681 | |
| Europe | | | 5,950,832 | | | | 221,697 | | | | | | | | 6,172,529 | |
| North America | | | 3,592,563 | | | | 382,628 | | | | | | | | 3,975,191 | |
| South and Central America | | | 44,556 | | | | 710,086 | | | | | | | | 754,642 | |
| Africa | | | | | | | 53,692 | | | | | | | | 53,692 | |
| Cost of sales | | | (17,440,018 | ) | | | (3,303,464 | ) | | | | | | | (20,743,482 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 3,587,668 | | | | 1,681,800 | | | | | | | | 5,269,468 | |
| Gross margin (%) | | | 17.1 | % | | | 33.7 | % | | | | | | | 20.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating income (expenses) | | | (2,089,286 | ) | | | (679,719 | ) | | | 128,115 | | | | (2,640,890 | ) |
| Selling | | | (1,503,775 | ) | | | (401,504 | ) | | | | | | | (1,905,279 | ) |
| General and administrative | | | (806,774 | ) | | | (366,584 | ) | | | | | | | (1,173,358 | ) |
| Other operating, net | | | 209,577 | | | | 68,062 | | | | 128,115 | | | | 405,754 | |
| Income from associates and joint ventures | | | 11,686 | | | | 20,307 | | | | | | | | 31,993 | |
| Operating profit before net financial income (“EBIT”) (1) | | | 1,498,382 | | | | 1,002,081 | | | | 128,115 | | | | 2,628,578 | |
| Operating margin (%) | | | 7.1 | % | | | 20.1 | % | | | | | | | 10.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial result, net | | | | | | | | | | | (6,725,781 | ) | | | (6,725,781 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) before taxes | | | 1,498,382 | | | | 1,002,081 | | | | (6,597,666 | ) | | | (4,097,203 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Income taxes | | | | | | | | | | | 1,282,461 | | | | 1,282,461 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) for the year | | | 1,498,382 | | | | 1,002,081 | | | | (5,315,205 | ) | | | (2,814,742 | ) |
| Profit (loss) margin for the year (%) | | | 7.1 | % | | | 20.1 | % | | | | | | | (10.8 | )% |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Result of the year attributable to controlling Shareholders | | | 1,498,382 | | | | 1,002,081 | | | | (5,317,981 | ) | | | (2,817,518 | ) |
| Result of the year attributed to non-controlling shareholders | | | | | | | | | | | 2,776 | | | | 2,776 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Depreciation, depletion and amortization | | | 7,575,630 | | | | 516,322 | | | | | | | | 8,091,952 | |
| 1) | Earnings before interest and tax. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| | | December 31,
��2018 | |
| | | Pulp | | | Paper | | | Not segmented | | | Total | |
| Net sales | | | 8,783,274 | | | | 4,660,102 | | | | | | | | 13,443,376 | |
| Domestic market (Brazil) | | | 744,566 | | | | 3,307,074 | | | | | | | | 4,051,640 | |
| Foreign market | | | 8,038,708 | | | | 1,353,028 | | | | | | | | 9,391,736 | |
| Asia | | | 3,837,998 | | | | 101,695 | | | | | | | | 3,939,693 | |
| Europe | | | 2,810,899 | | | | 225,111 | | | | | | | | 3,036,010 | |
| North America | | | 1,340,907 | | | | 210,831 | | | | | | | | 1,551,738 | |
| South and Central America | | | 48,904 | | | | 774,730 | | | | | | | | 823,634 | |
| Africa | | | | | | | 40,661 | | | | | | | | 40,661 | |
| Cost of sales | | | (3,965,912 | ) | | | (2,956,419 | ) | | | | | | | (6,922,331 | ) |
| Gross profit | | | 4,817,362 | | | | 1,703,683 | | | | | | | | 6,521,045 | |
| Gross margin (%) | | | 54.8 | % | | | 36.6 | % | | | | | | | 48.5 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating income (expenses) | | | (626,887 | ) | | | (886,347 | ) | | | | | | | (1,513,234 | ) |
| Selling expenses | | | (212,869 | ) | | | (385,857 | ) | | | | | | | (598,726 | ) |
| General and administrative expenses | | | (275,859 | ) | | | (549,350 | ) | | | | | | | (825,209 | ) |
| Other operating income (expenses), net | | | (138,159 | ) | | | 41,284 | | | | | | | | (96,875 | ) |
| Income from associates and joint ventures | | | | | | | 7,576 | | | | | | | | 7,576 | |
| Operating profit before net financial income (“EBIT”) (1) | | | 4,190,475 | | | | 817,336 | | | | | | | | 5,007,811 | |
| Operating margin (%) | | | 47.7 | % | | | 17.5 | % | | | | | | | 37.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial result, net | | | | | | | | | | | (4,842,513 | ) | | | (4,842,513 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) before taxes | | | 4,190,475 | | | | 817,336 | | | | (4,842,513 | ) | | | 165,298 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Income taxes | | | | | | | | | | | 154,516 | | | | 154,516 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) for the year | | | 4,190,475 | | | | 817,336 | | | | (4,687,997 | ) | | | 319,814 | |
| Profit margin for the year (%) | | | 47.7 | % | | | 17.5 | % | | | | | | | 2.5 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Result of the year attributable to controlling shareholders | | | 4,190,475 | | | | 817,336 | | | | (4,688,118 | ) | | | 319,693 | |
| Result of the year attributed to non-controlling shareholders | | | | | | | | | | | 121 | | | | 121 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Depreciation, depletion and amortization | | | 1,105,381 | | | | 457,842 | | | | | | | | 1,563,223 | |
| 1) | Earnings before interest and tax. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
With regard to the foreign market revenues of the pulp operating segment, China and USA are the main countries in relation to net revenue, 47.97% and 16.54%, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2020 (China and USA represented 40.00% and 16.54%, respectively, on December 31, 2019).
