Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2013
OR
o | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
FOR THE TRANSITION PERIOD FROM TO .
COMMISSION FILE NUMBER: 000-26076
SINCLAIR BROADCAST GROUP, INC.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
Maryland | | 52-1494660 |
(State or other jurisdiction of | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
incorporation or organization) | | |
10706 Beaver Dam Road
Hunt Valley, MD 21030
(Address of principal executive offices)
(410) 568-1500
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class | | Name of each exchange on which registered |
Class A Common Stock, par value $ 0.01 per share | | The NASDAQ Stock Market LLC |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer x | | Accelerated filer o | | Non-accelerated filer o | | Smaller reporting company o |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes o No x
Based on the closing sales price of $29.37 per share as of June 28, 2013, the aggregate market value of the voting common equity of the Registrant held by non-affiliates was approximately $2,132.8 million.
Indicate the number of shares outstanding of each of the registrant’s classes of common stock, as of the latest practicable date.
Title of each class | | Number of shares outstanding as of
February 24, 2014 | |
Class A Common Stock | | 71,998,554 | |
Class B Common Stock | | 26,028,357 | |
Documents Incorporated by Reference - Portions of our definitive Proxy Statement relating to our 2014 Annual Meeting of Shareholders are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Form 10-K. We anticipate that our Proxy Statement will be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of our fiscal year ended December 31, 2013.
Table of Contents
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This report includes or incorporates forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the Exchange Act), and the U.S. Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. We have based these forward-looking statements on our current expectations and projections about future events. These forward-looking statements are subject to risks, uncertainties and assumptions about us, including, among other things, the following risks:
General risks
· the impact of changes in national and regional economies and credit and capital markets;
· consumer confidence;
· the potential impact of changes in tax law;
· the activities of our competitors;
· terrorist acts of violence or war and other geopolitical events;
· natural disasters that impact our advertisers and our stations;
Industry risks
· the business conditions of our advertisers particularly in the automotive and service industries;
· competition with other broadcast television stations, radio stations, multi-channel video programming distributors (MVPDs), internet and broadband content providers such and other print and media outlets serving in the same markets;
· availability and cost of programming and the continued volatility of networks and syndicators that provide us with programming content;
· the effects of the Federal Communications Commission’s (FCC’s) National Broadband Plan and the auctioning and potential reallocation of our broadcasting spectrum;
· the effects of governmental regulation of broadcasting or changes in those regulations and court actions interpreting those regulations, including ownership regulations (including regulations relating to Joints Sales Agreements (JSA) and Shared Services Agreements (SSA)), indecency regulations, retransmission fee regulations and political or other advertising restrictions;
· labor disputes and legislation and other union activity associated with film, acting, writing and other guilds and professional sports leagues;
· the broadcasting community’s ability to create and adopt a new transmission standard, as well as viable mobile digital broadcast television (mobile DTV) strategy and platform and the consumer’s appetite for mobile television;
· the operation of low power devices in the broadcast spectrum, which could interfere with our broadcast signals;
· the impact of reverse network compensation payments charged by networks pursuant to their affiliation agreements with broadcasters requiring compensation for network programming;
· the effects of new ratings system technologies including “people meters” and “set-top boxes,” and the ability of such technologies to be a reliable standard that can be used by advertisers;
· the impact of new FCC rules requiring broadcast stations to publish, among other information, political advertising rates online;
· changes in the makeup of the population in the areas where stations are located;
Risks specific to us
· the effectiveness of our management;
· our ability to attract and maintain local and national advertising;
· our ability to service our debt obligations and operate our business under restrictions contained in our financing agreements;
· our ability to successfully renegotiate retransmission consent agreements;
· our ability to renew our FCC licenses;
· our ability to obtain FCC approval for any future acquisitions, as well as, in certain cases, customary antitrust clearance for any future acquisitions;
· our ability to successfully integrate any acquired businesses;
· our ability to maintain our affiliation and programming service agreements with our networks and program service providers and at renewal, to successfully negotiate these agreements with favorable terms;
3
Table of Contents
· our ability to effectively respond to technology affecting our industry and to increasing competition from other media providers;
· the popularity of syndicated programming we purchase and network programming that we air;
· the strength of ratings for our local news broadcasts including our news sharing arrangements;
· the successful execution of our multi-channel broadcasting initiatives including mobile DTV; and
· the results of prior year tax audits by taxing authorities.
Other matters set forth in this report and other reports filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), including the Risk Factors set forth in Item 1A of this report may also cause actual results in the future to differ materially from those described in the forward-looking statements. However, additional factors and risks not currently known to us or that we currently deem immaterial may also cause actual results in the future to differ materially from those described in the forward-looking statements. You are cautioned not to place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date on which they are made. We undertake no obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise. In light of these risks, uncertainties and assumptions, events described in the forward-looking statements discussed in this report might not occur.
4
Table of Contents
PART I
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
We are a diversified television broadcasting company that owns or provides certain programming, operating or sales services to more television stations than most other commercial broadcasting groups in the United States. As of March 1, 2014, we own, provide programming and operating services pursuant to local marketing agreements (LMAs) or provide sales services and other non-programming operating services pursuant to contracts to 149 television stations in 71 markets. For the purpose of this report, these 149 stations are referred to as “our” stations.
Our broadcast group is a single reportable segment for accounting purposes and includes the following network affiliations: FOX (39 stations); CBS (25 stations); ABC (19 stations); NBC (16 stations); The CW (23 stations); MyNetworkTV (20 stations; not a network affiliation; however, it is branded as such); Univision (5 stations), Azteca (1 station) and one independent station. In addition, certain stations broadcast programming on second and third digital signals through network affiliation or program service arrangements with CBS, ABC, and NBC (certain signals are rebroadcasted content from other primary channels within the same market), FOX, The CW, MyNetworkTV, This TV, ME TV, Weather Radar, Weather Nation, Live Well Network, Antenna TV, Bounce Network, Zuus Country Network, Retro TV, Estrella TV, MundoFox, Tele-Romantica, Inmigrante TV, Azteca and Telemundo. Refer to our Markets and Stations table later in this Item 1 for more information.
We broadcast free over-the-air programming to television viewing audiences in the communities we serve through our local television stations. The programming that we provide on our primary station channels consists of network provided programs, news produced locally, local sporting events, programming from program service arrangements, syndicated entertainment programs and other locally produced programs such as Ring of Honor wrestling, a franchise we acquired in 2011. We produce news at 84 stations in 47 markets, including one station where we produce news pursuant to a local news sharing arrangement with a competitive station in that market. We have 16 stations which have local news sharing arrangements with a competitive station in that market that produces the news aired on our station. We provide live local sporting events on many of our stations by acquiring the local television broadcast rights for these events. Additionally, we purchase and barter for popular syndicated programming from third party television producers. See Operating Strategy later in this Item 1 for more information regarding the programming we provide.
Our primary source of revenue is the sale of commercial inventory on our television stations to our advertising customers. Our objective is to meet the needs of our advertising customers by delivering significant audiences in key demographics. Our strategy is to achieve this objective by providing quality local news programming and popular network and syndicated programs to our viewing audience. We attract most of our national television advertisers through national marketing representation firms which have offices in New York City, Los Angeles, Chicago and Atlanta. Our local television advertisers are attracted through the use of a local sales force at each of our television stations, which is comprised of approximately 711 sales account executives and local sales managers company-wide.
We also earn revenue from our retransmission consent agreements through payments from MVPDs in our markets. The MVPDs are local cable companies, satellite television and local telecommunication video providers. The revenues primarily represent payments from the MVPDs for access to our broadcast signal and is typically based on the number of subscribers they have.
Our operating results are subject to cyclical fluctuations from political advertising. Political spending has been significantly higher in the even-number years due to the cyclicality of political elections. In addition, every four years, political spending is typically elevated further due to the advertising preceding the presidential election. Because of the political election cyclicality, there has been a significant difference in our operating results when comparing even-numbered years’ performance to the odd numbered years’ performance. Additionally, our operating results are impacted by the number and importance of individual race, and issues discussed. We believe political advertising will continue to be a strong advertising category in our industry, particularly in light of the 2010 United States Supreme Court decision in Citizens United v. Federal Election Commission in which the Supreme Court ruled that federal laws limiting issue advocacy by for-profit and non-profit corporations was unconstitutional. With increased spending by Political Action Committees (PACs), including so-called Super PACs and as political-activism around social, political, economic and environmental causes continues to draw attention, political advertising levels may increase further.
We continue to believe the prospects for a viable mobile television service can occur because of the significant advantages over the air, point to multipoint delivery has compared to the limitations and expenses the consumer is facing through the transitional cell phone delivery option. Television broadcasters have the potential capability of delivering significantly greater video and data at a fraction of the cost of the existing carrier network. We believe a change to the existing mobile broadcast standard to a standard that is comparable to that used in several other parts of the world is essential. We cannot predict at this time how or if any change to the current US mobile standard will take place.
5
Table of Contents
We have one reportable operating segment: “broadcast.” Our broadcast segment includes our television stations and the four radio stations we acquired from Fisher Communications, Inc. We also earned revenues in 2013 from sign design and fabrication, regional security alarm operating and bulk acquisitions, manufacturing and service of broadcasting antennas and transmitters, real estate ventures and a wrestling programming franchise, which we refer to as our “Other Operating Divisions.” Corporate and unallocated expenses primarily include our costs to operate as a public company and to operate our corporate headquarters location. Our Other Operating Divisions and Corporate are not reportable segments. See Note 13. Segment Data, in the Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements for more information regarding our operating segments.
We are a Maryland corporation formed in 1986. Our principal offices are located at 10706 Beaver Dam Road, Hunt Valley, Maryland 21030. Our telephone number is (410) 568-1500 and our website address is www.sbgi.net. The information contained on, or accessible through, our website is not part of this annual report on Form 10-K and is not incorporated herein by reference.
6
Table of Contents
TELEVISION BROADCASTING
Markets and Stations
As of December 31, 2013, we own and operate, provide programming services to, provide sales services to or have agreed to acquire the following television stations:
Market | | Market
Rank (a) | | Stations
in
Market | | Stations | | Channel | | Status (b) | | Network/
Program Service
Arrangement (c) | | Station
Rank in
Market (d) | | Expiration Date of FCC
License |
Seattle/Tacoma, WA | | 13 | | 2 | | KOMO KUNS KOMO KUNS | | Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O O&O | | ABC Univision This TV MundoFox | | 3 of 9 8 of 9 | | 2/01/15 |
Tampa/St. Petersburg, Florida | | 14 | | 1 | | WTTA | | Primary | | O&O | | MNT | | 7 of 9 | | 2/01/13 (f) |
Minneapolis/St. Paul, Minnesota | | 15 | | 1 | | WUCW WUCW | | Primary Second | | O&O | | CW Zuus Country | | 6 of 7 | | 4/01/14 |
St. Louis, Missouri | | 21 | | 1 | | KDNL KDNL | | Primary Second | | O&O | | ABC Zuus Country | | 4 of 7 | | 2/01/14 |
Portland, Oregon | | 22 | | 3 | | KATU KUNP/ KUNP-LD KATU KUNP | | Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O
O&O | | ABC Univision ME TV MundoFox | | 1 of 8 8 of 8 | | 2/01/15 2/01/15 |
Pittsburgh, PA | | 23 | | 2 | | WPGH WPMY WPGH | | Primary Primary Second | | O&O O&O | | FOX MNT Zuus Country | | 4 of 7 6 of 7 | | 8/01/15 8/01/15 |
Raleigh/Durham, North Carolina | | 24 | | 2 | | WLFL WRDC WLFL | | Primary Primary Second | | O&O O&O | | CW MNT Zuus Country | | 5 of 7 6 of 7 | | 12/01/04 (e) 12/01/04 (e) |
Baltimore, Maryland | | 27 | | 3 | | WBFF WUTB WNUV WBFF WUTB WBFF | | Primary Primary Primary Second Second Third | | O&O JSA/SSA(h) LMA(g) | | FOX MNT CW This TV Bounce Network Zuus Country | | 3 of 6 5 of 6 6 of 6 | | 10/01/04 (e) 10/01/12 (e) 10/01/12 (f) |
Nashville, Tennessee | | 29 | | 3 | | WZTV WUXP WNAB WNAB | | Primary Primary Primary Second | | O&O O&O JSA/SSA(h) | | FOX MNT CW Zuus Country | | 4 of 7 5 of 7 6 of 7 | | 8/01/13 (f) 8/01/13 (f) 8/01/21 |
Columbus, Ohio | | 32 | | 3 | | WSYX WTTE WWHO WSYX | | Primary Primary Primary Second | | O&O LMA(g) JSA/SSA(h) | | ABC FOX CW This TV and MNT | | 2 of 7 4 of 7 5 of 7 | | 10/01/13 (f) 10/01/05 (e) 10/01/13 (e) |
Salt Lake City/St. George, Utah | | 33 | | 3 | | KUTV KMYU KENV(j) KUTV KMYU | | Primary Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O O&O JSA/SSA(h) | | CBS MNT NBC MNT CBS | | 1 of 8 7 of 8 8 of 8 | | 10/01/14 10/01/14 10/01/14 |
Milwaukee, Wisconsin | | 34 | | 2 | | WVTV WCGV WCGV | | Primary Primary Second | | O&O O&O | | CW MNT Zuus Country | | 7 of 9 8 of 9 | | 12/01/13 (f) 12/01/05 (e) |
Cincinnati, Ohio | | 35 | | 2 | | WKRC WSTR WKRC | | Primary Primary Second | | O&O JSA/SSA(h) | | CBS MNT CW | | 1 of 7 5 of 7 | | 10/01/13 (f) 10/01/21 |
San Antonio, Texas | | 36 | | 3 | | WOAI KABB KMYS KABB WOAI | | Primary Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O O&O JSA/SSA(h) | | NBC FOX CW Zuus Country Live Well Network | | 3 of 6 4 of 6 5 of 6 | | 8/01/14 8/01/14 8/01/14 |
Asheville, North Carolina/ Greenville/Spartanburg/ Anderson, South Carolina | | 37 | | 2 | | WLOS WMYA WLOS WMYA | | Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O LMA(g) | | ABC MNT MNT Zuus Country | | 3 of 7 5 of 7 | | 12/01/04 (e) 12/01/04 (e) |
7
Table of Contents
Market | | Market
Rank (a) | | Stations
in
Market | | Stations | | Channel | | Status (b) | | Network/
Program Service
Arrangement (c) | | Station
Rank in
Market (d) | | Expiration
Date of FCC
License |
West Palm Beach/Fort Pierce, Florida | | 38 | | 4 | | WPEC WTVX WTCN-CA WWHB-CA WPEC WPEC WTVX WTVX | | Primary Primary Primary Primary Second Third Second Third | | O&O O&O O&O O&O | | CBS CW MNT Azteca(k) CBS Weather Radar Azteca(k) MNT | | 3 of 6 5 of 6 6 of 6 Not available | | 2/01/13 (f) 2/01/13 (f) 2/01/13 (f) 2/01/13 (f) |
Grand Rapids/Kalamazoo, Michigan | | 39 | | 1 | | WWMT WWMT | | Primary Second | | O&O | | CBS CW | | 1 of 6 | | 10/01/13(f) |
Austin, Texas | | 40 | | 1 | | KEYE KEYE | | Primary Second | | O&O | | CBS Telemundo | | 3 of 6 | | 8/01/14 |
Oklahoma City, Oklahoma | | 41 | | 2 | | KOKH KOCB KOKH | | Primary Primary Second | | O&O O&O | | FOX CW Zuus Country | | 4 of 7 5 of 7 | | 6/01/14 6/01/14 |
Las Vegas, Nevada | | 42 | | 2 | | KVMY KVCW KVMY KVCW KVCW | | Primary Primary Second Second Third | | O&O O&O | | MNT CW Estrella TV This TV Zuus Country | | 4 of 6 5 of 6 | | 10/01/14 10/01/14 |
Harrisburg/Lancaster/ Lebanon/York, Pennsylvania | | 43 | | 2 | | WHP WLYH WHP WLYH | | Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O LMA(g) | | CBS CW MNT Live Well Network | | 2 of 7 5 of 7 | | 8/01/15 8/01/07(e) |
Birmingham, Alabama | | 44 | | 3 | | WTTO WABM WDBB WTTO WDBB | | Primary Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O O&O LMA(g) | | CW MNT CW Zuus Country Zuus Country | | 5 of 7 6 of 7 5 of 7 | | 4/01/05 (e) 4/01/21 4/01/21 |
Norfolk, Virginia | | 45 | | 1 | | WTVZ WTVZ | | Primary Second | | O&O | | MNT Zuus Country | | 6 of 7 | | 10/01/12 (f) |
Greensboro/Winston- Salem/Highpoint, North Carolina | | 46 | | 2 | | WXLV WMYV WXLV | | Primary Primary Second | | O&O O&O | | ABC MNT Zuus Country | | 4 of 6 5 of 6 | | 12/01/04 (e) 12/01/04 (e) |
Buffalo, New York | | 52 | | 2 | | WUTV WNYO WUTV | | Primary Primary Second | | O&O O&O | | FOX MNT Zuus Country | | 4 of 6 6 of 6 | | 6/01/15 6/01/15 |
Fresno/Visalia, California | | 55 | | 3 | | KMPH/ KMPH-CD KFRE KMPH KFRE | | Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O O&O | | FOX CW This TV Estrella TV | | 3 of 11 7 of 11 | | 12/01/14 12/01/14 12/01/14 |
Richmond, Virginia | | 57 | | 1 | | WRLH WRLH | | Primary Second | | O&O | | FOX This TV and MNT | | 4 of 6 | | 10/01/12 (f) |
Albany, New York | | 58 | | 2 | | WRGB WCWN WRGB WCWN | | Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O O&O | | CBS CW This TV CBS | | 1 of 6 5 of 6 | | 6/01/15 6/01/15 |
Mobile, Alabama/ Pensacola, Florida | | 59 | | 4 | | WEAR WPMI WJTC WFGX WEAR WPMI | | Primary Primary Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O JSA/SSA(h) JSA/SSA(h) O&O | | ABC NBC IND MNT Zuus Country Weather Nation | | 2 of 7 4 of 7 5 of 7 7 of 7 | | 2/01/13 (f) 4/01/13 (e) 2/01/13 (f) 2/01/13 (f) |
Lexington, Kentucky | | 63 | | 1 | | WDKY | | Primary | | O&O | | FOX | | 3 of 8 | | 8/01/13 (f) |
8
Table of Contents
Market | | Market
Rank (a) | | Stations
in
Market | | Stations | | Channel | | Status (b) | | Network/
Program Service
Arrangement (c) | | Station
Rank in
Market (d) | | Expiration
Date of FCC
License |
Dayton, Ohio | | 64 | | 2 | | WKEF WRGT WRGT | | Primary Primary Second | | O&O LMA(g) | | ABC FOX MNT and This TV | | 3 of 5 4 of 5 | | 10/01/13 (f) 10/01/05 (e) |
Charleston/Huntington, West Virginia | | 65 | | 2 | | WCHS WVAH WVAH | | Primary Primary Second | | O&O LMA(g) | | ABC FOX Zuus Country | | 2 of 6 4 of 6 | | 10/01/12 (f) 10/01/04 (e) |
Wichita/Hutchinson Plus, Kansas | | 67 | | 6 | | KSAS/ KOCW/ KAAS/ KAAS-LP/ KSAS-LP KMTW KSAS KMTW | | Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O LMA(g) | | FOX MNT Antenna TV Zuus Country | | 4 of 6 6 of 6 | | 6/01/14 6/01/14 |
Flint/Saginaw/Bay City, Michigan | | 68 | | 3 | | WSMH WEYI WBSF WSMH WEYI WSBSF WEYI | | Primary Primary Primary Second Second Second Third | | O&O JSA/SSA(h) JSA/SSA(h) | | FOX NBC CW Zuus Country CW NBC Bounce Network | | 3 of 6 4 of 6 5 of 6 | | 10/01/13(f) 10/01/21 10/01/21 |
Des Moines, Iowa | | 72 | | 1 | | KDSM KDSM | | Primary Second | | O&O | | FOX Zuus Country | | 4 of 6 | | 2/01/14 |
Spokane, Washington | | 73 | | 1 | | KLEW | | Primary | | O&O | | CBS | | Not available | | 10/01/14 |
Omaha, Nebraska | | 74 | | 2 | | KPTM KXVO KPTM KXVO KPTM | | Primary Primary Second Second Third | | O&O LMA(g) | | FOX CW This TV and MNT This TV Estrella TV | | 4 of 7 5 of 7 | | 6/01/14 6/01/06(e) |
Toledo, Ohio | | 76 | | 1 | | WNWO WNWO | | Primary Second | | O&O | | NBC Retro TV | | 3 of 6 | | 10/01/21 |
Columbia, South Carolina | | 77 | | 1 | | WACH | | Primary | | O&O | | FOX | | 4 of 6 | | 12/01/20 |
Rochester, New York | | 78 | | 2 | | WHAM WUHF WHAM | | Primary Primary Second | | JSA/SSA(h) JSA/SSA(i) | | ABC FOX CW | | 2 of 5 4 of 5 | | 6/01/15 6/01/15 |
Portland, Maine | | 80 | | 2 | | WGME WPFO | | Primary Primary | | O&O JSA/SSA(h) | | CBS FOX | | 2 of 6 4 of 6 | | 4/01/15 4/01/07(f) |
Cape Girardeau, Missouri/ Paducah, Kentucky | | 81 | | 2 | | KBSI WDKA KBSI WDKA | | Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O LMA(g) | | FOX MNT MNT Zuus Country | | 4 of 6 5 of 6 | | 2/01/14 8/01/21 |
Madison, Wisconsin | | 83 | | 1 | | WMSN WMSN | | Primary Second | | O&O | | FOX Zuus Country | | 4 of 5 | | 12/01/13 (f) |
Springfield/Champaign/ Decatur, Illinois | | 84 | | 5 | | WICS/ WICD WRSP/ WCCU WBUI WICS WRSP WCCU WBUI | | Primary Primary Primary Second Second Second Second | | O&O JSA/SSA(h) JSA/SSA(h) | | ABC FOX CW Zuus Country ME TV ME TV This TV | | 3 of 6 4 of 6 6 of 6 | | 12/01/05 (e) 12/01/13 (f) 12/01/13 (f) 12/01/13 (f) |
Syracuse, New York | | 85 | | 3 | | WSTM WTVH WSTQ-LP WSTM WSTM | | Primary Primary Primary Second Third | | O&O JSA/SSA(h)O&O | | NBC CBS CW CW Local News & Weather | | 2 of 6 3 of 6 6 of 6 | | 6/01/15 6/01/15 6/01/15 |
Harlingen/Weslaco/ Brownsville/McAllen,TX | | 86 | | 1 | | KGBT KGBT | | Primary Second | | O&O | | CBS Inmigrante TV | | 5 of 16 | | 8/01/14 |
Chattanooga, Tennessee | | 87 | | 1 | | WTVC WTVC | | Primary Second | | O&O | | ABC This TV | | 1 of 6 | | 8/01/13 (f) |
9
Table of Contents
Market | | Market
Rank (a) | | Stations
in
Market | | Stations | | Channel | | Status (b) | | Network/
Program Service
Arrangement (c) | | Station
Rank in
Market (d) | | Expiration
Date of FCC
License |
Colorado Springs, Colorado | | 89 | | 2 | | KXRM KXTU-LD KXRM KXTU-LD | | Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O O&O | | FOX CW CW MundoFox | | 4 of 6 5 of 6 | | 8/01/14 8/01/14 |
Cedar Rapids, Iowa | | 90 | | 2 | | KGAN KFXA KFXA | | Primary Primary Second | | O&O JSA/SSA(h) | | CBS FOX Zuus Country | | 3 of 4 4 of 4 | | 2/01/14 2/01/14 |
El Paso, Texas | | 91 | | 2 | | KFOX KDBC KFOX KDBC KDBC | | Primary Primary Second Second Third | | O&O JSA/SSA(i) | | FOX CBS Retro TV This TV and MNT Tele-Romantica | | 3 of 6 4 of 6 | | 8/01/14 8/01/14 |
Charleston, South Carolina | | 95 | | 2 | | WTAT WMMP WMMP | | Primary Primary Second | | LMA(g) O&O | | FOX MNT Zuus Country | | 4 of 6 5 of 6 | | 12/01/04 (e) 12/01/04 (e) |
Myrtle Beach/Florence, SC | | 102 | | 2 | | WPDE WWMB WPDE WWMB | | Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O LMA(g) | | ABC CW Local News & Weather CW | | 2 of 6 5 of 6 | | 12/01/20 12/01/20 |
Johnstown/Altoona, PA | | 103 | | 1 | | WJAC WJAC | | Primary Second | | O&O | | NBC ME TV | | 2 of 5 | | 8/01/15 |
Tallahassee, Florida | | 106 | | 1 | | WTWC WTWC | | Primary Second | | O&O | | NBC Zuus Country | | 3 of 6 | | 2/01/13 (f) |
Reno, Nevada | | 107 | | 3 | | KRNV KRXI KAME KRXI KAME KRNV | | Primary Primary Primary Second Second Second | | JSA/SSA(h)O&O LMA(g) | | NBC FOX MNT Retro TV ME TV This TV | | 2 of 6 4 of 6 5 of 6 | | 10/01/14 10/01/14 10/01/14 |
Boise, Idaho | | 110 | | 2 | | KBOI KYUU-LD | | Primary Primary | | O&O O&O | | CBS CW | | 2 of 6 6 of 6 | | 10/01/14 10/01/14 |
Peoria/Bloomington, Illinois | | 117 | | 1 | | WHOI WHOI | | Primary Second | | JSA/SSA(i) | | ABC CW | | 3 of 6 | | 12/01/21 |
Traverse City/Cadillac, MI | | 119 | | 4 | | WPBN/ WTOM WGTU/ WGTQ WPBN/ WTOM WGTU/ WGTQ | | Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O JSA/SSA(h) | | NBC ABC ABC NBC | | 2 of 4 4 of 4 | | 10/01/21 10/01/21 |
Eugene, Oregon | | 121 | | 6 | | KVAL/ KCBY/ KPIC KMTR/ KMCB/ KTCW KVAL KMTR | | Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O JSA/SSA(h) | | CBS NBC This TV CW | | 1 of 5 3 of 5 | | 2/01/15 2/01/15 |
Yakima/Pasco/Richland/Kennewick, Washington | | 124 | | 4 | | KIMA/ KEPR KUNW-CD/ KVVK-CD KIMA | | Primary Primary Second | | O&O O&O | | CBS Univision CW | | 1 of 6 5 of 6 | | 2/01/15 2/01/15 |
Bakersfield, California | | 127 | | 2 | | KBAK KBFX-CD KBFX-CD | | Primary Primary Second | | O&O O&O | | CBS FOX This TV | | 2 of 6 5 of 6 | | 12/01/14 12/01/14 |
10
Table of Contents
Market | | Market
Rank (a) | | Stations
in
Market | | Stations | | Channel | | Status (b) | | Network/
Program Service
Arrangement (c) | | Station
Rank in
Market (d) | | Expiration
Date of FCC
License |
Amarillo, Texas | | 130 | | 2 | | KVII KVIH KVII KVIH | | Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O O&O | | ABC CW CW ABC | | 2 of 8 Not available | | 8/01/14 10/01/14 |
Columbia/Jefferson City, Missouri | | 138 | | 1 | | KRCG | | Primary | | O&O | | CBS | | 1 of 6 | | 2/01/14 |
Medford, Oregon | | 140 | | 1 | | KTVL KTVL | | Primary Second | | O&O | | CBS CW | | 2 of 4 | | 2/01/15 |
Beaumont, Texas | | 141 | | 2 | | KFDM KBTV KFDM KBTV | | Primary Primary Second Second | | O&O JSA/SSA(h) | | CBS FOX CW Bounce Network | | 1 of 6 3 of 6 | | 8/01/14 8/01/06 (e) |
Sioux City, Iowa | | 147 | | 4 | | KMEG KPTH/ KPTP-LD/ KBVK-LP KMEG KPTH | | Primary Primary Second Second | | JSA/SSA(h) O&O | | CBS FOX Azteca This TV and MNT | | 3 of 6 4 of 6 | | 2/01/14 2/01/14 |
Albany, Georgia | | 151 | | 1 | | WFXL WFXL | | Primary Second | | O&O | | FOX Bounce Network | | 3 of 6 | | 4/01/21 |
Steubenville, OH / Wheeling, WV | | 157 | | 1 | | WTOV WTOV | | Primary Second | | O&O | | NBC ME TV | | 1 of 4 | | 10/01/13 (f) |
Quincy, IL/Hannibal, MO/Keokuk, IA | | 170 | | 1 | | KHQA KHQA | | Primary Second | | O&O | | CBS ABC | | 2 of 5 | | 2/01/14 |
Marquette, Michigan | | 180 | | 1 | | WLUC WLUC | | Primary Second | | O&O | | NBC FOX | | 1 of 5 | | 10/01/21 |
Ottumwa, IA/Kirksville, MO | | 201 | | 1 | | KTVO KTVO | | Primary Second | | O&O | | ABC CBS | | 1 of 3 | | 2/01/14 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total television stations | | 149 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(a) Rankings are based on the relative size of a station’s Designated Market Area (DMA) among the 210 generally recognized DMAs in the United States as estimated by Nielsen as of September 2013.
(b) “O & O” refers to stations that we own and operate. “LMA” refers to stations to which we provide programming services pursuant to a local marketing agreement. “JSA/SSA” refers to stations to which we provide or receive sales services pursuant to an outsourcing agreement.
(c) When we negotiate the terms of our network affiliations or program service arrangements, we negotiate on behalf of all of our stations affiliated with that entity simultaneously. This results in substantially similar terms for our stations, including the expiration date of the network affiliations or program service arrangements. A summary of these expiration dates for our primary channels as of December 31, 2013 is as follows:
Network/
Program Service
Arrangement | | Expiration Date |
FOX | | Of the 39 agreements, eight agreements expire on June 30, 2014, one agreement expires on June 30, 2015, one agreement expires on June 30, 2016, five agreements expire on June 30, 2017 and twenty-four agreements expire on December 31, 2017. |
CBS | | Of the 25 agreements, two agreements expire on June 30, 2015, one agreement expires on December 31, 2015, five agreements expire on January 31, 2016, seven agreements expire on February 29, 2016, one agreement expires on March 3, 2016, two agreements expire on June 2, 2016, one agreement on August 31, 2016, one agreement expires December 31, 2016, two agreements expire on April 29, 2017 and three agreements expire on December 31, 2018 |
ABC | | Of the 19 agreements, two agreements expire on August 31, 2014, one agreement expires on December 31, 2014, nine agreements expire on August 31, 2015, one agreement expires on December 31, 2015, three agreements expire on December 31, 2017, and three agreements expire on December 31, 2018 |
NBC | | Of the 16 agreements, nine agreements expire on December 31, 2015, two agreements expire on January 1, 2016, one agreement expires on |
11
Table of Contents
| | January 1, 2017 and four agreements expire on December 31, 2017 |
CW | | Of the 23 agreements, sixteen expire on August 31, 2016, and seven expire at end of the 2015/2016 season. |
MNT | | All 20 agreements expire in the Fall of 2015 |
Univision | | All five agreements expire on December 31, 2014 |
Azteca | | Agreement expired on February 8, 2013 (k) |
(d) The first number represents the rank of each station in its market and is based upon the November 2013 Nielsen estimates of the percentage of persons tuned into each station in the market from 6:00 a.m. to 2:00 a.m., Monday through Sunday. The second number represents the estimated number of television stations designated by Nielsen as “local” to the DMA, excluding public television stations and stations that do not meet the minimum Nielsen reporting standards (weekly cumulative audience of at least 0.1%) for the Monday through Sunday 6:00 a.m. to 2:00 a.m. time period as of November 2013. This information is provided to us in a summary report by Franco Research Group.
(e) We, or subsidiaries of Cunningham Broadcasting Company (Cunningham), timely filed applications for renewal of these licenses with the FCC. Unrelated third parties have filed petitions to deny or informal objections against such applications. We opposed the petitions to deny and the informal objections and those applications are pending. See Note 10. Commitments and Contingencies, in the Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements for more information.
(f) We timely filed applications for renewal of these licenses with the FCC. We are currently waiting for FCC approval.
(g) The license assets for these stations are currently owned by a third party. We operate these stations under local marketing agreements.
(h) The license and programming assets for this station are currently owned by a third party. We operate this station under an outsourcing agreement with the third party to provide certain non-programming related sales, operational and administrative services to these stations.
(i) We have entered into outsourcing agreements with unrelated third parties, under which the unrelated third parties provide certain non-programming related sales, operational and managerial services to these stations. We continue to own all of the license and program assets of these stations and to program and control each station’s operations.
(j) KENV-TV is licensed in the Salt Lake City/St. George, Utah DMA, however, the station is a satellite of KRNV-TV in the Reno, Nevada MDA
(k) The station is continuing to operate under the existing affiliation agreement with Azteca on a temporary basis while we negotiate a new affiliation agreement.
Operating Strategy
Our operating strategy includes the following elements:
Programming to Attract Viewership. We seek to target our programming offerings to attract viewership, to meet the needs of the communities in which we serve and to meet the needs of our advertising customers. In pursuit of this strategy, we seek to obtain, at attractive prices, popular syndicated programming that is complementary to each station’s network programming. We also seek to broadcast live local and national sporting events that would appeal to a large segment of the local community. Moreover, we produce news at 84 stations in 47 markets, including one station which have a local news sharing agreement with a competitive station in that market. We have 16 stations which have local news sharing arrangements with a competitive station in that market, which produces the news aired on our station.
Television advertising prices are primarily based on ratings information measured and distributed by Nielsen. In 2010, the Media Rating Council, an independent organization that monitors rating services, revoked Nielsen’s accreditation in the 154 markets in which Nielsen measures ratings exclusively by its diary methodology. As of March 1, 2014, approximately 46 of our 71 markets are diary only markets. For certain markets, including some of our diary only markets, we entered into a contract with Rentrak Corporation, an alternative rating service provider, that uses set-top box television measurements to provide us additional measurement information to the ratings services Nielsen provides.
Attract and Retain High Quality Management. We believe that much of our success is due to our ability to attract and retain highly skilled and motivated managers at both the corporate and local station levels. We provide a combination of base salary, long-term incentive compensation including equity awards and, where appropriate, cash bonus pay designed to be competitive with comparable employers in the television broadcast industry. A significant portion of the compensation available to certain members of our senior management and our sales force is based on their achievement of certain performance goals.
Developing Local Franchises. We believe the greatest opportunity for a sustainable and growing customer base lies within our local communities. Therefore, we have focused on developing a strong local sales force at each of our television stations, which is comprised of
12
Table of Contents
approximately 711 sales account executives and local sales managers company-wide. Excluding political advertising revenue, 70.2% of our net time sales were local for the year ended December 31, 2013, compared to 70.0% in 2012. Excluding political, local revenues have increased 40.7% during 2013 versus 2012. Market share survey results reflect that our stations’ share of the local television advertising market increased to 22.2% in 2013 from 19.0% in 2012. Our goal is to grow our local revenues by increasing our market share and by developing new business opportunities.
Local News. We believe that the production and broadcasting of local news is an important link to the community and an aid to a station’s efforts to expand its viewership. In addition, local news programming can provide access to advertising sources targeted specifically to local news viewers. We assess the anticipated benefits and costs of producing local news prior to the introduction of local news at our stations because a significant investment in capital equipment is required and substantial operating expenses are incurred in introducing, developing and producing local news programming. We also continuously review the performance of our existing news operations to make sure they are economically viable. Excluding certain stations acquired during 2013, we have upgraded the majority of our markets to provide high—definition (HD) news programming. We expect to roll out HD news programming to our remaining news producing markets in the next couple of years. During 2013, we expanded news in 9 markets and plan to expand our news in an additional 11 markets in 2014.
Our local news initiatives are an important part of our strategy that have resulted in our entering into 17 local news sharing arrangements with other television broadcasters. We are the provider of news services in one instance while in 16 of our news share arrangements, we are the recipient of services. We believe in the markets where we have news share arrangements that such arrangements generally provide both higher viewer ratings and revenues for the station receiving the news and generate a profit for the news share provider. Generally, both parties and the local community are beneficiaries of these arrangements.
Developing New Business. We are always striving to develop new business models to complement or enhance our existing television broadcast business. We have developed new ways to bundle online, mobile text messaging and social media advertising with our traditional commercial broadcasting model. We plan to continue to expand our efforts in this area. In addition, we are making progress on standardizing and implementing a viable business platform for mobile DTV. See Mobile Digital Broadcast Television (mobile DTV) section below. We continue to explore new opportunities and plan to implement new initiatives in 2014.
Retransmission Consent Agreements. We have retransmission consent agreements with MVPDs, such as cable, satellite and telecommunications operators in our markets. MVPDs compensate us for the right to retransmit our broadcast signals. Our successful negotiations with MVPDs have created agreements that now produce meaningful sustainable revenue streams.
Ownership Duopolies and Utilization of Local Marketing Agreements. We have sought to increase our revenues and improve our margins through the ownership of two stations in a single market, called a duopoly, and by providing programming services pursuant to a LMA to a second station in DMAs where we already own one station. Duopolies and LMAs allow us to realize significant economies of scale in marketing, programming, overhead and capital expenditures. We also believe these arrangements enable us to air popular programming and contribute to the diversity of programming within each DMA. Although under the FCC ownership rules released in June 2003 (the 2003 Rules), we would be allowed to continue to program most of the stations with which we have a LMA, in the absence of a waiver, the 2003 Rules would require us to terminate or modify three of our LMAs. Under the ownership rules established in 2008, we may be required to terminate or modify three more of our LMAs that we executed after November 5, 1996. We also may be required to terminate or modify three other LMAs that we executed prior to November 5, 1996, if the FCC subsequently initiates a case-by-case review of those LMAs and determines not to extend the grandfathering period. In connection with our pending acquisition of the Allbritton station in Charleston, the FCC has taken the position that the stay granted by the D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals allowing the continuation of an LMA between us and Cunningham relating to WTAT-TV in that market is no longer effective. In response to this, we are currently restructuring the relationship with WTAT in order to comply with current ownership rules in the absence of such a stay. Such restructuring will include a JSA rather than an LMA and further action may subsequently be required as a result of any action the FCC takes with respect to JSAs. See Local Marketing Agreements under the Federal Regulation of Television Broadcasting section below and Risk Factors - The FCC’s multiple ownership rules limit our ability to operate multiple television stations in some markets and may result in a reduction in our revenue or prevent us from reducing costs. Changes in these rules may threaten our existing strategic approach to certain television markets.
Use of Outsourcing Agreements / Joint Sales Agreements (JSAs). In addition to our LMAs, we have entered into outsourcing agreements in which our stations currently provide non-programming related services such as, sales, operational and managerial services to twenty stations (excluding five satellite stations) in seventeen markets, of which twelve are affiliated with major networks (FOX, ABC, CBS, and NBC) and eight are affiliated with CW, MyNetwork TV, or are independent, and we may seek opportunities for additional outsourcing arrangements. Additionally, another party provides similar services to three of our stations. We believe the outsourcing structure allows stations to achieve operational efficiencies and economies of scale, which should improve broadcast cash flow and competitive positions and better serve the viewers in the community. While television JSAs are not currently “attributable,” as that term is defined by the FCC, on August 2, 2004, the FCC released a notice of proposed rulemaking seeking comments on its tentative conclusion that television JSAs should be attributable. The FCC is also considering the attribution of JSAs as part of its 2010 Quadrennial Regulatory Review of its broadcast ownership rules, released on December 22, 2011. Press and other reports indicate that the FCC is actively considering
13
Table of Contents
implementing new rules which would cause a station to be attributable to the owner of another station in the market which sells more than 15 percent of the advertising on the first station. Reports indicate that the FCC does not intend to “grandfather” existing JSAs, but rather to require parties to come into compliance with these new rules within a period of between eighteen months and two years. If the FCC were to enact such a rule we would no longer be able to enter into new transactions utilizing JSAs in the way we have done historically and would need to either terminate our existing JSAs or take action to modify the terms of our JSAs in a manner which complies with any such new rules. There can be no such assurance that the FCC will take the actions reported to be being considered and we cannot predict with any certainty the impact such rules might have on us until such rules are actually enacted. See Local Marketing Agreements under the Federal Regulation of Television Broadcasting section below and Risk Factors - The FCC’s multiple ownership rules limit our ability to operate multiple television stations in some markets and may result in a reduction in our revenue or prevent us from reducing costs. Changes in these rules may threaten our existing strategic approach to certain television markets.
Multi-Channel Digital Broadcasting. FCC rules allow broadcasters to transmit additional digital channels within the spectrum allocated to each FCC license holder. This provides viewers with additional programming alternatives at no additional cost to them. We are airing second and third digital channels comprised of: CBS, ABC, and NBC (certain signals are rebroadcasted content from other primary channels within the same market); FOX; The CW; MyNetworkTV; This TV, independent programming; ME TV; Weather Radar; Weather Nation; Live Well Network, Antenna TV; Bounce Network; Zuus Country; Retro TV; and Estrella TV, Azteca, Tele-Romantica, Inmigrante TV, MundoFox and Telemundo, Spanish-language television networks. In addition, as noted below, we believe mobile DTV will serve as an additional use of our digital spectrum. We may consider other alternative programming formats that we could air using our multi-channel digital spectrum space with the goal towards achieving higher profits and community service.
Mobile Digital Broadcast Television (mobile DTV). We are a founding member of the Open Mobile Video Coalition (OMVC) and Mobile500 (M500). The Open Mobile Video Coalition (OMVC), an alliance of broadcasters dedicated to accelerating the development and rollout of mobile television, has recently integrated functions with the National Association of Broadcasters. With mobile TV, viewers can tune in to live, local news, traffic information, weather, sporting events and entertainment programs from virtually any location — wherever they may be, using a variety of mobile and video devices.
The OMVC, working within the Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC), helped to develop a mobile broadcasting standard that allows digital television to be broadcast to numerous mobile devices including smart phones, laptop computers, tablet devices, video screens in vehicles, portable video players and other mobile and portable devices with the addition of a mobile DTV receiver. The ATSC is an international, non-profit organization developing voluntary standards for digital television.
We continue to believe that the technical ability to receive our television broadcast content on mobile devices will be attractive to individuals. We have installed and are running current mobile DTV services at WSYX-TV, WTTE-TV, WPEC-TV, WKRC-TV and KEYE-TV. We will continue to gauge our plans on the successes of these markets, and deploy within remaining markets accordingly.
Next Generation Broadcast Platforms (NextGen). Cunningham received FCC approval to test advanced services (including mobile broadcasting and 4K-Ultra High Definition TV) on WNUV-TV in Baltimore. With respect to WNUV-TV, the FCC granted the station authority to operate an experimental facility in order to evaluate the performance of the Next Generation Broadcast capabilities throughout the WNUV-TV service area.
On 26 March 2013 the ATSC announced a Call for Proposals for the “physical layer” of the next-generation broadcast TV standard that in the years ahead could replace the current digital broadcasting systems used in the United States and around the world. The physical layer is the core transmission system that is the basis for any over-the-air broadcast system. The ATSC is an international, non-profit organization developing voluntary standards for digital television.
There are many “Key Goals” for ATSC 3.0. It will be a system that is much more flexible and efficient with spectrum; provide for integration with other delivery technologies, such as mobile; support targeted advertising capabilities; integrate features for delivery of personalized content; bring immersive viewing experiences that would include 4K or Ultra HD as well as advanced audio; include better video compression, most likely using the new MPEG H.265/High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) standard; and plans to make the standard more compatible with systems used outside the U.S.
Sinclair, together with Coherent Logix, a specialist in software-defined radio technology, is among the 13 groups that submitted proposals to for the ATSC 3.0 transmission standard. The next-generation ATSC 3.0 broadcast television standard must provide improvements in performance, functionality and efficiency that are significant enough to warrant the challenges of a transition to a new system. The physical layer technologies will provide a foundation for the next terrestrial broadcast system. Robustness of service for devices operating within the ATSC 3.0 service area should exceed that of current ATSC systems and that of cell phone and other wireless devices.
Control of Operating and Programming Costs. By employing a disciplined approach to managing programming acquisition and other costs, we have been able to achieve operating margins that we believe are very competitive within the television broadcast industry. We believe our
14
Table of Contents
national reach of over 34.6% of the country provides us with a strong position to negotiate with programming providers and, as a result, the opportunity to purchase high quality programming at more favorable prices. Moreover, we emphasize control of each of our station’s programming and operating costs through program-specific profit analysis, detailed budgeting, regionalization of staff and detailed long-term planning models.
Popular Sporting Events. At some of our stations, we have been able to acquire local television broadcast rights for certain sporting events, including NBA basketball, Major League Baseball, NFL football, NHL hockey, ACC basketball and both Big Ten and SEC football and basketball and certain other college and high school sports. We seek to expand our sports broadcasting in DMAs as profitable opportunities arise such as our purchase of the Ring of Honor professional wrestling franchise in May 2011. Our CW and MyNetworkTV stations generally face fewer preemption restrictions on broadcasting live local sporting events compared with our FOX, ABC, CBS and NBC stations, which are required to broadcast a greater number of hours of programming supplied by the networks. In addition, our stations that are affiliated with FOX, ABC, CBS and NBC have network arrangements to broadcast certain NBA basketball games, MLB baseball games, NFL football games, NHL hockey games, NASCAR races and PGA golf events, as well as other popular sporting events.
Strategic Realignment of Station Portfolio. We continue to examine our television station group portfolio in light of the 2003 Rules. For a summary of these rules, refer to Ownership Matters, discussed under Federal Regulation of Television Broadcasting. Our objective has been to build our local franchises in the markets we deem strategic. We routinely review and conduct investigations of potential television station acquisitions, dispositions and station swaps. At any given time, we may be in discussions with one or more television station owners.
Non-broadcast Investments. We have sought ways to diversify our business and return additional value to our shareholders through investments in non-broadcast based businesses and real estate. We carry investments in various companies from different industries including sign design and fabrication and security alarm monitoring and bulk acquisition. In addition, we invest in various real estate ventures including developmental land, operating commercial and multi-family residential real estate properties and apartments. We also invest in private equity and structured debt / mezzanine financing investment funds. Currently, operating results from our investments represent a small portion of our overall operating results. Our ability to make additional investments is limited by the restrictions of our amended senior secured credit facility (Bank Credit Agreement). Activity related to these investments is included in Other Operating Divisions.
FEDERAL REGULATION OF TELEVISION BROADCASTING
The ownership, operation and sale of television stations are subject to the jurisdiction of the FCC, which acts under the authority granted by the Communications Act of 1934, as amended (the Communications Act). Among other things, the FCC assigns frequency bands for broadcasting; determines the particular frequencies, locations and operating power of stations; issues, renews, revokes and modifies station licenses; regulates equipment used by stations; adopts and implements regulations and policies that directly or indirectly affect the ownership, operation and employment practices of stations; and has the power to impose penalties for violations of its rules and regulations or the Communications Act.
The following is a brief summary of certain provisions of the Communications Act, the Telecommunications Act of 1996 (the 1996 Act) and specific FCC regulations and policies. Reference should be made to the Communications Act, the 1996 Act, FCC rules and the public notices and rulings of the FCC for further information concerning the nature and extent of federal regulation of broadcast stations.
License Grant and Renewal
Television stations operate pursuant to broadcasting licenses that are granted by the FCC for maximum terms of eight years and are subject to renewal upon application to the FCC. During certain periods when renewal applications are pending, petitions to deny license renewals can be filed by interested parties, including members of the public. The FCC will generally grant a renewal application if it finds:
· that the station has served the public interest, convenience and necessity;
· that there have been no serious violations by the licensee of the Communications Act or the rules and regulations of the FCC; and
· that there have been no other violations by the licensee of the Communications Act or the rules and regulations of the FCC that, when taken together, would constitute a pattern of misconduct.
All of the stations that we currently own and operate or provide programming services or sales services to, pursuant to Time Brokerage Agreements (sometimes called Local Marketing Agreements (LMAs)), JSAs or other agreements, are presently operating under regular licenses, which expire as to each station on the dates set forth under Television Broadcasting above. Although renewal of a license is granted in the vast majority of cases even when petitions to deny are filed, there can be no assurance that the license of any station will be renewed.
In 2004, we filed with the FCC an application for the license renewal of WBFF-TV in Baltimore, Maryland. Subsequently, an individual named Richard D’Amato filed a petition to deny the application. In 2004, we also filed with the FCC applications for the license renewal
15
Table of Contents
of television stations: WXLV-TV, Winston-Salem, North Carolina; WMYV-TV, Greensboro, North Carolina; WLFL-TV, Raleigh / Durham, North Carolina; WRDC-TV, Raleigh / Durham, North Carolina; WLOS-TV, Asheville, North Carolina and WMMP-TV, Charleston, South Carolina. An organization calling itself “Free Press” filed a petition to deny the renewal applications of these stations and also the renewal applications of two other stations in those markets, which we program pursuant to LMAs: WTAT-TV, Charleston, South Carolina and WMYA-TV, Anderson, South Carolina. Several individuals and an organization named “Sinclair Media Watch” also filed informal objections to the license renewal applications of WLOS-TV and WMYA-TV, raising essentially the same arguments presented in the Free Press petition. The FCC is in the process of considering these renewal applications and we believe the objections have no merit.
On July 21, 2005, we filed with the FCC an application to acquire the license and television broadcast assets of WNAB-TV in Nashville, Tennessee. The Rainbow / PUSH Coalition (Rainbow / PUSH) filed a petition to deny that application and also requested that the FCC initiate a hearing to investigate whether WNAB-TV was improperly operated with WZTV-TV and WUXP-TV, two of our stations located in the same market as WNAB-TV. The FCC application remains pending and we believe the Rainbow / PUSH petition has no merit.
On August 1, 2005, we filed applications with the FCC requesting renewal of the broadcast licenses for WICS-TV and WICD-TV in Springfield / Champaign, Illinois. Subsequently, various viewers filed informal objections requesting that the FCC deny these renewal applications. On September 30, 2005, we filed an application with the FCC for the renewal of the broadcast license for KGAN-TV in Cedar Rapids, Iowa. On December 28, 2005, an organization calling itself “Iowans for Better Local Television” filed a petition to deny that application. In April 2009, the FCC granted the license renewal application for WICD-TV. The FCC is in the process of considering the WICS-TV and KGAN-TV renewal applications and we believe the objections and petitions requesting denial have no merit.
On August 1, 2005, we filed applications with the FCC requesting renewal of the broadcast licenses for WCGV-TV and WVTV-TV in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. On November 1, 2005, the Milwaukee Public Interest Media Coalition filed a petition to deny these renewal applications. On June 13, 2007, the Video Division of the FCC denied the petition to deny, and subsequently, the Milwaukee Public Interest Media Coalition filed a petition for reconsideration of that decision, which we opposed. In July 2008, the Video Division granted the renewal application of WVTV-TV and separately denied the Milwaukee Public Interest Media Coalition’s petition for reconsideration. On August 11, 2008, the Milwaukee Public Interest Media Coalition and another organization filed another petition for reconsideration of the decision, which we opposed. On January 12, 2010, the FCC dismissed the second petition for reconsideration. On February 16, 2010, the Milwaukee Public Interest Media Coalition filed an application for review of the January 2010 dismissal decision, which we opposed. On December 12, 2010, the FCC dismissed the application for review. On January 11, 2011, the Milwaukee Public Interest Media Coalition filed a second application for review seeking review of the December 2010 dismissal decision, which we opposed. The WCGV-TV renewal of license application remains pending.
Action on many license renewal applications, including those we have filed, has been delayed because of the pendency of complaints that programming aired by the various networks contained indecent material and complaints regarding alleged violations of sponsorship identification rules. We cannot predict when the FCC will address these complaints and act on the renewal applications. We continue to have operating authority until final action is taken on our renewal applications.
The FCC has made it difficult for us to predict the impact on our license renewals from allegations related to the airing of indecent material that may arise in the ordinary course of our business. For example, on Veterans’ Day in November 2004, we preempted (did not air) “Saving Private Ryan,” a program that was aired during ABC’s network programming time. We were concerned that since the program contained the use of the “F-word” (indecent material as defined by the FCC) airing the programming could result in a fine or other negative consequences for one or more of our ABC stations. In February 2005, the FCC dismissed all complaints filed against ABC stations regarding this program. The FCC’s decision justified what some may consider indecent material as appropriate in the context of the program. Although this ruling has expanded the programming opportunities of our stations, it still leaves us at risk because what might be determined as legitimate context by us may not be deemed so by the FCC and the FCC will not rule beforehand as this may be considered a restriction of free speech. For example, in September 2006, we preempted a CBS network documentary on the events that happened on September��11, 2001 because the program contained what some have argued is indecent material and the FCC would not provide, in advance of the airing of the documentary, any guidance on whether that material was appropriate in the context of the program. In 2007, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit held that the FCC’s indecency policy regarding “fleeting expletives” was arbitrary and capricious when the FCC determined that “fleeting expletives” aired during the Golden Globes and Billboard Music Awards violated its indecency rules. The FCC challenged the decision and the case was argued before the Supreme Court in November 2008. Also in 2008 the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit rejected an FCC decision concluding, among other things, that a fleeting display of nudity during the Superbowl halftime show was indecent. On April 28, 2009, the Supreme Court overturned the Golden Globes and Billboard Music Awards decision of the Second Circuit and held that the FCC had adequately justified its departure from prior decisions in determining that it could sanction a station for a single “F-word” or “S-word” broadcast on that station. However, the Supreme Court also remanded the case back to the Second Circuit for further consideration to resolve any First Amendment Constitutional issues raised by the FCC’s enforcement policy. On May 16, 2009, the Supreme Court remanded the Superbowl halftime show case to the Third Circuit in order to consider the impact of the Supreme Court’s Golden Globes and Billboard Music Awards decision and to consider the same First Amendment issues that were remanded to the Second Circuit. On July 13, 2010, the Second Circuit struck down the FCC’s indecency policy in its
16
Table of Contents
entirety. On June 21, 2012, the Supreme Court vacated the Second Circuit’s decision that the FCC’s enforcement of its indecency rules was unconstitutional. Although the Supreme Court refused to address whether the FCC’s indecency rules and the enforcement of them was unconstitutional, it did find that the agency did not give ABC and Fox “fair warning” that they could be fined for so-called “fleeting expletives” and nudity. The Court’s opinion permits the FCC to modify its current indecency policy. It is unclear when the FCC might act as a result of the Court’s ruling and the FCC’s unclear policy make it difficult for us to determine what may be indecent programming.
Ownership Matters
General. The Communications Act prohibits the assignment of a broadcast license or the transfer of control of a broadcast license without the prior approval of the FCC. In determining whether to permit the assignment or transfer of control of, or the grant or renewal of, a broadcast license, the FCC considers a number of factors pertaining to the licensee, including compliance with various rules limiting common ownership of media properties, the “character” of the licensee and those persons holding “attributable” interests in that licensee and compliance with the Communications Act’s limitations on ownership by non-U. S. citizens or their representatives or by a foreign government or a representative thereof, or by any corporation organized under the laws of a foreign country (collectively, aliens). The FCC has indicated that in order to approve an assignment or transfer of a broadcast license the FCC must make an affirmative determination that the proposed transaction serves the public interest, not merely that the transaction does not violate its rules or shares factual elements with other transactions previously approved by the FCC, and that it may deny a transaction if it determines that the transaction could result in public interest harms by substantially frustrating or impairing the objectives or implementation of the Communications Act or related statutes.
To obtain the FCC’s prior consent to assign a broadcast license or transfer control of a broadcast license, appropriate applications must be filed with the FCC. If the application involves a “substantial change” in ownership or control, the application must be placed on public notice for a period of approximately 30 days during which petitions to deny the application may be filed by interested parties, including members of the public. If the application does not involve a “substantial change” in ownership or control, it is a “pro forma” application. The “pro forma” application is not subject to petitions to deny or a mandatory waiting period, but is nevertheless subject to having informal objections filed against it. If the FCC grants an assignment or transfer application, interested parties have approximately 30 days from public notice of the grant to seek reconsideration or review of the grant. Generally, parties that do not file initial petitions to deny, or informal objections against the application, face difficulty in seeking reconsideration or review of the grant. The FCC normally has an additional 10 days to set aside such grant on its own motion. When passing on an assignment or transfer application, the FCC is prohibited from considering whether the public interest might be served by an assignment or transfer to any party other than the assignee or transferee specified in the application.
The FCC generally applies its ownership limits to “attributable” interests held by an individual, corporation, partnership or other association. In the case of corporations holding, or through subsidiaries controlling, broadcast licenses, the interests of officers, directors and those who, directly or indirectly, have the right to vote 5% or more of the corporation’s stock (or 20% or more of such stock in the case of insurance companies, investment companies and bank trust departments that are passive investors) are generally attributable. In August 1999, the FCC revised its attribution and multiple ownership rules and adopted the equity-debt-plus rule that causes certain creditors or investors to be attributable owners of a station. Under this rule, a major programming supplier (any programming supplier that provides more than 15% of the station’s weekly programming hours) or same-market media entity will be an attributable owner of a station if the supplier or same-market media entity holds debt or equity, or both, in the station that is greater than 33% of the value of the station’s total debt plus equity. For the purposes of this rule, equity includes all stock, whether voting or non-voting, and equity held by insulated limited partners in partnerships. Debt includes all liabilities whether long-term or short-term. In addition, LMAs are attributable where a licensee holds an attributable interest in a television station and programs more than 15% of another television station in the same market.
The Communications Act prohibits the issuance of a broadcast license to, or the holding of a broadcast license by, any corporation of which more than 20% of the capital stock is owned of record or voted by aliens. The Communications Act also authorizes the FCC, if the FCC determines that it would be in the public interest, to prohibit the issuance of a broadcast license to, or the holding of a broadcast license by, any corporation directly or indirectly controlled by any other corporation of which more than 25% of the capital stock is owned of record or voted by aliens. The FCC has issued interpretations of existing law under which these restrictions in modified form apply to other forms of business organizations, including partnerships. In November 2013, the FCC indicated that it would consider indirect foreign ownership of broadcast licenses in excess of the 25% level on a case-by-case basis.
As a result of these provisions, the licenses granted to our subsidiaries by the FCC could be revoked if, among other restrictions imposed by the FCC, more than 25% of our stock were directly or indirectly owned or voted by aliens. Sinclair and its subsidiaries are domestic corporations, and the members of the Smith family (who together hold approximately 75.3% as of February 24, 2014 of the common voting rights of Sinclair) are all United States citizens. Our amended and restated Articles of Incorporation (the Amended Certificate) contain limitations on alien ownership and control that are substantially similar to those contained in the Communications Act. Pursuant to the Amended Certificate, we have the right to repurchase alien-owned shares at their fair market value to the extent necessary, in the judgment of the Board of Directors, to comply with the alien ownership restrictions.
17
Table of Contents
In February 2008, the FCC released a Report and Order that, with the exception of the newspaper / broadcast cross-ownership rule, essentially re-adopts the ownership rules the FCC originally introduced in 1999 and has enforced since then.
The relevant 2008 ownership rules are as follows:
Radio / Television Cross-Ownership Rule. The FCC’s radio / television cross-ownership rule (the “one to a market” rule) generally permits a party to own a combination of up to two television stations and six radio stations in the same market, depending on the number of independent media voices in the market.
Newspaper / Broadcast Cross-Ownership Rule. The FCC’s rule generally prohibits the common ownership of a radio or television broadcast station and a daily newspaper in the same market. However, the FCC will presume that, in the top 20 DMAs, it is not inconsistent with the public interest for one entity to own a daily newspaper and a radio station or, under the following circumstances, a daily newspaper and a television station if: (1) the television station is not ranked among the top-four stations in the DMA and (2) at least eight independent “major media voices” remain in the DMA. The FCC will presume that all other newspaper / broadcast mergers are not in the public interest, but it will allow applicants to seek a waiver and rebut this presumption by clear and convincing evidence that, post-merger, the merged entity will increase the diversity of independent news outlets and increase competition among independent news sources in the relevant market.
In addition, expansion of our broadcast operations on both a local and national level will continue to be subject to the FCC’s ownership rules, Department of Justice (DOJ) review and any changes the FCC or Congress may adopt. On December 22, 2011, the FCC released a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking in its Quadrennial Review of the Multiple Ownership Rules and is considering changes to the FCC’s rules regarding broadcast-newspaper cross ownership restrictions, the possible elimination of rules restricting the ownership of radio and TV in the same market, the potential attribution of TV JSAs and shared services agreements (SSAs) meaning potentially making JSAs and SSAs count as ownership interests in a multiple ownership analysis and other possible revisions to the local radio and TV ownership limitations or exceptions that would allow for waivers of the limits in defined circumstances. Press and other reports indicate that the FCC is actively considering implementing new rules which would cause a station to be attributable to the owner of another station in the market which sells more than 15 percent of the advertising on the first station. Reports indicate that the FCC does not intend to “grandfather” existing JSAs, but rather to require parties to come into compliance with these new rules within a period of between eighteen months and two years. If the FCC were to enact such a rule we would no longer be able to enter into new transactions utilizing JSAs in the way we have done historically and would need to either terminate our existing JSAs or take action to modify the terms of our JSAs in a manner which complies with any such new rules. There can be no such assurance that the FCC will take the actions reported to be being considered and we cannot predict with any certainty the impact such rules might have on us until such rules are actually enacted. Any further relaxation of the FCC’s ownership rules may increase the level of competition in one or more markets in which our stations are located, more specifically to the extent that any of our competitors may have greater resources and thereby may be in a superior position to take advantage of such changes. Conversely, any such relaxation or invalidation of such rules may provide us the opportunity to expand should we have the resources and find the terms advantageous.
Dual Network Rule. The four major television networks, FOX, ABC, CBS and NBC, are prohibited, absent a waiver, from merging with each other. In May 2001, the FCC amended its dual network rule to permit the four major television networks to own, operate, maintain or control other television networks, such as The CW or program service arrangements, such as MyNetworkTV.
National Ownership Rule. As of 2004, by statute, the national television viewing audience reach cap is 39%. Under this rule, where an individual or entity has an attributable interest in more than one television station in a market, the percentage of the national television viewing audience encompassed within that market is only counted once. Additionally, since historically, very high frequency, or VHF stations (channels 2 through 13) have shared a larger portion of the market than ultra-high frequency, or UHF stations (channels 14 through 51), only half of the households in the market area of any UHF station are included when calculating an entity’s national television viewing audience (commonly referred to as the UHF discount). On September 26, 2013, the FCC initiated a rulemaking seeking comment on whether (a) the FCC has the authority to modify the national ownership rule, including revision or elimination of the UHF discount; (b) the UHF discount should be eliminated; (c) if the UHF discount is eliminated, grandfathering should be accorded where owners of television groups would exceed the 39% national audience cap by virtue of the elimination of the discount; and should a discount for VHF station ownership be adopted. We cannot predict the outcome of that rulemaking.
All but nine of the stations we own and operate, or to which we provide programming services, are UHF. Counting all our present stations and pending transactions, we reach over 38% of U. S. television households or 24.3% taking into account the FCC’s UHF discount.
Local Television (Duopoly) Rule. A party may own television stations in adjoining markets, even if there is Grade B overlap between the two stations’ broadcast signals and generally may own two stations in the same market:
· if there is no Grade B overlap between the stations; or
18
Table of Contents
· if the market containing both the stations will contain at least eight independently owned full-power television stations post-merger (the eight voices test) and not more than one station is among the top-four ranked stations in the market.
In addition, a party may request a waiver of the rule to acquire a second or third station in the market if the station to be acquired is economically distressed or not yet constructed and there is no party who does not own a local television station who would purchase the station for a reasonable price.
Antitrust Regulation. DOJ and the Federal Trade Commission have increased their scrutiny of the television industry since the adoption of the 1996 Act and have reviewed matters related to the concentration of ownership within markets (including LMAs and JSAs) even when ownership or the LMA or JSA in question is permitted under the laws administered by the FCC or by FCC rules and regulations. The DOJ takes the position that an LMA or JSA entered into in anticipation of a station’s acquisition with the proposed buyer of the station constitutes a change in beneficial ownership of the station which, if subject to filing under the Hart-Scott-Rodino Anti Trust Improvements Act, cannot be implemented until the waiting period required by that statute has ended or been terminated.
Local Marketing Agreements
Certain of our stations have entered into what have commonly been referred to as time brokerage agreements or local marketing agreements or LMAs. One typical type of LMA is a programming agreement between two separately owned television stations serving the same market, whereby the licensee of one station programs substantial portions of the broadcast day and sells advertising time during such programming segments on the other licensee’s station subject to the latter licensee’s ultimate editorial and other controls. We believe these arrangements allow us to reduce our operating expenses and enhance profitability.
If we are required to terminate or modify our LMAs, our business could be adversely affected in several ways, including losses on investments and termination penalties. For more information on the risks, see Risk Factors — The FCC’s multiple ownership rules limit our ability to operate multiple television stations in some markets and may result in a reduction in our revenue or prevent us from reducing costs. Changes in these rules may threaten our existing strategic approach to certain television markets — Changes in rules on local marketing agreements.
The following paragraphs discuss various proceedings relevant to our LMAs.
In 1999, the FCC established a new local television ownership rule. LMAs fell under this rule, however, the rule grandfathered LMAs that were entered into prior to November 5, 1996, and permitted the applicable stations to continue operations pursuant to the LMAs until the conclusion of the FCC’s 2004 biennial review. The FCC stated it would conduct a case-by-case review of grandfathered LMAs and assess the appropriateness of extending the grandfathering periods. The FCC did not initiate any review of grandfathered LMAs in 2004 or as part of its subsequent quadrennial reviews. We do not know when, or if, the FCC will conduct any such review of grandfathered LMAs. For LMAs executed on or after November 5, 1996, the FCC required compliance with the 1999 local television ownership rule by August 6, 2001. We challenged the 1999 rules in the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit (D.C. Circuit), resulting in the exclusion of post-November 5, 1996 LMAs from the 1999 rules. In 2002, the D.C. Circuit ruled in Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. v. F.C.C., 284 F.3d 114 (D.C. Cir. 2002) that the 1999 local television ownership rule was arbitrary and capricious and sent the rule back to the FCC for further refinement.
In 2003, the FCC revised its ownership rules, including the local television ownership rule; however the U. S. Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit (Third Circuit) did not enable the 2003 rules to become effective and sent the 2003 rules back to the FCC for further refinement. Due to the court decisions, the FCC concluded the 1999 rules could not be justified as necessary in the public interest and, as a result, we took the position that an issue exists regarding whether the FCC has any current legal right to enforce any rules prohibiting the acquisition of television stations. Several parties, including us, filed petitions with the Supreme Court of the United States seeking review of the Third Circuit decision, but the Supreme Court denied the petitions in June 2005.
In July 2006, the FCC released a Further Notice of Proposed Rule Making seeking comment on how to address the issues raised by the Third Circuit’s decision. In January 2008, the FCC released an order containing ownership rules that re-adopted the 1999 rules. On February 29, 2008, several parties, including us, separately filed petitions for review in a number of federal appellate courts challenging the 1999 rules. Those petitions were consolidated in the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit (Ninth Circuit) and in November 2008, transferred by the Ninth Circuit to the Third Circuit and on July 7, 2011, the Third Circuit upheld the FCC’s local television ownership rules. On December 5, 2011, we joined with a number of other parties on a Petition for a Writ of Certiorari filed with the Supreme Court requesting that the Court overrule the decision of the Third Circuit. That request was denied by the Supreme Court.
On November 15, 1999, we entered into an agreement to acquire WMYA-TV (formerly WBSC-TV) in Anderson, South Carolina from Cunningham, but that transaction was denied by the FCC. Since none of the FCC rule changes ever became effective, we filed a petition for reconsideration with the FCC and amended our application to acquire the license of WMYA-TV. We also filed applications in November 2003 to acquire the license assets of the remaining five Cunningham stations: WRGT-TV, Dayton, Ohio; WTAT-TV, Charleston, South Carolina; WVAH-TV, Charleston, West Virginia; WNUV-TV, Baltimore, Maryland; and WTTE-TV, Columbus, Ohio.
19
Table of Contents
Rainbow / PUSH filed a petition to deny these five applications and to revoke all of our licenses. The FCC dismissed our applications and denied the Rainbow / PUSH petition due to the above mentioned 2003 Third Circuit decision. Rainbow / PUSH filed a petition for reconsideration of that denial and we filed an application for review of the dismissal. In 2005, we filed a petition with the D. C. Circuit requesting that the Court direct the FCC to take final action on our applications, but that petition was dismissed. On January 6, 2006, we submitted a motion to the FCC requesting that it take final action on our applications. The applications and the associated petition to deny are still pending. We believe the Rainbow / PUSH petition is without merit.
The Satellite Home Viewer Act (SHVA), The Satellite Home Viewer Improvement Act (SHVIA) and the Satellite Home Viewer Extension and Reauthorization Act (SHVERA)
In 1988, Congress enacted the Satellite Home Viewer Act (SHVA), which enabled satellite carriers to provide broadcast programming to those satellite subscribers who were unable to obtain broadcast network programming over-the-air. SHVA did not permit satellite carriers to retransmit local broadcast television signals directly to their subscribers. The Satellite Home Viewer Improvement Act of 1999 (SHVIA) revised SHVA to reflect changes in the satellite and broadcasting industry. This legislation allowed satellite carriers, until December 31, 2004, to provide local television signals by satellite within a station market, and effective January 1, 2002, required satellite carriers to carry all local signals in any market where they carry any local signals. On or before July 1, 2001, SHVIA required all television stations to elect to exercise certain “must-carry” or “retransmission consent” rights in connection with their carriage by satellite carriers. We have entered into compensation agreements granting the two primary satellite carriers retransmission consent to carry all our stations. In December 2004, President Bush signed into law the Satellite Home Viewer Extension and Reauthorization Act (SHVERA). SHVERA extended, until December 31, 2009, the rights of broadcasters and satellite carriers under SHVIA to retransmit local television signals by satellite. SHVERA also authorized satellite delivery of distant network signals, significantly viewed signals and local low-power television station signals into local markets under defined circumstances. With respect to digital signals, SHVERA established a process to allow satellite carriers to retransmit distant network signals and significantly viewed signals to subscribers under certain circumstances. In November 2005, the FCC completed a rulemaking proceeding enabling the satellite carriage of “significantly viewed” signals. In December 2005, the FCC concluded a study, as required by SHVERA, regarding the applicable technical standards for determining when a subscriber may receive a distant digital network signal. The carriage of programming from two network stations to a local market on the same satellite system could result in a decline in viewership of the local network station, adversely impacting the revenues of our affected owned and programmed stations. Congress extended SHVERA until December 31, 2014.
Must-Carry / Retransmission Consent
Pursuant to the Cable Act of 1992, television broadcasters are required to make triennial elections to exercise either certain “must-carry” or “retransmission consent” rights in connection with their carriage by cable systems in each broadcaster’s local market. We have elected to exercise our retransmission consent rights with respect to all our stations. This election was made by October 1, 2011 for the period January 1, 2012 through December 31, 2014. By electing to exercise must-carry rights, a broadcaster demands carriage and receives a specific channel on cable systems within its DMA, in general, as defined by the Nielsen DMA Market and Demographic Rank Report of the prior year. These must-carry rights are not absolute and their exercise is dependent on variables such as:
· the number of activated channels on a cable system;
· the location and size of a cable system; and
· the amount of programming on a broadcast station that duplicates the programming of another broadcast station carried by the cable system.
Therefore, under certain circumstances, a cable system may decline to carry a given station. Alternatively, if a broadcaster chooses to exercise retransmission consent rights, it can prohibit cable systems from carrying its signal or grant the appropriate cable system the authority to retransmit the broadcast signal for a fee or other consideration. The FCC has clarified that cable systems need only carry a broadcast station’s primary video stream and not any of the station’s other programming streams in those situations where a station chooses to transmit multiple programming streams.
Syndicated Exclusivity / Territorial Exclusivity
The FCC’s syndicated exclusivity rules allow local broadcast television stations to demand that cable operators black out syndicated non-network programming carried on “distant signals” (i.e. signals of broadcast stations, including so-called “superstations,” which serve areas substantially removed from the cable systems’ local community). The FCC’s network non-duplication rules allow local broadcast, network affiliated stations to require that cable operators black out duplicate network programming carried on distant signals. However, in a number of markets in which we own or program stations affiliated with a network, a station that is affiliated with the same network in a nearby market is carried on cable systems in our markets. This is not necessarily a violation of the FCC’s network non-duplication rules. However, the carriage of two network stations on the same cable system could result in a decline of viewership, adversely affecting the revenues of our owned or programmed stations.
20
Table of Contents
Digital Television
The FCC has taken a number of steps to implement digital television (DTV) broadcasting services and has ruled that television broadcast licensees may use their digital channels for a wide variety of services such as HD television, multiple standard definition television programming, audio, data and other types of communications, subject to the requirement that each broadcaster provide at least one free video channel equal in quality to the current technical standard and further subject to the requirement that broadcasters pay a fee of 5% of gross revenues from any DTV ancillary or supplementary service for which there is a subscription fee or for which the licensee receives a fee from a third party.
Implementation of digital television has imposed substantial additional costs on our television stations because of the need to replace equipment. In addition, the FCC has proposed imposing new public interest requirements on television licensees in exchange for their receipt of DTV channels.
We believe that the following developments regarding the FCC’s digital regulations may have effects on us:
Digital must-carry. In February 2005, the FCC adopted an order stating that cable television systems are required to carry a must-carry station’s primary video stream but is not required to carry any of the station’s other programming streams in those situations where a station chooses to transmit multiple programming streams. On September 11, 2007, the FCC adopted an order requiring, after the digital transition, all cable operators to make the primary digital stream of must-carry television stations viewable by all cable subscribers, regardless of whether they are using analog or digital television equipment. The FCC indicated that it would consider requests for a waiver of this requirement by small cable system operators, where compliance with that requirement would be unduly burdensome. In March 2008, the FCC adopted an order requiring satellite carriers to carry digital-only stations upon request in markets in which the satellite carriers are providing local-into-local service pursuant to the statutory copyright license. The FCC also required that satellite carriers carry the HD signals of digital-only stations in HD format if any broadcaster in the same market is carried in HD. This latter requirement is being implemented over a four-year phase-in period which started in February 2009 and ended February 2013. Any impairment on viewers’ ability to obtain our digital HD signals retransmitted by satellite in markets in which we operate could result in a loss of viewers for those stations and could negatively impact station revenues. On June 11, 2012, the FCC issued an Order which sunsets the commission’s viewability rules for larger cable systems on December 12, 2012, which requires hybrid, analog-digital cable systems to offer viewers TV broadcast signals in an analog format so that viewers with older analog television sets can continue to receive them.
Multi-Channel Digital Broadcasting. FCC rules allow broadcasters to transmit additional digital channels within the spectrum allocated to each FCC license holder. This provides viewers with additional programming alternatives at no additional cost to them. Our television stations are experimenting with broadcasting on second and third digital channels in accordance with these rules, airing various alternative programming formats. We are airing second and third digital channels comprised of: CBS, ABC, and NBC (certain signals are rebroadcasted content from other primary channels within the same market); FOX, The CW; MyNetworkTV; This TV, independent programming; ME TV; Weather Radar; Weather Nation; Live Well Network, Antenna TV; Bounce Network; Zuus Country; Retro TV; and Estrella TV, Azteca, Tele-Romantica, Inmigrante TV, MundoFox and Telemundo, Spanish-language television networks..
We may consider other alternative programming formats that we could air using our multi-channel digital spectrum space with the goal towards achieving higher profits and community service.
Capital and operating costs. We have incurred and will continue to incur costs to replace equipment in certain stations in order to provide high definition news programming.
Children’s programming. In 2004, the FCC established children’s educational and informational programming obligations for digital multicast broadcasters and placed restrictions on the increasing commercialization of children’s programming on both analog and digital broadcast and cable television systems. In addition to imposing its limit as to the amount of commercial matter in children’s programming (10.5 minutes per hour on weekends and 12 minutes per hour on weekdays) on all digital or video programming, free or pay, directed to children 12 years old and younger, the FCC also mandated that digital broadcasters air an additional half hour of “core” children’s programming for every 28-hour block of free video programming provided in addition to the main DTV program stream. The additional core children’s programming requirement for digital broadcasters took effect on January 2, 2007.
Emergency Alert System. In November 2005, the FCC adopted an order requiring that digital broadcasters comply with the FCC’s present Emergency Alert System (EAS) rules. It also issued a further notice of proposed rulemaking seeking comments on what actions the FCC should take to expedite the development of a digitally based public alert and warning system. On July 12, 2007, the FCC adopted an order allowing mandatory use of EAS by state governments and requiring that all EAS participants, including
21
Table of Contents
television broadcasters, be able to receive messages formatted pursuant to a procedure to be adopted by the Federal Emergency Management Agency. In a further notice, the FCC invited comments on, among other things, how the EAS rules could be modified to ensure that non-English speakers and persons with disabilities are reached by EAS messages and whether local, county, tribal, or other state governmental entities should be allowed to initiate mandatory state and local alerts. On November 23, 2010, the FCC issued an Order requiring all broadcasters to acquire and install the equipment necessary to use the Common Alerting Protocol (CAP) standard for EAS alerts by September 30, 2011. On February 3, 2011, the FCC released an Order which requires national testing of the EAS and requires broadcast stations to submit data from such tests to the FCC. On September 16, 2011, the FCC released an Order extending the CAP-compliance deadline until June 30, 2012. The new EAS requirements and any additional FCC EAS requirements on broadcasters could increase our costs.
Restrictions on Broadcast Programming
Advertising of cigarettes and certain other tobacco products on broadcast stations has been banned for many years. Various states also restrict the advertising of alcoholic beverages and, from time to time, certain members of Congress have contemplated legislation to place restrictions on the advertisement of such alcoholic beverages. FCC rules also restrict the amount and type of advertising which can appear in a program broadcast primarily for an audience of children 12 years old and younger. In addition, the Federal Trade Commission issued guidelines in December 2003 and continues to provide advice to help media outlets voluntarily screen out weight loss product advertisements that are misleading.
The Communications Act and FCC rules also place restrictions on the broadcasting of advertisements by legally qualified candidates for elective office. Those restrictions state that:
· stations must provide “reasonable access” for the purchase of time by legally qualified candidates for federal office;
· stations must provide “equal opportunities” for the purchase of equivalent amounts of comparable broadcast time by opposing candidates for the same elective office; and
· during the 45 days preceding a primary or primary run-off election and during the 60 days preceding a general or special election, legally qualified candidates for elective office may be charged no more than the station’s “lowest unit charge” for the same class and amount of time for the same period.
It is a violation of federal law and FCC regulations to broadcast obscene, indecent, or profane programming. FCC licensees are, in general, responsible for the content of their broadcast programming, including that supplied by television networks. Accordingly, there is a risk of being fined as a result of our broadcast programming, including network programming. As a result of legislation passed in June 2006, the maximum forfeiture amount for the broadcast of indecent or obscene material was increased to $325,000 from $32,500 for each violation with a cap of $3.0 million for any single act.
Programming and Operations
General. The Communications Act requires broadcasters to serve the “public interest.” The FCC has relaxed or eliminated many of the more formalized procedures it had developed in the past to promote the broadcast of certain types of programming responsive to the needs of a station’s community of license. FCC licensees continue to be required, however, to present programming that is responsive to the needs and interests of their communities and to maintain certain records demonstrating such responsiveness. Complaints from viewers concerning a station’s programming may be considered by the FCC when it evaluates renewal applications of a licensee, although such complaints may be filed at any time and generally may be considered by the FCC at any time. Stations also must pay regulatory and application fees and follow various rules promulgated under the Communications Act that regulate, among other things, political advertising, sponsorship identifications, obscene and indecent broadcasts and technical operations, including limits on radio frequency radiation.
Equal Employment Opportunity. On November 20, 2002, the FCC adopted rules, effective March 10, 2003, requiring licensees to create equal employment opportunity outreach programs and maintain records and make filings with the FCC evidencing such efforts. The FCC simultaneously released a notice of proposed rulemaking seeking comments on whether and how to apply these rules and policies to part-time positions, defined as less than 30 hours per week. That rulemaking is still pending.
Children’s Television Programming. Television stations are required to broadcast a minimum of three hours per week of “core” children’s educational programming, which the FCC defines as programming that:
· has the significant purpose of serving the educational and informational needs of children 16 years of age and under;
· is regularly scheduled weekly and at least 30 minutes in duration; and
· is aired between the hours of 7:00 a.m. and 10:00 p.m. local time.
22
Table of Contents
In addition, the FCC concluded that starting on January 2, 2007, a digital broadcaster must air an additional half hour of “core” children’s programming per every increment of 1 to 28 hours of free video programming provided in addition to the main DTV program stream. Furthermore, “core” children’s educational programs, in order to qualify as such, are required to be identified as educational and informational programs over-the-air at the time they are broadcast and are required to be identified in the children’s programming reports, which are required to be placed quarterly in stations’ public inspection files and filed quarterly with the FCC.
On April 17, 2007, the FCC requested comments on the status of children’s television programming and compliance with the Children’s Television Act and the FCC’s rules. That proceeding is still pending.
Violent Programming. In 2004, the FCC initiated a notice of inquiry seeking comments on issues relating to the presentation of violent programming on television and its impact on children. On April 25, 2007, the FCC released a report concluding that there is strong evidence that exposure to violence in the media can increase aggressive behavior in children, at least in the short term. Accordingly, the FCC concluded that it would be in the public interest to regulate such programming and Congress could do so consistent with the First Amendment. As possible solutions, the FCC suggested, among other things, a voluntary industry initiative to reduce the amount of excessively violent programming viewed by children and also proposed several viewer-initiated blocking proposals, such as the provision of video channels by MVPDs on family tiers or on an a la carte basis.
Television Program Content. The television industry has developed an FCC approved ratings system that is designed to provide parents with information regarding the content of the programming being aired. Furthermore, the FCC requires certain television sets to include the so-called “V-chip,” a computer chip that allows the blocking of rated programming. It is a violation of federal law and FCC regulations to broadcast obscene or indecent programming. FCC licensees are, in general, responsible for the content of their broadcast programming, including that supplied by television networks. Accordingly, there is a risk of being fined as a result of our broadcast programming, including network programming.
Localism. On October 27, 2011, the FCC issued an Order vacating its 2008 decision proposing to update the way television broadcasters inform the public about how they are serving their local communities. Specifically, the FCC has adopted rules to largely replace the requirement that television stations maintain a paper public file at their main studios with a requirement to submit documents for inclusion in an online public file to be hosted by the FCC. The new rules took effect on August 2, 2012. On and after August 2, 2012, broadcasters posted to the online public file any new documents that they determined must be placed in the public file. Broadcasters had six months after August 2, 2012 to post existing documents that were part of the public file prior to August 2, except in the case of the political file. With respect to the political file only, broadcasters are not required to upload any such documents that were part of their public file prior to August 2. Instead, only newly created political file documents must be uploaded. In addition, smaller broadcasters not affiliated with the top four networks in the top 50 markets are not required to post their political file documents to their online public file until July 1, 2014. In a related proceeding, on November 14, 2011, the FCC released a Notice of Inquiry regarding the use of a standardized disclosure form for television stations to provide the public with the information on how stations are serving the public interest in an effort to help stations meet their obligation to provide programming that addresses a local community’s needs and interests.
Closed Captioning. In November 2008, the FCC issued a declaratory ruling clarifying certain closed captioning obligations for stations transmitting digital programming, including the obligation to transmit captions in analog standard after the DTV transition and simplifying the close captioning complaint process for consumers. The 21st Century Communications and Video Accessibility Act (CVAA) requires that all nonexempt full-length video programming delivered over the Internet that first appeared on TV in the United States with captions also be captioned online. The first compliance deadline for the FCC’s new rules for the closed captioning of video programming delivered via Internet protocol (i.e., IP video), as required by the CVAA, was September 30, 2012. The effective date of the new rules was April 30, 2012, and all video programming that appeared on television with captions after that date is considered “covered IP video” and will need to be captioned when being shown online in the future. “Video programming” is defined as “programming by, or generally considered comparable to programming provided by a television broadcast station.” Beginning September 30, 2012, all pre-recorded programming not edited for Internet distribution must be captioned for online viewing. Pre-recorded programming is defined as programming other than live or near-live programming. Beginning March 30, 2013, all live and near-live programming must be captioned for online viewing. Live programming is defined as programming that airs on TV “substantially simultaneously” with its performance (i.e., news and sporting events). Near-live programming is video programming that is performed and recorded less than 24 hours prior to the first time it aired on television (i.e., the “Late Show with David Letterman”). Beginning September 30, 2013, all pre-recorded programming that is edited for Internet distribution was required to be captioned for online viewing. Programming edited for Internet distribution means video programming for which the TV version is “substantially edited” prior to its Internet distribution.
Pending Matters
Congress and the FCC have under consideration and in the future may consider and adopt, new laws, regulations and policies regarding a wide variety of matters that could affect, directly or indirectly, the operation, ownership and profitability of our broadcast stations, result in the loss of audience share and advertising revenues for our broadcast stations and affect our ability to acquire additional broadcast stations or finance such acquisitions.
23
Table of Contents
Other matters that could affect our broadcast properties include technological innovations and developments generally affecting competition in the mass communications industry, such as direct television broadcast satellite service, Class A television service, the continued establishment of wireless cable systems and low power television stations, digital television technologies, the internet and mobility and portability of our broadcast signal to hand-held devices.
For example, in November 2008, the FCC adopted an order allowing new low power devices to operate in the broadcast television spectrum at locations where channels in that spectrum are not in use. The operation of such devices could cause harmful interference to our broadcast signals adversely affecting the operation and profitability of our stations.
On December 22, 2011, the FCC released a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking in its Quadrennial Review of the Multiple Ownership Rules and is considering changes to the FCC’s rules regarding broadcast-newspaper cross ownership restrictions, the possible elimination of rules restricting the ownership of radio and TV in the same market, the potential attribution of TV JSAs and SSAs meaning potentially making JSAs and SSAs count as an ownership interests in a multiple ownership analysis and other possible revisions to the local radio and TV ownership limitations or exceptions that would allow for waivers of the limits in defined circumstances. Press and other reports indicate that the FCC is actively considering implementing new rules which would cause a station to be attributable to the owner of another station in the market which sells more than 15 percent of the advertising on the first station. Reports indicate that the FCC does not intend to “grandfather” existing JSAs, but rather to require parties to come into compliance with these new rules within a period of between eighteen months and two years. If the FCC were to enact such a rule we would no longer be able to enter into new transactions utilizing JSAs in the way we have done historically and would need to either terminate our existing JSAs or take action to modify the terms of our JSAs in a manner which complies with any such new rules. There can be no such assurance that the FCC will take the actions reported to be being considered and we cannot predict with any certainty the impact such rules might have on us until such rules are actually enacted.
Congress passed legislation providing the FCC with authority to conduct so-called “incentive auctions”, which is the process of auctioning and repurposing broadcast television spectrum for mobile broadband use. Incentive auction authority allows the FCC to share the proceeds of spectrum auctions with incumbent television station licensees who give up their licenses (or in some cases, move to a different channel) to facilitate spectrum auctions. The legislation contemplates that the FCC will encourage broadcasters to tender their licenses for auction. The FCC would then “repack” non-tendering broadcasters into the lower portions of the UHF band and auction new “flexible use” wireless licenses in the upper portion of the UHF band. The proposals for television stations to participate in the “incentive auctions” are voluntary and at this time we have not decided whether the company will participate on behalf of any of its stations. On September 28, 2012, the FCC voted in favor of a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that launches the incentive auction process to clear a portion of the television band that will make way for mobile broadband use. At this time we cannot predict the final outcome of this proceeding.
Other Considerations
The preceding summary is not a complete discussion of all provisions of the Communications Act, the 1996 Act or other congressional acts or of the regulations and policies of the FCC, or in some cases, the DOJ. For further information, reference should be made to the Communications Act, the 1996 Act, other congressional acts and regulations and public notices circulated from time to time by the FCC, or in some cases, the DOJ. There are additional regulations and policies of the FCC and other federal agencies that govern political broadcasts, advertising, equal employment opportunity and other matters affecting our business and operations.
ENVIRONMENTAL REGULATION
Prior to our ownership or operation of our facilities, substances or waste that are, or might be considered, hazardous under applicable environmental laws may have been generated, used, stored or disposed of at certain of those facilities. In addition, environmental conditions relating to the soil and groundwater at or under our facilities may be affected by the proximity of nearby properties that have generated, used, stored or disposed of hazardous substances. As a result, it is possible that we could become subject to environmental liabilities in the future in connection with these facilities under applicable environmental laws and regulations. Although we believe that we are in substantial compliance with such environmental requirements and have not in the past been required to incur significant costs in connection therewith, there can be no assurance that our costs to comply with such requirements will not increase in the future or that we will not become subject to new governmental regulations, including those pertaining to potential climate change legislation, that may impose additional restrictions or costs on us. We presently believe that none of our properties have any condition that is likely to have a material adverse effect on our consolidated balance sheets, consolidated statements of operations or consolidated statements of cash flows.
COMPETITION
Our television stations compete for audience share and advertising revenue with other television stations in their respective DMAs, as well as with other advertising media such as MVPDs, radio, newspapers, magazines, outdoor advertising, transit advertising,
24
Table of Contents
telecommunications providers, internet and broadband, yellow page directories and direct mail. Some competitors are part of larger organizations with substantially greater financial, technical and other resources than we have. Other factors that are material to a television station’s competitive position include signal coverage, local program acceptance, network affiliation or program service, audience characteristics and assigned broadcast frequency.
Competition in the television broadcasting industry occurs primarily in individual DMAs. Generally, a television broadcasting station in one DMA does not compete with stations in other DMAs. Our television stations are located in highly competitive DMAs. MVPDs can increase competition for a broadcast television station by bringing into its market additional cable network channels. These narrow cable network channels are typically low rated, and, as a result, advertisements are inexpensive to the local advertisers. In addition, certain of our DMAs are overlapped by over-the-air station from adjacent DMAs and MVPDs of stations from other DMAs, which tends to spread viewership and advertising expenditures over a larger number of television stations.
Television stations compete for audience share primarily on the basis of program popularity, which has a direct effect on advertising rates. Our network affiliated stations are largely dependent upon the performance of network provided programs in order to attract viewers. Non-network time periods are programmed by the station primarily with syndicated programs purchased for cash, cash and barter or barter-only, as well as through self-produced news, public affairs programs, live local sporting events, paid-programming and other entertainment programming.
Television advertising rates are based upon factors which include the size of the DMA in which the station operates, a program’s popularity among the viewers that an advertiser wishes to attract, the number of advertisers competing for the available time, the demographic makeup of the DMA served by the station, the availability of alternative advertising media in the DMA, the aggressiveness and knowledge of the sales forces in the DMA and development of projects, features and programs that tie advertiser messages to programming. We believe that our sales and programming strategies allow us to compete effectively for advertising revenues within our DMAs.
The broadcasting industry is continuously faced with technical changes and innovations, competing entertainment and communications media, changes in labor conditions and governmental restrictions or actions of federal regulatory bodies, including the FCC, any of which could possibly have a material effect on a television station’s operations and profits. For instance, the FCC has established Class A television service for qualifying low power television stations. This Class A designation provides low power television stations, which ordinarily have no broadcast frequency rights when the low power signal conflicts with a signal from any full power stations, some additional frequency rights. These rights may allow low power stations to compete more effectively with full power stations. We cannot predict the effect of increased competition from Class A television stations in markets where we have full power television stations.
Moreover, technology advances and regulatory changes affecting programming delivery through fiber optic lines, video compression, and new wireless uses could lower entry barriers for new video channels and encourage the further development of increasingly specialized “niche” programming. Telephone companies are permitted to provide video distribution services, on a common carrier basis, as “cable systems” or as “open video systems,” each pursuant to different regulatory schemes. Additionally, in January 2004, the FCC concluded an auction for licenses operating in the 12 GHz band that can be used to provide multi-channel video programming distribution. Those licenses were granted in July 2004. In addition, on March 18, 2008, the FCC concluded an auction for the rights to operate the 700 MHz frequency band that had been used by analog television broadcasters and became available when full power television stations ceased using the spectrum as a result of the digital television transition on June 12, 2009. The winning bidders were announced on March 20, 2008. The FCC has indicated that the spectrum may be used for flexible fixed, mobile, and broadcast uses, including fixed and mobile wireless commercial services; fixed and mobile wireless uses for private, internal radio needs;��mobile and other new digital broadcast operations; and, may include two-way interactive, cellular, and mobile television broadcasting services. We are unable to predict what other video technologies might be considered in the future or the effect that technological and regulatory changes will have on the broadcast television industry and on the future profitability and value of a particular broadcast television station.
DTV technology has the potential to permit us to provide viewers multiple channels of digital television over each of our existing standard digital channels, to provide certain programming in HD television format and to deliver other channels of information in the forms of data and programming to the internet, PCs, smart phones, tablet computers and mobile devices. These additional capabilities may provide us with additional sources of revenue, as well as additional competition.
We also compete for programming, which involves negotiating with national program distributors or syndicators that sell first-run and rerun packages of programming. Our stations compete for access to those programs against in-market broadcast station competitors for syndicated products and with national cable networks. Public broadcasting stations generally compete with commercial broadcasters for viewers, but not for advertising dollars.
We believe we compete favorably against other television stations because of our management skill and experience, our ability historically to generate revenue share greater than our audience share, our network affiliations and program service arrangements and our local program acceptance. In addition, we believe that we benefit from the operation of multiple broadcast properties, affording us certain non-
25
Table of Contents
quantifiable economies of scale and competitive advantages in the purchase of programming.
EMPLOYEES
As of February 24, 2014, we had approximately 6,400 employees. Approximately 556 employees are represented by labor unions under certain collective bargaining agreements. We have not experienced any significant labor problems and consider our overall labor relations to be good.
AVAILABLE INFORMATION
We regularly use our website as a source of company information and it can be accessed at www.sbgi.net. We make available, free of charge through our website, our annual report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act as soon as reasonably practicable after such documents are electronically submitted to the SEC. In addition, a replay of each of our quarterly earnings conference calls is available on our website until the subsequent quarter’s earnings call. The information contained on, or otherwise accessible through, our website is not a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and is not incorporated herein by reference.
26
Table of Contents
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
You should carefully consider the risks described below before investing in our securities. Our business is also subject to the risks that affect many other companies such as general economic conditions, geopolitical events, competition, technological obsolescence and employee relations. The risks described below, along with risks not currently known to us or that we currently believe are immaterial, may impair our business operations and our liquidity in an adverse way.
Our advertising revenue can vary substantially from period to period based on many factors beyond our control. This volatility affects our operating results and may reduce our ability to repay indebtedness or reduce the market value of our securities.
We rely on sales of advertising time for most of our revenues and, as a result, our operating results depend on the amount of advertising revenue we generate. If we generate less advertising revenue, it may be more difficult for us to repay our indebtedness and the value of our business may decline. Our ability to sell advertising time depends on:
· the levels of automobile advertising, which historically have represented about one quarter of our advertising revenue; however, for the year ended December 31, 2013, automobile advertising represented 25.2% of our net time sales;
· the health of the economy in the area where our television stations are located and in the nation as a whole;
· the popularity of our programming and that of our competition;
· the levels of political advertising, which are affected by campaign finance laws and the ability of political candidates and political action committees to raise and spend funds and are subject to seasonal fluctuations;
· the reliability of our ratings information measurements, including new ratings system technologies such as “people meters” and “set-top boxes”;
· changes in the makeup of the population in the areas where our stations are located;
· the activities of our competitors, including increased competition from other forms of advertising-based mediums, such as other broadcast television stations, radio stations, MVPDs, internet and broadband content providers and other print and media outlets serving in the same markets; and
· other factors that may be beyond our control.
After a severe economic recession in 2008 and 2009 that affected our advertising revenue, we experienced a rebound in advertising spending in 2010 due primarily to a resurgence of the automotive industry, our largest advertising category, and a contentious mid-term election resulting in record political revenues. In 2012, we recorded record levels of political advertising and benefited from strong results in our automotive advertising category. There can be no assurance that our advertising revenue will not be volatile in the future or that such volatility will not have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Our substantial indebtedness could adversely affect our financial condition and prevent us from fulfilling our debt obligations.
We have a high level of debt, totaling $3,034.0 million at December 31, 2013, compared to the book value of shareholders’ equity of $405.7 million on the same date. Our relatively high level of debt poses the following risks, particularly in periods of declining revenues:
· we may be unable to service our debt obligations, including payments on notes as they come due, especially during general negative economic and market industry conditions;
· we may use a significant portion of our cash flow to pay principal and interest on our outstanding debt, especially during general negative economic and market industry conditions;
· the amount available for working capital, capital expenditures, dividends and other general corporate purposes may be limited because a significant portion of cash flow is used to pay principal and interest on outstanding debt;
· our lenders may not be as willing to lend additional amounts to us for future working capital needs, additional acquisitions or other purposes;
· the cost to borrow from lenders may increase;
· our ability to access the capital markets may be limited, and we may be unable to issue securities with pricing or other terms that we find attractive, if at all;
· if our cash flow were inadequate to make interest and principal payments, we might have to restructure or refinance our indebtedness or sell one or more of our stations to reduce debt service obligations;
· we may be more vulnerable to adverse economic conditions than less leveraged competitors and thus, less able to withstand competitive pressures; and
27
Table of Contents
· because the interest rate under the Bank Credit Agreement is a floating rate, any increase will reduce the funds available to repay our obligations and for operations and future business opportunities and will make us more vulnerable to the consequences of our leveraged capital structure. As of December 31, 2013, approximately $1,146.4 million principal amount of our recourse debt relates to the Bank Credit Agreement.
Any of these events could reduce our ability to generate cash available for investment, debt repayment or capital improvements or to respond to events that would enhance profitability.
Commitments we have made to our lenders limit our ability to take actions that could increase the value of our securities and business or may require us to take actions that decrease the value of our securities and business.
Our existing financing agreements prevent us from taking certain actions and require us to meet certain tests. These restrictions and tests may require us to conduct our business in ways that make it more difficult to repay unsecured debt or decrease the value of our securities and business. These restrictions and tests include the following:
· restrictions on additional debt;
· restrictions on our ability to pledge our assets as security for indebtedness;
· restrictions on payment of dividends, the repurchase of stock and other payments relating to our capital stock;
· restrictions on some sales of certain assets and the use of proceeds from asset sales;
· restrictions on mergers and other acquisitions, satisfaction of conditions for acquisitions and a limit on the total amount of acquisitions without the consent of bank lenders;
· restrictions on permitted investments;
· restrictions on the lines of business we and our subsidiaries may operate; and
· financial ratio and condition tests including the ratio of adjusted earnings before interest, tax, depreciation and amortization, as adjusted (adjusted EBITDA) to adjusted interest expense, the ratio of first lien indebtedness to adjusted EBITDA and the ratio of Sinclair Television Group, Inc. (STG) total indebtedness to adjusted EBITDA.
Future financing arrangements may contain additional restrictions and tests. All of these restrictive covenants may limit our ability to pursue our business strategies, prevent us from taking action that could increase the value of our securities or may require actions that decrease the value of our securities. In addition, we may fail to meet the tests and thereby default on one or more of our obligations (particularly if the economy weakens and thereby reduces our advertising revenues). If we default on our obligations, creditors could require immediate payment of the obligations or foreclose on collateral. If this happens, we could be forced to sell assets or take other actions that could significantly reduce the value of our securities and business and we may not have sufficient assets or funds to pay our debt obligations.
A failure to comply with covenants under our debt instruments could result in a default under such debt instruments, acceleration of amounts due under our debt and loss of assets securing our loans.
Certain of our debt agreements contain cross-default provisions with our other debt, which means that a default under certain of our debt instruments may cause a default under certain indentures or the Bank Credit Agreement.
If we breach certain of our debt covenants, our lenders could require us to repay the debt immediately, and, if the debt is secured, could immediately take possession of the property securing such debt. In addition, if any other lender declared its loan due and payable as a result of a default, the holders of our outstanding notes, along with the lenders under the Bank Credit Agreement, might be able to require us to pay those debts immediately.
As a result, any default under our debt covenants could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and our ability to meet our obligations.
Any insolvency or bankruptcy proceeding relating to material third-party licensees as defined by our Bank Credit Agreement, would cause a default and potential acceleration under the Bank Credit Agreement.
Our Bank Credit Agreement contains certain cross-default provisions with certain material third-party licensees, defined as any party that owns the license assets of one or more television stations for which we provided services to pursuant to LMAs and/or other outsourcing agreements and those stations provide 10% or more of our aggregate broadcast cash flows. A default caused by an involuntary or voluntary petition filed for liquidation, reorganization or other relief of insolvency by a material third-party licensee, or a failure of a material third-party licensee to preserve and maintain its legal existence or any of its material rights, privileges or franchises including its broadcast licenses, would cause an event of default and potential acceleration under our Bank
28
Table of Contents
Credit Agreement. As of December 31, 2013, there were no material third party licensees as defined in our Bank Credit Agreement.
Despite current debt levels, we may be able to incur significantly more debt in the future, which could increase the foregoing risks related to our indebtedness.
At December 31, 2013, we had $154.5 million available (subject to certain borrowing conditions) for additional borrowings under the revolving credit facility (the Revolving Credit Facility) of the Bank Credit Agreement. Additionally, we have $200.0 million of Term Loan A to be drawn in 2014 to partially fund pending acquisitions. Under the terms of the debt instruments to which we are subject, and provided we meet certain financial and other covenants, we may be able to incur substantial additional indebtedness in the future, including additional senior debt and secured debt. If we incur additional indebtedness, the risks described in the risk factors in this report relating to having substantial debt could intensify.
Our strategic acquisitions could pose various risks and increase our leverage.
We have pursued and intend to selectively continue to pursue strategic acquisitions, subject to market conditions, our liquidity and the availability of attractive acquisition candidates, with the goal of improving our business. During 2013, we acquired certain assets related to, and/or equity of entities that own assets related to, and we began operating or providing certain services to 63 television stations.
We may not be able to identify other attractive acquisition targets or we may not be able to fund additional acquisitions in the future. Acquisitions involve inherent risks, such as increasing leverage and debt service requirements and combining company cultures and facilities, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and could strain our human resources. We may not be able to successfully implement effective costs controls or increase revenues as a result of an acquisition. In addition, future acquisitions may result in our assumption of unexpected liabilities and may result in the diversion of management’s attention from the operation of our core business.
Certain acquisitions, such as television stations, are subject to the approval of the FCC and potentially, other regulatory authorities. The need for FCC and other regulatory approvals could restrict our ability to consummate future transactions and potentially require us to divest certain television stations if the FCC believes that a proposed acquisition would result in excessive concentration in a market, even if the proposed combinations may otherwise comply with FCC ownership limitations.
Our investments in other operating divisions involve risks, including the diversion of resources, that may adversely affect our business or results of operations.
Our other operating divisions consist of businesses involved in sign design and fabrication, regional security alarm operations, fabrication and service of television broadcast antennas and transmitters, real estate ventures and a wrestling programming franchise and are reported separately from our broadcast segment. Managing the operations of these businesses and the costs incurred by these businesses involve risks, including the diversion of our management’s attention from managing the operations of our broadcast businesses and diverting other resources that could be used in our broadcast businesses. Such diversion of resources may adversely affect our business and results of operations. In addition, our investments in real estate ventures carry inherent risks related to owning interests in real property, including, among others, the relative illiquidity of real estate, potential adverse changes in real estate market conditions, and changes in tenant preferences. There can be no assurance that our investments in these businesses will yield a positive rate of return or otherwise be recoverable.
Financial and economic conditions may have an adverse impact on our industry, business, results of operations or financial condition.
Financial and economic conditions have been challenging and the continuation or worsening of such conditions could further reduce consumer confidence and have an adverse effect on the fundamentals of our business, results of operations and/or financial condition. Poor economic and industry conditions could have a negative impact on our industry or the industry of those customers who advertise on our stations, including, among others, the automotive industry and service businesses, each of which is a significant source of our advertising revenue. Additionally, financial institutions, capital providers, or other consumers may be adversely affected. Potential consequences of any financial and economic decline include:
· the financial condition of those companies that advertise on our stations, including, among others, the automobile manufacturers and dealers, may be adversely affected and could result in a significant decline in our advertising revenue;
· our ability to pursue the acquisition of attractive television and non-television assets may be limited if we are unable to obtain any necessary additional capital on favorable terms, if at all;
· our ability to pursue the divestiture of certain television and non-television assets at attractive values may be limited;
29
Table of Contents
· the possibility that our business partners, such as our counterparties to our outsourcing and news share arrangements, could be negatively impacted and our ability to maintain these business relationships could also be impaired; and
· our ability to refinance our existing debt on terms and at interest rates we find attractive, if at all, may be impaired;
· our ability to make certain capital expenditures may be significantly impaired.