With regard to the foreign market revenues of the paper operating segment, Argentina and USA are the main countries in relation to net revenue, representing 18.06% and 17.92%, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2020 (USA, Peru e Argentina represented 24.64%, 12.70% e 11.61% , respectively, on December 31, 2019).
There is no other individual foreign country that represents more than 10% of net revenue in the foreign market for the years ended December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019.
| 29.3. | Net sales by product |
The following table set forth the breakdown of consolidated net sales by product:
| Products | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | | | December 31, 2018 | |
| Market pulp (1) | | | 25,578,265 | | | | 21,027,686 | | | | 8,783,274 | |
| Printing and writing paper (2) | | | 3,891,002 | | | | 4,100,502 | | | | 3,834,380 | |
| Paperboard | | | 935,047 | | | | 823,360 | | | | 764,701 | |
| Other | | | 55,963 | | | | 61,402 | | | | 61,021 | |
| Net sales | | | 30,460,277 | | | | 26,012,950 | | | | 13,443,376 | |
| 1) | Net sale from fluff pulp represents approximately 0.6% of total net sales and, therefore, was included in market pulp net sales. |
| 2) | Tissue is a recently launched product and its revenues represent approximately 2.6% of total net sales and, therefore, was included in printing and writing paper net sales. |
| 29.4. | Goodwill based on expected future profitability |
The goodwill based on expected future profitability arising from the business combination were allocated to the disclosable segments, which correspond to the Company’s cash-generating units (“CGU”), considering the economic benefits generated by such intangible assets. The allocation of intangibles is set forth below:
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | |
| Pulp | | | 7,897,051 | | | | 7,942,486 | |
| Consumer goods | | | 119,332 | | | | 119,332 | |
| | | | 8,016,383 | | | | 8,061,818 | |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
| | | December 31, 2020 | | | December 31, 2019 | | | December 31, 2018 | |
| Cost of sales (1) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Personnel expenses | | | (997,080 | ) | | | (1,374,331 | ) | | | (649,741 | ) |
| Variable cost | | | (7,533,152 | ) | | | (10,067,716 | ) | | | (3,197,895 | ) |
| Logistics cost | | | (4,156,096 | ) | | | (2,776,021 | ) | | | (1,044,899 | ) |
| Depreciation, depletion and amortization (2) | | | (5,773,088 | ) | | | (7,135,049 | ) | | | (1,523,935 | ) |
| Operating expenses COVID-19 (3) | | | (95,024 | ) | | | | | | | | |
| Other (4) | | | (411,891 | ) | | | 609,635 | | | | (505,861 | ) |
| | | | (18,966,331 | ) | | | (20,743,482 | ) | | | (6,922,331 | ) |
| Selling expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Personnel expenses | | | (205,636 | ) | | | (215,640 | ) | | | (145,844 | ) |
| Services | | | (114,143 | ) | | | (85,161 | ) | | | (78,227 | ) |
| Logistics cost | | | (852,562 | ) | | | (618,089 | ) | | | (297,129 | ) |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | (905,880 | ) | | | (904,748 | ) | | | (4,471 | ) |
| Other (5) | | | (96,431 | ) | | | (81,641 | ) | | | (73,055 | ) |
| | | | (2,174,652 | ) | | | (1,905,279 | ) | | | (598,726 | ) |
| General and Administrative expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Personnel expenses | | | (862,308 | ) | | | (642,543 | ) | | | (469,661 | ) |
| Services | | | (311,975 | ) | | | (323,841 | ) | | | (235,544 | ) |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | (78,275 | ) | | | (26,221 | ) | | | (34,817 | ) |
| Social actions COVID-19 | | | (48,590 | ) | | | | | | | | |
| Operating expenses COVID-19 (3) | | | (41,076 | ) | | | | | | | | |
| Other (6) | | | (100,968 | ) | | | (180,753 | ) | | | (85,187 | ) |
| | | | (1,443,192 | ) | | | (1,173,358 | ) | | | (825,209 | ) |
| Other operating (expenses) income net | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Rents and leases | | | 4,303 | | | | 5,805 | | | | | |
| Result from sale of other products, net | | | 56,791 | | | | 15,229 | | | | 8,785 | |
| Result from sale and disposal of property, plant and equipment and biological assets, net (4) | | | 56,984 | | | | (63,454 | ) | | | 4,523 | |
| Result on fair value adjustment of biological assets | | | 466,484 | | | | 185,399 | | | | (129,187 | ) |
| Insurance reimbursement | | | 5,025 | | | | 7,917 | | | | | |
| Amortization of intangible assets | | | (15,537 | ) | | | (20,336 | ) | | | (9,947 | ) |
| Trade agreement credits (5) | | | | | | | 87,000 | | | | 51,846 | |
| Result on disposal of investmets | | | (9,404 | ) | | | | | | | | |
| Tax credits - gains in tax lawsuit (ICMS from the PIS/COFINS calculation basis) (6) | | | | | | | 128,115 | | | | 335 | |