We must purchase television programming in advance based on expectations about future revenues. Actual revenues may be lower than our expectations. If this happens, we could experience losses that may make our securities less valuable.
One of our most significant costs is television programming. Our ability to generate revenue to cover this cost may affect the value of our securities. If a particular program is not popular in relation to its costs, we may not be able to sell enough advertising time to cover the costs of the program. Since we generally purchase programming content from others rather than producing such content ourselves, we have limited control over the costs of the programming. Often we must purchase programming several years in advance and may have to commit to purchase more than one year’s worth of programming. We may replace programs that are doing poorly before we have recaptured any significant portion of the costs we incurred or before we have fully amortized the costs. Any of these factors could reduce our revenues or otherwise cause our costs to escalate relative to revenues. These factors are exacerbated during a weak advertising market. Additionally, our business is subject to the popularity of the programs provided by the networks with which we have network affiliation agreements or which provide us programming.
We may lose a large amount of programming if a network terminates its affiliation or program service arrangement with us, which could increase our costs and/or reduce revenue.
Out of our 135 full power television stations that we own and operate, or to which we provide (or for which we are provided) programming services and/or sales services, 134 are affiliated with networks, as of February 24, 2014. The networks produce and distribute programming in exchange for each station’s commitment to air the programming at specified times and for commercial announcement time during programming. The amount and quality of programming provided by each network varies.
The non-renewal or termination of any of our network affiliation agreements would prevent us from being able to carry programming of the relevant network. This loss of programming would require us to obtain replacement programming, which may involve higher costs and which may not be as attractive to our target audiences, resulting in reduced revenues. Upon the termination of any of our network affiliation agreements, we would be required to establish a new network affiliation agreement for the affected station with another network or operate as an independent station. At such time, the remaining value of the network affiliation asset could become impaired and we would be required to record impairment charges to write down the value of the asset to its estimated fair value.
We may not be able to negotiate our network affiliation agreements or program service arrangements at terms comparable to or more favorable than our current agreements upon their expiration.
As network affiliation agreements come up for renewal, we (or licensees of the stations we provide programming and/or sales services to), may not be able to negotiate terms comparable to or more favorable than our current agreements. On March 25, 2010, we agreed to terms on a renewal of nine of our ABC network affiliation agreements, expiring on August 31, 2015. On January 24, 2011, we extended 16 of our MyNetworkTV affiliation agreements, expiring fall 2014. In 2011 we extended ten of our CW network affiliation agreements, expiring August 31, 2016. On May 14, 2012, we agreed to terms of renewal of 20 FOX network affiliation agreements, expiring December 31, 2017. Pursuant to the terms, we are required to pay an annual license fee to ABC and a network programming fee to FOX for network programming. Effective January 1, 2013, we extended two of our CBS affiliation agreements, expiring December 31, 2018.
Our ABC, CBS, FOX, NBC, CW, MyNetworkTV, Azteca, and Univision affiliation agreements acquired in 2012 and 2013 have expirations dates ranging from June 30, 2014, through December 31, 2018. See footnote (c) in the table under “Business—Television broadcasting—Markets and stations” above.
We cannot predict the outcome of any future negotiations relating to our affiliation agreements or what impact, if any, they may have on our financial condition and results of operations. In addition, the impact of an increase in reverse network compensation payments, under which we compensate the network for programming pursuant to our affiliation agreements, may have a negative effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
We may not be able to renegotiate retransmission consent agreements at terms comparable to or more favorable than our current agreements and networks with which we are affiliated are currently, or in the future are expected to, require us to share revenue from retransmission consent agreements with them.
30
Table of Contents
As retransmission consent agreements expire, we may not be able to renegotiate such agreements at terms comparable to or more favorable than our current agreements. This may cause revenues and/or revenue growth from our retransmission consent agreements to decrease under the renegotiated terms despite the fact that our current retransmission consent agreements include automatic annual fee escalators. In addition, certain of our networks or program service providers with which we are affiliated are currently, or in the future are expected to, require us to share revenue from retransmission consent agreements with them as part of renewing expiring affiliation agreements or pursuant to certain rights contained in existing affiliation agreements. There can be no assurances that the amounts shared will not increase at expiration of the current contracts.
The effects of the economic environment could require us to record an asset impairment of goodwill and broadcast licenses.
We are required to analyze goodwill and certain other intangible assets for impairment. The accounting guidance establishes a method of testing goodwill and broadcast licenses for impairment on an annual basis, or on an interim basis if an event occurs that would reduce the fair value of a reporting unit or an indefinite-lived asset below its carrying value.
At least annually, we assess our goodwill and broadcast licenses for impairment. To perform this assessment, we review certain qualitative factors to conclude whether it is more likely than not that goodwill or broadcast licenses are impaired. If we conclude it is more likely than not that goodwill or broadcast licenses are impaired, we estimate the fair value of our reporting units or broadcast licenses using a combination of observed prices paid for similar assets and liabilities, discounted cash flow models and appraisals. We make certain critical estimates about the future revenue growth rates within each of our markets as well as the discount rates and comparable multiples that would be used by market participants in an arms-length transaction. If these growth rates or multiples decline, or if the discount rate increases, our goodwill and/or broadcast licenses’ carrying amounts could be in excess of the estimated fair values. An impairment of some or all of the value of these assets could result in a material effect on the consolidated statements of operations in the future. As of December 31, 2013, we had approximately $1,380.1 million and $101.0 million of goodwill and broadcast licenses, respectively. As of December 31, 2013, goodwill and broadcast licenses in aggregate represented 35.7% of our total assets. For additional information regarding impairments to our goodwill and broadcast licenses, see Note 5. Goodwill, Broadcast Licenses and Other Intangible Assets in the Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements.
Key officers and directors have financial interests that are different and sometimes opposite from ours and we may engage in transactions with these officers and directors that may benefit them to the detriment of other securityholders.
Some of our officers, directors and majority shareholders own stock or partnership interests in businesses that engage in television broadcasting, do business with us or otherwise do business that conflicts with our interests. They may transact some business with us upon approval by the independent members of our board of directors even if there is a conflict of interest or they may engage in business competitive to our business and those transactions may benefit the officers, directors or majority shareholders to the detriment of our securityholders. Each of David D. Smith, Frederick G. Smith, and J. Duncan Smith is an officer and director of Sinclair and Robert E. Smith is a director of Sinclair. Together, the Smiths hold shares of our common stock that control the outcome of most matters submitted to a vote of shareholders.
The Smiths own businesses that lease real property and tower space to us and engage in other transactions with us. Trusts established for the benefit of the children of our controlling shareholders and the estate of Carolyn C. Smith, a parent of our controlling shareholders, own Cunningham, which owns television stations in nine markets that we operate under LMAs or other outsourcing agreements. In addition, we have been granted the rights to acquire, subject to applicable FCC rules and regulations, Cunningham (although the present rules and regulations of the FCC would not allow us to control the stations of Cunningham (the Cunningham Stations) if we continue to hold television stations in the same market as the Cunningham Stations). David D. Smith, Frederick G. Smith, J. Duncan Smith, Robert E. Smith and David B. Amy, our Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, together own interests (less than 5% in aggregate) in Allegiance Capital Limited Partnership, a limited partnership in which we also hold an interest. Frederick G. Smith owns an interest (less than 1%) in Patriot Capital II, L.P., a limited partnership in which we also hold an interest. David Smith owns an interest (less than 3%) in Towson Row LLC, a real estate venture, which we also hold an interest. We can give no assurance that these transactions or any transactions that we may enter into in the future with our officers, directors or majority shareholders, have been, or will be, negotiated on terms as favorable to us as we would obtain from unrelated parties. Maryland law and our financing agreements limit the extent to which our officers, directors and majority shareholders may transact business with us and pursue business opportunities that we might pursue. These limitations do not, however, prohibit all such transactions.
For additional information regarding our related person transactions, see Note 11. Related Person Transactions, in the Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements.
We depend on key personnel and we may not be able to operate and grow our business effectively if we lose the services of our senior executive officers or are unable to attract and retain qualified personnel in the future.
31
Table of Contents
We depend on the efforts of our management and other key employees. The success of our business depends heavily on our ability to develop and retain management and to attract and retain qualified personnel in the future. Competition for senior management personnel is intense and we may not be able to retain our key personnel. If we are unable to do so, our business, financial condition or results of operations may be adversely affected.
The Smiths exercise control over most matters submitted to a shareholder vote and may have interests that differ from other securityholders. They may, therefore, take actions that are not in the interests of other securityholders.
David D. Smith, Frederick G. Smith, J. Duncan Smith and Robert E. Smith hold shares representing approximately 75.3% of the common stock voting rights of us as of February 20, 2014 and, therefore, control the outcome of most matters submitted to a vote of shareholders, including, but not limited to, electing directors, adopting amendments to our certificate of incorporation and approving corporate transactions. The Smiths hold substantially all of the Class B Common Stock, which have ten votes per share. Our Class A Common Stock has only one vote per share. In addition, the Smiths hold half our board of directors’ seats and, therefore, have the power to exert significant influence over our corporate management and policies. The Smiths have entered into a stockholders’ agreement pursuant to which they have agreed to vote for each other as candidates for election to our board of directors until June 13, 2015.
Although in the past the Smiths have recused themselves from related person transactions, circumstances may occur in which the interests of the Smiths, as the controlling securityholders, could be in conflict with the interests of other securityholders and the Smiths would have the ability to cause us to take actions in their interest. In addition, the Smiths could pursue acquisitions, divestitures or other transactions that, in their judgment, could enhance their equity investment, even though such transactions might involve risks to our other securityholders. Further, the concentration of ownership in the Smiths may have the effect of discouraging, delaying or preventing a future change of control, which could deprive our stockholders of an opportunity to receive a premium for their shares as part of a sale of our company and might reduce the price of our shares.
(See Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters and Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, which will be included as part of our Proxy Statement for our 2012 Annual Meeting.)
Significant divestitures by the Smiths could cause them to own or control less than 51% of the voting power of our shares, which would in turn give Cunningham the right to terminate the LMAs and other agreements with Cunningham due to a “change in control.” Any such terminations would have an adverse effect on our results of operations. The FCC’s multiple ownership rules limit our ability to operate multiple television stations in some markets and may result in a reduction in our revenue or prevent us from reducing costs. Changes in these rules may threaten our existing strategic approach to certain television markets. See Changes in rules on local marketing agreements in the risk factor below.
We may be subject to fines and other penalties related to violations of FCC indecency rules and other FCC rules and policies, the enforcement of which has increased in recent years, and complaints related to such violations may delay our renewal applications with the FCC.
We provide a significant amount of live news reporting that is provided by the broadcast networks or is controlled by our on-air news talent. Although both broadcast network and our on-air talent have generally been professional and careful in what they say, there is always the possibility that information may be reported that is inaccurate or even in violation of certain indecency rules promulgated by the FCC. In addition, entertainment and sports programming provided by broadcast networks may contain content that is in violation of the indecency rules promulgated by the FCC. Because the interpretation by the courts and the FCC of the indecency rules is not always clear, it is sometimes difficult for us to determine in advance what may be indecent programming. We have insurance to cover some of the liabilities that may occur, but the FCC has enhanced its enforcement efforts relating to the regulation of indecency. In addition, in 2006, Congress dramatically increased the penalties for broadcasting indecent programming and potentially subjects broadcasters to license revocation, renewal or qualification proceedings in the event that they broadcast indecent material. We are currently subject to pending FCC inquiries and proceedings relating to alleged violations of indecency, sponsorship identification, children’s programming and captioning rules. There can be no assurance that an incident that may lead to significant fines or other penalties by the FCC can be avoided.
In addition, action on many license renewal applications, including those we have filed, has been delayed because of, among other reasons, the pendency of complaints that programming aired by the various networks contained indecent material and complaints regarding alleged violations of sponsorship identification, children’s programming and captioning rules. We cannot predict when the FCC will address these complaints and act on the renewal applications. We continue to have operating authority until final action is taken on our renewal applications.
Federal regulation of the broadcasting industry limits our operating flexibility, which may affect our ability to generate revenue or reduce our costs.
32
Table of Contents
The FCC regulates our business, just as it does all other companies in the broadcasting industry. We must ask the FCC’s approval whenever we need a new license, seek to renew, assign or modify a license, purchase a new station, sell an existing station or transfer the control of one of our subsidiaries that hold a license. Our FCC licenses and those of the licensees for which we provide services to pursuant to LMAs, JSAs, SSAs, and other outsourcing agreements are critical to our operations; we cannot operate without them. We cannot be certain that the FCC will renew these licenses in the future or approve new acquisitions in a timely manner, if at all. If licenses are not renewed or acquisitions are not approved, we may lose revenue that we otherwise could have earned.
In addition, Congress and the FCC may, in the future, adopt new laws, regulations and policies regarding a wide variety of matters (including, but not limited to, technological changes in spectrum assigned to particular services) that could, directly or indirectly, materially and adversely affect the operation and ownership of our broadcast properties. (See Item 1. Business.)
The FCC’s multiple ownership rules limit our ability to operate multiple television stations in some markets and may result in a reduction in our revenue or prevent us from reducing costs. Changes in these rules may threaten our existing strategic approach to certain television markets.
Changes in rules on television ownership
Congress passed a bill requiring the FCC to establish a national audience reach cap of 39% that was signed into law on January 23, 2004. The FCC is currently considering elimination of the discount given to owners of UHF stations in determining compliance with the cap. Because we would be near the 39% cap without application of the UHF discount, the proposed change, if adopted, could limit our ability to acquire television stations in additional markets.
In June 2003, the FCC adopted new multiple ownership rules. In September 2003, the Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit stayed the effectiveness of the rules. In June 2004, the court issued a decision which upheld a portion of such rules and remanded the matter, including the local television ownership rule, to the FCC for further justification of the rules. The court left the stay of the 2003 rules in place pending the remand. Several parties, including us, filed petitions with the Supreme Court of the United States seeking review of the Third Circuit decision, but the Supreme Court denied the petitions in June 2005. In July 2006, as part of the FCC’s statutorily required quadrennial review of its media ownership rules, the FCC released a Further Notice of Proposed Rule Making seeking comment on how to address the issues raised by the Third Circuit’s decision, including the local television ownership rules. In February 2008, the FCC released an order containing its current ownership rules, which re-adopted its 1999 local television ownership rule. On February 29, 2008, several parties, including us, separately filed petitions for review in a number of federal appellate courts challenging the FCC’s current ownership rules. By lottery, those petitions were consolidated in the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit. In July 2008, several parties, including us, filed motions to transfer the consolidated proceedings in the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit and other parties requested transfer to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit. In November 2008, the Ninth Circuit transferred the consolidated proceedings to the Third Circuit. On July 7, 2011, the Third Circuit upheld the FCC’s local television ownership rules. On December 5, 2011, we joined with a number of other parties on a Petition for a Writ of Certiorari filed with the Supreme Court requesting that the Court overrule the decision of the Third Circuit and that request was denied by the Supreme Court. In a recent letter, the FCC’s staff took the position that the 2003 stay is not effective with regard to the Cunningham LMAs. Continuing to hold television stations in the same markets as the Cunningham Stations could force us to terminate or modify the LMAs with the Cunningham Stations. In addition, if Cunningham were to exercise its put rights under the acquisition and merger agreements and the LMAs, each as amended and/or restated, we may have to find a suitable third party to assume our purchase obligations because we are not permitted to purchase such stations under current FCC rules. We cannot assure you that we would be able to locate such a third party or that any such third party would continue the LMAs (or any alternative arrangements) with us on substantially similar terms that are as favorable to us or at all. While we do not agree with the FCC staff’s stated position, we are presently considering modification of the LMAs, effectively converting them to JSAs and SSAs.
On December 22, 2011, the FCC released a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking in its Quadrennial Review of the Multiple Ownership Rules and is considering changes to the FCC’s rules regarding broadcast-newspaper cross ownership restrictions, the possible elimination of rules restricting the ownership of radio and TV in the same market, the potential attribution of TV JSAs and SSAs meaning potentially making JSAs and SSAs count as an ownership interest in a multiple ownership analysis and other possible revisions to the local radio and TV ownership limitations or exceptions that would allow for waivers of the limits in defined circumstances. Press and other reports indicate that the FCC is actively considering implementing new rules which would cause a station to be attributable to the owner of another station in the market which sells more than 15 percent of the advertising on the first station. Reports indicate that the FCC does not intend to “grandfather” existing JSAs, but rather to require parties to come into compliance with these new rules within a period of between eighteen months and two years. If the FCC were to enact such a rule we would no longer be able to enter into new transactions utilizing JSAs in the way we have done historically and would need to either terminate our existing JSAs or take
33
Table of Contents
action to modify the terms of our JSAs in a manner which complies with any such new rules. There can be no such assurance that the FCC will take the actions reported to be being considered and we cannot predict with any certainty the impact such rules might have on us until such rules are actually enacted.
Changes in rules on local marketing agreements
Certain of our stations have entered into what have commonly been referred to as local marketing agreements or LMAs. One typical type of LMA is a programming agreement between two separately owned television stations serving the same market, whereby the licensee of one station programs substantial portions of the broadcast day and sells advertising time during such programming segments on the other licensee’s station subject to the ultimate editorial and other controls being exercised by the latter licensee. We believe these arrangements allow us to reduce our operating expenses and enhance profitability.
In 1999, the FCC established a new local television ownership rule and decided to attribute LMAs for ownership purposes. It grandfathered our LMAs that were entered into prior to November 5, 1996, permitting the applicable stations to continue operations pursuant to the LMAs until the conclusion of the FCC’s 2004 biennial review. The FCC stated it would conduct a case-by-case review of grandfathered LMAs and assess the appropriateness of extending the grandfathering periods. Subsequently, the FCC invited comments as to whether, instead of beginning the review of the grandfathered LMAs in 2004, it should do so in 2006. The FCC did not initiate any review of grandfathered LMAs in 2004 or as part of its 2006 quadrennial review. We do not know when, or if, the FCC will conduct any such review of grandfathered LMAs. With respect to LMAs executed on or after November 5, 1996, the FCC required that parties come into compliance with the 1999 local television ownership rule by August 6, 2001. We challenged the 1999 local television ownership rule in the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit, and that court stayed the enforcement of the divestiture of the post-November 5, 1996 LMAs. In 2002, the D.C. Circuit ruled that the 1999 local television ownership rule was arbitrary and capricious and remanded the rule to the FCC. Currently, three of our LMAs are grandfathered under the local television ownership rule because they were entered into prior to November 5, 1996 and the remainder are subject to the stay imposed by the D.C. Circuit. If the FCC were to eliminate the grandfathering of these three LMAs, or the D.C. Circuit were to lift its stay, we would have to terminate or modify these LMAs. In connection with our pending acquisition of the Allbritton station in Charleston, the FCC has taken the position that the stay granted by the D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals allowing the continuation of an LMA between us and Cunningham relating to WTAT-TV in that market is no longer effective. In response to this, we are currently restructuring the relationship with WTAT in order to comply with current ownership rules in the absence of such a stay. Such restructuring will include a JSA rather than an LMA and further action may subsequently be required as a result of any action the FCC takes with respect to JSAs.
In 2003, the FCC revised its ownership rules, including the local television ownership rule. The effective date of the 2003 ownership rules was stayed by the U. S. Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit and the rules were remanded to the FCC. Because the effective date of the 2003 ownership rules had been stayed and, in connection with the adoption of those rules, the FCC concluded the 1999 rules could not be justified as necessary in the public interest, we took the position that an issue exists regarding whether the FCC has any current legal right to enforce any rules prohibiting the acquisition of television stations. Several parties, including us, filed petitions with the Supreme Court of the United States seeking review of the Third Circuit decision, but the Supreme Court denied the petitions in June 2005.
On November 15, 1999, we entered into a plan and agreement of merger to acquire through merger WMYA-TV in Anderson, South Carolina from Cunningham, but that transaction was denied by the FCC. In light of the change in the 2003 ownership rules, we filed a petition for reconsideration with the FCC and amended our application to acquire the license of WMYA-TV. We also filed applications in November 2003 to acquire the license assets of, at the time, the remaining five Cunningham stations: WRGT-TV, Dayton, Ohio; WTAT-TV, Charleston, South Carolina; WVAH-TV, Charleston, West Virginia; WNUV-TV, Baltimore, Maryland; and WTTE-TV, Columbus, Ohio. The Rainbow / PUSH Coalition (Rainbow / PUSH) filed a petition to deny these five applications and to revoke all of our licenses on the grounds that such acquisition would violate the local television ownership rules. The FCC dismissed our applications in light of the stay of the 2003 ownership rules and also denied the Rainbow / PUSH petition. Rainbow / PUSH filed a petition for reconsideration of that denial and we filed an application for review of the dismissal. In 2005, we filed a petition with the U. S. Court of Appeals for the D. C. Circuit requesting that the Court direct the FCC to take final action on our applications, but that petition was dismissed. On January 6, 2006, we submitted a motion to the FCC requesting that it take final action on our applications. Both the applications and the associated petition to deny are still pending. We believe the Rainbow / PUSH petition is without merit. On February 8, 2008, we filed a petition with the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit requesting that the Court direct the FCC to take final action on these applications and cease its use of the 1999 local television ownership rule that it re-adopted as the permanent rule in 2008. In July 2008, the D.C. Circuit transferred the case to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit, and we filed a petition with the D.C. Circuit challenging that decision, which was denied. We also filed with the Ninth Circuit a motion to transfer that case back to the D.C. Circuit. In November 2008, the Ninth Circuit consolidated our petition seeking final FCC action on our applications with the petitions challenging the FCC’s
34
Table of Contents
current ownership rules and transferred the proceedings to the Third Circuit. In December 2008, we agreed voluntarily with the parties to the proceeding to dismiss the petition seeking final FCC action on the applications. In addition, if Cunningham were to exercise its put rights under the acquisition and merger agreements and the LMAs, each as amended and/or restated, we may have to find a suitable third party to assume our purchase obligations because we are not permitted to purchase such stations under current FCC rules. In the event of any such assignments, new applications will have to be filed to reflect the third party as the applicant. In that event, upon the closing of the assignment to such third party, our appeals relating to the 1999 local television ownership rules with respect to our three non-grandfathered LMAs may be moot and the three non-grandfathered LMAs may be terminated.
Use of outsourcing agreements
In addition to our LMAs, we have entered into outsourcing agreements whereby twenty-six stations (and may seek opportunities for additional) provide or are provided various non-programming related services such as sales, operational and managerial services to or by other stations within the same markets. Pursuant to these agreements, twenty-three of our stations currently provide services to one or more stations in each’s respective market and another party provides services to three of our stations. For additional information, refer to Markets and Stations under the Television Broadcasting section. We believe this structure allows stations to achieve operational efficiencies and economies of scale, which should otherwise improve broadcast cash flow and competitive positions. While television JSAs are not currently “attributable” under the FCC rules, on August 2, 2004, the FCC released a notice of proposed rulemaking seeking comments on its tentative conclusion that JSAs should be attributable. The FCC is also considering the attribution of JSAs as part of its 2010 Quadrennial Regulatory Review of its broadcast ownership rules, released on December 22, 2011, although it is widely reported that the FCC will not take action on the 2010 Quadrennial proceeding and will merge it with the 2014 Quadrennial proceeding. Press and other reports indicate that the FCC is actively considering implementing new rules which would cause a station to be attributable to the owner of another station in the market which sells more than 15 percent of the advertising on the first station. Reports indicate that the FCC does not intend to “grandfather” existing JSAs, but rather to require parties to come into compliance with these new rules within a period of between eighteen months and two years. If the FCC were to enact such a rule we would no longer be able to enter into new transactions utilizing JSAs in the way we have done historically and would need to either terminate our existing JSAs or take action to modify the terms of our JSAs in a manner which complies with any such new rules. There can be no such assurance that the FCC will take the actions reported to be being considered and we cannot predict with any certainty the impact such rules might have on us until such rules are actually enacted. We cannot predict the outcome of these proceedings, nor can we predict how any changes, together with possible changes to the ownership rules, would apply to our existing outsourcing agreements. If the FCC were to determine that our outsourcing arrangements were “attributable,” we would have to terminate or restructure such arrangements on terms that may not be as advantageous to us as the current arrangements.
If we are required to terminate or modify our LMAs/JSAs, our business could be affected in the following ways:
· Loss of revenues. If the FCC requires us to modify or terminate existing arrangements, we would lose some or all of the revenues generated from those arrangements. We would lose revenue because we will have less demographic options, a smaller audience distribution and lower revenue share to offer to advertisers. During the year ended December 31, 2013, we generated $118.2 million of net revenue from our 13 LMAs. During the year ended December 31, 2013, we earned $36.0 million of revenue from JSAs.
· Increased costs. If the FCC requires us to modify or terminate existing arrangements, our cost structure would increase as we would potentially lose significant operating synergies and we may also need to add new employees. With termination of LMAs, we likely would incur increased programming costs because we will be competing with the separately owned station for syndicated programming.
· Losses on investments. As part of certain of our arrangements, we own the non-license assets used by the stations with which we have arrangements. If certain of these arrangements are no longer permitted, we would be forced to sell these assets, restructure our agreements or find another use for them. If this happens, the market for such assets may not be as good as when we purchased them and, therefore, we cannot be certain of a favorable return on our original investments.
· Termination penalties. If the FCC requires us to modify or terminate existing arrangements before the terms of the arrangements expire, or under certain circumstances, we elect not to extend the terms of the arrangements, we may be forced to pay termination penalties under the terms of certain of our arrangements. Any such termination penalties could be material.
· Alternative arrangements. If the FCC requires us to terminate the existing arrangements, we may enter into one or more alternative arrangements. Any such arrangements may be on terms that are less beneficial to us than the existing arrangements.
35
Table of Contents
Failure of owner / licensee to exercise control
The FCC requires the owner / licensee of a station to maintain independent control over the programming and operations of the station. As a result, the owners / licensees of those stations with which we have LMAs or outsourcing agreements can exert their control in ways that may be counter to our interests, including the right to preempt or terminate programming in certain instances. The preemption and termination rights cause some uncertainty as to whether we will be able to air all of the programming that we have purchased under our LMAs and therefore, uncertainty about the advertising revenue that we will receive from such programming. In addition, if the FCC determines that the owner / licensee is not exercising sufficient control, it may penalize the owner licensee by a fine, revocation of the license for the station or a denial of the renewal of that license. Any one of these scenarios, especially the revocation of or denial of renewal of a license, might result in a reduction of our cash flow and an increase in our operating costs or margins. In addition, penalties might also affect our qualifications to hold FCC licenses, putting our own licenses at risk.
The pendency and indeterminacy of the outcome of these ownership rules, which may limit our ability to provide services to additional or existing stations pursuant to licenses, LMAs, outsourcing agreements or otherwise, expose us to a certain amount of volatility, particularly if the outcomes are adverse to us. Further, resolution of these ownership rules has been and will likely continue to be a cost burden and a distraction to our management and the continued absence of a resolution may have a negative effect on our business.
The FCC’s National Broadband Plan may result in a loss of spectrum for our stations potentially adversely impacting our ability to compete.
The FCC’s National Broadband Plan contemplates the voluntary reallocation of spectrum from broadcasters for other purposes which may include wireless broadband. On November 30, 2010, the FCC initiated a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that seeks comments on three methods that would permit up to 120 MHz of television spectrum to be reallocated for wireless broadband use: (a) encouraging broadcasters “voluntarily” to return 120 MHz of spectrum to be auctioned for wireless broadband service, with some currently unknown portion of the proceeds to be paid to broadcasters; (b) adoption of rules to encourage two or more digital television stations to share the same 6 MHz channel, thus lessening the spectrum occupied by each station; and (c) to adopt new engineering rules which would make VHF channels more desirable for digital television operations, thus encouraging stations to move from their current UHF channels into the VHF band, freeing UHF spectrum for wireless broadband use. This initiative raises a number of issues that could impact the broadcast industry. We cannot predict whether any of these proposals will be adopted, or, if adopted, the form of such final rules or whether they would have an adverse impact on our ability to compete. Moreover, we cannot predict whether the FCC might adopt even more stringent requirements, or incentives to abandon current spectrum, if its initiatives are adopted but do have the desired result in freeing what the agency deems sufficient spectrum for wireless broadband use.
Congress recently passed legislation providing the FCC with authority to conduct so-called “incentive auctions” to begin the process of auctioning and repurposing broadcast television spectrum for mobile broadband use. Incentive auction authority allows the FCC to share the proceeds of spectrum auctions with incumbent television station licensees who give up their licenses (or in some cases, move to a different channel) to facilitate spectrum auctions. The legislation includes specific provisions governing incentive auctions of spectrum that is used by television broadcasters today. The upper UHF bands allocated to television broadcasting will likely be used to provide service to mobile devices and are widely expected to draw bids from wireless operators at auction. The legislation contemplates that the FCC will encourage broadcasters to tender their licenses for auction. Using models it has been developing for the last two years (and will continue to develop) the FCC would then “repack” non-tendering broadcasters into the lower portion of the UHF band auction new “flexible use” wireless licenses in the upper portion of the UHF band. As a result of these changes, new companies will likely be able to enter our markets to compete with us. The proposals for television stations to participate in the incentive auctions are voluntary and at this time we have not decided whether the company will participate on behalf of any of its stations. On September 28, 2012, the FCC voted in favor of a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that launches the incentive auction process to clear a portion of the television band that will make way for mobile broadband use. We cannot predict the final outcome of this proceeding.
Competition from other broadcasters or other content providers and changes in technology may cause a reduction in our advertising revenues and/or an increase in our operating costs.
New technology and the subdivision of markets
Cable providers, direct broadcast satellite companies and telecommunication companies are developing new technology that allows them to transmit more channels on their existing equipment to highly targeted audiences, reducing the cost of creating channels and potentially leading to the division of the television industry into ever more specialized niche markets. Competitors who target programming to such sharply defined markets may gain an advantage over us for television
36
Table of Contents
advertising revenues. The decreased cost of creating channels may also encourage new competitors to enter our markets and compete with us for advertising revenue. In addition, technologies that allow viewers to digitally record, store and play back television programming may decrease viewership of commercials as recorded by media measurement services such as Nielsen Media Research and, as a result, lower our advertising revenues. The current ratings provided by Nielsen for use by broadcast stations are limited to live viewing Digital Video Recording playback and give broadcasters no credit whatsoever for viewing that occurs on a delayed basis after the original air date. However, the effects of new ratings system technologies, including “people meters” and “set-top boxes,” and the ability of such technologies to be a reliable standard that can be used by advertisers is currently unknown. In 2010, the Media Rating Council, an independent organization that monitors rating services, revoked Nielsen’s accreditation in the 154 markets it measures ratings exclusively by its diary methodology. Approximately 96 of our stations are diary only markets as of March 1, 2014.
Since digital television technology allows broadcasting of multiple channels within the additional allocated spectrum, this technology could expose us to additional competition from programming alternatives. In addition, technological advancements and the resulting increase in programming alternatives, such as cable television, direct broadcast Satellite systems, pay-per-view, home video and entertainment systems, video-on-demand, mobile video and the Internet have also created new types of competition to television broadcast stations and will increase competition for household audiences and advertisers. We cannot provide any assurances that we will remain competitive with these developing technologies.
Types of competitors
We also face competition from rivals that may have greater resources than we have. These include:
· other local free over-the-air broadcast television and radio stations;
· telecommunication companies;
· cable and satellite system operators;
· print media providers such as newspapers, direct mail and periodicals;
· internet search engines, internet service providers and websites; and
· other emerging technologies including mobile television.
Deregulation
The Telecommunications Act of 1996 and subsequent actions by the FCC and the courts have removed some limits on station ownership, allowing telephone, cable and some other companies to provide video services in competition with us. In addition, the FCC has reallocated and auctioned off a portion of the spectrum for new services including fixed and mobile wireless services and digital broadcast services. As a result of these changes, new companies are able to enter our markets and compete with us.
We could be adversely affected by labor disputes and legislation and other union activity.
The cost of producing and distributing entertainment programming has increased substantially in recent years due to, among other things, the increasing demands of creative talent and industry-wide collective bargaining agreements. Although we generally purchase programming content from others rather than produce such content ourselves, our program suppliers engage the services of writers, directors, actors and on-air and other talent, trade employees and others, some of whom are subject to these collective bargaining agreements. Also, as of March 1, 2014, approximately 556 of our employees, including certain new employees at the stations we acquired during 2013, are represented by labor unions under collective bargaining agreements. If we or our program suppliers are unable to renew expiring collective bargaining agreements, it is possible that the affected unions could take action in the form of strikes or work stoppages. Failure to renew these agreements, higher costs in connection with these agreements or a significant labor dispute could adversely affect our business by causing, among other things, delays in production that lead to declining viewers, a significant disruption of operations and reductions in the profit margins of our programming and the amounts we can charge advertisers for time. Our stations also broadcast certain professional sporting events, including NBA basketball games, MLB baseball games, NFL football games, and other sporting events, and our viewership may be adversely affected by player strikes or lockouts, which could adversely affect our advertising revenues and results of operations. Further, any changes in the existing labor laws, including the possible enactment of the Employee Free Choice Act, may further the realization of the foregoing risks.
Unrelated third parties may bring claims against us based on the nature and content of information posted on websites maintained by us.
We host internet services that enable individuals to exchange information, generate content, comment on our content, and engage in various online activities. The law relating to the liability of providers of these online services for activities of their users is currently unsettled both within the United States and internationally. Claims may be brought against us for defamation, negligence, copyright or trademark infringement, unlawful activity, tort, including personal injury, fraud, or other theories based
37
Table of Contents
on the nature and content of information that may be posted online or generated by our users. Our defense of such actions could be costly and involve significant time and attention of our management and other resources.
Costs of complying with changes in governmental laws and regulations may adversely affect our results of operations.
We cannot predict what other governmental laws or regulations will be enacted in the future, how future laws or regulations will be administered or interpreted or how future laws or regulations will affect us. Compliance with new laws or regulations, including proposed legislation to address climate change, or stricter interpretation of existing laws, may require us to incur significant expenditures or impose significant restrictions on us and could cause a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Changes in accounting standards can affect reported earnings and results of operations.
Generally accepted accounting principles and accompanying pronouncements and implementation guidelines for many aspects of our business, including those related to intangible assets, pensions, income taxes, share-based compensation and broadcast rights, are complex and involve significant judgments. Changes in rules or their interpretation could significantly change our reported earnings and results of operations.
Terrorism or armed conflict domestically or abroad may negatively impact our advertising revenues and results of operations. Future conflicts, terrorist attacks or other acts of violence may have a similar effect.
The commencement of the war in Iraq in 2002 and activities in Afghanistan resulted in a reduction of advertising revenues as a result of uninterrupted news coverage and/or general economic uncertainty. If the United States becomes engaged in similar conflicts in the future, there may be a similar adverse effect on our results of operations. Also, any terrorist attacks or other acts of violence may have a similar negative effect on our business or results of operations.
Cybersecurity risks and cyber incidents could adversely affect our business and disrupt operations.
Cyber incidents can result from deliberate attacks or unintentional events. These incidents can include, but are not limited to, gaining unauthorized access to digital systems for purposes of misappropriating assets or sensitive information, corruption data, or causing operational disruption. The result of these incidents could include, but are not limited to, disrupted operations, misstated financial data, liability for stolen assets or information, increased cybersecurity protection costs, litigation and reputational damage adversely affecting customer or investor confidence.
38
Table of Contents
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
Generally, each of our stations has facilities consisting of offices, studios and tower sites. Transmitter and tower sites are located to provide maximum signal coverage of our stations’ markets. We believe that all of our properties, both owned and leased, are generally in good operating condition, subject to normal wear and tear and are suitable and adequate for our current business operations. The following is a summary of our principal owned and leased real properties. Approximately 128,000 square feet of leased office and warehouse buildings is related to our corporate facilities and is not included in the table below. We believe that no one property represents a material amount of the total properties owned or leased. See Item 1. Business, for a listing of our station locations.
Broadcast Segment | | Owned | | Leased |
Office and studio buildings | | 1,451,060 square feet | | 572,009 square feet |
Office and studio land | | 658 acres | | 6 acres |
Transmitter building sites | | 205,730 square feet | | 87,842 square feet |
Transmitter and tower land | | 1,687 acres | | 282 acres |
Other Operating Divisions Segment | | Owned | | Leased |
Office and warehouse buildings | | — | | 84,760 square feet |
Recreational land | | 712 acres | | — |
Real estate rental property | | 452,466 square feet | | — |
Land held for development and sale | | 1,721 acres | | — |
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
We are a party to lawsuits and claims from time to time in the ordinary course of business. Actions currently pending are in various stages and no material judgments or decisions have been rendered by hearing boards or courts in connection with such actions. After reviewing developments to date with legal counsel, our management is of the opinion that the outcome of our pending and threatened matters will not have a material adverse effect on our consolidated balance sheets, consolidated statements of operations or consolidated statements of cash flows.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
None.
39
Table of Contents
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Our Class A Common Stock is listed for trading on the NASDAQ stock market under the symbol SBGI. Our Class B Common Stock is not traded on a public trading market or quotation system. The following tables set forth for the periods indicated the high and low closing sales prices on the NASDAQ stock market for our Class A Common Stock.
2013 | | High | | Low | |
First Quarter | | $ | 20.29 | | $ | 12.82 | |
Second Quarter | | $ | 29.94 | | $ | 19.61 | |
Third Quarter | | $ | 34.04 | | $ | 23.92 | |
Fourth Quarter | | $ | 35.73 | | $ | 31.35 | |
2012 | | High | | Low | |
First Quarter | | $ | 12.95 | | $ | 11.06 | |
Second Quarter | | $ | 11.33 | | $ | 7.92 | |
Third Quarter | | $ | 12.56 | | $ | 9.41 | |
Fourth Quarter | | $ | 12.92 | | $ | 10.39 | |
As of February 24, 2014, there were approximately 58 shareholders of record of our common stock. This number does not include beneficial owners holding shares through nominee names.
Dividend Policy
During 2012, our Board of Directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.12 per share in the months of February and May, which were paid in March and June, and $0.15 per share in the months of August and November, which were paid in September and December. A special cash dividend of $1.00 per share was also declared in November 2012, which was paid in December, for total dividend payments of $1.54 per share for the year ended December 31, 2012. During 2013, our Board of Directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.15 per share in the months of February, April, August and November, which were paid in March, June, September and December, respectively, for total dividend payments of $0.60 per share for the year ended December 31, 2013. In February 2014, our Board of Directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.15 per share. Future dividends on our common shares, if any, will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend on several factors including our results of operations, cash requirements and surplus, financial condition, covenant restrictions and other factors that the Board of Directors may deem relevant. The Class A Common Stock and Class B Common Stock holders have the same rights related to dividends. Under our Bank Credit Agreement, in certain circumstances, we may make up to $200.0 million in unrestricted annual cash payments including but not limited to dividends, of which $50.0 million may carry over to the next year. Under the indentures governing our 8.375% Senior Notes, due 2018 (the 8.375% Notes), our 6.125% Notes, due 2022 (the 6.125% Notes), our 5.375% Notes, due 2021 (the 5.375% Notes) and our 6.375% Notes, due 2021 (the 6.375% Notes) we are restricted from paying dividends on our common stock unless certain specified conditions are satisfied, including that:
· no event of default then exists under each indenture or certain other specified agreements relating to our indebtedness; and
· after taking account of the dividends payment, we are within certain restricted payment requirements contained in each indenture.
In addition, under certain of our debt instruments, the payment of dividends is not permissible during a default thereunder.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
During 2013, we did not repurchase any shares of Class A Common Stock or other equity securities of Sinclair.
Comparative Stock Performance
The following line graph compares the yearly percentage change in the cumulative total shareholder return on our Class A Common Stock with the cumulative total return of the NASDAQ Composite Index and the cumulative total return of the NASDAQ Telecommunications Index (an index containing performance data of radio and television broadcast companies and communication equipment and accessories manufacturers) from December 31, 2008 through December 31, 2013. The performance graph assumes that an investment of $100 was made in the Class A Common Stock and in each Index on December 31, 2008 and that all dividends were reinvested. Total shareholder return is measured by dividing total dividends (assuming dividend reinvestment) plus share price change for
40
Table of Contents
a period by the share price at the beginning of the measurement period.
Company/Index/Market | | 12/31/08 | | 12/31/09 | | 12/31/10 | | 12/31/11 | | 12/31/12 | | 12/31/13 | |
Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. | | 100.00 | | 130.00 | | 278.09 | | 404.72 | | 517.91 | | 1505.96 | |
NASDAQ Telecommunications Index | | 100.00 | | 144.88 | | 170.58 | | 171.30 | | 199.99 | | 283.39 | |
NASDAQ Composite Index | | 100.00 | | 137.81 | | 148.84 | | 131.52 | | 136.58 | | 189.00 | |
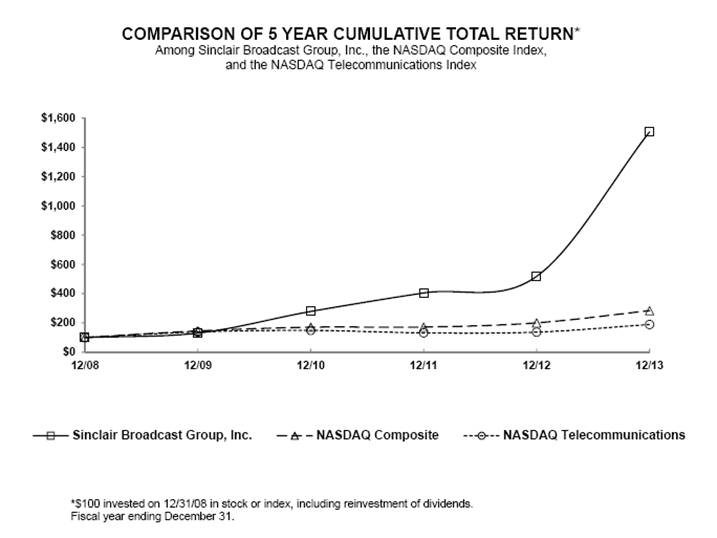
41
Table of Contents
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
The selected consolidated financial data for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012, 2011, 2010 and 2009 have been derived from our audited consolidated financial statements.
The information below should be read in conjunction with Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations and the consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this annual report on Form 10-K.
STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS DATA
(In thousands, except per share data)
| | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 | | 2009 | |
Statements of Operations Data: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net broadcast revenues (a) | | $ | 1,217,504 | | $ | 920,593 | | $ | 648,002 | | $ | 655,836 | | $ | 555,110 | |
Revenues realized from station barter arrangements | | 88,680 | | 86,905 | | 72,773 | | 75,210 | | 58,182 | |
Other operating divisions revenues | | 56,947 | | 54,181 | | 44,513 | | 36,598 | | 43,698 | |
Total revenues | | 1,363,131 | | 1,061,679 | | 765,288 | | 767,644 | | 656,990 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Station production expenses | | 385,104 | | 255,556 | | 178,612 | | 154,133 | | 142,415 | |
Station selling, general and administrative expenses | | 249,732 | | 171,279 | | 123,938 | | 127,091 | | 122,833 | |
Expenses recognized from station barter arrangements | | 77,349 | | 79,834 | | 65,742 | | 67,083 | | 48,119 | |
Depreciation and amortization (b) | | 141,374 | | 85,172 | | 51,103 | | 55,141 | | 65,247 | |
Amortization of program contract costs and net realizable value adjustments | | 80,925 | | 60,990 | | 52,079 | | 60,862 | | 73,087 | |
Other operating divisions expenses | | 48,109 | | 46,179 | | 39,486 | | 30,916 | | 45,520 | |
Corporate general and administrative expenses | | 53,126 | | 33,391 | | 28,310 | | 26,800 | | 25,632 | |
Loss(gain) on asset dispositions | | 3,392 | | — | | — | | — | | (4,945 | ) |
Impairment of goodwill, intangible and other assets | | — | | — | | 398 | | 4,803 | | 249,799 | |
Operating income (loss) | | 324,020 | | 329,278 | | 225,620 | | 240,815 | | (110,717 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest expense and amortization of debt discount and deferred financing cost | | (162,937 | ) | (128,553 | ) | (106,128 | ) | (116,046 | ) | (80,021 | ) |
(Loss) gain from extinguishment of debt (d) | | (58,421 | ) | (335 | ) | (4,847 | ) | (6,266 | ) | 18,465 | |
Income (loss) from equity and cost method investees | | 621 | | 9,670 | | 3,269 | | (4,861 | ) | 354 | |
Gain on insurance settlement | | 199 | | 47 | | 1,742 | | 344 | | 11 | |
Other income, net | | 2,026 | | 2,233 | | 1,717 | | 1,865 | | 1,448 | |
Income (loss) from continuing operations before income taxes | | 105,508 | | 212,340 | | 121,373 | | 115,851 | | (170,460 | ) |
Income tax (provision) benefit | | (41,249 | ) | (67,852 | ) | (44,785 | ) | (40,226 | ) | 32,512 | |
Income (loss) from continuing operations | | 64,259 | | 144,488 | | 76,588 | | 75,625 | | (137,948 | ) |
Discontinued operations: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of related income taxes | | 11,558 | | 465 | | (411 | ) | (577 | ) | (81 | ) |
Net income (loss) | | $ | 75,817 | | $ | 144,953 | | $ | 76,177 | | $ | 75,048 | | $ | (138,029 | ) |
Net (income) loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | | (2,349 | ) | (287 | ) | (379 | ) | 1,100 | | 2,335 | |
Net income (loss) attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 73,468 | | $ | 144,666 | | $ | 75,798 | | $ | 76,148 | | $ | (135,694 | ) |
Earnings (Loss) Per Common Share Attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic earnings (loss) per share from continuing operations | | $ | 0.66 | | $ | 1.78 | | $ | 0.95 | | $ | 0.96 | | $ | (1.70 | ) |
Basic earnings (loss) per share | | $ | 0.79 | | $ | 1.79 | | $ | 0.94 | | $ | 0.95 | | $ | (1.70 | ) |
Diluted earnings (loss) per share from continuing operations | | $ | 0.66 | | $ | 1.78 | | $ | 0.95 | | $ | 0.95 | | $ | (1.70 | ) |
Diluted earnings (loss) per share | | $ | 0.78 | | $ | 1.78 | | $ | 0.94 | | $ | 0.94 | | $ | (1.70 | ) |
Dividends declared per share | | $ | 0.60 | | $ | 1.54 | | $ | 0.48 | | $ | 0.43 | | $ | — | |
42
Table of Contents
| | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 | | 2009 | |
Balance Sheet Data: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 280,104 | | $ | 22,865 | | $ | 12,967 | | $ | 21,974 | | $ | 23,224 | |
Total assets | | $ | 4,147,472 | | $ | 2,729,697 | | $ | 1,571,417 | | $ | 1,485,924 | | $ | 1,590,029 | |
Total debt (c) | | $ | 3,034,040 | | $ | 2,273,379 | | $ | 1,206,025 | | $ | 1,212,065 | | $ | 1,366,308 | |
Total (deficit) equity | | $ | 405,704 | | $ | (100,053 | ) | $ | (111,362 | ) | $ | (157,082 | ) | $ | (202,222 | ) |
(a) Net broadcast revenues is defined as broadcast revenues, net of agency commissions.
(b) Depreciation and amortization includes depreciation and amortization of property and equipment and amortization of definite-lived intangible assets and other assets.
(c) Total debt is defined as notes payable, capital leases and commercial bank financing, including the current and long-term portions.
(d) During the year ended December 31, 2013, we recognized a loss on extinguishment of debt of $59.4 million related to the amendments of our Bank Credit Agreement in April and October 2013 and redemption of 9.25% Notes in October 2013, partially offset by a $1.0 million gain on extinguishment from our 3.0% Notes, resulting in a $58.4 loss from extinguishment of debt.
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following Management’s Discussion and Analysis provides qualitative and quantitative information about our financial performance and condition and should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and the accompanying notes to those statements. This discussion consists of the following sections:
Executive Overview — a description of our business, financial highlights from 2013, information about industry trends and sources of revenues and operating costs;
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates — a discussion of the accounting policies that are most important in understanding the assumptions and judgments incorporated in the consolidated financial statements and a summary of recent accounting pronouncements;
Results of Operations — a summary of the components of our revenues by category and by network affiliation or program service arrangement, a summary of other operating data and an analysis of our revenues and expenses for 2013, 2012 and 2011, including comparisons between years and certain expectations for 2014; and
Liquidity and Capital Resources — a discussion of our primary sources of liquidity, an analysis of our cash flows from or used in operating activities, investing activities and financing activities, a discussion of our dividend policy and a summary of our contractual cash obligations and off-balance sheet arrangements.
We have one reportable operating segment (broadcast), which includes our television and radio stations and is reported separately from our other operating divisions and corporate activities. The results of our other operating divisions consist primarily of revenues and expenses earned from sign design and fabrication; regional security alarm operating and bulk acquisitions; manufacturing and service of television broadcast antennas and transmitters; and real estate ventures.
STG, included in the broadcast segment and a wholly owned subsidiary of Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. (SBG), is the primary obligor under our Bank Credit Agreement, the 8.375% Notes, the 6.125% Notes, the 5.375% Notes and 6.375% Notes. SBG is a guarantor under the Bank Credit Agreement, the 8.375% Notes, the 6.125% Notes, the 5.375% Notes and 6.375% Notes. Our Class A Common Stock and Class B Common Stock remain obligations or securities of SBG and not obligations or securities of STG. SBG was the obligor of the 6.0% Notes and the 9.25% Notes until they were fully redeemed in 2011 and 2013, respectively.
EXECUTIVE OVERVIEW
2013 Events
Acquisitions / Divestments:
· In March 2013, we closed the sale of the assets of WLWC-TV (CW) in Providence, Rhode Island to an unrelated third party for $13.8 million. The related results from operations, net of related income taxes, have been reclassified from income from continuing operations and reflected as net income from discontinued operations;
43
Table of Contents
· In April 2013, we closed the sale of the assets of WLAJ-TV (ABC) in Lansing, MI to an unrelated third party for $14.4 million. The related results from operations, net of related income taxes, have been reclassified from income from continuing operations and reflected as net income from discontinued operations;
· Effective May 1, 2013, we completed the acquisition of certain stock and/or broadcast assets of four television stations, located in four markets, owned by Cox Media Group for $99.0 million, less $4.3 million of working capital adjustments, and less $0.4 million paid by Deerfield Media, Inc. (Deerfield) for the purchase of the license assets of one other station for which we provide sales and other non-programming support services pursuant to shared services and joint sales agreements;
· In June 2013, we acquired the assets of Dielectric from SPX Corporation, for an immaterial purchase price. Dielectric is the nation’s largest manufacturer of broadcast television, radio and wireless antennas, transmission lines, and RF systems;
· In July 2013, we entered into a definitive agreement to purchase the stock of Perpetual Corporation and the equity interest of Charleston Television, LLC, both owned and controlled by the Allbritton family (Allbritton), for an aggregate purchase price of $985.0 million. The Allbritton stations consist of seven ABC network affiliated television stations and NewsChannel 8, a 24-hour cable/satellite news network covering the Washington D.C. metropolitan area. The transaction is expected to close late in the second quarter of 2014, subject to approval of the FCC, antitrust clearance, and other customary closing conditions. We expect to fund the purchase price at closing through additional borrowings under our bank credit facility. Additionally, to comply with FCC local television ownership rules, we expect to sell the license and certain related assets of existing stations in Birmingham, AL — WABM (MNT) and WTTO (CW), Harrisburg/Lancaster/Lebanon/York, PA — WHP (CBS), and Charleston, SC — WMMP (MNT) and to provide sales and other non-programming support services to each of these stations pursuant to customary shared services and joint sales agreements;
· Effective August 8, 2013, we completed the merger with Fisher Communications, Inc. for an acquisition price of $373.2 million. Fisher owned twenty television stations in eight markets, plus two simulcasts, and four radio stations in the Seattle market;
· In September 2013, we entered into a definitive agreement to purchase the broadcast assets of eight television stations owned by New Age Media located in three markets, for an aggregate purchase price of $90.0 million. The transaction is expected to close in the second quarters of 2014, subject to approval of the FCC, and other customary closing conditions. We expect to fund the purchase price through cash on hand or a delayed draw under our bank credit agreement. Additionally, Wilkes/Barre/Scranton, PA — WSWB, Tallahassee, FL — WTLH and WTLF and Gainesville, FL — WMBW will be purchased by a third party; we will continue to provide sales and other non-programming support services to each of these stations, pursuant to customary share services and joint sales agreements;
· Effective September and October 2013, we completed the acquisition of nine stations for $115.3 million. The acquired stations were part of a definitive agreement entered into with TTBG in June 2013;
· In October 2013, we acquired the stock of the entity which owns KDBC (FOX) in El Paso, Texas for $21.0 million. A third party continues to provide sales and other related services pursuant to a JSA;
· In October 2013, we completed the purchase of the non-license assets of WPFO (FOX) in Portland, Maine for $13.6 million and entered into agreement to provide sales and other non-programming support services to the station;
· In November 2013, we closed on the acquisition of the non-license assets of KRNV in Reno, Nevada for $26.0 million and entered into agreements to provide sales and other non-programming support services to the station; and
· Effective November 2013, we completed the acquisition of broadcast assets of eighteen television stations owned by Barrington Broadcast Group, LLC and entered into agreements to operate or provide sales services for another six stations, for an aggregate purchase price of $370.0 million, which includes $7.5 million paid by certain third parties for the license assets of four stations. Due to FCC ownership conflict rules, we sold our station in Syracuse, NY (WSYT) and assigned our rights under an LMA to provide services to WNYS, to an unrelated third party for $15.0 million. We also sold our station in Peoria, IL (WYZZ) to Cunningham for $22.0 million.
Other:
· Effective January 1, 2013, we entered into a six-year affiliation agreement with the CBS Network on its Portland, ME and Cedar Rapids, IA affiliates, expiring December 31, 2018;
· In February 2013, our Board of Directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.15 per share which was paid on March 15, 2013, to the holders of record at the close of business on March 1, 2013;
· In February 2013, we announced a strategic initiative creating a small market television group. Also in February 2013, we announced that Steven J. Pruett would join our senior management team as Chief Operating Officer;
· In February 2013, we entered into a retransmission consent agreement with DirecTV for continued carriage in all of our markets and our next major MVPD that comes up for renewal is Charter Communications in March 2014;
· In April 2013, we issued $600.0 million aggregate principal amount of 5.375% Notes. The 5.375% Notes were priced at 100% of their par value and will bear interest at a rate of 5.375% per annum payable semi-annually on April 1 and October 1, commencing on October 1, 2013. The 5.375% Notes mature April 1, 2021 and are guaranteed by Sinclair and certain of its subsidiaries. See Liquidity and Capital Resources for more information;
· In April 2013, we filed registration statements on Form S-4 with the SEC to register the 6.125% Notes and the 5.375% Notes.
44
Table of Contents
Exchange offers were launched on May 23, 2013 to exchange the unregistered notes for notes registered under the Securities Act of 1933. The exchange offers were completed on June 28, 2013 with 100.0% of the 6.125% Notes and 5.375% Notes tendered;
· In April 2013, we entered into an amendment and restatement of our Bank Credit Agreement. We refinanced our existing facility and replaced the existing term loans under the facility with a new $500.0 million term loan A facility (Term Loan A), maturing April 2018 and priced at LIBOR plus 2.25%; and a $400.0 million term loan B facility (Term Loan B), maturing April 2020 and priced at LIBOR plus 2.25% with a LIBOR floor of 0.75%. In addition, Sinclair replaced its existing revolving line of credit with a new $100.0 million revolving line of credit maturing April 2018 and priced at LIBOR plus 2.25%. This new amendment also provides for increased incremental loan capacity, increased television station acquisition capacity and increased flexibility with restrictive covenants. See Note 4 Notes Payable and Commercial Bank Financing in of consolidated financial statements for more information.;
· In April 2013, we announced that we will begin broadcasting mobile-capable signals over 10 stations in nine markets over the next six months. Cunningham, one of our consolidated variable interest entities, currently provides mobile signals on two stations, WSYX-TV and WTTE-TV in Columbus, Ohio;
· In April 2013, our Board of Directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.15 per share payable on June 14, 2013, to the holders of record at the close of business on May 31, 2013;
· In April 2013, we commenced a public offering of 18.0 million shares of Class A common stock. The offering was priced at $27.25 per share on May 1, 2013 and closed on May 7, 2013. Net proceeds of $472.9 million were used to fund acquisitions in the third quarter 2013.
· In August 2013, our Board of Directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.15 per share, payable on September 13, 2013, to the holders of record at the close of business on August 30, 2013;
· In September 2013, 100% of the outstanding 4.875% Notes, representing principal of $5.7 million, were converted into 388,632 shares of Class A Common Stock, as permitted under the indenture;
· In October 2013, we issued $350.0 million aggregate principal amount of 6.375% Notes. The 6.375% Notes were priced at 100% of their par value and will bear interest at a rate of 6.375% per annum payable semi-annually on May 1 and November 1, commencing May 1, 2014. The 6.375% Notes mature on November 1, 2021 and are guaranteed by Sinclair and certain of its subsidiaries. See Note 4 Notes Payable and Commercial Bank Financing in our consolidated financial statements for more information;
· In October 2013, we used the proceeds from the issuance of the 6.375% Notes along with cash on hand to redeem the $500 million aggregate principal amount of 9.25% Notes;
· In October 2013, we amended our bank credit agreement (October Amendment). Pursuant to the October Amendment, we raised an additional $450 million of incremental loans, which consisted of $200 million in incremental delayed draw term loan A loans, maturing April 2018 and priced at LIBOR plus 2.25%; and $250.0 million in incremental term loan B loans, maturing April 2020 and priced at LIBOR plus 2.25% with a LIBOR floor of 0.75%. In addition, we obtained an additional $57.5 million of capacity under our revolving line of credit maturing April 2018. The terms loans are expected to be used to fund acquisitions and for general corporate purposes. We also amended certain other terms of our Bank Credit Agreement. See Note 4. Notes Payable and Commercial Bank Financing for more information.
· In October 2013, 100% of the outstanding 3.0% Notes, representing principal of $5.4 million, were converted and settled fully in cash for $10.5 million, as permitted under the indenture; and
· In November 2013, our Board of Directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.15 per share, payable on December 13, 2013, to the holders of record at the close of business on November 29, 2013;
2014 Events
· In January 2014, we exchanged 99.7% of our 6.375% Senior Unsecured Notes due 2021 for 6.375% Senior Notes due 2021 registered under the Securities Act of 1933.
· In February 2014, we entered into an agreement for a $0.5 million investment, purchasing Series A Preferred Units of Timeline Labs, and anticipates utilizing their products on 15 of our news-producing stations. Timeline Labs specializes in proprietary tools that discover, measure, and display trending social content in real time in such a way as to allow these items to be incorporated into live newscasts and shows.
· In February 2014, Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. (the “Company”) announced that, effective April 2, 2014, David B. Amy would be promoted to the position of Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer, and Christopher Ripley would become the Company’s Chief Financial Officer.
Industry Trends
· Political advertising increases in even-numbered years, such as 2012, due to the advertising expenditures from candidates running in local and national elections and issue-related advertiser spending. In every fourth year, such as 2012, political advertising is usually elevated further due to presidential elections;
45
Table of Contents
· The FCC has permitted broadcast television stations to use their digital spectrum for a wide variety of services including multi-channel broadcasts. The FCC “must-carry” rules only apply to a station’s primary digital stream;
· Retransmission consent rules provide a mechanism for broadcasters to seek payment from MVPDs who carry broadcasters’ signals. Recognition of the value of the programming content provided by broadcasters, including local news and other programming and network programming all in HD has generated increased local revenues;
· We, as well as a number of other broadcasters, have joined and worked together in organizations such as the NAB (along with OMVC now merged), M500 and the MCV to focus on efforts to accelerate the nationwide availability of mobile DTV and other advanced digital distribution services and work through the many programming, advertising, distribution and aggregation opportunities. There is potential for broadcasters to create an additional revenue stream by providing their signals to a wide variety of mobile / portable devices (tablets, laptops, smartphones, etc.) as well as through other multi-channel / multi-platform initiatives;
· Many broadcasters are enhancing / upgrading their websites to use the internet to deliver rich media content, such as newscasts and weather updates, to attract advertisers and to compete with other internet sites and smart phone and tablet device applications and other social media outlets;
· Seasonal advertising increases occur in the second and fourth quarters due to the anticipation of certain seasonal and holiday spending by consumers;
· Broadcasters have found ways to increase returns on their news programming initiatives while continuing to maintain locally produced content through the use of news sharing arrangements;
· Station outsourcing arrangements are becoming more common as broadcasters seek out ways to improve revenues and margins;
· Advertising revenue related to the Olympics occurs in even numbered years and the Super Bowl is aired on a different network each year. Both of these popularly viewed events can have an impact on our advertising revenues; and
Sources of Revenues and Costs
Our operating revenues are derived from local and national advertisers and, to a much lesser extent, from political advertisers. We also generate local revenues from our retransmission consent agreements with MVPDs. Our revenues from local advertisers have seen a continued upward trend, with the exception of 2008 and 2009 when non-political revenues fell due to the economic recession. Revenues from national advertisers have continued to trend downward when measured as a percentage of total broadcast revenues. We believe this trend is the result of our focus on increasing local advertising revenues as a percentage of total advertising revenues, combined with a decrease in overall spending by national advertisers and an increase in the number of competitive media outlets providing national advertisers multiple alternatives in which to advertise their goods or services. Our efforts to mitigate the effect of these increasingly competitive media outlets for national advertisers include continuing our efforts to increase local revenues and developing innovative sales and marketing strategies to sell traditional and non-traditional services to our advertisers including the success of multi-channel digital initiatives together with mobile DTV. In addition, our revenue success is dependent on the success and advertising spending levels of the automotive industry.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND ESTIMATES
This discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations is based on our consolidated financial statements which have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amount of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. On an on-going basis, we evaluate our estimates including those related to bad debts, program contract costs, intangible assets, income taxes, property and equipment, and investments. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. These estimates have been consistently applied for all years presented in this report and in the past we have not experienced material differences between these estimates and actual results. However, because future events and their effects cannot be determined with certainty, actual results could differ from our estimates and such differences could be material.
We have identified the policies below as critical to our business operations and to the understanding of our results of operations. For a detailed discussion of the application of these and other accounting policies, see Note 1. Nature of Operations and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, in the Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements.
Valuation of Goodwill, Long-Lived Assets, Intangible Assets and Equity and Cost Method Investments.
We periodically evaluate our goodwill, broadcast licenses, long-lived assets, intangible assets and equity and cost method investments for potential impairment indicators. Our judgments regarding the existence of impairment indicators are based on estimated future cash flows,
46
Table of Contents
market conditions, operating performance of our stations, legal factors and other various qualitative factors.
We have determined our broadcast licenses to be indefinite-lived intangible assets in accordance with the accounting guidance for goodwill and other intangible assets, which requires such assets along with our goodwill to be tested for impairment on an annual basis or more often when certain triggering events occur. As of December 31, 2013, we had $1,380.1 million of goodwill, $101.0 million in broadcast licenses, and $1,127.8 million in definite-lived intangibles. We perform our annual impairment tests for goodwill and broadcast licenses at the beginning of the fourth quarter each year.
In 2011, we early adopted the accounting guidance related to the annual goodwill impairment assessment, which allowed us, to first qualitatively assess whether it is more likely than not that goodwill has been impaired. As part of our qualitative assessment for goodwill impairment, we consider the following factors related to the reporting units, where applicable:
· Significant changes in the macroeconomic conditions;
· Significant changes in the regulatory environment;
· Significant changes in the operating model, management, products and services, customer base, cost structure and/or margin trends;
· Comparison of current and prior year operating performance and forecast trends for future operating performance; and
· The excess of the fair value over carrying value of the reporting units determined in prior quantitative assessments.
If we conclude that it is more likely than not that a reporting unit is impaired, we will apply the quantitative two-step method for goodwill. Prior to 2011, the annual impairment test for goodwill was performed using the quantitative two-step method for all reporting units. Our quantitative assessment for goodwill consists of estimating the fair value of our reporting units, using a combination of a market approach, using recent comparable market transactions and estimated market multiples, and an income approach, using a discounted cash flow model. The key assumptions used to determine the fair value of our reporting units to test our goodwill for impairment consist of discount rates, revenue and expense growth rates and comparable business multiples. The projected growth rates are based on our internal forecast of future performance, historical trends, and projected long-range inflation and long-term industry projections. The discount rate is based on a number of factors including market interest rates, a weighted average cost of capital analysis based on the target capital structure for a television station, and includes adjustments for market risk and company specific risk. For goodwill, if we determine that the fair value of the reporting unit is less than the carrying value, we then perform the second step which requires allocation of the reporting unit’s fair value to all of its assets and liabilities in a manner similar to a purchase price allocation, with any residual fair value being allocated to goodwill to determine the implied fair value. An impairment charge will be recognized only when the implied fair value of a reporting unit’s goodwill is less than its carrying amount.
We early adopted the recent accounting guidance related to the annual indefinite-lived intangible asset impairment test, which allowed us, beginning with our 2012 indefinite-lived intangible impairment test, to first qualitatively assess whether it is more likely than not that an indefinite-lived intangible asset has been impaired. As part of our qualitative assessment for indefinite-lived intangible assets, we consider the following factors related to the indefinite-lived intangible asset, where applicable:
· Significant changes in cost factors that could affect the inputs used to determine the fair value of the indefinite-lived intangible asset;
· Significant changes in the legal or regulatory environment;
· Significant changes in management, key personnel, strategy or customers that could affect the inputs used to determine the fair value of the indefinite-lived intangible asset;
· Significant changes in the industry and/or market;
· Significant changes in macroeconomic conditions;
· Comparison of current and prior year operating performance and forecast trends for future operating performance; and
· The excess of the fair value over carrying value of the indefinite-lived intangible assets determined in prior quantitative assessments.
If we conclude that it is more likely than not that an indefinite-lived intangible asset is impaired, we will calculate the fair market value of the indefinite-lived intangible asset and compare to the book value. Prior to 2012, the annual impairment test for our indefinite-lived intangibles, broadcast licenses, involved a quantitative assessment in which we estimated the fair market value of our broadcast licenses and compared to the book value. We estimated the fair market value of our broadcast licenses using a discounted cash flow model. The key assumptions used to determine the fair value of our broadcast licenses consist of discount rates, normalized market share, normalized profit margin, expected future growth rates and estimated start-up costs. We then compared the estimated fair market value to the book value of these assets to determine if impairment exists. For the broadcast licenses, if the fair value is less than book value, we would record the resulting impairment.
47
Table of Contents
We aggregate our stations by market for purposes of our goodwill and license impairment testing and we believe that our markets are most representative of our broadcast reporting units because segment management views, manages and evaluates our stations on a market basis. Furthermore, in our markets where we operate or provide services to more than one station, certain costs of operating the stations are shared including the use of buildings and equipment, the sales force and administrative personnel. Our discounted cash flow model is based on our judgment of future market conditions within each designated marketing area, as well as discount rates that would be used by market participants in an arms-length transaction.
Based on the annual qualitative assessment for goodwill impairment performed in 2013, we concluded that it was more likely than not that the fair values of all reporting units would sufficiently exceed their carrying value and thus it was not necessary to perform the quantitative two-step method. Based on the results of our annual qualitative assessment for goodwill impairment performed in 2013, we concluded that we would need to perform a quantitative “Step 1” test for three of our markets which had aggregate goodwill of $79.5 million as of October 1, 2012, the date of our annual impairment test. These markets had a decrease in operating results for the past few years and therefore, we estimated the fair value of these reporting units based on a market approach and income approach. For all three markets, the fair value of the reporting unit exceeded the respective carrying value by more than 10%. For all our other reporting units, we concluded based on the qualitative assessment that it was more likely than not that the fair values of these reporting units would sufficiently exceed their carrying values and it was not necessary to perform the quantitative two-step method.
For the year ended December 31, 2012, an increase in our discount rate and/or a decrease in our multiple of 10% would not have resulted in goodwill impairment. Based on the annual qualitative assessment for goodwill impairment performed in 2011, we concluded that it was more likely than not that the fair values of all reporting units would sufficiently exceed their carrying value and thus it was not necessary to perform the quantitative two-step method. The qualitative factors for our reporting units reviewed during our annual assessments, with the exception of the three markets in which we performed a quantitative assessment in 2012, indicated stable or improving margins and favorable or stable forecasted economic conditions including stable discount rates and comparable or improving business multiples. Additionally, the results of prior quantitative assessments supported significant excess fair value over carrying value of our reporting units.
Based on the annual qualitative assessment for broadcast license impairment performed in 2013 and 2012, we concluded that it was more likely than not that the fair values of all broadcast licenses would sufficiently exceed their carrying values and thus it was not necessary to perform a quantitative test. The qualitative factors for our broadcast licenses indicated an increase in market revenues, consistent expected market growth rates, stable market shares and stable cost factors from 2011 through 2013. We recorded a $0.4 million interim impairment charge in the first quarter of 2011 due to an anticipated increase in construction costs for one of our stations as a result of converting to full power. As a result of our annual impairment test for broadcast licenses in 2011, under which we applied the required quantitative test, we concluded that impairment did not exist.
We believe we have made reasonable estimates and utilized appropriate assumptions to evaluate whether it was more likely than not that the fair value of our reporting units and broadcast licenses was less than their carrying values. If future results are not consistent with our assumptions and estimates, including future events such as a deterioration of market conditions or significant increases in discount rates, we could be exposed to impairment charges in the future. Any resulting impairment loss could have a material adverse impact on our consolidated balance sheets, consolidated statements of operations and consolidated statements of cash flows.
For all other long-lived assets, including fixed assets and definite-lived intangibles, we assess recoverability of the assets whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the net book value of the assets may not be recoverable. If we conclude that such triggering event has occurred, we perform a two-step quantitative test to first assess whether the asset is recoverable by comparing the sum of undiscounted cash flows of the asset group to the carrying value of the asset group, including goodwill. If the sum of undiscounted cash flows is less than the carrying value of the asset group, we then measure and allocate the amount of impairment to record for each of the assets in the asset group by comparing the respective fair value of the assets to their carrying values. We did not have any indicators of impairment of our long-lived assets in 2011, 2012 or 2013.
When factors indicate that there may be a decrease in value of an equity or cost method investment, we assess that investment and determine whether a loss in value has occurred. If that loss is deemed to be other than temporary, an impairment loss is recorded. For any investments that indicate a potential impairment, we estimate the fair value of those investments using discounted cash flow models, unrelated third party valuations or industry comparables, based on the various facts available to us. During 2013 and 2012, we recorded $0.6 million and $1.3 million of impairment on equity method investments, respectively. No impairment of our equity or cost method investments was recorded 2011.
Revenue Recognition. Advertising revenues, net of agency commissions, are recognized in the period during which commercials are aired. All other revenues are recognized as services are provided. The revenues realized from station barter arrangements are recorded as the programs are aired at the estimated fair value of the advertising airtime given in exchange for the program rights. Some of our retransmission consent agreements contain both advertising and retransmission consent elements that are paid in cash. We have determined that these agreements are revenue arrangements with multiple deliverables. Advertising and retransmission consent
48
Table of Contents
deliverables sold under our agreements are separated into different units of accounting based on fair value. Revenue applicable to the advertising element of the arrangement is recognized consistent with the advertising revenue policy noted above. Revenue applicable to the retransmission consent element of the arrangement is recognized over the life of the agreement.
Program Contract Costs. We have agreements with distributors for the rights to televise programming over contract periods, which generally run from one to seven years. Contract payments are made in installments over terms that are generally equal to or shorter than the contract period. Each contract is recorded as an asset and a liability at an amount equal to its gross cash contractual commitment when the license period begins and the program is available for its first showing. The portion of program contracts which become payable within one year is reflected as a current liability in the consolidated balance sheets. As of December 31, 2013 and 2012, we recorded $99.0 million and $69.3 million, respectively, in program contract assets and $125.6 million and $104.4 million, respectively, in program contract liabilities.
The programming rights are reflected in the consolidated balance sheets at the lower of unamortized cost or estimated net realizable value (NRV). Estimated NRVs are based on management’s expectation of future advertising revenue, net of sales commissions, to be generated by the remaining program material available under the contract terms. Amortization of program contract costs is generally computed using a four-year accelerated method or a straight-line method, depending on the length of the contract. Program contract costs estimated by management to be amortized within one year are classified as current assets. Program contract liabilities are typically paid on a scheduled basis and are not impacted by adjustments for amortization or estimated NRV. If our estimate of future advertising revenues declines, then additional write downs to NRV may be required.
Income Tax. We recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities based on the differences between the financial statements carrying amounts and the tax bases of assets and liabilities. As of December 31, 2013 and 2012, we recorded $312.8 million and $235.4 million, respectively, in net deferred tax liabilities. We provide a valuation allowance for deferred tax assets if we determine that it is more likely than not that some or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. In evaluating our ability to realize net deferred tax assets, we consider all available evidence, both positive and negative, including our past operating results, tax planning strategies and forecasts of future taxable income. In considering these sources of taxable income, we must make certain judgments that are based on the plans and estimates used to manage our underlying businesses on a long-term basis. A valuation allowance has been provided for deferred tax assets related to a substantial portion of our available state net operating loss carryforwards, based on past operating results, expected timing of the reversals of existing temporary book/tax basis differences, alternative tax strategies and projected future taxable income.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In July 2012, the FASB issued new guidance for testing indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment. The new guidance allows companies to perform a qualitative assessment to determine whether further impairment testing of indefinite-lived intangible assets is necessary, similar to the approach now applied to goodwill. Companies can first determine based on certain qualitative factors whether it is “more likely than not” (a likelihood of more than 50 percent) that an indefinite-lived intangible asset is impaired. The new standard is intended to reduce the cost and complexity of testing indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment. The revised standard is effective for annual and interim impairment tests performed for fiscal years beginning after September 30, 2012 and early adoption is permitted. We adopted this new guidance in the fourth quarter of 2012 when completing our annual impairment analysis. This guidance impacted how we perform our annual impairment testing for indefinite-lived intangible assets and changed our related disclosures for 2012; however, it does not have an impact on our consolidated financial statements as the guidance does not impact the timing or amount of any resulting impairment charges.
In February 2013, the FASB issued new guidance requiring disclosure of items reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income (AOCI). This new guidance requires entities to present (either on the face of the income statement or in the notes) the effects on the line items of the income statement for amounts reclassified out of AOCI. The new guidance is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2012. This guidance does not have a material impact on our financial statements.
In July 2013, the FASB issued new guidance requiring new disclosure of unrecognized tax benefit, or a portion of an unrecognized tax benefit, in the financial statements as a reduction to a deferred tax asset for a net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss, or a tax credit carryforward. If a company does not have: (i) a net operating loss carryforward; (ii) a similar tax loss; or (iii) a tax credit carryforward is not available at the reporting date under the tax law of the applicable jurisdiction to settle any additional income taxes that would result from the disallowance of a tax position or the entity does not intend to use the deferred tax asset for such purpose, the unrecognized tax benefit should be presented in the financial statements as a liability and should not be combined with deferred tax assets. The authoritative guidance is effective for fiscal years and the interim periods within those fiscal years beginning on or after December 15, 2013 and should be applied on a prospective basis. We do not expect this requirement to have a material impact on our financial statements.
49
Table of Contents
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
In general, this discussion is related to the results of our continuing operations, except for discussions regarding our cash flows, which also include the results of our discontinued operations The results of the acquired stations from Freedom Communications (Freedom) as of April 1, 2012, Newport Television (Newport) as of December 1, 2012 (acquisition date), Cox Media Group (Cox) as of May 1, 2013 (acquisition date), Fisher Communications (Fisher) as of August 8, 2013, TTBG as of October 1, 2013, Barrington as of November 22, 2013, and six other television stations during the year ended 2012 and 2013 are included in our results of our continuing operations. In 2012, we determined that the operating results of WLAJ-TV, which was one of the stations acquired in the Freedom acquisition, and WLWC-TV, which was one of the stations acquired in the Four Points acquisition, should be accounted for as discontinued operations and therefore the results are not included in our consolidated results of continuing operations year ended December 31, 2013. Unless otherwise indicated, references in this discussion and analysis to 2013, 2012 and 2011 are to our fiscal years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively. Additionally, any references to the first, second, third or fourth quarters are to the three months ended March 31, June 30, September 30 and December 31, respectively, for the year being discussed. We have one reportable segment, “broadcast” that is disclosed separately from our other operating division and corporate activities.
Seasonality / Cyclicality
Our operating results are usually subject to seasonal fluctuations. Usually, the second and fourth quarter operating results are higher than the first and third quarters’ because advertising expenditures are increased in anticipation of certain seasonal and holiday spending by consumers.
Our operating results are usually subject to fluctuations from political advertising. In even numbered years, political spending is usually significantly higher than in odd numbered years due to advertising expenditures preceding local and national elections. Additionally, every four years, political spending is usually elevated further due to advertising expenditures preceding the presidential election.
Operating Data
The following table sets forth certain of our operating data from continuing operations for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 (in millions). For definitions of terms, see the footnotes to the table in Item 6. Selected Financial Data.
| | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
Net broadcast revenues | | $ | 1,217.5 | | $ | 920.6 | | $ | 648.0 | |
Revenues realized from station barter arrangements | | 88.7 | | 86.9 | | 72.8 | |
Other operating divisions revenues | | 56.9 | | 54.2 | | 44.5 | |
Total revenues | | 1,363.1 | | 1061.7 | | 765.3 | |
Station production expenses | | 385.1 | | 255.5 | | 178.6 | |
Station selling, general and administrative expenses | | 249.7 | | 171.3 | | 123.9 | |
Expenses recognized from station barter arrangements | | 77.3 | | 79.8 | | 65.7 | |
Depreciation and amortization | | 222.4 | | 146.2 | | 103.3 | |
Other operating divisions expenses | | 48.1 | | 46.2 | | 39.5 | |
Corporate general and administrative expenses | | 53.1 | | 33.4 | | 28.3 | |
Loss on asset dispositions | | 3.4 | | — | | — | |
Impairment of goodwill, intangible and other assets | | — | | — | | 0.4 | |
Operating income | | $ | 324.0 | | $ | 329.3 | | $ | 225.6 | |
Net income attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 73.5 | | $ | 144.7 | | $ | 75.8 | |
50
Table of Contents
BROADCAST SEGMENT
Broadcast Revenues
The following table presents our revenues from continuing operations, net of agency commissions, for the three years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 (in millions):
| | | | | | | | Percent Change | |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | ‘13 vs. ‘12 | | ‘12 vs. ‘11 | |
Local revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Non-political | | $ | 954.5 | | $ | 643.5 | | $ | 498.7 | | 48.3 | % | 29.0 | % |
Political | | 1.5 | | 12.9 | | 2.5 | | | (a) | | (a) |
Total local | | 956.0 | | 656.4 | | 501.2 | | 45.6 | % | 31.0 | % |
National revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Non-political | | 251.2 | | 180.2 | | 141.0 | | 39.4 | % | 27.8 | % |
Political | | 10.3 | | 84.0 | | 5.8 | | | (a) | | (a) |
Total national | | 261.5 | | 264.2 | | 146.8 | | (1.0 | )% | 80.0 | % |
Total net broadcast revenues | | $ | 1,217.5 | | $ | 920.6 | | $ | 648.0 | | 32.3 | % | 42.1 | % |
(a) Political revenue is not comparable from year to year due to the cyclicality of elections. See Political Revenues below for more information.
Our largest categories of advertising and their approximate percentages of 2013 net time sales, which include the advertising portion of our local and national broadcast revenues, were automotive (25.2%), services (16.6%), retail / department stores(6.1%), schools (5.5%), medical (5.3%) and fast food (5.1%). No other advertising category accounted for more than 5.0% of our net time sales in 2013. No advertiser accounted for more than 1.5% of our consolidated revenue in 2013. We conduct business with thousands of advertisers.
Our primary types of programming and their approximate percentages of 2013 net time sales were syndicated programming (33.4%), network programming (27.8%), local news (26.2%), sports programming (8.0%) and direct advertising programming (4.6%).
From a network affiliation or program service arrangement perspective, the following table sets forth our affiliate percentages of net time sales for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012:
| | # of | | Percent of Net Time Sales for the
Twelve Months Ended December 31, | | Net Time Sales
Percent Change | |
| | Stations(a) | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | ‘13 vs. ‘12 | | ‘12 vs. ‘11 | |
FOX | | 39 | | 31.2 | % | 36.9 | % | 47.4 | % | 2.4 | % | 9.6 | % |
ABC | | 19 | | 19.1 | % | 19.5 | % | 20.5 | % | 18.6 | % | 33.1 | % |
CBS | | 25 | | 21.3 | % | 18.6 | % | 3.0 | % | 38.5 | % | 786.2 | % |
MyNetworkTV | | 20 | | 10.3 | % | 12.5 | % | 15.8 | % | -0.2 | % | 11.0 | % |
The CW | | 23 | | 9.8 | % | 10.7 | % | 12.4 | % | 10.4 | % | 22.0 | % |
NBC | | 16 | | 6.1 | % | 1.0 | % | 0.5 | % | n/m | | 169.7 | % |
Digital | | (b) | | 1.7 | % | 0.7 | % | 0.4 | % | n/m | | 110.8 | % |
Other | | 7 | | 0.5 | % | 0.1 | % | n/a | | n/m | | 110.8 | % |
Total | | 149 | | | | | | | | | | | |
n/m- Not meaningful
n/a- Not applicable
(a) During 2013, we acquired or entered into outsourcing agreements to provide certain non-programming related sales, operational and administrative services to 63 stations with the following network affiliation or program service arrangements: CBS (ten stations in the third quarter and four in the fourth quarter), FOX (two stations in the second quarter, three in the third quarter and eight in the fourth quarter), NBC (two stations in the second quarter, three in the third quarter and eight in the fourth quarter), ABC (two stations in the third quarter and six in the fourth quarter), CW (one station in the third quarter and seven the fourth quarter), Univision (five stations in the third quarter), and MyNetworkTV (two stations in the second quarter). We reclassified the results of operations of WLAJ-TV, an ABC station acquired in the second quarter of 2012 and WLWC-TV a CW station acquired in the first quarter of 2012, as discontinued operations as discussed in Note 1. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies and therefore the net time sales of WLAJ-TV and WLWC-TV are not included in the percentages above and are excluded from the number of stations.
(b) We broadcast programming from network affiliations or program service arrangements with CBS (rebroadcasted content from other primary channels within the same markets), The CW, MyNetworkTV, This TV, ME TV, Retro TV, Weather Radar, Weather Nation, Live Well Network,
51
Table of Contents
Antenna TV, Bounce Network, Retro TV, Zuus Country, Azteca, Tele-Romantica, Inmigrante TV, MundoFox, Telemundo and Estrella TV on additional channels through our stations’ second and third digital signals.
Net Broadcast Revenues. Net broadcast revenues increased $296.9 million in 2013 when compared to 2012, of which $326.7 million was related to stations acquired during 2013. The remaining decrease was due to decreases in advertising revenues generated from the political, direct response and school sectors. These decreases were partially offset by an increase in retransmission revenues from multichannel video programming distributors (MVPD) and increases in advertising revenues generated from the automotive, food-grocery/other, and services sectors. Excluding the stations acquired in 2013, automotive, which typically is our largest category, represented 25.1% of net time sales for the year ended December 31, 2013.
Net broadcast revenues increased $272.6 million in 2012 when compared to 2011, of which $164.2 million was related to stations acquired during 2012. Additionally, revenues earned pursuant to the LMA with the Freedom stations during the first quarter of 2012 included $2.2 million for management services performed and $7.8 million of pass-through costs. The remaining increase was due to increases in advertising revenues generated from the political, direct response and beer / wine sectors. These increases were partially offset by decreases in the internet, soft drinks, movies and drugs / cosmetic sectors. Excluding the stations acquired in 2012, automotive, which typically is our largest category, represented 20.3% of net time sales for the year ended December 31, 2012.
Political Revenues. Political revenues, which include time sales from political advertising, decreased by $85.1 million to $11.8 million for 2013 when compared to 2012. Political revenues increased by $88.6 million to $96.9 million for 2012 when compared to 2011. Political revenues are typically higher in election years such as 2012 and 2010. Accordingly, we expect political revenues to increase in 2014 from 2013 levels.
Local Revenues. Excluding political revenues, our local broadcast revenues, which include local times sales, retransmission revenues and other local revenues, were up $311.0 million for 2013 when compared to 2012, of which $250.9 million related to the stations acquired in 2013. The remaining increase is due to an increase in advertising spending particularly in the automotive, services, and grocery/other sectors and an increase in retransmission revenues from MVPDs. These increases were partially offset by a decrease due to a decline in advertising revenues from the restaurants, schools and retail/department stores sectors. Excluding political revenues, our local broadcast revenues, which include local times sales, retransmission revenues and other local revenues, were up $144.8 million for 2012, compared to 2011, of which $112.1 million was related to the stations acquired in 2012. The remaining increase is due to an increase in advertising spending particularly in the automotive and direct response sectors and an increase in retransmission revenues from MVPDs. These increases were partially offset by declines in advertising revenues from the schools, fast food and services sectors and a change in networks for the Super Bowl programming from FOX to NBC as we had 20 FOX stations compared to one NBC station at the time when the Super Bowl aired in February 2012.
National Revenues. Our national broadcast revenues, excluding political revenues, which include national time sales and other national revenues, were up $71.0 million for 2013 when compared to 2012, of which $70.2 million related to the stations acquired in 2013. The remaining increase was due to increases in advertising revenues generated from the automotive, media and restaurants sectors. These increases were partially offset by a decline in advertising revenues in the fast food, other and movie sectors. Excluding political revenues, our national broadcast revenues increased $39.2 million for 2012 when compared to 2011, of which $38.5 million related to the stations acquired in 2012. The remaining increase was due to increases in advertising revenues generated from the direct response and services sectors.
52
Table of Contents
Broadcast Expenses
The following table presents our significant operating expense categories for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 (in millions):
| | | | | | | | Percent Change
(Increase/(Decrease)) | |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | ‘13 vs. ‘12 | | ‘12 vs. ‘11 | |
Station production expenses | | $ | 385.1 | | $ | 255.5 | | $ | 178.6 | | 50.7 | % | 43.1 | % |
Station selling, general and administrative expenses | | $ | 249.7 | | $ | 171.3 | | $ | 123.9 | | 45.8 | % | 38.3 | % |
Amortization of program contract costs and net realizable value adjustments | | $ | 80.9 | | $ | 61.0 | | $ | 52.1 | | 32.6 | % | 17.1 | % |
Corporate general and administrative expenses | | $ | 47.3 | | $ | 28.9 | | $ | 24.8 | | 63.7 | % | 16.5 | % |
Impairment of goodwill, intangible and other assets | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 0.4 | | — | | (100.0 | )% |
Depreciation and amortization expenses | | $ | 133.1 | | $ | 77.5 | | $ | 44.6 | | 71.7 | % | 73.8 | % |
Station production expenses. Station production expenses increased $129.6 million during 2013 compared to 2012, of which $107.2 million related to the stations acquired in 2013 and 2012. The remaining increases for the year were primarily due to an increase in fees pursuant to network affiliation agreements and increased compensation expense, including incentive compensation.
Station production expenses increased $76.9 million during 2012 compared to 2011. This increase was primarily due to an increase in fees pursuant to network affiliation agreements, increased compensation expense (including amounts related to the Four Points and Freedom stations pursuant to the LMAs prior to acquisition, which were pass-through costs), increased promotional advertising expenses and increased rating service fees due to annual scheduled rate increases. Additionally, news profit share expenses increased due to better news performance which resulted in higher payments to our news share partners.
Station selling, general and administrative expenses. Station selling, general and administrative expenses increased $78.4 million during 2013 compared to 2012, of which $75.4 million related to the stations acquired in 2013 and 2012. The remaining increases for the year were primarily due to an increase in compensation expense, including incentive compensation, partially offset by lower national sales commissions.
Station selling, general and administrative expenses increased $47.4 million during 2012 compared to 2011, of which $38.4 million related to the stations acquired in 2012. The remaining increases for the year were primarily due to an increase in national sales commissions and increased compensation expense, including incentive compensation.
Amortization of program contract costs and net realizable value adjustments. The amortization of program contract costs increased $19.9 million during 2013 compared to 2012, of which $14.8 million related to the stations acquired in 2013 and 2012. The remaining increase is due to higher programming costs.
The amortization of program contract costs increased $8.9 million during 2012 compared to 2011. $7.1 million of this increase was due primarily to stations acquired in 2012. The remaining increase is due to higher programming costs.
Corporate general and administrative expenses. See explanation under Corporate and Unallocated Expenses
Impairment of goodwill, intangible and other assets. We completed our annual test of goodwill and broadcast licenses for impairment in fourth quarter 2013, 2012 and 2011. We recorded no impairment in 2013 and 2012. During 2011, we recorded impairments of $0.4 million related to our broadcast licenses.
Depreciation and amortization expenses. Depreciation of property and equipment and amortization of definite-lived intangibles and other assets increased $55.6 million during 2013 compared 2012, of which $57.3 million related to the stations acquired in 2013 and 2012. Depreciation and amortization expenses increased $32.9 million during 2012 compared to 2011. This increase was primarily due to stations being acquired in 2012.
53
Table of Contents
OTHER OPERATING DIVISIONS REVENUE AND EXPENSE
The following table presents our other operating divisions revenue and expenses which is comprised of the following for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 (in millions): Triangle Signs & Services, LLC (Triangle), a sign designer and fabricator; Alarm Funding Associates, LLC. (Alarm Funding), a regional security alarm operating and bulk acquisition company; real estate ventures and other nominal businesses.
| | | | | | | | Percent Change | |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | ‘13 vs. ‘12 | | ‘12 vs. ‘11 | |
Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Triangle | | $ | 26.8 | | $ | 26.5 | | $ | 23.1 | | 1.1 | % | 14.7 | % |
Alarm Funding | | $ | 18.3 | | $ | 16.0 | | $ | 12.8 | | 14.4 | % | 25.0 | % |
Real Estate Ventures | | $ | 7.4 | | $ | 9.3 | | $ | 7.1 | | (20.4 | )% | 31.0 | % |
Other | | $ | 4.3 | | $ | 2.4 | | $ | 1.5 | | 79.2 | % | 60.0 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Expenses: (a) | | | | | | | | | | | |
Triangle | | $ | 24.6 | | $ | 25.9 | | $ | 21.8 | | (5.0 | )% | 18.8 | % |
Alarm Funding | | $ | 9.1 | | $ | 12.9 | | $ | 12.7 | | (29.5 | )% | 1.6 | % |
Real Estate Ventures | | $ | 7.2 | | $ | 12.6 | | $ | 9.6 | | (42.9 | )% | 31.3 | % |
Other | | $ | 7.2 | | $ | 4.6 | | $ | 2.7 | | 56.5 | % | 70.4 | % |
(a) Comprises total expenses of the entity including other operating divisions expenses, depreciation and amortization and applicable other income (expense) items such as interest expense and non-cash stock-based compensation expense related to issuances of subsidiary stock awards.
The year over year increases in Triangle’s revenue and expenses during 2013 compared to 2012 and 2012 compared to 2011 was primarily due to increases in sales volume due to new service contracts. The increases in Alarm Funding’s revenue and expenses during 2013 compared to 2012 and 2012 compared to 2011 were primarily due to the acquisition of new alarm monitoring contracts. Revenues and expenses decreased for our consolidated real estate ventures over the same periods due to a decrease in leasing activity for operating real estate properties and sales of property under development in 2013 compared to 2012. As of December 31, 2013, we held $82.3 million of real estate for development and sale. The increases in revenue and expenses during 2013 compared to 2012 for Other were primarily due to the acquisition of Dielectric, LLC during 2013.
Income (loss) from Equity and Cost Method Investments. As of December 31, 2013 and 2012, the carrying value of our investments in private equity funds and real estate ventures, accounted for under the equity or cost method, was $23.2 million and $71.3 million in 2013 and $27.3 million and $65.9 million in 2012, respectively. Results of our equity and cost method investments in private investment funds and real estate ventures are included in income from equity and cost method investments in our consolidated statements of operations. During 2013, we recorded income of $2.0 million related to certain private investment funds and a loss of $1.4 million related to our real estate ventures. During 2012, we recorded income of $2.2 million related to certain private investment funds and income of $7.4 million related to our real estate ventures, including a $7.9 million gain on the sale of three of our real estate ventures, partially offset by a $0.9 million impairment charge related to one of our real estate ventures. During 2011, we recorded income of $2.3 million related to certain private equity funds and income of $1.0 million related to our real estate ventures, including a $1.1 million gain on sale of one of our real estate ventures.
CORPORATE AND UNALLOCATED EXPENSES
| | | | | | | | Percent Change
(Increase/(Decrease)) | |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | ‘13 vs. ‘12 | | ‘12 vs. ‘11 | |
Corporate general and administrative expenses | | $ | 4.5 | | $ | 2.8 | | $ | 2.4 | | 60.7 | % | 16.7 | % |
Interest expense | | $ | 159.7 | | $ | 125.3 | | $ | 102.4 | | 27.5 | % | 22.4 | % |
Loss from extinguishment of debt | | $ | 58.4 | | $ | 0.3 | | $ | 4.8 | | n/m | | (93.8 | )% |
Income tax provision | | $ | 41.2 | | $ | 67.9 | | $ | 44.8 | | (39.3 | )% | 51.6 | % |
n/m — not meaningful
54
Table of Contents
Corporate general and administrative expenses. We allocate most of our corporate general and administrative expenses to the broadcast segment. The explanation that follows combines corporate general and administrative expenses found in the Broadcast Segment section with the corporate general and administrative expenses found in this section, Corporate and Unallocated Expenses. These results exclude general and administrative costs from our other operating divisions segment which are included in our discussion of expenses in the Other Operating Divisions Segment section.
Combined corporate general and administrative expenses increased to $51.8 million in 2013 from $31.7 million in 2012. This is primarily due to an increase in transaction costs due to our recent acquisitions, an increase in higher health insurance costs, due to increased employee headcount from acquisitions, and higher compensation expense, including incentive compensation.
Combined corporate general and administrative expenses increased to $31.7 million in 2012 from $27.2 million in 2011. This is primarily due to an increase in transaction costs due to our recent acquisitions, an increase in higher health insurance costs and higher employee incentive / performance bonuses.
We expect corporate general and administrative expenses to increase in 2014 compared to 2013.
Interest expense. Interest expense increased in 2013 compared to 2012 primarily due to the issuance of $500 million of 6.125% Notes in the fourth quarter 2012, the incremental borrowings on our Term Loan A and Term Loan B under our Bank Credit Agreement for our acquisitions in 2013, the issuance of $600.0 million of 5.375% Notes in the second quarter of 2013, and the issuance of $350.0 million of 6.375% Notes in the fourth quarter of 2013. Interest expense was partially offset by a decrease due to the redemption of our 9.25% Notes, our 4.875% Notes and our 3.0% Notes in the fourth quarter of 2013.
Interest expense increased in 2012 compared to 2011 primarily due to the incremental borrowings on our Term Loan A and Term Loan B under our Bank Credit Agreement for our acquisitions in 2012, the issuance of $500.0 million of 6.125% notes in the fourth quarter of 2012, as well as financing costs of $6.3 million related to the amendment of our Bank Credit Agreement, which were incurred in 2012. The increase in interest was partially offset by a decrease due to the full extinguishment of our 6.0% Notes in the second quarter of 2011.
We expect interest expense to decrease in 2014 compared to 2013 when excluding the financing of pending acquisitions.
Loss from extinguishment of debt. We recognized a loss on extinguishment of debt of $59.4 million related to the amendments of our Bank Credit Agreement in April and October 2013 and redemption of 9.25% Notes in October 2013, partially offset by a $1.0 million gain on extinguishment from our 3.0% Notes, resulting in a $58.4 loss from extinguishment of debt for the year ended December 31, 2013.
During the year ended December 31, 2012, we drew down on our incremental borrowings under the Bank Credit Agreement and wrote off a portion of our deferred financing costs and debt discount on the Term Loan B, resulting in a loss of $0.3 million from extinguishment of debt. During the year ended December 31, 2011, we amended our Bank Credit Agreement and paid down a portion of our Term Loan B, completed the redemption of all $70.0 million of the remaining 6.0% Notes and repurchased certain of our 8.375% Notes, resulting in a loss of $4.8 million from extinguishment of debt.
Income tax (provision) benefit. The 2013 income tax provision for our pre-tax income from continuing operations (including the effects of the noncontrolling interest) of $103.2 million resulted in an effective tax rate of 40.0%. The 2012 income tax provision for our pre-tax income from continuing operations (including the effects of the noncontrolling interest) of $212.1 million resulted in an effective tax rate of 32.0%. The increase in the effective tax rate from 2012 to 2013 is primarily due to the following items: 1) greater expenses of consolidated VIEs in 2013 that are treated as pass-through entities for income tax purposes; and 2) a 2012 release of valuation allowance of $7.7 million related to certain deferred tax assets of Cunningham, one of our consolidated VIEs, as the weight of all available evidence supports realization of the deferred tax assets. The valuation allowance release determination was based primarily on the sufficiency of forecasted taxable income necessary to utilize NOLs expiring in years 2022 — 2029. This VIE files separate income tax returns. Any resulting tax liabilities are nonrecourse to us and we are not entitled to any benefit resulting from the deferred tax assets of the VIE.
The 2012 income tax provision for our pre-tax income from continuing operations (including the effects of the non-controlling interest) of $212.1 million resulted in an effective tax rate of 32.0%. The 2011 income tax provision for our pre-tax income from continuing operations (including the effects of the non-controlling interest) of $121.0 million resulted in an effective tax rate of 37.0%. The decrease in the effective tax rate from 2011 to 2012 is primarily due to the release of valuation allowance in 2012 of $7.7 million related to certain deferred tax assets of Cunningham, one of our consolidated VIEs, as discussed above.
As of December 31, 2013, we had a net deferred tax liability of $312.8 million as compared to a net deferred tax liability of $235.4 million as of December 31, 2012. The increase primarily relates to an increase in deferred tax liabilities resulting from the 2013 stock acquisitions with greater book basis in intangible and fixed assets.
As of December 31, 2013, we had $16.9 million of gross unrecognized tax benefits. Of this total, $15.6 million (net of federal effect on state tax issues) represents the amount of unrecognized tax benefits that, if recognized, would favorably affect our effective tax rates from
55
Table of Contents
continuing operations. As of December 31, 2012, we had $26.0 million of gross unrecognized tax benefits. Of this total, $15.0 million (net of federal effect on state tax issues) and $6.8 million (net of federal effect on state tax issues) represent the amounts of unrecognized tax benefits that, if recognized, would favorably affect our effective tax rates from continuing operations and discontinued operations, respectively. We recognized $1.2 million and $1.5 million of income tax expense for interest related to uncertain tax positions for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively. See Note 9. Income Taxes in the Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements for further information.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
As of December 31, 2013, we had $280.1 million in cash and cash equivalent balances and net positive working capital of approximately $354.5 million. Cash generated by our operations and borrowing capacity under the Bank Credit Agreement are used as our primary sources of liquidity. As of December 31, 2013, we had no amounts drawn on our Revolving Credit Facility and $154.5 million of borrowing capacity available. We anticipate that existing cash and cash equivalents, cash flow from our operations and borrowing capacity under the Revolving Credit Facility and general uncommitted incremental term loan capacity of $200.0 million under our Bank Credit Agreement will be sufficient to satisfy our debt service obligations, capital expenditure requirements and working capital needs for the next twelve months. We anticipate raising additional funds for our pending acquisitions. For our long-term liquidity needs, in addition to the sources described above, we may rely upon the issuance of long-term debt, the issuance of equity or other instruments convertible into or exchangeable for equity, or the sale of non-core assets. However, there can be no assurance that additional financing or capital or buyers of our non-core assets will be available, or that the terms of any transactions will be acceptable or advantageous to us.
On April 9, 2013, we entered into an amendment and restatement (the Amendment) of our Bank Credit Agreement. Pursuant to the Amendment, we refinanced the existing facility and replaced the existing term loans under the facility with a new $500.0 million term loan A facility (Term Loan A), maturing April 2018 and priced at LIBOR plus 2.25%; and a $400.0 million term loan B facility (Term Loan B), maturing April 2020 and priced at LIBOR plus 2.25% with a LIBOR floor of 0.75%. $445.0 million of the Term Loan A was drawn on a delayed basis in October 2013.
In addition, we replaced our existing revolving line of credit with a new $100.0 million revolving line of credit maturing April 2018 and priced at LIBOR plus 2.25%. The proceeds from the term loans, along with cash on hand, was used to fund acquisitions and for general corporate purposes.
In October 2013, we further amended certain terms of our Bank Credit Agreement. Pursuant to this amendment, we increased the capacity of Term Loan A from $500 million to $700 million and increased the capacity of Term Loan B from $400 million to $650 million through an incremental Term Loan B loan of $250.0 million, which was drawn in October 2013. The incremental Term Loan B of $250.0 million was used to fund fourth quarter acquisitions, the redemption of the 9.25% Notes and for general corporate purposes. We also increased the capacity of our revolving line of credit from $100.0 million to $157.5 million maturing in April 2018. Additional terms of the amendment are as follows:
· We increased our ratio of our First Lien Indebtedness from 3.50 times EBITDA to 3.75 times EBITDA for the period January 1, 2015 through maturity of the agreement.
· We increase our threshold for determining material third-party licensees from 5% to 10%
· Other amended terms provided us with increased television station acquisition capacity, more flexibility under the other restrictive covenants and prepayments of the existing term loans.
In May 2013, we issued 18.0 million shares of Class A Common Stock for net proceeds of $472.9 million. The net proceeds were used to fund acquisitions in the third quarter 2013.
In April 2013, we issued $600.0 million of 5.375% Notes, which bear interest at a rate of 5.375% per annum and mature on April 1, 2021, pursuant to an indenture dated April 2, 2013 (the 5.375% Indenture). The 5.375% Notes were priced at 100% of their par value and interest is payable semi-annually on April 1 and October 1, commencing on October 1, 2013. Prior to April 1, 2016, we may redeem the 5.375% Notes, in whole or in part, at any time or from time to time at a price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the 5.375% Notes plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the redemption date, plus a “make-whole” premium as set forth in the 5.375% Indenture. Beginning on April 1, 2016, we may redeem some or all of the 5.375% Notes at any time or from time to time at a redemption price set forth in the 5.375% Indenture. In addition, on or prior to April 1, 2016, we may redeem up to 35% of the 5.375% Notes using proceeds of certain equity offerings. Upon the sale of certain of our assets or certain changes of control, the holders of the 5.375% Notes may require us to repurchase some or all of the notes. The net proceeds from the offering of the 5.375% Notes were used to pay down outstanding indebtedness under our bank credit facility.
In September 2013, 100% of the outstanding 4.875% Notes, representing aggregate principal of $5.7 million, were converted into 388,632 shares of Class A Common Stock, as permitted under the indenture, resulting in an increase in additional paid-in capital of $7.3
56
Table of Contents
million, net of income taxes.
In October 2013, we issued $350.0 million in senior unsecured notes, which bear interest at a rate of 6.375% Notes per annum and mature on November 1, 2021, pursuant to an indenture dated October 11, 2013 (the 6.375% Indenture). The 6.375% Notes were priced at 100% of their par value and interest is payable semi-annually on May 1 and November 1, commencing on May 1, 2014. Prior to November 1, 2016, we may redeem the 6.375% Notes, in whole or in part, at any time or from time to time at a price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the Notes plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the date of redemption, plus a “make-whole” premium as set forth in the 6.375% Indenture. In addition, on or prior to November 1, 2016, we may redeem up to 35% of the 6.375% Notes using the proceeds of certain equity offerings. Upon the sale of certain of our assets or certain changes of control, the holders of the 6.375% Notes may require us to repurchase some or all of the notes. The proceeds from the offering of the 6.375% Notes were used to partially fund the redemption of the 9.25% Notes, as discussed further below.
Effective October 12, 2013, we redeemed all of the outstanding 9.25% Notes, representing $500.0 million in aggregate principal amount. Upon the redemption, along with the principal, we paid the accrued and unpaid interest and a make whole premium of $25.4 million, for a total of $546.1 million paid to noteholders. We recorded a loss on extinguishment of $43.1 million in the fourth quarter of 2013 related to this redemption.
In October 2013, 100% of the outstanding 3.0% Notes, representing aggregate principal of $5.4 million, were converted and settled fully in cash of $10.5 million, as permitted under the indenture. As the original terms of the indenture included a cash conversion feature, the effective settlement of the liability and equity components were accounted for separately. The redemption of the liability component to resulted in a $1.0 million gain on extinguishment, and the redemption of the equity component was recorded as a reduction in additional paid-in capital, net of taxes.