| Provision for loss and write-off of property, plant and equipment and biological assets | | | | | | | | | | | (18,103 | ) |
| Other operating income (expenses), net | | | (33,496 | ) | | | 60,079 | | | | (5,127 | ) |
| | | | 531,150 | | | | 405,754 | | | | (96,875 | ) |
| 1) | Includes R$524,411 related to idle capacity and maintenance downtime (R$615,394 as of December 31, 2019). |
| 2) | In the year ended December 31, 2020 includes amortization of the inventories step up, arising from the business combination with Fibria, in the amount of R$2,178,903. |
| 3) | Includes, mainly, expenses in the facilities units for the upgrading of cafeterias and workplaces, expansion of the frequency of conservation, cleaning, hygiene and maintenance of common areas, public transport with more space between passengers, distribution of masks and realization rapid tests on employees working in facilities units. |
| 4) | Includes R$3,177 related to dismantling cost arising from land lease agreement used in the formation of the cost of biological assets. |
| 5) | Includes expected credit losses, insurance, materials of use and consumption, travel, accommodation, trade fairs and events. |
| 6) | Includes corporate expenses, insurance, materials of use and consumption, social programs and donations, travel and accommodation. |
Suzano S.A. Explanatory notes to the consolidated financial statements
Year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |  |
The Company has insurance coverage for operational risks, with a maximum coverage of US$1,000,000 corresponding to R$5,196,700. Additionally, the Company has insurance coverage for civil general liabilities in the amount of US$20,000 corresponding to R$103,934 on December 31, 2020.
Company’s Management considers these amounts adequate to cover any potential liability, risks and damages to its assets and loss of profits.
The Company does not have insurance coverage for its forests. To mitigate the risk of fire, the Company maintains internal fire brigades, a watchtower network, and a fleet of fire trucks. There is no history of material losses from forest fires.
The Company has a domestic and international transportation insurance policy effective through May 2021, renewable for additional 12 months.
In addition, it has insurance coverage for civil responsibility for Directors and Executives (D&O) for amounts considered adequate by Management.
The assessment of the sufficiency of insurance coverage is not part of the scope of the examination of the financial statements by our independent auditors.
| 32.1. | Conclusion of commitment to purchase and sale of rural properties and forests with conditions precedent (“Closing”) |
On January 5, 2021, through a Notice to the Market, the Company informs the conclusion of the transaction with Bracell SP Celulose Ltda. and Turvinho Participações Ltda., receiving the final purchase price of R$1,056,755 in connection with the terms of the purchase and sale of rural properties and forests, with the conditions precedent agreement signed between the parties (Note 1.2.2).
From the total amount received:
| (i) | R$375,850 was recognized in other liabilities, since it is related to the sale of eucalyptus forests (mature) and biological assets in formation (immature), which will be recognized in other operating results upon delivery of the wood; and |
| (ii) | R$680,895 was recognized other operating results, in compliance with the obligation to delivery and transfer the possession of the rural properties. The cost of properties in the amount of R$ 289,867, previously classified non-current assets held for sale, was realized and recognized in other operating results, generating a net income of R$391,028. |
The transfer of lease agreements in the amount of R$1, mentioned in note 1.2.2, was deducted from the amount received, without impacting the object of purchase and sale of the Transaction mentioned above.
In addition, of the amount received for the sale of rural properties, R$50,415 was classified as marketable securities of long-term as escrow account, whose amount will only be released after compliance with the documentary regularization of certain rural properties as defined in the terms of the purchase and sale. Regularization costs were estimated at R$ 8,000 and were provisioned in the other operating results.
| 32.2. | Early settlement of financing with BNDES |
On February 9, 2021, the Company early settled a financing contract with BNDES, in the principal amount of R$1,453,842, with original maturity in May 2026 and monthly interest rate indexed to SELIC + 3% p.a. and TJLP + 2% and transaction cost in the amount of R$30,000.