Sources and Uses of Cash
The following table sets forth our cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 (in millions):
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
Net cash flows from operating activities | | $ | 160.6 | | $ | 237.5 | | $ | 148.5 | |
| | | | | | | |
Cash flows from (used in) investing activities: | | | | | | | |
Acquisition of property and equipment | | $ | (43.4 | ) | $ | (44.0 | ) | $ | (35.8 | ) |
Payments for acquisitions of television stations | | (1,006.1 | ) | (1,135.3 | ) | — | |
Proceeds from the sale of broadcast assets | | 49.7 | | — | | — | |
Payments for acquisitions of assets of other operating divisions | | (4.7 | ) | — | | — | |
Purchase of alarm monitoring contracts | | (23.7 | ) | (12.5 | ) | (8.9 | ) |
(Increase) decrease in restricted cash | | (11.5 | ) | 58.5 | | (53.4 | ) |
Investments in equity and cost method investees | | (10.8 | ) | (24.1 | ) | (11.6 | ) |
Investment in marketable securities | | (11.6 | ) | (1.5 | ) | (4.9 | ) |
Other, net | | 10.9 | | 9.6 | | 2.4 | |
Net cash flows (used in) from investing activities | | $ | (1,051.2 | ) | $ | (1,149.3 | ) | $ | (112.2 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
Cash flows from (used in) financing activities: | | | | | | | |
Proceeds from notes payable, commercial bank financing and capital leases | | $ | 2,278.3 | | $ | 1,247.2 | | $ | 151.7 | |
Repayments of notes payable, commercial bank financing and capital leases | | (1,509.8 | ) | (179.3 | ) | (150.4 | ) |
Proceeds from the sale of Class A Common Stock | | 472.9 | | — | | — | |
Dividends paid on Class A and Class B common stock | | (56.8 | ) | (123.9 | ) | (38.4 | ) |
Payments for deferred financing costs | | (27.7 | ) | (18.7 | ) | (5.5 | ) |
Noncontrolling distributions contributions | | (10.3 | ) | (1.1 | ) | (0.6 | ) |
Other, net | | 1.3 | | (2.5 | ) | (2.1 | ) |
Net cash flows from (used in) financing activities | | $ | 1,147.9 | | $ | 921.7 | | $ | (45.3 | ) |
57
Table of Contents
Operating Activities
Net cash flows from operating activities decreased during the year ended December 31, 2013 compared to the same period in 2012. During 2013, we had higher program payments, higher cash payments to vendors, and higher compensation expenses which are primarily due to our acquisitions since the same period in 2012, partially offset by higher cash receipts from customers.
Net cash flows from operating activities increased during the year ended December 31, 2012 compared to the same period in 2011. During 2012, we received more cash receipts from customers, net of cash payments to vendors, partially offset by higher interest and tax payments and the $25.0 million payments to FOX pursuant to the agreements entered into during the second quarter of 2012.
Investing Activities
Net cash flows used in investing activities decreased during the year ended December 31, 2013 compared to the same period in 2012. This increase is primarily due to $1,006.1 million in payments for acquisitions of television stations during 2013 compared to $1,135.3 million during 2012, the proceeds from sales of certain television stations during 2013, and lower investments in equity and cost investees. This increase was partially offset by higher purchases of alarm monitoring contracts and an increase in restricted cash for pending acquisitions.
Net cash flows used in investing activities increased during the year ended December 31, 2012 compared to the same period in 2011. This increase is due to $1,135.3 million in payments for acquisitions of television stations, additional investment in equity investees, higher capital expenditures and the purchases of alarm monitoring contracts. This increase was partially offset by the use of the restricted cash held in escrow for our acquisitions and distributions received upon sale of three of our equity method investments during 2012.
In 2014, we anticipate incurring higher capital expenditures than incurred in 2013.
Financing Activities
Net cash flows from financing activities increased during the year ended December 31, 2013 compared to the same period in 2012. The increase is primarily due to issuing $600.0 million and $350.0 million of 5.375% and 6.375% Notes, respectively, and $250.0 million net proceeds from our Bank Credit Agreement, $472.9 proceeds received from our offering of Class A common stock, decreases in dividends paid from $1.54 per share during 2012 to $0.60 per share during 2013, and increases in loans by our consolidated variable interest entities. This increase is partially offset by redemption of our 9.375% Notes and increased payments for deferred financing costs.
Net cash flows from financing activities increased during the year ended December 31, 2012 compared to the same period in 2011. During 2012, we drew $530.0 million of incremental term loans to fund the asset acquisitions of both Four Points and Freedom, which closed in January 2012 and April 2012, respectively. We also issued $500.0 million of Senior Unsecured Notes and used the proceeds to fund the acquisitions in the fourth quarter. This was slightly offset by higher stock dividends paid in 2012 totaling $1.54 per share, which included the $1.00 per share special dividend paid in December, versus $0.48 per share in 2011, as well as, $13.2 million more in payments for deferred financing costs related to the incremental borrowings in 2012.
During 2012, our Board of Directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.12 per share in the months of February and May, which were paid in March and June, and $0.15 per share in the months of August and November, which were paid in September and December. A special cash dividend of $1.00 per share was also declared in November 2012, which was paid in December, for total dividend payments of $1.54 per share for the year ended December 31, 2012. During 2013, our Board of Directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.15 per share in the months of February, April, August and November, which were paid in March, June, September and December, respectively, for total dividend payments of $0.60 per share for the year ended December 31, 2013. In February 2014, our Board of Directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.15 per share. Future dividends on our common shares, if any, will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend on several factors including our results of operations, cash requirements and surplus, financial condition, covenant restrictions and other factors that the Board of Directors may deem relevant. The Class A Common Stock and Class B Common Stock holders have the same rights related to dividends. Under our Bank Credit Agreement, in certain circumstances, we may make up to $200.0 million in unrestricted annual cash payments including but not limited to dividends, of which $50.0 million may carry over to the next year.
Contractual Obligations
We have various contractual obligations which are recorded as liabilities in our consolidated financial statements. Other items, such as certain purchase commitments and other executory contracts are not recognized as liabilities in our consolidated financial statements but are required to be disclosed. For example, we are contractually committed to acquire future programming and make certain minimum lease payments for the use of property under operating lease agreements.
The following table reflects a summary of our contractual cash obligations as of December 31, 2013 and the future periods in which
58
Table of Contents
such obligations are expected to be settled in cash (in millions):
CONTRACTUAL OBLIGATIONS RELATED TO CONTINUING OPERATIONS (a)
| | Total | | 2014 | | 2015-2016 | | 2017-2018 | | 2019 and
thereafter (b) | |
Notes payable, capital leases and commercial bank financing (c), (d) | | $ | 3,829.2 | | $ | 155.9 | | $ | 423.7 | | $ | 874.5 | | $ | 2,375.1 | |
Notes and capital leases payable to affiliates (c) | | 32.0 | | 4.5 | | 8.5 | | 6.0 | | 13.0 | |
Operating leases | | 86.2 | | 13.3 | | 22.8 | | 19.2 | | 30.9 | |
Program content (e) | | 736.5 | | 223.6 | | 346.1 | | 158.9 | | 7.9 | |
Programming services (f) | | 101.6 | | 42.9 | | 29.9 | | 19.7 | | 9.1 | |
LMA and outsourcing agreements (g) | | 2.2 | | 0.7 | | 1.2 | | 0.3 | | — | |
Investments and loan commitments (h) | | 17.0 | | 17.0 | | — | | — | | — | |
Other (i) | | 34.5 | | 4.7 | | 6.5 | | 5.6 | | 17.7 | |
Total contractual cash obligations | | $ | 4,839.2 | | $ | 462.6 | | $ | 838.7 | | $ | 1,084.2 | | $ | 2,453.8 | |
(a) Excluded from this table are $16.9 million of accrued unrecognized tax benefits. Due to inherent uncertainty, we cannot make reasonable estimates of the amount and period payments will be made.
(b) Includes a one-year estimate of $8.9 million in payments related to contracts that automatically renew. We have not calculated potential payments for years after 2019.
(c) Includes interest on fixed rate debt and capital leases. Estimated interest on our recourse variable rate debt has been excluded. Recourse variable rate debt represents $1.2 billion of our $3.0 billion total face value of debt as of December 31, 2013.
(d) During 2013 issued $600.0 million and $350.0 million of 5.375% and 6.375% Notes, and $250.0 million net proceeds from our Bank Credit Agreement. Additionally, during 2013, we redeemed $500.0 million of 9.25% Notes, $5.4 million of 3% Notes, and $5.7 million of 4.875% Notes. Also, included in these amounts are $55.6 million of debt of our variable interest entities.
(e) Our Program content includes contractual amounts owed through the expiration date of the underlying agreement for active and future program contracts, network programming and additional advertising inventory in various dayparts. Active program contracts are included in the balance sheet as an asset and liability while future program contracts are excluded until the cost is known, the program is available for its first showing or telecast and the licensee has accepted the program. Industry protocol typically enables us to make payments for program contracts on a three-month lag, which differs from the contractual timing within the table. Network programming agreements may include variable fee components such as subscriber levels, which in certain circumstances have been estimated and reflected in the table.
(f) Includes obligations related to rating service fees, music license fees, market research, weather and news services.
(g) Excluded from the table are estimated amounts due pursuant to LMAs and outsourcing agreements where we consolidate the counterparty. The fees that we are required to pay under these agreements total $6.9 million, $10.9 million, $2.9 million and $4.1 million for the periods 2014, 2015-2016, 2017-2018 and 2019 and thereafter, respectively. Certain station related operating expenses are paid by the licensee and reimbursed by us under the LMA agreements. Certain of these expenses that are in connection with contracts are included in table above.
(h) Commitments to contribute capital or provide loans to Allegiance Capital, LP, Sterling Ventures Partners, LP, Patriot Capital II, LP and Patriot III, LP.
(i) Other includes obligations post-retirement benefits, maintenance and support, other corporate contracts and other long term liabilities.
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
Off balance sheet arrangements as defined by the SEC means any transaction, agreement or other contractual arrangement to which an entity unconsolidated with the registrant is a party, under which the registrant has: obligations under certain guarantees or contracts; retained or contingent interest in assets transferred to an unconsolidated entity or similar arrangements; obligations under certain derivative arrangements; and obligations arising out of a material variable interest in an unconsolidated entity. As of December 31, 2013, we do not have any material off balance sheet arrangements.
59
Table of Contents
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
We are exposed to market risk from changes in interest rates. At times we enter into derivative instruments primarily for the purpose of reducing the impact of changing interest rates on our floating rate debt and to reduce the impact of changing fair market values on our fixed rate debt. See Note 6. Notes Payable and Commercial Bank Financing, in the Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements. As of December 31, 2013, we did not have any outstanding derivative instruments.
We are exposed to risk from the changing interest rates of our variable rate debt, primarily related to our Bank Credit Agreement. For the year ended December 31, 2013, interest expense on our term loans and revolver related to our Bank Credit Agreement was $27.3 million. We estimate that adding 1.0% to respective interest rates would result in an increase in our interest expense of $7.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. We also have $86.3 million of variable rate debt associated with our other operating divisions. We estimate that adding 1.0% to respective interest rates would result in $0.7 million of additional interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2013. Our consolidated VIEs have $55.6 million of variable rate debt associated with the stations that we provide services to pursuant to LMAs and other outsourcing arrangements.. We estimate that adding 1.0% to respective interest rates would an increase interest expense of the VIEs by $0.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2013.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
The financial statements and supplementary data required by this item are filed as exhibits to this report, are listed under Item 15(a)(1) and (2) and are incorporated by reference in this report.
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
There were no changes in and/or disagreements with accountants on accounting and financial disclosure during the year ended December 31, 2013.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures and Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management, under the supervision and with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, evaluated the design and effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures and our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013.
The term “disclosure controls and procedures,” as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act, means controls and other procedures of a company that are designed to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to the our management, including its principal executive and principal financial officers, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. Management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving their objectives and management necessarily applies its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures.
The term “internal control over financial reporting,” as defined in Rules 13a-15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act, means a process designed by, or under the supervision of our Chief Executive and Chief Financial Officers and effected by our Board of Directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and includes those policies and procedures that:
· pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of our assets;
· provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP and that our receipts and expenditures are being made in accordance with authorizations of
60
Table of Contents
management or our Board of Directors; and
· provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of our assets that could have a material adverse effect on our financial statements.
Assessment of Effectiveness of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Based on the evaluation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2013, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that, as of such date, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective at the reasonable assurance level.
Report of Management on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, we assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013 based on the criteria set forth in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (1992 framework) (COSO). Based on our assessment, management has concluded that, as of December 31, 2013, our internal control over financial reporting was effective based on those criteria.
Management has excluded the assets, liabilities and operations of the television stations acquired from Cox Media Group LLC, Fisher Communications, Barrington Broadcasting LLC, TTBG LLC as well as WUTB-TV, KDBC-TV, KENV-TV, KRNV-TV, WPFO-TV from its assessment of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013 because these television stations were acquired by the Company in a purchase business combination during 2013. These assets acquired represent 7% of total assets as of December 31, 2013 and 11% of total revenues for the year ended December 31, 2013.
The effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013 has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report which is included herein.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There have been no changes in our internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act) during the quarter ended December 31, 2013, that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Limitations on the Effectiveness of Controls
Management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, do not expect that our disclosure controls and procedures or our internal control over financial reporting will prevent all errors and all fraud. A control system, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met. Further, the design of a control system must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints and the benefits of controls must be considered relative to their costs. Because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, within our company have been detected. These inherent limitations include the realities that judgments in decision-making can be faulty and that breakdowns can occur because of simple error or mistake. Additionally, controls can be circumvented by the individual acts of some persons, by collusion of two or more people, or by management’s override of the control. The design of any system of controls also is based in part upon certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions; over time, controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate. Because of the inherent limitations in a cost-effective control system, misstatements due to error or fraud may occur and not be detected.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
None.
61
Table of Contents
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
The information required by this Item will be included in our Proxy Statement for the 2014 Annual Meeting of shareholders under the captions, “Directors, Executive Officers and Key Employees,” “Section 16(A) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance,” “Code of business Conduct and Ethics” and “Corporate Governance,” which will be filed with the SEC no later than 120 days after the close of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2013 and is incorporated by reference in this report.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The information required by this Item will be included in our Proxy Statement for the 2014 Annual Meeting of shareholders under the captions, “Compensation Discussion and Analysis”, “Director Compensation for 2013,” “Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation” and “Compensation Committee Report,” which will be filed with the SEC no later than 120 days after the close of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2013 and is incorporated by reference in this report.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
The information required by this Item will be included in our Proxy Statement for the 2014 Annual Meeting of shareholders under the caption, “Security Ownership Of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management,” which will be filed with the SEC no later than 120 days after the close of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2013 and is incorporated by reference in this report.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
The information required by this Item will be included in our Proxy Statement for the 2014 Annual Meeting of shareholders under the captions, “Related Person Transactions” and “Director Independence,” which will be filed with the SEC no later than 120 days after the close of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2013 and is incorporated by reference in this report.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
The information required by this Item will be included in our Proxy Statement for the 2014 Annual Meeting of shareholders under the caption, “Disclosure of Fees Charged by Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm,” which will be filed with the SEC no later than 120 days after the close of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2013 and is incorporated by reference in this report.
62
Table of Contents
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
(a) (1) Financial Statements
The following financial statements required by this item are submitted in a separate section beginning on page F-1 of this report.
Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. Financial Statements: | | Page: |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | | F-2 |
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 | | F-3 |
Consolidated Statements of Operations for the Years Ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 | | F-4 |
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the Years Ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 | | F-5 |
Consolidated Statements of Equity (Deficit) for the Years Ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 | | F-6 |
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 | | F-9 |
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | | F-10 |
(a) (2) Financial Statements Schedules
All schedules are omitted because they are not applicable or the required information is shown in the Financial Statements or the accompanying notes.
(a) (3) Exhibits
The following exhibits are filed with this report:
EXHIBIT NO. | | EXHIBIT DESCRIPTION |
2.1 | | Purchase Agreement, dated as of July 28, 2013, among Barbara B. Allbritton, Robert L. Allbritton, The Estate of Joe L. Allbritton, Barbara B. Allbritton 2008 Marital Trust, Robert Lewis Allbritton 1996 Trust, Allholdco, Inc. and Sinclair Television Group, Inc., with respect to the acquisition of Perpetual Corporation and Charleston Television, LLC. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Current Report on Form 10-Q filed on November 12, 2013.) |
3.1 | | Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 1998). |
3.2 | | Amended By-Laws of Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. as further amended by the Second Amendment to the Amended By-Laws of Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc., dated March 3, 2009. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed March 6, 2009). |
4.1 | | Indenture, dated as of May 20, 2003, between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and Wachovia Bank, National Association. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-4 (333-107522) filed on July 31, 2003). |
4.2 | | Senior Indenture, dated as of May 10, 2007, between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed on May 11, 2007). |
4.3 | | First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of May 10, 2007, between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed on May 11, 2007). |
4.4 | | Indenture, dated as of October 29, 2009, among Sinclair Television Group, Inc., the guarantors named therein and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee and collateral agent. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed on October 29, 2009). |
4.5 | | Indenture, dated as of October 4, 2010, by and among Sinclair Television Group, Inc., the guarantors identified therein and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2010). |
4.6 | | Indenture, dated as of October 12, 2012, by and among Sinclair Television Group, Inc., the guarantors identified therein and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed on October 17, 2012). |
4.7 | | Indenture, dated as of April 2, 2013, by and among Sinclair Television Group, Inc., the guarantors identified therein and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed on April 4, 2013). |
63
Table of Contents
4.8 | | Indenture, dated as of October 11, 2013, by and among Sinclair Television Group, Inc., the guarantors identified therein and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed on October 17, 2013). |
10.1 | | Common Non-Voting Capital Stock Option between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and William Richard Schmidt, as trustee. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 No. 33-90682). |
10.2 | | Common Non-Voting Capital Stock Option between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and C. Victoria Woodward, as trustee. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 No. 33-90682). |
10.3 | | Common Non-Voting Capital Stock Option between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and Dyson Ehrhardt, as trustee. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 No. 33-90682). |
10.4 | | Common Non-Voting Capital Stock Option between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and Mark Knobloch, as trustee. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 No. 33-90682). |
10.5* | | First Amendment to Incentive Stock Option Plan for Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc., adopted April 10, 1996. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K/A for the year ended December 31, 1996). |
10.6* | | Second Amendment to Incentive Stock Option Plan for Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc., adopted May 31, 1996. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K/A for the year ended December 31, 1996). |
10.7* | | 1996 Long-Term Incentive Plan for Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K/A for the year ended December 31, 1996). |
10.8* | | First Amendment to 1996 Long-Term Incentive Plan for Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A for the year ended December 31, 1998). |
10.9* | | Employment Agreement by and between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and Frederick G. Smith, dated June 12, 1998. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 1998). |
10.10* | | Employment Agreement by and between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and J. Duncan Smith, dated June 12, 1998. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 1998). |
10.11* | | Employment Agreement by and between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and Lucy Rutishauser dated March 19, 2001. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K/A filed on April 29, 2005). |
10.12 | | Amendment No. 2, dated as of July 1, 2005 and effective July 1, 2005, by and between Cunningham Communications, Inc. (“Lessor”) and Sinclair Communications, LLC, as successor by merger of Chesapeake Television, Inc. (“Lessee”) to the Lease Agreement (the “Agreement”) between Lessor and Lessee, effective as of July 1, 1987, as amended July 1, 1997. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed on July 1, 2005). |
10.13* | | Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2006). |
10.14* | | Stock Appreciation Right Agreement between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and David D. Smith dated April 2, 2007. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2007). |
10.15 | | Agreement of Lease dated as of March 28, 2008 by and between Beaver Dam Limited Liability Company and Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed on April 3, 2008). |
10.16 | | Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of October 29, 2009, by and among Sinclair Television Group, Inc., JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A and the lenders party thereto. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2009). |
10.17 | | Amended and restated lease dated as of February 8, 2010 between Gerstell Development Limited Partnership and Sinclair Media I, Inc. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2009). |
10.18 | | Amended and restated lease dated as of February 8, 2010 between Cunningham Communications, Inc. and Sinclair Communications, LLC. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2009). |
10.19 | | Amended and restated lease dated as of February 8, 2010 between Keyser Investment Group, Inc. and Sinclair Communications, LLC. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2009). |
10.20 | | Amended and restated lease dated as of February 8, 2010 between Keyser Investment Group, Inc. and Sinclair Communications, LLC. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2009). |
10.21 | | Amendment No. 1 to the Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated August 19, 2010, by and |
64
Table of Contents
| | among Sinclair Television Group, Inc., the guarantors party thereto, JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A as administrative agent, and the lenders party thereto. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2010). |
10.22 | | Second Amendment to the Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of March 15, 2011, by and among Sinclair Television Group, Inc., JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A and the lenders party thereto. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed on March 16, 2011). |
10.23* | | Stock Appreciation Right Agreement, between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and David D. Smith dated March 22, 2011. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010). |
10.24 | | Asset Purchase Agreement dated September 8, 2011 between Four Points Media Group LLC and Sinclair Television Group, Inc. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2011). |
10.25 | | Asset Purchase Agreement dated November 1, 2011, between Freedom Communications Holdings, Inc. and Sinclair Television Group, Inc. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011). |
10.26* | | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement by and between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and David B. Amy, dated November 11, 2011. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011). |
10.27* | | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement by and between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and Barry M. Faber, dated November 11, 2011. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011). |
10.28* | | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement by and between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and Steven M. Marks, dated November 14, 2011. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011). |
10.29 | | Third Amendment to the Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of December 16, 2011, by and among Sinclair Television Group, Inc., JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A. and the lenders party thereto. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed on December 19, 2011). |
10.30* | | Stock Appreciation Right Agreement, between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and David D. Smith dated March 9, 2012. (Incorporated by reference form Registrant’s Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2012) |
10.31 | | Option Agreement dated May 14, 2012 between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and Fox Television Stations, Inc. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2012). |
10.32 | | Asset Purchase Agreement dated July 19, 2012 between Newport Television LLC, Newport Television License LLC and Sinclair Television Group. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2012.) |
10.33 | | Fourth Amendment to the Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of September 20, 2012, by and among Sinclair Television Group, Inc., the guarantors party thereto, JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and the lenders party thereto. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed on September 26, 2012). |
10.34 | | Amended and restated lease dated January 1, 2013 between Keyser Investment Group, Inc. and Sinclair Communications LLC. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K filed on March 12, 2014). |
10.35* | | Stock Appreciation Right Agreement, between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and David D. Smith dated February 5, 2013. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K filed on March 12, 2014). |
10.36* | | Employment Agreement for Steven J. Pruett, Chief Operating Officer. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed on April 3, 2008). |
10.37 | | Fifth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of April 9, 2013, by and among Sinclair Television Group, Inc., the guarantors party thereto, JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and the lenders party thereto. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 12, 2013.) |
10.38 | | Second Amendment to the Fifth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of October 23, 2013, by and among Sinclair Television Group, Inc., the guarantors party thereto, JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and the lenders party thereto. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 29, 2013.) |
10.39* | | Amendment to the 1996 Long-Term Incentive Plan of Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc., by and among Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc |
10.40* | | Stock Appreciation Right Agreement, between Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and David D. Smith dated February 11, 2014. |
65
Table of Contents
12 | | Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges. |
21 | | Subsidiaries of the Registrant. |
23 | | Consent of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. |
24 | | Power of Attorney; included above registrants signatures of this Form 10-K. |
31.1 | | Certification by David D. Smith, as Chief Executive Officer of Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc., pursuant to § 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (15 U.S.C. § 7241). |
31.2 | | Certification by David B. Amy, as Chief Financial Officer of Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc., pursuant to § 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (15 U.S.C. § 7241). |
32.1 | | Certification by David D. Smith, as Chief Executive Officer of Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc., pursuant to § 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (18 U.S.C. § 1350). |
32.2 | | Certification by David B. Amy, as Chief Financial Officer of Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc., pursuant to § 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (18 U.S.C. § 1350). |
99 | | Stockholders’ Agreement dated April 19, 2005 by and among the Smith Brothers. (Incorporated by reference from Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed on April 26, 2005). |
101.INS | | XBRL Instance Document |
101.SCH | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema |
101.CAL | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase |
101.LAB | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase |
101.PRE | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase |
101.DEF | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase |
* Management contracts and compensatory plans or arrangements required to be filed as an exhibit pursuant to Item 15(b) of Form 10-K.
(b) Exhibits
The exhibits required by this Item are listed under Item 15 (a) (3).
66
Table of Contents
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report on Form 10-K to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized on this 3rd day of March 2014.
| SINCLAIR BROADCAST GROUP, INC. |
| | |
| By: | /s/ David D. Smith |
| | David D. Smith |
| | Chief Executive Officer |
POWER OF ATTORNEY
KNOW ALL MEN BY THESE PRESENTS, that each person whose signature appears below under the heading “Signature” constitutes and appoints David B. Amy as his true and lawful attorney-in-fact each acting alone, with full power of substitution and resubstitution, for him and in his name, place and stead in any and all capacities to sign any or all amendments to this 10-K and to file the same, with all exhibits thereto, and other documents in connection therewith, with the SEC, granting unto said attorney-in-fact full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary to be done in and about the premises, as fully for all intents and purposes as he might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorney-in-fact, or their substitutes, each acting alone, may lawfully do or cause to be done in virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Signature | | Title | | Date |
| | | | |
/s/ David D. Smith | | Chairman of the Board, President and | | |
David D. Smith | | Chief Executive Officer | | March 3, 2014 |
| | | | |
/s/ David B. Amy | | Executive Vice President and | | |
David B. Amy | | Chief Financial Officer | | March 3, 2014 |
| | | | |
/s/ David R. Bochenek | | Senior Vice President and | | |
David R. Bochenek | | Chief Accounting Officer | | March 3, 2014 |
| | | | |
/s/ Frederick G. Smith | | | | |
Frederick G. Smith | | Director | | March 3, 2014 |
| | | | |
/s/ J. Duncan Smith | | | | |
J. Duncan Smith | | Director | | March 3, 2014 |
| | | | |
/s/ Robert E. Smith | | | | |
Robert E. Smith | | Director | | March 3, 2014 |
| | | | |
/s/ Lawrence E. McCanna | | | | |
Lawrence E. McCanna | | Director | | March 3, 2014 |
| | | | |
/s/ Daniel C. Keith | | | | |
Daniel C. Keith | | Director | | March 3, 2014 |
| | | | |
/s/ Martin R. Leader | | | | |
Martin R. Leader | | Director | | March 3, 2014 |
67
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc.
In our opinion, the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and the related consolidated statements of operations, of equity (deficit), of comprehensive income, and of cash flows present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. and its subsidiaries (the Company) at December 31, 2013 and December 31, 2012, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2013 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the Report of Management on Internal Control over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A. Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements and on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our integrated audits. We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
The operations of the television stations acquired during 2013 from Cox Media Group LLC, Fisher Communications Inc, Barrington Broadcasting LLC and TTBG LLC as well as the operations of WUTB-TV, KDBC-TV, KENV-TV, KRNV-TV and WPFO-TV were excluded from Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A and our audit of internal control over financial reporting represent 7% of total assets and 11% of total revenues, respectively, of the related consolidated financial statement amounts as of and for the year ended December 31, 2013.
/s/PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
Baltimore, Maryland
March 3, 2014
F-2
Table of Contents
SINCLAIR BROADCAST GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| | As of December 31, | |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | |
ASSETS | | | | | |
CURRENT ASSETS: | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 280,104 | | $ | 22,865 | |
Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $3,379 and $3,091, respectively | | 308,974 | | 183,480 | |
Affiliate receivable | | 182 | | 416 | |
Current portion of program contract costs | | 74,324 | | 56,581 | |
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | 30,599 | | 7,404 | |
Assets held for sale | | — | | 30,357 | |
Deferred barter costs | | 3,688 | | 3,345 | |
Total current assets | | 697,871 | | 304,448 | |
| | | | | |
PROGRAM CONTRACT COSTS, less current portion | | 24,708 | | 12,767 | |
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, net | | 596,071 | | 439,713 | |
RESTRICTED CASH | | 11,747 | | 225 | |
GOODWILL | | 1,380,082 | | 1,074,032 | |
BROADCAST LICENSES | | 101,029 | | 85,122 | |
DEFINITE-LIVED INTANGIBLE ASSETS, net | | 1,127,755 | | 623,406 | |
OTHER ASSETS | | 208,209 | | 189,984 | |
Total assets (a) | | $ | 4,147,472 | | $ | 2,729,697 | |
| | | | | |
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY (DEFICIT) | | | | | |
CURRENT LIABILITIES: | | | | | |
Accounts payable | | $ | 13,989 | | $ | 10,086 | |
Accrued liabilities | | 182,185 | | 143,731 | |
Income taxes payable | | 2,504 | | 9,939 | |
Current portion of notes payable, capital leases and commercial bank financing | | 46,346 | | 47,622 | |
Current portion of notes payable and capital leases payable to affiliates | | 2,367 | | 1,704 | |
Current portion of program contracts payable | | 90,933 | | 88,015 | |
Liabilities held for sale | | — | | 2,397 | |
Deferred barter revenues | | 3,319 | | 3,499 | |
Deferred tax liabilities | | 1,738 | | 607 | |
Total current liabilities | | 343,381 | | 307,600 | |
| | | | | |
LONG-TERM LIABILITIES: | | | | | |
Notes payable, capital leases and commercial bank financing, less current portion | | 2,966,402 | | 2,210,866 | |
Notes payable and capital leases to affiliates, less current portion | | 18,925 | | 13,187 | |
Program contracts payable, less current portion | | 34,681 | | 16,341 | |
Deferred tax liabilities | | 311,041 | | 233,465 | |
Other long-term liabilities | | 67,338 | | 48,291 | |
Total liabilities (a) | | 3,741,768 | | 2,829,750 | |
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES (See Note 10) | | | | | |
EQUITY (DEFICIT): | | | | | |
SINCLAIR BROADCAST GROUP SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT): | | | | | |
Class A Common Stock, $.01 par value, 500,000,000 shares authorized, 74,145,569 and 52,332,012 shares issued and outstanding, respectively | | 741 | | 523 | |
Class B Common Stock, $.01 par value, 140,000,000 shares authorized, 26,028,357 and 28,933,859 shares issued and outstanding, respectively, convertible into Class A Common Stock | | 260 | | 289 | |
Additional paid-in capital | | 1,094,918 | | 600,928 | |
Accumulated deficit | | (696,996 | ) | (713,697 | ) |
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | | (2,553 | ) | (4,993 | ) |
Total Sinclair Broadcast Group shareholders’ deficit | | 396,370 | | (116,950 | ) |
Noncontrolling interests | | 9,334 | | 16,897 | |
Total equity (deficit) | | 405,704 | | (100,053 | ) |
Total liabilities and equity (deficit) | | $ | 4,147,472 | | $ | 2,729,697 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
(a) Our consolidated total assets as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 include total assets of variable interest entities (VIEs) of $194.1 million and $107.9 million, respectively, which can only be used to settle the obligations of the VIEs. Our consolidated total liabilities as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 include total liabilities of the VIEs of $31.6 million and $7.9 million, respectively, for which the creditors of the VIEs have no recourse to us. See Note 1: Nature of Operations and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies.
F-3
Table of Contents
SINCLAIR BROADCAST GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2013, 2012 AND 2011
(In thousands, except per share data)
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
REVENUES: | | | | | | | |
Station broadcast revenues, net of agency commissions | | $ | 1,217,504 | | $ | 920,593 | | $ | 648,002 | |
Revenues realized from station barter arrangements | | 88,680 | | 86,905 | | 72,773 | |
Other operating divisions revenues | | 56,947 | | 54,181 | | 44,513 | |
Total revenues | | 1,363,131 | | 1,061,679 | | 765,288 | |
| | | | | | | |
OPERATING EXPENSES: | | | | | | | |
Station production expenses | | 385,104 | | 255,556 | | 178,612 | |
Station selling, general and administrative expenses | | 249,732 | | 171,279 | | 123,938 | |
Expenses recognized from station barter arrangements | | 77,349 | | 79,834 | | 65,742 | |
Amortization of program contract costs and net realizable value adjustments | | 80,925 | | 60,990 | | 52,079 | |
Other operating divisions expenses | | 48,109 | | 46,179 | | 39,486 | |
Depreciation of property and equipment | | 70,554 | | 47,073 | | 32,874 | |
Corporate general and administrative expenses | | 53,126 | | 33,391 | | 28,310 | |
Amortization of definite-lived intangible and other assets | | 70,820 | | 38,099 | | 18,229 | |
Loss (gain) on asset dispositions | | 3,392 | | (7 | ) | (18 | ) |
Impairment of goodwill, intangible and other assets | | — | | — | | 398 | |
Total operating expenses | | 1,039,111 | | 732,394 | | 539,650 | |
Operating income | | 324,020 | | 329,285 | | 225,638 | |
| | | | | | | |
OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE): | | | | | | | |
Interest expense and amortization of debt discount and deferred financing costs | | (162,937 | ) | (128,553 | ) | (106,128 | ) |
Loss from extinguishment of debt | | (58,421 | ) | (335 | ) | (4,847 | ) |
Income (loss) from equity and cost method investments | | 621 | | 9,670 | | 3,269 | |
Gain on insurance settlement | | 199 | | 47 | | 1,742 | |
Other income (loss), net | | 2,026 | | 2,226 | | 1,699 | |
Total other expense | | (218,512 | ) | (116,945 | ) | (104,265 | ) |
Income from continuing operations before income taxes | | 105,508 | | 212,340 | | 121,373 | |
INCOME TAX PROVISION | | (41,249 | ) | (67,852 | ) | (44,785 | ) |
Income from continuing operations | | 64,259 | | 144,488 | | 76,588 | |
DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS: | | | | | | | |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations, includes income tax benefit (provision) of $10,806, ($663) and ($477), respectively | | 11,558 | | 465 | | (411 | ) |
NET INCOME | | 75,817 | | 144,953 | | 76,177 | |
Net (income) attributable to the noncontrolling interests | | (2,349 | ) | (287 | ) | (379 | ) |
NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO SINCLAIR BROADCAST GROUP | | $ | 73,468 | | $ | 144,666 | | $ | 75,798 | |
Dividends declared per share | | $ | 0.60 | | $ | 1.54 | | $ | 0.48 | |
EARNINGS PER COMMON SHARE ATTRIBUTABLE TO SINCLAIR BROADCAST GROUP: | | | | | | | |
Basic earnings per share from continuing operations | | $ | 0.66 | | $ | 1.78 | | $ | 0.95 | |
Basic earnings per share | | $ | 0.79 | | $ | 1.79 | | $ | 0.94 | |
Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations | | $ | 0.66 | | $ | 1.78 | | $ | 0.95 | |
Diluted earnings per share | | $ | 0.78 | | $ | 1.78 | | $ | 0.94 | |
Weighted average common shares outstanding | | 93,207 | | 81,020 | | 80,217 | |
Weighted average common and common equivalent shares outstanding | | 93,845 | | 81,310 | | 80,532 | |
| | | | | | | |
AMOUNTS ATTRIBUTABLE TO SINCLAIR BROADCAST GROUP COMMON SHAREHOLDERS: | | | | | | | |
Income from continuing operations, net of tax | | $ | 61,910 | | $ | 144,201 | | $ | 76,209 | |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax | | 11,558 | | 465 | | (411 | ) |
Net income | | $ | 73,468 | | $ | 144,666 | | $ | 75,798 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-4
Table of Contents
SINCLAIR BROADCAST GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2013, 2012 AND 2011
(In thousands)
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
| | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 75,817 | | $ | 144,953 | | $ | 76,177 | |
Amortization of net periodic pension benefit costs, net of taxes | | (392 | ) | (145 | ) | (934 | ) |
Adjustments to pension obligations, net of taxes | | 2,571 | | — | | — | |
Unrealized gain on investments, net of taxes | | 261 | | — | | — | |
Comprehensive income | | 78,257 | | 144,808 | | 75,243 | |
Comprehensive (income) loss attributable to the noncontrolling interests | | (2,349 | ) | (287 | ) | (379 | ) |
Comprehensive income attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 75,908 | | $ | 144,521 | | $ | 74,864 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
F-5
Table of Contents
SINCLAIR BROADCAST GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EQUITY (DEFICIT)
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2013, 2012 AND 2011
(In thousands)
| | Sinclair Broadcast Group Shareholders | | | | | |
| | Class A
Common Stock | | Class B
Common Stock | | Additional
Paid-In | | Accumulated | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive | | Noncontrolling | | Total Equity | |
| | Shares | | Values | | Shares | | Values | | Capital | | Deficit | | Loss | | Interests | | (Deficit) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
BALANCE, December 31, 2010 | | 50,284,052 | | $ | 503 | | 30,083,819 | | $ | 301 | | $ | 609,640 | | $ | (771,953 | ) | $ | (3,914 | ) | $ | 8,341 | | $ | (157,082 | ) |
Dividends declared on Class A and Class B Common Stock | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (38,356 | ) | — | | — | | (38,356 | ) |
Class A Common Stock issued pursuant to employee benefit plans | | 586,759 | | 5 | | — | | — | | 5,826 | | — | | — | | — | | 5,831 | |
Class B Common Stock converted into Class A Common Stock | | 1,149,960 | | 12 | | (1,149,960 | ) | (12 | ) | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
Class A Common Stock sold by variable interest entity | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 1,808 | | — | | — | | — | | 1,808 | |
6% Notes converted into Class A Common Stock | | 1,315 | | — | | — | | — | | 30 | | — | | — | | — | | 30 | |
Tax benefit on share based awards | | — | | | | — | | — | | 734 | | — | | — | | — | | 734 | |
Distributions to noncontrolling interests | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (270 | ) | (270 | ) |
Issuance of subsidiary share awards | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 3,201 | | 3,201 | |
Purchase of subsidiary shares from noncontrolling interests | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (663 | ) | — | | — | | (1,838 | ) | (2,501 | ) |
Other comprehensive income | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (934 | ) | — | | (934 | ) |
Net income | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 75,798 | | — | | 379 | | 76,177 | |
BALANCE, December 31, 2011 | | 52,022,086 | | $ | 520 | | 28,933,859 | | $ | 289 | | $ | 617,375 | | $ | (734,511 | ) | $ | (4,848 | ) | $ | 9,813 | | $ | (111,362 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-6
Table of Contents
SINCLAIR BROADCAST GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EQUITY (DEFICIT)
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2013, 2012 AND 2011
(In thousands)
| | Sinclair Broadcast Group Shareholders | | | | | |
| | Class A
Common Stock | | Class B
Common Stock | | Additional
Paid-In | | Accumulated | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive | | Noncontrolling | | Total Equity | |
| | Shares | | Values | | Shares | | Values | | Capital | | Deficit | | Loss | | Interests | | (Deficit) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
BALANCE, December 31, 2011 | | 52,022,086 | | $ | 520 | | 28,933,859 | | $ | 289 | | $ | 617,375 | | $ | (734,511 | ) | $ | (4,848 | ) | $ | 9,813 | | $ | (111,362 | ) |
Dividends declared on Class A and Class B Common Stock | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (123,852 | ) | — | | — | | (123,852 | ) |
Class A Common Stock issued pursuant to employee benefit plans | | 309,926 | | 3 | | — | | — | | 5,102 | | — | | — | | — | | 5,105 | |
Purchase of assets from entity under common control | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (23,638 | ) | — | | — | | — | | (23,638 | ) |
Tax benefit on share based awards | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 271 | | — | | — | | — | | 271 | |
Distributions to noncontrolling interests | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (1,142 | ) | (1,142 | ) |
Issuance of subsidiary share awards | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 707 | | 707 | |
Consolidation of variable interest entity | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 9,050 | | 9,050 | |
Purchase of subsidiary shares from noncontrolling interests | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 1,818 | | — | | — | | (1,818 | ) | — | |
Other comprehensive income | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (145 | ) | — | | (145 | ) |
Net income | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 144,666 | | — | | 287 | | 144,953 | |
BALANCE, December 31, 2012 | | 52,332,012 | | $ | 523 | | 28,933,859 | | $ | 289 | | $ | 600,928 | | $ | (713,697 | ) | $ | (4,993 | ) | $ | 16,897 | | $ | (100,053 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-7
Table of Contents
SINCLAIR BROADCAST GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EQUITY (DEFICIT)
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2013, 2012 AND 2011
(In thousands)
| | Sinclair Broadcast Group Shareholders | | | | | |
| | Class A
Common Stock | | Class B
Common Stock | | Additional
Paid-In | | Accumulated | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive | | Noncontrolling | | Total Equity | |
| | Shares | | Values | | Shares | | Values | | Capital | | Deficit | | Loss | | Interests | | (Deficit) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
BALANCE, December 31, 2012 | | 52,332,012 | | $ | 523 | | 28,933,859 | | $ | 289 | | $ | 600,928 | | $ | (713,697 | ) | $ | (4,993 | ) | $ | 16,897 | | $ | (100,053 | ) |
Dividends declared on Class A and Class B Common Stock | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (56,767 | ) | — | | — | | (56,767 | ) |
Issuance of common stock, net of issuance costs | | 18,000,000 | | 180 | | — | | — | | 472,733 | | — | | — | | — | | 472,913 | |
Class B Common Stock converted into Class A Common Stock | | 2,905,502 | | 29 | | (2,905,502 | ) | (29 | ) | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
Redemption of 3% Convertible Debentures, net of taxes | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (5,100 | ) | — | | — | | — | | (5,100 | ) |
4.875% Convertible Debentures converted into Class A Common Stock, net of taxes | | 338,632 | | 3 | | — | | — | | 8,599 | | — | | — | | — | | 8,602 | |
Class A Common Stock issued pursuant to employee benefit plans | | 569,423 | | 6 | | — | | — | | 10,229 | | — | | — | | — | | 10,235 | |
Tax benefit on share based awards | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 521 | | — | | — | | — | | 521 | |
Distributions to noncontrolling interests | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (10,256 | ) | (10,256 | ) |
Issuance of subsidiary share awards | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 344 | | 344 | |
Class A Common Stock sold by variable interest entity, net of taxes | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 7,008 | | — | | — | | — | | 7,008 | |
Other comprehensive income | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 2,440 | | — | | 2,440 | |
Net income | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 73,468 | | — | | 2,349 | | 75,817 | |
BALANCE, December 31, 2013 | | 74,145,569 | | $ | 741 | | 26,028,357 | | $ | 260 | | $ | 1,094,918 | | $ | (696,996 | ) | $ | (2,553 | ) | $ | 9,334 | | $ | 405,704 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-8
Table of Contents
SINCLAIR BROADCAST GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2013, 2012 AND 2011
(In thousands)
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 75,817 | | $ | 144,953 | | $ | 76,177 | |
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | | | |
Depreciation of property and equipment | | 70,554 | | 48,871 | | 33,153 | |
Impairment of goodwill, intangible and other assets | | — | | — | | 398 | |
Amortization of definite-lived intangible assets | | 70,820 | | 38,671 | | 18,229 | |
Amortization of program contract costs and net realizable value adjustments | | 80,925 | | 61,943 | | 52,079 | |
Loss on extinguishment of debt, non-cash portion | | 33,049 | | 335 | | 4,985 | |
Deferred tax provision | | 22,518 | | 8,313 | | 43,972 | |
Changes in assets and liabilities, net of effects of acquisitions and dispositions: | | | | | | | |
(Increase) in accounts receivable, net | | (90,635 | ) | (23,225 | ) | (11,616 | ) |
Decrease in income taxes receivable | | — | | — | | 74 | |
Increase in prepaid expenses and other current assets | | 8,295 | | (8,360 | ) | (10,449 | ) |
Increase in other assets | | (3,686 | ) | (23,200 | ) | (1,247 | ) |
Increase in accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | 7,954 | | 35,885 | | 8,878 | |
(Decrease) increase in income taxes payable | | (4,937 | ) | 9,150 | | (780 | ) |
(Decrease) increase in other long-term liabilities | | (16,178 | ) | (3,941 | ) | 913 | |
Payments on program contracts payable | | (90,080 | ) | (70,061 | ) | (67,319 | ) |
Original debt issuance discount paid | | (23,766 | ) | — | | (13,785 | ) |
Other, net | | 19,927 | | 18,141 | | 14,851 | |
Net cash flows from operating activities | | 160,577 | | 237,475 | | 148,513 | |
CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | | | |
Acquisition of property and equipment | | (43,388 | ) | (43,986 | ) | (35,835 | ) |
Payments for acquisitions of television stations | | (1,006,144 | ) | (1,135,348 | ) | — | |
Proceeds from the sale of broadcast assets | | 49,738 | | — | | — | |
Payments for acquisitions of assets of other operating divisions | | (4,650 | ) | — | | (3,072 | ) |
Purchase of alarm monitoring contracts | | (23,721 | ) | (12,454 | ) | (8,850 | ) |
(Increase) decrease in restricted cash | | (11,522 | ) | 58,501 | | (53,445 | ) |
Distributions from equity and cost method investees | | 5,258 | | 9,590 | | 3,798 | |
Investments in equity and cost method investees | | (10,767 | ) | (24,052 | ) | (11,577 | ) |
Investment in marketable securities | | (11,604 | ) | (1,493 | ) | (4,911 | ) |
Other, net | | 5,559 | | (42 | ) | 1,644 | |
Net cash flows (used in) from investing activities | | (1,051,241 | ) | (1,149,284 | ) | (112,248 | ) |
CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | | | |
Proceeds from notes payable, commercial bank financing and capital leases | | 2,278,293 | | 1,247,255 | | 151,733 | |
Repayments of notes payable, commercial bank financing and capital leases | | (1,509,760 | ) | (179,356 | ) | (150,447 | ) |
Redemption of 3% convertible notes | | (10,500 | ) | — | | — | |
Proceeds from the sale of Class A Common Stock | | 472,913 | | — | | — | |
Dividends paid on Class A and Class B Common Stock | | (56,767 | ) | (123,852 | ) | (38,356 | ) |
Payments for deferred financing costs | | (27,724 | ) | (18,707 | ) | (5,483 | ) |
Proceeds from Class A Common Stock sold by variable interest entity | | 10,908 | | — | | 1,808 | |
Noncontrolling interests distributions | | (10,256 | ) | (1,142 | ) | (610 | ) |
Repayments of notes and capital leases to affiliates | | (1,959 | ) | (2,882 | ) | (3,210 | ) |
Other, net | | 2,755 | | 391 | | (707 | ) |
Net cash flows from (used in) financing activities | | 1,147,903 | | 921,707 | | (45,272 | ) |
NET INCREASE (DECREASE) IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | | 257,239 | | 9,898 | | (9,007 | ) |
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, beginning of year | | 22,865 | | 12,967 | | 21,974 | |
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, end of year | | $ | 280,104 | | $ | 22,865 | | $ | 12,967 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-9
Table of Contents
SINCLAIR BROADCAST GROUP, INC.
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. NATURE OF OPERATIONS AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES:
Nature of Operations
Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. is a diversified television broadcasting company that owns or provides certain programming, operating or sales services to television stations pursuant to broadcasting licenses that are granted by the Federal Communication Commission (the FCC or Commission). We owned and provided programming and operating services pursuant to local marketing agreements (LMAs) or provided or were provided sales services pursuant to outsourcing agreements to 149 television stations in 71 markets, as of December 31, 2013. For the purpose of this report, these 149 stations are referred to as “our” stations.
Our broadcast group is a single reportable segment for accounting purposes and includes the following network affiliations: FOX (39 stations); CBS (25 stations); ABC (19 stations); NBC (16 stations); The CW (23 stations); MyNetworkTV (20 stations; not a network affiliation; however, it is branded as such); Univision (5 stations), Azteca (1 station) and one independent station. In addition, certain stations broadcast programming on second and third digital signals through network affiliation or program service arrangements with CBS, ABC, and NBC (certain signals are rebroadcasted content from other primary channels within the same market), FOX, The CW, MyNetworkTV, This TV, ME TV, Weather Radar, Weather Nation, Live Well Network, Antenna TV, Bounce Network, Zuus Country Network, Retro TV, Estrella TV, MundoFox, Tele-Romantica, Inmigrante TV, Azteca and Telemundo.
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include our accounts and those of our wholly-owned and majority-owned subsidiaries and VIEs for which we are the primary beneficiary. Noncontrolling interest represents a minority owner’s proportionate share of the equity in certain of our consolidated entities. All intercompany transactions and account balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
Discontinued Operations
In accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board’s (FASB) guidance on reporting assets held for sale, we reported the financial position and results of operations of our stations in Lansing, Michigan (WLAJ-TV) and Providence, Rhode Island (WLWC-TV), as assets and liabilities held for sale in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and consolidated statements of operations. Discontinued operations have not been segregated in the consolidated statements of cash flows and, therefore, amounts for certain captions will not agree with the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and consolidated statements of operations. WLAJ-TV was recently acquired in the second quarter of 2012 in connection with the acquisition of the television stations from Freedom Communications (Freedom). WLWC-TV was recently acquired in the first quarter of 2012 in connection with the acquisition of the television stations from Four Points Media Group LLC (Four Points). See Note 2. Acquisitions for more information. In October 2012, we entered into an agreement to sell all the assets of WLAJ-TV to an unrelated third party for $14.4 million. In January 2013, we entered into an agreement to sell the assets of WLWC-TV to an unrelated third party for $13.8 million. The operating results of WLAJ-TV, which was sold effective March 1, 2013, and WLWC-TV, which was sold effective April 1, 2013, are not included in our consolidated results of operations from continuing operations for the year ended December 31, 2013. Total revenues for WLAJ-TV and WLWC-TV, which are included in discontinued operations for the year ending December 31, 2013, were $0.6 million and $1.6 million, respectively. Total revenues of WLAJ-TV and WLWC-TV, which are included in discontinued operations for the year ending December 31, 2012, are $3.7 million and $6.3 million, respectively. Total income before taxes for WLAJ-TV and WLWC-TV, which are included in discontinued operations for the year ending December 31, 2013, are $0.2 million and $0.4 million, respectively, and total income(loss) before taxes of WLAJ-TV and WLWC-TV, which are included in discontinued operations for the year ending December 31, 2012, are $0.9 million and $0.2 million, respectively. The resulting gain on the sale of these stations in 2013 was negligible.
Additionally, we recognized a $11.2 million income tax benefit during the year ended December 31, 2013, attributable to the adjustment of certain liabilities for unrecognized tax benefits related to discontinued operations. See Note 9. Income Taxes for further information.
F-10
Table of Contents
Variable Interest Entities
In determining whether we are the primary beneficiary of a VIE for financial reporting purposes, we consider whether we have the power to direct the activities of the VIE that most significantly impact the economic performance of the VIE and whether we have the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive returns that would be significant to the VIE. We consolidate VIEs when we are the primary beneficiary. The assets of each of our consolidated VIEs can only be used to settle the obligations of the VIE. All the liabilities are non-recourse to us except for certain debt of VIEs which we guarantee. See Note 6. Notes Payable and Commercial Bank Financing for more information.
We have entered into LMAs to provide programming, sales and managerial services for seven television stations of Cunningham Broadcasting Company (Cunningham), the license owner of these television stations as of December 31, 2013. We pay LMA fees to Cunningham and also reimburse all operating expenses. We also have an acquisition agreement in which we have a purchase option to buy the license assets of these television stations which includes the FCC license and certain other assets used to operate the station (License Assets). Our applications to acquire these FCC license related assets are pending FCC approval. We also perform sales and other non-programming support services to two other stations owned by Cunningham (acquired in November 2013) pursuant to joint sales agreements (JSAs) and shared services agreements (SSAs). We have purchase options to acquire the license assets of these stations. We own the majority of the non-license assets of these nine Cunningham stations and we have guaranteed the debt of Cunningham. We have determined that Cunningham and these nine stations are VIEs and that based on the terms of the agreements, the significance of our investment in the stations and our guarantee of the debt of Cunningham, we are the primary beneficiary of the variable interests because, subject to the ultimate control of the licensees, we have the power to direct the activities which significantly impact the economic performance of the VIEs through the services we provide pursuant to the LMAs, and other outsourcing agreements, and we absorb losses and returns that would be considered significant to Cunningham. See Note 11. Related Person Transactions for more information on our arrangements with Cunningham. Included in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 are net revenues of $107.6 million, $105.5 million and $90.3 million, respectively, which relates to LMAs with Cunningham.
We have certain outsourcing agreements, including certain joint sales and shared services agreements, with certain other license owners, under which we provide certain non-programming related sales, operational and administrative services. The terms of the agreements vary, but generally have initial terms of over five years with several optional renewal terms. We own the majority of the non-license assets of these stations and in certain cases have guaranteed the debt of licensee (see Note 6. Notes Payable and Commercial Bank Financing). We also have purchase options to buy the assets of the licensees. We have determined that these licensees (18 and 10 licensees as of December 31, 2013 and 2012) are VIEs, and, based on the terms of the agreements and the significance of our investment in the stations, we are the primary beneficiary of the variable interests because, subject to the ultimate control of the licensees, we have the power to direct the activities which significantly impact the economic performance of the VIE through the sales and managerial services we provide and because we absorb losses and returns that would be considered significant to the VIEs. Included in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 are net revenues of $128.2 million, $49.1 million and $11.9 million, respectively which relates to these arrangements.
F-11
Table of Contents
As of the dates indicated, the carrying amounts and classification of the assets and liabilities of the VIEs mentioned above which have been included in our consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 were as follows (in thousands):
| | 2013 | | 2012 | |
ASSETS | | | | | |
CURRENT ASSETS: | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 4,916 | | $ | 3,805 | |
Accounts receivable | | 18,468 | | 110 | |
Current portion of program contract costs | | 10,725 | | 6,113 | |
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | 247 | | 218 | |
Total current asset | | 34,356 | | 10,246 | |
| | | | | |
PROGRAM CONTRACT COSTS, less current portion | | 5,075 | | 1,484 | |
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, net | | 11,081 | | 10,806 | |
GOODWILL | | 6,357 | | 6,357 | |
BROADCAST LICENSES | | 16,768 | | 14,927 | |
DEFINITE-LIVED INTANGIBLE ASSETS, net | | 97,496 | | 51,368 | |
OTHER ASSETS | | 22,935 | | 12,723 | |
Total assets | | $ | 194,068 | | $ | 107,911 | |
LIABILITIES | | | | | |
CURRENT LIABILITIES: | | | | | |
Accounts payable | | $ | 86 | | $ | 15 | |
Accrued liabilities | | 2,536 | | 186 | |
Current portion of notes payable, capital leases and commercial bank financing | | 5,731 | | 2,123 | |
Current portion of program contracts payable | | 11,552 | | 8,991 | |
Total current liabilities | | 19,905 | | 11,315 | |
| | | | | |
LONG-TERM LIABILITIES: | | | | | |
Notes payable, capital leases and commercial bank financing, less current portion | | 49,850 | | 20,238 | |
Program contracts payable, less current portion | | 6,597 | | 2,080 | |
Long term liabilities | | 10,838 | | — | |
Total liabilities | | $ | 87,190 | | $ | 33,633 | |
The amounts above represent the consolidated assets and liabilities of the VIEs described above, for which we are the primary beneficiary, and have been aggregated as they all relate to our broadcast business. Excluded from the amounts above are payments made to Cunningham under the LMA which are treated as a prepayment of the purchase price of the stations and capital leases between us and Cunningham which are eliminated in consolidation. The total payment made under these LMAs as of December 31, 2013 and 2012, which are excluded from liabilities above, were $32.4 million and $29.8 million, respectively. The total capital lease assets excluded from above were $11.2 million and $11.7 million, respectively for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2013, Cunningham sold a portion of its investment in our Class A Common Stock which is eliminated in consolidation and excluded from assets shown above, for $7.0 million, net of income taxes and has been reflected as an increase in additional paid in capital in the consolidated balance sheet. Also excluded from the amounts above are liabilities associated with the certain outsourcing agreements and purchase options with certain VIEs totaling $59.9 million and $36.2 million as of December 31, 2013 and December 31, 2012, respectively, as these amounts are eliminated in consolidation. The risk and reward characteristics of the VIEs are similar.
In the fourth quarter of 2011, we began providing sales, programming and management services to the Freedom stations pursuant to a LMA. Effective April 1, 2012, we completed the acquisition of the Freedom stations and the LMA was terminated. We determined that the Freedom stations were VIEs during the period of the LMA based on the terms of the agreement. We were not the primary beneficiary because the owner of the stations had the power to direct the activities of the VIEs that most significantly impacted the economic performance of the VIEs. In the consolidated statements of operations for the year ended December 31, 2012 are net broadcast revenues of $10.0 million and station production expenses of $7.8 million related to the Freedom LMAs, and for the year ended December 31, 2011 are net revenues of $10.8 million and station production expenses of $7.7 million related to the Four Points and Freedom LMAs.
We have investments in other real estate ventures and investment companies which are considered VIEs. However, we do not participate in the management of these entities including the day-to-day operating decisions or other decisions which would allow us to control the entity, and therefore, we are not considered the primary beneficiary of these VIEs. We account for these entities using the equity or cost method of accounting.
F-12
Table of Contents
The carrying amounts of our investments in these VIEs for which we are not the primary beneficiary as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 was $26.7 million and $31.0 million, respectively, which are included in other assets in the consolidated balance sheets. Our maximum exposure is equal to the carrying value of our investments. The income and loss related to these investments are recorded in income from equity and cost method investments in the consolidated statement of operations. We recorded income of $2.1 million, $6.4 million and $2.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively, related to these investments.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses in the consolidated financial statements and in the disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In July 2012, the FASB issued new guidance for testing indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment. The new guidance allows companies to perform a qualitative assessment to determine whether further impairment testing of indefinite-lived intangible assets is necessary, similar to the approach now applied to goodwill. Companies can first determine based on certain qualitative factors whether it is “more likely than not” (a likelihood of more than 50 percent) that an indefinite-lived intangible asset is impaired. The new standard is intended to reduce the cost and complexity of testing indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment. The revised standard is effective for annual and interim impairment tests performed for fiscal years beginning after September 30, 2012 and early adoption is permitted. We adopted this new guidance in the fourth quarter of 2012 when completing our annual impairment analysis. This guidance impacted how we perform our annual impairment testing for indefinite-lived intangible assets and changed our related disclosures for 2012; however, it does not have an impact on our consolidated financial statements as the guidance does not impact the timing or amount of any resulting impairment charges.
In February 2013, the FASB issued new guidance requiring disclosure of items reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income (AOCI). This new guidance requires entities to present (either on the face of the income statement or in the notes) the effects on the line items of the income statement for amounts reclassified out of AOCI. The new guidance is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2012. This guidance did not have a material impact on our financial statements.
In July 2013, the FASB issued new guidance requiring new disclosure of unrecognized tax benefit, or a portion of an unrecognized tax benefit, in the financial statements as a reduction to a deferred tax asset for a net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss, or a tax credit carryforward. If a company does not have: (i) a net operating loss carryforward; (ii) a similar tax loss; or (iii) a tax credit carryforward is not available at the reporting date under the tax law of the applicable jurisdiction to settle any additional income taxes that would result from the disallowance of a tax position or the entity does not intend to use the deferred tax asset for such purpose, the unrecognized tax benefit should be presented in the financial statements as a liability and should not be combined with deferred tax assets. The authoritative guidance is effective for fiscal years and the interim periods within those fiscal years beginning on or after December 15, 2013 and should be applied on a prospective basis. We do not expect this guidance to have a material impact on our financial statements.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
We consider all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents.
Restricted Cash
Under the terms of certain lease agreements, as of December 31, 2013 and December 31, 2012, we were required to hold $0.2 million of restricted cash related to the removal of analog equipment from some of our leased towers.
Additionally, during 2013, we entered into definitive agreements to purchase the assets of pending acquisitions. We were required to deposit 10% of the purchase price for each acquisition into an escrow account. As of December 31, 2013, we held $11.4 million in restricted cash classified as noncurrent related to the amount held in escrow for these acquisitions.
Accounts Receivable
Management regularly reviews accounts receivable and determines an appropriate estimate for the allowance for doubtful
F-13
Table of Contents
accounts based upon the impact of economic conditions on the merchant’s ability to pay, past collection experience and such other factors which, in management’s judgment, deserve current recognition. In turn, a provision is charged against earnings in order to maintain the appropriate allowance level.
A rollforward of the allowance for doubtful accounts for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 is as follows (in thousands):
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
Balance at beginning of period | | $ | 3,091 | | $ | 3,008 | | $ | 3,242 | |
Charged to expense | | 1,802 | | 1,141 | | 751 | |
Net write-offs | | (1,514 | ) | (1,058 | ) | (985 | ) |
Balance at end of period | | $ | 3,379 | | $ | 3,091 | | $ | 3,008 | |
Programming
We have agreements with distributors for the rights to television programming over contract periods, which generally run from one to seven years. Contract payments are made in installments over terms that are generally equal to or shorter than the contract period. Pursuant to accounting guidance for the broadcasting industry, an asset and a liability for the rights acquired and obligations incurred under a license agreement are reported on the balance sheet where the cost of each program is known or reasonably determinable, the program material has been accepted by the licensee in accordance with the conditions of the license agreement and the program is available for its first showing or telecast. The portion of program contracts which becomes payable within one year is reflected as a current liability in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
The rights to this programming are reflected in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets at the lower of unamortized cost or estimated net realizable value. With the exception of one-year contracts amortization of program contract costs is computed using either a four-year accelerated method or based on usage, whichever method results in the earliest recognition of amortization for each program. Program contract costs are amortized on a straight-line basis for one-year contracts. Program contract costs estimated by management to be amortized in the succeeding year are classified as current assets. Payments of program contract liabilities are typically made on a scheduled basis and are not affected by adjustments for amortization or estimated net realizable value.
Estimated net realizable values are based on management’s expectation of future advertising revenues, net of sales commissions, to be generated by the program material. We perform a net realizable value calculation quarterly for each of our program contract costs in accordance with FASB guidance on Financial Reporting for Broadcasters. We utilize sales information to estimate the future revenue of each commitment and measure that amount against the commitment. If the estimated future revenue is less than the amount of the commitment, a loss is recorded in amortization of program contract costs and net realizable value adjustments in the consolidated statements of operations.
Barter Arrangements
Certain program contracts provide for the exchange of advertising airtime in lieu of cash payments for the rights to such programming. The revenues realized from station barter arrangements are recorded as the programs are aired at the estimated fair value of the advertising airtime given in exchange for the program rights. Program service arrangements are accounted for as station barter arrangements, however, network affiliation programming is excluded from these calculations. Revenues are recorded as revenues realized from station barter arrangements and the corresponding expenses are recorded as expenses recognized from station barter arrangements.
We broadcast certain customers’ advertising in exchange for equipment, merchandise and services. The estimated fair value of the equipment, merchandise or services received is recorded as deferred barter costs and the corresponding obligation to broadcast advertising is recorded as deferred barter revenues. The deferred barter costs are expensed or capitalized as they are used, consumed or received and are included in station production expenses and station selling, general and administrative expenses, as applicable. Deferred barter revenues are recognized as the related advertising is aired and are recorded in revenues realized from station barter arrangements.
Other Assets
Other assets as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 consisted of the following (in thousands):
F-14
Table of Contents
| | 2013 | | 2012 | |
Equity and cost method investments | | $ | 98,385 | | $ | 94,924 | |
Unamortized costs related to debt issuances | | 46,150 | | 40,260 | |
Other | | 63,674 | | 54,800 | |
Total other assets | | $ | 208,209 | | $ | 189,984 | |
We have equity and cost method investments primarily in private investment funds and real estate ventures. In the event that one or more of our investments are significant, we are required to disclose summarized financial information. For the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011, none of our investments were significant individually or in the aggregate.
As of December 31, 2013 and 2012, our unfunded commitments related to private equity investment funds totaled $17.0 million and $8.9 million, respectively.
When factors indicate that there may be a decrease in value of an equity or cost method investment, we assess whether a loss in value has occurred related to the investment. If that loss is deemed to be other than temporary, an impairment loss is recorded accordingly. For any investments that indicate a potential impairment, we estimate the fair values of those investments using discounted cash flow models, unrelated third party valuations or industry comparables, based on the various facts available to us. For the year ended December 31, 2011 we recorded no impairments. For the year ended December 31, 2012, we recorded impairments of $1.3 million related to two of our investments. For the year ended December 31, 2013, we recorded impairments of $0.6 million related to two of our investments. The impairments are recorded in the income (loss) from equity and cost method investees in our consolidated statement of operations.
Unamortized costs related to debt issuances represent direct costs incurred to obtain long-term financing and are amortized to interest expense over the term of the related debt using the effective interest method. Previously capitalized debt financing costs are expensed and included in loss on extinguishment of debt if we determine that there has been a substantial modification of the related debt.
The increase in other, in the table above, in 2013 was primarily due to acquisitions of marketable securities by our consolidated variable interest entities.
Impairment of Intangible and Long-Lived Assets
We assess annually, in the fourth quarter, whether goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets are impaired. Additionally, impairment assessments may be performed on an interim basis when events or changes in circumstances indicate that impairment potentially exists. We aggregate our stations by market for purposes of our goodwill and license impairment testing. We believe that our markets are most representative of our broadcast reporting units because segment management views, manages and evaluates our stations on a market basis. Furthermore, in our markets, where we operate or provide services to more than one station, certain costs of operating the stations are shared including the use of buildings and equipment, the sales force and administrative personnel. In our assessment of goodwill for impairment we first determined, based upon a qualitative assessment, whether it is more likely than not a reporting unit has been impaired. Our qualitative assessment includes, but is not limited to, assessing the changes in macroeconomic conditions, regulatory environment, industry and market conditions, and the specific financial performance of the reporting units, as well as any other events or circumstances specific to the reporting units. If we conclude that it is more likely than not that a reporting unit is impaired, we will apply the quantitative two-step method. In the first step, the Company determines the fair value of the reporting unit and compares that fair value to the net book value of the reporting unit. The fair value of the reporting unit is determined using various valuation techniques, including quoted market prices, observed earnings/cash flow multiples paid for comparable television stations and discounted cash flow models. Our discounted cash flow model is based on our judgment of future market conditions within each designated market area, as well as discount rates that would be used by market participants in an arms-length transaction. If the net book value of the reporting unit were to exceed the fair value, we would then perform the second step of the impairment test, which requires allocation of the reporting unit’s fair value to all of its assets and liabilities in a manner similar to a purchase price allocation, with any residual fair value being allocated to goodwill to determine the implied fair value. An impairment charge will be recognized only when the implied fair value of a reporting unit’s goodwill is less than its carrying amount.
For our annual impairment test for indefinite-lived intangibles, broadcast licenses, we applied a qualitative assessment to assess whether it is more likely than not that a broadcast license is impaired. Our qualitative assessment for indefinite-lived intangible asset impairment includes, but it not limited to, review of operating results, assessing the changes in macroeconomic conditions, cost factors, regulatory environment, industry and market conditions, and other events and circumstances that could affect the significant inputs used to determine the fair value of our broadcast license assets. When evaluating our broadcast licenses for impairment, the qualitative assessment is done at the unit of accounting level, each station’s broadcast license, and we aggregate
F-15
Table of Contents
the broadcast licenses for each market because the broadcast licenses within the market are complementary and together enhance the single broadcast license of each station. If we conclude that it is more likely than not that one of our broadcast licenses is impaired, we will calculate the fair value of the broadcast license in accordance with the quantitative test for indefinite-lived intangible assets. If a quantitative test is performed, we use the income approach method. The income approach method involves a discounted cash flow model that incorporates several variables, including, but not limited to, discounted cash flows of a typical market participant, market revenue and long term growth projections, estimated market share for the typical participant and estimated profit margins based on market size and station type. The model also assumes outlays for capital expenditures, future terminal values, an effective tax rate assumption and a discount rate based on the weighted-average cost of capital of the television broadcast industry. We will compare the fair value of the broadcast licenses, at a market level, to the carrying amount of those same broadcast licenses. If the carrying amount of the broadcast licenses exceeds the fair value, then an impairment loss is recorded to the extent that the carrying value of the broadcast licenses exceeds the fair value.
We periodically evaluate our long-lived assets for impairment and continue to evaluate them as events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of such assets may not be fully recoverable. We evaluate the recoverability of long-lived assets by measuring the carrying amount of the assets against the estimated undiscounted future cash flows associated with them. At the time that such evaluations indicate that the future undiscounted cash flows of certain long-lived assets are not sufficient to recover the carrying value of such assets, the assets are tested for impairment by comparing their estimated fair value to the carrying value. We typically estimate fair value using discounted cash flow models and appraisals. See Note 5. Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets, for more information.
Accrued Liabilities
Accrued liabilities consisted of the following as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 (in thousands):
| | 2013 | | 2012 | |
Compensation and employee health insurance | | $ | 44,800 | | $ | 32,099 | |
Interest | | 25,133 | | 18,885 | |
Deferred revenue | | 20,128 | | 14,734 | |
Other accruals relating to operating expenses (a) | | 92,124 | | 78,013 | |
Total accrued liabilities | | $ | 182,185 | | $ | 143,731 | |
(a) Included in other accruals relating to operating expenses as of December 31, 2012 is $25.0 million which was paid to Fox in April 2013 as discussed further in Network Affiliation Agreements and Program Service Agreements under Note 10. Commitments and Contingencies.
We expense these activities when incurred.
Income Taxes
We recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities based on the differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and the tax bases of assets and liabilities. We provide a valuation allowance for deferred tax assets if we determine that it is more likely than not that some or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. In evaluating our ability to realize net deferred tax assets, we consider all available evidence, both positive and negative, including our past operating results, tax planning strategies and forecasts of future taxable income. In considering these sources of taxable income, we must make certain judgments that are based on the plans and estimates used to manage our underlying businesses on a long-term basis. As of December 31, 2013, a valuation allowance has been provided for deferred tax assets related to a substantial amount of our available state net operating loss carryforwards, based on past operating results, expected timing of the reversals of existing temporary book/tax basis differences, alternative tax strategies and projected future taxable income. Management periodically performs a comprehensive review of our tax positions and accrues amounts for tax contingencies. Based on these reviews, the status of ongoing audits and the expiration of applicable statute of limitations, accruals are adjusted as necessary in accordance with income tax accounting guidance. The resolution of audits is unpredictable and could result in tax liabilities that are significantly higher or lower than for what we have provided.
Supplemental Information — Statements of Cash Flows
During 2013, 2012 and 2011, we had the following cash transactions (in thousands):
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
Income taxes paid related to continuing operations | | $ | 26,037 | | $ | 46,964 | | $ | 897 | |
Income tax refunds received related to continuing operations | | $ | 4,414 | | $ | 194 | | $ | 5 | |
Interest paid | | $ | 147,083 | | $ | 110,973 | | $ | 98,643 | |
F-16
Table of Contents
Non-cash transactions related to capital lease obligations were $10.4 million, $0.3 million and $2.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively. The non-cash conversion of the 4.875% Notes was $8.6 million, net of taxes for the year ended December 31, 2013.
Revenue Recognition
Total revenues include: (i) cash and barter advertising revenues, net of agency commissions; (ii) retransmission consent fees; (iii) network compensation; (iv) other broadcast revenues and (v) revenues from our other operating divisions.
Advertising revenues, net of agency commissions, are recognized in the period during which time spots are aired.
Our retransmission consent agreements contain both advertising and retransmission consent elements. We have determined that our retransmission consent agreements are revenue arrangements with multiple deliverables. Advertising and retransmission consent deliverables sold under our agreements are separated into different units of accounting at fair value. Revenue applicable
to the advertising element of the arrangement is recognized similar to the advertising revenue policy noted above. Revenue applicable to the retransmission consent element of the arrangement is recognized over the life of the agreement.
Network compensation revenue is recognized over the term of the contract. All other significant revenues are recognized as services are provided.
Advertising Expenses
Promotional advertising expenses are recorded in the period when incurred and are included in station production and other operating division expenses. Total advertising expenses from continuing operations, net of advertising co-op credits, were $15.4 million, $12.2 million and $8.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
Financial Instruments
Financial instruments, as of December 31, 2013 and 2012, consisted of cash and cash equivalents, trade accounts receivable, accounts payable, accrued liabilities and notes payable. The carrying amounts approximate fair value for each of these financial instruments, except for the notes payable. See Note 6. Notes Payable and Commercial Bank Financing, for additional information regarding the fair value of notes payable.
Post-retirement Benefits
We are required to recognize the funded status (i.e., the difference between the fair value of plan assets and the projected
benefit obligations) of our pension plan in our consolidated financial statements. As of December 31, 2013 and 2012, we held a liability of $1.9 million and $5.5 million, respectively, representing the underfunded status of our defined benefit pension plan.
In connection with acquisition of Fisher Communications, Inc. (Fisher) in 2013 (see Note 2. Acquisitions), we assumed a nonqualified noncontributory supplemental retirement program (Fisher SERP) that was originally established for former executives of Fisher. No new participants have been admitted to this program since 2001 and the benefits of active participants were frozen in 2005. The program participants do not include any active employees. The Fisher SERP required continued employment or disability through the date of expected retirement, unless involuntarily terminated. The cost of the program is accrued over the average expected future lifetime of the participants. While the nonqualified plan is unfunded, but Fisher had made investments in annuity contracts and life insurance policies on the lives of certain individual participants to assist in future payment of retirement benefits. The Company is the owner and beneficiary of the annuity contracts and life insurance policies; accordingly, the cash value of the annuity contracts and the cash surrender value of the life insurance policies are reported at fair value as assets in our consolidated balance sheet and any appreciation value is included in other income in our consolidated statement of operations. The carrying value of the annuity contracts and life insurance policies was $18.2 million as of December 31, 2013.
As of December 31, 2013, the estimated projected benefit obligation of Fisher SERP was $22.0 million, of which $1.5 million is included in accrued expenses in the consolidated balance sheet and the $20.5 million is included in other long-term liabilities. During the year ended December 31, 2013, since acquiring Fisher, we made $0.5 million in benefit payments, recognized $0.4 million of periodic
F-17
Table of Contents
pension expense, reported in other expenses in the consolidated statement of operations, and $0.2 million of actuarial gains through other comprehensive income.
At December 31, 2013 the projected benefit obligation was measured using a 4.51% discount rate. We estimated its discount rate, in consultation with our independent actuaries, based on a yield curve constructed from a portfolio of high quality bonds for which the timing and amount of cash outflows approximate the estimated payouts of the plan.
We estimate that benefits expected to be paid to participants under the Fisher SERP as follows (in thousands):
| | December 31,
2013 | |
2014 | | $ | 1,489 | |
2015 | | 1,601 | |
2016 | | 1,686 | |
2017 | | 1,624 | |
2018 | | 1,580 | |
Next 5 years | | 7,366 | |
| | $ | 15,346 | |
Reclassifications
Certain reclassifications have been made to prior years’ consolidated financial statements to conform to the current year’s presentation.
2. ACQUISITIONS
Four Points
Effective January 1, 2012, we completed the acquisition of the broadcast assets of Four Points, which we had previously operated pursuant to a LMA since October 1, 2011. The acquired assets consist of the following seven stations in four markets along with the respective network affiliation or program service arrangements: KUTV (CBS) and KMYU (MNT / This TV) in Salt Lake City / St. George, UT; KEYE (CBS) in Austin, TX; WTVX (CW), WTCN (MNT) and WWHB (Azteca) in West Palm Beach / Fort Pierce / Stuart, FL; and WLWC (CW) in Providence, RI / New Bedford, MA. This acquisition provides expansion into additional markets and increases value based on the synergies we can achieve.
We paid Four Points $200.0 million in cash, less a working capital adjustment of $0.9 million. The acquisition was financed with a $180.0 million draw under an incremental Term B Loan commitment under our amended Bank Credit Agreement plus a $20.0 million cash escrow previously paid in September 2011.
Under the acquisition method of accounting, the results of the acquired operations are included in the financial statements of the Company beginning January 1, 2012. The purchase price has been allocated to the acquired assets and assumed liabilities based on estimated fair values. The allocated fair value of acquired assets and assumed liabilities is summarized as follows (in thousands):
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | $ | 456 | |
Program contract costs | | 3,731 | |
Property and equipment | | 34,578 | |
Broadcast licenses | | 10,658 | |
Definite-lived intangible assets | | 93,800 | |
Other assets | | 548 | |
Accrued liabilities | | (381 | ) |
Program contracts payable | | (5,157 | ) |
Fair value of identifiable net assets acquired | | 138,233 | |
Goodwill | | 60,843 | |
Total | | $ | 199,076 | |
The final allocation presented above is based upon management’s estimate of the fair values using valuation techniques including income, cost and market approaches. In estimating the fair value of the acquired assets and assumed liabilities, the fair value estimates are based on, but not limited to, expected future revenue and cash flows, expected future growth rates, and
F-18
Table of Contents
estimated discount rates. The amount allocated to definite-lived intangible assets represents the estimated fair values of network affiliations of $66.9 million, the decaying advertiser base of $9.8 million, and other intangible assets of $17.1 million. These intangible assets will be amortized over the estimated remaining useful lives of 15 years for network affiliations, 10 years for the decaying advertiser base and a weighted average of 14 years for the other intangible assets. Acquired property and equipment will be depreciated on a straight-line basis over the respective estimated remaining useful lives. Goodwill is calculated as the excess of the consideration transferred over the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired and represents the future economic benefits expected to arise from other intangible assets acquired that do not qualify for separate recognition, including assembled workforce and noncontractual relationships, as well as expected future synergies. We expect that goodwill will be deductible for tax purposes. Certain measurement period adjustments have been made since the initial allocation in the first quarter of 2012, which were not material to the consolidated financial statements.
Prior to the acquisition, since October 1, 2011, we provided sales, programming and management services to the stations pursuant to an LMA. During that period, we funded the working capital needs of the stations, which totaled $8.1 million as of December 31, 2011 and was reflected as cash flows used in operating activities within the consolidated statement of cash flows for that period. This working capital is not reflected in the purchase price allocation presented above.
The results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012 include the results of the Four Points stations since January 1, 2012. Net broadcast revenues and operating income of the Four Points stations included in our consolidated statements of operations, were $73.7 million and $70.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively and $19.8 million and $17.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively. These amounts exclude the operations of WLWC-TV which are classified as discontinued operations in the consolidated statements of operations. See Note 1. Nature of Operations and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies. Net broadcast revenues and operating losses of WLWC-TV were $1.4 million and $0.2 million, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2013 and $5.5 million and $0.2 million, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2012. Additionally, during the year ended December 31, 2011, prior to the acquisition, we recorded net broadcast revenues of $8.8 million related to the Four Points LMA.
Freedom
Effective April 1, 2012, we completed the acquisition of the broadcast assets of Freedom, which we had previously operated pursuant to a LMA since December 1, 2011. The acquired assets consist of the following eight stations in seven markets along with the respective network affiliation or program service arrangements: WPEC (CBS) in West Palm Beach, FL; WWMT (CBS) in Grand Rapids/Kalamazoo/Battle Creek, MI; WRGB (CBS) and WCWN (CW) in Albany, NY; WTVC (ABC) in Chattanooga, TN; WLAJ (ABC) in Lansing, MI; KTVL (CBS) in Medford-Klamath Falls, OR; and KFDM (CBS) in Beaumont/Port Arthur/Orange, TX. This acquisition provides expansion into additional markets and increases value based on the synergies we can achieve.
We paid Freedom $385.0 million plus a working capital adjustment of $0.3 million. The acquisition was financed with a draw under a $157.5 million incremental Term Loan A and a $192.5 million incremental Term B Loan commitment under our amended Bank Credit Agreement, plus a $38.5 million cash escrow previously paid in November 2011.
Under the acquisition method of accounting, the results of the acquired operations are included in the financial statements of the Company beginning April 1, 2012. The purchase price has been allocated to the acquired assets and assumed liabilities based on estimated fair values. The allocated fair value of acquired assets and assumed liabilities is summarized as follows (in thousands):
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | $ | 373 | |
Program contract costs | | 3,520 | |
Property and equipment | | 54,109 | |
Broadcast licenses | | 10,424 | |
Definite-lived intangible assets | | 140,963 | |
Other assets | | 278 | |
Accrued liabilities | | (589 | ) |
Program contracts payable | | (3,404 | ) |
Fair value of identifiable net assets acquired | | 205,674 | |
Goodwill | | 179,609 | |
Total | | $ | 385,283 | |
The final allocation presented above is based upon management’s estimate of the fair values using valuation techniques including income, cost and market approaches. In estimating the fair value of the acquired assets and assumed liabilities, the fair value estimates are based on, but not limited to, expected future revenue and cash flows, expected future growth rates, and
F-19
Table of Contents
estimated discount rates. The amount allocated to definite-lived intangible assets represents the estimated fair values of network affiliations of $93.1 million, the decaying advertiser base of $25.1 million, and other intangible assets of $22.8 million. These intangible assets will be amortized over the estimated remaining useful lives of 15 years for network affiliations, 10 years for the decaying advertiser base and a weighted average life of 16 years for the other intangible assets. Acquired property and equipment will be depreciated on a straight-line basis over the respective estimated remaining useful lives. Goodwill is calculated as the excess of the consideration transferred over the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired and represents the future economic benefits expected to arise from other intangible assets acquired that do not qualify for separate recognition, including assembled workforce and noncontractual relationships, as well as expected future synergies. We expect that goodwill will be deductible for tax purposes. Certain measurement period adjustments have been made since the initial allocation in the second quarter of 2012, which were not material to the consolidated financial statements
Prior to the acquisition, since December 1, 2011, we provided sales, programming and management services to the stations pursuant to an LMA. During that period, we funded the working capital needs of the stations, which totaled $1.5 million as of December 31, 2011 and $9.6 million as of March 31, 2012 and was reflected as cash flows used in operating activities within the consolidated statement of cash flows for those periods. This working capital is not reflected in the purchase price allocation presented above.
The results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012 includes the results of the Freedom stations since April 1, 2012. Net broadcast revenues and operating income of the Freedom stations included in our consolidated statements of operations, were $108.6 million and $91.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively, and$29.4 million and $32.5 million for the years ended December 31 2013, and 2012, respectively. These amounts exclude the operations of WLAJ-TV which are classified as discontinued operations in the consolidated statements of operations. See Note 1. Nature of Operations and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies. Net broadcast revenues and operating losses of WLAJ-TV were $0.7 million and $0.1 million, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2013 and $3.8 million and $0.9 million, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2012. Additionally, during the first quarter 2012 and year ended December 31, 2011, prior to the acquisition, we recorded net broadcast revenues of $10.0 million and $2.0 million, respectively, related to the Freedom LMA.
Newport
Effective December 1, 2012, we completed the acquisition of certain broadcast assets of Newport Television (Newport). The acquired assets relate to the following seven stations in six markets along with the respective network affiliation or program service arrangements: WKRC (CBS) in Cincinnati, OH; WOAI (NBC) in San Antonio, TX; WHP (CBS) in Harrisburg/Lancaster/Lebanon/York, PA; WPMI (NBC) and WJTC (IND) in Mobile, AL/Pensacola, FL; KSAS (FOX) in Wichita/Hutchinson, KS; and WHAM (ABC) in Rochester, NY. We also acquired Newport’s rights under the local marketing agreements with WLYH (CW) in Harrisburg, PA and KMTW (MNT) in Wichita, KS, as well as options to acquire the license assets. This acquisition provides expansion into additional markets and increases value based on the synergies we can achieve.
We paid Newport $460.5 million in cash, less a working capital adjustment of $1.0 million. We financed the $460.5 million purchase price, less the $41.3 million in escrow with the net proceeds from the 6.125% Notes issued in October 2012. See Note 6. Notes Payable and Commercial Bank Financing for more information.
Our right to acquire certain of the license assets of WPMI and WJTC in Mobile, AL was assigned to a third party, who acquired these assets effective December 1, 2012 for $6.0 million. Additionally, a third party acquired the license assets of WHAM in Rochester, NY from Newport effective February 1, 2013 for $6.0 million. Concurrent with the acquisition of WKRC in Cincinnati, OH and WOAI in San Antonio, TX from Newport, we sold the license assets of two of our existing stations located in Cincinnati, OH (WSTR MNT) and San Antonio, TX (KMYS CW) for a total of $10.7 million to third parties. All of the aforementioned third party licensees are part of the Deerfield Media group of companies (Deerfield), which are under common ownership. Deerfield financed these purchases with third party bank financing which we have guaranteed. See Note 6. Notes Payable and Commercial Bank Financing for more information. We provide non-programming related sales, operational and administrative services to these stations pursuant to certain outsourcing agreements and we have assignable purchase options with these licensees to acquire the license assets upon FCC approval. We consolidate the license assets of these stations because the licensee companies are VIEs and we are the primary beneficiary. Prior to Deerfield acquiring the license assets of WHAM in Rochester, NY on February 1, 2013, we provided non-programming related sales, operational and administrative services to the station pursuant to certain outsourcing agreements with Newport. We consolidated the license assets owned by Newport from December 1, 2012 to January 31, 2013 because the licensee company was a VIE and the Company was the primary beneficiary. See Variable Interest Entities in Note 1. Nature of Operations and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies. The purchase of the license assets by Deerfield in February 2013 was accounted for as a transaction between parties under common control.
Under the acquisition method of accounting, the results of the acquired operations are included in the financial statements of the Company beginning December 1, 2012. The initial purchase price has been allocated to the acquired assets and assumed
F-20
Table of Contents
liabilities based on estimated fair values. The initial purchase price allocated includes $460.5 million paid for certain broadcast assets of the seven stations from Newport and the rights under the LMAs with the two other stations, $6.0 million paid by Deerfield for the license assets of WPMI and WJTC and $6.0 million paid by third parties for the license assets of WHAM, and $0.2 million of noncontrolling interests related to the WLYH VIE, less a working capital adjustment of $1.3 million. The sale of the license assets of WSTR in Cincinnati, OH and KMYS in San Antonio, TX was considered a transaction between parties under common control and therefore was not included in the purchase price allocation. The final allocated fair value of acquired assets and assumed liabilities, including the assets owned by VIEs, is summarized as follows (in thousands):
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | $ | 1,390 | |
Program contract costs | | 10,378 | |
Property and equipment | | 53,883 | |
Broadcast licenses | | 15,581 | |
Definite-lived intangible assets | | 240,013 | |
Other assets | | 1,097 | |
Accrued liabilities | | (3,928 | ) |
Program contracts payable | | (11,634 | ) |
Fair value of identifiable net assets acquired | | 306,780 | |
Goodwill | | 164,621 | |
Total | | $ | 471,401 | |
The final allocation presented above is based upon management’s estimate of the fair values using valuation techniques including income, cost and market approaches. In estimating the fair value of the acquired assets and assumed liabilities, the fair value estimates are based on, but not limited to, expected future revenue and cash flows, expected future growth rates, and estimated discount rates. The amount allocated to definite-lived intangible assets represents the estimated fair values of network affiliations of $176.0 million, the decaying advertiser base of $23.7 million, and other intangible assets of $40.3 million. These intangible assets will be amortized over the estimated remaining useful lives of 15 years for network affiliations, 10 years for the decaying advertiser base and a weighted average of 14 years for the other intangible assets. Acquired property and equipment will be depreciated on a straight-line basis over the respective estimated remaining useful lives. Goodwill is calculated as the excess of the consideration transferred over the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired and represents the future economic benefits expected to arise from other intangible assets acquired that do not qualify for separate recognition, including assembled workforce and noncontractual relationships, as well as expected future synergies. We expect that goodwill will be deductible for tax purposes. Certain measurement period adjustments have been made since the initial allocation in the fourth quarter of 2012, which were not material to our consolidated financial statements.
The results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2012 include the results of the Newport stations since December 1, 2012. Net broadcast revenues and operating income of the Newport stations included in our consolidated statements of operations, were $149.0 million and $11.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively, and $35.8 million and $2.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Fisher Communications
Effective August 8, 2013, we completed the acquisition of all of the outstanding common stock of Fisher Communications, Inc. (Fisher). We paid $373.2 million to the shareholders of the Fisher common stock, representing $41.0 per common share. We financed the total purchase price with cash on hand. Fisher owns certain broadcast assets related to the following twenty-two stations, and four radio stations in 8 markets along with the respective network affiliation or program service arrangements: KOMO (ABC) and KUNS (Univision) in Seattle-Tacoma, WA; KATU (ABC), KUNP(Univision), and KUNP-LP (Univision) in Portland, OR; KLEW (CBS) in Spokane, WA; KBOI (CBS) and KYUU-LD (CW) in Boise, ID; KVAL (CBS), KCBY (CBS), KPIC (CBS), KMTR (NBC), KMCB (NBC), and KTCW (NBC) in Eugene, OR; KIMA (CBS), KEPR (CBS), KUNW-CD (Univision), and KVVK-CD (Univision), in Yakima/Pasco/Richland/Kennewick, WA; KBAK (CBS) and KBFX-CD (FOX) in Bakersfield, CA; as well as KIDK (CBS/FOX) and KXPI (FOX) in Idaho Falls/Pocatello, ID. The four radio stations are: KOMO (AM/FM), KPLZ (FM) and KVI (AM) in the Seattle/Tacoma, WA market. This acquisition provides expansion into additional markets and increases value based on the synergies we can achieve.
The results of the acquired operations are included in the financial statements of the Company beginning on August 8, 2013. Under the acquisition method of accounting, the initial purchase price has been allocated to the acquired assets and assumed liabilities based on estimated fair values. The allocation reflects the consolidation of net assets of the third party which owns the license and related assets of KMTR in Eugene, OR, which we have consolidated, as the licensee is considered to be a VIE and we are the primary beneficiary of the variable interests. Additionally, another third party that performs certain services pursuant to an
F-21
Table of Contents
outsourcing agreement to our stations in Idaho Falls, ID (KIDK and KXPI), exercised an existing purchase option to purchase the broadcast assets of the two stations for $6.3 million, which closed in November 2013. The assets of these stations were classified as assets held for sale in the initial purchase price allocation. The purchase price allocation is preliminary pending a final determination of the fair values of the assets and liabilities. The allocated fair value of acquired assets and assumed liabilities is summarized as follows (in thousands):
Cash | | $ | 13,531 | |
Accounts receivable | | 29,962 | |
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | 19,337 | |
Program contract costs | | 10,968 | |
Property and equipment | | 48,616 | |
Broadcast licenses | | 11,058 | |
Definite-lived intangible assets | | 155,073 | |
Other assets | | 8,348 | |
Assets held for sale | | 6,339 | |
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | (20,384 | ) |
Program contracts payable | | (10,977 | ) |
Deferred tax liability | | (51,024 | ) |
Other long-term liabilities | | (22,127 | ) |
Fair value of identifiable net assets acquired | | 198,720 | |
Goodwill | | 174,476 | |
Total | | $ | 373,196 | |
The preliminary allocation presented above is based upon management’s estimate of the fair values using valuation techniques including income, cost and market approaches. In estimating the fair value of the acquired assets and assumed liabilities, the fair value estimates are based on, but not limited to, expected future revenue and cash flows, expected future growth rates, and estimated discount rates. The amount allocated to definite-lived intangible assets represents the estimated fair values of network affiliations of $100.6 million, the decaying advertiser base of $15.0 million, and other intangible assets of $39.5 million. These intangible assets will be amortized over the estimated remaining useful lives of 15 years for network affiliations, 10 years for the decaying advertiser base and a weighted average life of 15 years for the other intangible assets. Acquired property and equipment will be depreciated on a straight-line basis over the respective estimated remaining useful lives. Goodwill is calculated as the excess of the consideration transferred over the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired and represents the future economic benefits expected to arise from other intangible assets acquired that do not qualify for separate recognition, including assembled workforce and noncontractual relationships, as well as expected future synergies. We expect that goodwill deductible for tax purposes will be approximately $11.1 million. The initial purchase price allocation is based upon all information available to us at the present time and is subject to change, and such changes could be material. Certain measurement period adjustments have been made since the initial allocation in the third quarter of 2013, which were not material to our consolidated financial statements.
The results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2013 includes the results of the Fisher stations since August 8, 2013. Net broadcast revenues and operating income of the Fisher stations included in our consolidated statements of operations, were $79.1 million and $19.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. Post-acquisition, we recognized $4.3 million of severance expense related to certain Fisher executives and employees that have been or will be terminated who had existing agreements in place prior to close.
Barrington
Effective November 22, 2013, we completed the acquisition of the broadcast assets of Barrington Broadcasting Company, LLC for $370.0 million, less working capital of $2.4 million, and entered into agreements to operate or provide sales and administrative services to another five stations. The purchase price includes $7.5 million paid by third parties for the license related assets of certain stations. The acquired assets relate to the following twenty four stations located in fifteen markets along with the respective network affiliation or program service arrangements: WEYI (NBC) and WBSF (CW) in Flint/Saginaw/Bay City/Midland, MI; WNWO (NBC) in Toledo, OH; WACH (FOX) in Columbia, SC; WSTM (NBC), WTVH (CBS) and WSTQ (CW) in Syracuse, NY; KGBT (CBS) in Harlingen/Weslaco/Brownsville/McAllen, TX; KXRM (FOX) and KXTU (CW) in Colorado Springs, CO; WPDE (ABC) and WWMB (CW) in Myrtle Beach/Florence, SC; WHOI (ABC) in Peoria/Bloomington, IL; WPBN/WTOM (NBC), and WGTU/WGTQ (ABC) in Traverse City/Cadillac, MI; KVII (ABC) and KVIH (ABC) in Amarillo, TX; KRCG (CBS) in Columbia/Jefferson City, MO; WFXL (FOX) in Albany, GA; KHQA (CBS) in Quincy, IL/Hannibal, MO/Keokuk, IA; WLUC (NBC) in Marquette, MI; and KTVO (ABC) in Ottumwa, IA/Kirksville, MO.
F-22
Table of Contents
Concurrent with the Barrington acquisition, due to FCC conflict ownership rules, we sold our station, WSYT (FOX), and assigned its LMA with WNYS-TV (MNT), in Syracuse, NY to a third party for $15 million less, and recognized a loss on sale of approximately $3.3 million. We also sold our station, WYZZ (FOX) in Peoria, IL, which currently receives non-programming related sales, operational and administrative services from Nexstar Broadcasting pursuant to certain outsourcing agreements, to Cunningham for $22.0 million. Although we have no continuing involvement in the operations of this station, because Cunningham is a consolidated VIE and we have a purchase plan option to acquire these assets from Cunningham, the assets of WYZZ were not derecognized and the transaction was accounted for a transaction between parties under common control. Thus no gain or loss has been recognized in the consolidated statement of operations for sale of WYZZ.
The results of the acquired operations are included in the financial statements of the Company beginning on November 22, 2013. Under the acquisition method of accounting, the initial purchase price has been allocated to the acquired assets and assumed liabilities based on estimated fair values. The allocation reflects the consolidation of net assets of the third party licensees which own the license and related assets of WEYI and WBSF in Flint, MI, WWMB in Myrtle Beach, SC and WGTU/WGTQ in Traverse City, MI, which we have consolidated, as the licensees are considered to be VIEs and we are the primary beneficiary of the variable interests. The purchase price allocation is preliminary pending a final determination of the fair values of the assets and liabilities. The allocated fair value of acquired assets and assumed liabilities is summarized as follows (in thousands):
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | $ | 681 | |
Program contract costs | | 3,813 | |
Property and equipment | | 67,519 | |
Broadcast licenses | | 719 | |
Definite-lived intangible assets | | 220,535 | |
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | (2,725 | ) |
Program contracts payable | | (3,813 | ) |
Other long-term liabilities | | (65 | ) |
Fair value of identifiable net assets acquired | | 286,664 | |
Goodwill | | 81,022 | |
Total | | $ | 367,686 | |
The preliminary allocation presented above is based upon management’s estimate of the fair values using valuation techniques including income, cost and market approaches. In estimating the fair value of the acquired assets and assumed liabilities, the fair value estimates are based on, but not limited to, expected future revenue and cash flows, expected future growth rates, and estimated discount rates. The amount allocated to definite-lived intangible assets represents the estimated fair values of network affiliations of $99.3 million, the decaying advertiser base of $43.8 million, and other intangible assets of $77.4 million. These intangible assets will be amortized over the estimated remaining useful lives of 15 years for network affiliations, 10 years for the decaying advertiser base and a weighted average life of 14 years for the other intangible assets. Acquired property and equipment will be depreciated on a straight-line basis over the respective estimated remaining useful lives. Goodwill is calculated as the excess of the consideration transferred over the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired and represents the future economic benefits expected to arise from other intangible assets acquired that do not qualify for separate recognition, including assembled workforce and noncontractual relationships, as well as expected future synergies. We expect that goodwill will be deductible for tax purposes. The initial purchase price allocation is based upon all information available to us at the present time and is subject to change, and such changes could be material.
The results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2013 includes the results of the Barrington stations since November 22, 2013. Net broadcast revenues and operating income of the Barrington stations included in our consolidated statements of operations, were $16.9 million and $4.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2013.
Pro Forma Information
The following table sets forth unaudited pro forma results of operations, assuming that the above acquisitions, along with transactions necessary to finance the acquisitions, occurred at the beginning of the year preceding the year of acquisition. The pro forma results exclude acquisitions presented under Other Acquisitions below, as they were deemed not material both individually and in the aggregate. The 2011 period does not include the pro forma effects of the 2013 acquisitions, and as such will not provide comparability to the 2012 and 2013 pro forma periods presented in the following table (in thousands, except per share data):
| | (Unaudited) | |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
Total revenues | | $ | 1,580,883 | | $ | 1,513,975 | | $ | 1,210,257 | |
Net Income | | $ | 56,657 | | $ | 153,807 | | $ | 151,751 | |
Net Income attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 54,308 | | $ | 153,370 | | $ | 151,352 | |
Basic and diluted earnings per share attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 0.58 | | $ | 1.89 | | $ | 1.86 | |
F-23
Table of Contents
This pro forma financial information is based on historical results of operations, adjusted for the allocation of the purchase price and other acquisition accounting adjustments, and is not indicative of what our results would have been had we operated the businesses since the beginning of the annual period presented because the pro forma results do not reflect expected synergies. The pro forma adjustments reflect depreciation expense, amortization of intangibles and amortization of program contract costs related to the fair value adjustments of the assets acquired, additional interest expense related to the financing of the transactions, exclusion of nonrecurring financing and transaction related costs, alignment of accounting policies and the related tax effects of the adjustments. Depreciation and amortization expense are higher than amounts recorded in the historical financial statements of the acquirees due to the fair value adjustments recorded for long-lived tangibles and intangible assets in purchase accounting. The pro forma revenues exclude the revenues of WLAJ-TV and WLWC-TV which are classified as discontinued operations in the consolidated statements of operations.
In connection with these acquisitions, for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011, we incurred a total of $2.8 million, $1.2 million, and $0.6 million, respectively, of costs primarily related to legal and other professional services,, which we expensed as incurred and classified as corporate general and administrative expenses in the consolidated statements of operations. These costs were not included in the pro forma amounts above as they are nonrecurring in nature.
Other Acquisitions
We acquired five other television stations during the year ended December 31, 2012 in three markets. The initial purchase price allocated includes $45.1 million paid for certain broadcast assets of these stations, less working capital adjustments of $0.7 million, and $4.4 million of non-controlling interests related to, and amounts paid by certain VIEs for the license assets of certain of these stations owned by VIEs that we consolidate. In addition to the Fisher and Barrington acquisitions, we acquired nineteen television stations during the year ended December 31, 2013 in ten markets, of which five station in four of the ten markets were acquired from Cox Media Group in May 2013. Additionally, ten of the nineteen stations were acquired in four markets from TTBG LLC (TTBG) during September 2013 and October 2013. The initial purchase price allocated includes $272.7 million paid for certain broadcast assets of these stations, working capital of $9.5 million, and $0.7 million paid by certain VIEs for the license assets of certain of these stations owned by VIEs that we consolidate. We allocated the total purchase price of these within the respective years, as follows (in thousands):
| | 2013 | | 2012 | |
Accounts receivable | | $ | 8,226 | | $ | — | |
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | 5,217 | | 160 | |
Program contract costs | | 6,182 | | 1,638 | |
Property and equipment | | 54,148 | | 16,545 | |
Deferred tax asset | | 3,888 | | — | |
Broadcast licenses | | 3,736 | | 2,679 | |
Definite-lived intangible assets | | 147,191 | | 22,546 | |
Accrued liabilities | | (3,926 | ) | (1,178 | ) |
Program contracts payable | | (6,331 | ) | (4,252 | ) |
Other long term liabilities | | (10,300 | ) | — | |
Fair value of identifiable net assets acquired | | 208,031 | | 38,138 | |
Goodwill | | 74,847 | | 10,661 | |
Total | | $ | 282,878 | | $ | 48,799 | |
The definite-lived intangible assets in the table above, will be amortized over the remaining useful lives of 15 years for network affiliations, 10 years for decaying advertiser base, and a weighted average of 14 years for the other intangible assets. In conjunction with these acquisitions, for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, we incurred transaction costs of approximately $0.6 million and $0.7 million respectively, which are reported in general and administrative expenses in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Net broadcast revenues for the year ended December 31, 2013 related to stations acquired in 2013 were $52.4 million. Net broadcast revenues for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012 related to the stations acquired in 2012 were $21.5 million and $5 million, respectively.
In December 2012, we acquired the license assets of WTTA-TV in Tampa/St. Petersburg, Florida from Bay Television, Inc. (Bay TV). Prior to December 1, 2012, we performed sales, programming and other management services to the station pursuant
F-24
Table of Contents
to an LMA which was terminated upon closing. As discussed in Note 11. Related Person Transactions, our controlling shareholders own a controlling interest in Bay TV. As this was considered a transaction between entities under common control, the acquisition method of accounting was not applied, and the assets acquired were recorded at their historical cost basis and the difference between the purchase price and the historical cost basis of the assets of $23.6 million, net of taxes of $15.6 million, was recorded as a reduction in additional paid-in capital. A substantial portion of the purchase price will be deductible for tax purposes in future periods.
3. STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION PLANS:
Description of Awards
We have seven types of stock-based compensation awards: compensatory stock options (options), restricted stock awards (RSAs), an employee stock purchase plan (ESPP), employer matching contributions (the Match) for participants in our 401(k) plan, stock-settled appreciation rights (SARs), subsidiary stock awards and stock grants to our non-employee directors. Stock-based compensation expense has no effect on our consolidated cash flows. Below is a summary of the key terms and methods of valuation of our stock-based compensation awards:
Options. In June 1996, our Board of Directors adopted, upon approval of the shareholders by proxy, the 1996 Long-Term Incentive Plan (LTIP). The purpose of the LTIP is to reward key individuals for making major contributions to our success and the success of our subsidiaries and to attract and retain the services of qualified and capable employees. Options granted pursuant to the LTIP must be exercised within 10 years following the grant date. A total of 14,000,000 shares of Class A Common Stock are reserved for awards under this plan. As of December 31, 2013, 8,682,809 shares (including forfeited shares) were available for future grants. We have not issued any options subsequent to accelerating the vesting in 2005.
The following is a summary of changes in outstanding stock options:
| | Options | | Weighted-Average
Exercise Price | | Exercisable | | Weighted-Average
Exercise Price | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2012 | | 129,500 | | $ | 11.73 | | 129,500 | | $ | 11.73 | |
2013 Activity: | | | | | | | | | |
Granted | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
Exercised | | (100,000 | ) | 11.86 | | — | | — | |
Cancelled | | (17,000 | ) | 11.71 | | — | | — | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2013 | | 12,500 | | 10.75 | | 12,500 | | 10.75 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
RSAs. RSAs are granted to employees pursuant to the LTIP. RSAs issued in 2013, 2012 and 2011 have certain restrictions that lapse over two years at 50% and 50%, respectively. RSAs issued prior to 2010 have certain restrictions that lapse over three years at 25%, 25% and 50%, respectively. As the restrictions lapse, the Class A Common Stock may be freely traded on the open market. Unvested RSAs are entitled to dividends. The fair value assumes the value of the stock on the grant date.
The following is a summary of changes in unvested restricted stock:
| | RSAs | | Weighted-Average
Price | |
Unvested shares at December 31, 2012 | | 158,500 | | $ | 11.79 | |
2013 Activity: | | | | | |
Granted | | 314,000 | | 14.19 | |
Vested | | (102,500 | ) | 11.84 | |
Forfeited | | — | | — | |
Unvested shares at December 31, 2013 | | 370,000 | | 13.81 | |
| | | | | | |
For the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, we recorded compensation expense of $2.7 million, $1.2 million and $1.0 million, respectively. The majority of the unrecognized compensation expense of $2.5 million, as of December 31, 2013, will be recognized in 2014.
ESPP. In March 1998, the Board of Directors adopted, subject to approval of the shareholders, the ESPP. The ESPP provides our employees with an opportunity to become shareholders through a convenient arrangement for purchasing shares of Class A Common Stock. On the first day of each payroll deduction period, each participating employee receives options to purchase a number of shares of our common stock with money that is withheld from his or her paycheck. The number of shares
F-25
Table of Contents
available to the participating employee is determined at the end of the payroll deduction period by dividing the total amount of money withheld during the payroll deduction period by the exercise price of the options (as described below). Options granted under the ESPP to employees are automatically exercised to purchase shares on the last day of the payroll deduction period unless the participating employee has, at least thirty days earlier, requested that his or her payroll contributions stop. Any cash accumulated in an employee’s account for a period in which an employee elects not to participate is distributed to the employee.
The initial exercise price for options under the ESPP is 85% of the lesser of the fair market value of the common stock as of the first day of the quarter and as of the last day of that quarter. No participant can purchase more than $25,000 worth of our common stock over all payroll deduction periods ending during the same calendar year. We value the stock options under the ESPP using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, which incorporates the following assumptions as of December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011:
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
Risk-free interest rate | | 0.1% | | 0.1% | | 0.4% | |
Expected life | | 3 months | | 3 months | | 3 months | |
Expected volatility | | 37%-60% | | 38%-53% | | 38%-67% | |
Weighted average volatility | | 44% | | 44% | | 51% | |
Annual dividend yield | | 1.8%-4.7% | | 4.3%-6.7% | | 3.8%-6.6% | |
Weighted average dividend yield | | 4.2% | | 5.2% | | 5.4% | |
We use the Black-Scholes model as opposed to a lattice pricing model because employee exercise patterns are not relevant to this plan. The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant with short-term maturities that approximate the expected life of the options of three months. The expected volatility is based on our historical stock prices over the previous three month period. The annual dividend yield is based on the annual dividend per share divided by the share price on the grant date.
The stock-based compensation expense recorded related to the ESPP for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 was $0.3 million, $0.2 million and $0.1 million, respectively. Less than 0.1 million shares were issued to employees during the year ended December 31, 2013.
Match. The Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. 401(k) Profit Sharing Plan and Trust (the 401(k) Plan) is available as a benefit for our eligible employees. Contributions made to the 401(k) Plan include an employee elected salary reduction amount, the Match and an additional discretionary amount determined each year by the Board of Directors. The Match and any additional discretionary contributions may be made using our Class A Common Stock if the Board of Directors so chooses. Typically, we make the Match using our Class A Common Stock.
The value of the Match is based on the level of elective deferrals into the 401(k) plan. The amount of shares of our Class A Common Stock used to make the Match is determined using the closing price on or about March 1st of each year for the previous calendar year’s Match. The Match is discretionary and is equal to a maximum of 50% of elective deferrals by eligible employees, capped at 4% of the employee’s total cash compensation. For the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, we recorded $3.1 million, $1.6 million and $1.3 million, respectively, of compensation expense related to the Match.
SARs. On February 5, 2013, 500,000 SARs were granted to David Smith, our President and Chief Executive Officer, pursuant to the LTIP. The base value of each SAR is $14.21 per share, which was the closing price of our Class A Common Stock on the grant date. The SARs had a grant date fair value of $3.2 million. On March 9, 2012, 400,000 SARs were granted to David Smith, our President and Chief Executive Officer, pursuant to the LTIP. The base value of each SAR is $11.68 per share, which was the closing price of our Class A Common Stock on the grant date. The SARs had a grant date fair value of $2.0 million. On March 22, 2011, 300,000 SARs were granted to David Smith, our President and Chief Executive Officer, pursuant to the LTIP. The base value of each SAR is $12.07 per share, which was the closing price of our Class A Common Stock on the grant date. The SARs had a grant date fair value of $2.2 million. The SARs have a 10-year term and vest immediately. We valued the SARs using the Black-Scholes model and the following assumptions:
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
Risk-free interest rate | | 0.9% | | 0.9% | | 3.6% | |
Expected life | | 5 years | | 5 years | | 10 years | |
Expected volatility | | 73% | | 73% | | 68% | |
Annual dividend yield | | 4.3% | | 5.2% | | 2.3% | |
The following is a summary of the changes in SARS:
F-26
Table of Contents
| | SARs | | Weighted-Average Price | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2012 | | 900,000 | | $ | 12.72 | |
2013 Activity: | | | | | |
Granted | | 500,000 | | 14.21 | |
Exercised | | — | | — | |
Outstanding SARs at December 31, 2013 | | 1,400,000 | | 13.25 | |
| | | | | | |
For the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, we recorded compensation expense, at the grant date, of $3.2 million, $2.0 million and $2.2 million, respectively, related to these grants. In 2011, David Smith exercised 650,000 of his then outstanding SARs for 237,947 shares. During 2013, 2012 and 2011, outstanding SARs increased the weighted average shares outstanding for purposes of determining dilutive earnings per share. As of December 31, 2013, 1,400,000 SARs were outstanding.
Subsidiary Stock Awards. From time to time, we grant subsidiary stock awards to employees. The subsidiary stock is typically in the form of a membership interest in a consolidated limited liability company, not traded on a public exchange and valued based on the estimated fair value of the subsidiary. Fair value is typically estimated using discounted cash flow models and/or appraisals. These stock awards vest immediately. For the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, we recorded compensation expense of $0.3 million, $0.7 and $2.9 million, respectively, related to these awards. These awards have no effect on the shares used in our basic and diluted earnings per share.
Stock Grants to Non-Employee Directors. In addition to directors fees paid, on the date of each of our annual meetings of shareholders, each non-employee director receives a grant of shares of Class A Common Stock pursuant to the LTIP. In 2013, each non-employee director received 6,250 shares and in 2012 and 2011, each non-employee director received 5,000 shares, respectively. On June 6, 2013, we granted 31,250 shares that had a fair value of $24.30 per share. On June 14, 2012 and June 3, 2011, we granted 25,000 shares that had a fair value of $8.12 per share, 25,000 shares that had a fair value of $9.39 per share, respectively. The fair value assumes the closing value of the stock on the date of grant. We recorded expense of $0.8 million, $0.2 million and $0.2 million for each of the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011. Additionally, these shares are included in the total shares outstanding, which results in a dilutive effect on our basic and diluted earnings (loss) per share.
4. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT:
Property and equipment are stated at cost, less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is generally computed under the straight-line method over the following estimated useful lives:
Buildings and improvements | | 10 - 30 years | |
Station equipment | | 5 - 10 years | |
Office furniture and equipment | | 5 - 10 years | |
Leasehold improvements | | Lesser of 10 - 30 years or lease term | |
Automotive equipment | | 3 - 5 years | |
Property and equipment under capital leases | | Lease term | |
Acquired property and equipment as discussed in Note 2. Acquisitions, is depreciated on a straight-line basis over the respective estimated remaining useful lives.
Property and equipment consisted of the following as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 (in thousands):
| | 2013 | | 2012 | |
Land and improvements | | $ | 37,517 | | $ | 33,932 | |
Real estate held for development and sale | | 67,037 | | 56,419 | |
Buildings and improvements | | 168,441 | | 135,162 | |
Station equipment | | 572,851 | | 425,823 | |
Office furniture and equipment | | 50,210 | | 41,134 | |
Leasehold improvements | | 19,453 | | 18,362 | |
Automotive equipment | | 23,443 | | 20,634 | |
Capital leased assets | | 81,602 | | 79,126 | |
Construction in progress | | 17,078 | | 18,274 | |
| | 1,037,632 | | 828,866 | |
Less: accumulated depreciation | | (441,561 | ) | (389,153 | ) |
| | $ | 596,071 | | $ | 439,713 | |
F-27
Table of Contents
Capital leased assets are related to building, tower and equipment leases. Depreciation related to capital leases is included in depreciation expense in the consolidated statements of operations. We recorded capital lease depreciation expense of $4.0 million, $3.5 million and $3.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
5. GOODWILL, BROADCAST LICENSES AND OTHER INTANGIBLE ASSETS:
Goodwill, which arises from the purchase price exceeding the assigned value of the net assets of an acquired business, represents the value attributable to unidentifiable intangible elements being acquired. Goodwill totaled $1,380.1 million and $1,074.0 million at December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The change in the carrying amount of goodwill related to continuing operations was as follows (in thousands):
| | Broadcast | | Other
Operating
Divisions | | Consolidated | |
Balance at December 31, 2011 | | | | | | | |
Goodwill | | $ | 1,070,202 | | $ | 3,488 | | $ | 1,073,690 | |
Accumulated impairment losses | | (413,573 | ) | — | | (413,573 | ) |
| | 656,629 | | 3,488 | | 660,117 | |
Acquisition of television stations (a) | | 425,822 | | — | | 425,822 | |
Reclassification of goodwill to assets held for sale (b) | | (11,907 | ) | — | | (11,907 | ) |
Balance at December 31, 2012 (c) | | | | | | | |
Goodwill (a) | | 1,484,117 | | 3,488 | | 1,487,605 | |
Accumulated impairment losses | | (413,573 | ) | — | | (413,573 | ) |
| | 1,070,544 | | 3,488 | | 1,074,032 | |
Acquisition of television stations (a) | | 330,309 | | — | | 330,309 | |
Sale of broadcast assets (d) | | (14,724 | ) | — | | (14,724 | ) |
Measurement period adjustments related to 2012 acquisitions (e) | | (9,535 | ) | — | | (9,535 | ) |
Balance at December 31, 2013 (c) | | | | | | | |
Goodwill | | 1,790,167 | | 3,488 | | 1,793,655 | |
Accumulated impairment losses | | (413,573 | ) | — | | (413,573 | ) |
| | $ | 1,376,594 | | $ | 3,488 | | $ | 1,380,082 | |
(a) In 2013 and 2012, we acquired goodwill as a result of acquisitions as discussed in Note 2. Acquisitions.
(b) In 2012, we reclassified goodwill to assets held for sale as a result of the pending sales of WLAJ-TV in Lansing, Michigan, and WLWC-TV in Providence, Rhode Island as discussed in Discontinued Operations under Note 1. Nature of Operations and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
(c) Approximately $6.4 million of goodwill relates to consolidated VIEs as of December 31, 2013 and 2012.
(d) Amounts relate to the sale of WSYT (FOX) (including certain assets of WNYS (MNT), which we performed service to under an LMA) in Syracuse, NY, in connection with the acquisition of stations from Barrington, as discussed in Note 2. Acquisitions.
(e) Amounts relate to immaterial measurement period adjustments related to 2012 acquisitions.
As of December 31, 2013 and 2012, the carrying amount of our broadcast licenses related to continuing operations was as follows (in thousands):
| | 2013 | | 2012 | |
Beginning balance | | $ | 85,122 | | $ | 47,002 | |
Acquisition of television stations (a) | | 15,514 | | 38,924 | |
Sale of broadcast assets (e) | | (25 | ) | — | |
Measurement period adjustments related to 2012 acquisitions (d) | | 418 | | — | |
Reclassification of broadcast license to assets held for sale (b) | | — | | (804 | ) |
Ending balance (c) | | $ | 101,029 | | $ | 85,122 | |
F-28
Table of Contents
(a) In 2013, we acquired broadcast licenses as a result of acquisitions as discussed in Note 2. Acquisitions.
(b) In 2012, we reclassified the broadcast license of WLAJ-TV in Lansing, Michigan and WLWC-TV in Providence, Rhode Island to assets held for sale as discussed in Discontinued Operations under Note 1. Nature of Operations and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies.
(c) Approximately $16.8 million and $14.9 million of broadcast licenses relate to consolidated VIEs as of December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
(d) Amounts relate to immaterial measurement period adjustments related to 2012 acquisitions, as discussed in Note 2. Acquisitions
(e) Amounts relate to the sale of WSYT (FOX) (including certain assets of WNYS (MNT), which we performed service to under an LMA) in Syracuse, NY, in connection with the acquisition of stations from Barrington, as discussed in Note 2. Acquisitions.
We did not have any indicators of impairment in any interim period in 2013 or 2012 and therefore did not perform interim impairment tests for goodwill or broadcast licenses during those periods. We performed our annual impairment tests for goodwill and indefinite-lived intangibles in the fourth quarter of 2013 and 2012 and we did not recognize any impairment as a result of our qualitative and/or quantitative assessments. In 2013, we concluded based on our qualitative assessment that it was more likely than not that the fair values of the reporting units would sufficiently exceed their carrying values and it was unnecessary to perform the quantitative two-step method. Based on the results of our annual qualitative assessment for goodwill impairment performed in 2012, we concluded that we would need to perform a quantitative “Step 1” test for three of our markets which had aggregate goodwill of $79.5 million as of October 1, 2012, the date of our annual impairment test. These markets had a decrease in operating results for the past few years and therefore, we estimated the fair value of these reporting units based on a market approach and income approach. For all three markets, the fair value of the reporting unit exceeded the respective carrying value by more than 10%. For all our other reporting units, we concluded based on the qualitative assessment that it was more likely than not that the fair values of these reporting units would sufficiently exceed their carrying values and it was not necessary to perform the quantitative two-step method.
We did not have any indicators of impairment in the first, second or third quarters of 2011 and therefore did not perform interim impairment tests for goodwill during those periods. In the first quarter 2011, we recorded an impairment charge of $0.4 million for our broadcast licenses due to anticipated increase in costs for one of our stations as a result of converting to full power. We performed our annual impairment tests in the fourth quarter of 2011, and did not recognize any impairment as a result of the assessments. Based on the annual qualitative assessment for goodwill impairment performed in 2011, we concluded that it was more likely than not that the fair values of all reporting units would sufficiently exceed their carrying value and thus it was not necessary to perform the quantitative two-step method.
The qualitative factors for our reporting units reviewed during our annual assessments, with the exception of the three markets in which we performed a quantitative assessment in 2012, indicated stable or improving margins and favorable or stable forecasted economic conditions including stable discount rates and comparable or improving business multiples. Additionally, the results of prior quantitative assessments supported significant excess fair value over carrying value of our reporting units.
F-29
Table of Contents
The carrying value, fair value and impairment loss of the broadcast licenses which were impaired during 2011 were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | Fair Value Measurements Using | | | |
Description | | Carrying Value | | Quoted
Prices in
Active
Markets for
Identical
Assets
(Level 1) | | Significant
Other
Observable
Inputs
(Level 2) | | Significant
Unobservable
Inputs
(Level 3) | | Total
Impairment
Losses | |
Year Ended December 31, 2011 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Broadcast licenses (a) | | $ | 1,265 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 1,265 | | $ | 398 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(a) The fair value above represents the fair value of the broadcast licenses that were impaired in 2011 and written down to fair value. It excludes carrying values of $45.7 million related to broadcast licenses as of December 31, 2011, which were not impaired and had fair values in excess of carrying value.
The key assumptions used to determine the fair value of our broadcast licenses consist of discount rates, estimated market revenues, normalized market share, normalized profit margin, and estimated start-up costs. The qualitative factors for our broadcast licenses indicated an increase in market revenues, stable market shares and stable cost factors. The revenue, expense and growth rates used in determining the fair value of our broadcast licenses remained constant or increased slightly from 2012 to 2013. The growth rates are based on market studies, industry knowledge and historical performance. The discount rates used to determine the fair value of our broadcast licenses did not change significantly over the last three years. The discount rate is based on a number of factors including market interest rates, a weighted average cost of capital analysis based on the target capital structure for a television station, and includes adjustments for market risk and company specific risk.
The following table shows the gross carrying amount and accumulated amortization of definite-lived intangibles related to continuing operations (in thousands):
| | As of December 31, 2013 | |
| | Gross Carrying Amount | | Accumulated
Amortization | | Net | |
| | | | | | | |
Amortized intangible assets: | | | | | | | |
Network affiliation (a) | | $ | 869,535 | | $ | (195,037 | ) | $ | 674,498 | |
Decaying advertiser base (b) | | 260,454 | | (135,978 | ) | 124,476 | |
Other (c) | | 389,769 | | (60,988 | ) | 328,781 | |
Total | | $ | 1,519,758 | | $ | (392,003 | ) | $ | 1,127,755 | |
| | As of December 31, 2012 | |
| | Gross Carrying Amount | | Accumulated
Amortization | | Net | |
| | | | | | | |
Amortized intangible assets: | | | | | | | |
Network affiliation | | $ | 580,929 | | $ | (160,166 | ) | $ | 420,763 | |
Decaying advertiser base | | 178,094 | | (121,919 | ) | 56,175 | |
Other (d) | | 195,103 | | (48,635 | ) | 146,468 | |
Total | | $ | 954,126 | | $ | (330,720 | ) | $ | 623,406 | |
(a) The increase in network affiliation assets includes amounts from acquisitions of $279.0 million and $343.0 million in 2013 and 2012, respectively. See Note 2. Acquisitions for more information.
(b) The increase in decaying advertiser base includes amounts from acquisitions of $84.3 million and $56.9 million in 2013 and 2012, respectively.
F-30
Table of Contents
(c) The increase in other intangible assets includes the amounts from acquisitions of $159.5 million and $79.4 million in 2013 and 2012, respectively. See Note 2. Acquisitions for more information.
Definite-lived intangible assets and other assets subject to amortization are being amortized on a straight-line basis over their estimated useful lives which generally range from 5 to 25 years. The total weighted average useful life of all definite-lived intangible assets and other assets subject to amortization acquired as a result of the acquisitions discussed in Note 2. Acquisitions is 14 years. The amortization expense of the definite-lived intangible assets for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 was $70.8 million, $38.1 million and $18.2 million, respectively. We analyze specific definite-lived intangibles for impairment when events occur that may impact their value in accordance with the respective accounting guidance for long-lived assets. There were no impairment charges recorded for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011.
The following table shows the estimated amortization expense of the definite-lived intangible assets for the next five years (in thousands):
For the year ended December 31, 2014 | | $ | 97,242 | |
For the year ended December 31, 2015 | | 96,845 | |
For the year ended December 31, 2016 | | 96,275 | |
For the year ended December 31, 2017 | | 95,696 | |
For the year ended December 31, 2018 | | 86,313 | |
Thereafter | | 655,384 | |
| | $ | 1,127,755 | |
6. NOTES PAYABLE AND COMMERCIAL BANK FINANCING:
Bank Credit Agreement
In January 2012, we drew $180.0 million of the incremental Term Loan B under our Bank Credit Agreement to fund the asset acquisition of Four Points, which closed January 1, 2012. In addition, in April 2012, we drew $157.5 million of the incremental Term Loan A and $192.5 million of the incremental Term Loan B under our Bank Credit Agreement to fund the asset acquisition of Freedom, which closed April 1, 2012. As of December 31, 2012, we had $48.0 million drawn on our revolver.
On April 9, 2013, we entered into an amendment and restatement (the Amendment) of our credit agreement (as amended, the Bank Credit Agreement). Pursuant to the Amendment, we refinanced the existing facility and replaced the existing term loans under the facility with a new $500.0 million term loan A facility (Term Loan A), maturing April 2018 (which included a $445.0 million delayed draw of the Term Loan A that was drawn on in October 2013) and priced at LIBOR plus 2.25%; and a $400.0 million term loan B facility (Term Loan B), maturing April 2020 and priced at LIBOR plus 2.25% with a LIBOR floor of 0.75%.
In addition, we replaced our existing revolving line of credit with a new $100.0 million revolving line of credit maturing April 2018 and priced at LIBOR plus 2.25%. The proceeds from the term loans, along with cash on hand and/or a borrowings under the revolving line of credit, were used to fund acquisitions.
In October 2013, we further amended certain terms of our Bank Credit Agreement. Pursuant to the agreement, we increased the capacity of Term Loan A from $500 million to $700 million through a $200.0 million delayed draw tranche and increased the capacity of Term Loan B from $400 million to $650 million. We drew $250.0 million of the incremental Term Loan B in October 2013 which was used to fund fourth quarter acquisitions, the redemption of the 9.25% Senior Secured Second Lien Notes and for general corporate purposes. We also increased the capacity of our revolving line of credit from $100.0 million to $157.5 million maturing in April 2018. We also amended certain terms of the Bank Credit Agreement. The final terms of the amendment are as follows:
· We increased our ratio of our First Lien Indebtedness from 3.50 times EBITDA to 3.75 times EBITDA for the period January 1, 2015 through maturity of the agreement.
· Other amended terms provided us with increased television station acquisition capacity, more flexibility under the other restrictive covenants and prepayments of the existing term loans.
F-31
Table of Contents
Interest expense related to the Bank Credit Agreement, including the revolver, on our consolidated statement of operations was $27.3 million, $35.7 million and $19.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively. Included in these amounts were debt refinancing costs of $2.4 million, $6.3 million and $6.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, and 2011 respectively, in accordance with debt modification accounting guidance that applied to the amendments. In connection with the amendments, we capitalized $14.9 million and $2.3 million as deferred financing costs, which are included in other assets in our consolidated financial statements during the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The weighted average effective interest rate of the Term Loan B for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012 was 3.29% and 4.40%, respectively. The weighted average effective interest rate of the Term Loan A for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012 was 2.51% and 2.53%, respectively.
Our Bank Credit Agreement contains certain cross-default provisions with certain material third-party licensees, defined as any party that owns the license assets of one or more television stations for which we provided services to pursuant to LMAs and/or other outsourcing agreements and those stations provide 10% or more of our aggregate broadcast cash flows. A default by a material third-party licensee under our agreements with such parties, including a default caused by insolvency, would cause an event of default under our Bank Credit Agreement. As of December 31, 2013, there were no material third party licensees as defined in our Bank Credit Agreement.
Our Bank Credit Agreement and indentures governing our outstanding notes contain a number of covenants that, among other things, restrict our ability and our subsidiaries’ ability to incur additional indebtedness, pay dividends, incur liens, engage in mergers or consolidations, make acquisitions, investments or disposals and engage in activities with affiliates. In addition, under the Bank Credit Agreement, we are required to satisfy specified financial ratios. As of December 31, 2013, we were in compliance with all financial ratios and covenants.
Substantially all of our stock in our wholly-owned subsidiaries has been pledged as security for the Bank Credit Agreement.
6.375% Senior Notes, due 2021
On October 11, 2013, we issued $350.0 million in senior unsecured notes, which bear interest at a rate of 6.375% per annum and mature on November 1, 2021 (the 6.375% Notes), pursuant to an indenture dated October 11, 2013 (the 6.375% Indenture). The 6.375% Notes were priced at 100% of their par value and interest is payable semi-annually on May 1 and November 1, commencing on May 1, 2014. Prior to November 1, 2016, we may redeem the 6.375% Notes, in whole or in part, at any time or from time to time at a price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the Notes plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the date of redemption, plus a “make-whole” premium as set forth in the 6.375% Indenture. In addition, on or prior to November 1, 2016, we may redeem up to 35% of the 6.375% Notes using the proceeds of certain equity offerings. If we sell certain of our assets or experience specific kinds of changes of control, holder of the 6.375% Notes may require us to repurchase some or all of the Notes. Upon the sale of certain of our assets or certain changes of control, the holders of the 6.375% Notes may require us to repurchase some or all of the notes. The proceeds from the offering of the 6.375% Notes were used to partially fund the redemption of the 9.25% Senior Secured Second Lien Notes, Due 2017 (the 9.25% Notes), as discussed further below. Concurrent with entering into an indenture for the 6.375% Notes in October 2013, we also entered into a registration rights agreement requiring us to complete an offer of an exchange of the 6.375% Notes for registered securities with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the SEC) by July 8, 2014. We filed a registration statement on Form S-4 with the SEC on December 6, 2013, which became effective on December 19, 2013. An exchange offer was launched on December 19, 2013 to exchange the unregistered 6.375% Notes with the holders for 6.375% Notes registered under the Securities Act of 1933. The exchange offer was completed on January 24, 2014 with 99.7% of the $350.0 million 6.375% Senior Unsecured Notes due 2021 tendered in the exchange offer.
Interest expense was $4.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The weighted average effective interest rate for the 6.375% Notes was 6.375% for the year ended December 31, 2013.
5.375% Senior Unsecured Notes, due 2021
On April 2, 2013, we issued $600.0 million of senior unsecured notes, which bear interest at a rate of 5.375% per annum and mature on April 1, 2021 (the 5.375% Notes), pursuant to an indenture dated April 2, 2013 (the 5.375% Indenture). The 5.375% Notes were priced at 100% of their par value and interest is payable semi-annually on April 1 and October 1, commencing on October 1, 2013. Prior to April 1, 2016, we may redeem the 5.375% Notes, in whole or in part, at any time or from time to time at a price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the 5.375% Notes plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the redemption date, plus a “make-whole” premium as set forth in the 5.375% Indenture. Beginning on April 1, 2016, we may redeem some or all of the 5.375% Notes at any time or from time to time at a redemption price set forth in the 5.375% Indenture. In addition, on or prior to April 1, 2016, we may redeem up to 35% of the 5.375% Notes using proceeds of certain equity offerings. Upon the
F-32
Table of Contents
sale of certain of our assets or certain changes of control, the holders of the 5.375% Notes may require us to repurchase some or all of the notes. The net proceeds from the offering of the 5.375% Notes were used to pay down outstanding indebtedness under our bank credit facility. Concurrent with entering into an indenture for the 5.375% Notes in April 2013, we also entered into a registration rights agreement requiring us to complete an offer of an exchange of the 5.375% Notes for registered securities with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the SEC) by December 28, 2013. We filed a registration statement on Form S-4 with the SEC on April 4, 2013, which became effective on April 16, 2013. An exchange offer was launched on May 23, 2013 to exchange the unregistered 5.375% Notes with the holders for 5.375% Notes registered under the Securities Act of 1933. The exchange offer was completed on June 28, 2013 with 100% of the $600.0 million 5.375% Senior Unsecured Notes due 2021 tendered in the exchange offer.
Interest expense was $24.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The weighted average effective interest rate for the 5.375% Notes was 5.375% for the year ended December 31, 2013.
6.125% Senior Unsecured Notes, due 2022
On October 12, 2012, we issued $500.0 million of senior unsecured notes, which bear interest at a rate of 6.125% per annum and mature on October 1, 2022 (the 6.125% Notes), pursuant to an indenture dated October 12, 2012 (the 2012 Indenture). The 6.125% Notes were priced at 100% of their par value and interest is payable semi-annually on April 1 and October 1, commencing on April 1, 2013. Prior to October 1, 2017, we may redeem the 6.125% Notes, in whole or in part, at any time or from time to time at a price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the 6.125% Notes plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the redemption date, plus a “make-whole” premium as set forth in the 2012 Indenture. Beginning on October 1, 2017, we may redeem some or all of the 6.125% Notes at any time or from time to time at a redemption price set forth in the 2012 Indenture. In addition, on or prior to October 1, 2015, we may redeem up to 35% of the 6.125% Notes using proceeds of certain equity offerings. Upon the sale of certain of our assets or certain changes of control, the holders of the 6.125% Notes may require us to repurchase some or all of the notes. The net proceeds from the offering of the 6.125% Notes were used to pay down outstanding indebtedness under the revolving credit facility under our Bank Credit Agreement and fund certain acquisitions as described under Note 2. Acquisitions, and for general corporate purposes. Concurrent with entering into the 2012 Indenture, we also entered into a registration rights agreement requiring us to complete an offer of an exchange of the 6.125% Notes for registered securities with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the SEC) by July 8, 2013. We filed a registration statement on Form S-4 with the SEC on April 4, 2013 which became effective on April 16, 2013. An exchange offer was launched on May 23, 2013 to exchange the unregistered 6.125% Notes with the holders for 6.125% Notes registered under the Securities Act of 1933. The exchange offer was completed on June 28, 2013 with 100.0% of the $500.0 million 6.125% Senior Unsecured Notes due 2022 tendered in the exchange offer
Interest expense was $30.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The weighted average effective interest rate for the 6.125% Notes was 6.125% for the year ended December 31, 2013.
8.375% Senior Unsecured Notes, due 2018
On October 4, 2010, we issued $250.0 million aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes, which bear interest at a rate of 8.375% per annum and mature on October 15, 2018 (the 8.375% Notes), pursuant to an indenture dated as of October 4, 2010 (the 2010 Indenture). The 8.375% were issued at 98.567% of their par value and interest is payable semi-annually on April 15 and October 15 of each year, commencing on April 15, 2011. Prior to October 15, 2014, we may redeem the 8.375% Notes in whole or in part, at any time or from time to time at a price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the 8.375% Notes plus accrued and unpaid interest, plus a “make-whole premium” as set forth in the 2010 Indenture. Beginning on October 15, 2014, we may redeem some or all of the 8.375% Notes at any time or from time to time at the redemption prices set forth in the 2010 Indenture. In addition, on or prior to October 15, 2013, we may redeem up to 35% of the 8.375% Notes using the proceeds of certain equity offerings. Upon certain changes of control, we must offer to purchase the 8.375% Notes at a price equal to 101% of the face amount of the notes plus accrued and unpaid interest. Upon the sale of certain of our assets or certain changes of control, the holders of the 8.375% Notes may require us to repurchase some or all of the 8.375% Notes. Concurrent to entering into the 2010 Indenture we also entered into a registration rights agreement requiring us to complete an offer of an exchange of the 8.375% Notes for registered securities with the SEC by July 1, 2011. The 8.375% Notes registration became effective on November 23, 2010.
In 2011, we repurchased, in the open market, $12.5 million principal amount of the 8.375% Notes. We recognized a loss on these extinguishments of $0.3 million. As of December 31, 2012, the principal amount of the outstanding 8.375% Notes was $237.5 million.
F-33
Table of Contents
Interest expense was $20.3 million, $20.2 million and $21.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively. The weighted average effective interest rate of the 8.375% Notes, including amortization of its bond discount, was 8.65% for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
9.25% Senior Secured Second Lien Notes, Due 2017
Effective October 12, 2013, we redeemed all of the outstanding 9.25% Senior Secured Second Lien Notes, representing $500.0 million in aggregate principal amount. Upon the redemption, along with the principal, we paid the accrued and unpaid interest and a make whole premium of $25.4 million, for a total of $546.1 million paid to noteholders. We recorded a loss on extinguishment of $43.1 million in the fourth quarter of 2013 related to this redemption, which included the write-off of the unamortized deferred financing costs of $9.5 million and debt discount of $8.2 million.
Interest expense was $37.3 million, $47.7 million and $47.6 for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively. The weighted average effective interest rate for the 9.25% Notes, including the amortization of its bond discount, was 9.74% for the year ended December 31, 2012.
4.875% Convertible Senior Notes, due 2018 and 3.0% Convertible Senior Notes, Due 2027
In September 2013, 100% of the outstanding 4.875% Convertible Senior Notes, due in 2018 (the 4.875% Notes), representing aggregate principal of $5.7 million, were converted into 388,632 shares of Class A Common Stock, as permitted under the indenture, resulting in an increase in additional paid-in capital of $8.6 million, net of $2.4 million of taxes.
In October 2013, 100% of the outstanding 3.0% Convertible Senior Notes, due in 2027 (the 3.0% Notes), representing aggregate principal of $5.4 million, were converted and settled fully in cash of $10.5 million, as permitted under the indenture. As the original terms of the indenture included a cash conversion feature, the effective settlement of the liability and equity components were accounted for separately. The redemption of the liability component to result in a $1.0 million gain on extinguishment, and the redemption of the equity component was recorded as a $5.1 million reduction in additional paid-in capital, net of $0.9 million of taxes.
Other Operating Divisions Debt
Other operating divisions debt includes the debt of our consolidated subsidiaries with non-broadcast related operations. This debt is non-recourse to us. Interest was paid on this debt at rates typically ranging from LIBOR plus 2.5% to a fixed 6.50% during 2013. During 2013, 2012 and 2011, interest expense on this debt was $3.2 million, $3.1 million and $3.7 million, respectively.
Debt of Variable Interest Entities
Our consolidated VIEs have $55.6 million in outstanding debt for which the proceeds were used to purchase the license assets of certain stations. See Note 1. Nature of Operations and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies and Note 2. Acquisitions for more information. The credit agreement and term loans of these VIEs bear interest of LIBOR plus 2.50%. We have jointly and severally, unconditionally and irrevocably guaranteed the debt of the VIEs, as a primary obligor, including the payment of all unpaid principal of and interest on the loans.
For the year ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, the interest expense relating to the debt of our VIEs which was jointly and severally, unconditionally and irrevocably guaranteed was $1.2 million and $0.1 million, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2012 and 2011, one of our VIEs had debt outstanding that was non-recourse to us and that debt was repaid in full on October 1, 2012. The interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2012 and 2011 related to that debt was $0.3 million and $1.0 million, respectively.
Summary
Notes payable, capital leases and the Bank Credit Agreement consisted of the following as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 (in thousands):
F-34
Table of Contents
| | 2013 | | 2012 | |
Bank Credit Agreement, Term Loan A | | $ | 500,000 | | $ | 263,875 | |
Bank Credit Agreement, Term Loan B | | 646,375 | | 587,656 | |
Revolving Credit Facility | | — | | 48,000 | |
9.25% Senior Secured Second Lien Notes, due 2017 | | — | | 500,000 | |
8.375% Senior Unsecured Notes, due 2018 | | 237,530 | | 237,530 | |
6.375% Senior Unsecured Notes, due 2021 | | 350,000 | | — | |
5.375% Senior Unsecured Notes, due 2021 | | 600,000 | | — | |
6.125% Senior Unsecured Notes, due 2022 | | 500,000 | | 500,000 | |
4.875% Convertible Senior Notes, due 2018 | | — | | 5,685 | |
3.0% Convertible Senior Notes, due 2027 | | — | | 5,400 | |
Debt of variable interest entities | | 30,231 | | 19,950 | |
Debt of variable interest entities (non-recourse) | | 25,350 | | — | |
Other operating divisions debt (all non-recourse) | | 86,263 | | 65,663 | |
Capital leases | | 42,946 | | 43,364 | |
Total outstanding principal | | 3,018,695 | | 2,277,123 | |
Plus: Accretion on 4.875% Convertible Senior Notes, due 2018 | | — | | 332 | |
Less: Discount on Bank Credit Agreement, Term Loan B | | (3,642 | ) | (6,807 | ) |
Less: Discount on 9.25% Senior Secured Second Lien Notes, due 2017 | | — | | (9,483 | ) |
Less: Discount on 8.375% Senior Unsecured Notes, due 2018 | | (2,305 | ) | (2,677 | ) |
Less: Current portion | | (46,346 | ) | (47,622 | ) |
Net carrying value of long-term debt | | $ | 2,966,402 | | $ | 2,210,866 | |
Indebtedness under the notes payable, capital leases and the Bank Credit Agreement as of December 31, 2013 matures as follows (in thousands):
| | Notes and Bank
Credit
Agreement | | Capital Leases | | Total | |
2014 | | $ | 41,449 | | $ | 8,137 | | $ | 49,586 | |
2015 | | 106,849 | | 5,435 | | 112,284 | |
2016 | | 93,986 | | 5,039 | | 99,025 | |
2017 | | 90,113 | | 5,078 | | 95,191 | |
2018 | | 565,076 | | 5,120 | | 570,196 | |
2019 and thereafter | | 2,078,299 | | 44,204 | | 2,122,503 | |
Total minimum payments | | 2,975,772 | | 73,013 | | 3,048,785 | |
Less: Discount on Term Loan B | | (3,642 | ) | — | | (3,642 | ) |
Less: Discount on 8.375% Senior Unsecured Notes, due 2018 | | (2,305 | ) | — | | (2,305 | ) |
Less: Amount representing future interest | | — | | (30,090 | ) | (30,090 | ) |
| | $ | 2,969,825 | | $ | 42,923 | | $ | 3,012,748 | |
As of December 31, 2013, our broadcast segment had 28 capital leases with non-affiliates, including 25 tower leases, two building leases and one software lease; our other operating divisions segment had five capital equipment leases and corporate has one building lease. All of our tower leases will expire within the next 18 years and the building leases will expire within the next 3 years. Most of our leases have 5-10 year renewal options and it is expected that these leases will be renewed or replaced within the normal course of business. For more information related to our affiliate notes and capital leases, see Note 11. Related Person Transactions.
7. PROGRAM CONTRACTS:
Future payments required under program contracts as of December 31, 2013 were as follows (in thousands):
2014 | | $ | 90,933 | |
2015 | | 16,803 | |
2016 | | 8,693 | |
2017 | | 5,626 | |
2018 | | 3,559 | |
Total | | 125,614 | |
Less: Current portion | | (90,933 | ) |
Long-term portion of program contracts payable | | $ | 34,681 | |
Each future periods’ film liability includes contractual amounts owed, however, what is contractually owed does not necessarily
F-35
Table of Contents
reflect what we are expected to pay during that period. While we are contractually bound to make the payments reflected in the table during the indicated periods, industry protocol typically enables us to make film payments on a three-month lag. Included in the current portion amounts are payments due in arrears of $22.6 million. In addition, we have entered into non-cancelable commitments for future program rights aggregating to $163.8 million as of December 31, 2013.
8. COMMON STOCK:
Holders of Class A Common Stock are entitled to one vote per share and holders of Class B Common Stock are entitled to ten votes per share, except for votes relating to “going private” and certain other transactions. The Class A Common Stock and the Class B Common Stock vote together as a single class, except as otherwise may be required by Maryland law, on all matters presented for a vote. Holders of Class B Common Stock may at any time convert their shares into the same number of shares of Class A Common Stock. During 2013, 2,905,502 Class B Common Stock shares were converted into Class A Common Stock shares. There were no Class B Common Stock shares converted into Class A Common Stock shares in 2012.
Our Bank Credit Agreement and some of our subordinated debt instruments have restrictions on our ability to pay dividends. Under our Bank Credit Agreement, in certain circumstances, we may make up to $200.0 million in unrestricted annual cash payments including but not limited to dividends, of which $50.0 million may carry over to the next year. Under the indentures governing the 8.375% Notes, 6.125% Notes, 5.375% Notes and 6.375% Notes, we are restricted from paying dividends on our common stock unless certain specified conditions are satisfied, including that:
· no event of default then exists under the indenture or certain other specified agreements relating to our indebtedness; and
· after taking into account the dividends payment, we are within certain restricted payment requirements contained in the indenture.
In addition, under certain of our debt instruments, the payment of dividends is not permissible during a default thereunder.
In April 2013, we commenced a public offering of 18.0 million shares of Class A common stock. The offering was priced at $27.25 per share on May 1, 2013 and closed on May 7, 2013. The net proceeds of $472.9 million were used to fund 2013 acquisitions and for general corporate purposes.
During 2012, our Board of Directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.12 per share in the months of February and May, which were paid in March and June, and $0.15 per share in the months of August and November, which were paid in September and December. A special cash dividend of $1.00 per share was also declared in November 2012, which was paid in December, for total dividend payments of $1.54 per share for the year ended December 31, 2012. During 2013, our Board of Directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.15 per share in the months of February, April, August and November, which were paid in March, June, September and December, respectively. Total dividend payments for the year ended December 31, 2013 were $0.60 per share. In February 2014, our Board of Directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.15 per share. Future dividends on our common shares, if any, will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend on several factors including our results of operations, cash requirements and surplus, financial condition, covenant restrictions and other factors that the Board of Directors may deem relevant. The Class A Common Stock and Class B Common Stock holders have the same rights related to dividends.
9. INCOME TAXES:
The provision (benefit) for income taxes consisted of the following for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 (in thousands):
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
Provision for income taxes - continuing operations | | $ | 41,249 | | $ | 67,852 | | $ | 44,785 | |
(Benefit) provision for income taxes - discontinued operations | | (10,806 | ) | 663 | | 477 | |
| | $ | 30,443 | | $ | 68,515 | | $ | 45,262 | |
Current: | | | | | | | |
Federal | | $ | 16,229 | | $ | 56,106 | | $ | 678 | |
State | | (8,305 | ) | 4,095 | | 1,055 | |
| | 7,924 | | 60,201 | | 1,733 | |
Deferred: | | | | | | | |
Federal | | 20,214 | | 9,151 | | 41,361 | |
State | | 2,305 | | (837 | ) | 2,168 | |
| | 22,519 | | 8,314 | | 43,529 | |
| | $ | 30,443 | | $ | 68,515 | | $ | 45,262 | |
F-36
Table of Contents
The following is a reconciliation of federal income taxes at the applicable statutory rate to the recorded provision from continuing operations:
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
Federal statutory rate | | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % |
Adjustments- | | | | | | | |
State income taxes, net of federal tax benefit | | 8.3 | % | (0.4 | )% | 1.9 | % |
Non-deductible expenses | | 1.4 | % | 0.3 | % | 0.4 | % |
Domestic Production Activities Deduction | | (3.8 | )% | (1.4 | )% | — | |
Effect of consolidated VIEs | | 3.7 | % | (3.4 | )% | (0.7 | )% |
Change in state tax laws and rates | | (5.5 | )% | 0.2 | % | 0.5 | % |
Other | | 0.9 | % | 1.7 | % | (0.1 | )% |
Effective income tax rate | | 40.0 | % | 32.0 | % | 37.0 | % |
For the year ended December 31, 2013 we recorded $3.4 million of income tax provision related to expenses of our consolidated VIEs that are treated as pass-through entities for income tax purposes. Included in state income taxes above are deferred income tax effects related to certain acquisitions and intercompany mergers. Additionally, during the year ended December 31, 2013 we recorded $2.0 million of additional benefit related to domestic production activities deduction upon filing the 2012 federal income tax return.
For the year ended December 31, 2012, the taxes on consolidated VIEs include a release of $7.7 million of valuation allowance related to certain deferred tax assets of Cunningham, one of our consolidated VIEs, as the weight of all available evidence supports realization of the deferred tax assets. This assessment was based primarily on the sufficiency of forecasted taxable income necessary to utilize net operating loss carryforwards expiring in years 2022 — 2029. This VIE files separate income tax returns. Any resulting tax liabilities are nonrecourse to us, and we are not entitled to any benefit resulting from the deferred tax assets of the VIE.
Temporary differences between the financial reporting carrying amounts and the tax bases of assets and liabilities give rise to deferred taxes. Total deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 were as follows (in thousands):
| | 2013 | | 2012 | |
Current and Long-Term Deferred Tax Assets: | | | | | |
Net operating and capital losses: | | | | | |
Federal | | $ | 5,027 | | $ | 5,738 | |
State | | 63,051 | | 66,990 | |
Broadcast licenses | | 27,652 | | 29,170 | |
Intangibles | | 3,451 | | 5,871 | |
Other | | 35,677 | | 33,803 | |
| | 134,858 | | 141,572 | |
Valuation allowance for deferred tax assets | | (51,062 | ) | (59,407 | ) |
Total deferred tax assets | | $ | 83,796 | | $ | 82,165 | |
| | | | | |
Current and Long-Term Deferred Tax Liabilities: | | | | | |
Broadcast licenses | | $ | (20,395 | ) | $ | (13,090 | ) |
Intangibles | | (270,008 | ) | (216,505 | ) |
Property & equipment, net | | (52,514 | ) | (25,359 | ) |
Contingent interest obligations | | (51,621 | ) | (52,388 | ) |
Other | | (2,037 | ) | (10,213 | ) |
Total deferred tax liabilities | | (396,575 | ) | (317,555 | ) |
Net tax liabilities | | $ | (312,779 | ) | $ | (235,390 | ) |
Our remaining federal and state capital and net operating losses will expire during various years from 2014 to 2033, and some of them are subject to annual limitations under the Internal Revenue Code Section 382 and similar state provisions.
F-37
Table of Contents
As discussed in Note 1. Income taxes, we establish valuation allowances in accordance with the guidance related to accounting for income taxes. As of December 31, 2013, a valuation allowance has been provided for deferred tax assets related to a substantial portion of our available state net operating loss carryforwards based on past operating results, expected timing of the reversals of existing temporary book/tax basis differences, alternative tax strategies and projected future taxable income. Although realization is not assured for the remaining deferred tax assets, we believe it is more likely than not that they will be realized in the future. During the year ended December 31, 2013, we decreased our valuation allowance by $8.3 million from $59.4 million. The reduction in valuation allowance was primarily due to a law change in a state tax jurisdiction, effective for years beginning after December 31, 2014, which we expect will significantly increase the forecasted future taxable income attributable to that state and result in utilization of the state NOL carryforwards. During the year ended December 31, 2012, we decreased out valuation allowance by $19.7 million, from $79.1 million. The reduction in valuation allowance was primarily due to the settlement of several audits, which resulted in the utilization of certain state net operating loss carryforwards which were previously fully reserved, as well as due to changes in estimates of apportionment for certain states. During the year ended December 31, 2011, we increased our valuation allowance by $1.6 million, from $77.6 million. The change in valuation allowance was primarily due to the creation of additional state net operating loss carryforwards.
As of December 31, 2013 and 2012, we had $16.9 million and $26.0 million of gross unrecognized tax benefits, respectively. Of this total, for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, $15.6 and $15.0 million from respective continuing operations (net of federal effect on state tax issues) and $6.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2012 from discontinued operations (net of federal effect on state tax issues) represent the amounts of unrecognized tax benefits that, if recognized, would favorably affect our effective tax rates.
The following table summarizes the activity related to our accrued unrecognized tax benefits (in thousands):
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
Balance at January 1, | | $ | 25,965 | | $ | 26,088 | | $ | 26,125 | |
Reductions related to prior years tax position | | (8,928 | ) | (123 | ) | (127 | ) |
Increases related to current year tax positions | | 693 | | — | | 90 | |
Reductions related to settlements with taxing authorities | | (847 | ) | — | | — | |
Reductions related to expiration of the applicable statute of limitations | | — | | — | | — | |
Balance at December 31, | | $ | 16,883 | | $ | 25,965 | | $ | 26,088 | |
In addition, we recognize accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense. We recognized $1.2 million, $1.5 million and $1.3 million of income tax expense for interest related to uncertain tax positions for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
Management periodically performs a comprehensive review of our tax positions and accrues amounts for tax contingencies. Based on these reviews, the status of ongoing audits and the expiration of applicable statute of limitations, these accruals are adjusted as necessary. Amounts accrued for these tax matters are included in the table above and long-term liabilities in our consolidated balance sheets. We believe that adequate accruals have been provided for all years.
As previously discussed under Discontinued Operations within Note 1. Nature of Operations and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, during the year ended December 31, 2013, we reduced our liability for unrecognized tax benefits by $11.2 million related to discontinued operations. During the third quarter of 2013, we concluded that it was more likely than not that our previously unrecognized state tax position would be sustained upon review of the state tax authority, based on new information obtained during the period, resulting in a reduction in the liability of $6.1 million. The remaining $5.1 million reduction in the second quarter of 2013, was the result of application of limits under an available state administrative practice exception.
We are subject to U.S. federal income tax as well as income tax of multiple state jurisdictions. All of our 2010 and subsequent federal and state tax returns remain subject to examination by various tax authorities. Some of our pre-2010 federal and state tax returns may also be subject to examination. We do not anticipate the resolution of these matters will result in a material change to our consolidated financial statements. In addition, we believe it is reasonably possible that our liability for unrecognized tax benefits related to continuing operations could be reduced by up to $8.3 million, in the next twelve months, as a result of expected statute of limitations expirations, the application of limits under available state administrative practice exceptions, and the resolution of examination issues and settlements with federal and certain state tax authorities.
In April, 2013, we entered into a settlement agreement with the Internal Revenue Service’s Appeals Office with respect to our 2006 and 2007 federal income tax returns. There was no material impact on our financial statements as a result of this settlement.
F-38
Table of Contents
10. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES:
Litigation
We are a party to lawsuits and claims from time to time in the ordinary course of business. Actions currently pending are in various stages and no material judgments or decisions have been rendered by hearing boards or courts in connection with such actions. After reviewing developments to date with legal counsel, our management is of the opinion that the outcome of our pending and threatened matters will not have a material adverse effect on our consolidated balance sheets, consolidated statements of operations or consolidated statements of cash flows.
Various parties have filed petitions to deny our applications or our LMA partners’ applications for the following stations’ license renewals: WXLV-TV, Winston-Salem, North Carolina; WMYV-TV, Greensboro, North Carolina; WLFL-TV, Raleigh / Durham, North Carolina; WRDC-TV, Raleigh / Durham, North Carolina; WLOS-TV, Asheville, North Carolina, WMMP-TV, Charleston, South Carolina; WTAT-TV, Charleston, South Carolina; WMYA-TV, Anderson, South Carolina; WICS-TV Springfield, Illinois; WBFF-TV, Baltimore, Maryland; KGAN-TV, Cedar Rapids, Iowa; WTTE-TV, Columbus, Ohio; WRGT-TV, Dayton, Ohio; WVAH-TV, Charleston / Huntington, West Virginia; WCGV-TV, Milwaukee, Wisconsin; WTTO-TV, Birmingham, AL; KXVO-TV, Omaha, NE (acquired on October 1, 2013); WNAB-TV, Nashville, TN; WPMI-TV, Mobile, AL; WWHO-TV, Chillicothe, OH and WUTB-TV in Baltimore, MD. The FCC is in the process of considering the renewal applications and we believe the petitions have no merit.
Operating Leases
We have entered into operating leases for certain property and equipment under terms ranging from one to 40 years. The rent expense from continuing operations under these leases, as well as certain leases under month-to-month arrangements, for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 was approximately $10.3 million, $6.7 million and $3.9 million, respectively.
Future minimum payments under the leases are as follows (in thousands):
2014 | | $ | 13,318 | |
2015 | | 11,846 | |
2016 | | 10,924 | |
2017 | | 10,188 | |
2018 | | 9,012 | |
2019 and thereafter | | 30,959 | |
| | $ | 86,247 | |
As of December 31, 2013, we had outstanding letters of credit totaling $3.1 million.
Network Affiliation Agreements
On May 14, 2012, the Company and the licensees of stations to which we provide services, representing 20 affiliates of Fox Broadcast Company (FOX), extended the network affiliation agreements with FOX from the existing term of December 31, 2012 to December 31, 2017. Concurrently, we entered into an assignable option agreement with Fox Television Stations, Inc. (FTS) giving us or our assignee the right to purchase substantially all the assets of the WUTB station (Baltimore, MD) owned by FTS, which has a program service arrangement with MyNetworkTV, for $2.7 million. In October 2012, we exercised our option and purchased the assets of WUTB effective June 1, 2013. As part of this transaction, we also granted options to FTS to purchase the assets of televisions stations we own in up to three out of four designated markets, which options expired unexercised. In the second quarter of 2012, we paid $25.0 million to FOX pursuant to the agreements and we recorded $50.0 million in other assets and $25.0 million of other accrued liabilities within the consolidated balance sheet, representing the additional obligation due to FOX which was paid in the second quarter of 2013. The $50.0 million asset is being amortized through the current term of the affiliation agreement ending on December 31, 2017. Approximately $8.9 million and $5.6 million of amortization expense has been recorded in the consolidated statement of operations during the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012. In addition, we are required to pay to FOX programming payments under the terms of the affiliation agreements. These payments are recorded in station production expenses as incurred.
F-39
Table of Contents
Changes in the Rules on Television Ownership and Local Marketing Agreements
Certain of our stations have entered into what have commonly been referred to as local marketing agreements or LMAs. One typical type of LMA is a programming agreement between two separately owned television stations serving the same market, whereby the licensee of one station programs substantial portions of the broadcast day and sells advertising time during such programming segments on the other licensee’s station subject to the latter licensee’s ultimate editorial and other controls. We believe these arrangements allow us to reduce our operating expenses and enhance profitability.
If we are required to terminate or modify our LMAs, our business could be affected in the following ways:
Losses on investments. In some cases, we own the non-license assets used by the stations we operate under LMAs. If certain of these LMA arrangements are no longer permitted, we would be forced to sell these assets, restructure our agreements or find another use for them. If this happens, the market for such assets may not be as good as when we purchased them and, therefore, we cannot be certain of a favorable return on our original investments.
Termination penalties. If the FCC requires us to modify or terminate existing LMAs before the terms of the LMAs expire, or under certain circumstances, we elect not to extend the terms of the LMAs, we may be forced to pay termination penalties under the terms of some of our LMAs. Any such termination penalties could be material.
The following paragraphs discuss various proceedings relevant to our LMAs.
In 1999, the FCC established a new local television ownership rule. LMAs fell under this rule, however the rule grandfathered LMAs that were entered into prior to November 5, 1996, and permitted the applicable stations to continue operations pursuant to the LMAs until the conclusion of the FCC’s 2004 biennial review. The FCC stated it would conduct a case-by-case review of grandfathered LMAs and assess the appropriateness of extending the grandfathering periods. The FCC did not initiate any review of grandfathered LMAs in 2004 or as part of its 2006 quadrennial review. We do not know when, or if, the FCC will conduct any such review of grandfathered LMAs. For LMAs executed on or after November 5, 1996, the FCC required compliance with the 1999 local television ownership rule by August 6, 2001. We challenged the 1999 rules in the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit (D.C. Circuit), resulting in the exclusion of post-November 5, 1996 LMAs from the 1999 rules. In 2002, the D.C. Circuit ruled in Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. v. F.C.C., 284 F.3d 114 (D.C. Cir. 2002) that the 1999 local television ownership rule was arbitrary and capricious and sent the rule back to the FCC for further refinement.
In 2003, the FCC revised its ownership rules, including the local television ownership rule; however the U. S. Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit (Third Circuit) did not enable the 2003 rules to become effective and sent the 2003 rules back to the FCC for further refinement. Due to the court decisions, the FCC concluded the 1999 rules could not be justified as necessary in the public interest and as a result, we took the position that an issue exists regarding whether the FCC has any current legal right to enforce any rules prohibiting the acquisition of television stations. Several parties, including us, filed petitions with the Supreme Court of the United States seeking review of the Third Circuit decision, but the Supreme Court denied the petitions in June 2005.
In July 2006, the FCC released a Further Notice of Proposed Rule Making seeking comment on how to address the issues raised by the Third Circuit’s decision. In January 2008, the FCC released an order containing ownership rules that re-adopted the 1999 rules. On February 29, 2008, several parties, including us, separately filed petitions for review in a number of federal appellate courts challenging the 1999 rules. Those petitions were consolidated in the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit (Ninth Circuit) and in November 2008, transferred by the Ninth Circuit to the Third Circuit. On July 7, 2011, the Third Circuit upheld the FCC’s local television ownership rules. On December 5, 2011, we joined with a number of other parties on a Petition for a Writ of Certiorari filed with the Supreme Court requesting that the Court overrule the decision of the Third Circuit. That request remains pending before the Supreme Court.
On November 15, 1999, we entered into an agreement to acquire WMYA-TV (formerly WBSC-TV) in Anderson, South Carolina from Cunningham Broadcasting Corporation (Cunningham), but that transaction was denied by the FCC. Since none of the FCC rule changes ever became effective, we filed a petition for reconsideration with the FCC and amended our application to acquire the license of WMYA-TV. We also filed applications in November 2003 to acquire the license assets of, at that time, the remaining five Cunningham stations: WRGT-TV, Dayton, Ohio; WTAT-TV, Charleston, South Carolina; WVAH-TV, Charleston, West Virginia; WNUV-TV, Baltimore, Maryland; and WTTE-TV, Columbus, Ohio. Rainbow / PUSH filed a petition to deny these five applications and to revoke all of our licenses. The FCC dismissed our applications and denied the Rainbow / PUSH petition due to the abovementioned 2003 Third Circuit decision. Rainbow / PUSH filed a petition for reconsideration of that denial and we filed an application for review of the dismissal. In 2005, we filed a petition with the D. C. Circuit requesting that the Court direct the FCC to take final action on our applications, but that petition was dismissed. On January 6, 2006, we submitted a motion to the FCC requesting that it take final action on our applications. The applications and the associated petition to deny are still pending. We believe the Rainbow / PUSH petition is without merit. On February 8, 2008, we filed a petition with the D.C. Circuit requesting that the Court direct the FCC to act on our applications and cease its use of the 1999 rules. In July 2008, the D.C. Circuit transferred the case to the Ninth Circuit, and we filed a petition with the D.C.
F-40
Table of Contents
Circuit challenging that decision; however, it was denied. We also filed with the Ninth Circuit a motion to transfer that case back to the D.C. Circuit. In November 2008, the Ninth Circuit consolidated and sent our petition seeking final FCC action on our applications to the Third Circuit. In December 2008, we agreed voluntarily with the parties to our proceeding to dismiss our petition seeking final FCC action on our applications.
Pending Acquisitions
In July 2013, we entered into a definitive agreement to purchase the stock of Perpetual Corporation and the equity interest of Charleston Television, LLC, both owned and controlled by the Allbritton family (Allbritton), for an aggregate purchase price of $985.0 million. The Allbritton stations consist of seven ABC Network affiliates and NewsChannel 8, a 24-hour cable/satellite news network covering the Washington D.C. metropolitan area. The transaction is expected to close late in the second quarter of 2014, subject to approval of the FCC, antitrust clearance, and other customary closing conditions. We expect to fund the purchase price at closing through additional borrowings under our bank credit facility. Additionally, to comply with FCC local television ownership rules, we expect to sell the license and certain related assets of existing stations in Birmingham, AL - WABM (MNT) and WTTO (CW), Harrisburg/Lancaster/Lebanon/York, PA - WHP (CBS), and Charleston, SC - WMMP (MNT) and to provide sales and other non-programming support services to each of these stations pursuant to customary shared services and joint sales agreements.
In September 2013, we entered into a definitive agreement to purchase the broadcast assets of eight television stations owned by New Age Media located in three markets, for an aggregate purchase price of $90.0 million. The transaction is expected to close in the second quarters of 2014, subject to approval of the FCC and other customary closing conditions. We expect to fund the purchase price through cash on hand or a delayed draw under our bank credit agreement. Additionally, Wilkes/Barre/Scranton, PA — WSWB, Tallahassee, FL — WTLH and WTLF and Gainesville, FL — WMBW will be purchased by a third party; we will continue to provide sales and other non-programming support services to each of these stations, pursuant to customary share services and joint sales agreements.
11. RELATED PERSON TRANSACTIONS:
Transactions with our controlling shareholders. David, Frederick, J. Duncan and Robert Smith (collectively, the controlling shareholders) are brothers and hold substantially all of the Class B Common Stock and some of our Class A Common Stock. We engaged in the following transactions with them and/or entities in which they have substantial interests.
Leases. Certain assets used by us and our operating subsidiaries are leased from Cunningham Communications Inc., Keyser Investment Group, Gerstell Development Limited Partnership and Beaver Dam, LLC (entities owned by the controlling shareholders). Lease payments made to these entities were $5.2 million, $4.7 million and $4.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
Bay TV. In January 1999, we entered into an LMA with Bay TV, which owns the television station WTTA-TV in the Tampa / St. Petersburg, Florida market. Each of our controlling shareholders owns a substantial portion of the equity of Bay TV and collectively they have a controlling interest. On December 1, 2012, we purchased substantially all of the assets of Bay TV for $40.0 million. Our board of directors obtained a fairness opinion on the purchase price from a third party valuation firm. Concurrent with the acquisition, our LMA with Bay TV was terminated. Payments made to Bay TV were $2.9 million and $2.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively. The LMA with Bay TV has been approved pursuant to the current related person transaction policy.
Charter Aircraft. From time to time, we charter aircraft owned by certain controlling shareholders. We incurred expenses of $0.9 million, $0.6 million and $0.2 million during the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
Capital leases payable related to the aforementioned relationships consisted of the following as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 (in thousands):
| | 2013 | | 2012 | |
Capital lease for building, interest at 8.54% | | $ | 6,267 | | $ | 7,405 | |
Capital leases for building and tower, interest at 7.93% | | 1,106 | | 1,221 | |
Capital leases for building, interest at 8.11% | | 8,141 | | — | |
Capital leases for broadcasting tower facilities, interest at 9.0% | | 860 | | 1,275 | |
Capital leases for broadcasting tower facilities, interest at 10.5% | | 4,918 | | 4,990 | |
| | 21,292 | | 14,891 | |
Less: Current portion | | (2,367 | ) | (1,704 | ) |
| | $ | 18,925 | | $ | 13,187 | |
F-41
Table of Contents
Capital leases payable related to the aforementioned relationships as of December 31, 2013 mature as follows (in thousands):
2014 | | $ | 4,388 | |
2015 | | 4,402 | |
2016 | | 4,138 | |
2017 | | 4,102 | |
2018 | | 1,880 | |
2019 and thereafter | | 13,045 | |
Total minimum payments due | | 31,955 | |
Less: Amount representing interest | | (10,631 | ) |
| | $ | 21,324 | |
Cunningham Broadcasting Corporation. As of December 31, 2013, Cunningham was the owner-operator and FCC licensee of: WNUV-TV Baltimore, Maryland; WRGT-TV Dayton, Ohio; WVAH-TV Charleston, West Virginia; WTAT-TV Charleston, South Carolina; WMYA-TV Anderson, South Carolina; WTTE-TV Columbus, Ohio; WDBB-TV Birmingham, Alabama; WBSF-TV Flint, Michigan; and WGTU-TV/WGTQ-TV Traverse City/Cadillac, Michigan (collectively, the Cunningham Stations) and WYZZ Peoria/Bloomington, IL.
During the first quarter of 2013, the estate of Carolyn C. Smith, a parent of our controlling shareholders, distributed all of the non-voting stock owned by the estate to our controlling shareholders, and a portion was repurchased by Cunningham for $1.7 million in the aggregate. As of December 31, 2013, our controlling shareholders own approximately 4.4% of the total capital stock of Cunningham, none of which have voting rights. The remaining amount of non-voting stock is owned by trusts established for the benefit of the children of our controlling shareholders. The estate of Mrs. Smith currently owns all of the voting stock. The sale of the voting stock by the estate to an unrelated party is pending approval of the FCC. We have options from the trusts, which grant us the right to acquire, subject to applicable FCC rules and regulations, 100% of the voting and nonvoting stock of Cunningham. We also have options from each of Cunningham’s subsidiaries, which are the FCC licensees of the Cunningham stations, which grant us the right to acquire, and grant Cunningham the right to require us to acquire, subject to applicable FCC rules and regulations, 100% of the capital stock or the assets of Cunningham’s individual subsidiaries.
In addition to the option agreements, certain of our stations provide programming, sales and managerial services pursuant to LMAs to seven of their stations: WNUV-TV, WRGT-TV, WVAH-TV, WTAT-TV, WMYA-TV, WTTE-TV, and WDBB-TV (collectively, the Cunningham LMA Stations). Each of these LMAs has a current term that expires on July 1, 2016 and there are three additional 5-year renewal terms remaining with final expiration on July 1, 2031.
Effective November 5, 2009, we entered into amendments and/or restatements of the following agreements between Cunningham and us: (i) the LMAs, (ii) option agreements to acquire Cunningham stock and (iii) certain acquisition or merger agreements relating to the Cunningham LMA Stations.
Pursuant to the terms of the LMAs, options and other agreements, beginning on January 1, 2010 and ending on July 1, 2012, we were obligated to pay Cunningham the sum of approximately $29.1 million in 10 quarterly installments of $2.75 million and one quarterly payment of approximately $1.6 million, which amounts were used to pay down Cunningham’s bank credit facility and which amounts were credited toward the purchase price for each Cunningham station. An additional $1.2 million was paid on July 1, 2012 and another installment of $2.75 million was paid on October 1, 2012 as an additional LMA fee and was used to pay off the remaining balance of Cunningham’s bank credit facility. The aggregate purchase price of the television stations, which was originally $78.5 million pursuant to certain acquisition or merger agreements subject to 6% annual increases, was decreased by each payment made by us to Cunningham, through 2012, up to $29.1 million in the aggregate, pursuant to the foregoing transactions with Cunningham as such payments are made. Beginning on January 1, 2013, we are obligated to pay Cunningham an annual LMA fee for the television stations equal to the greater of (i) 3% of each station’s annual net broadcast revenue and (ii) $5.0 million, of which a portion of this fee will be credited toward the purchase price to the extent of the annual 6% increase. The remaining purchase price as of December 31, 2013 was approximately $57.1 million. Additionally, we reimburse Cunningham for 100% of its operating costs, and paid Cunningham a monthly payment of $50,000 through December 2012 as an LMA fee.
We made payments to Cunningham under these LMAs and other agreements with the Cunningham LMA Stations of $9.8 million, $15.7 million and $16.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, Cunningham LMA Stations provided us with approximately $107.6 million, $105.5 million and $90.3 million, respectively, of total revenue. The financial statements for Cunningham are included in our consolidated financial statements for all periods presented.
F-42
Table of Contents
In November 2013, concurrent with our acquisition of the Barrington stations, Cunningham acquired the license related assets of WBSF-TV and WGTU-TV/WGTQ-TV, which was funded by bank debt, for which we have provided a guarantee. We provide certain non-programming related sales, operational and administrative services to these stations pursuant to certain outsourcing agreements. The agreements for WBSF-TV and WGTU-TV/WGTQ-TV expire in November 2021 and August 2015, respectively, and each have renewal provisions for successive eight year periods. Under these arrangements, we earned $0.6 million from the services we perform for these stations. As we consolidate the licensees as VIEs, the amounts we earn under the arrangements are eliminated in consolidation and the gross revenues of the stations are reported within our consolidated statement of operations. For the December 31, 2013, our consolidated revenues include $0.7 million related to these stations.
Also, concurrent with the Barrington acquisition, we also sold our station, WYZZ (FOX) in Peoria, IL, which currently receives non-programming related sales, operational and administrative services from Nexstar Broadcasting pursuant to certain outsourcing agreements, to Cunningham for $22 million. Although we have no continuing involvement in the operations of this station, because Cunningham is a consolidated VIE and we have a purchase plan option to acquire these assets from Cunningham, the assets of WYZZ were not derecognized and the transaction was accounted for a transaction between parties under common control and thus no gain or loss has been recognized in the consolidated statement of operations
During October 2013, we purchased the outstanding membership interests of KDBC-TV from Cunningham for $21.2 million, plus a working capital adjustment of $0.2 million. See Other Acquisitions within Note 2. Acquisitions, for further information.
Atlantic Automotive Corporation. We sold advertising time to and purchased vehicles and related vehicle services from Atlantic Automotive Corporation (Atlantic Automotive), a holding company that owns automobile dealerships and an automobile leasing company. David D. Smith, our President and Chief Executive Officer, has a controlling interest in, and is a member of the Board of Directors of Atlantic Automotive. We received payments for advertising totaling $0.2 million, $0.1 million and $0.2 million during the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively. We paid $1.1 million, $1.8 million and $1.1 million for vehicles and related vehicle services from Atlantic Automotive during the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively. Additionally, in August 2011, Atlantic Automotive entered into an office lease agreement with Towson City Center, LLC (Towson City Center), a subsidiary of one of our real estate ventures. Atlantic Automotive paid $1.0 million in rent during the year ended December 31, 2013.
Leased property by real estate ventures. Certain of our real estate ventures have entered into leases with entities owned by David Smith to lease restaurant space. There are leases for three restaurants in a building owned by one of our consolidated real estate ventures in Baltimore, MD. Total rent received under these leases was $0.5 million, $0.3 million and $0.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011. There is also one lease for a restaurant in a building owned by one of our real estate ventures, accounted for under the equity method, in Towson, MD. This investment received $0.2 million in rent pursuant to the lease for the year ended December 31, 2013.
Thomas & Libowitz, P.A. Steven A. Thomas, a partner and founder of Thomas & Libowitz, P.A. (Thomas & Libowitz), a law firm providing legal services to us on an ongoing basis, is the son of a former member of the Board of Directors, Basil A. Thomas. We paid fees of $1.6 million, $1.0 million and $0.5 million to Thomas & Libowitz during 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
12. EARNINGS PER SHARE:
The following table reconciles income (numerator) and shares (denominator) used in our computations of earnings per share for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 (in thousands):
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
Income (Numerator) | | | | | | | |
Income from continuing operations | | $ | 64,259 | | $ | 144,488 | | $ | 76,588 | |
Income impact of assumed conversion of the 4.875% Notes, net of taxes | | — | | 180 | | 180 | |
Net (income) attributable to noncontrolling interests included in continuing operations | | (2,349 | ) | (287 | ) | (379 | ) |
Numerator for diluted earnings per common share from continuing operations available to common shareholders | | 61,910 | | 144,381 | | 76,389 | |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes | | 11,558 | | 465 | | (411 | ) |
Numerator for diluted earnings available to common shareholders | | $ | 73,468 | | $ | 144,846 | | $ | 75,978 | |
| | | | | | | |
Shares (Denominator) | | | | | | | |
Weighted-average common shares outstanding | | 93,207 | | 81,020 | | 80,217 | |
Dilutive effect of outstanding stock settled appreciation rights, restricted stock awards and stock options | | 638 | | 36 | | 61 | |
Dilutive effect of 4.875% Notes | | — | | 254 | | 254 | |
Weighted-average common and common equivalent shares outstanding | | 93,845 | | 81,310 | | 80,532 | |
F-43
Table of Contents
Potentially dilutive securities representing zero shares, 1.5 million and 1.1 million shares of common stock for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively, were excluded from the computation of diluted earnings (loss) per common share for these periods because their effect would have been antidilutive. The decrease in 2013 compared to 2012 of potentially dilutive securities is primarily related to the increase of stock price in 2013. The increase in 2012 compared to 2011 of potentially dilutive securities is primarily related to the issuance of new stock settled appreciation rights in 2012. The net earnings per share amounts are the same for Class A and Class B Common Stock because the holders of each class are legally entitled to equal per share distributions whether through dividends or in liquidation.
13. SEGMENT DATA:
We measure segment performance based on operating income (loss). Excluding discontinued operations, our broadcast segment includes stations in 71 markets located throughout the continental United States. The operating results of WLAJ-TV and WLWC-TV, which were sold effective March 1, 2013 and April 1, 2013, respectively, are classified as discontinued operations and are not included in our consolidated results of continuing operations for the years ended 2013 and 2012. Our other operating divisions primarily consist of sign design and fabrication; regional security alarm operating and bulk acquisitions; manufacturing and service of broadcast antennas and transmitters and real estate ventures. All of our other operating divisions are located within the United States. Corporate costs primarily include our costs to operate as a public company and to operate our corporate headquarters location. Other Operating Divisions and Corporate are not reportable segments but are included for reconciliation purposes. We had approximately $171.9 million and $171.2 million of intercompany loans between the broadcast segment, other operating divisions and corporate as of December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively. We had $20.0 million in intercompany interest expense related to intercompany loans between the broadcast segment, other operating divisions and corporate for the both years ended December 31, 2013, and 2012, and $19.7 million in interest expense in 2011. All other intercompany transactions are immaterial.
Financial information for our operating segments is included in the following tables for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 (in thousands):
For the year ended December 31, 2013 | | Broadcast | | Other
Operating
Divisions | | Corporate | | Consolidated | |
Revenue | | $ | 1,306,187 | | $ | 56,944 | | $ | — | | $ | 1,363,131 | |
Depreciation of property and equipment | | 67,320 | | 1,891 | | 1,343 | | 70,554 | |
Amortization of definite-lived intangible assets and other assets | | 65,786 | | 5,034 | | — | | 70,820 | |
Amortization of program contract costs and net realizable value adjustments | | 80,925 | | — | | — | | 80,925 | |
General and administrative overhead expenses | | 47,272 | | 1,350 | | 4,504 | | 53,126 | |
Operating income (loss) | | 329,312 | | 555 | | (5,847 | ) | 324,020 | |
Interest expense | | — | | 3,251 | | 159,686 | | 162,937 | |
Income from equity and cost method investments | | — | | 621 | | — | | 621 | |
Goodwill | | 1,376,594 | | 3,488 | | — | | 1,380,082 | |
Assets | | 3,493,603 | | 294,921 | | 376,726 | | 4,165,250 | |
Capital expenditures | | 37,665 | | 4,994 | | 2,700 | | 45,359 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
F-44
Table of Contents
For the year ended December 31, 2012 | | Broadcast | | Other
Operating
Divisions | | Corporate | | Consolidated | |
Revenue | | $ | 1,007,498 | | $ | 54,181 | | $ | — | | $ | 1,061,679 | |
Depreciation of property and equipment | | 44,054 | | 1,496 | | 1,523 | | 47,073 | |
Amortization of definite-lived intangible assets and other assets | | 33,701 | | 4,398 | | — | | 38,099 | |
Amortization of program contract costs and net realizable value adjustments | | 60,990 | | — | | — | | 60,990 | |
General and administrative overhead expenses | | 28,854 | | 1,697 | | 2,840 | | 33,391 | |
Operating income (loss) | | 333,164 | | 491 | | (4,377 | ) | 329,278 | |
Interest expense | | — | | 3,282 | | 125,271 | | 128,553 | |
Income from equity and cost method investments | | — | | 9,670 | | — | | 9,670 | |
Goodwill | | 1,070,544 | | 3,488 | | — | | 1,074,032 | |
Assets | | 2,436,537 | | 284,583 | | 8,577 | | 2,729,697 | |
Capital expenditures | | 35,161 | | 2,341 | | 6,484 | | 43,986 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
For the year ended December 31, 2011 | | Broadcast | | Other
Operating
Divisions | | Corporate | | Consolidated | |
Revenue | | $ | 720,775 | | $ | 44,513 | | $ | — | | $ | 765,288 | |
Depreciation of property and equipment | | 29,929 | | 1,323 | | 1,622 | | 32,874 | |
Amortization of definite-lived intangible assets and other assets | | 14,643 | | 3,586 | | — | | 18,229 | |
Amortization of program contract costs and net realizable value adjustments | | 52,079 | | — | | — | | 52,079 | |
Impairment of goodwill, intangible and other assets | | 398 | | — | | — | | 398 | |
General and administrative overhead expenses | | 24,760 | | 1,158 | | 2,392 | | 28,310 | |
Operating income (loss) | | 230,679 | | (1,041 | ) | (4,018 | ) | 225,620 | |
Interest expense | | — | | 2,528 | | 103,600 | | 106,128 | |
Income from equity and cost method investments | | — | | 3,269 | | — | | 3,269 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
14. FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS:
Accounting guidance provides for valuation techniques, such as the market approach (comparable market prices), the income approach (present value of future income or cash flow), and the cost approach (cost to replace the service capacity of an asset or replacement cost). A fair value hierarchy using three broad levels prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value. The following is a brief description of those three levels:
· Level 1: Observable inputs such as quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
· Level 2: Inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly. These include quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets and quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active.
· Level 3: Unobservable inputs that reflect the reporting entity’s own assumptions.
The carrying value and fair value of our notes, debentures, program contracts payable and non-cancelable programming commitments as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 were as follows (in thousands):
F-45
Table of Contents
| | 2013 | | 2012 | |
| | Carrying Value | | Fair Value | | Carrying Value | | Fair Value | |
Level 2: | | | | | | | | | |
9.25% Senior Second Lien Notes due 2017 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 490,517 | | $ | 552,500 | |
8.375% Senior Notes due 2018 | | 235,225 | | 259,547 | | 234,853 | | 265,886 | |
6.375% Senior Unsecured Notes due 2021 | | 350,000 | | 360,938 | | — | | — | |
6.125% Senior Unsecured Notes due 2022 | | 500,000 | | 497,525 | | 500,000 | | 533,125 | |
5.375% Senior Unsecured Notes due 2021 | | 600,000 | | 582,078 | | — | | — | |
Term Loan A | | 500,000 | | 495,000 | | 263,875 | | 262,556 | |
Term Loan B | | 642,734 | | 641,205 | | 580,850 | | 589,125 | |
Debt of variable interest entities | | 55,581 | | 55,581 | | 19,950 | | 19,950 | |
Debt of other operating divisions | | 86,263 | | 86,263 | | 65,666 | | 65,666 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Not included in the table above are the fair values and carrying values for our 4.875% Notes and 3.0% Notes as of 2012, which we believe their fair values approximate their carrying values based on discounted cash flows using Level 3 inputs described above. The 4.875% Notes and 3.0% Notes were redeemed in full during 2013.
Additionally, Cunningham, one of our consolidated VIEs has certain investments in securities that are recorded at fair value using Level 1 inputs described above. As of December 31, 2013 and 2012, $18.1 million and $6.4 million were included in other assets in our consolidated balance sheets.
15. CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:
Sinclair Television Group, Inc. (STG), a wholly-owned subsidiary and the television operating subsidiary of Sinclair Broadcast Group, Inc. (SBG), is the primary obligor under the Bank Credit Agreement, the 5.375% Notes, 6.125% Notes, 8.375% Notes, and 6.375% Notes (issued October 2013). Our Class A Common Stock and Class B Common Stock as of December 31, 2013, were obligations or securities of SBG and not obligations or securities of STG. SBG is a guarantor under the Bank Credit Agreement, the 5.375% Notes, 6.125% Notes, 8.375% Notes, and 6.375% Notes. As of September 30, 2013, our consolidated total debt of $2,475 million included $2,380.6 million of debt related to STG and its subsidiaries of which SBG guaranteed $2,338.4 million.
SBG, KDSM, LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of SBG, and STG’s wholly-owned subsidiaries (guarantor subsidiaries), have fully and unconditionally guaranteed, subject to certain customary automatic release provisions, all of STG’s obligations. Those guarantees are joint and several. There are certain contractual restrictions on the ability of SBG, STG or KDSM, LLC to obtain funds from their subsidiaries in the form of dividends or loans.
The following condensed consolidating financial statements present the consolidated balance sheets, consolidated statements of operations and consolidated statements of cash flows of SBG, STG, KDSM, LLC and the guarantor subsidiaries, the direct and indirect non-guarantor subsidiaries of SBG and the eliminations necessary to arrive at our information on a consolidated basis. These statements are presented in accordance with the disclosure requirements under SEC Regulation S-X, Rule 3-10.
F-46
Table of Contents
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET
AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2013
(In thousands)
| | Sinclair
Broadcast
Group, Inc. | | Sinclair
Television
Group, Inc. | | Guarantor
Subsidiaries
and KDSM,
LLC | | Non-Guarantor
Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | Sinclair
Consolidated | |
Cash | | $ | — | | $ | 237,974 | | $ | 28,594 | | $ | 13,536 | | $ | — | | $ | 280,104 | |
Accounts and other receivables | | 59 | | 818 | | 281,822 | | 27,479 | | (1,022 | ) | 309,156 | |
Other current assets | | 5,500 | | 25,887 | | 67,279 | | 16,391 | | (6,446 | ) | 108,611 | |
Total current assets | | 5,559 | | 264,679 | | 377,695 | | 57,406 | | (7,468 | ) | 697,871 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Property and equipment, net | | 5,017 | | 13,561 | | 454,917 | | 130,019 | | (7,443 | ) | 596,071 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Investment in consolidated subsidiaries | | 363,231 | | 2,508,058 | | 4,179 | | — | | (2,875,468 | ) | — | |
Restricted cash — long term | | — | | 11,524 | | 223 | | — | | — | | 11,747 | |
Other long-term assets | | 78,849 | | 503,674 | | 62,435 | | 132,840 | | (544,881 | ) | 232,917 | |
Total other long-term assets | | 442,080 | | 3,023,256 | | 66,837 | | 132,840 | | (3,420,349 | ) | 244,664 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Goodwill and other intangible assets | | — | | — | | 2,486,794 | | 214,325 | | (92,253 | ) | 2,608,866 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 452,656 | | $ | 3,301,496 | | $ | 3,386,243 | | $ | 534,590 | | $ | (3,527,513 | ) | $ | 4,147,472 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | $ | 234 | | $ | 51,781 | | $ | 126,245 | | $ | 17,914 | | $ | — | | $ | 196,174 | |
Current portion of long-term debt | | 556 | | 37,335 | | 1,007 | | 7,448 | | — | | 46,346 | |
Current portion of affiliate long-term debt | | 1,294 | | — | | 1,073 | | 1,003 | | (1,003 | ) | 2,367 | |
Other current liabilities | | 3,529 | | — | | 87,612 | | 9,645 | | (2,292 | ) | 98,494 | |
Total current liabilities | | 5,613 | | 89,116 | | 215,937 | | 36,010 | | (3,295 | ) | 343,381 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Long-term debt | | 529 | | 2,793,334 | | 35,709 | | 136,830 | | — | | 2,966,402 | |
Affiliate long-term debt | | 4,972 | | — | | 13,984 | | 294,919 | | (294,950 | ) | 18,925 | |
Other liabilities | | 45,172 | | 23,645 | | 610,491 | | 145,828 | | (412,076 | ) | 413,060 | |
Total liabilities | | 56,286 | | 2,906,095 | | 876,121 | | 613,587 | | (710,321 | ) | 3,741,768 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Sinclair Broadcast Group equity (deficit) | | 396,370 | | 395,401 | | 2,510,122 | | (88,331 | ) | (2,817,192 | ) | 396,370 | |
Noncontrolling interests in consolidated subsidiaries | | — | | — | | — | | 9,334 | | — | | 9,334 | |
Total liabilities and equity (deficit) | | $ | 452,656 | | $ | 3,301,496 | | $ | 3,386,243 | | $ | 534,590 | | $ | (3,527,513 | ) | $ | 4,147,472 | |
F-47
Table of Contents
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET
AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2012
(In thousands)
| | Sinclair
Broadcast
Group, Inc. | | Sinclair
Television
Group, Inc. | | Guarantor
Subsidiaries
and KDSM,
LLC | | Non-
Guarantor
Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | Sinclair
Consolidated | |
Cash | | $ | — | | $ | 7,230 | | $ | 199 | | $ | 15,436 | | $ | — | | $ | 22,865 | |
Accounts and other receivables | | 152 | | 907 | | 175,837 | | 7,622 | | (622 | ) | 183,896 | |
Other current assets | | 2,821 | | 2,342 | | 56,522 | | 9,028 | | (3,383 | ) | 67,330 | |
Assets held for sale | | — | | — | | 30,357 | | — | | — | | 30,357 | |
Total current assets | | 2,973 | | 10,479 | | 262,915 | | 32,086 | | (4,005 | ) | 304,448 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Property and equipment, net | | 6,315 | | 8,938 | | 321,873 | | 113,454 | | (10,867 | ) | 439,713 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Investment in consolidated subsidiaries | | — | | 1,636,504 | | 1,956 | | — | | (1,638,460 | ) | — | |
Restricted cash — long term | | — | | 2 | | 223 | | — | | — | | 225 | |
Other long-term assets | | 84,055 | | 375,687 | | 60,114 | | 112,757 | | (429,862 | ) | 202,751 | |
Total other long-term assets | | 84,055 | | 2,012,193 | | 62,293 | | 112,757 | | (2,068,322 | ) | 202,976 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Goodwill and other intangible assets | | — | | — | | 1,706,646 | | 153,961 | | (78,047 | ) | 1,782,560 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 93,343 | | $ | 2,031,610 | | $ | 2,353,727 | | $ | 412,258 | | $ | (2,161,241 | ) | $ | 2,729,697 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | $ | 326 | | $ | 61,165 | | $ | 83,049 | | $ | 9,379 | | $ | (102 | ) | $ | 153,817 | |
Current portion of long-term debt | | 483 | | 31,113 | | 800 | | 15,226 | | — | | 47,622 | |
Current portion of affiliate long-term debt | | 1,102 | | — | | 602 | | 433 | | (433 | ) | 1,704 | |
Other current liabilities | | — | | — | | 96,288 | | 8,871 | | (3,099 | ) | 102,060 | |
Liabilities held for sale | | — | | — | | 2,397 | | — | | — | | 2,397 | |
Total current liabilities | | 1,911 | | 92,278 | | 183,136 | | 33,909 | | (3,634 | ) | 307,600 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Long-term debt | | 12,502 | | 2,088,586 | | 36,705 | | 73,073 | | — | | 2,210,866 | |
Affiliate long-term debt | | 6,303 | | — | | 6,884 | | 267,521 | | (267,521 | ) | 13,187 | |
Dividends in excess of investment in consolidated subsidiaries | | 178,869 | | — | | — | | — | | (178,869 | ) | — | |
Other liabilities | | 10,708 | | 2,509 | | 491,845 | | 103,007 | | (309,972 | ) | 298,097 | |
Total liabilities | | 210,293 | | 2,183,373 | | 718,570 | | 477,510 | | (759,996 | ) | 2,829,750 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Sinclair Broadcast Group shareholders’ (deficit) equity | | (116,950 | ) | (151,763 | ) | 1,635,157 | | (82,149 | ) | (1,401,245 | ) | (116,950 | ) |
Noncontrolling interests in consolidated subsidiaries | | — | | — | | — | | 16,897 | | — | | 16,897 | |
Total liabilities and equity (deficit) | | $ | 93,343 | | $ | 2,031,610 | | $ | 2,353,727 | | $ | 412,258 | | $ | (2,161,241 | ) | $ | 2,729,697 | |
F-48
Table of Contents
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2013
(In thousands)
| | Sinclair
Broadcast
Group, Inc. | | Sinclair
Television
Group, Inc. | | Guarantor
Subsidiaries
and KDSM,
LLC | | Non-
Guarantor
Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | Sinclair
Consolidated | |
Net revenue | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 1,296,736 | | $ | 123,017 | | $ | (56,622 | ) | $ | 1,363,131 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Program and production | | 15 | | 357 | | 391,410 | | 50,950 | | (57,628 | ) | 385,104 | |
Selling, general and administrative | | 3,733 | | 48,363 | | 241,548 | | 9,132 | | 82 | | 302,858 | |
Depreciation, amortization and other operating expenses | | 1,307 | | 3,105 | | 275,889 | | 71,319 | | (471 | ) | 351,149 | |
Total operating expenses | | 5,055 | | 51,825 | | 908,847 | | 131,401 | | (58,017 | ) | 1,039,111 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating (loss) income | | (5,055 | ) | (51,825 | ) | 387,889 | | (8,384 | ) | 1,395 | | 324,020 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity in earnings of consolidated subsidiaries | | 97,138 | | 309,388 | | 1,009 | | — | | (407,535 | ) | — | |
Interest expense | | (1,083 | ) | (152,174 | ) | (4,965 | ) | (25,624 | ) | 20,909 | | (162,937 | ) |
Other income (expense) | | 4,633 | | (59,033 | ) | 245 | | 5,361 | | (6,781 | ) | (55,575 | ) |
Total other (expense) income | | 100,688 | | 98,181 | | (3,711 | ) | (20,263 | ) | (393,407 | ) | (218,512 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income tax benefit | | (22,165 | ) | 47,645 | | (73,266 | ) | 2,637 | | 3,900 | | (41,249 | ) |
Income from discontinued operations, net of taxes | | — | | 11,063 | | 495 | | — | | — | | 11,558 | |
Net income (loss) | | 73,468 | | 105,064 | | 311,407 | | (26,010 | ) | (388,112 | ) | 75,817 | |
Net loss attributable to the noncontrolling interests | | — | | — | | — | | (2,349 | ) | — | | (2,349 | ) |
Net income (loss) attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 73,468 | | $ | 105,064 | | $ | 311,407 | | $ | (28,359 | ) | $ | (388,112 | ) | $ | 73,468 | |
Comprehensive income | | $ | 78,257 | | $ | 107,243 | | $ | 311,407 | | $ | (28,098 | ) | $ | (390,552 | ) | $ | 78,257 | |
F-49
Table of Contents
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2012
(In thousands)
| | Sinclair
Broadcast
Group, Inc. | | Sinclair
Television
Group, Inc. | | Guarantor
Subsidiaries
and KDSM,
LLC | | Non-
Guarantor
Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | Sinclair
Consolidated | |
Net revenue | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 1,008,146 | | $ | 64,909 | | $ | (11,376 | ) | $ | 1,061,679 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Program and production | | — | | 322 | | 263,802 | | 1,400 | | (9,968 | ) | 255,556 | |
Selling, general and administrative | | 2,853 | | 28,762 | | 168,540 | | 6,082 | | (1,567 | ) | 204,670 | |
Depreciation, amortization and other operating expenses | | 1,523 | | 1,890 | | 213,681 | | 55,802 | | (728 | ) | 272,168 | |
Total operating expenses | | 4,376 | | 30,974 | | 646,023 | | 63,284 | | (12,263 | ) | 732,394 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating (loss) income | | (4,376 | ) | (30,974 | ) | 362,123 | | 1,625 | | 887 | | 329,285 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity in earnings (losses) of consolidated subsidiaries | | 144,620 | | 194,686 | | (123 | ) | — | | (339,183 | ) | — | |
Interest expense | | (1,317 | ) | (118,491 | ) | (4,840 | ) | (24,780 | ) | 20,875 | | (128,553 | ) |
Other income (expense) | | 5,245 | | 38,677 | | (39,781 | ) | 8,690 | | (1,223 | ) | 11,608 | |
Total other (expense) income | | 148,548 | | 114,872 | | (44,744 | ) | (16,090 | ) | (319,531 | ) | (116,945 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income tax benefit | | 494 | | 41,709 | | (118,519 | ) | 8,464 | | — | | (67,852 | ) |
Loss from discontinued operations, net of taxes | | — | | (269 | ) | 734 | | — | | — | | 465 | |
Net (loss) income | | 144,666 | | 125,338 | | 199,594 | | (6,001 | ) | (318,644 | ) | 144,953 | |
Net loss attributable to the noncontrolling interests | | — | | — | | — | | (287 | ) | — | | (287 | ) |
Net (loss) income attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 144,666 | | $ | 125,338 | | $ | 199,594 | | $ | (6,288 | ) | $ | (318,644 | ) | $ | 144,666 | |
Comprehensive income | | $ | 144,808 | | $ | 125,193 | | $ | 199,594 | | $ | (6,288 | ) | $ | (318,499 | ) | $ | 144,808 | |
F-50
Table of Contents
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2011
(In thousands)
| | Sinclair
Broadcast
Group, Inc. | | Sinclair
Television
Group, Inc. | | Guarantor
Subsidiaries
and KDSM,
LLC | | Non-
Guarantor
Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | Sinclair
Consolidated | |
Net revenue | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 721,936 | | $ | 52,295 | | $ | (8,943 | ) | $ | 765,288 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Program and production | | — | | 1,298 | | 185,038 | | 338 | | (8,062 | ) | 178,612 | |
Selling, general and administrative | | 2,396 | | 25,160 | | 121,391 | | 3,765 | | (464 | ) | 152,248 | |
Depreciation, amortization and other operating expenses | | 1,622 | | 688 | | 160,414 | | 46,618 | | (552 | ) | 208,790 | |
Total operating expenses | | 4,018 | | 27,146 | | 466,843 | | 50,721 | | (9,078 | ) | 539,650 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating (loss) income | | (4,018 | ) | (27,146 | ) | 255,093 | | 1,574 | | 135 | | 225,638 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity in earnings of consolidated subsidiaries | | 83,354 | | 134,996 | | — | | — | | (218,350 | ) | — | |
Interest expense | | (3,285 | ) | (94,556 | ) | (4,931 | ) | (23,978 | ) | 20,622 | | (106,128 | ) |
Gain on Sales of Securities | | — | | — | | — | | 391 | | (391 | ) | — | |
Other income (expense) | | 1,781 | | 35,255 | | (36,160 | ) | 1,560 | | (573 | ) | 1,863 | |
Total other income (expense) | | 81,850 | | 75,695 | | (41,091 | ) | (22,027 | ) | (198,692 | ) | (104,265 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income tax (provision) benefit | | (2,034 | ) | 29,783 | | (75,449 | ) | 2,915 | | — | | (44,785 | ) |
Loss from discontinued operations, net of taxes | | — | | (411 | ) | — | | — | | — | | (411 | ) |
Net income (loss) | | 75,798 | | 77,921 | | 138,553 | | (17,538 | ) | (198,557 | ) | 76,177 | |
Net loss attributable to the noncontrolling interests | | — | | — | | — | | (379 | ) | — | | (379 | ) |
Net income (loss) attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 75,798 | | $ | 77,921 | | $ | 138,553 | | $ | (17,917 | ) | $ | (198,557 | ) | $ | 75,798 | |
Comprehensive income | | $ | 75,243 | | $ | 76,987 | | $ | 138,553 | | $ | (17,917 | ) | $ | (197,623 | ) | $ | 75,243 | |
F-51
Table of Contents
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2013
(In thousands)
| | Sinclair
Broadcast
Group,
Inc. | | Sinclair
Television
Group, Inc. | | Guarantor
Subsidiaries
and KDSM,
LLC | | Non-
Guarantor
Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | Sinclair
Consolidated | |
NET CASH FLOWS (USED IN) FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | $ | (37,107 | ) | $ | (264,925 | ) | $ | 444,680 | | $ | (40,414 | ) | $ | 58,343 | | $ | 160,577 | |
CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Acquisition of property and equipment | | — | | (2,700 | ) | (35,659 | ) | (5,029 | ) | — | | (43,388 | ) |
Payments for acquisitions of television stations | | — | | — | | (998,664 | ) | (50,480 | ) | 43,000 | | (1,006,144 | ) |
Proceeds from the sale of broadcast assets | | — | | — | | 71,738 | | 21,000 | | (43,000 | ) | 49,738 | |
Payments for acquisitions of assets of other operating divisions | | — | | — | | — | | (4,650 | ) | — | | (4,650 | ) |
Purchase of alarm monitoring contracts | | — | | — | | — | | (23,721 | ) | — | | (23,721 | ) |
(Increase) decrease in restricted cash | | — | | (11,522 | ) | — | | — | | — | | (11,522 | ) |
Investments in equity and cost method investees | | 1,655 | | — | | — | | 3,603 | | — | | 5,258 | |
Distributions from equity and cost method investees | | — | | — | | — | | (10,767 | ) | — | | (10,767 | ) |
Investment in marketable securities | | — | | — | | — | | (696 | ) | (10,908 | ) | (11,604 | ) |
Other, net | | (7 | ) | — | | 50 | | 5,516 | | — | | 5,559 | |
Net cash flows (used in) from investing activities | | 1,648 | | (14,222 | ) | (962,535 | ) | (65,224 | ) | (10,908 | ) | (1,051,241 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Proceeds from notes payable, commercial bank financing and capital leases | | — | | 2,189,753 | | — | | 88,540 | | — | | 2,278,293 | |
Repayments of notes payable, commercial bank financing and capital leases | | (482 | ) | (1,473,898 | ) | (1,069 | ) | (34,311 | ) | — | | (1,509,760 | ) |
Proceeds from the sale of Class A Common Stock | | 472,913 | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 472,913 | |
Dividends paid on Class A and Class B common stock | | (56,767 | ) | — | | — | | — | | — | | (56,767 | ) |
Payments for deferred financing costs | | — | | (27,724 | ) | — | | — | | — | | (27,724 | ) |
Noncontrolling interest distributions (contributions) | | — | | — | | — | | (10,256 | ) | — | | (10,256 | ) |
Increase (decrease) in intercompany payables | | (371,331 | ) | (178,240 | ) | 548,139 | | 59,765 | | (58,333 | ) | — | |
Other, net | | (8,874 | ) | — | | (820 | ) | — | | 10,898 | | 1,204 | |
Net cash flows from (used in) financing activities | | 35,459 | | 509,891 | | 546,250 | | 103,738 | | (47,435 | ) | 1,147,903 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
NET INCREASE (DECREASE) IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | | — | | 230,744 | | 28,395 | | (1,900 | ) | — | | 257,239 | |
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, beginning of period | | — | | 7,230 | | 199 | | 15,436 | | — | | 22,865 | |
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, end of period | | $ | — | | $ | 237,974 | | $ | 28,594 | | $ | 13,536 | | $ | — | | $ | 280,104 | |
F-52
Table of Contents
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2012
(In thousands)
| | Sinclair
Broadcast
Group, Inc. | | Sinclair
Television
Group, Inc. | | Guarantor
Subsidiaries
and KDSM,
LLC | | Non-
Guarantor
Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | Sinclair
Consolidated | |
NET CASH FLOWS (USED IN) FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | $ | (4,038 | ) | $ | (56,760 | ) | $ | 282,446 | | $ | 12,999 | | $ | 2,828 | | $ | 237,475 | |
CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Acquisition of property and equipment | | 396 | | (4,057 | ) | (37,635 | ) | (2,690 | ) | — | | (43,986 | ) |
Payments for acquisitions of television stations | | — | | (1,127,848 | ) | — | | (18,200 | ) | 10,700 | | (1,135,348 | ) |
Purchase of alarm monitoring contracts | | — | | — | | — | | (12,454 | ) | — | | (12,454 | ) |
Decrease (increase) in restricted cash | | — | | 58,501 | | | | — | | — | | 58,501 | |
Distributions from investments | | 836 | | — | | — | | 8,754 | | — | | 9,590 | |
Investments in equity and cost method investees | | (2,000 | ) | — | | — | | (22,052 | ) | — | | (24,052 | ) |
Investment in debt securities | | — | | — | | — | | (1,493 | ) | — | | (1,493 | ) |
Proceeds from sale of assets | | — | | 10,700 | | 10 | | — | | (10,700 | ) | 10 | |
Other, net | | (94 | ) | — | | 42 | | — | | — | | (52 | ) |
Net cash flows (used in) from investing activities | | (862 | ) | (1,062,704 | ) | (37,583 | ) | (48,135 | ) | — | | (1,149,284 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Proceeds from notes payable, commercial bank financing and capital leases | | — | | 1,201,275 | | — | | 45,980 | | — | | 1,247,255 | |
Repayments of notes payable, commercial bank financing and capital leases | | (419 | ) | (154,989 | ) | (586 | ) | (23,362 | ) | — | | (179,356 | ) |
Proceeds from share based awards | | 391 | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 391 | |
Dividends paid on Class A and Class B Common Stock | | (125,100 | ) | — | | — | | — | | 1,248 | | (123,852 | ) |
Payments for deferred financing costs | | — | | (17,660 | ) | — | | (1,047 | ) | — | | (18,707 | ) |
Noncontrolling interest distributions (contributions) | | — | | — | | — | | (1,142 | ) | — | | (1,142 | ) |
Repayments of notes and capital leases to affiliates | | (998 | ) | — | | (1,884 | ) | — | | — | | (2,882 | ) |
Increase (decrease) in intercompany payables | | 131,026 | | 97,880 | | (242,507 | ) | 17,677 | | (4,076 | ) | — | |
Net cash flows from (used in) financing activities | | 4,900 | | 1,126,506 | | (244,977 | ) | 38,106 | | (2,828 | ) | 921,707 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
NET INCREASE (DECREASE) IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | | — | | 7,042 | | (114 | ) | 2,970 | | — | | 9,898 | |
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, beginning of period | | — | | 188 | | 313 | | 12,466 | | — | | 12,967 | |
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, end of period | | $ | — | | $ | 7,230 | | $ | 199 | | $ | 15,436 | | $ | — | | $ | 22,865 | |
F-53
Table of Contents
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2011
(In thousands)
| | Sinclair
Broadcast
Group, Inc. | | Sinclair
Television
Group, Inc. | | Guarantor
Subsidiaries
and KDSM,
LLC | | Non-
Guarantor
Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | Sinclair
Consolidated | |
NET CASH FLOWS (USED IN) FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | $ | (10,424 | ) | $ | (65,150 | ) | $ | 225,516 | | $ | 704 | | $ | (2,133 | ) | $ | 148,513 | |
CASH FLOWS (USED IN) FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Acquisition of property and equipment | | — | | (3,503 | ) | (30,950 | ) | (1,382 | ) | — | | (35,835 | ) |
Purchase of alarm monitoring contracts | | — | | — | | — | | (8,850 | ) | — | | (8,850 | ) |
Increase in restricted cash | | — | | (53,445 | ) | — | | — | | — | | (53,445 | ) |
Distributions from investments | | — | | — | | — | | 3,798 | | — | | 3,798 | |
Investments in equity and cost method investees | | (4,000 | ) | — | | — | | (7,577 | ) | — | | (11,577 | ) |
Investment in debt securities | | — | | — | | — | | (4,911 | ) | — | | (4,911 | ) |
Payments for acquisitions of assets of other operating divisions | | — | | — | | — | | (3,072 | ) | — | | (3,072 | ) |
Proceeds from sale of assets | | — | | — | | 59 | | 10 | | — | | 69 | |
Proceeds from sale of securities | | — | | — | | — | | 1,808 | | (1,808 | ) | — | |
Proceeds from insurance settlement | | — | | — | | 1,739 | | — | | — | | 1,739 | |
Loans to affiliates | | (194 | ) | (212 | ) | — | | — | | — | | (406 | ) |
Proceeds from loans to affiliates | | 199 | | — | | — | | 43 | | — | | 242 | |
Net cash flows used in investing activities | | (3,995 | ) | (57,160 | ) | (29,152 | ) | (20,133 | ) | (1,808 | ) | (112,248 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Proceeds from notes payable, commercial bank financing and capital leases | | — | | 136,719 | | — | | 15,014 | | — | | 151,733 | |
Repayments of notes payable, commercial bank financing and capital leases | | (57,120 | ) | (70,234 | ) | (432 | ) | (22,661 | ) | — | | (150,447 | ) |
Proceeds from share based awards | | 1,794 | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 1,794 | |
Purchase of subsidiary shares from noncontrolling interests | | — | | — | | — | | (2,501 | ) | — | | (2,501 | ) |
Dividends paid on Class A and Class B Common Stock | | (38,820 | ) | — | | — | | — | | 464 | | (38,356 | ) |
Payments for deferred financing costs | | — | | (5,417 | ) | — | | (66 | ) | — | | (5,483 | ) |
Proceeds from Class A Common Stock sold by variable interest entity | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 1,808 | | 1,808 | |
Noncontrolling interest distributions | | — | | — | | — | | (610 | ) | — | | (610 | ) |
Repayments of notes and capital leases to affiliates | | (869 | ) | — | | (2,341 | ) | — | | — | | (3,210 | ) |
Increase (decrease) in intercompany payables | | 109,434 | | 56,359 | | (194,300 | ) | 26,838 | | 1,669 | | — | |
Net cash flows from (used in) financing activities | | 14,419 | | 117,427 | | (197,073 | ) | 16,014 | | 3,941 | | (45,272 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
NET DECREASE IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | | — | | (4,883 | ) | (709 | ) | (3,415 | ) | — | | (9,007 | ) |
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, beginning of period | | — | | 5,071 | | 1,022 | | 15,881 | | — | | 21,974 | |
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, end of period | | $ | — | | $ | 188 | | $ | 313 | | $ | 12,466 | | $ | — | | $ | 12,967 | |
F-54
Table of Contents
QUARTERLY FINANCIAL INFORMATION (UNAUDITED):
(in thousands, except per share data)
| | For the Quarter Ended | |
| | 03/31/13 | | 06/30/13 | | 09/30/13 | | 12/31/13 | |
Total revenues, net | | $ | 282,618 | | $ | 314,154 | | $ | 338,644 | | $ | 427,715 | |
Operating income | | $ | 63,656 | | $ | 84,280 | | $ | 72,798 | | $ | 103,286 | |
Income from continuing operations | | $ | 16,515 | | $ | 12,956 | | $ | 30,551 | | $ | 4,237 | |
Income from discontinued operations | | $ | 355 | | $ | 5,103 | | $ | 6,100 | | $ | — | |
Net income attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 16,997 | | $ | 17,826 | | $ | 36,342 | | $ | 2,303 | |
Basic earnings per common share from continuing operations attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 0.20 | | $ | 0.14 | | $ | 0.30 | | $ | 0.02 | |
Basic earnings per common share attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 0.21 | | $ | 0.19 | | $ | 0.37 | | $ | 0.02 | |
Diluted earnings per common share from continuing operations attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 0.20 | | $ | 0.14 | | $ | 0.30 | | $ | 0.02 | |
Diluted earnings per common share attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 0.21 | | $ | 0.19 | | $ | 0.36 | | $ | 0.02 | |
| | For the Quarter Ended | |
| | 03/31/12 | | 06/30/12 | | 09/30/12 | | 12/31/12 | |
Total revenues, net | | $ | 222,375 | | $ | 251,074 | | $ | 258,713 | | $ | 329,517 | |
Operating income | | $ | 59,895 | | $ | 71,887 | | $ | 78,399 | | $ | 119,097 | |
Income from continuing operations | | $ | 29,126 | | $ | 30,131 | | $ | 26,479 | | $ | 58,752 | |
(Loss) income from discontinued operations | | $ | (51 | ) | $ | (1 | ) | $ | (126 | ) | $ | 643 | |
Net income attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 29,360 | | $ | 30,058 | | $ | 26,246 | | $ | 59,002 | |
Basic earnings per common share from continuing operations attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 0.36 | | $ | 0.37 | | $ | 0.33 | | $ | 0.72 | |
Basic earnings per common share attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 0.36 | | $ | 0.37 | | $ | 0.33 | | $ | 0.73 | |
Diluted earnings per common share from continuing operations attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 0.36 | | $ | 0.37 | | $ | 0.33 | | $ | 0.72 | |
Diluted earnings per common share attributable to Sinclair Broadcast Group | | $ | 0.36 | | $ | 0.37 | | $ | 0.32 | | $ | 0.73 | |
F-55
